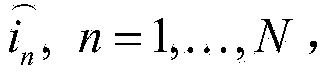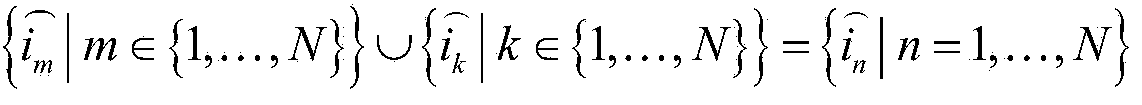Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
55 results about "Citation database" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
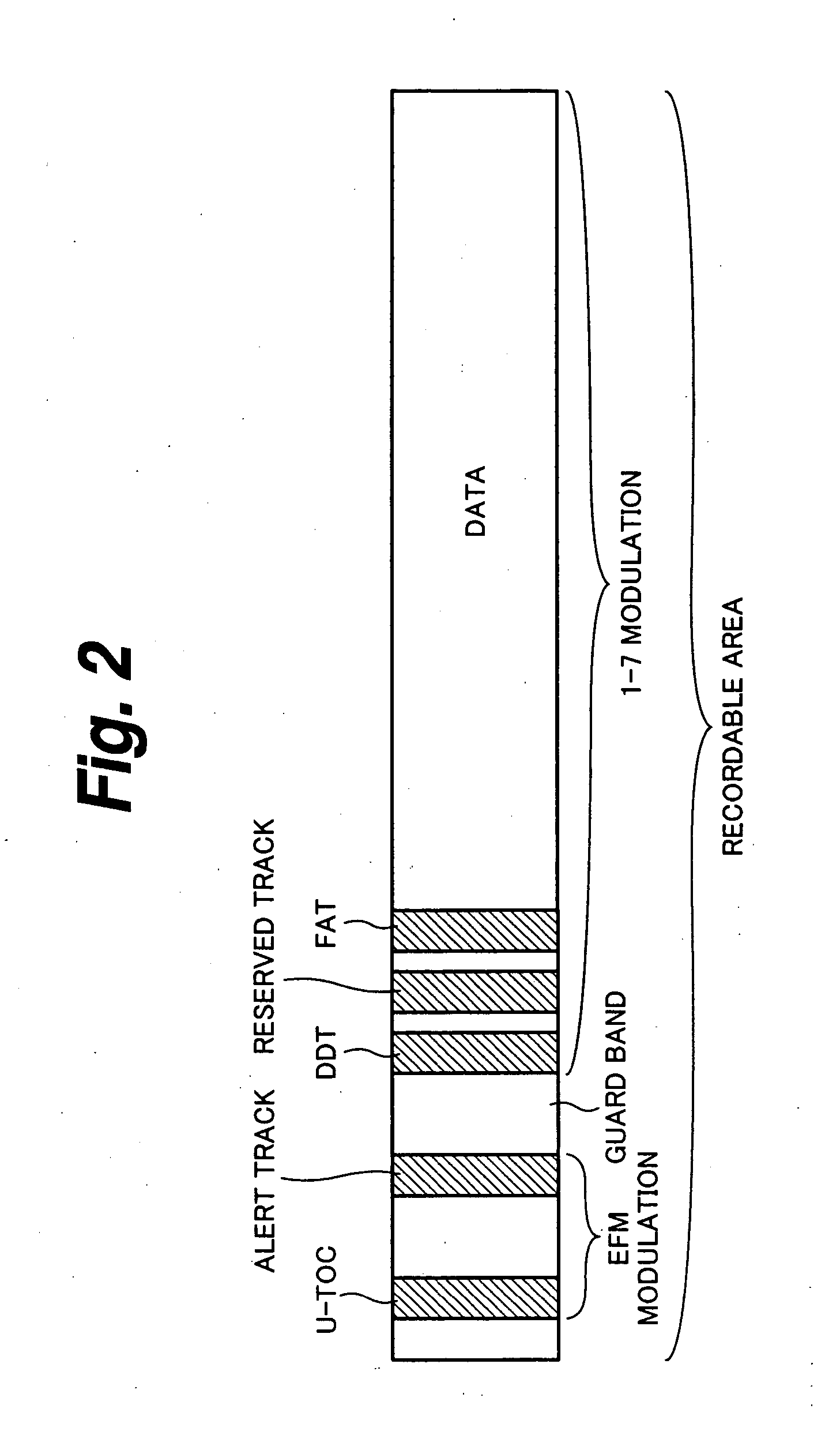
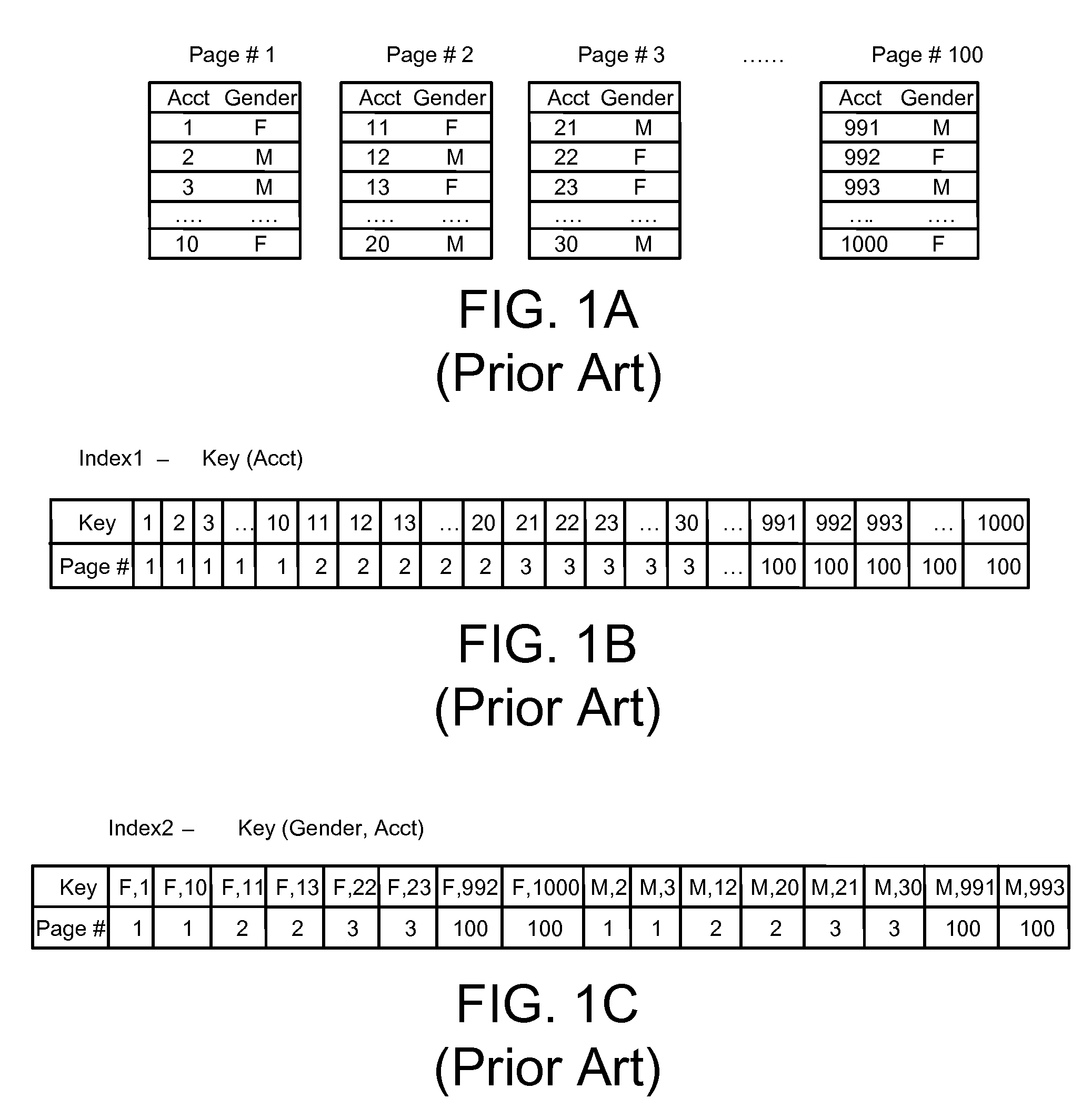
Basic information. Citation databases are databases that have been developed for evaluating publications. The citation databases enable you to count citations and check, for example, which articles or journals are the most cited ones. Note: None of the citation databases cover all publications.
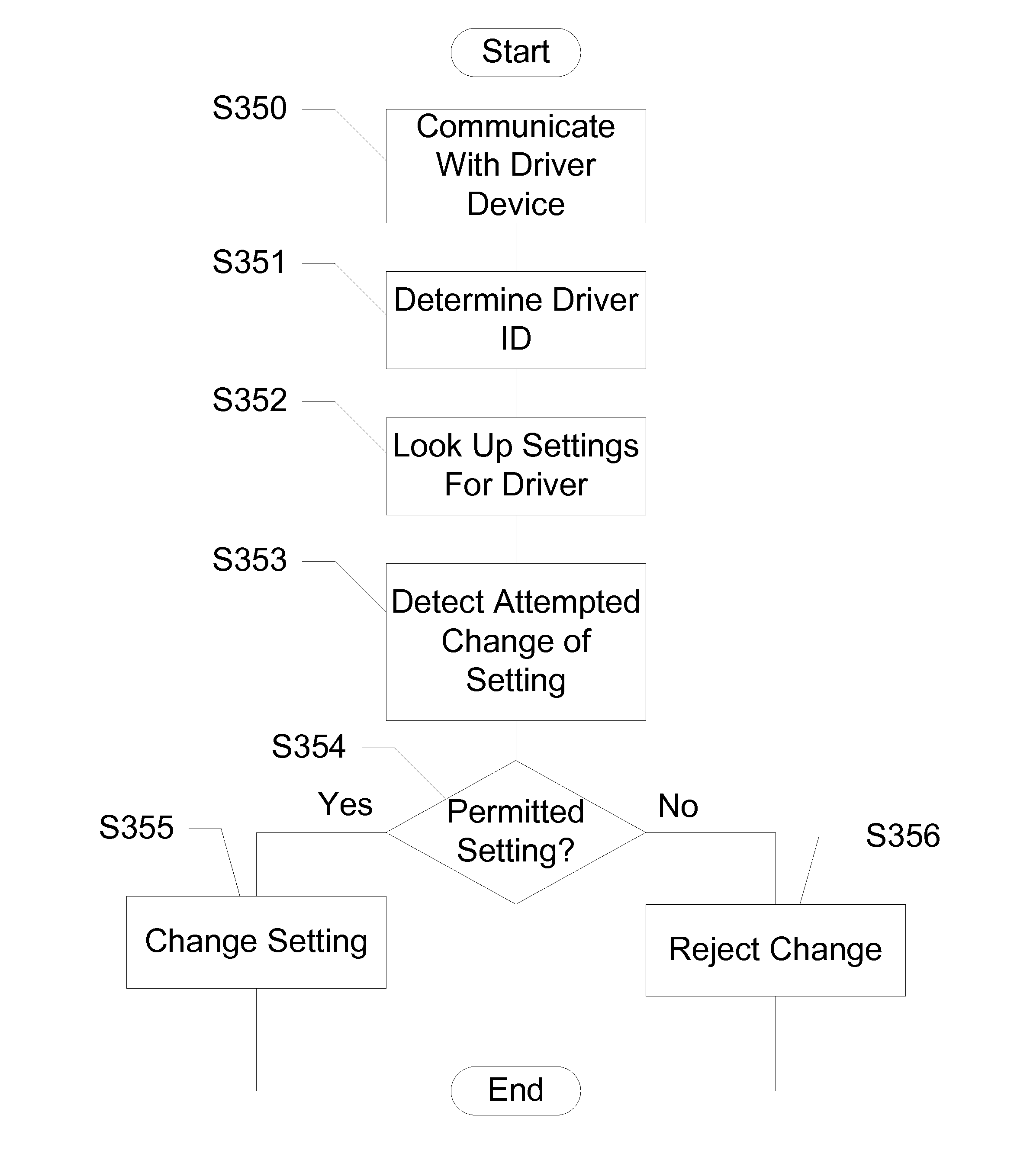
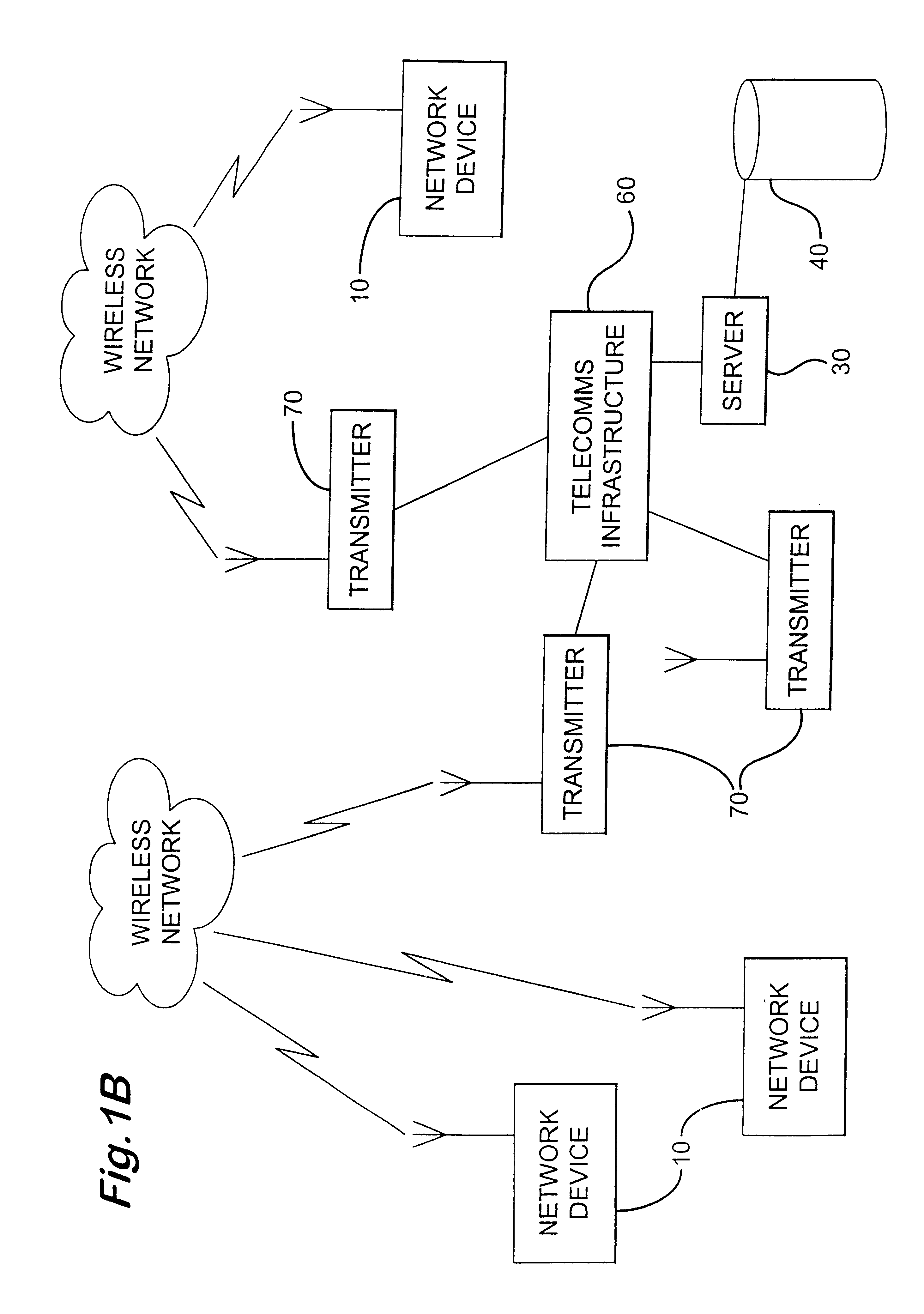
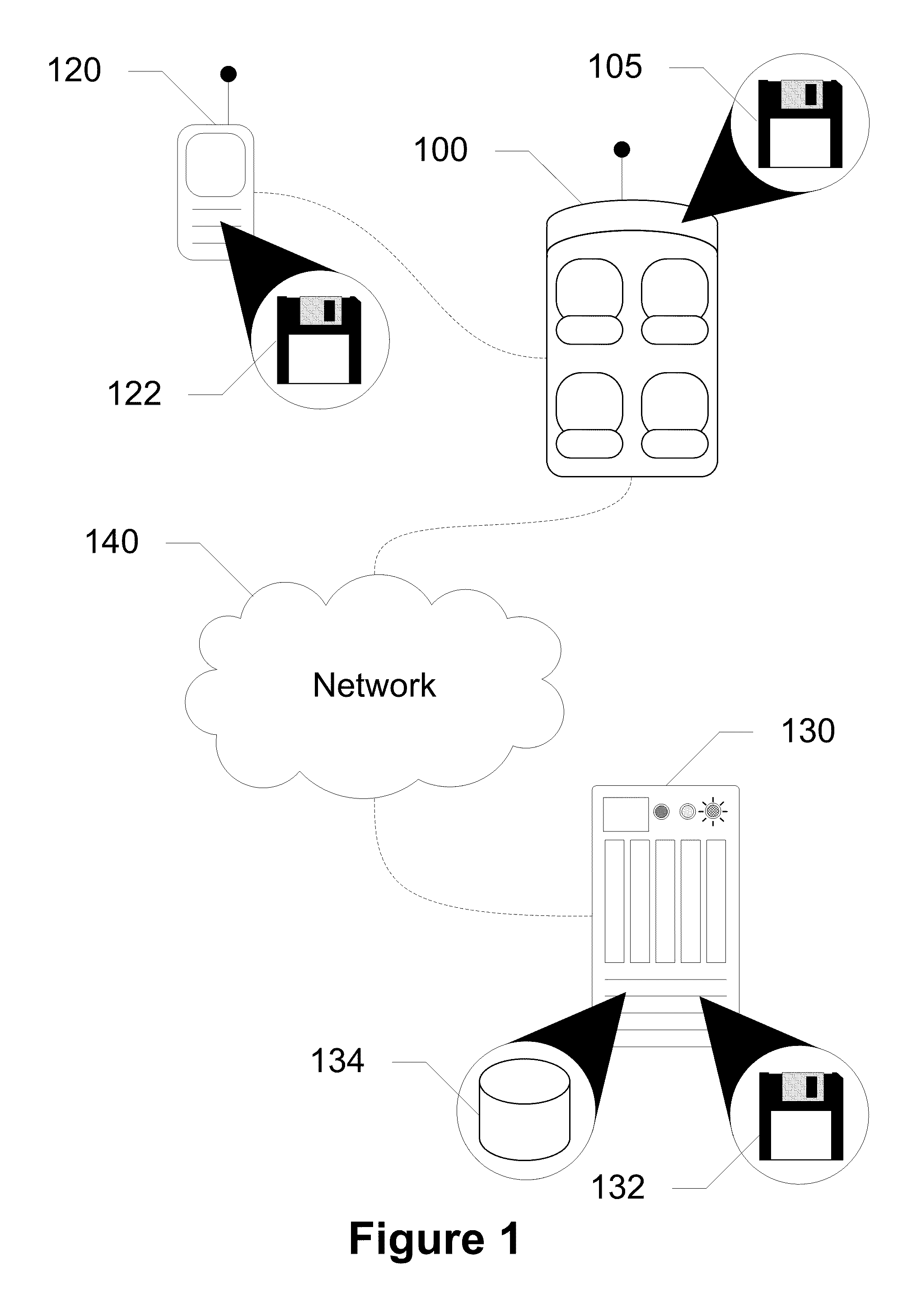
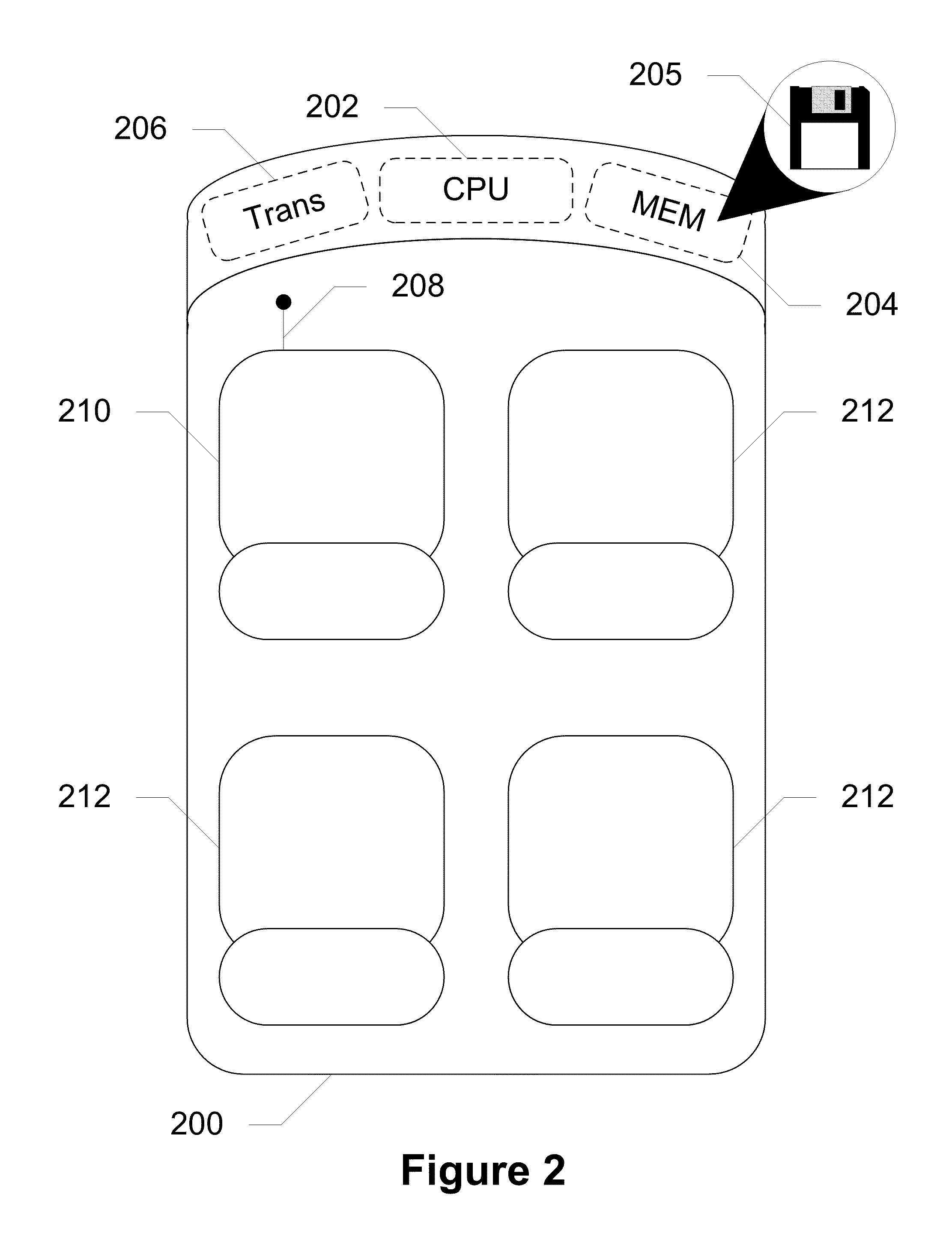
Devices, Systems and Methods for Controlling Permitted Settings on a Vehicle
ActiveUS20110137520A1Limiting distractionNetwork traffic/resource managementAnalogue computers for trafficDistractionDriver/operator
Devices, systems, and methods are disclosed for altering permitted settings of a vehicle according to a driver identified through short range wireless communication. The vehicle captures a unique identifier from a wireless communication device of the driver of the vehicle. This unique identifier is used to reference a database to determine the identity of the driver as well as settings for the driver created by a controlling authority. The controlling authority may be, for instance, a parent or employer of the driver. The settings may limit certain devices within the vehicle and / or the vehicle itself. Speed control settings, radio settings, wireless communication device settings, and various other settings are all possible to limit distractions to the driver. Further, the settings may be influenced by the number or identities of passengers within the vehicle.
