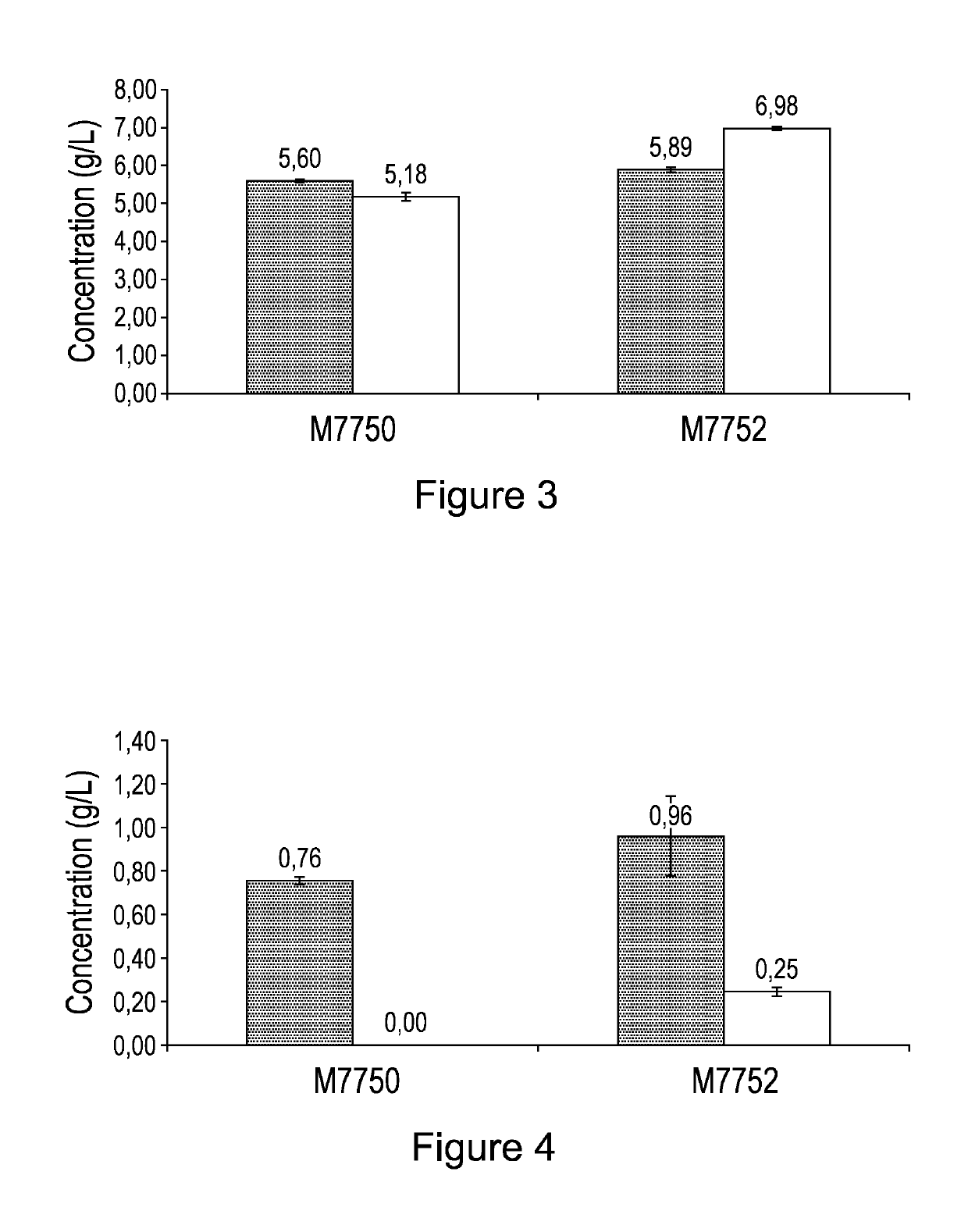
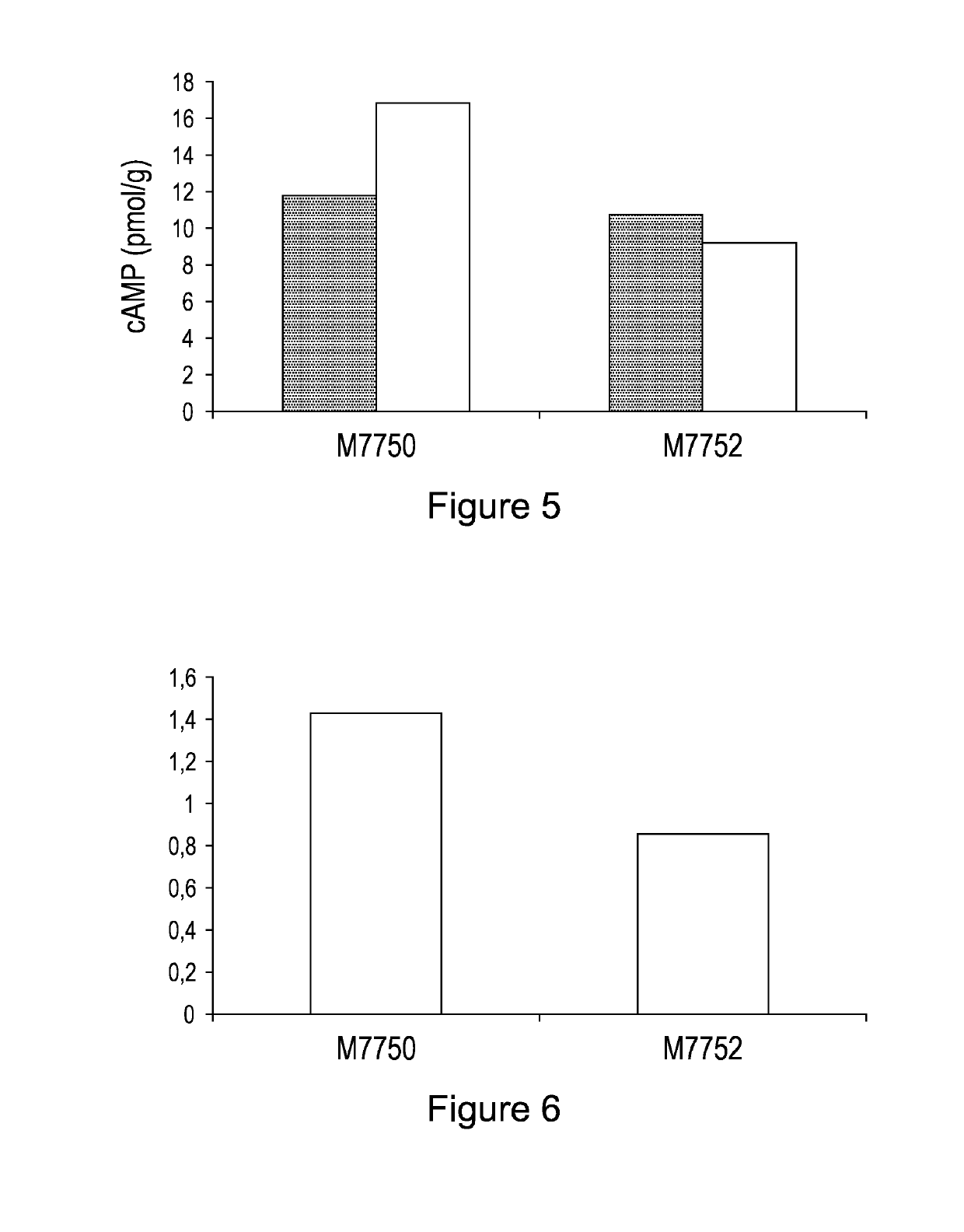
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
48 results about "Notch signaling pathway" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
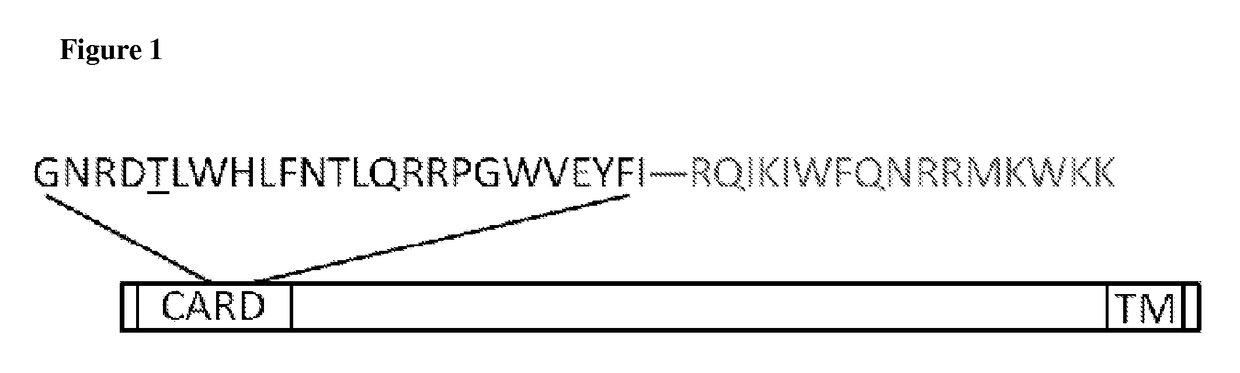
The Notch signaling pathway is a highly conserved cell signaling system present in most animals. Mammals possess four different notch receptors, referred to as NOTCH1, NOTCH2, NOTCH3, and NOTCH4. The notch receptor is a single-pass transmembrane receptor protein. It is a hetero-oligomer composed of a large extracellular portion, which associates in a calcium-dependent, non-covalent interaction with a smaller piece of the notch protein composed of a short extracellular region, a single transmembrane-pass, and a small intracellular region.
Method for Diagnosing, Prognosing and Treating Glioma
InactiveUS20070141066A1Long median patient survivalShort overall survivalHeavy metal active ingredientsCompound screeningAbnormal tissue growthAnti mitotic
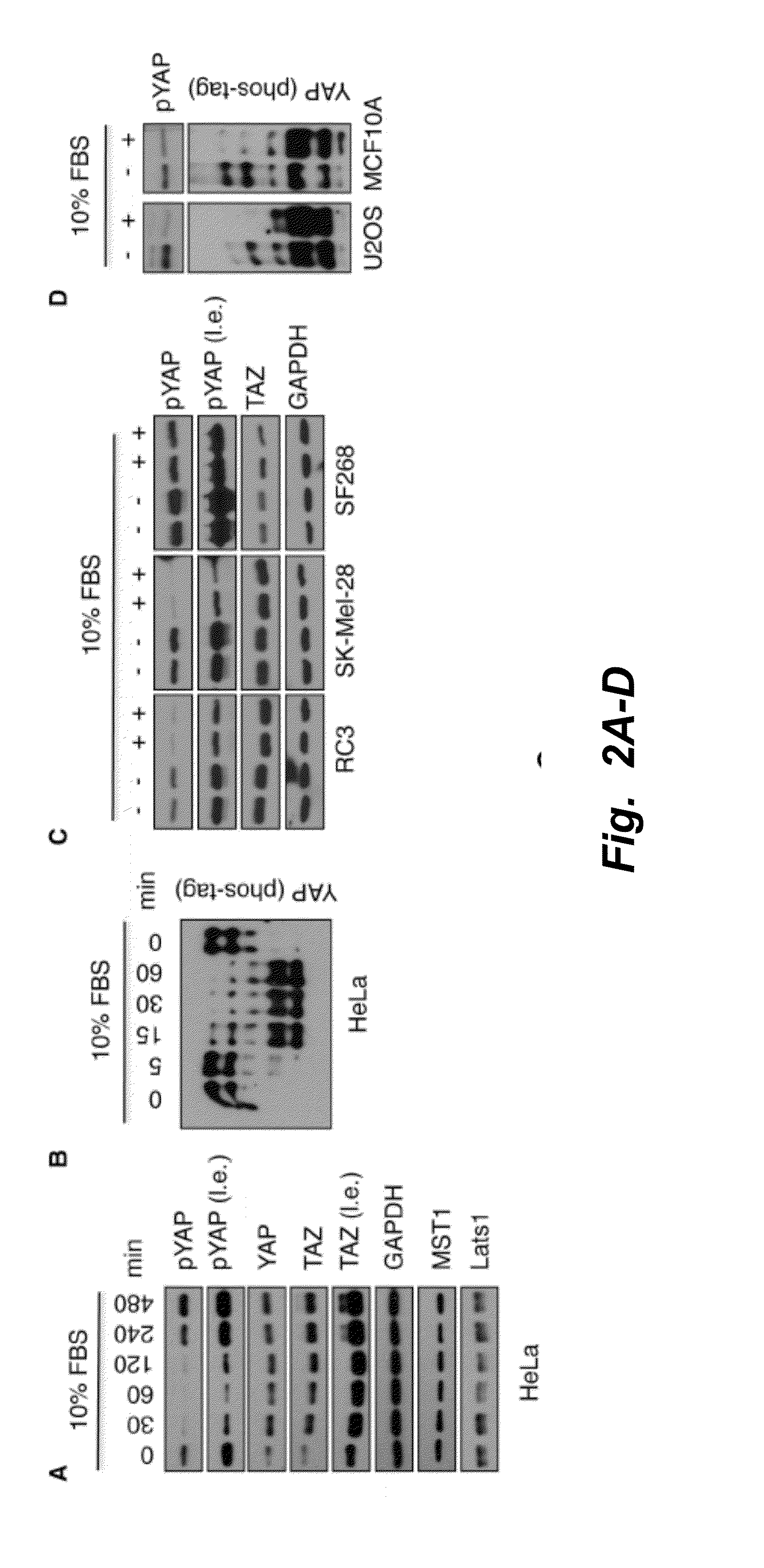
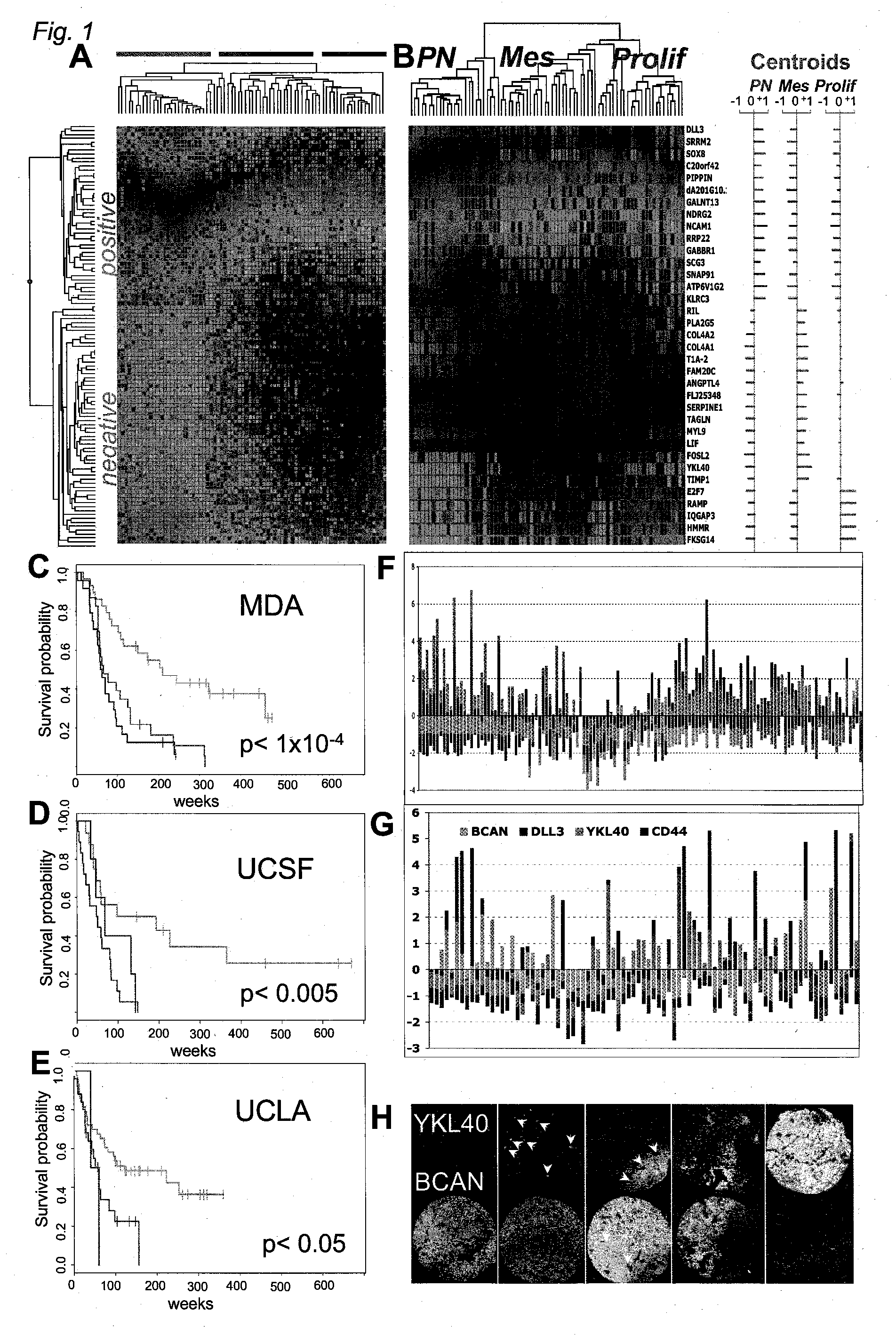
