Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
71 results about "Cell delay" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
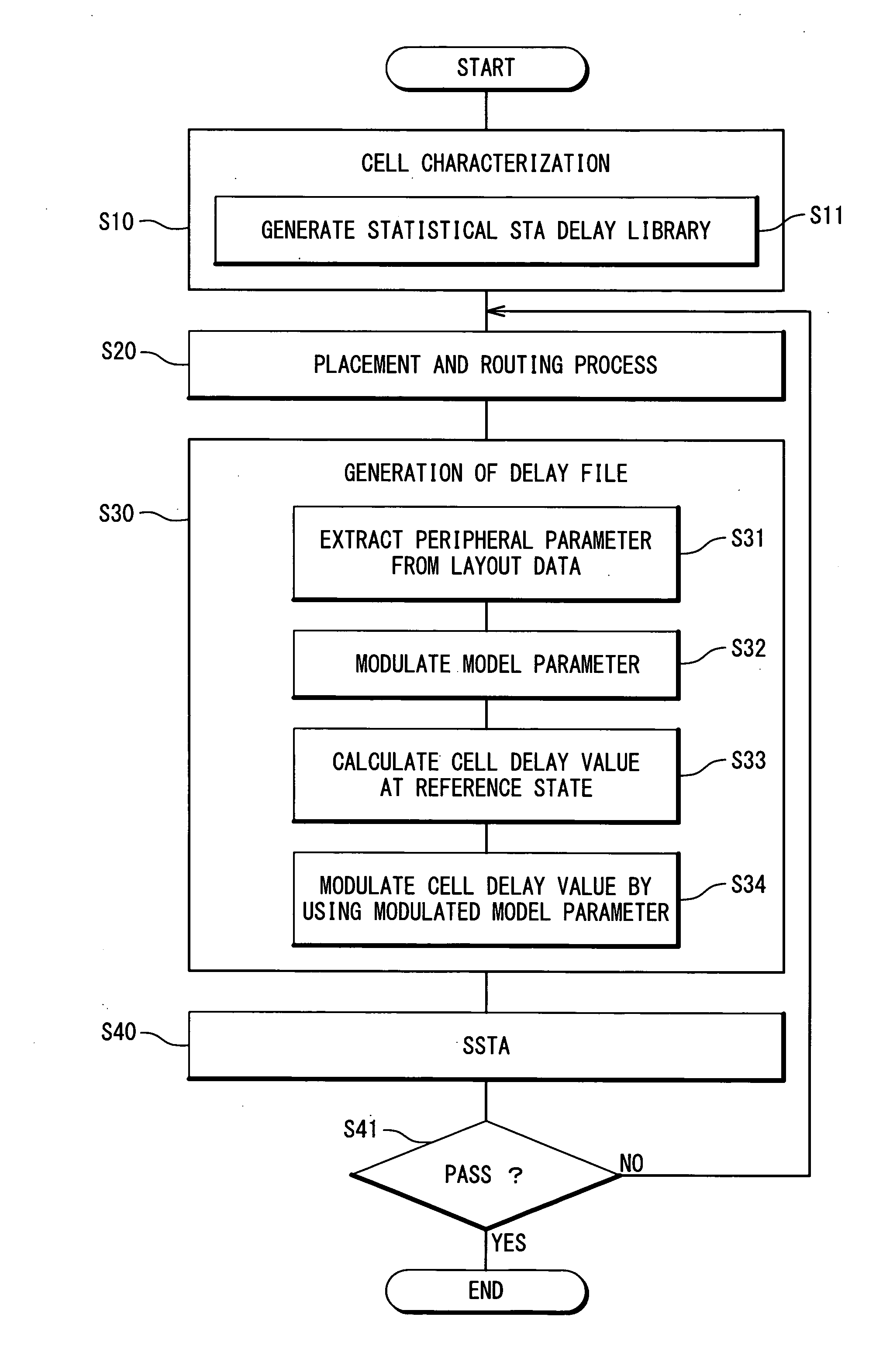
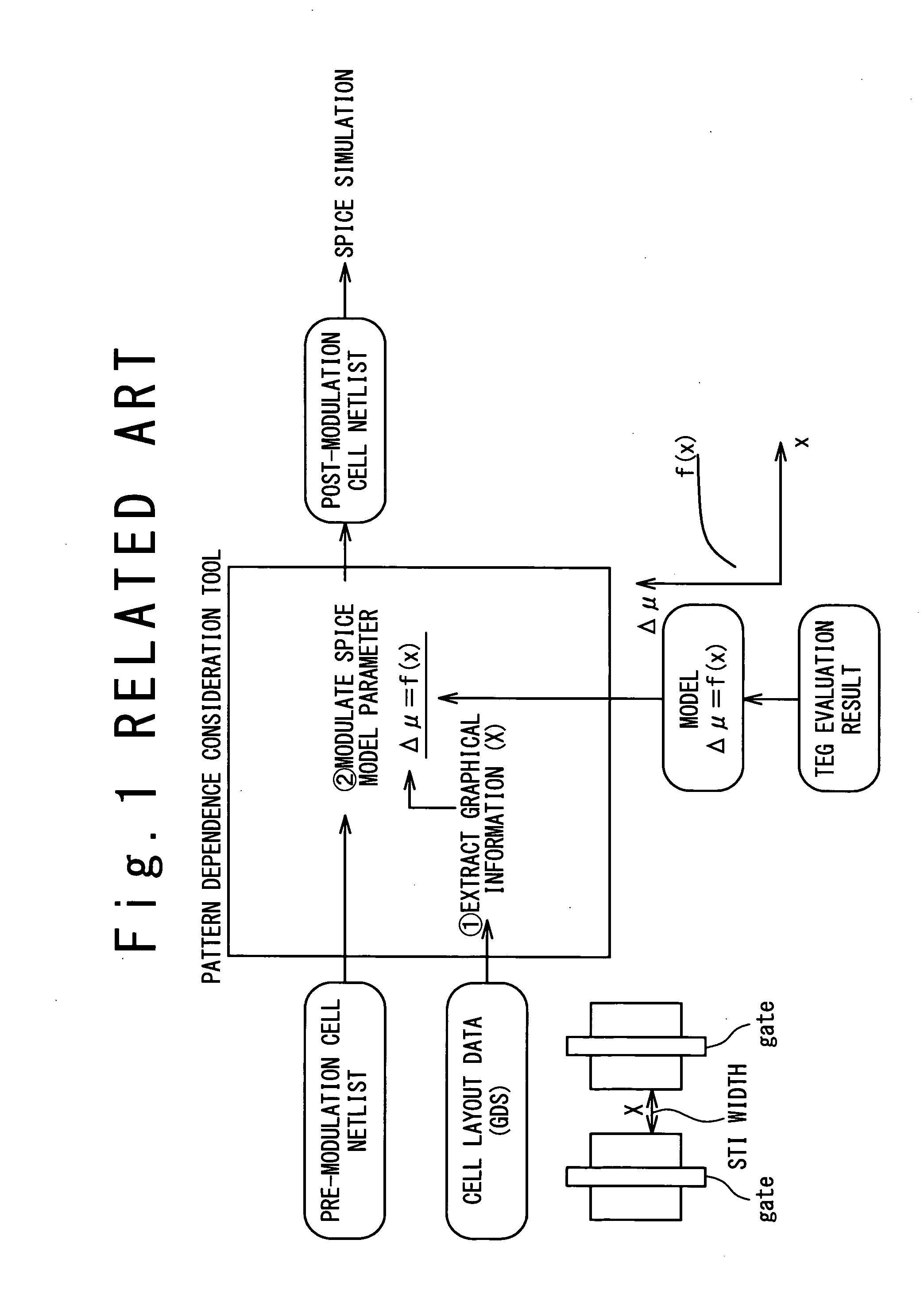
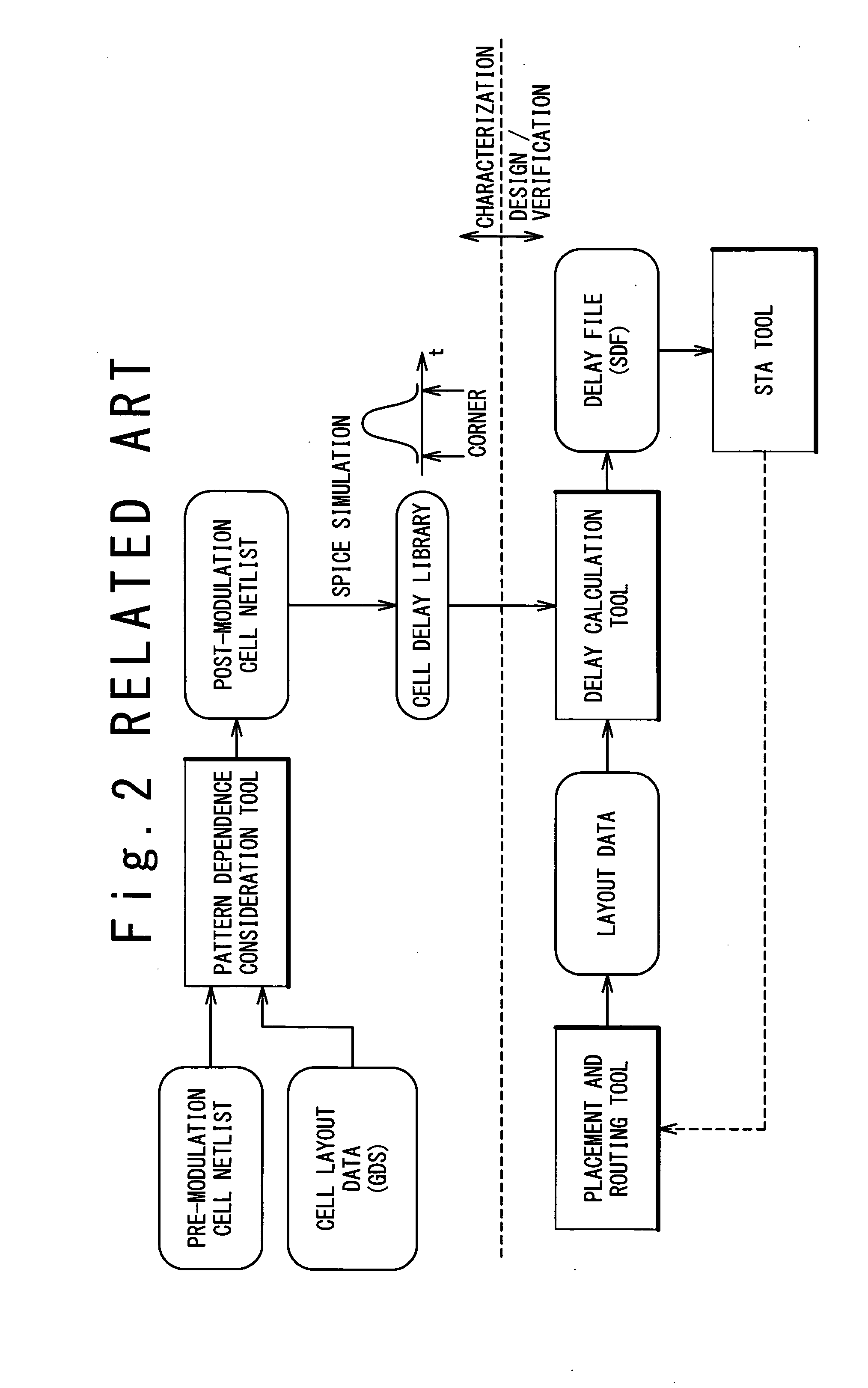
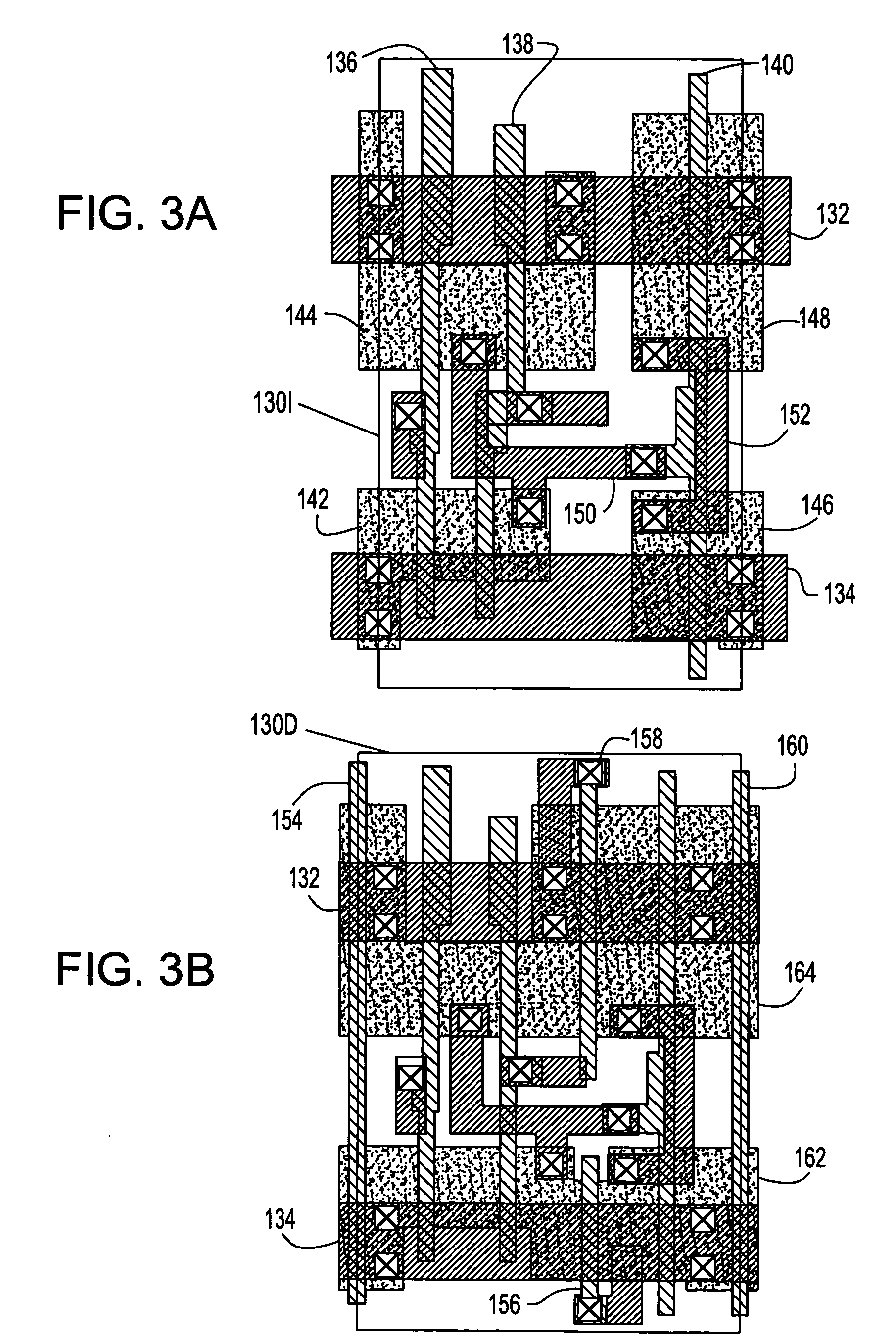
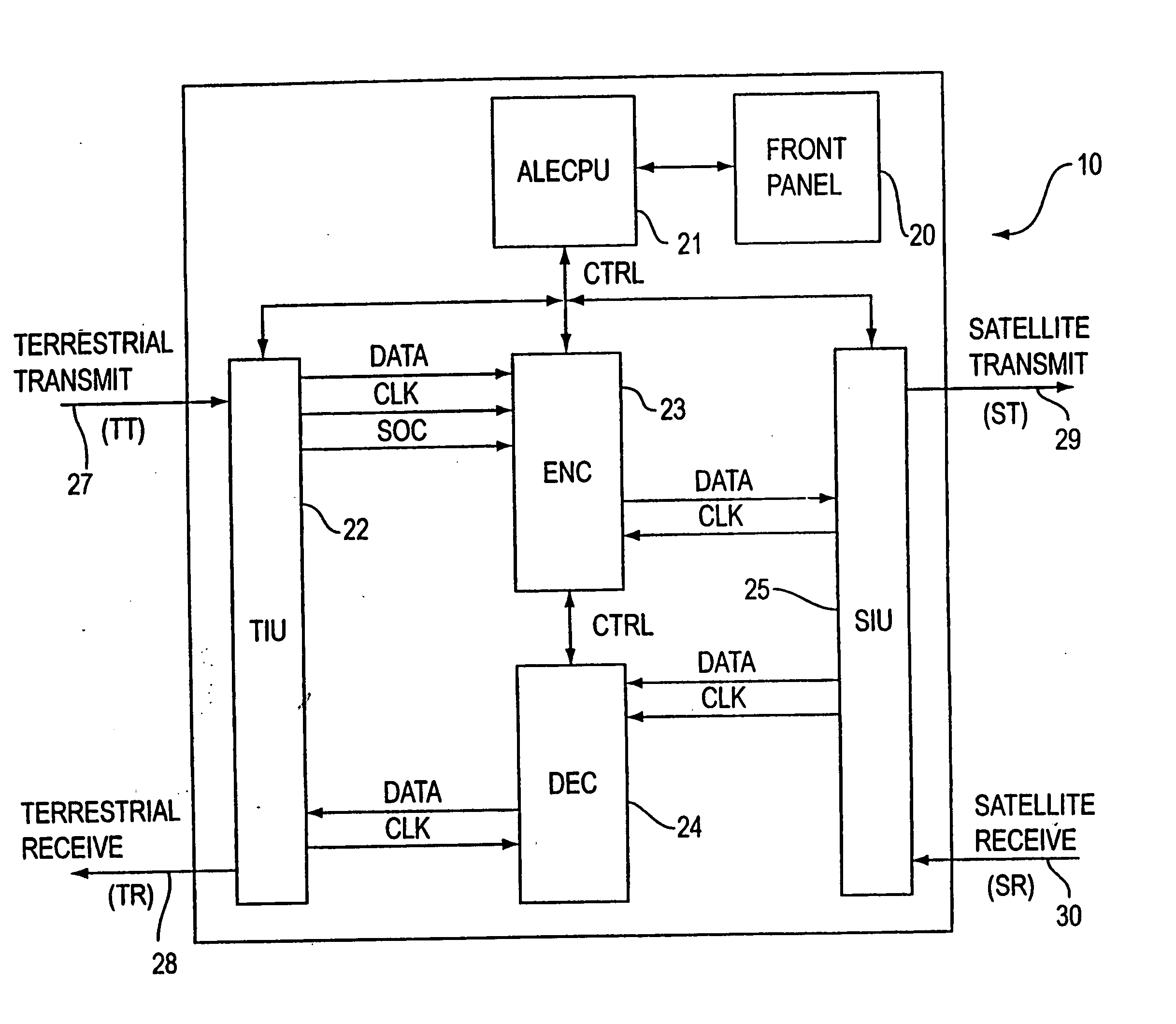
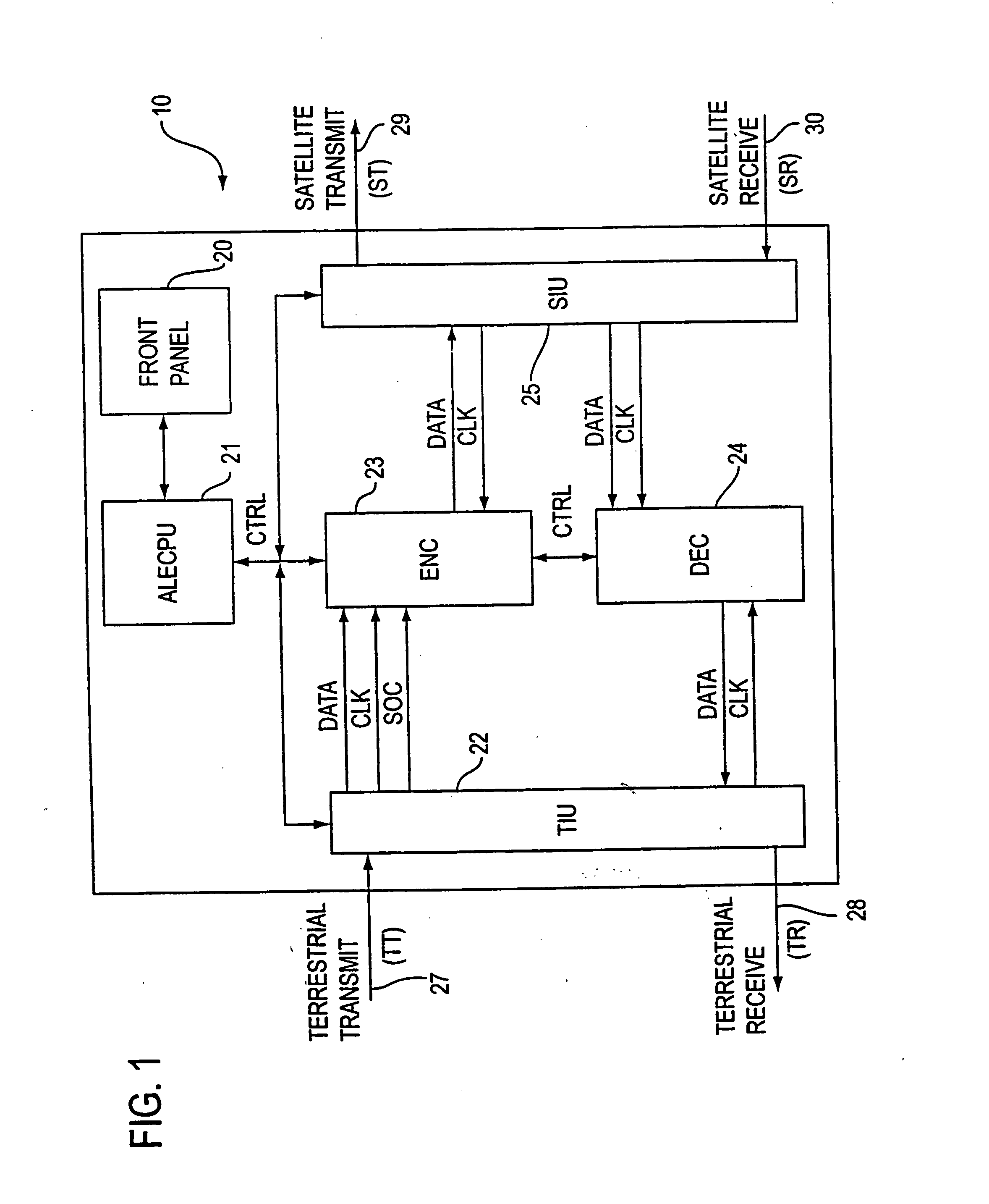
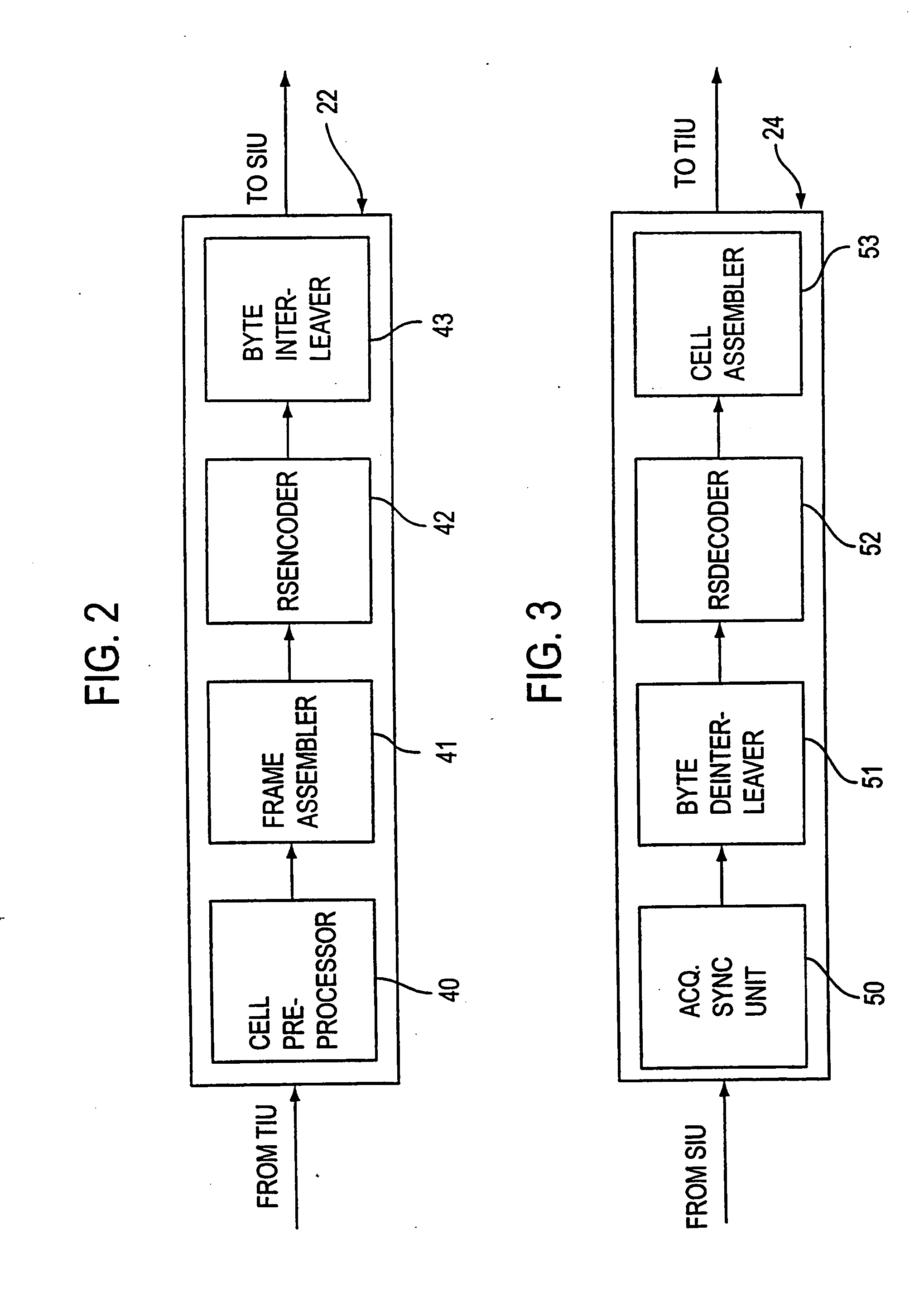
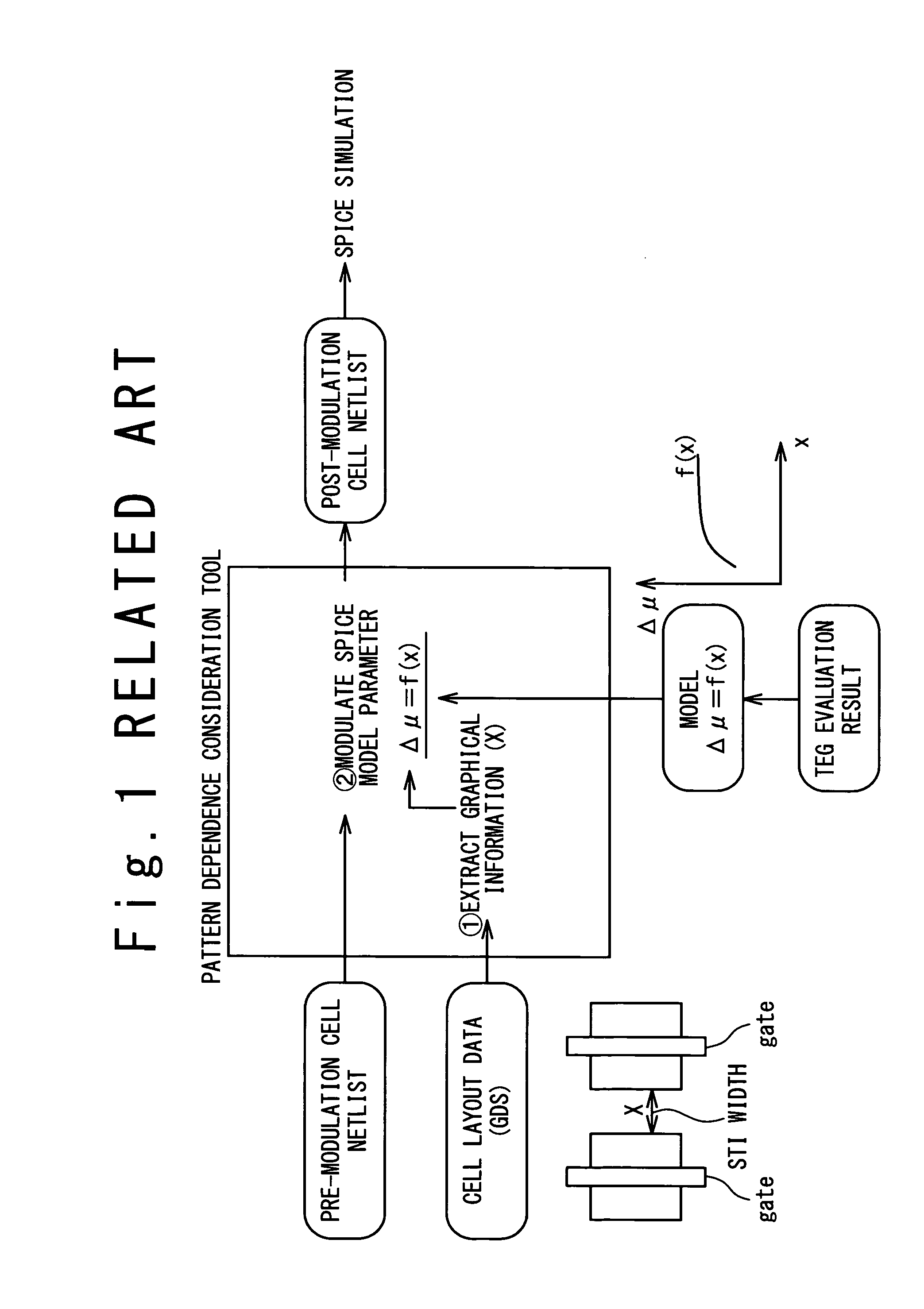
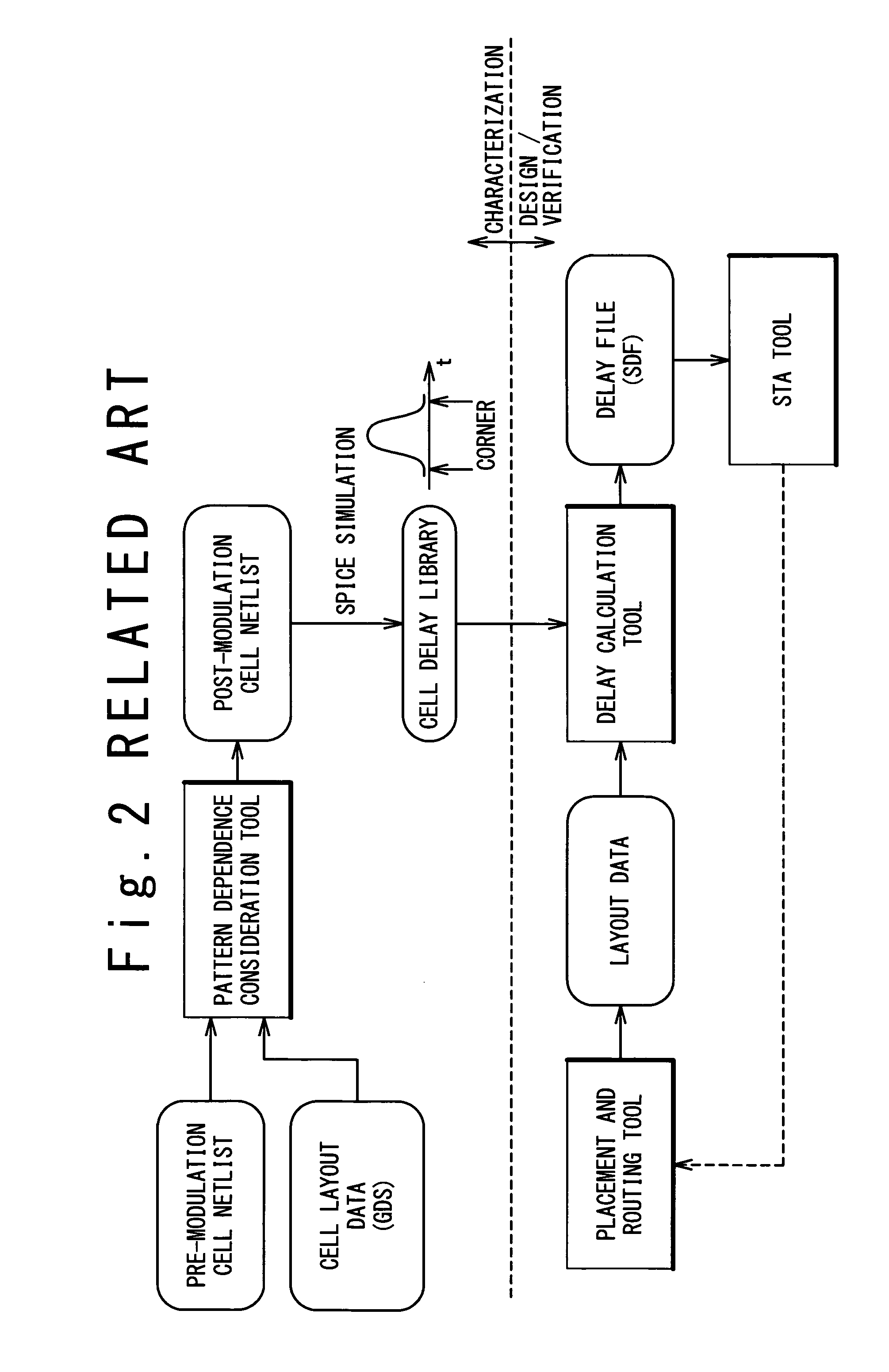
Method and program for designing semiconductor integrated circuit
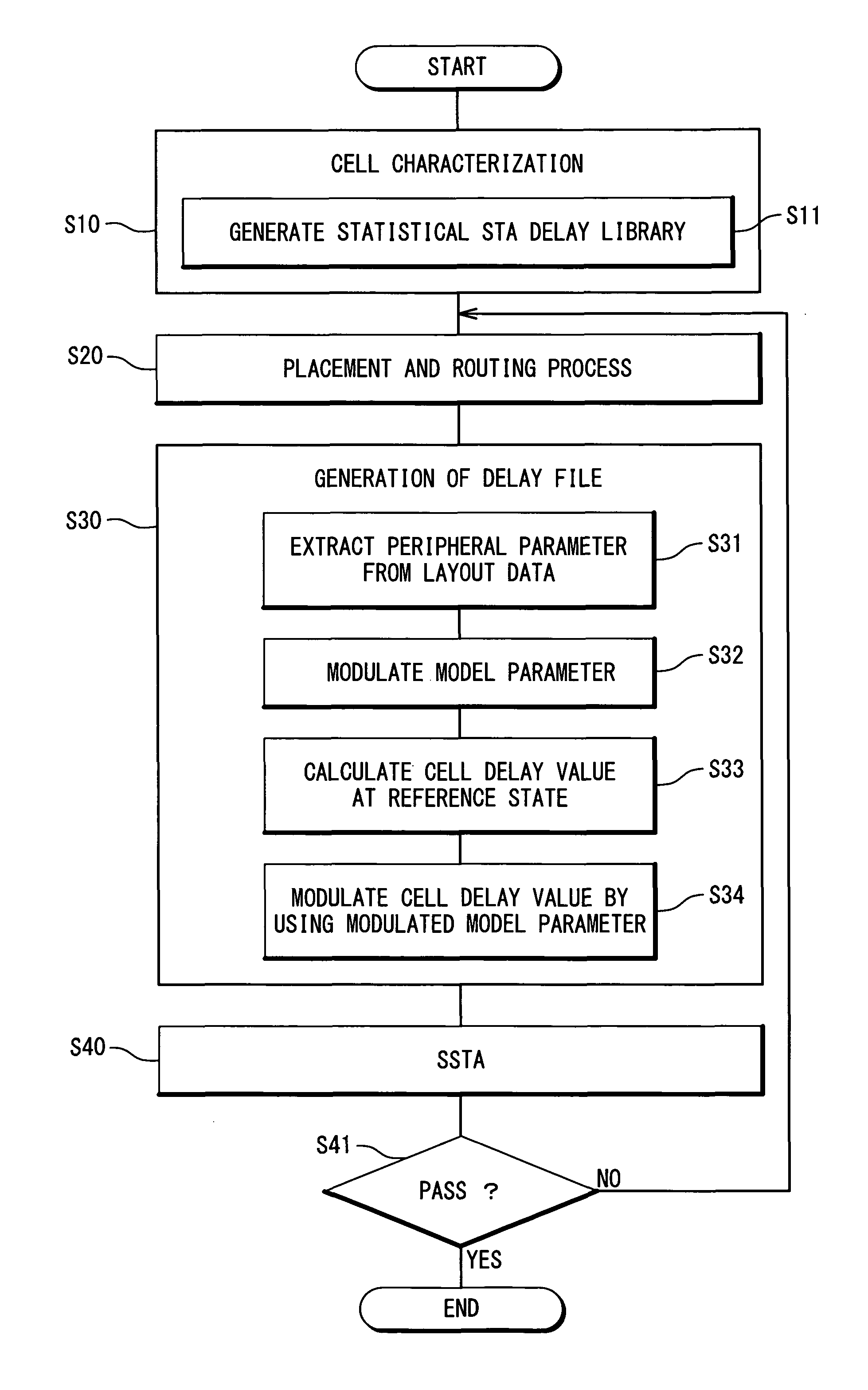
InactiveUS20090024974A1Increase in design/verification TAT can be preventedHigh delay accuracyCAD circuit designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationModel parametersCell based
A design method for an LSI includes: generating a delay library for use in a statistical STA, wherein the delay library provides a delay function that expresses a cell delay value as a function of model parameters of a transistor; generating a layout data; and calculating a delay value of a target cell based on the delay library and the layout data. The calculating includes: referring to the layout data to extract a parameter specifying a layout pattern around a target transistor; modulating model parameters of the target transistor such that the characteristics corresponding to the extracted parameter is obtained in a circuit simulation; calculating, by using the delay function, a reference delay value of the target cell; and calculating, by using the delay function and the modulation amount of the model parameter, a delay variation from the reference delay value depending on the modulation amount.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Integrated circuit logic with self compensating block delays
ActiveUS20050189604A1Reduce logic path variabilityMinimize fabrication parameter variationTransistorSolid-state devicesField-effect transistorCell delay
An integrated circuit (IC) including at least one combinational logic path. The combinational logic path includes two types of logic blocks cells that compensate each other for fabrication parameter effects on cell transistors. The two types may be dense cells with field effect transistor (FET) gates on contacted pitch and isolated cells with FET gates on wider than contacted pitch. Dense cell delay changes from the FET gates being printed out of focus are offset by isolated cell delay changes.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
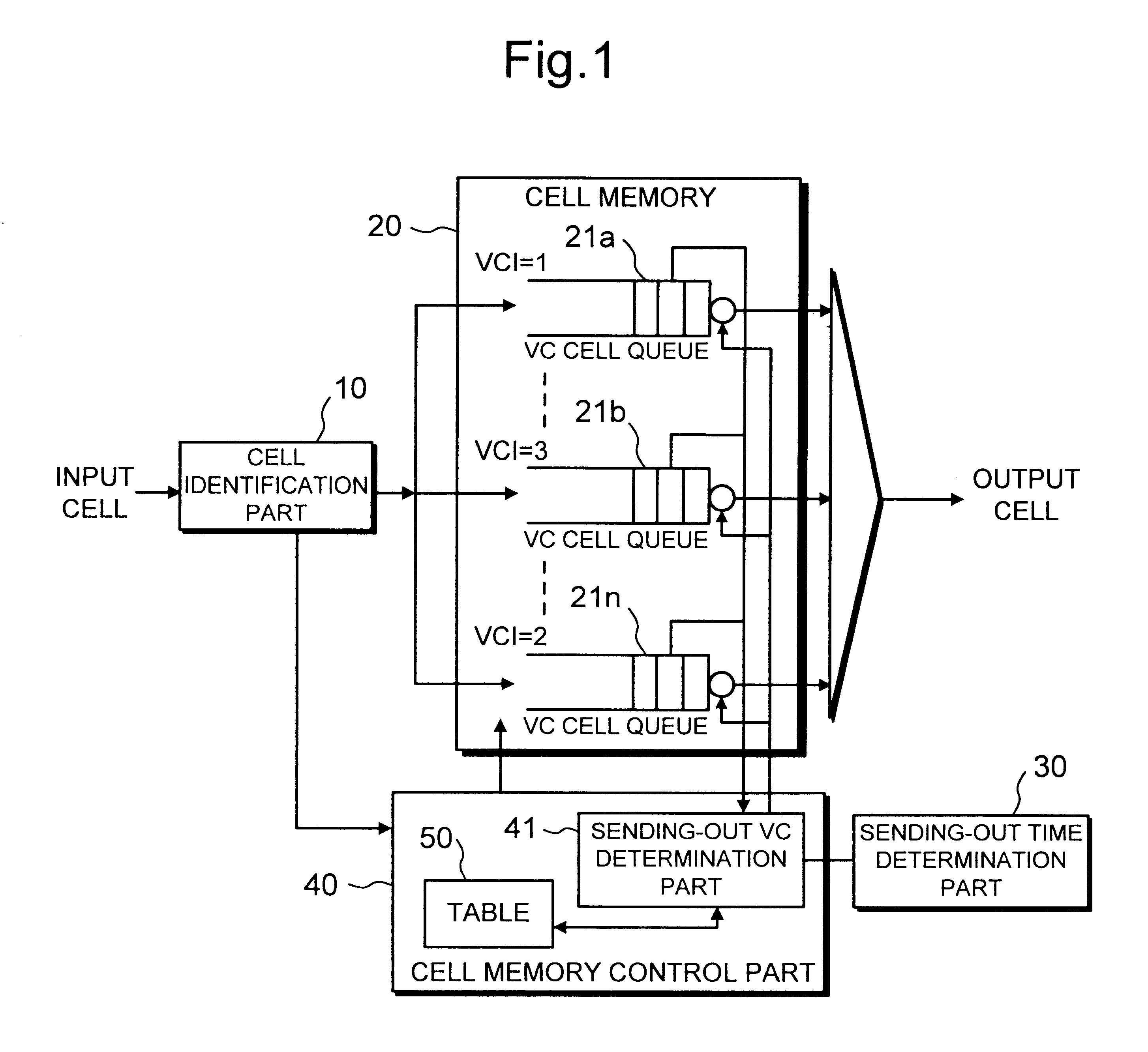
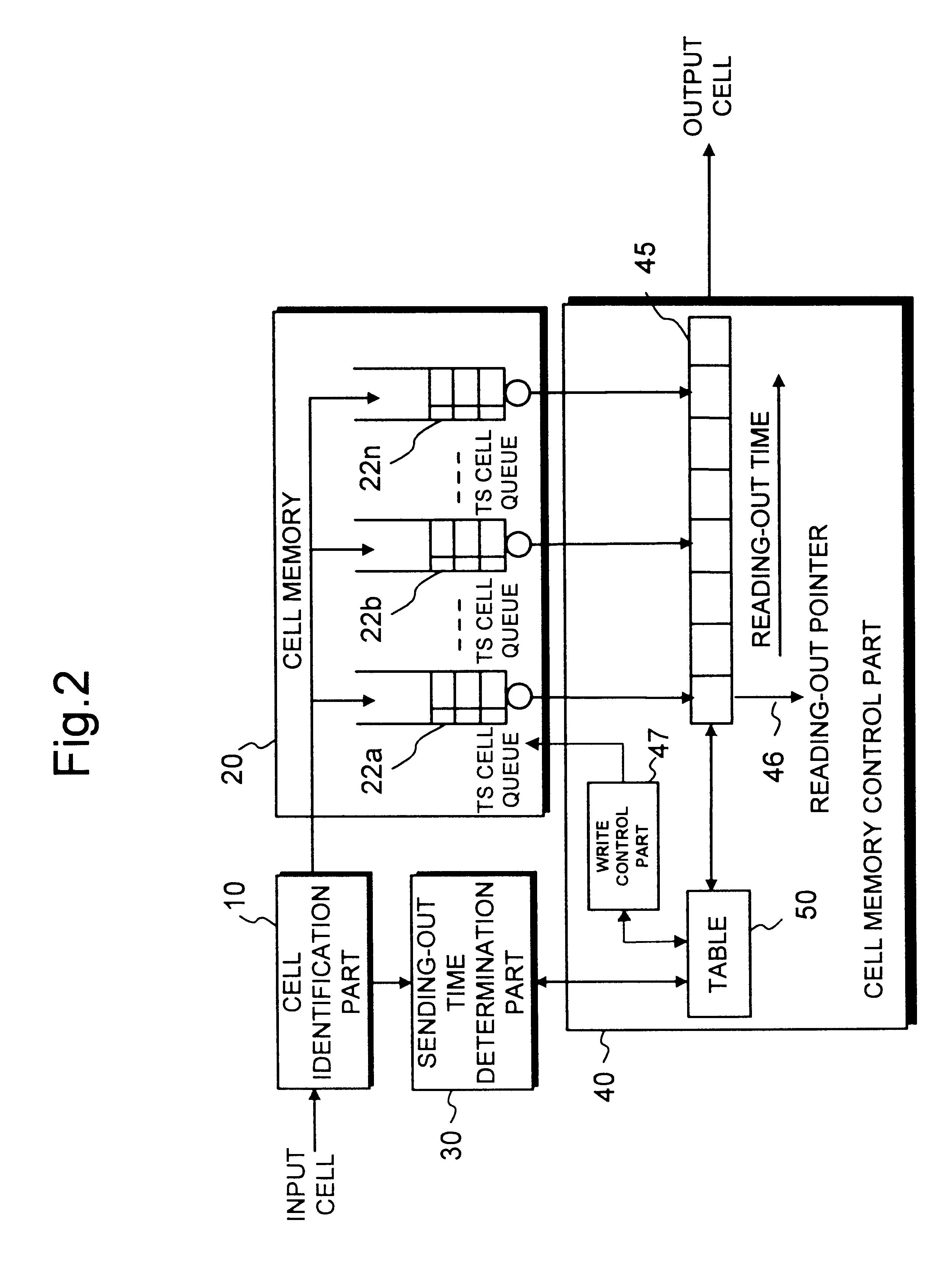
Traffic shaper
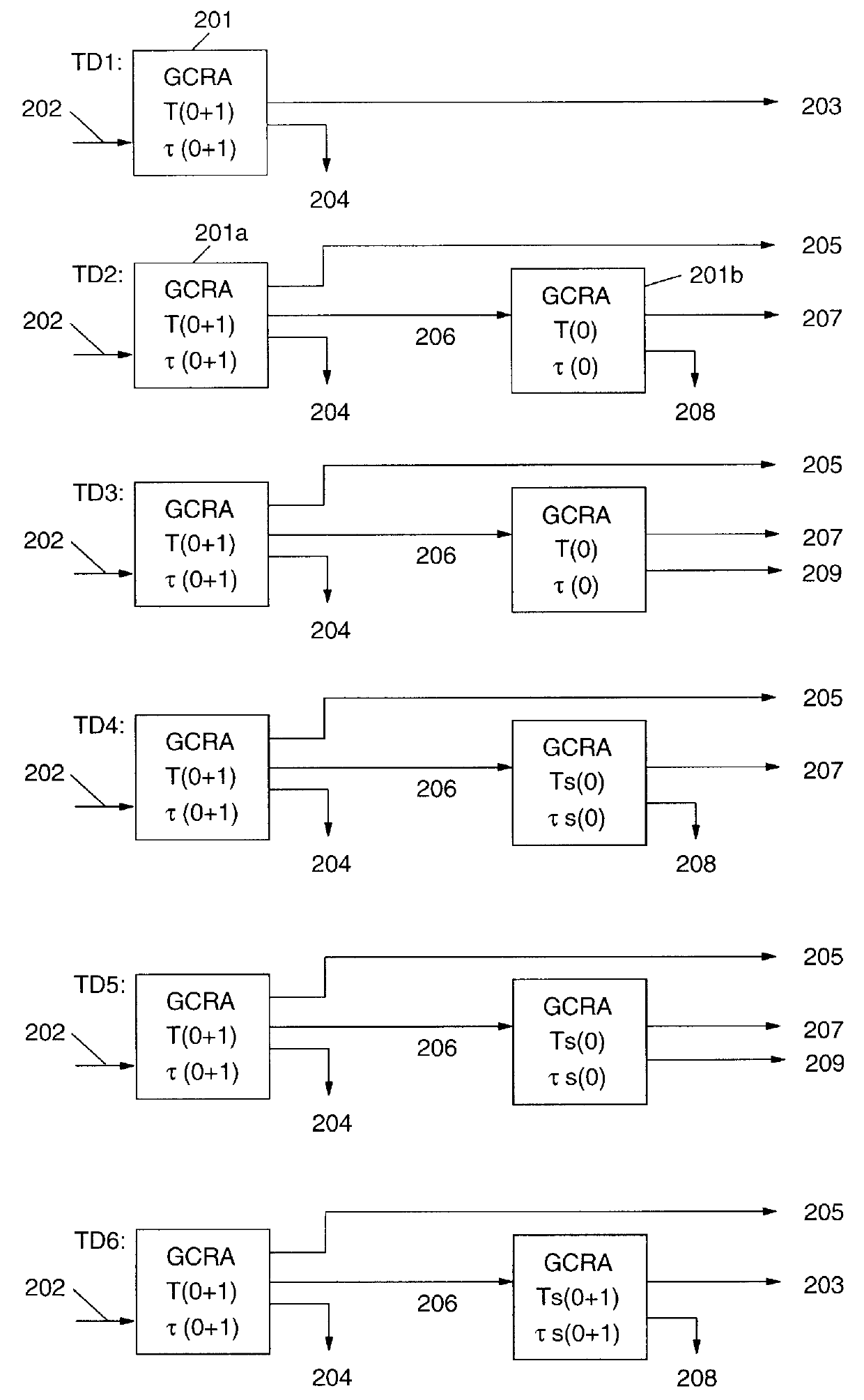
InactiveUS6704321B1Decreasing cell delay variationError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsCell delayDistributed computing
