Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
234 results about "Bayesian estimator" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
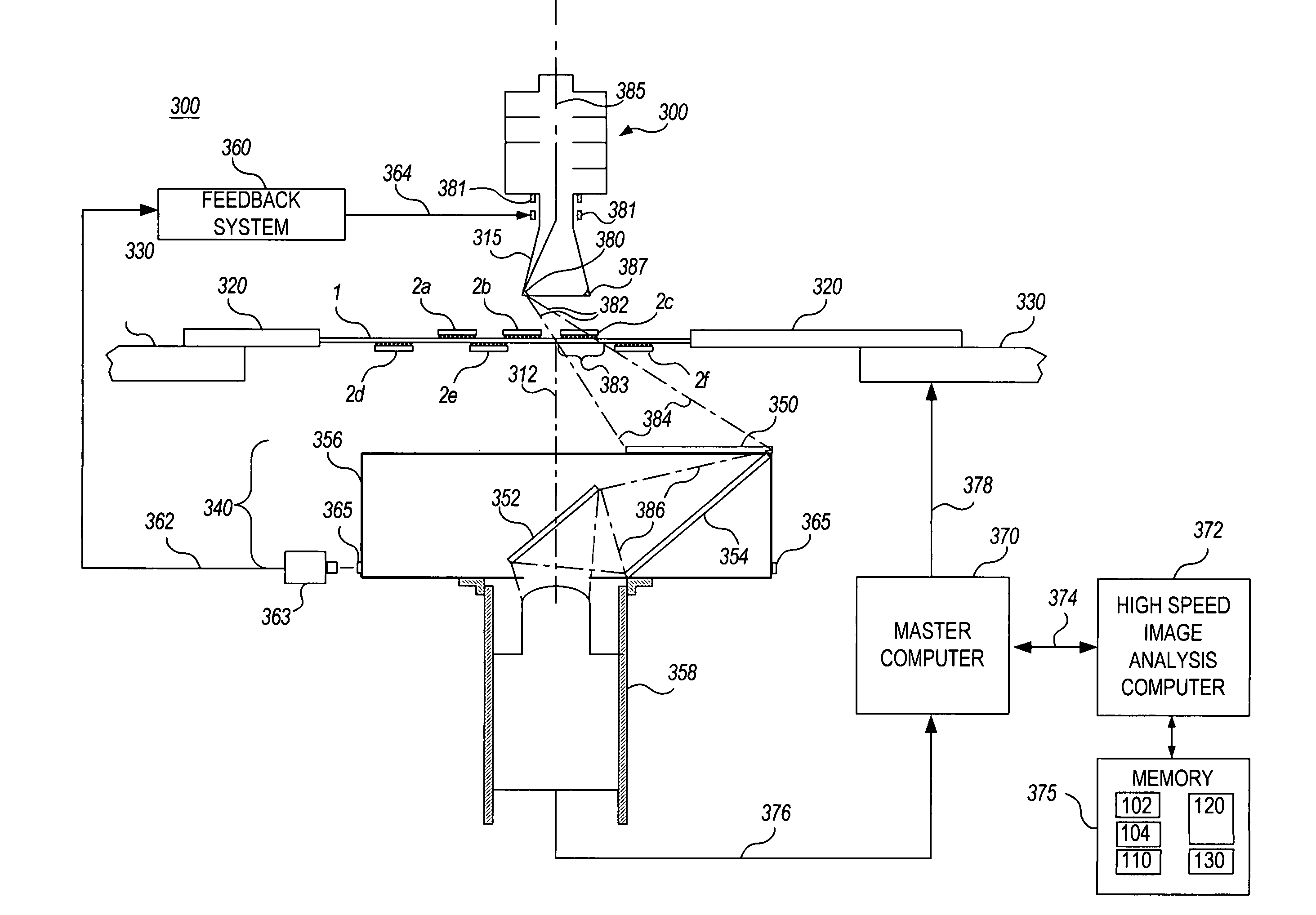
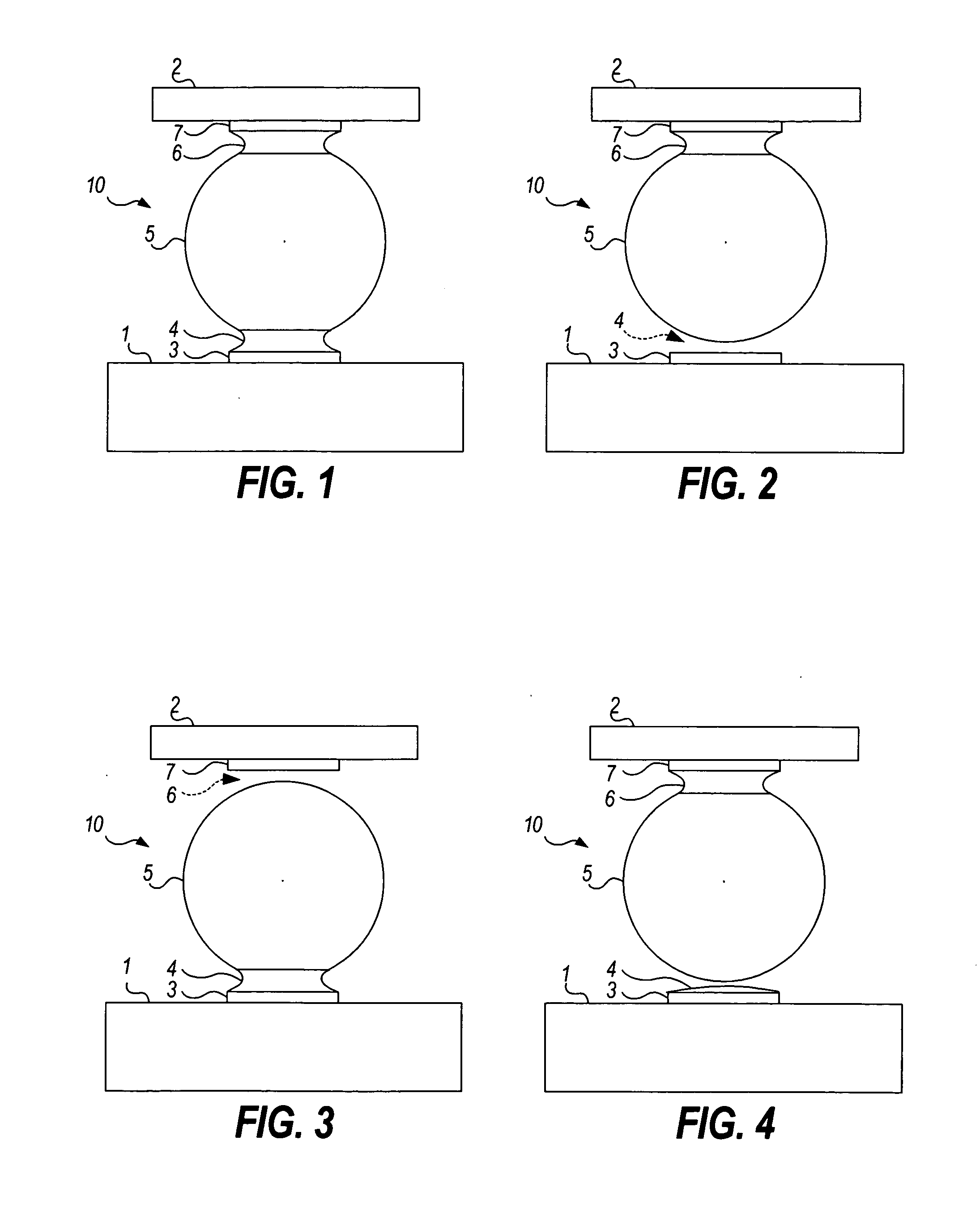
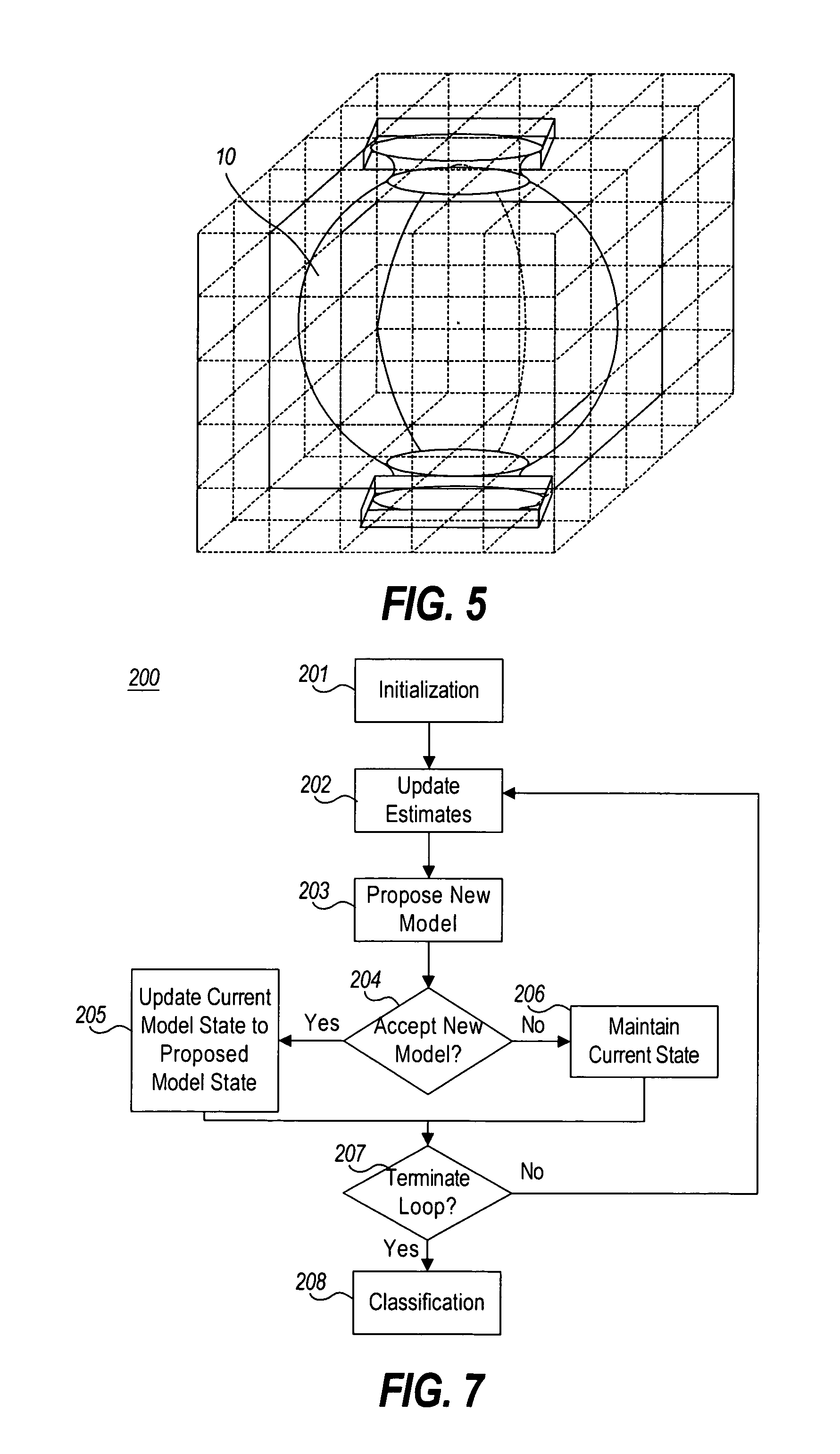
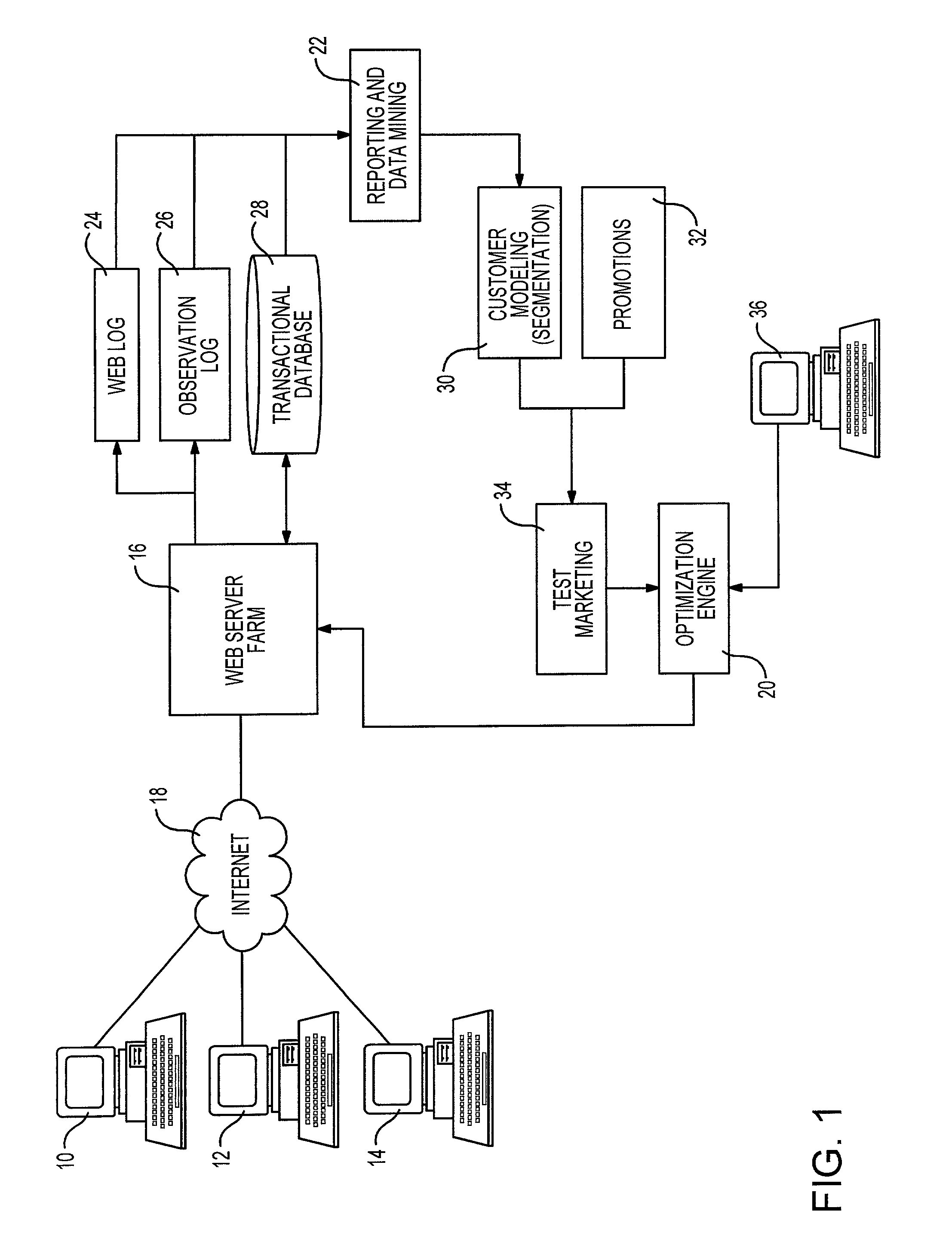
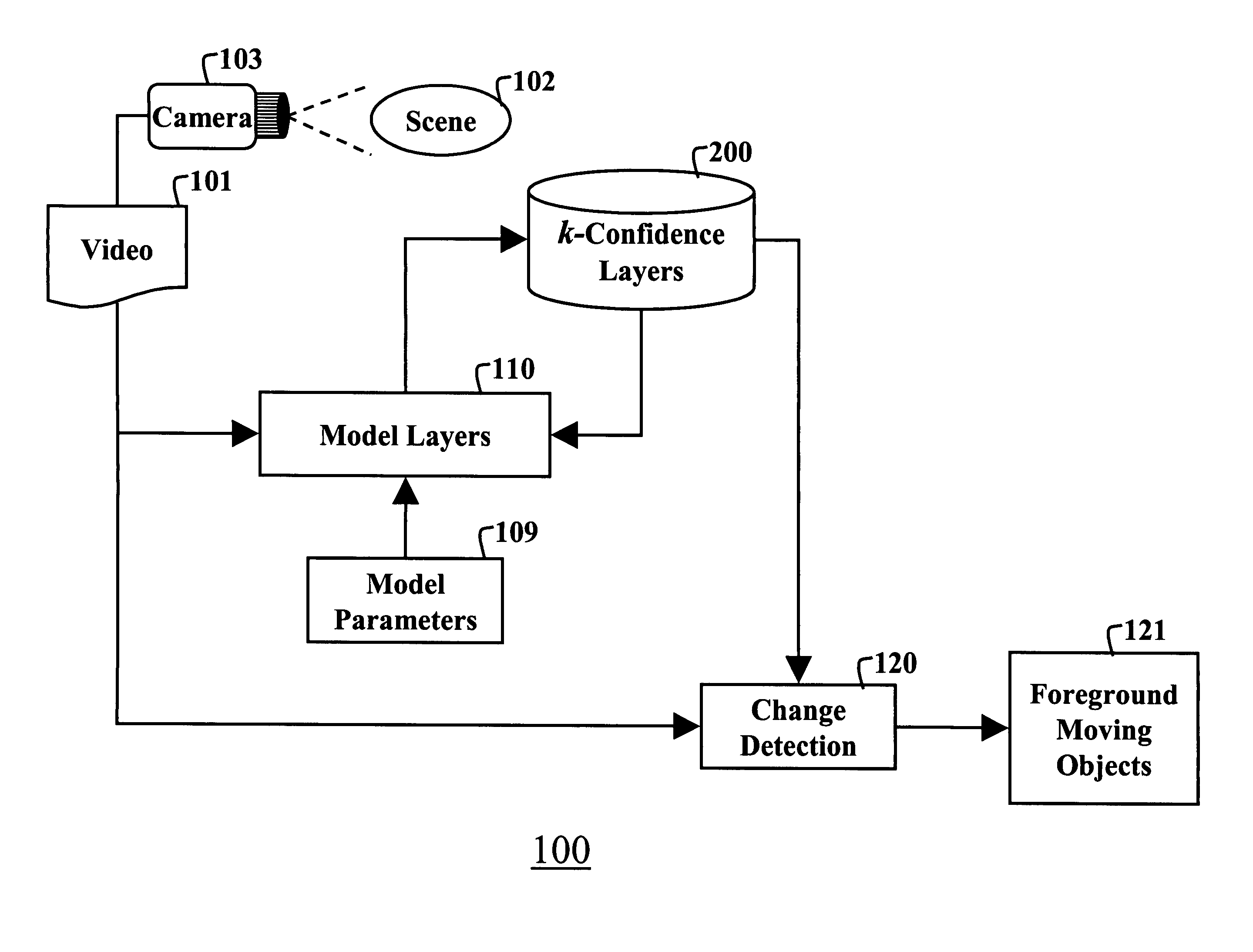
Highly constrained tomography for automated inspection of area arrays
InactiveUS20050105682A1Radiation/particle handlingUsing wave/particle radiation meansPattern recognitionPrior information
A tomographic reconstruction method and system incorporating Bayesian estimation techniques to inspect and classify regions of imaged objects, especially objects of the type typically found in linear, areal, or 3-dimensional arrays. The method and system requires a highly constrained model M that incorporates prior information about the object or objects to be imaged, a set of prior probabilities P(M) of possible instances of the object; a forward map that calculates the probability density P(D|M), and a set of projections D of the object. Using Bayesian estimation, the posterior probability p(M|D) is calculated and an estimated model MEST of the imaged object is generated. Classification of the imaged object into one of a plurality of classifications may be performed based on the estimated model MEST, the posterior probability p(M|D) or MAP function, or calculated expectation values of features of interest of the object.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
Highly constrained tomography for automated inspection of area arrays
InactiveUS7099435B2Radiation/particle handlingUsing wave/particle radiation meansPrior informationTomographic reconstruction
