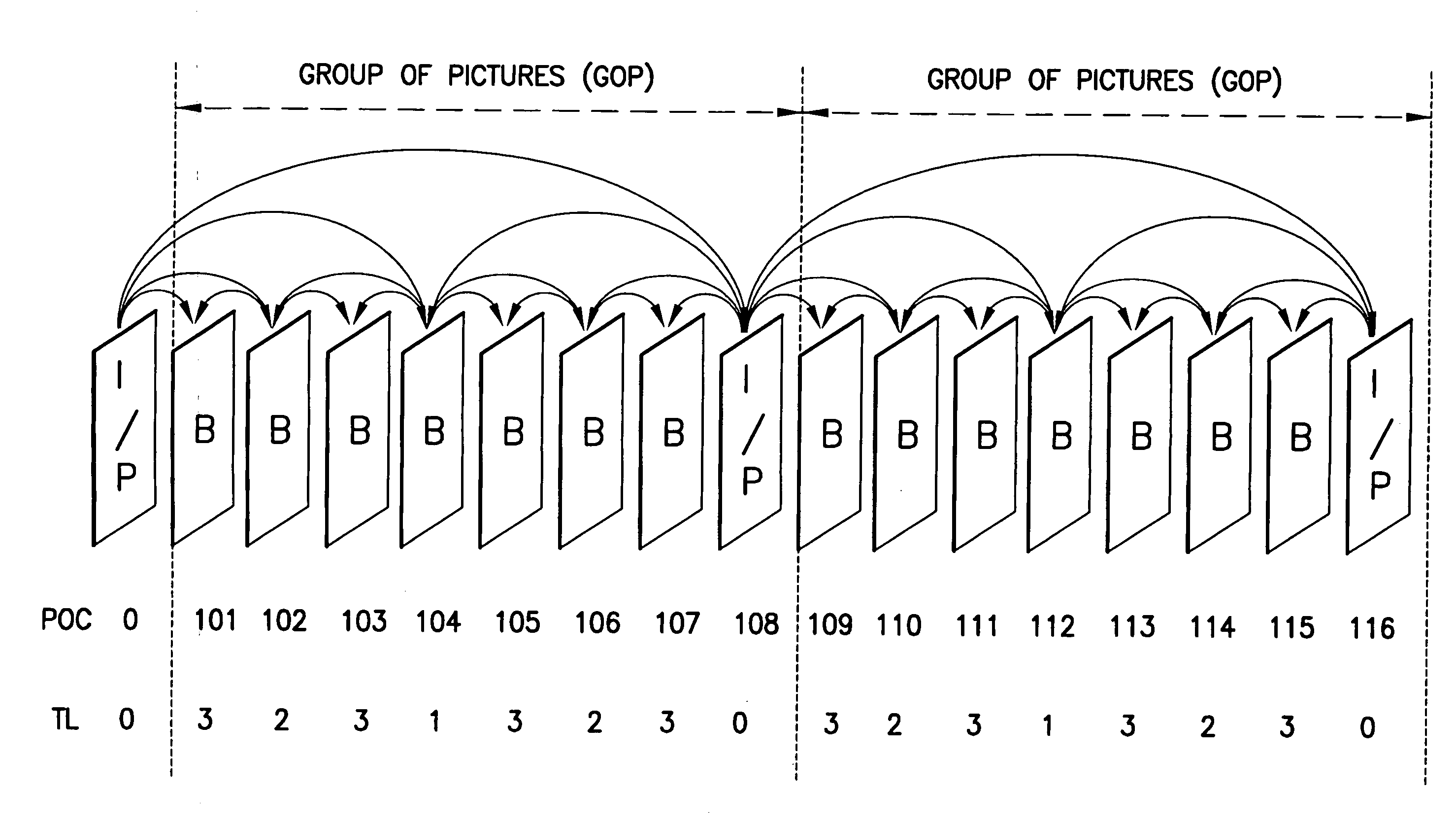
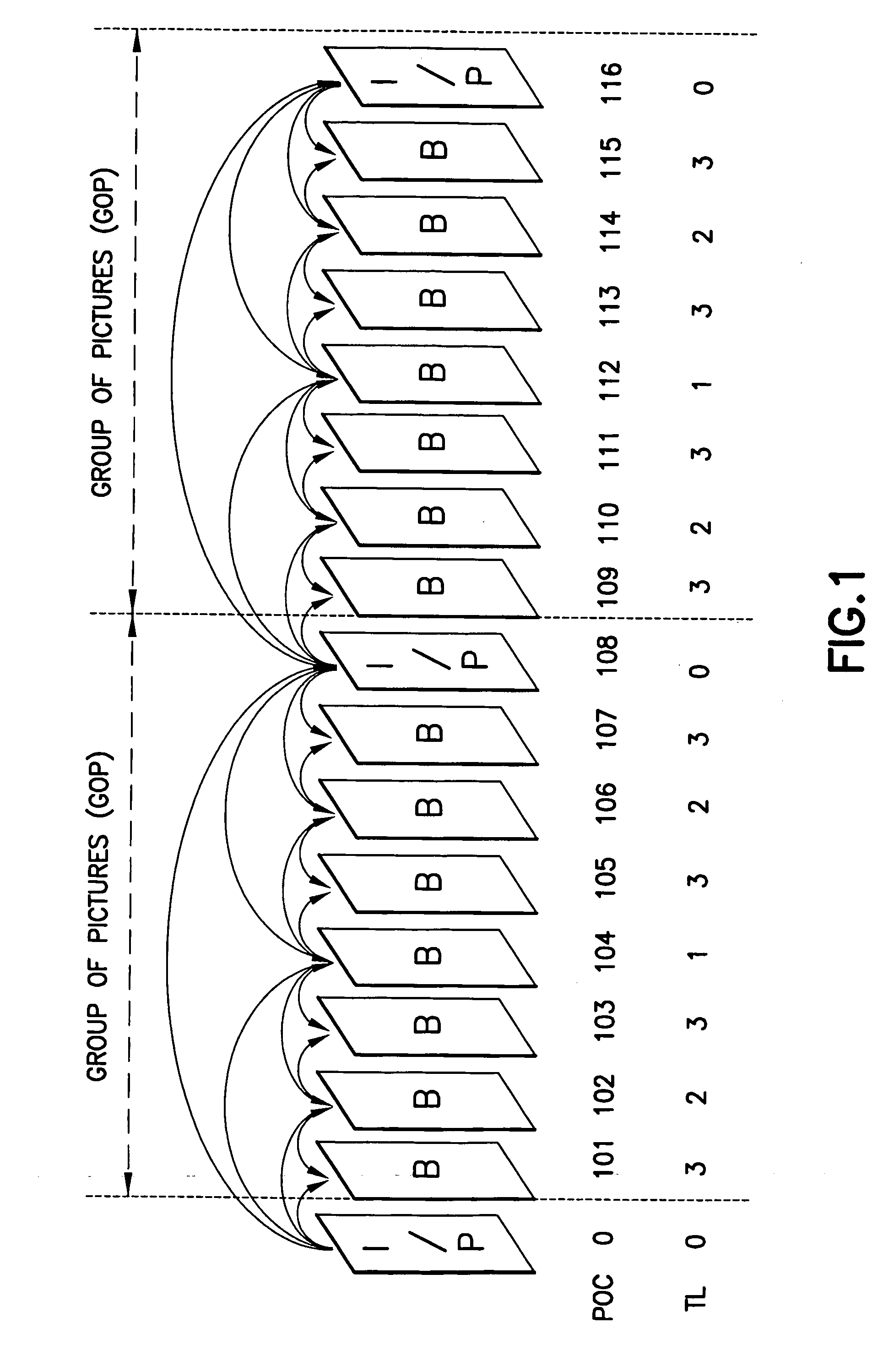
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
119 results about "CONSECUTIVE SAMPLE" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
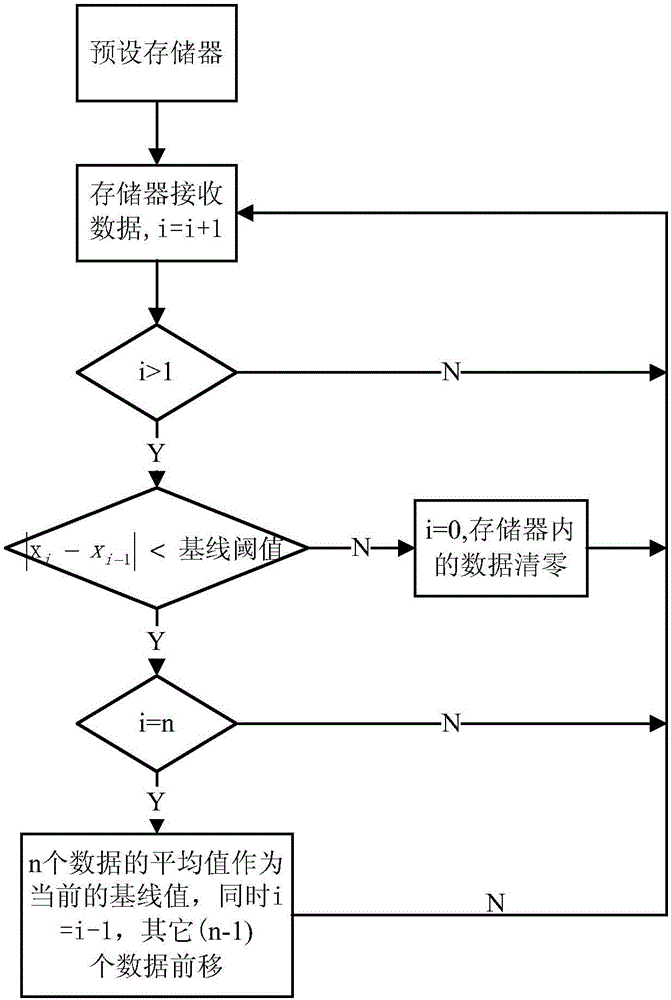
Consecutive sampling. Jump to navigation Jump to search. In the design of experiments, consecutive sampling, also known as total enumerative sampling, is a sampling technique in which every subject meeting the criteria of inclusion is selected until the required sample size is achieved.
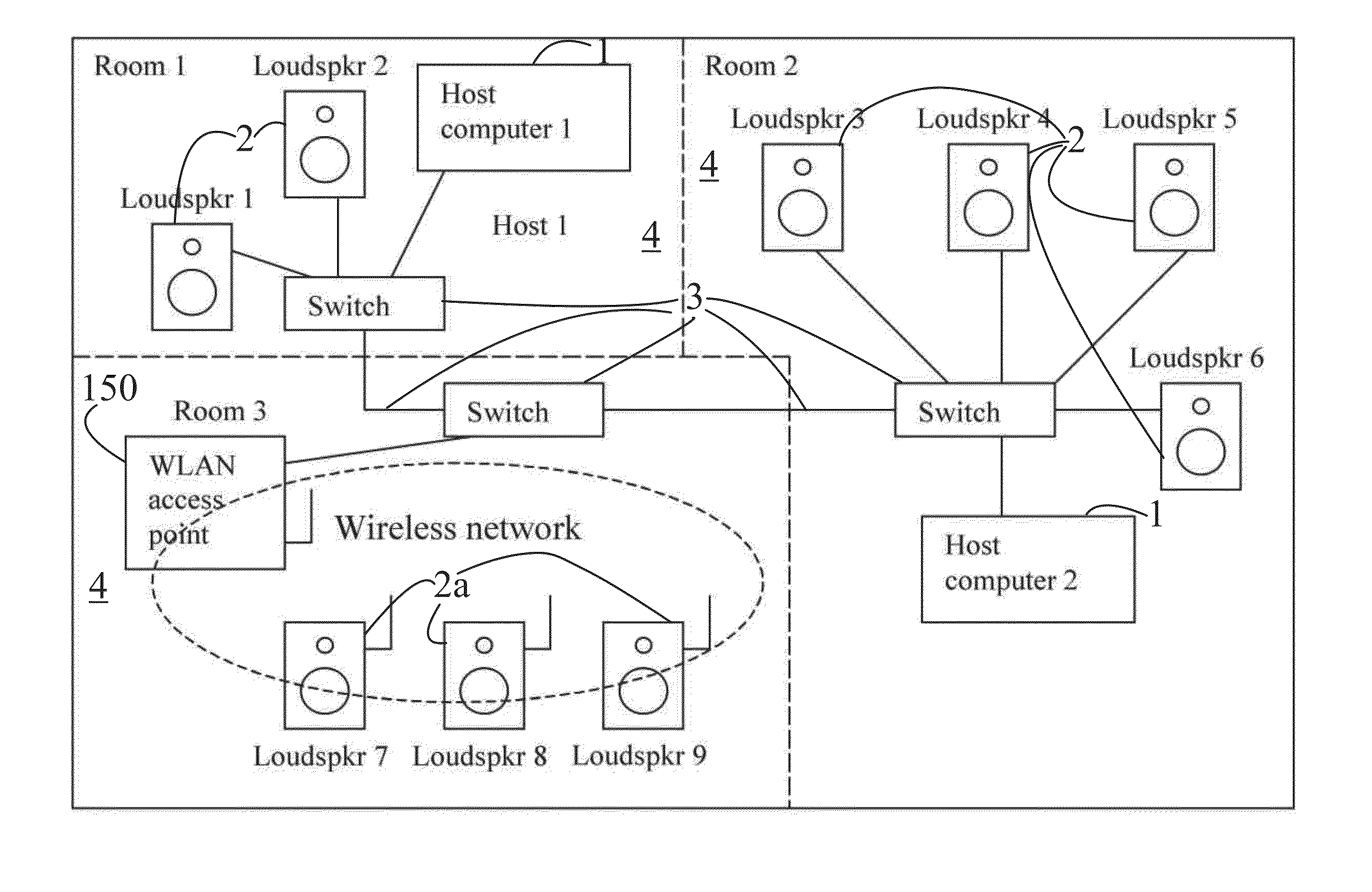
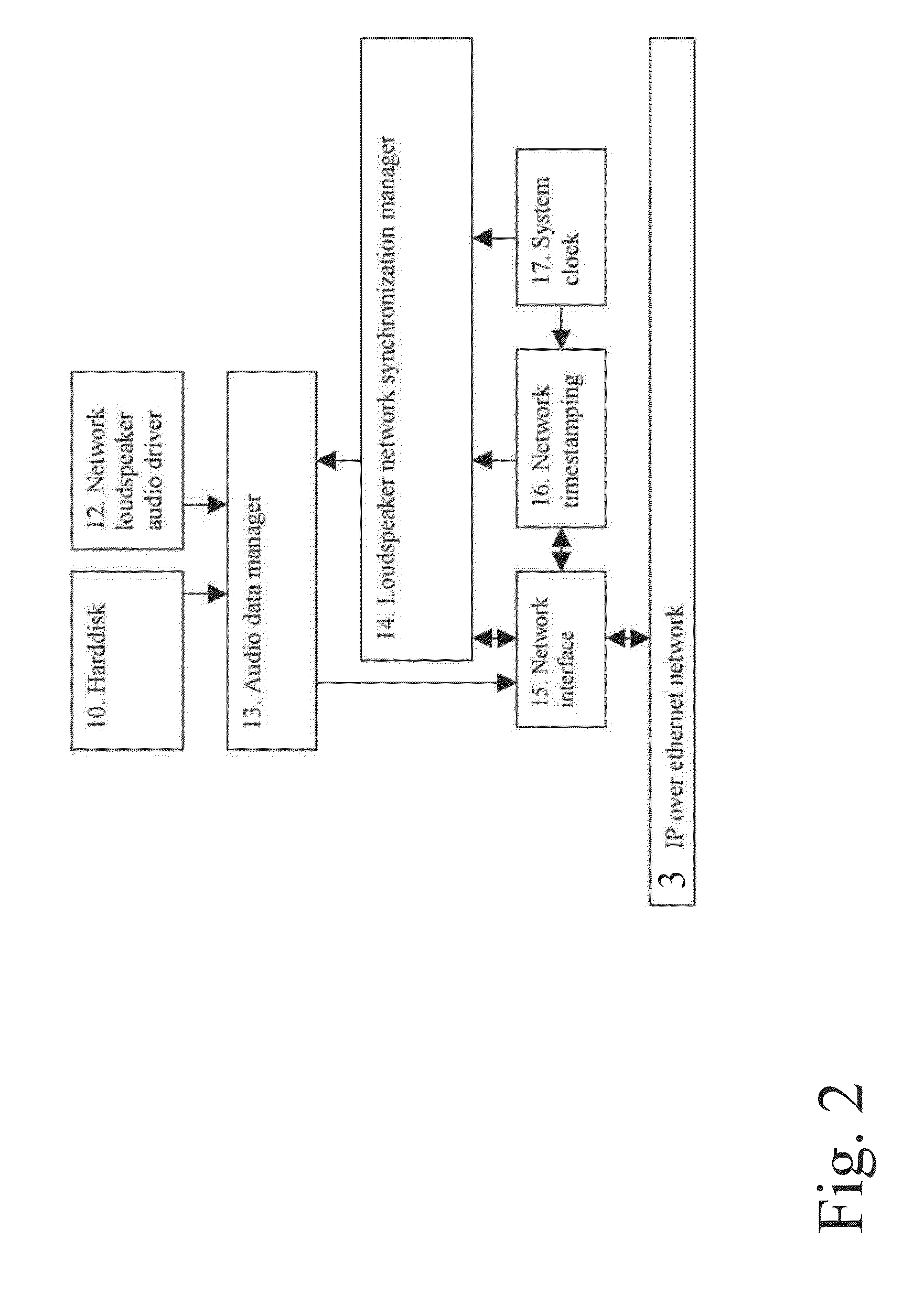
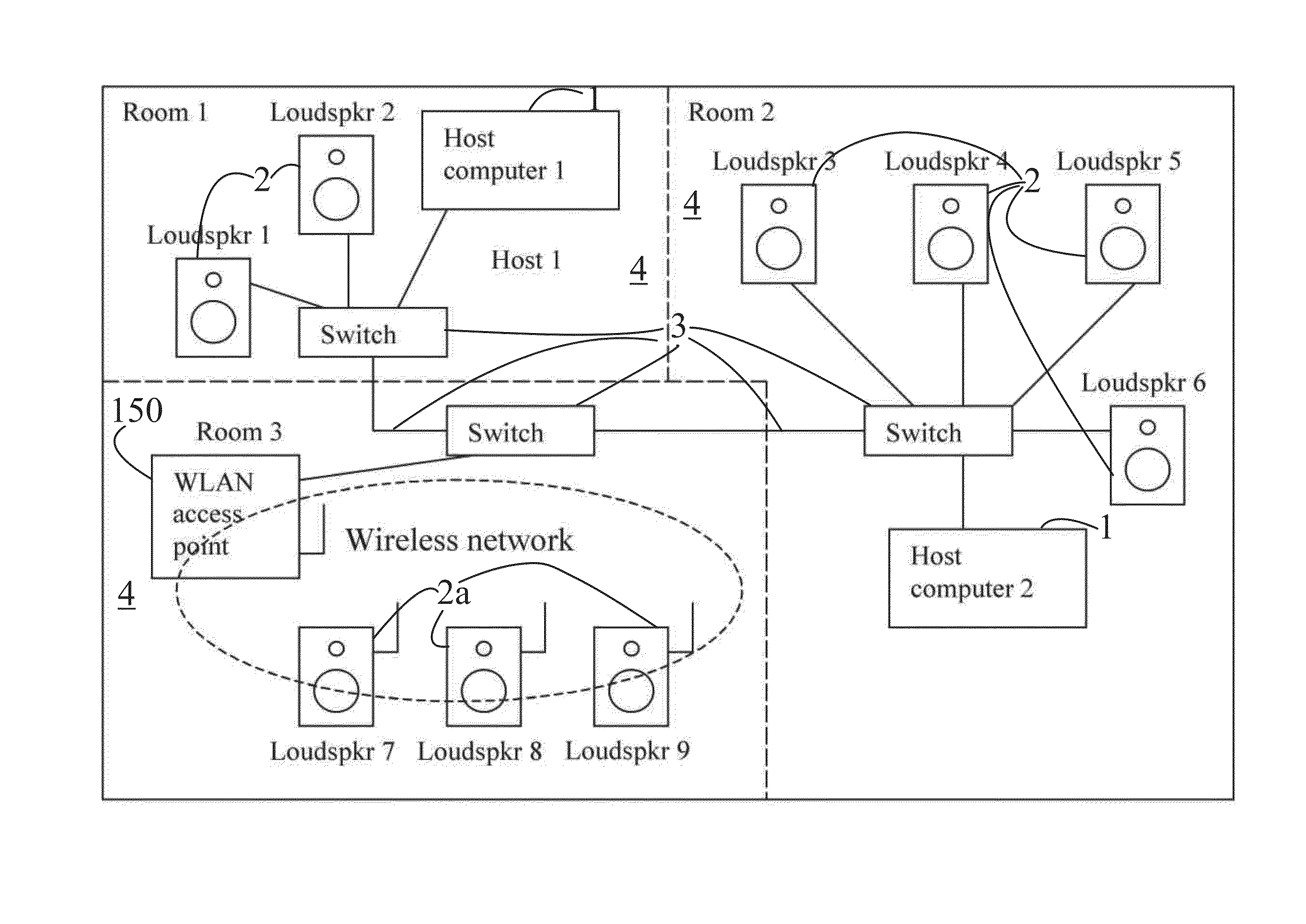
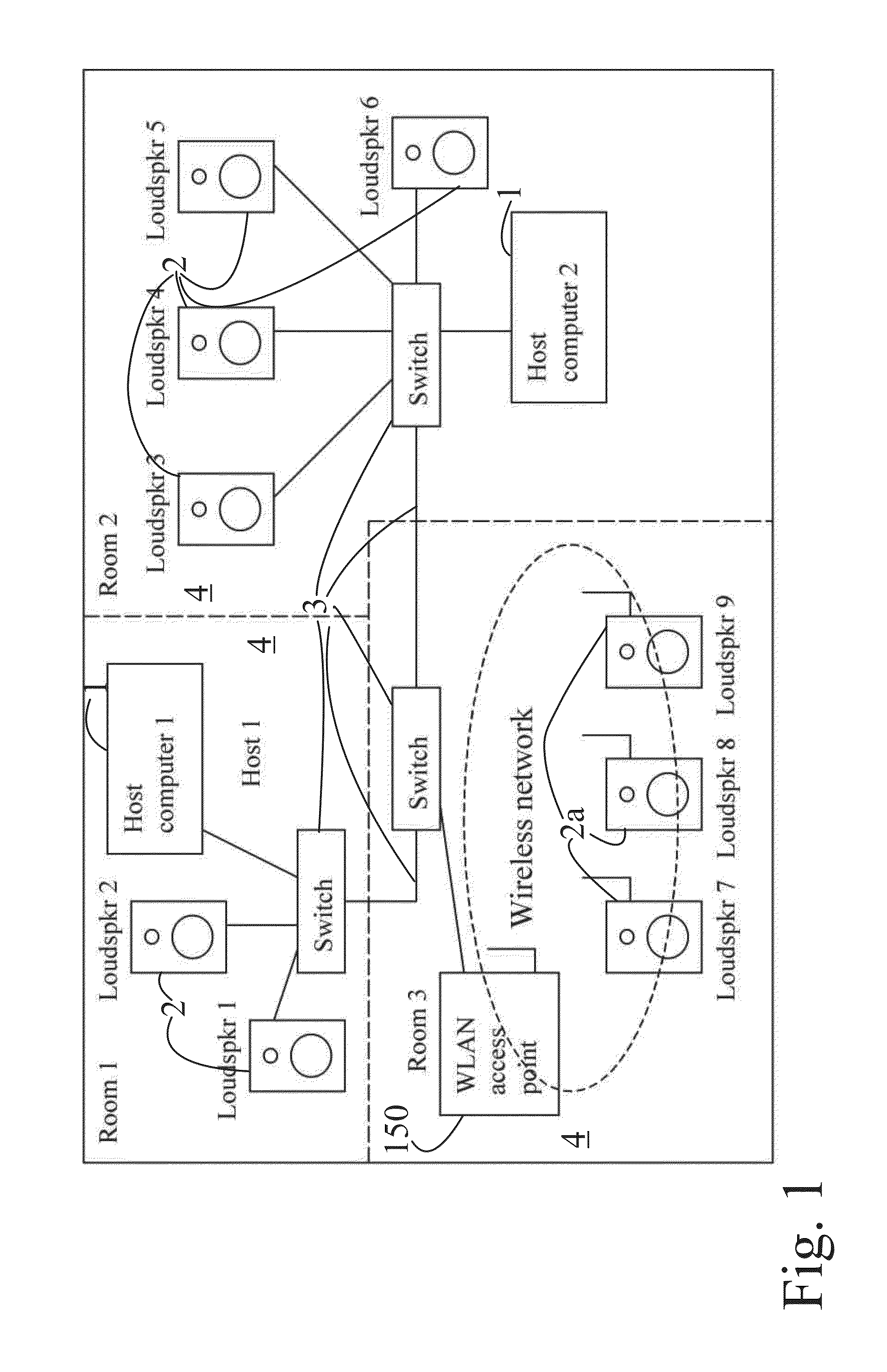
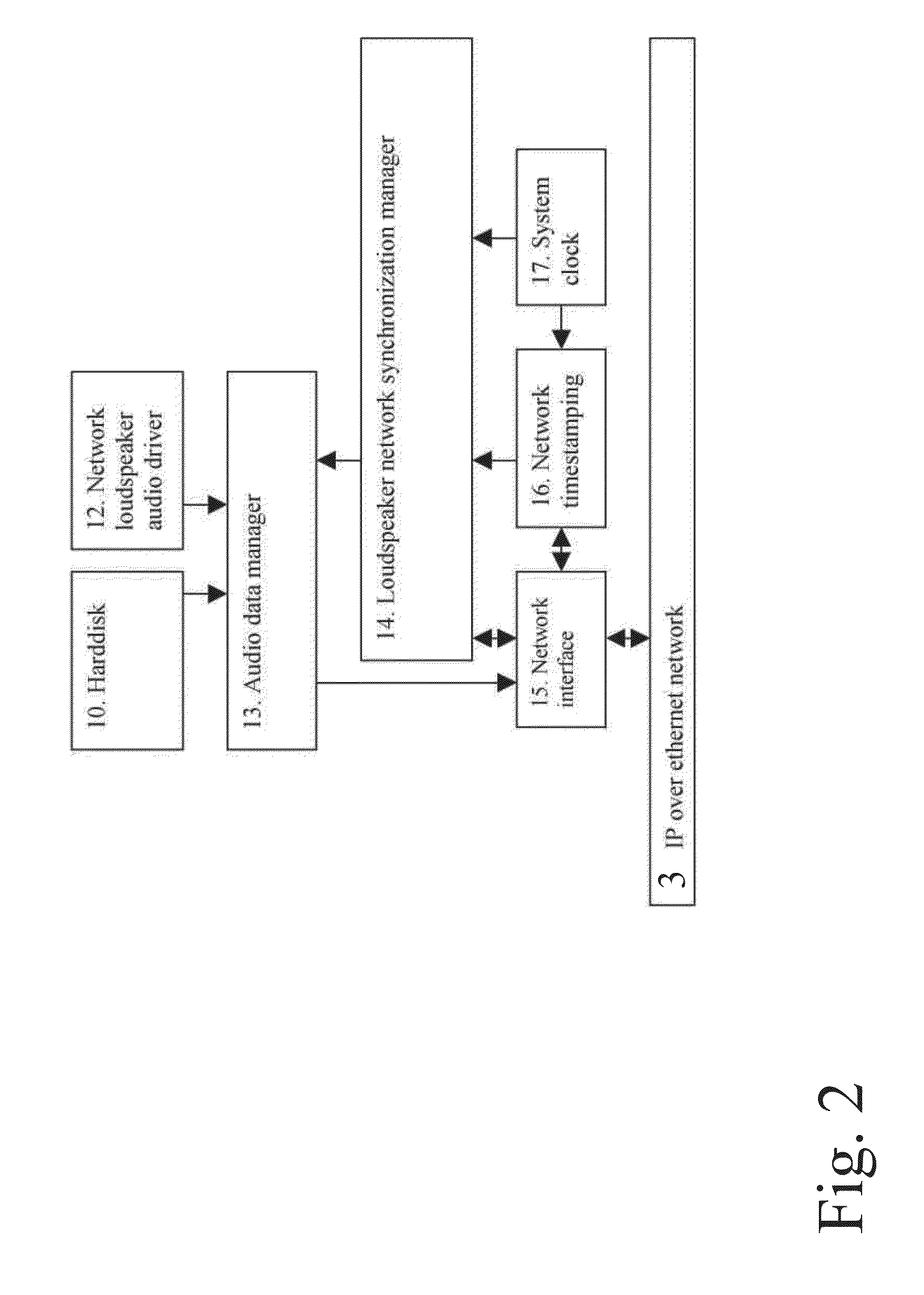
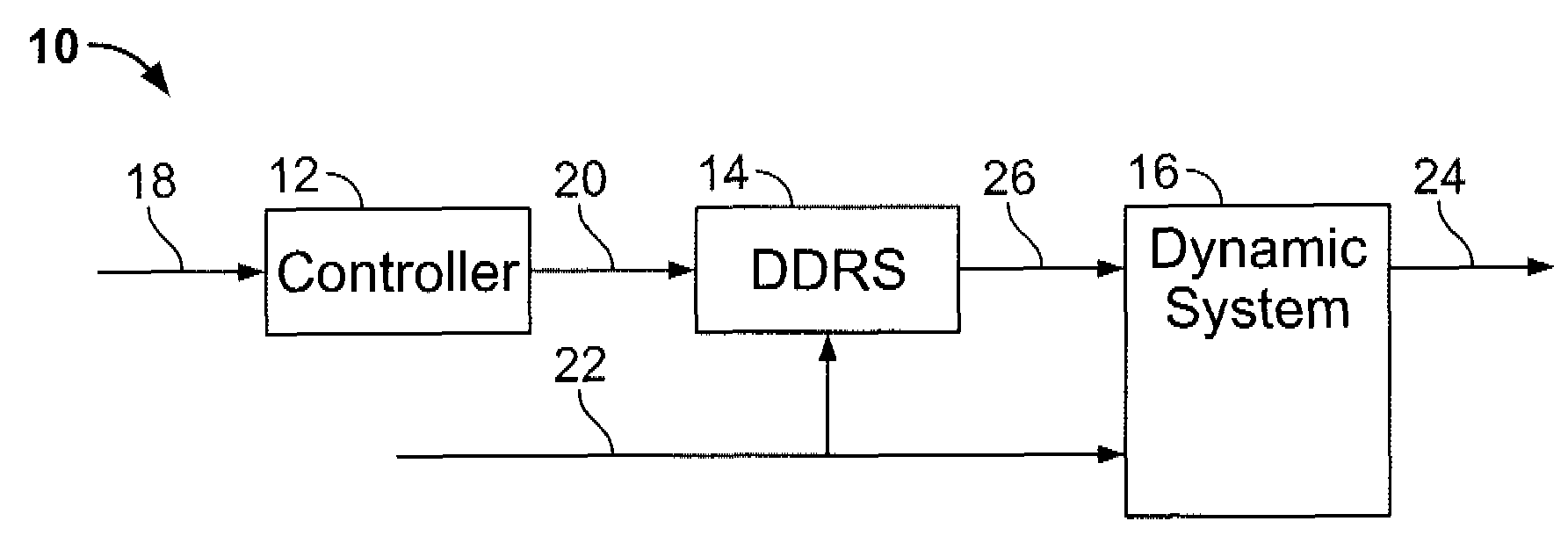
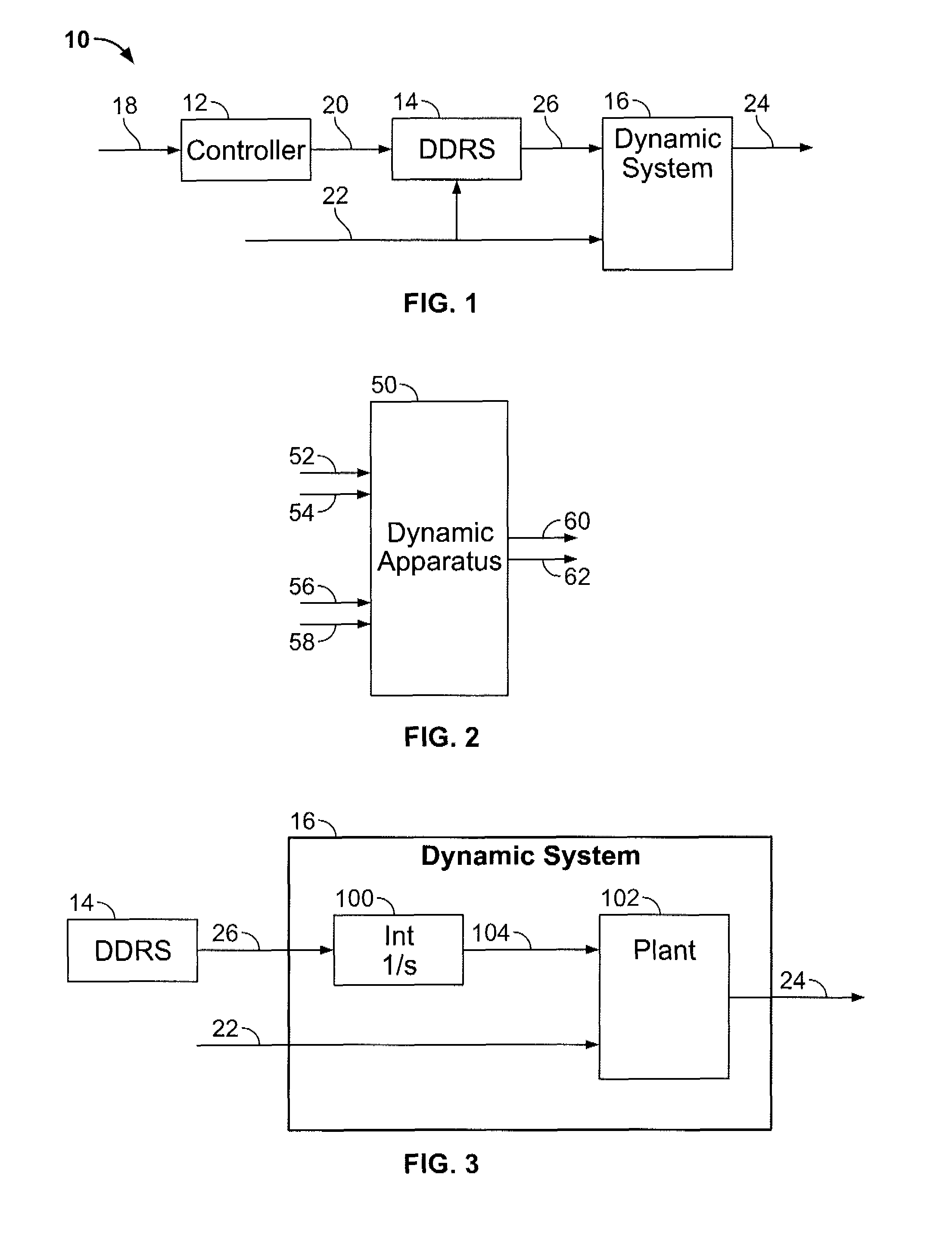
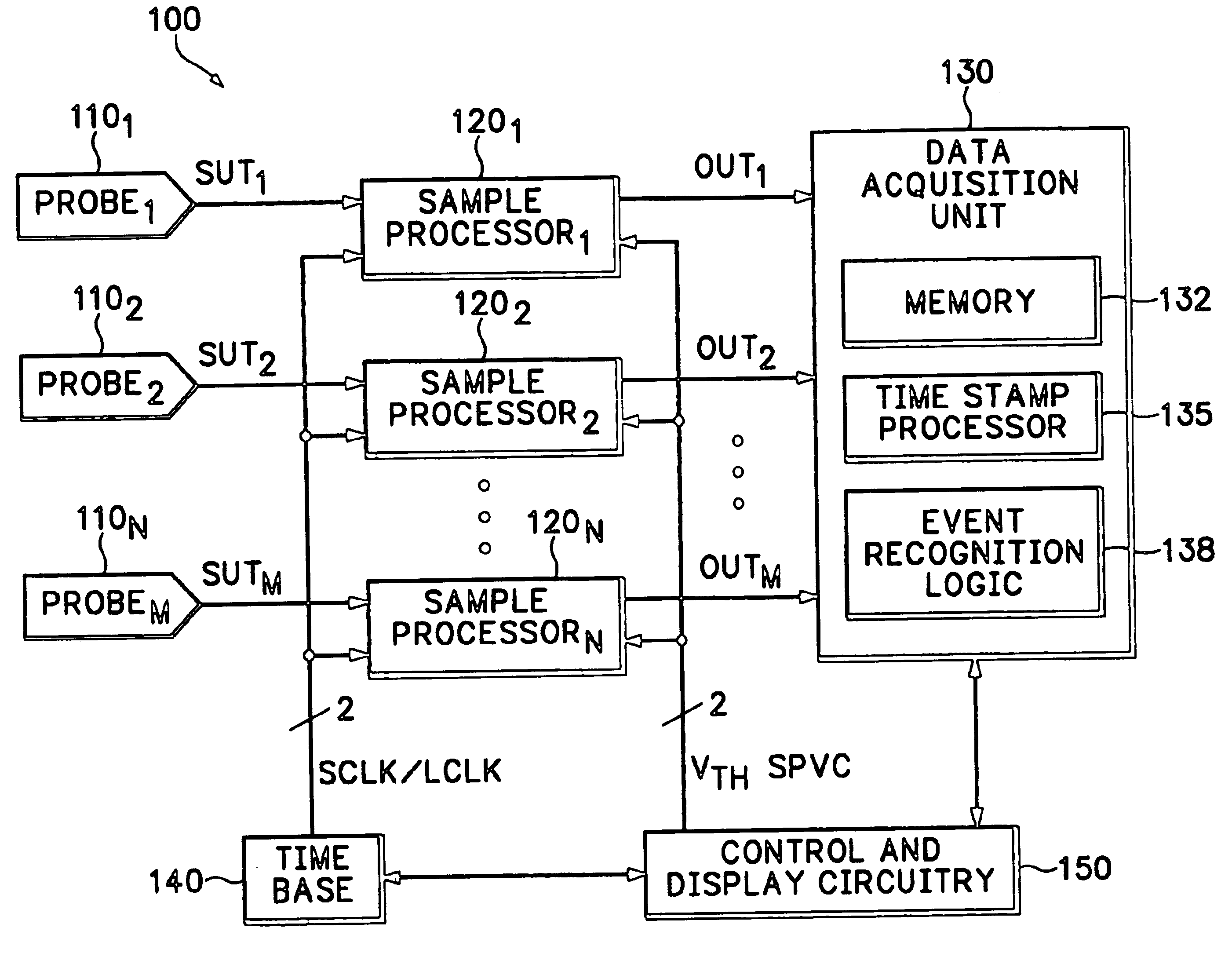
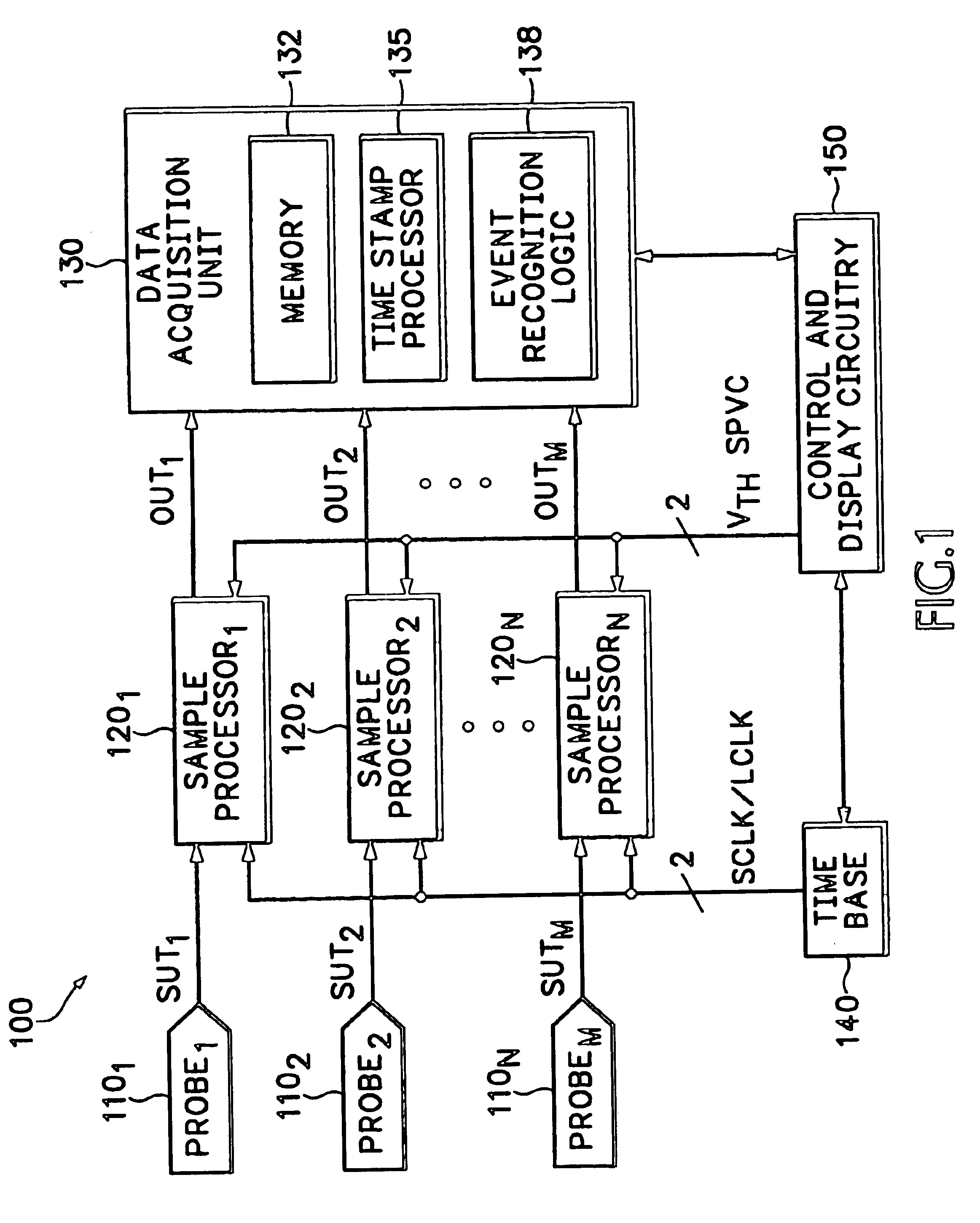
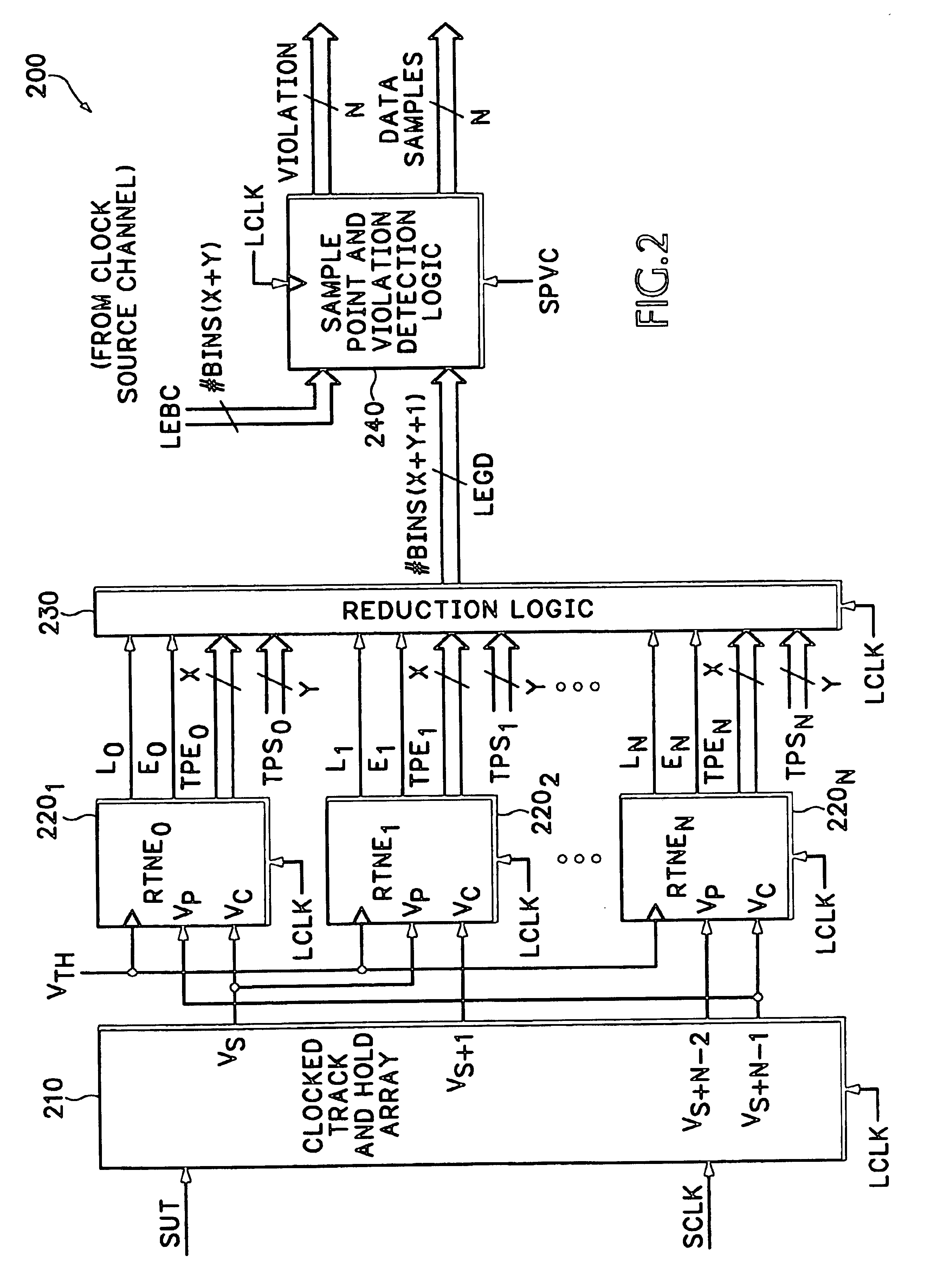
Data transfer method and system for loudspeakers in a digital sound reproduction system
ActiveUS8930006B2Accurate timingAccurate operationPublic address systemsTime-division multiplexMicrocontrollerDigital data
The present publication describes a data transfer method and system in a digital sound reproduction system. The method comprises method steps for generating a digital audio stream for multiple channels in a host data source, e.g. a computer, the audio stream is formed by multiple consecutive samples, receiving the digital audio stream sent by the host data source through a digital data transmission network by several digital receivers each of which including a microcontroller with a clock, the receivers further including means for generating an audio signal. In accordance with the invention the host data source sends repeatedly a synchronization sample to at least one receiver, the receiver replies to the synchronization sample by a return sample, the host calculates a latency (T) for each receiver based on the sending time (Th1) of the synchronization sample and the reception time (Th2) of the return sample and the processing time (Tt1-Tt2) of the receiver, the host sends to the receiver information of the calculated latency (T) in combination with the time stamp the measurement time, based on this information the receiver adjusts the function of its clock, and the above synchronization steps are repeated continuously.
