Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
105results about How to "Uniform section" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
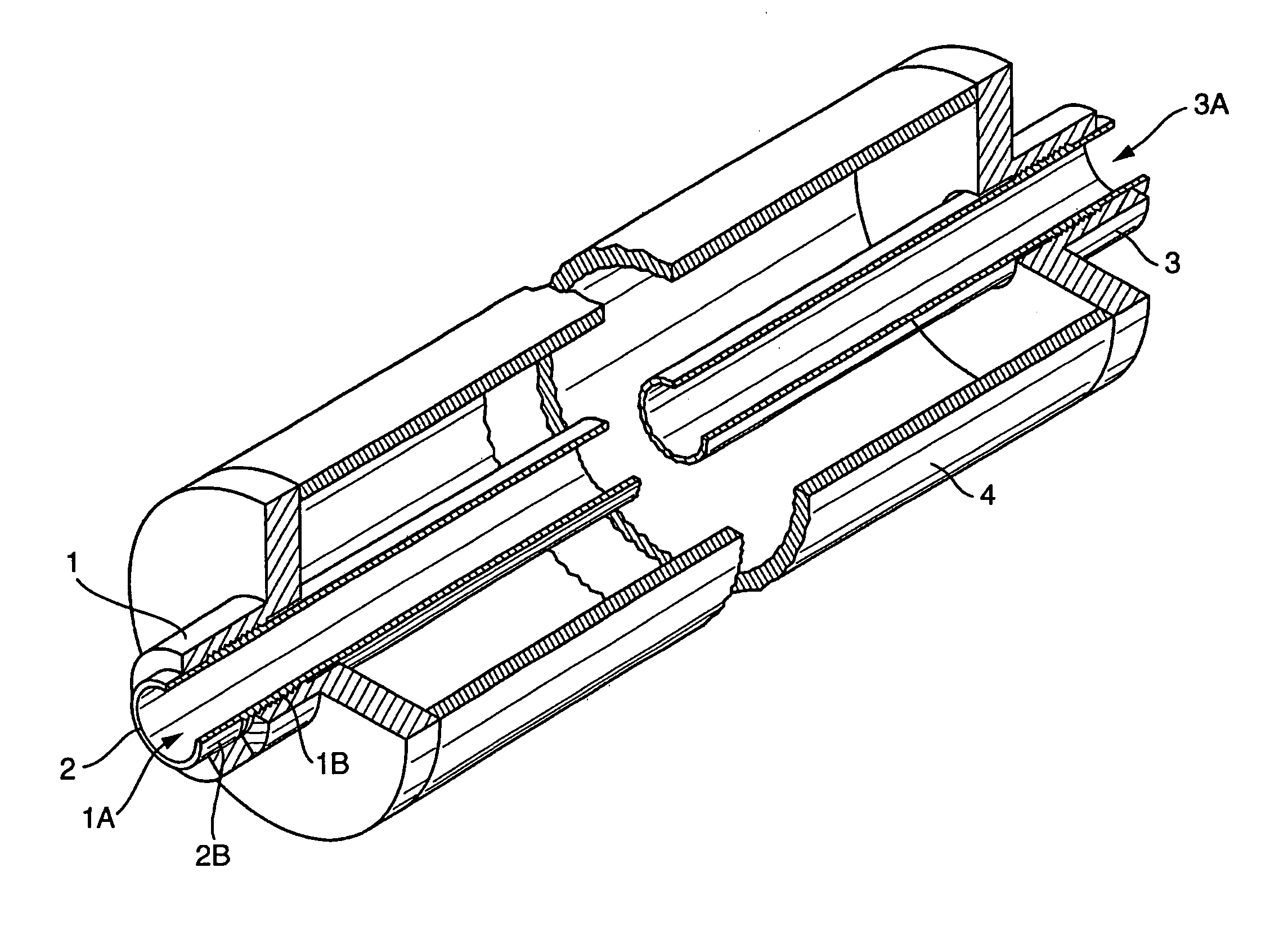
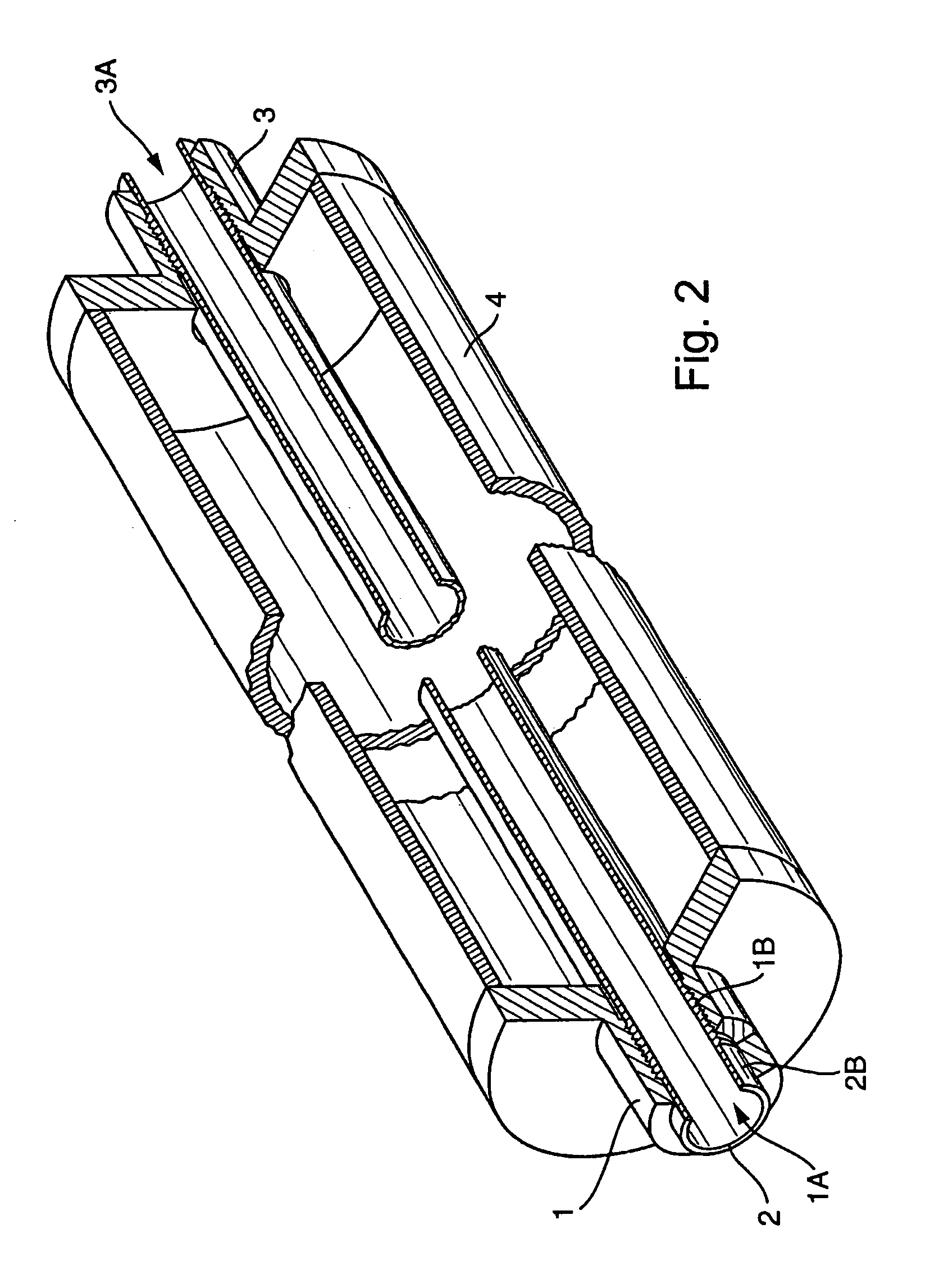
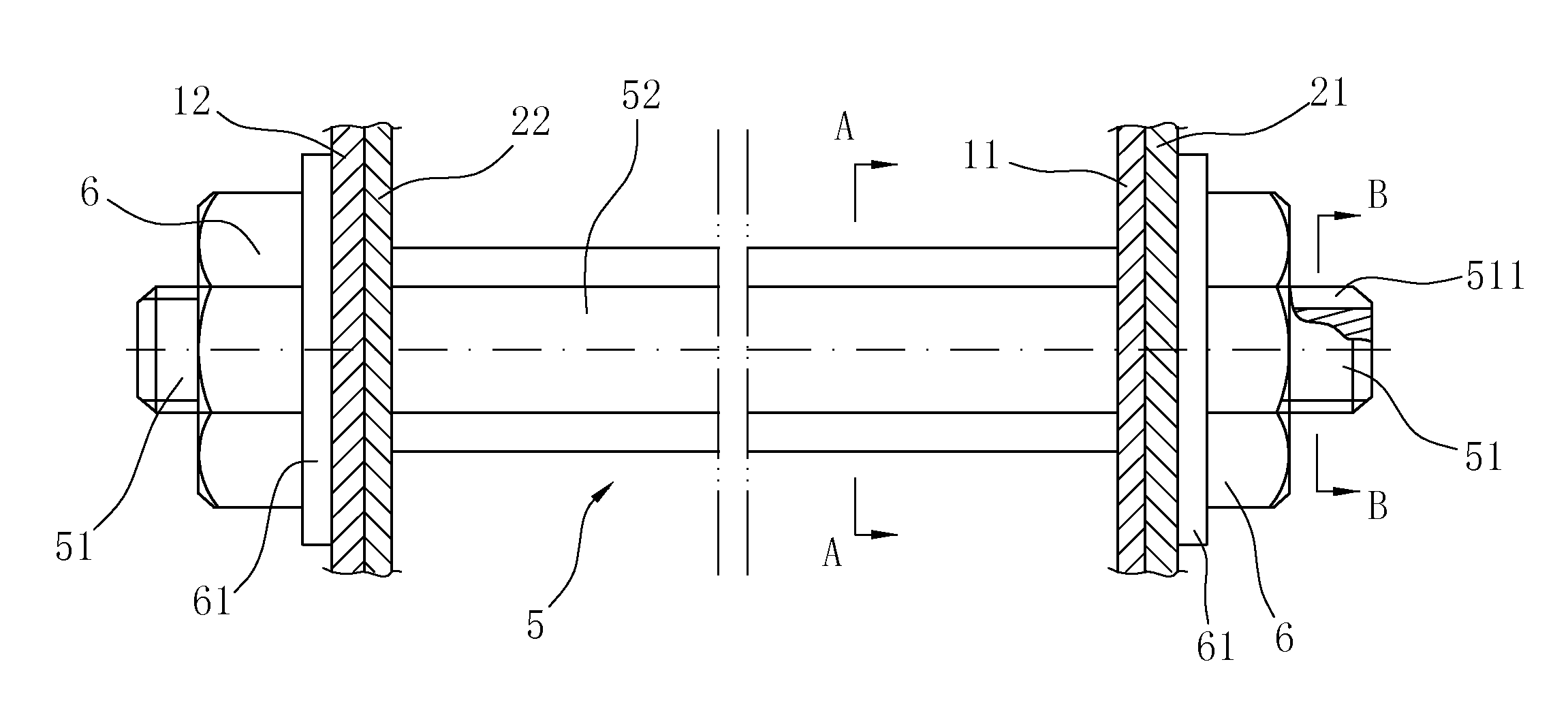
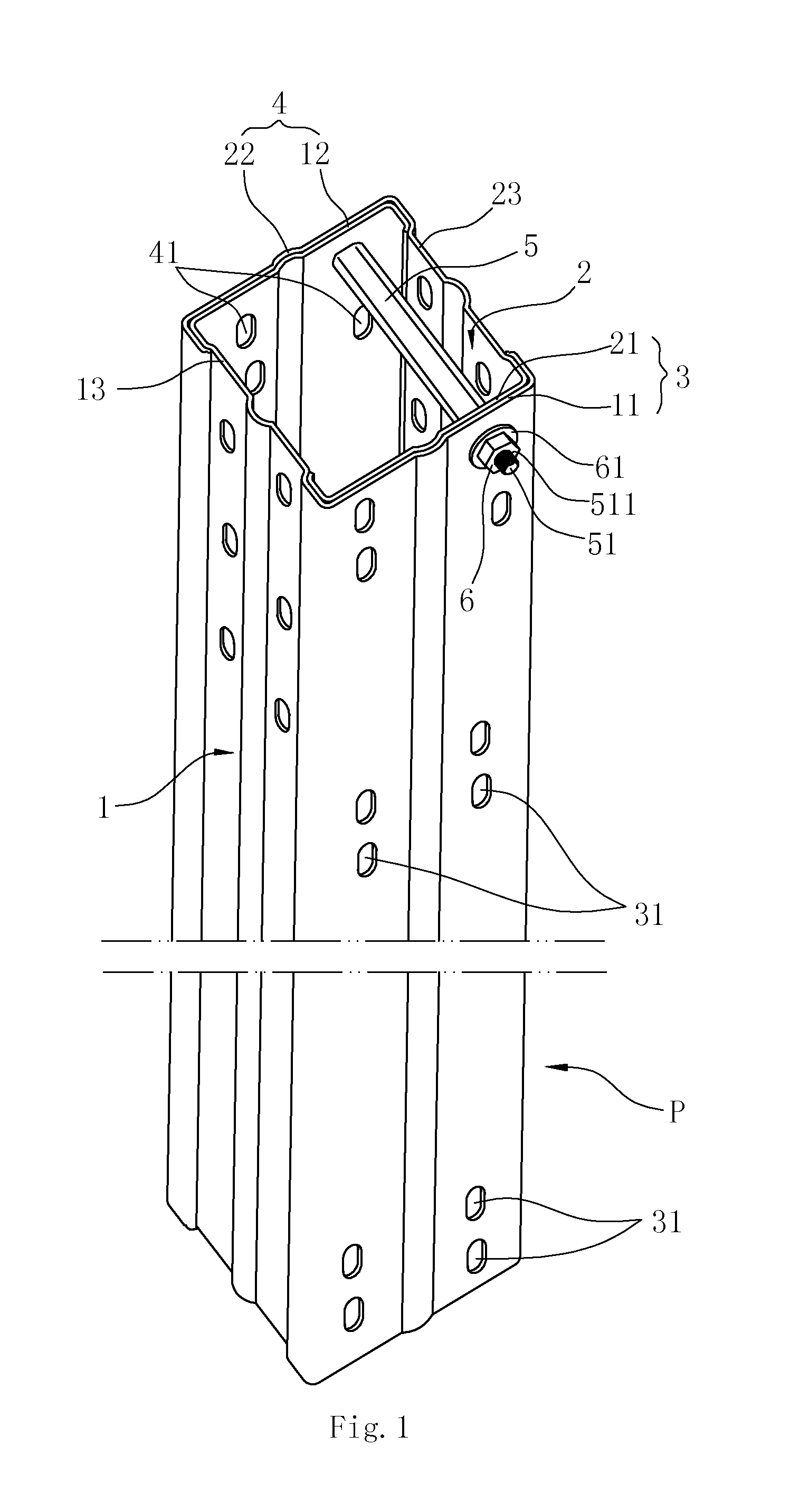