A tomographic reconstruction method and system incorporating Bayesian estimation techniques to inspect and classify regions of imaged objects, especially objects of the type typically found in linear, areal, or 3-dimensional arrays. The method and system requires a highly constrained model M that incorporates prior information about the object or objects to be imaged, a set of prior probabilities P(M) of possible instances of the object; a forward map that calculates the probability density P(D|M), and a set of projections D of the object. Using Bayesian estimation, the posterior probability p(M|D) is calculated and an estimated model MEST of the imaged object is generated. Classification of the imaged object into one of a plurality of classifications may be performed based on the estimated model MEST, the posterior probability p(M|D) or MAP function, or calculated expectation values of features of interest of the object.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
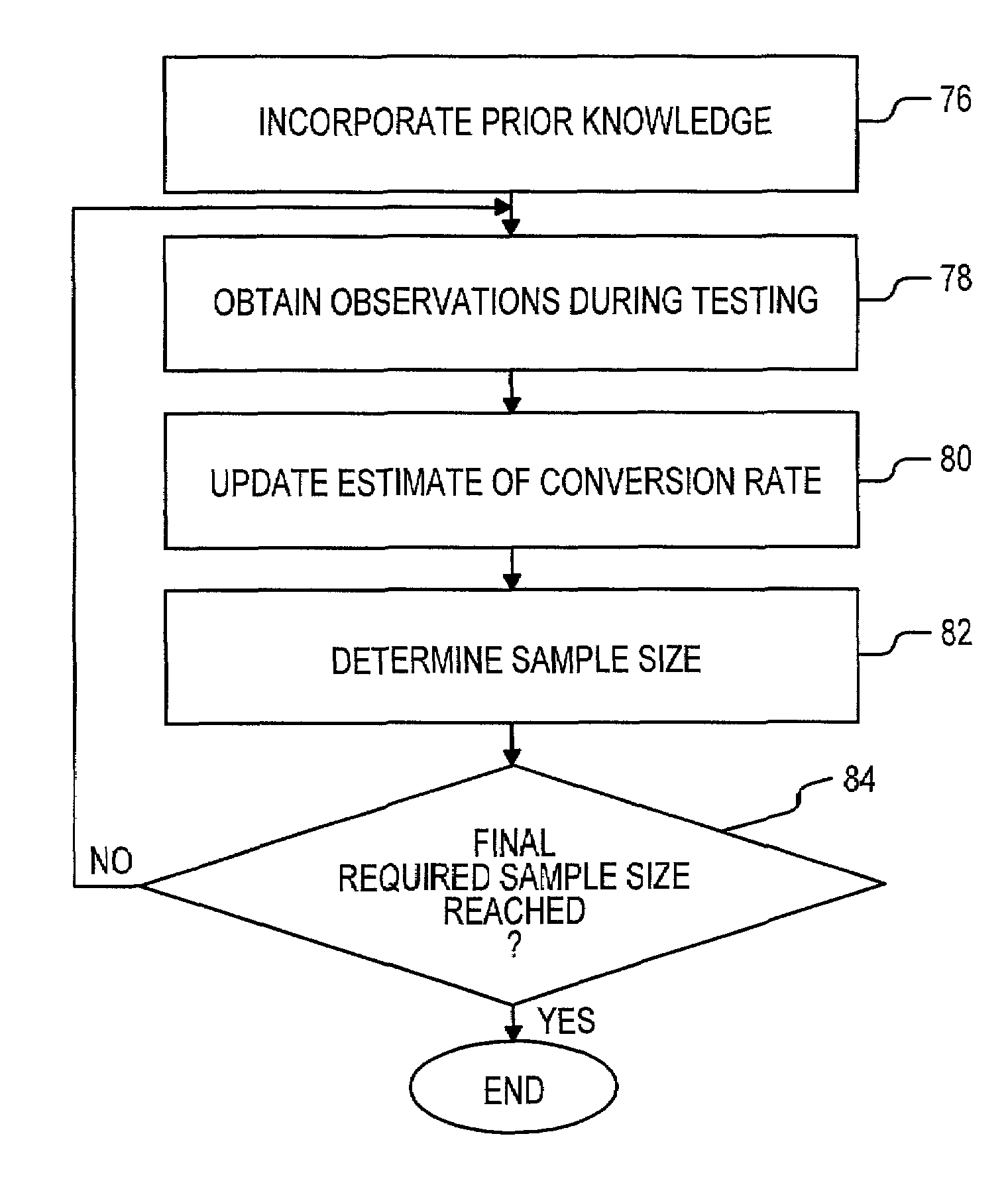
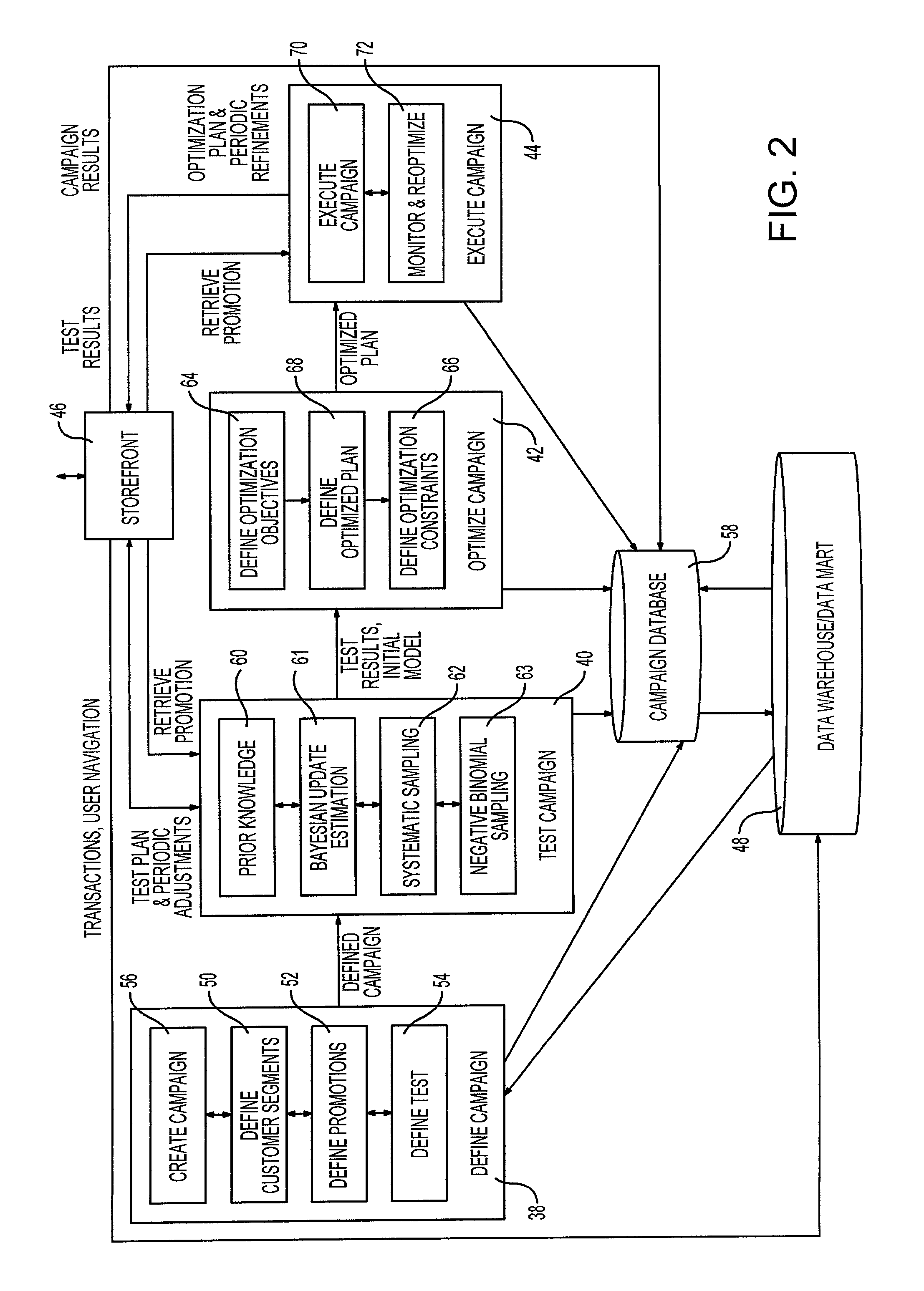
System and method for generating conversion-related estimates utilizing adaptive sample size
InactiveUS7058590B2Operational agilityMaintaining confidenceCash registersMarket data gatheringTest sampleStatistical Confidence
A method and system for processing test data relevant to specific behavior of visitors of a network accessible site, such as a website, includes a number of components. A first component is configured to determine an initial estimate of visitor behavior on the basis of pre-testing information. Such information may be entered by a manager of the site. A second component is configured to generate updates of the estimate in response to monitored behavior. Bayesian estimation may be employed in this component. The third and fourth components cooperate to dynamically adjust a measure of the required test sample size of the visitors so as to maintain a target statistical confidence level. The third component utilizes systematic sampling, while the fourth component uses negative binomial sampling.