Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
109results about "Reed-muller codes" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
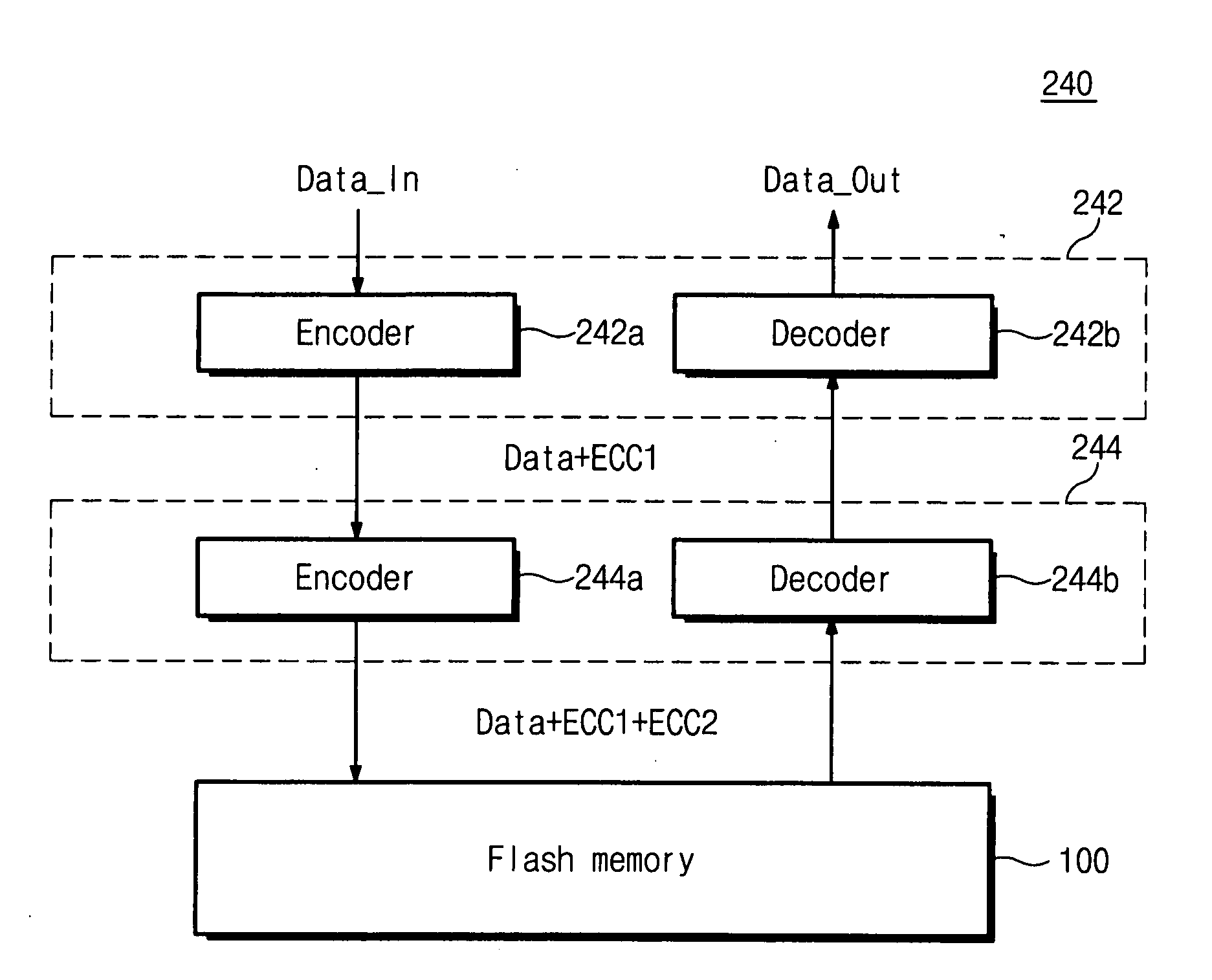
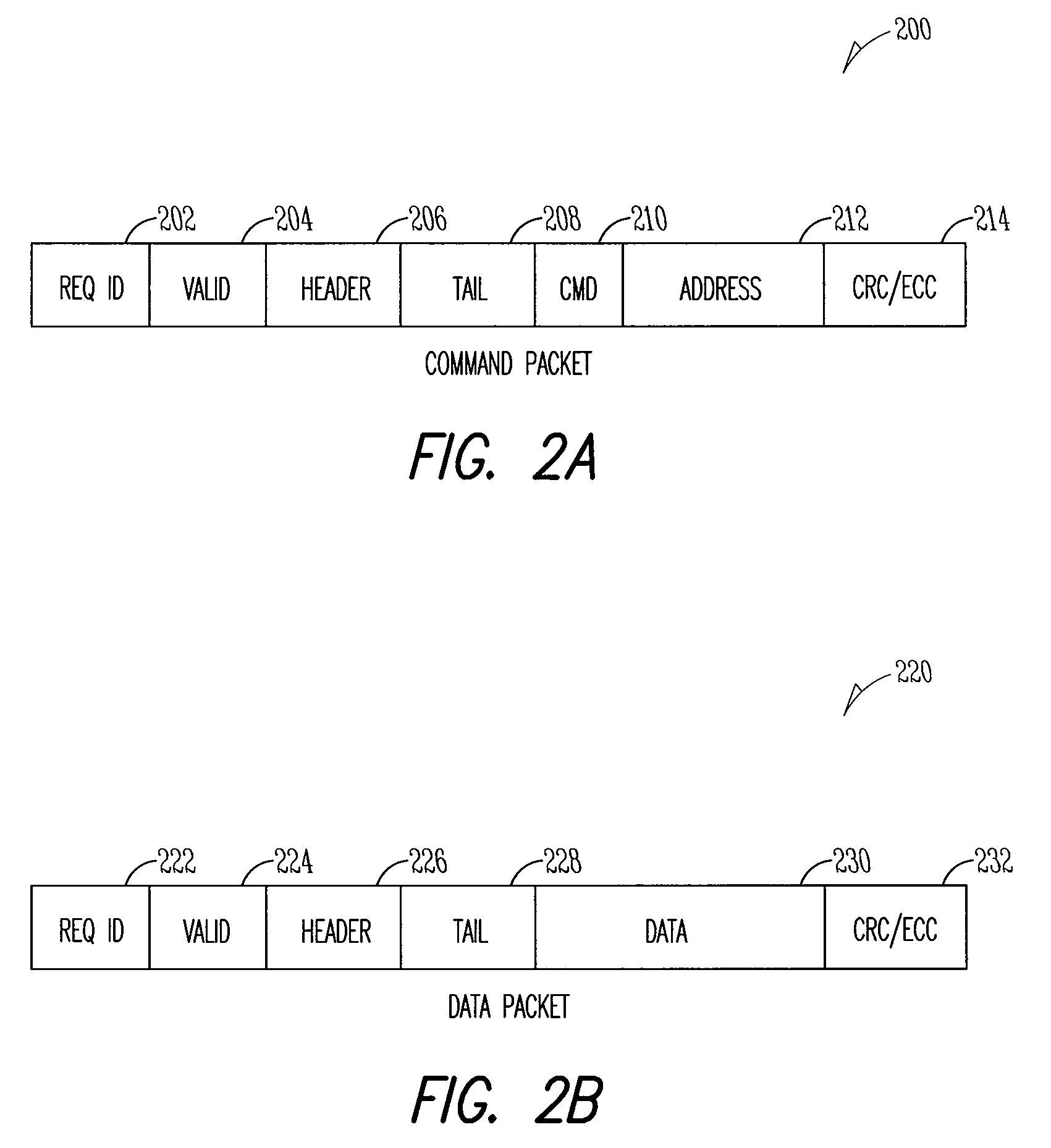
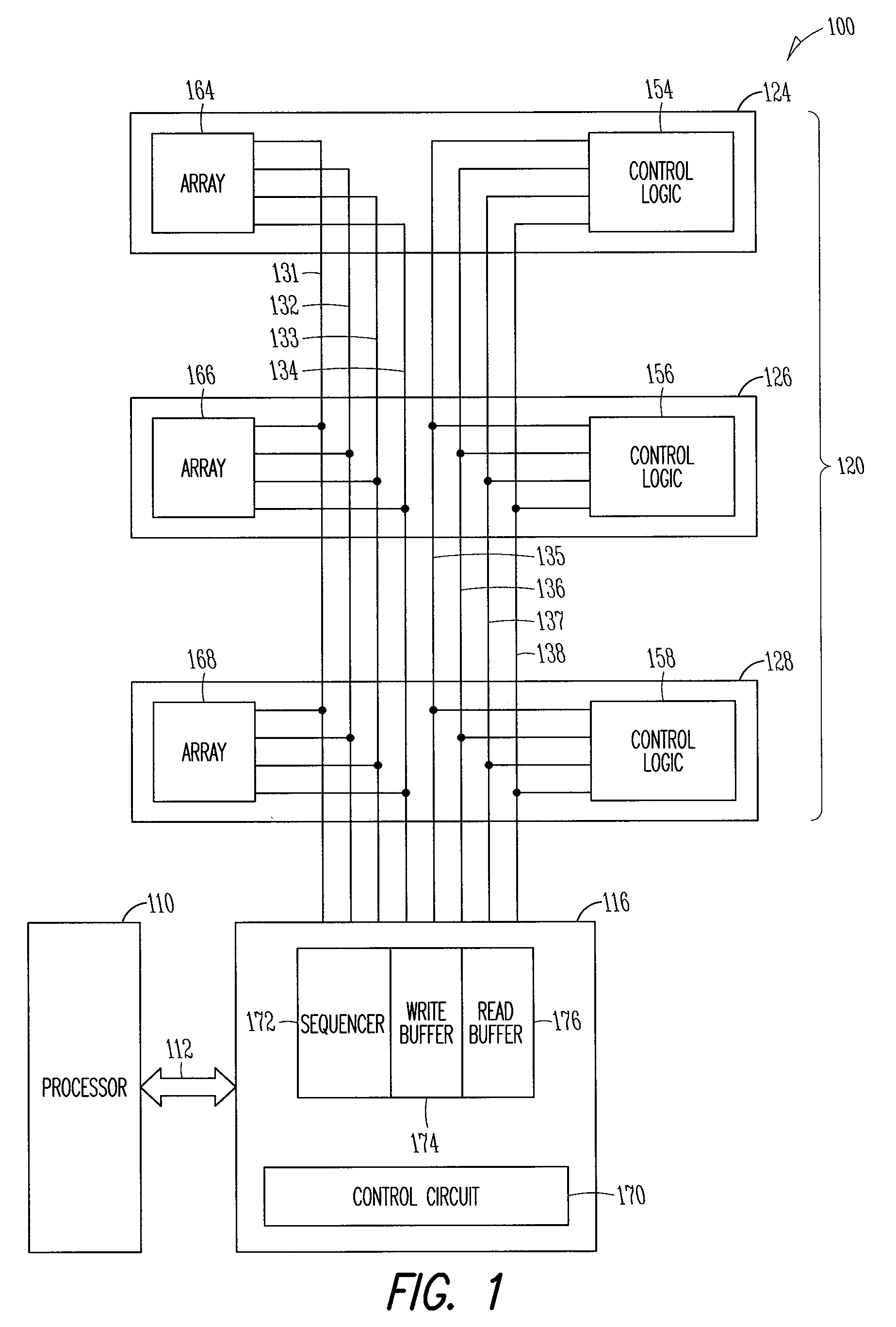
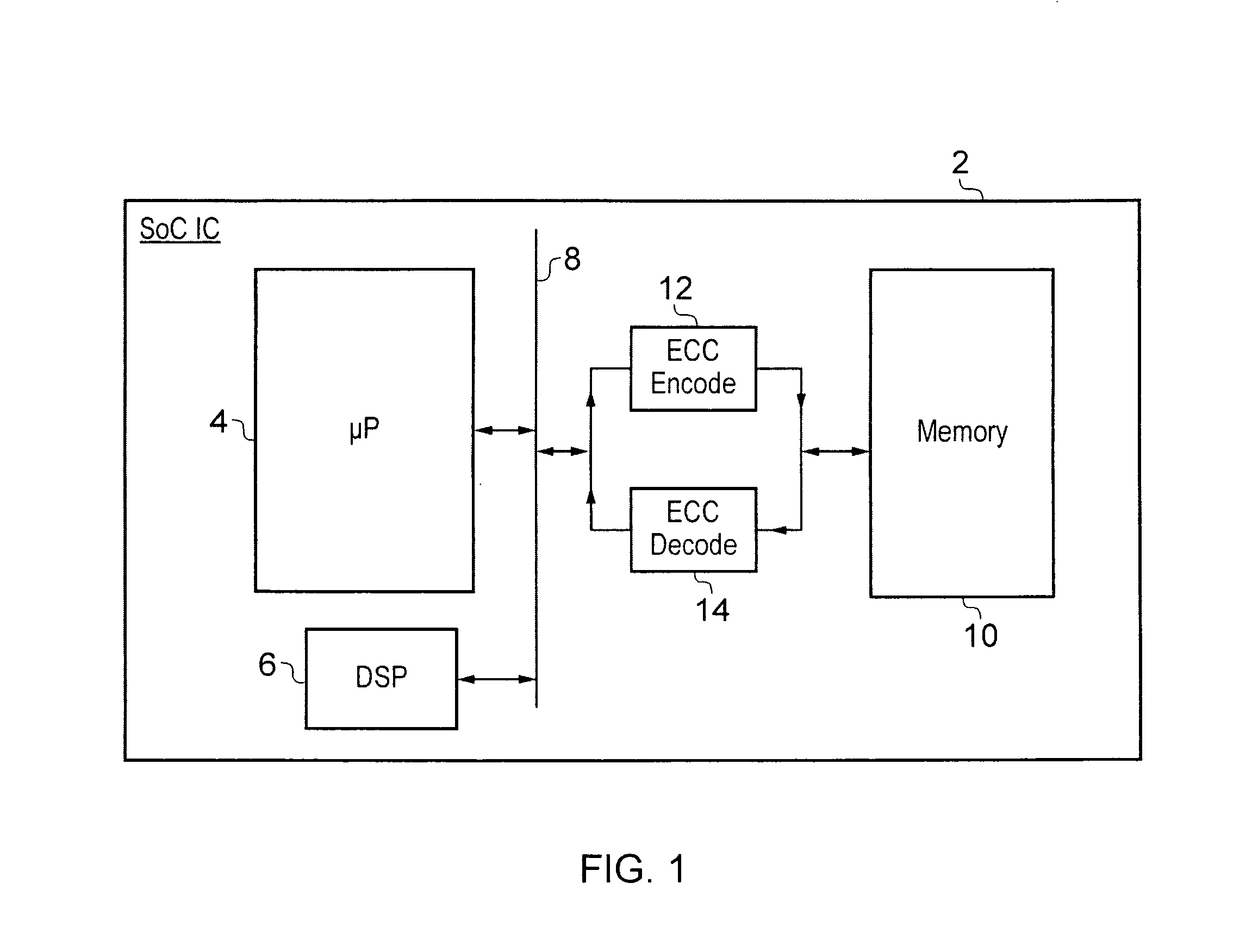
ECC controller for use in flash memory device and memory system including the same
An ECC (error correction code) controller of a flash memory device which stores an M-bit data (M being a positive integer equal to or greater than 2) comprises a first ECC block which generates a first ECC data from a program data to be stored in the flash memory device according to a first error correcting method and a second ECC block which generates a second ECC data from the first ECC data and the program data output from the first ECC block according to a second error correcting method, the program data, the first ECC data, and the second ECC data being stored in the flash memory device.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Multiple device apparatus, systems, and methods
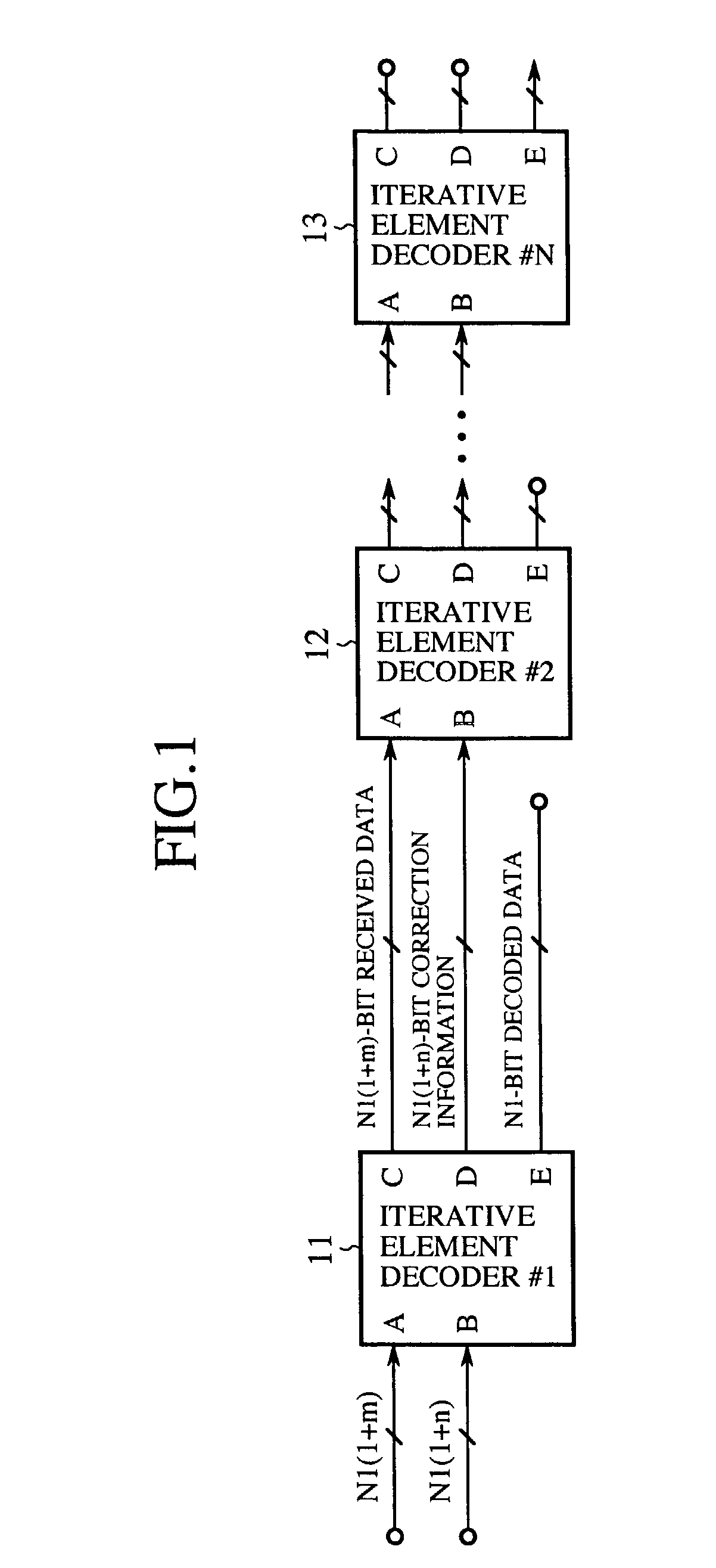
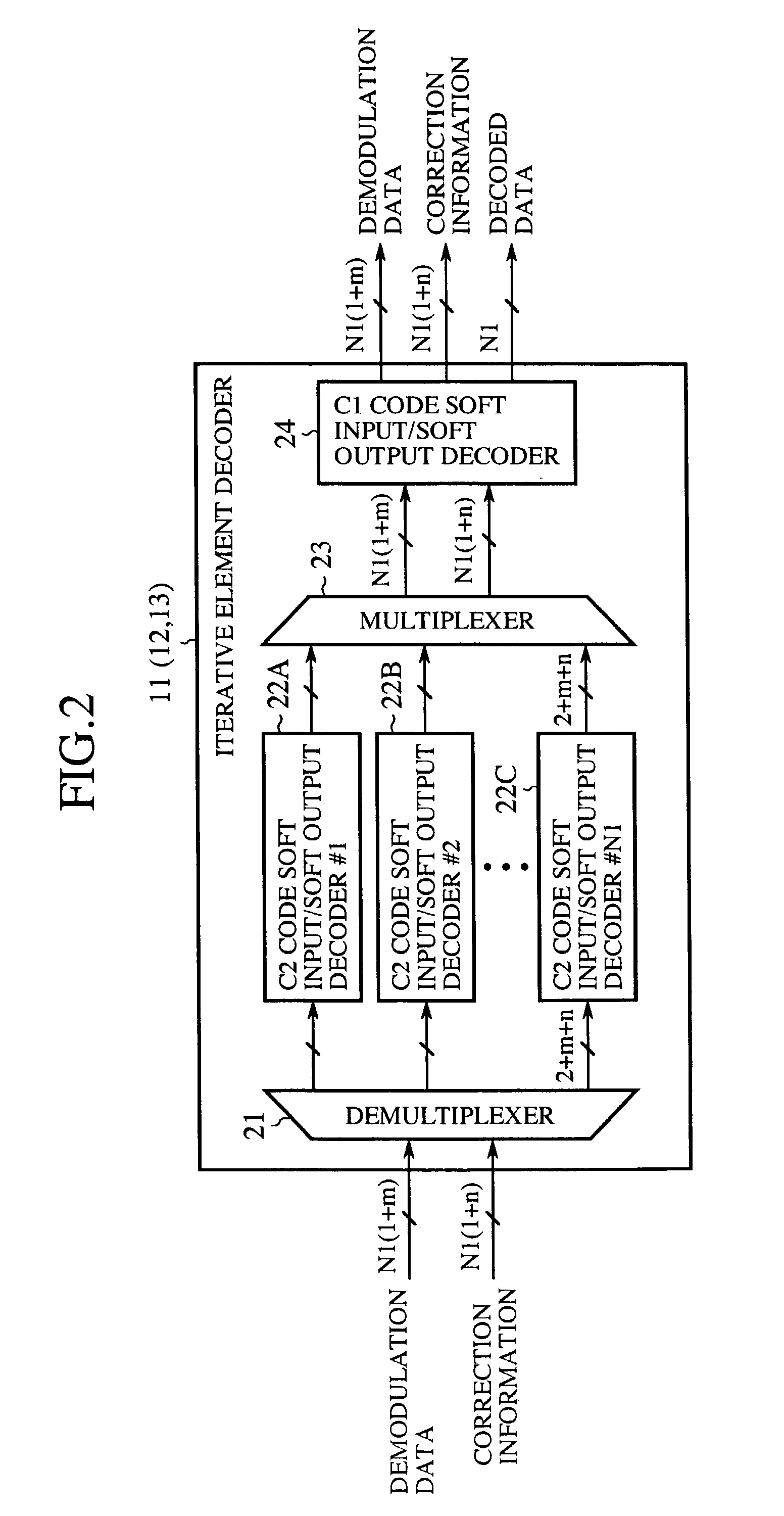
Data digits and correction digits are received in each of a number of integrated circuit (IC) devices. Apparatus, systems, and methods are disclosed that operate to check the data digits for error in each IC device according to an algorithm associated with the IC device, the algorithm being different for each IC device. Each IC device will act in response to the data digits if no error is detected in the data digits. Additional apparatus, systems, and methods are disclosed.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
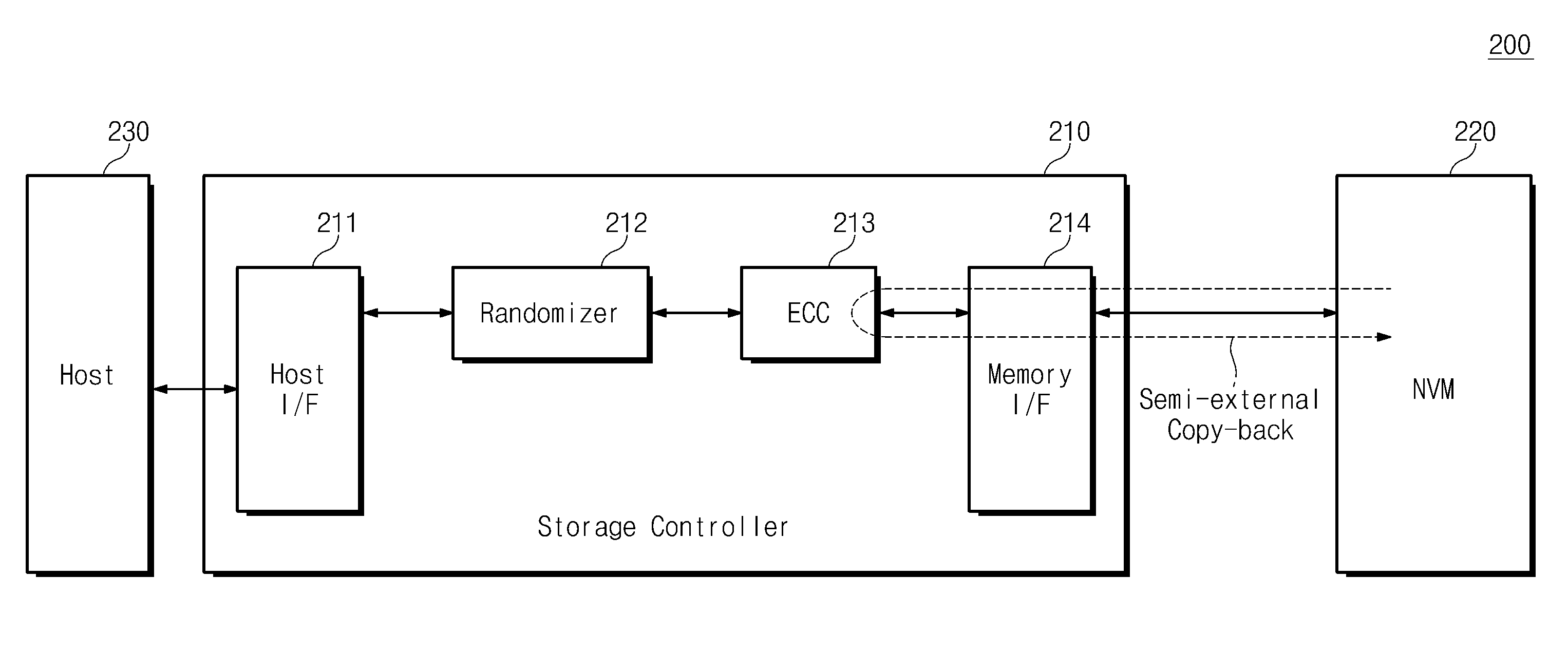
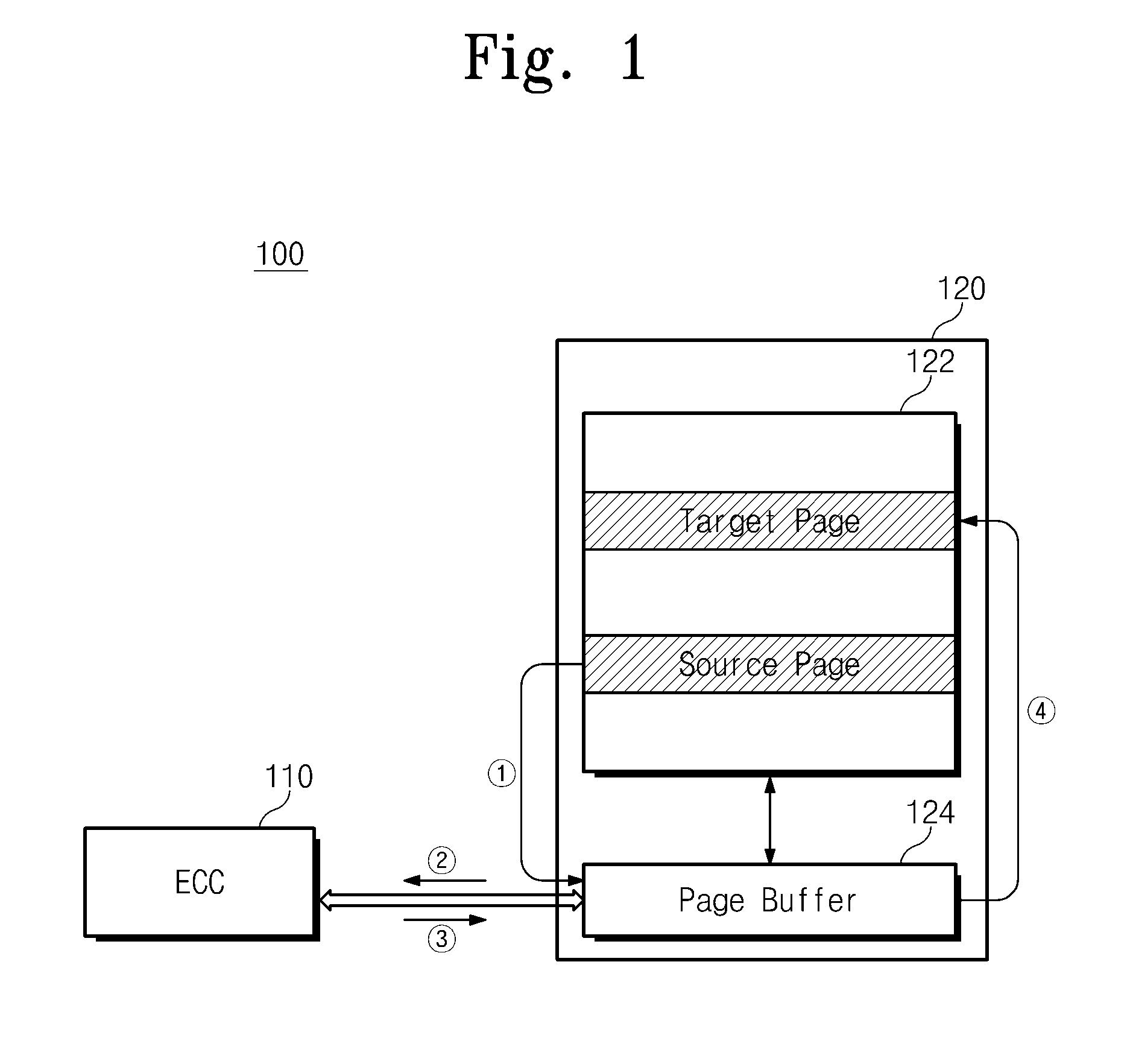
Storage device having a non-volatile memory device and copy-back method thereof
A storage device includes a non-volatile memory device outputting read data from a source area and a memory controller configured to execute an ECC operation on a plurality of vectors in the read data and to write the error-corrected read data into target area of the non-volatile memory device. The memory controller declares that a vector corresponding to a clean area is decoding pass without using a flag bit among the plurality of vectors during the error correction operation.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
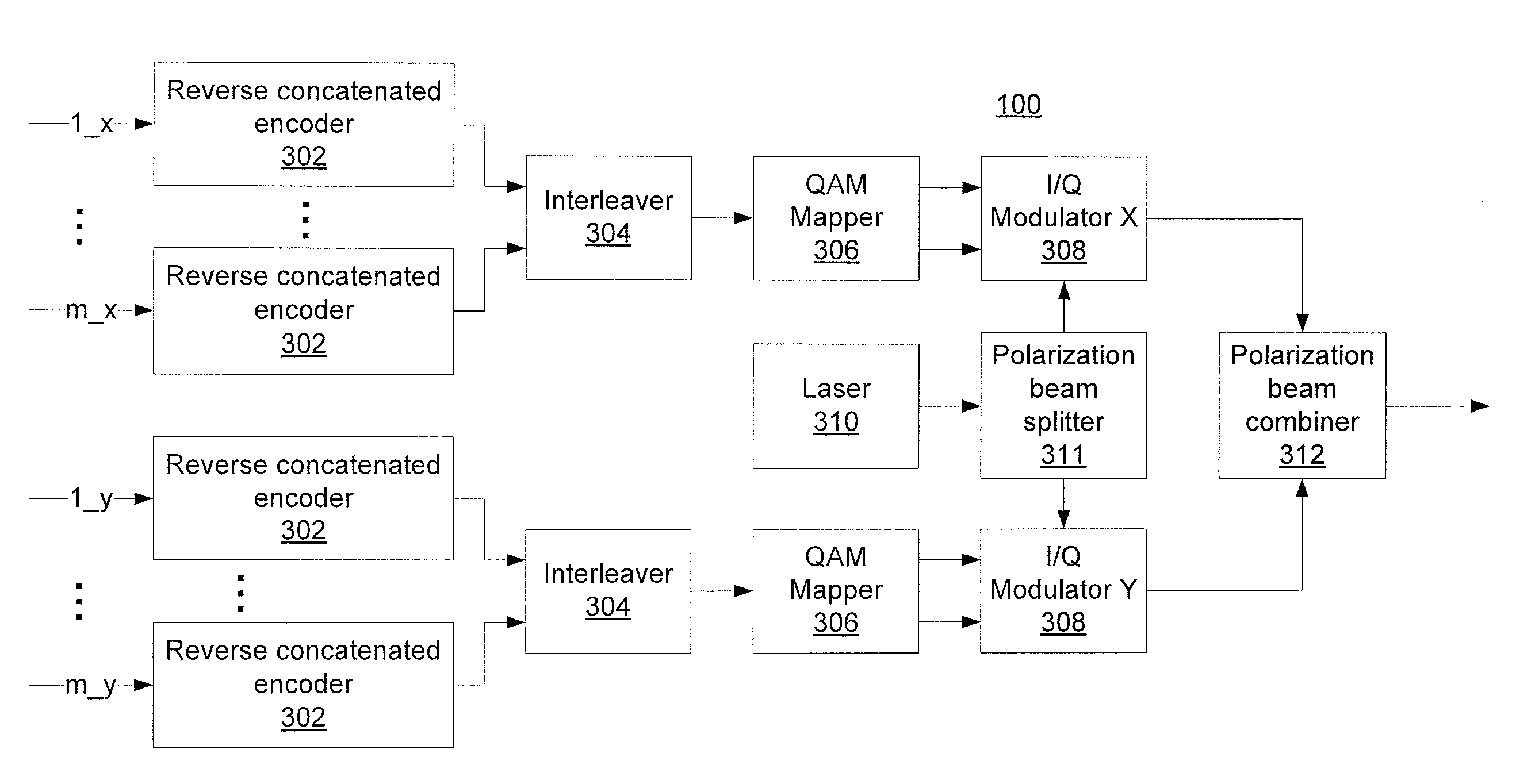
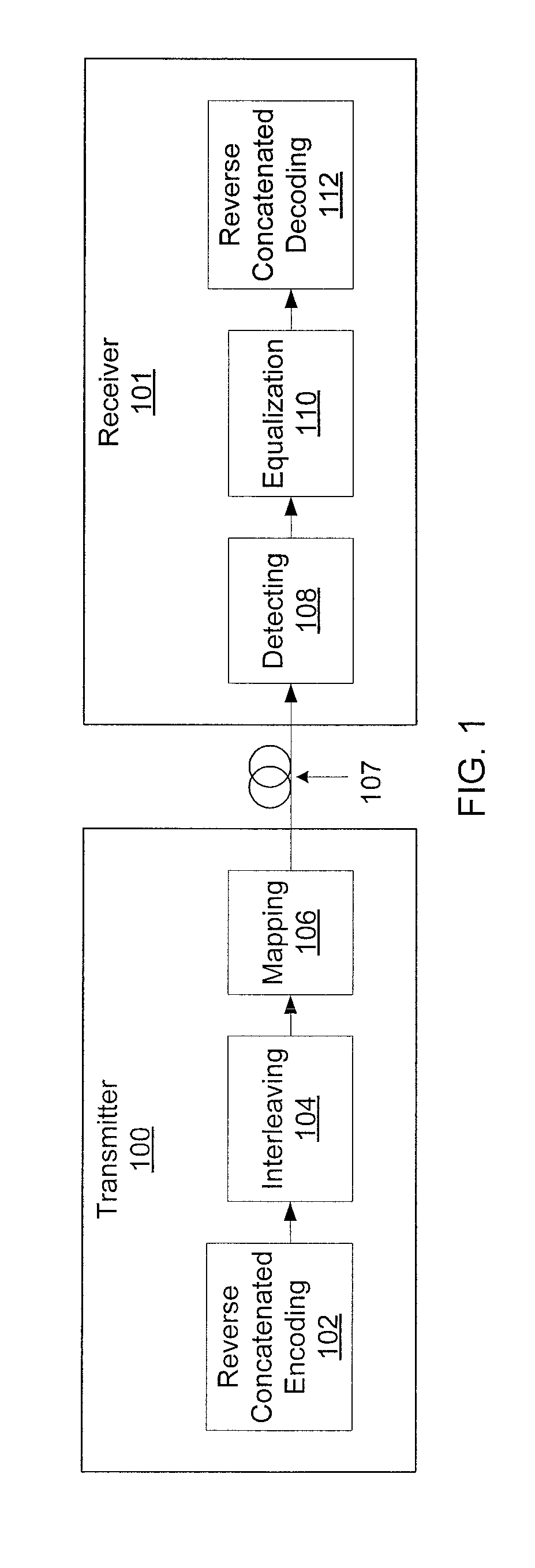
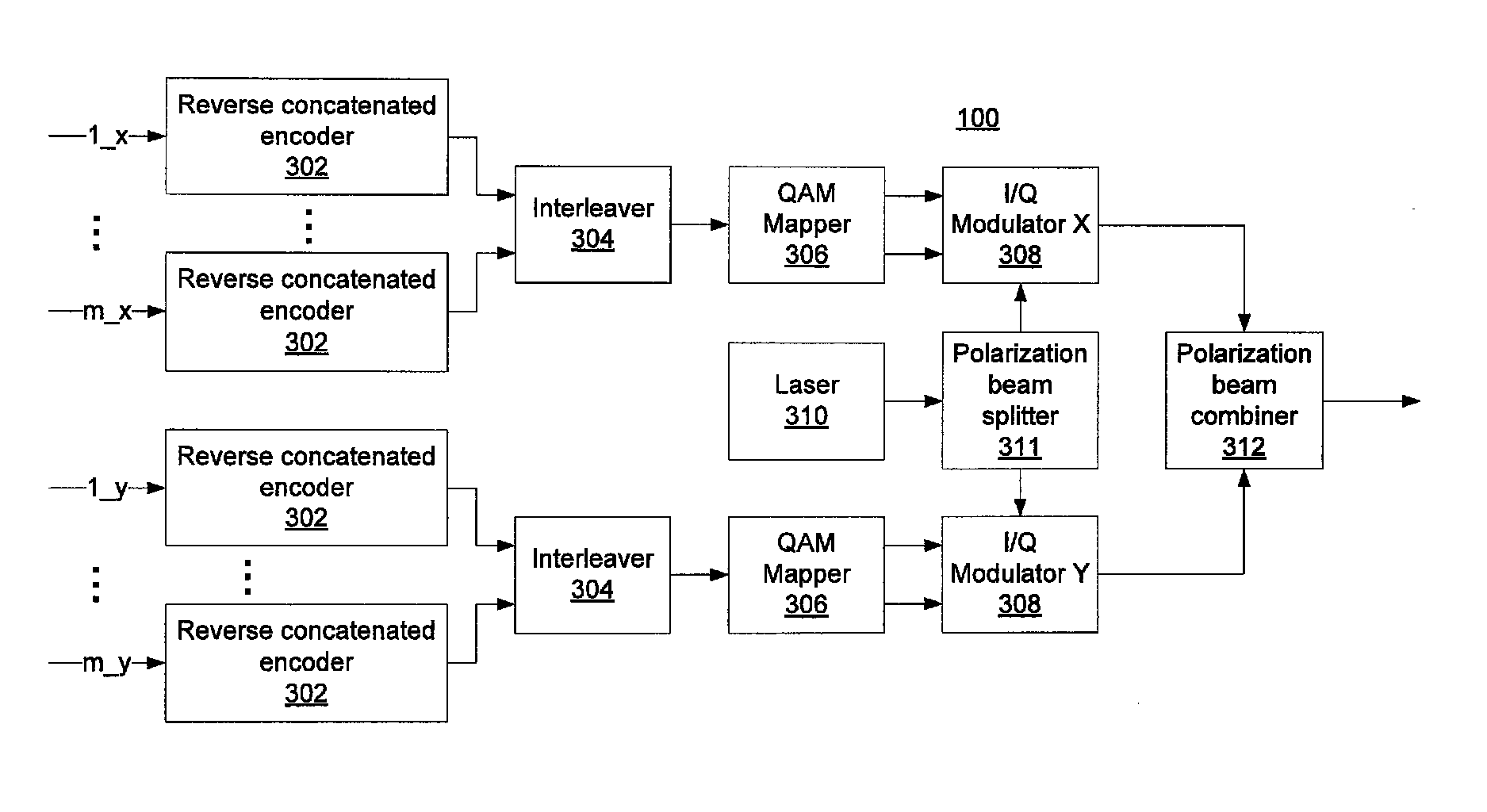
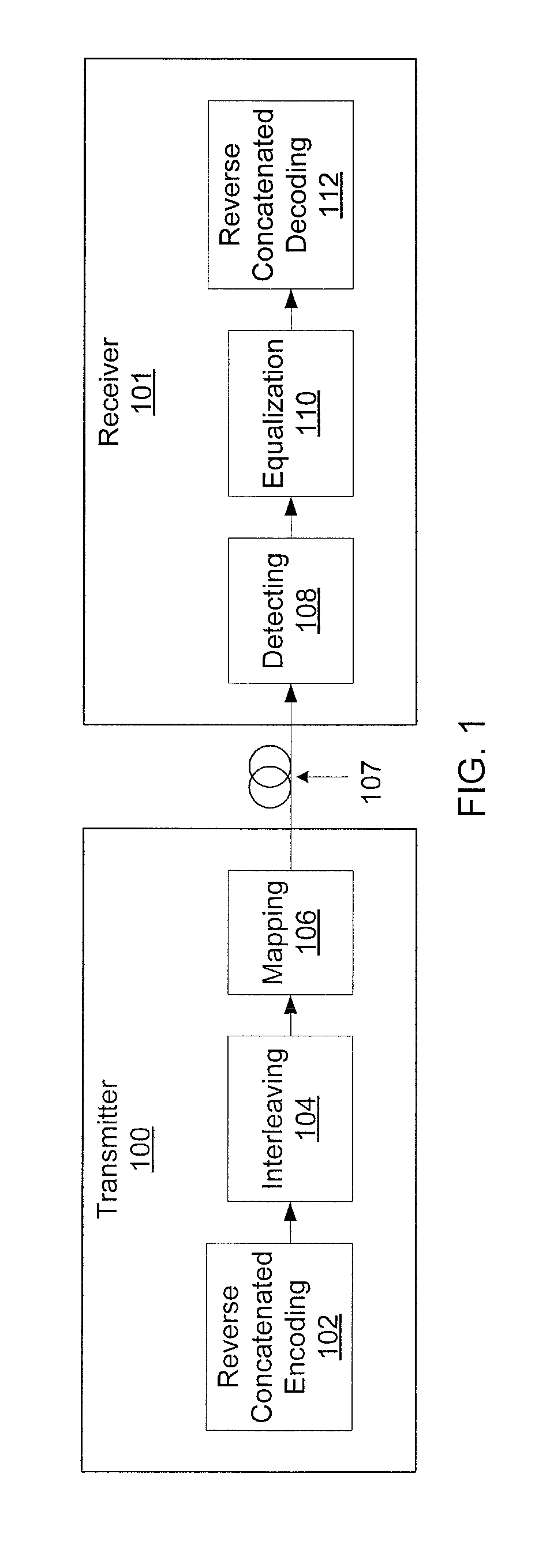
Reverse concatenated encoding and decoding
ActiveUS20120047415A1Improve decoding performanceReed-muller codesCode conversionComputer hardwareBlock code
