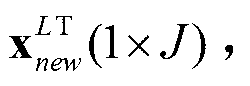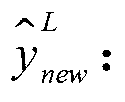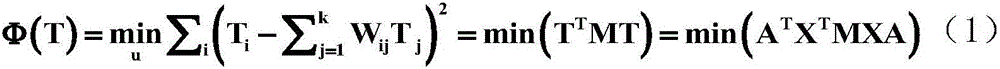Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
134 results about "Latent variable" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In statistics, latent variables (from Latin: present participle of lateo (“lie hidden”), as opposed to observable variables) are variables that are not directly observed but are rather inferred (through a mathematical model) from other variables that are observed (directly measured). Mathematical models that aim to explain observed variables in terms of latent variables are called latent variable models. Latent variable models are used in many disciplines, including psychology, demography, economics, engineering, medicine, physics, machine learning/artificial intelligence, bioinformatics, chemometrics, natural language processing, econometrics, management and the social sciences.
Automated Compilation of Probabilistic Task Description into Executable Neural Network Specification
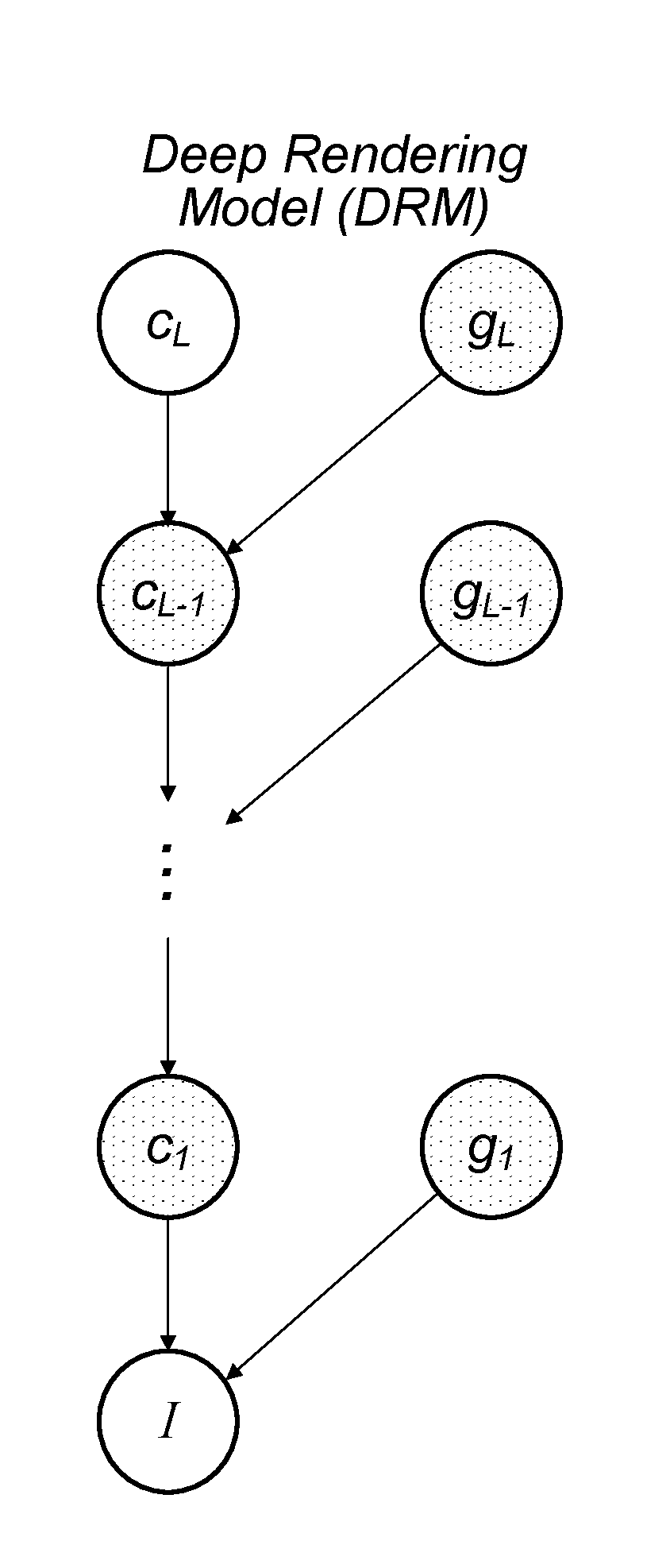
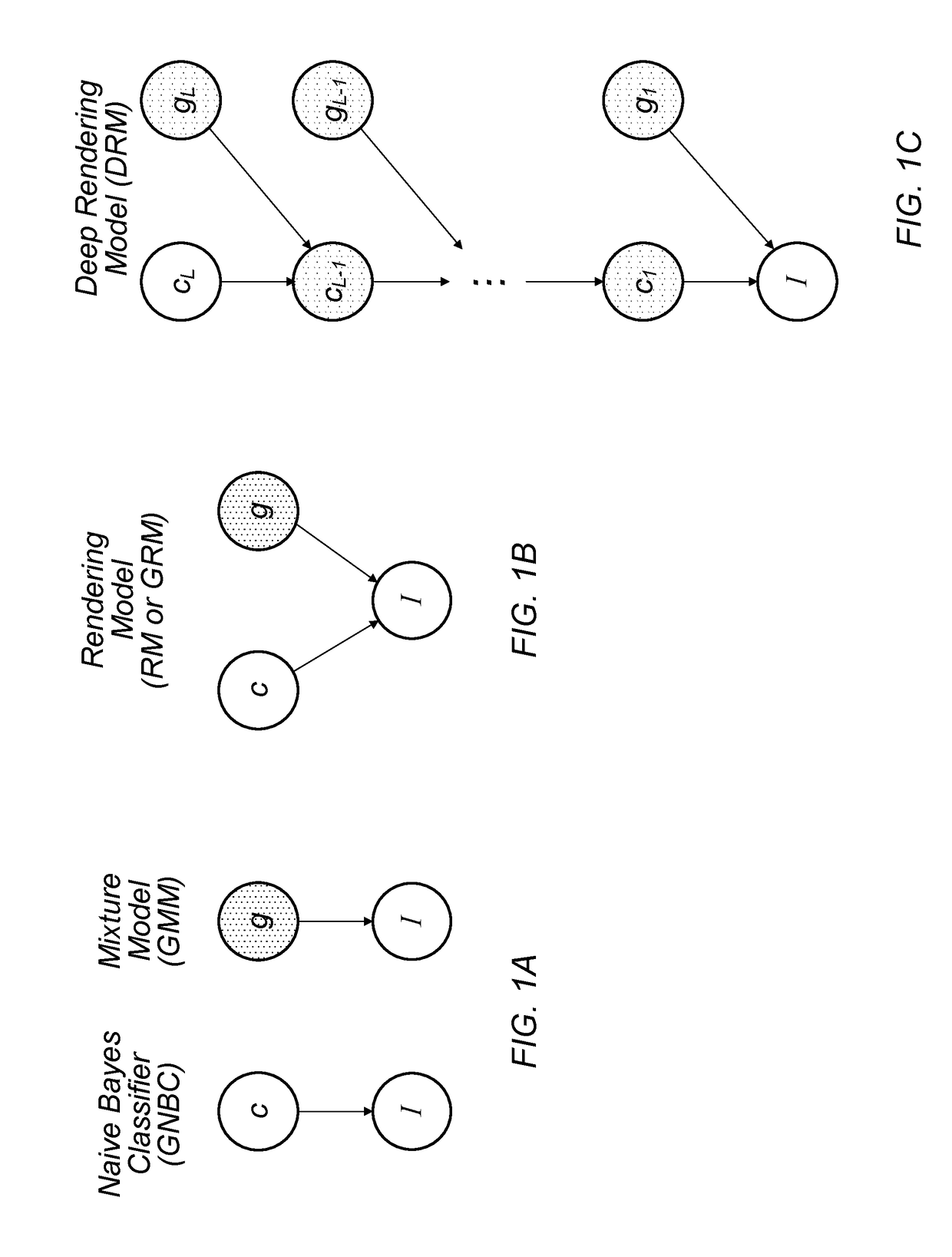
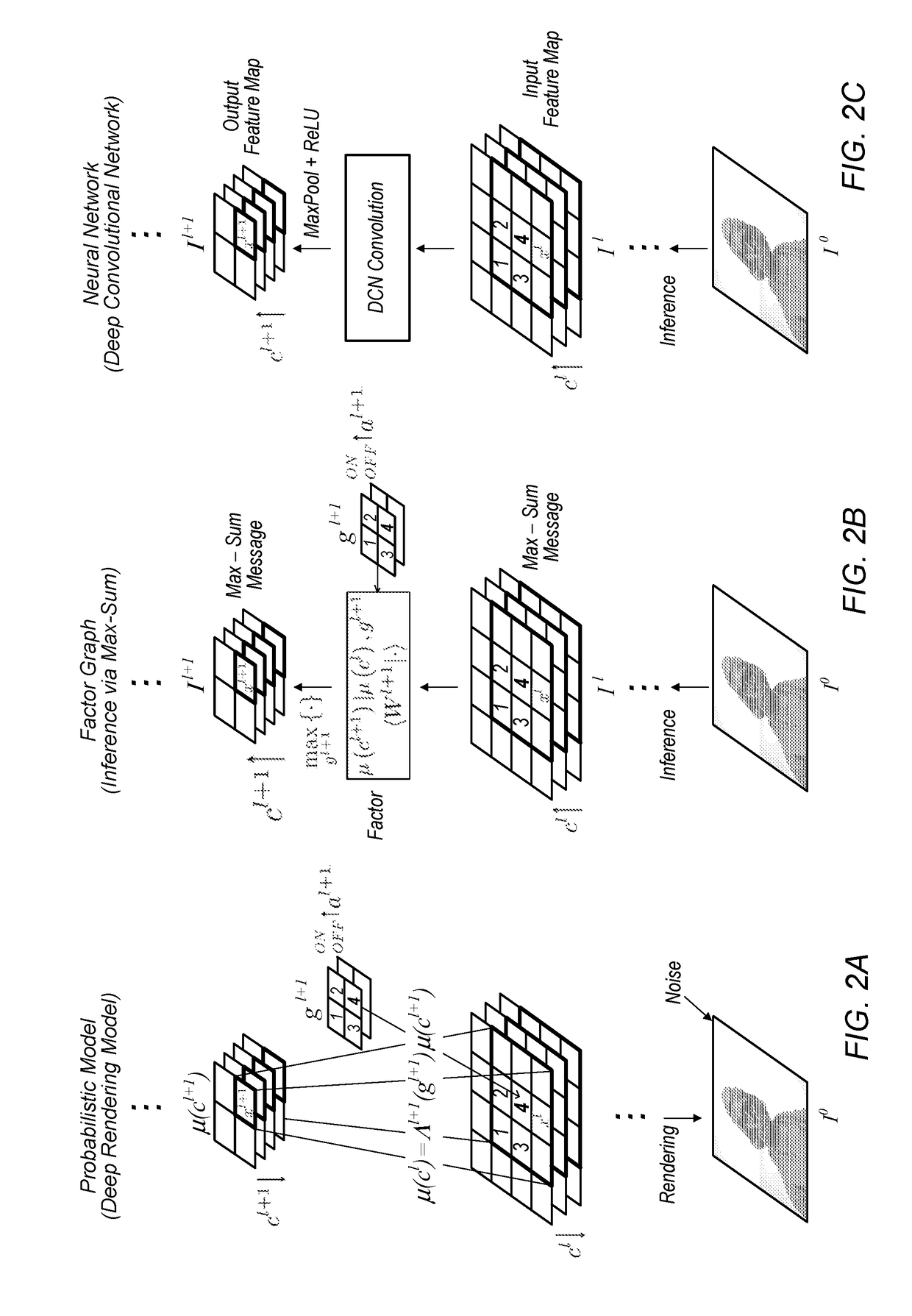
A mechanism for compiling a generative description of an inference task into a neural network. First, an arbitrary generative probabilistic model from the exponential family is specified (or received). The model characterizes a conditional probability distribution for measurement data given a set of latent variables. A factor graph is generated for the generative probabilistic model. Each factor node of the factor graph is expanded into a corresponding sequence of arithmetic operations, based on a specified inference task and a kind of message passing algorithm. The factor graph and the sequences of arithmetic operations specify the structure of a neural network for performance of the inference task. A learning algorithm is executed, to determine values of parameters of the neural network. The neural network is then ready for performing inference on operational measurements.
Owner:RICE UNIV
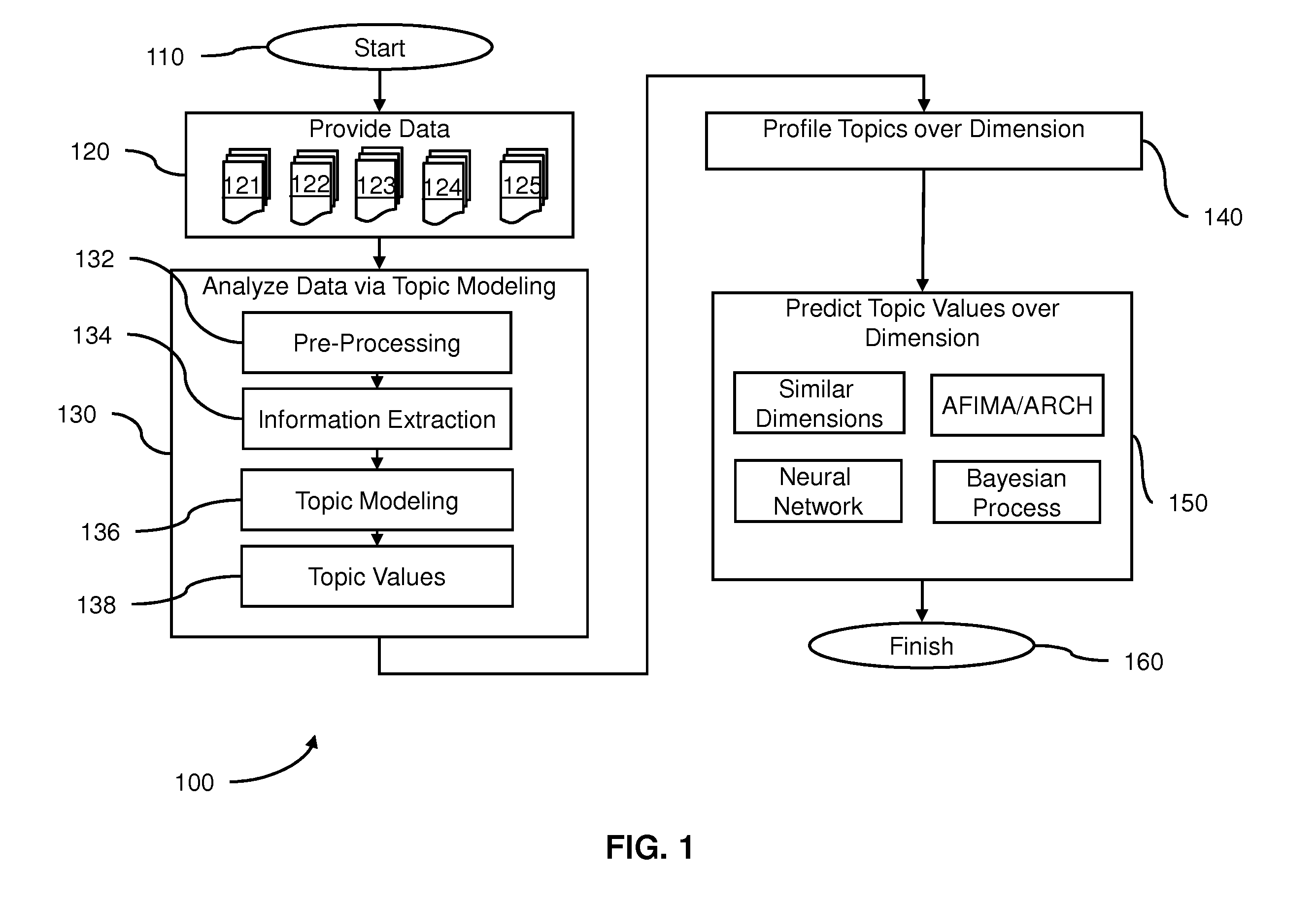
Method and system to predict a data value
ActiveUS20110106743A1Reduce the possibilityReduce the impactKnowledge representationSpecial data processing applicationsTime courseLatent variable
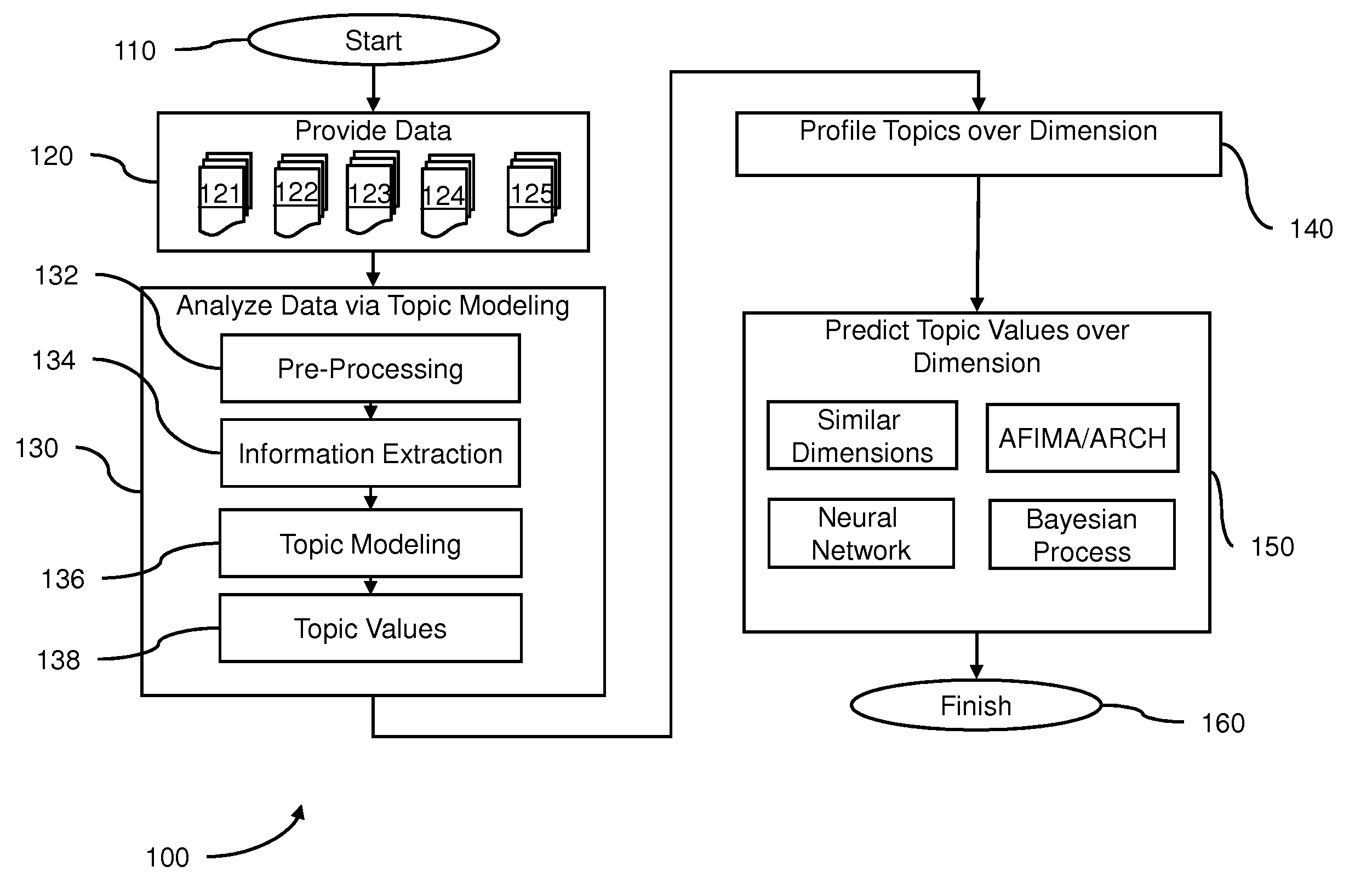
Embodiments of the present invention include methods and systems for predicting the likelihood of topics appearing in a set of data such as text. A number of latent variable methods are used to convert the data into a set of topics, topic values and topic profiles. A number of time-course methods are used to model how topic values change given previous topic profiles, or to find historical times with similar topic values and then projecting the topic profile forward from that historical time to predict the likelihood of the topics appearing. Embodiments include utilizing focus topics, such as valence topics, and data representing financial measures to predict the likelihood of topics. Methods and systems for modeling data and predicting the likelihood of topics over other dimensions are also contemplated.
Owner:APTIMA
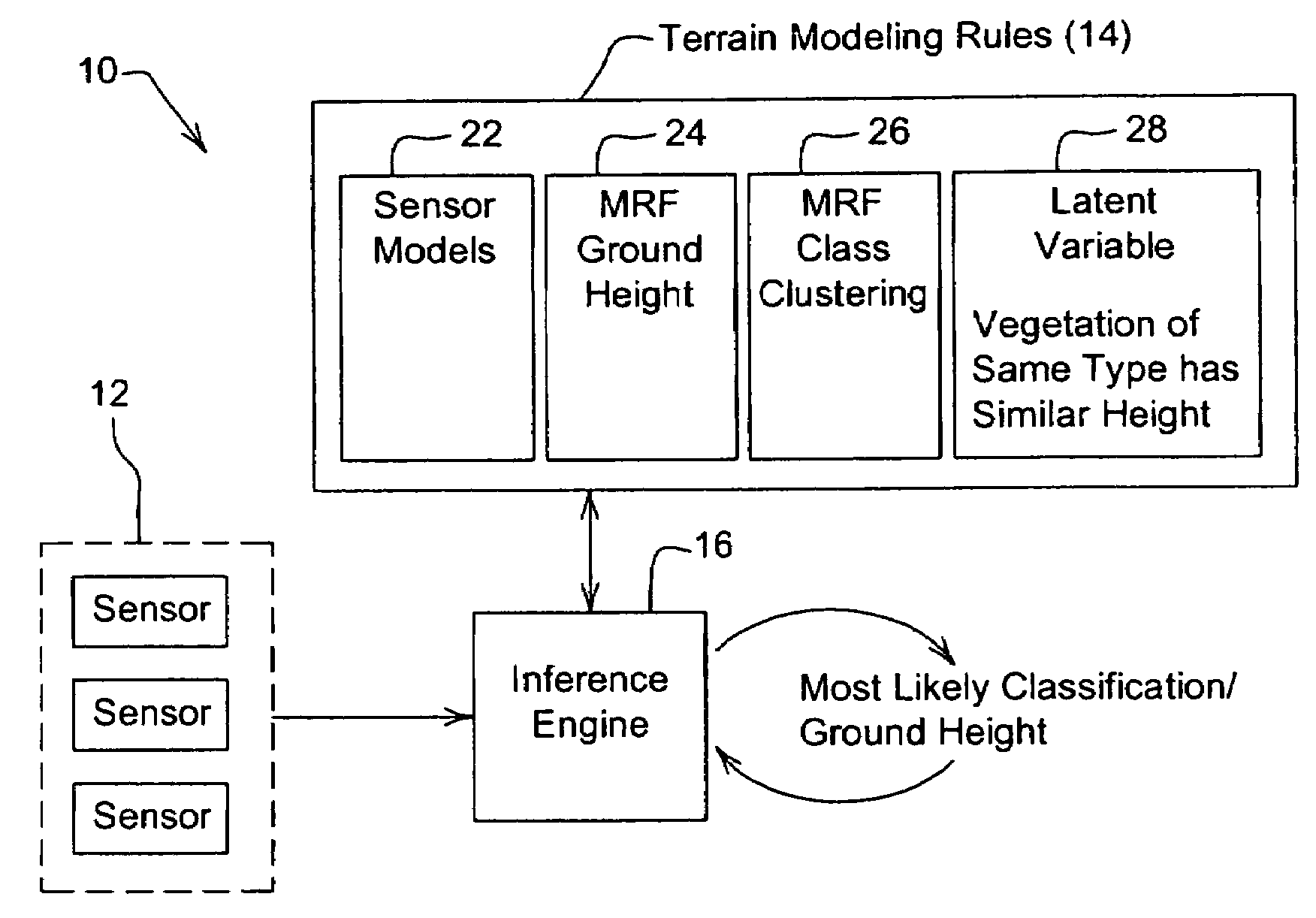
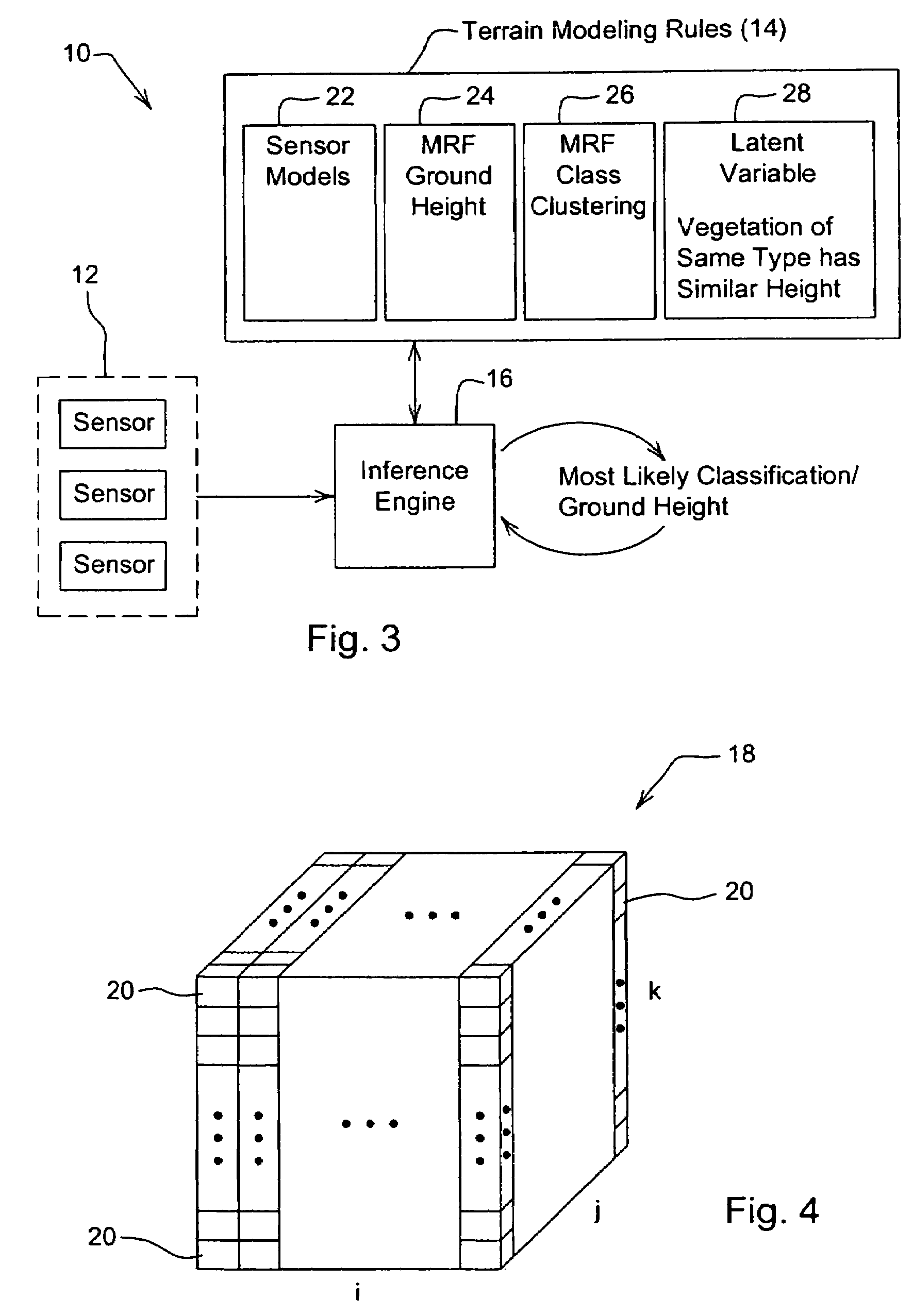
System and method for generating a terrain model for autonomous navigation in vegetation
ActiveUS20070280528A1Stable and robust navigationAccurate estimateVehicle position/course/altitude controlVehiclesProbabilistic methodTerrain
The disclosed terrain model is a generative, probabilistic approach to modeling terrain that exploits the 3D spatial structure inherent in outdoor domains and an array of noisy but abundant sensor data to simultaneously estimate ground height, vegetation height and classify obstacles and other areas of interest, even in dense non-penetrable vegetation. Joint inference of ground height, class height and class identity over the whole model results in more accurate estimation of each quantity. Vertical spatial constraints are imposed on voxels within a column via a hidden semi-Markov model. Horizontal spatial constraints are enforced on neighboring columns of voxels via two interacting Markov random fields and a latent variable. Because of the rules governing abstracts, this abstract should not be used to construe the claims.
