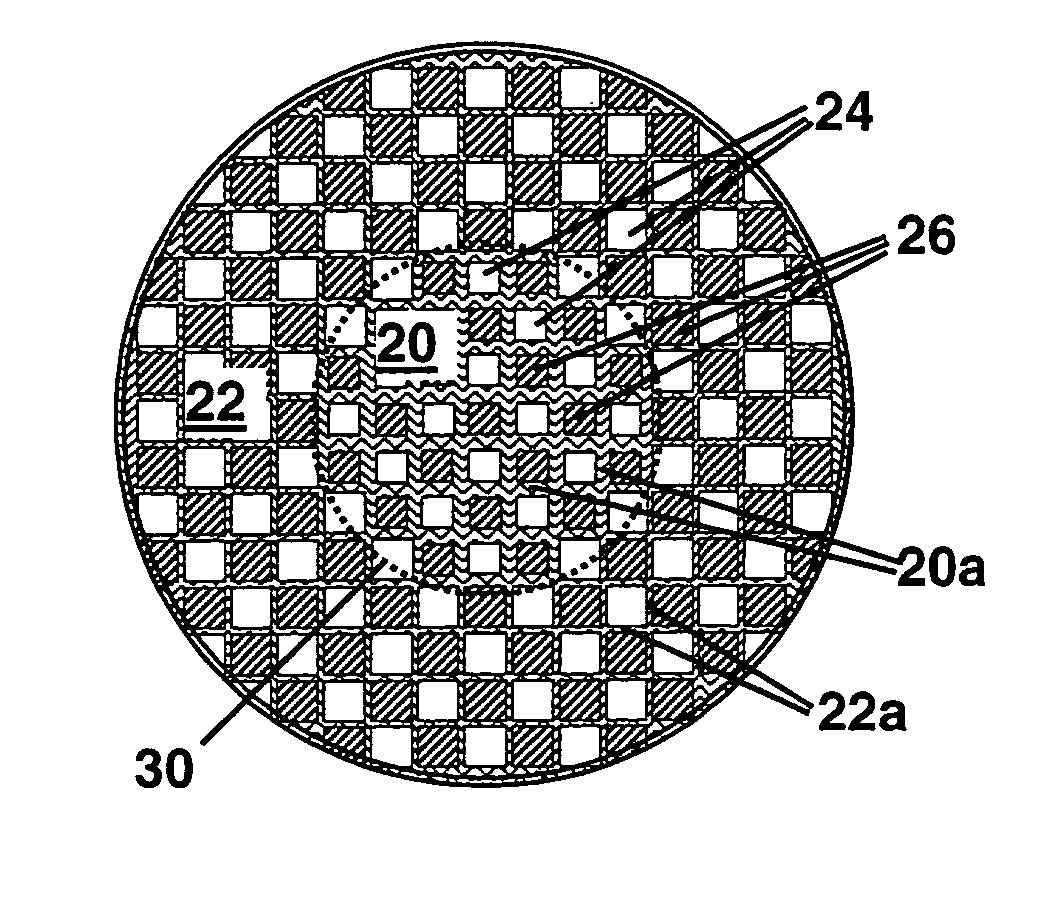
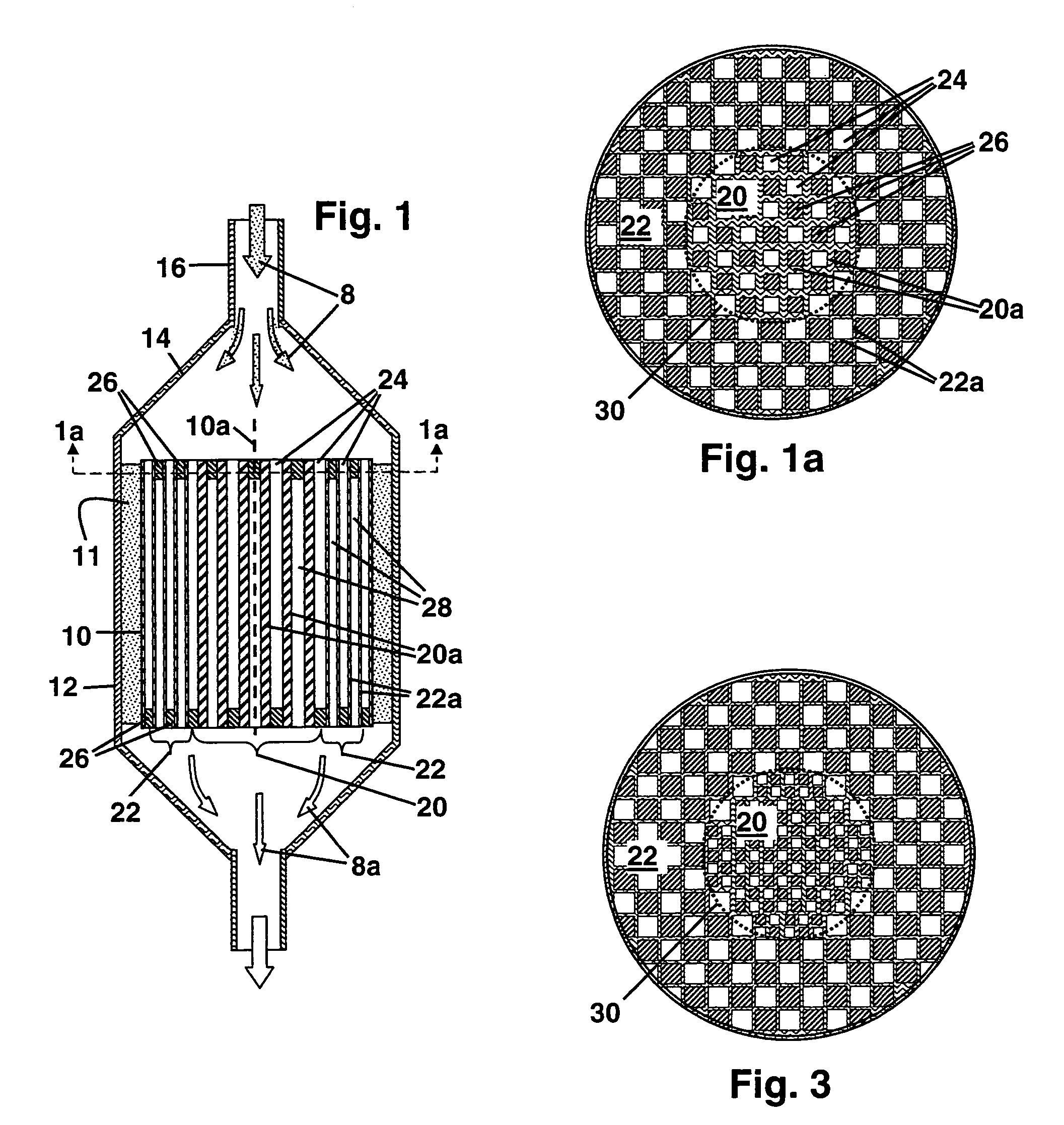
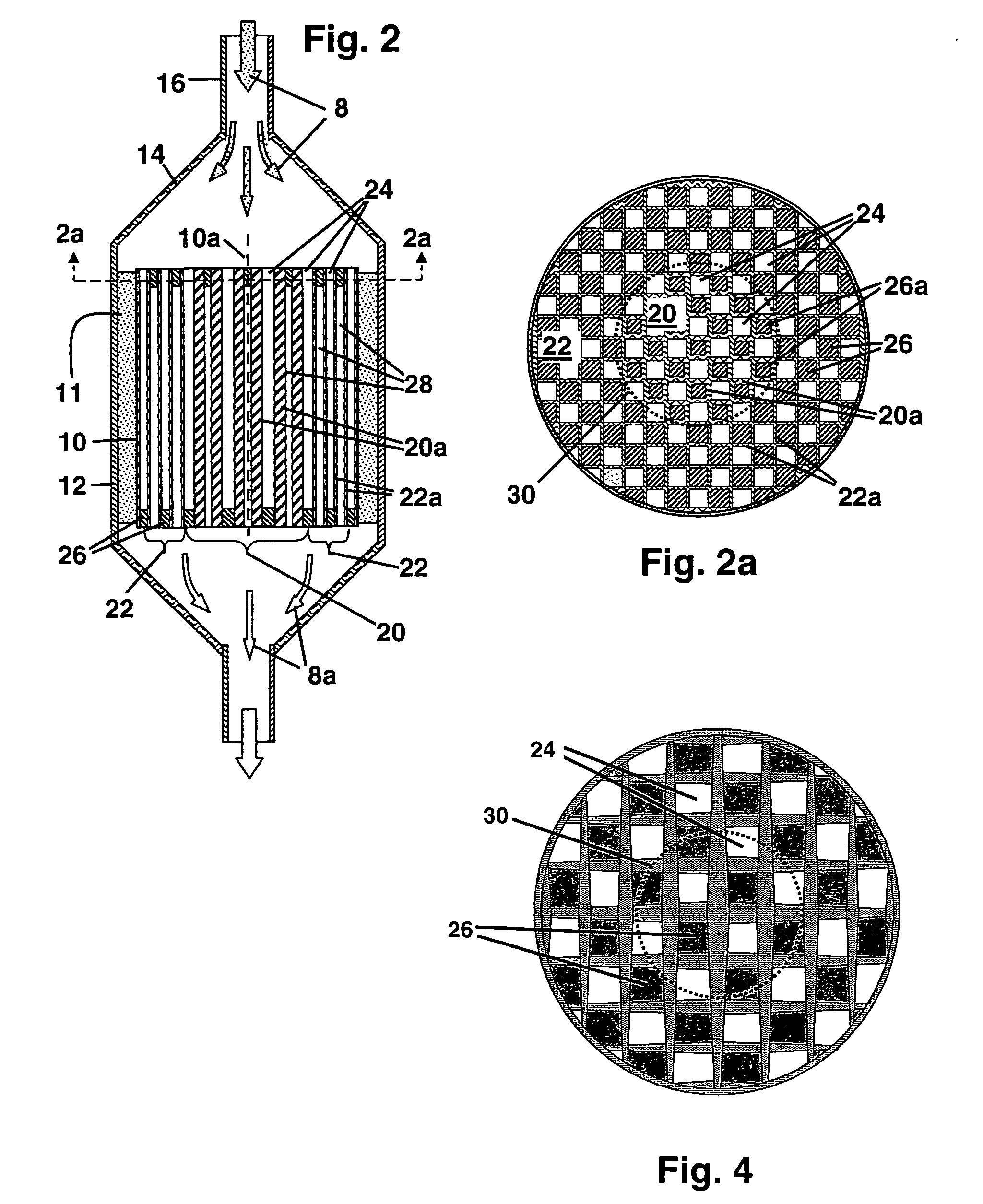
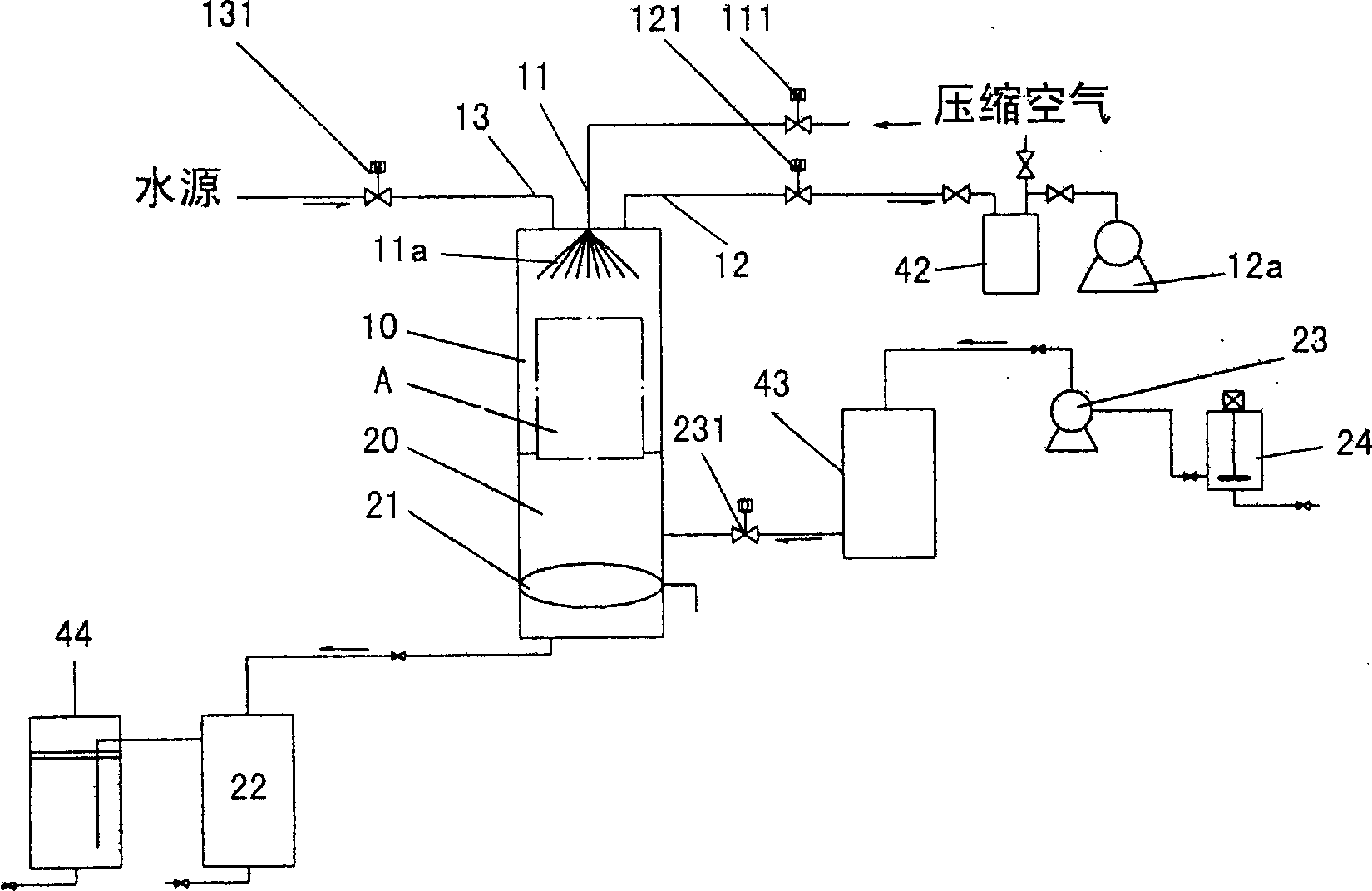
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
695 results about "Ceramic honeycomb" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
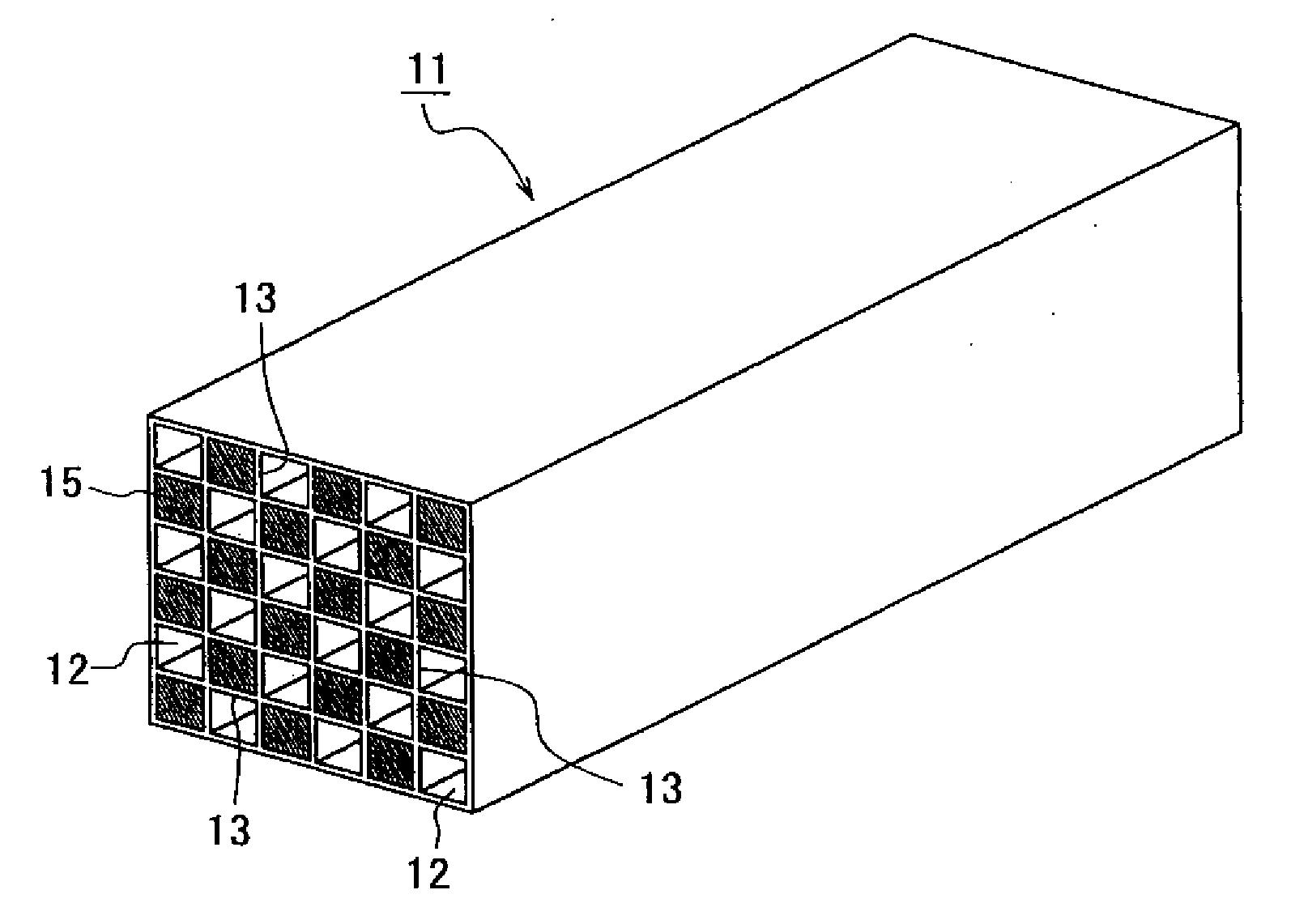
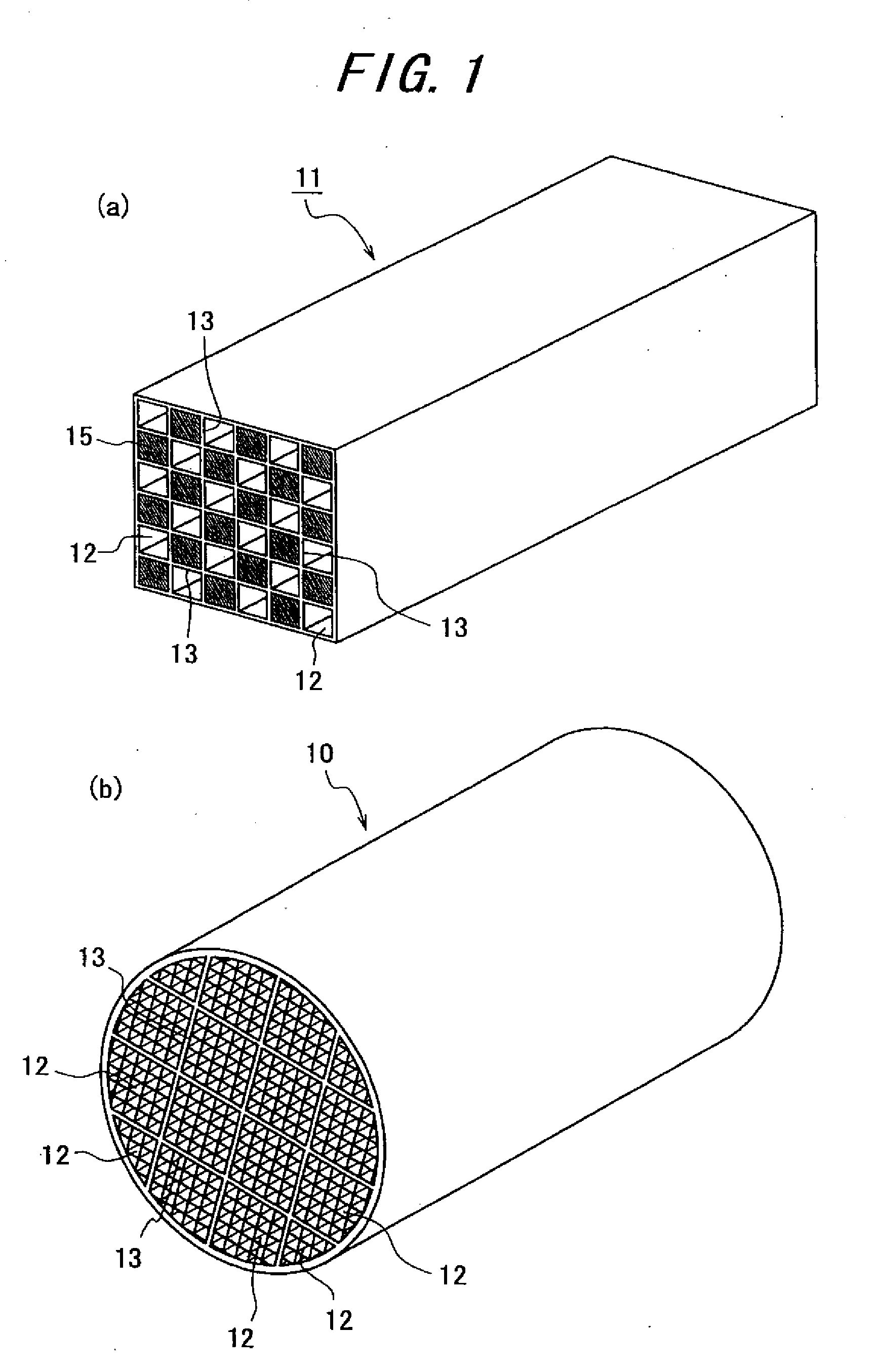
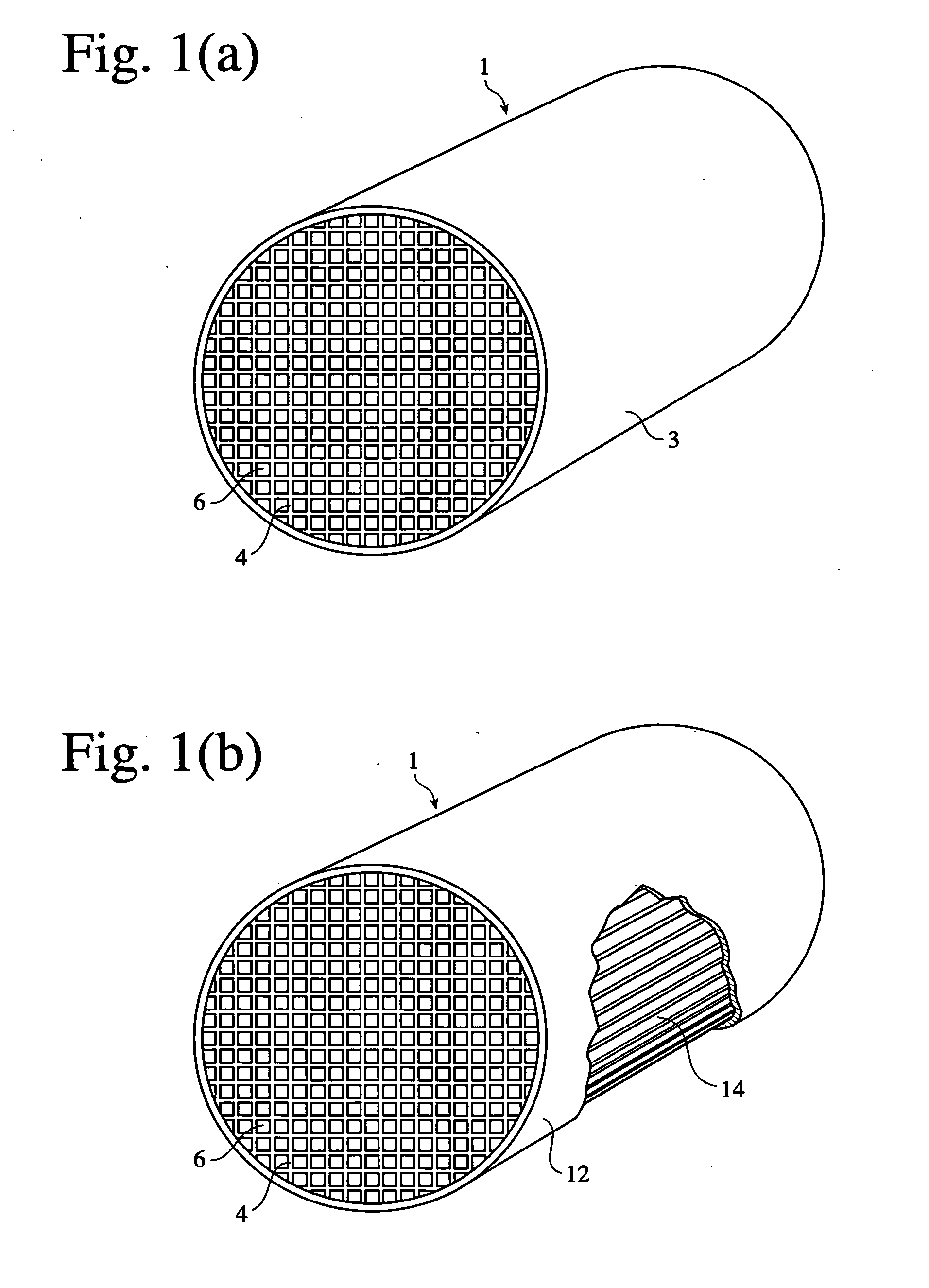
Ceramic Honeycomb Structural Body and Method of Manufacturing the Same
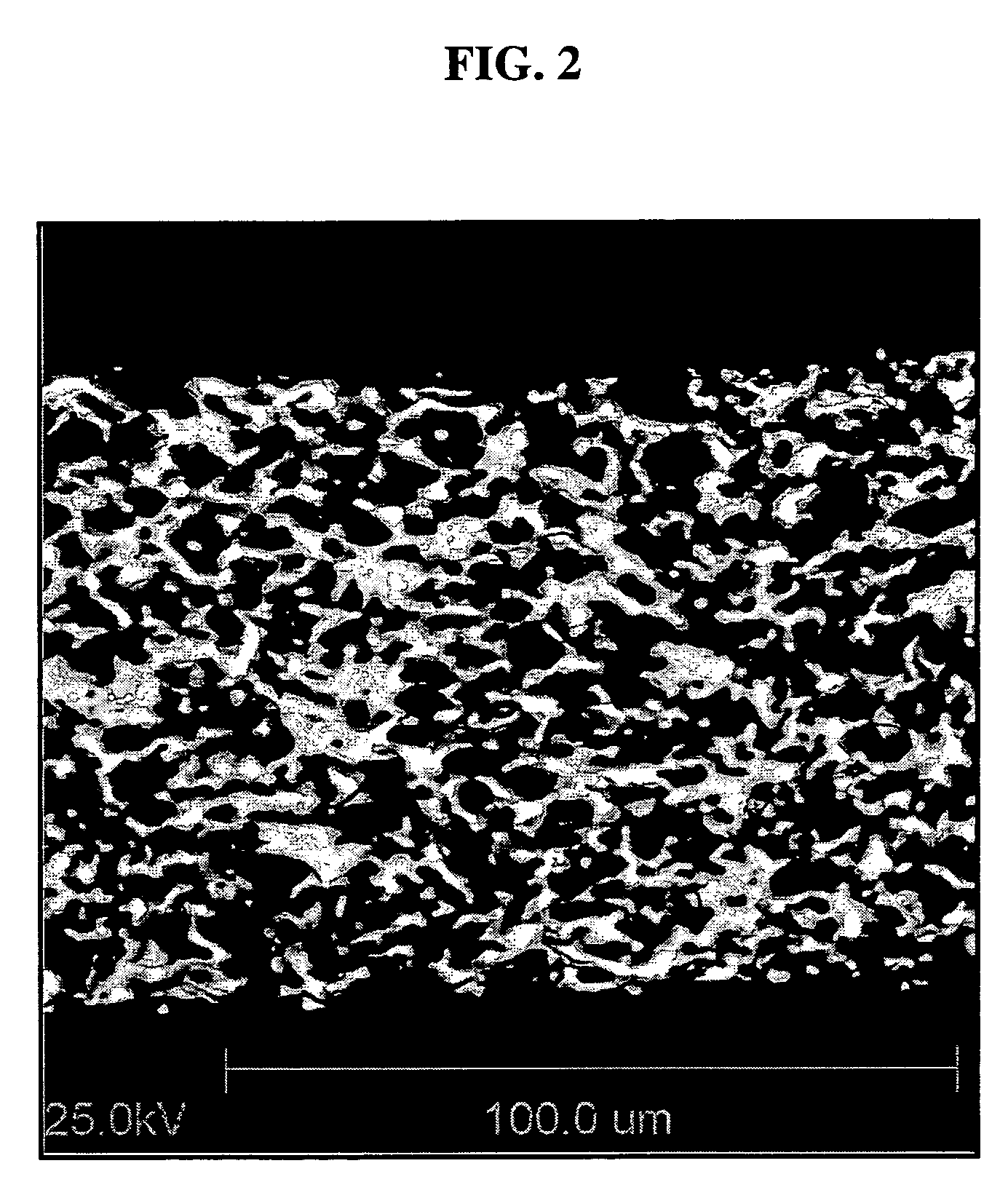
A ceramic honeycomb structural body is manufactured by molding silicon carbide raw powders into a honeycomb pillar shape and then firing it to form a sintered body. The silicon carbide raw powders are comprised of about 60 to about 80% by mass of particles of first particle group having one frequency peak in the particle size distribution and a particle size of 1.0 μm to about 100 μm, and about 20 to about 40% by mass of particles of a second particle group having a particle size of about 0.1 μm or more and less than 1.0 μm.