Owner:HYUNDAI MOTOR CO LTD +1
Method and apparatus for automatic entity disambiguation
ActiveUS7672833B2Efficiently findImprove throughputNatural language data processingOffice automationSemi-structured dataWeight of evidence
Owner:FAIR ISAAC & CO INC
Network based classified information systems
A system for automatically creating databases containing industry, service, product and subject classification data, contact data, geographic location data (CCG-data) and links to web pages from HTML, XML or SGML encoded web pages posted on computer networks such as the Internet or Intranets. The web pages containing HTML, XML or SGML encoded CCG-data, database update controls and web browser display controls are created and modified by using simple text editors, HTML, XML or SGML editors or purpose built editors. The CCG databases may be searched for references (URLs) to web pages by use of enquiries which reference one or more of the items of the CCG-data. Alternatively, enquiries referencing the CCG-data in the databases may supply contact data without web page references. Data duplication and coordination is reduced by including in the web page CCG-data display controls which are used by web browsers to format for display the same data that is used to automatically update the databases.
Owner:HANGER SOLUTIONS LLC +1
System and method for managing distribution of content to a device
InactiveUS6886017B1Improve efficiencyEasy to useData processing applicationsProgram loading/initiatingContent IdentifierCitation database
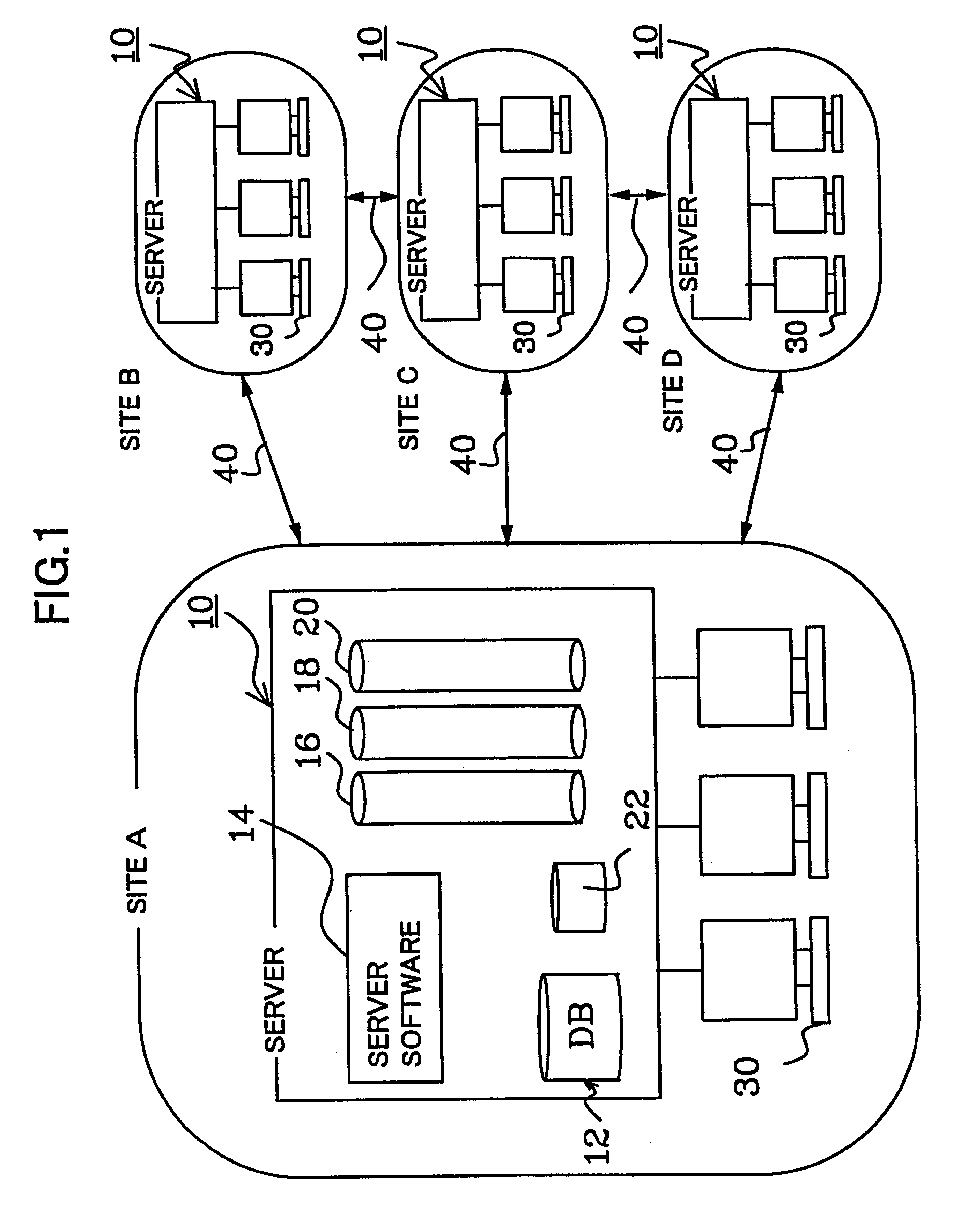
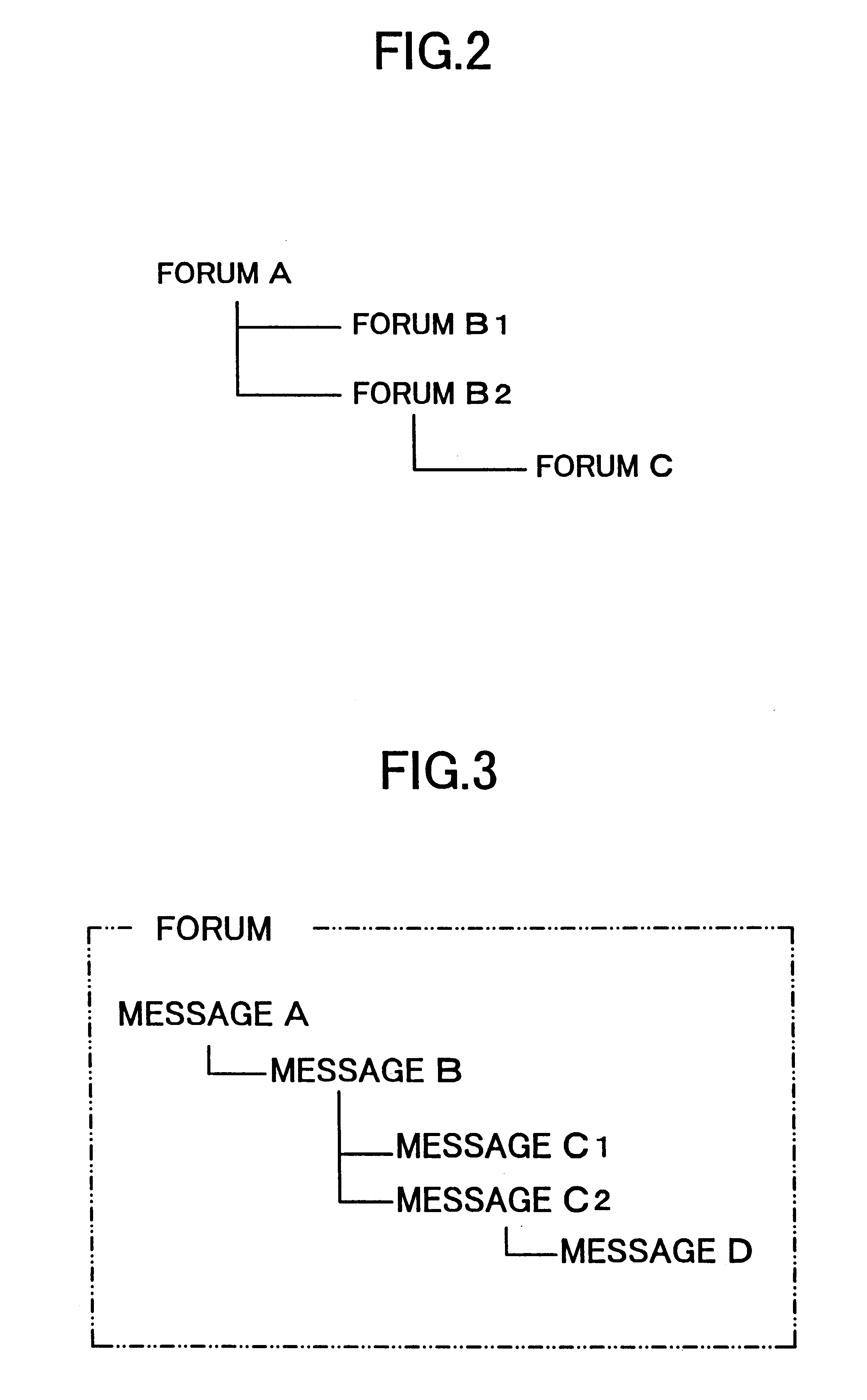
The present invention provides a system and method for managing distribution of content to a device, the system comprising a database for storing a number of elements as a hierarchical structure, content identifiers being able to be associated with elements in the hierarchical structure, and one of the elements representing the device, and a server for referencing the hierarchical structure in the database to generate a profile for the device, the profile containing a number of content identifiers indicating content to be provided to the device. A device manager is associated with the device and arranged to receive the profile from the server and to use the content identifiers in the profile to cause the content indicated by the profile to be provided to the device, a record being kept identifying the content provided to the device in accordance with the profile. The device manager is arranged upon receipt of a subsequent profile from the server to compare the content identifiers in the subsequent profile with the record to determine new content not yet provided on the device and old content no longer to be provided on the device, the device manager being arranged to use the relevant content identifiers to cause the new content to be provided to the device, and to cause the old content to be removed. This approach facilitates the efficient management of distribution of content to devices.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
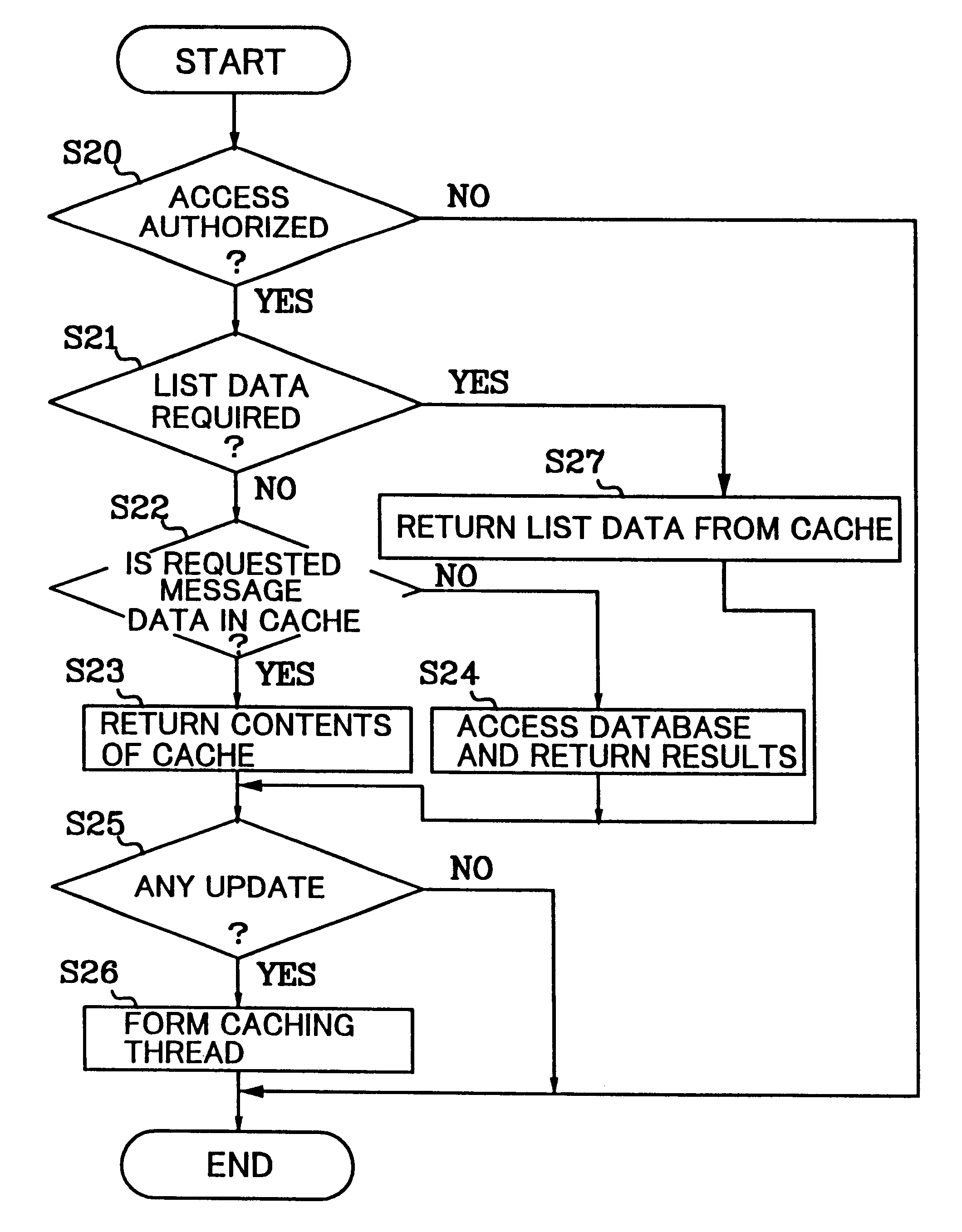
Data caching apparatus, data caching method and medium recorded with data caching program in client/server distributed system
InactiveUS6243719B1Improve response speedShorten speedData processing applicationsMemory adressing/allocation/relocationCitation databaseClient-side
A data caching apparatus, data caching method and medium recorded with data caching program in client / server distributed systems, wherein, when there is a request from a client for reference to a database, duplicate of reference request data retained in a cache file is preferentially sent back to the client, and the duplicate data retained in the cache file is updated in the server background.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
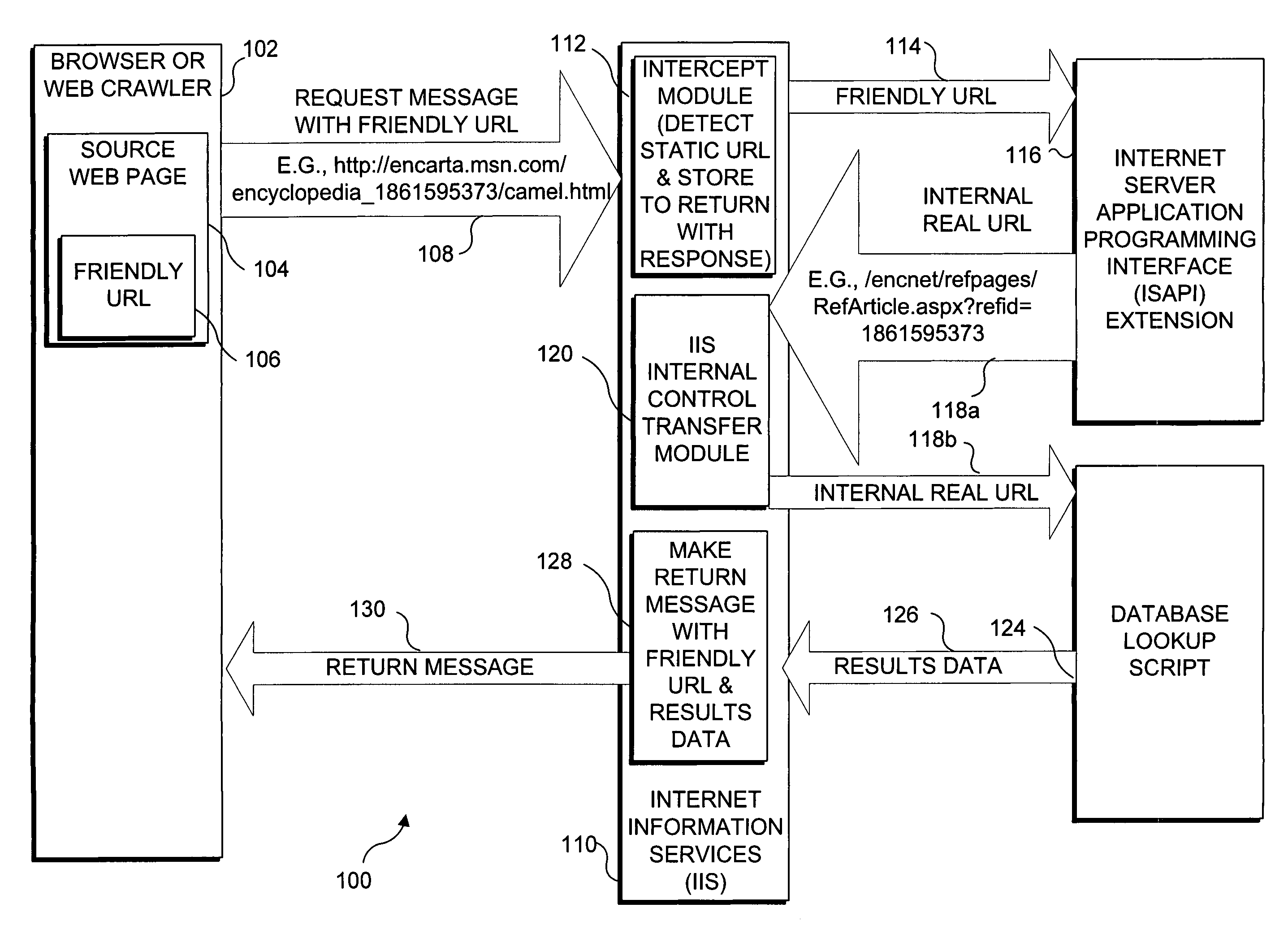
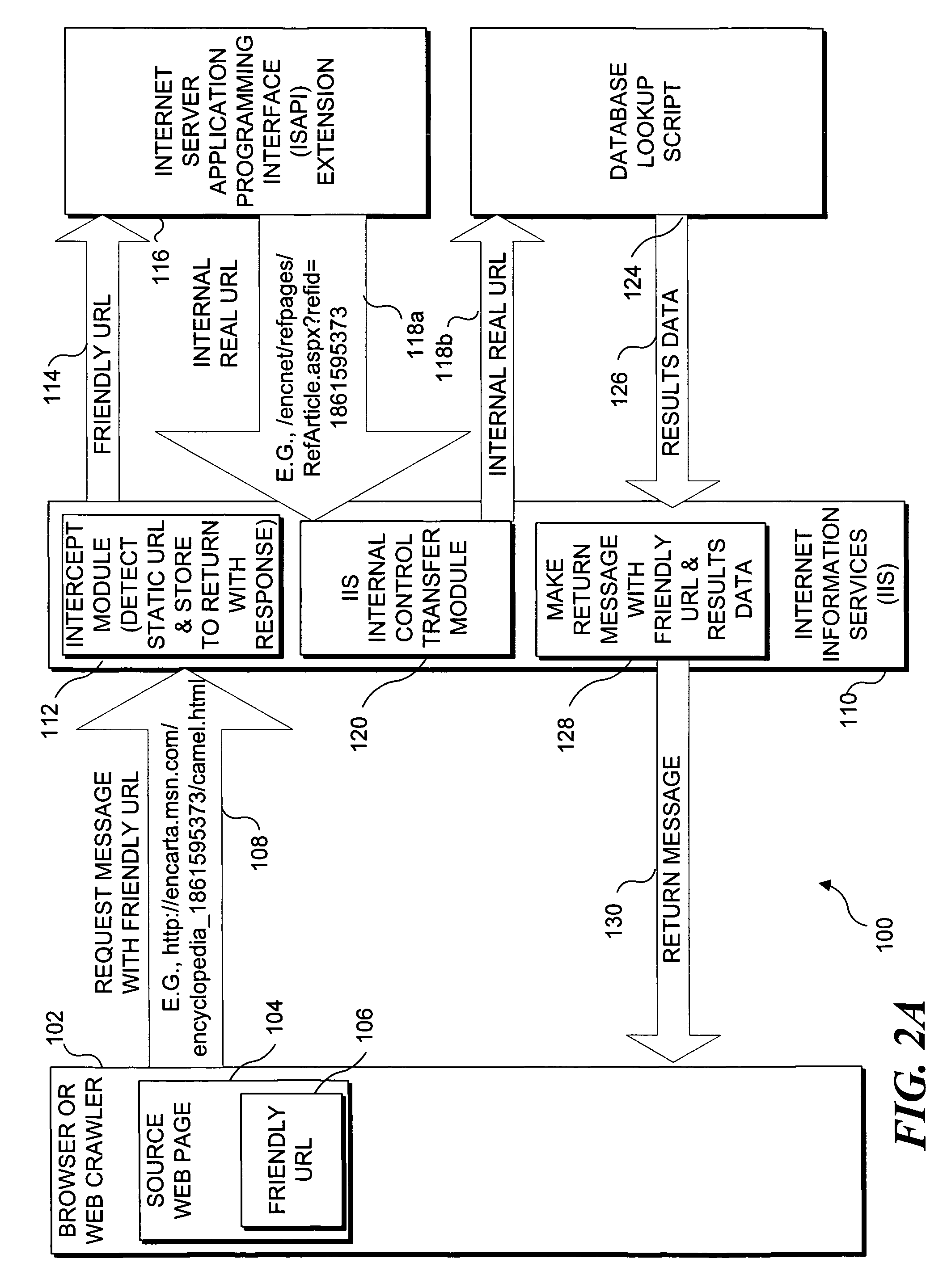
Friendly URLs
ActiveUS7293012B1Easy to readEasy to understandData processing applicationsWeb data indexingCitation databaseData source