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
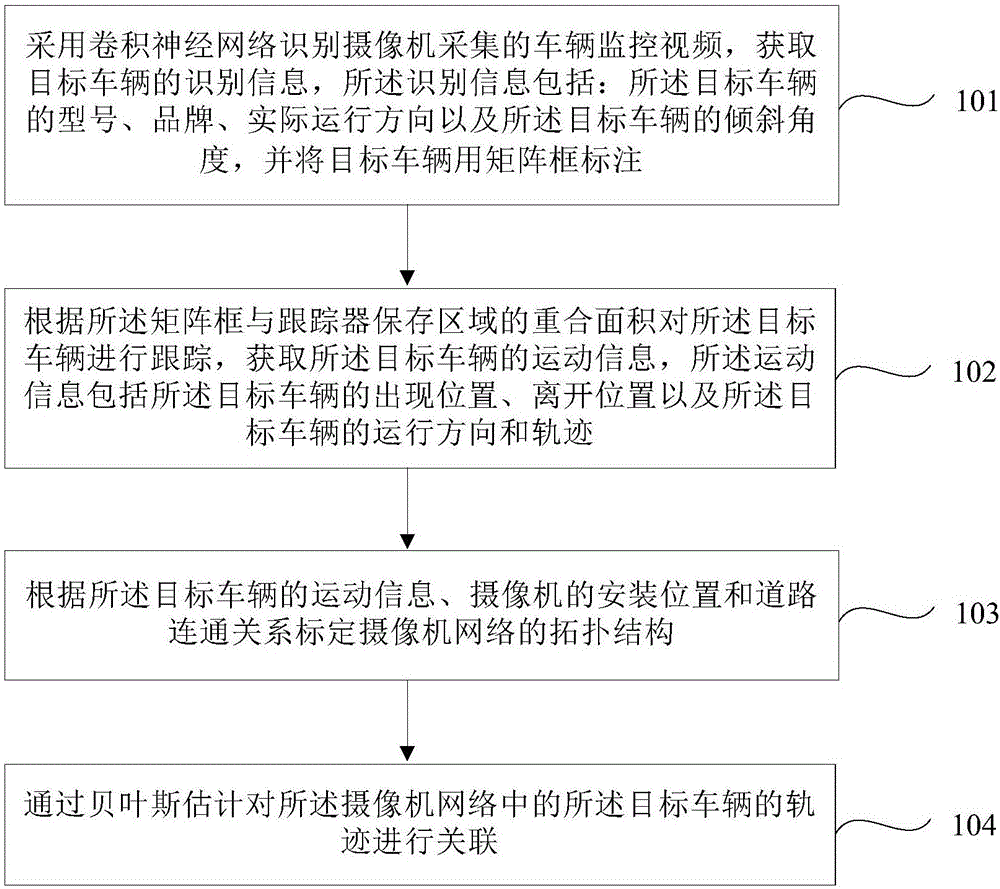
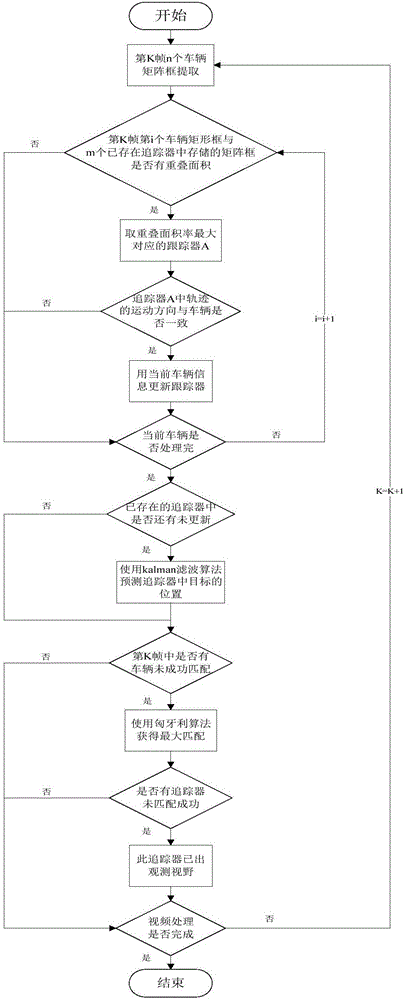
Method for calculating traces of vehicle in multi-camera scene
ActiveCN106846374AAccurate trackingImage analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionMulti cameraComputer graphics (images)
The invention provides a method for calculating traces of a vehicle in a multi-camera scene, comprising the steps of identifying vehicle monitoring videos collected by the cameras by use of a convolutional neural network to acquire identification information of a target vehicle, wherein the identification information includes a model, a brand, an actual running direction and an inclination angle of the target vehicle, and a position of the target vehicle is labeled by a matrix frame; tracking the target vehicle according to an overlapping area of the matrix frame and a tracker storage region to acquire motion information of the target vehicle, wherein the motion information includes an occurrence position, a departure position, a running direction and a running trace of the target vehicle; calibrating a topological structure of a camera network according to the motion information of the target vehicle, mounting positions of the cameras and a path connected relation; and associating the traces of the target vehicle in the camera network through Bayesian estimation. The method improves the accuracy rate of calculation of the traces of the vehicle in the multi-camera scene.