Methods and systems for transmitting and receiving data include reverse concatenated encoding and decoding. Reverse concatenated decoding includes inner decoding the encoded stream with an inner decoder that uses a low-complexity linear-block code to produce an inner-decoder output stream, outer decoding the inner-decoder output stream with an outer decoder that uses a low-density parity-check code to produce an information stream, and iterating extrinsic bit reliabilities from the outer decoding for use in subsequent inner decoding to improve decoding performance.
Owner:NEC CORP
Multi-dimensional irregular array codes and methods for forward error correction, and apparatuses and systems employing such codes and methods
InactiveUS7296212B1Reed-muller codesError detection/correctionArray data structureTheoretical computer science
Owner:OPTIC153 LLC
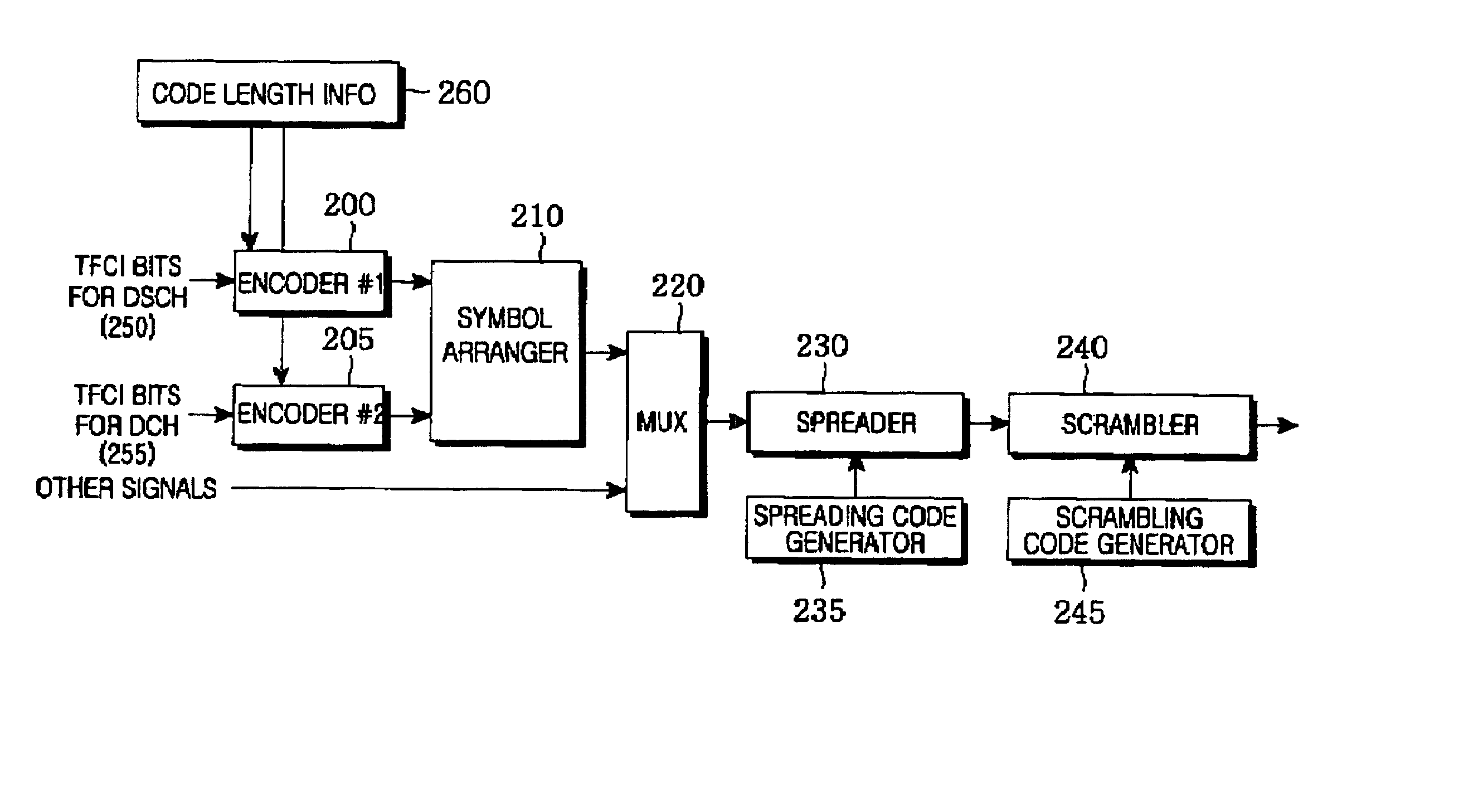
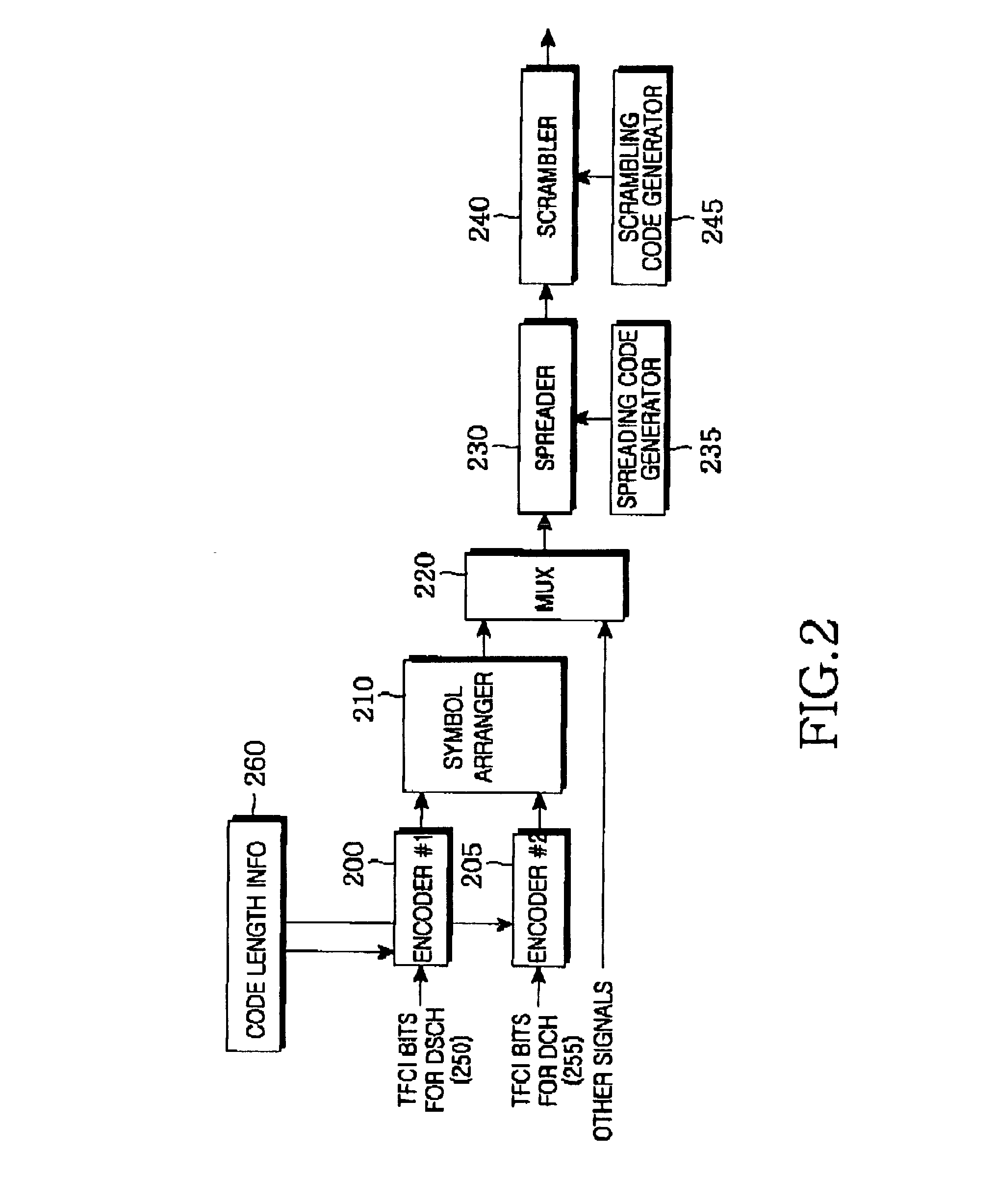
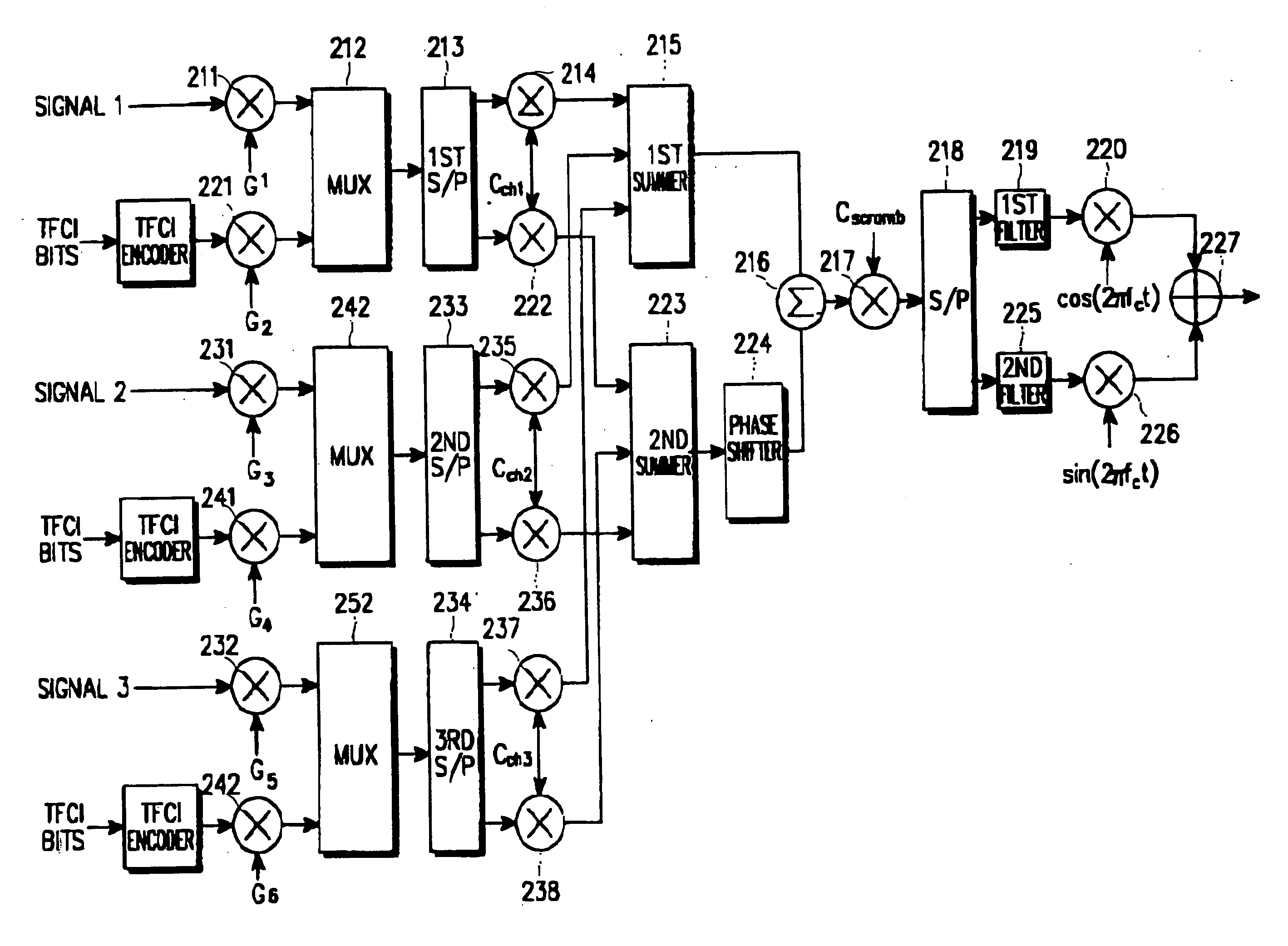
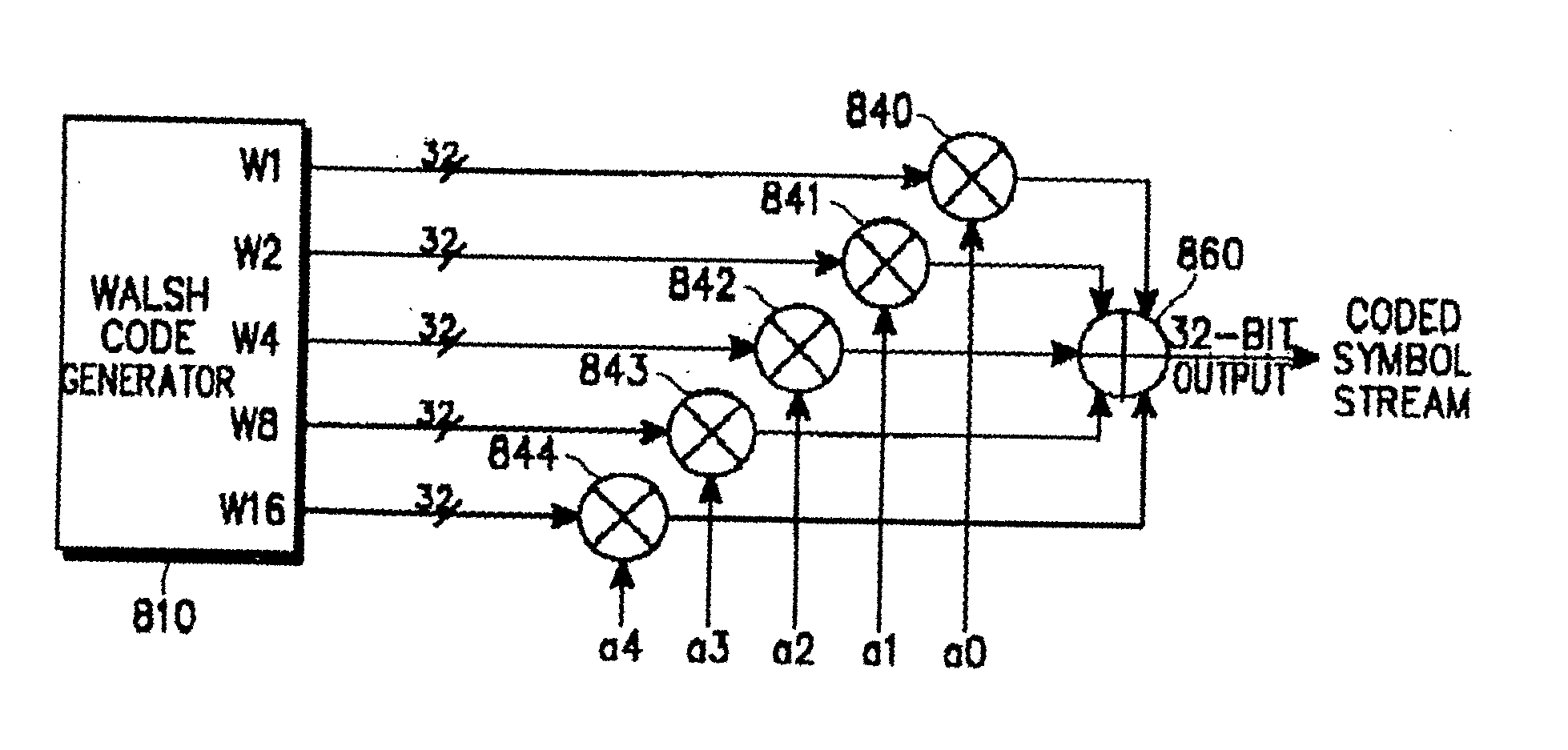
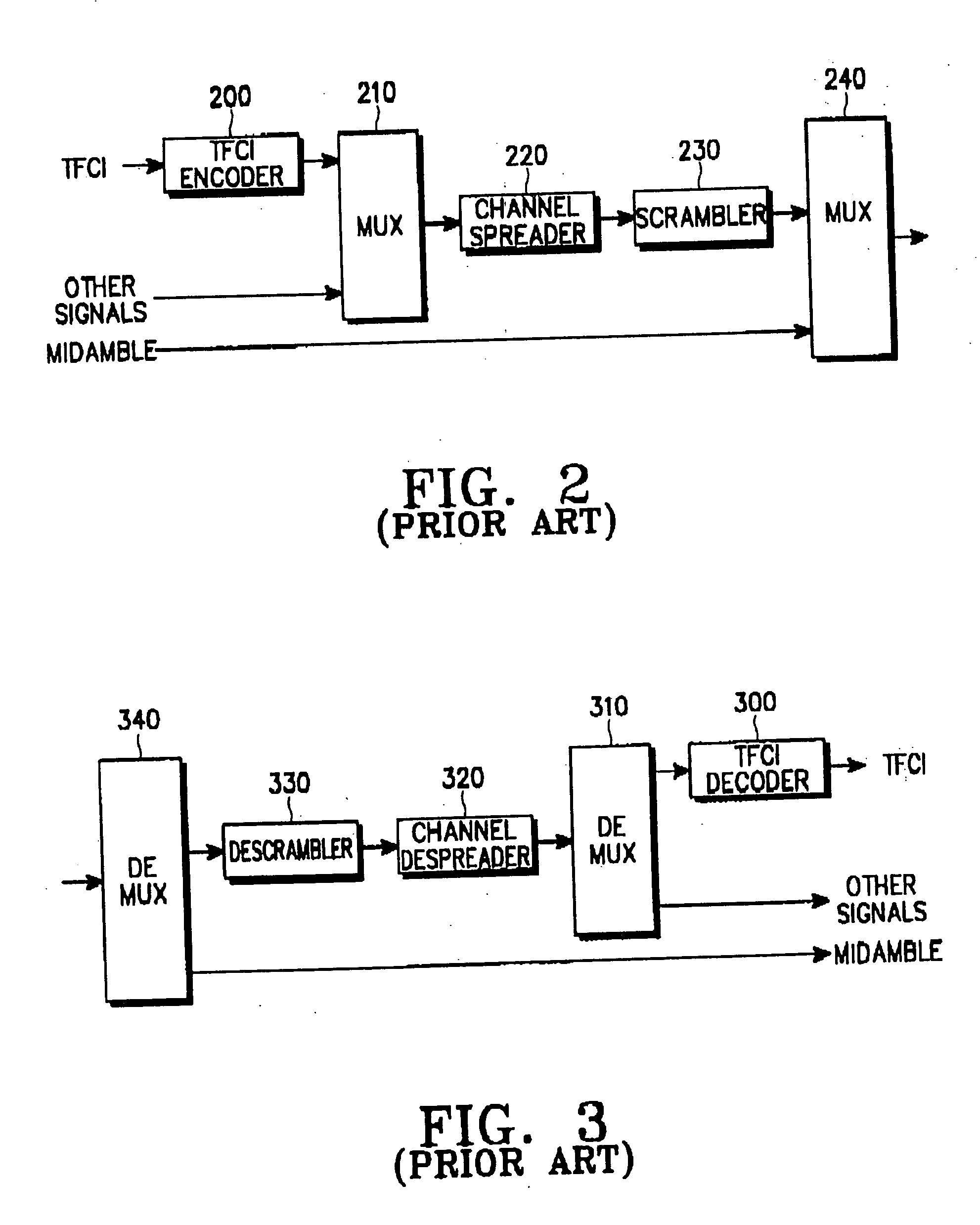
Apparatus and method for symbol mapping TFCI bits for a hard split mode in a CDMA mobile communication system
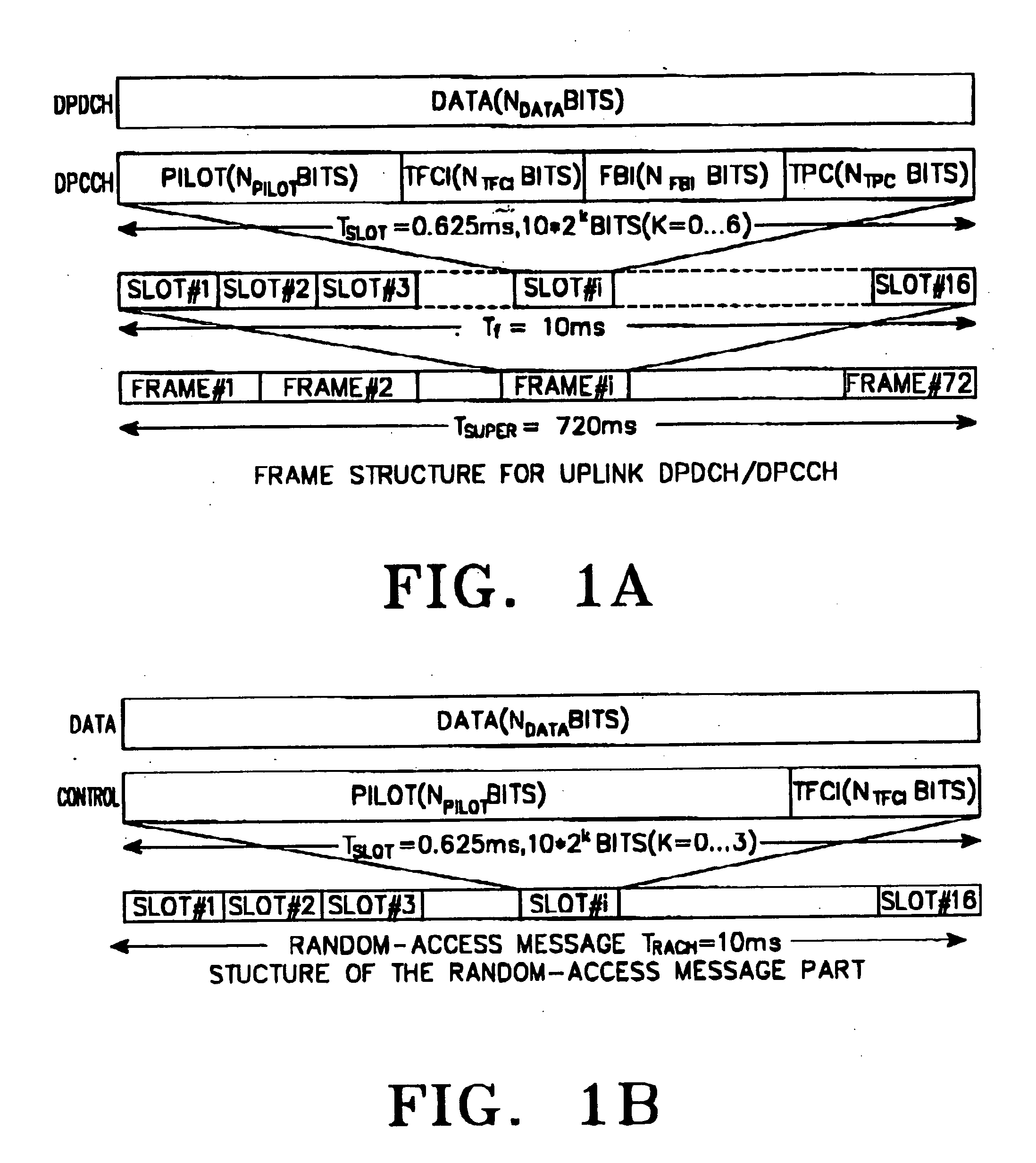
A method for mapping first coded TFCI symbols and second coded TFCI symbols to a radio frame in a transmission apparatus of a mobile communication system for encoding k first TFCI bits and (10-k) second TFCI bits, a sum of the first coded TFCI symbols and the second coded TFCI symbols being 32. The method comprises multiplexing the coded symbols such that the first coded TFCI symbols and the second coded TFCI symbols are uniformly distributed according to a transmission mode and a data rate of the radio frame, and outputting 32 coded symbols; and mapping the 32 multiplexed coded symbols to the radio frame to satisfy the number of the coded symbols that can be mapped to one radio frame, determined according to the transmission mode and the data rate of the radio frame.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Decoding Reed-Solomon codes and related codes represented by graphs
InactiveUS7191376B2Low costError prevention/detection by using return channelReed-muller codesProgramming languageError correcting
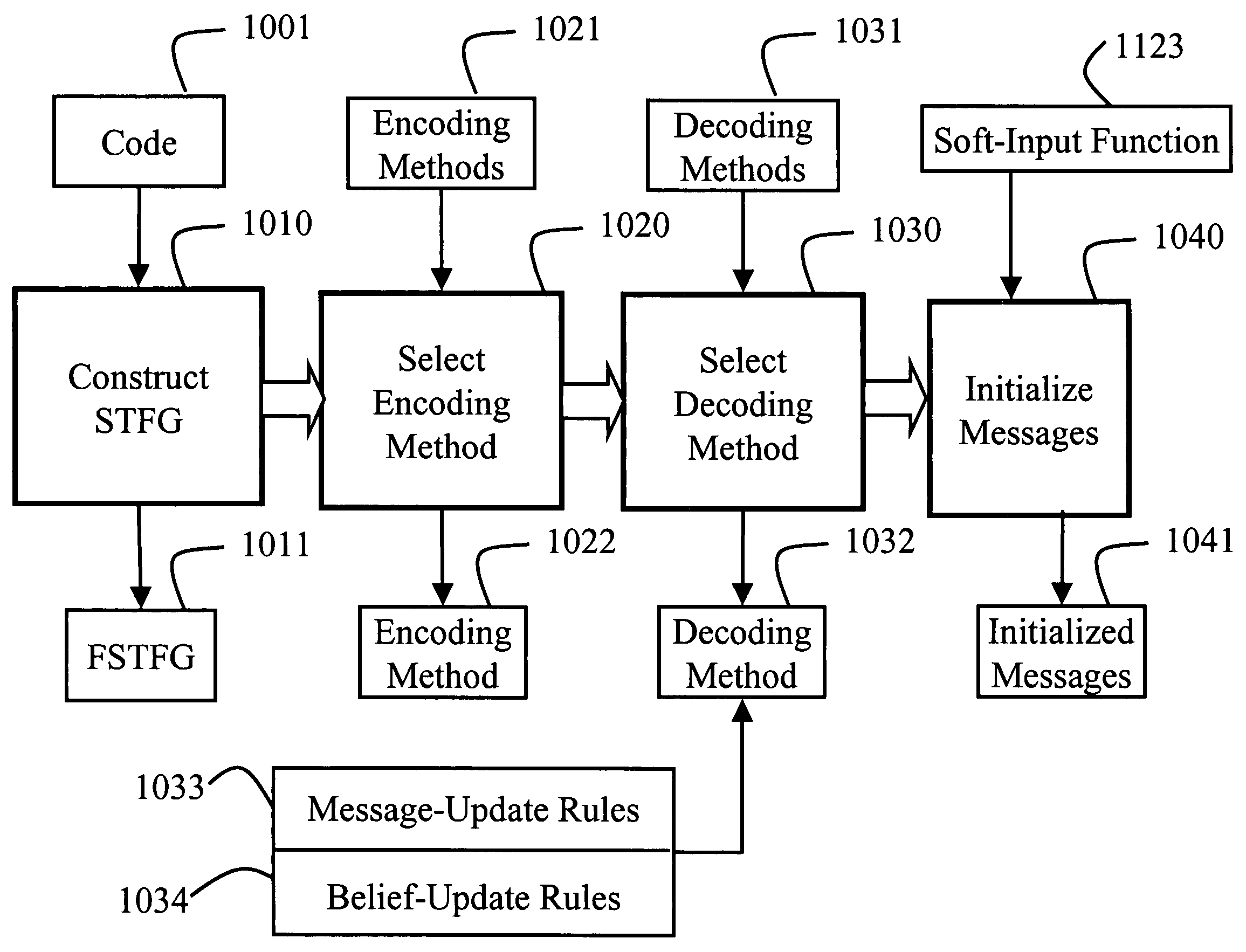
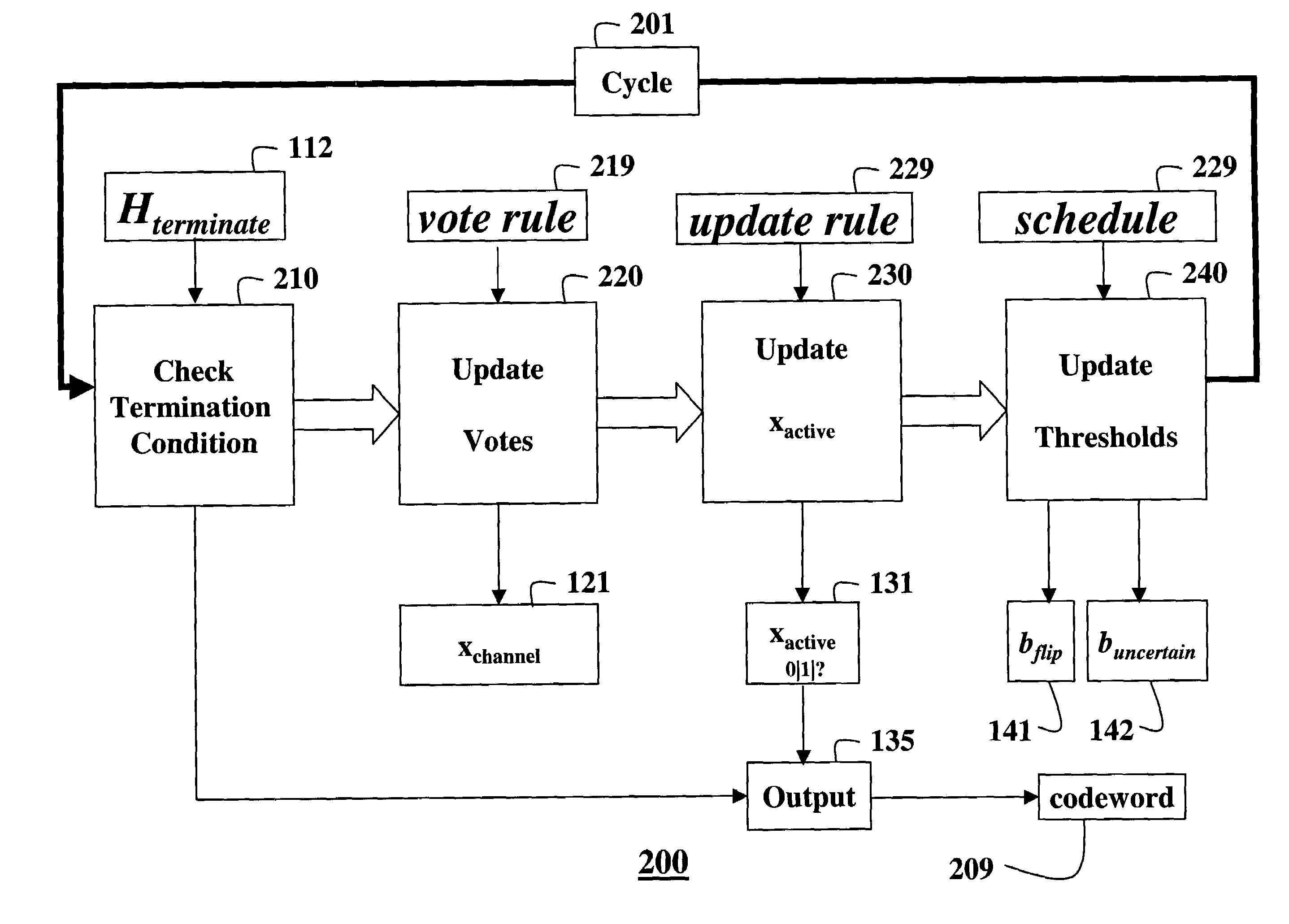
A method decodes a soft-input cost function for an error-correcting code. First, the code is selected and its FSTFG representation is constructed. The representation is simplified, and an encoding method consistent with the representation is selected. A set of message-update and belief-update rules are selected. Messages are initialized according to a soft-input cost function. An iterative decoding cycle is then begun. The first