Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
43 results about "Antipsychotic Agent" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Also known as neuroleptics, major tranquilizers, or antischizophrenics, natural or synthetic. Antipsychotic Agents relieve and control the symptoms of schizophrenic illness (hallucinations, delusions, dementia). Most antipsychotic agents interfere with various neurotransmitter functions, often blocking dopamine receptors, and induce diverse behavioral, endocrine, motor-kinetic effects. (NCI04)
Aripiprazole complex formulation and method
An aripiprazole formulation is provided which includes the antipsychotic agent aripiprazole in the form of an inclusion complex in a β-cyclodextrin, preferably, sulfobutyl ether β-cyclodextrin (SBECD), which in the form of an injectable produces reversible generally minimal to mild irritation at the intramuscular injection site. A method for minimizing or reducing irritation caused by aripiprazole at an intramuscular injection site and a method for treating schizophrenia employing the above formulation are also provided.
Owner:OTSUKA PHARM CO LTD
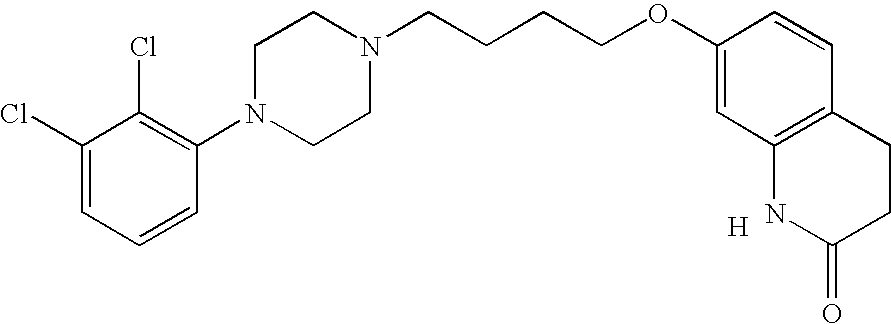
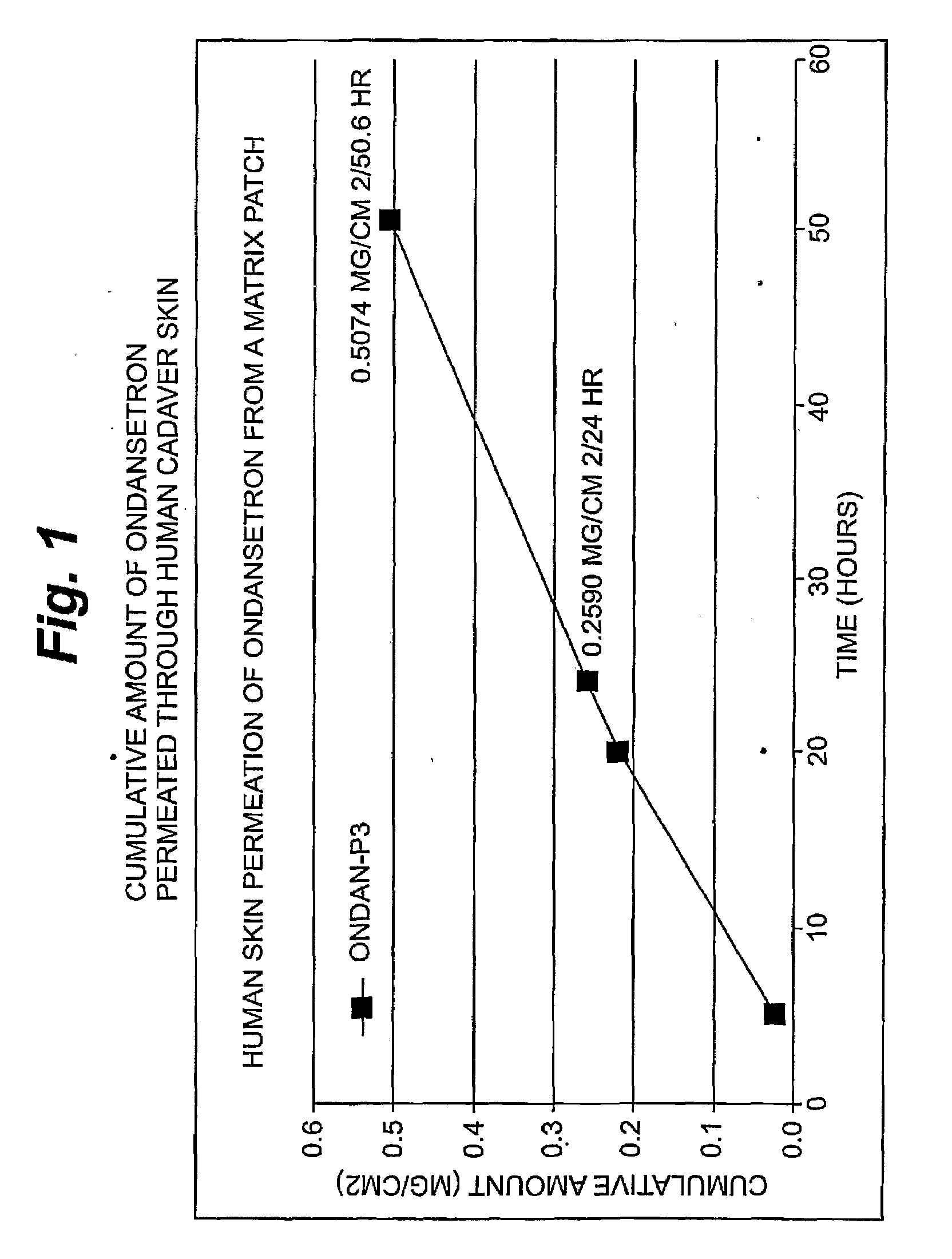
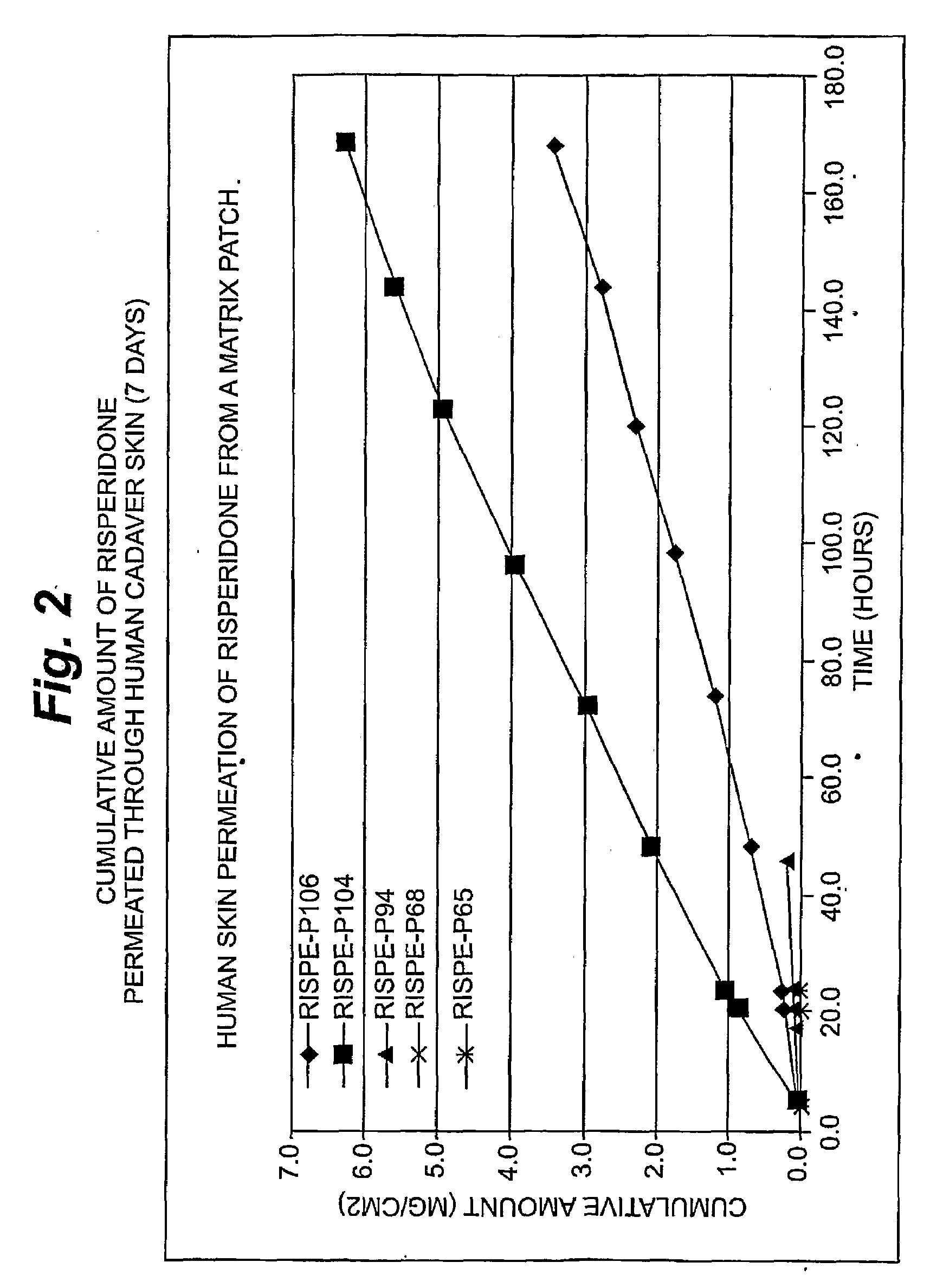
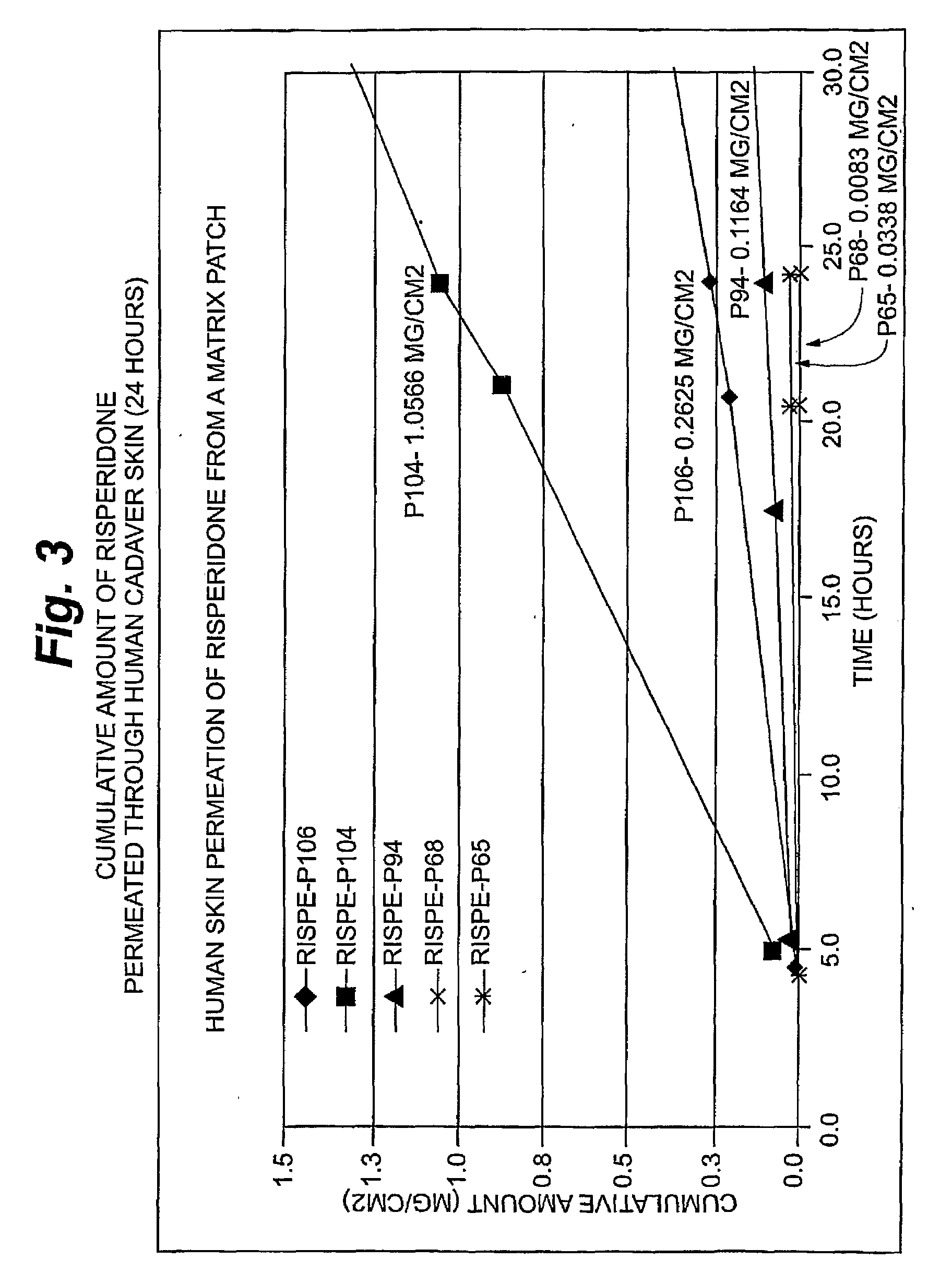
Transdermal Delivery of Hydrophobic Bioactive Agents
InactiveUS20080262445A1Improve solubilityImprove permeabilityBiocideAdhesive dressingsSerotoninFlumazenil
A method and related compositions, including the use of N-acyl derivatives of sarcosine, provide for the delivery of bioactive agents through tissue surfaces such as the skin. The method and composition are particularly well suited for hydrophobic active agents such as serotonin (5HT3) receptor antagonists (e.g., ondansetron), antipsychotic agents (e.g., risperidone), benzodiazepines (e.g., flumazenil), and progestins (e.g., levonorgestrel).
Owner:DERMATRENDS INC
Treatment of psychosis with a muscarinic m1 receptor ectopic activator
A muscarinic M1 receptor ectopic activator, such as a muscarinic M1 receptor allosteric potentiator or a muscarinic M1 receptor ectopic agonist is useful, alone or in combination with other antipsychotic agents, for treating or preventing psychosis, such as a schizophrenic disorder or psychosis in Alzheimer's disease or bipolar disorder, for enhancing cognition and for neuropathic pain.