A Web crawler, search engine, browser program, or other client application dynamically accesses data by using “friendly” Uniform Resource Locaters (URLs) that do not require query parameters or other non-intuitive coding. A friendly URL includes a static URL that appears to identify a static resource, such as a Hyper Text Markup Language document. A friendly URL can be a link or entered in a browser program's address field. A data type in the friendly URL is mapped to a data source that dynamically accesses data associated with an intuitive data key in the friendly URL. The data key refers to a specific document, and / or is a search term. A query URL is constructed with the data key, and a data source identifier that preferably refers to a database function and is mapped to the data type. The resulting dynamically accessed data are communicated back to the requesting client application.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
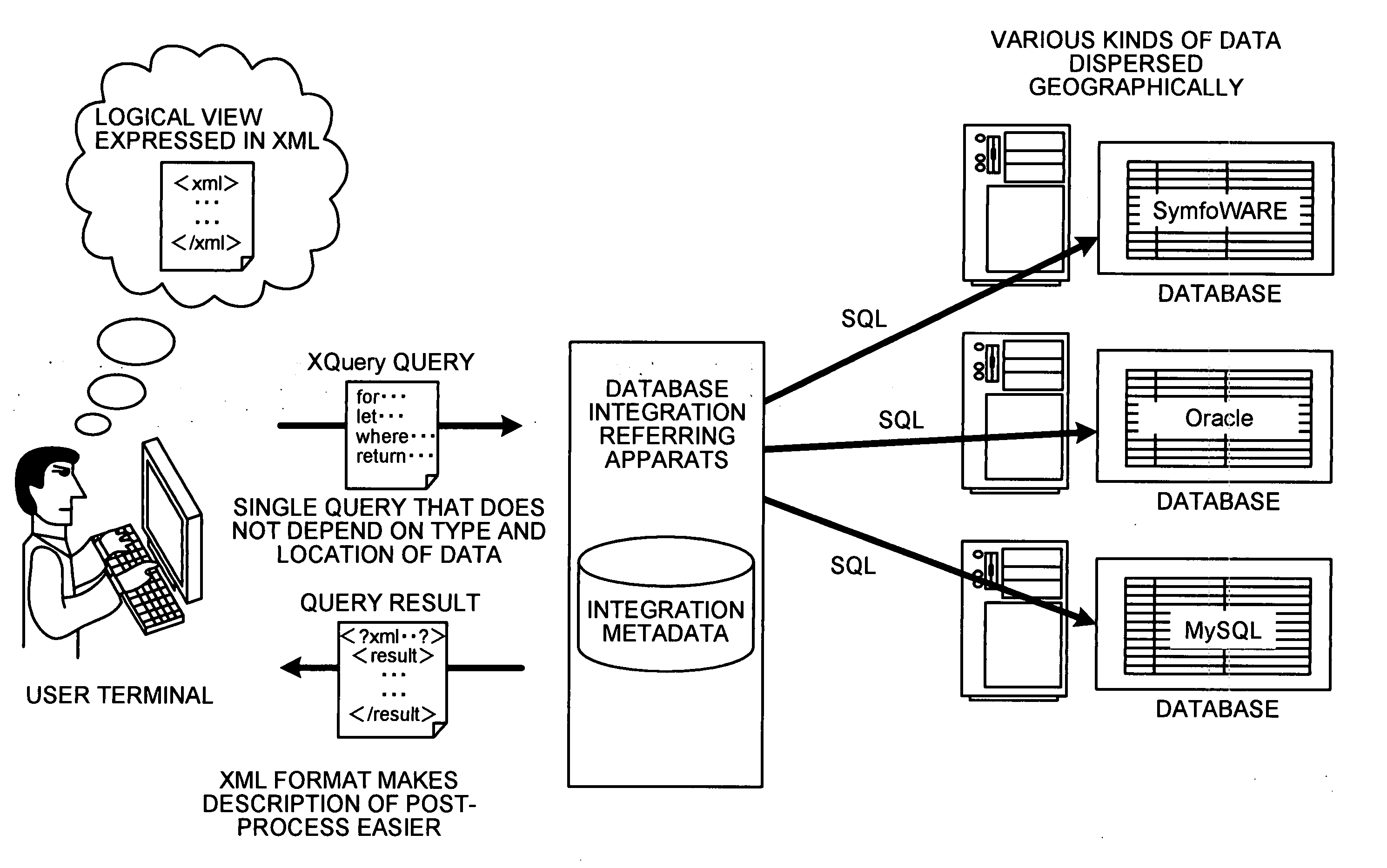
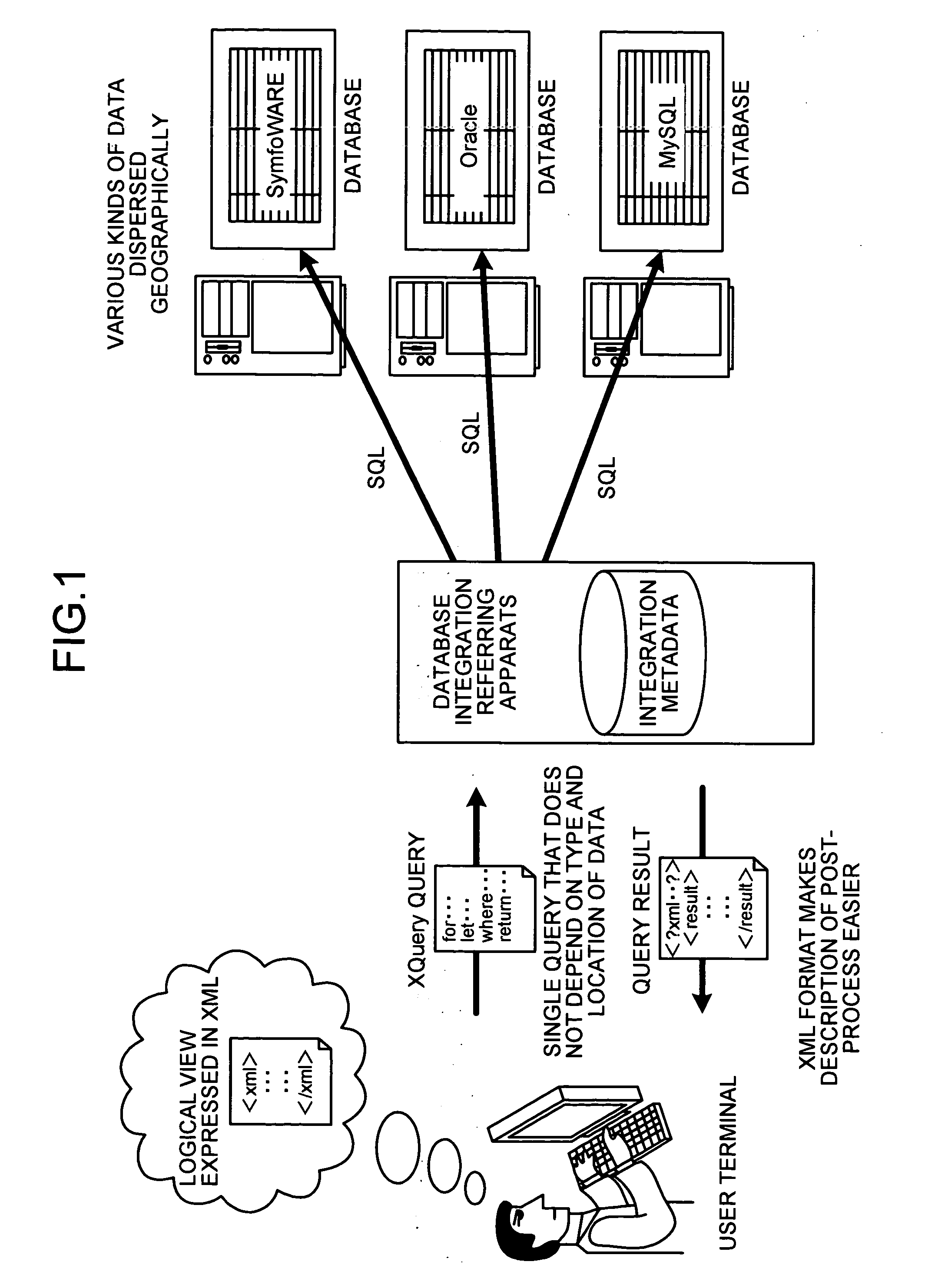
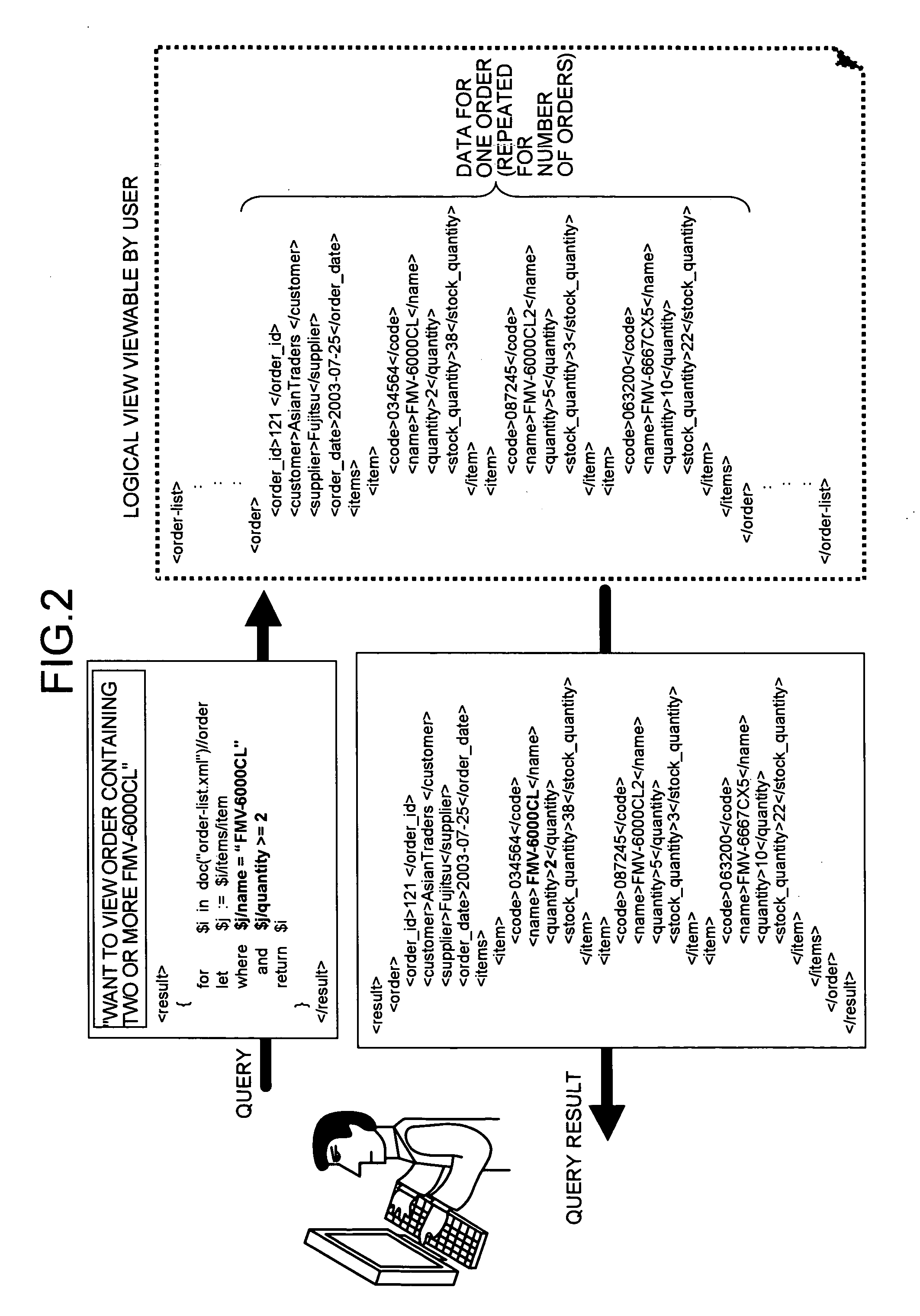
Method and apparatus for referring to database integration, and computer product
InactiveUS20050160076A1Solve problemsDatabase management systemsSpecial data processing applicationsReference databaseCitation database
When referring to database integration, integration metadata is stored. The integration metadata defines a format of a tagged document used for outputting a result of a query for data reference to a plurality of databases, a relation between each element in the tagged document and each element in each database, and a relation between the elements in each database. When a query is received in a format of the tagged document, the integration metadata is referred to and queries are made to various databases to acquire data. Finally a result of the queries is generated in the format of the tagged document.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
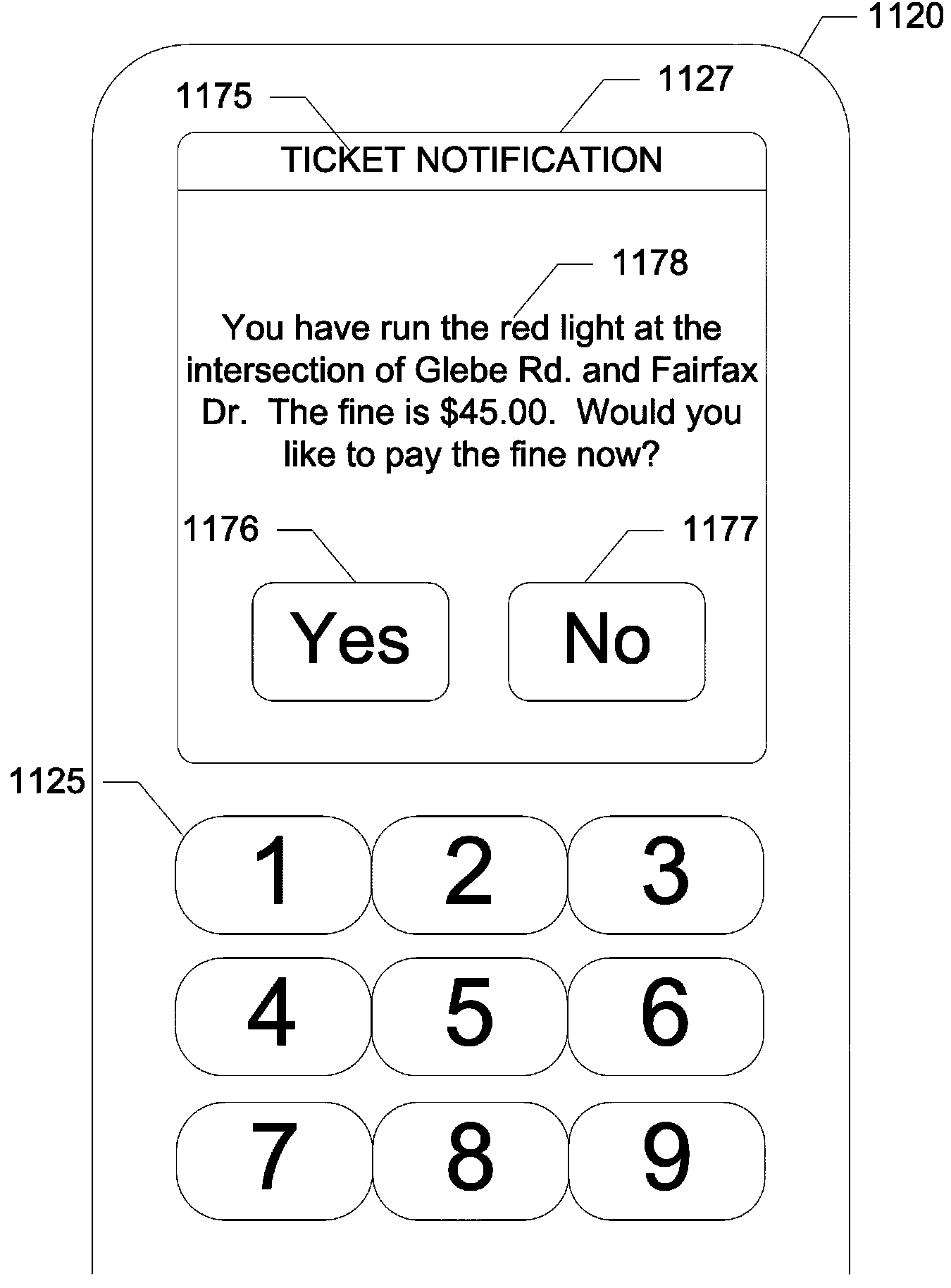
Devices, Systems and Methods for Detecting a Traffic Infraction
ActiveUS20110133952A1Arrangements for variable traffic instructionsDetection of traffic movementPaymentDriver/operator
Devices, systems, and methods are disclosed for identifying a driver within a vehicle using short range wireless communication in order to ticket or alert the driver in response to a traffic infraction by the driver. In exemplary embodiments, a short range wireless communication device registers drivers of vehicles at a certain location. The registration captures a unique identifier for each driver at the location from the driver's wireless communication device. When a vehicle commits a traffic infraction, the unique identifier is used to reference a database to determine the identity and address of the driver. The driver may then be sent a notification of the infraction as well as payment options. This notification may be sent directly to the wireless communication device of the driver. In embodiments of the present invention, a smart vehicle acts as a proxy to capture the unique identifier from the driver's wireless communication device and communicates with the short range wireless communication device.
Owner:AT&T MOBILITY II LLC
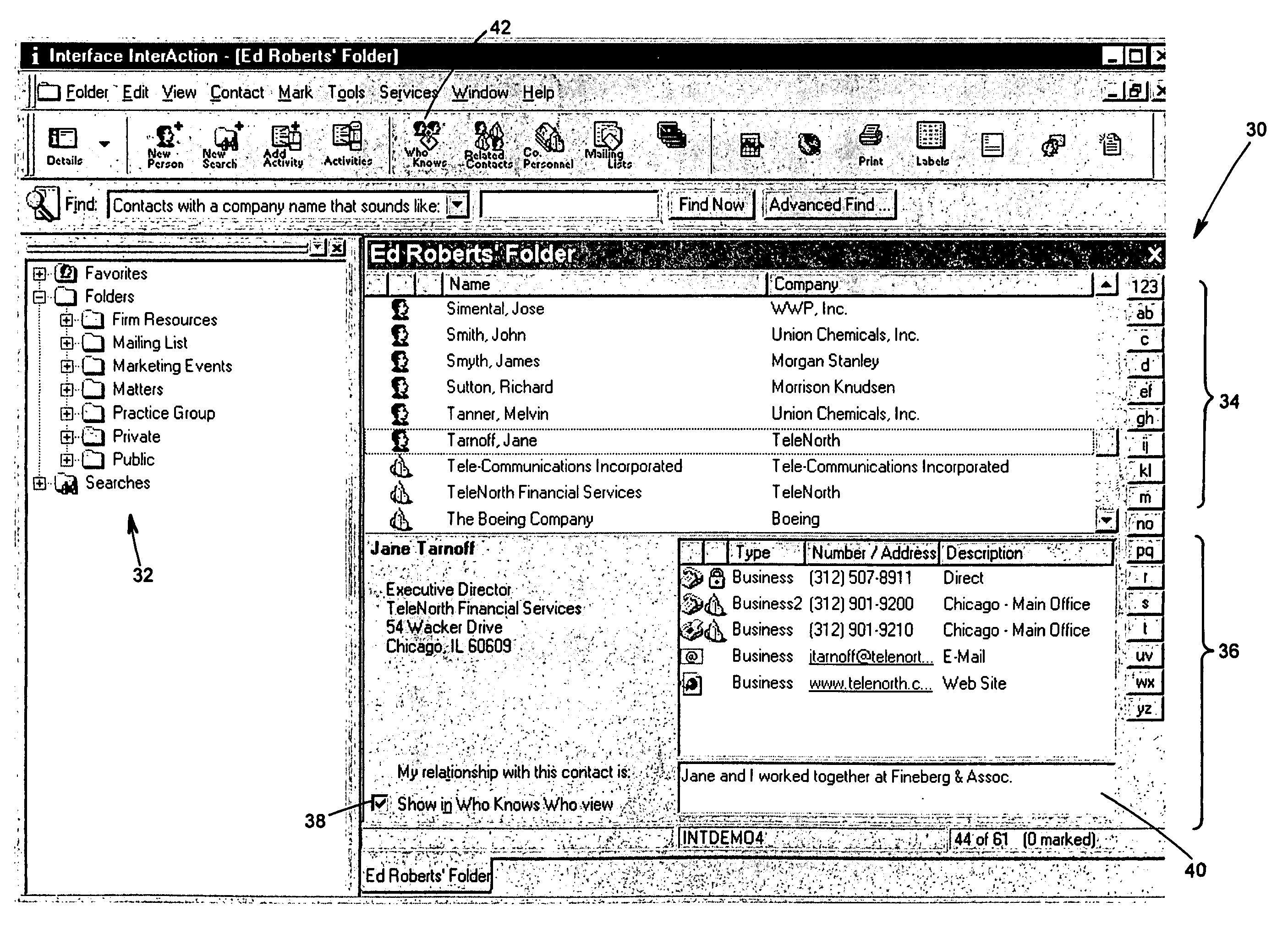
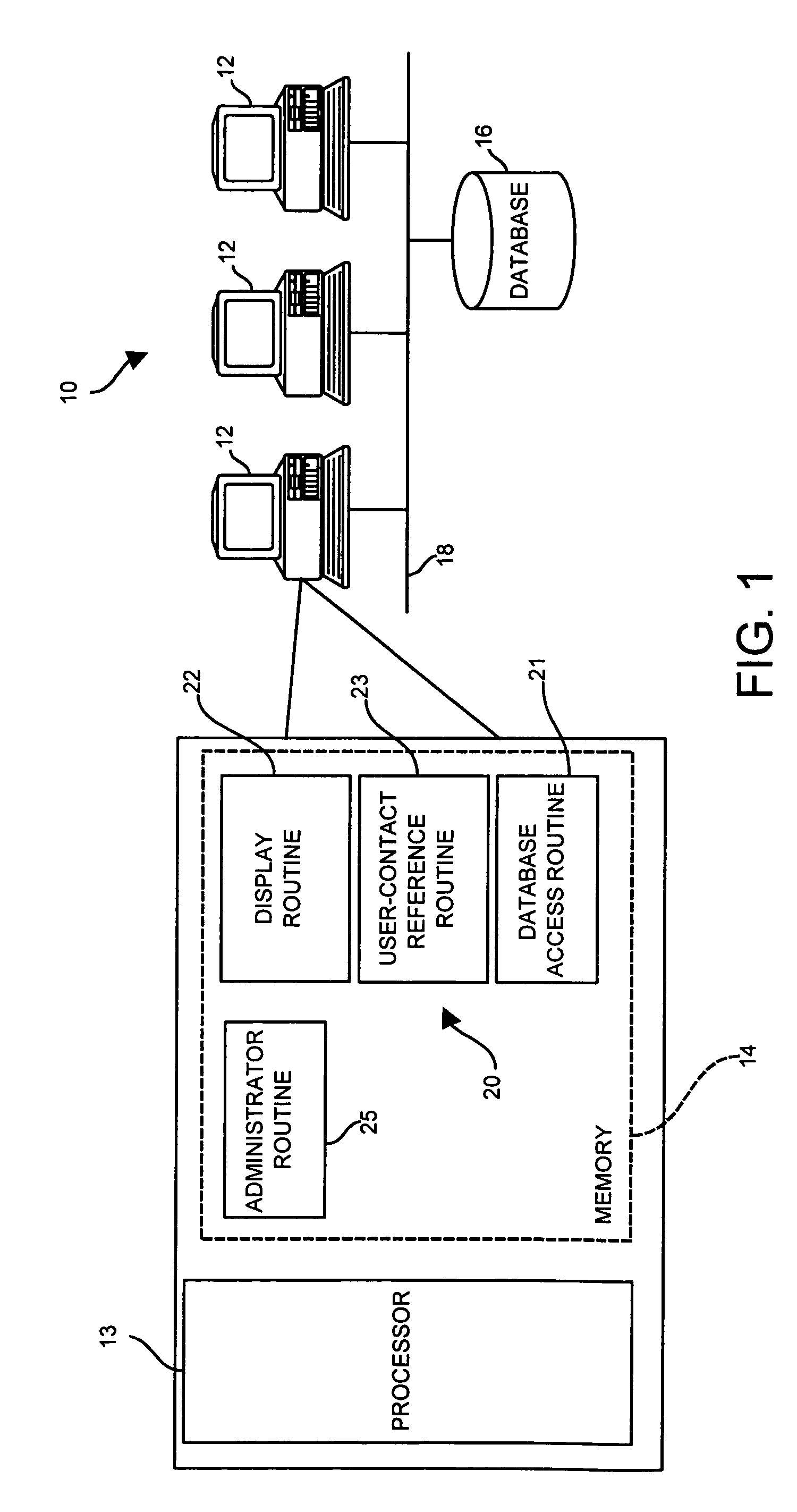
Relationship management system that provides an indication of users having a relationship with a specified contact
InactiveUS7613695B1More readableMore useableData processing applicationsDigital data information retrievalCustomer relationship managementCitation database
A relationship management system uses a database to store contact information related to a number of contacts and to store a number of folders, each of which reference one or more of the contacts within the database. The relationship management system also stores a set of contact-user pairs defining known relationships between users of the relationship management system and the contacts stored in the database. For each contact-user pair, an opt-in field indicating if the contact-user relationship is to be available for use in determining which users know a specified user is stored. If the opt-in flag is set, information pertaining to the nature of the relationship between the user and the contact, such as a relationship description, an indication of the type or strength of the relationship, etc. is also stored. At any desired time, a user may implement a user-contact reference routine to determine which users know a specified contact. The user-contact reference routine accesses the contact-user pairs within the database to determine the users which are associated with a contact-user pair that references the specified contact and that has an opt-in flag set to enable the contact-user relationship to be discovered. The user-contact reference routine then lists all of the determined users and may display the relationship information stored for each discovered contact-user pair.