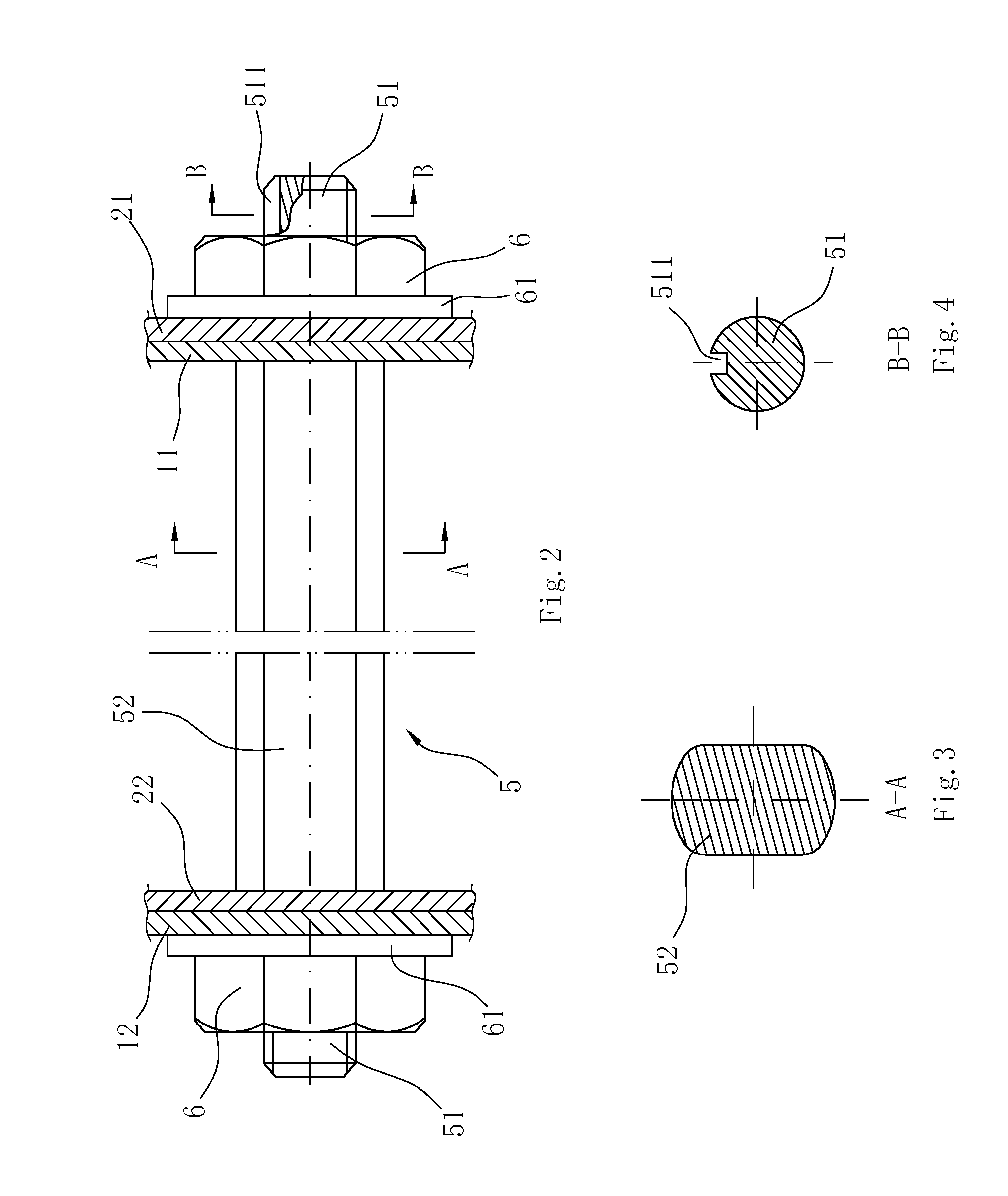
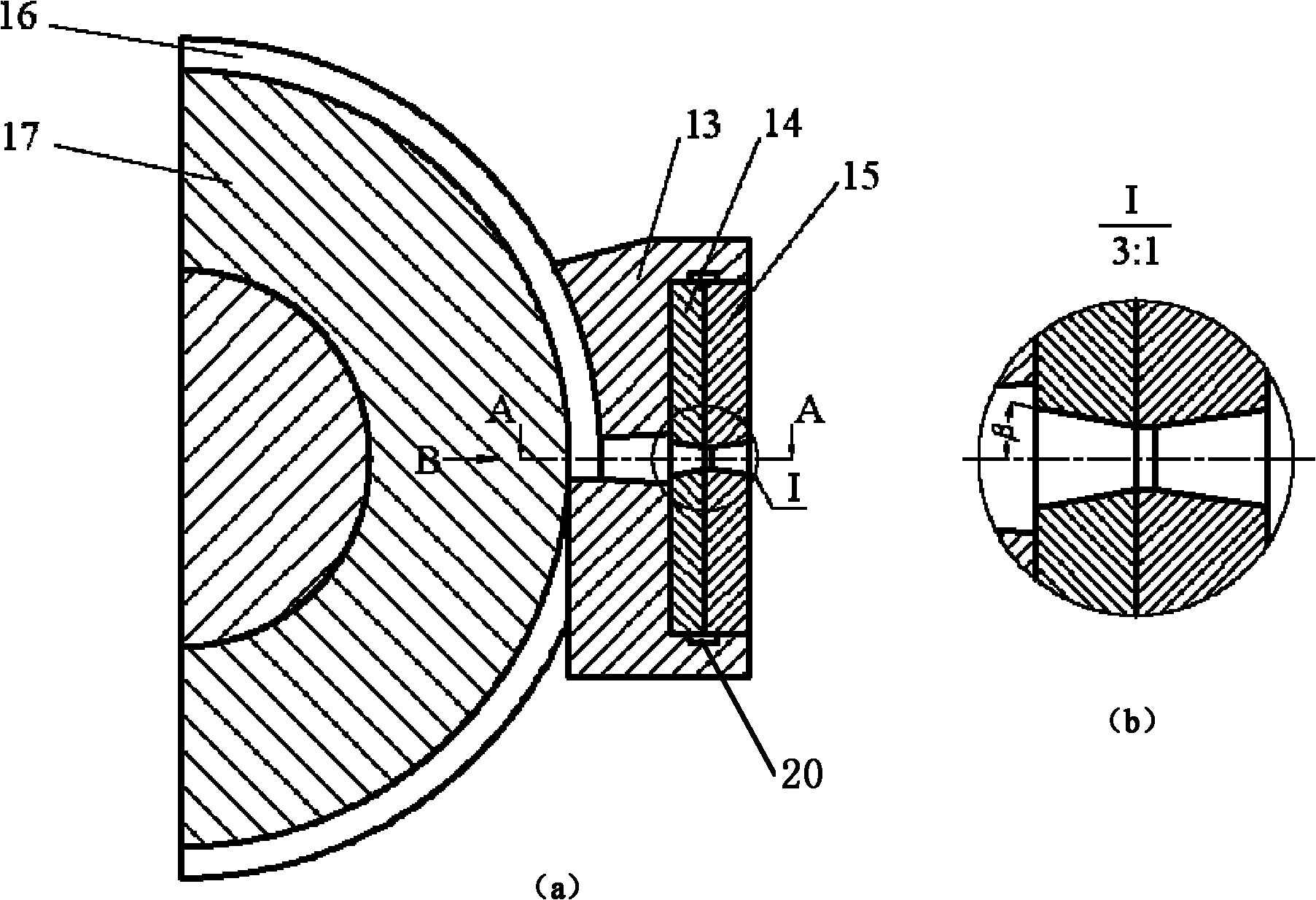
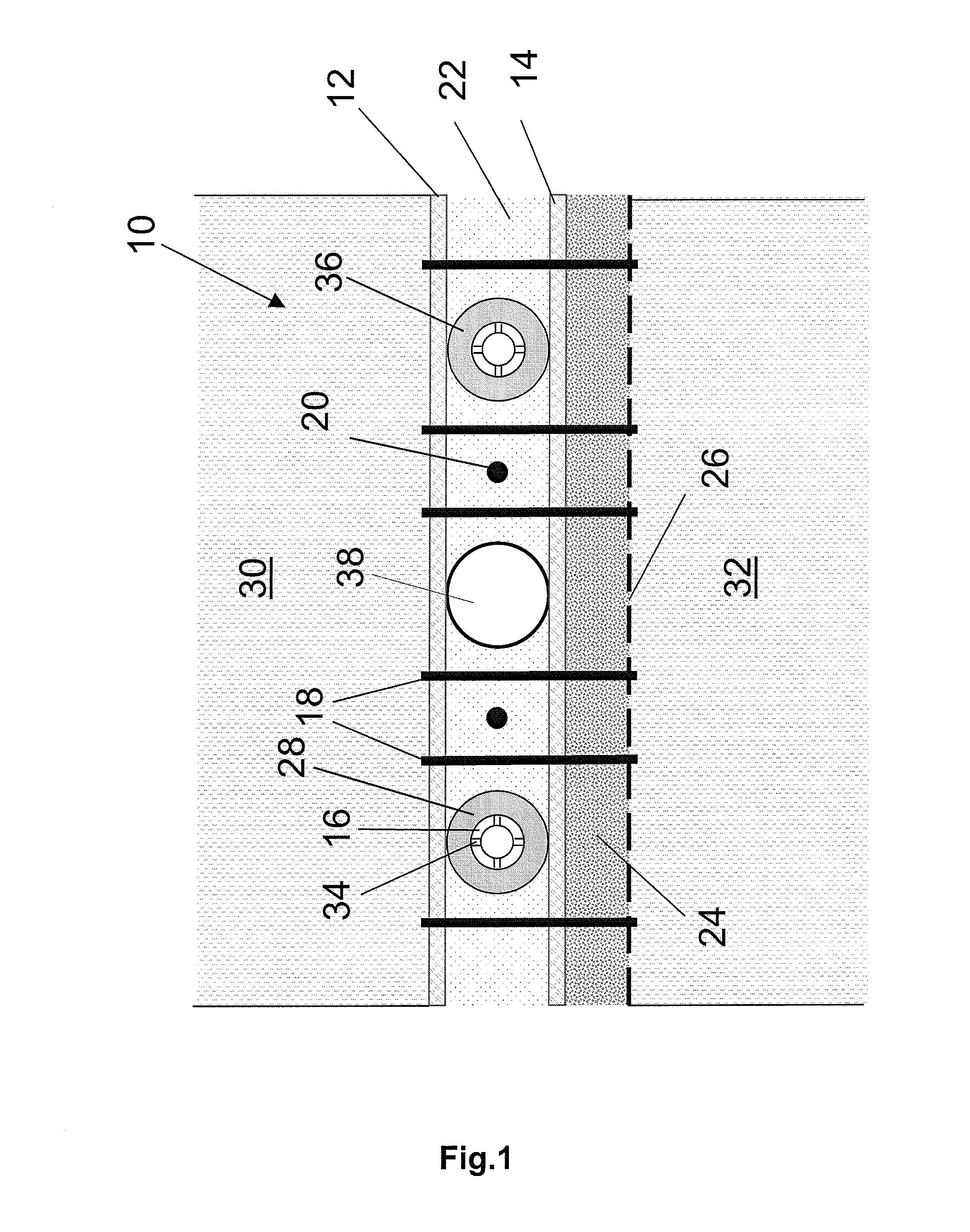
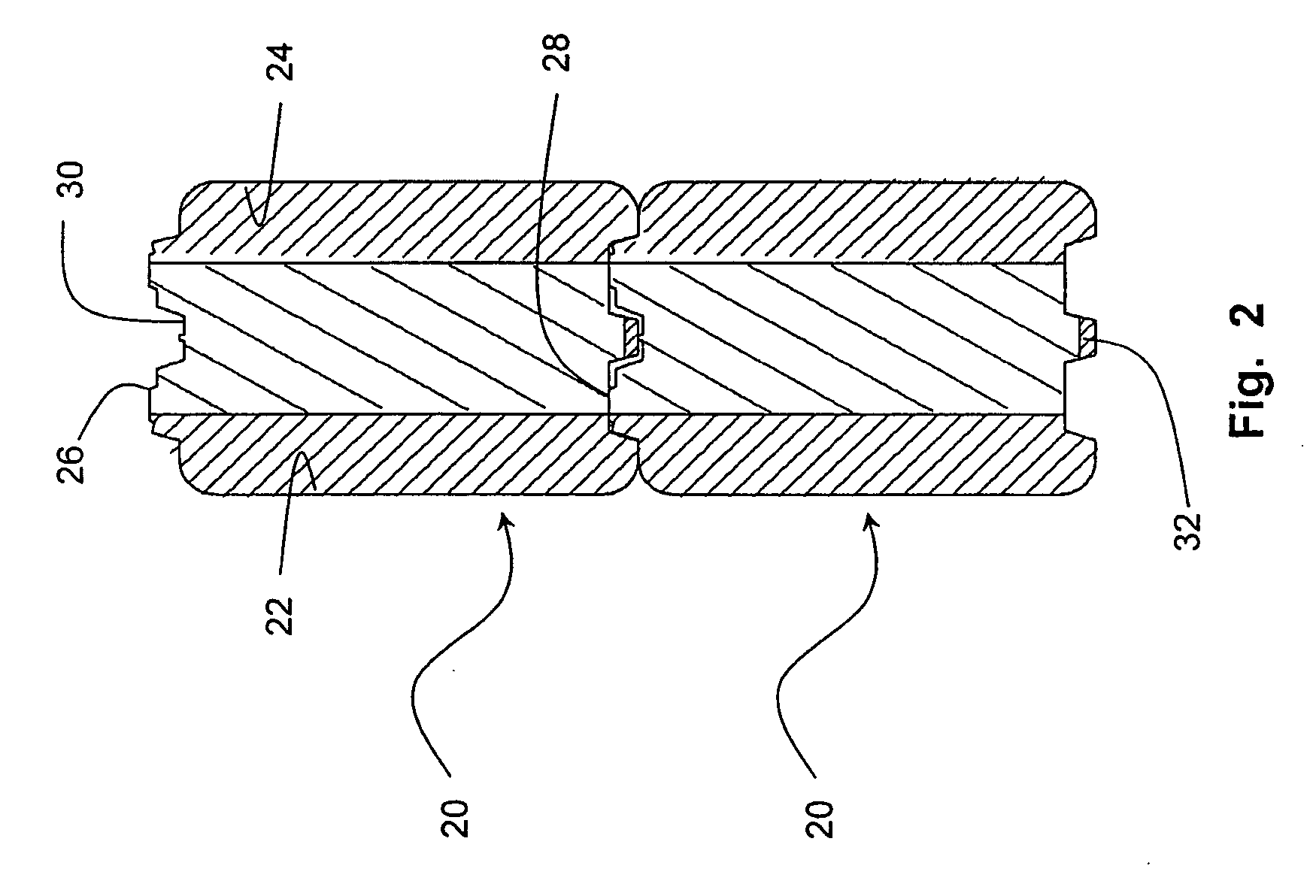
Composite system, method for its manufacture, and measurement pickup using such a composite system