Owner:MERCK & CO INC
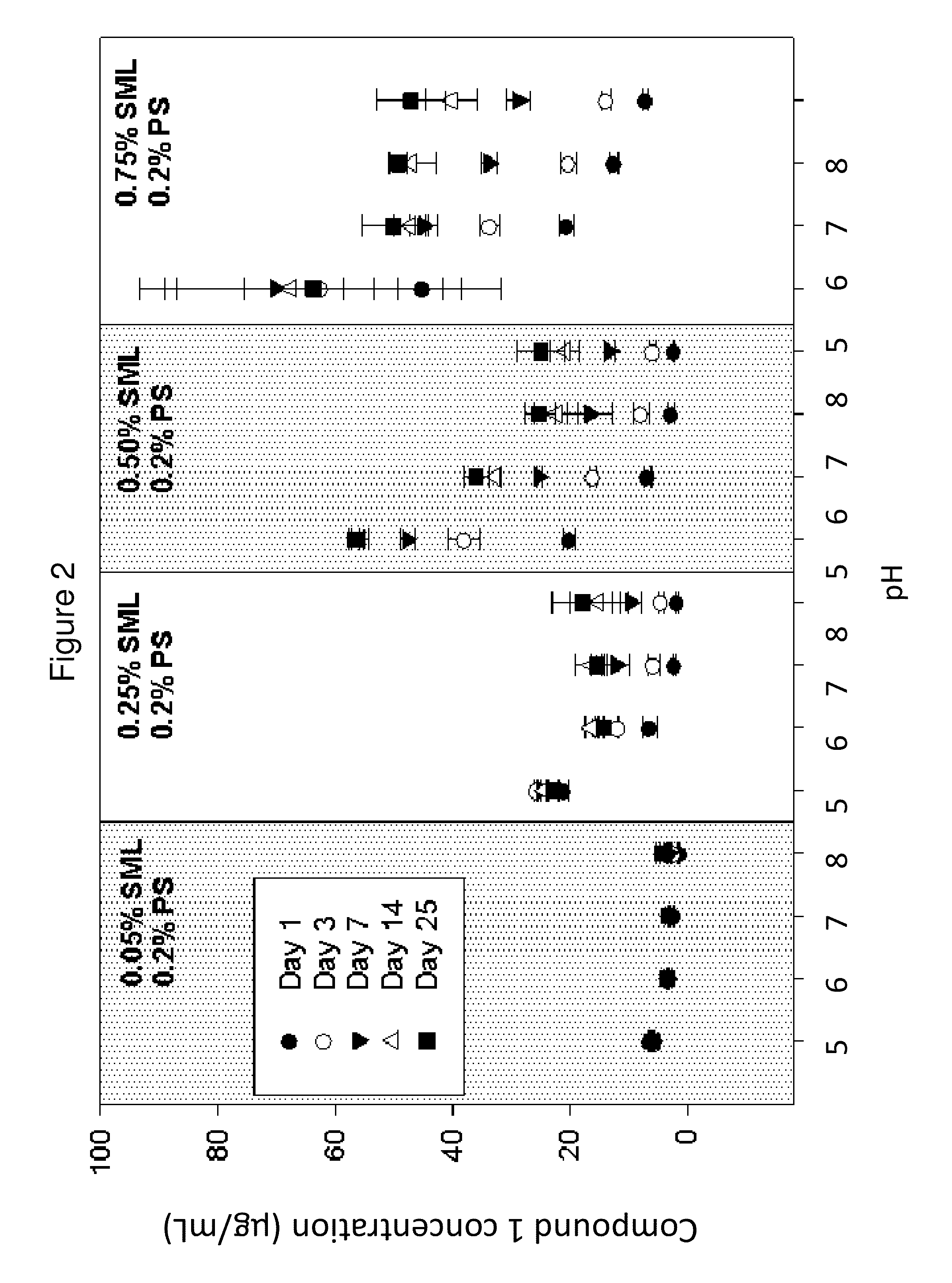
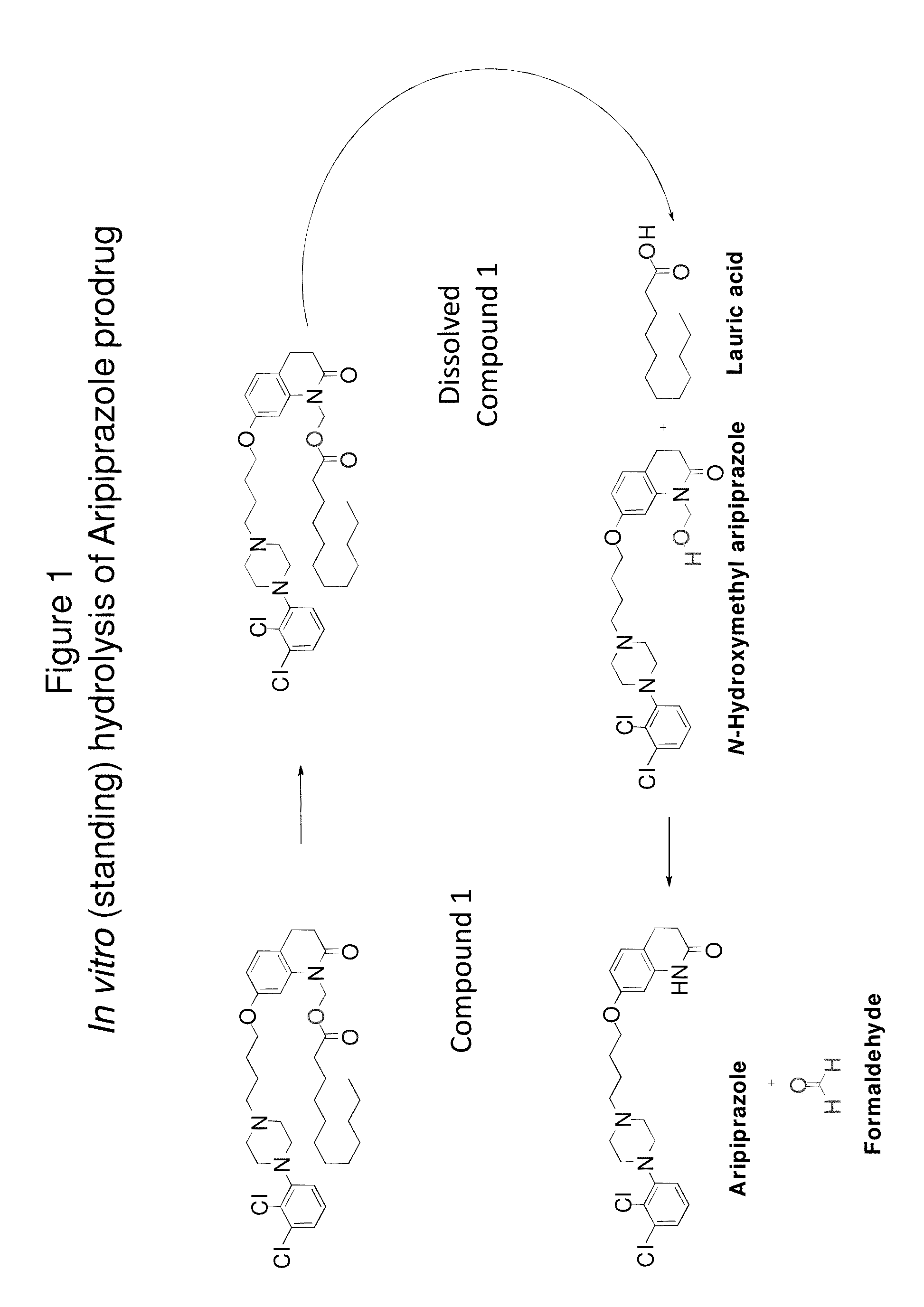
Pharmaceutical compositions having improved storage stability
ActiveUS20140088115A1Easily resuspendedMinimize in vitro degradationOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderAntipsychotic AgentPharmacology
The present invention relates to a pharmaceutical composition that provides long-term stability of a hydrolytically labile antipsychotic agent
Owner:ALKERMES PHARMA IRELAND LTD
Antipsychotic sulfonamide-heterocycles, and methods of use thereof
One aspect of the present invention relates to heterocyclic compounds comprising a sulfonamide moiety. A second aspect of the present invention relates to the use of the heterocyclic compounds comprising a sulfonamide moiety to treat diseases, afflictions or maladies caused at least in part by abnormal activity of one or more GPCRs or ligand-gated ion channels. An additional aspect of the present invention relates to the synthesis of combinatorial libraries of the heterocyclic compounds comprising a sulfonamide moiety, and the screening of those libraries for biological activity, e.g., in animal models of psychosis.
Owner:SEPACOR INC
Pharmaceutical compositions having improved storage stability
ActiveUS9193685B2Easily resuspendedMinimize in vitro degradationOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderAntipsychotic AgentDrug
The present invention relates to a pharmaceutical composition that provides long-term stability of a hydrolytically labile antipsychotic agent
Owner:ALKERMES PHARMA IRELAND LTD
Adenosine A2a receptor antagonists for the treatment of extra-pyramidal syndrome and other movement disorders
There is disclosed a method for the treatment or prevention of Extra Pyramidal syndrome (EPS), dystonia, restless legs syndrome (RLS) or periodic leg movement in sleep (PLMS) comprising the administration of an adenosine A2a receptor antagonist, alone or in combination with other agents useful for treating EPS, dystonia, RLS or PLMS; also claimed are pharmaceutical compositions consisting of an adenosine A2a receptor antagonist in combination with an antipsychotic agent, an anticonvulsant agent, lithium or an opioid.
Owner:SCHERING CORP
Combination therapy
InactiveUS20100099762A1Eliminate side effectsIncreasing glutathione levelBiocideNervous disorderCombined Modality TherapyPsychiatry
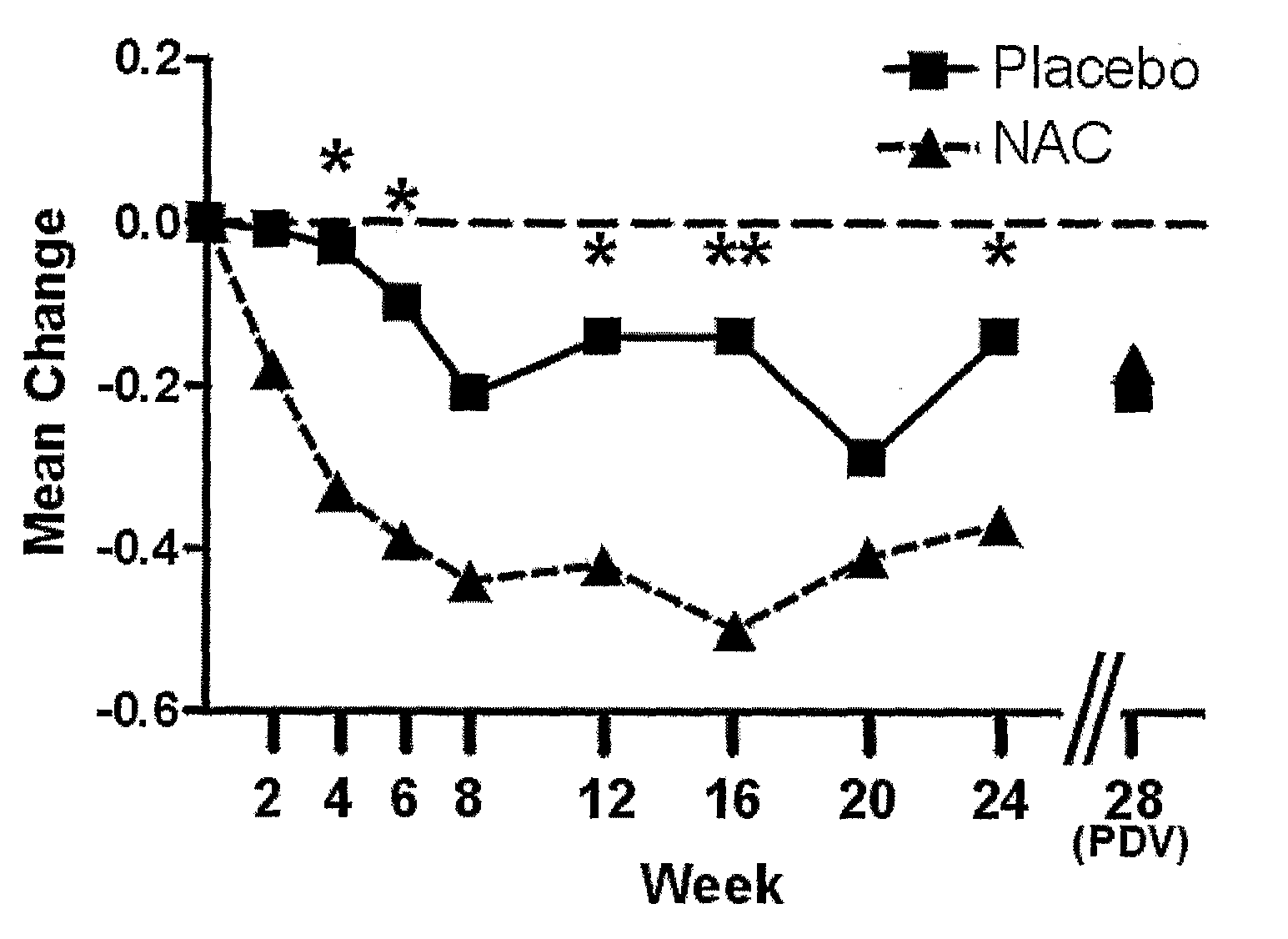
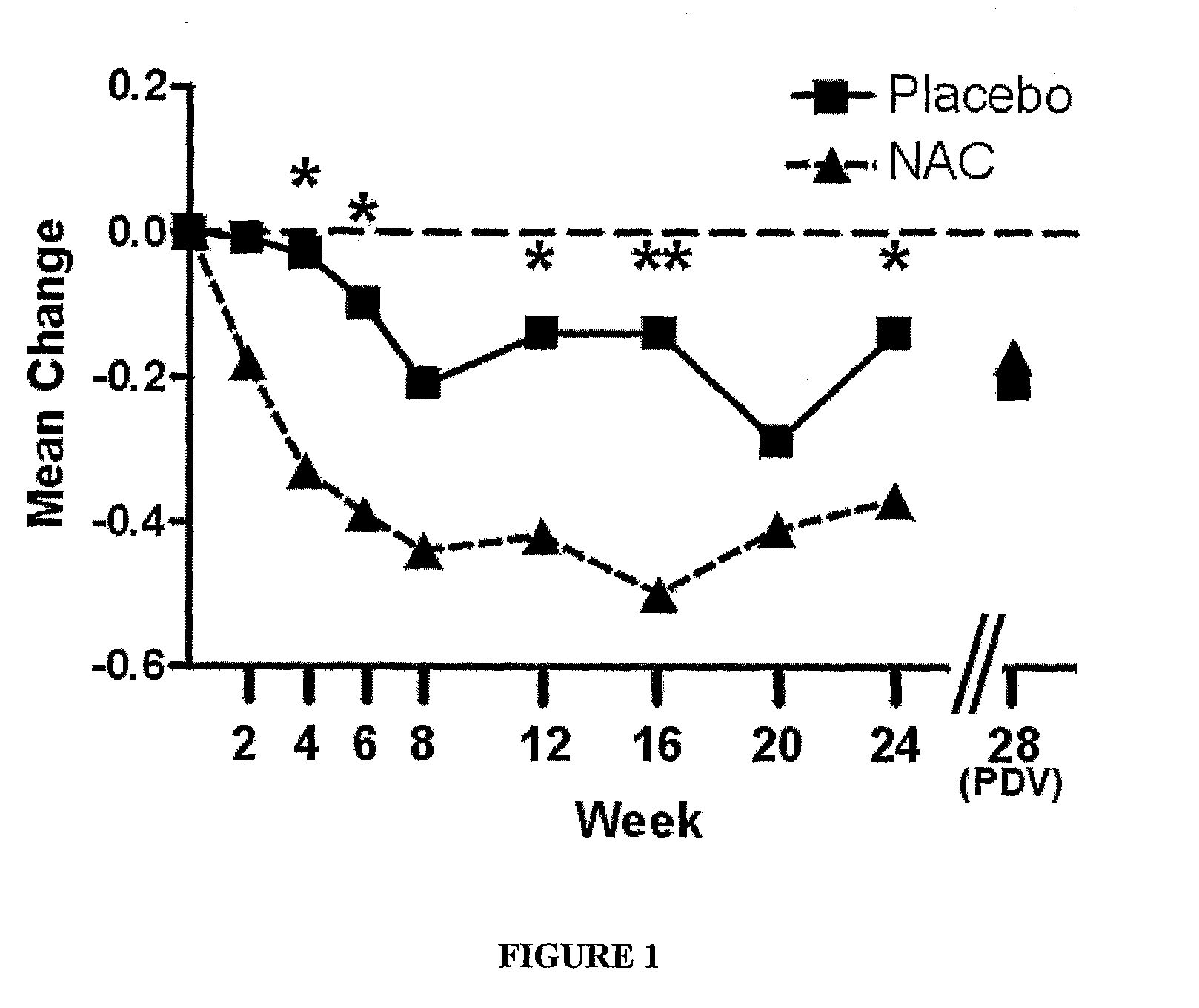
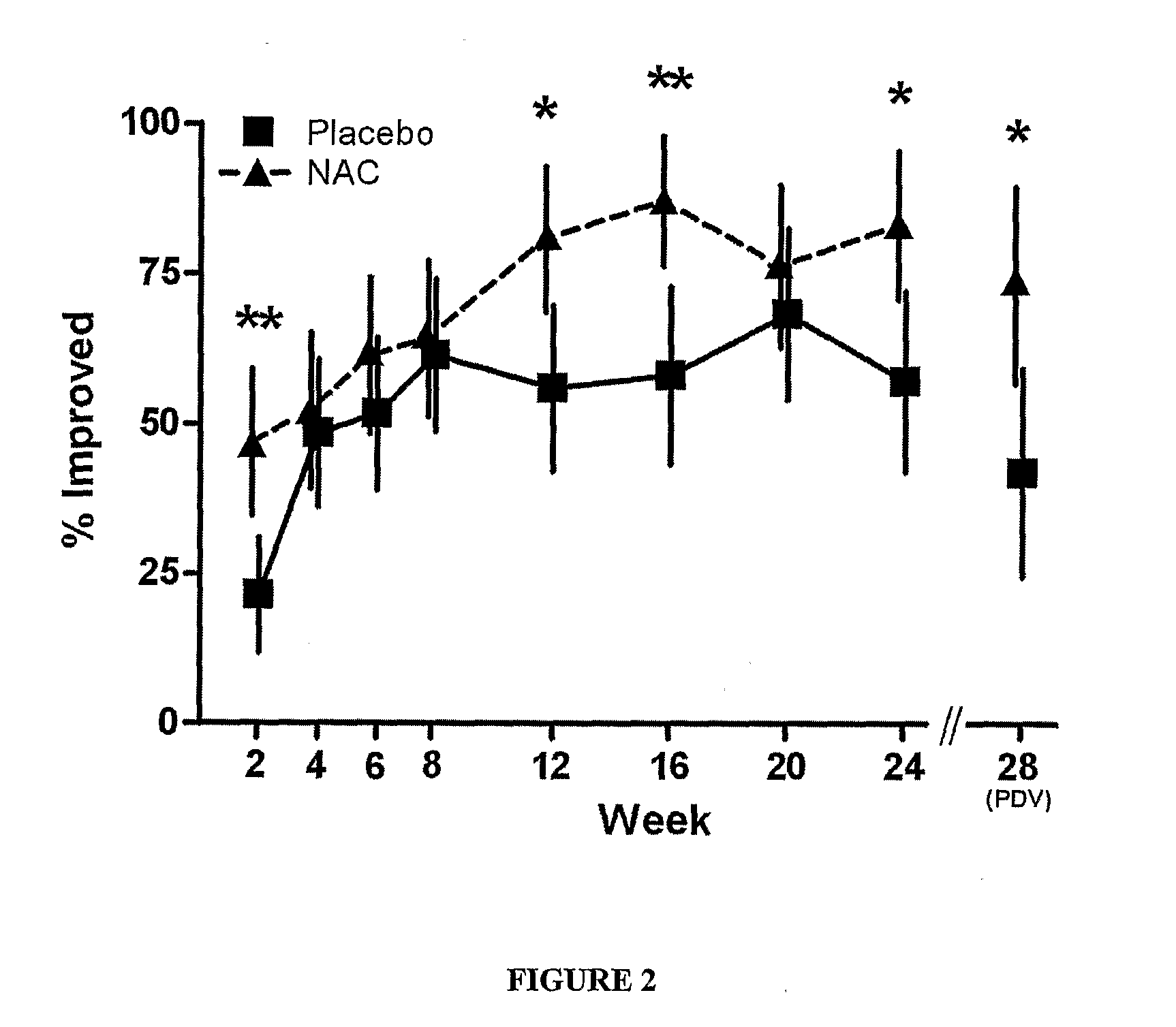
The present invention relates generally to a method of treating a psychiatric or neuropsychiatric condition in a mammal with a combination therapy. More particularly, the present invention relates to a combination therapy comprising an antipsychotic agent and a compound that increases levels of glutathione in the body.
