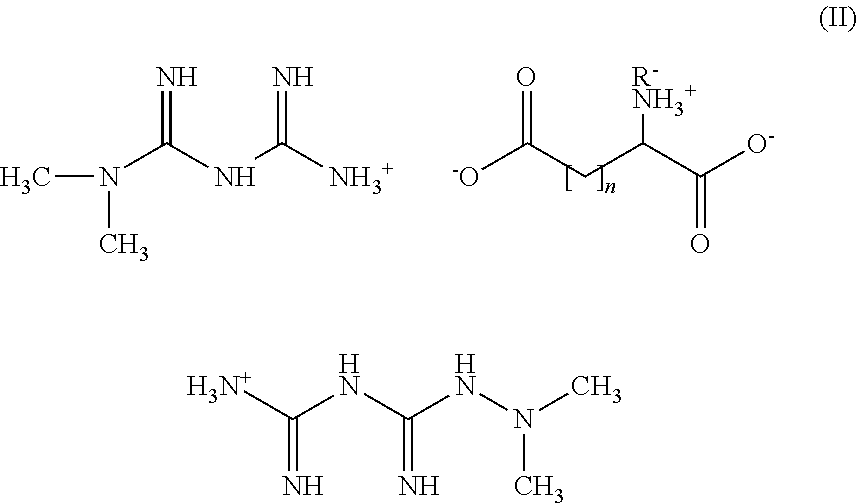
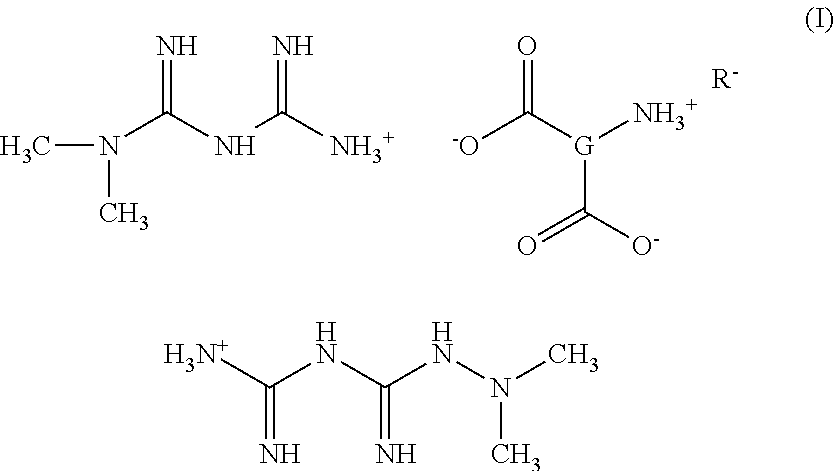
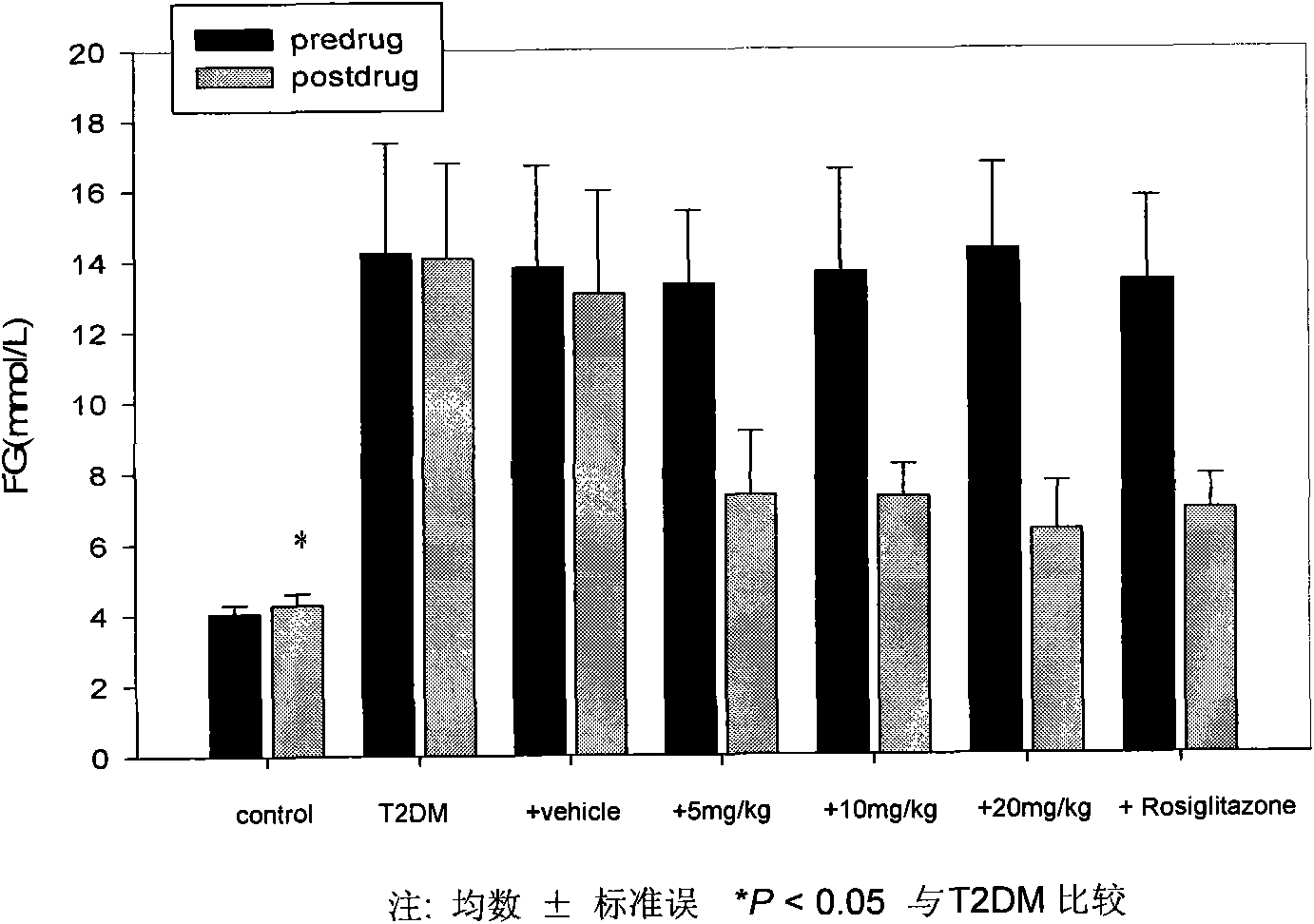
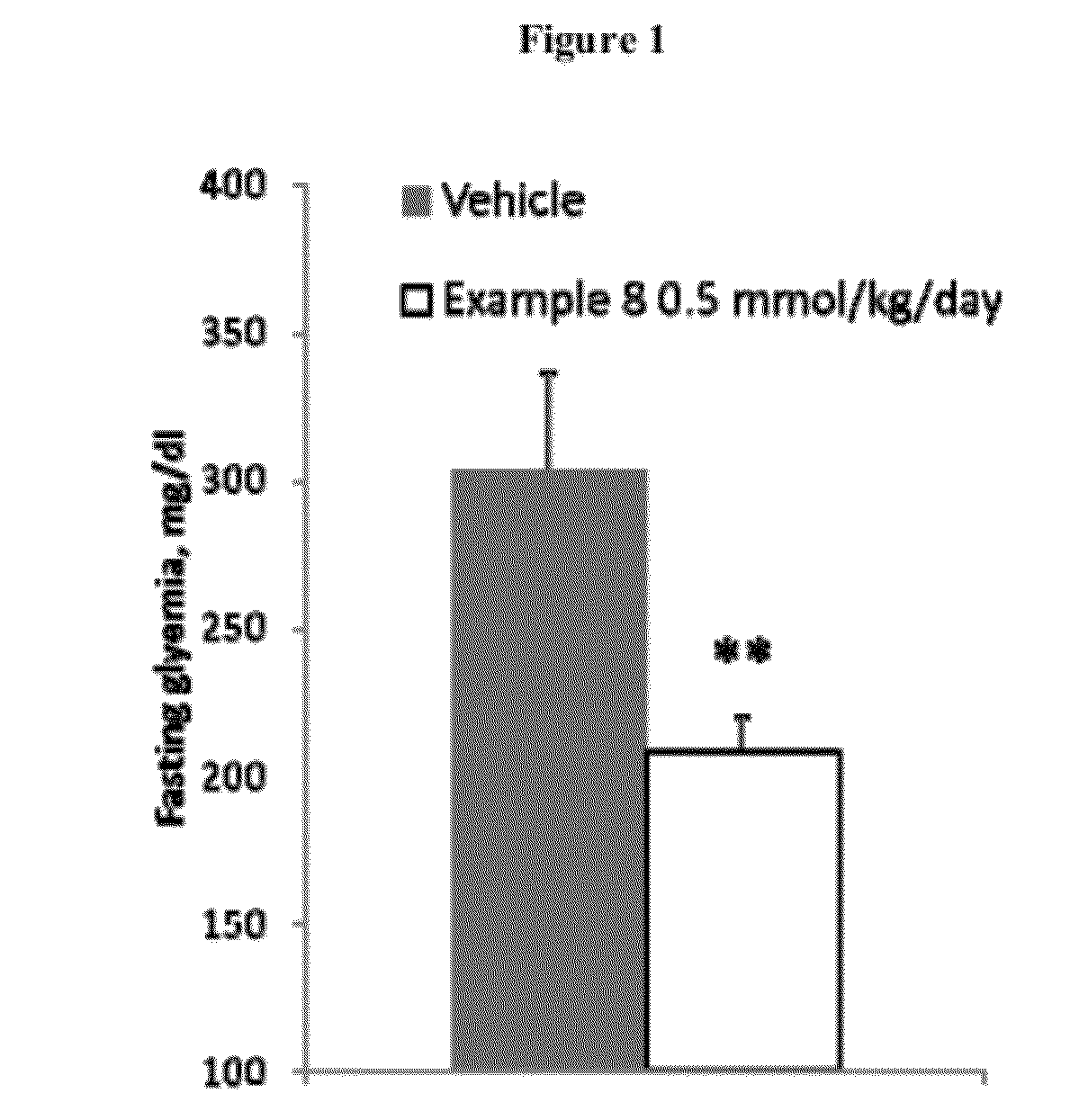
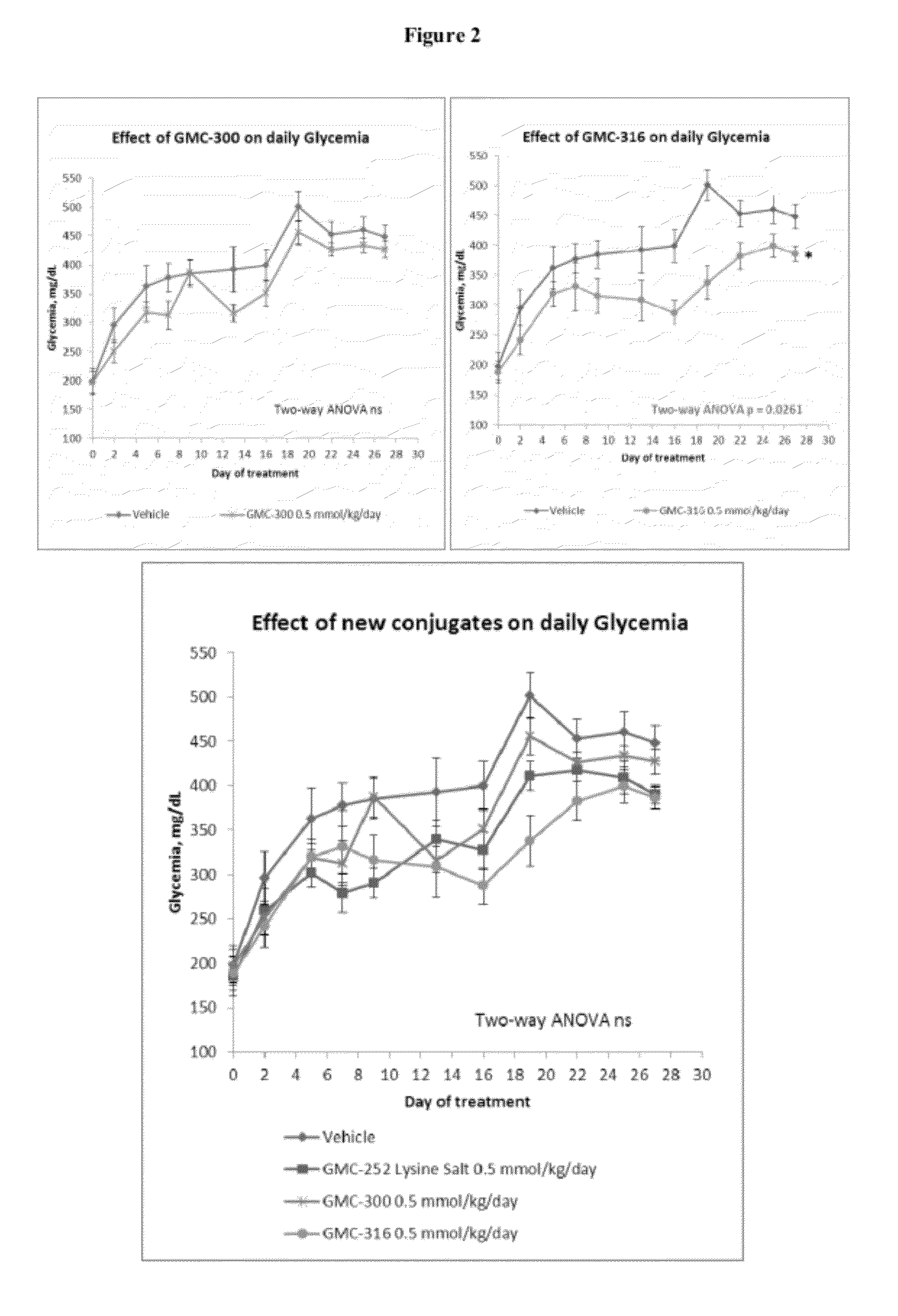
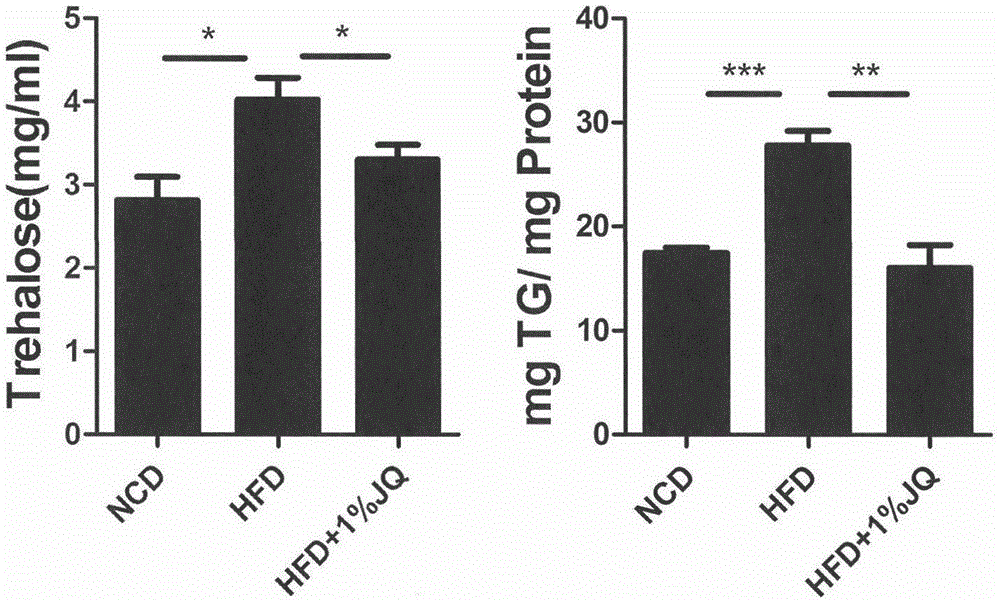
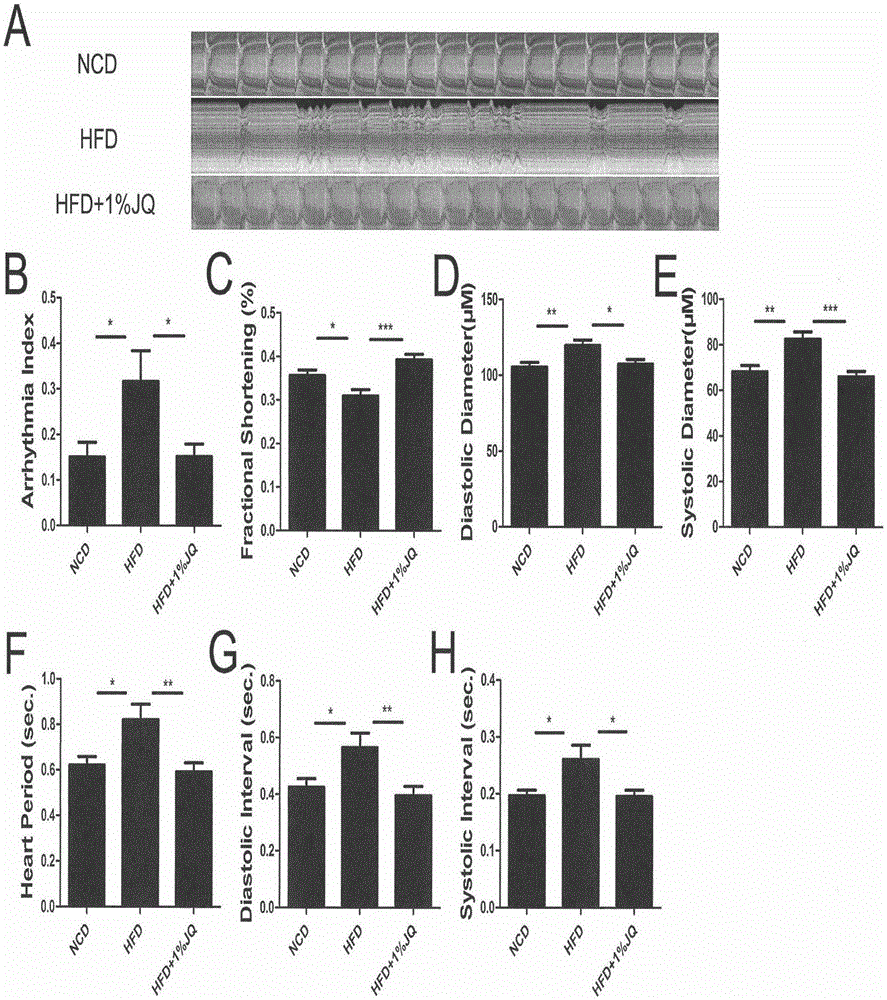
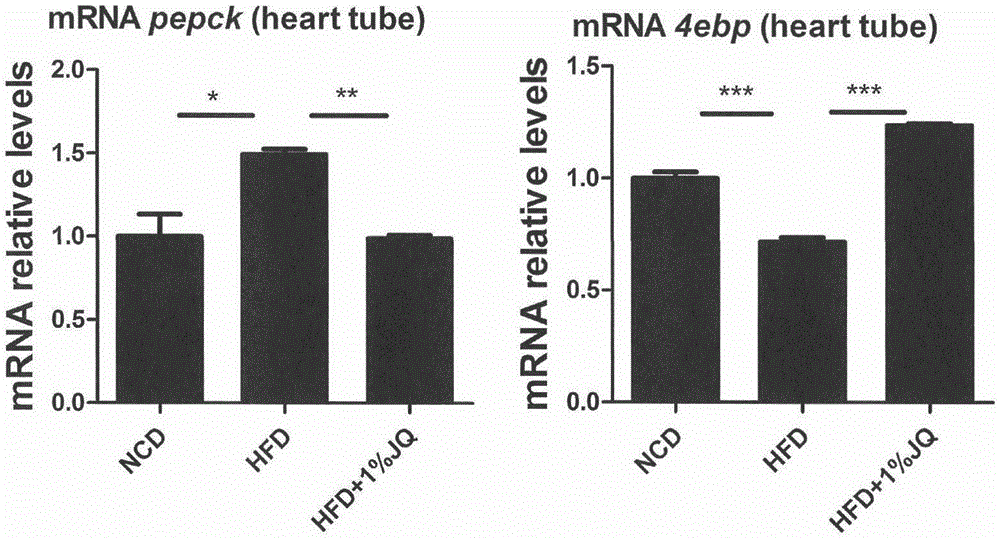
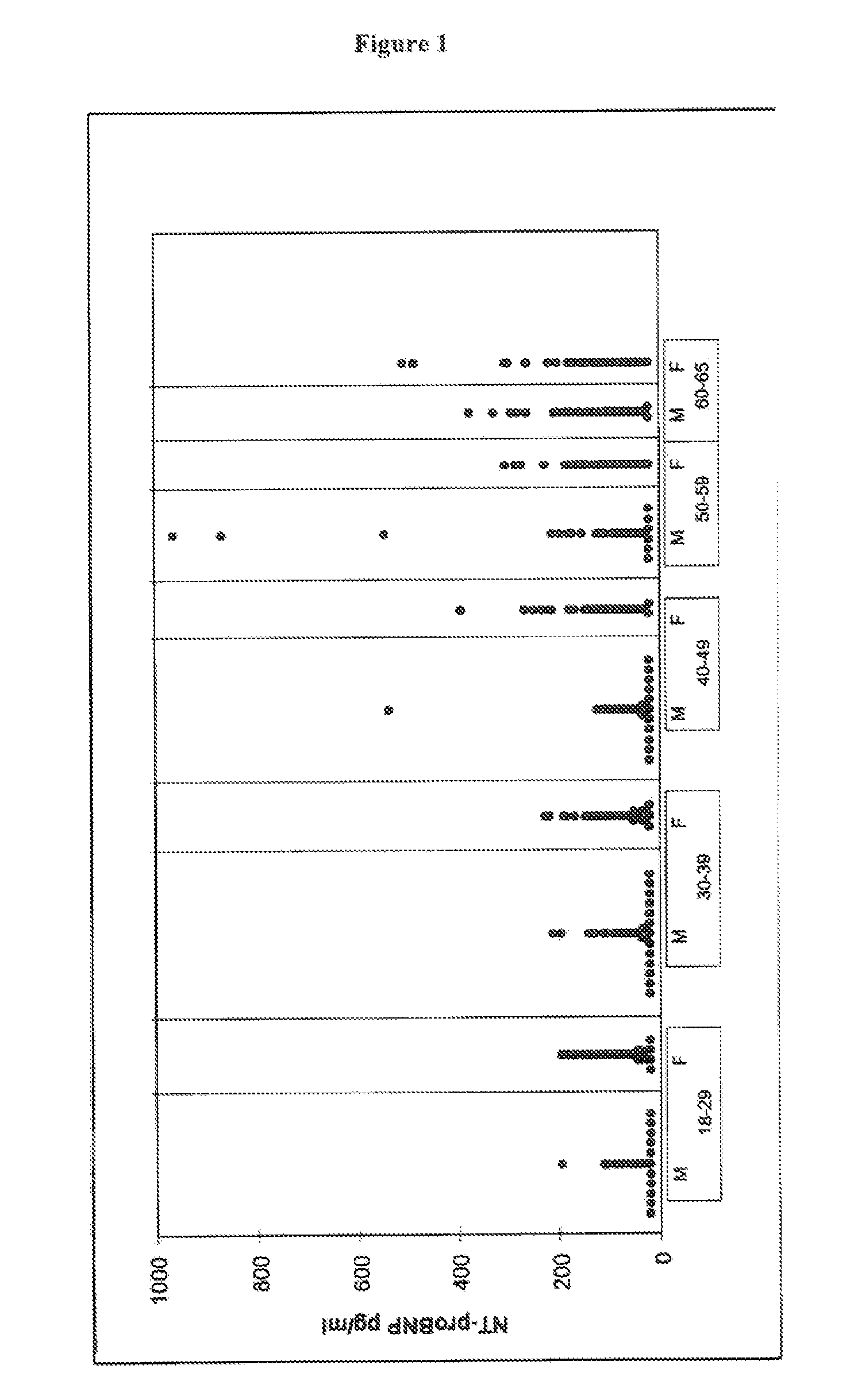
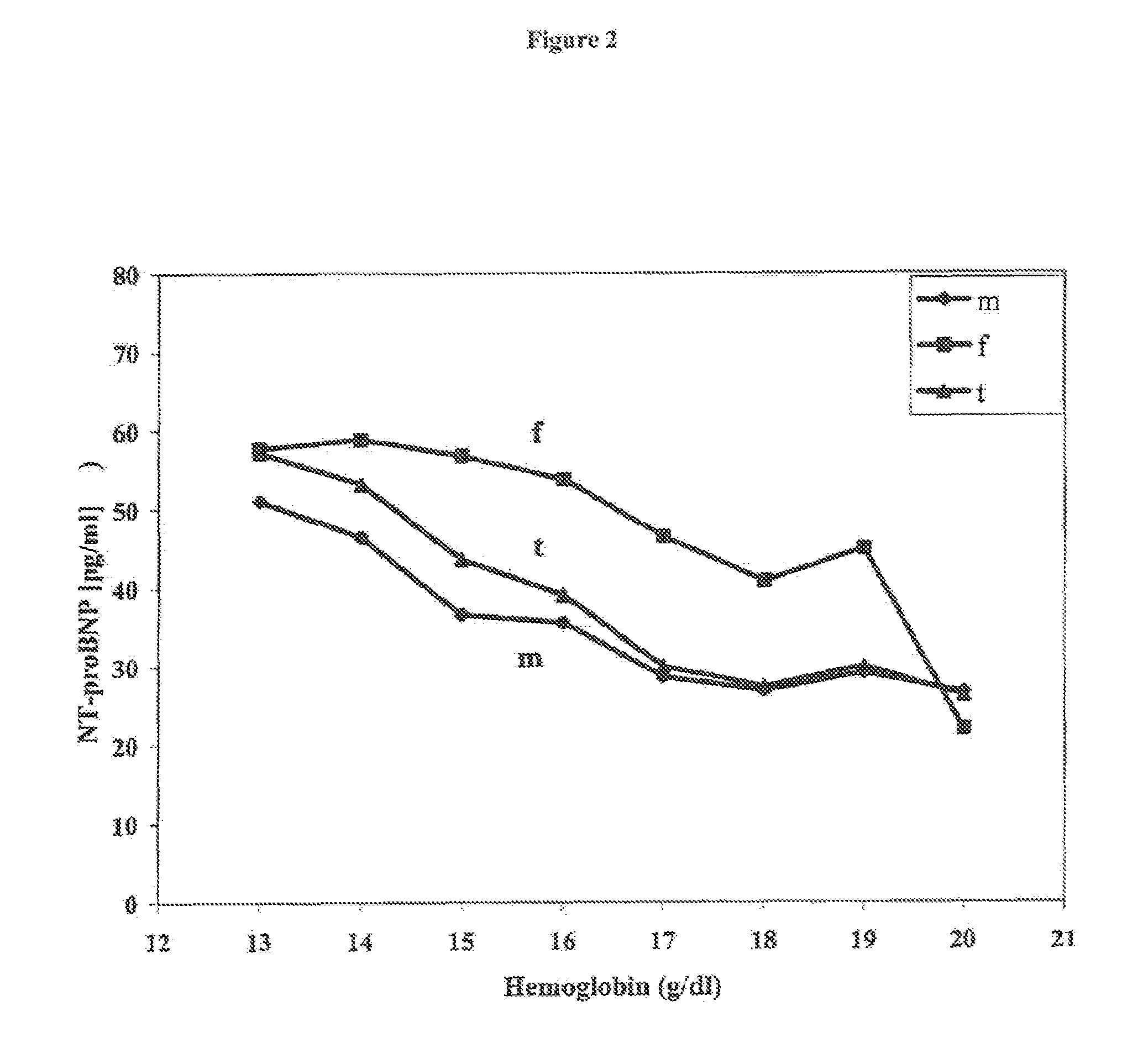
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
87 results about "Cardiovascular Complication" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Any heart or vascular disorder occurring as a consequence of injury to the cardiovascular system.