Owner:IBIDEN CO LTD
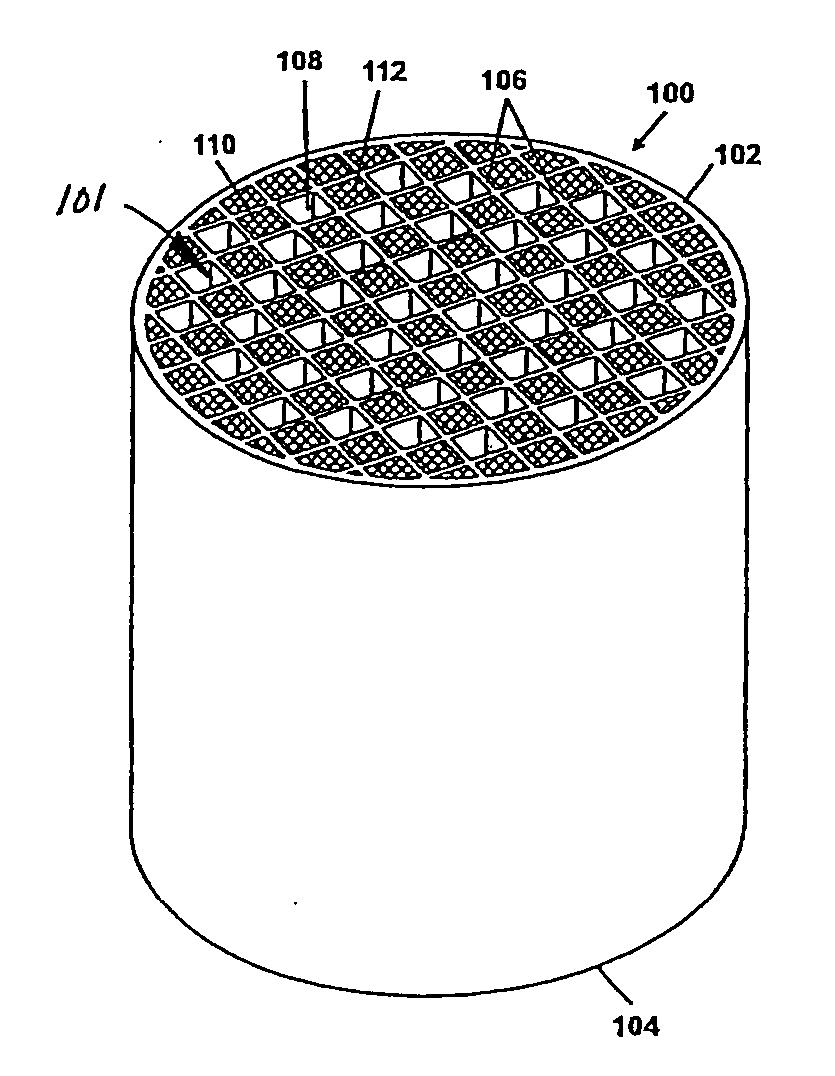
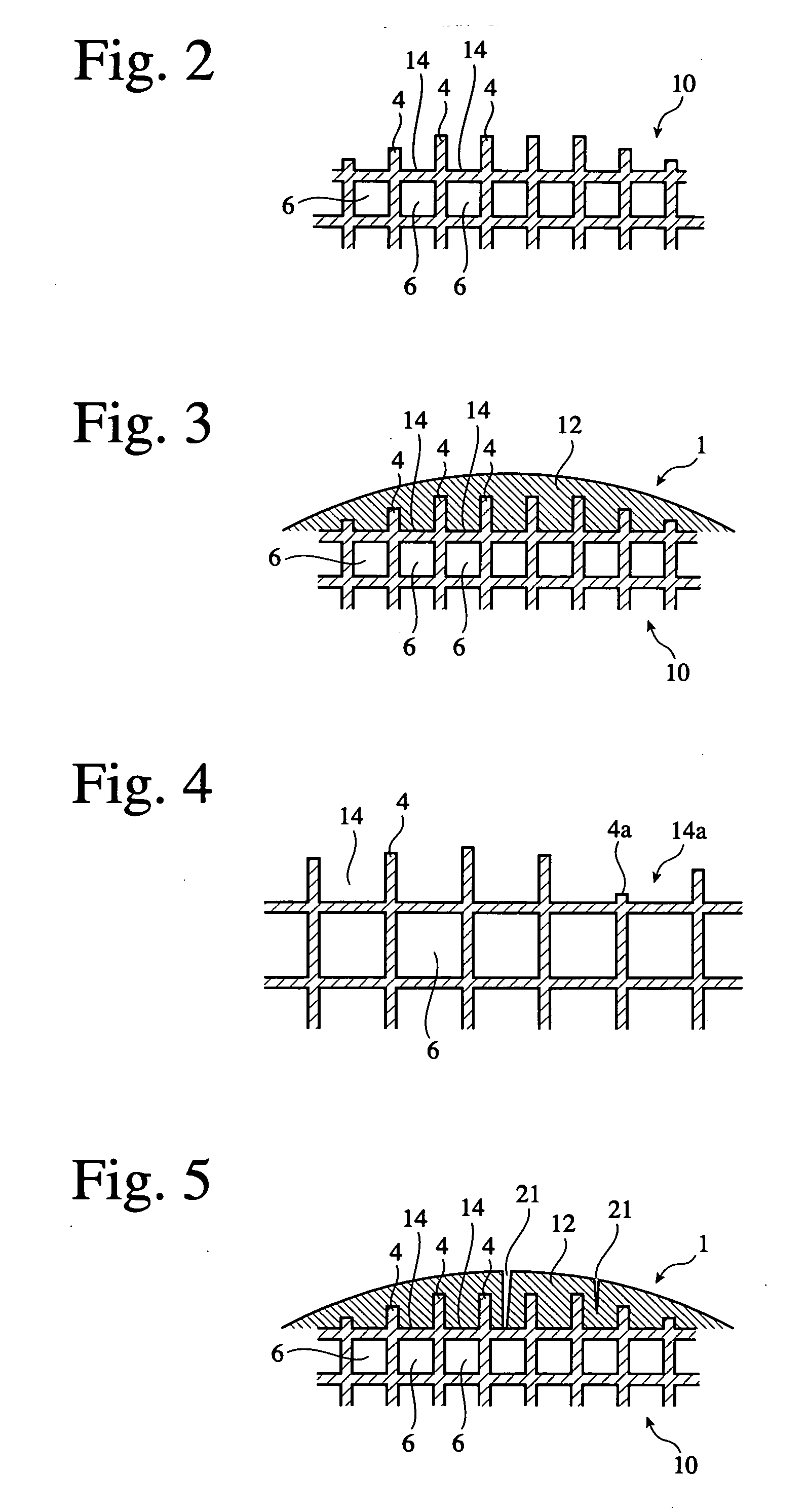
Ceramic honeycomb structure
ActiveUS20060166820A1Excellent in pressure loss and catching efficiencyHigh catalytic activityDispersed particle filtrationExhaust apparatusPore distributionSurface roughness
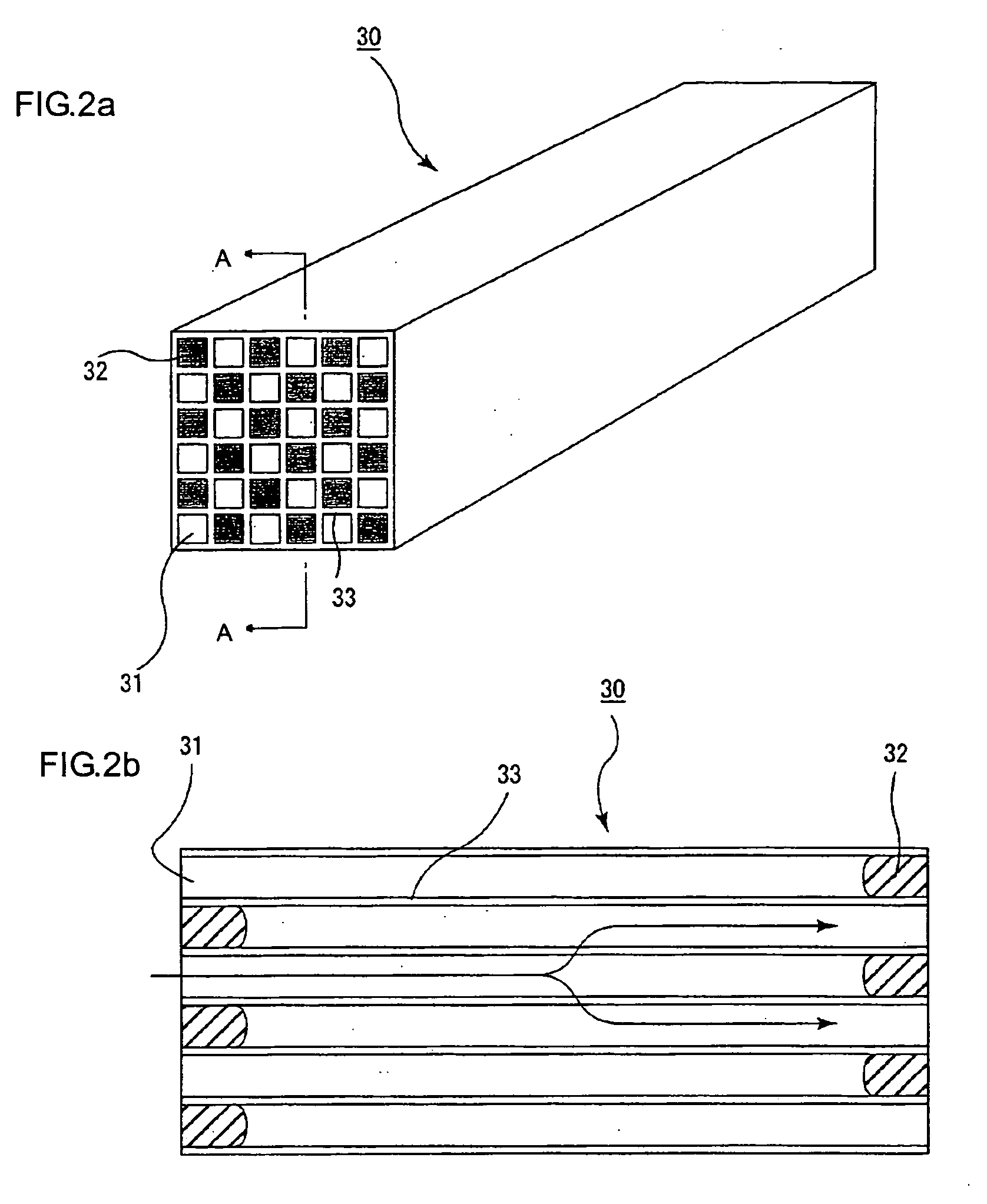
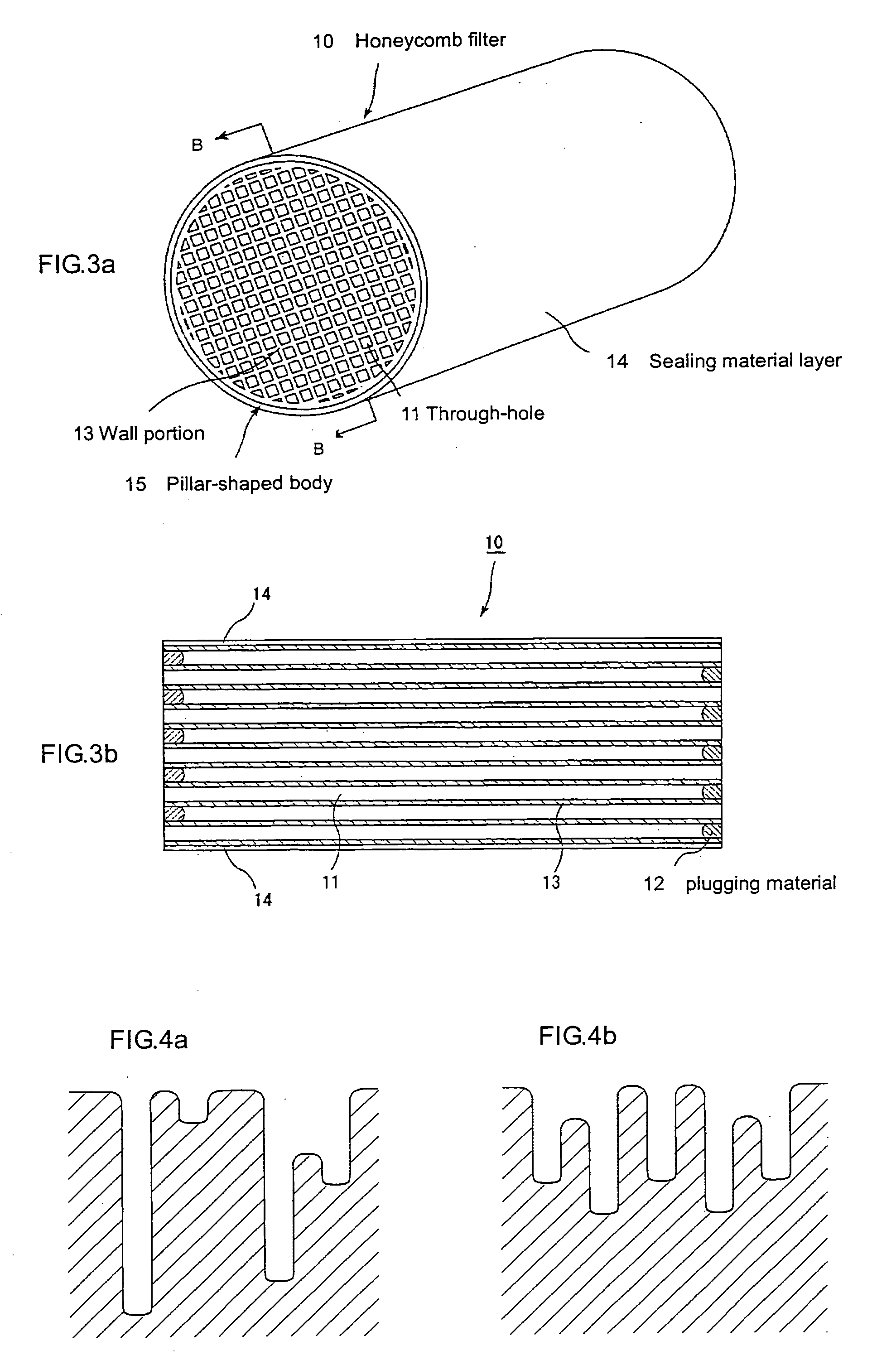
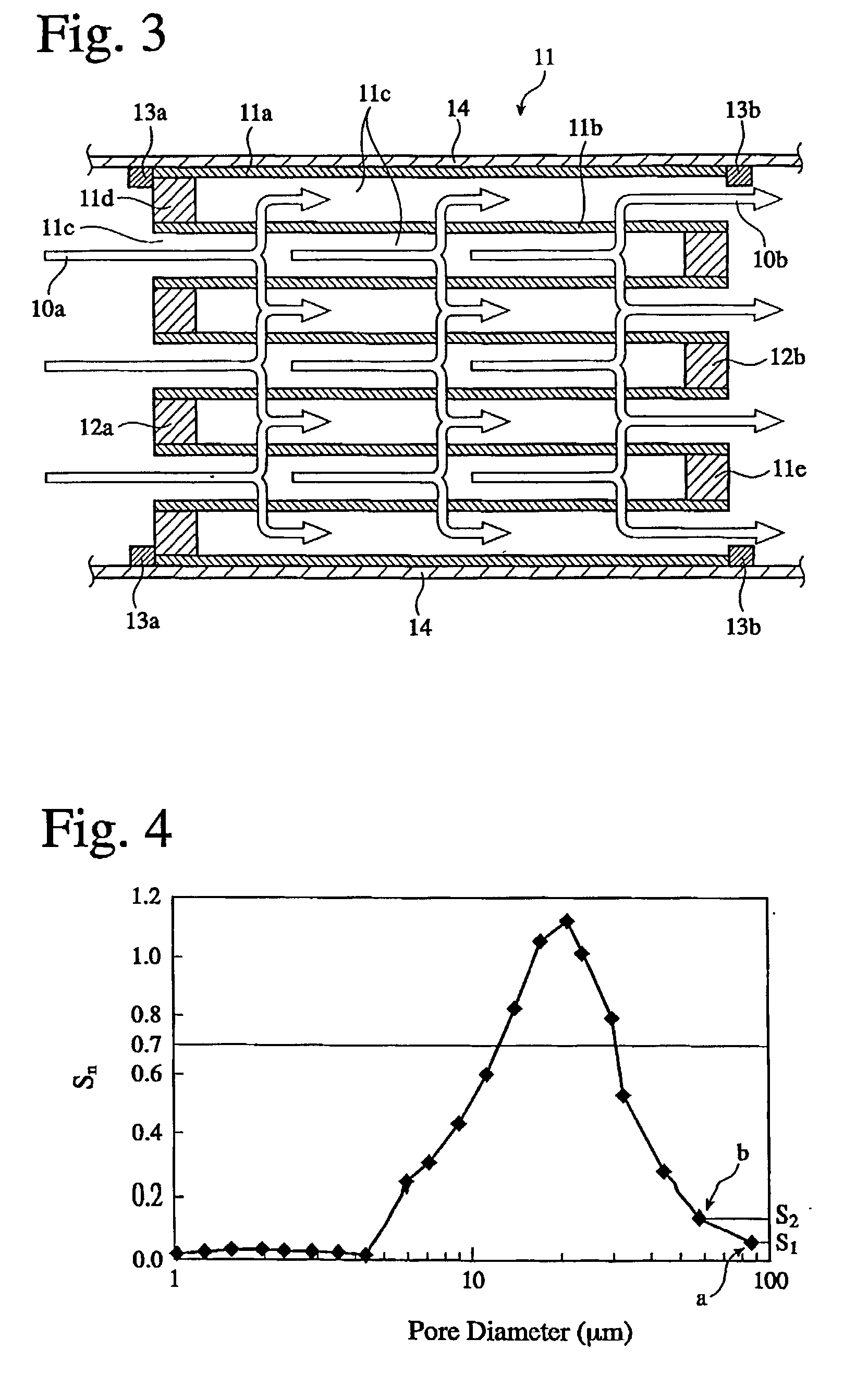
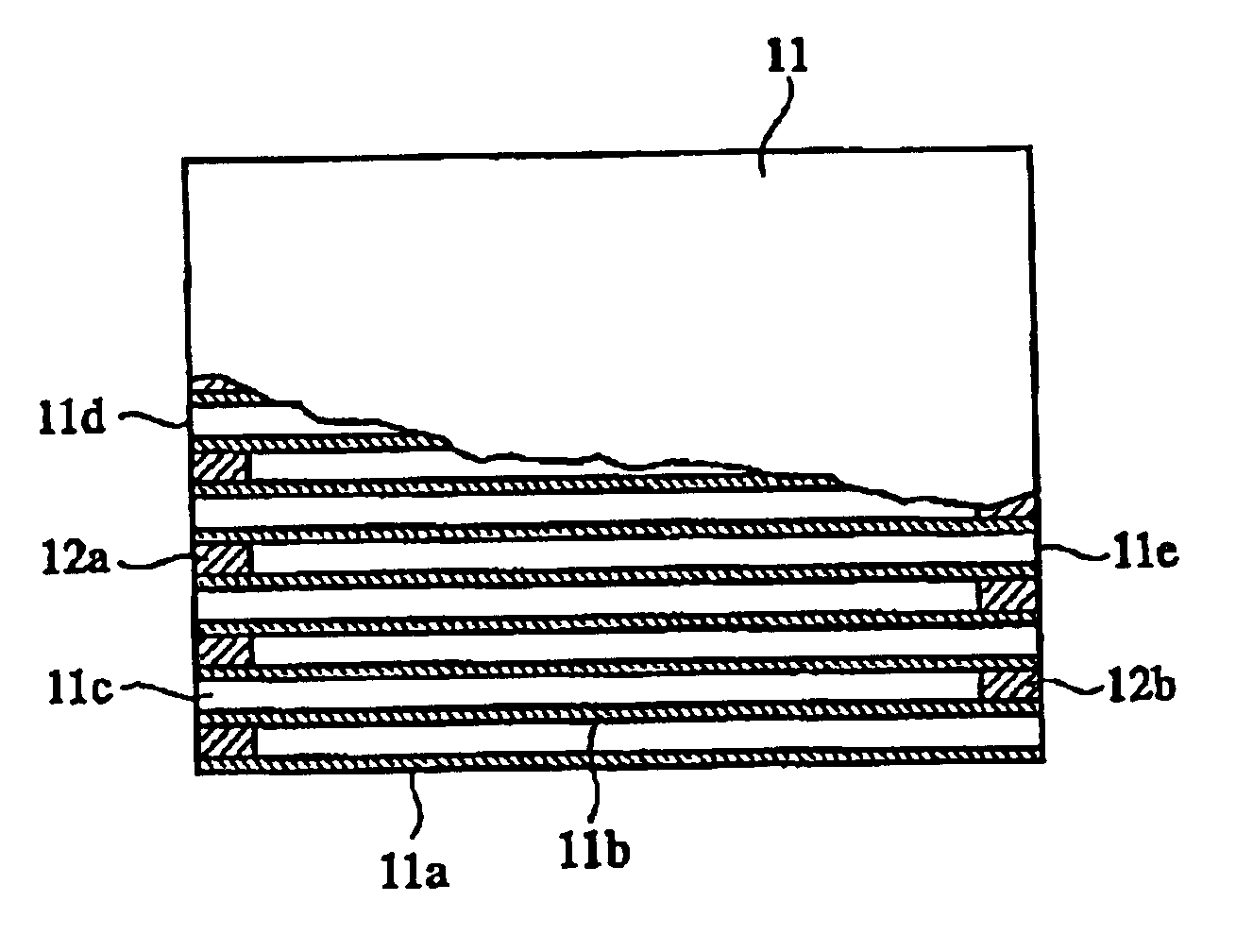
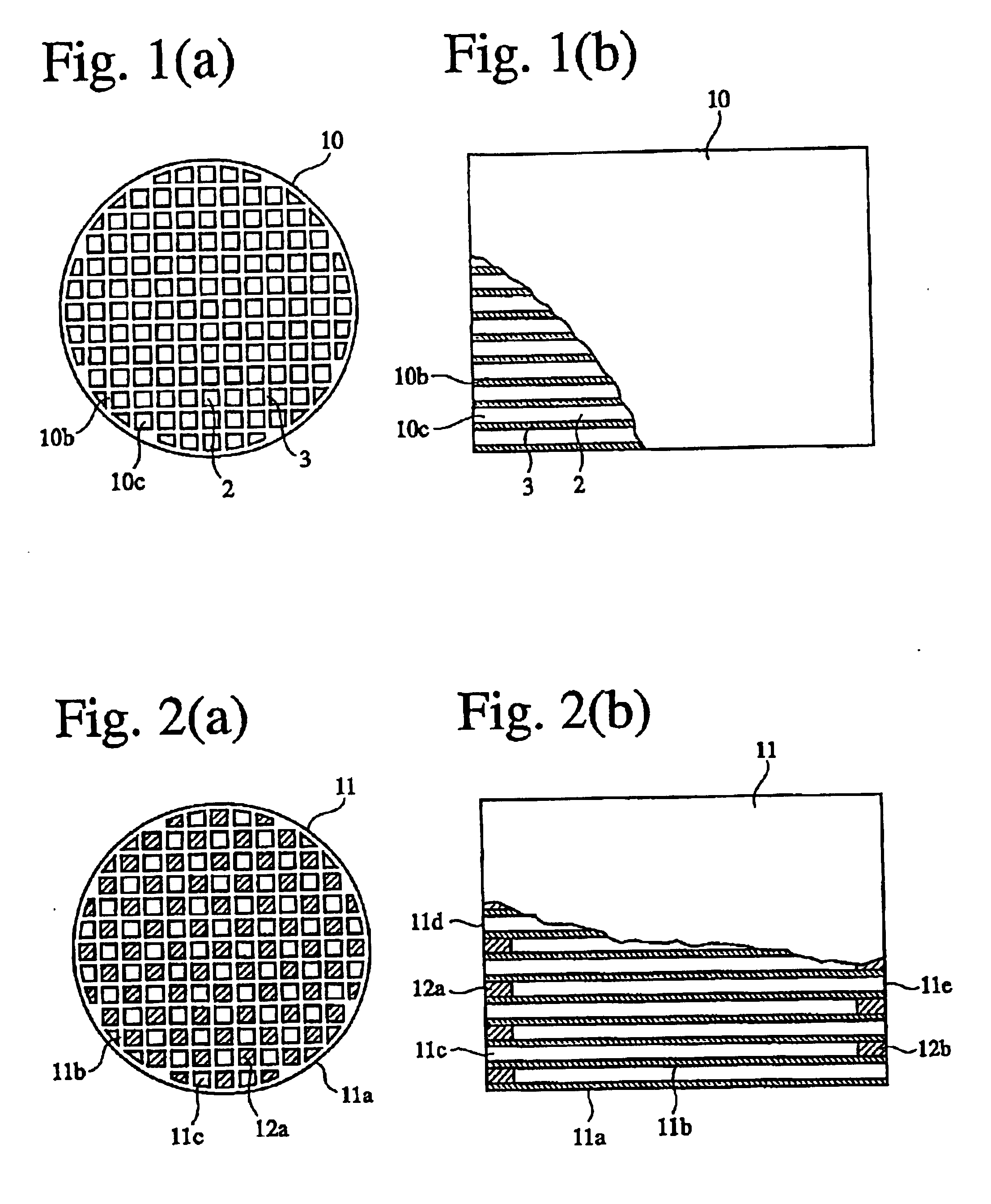
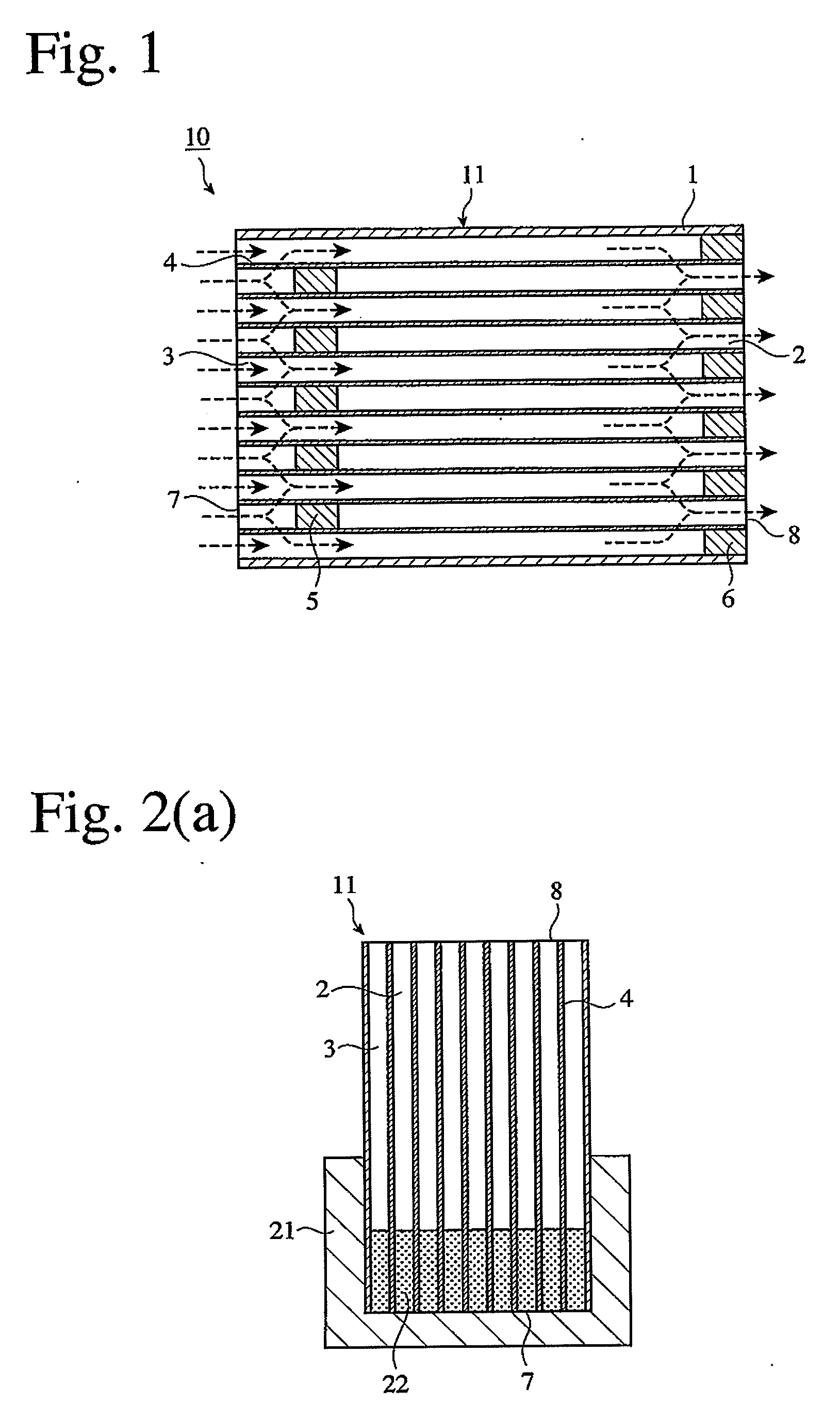
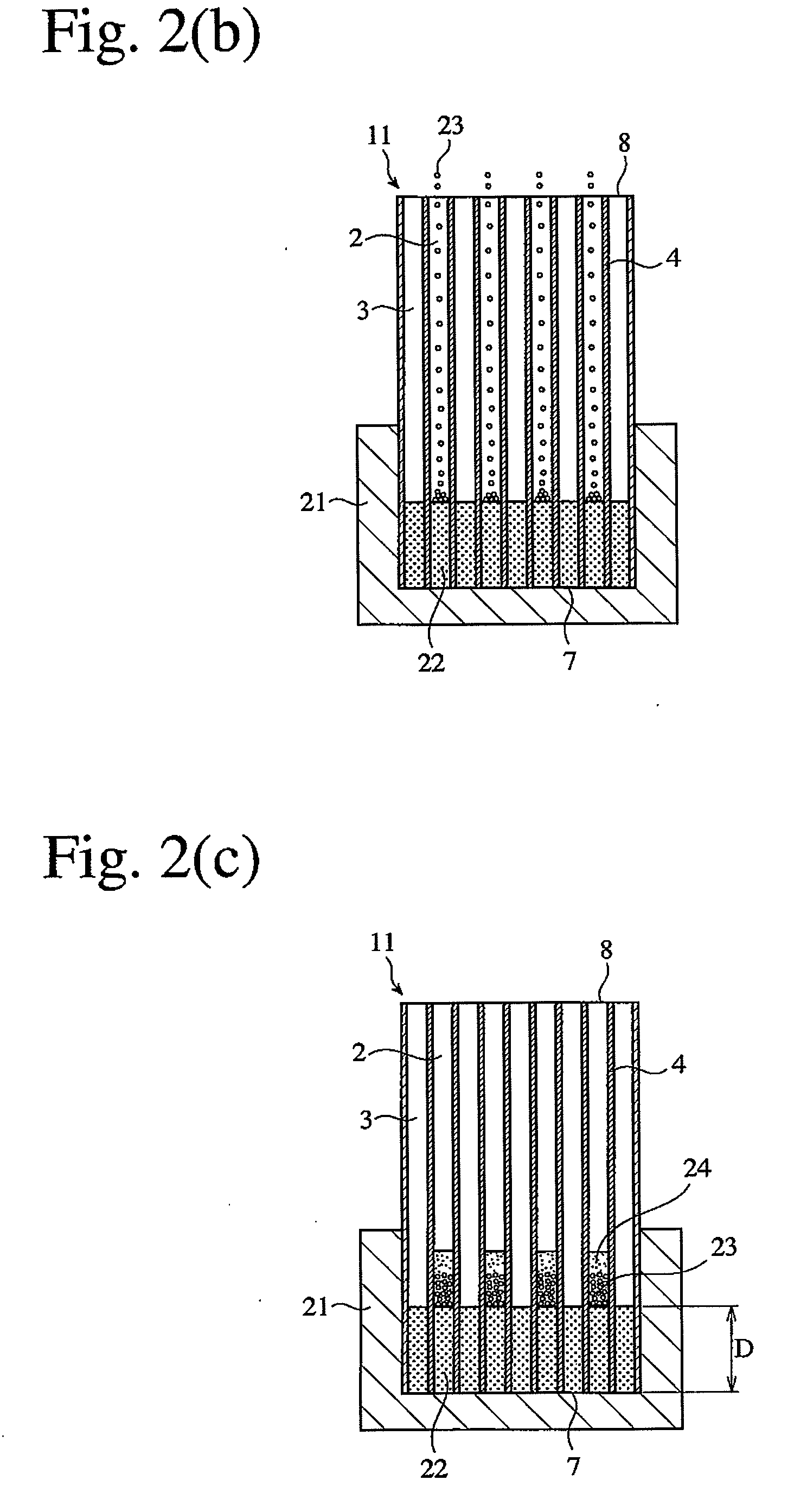
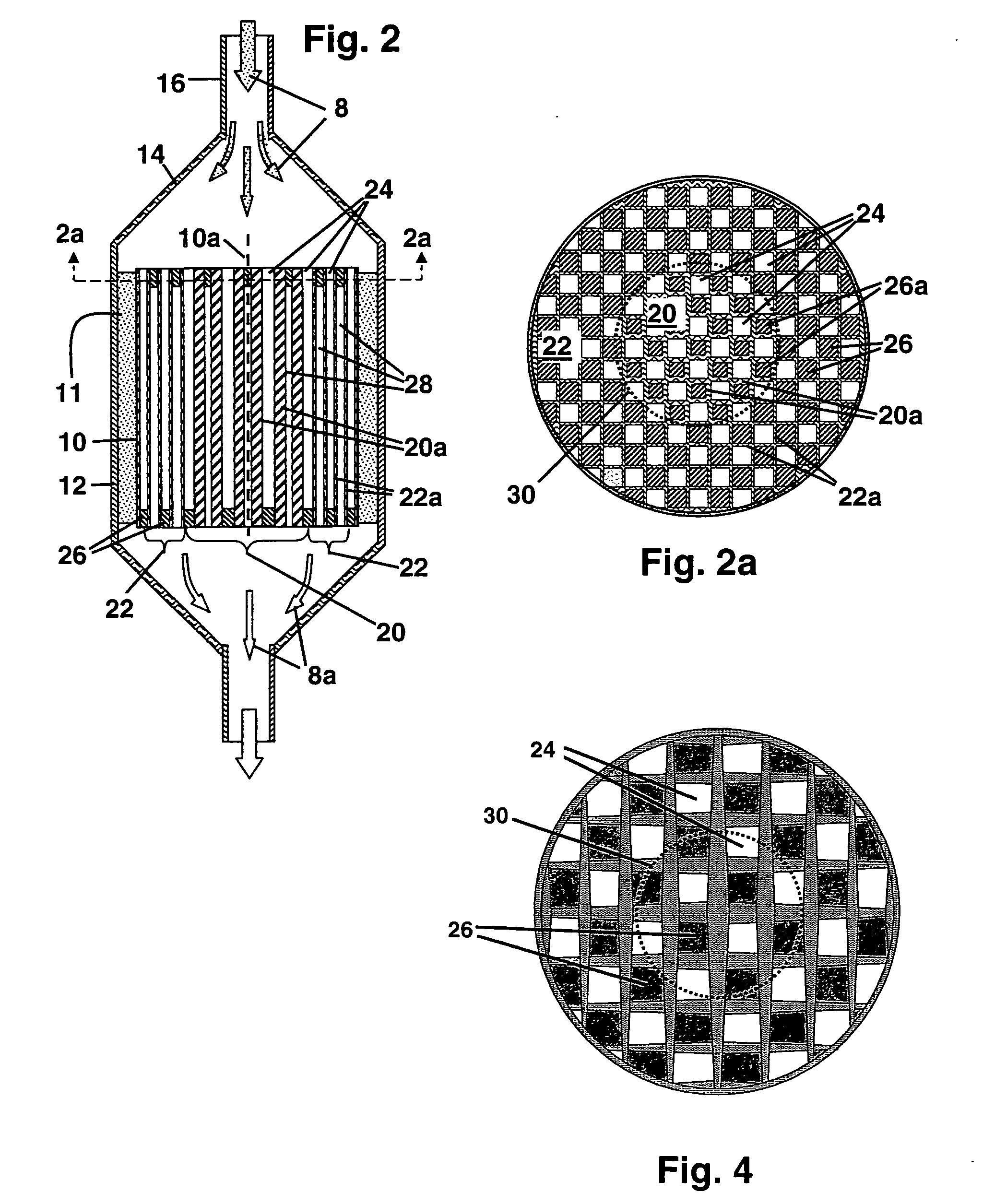
A honeycomb structural body comprises one or plural pillar-shaped porous ceramic members in which many through-holes are arranged side by side in a longitudinal direction through partition walls and either one end portions of these through-holes are sealed. The partition wall forming the structural body has a surface roughness of not less than 10 μm as a maximum roughness Rz defined in JIS B0601-2001 and an average pore size of 5-100 μm in a pore distribution measured by a mercury pressure method, and satisfies the following relationship: A≧90−B / 20 or A≦100−B / 20 when a ratio pores having a pore size of 0.9-1.1 times the average pore size to total pore volume is A (%) and a thickness of the partition wall is B (μm), and there is proposed an effective honeycomb structural body having excellent pressure loss and catching efficiency and a high catalyst reactivity.
Owner:IBIDEN CO LTD
High porosity honeycomb and method
ActiveUS20050069469A1Improved light off performanceHigh porosityCombination devicesDispersed particle filtrationPorosityMicrometer