Owner:THE MENTAL HEALTH RES INST OF VICTORIA
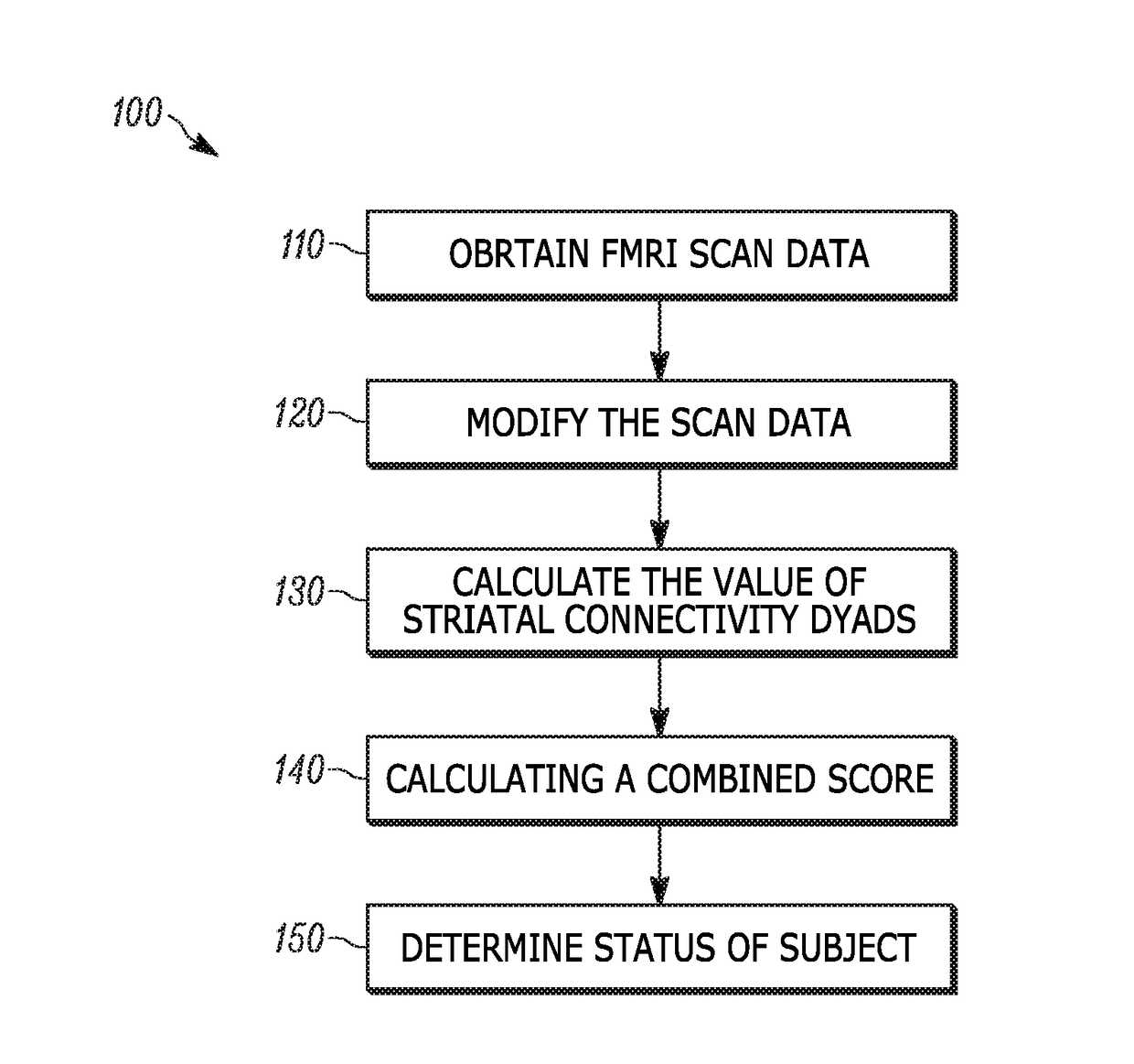
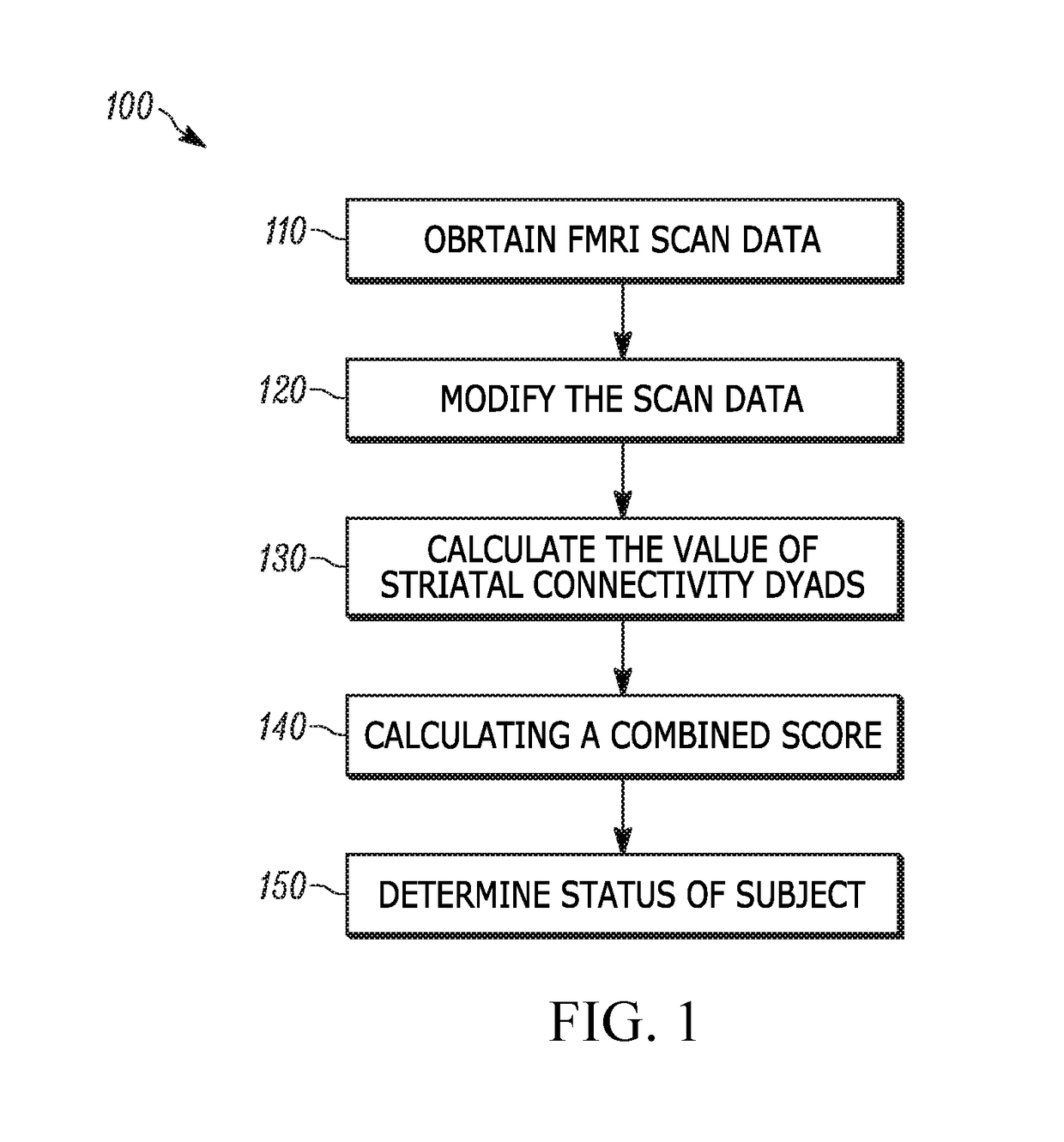
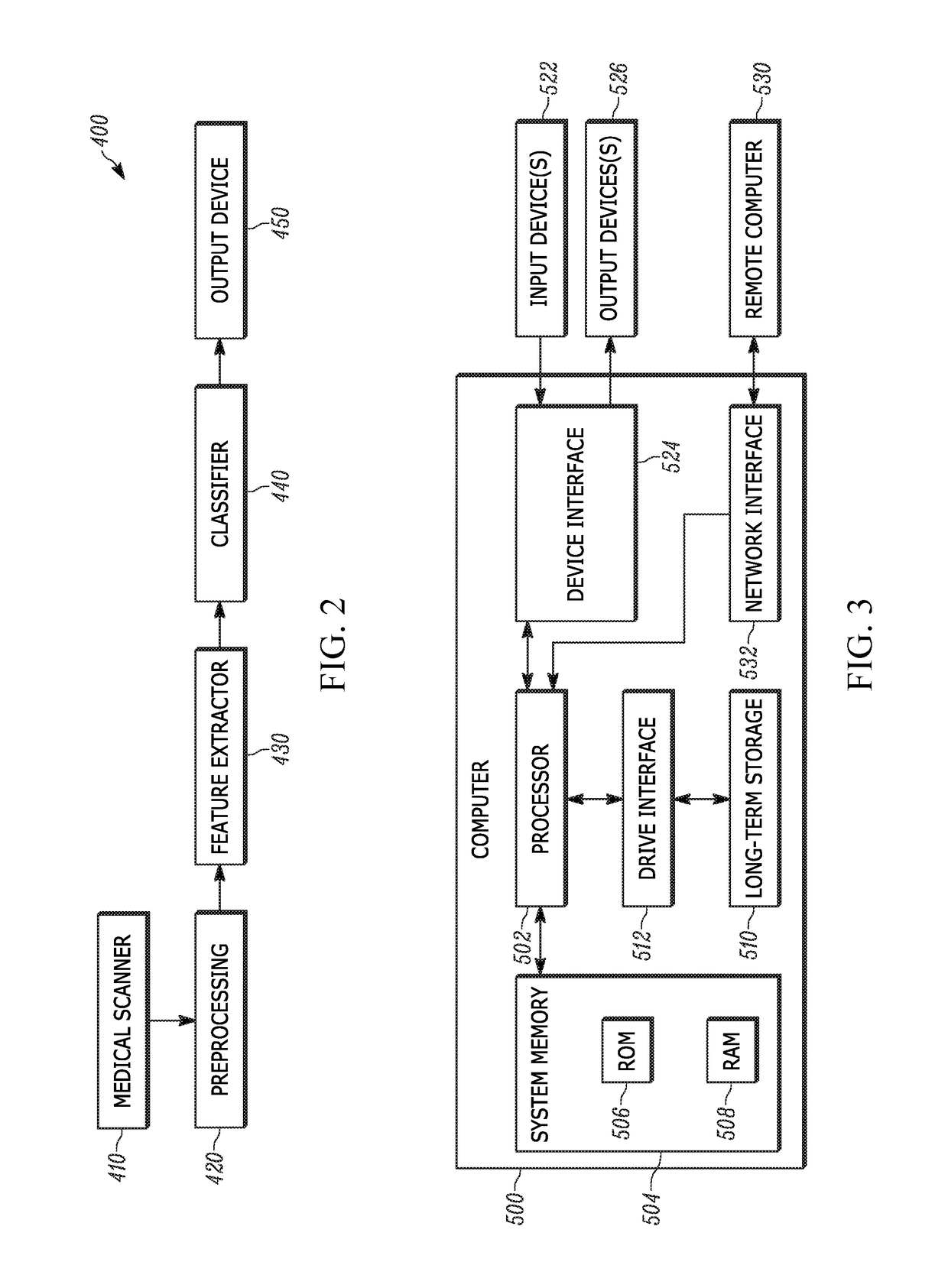
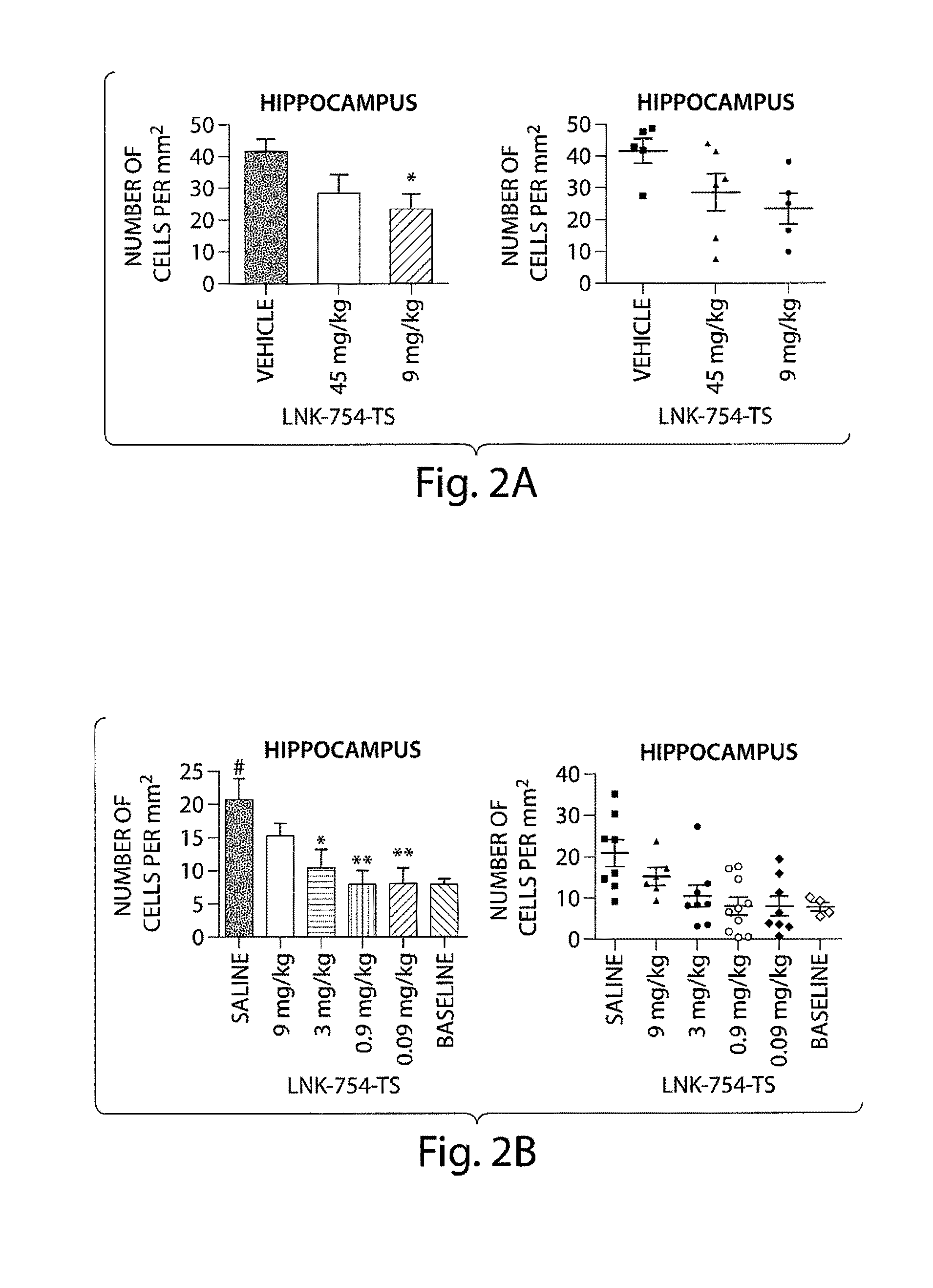
Use of striatal connectivity patterns for evaluating antipsychotic agents
InactiveUS20170343634A1Medical imagingMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsCombination algorithmComputer science
A method of predicting the response of a subject to an antipsychotic agent is described. The method includes obtaining functional MRI (fMRI) scan data of the brain of the subject, modifying the scan data using a standardizing algorithm to provide modified scan data, calculating the value of a plurality of striatal connectivity dyads from the modified scan data using an extraction algorithm, calculating a combined score from the values of the striatal connectivity dyads using a combining algorithm; and comparing the combined score to a classifier value to determine if the subject is a responder or a non-responder. Systems for carrying out the method of predicting the response of a subject to an antipsychotic agent are also described.
