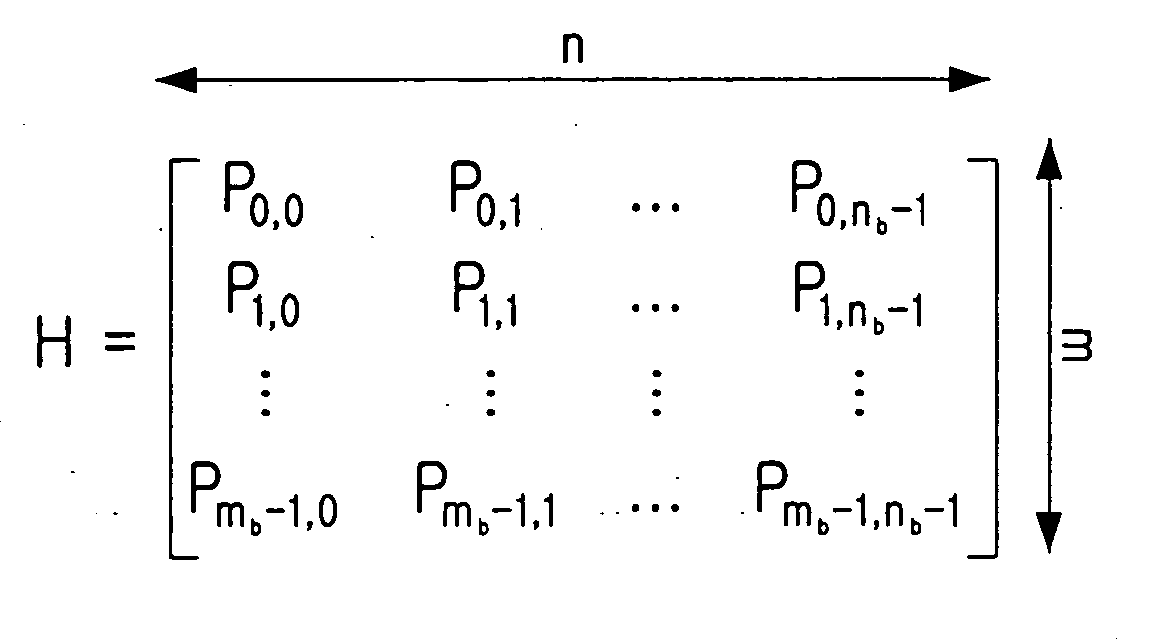Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
298 results about "Factor graph" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
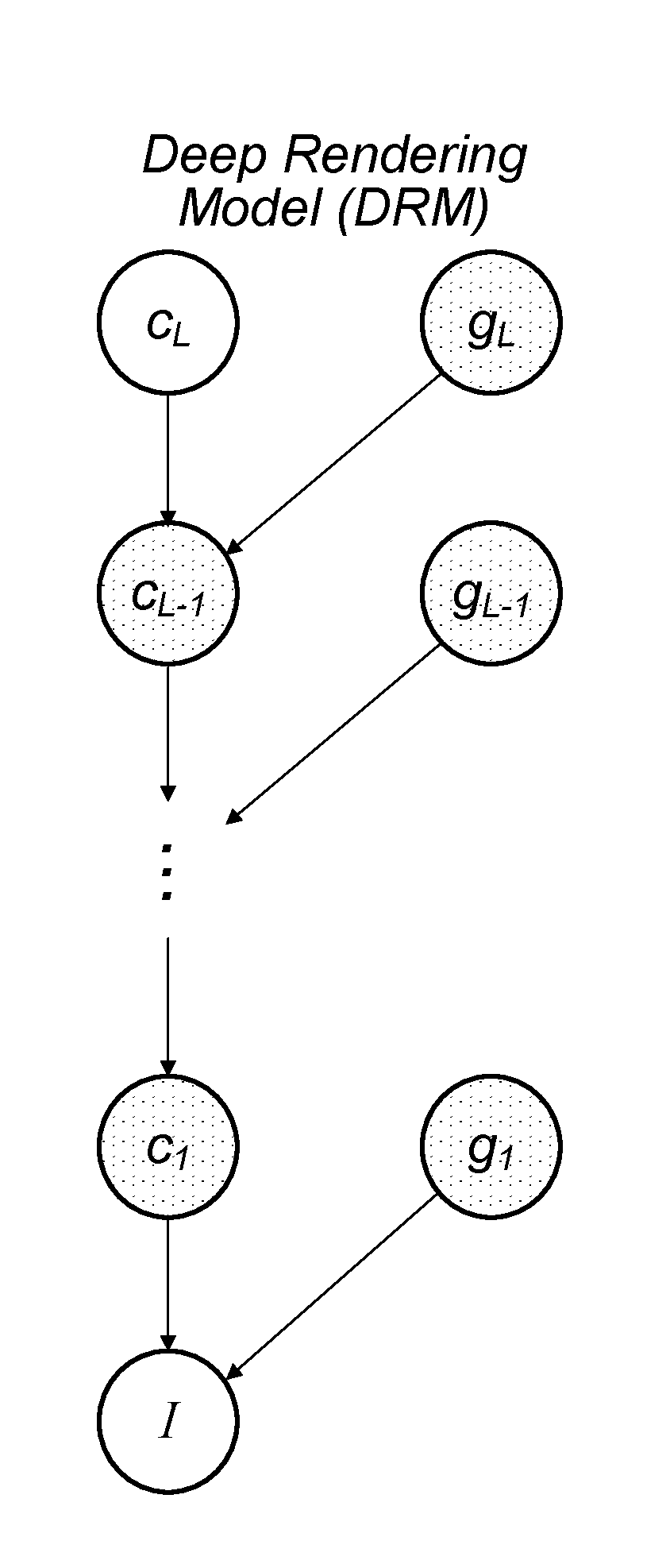
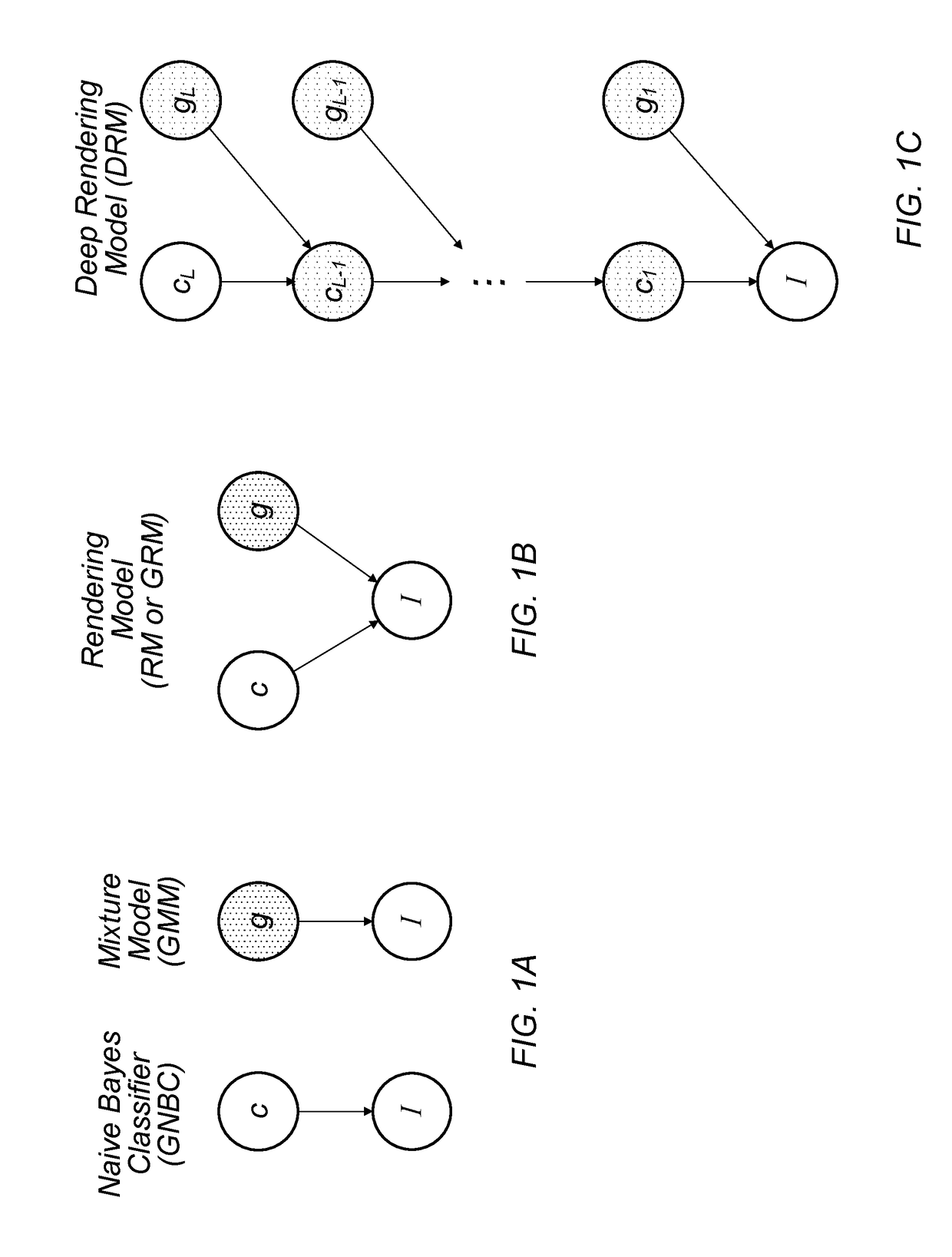
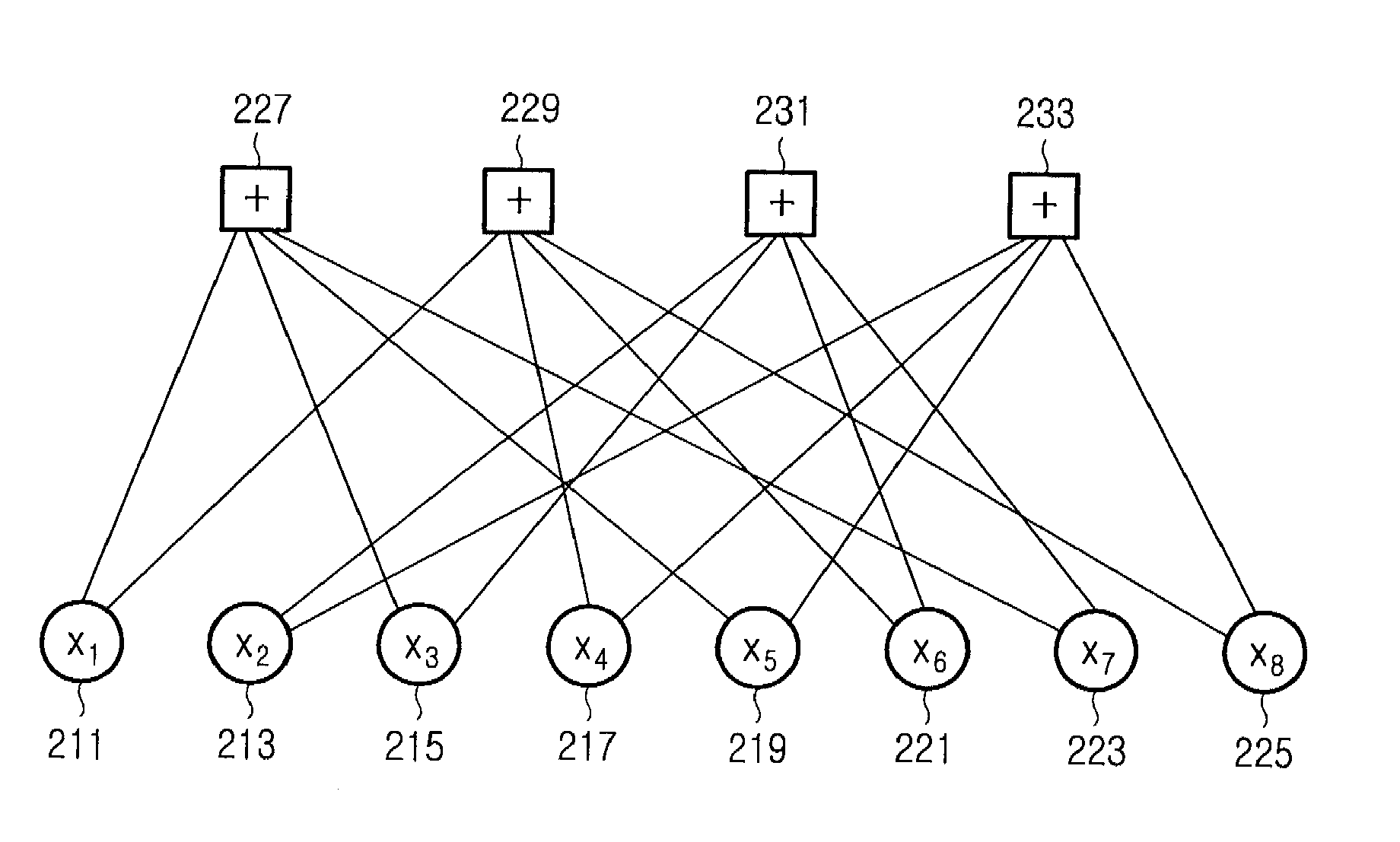
A factor graph is a bipartite graph representing the factorization of a function. In probability theory and its applications, factor graphs are used to represent factorization of a probability distribution function, enabling efficient computations, such as the computation of marginal distributions through the sum-product algorithm. One of the important success stories of factor graphs and the sum-product algorithm is the decoding of capacity-approaching error-correcting codes, such as LDPC and turbo codes.