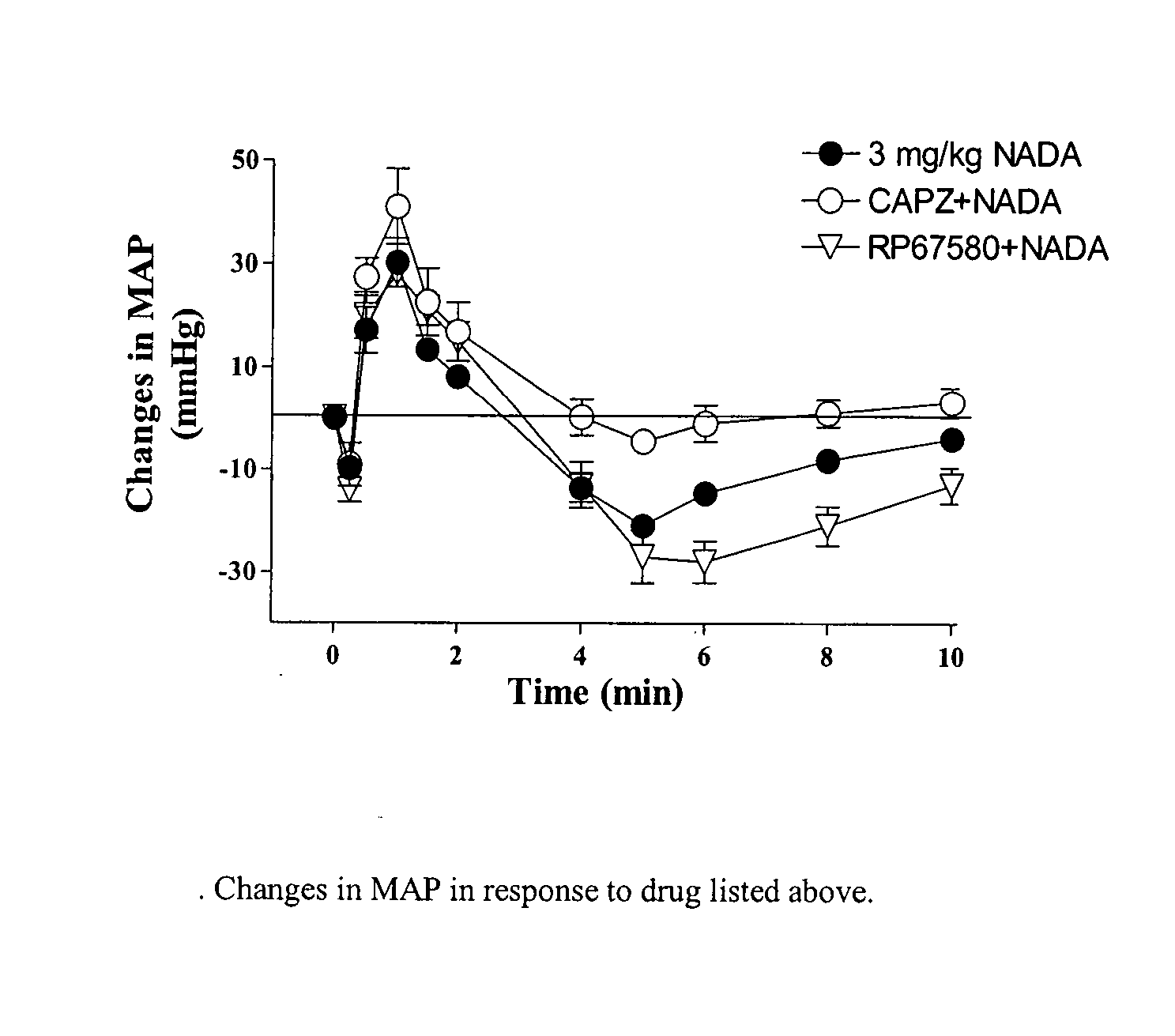
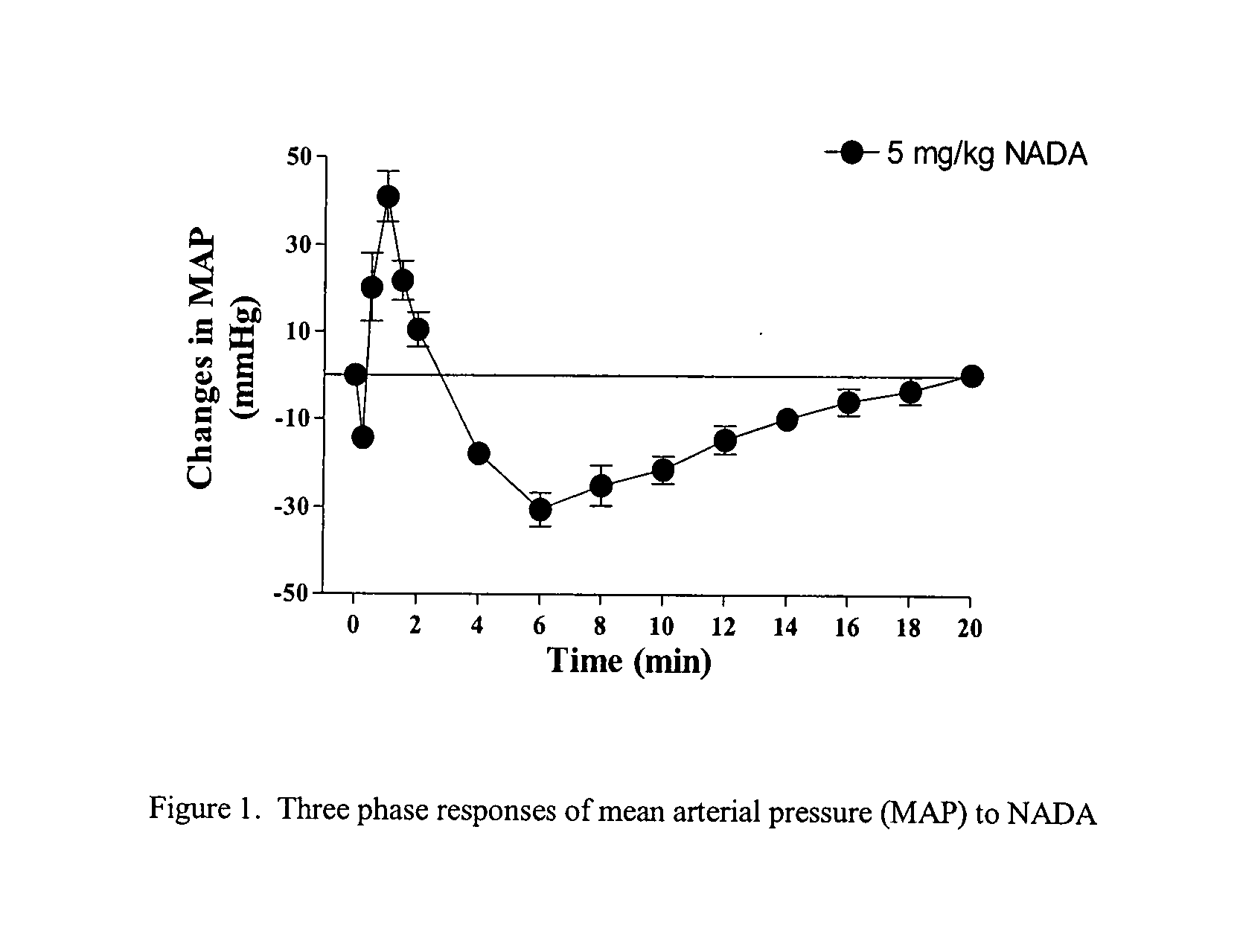
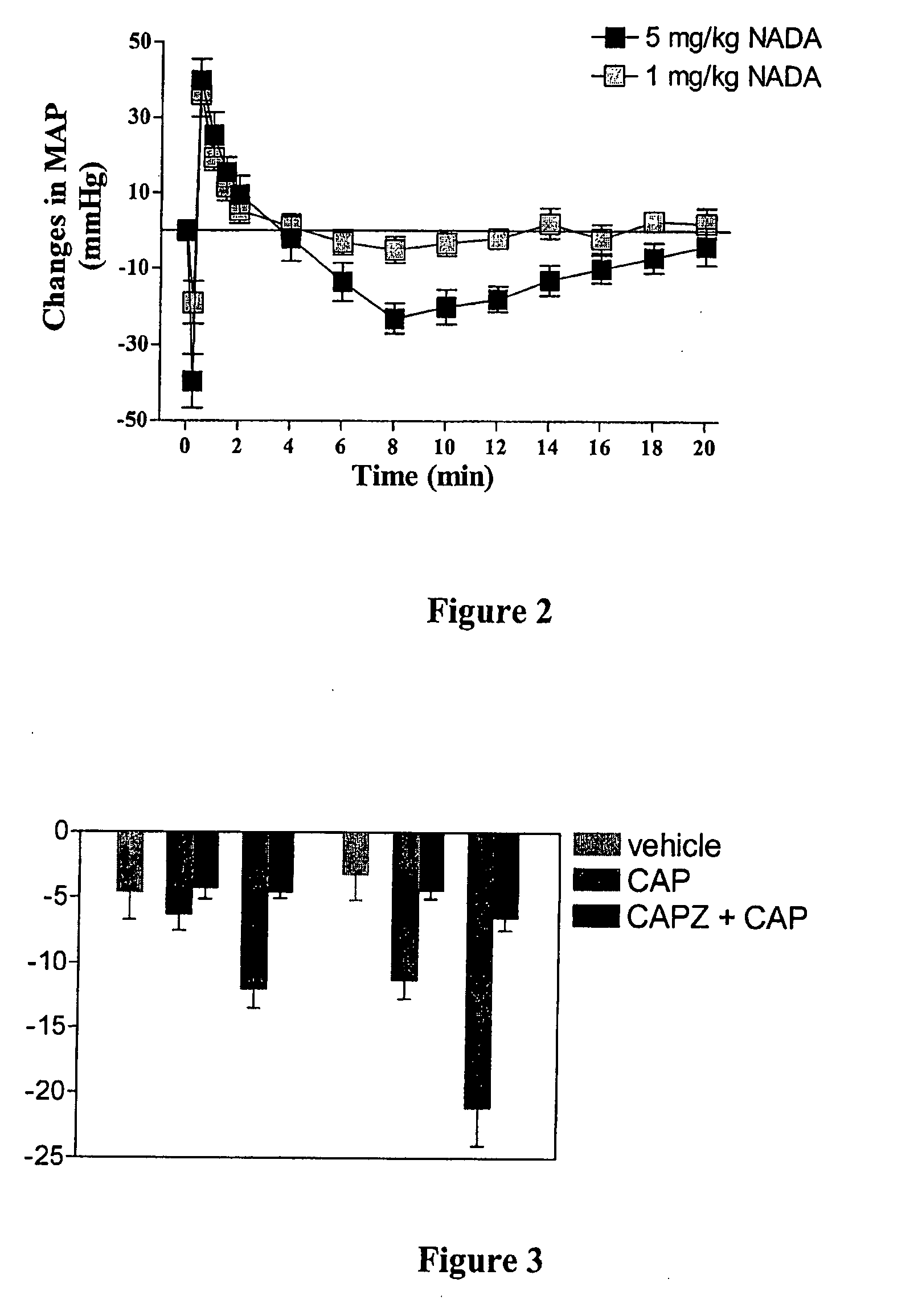
Compositions and methods for transient receptor potential vanilloid (TRPV) channel mediated treatments
InactiveUS20080051454A1Increasing TRPV1-responsesCompound screeningBiocideScreening methodArachidonic acid supplementation
The present inventions relate to therapeutic compositions comprising, and methods utilizing, arachidonic acid derivatives and analogs for treatment of patients demonstrating symptoms of pathological conditions. Specifically, the inventions relate to therapeutic compositions for activating transient receptor potential vanilloid-1 channels (TRPV1). Additionally, therapeutic compositions are provided for increasing TRPV1-type responses. These pathological conditions include, but are limited to, hypertension, in particular salt induced hypertension, and cardiovascular complications, including myocardial infarction, kidney dysfunction, diabetes, and inflammation. Further, the inventions relate to drug screening methods for providing additional therapeutic compounds.
Owner:MICHIGAN STATE UNIV
Dual glucose-turbidimetric analytical sensors
InactiveUS20060051738A1Simple data analysisImprove compatibilityAnalysis using chemical indicatorsWeather/light/corrosion resistanceChylomicronTurbidity
Diagnostic dry reagent tests capable of reacting with a single drop of whole blood and reporting both glucose and light-scattering analytes, such as chylomicrons, are taught. Such dry reagent tests may employ electrochemical detection methodologies, optical detection methodologies, or both methodologies. These tests alert diabetics to excessive levels of postprandial lipemia caused by meals with excessive amounts of fat, and thus can help reduce the risk of cardiovascular complications in diabetic patients.
Owner:ZWEIG STEPHEN ELIOT
Notch inhibition in the treatment and prevention of a metabolic disease or disorder and cardiovascular complications thereof
ActiveUS20130064832A1Improve the level ofIncreased riskSenses disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsNotch signalling pathwayImaging analysis
The present invention is directed to methods of treating or preventing a metabolic disease or disorder and cardiovascular complications and other complications thereof by administering agents that inhibit the NOTCH signaling pathway. In addition, the invention encompasses methods for determining whether a patient is at increased risk for developing these conditions by determining the amount, function, or activity of NOTCH pathway components in biological samples derived from the patient or in imaging analyses.