A ceramic honeycomb substrate for use in an automotive catalytic converter system which exhibits improved light-off performance by virtue of a high porosity of 45 to 75% while still maintaining a wall thickness of greater than 2.0 mil (0.0020 inch, 0.0508 mm), preferably 2.5 mil (0.0025 in., 0.0635 mm) to 7 mil (0.0070 in., 0.1778 mm), and more preferably 2.5 mil (0.0025 in., 0.0635 mm) to 3 mil (0.0030 in., 0.0762 mm). The median pore size is in the range of 2-10 micrometers, and a coefficient of thermal expansion (CTE) (25-800° C.) of less than 15×10−7 / ° C.
Owner:CORNING INC
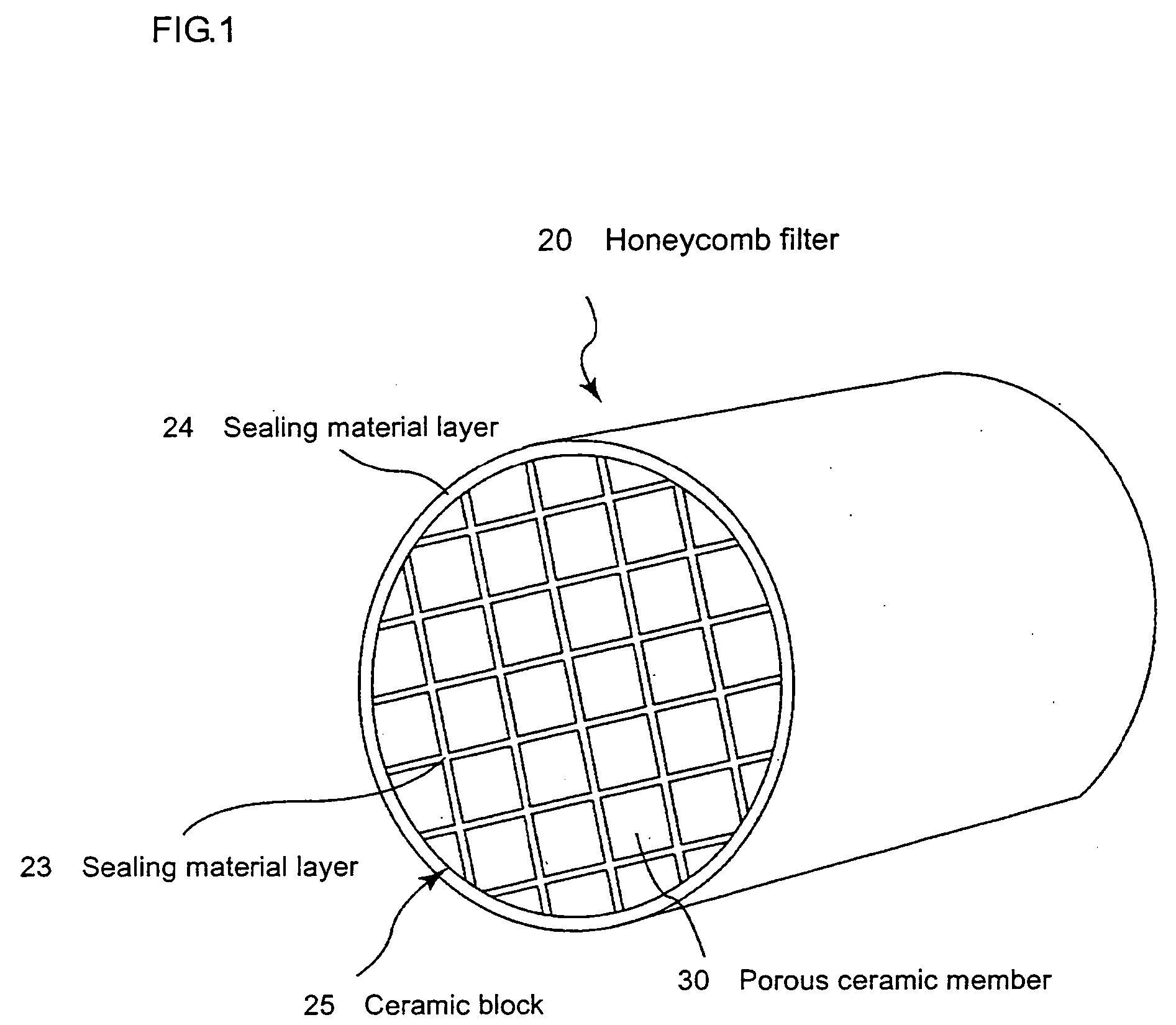
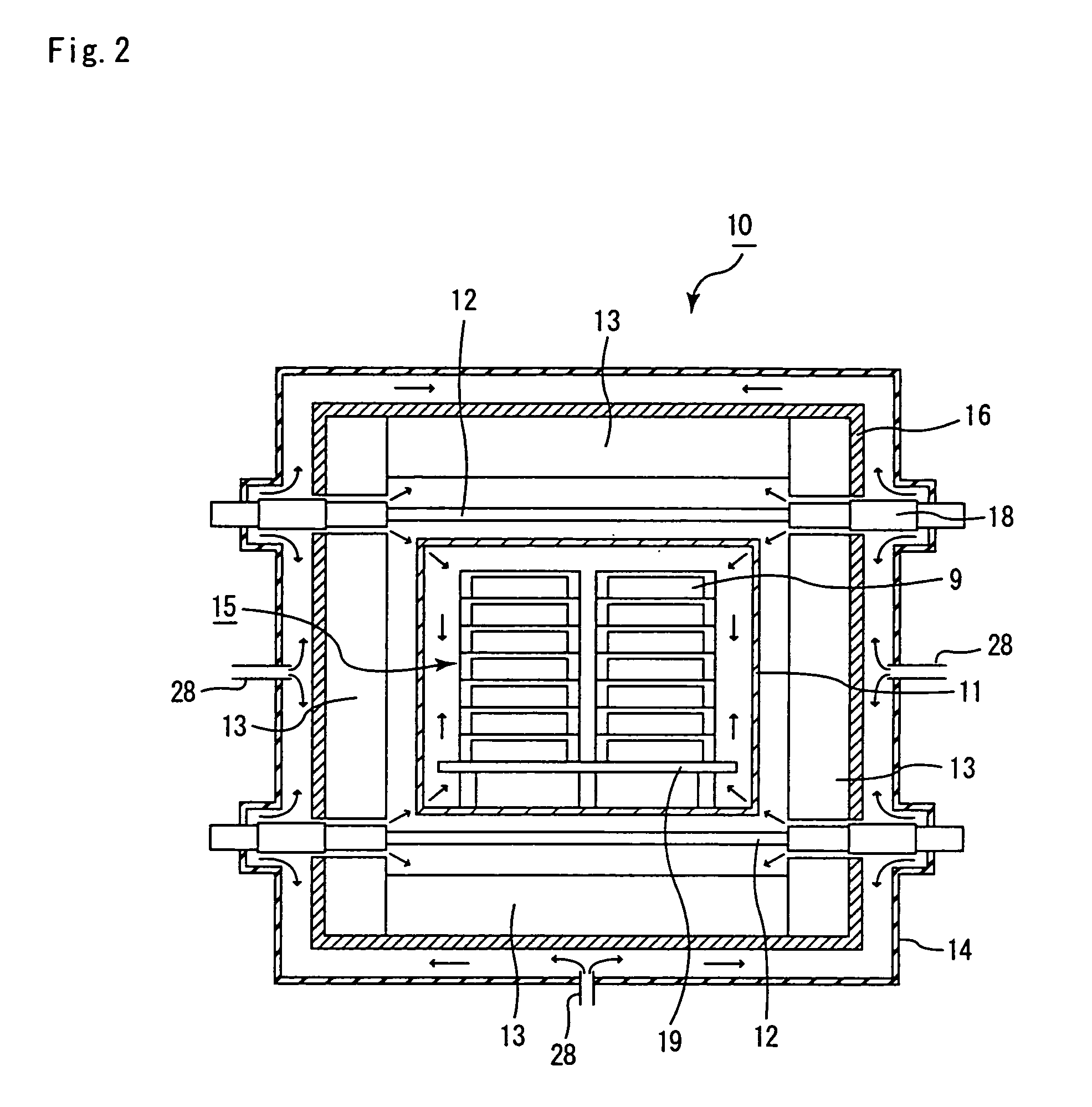
Continuous firing furnace, manufacturing method of porous ceramic member using the same, porous ceramic member, and ceramic honeycomb filter
InactiveUS20060029897A1Ensuring spaceMaintainance of heating chambersCharge manipulationMetallurgyPorous ceramics
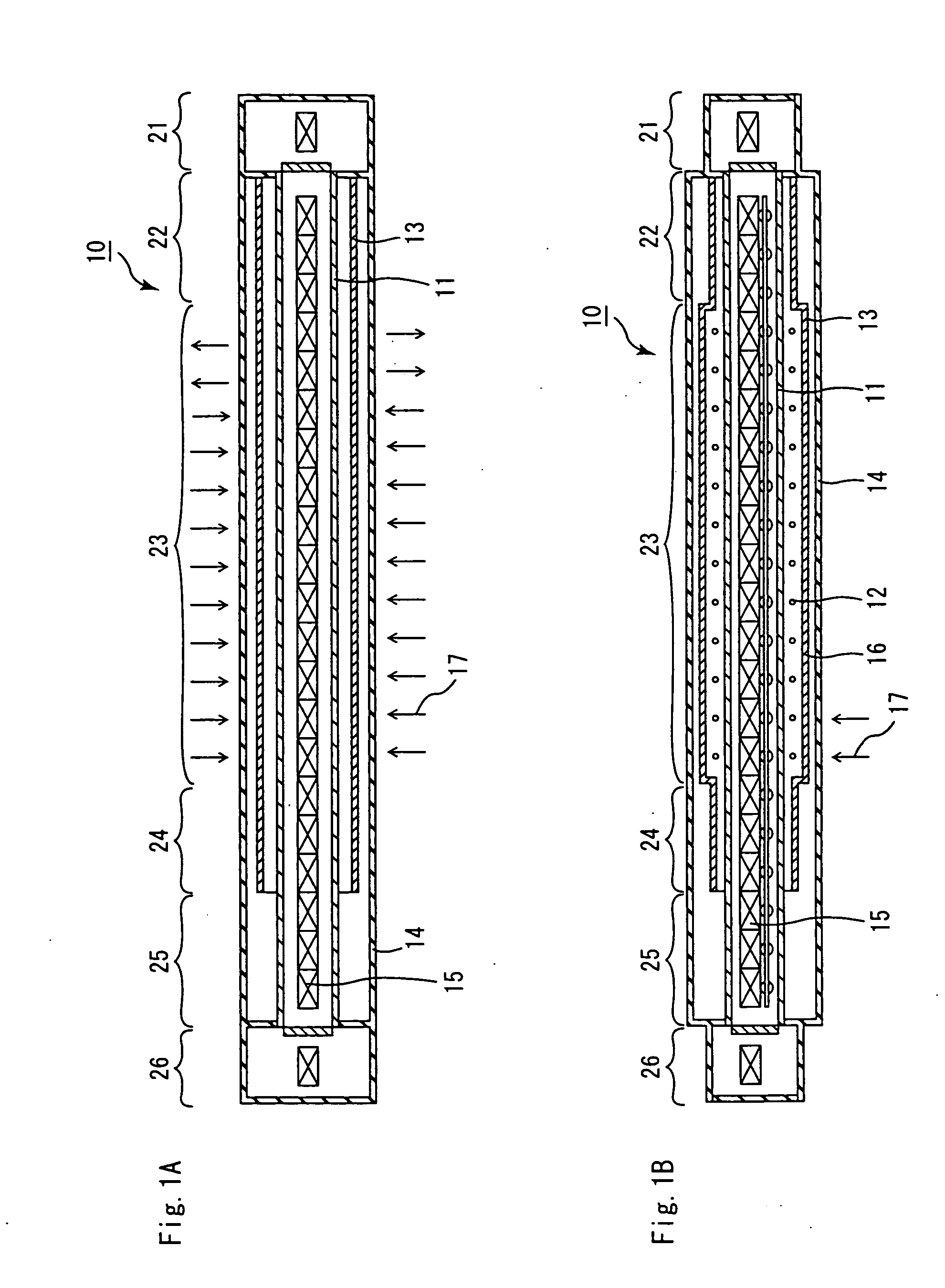
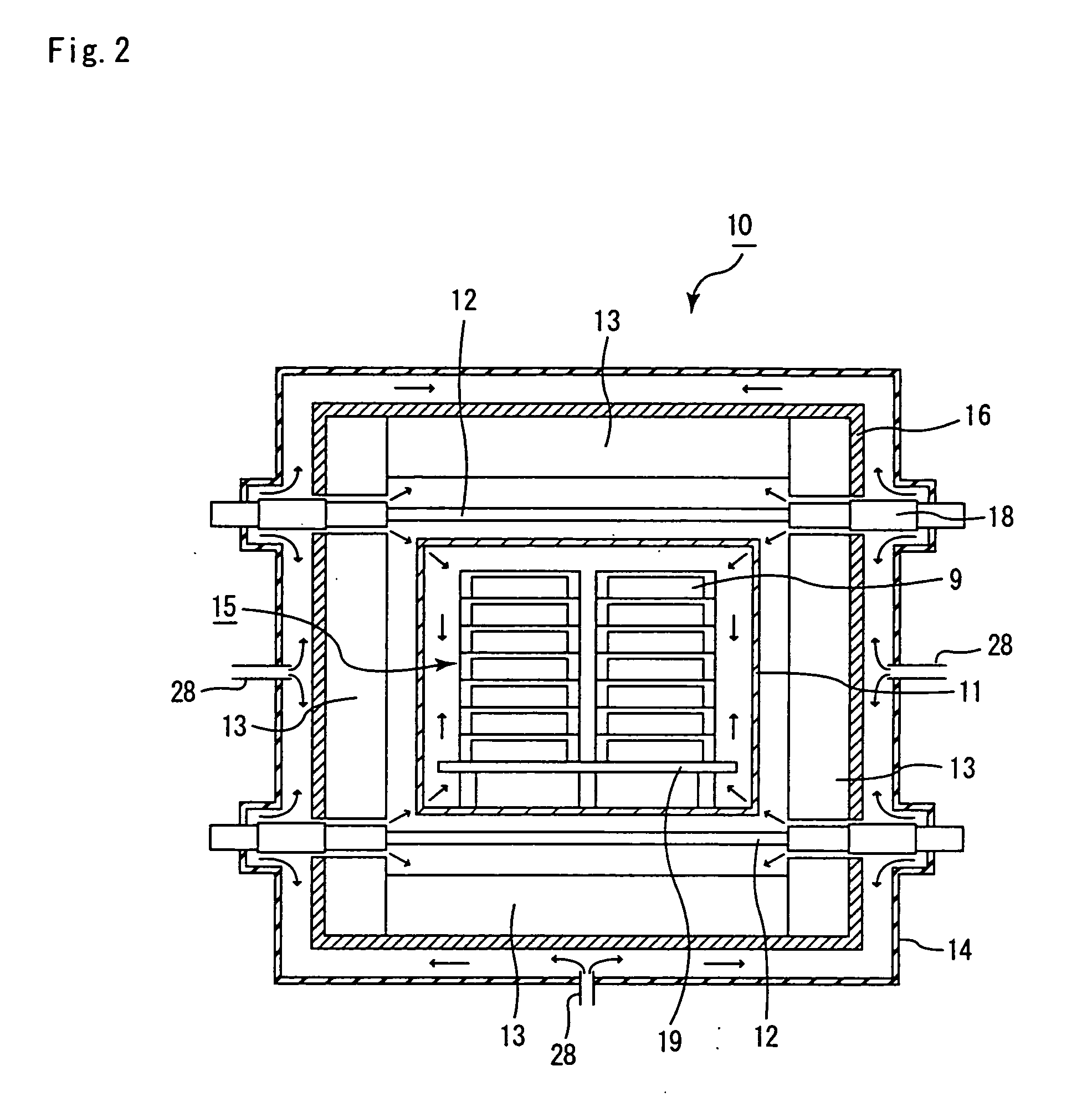
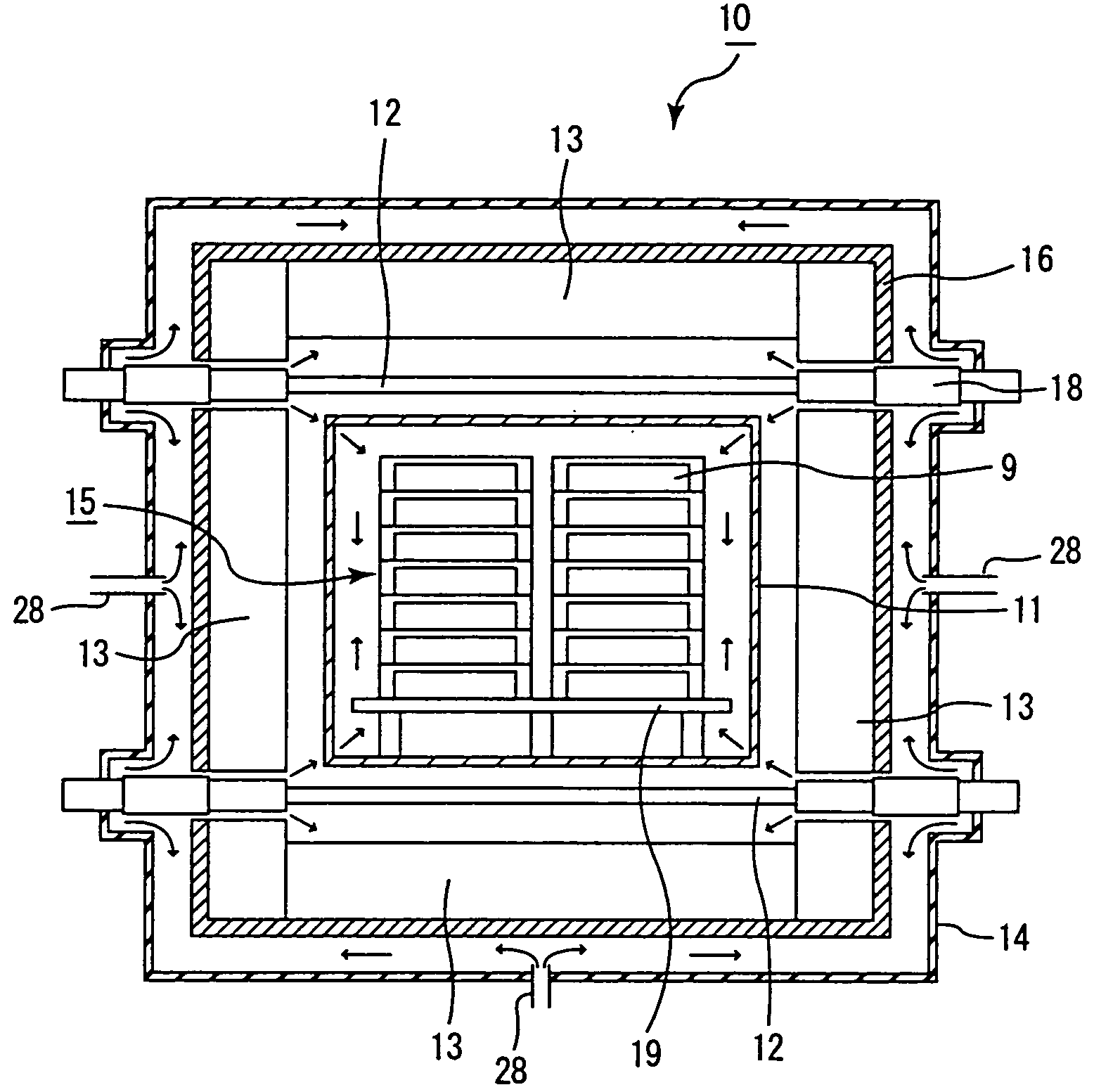
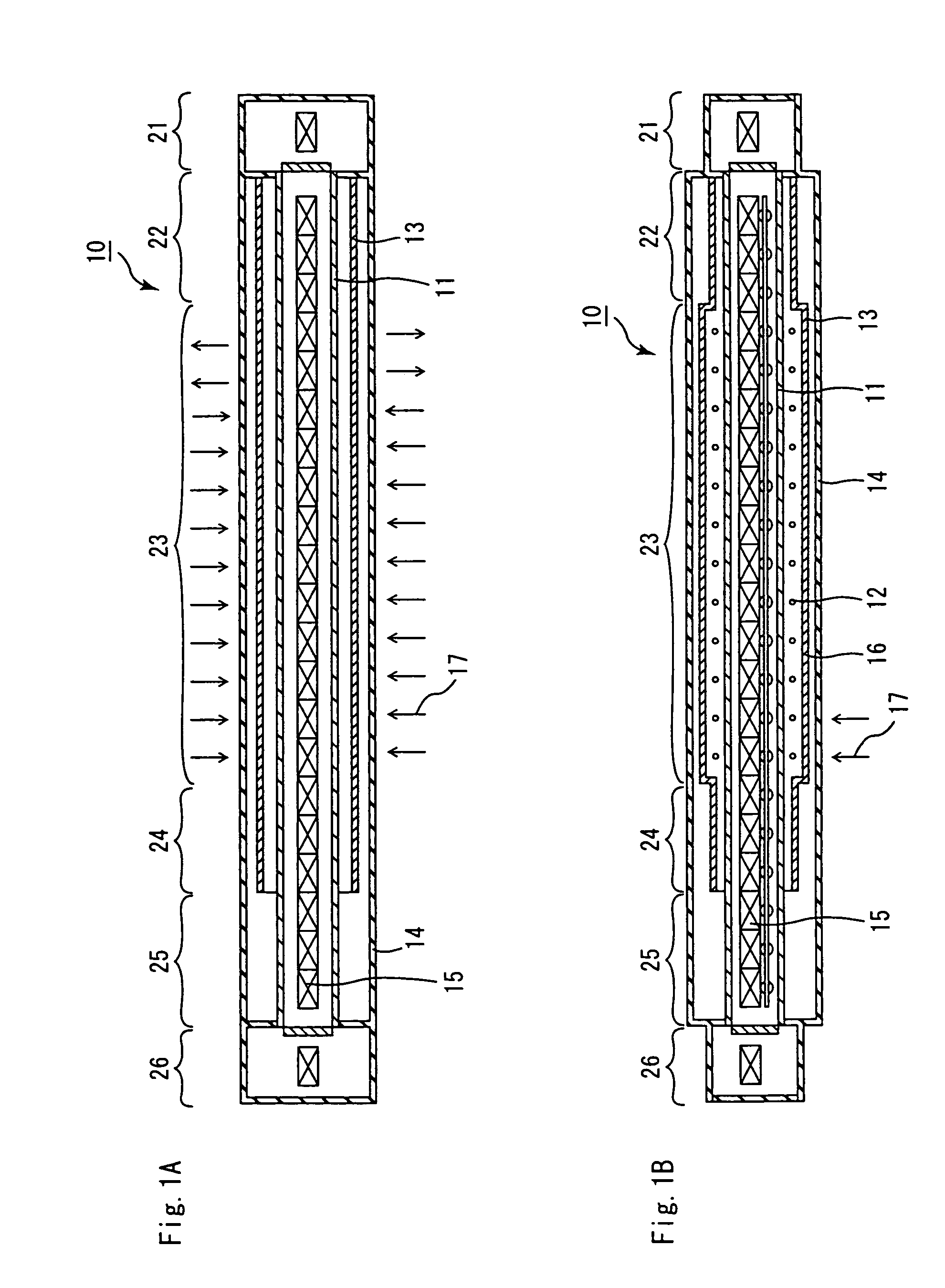
A continuous firing furnace of the present invention comprises: a muffle formed into a cylindrical shape so as to ensure a predetermined space; a plurality of heat generators placed at the peripheral direction from the muffle; and a heat insulating layer formed in a manner so as to enclose said muffle and said heat generators therein, said continuous firing furnace being configured such that a formed body to be fired, which is transported from an inlet side, passes through the inside of said muffle at a predetermined speed in an inert gas atmosphere and, then, is discharged from an outlet so that said formed body is fired, wherein said inert gas flows through: a space between said muffle and said heat insulating layer; and a space inside the muffle, in sequence.