Automated Compilation of Probabilistic Task Description into Executable Neural Network Specification
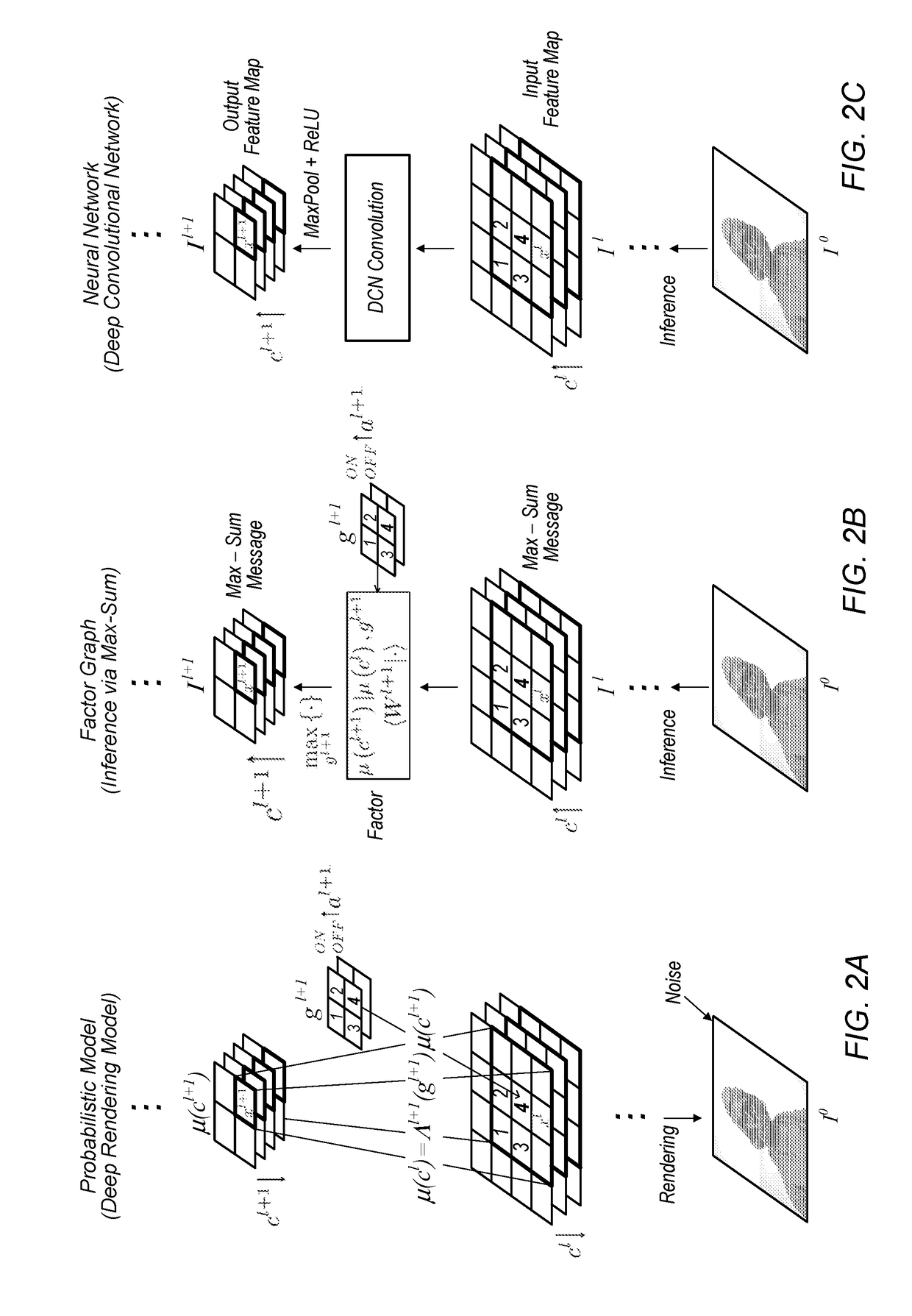
A mechanism for compiling a generative description of an inference task into a neural network. First, an arbitrary generative probabilistic model from the exponential family is specified (or received). The model characterizes a conditional probability distribution for measurement data given a set of latent variables. A factor graph is generated for the generative probabilistic model. Each factor node of the factor graph is expanded into a corresponding sequence of arithmetic operations, based on a specified inference task and a kind of message passing algorithm. The factor graph and the sequences of arithmetic operations specify the structure of a neural network for performance of the inference task. A learning algorithm is executed, to determine values of parameters of the neural network. The neural network is then ready for performing inference on operational measurements.
Owner:RICE UNIV
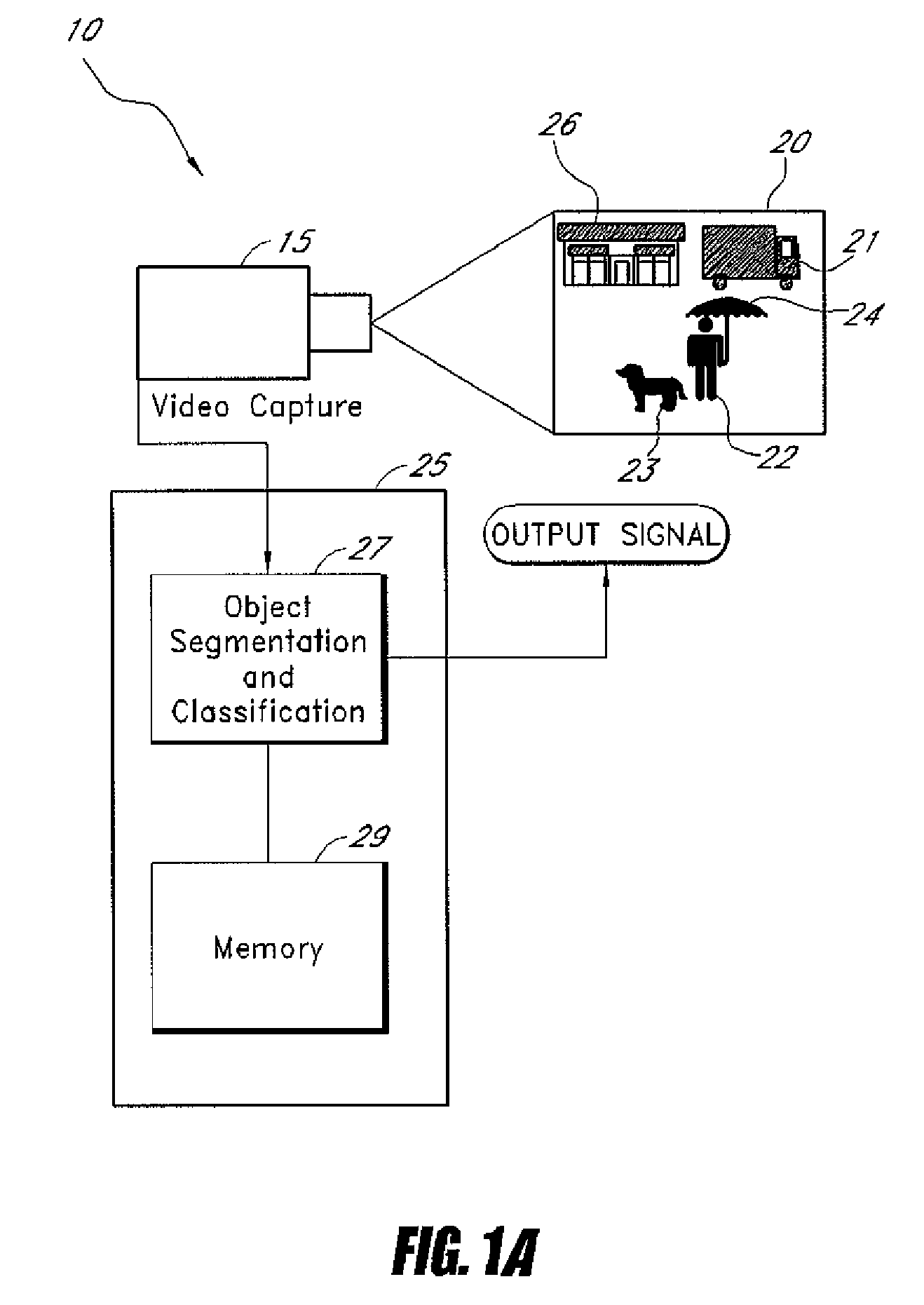
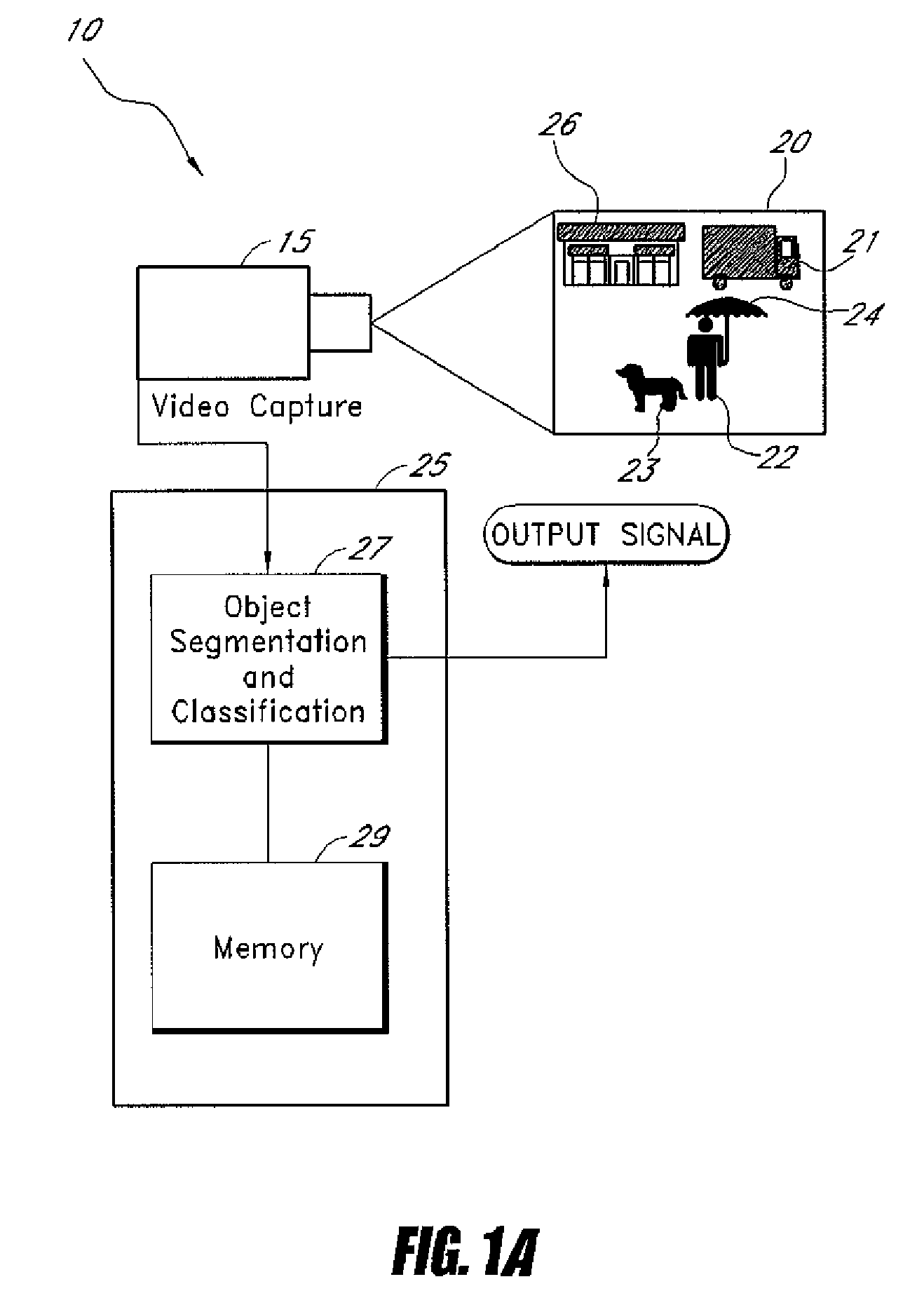
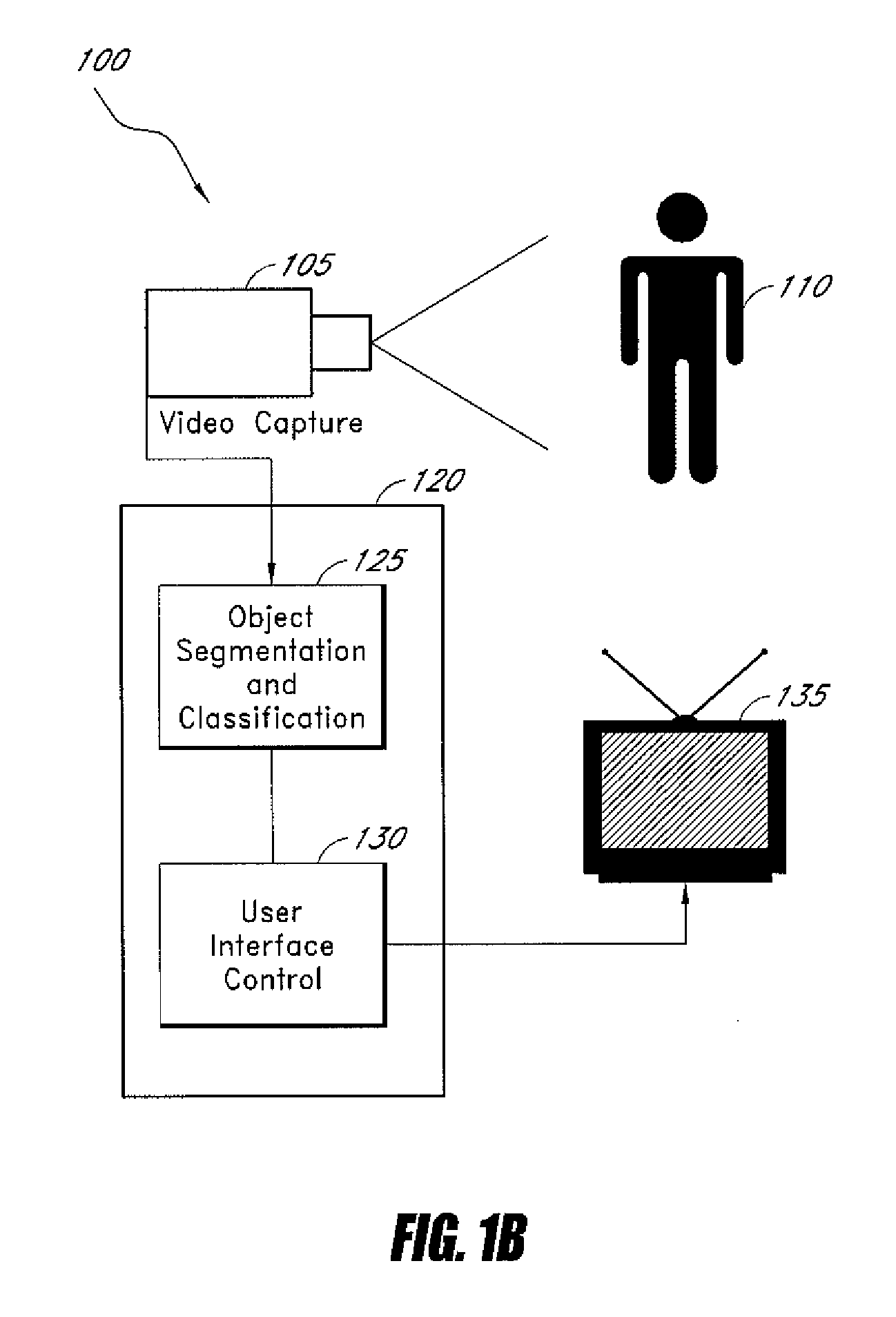
System and method for class-specific object segmentation of image data
Systems and methods for processing an image to determine whether segments of the image belong to an object class are disclosed. In one embodiment, the method comprises receiving digitized data representing an image, the image data comprising a plurality of pixels, segmenting the pixel data into segments at a plurality of scale levels, determining feature vectors of the segments at the plurality of scale levels, the feature vectors comprising one or more measures of visual perception of the segments, determining one or more similarities, each similarity determined by comparing two or more feature vectors, determining, for each of a first subset of the segments, a first measure of probability that the segments is a member of an object class, determining probability factors based on the determined first measures of probability and similarity factors based on the determined similarities, and performing factor graph analysis to determine a second measure of probability for each of a second subset of the segments based on the probability factors and similarity factors.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
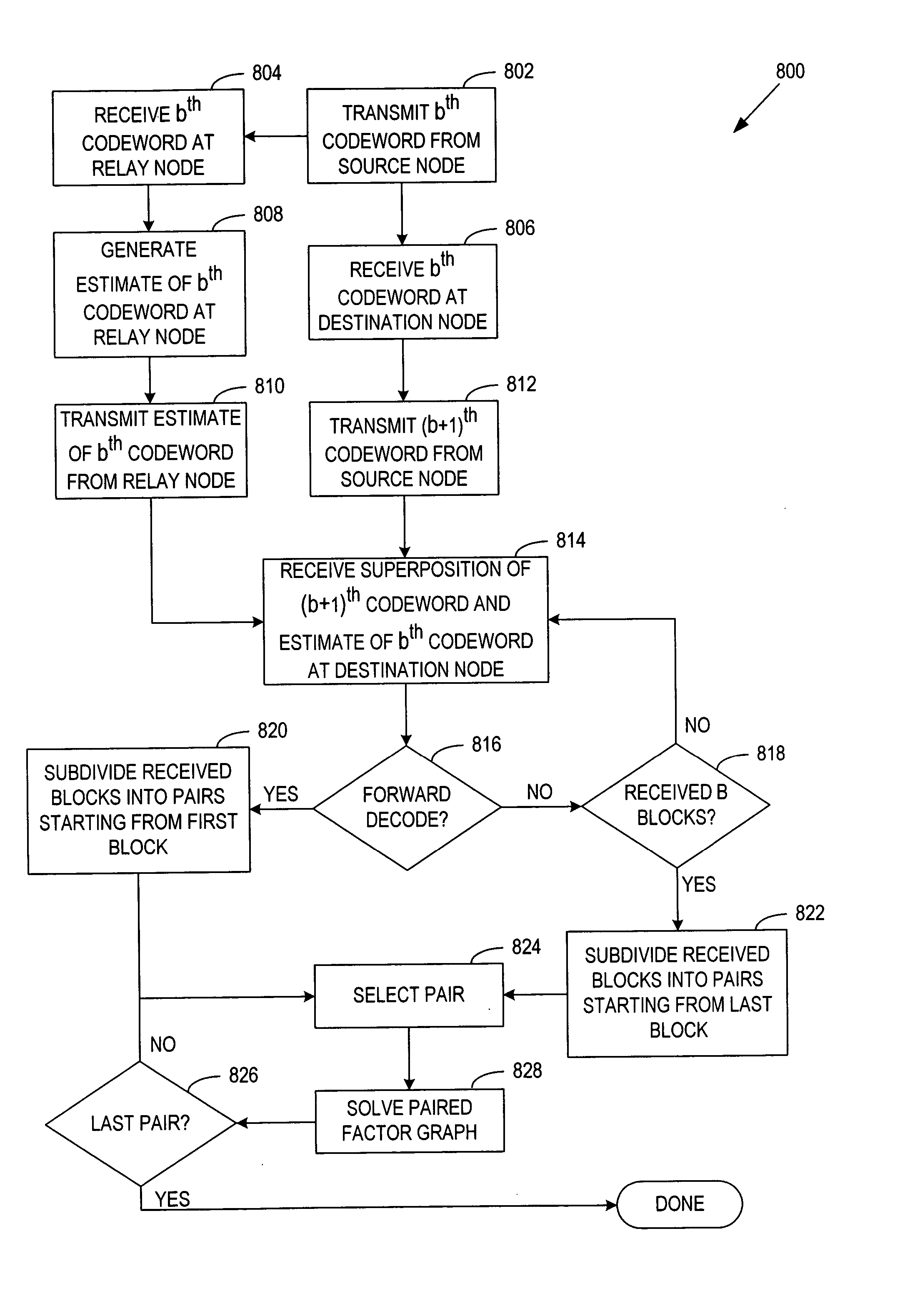
General code design for the relay channel and factor graph decoding
InactiveUS20050265387A1Improve accuracyImprove decoding accuracyError correction/detection using convolutional codesCode conversionParallel computingCODE protocol
A system and method of relay code design and factor graph decoding using a forward and a backward decoding scheme. The backward decoding scheme exploits the idea of the analytical decode-and-forward coding protocol and hence has good performance when the relay node is located relatively close to the source node. The forward decoding scheme exploits the idea of the analytical estimate-and-forward protocol and hence has good performance when the relay node is located relatively far from the source node. The optimal decoding factor graph is first broken into partial factor graphs and then solved iteratively using either the forward or backward decoding schemes.