Owner:THE FEINSTEIN INST FOR MEDICAL RES
Use of a CB1 Antagonist for Treating Side Effects and Negative Symptoms of Schizophrenia
InactiveUS20080221078A1Useful in treatmentSymptoms improvedOrganic active ingredientsBiocideDiseaseNegative symptom
The present invention discloses and claims a method of treating cognition deficits in a patient suffering from schizophrenia by administering to said patient a therapeutically effective amount of a CB1 receptor antagonist as described herein. In another aspect, this invention also discloses and claims a combination of one or more CB1 receptor antagonists and of one or more antipsychotic agents useful in the treatment of psychiatric disorders. The combination of this invention provides synergistic results in that the combination improves positive and negative symptoms of schizophrenia, weight gain and catalepsy.
Owner:AVENTIS PHARMA INC
7-keto DHEA for psychiatric use
InactiveUS20080070879A1Improve depressive symptomsFunction increaseBiocideOrganic active ingredientsAnti-Anxiety AgentsDisease
The present invention comprises novel methods for the use of compositions comprising 7-keto DHEA for treating psychiatric conditions. These methods include administering an effective amount of a composition comprising 7-keto DHEA in an acceptable carrier, alone or in combination with other psychiatric drugs, such as analgesic agents, anticonvulsants, anti-anxiety agents, antidepressants, anti-panic agents, antipsychotic agents, bipolar agents, psychostimulants to reduce or ameliorate symptoms of a psychiatric condition. This method may be used alone or as an adjunctive treatment for treating a wide variety of psychiatric conditions such as stress disorders, anxiety disorders and depressive disorders.
Owner:SAGEMAN SHARON +1
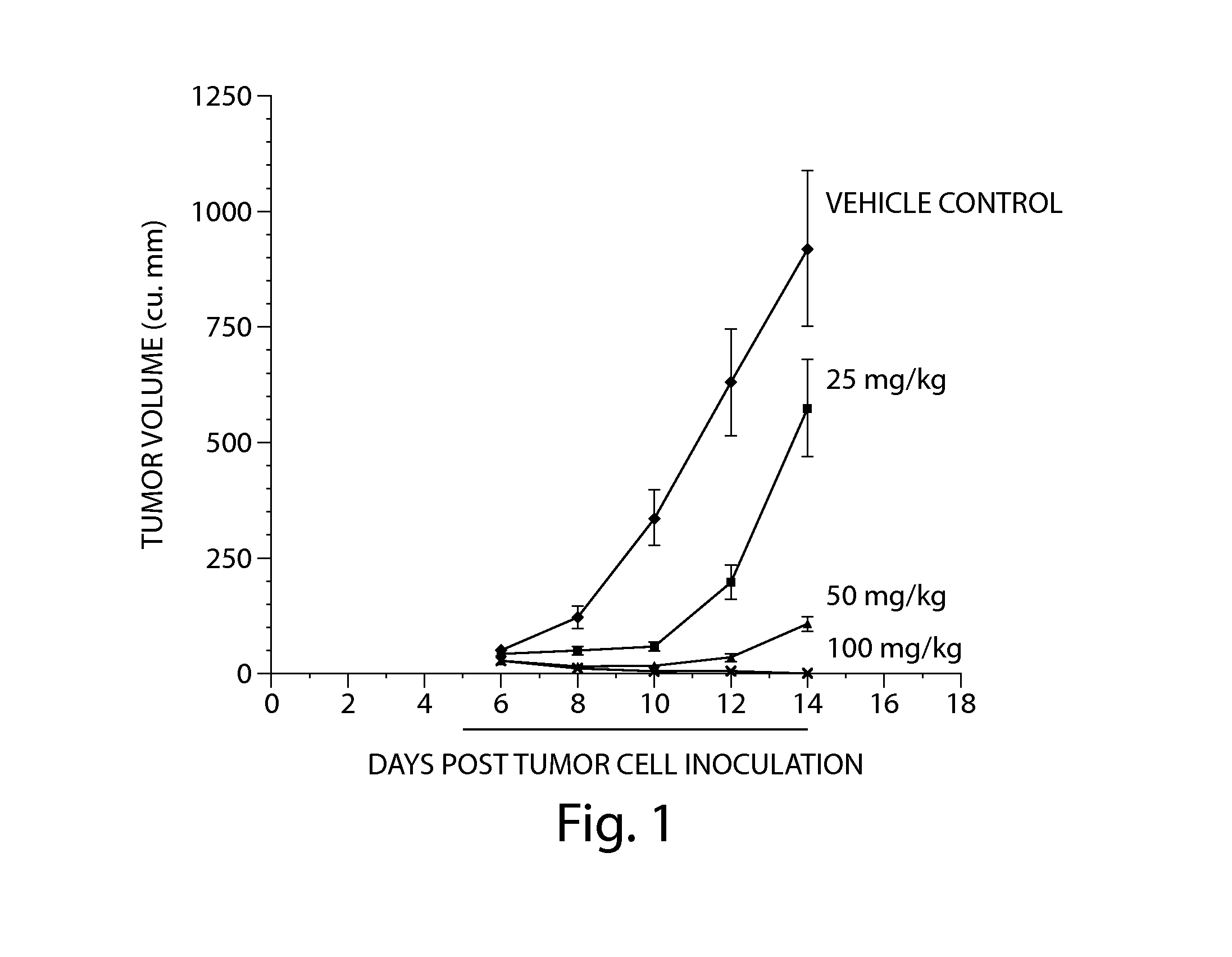
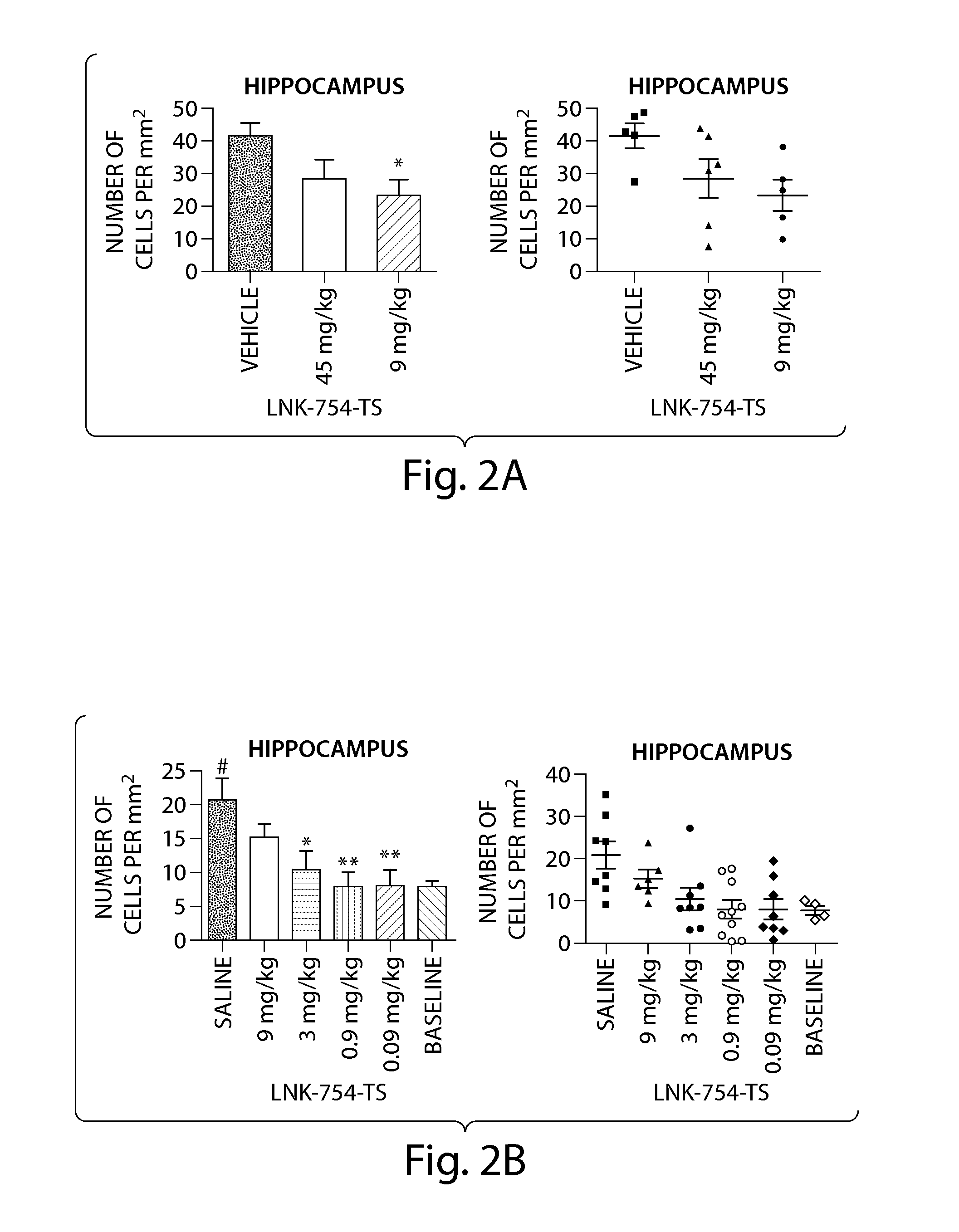
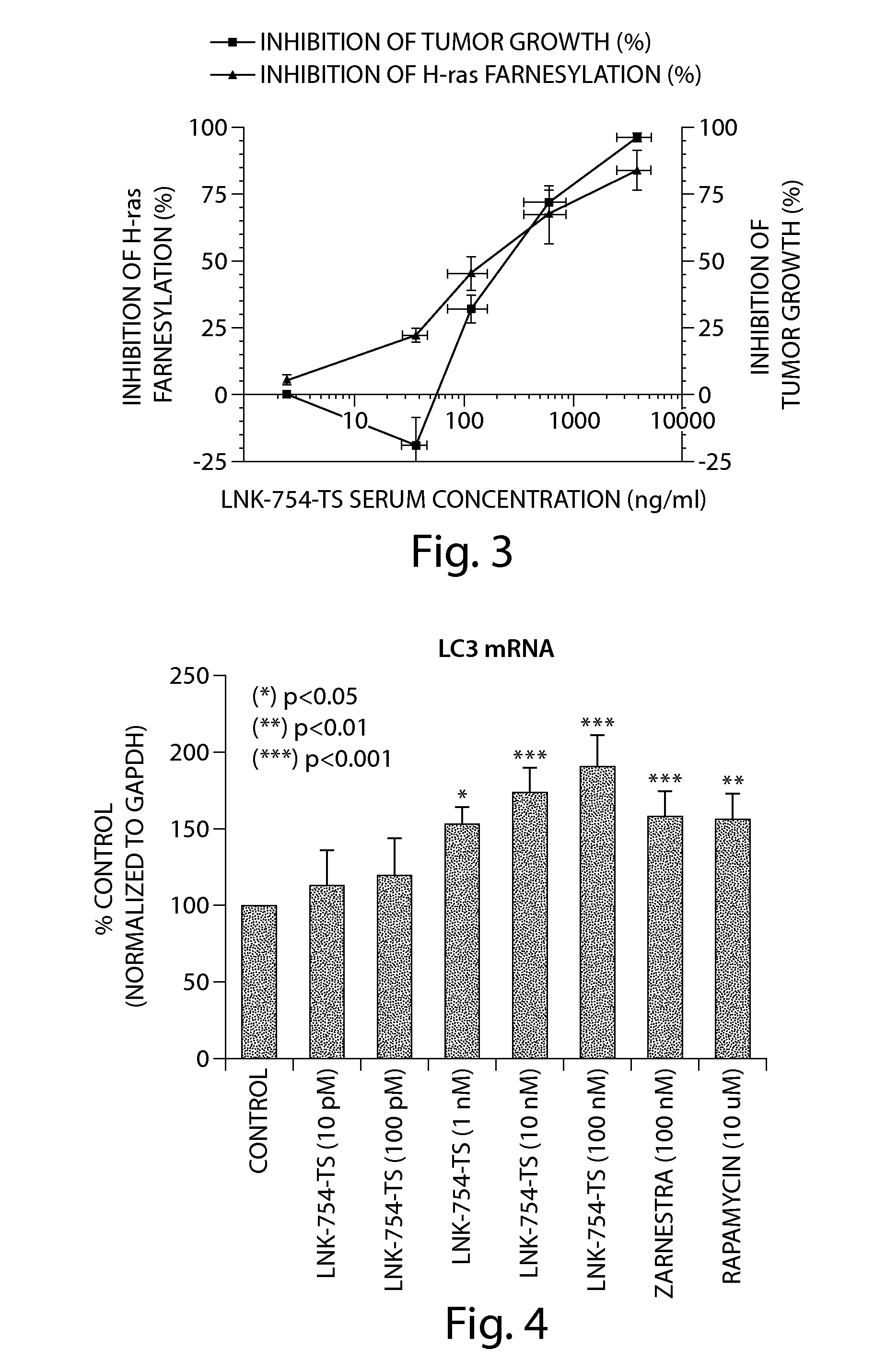
Treatment of mitochondrial disorders using a farnesyl transferase inhibitor
InactiveUS20100331363A1Avoid cell deathIncreased insulin secretionBiocideNervous disorderAntioxidantDepressant
Methods and pharmaceutical compositions comprising a low dose of a farnesyl transferase inhibitor useful in the treatment of proteinopathies are provided. These low doses are below the doses used in oncological treatments for which these compounds were initially designed. The treatment includes administering to a subject an amount of a farnesyl transferase inhibitor, wherein the amount administered is sufficient to cause an improvement in mitochondrial health in said subject. Treatments in accordance with the present invention may also include an acetylcholinesterase inhibitor, an activator of neurotrophic receptors, an NMDA anatagonist, an amyloid deposit inhibitor, an antipsychotic agent, an antidepressant, an anxiolytic, or an antioxidant.
Owner:ASTRAZENECA AB
Augmentation of antipsychotic agent pharmacotherapy with chromium picolinate supplementation
InactiveUS20050096305A1Reduce morbidityMinimize side effectsBiocideAnimal repellantsSide effectAntipsychotic Agent
The present invention relates to pharmaceutical compositions comprising an antipsychotic agent in combination with a chromium salt, which are used for minimizing side effects in a patient taking an antipsychotic agent.