Owner:REED ELSEVIER INC
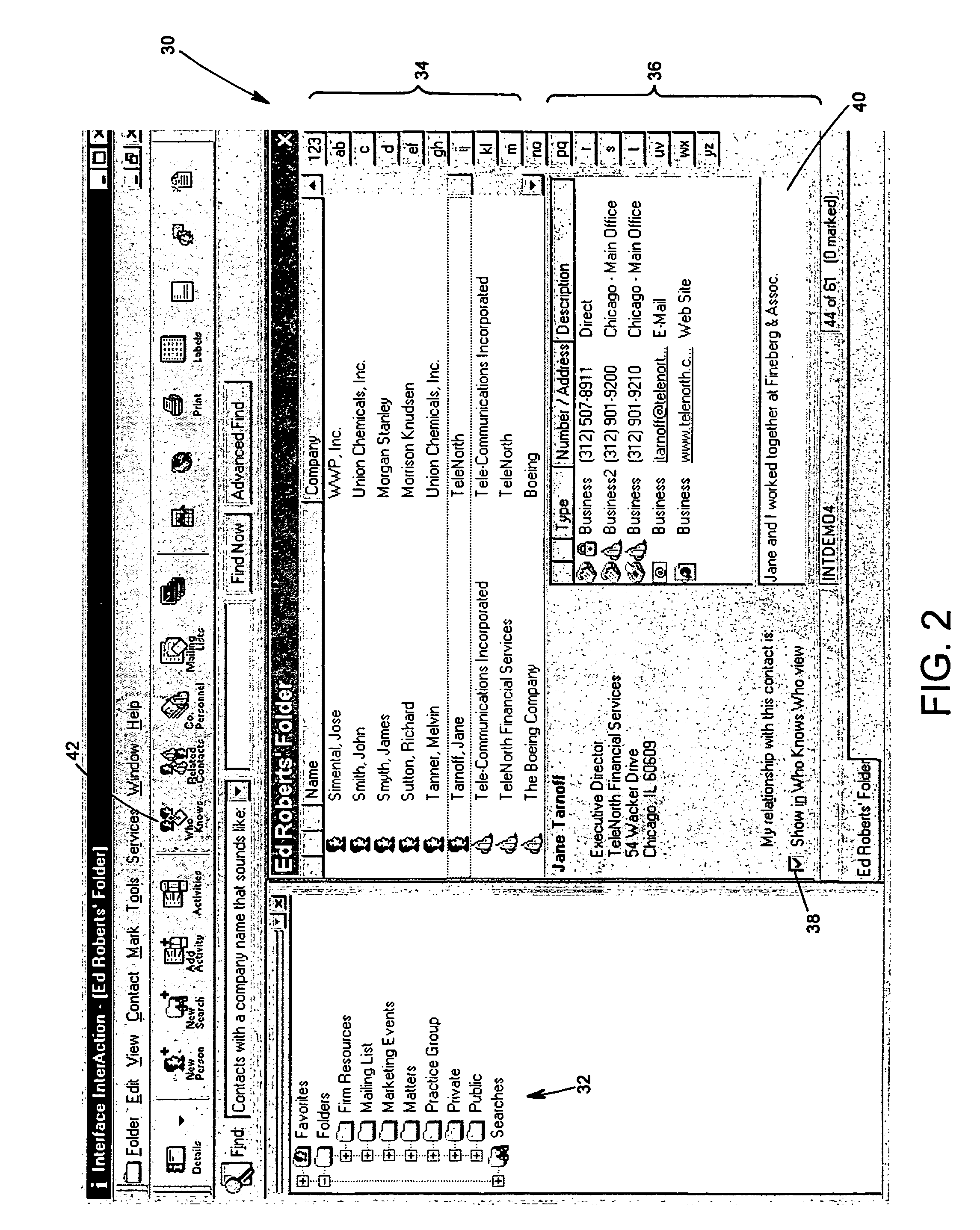
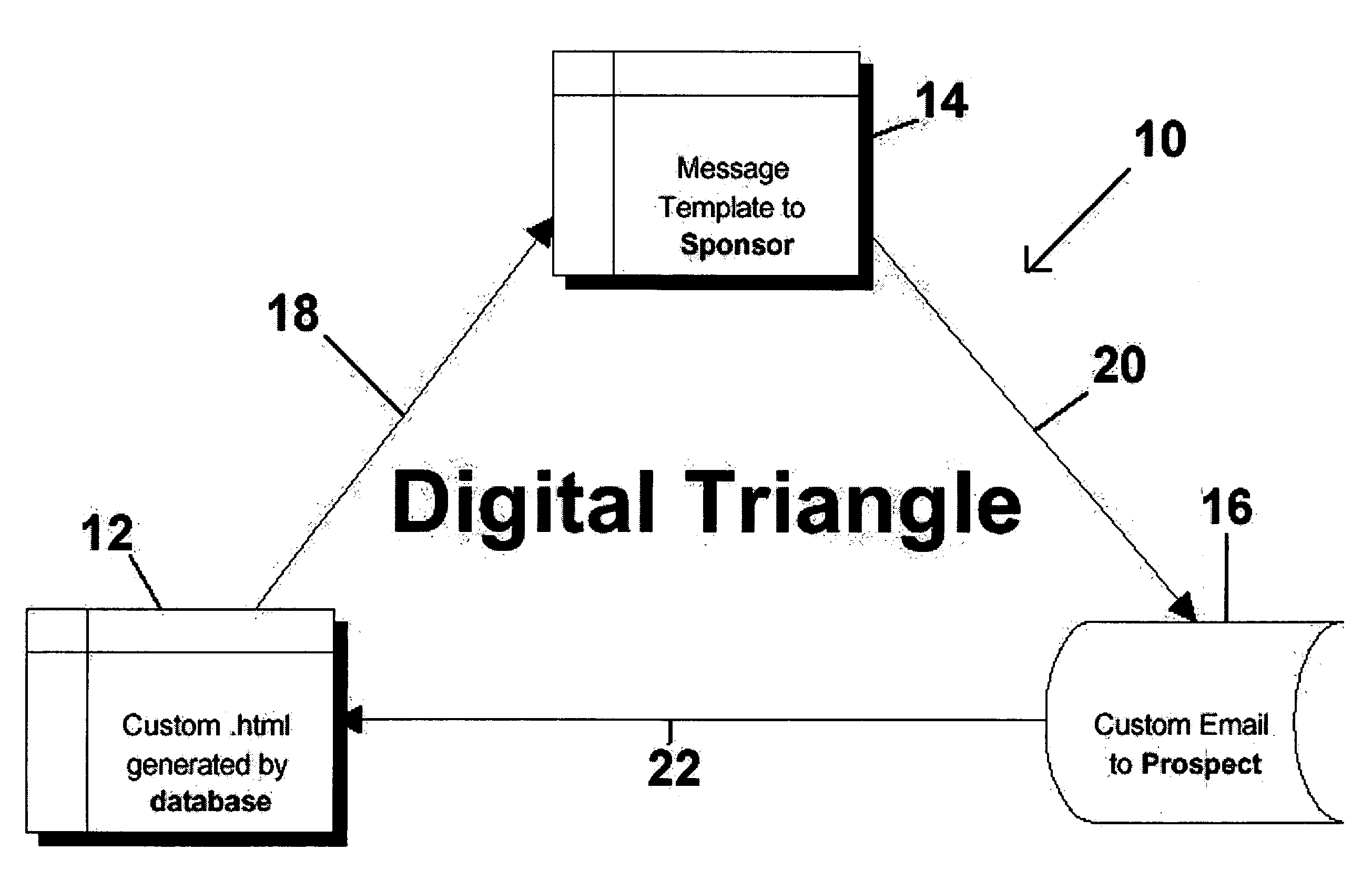
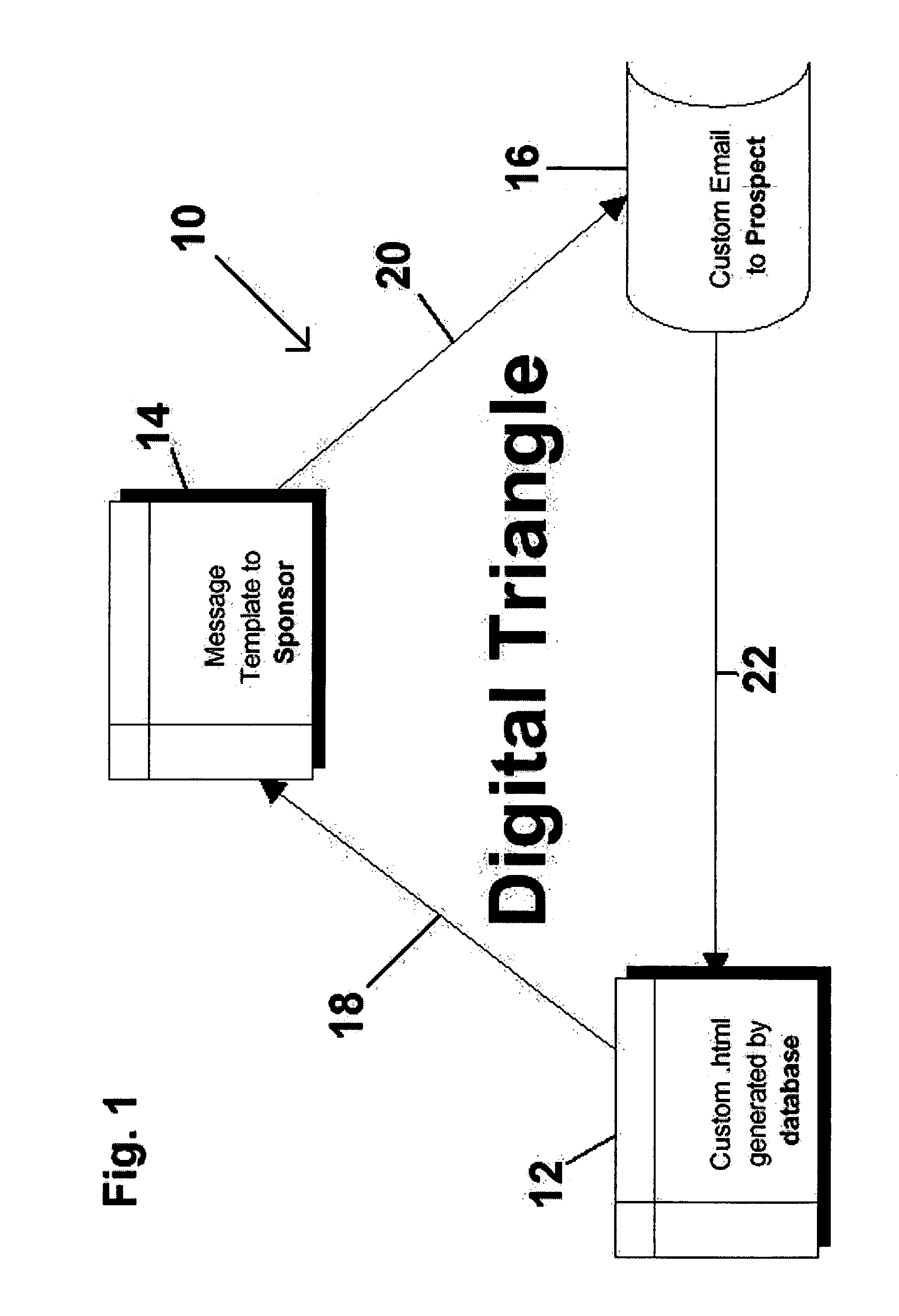
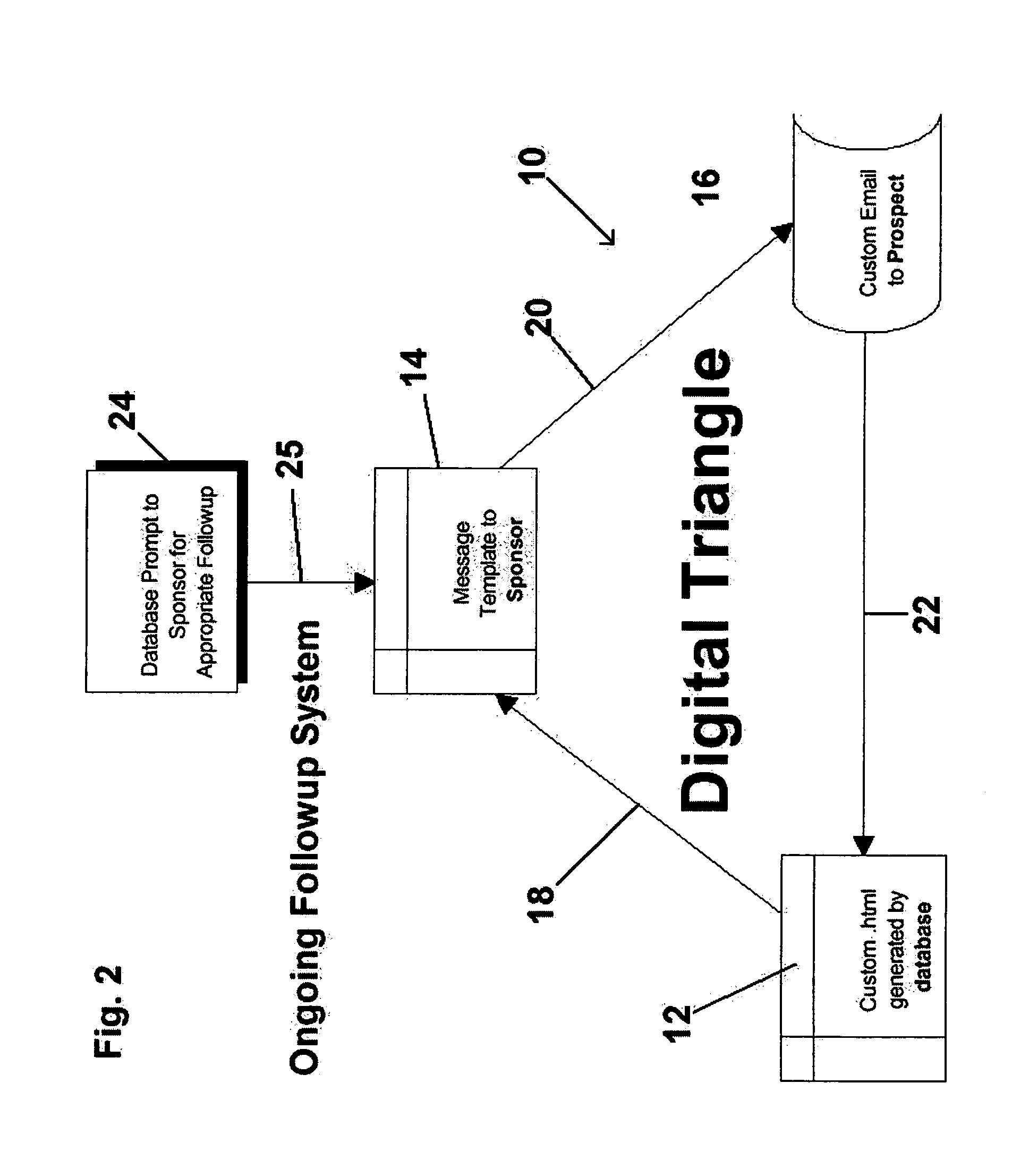
Method for automated electronic mail communication
InactiveUS6993489B1Efficient analysisAnalyze the effectiveness of the messageResourcesMarketingElectronic communicationCitation database
A method of controlling the automated electronic communication between a host database and a prospect that was referred to the database by a sponsor. Initially, a sponsor accesses the host database and answers survey questions related to the sponsor and additional survey questions about each of the prospects being referred to the host database. Based upon the information received about each of the prospects from the sponsor, the host database generates a message template that is delivered electronically to the sponsor. After receiving the message template, the sponsor forwards the message to the prospect such that the prospect believes that the message has been originated directly from the sponsor, rather than the host database. The message template sent to the prospect from the sponsor includes an electronic link to a customized web page generated by the host database. The customized web page is created based upon the information received about the prospect from the sponsor. Based upon the information about the prospect, the web page is created containing information relevant to the prospect. Upon accessing the web page, the prospect is asked if they would like to receive further information. If further information is required, the host database again generates a message template that is sent to the sponsor for forwarding onto the prospect. The method of automated electronic communication allows the host database to generate messages that are first sent to the sponsor prior to their receipt by the prospect.
Owner:MIGLAUTSCH JOHN R
Method and system for quantifying a data page repetition pattern for a database index in a database management system
InactiveUS20080243761A1Overcomes shortcomingDigital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsDatabase queryCitation database
A method and system are presented for quantifying a data page repetition pattern for a database index in a database management system. In one embodiment, the method includes identifying a database index to provide a basis for collecting a data page repetition statistic, the database index having a database index key. The method may also include collecting the data page repetition statistic based on the database index key, wherein the data page repetition statistic quantifies a data page repetition pattern associated with database queries that reference sequential entries of the database index. The method may further include optimizing a data page access process based on the data page repetition statistic. In a further embodiment, the method may utilize both cluster ratio and data page repetition statistics to evaluate data page I / O and CPU cost.
Owner:IBM CORP
Content data transmission system and content data transmission method
InactiveUS20050273632A1Easy to updateSynchronization is simpleDigital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationComputer hardwareCompact disc
A library of a PC is easily synchronized with recorded contents of a disc loaded into a recording and reproducing apparatus (PD). The PC has a dynamic group and a database. Contents of the dynamic group are, dynamically changed. The dynamic group is correlated with the ID of the disc on which the contents of the dynamic group have been recorded. When the CP and the PD are connected, the ID of the disc loaded into the PD is read. The database is referenced for the ID of the disc. When there is a corresponding dynamic group, the dynamic group is compared with the recorded contents of the disc. Contents that exist in the dynamic group and that do not exist on the disc are checked out to the disc. In contrast, contents that exist on the disc and that do not exist in the dynamic group are checked in to the PC. In addition, the reproduction order of contents of the dynamic group is reflected to contents of the disc. The user can synchronize the recorded contents of the disc with the library of the PC only by connecting the PC and the PD.