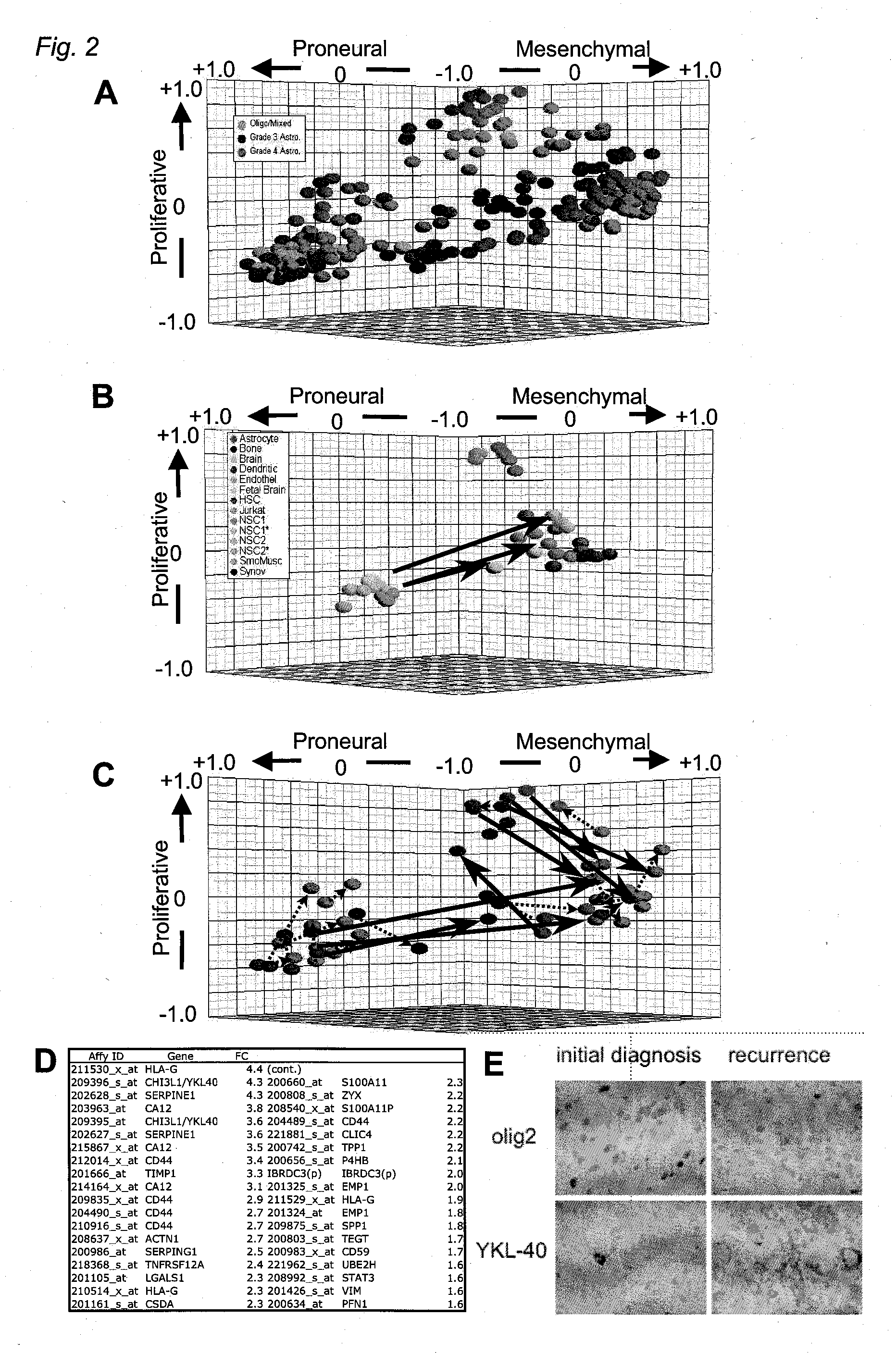
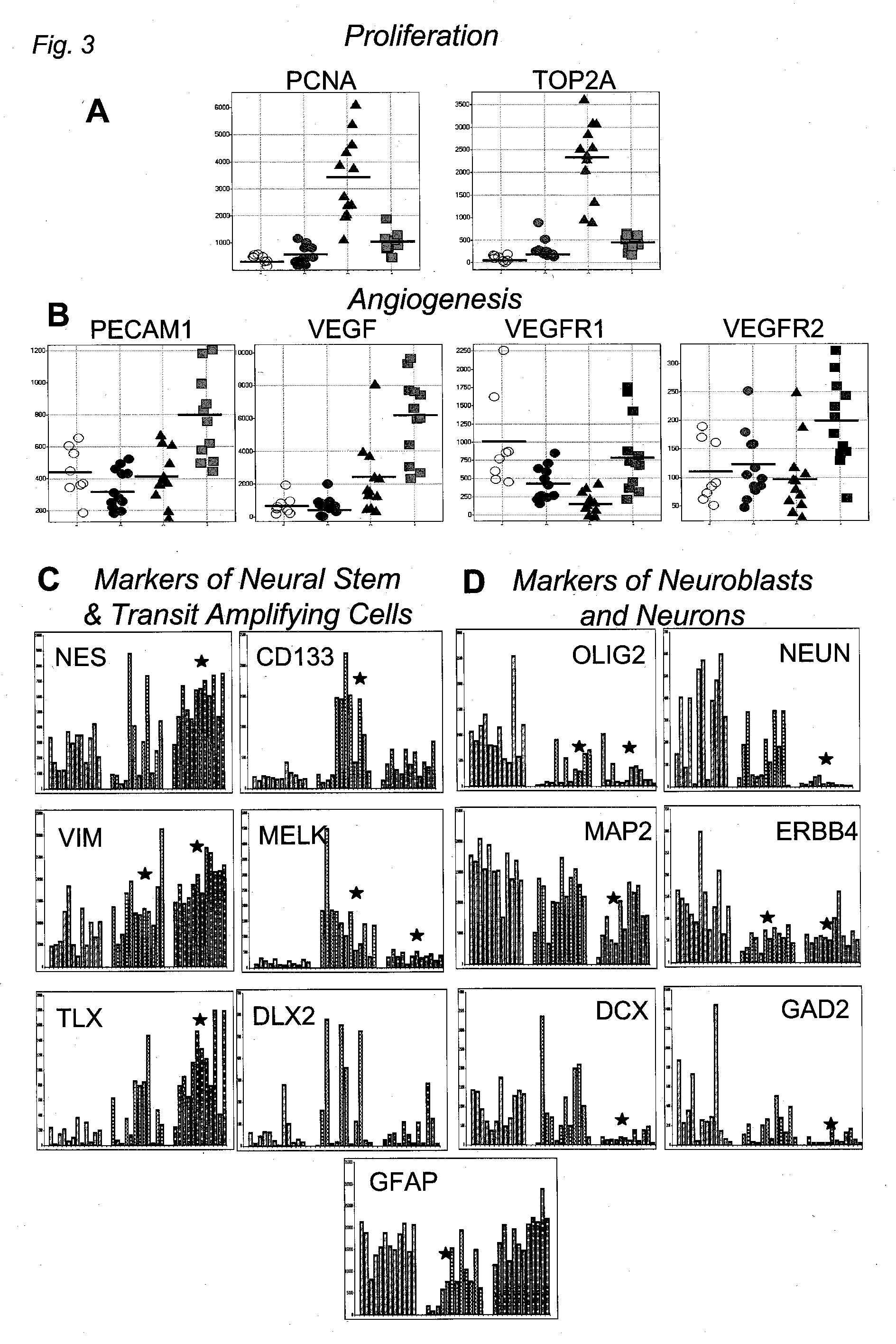
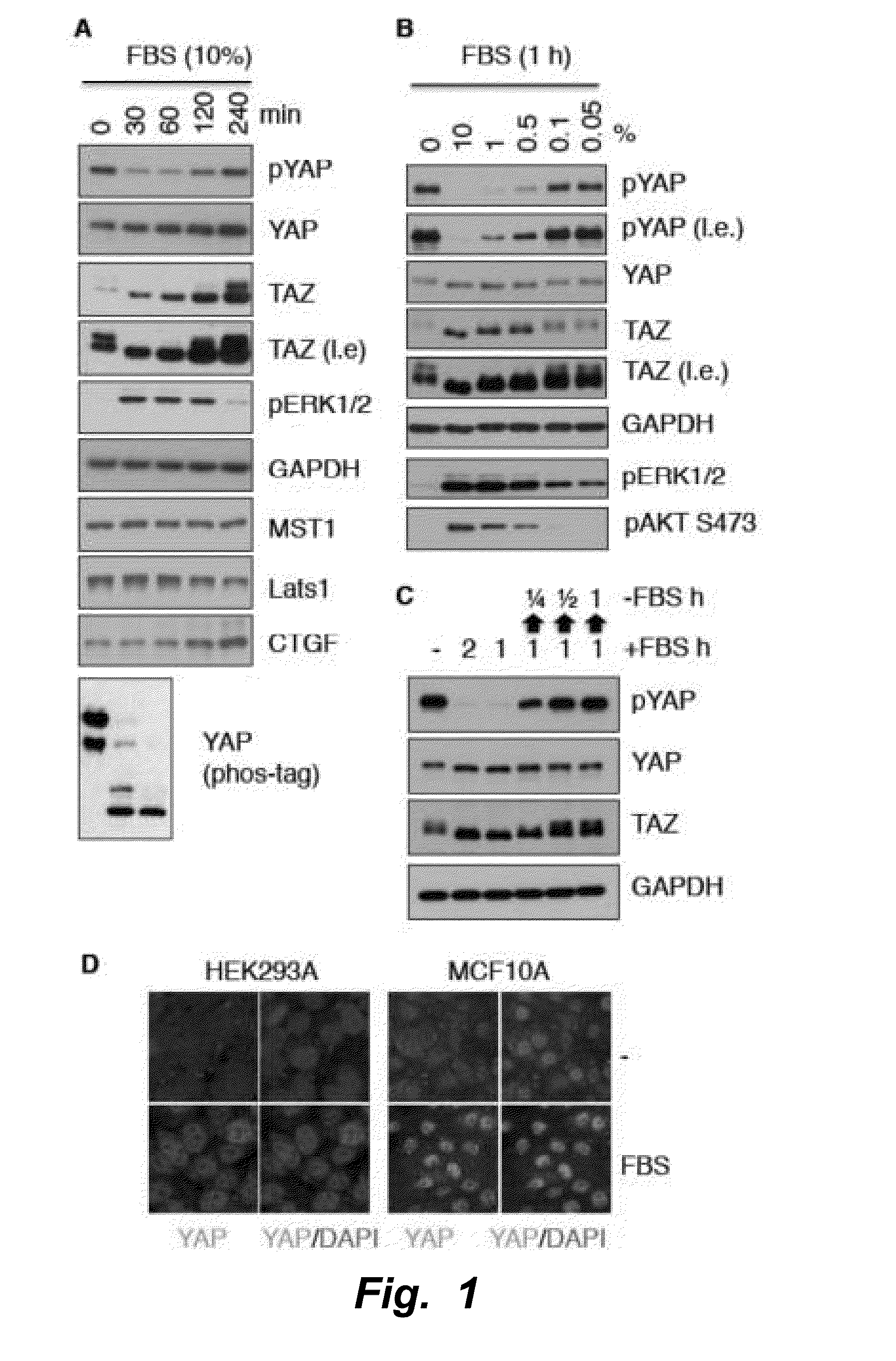
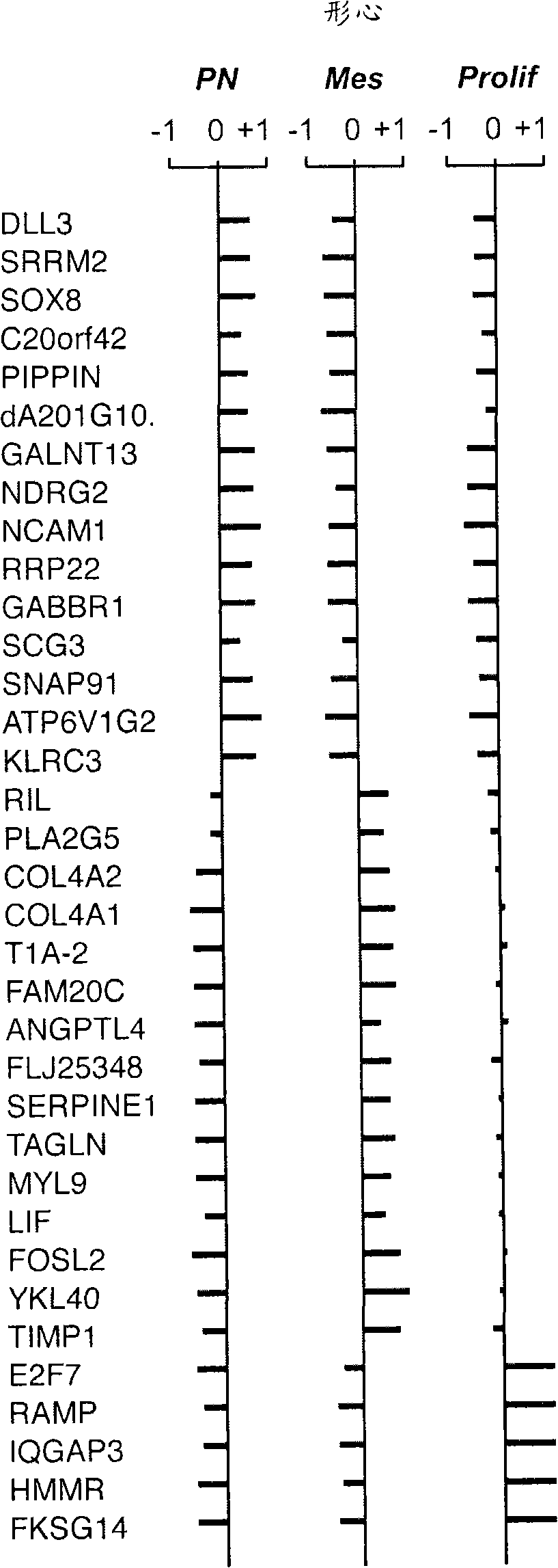
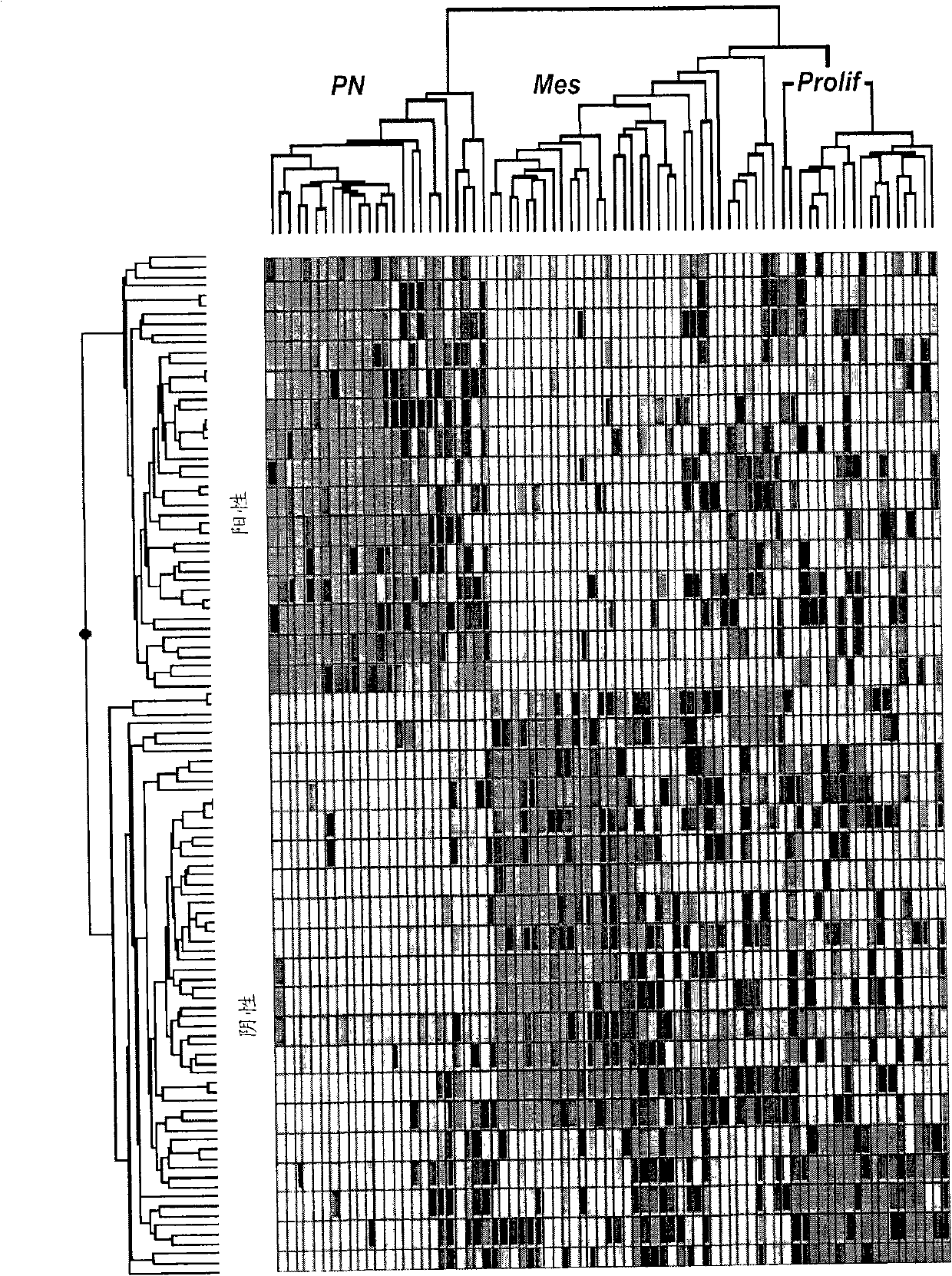
The invention provides generally a method of monitoring, diagnosing, prognosing and treating glioma. Specifically, the invention provides for three (3) prognostic subclasses of glioma, which are differentially associated with activation of the akt and notch signaling pathways. Tumor displaying neural or proneural PN lineage markers (including notch pathway elements) show longer median patient survival, while the two remaining tumor markers Prolif and Mes are associated with shortened survival. Tumors classified in this manner may also be treated with the appropriate PN- Prolif- or Mes-therapeutic corresponding to the subclassification in combination with anti-mitotic agents, anti-angiogenic agents, Akt antagonists, and neural differentiation agents. Alternatively, the invention also provides for method of prognosing and diagnosing glioma with a two-gene model based on the expression levels of PTEN and DLL3.