Owner:GENELEC
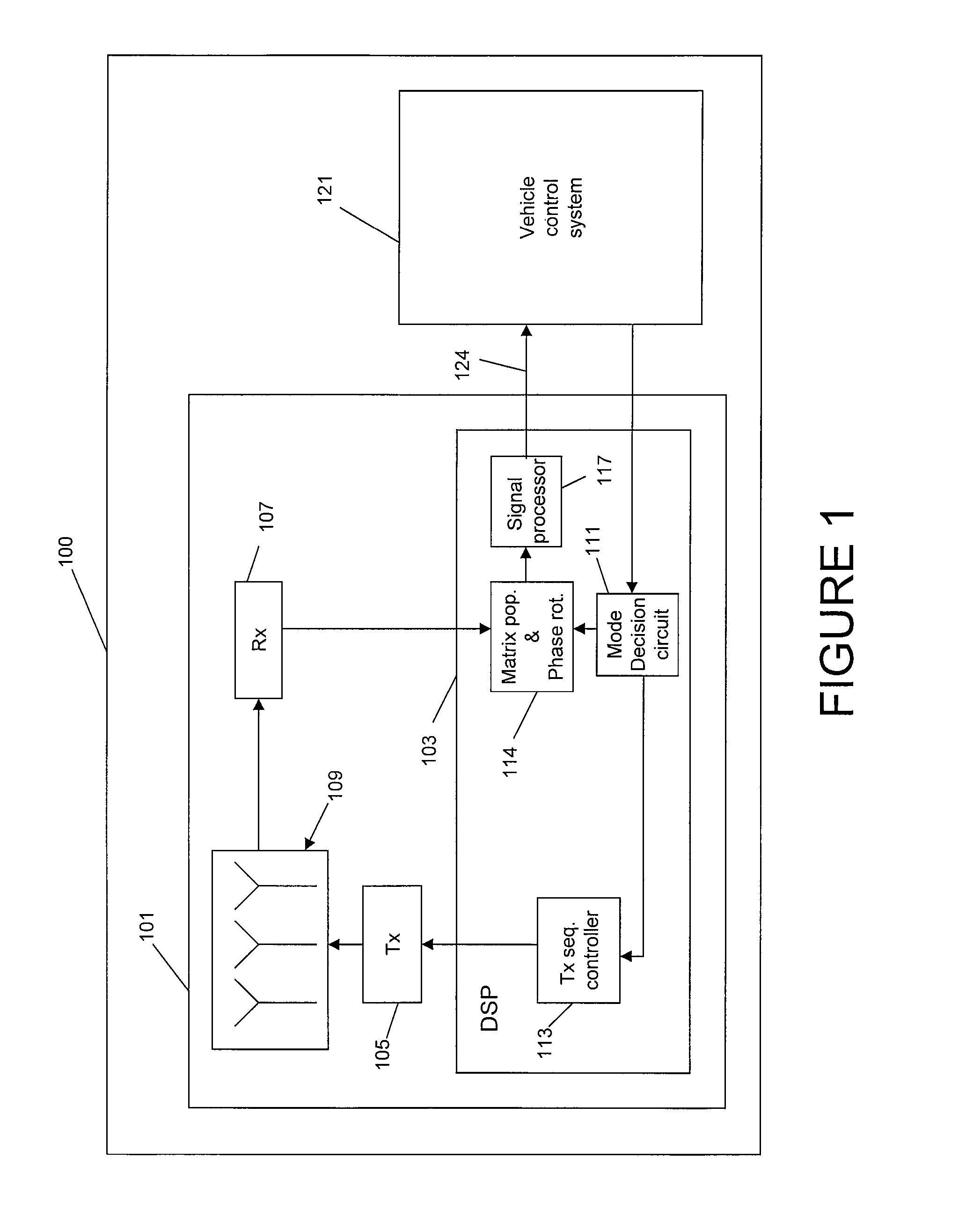
Method and apparatus for radar signal processing
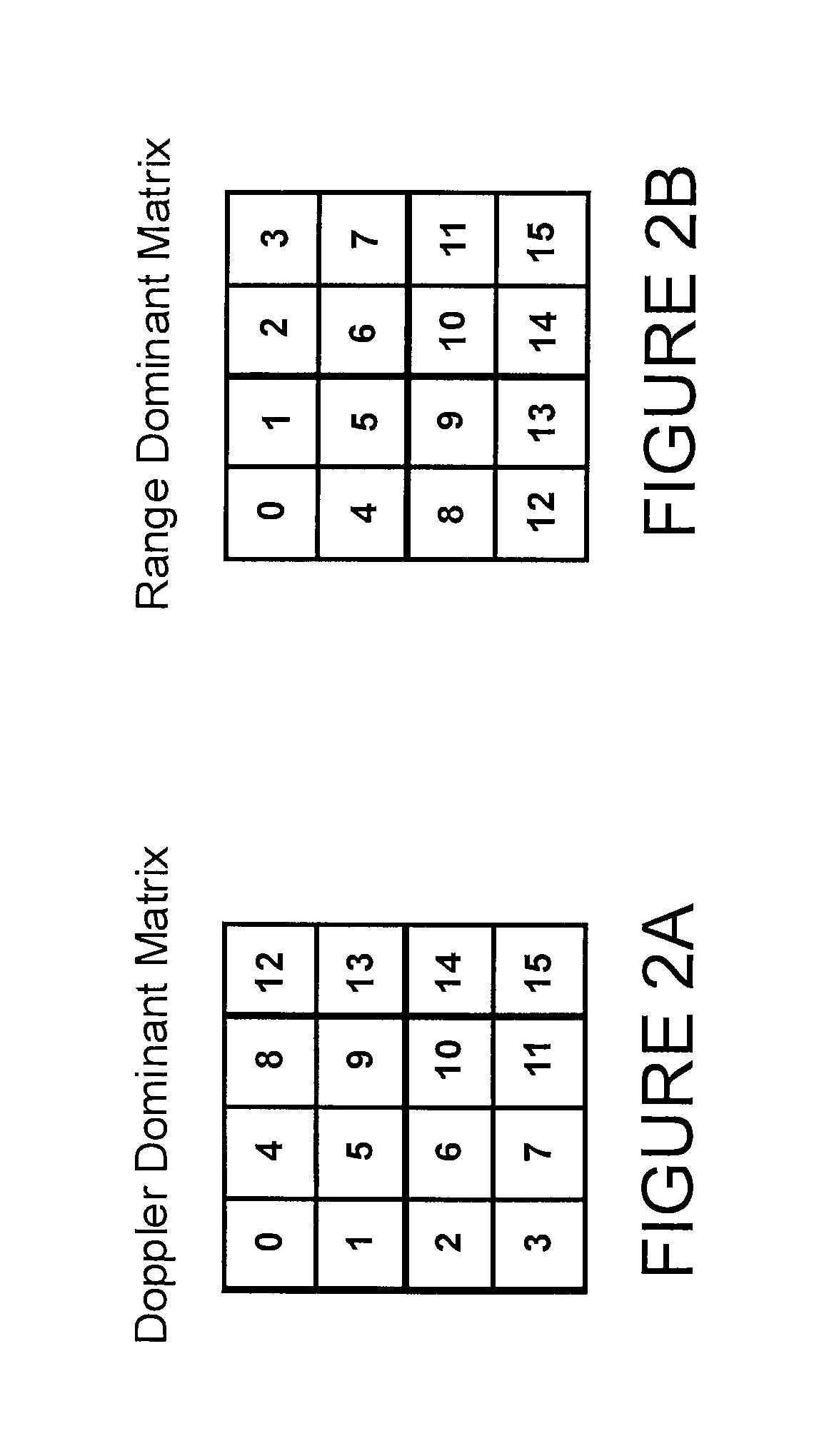
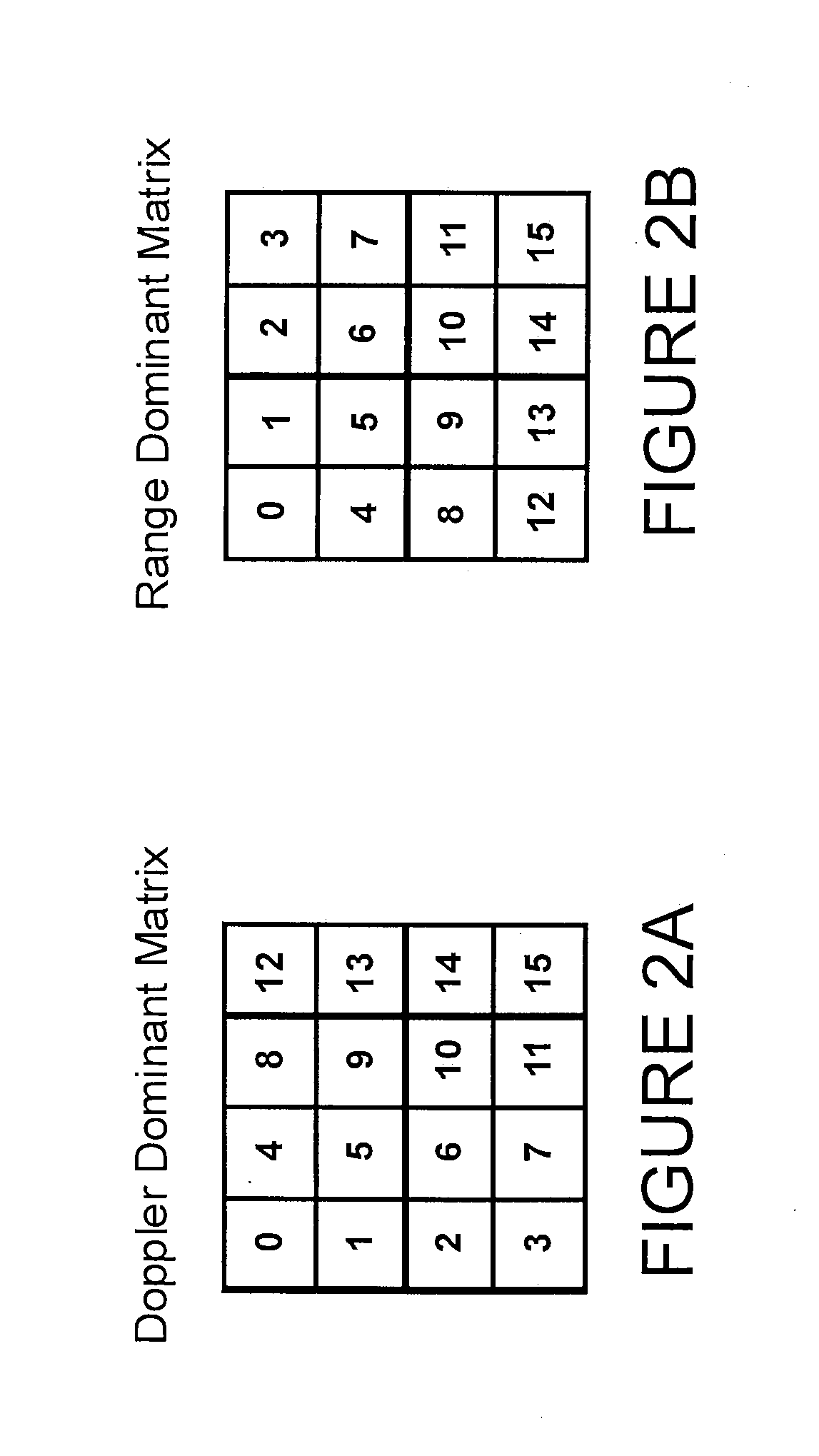
A radar apparatus and method for determining the range to and velocity of at least one object comprising, transmitting a plurality of RF signals, each comprising a particular frequency and being transmitted during a particular unique finite period, the plurality of signals collectively comprising at least one first subset of signals having the same frequency and at least one second subset of signals having different frequencies, receiving the plurality of signals after reflection from an object, determining a phase difference between each of the signals and the corresponding reflected signal, each piece of phase difference information herein termed a sample, organizing the samples in two-dimensions wherein, in a first dimension, all samples have the same frequency and, in a second dimension, all consecutive samples are separated from each other by a fixed time interval; processing the samples in the first dimension to determine a phase rotation frequency corresponding to the samples in the first dimension, the phase rotation frequency comprising a Doppler frequency for the at least one object, processing the samples in the second dimension to determine a second phase rotation frequency corresponding to the samples in the second dimension; the phase rotation frequency comprising Doppler frequency and range frequency for the at least one object; comparing the first phase rotation frequency to the second phase rotation frequency to distinguish range frequency from Doppler frequency of the at least one object; and converting the Doppler frequency to a velocity of the object and converting the range frequency to a range of the object.