Owner:IBIDEN CO LTD
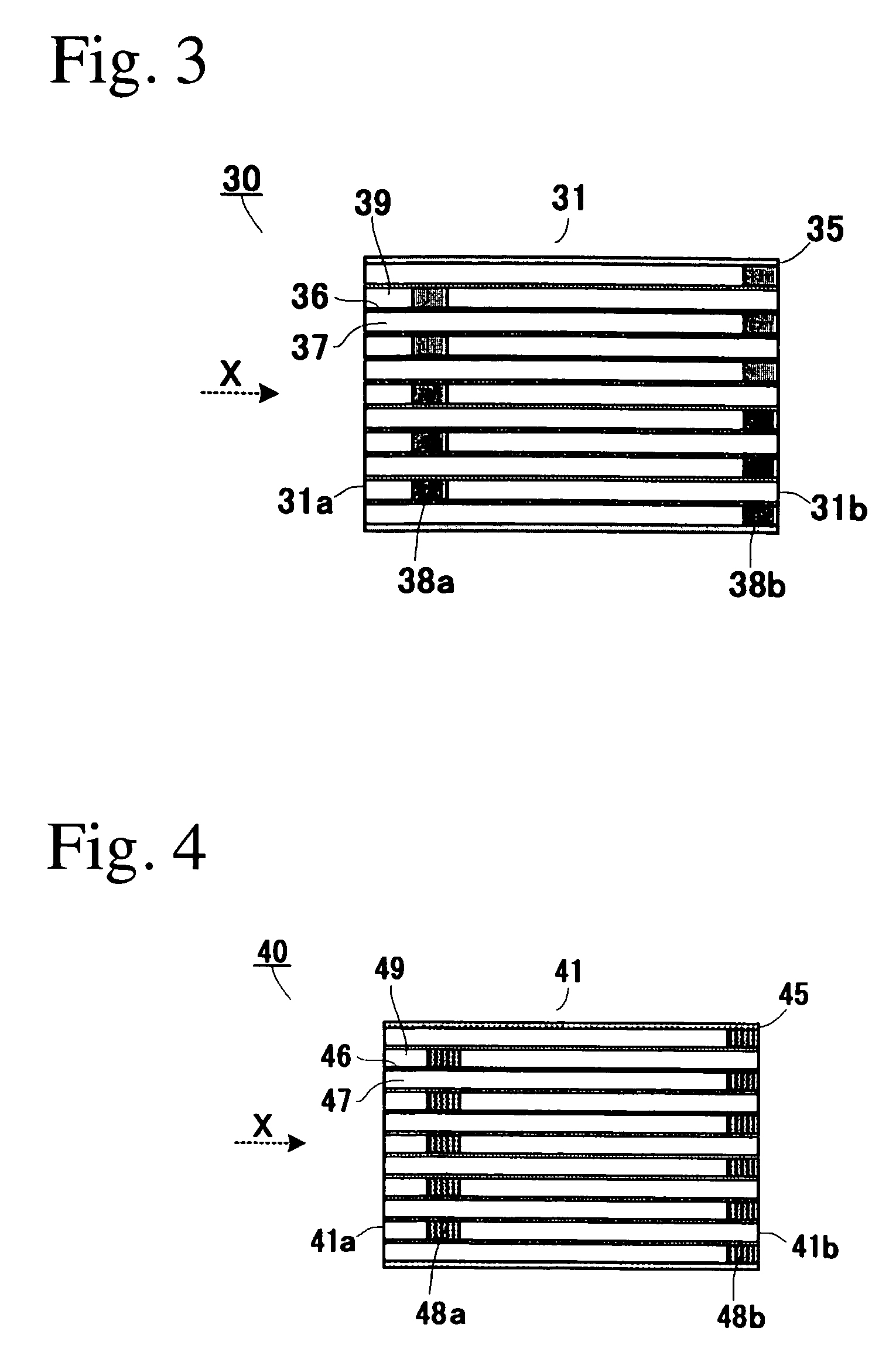
Ceramic honeycomb filter
InactiveUS20030093982A1Increased durabilityHigh strengthCombination devicesAuxillary pretreatmentParticulatesMeasurement point
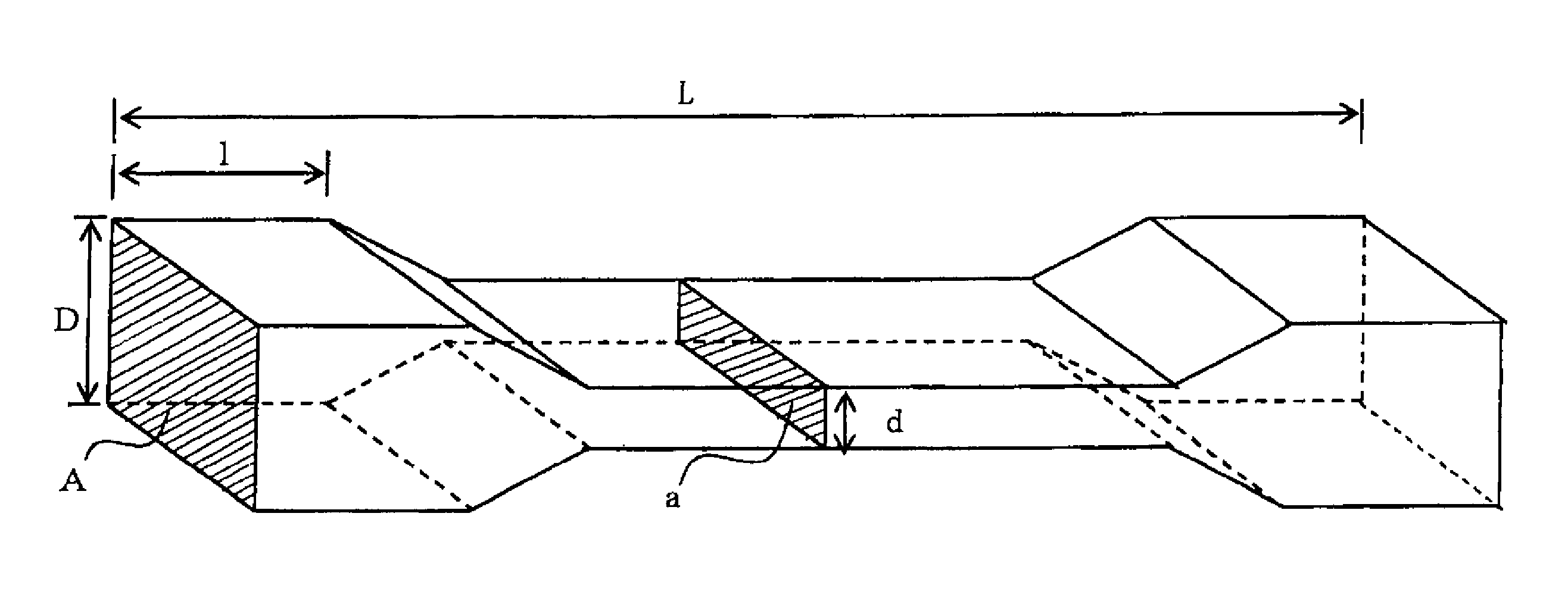
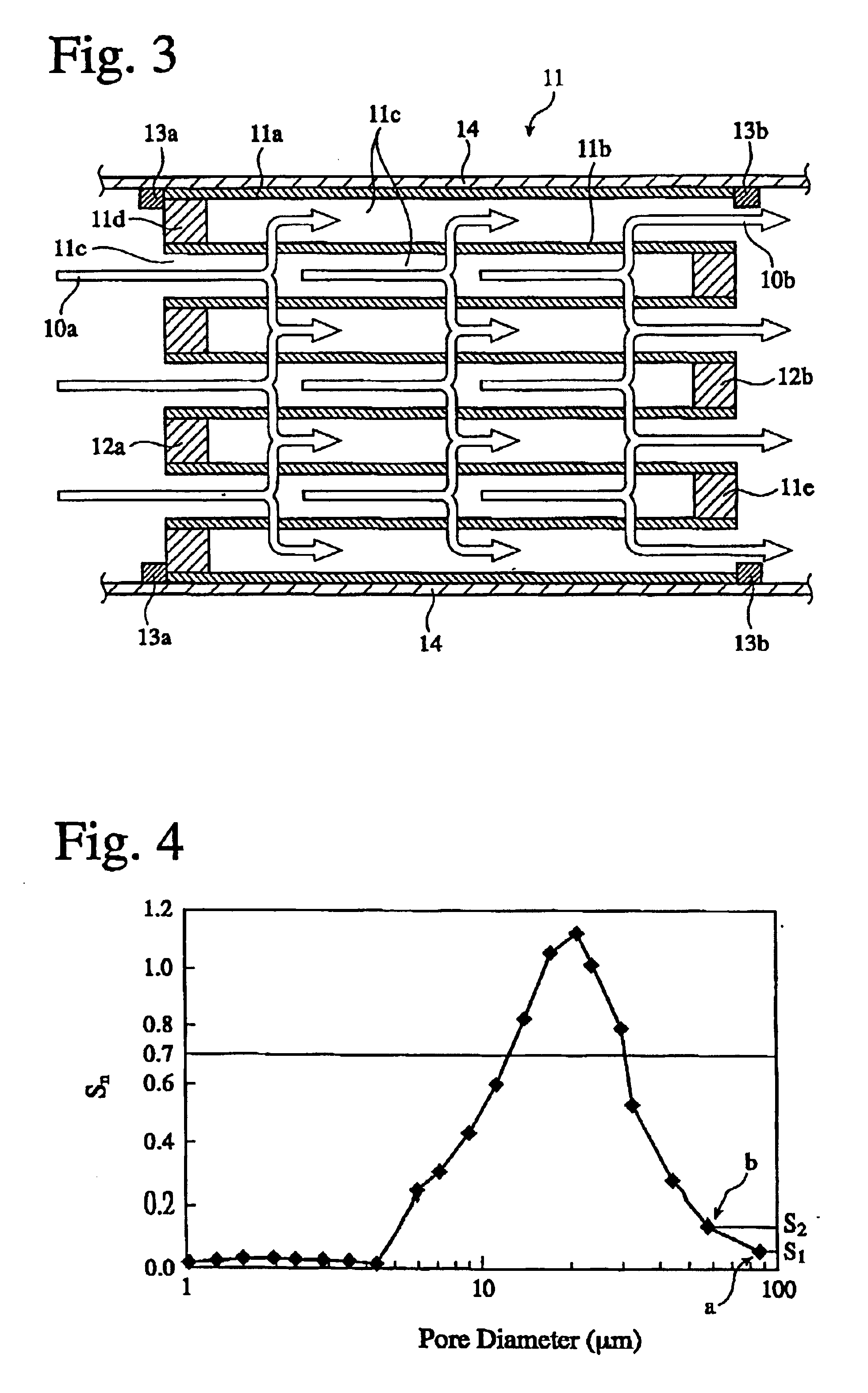
A ceramic honeycomb filter comprising a ceramic honeycomb structure having porous partition walls defining a plurality of flow paths for flowing an exhaust gas through the porous partition walls to remove particulates from the exhaust gas, the predetermined flow paths among the flow paths being sealed at their ends, a catalyst being carried by the porous partition walls, the porous partition walls having a porosity of 60-75% and an average pore diameter of 15-25 mum when measured according to a mercury penetration method, and the maximum of a slope Sn of a cumulative pore volume curve of the porous partition walls relative to a pore diameter obtained at an n-th measurement point being 0.7 or more, the Sb being represented by the following formula (1): Sn=-(Vb-Vn-1) / [log Dn-log (Dn-1)] (1), wherein Dn is a pore diameter (mum) at an n-th measurement point, Dn-1 is a pore diameter (mum) at an (n-1)-th measurement point, Vn is a cumulative pore volume (cm3 / g) at an n-th measurement point, and Vn-1 is a cumulative pore volume (cm3 / g) at an (n-1)-th measurement point.
Owner:HITACHI METALS LTD +1
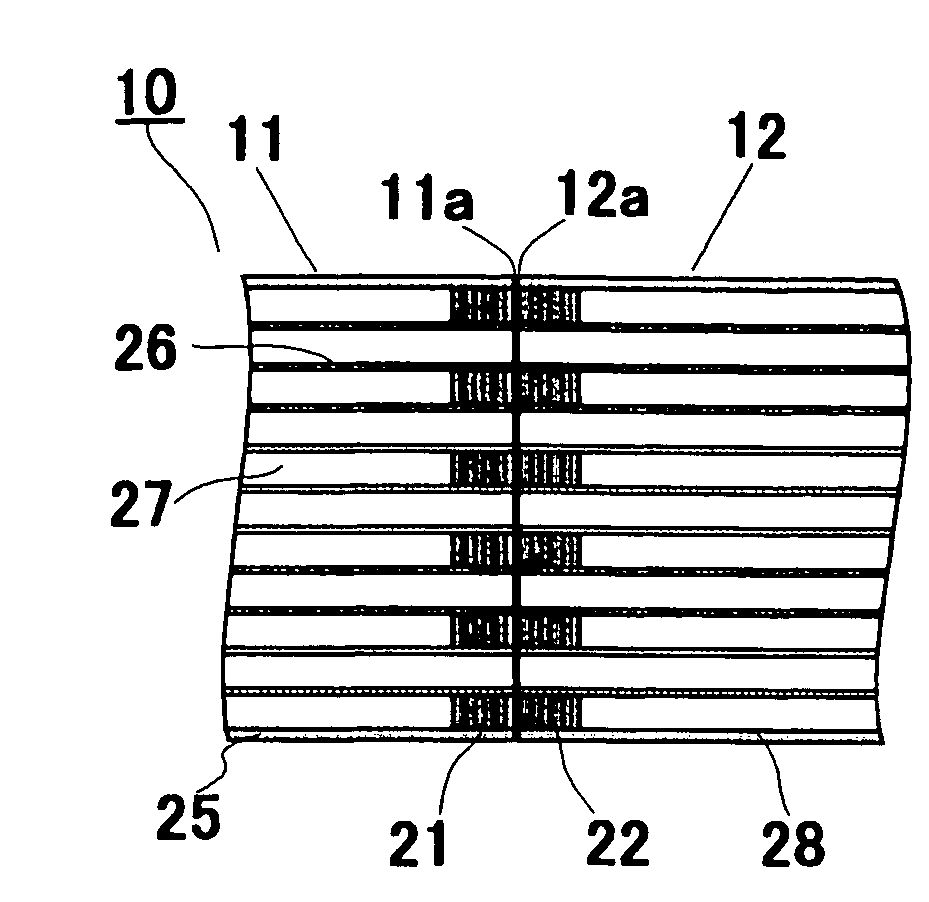
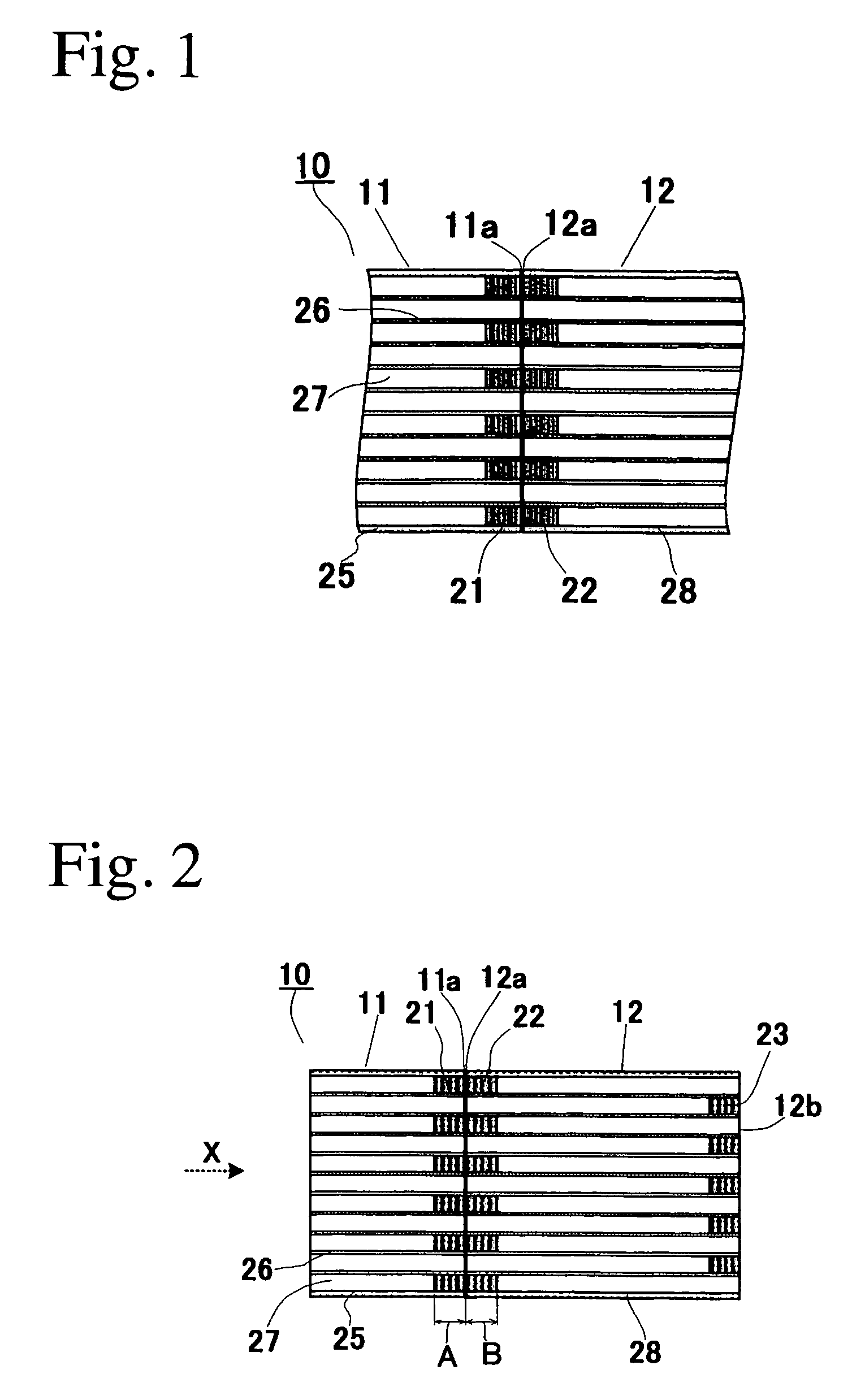
Ceramic honeycomb structural body
ActiveUS7438967B2Increase the cross-sectional areaPhysical/chemical process catalystsDispersed particle filtrationCell wallMaterials science
Owner:IBIDEN CO LTD
Ceramic honeycomb filter
InactiveUS6827754B2Increased durabilityHigh strengthCombination devicesAuxillary pretreatmentParticulatesMeasurement point
A ceramic honeycomb filter comprising a ceramic honeycomb structure having porous partition walls defining a plurality of flow paths for flowing an exhaust gas through the porous partition walls to remove particulates from the exhaust gas, the predetermined flow paths among the flow paths being sealed at their ends, a catalyst being carried by the porous partition walls, the porous partition walls having a porosity of 60-75% and an average pore diameter of 15-25 mum when measured according to a mercury penetration method, and the maximum of a slope Sn of a cumulative pore volume curve of the porous partition walls relative to a pore diameter obtained at an n-th measurement point being 0.7 or more, the Sn being represented by the following formula (1):wherein Dn is a pore diameter (mum) at an n-th measurement point, Dn-1 is a pore diameter (mum) at an (n-1)-th measurement point, Vn is a cumulative pore volume (cm<3> / g) at an n-th measurement point, and Vn-1 is a cumulative pore volume (cm<3> / g) at an (n-1)-th measurement point.
Owner:HITACHI METALS LTD +1
Porous cordierite ceramic honeycomb article with improved strength and method of manufacturing same
ActiveUS20070119133A1Reduce the amount requiredIncrease volume fractionCombination devicesAuxillary pretreatmentCordieritesSilicon dioxide
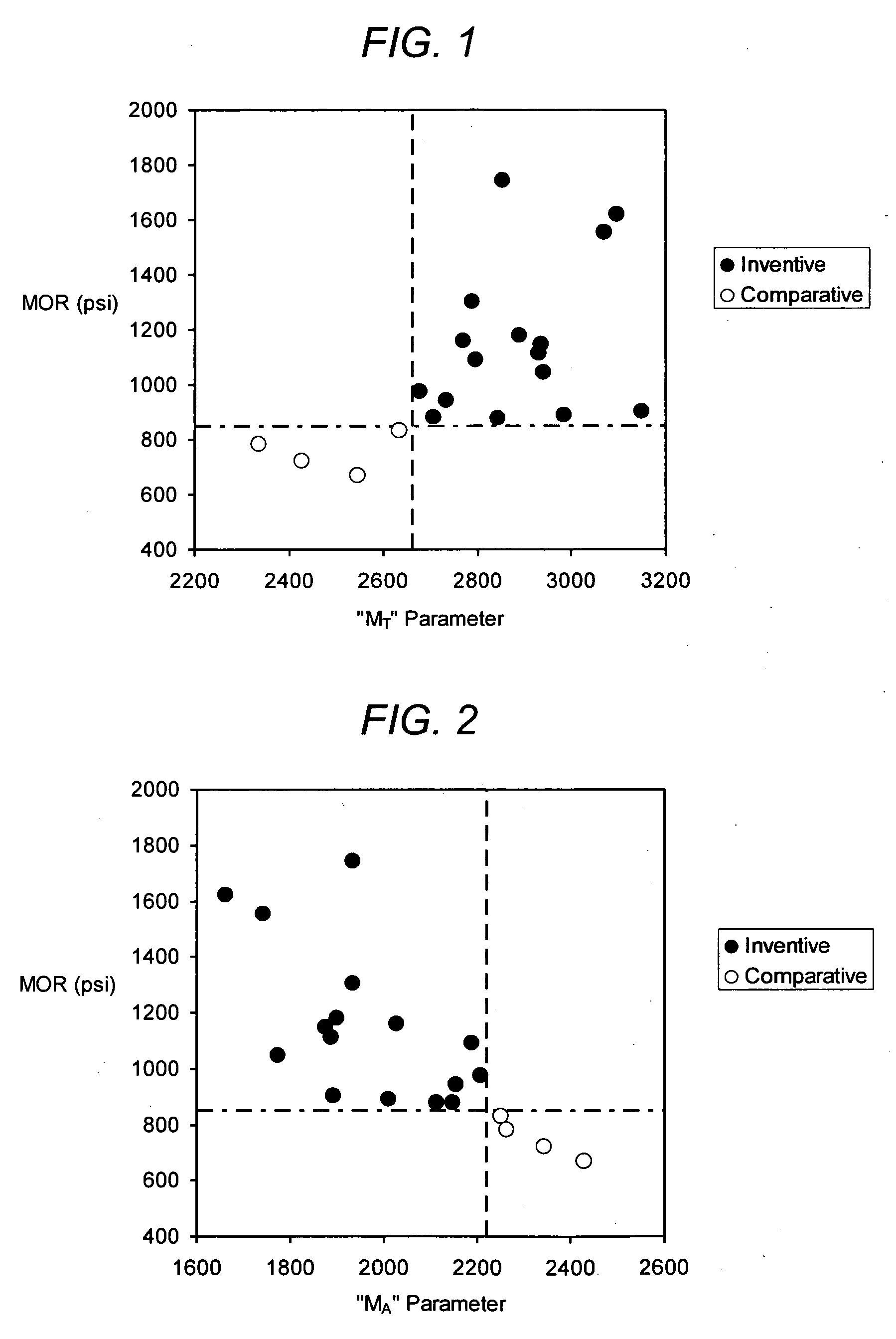
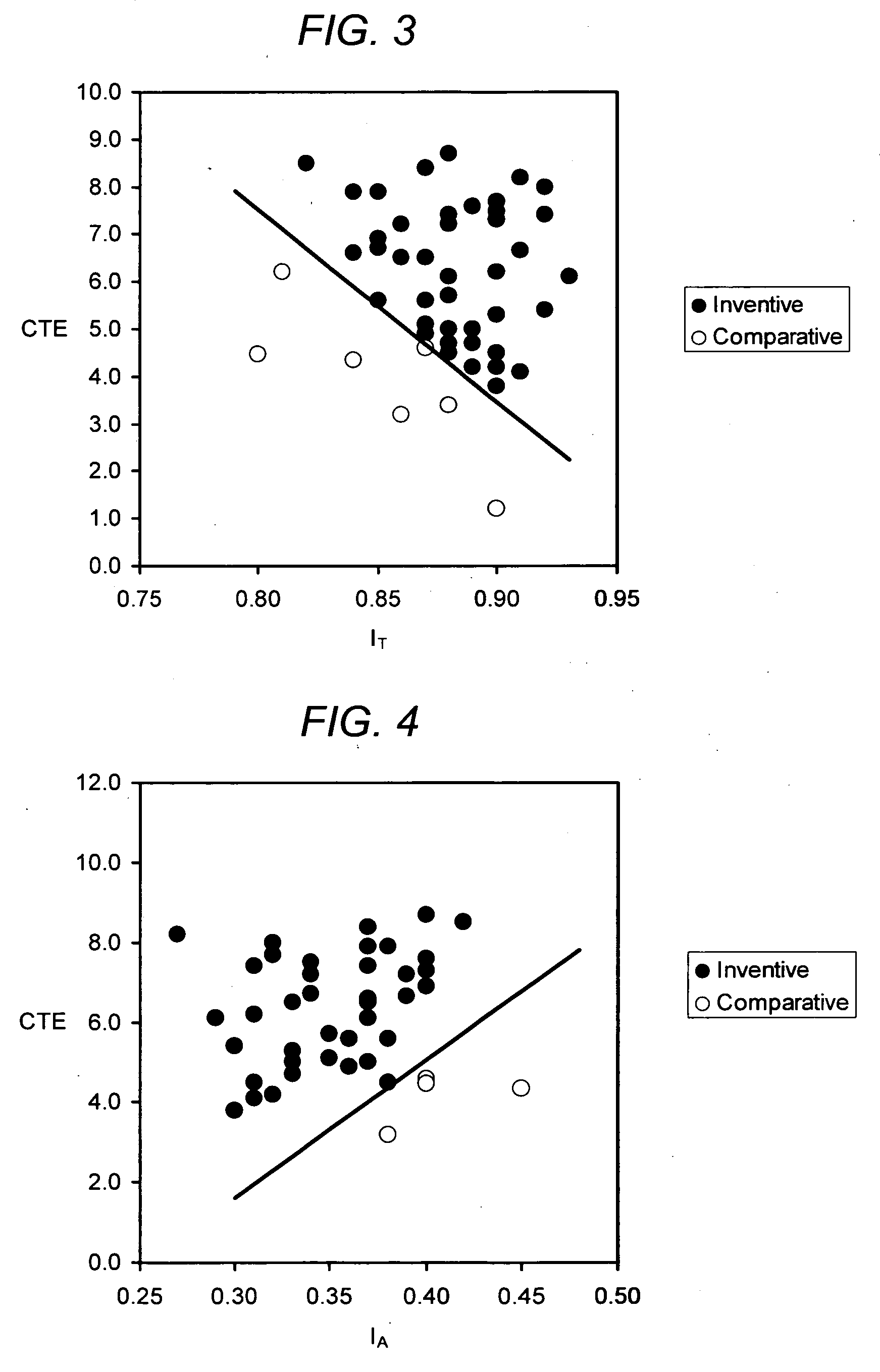
A porous cordierite ceramic honeycomb article with increased mechanical strength and thermal shock resistance. The porous cordierite ceramic honeycomb article has MA<2220, or MT>2660 wherein MA=3645 (IA)−106 (CTE)+19 (d90)+17 (% porosity), MT=4711 (IT)+116 (CTE)−26 (d90)−28 (% porosity), and a CTE≦9×10−7 / ° C. in at least one direction. A method of manufacturing is also disclosed wherein the inorganic raw material mixture contains talc, an alumina-forming source, a silica-forming source, and 0-18 wt. % of a kaolin or calcined kaolin containing not more than 8 wt. % of a fine kaolin source having a median particle diameter of less than 7 μm, wherein the fired porous ceramic cordierite honeycomb article has a porosity<54% . Alternatively, if greater than 8 wt. % of the fine kaolin source is used, then a slow ramp rate is utilized from 1200° C. to 1300° C. of not more than 20° C. / hr.