Owner:CARNEGIE MELLON UNIV
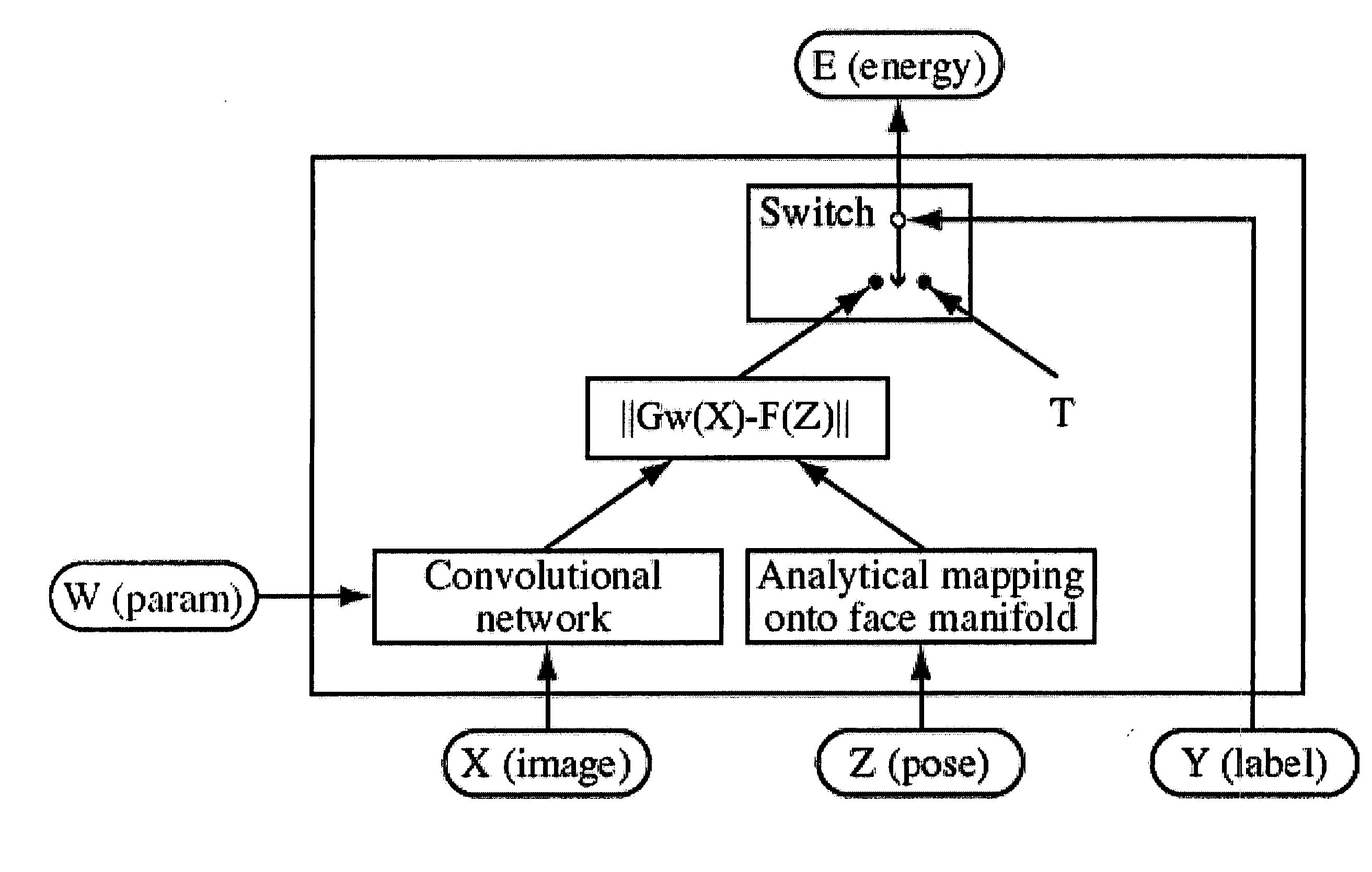
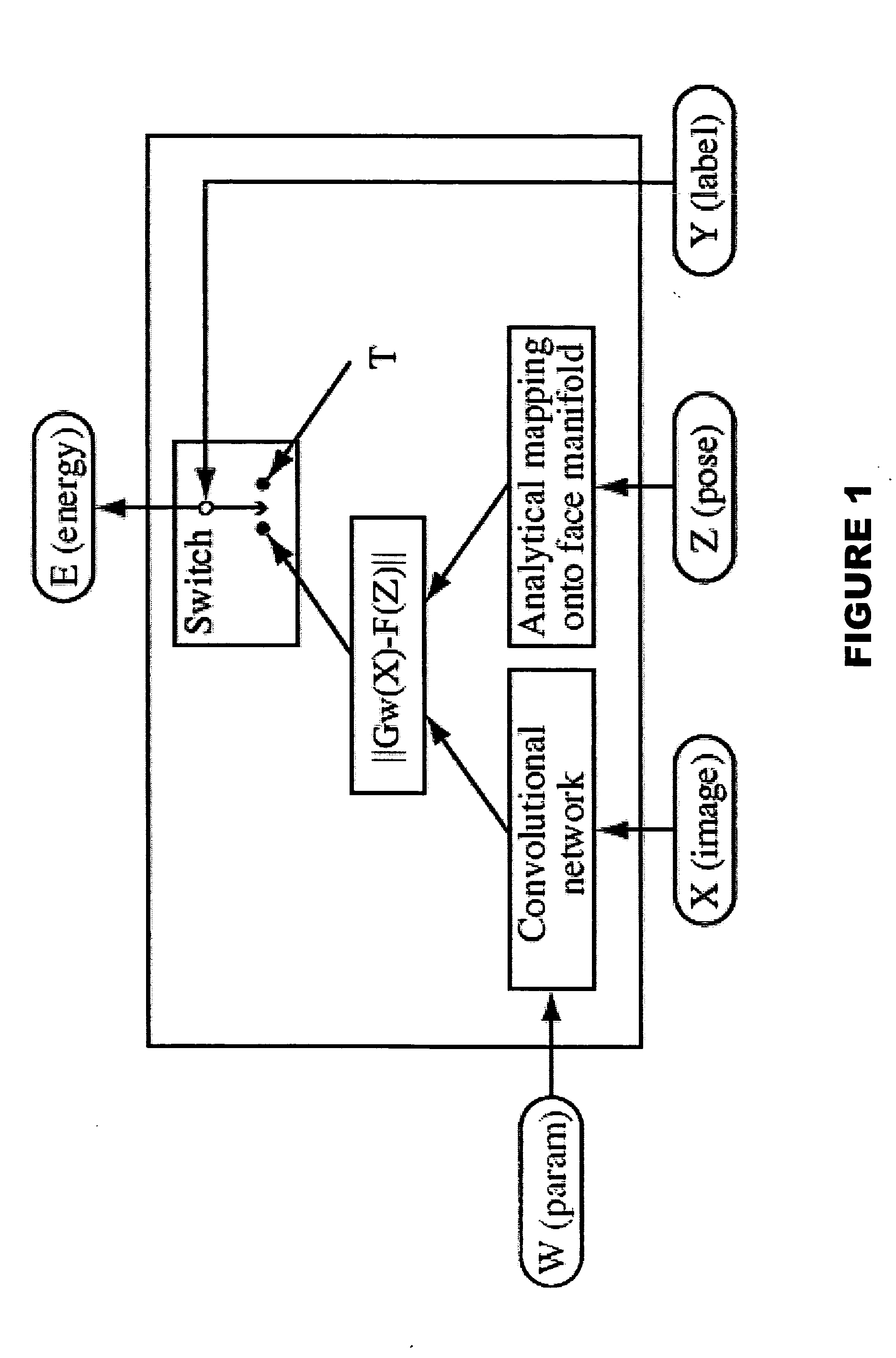
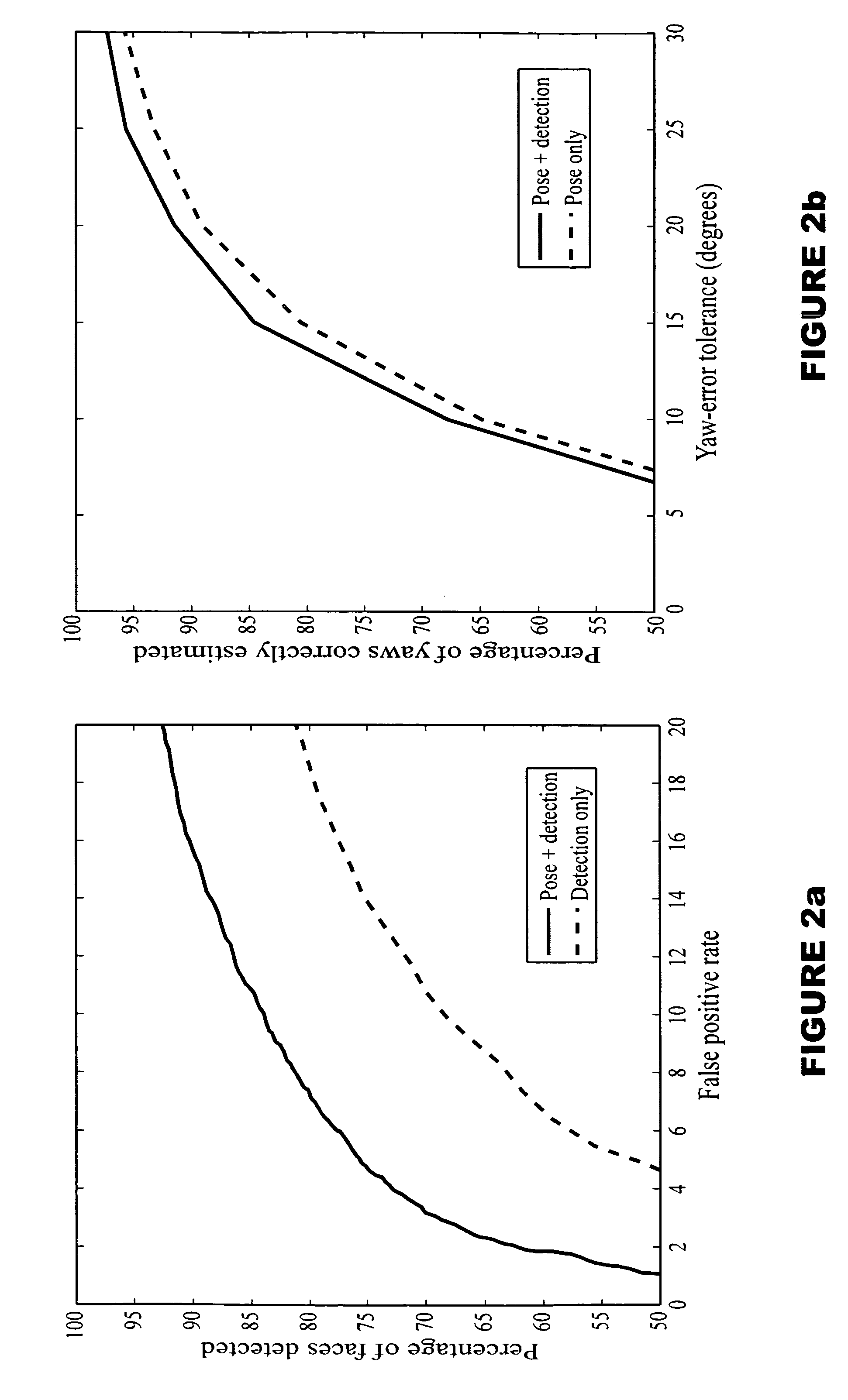
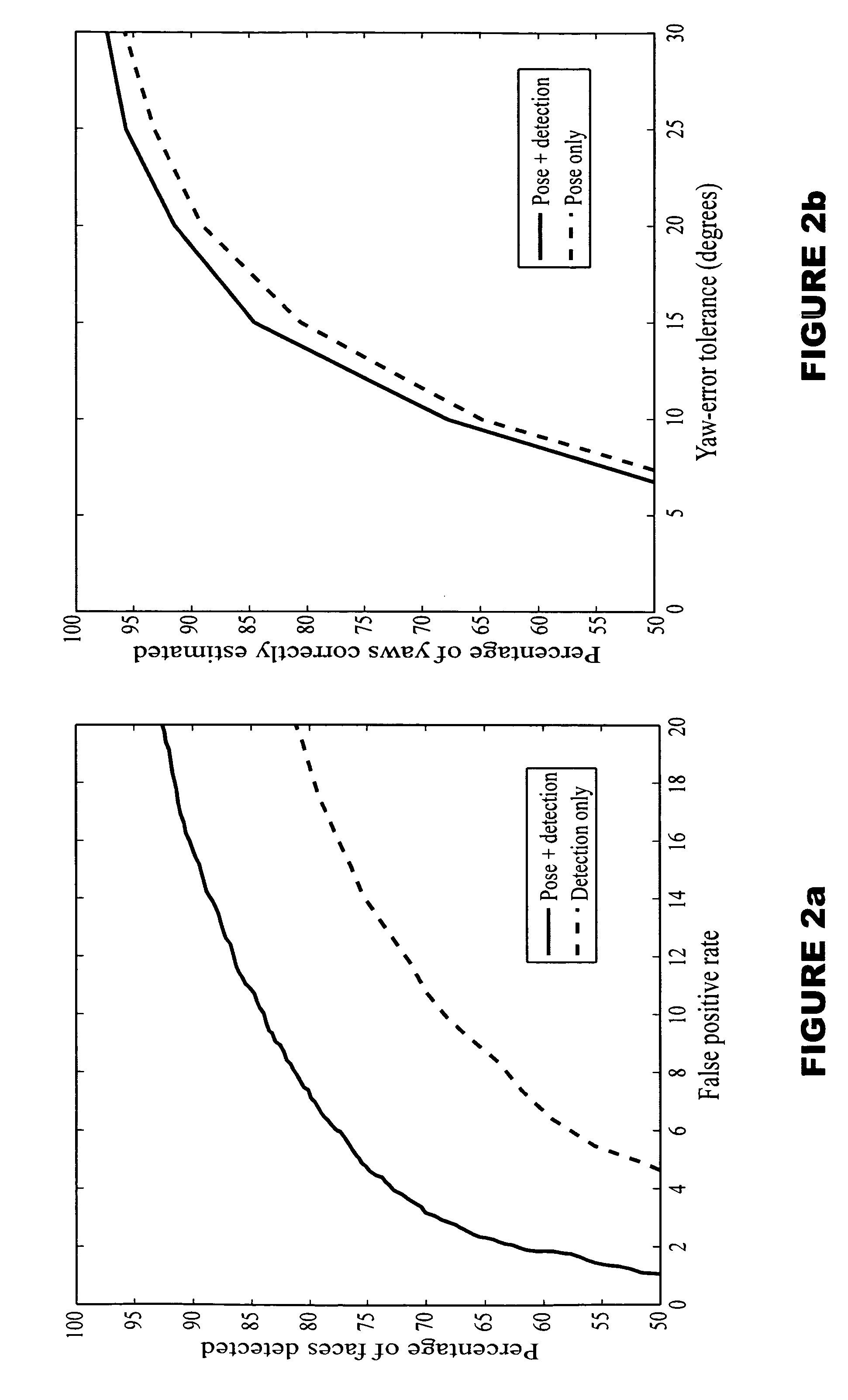
Synergistic face detection and pose estimation with energy-based models
ActiveUS20060034495A1Improve reliabilityThree-dimensional object recognitionFace detectionEnergy minimization
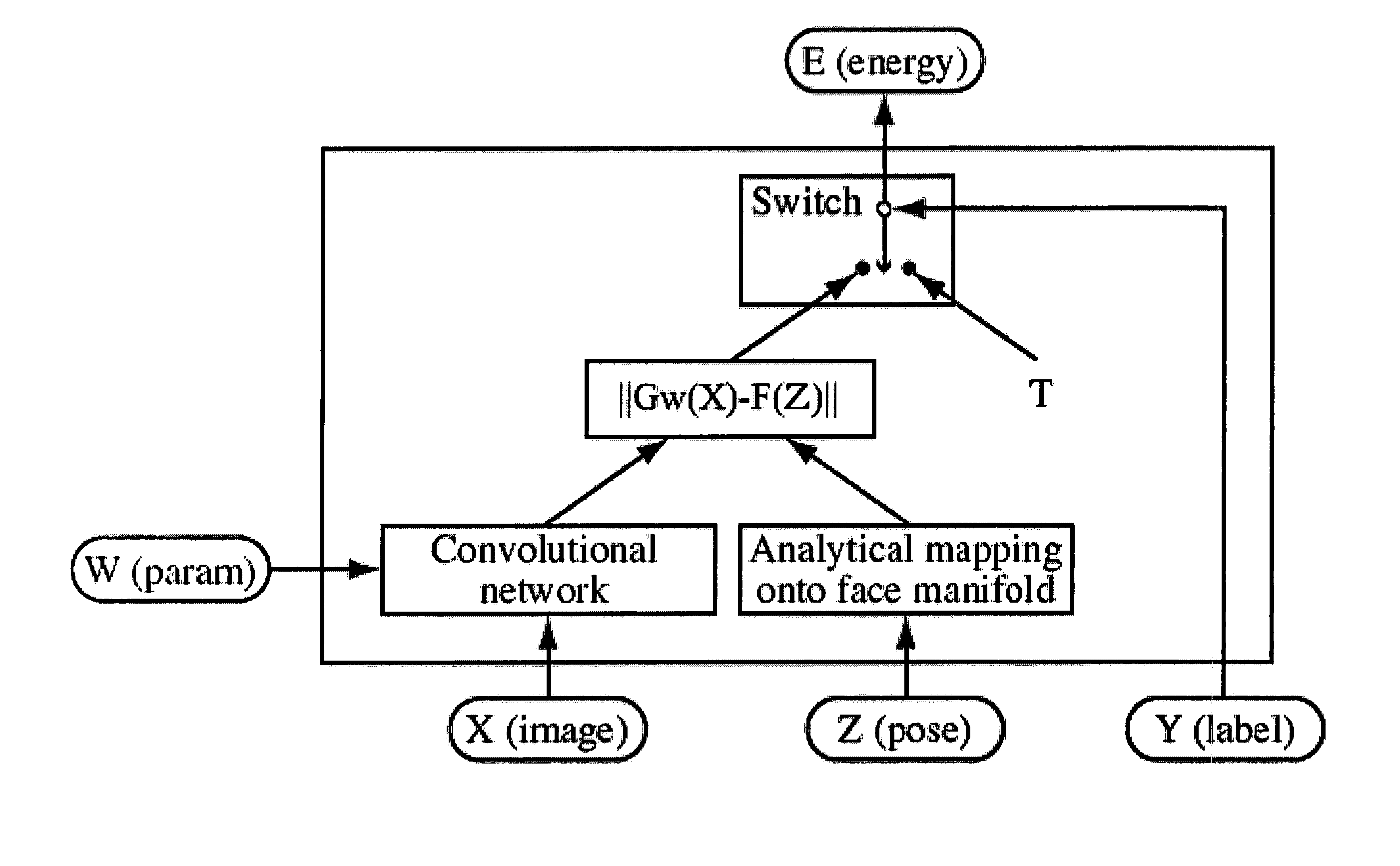
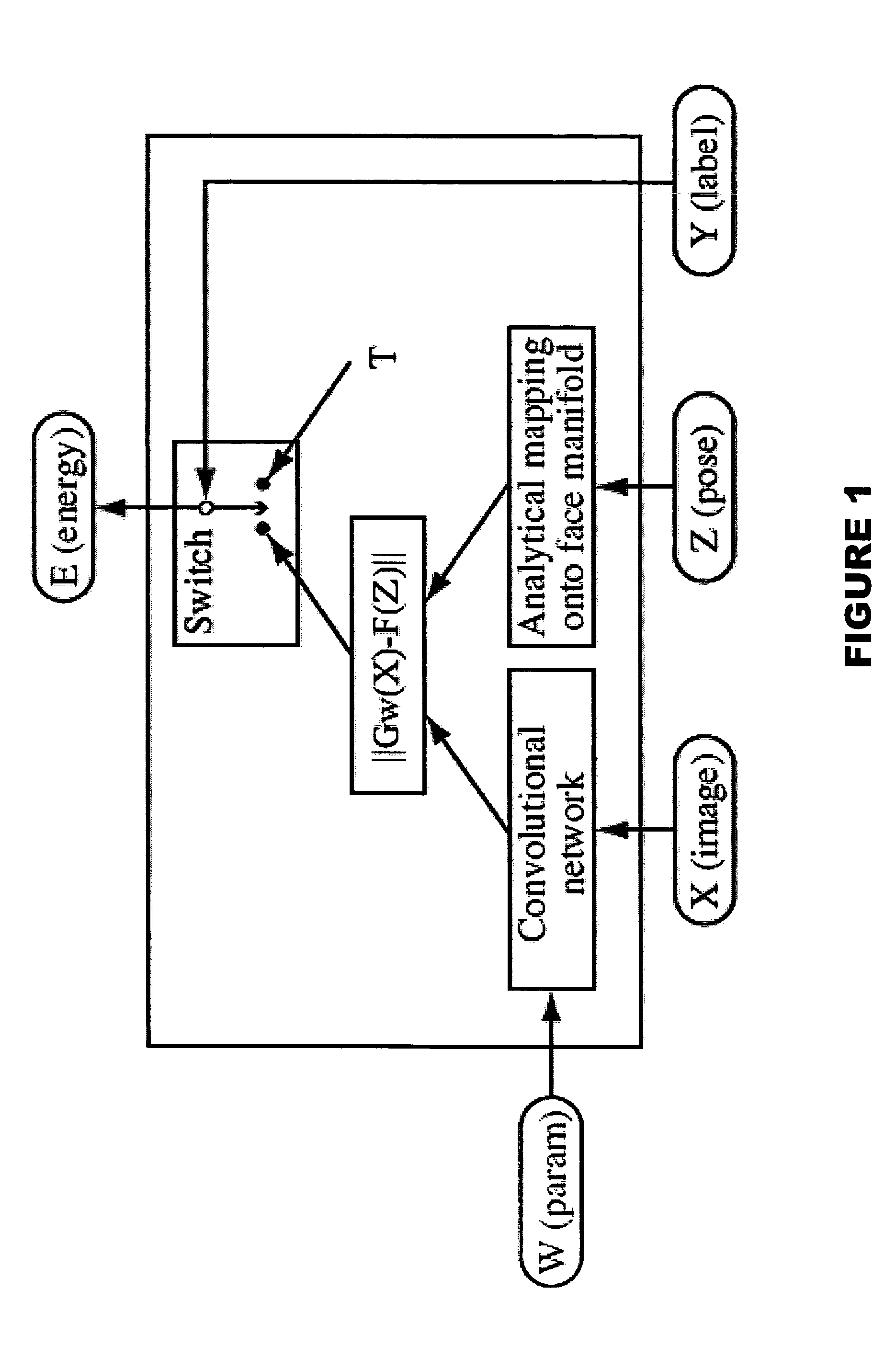
A method for human face detection that detects faces independently of their particular poses and simultaneously estimates those poses. Our method exhibits an immunity to variations in skin color, eyeglasses, facial hair, lighting, scale and facial expressions, and others. In operation, we train a convolutional neural network to map face images to points on a face manifold, and non-face images to points far away from that manifold, wherein that manifold is parameterized by facial pose. Conceptually, we view a pose parameter as a latent variable, which may be inferred through an energy-minimization process. To train systems based upon our inventive method, we derive a new type of discriminative loss function that is tailored to such detection tasks. Our method enables a multi-view detector that can detect faces in a variety of poses, for example, looking left or right (yaw axis), up or down (pitch axis), or tilting left or right (roll axis). Systems employing our method are highly-reliable, run at near real time (5 frames per second on conventional hardware), and is robust against variations in yaw (±90°), roll (±45°), and pitch (±60°).