Owner:THE BRIGHAM & WOMEN S HOSPITAL INC
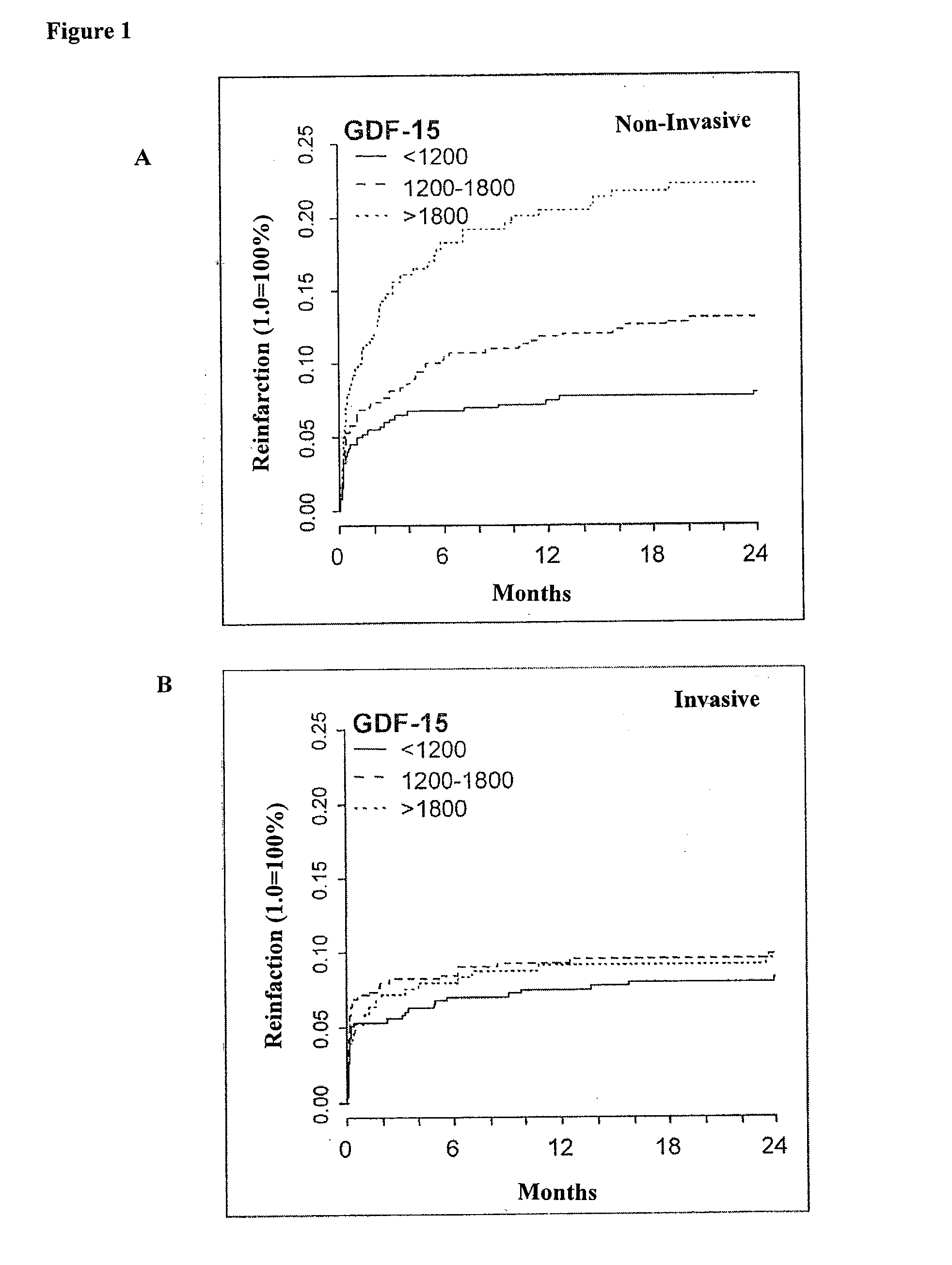
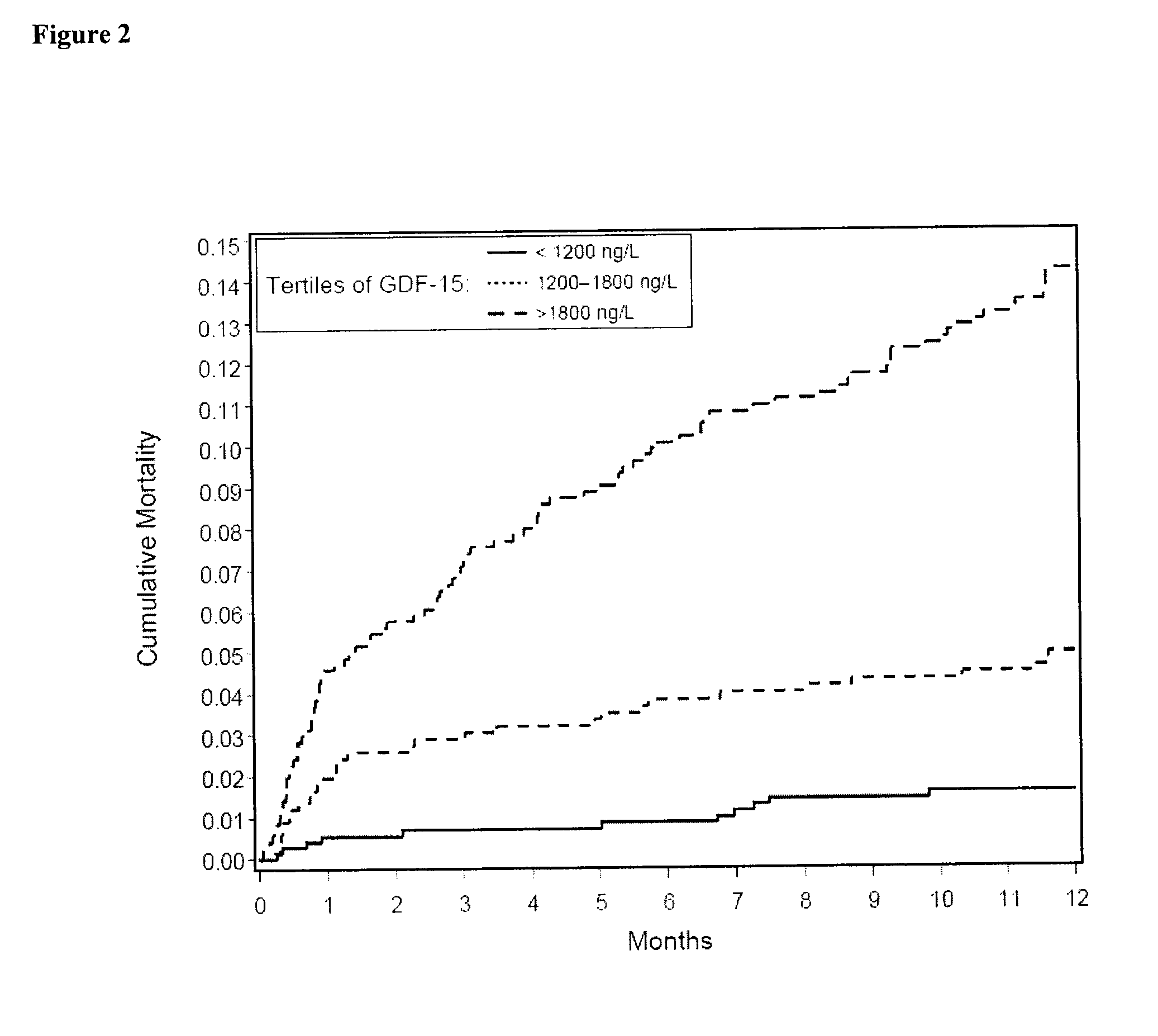
Assessing risk of cardiac intervention based on gdf-15
ActiveUS20110065204A1Analysis using chemical indicatorsComponent separationRisk of mortalityNatriuretic peptide
The present invention relates to a method of identifying a subject being susceptible to a cardiac intervention based on the determination of GDF-15 in a sample of a subject in need of a cardiac intervention. Moreover, the present invention pertains to a method for predicting the risk of mortality or a further acute cardiovascular event for a subject suffering from a cardiovascular complication based on the determination of GDF-15 and a natriuretic peptide and / or a cardiac troponin in a sample the said subject. Also encompassed by the present invention are devices and kits for carrying out the aforementioned methods.
Owner:MEDIZINISCHE HOCHSCHULE HANNOVER
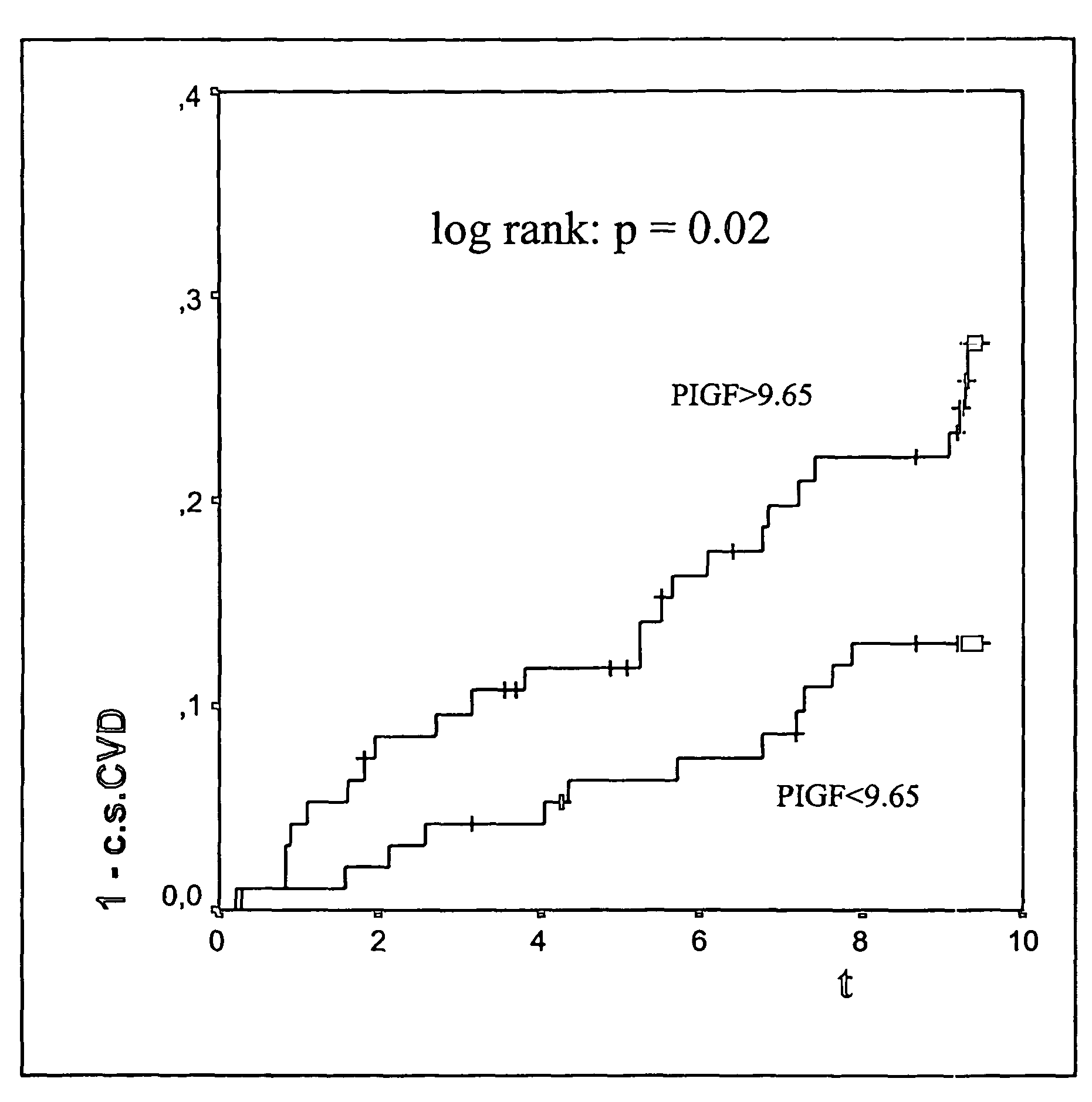
Multimarker panel based on PIGF for diabetes type 1 and 2
InactiveUS20060008829A1Peptide/protein ingredientsAntipyreticBlood vesselCardiovascular Complication
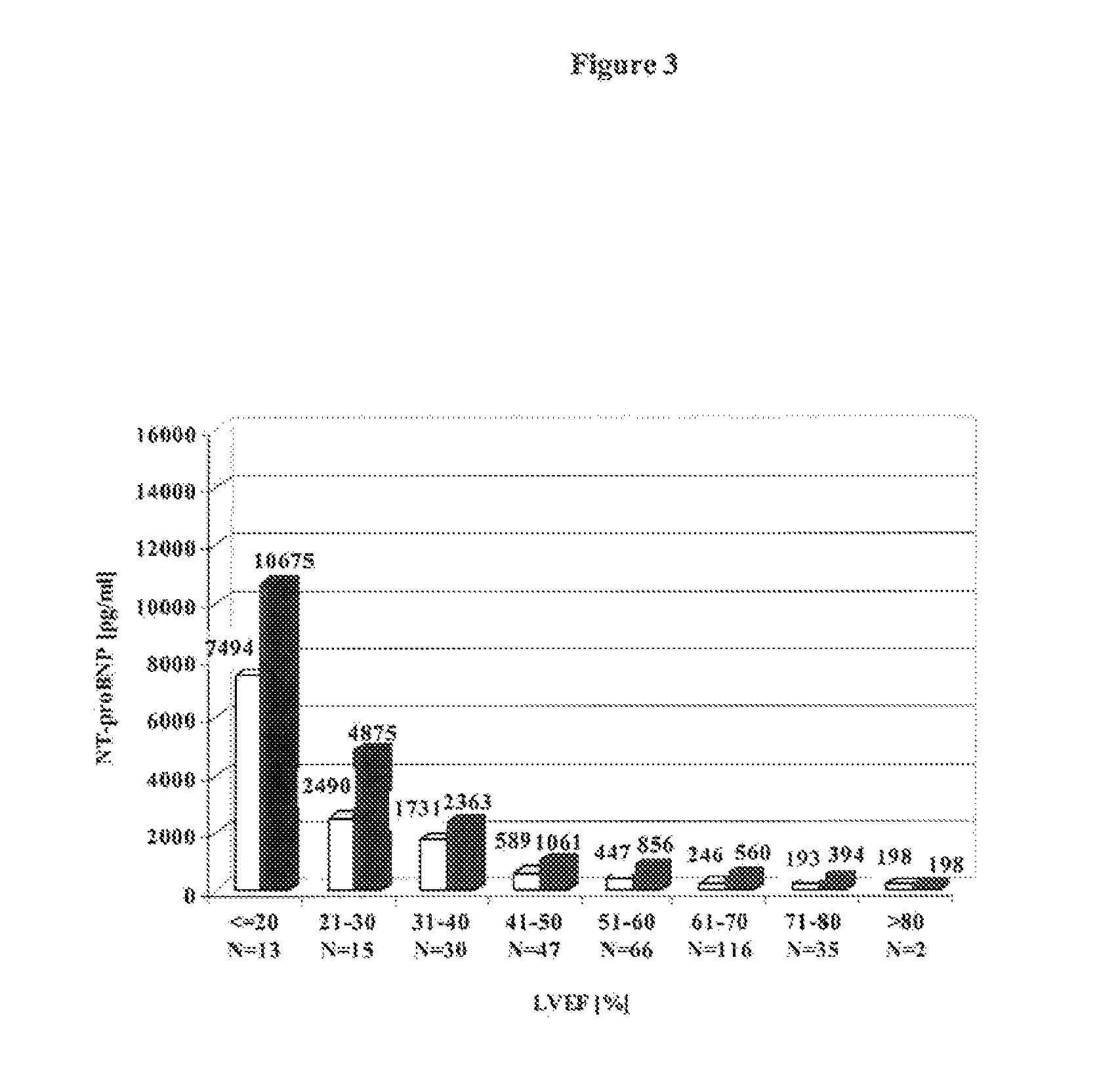
The present invention relates to a method and means for diagnosing or risk stratification of co-morbidities, particularly cardiovascular complications in diabetes patients. The invention particularly relates to a method for diagnosing whether a diabetes patient is suffering from a cardiovascular complication or is at risk of suffering from a cardiovascular complication, said method comprising the steps of (a) measuring, preferably in vitro, the level(s) of at least one cardiac hormone or a variant thereof in a sample from the patient, and (b) diagnosing the cardiovascular complication or the risk of suffering from cardiovascular complication by comparing the measured level(s) to known level(s) associated with the cardiovascular complication or risk. The present invention also relates to combining the measurement of markers comprising cardiac hormones, natriuretic peptides, inflammation-associated markers, angiogenesis markers, and markers for platelet activation. Preferred markers are brain natriuretic peptides (particularly NT-proBNP), PIGF, and sCD40L.
Owner:ROCHE DIAGNOSTICS OPERATIONS INC
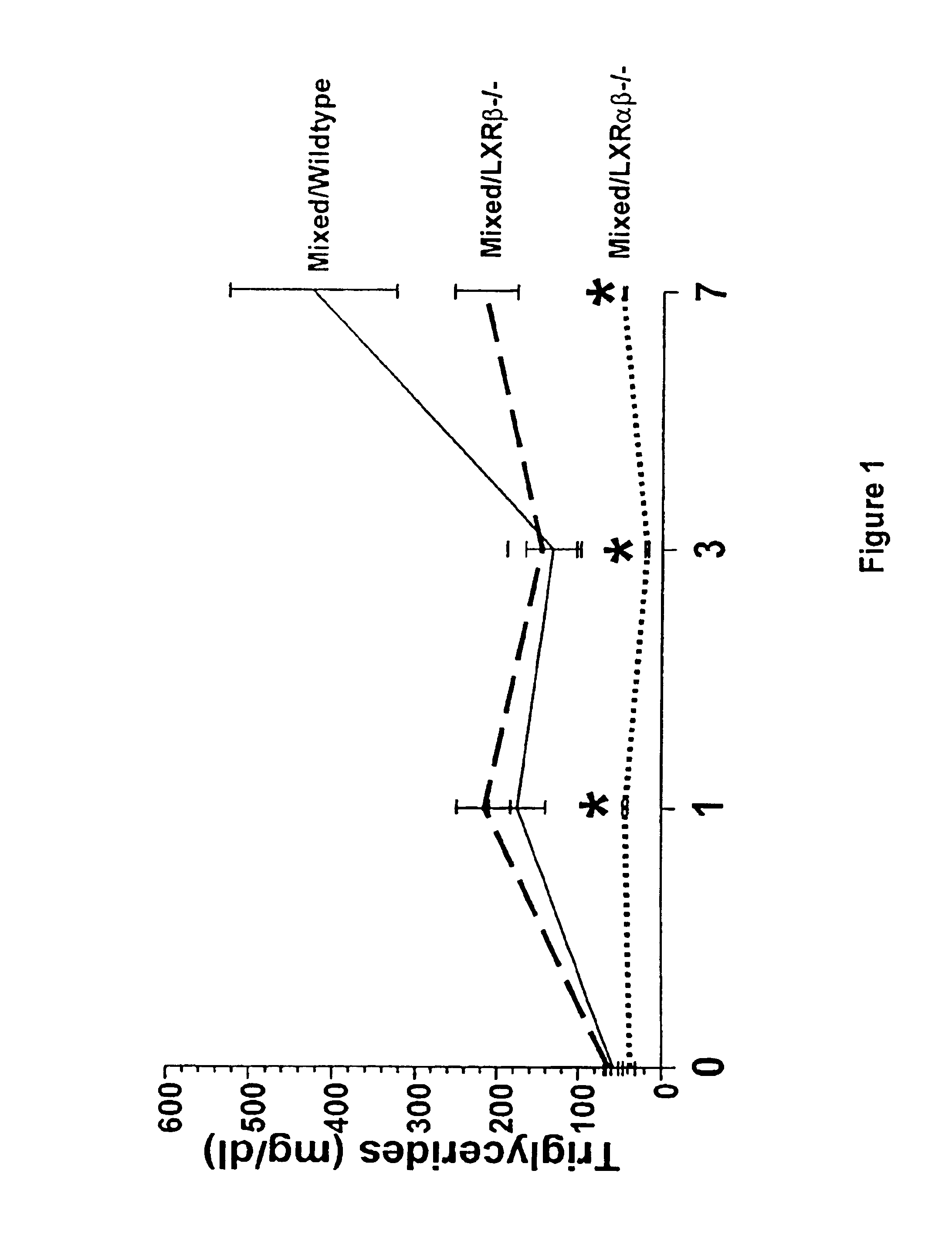
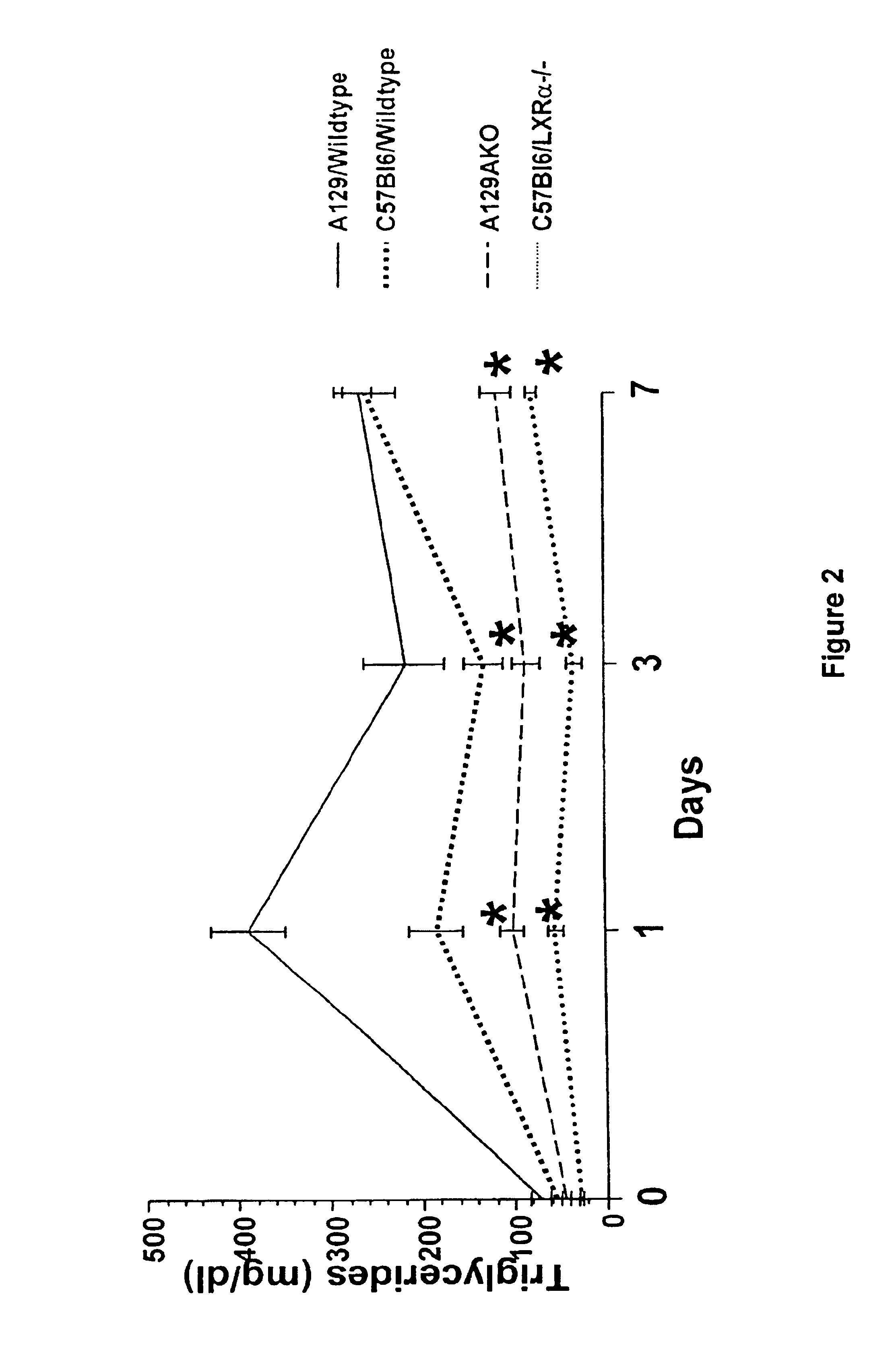
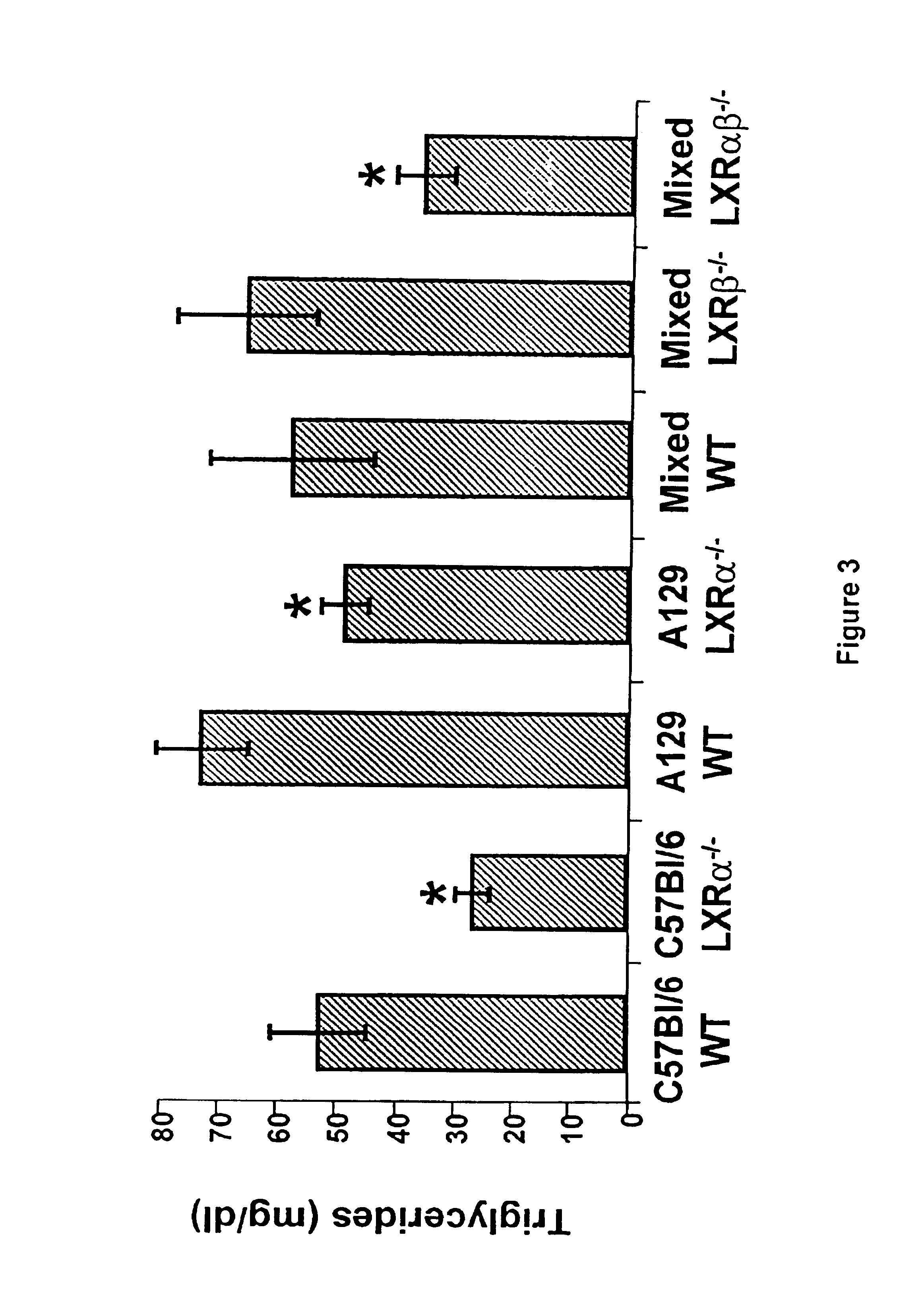
Methods for affecting various diseases utilizing LXR compounds
The present invention relates to methods for elevating high density lipoprotein (HDL) plasma levels, decreasing the absorption of dietary cholesterol in the intestine, decreasing the plasma level of low density lipoprotein (LDL), and increasing the conversion of cholesterol to bile acids, utilizing LXRβ selective agonists, usually without elevating the plasma levels of triglycerides. Also provided are methods of using such agonists to treat metabolic diseases alone or in combination with other active agents. Also provided are methods for decreasing hyperglycemia and insulin resistance methods for treating type II diabetes, and methods for treating type II diabetes and reducing the cardiovascular complications of type II diabetes, utilizing an LXR agonist. Further provided are methods for treating obesity and methods for treating the complications of obesity including type II diabetes, cardiovascular disease, hyperlipidemia, and hypertension, administering an LXRα-selective antagonist.