Owner:COMPREHENSIVE NEUROSCI
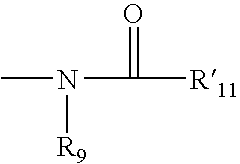
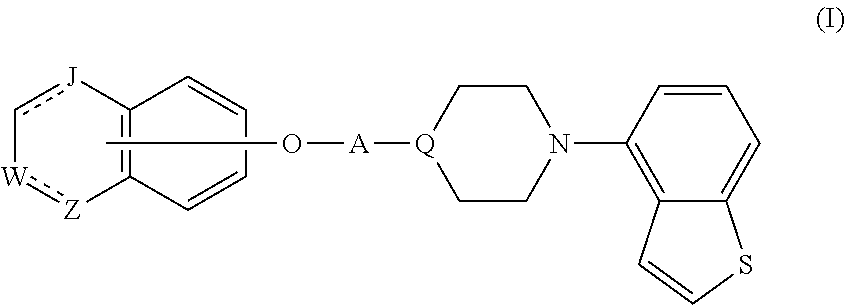
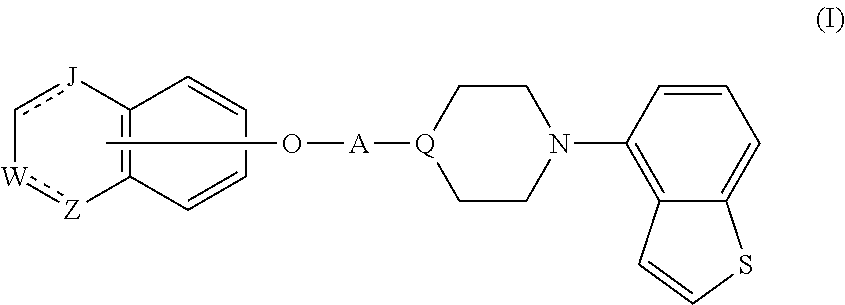
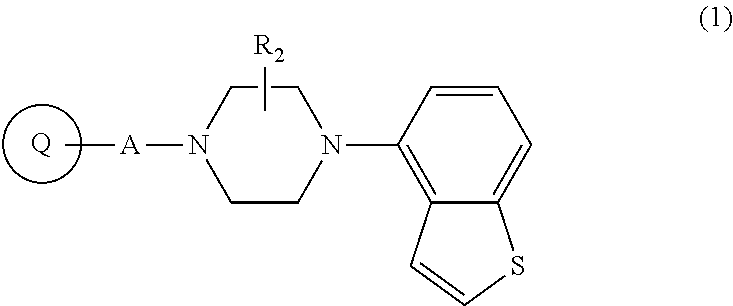
Piperazine-substituted benzothiophene derivatives as antipsychotic agents
ActiveUS9260420B2Suppresses dopaminergic (DA) neurotransmissionIncrease neurotransmissionGroup 4/14 element organic compoundsNervous disorderSide effectTolerability
Provided is a superior, novel heterocyclic compound with improved solubility in oil such as sesame oil and benzyl benzoate, which has a broader treatment spectrum, causes less side effects, and is superior in tolerability and safety, and use thereof. A heterocyclic compound represented by the formula (I) wherein each symbol is as defined in the specification, or a salt thereof.
Owner:OTSUKA PHARM CO LTD
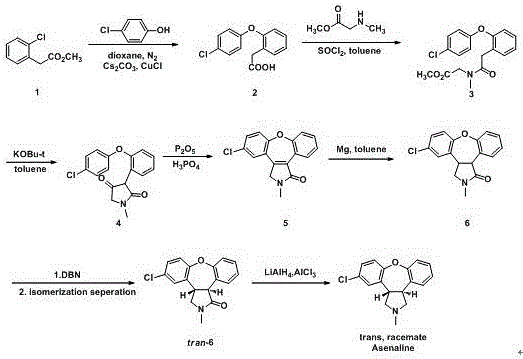
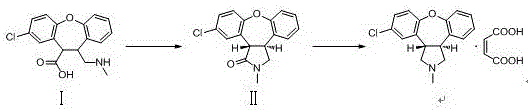
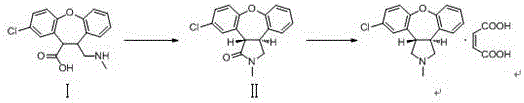
Preparation method of maleic acid asenapine
The invention relates to an industrialization-suitable synthesis process for antipsychotic medicine asenapine. The synthesis process includes the following steps that in an organic solvent, a compound I is cyclized under an acidic condition to obtain an intermediate II; the intermediate II is subjected to a reduction reaction under the effect of a strong reducing agent, the intermediate II and maleic acid are salified, and the target compound maleic acid asenapine is obtained.
Owner:AVENTIS PHARMA HAINAN
Aripiprazole complex formulation and method
An aripiprazole formulation is provided which includes the antipsychotic agent aripiprazole in the form of an inclusion complex in a β-cyclodextrin, preferably, sulfobutyl ether β-cyclodextrin (SBECD), which in the form of an injectable produces reversible generally minimal to mild irritation at the intramuscular injection site. A method for minimizing or reducing irritation caused by aripiprazole at an intramuscular injection site and a method for treating schizophrenia employing the above formulation are also provided.
Owner:OTSUKA PHARM CO LTD
7-keto DHEA for psychiatric use
InactiveUS8124598B2Improve depressive symptomsFunction increaseOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderAnti-Anxiety AgentsPsychosis drug
The present invention comprises novel methods for the use of compositions comprising 7-keto DHEA for treating psychiatric conditions. These methods include administering an effective amount of a composition comprising 7-keto DHEA in an acceptable carrier, alone or in combination with other psychiatric drugs, such as analgesic agents, anticonvulsants, anti-anxiety agents, antidepressants, anti-panic agents, antipsychotic agents, bipolar agents, psychostimulants to reduce or ameliorate symptoms of a psychiatric condition. This method may be used alone or as an adjunctive treatment for treating a wide variety of psychiatric conditions such as stress disorders, anxiety disorders and depressive disorders.
Owner:SAGEMAN SHARON +1
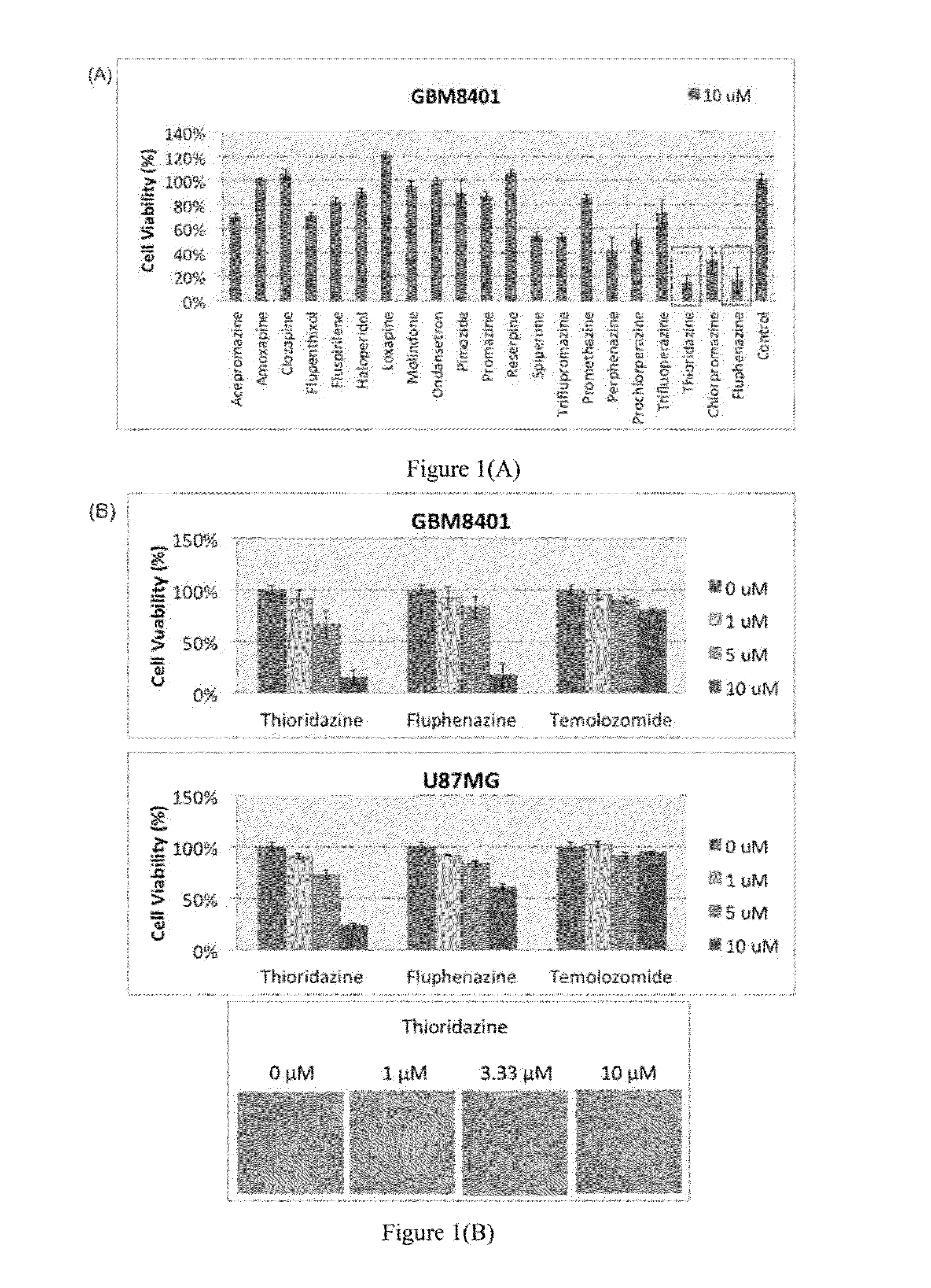
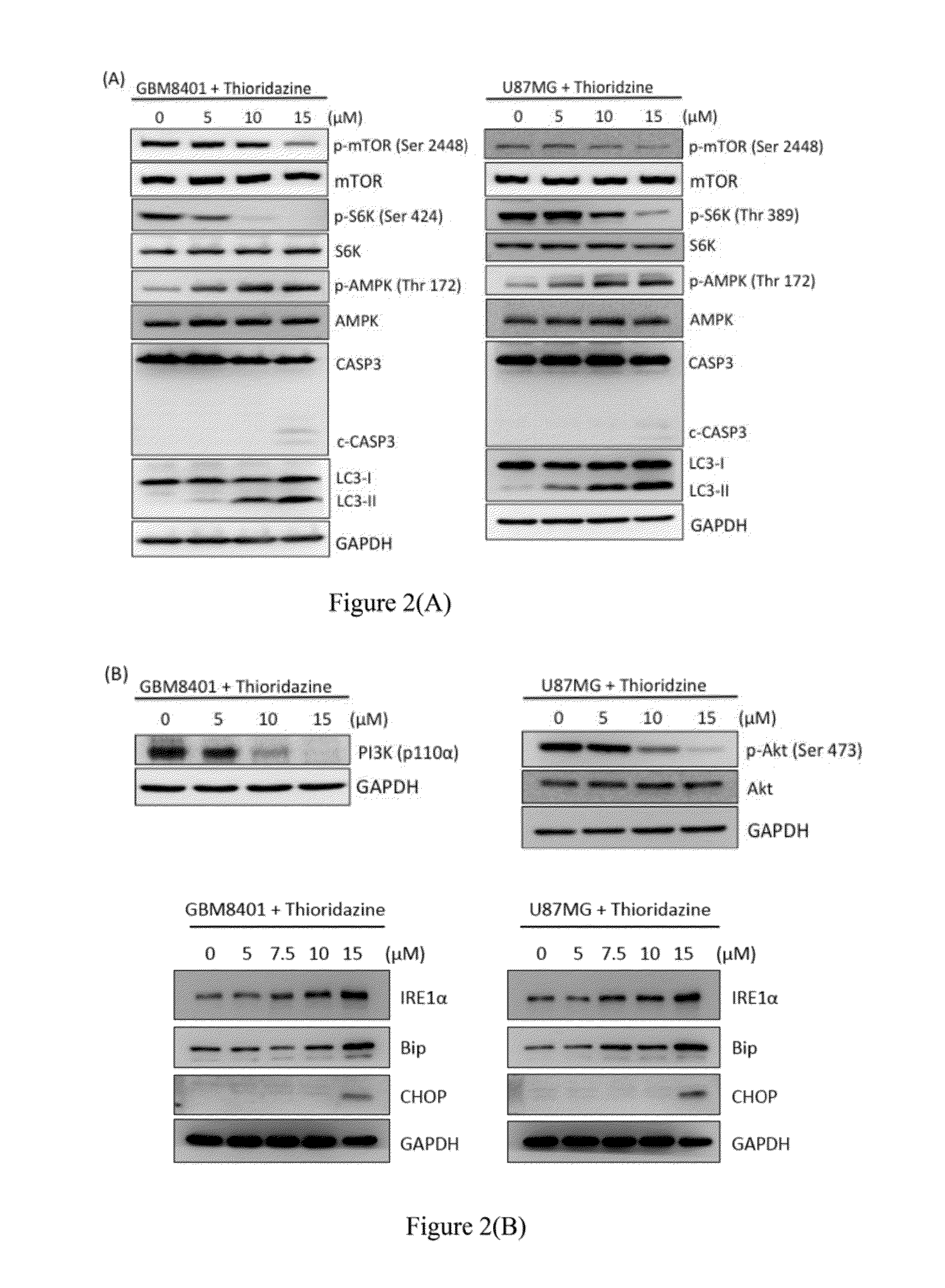
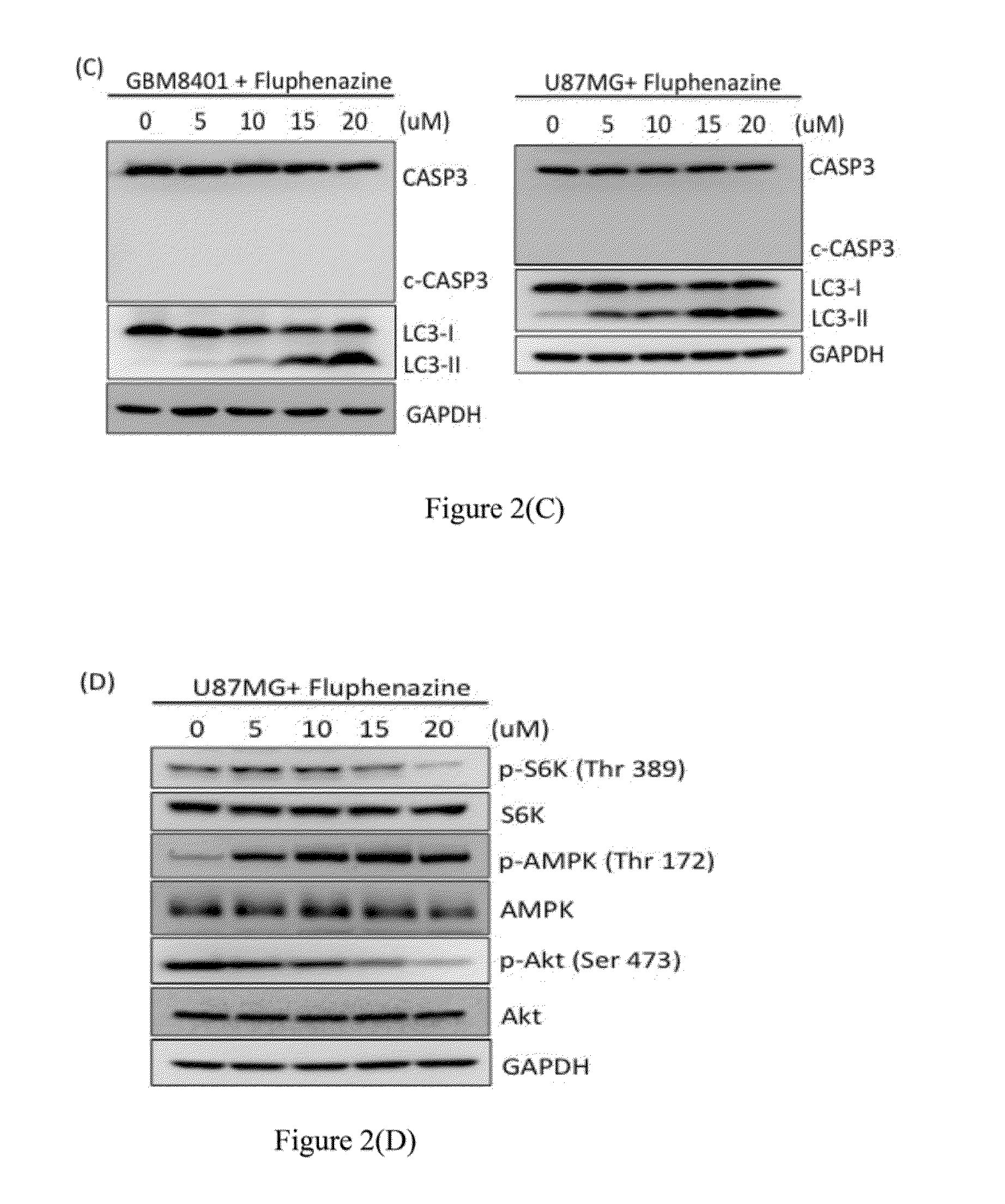
Method for treating brain tumor
The preset invention relates to a new method for treating brain tumor with an antipsychotic phenothiazine derivative as a brain tumor cell inhibitor or a brain tumor stem cell inhibitor. In particular, an antipsychotic phenothiazine is accessible to brain via blood-brain barrier, which should be beneficially in treatment of brain tumor.