Owner:VEONEER US LLC
Data replacement policy
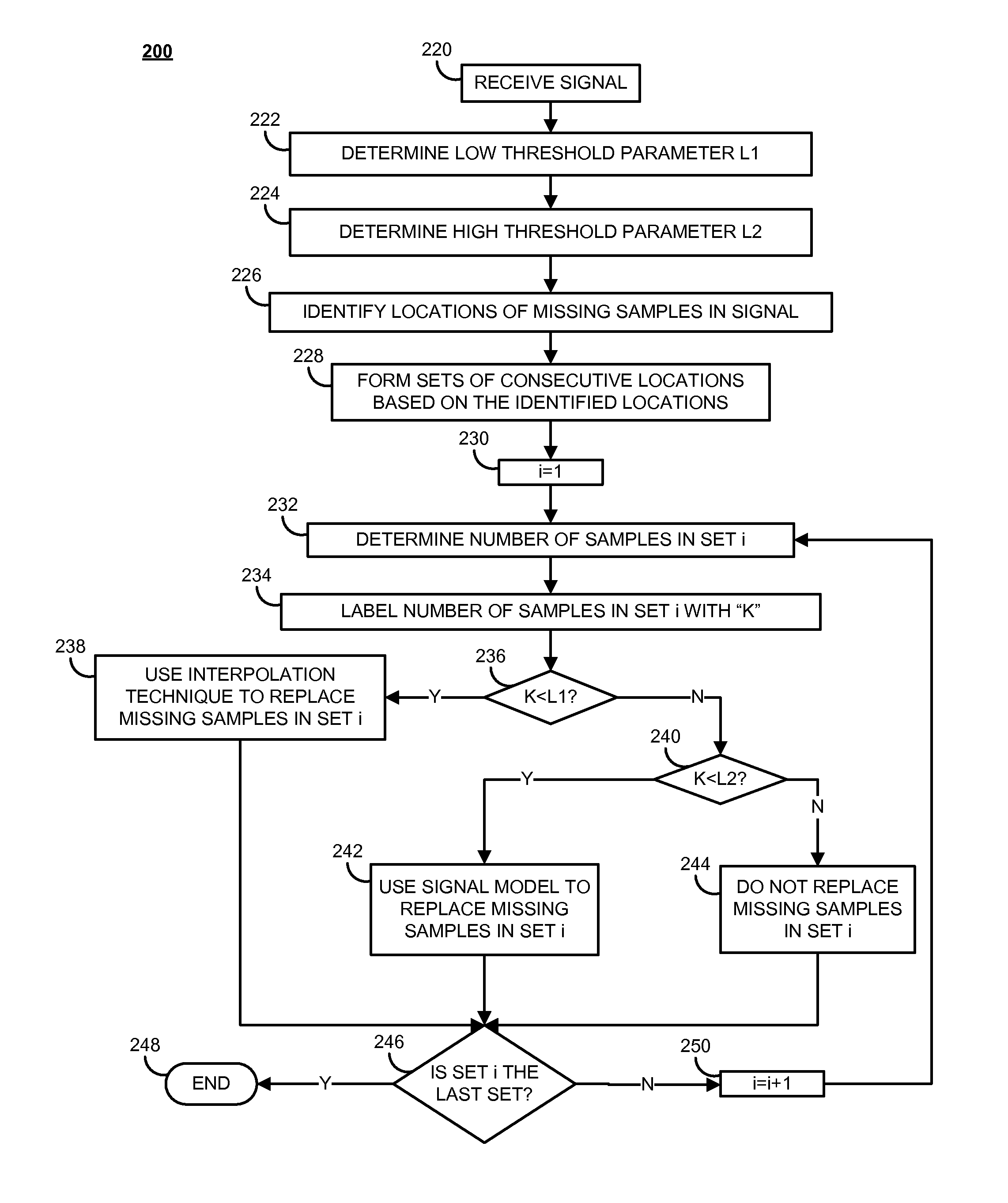
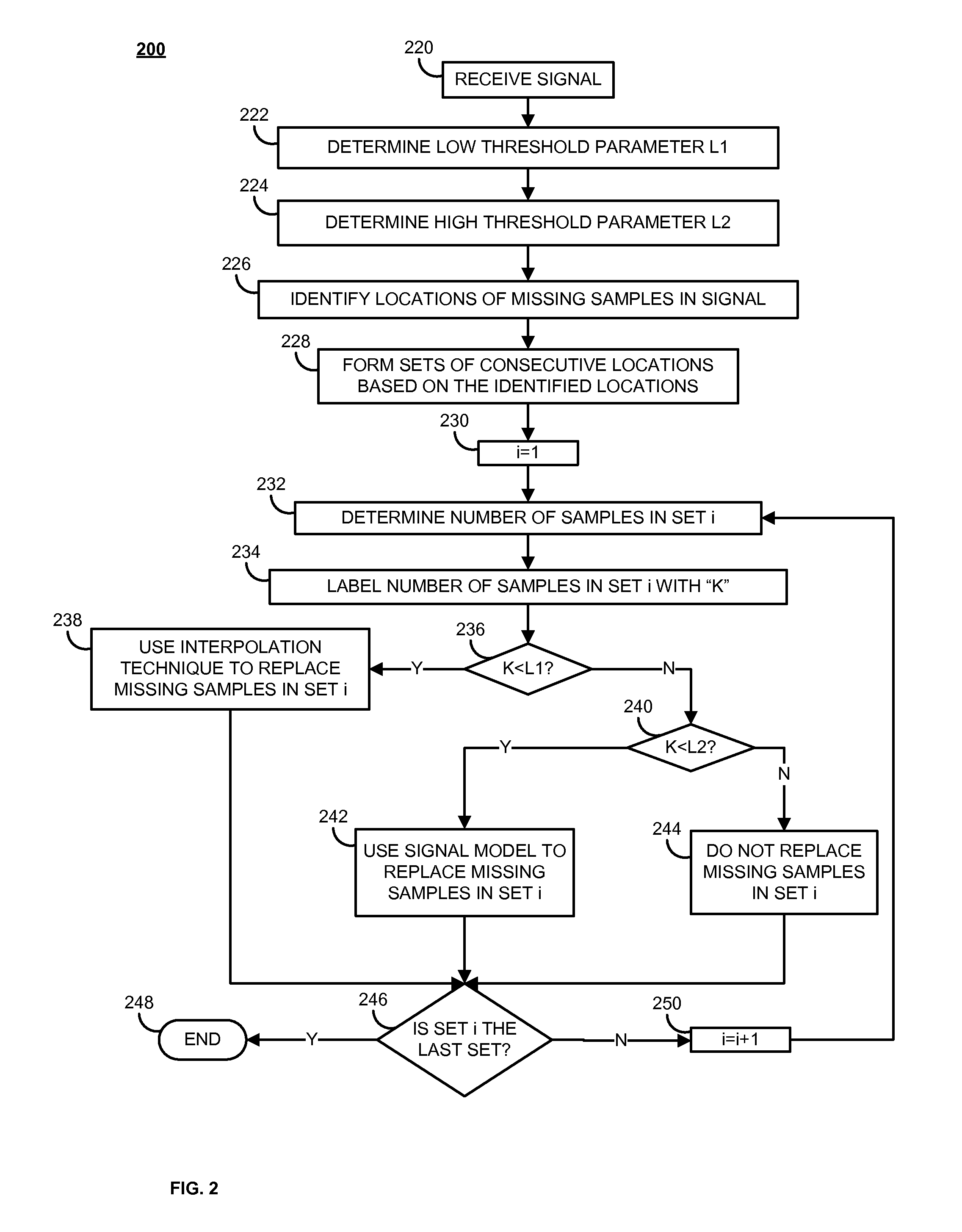
Systems and methods are provided for estimating missing samples in a signal. A plurality of samples in the signal is received, and a respective sample corresponds to a respective sample location in a plurality of sample locations. A subset of sample locations representing missing samples in the signal is identified, and a first and a second threshold are determined. Each threshold is an integer number of samples, and the second threshold is greater than the first threshold. A first set of consecutive sample locations from the identified subset of sample locations is formed, and the missing samples in the first set of consecutive sample locations are replaced based on a comparison between a number of locations in the first set of consecutive locations, the first threshold, and the second thresholds.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Signaling of multiple decoding times in media files
ActiveUS20080292003A1Pulse modulation television signal transmissionPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesComputer scienceSample number
The exemplary embodiments of this invention provide in one aspect thereof an ability to signal multiple decoding times for each sample in a file format level in order to allow, for example, different decoding times for each sample (or sample subset) between decoding an entire stream and decoding a subset of the stream. An alternate decoding time box is specified to allow for the signaling of multiple decoding times for each sample. Such a box can contain a compact version of a table that allows indexing from an alternate decoding time to a sample number, where an alternate decoding time is a decoding time to be used with a sample when only a subset of an elementary stream stored in a track is to be decoded. Furthermore, each entry in the table provides the number of consecutive samples with the same time delta, and the delta between those consecutive samples. By adding the deltas a complete time-to-sample map can be constructed.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
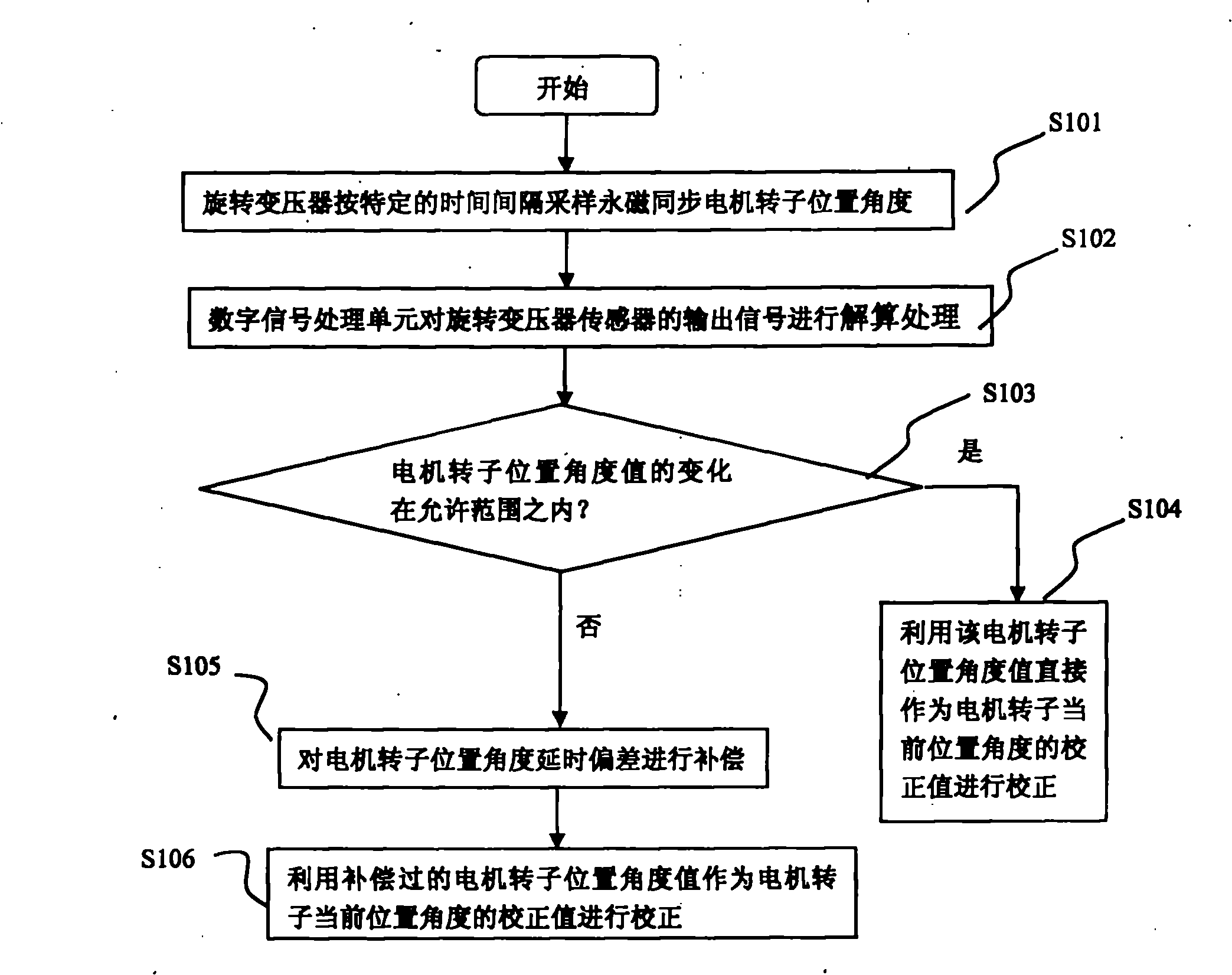
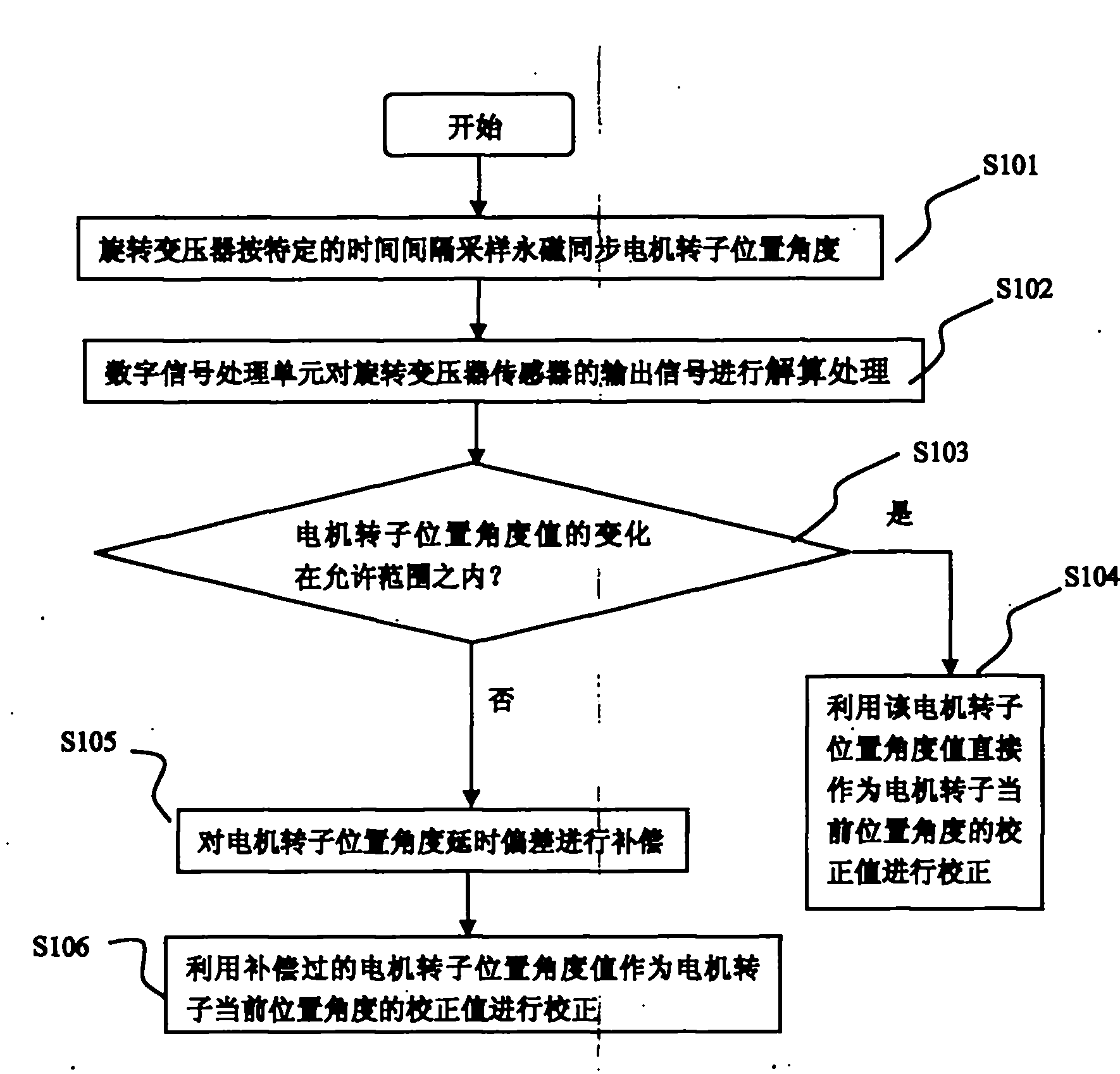
Compensation method for rotor position angle of permanent-magnet motor
InactiveCN101924510AEasy to operateGuaranteed uptimeElectronic commutatorsDigital signal processingTime delays
The invention provides a compensation method for the rotor position angle of a permanent-magnet motor, which can enable a permanent-magnet synchronous motor to keep on stable operation under the conditions of a high speed and large rotary transformer errors. The method specifically comprises the following steps: sampling the rotor position angle of the permanent-magnet synchronous motor by using a rotary transformer coaxial with the permanent-magnet synchronous motor at a specific time interval, resolving output signals of a rotary transformer sensor by using a digital signal processing unit after each sampling operation, and judging whether the variation of the rotor position angle of the motor is within the allowed range; if so, directly using the rotor position angle value of the motor as a correction value of the current rotor position angle of the motor; and if not, calculating the correction value of the current rotor position angle of the motor based on the angular speed of the motor in the last sampling operation and the time interval between two consecutive sampling operations, and compensating for the time delay deviation of the rotor position angle of the motor by using a processor.
Owner:CHERY AUTOMOBILE CO LTD
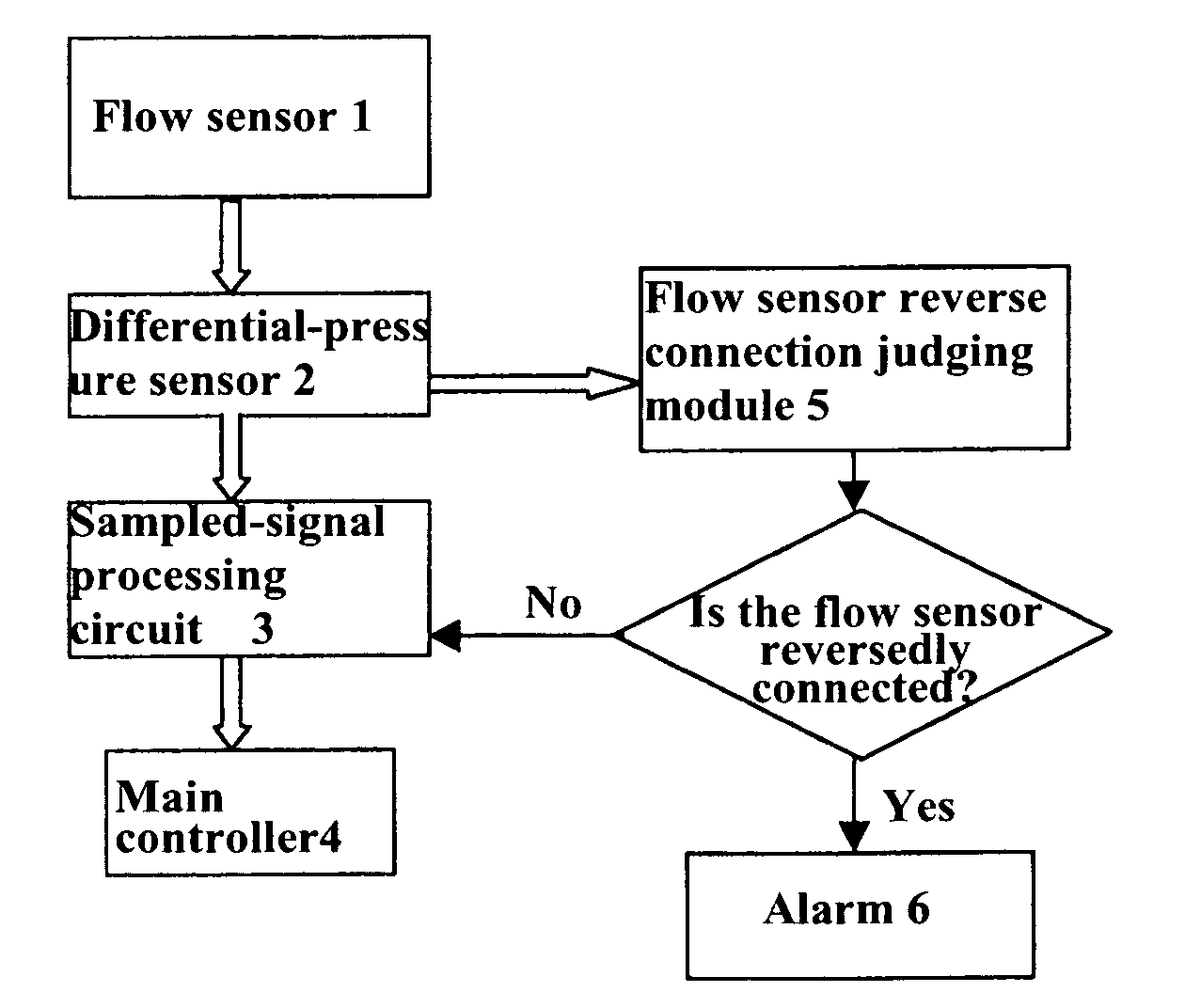
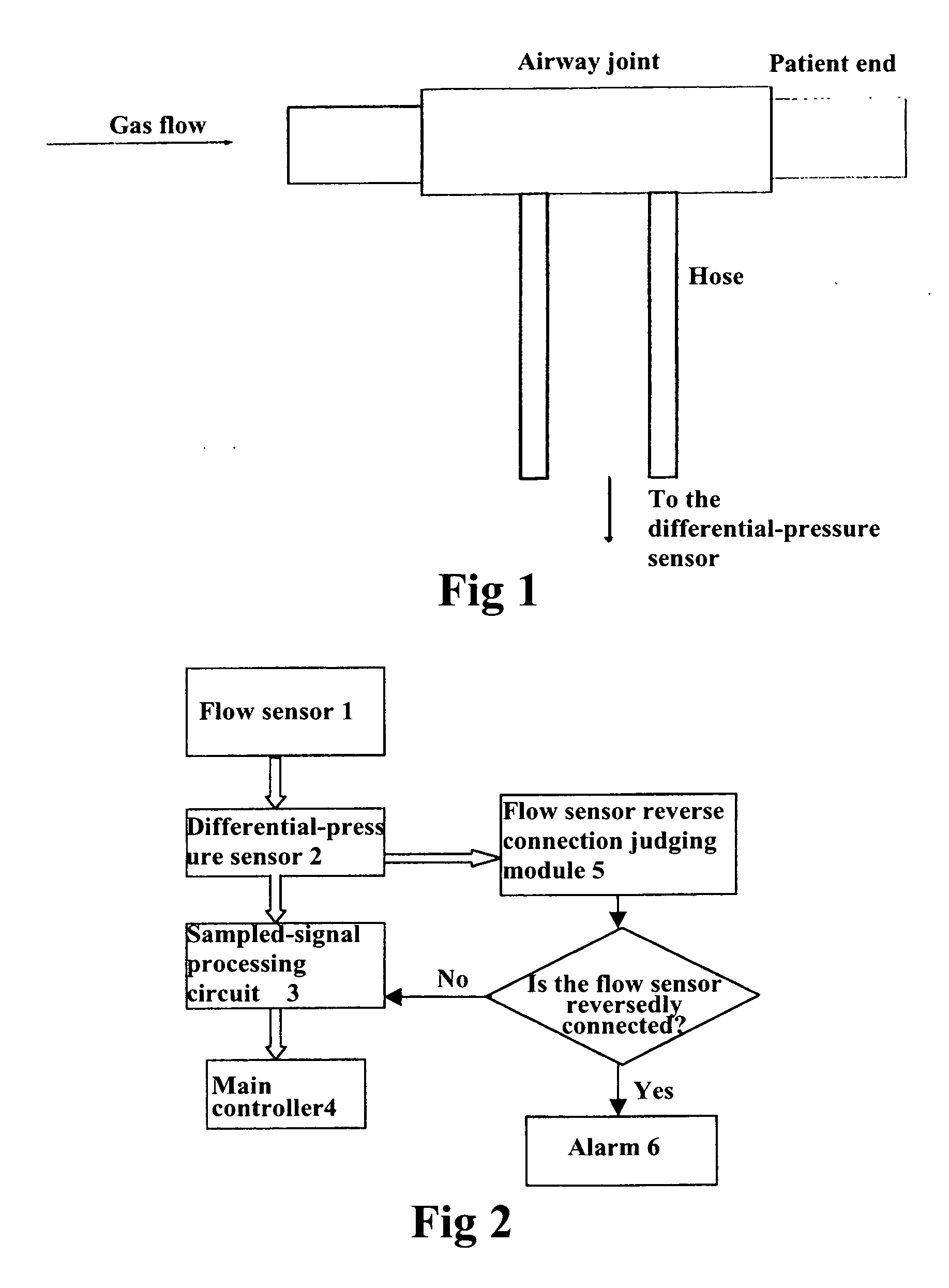
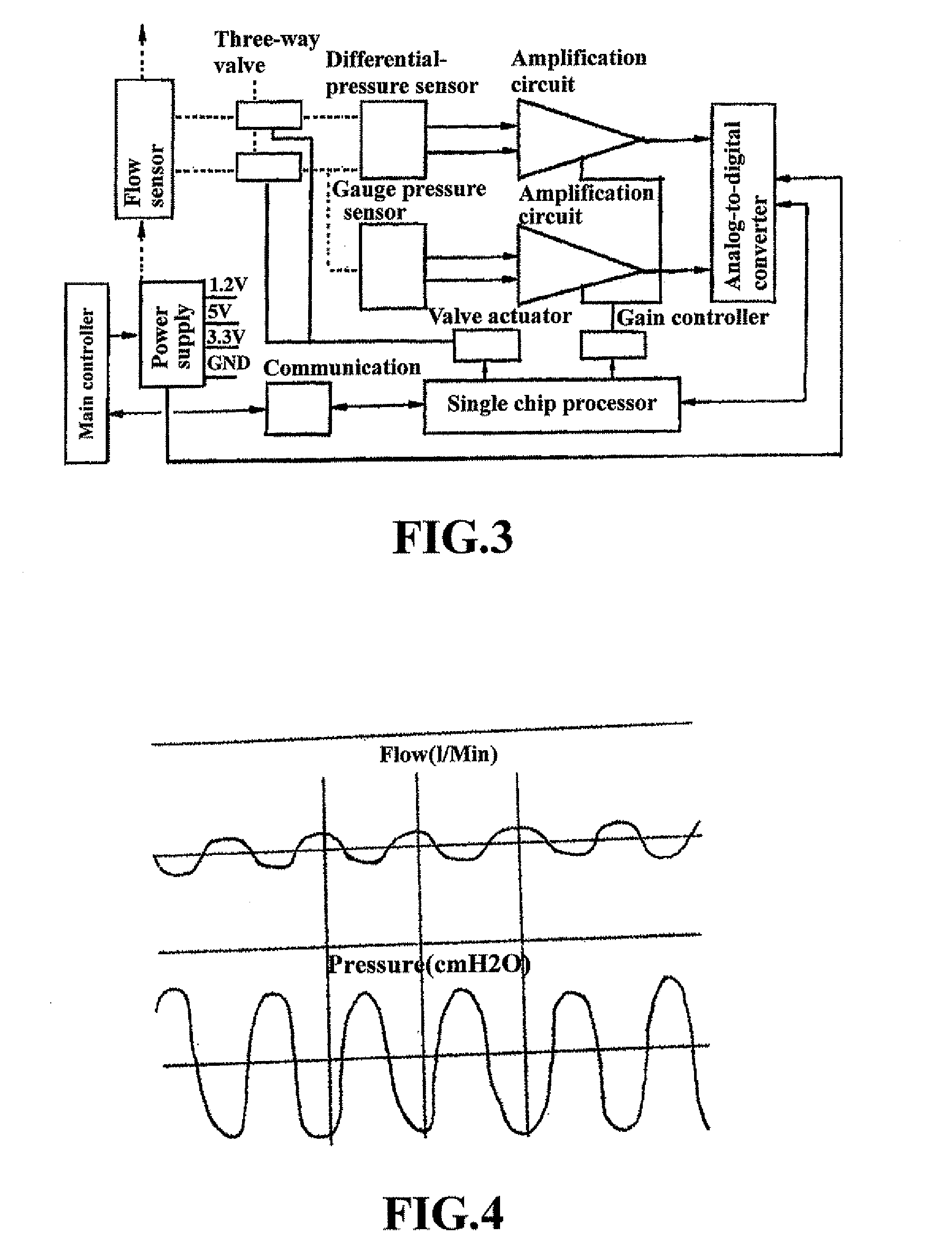
Method for judging the reverse connection of a flow sensor and a respiratory mechanics measuring module used therein
ActiveUS20070181127A1Reduce manufacturing costImprove efficiencyRespiratorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesEngineeringReverse connection
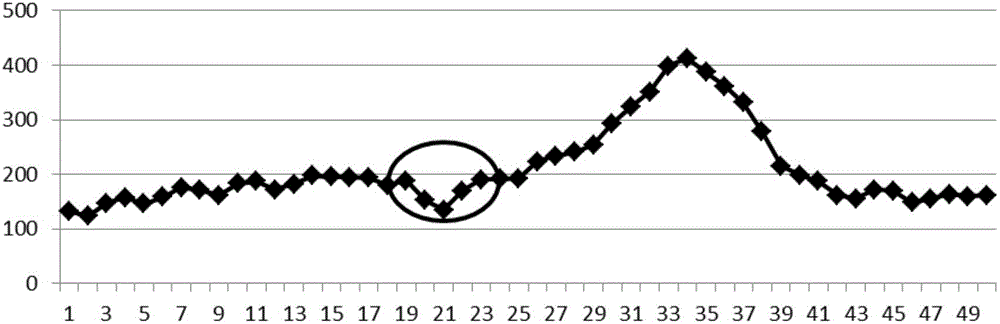
A method for judging the reverse connection of a flow sensor comprises the steps of: collecting a time sequence of pressure intensity x1, x2, x3 and x4 at four consecutive sampling points of time and the flow value S corresponding to that time sequence as basis for judgment; calculating three variables dx1=x1−x2, dx2=x2−x3 and dx3=x3−x4; judging a reverse connection of the flow sensor and giving an alarm signal when any one of the two instances appears: 1) x1, x2 and x3 are all smaller than zero and x1 and x3 are equal to or greater than x2, and flow value S is smaller than a predetermined first threshold value f1; 2) dx1, dx2 and dx3 are all greater than zero and dx1 and dx3 are smaller than or equal to dx2, and flow value S is greater than a predetermined second threshold value f2.