Owner:EXELIXIS INC
Gdf-15 as biomarker in type 1 diabetes
InactiveUS20110033886A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsFAILURE KIDNEYRenal Failures
Owner:ROCHE DIAGNOSTICS OPERATIONS INC
Cardiac hormones for assessing cardiovascular risk
Owner:ROCHE DIAGNOSTICS OPERATIONS INC
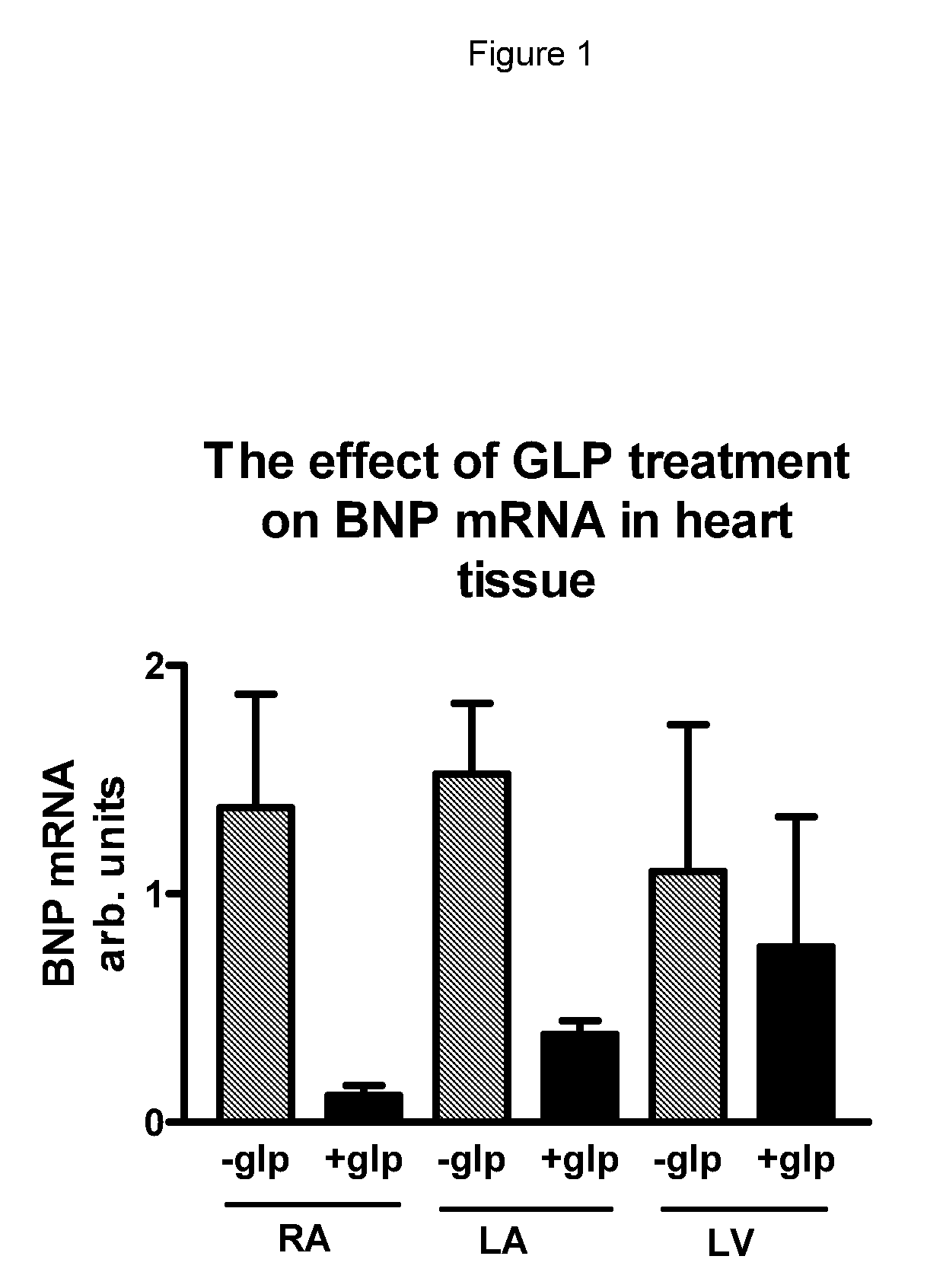
GLP-I Agonist And Cardiovascular Complications
InactiveUS20090215688A1Easy to useLower Level RequirementsPeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderGLP-1 AgonistsCardiovascular Complication
Methods and uses for the treatment and prevention of cardiac and cardiovascular diseases comprising administration of a GLP-1 agonist.
Owner:NOVO NORDISK AS
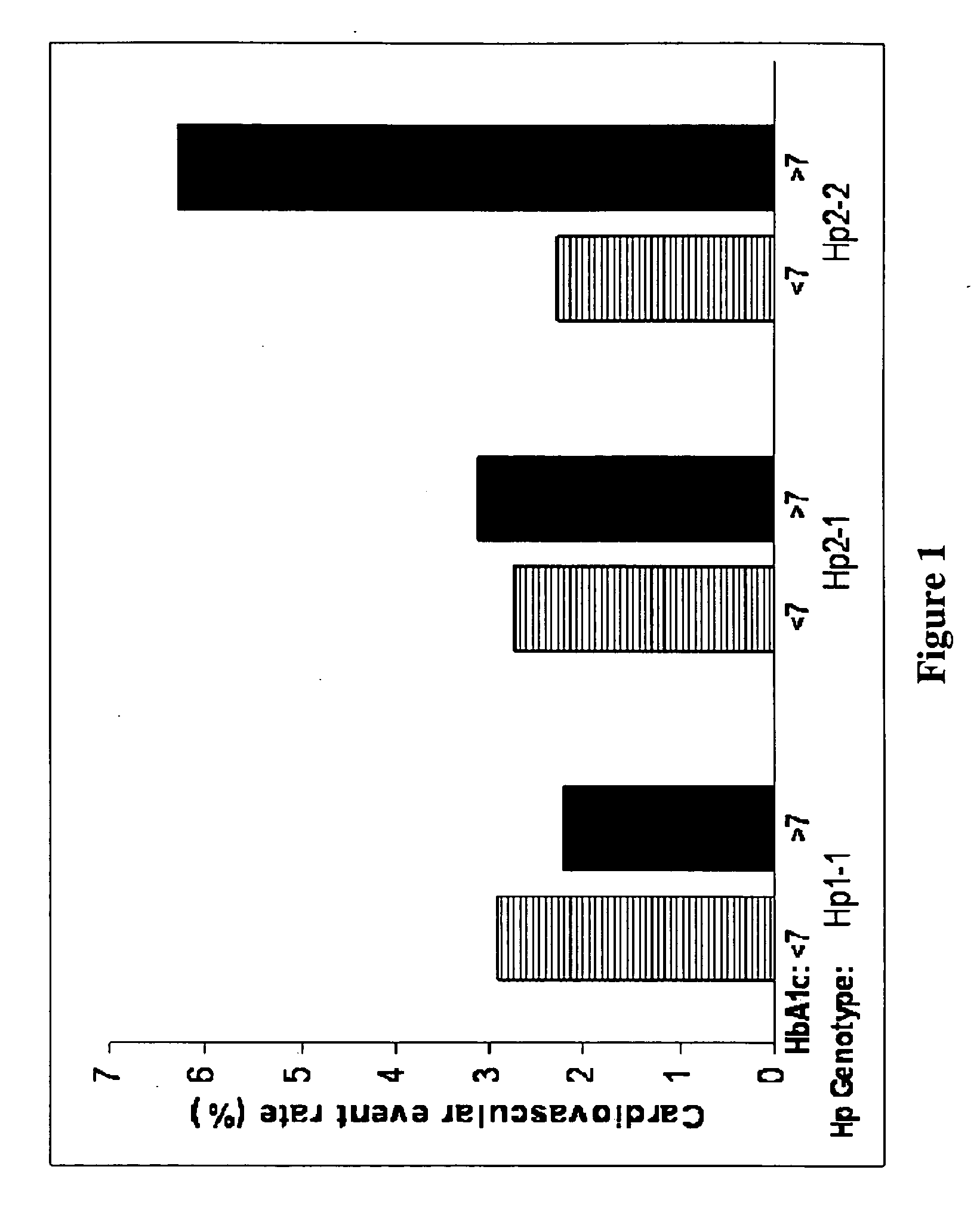
Glycemic control for reduction of cardiovascular disease risk in diabetic patients expressing haptoglobin 2-2
InactiveUS20090246770A1Reduce riskMetabolism disorderMicrobiological testing/measurementGlycemicAllele
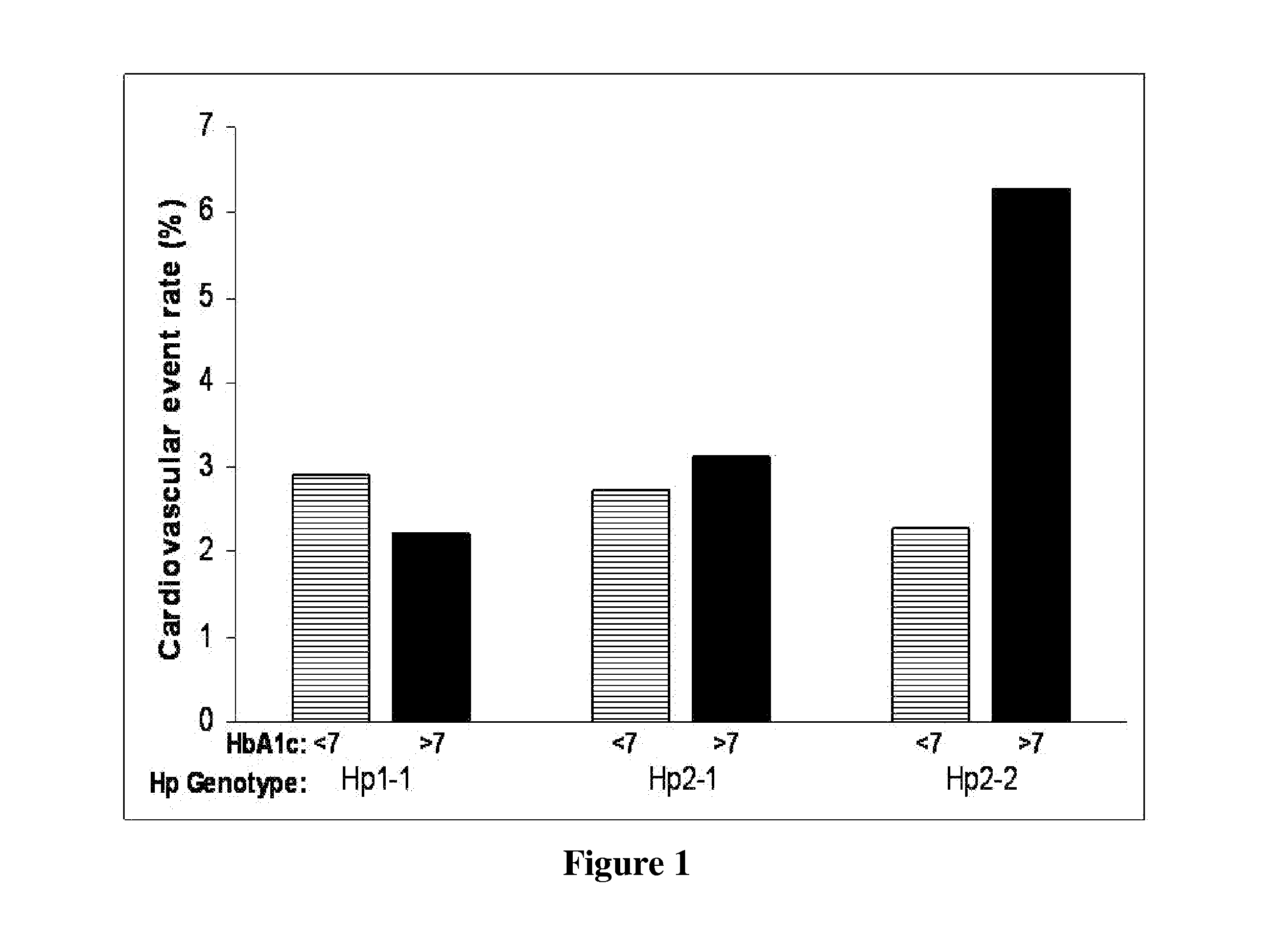
This invention relates to methods of reducing risk of developing cardiovascular complications in diabetic patients. Specifically, the invention relates to the use of haptoglobin genotyping for determining the importance of maintaining tight glycemic control in diabetic subjects expressing Hp 2-2 allele.
Owner:RAPPAPORT FAMILY INSTITUTE FOR RESEACH IN THE MEDICAL SCIENCES
Multimarker panel for diabetes type 1 and 2
The present invention relates to a method and means for diagnosing or risk stratification of co-morbidities, particularly cardiovascular complications in diabetes patients. The invention particularly relates to a method for diagnosing whether a diabetes patient is suffering from a cardiovascular complication or is at risk of suffering from a cardiovascular complication, said method comprising the steps of (a) measuring, preferably in vitro, the level(s) of at least one cardiac hormone or a variant thereof in a sample from the patient, and (b) diagnosing the cardiovascular complication or the risk of suffering from cardiovascular complication by comparing the measured level(s) to known level(s) associated with the cardiovascular complication or risk. The present invention also relates to combining the measurement of markers comprising cardiac hormones, natriuretic peptides, inflammation-associated markers, angiogenesis markers, and markers for platelet activation. Preferred markers are brain natriuretic peptides (particularly NT-proBNP), PIGF, and sCD40L.