Owner:NATIONAL YANG MING UNIVERSITY
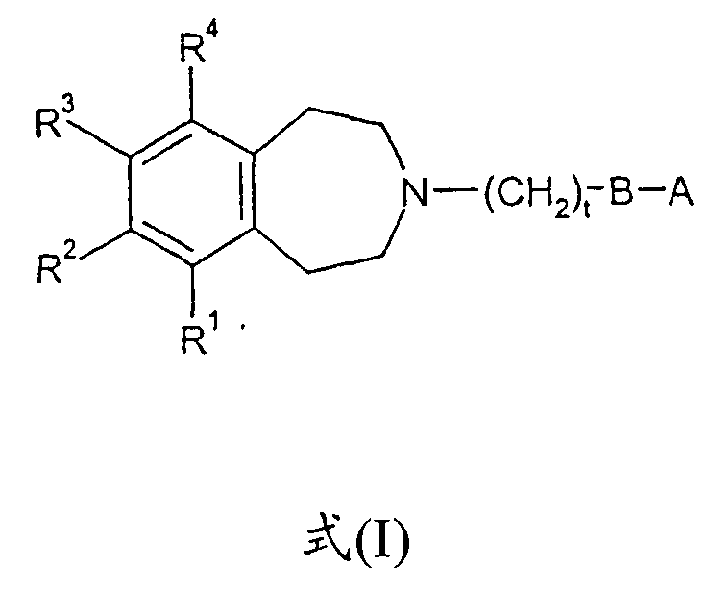
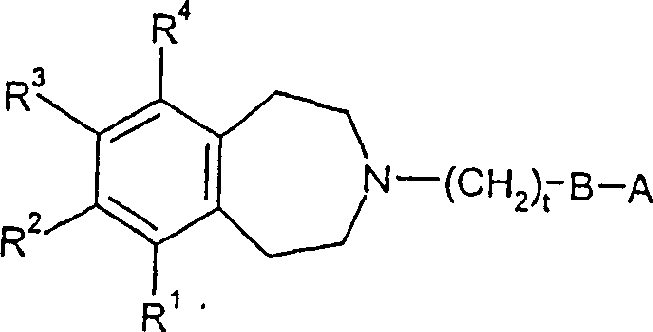
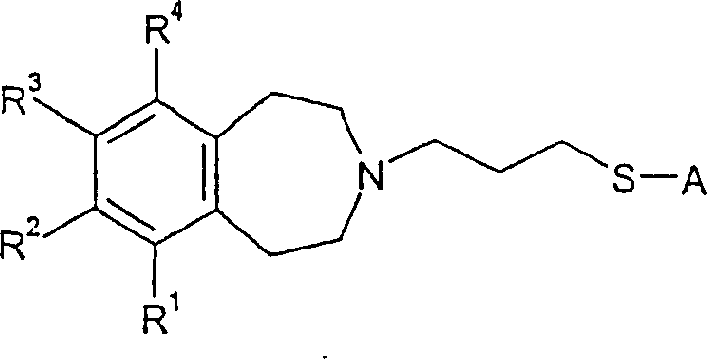
Tetrahydroazepine derivatives useful as dopamine d3 receptor modulators (antipsychotic agents)
The invention provides compounds of formula (I), wherein R1-R4, A, B and t are as defined in claim 1. The compounds are modulators of dopamine D3 receptors and have potential in the treatment of psychotic conditions (e.g. schizophrenia) or substance abuse.
Owner:SMITHKLINE BECKMAN CORP
Treatment of mitochondrial disorders using a farnesyl transferase inhibitor
InactiveUS20110060005A1Avoid cell deathIncreased insulin secretionBiocideNervous disorderAntioxidantMITOCHONDRIAL PHERS
Methods and pharmaceutical compositions comprising a low dose of a farnesyl transferase inhibitor useful in the treatment of proteinopathies and mitochondrial disorders are provided. These low doses are below the doses used in oncological treatments for which these compounds were initially designed. The treatment includes administering to a subject an amount of a farnesyl transferase inhibitor, wherein the amount administered is sufficient to stimulate mitophagy in said subject. Treatments in accordance with the present invention may also include an acetylcholinesterase inhibitor, an activator of neurotrophic receptors, an NMDA anatagonist, an amyloid deposit inhibitor, an antipsychotic agent, an antidepressant, an anxiolytic, or an antioxidant.
Owner:ASTRAZENECA AB
Piperazine-substituted benzothiophene derivatives as antipsychotic agents
ActiveUS20150045356A1Suppression problemAccelerates DAergic neurotransmissionGroup 4/14 element organic compoundsNervous disorderBenzyl benzoatSide effect
Provided is a superior, novel heterocyclic compound with improved solubility in oil such as sesame oil and benzyl benzoate, which has a broader treatment spectrum, causes less side effects, and is superior in tolerability and safety, and use thereof. A heterocyclic compound represented by the formula (I) wherein each symbol is as defined in the specification, or a salt thereof.
Owner:OTSUKA PHARM CO LTD
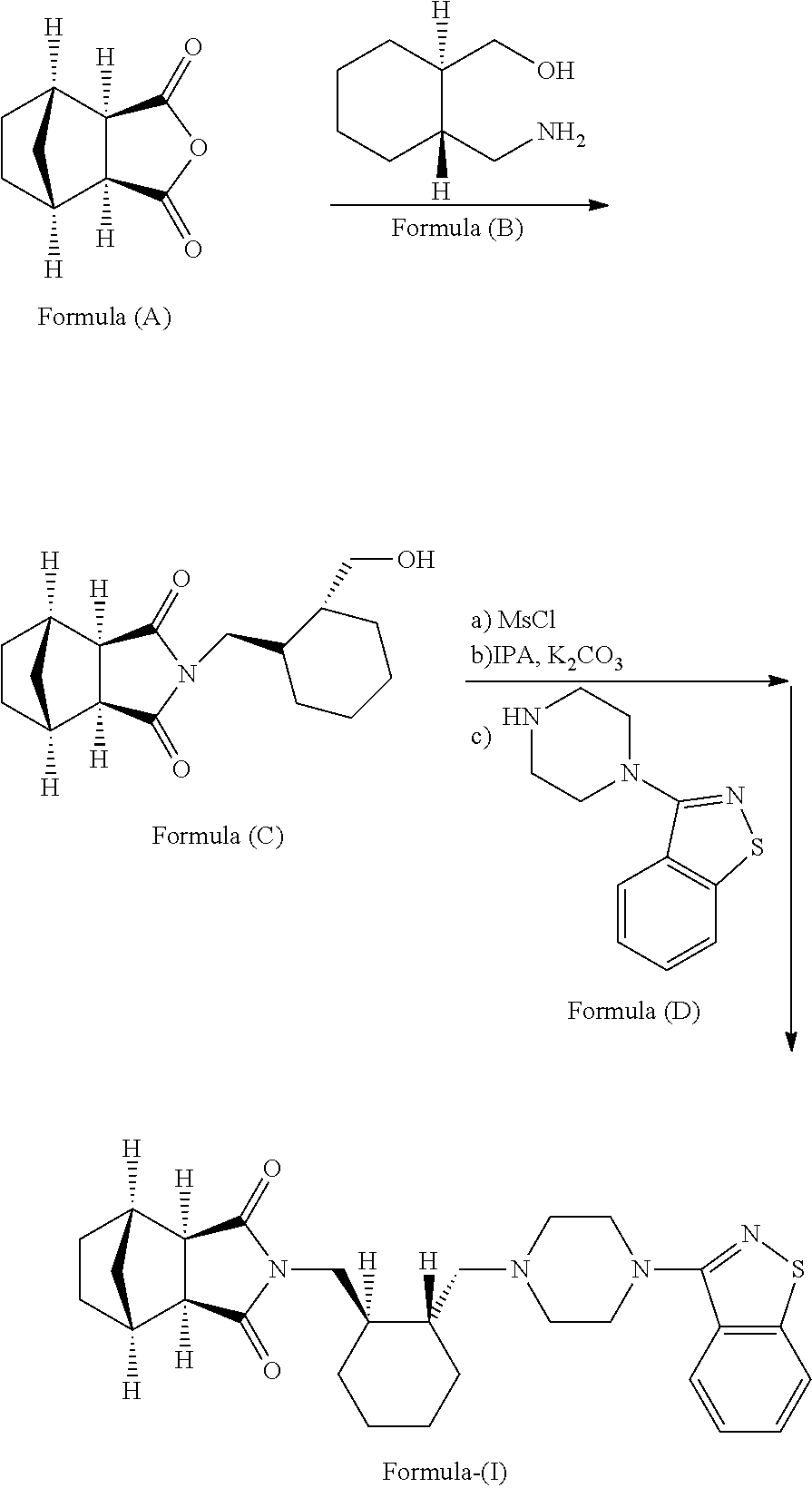
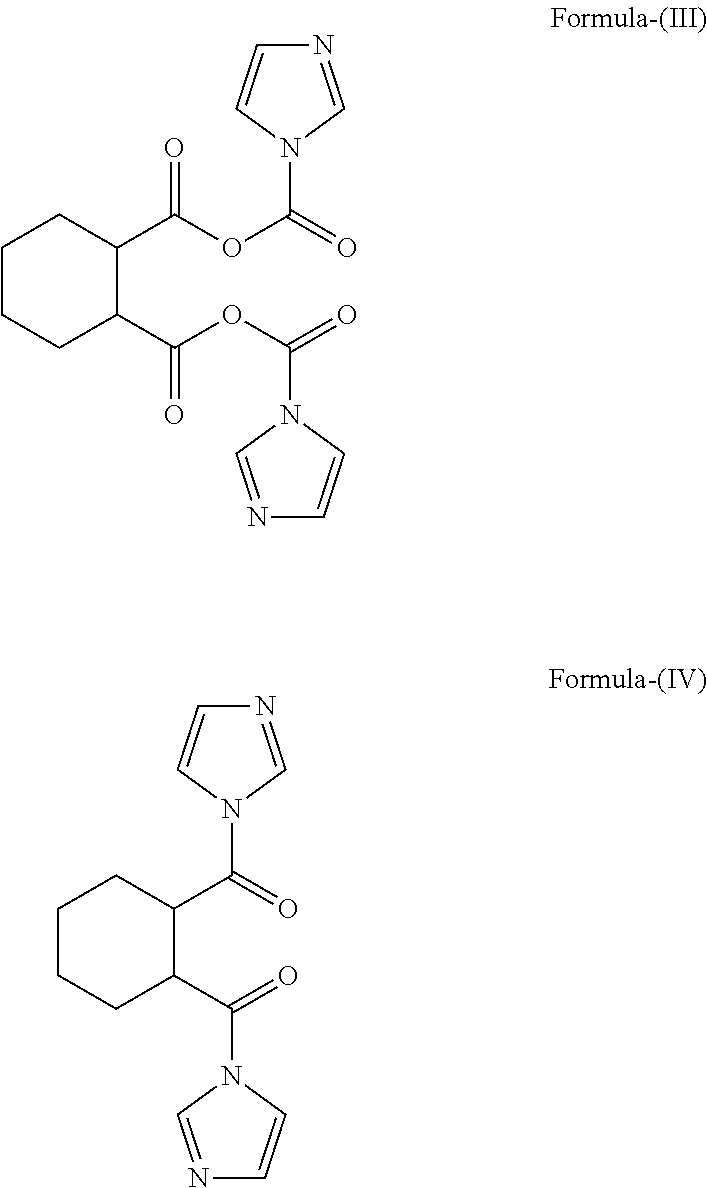
An improved process for the preparation of lurasidone hydrochloride
ActiveUS20170246165A1Useful in treatmentCost-effective and industrially amenableOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryLurasidone HydrochlorideIndustrial scale
Disclosed herein is an improved process for the preparation of Lurasidone and its pharmaceutically acceptable salts via novel intermediate and use thereof for the preparation of an antipsychotic agent useful for the treatment of schizophrenia and bipolar disorder. Further, present invention provides a cost effective and eco-friendly process for producing Lurasidone hydrochloride of formula (I) substantially free of residual solvent(s) at industrial scale.