Owner:NOKIA CORP
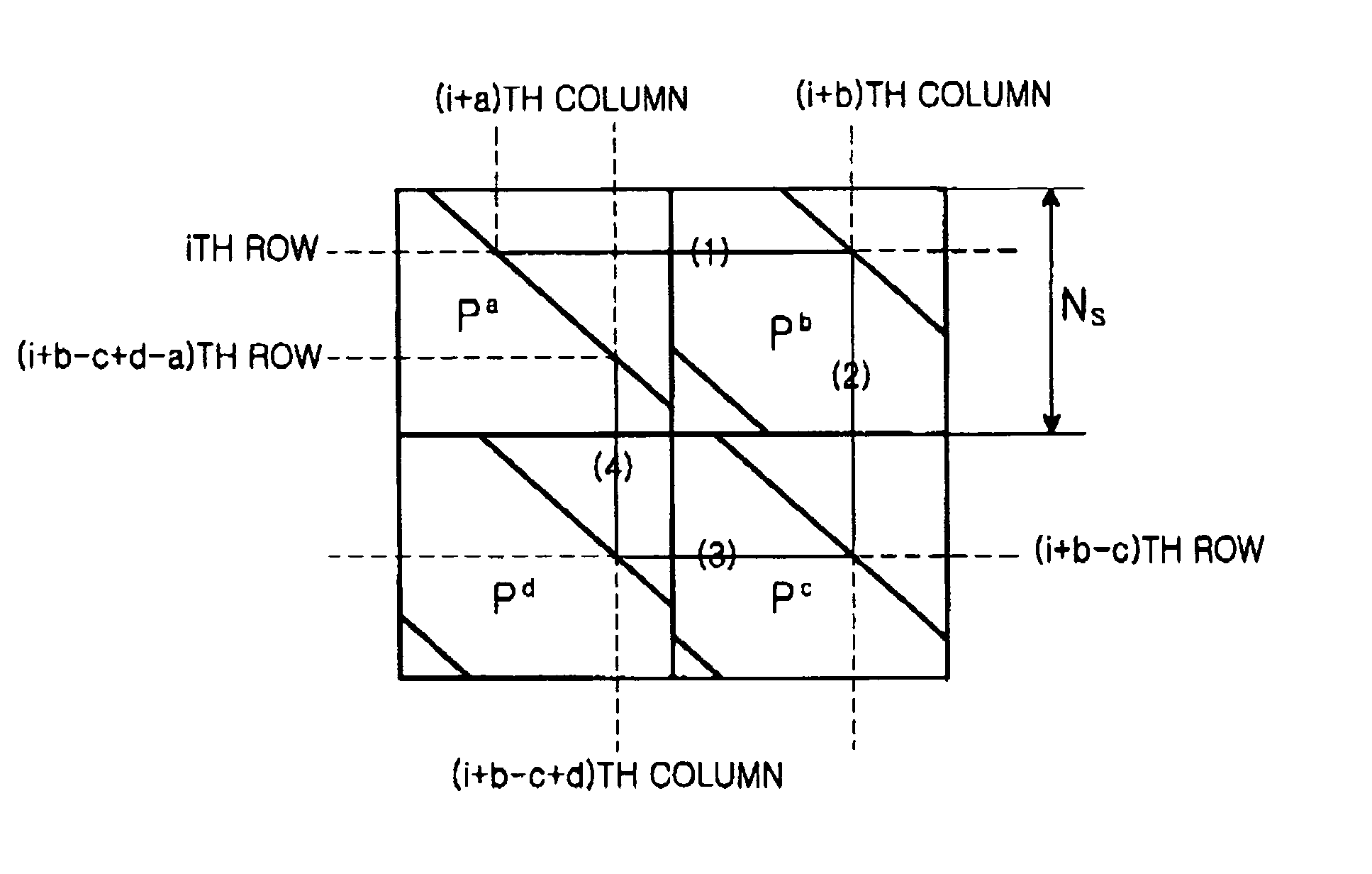
Apparatus and method for coding/decoding block low density parity check code in a mobile communication system
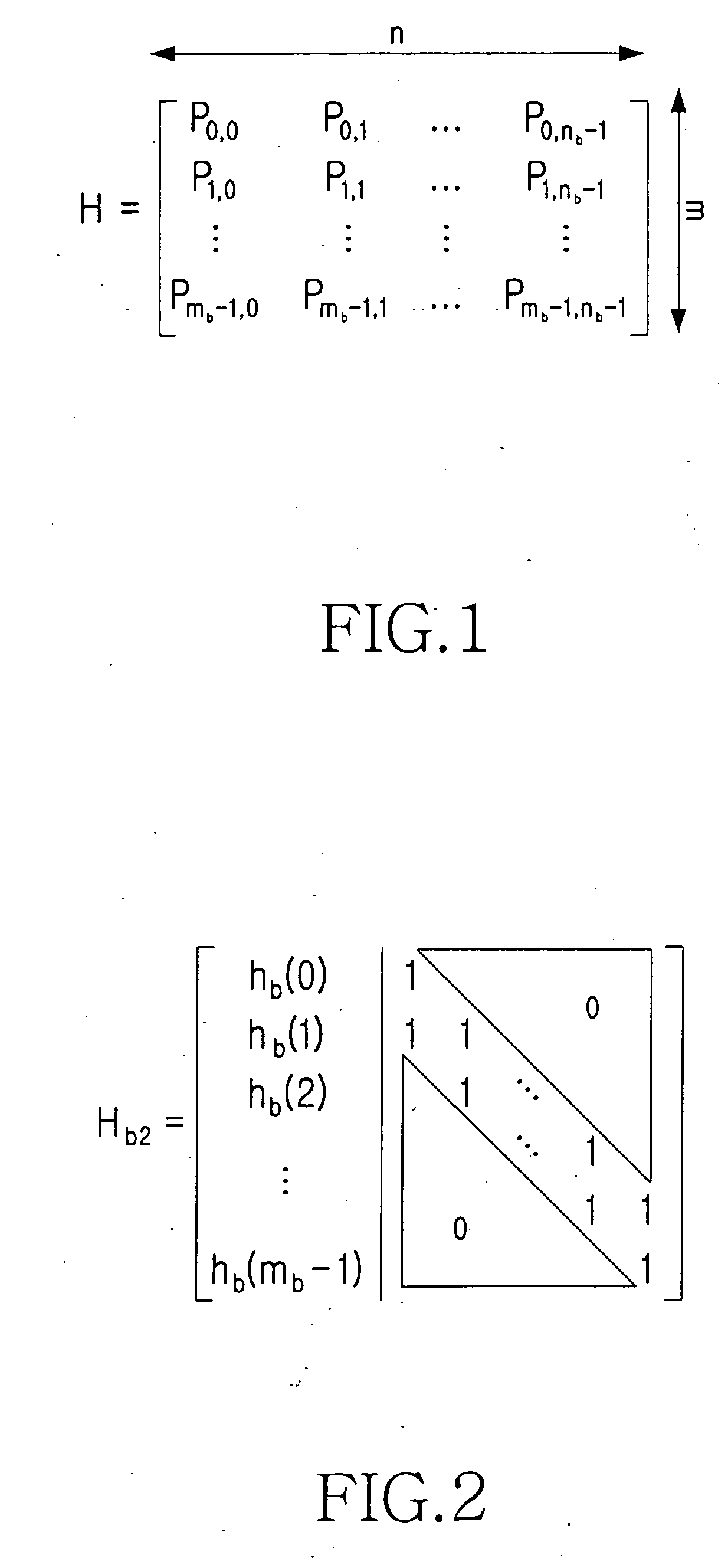
ActiveUS20050050435A1Maximized error correction capabilityMaximized minimum cycle lengthError preventionError detection/correctionTheoretical computer scienceParity-check matrix
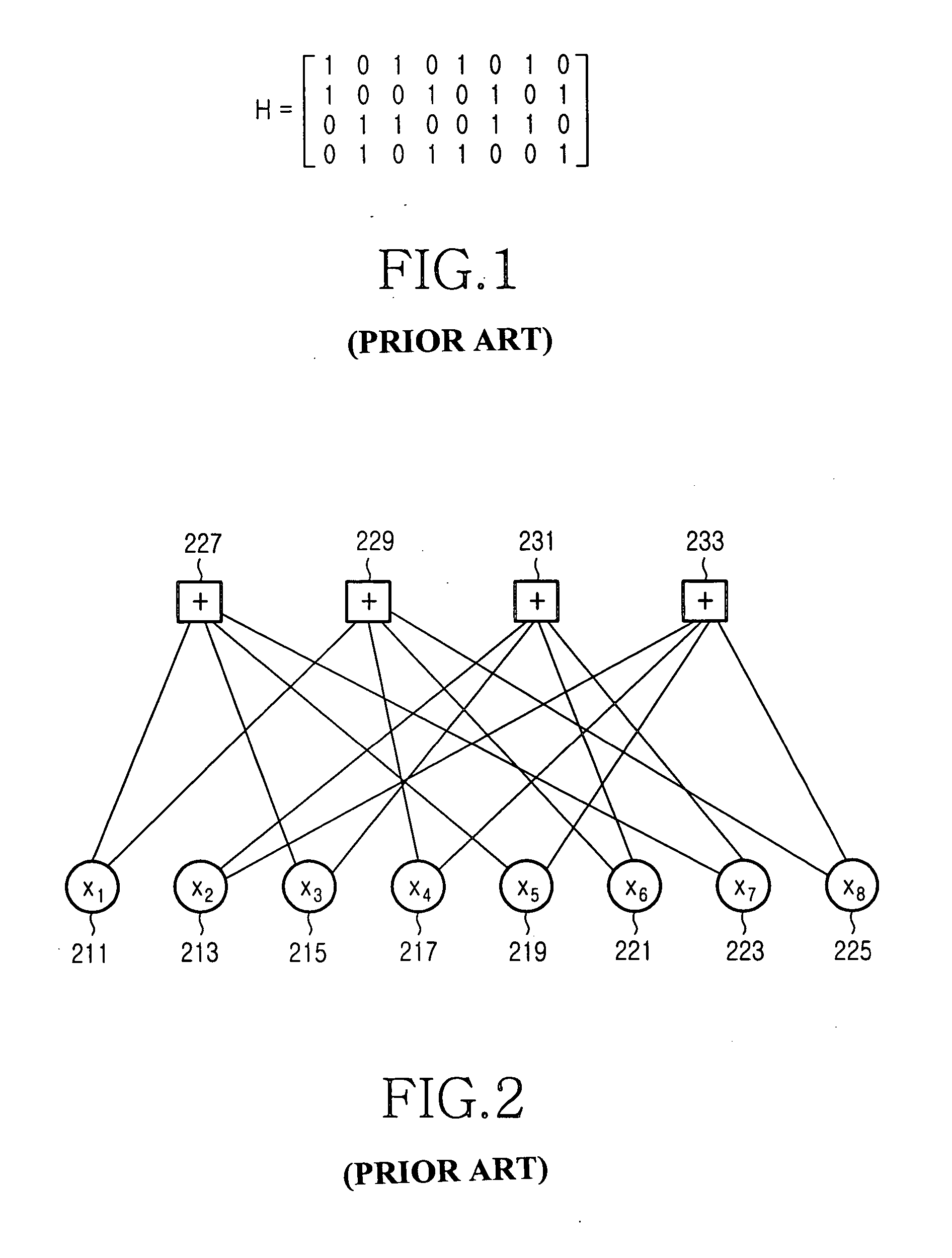
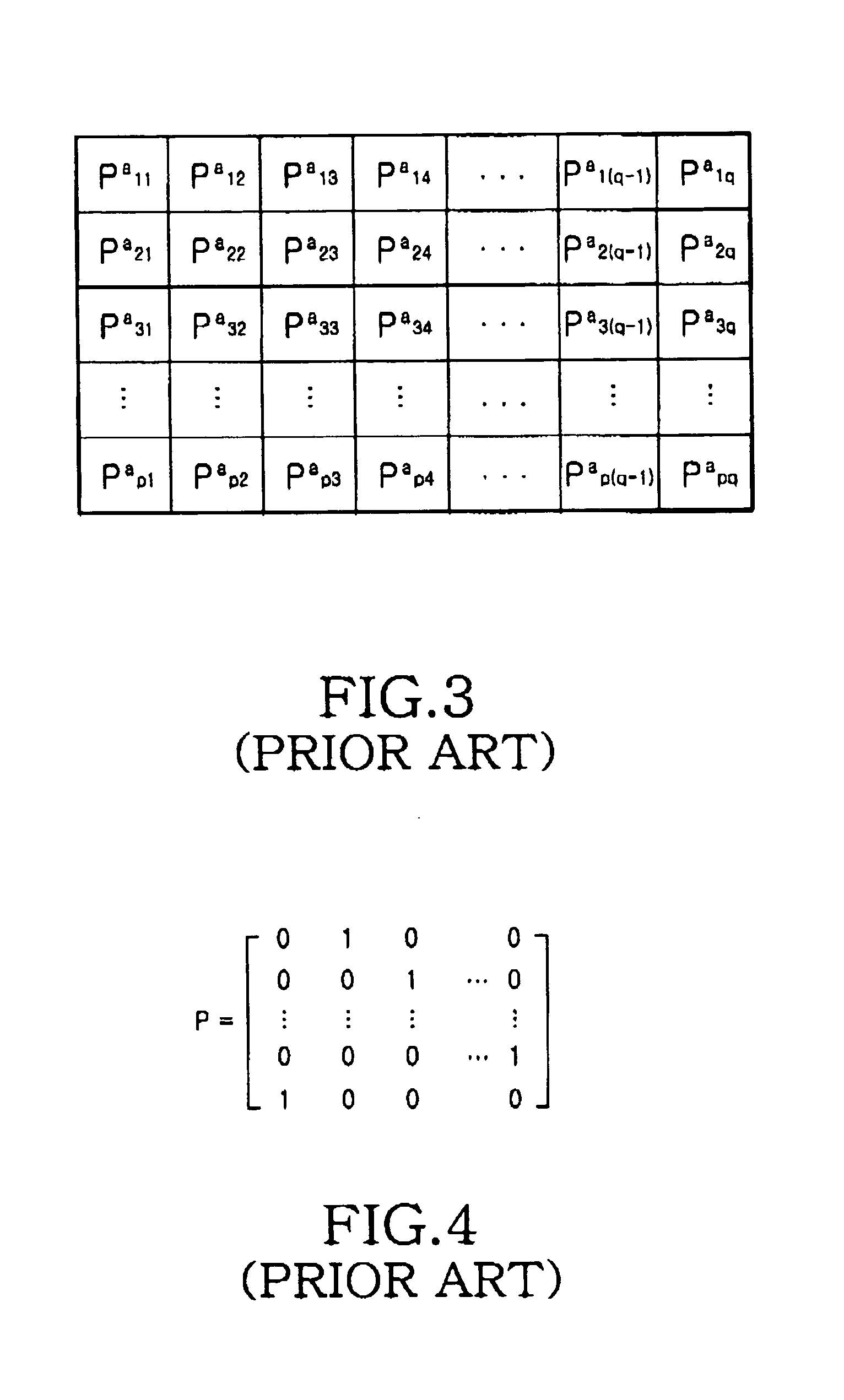
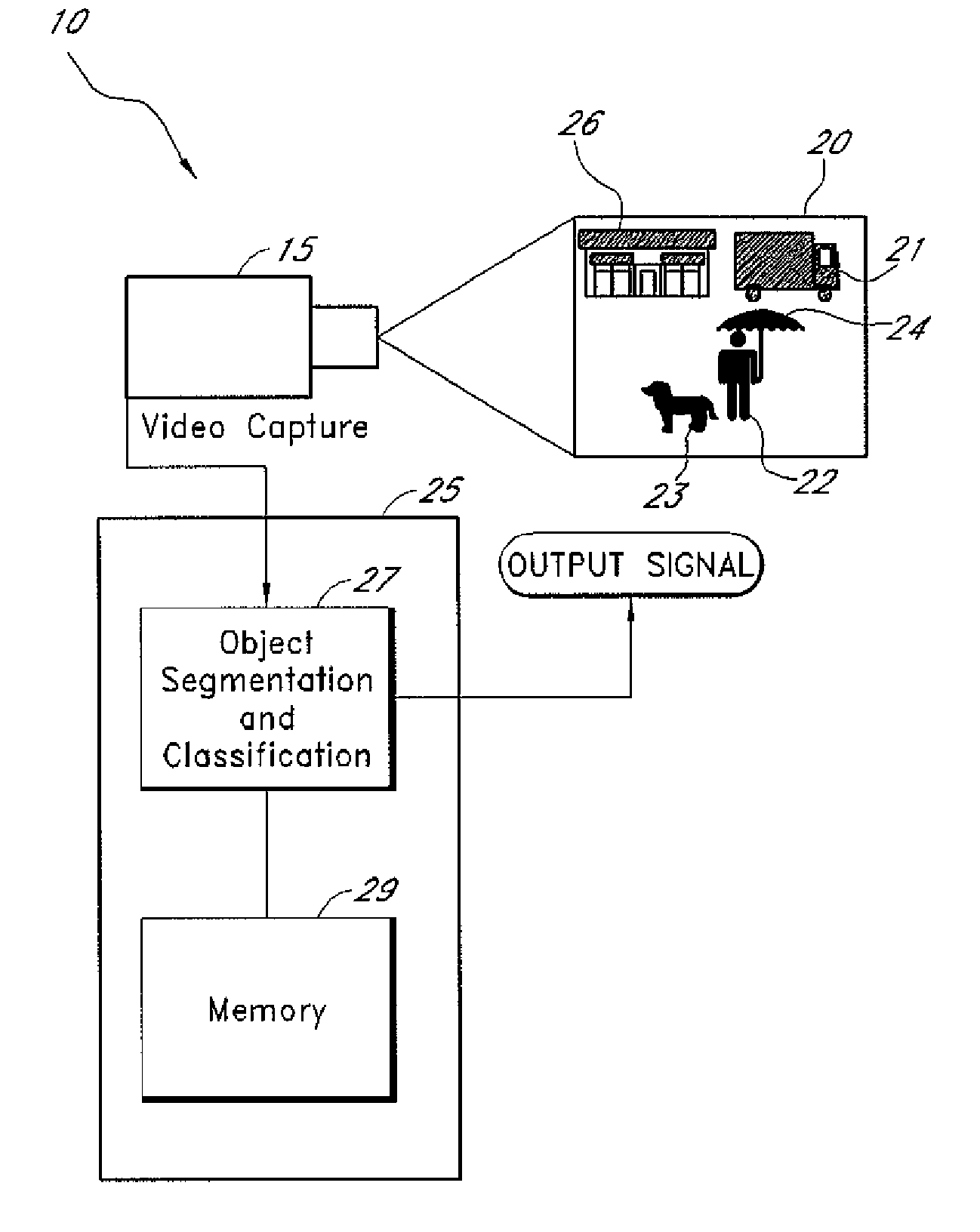
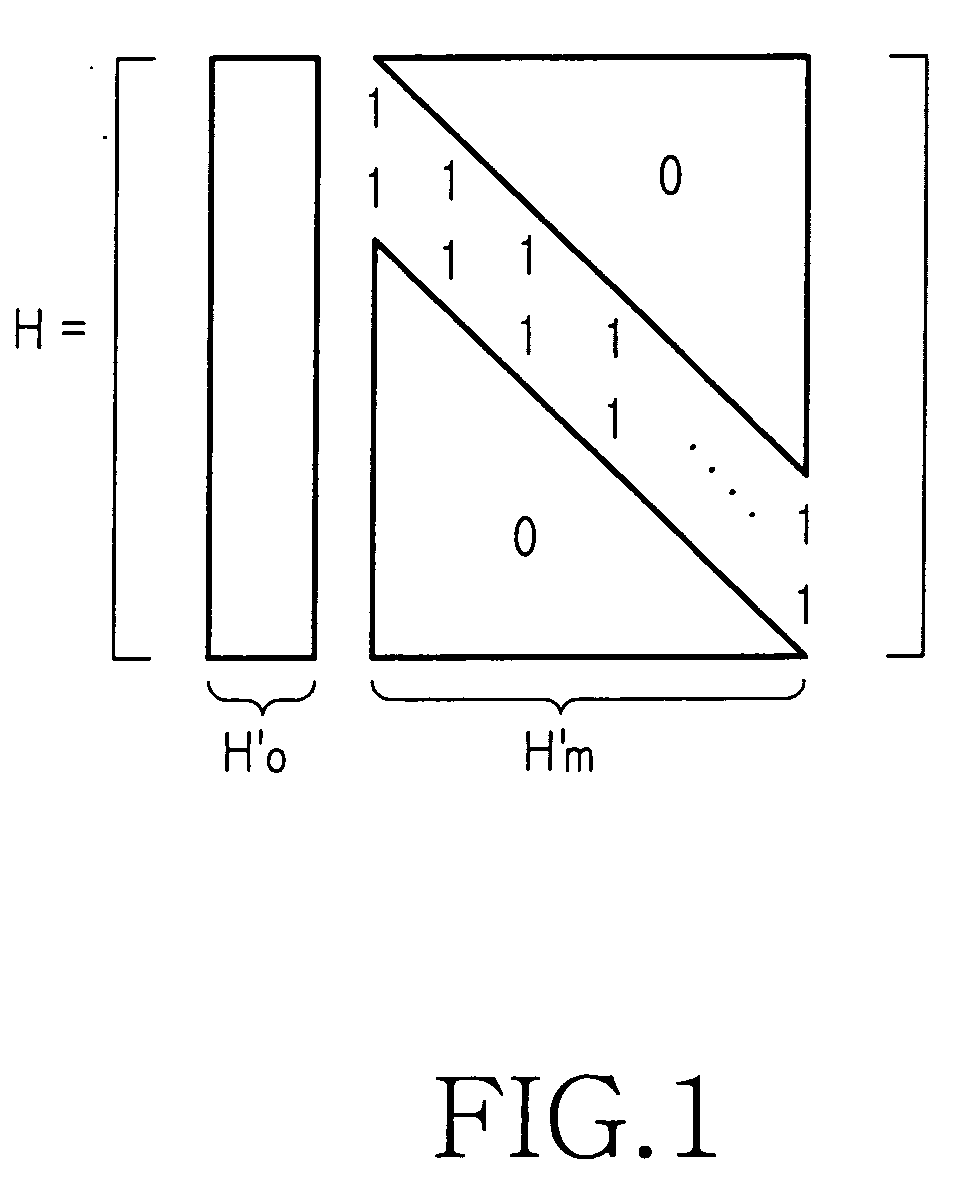
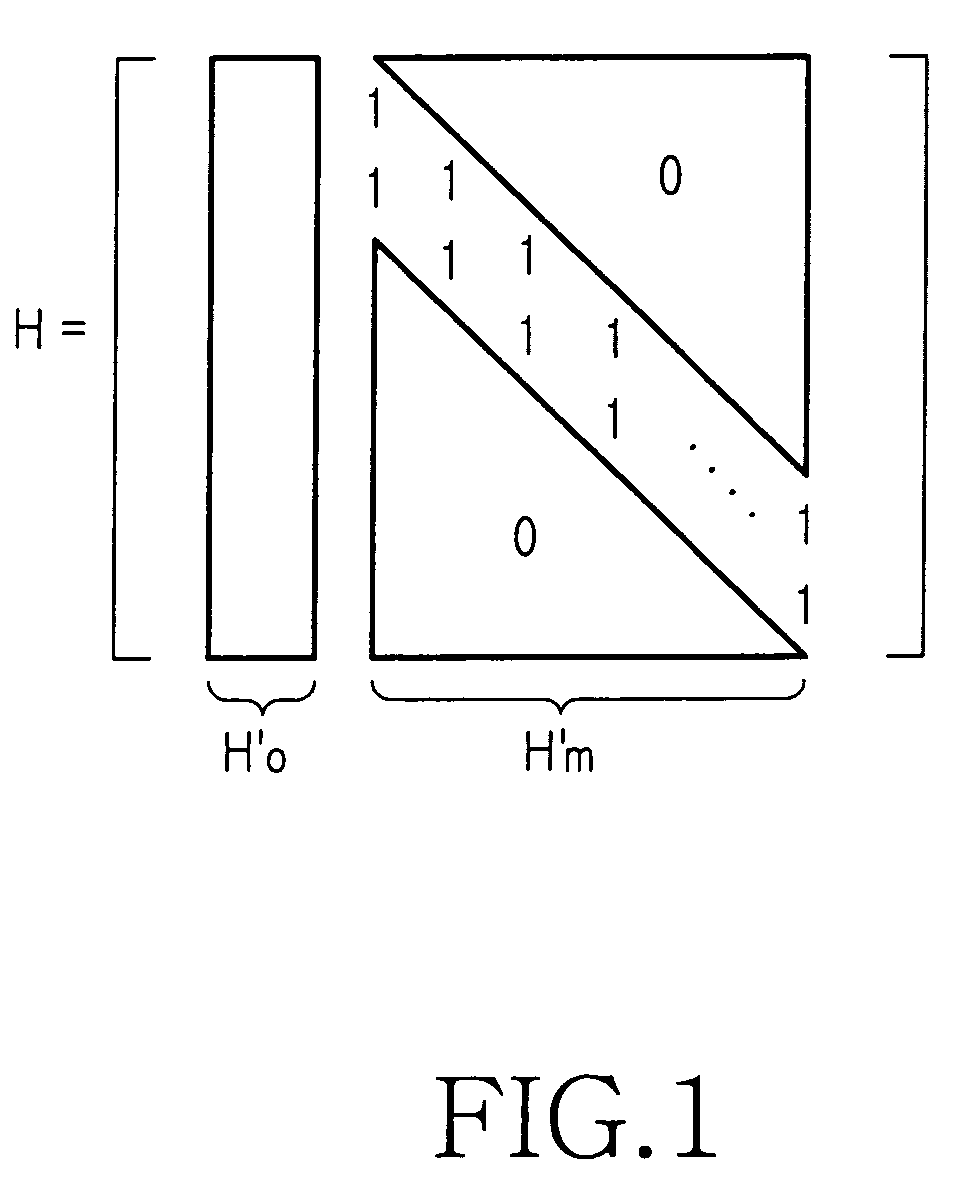
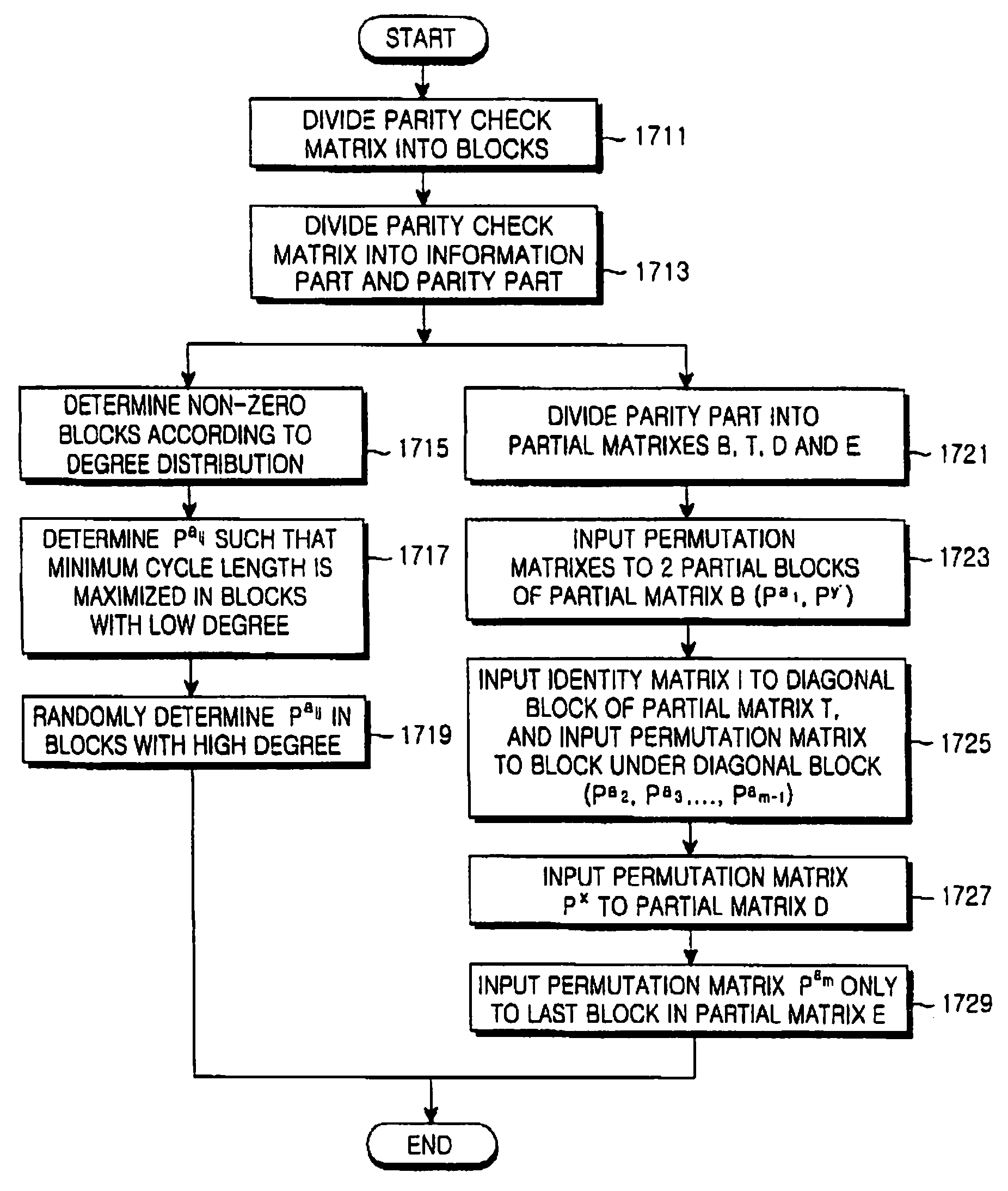
A method for generating a parity check matrix of a block LDPC code is disclosed. The parity check matrix includes an information part corresponding to an information word and a first parity part and a second parity part each corresponding to a parity. The method includes determining a size of the parity check matrix based on a coding rate applied when coding the information word with the block LDPC code, and a codeword length; dividing a parity check matrix with the determined size into a predetermined number of blocks; classifying the blocks into blocks corresponding to the information part, blocks corresponding to the first parity part, and blocks corresponding to the second parity part; arranging permutation matrixes in predetermined blocks from among the blocks classified as the first parity part, and arranging identity matrixes in a full lower triangular form in predetermined blocks from among the blocks classified as the second parity part; and arranging the permutation matrixes in the blocks classified as the information part such that a minimum cycle length is maximized and weight values are irregular on a factor graph of the block LDPC code.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Electronic device management using interdomain profile-based inferences
InactiveUS20130110992A1Digital data information retrievalInformation formatContext dataDevice status
A system and method for generating action cues and recommendations for provision to an electronic device are provided. Context data associated with an electronic device and derived from one or more of sensor data, device state data, and application data is received, and a profile for the electronic device or a user thereof is defined using the context data, representing probability distribution. A selected action from a plurality of actions executable at the electronic device is identified using the profile, and a cue is returned to the electronic device for execution. The profile may be constructed as a factor graph representation using random coding techniques.
Owner:BLACKBERRY LTD
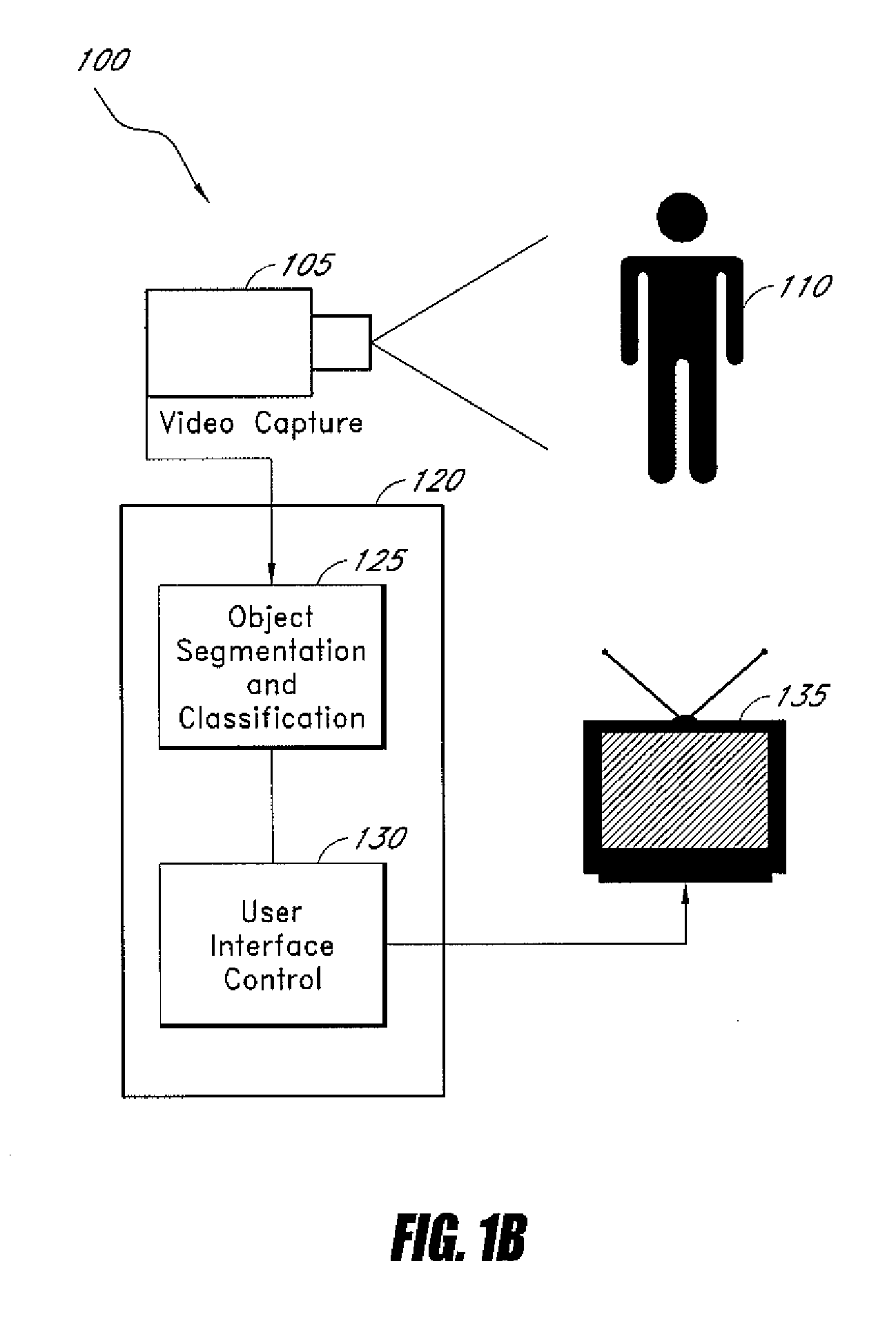
System and method for class-specific object segmentation of image data
Systems and methods for processing an image to determine whether segments of the image belong to an object class are disclosed. In one embodiment, the method comprises receiving digitized data representing an image, the image data comprising a plurality of pixels, segmenting the pixel data into segments at a plurality of scale levels, determining feature vectors of the segments at the plurality of scale levels, the feature vectors comprising one or more measures of visual perception of the segments, determining one or more similarities, each similarity determined by comparing two or more feature vectors, determining, for each of a first subset of the segments, a first measure of probability that the segments is a member of an object class, determining probability factors based on the determined first measures of probability and similarity factors based on the determined similarities, and performing factor graph analysis to determine a second measure of probability for each of a second subset of the segments based on the probability factors and similarity factors.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