Owner:GENENTECH INC
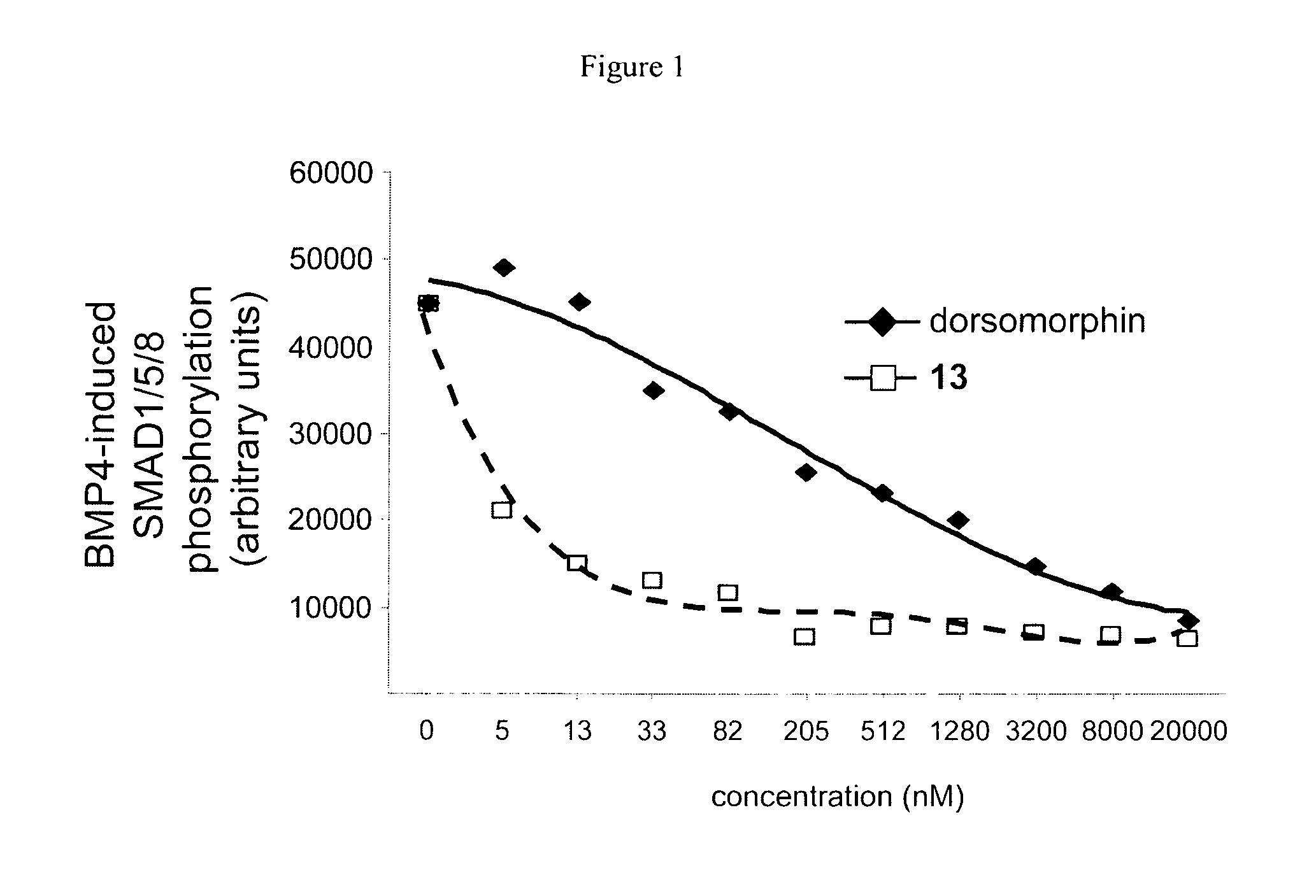
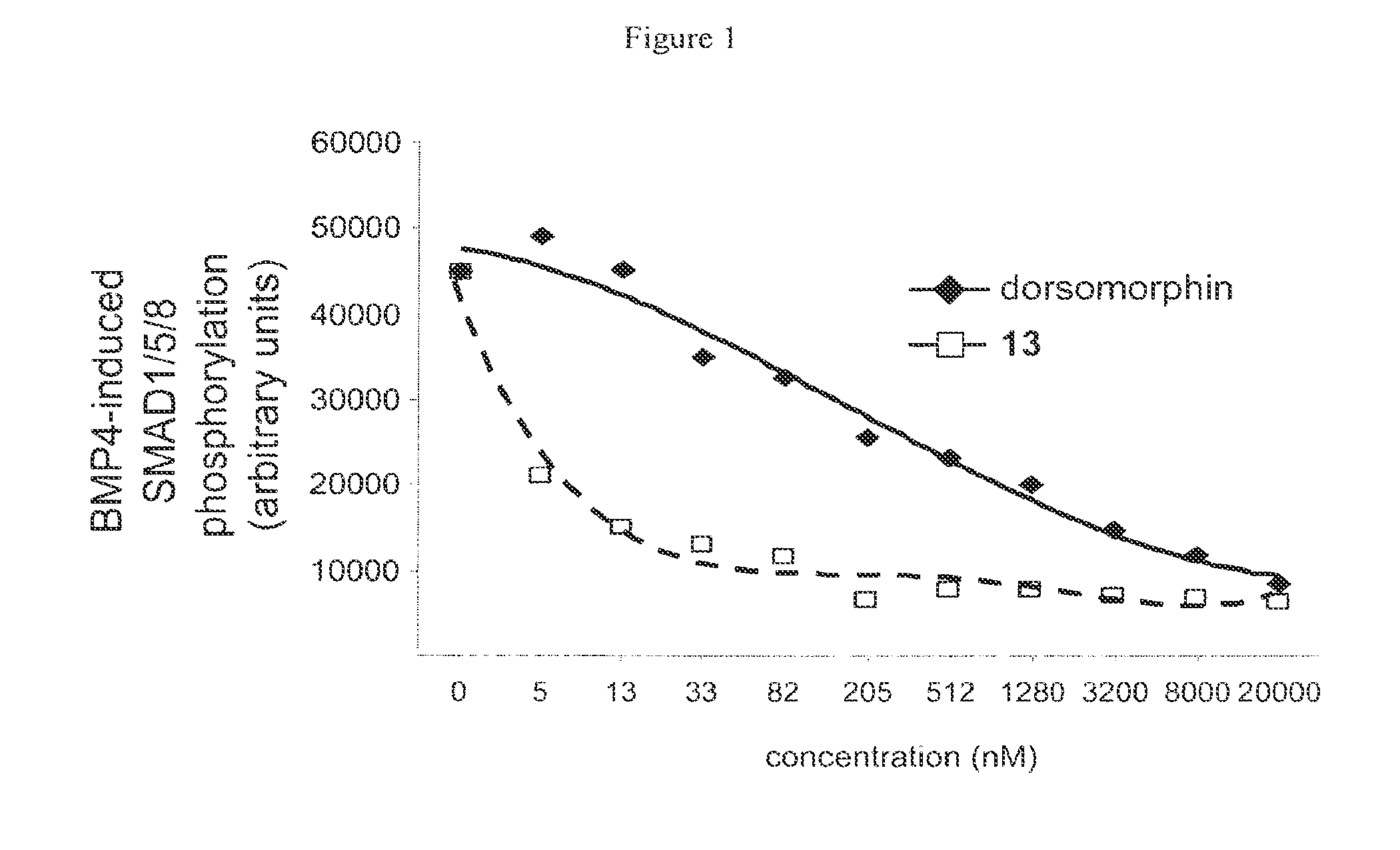
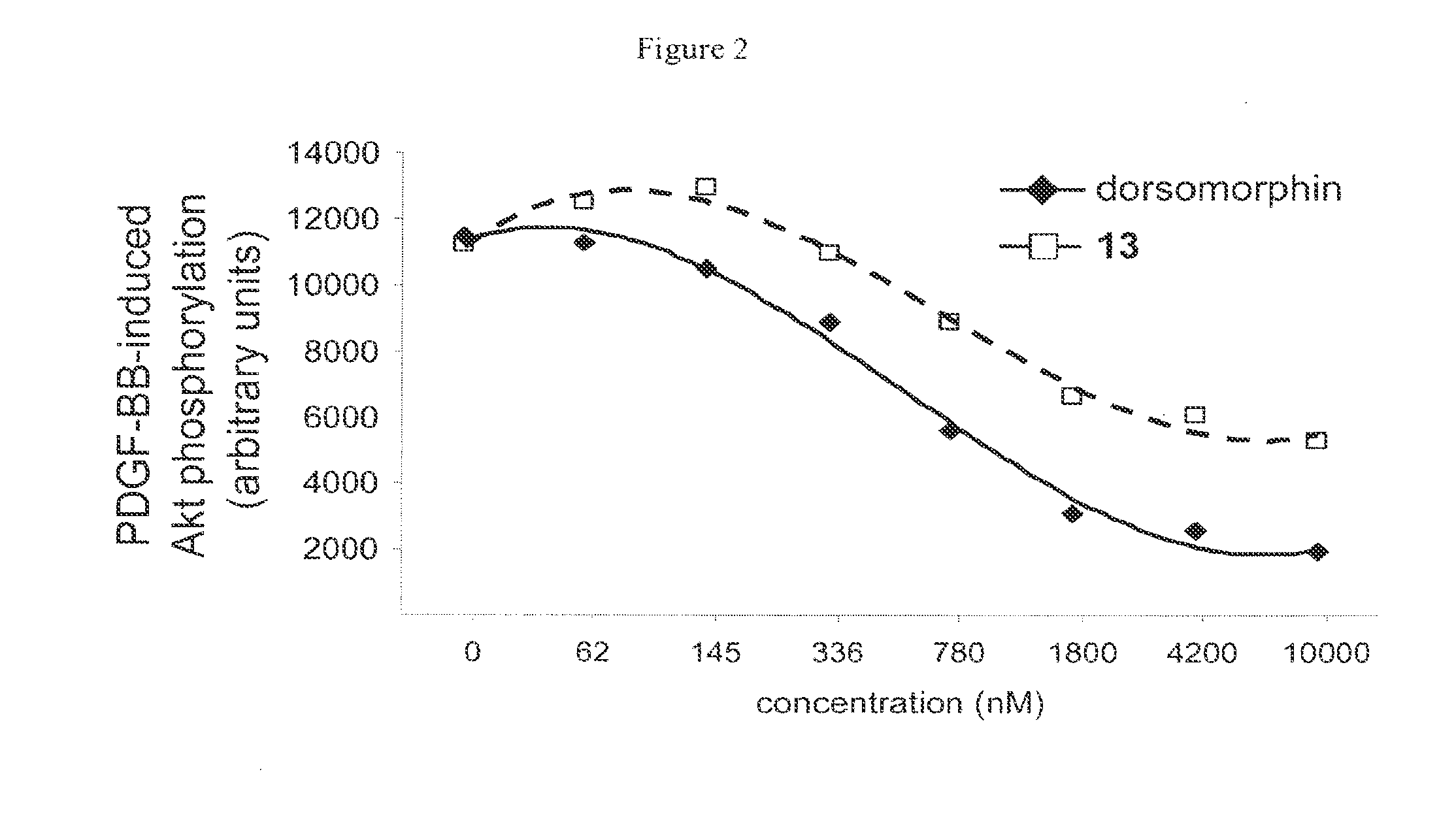
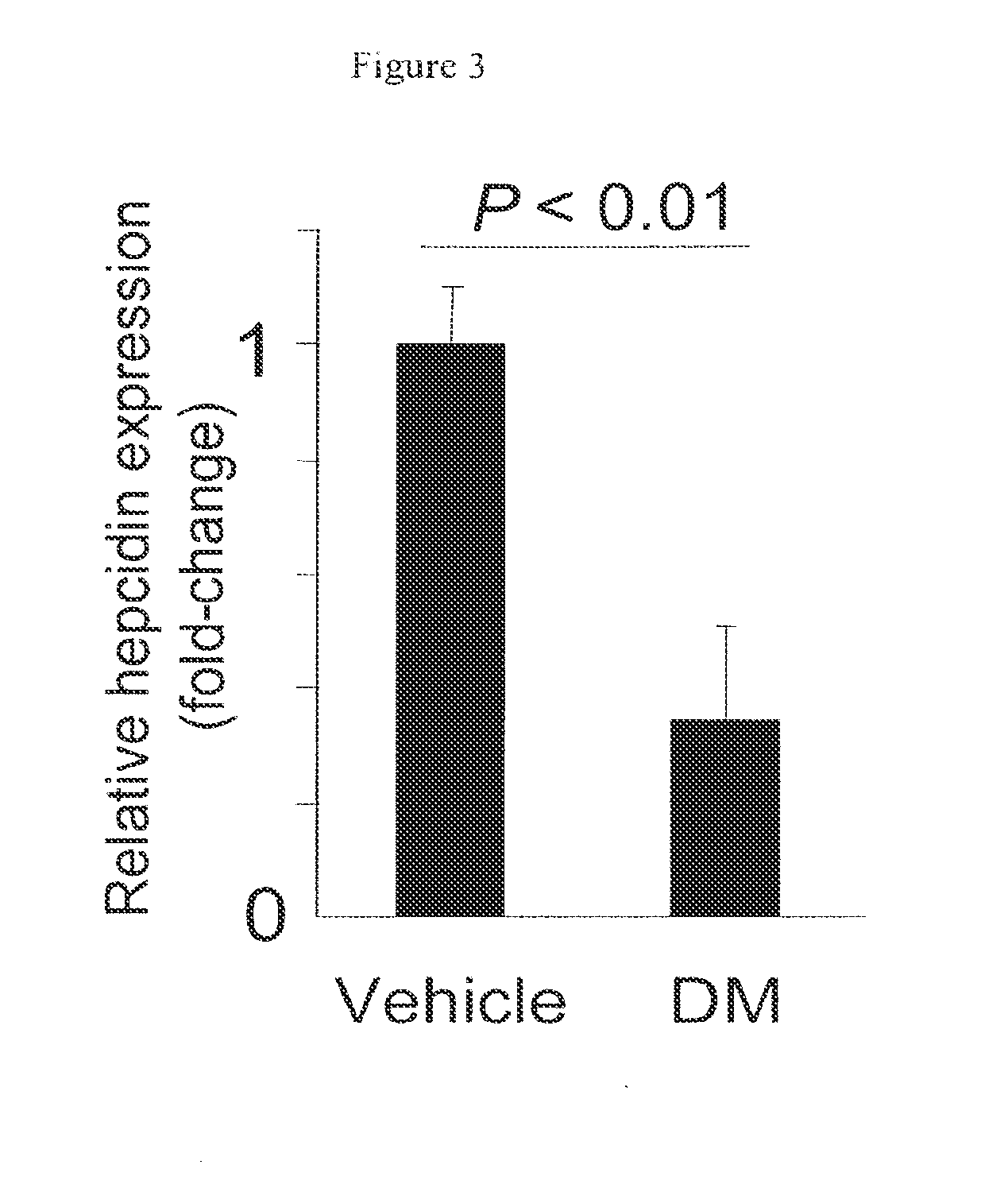
Inhibitors of the bmp signaling pathway
The present invention provides small molecule inhibitors of BMP signaling. These compounds may be used to modulate cell growth, differentiation, proliferation, and apoptosis, and thus may be useful for treating diseases or conditions associated with BMP signaling, including inflammation, cardiovascular disease, hematological disease, cancer, and bone disorders, as well as for modulating cellular differentiation and / or proliferation.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP +1
Preparation method of zebrafish notch2 gene mutant
ActiveCN108707628AGenetic stabilityFacilitate in-depth researchHydrolasesStable introduction of DNAPUC19Embryo
The invention discloses a preparation method of a zebrafish notch2 gene mutant. The preparation method includes: determining positions of knock-out target spots of the notch2 gene; utilizing pUC19-gRNA scaffold plasmid as a template, and performing PCR (polymerase chain reaction) amplification with primers T7-notch2-sfd and tracr rev; subjecting a PCR product to purification and in-vitro transcription to obtain gRNA (guide ribose nucleic acid); introducing the gRNA and Cas9 protein into a cell-stage embryo of zebrafish through micro-injection, and screening to obtain the notch2 gene mutant stable in inheritance. The preparation method has the advantages that by the aid of the CRISPR / Cas9 (clustered regularly interspersed short palindromic repeats, CRISPR / CRISPR-associated genes, cas gene)technology, and by means of selecting a specific section of targeting domain, the notch2 gene in the zebrafish is knocked out, other genes are protected from being 'injured accidentally', the zebrafish without the Notch2 gene is formed, experimental materials are provided for in-depth study on follow-up gene functions, and great significance is achieved on study of Notch signal channels.