Owner:JUBILANT GENERICS
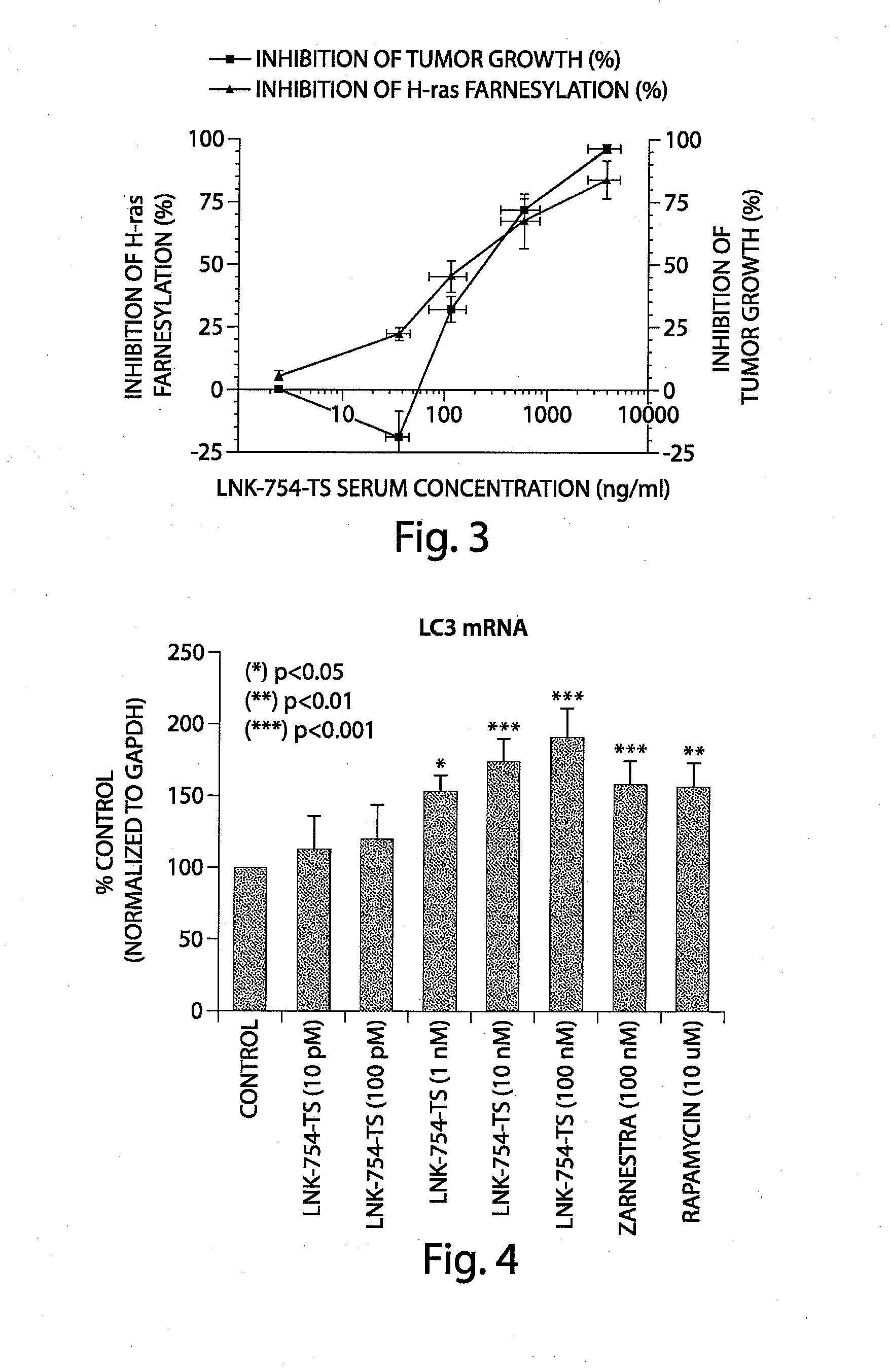
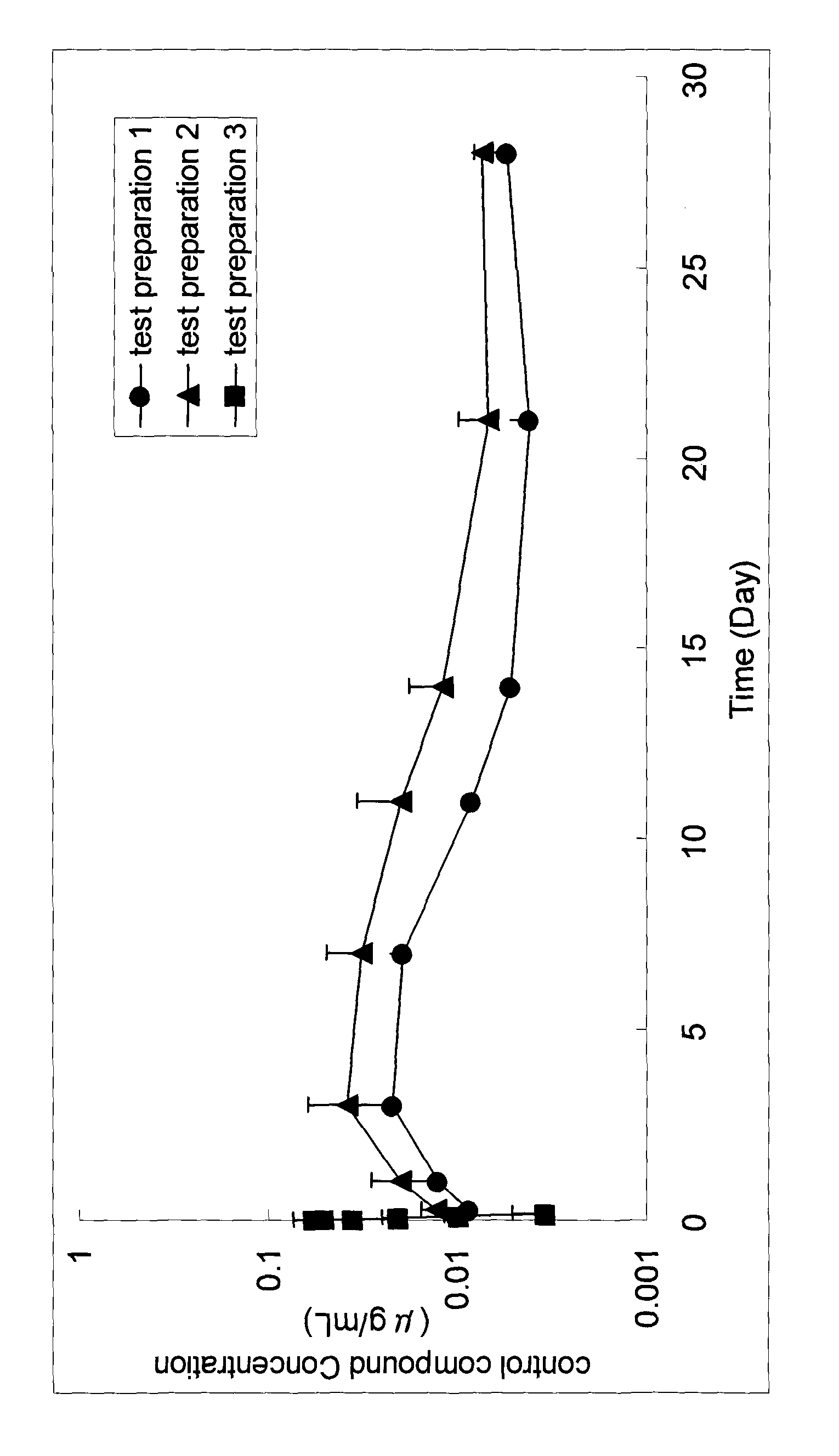
Treatment of proteinopathies using a farnesyl transferase inhibitor
InactiveUS20100160372A1Reduces α-synuclein levelLess inclusionBiocideSenses disorderAntioxidantDepressant
Methods and pharmaceutical compositions comprising a low dose of a farnesyl transferase inhibitor useful in the treatment of proteinopathies are provided. These low doses are below the doses used in oncological treatments for which these compounds were initially designed. The treatment includes administering to a subject in need thereof a therapeutically effective amount of a farnesyl transferase inhibitor, wherein the amount is effective to inhibit the farnesylation of a non-Ras FTase substrate involved in the autophagy pathway without substantially affecting the farnesylation of Ras or other oncology related substrates. Treatments in accordance with the present invention may also include an acetylcholinesterase inhibitor, an activator of neurotrophic receptors, an NMDA antagonist, an amyloid deposit inhibitor, an antipsychotic agent, an antidepressant, an anxiolytic, or an antioxidant.
Owner:ASTRAZENECA AB
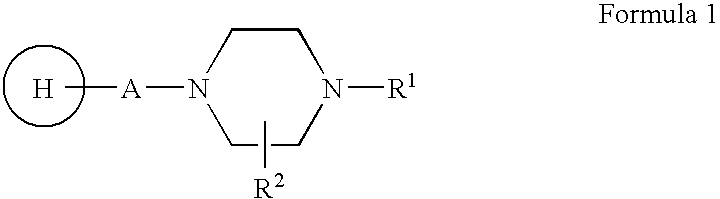
Antipsychotic agents and standardized antipsychotic fractions from Rauwolfia tetraphylla and process of their isolation
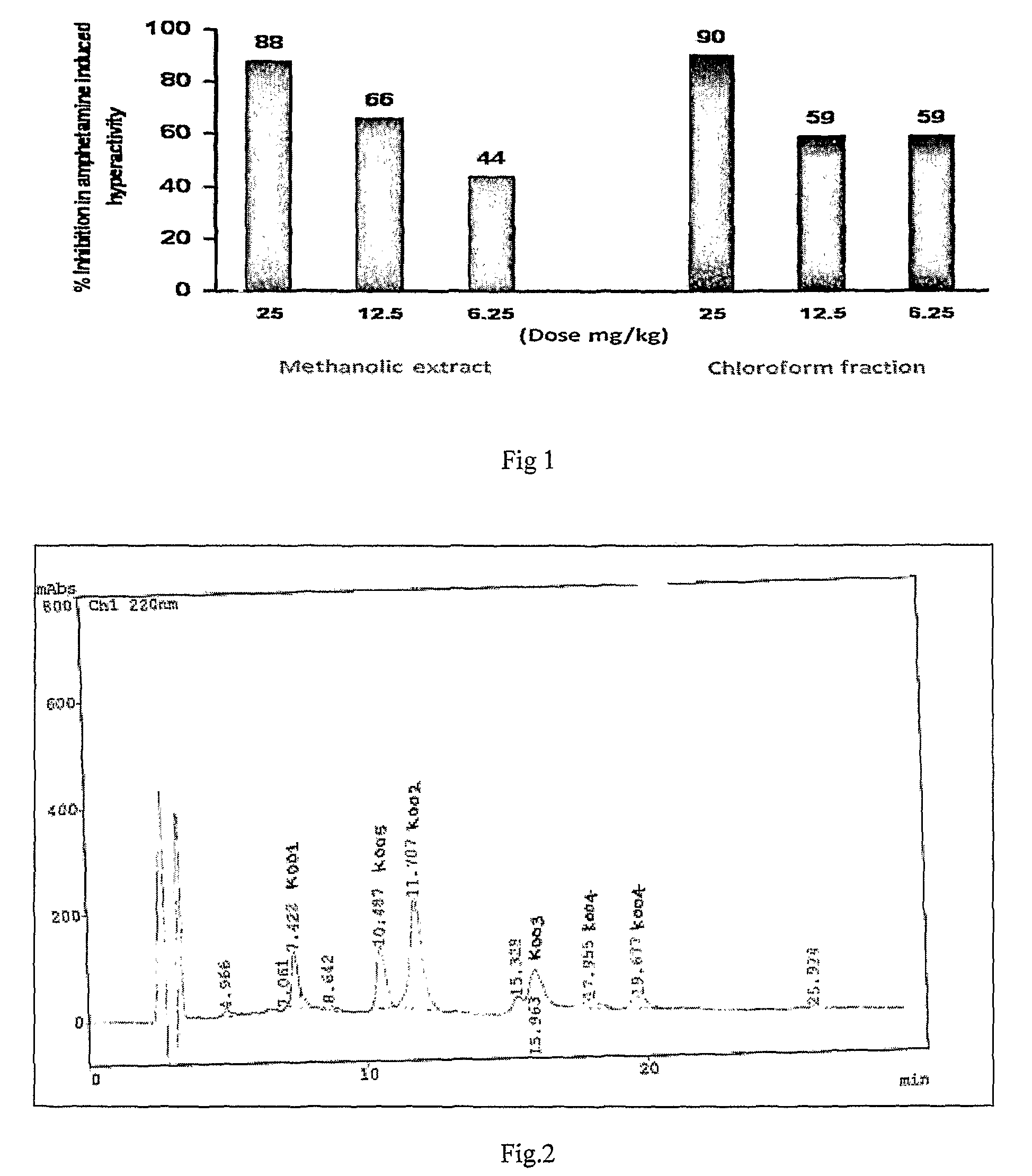
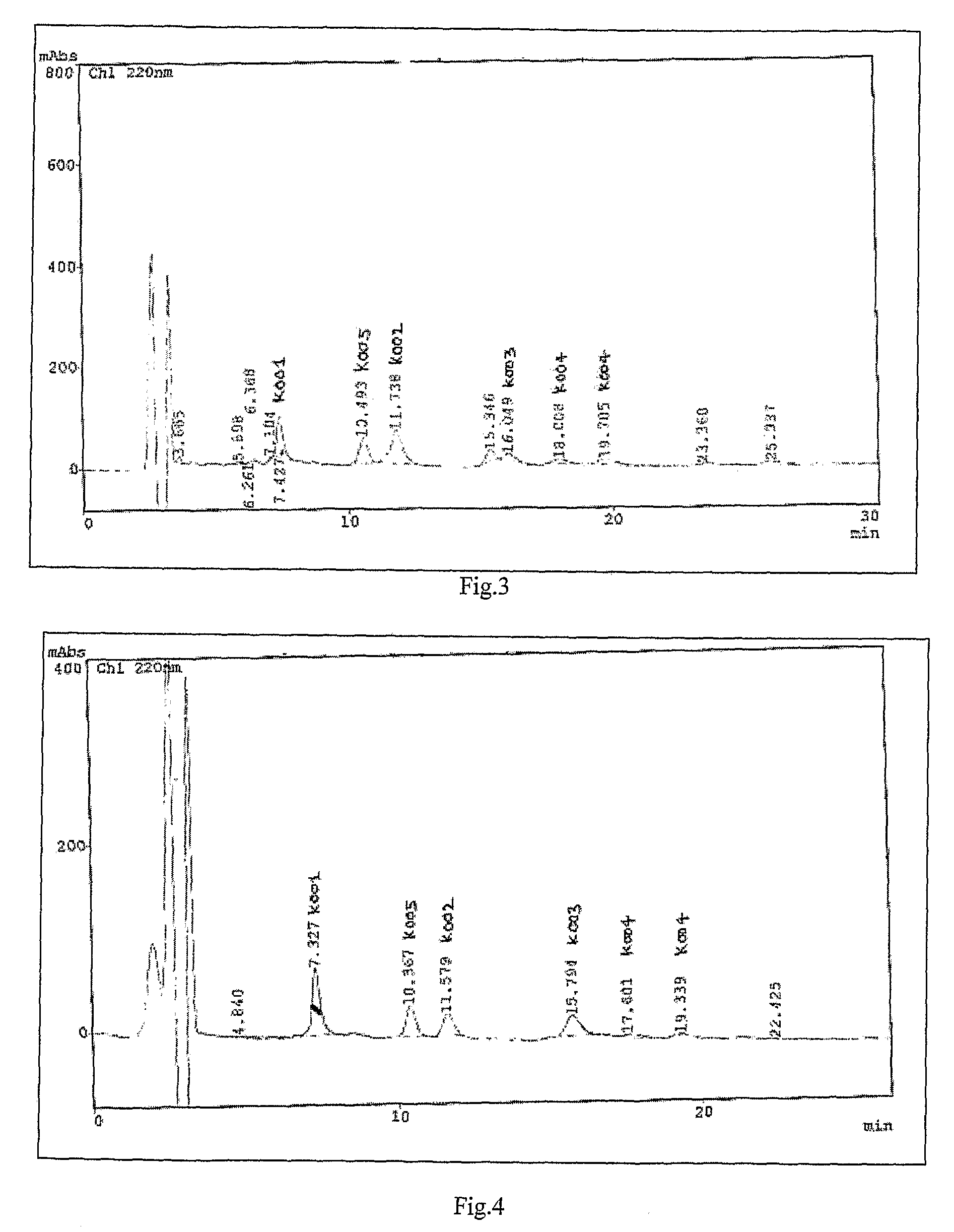
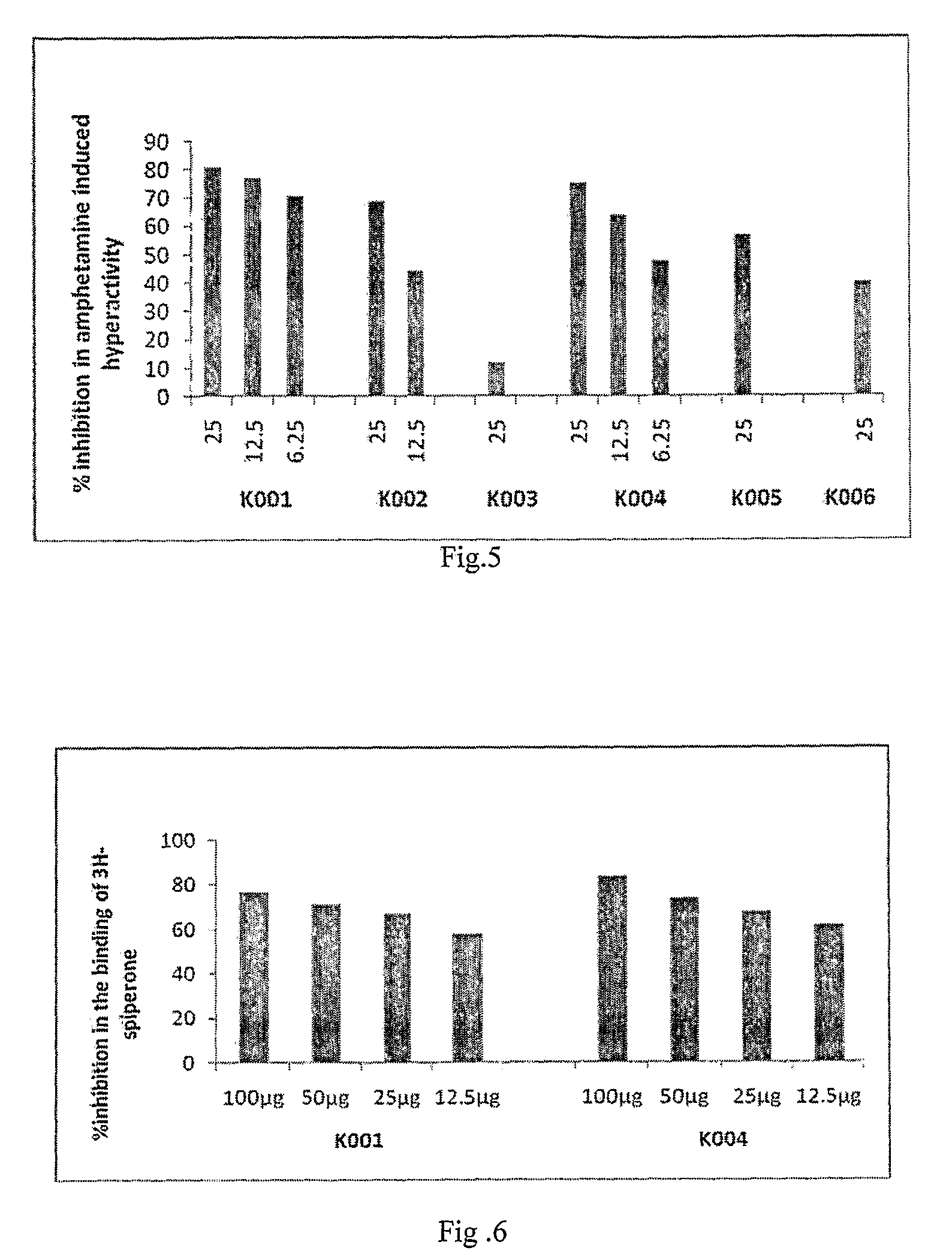
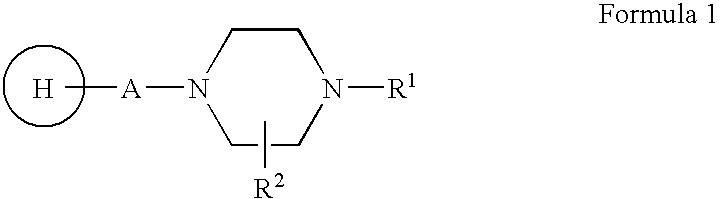
The present invention relates to bioactive extracts its fractions and isolation of compound from Rauwolfia tetraphylla. The extracts and fractions are useful for the treatment of psychosis based on in-vivo validation on animal model and proportional binding affinities for dopaminergic-D2, Cholinergic (muscarinic) and Serotonergic (5HT2A) receptors for antipsychotic activity. The present invention relates to novel antipsychotic activity in the leaf alkaloids of Formula 1 and 2 named tetrahydroalstonine, 10-methoxytetrahydroalstonine, isoreserpiline, 10-demethoxyreserpiline, 11-demethoxyreserpiline, reserpiline and α-yohimbine. The present invention also relates to processes for obtaining antipsychotic extracts as well as for the isolation of alkaloids of formula 1 and 2 from the leaves of Rauwolfia tetraphylla. The present invention particularly relates to significant antipsychotic activity in the MeOH extract, ethylacetate and chloroform fractions of R. tetraphylla and in the isolated compounds α-yohimbine, reserpiline and in a mixture 10-demethoxyreserpiline and 11-demethoxyreserpiline in 1:1.5 ratios for treating psychosis without any extra pyramidal symptoms (EPS).
