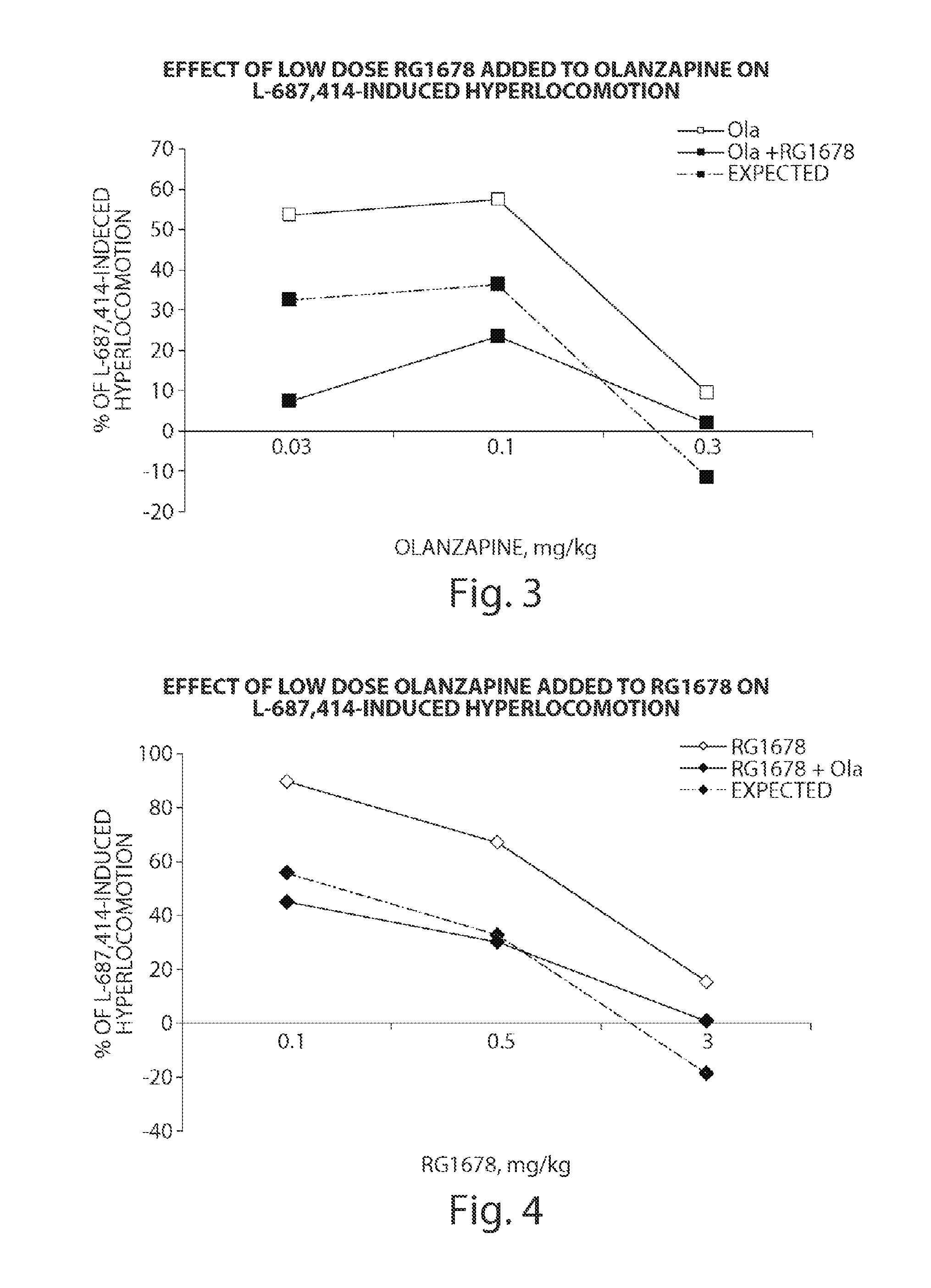
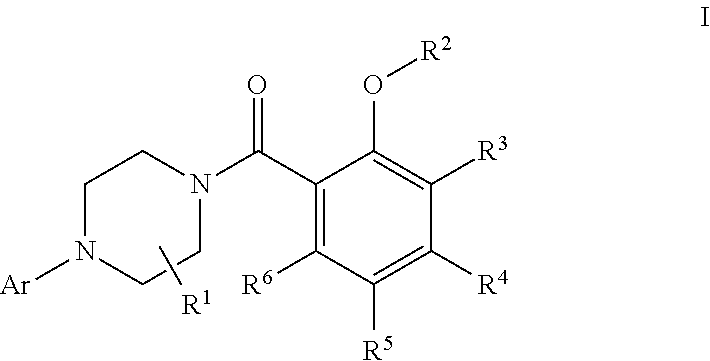
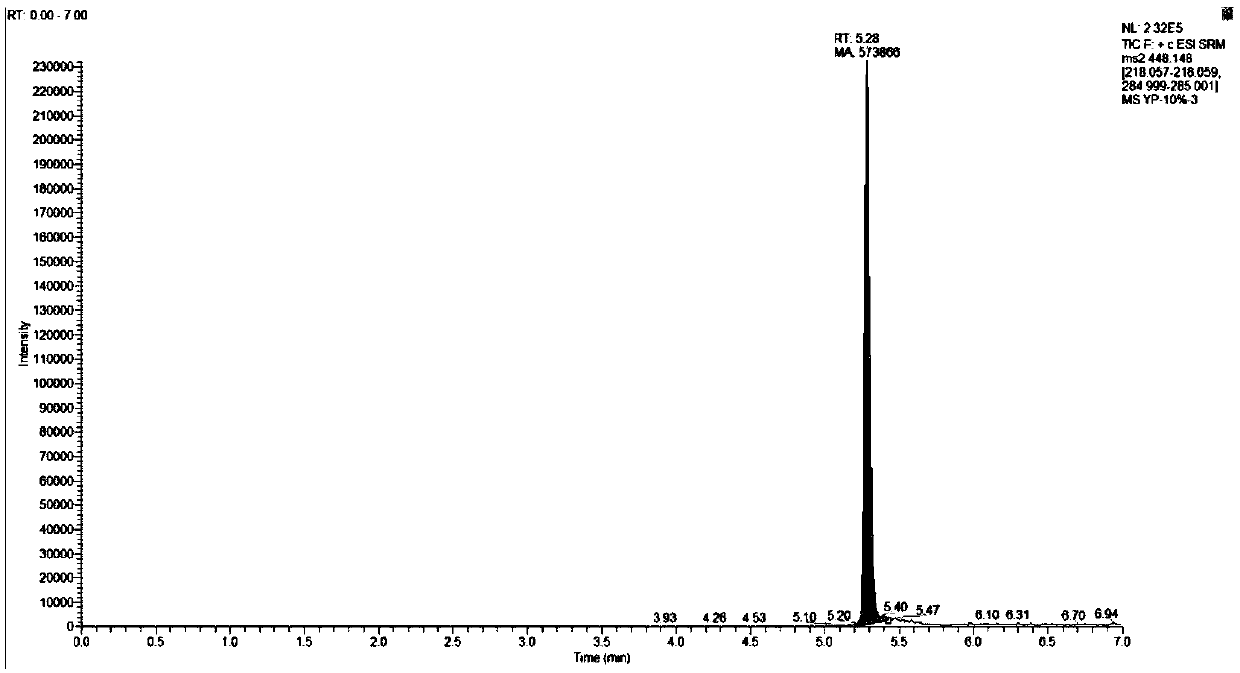
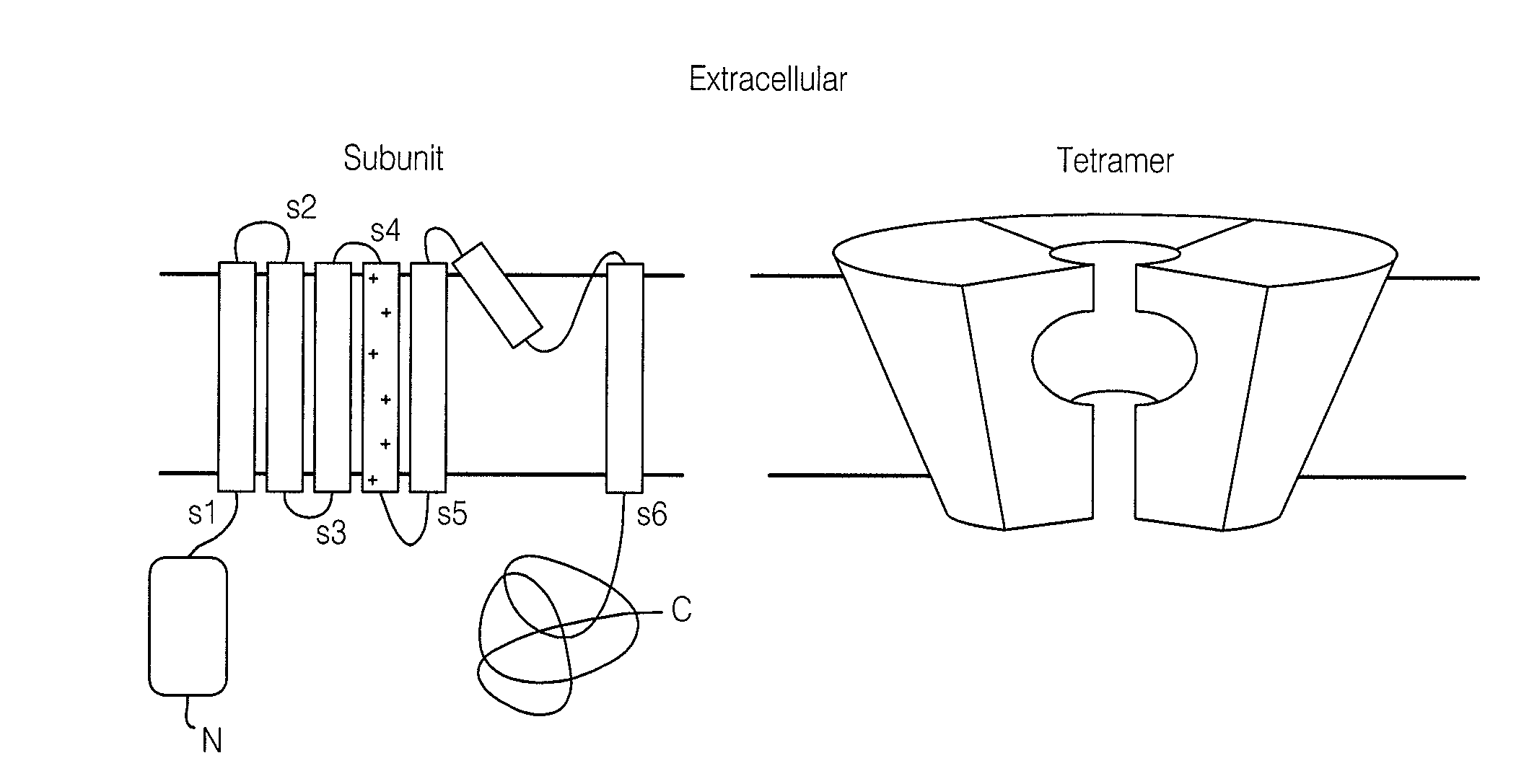
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
148 results about "Antipsychotic Medications" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Antipsychotic medications are used as a short-term treatment for bipolar disorder to control psychotic symptoms such as hallucinations, delusions, or mania symptoms. These symptoms may occur ...
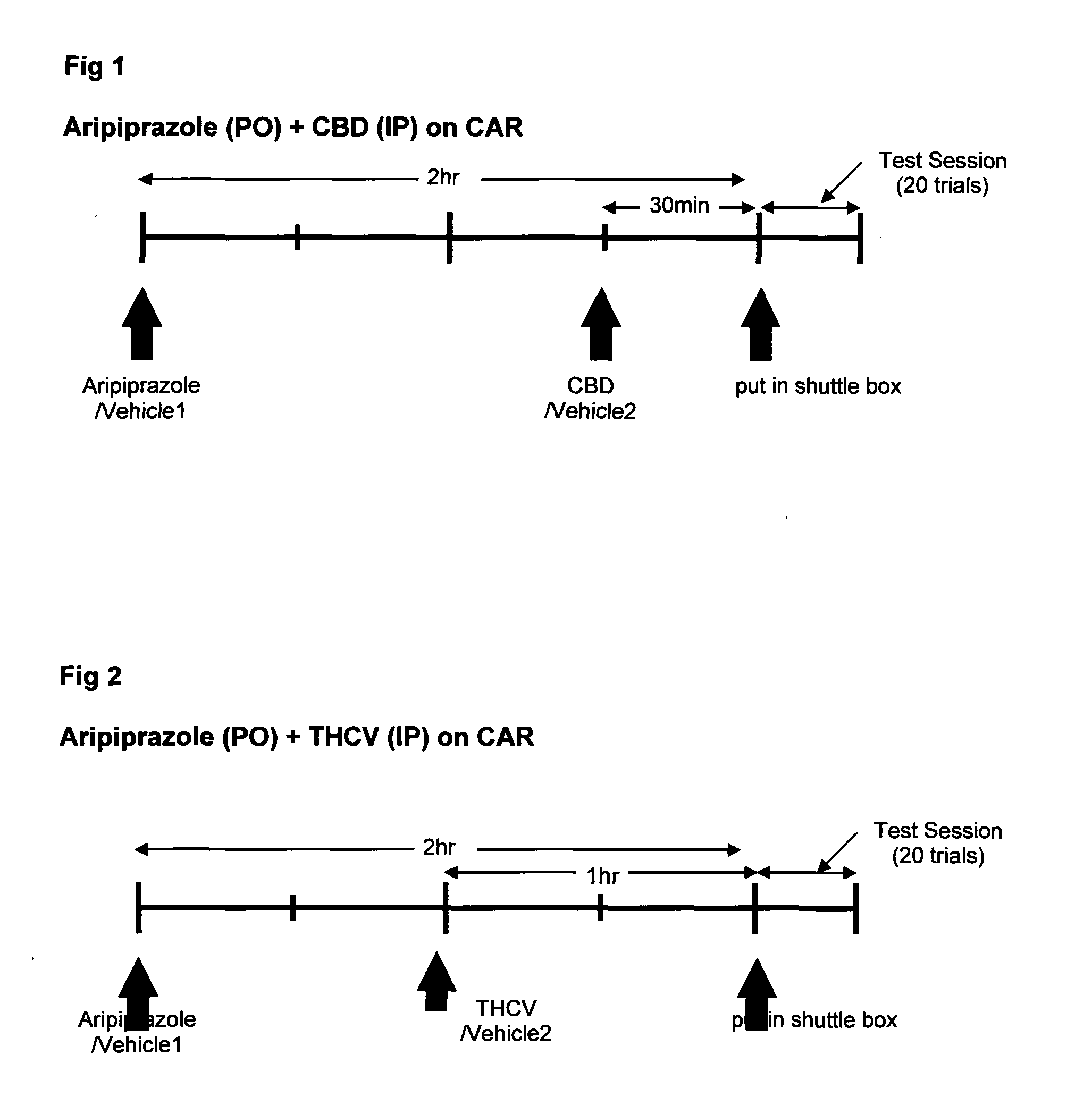
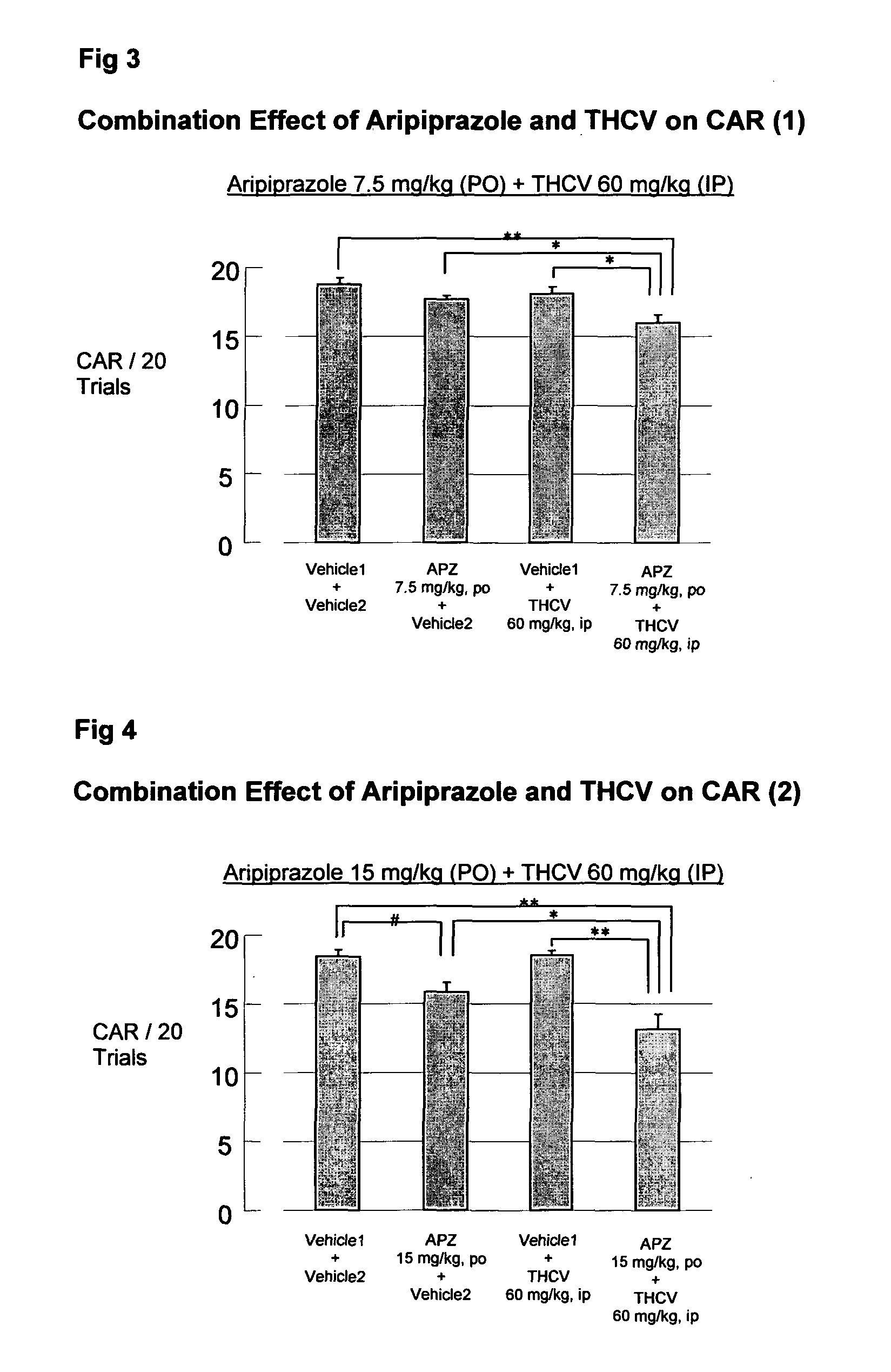
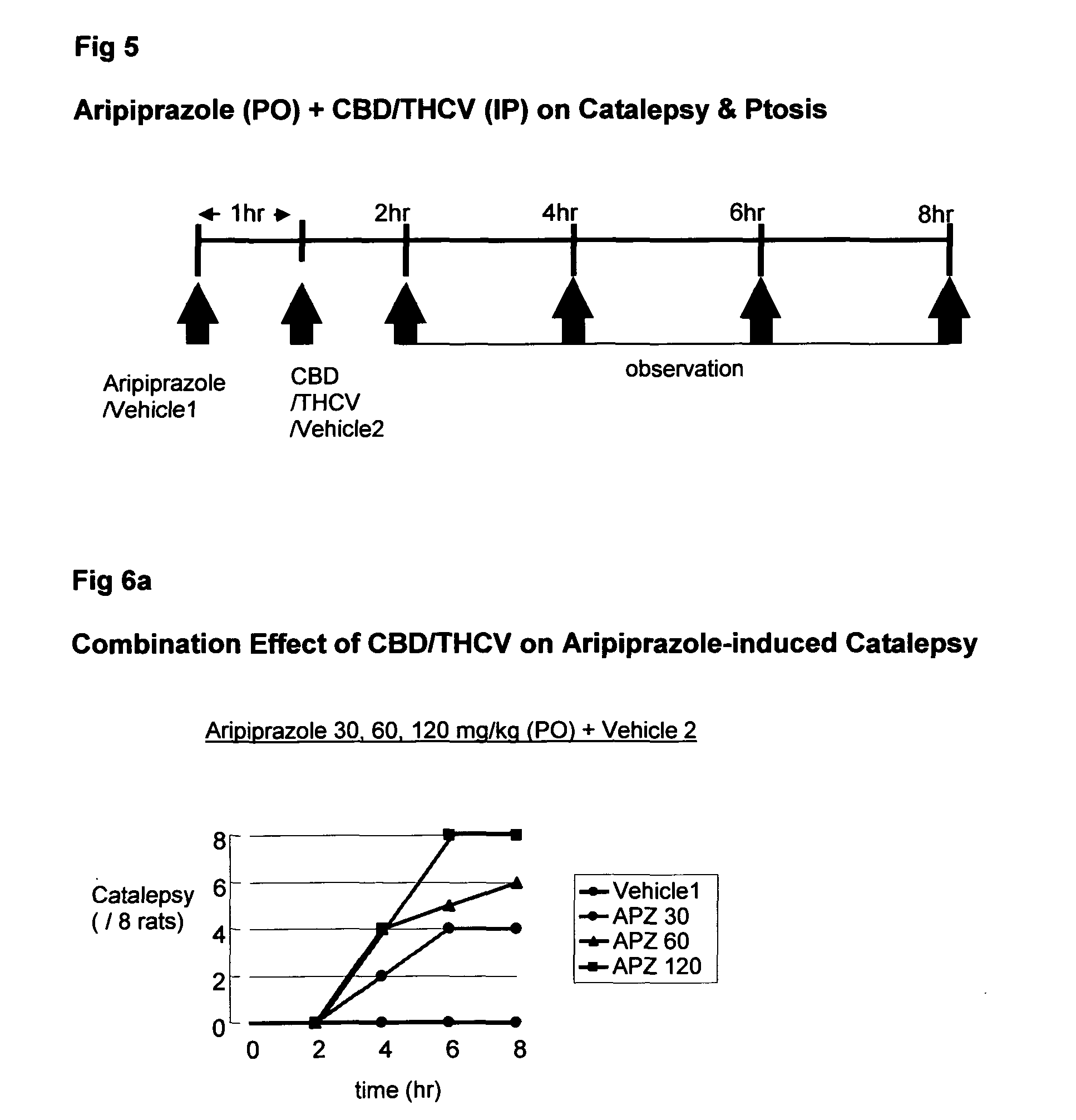
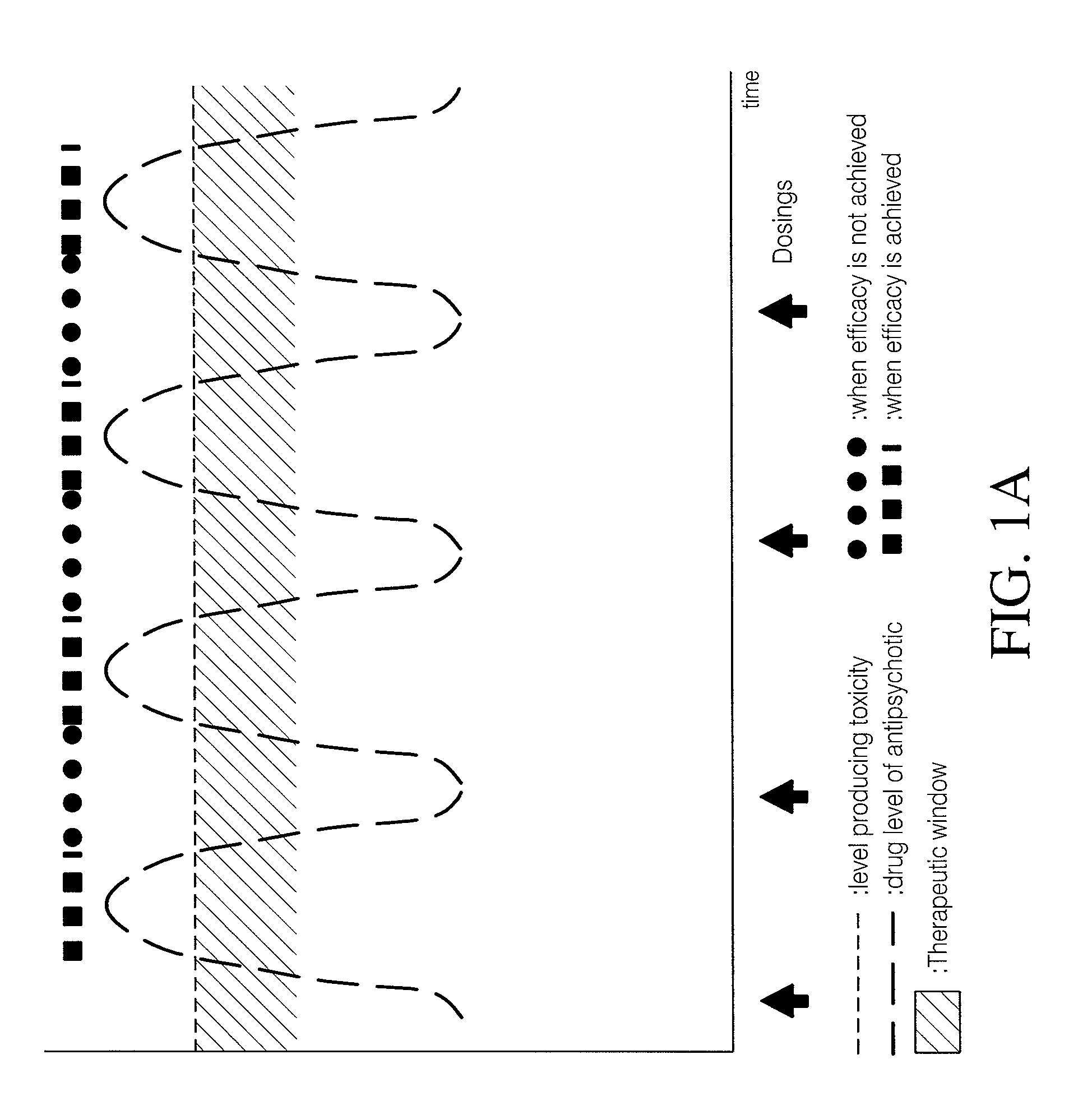
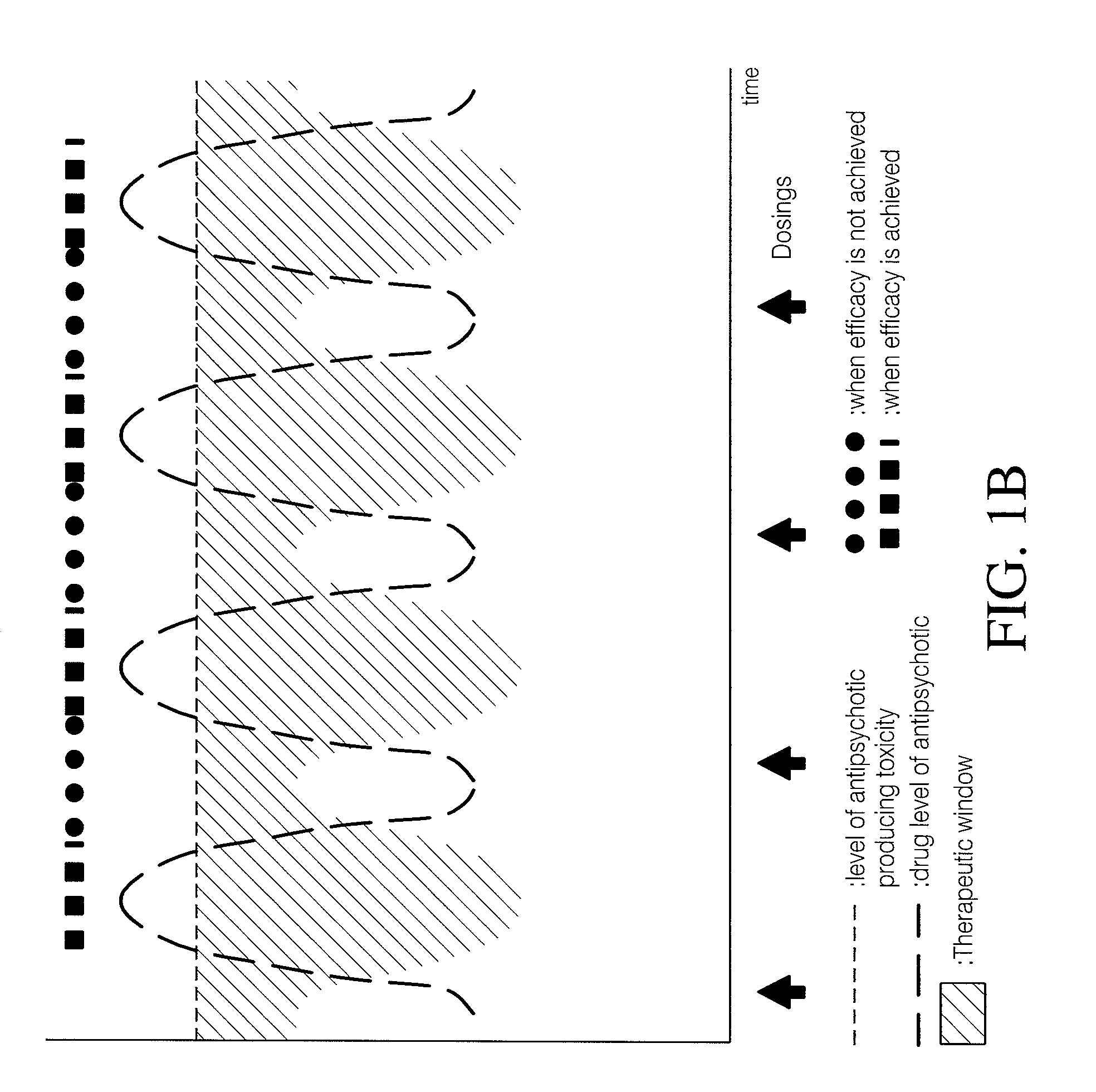
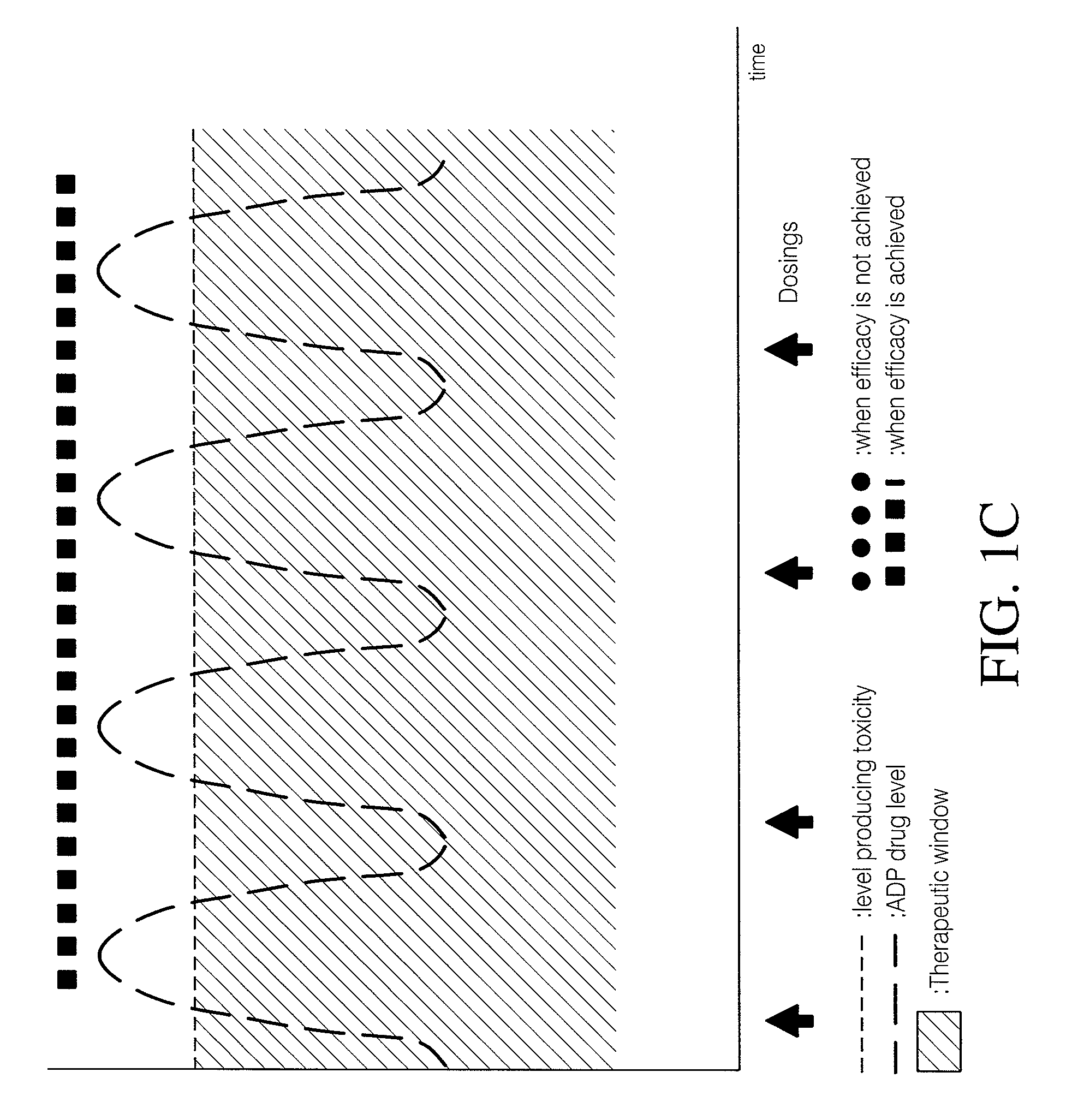
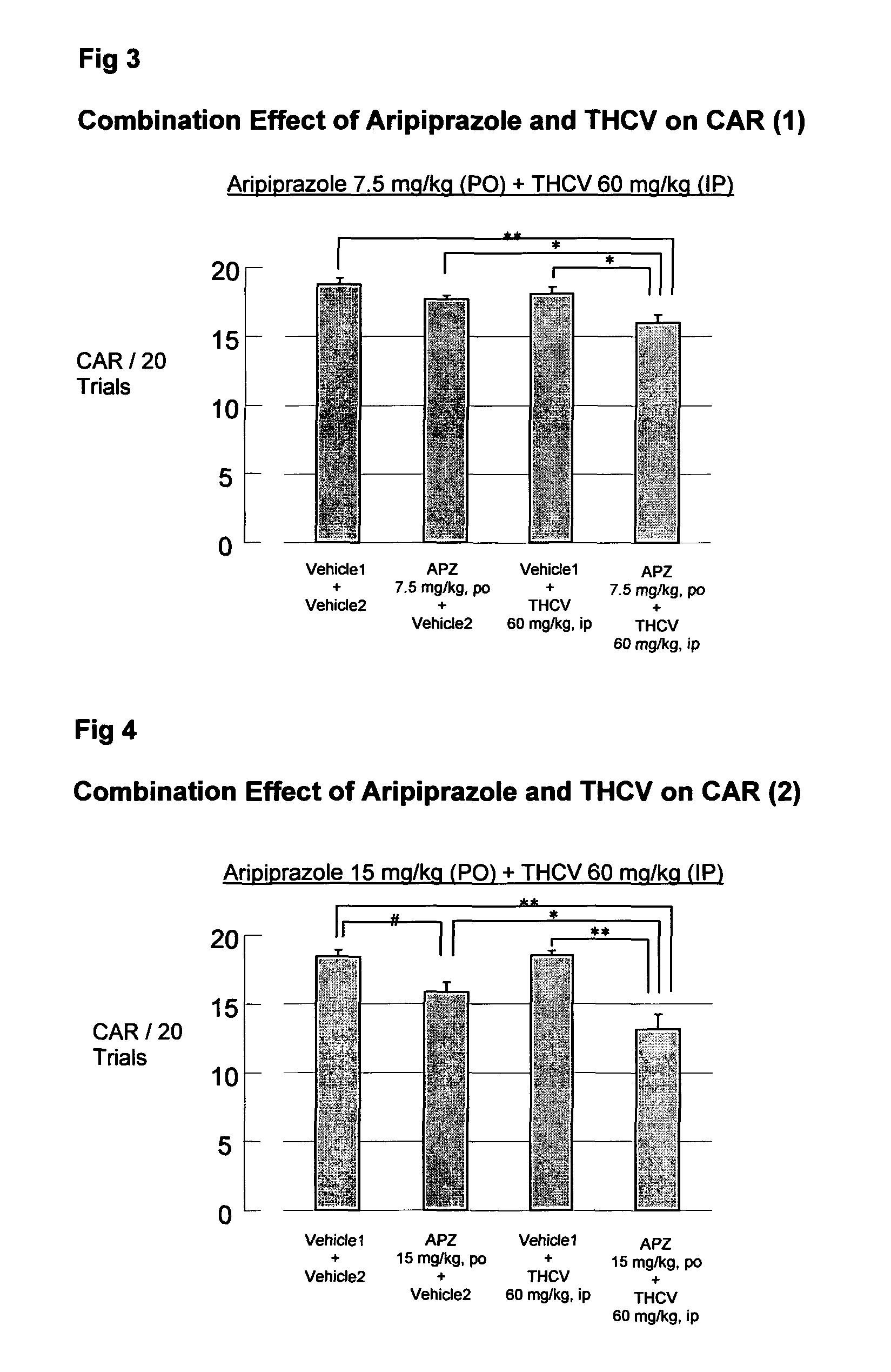