Owner:SHANGHAI OCEAN UNIV
Preparation method of zebrafish notch1b gene mutant
PendingCN108707629AGenetic background is clear and cleanFacilitate in-depth researchHydrolasesStable introduction of DNAPUC19Embryo
The invention discloses a preparation method of a zebrafish notch1b gene mutant. The preparation method includes: determining positions of knock-out target spots of the notch1b gene; utilizing pUC19-gRNA scaffold plasmid as a template, and performing PCR (polymerase chain reaction) amplification with primers T7-notch1b-sfd and tracr rev; subjecting a PCR product to purification and in-vitro transcription to obtain gRNA (guide ribose nucleic acid); introducing the gRNA and Cas9mRNA into a cell-stage embryo of zebrafish, and culturing to obtain the notch1b gene mutant stable in inheritance. Thepreparation method has the advantages that by the aid of the CRISPR / Cas9 (clustered regularly interspersed short palindromic repeats, CRISPR / CRISPR-associated genes, cas gene) technology, and by meansof selecting a specific section of targeting domain, the notch1b gene in the zebrafish is knocked out, other genes are protected from being 'injured accidentally', the zebrafish without the Notch1b gene is formed, and great significance is achieved on study of Notch signal channels.
Owner:SHANGHAI OCEAN UNIV
Inhibitors of hippo-yap signaling pathway
This invention provides methods of preventing, reducing, delaying or inhibiting the proliferation, growth, migration and / or metastasis of cancer by administering an effective amount of an inhibitor of the Hippo-YAP signaling pathway.
Owner:THE J DAVID GLADSTONE INST A TESTAMENTARY TRUST ESTABLISHED UNDER THE WILL OF J DAVID GLADS
Reagent for detecting Notch signal path as well as PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) detecting method and application thereof
The invention provides a reagent for detecting a Notch signal path as well as a PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) detecting method and application thereof. The detecting reagent comprises PCR reaction primers for detecting an ADAM10 gene, an ADAM17 gene, an AES gene, a CBL gene, a CCND1gene, a CD44 gene, and the like, and primers of corresponding internal-reference regulatory genes GAPDH (Reduced Glyceraldehyde-Phosphate Dehydrogenase), ACTB (Beta-Actin) and B2M (Beta-2-Microglobulin). The invention provides the reagent for detecting core molecule changes of the NOTCH signal channel; by virtue of the detecting reagent, genes associated with the NOTCH channel can be quickly detected on transcriptional level by virtue of real-time fluorescent quantitative PCR; on this basis, core molecules and a mechanism of action of a tumor NOTCH signal channel are analyzed and researched, so that an NOTCH regulatory channel of tumor-associated medicaments is quickly and accurately found, and therefore, a powerful tool is provided for screening anti-tumor medicaments, discussing the mechanism of a novel targeted medicament, and the like.
Owner:HOSPITAL ATTACHED TO QINGDAO UNIV
Method for diagnosing, prognosing and treating glioma
The invention provides generally a method of monitoring, diagnosing, prognosing and treating glioma. Specifically, the invention provides for three (3) prognostic subclasses of glioma, which are differentially associated with activation of the akt and notch signaling pathways. Tumor displaying neural or proneural PN lineage markers (including notch pathway elements) show longer median patient survival, while the two remaining tumor markers Prolif and Mes are associated with shortened survival. Tumors classified in this manner may also be treated with the appropriate PN- Prolif- or Mes- therapeutic corresponding to the subclassification in combination with anti-mitotic agents, anti-angiogenic agents, Akt antagonists, and neural differentiation agents. Alternatively, the invention also provides for method of prognosing and diagnosing glioma with a two- gene model based on the expression levels of PTEN and DLL3.
Owner:GENENTECH INC
Novel human septin and uses therefor
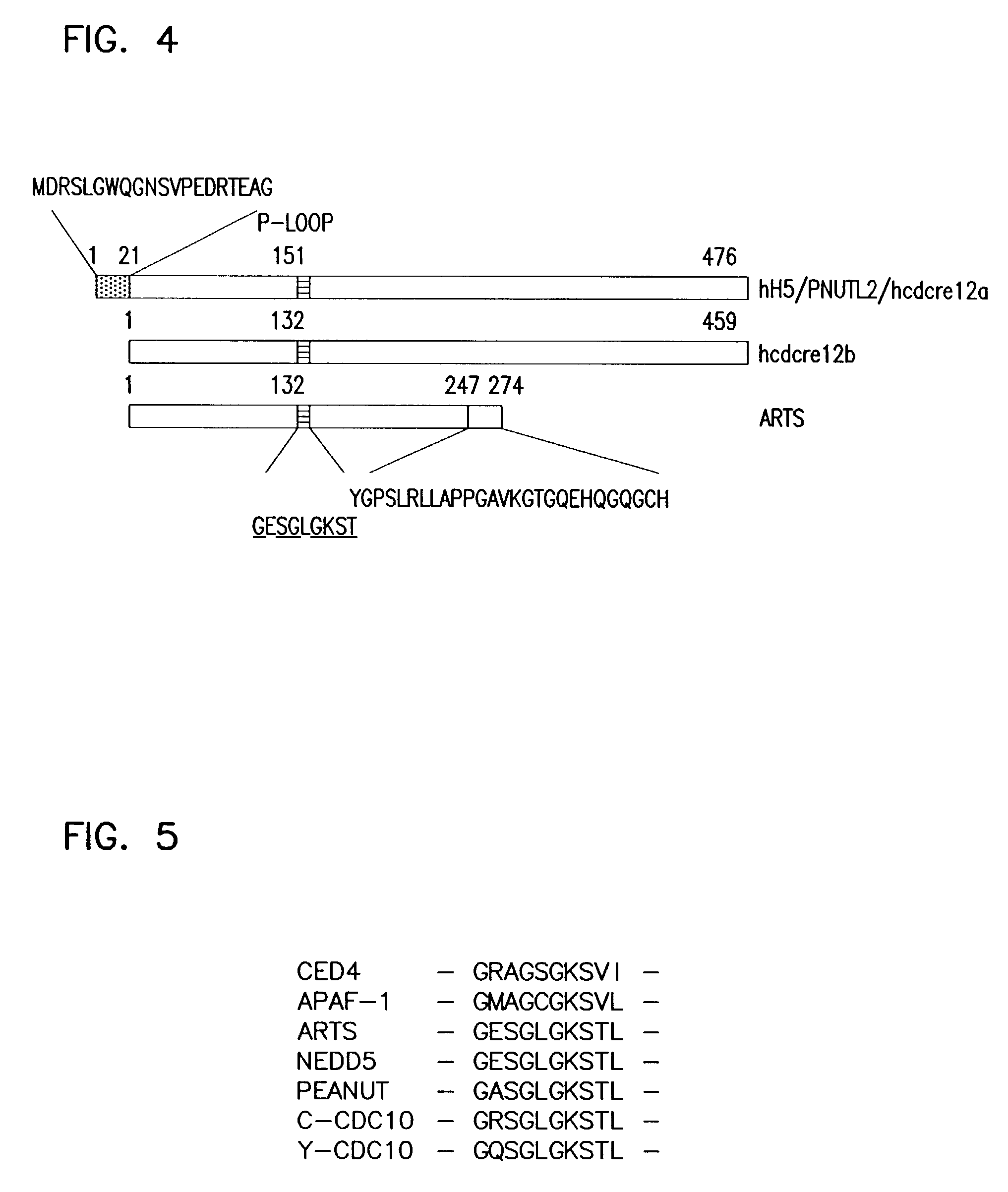
The invention provides a newly identified and isolated nucleotide sequence encoding a polypeptide referred to in the present application as ARTS, for Apoptosis Related protein in the TGF-beta Signaling pathway.
Owner:HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES UNITED STATES OF AMERICA REPRESENTED BY THE SEC DEPT OF
Method and apparatus for electromagnetic enhancement of biochemical signaling pathways for therapeutics and prophylaxis in plants, animals and humans
InactiveUS20150217126A1Enhance CaM-dependent signalingIncrease blood flowElectrotherapySeed and root treatmentBiological bodyLiving systems
Apparatus and methods for delivering electromagnetic signals configured specifically to accelerate the asymmetrical kinetics of the binding of intracellular ions to their respective intracellular buffers, to enhance the biochemical signaling pathways plant animal and human molecules, cells, tissues, organs, portions of entire organisms and entire organisms employ for growth, repair and maintenance. Described herein are devices and methods that utilize repetitive bursts of waveforms configured to maximize the bound concentration of intracellular ions at their associated molecular buffers to enhance the biochemical signaling pathways living systems employ for growth, repair and maintenance. For example the systems and methods described herein may drive the binding of calcium to calmodulin (CaM), thereby enhancing the CaM-dependent nitric oxide (NO) / cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP) signaling pathway.
Owner:ENDONOVO THERAPEUTICS INC
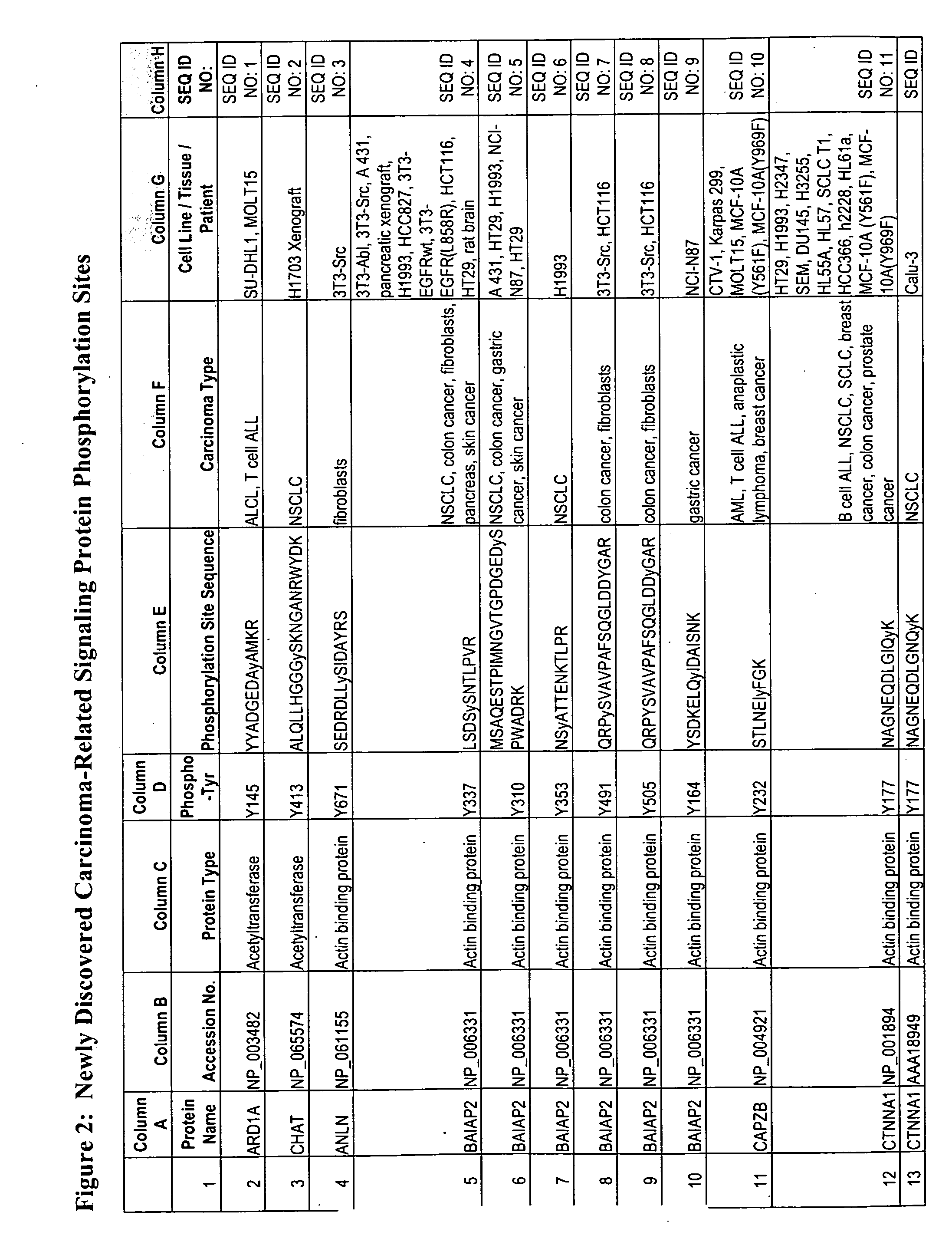
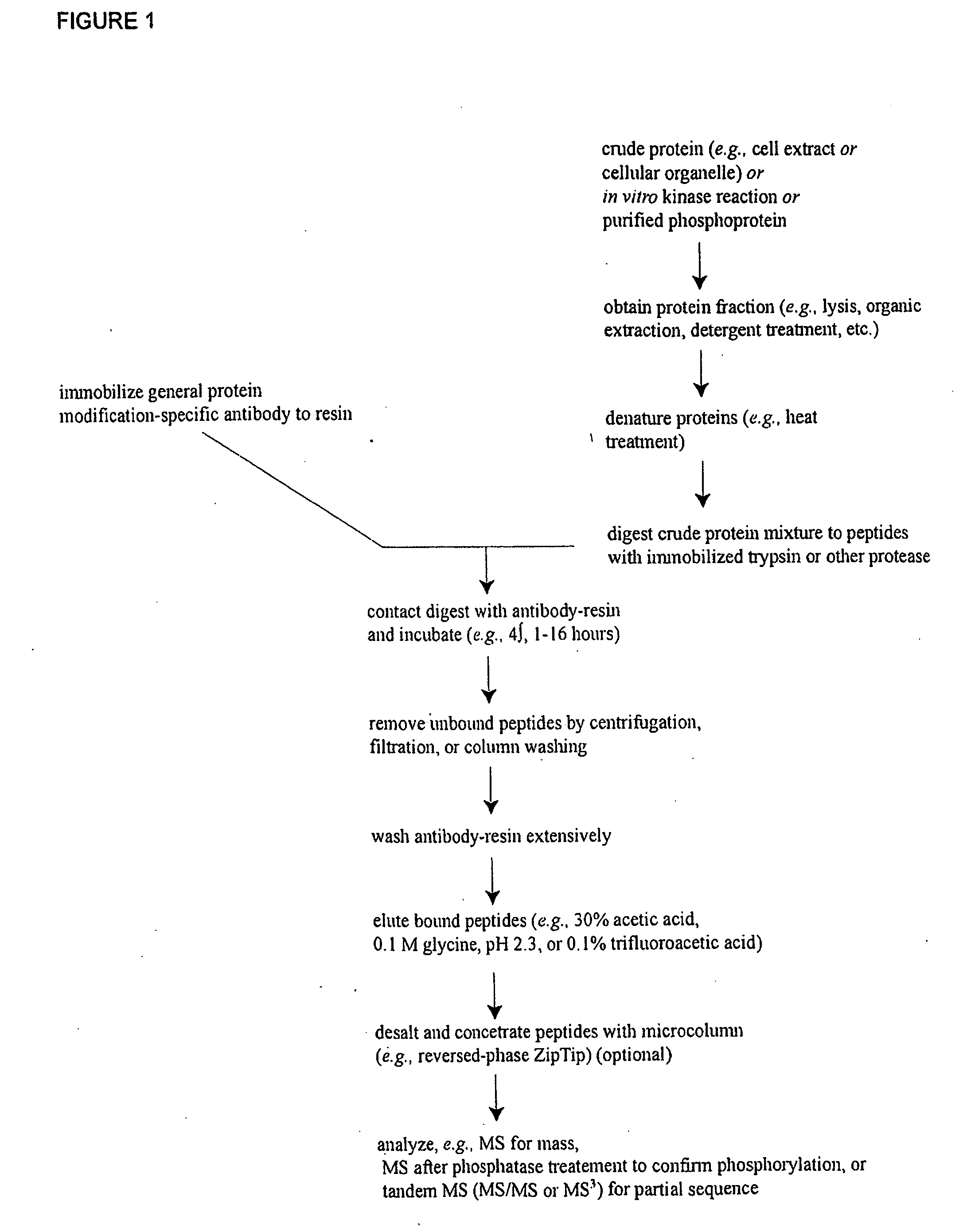
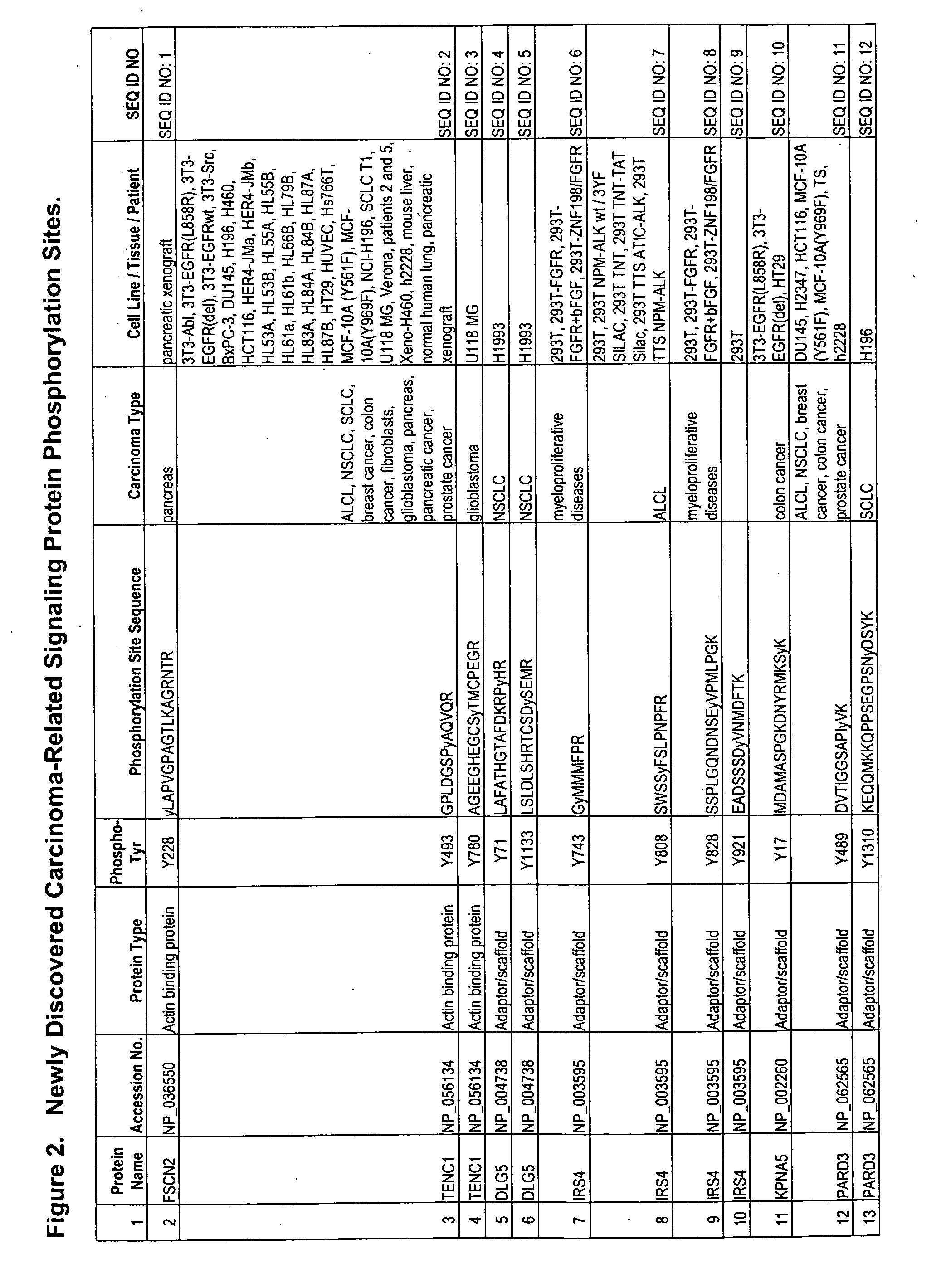
Reagents for the detection of protein phosphorylation in carcinoma signaling pathways
InactiveUS20090258442A1Immunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsFermentationPhospholipaseADAMTS Proteins
The invention discloses nearly 474 novel phosphorylation sites identified in signal transduction proteins and pathways underlying human carcinoma, and provides phosphorylation-site specific antibodies and heavy-isotope labeled peptides (AQUA peptides) for the selective detection and quantification of these phosphorylated sites / proteins, as well as methods of using the reagents for such purpose. Among the phosphorylation sites identified are sites occurring in the following protein types: Kinase, Adaptor / Scaffold proteins, Phosphatase, G protein Regulator / Guanine Nucleotide Exchange Factors / GTPase Activating Proteins, Cytoskeleton Proteins, DNA Binding Proteins, Phospholipase, Receptor Proteins, Enzymes, DNA Repair / Replication Proteins, Adhesion Proteins, and Proteases, as well as other protein types.