Owner:COUNCIL OF SCI & IND RES
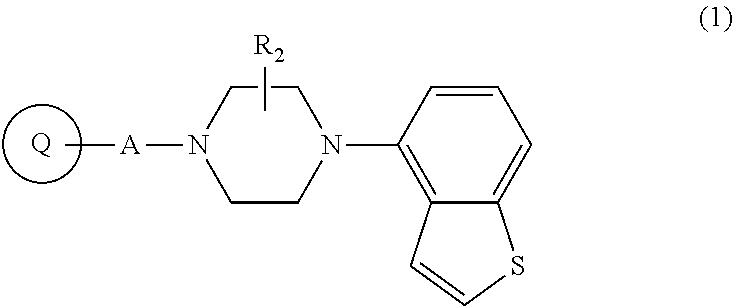
Compositions, synthesis, and methods of using piperazine based antipsychotic agents
ActiveUS8207163B2Reduce adverse side effectsEffective treatmentOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderBipolar mood disorderAntipsychotic Agent
The present invention provides novel piperazine derivatives which can be advantageously used for treating schizophrenia and related psychoses such as acute manic, bipolar disorder, autistic disorder and depression.
Owner:REVIVA PHARMA INC
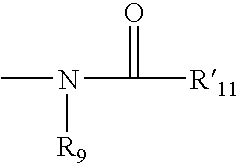
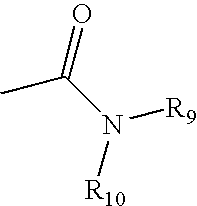
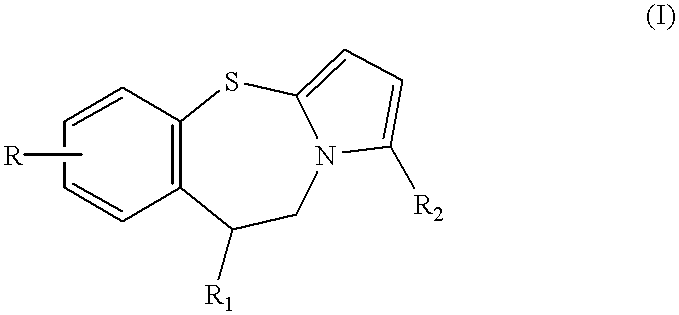
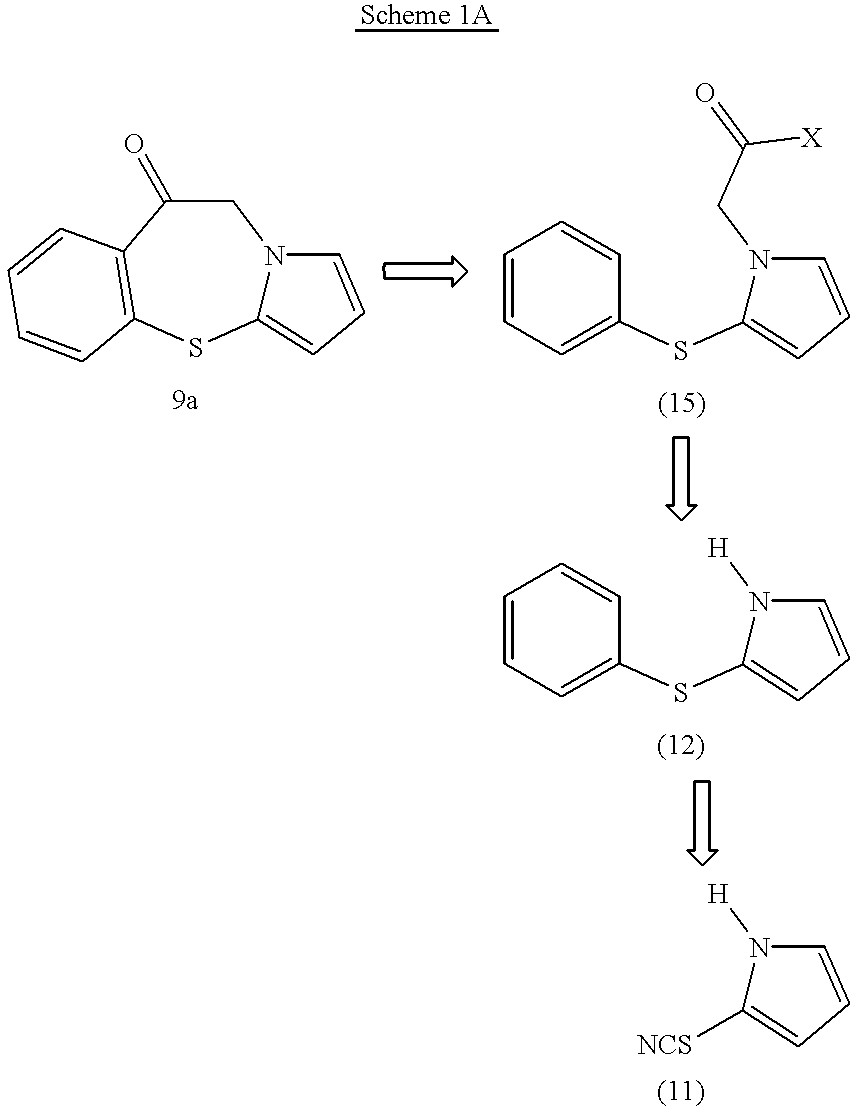
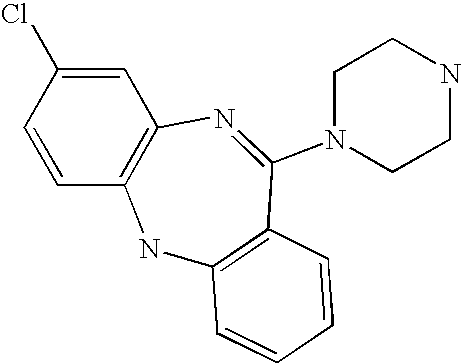
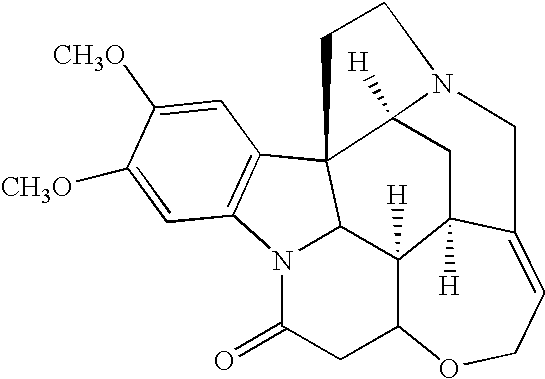
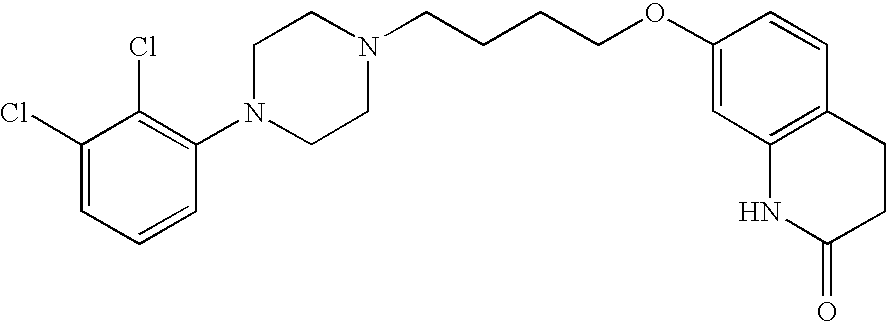
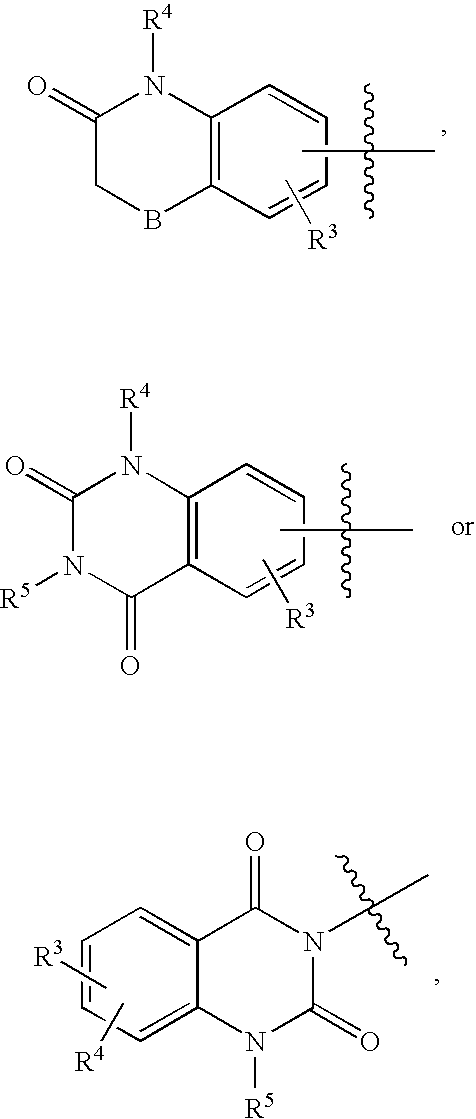
Pyrrolo [2,1-b][1,3]benzothiazepines with atypical antipsychotic activity
InactiveUS6391870B2High yieldReduce doseBiocideNervous disorderAtypical antipsychoticAntipsychotic Agent
Polycondensated heterocycles with a pyrrole[2,1-b][1,3]benzothiazepine structure of the following formula (I)where the groups are defined as in the description are disclosed. As compared to known antipsychotic agents, these compounds present substantial activity associated with a simultaneous reduction in unwanted extrapyramidal symptoms. These compounds can be formulated in pharmaceutical compositions for the treatment of psychoses such as, for example, schizophrenia.
Owner:SIGMA TAU IND FARMACEUTICHE RIUNITE SPA
Treatment of proteinopathies using a farnesyl transferase inhibitor
InactiveUS20110294794A1Lower Level RequirementsLess inclusionBiocideSenses disorderReceptorAntioxidant
Methods and pharmaceutical compositions comprising a low dose of a farnesyl transferase inhibitor useful in the treatment of proteinopathies are provided. These low doses are below the doses used in oncological treatments for which these compounds were initially designed. The treatment includes administering to a subject in need thereof a therapeutically effective amount of a farnesyl transferase inhibitor, wherein the amount is effective to inhibit the farnesylation of a non-Ras FTase substrate involved in the autophagy pathway without substantially affecting the farnesylation of Ras or other oncology related substrates. Treatments in accordance with the present invention may also include an acetylcholinesterase inhibitor, an activator of neurotrophic receptors, an NMDA anatagonist, an amyloid deposit inhibitor, an antipsychotic agent, an antidepressant, an anxiolytic, or an antioxidant.
Owner:ASTRAZENECA AB
Antipsychotic sulfonamide-heterocycles, and methods of use thereof
One aspect of the present invention relates to heterocyclic compounds comprising a sulfonamide moiety. A second aspect of the present invention relates to the use of the heterocyclic compounds comprising a sulfonamide moiety to treat diseases, afflictions or maladies caused at least in part by abnormal activity of one or more GPCRs or ligand-gated ion channels. An additional aspect of the present invention relates to the synthesis of combinatorial libraries of the heterocyclic compounds comprising a sulfonamide moiety, and the screening of those libraries for biological activity, e.g., in animal models of psychosis.
Owner:SEPACOR INC
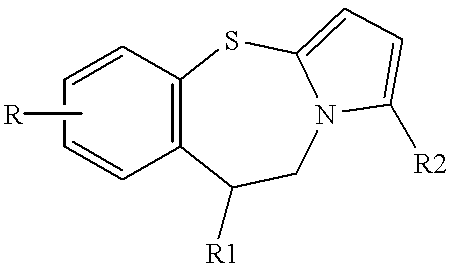
Pyrrolo {2,1-b}{1,3}benzothiazepines with atypical antipsychotic activity
InactiveUS20020006921A1Reduce doseReduce accumulationBiocideOrganic active ingredientsAtypical antipsychoticPyrrole
Polycondensated heterocycles with a pyrrole[2,1-b][1,3]benzothiazepine structure of the following formula (I) where the groups are defined as in the description are disclosed. As compared to known antipsychotic agents, these compounds present substantial activity associated with a simultaneous reduction in unwanted extrapyramidal symptoms. These compounds can be formulated in pharmaceutical compositions for the treatment of psychoses such as, for example, schizophrenia.
Owner:SIGMA TAU IND FARMACEUTICHE RIUNITE SPA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com
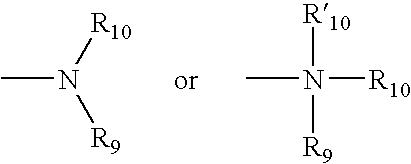











![Pyrrolo [2,1-b][1,3]benzothiazepines with atypical antipsychotic activity Pyrrolo [2,1-b][1,3]benzothiazepines with atypical antipsychotic activity](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/7a49d776-db2d-40f9-b31e-3d45f9f0d6fd/US06391870-20020521-C00001.png)
![Pyrrolo [2,1-b][1,3]benzothiazepines with atypical antipsychotic activity Pyrrolo [2,1-b][1,3]benzothiazepines with atypical antipsychotic activity](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/7a49d776-db2d-40f9-b31e-3d45f9f0d6fd/US06391870-20020521-C00002.png)
![Pyrrolo [2,1-b][1,3]benzothiazepines with atypical antipsychotic activity Pyrrolo [2,1-b][1,3]benzothiazepines with atypical antipsychotic activity](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/7a49d776-db2d-40f9-b31e-3d45f9f0d6fd/US06391870-20020521-C00003.png)