Owner:NEC CORP
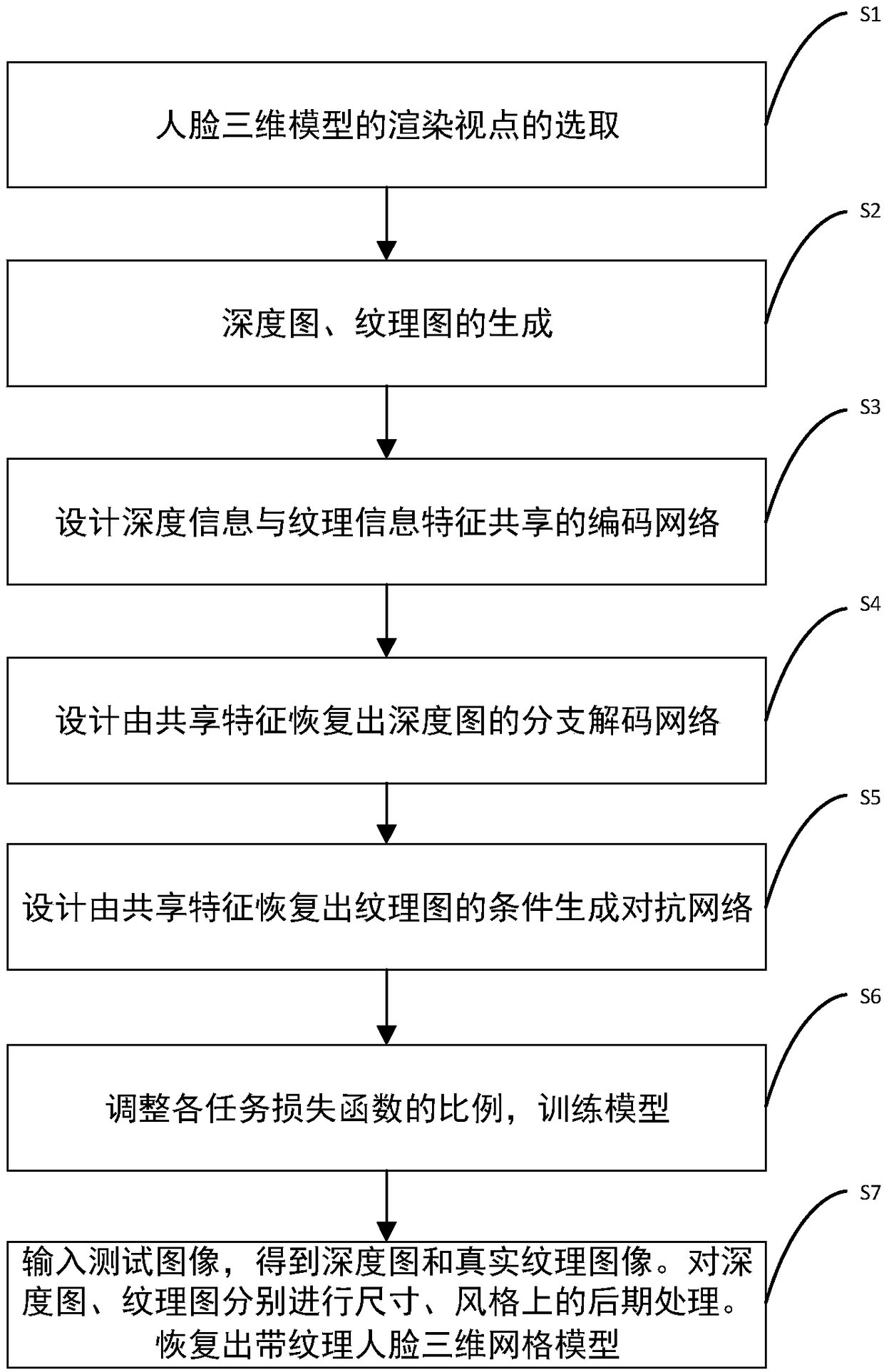
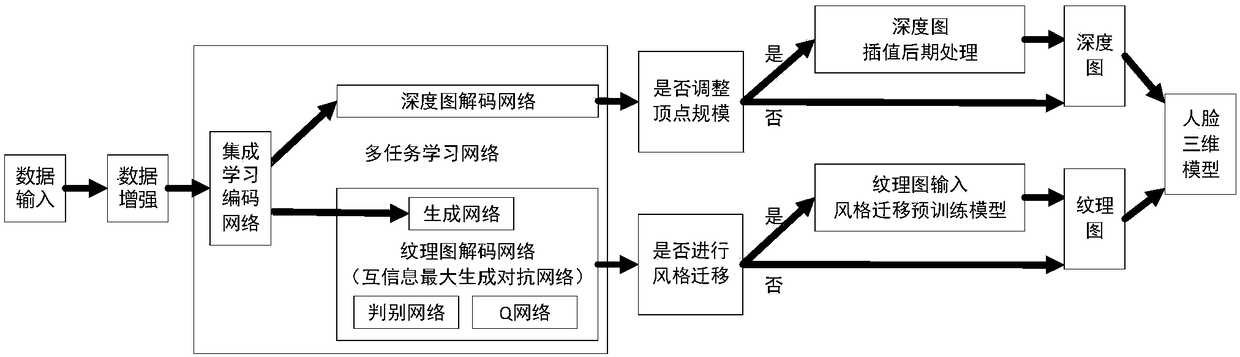
A method for 3D reconstruction and texture generation from single-view face based on multi-task learning
The invention discloses a method for 3D reconstruction and texture generation from single-view face based on multi-task learning, belonging to the computer vision field. The method comprises the following steps of: selecting a special viewpoint for rendering a three-dimensional human face model; generating depth map and texture map as truth value data from special viewpoint; designing an integrated learning and coding network based on feature sharing of depth information and texture information; designing the branch decoding network to recover the depth map from the shared features, and recovering the depth map, designing the mutual information with shared features as latent variables to maximize the generation of antagonistic network, and restoring the texture unwrapping map, adjusting the proportion of each task loss function and training the model; interpolating the depth map and using texture map to reconstruct the 3D face mesh model with texture details. The invention utilizes multi-task learning to carry out single-view face three-dimensional reconstruction, texture generation and style migration, and has the advantages of high speed, low cost and the like.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Synergistic face detection and pose estimation with energy-based models
ActiveUS7236615B2Improve reliabilityPictoral communicationThree-dimensional object recognitionFace detectionEnergy minimization
A method for human face detection that detects faces independently of their particular poses and simultaneously estimates those poses. Our method exhibits an immunity to variations in skin color, eyeglasses, facial hair, lighting, scale and facial expressions, and others. In operation, we train a convolutional neural network to map face images to points on a face manifold, and non-face images to points far away from that manifold, wherein that manifold is parameterized by facial pose. Conceptually, we view a pose parameter as a latent variable, which may be inferred through an energy-minimization process. To train systems based upon our inventive method, we derive a new type of discriminative loss function that is tailored to such detection tasks. Our method enables a multi-view detector that can detect faces in a variety of poses, for example, looking left or right (yaw axis), up or down (pitch axis), or tilting left or right (roll axis). Systems employing our method are highly-reliable, run at near real time (5 frames per second on conventional hardware), and is robust against variations in yaw (±90°), roll(±45°), and pitch(±60°).
Owner:NEC CORP
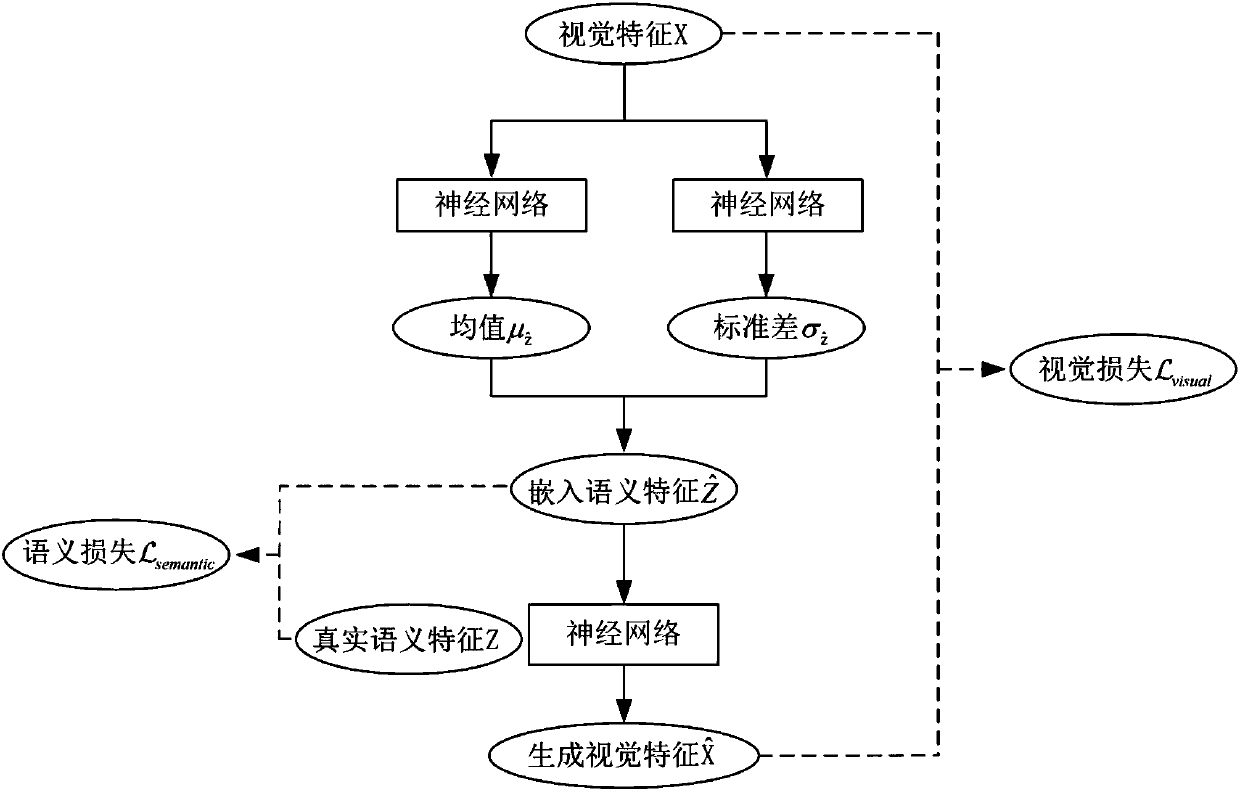
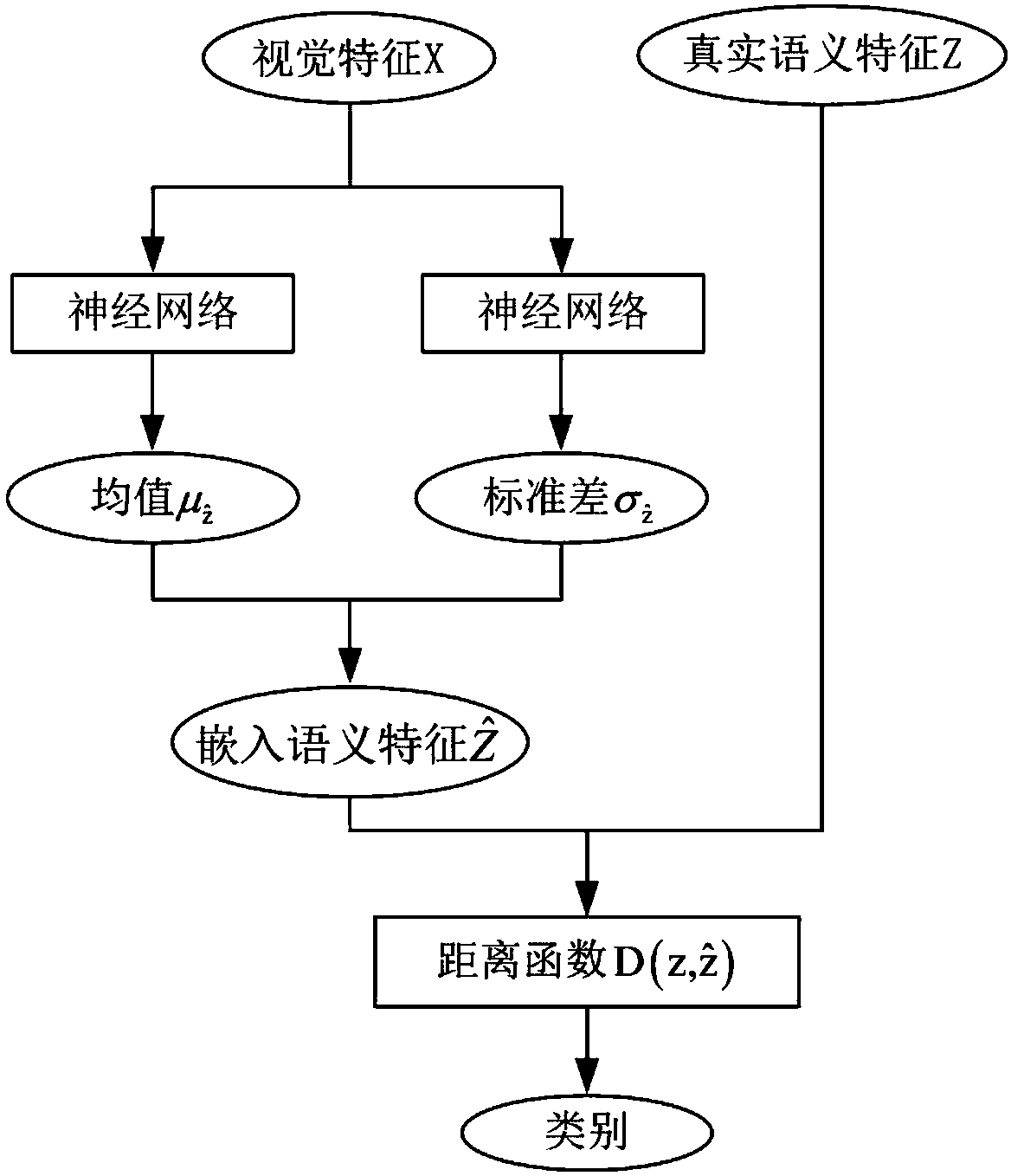
Variational automatic encoder-based zero-sample image classification method
InactiveCN107679556AEffective semantic associationFully consider the probability distribution characteristicsCharacter and pattern recognitionNeural architecturesClassification methodsSample image
The present invention relates to a zero-sample classification technology in the computer vision field, in particular, a variational automatic encoder-based zero-sample image classification method. Asto the zero-sample image classification method, the distribution of the mappings of semantic features and visual features of categories in a semantic space is fitted, and more efficient semantic associations between the visual features and category semantics are built. According to the variational automatic encoder-based zero-sample image classification method, a variational automatic encoder is adopted to generate embedded semantic features on the basis of the visual features; it is regarded that the variational automatic encoder has a latent variable Z<^>; the latent variable Z<^> is adoptedas an embedded semantic feature; as for a zero-sample image classification task and the visual feature xj of a category-unknown sample, the encoding network of the variational automatic encoder whichis trained on visual categories is utilized to calculate a latent variable Z<^>j which is generated through encoding; the latent variable Z<^>j is adopted as an embedded semantic feature, cosine distances between the latent variable Z<^>j and the semantic feature of each invisible category are calculated, wherein the semantic feature of each invisible category is represented by a symbol describedin the descriptions of the invention; and a category of which the semantic feature is separated from the latent variable Z<^>j by the smallest distance is regarded as the category of the vision sample. The method of the present invention is mainly applied to video classification conditions.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
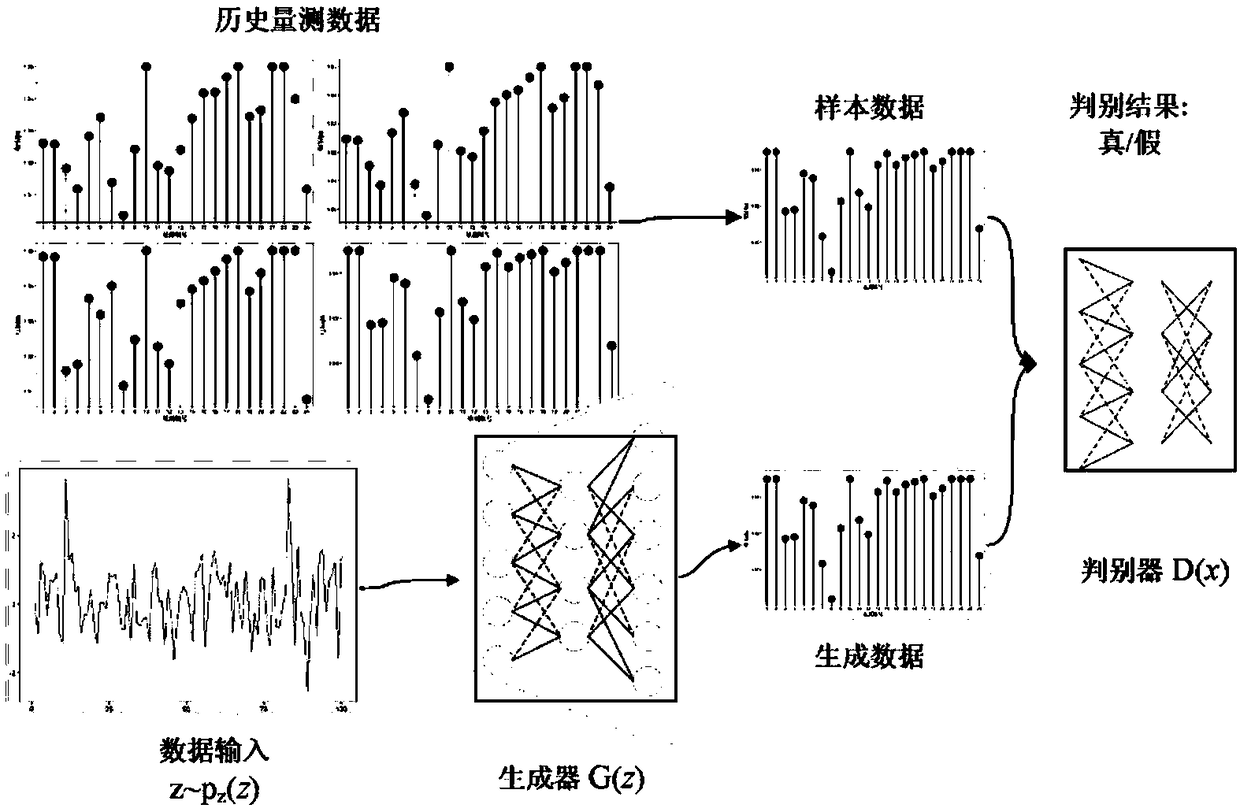
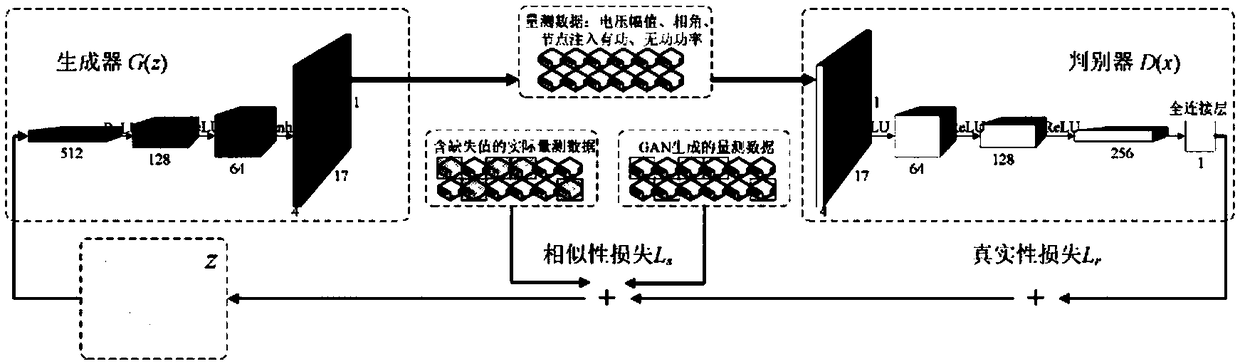
Power system measurement missing value reconstruction method based on depth learning and application thereof
InactiveCN109144987AHigh precisionImprove reconstruction accuracyData processing applicationsDigital data information retrievalNerve networkAlgorithm
The invention relates to a power system measurement missing value reconstruction method based on depth learning. The reconstruction method comprises the following steps: cleaning and selecting the measured historical data from SCADA to obtain a training set of a neural network; an improved generative countermeasure network based on Wasserstein distance being constructed and trained; Adam being chosen as the optimizer to optimize the latent variable of WGAN network, and the improved GAN based on Wasserstein distance being obtained; the measurement data with missing values and corresponding binary mask matrix being inputted into the WGAN network model, and the reconstructed measurement data being finally obtained. The method can be applied to data cleaning and correction or to reconstructionof lost measurements when the system is attacked by communication. As the neural network of the invention automatically learn the complex spatio-temporal relationship which is difficult to be explicitly modeled such as the correlation between measurement and the load fluctuation rule, the feasibility of taking the reconstructed data as a pseudo measurement is ensured.
Owner:天津相和电气科技有限公司
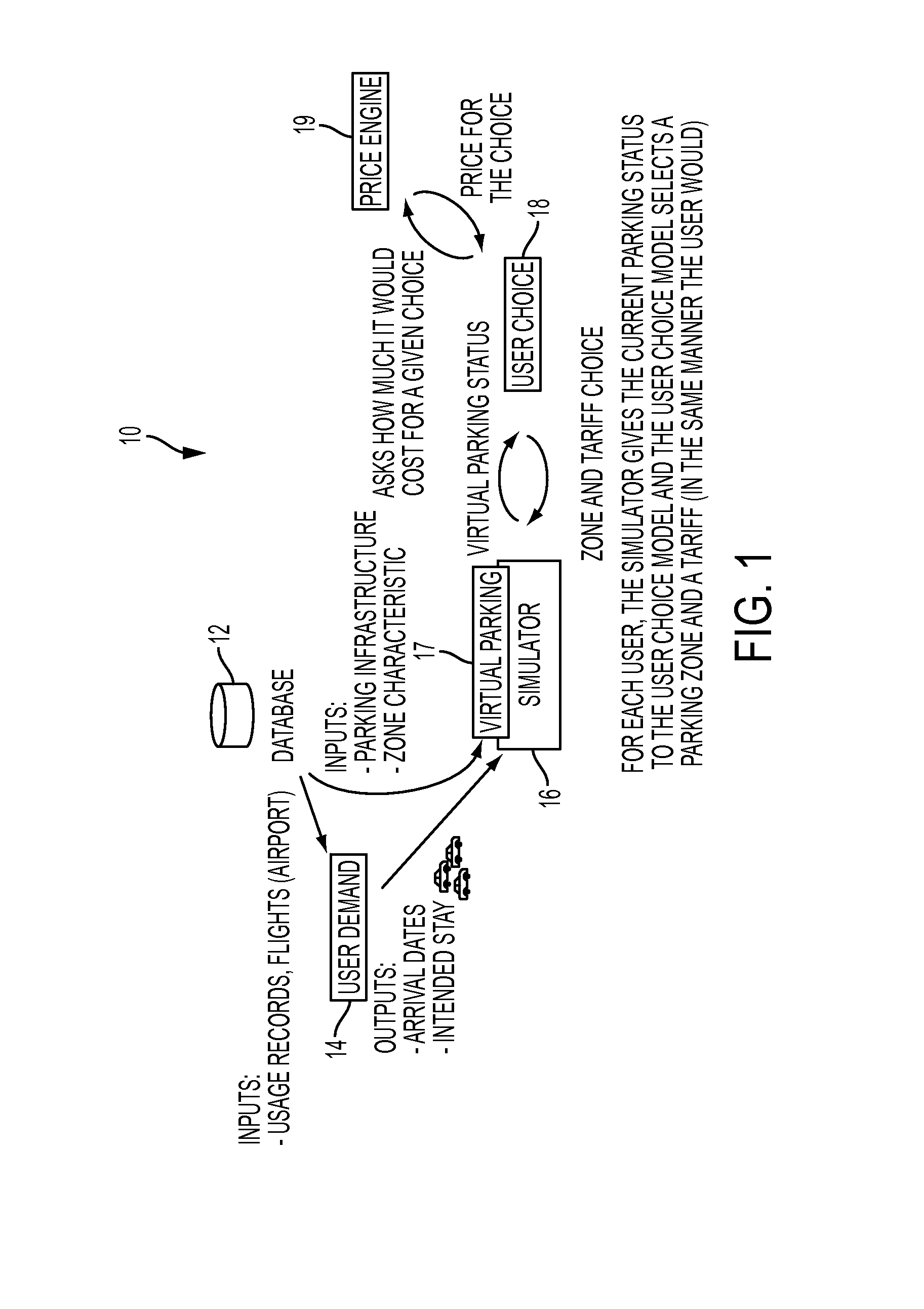
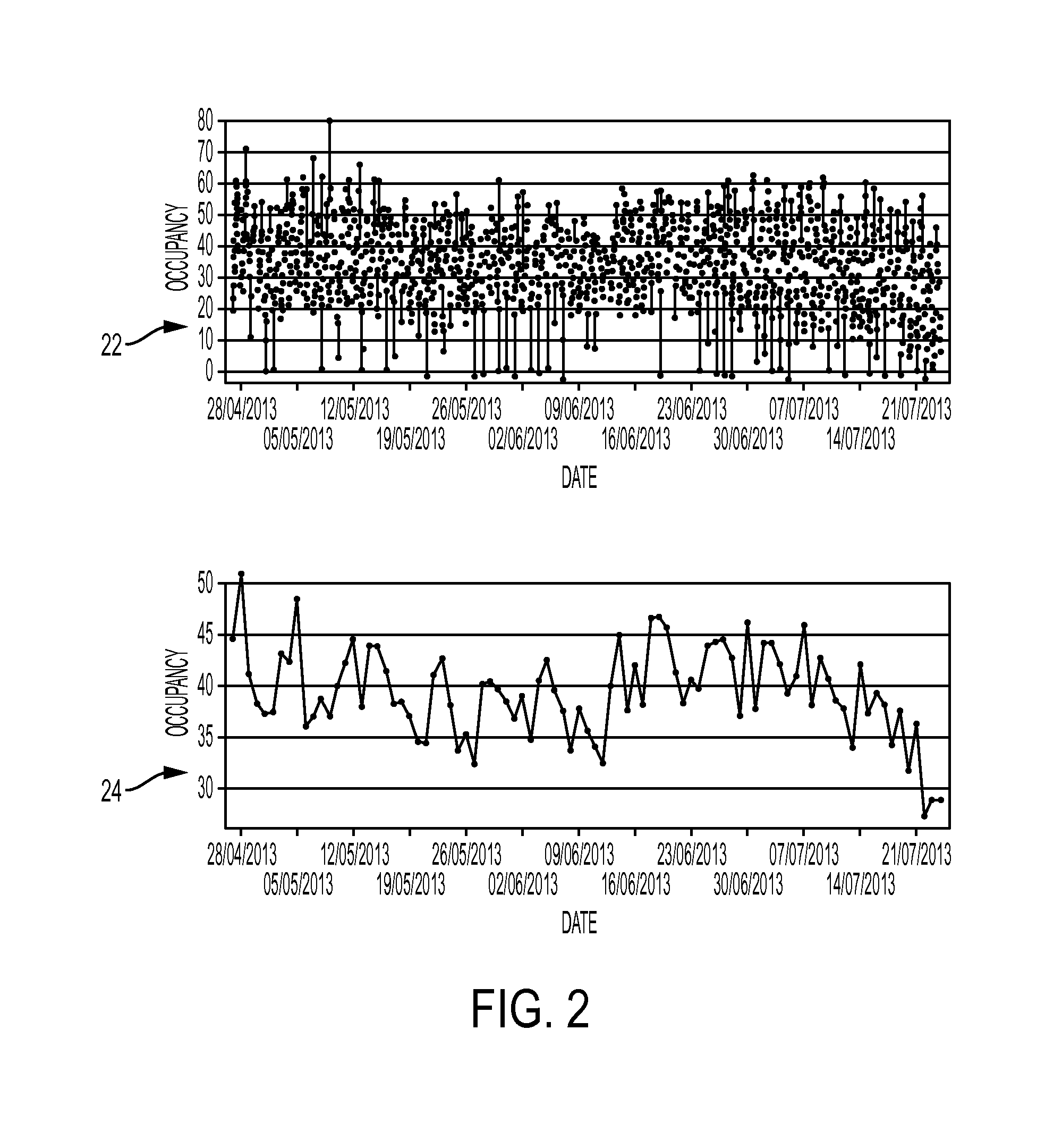
Method and system for simulating users in the context of a parking lot based on the automatic learning of a user choice decision function from historical data considering multiple user behavior profiles
ActiveUS20160247326A1Simple methodMathematical modelsTicket-issuing apparatusLatent variableUser profile
Methods and systems for modeling user arrival and choice in the context of off-street parking solutions. A first component models the arrival and duration of stay of users as a function of time, taking into account different user profiles (or “clusters”), captured by a latent variable. A second component provides a ranking function (for each user cluster), wherein the input features describing the “choice” constitute status variables associated different car park(s), and the output constitutes a preferred car park and a pricing scheme. The system simulates different user behaviors by assuming some standard groups of users will behave similarly. Groups of users or user profiles are learned automatically. The profiles are then employed as a key element for automatically learning a decision function of parking users, and automatically learning one decision function per profile.