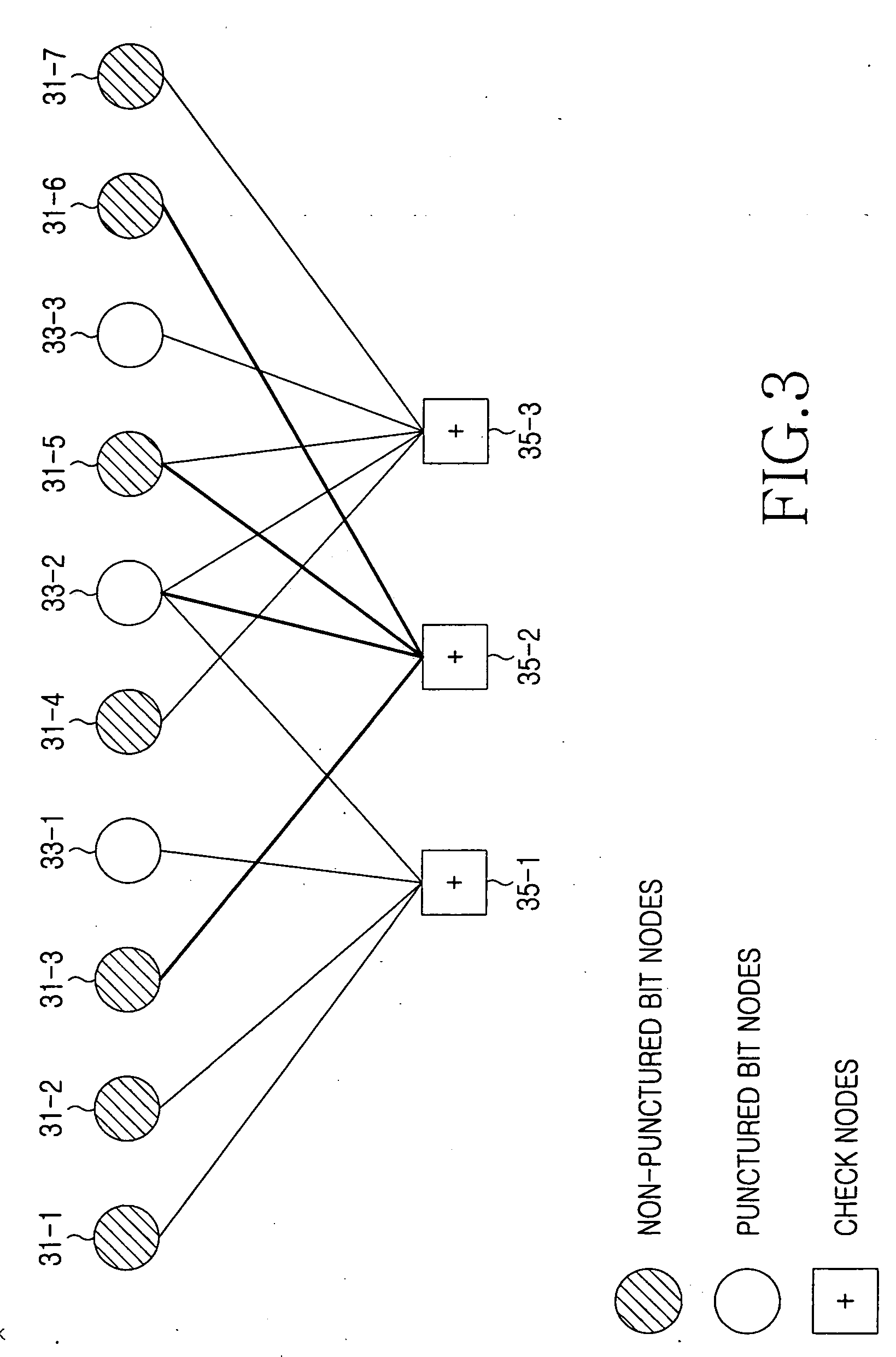
Method for puncturing an LDPC channel code
ActiveUS20060156181A1Improve performanceData representation error detection/correctionError detection/correctionTheoretical computer scienceParity-check matrix
A method for puncturing a low density parity check (LDPC) code that is decoded through a parity check matrix expressed by a factor graph including check nodes and bit nodes connected to the check nodes through edges. The method includes classifying the bit nodes mapped to a parity part of a codeword into hierarchical groups according to their decoding facilities when the bit nodes are punctured, determining puncturing order of the groups, and sequentially performing puncturing on the bit nodes from a bit node belonging to a corresponding group according to the puncturing order of the groups to acquire a codeword with a desired coding rate.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
Apparatus and method for coding and decoding irregular repeat accumulate codes
ActiveUS20050132260A1Minimize complexityError prevention/detection by using return channelError correction/detection using multiple parity bitsParity-check matrixDiagonal matrix
An apparatus and method for coding an irregular Repeat Accumulate (RA) code. A repeater repeats a received information word such that the information word corresponds to weights of a first information part and a second information part of a parity check matrix in which permutation matrixes are arranged in the first information part and the second information part corresponding to the information word such that a minimum length of a cycle on a factor graph of the irregular RA code becomes a predetermined length and weights are irregular, and a dual diagonal matrix is arranged in a parity part corresponding to a parity. An interleaver interleaves a signal output from the repeater using an interleaving scheme predefined for the parity check matrix. An accumulator generates the irregular RA code by accumulating a signal output from the interleaver according to a weight of the parity part.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method for predicting dynamic social network user behaviors
InactiveCN102117325AAccurate predictionSpecial data processing applicationsStatistical analysisSocial effects
The invention discloses a method for predicting dynamic social network user behaviors based on a computer probability graph model, which comprises the following steps of: 1, performing objective statistical analysis on the dynamic social network user behaviors in terms of social influence, time dependence and network correlation; 2, performing formal definition on the dynamic social network user behaviors by adopting computer technical means such as a graph theory, a set, a matrix theory and the like; 3, establishing a dynamic anti-noise factor graph model according to the definition in the step 2; 4, learning the dynamic anti-noise factor graph model, and estimating a value Theta of a series parameter from given historic records; and 5, predicting the user behaviors according to the Theta to obtain prediction results. By the method, modeling and accurate prediction are performed on the dynamic social network user behaviors from a micro level.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
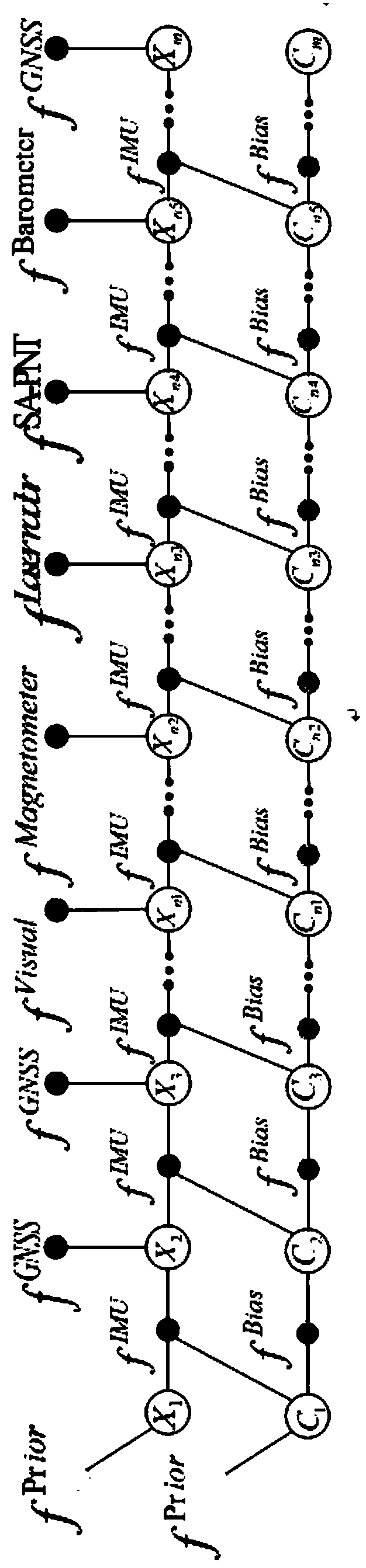
Multisource navigation information fusion method based on factor graph
InactiveCN106197408AHigh precisionImprove fault toleranceNavigational calculation instrumentsNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsInformation integrationFusion frame