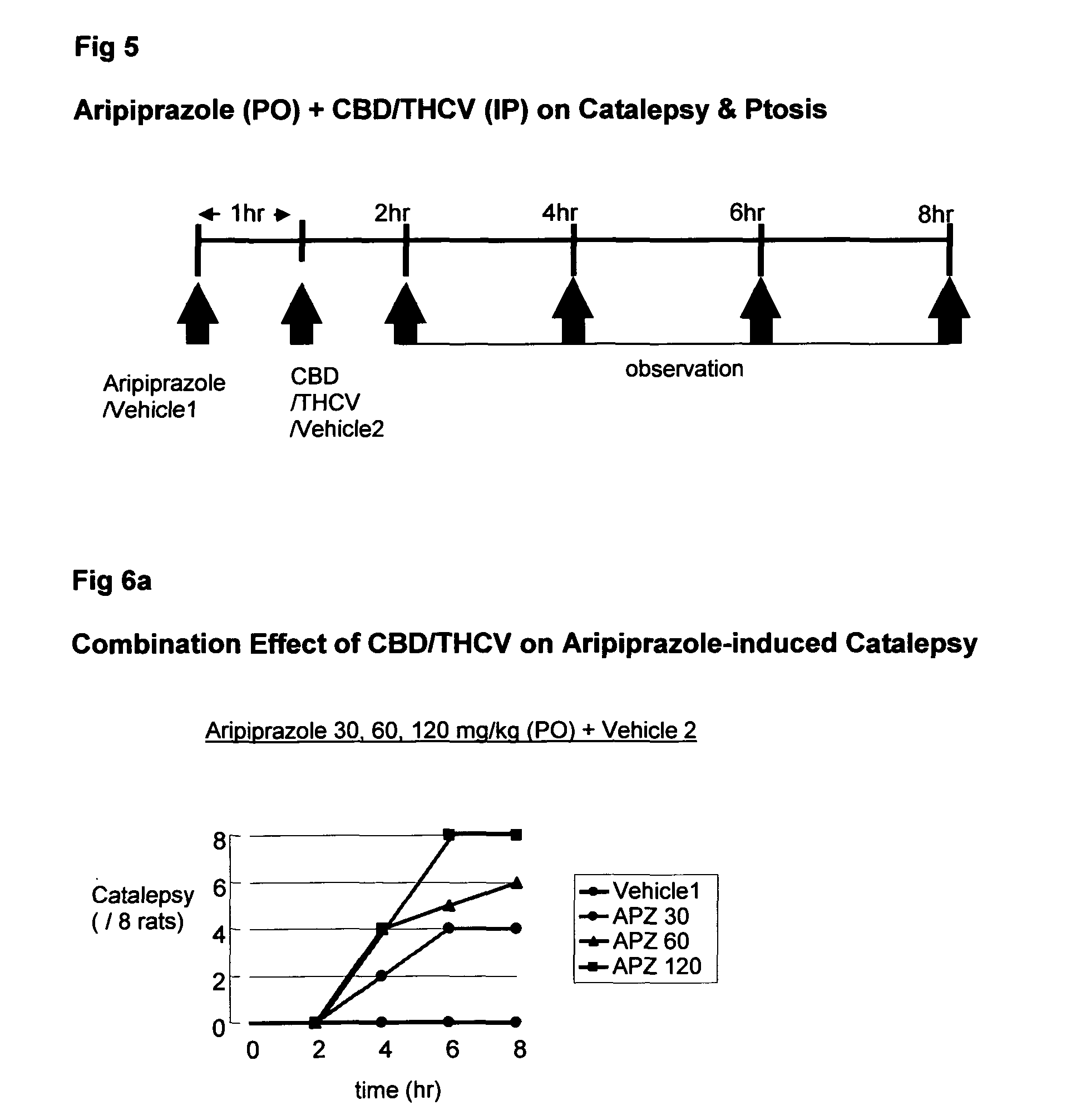
Use of cannabinoids in combination with an Anti-psychotic medicament
ActiveUS20110038958A1High activityLess degree of activityBiocideSenses disorderPsychosis drugTypical antipsychotic
The present invention relates to the use of one or more cannabinoids in combination with one or more anti-psychotic medicaments for use in the prevention or treatment of psychosis and psychotic disorders. Preferably the one or more cannabinoids are taken from the group: cannabidiol (CBD); cannabidiolic acid (CBDA); tetrahydrocannbidivarin (THCV); tetrahydrocannbidivarinin acid (THCVA); cannabichromene (CBC); cannabichromenic acid (CBCA); cannabigerol (CBG) and cannabigerolic acid (CBGA). Preferably the anti-psychotic medication is an atypical anti-psychotic medication.