Owner:CONDUENT BUSINESS SERVICES LLC
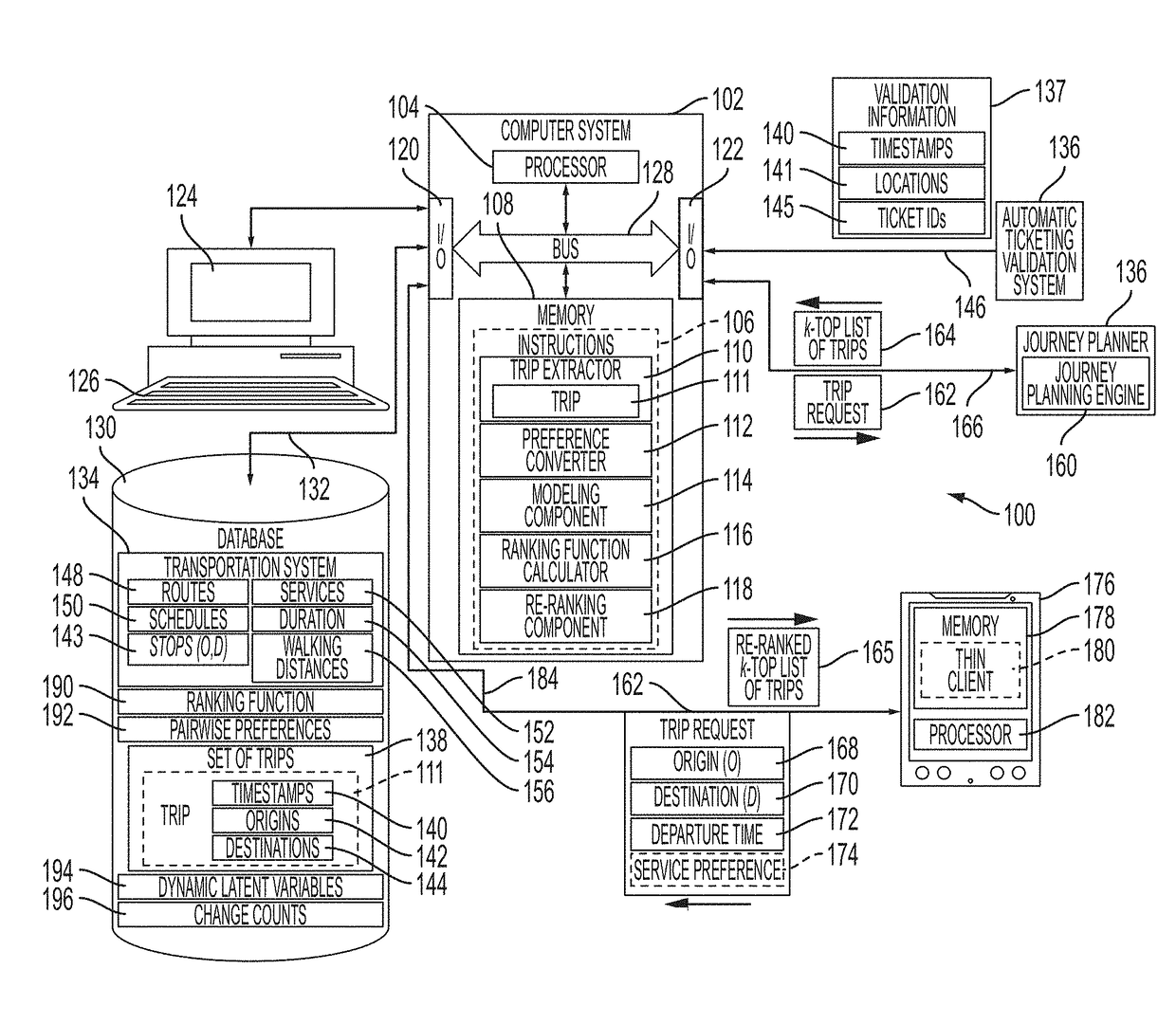
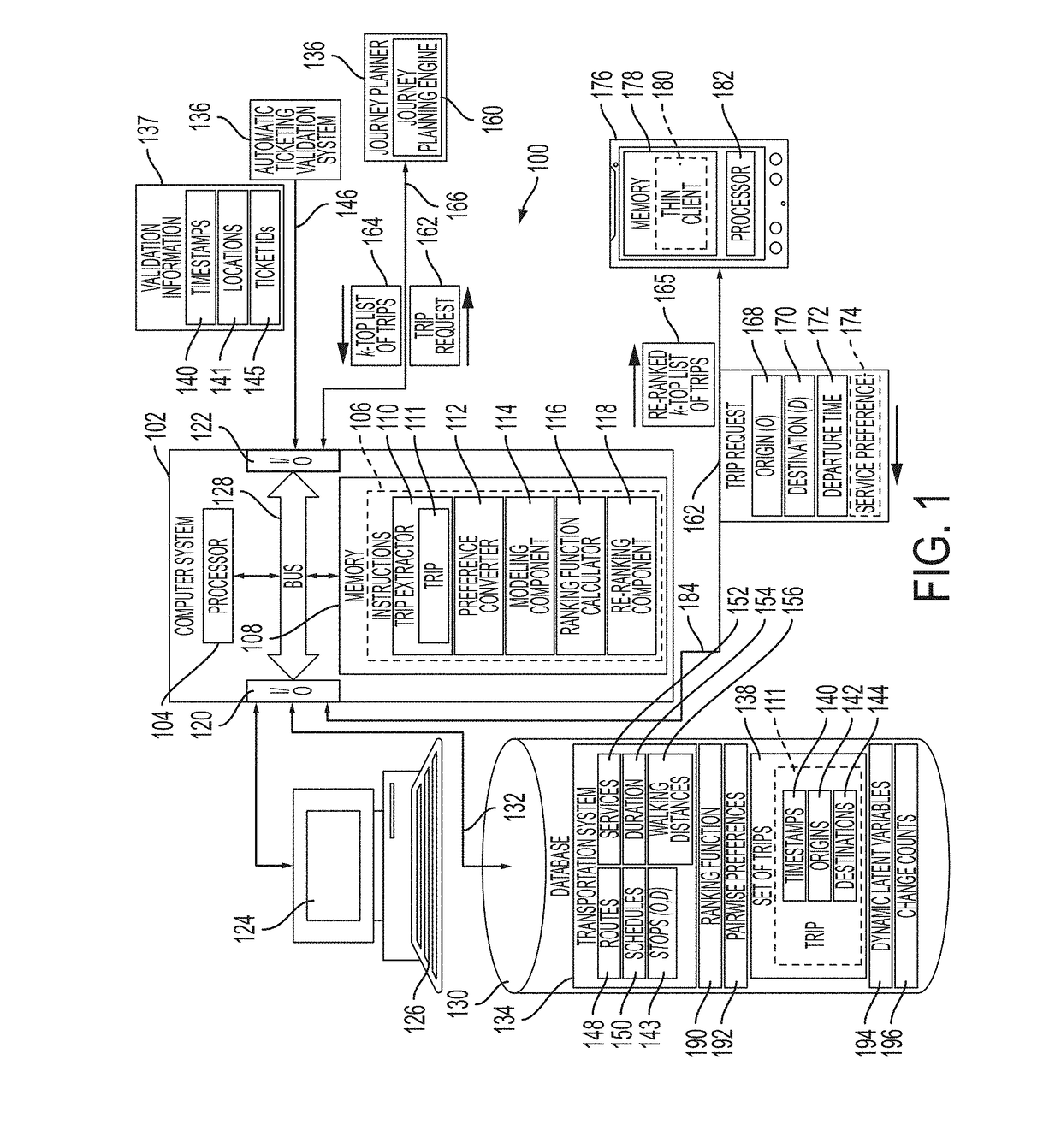
Smoothed dynamic modeling of user traveling preferences in a public transportation system
A method and system are disclosed for generating a list of trips on an associated transportation network, the list ranked in accordance with time-dependent modeling of passenger preferences. User preferences of choosing a specific public transportation service or change point are modeled by a set of latent variables. Any actual trip on the network is converted into a set of pairwise preferences implicitly made by the passenger during the trip. Sequences of services matrices and change points matrices from the retrieved set of trips and non-negative factorization of the services and change points matrices is performed to smooth the matrices. The set of pairwise preferences are used to learn a ranking function and the output of a journey planner is re-ranked using the ranking function.
Owner:CONDUENT BUSINESS SERVICES LLC
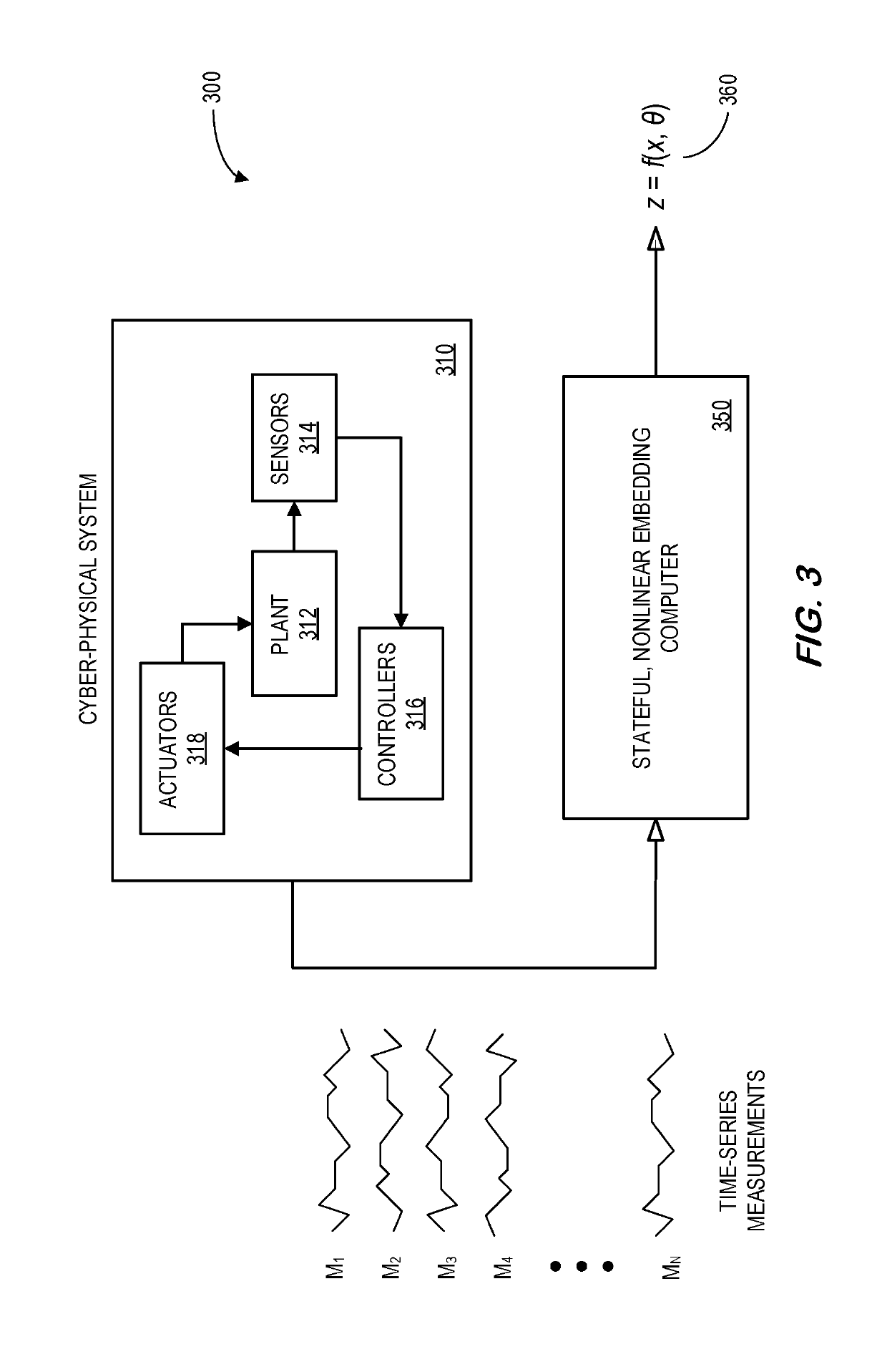
System and method for abstracting characteristics of cyber-physical systems
PendingUS20190228110A1Rapid and accurate mannerRedundant informationNeural architecturesTransmissionNonlinear embeddingData source
A data source may provide a plurality of time-series measurements that represent normal operation of a cyber-physical system (e.g., in substantially real-time during online operation of the cyber-physical system). A stateful, nonlinear embedding computer may receive the plurality of time-series measurements and execute stateful, nonlinear embedding to project the plurality of time-series measurements to a lower-dimensional latent variable space. In this way, redundant and irrelevant information may be reduced, and temporal and spatial dependence among the measurements may be captured. The output of the stateful, nonlinear embedding may be utilized to automatically identify underlying system characteristics of the cyber-physical system. In some embodiments, a stateful generative adversarial network may be used to achieve stateful embedding.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
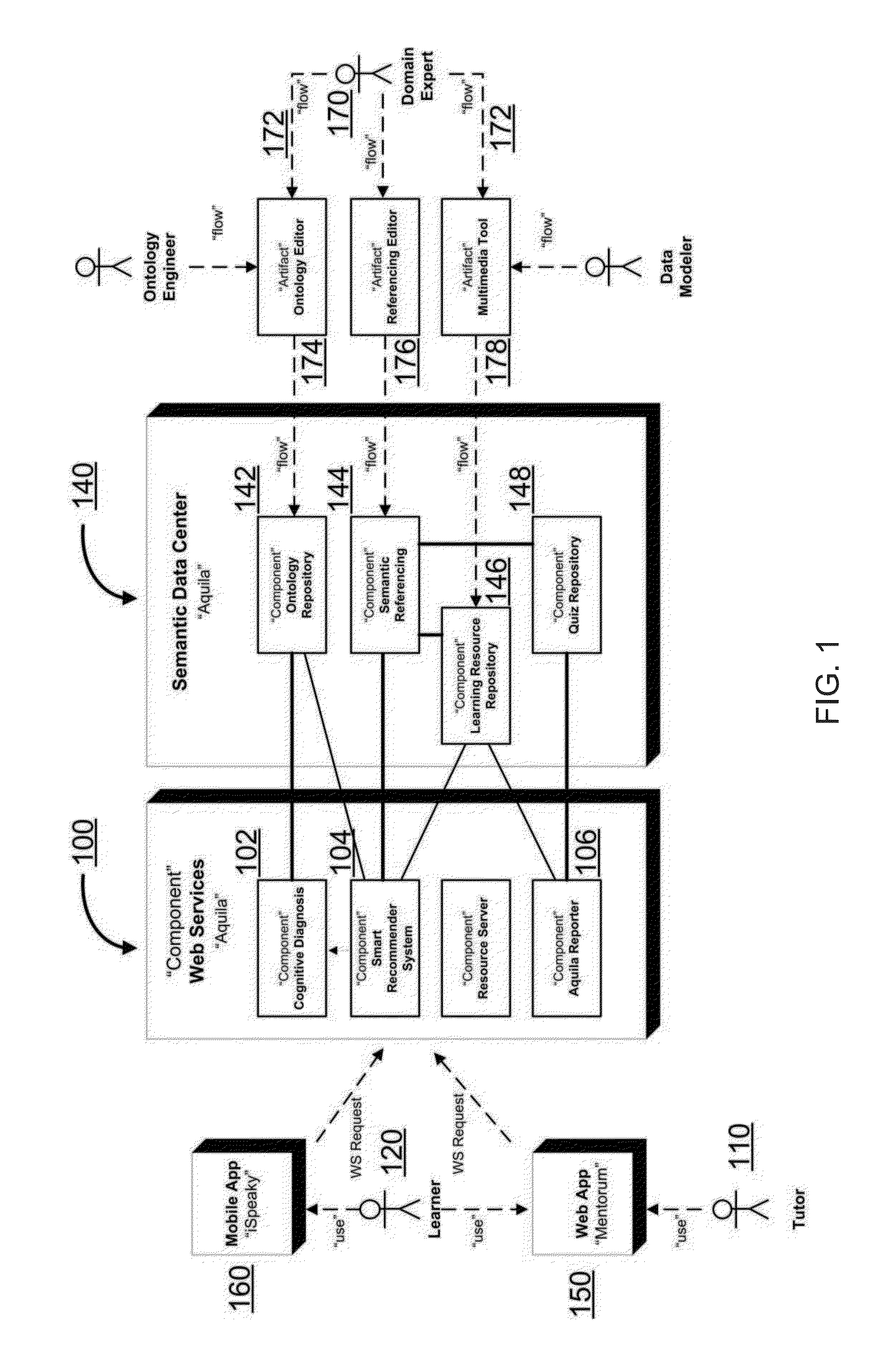
Adaptive e-learning system and method
InactiveUS20160005323A1Low costReduce training timeKnowledge representationInference methodsStudy methodsLearning methods
An adaptive computer-implemented e-learning system and method able to deliver a learning approach that customizes and adapts to each learners' skills and knowhow. A computer-implemented cognitive diagnosis process for predictions on skills and knowledge of a learner comprising the steps of: building a domain ontology; establishing a items bank; referencing the items bank using elements from the domain ontology elements (semantic-grounding of the items); establishing a training database of learners answers; estimating Cognitive Diagnostic Model (CDM) parameters and determining an appropriate model to be used; running the model to estimate a learner level on non-abstract latent variables; applying a Mastery of domain Knowledge and competency Skill (MKS) approach to estimate the learner level on abstract latent variables, or extracting relevant hierarchies from the ontology and use the CDM appropriate model to estimate those attributes; and building a diagnosis report from the results of steps 6) and 7).