step updates the messages according to the pre-selected message-update rules. The second step determines a trial code word from the messages, the pre-selected message-update rules, and the encoding method. The third step replaces a tentative output code word of the decoding method with the trial code word if the trial code word has lower cost. The decoding cycle terminates if a termination condition is true, and outputs the tentative code word.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC RES LAB INC
System and method for signaling control information in a mobile communication network
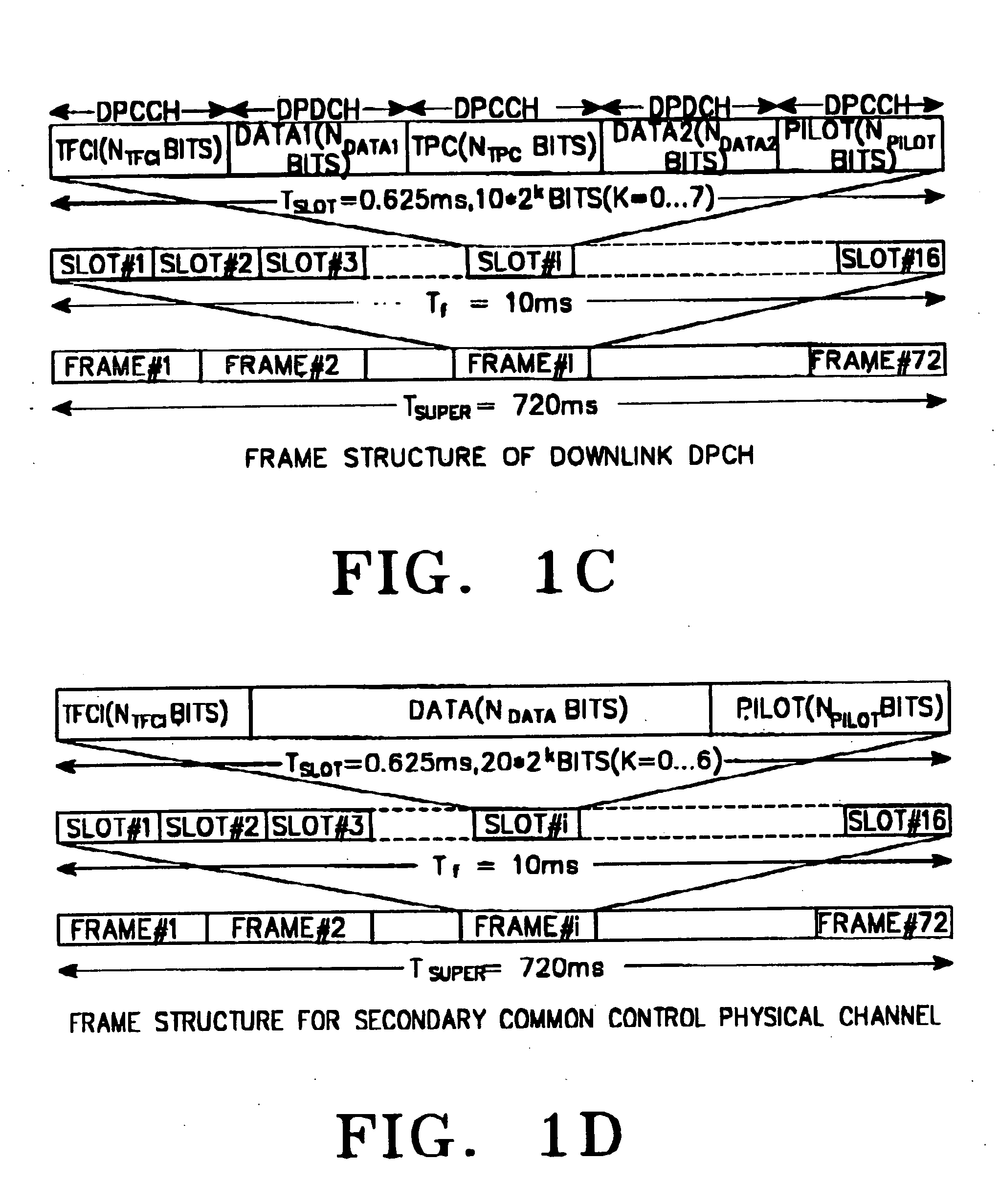
ActiveUS20110243278A1Reduce overheadControl overheadPower managementReed-muller codesReed–Muller codeHadamard transform
A method of decoding encoded information communicated over a radio channel includes receiving a vector of encoded information transmitted by a wireless terminal. The encoded information includes an encoded representation of unencoded information bits that have been encoded using a first order Reed-Muller code. The method also includes generating a vector of transform values by performing a Hadamard Transform on the received vector and identifying a subset of the transform values based on scheduling information associated with the wireless terminal. Additionally, the method includes selecting, from the subset of transform values, one of the transform values based on a magnitude of the selected transform value and determining an estimate of the unencoded information bits based on a bit sequence associated with the selected transform value. In accordance with another embodiment of the present disclosure, an apparatus is operable to implement this method.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Multiple device apparatus, systems, and methods
ActiveUS20100031129A1Improve efficiencyReduce bandwidth usageReed-muller codesError preventionIc devicesEmbedded system
Data digits and correction digits are received in each of a number of integrated circuit (IC) devices. Apparatus, systems, and methods are disclosed that operate to check the data digits for error in each IC device according to an algorithm associated with the IC device, the algorithm being different for each IC device. Each IC device will act in response to the data digits if no error is detected in the data digits. Additional apparatus, systems, and methods are disclosed.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
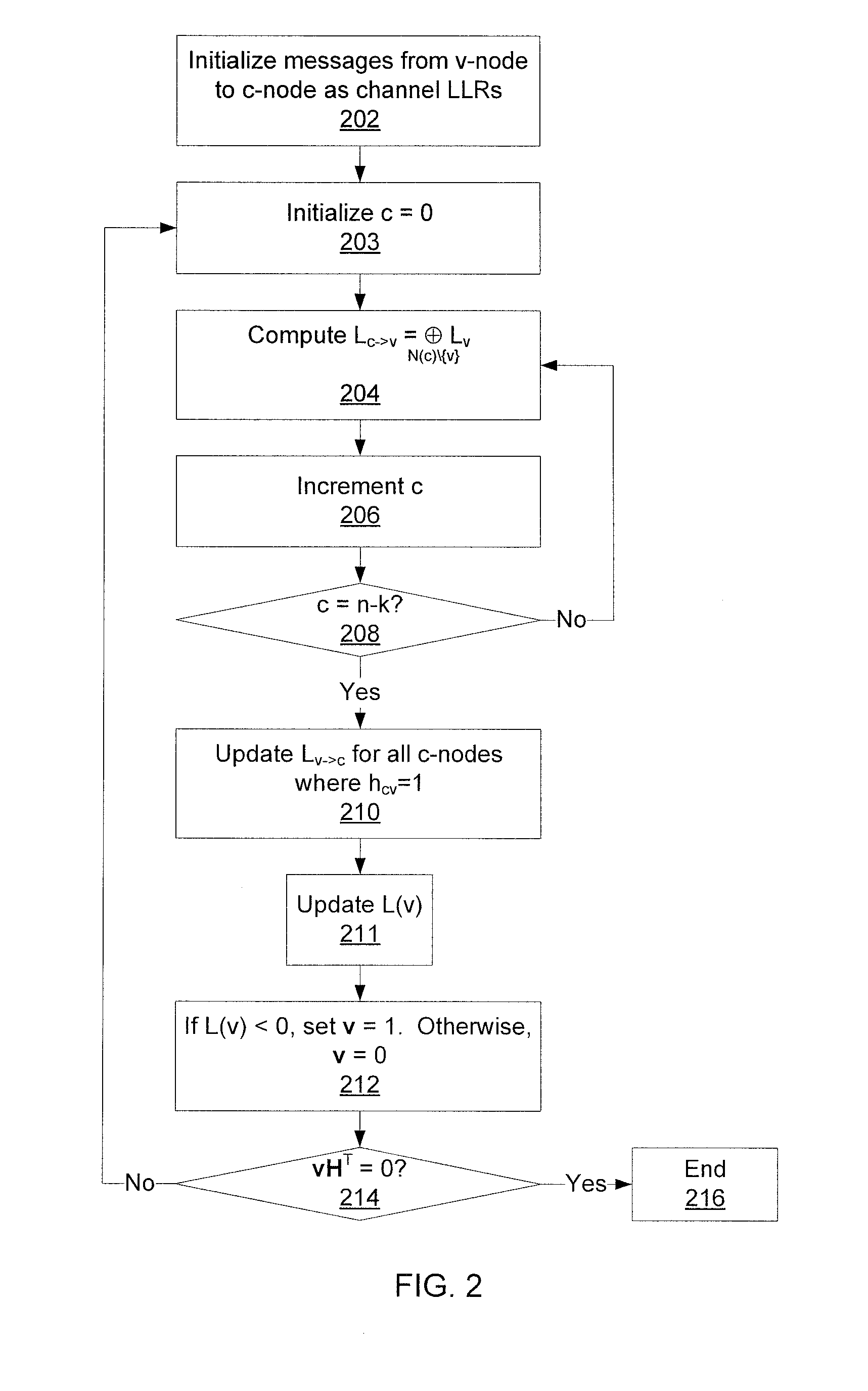
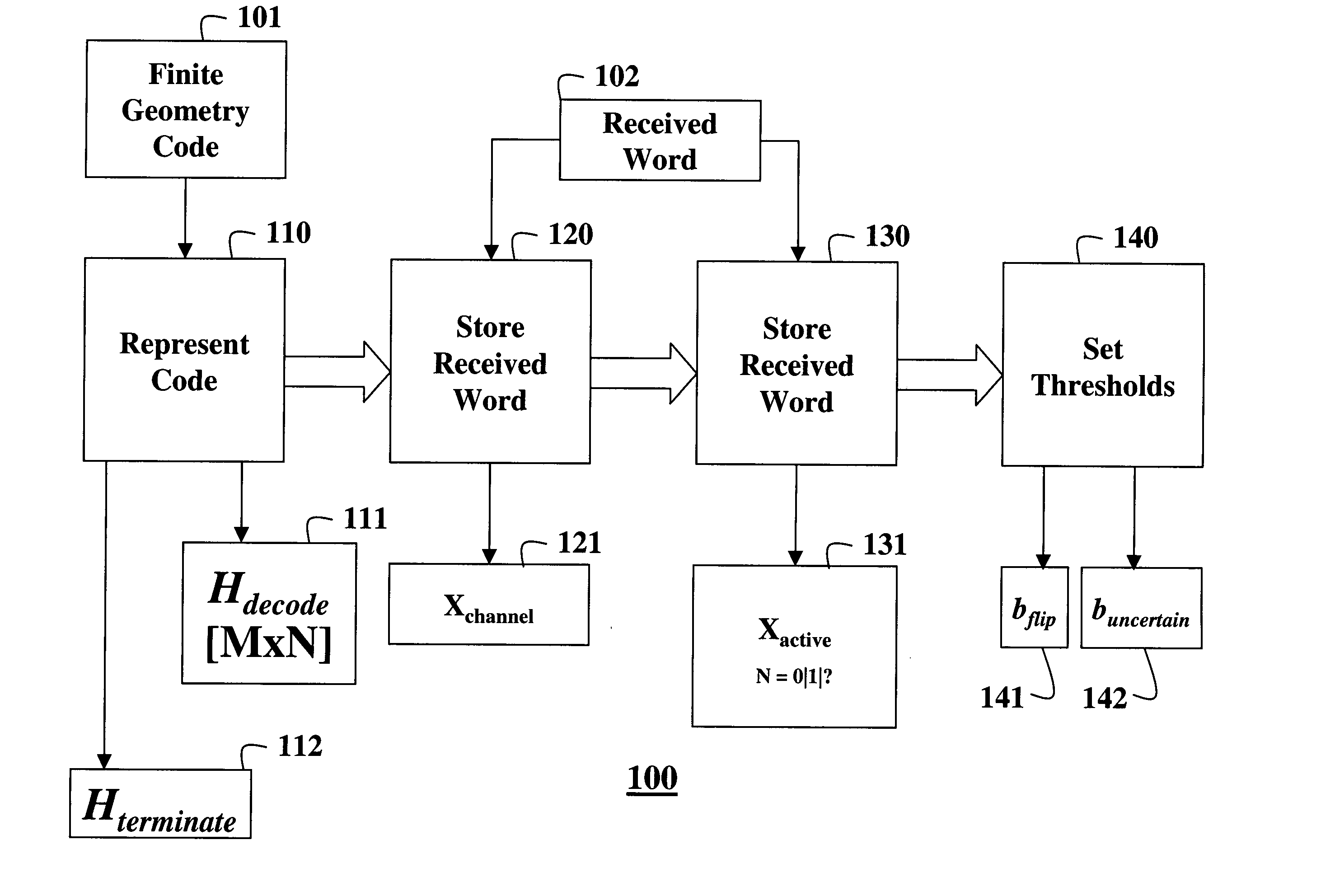
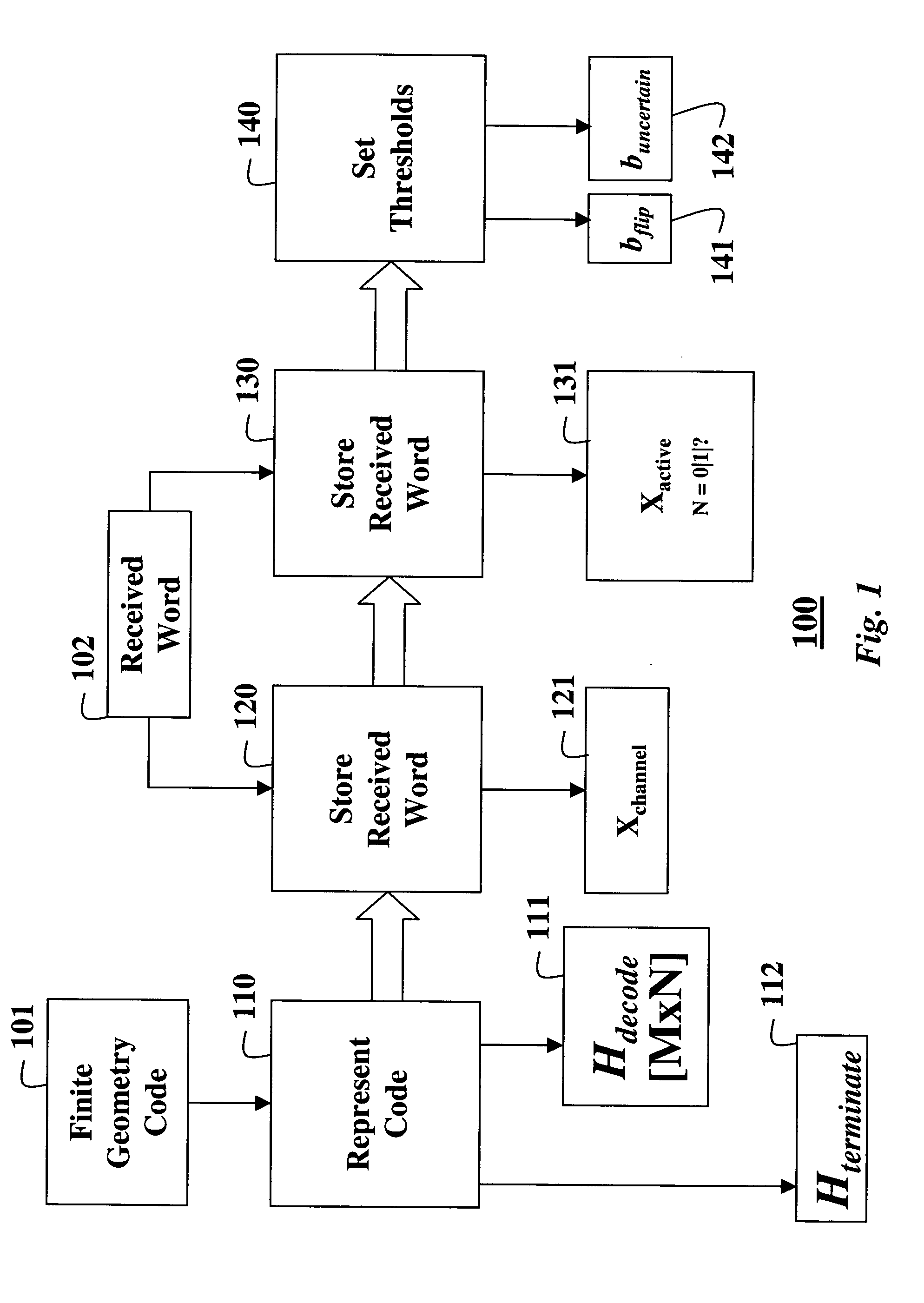
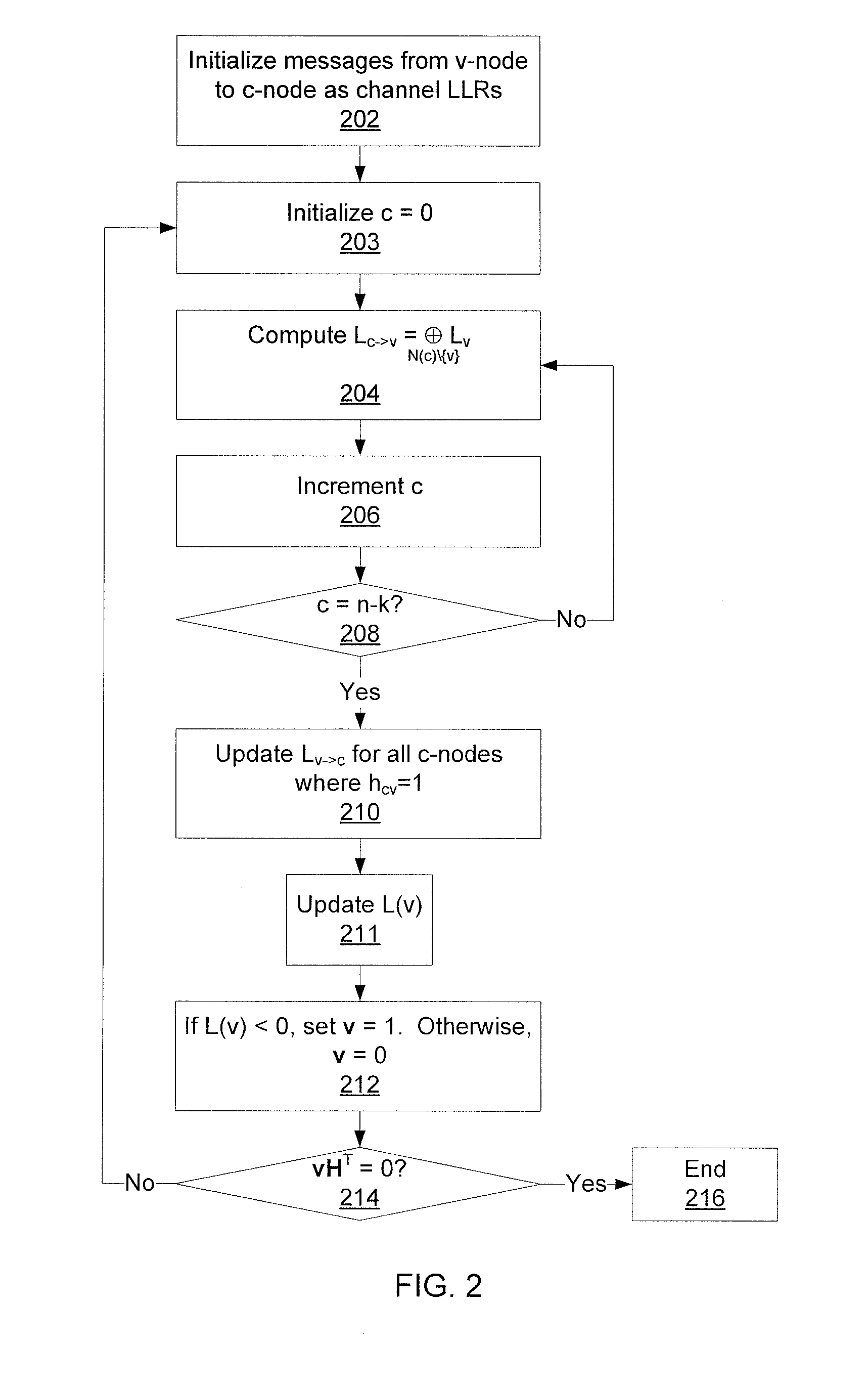
Decoding error-correcting codes based on finite geometries