A traffic shaper for absorbing a cell delay variation of cell flow in each of virtual connections in an ATM (asynchronous transmission mode) network is realized. The traffic shaper comprises a cell identification part, a cell memory, a sending-out time determination part and a cell memory control part. The cell identification part is provided for identifying a virtual connection allocated to an input cell, the cell memory is provided for storing input cells into respective virtual queues, each queue is corresponding to the virtual connection, in accordance with the identified virtual connection of each input cell, the sending-out time determination part is provided for determining a sending-out time for each cell stored in the cell memory on the virtual connection basis, and the cell memory control part is provided for performing a cell output from each virtual queue in accordance with the sending-out time determined for each cell, and performing an output competition control by selecting a cell to be output among cells having the same sending-out time in different virtual queues in accordance with a predetermined output priority assigned to each virtual connection.
Owner:JUMIPER NETWORKS INC
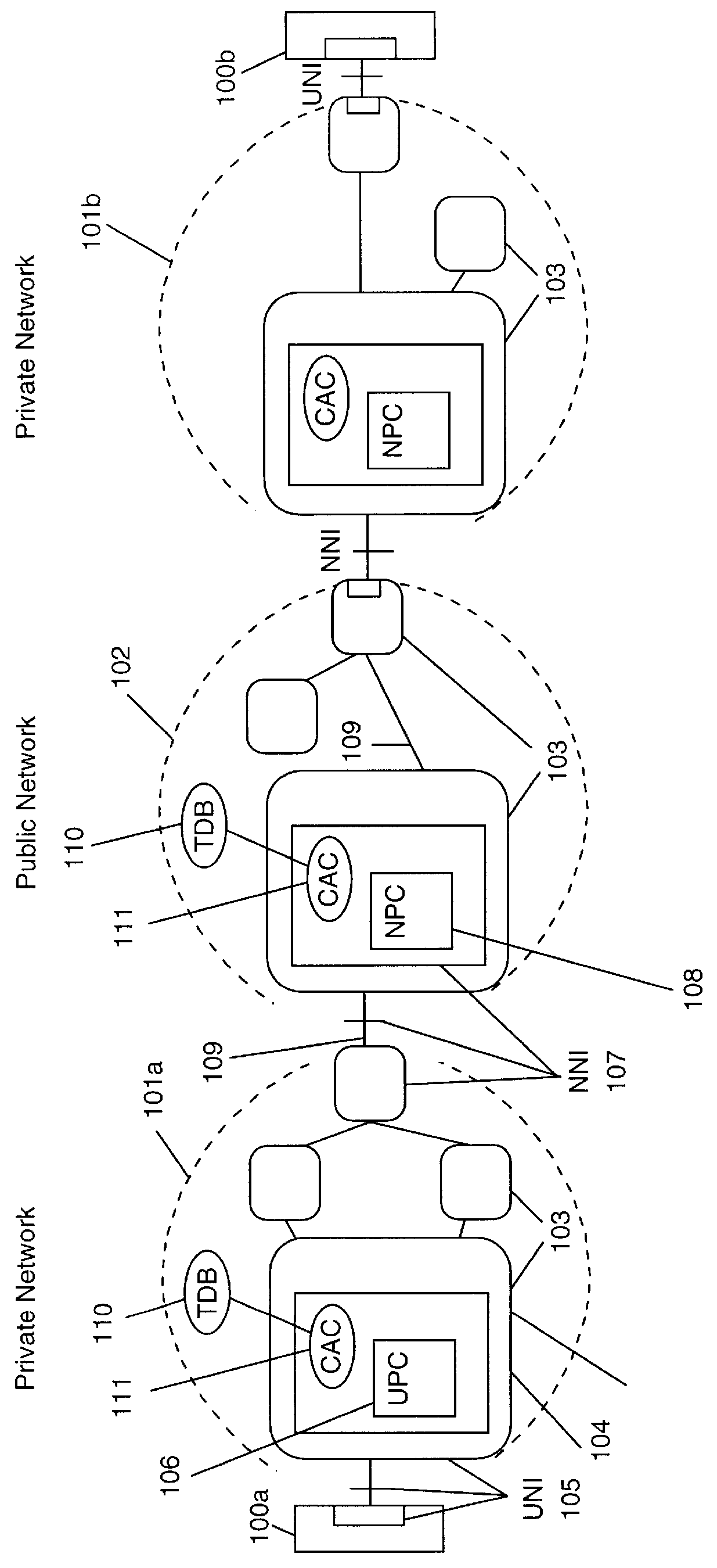
Flow control for very bursty connections in high speed cell switching networks
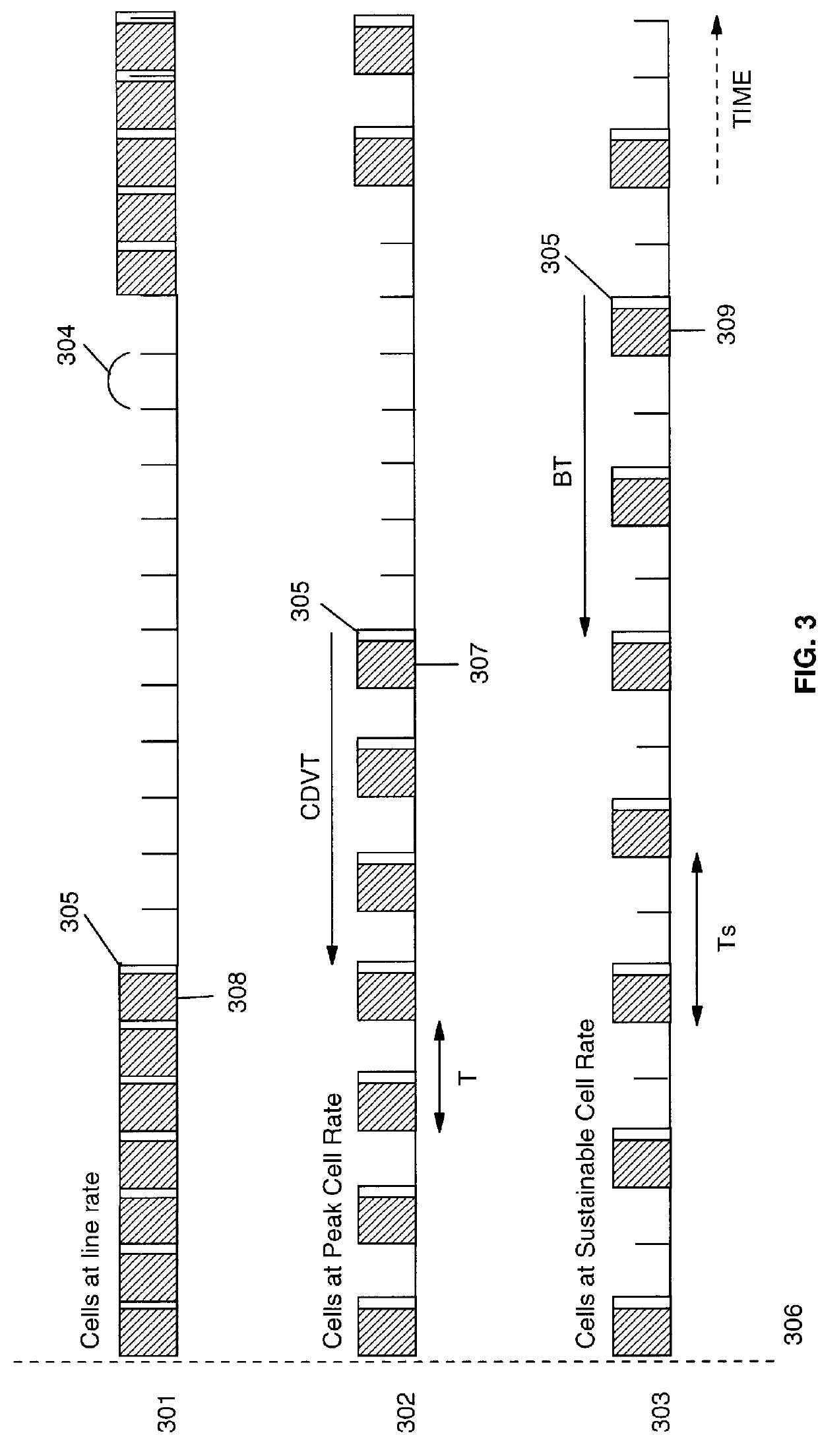
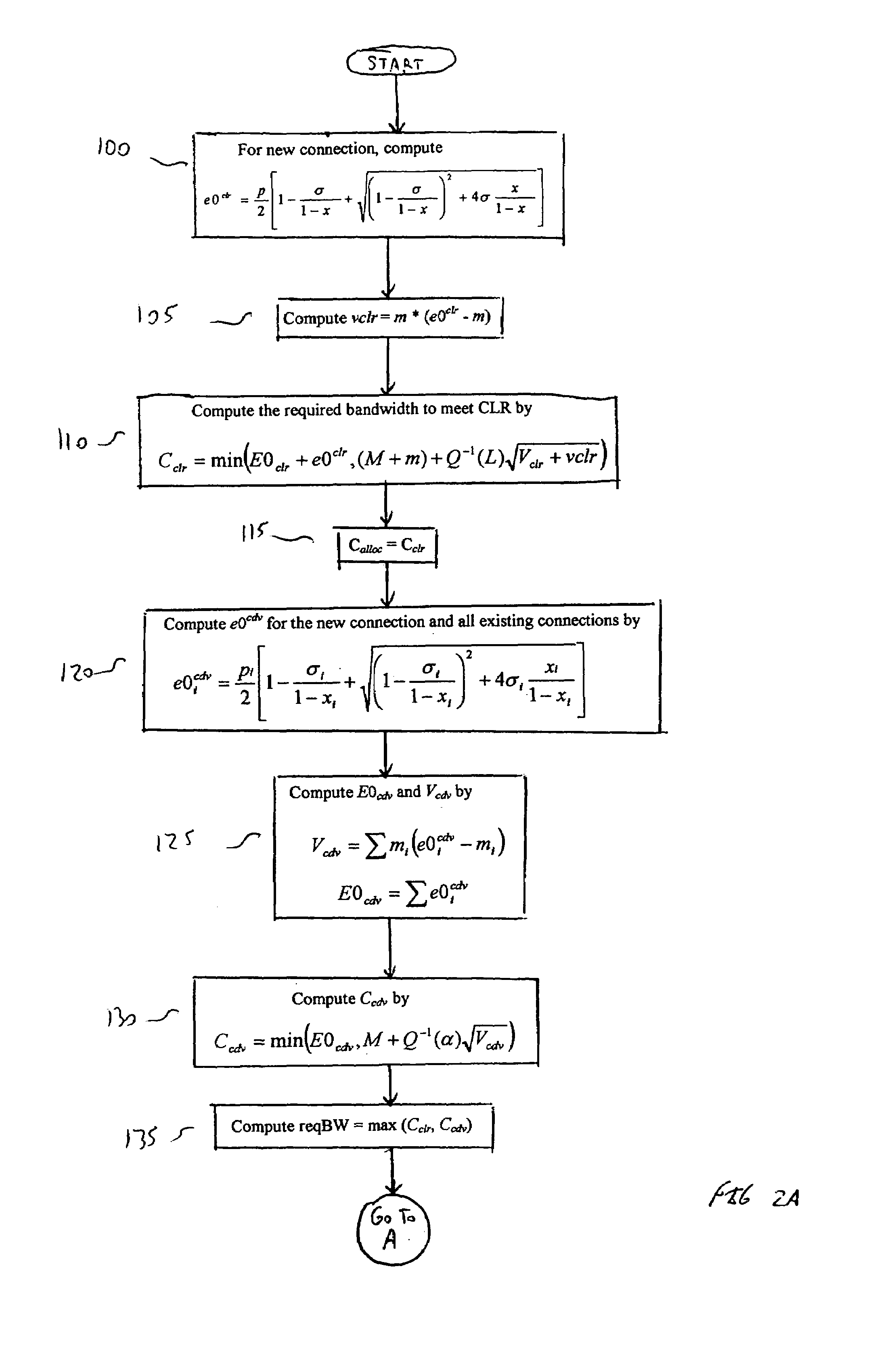
In high speed cell switching networks, a Call Admission Control (CAC) procedure is performed on each connection according to a specified Traffic Descriptor. A mandatory parameter of the Traffic Descriptor is the Peak Cell Rate (PCR), associated with a Cell Delay Variation Tolerance (CDVT). Connections which specify a high CDVT value may potentially send into the network bursts of cells at a rate much higher than the declared Peak Cell Rate, which may lead to congestion in cell buffers of intermediate network nodes. Guaranteeing the Quality of Service (QoS) for such connections may require the reservation of a high amount of resources in the network, leading to poor utilization of those resources. A Call Admission Control procedure, associated with an Usage Parameter Control / Network Parameter Control mechanism, provides: accepting not bursty connections and guaranteeing the Quality of Service requested at connection setup, accepting very bursty connections and guaranteeing a minimal Quality of Service rather than simply rejecting them, protecting the network from potentially too bursty traffic, determining a bandwidth reservation method based on a Mean Burst Length, for every connection, minimizing the bandwidth reservation while satisfying the required Quality of Service.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Programmable application specific integrated circuit and logic cell
A field programmable gate array includes a programmable routing network, a programmable configuration network integrated with the programmable routing network; and a logic cell integrated with the programmable configuration network. The logic cell includes four two-input AND gates, two six-input AND gates, three multiplexers, and a delay flipflop. The logic cell is a powerful general purpose universal logic building block suitable for implementing most TTL and gate array macrolibrary functions. A considerable variety of functions are realizable with one cell delay, including combinational logic functions as wide as thirteen inputs, all boolean transfer functions for up to three inputs, and sequential flipflop functions such as T, JK and count with carry-in.