Owner:DALIAN MARITIME UNIVERSITY
Modeling low frame rate videos with bayesian estimation
InactiveUS20060262959A1Accurate scene modelEasy to trackImage analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionPattern recognitionRecursive Bayesian estimation
A video is acquired of a scene. Each pixel in each frame of the video is represented by multiple of layers. Each layer includes multiple Gaussian distributions. Each Gaussian distribution includes a mean and a covariance. The covariance is an inverse Wishart distribution. Then, the layers are updated for each frame with a recursive Bayesian estimation process to construct a model of the scene. The model can be used to detect foreground and background pixels according to confidence scores of the layers.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC RES LAB INC
Sensor information fuse device and method
InactiveCN101441718AImprove reliabilityConfidenceCharacter and pattern recognitionAdaptive weightingPosteriori probability
The invention discloses a device and a method for fusing sensor information. The sensor-information fusion method comprises the steps of adopting a self-adaptive weighted-data fusion algorithm to allocate corresponding weight numbers for induction information from a plurality of sensors, adopting a Kalman filtering algorithm to perform optimal estimation to the induction information of the corresponding weight numbers so as to acquire the locally fused induction information, adopting a D-S theory estimation algorithm to perform interval estimation to the uncertain induction information in the locally fused induction information, adopting a multi-Bayesian estimation algorithm to perform individual association probability distribution for the induction information after interval estimation so as to synthesize a joint posteriori probability distribution function, and utilizing the joint distribution function to output a final fusion value of the induction information. The invention has the advantages of improving the reliability, confidence and efficiency of sensor information fusion.
Owner:FUJIAN SUNNADA COMM
Train navigator with integral constrained GPS solution and track database compensation
The present invention provides a new set of algorithmic solutions to accommodate track inaccuracy information in track databases. Navigation and measurement aiding processes are defined by a stochastic mode relative to a moving rail frame defined so that it is aligned with the heading of the compensated track database at the current along track-position. Filtering generates long and short wavelength track alignment disturbances commensurate with track grade to compensate for track database errors; a stochastic error model is defined as the difference between the deterministic implementation and the actual stochastic processes Bayesian estimation of the error variables is implemented via a digital Kalman filter with the navigation, database, and measurement errors removed by subtracting the filter estimates.
Owner:AUSTRALIAN RAIL TRACK CORP
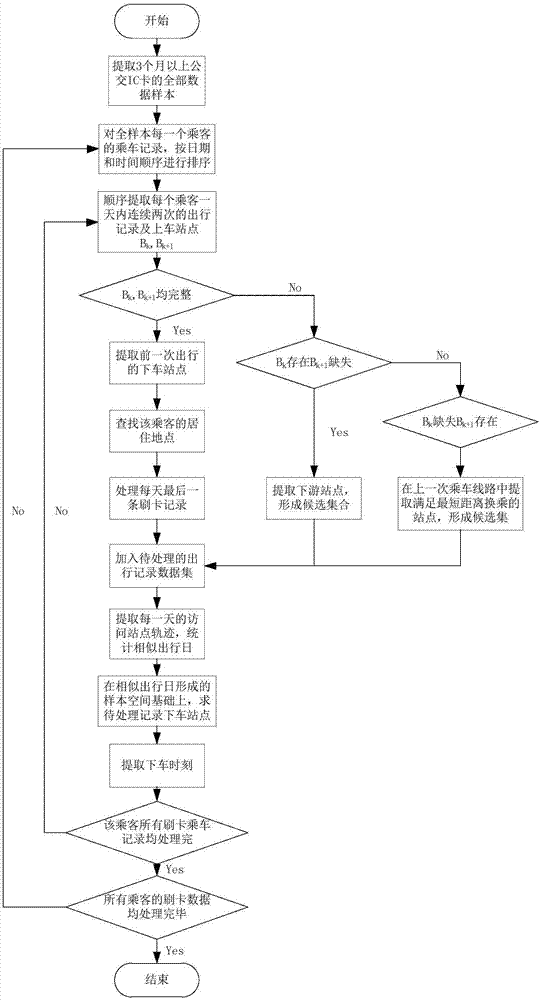
Method for extracting public transport passenger trip space-time tracks
ActiveCN106874432AAvoid the pitfalls of overriding individual featuresRespond effectively to distractionsData processing applicationsSpecial data processing applicationsTransit networkSimulation
The invention discloses a method for extracting public transport passenger trip space-time tracks. Data resources of full-sample passenger bus-taking records and bus running records are fused; based on the continuous trip chain method, starting from similarity analysis of everyday bus station tracks of each passenger, similar trip days are extracted; a statistical sample space is constructed to mine passenger activity rules; by means of the Bayesian estimation method, getting-off stations of one-ticket bus passenger card-swiping bus-taking records are extracted more reasonably and accurately, and trip tracks of the passengers are reduced from missing information. According to the method, implicit passenger individual activity rules in full-sample card-swiping data can be fully utilized for reasonably deducing the card-swiping getting-off stations of the passengers, and follow-up public transit network section flow statistics and data mining are promoted.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
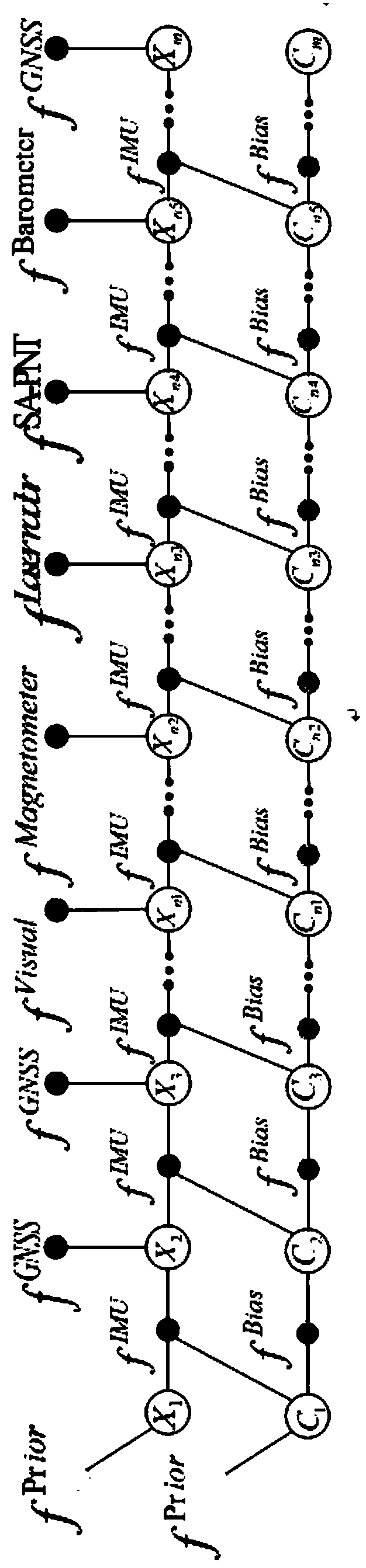
Multi-source information fusion method based on factor graph
PendingCN108364014ARealize plug and playImprove navigation accuracyCharacter and pattern recognitionMultiple sensorInertial navigation system
The invention relates to a multi-source information fusion method based on a factor graph. The multi-source information fusion method aims to realize full-source positioning and navigation without relying on satellite navigation in a complex environment, takes an inertial navigation system as the core, utilizes all available navigation information sources, and performs rapid fusion, optimal configuration and self-adaptive switching on asynchronous heterogeneous sensor information. A factor graph model is constructed by means of recursive Bayesian estimation, the factor graph is broadened by means of a variable node and a factor node of the system after measurement information of different sensors are acquired, state recursion and updating are completed based on a set cost function, and thefactor graph optimization problem is solved through sparse QR decomposition by adopting an increment smoothing method. The multi-source information fusion method effectively solves the time-varying state space problem generated between carrier motion and measurement availability, can calculate a solution of precise navigation according to dynamic changes of a carrying platform, realizes plug-and-play of multiple sensors, and meets the requirements of carriers changing in complex environment and different tasks.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
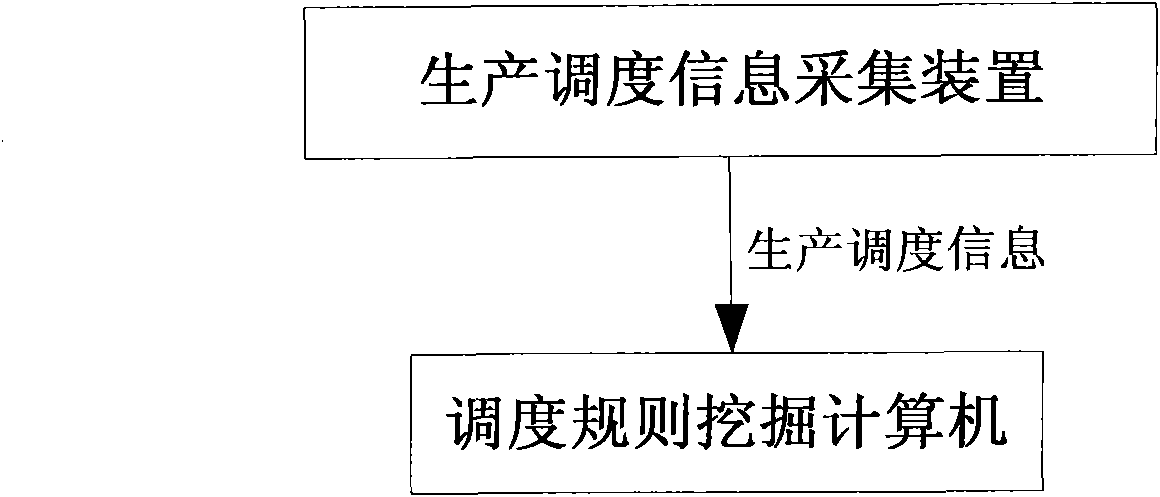
Scheduling rule intelligent excavating method based on rule parameter global coordination optimization
The invention relates to a scheduling rule intelligent excavating method based on rule parameter global coordination optimization, belonging to the automatic control, information technology and advanced manufacturing field, in particular relates to a complex production process oriented scheduling rule intelligent excavating method for scheduling environment in real time. The invention is characterized in that the method includes the following steps: a complex production process oriented scheduling rule intelligent excavating frame for scheduling environment in real time is built, a scheduling problem instance classification model is build, and scheduling rule parameter global coordination optimization problem is constructed and solved. The invention is based on the scheduling rule intelligent excavating frame provided by the invention and adopts double-layer fuzzy C-means clustering method to classify scheduling problem instances. Rule parameter global coordination optimization problem is constructed directing at scheduling problem instance in each class and linear partition based particle swarm optimization is adopted to solve and optimize the problem, wherein Bayes estimation method is adopted to carry out comprehensive evaluation on scheduling rule performance. The obtained scheduling rule has better scheduling effect on different problem instances in similar scheduling environment.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