Owner:GW PHARMA LTD
Combinations of 5-ht2a inverse agonists and antagonists with antipsychotics
InactiveUS20090053329A1Achieve effectQuick effectCompounds screening/testingBiocideSide effectAntipsychotic drug therapy
Combinations of 5-HT2A inverse agonists or antagonists such as pimavanserin with antipsychotics such as risperidone are shown to induce a rapid onset of antipsychotic action and increase the number of responders when compared to therapy with the antipsychotic alone. These effects can be achieved at a low dose of the antipsychotic, thereby reducing the incidence of side effects. The combinations are also effective at decreases the incidence of weight gain and increased glucose or prolactin levels caused by the antipsychotic.
Owner:ACADIA PHARMA INC
Use of cannabinoids in combination with an anti-psychotic medicament
ActiveUS9017737B2High activityLess degree of activityBiocideSenses disorderTypical antipsychoticPsychosis drug
The present invention relates to the use of one or more cannabinoids in combination with one or more anti-psychotic medicaments for use in the prevention or treatment of psychosis and psychotic disorders. Preferably the one or more cannabinoids are taken from the group: cannabidiol (CBD); cannabidiolic acid (CBDA); tetrahydrocannbidivarin (THCV); tetrahydrocannbidivarinin acid (THCVA); cannabichromene (CBC); cannabichromenic acid (CBCA); cannabigerol (CBG) and cannabigerolic acid (CBGA). Preferably the anti-psychotic medication is an atypical anti-psychotic medication.
Owner:GW PHARMA LTD
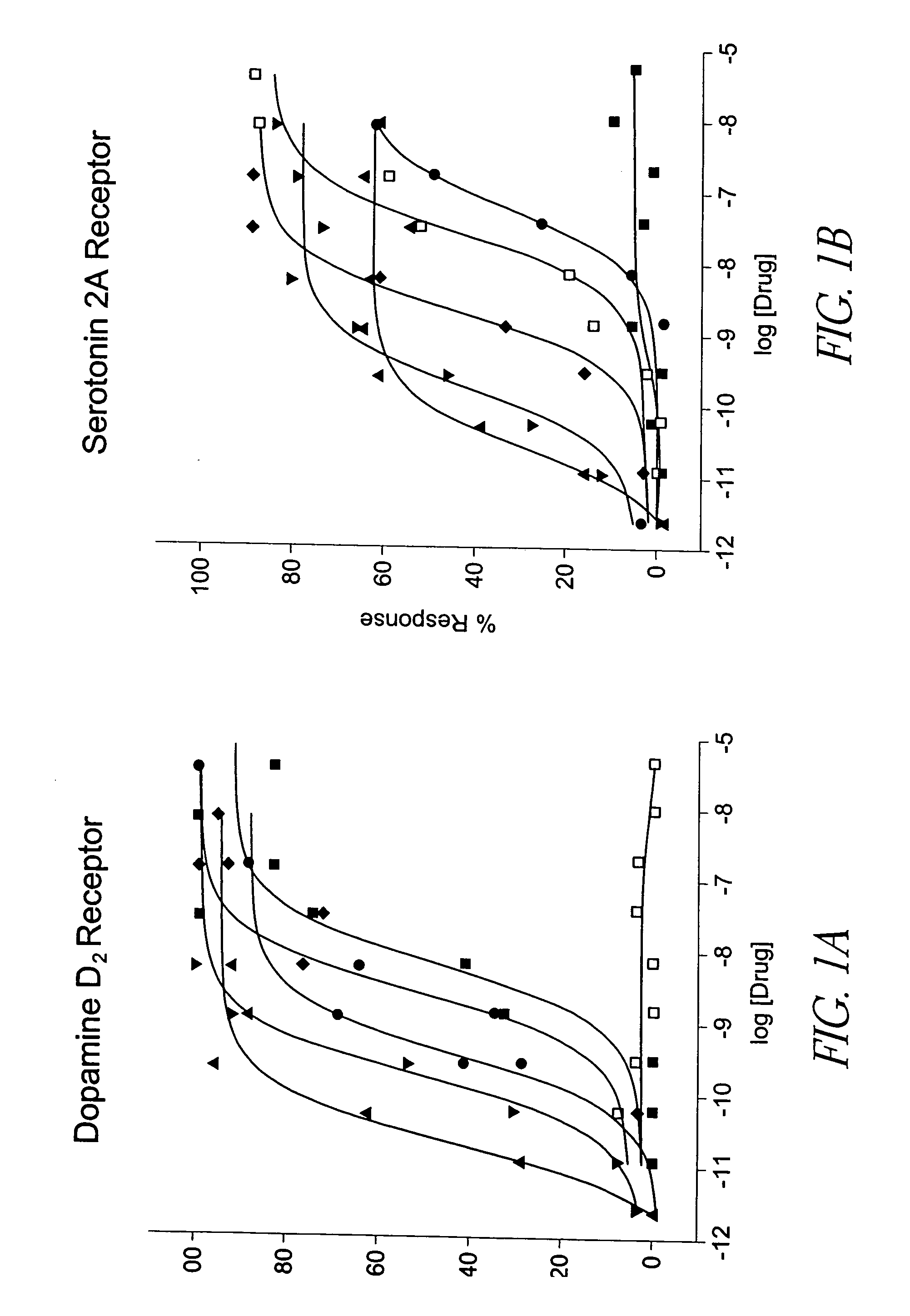
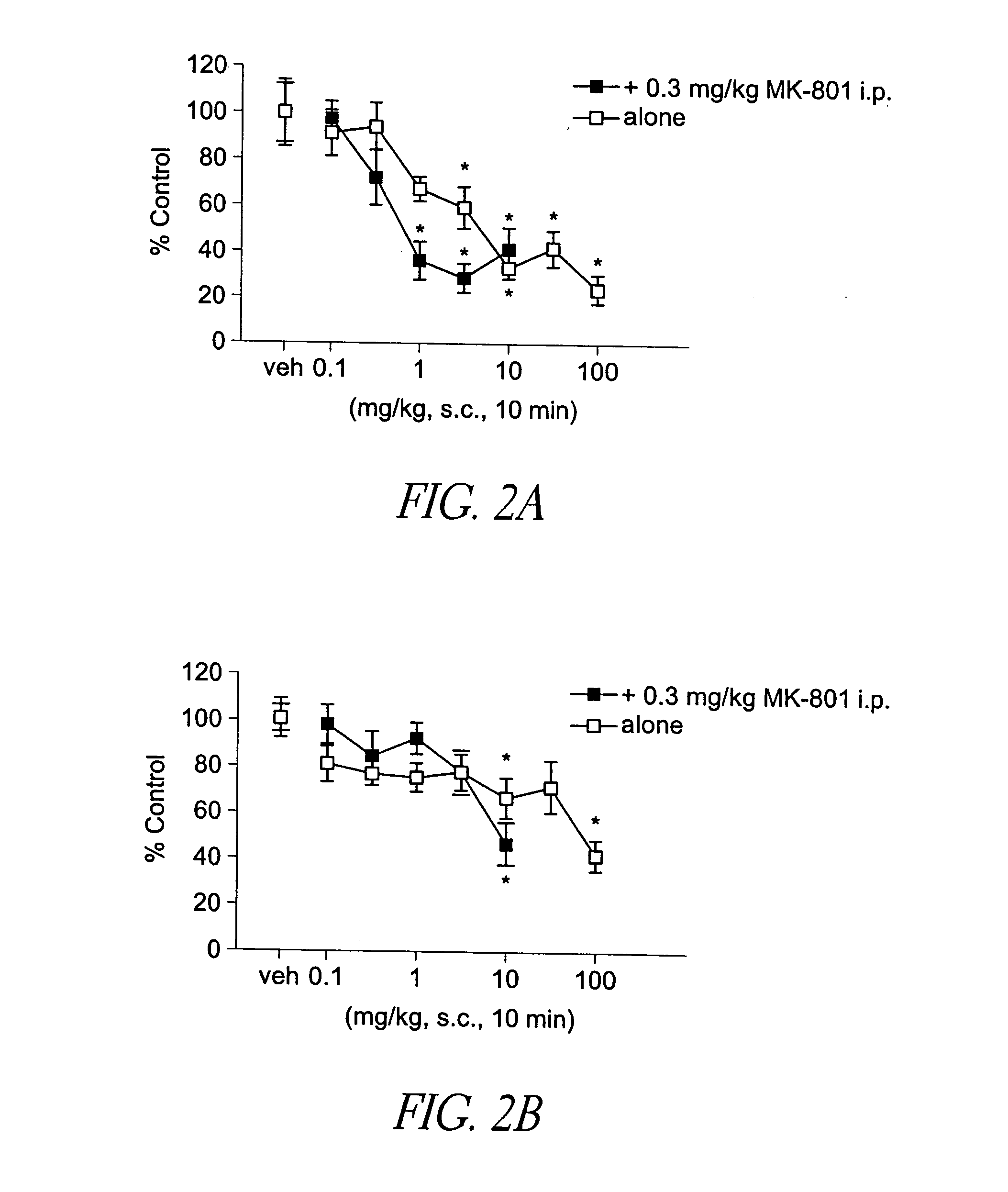
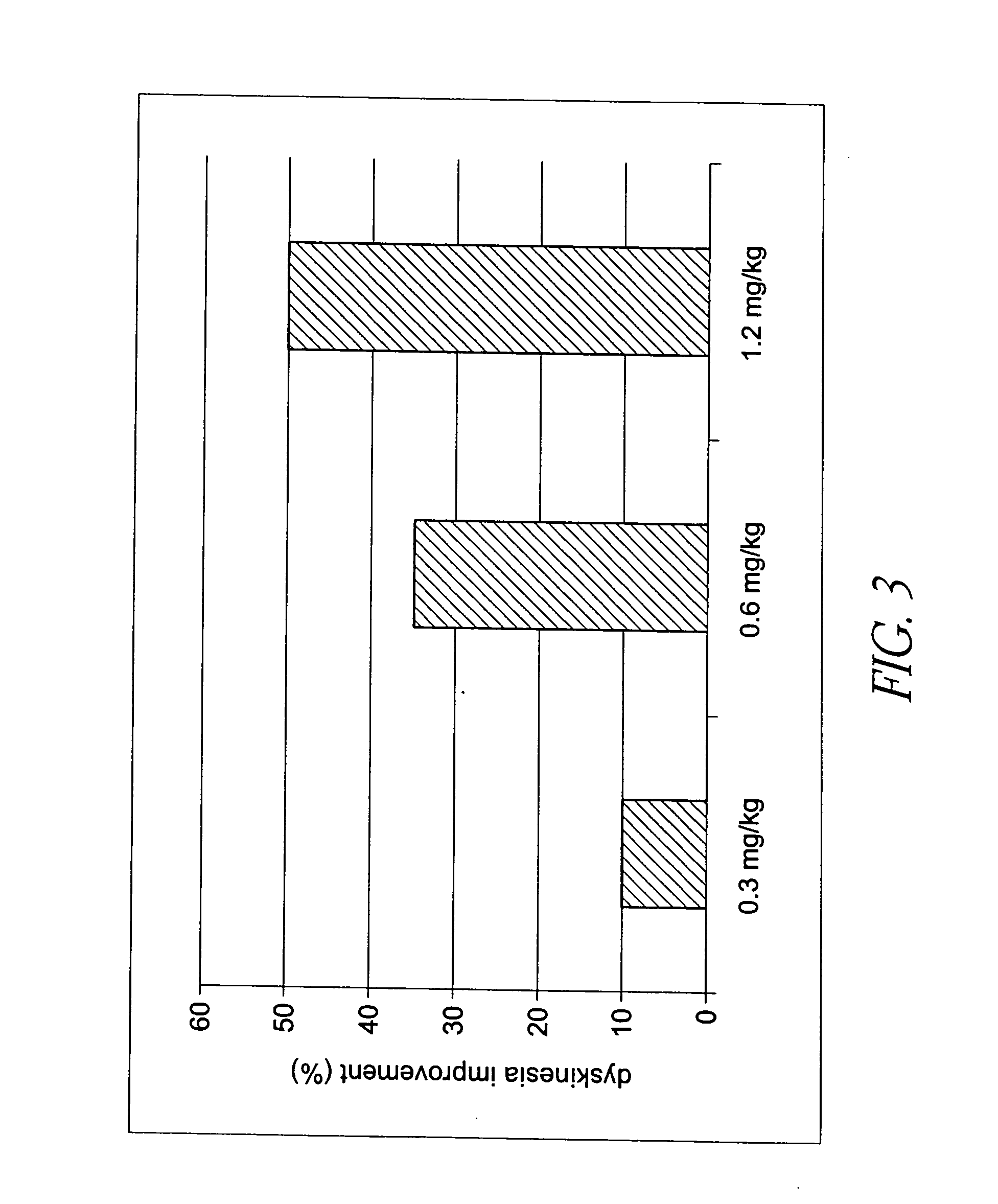
Selective serotonin 2A/2C receptor inverse agonists as therapeutics for neurodegenerative diseases
Behavioral pharmacological data with the compound of formula (I), a novel and selective 5HT2A / 2C receptor inverse agonist, demonstrate in vivo efficacy in models of psychosis and dyskinesias. This includes activity in reversing MK-801 induced locomotor behaviors, suggesting that this compound may be an efficacious anti-psychotic, and activity in an MPTP primate model of dyskinesias, suggesting efficacy as an anti-dyskinesia agent. These data support the hypothesis that 5HT2A / 2C receptor inverse agonism may confer antipsychotic and anti-dyskinetic efficacy in humans, and indicate a use of the compound of formula (I) and related agents as novel therapeutics for Parkinson's Disease, related human neurodegenerative diseases, and psychosis.
Owner:ACADIA PHARMA INC
Methods and compositions for treating schizophrenia using antipsychotic combination therapy
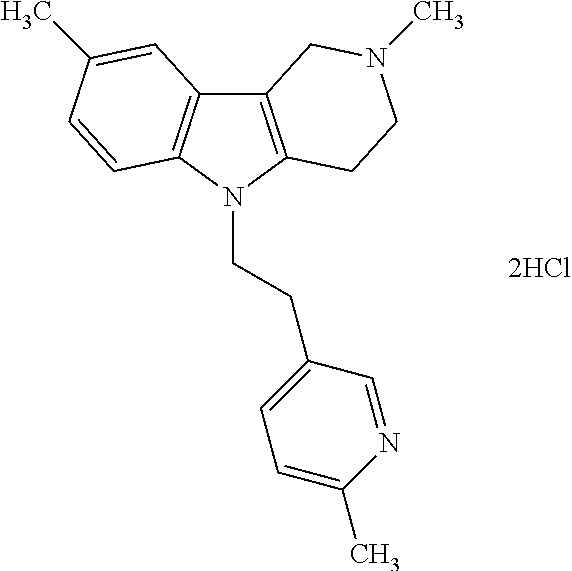
The present invention relates to combination therapies and methods for treating, preventing and / or delaying the onset and / or development of schizophrenia, wherein the combination therapies comprise a hydrogenated pyrido[4,3-b]indole or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, such as dimebon, and an antipsychotic.