Owner:QUICKLOGIC
Delay locked loop circuitry and method for optimizing delay timing in mixed signal systems
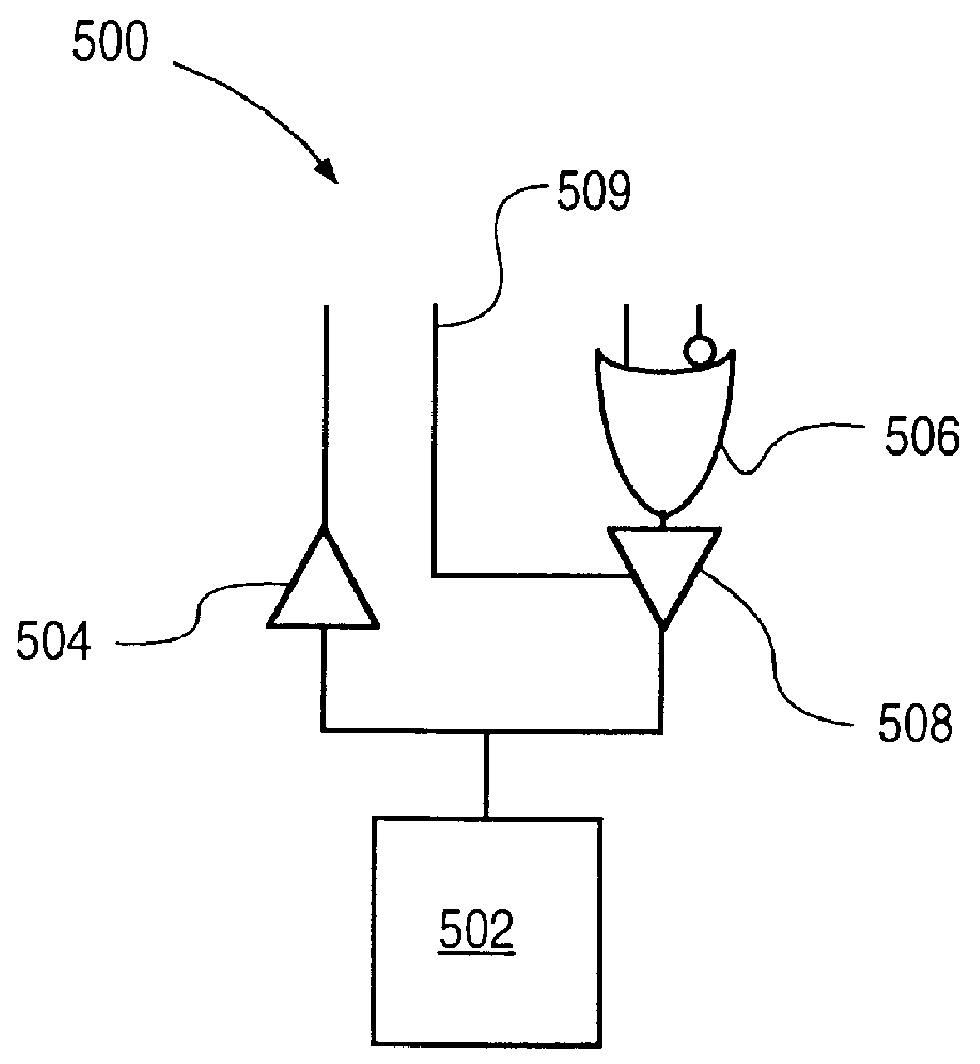
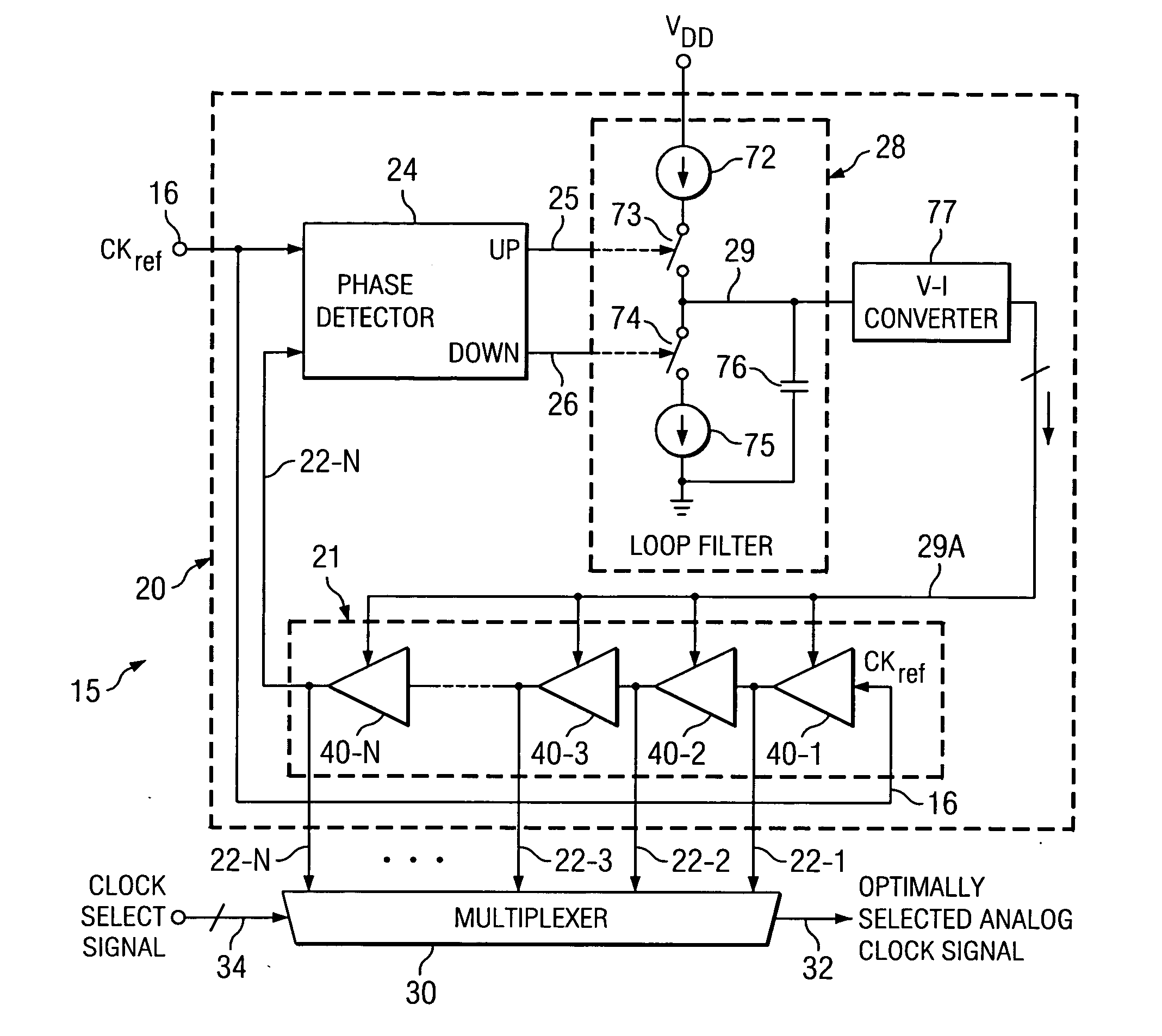
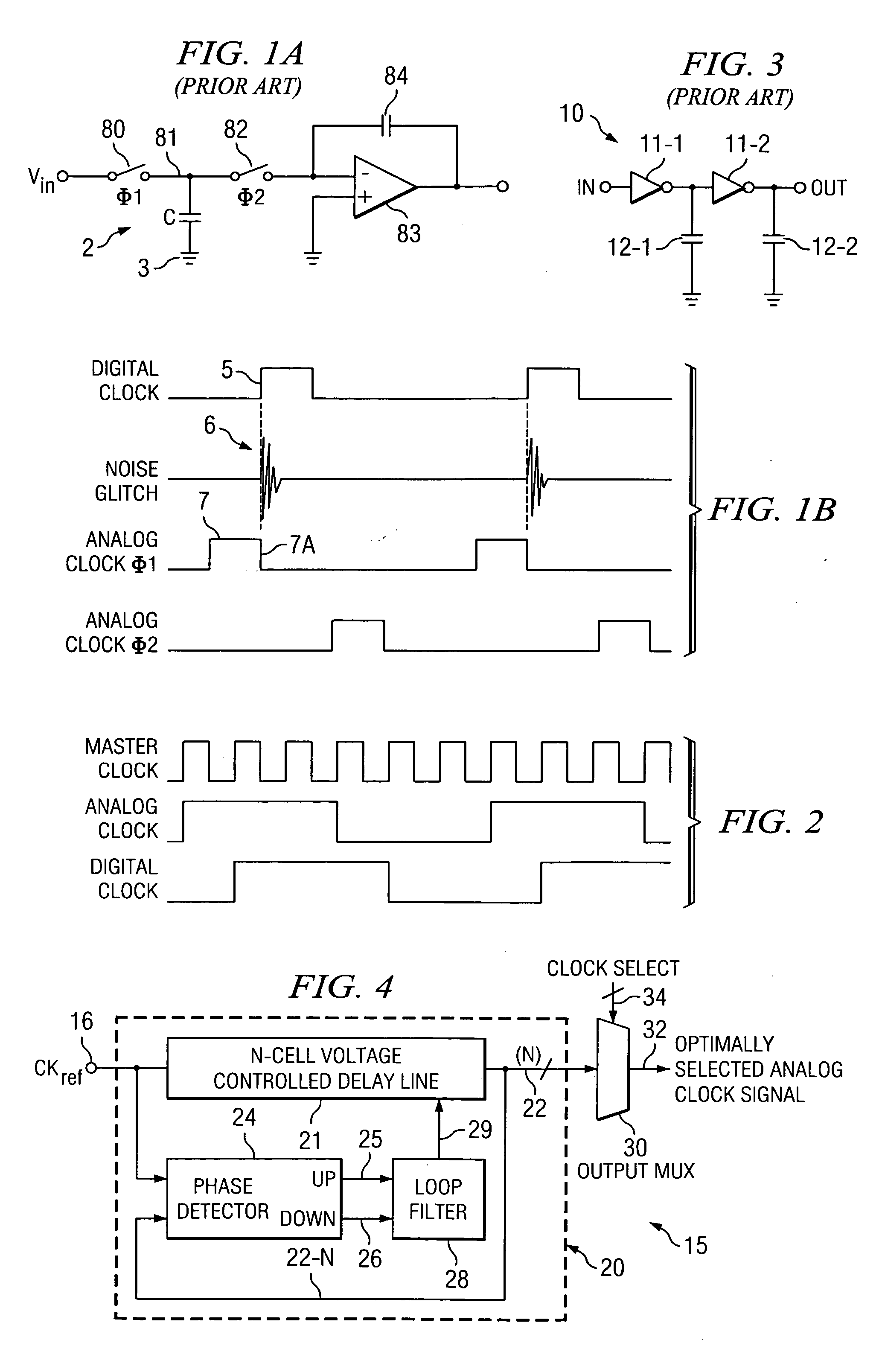
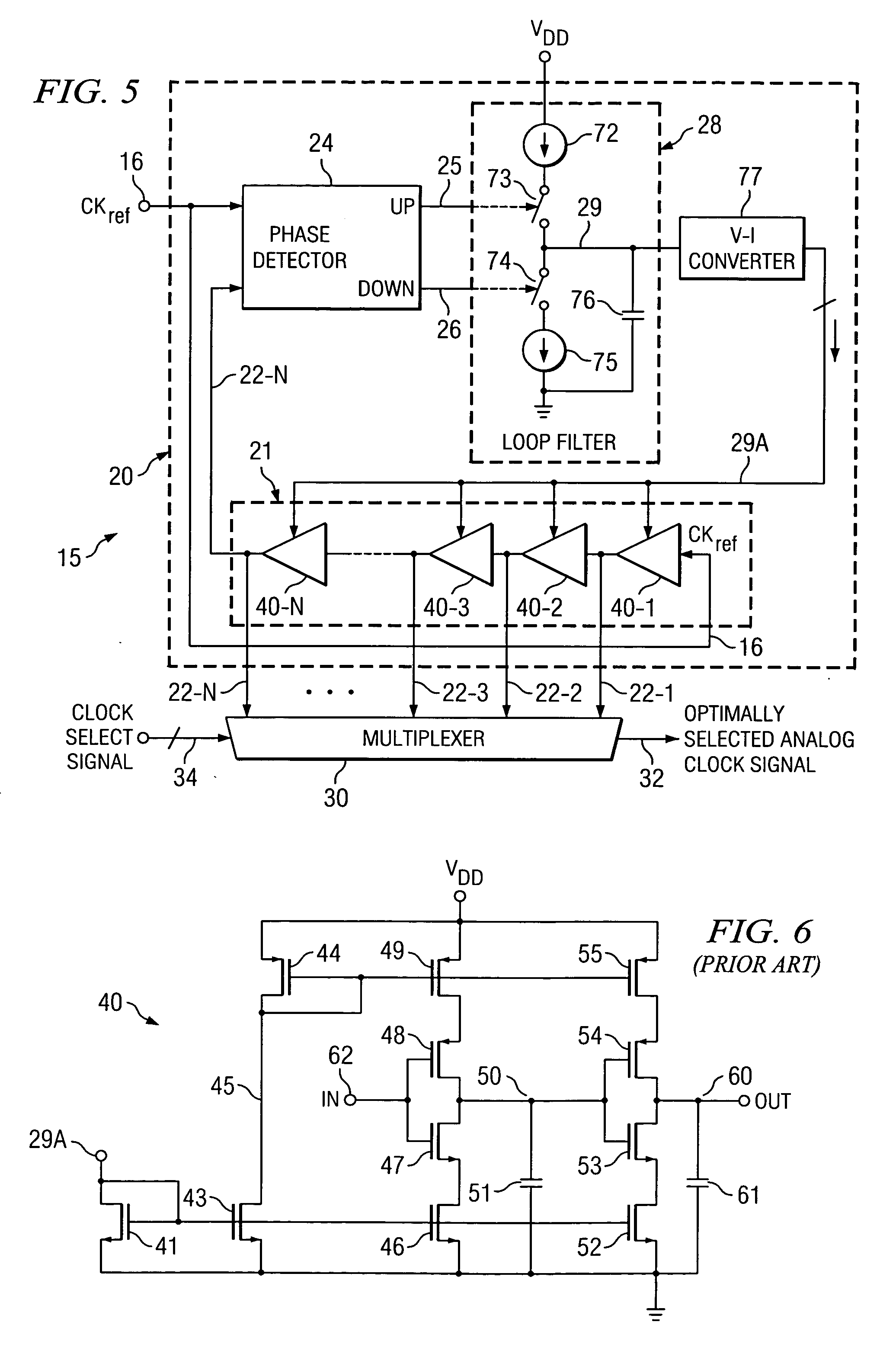
InactiveUS20060038596A1Minimizing degradationAvoid problemsAnalogue/digital conversionPulse automatic controlMultiplexerDigital clock
A mixed signal system includes a digital circuit (17) clocked by a digital clock signal, an analog circuit (18) clocked by an analog clock signal, and clock generation circuitry (15) including a delay locked loop (20) including a N-cell delay line (21) having an input for receiving a reference clock signal and a plurality of delay outputs (22), and a multiplexer (30) having a plurality of inputs coupled to the plurality of delay outputs (22), respectively. A selection signal (34) causes the multiplexer (30) to couple a selected one of the delay outputs (22) to an output (32) of the multiplexer (30) so as to cause the analog clock signal and the digital clock signal to be sufficiently skewed from each other to minimize an inaccuracy in the analog circuit (18) caused by a noise glitch associated with the digital clock signal.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Virtual loop carrier system with network clock recovery
InactiveUS6982993B1Lower unit costGood serviceTime-division multiplexNetwork connectionsClock driftTelecommunications link
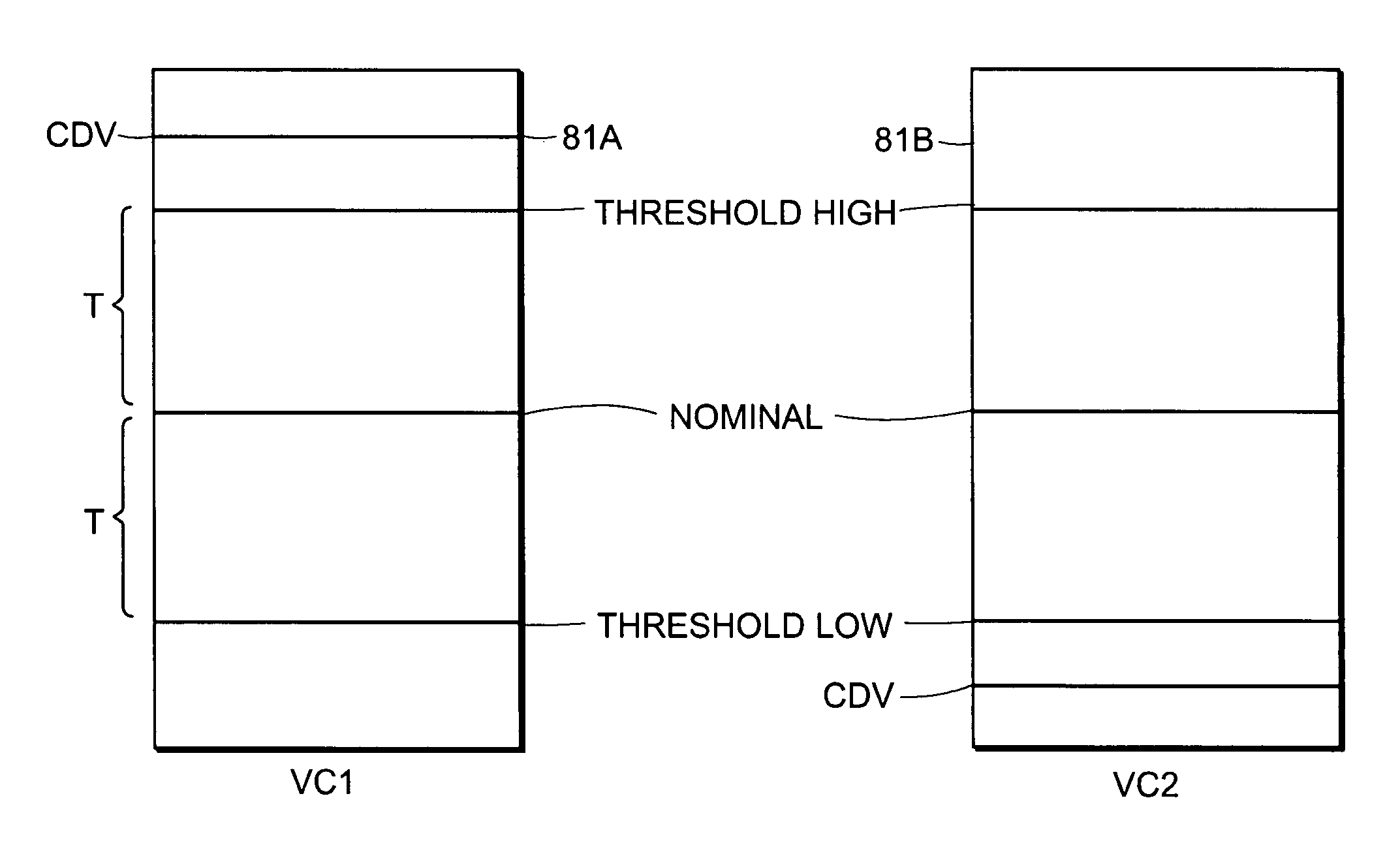
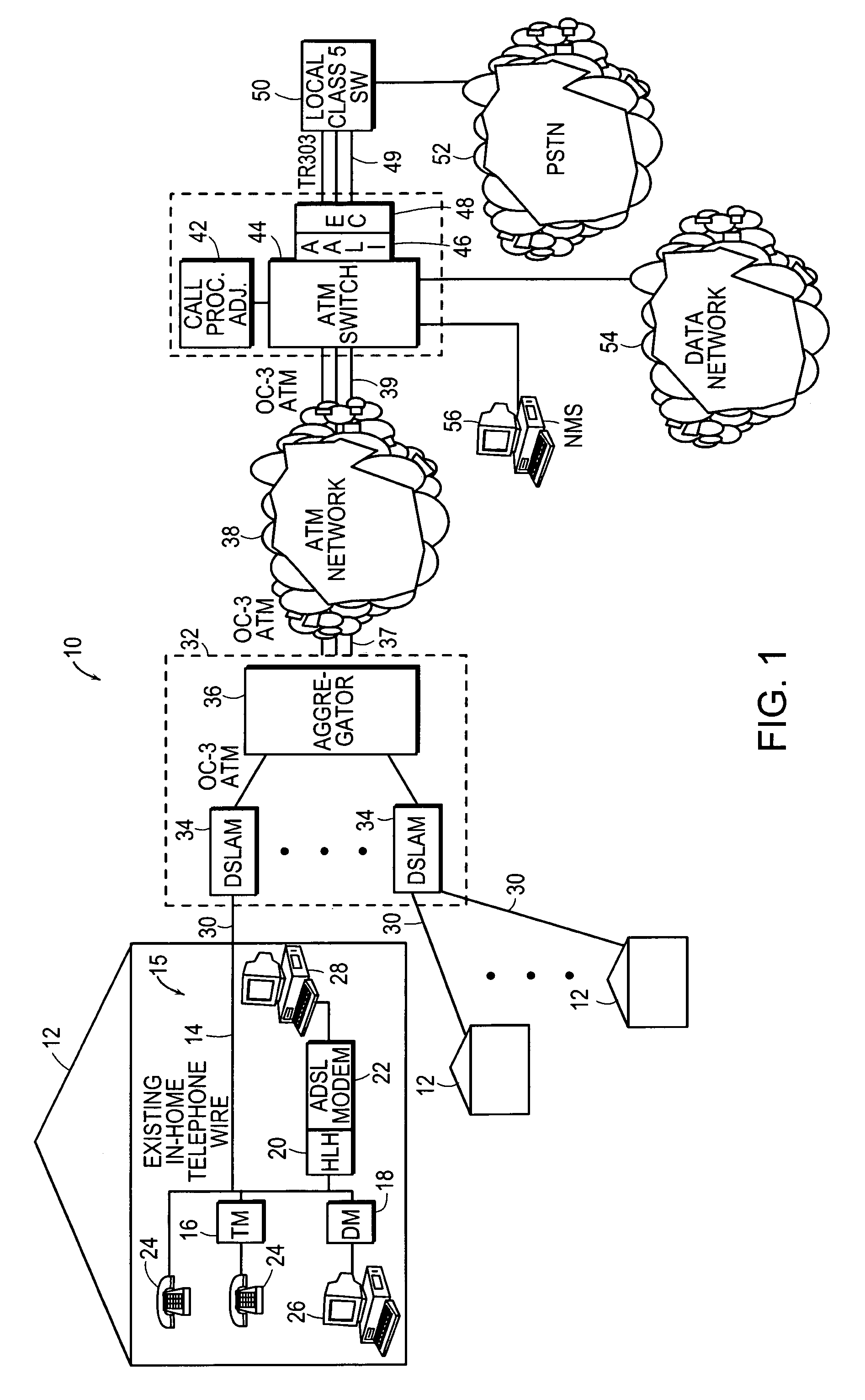
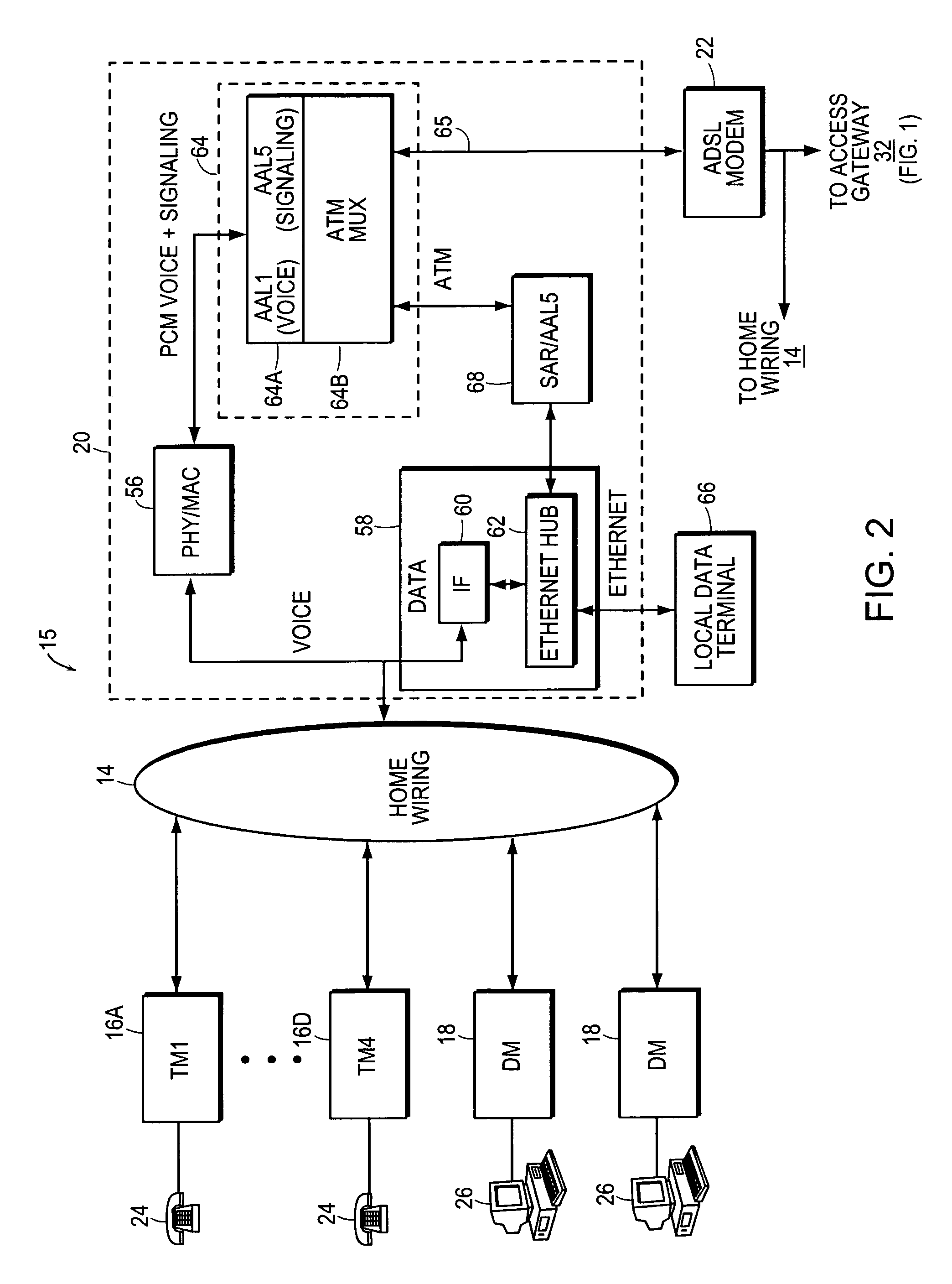
A loop carrier system includes a home local area network having plural telephone modules and a hub coupled to in-home telephone wiring. The telephone modules and the hub communicate voice signals over the in-home wiring in a dedicated frequency band above baseband POTS. The hub converts between voice signals and voice packets and is connected to a network access device for transferring the voice packets from the home local area network to a telecommunications network which routes the voice packets to a gateway. The gateway converts between the voice packets and a circuit format compatible with a local digital voice switch. The home local area network includes a timing recovery mechanism which in the absence of a clock that is traceable to the Primary Reference Clock on the public network is robust to clock drift, cell delay variation and cell impairments.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
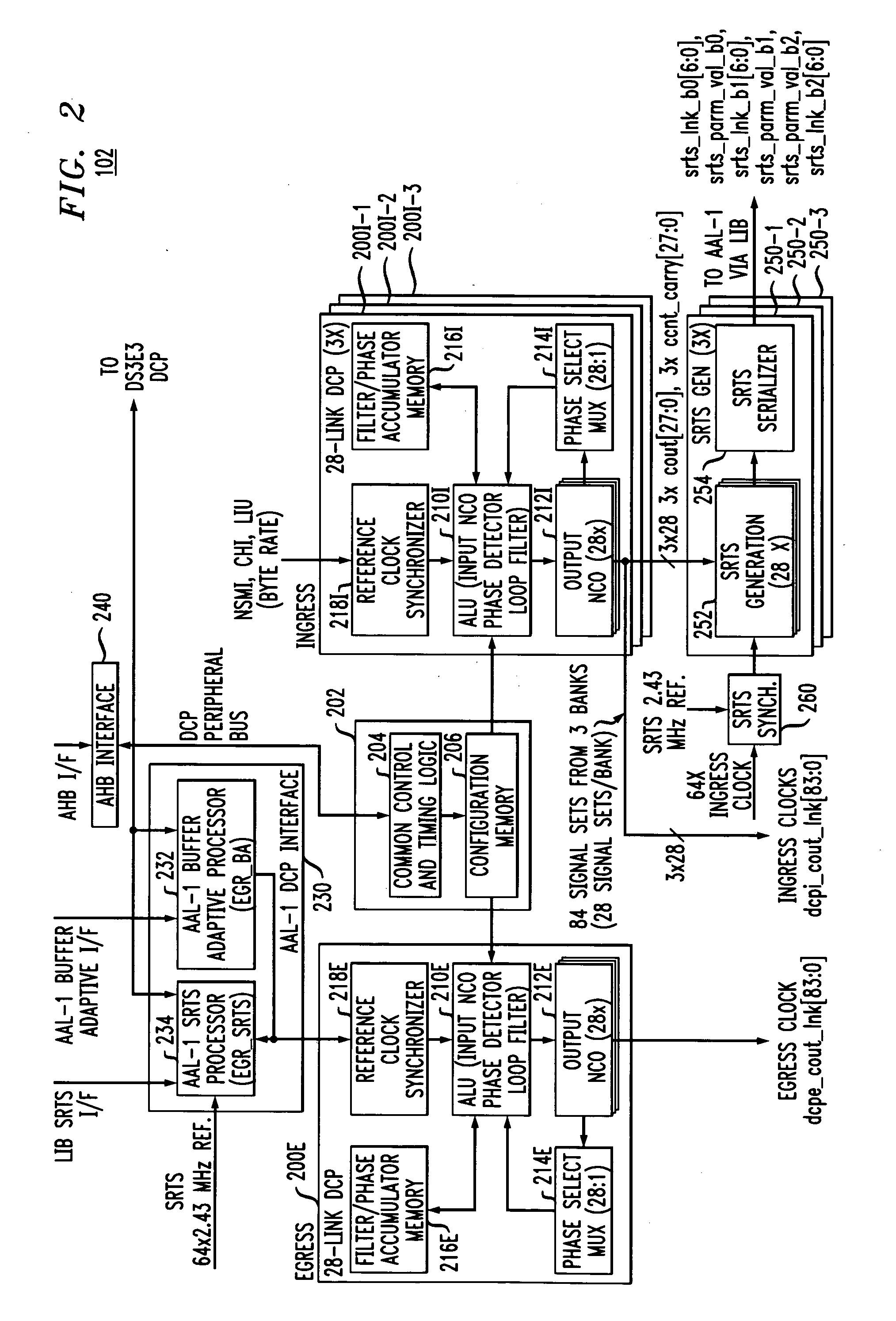
Link layer device with clock processing hardware resources shared among multiple ingress and egress links
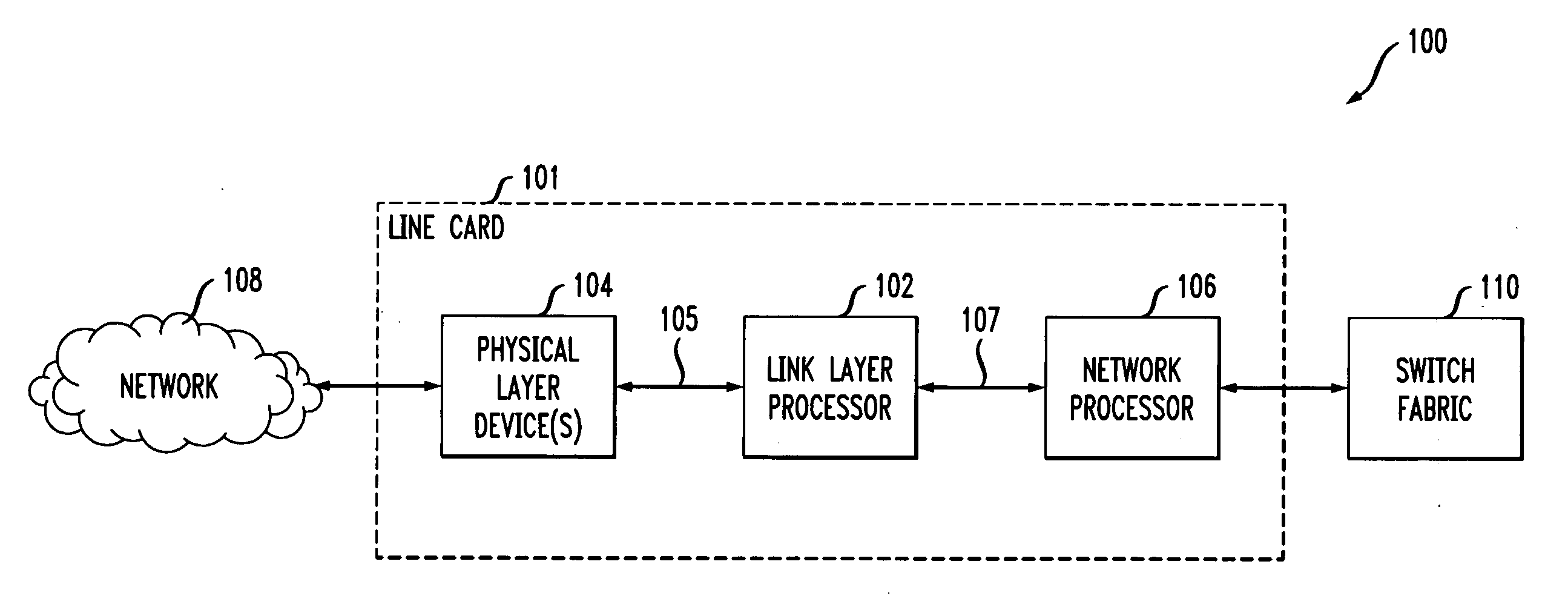
InactiveUS20070274348A1Improve robustnessReduced Power RequirementsTime-division multiplexData switching by path configurationCommunications systemPhysical layer
In a communication system comprising a link layer device connectable to one or more physical layer devices, the link layer device is configured using an efficient shared architecture for processing data associated with a plurality of links including at least one ingress link and at least one egress link. The link layer device comprises an ingress data clock processor configured to generate an ingress clock signal for processing data associated with said at least one ingress link, an egress data clock processor configured to generate an egress clock signal for processing data associated with said at least one egress link, and a control and configuration unit shared by the ingress data clock processor and the egress data clock processor. Another aspect of the invention relates to a buffer adaptive processor that in an illustrative embodiment limits clock variability in the presence of cell delay variation or cell loss.