Owner:CELL SIGNALING TECHNOLOGY
Construction method for conditional overexpression Yap1 gene mice model at H11 locus
InactiveCN110093369AHigh precisionReduce dependenceAnimals/human peptidesVector-based foreign material introductionDevelopmental stageHippo signaling
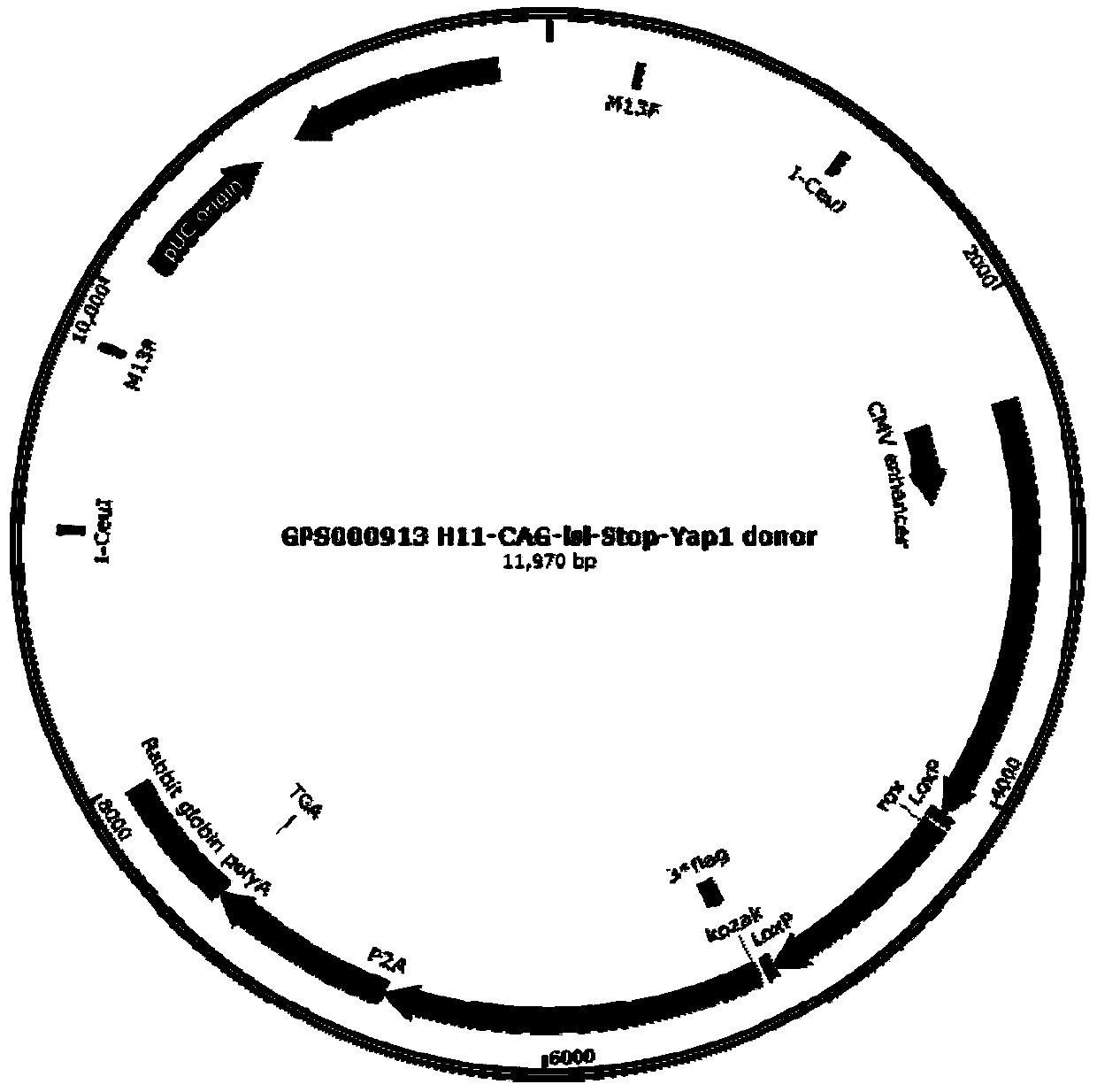
The invention discloses a construction method for a conditional overexpression Yap1 gene mice model at an H11 locus. The construction method comprises the steps: firstly, obtaining an inducible Yap1 overexpression transgenic vector; then, obtaining transgenic F0-generation mice; next, enabling the F0-generation mice to mate with wild-type mice, carrying out passage and line establishment, and thusobtaining F1-generation mice; and carrying out expanding propagation of positive F1-generation mice, then mutually mating, and thus obtaining the conditional overexpression mice Yap1 animal model. The transgenic mice model constructed by the method can be used for studying the function of Yap1 in different tissues and different developmental stages and the action mechanism of Hippo signaling pathways, can also be used for studying the function of the Hippo signaling pathway in animal development, biotumorigenesis, regenerative medicine and other disciplines, and has important guiding significance on biological signal transduction studies.
Owner:成都药康生物科技有限公司
Inhibitors of the BMP signaling pathway
The present invention provides small molecule inhibitors of BMP signaling. These compounds may be used to modulate cell growth, differentiation, proliferation, and apoptosis, and thus may be useful for treating diseases or conditions associated with BMP signaling, including inflammation, cardiovascular disease, hematological disease, cancer, and bone disorders, as well as for modulating cellular differentiation and / or proliferation.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP +1
Compounds, methods, and treatments for abnormal signaling pathways for prenatal and postnatal development
InactiveUS20110218176A1Inhibits cancer growthAvoid survivalBiocideMetabolism disorderDiseaseBiological body
The present invention relates to prevention of congenital deformations. The invention further relates to cancer inhibition and prevention. The invention further relates to methods and compositions to modulate, antagonize, or agonize disparate signaling pathways that may converge to regulate patterning events and gene expression during prenatal development, post-natal development, and during development in the adult organism. The invention also relates to activators or deactivators of pyruvate kinase M2 (PKM2) for the treatment, prevention, or amelioration of diseases related to PKM2 function.
Owner:JENNINGS SPRING BARBARA BROOKE
Regulation of the ras/camp/pka signaling pathway in yeasts
The present disclosure relates to the modulation in the RAS / cAMP / PKA signaling pathway for maintaining the propagation efficiency and increasing fermentation efficiency of yeast cells. The present disclosure provides yeast cells having or engineered to exhibit a modulation in signaling in a RAS / cAMP / PKA pathway, depending on conditions. For example the yeast cells can be selected or genetically modified to express a mutated Ras1 protein, a mutated Ras2 protein, a mutated Ira1 protein and / or a mutated Ira2 protein, optionally in combination with specific promoters. Also provided herewith are methods for propagating the yeast cells as well as using the yeast cells to generate a fermented product (such as ethanol).
Owner:LALLEMAND HUNGARY LIQUIDITY MANAGEMENT LLC
Applications of bruceine D in preparing Wnt/Notch signal channel inhibitor drugs
InactiveCN106491595ARevealing anti-tumor activity in vitro and in vivoOrganic active ingredientsDigestive systemDevelopmental anomalyBULK ACTIVE INGREDIENT
The invention provides applications of bruceine D in preparing a Wnt / Notch signal channel inhibitor preventing / treating drug. The Wnt / Notch signal channel inhibitor preventing / treating drug is a drug composition which is prepared by taking bruceine D as an active ingredient, and is prepared from bruceine D and a pharmaceutic adjuvant, and can be prepared into oral preparations, injection preparations, or transdermal drugs. A human liver cancer tumor cell line model and a human normal liver cell line model are used for evaluating in vitro antitumor effect of bruceine D, a zebra fish model is used for evaluating inhibition effect of bruceine D on Wnt / Notch signal channel, and it is confirmed by experiment results that body axis dysplasia caused by inhibition of Wnt signal channel is observed when death of zebra fish is not caused by 100<mu>M of bruceine D. Influences of bruceine D on Wnt-Notch signal channel key proteins are disclosed by in vitro and vivo antitumor activity experiments of bruceine D for the first time, the important effect of Wnt-Notch signal channel on liver cancer, and the inner relationship of Wnt-Notch signal channel are confirmed, novel applications of bruceine D in preparing the drugs used for preventing / treating liver cancer are provided, the drugs used for preventing / treating liver cancer are provided for clinical therapy, and high application value is achieved.
Owner:SHANXI ZHENDONG LEADING BIOTECH CO LTD
Reagents for the detection of protein phosphorylation in carcinoma signaling pathways
InactiveUS20090099340A1Immunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsFermentationADAMTS ProteinsProtein phosphorylation
The invention discloses 214 novel phosphorylation sites identified in signal transduction proteins and pathways underlying human carcinoma, and provides phosphorylation-site specific antibodies and heavy-isotope labeled peptides (AQUA peptides) for the selective detection and quantification of these phosphorylated sites / proteins, as well as methods of using the reagents for such purpose. Among the phosphorylation sites identified are sites occurring in the following protein types: Adaptor / Scaffold proteins, Cytoskeleton proteins, GTP Signaling proteins, Kinases, Metabolism proteins, Phosphatases / Phospho-diesterases / Proteases, Receptor proteins, RNA Processing proteins, Transcription proteins, Translation proteins, Transporter proteins, and Ubitquitin proteins, as well as other protein types.
Owner:CELL SIGNALING TECHNOLOGY
Hepatocyte growth factor pathway activators in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
ActiveUS7879898B1Promotes compensatory lung growthInduce angiogenesisBiocideAnimal repellantsObstructive Pulmonary DiseasesHepatocyte growth factor
Methods are provided for treating chronic obstructive pulmonary diseases such as emphysema using compounds that activate the signaling pathways of hepatocyte growth factor.
Owner:ANGION BIOMEDICA CORP
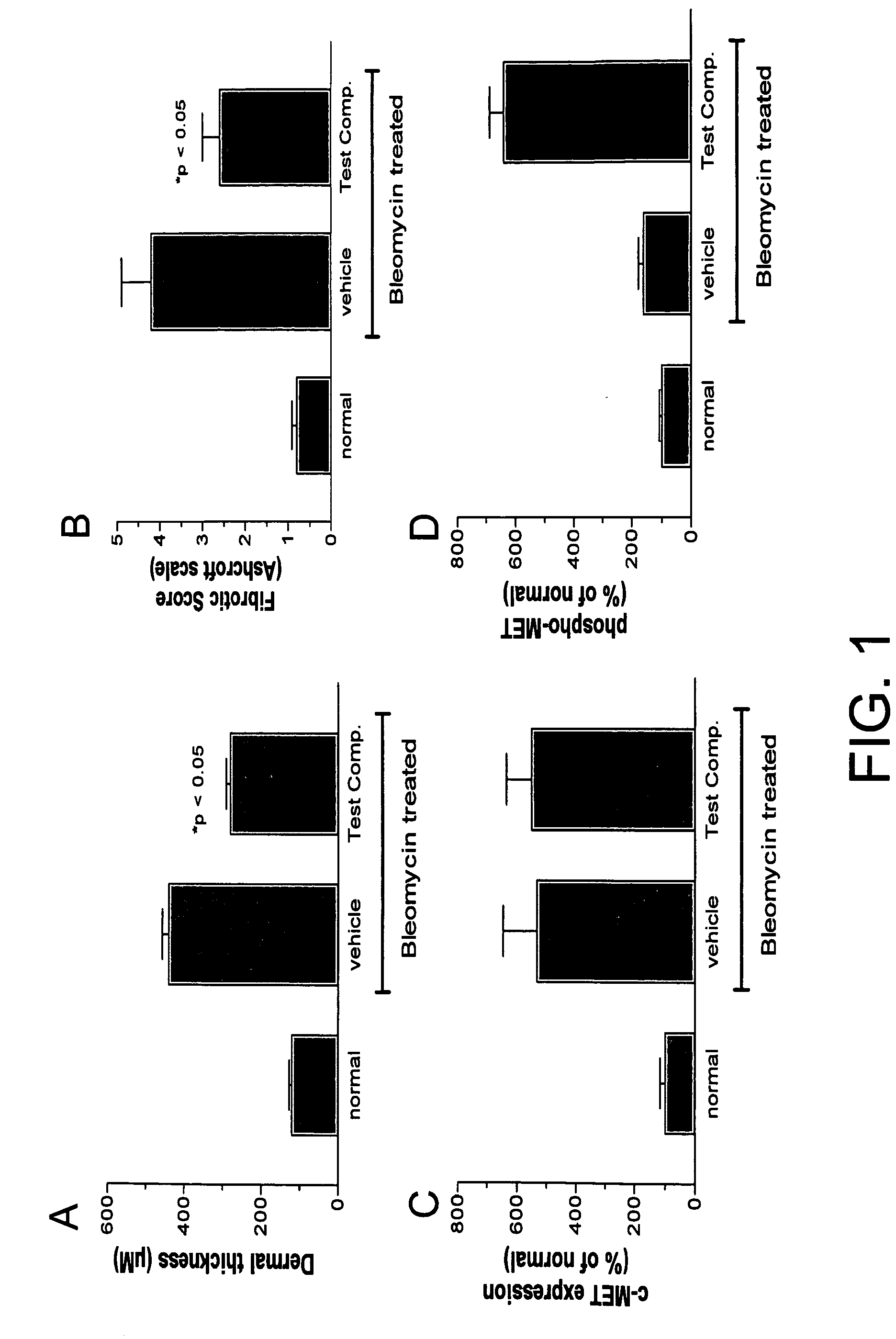
Hepatocyte growth factor pathway activators in fibrotic connective tissue diseases
Methods are provided for treating fibrotic connective tissue diseases such as scleroderma and conditions such as surgically-induced adhesions using compounds that activate the signaling pathways of hepatocyte growth factor.