Owner:MEDIVATION TECH INC
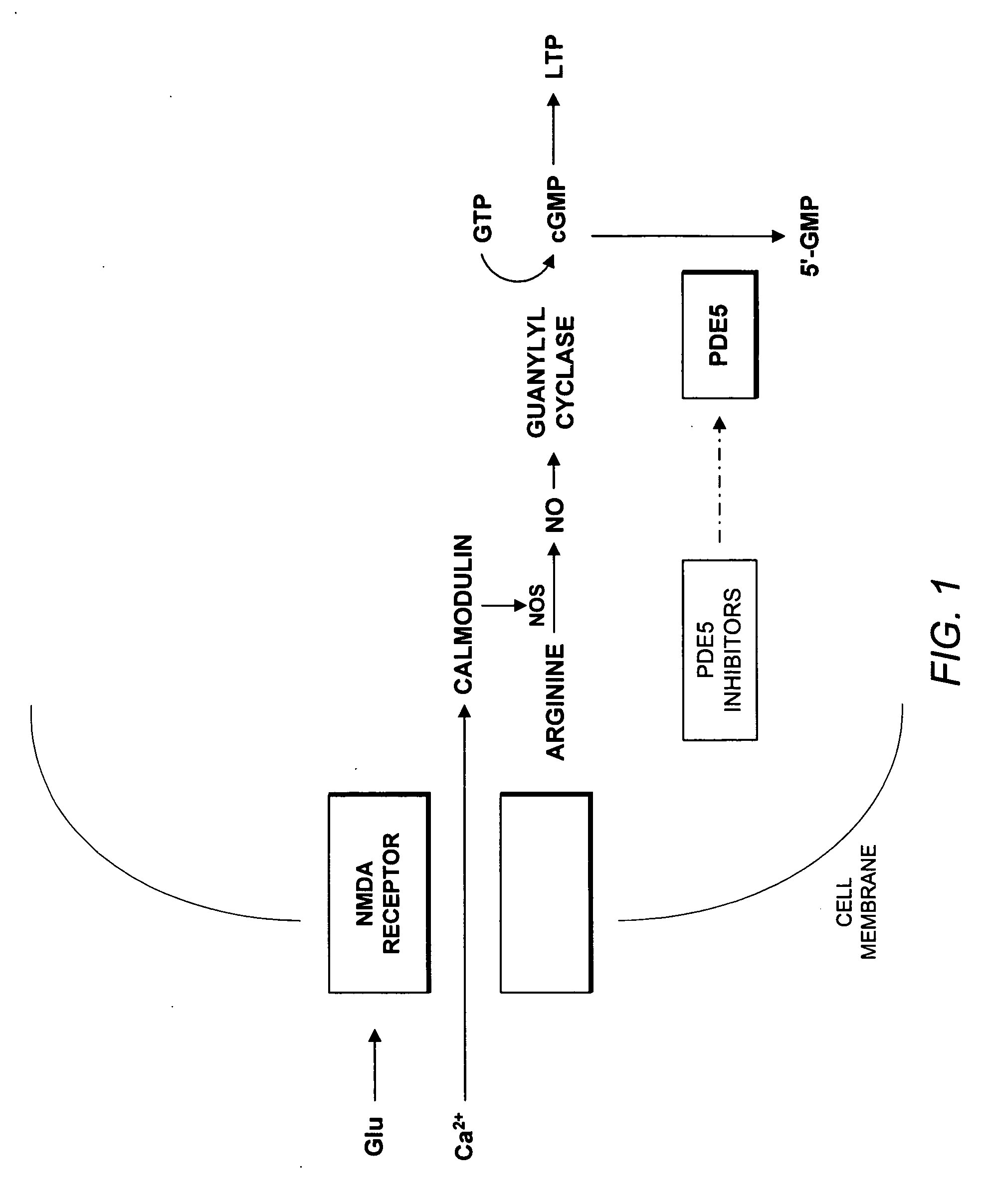
Use of phosphodiesterase 5 (PDE5) inhibitors in the treatment of schizophrenia
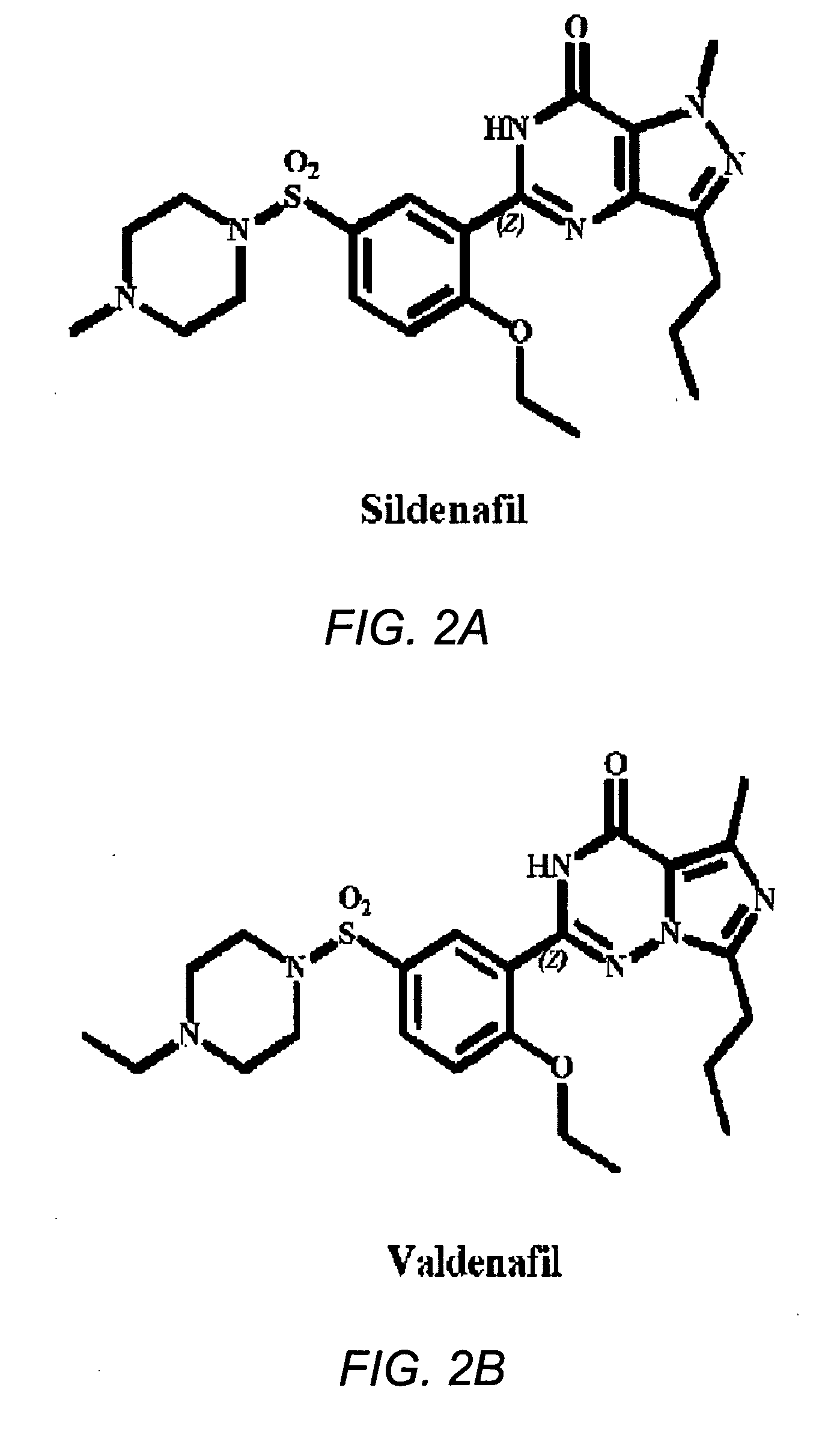
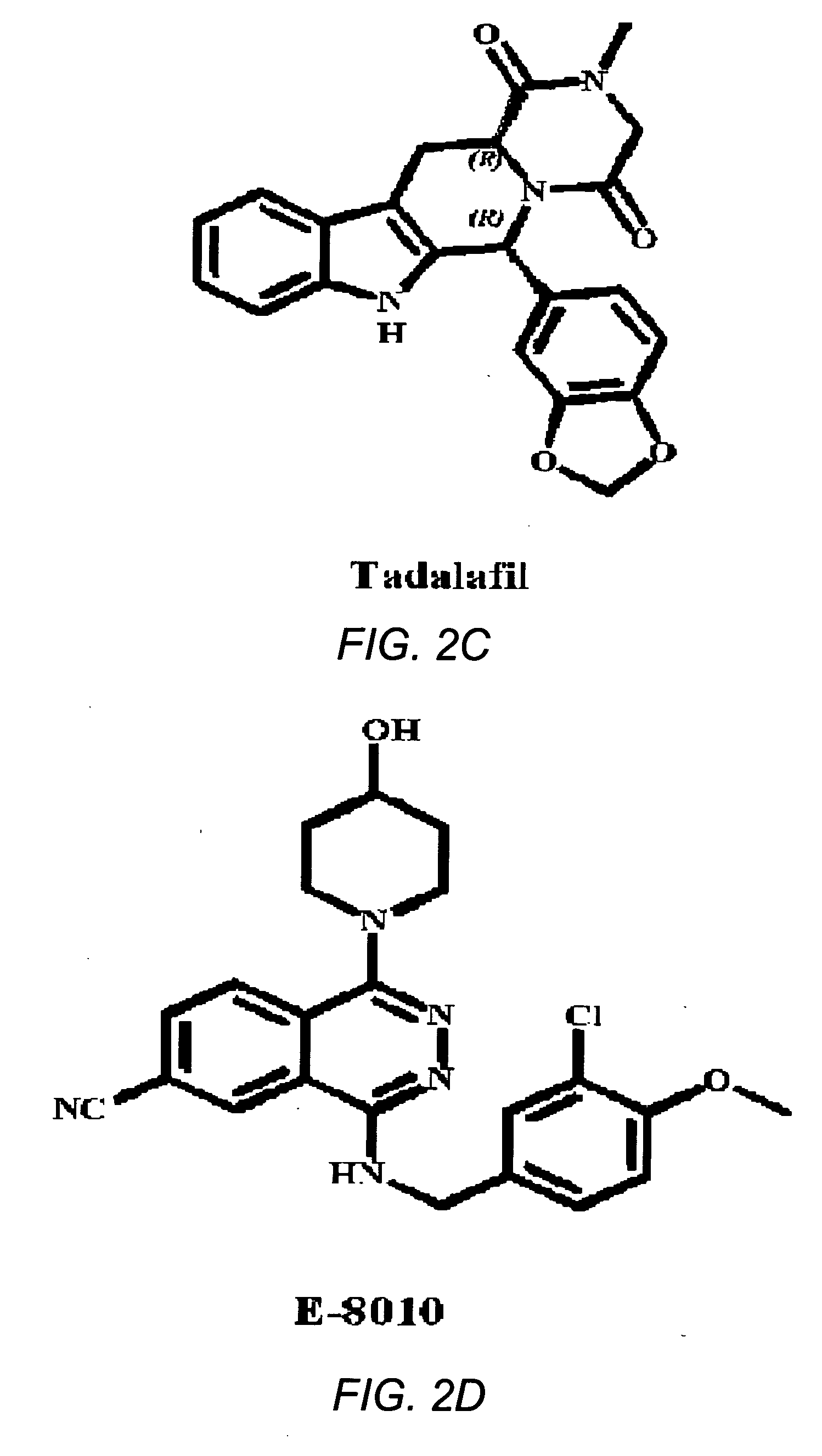
The use of phosphodiesterase 5 (PDE5) inhibitors for treatment of schizophrenia is described. Suitable PDE5 inhibitors for use for treatment of schizophrenia include sildenafil, vardenafil, tadalafil, E-8010, zaprinast, and E-4021. In one embodiment, for example, a method is described for treating schizophrenia in a patient which comprises treating the patient with an effective amount of a PDE5 inhibitor, or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt, solvate, or composition thereof. The PDE5 inhibitor may be administered orally. The PDE5 inhibitor may also be administered together with one or more conventional antipsychotic medications such as risperidone, olanzapine, quetiapine, ziprasidone, aripiprazole, clozapine, haloperidol, and fluphenazine.
Owner:SHARY CIRCLE
Antipsychotic molecular-targeting epithelial growth factor receptor
The purpose of this invention is to provide an agent useful for prevention and / or treatment of psychosis, schizophrenia and cognitive impairments. To solve this problem, this invention provides epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitors as therapeutic agents for psychosis, schizophrenia and cognitive impairments.
Owner:HIROYUKI NAWA
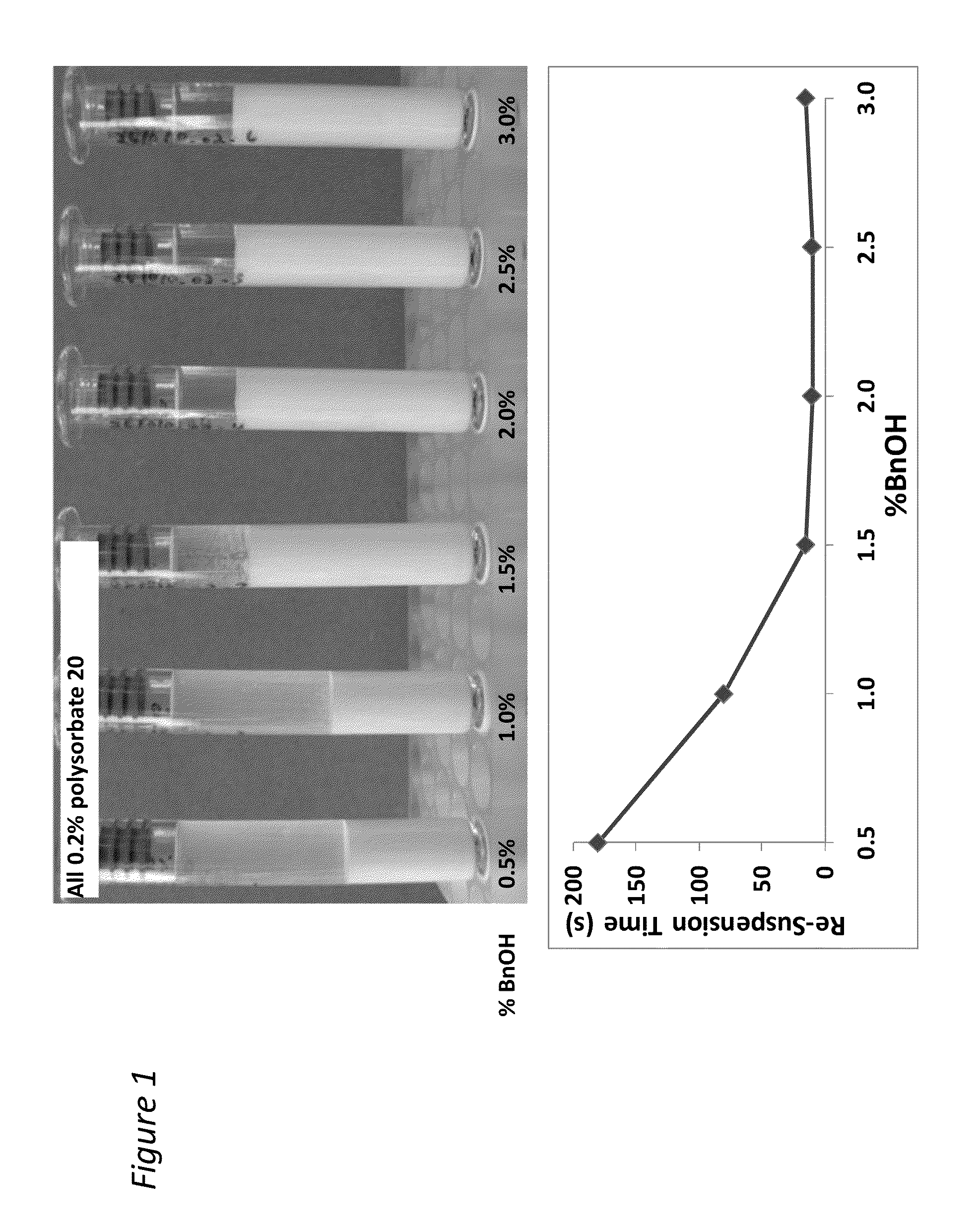
Pharmaceutical compositions comprising benzyl alcohol
ActiveUS20130267505A1Patient compliance is goodOptimizing pharmacological profileBiocideNervous disorderCarboxylic acidBENZYL ALCOHOL/WATER
The present invention relates to a pharmaceutical composition comprising benzyl alcohol and polyoxyethylene derivatives of sorbitan esters of carboxylic acids that are useful for the delivery of anti-psychotic drugs.