The invention discloses a multisource navigation information fusion method based on a factor graph. The multisource navigation information fusion method comprises the following steps: firstly obtaining a track meeting the actual environment and task requirement by carrying out track setting, obtaining sensor measurement information by virtue of various sensors, obtaining inertial navigation IMU data by virtue of an inertia measurement unit, constructing a multisource navigation information fusion frame by virtue of the factor graph, and finally obtaining navigation information through multisource information filtering fusion. The multisource navigation information fusion method disclosed by the invention has the advantages that the factor graph and a multisource information fusion algorithm are combined together and processing on asynchronous measurement information and requirement on navigation accuracy are realized.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Method for puncturing low density parity check code
InactiveUS20060206781A1Avoid performanceError correction/detection using multiple parity bitsCode conversionTheoretical computer scienceDiagonal matrix
Owner:K2M +1
Method for padding and puncturing low density parity check code
InactiveUS20070011567A1Simple calculationReduce latencyError correction/detection using multiple parity bitsCode conversionTheoretical computer scienceDiagonal matrix
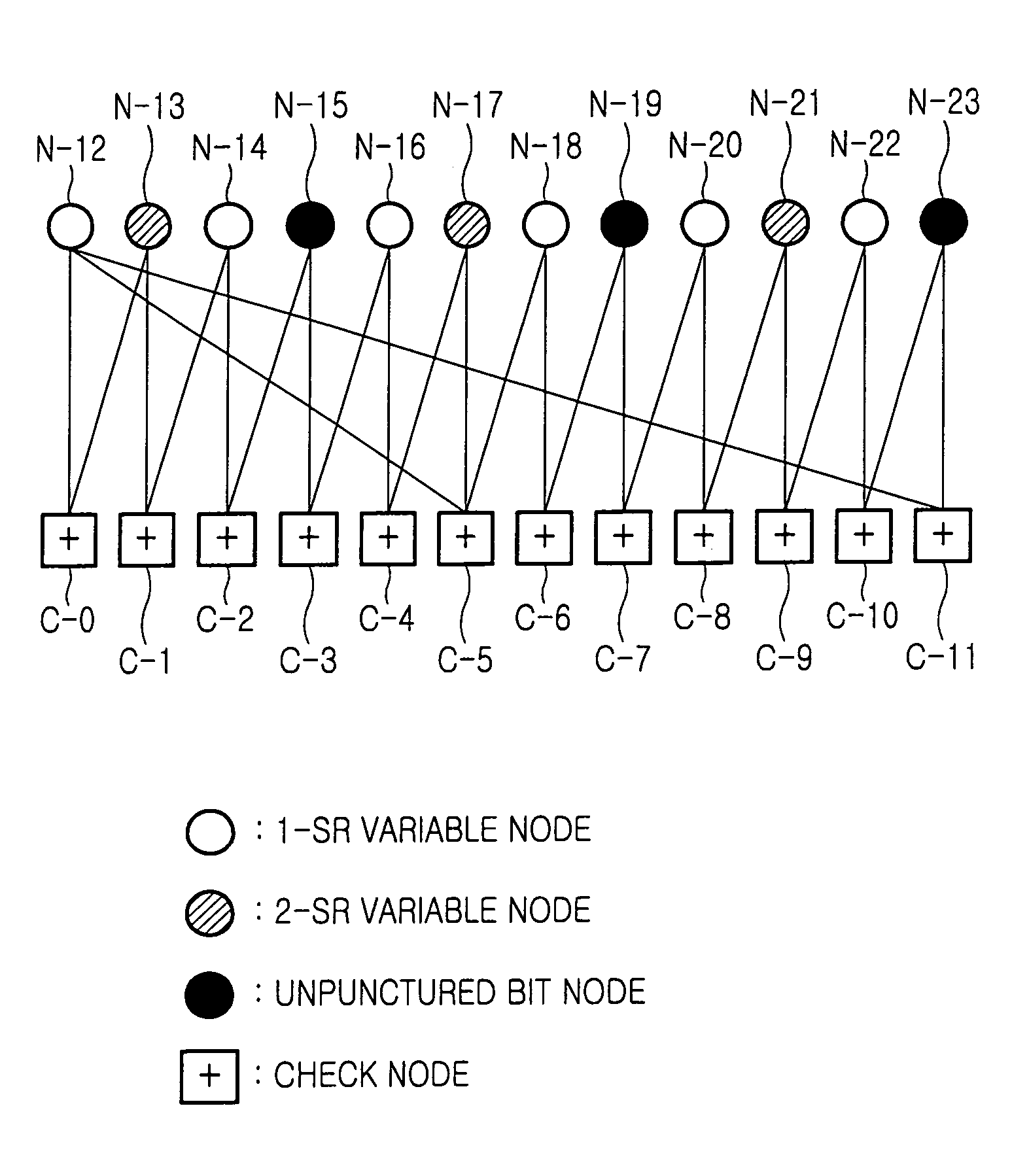
Disclosed is a method for puncturing a Low Density Parity Check (LDPC) code that is expressed by a factor graph having a check node and a variable node, connected to each other by an edge, and is decoded by a parity check matrix including a parity part having a single weight-3 column and a dual-diagonal matrix. The method includes selecting 1-step recoverable (1-SR) variable nodes with the highest quality including a variable node mapped to a weight-3 column, and setting a first puncturing priority group using the selected 1-SR variable nodes, selecting k-step recoverable (k-SR) variable nodes with the highest quality in the next step k taking into account the variable nodes selected in the current step, and setting a priority group for each individual step, puncturing an LDPC code mapped to a variable node belonging to a corresponding group according to priority of each group obtained in the preceding steps.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
BP decoding method and device for polarization code
ActiveCN105187073AEasy to implementReduce the number of decoding iterationsError correction/detection using multiple parity bitsCode conversionSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Computation complexity
The invention discloses a BP decoding method and device for a polarization code, and belongs to the technical field of channel coding. A BP decoding algorithm based on an early termination iteration strategy is used for decoding the polarization code, and a judgment condition of early termination of the BP decoding algorithm based on the early termination iteration strategy is that a symbol of the log-likelihood ratio of the leftmost end of a factor graph does not change in continuous two iteration processes. The invention also discloses a BP decoding device for the polarization code. Through the convergence characteristic of the symbol of the log-likelihood ratio, the method and device carry out the judgment of iteration termination of BP coding, can remarkably reduce the number of iteration times under the condition of causing no loss of decoding performance, and are more remarkable in effects under the conditions of medium and high signal-to-noise ratios. The method is simple and easy, is low in calculating complexity, and is simple in hardware implementation.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Multi-source fusion navigation method based on factor graph and observability analysis
ActiveCN111780755AFlexible configurationFlexible useNavigational calculation instrumentsNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsMultiple sensorEngineering