Owner:SHENZHEN MINDRAY BIO MEDICAL ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Serial link scheme based on delay lock loop
InactiveUS7113560B1Efficient methodConfidenceModulated-carrier systemsCode conversionDelay-locked loopPhase state
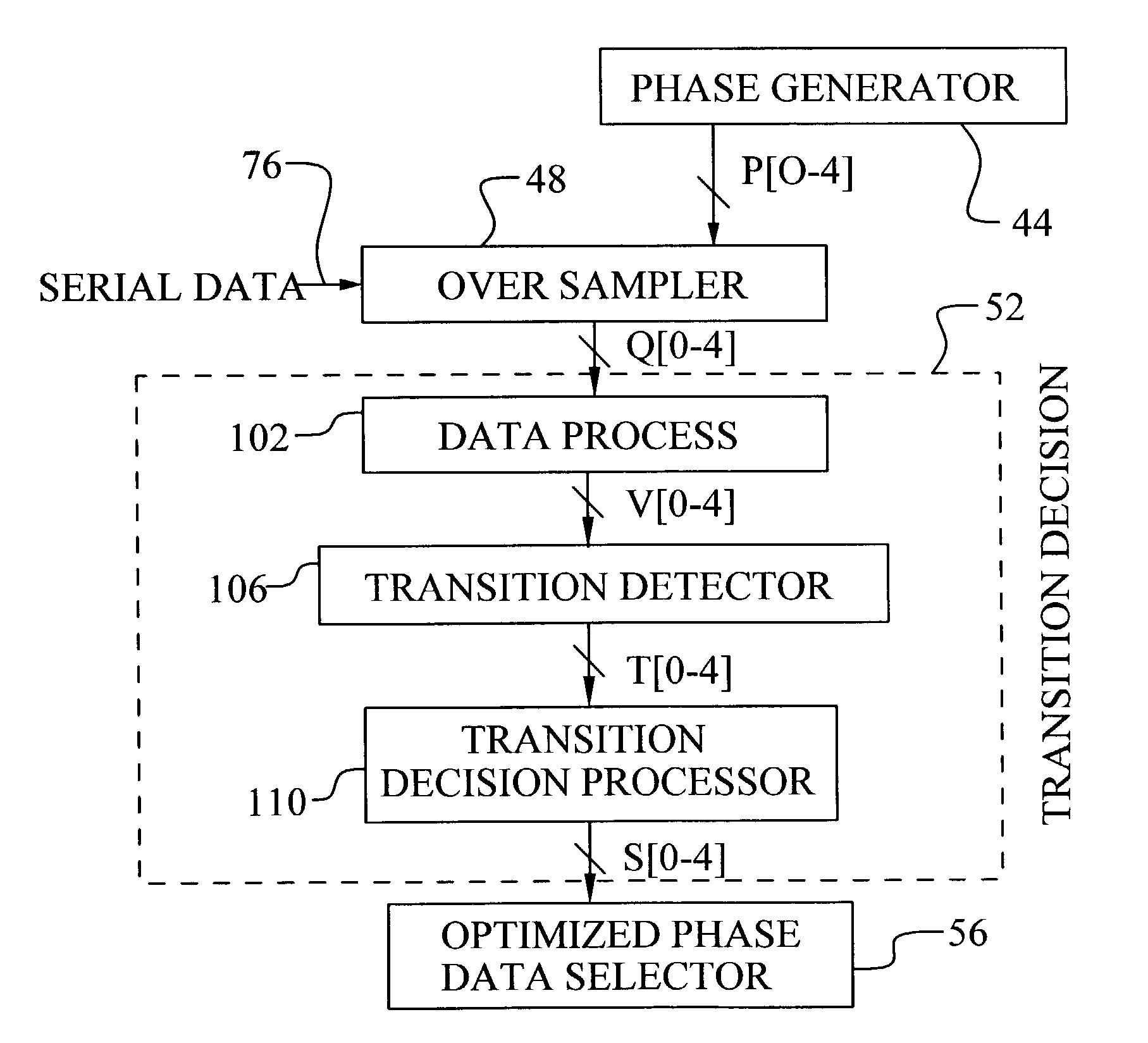
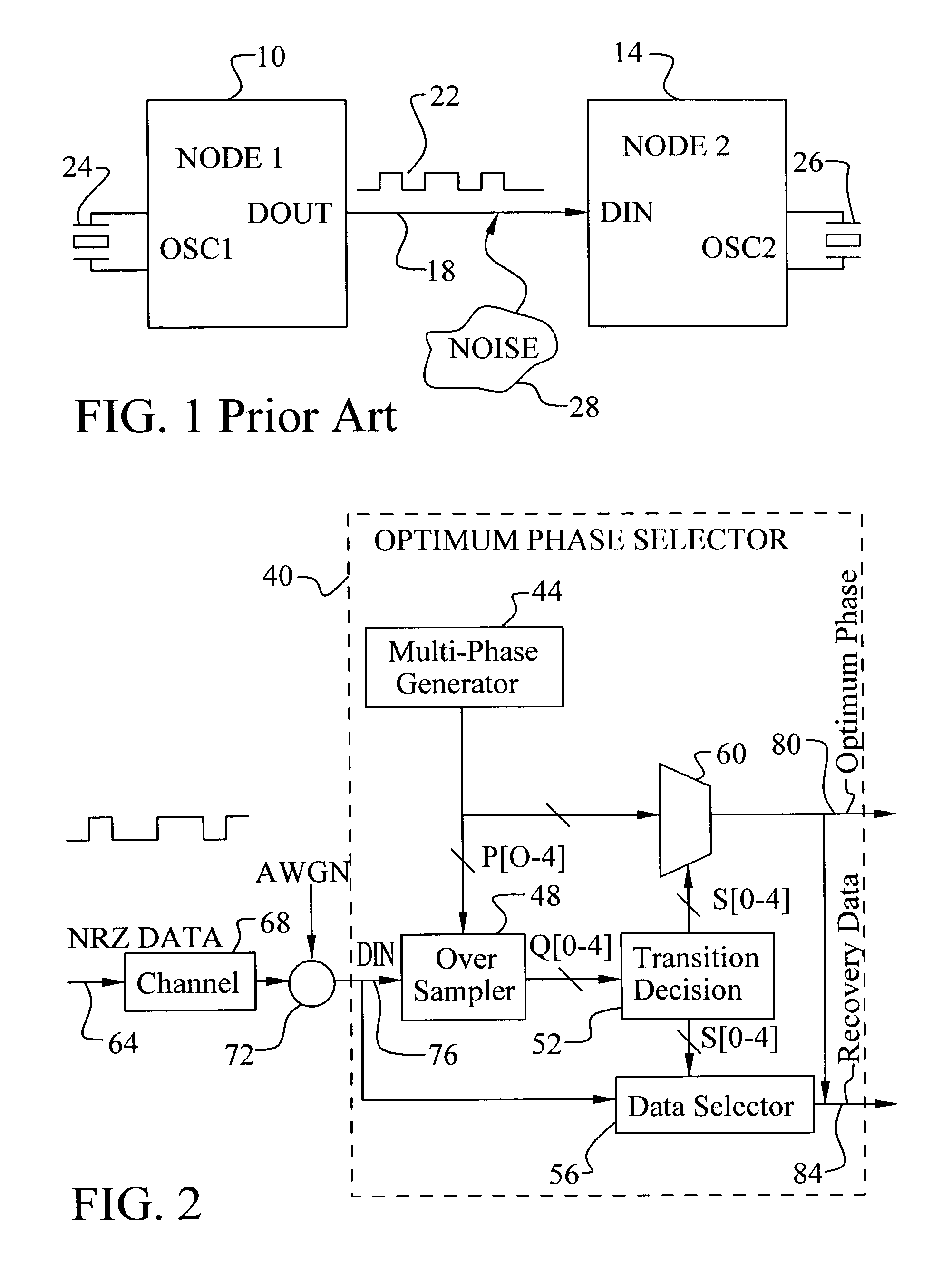
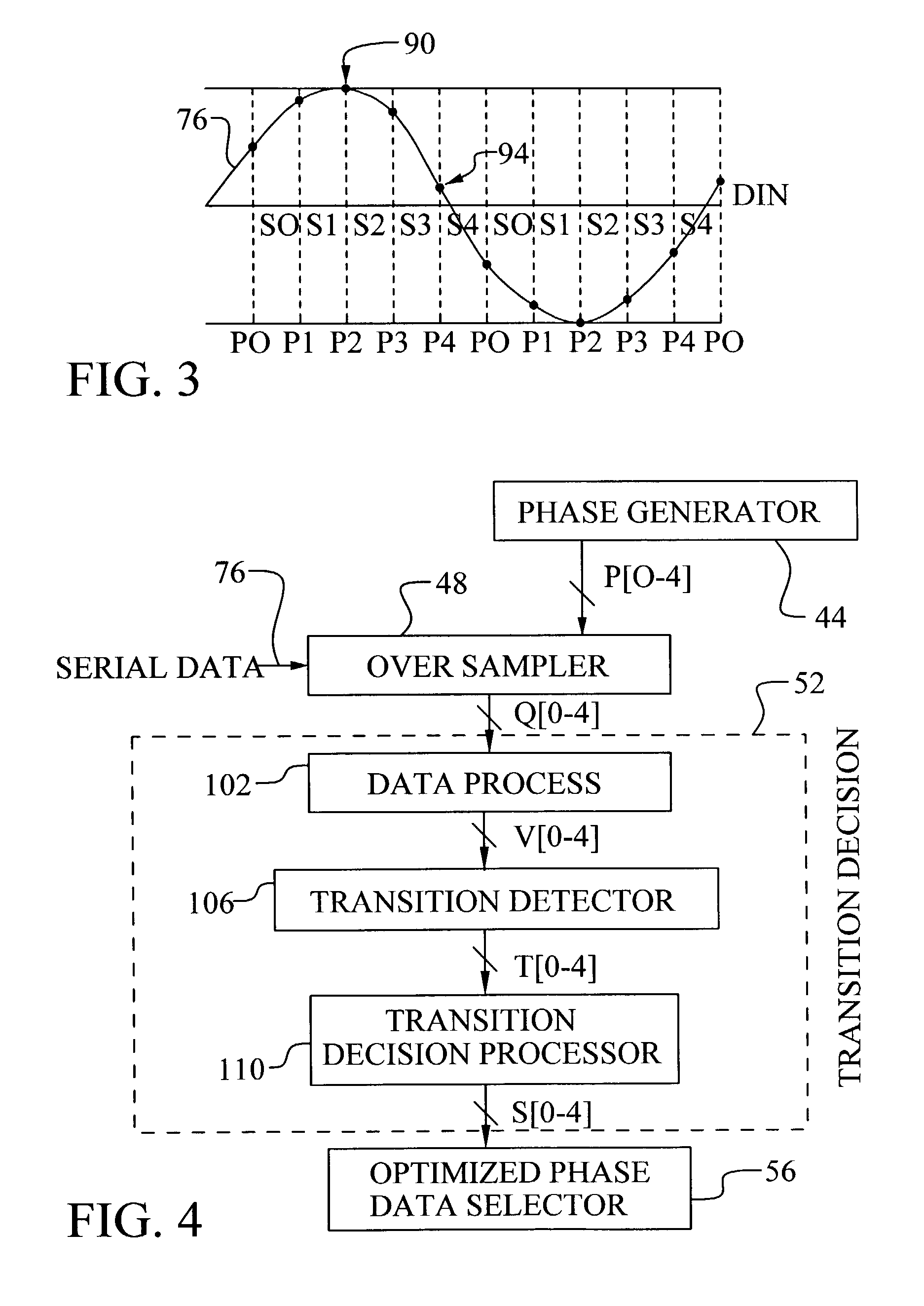
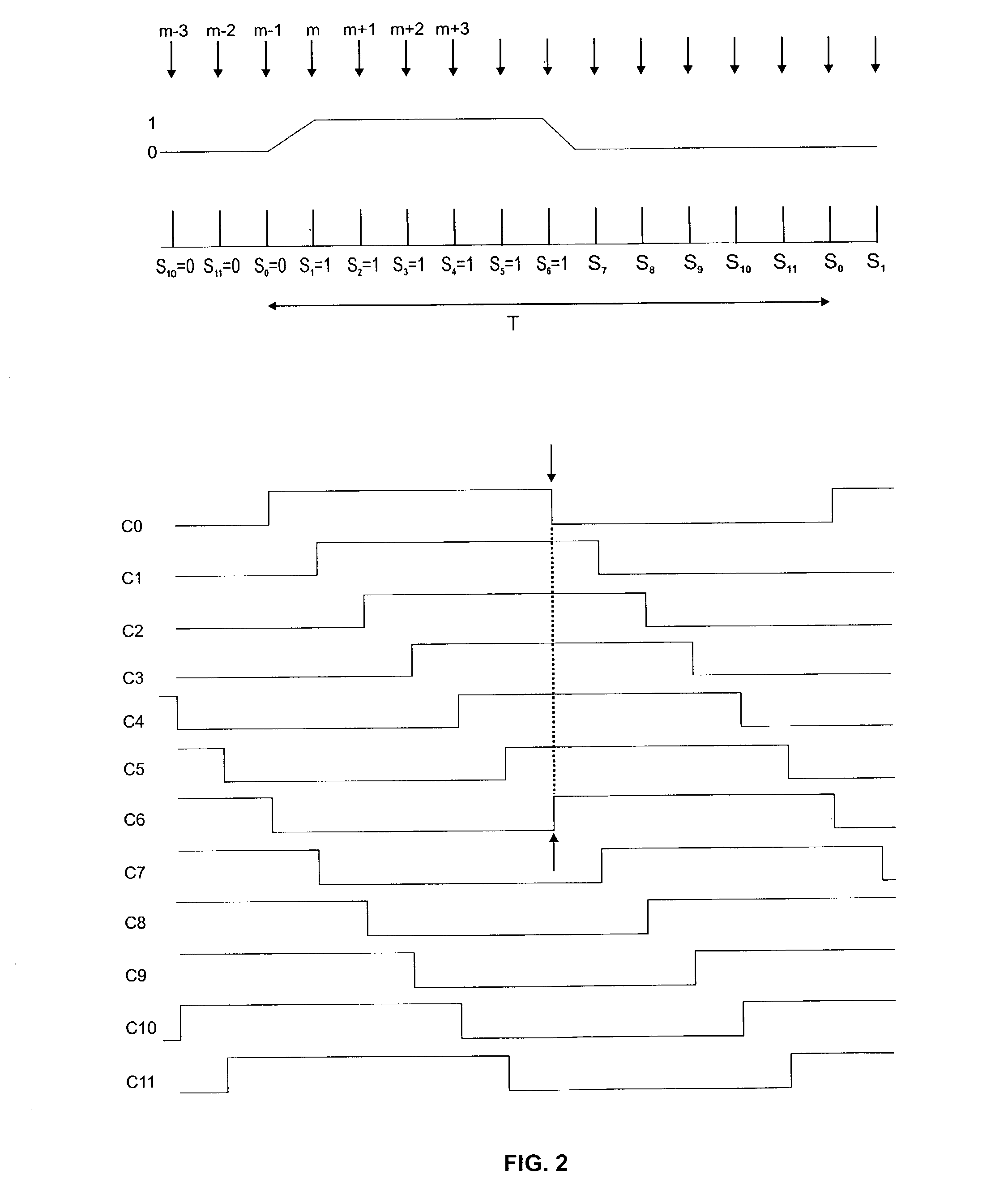
A method and circuit to produce an optimal sampling phase for recovery of a digital signal is achieved. A digital signal is over-sampled by sampling on each phase of a multiple phase clock to generate a sample value per phase. The multiple phase clock may be generated by a DLL. A voted value is determined per phase comprising a majority value of a set of consecutive sample values. Transition phases are sensed. A transition phase is defined as two consecutive voted phases comprising different values. The transition phases are compared to a stored phase state to determine a signal shift direction. The signal shift direction is filtered to generate a state update signal. The stored phase state is updated based on the state update signal. The stored phase state corresponds to an optimal sampling phase for recovery of the digital signal.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Self-adjusting hold-off trigger
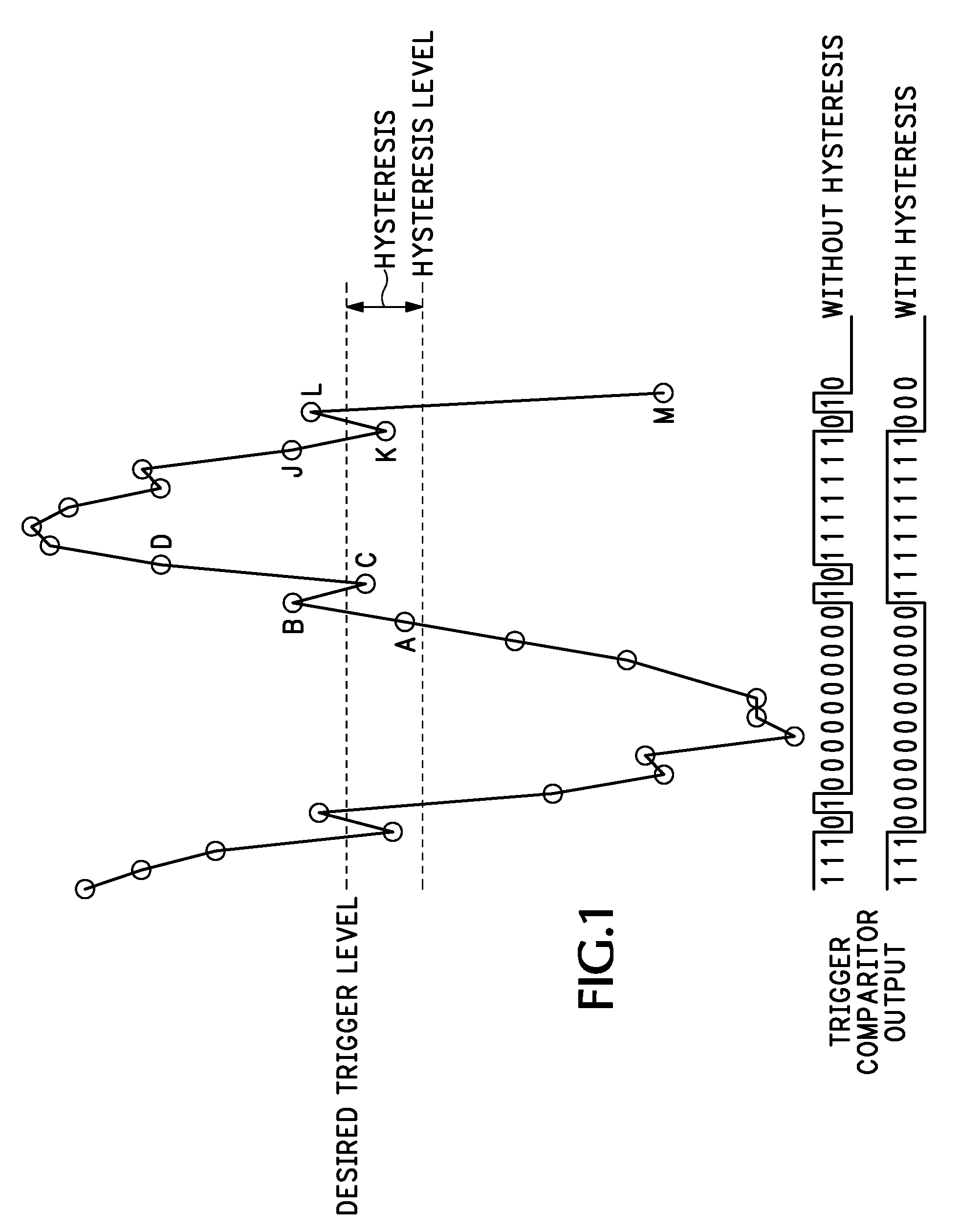
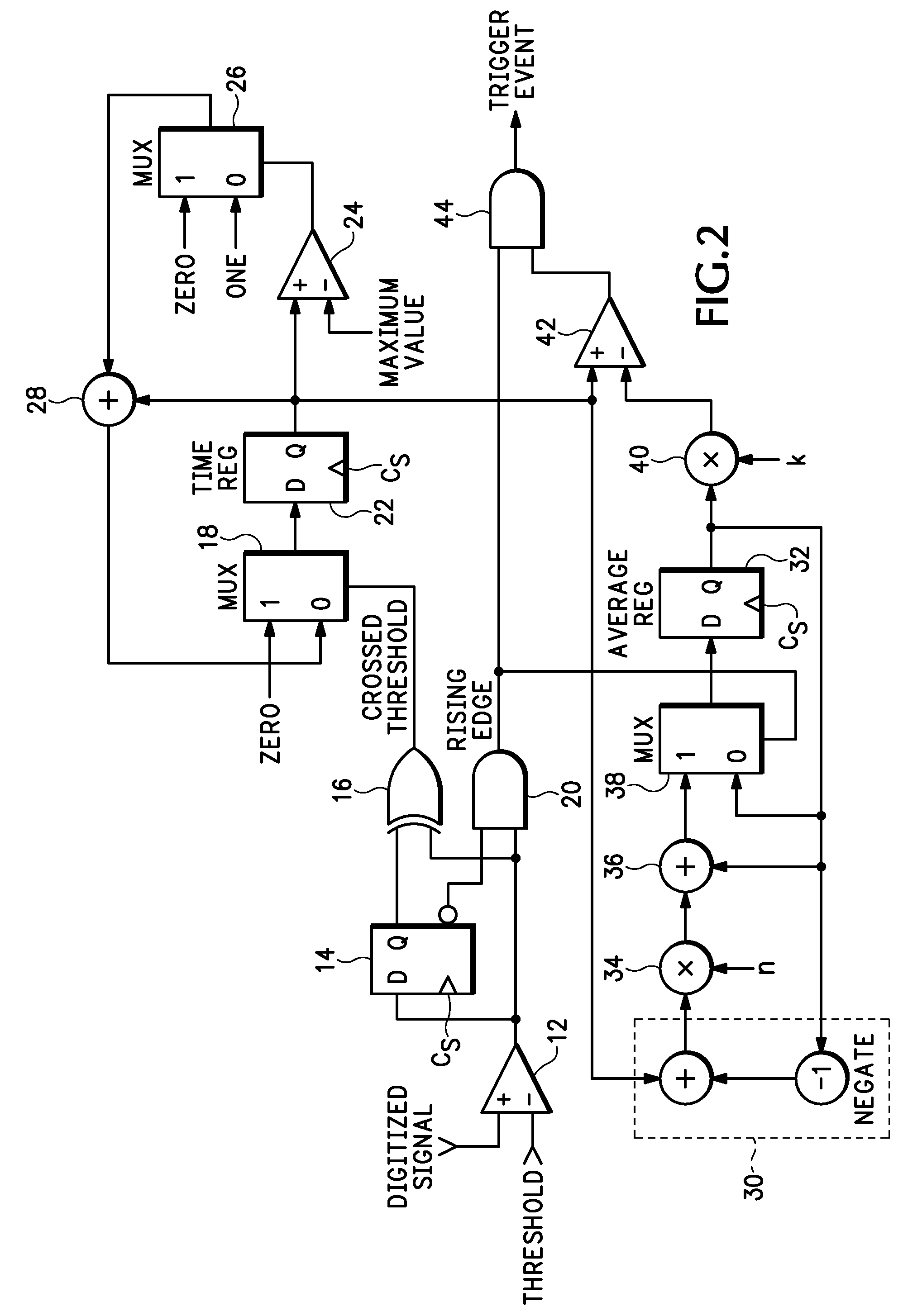
InactiveUS20080030239A1Multiple input and output pulse circuitsProduction of permanent recordsPeak valueComputer science
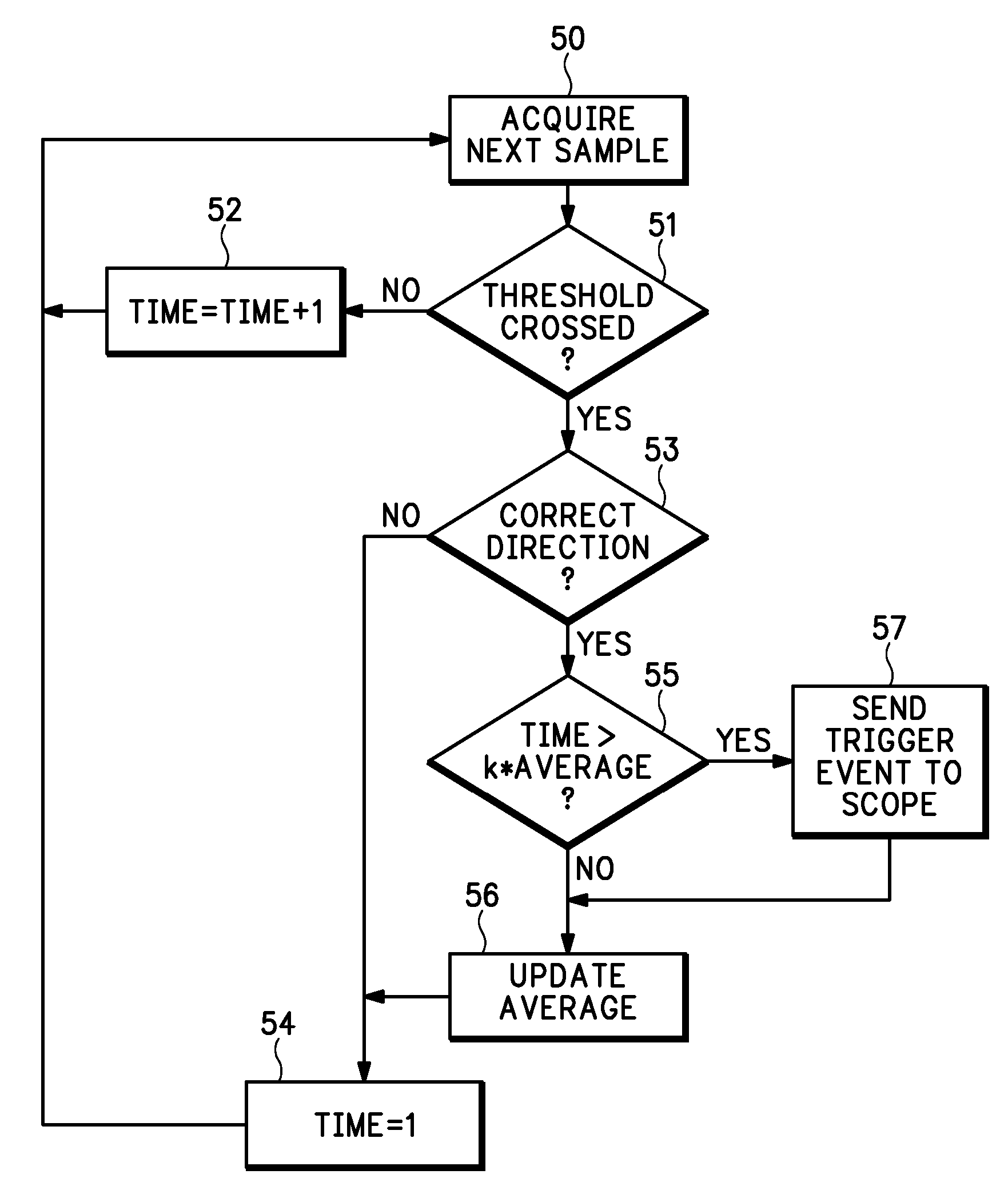
A self-adjusting hold-off trigger circuit and method detects a threshold crossing between consecutive samples of a digitized input signal as edge events, identifies the crossing as a qualified trigger event if the crossing is in a desired direction based upon trigger criteria, and provides a trigger output when the qualified trigger event occurs greater than an approximate average or peak time after a preceding edge event.
Owner:TEKTRONIX INC
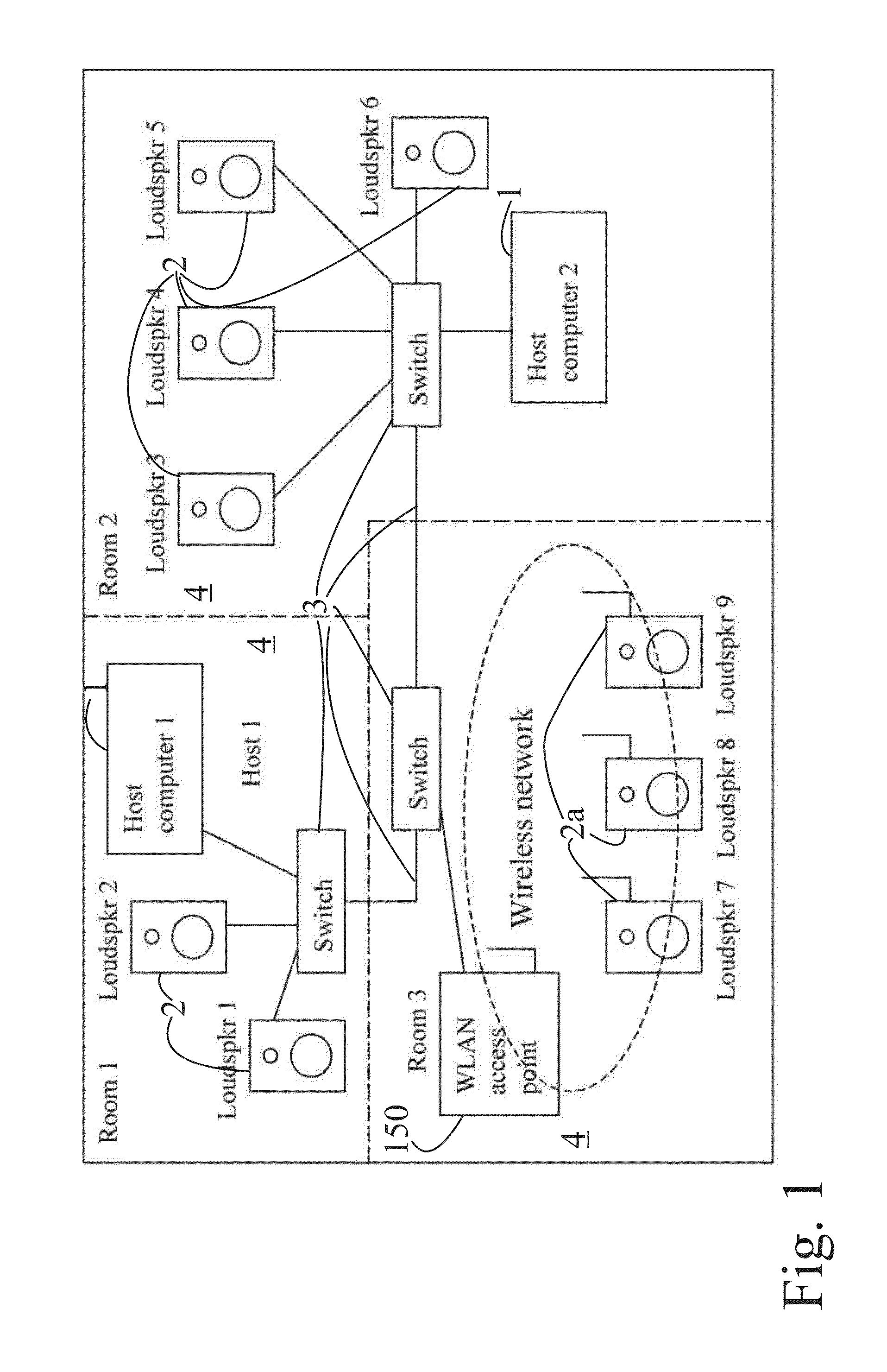
Data transfer method and system for loudspeakers in a digital sound reproduction system
ActiveUS20130336498A1Reduce defectsNew typePublic address systemsTime-division multiplexMicrocontrollerDigital data
The present publication describes a data transfer method and system in a digital sound reproduction system. The method comprises method steps for generating a digital audio stream for multiple channels in a host data source, e.g. a computer, the audio stream is formed by multiple consecutive samples, receiving the digital audio stream sent by the host data source through a digital data transmission network by several digital receivers each of which including a microcontroller with a clock, the receivers further including means for generating an audio signal. In accordance with the invention the host data source sends repeatedly a synchronization sample to at least one receiver, the receiver replies to the synchronization sample by a return sample, the host calculates a latency (T) for each receiver based on the sending time (Th1) of the synchronization sample and the reception time (Th2) of the return sample and the processing time (Tt1-Tt2) of the receiver, the host sends to the receiver information of the calculated latency (T) in combination with the time stamp the measurement time, based on this information the receiver adjusts the function of its clock, and the above synchronization steps are repeated continuously.
Owner:GENELEC
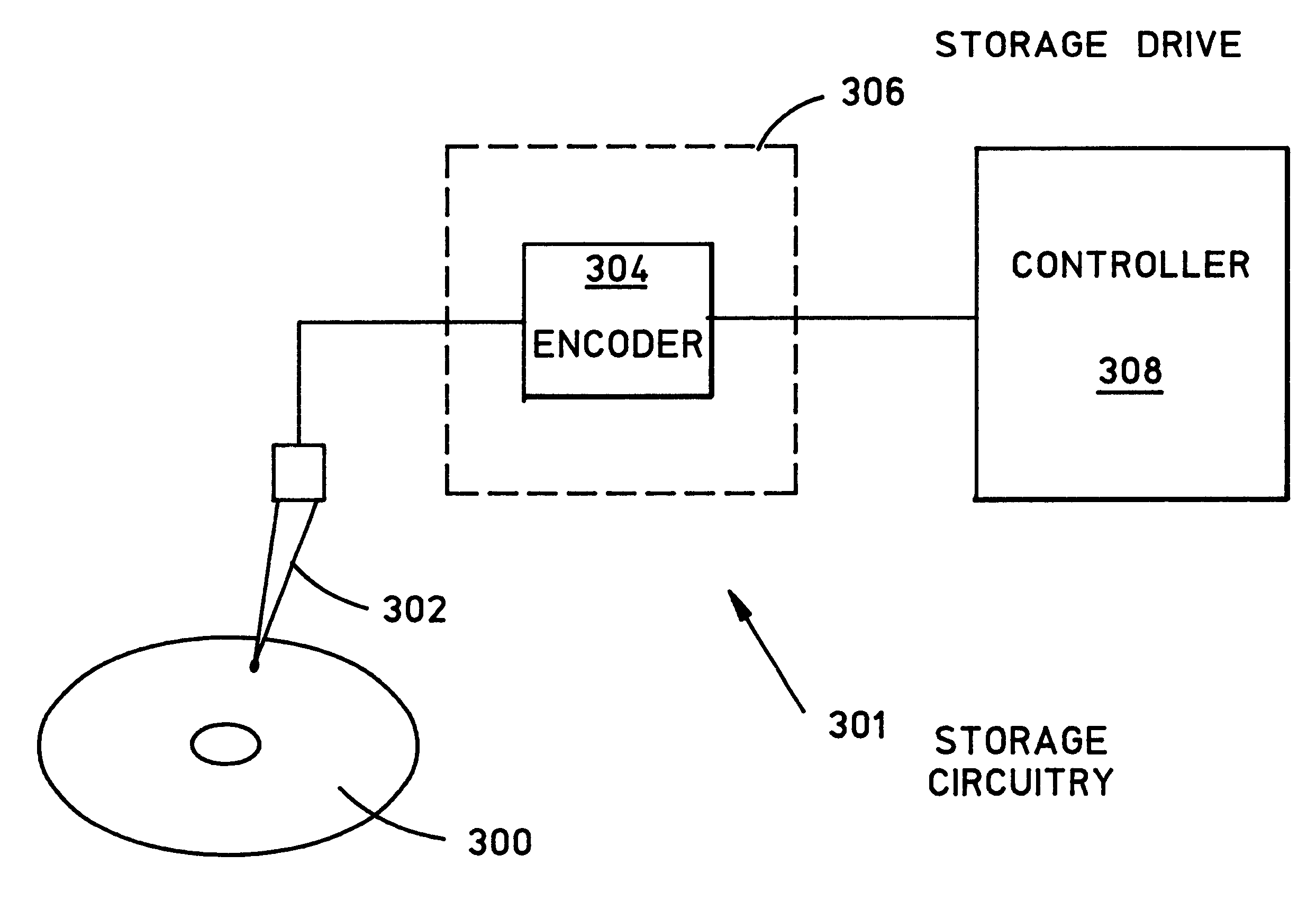
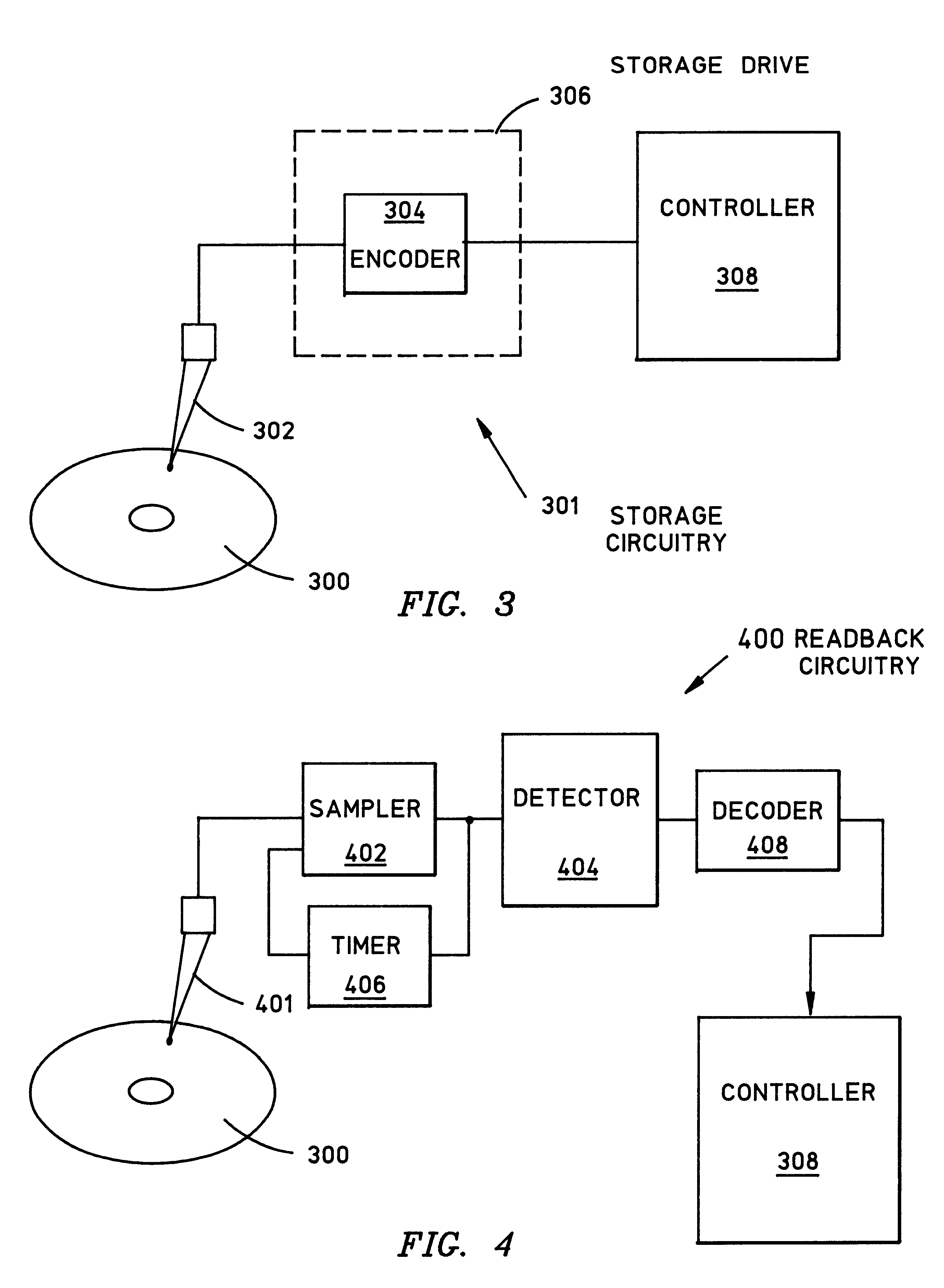
Data storage to enhance timing recovery in high density magnetic recording
InactiveUS6429986B1Improve storage efficiencyRecord information storageDigital recordingHigh densityBlock code
A timing recovery system encodes data while impressing recognizable patterns thereon, enabling precise timing during subsequent readback operations. An uncoded binary sequence is encoded using an m / n rate block coded sequence, incorporating a unique predetermined binary bit pattern that occurs with a selected level of frequency. The encoded sequence is stored on the recording medium as a series of flux transitions. To read back the stored data, a read head measures the flux transitions stored on the medium and generates a representative analog waveform. A sampler samples the waveform in accordance with a timing scheme provided by a timing circuit. The timing circuit adjusts the timing of the samples to ensure that the analog waveform is sampled at appropriate times to yield the most accurate results. The timing circuit evaluates two consecutive samples to identify samples associated with features of the analog readback waveform that corresponds to the predetermined bit patterns. Identified samples are then compared to determine whether timing of samples should be advanced, retarded, or retained with respect to the analog waveform. After a detector translates samples into an enclosed binary bit stream, a decoder decodes the detector's binary bit stream by revising the original encoding process, recreating the original encoded binary sequence.