Owner:SONY CORP
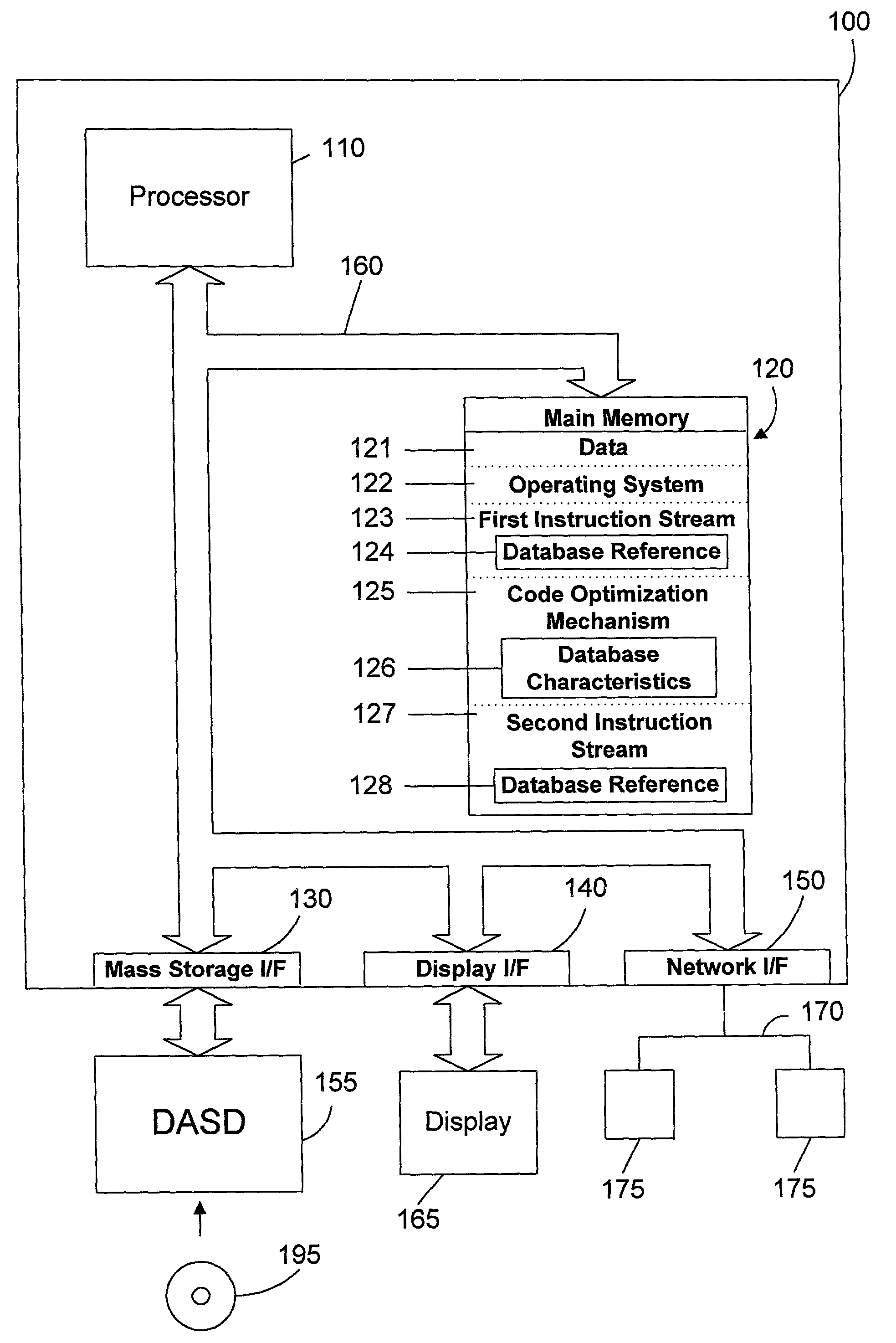
Apparatus and method for using database knowledge to optimize a computer program
A code optimizer is used to optimize a computer program that references a database by determining the characteristics of the database and making suitable optimizations based on the characteristics of the database. By taking into account the characteristics of a database referenced in the computer program, the optimizer may make suitable optimizations to the computer program. Such optimizations include, without limitation, removing unnecessary calls to the database, removing unnecessary loops, removing unnecessary database operations, providing compile-time errors, and replacing dynamic calls with static data.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Method for analyzing and sequencing academic influence of theme literature in citation database
ActiveCN103729432AImplement sortingSpecial data processing applicationsCitation databaseSubject matter
The invention discloses a method for analyzing and sequencing academic influence of theme literature in a citation database. The method includes performing theme retrieval in the citation database to acquire metadata information of the theme literature and citation relation among the theme literature; according to the acquired metadata information of the theme literature and the acquired citation relation among the theme literature, creating a theme citation network; on the basis of the citation network, building a factor graph model containing various literature academic influence factors; using a circulating maximum sum algorithm for approximate reasoning on a factor graph to determine marginal probability values of all variables in the factor graph; according to a descending order result of the marginal probability values, acquiring and outputting an academic influence sequence of all theme literature. By the method, sequencing of the academic influence of literature with a theme given by a user can be realized.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
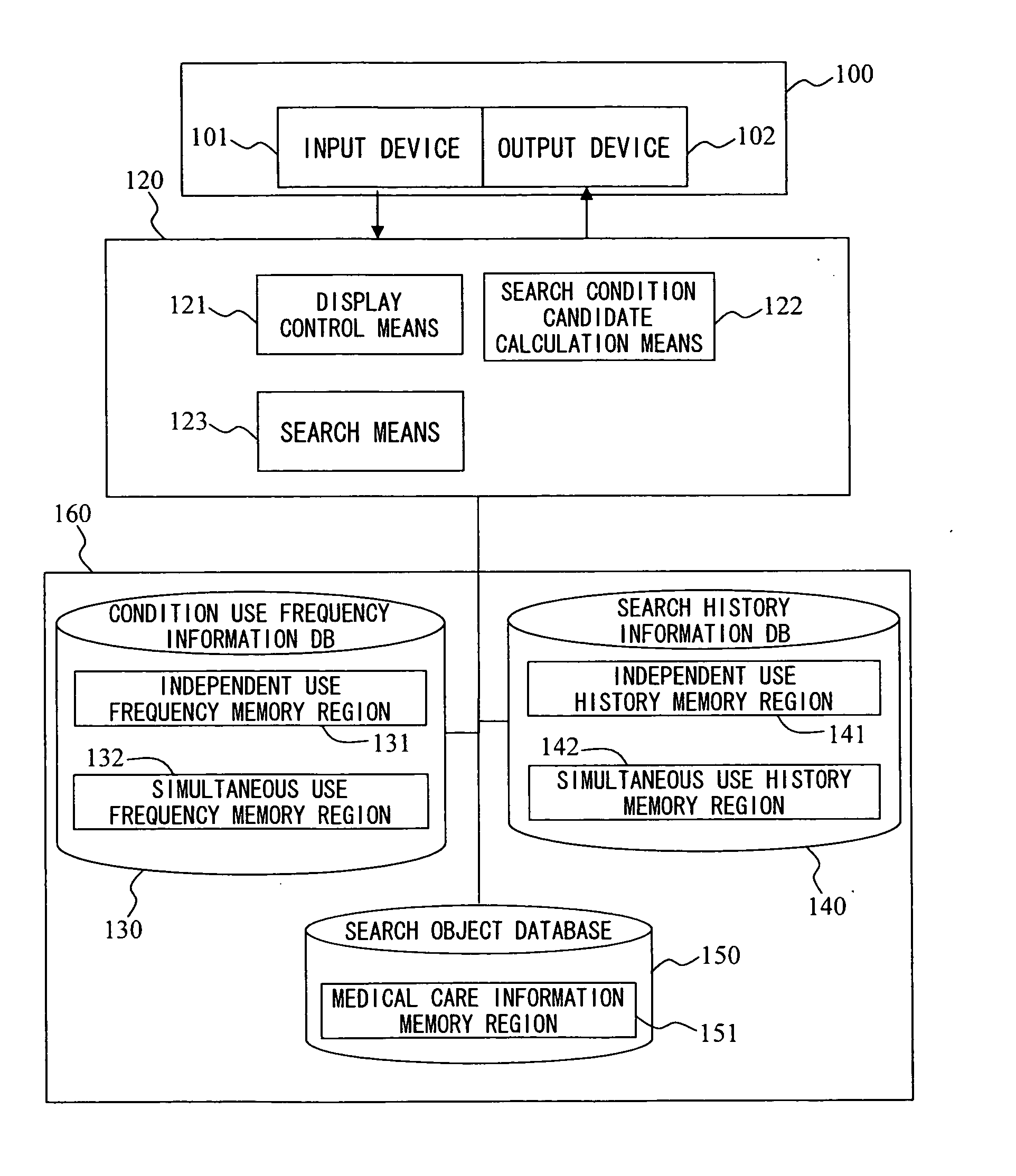
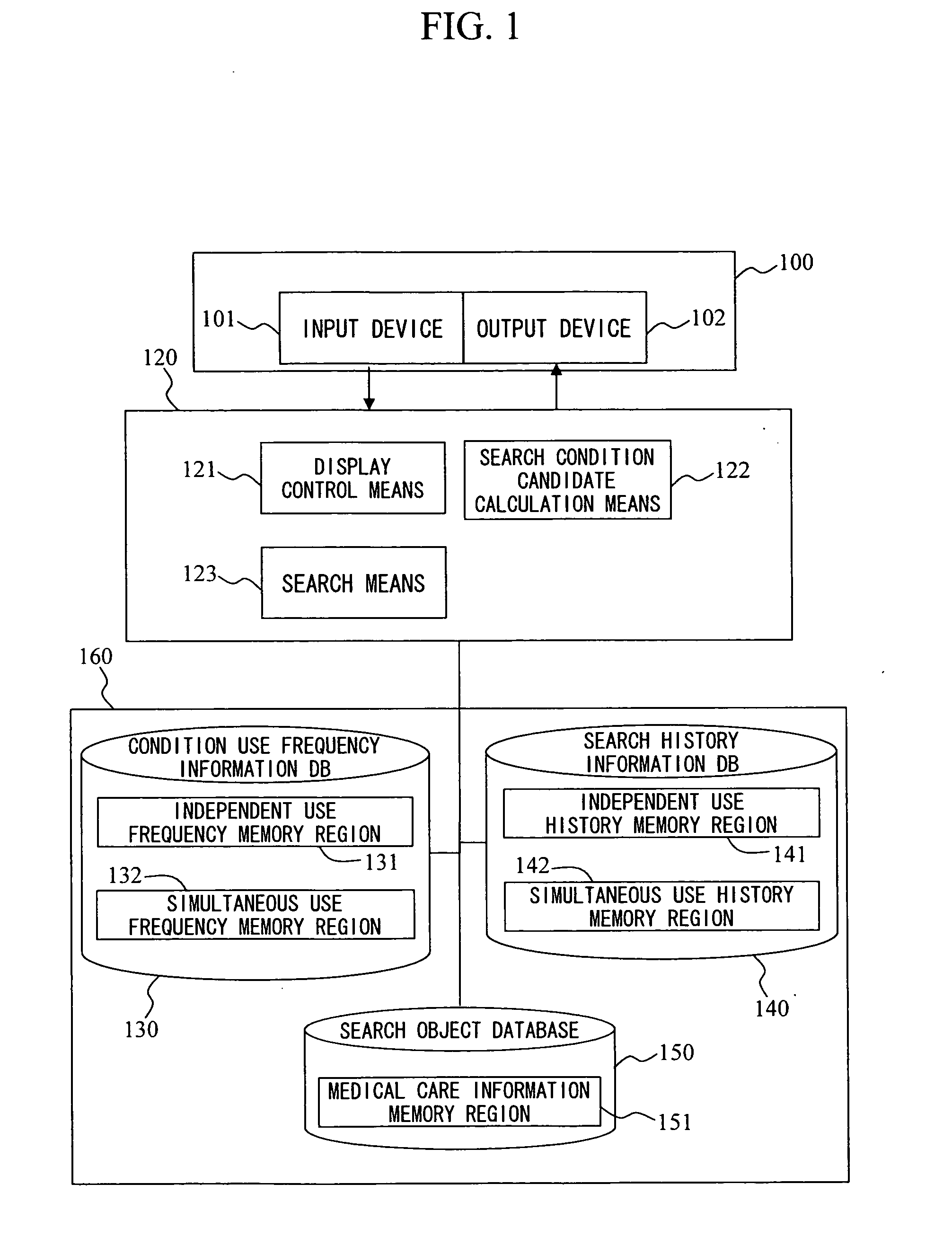
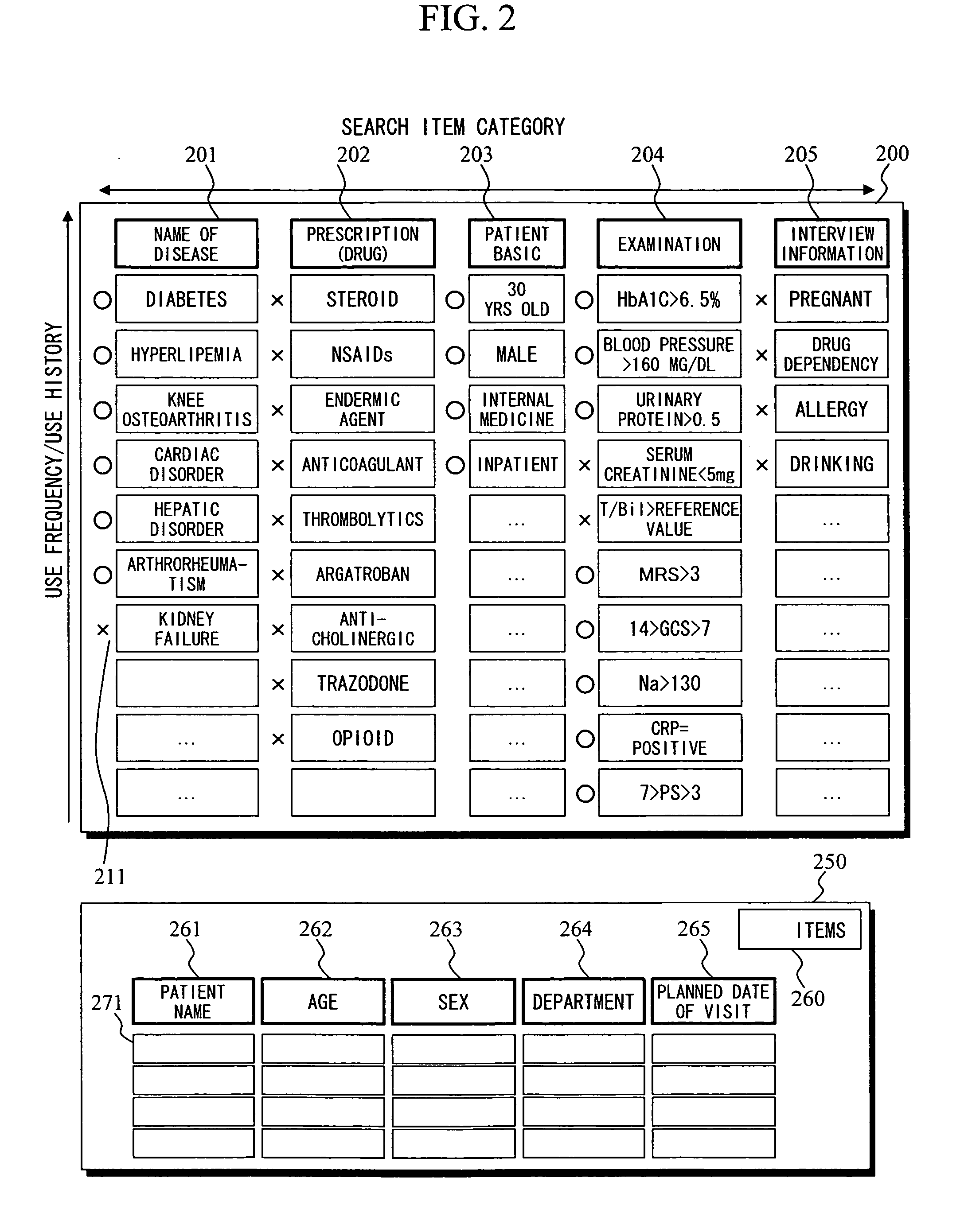
Search apparatus
ActiveUS20070276857A1Digital data information retrievalData processing applicationsCitation databaseCo-occurrence
The setting of a search condition is supported. Databases 130 and 140 store use frequency information about search conditions, co-occurrence frequency information between search conditions, relationship information unique to a particular field, use history information for each search condition, and simultaneous use history information. Based on a search condition that is already set, the database are referred to so as to calculate the recommendation level of other search conditions, and search conditions that have high recommendation levels and that are likely to be used simultaneously with the already-set search condition are arranged at conspicuous positions. The recommendation level is calculated based on the value of a co-occurrence frequency between search conditions, the history of simultaneous setting, or the estimated number of search results, for example.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
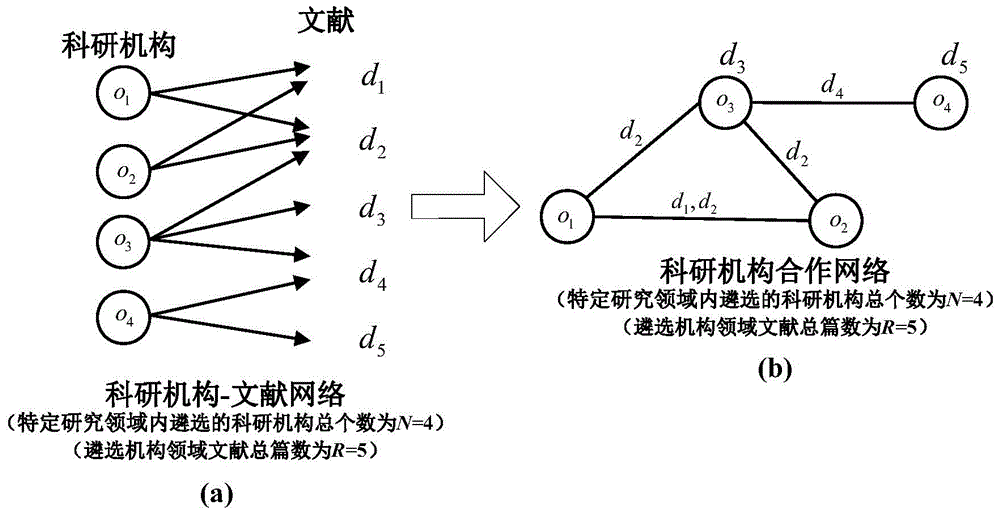
Multi-factor comprehensive quantitative analysis and sorting method for academic influences of scientific research institutions
InactiveCN104636426AImprove effectivenessImprove practicalitySpecial data processing applicationsResearch efficiencyCitation database
The invention discloses a multi-factor comprehensive quantitative analysis and sorting method for academic influences of scientific research institutions. The method includes the steps that document retrieval of a specific research field is performed in a citation database, and document metadata of the field are acquired; metadata of the relevant scientific research institutions are extracted according to the document metadata of the field; a weighed cooperation network of the scientific research institutions is constructed according to the metadata of the scientific research institutions; on the basis of the weighed cooperation network of the scientific research institutions, a factor graph model including multiple factors of the academic influences of the scientific research institutions is established; a circulation max-sum algorithm is used for performing approximate reasoning on a factor graph, variables of the factor graph are determined and edge probability values of all the factors are concentrated; academic influence sorting of the scientific research institutions in the research field retrieved by users is acquired and output according the descending sort result of the edge probability values. Due to the multi-factor comprehensive quantitative analysis and sorting method for the academic influences of the scientific research institutions, scientific research personnel can accurately position the high-academic-influence scientific research institutions, track research results and improve scientific research efficiency easily.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
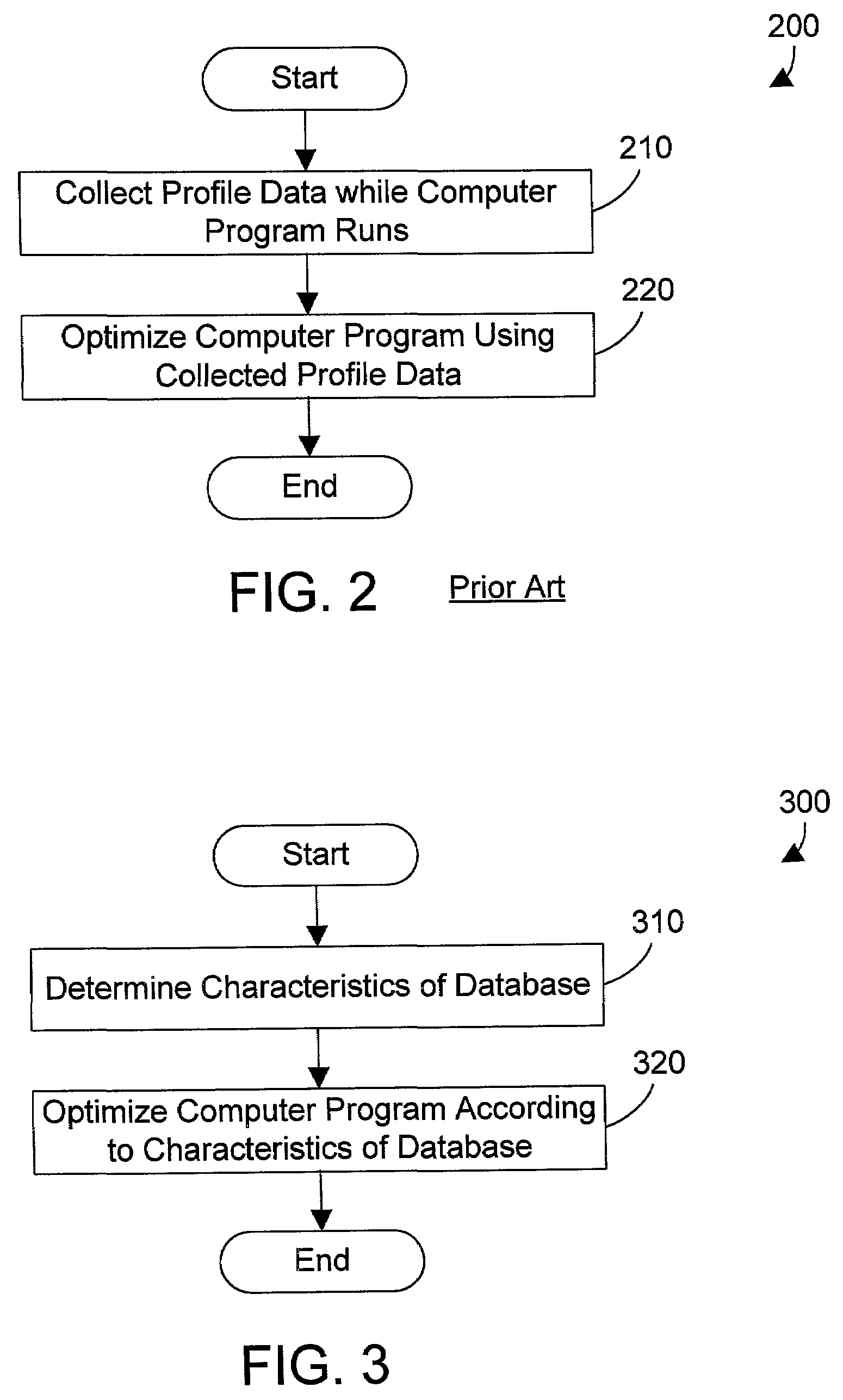
Method for optimizing the performance of a database
InactiveUS20010032199A1Improve performanceReduced persistent sizeData processing applicationsProgram loading/initiatingCitation databaseData field
Methods for Optimizing the Installation of a Software Product onto a Target Computer System Optimizations for the process of installing a software product onto a target computer system. A relational installation database for storing data elements in the form of strings, objects, etc. is aliased with integer identifiers corresponding to each data element. The integer identifiers are obtained from an index that sequentially stores a copy of each unique occurrences of a data element. Populating an installation database with only integers reduces persistent size and provides uniformity to the data fields underlying the database tables, and provides a significant improvement in database performance The uniform data fields may be expanded and contracted to add temporary rows and columns directly to a database table. In this way, temporary data elements may be stored directly in a database table without the need for creating a view of the database table. Temporary data elements are lost when the database table is no longer referenced, and temporary data is ignored when persisting the database. Aliased installation databases are easily manageable and provide greater flexibility to software developers in the creation and shipping of a software product. Database tables may be created in a modular fashion and may be efficiently merged together when the software product is complete. Also, differences between various versions of the software product may be recorded in database transforms. Database transforms may be shipped to the end-user and applied to a prior installation database, so as to provided enhancements, patches, upgrades, custom installations, etc. without the need to ship an entire modified installation database.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
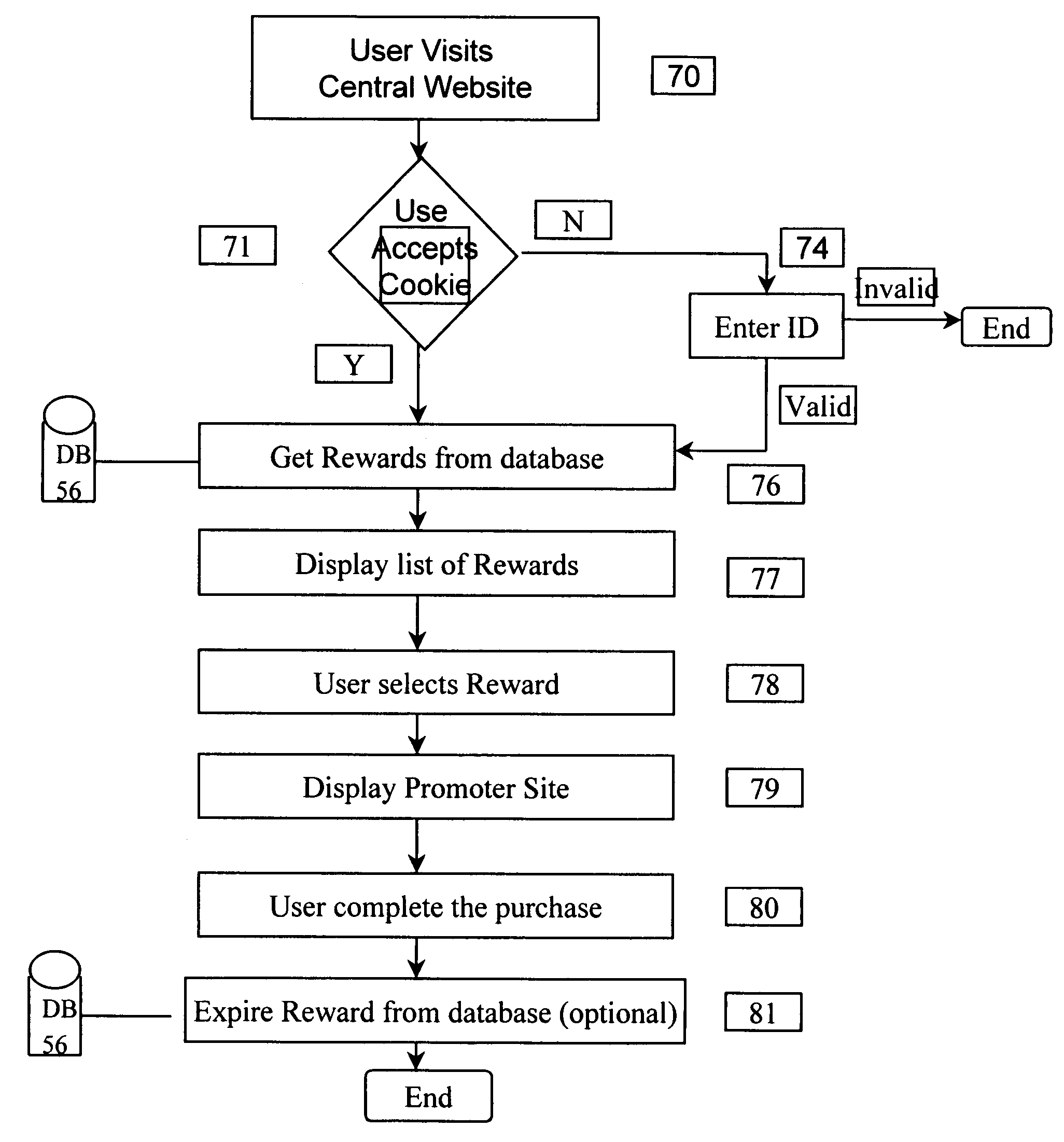
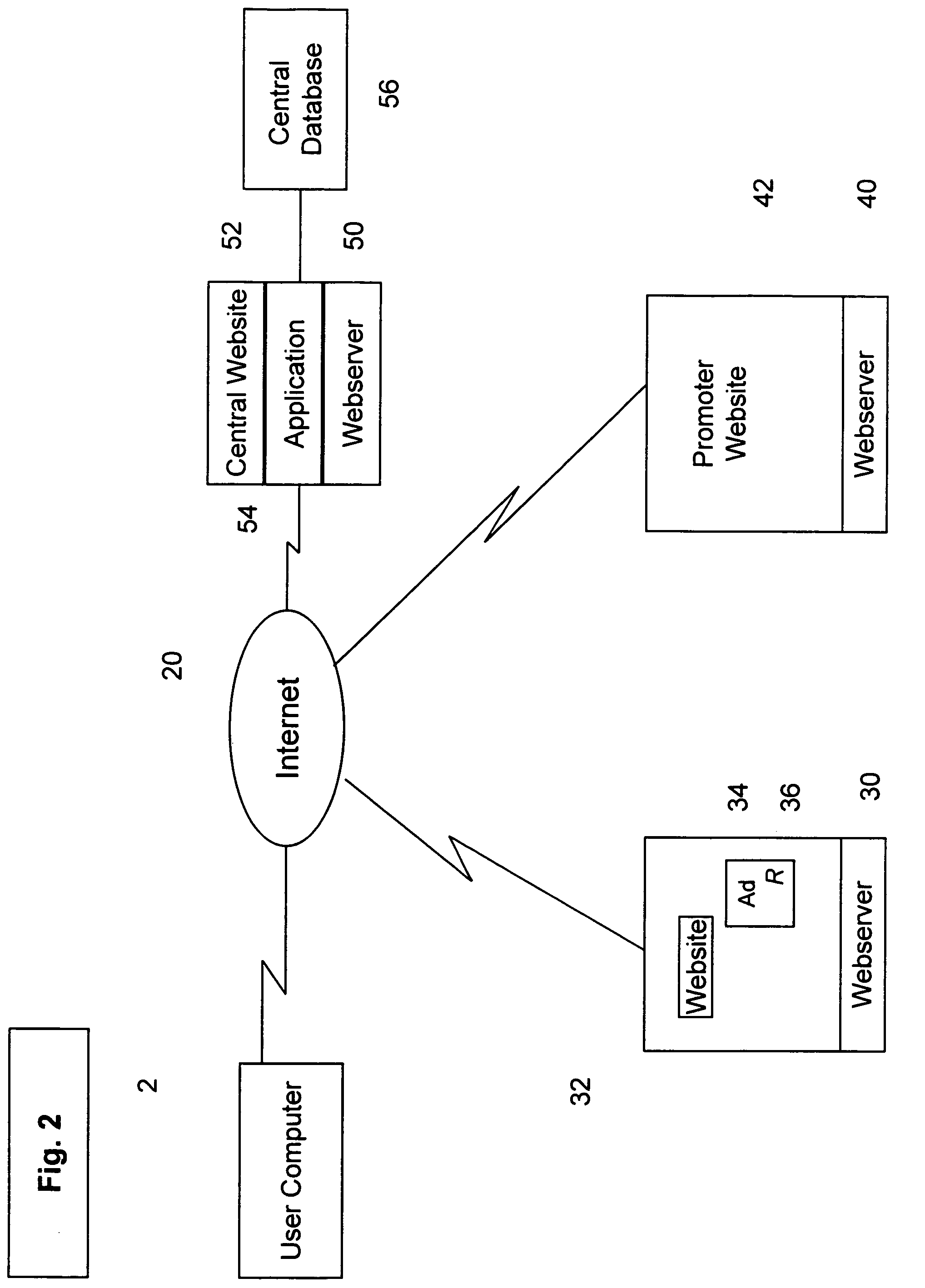
Interactive reward system and method
InactiveUS7624038B1No cost and wasted time in collectingSimple for to redeemMarketingReward systemCitation database
An interactive reward system to allow a user to collect and redeem rewards is disclosed. The system can operate over the Internet or any other network of linked mirco-processors which can reference a database. The user can obtain rewards when using a user computer. A reward can be obtained when the user selects an image or text, such as an advertisement, that has an associated (optional) reward indicator. A reward indicator can be, for example, a special logo or icon. When an image with a reward indicator is selected by the user, control is passed to a central computer that identifies the user and adds the reward to a database storing a list of rewards available for redemption by that user. Each reward is associated with a promoter's offer. Typically, each promoter will have a computer, such as a webserver. After a reward has been allocated to the user, the central computer passes control to the promoter's computer associated with the selected image. The users can access the central computer to see what rewards the user has collected, to transfer rewards, and to redeem rewards or to print reward coupons for redemption in a physical outlet. Rewards can also be redeemed at the promoter's computer, which will communicate with the central computer to ascertain if the selected reward is valid. The system has application to other networked devices other than the Internet, such as ATMs and telephones.