InactiveUS20050044475A1Non-binary linear block codesReed-muller codesBinary linear block codesTheoretical computer science
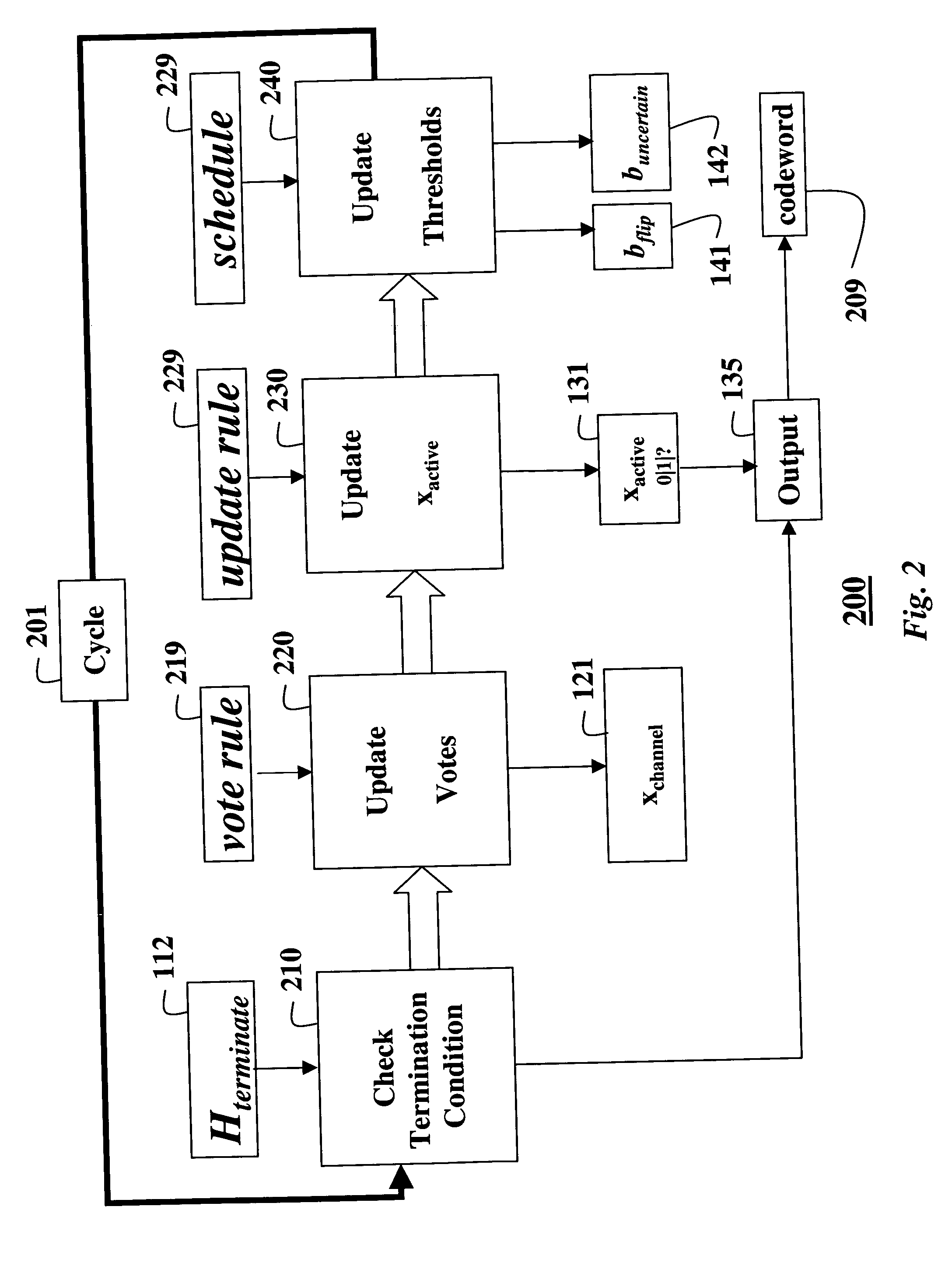
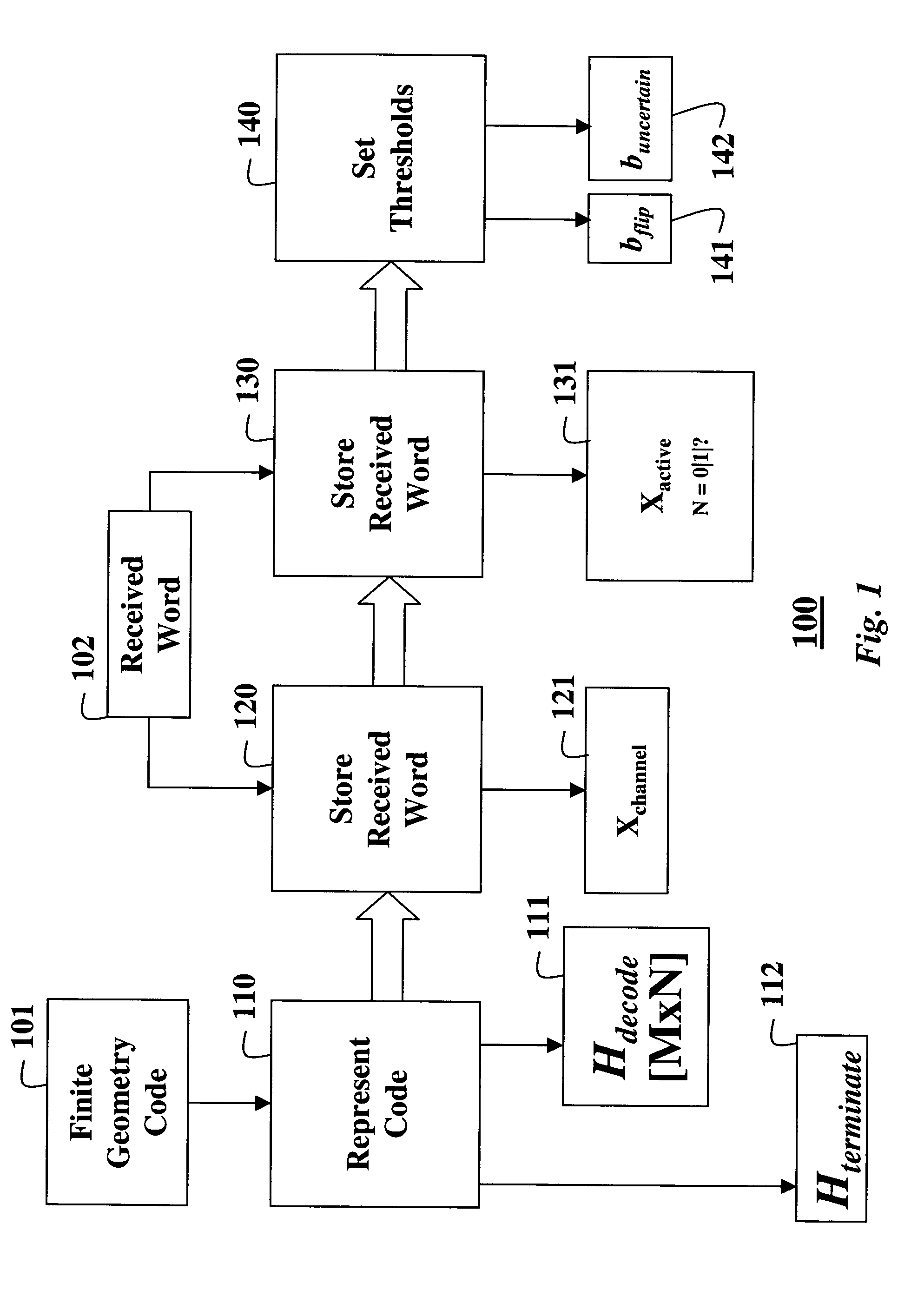
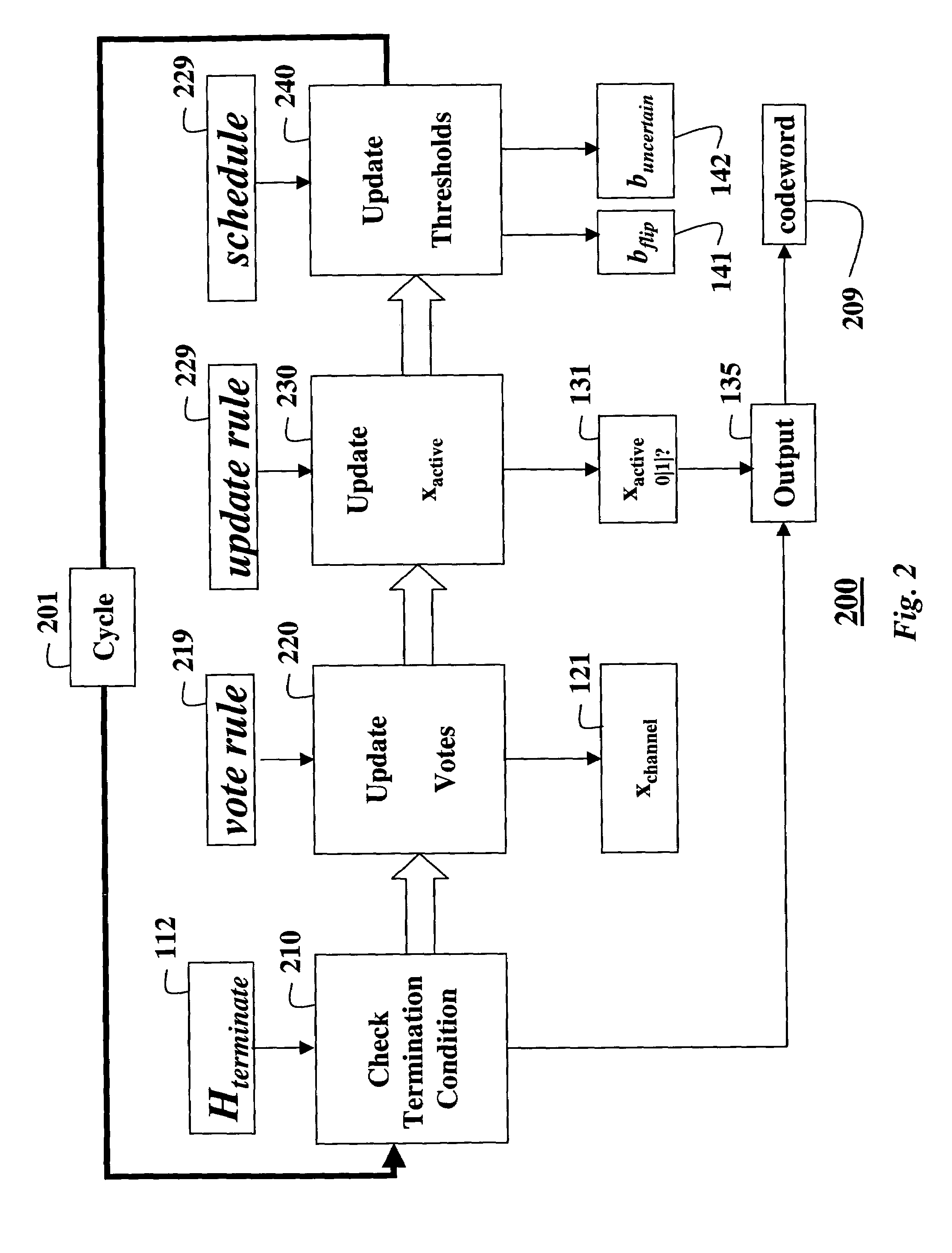
A method decodes a received word for a binary linear block code based on a finite geometry. First, a parity check matrix representation of the code is defined. The received word is stored in a channel register. An active register represents a current state of the decoder. Each element in the active register can take three states, representing the two possible states of the corresponding bit in the word, and a third state representing uncertainty. Votes from parity checks to elements of the active register are determined from parity checks in the matrix, and the current state of the active register. A recommendation and strength of recommendation for each element in the active register is determined from the votes. The elements in the active register are then updated by comparing the recommendation and strength of recommendation with two thresholds, and the state of the corresponding bit in the received word. When termination conditions are satisfied, the decoder outputs the state of the active register. If the decoder outputs a state of the active register that does not correspond to a codeword, a new representation for the code using a parity check matrix with substantially more rows is chosen, and the decoding cycle is restarted.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC INFORMATION TECH CENT AMERICA ITA
System and Method for Mapping and Decoding Codewords in Acknowledgement Information Communications
ActiveUS20110268090A1Fluctuating performanceImprove performanceReed-muller codesTransmission path divisionHybrid automatic repeat request harqAlgorithm
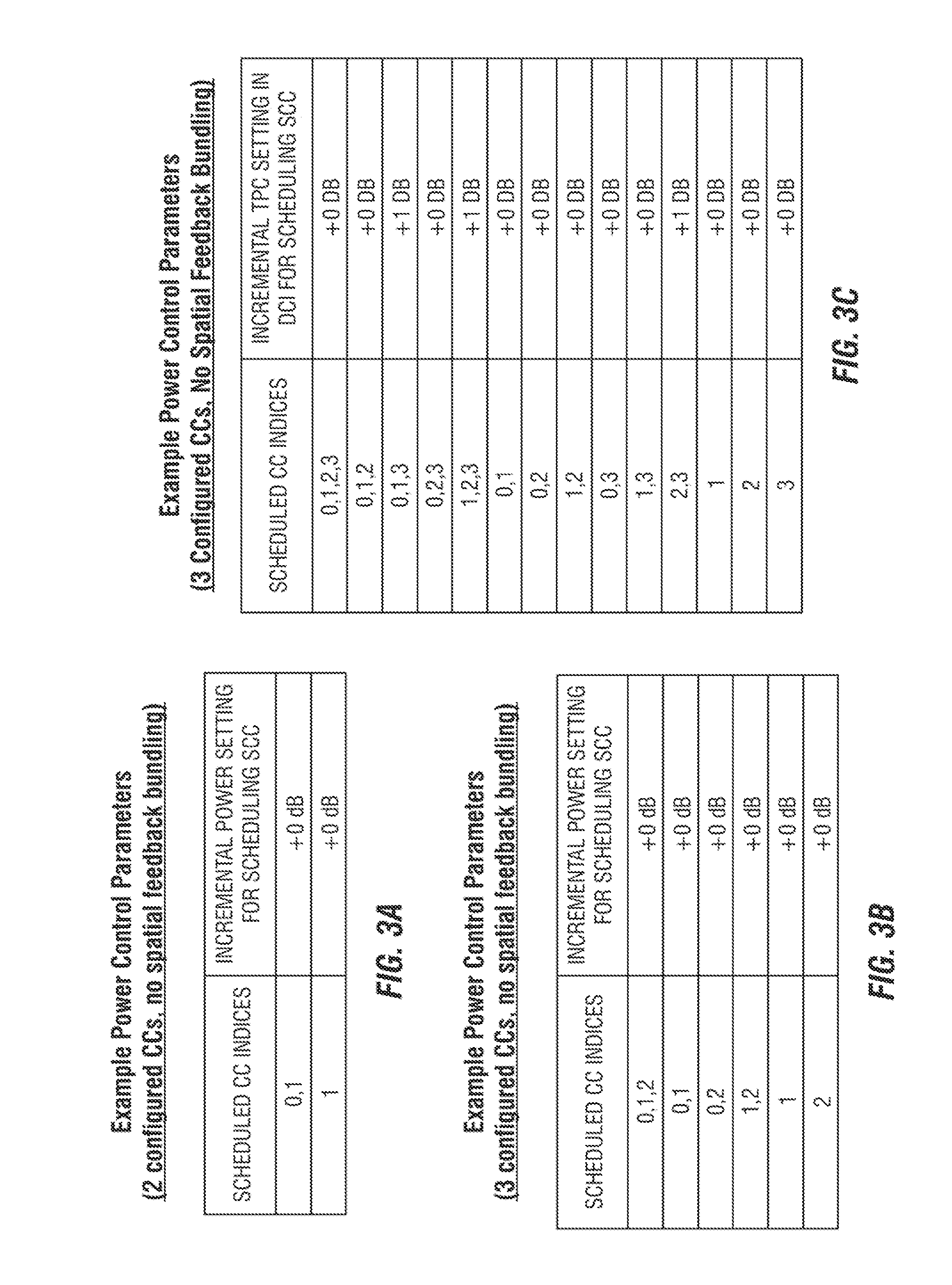
A system and method for mapping and decoding codewords in acknowledgement information communications are provided. A method for communications device operations includes determining a hybrid automatic repeat request (HARQ) response for each component carrier (CC) in a set of configured CCs, thereby producing a set of HARQ responses, generating an information vector from the set of HARQ responses, encoding the information vector based on a (n, k) linear block code corresponding to the set of configured CCs, and transmitting the encoded information vector. A unique set of bits selected from the information vector is assigned to represent a HARQ response for each different CC in the set of configured CCs. the (n, k) linear block code is obtained by a linear transformation of an original (n, k) linear block code, where n is a length of code words, and k is a length of information vectors.