Owner:ALKERMES PHARMA IRELAND LTD
Sustained-release microsphere containing risperidone and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101292960AHigh drug loadingHigh encapsulation efficiencyOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderMicrosphereAntipsychotic Medications
The invention relates to a sustained-release microsphere of antipsychotic drug risperidone and the preparation method thereof.
Owner:INST OF PHARMACOLOGY & TOXICOLOGY ACAD OF MILITARY MEDICAL SCI P L A
Pharmaceutical compositions comprising sorbitan esters
ActiveUS9034867B2Optimizing pharmacological profilePatient compliance is goodBiocideNervous disorderCarboxylic acidSorbitan
Owner:ALKERMES PHARMA IRELAND LTD
Antipsychotic Injectable Depot Composition
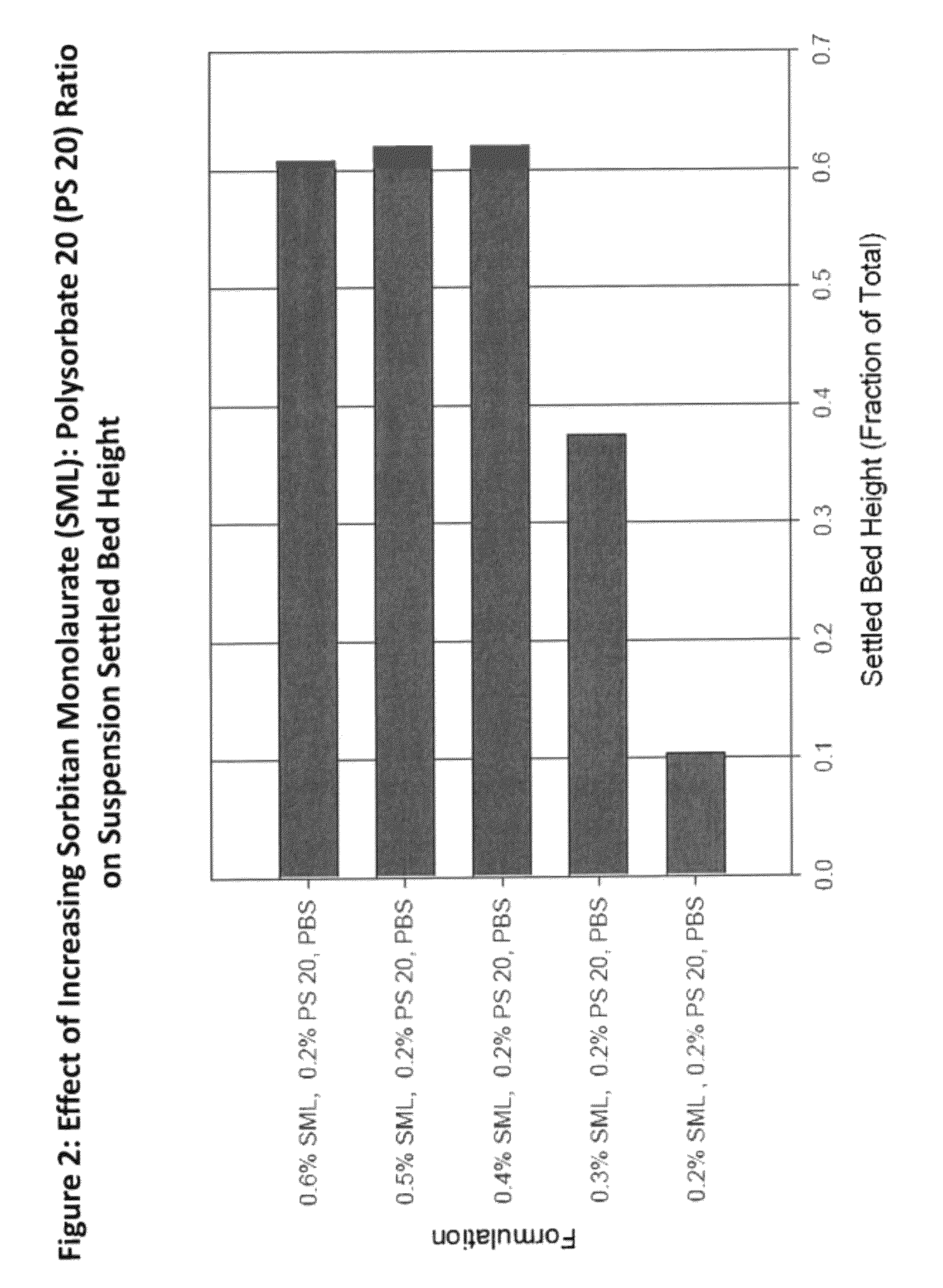
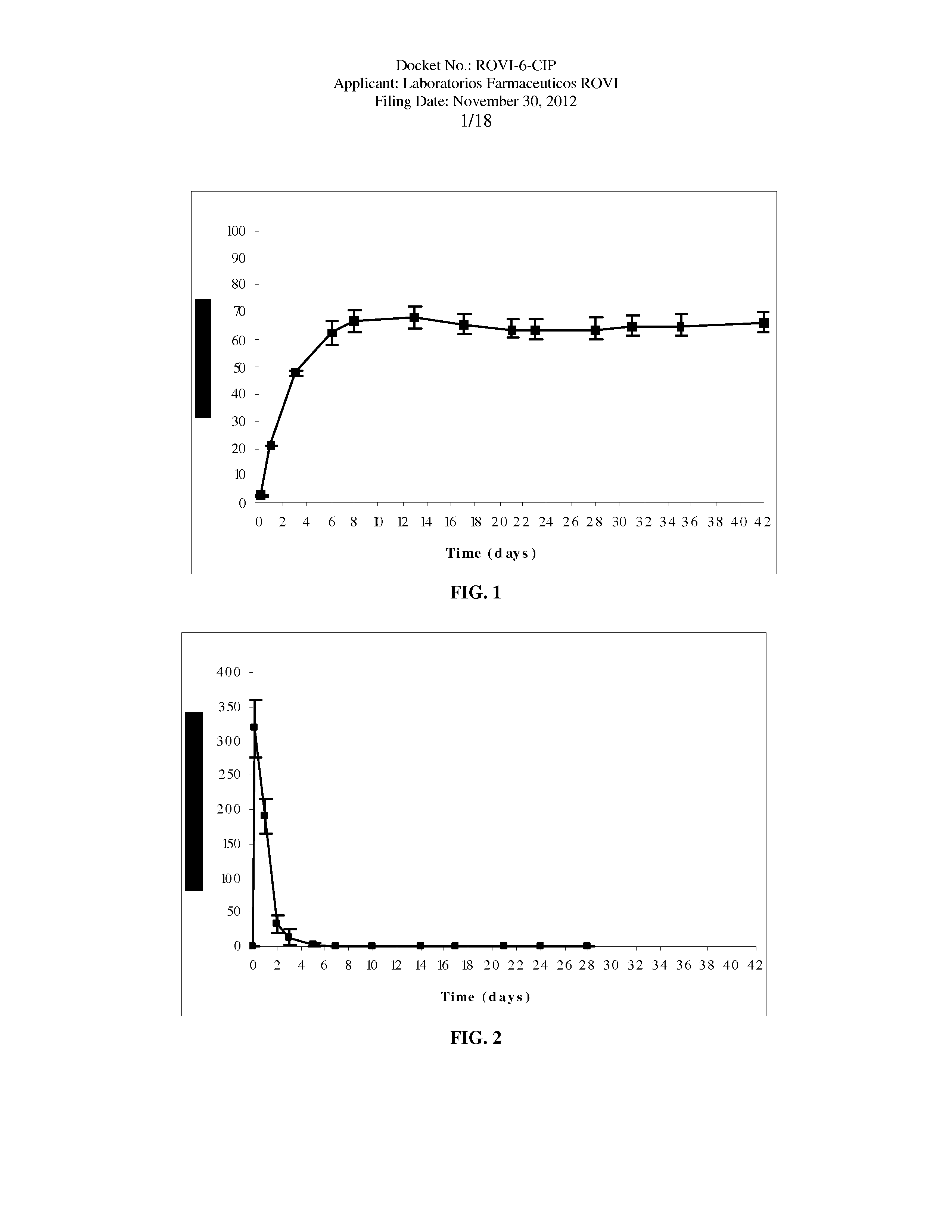
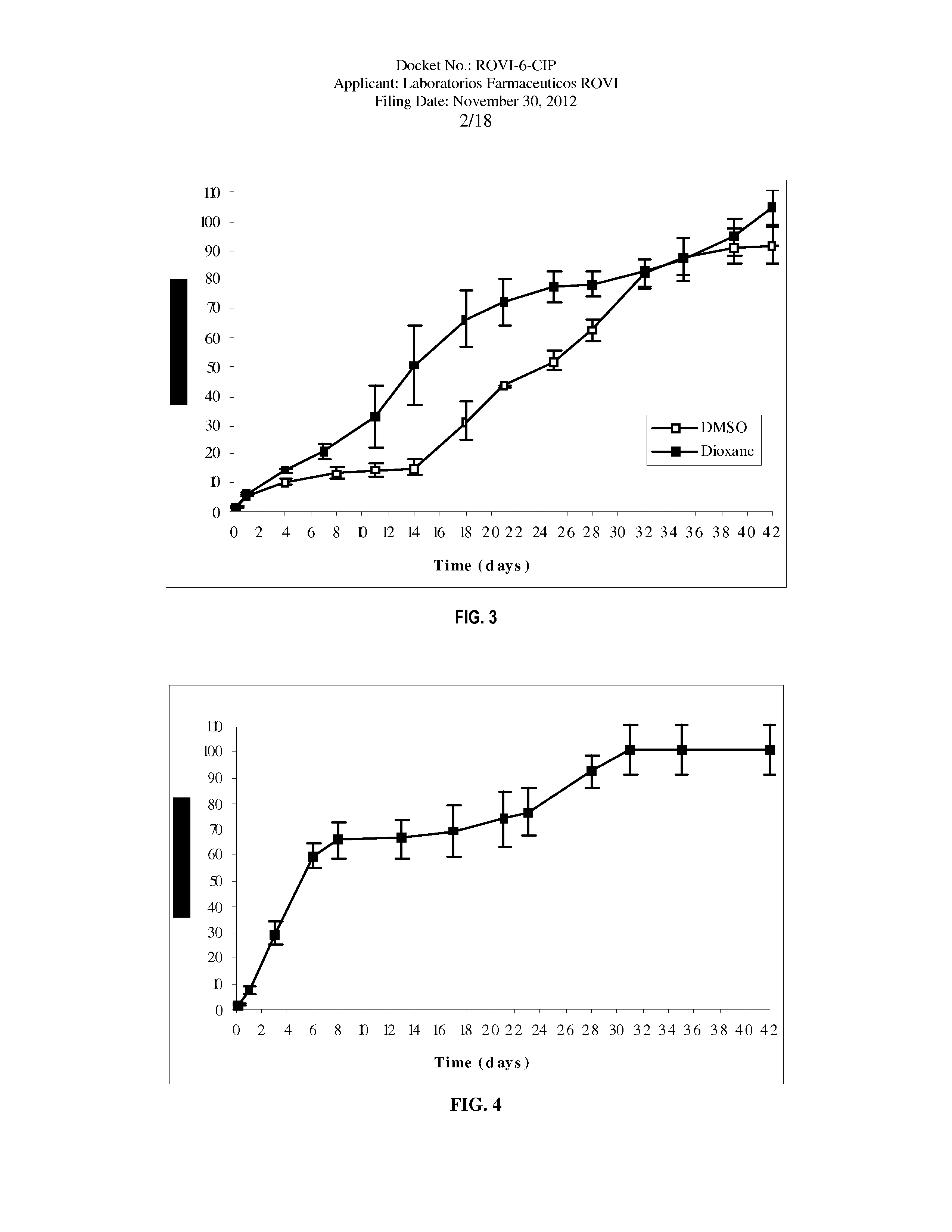
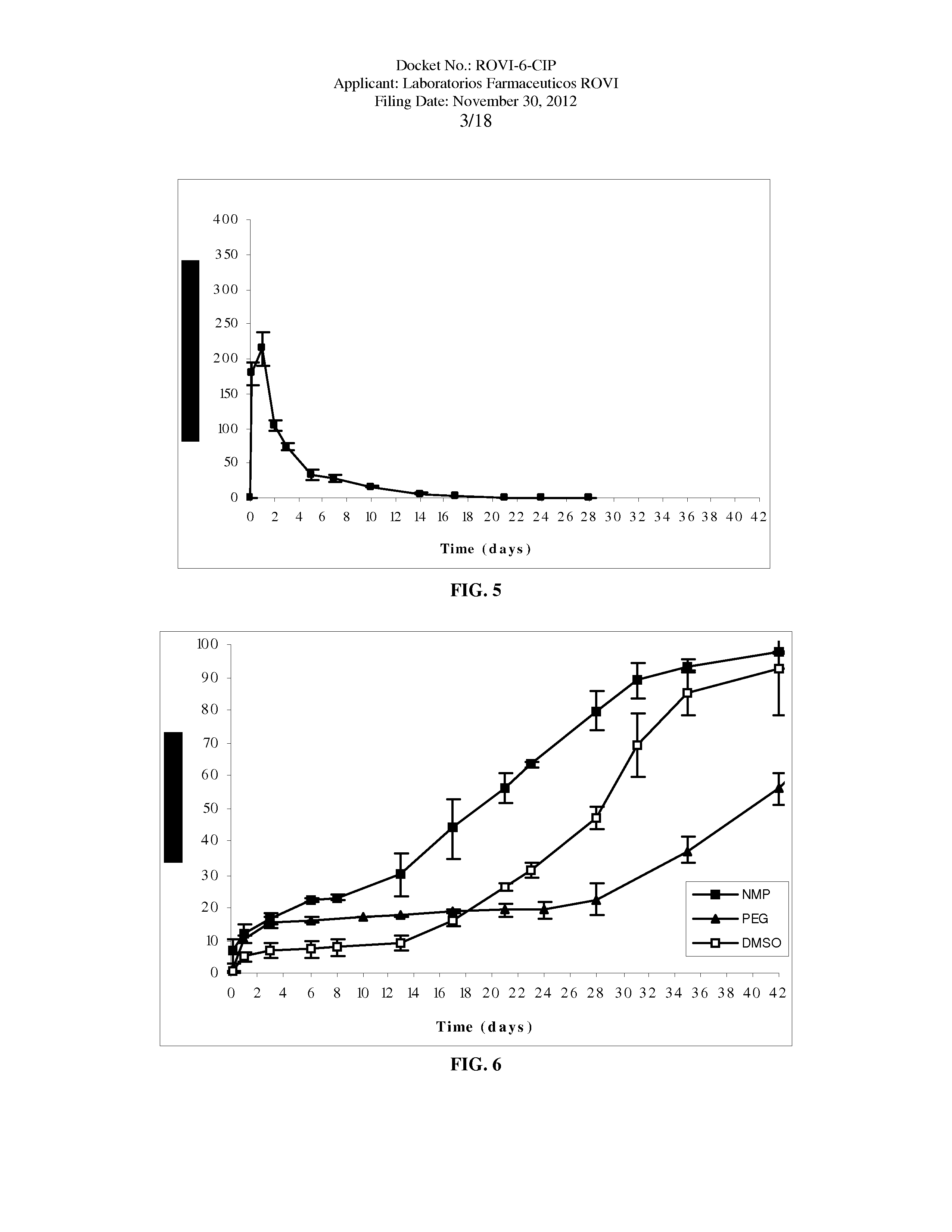
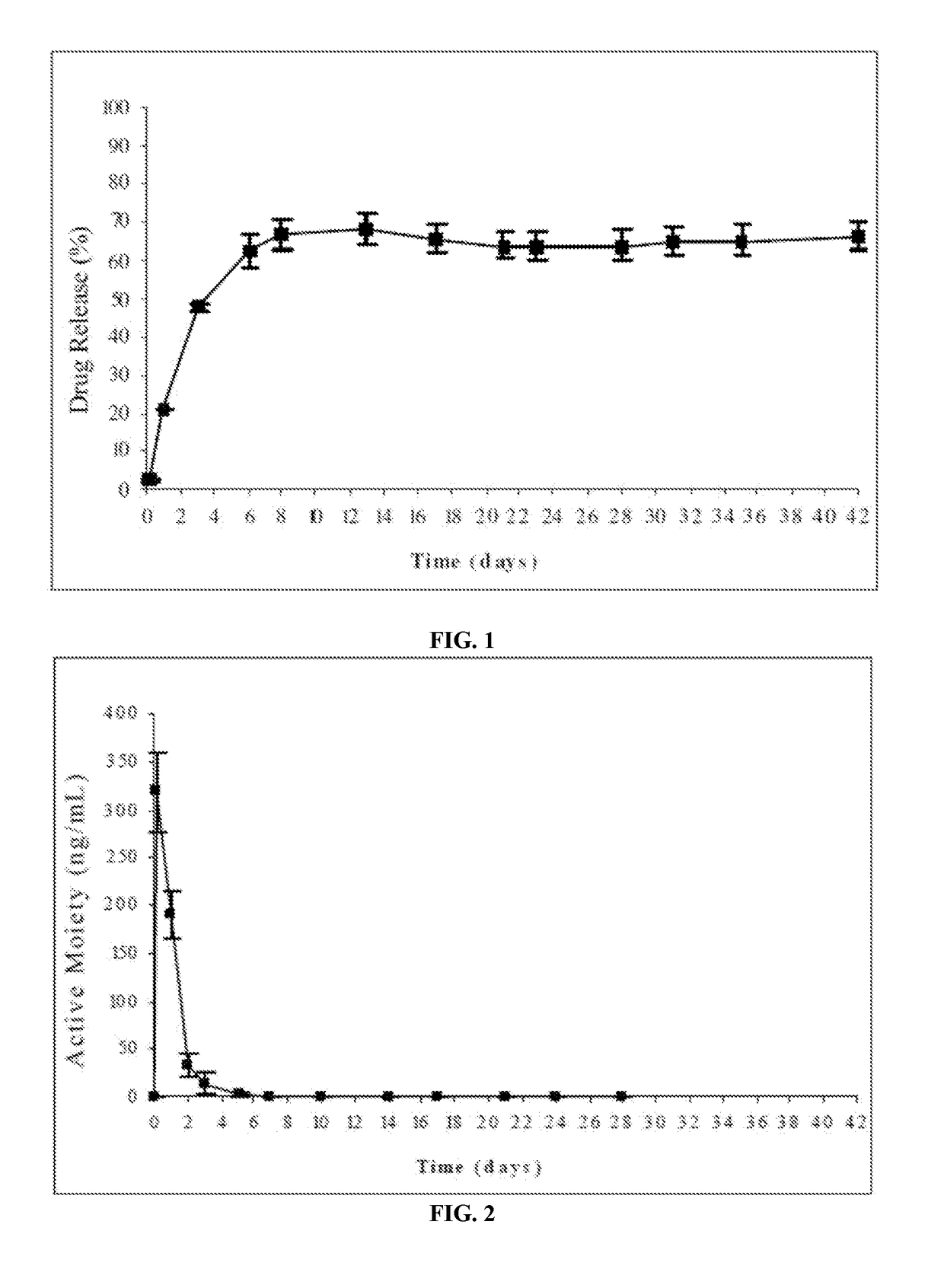
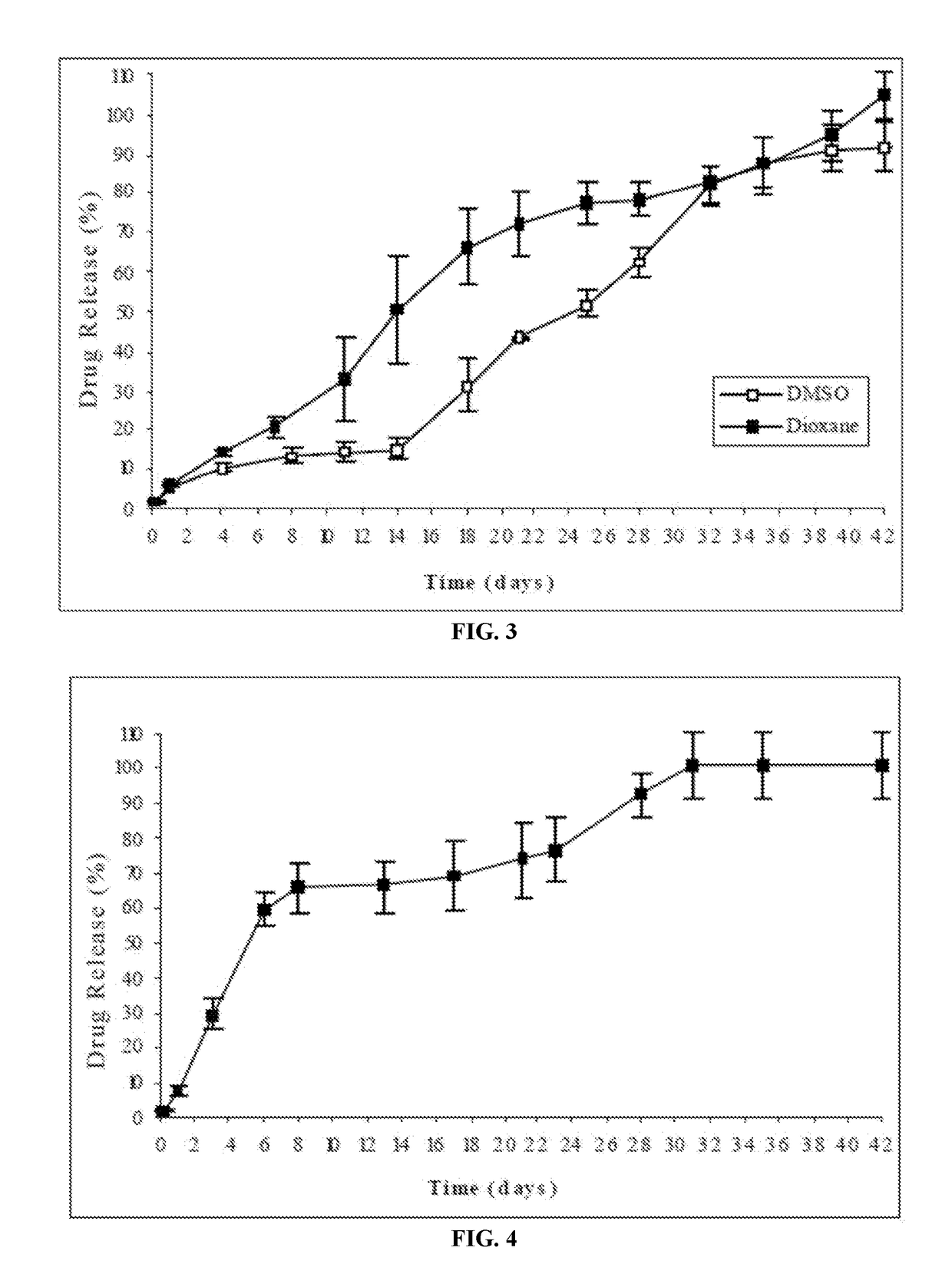
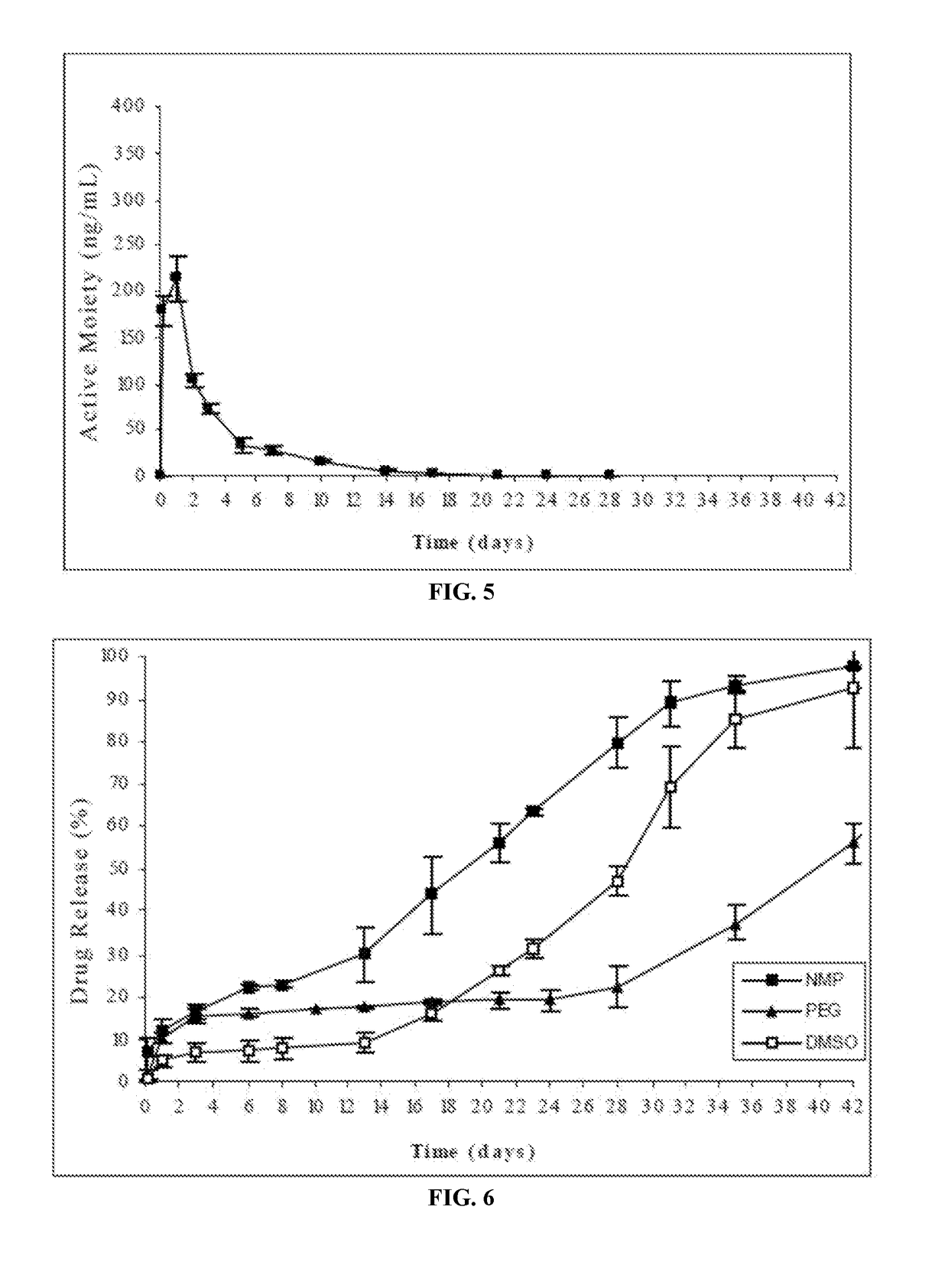
The present invention is directed to a composition that can be used to deliver an antipsychotic drug such as risperidone as an injectable in-situ forming biodegradable implant for extended release providing therapeutic plasma levels from the first day. The composition is in the form of drug suspension on a biodegradable and biocompatible copolymer or copolymers solution using water miscible solvents that is administered in liquid form. Once the composition contacts the body fluids, the polymer matrix hardens retaining the drug, forming a solid or semisolid implant that releases the drug in a continuous manner. Therapeutic plasma levels of the drug can be achieved since the first day up to at least 14 days or more even up to at least four weeks.