Owner:INTEL CORP
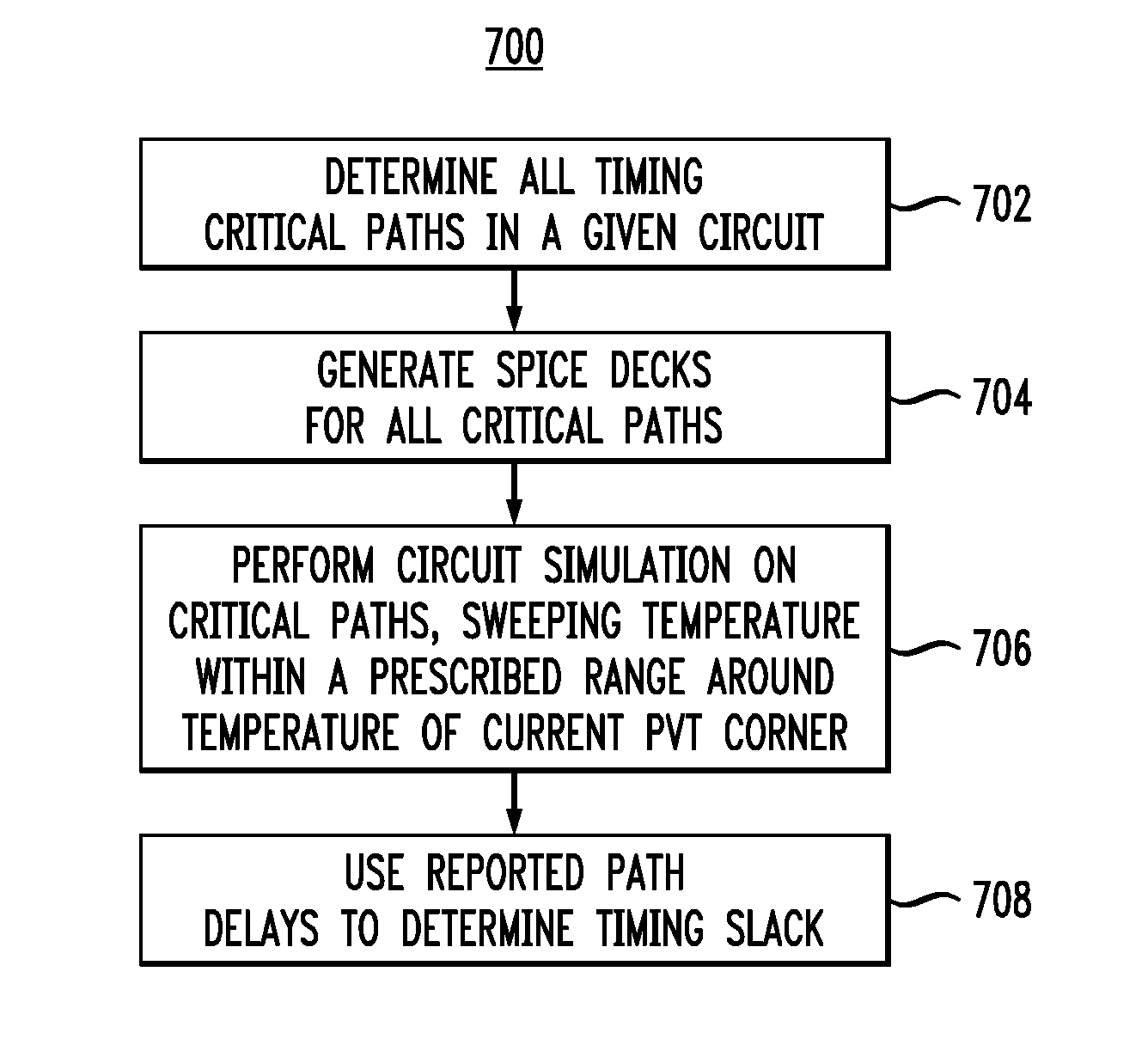
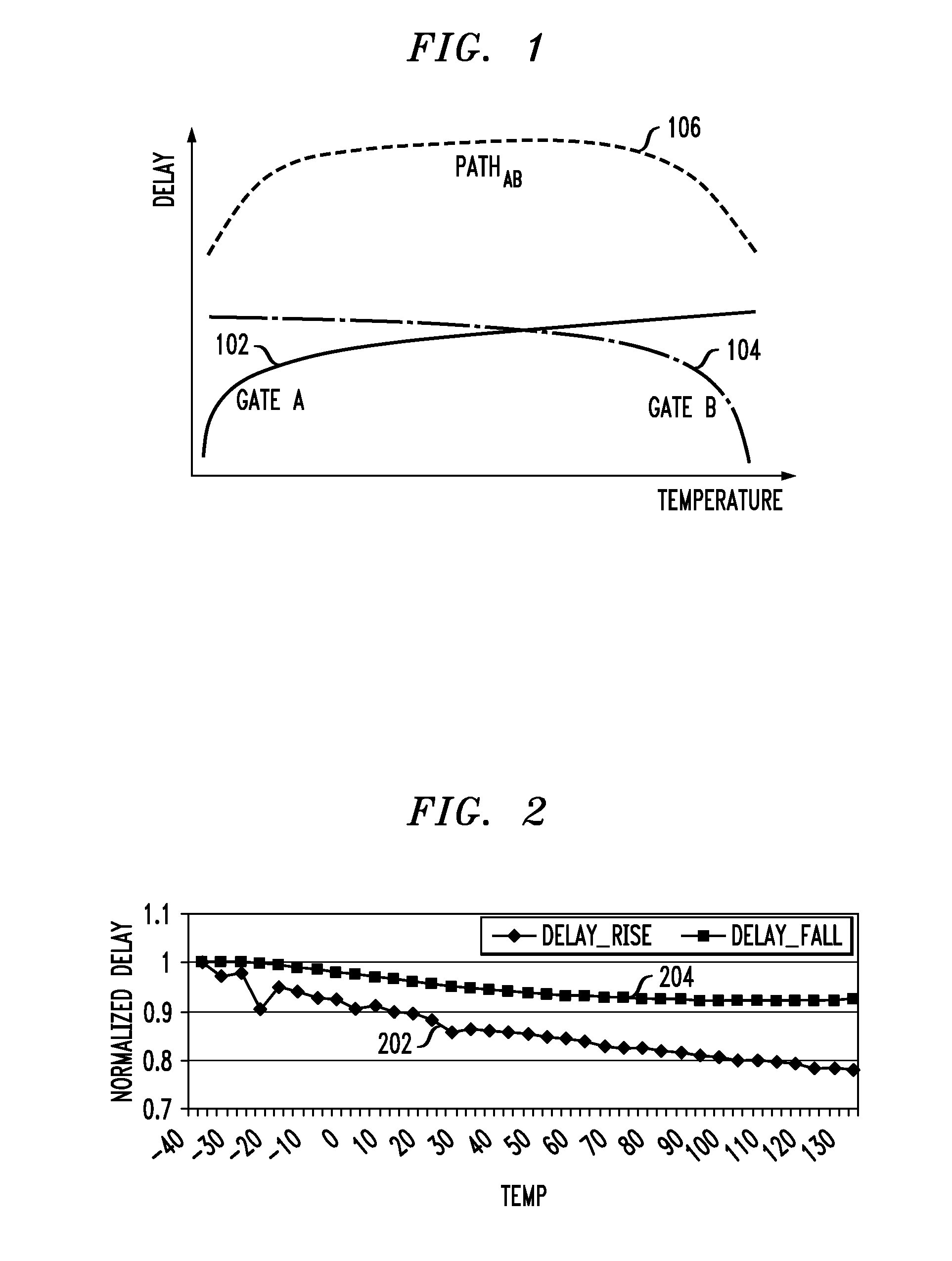
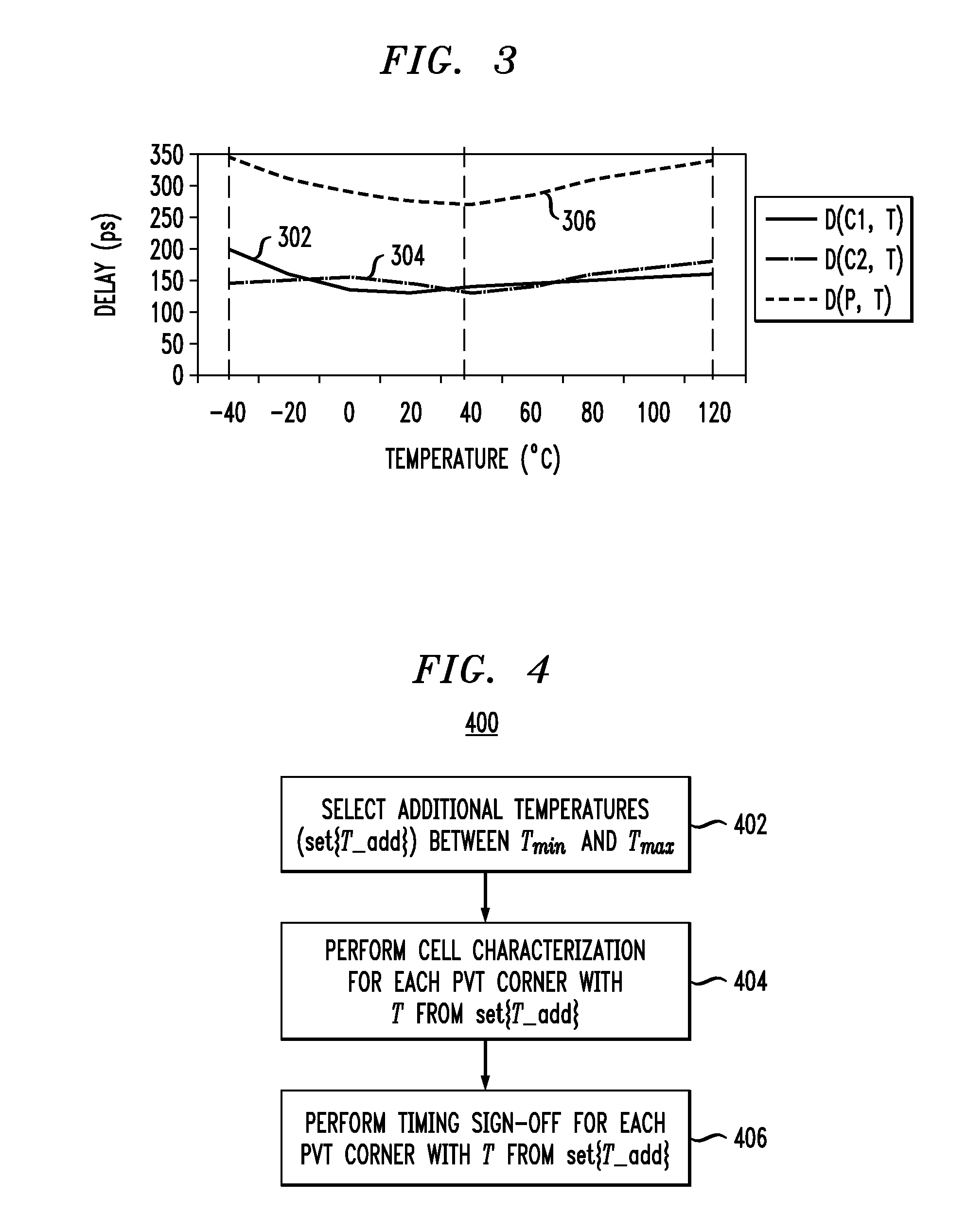
Circuit Timing Analysis Incorporating the Effects of Temperature Inversion
ActiveUS20100095259A1Improve accuracyHigh time accuracyCAD circuit designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationComputer scienceCell delay
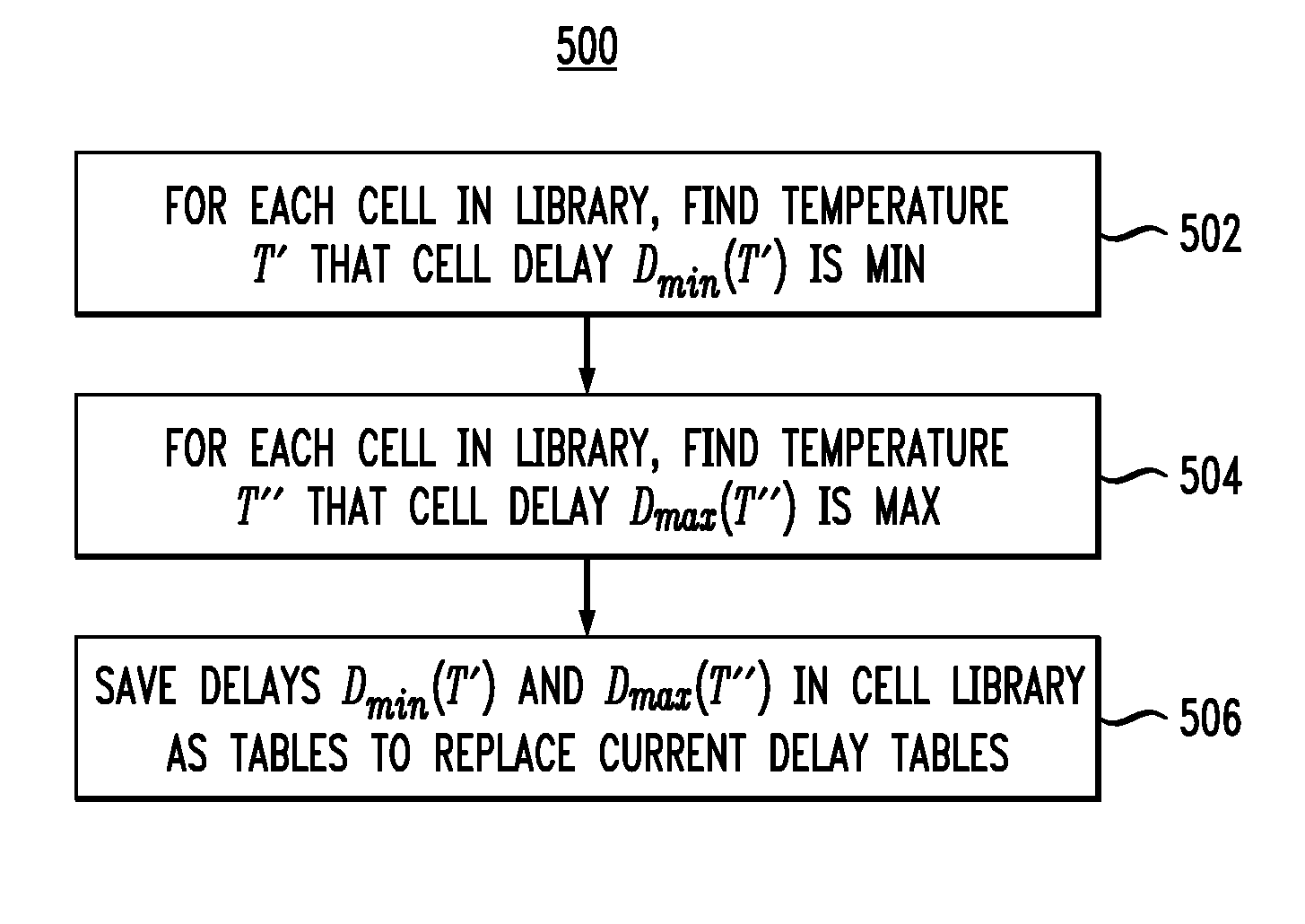
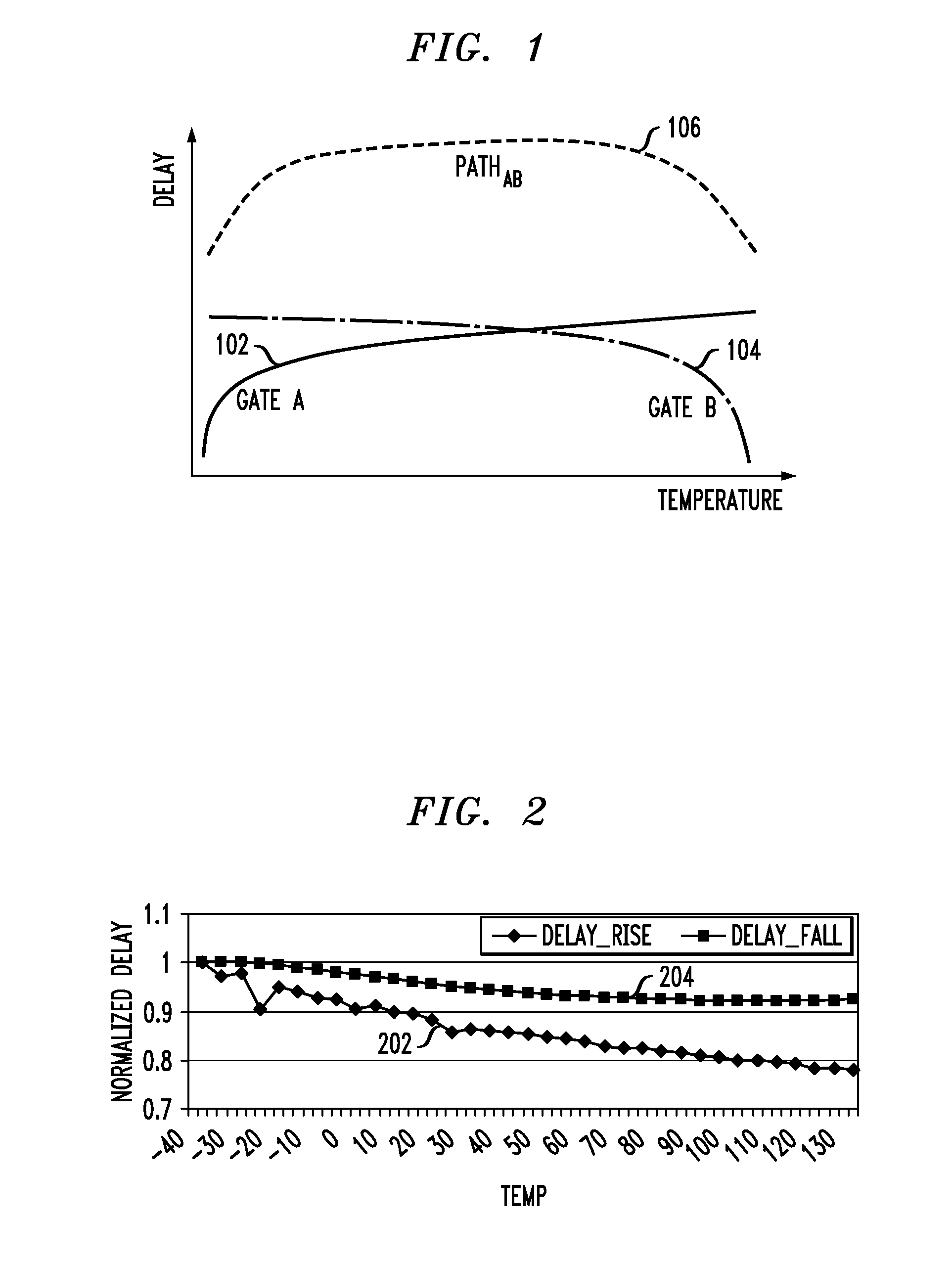
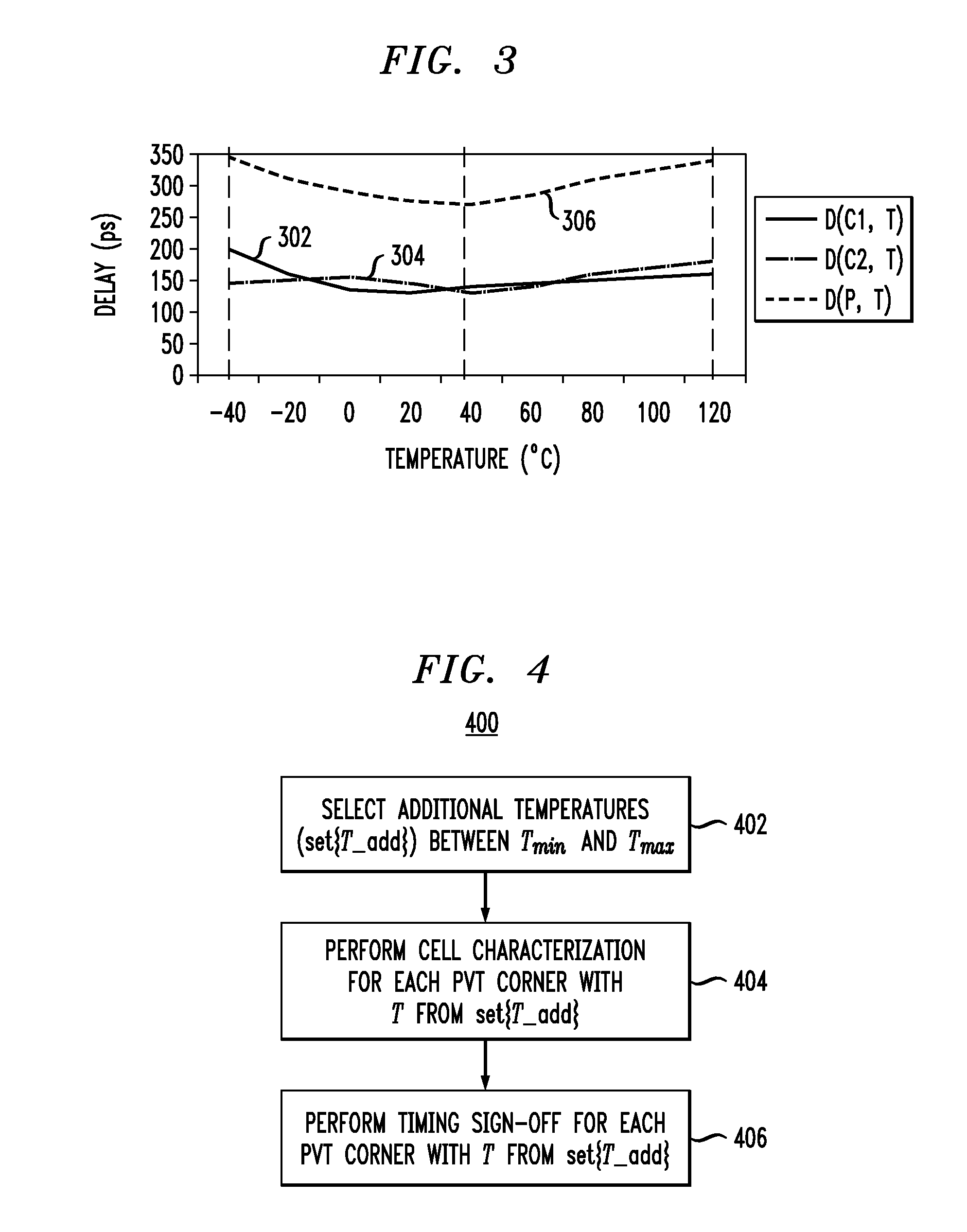
Methods and apparatus for increasing the accuracy of timing characterization of a circuit including one or more cells in a cell library are provided. One method includes the steps of: performing cell library timing characterization for each of the cells in the circuit for at least first and second prescribed temperatures, the first and second temperatures corresponding to first and second PVT corners, respectively, in the cell library; calculating respective cell delays for the one or more cells in the circuit, the cell delay calculation being a function of temperature for each instance of the one or more cells; and incorporating the cell delay calculation into the timing characterization for each of the cells in the circuit to thereby increase the accuracy of the timing characterization.
Owner:BELL SEMICON LLC
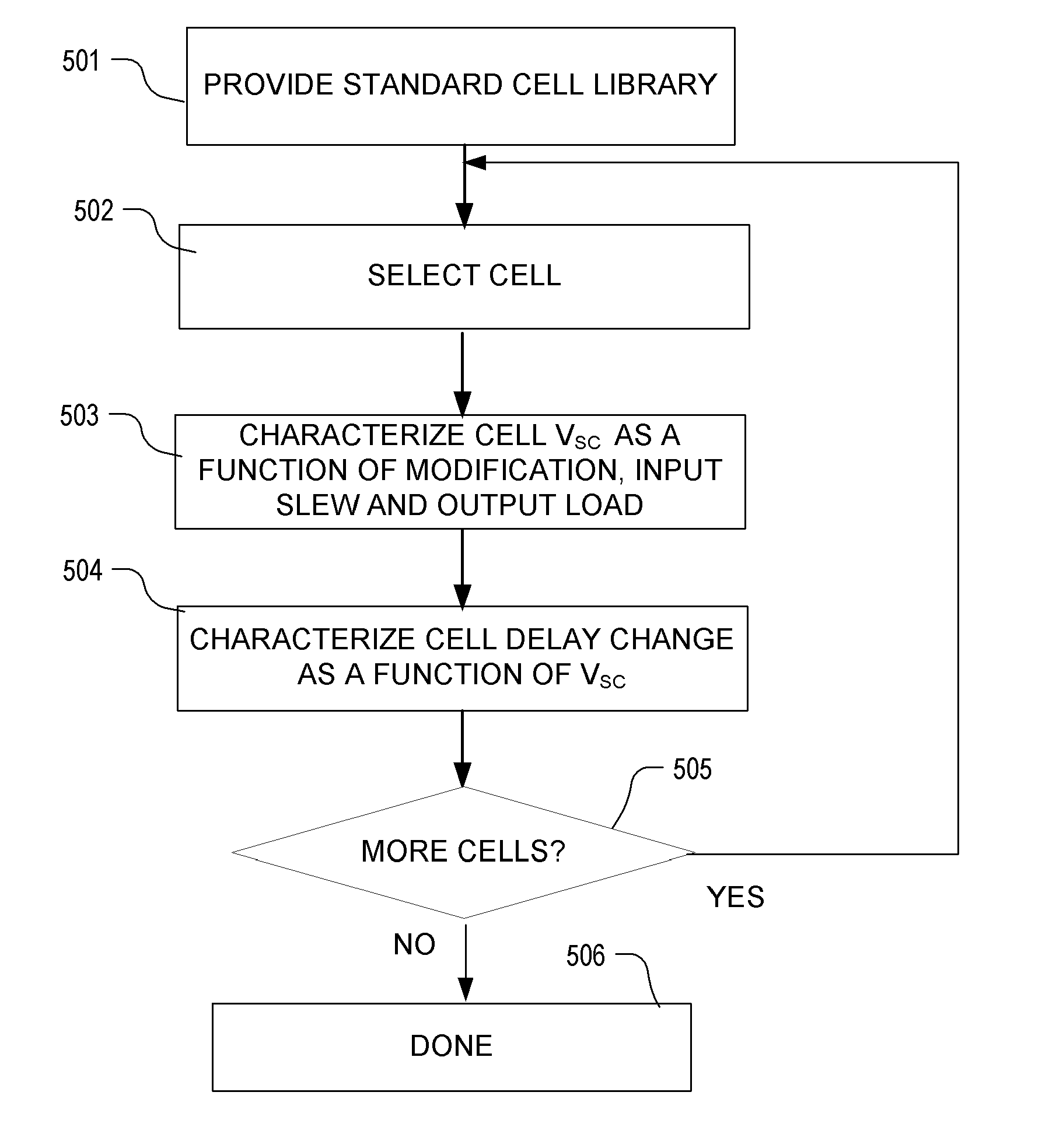
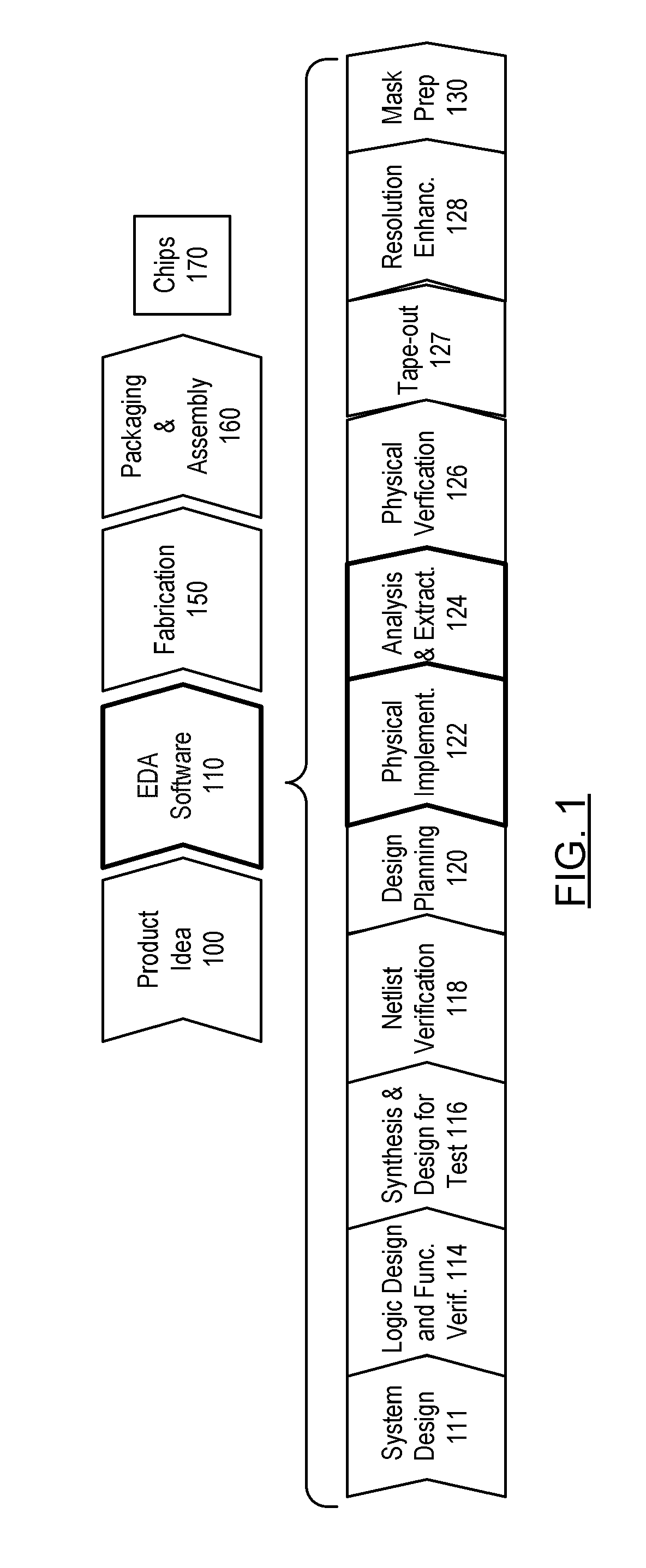
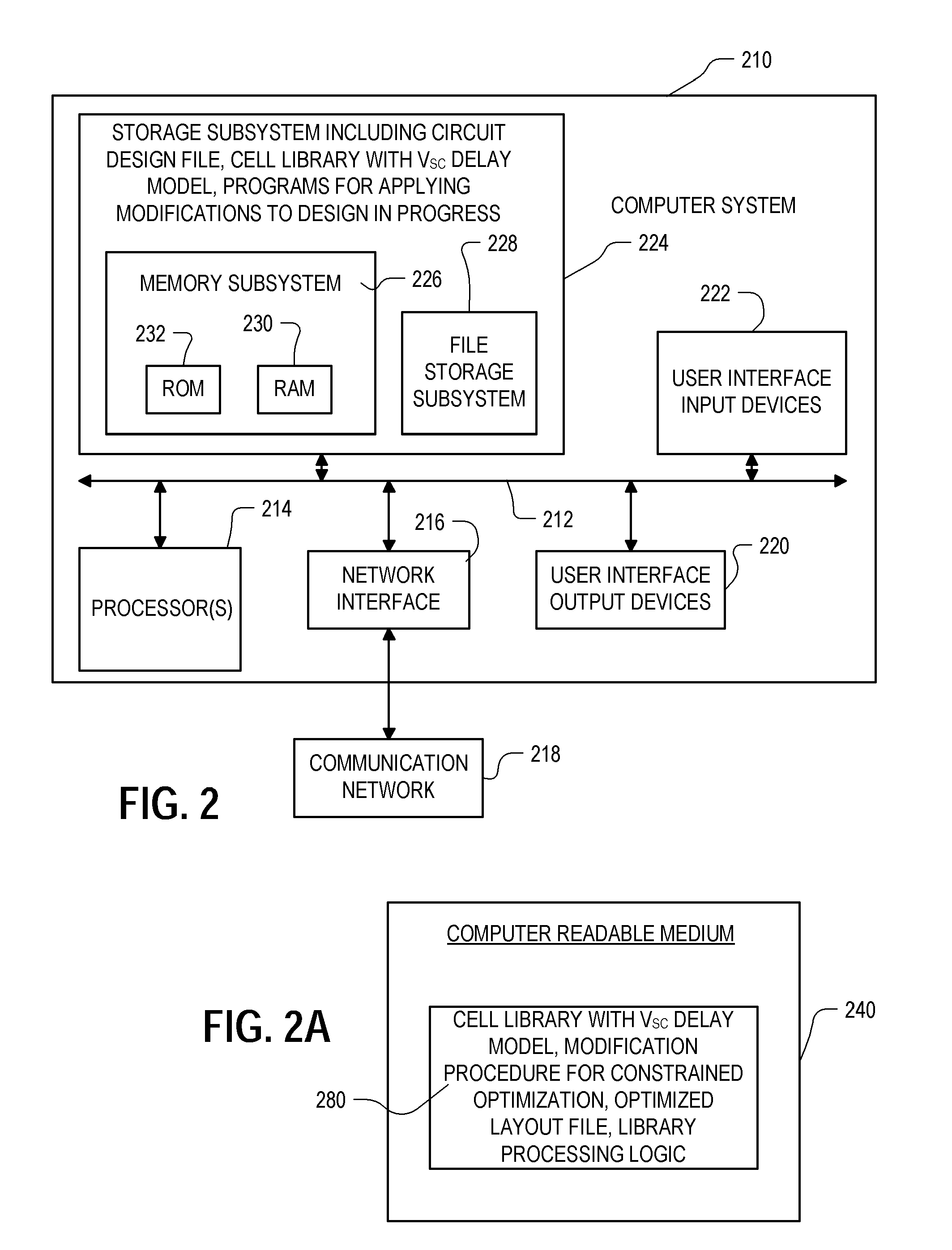
Modeling of cell delay change for electronic design automation
ActiveUS20110231811A1Reduce the required powerDesign optimisation/simulationCAD circuit designCell featureLeakage power
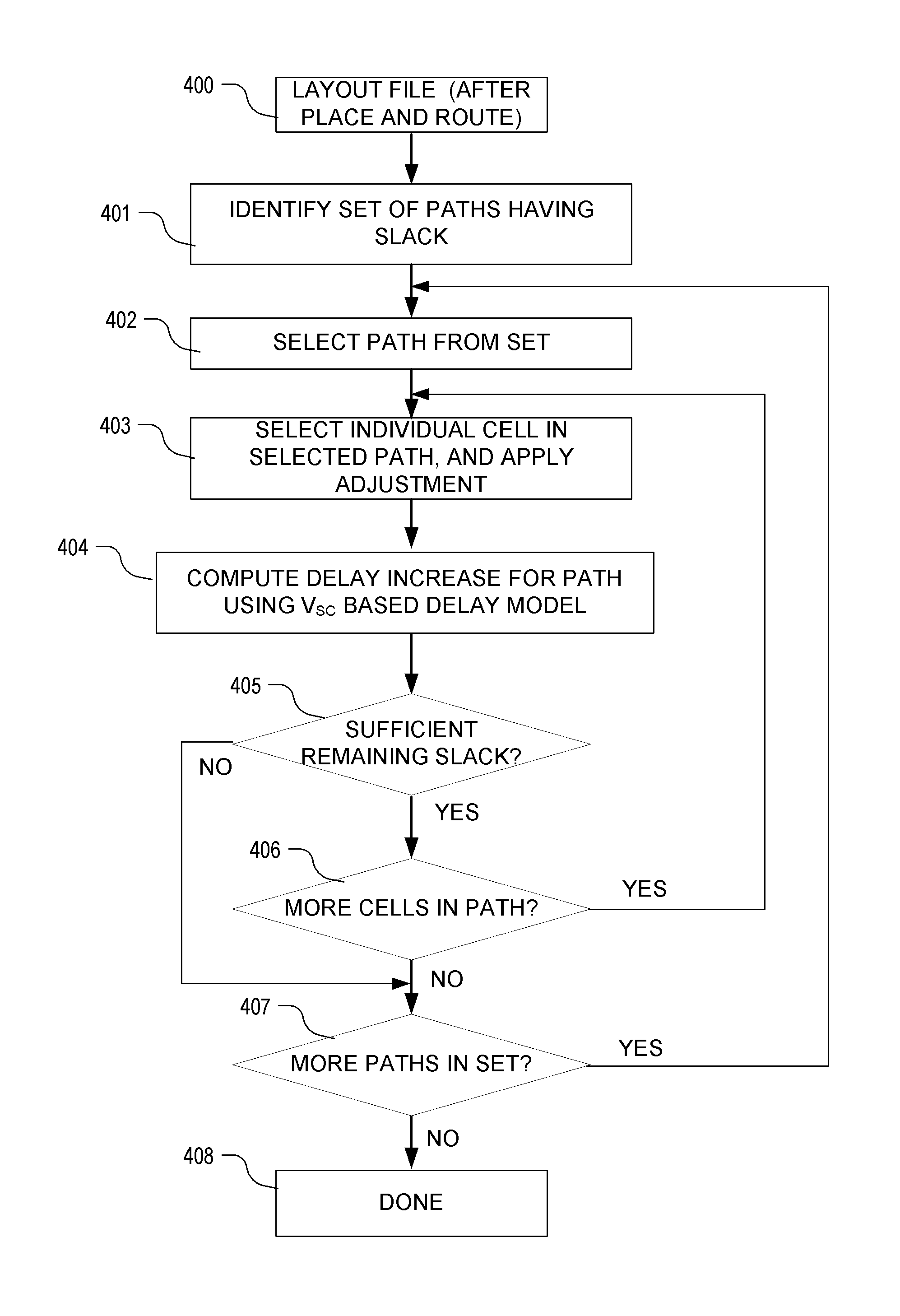
An integrated circuit design optimization procedure to modify a cell feature, such as gate length, models changes in delay as a result of the modification. In the delay change calculation, a characteristic of an event in cell switching behavior, such as the output short-circuit voltage VSC, is determined for the modified cell, where changes in the determined characteristic correlate with changes in delay of the cell due to the modification. Next, a value for delay of the modified cell is determined as a function of the determined characteristic of the event. The procedure can be applied after placement and routing. A timing-constrained, leakage power reduction is described using the delay change model.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
Method of delay calculation for variation in interconnect metal process
InactiveUS6880142B2CAD circuit designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationElectrical resistance and conductanceCapacitance
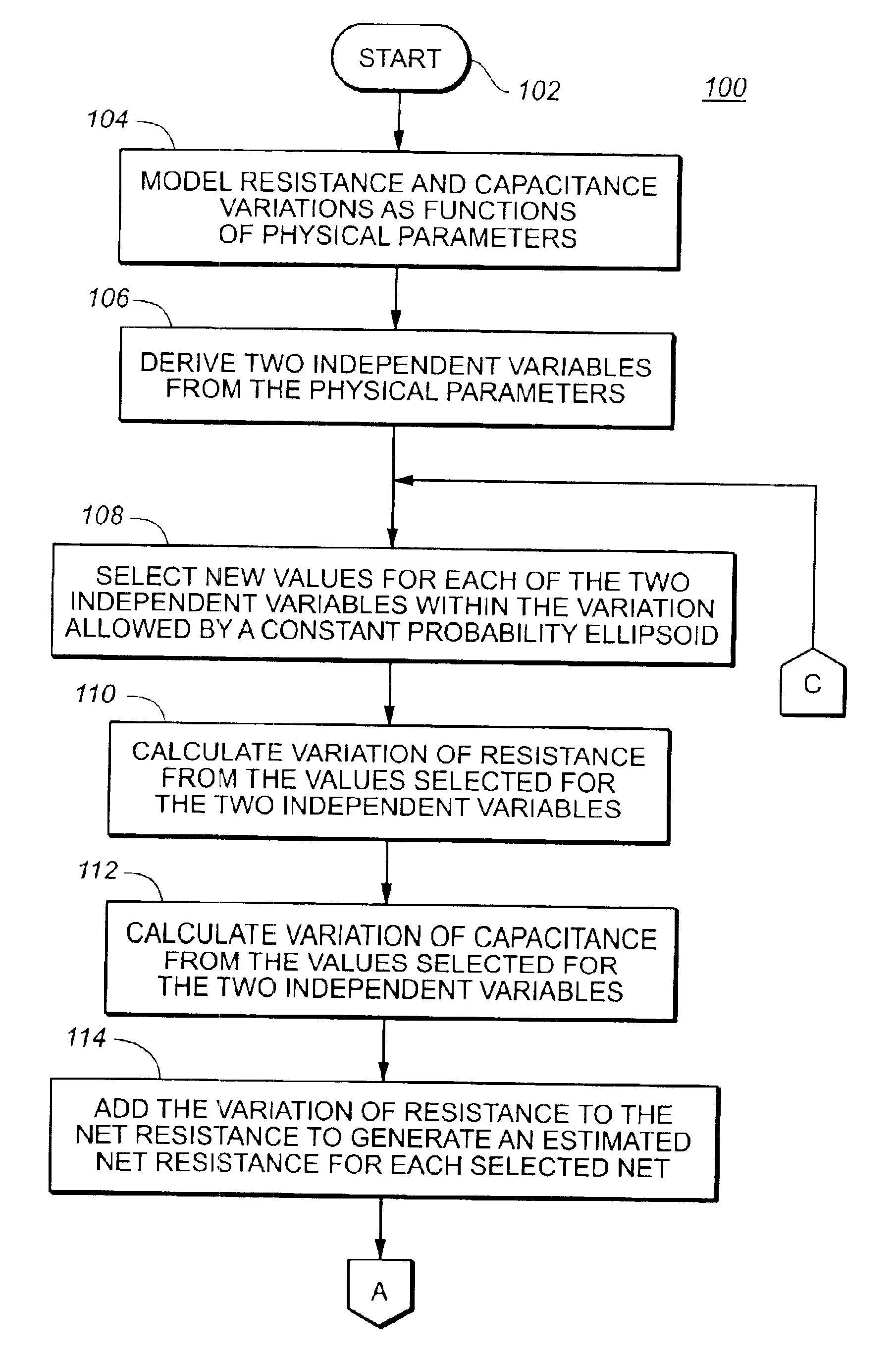
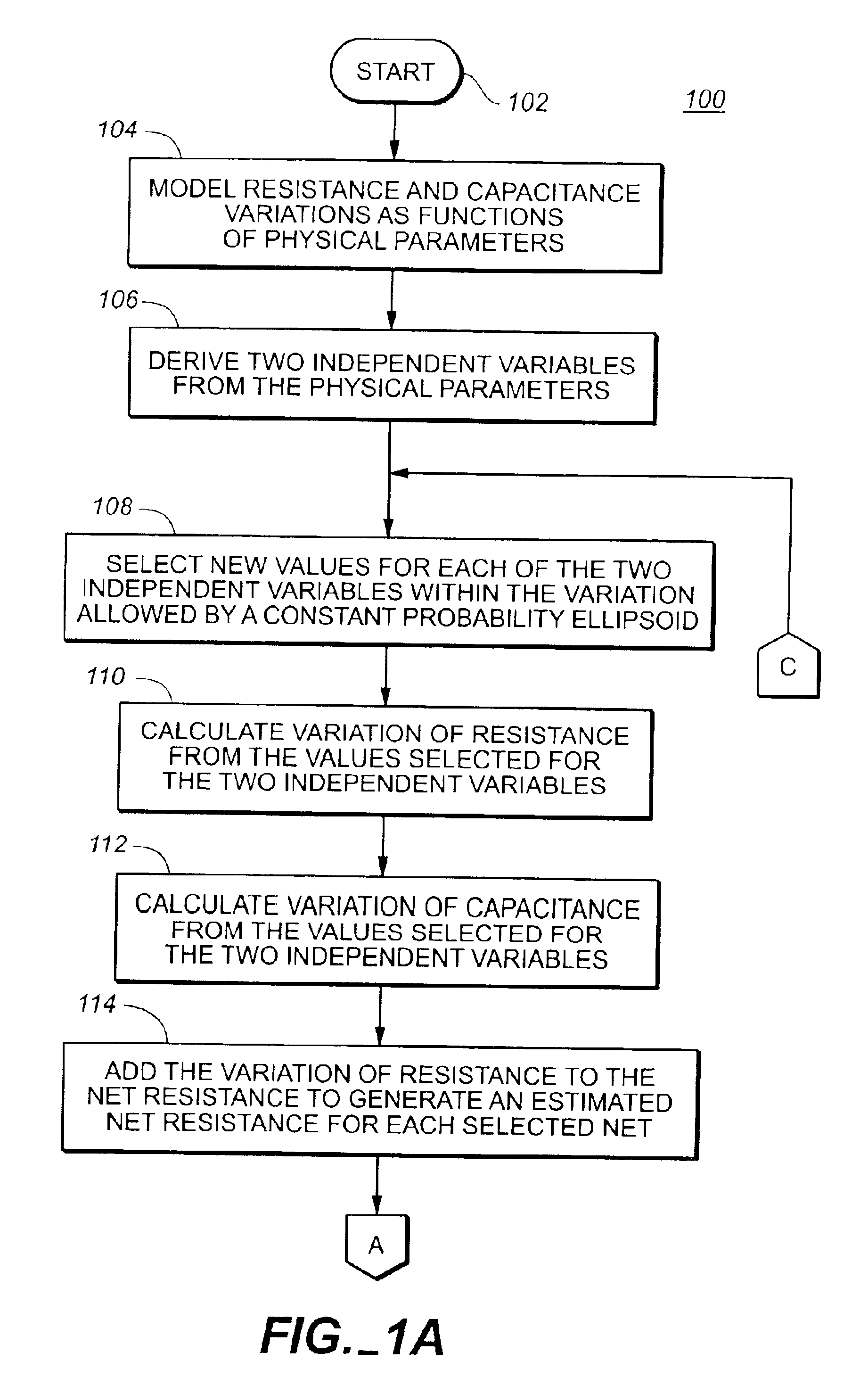
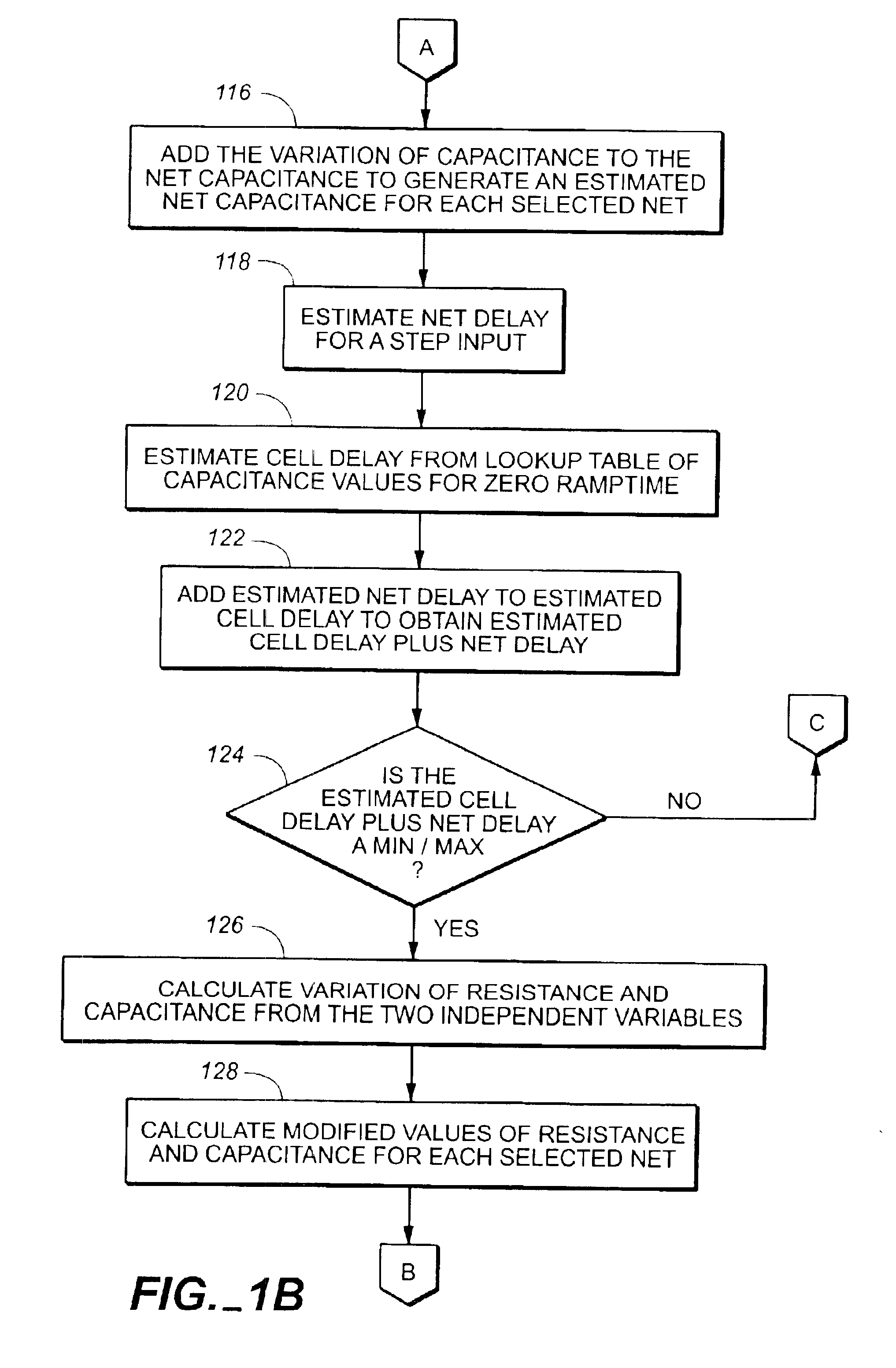
A method of calculating delay for a process variation includes finding a value for each of exactly two independent variables that results in a maximum or minimum variation of estimated cell delay plus net delay, calculating a variation of resistance from the value found for each of the exactly two independent variables, calculating a variation of capacitance from the value found for each of the exactly two independent variables, adding the calculated variation of resistance to a net resistance to generate a modified net resistance for a selected net, adding the calculated variation of capacitance to a net capacitance to generate a modified net capacitance for the selected net, and calculating the cell delay plus net delay from the modified net resistance and the modified net capacitance.