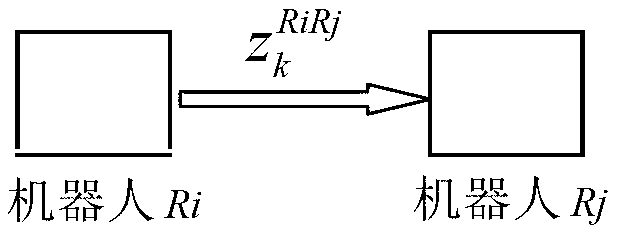
Distributed multi-robot synergetic location algorithm
ActiveCN103135117AAvoid precision lossReduce constraintsSatellite radio beaconingExtensibilityFault tolerance
The invention discloses a distributed multi-robot synergetic location algorithm. The Distributed multi-robot synergetic location algorithm aims at n robots (respectively identified as R1, R2...Rn) which are provided with locating devices and can communicate mutually and steps such as a synergetic location algorithm at time of k=1 and a synergetic location algorithm at time of k+1 (k=1,2...). The method is a distributed bayes estimation algorithm. Under the premise that a decoupling approximation is not carried out on a system model, three-type alignment sensor data such as movement metrical information of the robots, external observation information of a single robot and relative observation information between the robots are fused in robot local; the communication of the robot is point-to-point communication which comprises two parts: one of the parts is the communicated of the relative observation information between two robots which relatively observe, the other of the parts is all robots form a communication chain, and the communication content of adjacent robots is associated state estimation of robots after a sender fuses local alignment sensor data. The method has the advantages of being modularized, good in expandability, good in fault tolerance and the like.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
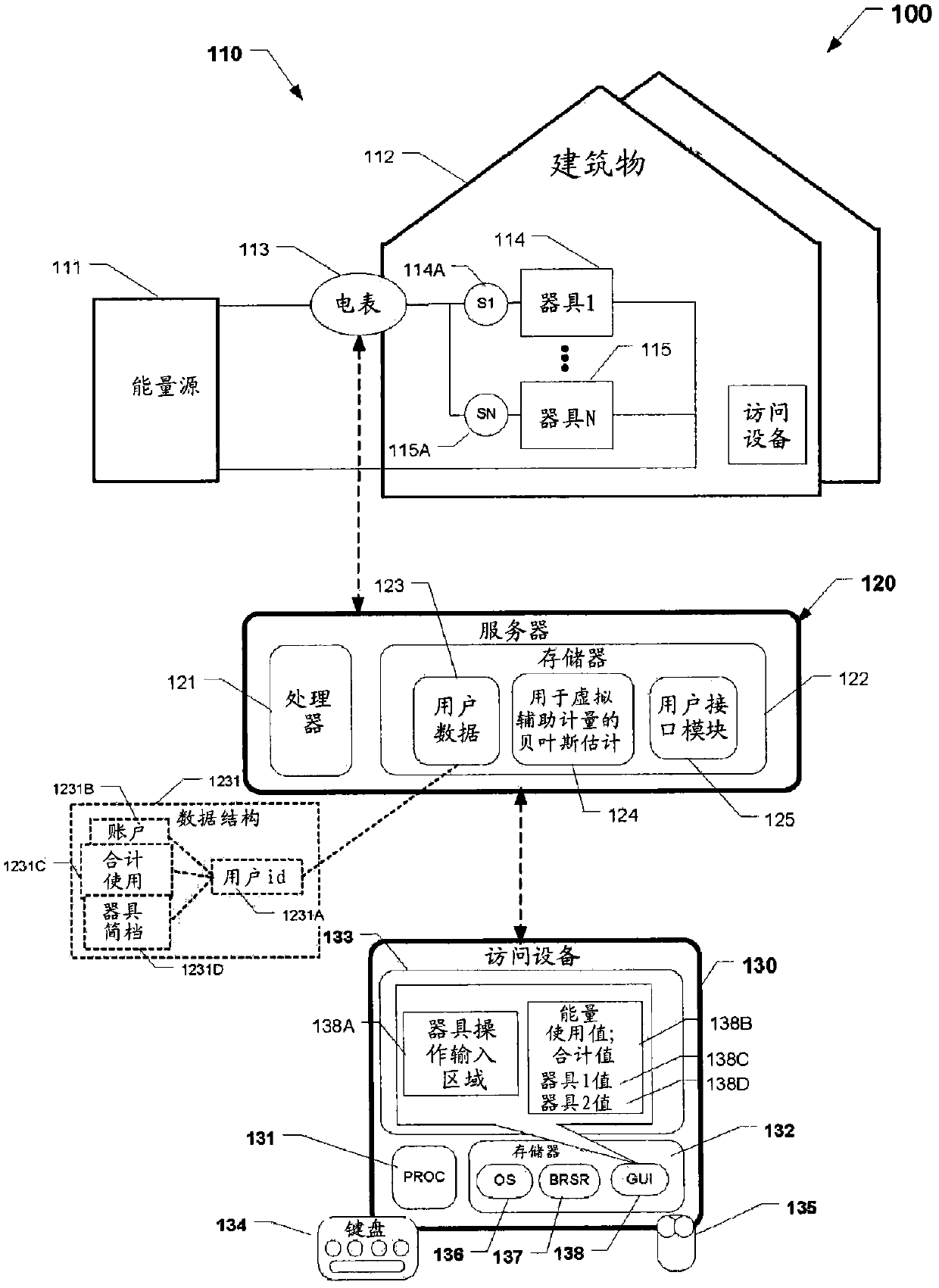
Systems and methods for virtual sub-metering
The invention discloses systems and methods for virtual sub-metering. The present inventors devised, among other things, systems (100) and methods (200) for estimating the energy usage of individual appliances (114, 115) based on cumulative household energy usage data (1231C) and energy consumption profiles (1231D) of the appliances. One exemplary system receives cumulative or aggregate energy usage for a building (112) or other structure including a set of two or more appliances (114, 115) having different load ratings. Based on the aggregate energy usage (1231C) and predefined usage profiles (1231D) for the appliances, the exemplary system estimates individual energy usage (138C, 138D, 230) of the appliances. In one embodiment, the system estimates individual energy usage of the appliances using a Bayesian estimator (124) and displays the usage estimates (130, 240), referred to as virtual submeter readings, on a graphical user interface (138).
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Particle filter-based gravity sampling vector matching positioning method
ActiveCN105180938AOvercome the shortcoming of easy divergenceImprove robust performanceNavigational calculation instrumentsBayesian estimatorSingle point
The present invention provides a particle filter-based gravity sampling vector matching positioning method. The vector matching algorithm takes into account the position correlation of the matching points, and solves the problem of low credibility of a traditional matching algorithm. The present invention utilizes vector consisting of gravity sampling points for matching; and the second estimation of the single point matching results is achieved by using Bayesian estimation based particle filter. After the single-point matching, Euclidean distance between adjacent points of the matching results is calculated to determine whether the distance meets the scope determined by the Euclidean distance between two adjacent sampling points in a non-error inertial navigation system. If the distance meets the scope, the matching result of the point is reliable; and if the distance does not meet the scope, single point matching is carried out again according to limitation conditions.
Owner:BEIJING CNTEN SMART TECH CO LTD
System and method for face recognition
ActiveUS7783082B2Improve accuracyVolume of data required for face recognition can be minimizedCharacter and pattern recognitionViewpointsImaging data
A face recognition system includes a component learning / extraction module, component classifier training module, knowledge base for component classification (KBCC), component extraction module (CEM), object identification training module (OITM), knowledge base for face identification (KBFI), and object identification module (OIM). The CEM receives image data of faces at various viewpoints and extracts outputs of classification of the component data, using the results of classifier training of the component data, stored in the KBCC. The OITM receives the outputs of classification of the component data and determines indicator component for each person by Bayesian estimation so that posterior probability of a predetermined attention class is maximized under the outputs of classification of the component data at various viewpoints. The KBFI stores indicator components for the individuals. The OIM receives the outputs of classification of the component data and identifies faces using the indicator components stored in the KBFI.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
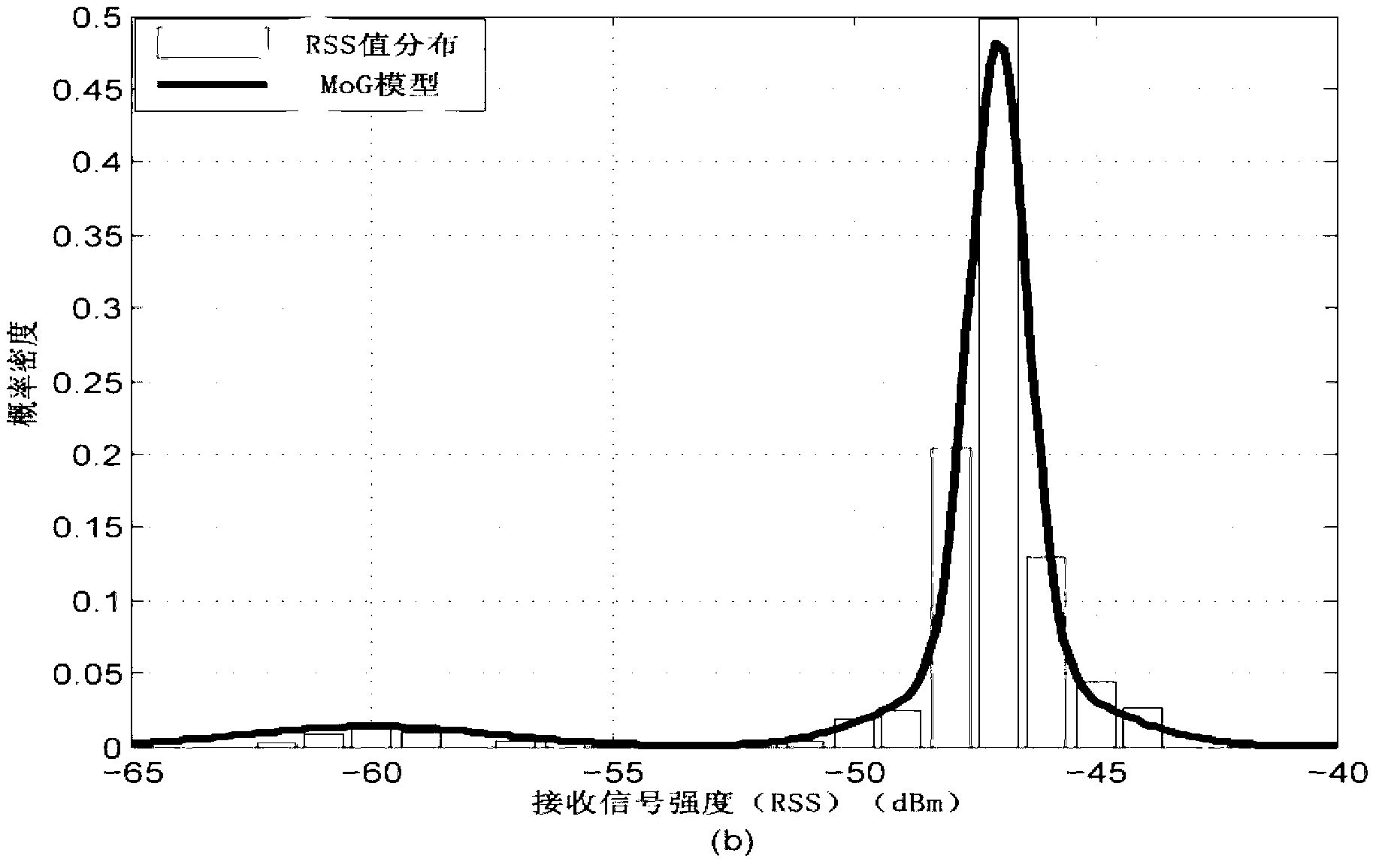
Collaboration node positioning method based on wireless sensor network
InactiveCN102711244AReduce distractionsImprove node positioning accuracyPosition fixationTransmission monitoringWireless mesh networkStudy methods
The invention relates to a collaboration node positioning method based on a wireless sensor network. The collaboration node positioning method based on the wireless sensor network comprises the following steps: 1) establishing a Gaussian mixture model for RSS (Received Signal Strength) values of each link circuit; 2) separating background RRS values from the RRS values through a background learning method; and 3) converting the background RRS values into distance information among nodes according to a path loss model, and using Bayesian estimation method to calculate and then obtain the coordinates of unknown nodes. The collaboration node positioning method provided by the invention has reasonable design; the interference of obstacles on the signal reception strength is effectively reduced by separating the measured RSS values from the background RSS values through establishing the Gaussian mixture model for RSS values of link circuits and background learning method according to the change characteristics of the RSS in the case of movable obstacles and then using Bayesian estimation method (LS) to achieve a collaboration positioning function, so that the higher node positioning accuracy is acquired.