Owner:FUTUREWEI TECH INC
Decoding Reed-Solomon codes and related codes represented by graphs
InactiveUS20050138516A1Low costError prevention/detection by using return channelReed-muller codesComputer scienceFactor graph
A method decodes a soft-input cost function for an [N,k]q linear block error- correcting code that has a fast sparse transform factor graph (FSTFG) representation, such as Reed-Solomon codes. First, the code is selected and its FSTFG representation is constructed. The representation is simplified and is made redundant if the improved performance is more important than the increased decoding complexity. An encoding method consistent with the representation is selected. A set of message-update and belief-update rules are selected. The messages are initialized according to a soft-input cost function. An iterative decoding cycle is then begun, in which the first step consists of updating the messages according to the pre-selected message-update rules. In the second step of the decoding cycle, a trial code word is determined from the messages, the pre- selected message-update rules, and the encoding method. In the third step of the decoding cycle, the tentative output code word of the decoding method is replaced with the trial code word if the trial code word has lower cost. Finally, the decoding cycle terminates if a termination condition is true, and outputs the tentative code word, and otherwise repeats the decoding cycle. The decoding method can be combined or concatenated with other decoding methods for FSTFG codes.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC RES LAB INC
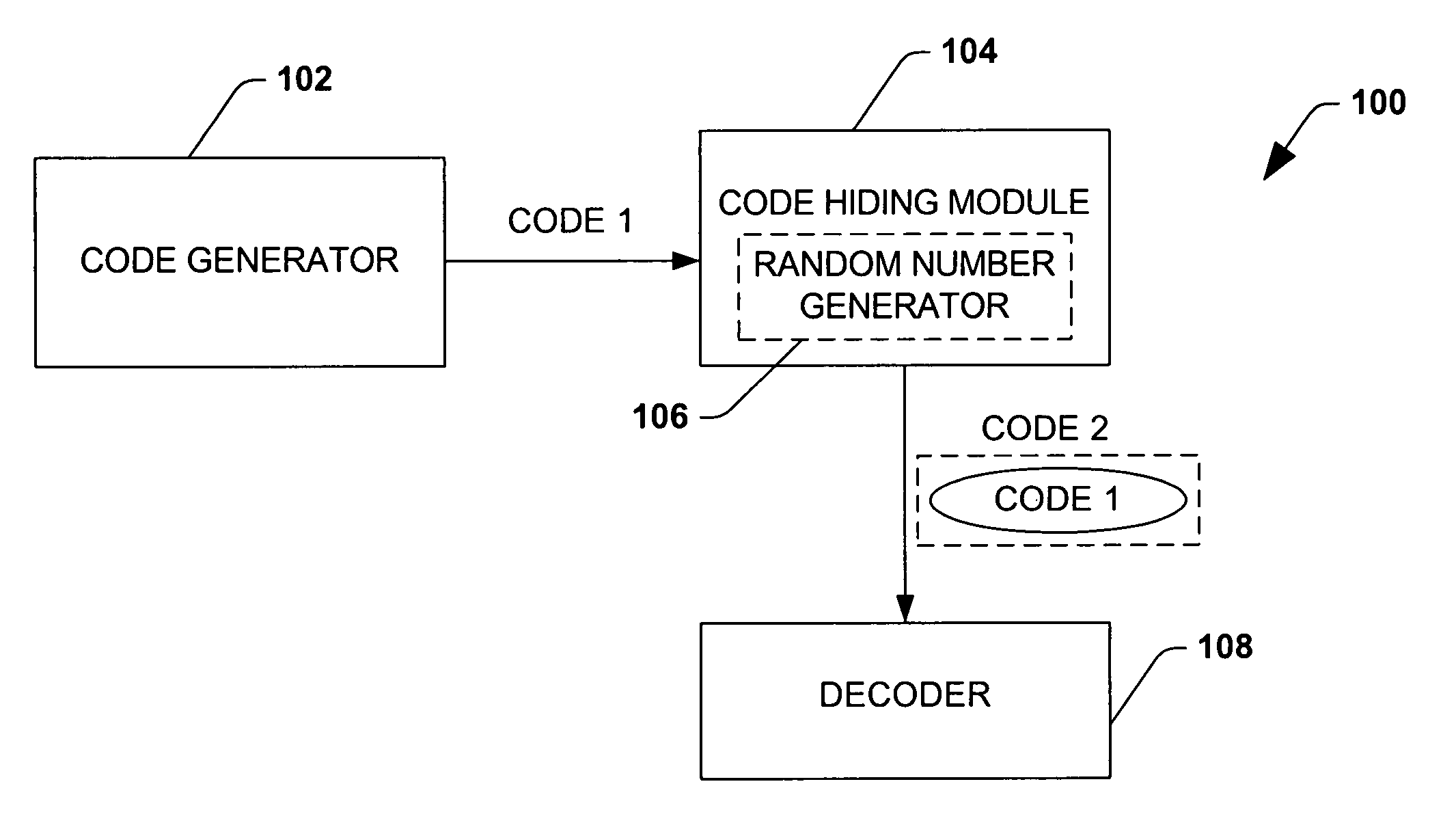
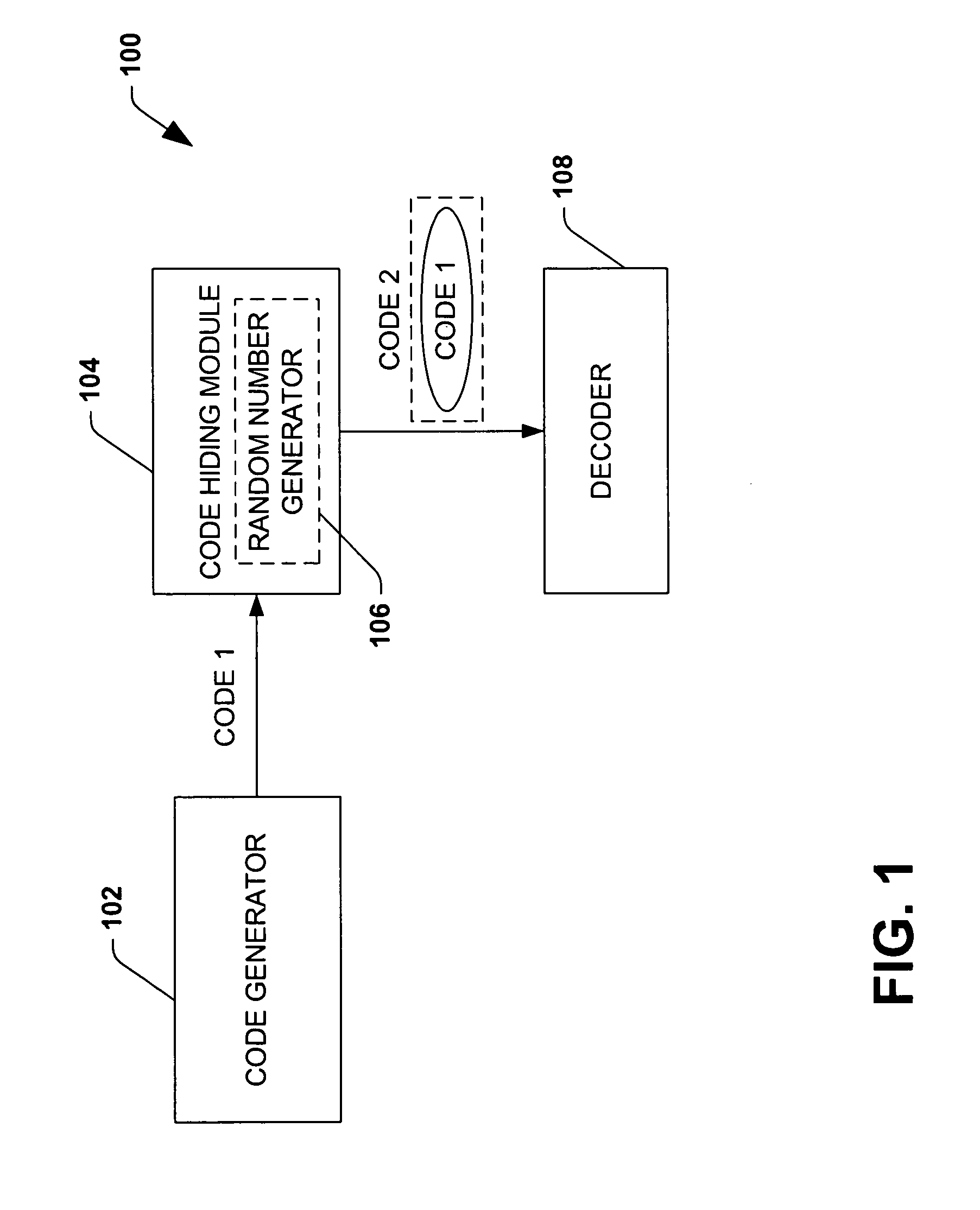
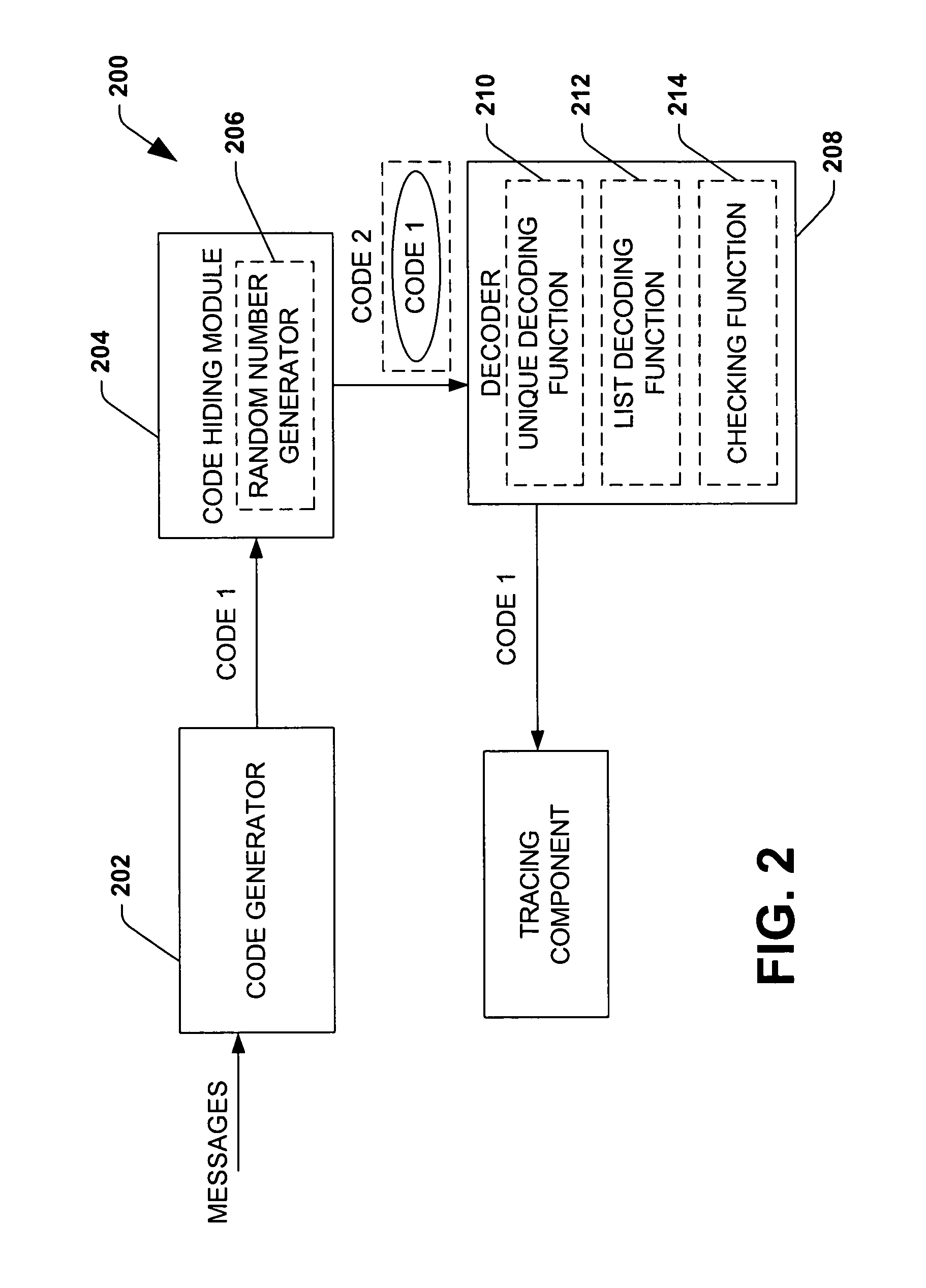
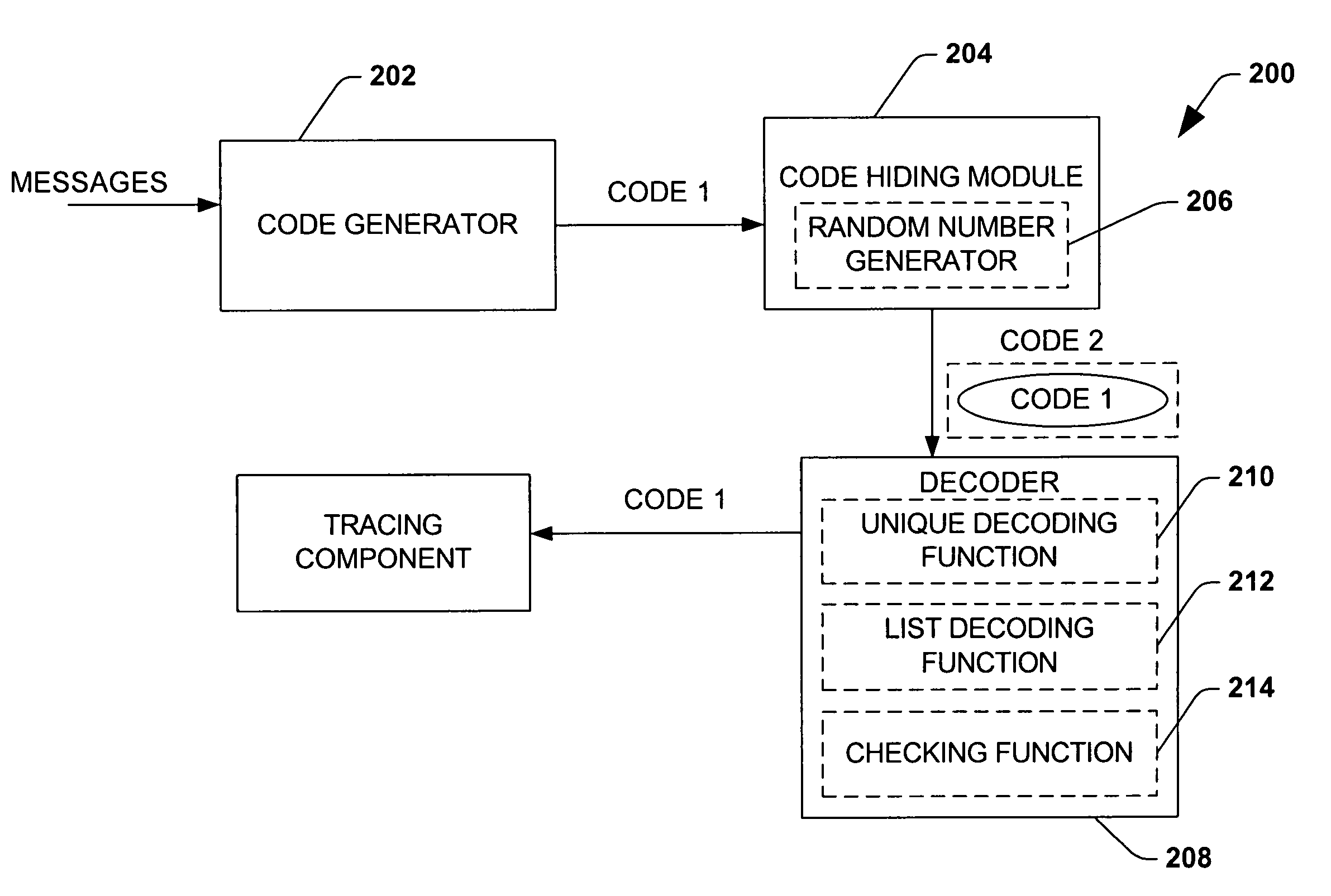
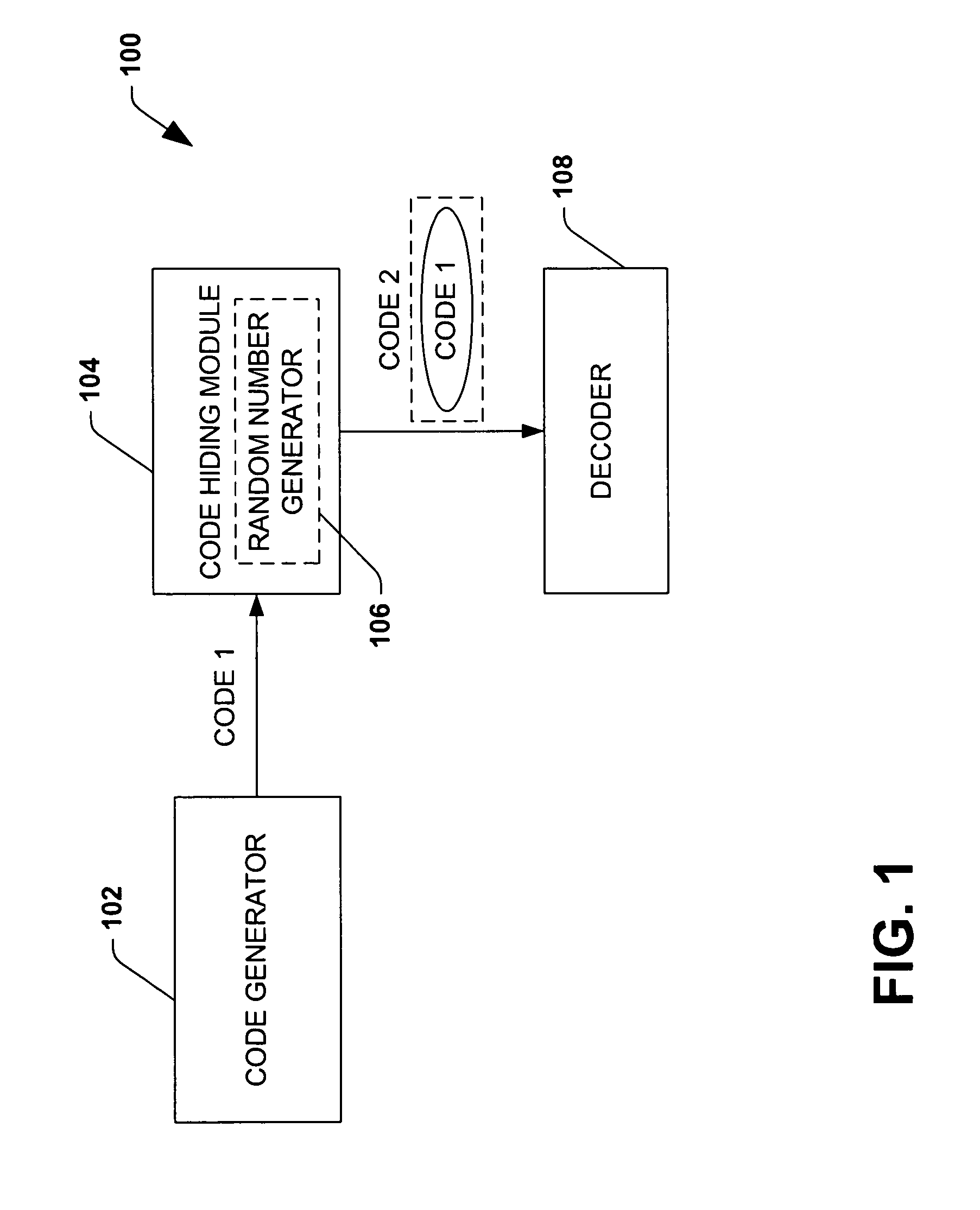
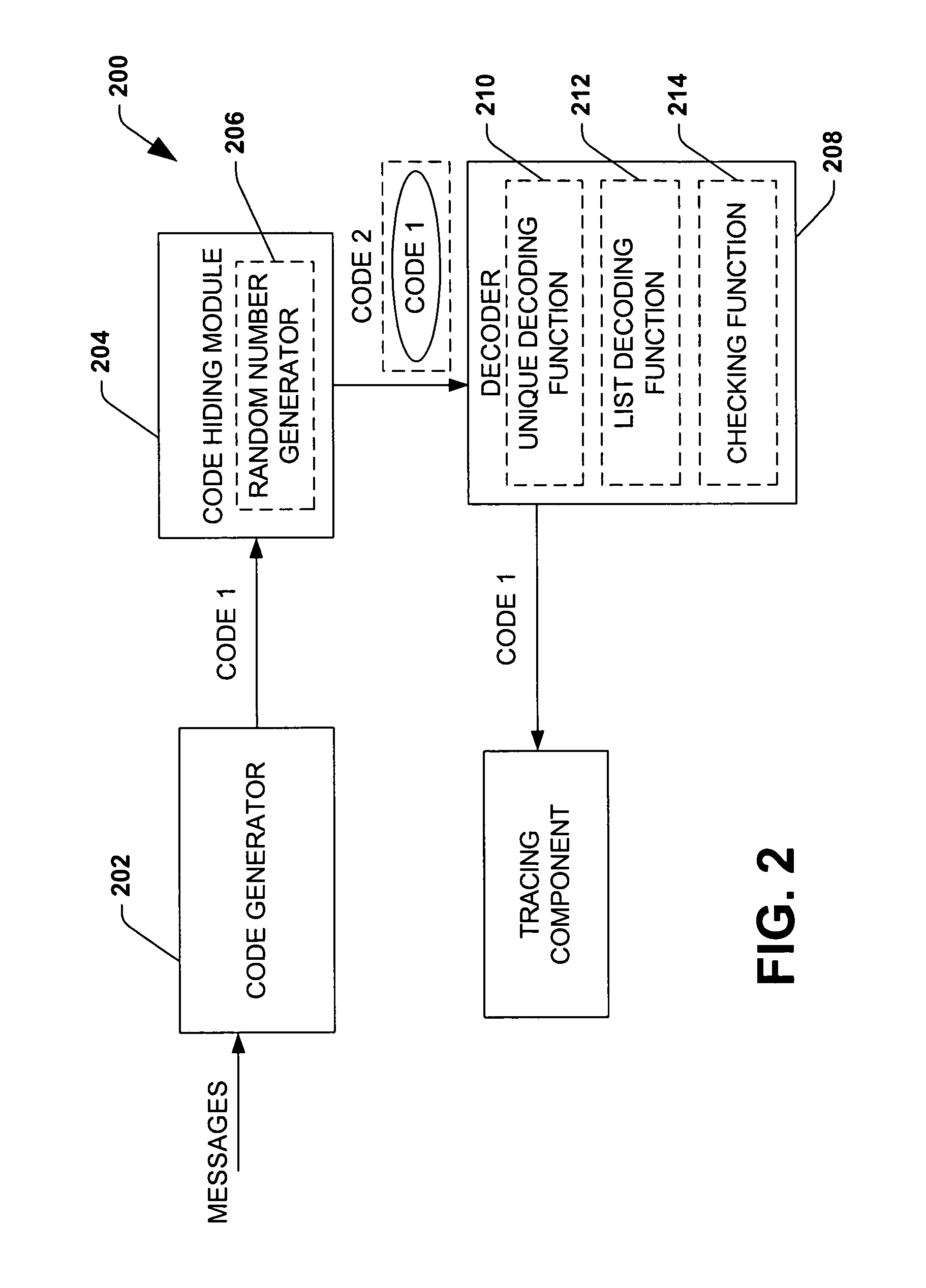
Efficient code constructions via cryptographic assumptions
InactiveUS20050175180A1High level of performanceEffectively randomizesReed-muller codesSynchronising transmission/receiving encryption devicesCryptographic hash functionTheoretical computer science
A system that facilitates efficient code construction comprises a component that receives a first code and a transformation component that transforms the first code to a new code. The new code has essentially same length parameters as the first code but is hidden to a computationally bounded adversary. The first code can be designed in the noise model and appear random to a computationally bounded adversary upon transformation.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
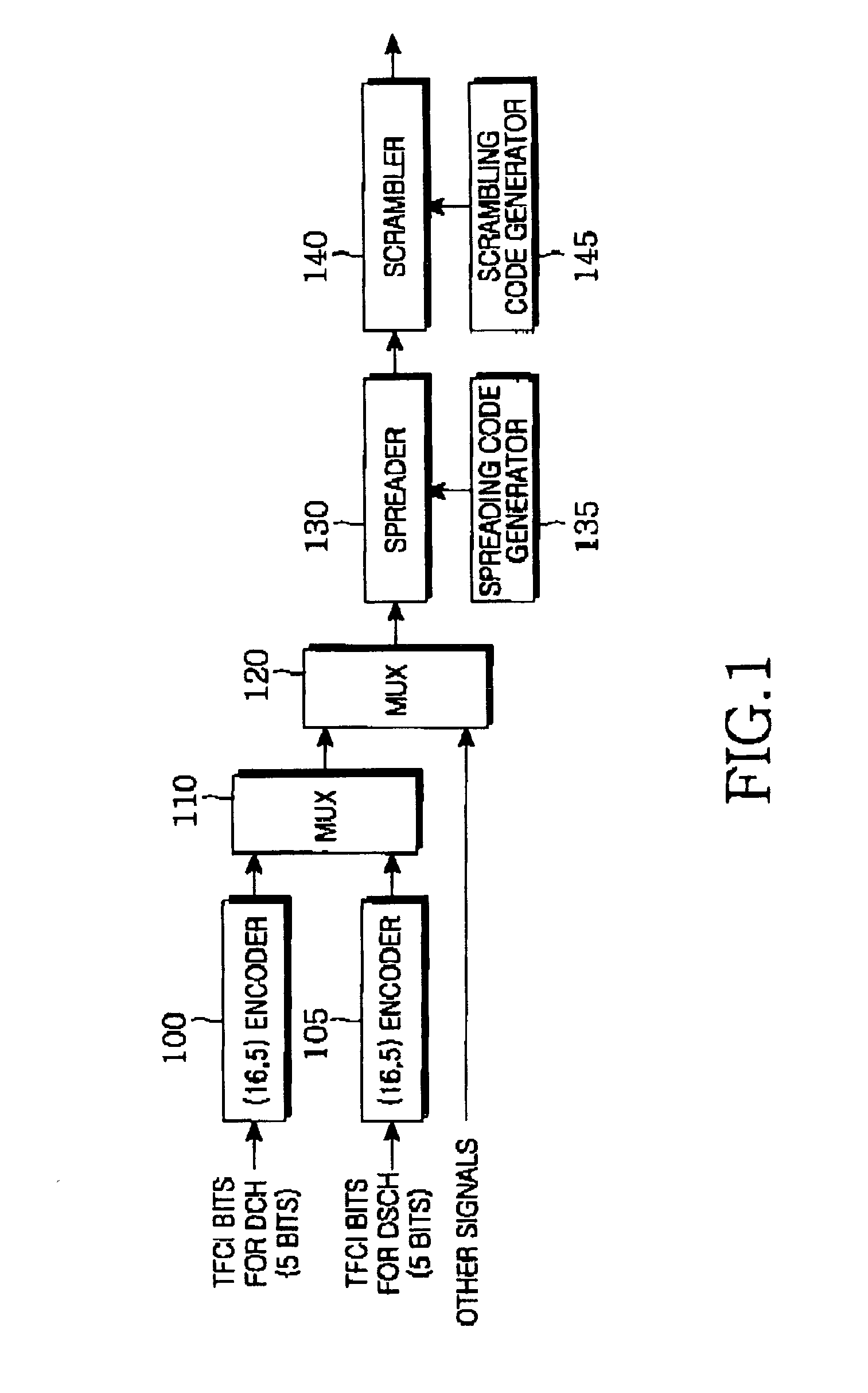
Apparatus and method for encoding/decoding transport format combination indicator in CDMA mobile communication system
InactiveUS20050083901A1Reed-muller codesNetwork traffic/resource managementCommunications systemOrthogonal sequence
An apparatus and method for encoding / decoding a transport format combination indicator (TFCI) in a CDMA mobile communication system. In the TFCI encoding apparatus, a one-bit generator generates a sequence having the same symbols. A basis orthogonal sequence generator generates a plurality of basis orthogonal sequences. A basis mask sequence generator generates a plurality of basis mask sequences. An operation unit receives TFCI bits that are divided into a first information part representing biorthogonal sequence conversion, a second information part representing orthogonal sequence conversion, and a third information part representing mask sequence conversion and combines an orthogonal sequence selected from the basis orthogonal sequence based on the second information, a biorthogonal sequence obtained by combining the selected orthogonal sequence with the same symbols selected based on the first information part, and a mask sequence selected based on the biorthogonal sequence and the third information part, thereby generating a TFCI sequence.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Decoding error-correcting codes based on finite geometries
InactiveUS7103825B2Non-binary linear block codesReed-muller codesProcessor registerBinary linear block codes
A method decodes a received word for a binary linear block code based on a finite geometry. First, a parity check matrix representation of the code is defined. The received word is stored in a channel register. An active register represents a current state of the decoder. Each element in the active register can take three states, representing the two possible states of the corresponding bit in the word, and a third state representing uncertainty. Votes from parity checks to elements of the active register are determined from parity checks in the matrix, and the current state of the active register. A recommendation and strength of recommendation for each element in the active register is determined from the votes. The elements in the active register are then updated by comparing the recommendation and strength of recommendation with two thresholds, and the state of the corresponding bit in the received word. When termination conditions are satisfied, the decoder outputs the state of the active register. If the decoder outputs a state of the active register that does not correspond to a codeword, a new representation for the code using a parity check matrix with substantially more rows is chosen, and the decoding cycle is restarted.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC INFORMATION TECH CENT AMERICA ITA
System and method for iterative decoding of Reed-Muller codes
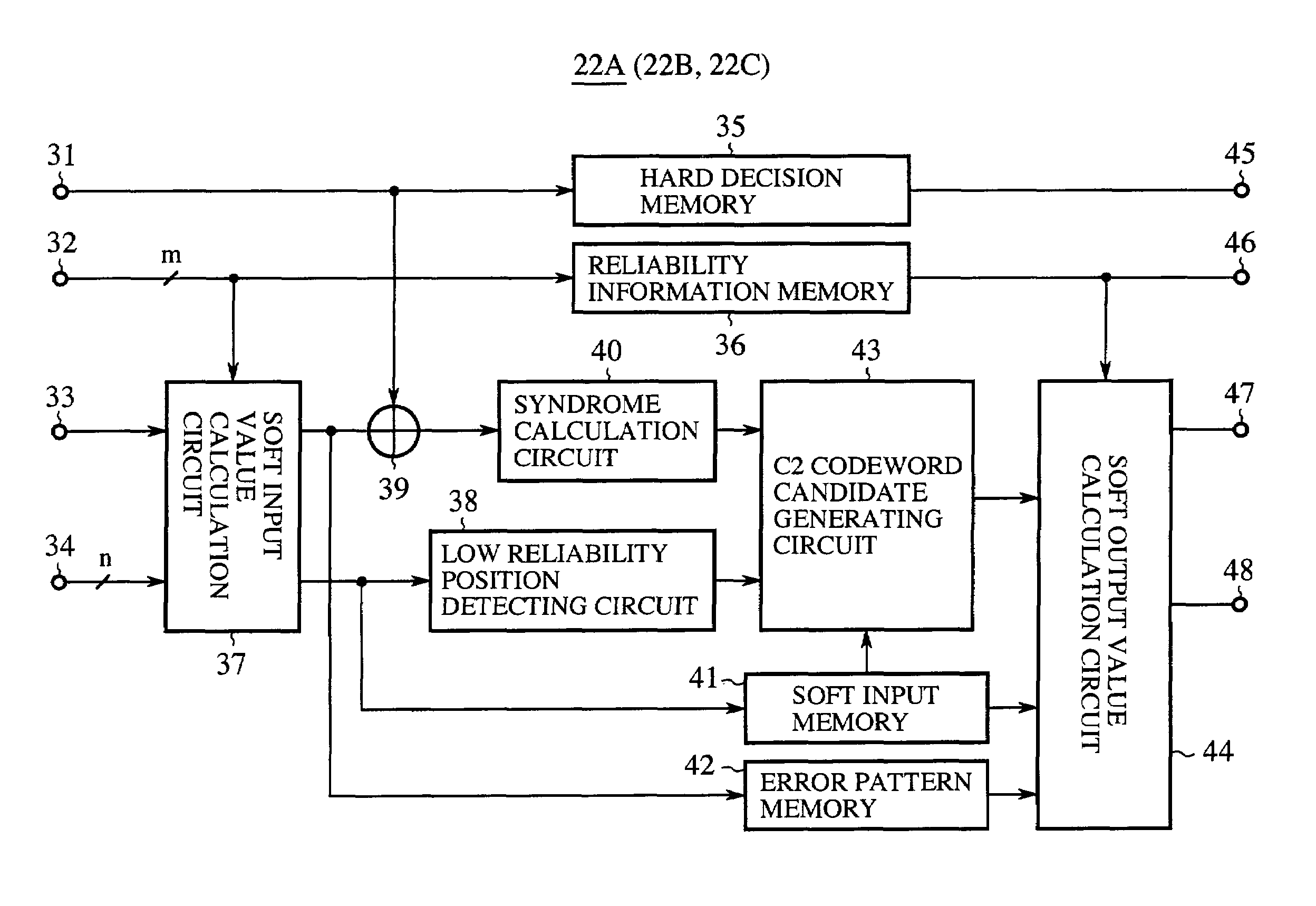
A system for soft-decoding of Reed-Muller coded information has one or more rows of decoding blocks, each decoding block having a soft-output device and a Reed-Muller message passing device. A first soft-output device of a first decoding block processes a coded signal and a zero value probability vector. Each subsequent soft-output device processes the coded information and a non-zero value probability vector. The system for soft-decoding Reed-Muller coded information decodes a code-bit reliability vector from a soft-output device to generate an updated codeword reliability vector, which is used by a next decoding block in a sequence of decoding blocks to reprocess the coded information using the updated reliability vector. The reliability vector is updated through processing in each decoding block to optimize the reliability vector for extraction of the transmitted information from the received information.