Owner:MENTORUM SOLUTIONS
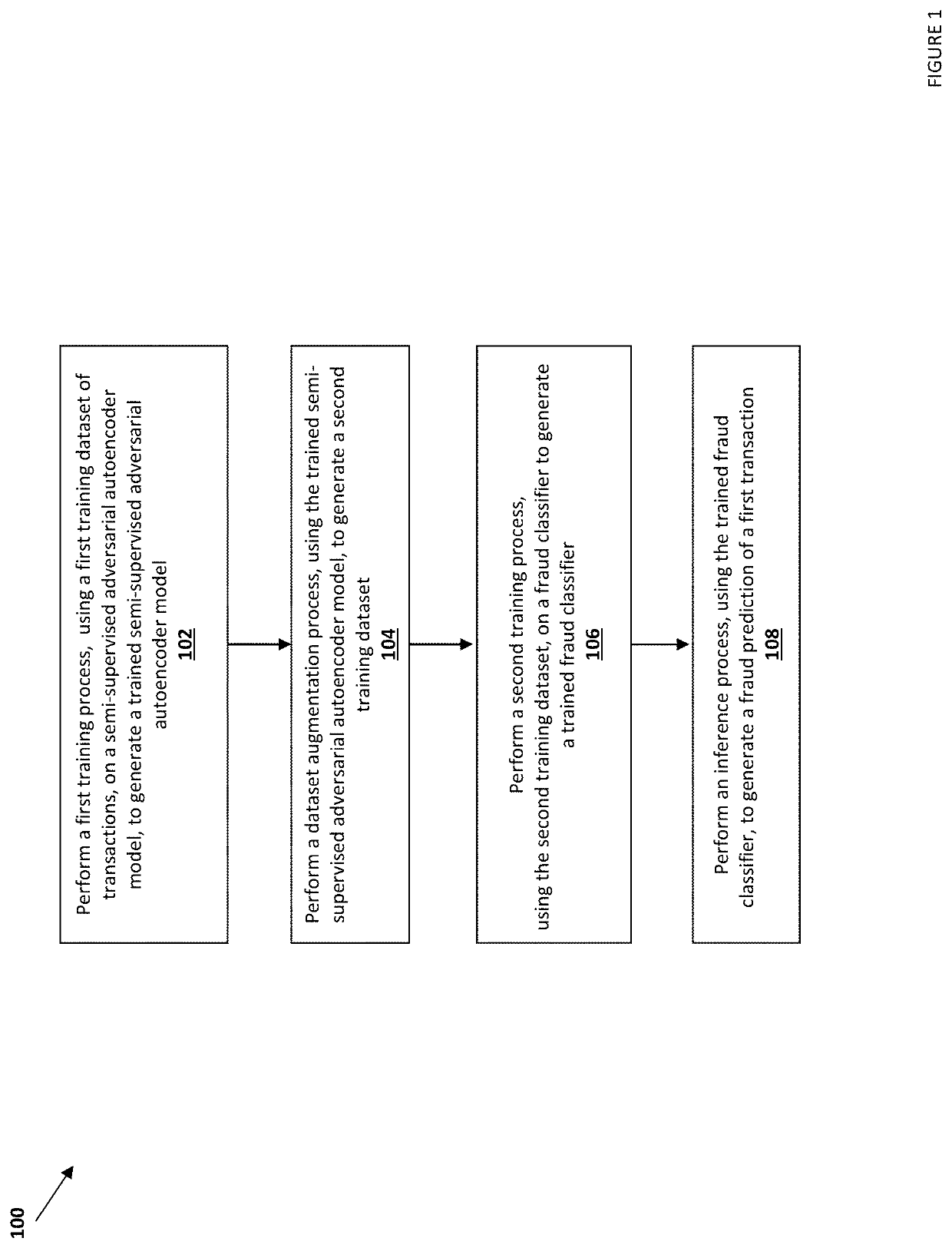
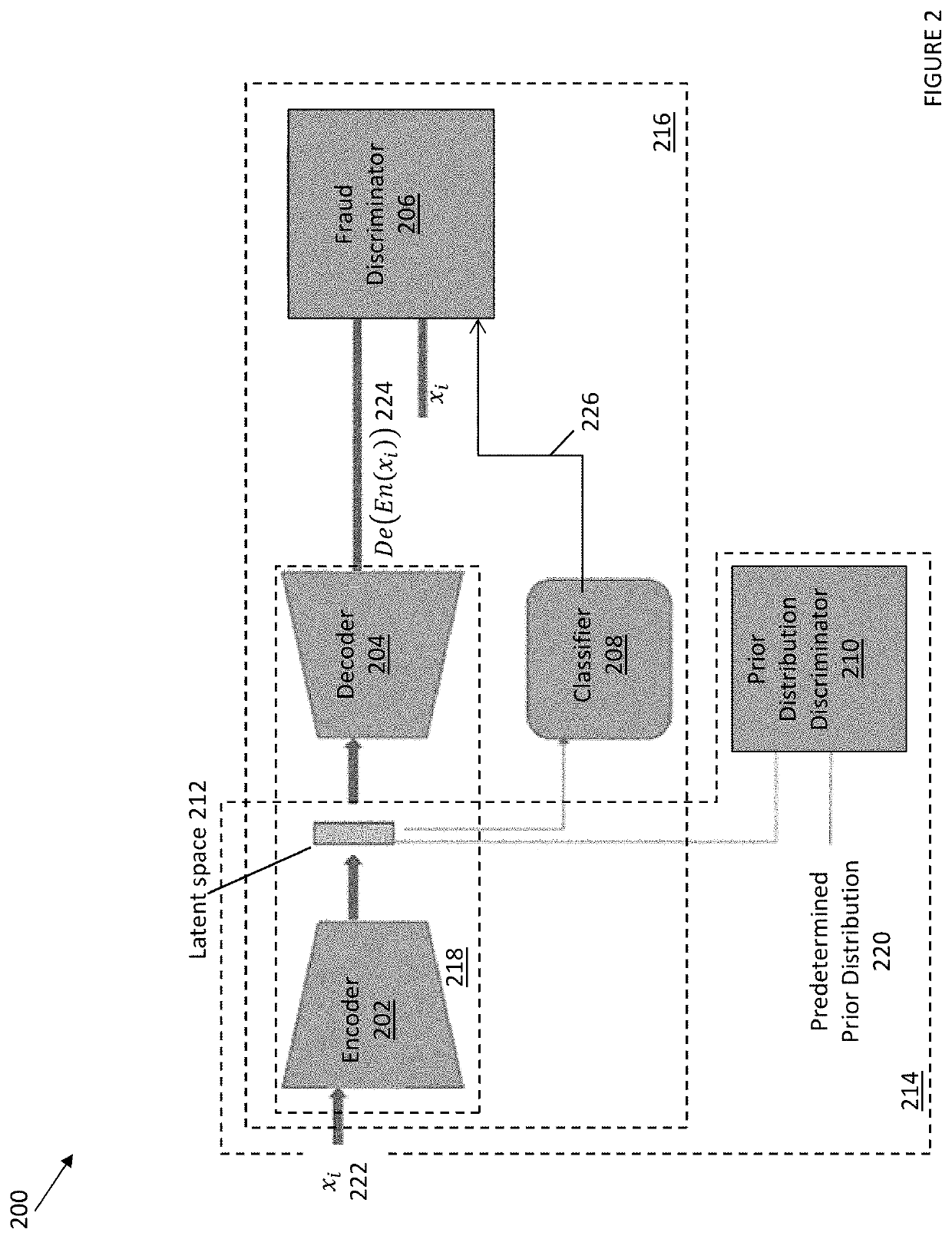
Data augmentation in transaction classification using a neural network
ActiveUS20200210808A1Character and pattern recognitionProbabilistic networksNeural network systemNetworked system
Owner:PAYPAL INC
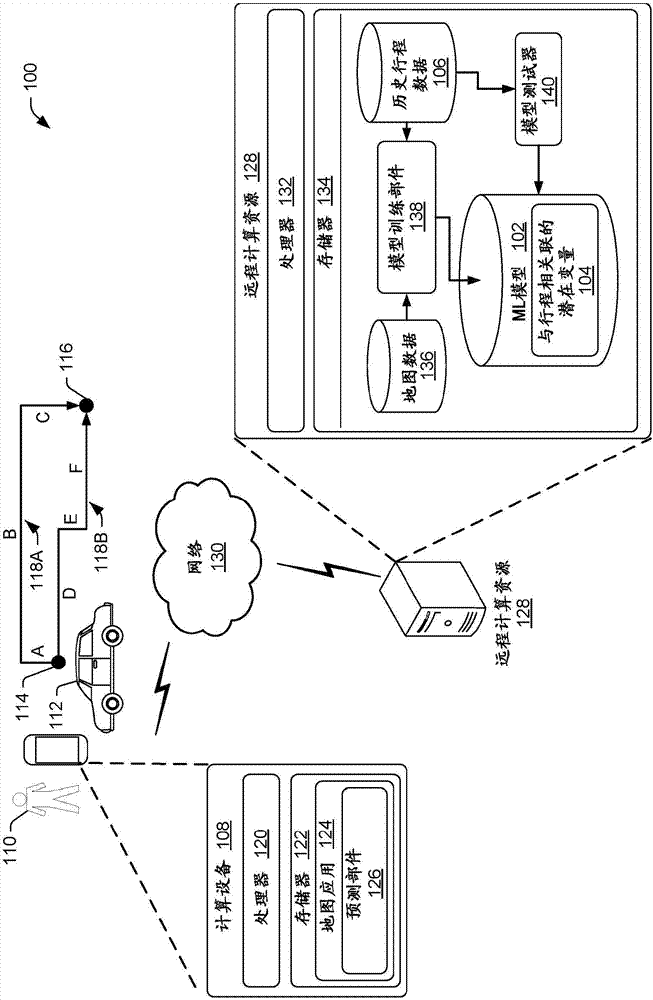
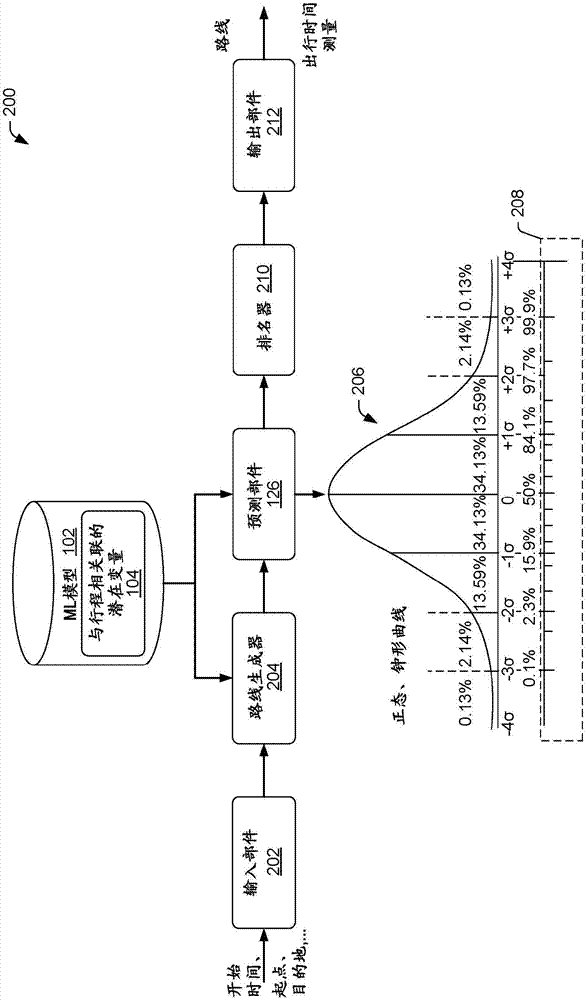
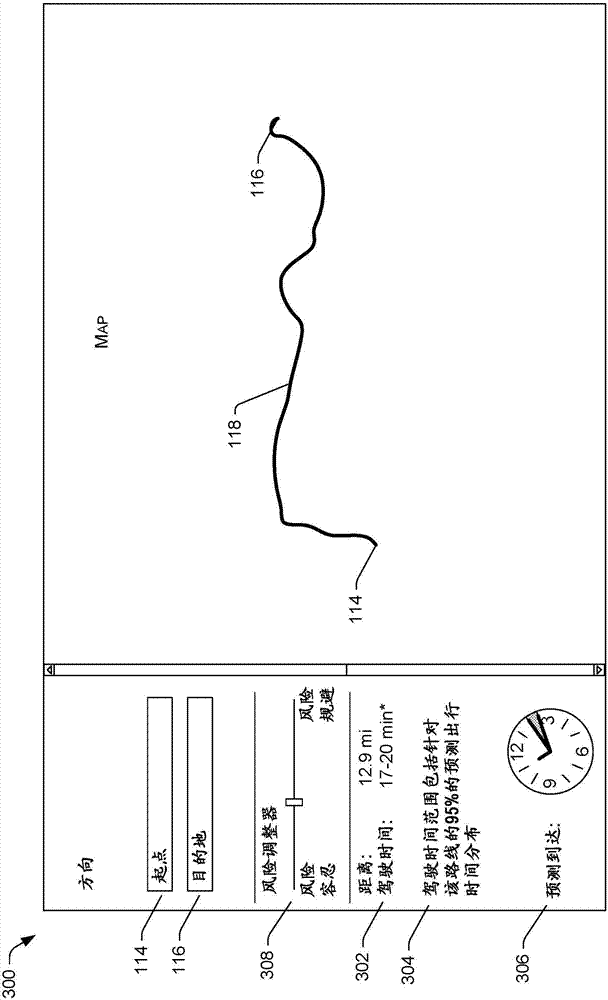
Predicting and utilizing variability of travel times in mapping services
ActiveCN107111794AComputationally efficientImprove experienceInstruments for road network navigationForecastingStart timeLatent variable
A system for predicting variability of travel time for a trip at a particular time may utilize a machine learning model including latent variables that are associated with the trip. The machine learning model may be trained from historical trip data that is based on location-based measurements reported from mobile devices. Once trained, the machine learning model may be utilized for predicting variability of travel time. A process may include receiving an origin, a destination, and a start time associated with a trip, obtaining candidate routes that run from the origin to the destination, and predicting, based at least in part on the machine learning model, a probability distribution of travel time for individual ones of the candidate routes. One or more routes may be recommended based on the predicted probability distribution, and a measure of travel time for the recommended route(s) may be provided.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
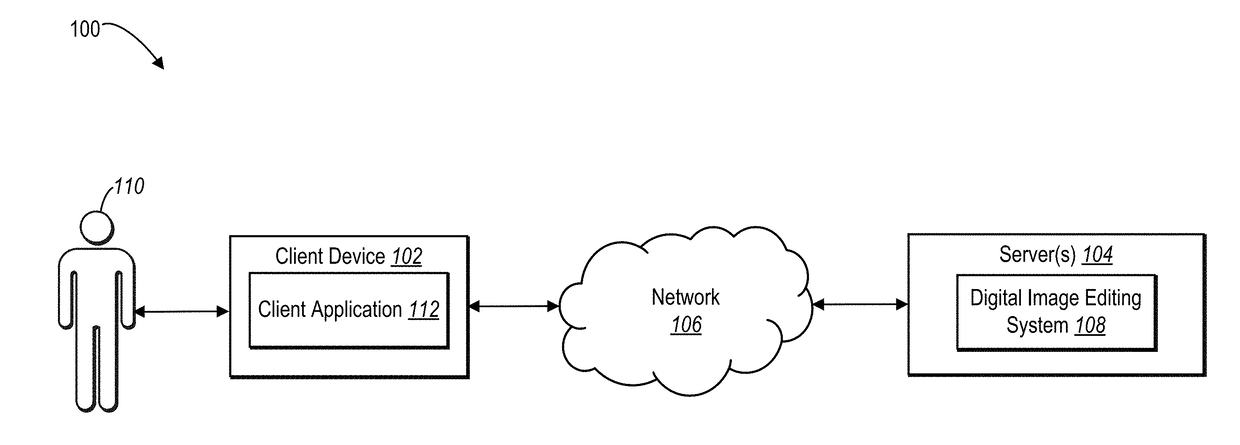
Generating multimodal image edits for a digital image
The present disclosure is directed towards methods and systems for determining multimodal image edits for a digital image. The systems and methods receive a digital image and analyze the digital image. The systems and methods further generate a feature vector of the digital image, wherein each value of the feature vector represents a respective feature of the digital image. Additionally, based on the feature vector and determined latent variables, the systems and methods generate a plurality of determined image edits for the digital image, which includes determining a plurality of set of potential image attribute values and selecting a plurality of sets of determined image attribute values from the plurality of sets of potential image attribute values wherein each set of determined image attribute values comprises a determined image edit of the plurality of image edits.
Owner:ADOBE INC
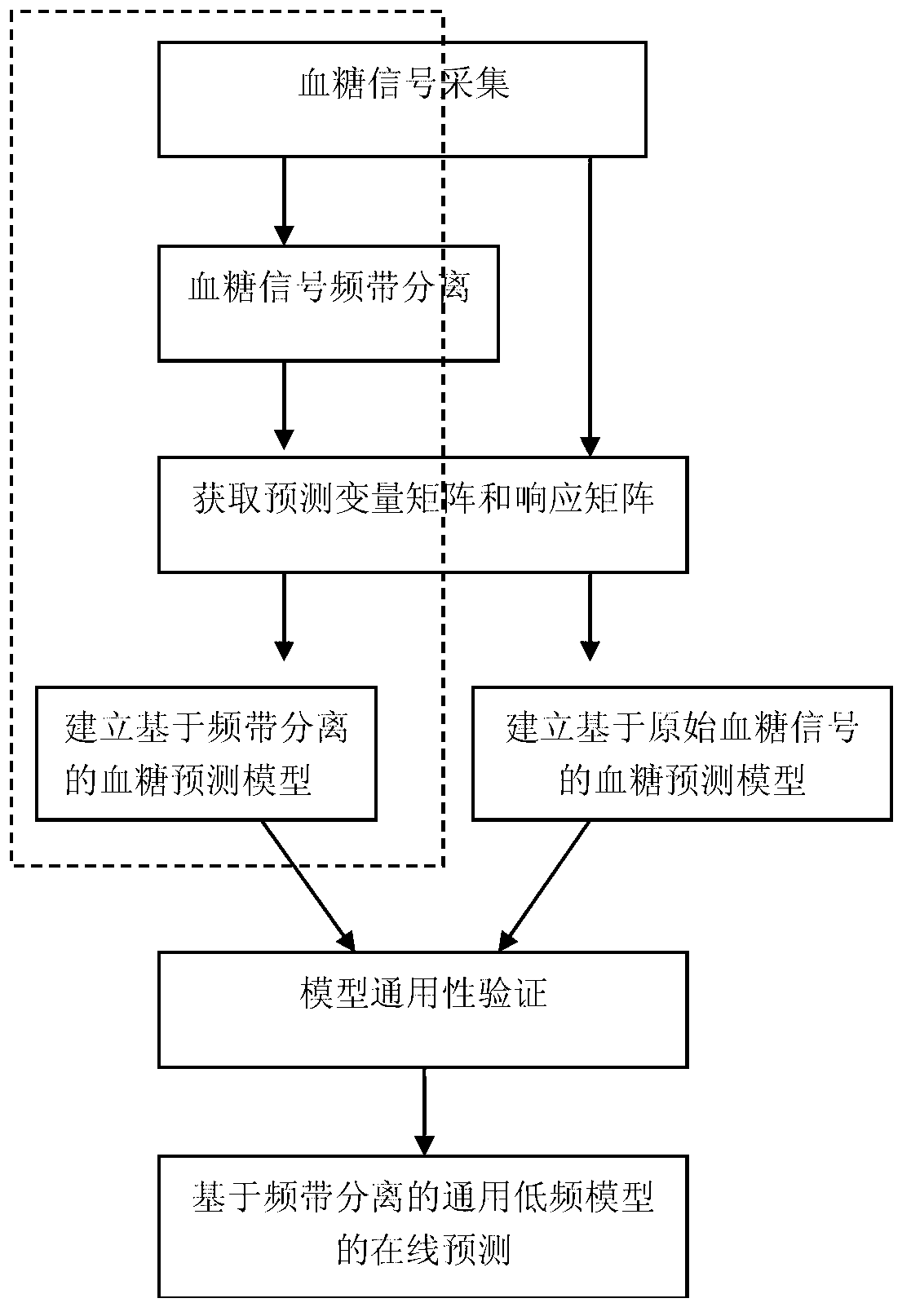
Universal blood glucose prediction method based on frequency band separation and data modeling
ActiveCN103310113ASimplify workloadSimplify complexitySpecial data processing applicationsData modelingBlood Glucose Measurement
The invention discloses a universal blood glucose prediction method based on frequency band separation and data modeling, which comprises the steps that a human body subcutaneous blood glucose measurement signal is analyzed; the latent timing sequence dynamic characteristic of the human body subcutaneous blood glucose measurement signal is extracted; a frequency band separation threshold is defined; the subcutaneous blood glucose measurement signal is divided into a high frequency band and a low frequency band; timing sequence autocorrelation of a low frequency blood glucose signal is analyzed; and an autoegression blood glucose prediction model is established. According to the universal blood glucose prediction method, re-modeling for a new object is not required after the sufficient blood glucose measurement signals are acquired, and real-time blood glucose prediction can be performed by directly calling a prediction model of other individual, so that the modeling working capacity and the complexity are simplified greatly; the modeling cost can be lowered greatly; the prediction precision is improved due to the fact that a universal model adopts a method based on frequency band separation and latent variable modeling; and the universal blood glucose prediction method is easy to implement, and indicates a new direction for research of a blood glucose prediction modeling method.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
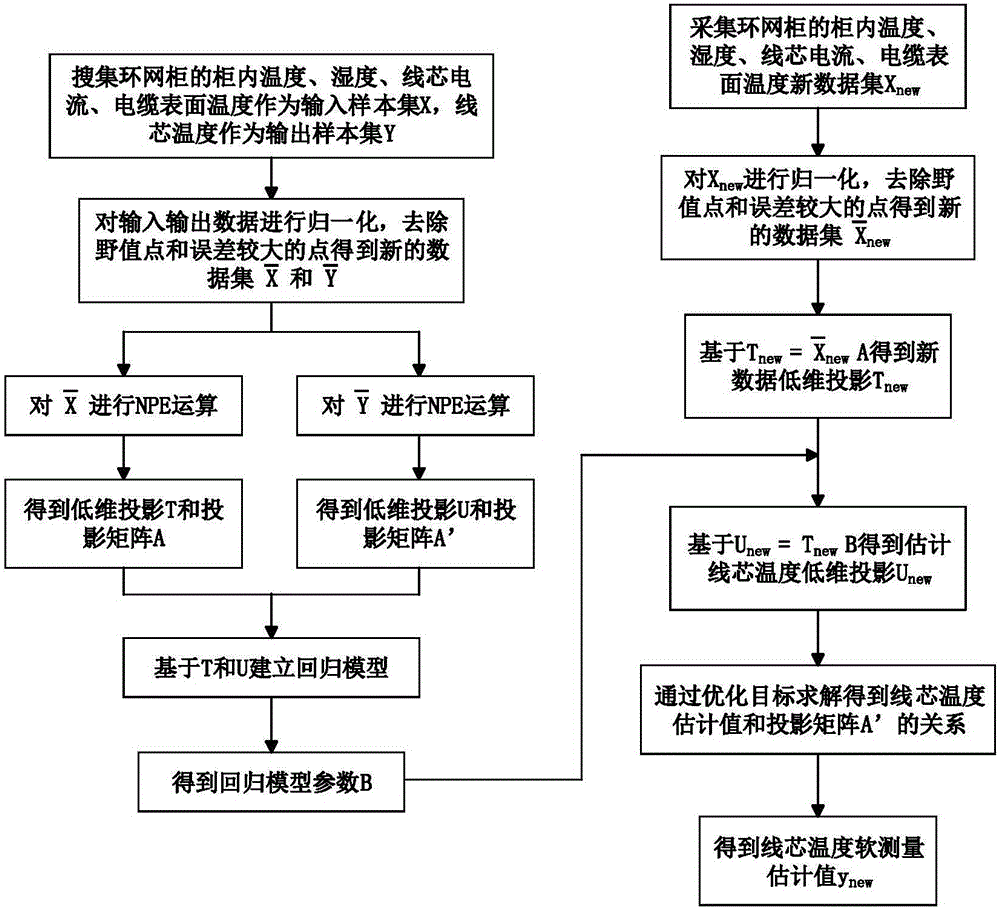
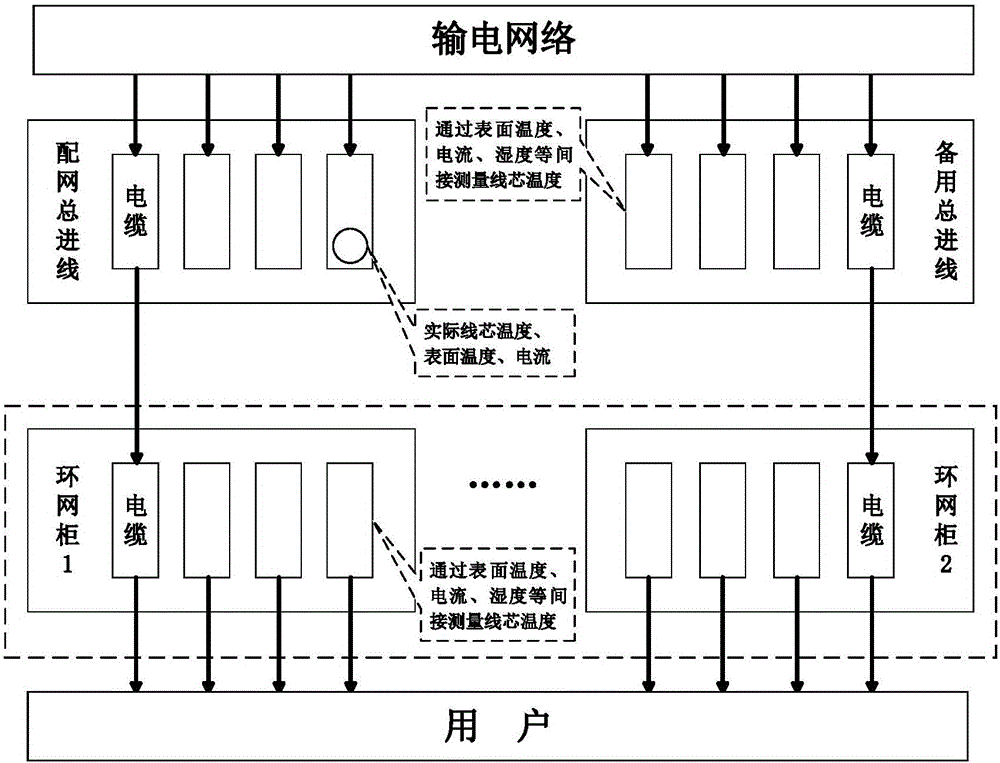
Ring main unit cable core temperature soft measurement method based on neighborhood preserving embedded regression algorithm
ActiveCN106644162ARealize online estimationEasy to measureThermometer applicationsFeature extractionOperability
The invention discloses a ring main unit cable core temperature soft measurement method based on a neighborhood preserving embedded regression algorithm. The ring main unit cable core temperature soft measurement method comprises that firstly, based on the local feature extraction strategy of the neighborhood preserving embedded algorithm, a regression optimization function which takes the internal temperature and the internal humidity of a ring main unit, the cable core current and the cable surface temperature as input, and takes the cable core temperature of a cable in the ring main unit as output is established, local features of input data and output data are reserved, and the maximum relationship between data is obtained; then based on lower-dimension latent variables of data, input and output features which construct data regression are obtained; and a cable core temperature soft measurement model is established. The ring main unit cable core temperature soft measurement method is advantaged in that by means of a data local feature extraction method, a traditional neighborhood preserving embedded algorithm is modified to be a regression model, and key variable information, of the ring main unit, which cannot be measured easily is obtained. According to the invention, the problem that the temperature of the cable core in the ring main unit cannot be measured easily is solved, and the accuracy and operability of on-line monitoring and fault locating of the ring main unit are improved.