The invention discloses a multi-source fusion navigation method based on a factor graph and observability analysis. The method comprises the following steps: constructing a multi-source integrated navigation system based on an inertial navigation / auxiliary sensor integrated navigation model to obtain an integrated navigation robust Kalman sub-filter taking inertial navigation as a core and takingtwo or more than two of satellites, vision and odometers as auxiliary sensors; based on the navigation calculation result of each integrated navigation robust Kalman sub-filter, measuring the observability degree of the state variable of each integrated navigation robust Kalman sub-filter; using an incremental factor graph architecture, selecting an optimal factor online to participate in fusion according to credibility evaluation of multi-source integrated navigation factors, and automatically adjusting the weight of information distribution so that cross-scene multi-source fusion navigationis realized. According to the invention, adaptive fusion and safe and reliable navigation positioning of multiple sensors can be realized, and the precision and reliability of multi-source navigationinformation fusion of inertia / satellite / vision and the like are improved.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
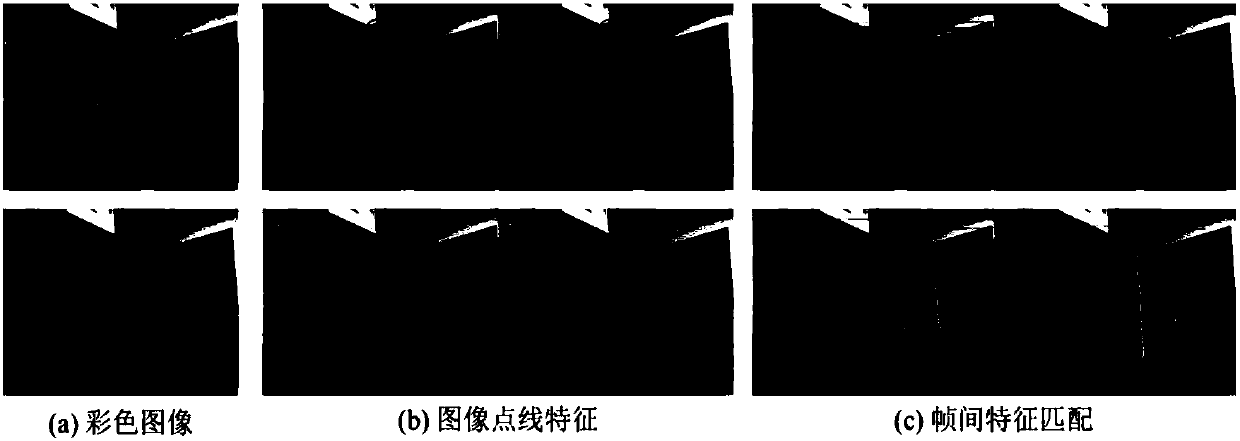
VSLAM method based on multi-characteristic visual odometer and graph optimization model
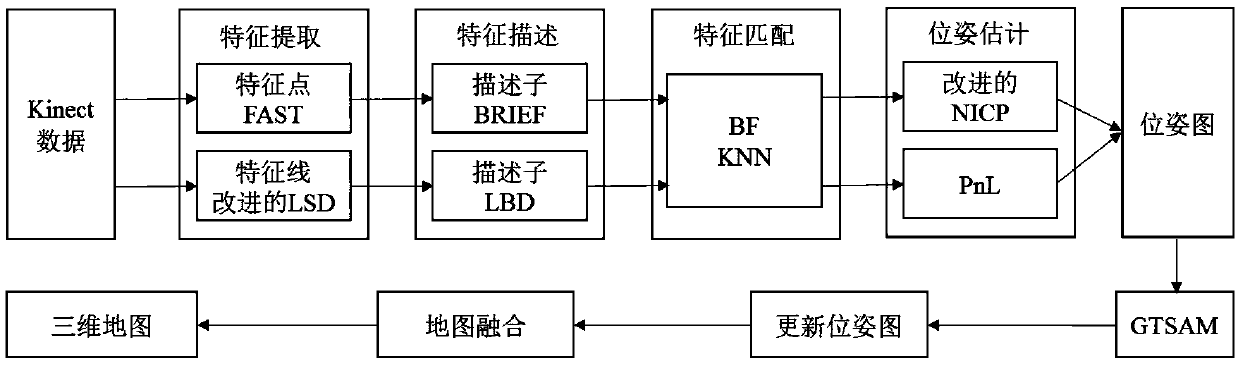
The invention discloses a VSLAM method based on a multi-characteristic visual odometer and a graph optimization model, and belongs to the robot SLAM field; the method comprises the following steps: firstly using a FAST (features from accelerated segment test) and an improved LSD algorithm to extract point and line features in a color image; further using different descriptors to describe characteristics; then carrying out characteristic matching; finally using an improved NICP (normal iterative closest point) algorithm and a PnL (perspective n line) algorithm to estimate a robot initial posture. The method can extract image line features so as to enlarge algorithm application scenes, can obtain a well robot initial posture, uses a Bayes network to express a multi-characteristic visual odometer, obtains a factor graph on the basis of the Bayes network, uses a maximum posterior probability to estimate a robot global posture in the factor graph, and uses a Gauss-Newton method to solve themaximum posterior probability to obtain the updated posture graph; finally, the posture graph and three dimensional points of corresponding frames are fused to obtain a reconstructed three dimensional map.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Stochastic decoding of LDPC codes
ActiveUS20080077839A1Low-complexity hardwareImprove decoding performanceCode conversionSingle error correctionNoise levelTheoretical computer science
The present invention relates to a decoding method and system for stochastic decoding of LDPC codes. Each encoded sample of a set of encoded samples is first scaled by a scaling factor proportional to a noise level of the set of encoded samples. Each of the scaled encoded samples is then converted into a corresponding probability. For each probability a corresponding probability message is the generated by encoding each probability as a sequence of digital bits. Each probability message is then provided to a respective node of a logic circuitry for stochastic decoding. The logic circuitry represents a factor graph of the parity check matrix of the LDPC code. Using the logic circuitry each probability message is processed for determining an estimated sequence of information bits. If an equality node is in a hold state a chosen bit is provided from a corresponding edge memory which is updated by storing output bits from the equality node when the same is in a state other than a hold state.