Owner:CORNING INC
Microwave drying of ceramic structures
ActiveUS7596885B2Dry evenlySimple structureDielectric heatingDrying solid materials with heatStructural degradationMetallurgy
Owner:CORNING INC
Ceramic honeycomb filter and its production method
ActiveUS8388721B2High PM-capturing efficiencyEasy to optimizeCombination devicesLiquid surface applicatorsCross-linkHoneycomb structure
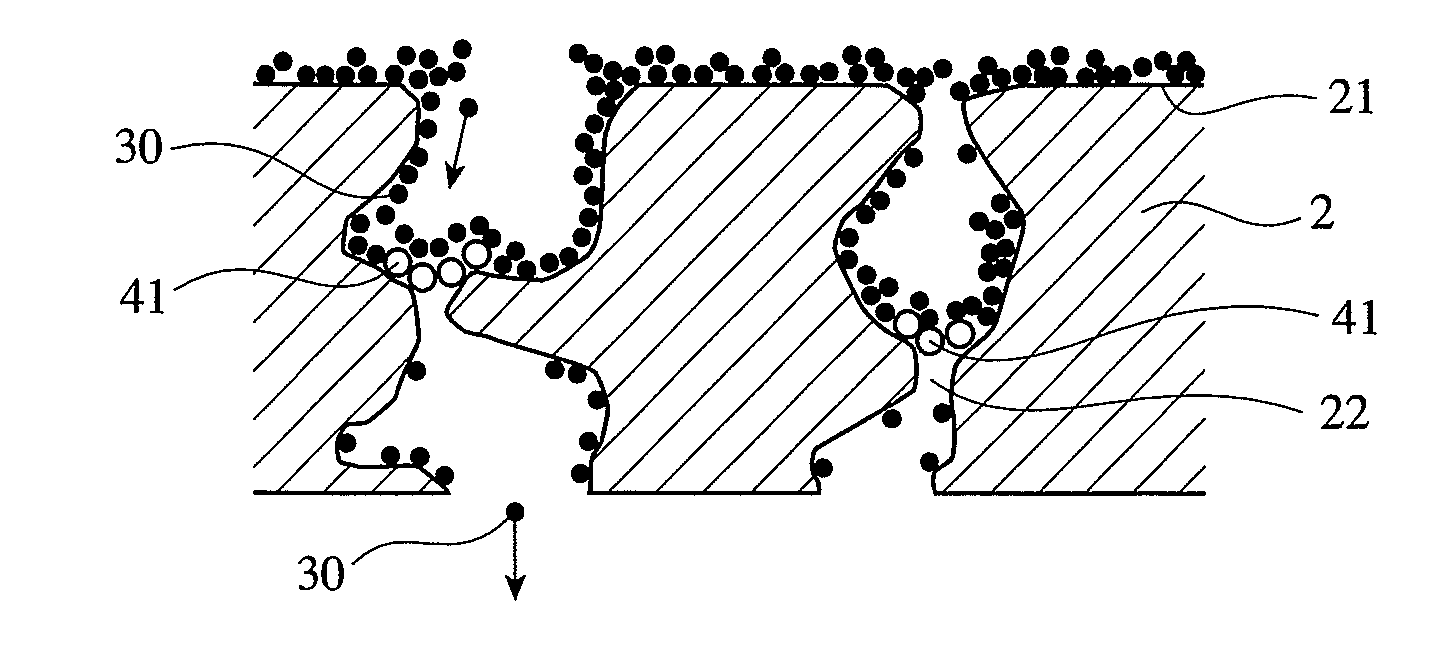
A ceramic honeycomb filter comprising a honeycomb structure having large numbers of flow paths partitioned by porous cell walls, and plugs alternately formed in the flow paths on the exhaust-gas-inlet and outlet sides, the area ratio of pores opening at the cell wall surfaces being 20% or more, porous, cross-linked structures being formed by heat-resistant particles introduced together with a gas into penetrating holes constituted by communicating pores in the cell walls, such that they clog the penetrating holes, and the cross-linked structures being formed more on the exhaust-gas-outlet side of the ceramic honeycomb filter than on the exhaust-gas-inlet side.
Owner:HITACHI METALS LTD
Ceramic honeycomb filter and its production method
InactiveUS7578864B2Efficient conductionCombination devicesAuxillary pretreatmentHoneycomb structureMaterials science
A ceramic honeycomb filter comprising pluralities of ceramic honeycomb structures each having large numbers of flow paths partitioned by cell walls, which are bonded in the direction of the flow paths, predetermined flow paths being sealed by plugs, plugs formed at one end of at least one honeycomb structure being bonded to at least part of plugs formed at one end of a honeycomb structure adjacent to the end of this honeycomb structure.
Owner:HITACHI METALS LTD
Low-microcracked, porous ceramic honeycombs and methods of manufacturing same
ActiveUS20080032090A1Improve efficiencyHigh strengthLayered productsCeramic shaping apparatusThermal expansionInterconnected porosity
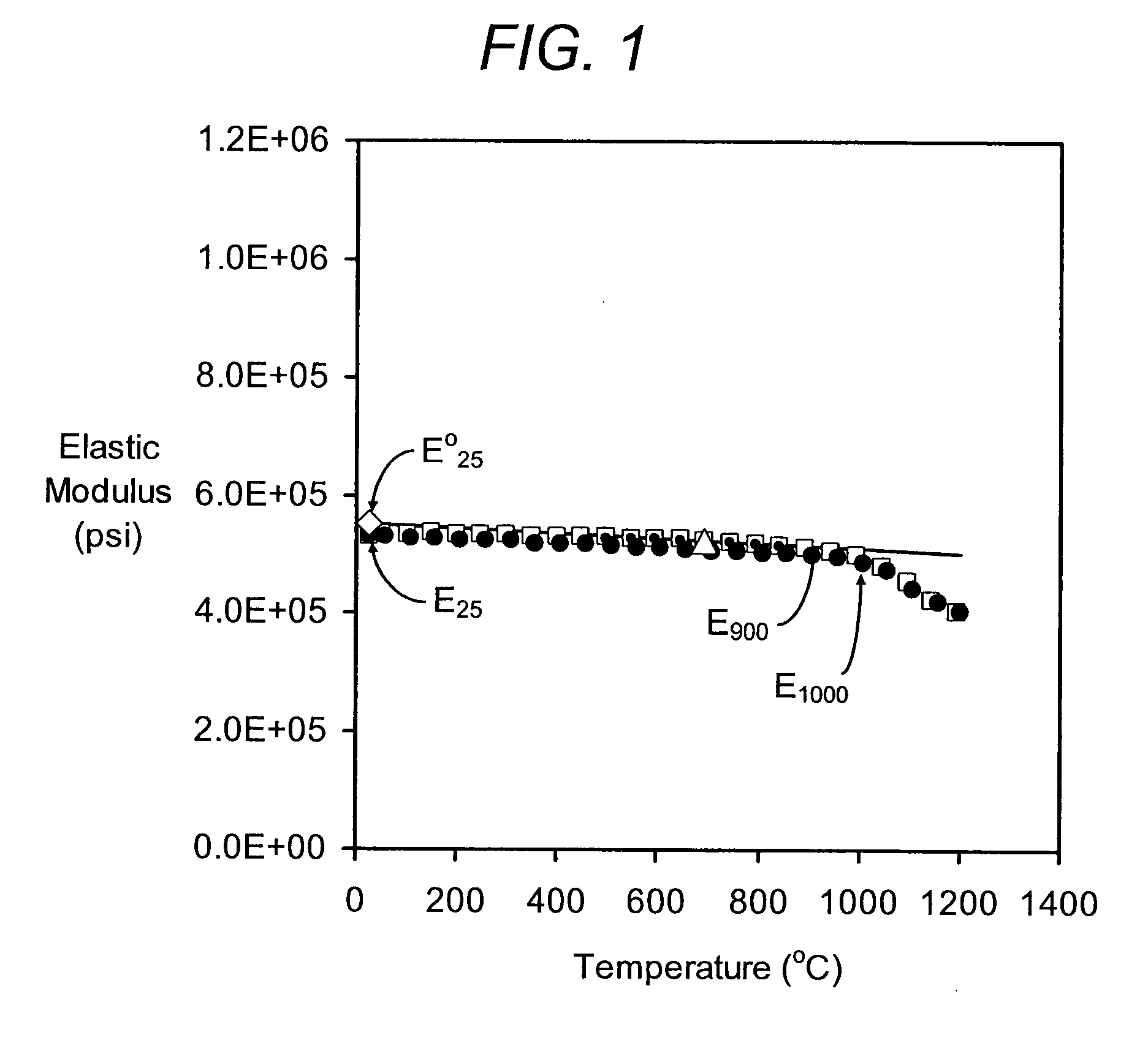
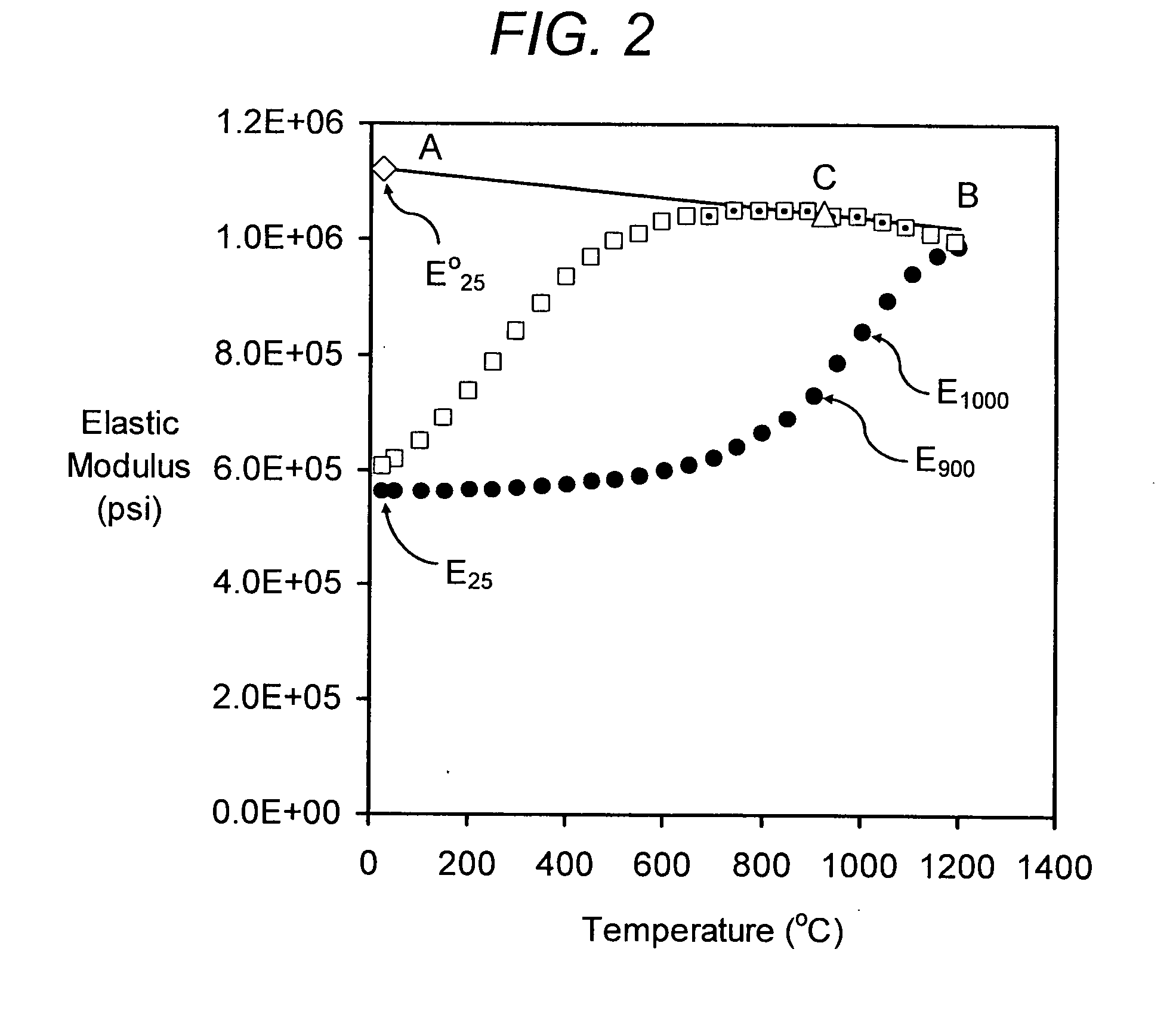
Substantially non-microcracked, porous, cordierite ceramic honeycomb bodies are provided. Although exhibiting moderately high thermal expansion (CTE) between 7×10−7 to 16×10−7 / ° C. (25-800° C.), the honeycomb bodies exhibit relatively high thermal shock parameter (TSP), such as TSR≧525° C. by virtue of a high MOR / E ratio, and / or low Eratio=ERT / E1000° C. and well interconnected porosity, as witnessed by a relatively high pore connectivity factor (PCF). A method of manufacturing the honeycomb ceramic structure is also provided.
Owner:CORNING INC
Continuous firing furnace, manufacturing method of porous ceramic member using the same, porous ceramic member, and ceramic honeycomb filter
A continuous firing furnace of the present invention comprises: a muffle formed into a cylindrical shape so as to ensure a predetermined space; a plurality of heat generators placed at the peripheral direction from the muffle; and a heat insulating layer formed in a manner so as to enclose said muffle and said heat generators therein, said continuous firing furnace being configured such that a formed body to be fired, which is transported from an inlet side, passes through the inside of said muffle at a predetermined speed in an inert gas atmosphere and, then, is discharged from an outlet so that said formed body is fired, wherein said inert gas flows through: a space between said muffle and said heat insulating layer; and a space inside the muffle, in sequence.
Owner:IBIDEN CO LTD
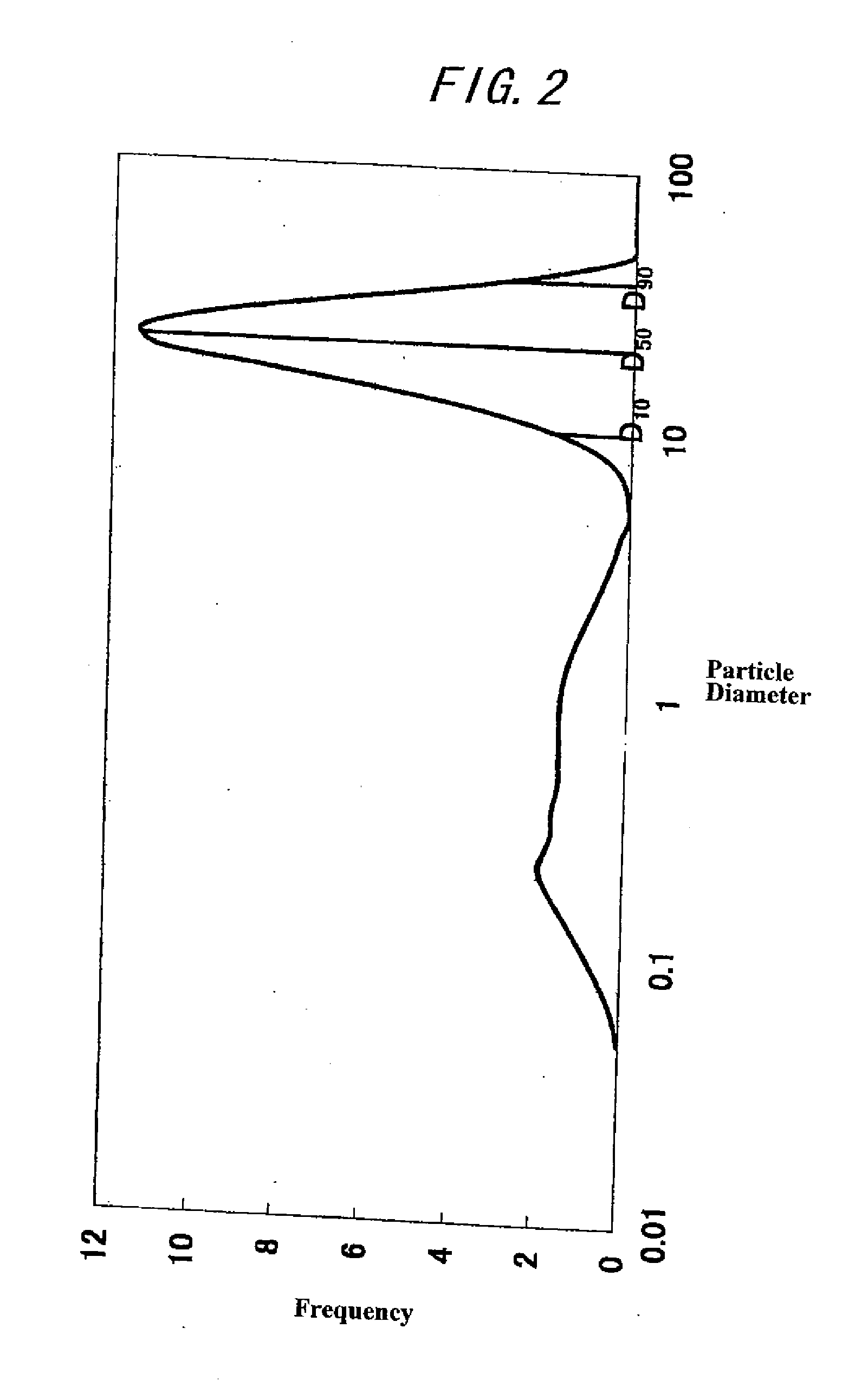
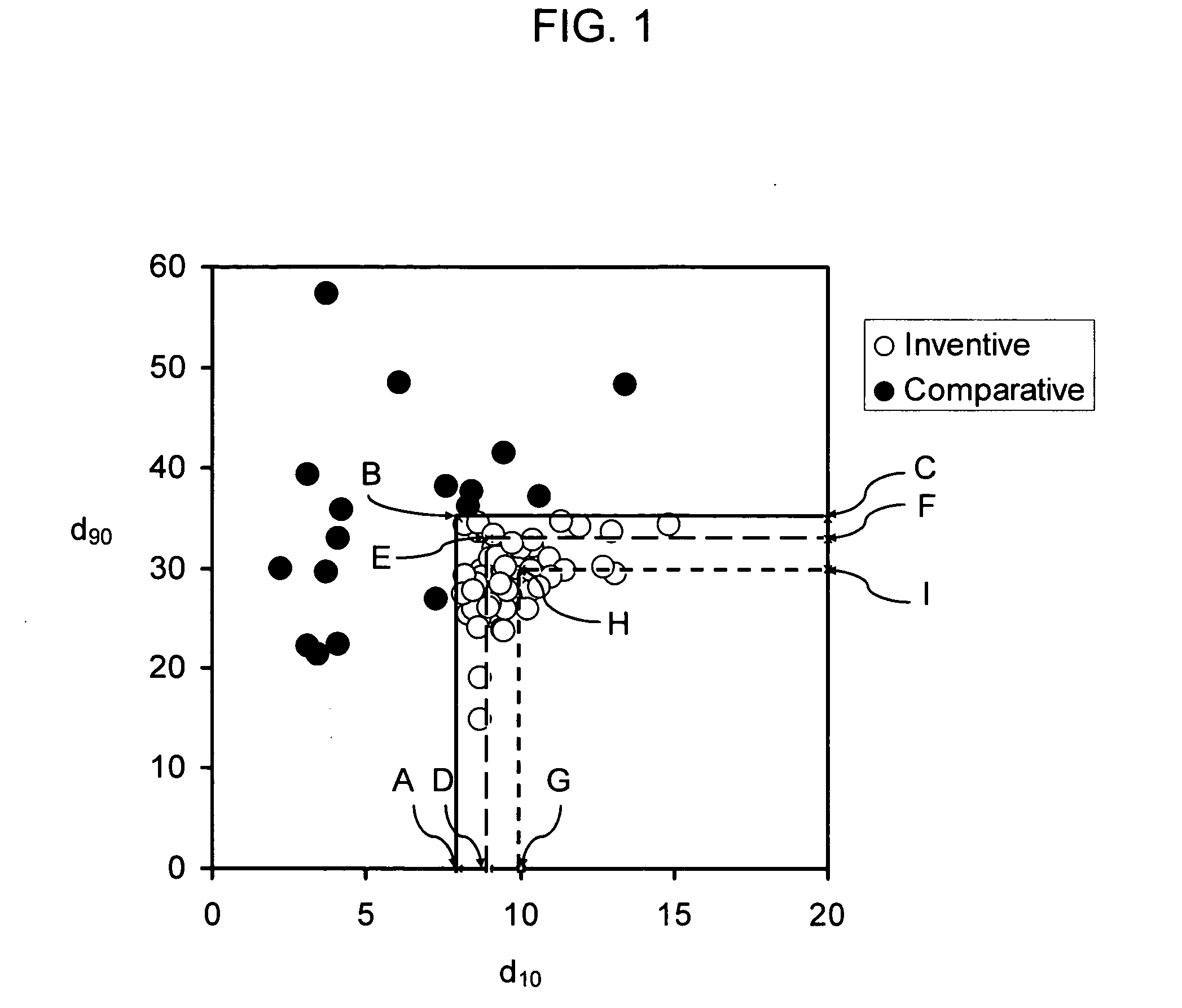
Narrow pore size distribution cordierite ceramic honeycomb articles and methods for manufacturing same
ActiveUS20080047243A1Low cleanlinessLow pressureCombination devicesDispersed particle filtrationFiltrationHeat resistance
Disclosed are ceramic honeycomb articles, which are composed predominately of a crystalline phase cordierite composition. The ceramic honeycomb articles possess a microstructure characterized by a unique combination of relatively high total porosity of less than 54%, and relatively narrow pore size distribution having a d10 pore diameter of not less than 8 μm, a d90 pore diameter of not greater than 35 μm, and a value of df=(d50−d10) / d50 of less than 0.50. The articles exhibit high thermal durability and high filtration efficiency coupled with low pressure drop across the filter. Such ceramic articles are particularly well suited for filtration applications, such as diesel exhaust filters or DPFs. Also disclosed are methods for manufacturing the ceramic articles of the present invention.
Owner:CORNING INC
Ceramic honeycomb structure
ActiveUS7504359B2Excellent in pressure loss and catching efficiencyHigh catalytic activityDispersed particle filtrationExhaust apparatusPore distributionSurface roughness
A honeycomb structural body comprises one or plural pillar-shaped porous ceramic members in which many through-holes are arranged side by side in a longitudinal direction through partition walls and either one end portions of these through-holes are sealed.The partition wall forming the structural body has a surface roughness of not less than 10 μm as a maximum roughness Rz defined in JIS B0601-2001 and an average pore size of 5-100 μm in a pore distribution measured by a mercury pressure method, and satisfies the following relationship:A≧90−B / 20 or A≦100−B / 20when a ratio pores having a pore size of 0.9-1.1 times the average pore size to total pore volume is A (%) and a thickness of the partition wall is B (μm), and there is proposed an effective honeycomb structural body having excellent pressure loss and catching efficiency and a high catalyst reactivity.
Owner:IBIDEN CO LTD
Natural gas vehicle tai-gas clean-up catalyst and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101549301AReduce dosageImprove purification effectNitrous oxide captureMolecular sieve catalystsCeriumCordierite
The invention relates to a high-performance natural gas vehicle tail-gas clean-up catalyst and preparation method thereof, wherein the catalyst has higher catalytic conversion performance to CO, HC, NOx, especially capable of effectively conversing methane at low temperature. The catalyst comprises a first carrier, a second carrier on the first carrier and active components, characterized in that: the second carrier comprises a molecular sieve modified by the metal oxides and cerium zirconium solid solution; the active components comprise two or three kinds of noble metal platinum, palladium and rhodium. The first carrier is cordierite ceramic honeycomb carrier and the second carrier loads and the cerium, zirconium solid solution loaded with one or more than one noble metal selected from the platinum, palladium and rhodium is used as the first layer load on the cordierite ceramic honeycomb carrier and the molecular sieve modified by the metal oxide and loaded with one or more than one noble metal selected from the platinum, palladium and rhodium is used as the second layer load on the first load.
Owner:昆明贵研催化剂有限责任公司
Ceramic structures having hydrophobic coatings
InactiveUS20050159308A1Reduce absorptionGas treatmentInternal combustion piston enginesCordieriteAqueous medium
A catalyst support structure for use as either a NOx catalyst support or as a DPF including (i) a multicellular ceramic body, preferably a monolithic ceramic honeycomb composed e.g., of cordierite or aluminum titanate, and (ii) a hydrophobic coating on at least the exterior surface thereof which results in a ceramic honeycomb exhibiting reduced or low absorption when exposed to both liquid catalytic coating media and aqueous media utilized in the process of applying the catalytic coating. In a preferred embodiment the hydrophobic coating is formed within or on an applied external skin layer provided on the multicellular ceramic body.
Owner:CORNING INC
Method for Producing Ceramic Honeycomb Filter
ActiveUS20090008830A1Formed surelyGas treatmentInternal combustion piston enginesCell wallMaterials science
A method for producing a ceramic honeycomb filter having large numbers of flow paths partitioned by cell walls, the flow paths having plugs at positions separate from an end surface of the honeycomb filter, comprising the steps of introducing a base-forming material into the flow paths on one end surface side, charging a plug-forming material into flow paths to be provided with plugs from the other end surface side, and sintering it.