Owner:LINKEDIN
Self-synchronization longitudinal current differential protection method suitable for power transmission line
ActiveCN107359602AAchieve synchronizationSimple and reliable protection methodEmergency protective circuit arrangementsTime informationData synchronization
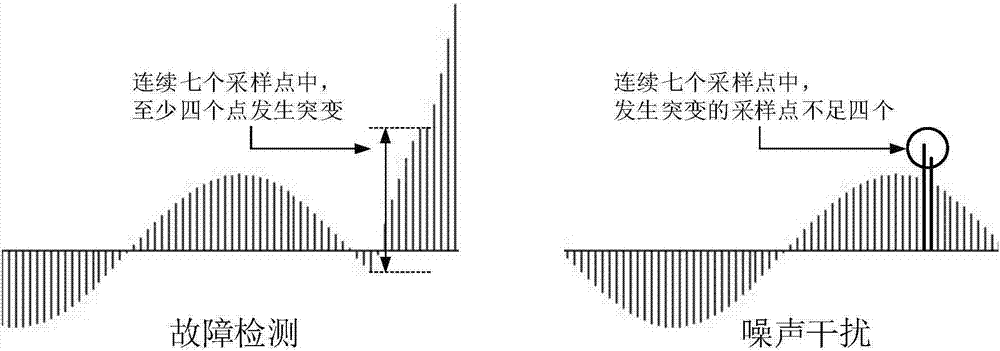
The present invention discloses a self-synchronization longitudinal current differential protection method suitable for a power transmission line. The method includes the following steps that: fault condition detection and fault time point extraction are realized according to the fault features of the line; with the fault time points of two ends of the protected line adopted as time reference, current data are synchronized, and therefore, excellent effects can be realized in the vicinity of a zero crossing point; and according to the influence of the reflection and reflection process of traveling waves, noise interference and the like, seven consecutive sampling points are detected, and it is confirmed that a fault occurs when at least four points change suddenly, and therefore, the reliability of protection and the precision of the time point of the fault are both guaranteed. The method of the invention does not depend on synchronous clocks and does not need to adopt extra equipment; and the method fully utilizes the fault features to realize the data synchronization, thereby reducing the transmission of time information. The method has the advantages of small communication traffic, high channel utilization efficiency, and the like, and can tolerate the influence of channel delay, sampling delay and the like.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
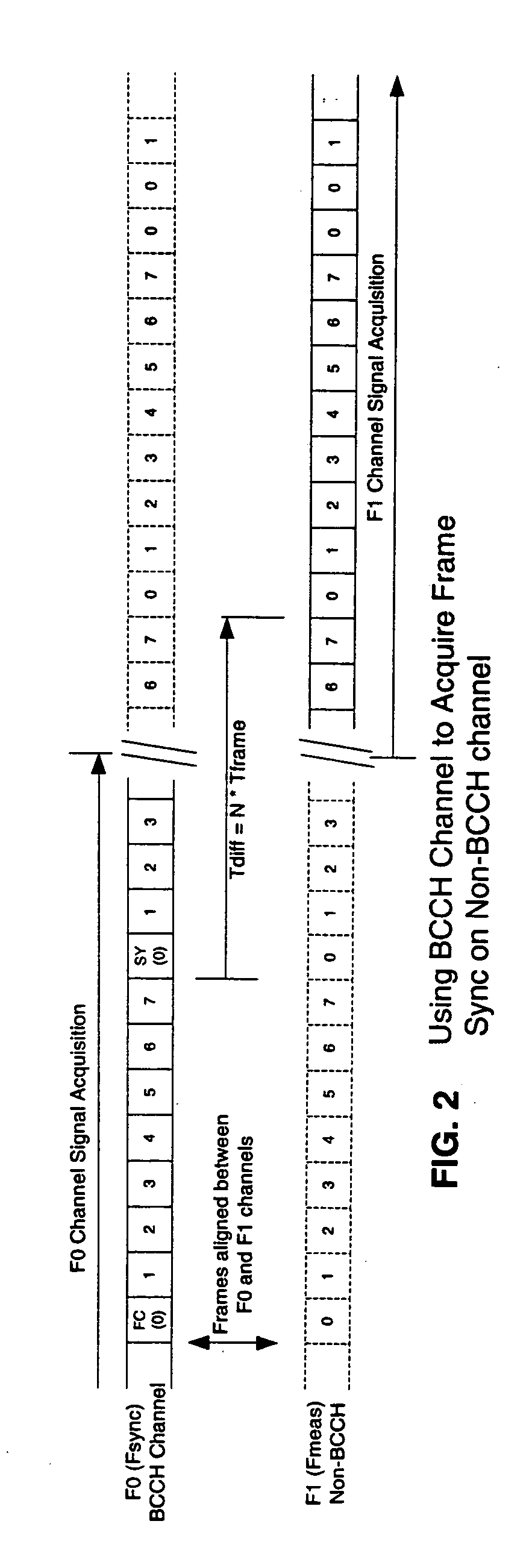
Synchronizing to GSM RF downlink signal frame timing
InactiveUS20050238060A1Time-division multiplexRadio transmission for post communicationTime rangeCONSECUTIVE SAMPLE
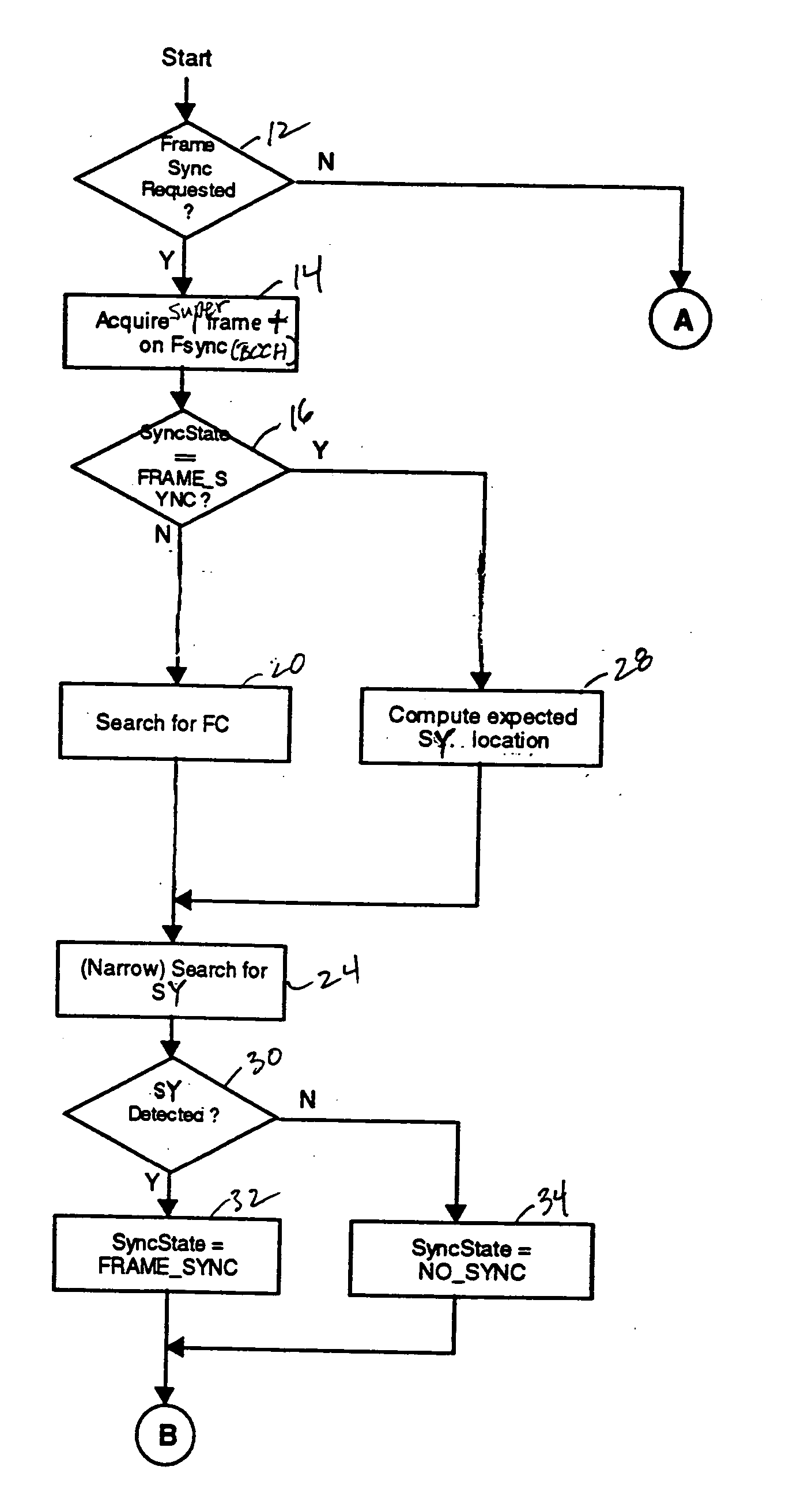
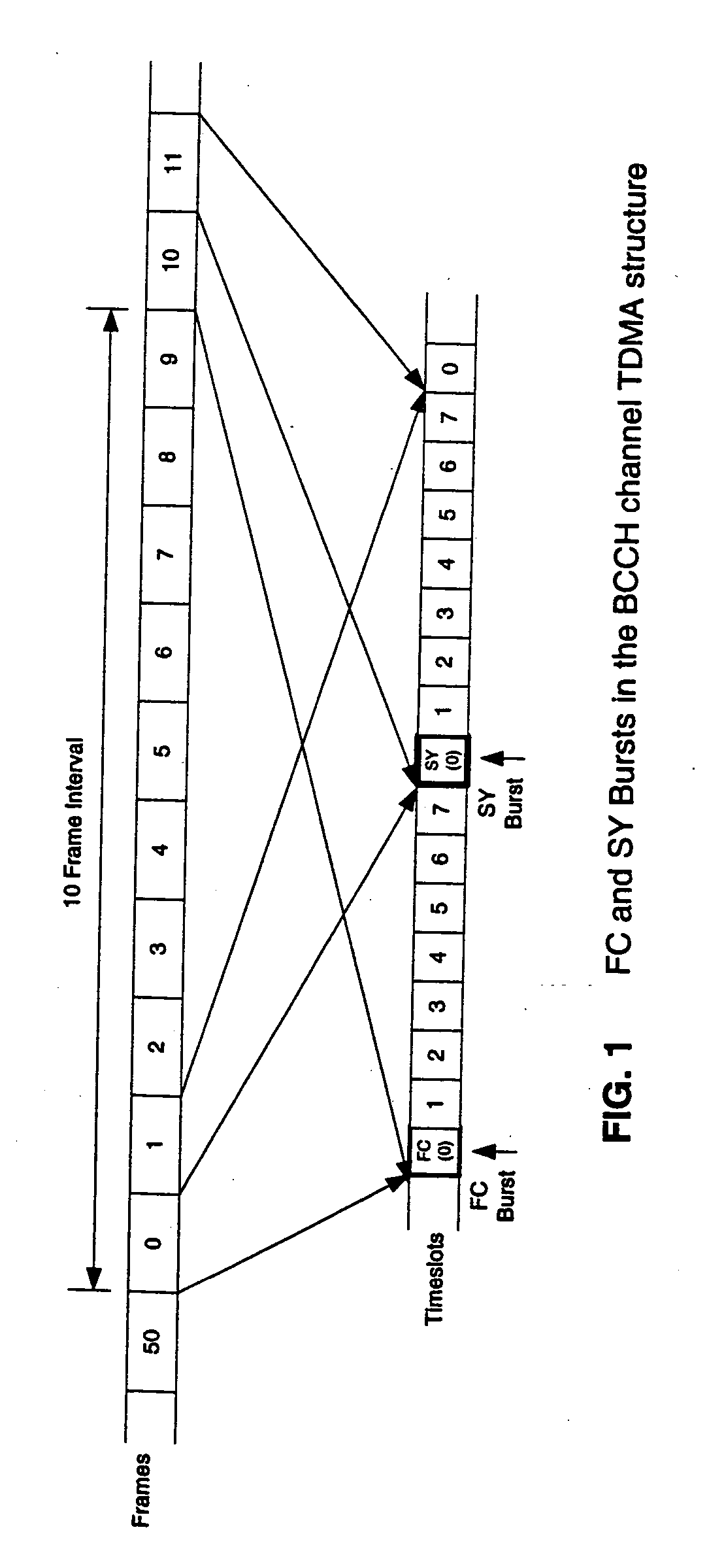
A method of synchronizing to GSM RF downlink signal frame timing includes acquiring a continuous sample data record from a base RF channel (BCCH) of the RF downlink signal that encompasses multiple frames of the GSM RF downlink signal to guarantee inclusion of synchronization frames. The location of a frequency correction burst within the sample data record is searched for and, once the frequency correction burst location is found, a synchronization burst is searched for within a limited time range about a predicted location to determine a precise indication of frame location. With frames precisely located, data may be extracted from any desired slot of the frames from the continuous sample data record, or of frames in a continuous sample data record acquired from a related measurement channel, for further measurement processing.
Owner:KUNTZ THOMAS L +1
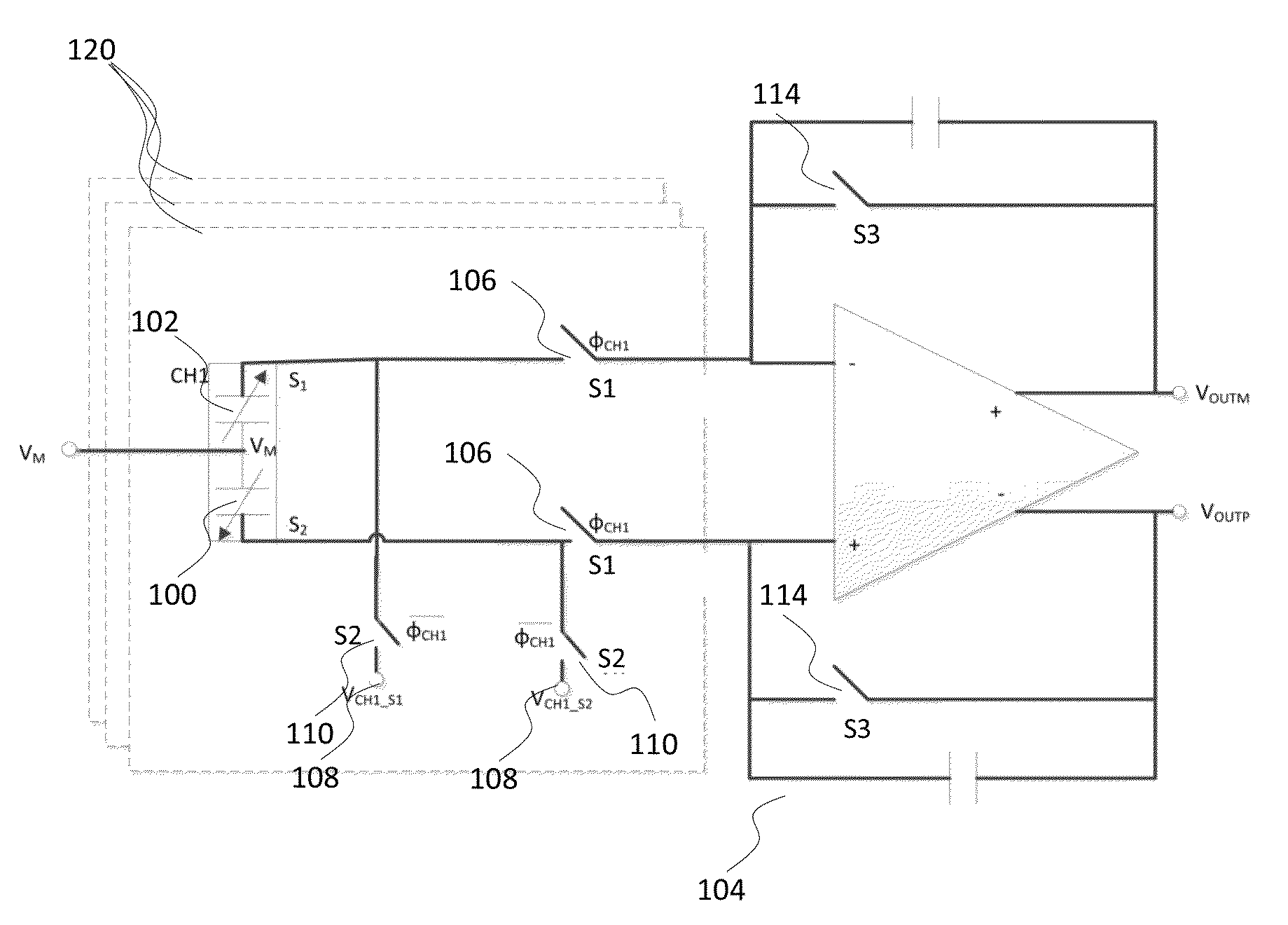
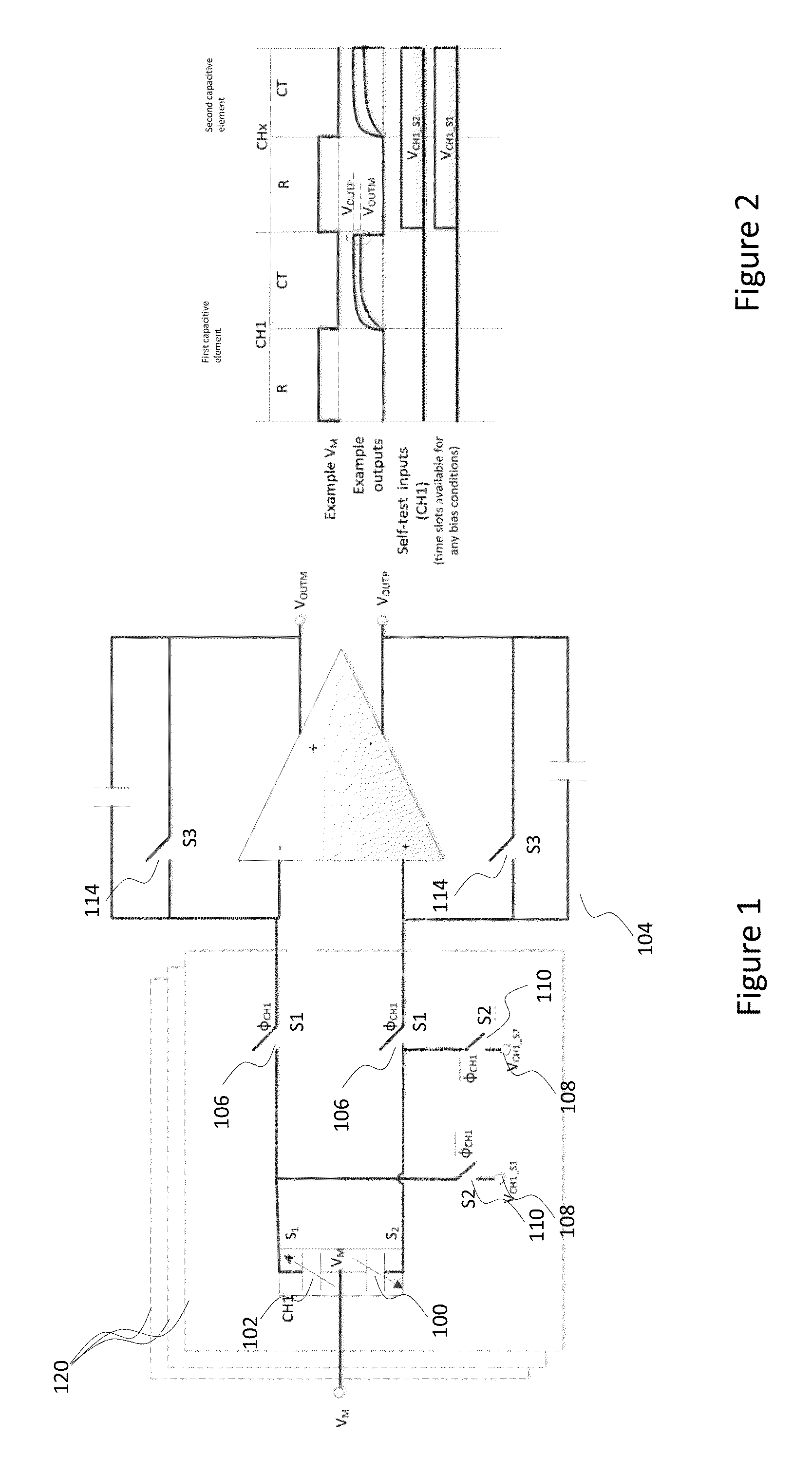
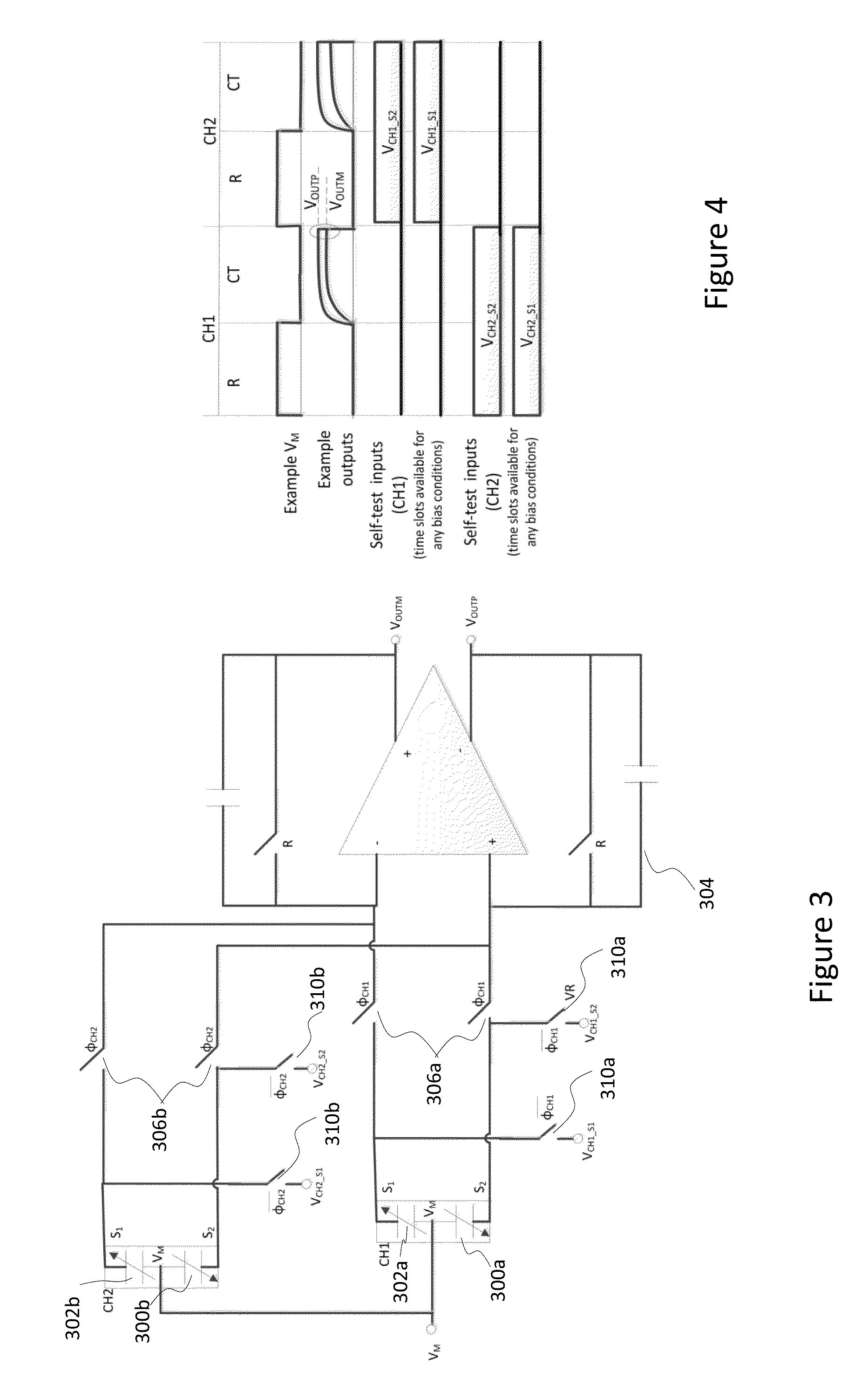
Continuous self-test in capacitive sensor
ActiveUS20160202286A1Cause parasitic effectIncrease consumptionAcceleration measurement using interia forcesElectrical testingMultiplexingElectrical polarity
A capacitive sensor device includes capacitive elements for detecting at least two inertial channels. At least one of the inertial channels comprises at least two self-test tones with distinctive fundamental frequencies. Inertial signals in the at least two inertial channels are caused by change of capacitance in the capacitive elements due to movements of rotor masses. Self-test tones are fed into at least one capacitive element under control of a self-test control module and the at least two inertial channels are temporally multiplexed to allow feeding of the self-test tones during normal operation of the capacitive sensor device. Signals in the inertial channels are processed for extracting self-test signals corresponding to the self-test tones, and the self-test signals are analyzed for self-test purposes. Alarm is triggered if multiple consecutive samples of predefined set of self-test signals indicate error with same polarity.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
Systems and methods for reducing an effect of a disturbance
InactiveUS7421354B2Noise figure or signal-to-noise ratio measurementDigital variable/waveform displaySignal onComputer science
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
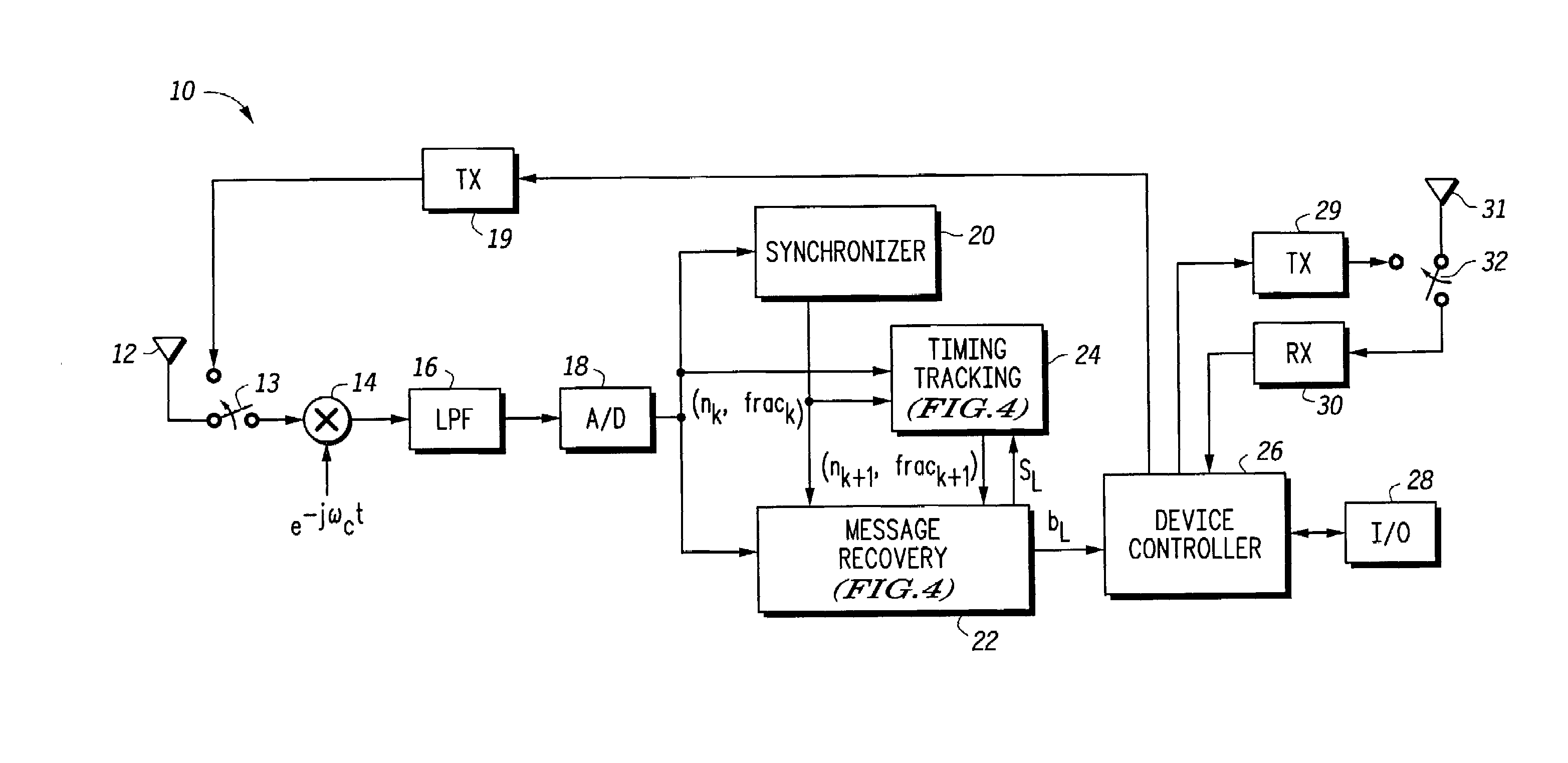
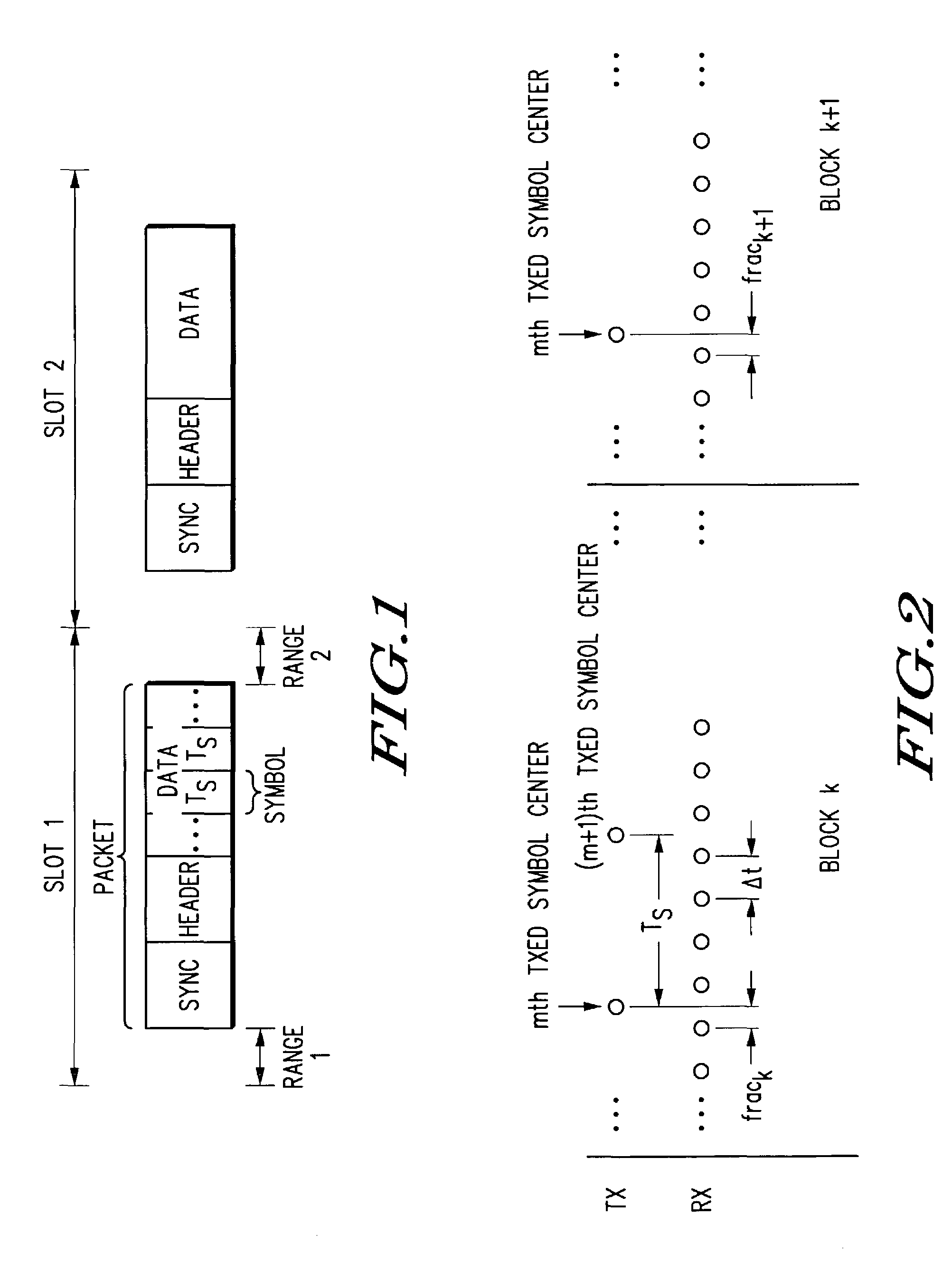
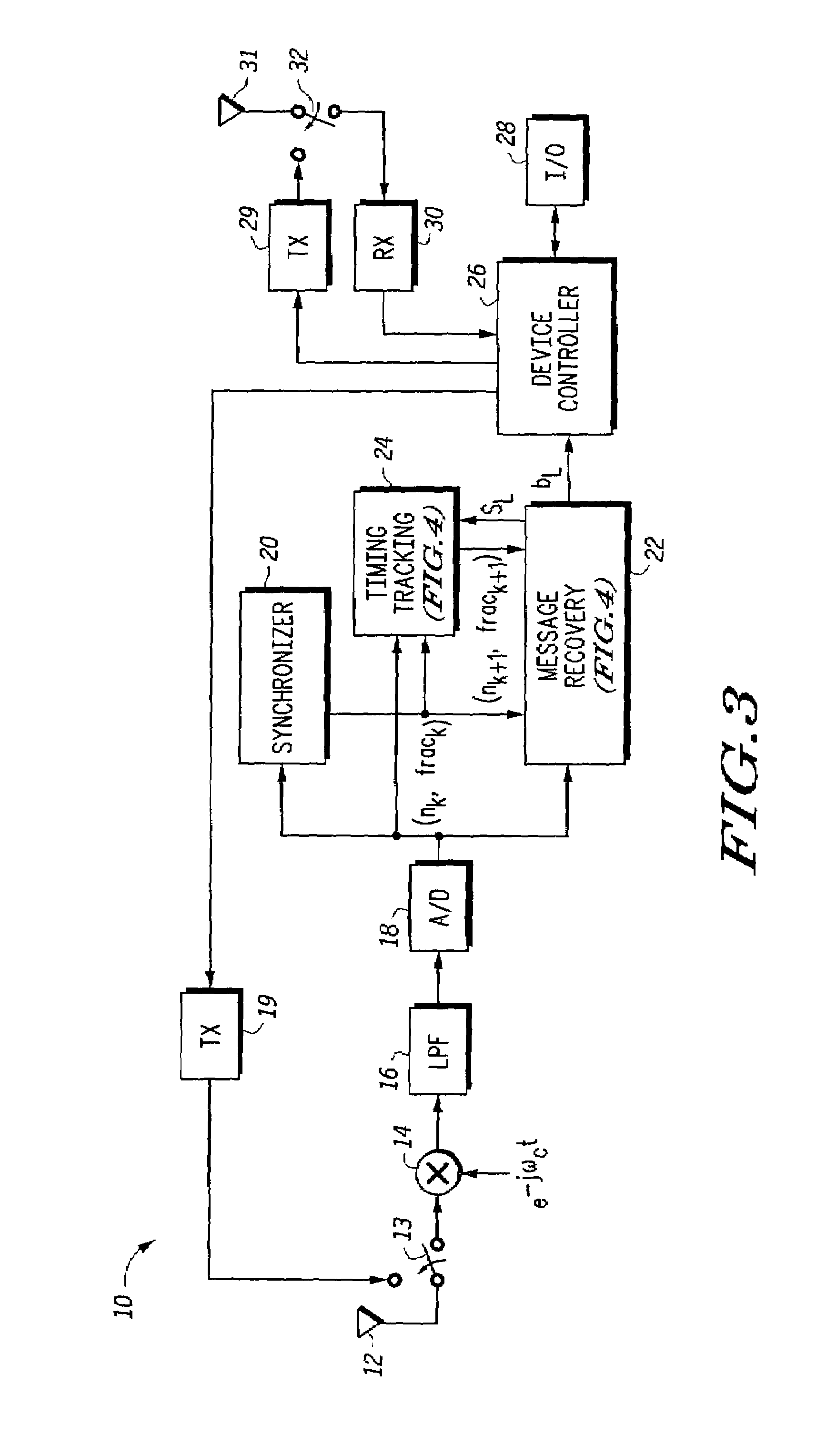
Symbol timing tracking and method therefor
A system and method in a communication device (10) uses timing tracking to correct timing drifting due to the difference in frequency of a transmitter clock and a receiver clock. With the timing tracking, correlation values of three consecutive samples are calculated using the receive signal and the recovered symbols and then summed. A timing signal, (nk, frack) is updated based upon a metric calculated from a previous correlation value, R−1, present correlation value (R0) and a next con-elation value (R+1). Adjustment of timing signal is based on the relative location with respect to the current timing of a peak of a second order polynomial curve formed by the first correlation value R−1, the second correlation value R0 and the third correlation value R+1.