Owner:INTERNET MONEY EXCHANGE PTY LTD THE
SQL execution analysis
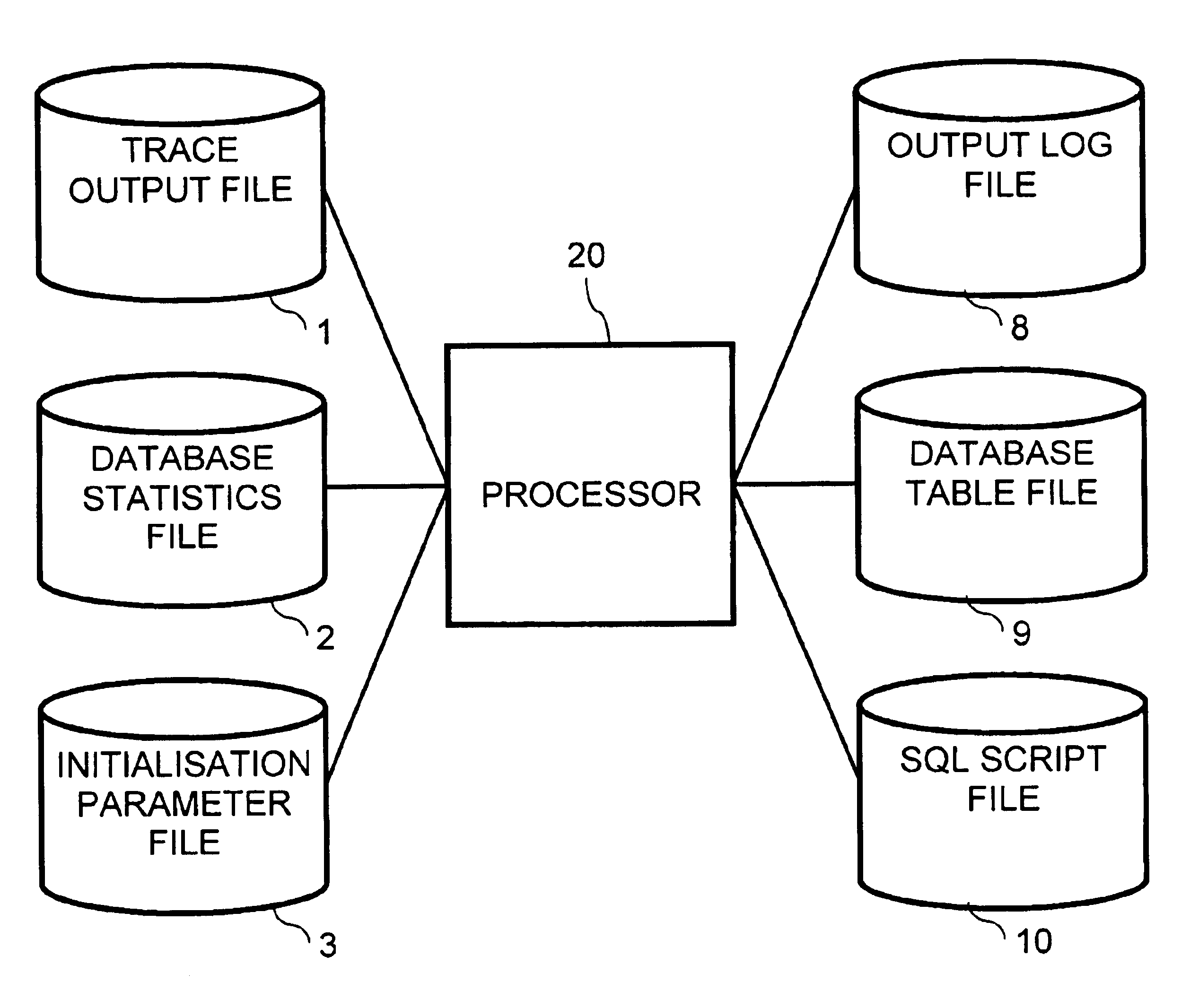
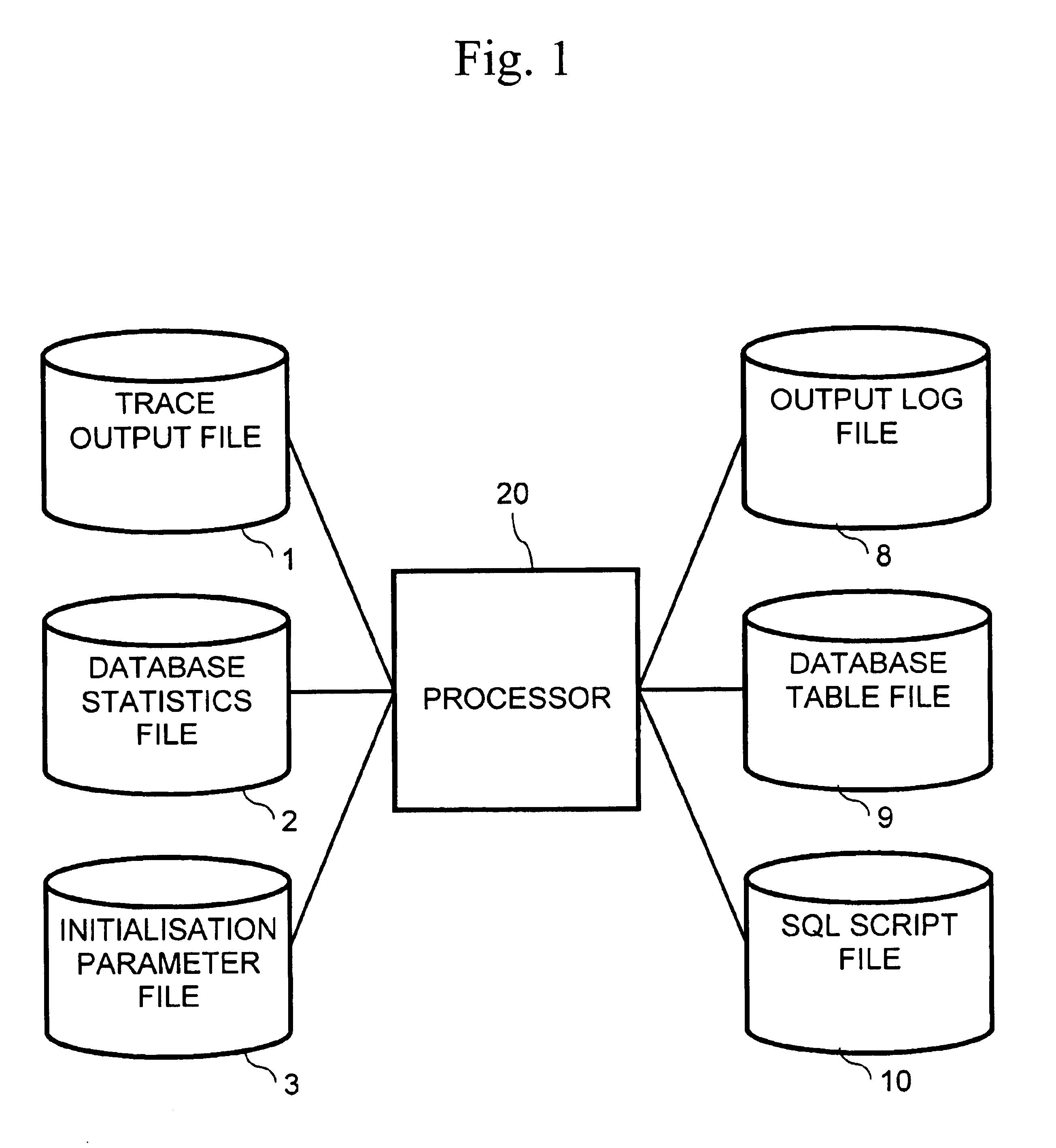
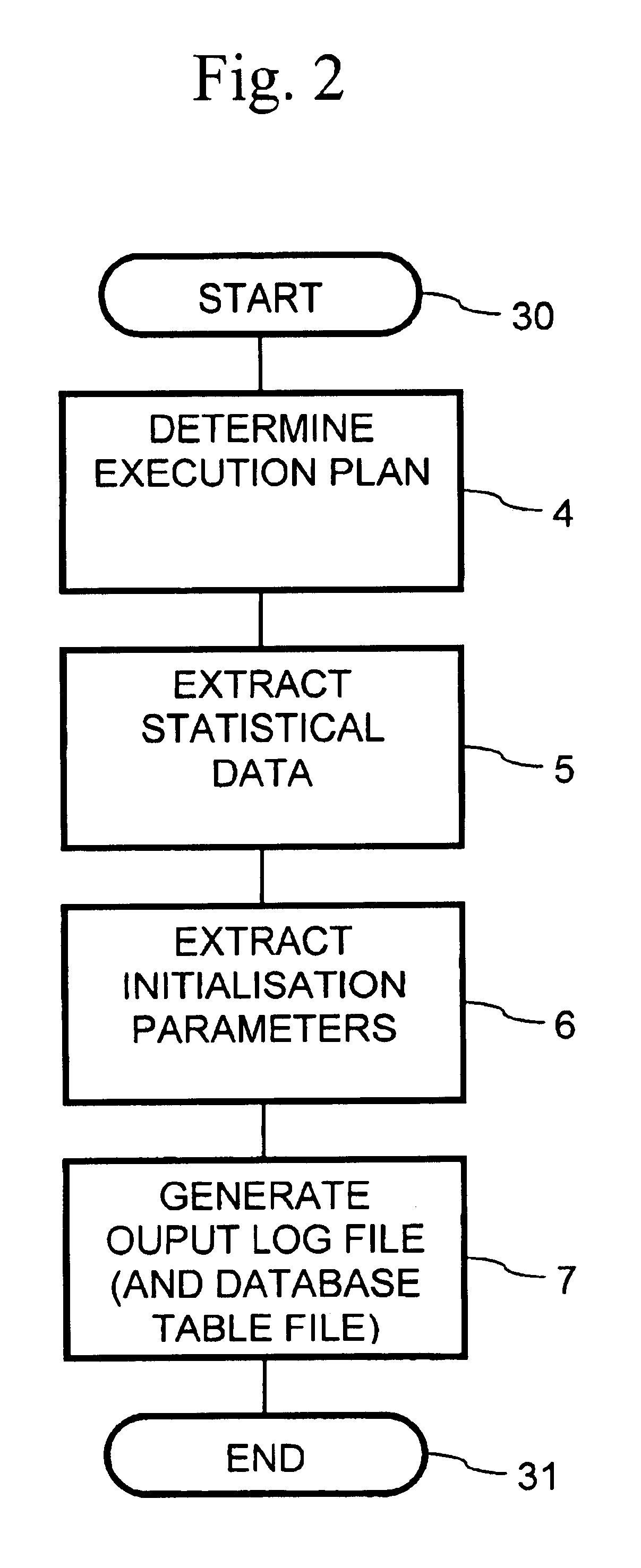
InactiveUS20030033291A1Data processing applicationsDigital data information retrievalExecution planCitation database
A method of collecting data is described. The method relates to the manner in which a SQL statement referencing a database was executed, and comprises the following steps: a. obtaining an execution plan and associated performance factors for the SQL statement; b. obtaining predetermined statistical data relating to the database referenced by the SQL statement; and, c. generating an output file containing the SQL statement, the execution plan, the performance factors and the predetermined statistical data.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Devices, systems and methods for controlling permitted settings on a vehicle
ActiveUS8706349B2Limiting distractionNetwork traffic/resource managementAssess restrictionDistractionDriver/operator
Devices, systems, and methods are disclosed for altering permitted settings of a vehicle according to a driver identified through short range wireless communication. The vehicle captures a unique identifier from a wireless communication device of the driver of the vehicle. This unique identifier is used to reference a database to determine the identity of the driver as well as settings for the driver created by a controlling authority. The controlling authority may be, for instance, a parent or employer of the driver. The settings may limit certain devices within the vehicle and / or the vehicle itself. Speed control settings, radio settings, wireless communication device settings, and various other settings are all possible to limit distractions to the driver. Further, the settings may be influenced by the number or identities of passengers within the vehicle.
Owner:HYUNDAI MOTOR CO LTD +1
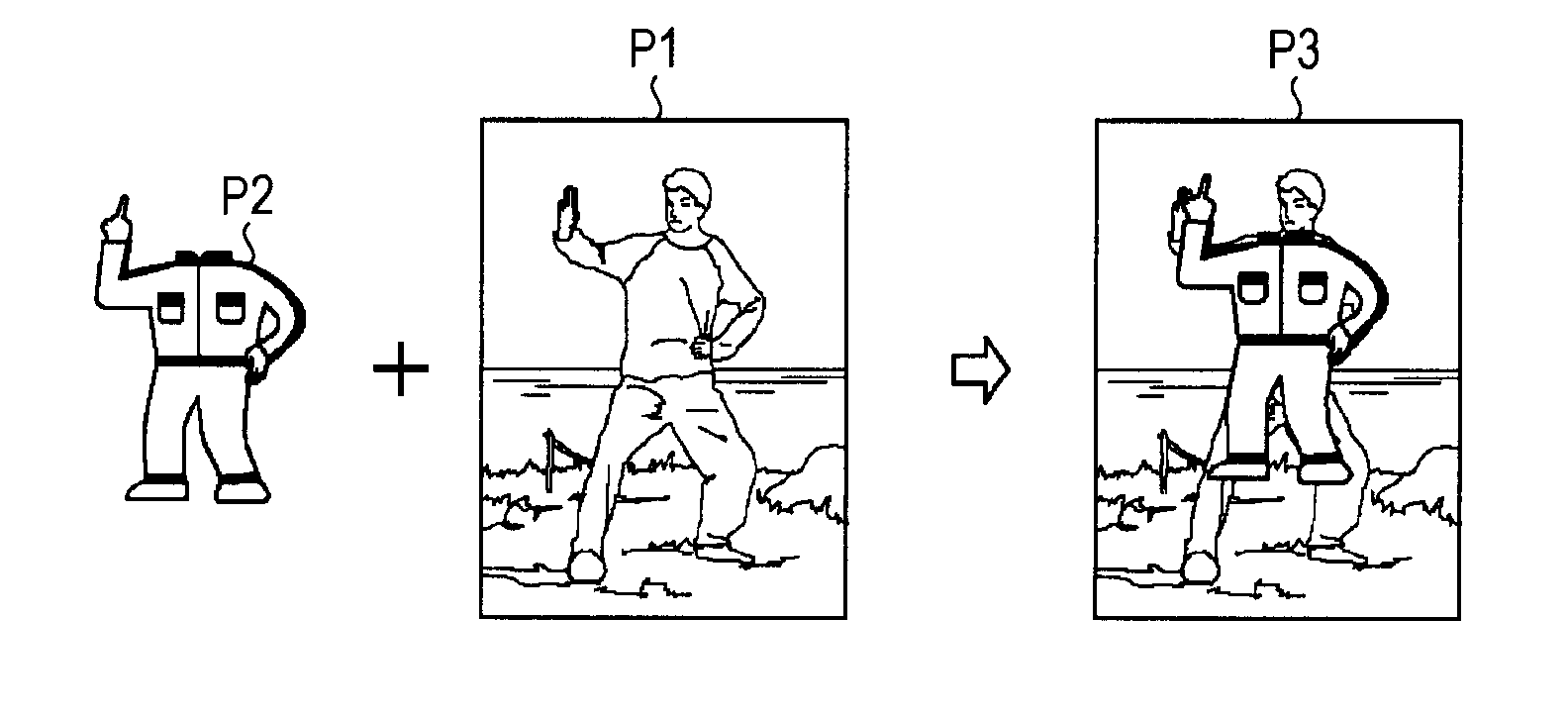
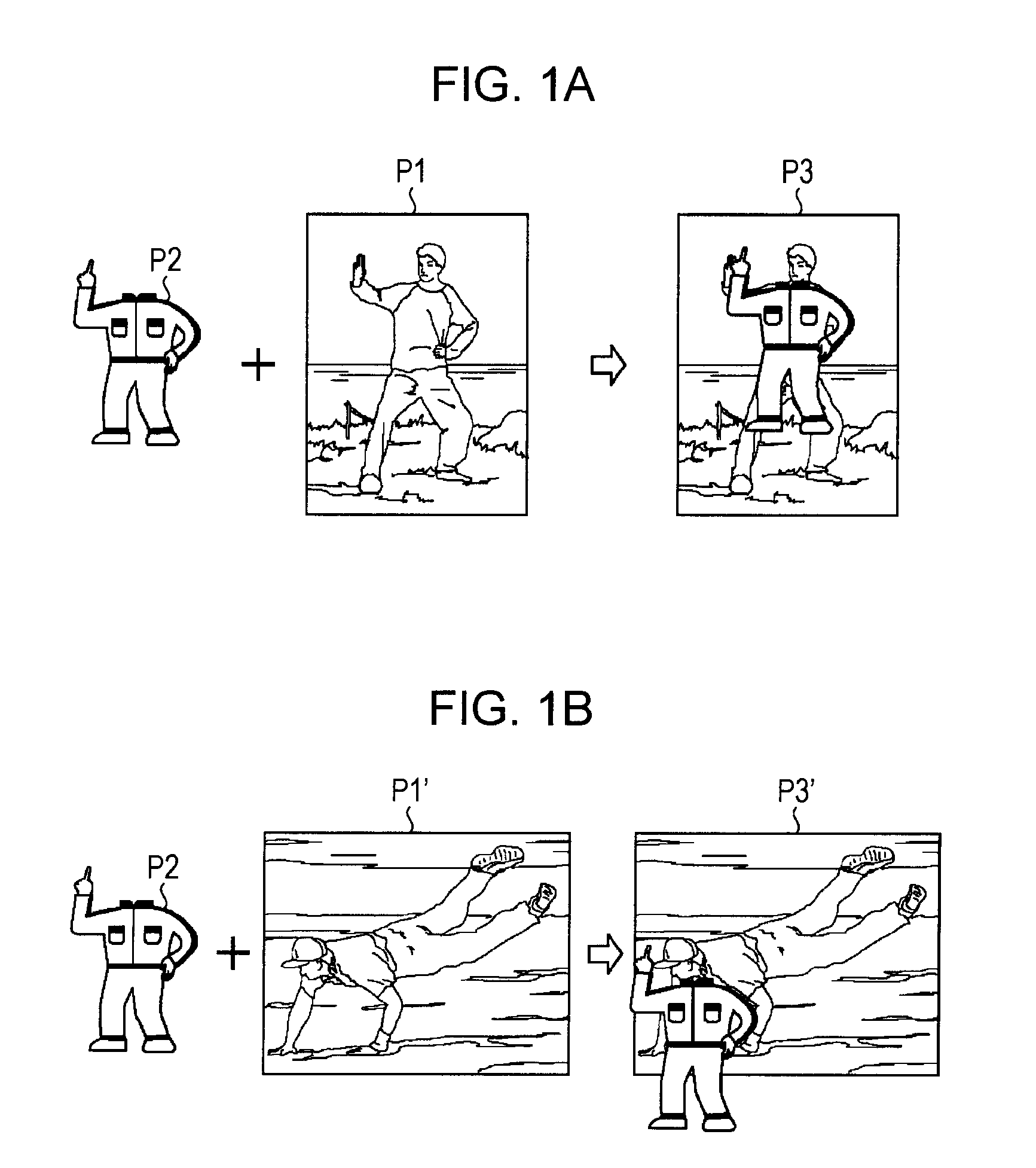
Image processing system, image processing apparatus, image processing method, and program
An image processing system includes a storing section that stores a database in which specific pose data representing each of specific poses of a human, and effect manipulation data specifying each of manipulations applied to an image are registered in association with each other, a human region detecting section that detects a human region that is a region where a human appears in an image on which to perform image processing, a human pose recognizing section that recognizes a pose of the human in the human region detected by the human region detecting section, a matching section that finds the specific pose data matching the pose recognized by the human pose recognizing section, by referencing the database, and a manipulating section that applies a manipulation to the image on the basis of the effect manipulation data associated with the specific pose data found by the matching section.