Owner:ROCHE DIAGNOSTICS OPERATIONS INC
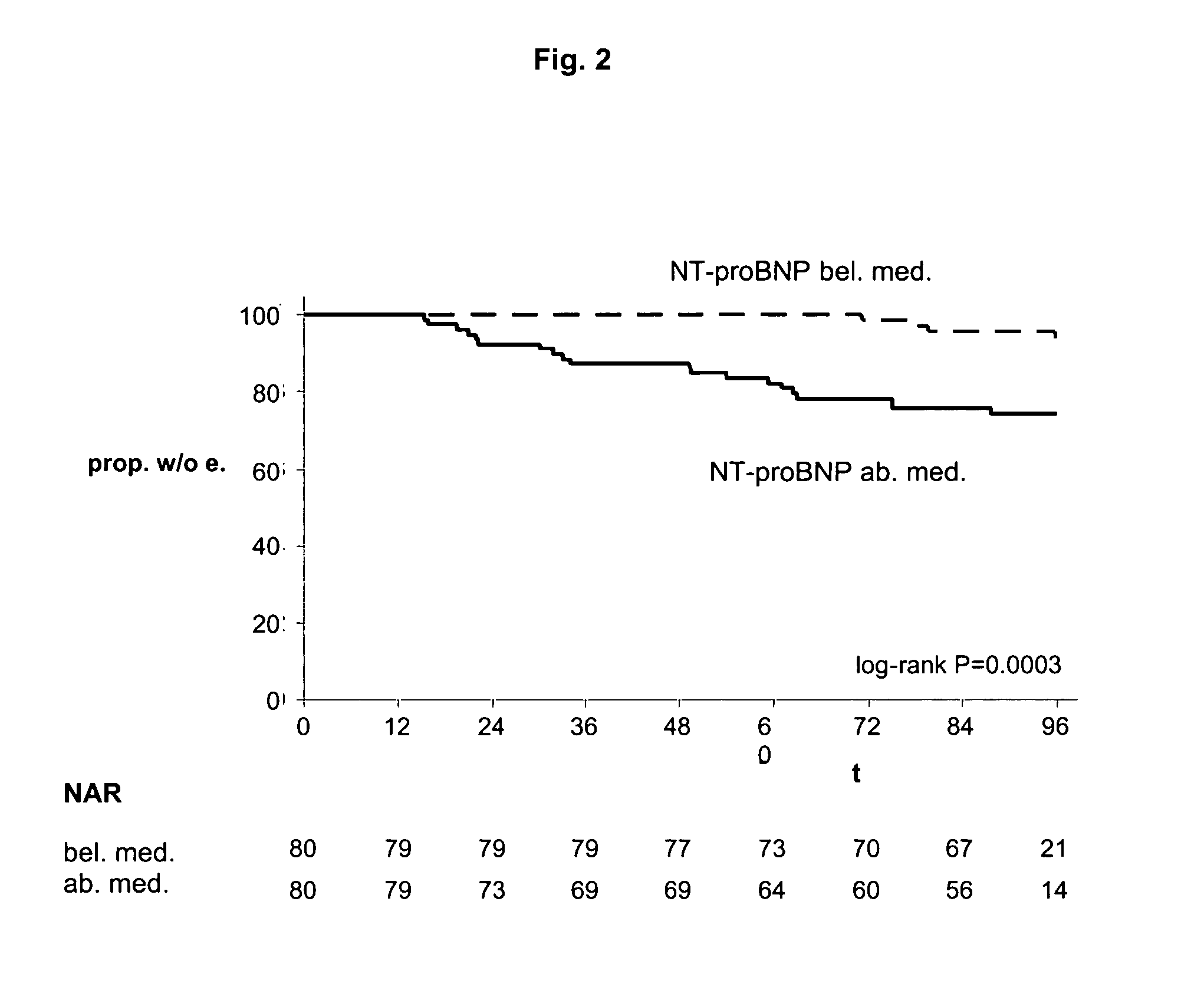
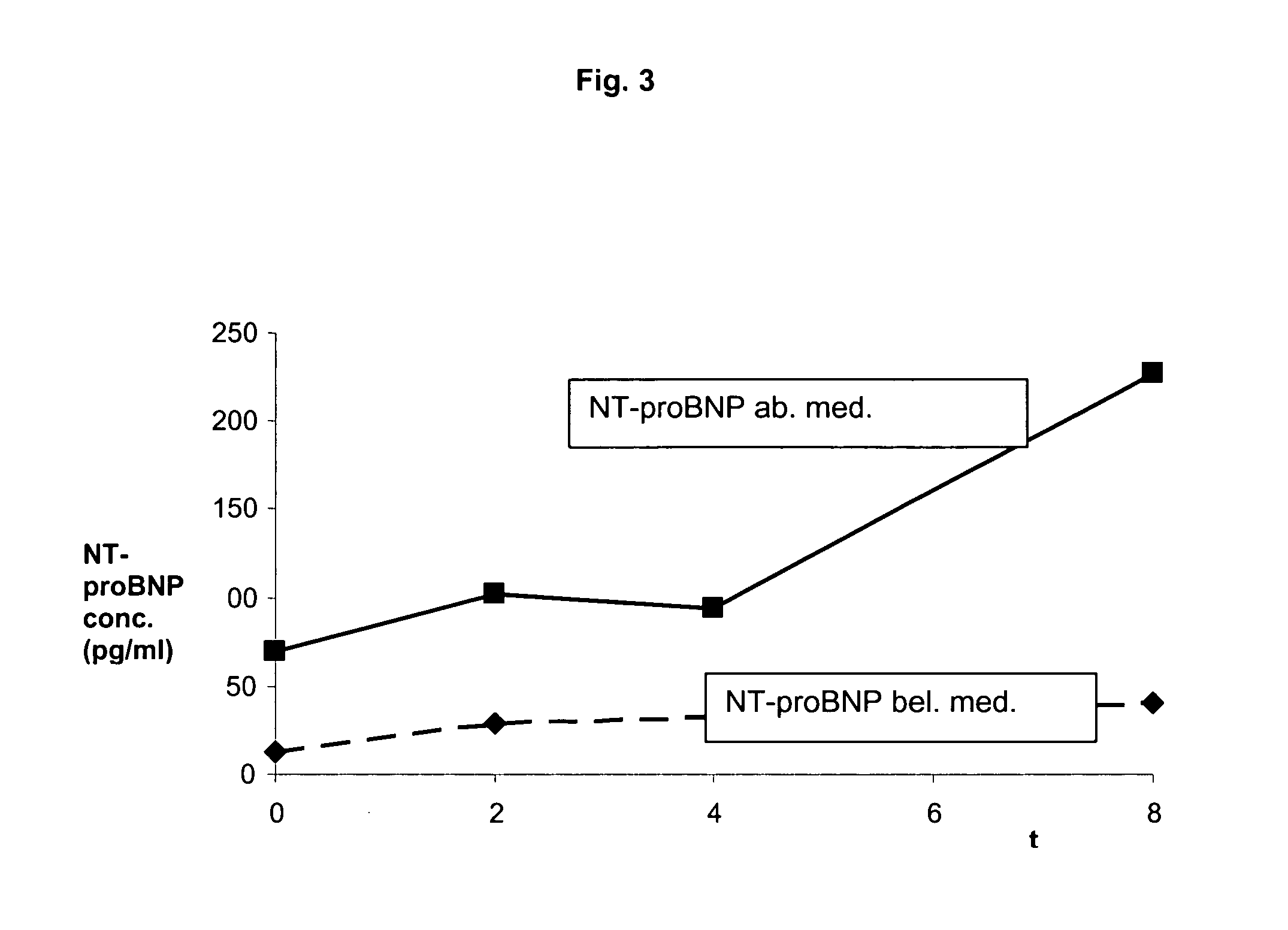
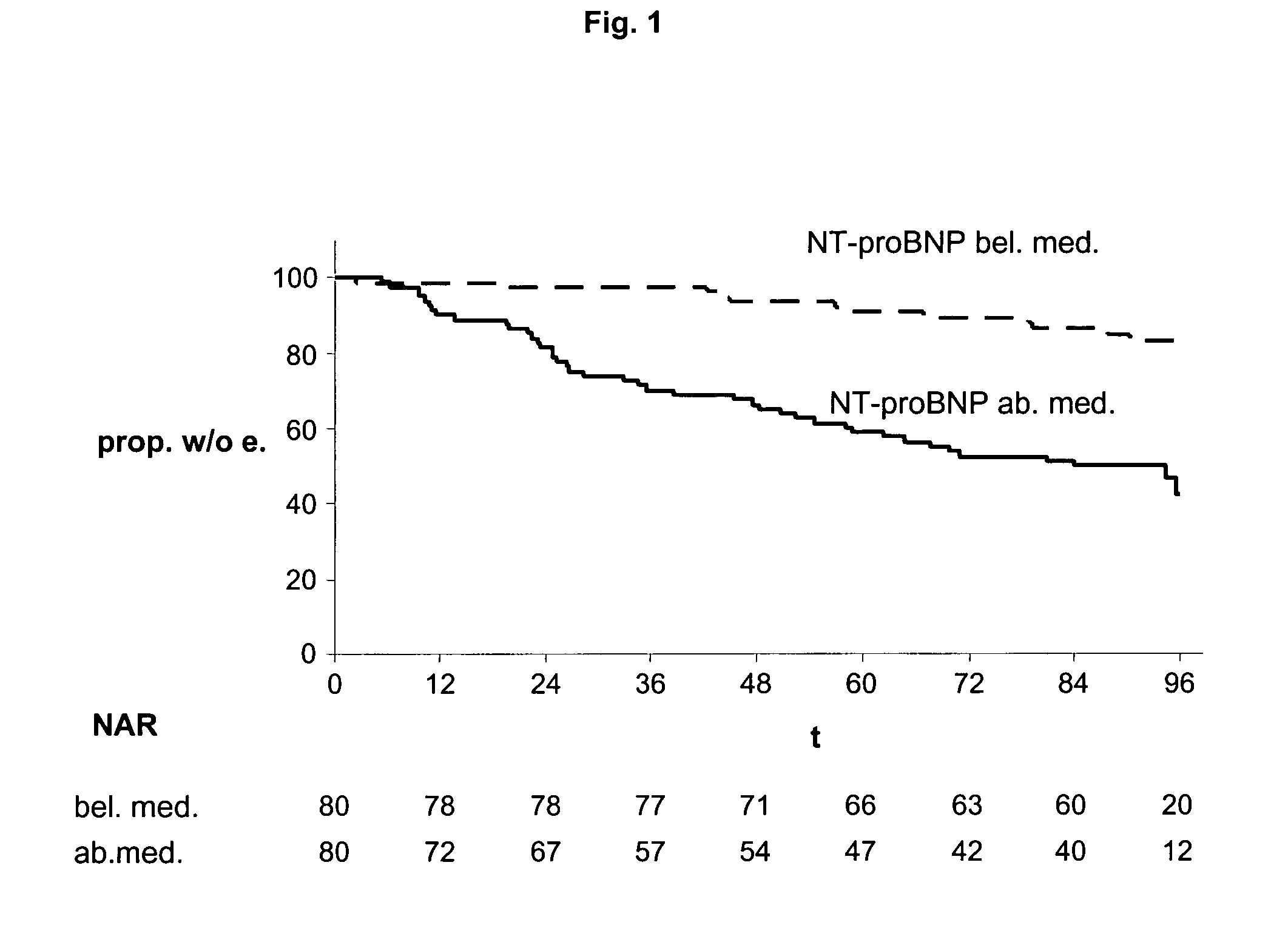
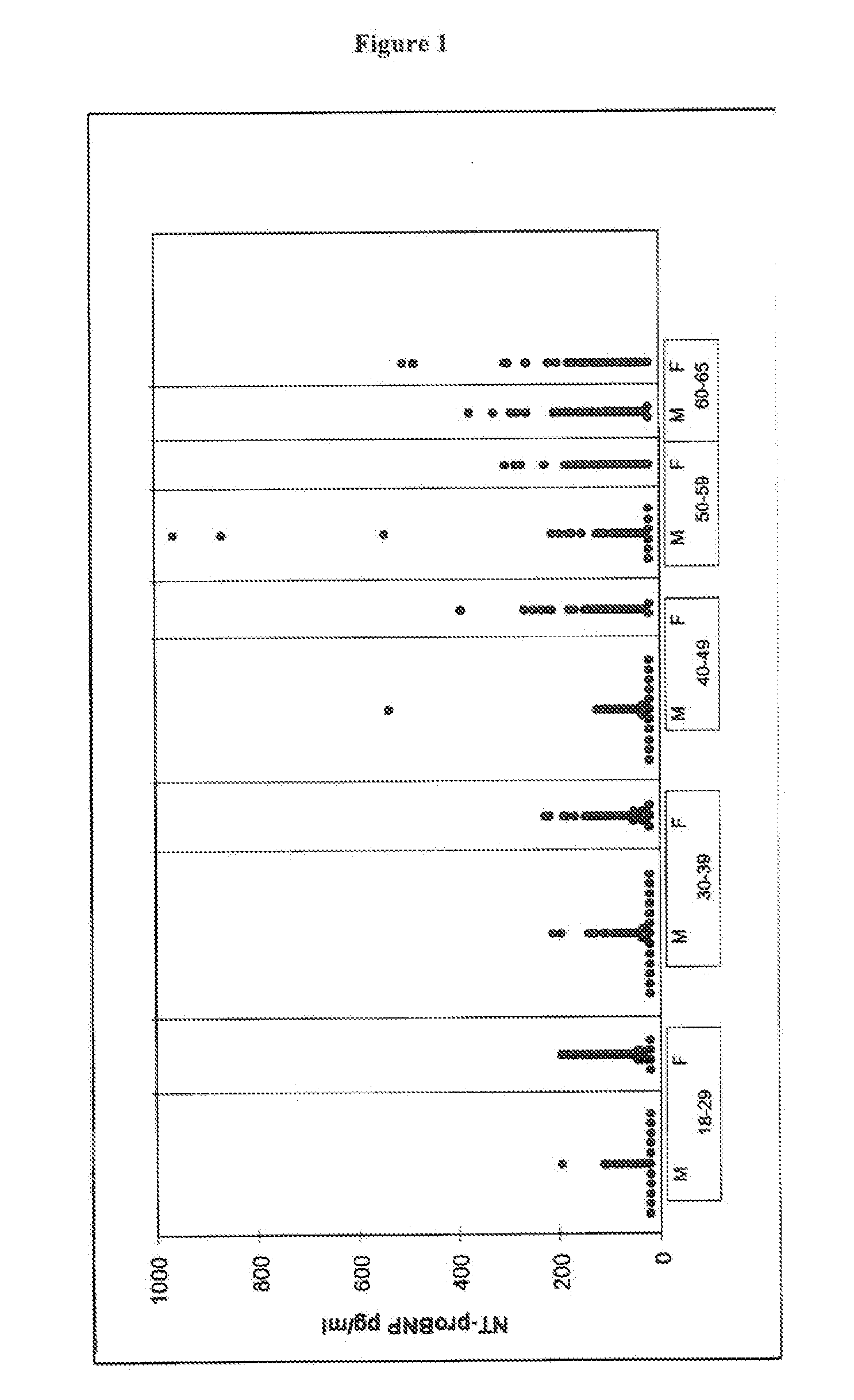
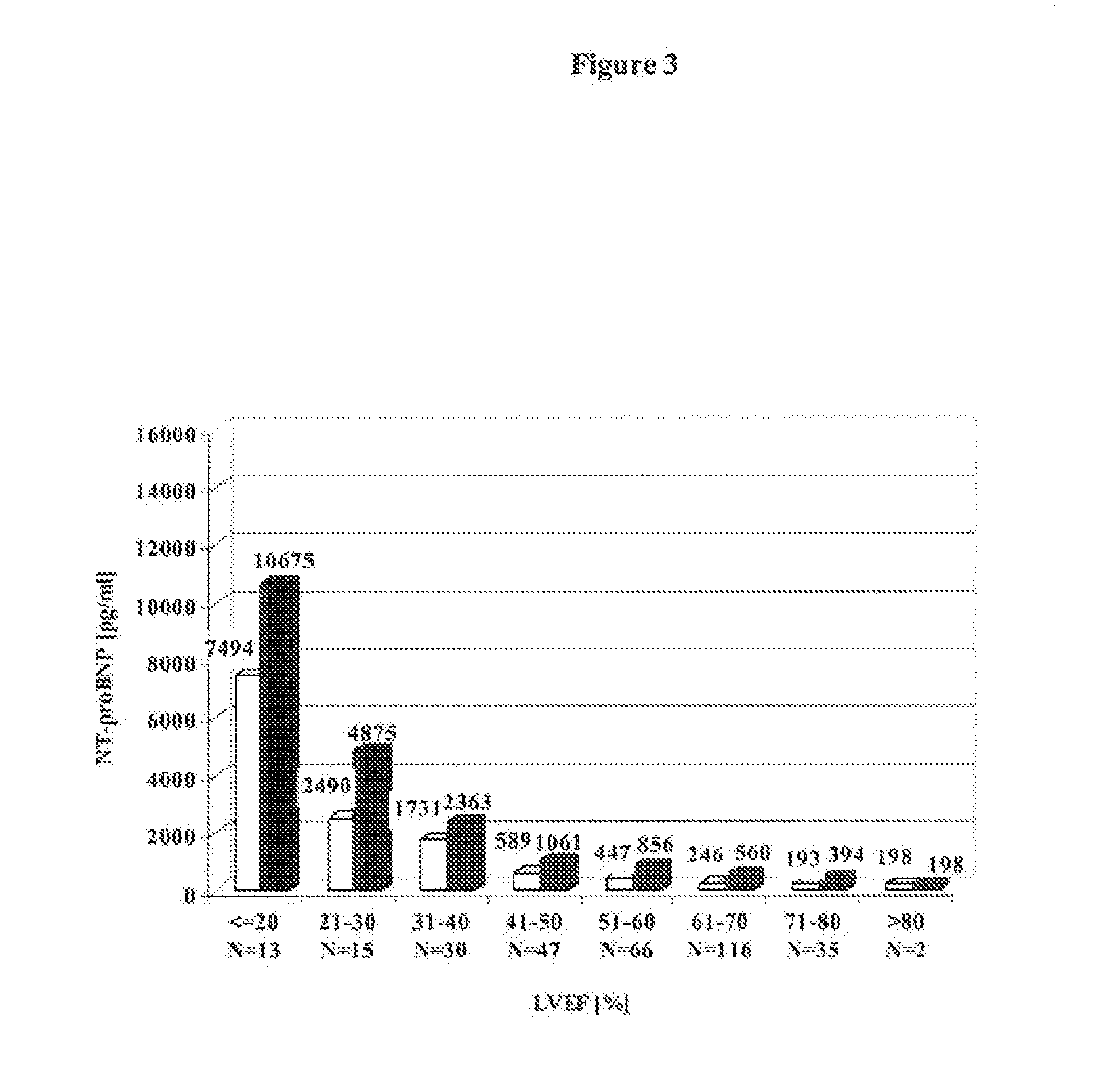
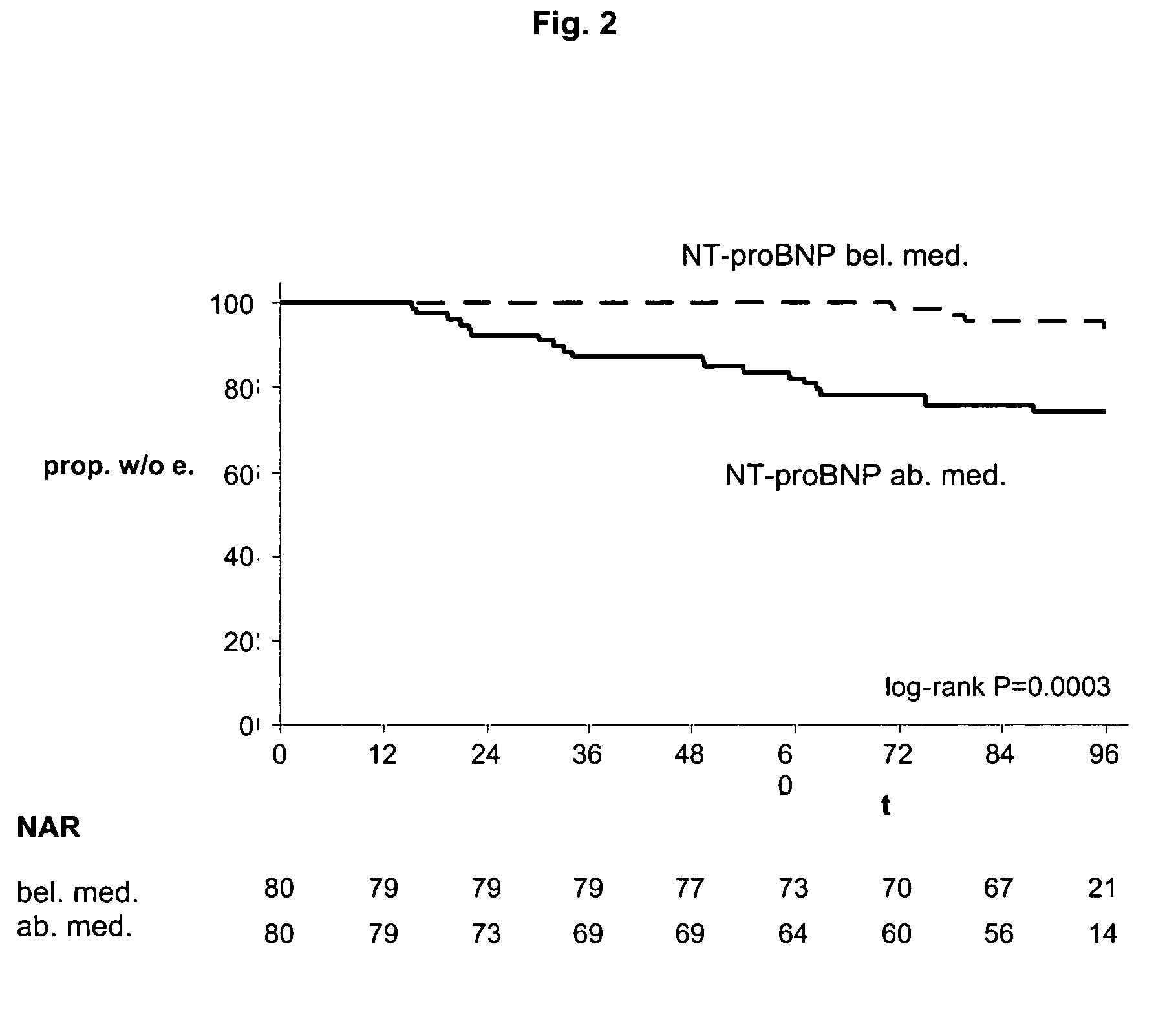
Diagnosing risk of cardiovascular complications using natiuretic peptides
ActiveUS20070190573A1Simple inexpensiveRisk minimizationEnzymologyDisease diagnosisHeart diseaseCardiovascular Complication
The present invention relates to the use of cardiac hormones, particularly natriuretic peptides, for diagnosing the risk of suffering from a cardiovascular complication, particularly heart disease or acute coronary syndrome, as a consequence of cardiotoxic medication, in particular chemotherapeutics, including anthracyclines. In particular, the invention relates to a method for diagnosing the risk of a patient who is going to receive cardiotoxic medication of suffering from a cardiovascular complication as a consequence of the cardiotoxic medication, comprising the steps of (a) taking a body fluid or tissue sample, and (b) measuring, preferably in vitro, the level of a cardiac hormone. Preferred cardiac hormones in the context of the present invention are ANP, NT-proANP, BNP, and NT-proBNP.
Owner:ROCHE DIAGNOSTICS OPERATIONS INC
Method for preparing crystals and application of crystals
ActiveCN104230907AStable productionProduction repeatableOrganic active ingredientsSenses disorderEccentric hypertrophyDiabetic complication
The invention discloses novel crystal form III and crystal form IV of 1-(beta-D-glucopyranosyl)-4-methyl-3-[5-(4-fluorophenyl)-2-thienylmethyl, a preparation method of the crystal form III and the crystal form IV and a medicinal application of the crystal form III and the crystal form IV in treatment of diabetes mellitus. The crystal form III serving as an octanol compound has a more remarkable action effect on treatment of diabetes mellitus, and is prepared by carrying out supersaturated precipitation or re-crystallization in octanol or a solution containing octanol. The octanol serving as a gap junction blocker has an effect of reducing diabetic complications, such as a pharmacological action for resisting cardiomyocyte edema and hypertrophy and a neuroprotective effect, so that compared with other crystal forms, the crystal form III has a more remarkable action effect on diabetes mellitus treatment, especially prevention of cardiovascular complications of patients with early diabetes mellitus.