Owner:LAB FARM ROVI SA
Aripiprazole formulations having increased injection speeds
ActiveUS20150265529A1Organic active ingredientsNervous disorderAntipsychotic MedicationsInjection rate
The present invention relates to pharmaceutical compositions comprising a compound of Formula (I) that are useful for the intramuscular delivery of antipsychotic drugs using rapid injection rates.
Owner:ALKERMES PHARMA IRELAND LTD
Combination of glyt1 compound with antipsychotics
InactiveUS20120035156A1Affecting/increasing side-effect profileBiocideNervous disorderNegative symptomAtypical antipsychotic
The present invention relates to a pharmaceutical combination of a glycine transporter inhibitor (GlyT1) and an atypical antipsychotic drug which may be used for the treatment of positive and negative symptoms of schizophrenia.
Owner:F HOFFMANN LA ROCHE & CO AG
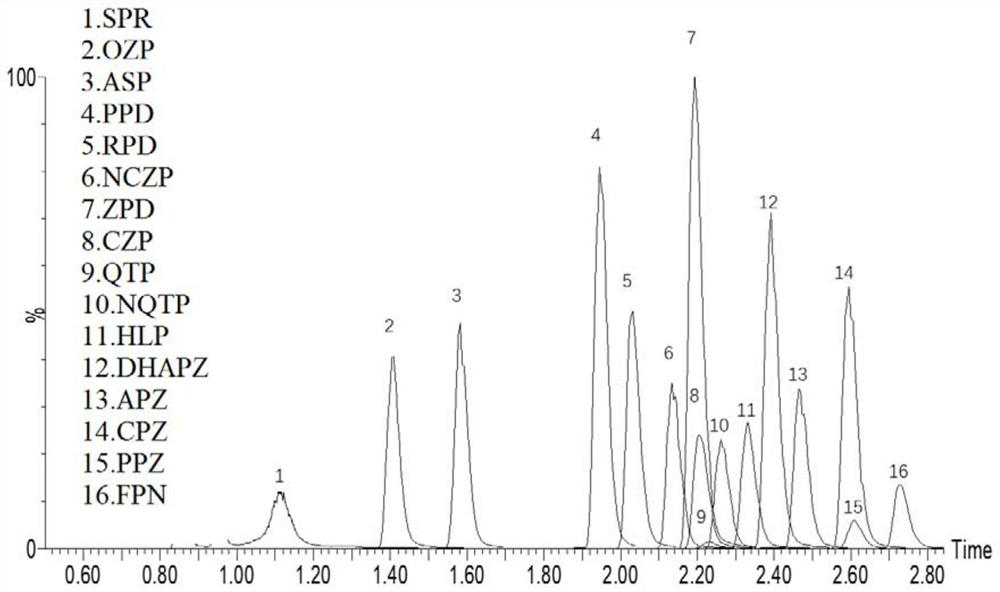
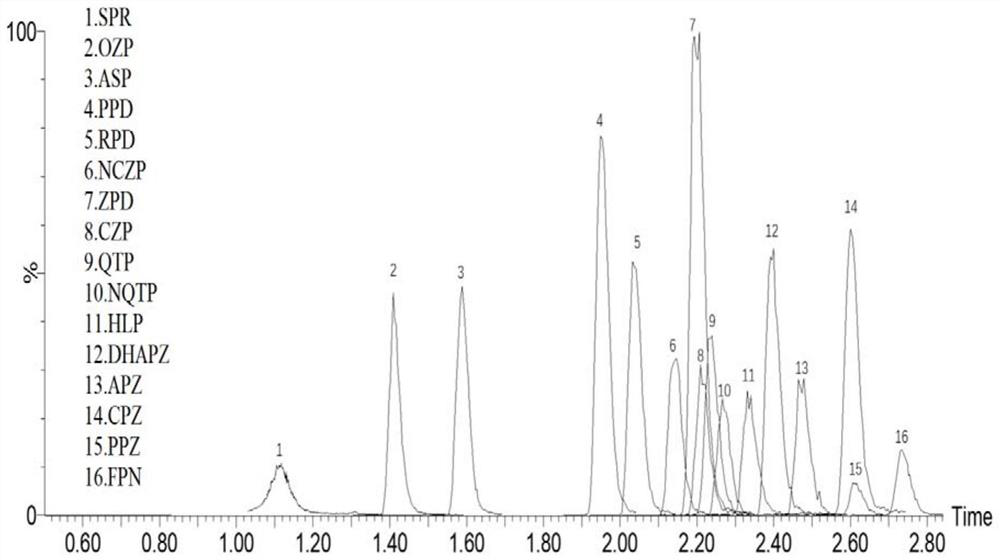
Method for synchronously detecting seventeen antipsychotics in blood sample
InactiveCN109668979ARealize detectionAchieving Simultaneous DetectionComponent separation9-HydroxyrisperidoneSolvent
The invention discloses a method for synchronously detecting seventeen antipsychotics in a blood sample. The method comprises the steps that the sample is extracted with a mixed solution of methanol and acetonitrile to obtain supernate, and after a solvent is removed from the supernate, the supernate is dissolved in a methanol aqueous solution and filtered to obtain a specimen; a high performanceliquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry method is adopted to detect the specimen; the sample is serum or plasma, and the antipsychotics are amisulpride, aripiprazole, dehydro aripiprazole, chlorpromazine, clozapine, desmethylclozapine, fluphenazine, haloperidol, olanzapine, paliperidone, perphenazine, quetiapine, risperidone, 9-hydroxyrisperidone, sulpiride, ziprasidone and thioridazine; inthe high performance liquid chromatography, a mobile phase A is an aqueous solution of formic acid, and a mobile phase B is a methanol solution of the formic acid; and the mass spectrometry adopts amulti-ion reaction monitoring mode of positive ion electrospray ionization.
Owner:JINAN YING SHENG BIOTECH
Method for classification of anti-psychotic drugs
The present invention provides a method for identifying an agent to be tested for an ability to treat a psychotic disorder in a patient in need of such treatment. The invention provides a method for screening candidate drugs for anti-psychotic drug activity, preferably atypical anti-psychotic activity, comprising contacting cells or tissues with a candidate drug, determining levels of phosphorylation of the intracellular signaling proteins, DARPP-32, ERK1, ERK2 and CREB, in said cells or tissues and determining the pattern of the levels of phosphorylation of the proteins. The pattern of the levels of phosphorylation of DARPP-32, ERK1, ERK2 and CREB is, in certain embodiments, compared with the pattern of the levels of phosphorylation of DARPP-32, ERK1, ERK2 and CREB in the presence of an atypical anti-psychotic drug.
Owner:THE ROCKEFELLER UNIV
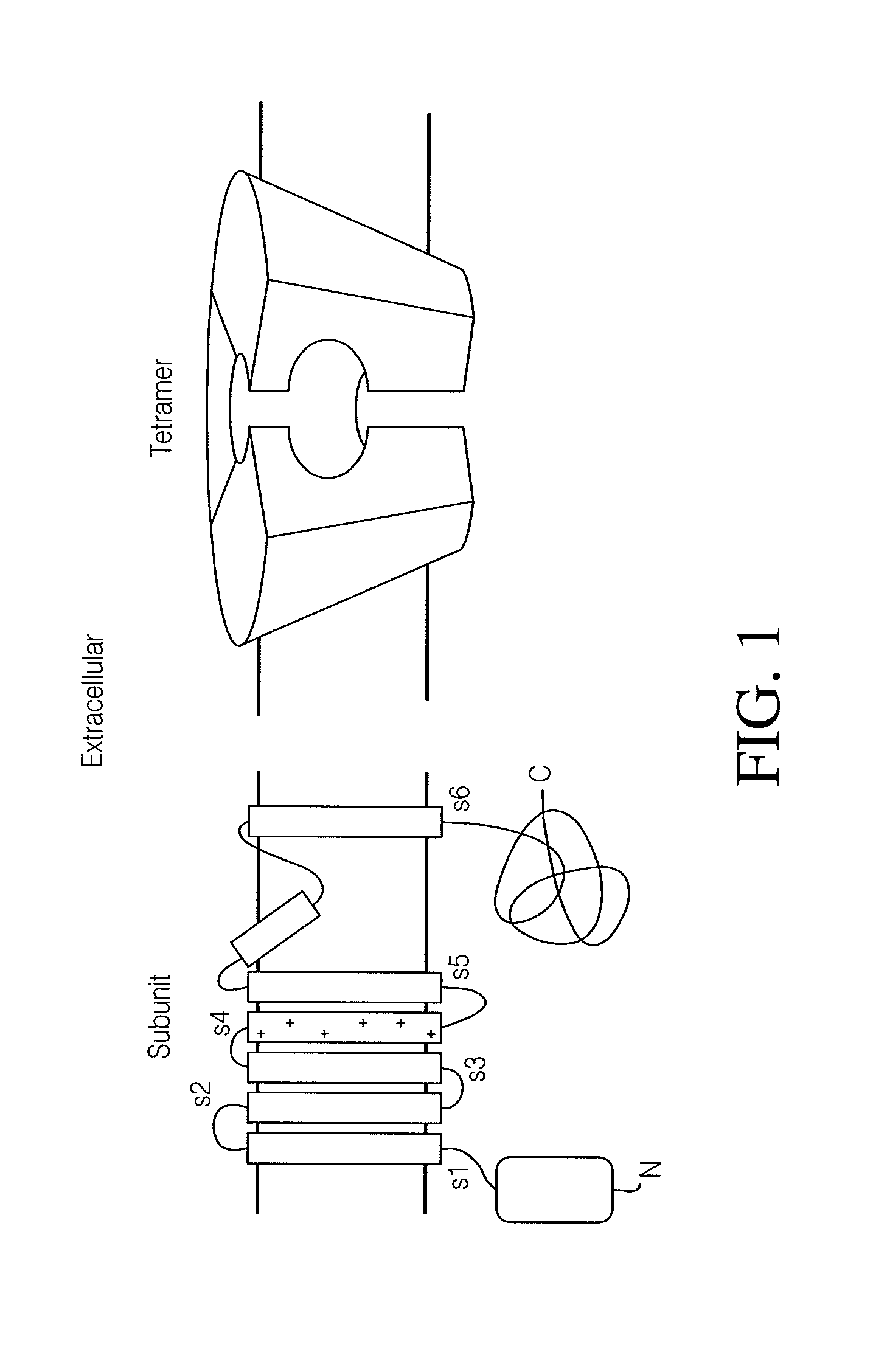
Schizophrenia-related isoform of kcnh2 and development of antipsychotic drugs
The invention is related to a novel primate specific brain isoform of the potassium channel KCNH2 and genetic association with risk for schizophrenia.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
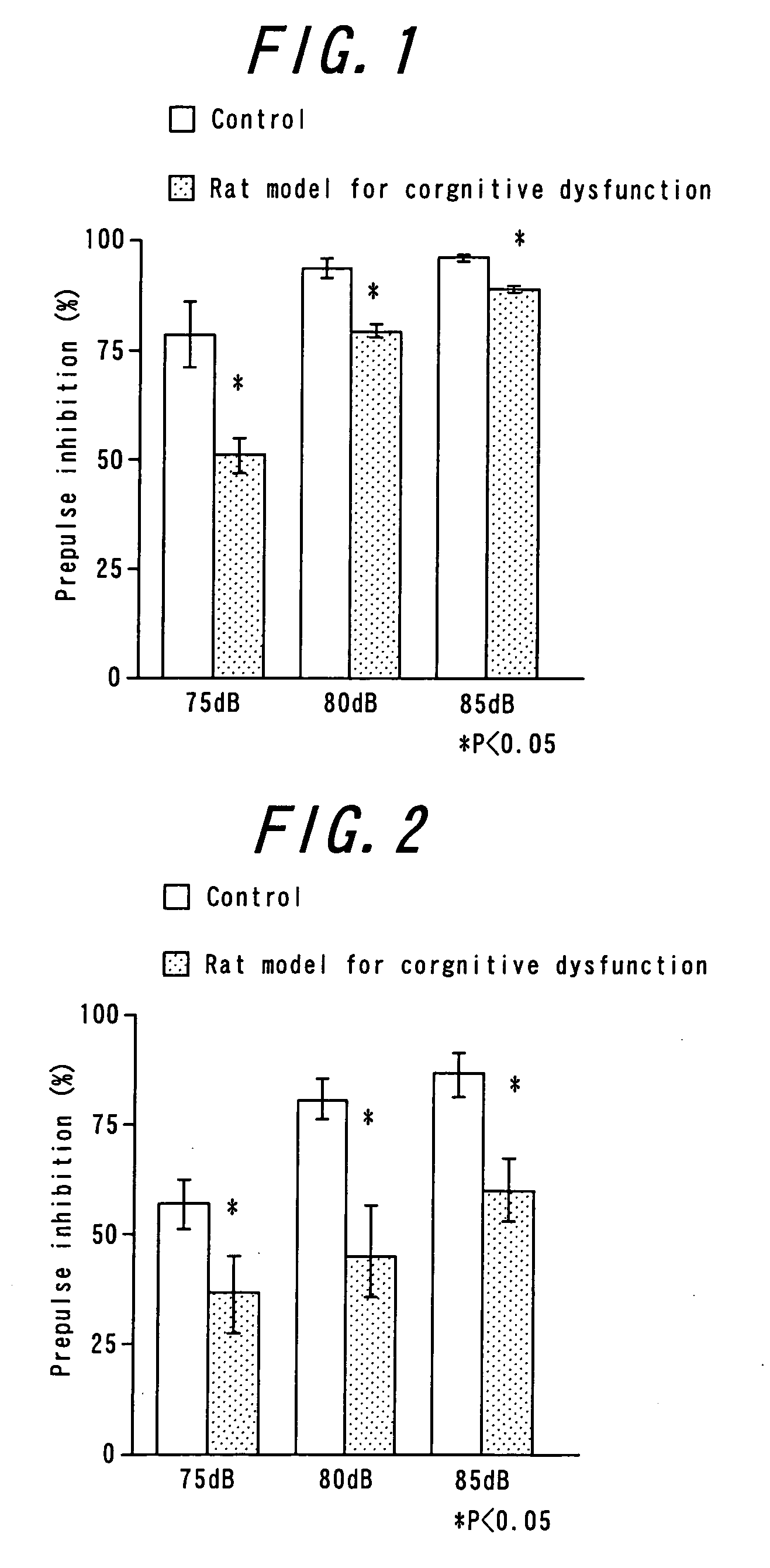
In vivo screening method of therapeutic agent for memory/learning dysfunctions by schizophrenia
ActiveUS20090176800A1High activityImprove cognitive impairmentCompounds screening/testingNervous disorderPsychosis drugScreening method
Owner:SUMITOMO DAINIPPON PHARMA CO LTD
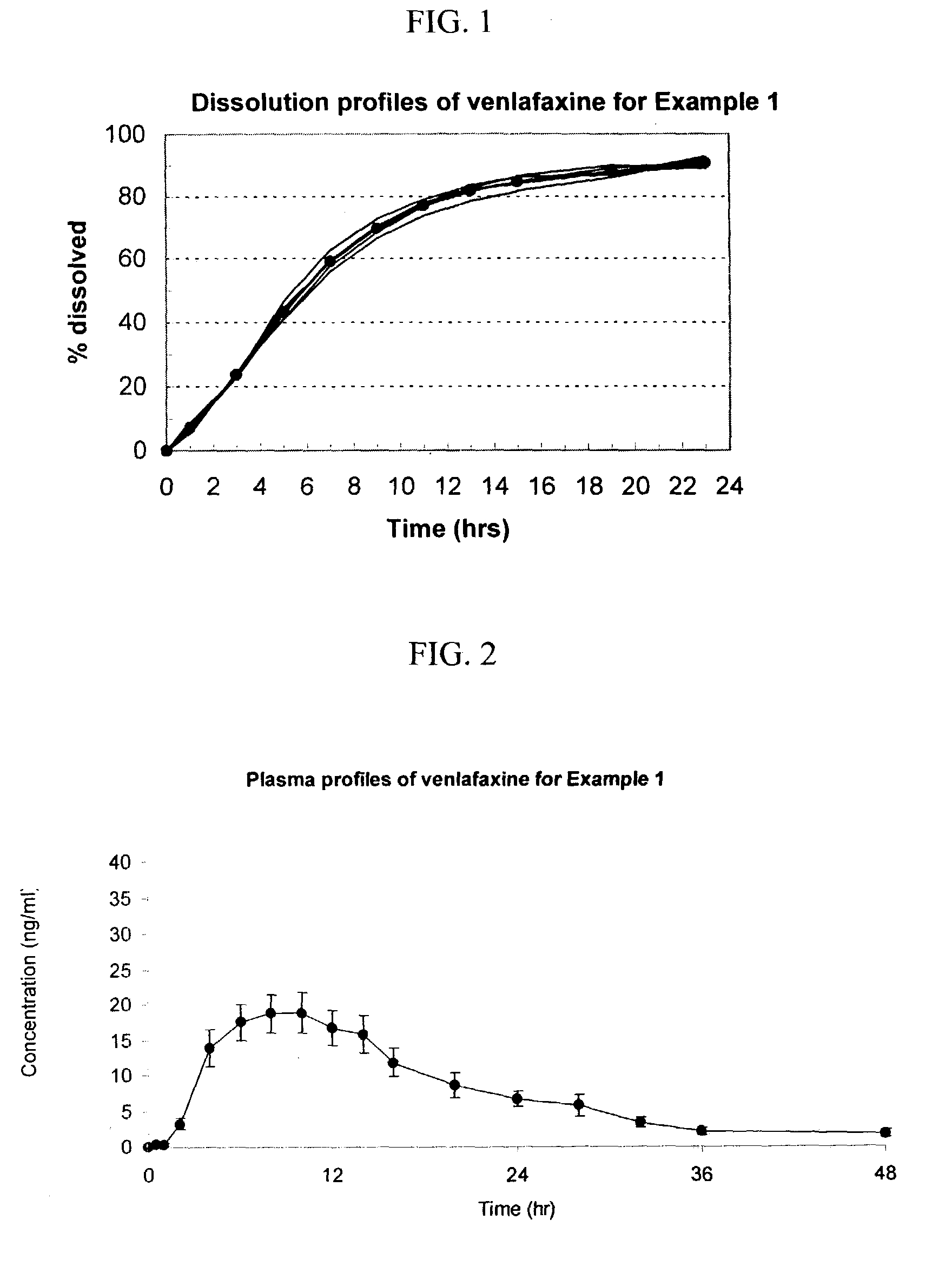
Osmotic device containing venlafaxine and an anti-psychotic agent
The present invention provides an osmotic device containing controlled release venlafaxine in the core in combination with an anti-psychotic agent in a rapid release external coat. A wide range of anti-psychotic agents can be used in this device. Particular embodiments of the invention provide osmotic devices having predetermined release profiles. One embodiment of the osmotic device includes an external coat that has been spray-coated rather compression-coated onto the device. The device with spray-coated external core is smaller and easier to swallow than the similar device having a compression-coated external coat. The device is useful for the treatment of depression, anxiety or psychosis related disorders.