Owner:SEAGATE TECH LLC
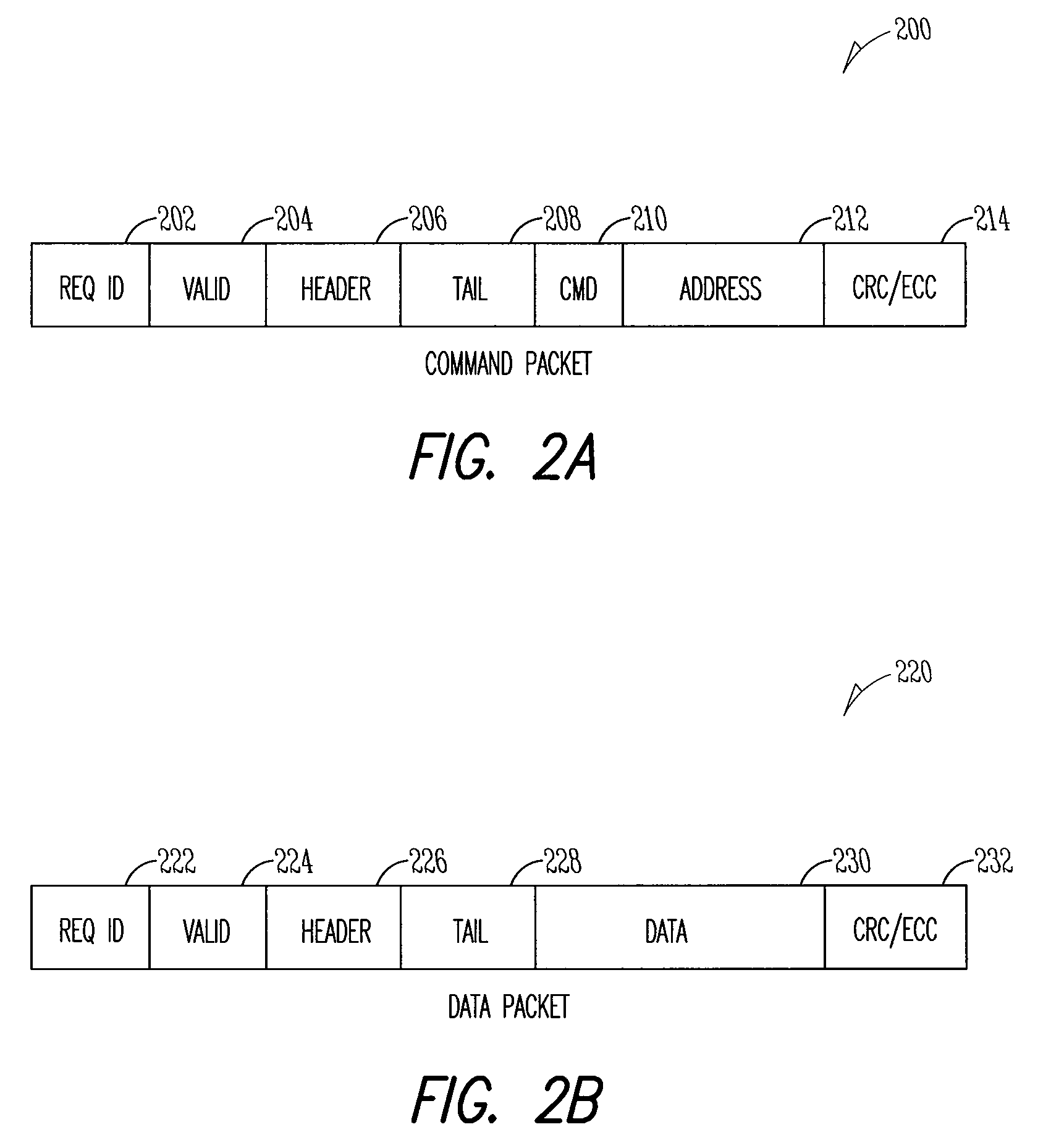
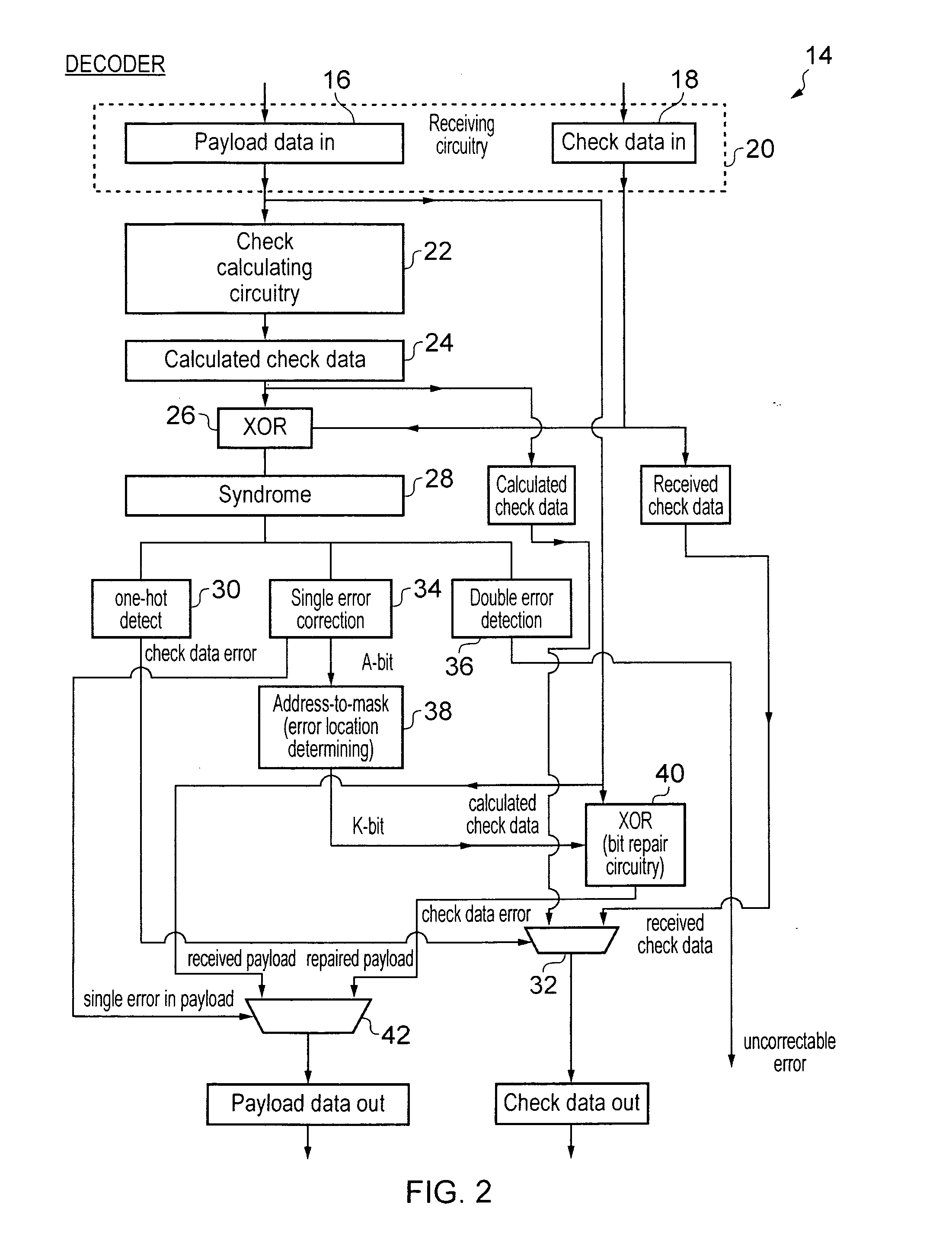
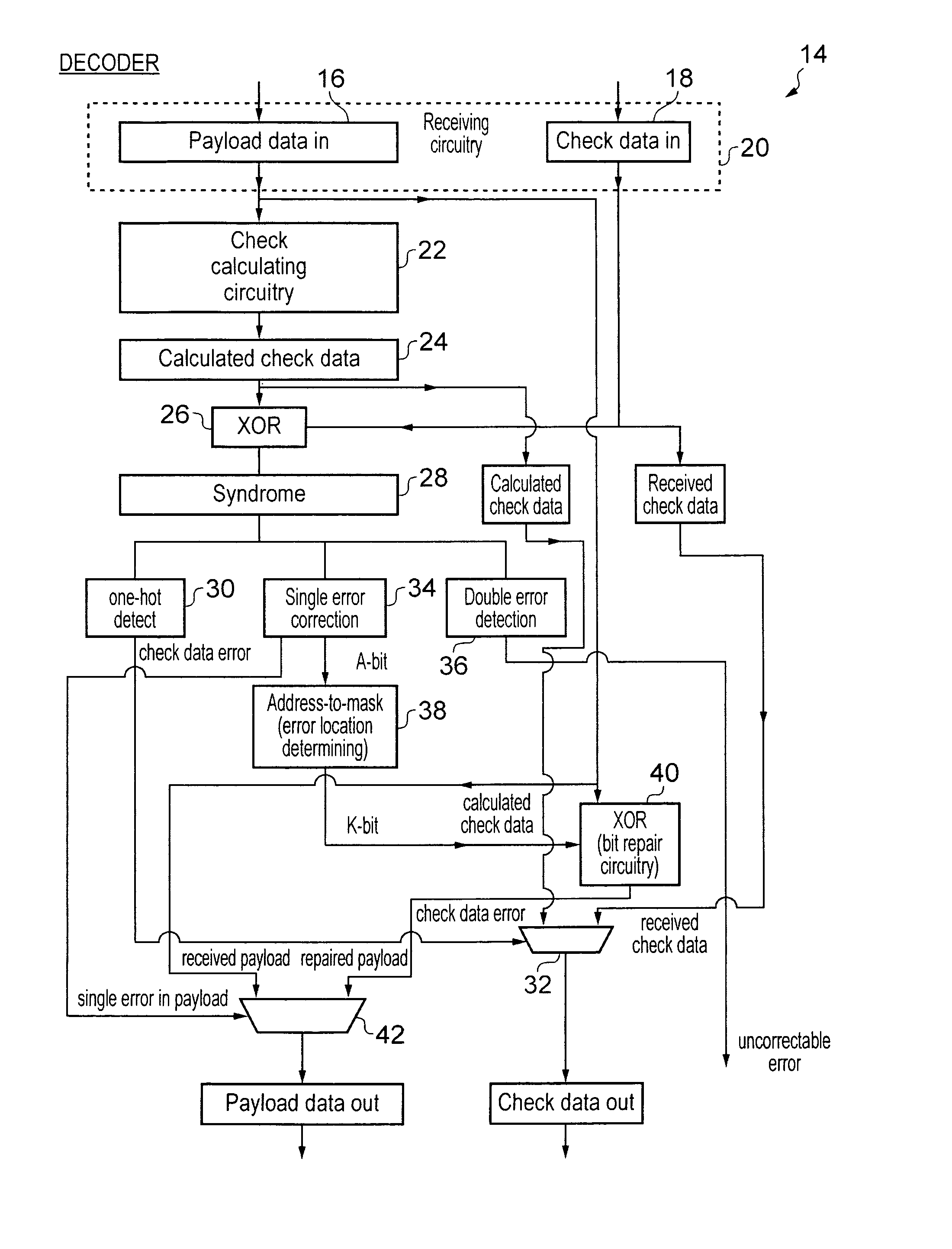
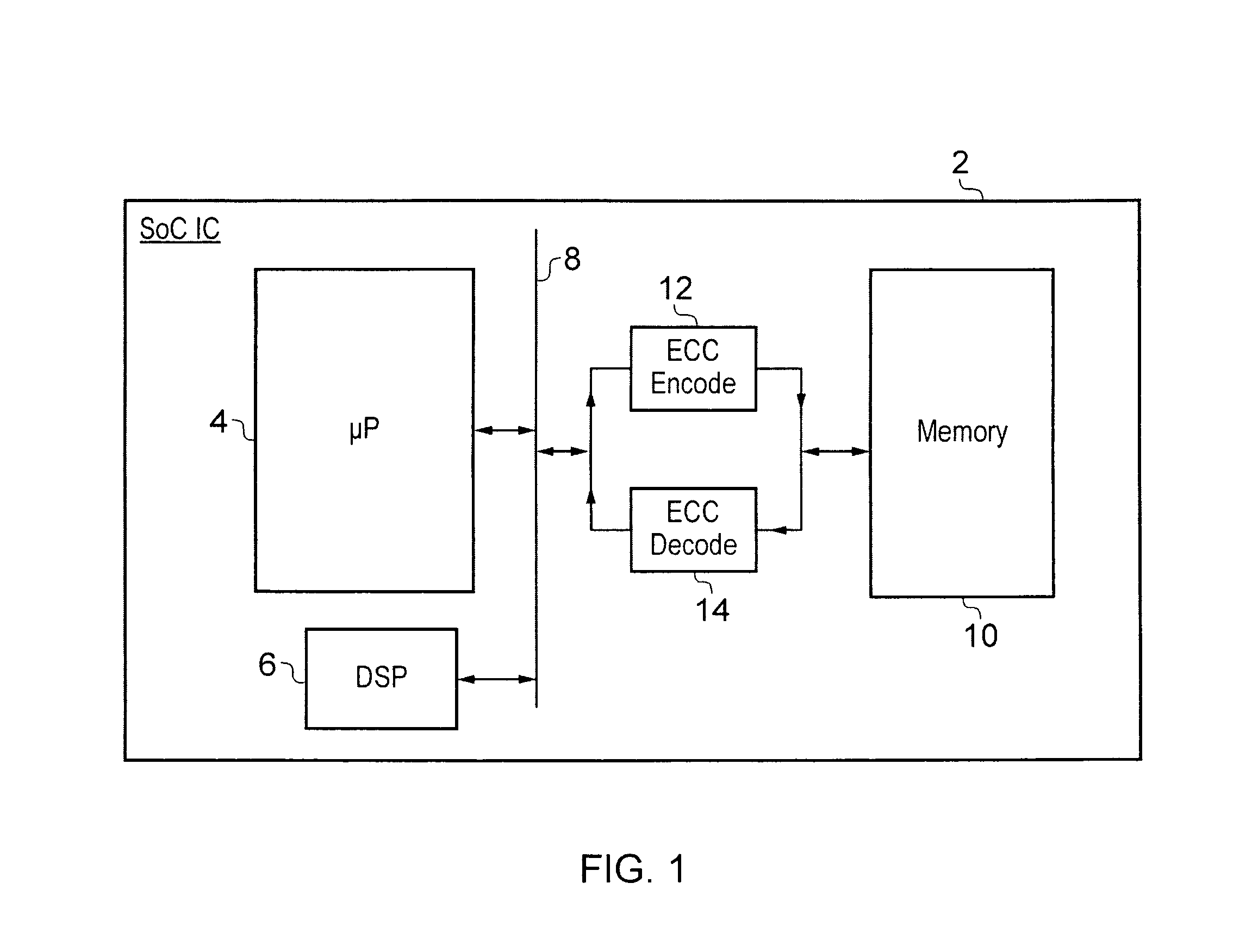
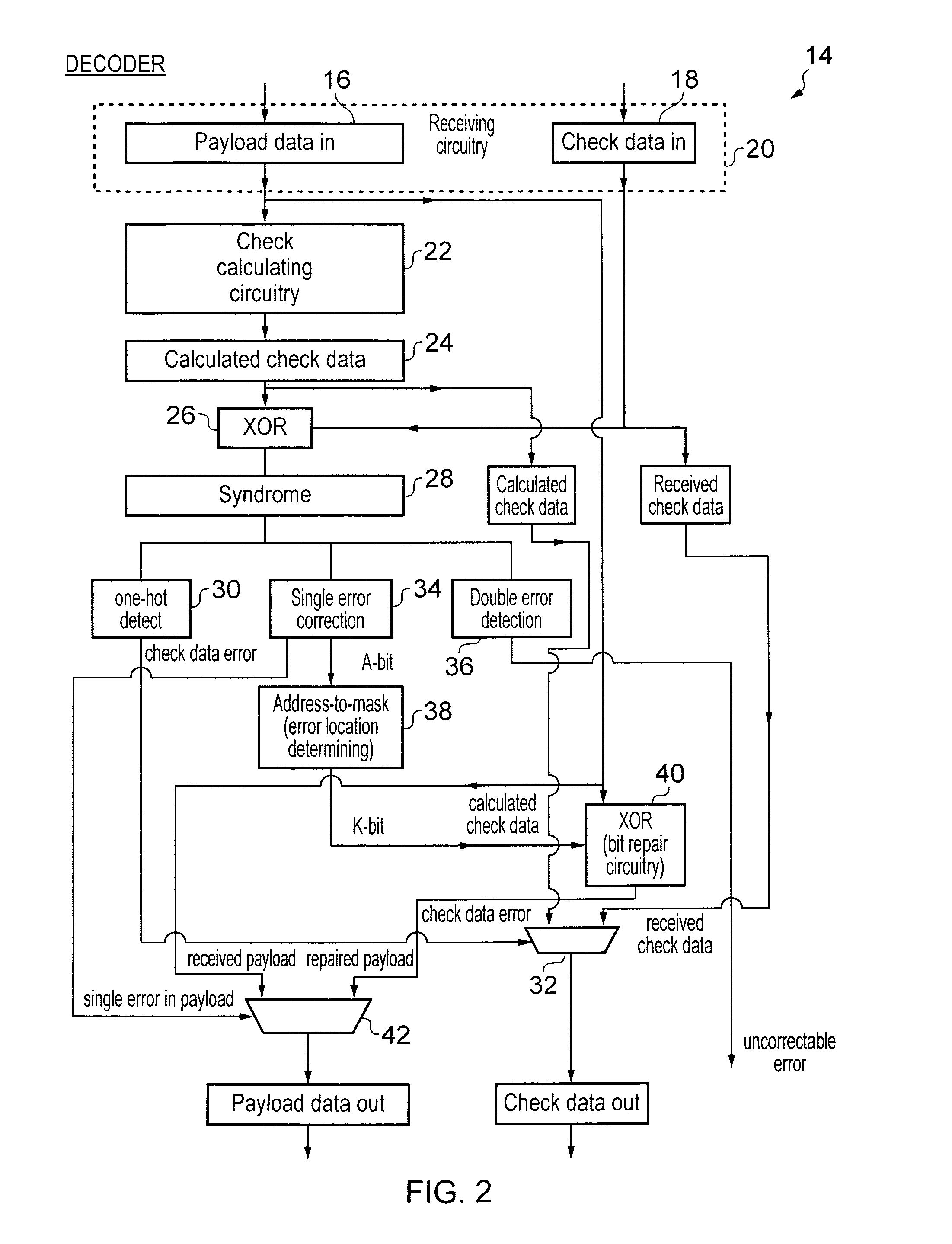
Error control coding for single error correction and double error detection
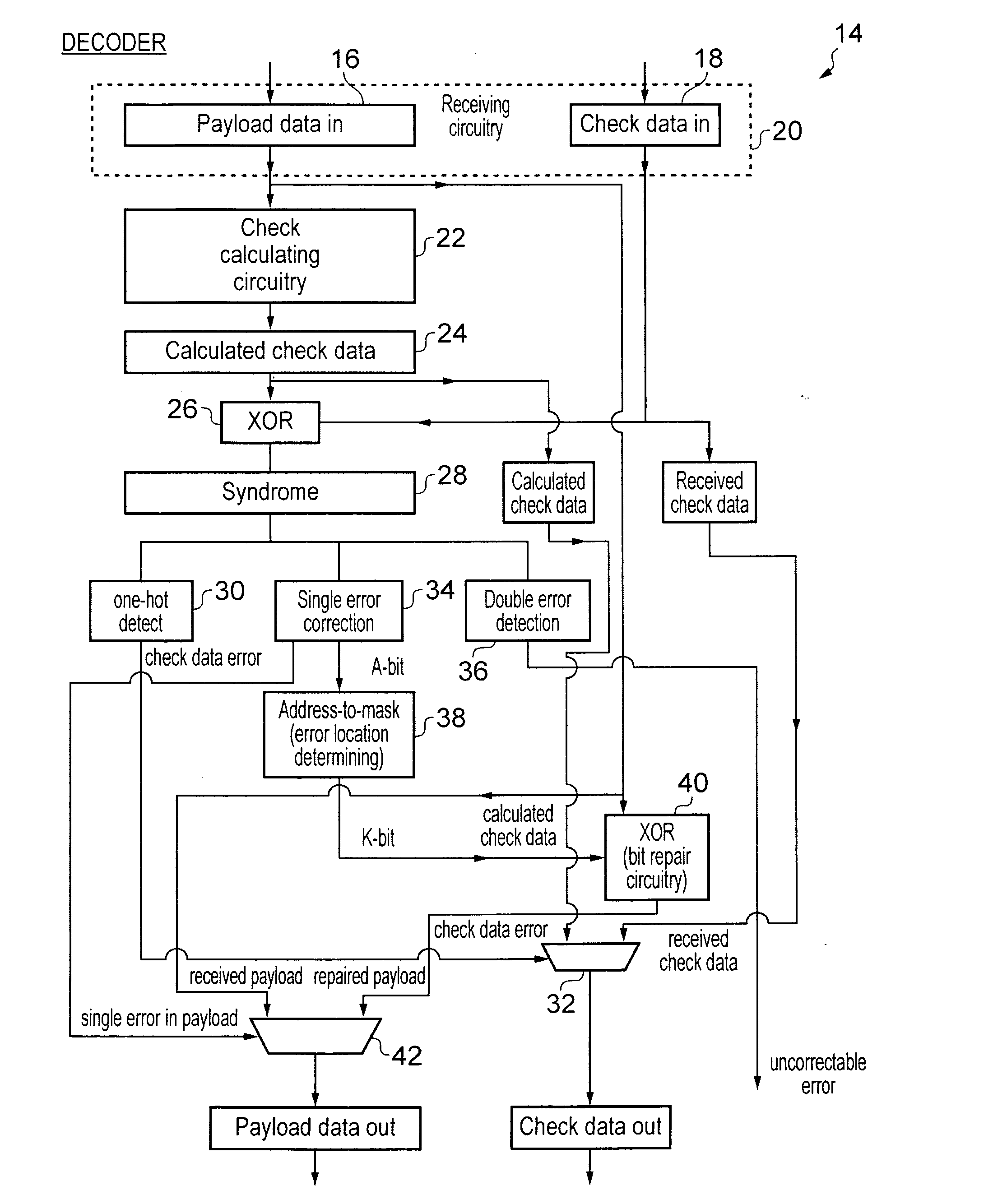
ActiveUS20110099451A1Good error correction/detectionLow overhead implementationReed-muller codesChecking code calculationsComputer hardwareChecksum
An error correction coding is provided that generates P bits of check data from K M-bit words of payload data. The P bits of check data include an address field A, a bit error indicating field E and an auxiliary field P−(E+A). The address field encodes a set of error addresses which has a cardinality equal to the bit size K of the payload data and providing a one-to-one mapping between values of the address field and the locations of a single bit error within the payload data. The bit error indicating field indicates if a bit error is present. The auxiliary field is a minimum size bit vector such that together with the address field and the bit area indicating field it provides a checksum for a systematic code for the payload data with a minimum Hamming distance serving to provide either single error correction capability or single error correction and double error detection capability.