Owner:王军
NOTCH inhibition in the treatment and prevention of a metabolic disease or disorder and cardiovascular complications thereof
Owner:THE BRIGHAM & WOMEN S HOSPITAL INC
Tri-salt form of metformin
Owner:THETIS PHARMA
Nitric oxide-donating chrysin derivatives, preparation method thereof, medical use thereof
InactiveCN101768145APromote generationFunction increaseOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryVascular endotheliumNitric oxide
The invention relates to the fields of pharmaceutical chemistry and particularly provides a series of nitric oxide-donating chrysin derivatives, which are prepared by modifying the chrysin at position 5 and position 7. The nitric oxide-donating chrysin derivatives release nitric oxide and chrysin derivatives in vivo and therefore can conduct functions of reducing blood sugar and blood pressure, promoting angiogenesis, improving a vascular endothelial function and lipid metabolism disorders and can be used in the preparation of medicaments for treating diabetes, diabetic cardiovascular complications, metabolic syndrome and endothelial dysfunction.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Thiocarbonates as Anti-Inflammatory and Antioxidant Compounds Useful For Treating Metabolic Disorders
InactiveUS20120149769A1Delaying and preventing cardiovascular complicationReducing free fatty acids (FFA)BiocideOrganic active ingredientsFatty acidInsulin resistance
The invention is directed to thiocarbonate compounds of Formula (I)-(III) and methods of treating atherosclerosis, neuropathy, nephropathy, retinopathy, inflammatory disorders, COPD, cardiovascular diseases, metabolic disorders, type I diabetes mellitus, type II diabetes mellitus, LADA, Wolfram Syndrome 1, Wolcott-Rallison syndrome, metabolic syndrome, dyslipidemia, hyperglycemia, or insulin resistance. The compounds of the invention are also useful for protecting pancreatic beta-cells and for reducing free fatty acids, triglycerides, advanced glycated end products, ROS, lipid peroxidation, tissue and plasma TNFalpha and IL6 levels, or for delaying or preventing cardiovascular complications associated with atherosclerosis.
Owner:GENMEDICA
Jinqi glucose-lowering tablet for treating diabetic cardiovascular complications
The invention relates to an application of a jinqi glucose-lowering tablet in preparation of compositions for treating diabetic cardiovascular complications. The jinqi glucose-lowering tablet is prepared from the following raw materials: coptis chinensis, astragalus membranaceus and honeysuckle.
Owner:CHINA PHARM UNIV
Diagnosing risk of cardiovascular complications using natiuretic peptides
ActiveUS7655416B2Simple and inexpensive methodRisk minimizationEnzymologyDisease diagnosisCvd riskHeart disease
The present invention relates to the use of cardiac hormones, particularly natriuretic peptides, for diagnosing the risk of suffering from a cardiovascular complication, particularly heart disease or acute coronary syndrome, as a consequence of cardiotoxic medication, in particular chemotherapeutics, including anthracyclines. In particular, the invention relates to a method for diagnosing the risk of a patient who is going to receive cardiotoxic medication of suffering from a cardiovascular complication as a consequence of the cardiotoxic medication, comprising the steps of (a) taking a body fluid or tissue sample, and (b) measuring, preferably in vitro, the level of a cardiac hormone. Preferred cardiac hormones in the context of the present invention are ANP, NT-proANP, BNP, and NT-proBNP.
Owner:ROCHE DIAGNOSTICS OPERATIONS INC
Glycemic control for reduction of cardiovascular disease risk in diabetic patients expressing haptoglobin 2-2
This invention relates to methods of reducing risk of developing cardiovascular complications in diabetic patients. Specifically, the invention relates to the use of haptoglobin genotyping for determining the importance of maintaining tight glycemic control in diabetic subjects expressing Hp 2-2 allele.
Owner:RAPPAPORT FAMILY INSTITUTE FOR RESEACH IN THE MEDICAL SCIENCES
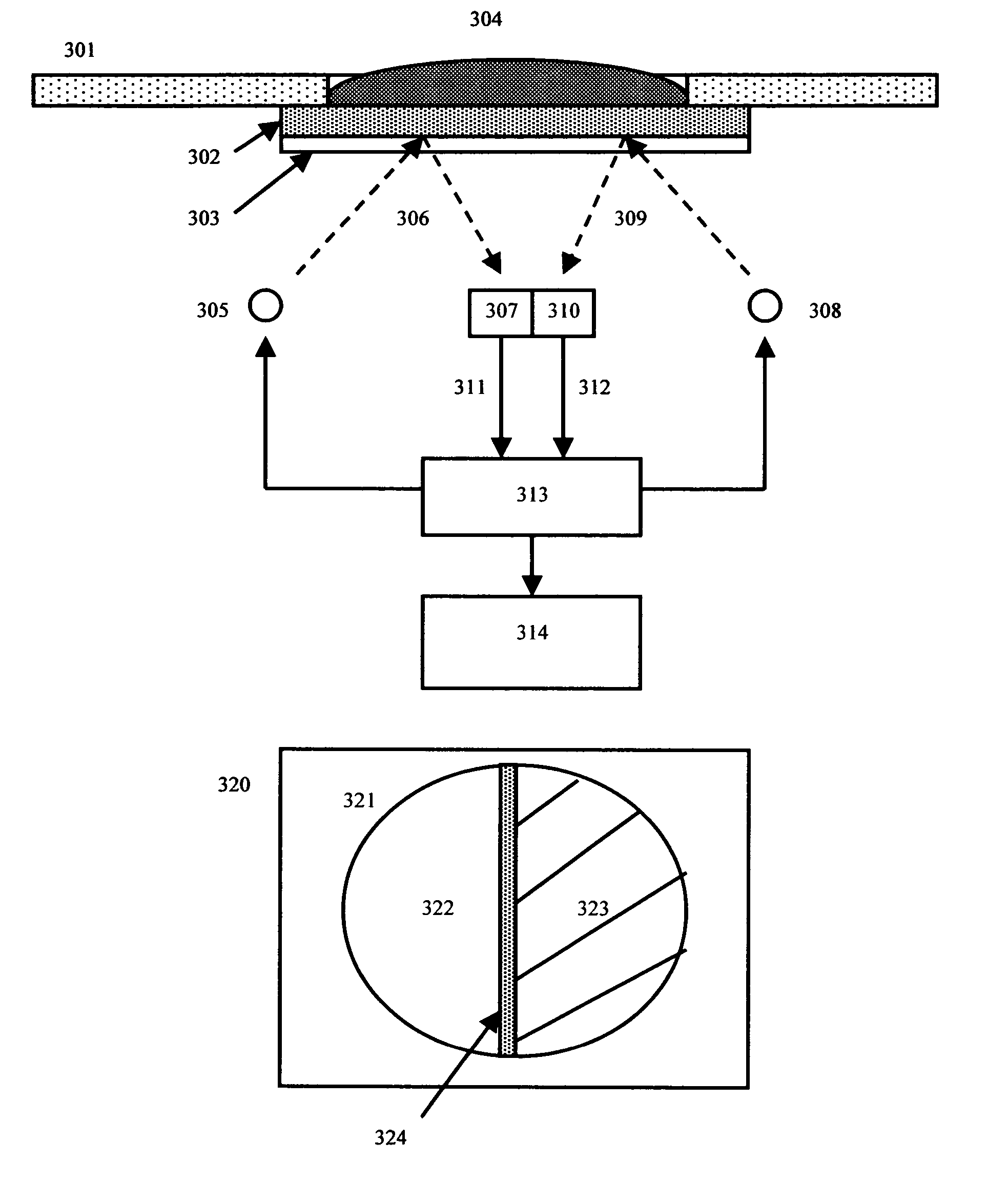
Method and Device for Assessing the Risk of Cardiovascular Complications
InactiveUS20150297098A1Improve reliabilityImprove objectivityElectrocardiographyEvaluation of blood vesselsDigital signal processingCapillaroscopies
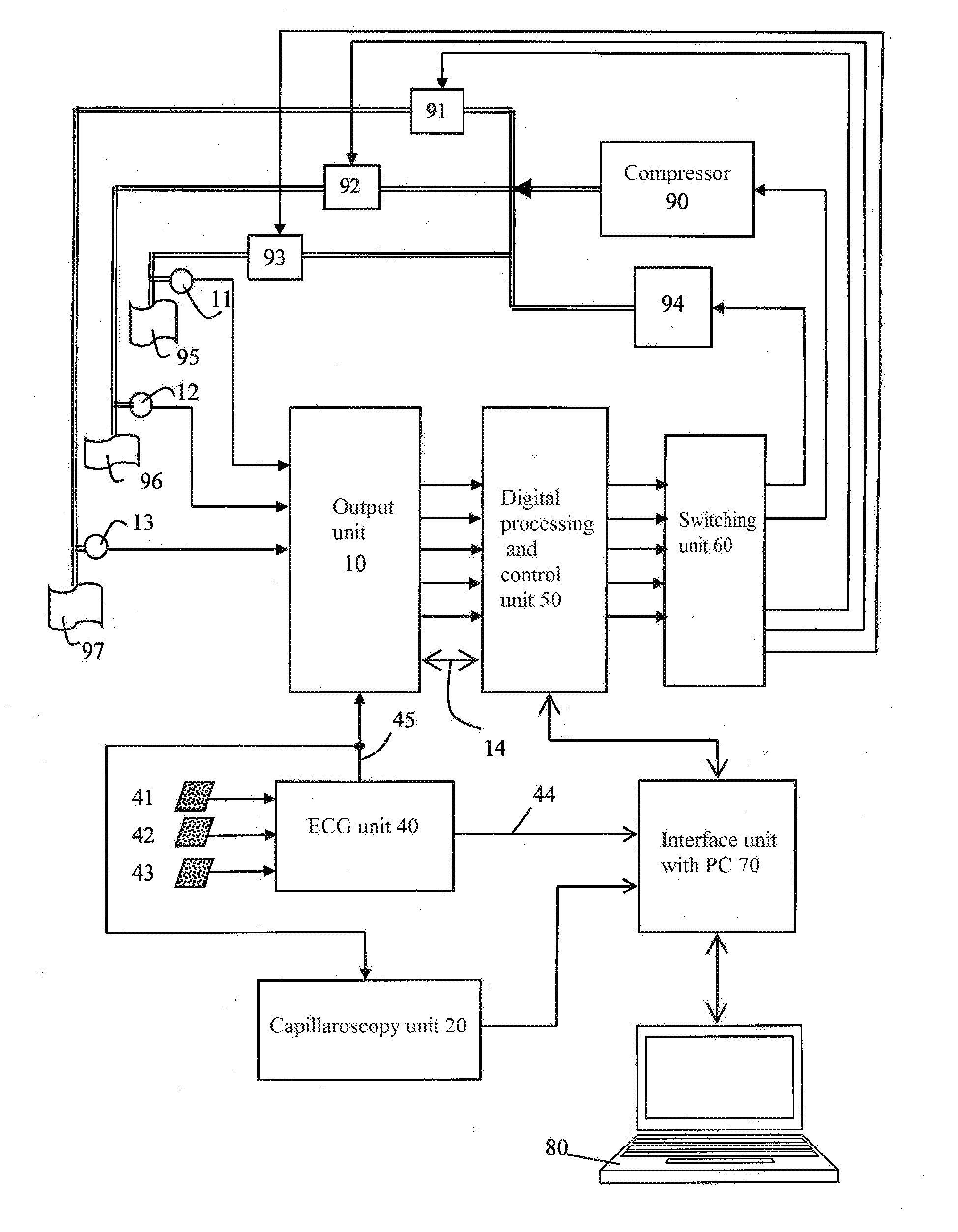
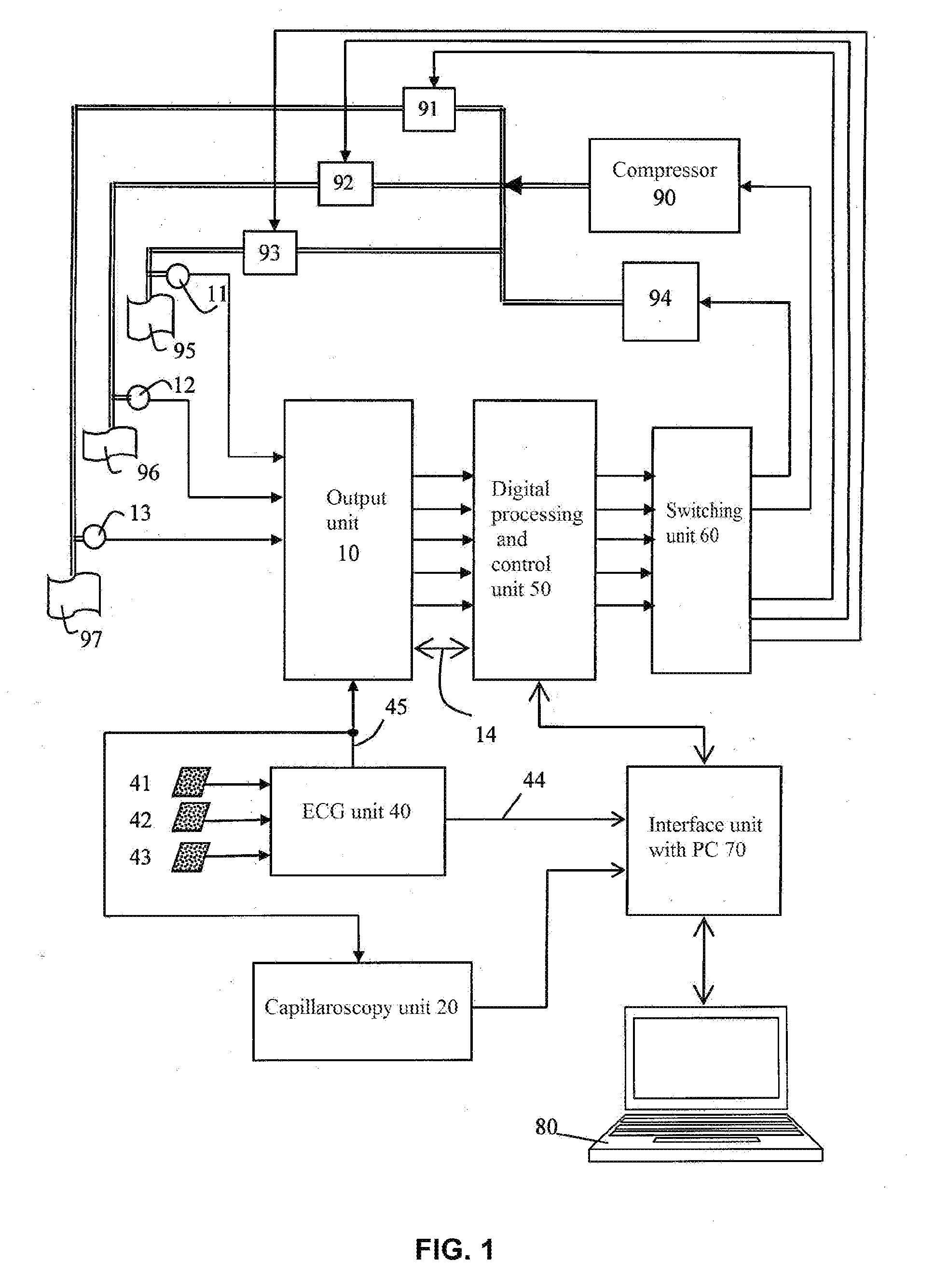
The group of inventions is directed to improving the reliability and objectivity of assessment of the risk of cardiovascular complications. Using optical capillaroscopy of the nail fold of a finger in a state of reactive hyperemia and in the absence thereof, the size of the perivascular area and the diameters of the venous and arterial portions of the capillaries are measured. pulse wave velocity and the level of endothelial function in the upper limb are measured simultaneously relative to the R peak of an electrocardiogram, and an index K of the risk of cardiovascular complications is calculated using the given expression and categorized. The device comprises: a pneumatic means for creating occlusion in a limb of the patient and pressure sensors connected to occlusion cuffs; an input unit capable of receiving and regulating the level of signals from the output of the pressure sensors and of amplifying and pre-filtering said signals; an optical capillaroscopy unit capable of measuring the size of the perivascular zone and the diameters of the venous and arterial portions of the nail fold capillaries of a finger in a state of reactive hyperemia and in the absence thereof; an electrocardiogram recording unit capable of generating a pulsed synchronization signal based on the R wave of the electrocardiogram; a unit for amplitude-to-digital conversion, digital signal processing and control, a switching unit, and a unit for communicating with a computer.
Owner:CARDIOBIONICA
Receptor-Based Blood Detoxification System
InactiveUS20110082421A1Immunoglobulin superfamilyOther blood circulation devicesWhole blood productMedicine
The invention discloses compositions of matter and methods of using such compositions to detoxify blood and blood products. The invention as particular use in the treatment of diabetes, Alzheimer's disease, hemodialysis associated amyloidosis, and cardiovascular complications.
Owner:NORTHSHORE UNIV HEALTHSYST +1
Biomarker for predicting II-type diabetic vascular complication risk and application thereof
InactiveCN106906278AImprove responsePersonalized Intervention TherapyOrganic active ingredientsMetabolism disorderScreening methodWestern blot
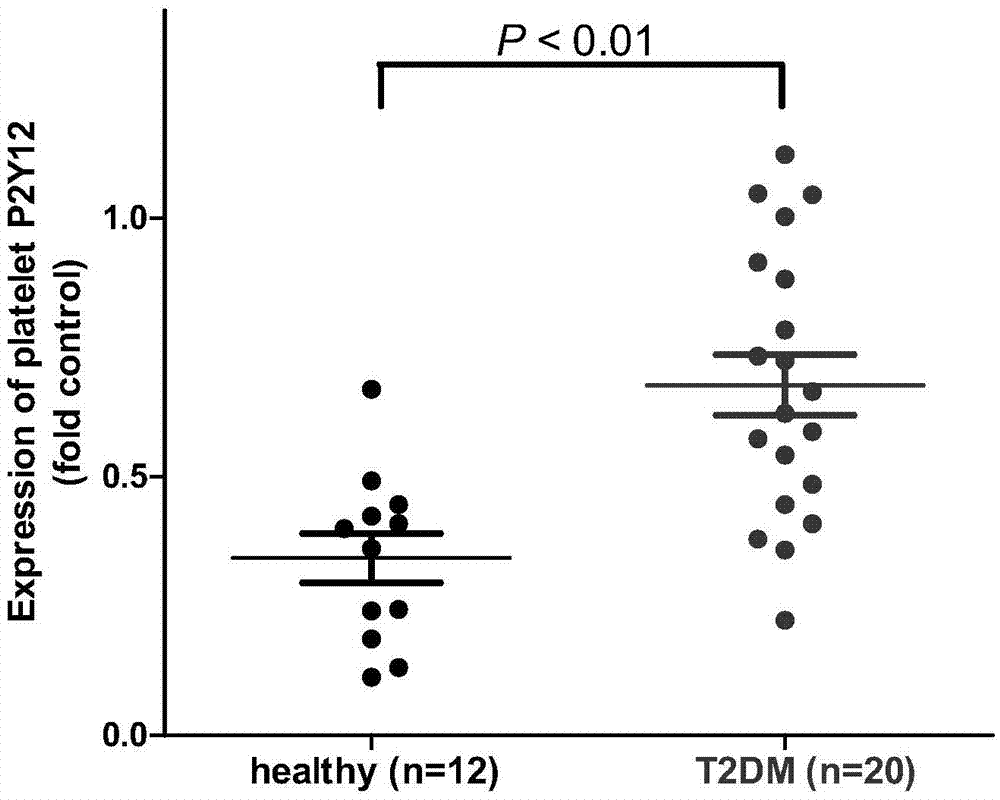
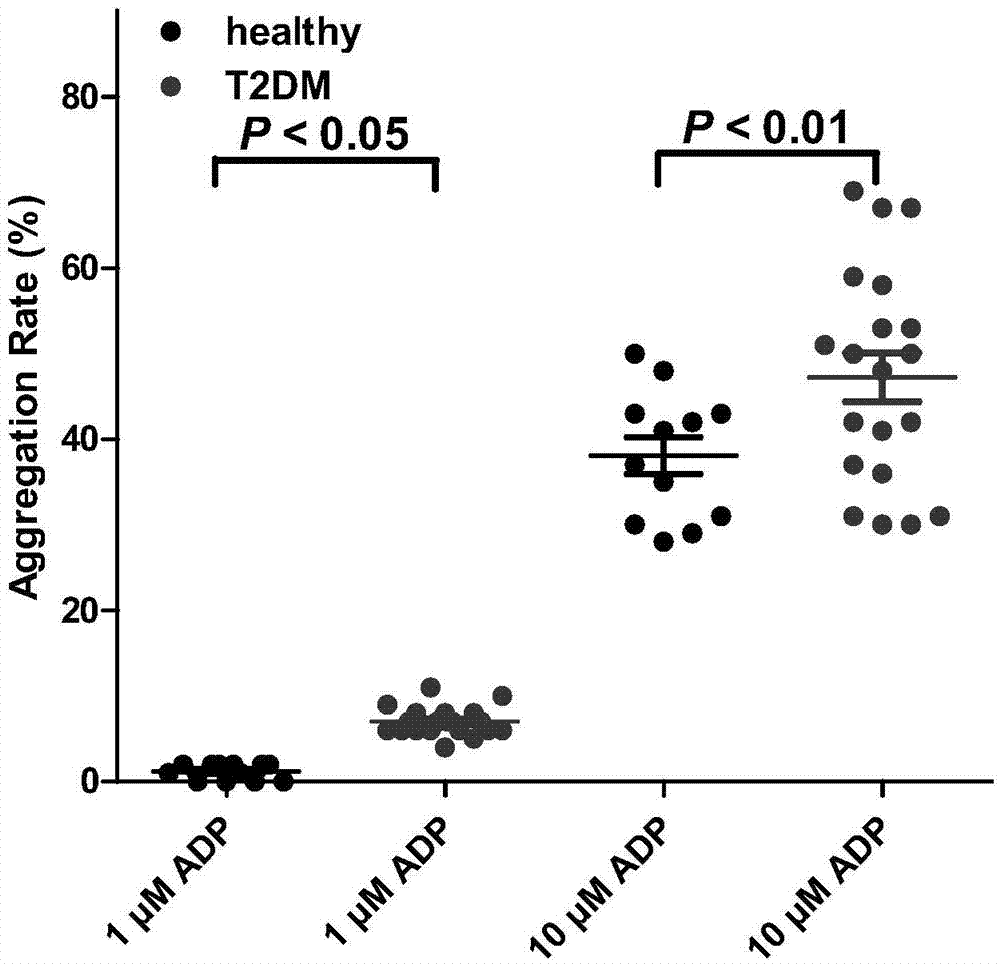
The invention belongs to the technical field of biology and diagnosis, and relates to a receptor of a definite, effective and visualized platelet reactivity biomarker P2Y12 and an application thereof for diagnosing and predicting the II-type diabetic vascular complication risk. The platelet activation biomarker P2Y12 can detect expression levels of platelet through fluorescent quantitative polymerase chain reaction (PCR), Western blot, enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA), flow cytometry, UV spectrophotometry-near infrared spectrometry, high performance liquid chromatography, colorimetry, a mass spectrum identification method and the like and detect content of P2Y12 in whole blood. The invention also provides a method of biomarker P2Y12 for diagnosing and predicting vascular complication of subjects as well as a medicine for treating II-type diabetic vascular complication and a screening method of the medicine. The invention further provides an intervene plane for individualizing P2Y12 inverse agonist and accurately treating the vascular complication of II-type diabetic patients.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Biological medicated food equivalent to acarbose physical method for reducing postprandial blood sugar
InactiveCN104473152ASettle the priceAddress issues such as side effects that can damage the liverMetabolism disorderFood preparationGlycosuriaDrug efficiency
The invention relates to a biological medicated food equivalent to an acarbose physical method for reducing postprandial blood sugar. The biological medicated food is prepared from the following raw materials in part by weight: 2-5 parts of barley beta-glucan, 1-3 parts of mulberry leaf extract, 1-3 parts of Chinese yam extract, 1-2 parts of konjaku flour and 3-5 parts of oat powder. According to the biological medicated food, the attributes of the raw materials are fully considered, all raw materials are mixed, the advantages of all raw materials can be fully played, the prepared biological medicated food and the acarbose are equivalent in drug efficiency, the prepared biological medicated food can effectively reduce the postprandial blood sugar of diabetes, can reduce excessive energy intake, control the blood sugar level, prevent postprandial blood sugar from elevation and enable blood glucose to become stable, can improve the symptom of a diabetic patient, can reduce the dependence of the diabetic patient on insulin, and can relieve cardiovascular complication of the diabetic patient.