Owner:NXP USA INC
A concentration gradient diffusion sampling device for an online detection system of a bioreactor
The invention relates to a sampling device suitable for bioreactors such as microbial fermentation and cell culture, in particular to a concentration gradient diffusion sampling device, which is based on the concentration difference caused by the concentration difference of each component in the liquid in the solution on both sides of the separation membrane. The principle is to form a concentration gradient distribution of components (measured samples) in the sampling pipeline, and the flux or rate of diffusion follows Fick's law. Using this device to sample the samples in the bioreactor has the advantages of effectively preventing sampling pollution and good safety; there is no filtration process of the solution, the membrane pores should not be blocked, and the stability of continuous sampling is high; the sample components are in the sampling pipeline A gradient distribution is formed, which can be measured without cumbersome dilution, making the online detection system simpler, with faster measurement speed and wider linear range, and is especially suitable for on-line detection of various flow injection analysis systems.
Owner:BIOLOGY INST OF SHANDONG ACAD OF SCI
Method and apparatus for high-speed synchronous digital acquisition derived in real -time from analog samples
InactiveUS6912474B2Increase chanceTwo-way loud-speaking telephone systemsTelevision system detailsDigital clockComputer science
A method and apparatus for real-time derivation of precise digital clock edges and synchronous logic samples from a digital signal having a clock channel and at least one data channel acquires a plurality of temporally offset analog samples during each of a sequence of sample periods and from consecutive samples where there is a logic level transition estimates an edge time. From the edge times for the clock channel an offset is added and applied to the at least one data channel to determine the synchronous logic samples for the data channel at each offset clock edge time.
Owner:TEKTRONIX INC
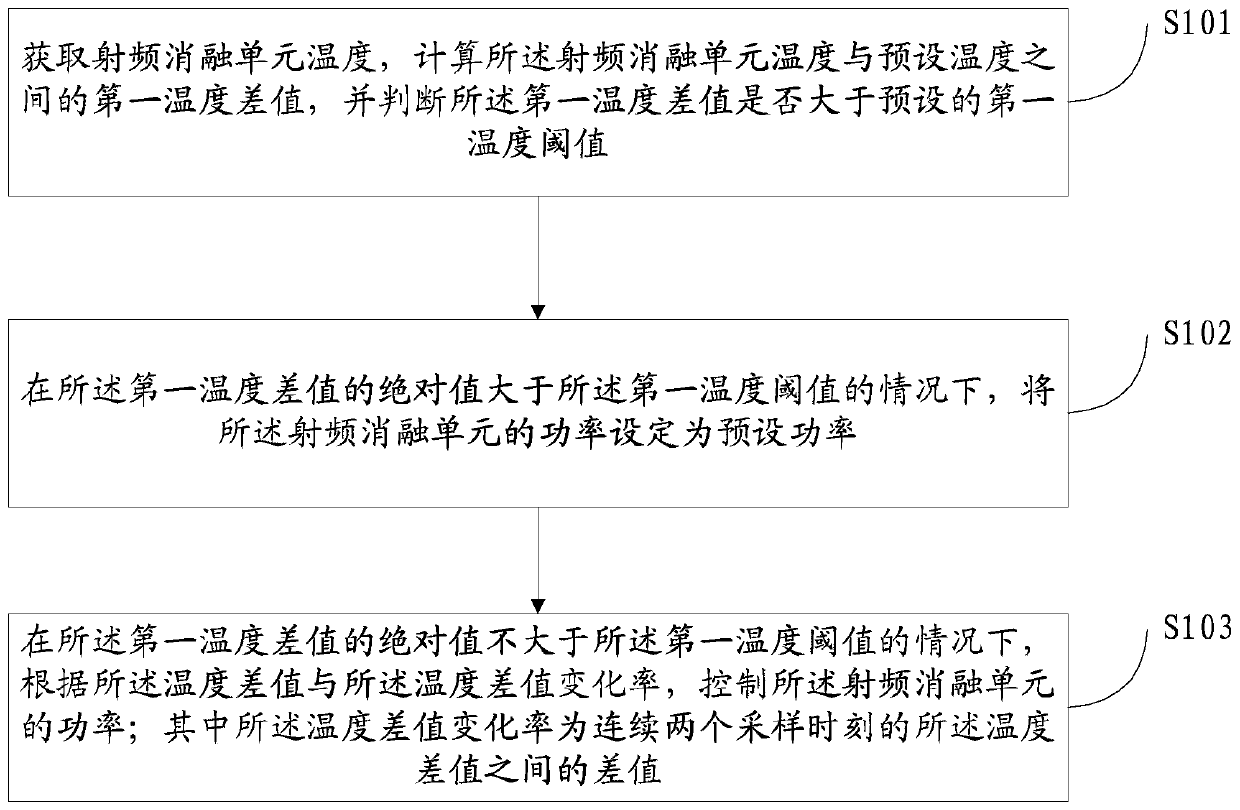
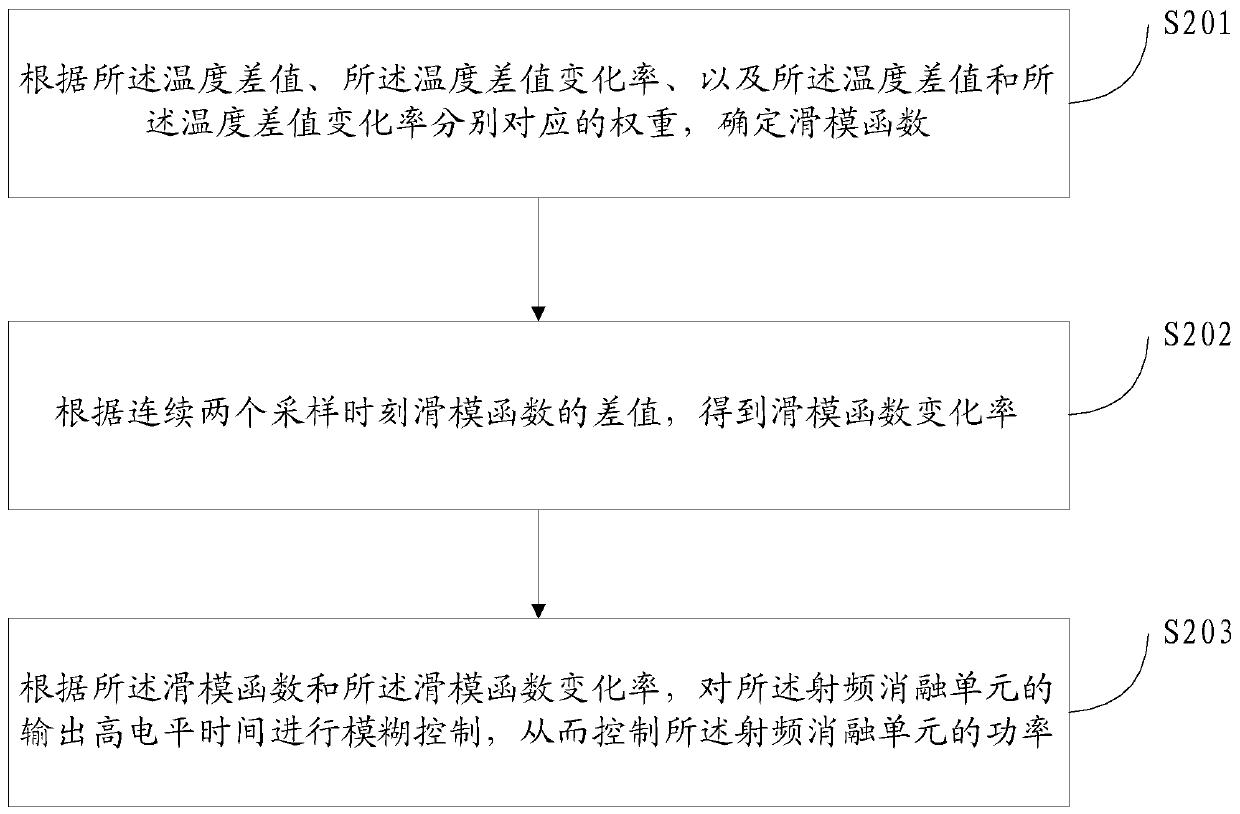
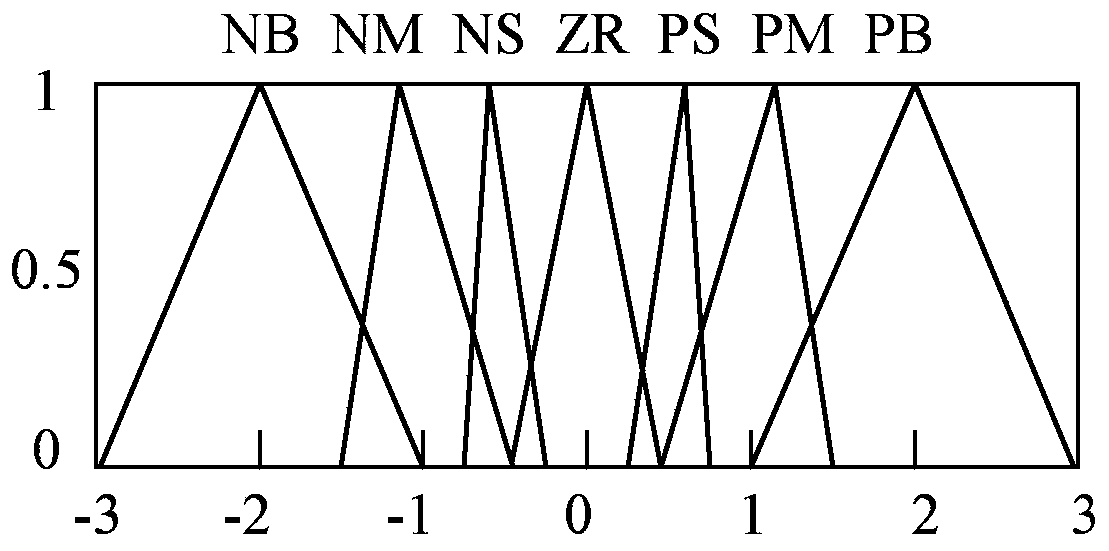
Temperature control method and device for radio frequency ablation device
ActiveCN110063787ATemperature controlGuaranteed therapeutic effectSurgical instruments for heatingTemperature controlEngineering
The invention discloses a temperature control method and device for a radio frequency ablation device, and relates to medical device technologies. The method includes the steps of acquiring a temperature of a radio frequency ablation unit, calculating a first temperature difference between the temperature of the radio frequency ablation unit and a preset temperature, and determining whether an absolute value of the first temperature difference is greater than a preset first temperature threshold; when the absolute value of the first temperature difference is greater than the first temperaturethreshold, setting the power of the radio frequency ablation unit to a preset power; otherwise, controlling the power of the radio frequency ablation unit according to the first temperature differenceand the temperature difference change rate; the temperature difference change rate is a difference between the first temperature differences of two consecutive sampling instants. The method can quickly and stably make the temperature of the radio frequency ablation device reach the set temperature range, after the set temperature range is reached, and the temperature of the radio frequency ablation device is kept stable, thereby ensuring the therapeutic effect and treatment safety of the radio frequency ablation technique.
Owner:BEIJING BOHAIKANGYUAN MEDICAL DEVICES
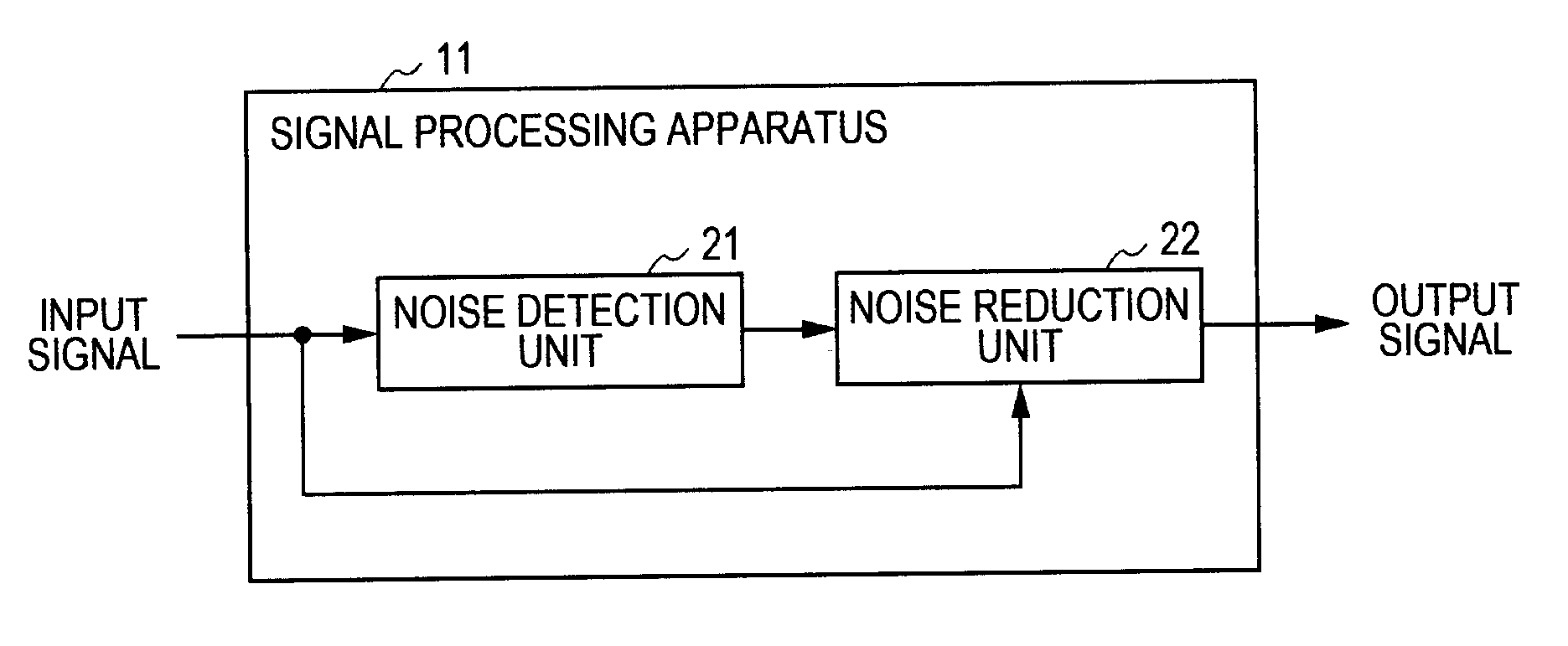
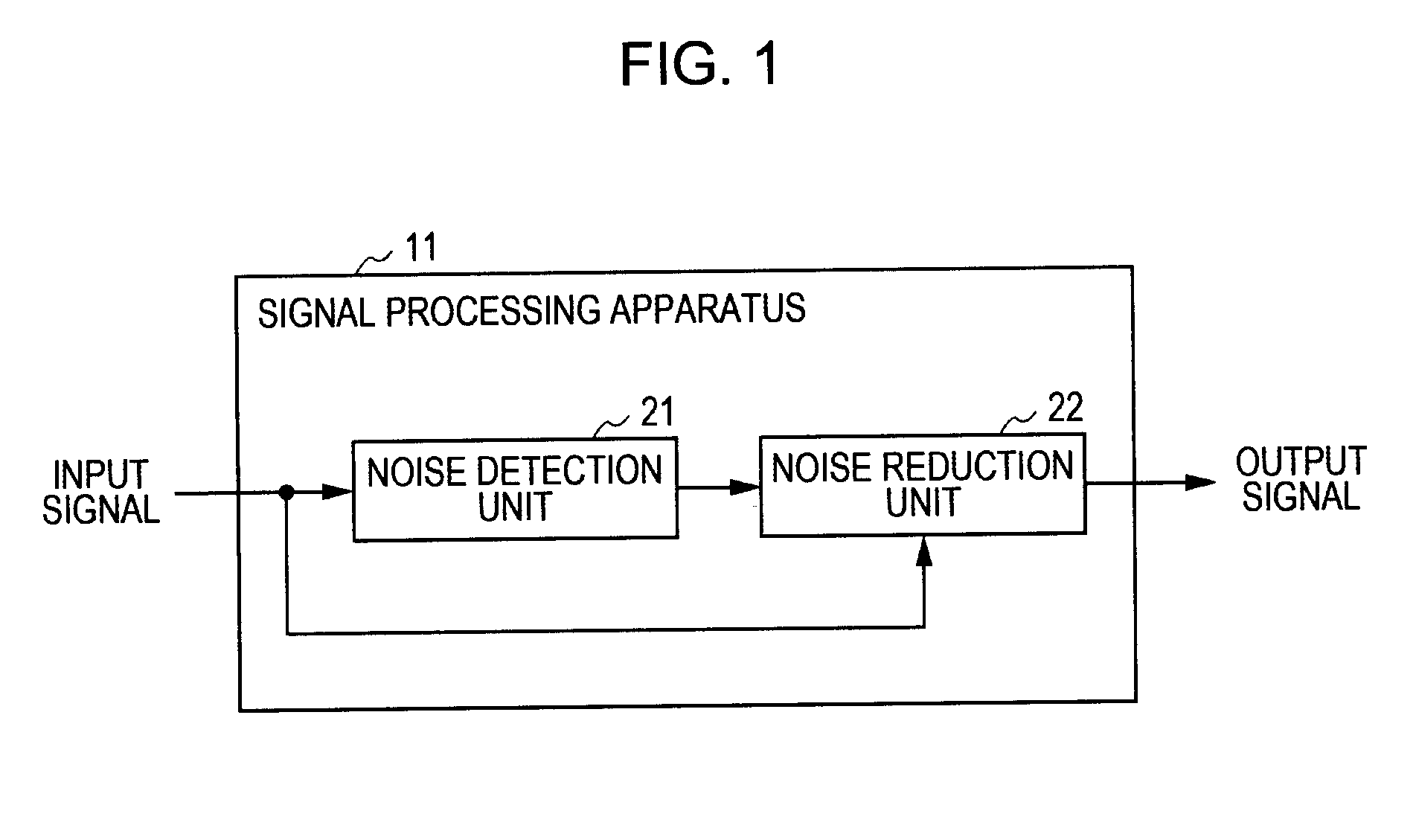
Signal processing apparatus, signal processing method, and program
InactiveUS20110255710A1Reliable detectionEasy to detectSpeech analysisTransducer protection circuitsAlgorithmEngineering
A signal processing apparatus includes an absolute value unit configured to convert an audio signal into absolute values, a representative value calculation unit configured to calculate representative values of consecutive sample values included in blocks of the audio signal which has been converted into the absolute values using at least maximum sample values among values of the samples included in the blocks for individual blocks, an average value calculation unit configured to determine a section which includes a predetermined number of consecutive blocks as a frame and calculate a maximum value of the representative values of the blocks included in the frame and an average value of the representative values of the blocks included in the frame, and a detector configured to detect click noise in the frame on the basis of a ratio of the maximum value to the average value.
Owner:SONY CORP
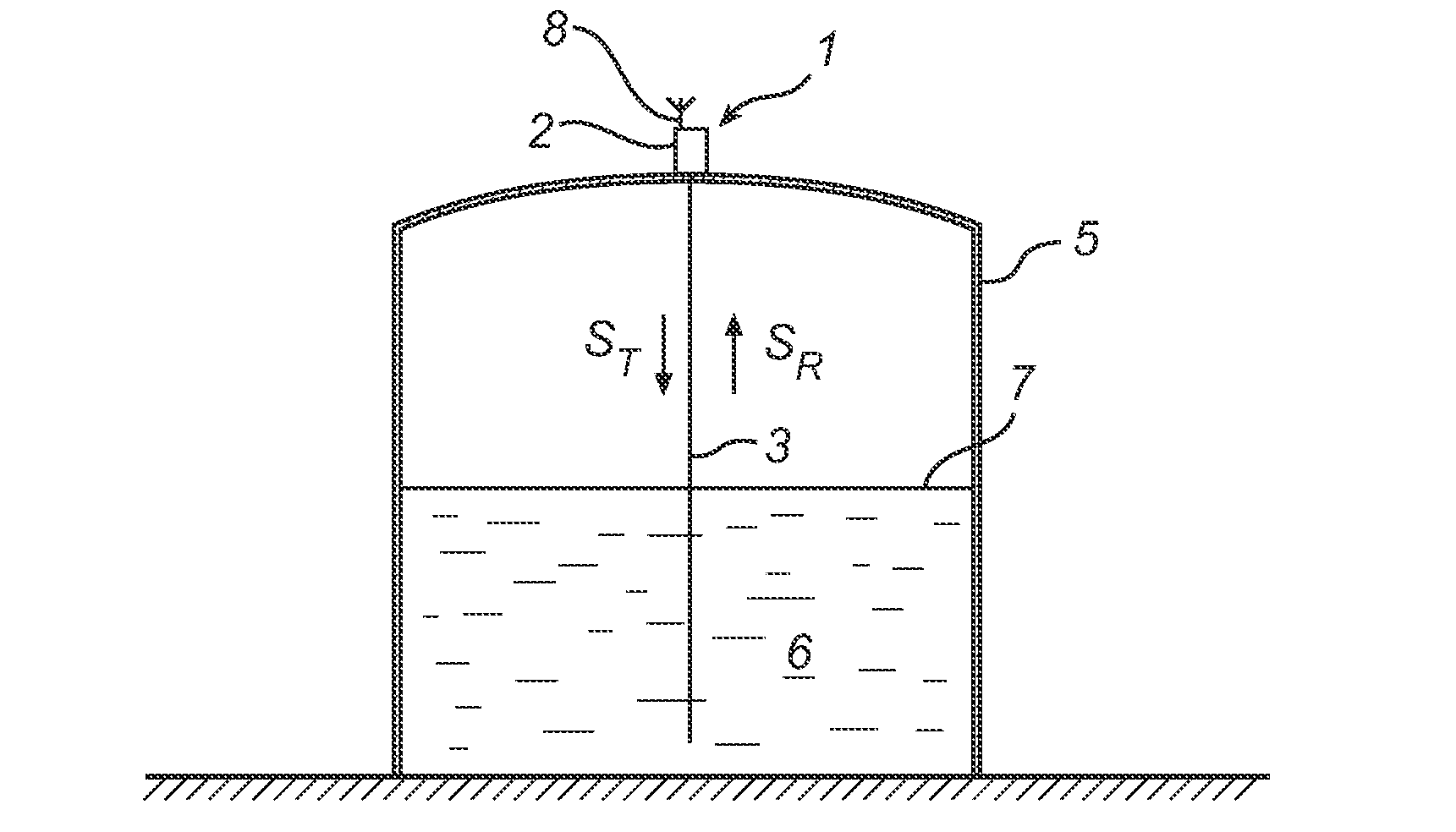
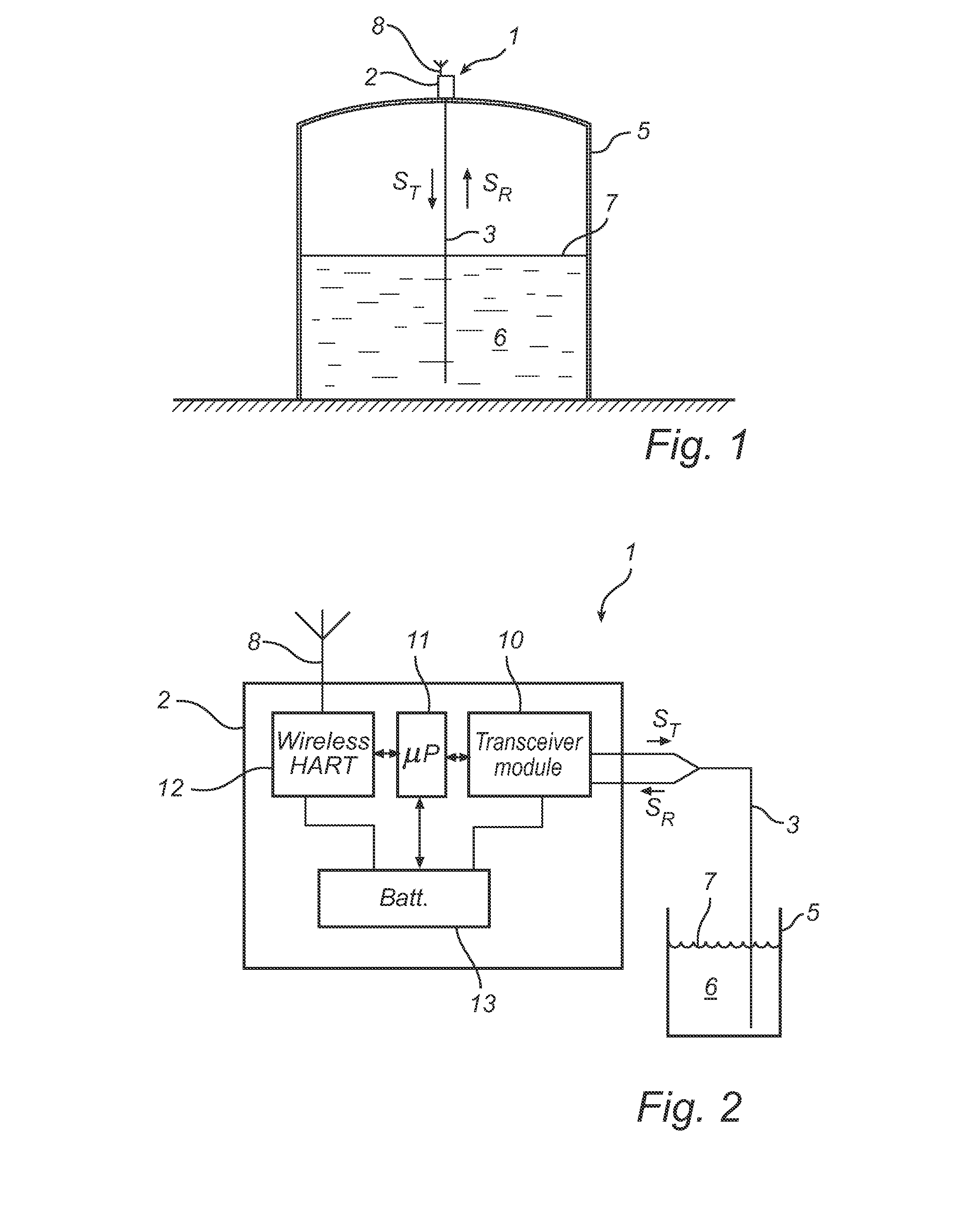
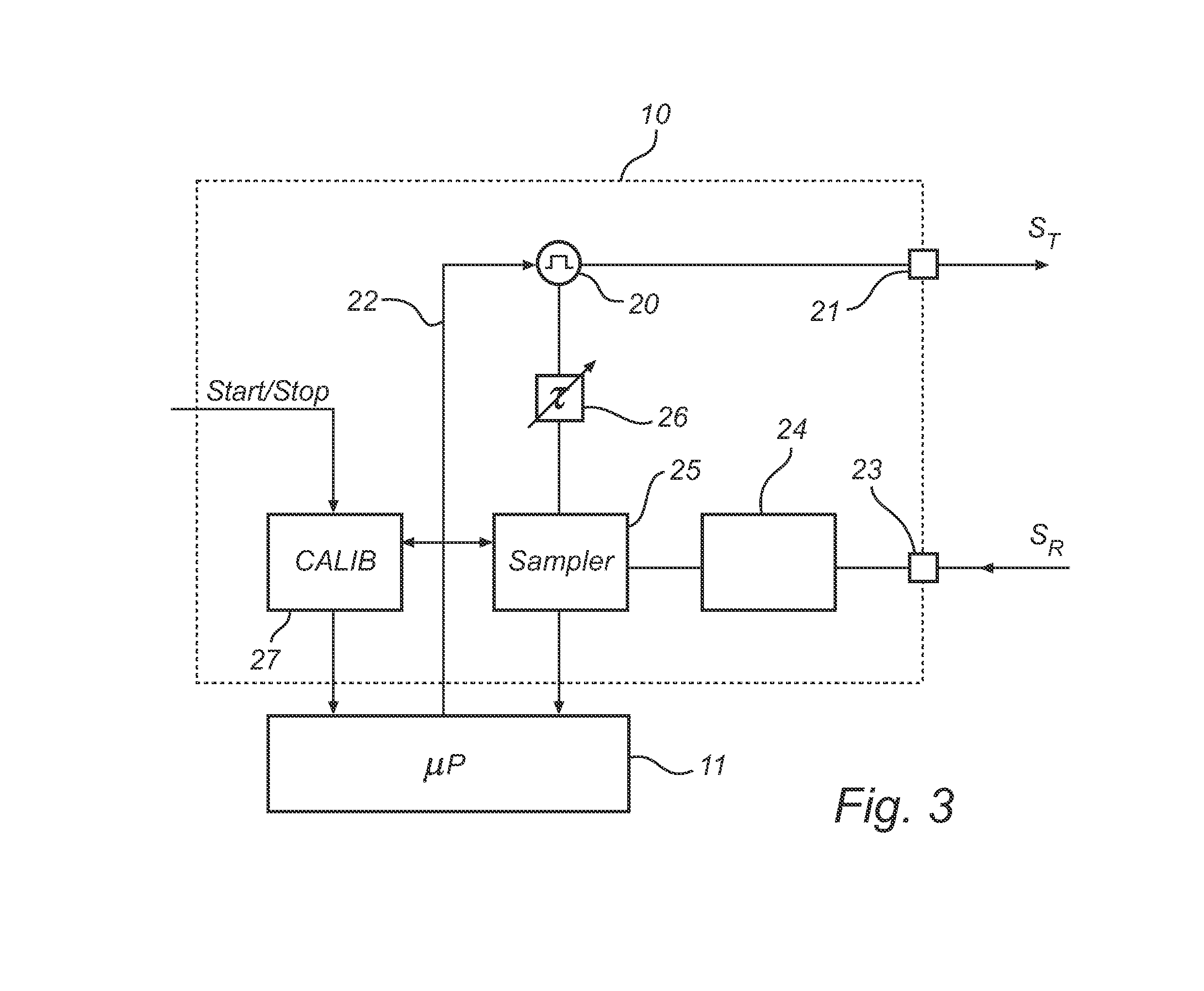
Calibration of a level gauge system
ActiveUS20130069795A1Improve accuracyGood estimateElectric signal transmission systemsTesting/calibration apparatusElectricityCONSECUTIVE SAMPLE
A method of calibrating a level gauge system using electromagnetic signals to determine a filling level of a product in a tank. The level gauge system comprises a real time sampler for sampling a reflection signal with a sampling period between consecutive samples. The method comprises the steps of: receiving timing signals from a wireless communication network; generating time stamp signals based on the timing signals; registering a number of the sampling periods between a first time stamp signal and a second time stamp signal; and determining the sampling period based on the registered number of sampling periods and a time between the first time stamp signal and the second time stamp signal. Various embodiments of the present invention provide for high accurate determination of the filling level in a tank without the need for a temperature stable and highly accurate clock reference in the level gauge system.