Owner:ANGION BIOMEDICA CORP
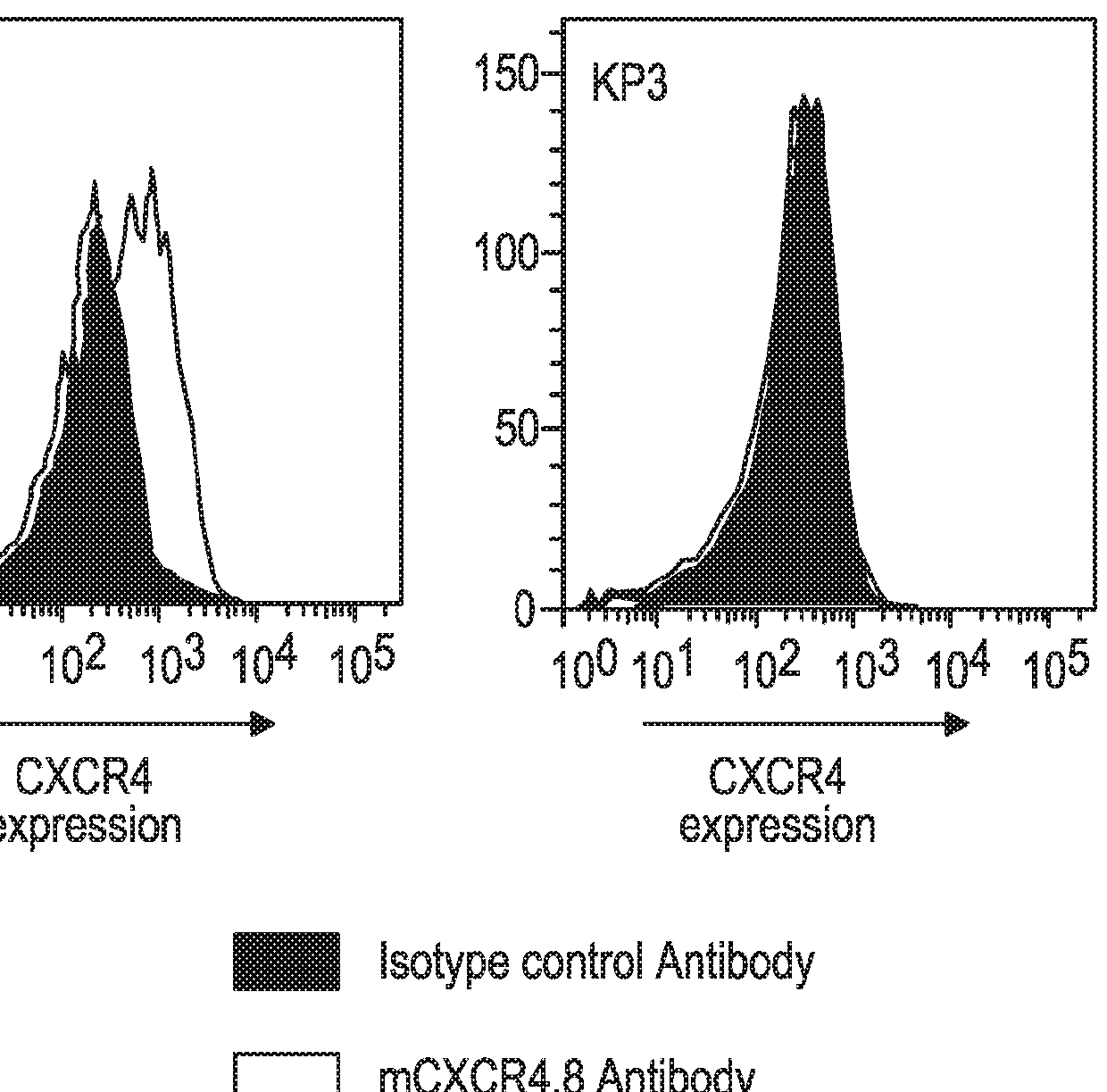
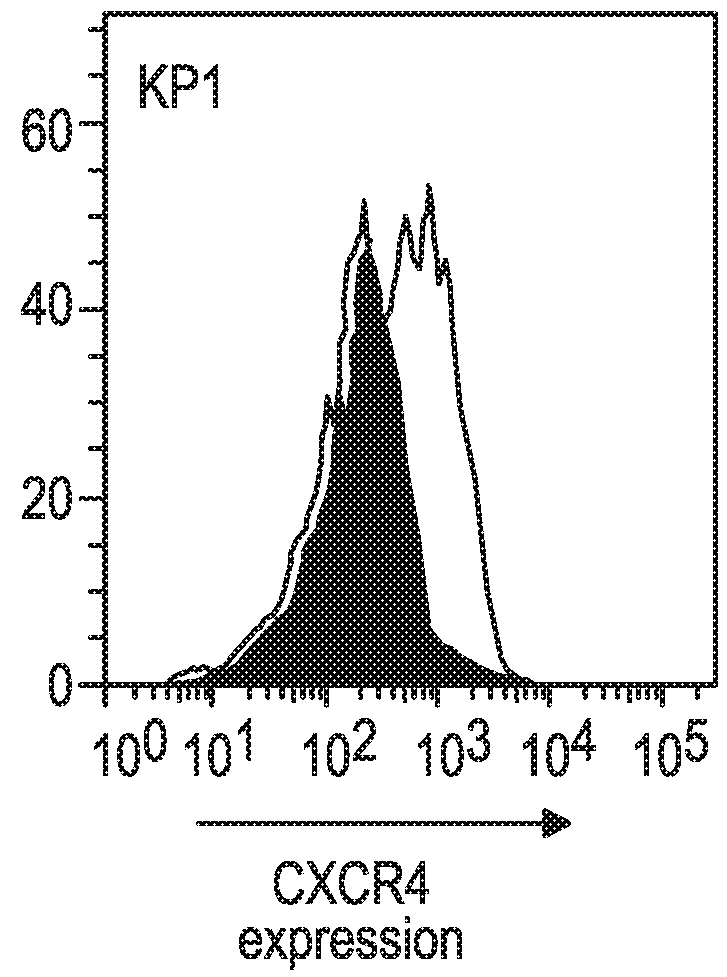
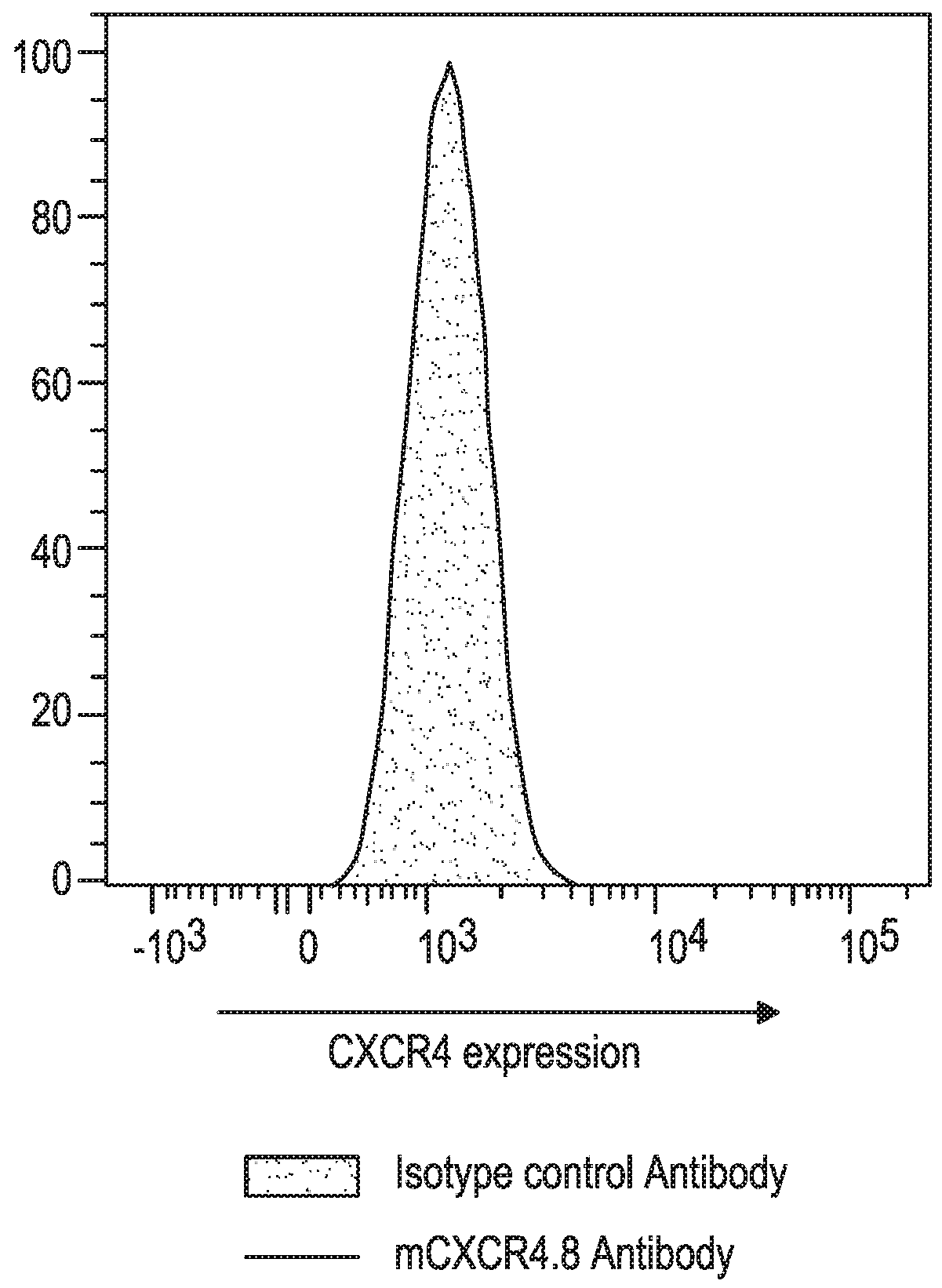
Treatment of cancer by combined blockade of the pd-1 and cxcr4 signaling pathways
InactiveUS20180179282A1Avoid signalingImmunoglobulins against cytokines/lymphokines/interferonsImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsCXCR4 Signaling PathwayAntigen binding
This disclosure provides a method for treating a subject afflicted with a cancer comprising administering to the subject a combination of therapeutically effective amounts of an antibody or an antigen-binding portion thereof that binds specifically to Programmed Death-1 (PD-1) or to Programmed Death Ligand-1 (PD-L1), and an antibody or an antigen-binding portion thereof that binds specifically to C-X-C Chemokine Receptor 4 (CXCR4) or to C-X-C motif chemokine 12 (CXCL12). The disclosure also provides a kit for treating a subject afflicted with a cancer, the kit comprising one or more dosages of an antibody or an antigen-binding portion thereof that binds specifically to PD-1 or to PD-L1, one or more dosages of an antibody or an antigen-binding portion thereof that binds specifically to CXCR4 or to CXCL12, and instructions for using the antibodies or portions thereof for treating the subject.
Owner:BRISTOL MYERS SQUIBB CO
Compositions and methods for regulating cancer-related signaling pathways
InactiveUS20140348744A1Improve survivabilityLibrary screeningImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsADAMTS ProteinsTreatment targets
Owner:PINSKI JACEK K
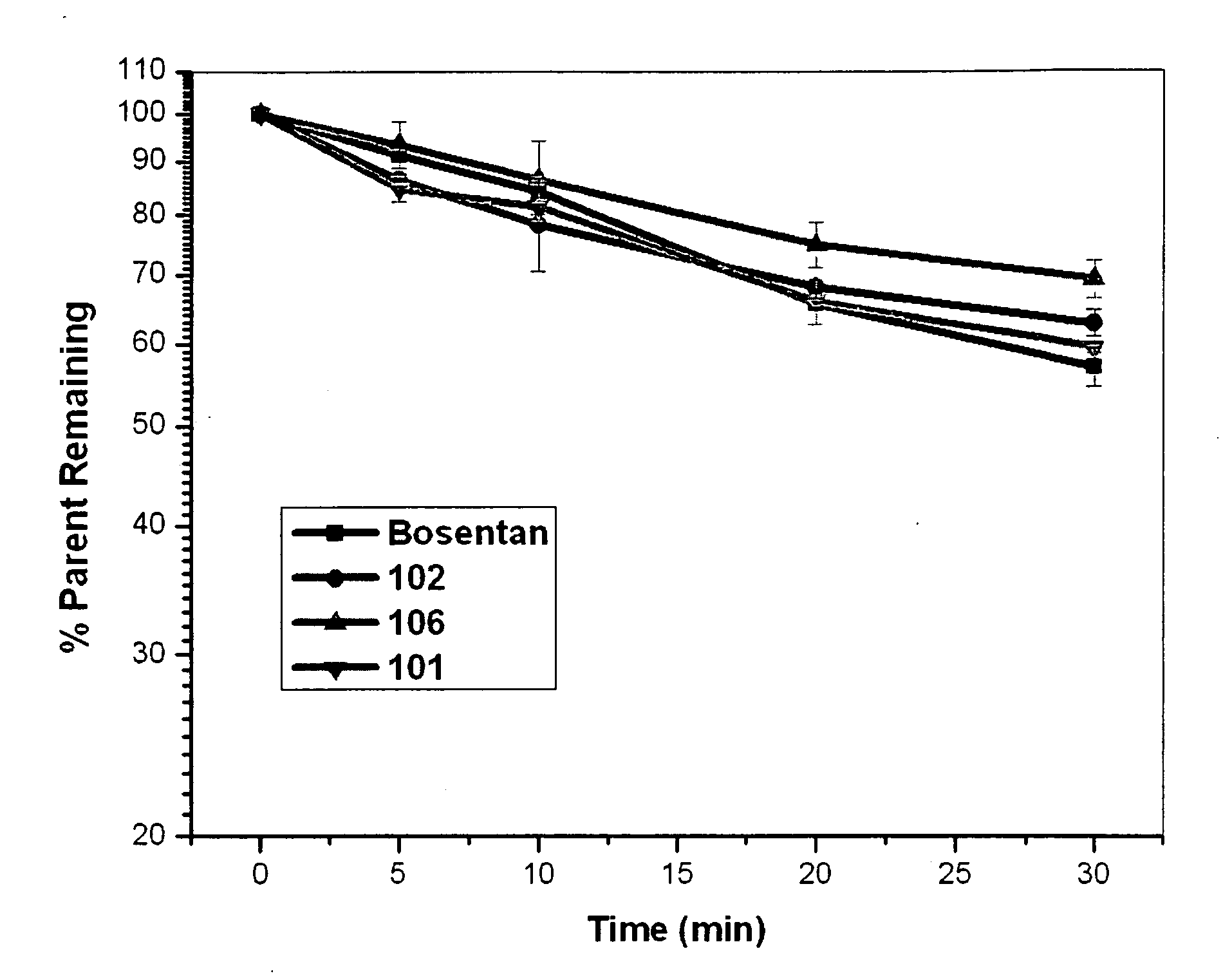
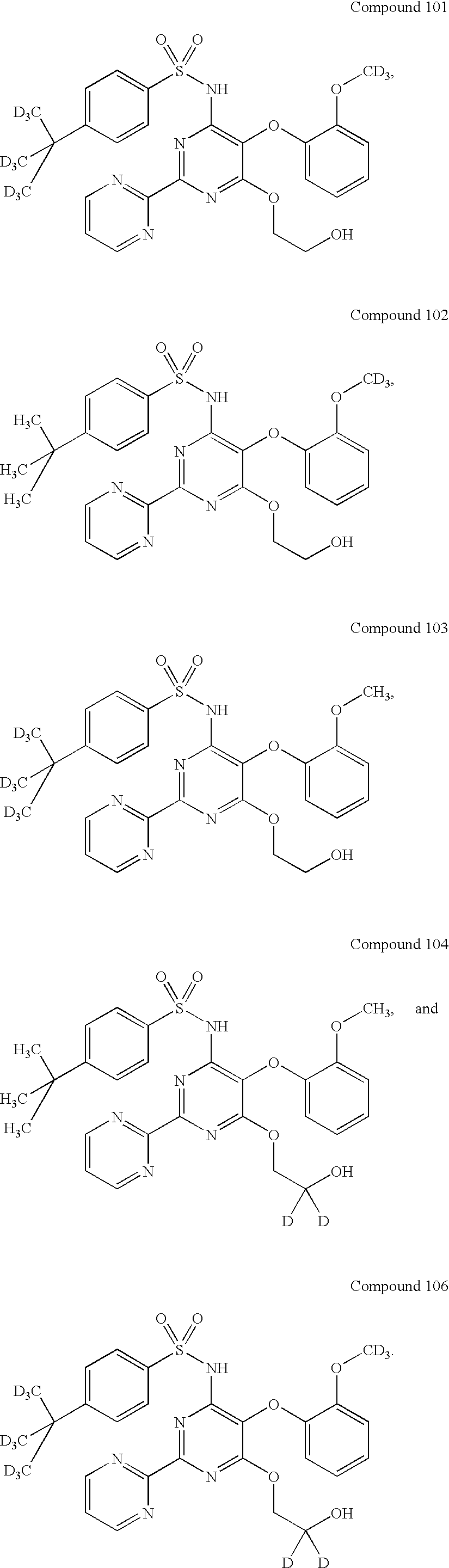
Endothelin receptor antagonists
This invention relates to novel endothelin receptor antagonists, derivatives, acceptable acid addition salts thereof. The invention also provides compositions comprising a compound of this invention and the use of such compositions in methods of treating diseases and conditions that are beneficially treated by compounds that block the endothelin signaling pathway that leads to vasoconstriction and in particular those diseases or conditions beneficially treated by endothelin receptor antagonists.