Owner:HITACHI METALS LTD
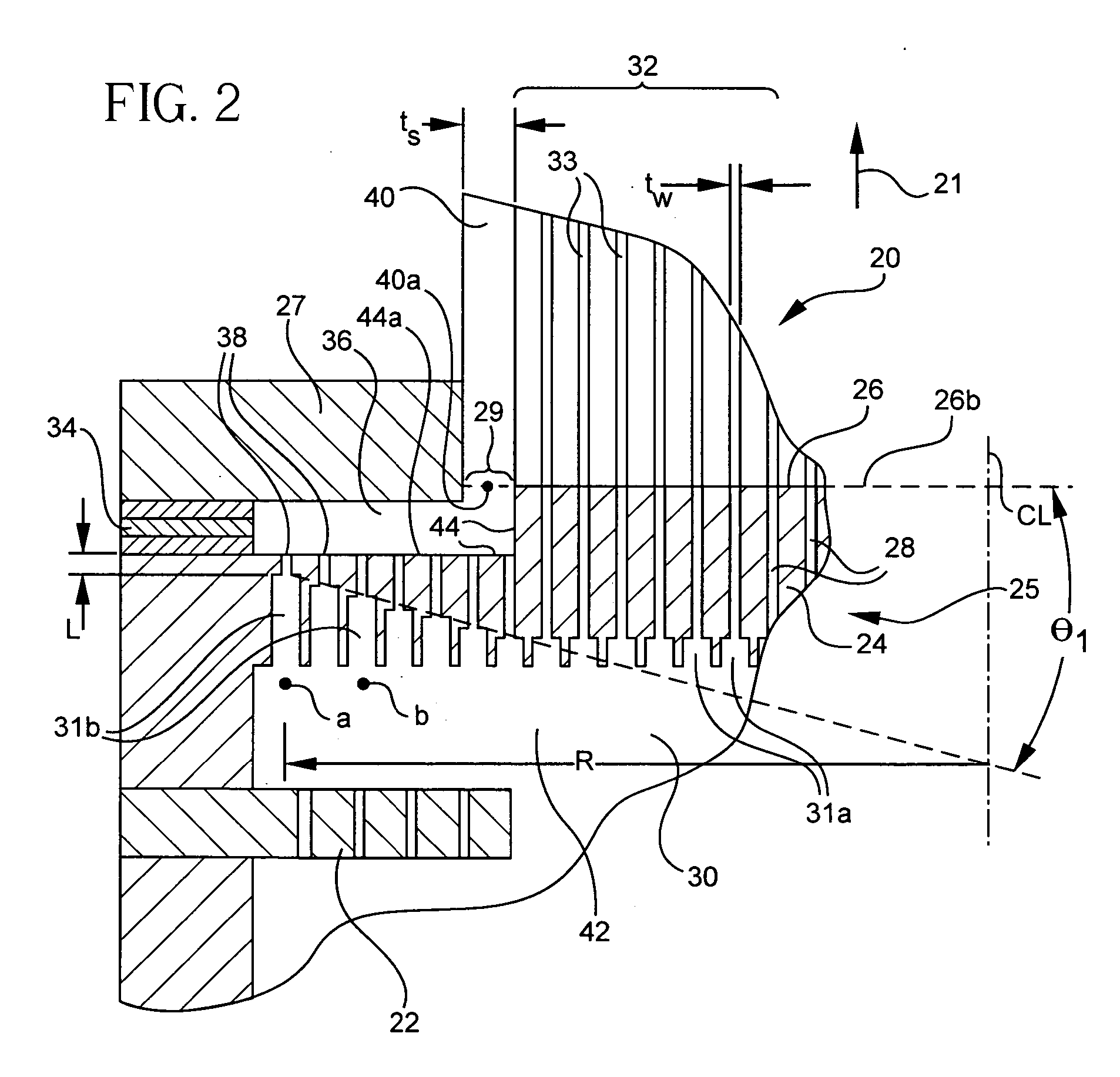
Method and apparatus for extruding honeycomb articles and thick-skinned ceramic honeycomb articles manufactured thereby
ActiveUS20070026188A1Reduction tendencyEasy alignmentLayered productsConfectioneryParticle alignmentMaterials science
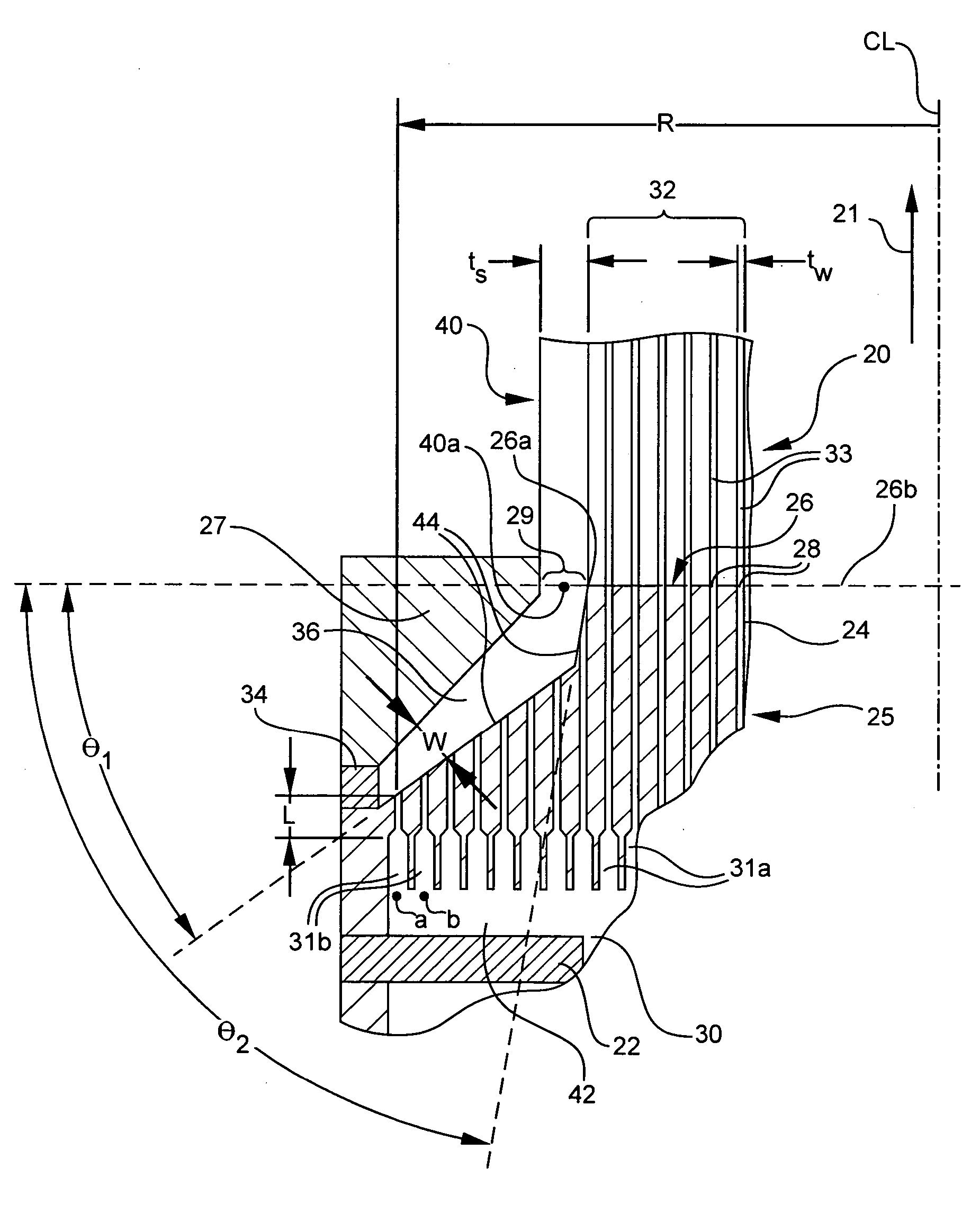
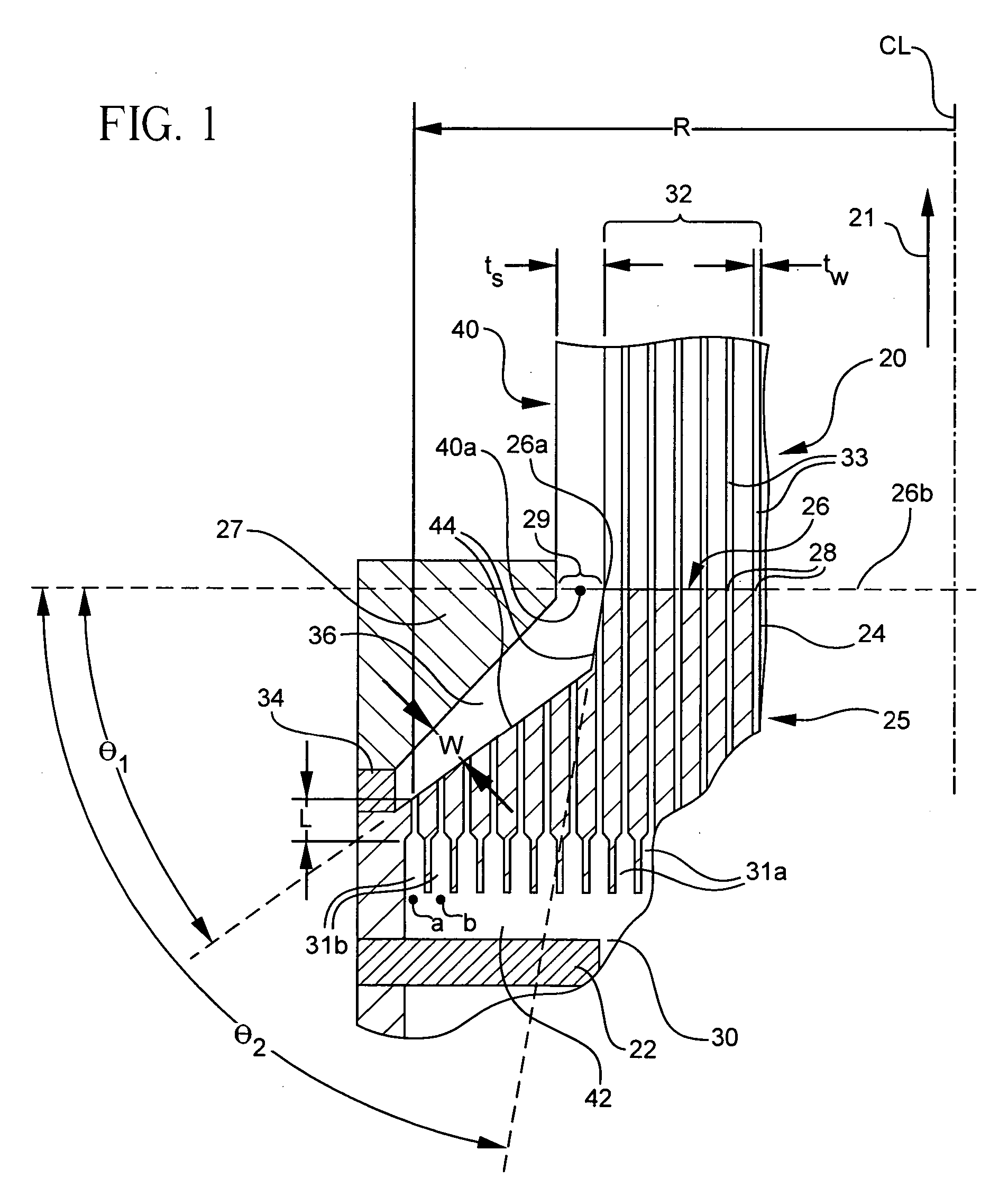
Disclosed is a method and apparatus for forming a circumferential skin surrounding a central cellular structure of an extruded honeycomb article. The method and apparatus may be used to produce defect-free skins and / or skins having large thickness and a high degree of particle alignment thereby preferably exhibiting CTE comparable to the extruded webs. These benefits are achieved by providing a die and method wherein a flow, Q, exiting any two active ones of a plurality of peripheral slots forming the skin is substantially equal. Also disclosed is a thick-skinned ceramic article having a thick extruded skin (ts′>5 tw′) with an I-value comparable to the webs.
Owner:CORNING INC
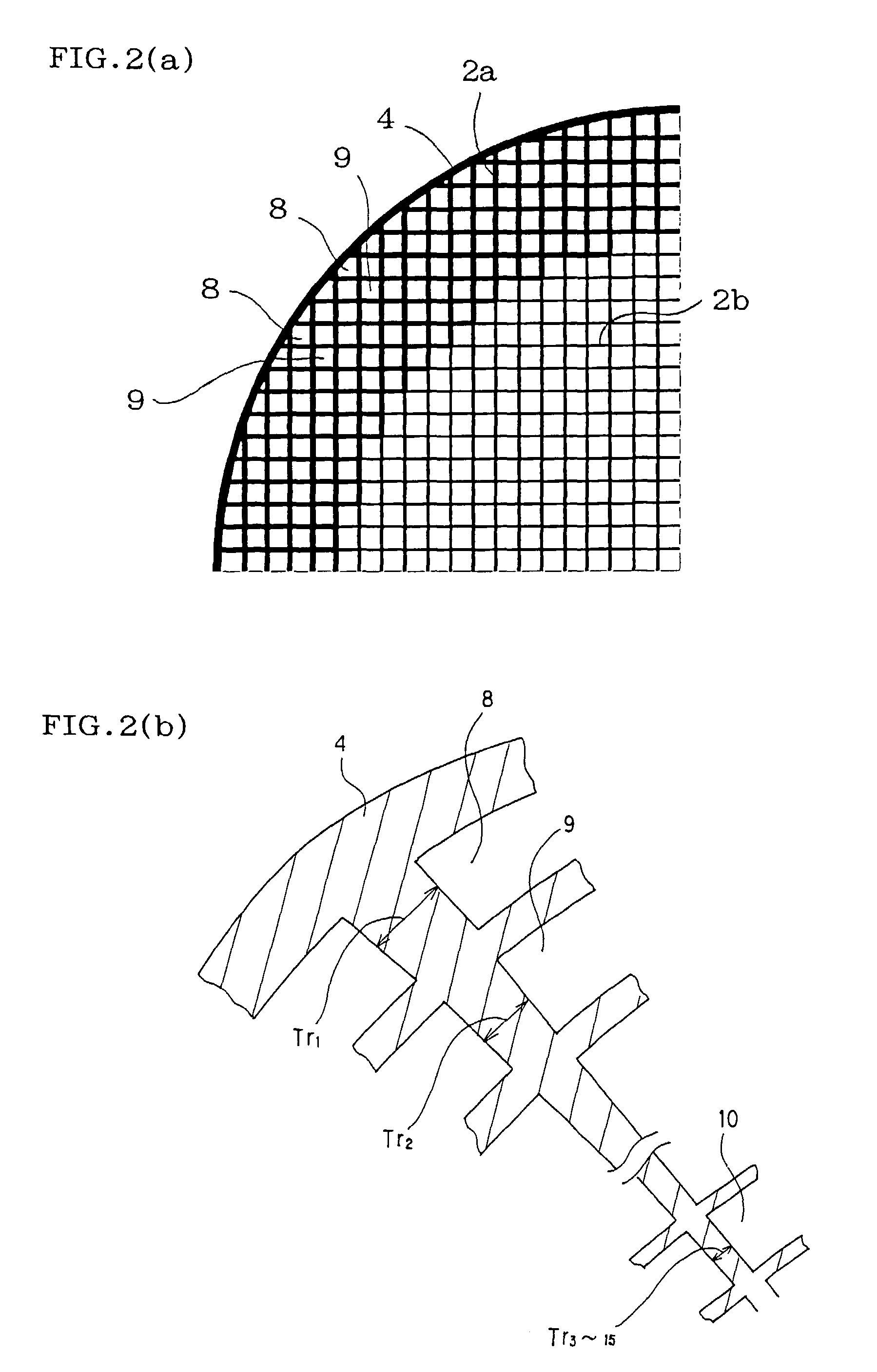
Ceramic honeycomb structure
InactiveUS20020192426A1Increased pressure lossReduced thermal shock resistanceCombination devicesDead plant preservationCell wallHoneycomb structure
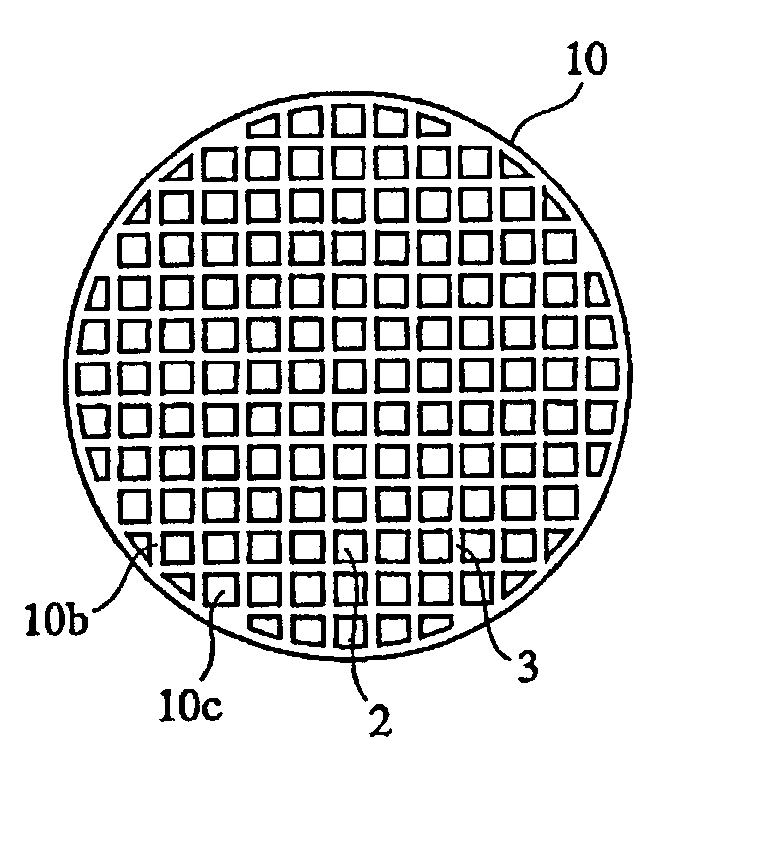
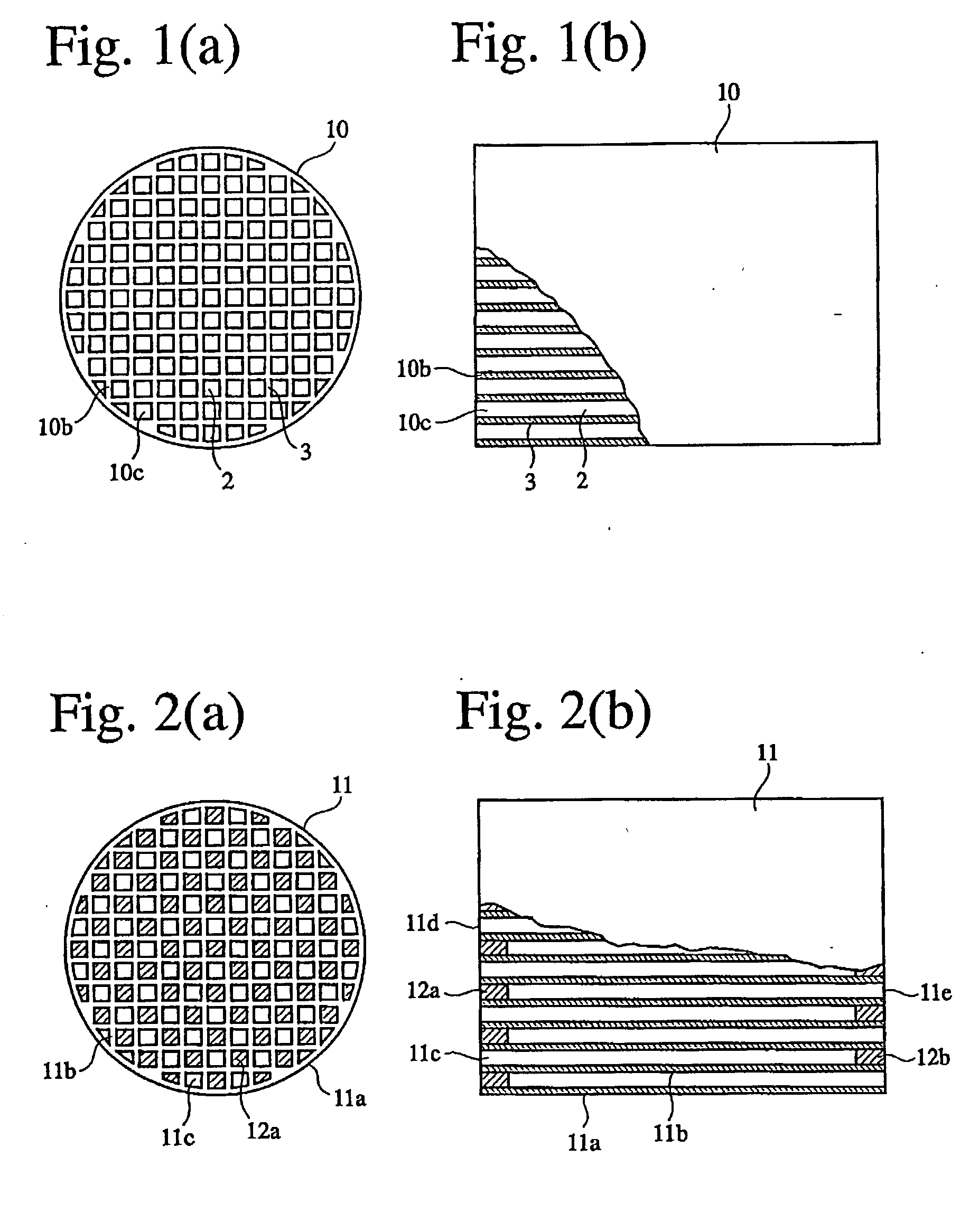
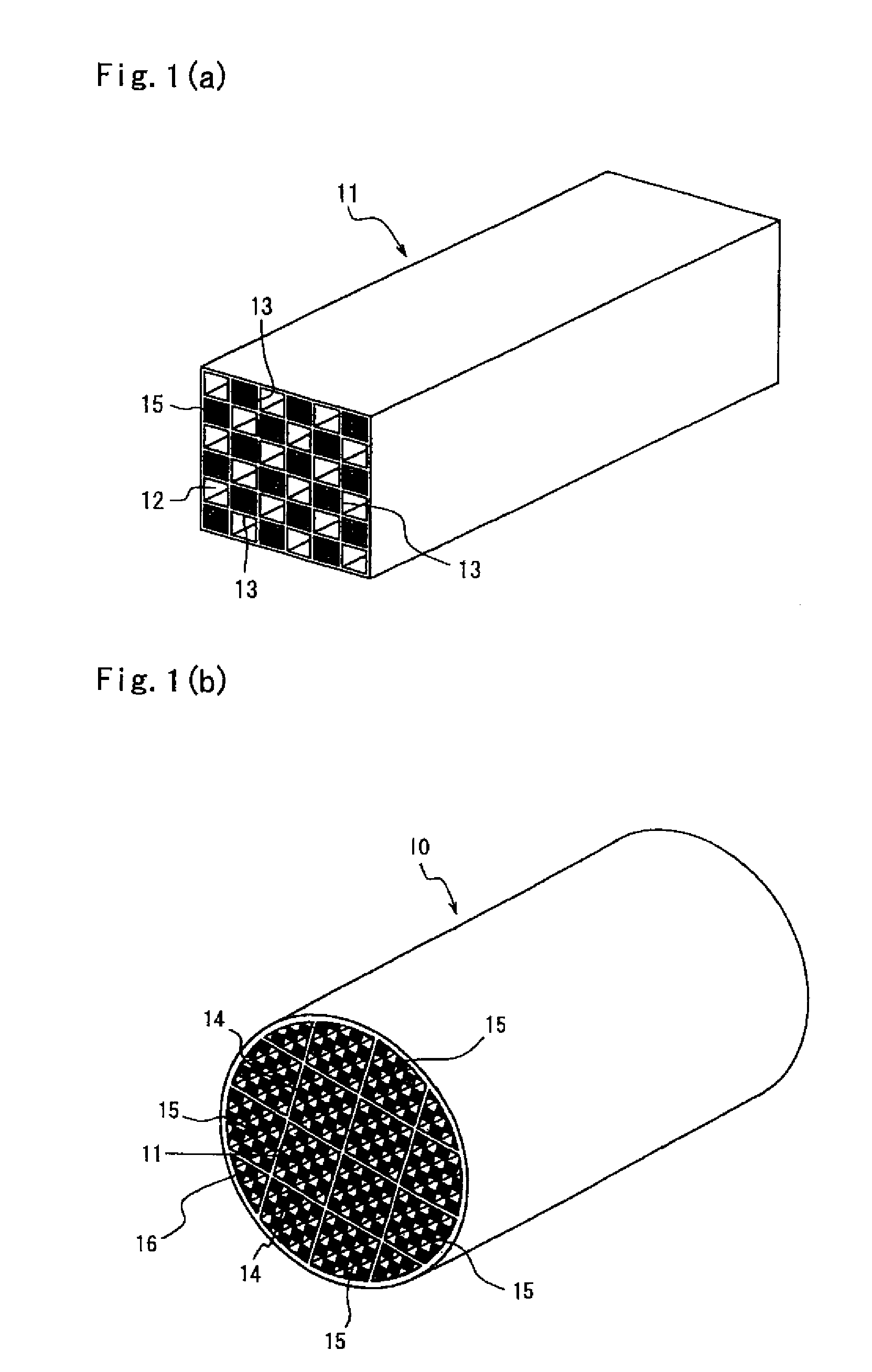