Owner:ROSEMOUNT TANK RADAR
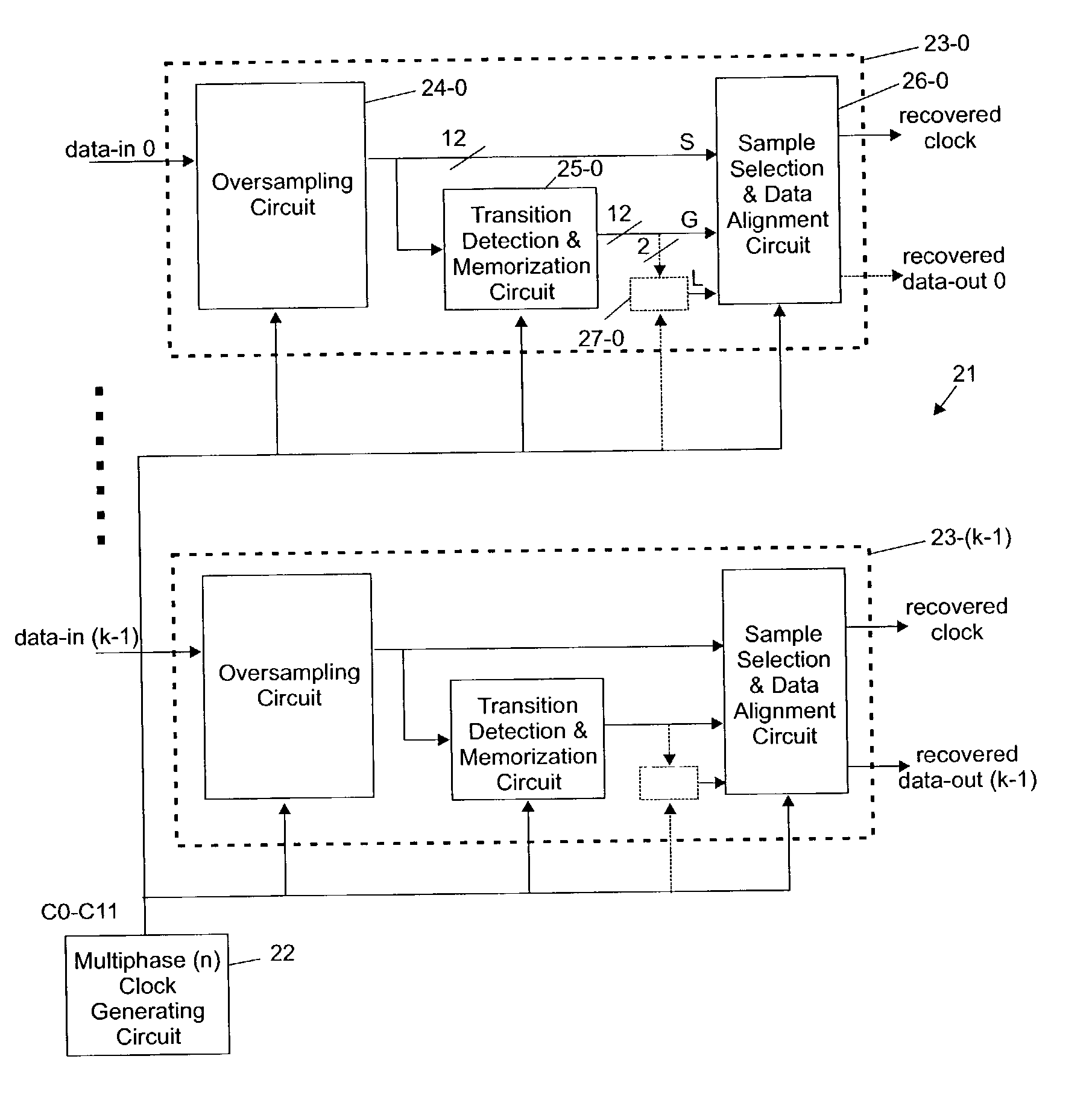
Transition detection, validation and memorization circuit
InactiveUS7180966B2Optimize dataImprove noise immunityDc level restoring means or bias distort correctionAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsData streamControl signal
A transition detection, validation and memorization (TDVM) circuit detects the position of a transition in a stream of serially transmitted binary data (bits) that are over sampled and generates a control signal indicating which sampled signal represents the best data. The incoming data stream is over sampled by the n phases of a multiple phase clock signal. Then n over sampled signals are fed into the TDVM circuit which includes a first section for detecting the transition at the positions of two consecutive sampled signals according to a specific signal processing, a second section for validating the transition position, and a third section for memorizing the validated transition position and generating a control signal that is used to recover the data.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Frequency analyzer
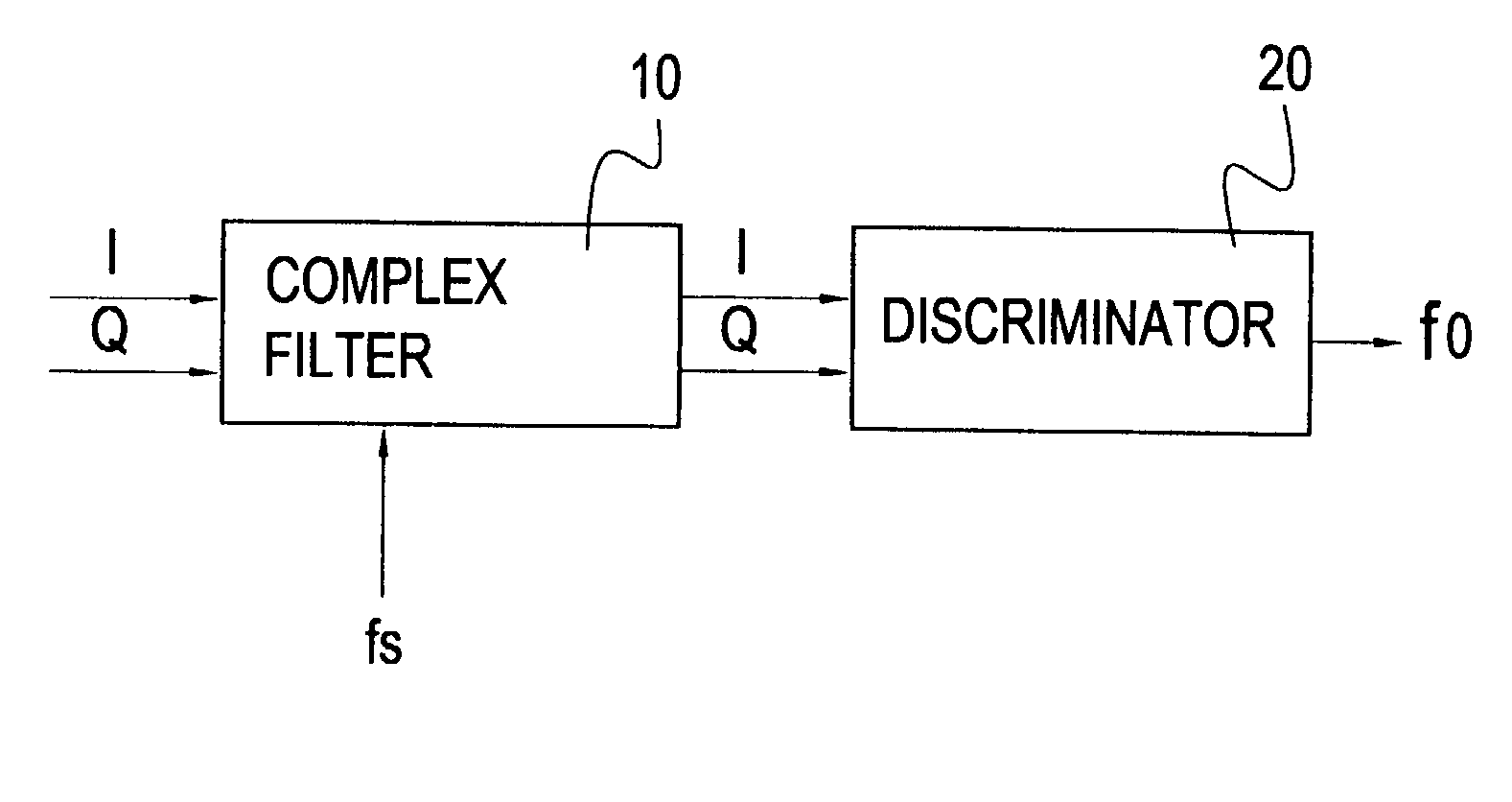
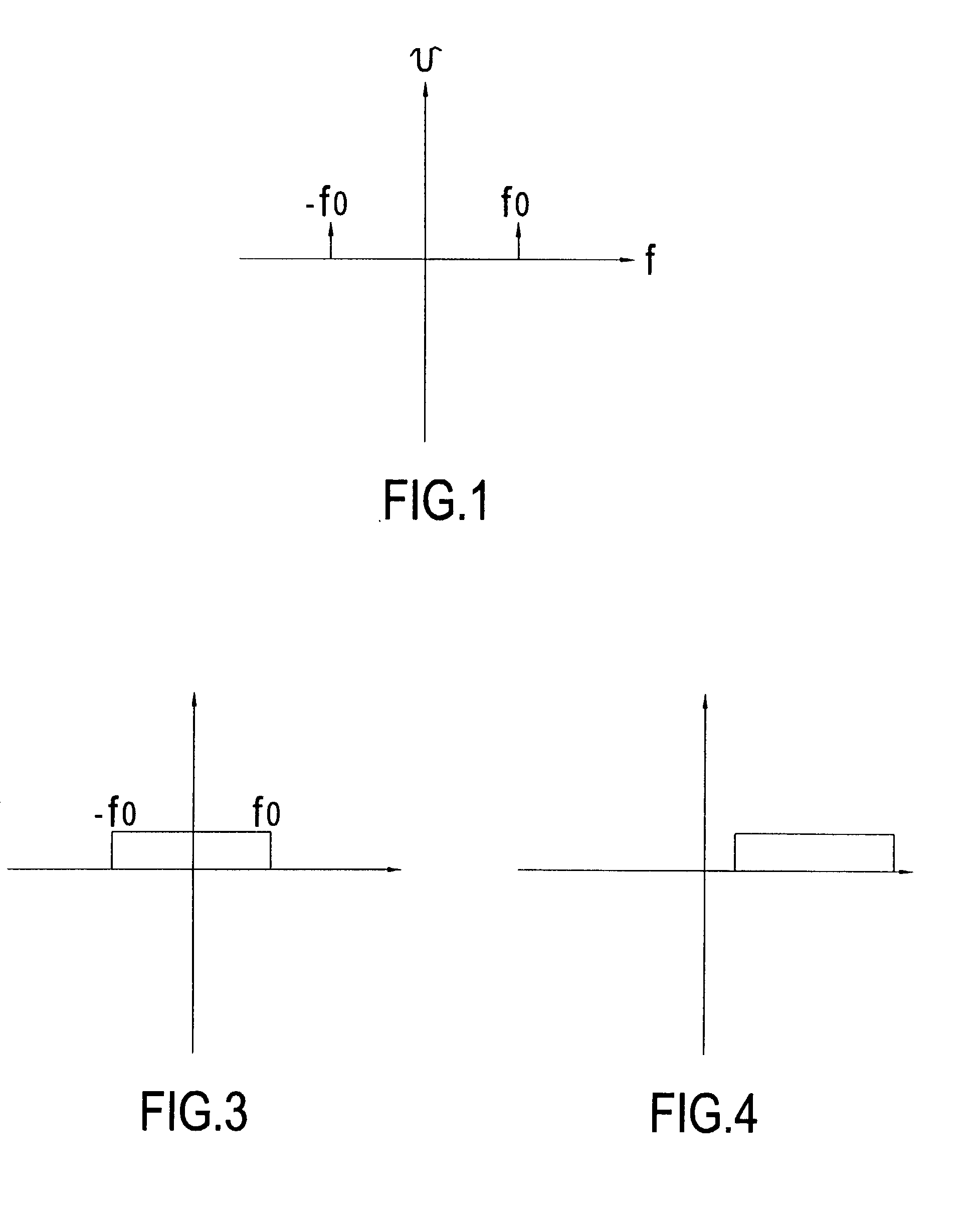
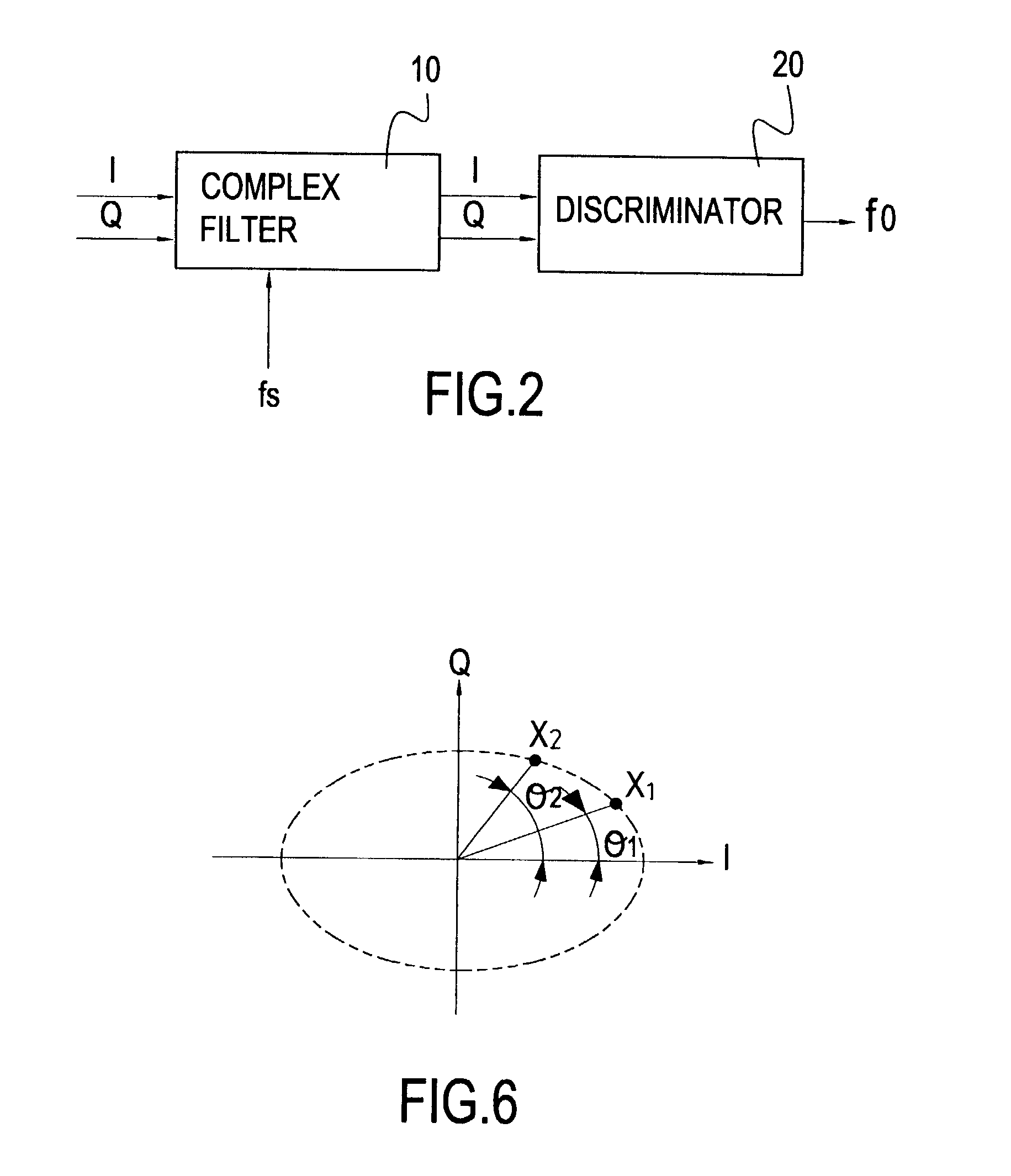
InactiveUS20030185315A1Peak efficiencyMinimize powerFrequency analysisAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsDiscriminatorFrequency spectrum
A frequency analyzer uses a new approach to determine simple and multi-frequency components. The invention mainly comprises a complex filter and a frequency discriminator. The real number part of the input frequency can be represented by a frequency spectrum composed of both positive frequencies and negative frequencies. The complex filter receives an input signal through two sampling points, and then the frequency discriminator computes the phase difference between two sampled signals from these two consecutive sampling points. After applying an inverse trigonometric function, the demodulated frequency is derived from the phase difference. Using a complex function to derive the demodulated frequency is more advantageous in that many high-frequency sampling circuits become unnecessary, thus reducing the power consumption of the frequency demodulation circuit.
Owner:WINBOND ELECTRONICS CORP
Method and apparatus for radar signal processing
A radar apparatus and method for determining the range to and velocity of at least one object comprising, transmitting a plurality of RF signals, each comprising a particular frequency and being transmitted during a particular unique finite period, the plurality of signals collectively comprising at least one first subset of signals having the same frequency and at least one second subset of signals having different frequencies, receiving the plurality of signals after reflection from an object, determining a phase difference between each of the signals and the corresponding reflected signal, each piece of phase difference information herein termed a sample, organizing the samples in two-dimensions wherein, in a first dimension, all samples have the same frequency and, in a second dimension, all consecutive samples are separated from each other by a fixed time interval; processing the samples in the first dimension to determine a phase rotation frequency corresponding to the samples in the first dimension, the phase rotation frequency comprising a Doppler frequency for the at least one object, processing the samples in the second dimension to determine a second phase rotation frequency corresponding to the samples in the second dimension; the phase rotation frequency comprising Doppler frequency and range frequency for the at least one object; comparing the first phase rotation frequency to the second phase rotation frequency to distinguish range frequency from Doppler frequency of the at least one object; and converting the Doppler frequency to a velocity of the object and converting the range frequency to a range of the object.
Owner:VEONEER US LLC
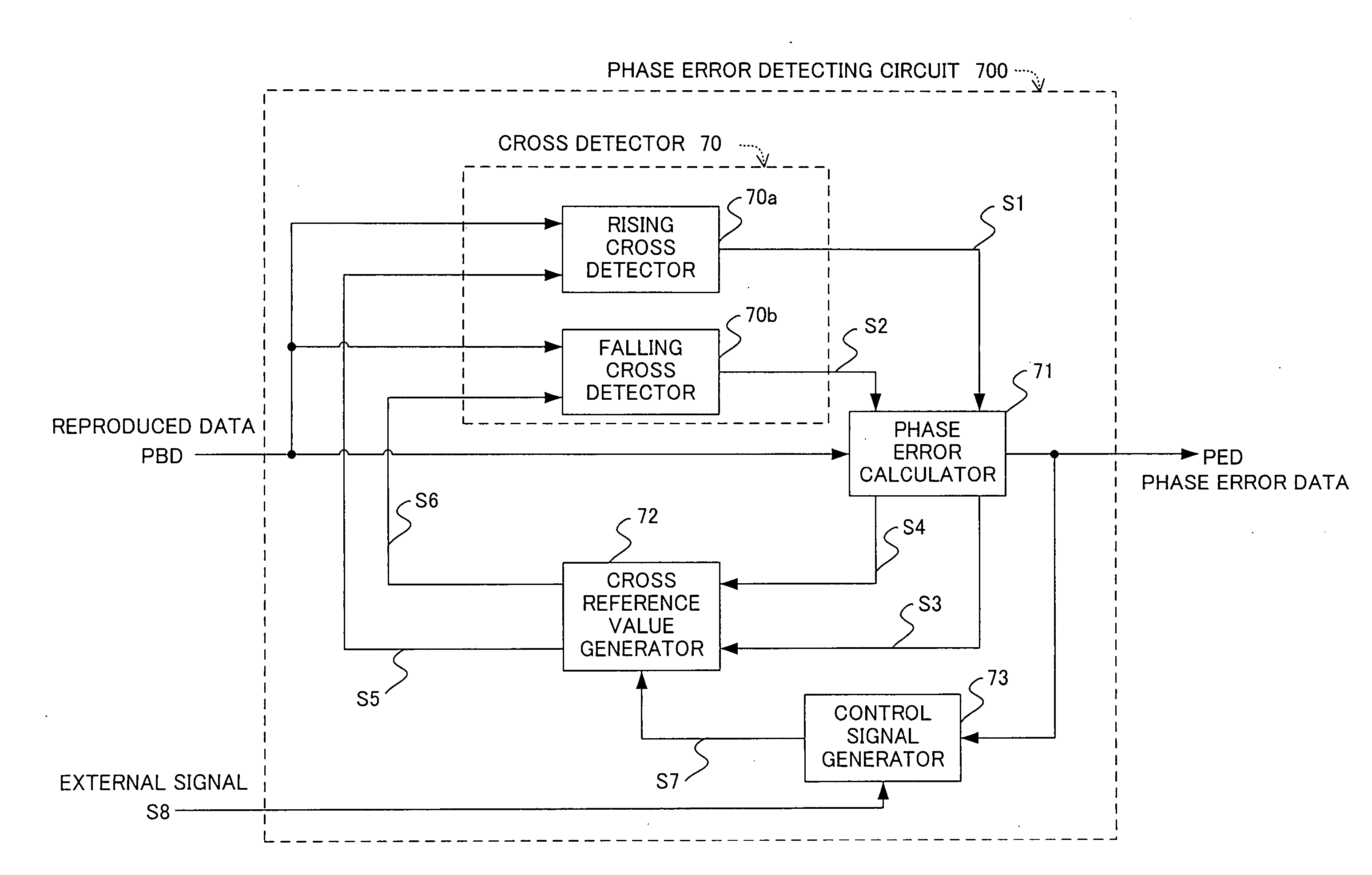
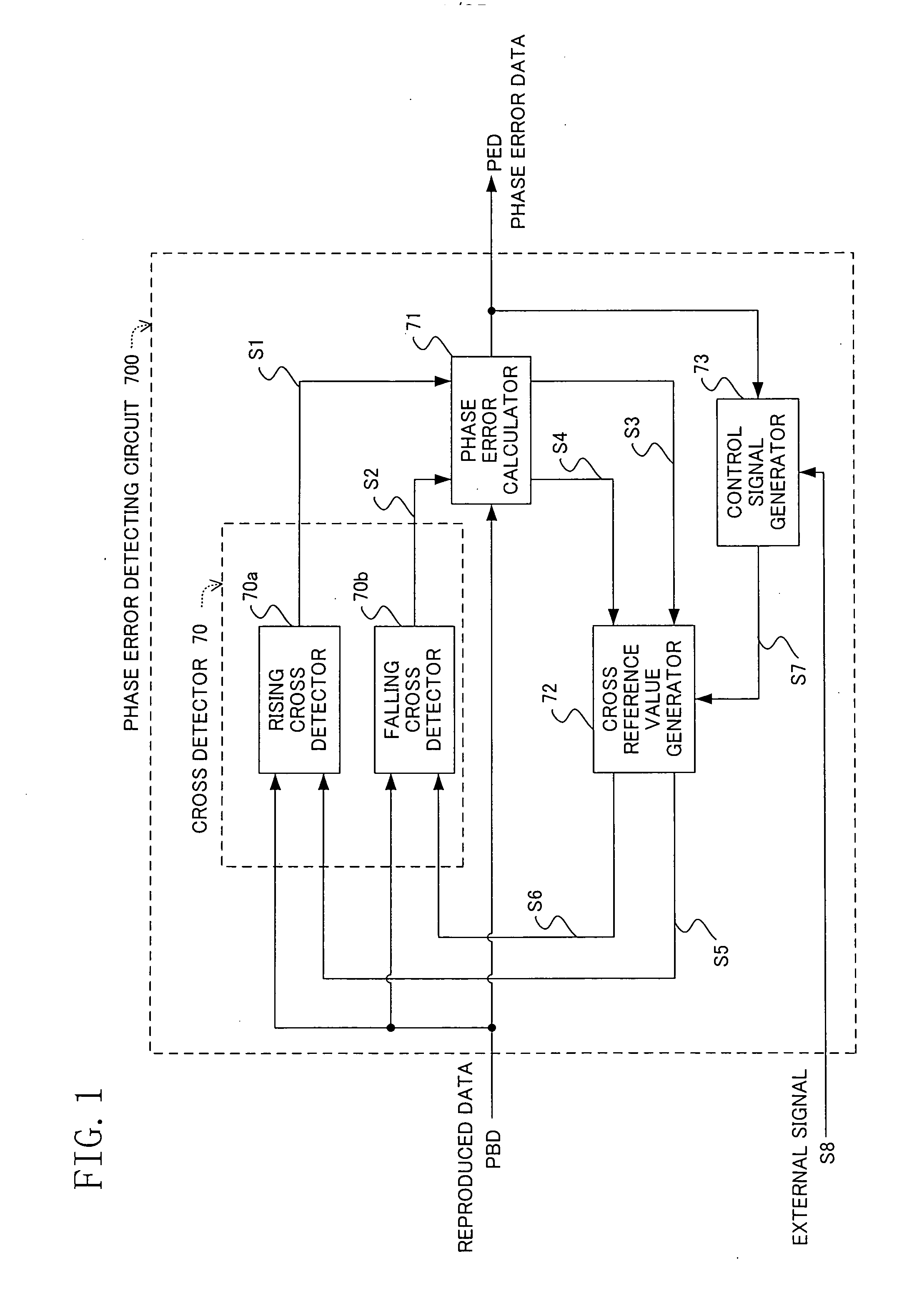
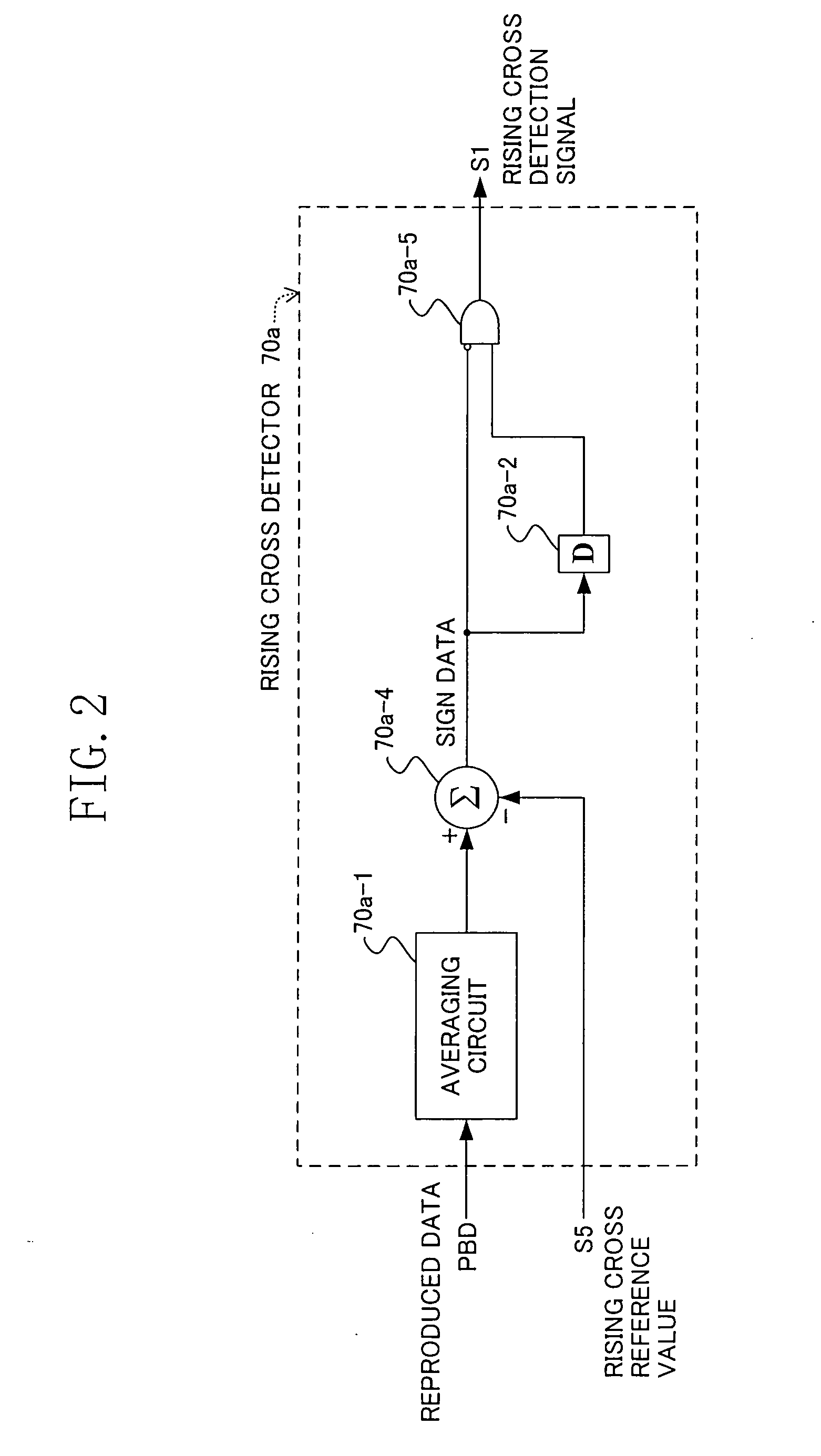
Phase error detecting circuit and synchronization clock extraction circuit
InactiveUS20060044990A1Accurate detectionExpand the capture rangeCombination recordingModification of read/write signalsComputer scienceCONSECUTIVE SAMPLE
In a phase error detecting circuit used in a synchronous clock extracting circuit for extracting a clock which is synchronized with reproduced data, a cross reference value generator 72 inputs, as a rising cross reference value S5, rising phase error data S3 calculated in a phase error calculator 71 to a rising cross detector 70a and inputs, as a falling cross reference value S6, falling phase error data S4 similarly calculated to a falling cross detector 70b. Each of the cross detectors 70a and 70b calculates a difference value between the value of the reproduced data at a sampling point and the inputted cross reference value (cross offset value) S5 or S6 and outputs a rising or falling cross detection signal when one of two difference values at consecutive sampling points is negative and the other thereof is positive. Accordingly, a capture range is enlarged.