Owner:BEIJING ZHONGFANG SHIXIN TECH
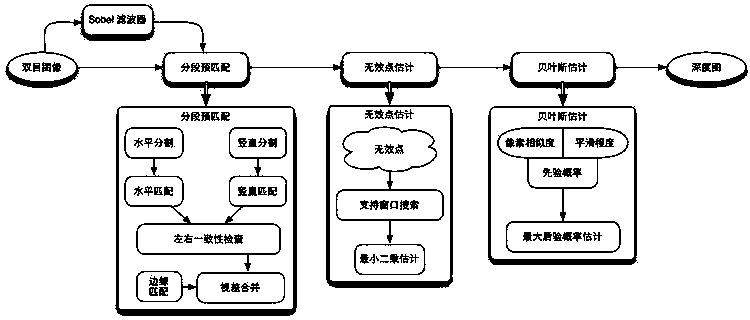
Progressive type three-dimensional matching algorithm based on sectional matching and bayes estimation
InactiveCN103383776AReduce the occurrence of mismatchesImage analysisStereo matchingMaximum a posteriori estimation
The invention discloses a progressive type three-dimensional matching algorithm based on sectional matching and bayes estimation. The progressive type three-dimensional matching algorithm includes: 1) dividing an image into an edge area and a sectional area on the basis of responding of a Sobel filter, matching through a three-dimensional matching strategy based on a window and a sectional matching strategy, and combining to obtain a pre-matching depth image; 2) for invalid points in the pre-matching depth image, fitting a least square plane through effective points in a support window, estimating the depth of the invalid point position, and thickening the pre-matching image; 3) for the obtained pre-matching image, revising the depth of each point through a bayes maximum posterior probability method, considering using pre-matching values as the prior probability, and considering using smoothness of similarity and depth of the image as the posterior probability. By means of the progressive type three-dimensional matching algorithm, extraction of depth images from thick to dense and from coarse to fine can be finished through a progressive structure, and meanwhile, edge characteristics and smoothness are considered, so that the accurate and smooth depth images can be obtained.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Moving target detection method based on particle filtering visual attention model
InactiveCN104050685AConform to visual characteristicsReduce estimation errorImage analysisAttention modelSaliency map
The invention discloses a moving target detection method based on a particle filtering visual attention model. First of all, a particle filtering bidirectional fusion attention model is constructed according to the Bayesian estimation principle; next, on the basis of the particle filtering bidirectional fusion attention model, movement attention and target color attention serve as B-U attention input and T-D attention input respectively, the particle distribution state is changed by calculating particle weights, an attention saliency map is formed, and finally the position of a moving target is determined. According to the method, time attention and space attention are fused, so that the movement attention is calculated more accurately; bottom-to-top attention and top-to-bottom attention are fused, so that the forming process of human visual attention is simulated simply and effectively; with respect to a complex global movement scene, the effectiveness and accuracy of moving target detection are improved.
Owner:XIAN UNIV OF TECH
Reservoir resistivity characterization incorporating flow dynamics
InactiveUS20180231681A1Accurate measurementEasy to optimizeGeomodellingDesign optimisation/simulationElectrical resistivity and conductivityInversion methods
Systems and methods for reservoir resistivity characterization are provided. In various aspects, an integrated framework for the estimation of Archie's parameters for a strongly heterogeneous reservoir utilizing the dynamics of the reservoir are provided. The framework can encompass a Bayesian estimation / inversion method for estimating the reservoir parameters, integrating production and time lapse formation conductivity data to achieve a better understanding of the subsurface rock conductivity properties and hence improve water saturation imaging.
Owner:KING ABDULLAH UNIV OF SCI & TECH
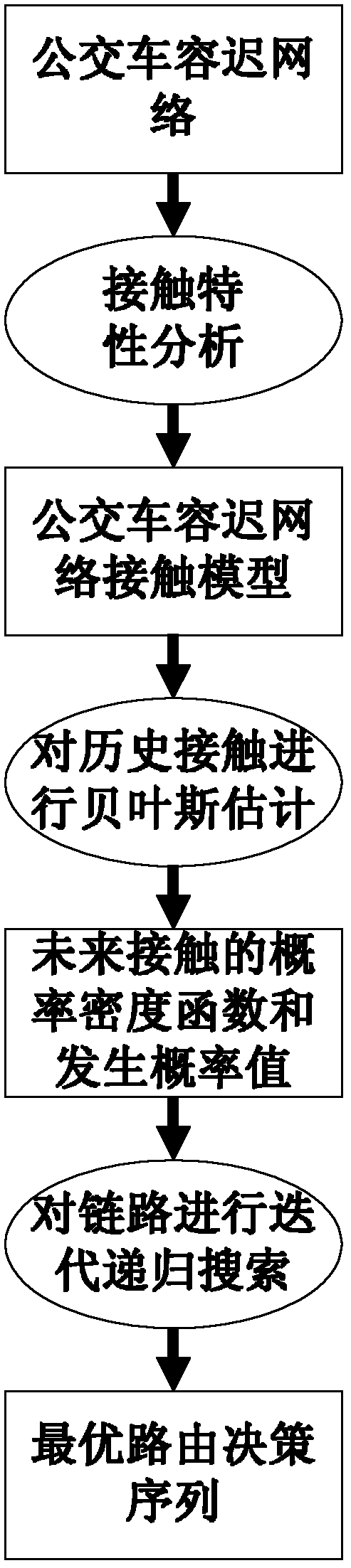
Predictive routing method for bus delay tolerant network
The invention discloses a predictive routing method for a bus delay tolerant network (DTN). The method specifically comprises the following steps of: (1) disclosing an interval algebra-based extract network topological representation method for the semidefiniteness of a bus net node motion mode; (2) quantitatively calculating the possibility of future contact by utilizing the historical contact information of a node and adopting Bayesian estimation to obtain the probability of the future contact and a density function thereof; and (3) calculating an optimal decision sequence for a future communication path by adopting an iteration and recursion algorithm according to obtained future contact information. In a bus net scenario, a delivery rate is higher than those of most of other DTN routing, a high overhead rate and a good average delay are ensured, and the requirements of the bus DTN can be met.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
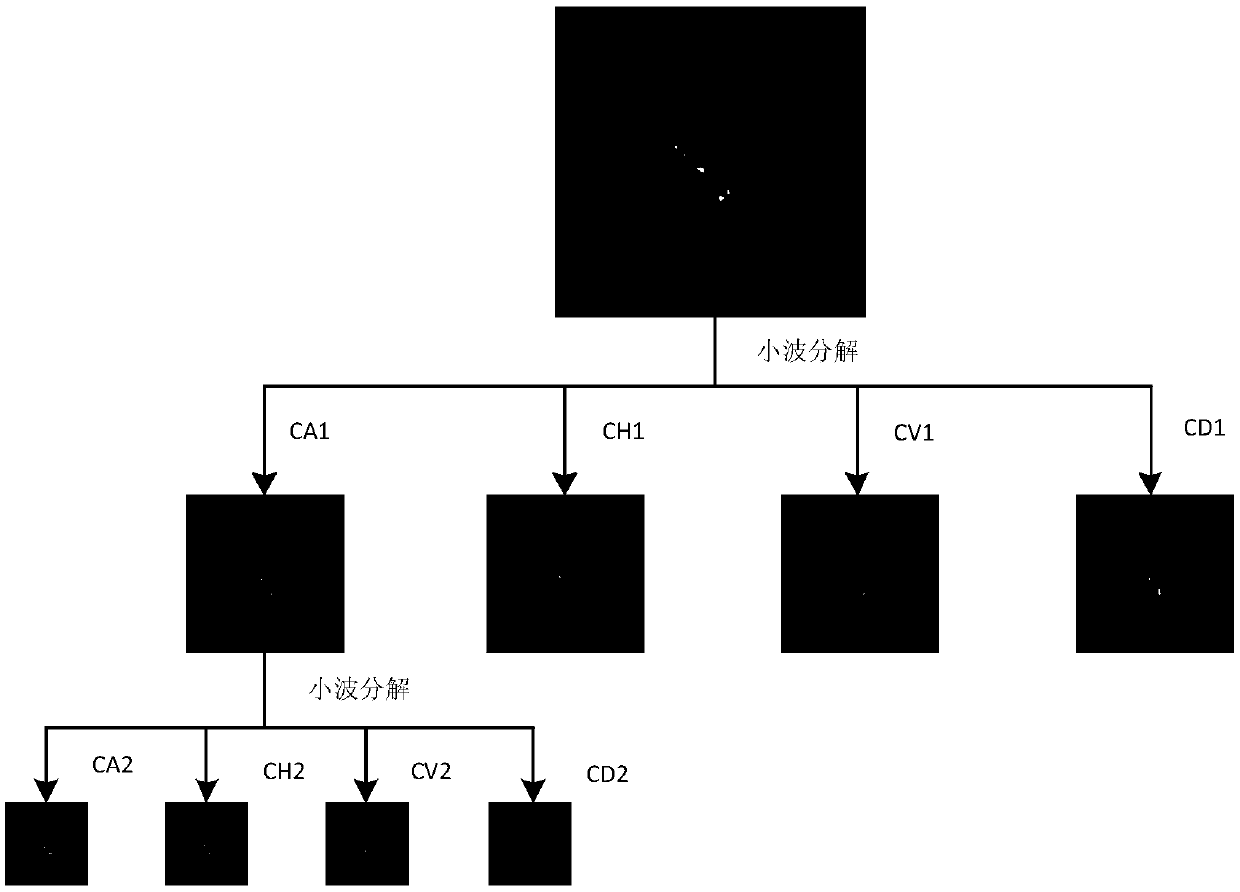
SAR image target recognition method based on wavelet threshold denoising combined with convolutional neural network
InactiveCN108898155AImprove target recognition abilityReduce dependenceCharacter and pattern recognitionNeural architecturesWavelet decompositionWavelet
A SAR image target recognition method based on wavelet threshold denoising combined with a convolutional neural network includes the following steps: a step 1, performing 2-layer 2D wavelet decomposition on a SAR target image; a step 2, using a Bayesian estimated threshold to quantize a high frequency coefficient after wavelet decomposition; a step 3, performing wavelet image reconstruction on a low-frequency coefficients after wavelet decomposition and the high-frequency coefficient after threshold quantization; and a step 4, using the convolutional neural network to automatically learn multi-layer features from the reconstructed SAR target image to characterize the image, and using a Softmax classifier to recognize a target type. The method can overcome the influence of speckle noise oncontour details of the image and reduce the dependence on artificial design, selection features and classifiers, and improve the performance of SAR image target recognition.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Bayesian estimation-based particle filter gravity-assisted inertial navigation matching method