Owner:ARM LTD
Efficient code constructions via cryptographic assumptions
InactiveUS7643637B2High levelSynchronising transmission/receiving encryption devicesReed-muller codesCryptographic hash functionTheoretical computer science
A system that facilitates efficient code construction comprises a component that receives a first code and a transformation component that transforms the first code to a new code. The new code has essentially same length parameters as the first code but is hidden to a computationally bounded adversary. The first code can be designed in the noise model and appear random to a computationally bounded adversary upon transformation.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Method and apparatus of generating codewords in wireless communication system
ActiveUS20110043391A1Improve encoding performanceImprove performanceReed-muller codesCode conversionCommunications systemVariable length
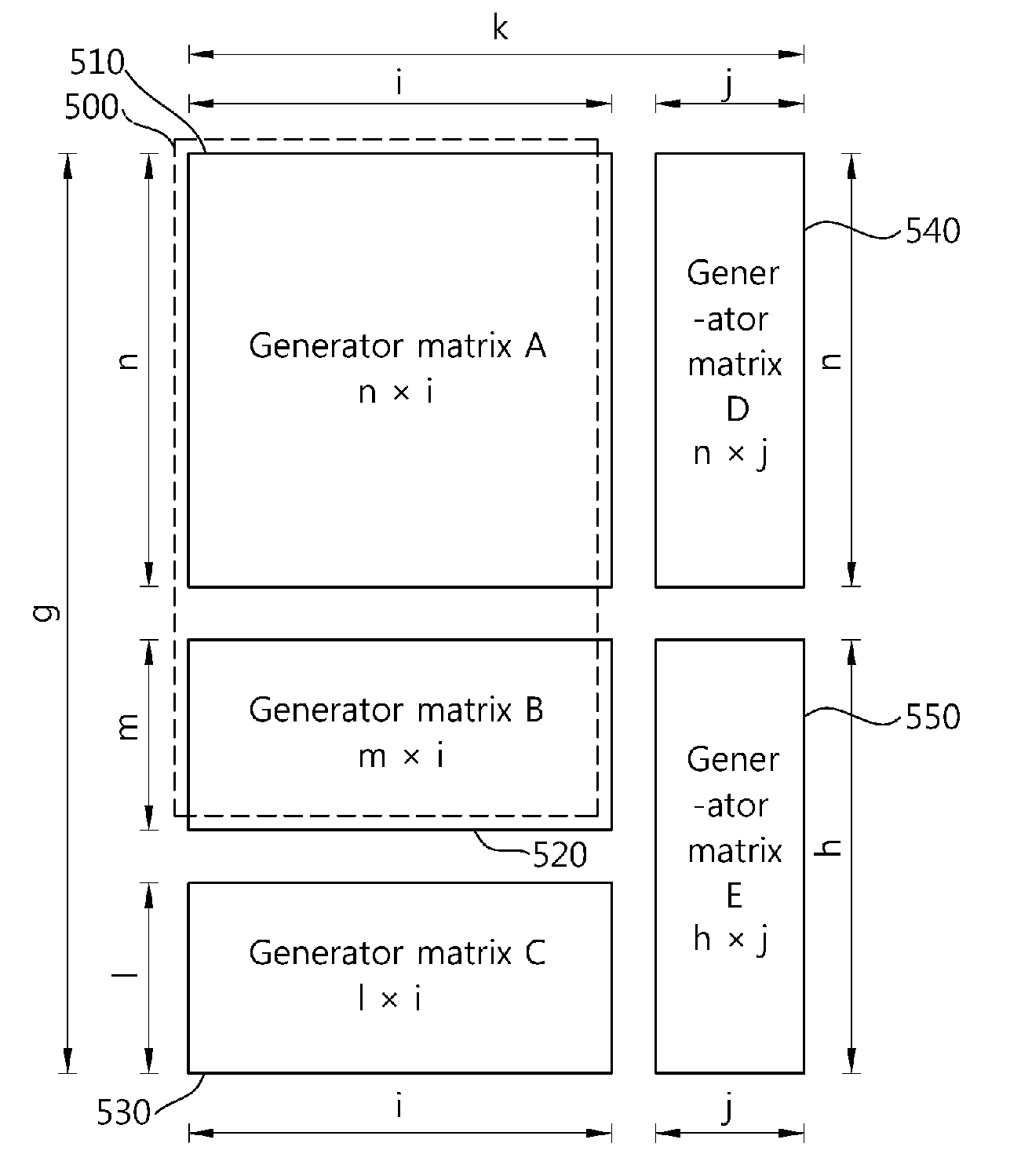
A method and apparatus for generating and transmitting codewords is provided. The method includes receiving information bits with a variable length, selecting vectors by the length of the information bits from a generator matrix, and generating a codeword based on the information bits and the generator matrix. Codewords with a certain length providing a coding performance with respect to received variable information bits can be obtained.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
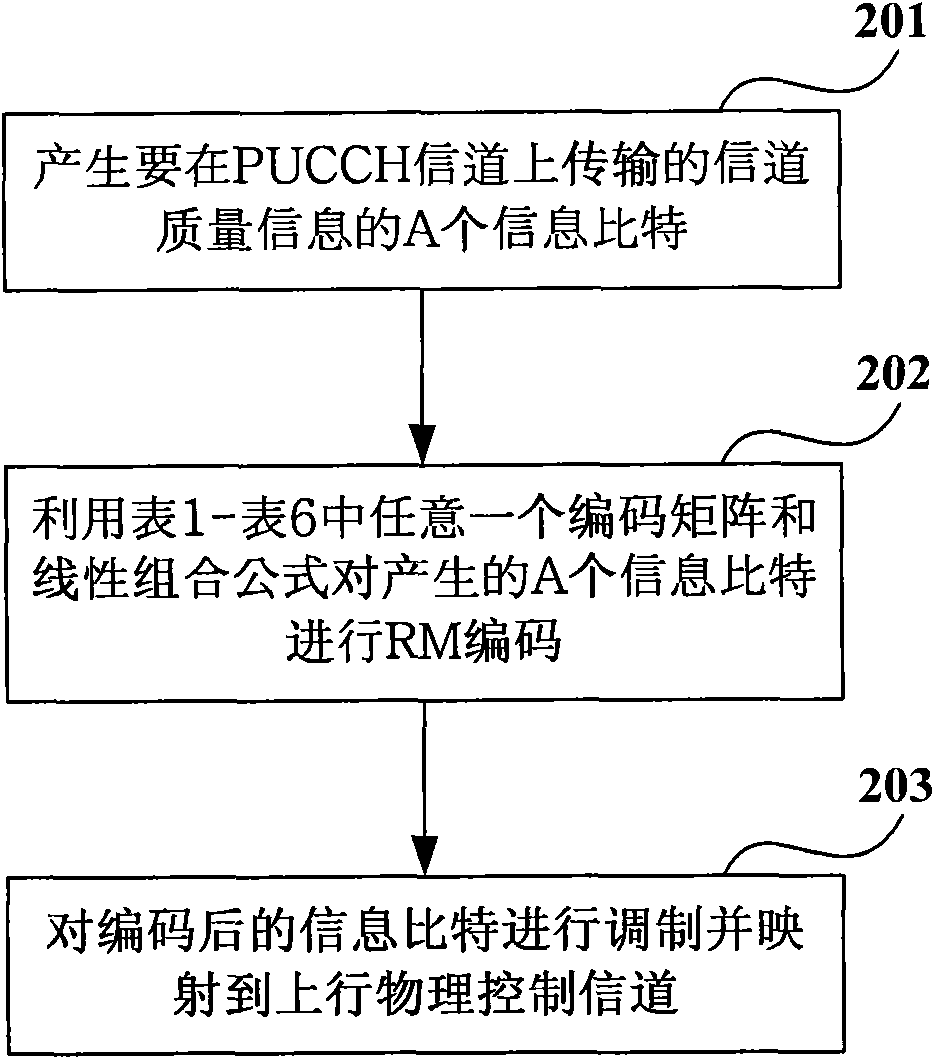
Encoding method and device thereof
ActiveCN101771418AImprove transmission performanceEnough timeReed-muller codesCode conversionComputer scienceTime diversity
The invention provides an encoding method and a device thereof. The method comprises the following step of encoding an input information bit according to an encoding matrix G and a linear combination formula; the linear combination formula is as follows: bi is equal to the sum of (an*M1,n)mod2 from n to A-1,, wherein bi is the encoded output bits, and i is equal to 0, 1, 2 until B-1; M1,n is corresponding elements in the encoding matrix; an is the input information bit, and n ranges from 0 to A-1; A and B are positive integers greater than zero; and the encoding matrix G is an encoding matrix obtained by carrying out row replacement on an encoding matrix H with at least one line having a plurality of continuous zeros. The information bits are uniformly distributed on all encoded output bits as far as possible through utilizing the encoding matrix G of the encoding method to encode or through carrying out bit mapping on the encoded information, thereby ensuring that the information bit obtains sufficient frequency diversity and time diversity after channel mapping and effectively improving the transmission performance of control information.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
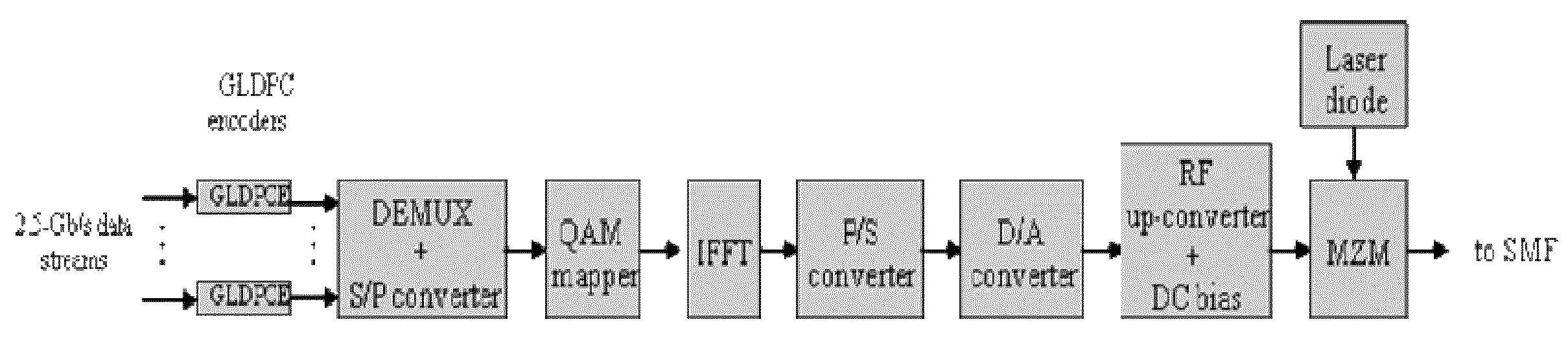
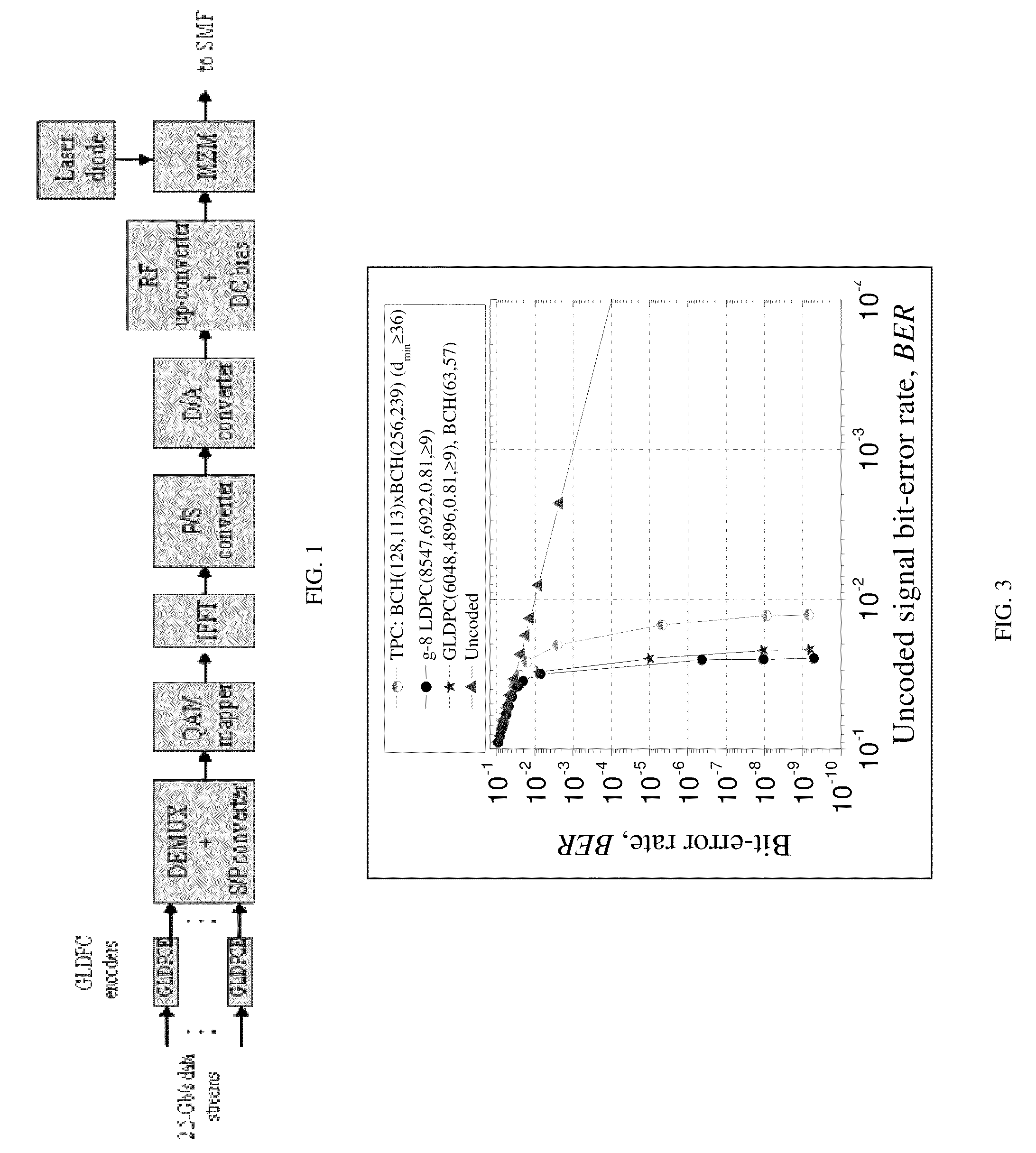
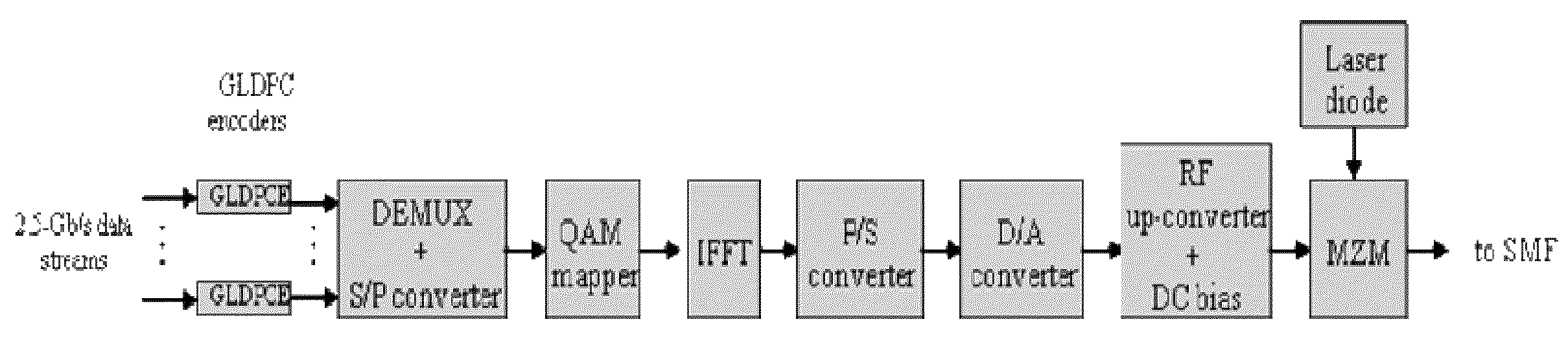
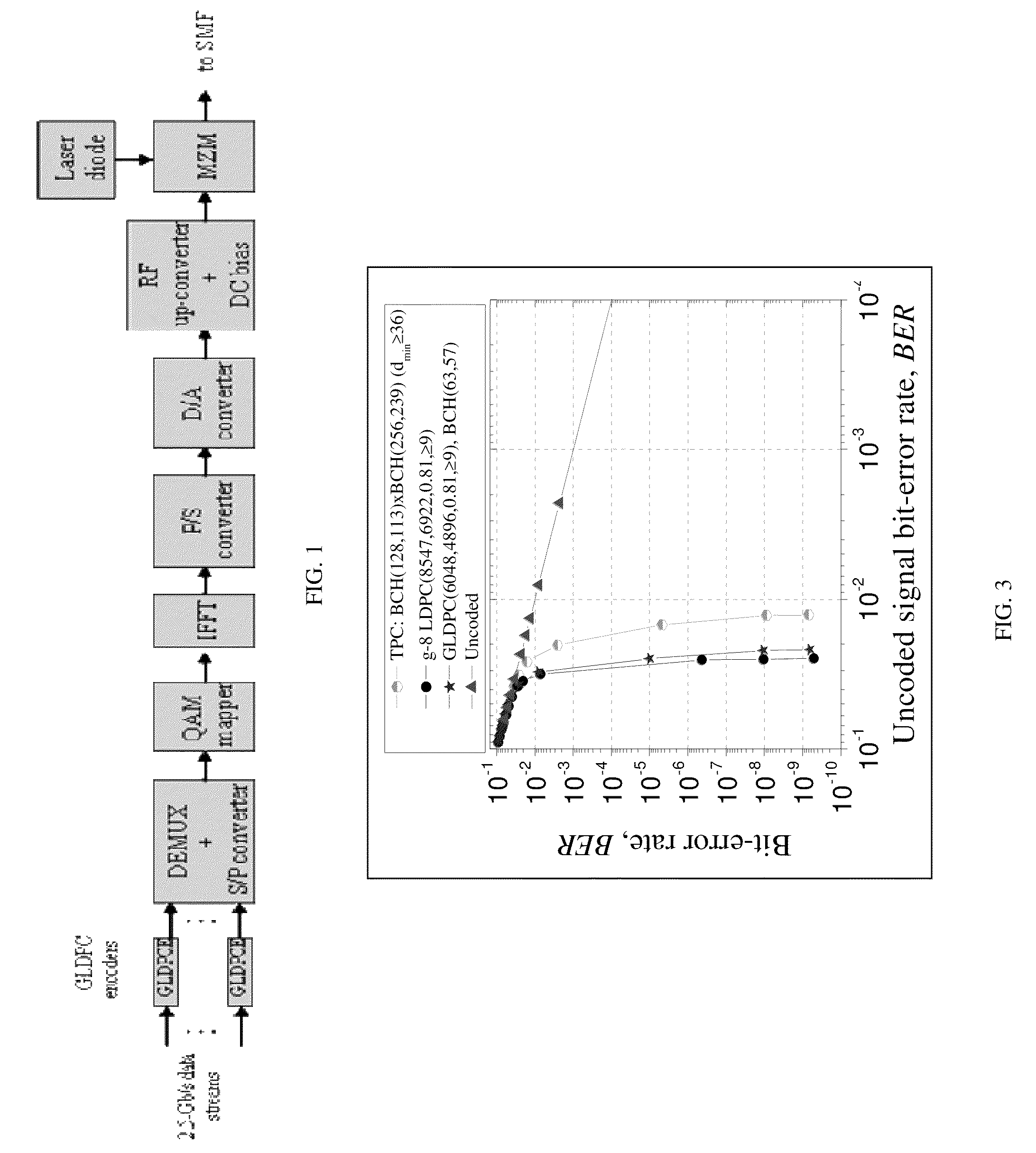
GLDPC encoding with Reed-Muller component codes for optical communications
ActiveUS8386879B2Reed-muller codesError detection/correctionComputer hardwareMaximum a posteriori estimation
Owner:NEC CORP
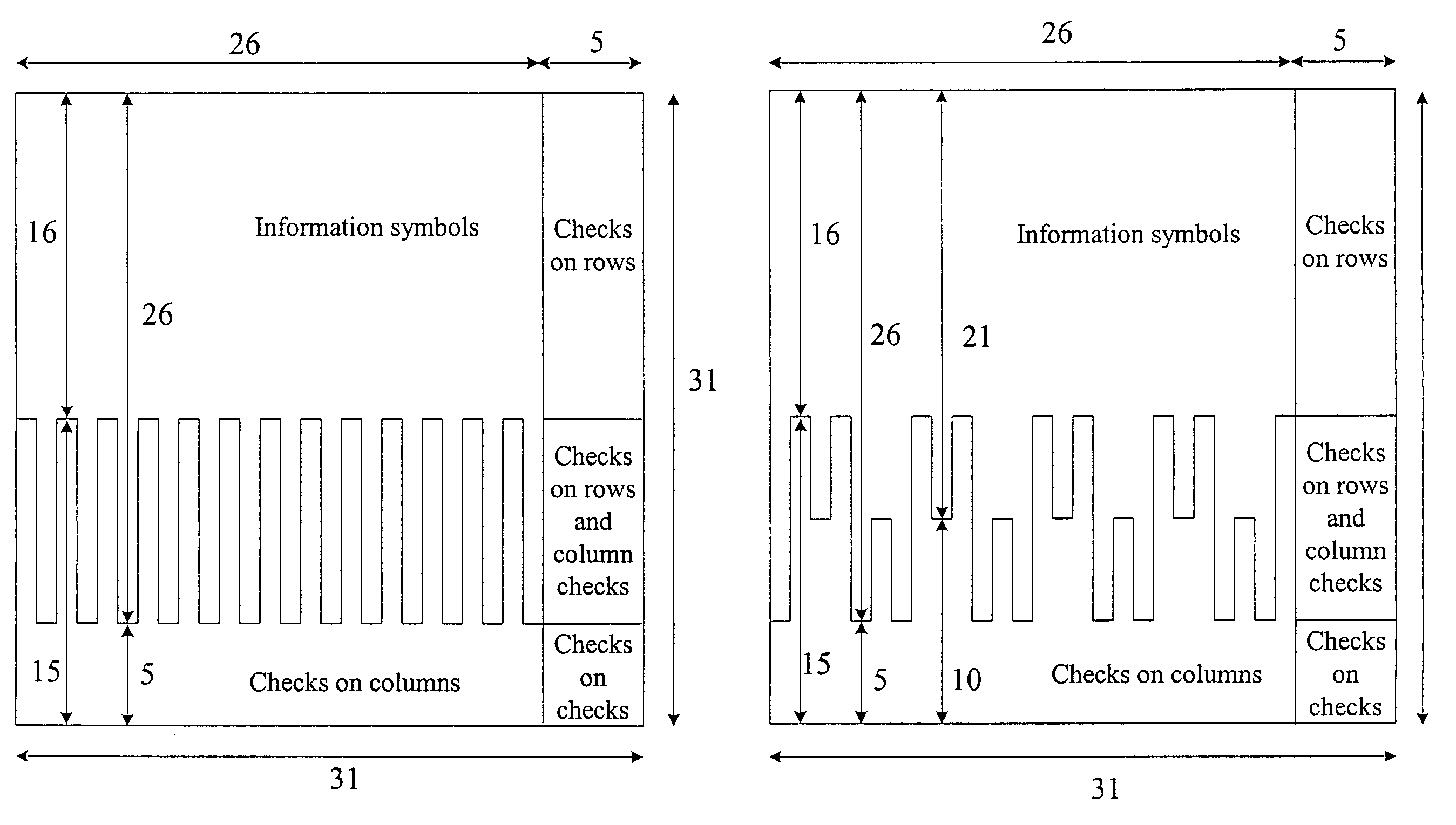
Decoding method, decoding apparatus and digital transmission system of product code
InactiveUS7069496B2Efficient use ofAccurate valueError prevention/detection by using return channelReed-muller codesError locationDependability
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Reverse concatenated encoding and decoding
ActiveUS8595585B2Improve decoding performanceReed-muller codesError detection/correctionComputer hardwareBlock code
Methods and systems for transmitting and receiving data include reverse concatenated encoding and decoding. Reverse concatenated decoding includes inner decoding the encoded stream with an inner decoder that uses a low-complexity linear-block code to produce an inner-decoder output stream, outer decoding the inner-decoder output stream with an outer decoder that uses a low-density parity-check code to produce an information stream, and iterating extrinsic bit reliabilities from the outer decoding for use in subsequent inner decoding to improve decoding performance.
Owner:NEC CORP
Error control coding for single error correction and double error detection
ActiveUS8381083B2Reduce overheadReduce circuitReed-muller codesError detection/correctionComputer hardwareChecksum
An error correction coding is provided that generates P bits of check data from K M-bit words of payload data. The P bits of check data include an address field A, a bit error indicating field E and an auxiliary field P−(E+A). The address field encodes a set of error addresses which has a cardinality equal to the bit size K of the payload data and providing a one-to-one mapping between values of the address field and the locations of a single bit error within the payload data. The bit error indicating field indicates if a bit error is present. The auxiliary field is a minimum size bit vector such that together with the address field and the bit area indicating field it provides a checksum for a systematic code for the payload data with a minimum Hamming distance serving to provide either single error correction capability or single error correction and double error detection capability.
Owner:ARM LTD
Gldpc encoding with reed-muller component codes for optical communications
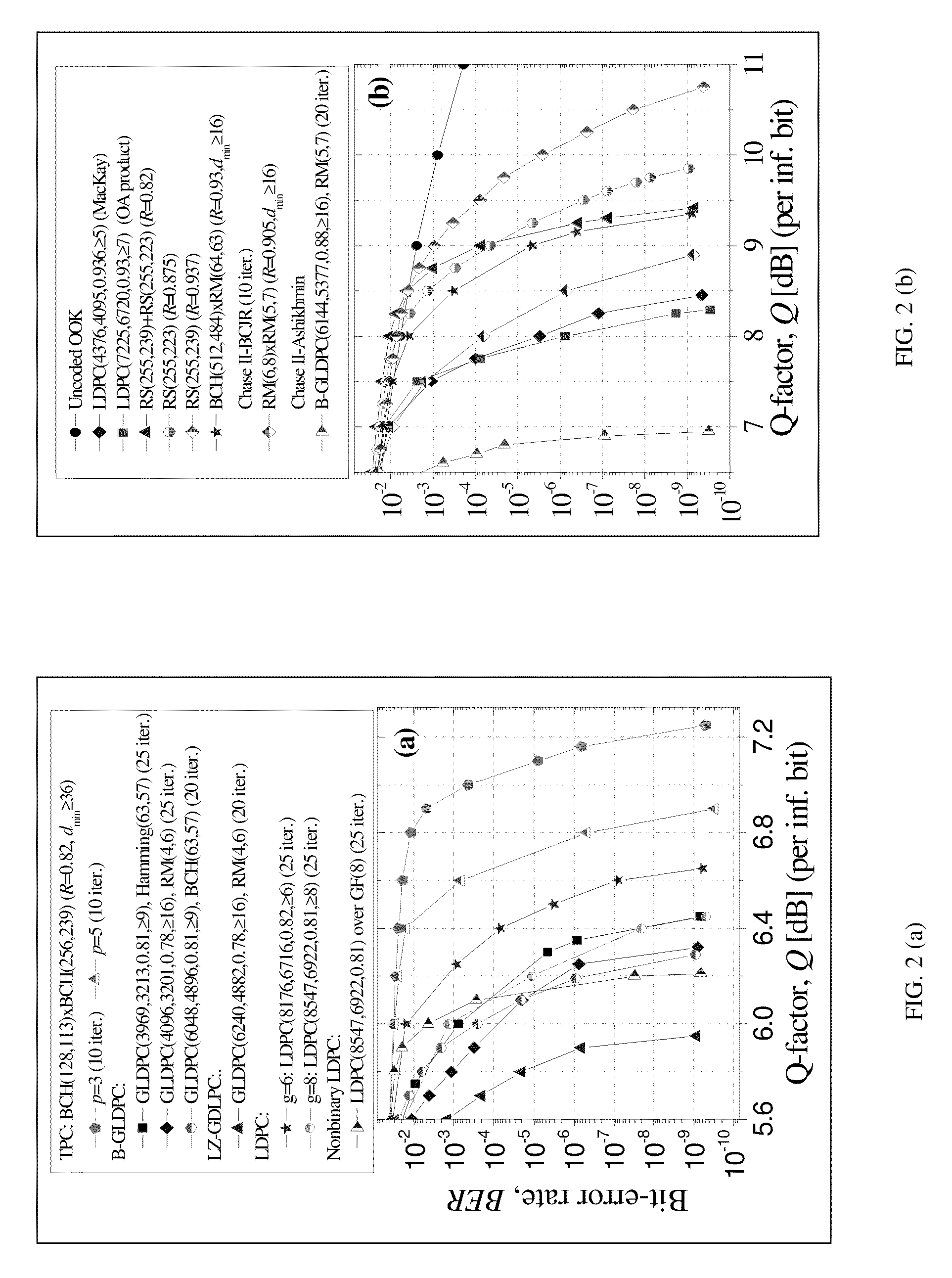
A method of encoding for optical transmission of information includes encoding information with a generalized low-density parity-check (GLDPC) code for providing coding gains, and constructing the GLDPC code with a Reed-Muller RM code as a component code, the component code being decodable using a maximum posterior probability (MAP) decoding. In a preferred embodiment, the GLDPC code includes a codeword length of substantially 4096, an information word length of substantially 3201, a lower-bound on minimum distance of substantially greater than or equal to 16, a code rate of substantially 0.78 and the RM component code includes an order of substantially 4 and an r parameter of substantially 6.