Owner:SOCIONEXT INC
Pulse baseline value calculation method and particle counting method for blood cell analyzer
ActiveCN105866011AReduce misjudgmentAccurate countIndividual particle analysisPulse characteristics measurementsComputational physicsComputer science
The invention relates to a pulse baseline value calculation method and a particle counting method for a blood cell analyzer. The pulse baseline value calculation method comprises the step of calculating the average value of n consecutive sampling data on the condition that the absolute value of the difference between two arbitrary adjacent data among the n consecutive sampling data is smaller than a baseline threshold value and the n consecutive sampling data are nearest to a pulse starting point within a pulse non-sustainable period, wherein the average value represents the baseline threshold value. According to the technical scheme of the invention, the baseline threshold value is preset and compared, and the sampling data of a noise-superimposed baseline are avoided. Meanwhile, sampling data within a noise / interference allowable range are selected and calculated. In this way, the noise is accumulated onto a final baseline value, so that the baseline value is more close to real data. The misjudgment of the baseline value is greatly reduced, so that the particle counting result is more accurate. The method can be applied to the particle counting operations of three-category type blood cell analyzers, five-category type blood cell analyzers, flow cytometers and other biochemical instruments.
Owner:ACON BIOTECH (HANGZHOU) CO LTD
Phase-alternating mixer with alias and harmonic rejection
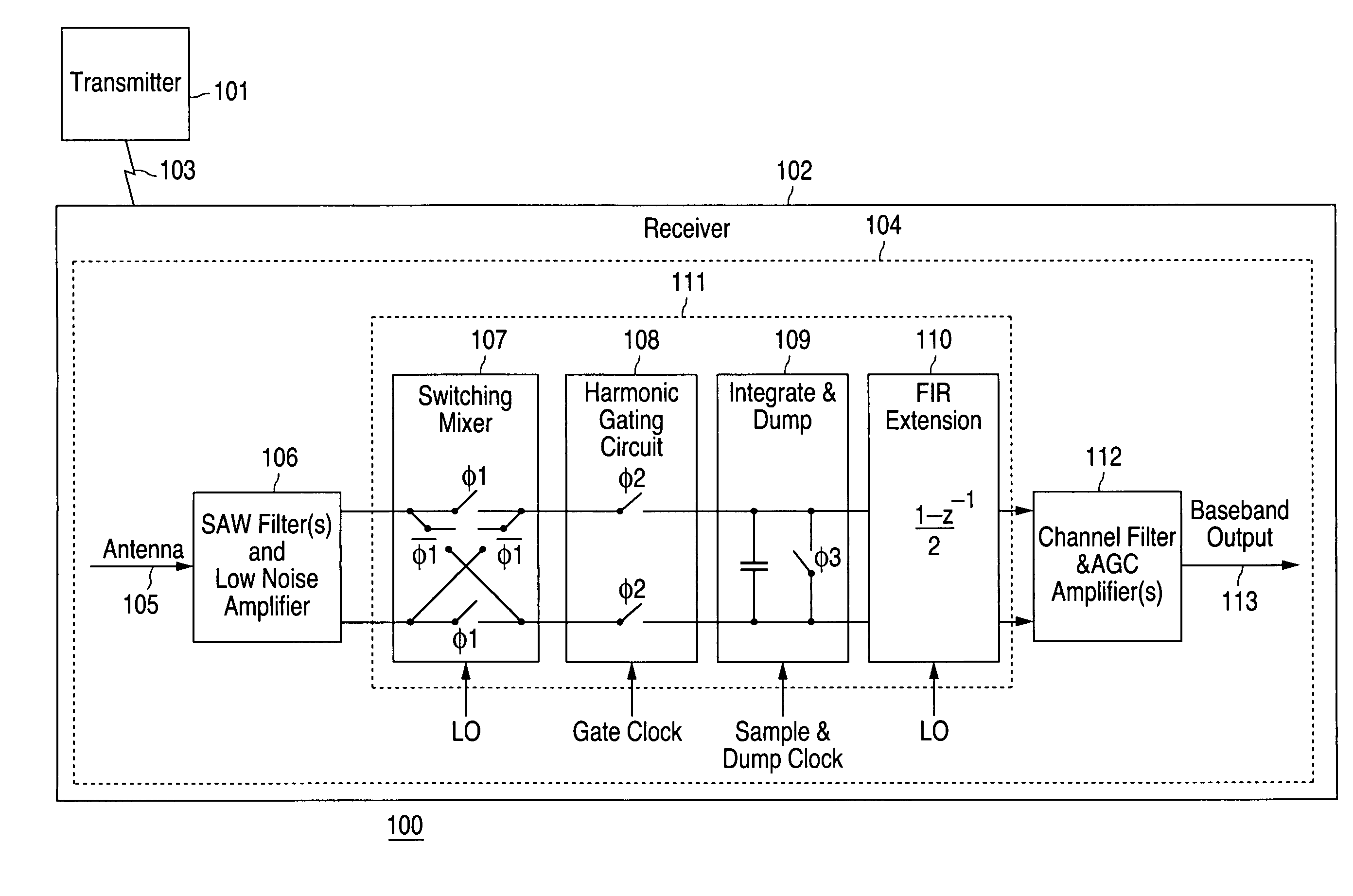
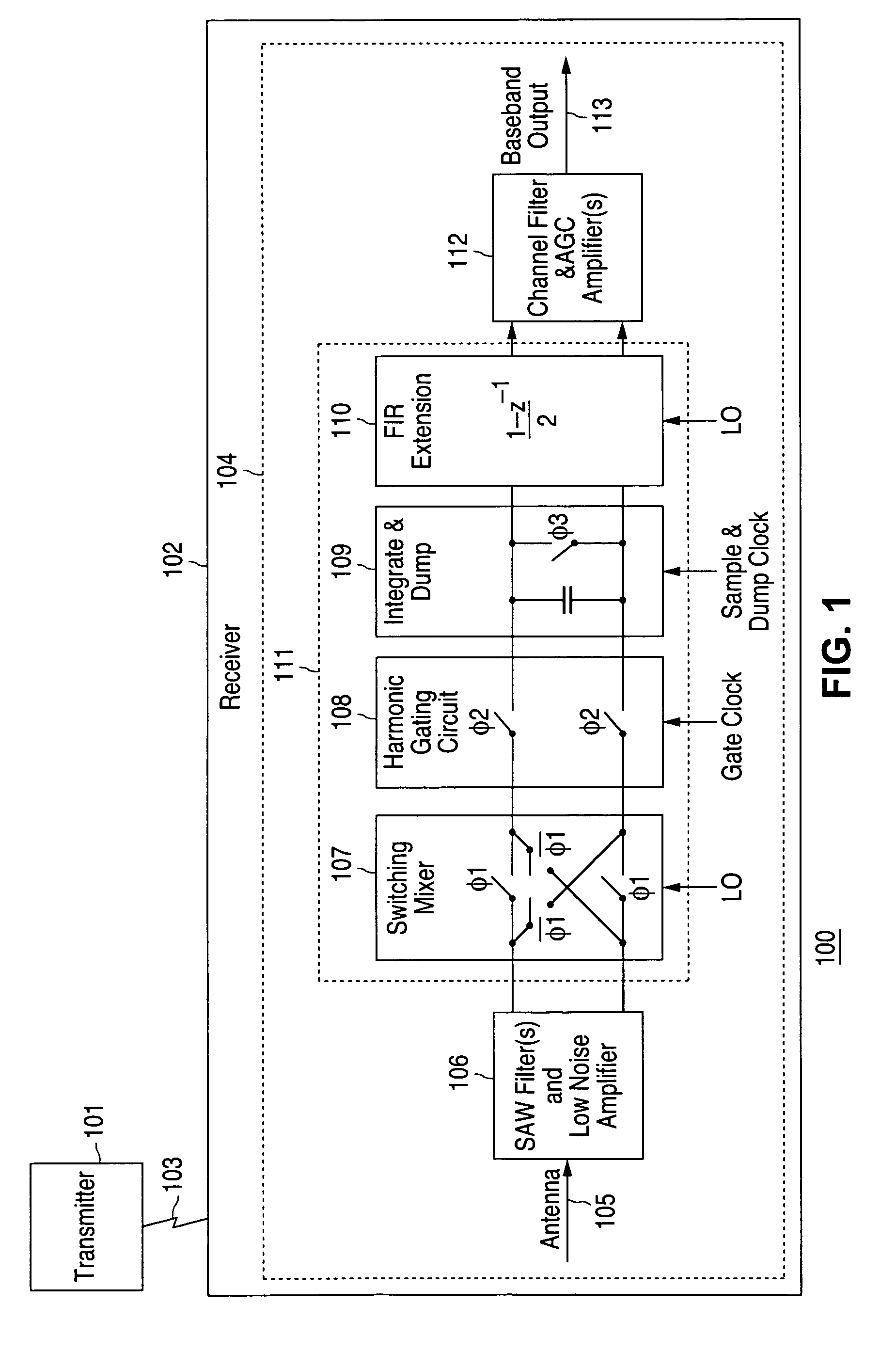
ActiveUS7336938B1Suppresses harmonic responseEasy to integrateModulation transference balanced arrangementsTransmissionIntegratorCascading effects
Rejection of local oscillator alias response is provided in a mixing circuit by (1) a switching mixer producing an output that changes at least twice between two states (e.g., high-low-high or low-high-low) during each local oscillator period, and (2) a charge integrator integrating current output from the switching mixer over the local oscillator period. The switching mixer and charge integrator produce a sampled data format, double sideband signal with serial cancellation of the switching mixer's alias responses. An extension unit connected in series with the switching mixer and charge integrator, and implementing a transform function computing a difference between consecutive samples, produces a cascading effect with the switching mixer and charge integrator, optionally producing additional nulls suppressing alias response at frequencies near the local oscillator frequency. A harmonic gating circuit between the switching mixer and charge integrator, controlled at a multiple of the local oscillator frequency, suppresses harmonic responses of the switching mixer.
Owner:NAT SEMICON CORP
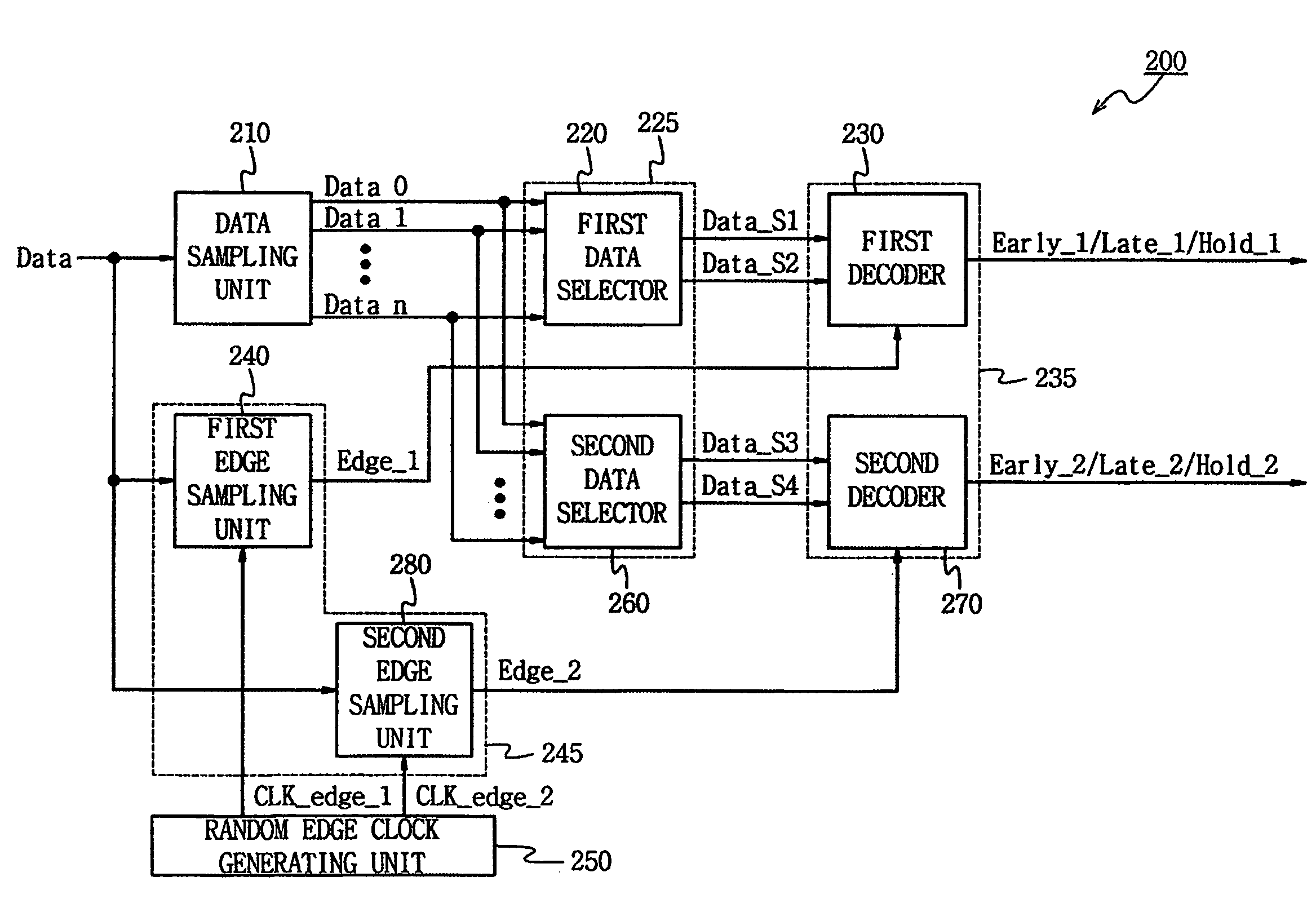
Clock and data recovery circuits using random edge sampling and recovery method therefor
A clock and data recovery (CDR) circuit comprises a data sampling unit which latches serial data input in response to data clock signals, and outputs a plurality of sampling data, the data clock signals maintaining a constant phase difference and having mutually different phases, an edge sampling unit which outputs an edge sampling signal generated by sampling edge information of the serial data in response to a selection edge clock signal, the selection edge clock signal being randomly selected from among a plurality of edge clock signals, a data selection unit which selects at least two consecutive sampling data from among the plurality of sampling data, and a decoding unit which performs a logical operation of the sampling data selected by the data selection unit and the edge sampling signal.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Sliding-window based signal monitoring
InactiveUS20050013354A1Reduce complexityReduce detection time latencyPulse train pattern monitoringTransmission monitoringOversamplingSignal monitoring
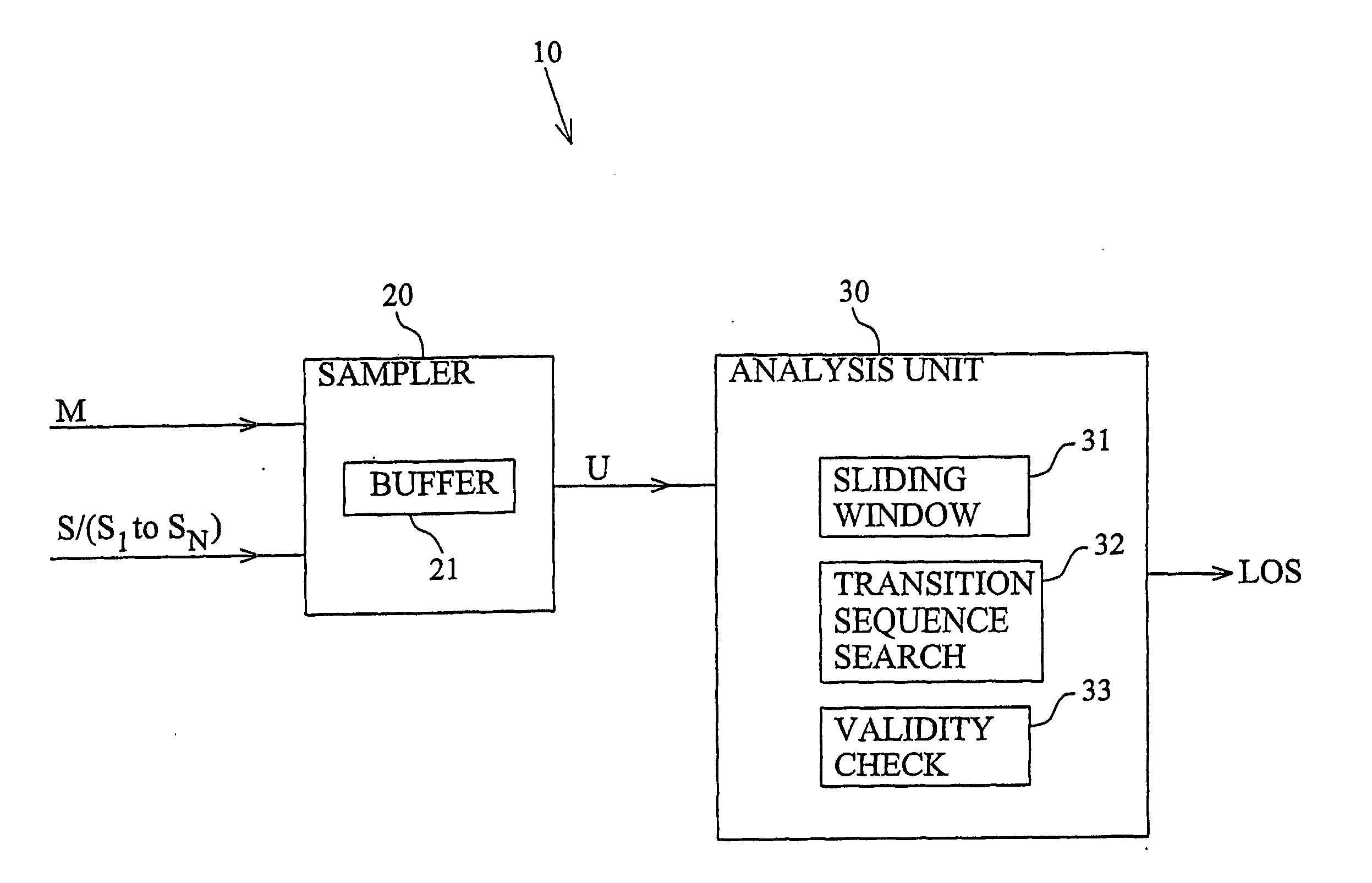
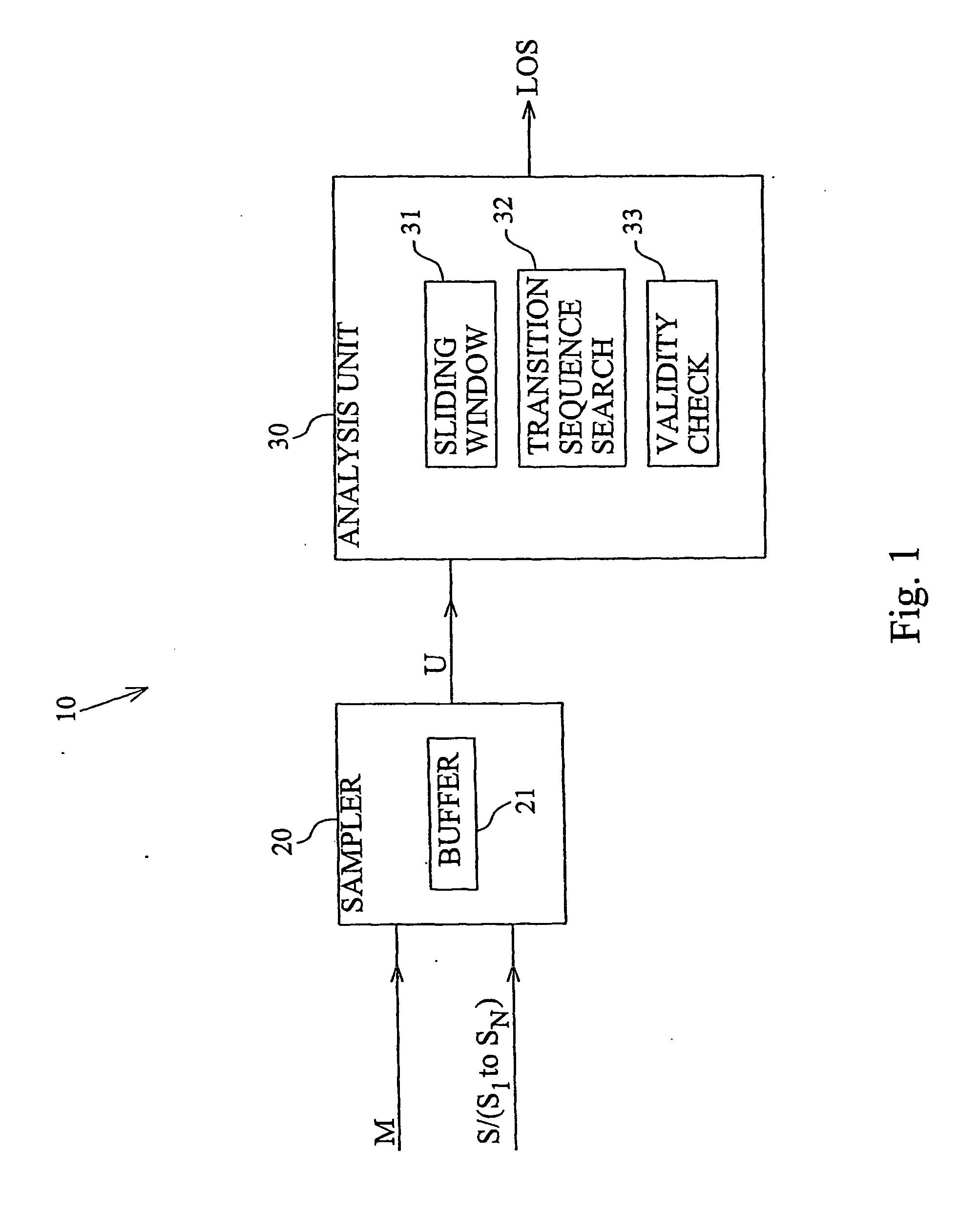
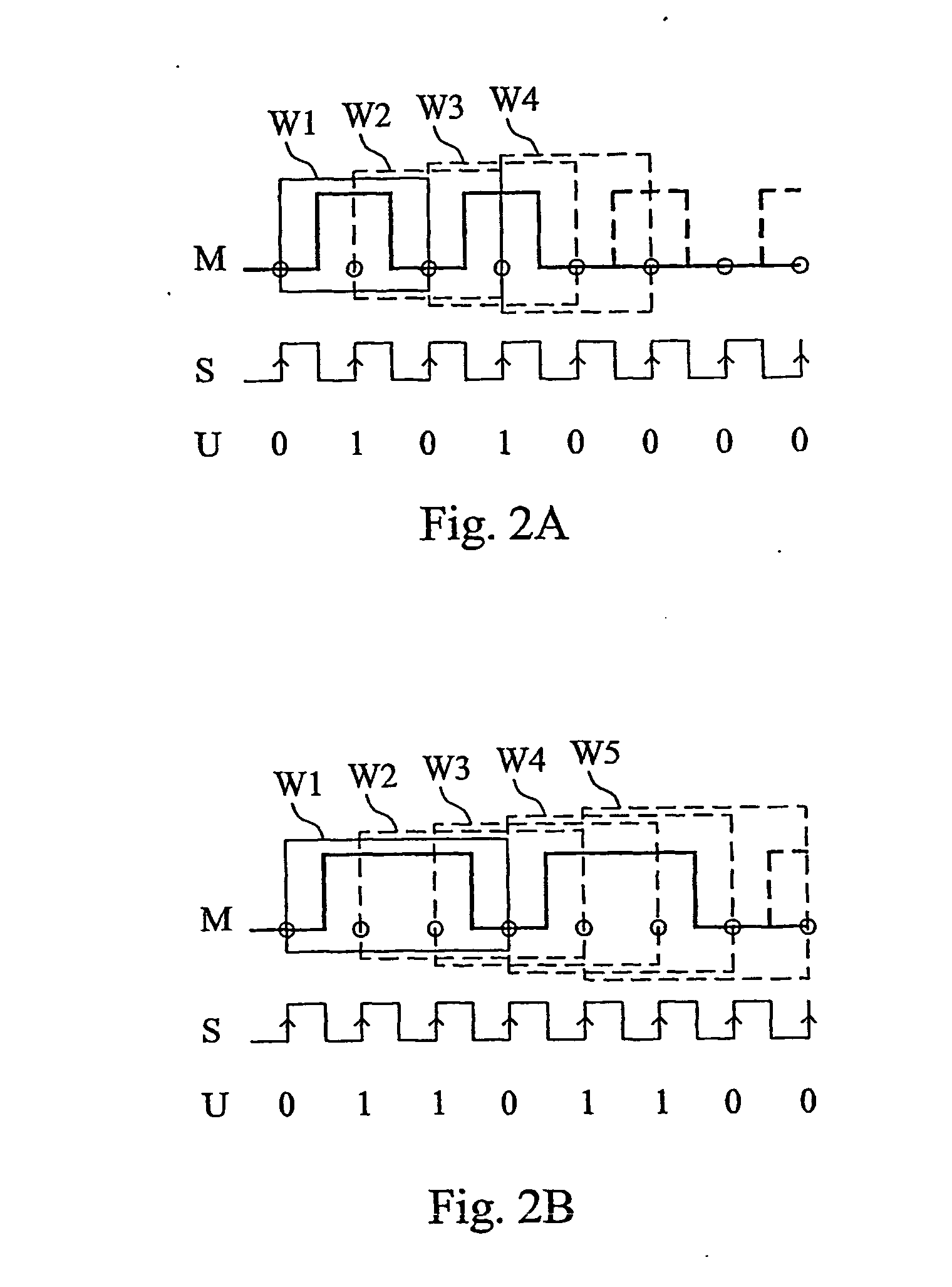
The invention is generally directed towards monitoring of a signal (M), such as a clock signal or a data signal, by sampling the signal to obtain a discrete sample representation of the signal and analyzing the sample representation. The idea according to the invention is to slide a sample window (SW) over the sampled signal and determine whether the samples currently within the window include a valid transition sequence. In the general case, the existence of a valide signal is confirmed as long as a valid transition sequence is present in at least one of a predetermined number of consecutive sample windows. In order to reduce the need for oversampling in high-frequency applications, the invention furthermore proposes a multi-phase sampling technique according to which a number of phase-shifted sample clocks (S1 to SN) are generated for the purpose of sampling the signal to be monitored. Higher-frequency oversampling is thus replace by a higher resolution in the time domain.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Timing recovery methods and apparatuses
InactiveUS20060158358A1Electric signal transmission systemsSynchronisation error detectionRecovery methodComputer science
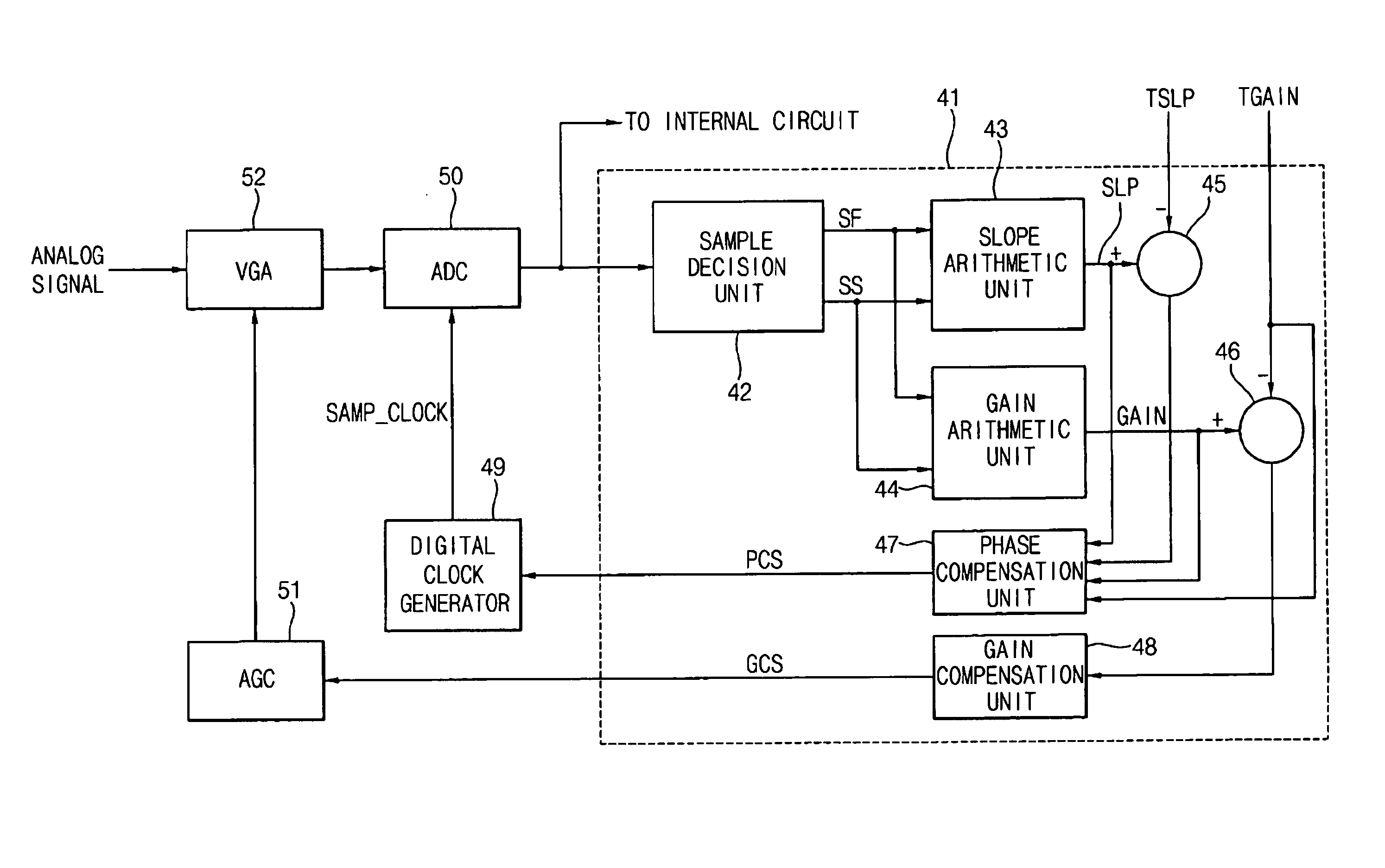
In a timing recovery method, two consecutive sampling values may be generated based on a sampled input signal. The input signal may be sampled according to a phase interval of a sampling clock. A slope between the two consecutive sampling values may be calculated, and a difference between a target slope and the calculated slope may be determined. A phase of the sampling clock may be compensated based on the difference between the target slope and the calculated slope.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Display screen brightness adjustment method and device
ActiveCN106297628ARealize automatic adjustmentAvoid the problem of incorrectly generating display brightness adjustment commandsCathode-ray tube indicatorsLight sensingComputer science
Embodiments of the invention relate to the technical field of infrared touch control devices, and particularly relate to a display screen brightness adjustment method and device. The method comprises: when there is no user touch control action, periodical sampling of an infrared receiving tube in an infrared touch control frame is performed; whether the difference values between infrared signal parameter values of N consecutive samplings and a reference parameter value are all greater than an abrupt change threshold is determined, wherein the N is an integer not less than 2; when the difference values between the infrared signal parameter values of N consecutive samplings and the reference parameter value are all greater than the abrupt change threshold, a display brightness adjustment command is generated. According to the technical scheme, the method and the device can adjust the brightness of high-sensitivity display screen without adding extra light sensing elements.
Owner:HISENSE VISUAL TECH CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com