Owner:石泽 +1
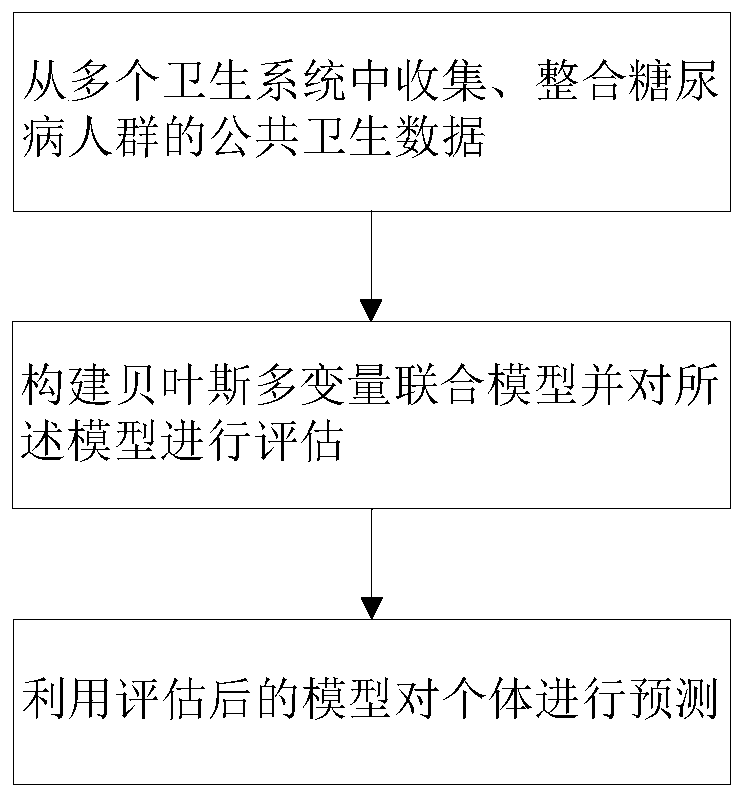
Method and system for predicting dynamic morbidity risk of cardiovascular complication of diabetes mellitus patient
ActiveCN111297329AImprove compliance with doctor's ordersGood outcomeDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsEmergency medicineIntensive care medicine
The invention relates to a method and a system for predicting a dynamic morbidity risk of the cardiovascular complication of a diabetes mellitus patient. The method comprises the following steps of: collecting and integrating the public health data of a diabetes mellitus crowd from a plurality of health systems; constructing a Bayes multivariable combined model, and evaluating the model; and utilizing the evaluated model to predict an individual. According to the method, a purpose of preventing and stopping progression of diseases can be achieved.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
Prophylactic/therapeutic agent for cardiovascular complications of diabetes
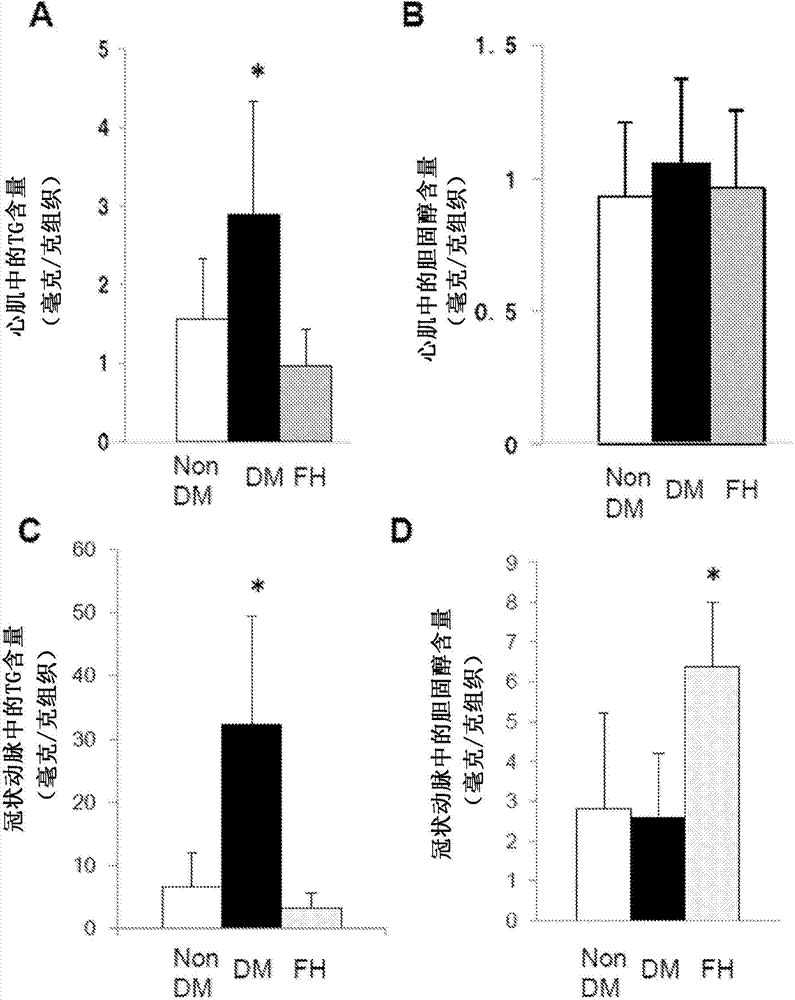
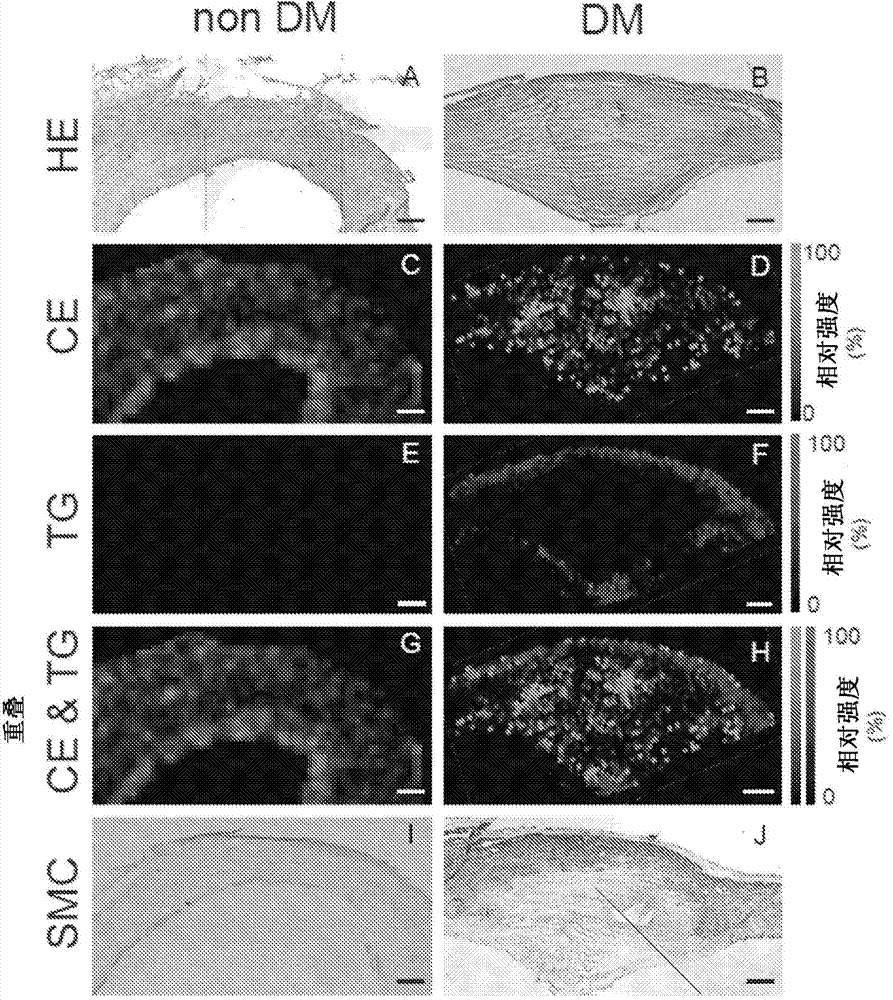
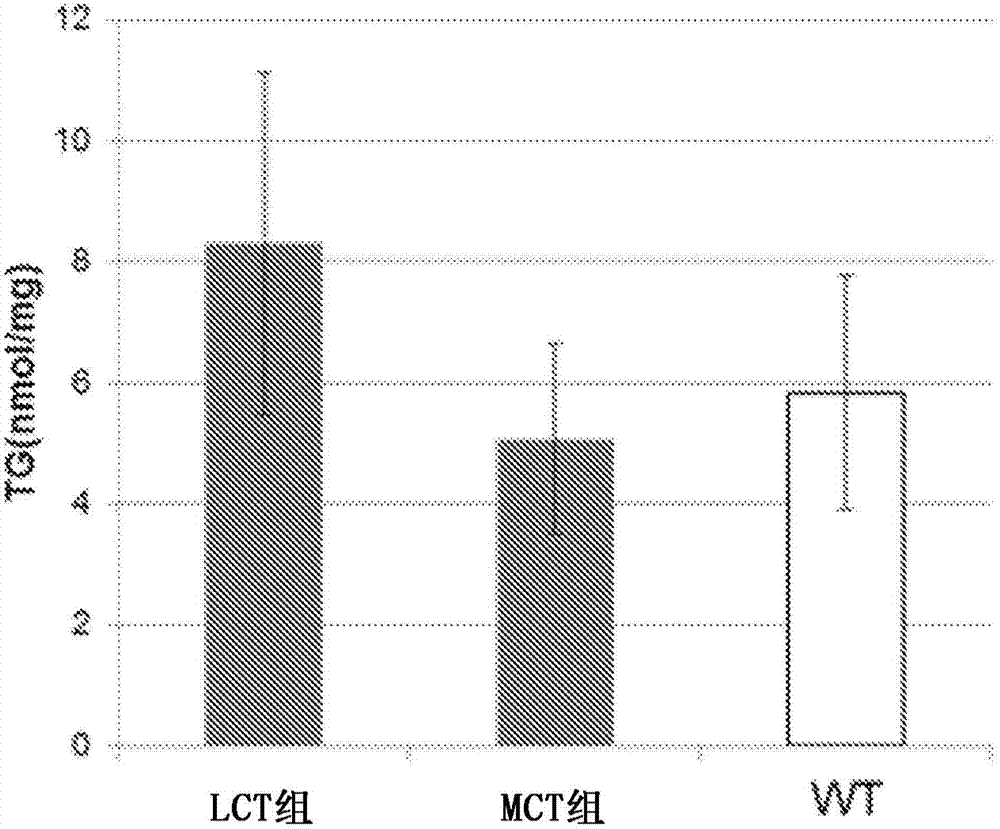
InactiveCN103945840AEasy to solveGood treatment effectSenses disorderNervous disorderTG - TriglycerideTherapeutic effect
The purpose of the present invention is to provide a drug having excellent prophylactic or therapeutic effect against cardiovascular complications of diabetes, the drug containing a compound for inhibiting neutral fat accumulation in cardiovascular tissue or cells. The present invention pertains to a prophylactic / therapeutic drug for cardiovascular complications of diabetes, the drug containing a compound for inhibiting neutral fat accumulation (preferably, medium-chain fatty acid and / or medium-chain triglyceride).
Owner:OSAKA UNIV
Multimarker panel based on PIGF for diabetes types 1 and 2
Owner:ROCHE DIAGNOSTICS OPERATIONS INC
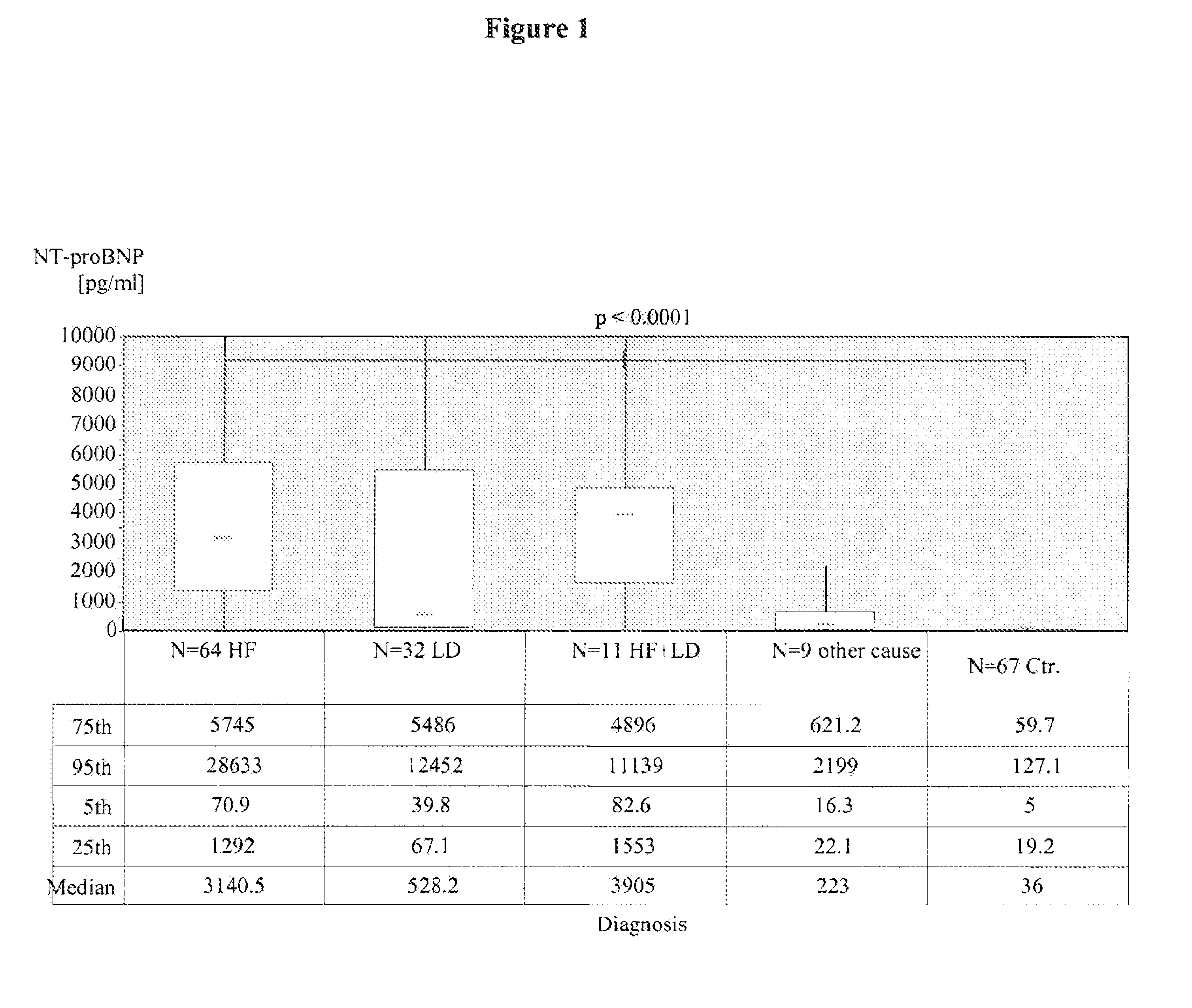
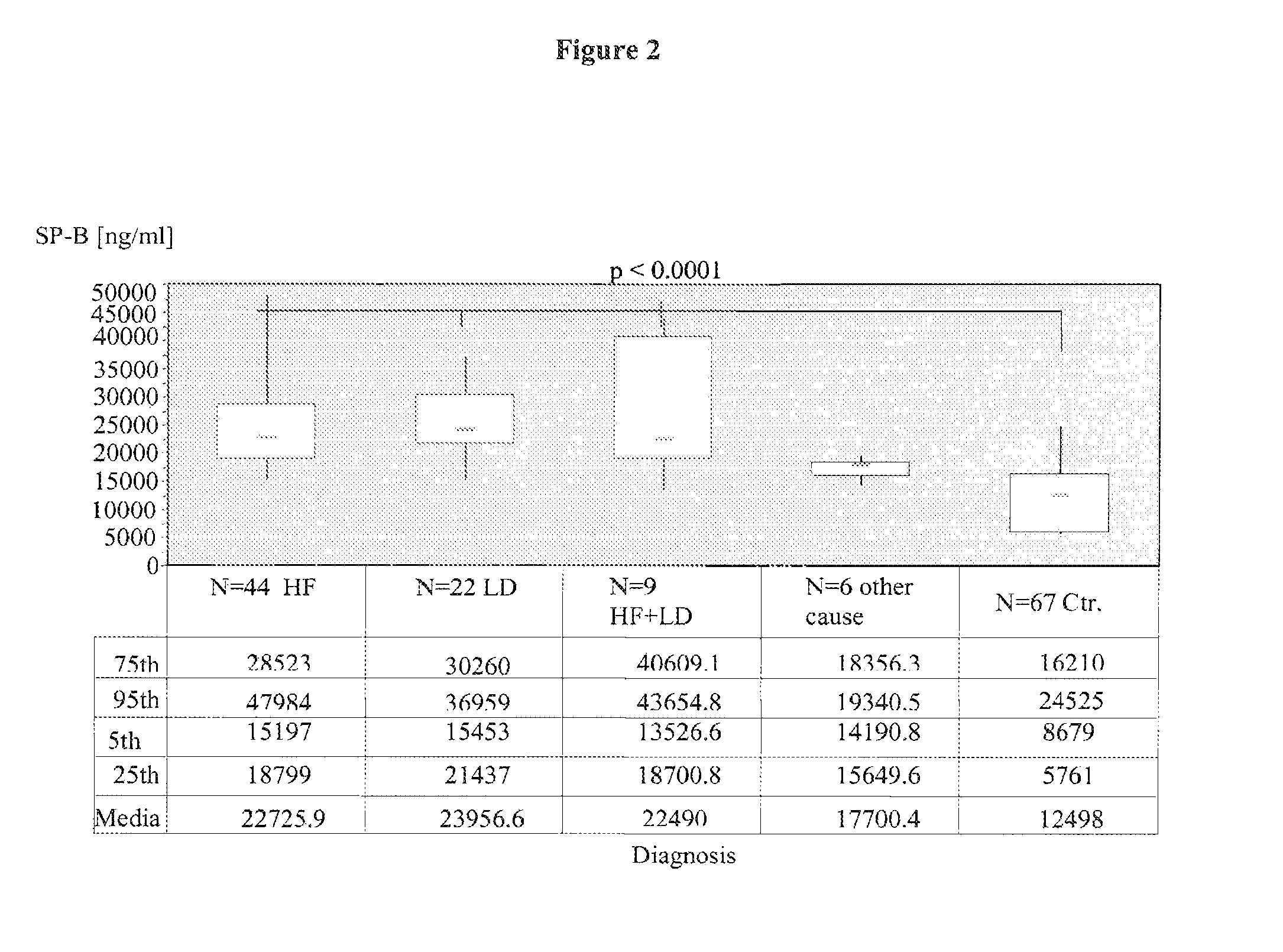
Differentiation of cardiac and pulmonary causes of acute shortness of breath
InactiveUS7892844B2Effective diagnosisAvoid disadvantagesDisease diagnosisBiological testingN-terminal pro-Brain Natriuretic PeptideDecreased surfactant
The present invention relates to a method for differentiating in a subject suffering from acute shortness of breath (dyspnea) between (i) a pulmonary disease, (ii) a cardiovascular complication, (iii) a cardiovascular complication accompanied by a pulmonary disease or (iv) acute dyspnea without cardiovascular or pulmonary causes comprising the steps of determining the amount of pulmonary surfactant protein B (SP-B) in a sample of a subject, determining the amount of N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP) in a sample of the subject, and differentiating between (i) a pulmonary disease, (ii) a cardiovascular complication, (iii) a cardiovascular complication accompanied by a pulmonary disease or (iv) acute dyspnea without cardiovascular or pulmonary causes by comparing the determined amounts with reference amounts.