Owner:LSI LIGIC CORP +1
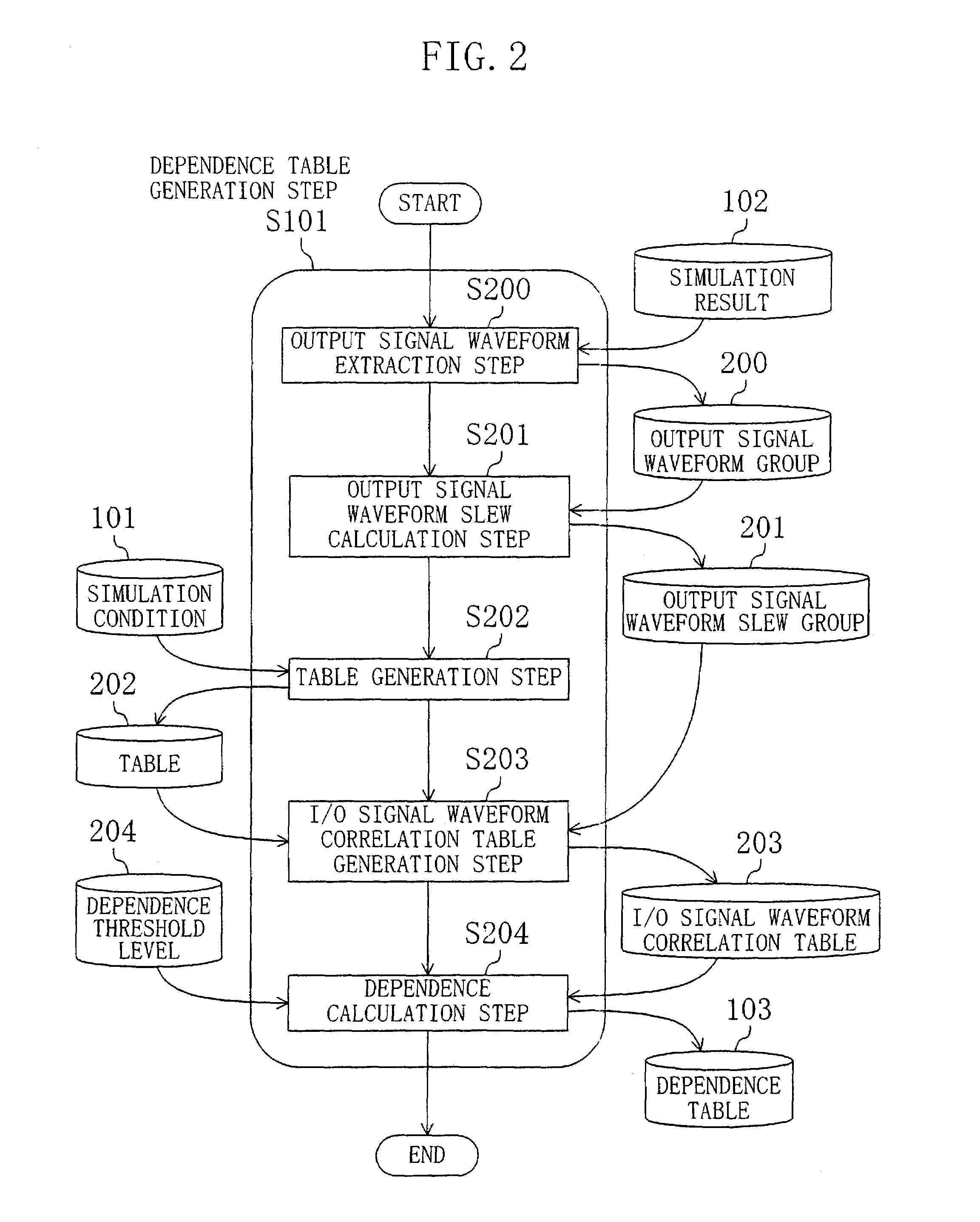
Method for calculation of cell delay time and method for layout optimization of semiconductor integrated circuit
InactiveUS7107557B2Improve accuracyAccuracy is inferiorLogic circuits characterised by logic functionElectronic circuit testingCapacitanceEngineering
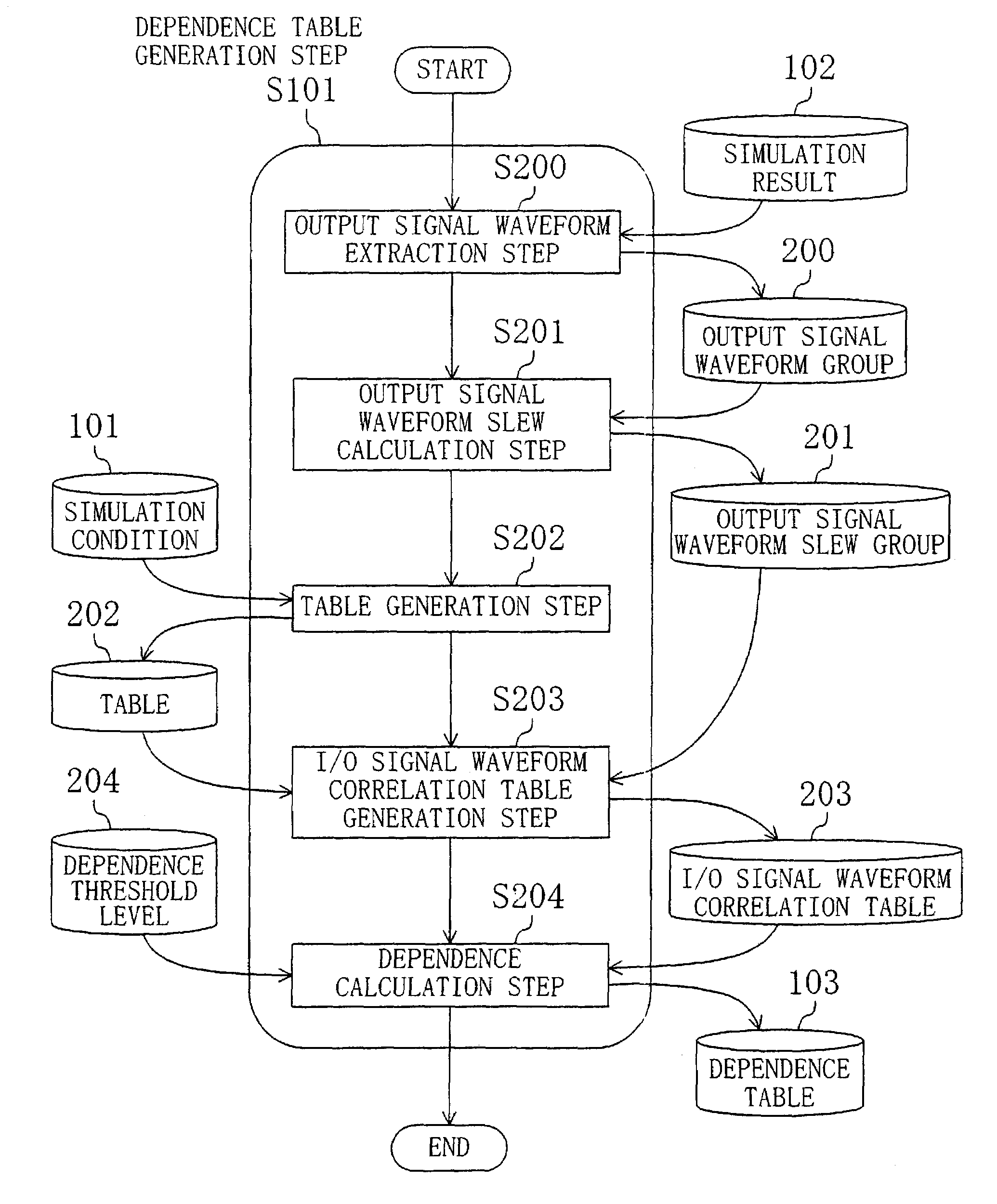
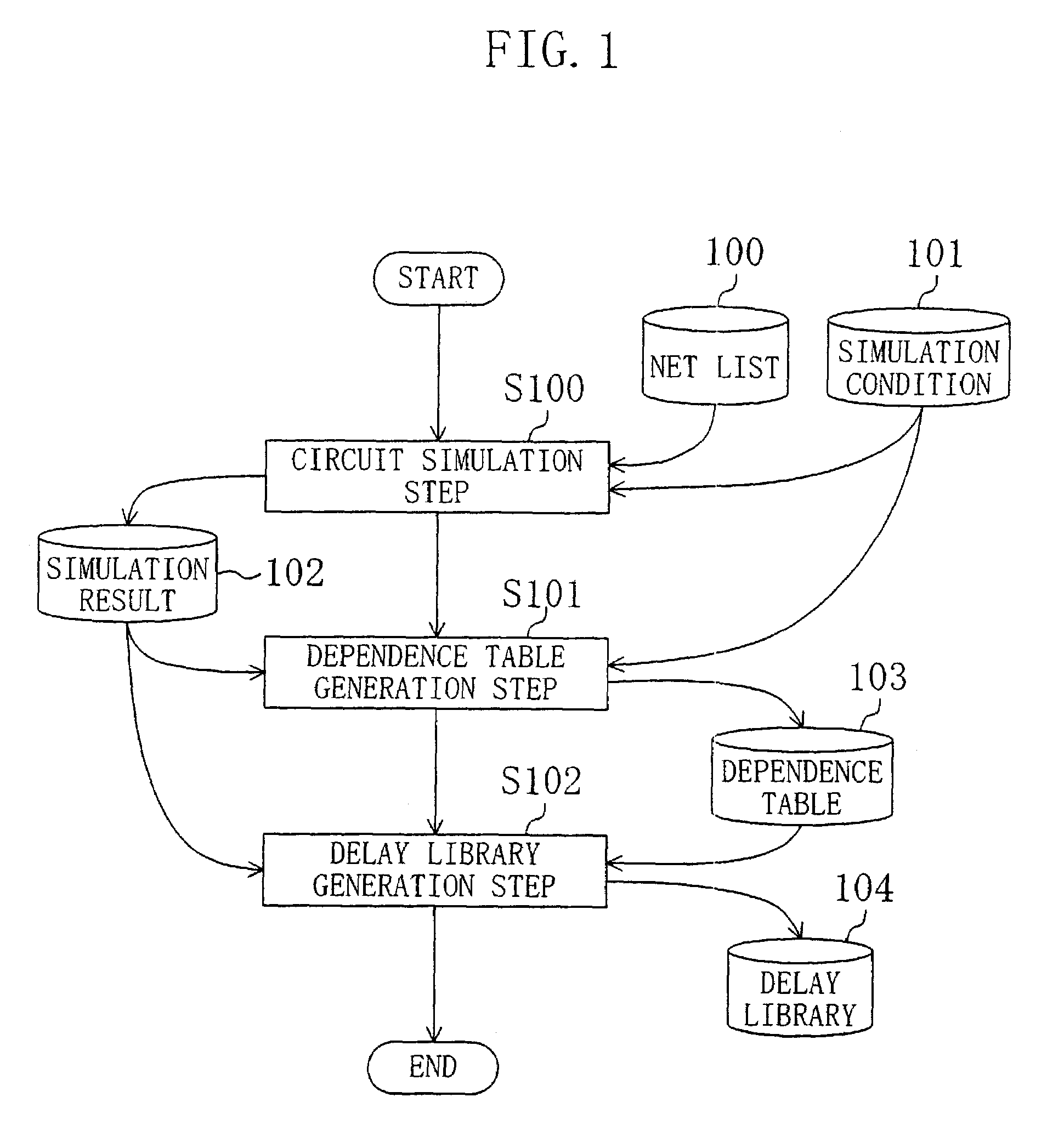
In a circuit simulation step, a cell transistor level net list is input, the slew of an input signal waveform and the magnitude of a load capacitance connected to a cell output terminal are varied for each cell, to perform a circuit simulation of each cell for obtaining an output signal waveform. Next, in a dependence table generation step, the dependence of the output signal waveform slew upon the input slew rate and the load capacitance is calculated for each cell, the dependence thus calculated is compared with a predetermined threshold level, and according to the dependence level, a delay calculation expression with consideration taken to the delay of signal propagation between the cell input and output terminals and another without such consideration are selectively used. Accordingly, the delay times of the cells forming a semiconductor integrated circuit can be calculated at high accuracy and at high processing speed.
Owner:SOCIONEXT INC
Method and apparatus for improving asynchronous transfer mode operation over noisy, high speed wireless links
InactiveUS20050122925A1Error correction/detection using convolutional codesCode conversionPattern detectionByte
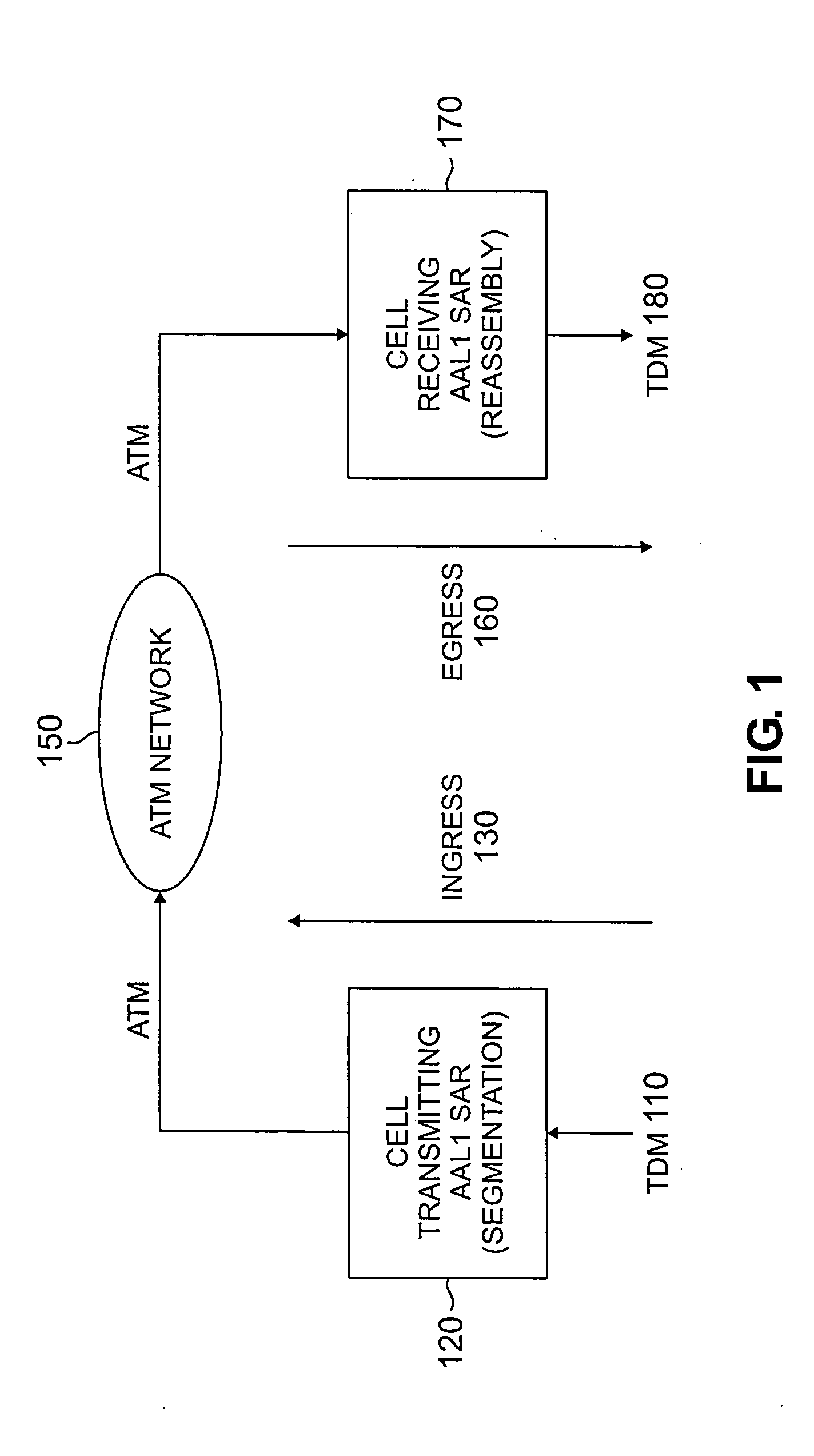
In an asynchronous transfer mode (ATM) system, an apparatus is used to improve the transmission and reception of encoded ATM information over a wireless link having an encoder for encoding the information, assembling the information into a frame format and interleaving of the information for transmission over the wireless link. In addition, the apparatus also has a decoder for decoding information received via the wireless link which was encoded by a similar apparatus transmitting the information over the wireless link. Further, methods utilized by the encoder and decoder to improve transmission include increasing the bandwidth efficiency by dropping a header byte from every ATM cell; assembling separate header and payload frames; utilizing and rearranging idle / unassigned cells in the payload frame for storing and, thereby, increasing error correction code in the frame; dynamically changing the coding of frame in real time from one payload frame to optimize utilization of the mumber of available idle / unassigned cells occurring in each frame; restoring the positions of all idle / unassigned cells to their original position at a receiving end in order to leave the Cell Delay Variation unaffected; interleaving the frames to reduce burst errors during transmission; preservation of overhead parity bits present in the original frames received from a wireline link; cell Header error detection and correction through the use of a generated syndrome; and a synchronization pattern detection method during decoding.
Owner:VIASAT CORP
Method and apparatus for ATM adaptation layer staggered constant bit rate cell scheduling
A method and apparatus are disclosed for ATM Adaptation Layer (AAL) staggered constant bit rate cell scheduling. Cells from a plurality of virtual circuits are scheduled. Each of the virtual circuits have a transmission characteristic and each of the plurality of virtual circuits are classified into one of a plurality of stagger groups based on similar transmission characteristics. For each frame synchronization, a cell is transmitted from a given virtual circuit until a predefined cell threshold is exceeded for the stagger group containing the given virtual circuit. A Cell Delay Variation of each of the virtual circuits will not exceed a given time interval. A scheduler can be allocated for each connection or for each period.
Owner:AGERE SYST INC
Circuit timing analysis incorporating the effects of temperature inversion
ActiveUS8181144B2Improve accuracyHigh time accuracyCAD circuit designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationEngineeringComputational physics
Methods and apparatus for increasing the accuracy of timing characterization of a circuit including one or more cells in a cell library are provided. One method includes the steps of: performing cell library timing characterization for each of the cells in the circuit for at least first and second prescribed temperatures, the first and second temperatures corresponding to first and second PVT corners, respectively, in the cell library; calculating respective cell delays for the one or more cells in the circuit, the cell delay calculation being a function of temperature for each instance of the one or more cells; and incorporating the cell delay calculation into the timing characterization for each of the cells in the circuit to thereby increase the accuracy of the timing characterization.
Owner:BELL SEMICON LLC
Method and device for deactivating a cell
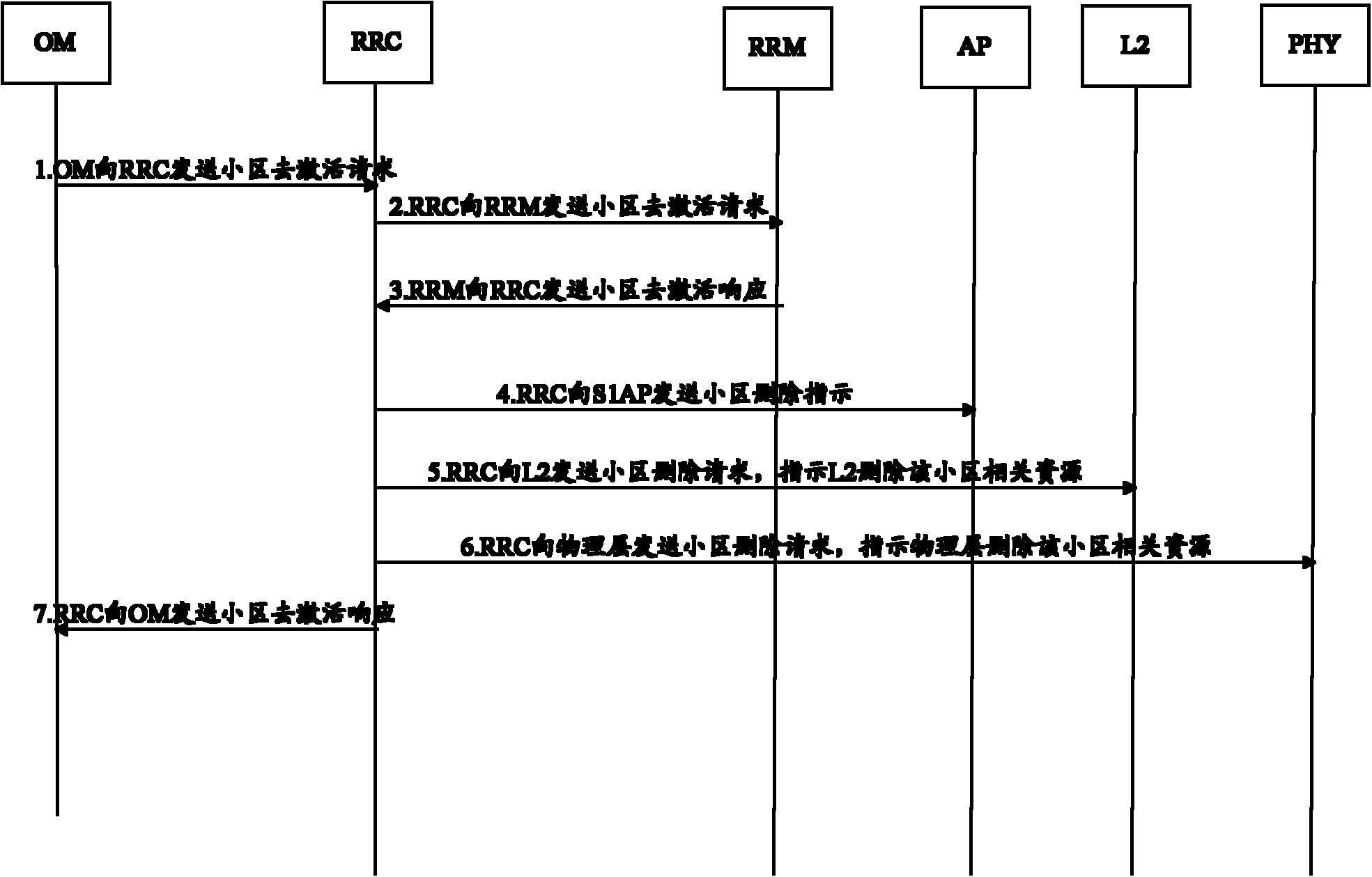
InactiveCN102281578AAvoid dropped callsGuaranteed normal switchingConnection managementTelecommunicationsBiological activation
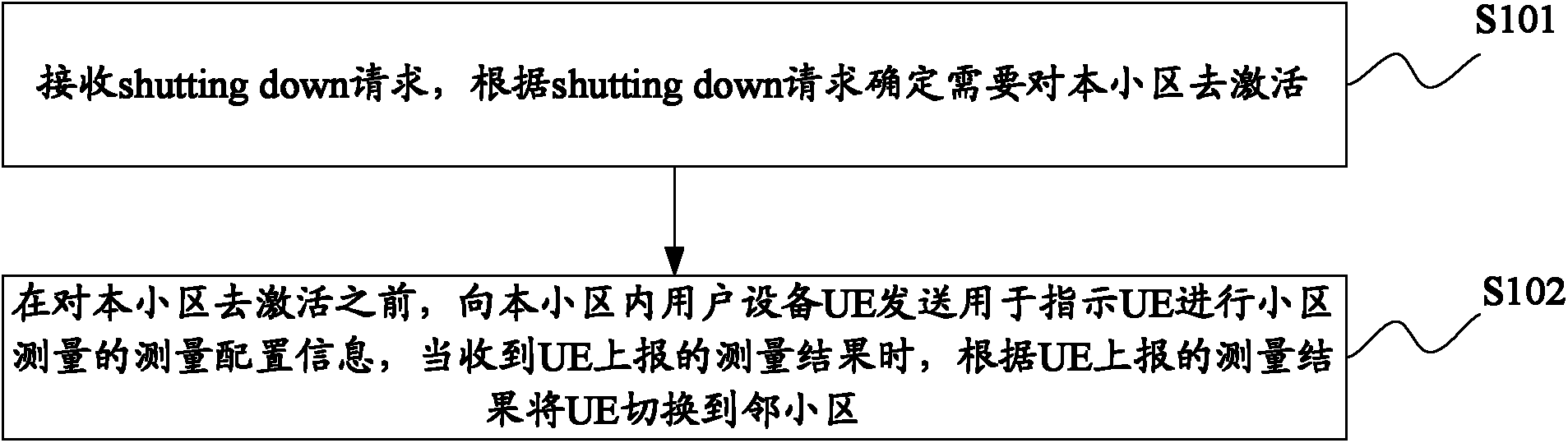
The invention discloses a method and device for deactivating a cell, which are used to avoid user call drop caused by the deactivating cell. A method for deactivating a cell provided by the present invention includes: receiving a cell delay deactivation shutting down request, determining that the cell needs to be deactivated according to the shutting down request; before deactivating the cell, sending a message to a user equipment UE in the cell Measurement configuration information that instructs the UE to perform cell measurement. When the measurement result reported by the UE is received, the UE is handed over to a neighboring cell according to the measurement result reported by the UE.