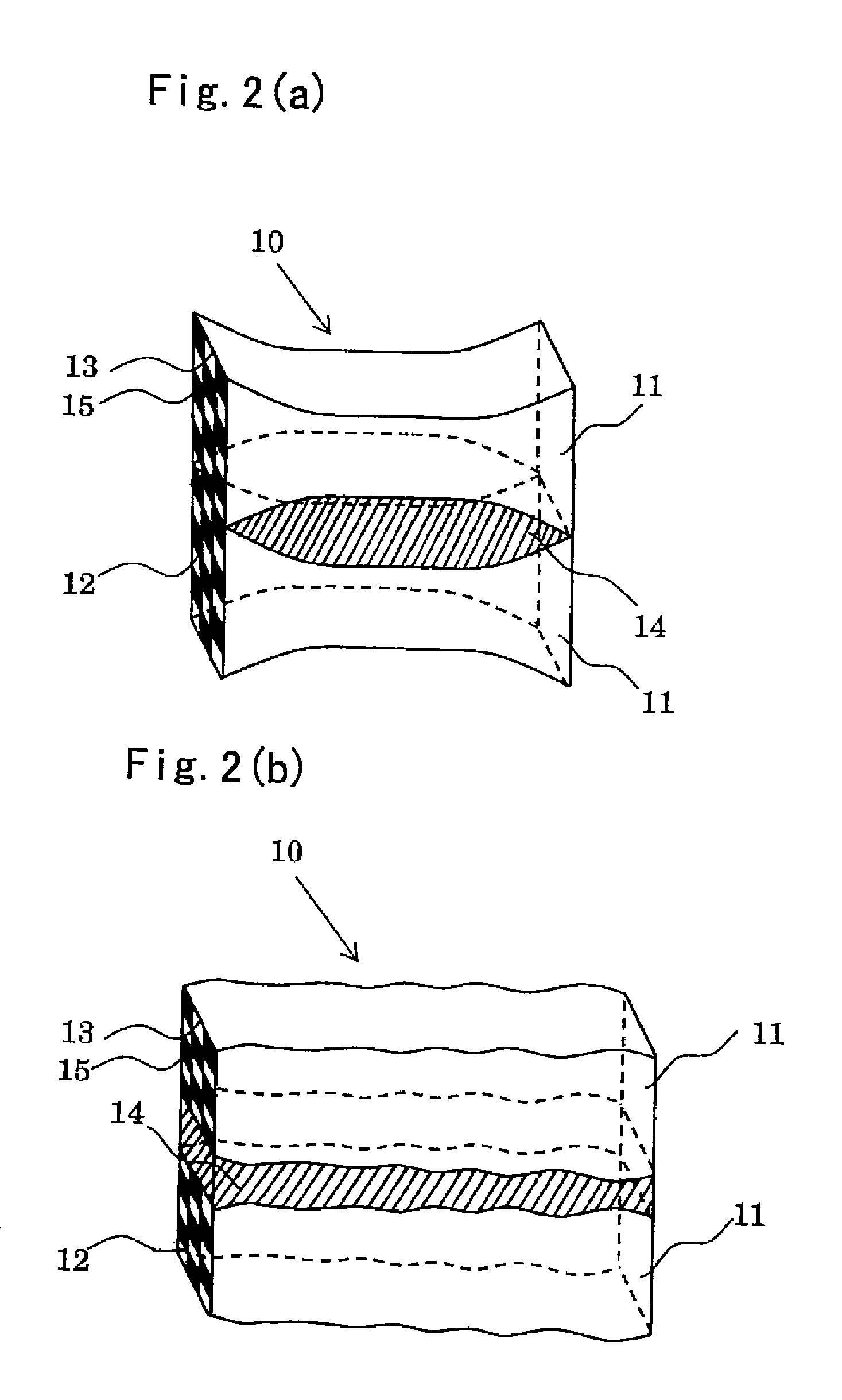
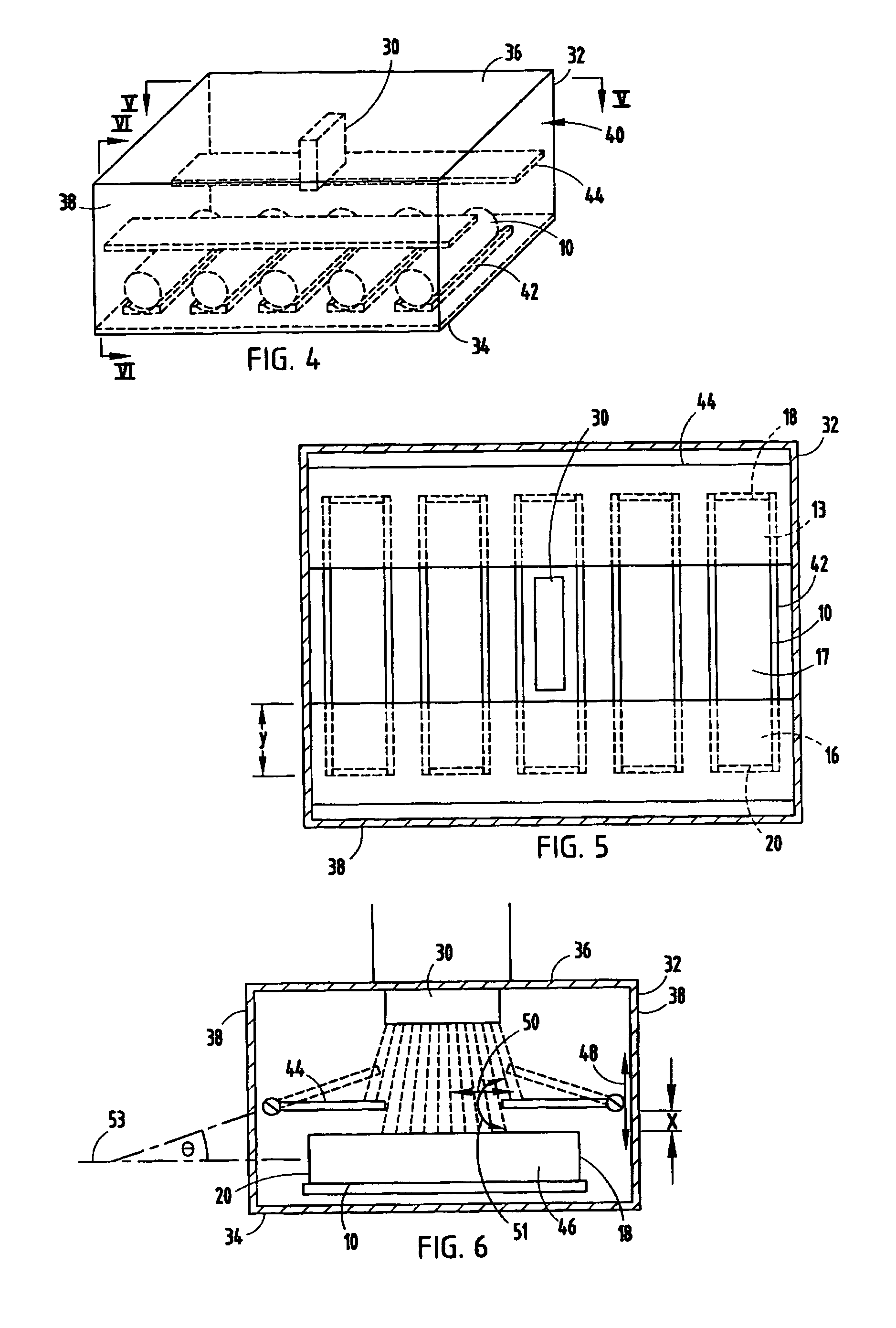
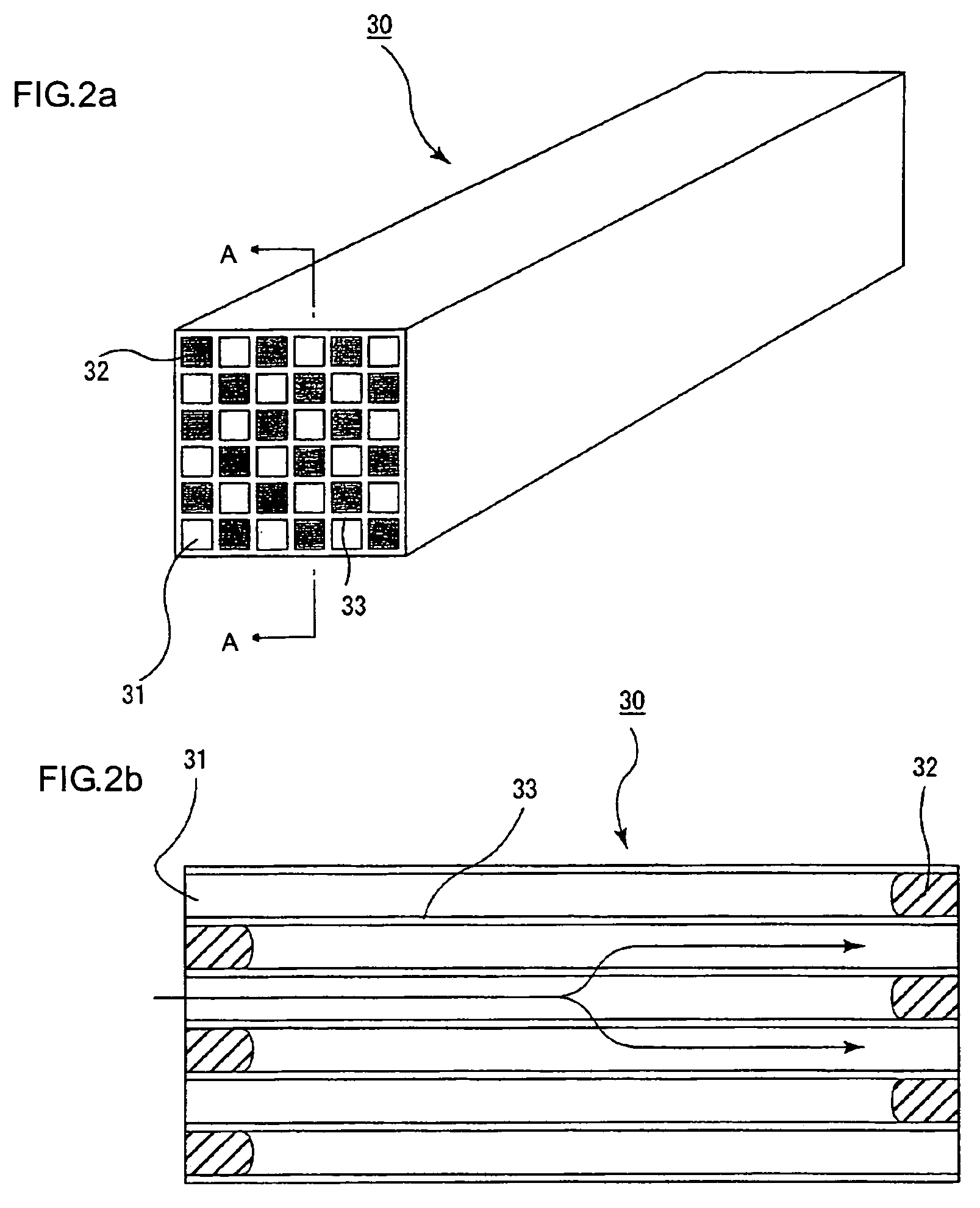
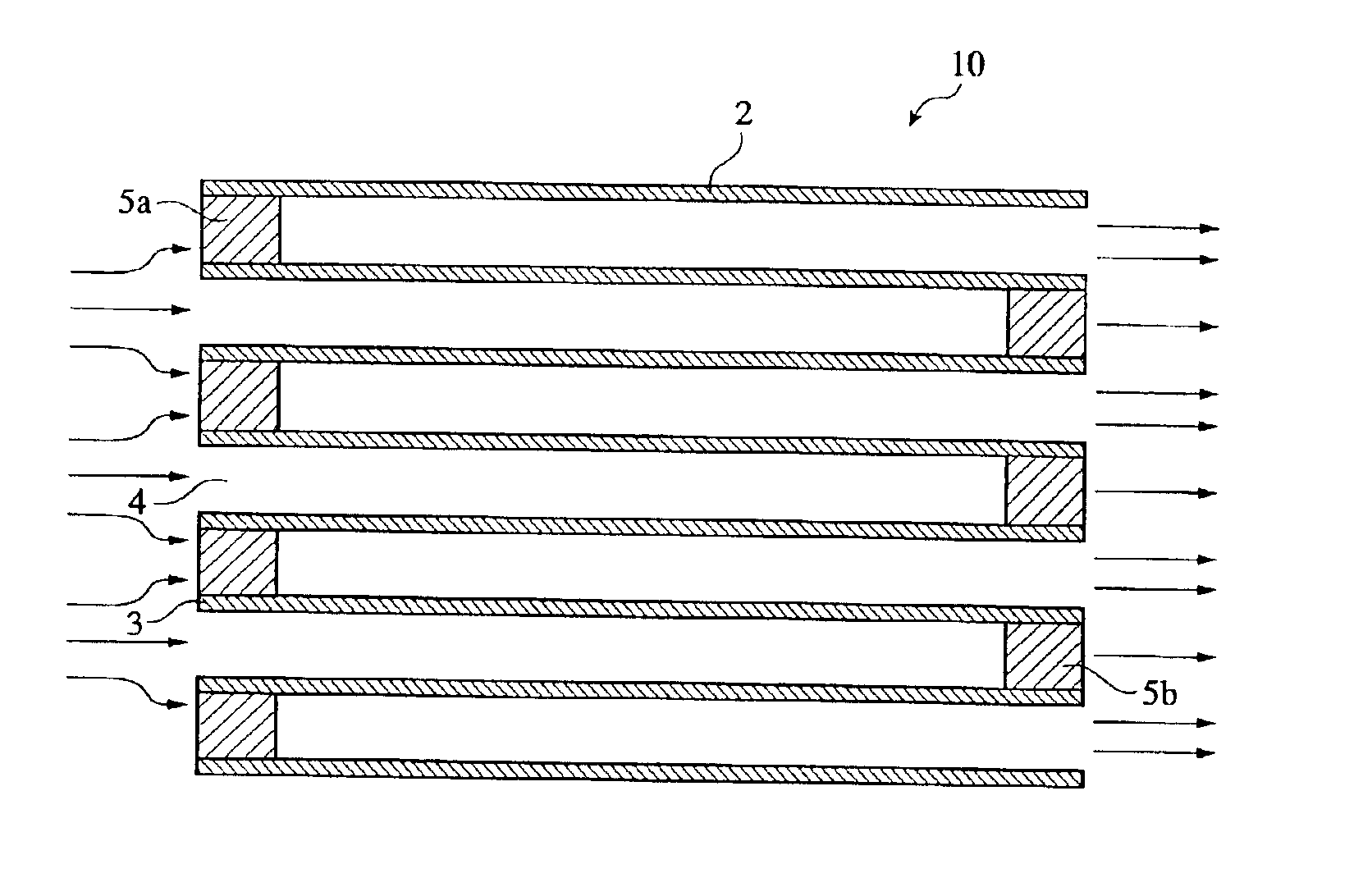
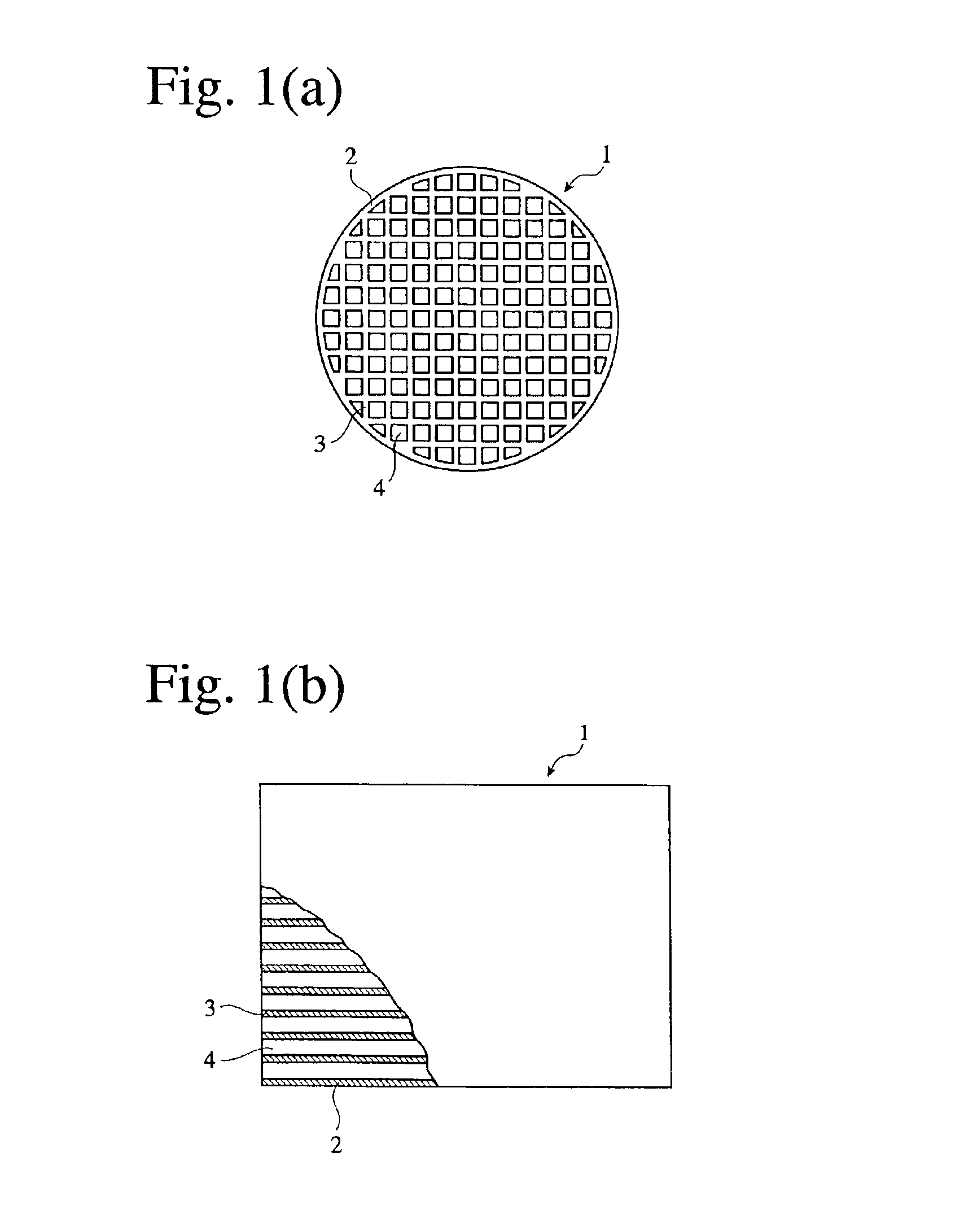
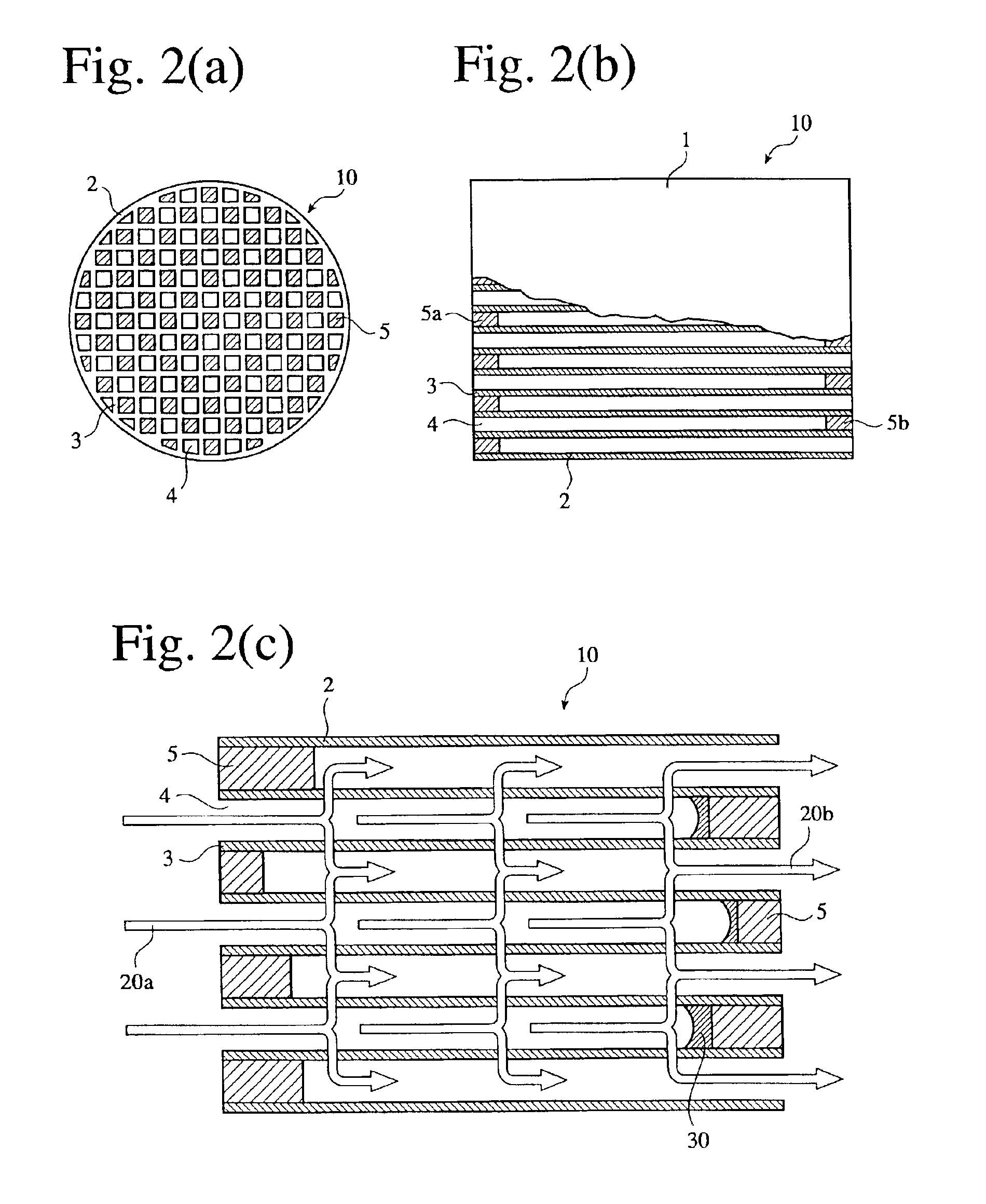
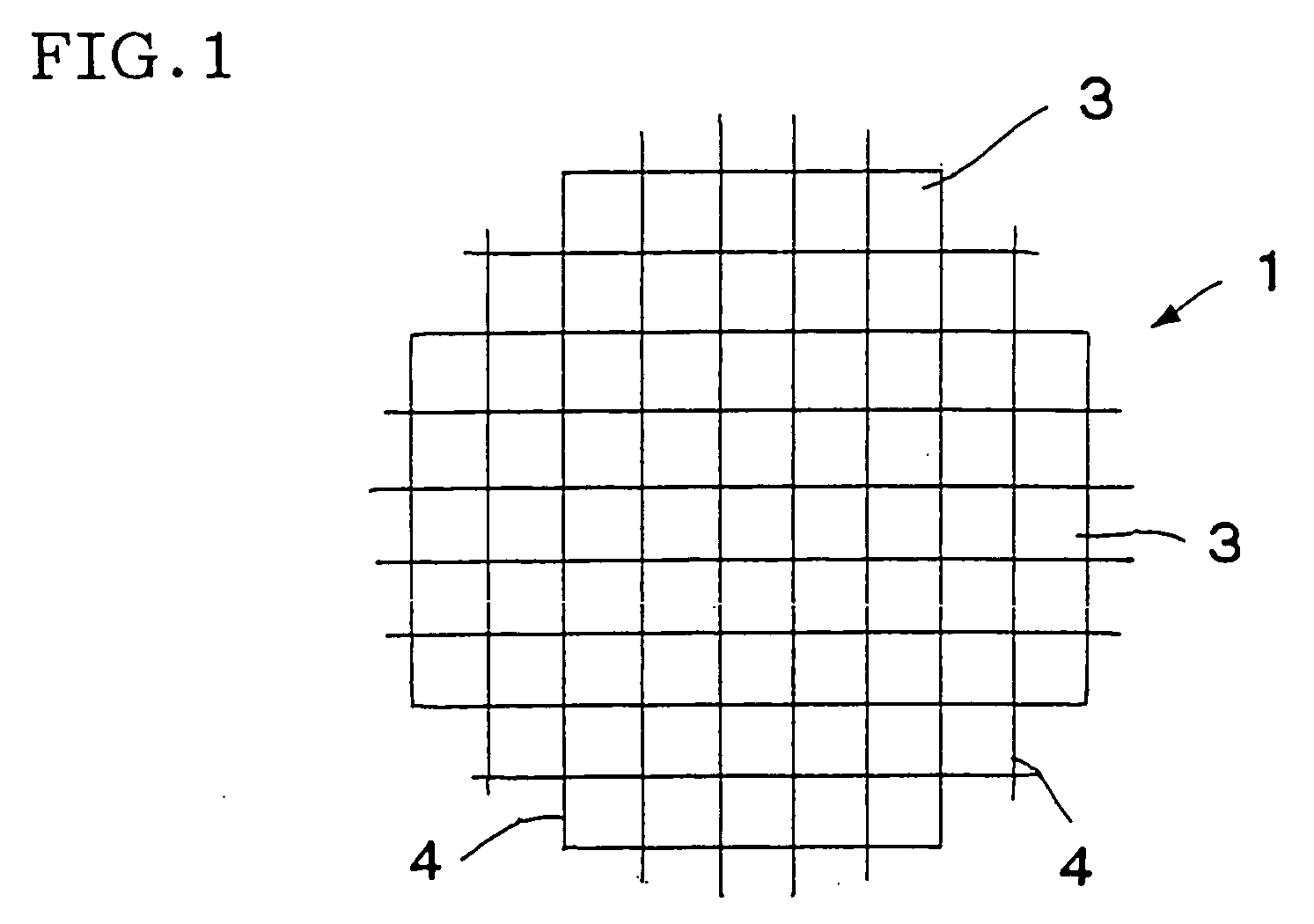
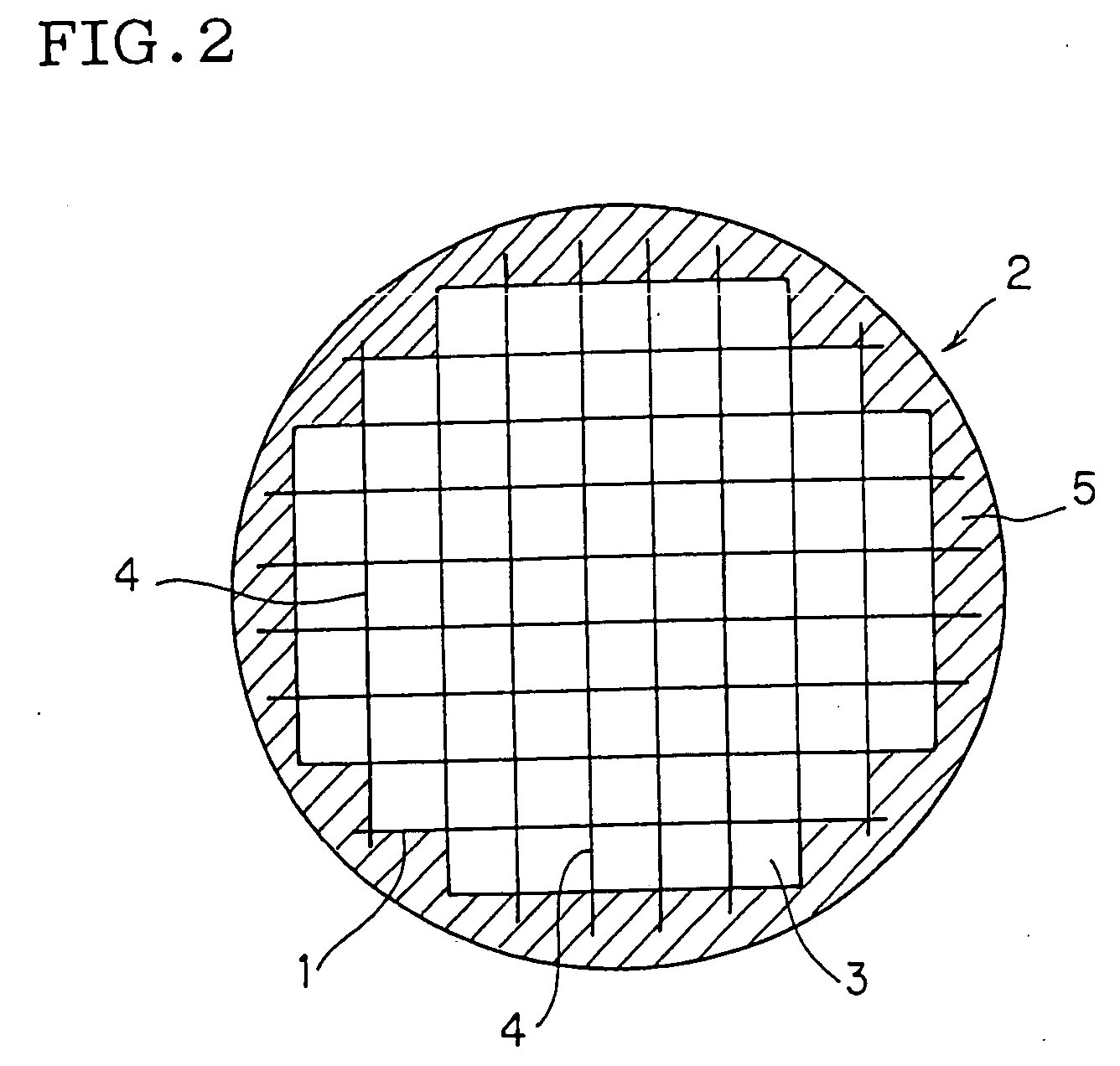
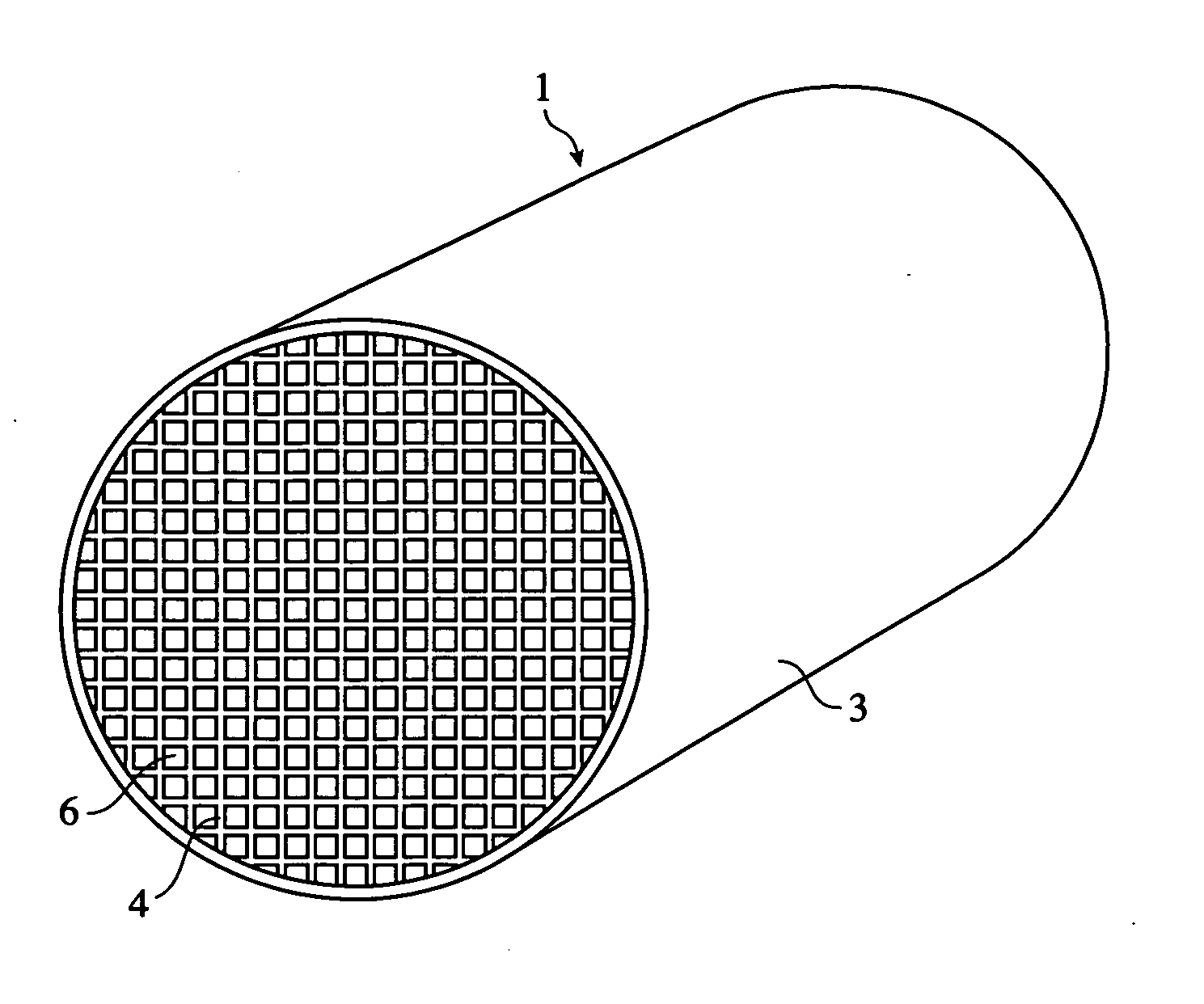
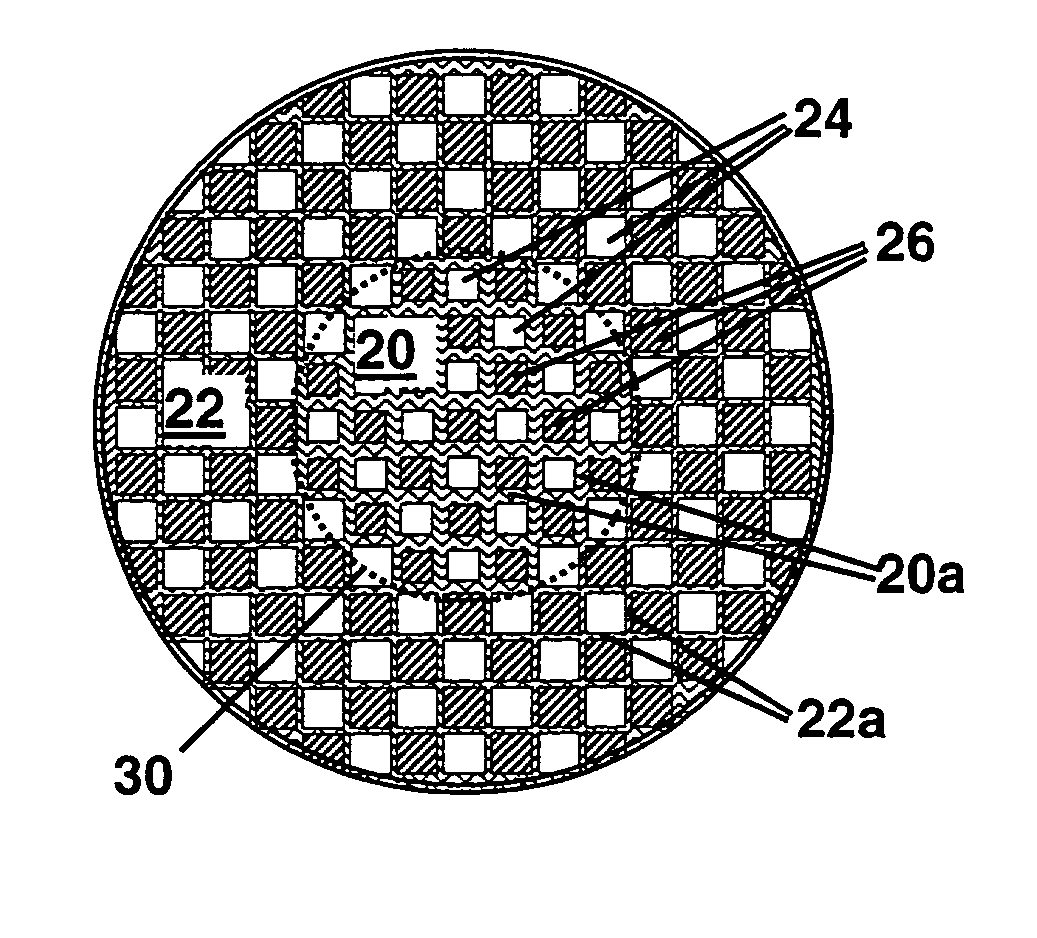
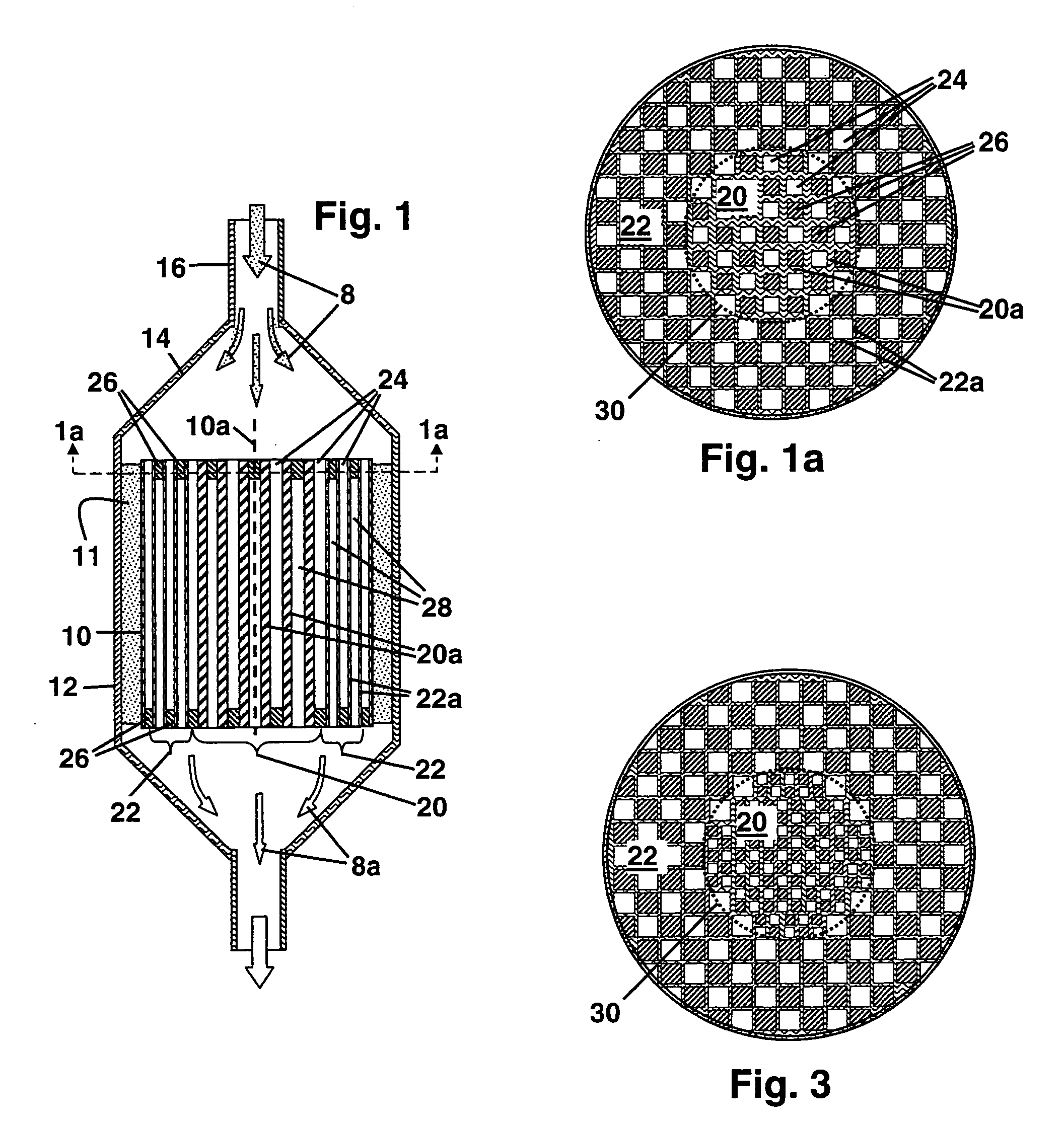
A ceramic honeycomb structure (1) constituted by cell walls (ribs) (2) forming a composite structure from a plurality of cells (3) being adjacent each other and a honeycomb outer wall (4) surrounding and holding the outermost peripheral cells located at the circumference of the composite structure; said composite structure satisfying the followings: the basic thickness of the cell walls (2) (the basic cell wall thickness) (Tc) is Tc<=0.12 mm, the outer wall thickness (Ts) of the honeycomb structure is Ts >=0.05 mm, and the open frontal area (P) is P>==80%, and there is a relation shown by formula: <paragraph lvl="0"><in-line-formula>1.10<=(Tr1~Tr3-20) / Tc<=3.00 < / in-line-formula>between the basic cell wall thickness (Tc) and each cell wall thickness (Tr1~Tr3-20) of cells existing between an outermost peripheral cell and any cell within a first end cell from a fifth cell to a twentieth cell extending inwardly, taking the outermost peripheral cell as a first staring cell.