Owner:OSMOTICA KERESKEDELMI & SZOLGALTATO +1
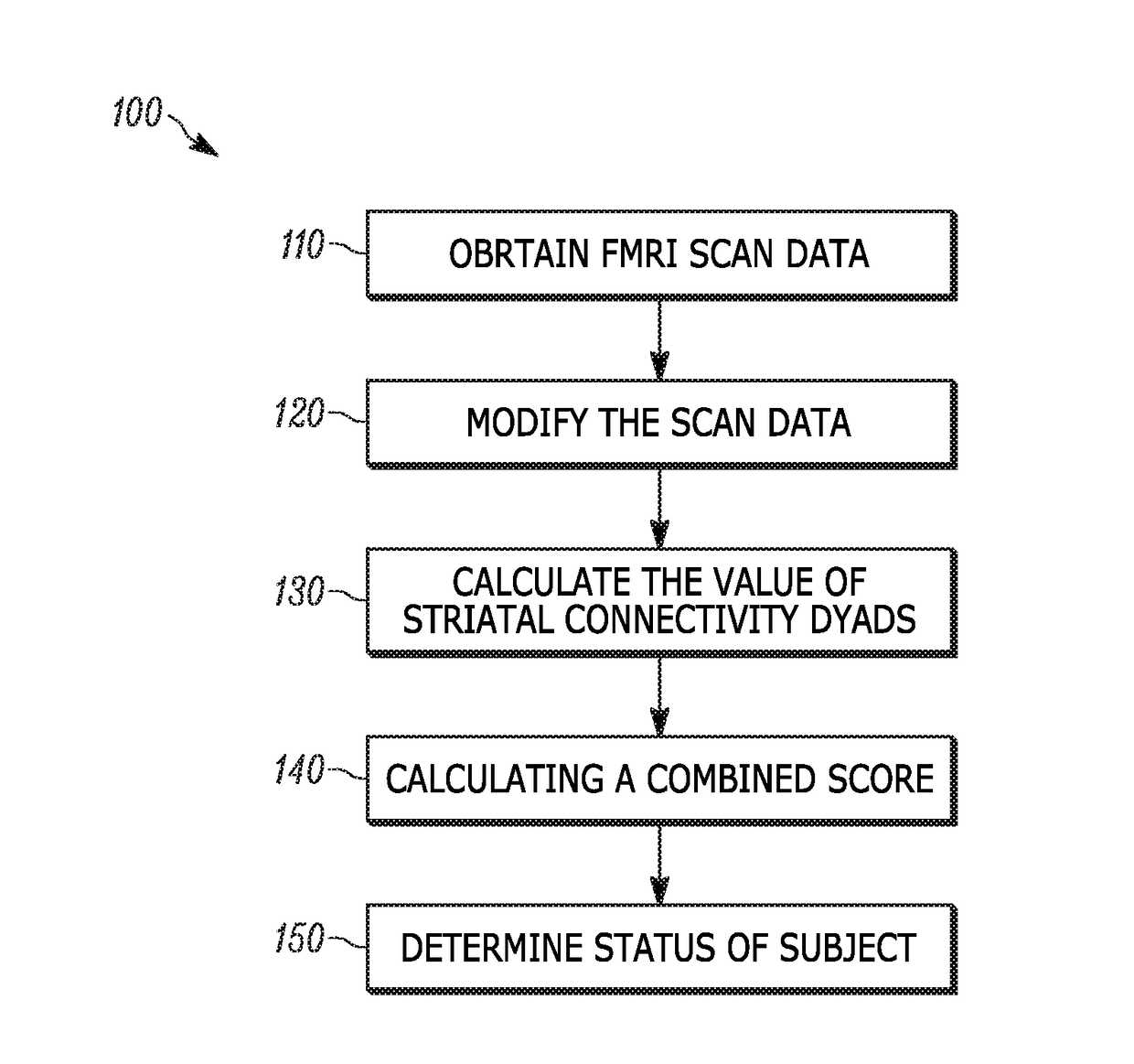
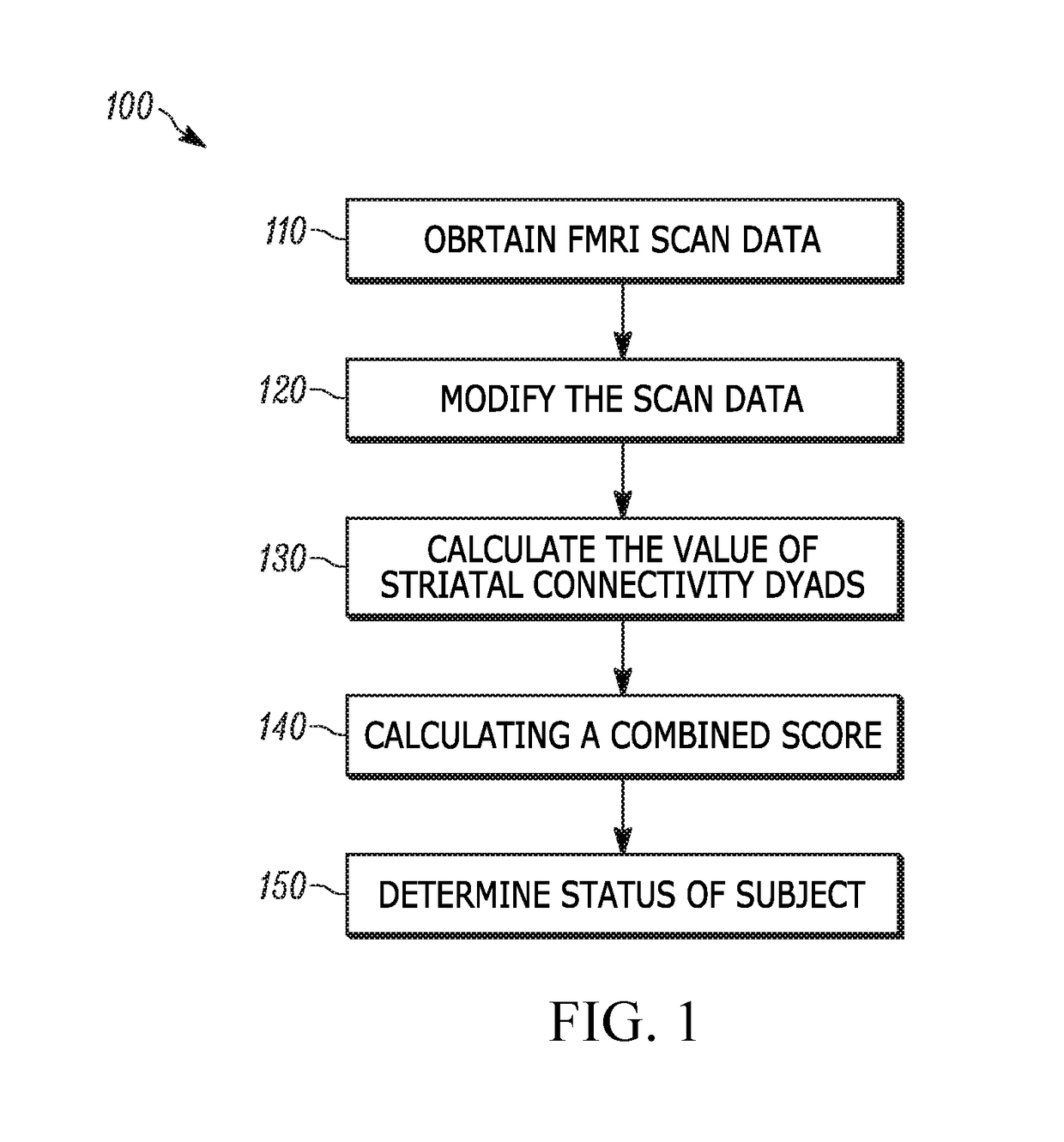
Use of striatal connectivity patterns for evaluating antipsychotic agents
InactiveUS20170343634A1Medical imagingMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsCombination algorithmComputer science
A method of predicting the response of a subject to an antipsychotic agent is described. The method includes obtaining functional MRI (fMRI) scan data of the brain of the subject, modifying the scan data using a standardizing algorithm to provide modified scan data, calculating the value of a plurality of striatal connectivity dyads from the modified scan data using an extraction algorithm, calculating a combined score from the values of the striatal connectivity dyads using a combining algorithm; and comparing the combined score to a classifier value to determine if the subject is a responder or a non-responder. Systems for carrying out the method of predicting the response of a subject to an antipsychotic agent are also described.
Owner:THE FEINSTEIN INST FOR MEDICAL RES
Method for preparing aripiprazole and its intermediate
ActiveCN1634889AShort reaction timeImprove reaction efficiencyNervous disorderOrganic chemistryChemical synthesisSolvent
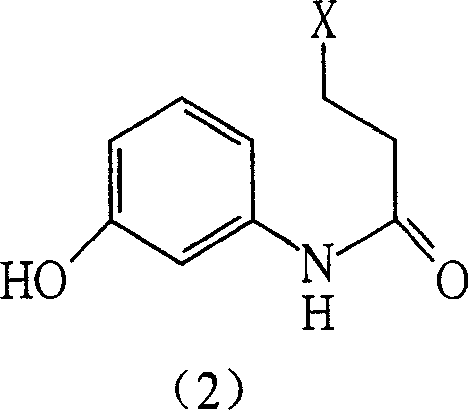
The invention discloses a chemical synthesis method of psychotolytic medicine, especially a preparation method of aripiprazole and its intermediate. Intermediate (4) can be prepared by six different processes in the invention, and the targeted compound aripiprazole is produced from the intermediate (4) by ring-closing reaction. Compared to available method, the invention has short reaction time and high reaction efficiency.
Owner:CHENGDU KANGHONG PHARMA GRP
Artemisinin Derivatives
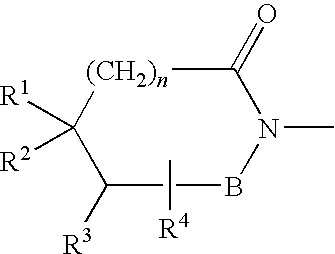
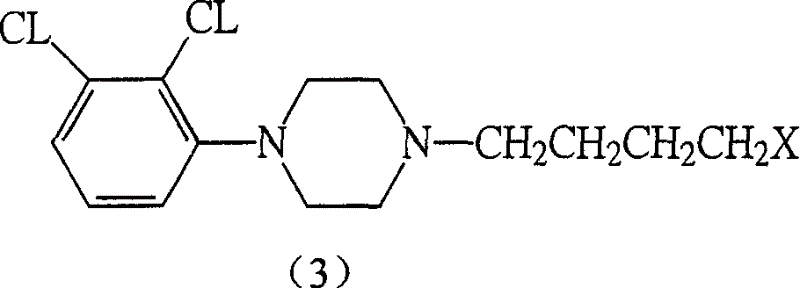
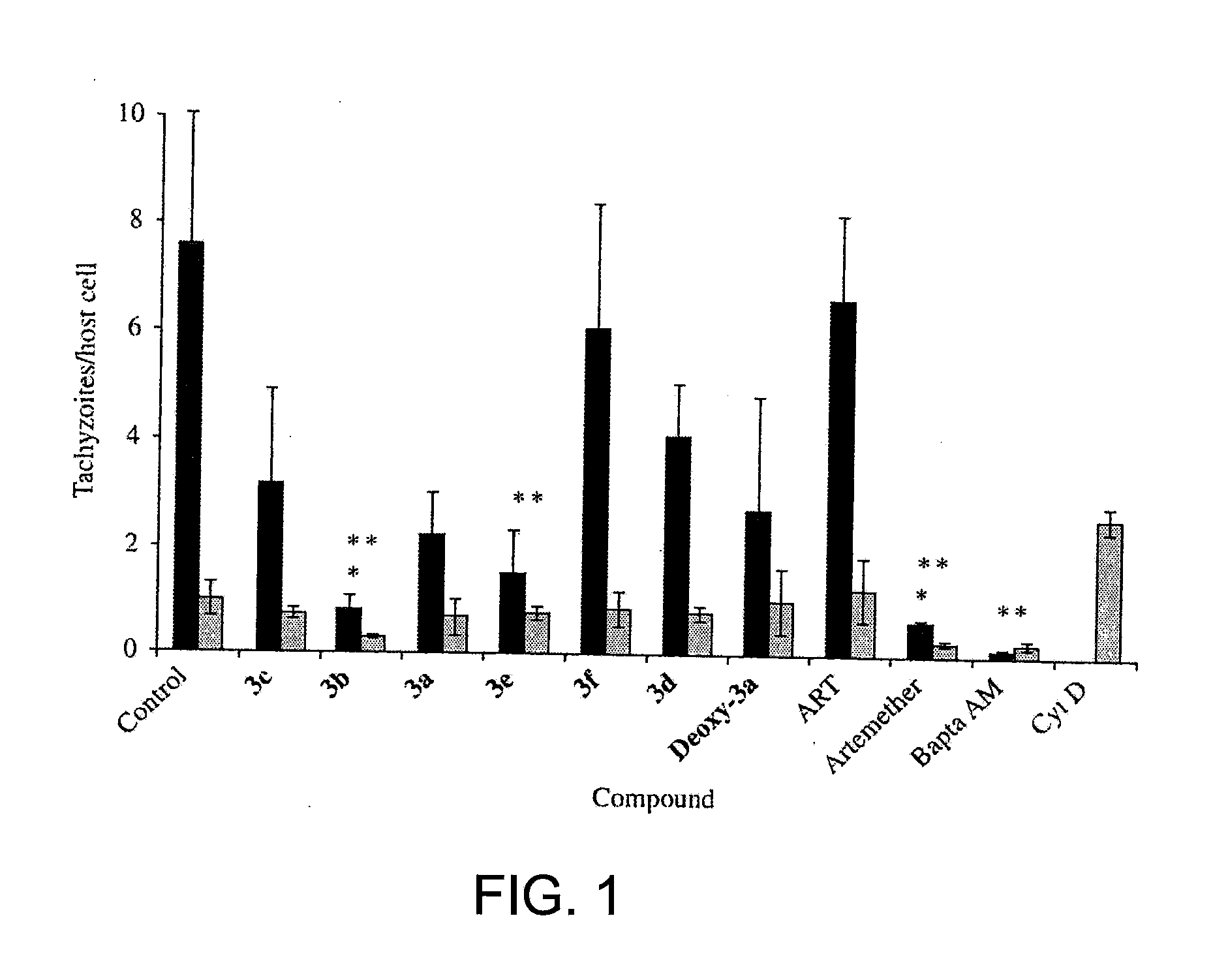
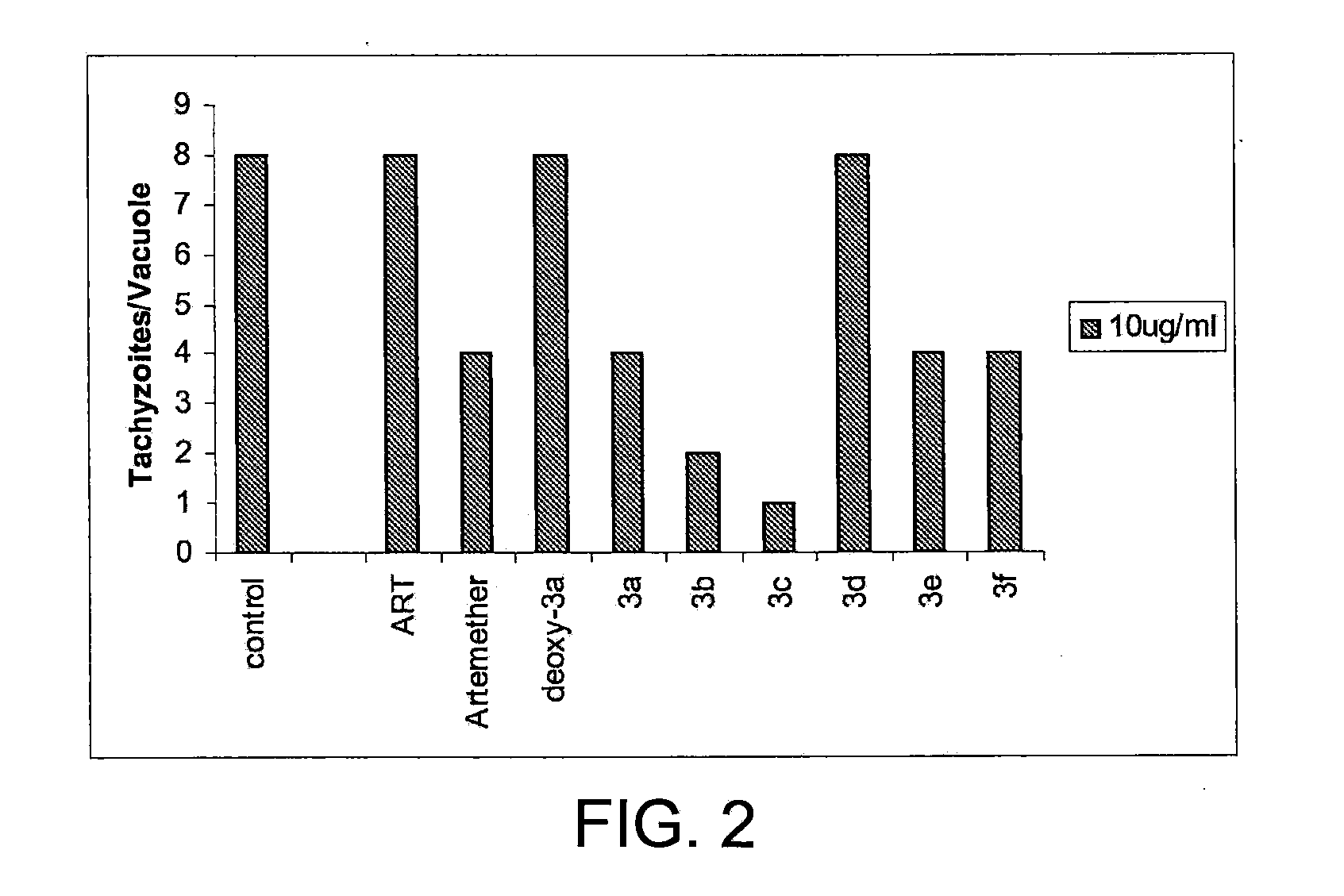
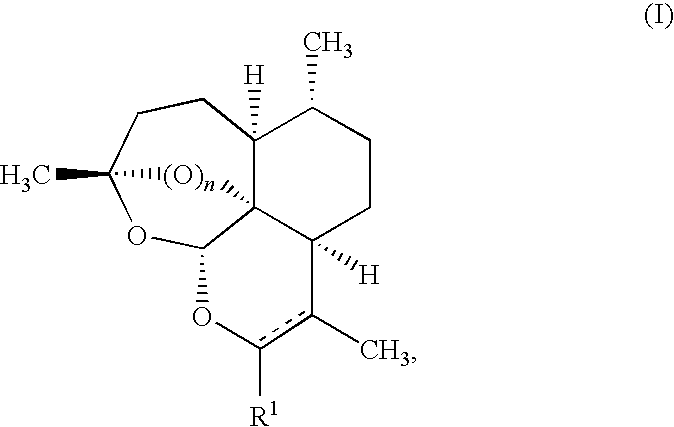
This disclosure provides improved derivatives of artemisinin; pharamaceutical compositions containing these compounds; methods for preparing these compounds and compositions; methods of using these compounds and compositions for preventing, controlling or treating infectious diseases including but not limited to parasitic infectious diseases such as T. gondii infection, trypanosome parasite infection, plasmodia parasite infection, and cryptosporidium parasite infection; methods for preventing, controlling or treating toxoplasma infection; and methods for treating psychiatric disorders associated with toxoplasma infection including but not limited to schizophrenia using the disclosed compounds and compositions alone or in combination with one or more antipsychotic drugs.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Stabilized Atypical Antipsychotic Formulation
A pharmaceutical composition that contains an atypical antipsychotic drug and succinic acid, fumaric acid or a mixture of succinic acid and fumaric acid.
Owner:HANDA PHARM LLC
Methods of treating schizophrenia
InactiveUS7115256B1Improve cognitive functionImproving cognitive deficitsBiocideNervous disorderSide effectNeurotrophic factors
The invention provides methods for the treatment of abnormal psychiatric states, particularly the negative symptoms of schizophrenia and extrapyramidal side effects (EPS) of antipsychotic drugs. The inventive methods relate to the administration of therapeutic cells (which produce dopamine or dopamine precursors) adhered to support matrices to subjects suffering from the negative symptoms of schizophrenia and / or EPS. The therapeutic cells may be coadministered with cells which protect the therapeutic cells from immune rejection and / or cells which produce neurotrophic factors which improve the viability of the therapeutic cells.