Owner:MCGILL UNIV
Whole-course pose estimation method based on global map and multi-sensor information fusion
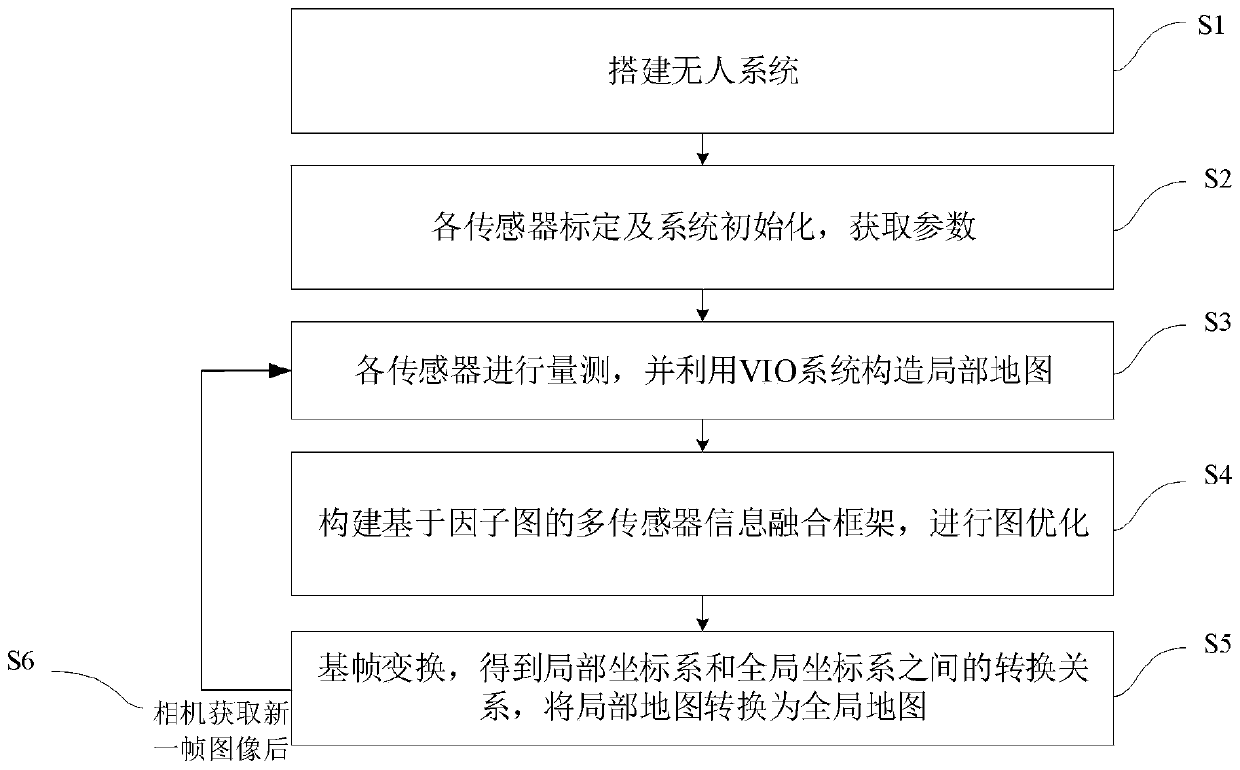
ActiveCN110706279AAccurate pose estimation throughout the processHigh precisionImage analysisUncrewed vehicleOdometer
The invention provides a whole-course pose estimation method based on global map and multi-sensor information fusion, and relates to the field of navigation. The method comprises: firstly, building anunmanned aerial vehicle system comprising sensors; calibrating the sensors to obtain corresponding parameters of each sensor, and initializing an unmanned aerial vehicle system; acquiring measurementinformation of the current pose of the carrier unmanned aerial vehicle by utilizing each sensor, and constructing and maintaining a local map by utilizing image information of a visual inertia odometer VIO system; and constructing a factor graph-based multi-sensor information fusion framework, optimizing by utilizing the factor graph to obtain an optimal state variable of each current frame of the VIO system corresponding to the unmanned aerial vehicle system, updating a conversion relationship between a local coordinate system and a global coordinate system under the current frame, and converting a local map into a global map. Measurement of all sensors carried by the unmanned aerial vehicle and global map information can be fused by using a global optimization mode so that accuracy andreliability of pose estimation of the unmanned aerial vehicle system can be enhanced.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Method for padding and puncturing low density parity check code
InactiveUS8006162B2Error correction/detection using multiple parity bitsCode conversionAlgorithmParity-check matrix
Disclosed is a method for puncturing a Low Density Parity Check (LDPC) code that is expressed by a factor graph having a check node and a variable node, connected to each other by an edge, and is decoded by a parity check matrix including a parity part having a single weight-3 column and a dual-diagonal matrix. The method includes selecting 1-step recoverable (1-SR) variable nodes with the highest quality including a variable node mapped to a weight-3 column, and setting a first puncturing priority group using the selected 1-SR variable nodes, selecting k-step recoverable (k-SR) variable nodes with the highest quality in the next step k taking into account the variable nodes selected in the current step, and setting a priority group for each individual step, puncturing an LDPC code mapped to a variable node belonging to a corresponding group according to priority of each group obtained in the preceding steps.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method and System for Decoding Graph-Based Codes Using Message-Passing with Difference-Map Dynamics
InactiveUS20110041029A1Increase heightImprove errorDigital data processing detailsCode conversionDifference-map algorithmTheoretical computer science
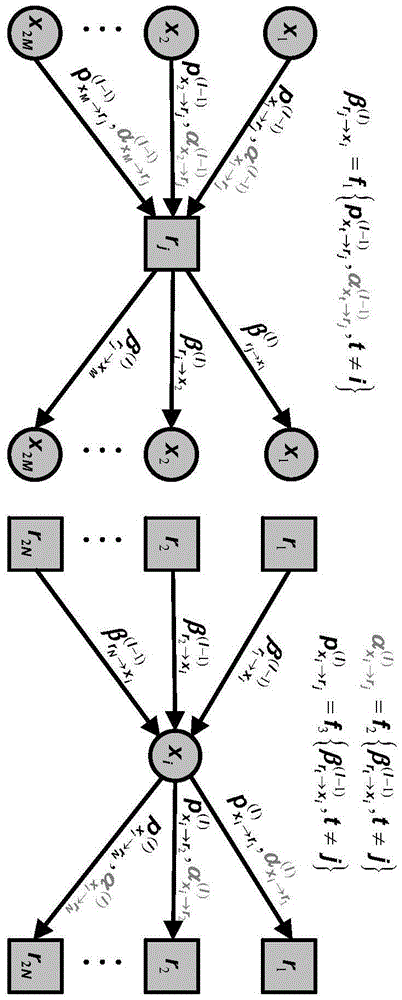
A code to be decoded by message-passing is represented by a factor graph. The factor graph includes variable nodes indexed by i and constraint nodes indexed by a connected by edges for transferring messages mi→a outgoing from the variable nodes to the constraint nodes and messages ma→i incoming from the constraint nodes to the variable nodes. The messages mi→a are initialized based on beliefs bi of a received codeword. The messages ma→i are generated by overshooting the messages mi→a at the constraint nodes. The beliefs bi are updated at the variable nodes using the messages ma→i. The codeword is outputted if found, otherwise, the messages mi→a are updated using a correction for the overshooting.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC RES LAB INC
Method for analyzing and sequencing academic influence of theme literature in citation database
ActiveCN103729432AImplement sortingSpecial data processing applicationsCitation databaseSubject matter
The invention discloses a method for analyzing and sequencing academic influence of theme literature in a citation database. The method includes performing theme retrieval in the citation database to acquire metadata information of the theme literature and citation relation among the theme literature; according to the acquired metadata information of the theme literature and the acquired citation relation among the theme literature, creating a theme citation network; on the basis of the citation network, building a factor graph model containing various literature academic influence factors; using a circulating maximum sum algorithm for approximate reasoning on a factor graph to determine marginal probability values of all variables in the factor graph; according to a descending order result of the marginal probability values, acquiring and outputting an academic influence sequence of all theme literature. By the method, sequencing of the academic influence of literature with a theme given by a user can be realized.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
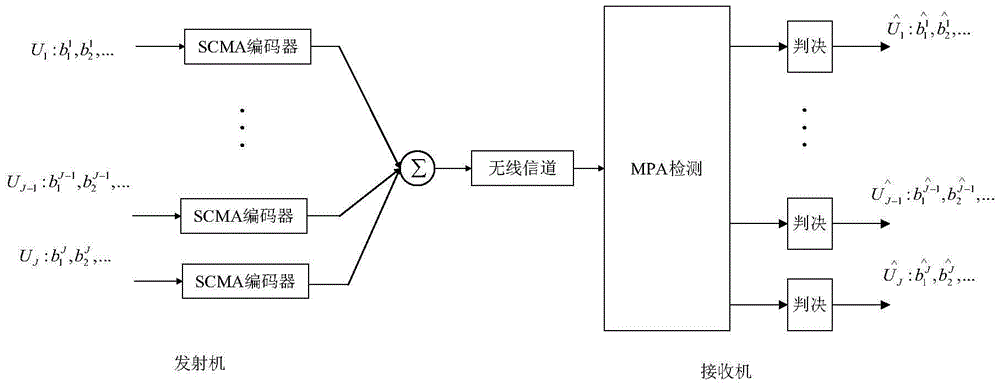
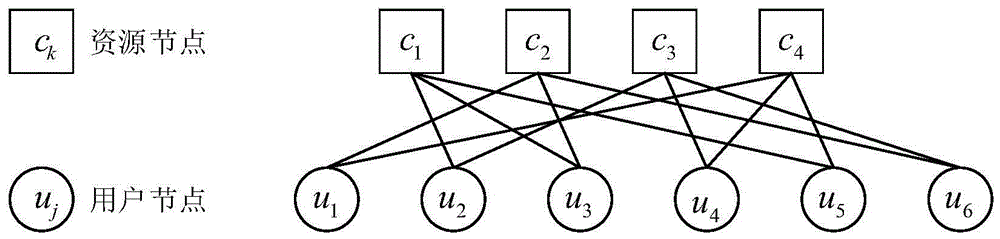
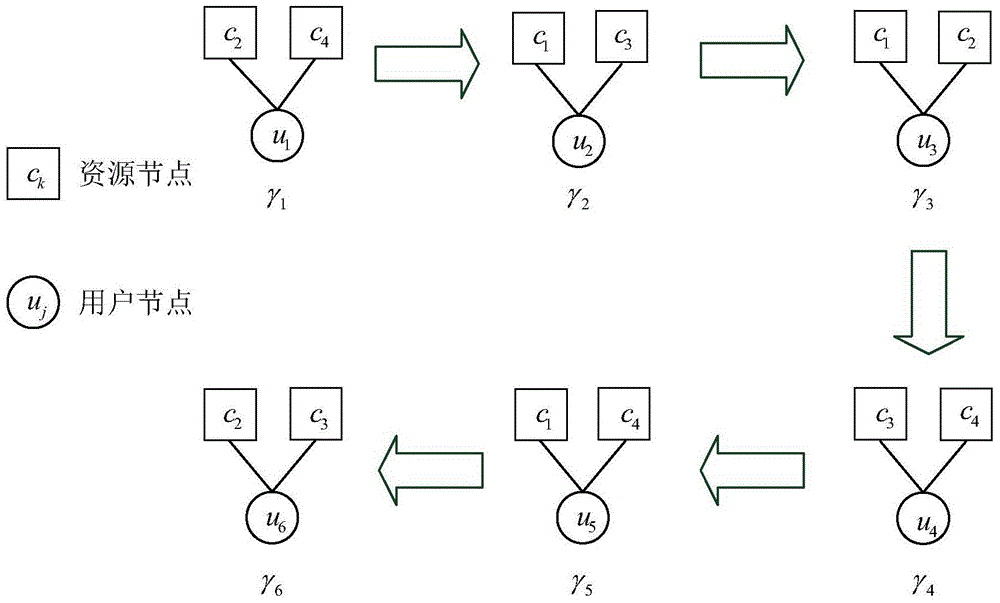
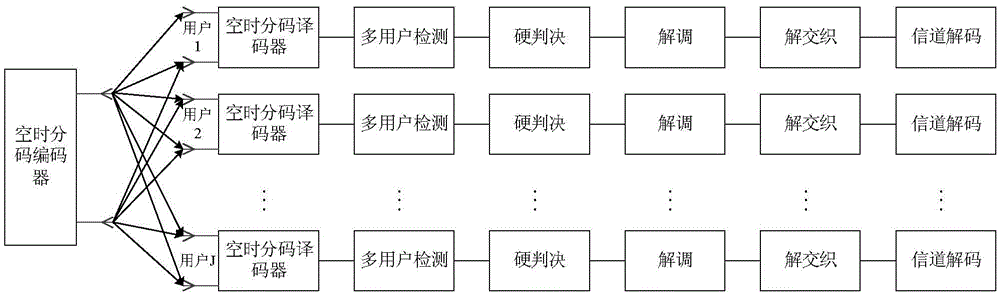
Multiuser detection method based on serial strategy for SCMA (Sparse Code Multiple Access) uplink communication system
InactiveCN105721106AIncrease profitImprove BER performanceTransmitter/receiver shaping networksForward error control useMultiuser detectionNODAL
The invention provides a multiuser detection method based on a serial strategy for an SCMA (Sparse Code Multiple Access) uplink communication system, and belongs to the field of signal detection of wireless communication systems. The method is characterized in that nodes in a conventional SCMA factor graph are divided into J groups (J is a quantity of user nodes); each group comprises one user node and all resource nodes connected with the user node; and all nodes (one user node and all the resource nodes which are connected with the user node) of each group are updated in sequence in each iteration process. According to the multiuser detection method, already-updated node messages are utilized in each iteration process, so that a utilization ratio of the already-updated node messages can be effectively increased. The BER (Bit Error Rate) performance of the method is far superior to the BER performance of a method in the prior art under the condition of less iteration times. The calculation complexity of the method is much lower than the calculation complexity of the method in the prior art under the condition of hardly any loss of the BER performance.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
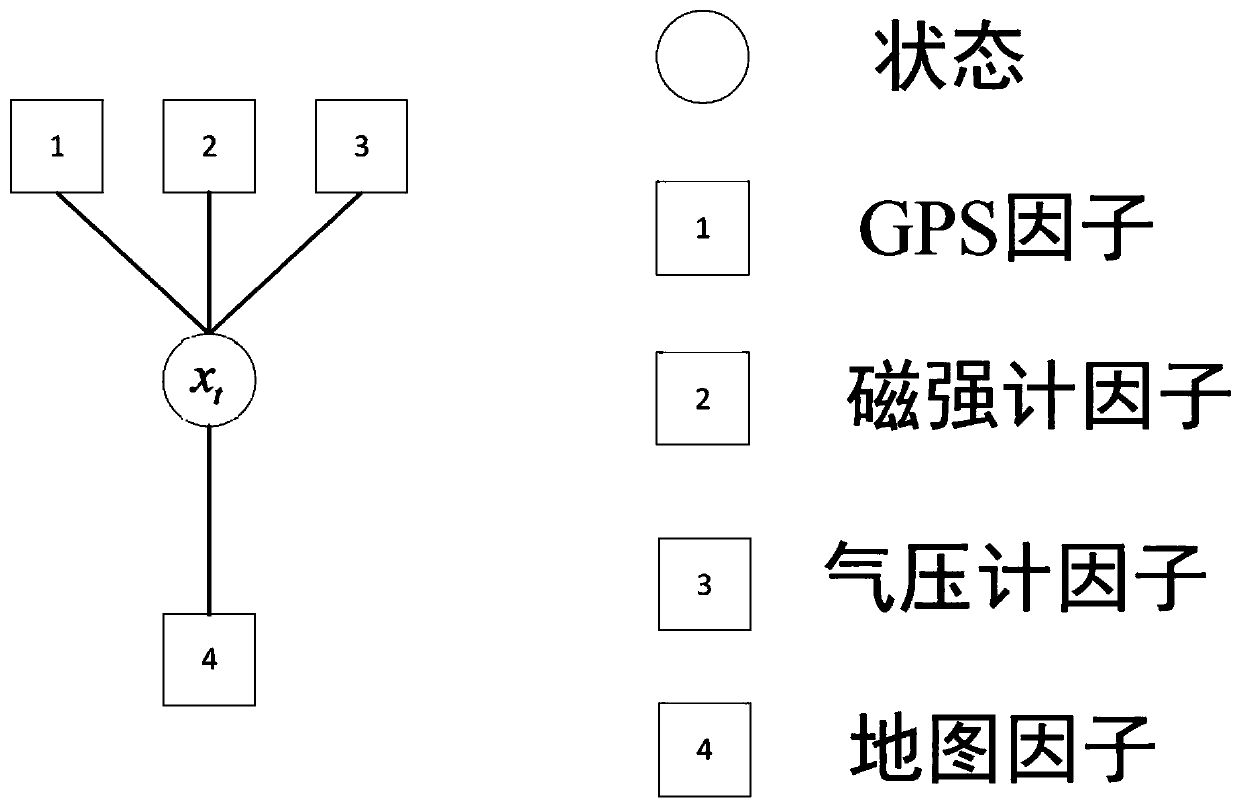
Multi-source information fusion method based on factor graph
PendingCN108364014ARealize plug and playImprove navigation accuracyCharacter and pattern recognitionMultiple sensorInertial navigation system
The invention relates to a multi-source information fusion method based on a factor graph. The multi-source information fusion method aims to realize full-source positioning and navigation without relying on satellite navigation in a complex environment, takes an inertial navigation system as the core, utilizes all available navigation information sources, and performs rapid fusion, optimal configuration and self-adaptive switching on asynchronous heterogeneous sensor information. A factor graph model is constructed by means of recursive Bayesian estimation, the factor graph is broadened by means of a variable node and a factor node of the system after measurement information of different sensors are acquired, state recursion and updating are completed based on a set cost function, and thefactor graph optimization problem is solved through sparse QR decomposition by adopting an increment smoothing method. The multi-source information fusion method effectively solves the time-varying state space problem generated between carrier motion and measurement availability, can calculate a solution of precise navigation according to dynamic changes of a carrying platform, realizes plug-and-play of multiple sensors, and meets the requirements of carriers changing in complex environment and different tasks.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
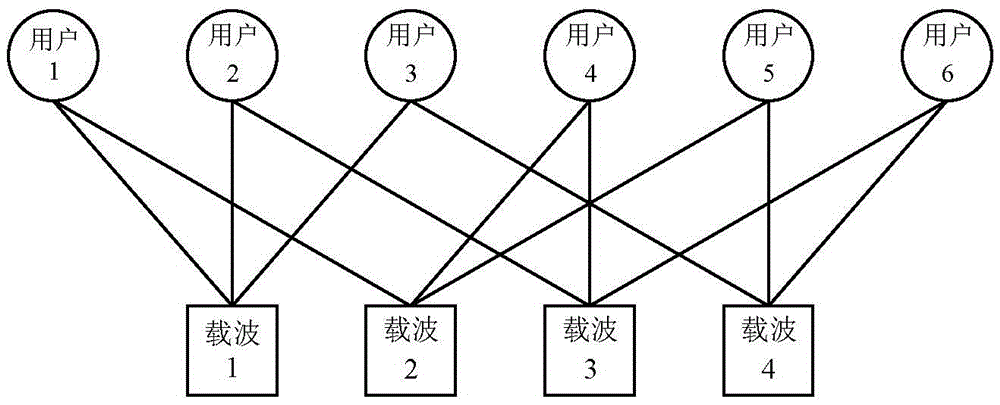
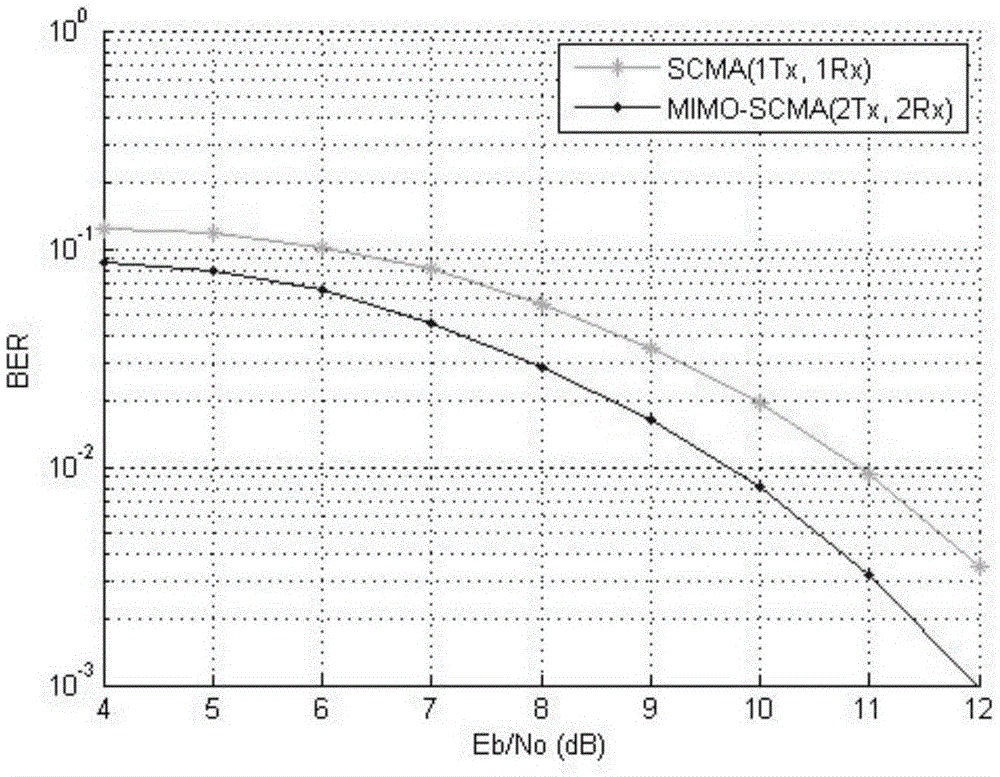
MIMO-SCMA system downlink design method based on STBC
ActiveCN105554865AImprove spectrum utilizationImprove bit error rate performancePower managementCarrier signalEngineering
The invention provides an MIMO-SCMA system downlink design method based on STBC, and relates to the MIMO-SCMA system downlink design method. The MIMO-SCMA system downlink design method based on the STBC aims at the problems that error rate requires to be reduced by an SCMA technology and an MOMO-OFDM technology is difficult to meet the requirement of 5G for transmission rate. The method is realized by the steps that step one, two antennas of a base station are utilized to transmit TW and T'W; step two, user terminals are utilized to receive signals SW and S'W; step three, STBC decoding is performed on the signals SW and S'W received by each user terminal and then the decoded signals YW=[xw1xw2...xwK]T are obtained; step four, a factor graph is determined according to J users, occupation of K subcarriers, overload coefficient of J / K and a configuration matrix F; step five, the probability value of information transmitting of each user is obtained; and step six, information bits are obtained. The MIMO-SCMA system downlink design method based on the STBC is applied to the field of MIMO-SCMA system downlink design.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