Owner:YUNNAN UNIV +1
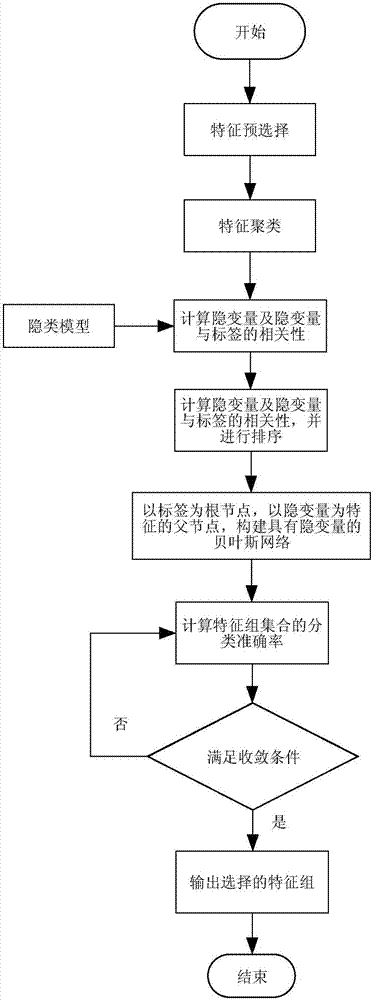
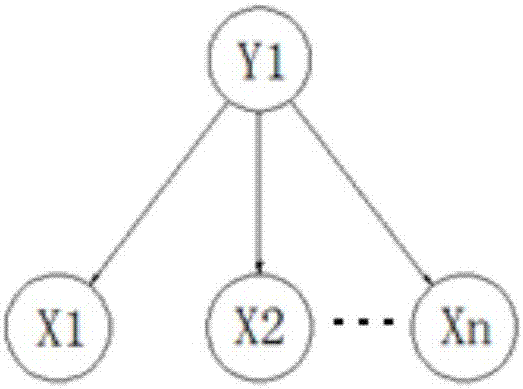
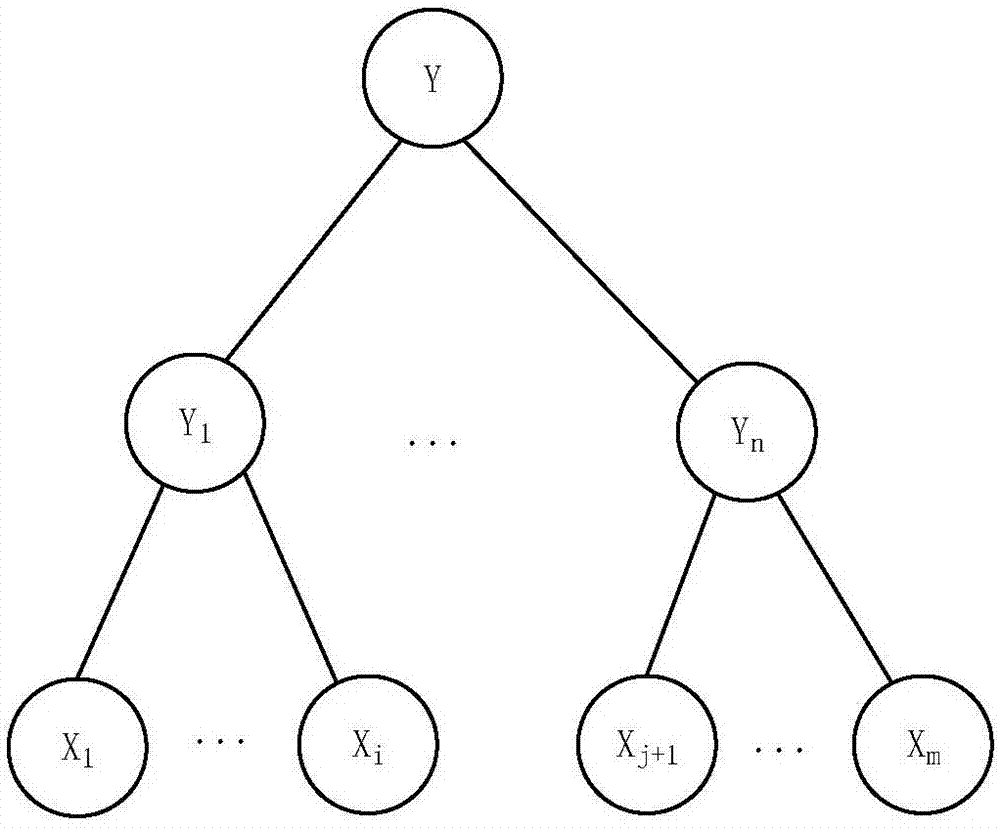
Feature selection method and traditional Chinese medicine main-symptom selection method based on feature groups
ActiveCN107292097ACharacter and pattern recognitionSpecial data processing applicationsCluster algorithmFeature set
The invention discloses a feature selection method and a traditional Chinese medicine main-symptom selection method based on feature groups. The feature selection method based on the feature groups comprises the following steps: 1, screening an original feature set; 2, utilizing a feature clustering algorithm to cluster the screened feature set to obtain the corresponding feature groups; 3, introducing a latent variable to each feature group to obtain a corresponding latent class model (LCM), and calculating correlation between the latent variables and labels; 4, sorting the feature groups sequentially with decreasing according to the correlation between the latent variables and the labels; 5, adding the sorted feature groups into selected feature subsets in turn, and establishing a Bayesian network with the latent variables; and 6, calculating classification accuracy rates of the Bayesian network, then obtaining a curve of the numbers of the added feature groups and the classification accuracy rates, and obtaining the corresponding optimal feature subset through judging the convergence of the curve or the highest accuracy rate. According to the method, the feature groups are used as selected targets, and the feature groups composed of a plurality of features have better representation capacity for original data.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH +1
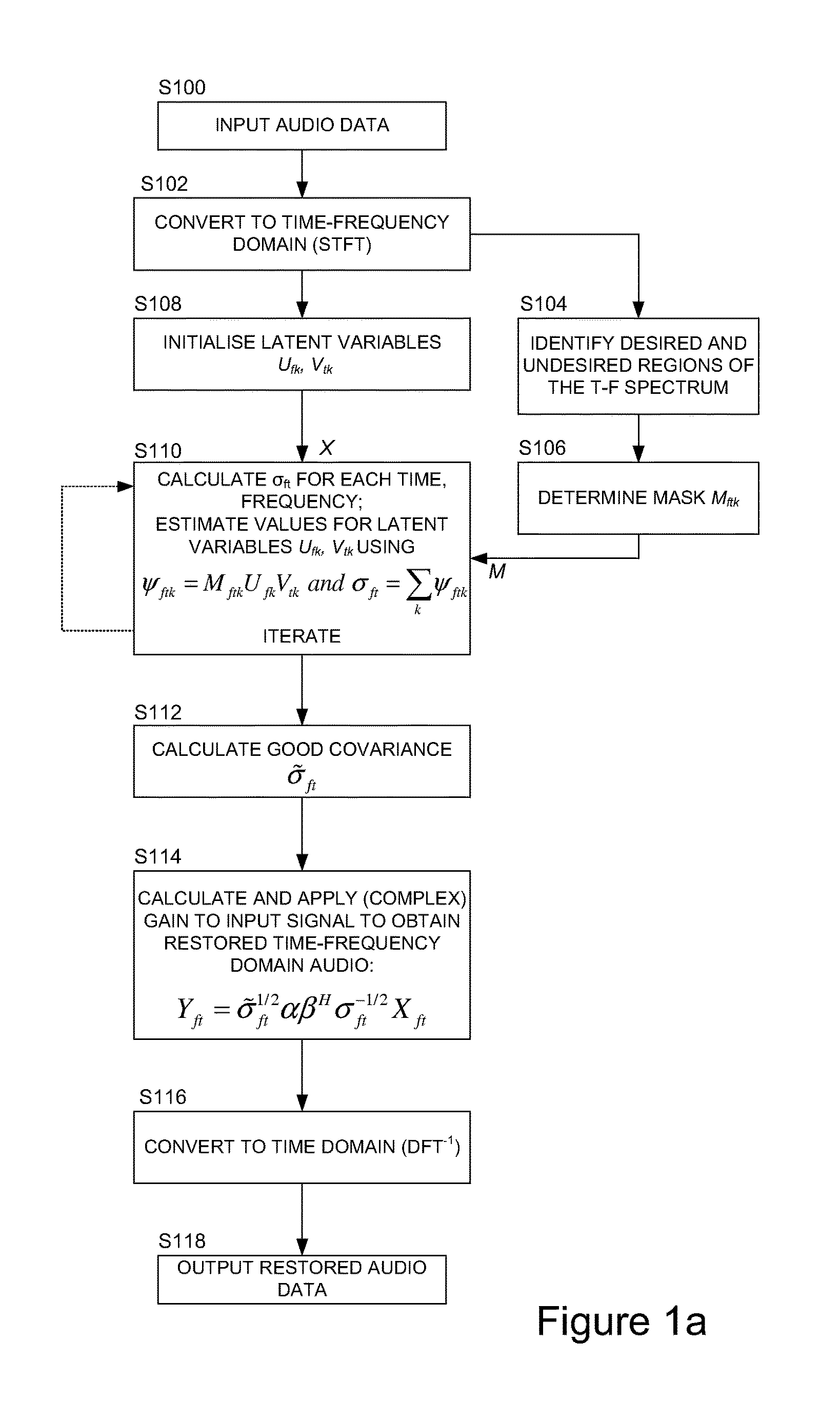
Restoring audio signals with mask and latent variables
We describe techniques for restoring an audio signal. In embodiments these employ masked positive semi-definite tensor factorization to process the signal in the time-frequency domain. Broadly speaking the methods estimate latent variables which factorize a tensor representation of the (unknown) variance / covariance of an input audio signal, using a mask so that the audio signal is separated into desired and undesired audio source components. In embodiments a masked positive semi-definite tensor factorization of ψftk=MftkUfkVtk is performed, where M defines the mask and U, V the latent variables. A restored audio signal is then constructed by modifying the input signal to better match the variance / covariance of the desired components.
Owner:CEDAR AUDIO
Generative adversarial network based intra prediction for video coding
ActiveUS20200137384A1Generate flexiblePredict in advanceDigital video signal modificationNeural architecturesEncoder decoderAlgorithm
Systems and methods which provide Generative Adversarial Network (GAN) based intra prediction for video coding are described. GAN based intra prediction as implemented according to embodiments may be modeled as an inpainting task. For example, intra prediction may be formulated as a learning based inpainting task, wherein a latent variable is designed to control different generation modes. GAN based intra prediction provided according to embodiments of the invention may be implemented alone or in combination with one or more other video compression technique, such as a direction intra prediction technique. The intra prediction module of such a HEVC encoder / decoder may be redesigned to also apply GAN based inpainting in intra prediction, wherein Rate-Distortion Optimization (RDO) may be performed to select the best intra prediction mode between the intra prediction approaches.
Owner:CITY UNIVERSITY OF HONG KONG
Computer-implemented method, computer program product and system for anomaly detection and/or predictive maintenance
PendingCN112655004AEfficient detectionReduce distractionsTesting/monitoring control systemsCharacter and pattern recognitionHidden layerData set
Owner:SARTORIUS STEDIM DATA ANALYTICS AB
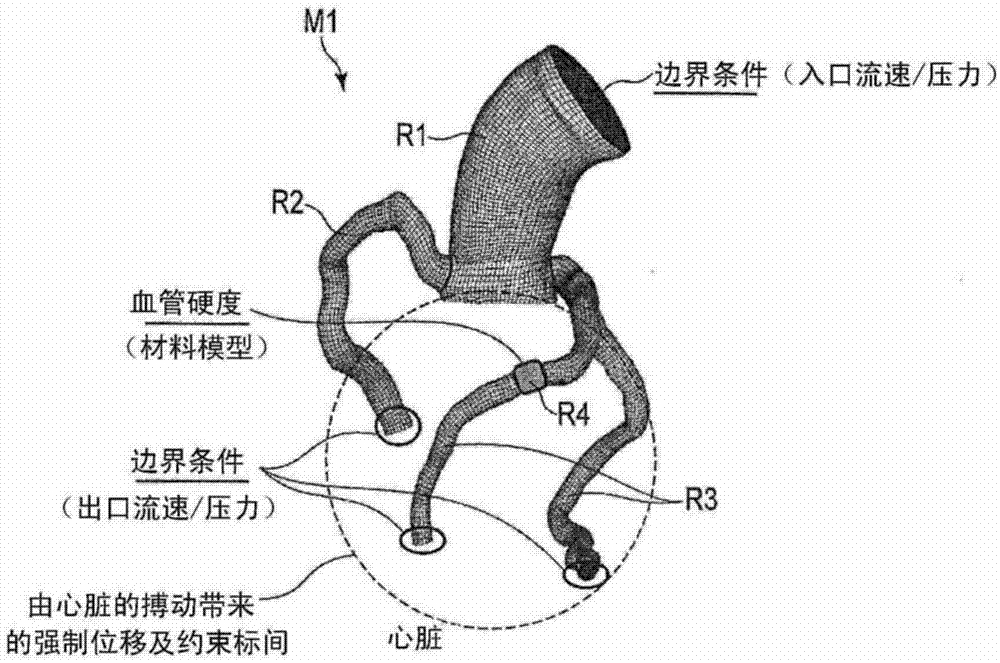
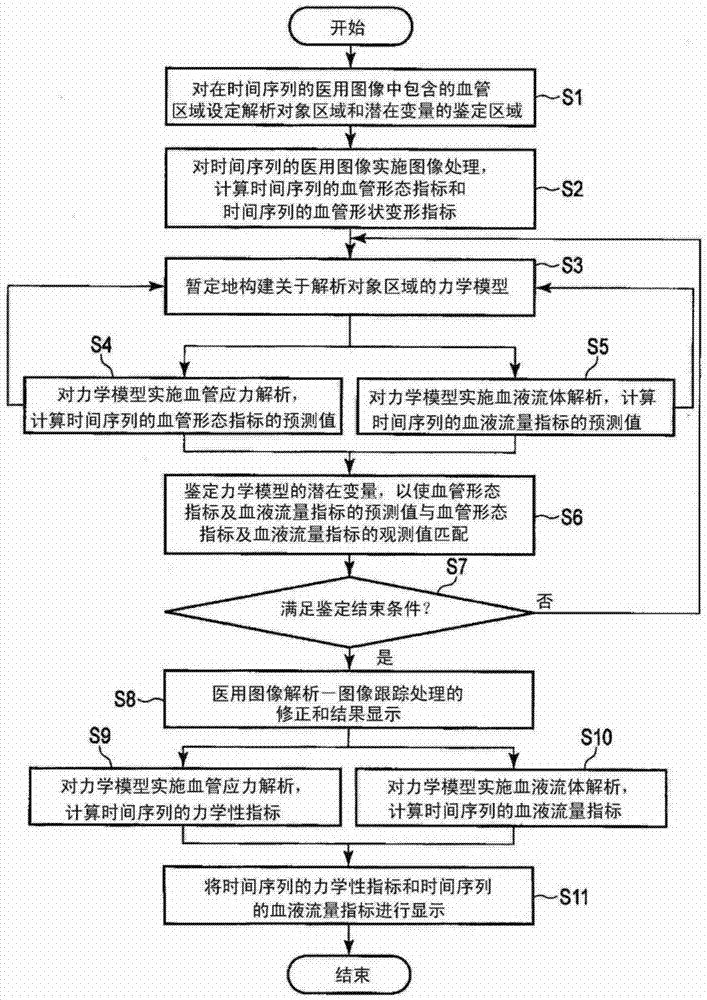
Blood vessel analysis device, medical image diagnostic device, and blood vessel analysis method
The present invention enhances the precision of blood vessel structure and fluid analysis. An image analysis / tracking processing unit (53) performs image analysis of a time series medical image and calculates a time series form index and a time series shape deformation index for an analysis subject region. A dynamic model constructing unit (55) provisionally constructs a dynamic model relating to structure and fluid analysis of the analysis subject region on the basis of the time series form index, the time series shape deformation index, and the time series medical image. A statistical identification unit (61) identifies a latent variable relating to a latent variable identification region so that a predicted value for a blood vessel form index and / or a predicted value for a blood vessel flow rate index based on the provisionally constructed dynamic model is / are consistent with an observed value for the blood vessel form index and / or an observed value for the blood vessel flow rate index. Calculation units (57, 59) perform structure analysis, fluid analysis, or structure-fluid interaction analysis on the dynamic model in which the latent variable is allocated to the latent variable identification region, and calculate a predicted value for a time series dynamic index and / or a predicted value for a time series blood flow rate index.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
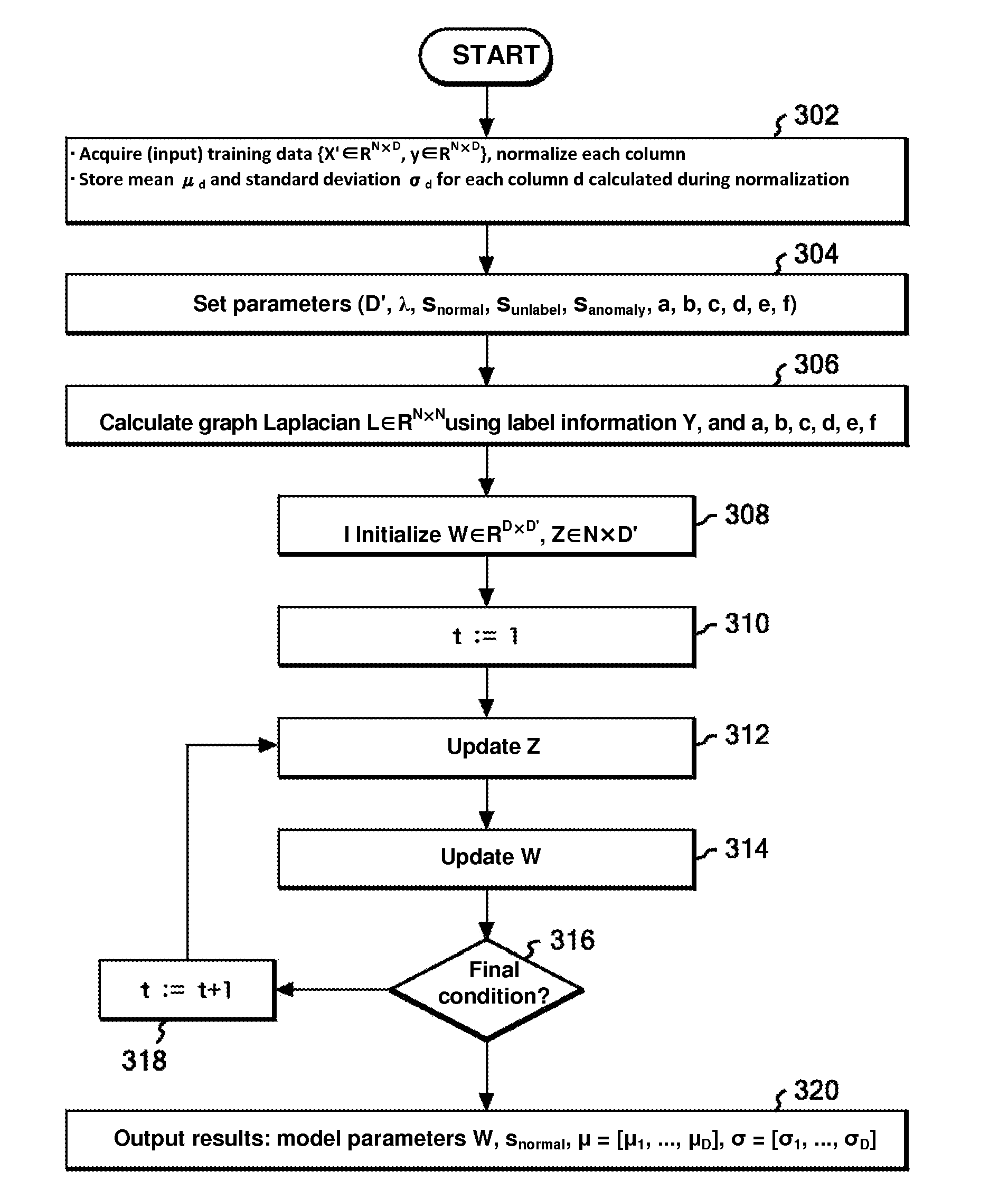
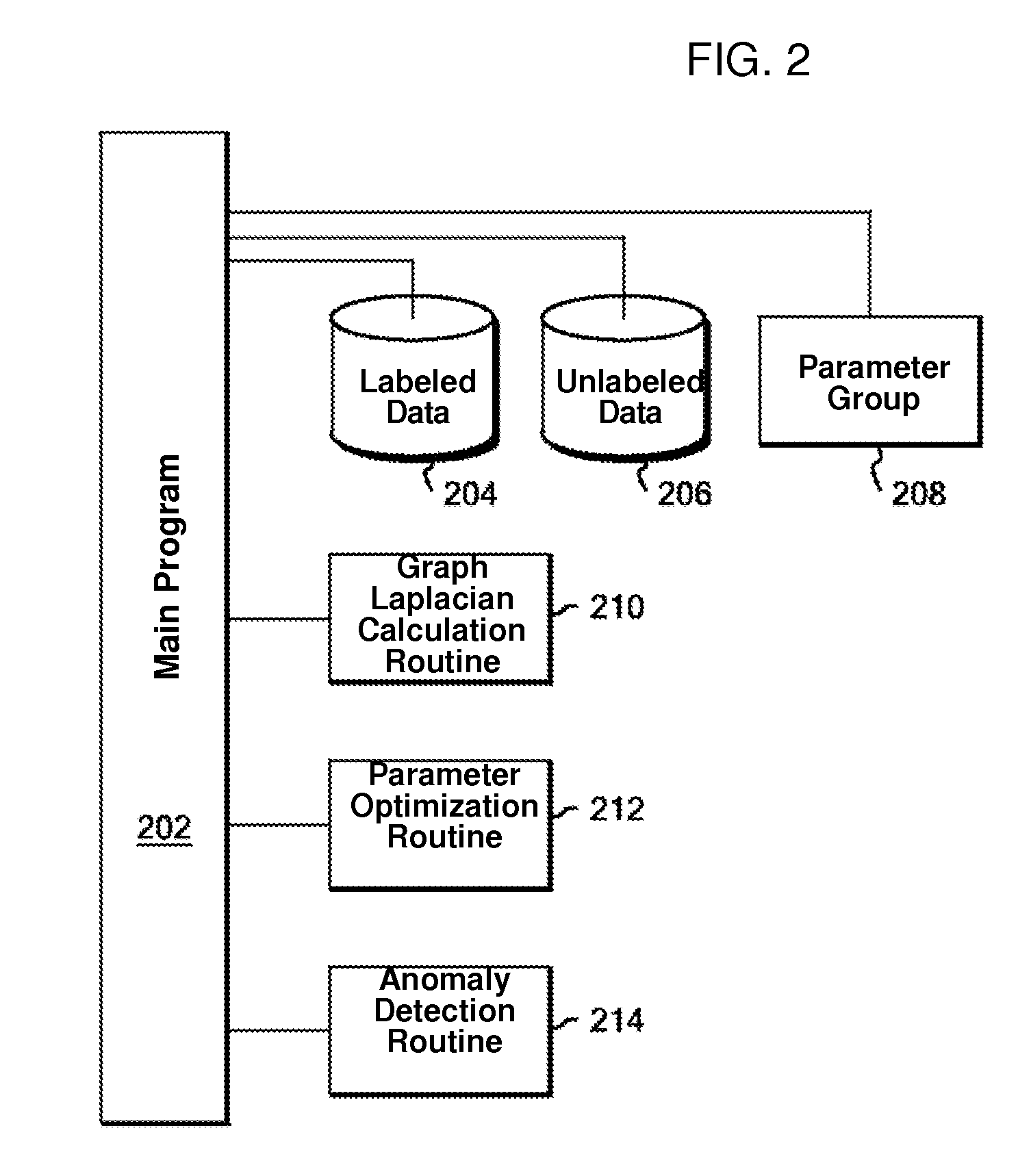
Anomaly Detection Method, Program, and System
ActiveUS20130338965A1Efficient use ofReduce randomnessMeasurement devicesDigital computer detailsAnomaly detectionTest sample
A method providing an analytical technique introducing label information into an anomaly detection model. Effective utilization of label information is based on introducing the degree of similarity between samples. Assuming, for example, there is a degree of similarity between normally labeled samples and no similarity between normally labeled and abnormally labeled samples. Also each sensor value is generated by the linear sum of a latent variable and a coefficient vector specific to each sensor. However, the magnitude of observation noise is formulated to vary according to the label information for the sensor values, and set so that normal label unlabeled anomalously labeled. A graph Laplacian is created based on the degree of similarity between samples, and determines the optimal linear transformation matrix according to a gradient method. A optimal linear transformation matrix is used to calculate an anomaly score for each sensor in the test samples.
Owner:IBM CORP
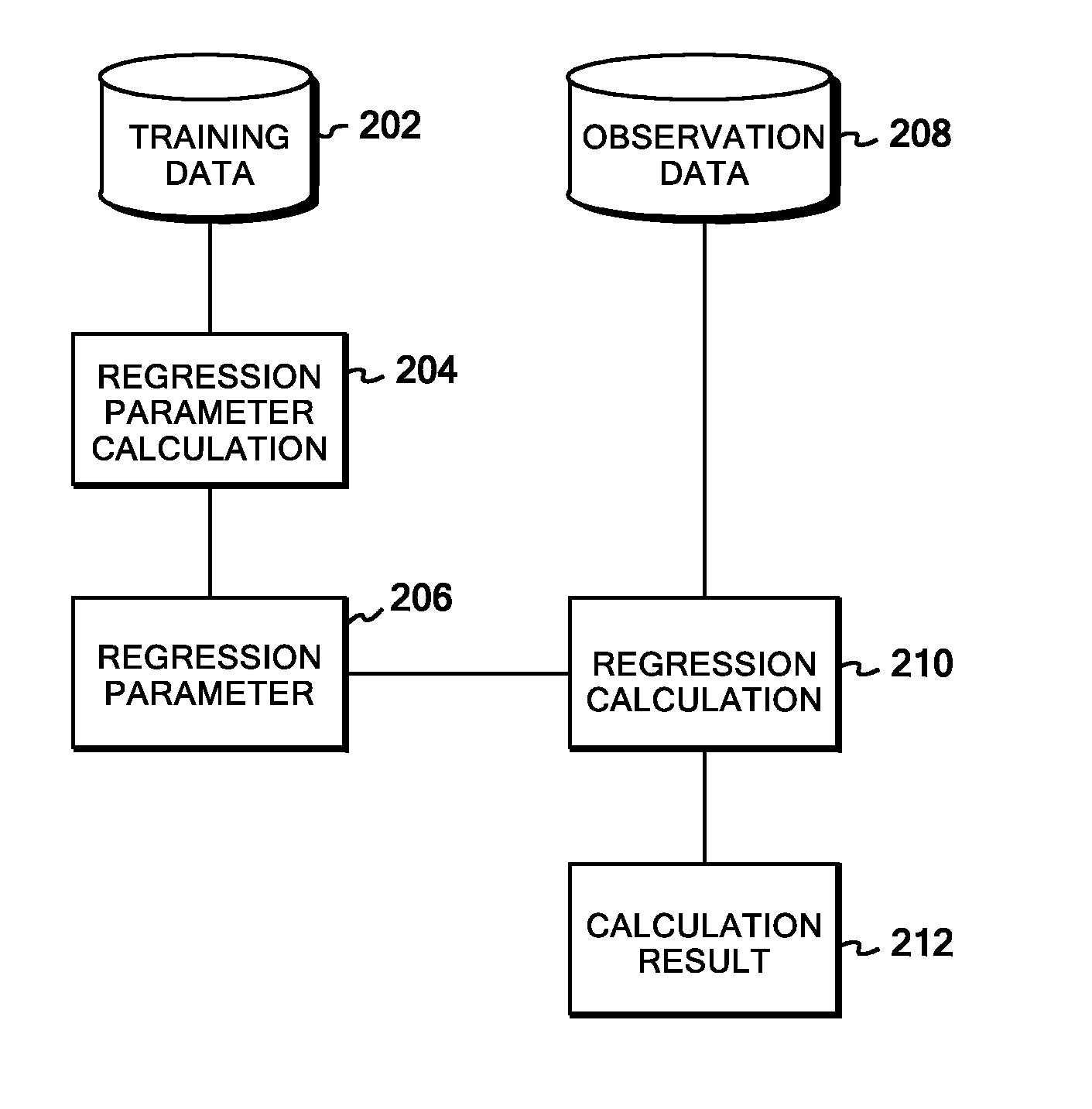
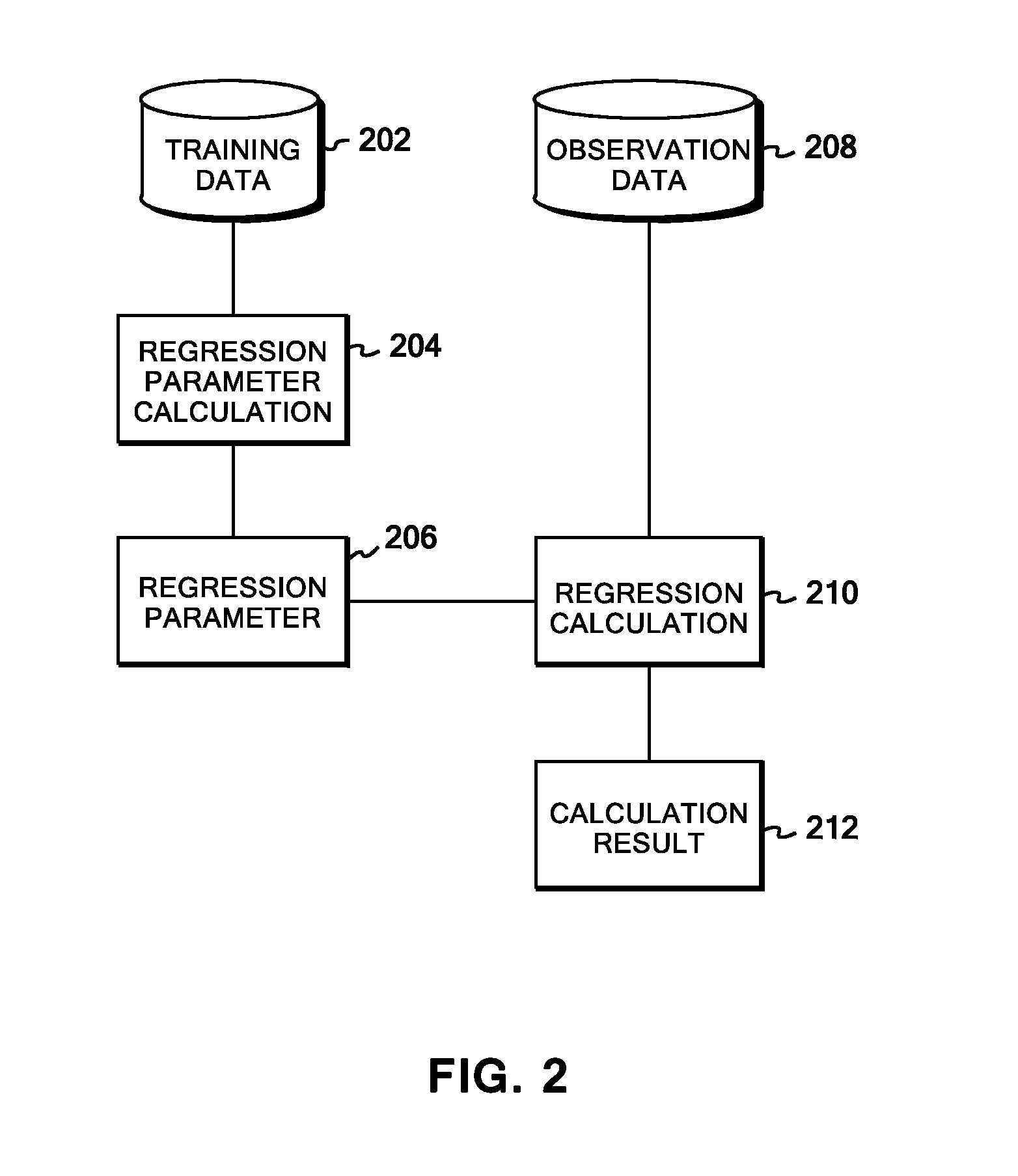
Kernel regression system, method, and program
InactiveUS20110238606A1Reduce computing costDigital computer detailsForecastingKernel regressionAlgorithm
In training data, a similarity matrix is generated for each of types of data corresponding to different kernels, and graph Laplacians are formed individually from the similarity matrices. An entire graph Laplacian is defined as linear combination of the individual graph Laplacians with coupling constants. Observation variables and latent variables associated therewith are assumed to form normal distributions, and the coupling constants are assumed to form a gamma distribution. Then, on the basis of a variational Bayesian method, a variance of the observation variables and the coupling constants can be figured out with a reasonable computational cost. Once the variance of the observation variables and the coupling constants are figured out, a predictive distribution for any input data can be figured out by means of a Laplace approximation.