InactiveCN105157704AOvercome the shortcoming of easy divergenceAvoid errorsNavigational calculation instrumentsNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsGravity assistPoint match
The invention provides a bayesian estimation-based particle filter gravity-assisted inertial navigation matching method. When solving non-linear problems, particle filter prevents linearization-caused errors and solves the problem that the traditional point matching Sandia algorithm easily produces divergence in a large-gravity anomalous change matching area. Through use of inertial navigation position information as quantity of state, a gravimeter measured value as observed quantity, bayesian estimation-based particle filter, and a random sample average replacing a probability density function conditional mean, inertial navigation system state variable is estimated.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Improved spectrum subtraction method based on human ear masking effect and Bayesian estimation
InactiveCN108735225AQuick response to changesOvercoming the defect of inaccurate noise estimationSpeech analysisNoise power spectrumNoise estimation
The invention discloses an improved spectrum subtraction method based on a human ear masking effect and Bayesian estimation. The improved spectrum subtraction method comprises the steps of: (1) adopting an improved minimum control value recursive averaging algorithm to obtain noise power spectrum estimation of an original noisy speech; (2) combining the obtained noise power spectrum estimation forperforming preliminary spectrum subtraction on a noisy speech signal; (3) performing Bayesian estimation based on weighted likelihood ratio distortion measurement on the signal after preliminary spectrum subtraction, and calculating the optimal estimated amplitude spectrum of the signal; (4) calculating a subtraction parameter of secondary spectrum subtraction by utilizing the human ear masking effect; (5) performing IMCRA noise estimation again before secondary spectrum subtraction, and carrying out secondary spectrum subtraction to obtain a final enhanced speech signal; (6) and performing inverse Fourier transform on the enhanced speech signal to obtain a final enhanced speech. The improved spectrum subtraction method better guarantees the intelligibility of the speech while improving the noise elimination capability of the algorithm, thereby improving the overall effect of speech enhancement.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
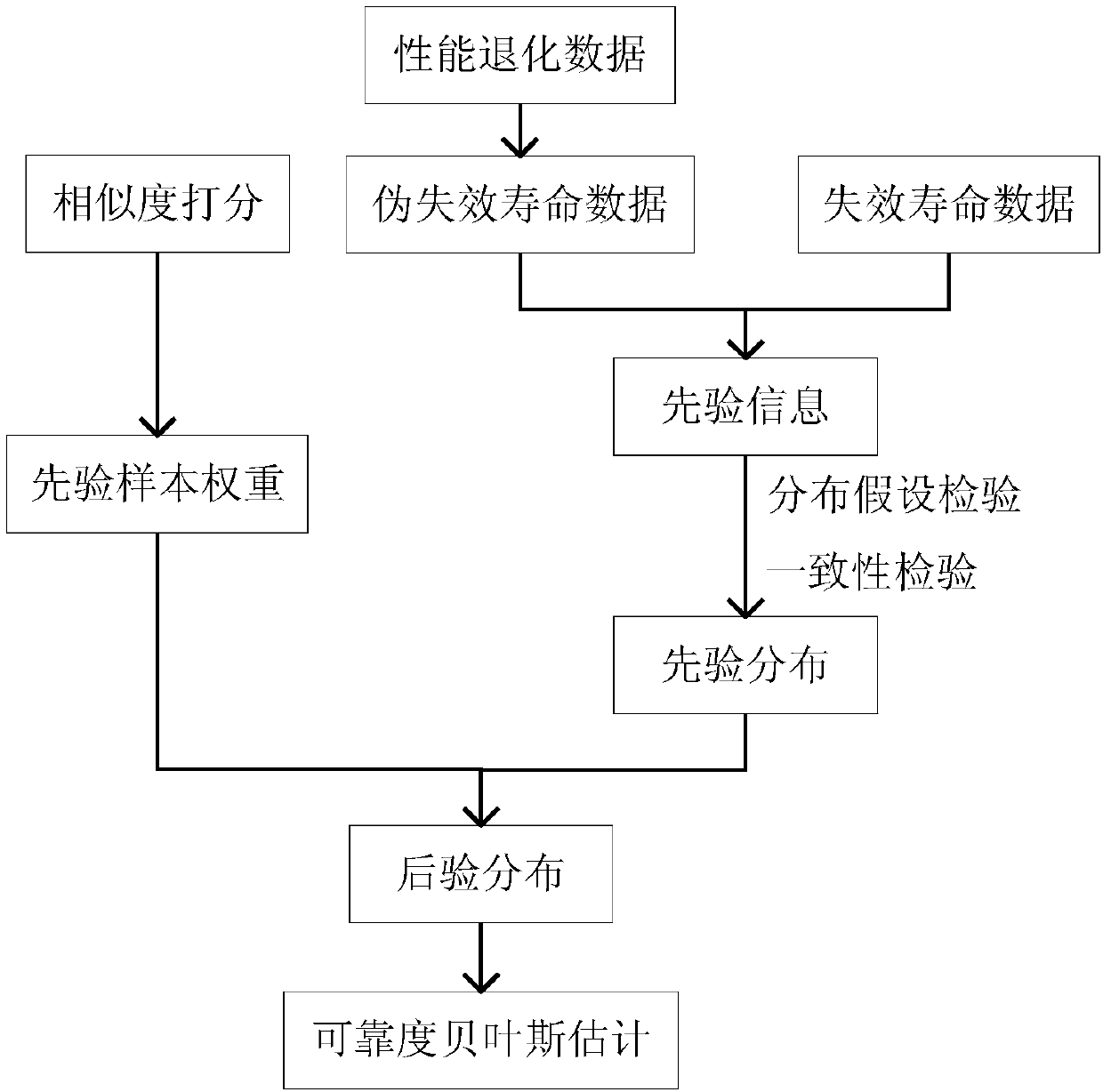
Similar product information-based bayesian reliability evaluation method of small number samples
ActiveCN106570281AMake up for the problem of insufficient sample sizeHigh precisionDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsComputing MethodologiesPrior information
The invention relates to a similar product information-based bayesian reliability evaluation method of small number samples. The method comprises the steps of (S1) carrying out similarity scoring on similar products and determining a prior sample set; (S2) acquiring prior information, which includes failure life data and pseudo failure life data of the similar products; (S3) determining a prior distribution form; (S4) checking the failure mechanism consistency of the similar products; and (S5) determining prior distribution and posterior distribution and achieving bayesian reliability evaluation. According to the method provided by the invention, the sample quantity of the small number samples is effectively improved; and the prior information includes the failure life data and the pseudo failure life data and a two-parameter bayesian reliability evaluation problem is converted into single-parameter bayesian reliability evaluation, so that the bayesian reliability evaluation accuracy of the products is effectively improved and the calculation method of bayesian reliability parameter evaluation is simplified.
Owner:SHANGHAI RADIO EQUIP RES INST
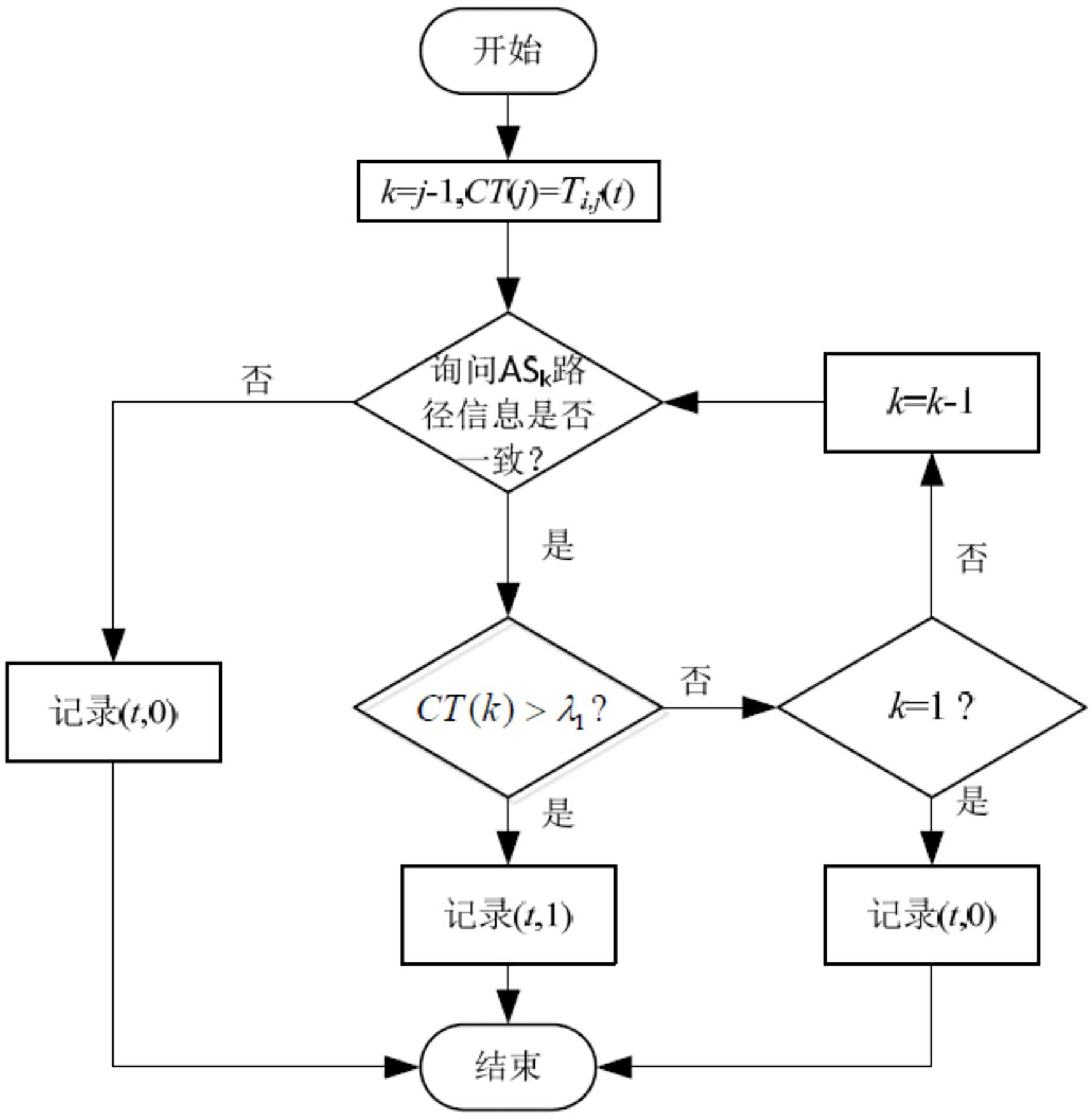
Method for building and maintaining trust relation between autonomy systems in inter-domain routing system
InactiveCN102104550AInhibition of spreadEnsure safetyData switching networksNetwork packetTrust level
The invention relates to a method for building and maintaining a trust relation between autonomy systems in an inter-domain routing system. The building and maintaining of a trust relation between autonomy systems are completed by the following steps: (1) initialization of parameters, namely defining and initializing the parameters needed to build the trust relation between the autonomy systems; (2) detection for the authenticity of an inter-domain routing message, namely judging whether the received inter-domain routing message conforms to a real network topology or not by the autonomy systems; (3) trust degree update based on a routing detection, namely updating the trust degrees in real time by the autonomy systems according to the detection result of the routing message from the adjacent autonomy system; (4) trust level judgment of the autonomy systems, namely dividing the autonomy systems into low, middle and high trust levels according to the current trust degrees of the autonomy systems, and directly discarding the routing update data packets transmitted by the autonomy systems according to the levels, or detecting the data packets, or directly updating a route list.