Owner:NEC CORP
Method for performing soft decision decoding of euclidean space reed-muller codes
ActiveUS20120185755A1Improve performanceReed-muller codesError preventionDecoding methodsReed–Muller code
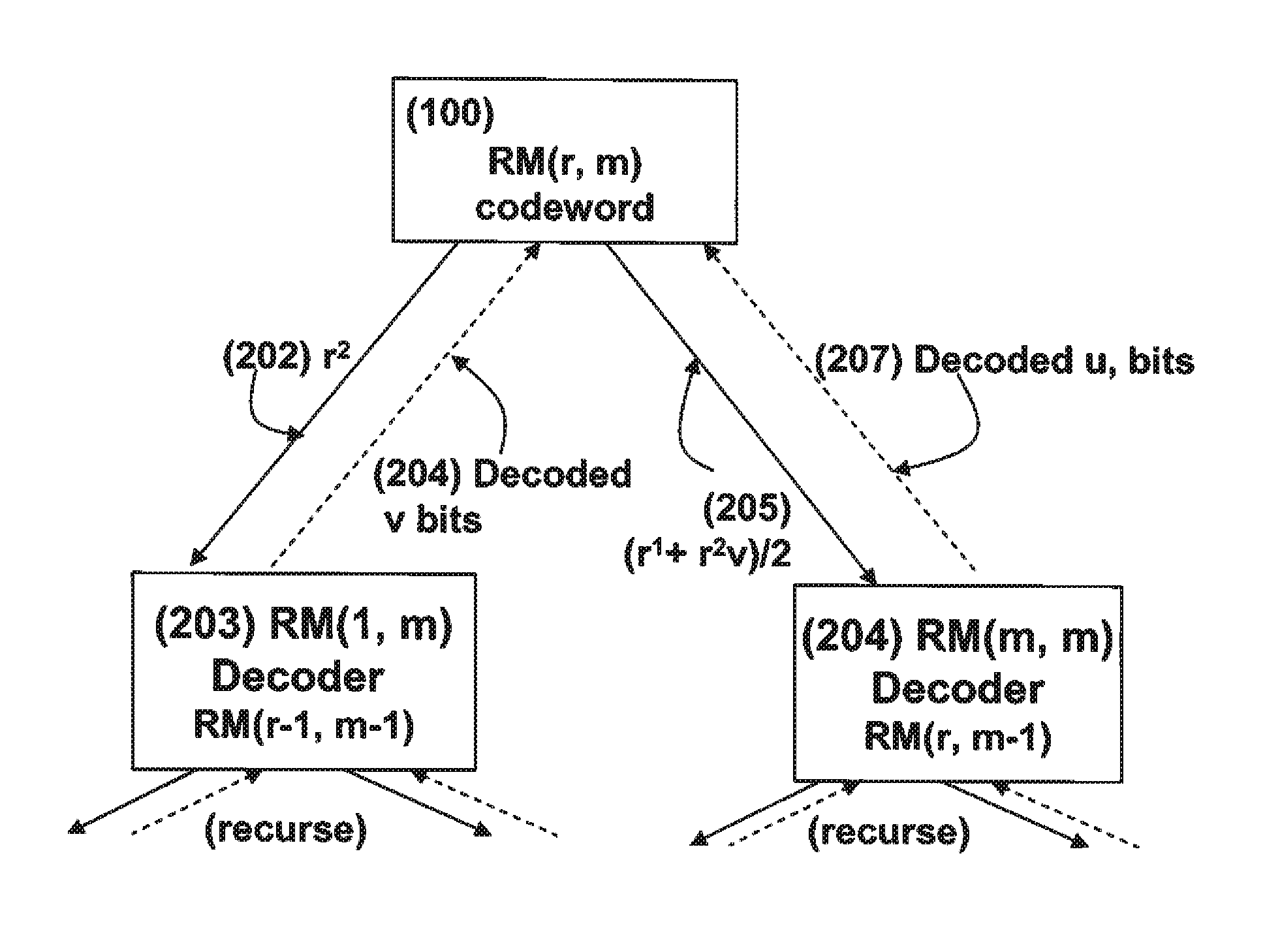
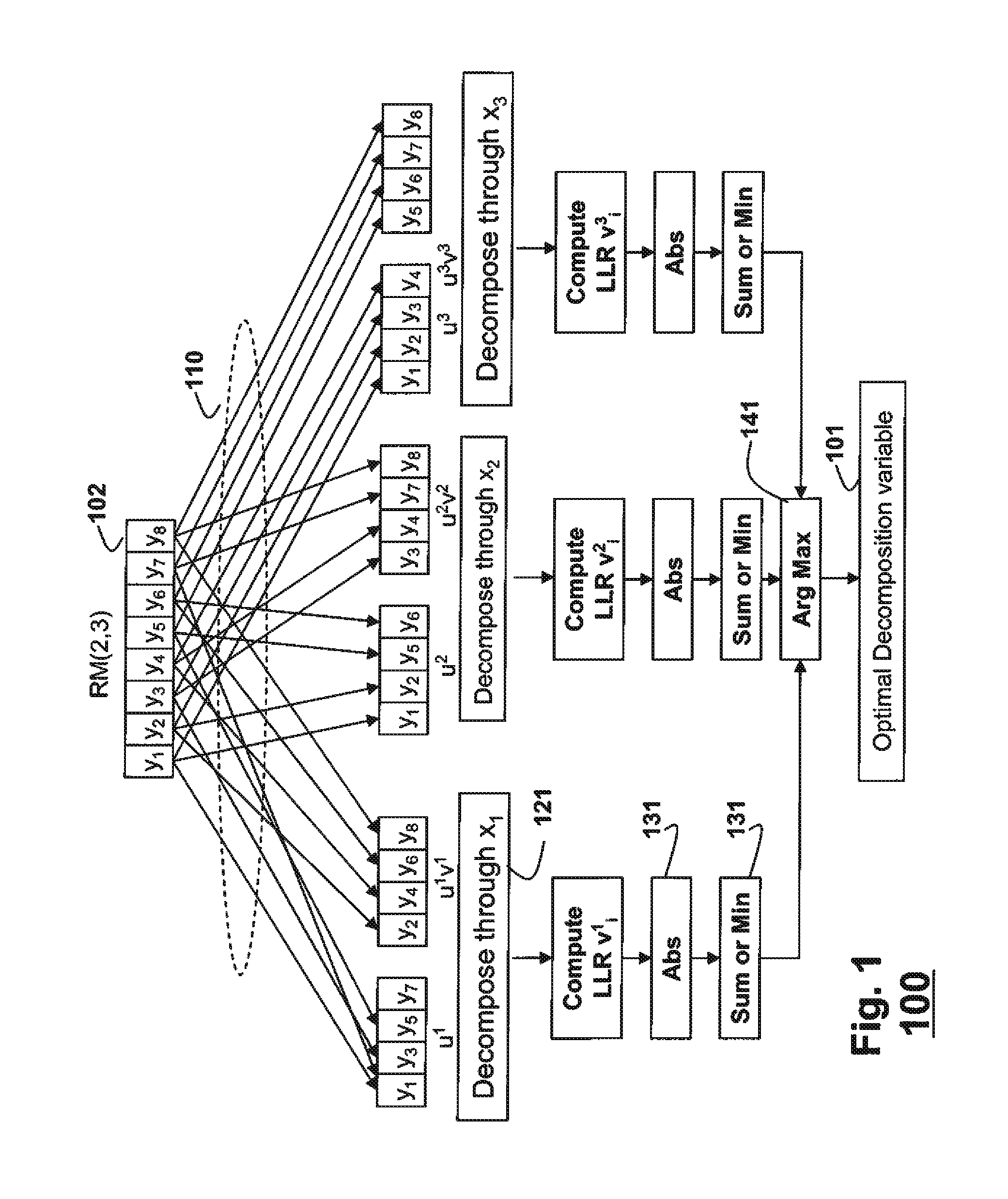
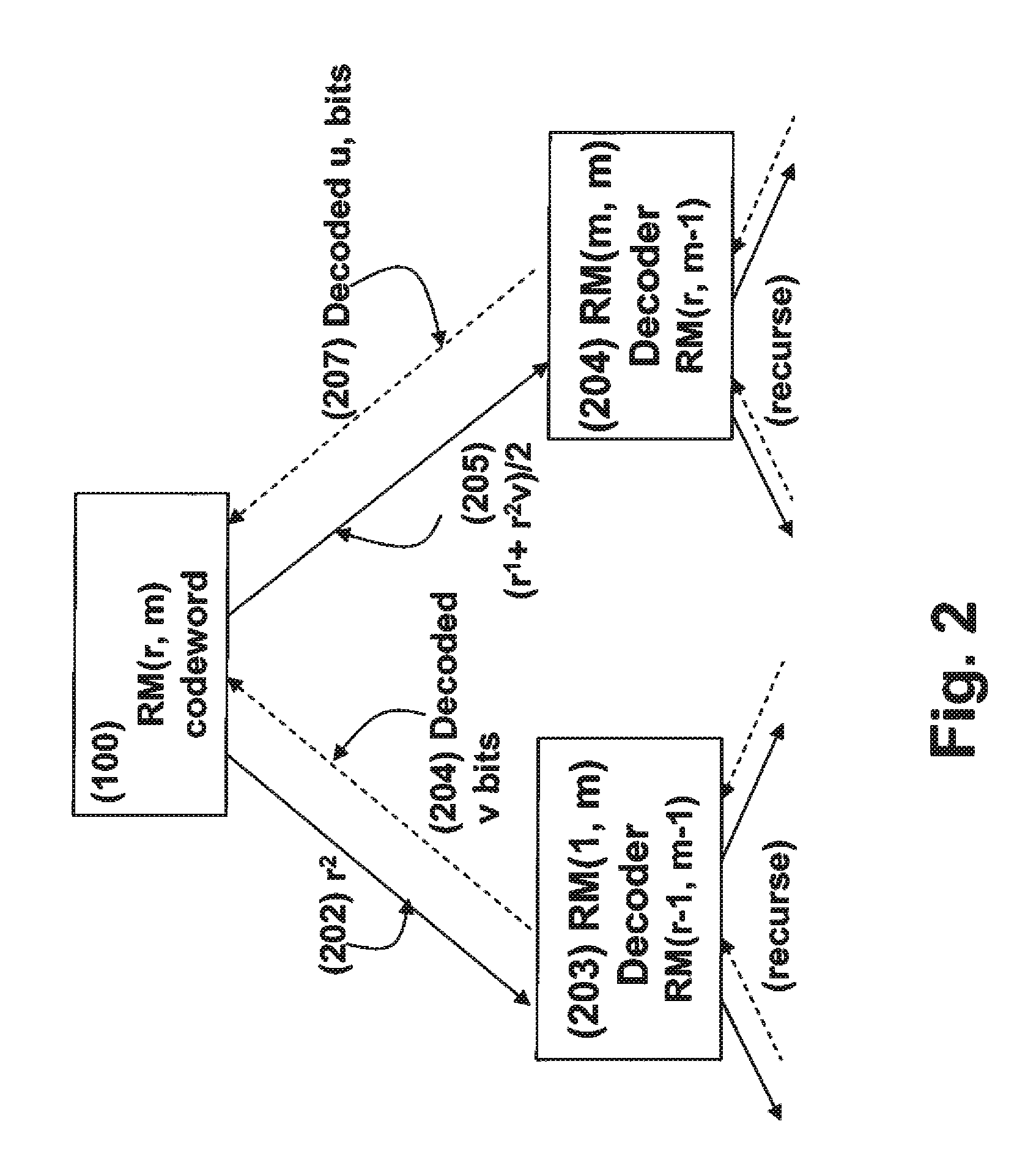
Soft decision decoding of a codeword of a Reed-Muller (RM) code byselecting an optimal decomposition variable i using a likelihood calculation. A code RM(r, m) is expressed as {(u, uv)|uεRM(r, m−1) and vεRM(r−1, m−1)) where uv denotes a component-wise multiplication of u and v, and (u, uv)=(r1, r2). A receive codeword is separated into r1=u and r2=uv based on the optimal decomposition variable, and r2 is decoded according to the optimal decomposition variable, using a RM(r−1, m−1) decoder to obtain a decoded v and a first set of decoded bits. The decoded v is combined with r1 using (r1+r2v) / 2, and(r1+r2V) / 2 is decoded using a RM(r, m−1) decoder to obtain a decoded u and a second set of decoded bits.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC RES LAB INC
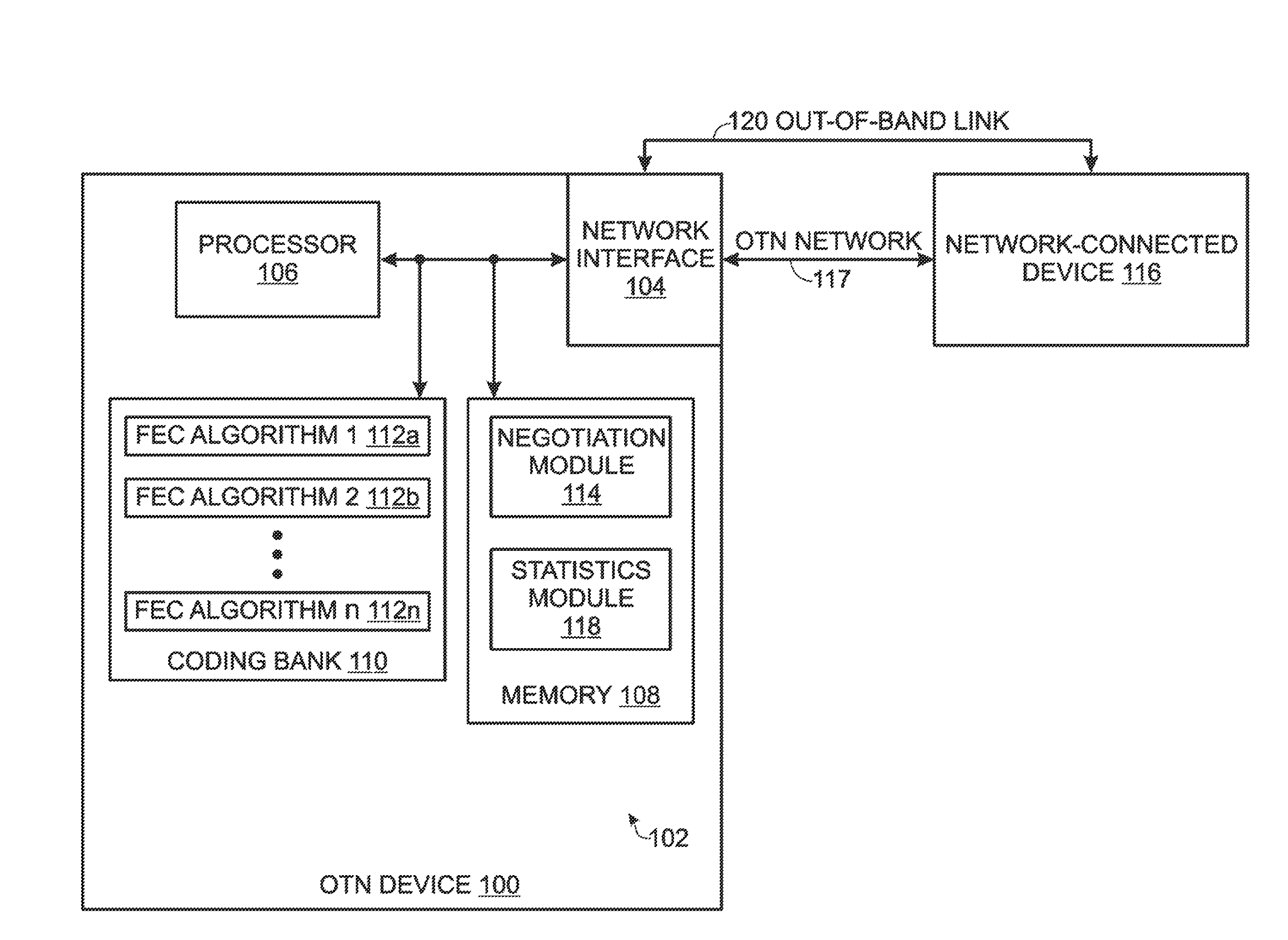
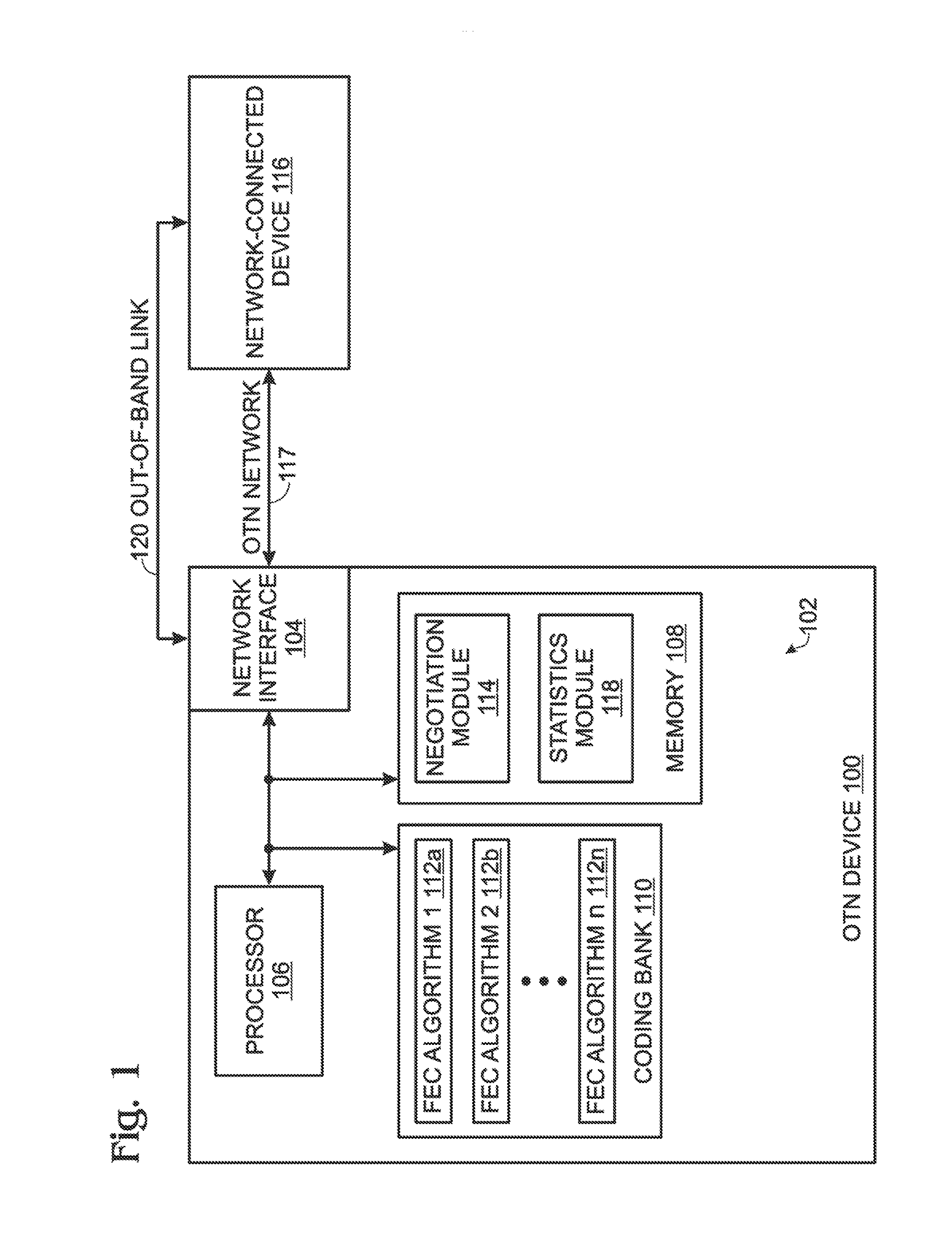
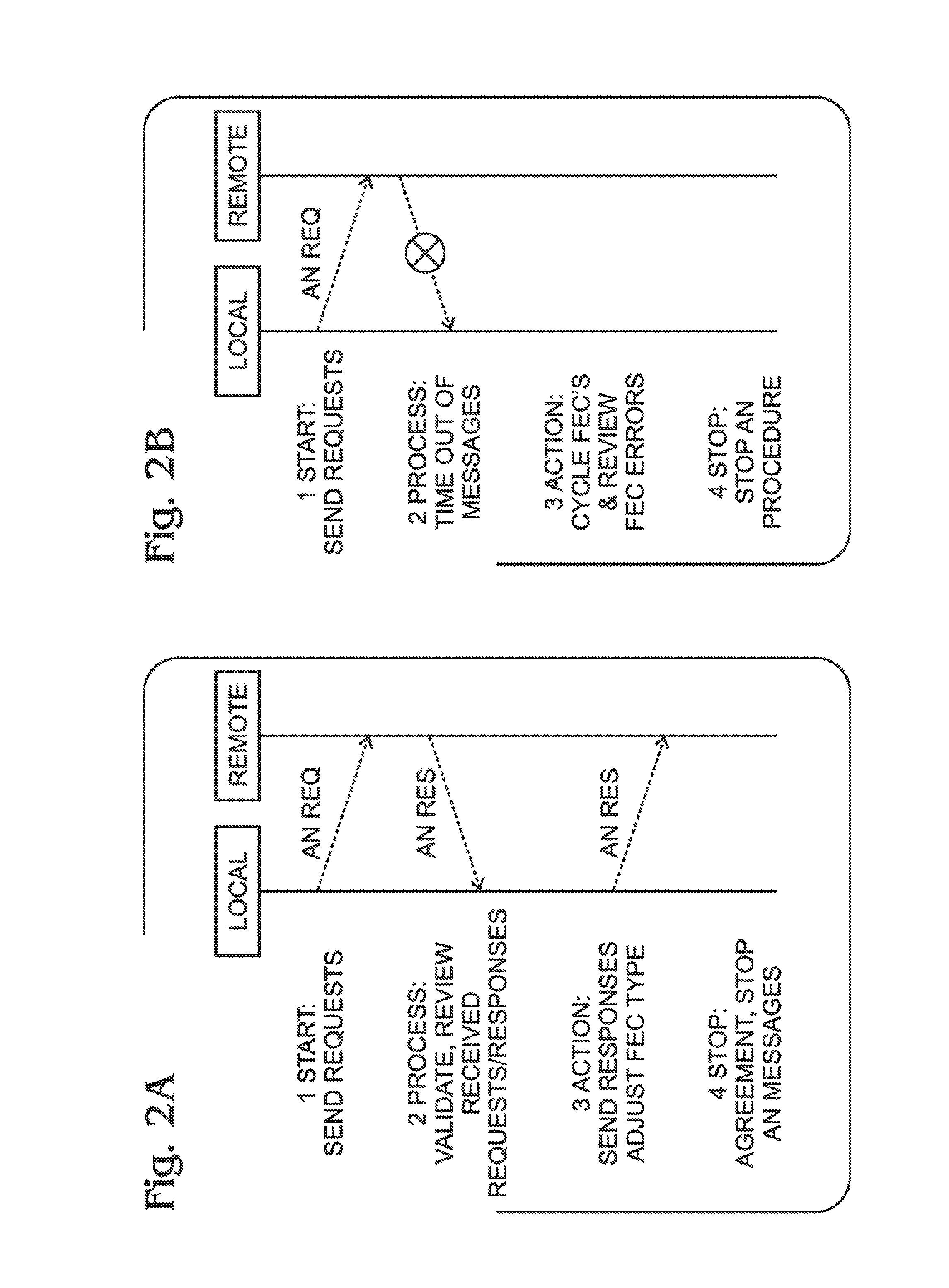
Forward error correction (FEC) auto negotiation for an optical transport network (OTN)
ActiveUS8433969B1Correction errorError prevention/detection by using return channelReed-muller codesNetwork connectionTrial and error
In an Optical Transport Network communication device using a plurality of forward error correction (FEC) algorithms, a method is provided for auto negotiating an FEC algorithm between network-connected devices. The first device sends an FEC auto negotiation (AN) request message to a second device. If the first device receives the FEC AN response from the second device, the first device selects the FEC algorithm suggested in the FEC AN response. In the event that the first device is unable to negotiate a mutually agreed upon FEC algorithm with the second device, the first device enters a trial-and-error mode, beginning with a first FEC algorithm. The first device iteratively cycles through each of the plurality of n FEC algorithms, and measures error statistics associated with the nth FEC algorithms. The first device compares the n sets of error statistics and selects an FEC algorithm associated with the minimum number of errors.
Owner:MACOM CONNECTIVITY SOLUTIONS LLC
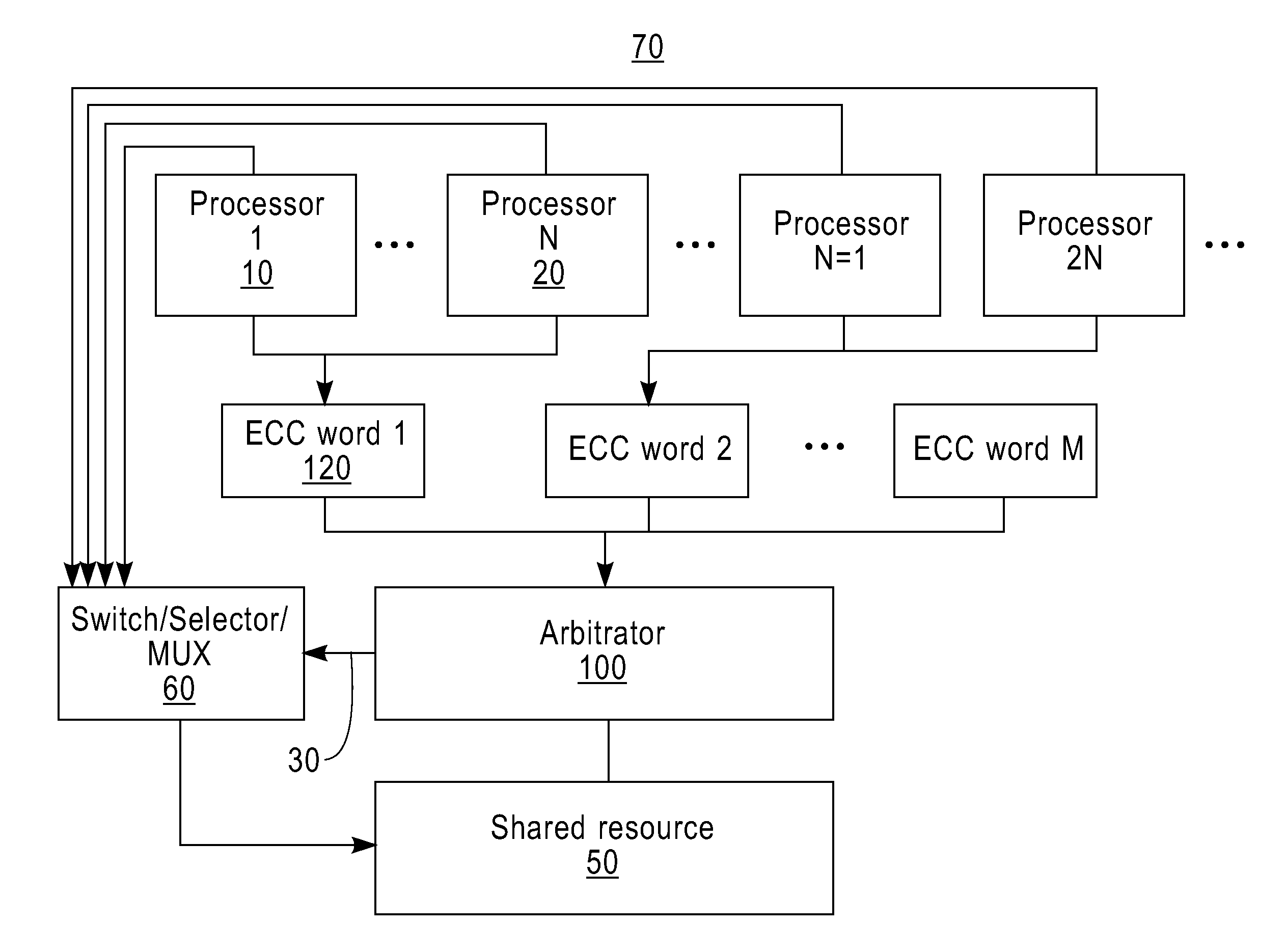
Low delay and area efficient soft error correction in arbitration logic
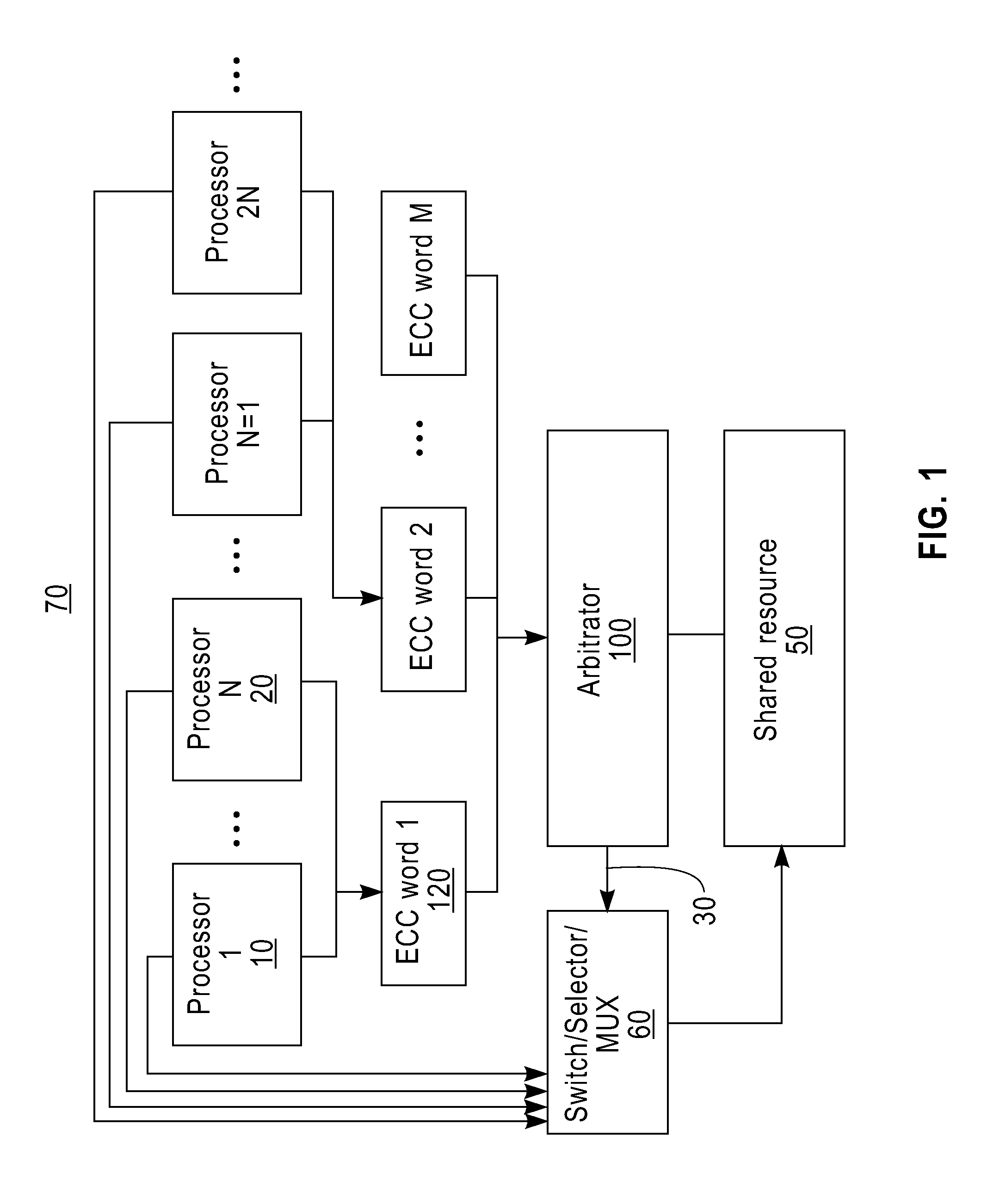
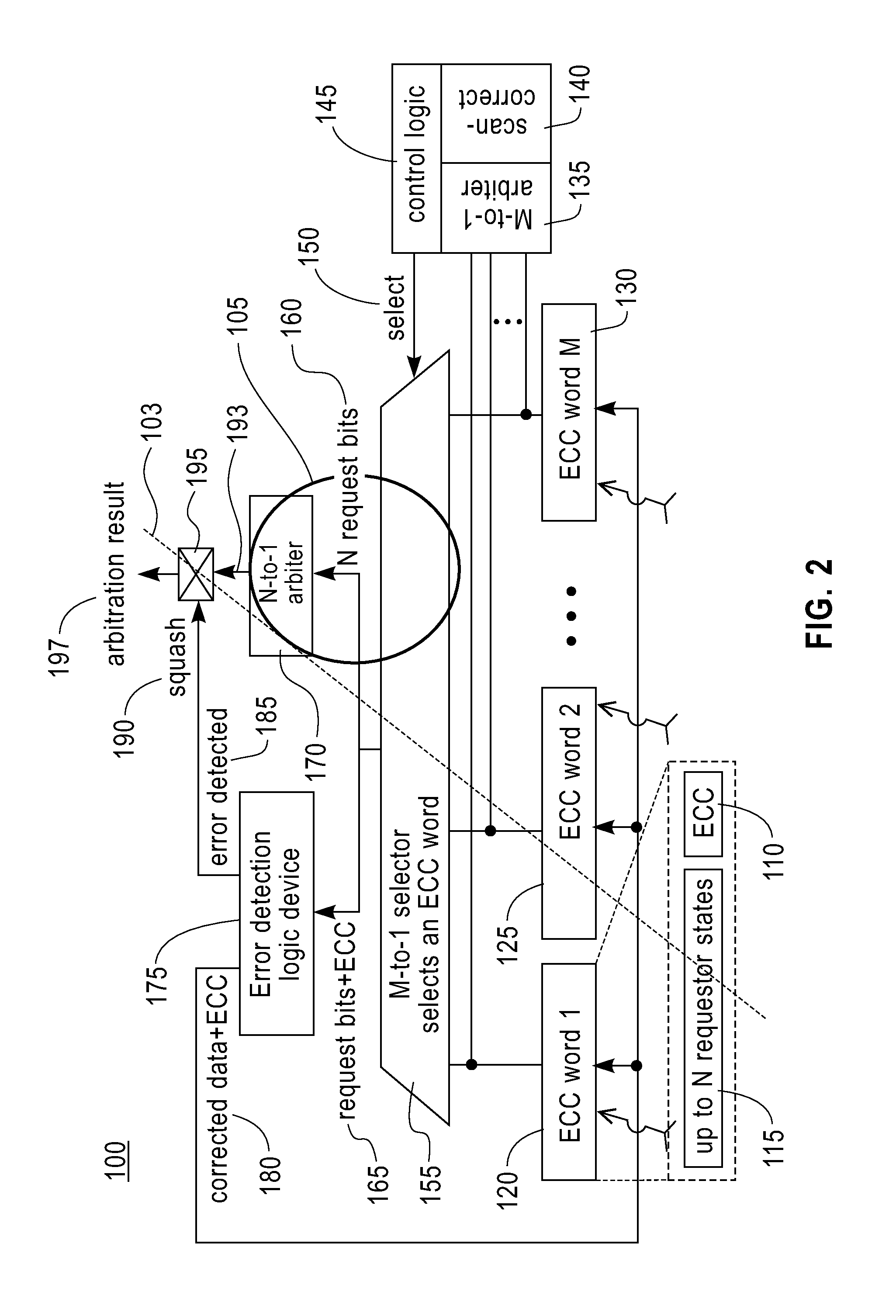
InactiveUS20120036412A1Reed-muller codesError correction/detection using convolutional codesLow delayShared resource
There is provided an arbitration logic device for controlling an access to a shared resource. The arbitration logic device comprises at least one storage element, a winner selection logic device, and an error detection logic device. The storage element stores a plurality of requestors' information. The winner selection logic device selects a winner requestor among the requestors based on the requestors' information received from a plurality of requestors. The winner selection logic device selects the winner requestor without checking whether there is the soft error in the winner requestor's information.
Owner:IBM CORP
Channel coding/decoding apparatus and method for a CDMA mobile communication system
InactiveUS20050210364A1Improve error correction performanceCorrection capabilityReed-muller codesError preventionReed–Muller codeTheoretical computer science
A apparatus for generating (2k-2t) first order Reed-Muller codes from 2k first order Reed-Muller codes based on k input information bits. The apparatus includes a code generator configured to generate (2k-2t) bits first order Reed-Muller codes, and an encoder for multiplying the k input information bits with the (2k-2t) bits first order Reed-Muller codes. The encoding apparatus also includes a memory for storing a number of first order Reed-Muller codes.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
System and Method for Signaling Control Information in a Mobile Communication Network
ActiveUS20140321395A1Reduce overheadControl overheadPower managementReed-muller codesComputer terminalMobile communication network
A method of operating a wireless communication terminal includes receiving one or more downlink control messages that each contain scheduling information scheduling the wireless terminal to receive a downlink transmission on either a primary carrier or a secondary carrier. The method also includes determining, for each of the downlink control messages, whether that message includes scheduling information for the primary carrier or for a secondary carrier. Additionally, the method includes selecting a format for an uplink control message based on whether any of the downlink control messages includes scheduling information for a secondary carrier, generating an uplink control message based on the selected format, and transmitting the uplink control message to the base station.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com