Owner:IBM CORP +1
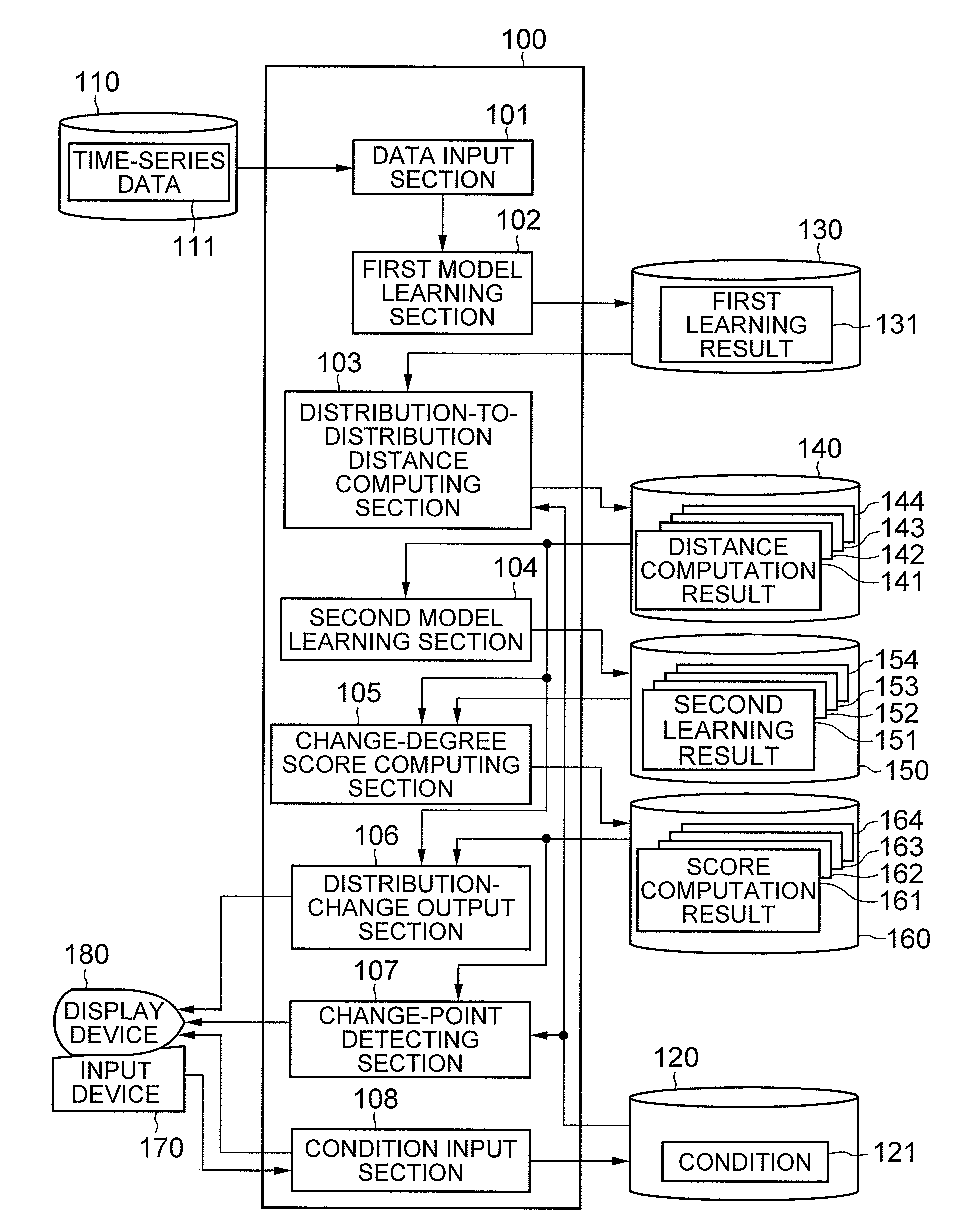
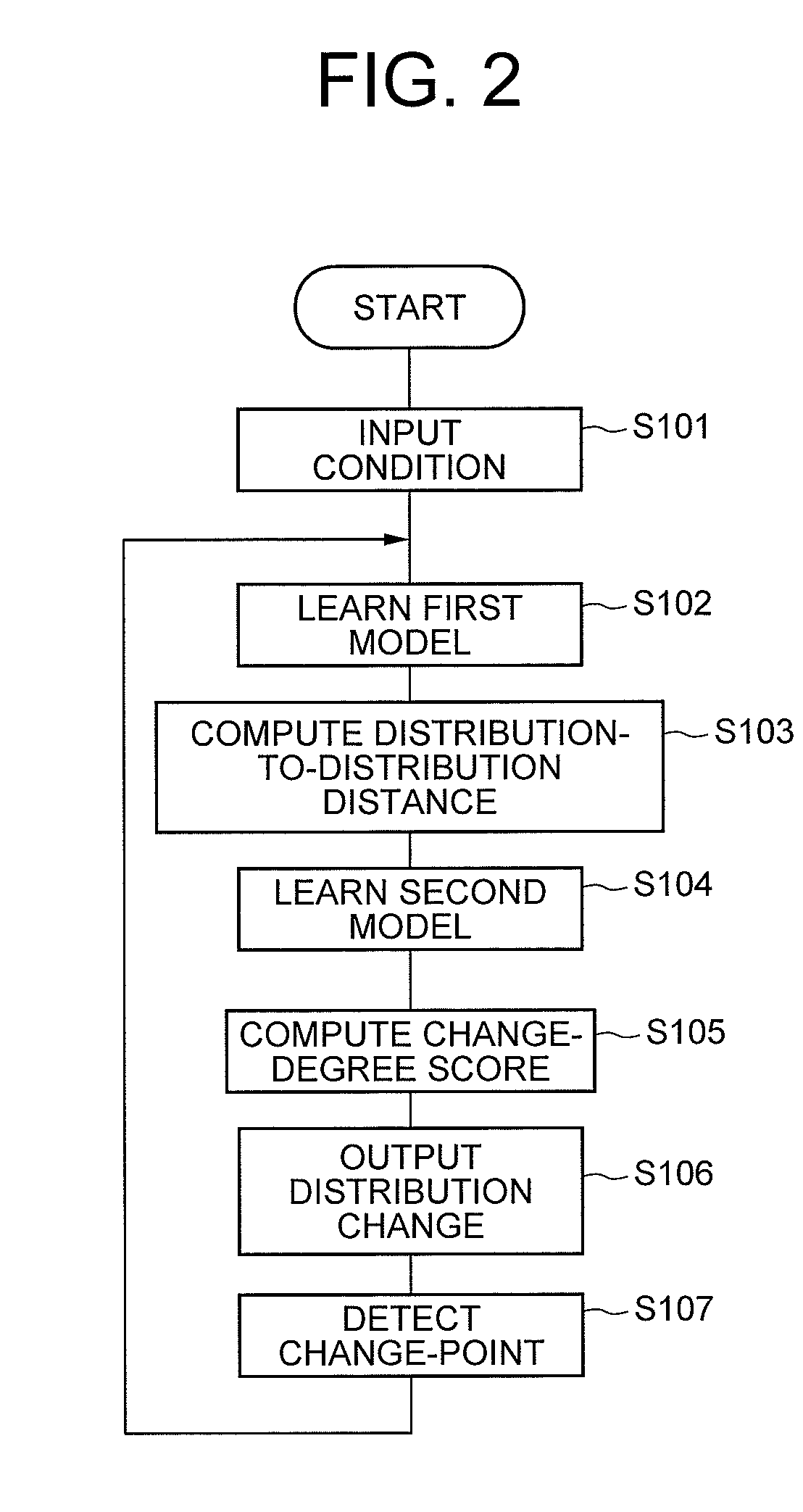
Change-point detecting method and apparatus
ActiveUS20100100511A1Realize functionDigital computer detailsCharacter and pattern recognitionTemporal changeConditional probability
To detect a statistical change-point that appears in time-series data with a high accuracy. A first model learning section 102 learns the occurrence probability distribution of time-series data 111 as a first statistical model (for example, a latent Markov model) defined by a finite number of variables including a latent variable. In the subsequent processing, the degree of a temporal change in the probability distribution is computed for each of the probability distribution of the entire first statistical model, its partial probability distribution (the probability distribution of the latent variable and conditional probability distribution contingent on the value of the latent variable), and the probability distribution in which the above plural probability distributions are linearly-combined with a weight. The change-point of the time-series data 111 is detected on the basis of the computed degree of the change.
Owner:NEC CORP
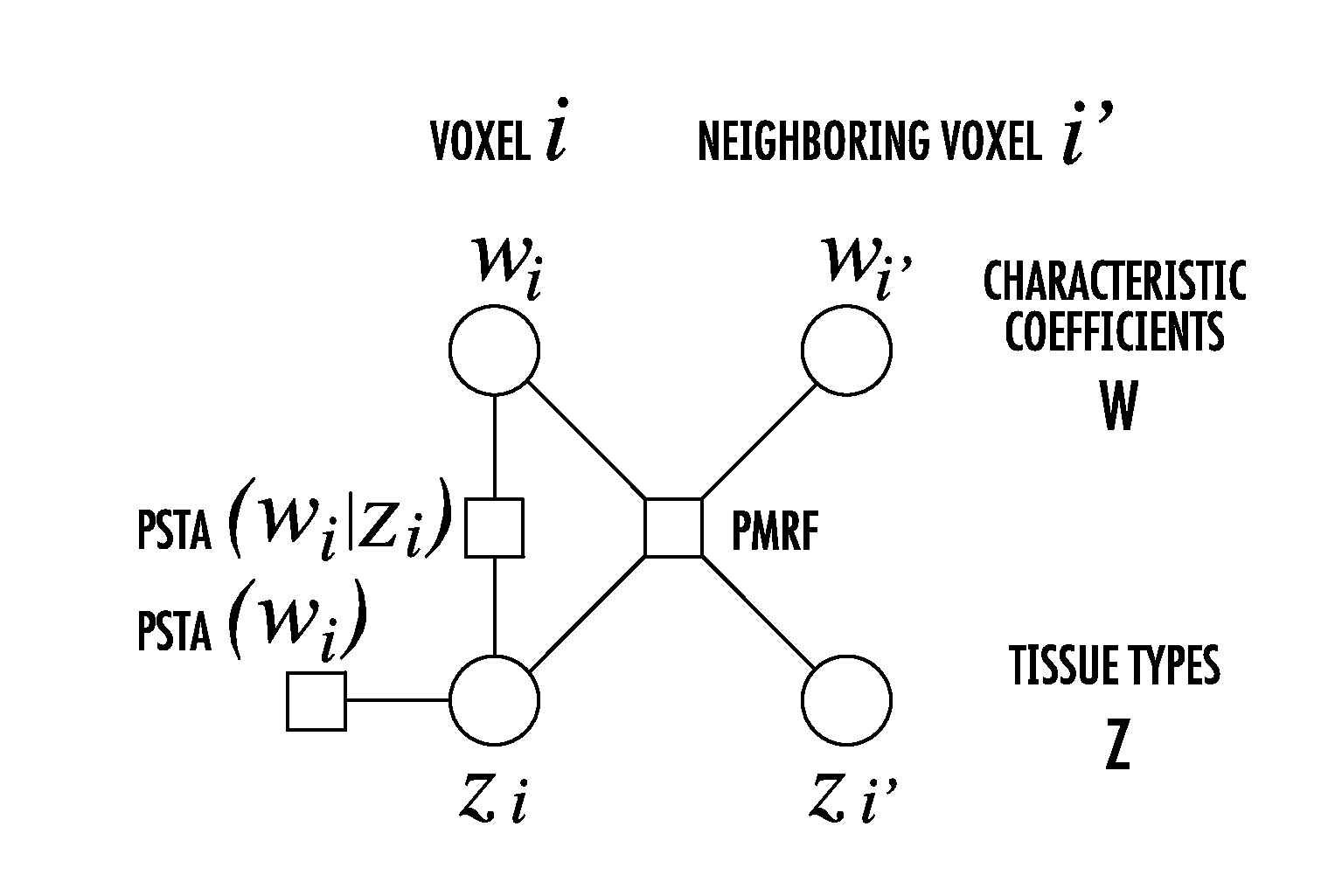
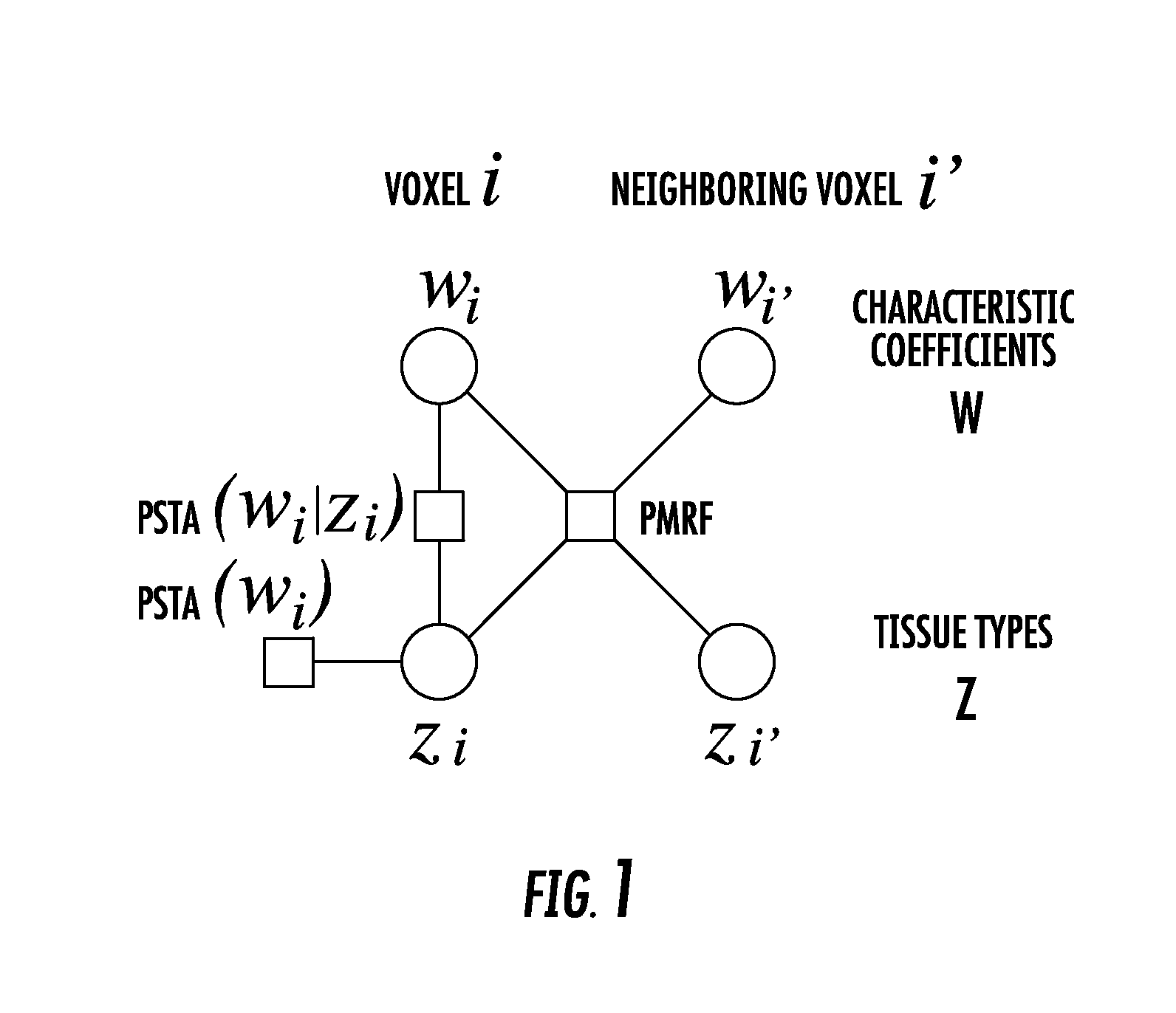
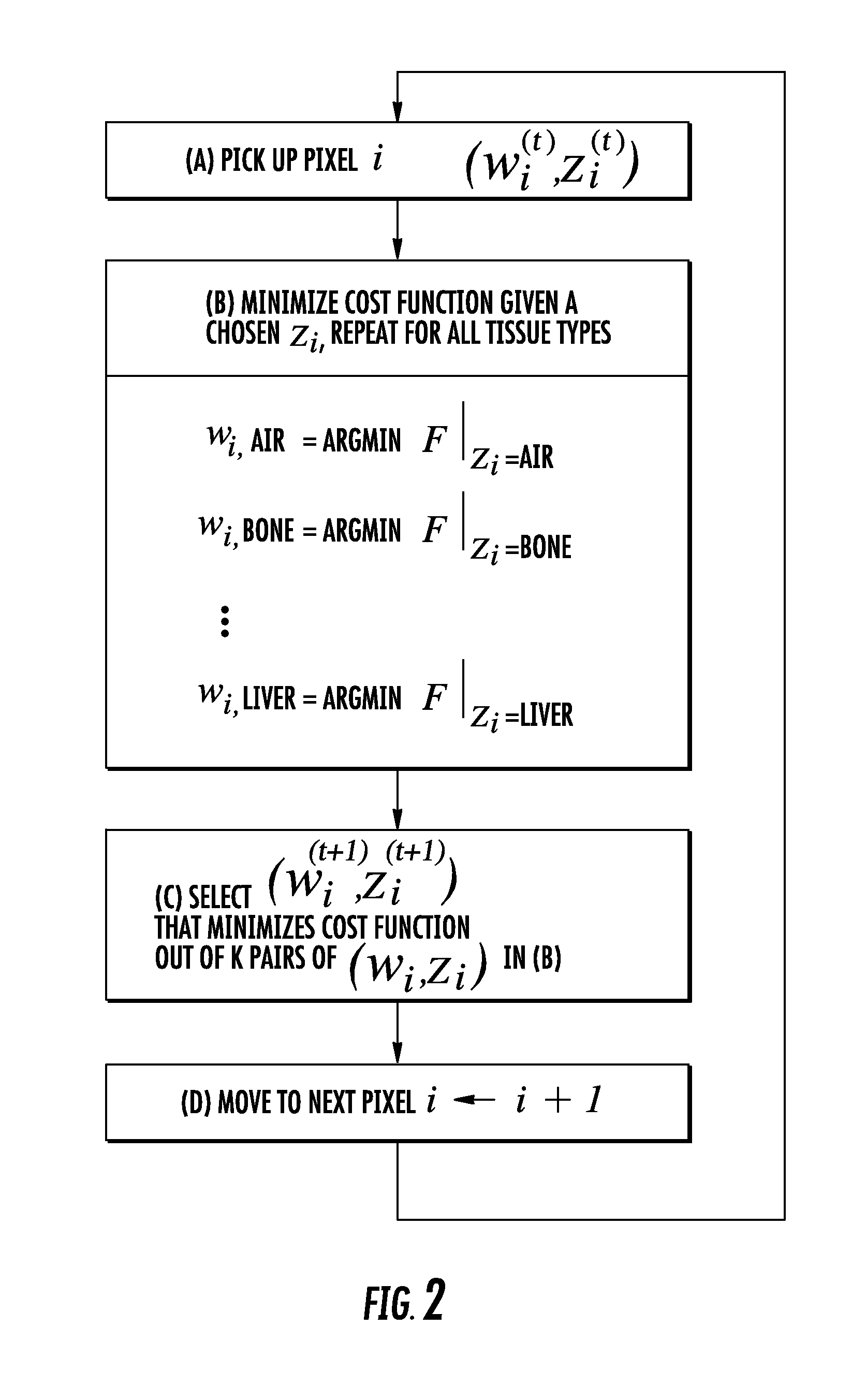
Joint estimation of tissue types and linear attenuation coefficients for computed tomography
ActiveUS20150131883A1Image enhancementReconstruction from projectionAttenuation coefficientUltrasound attenuation
The present invention is directed to a new joint estimation framework employing MAP estimation based on pixel-based latent variables for tissue types. The method combines the geometrical information described by latent MRF, statistical relation between tissue types and P-C coefficients, and Poisson noise models of PCD data, and makes possible the continuous Baysian estimation from detected photon counts. The proposed method has better accuracy and RMSE than the method using FBP and thresholding. The joint estimation framework has the potential to further improve the accuracy by introducing more information about tissues in human body, e.g., the location, size, and number of tissues, or limited variation of neighboring tissues, which will be easily formulated by pixel-based latent variables.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
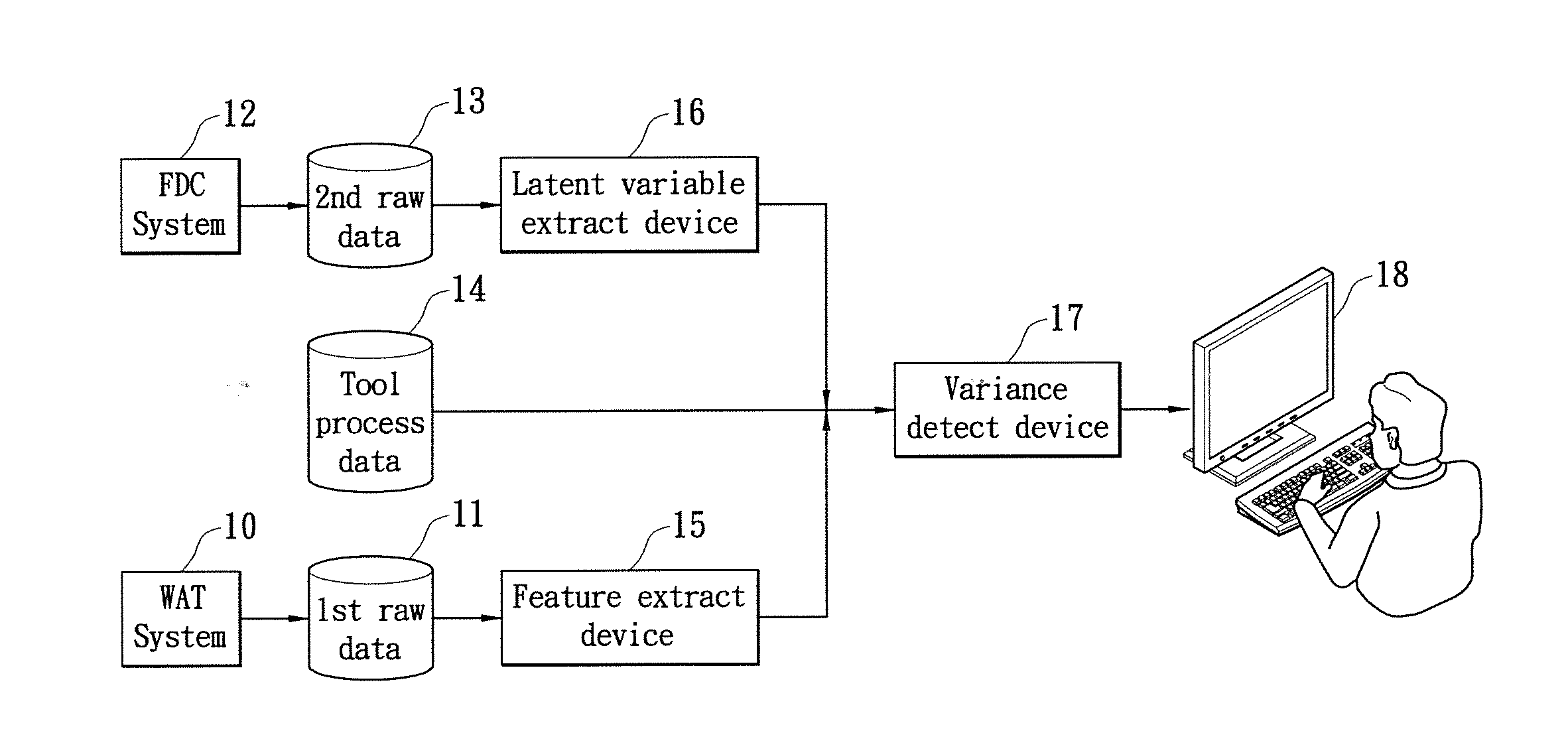
Method for detecting variance in semiconductor processes
ActiveUS20110257932A1Improve Wafer YieldLow production costProgramme controlTesting/monitoring control systemsPrincipal component analysisLatent variable
A method of detecting variance by regression model has the following steps. Step 1 is preparing the FDC data and WAT data for analysis. Step 2 is figuring out what latent variable effect of WAT data by Factor Analysis Step 3 is utilizing Principal Component Analysis to reduce the number of FDC variables to a few independent principal components. Step 4 is demonstrating how the tools and FDC data affect WAT data by Analysis of covariance model, and constructing interrelationship among FDC, WAT and tools. The interrelationship can point out which parameter effect WAT significantly. By the method, when WAT abnormal situation happened, it is easier for engineers to trace where the problem is.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
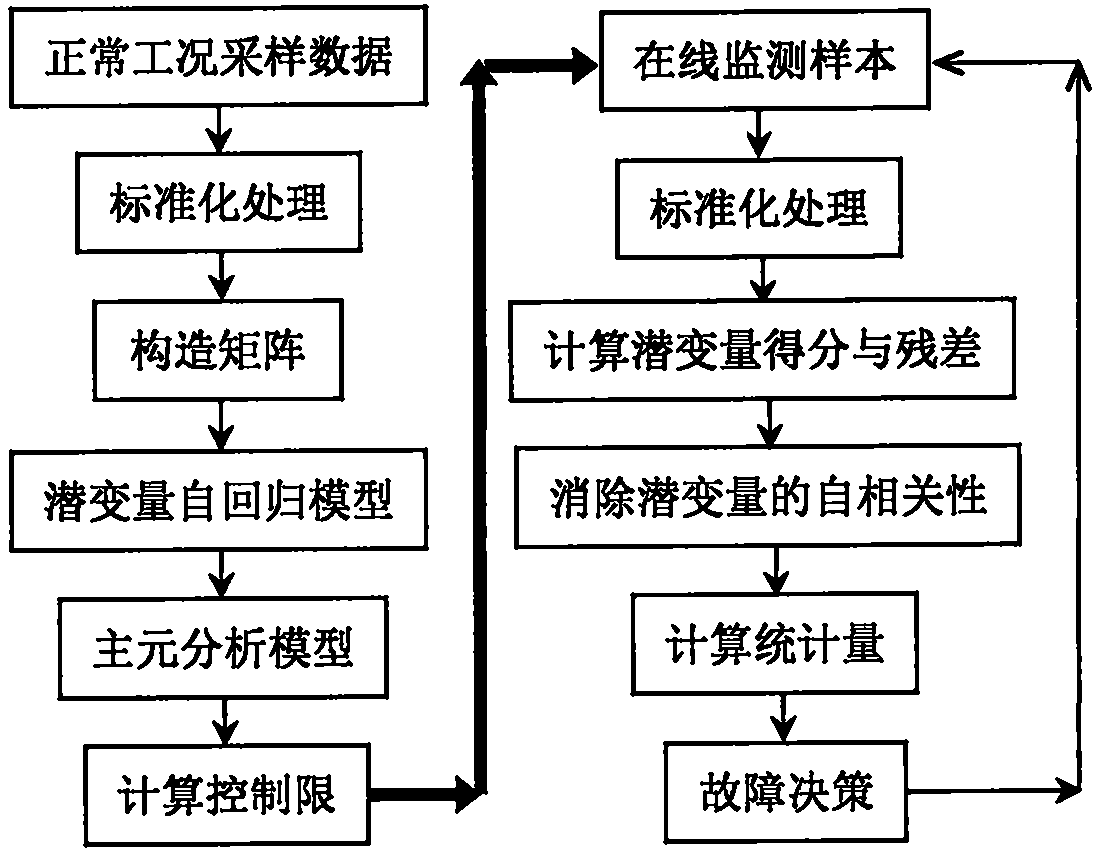
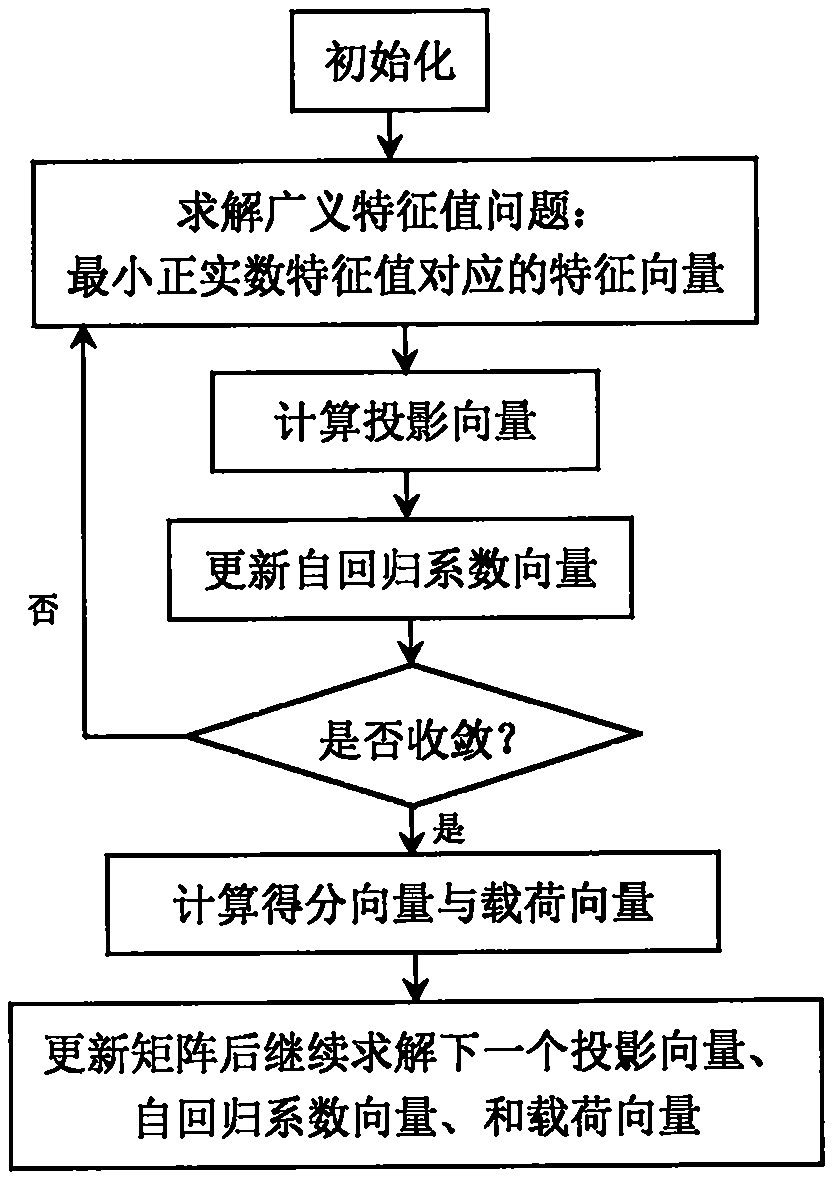
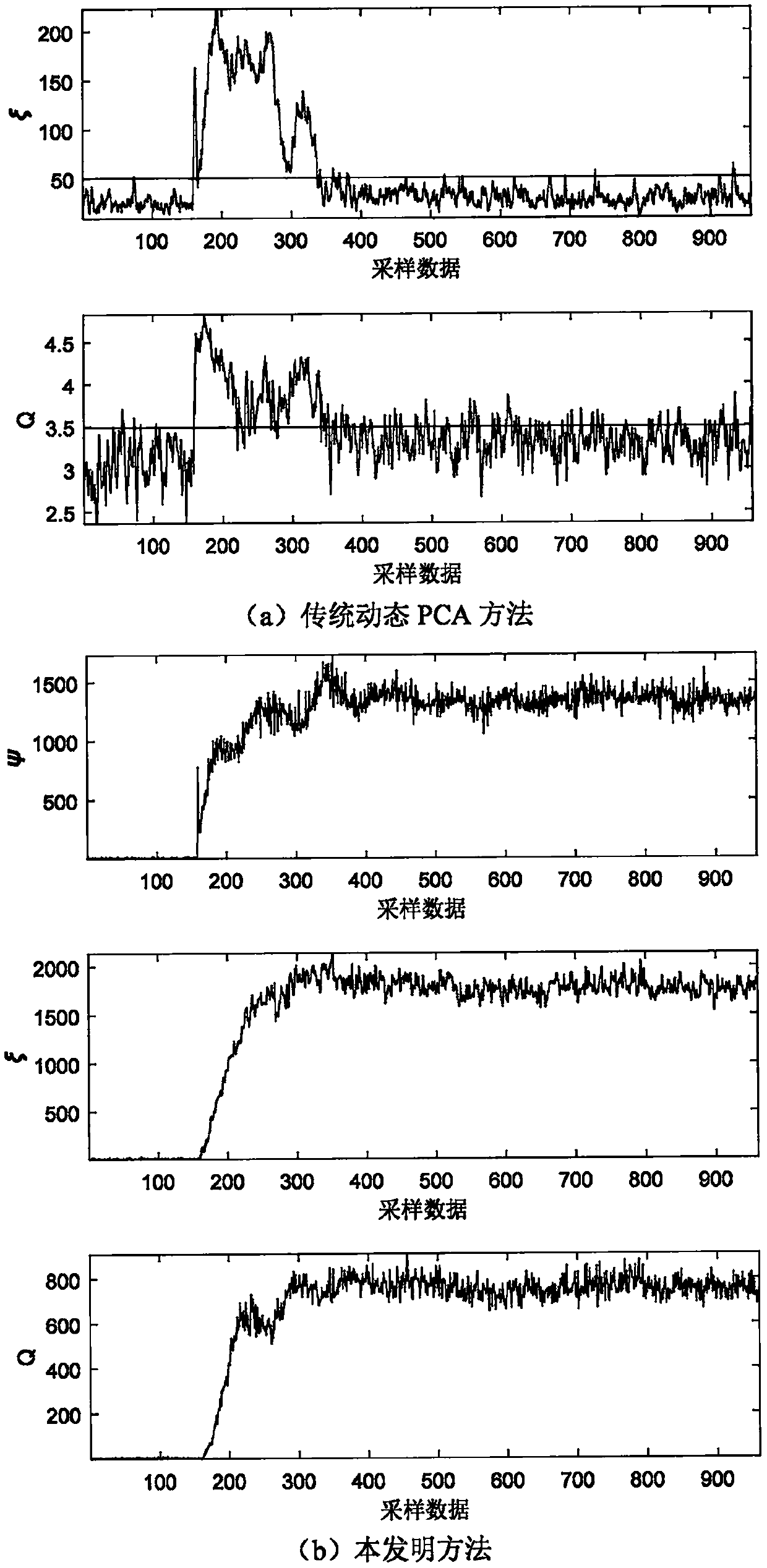
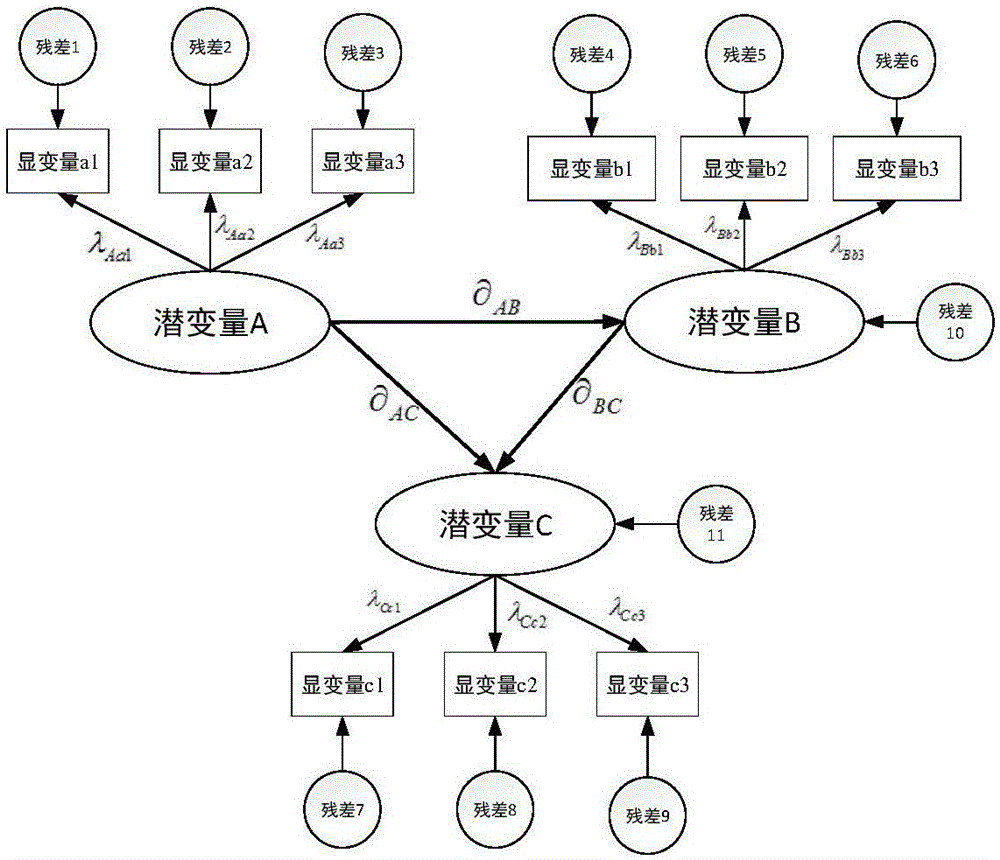
Dynamic process monitoring method based on a latent variable autoregression model
ActiveCN109522972AEliminate the effects of autocorrelationStrong explainabilityCharacter and pattern recognitionComplex mathematical operationsFeature miningData mining