Owner:THE PLA INFORMATION ENG UNIV
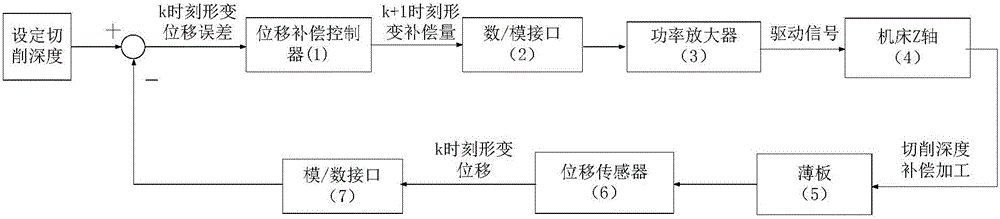
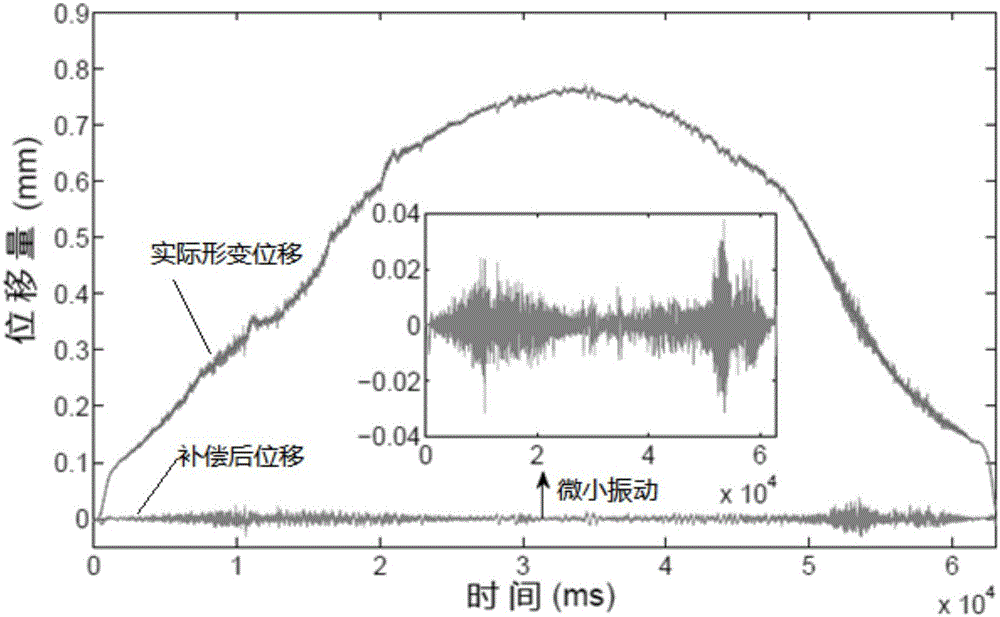
Thin-walled part milling system with real-time deformation compensation function
ActiveCN105904012AAccurate estimateQuality improvementAutomatic control devicesWorkpiecesEngineeringTime control
The invention discloses a thin-walled part milling system with a real-time deformation compensation function. The thin-walled part milling system with the real-time deformation compensation function comprises a machine tool, a rigid chassis, a stand column, a fixing support, a laser displacement sensor, a displacement compensation controller, a power amplifier and a computer. A sheet to be machined is fixed to the rigid chassis through the stand column and installed on a machining groove of the machine tool, deformation and displacement of the sheet are detected through the laser displacement sensor, the machining path is predicted by the displacement compensation controller through a Bayes estimation algorithm, a cutting depth compensating signal is obtained, and a control command is output to control feeding of a spindle of the machine tool. By means of the thin-walled part milling system with the real-time deformation compensation function, deformation of thin-walled parts in the milling process can be detected in real time, deformation of the thin-walled parts in the subsequent machining path is predicted, Z-direction deformation during milling of the sheet is compensated through real-time control over the Z axis of the machine tool, the effect of the same milling depth of the thin-walled parts on the machining path is ensured, and accordingly the surface quality and precision for milling of the thin-walled parts are greatly improved.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Channel estimation method based on Bayesian algorithm
InactiveCN107086970APrevent inversionImprove accuracyRadio transmissionTransmission monitoringEstimation methodsAlgorithm
The invention belongs to the technical field of wireless communication, and specifically relates to a channel estimation method based on the Bayesian algorithm. According to the method provided by the invention, a shared variance parameter of a shared sparse position is calculation in junction with the Bayesian algorithm, compared with the ordinary Bayesian variance parameter estimation method, the accuracy of variance estimation is greatly improved, and meanwhile the Bayesian algorithm is replaced by the GAMP algorithm to avoid a direct matrix inversion process of a posterior probability. Compared with the traditional method, the method provided by the invention has the beneficial effects of simplifying the calculated amount, improves the operation speed and the operation precision, and improves the channel estimation accuracy.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Apparatus and method for an overload control procedure against denial of service attack
ActiveUS7313092B2Suppress noiseError detection/prevention using signal quality detectorTransmission systemsOne passOverload control
The present invention is a methodology to prioritize packets based on the conditional probability that given the values of attributes carried by packet, the packet is a legitimate one. We will call this the conditional legitimate probability of a packet from here onward. The conditional probability of each packet is evaluated based on Bayesian estimation technique. This is accomplished by comparing the attributes carried by an incoming packet against the “nominal” distribution of attributes of legitimate packet stream. Since an exact prioritization of packets based on their conditional legitimate probability would require offline, multiple-pass operations, e.g. sorting, we take the following alternative approach to realize an online, one-pass selectively dropping scheme. In particular, we maintain the cumulative distribution function (CDF) of the conditional legitimate probability of all incoming packets and apply a threshold-based selective dropping mechanism according to the conditional probability value computed for each incoming packet. To speed-up the computation of the conditional legitimate probability for each incoming packet, we may, as an alternative, use the logarithmic version of the equation to implement the Bayesian estimation process. Other features of the invention include: providing means to guarantee minimum throughput of particular (pre-configured) type(s) of packets; providing a. Filtering Mechanism to suppress the noise during estimation / maintenance of nominal attributes distribution; applying state-of-the-art efficient algorithm / data-structures for quantile and histogram building / updates; using the proven, industrial-strength load-shedding algorithms as a submodule in the overload control algorithm; and being amenable to practical implementation to support online, one-pass processing on high-speed communication links.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
Cloud and rain microphysical parameter inversion method based on space-borne three-frequency millimeter wave radar
ActiveCN110361742AHigh spatio-temporal resolutionSmall cost functionWeather condition predictionICT adaptationImage resolutionPhysical model
The invention discloses a cloud and rain microphysical parameter inversion method based on a space-borne three-frequency millimeter wave radar. The method comprises the following steps of firstly, calculating and analyzing cloud and rain particle temporal and spatial distribution characteristics and summarizing, using a generalized Gamma distribution function to characterize cloud raindrop particle distribution and carrying out parameterization; then, based on an idea of a Bayesian estimation theory, establishing an inversion model, presetting prior distribution of the parameters, inputting space-borne W, Ka and Ku three-frequency millimeter wave radar reflectivity factors into a physical model, inputting space-time matching ground-based millimeter-wave radar data as an adjustment factor,carrying out posterior, after iterative calculation, continuously correcting prior probability distribution to minimize the cost function and outputting an optimal inversion result; and finally, carrying out linear processing on an inversion result in each distance library to obtain the inversion result of an entire profile. In the invention, a space-time resolution is high, cost is low, the inversion result is fine and actual distribution of cloud and rain particles can be simultaneously inverted.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
Visible light channel estimation method and system
ActiveCN105471777AAccurate estimateComplete and accurate channel estimation parametersClose-range type systemsChannel estimationTime delaysCovariance
The invention provides a visible light channel estimation method and system. The method comprises the following steps: performing least square estimation on a channel transfer function corresponding to a pilot signal, and performing maximum likelihood estimation on time domain channel impulse response of a spatial position which receives the pilot signal so as to acquire the maximum likelihood estimation of the time domain channel impulse response at different positions in the visible light channel, computing a covariance coefficient of each tapping in the visible light channel under same moment and different time delays, self-adaptively selecting an optimal variable statistic window length, and then computing a time domain estimation value of each tapping as a mean value required by Bayes estimation, and acquiring the time domain Bayes estimation of the channel impulse response. In the whole process, the length of an optimal statistic window is self-adaptively determined according to the covariance coefficient of each tapping, the parameter required by the Bayes estimation is computed, thereby providing a complete and precise channel estimation parameter for a visible light communication system, and realizing the accurate estimation of the visible light channel.
Owner:SYSU CMU SHUNDE INT JOINT RES INST +1
Intercerebral current source estimation method intercerebral current source estimation program recording medium containing the intercerebral current source estimation program and intercerebral current source estimation apparatus
InactiveUS7769424B2Improve accuracyMedical automated diagnosisDiagnostic recording/measuringObservation dataEstimation methods
Based on the fact that by causing an appropriate current flow on a virtual curved surface between a current source and an observation surface, an electromagnetic field generated by the current source can be recovered, and that as the curved surface comes closer to the true current source, current distribution on the curved surface becomes smaller, Bayesian estimation of the current source that recovers the observed data is performed. In this estimation, the fact that the model posterior probability attains the maximum when the curved surface includes the current source is utilized, that is, the model posterior probability is considered, to estimate the position of the current source including the depth direction. When observation data obtained by other observation means is available simultaneously, such information is incorporated in hierarchical prior distribution for Bayesian estimation, to enable estimation with higher precision.
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com