Owner:DATANG MOBILE COMM EQUIP CO LTD
Method and program for designing semiconductor integrated circuit
InactiveUS7913214B2Increase in design/verification TAT can be preventedHigh delay accuracyCAD circuit designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationModel parametersCell based
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
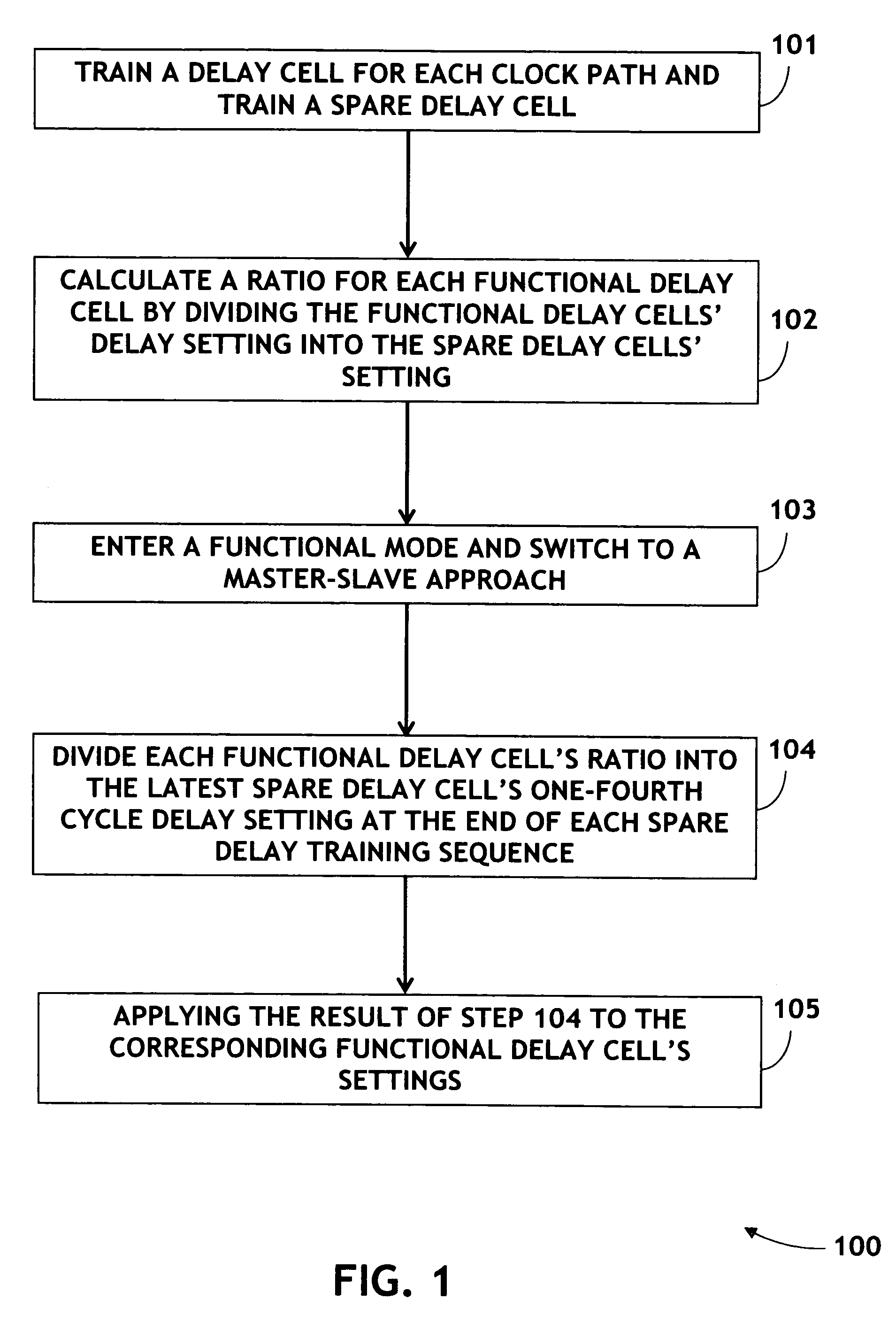
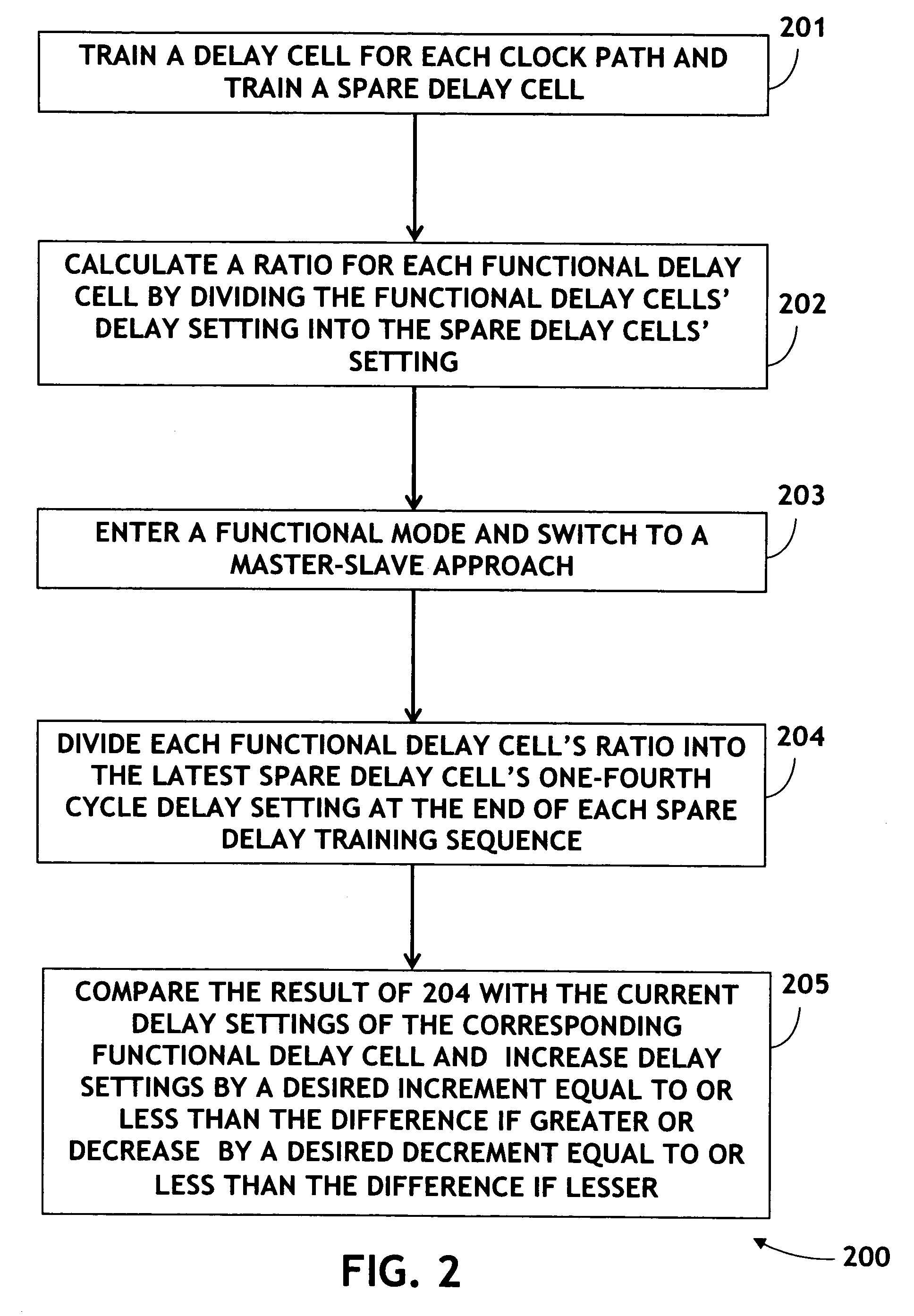
System and method for compensating for PVT variation effects on the delay line of a clock signal
The present invention is directed to a method for compensating for process, voltage, and temperature variation without complex online / offline swapping of data paths requiring a dedicated FIFO(First-in First-out) buffer design. Delay cells are trained for each clock path (namely a Functional delay) and a spare delay cell is trained. A ratio is calculated for each Functional delay cell by dividing the Functional delay cells' setting into the spare delay cells' one-fourth cycle setting. These ratios reflect any process variation. Functional mode is then entered and a Master-Slave approach switched to, during which the spare delay cell repeats the training sequence continuously while the Functional delay cells delay the clocks from the RAM(Random Access Memory). Each Functional delay cell is updated at the end of each training sequence of the spare delay cell, compensating for voltage and temperature change, by dividing the ratio into the new spare delay cell one-fourth cycle setting.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
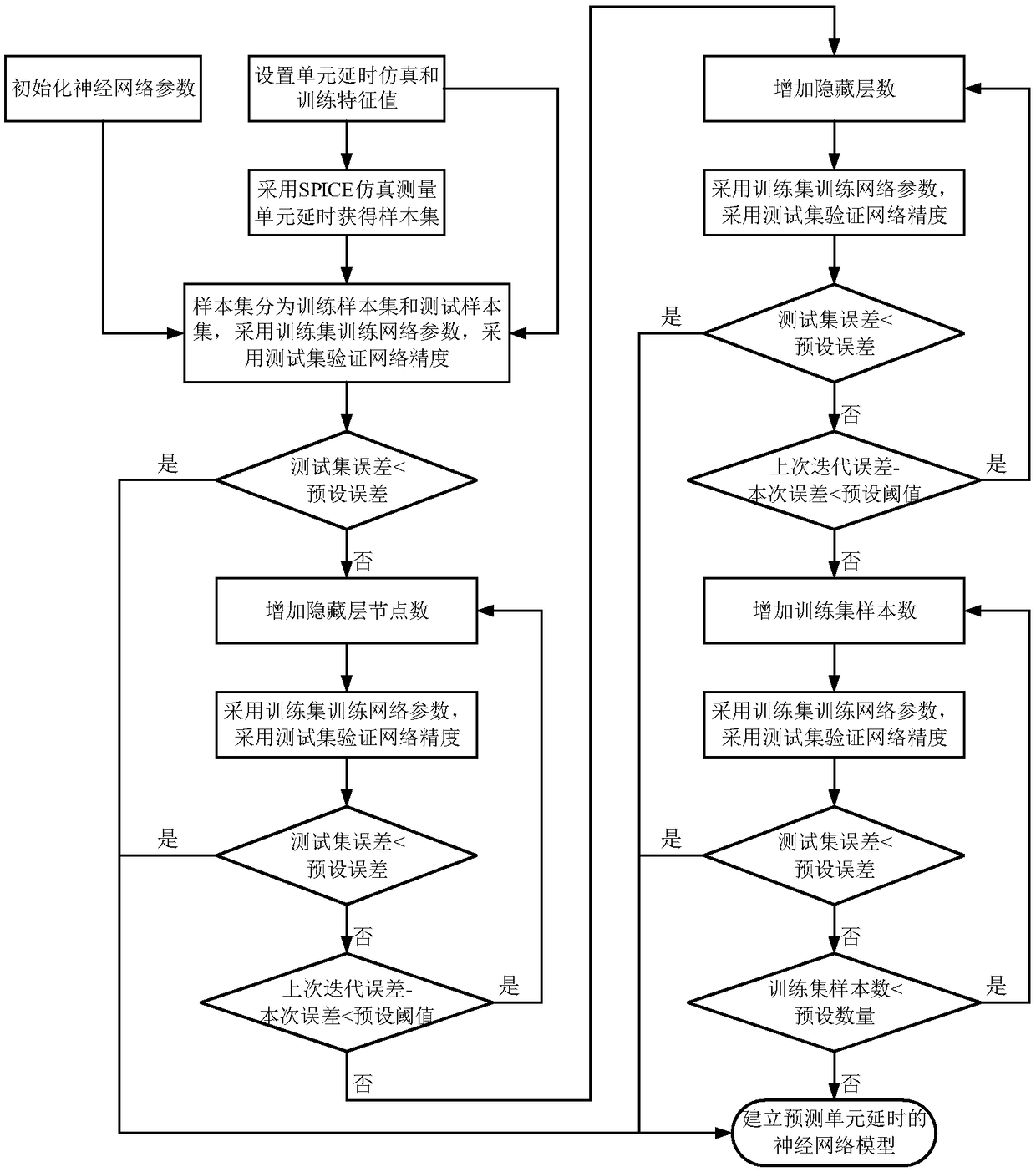
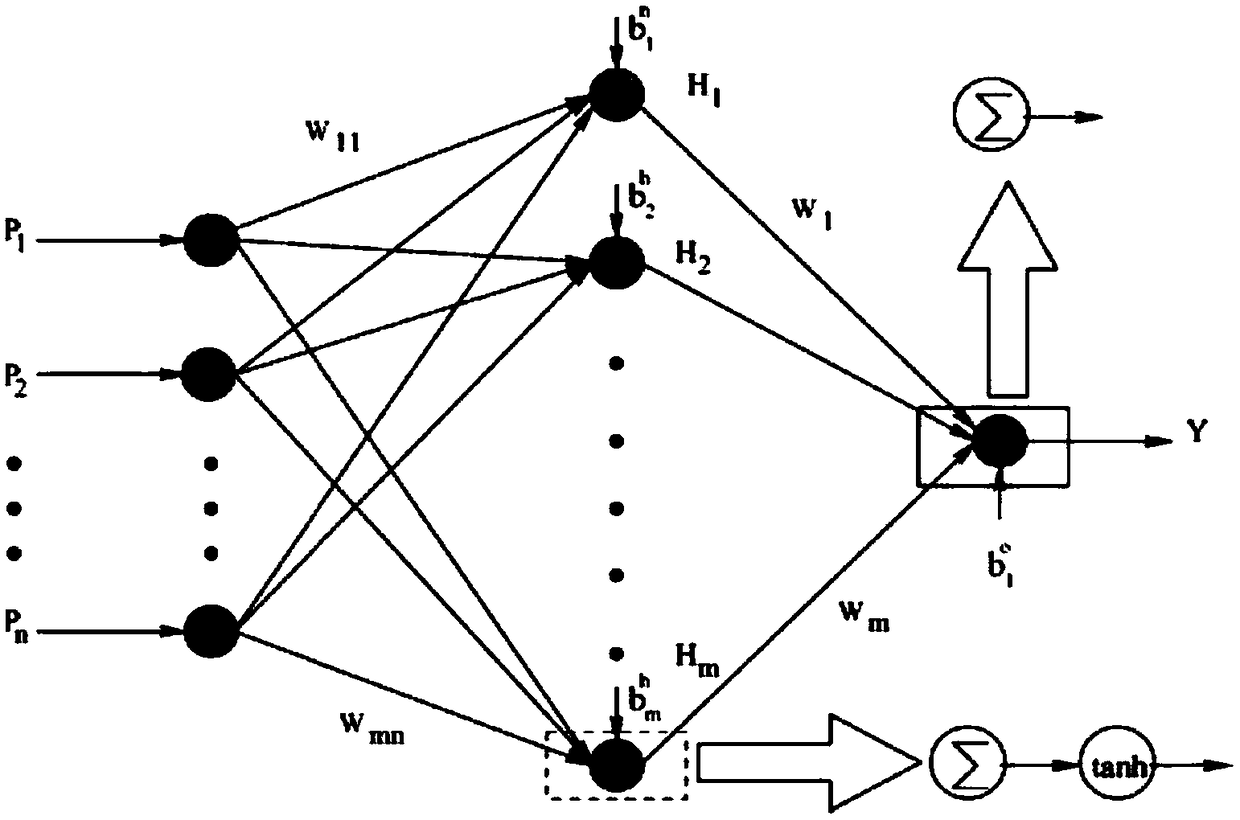
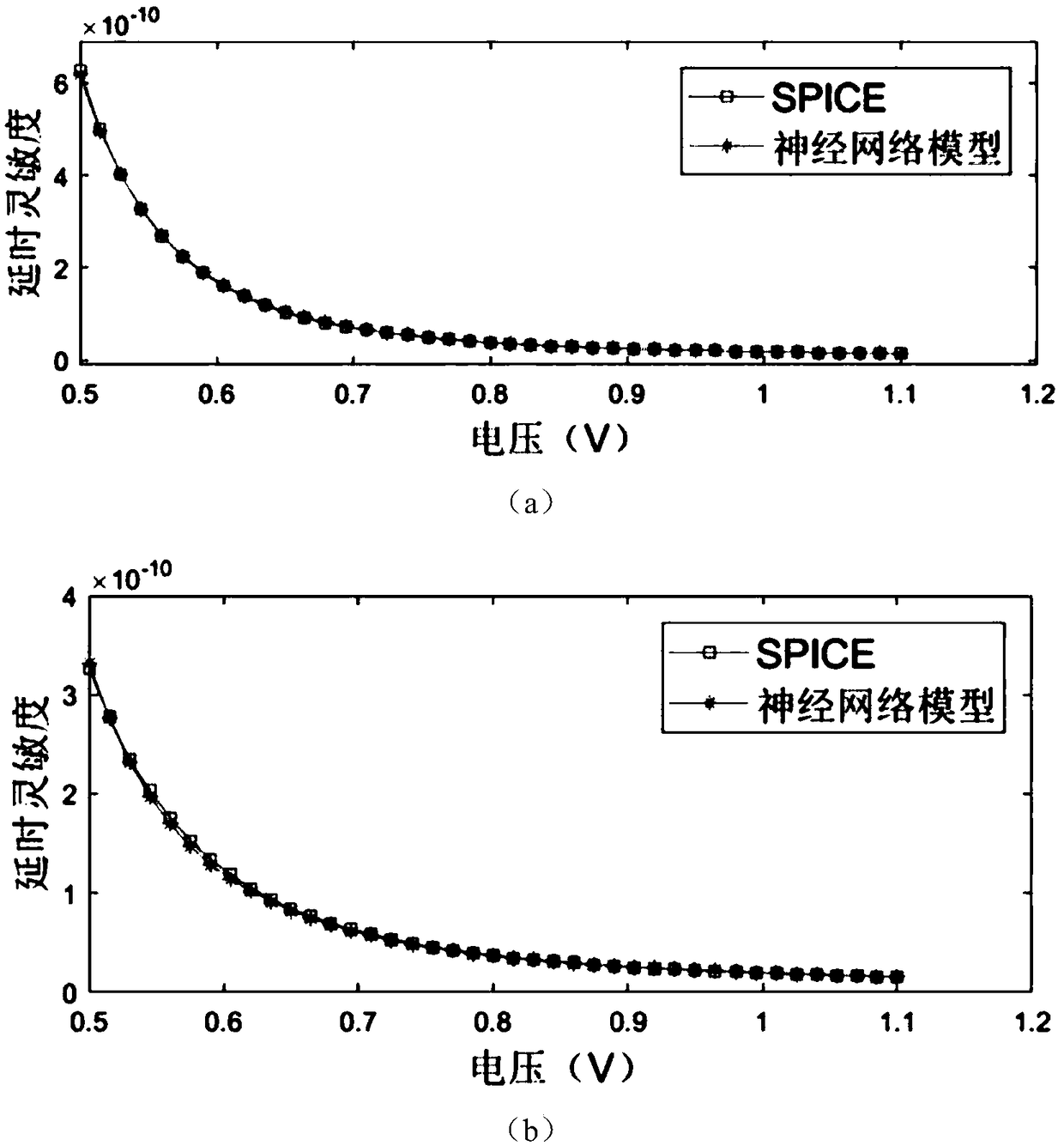
Unit delay prediction method and element delay sensitivity calculation method based on neural network
ActiveCN109255160AHigh accuracy of delay predictionOvercoming the high costCAD circuit designSpecial data processing applicationsComparative testNerve network
The invention discloses a unit delay prediction method based on a neural network, comprising the following steps: S1, selecting characteristic quantities required by SPICE simulation and neural network training; 2, randomly selecting that characteristic value, adopting SPICE to simulate and measure the delay of the unit, and establishing a sample set of the delay of the unit; S3, dividing the unitdelay sample set obtained by SPICE simulation into training sample set and test sample set, training the neural network model by a training sample set, and verifying the accuracy of neural network bytesting sample set, comparing the error between the unit delay predicted by testing sample set and the unit delay measured by SPICE simulation, and optimizing repeatedly the neural network parametersto reduce the error. The neural network model is a prediction model of unit delay. The invention also discloses a cell delay sensitivity calculation method. The invention has the advantages of high precision, low modeling cost and fast prediction speed.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Modeling of cell delay change for electronic design automation
ActiveUS8359558B2Detecting faulty computer hardwareDesign optimisation/simulationEngineeringCell feature
An integrated circuit design optimization procedure to modify a cell feature, such as gate length, models changes in delay as a result of the modification. In the delay change calculation, a characteristic of an event in cell switching behavior, such as the output short-circuit voltage VSC, is determined for the modified cell, where changes in the determined characteristic correlate with changes in delay of the cell due to the modification. Next, a value for delay of the modified cell is determined as a function of the determined characteristic of the event. The procedure can be applied after placement and routing. A timing-constrained, leakage power reduction is described using the delay change model.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
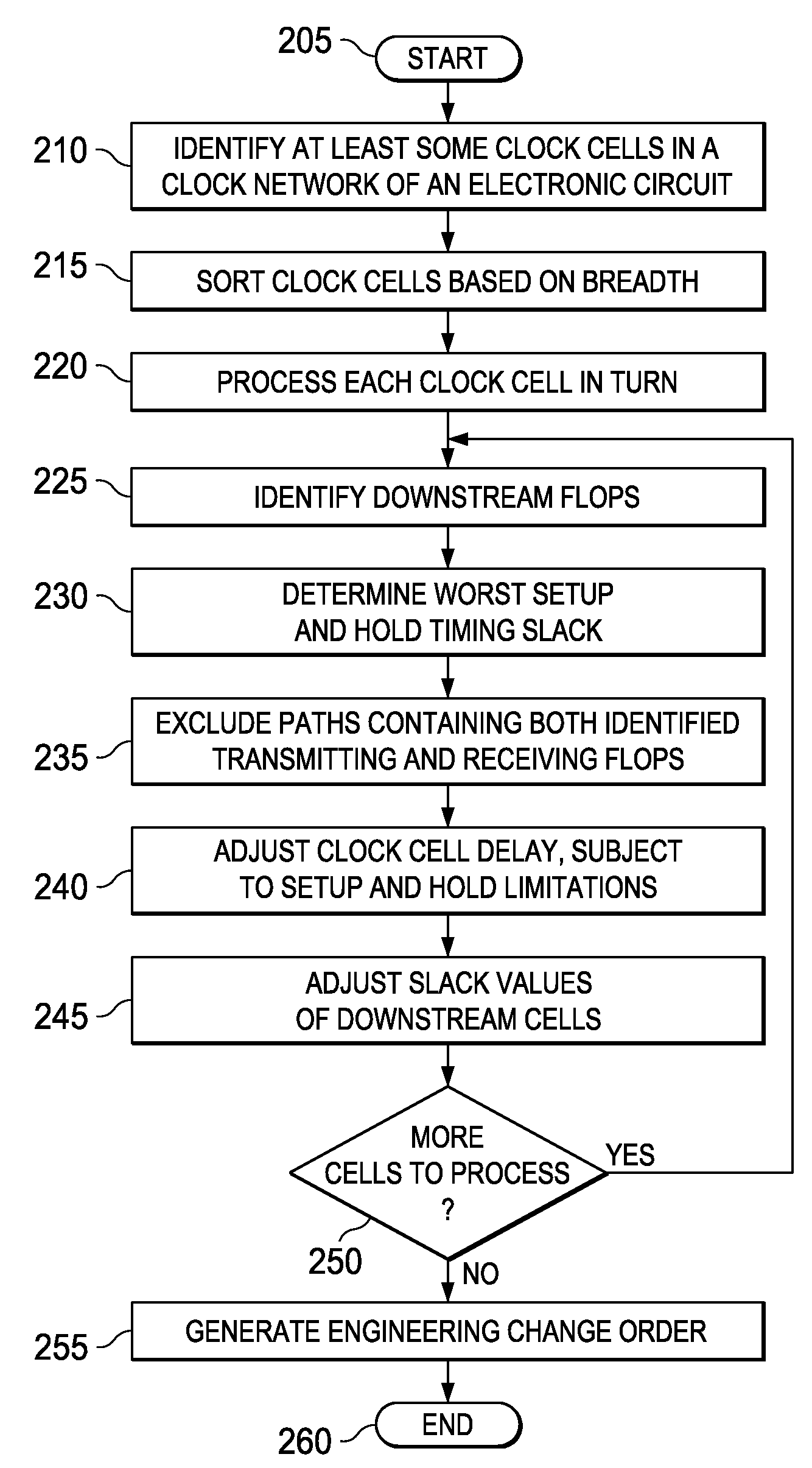
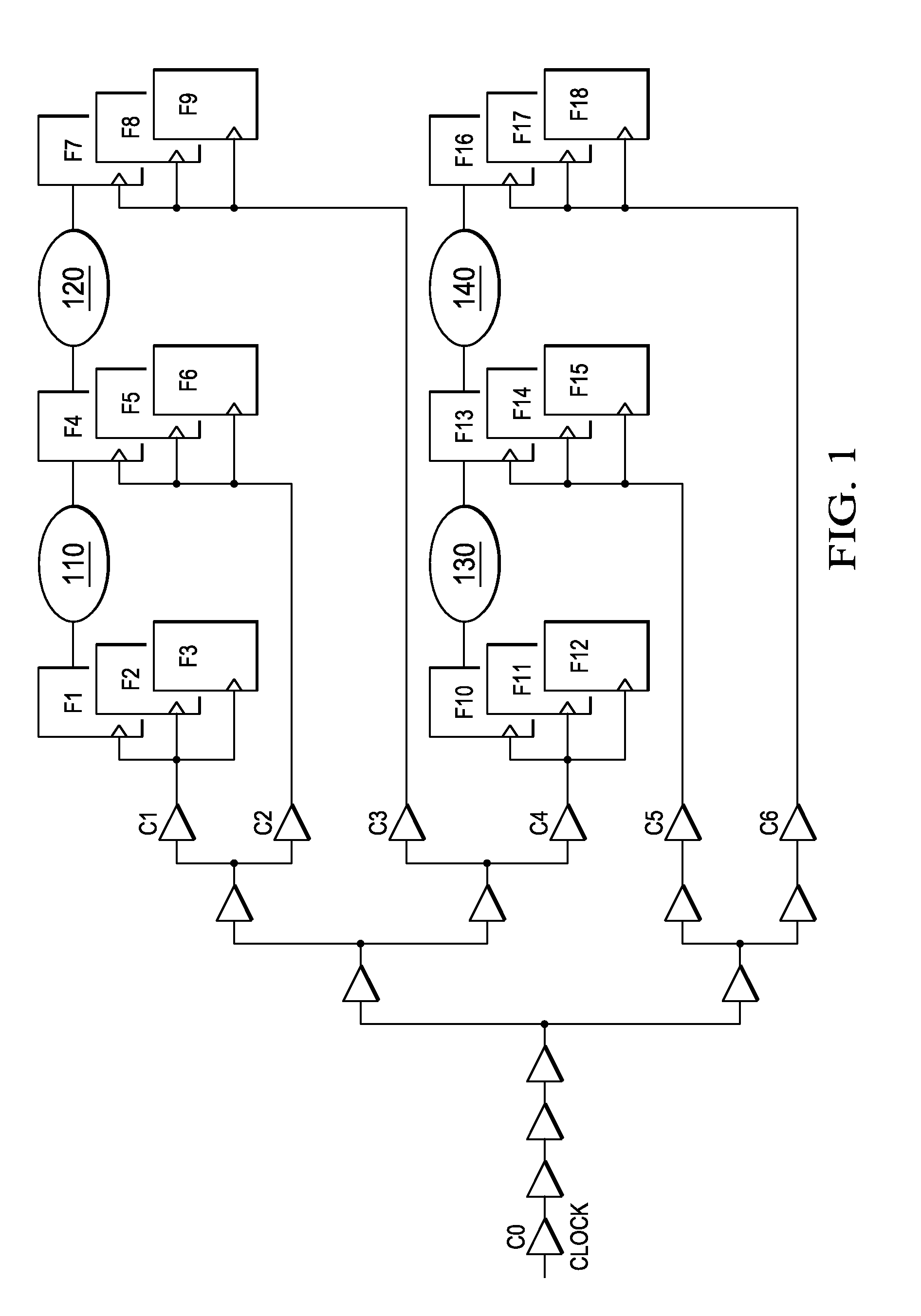
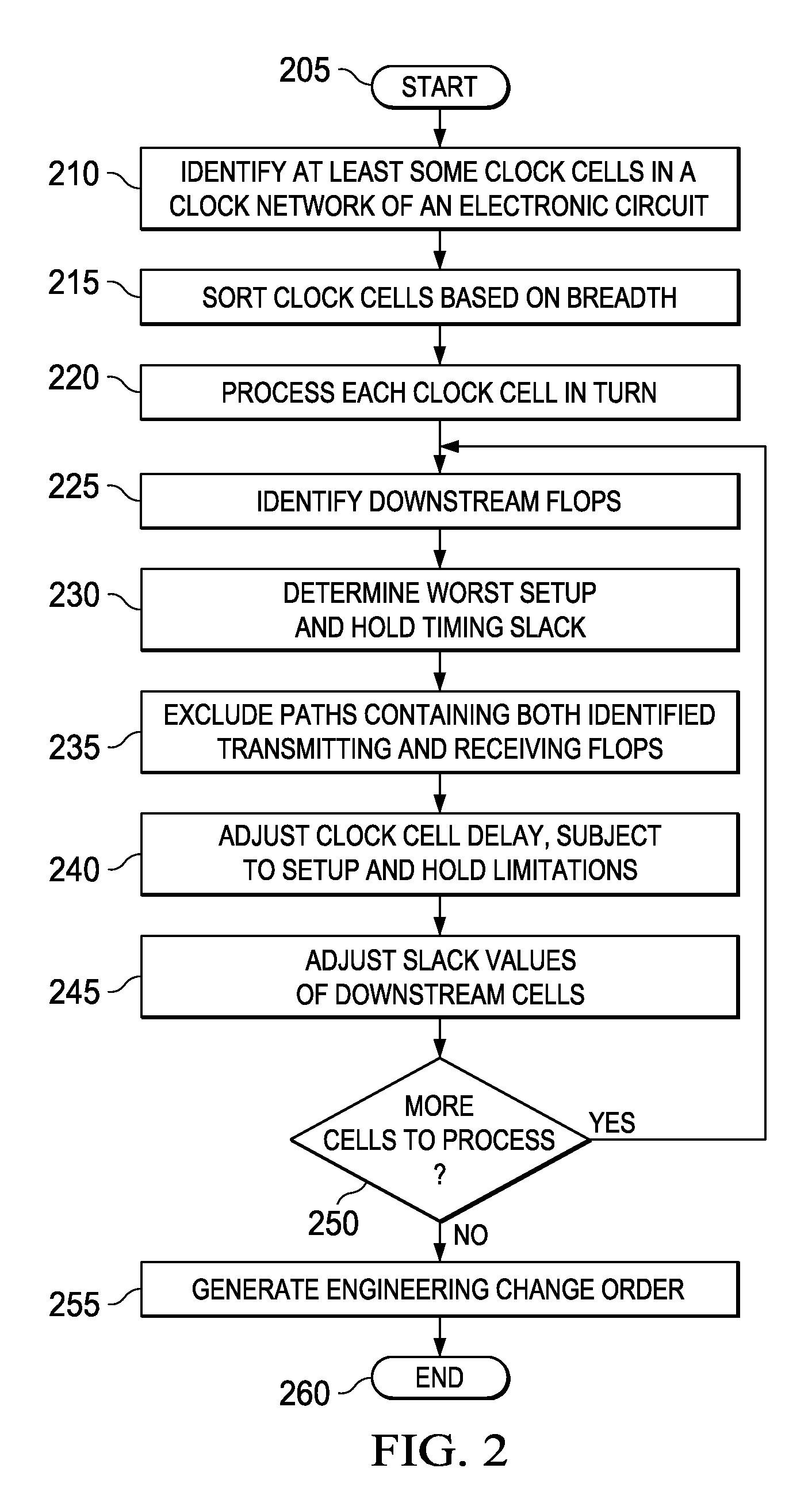
System and method for clock optimization to achieve timing signoff in an electronic circuit and electronic design automation tool incorporating the same
InactiveUS20100262939A1Computer aided designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationEngineeringClock network
A system and method for clock optimization to achieve timing signoff in an electronic circuit and an EDA tool that embodies the system or the method. In one embodiment, the system includes: (1) a clock cell identifier / sorter configured to identify at least some clock cells in a clock network associated with an electronic circuit design and sort the cells according to breadth, (2) a slack analyzer associated with the clock cell identifier / sorter and configured to identify flops that are downstream of the cells and determine a worst setup and hold timing slack thereof and (3) a clock cell delay adjuster associated with the slack analyzer and configured to adjust delays of the cells subject to the worst setup and hold timing slack.
Owner:BELL SEMICON LLC +1
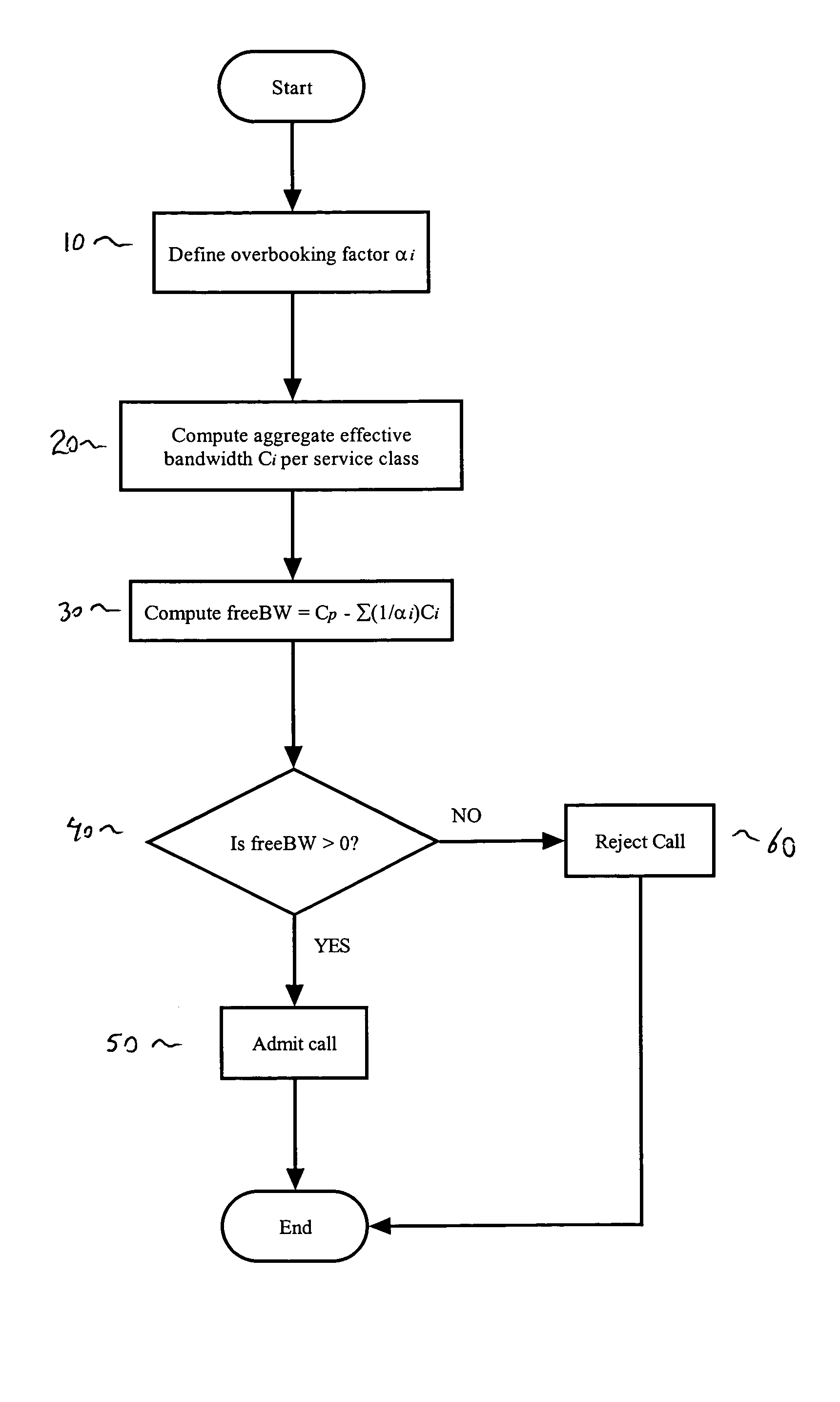
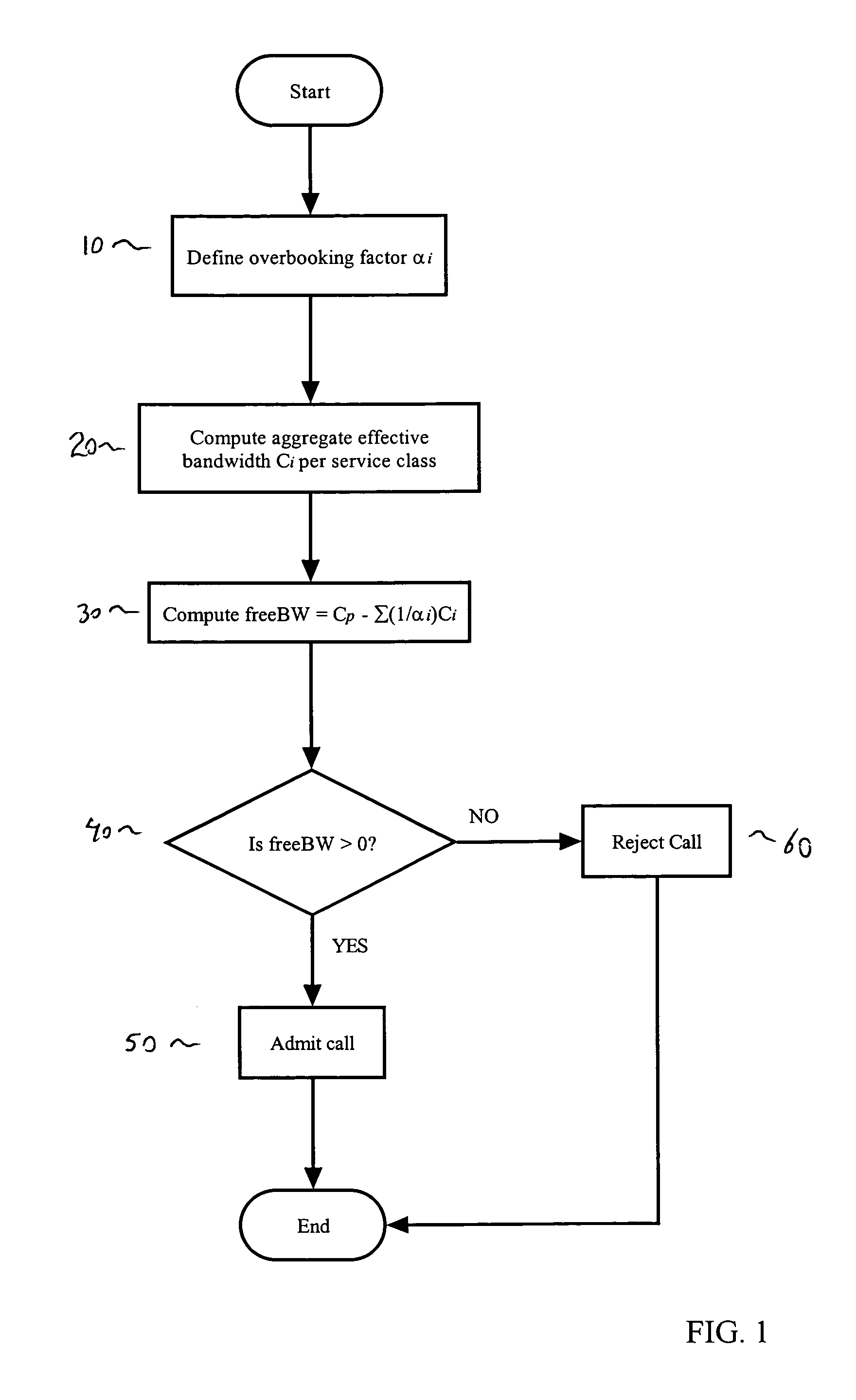
Call admission control with overbooking support and cell loss ratio and cell delay variation guarantee
ActiveUS7400630B1Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsTelecommunicationsCall Admission Control
Call admission methods for admitting connections into ATM / IP networks having a plurality of communication channels are disclosed. An overbooking technique is utilized which distinguishes among the different service classes. Each service class is assigned an overbooking factor. The call admission is determined based on the overbooking factor assigned to the class and the effective bandwidth for that service class. In addition, methods are disclosed for performing appropriate bookkeeping, i.e., updating and maintaining information concerning the state of the system.