Owner:TITAN PHARMA
Antipsychotic Injectable Depot Composition
ActiveUS20180221272A1Simple methodConstant effectiveNervous disorderPharmaceutical delivery mechanismSolventBlood plasma
Owner:LAB FARM ROVI SA
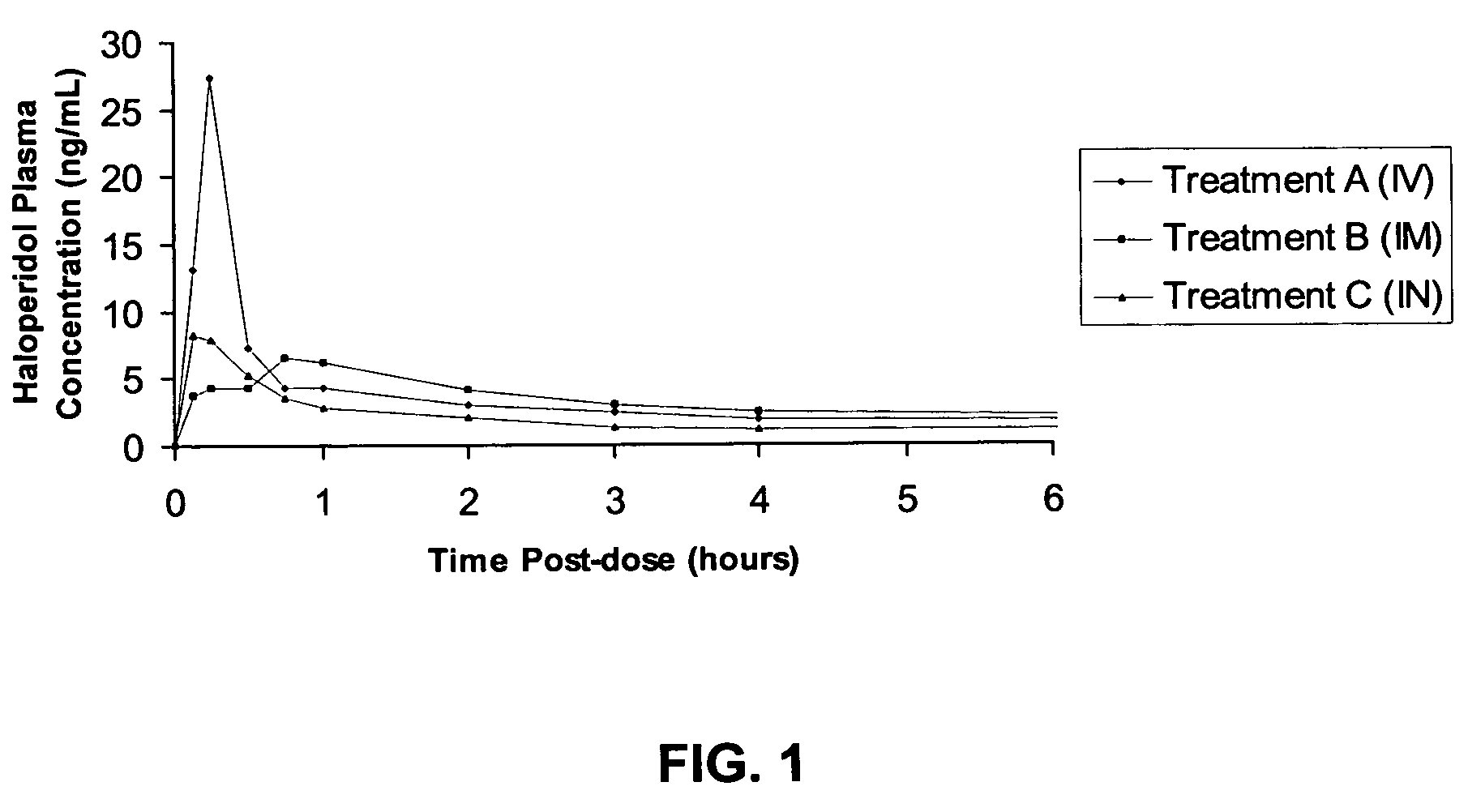
Intranasal delivery of antipsychotic drugs
InactiveUS20060039869A1Rapid systemic availabilityAvoidance of hepatic first metabolismBiocidePowder deliveryPsychosis drugNebulizer
An intranasal drug product is provided including an antipsychotic drug, such as haloperidol, in sprayable solution in an intranasal metered dose sprayer. Also provided is a method of administering an antipsychotic drug, such as haloperidol, to a patient, including the step of delivering an effective amount of the antipsychotic drug to a patient intranasally using an intranasal metered dose sprayer. A method of treating a psychotic episode also is provided, the method including the step of delivering an antipsychotic drug, such as haloperidol, intranasally in an amount effective to control the psychotic episode.
Owner:UNIV OF KENTUCKY RES FOUND
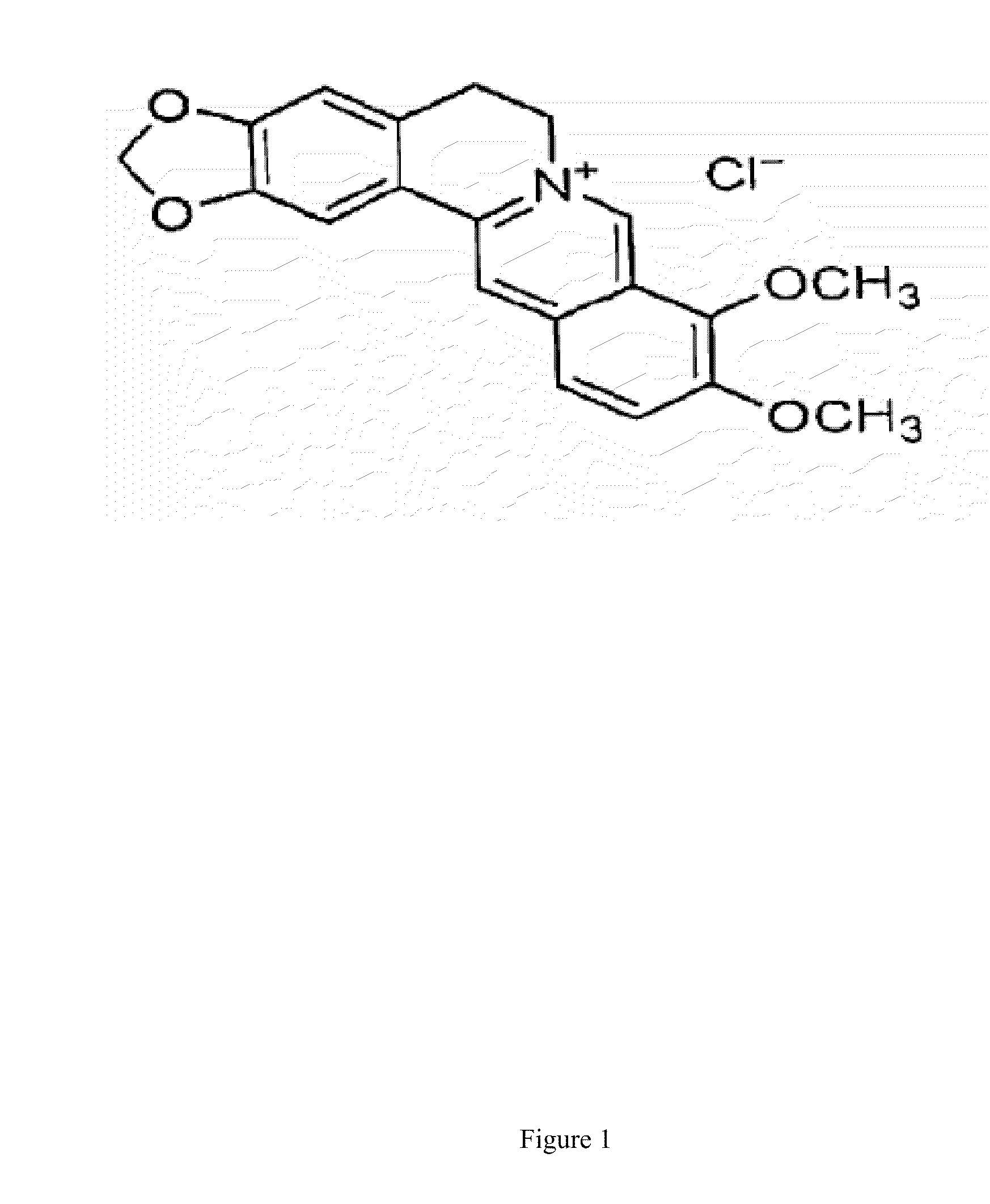
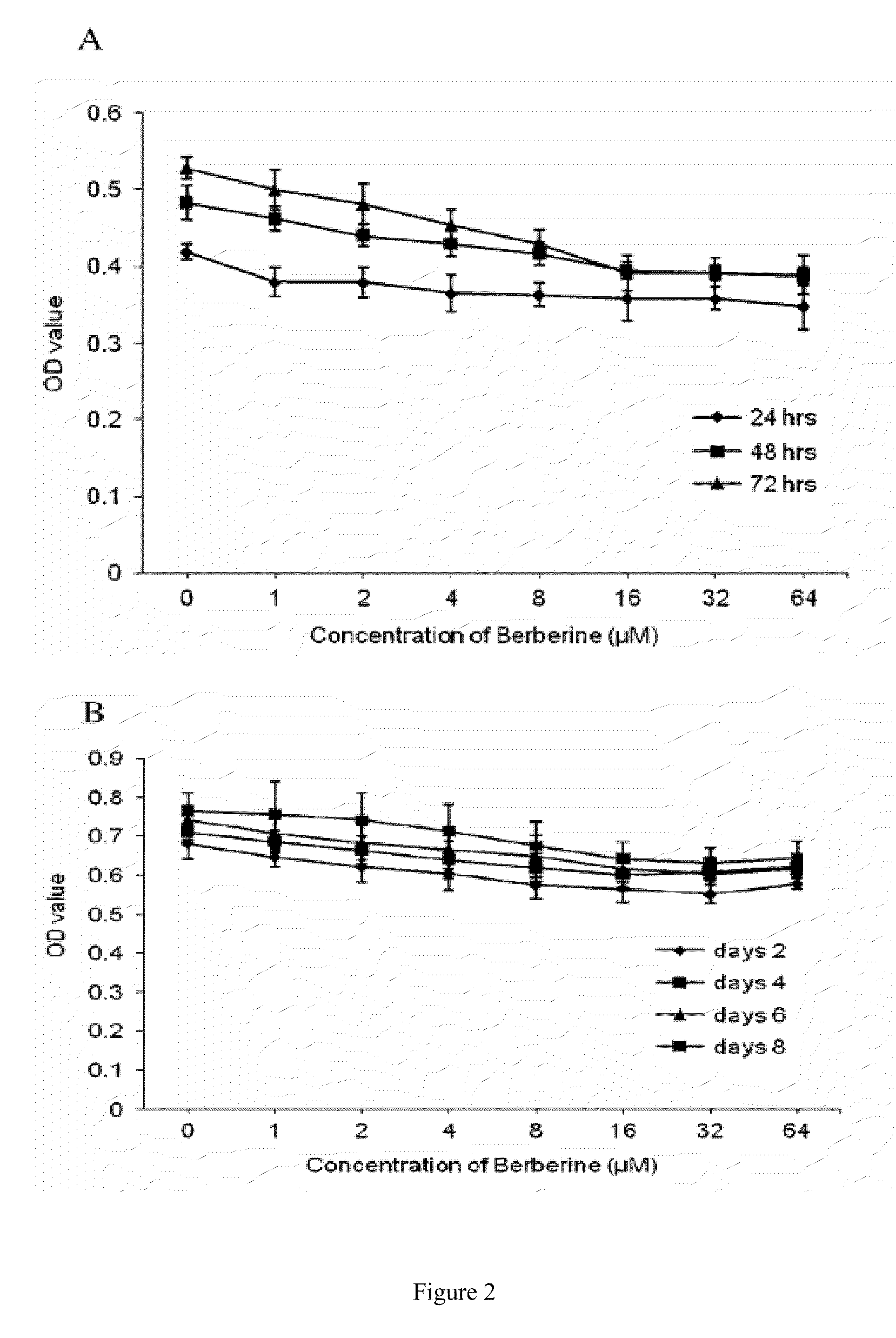
Pharmaceutical compositions containing berberine for treatment or prevention of weight gain and obesity associated with anti-psychotic drugs
InactiveUS20110281852A1Reduce weightInhibit weight gainBiocideNervous disorderBerberineNatural product
The compositions and methods disclosed herein are of use for the treatment and prevention of weight gain and obesity. In particular, the compositions and methods include treatment of weight gain and obesity with berberine and / or berberine analogs alone or in combination thereof to cause a reduction in an individual's weight or prevent weight gain or obesity. In certain embodiments, the weight gain and obesity are associated with administration of anti-psychotic drugs. In an alternative embodiment, the compositions and methods provide berberine or berberine analogs alone or for coadministration with an anti-psychotic agent. In an additional embodiment, the compositions and methods further include a natural product. The usefulness of the present invention is that berberine and berberine analogs do not have synergistic effects with other drugs and administration results in few side effects. Such characteristics of berberine or berberine analogs are a great improvement able to support the widespread use of the compositions and methods of the present invention as therapeutics for the treatment and prevention of weight gain and obesity.
Owner:DAVIES GARETH +1
Medicament for treating amphetamine type stimulant dependency and mixed dependency of amphetamine type stimulants and opiates substances
InactiveCN103495172AGood effectControl withdrawal symptomsOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderBenzodiazepineDrug withdrawal symptoms
The invention discloses a medicament for treating amphetamine type stimulant dependency and mixed dependency of amphetamine type stimulants and opiates substances. The medicament is prepared from the following components by weight percent: 2-95% of antipsychotics, 0.001-5% of alpha2 adrenergic agonists, 0-5% of anticholinergic agent, 0-80% of nonopioid analgesic, and 0-10% of benzodiazepine. The pharmaceutical composition disclosed by the invention achieves an ideal effect when the symptoms of a sufferer abusing stimulants such as benzedrine, or abusing the opiates substances in a merging manner are treated; the withdrawal symptom can be rapidly and obviously controlled; the detoxification recovery rate can be up to over 90%.
Owner:卢正堂 +1
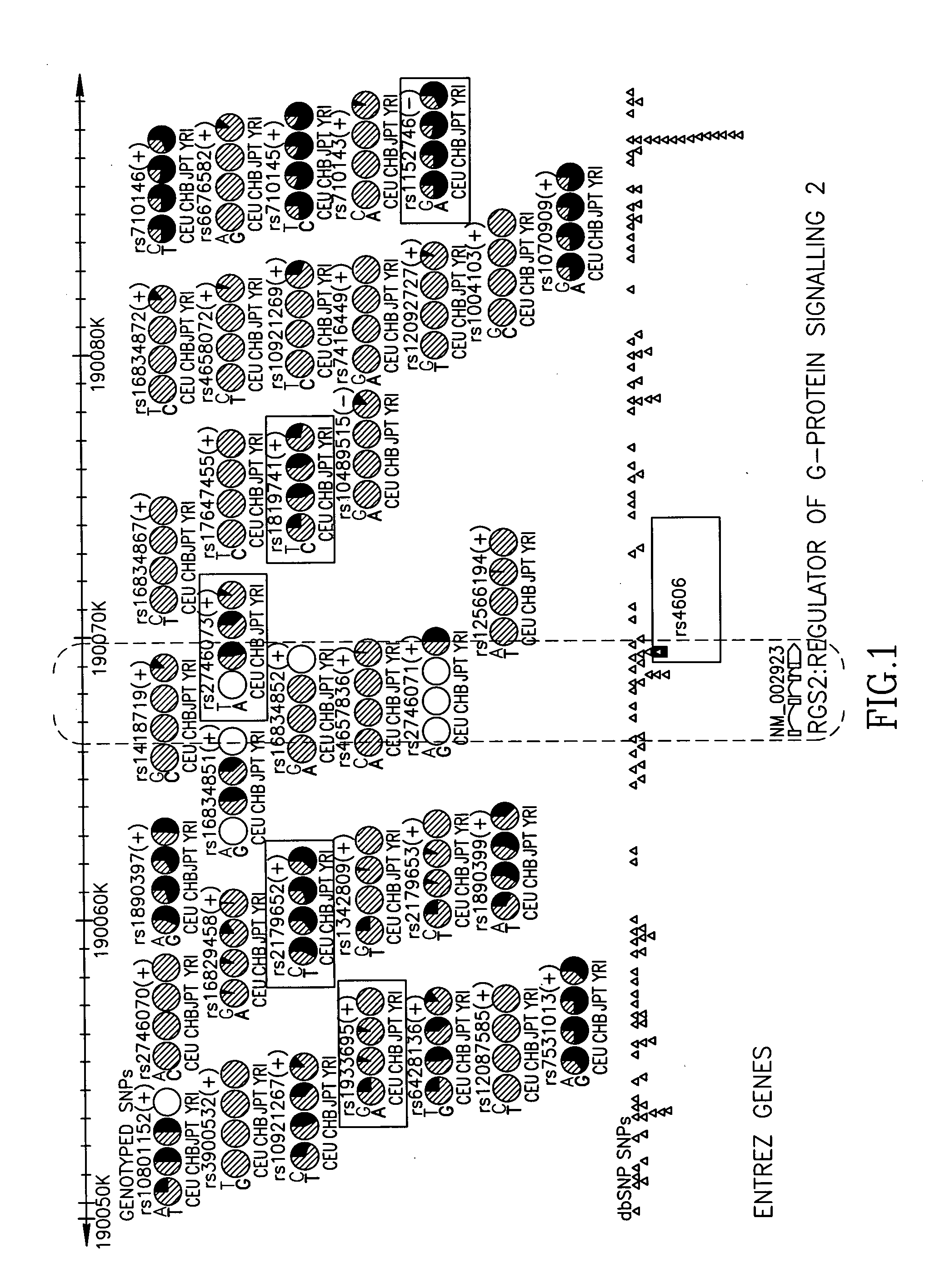
Rgs2 genotypes associated with extrapyramidal symptoms induced by antipsychotic medication
The present invention identifies genotypes associated with resistance to extrapyramidal symptoms induced by antipsychotic drugs. The present invention further identifies genotypes associated with predisposition to the onset or aggravation of extrapyramidal symptoms induced by antipsychotic drugs and use thereof for assessment of patient populations. Specifically, the present invention relates to particular polymorphisms in the RGS2 gene that are associated with resistance or susceptibility to drug-induced extrapyramidal symptoms.
Owner:HADASIT MEDICAL RES SERVICES & DEVMENT
Method for simultaneously detecting concentrations of various antipsychotic drugs in serum
ActiveCN111812218AHigh sensitivityStrong specificityComponent separationMetabolitePharmaceutical drug
The invention provides a method for simultaneously detecting the concentrations of various antipsychotic drugs in serum. According to the method, 16 kinds of antipsychotic drugs can be detected at a time; target drugs and metabolites are monitored at the same time; the method is high in sensitivity, high in specificity, good in accuracy and simple in pretreatment process; separation and detectionof the antipsychotic drugs in serum are completed within 5.0 minutes, and the accuracy and precision of the method basically meet requirements; and the method can be used for quantitative analysis ofantipsychotic drugs in serum clinically, and a simple and rapid detection method is provided for concentration monitoring of antipsychotic drugs clinically.
Owner:NANJING QLIFE MEDICAL TESTING LAB CO LTD +1
Augmentation of antipsychotic agent pharmacotherapy with chromium picolinate supplementation
InactiveUS20050096305A1Reduce morbidityMinimize side effectsBiocideAnimal repellantsSide effectAntipsychotic Agent
The present invention relates to pharmaceutical compositions comprising an antipsychotic agent in combination with a chromium salt, which are used for minimizing side effects in a patient taking an antipsychotic agent.
Owner:COMPREHENSIVE NEUROSCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com