Owner:SONY CORP
Devices, systems and methods for detecting a traffic infraction
ActiveUS8493234B2Arrangements for variable traffic instructionsParticular environment based servicesPaymentDriver/operator
Devices, systems, and methods are disclosed for identifying a driver within a vehicle using short range wireless communication in order to ticket or alert the driver in response to a traffic infraction by the driver. In exemplary embodiments, a short range wireless communication device registers drivers of vehicles at a certain location. The registration captures a unique identifier for each driver at the location from the driver's wireless communication device. When a vehicle commits a traffic infraction, the unique identifier is used to reference a database to determine the identity and address of the driver. The driver may then be sent a notification of the infraction as well as payment options. This notification may be sent directly to the wireless communication device of the driver. In embodiments of the present invention, a smart vehicle acts as a proxy to capture the unique identifier from the driver's wireless communication device and communicates with the short range wireless communication device.
Owner:AT&T MOBILITY II LLC
SQL execution analysis
InactiveUS6708185B2Data processing applicationsDigital data information retrievalExecution planCitation database
A method of collecting data relating to the manner in which a SQL statement referencing a database was executed and a computer program and computer program product implementing the method are provided. The method comprises obtaining an execution plan and associated performance factors for the SQL statement, obtaining predetermined statistical data relating to the database referenced by the SQL statement, generating at least one output file containing the SQL statement, the execution plan, the performance factors and the predetermined statistical data, and generating a SQL script which enables the predetermined statistical data to be recreated when executed on a second database, wherein the SQL script is executed on the second database to recreate the predetermined statistical data on the second database and wherein the SQL statement is analyzed by executing it on the second database after recreating the predetermined statistical data.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Misoperation-preventive locking logic automatic test system for intelligent transformer substation
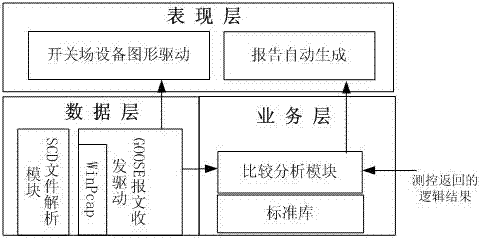
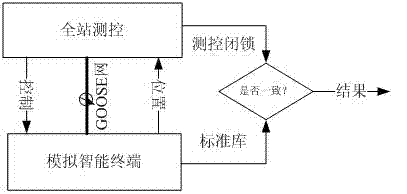
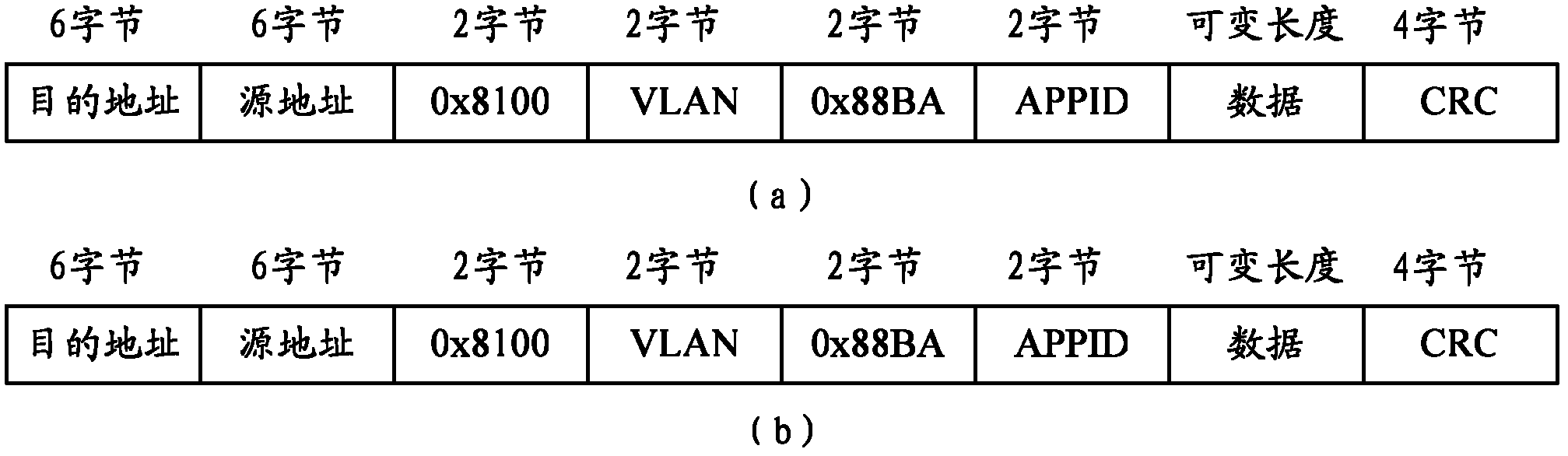
InactiveCN102832707ASpeed up the debugging processImprove efficiencyCircuit arrangementsInformation technology support systemSmart substationCitation database
The invention discloses a misoperation-preventive locking logic automatic test system for an intelligent transformer substation, comprising a data layer, a business layer and a presentation layer, wherein the data layer comprises a GOOSE (Generic Object Oriented Substation Event) message receiving and sending module for receiving a GOOSE signal, a switch and disconnecting link deflection signal and a switching value signal from a monitoring system of the intelligent transformer substation and sending the received data to a comparison and analysis module of the business layer, and an SCD (Science Citation Database) file parsing module for analyzing the GOOSE signal from the system of the intelligent transformer substation; and the business layer comprises a standard library for storing an input misoperation-preventive locking logic database, and the comparison and analysis module used for performing real-time logical operation by different switch and disconnecting link position combinations received from the GOOSE message receiving and sending module according to the input misoperation-preventive locking logic database, comparing the standard output result with the locking result fed back by a monitoring device and verifying validity of the misoperation-preventive locking logic of the monitoring device. The system can verify the validity and integrity of the misoperation-preventive locking logic of the monitoring device.
Owner:STATE GRID JIANGSU ELECTRIC POWER CO ELECTRIC POWER RES INST +3
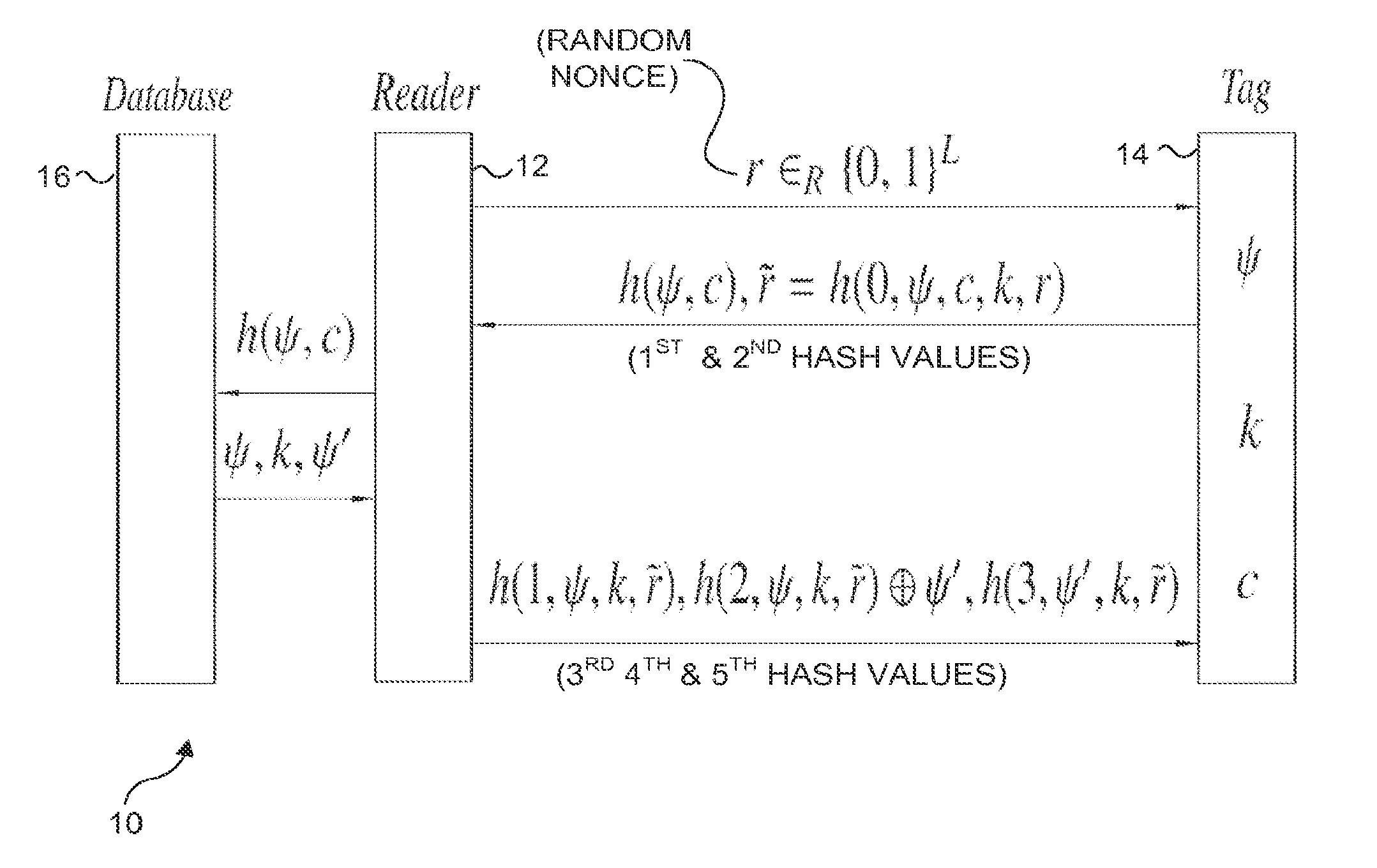
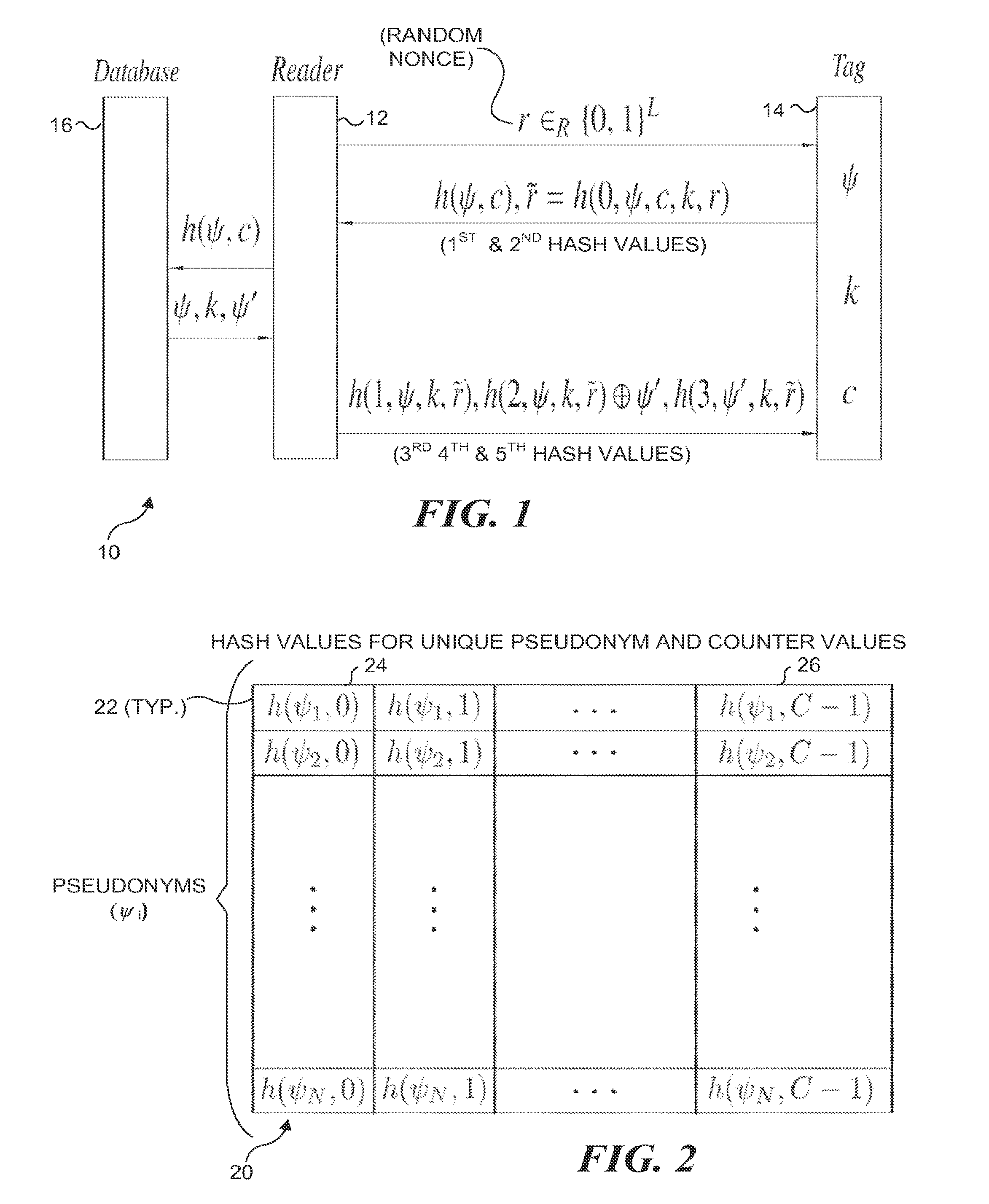
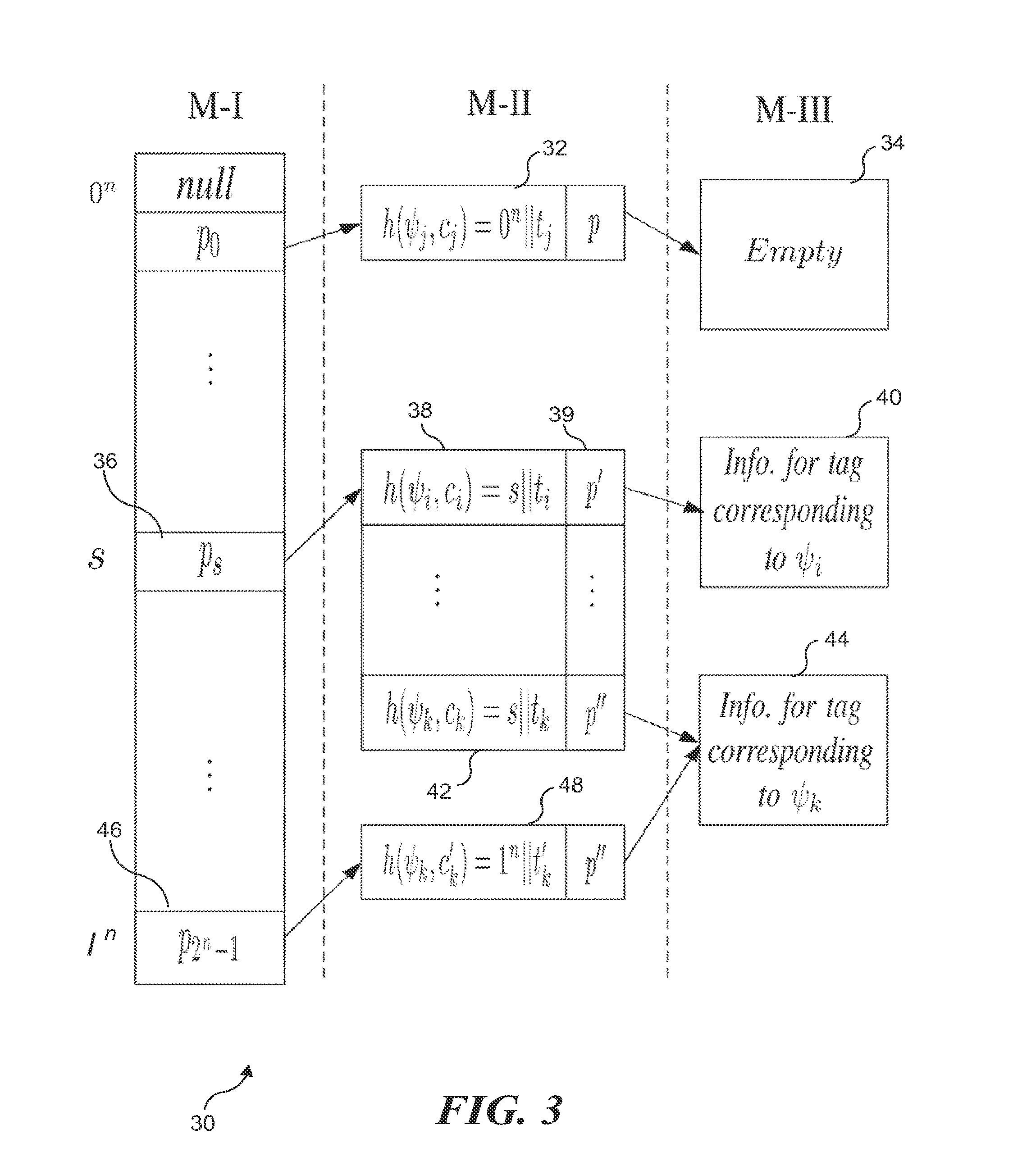
Scalable RFID systems: a privacy-preserving protocol with constant-time identification
InactiveUS20130207780A1Minimizes probability of collisionMinimizes probabilitySubscribers indirect connectionRecord carriers used with machinesComputer hardwareHash function
A protocol with constant-time complexity solves the problem of private identification of tags in low-cost, large-scale radio frequency identification (RFID) systems—assuming that an adversary has complete control over the communication channel. Each RFID tag has an internal counter, c, and is preloaded with a unique pseudonym, ψ, and a secret key, k. A RFID reader attempting to identify and authenticate a tag within its range generates and transmits a random nonce to the RFID tag, which returns a first hash of its current pseudonym and counter, and a second hash that is a function of the secret key. The reader uses the returned data to identify the RFID tag and its secret key by reference to a database and returns other hash values that authenticate the reader to the RFID tag. The most expensive operation that RFID tags are required to perform is a hash function.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON
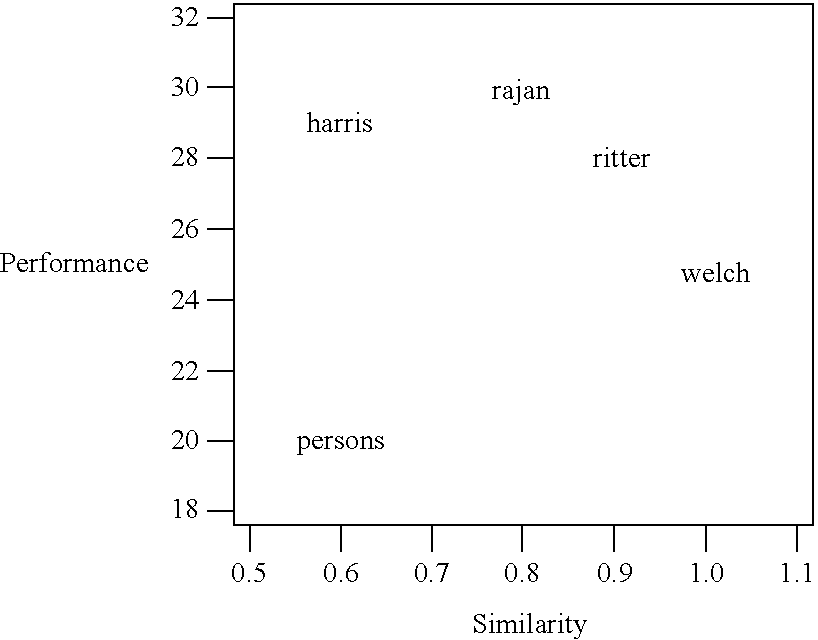
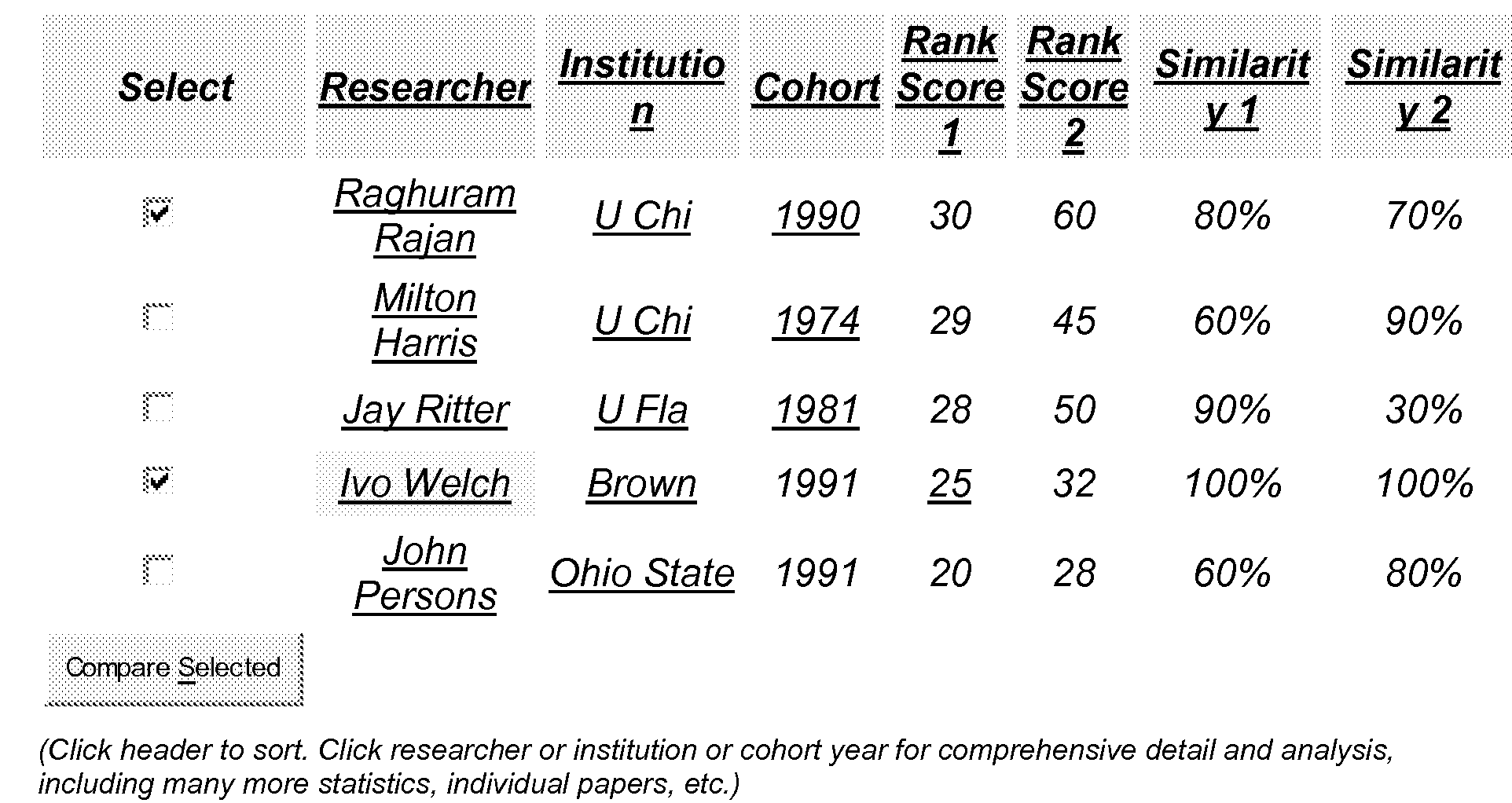
Automated peer performance measurement system for academic citation databases
InactiveUS20080133476A1Easy accessHigh similarityDigital data information retrievalSpecial data processing applicationsCitation databaseRanking
An automated query interface for searching academic citation databases is provided. The system of the present invention allows a user to query not just either the relative performance metrics and rankings of academic publications or the similarity of academic publications, but to query for the relative ranking of aggregations such as researchers, institutions and journals and relative to a set of similar “peers” that (usually) have also been obtained by the system itself via an automated similarity rating engine. The system intentionally deemphasizes or suppresses results for dissimilar researchers, institutions or journals, and seeks to present similar researchers, institutions, and journals together and relative to one another.