The invention discloses a dynamic process monitoring method based on a latent variable autoregression model, and aims to establish the latent variable autoregression model and implement dynamic process monitoring on the basis of the latent variable autoregression model. Specifically, the method comprises the steps of defining a least square objective function of an autoregression model of a latentvariable, inferring a corresponding feature mining algorithm, and then establishing a fault monitoring model so as to implement online fault monitoring. According to the method disclosed by the invention, the dynamic autocorrelation latent variable is mined by establishing the target of the latent variable autoregression model, and the autoregression model meeting the least square condition is given correspondingly. Through the latent variable autoregression model, autocorrelation characteristics in original training data can be mined, and the influence of latent variable autocorrelation canbe eliminated. Therefore, the method provided by the invention is obviously different from the traditional dynamic process monitoring method, and the interpretability of the model is stronger. In other words, the method provided by the invention is a more preferable dynamic process monitoring method.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
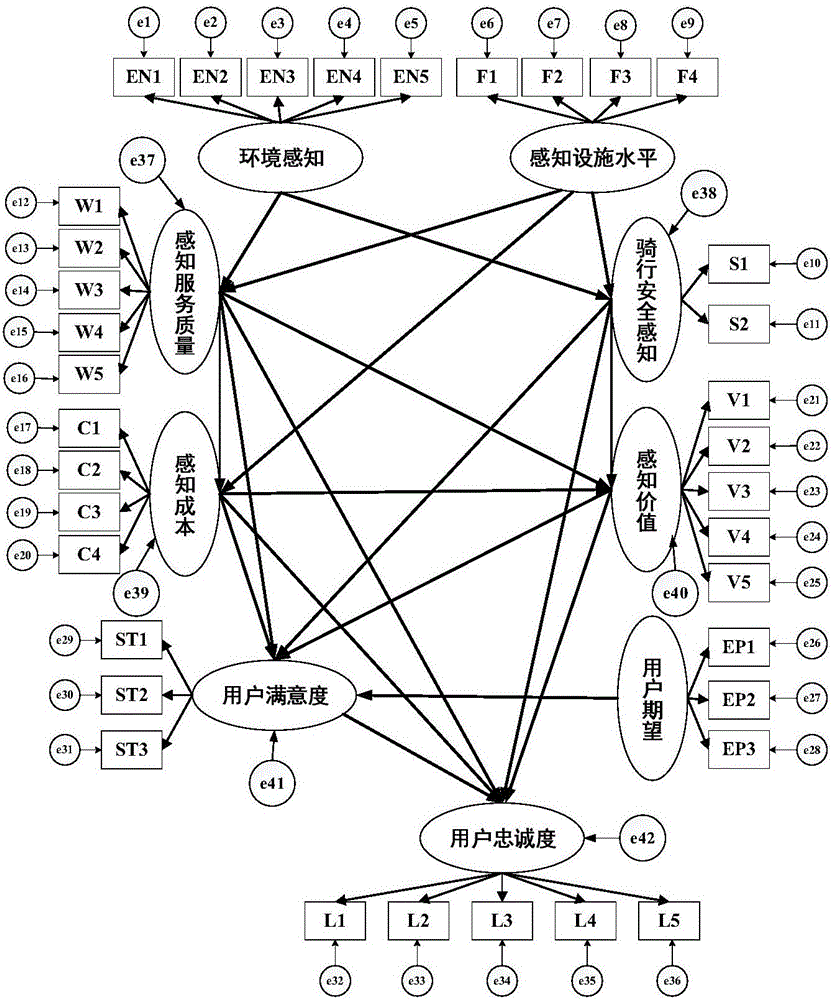
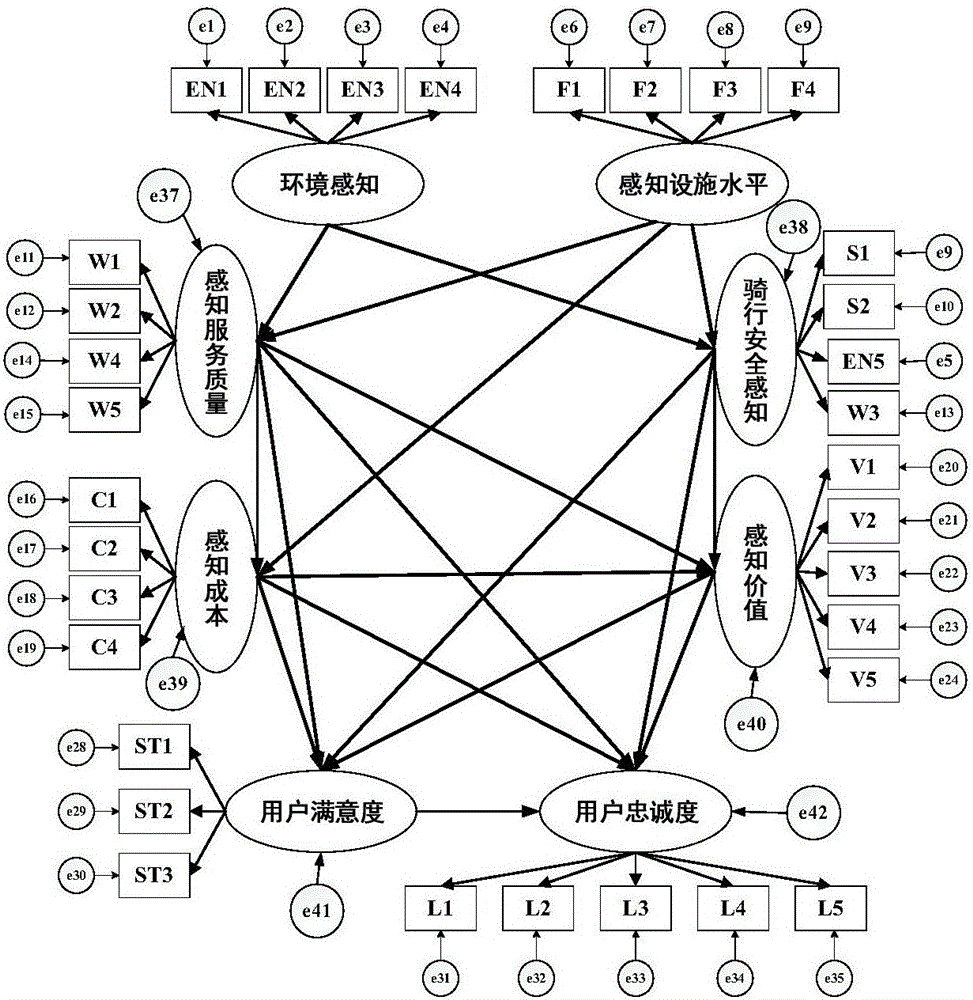
SEM model-based determination method of user loyalty degree of public bicycle
InactiveCN107180160AIncrease baseIncrease usageData processing applicationsSpecial data processing applicationsRegular distributionTraffic congestion
The invention discloses an SEM model-based determination method of a user loyalty degree of a public bicycle. The method comprises the following steps: constructing a structural equation model-based initial theoretical model of the user loyalty degree of the public bicycle; collecting data through a pre-survey questionnaire, using questionnaire data to calculate a KMO value, an alpha coefficient, factor loadings and a cumulative explained variance, and testing the questionnaire quality; calculating multivariate kurtosis values and multivariate skew values of the questionnaire data, carrying out a normal distribution test on the acquired valid data, and testing and correcting the model of the user loyalty degree of the public bicycle; and calculating a utility value of each latent variable on the loyalty degree and satisfaction degree indexes of influencing variables of the loyalty degree of the public bicycle according to a result output by the model. By adopting the method of the invention, quantitative evaluation can be carried out on the user loyalty degree of the public bicycle and the influencing factors thereof, then a public-bicycle share rate and even a slow-traffic share rate can be increased, and thus important contributions are made in an aspect of alleviating urban traffic congestion.
Owner:SOUTHWEST JIAOTONG UNIV
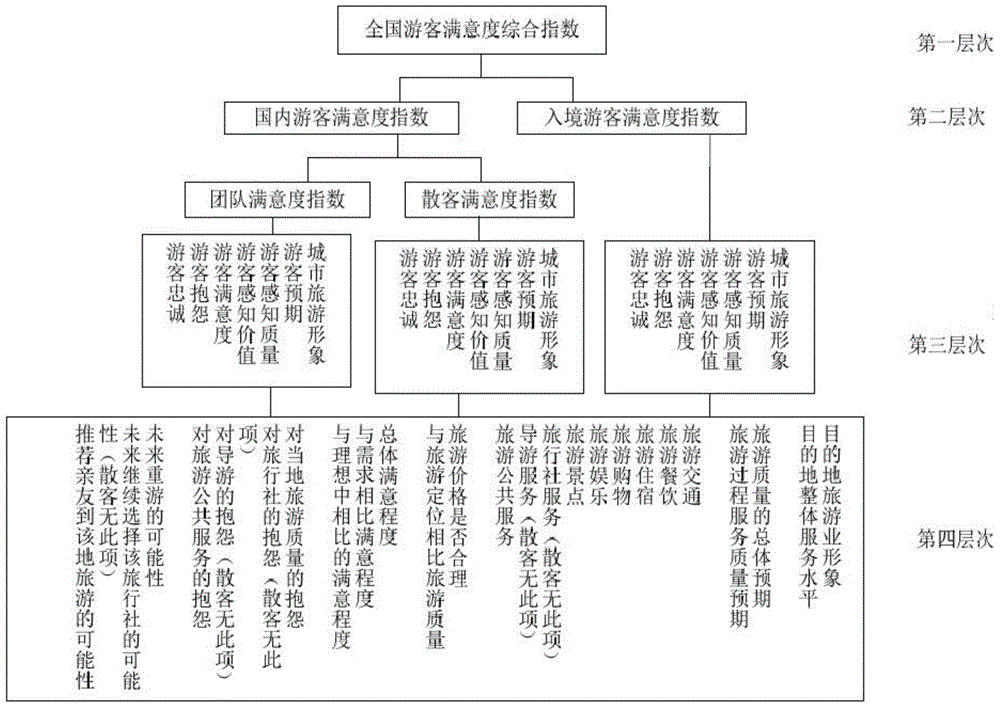
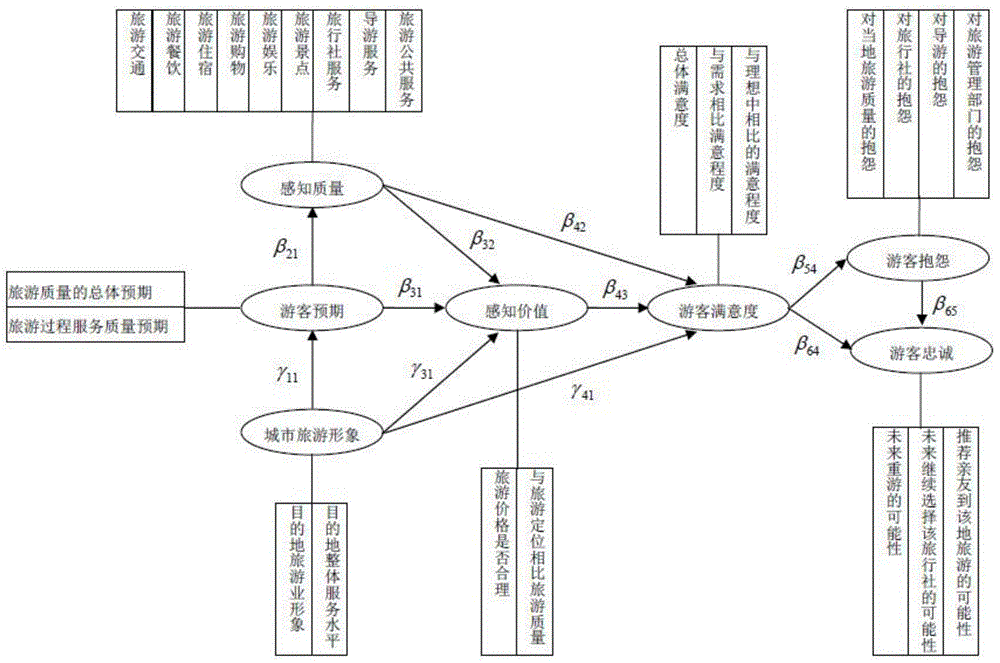
Tourist satisfaction investigation method
InactiveCN104809633AComprehensive research indexComprehensive treatment of statistical methodsMarketingInvestigation methodsIndex system
The invention relates to the technical field of data research, and particularly discloses a tourist satisfaction investigation method. The tourist satisfaction investigation method comprises the following steps: calculation and analysis of comprehensive indexes of tourist satisfaction in the whole nation: firstly constructing a four-layer index system of the comprehensive indexes of tourist satisfaction, wherein the first layer of the index system comprising comprehensive indexes of tourist satisfaction in the whole nation, the second layer of the index system comprising the indexes of satisfaction of national and inbound tourists, the third layer of the index system comprising latent variables, and the fourth layer of the index system comprising the measured variables of the latent variables; determining the weights of the four-layer indexes; calculating the indexes of tourist satisfaction in the fourth layer of indexes according to the weights; successively analogizing to calculate the indexes of tourist satisfaction of the third layer and the second layer of indexes according to the weights of the calculated indexes of tourist satisfaction and each layer of indexes; finally, calculating the comprehensive indexes of tourist satisfaction in the whole nation for the first layer of indexes. The capacity for scientific research is promoted, the research cost is reduced, and technical support and data foundation are provided for promoting the service quality in tourism, standardizing tourism market order and promoting tourism development.
Owner:中国旅游研究院
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com