Self-adaptive energy-saving dispatching method in isomorphic cluster system based on dynamic voltage regulation technology
A dynamic voltage adjustment and cluster system technology, applied in energy-saving computing, data processing power supply, resource allocation, etc., can solve problems such as ignoring network communication energy consumption, not being able to adjust adaptively, and only considering performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
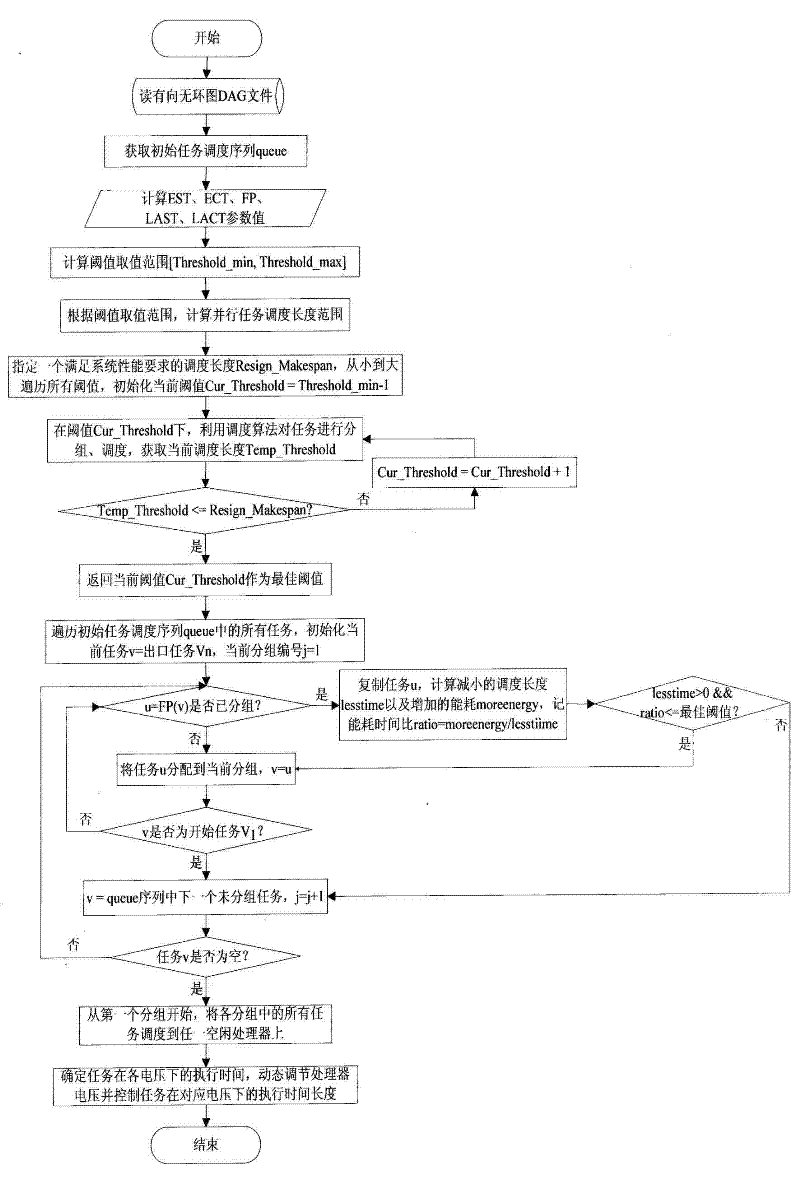
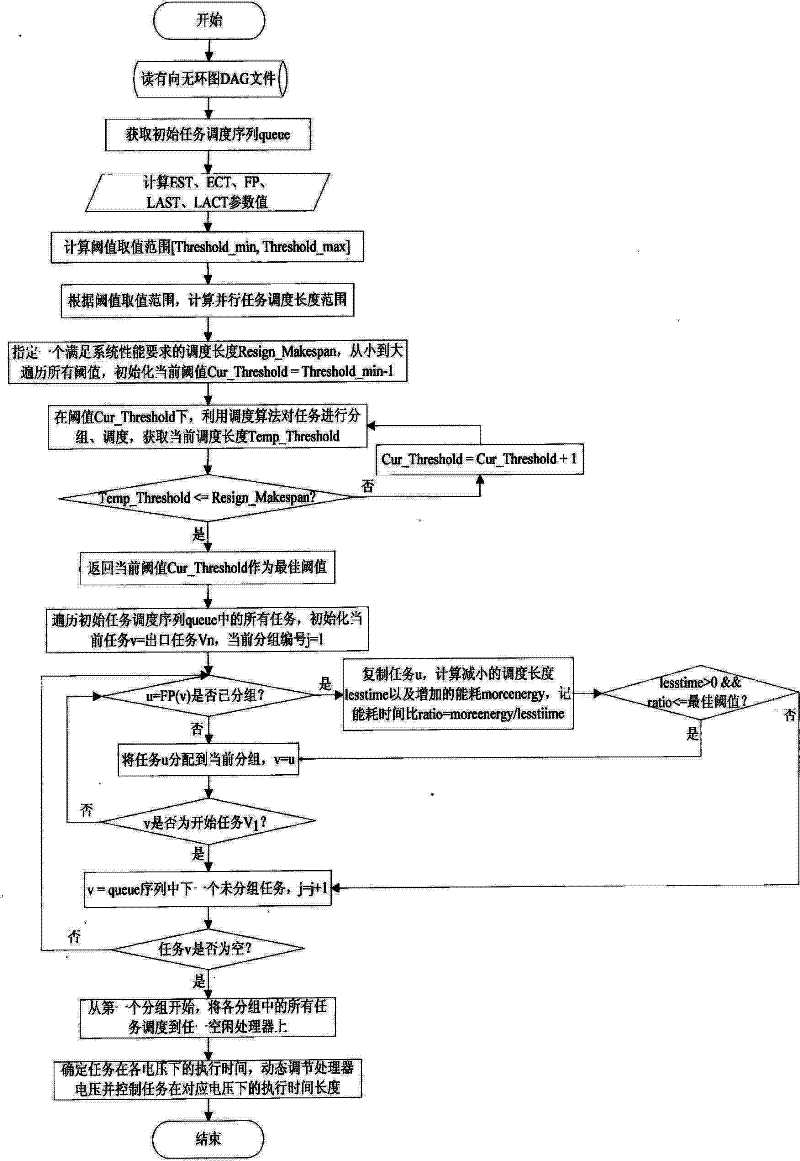
[0023] The present invention will be described in further detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings.
[0024] Parallel task: the task submitted by the user is represented by a directed acyclic graph DAG, which is defined as . in Represents a task set containing n tasks. For each task in V, t i is the task v i the computation time required to execute on the processor at the highest voltage and frequency, cc i is the task v i The calculation cycle of , it does not change with the change of the processor voltage, where 1≤i≤n. In particular, when the task When idle time exists, it can be divided into h task block { v i1 ,v i2 ,…,v ih}, each task block v ik at its corresponding voltage V k The execution time under is τ ik . E is the message set, e ij = (v i , v j ) E stands for task to task delivered message, express message The communication time charged. Furthermore, we use and Indicates the task A set of successor ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com