Owner:RPX CORP +1
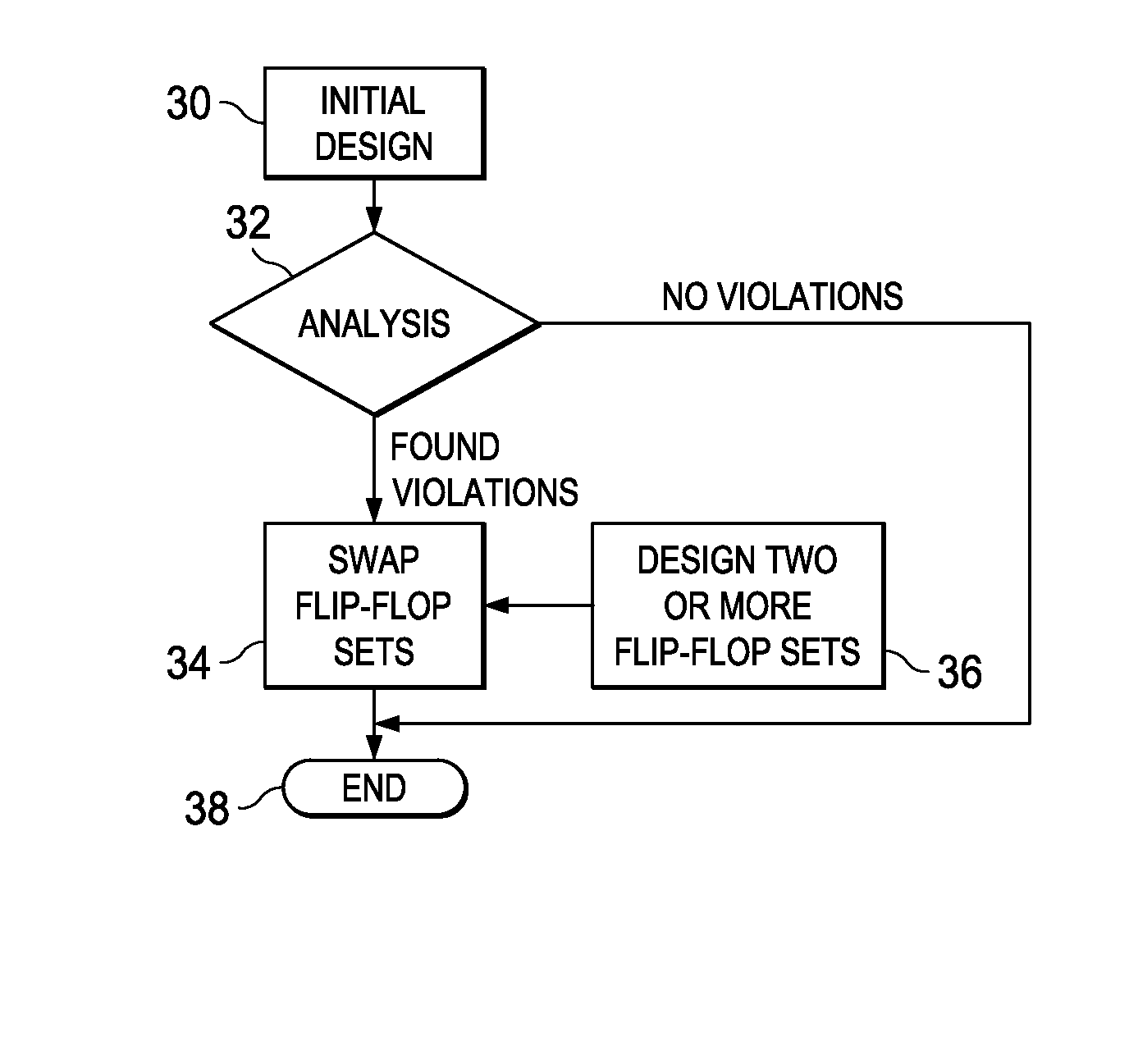
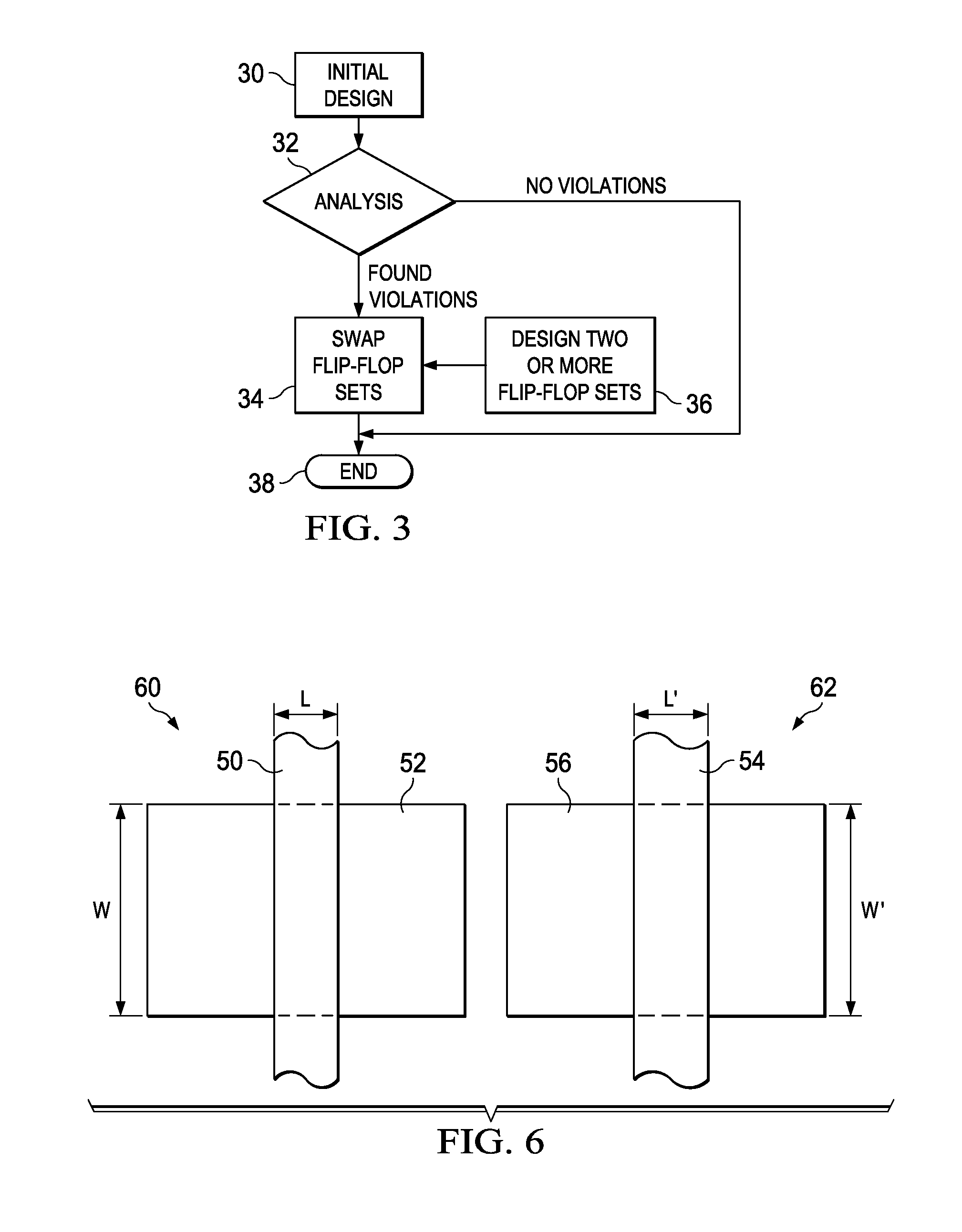
Fixing full-chip violations using flip-flops
A method of forming an integrated circuit includes providing a first design of the integrated circuit; analyzing the first design to identify a first flip-flop having setup / hold violations and a second flip-flop not having setup / hold violations; and replacing the first flip-flop with a third flip-flop having a substantially same cell delay as the first flip-flop to form a second design of the integrated circuit. The first flip-flop and the third flip-flop have different setup and hold windows.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Apparatus and method for intra-cell delay time analysis
ActiveUS20050025062A1Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsAnalysis methodComputer science
Method and apparatus for analyzing intra-cell delay times. The delay time between cells is measured and the number of times the measured delay times equals each of a plurality of predefined values is calculated. A graph is displayed indicating the count for each of the plurality of predefined values.
Owner:VIAVI SOLUTIONS INC
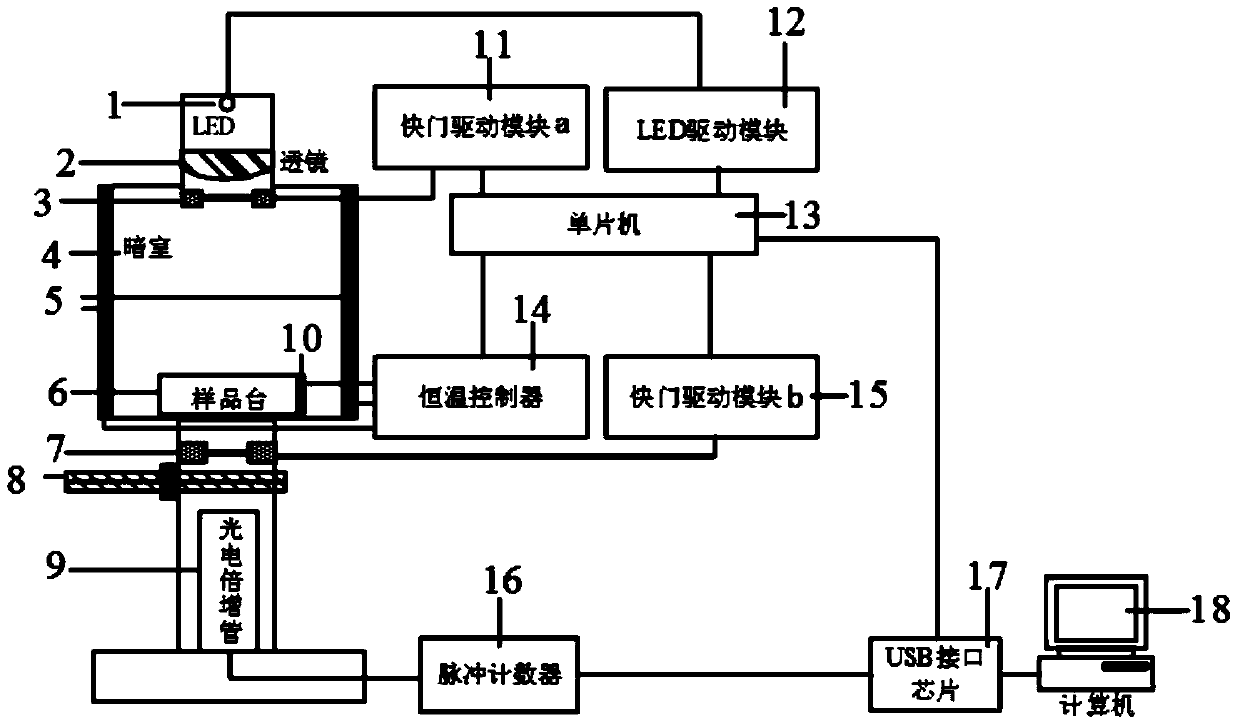
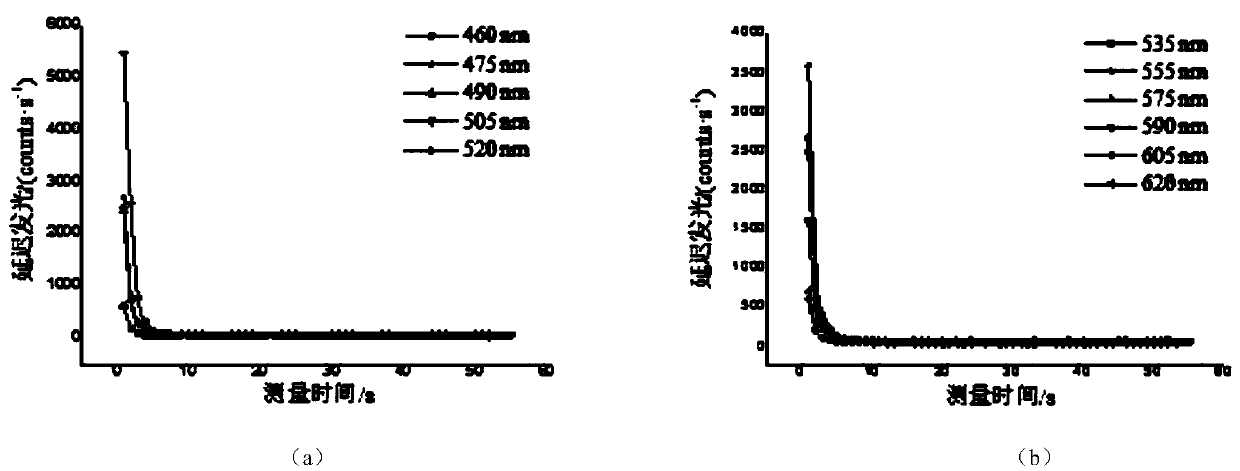
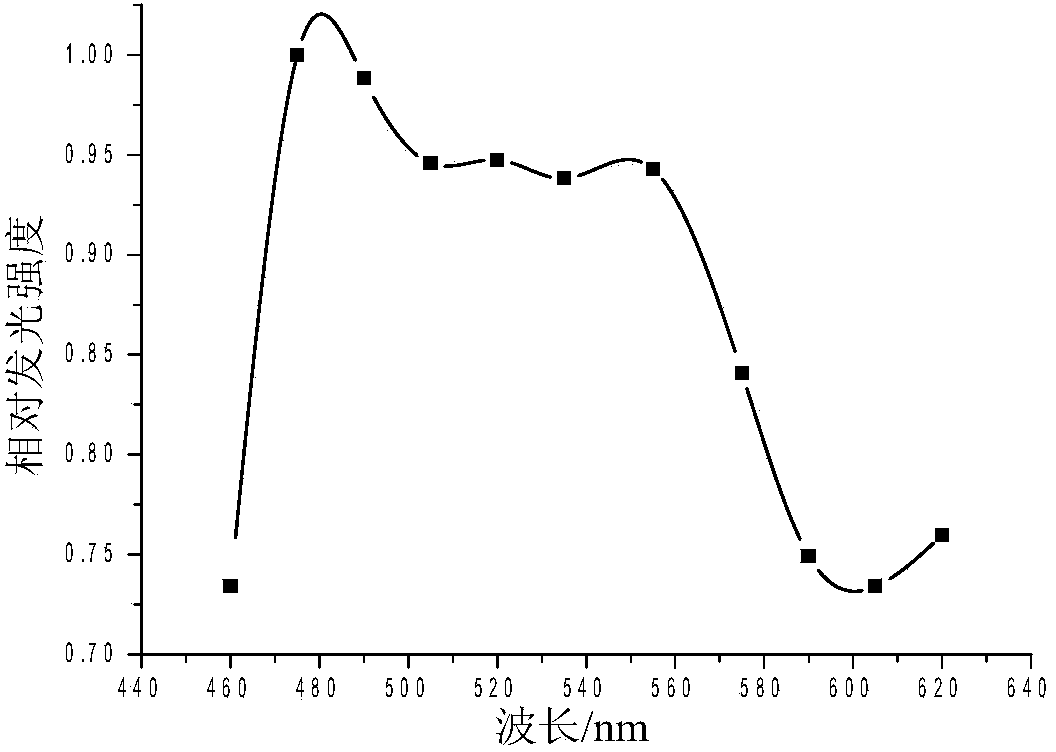
Method for detecting biological ultra-weak photon radiation spectrum
The invention discloses a method for detecting a biological ultra-weak photon radiation spectrum. The method includes the steps firstly, delayed luminescence curve data of a living biological sample on different wave lengths are collected accurately, and then fitting is performed on measurement data under the wave lengths by the utilization of the least square method according to the kinetic equation of cell delayed luminescence. Kinetic equation parameters obtained in fitting comprise parameters ISL for describing spontaneous luminescence of the sample, and the parameters are the spontaneous luminescence intensity under the wave lengths. Through the method, the spontaneous photon radiation spectrum of the sample can be measured indirectly. The problem that due to the fact that the spontaneous photon radiation intensity of the sample is too low, the spectrum of the sample cannot be detected directly is avoided.
Owner:XIAN UNIV OF TECH
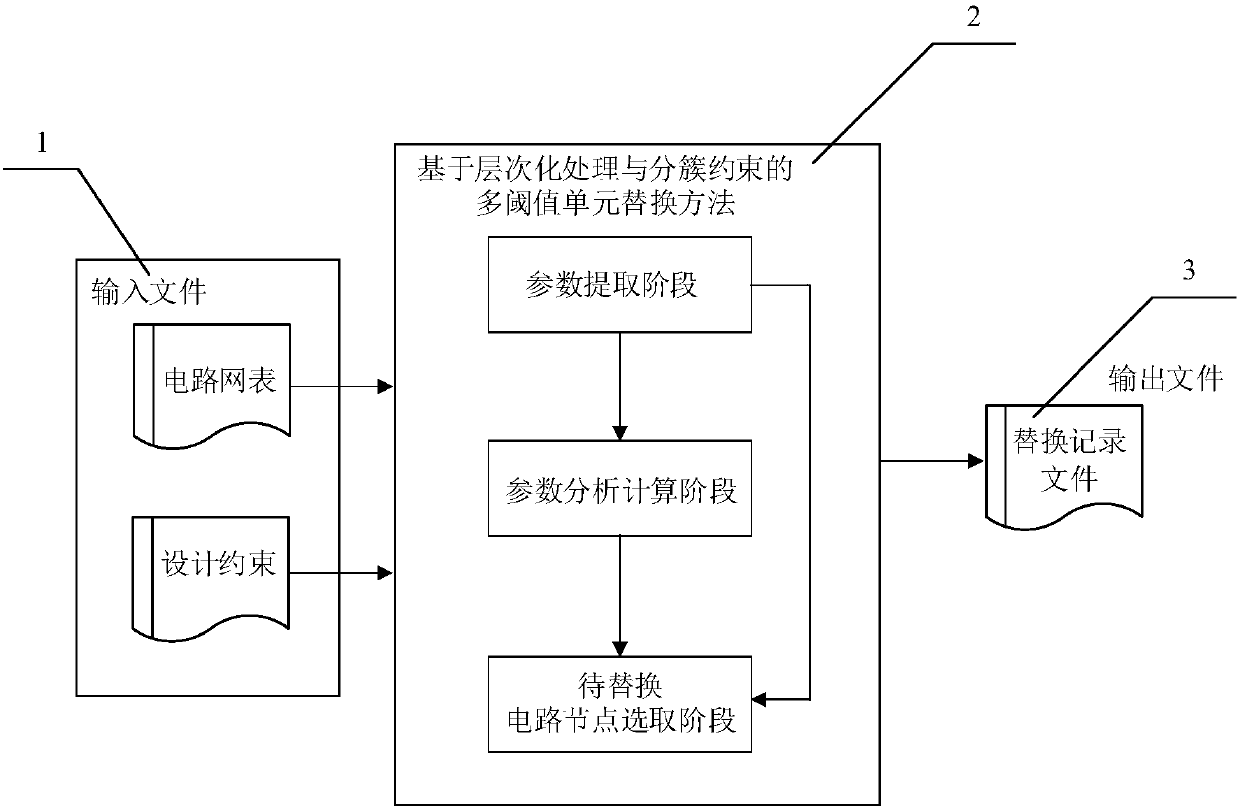
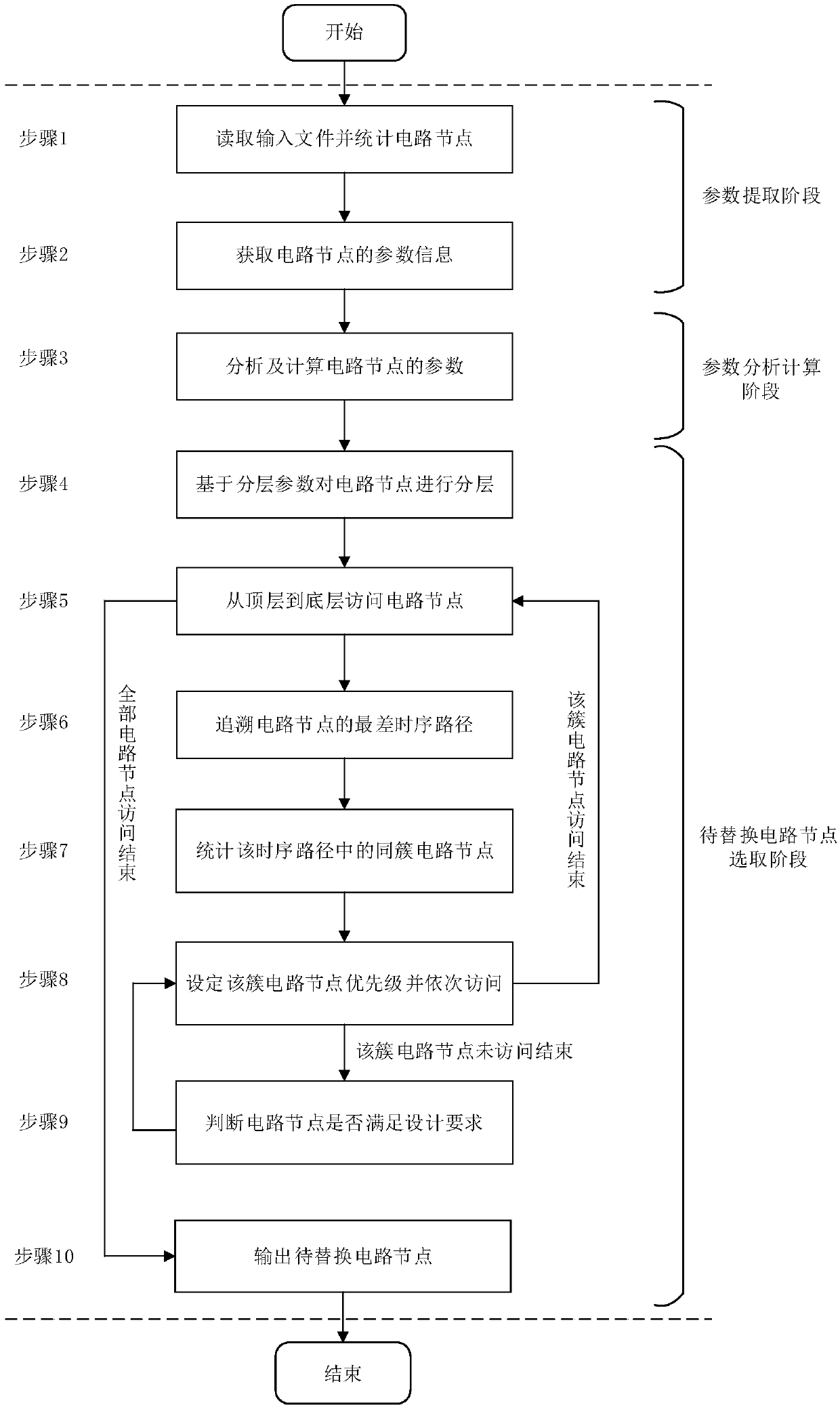
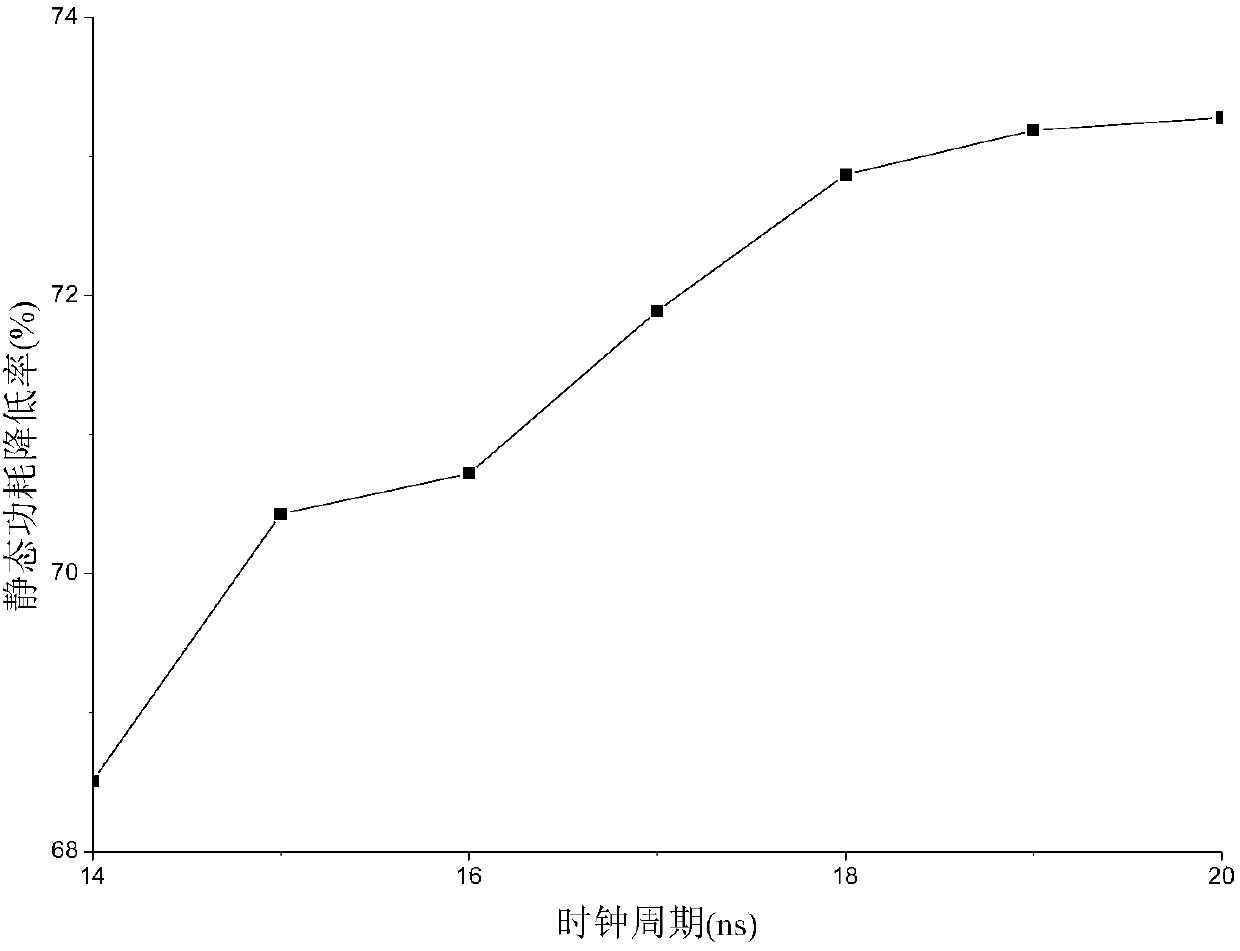
Multi-threshold-value unit replacing method based on hierarchical processing and cluster constraint
ActiveCN107862161ANo need to buildNo format conversion problemSpecial data processing applicationsParallel algorithmComputer science
The invention discloses a multi-threshold-value unit replacing method based on hierarchical processing and cluster constraint. The multi-threshold-value unit replacing method based on hierarchical processing and cluster constraint comprises the following steps: in parameter extracting stage, reading a parallel algorithm and a design constraint, counting combinational logic circuit nodes, and acquiring cell delay of the circuit nodes, static power consumption and a sequential path number; in a parameter analyzing and computing stage, computing cell delay variable quantity of the circuit nodes,static power consumption variable quantity and the ratio of the static power consumption variable quantity to the cell delay variable quantity; and in a to-be-replaced circuit node selecting stage, layering the circuit nodes on the basis of layering parameters, visiting the circuit nodes from the top layer to the bottom layer, tracing the worst timing sequence path of the circuit nodes, counting same-cluster circuit nodes in the time sequence path, setting a same-cluster circuit node priority and successively visiting the same-cluster circuit nodes, judging whether the circuit nodes meet design requirements or not, and outputting to-be-replaced circuit nodes. Selection of ASIC design to-be-replaced circuit nodes can be finished automatically, complexity caused by a traditional method is reduced, and the working efficiency is improved.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
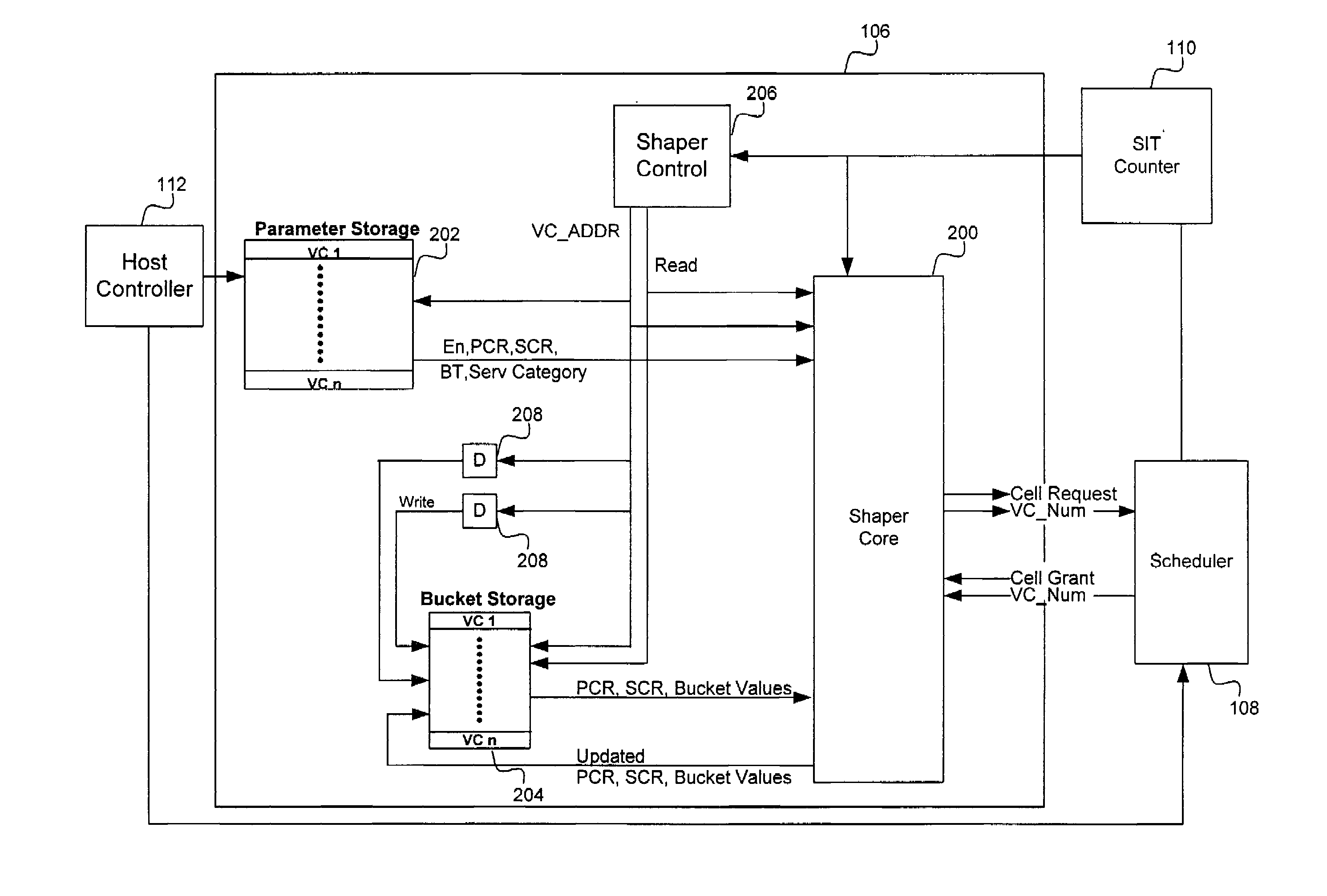
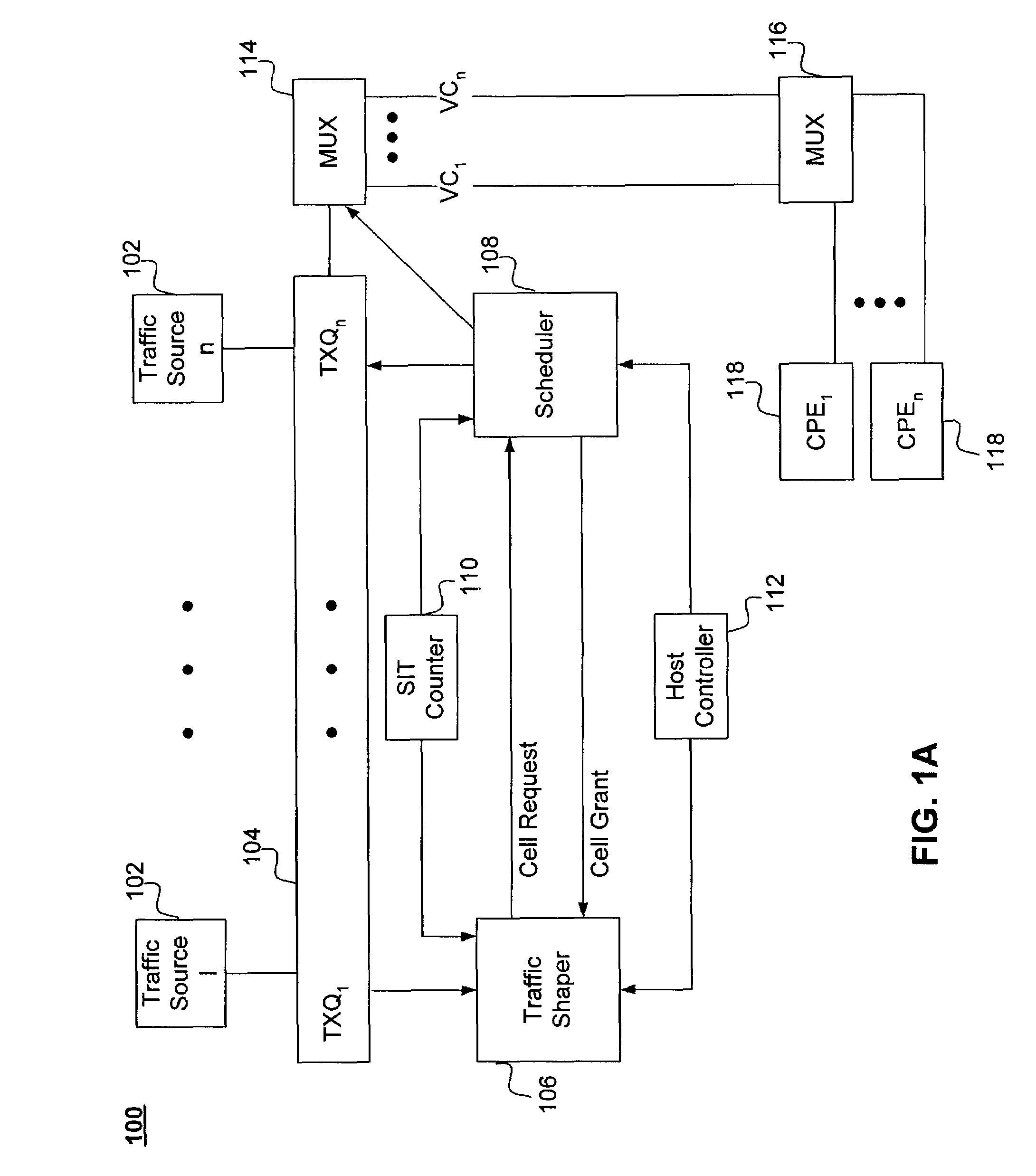
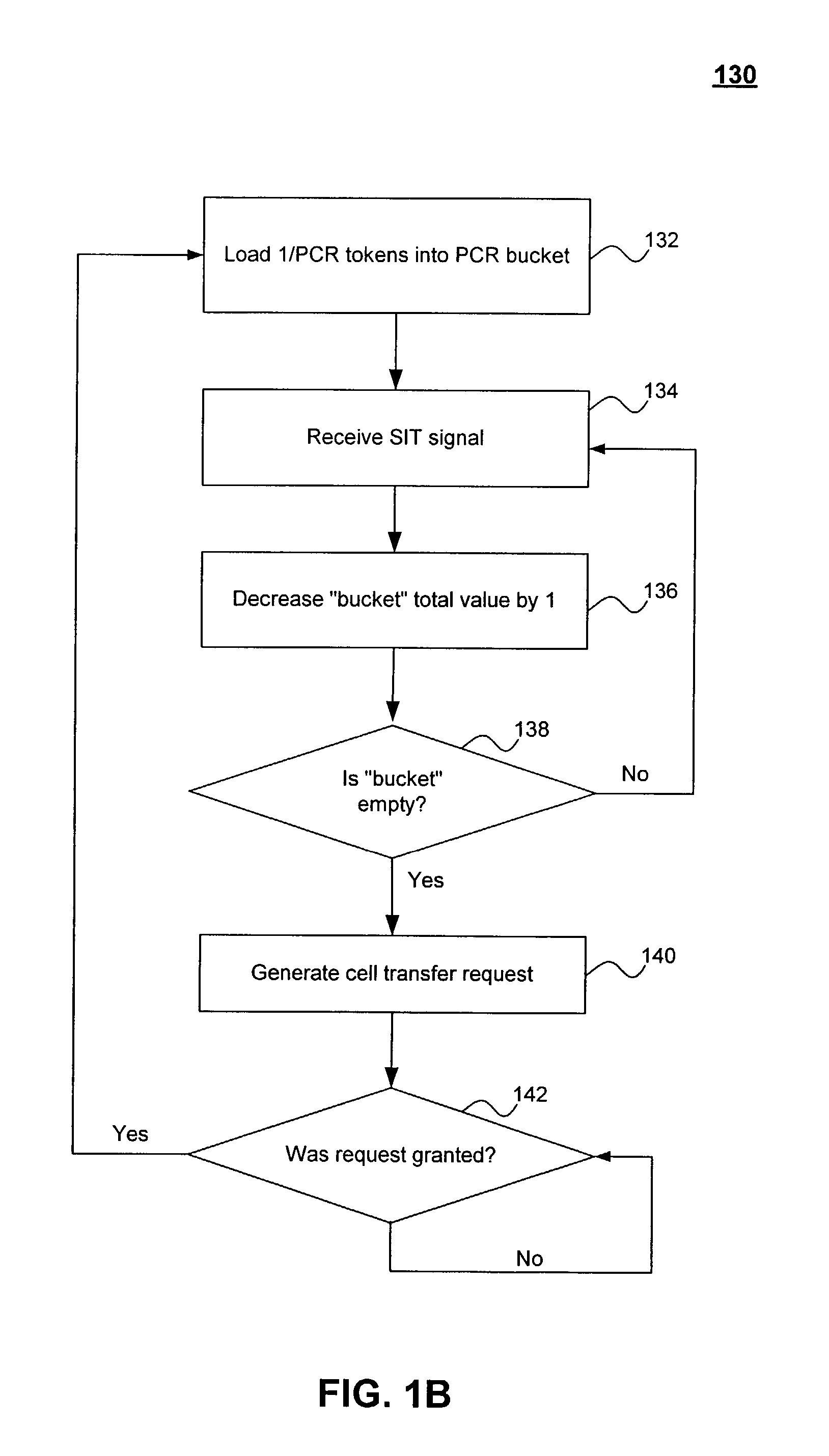
Scalable, high-resolution asynchronous transfer mode traffic shaper and method
InactiveUS7339890B2Low costZero and substantially zero cell delay variationError preventionTransmission systemsQuality of serviceVia device