Owner:SUN PHARMA IND INC
Application of chlorogenic acid in activation of immune related signaling pathway of organism and research method of chlorogenic acid
InactiveCN105106187AIncrease credibilityAvoid false positivesOrganic active ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsChlorogenic acidMolecular level
The invention discloses an application of a chlorogenic acid in activation of an immune related signaling pathway of an organism and a research method of the chlorogenic acid, belongs to the field of biological medicines, and provides a new application of the chlorogenic acid for regulating and controlling the organism immunoreaction from gene and molecular level, namely an application of the chlorogenic acid in activation of the immune related signaling pathway of the organism. A molecular contact between the immune related signaling pathway and the anti-cancer function of the chlorogenic acid is established. A method for accurately regulating and controlling the immune related signaling pathway of the organism through the chlorogenic acid is provided. Through the application, the chlorogenic acid can be further used for guiding treatment of tumors, and can also be used for building related research models for the specific action principle of the immune related signaling pathway or other related applications.
Owner:SICHUAN JIUZHANG BIO TECH CO LTD
Medical application of camptothecin and its derivative in resisting Alzheimer disease
The invention relates to the field of crude drugs, specifically relates to a medical application of camptothecin and its derivative in resisting Alzheimer disease. Pharmacological experiments prove that: the camptothecin and its derivative have significant effect on inhibiting production of A beta, the IC50 is within the range of 0.1-10 nM, and the molecular weights of the compounds are all less than 500 Dalton, which mean the compounds has latent capacity of permeating a blood cerebral barrier. More importantly, the camptothecin and its analogues have no influence on cytotoxicity and apoptosis in inhibiting the concentration range of A beta, and simultaneously have no side effect on Notch signal passages.
Owner:CHINA PHARM UNIV
Modulators of antiviral signaling pathways and therapeutic uses thereof
ActiveUS9650427B2Reduce deliveryGood effectCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsPeptide/protein ingredientsDiseaseRIG-I-like receptor
The invention provides methods, compositions, and kits featuring novel RIG-I like receptor activators or inhibitors for use in preventing or treating virus infection or autoimmune disease.
Owner:CHILDRENS MEDICAL CENT CORP
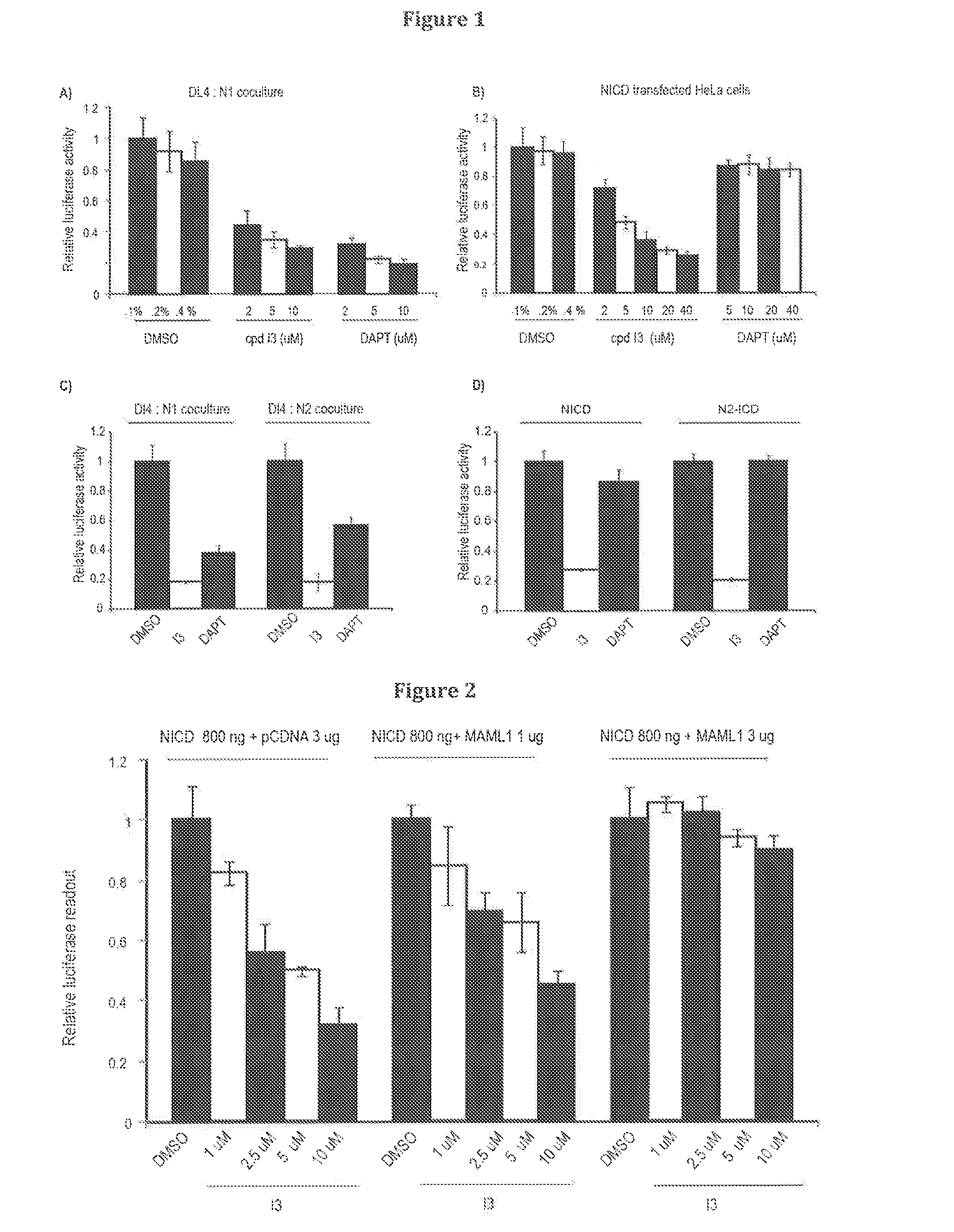
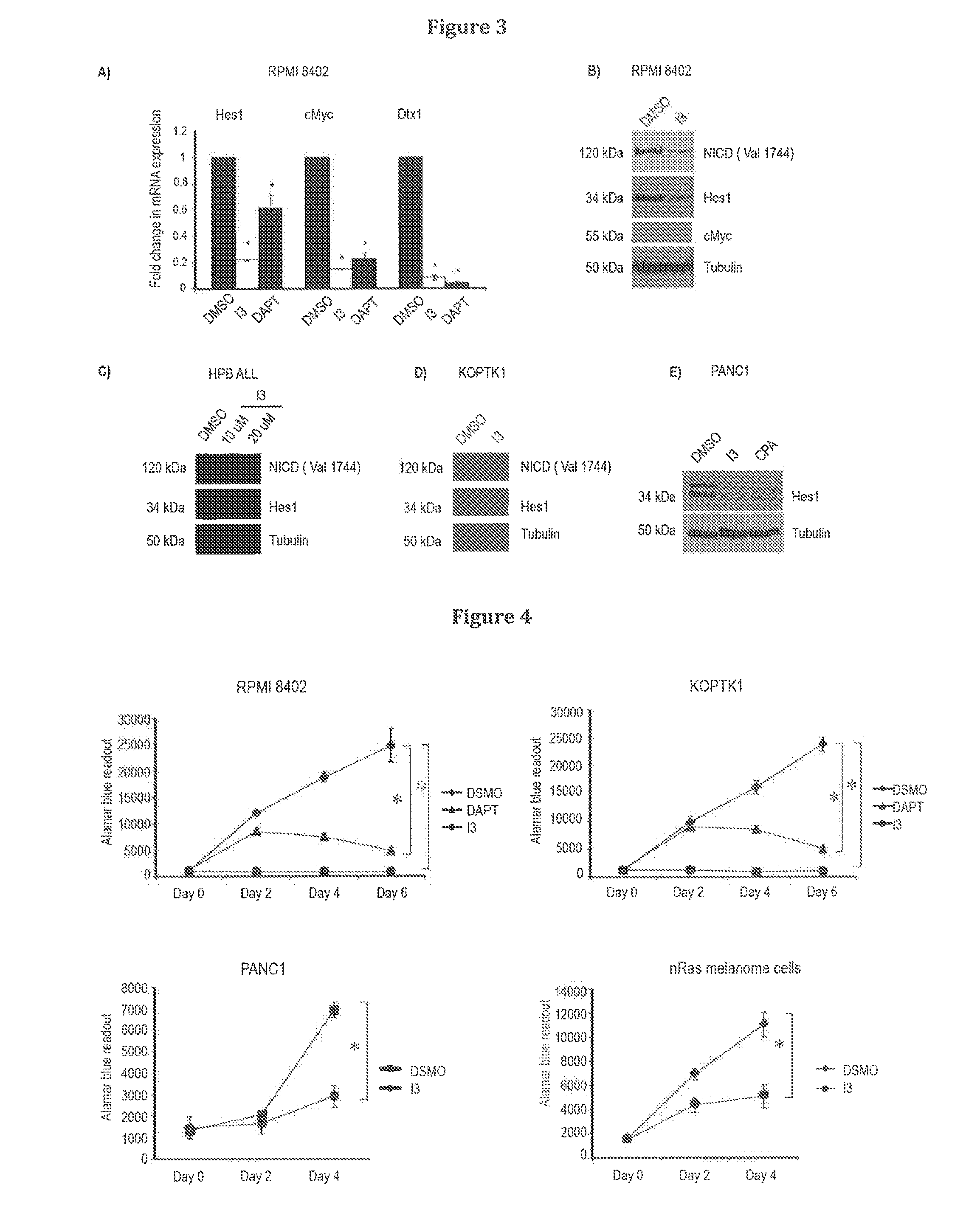
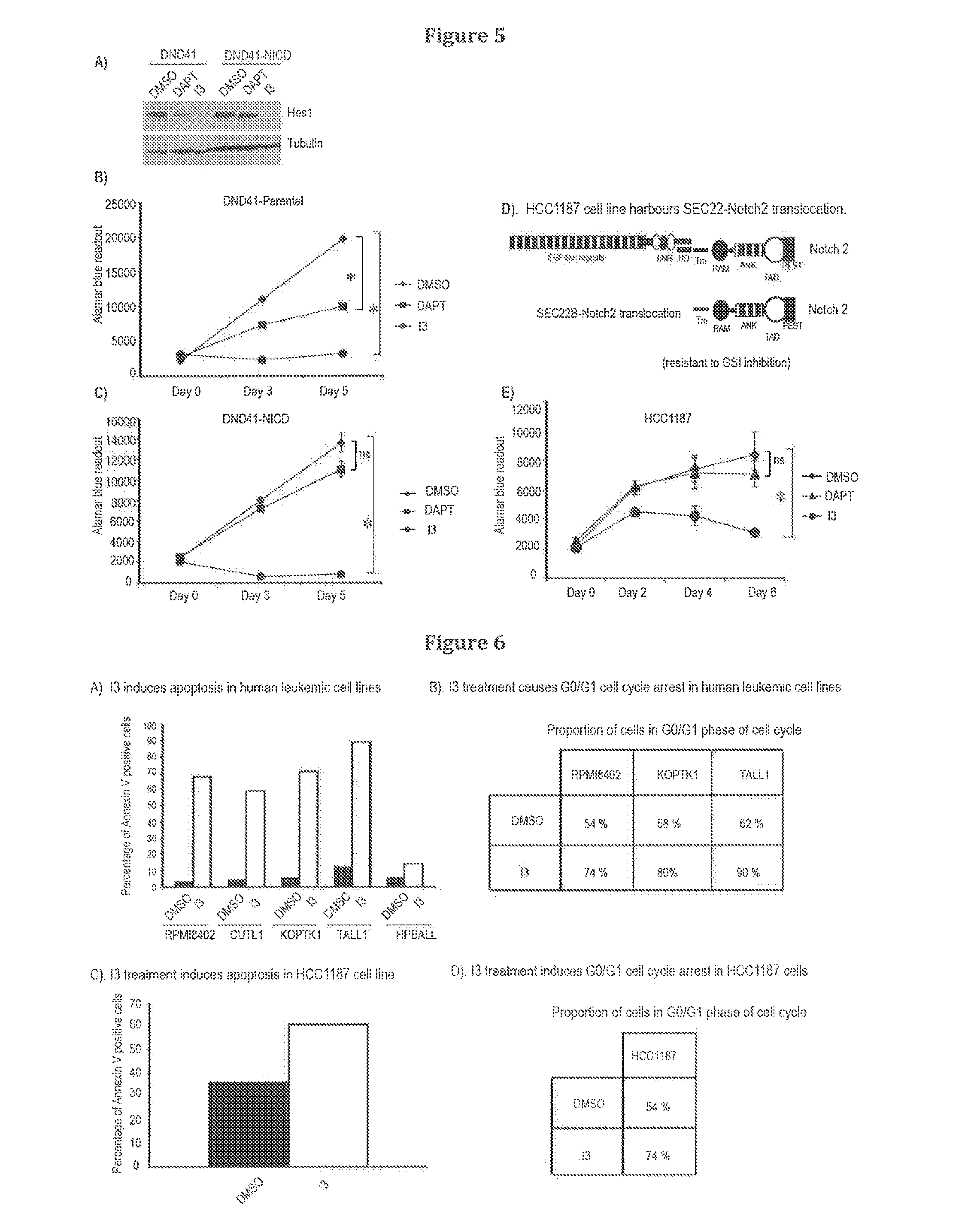
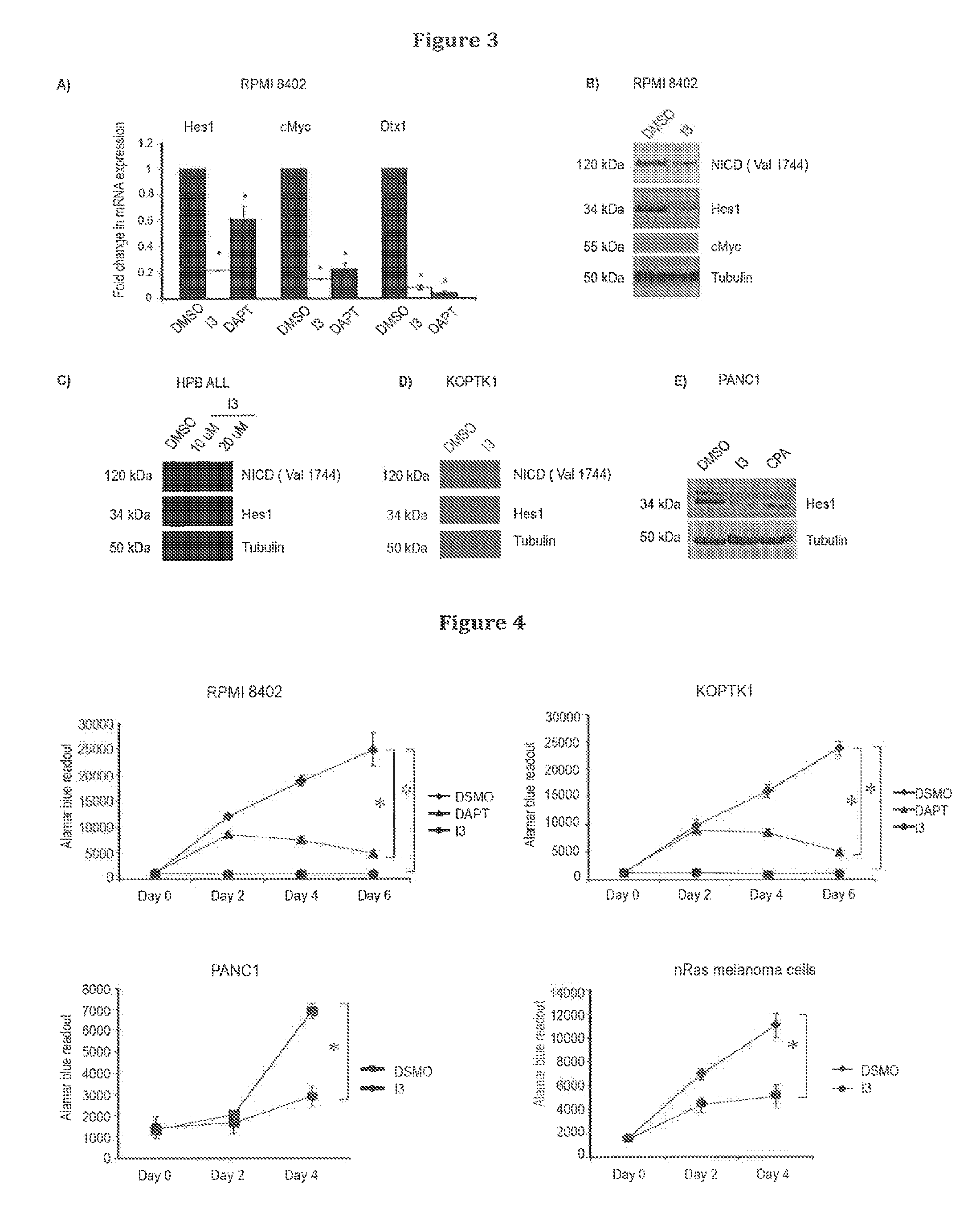
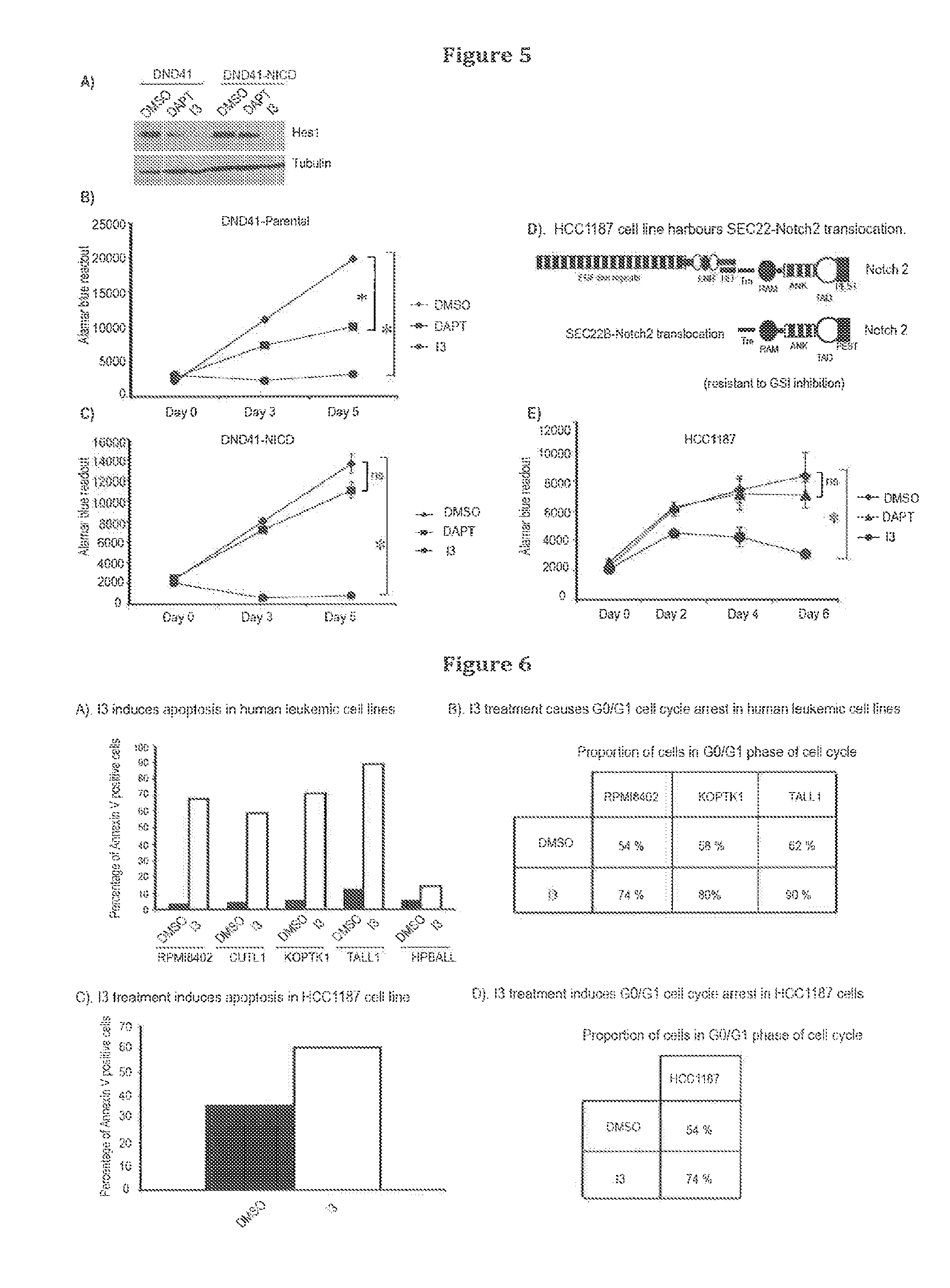
Inhibitors of notch signalling pathway and use thereof in treatment of cancers
ActiveUS20140329867A1Organic active ingredientsOrganic compound preparationCancer therapyCancer research
The present invention relates to use of inhibitors of Notch signalling pathway selected from the group consisting of 6-(4-Tert-Butylphenoxy)Pyridin-3-Amine (I3), its derivatives, in treating and / or preventing cancers.