Owner:ROCHE DIAGNOSTICS OPERATIONS INC
Dual glucose-turbidimetric analytical sensors
InactiveUS7758744B2Minimize cross-talkAccurate estimateAnalysis using chemical indicatorsWeather/light/corrosion resistanceChylomicronTurbidity
Diagnostic dry reagent tests capable of reacting with a single drop of whole blood and reporting both glucose and light-scattering analytes, such as chylomicrons, are taught. Such dry reagent tests may employ electrochemical detection methodologies, optical detection methodologies, or both methodologies. These tests alert diabetics to excessive levels of postprandial lipemia caused by meals with excessive amounts of fat, and thus can help reduce the risk of cardiovascular complications in diabetic patients.
Owner:ZWEIG STEPHEN ELIOT
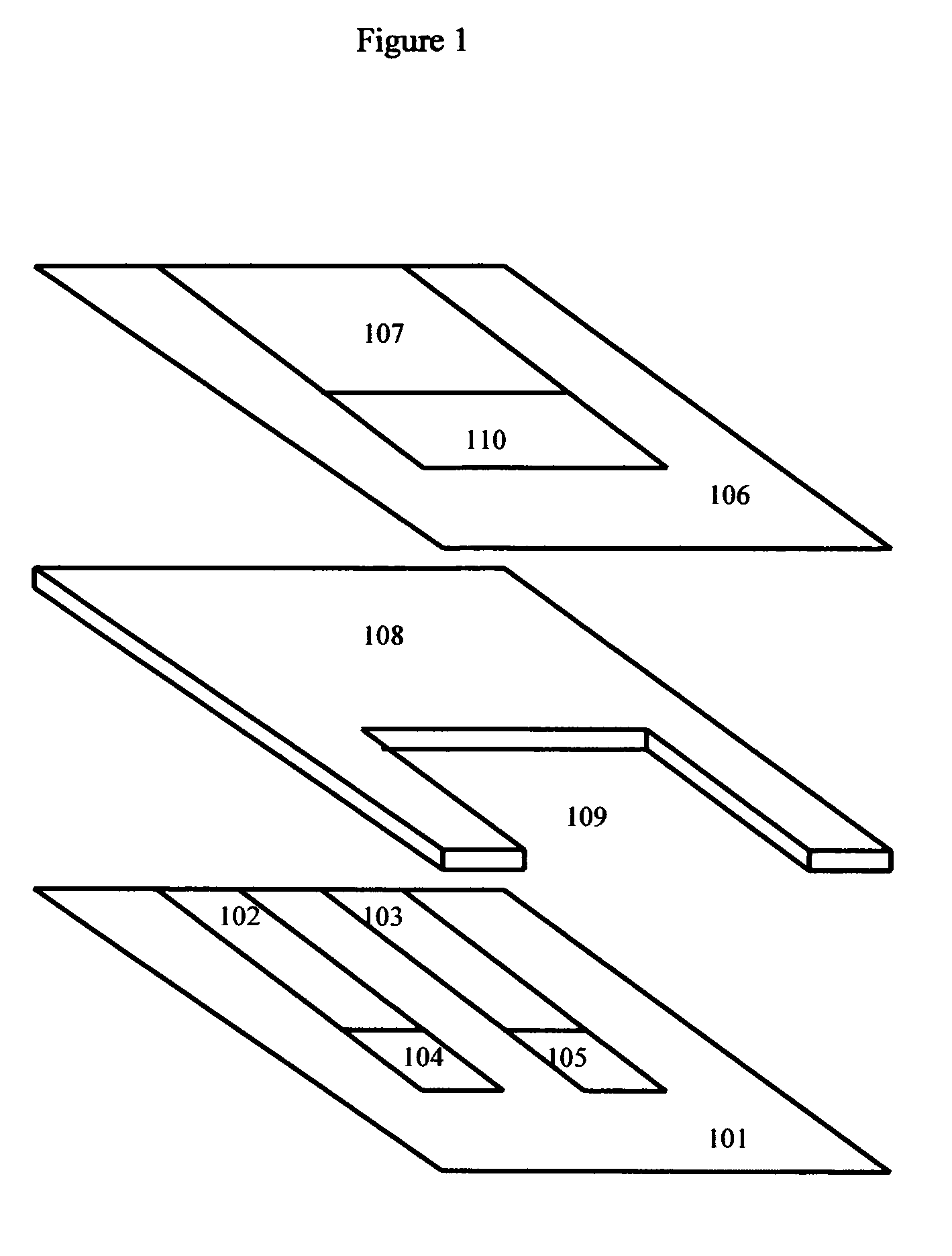
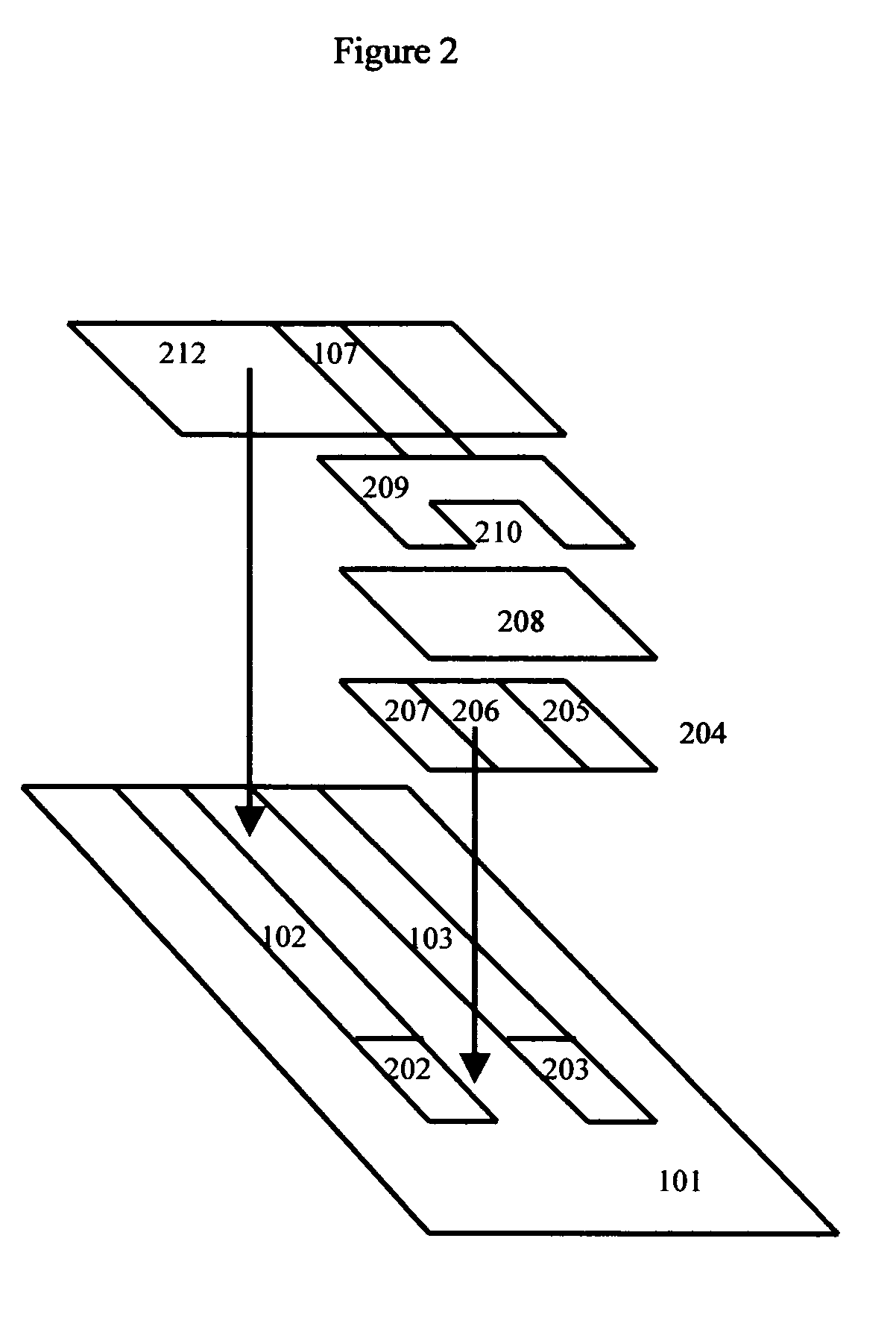
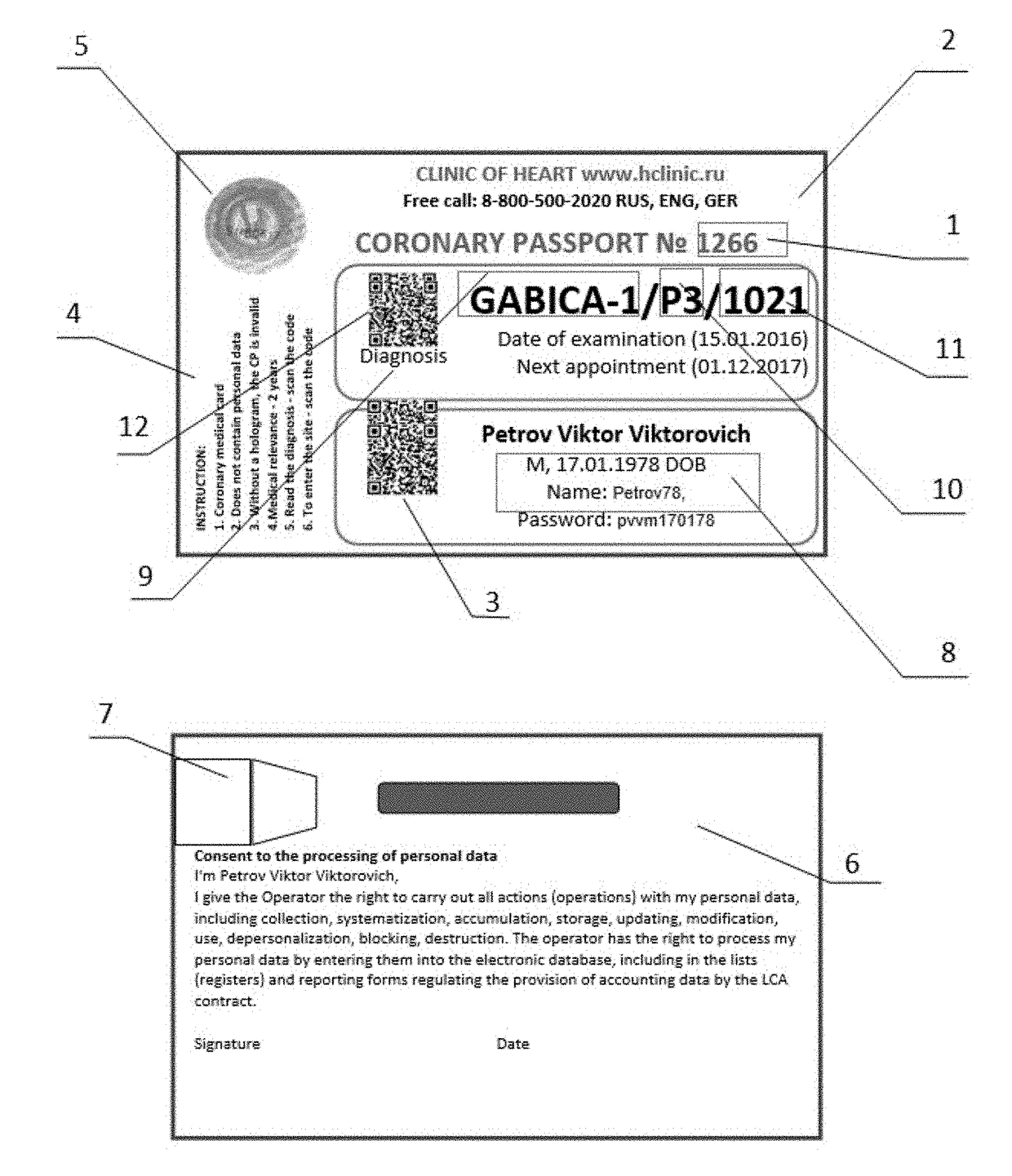
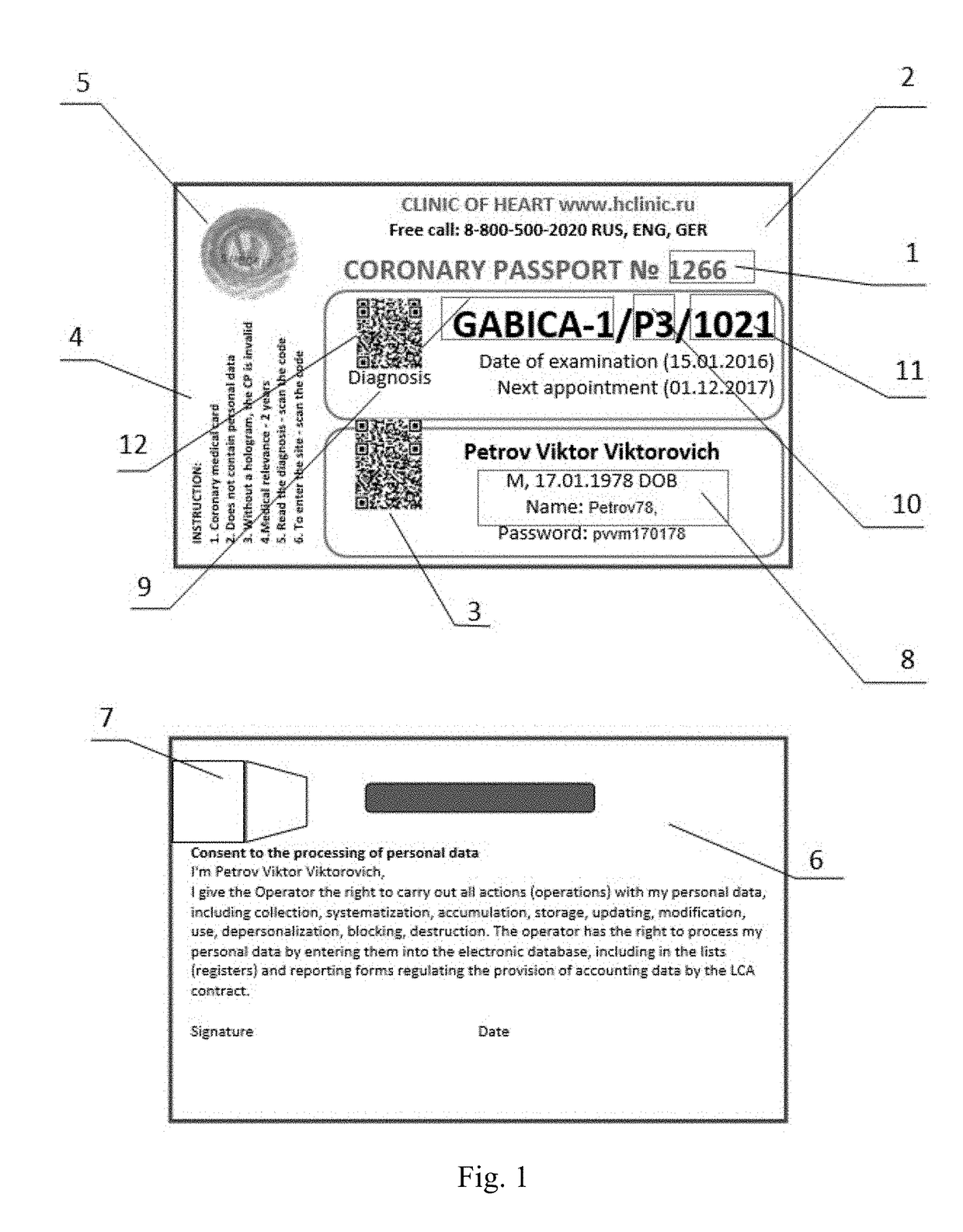
Human coronary passport
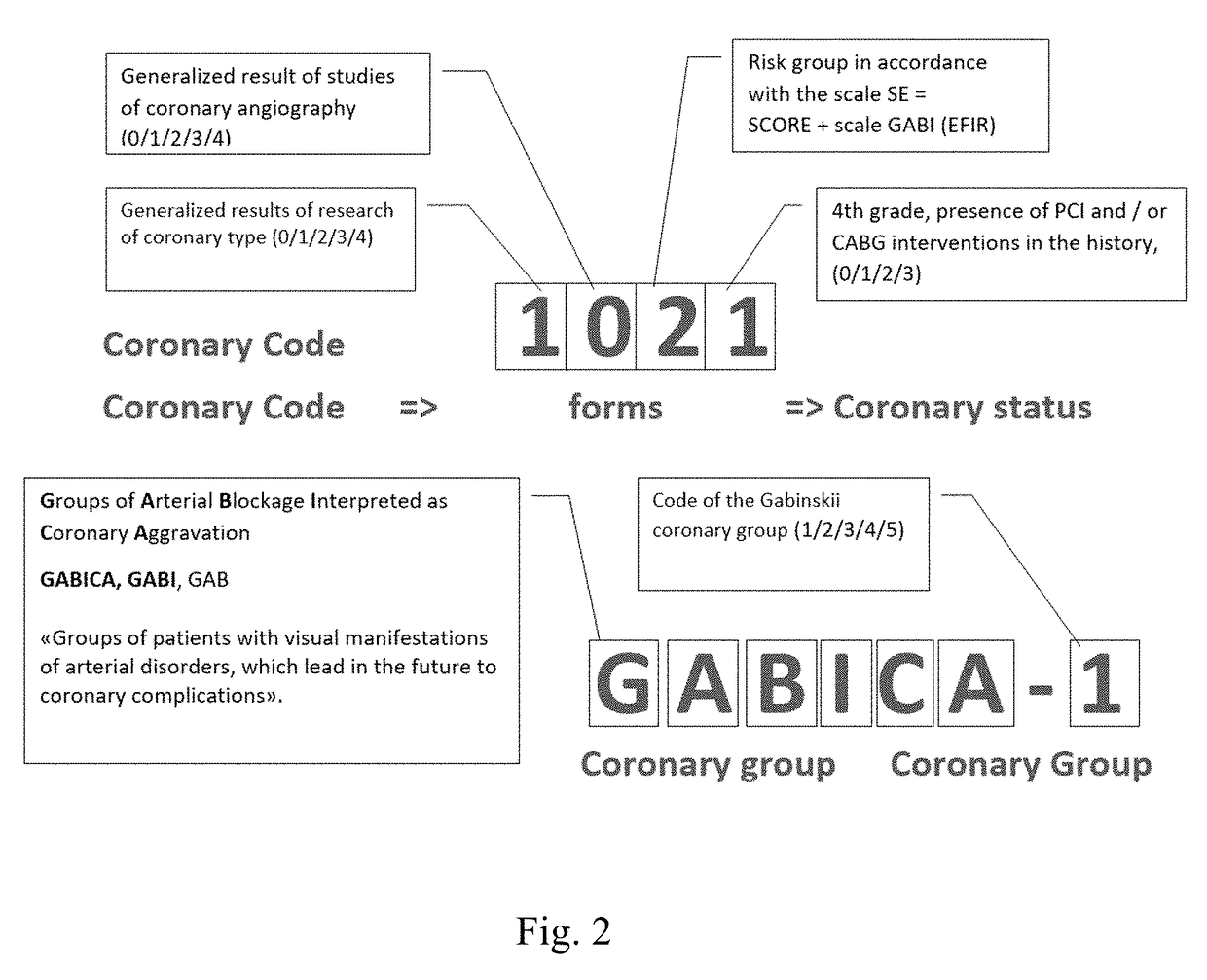
InactiveUS20180075206A1Early detection of riskReduce riskMedical communicationTherapiesPlan treatmentHeart disease
The invention relates to medicine, therapy, cardiology, in particular it relates to the planning of prevention and treatment of patients in a risk group or already suffering from illnesses such as cardiovascular diseases.The goal of the proposed invention is the prevention of the risk of developing cardiovascular diseases and an early detection of the risk of fatal cardiovascular complications for all people, especially those not previously assigned to risk groups.The technical result consists in the development of a universal automated system of monitoring and prevention of the development of cardiovascular diseases, based on a method of identifying the risk of developing cardiovascular diseases.The technical result is accomplished by virtue of the fact that the present invention represents a universal automated system which is able to identify the risk of developing cardiovascular diseases, plan a treatment, and recommend lifestyle changes, for all people, particularly those not previously assigned to risk groups, with the purpose of warning and preventing CVD (cardiovascular diseases). For the best solution of this problem, the proposed invention of a coronary passport for a person includes: a method of comprehensive evaluation of the coronary status of a person; a system of prevention and monitoring of the risk of development of cardiovascular diseases.
Owner:GABINSKII IAN LVOVICH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com