An ATM network traffic shaper is implemented in hardware. The traffic shaper shapes transmit data on one or more virtual circuits (VCs) according to the specified quality of service (QoS) parameters. Thus, the traffic shaper provides for the delivery of associated data cells in accordance with the specified QoS parameters. The traffic shaper is scalable in that the number of supported VCs can be increased with a relatively small increase in the size of the device and associated logic gates. The traffic shaper supports constant bit rate (CBR), variable bit rate (VBR), and unknown bit rate (UBR) service types and generates cell transmit requests with zero cell delay variation (CDVT). The traffic shaper also provides very high resolution in terms of bit rate specification. Varying shaping resolutions are achieved by varying a shaping interval time (SIT) generated by a SIT counter.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
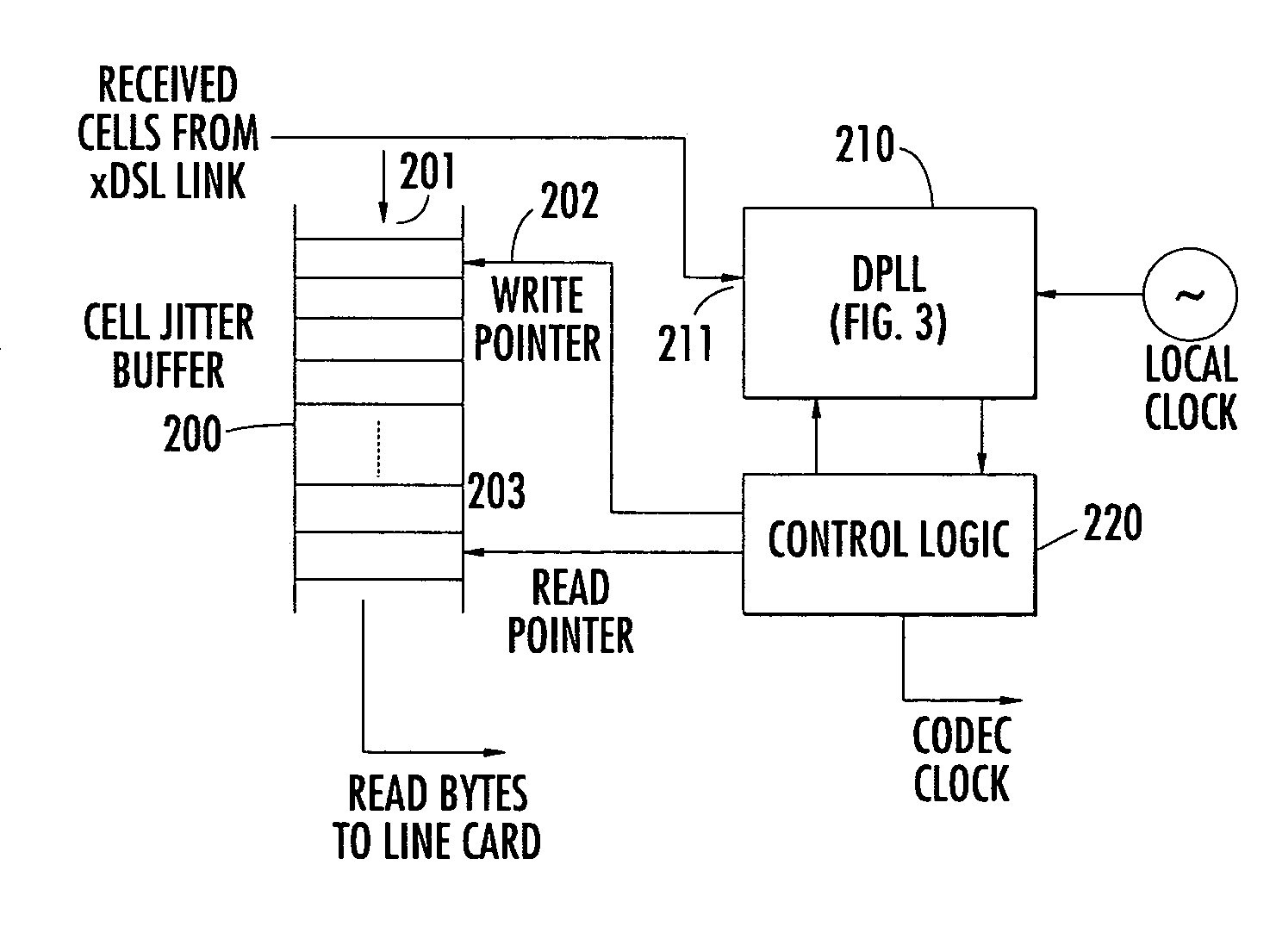
Method and apparatus for providing reliable voice and voice-band data transmission over asynchronous transfer mode (ATM) network
ActiveUS6990109B2Acquisition speed is fastShorten the timeError preventionModulated-carrier systemsModem deviceCommunications system
Adaptive clock recovery for the receiving entity of a communication system transporting constant bit-rate (CBR) services over an asynchronous transfer mode (ATM) or ATM-like network is performed by a digital phase locked loop (DPLL). The recovered clock is based on the DPLL's phase detector's count of high frequency service clock cycles between transitions in an input signal representative of instances of receipt of ATM cells subject to cell delay variations through the network, and a reference clock signal whose frequency is a prescribed fraction of that of the output clock. The DPLL's VCO function is an increment / decrement of the service clock frequency, which avoids constraining the operation of a high performance modem (such as a V.90 modem).
Owner:ADTRAN
Characterizing performance of an electronic system
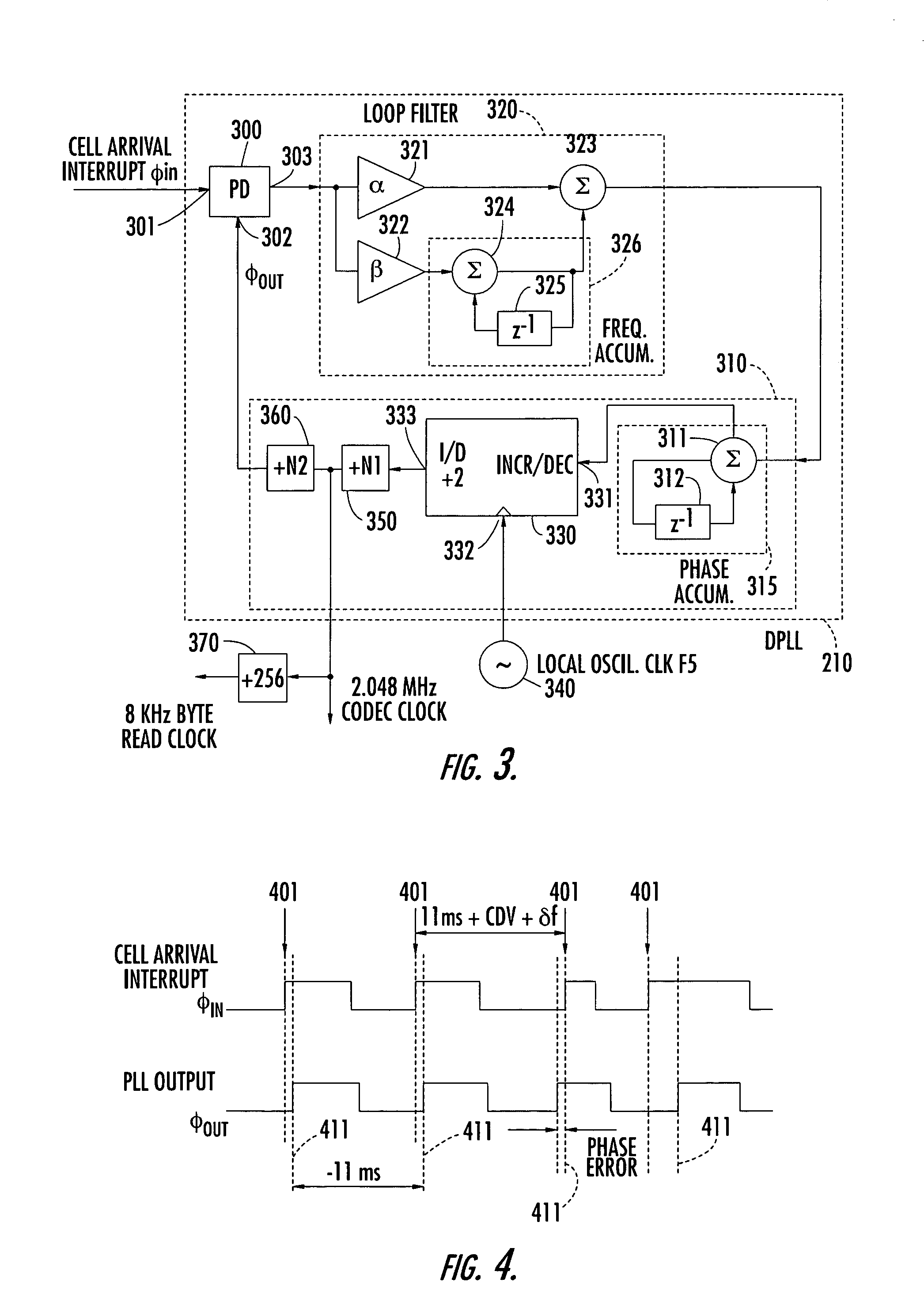
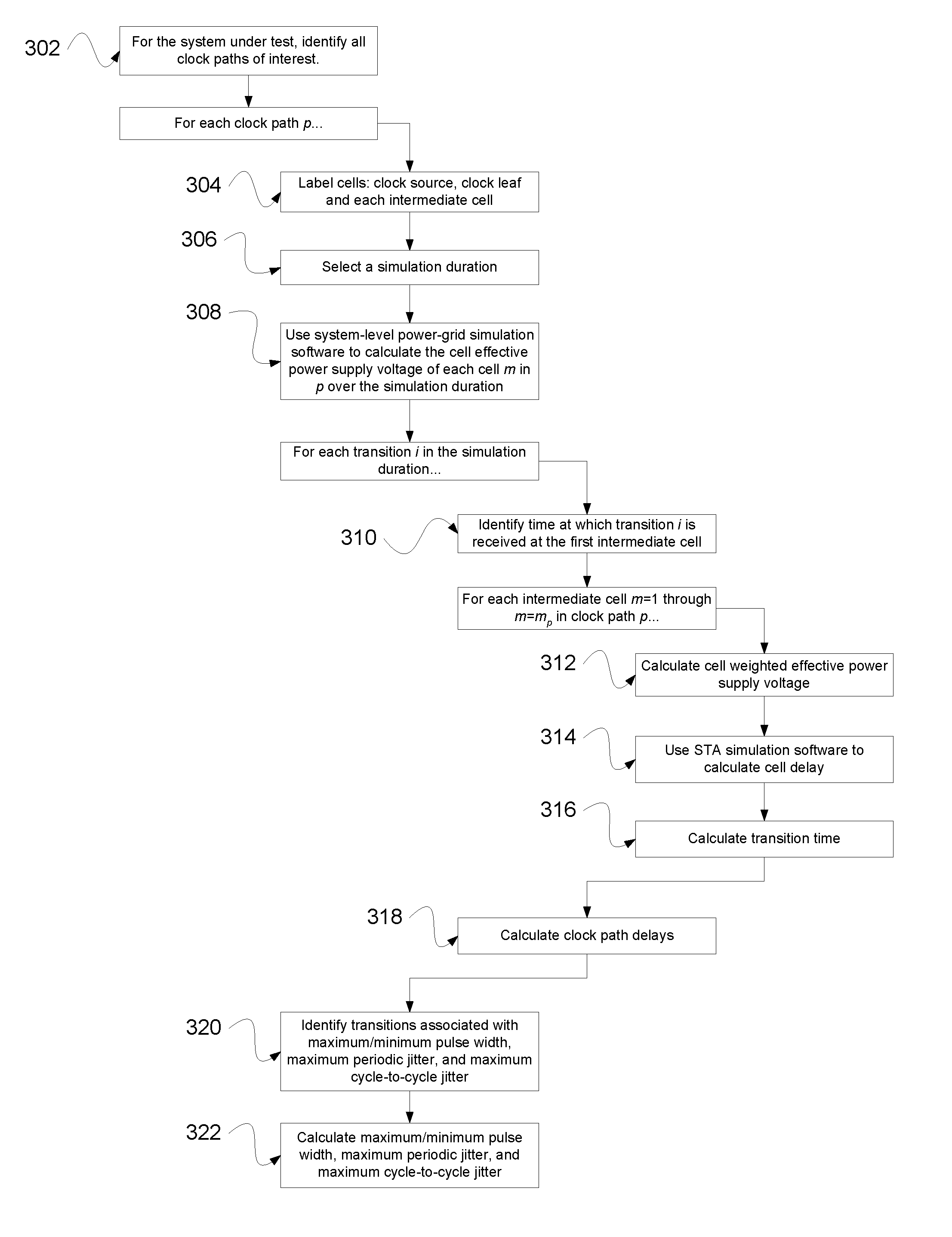
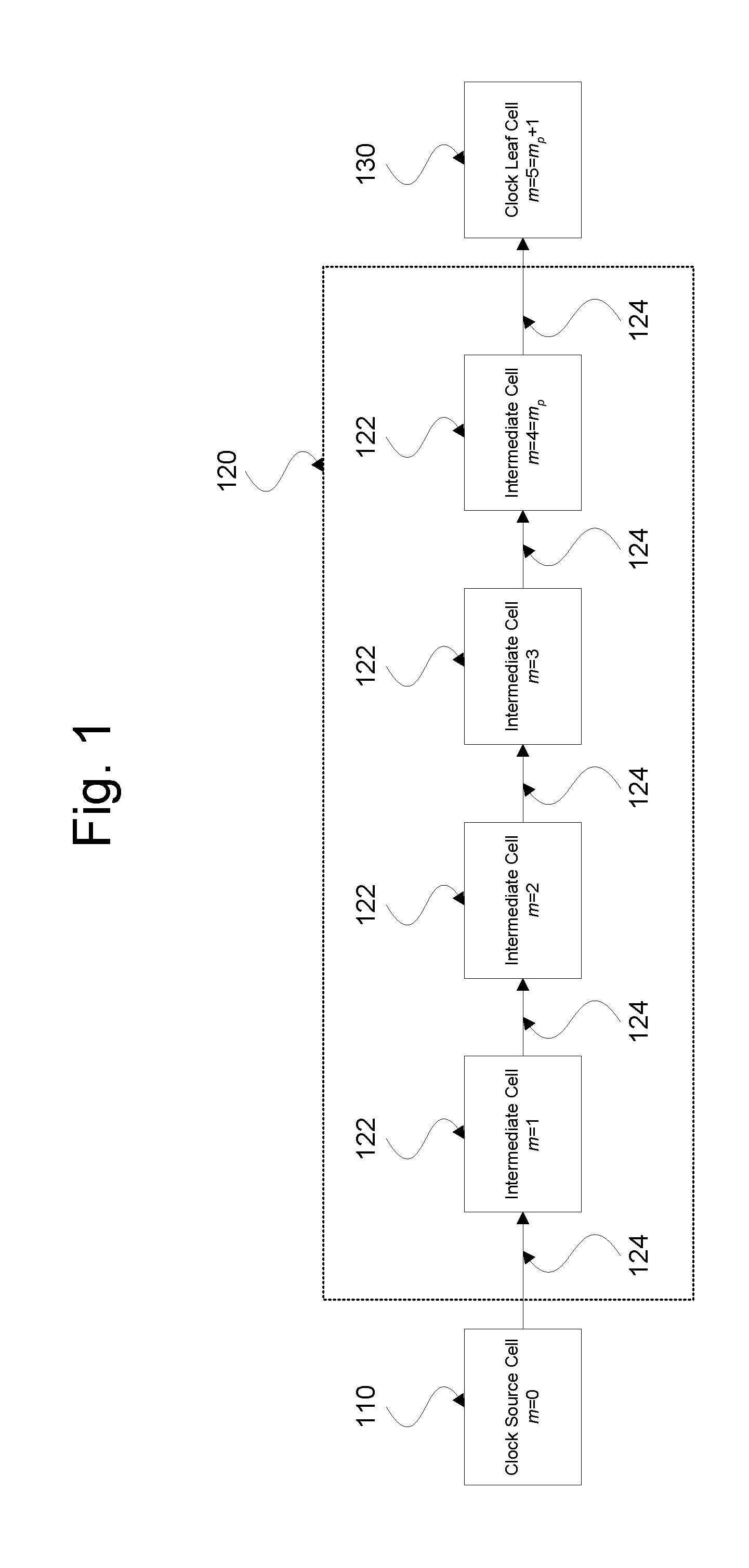
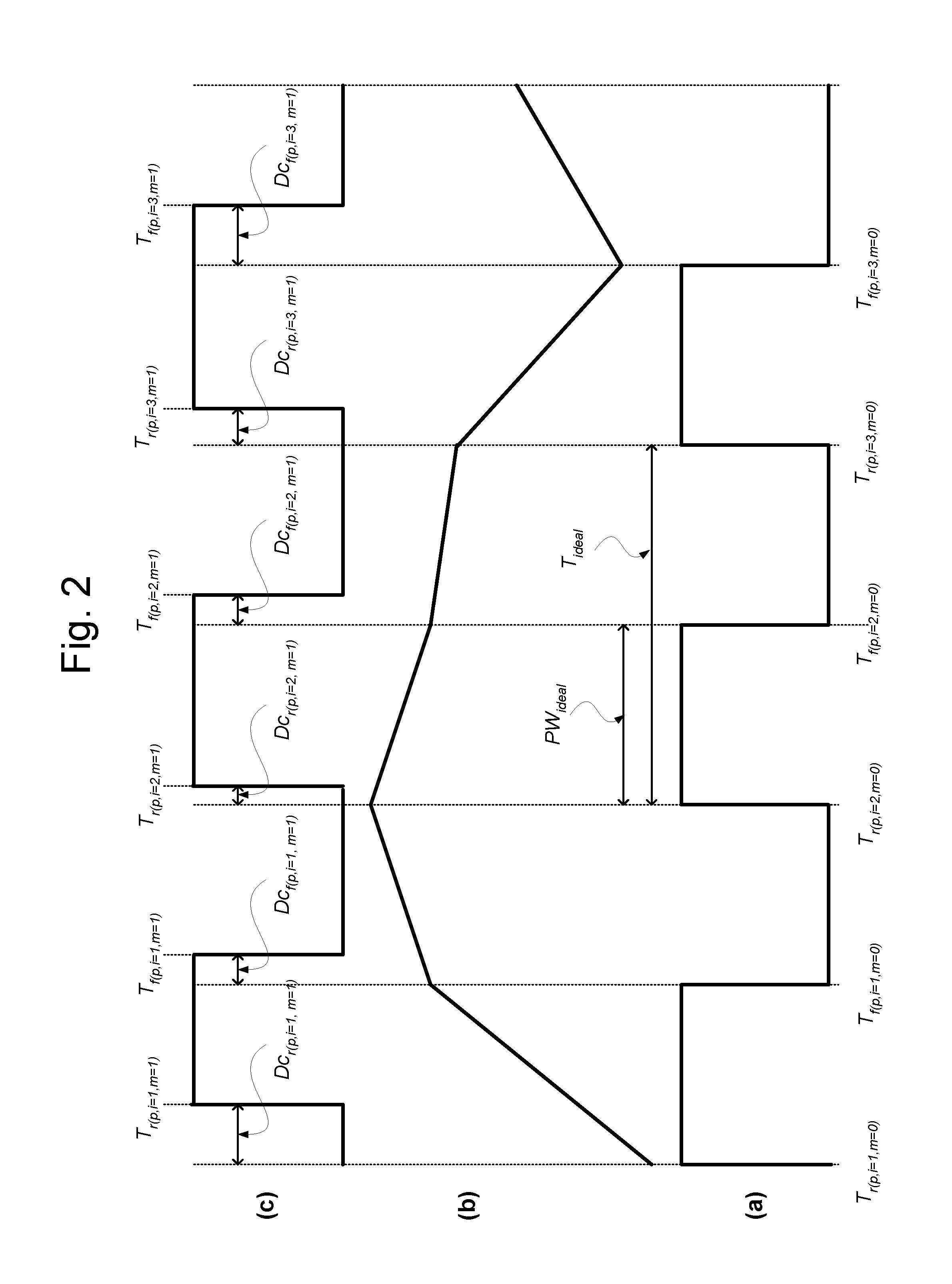
InactiveUS20090287462A1Near-SPICE accuracy in the resultsError detection/correctionComputation using non-denominational number representationStatic timing analysisEffective power
In one embodiment of the present invention, the performance of an electronic circuit having a clock path between a clock source cell and a clock leaf cell is characterized over a simulation duration, where the clock path has one or more intermediate cells. Variations in the effective power supply voltage level at at least one intermediate cell over the simulation duration are determined using a system-level power-grid simulation tool. Static timing analysis (STA) software is used to determine cell delays for at least one of the intermediate cells for different clock-signal transitions at different times during the simulation duration. The cell delays are then used to generate one or more metrics characterizing the performance of the electronic circuit, such as maximum and minimum pulse widths, maximum cycle-to-cycle jitter, and maximum periodic jitter.
Owner:BELL SEMICON LLC
Apparatus and method for processing cells in a communications system
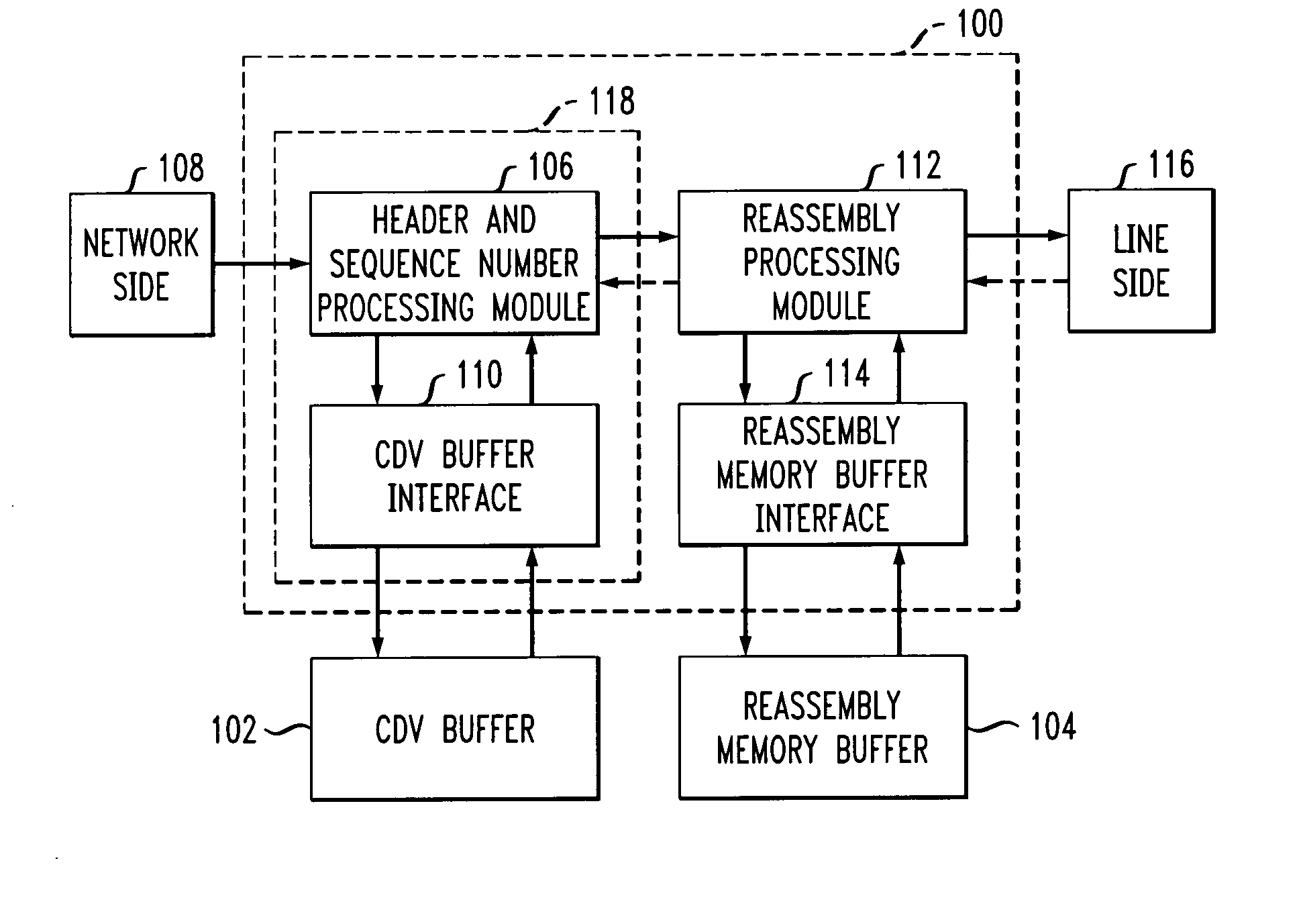
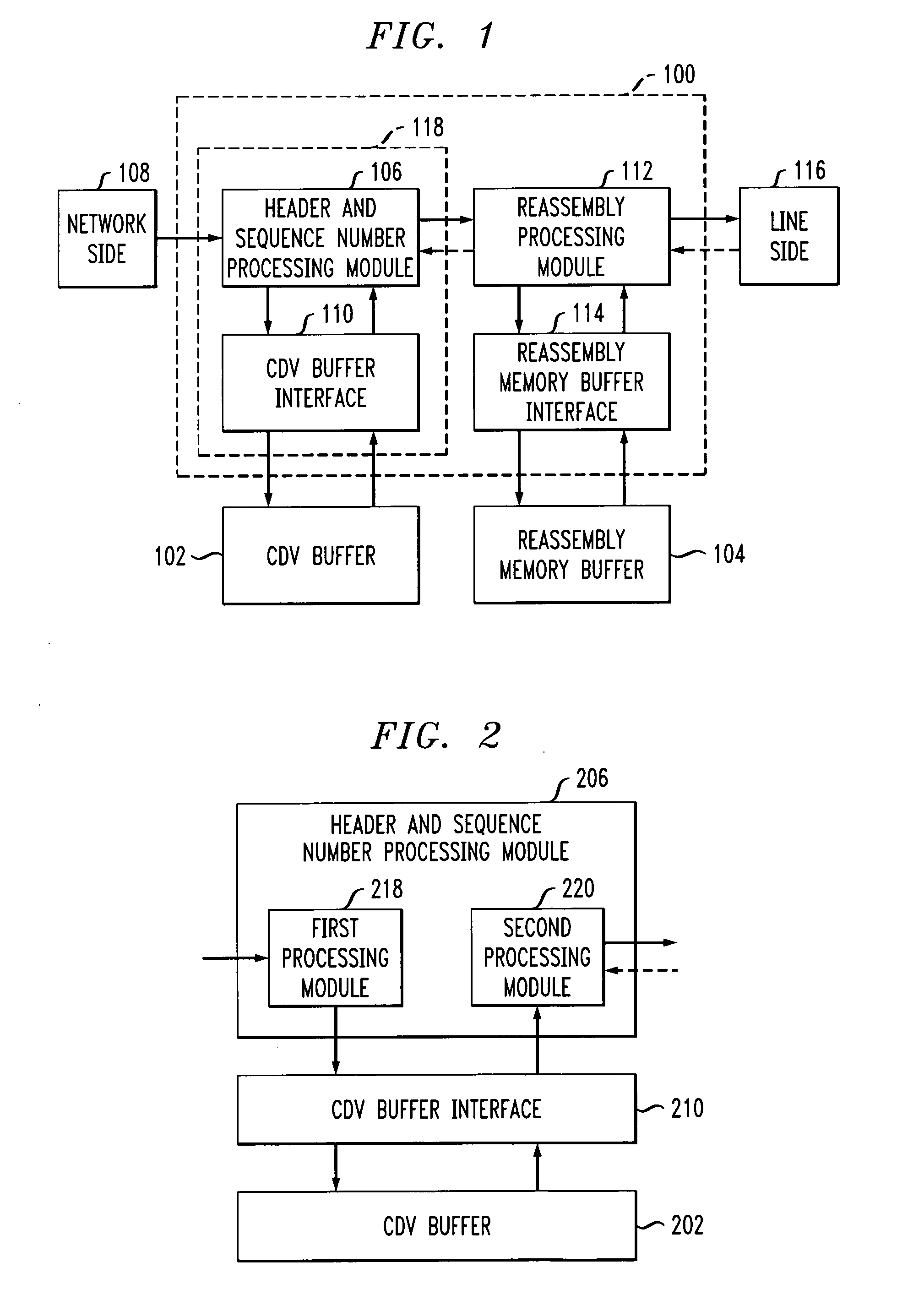
InactiveUS20060221976A1Time-division multiplexData switching by path configurationCommunications systemCell delay
An apparatus for interfacing with a cell delay variation buffer and a re-assembly memory buffer includes a header and sequence number processing module that can interface with the cell delay variation buffer and a re-assembly processing module that can interface with the re-assembly memory buffer. The header and sequence number processing module causes payloads from the cells to be stored in annotated form in the cell delay variation buffer and then extracted. Payload information from the extracted annotated payload can be passed to the re-assembly processing module which causes it to be stored in the re-assembly memory buffer and extracted therefrom as needed. By splitting the cell delay variation and re-assembly buffer functions, less expensive commodity memory can be used for the cell delay variation buffer function.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com