Owner:WELCH IVO
Method and system for quantifying a data page repetition pattern for a database index in a database management system
InactiveUS7921085B2Digital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsCitation databaseDatabase index
A method and system are presented for quantifying a data page repetition pattern for a database index in a database management system. In one embodiment, the method includes identifying a database index to provide a basis for collecting a data page repetition statistic, the database index having a database index key. The method may also include collecting the data page repetition statistic based on the database index key, wherein the data page repetition statistic quantifies a data page repetition pattern associated with database queries that reference sequential entries of the database index. The method may further include optimizing a data page access process based on the data page repetition statistic. In a further embodiment, the method may utilize both cluster ratio and data page repetition statistics to evaluate data page I / O and CPU cost.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Method and system for verifying of the authenticity of a consumer product
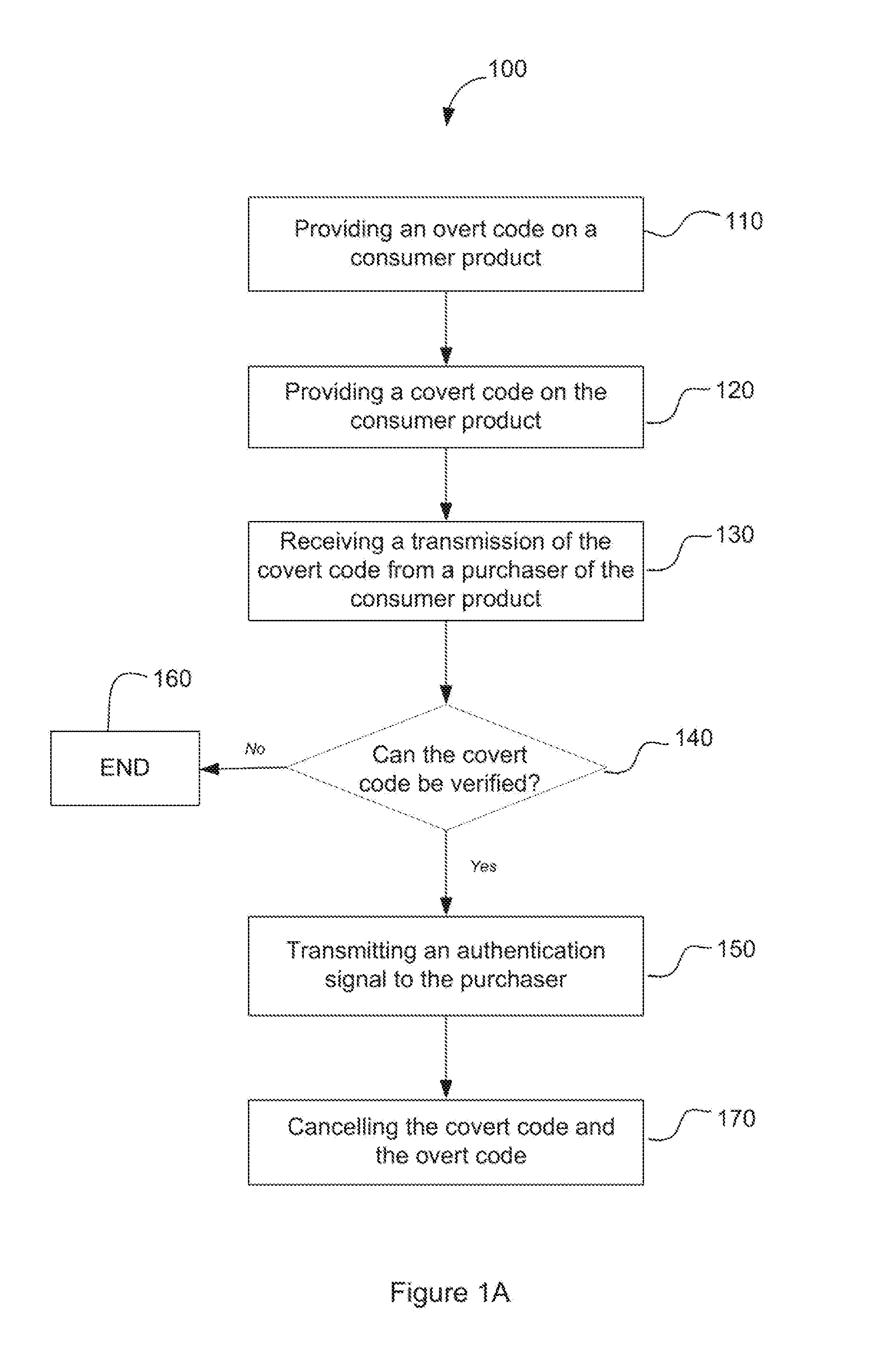
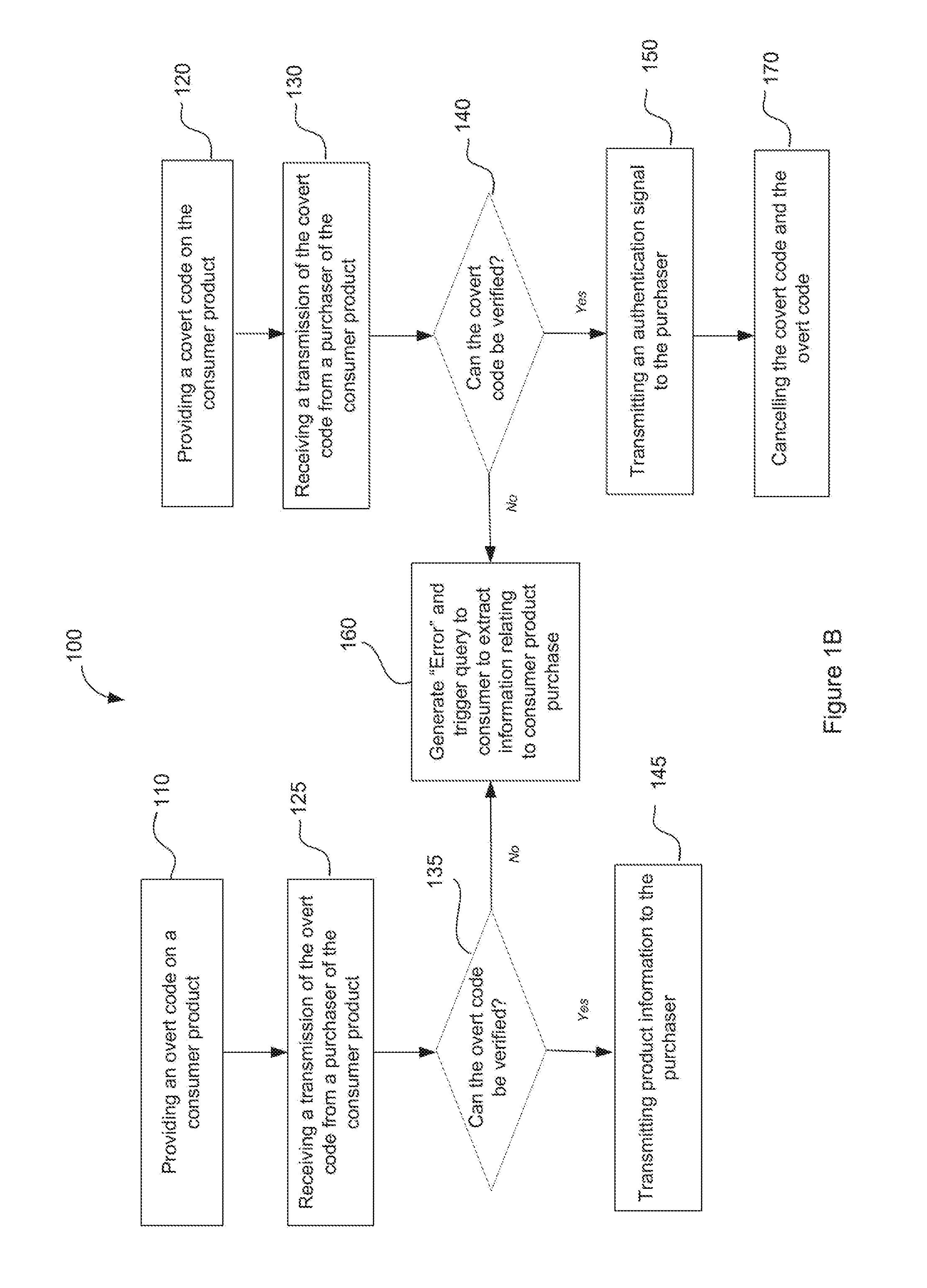
InactiveUS20160314475A1Simple procedureDigital data information retrievalCharacter and pattern recognitionCitation databaseAuthentication
A method and system is provided for verifying of the authenticity of a consumer product, the method including: providing an overt code on a consumer product, the overt code being readable prior to sale of the consumer product; providing a covert code on the consumer product, the covert code being revealed post sale of the consumer product; receiving a transmission of the covert code from a purchaser of the consumer product; verifying the covert code by reference to a database; if the covert code verifies the authenticity of the consumer product, transmitting an authentication signal to the purchaser; and cancelling the covert code and the overt code once the covert code has been used to verify the authenticity of the consumer product.
Owner:OMNIBLEND INNOVATION
Method and system for ensuring switch to carry out automatic learning on intelligent electronic equipment ports
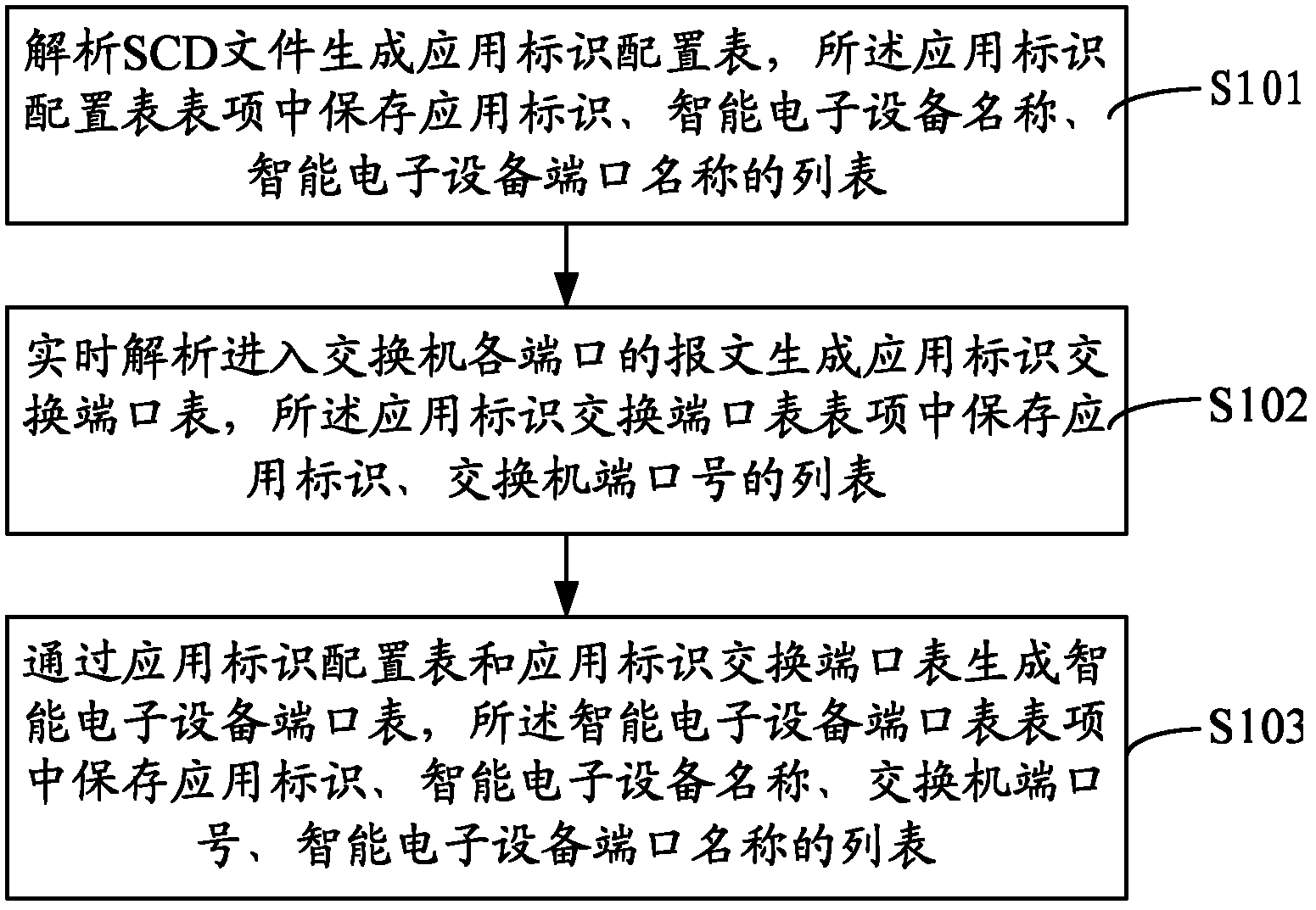
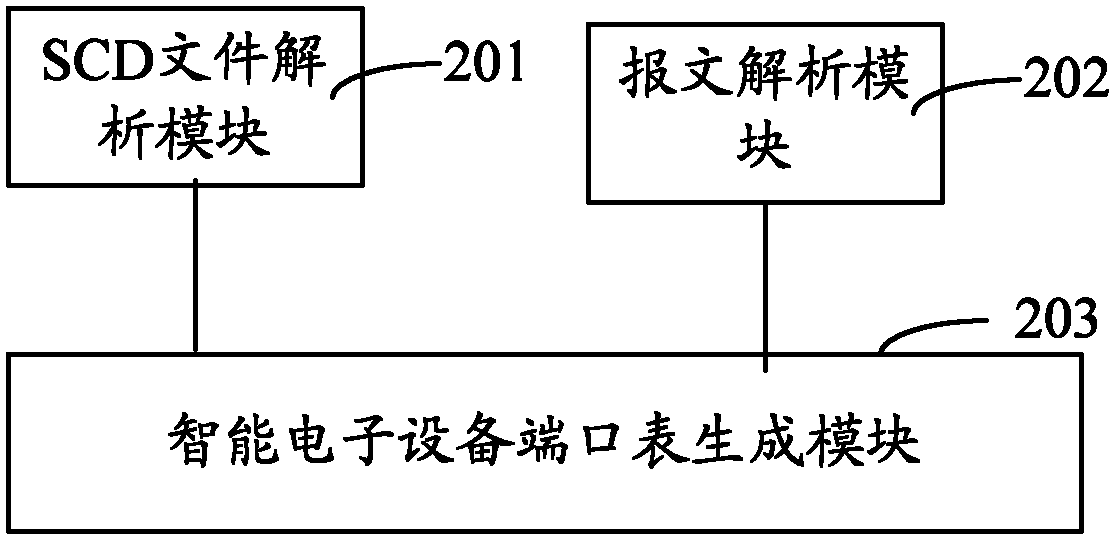
ActiveCN102624943AEasy to viewAchieving learning abilityData switching networksComputer architectureCitation database
The invention discloses a method and a system for ensuring a switch to carry out automatic learning on intelligent electronic equipment ports. The method comprises the following steps: analyzing an SCD (Science Citation Database) file to generate an application identifier configuration table, wherein lists of application identifiers, names of intelligent electronic equipment and names of the intelligent electronic equipment ports are stored in table items of the application identifier configuration table; analyzing a massage entering each port of the switch in real time to generate an application identifier switching port table, wherein lists of the application identifiers and port numbers of the switch are stored in table items of the application identifier switching port table; and generating an intelligent electronic equipment port table by the application identifier configuration table and the application identifier switching port table, wherein the lists of the application identifiers, the names of the intelligent electronic equipment, the port numbers of the switch and the names of the intelligent electronic equipment ports are stored in table items of the intelligent electronic equipment port table. The invention provides the basis for implementing more application functions of the switch.
Owner:GUANGDONG POWER GRID POWER DISPATCHING CONTROL CENT +1
Test stream generating method and apparatus for supporting various standards and testing levels
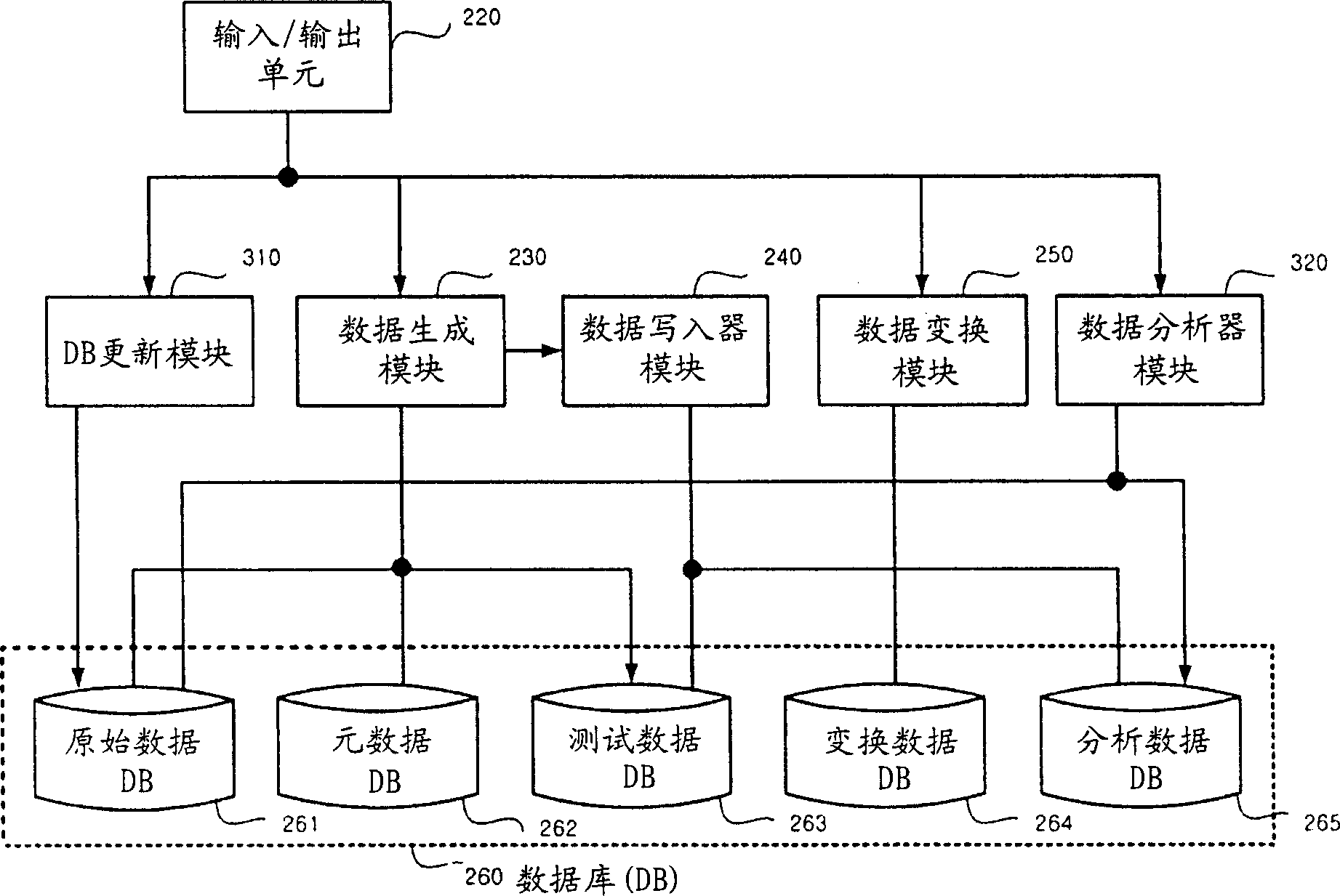
InactiveCN1551640ATest supportData processing applicationsTelevision systemsData transformationCitation database
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com