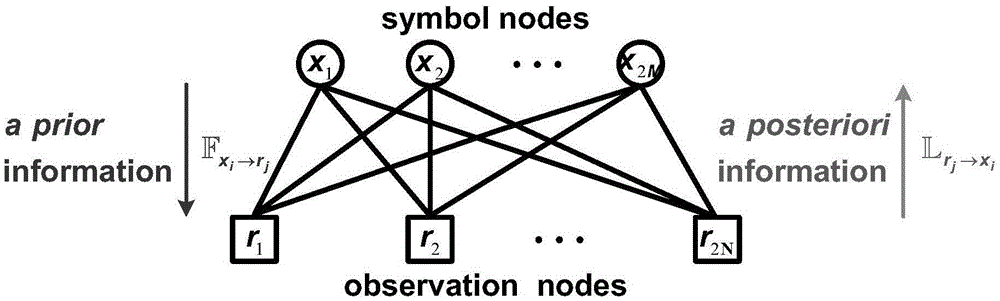
Low-complexity belief propagation detection algorithm for large-scale MIMO system
InactiveCN105656538AImprove performancePrevent inversionSpatial transmit diversityNODALPrior information
The invention discloses a low-complexity belief propagation detection algorithm for a large-scale MIMO system. A corresponding factor graph is built by utilizing an equivalent real number field model, and complex number field operation is translated into real number field operation, thereby implementing BP-based iteration detection; wherein the factor graph is used for representing a dependency relation between a receiving signal and a transmitting signal, the transmitting signal is utilized as a signal node, and the receiving signal is utilized as an observation node; each signal node updates prior information according to posterior information obtained from the observation node, and then transmits the updated prior information to all observation nodes connected with the signal node; each observation node calculates updates posterior information according to prior information obtained from the signal node, and then transmits the updated posterior information to a signal node connected with the observation node. According to the low-complexity belief propagation detection algorithm for the large-scale MIMO system, a symbol-based large-scale MIMO detection algorithm is implemented; high-dimensional matrix inversion is avoided, and the low-complexity belief propagation detection algorithm can be greatly suitable for application scenarios of the large-scale MIMO.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Apparatus and method for transmitting/receiving signal in a communication system
InactiveUS20070283216A1Error preventionError correction/detection using LDPC codesCommunications systemLow-density parity-check code
A signal transmission apparatus in a communication system is disclosed. A channel interleaver generates an interleaved vector by channel-interleaving a Low Density Parity Check (LDPC) codeword according to a channel interleaving rule, and a modulator generates a modulation symbol by modulating the interleaved vector according to a modulation scheme. The channel interleaving rule is one of a first channel interleaving rule and a second channel interleaving rule. The first channel interleaving rule is a rule for setting degree distribution for nodes in a factor graph of the LDPC codeword separately for individual levels supported by the modulation scheme. The second channel interleaving rule is a rule for allowing coded bits included in the LDPC codeword to be interleaved according to an unequal error characteristic of the modulation scheme.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
Assembly-line architecture of polarization code belief propagation decoder
ActiveCN105634507AReduce complexityImprove throughputCode conversionCyclic codesNODALRound complexity
Disclosed in the invention is assembly-line architecture of a polarization code belief propagation decoder. The assembly-line architecture comprises a BP decoder and a calculation module BCB. A BP decoding algorithm of the BP decoder is realized by iteration of n-order factor graph including (n+1) N nodes, wherein the N expresses a code length. Each node includes two kinds of likelihood probabilities: a first likelihood probability and a second likelihood probability; an input terminal of the BP decoder serves as a left end and an output terminal of the decoder serves as a right end; the first likelihood probability is used for message updating and transmission from the left side to the right side; and the second likelihood probability is used for message updating and transmission from the right side to the left side. The calculation module BCB is used for message updating and transmission between four nodes at an interval of an N / 2 bit at adjacent orders. According to the invention, the high-throughput-rate and low-complexity BP decoder architecture of the polarization code is realized; and the hardware realization complexity can be reduced and the processing speed is enhanced.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Decoding Reed-Solomon codes and related codes represented by graphs
InactiveUS20050138516A1Low costError prevention/detection by using return channelReed-muller codesComputer scienceFactor graph
A method decodes a soft-input cost function for an [N,k]q linear block error- correcting code that has a fast sparse transform factor graph (FSTFG) representation, such as Reed-Solomon codes. First, the code is selected and its FSTFG representation is constructed. The representation is simplified and is made redundant if the improved performance is more important than the increased decoding complexity. An encoding method consistent with the representation is selected. A set of message-update and belief-update rules are selected. The messages are initialized according to a soft-input cost function. An iterative decoding cycle is then begun, in which the first step consists of updating the messages according to the pre-selected message-update rules. In the second step of the decoding cycle, a trial code word is determined from the messages, the pre- selected message-update rules, and the encoding method. In the third step of the decoding cycle, the tentative output code word of the decoding method is replaced with the trial code word if the trial code word has lower cost. Finally, the decoding cycle terminates if a termination condition is true, and outputs the tentative code word, and otherwise repeats the decoding cycle. The decoding method can be combined or concatenated with other decoding methods for FSTFG codes.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC RES LAB INC
Apparatus and method for coding/decoding block low density parity check code in a mobile communication system
ActiveUS20070283221A1Maximized error correction capabilityMaximized minimum cycle lengthError preventionError detection/correctionTheoretical computer scienceParity-check matrix
A method for generating a parity check matrix of a block LDPC code. The parity check matrix includes an information part corresponding to an information word and a first parity part and a second parity part each corresponding to a parity. The method includes determining a size of the parity check matrix based on a coding rate applied when coding the information word with the block LDPC code, and a codeword length; dividing a parity check matrix with the determined size into a predetermined number of blocks; classifying the blocks into blocks corresponding to the information part, blocks corresponding to the first parity part, and blocks corresponding to the second parity part; arranging permutation matrixes in predetermined blocks from among the blocks classified as the first parity part, and arranging identity matrixes in a full lower triangular form in predetermined blocks from among the blocks classified as the second parity part; and arranging the permutation matrixes in the blocks classified as the information part such that a minimum cycle length is maximized and weight values are irregular on a factor graph of the block LDPC code.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Factor graph-based sparse code multiple access (SCMA) and low density parity check (LDPC) joint detection decoding algorithm and apparatus
ActiveCN106330199AMeet performance needsFast convergenceError correction/detection using block codesMulti user detectionAlgorithm
The present invention discloses a factor graph-based sparse code multiple access (SCMA) and low density parity check (LDPC) joint detection decoding algorithm and apparatus. Decoding information of LDPC is used to assist SCMA multi-user detection, an SCMA detection iteration process and an LDPC decoding iteration process are jointed on a factor graph so as to obtain a joint factor graph of SCMA detection and LDPC decoding, so that information integration of SCMA detection and LDPC decoding is performed in each iteration process. From the point of bit energy efficiency, ideal single-user transmission performance can be almost reached; and from the point of average iteration times, the iteration times of the present invention is far less than that of an outer iteration solution and is equivalent to that of a traditional non-feedback solution. The convergence speed is high, and no obvious, extra detection and decoding complexity is caused. The algorithm and apparatus better meet performance demands of a 5G system in the future.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA +1
Systems and methods for providing reputation management
ActiveUS20130173616A1Digital data processing detailsRelational databasesComputation complexityAttack
Systems and methods for providing efficient reputation management schemes resilient to malicious attacks. Methods for providing a reputation management scheme can comprise representing sets of service providers, raters, and ratings of service providers as a factor graph, wherein a factor node is associated with a function representing the probability distributions of the arguments of the function given the trustworthiness value and the ratings associated with a rater; and calculating the probability distributions of each variable in the reputation values of the set of providers using a belief propagation algorithm. In some embodiments, the computational complexity of the method is linear in the number of service providers and raters. In some embodiments, the method can identify malicious behavior and accordingly adjust the trustworthiness value for raters associated with malicious behavior.
Owner:GEORGIA TECH RES CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com