Owner:ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE FEDERALE DE LAUSANNE (EPFL)
Inhibitors of notch signalling pathway and use thereof in treatment of cancers
ActiveUS20160266095A1Ether/acetal active ingredientsImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsCancer preventionCancer therapy
The present invention relates to use of inhibitors of Notch signalling pathway selected from the group consisting of 6-(4-Tert-Butylphenoxy)Pyridin-3-Amine (I3), its derivatives, in treating and / or preventing cancers.
Owner:ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE FEDERALE DE LAUSANNE (EPFL)
Reagents for the detection of protein phosphorylation in carcinoma signaling pathways
The invention discloses nearly 443 novel phosphorylation sites identified in signal transduction proteins and pathways underlying human carcinoma, and provides phosphorylation-site specific antibodies and heavy-isotope labeled peptides (AQUA peptides) for the selective detection and quantification of these phosphorylated sites / proteins, as well as methods of using the reagents for such purpose. Among the phosphorylation sites identified are sites occurring in the following protein types: Protein kinases (including Serine / Threonine dual specificity, and Tyrosine kinases), Adaptor / Scaffold proteins, Transcription factors, Phospoatases, Tumor supressors, Ubiquitin conjugating system proteins, Translation initiation complex proteins, RNA binding proteins, Apoptosis proteins, Adhesion proteins, G protein regulators / GTPase activating protein / Guanine nucleotide exchange factor proteins, and DNA binding / replication / repair proteins, as well as other protein types.
Owner:CELL SIGNALING TECHNOLOGY
Pharmaceutical targeting of a mammalian cyclic di-nucleotide signaling pathway
Cyclic-GMP-AMP (cGAMP), including 2′,3′-cGAMP, are used in pharmaceutical formulations (including vaccine adjuvants), drug screens, therapies and diagnostics.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Reagents for the detection of protein phosphorylation in carcinoma signaling pathways
The invention discloses nearly 443 novel phosphorylation sites identified in signal transduction proteins and pathways underlying human carcinoma, and provides phosphorylation-site specific antibodies and heavy-isotope labeled peptides (AQUA peptides) for the selective detection and quantification of these phosphorylated sites / proteins, as well as methods of using the reagents for such purpose. Among the phosphorylation sites identified are sites occurring in the following protein types: Protein kinases (including Serine / Threonine dual specificity, and Tyrosine kinases), Adaptor / Scaffold proteins, Transcription factors, Phospoatases, Tumor supressors, Ubiquitin conjugating system proteins, Translation initiation complex proteins, RNA binding proteins, Apoptosis proteins, Adhesion proteins, G protein regulators / GTPase activating protein / Guanine nucleotide exchange factor proteins, and DNA binding / replication / repair proteins, as well as other protein types.
Owner:CELL SIGNALING TECHNOLOGY
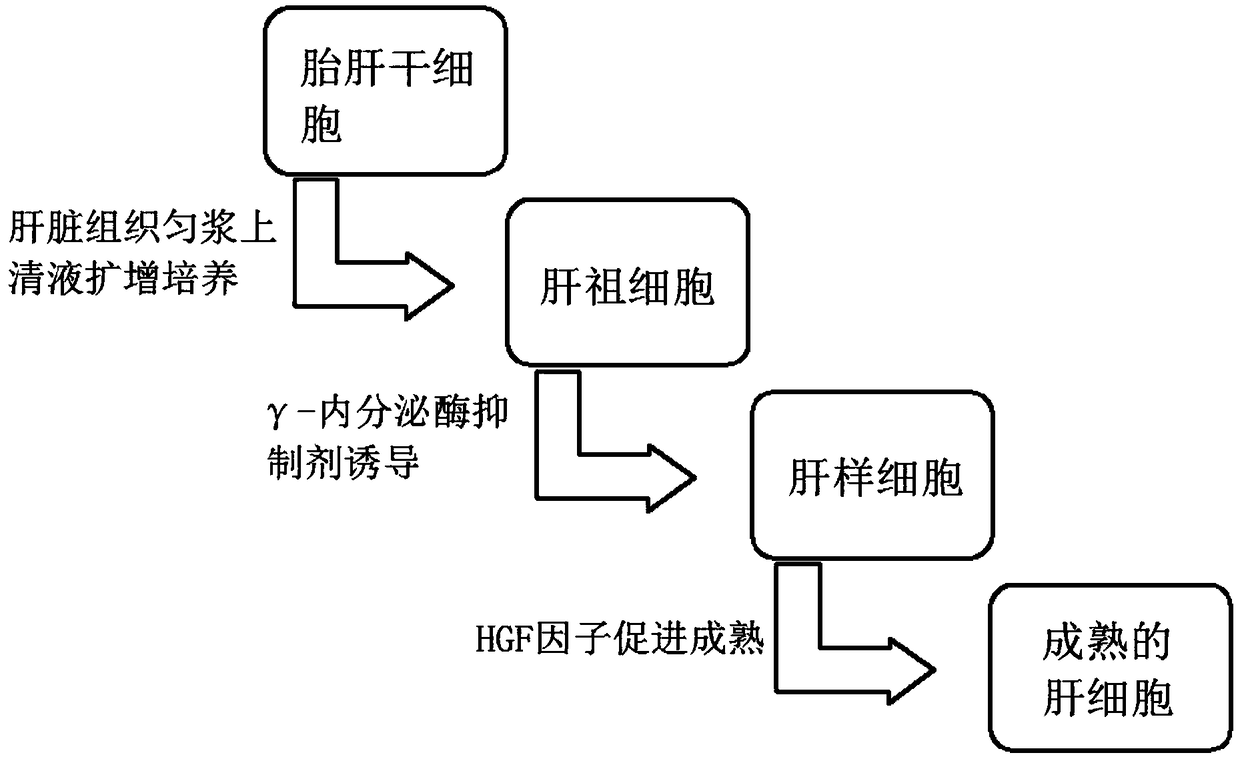
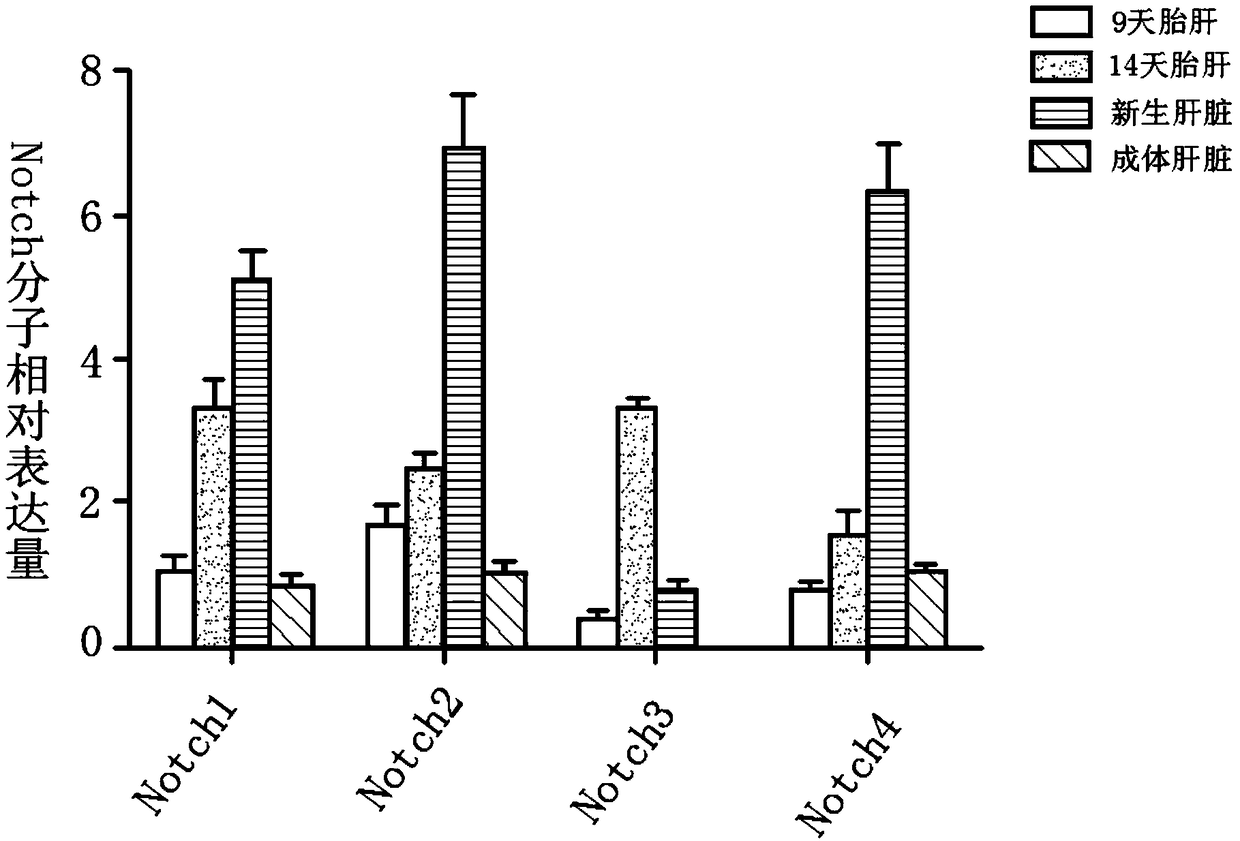
Method for inducing fetal hepatic stem cells to differentiate into mature hepatic cells in three-step sequential mode
PendingCN109251884ARich sourcesRecovery levelHepatocytesArtificial cell constructsBiotechnologyProgenitor
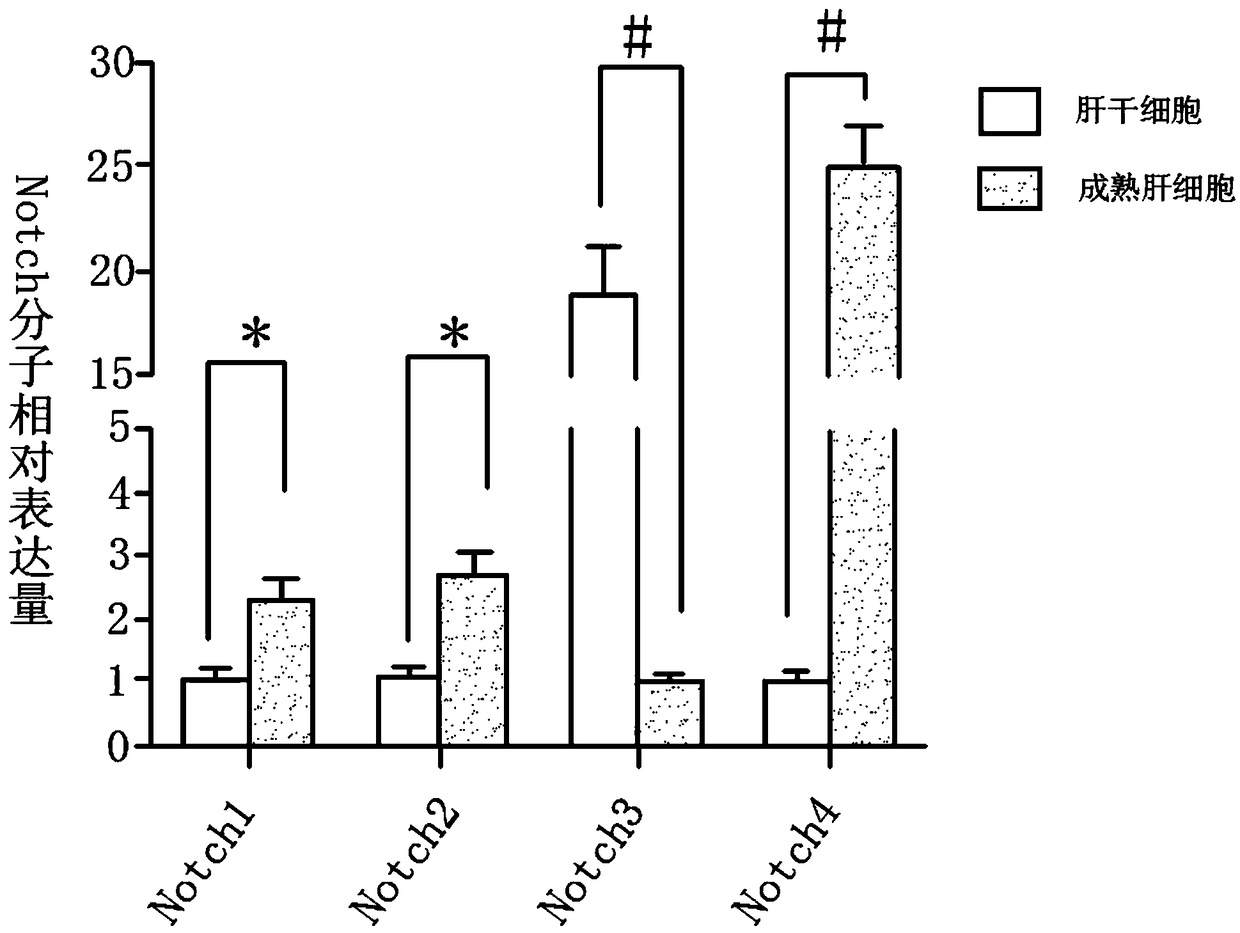
The invention discloses a method for inducing fetal hepatic stem cells to differentiate into mature hepatic cells in a three-step sequential mode, and belongs to the technical field of biology. The method comprises the following steps that (1) the fetal hepatic stem cells are obtained and identified, specifically, (a) the fetal hepatic steam cells are separated and amplified, and (b) the fetal hepatic stem cells are identified; (2) the fetal hepatic steam cells are induced to differentiate, specifically, (a) a tissue suspension prepared from normal hepatic tissue which is ground and homogenized is collected on dry ice at a low temperature, supernatant is collected after centrifuging and added into a Williams'E cell culture medium, and the fetal hepatic stem cells in the step (1) are cultivated to obtain hepatic progenitor cells, (b) the cells obtained in the step (a) are continuously cultivated through the Wiliams'E culture medium added with a Notch signal channel inhibitor to obtain hepatocyte-like cells, and (c) the cells obtained in the step (b) are cultivated through a rapid cell expansion culture medium added with HGF to obtain functional hepatic cells. Through the method, thefetal hepatic stem cells obtained early can be induced into the functional hepatic cells rapidly, accurately and efficiently.
Owner:刘卫辉
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com