Owner:NGK INSULATORS LTD
Ceramic honeycomb filter and its structure
InactiveUS6890616B2Small pressure lossLong-term useCombination devicesInternal combustion piston enginesPorosityParticulates
A ceramic honeycomb filter comprising a ceramic honeycomb structure having porous partition walls defining a plurality of flow paths for flowing an exhaust gas through the porous partition walls to remove particulates from the exhaust gas, wherein one end of each flow path is provided with a sealer, such that sealers of the flow paths in an inlet and an outlet of the ceramic honeycomb structure in a desired pattern; wherein the partition walls have thickness of 0.1-0.5 mm and a porosity of 50-80%; wherein the porosity of the sealers is larger than that of partition walls; and wherein the depth of the sealers is 3-15 mm.
Owner:HITACHI METALS LTD
Coating material, ceramic honeycomb structure and method for production thereof
InactiveUS20060121240A1Dispersed particle filtrationLayered productsThird generationVolumetric Mass Density
A coating material of the present invention is a coating material comprising: cordierite powder as a main component having a tap bulk density of 1.3 g / cm3 or more; and water. The coating material is capable of forming a coated wall (outer wall), for example, on the surface of a porous body formed of a ceramic in such a manner that defects such as generation of cracks, and peeling, and a manufacturing yield is satisfactory are not easily generated.
Owner:NGK INSULATORS LTD
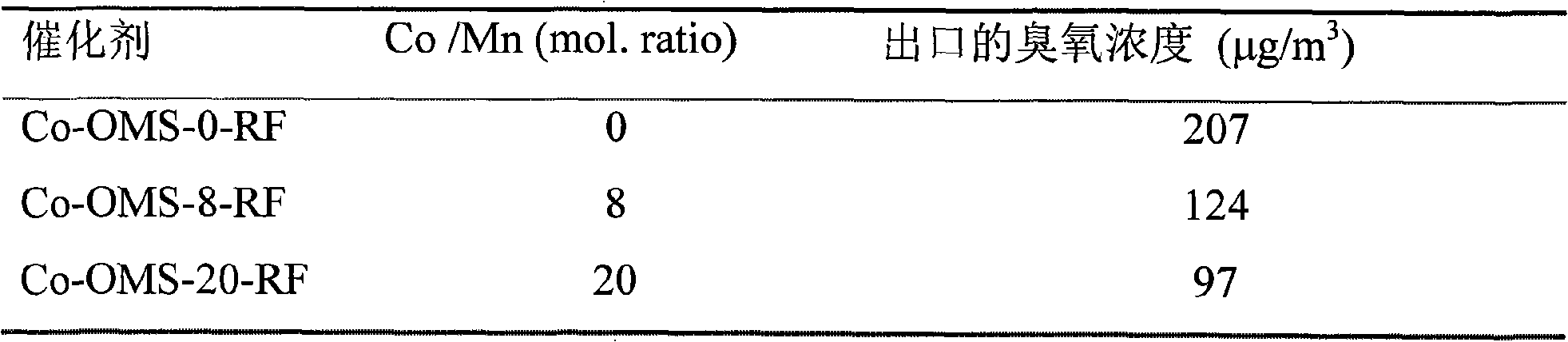
Room-temperature decomposition ozone catalysis material and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101357331AImprove moisture resistanceImprove processing efficiencyDispersed particle separationMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsAir volumeDecomposition
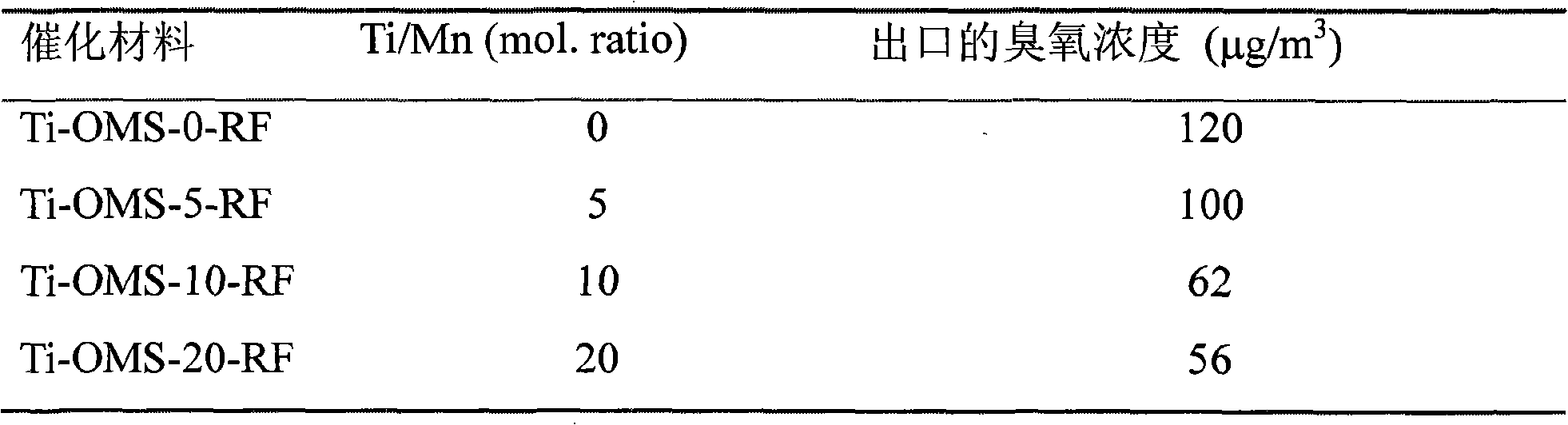
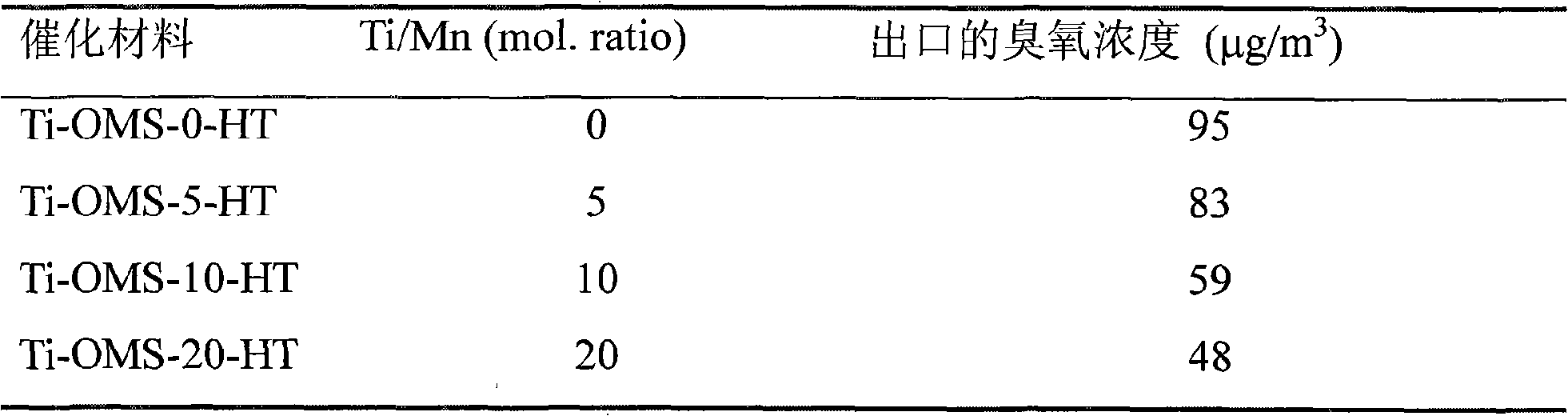
The invention discloses a manganese oxide molecular sieve-doped monolithic catalyst for decomposing ozone (O3) at room temperature and a preparation method thereof, which relates to the fields of catalysis and environmental protection. The preparation method is characterized in that a ceramic honeycomb monolithic type or porous foam metal carrier is adopted, and the manganese oxide molecular sieve doped with cobalt or titanium is taken as an active component. The manganese oxide molecular sieve doped with the cobalt or titanium is characterized in that: 1) the manganese oxide molecular sieve has Hollandite-typed manganese oxide octahedral molecular sieves (OMS-2) structure, the pore size is about 0.46nm multiplied by 0.46nm; 2) cobalt or titanium ions are introduced on a framework of the Hollandite-typed manganese oxide octahedral molecular sieves to form the manganese oxide molecular sieve doped with cobalt or titanium. An ozone decomposition catalyst is prepared by an oxidation reduction-refluxing method or an oxidation reduction-hydrothermal synthesis method, namely, the solution with manganese salt and cobalt salt or titanium salt is added with a strong oxidizer to synthesize the ozone decomposition catalyst by refluxing at the temperature of 90-200 DEG or hydrothermal process for more than 12 hours. The monolithic catalyst is characterized in that the input of additional energy sources such as light, heat, electricity, and the like, is unnecessary, and the ozone can be stably decomposed into oxygen under the conditions of normal temperature, normal humidity and large air volume.
Owner:李永刚
High porosity honeycomb and method
A ceramic honeycomb substrate for use in an automotive catalytic converter system which exhibits improved light-off performance by virtue of a high porosity of 45 to 75% while still maintaining a wall thickness of greater than 2.0 mil (0.0020 inch, 0.0508 mm), preferably 2.5 mil (0.0025 in., 0.0635 mm) to 7 mil (0.0070 in., 0.1778 mm), and more preferably 2.5 mil (0.0025 in., 0.0635 mm) to 3 mil (0.0030 in., 0.0762 mm). The median pore size is in the range of 2-10 micrometers, and a coefficient of thermal expansion (CTE) (25-800° C.) of less than 15×10−7 / ° C.
Owner:CORNING INC
Ceramic honeycomb structure, process for producing the same and coat material for use in the production
ActiveUS20060105139A1Improve reliabilityImprove thermal shock resistancePhysical/chemical process catalystsDispersed particle filtrationThermal expansionCell wall
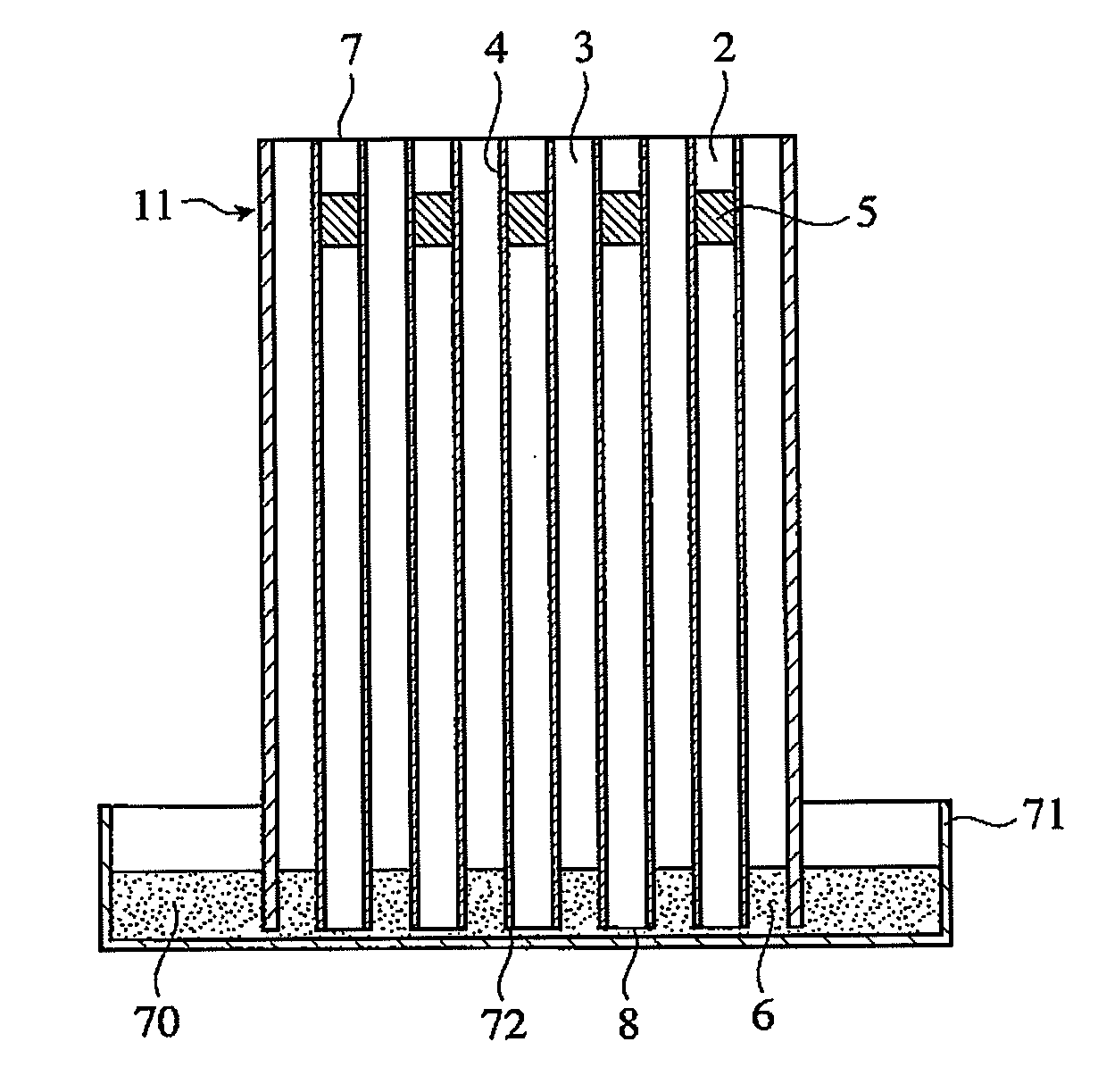
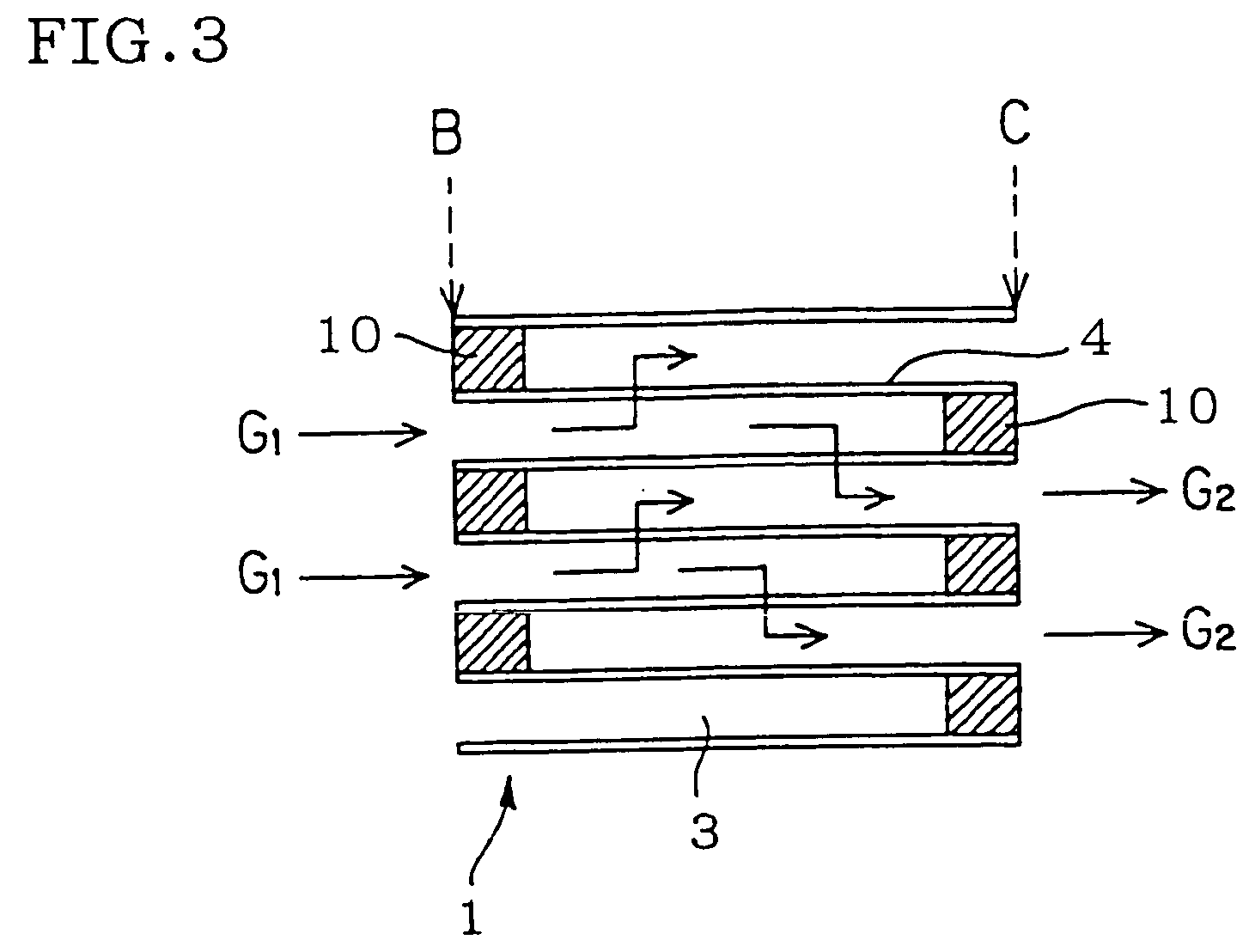
A ceramic honeycomb structure comprising a ceramic honeycomb body comprising axial grooves on its periphery and cell walls constituting a larger number of flow paths inside the grooves, and a peripheral wall layer covering the grooves, wherein there are stress release portions at least partially in the peripheral wall layer and / or between the peripheral wall layer and the grooves. The thermal expansion coefficient of the peripheral wall layer is preferably smaller than those of the cell walls in a radial direction. The peripheral wall layer is preferably formed on the ceramic honeycomb body formed by removing a peripheral wall from a ceramic green body, before or after firing the ceramic honeycomb body.
Owner:HITACHI METALS LTD
Diesel engine exhaust filters
ActiveUS20050235622A1Speed up the processResist damageCombination devicesGas treatmentFiltrationEngineering
Diesel engine exhaust filtration systems, and ceramic honeycomb wall flow exhaust filters for such systems, wherein the filters comprise axially centralized filter sections having a higher heat capacity and / or a higher gas flow resistance than peripheral filter sections disposed radially outwardly thereof, the filters thereby exhibiting increased resistance to thermal damage from filter regeneration over-heating.
Owner:CORNING INC
Method for introducing a catalytic coating into the pores of a ceramic honeycomb flow body
ActiveUS20100093527A1Increase pressureA large amountDispersed particle filtrationPretreated surfacesMaterials scienceBlow out
The invention relates to a process for coating ceramic honeycomb bodies with a catalyst suspension comprising catalyst components as solids and / or in dissolved form in a carrier liquid. Parallel flow channels run through the honeycomb bodies. The walls of the flow channels have an open pore structure. To coat the channel walls and in particular also the interior surfaces of the pores with the catalyst suspension, the entry and exit end faces of the vertically aligned honeycomb bodies are each brought into contact with a perforated mask, with the perforated masks being arranged so that the open regions of the perforated mask on the one end face are opposite the closed regions of the perforated mask on the other end face and vice versa. The catalyst suspension is then pumped or sucked from below into the honeycomb bodies until it exits at the upper end face. Excess suspension is then removed by blowing-out or sucking-out, the contact with the perforated masks is released and the honeycomb body is calcined to fix the coating.
Owner:UMICORE AG & CO KG
Diesel engine exhaust filters
ActiveUS7238217B2Resist damageSpeed up the processCombination devicesGas treatmentDieselingMechanical engineering
Diesel engine exhaust filtration systems, and ceramic honeycomb wall flow exhaust filters for such systems, wherein the filters comprise axially centralized filter sections having a higher heat capacity and / or a higher gas flow resistance than peripheral filter sections disposed radially outwardly thereof, the filters thereby exhibiting increased resistance to thermal damage from filter regeneration over-heating.
Owner:CORNING INC
Method and equipment for coating slurry layer on cellular carrier of ceramics
InactiveCN1660508AImprove efficiencyControl thicknessLiquid surface applicatorsCoatingsAutomatic controlPositive pressure
A process for coating the slurry on the surface of cellular ceramic carrier inclues such steps as arranging the cellular ceramic carrier to a particular working position by automatic fixture, sealing it, delivering the slurry via tube, negative-pressure coating, and positive-pressure scavenge to remove excessive slurry.
Owner:RES CENT FOR ECO ENVIRONMENTAL SCI THE CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Ceramic honeycomb filter, its production method, and plugging material for ceramic honeycomb filter
ActiveUS20070039298A1Small differenceImprove thermal shock resistanceCombination devicesAuxillary pretreatmentParticulatesOxide matrix
A ceramic honeycomb filter comprising a sintered ceramic honeycomb body having porous partition walls defining flow paths, and plugs formed in predetermined flow paths for removing particulate matter from an exhaust gas passing through the porous partition walls, the sintered ceramic honeycomb body being formed by a cordierite-based ceramic material, at least part of the plugs comprising ceramic particles and an amorphous oxide matrix formed from colloidal oxide.
Owner:HITACHI METALS LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com