ActiveUS7299699B2Stable, high-strength and lasting,Increased pull-out strengthMaterial analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesPig casting plantsEngineeringCompound system
A composite system includes a first component, for instance of metal, and a second component extending at least partly through the first component along an imaginary longitudinal axis of the composite system. The second component contacts, with an at least partially curved, especially cylindrical, outer surface, an inner surface of the first component flushly such that the first component at least sectionally, at least partly, grips around the second component. Joining surfaces of the composite system, which are formed by the mutually contacting surfaces of the two components, are formed in such a manner that the two components exhibit contour portions in the area of these joining surfaces embodied as self-closing, peripheral surfaces. The contour portions fit at least partly into one another, to form a mechanical interference locking effective, at least in part, likewise in the direction of the longitudinal axis. Additionally, the second component, with its outer surface, contacts the inner surface of the first component flushly, such that the two components are mechanically tightly connected together also by means of a frictional locking effective at least partly in the direction of the longitudinal axis. Alternatively, or in supplementation thereof, at least one of the components is subjected at least partly to lastingly elastic, especially mixed plastic-elastic, deformations. The composite system is distinguished by a high pull-out strength, even in the presence of repeatedly arising vibrations in one of the components and is, therefore, especially suited also for use in a vibration-type measurement pickup.
Owner:ENDRESS HAUSER FLOWTEC AG
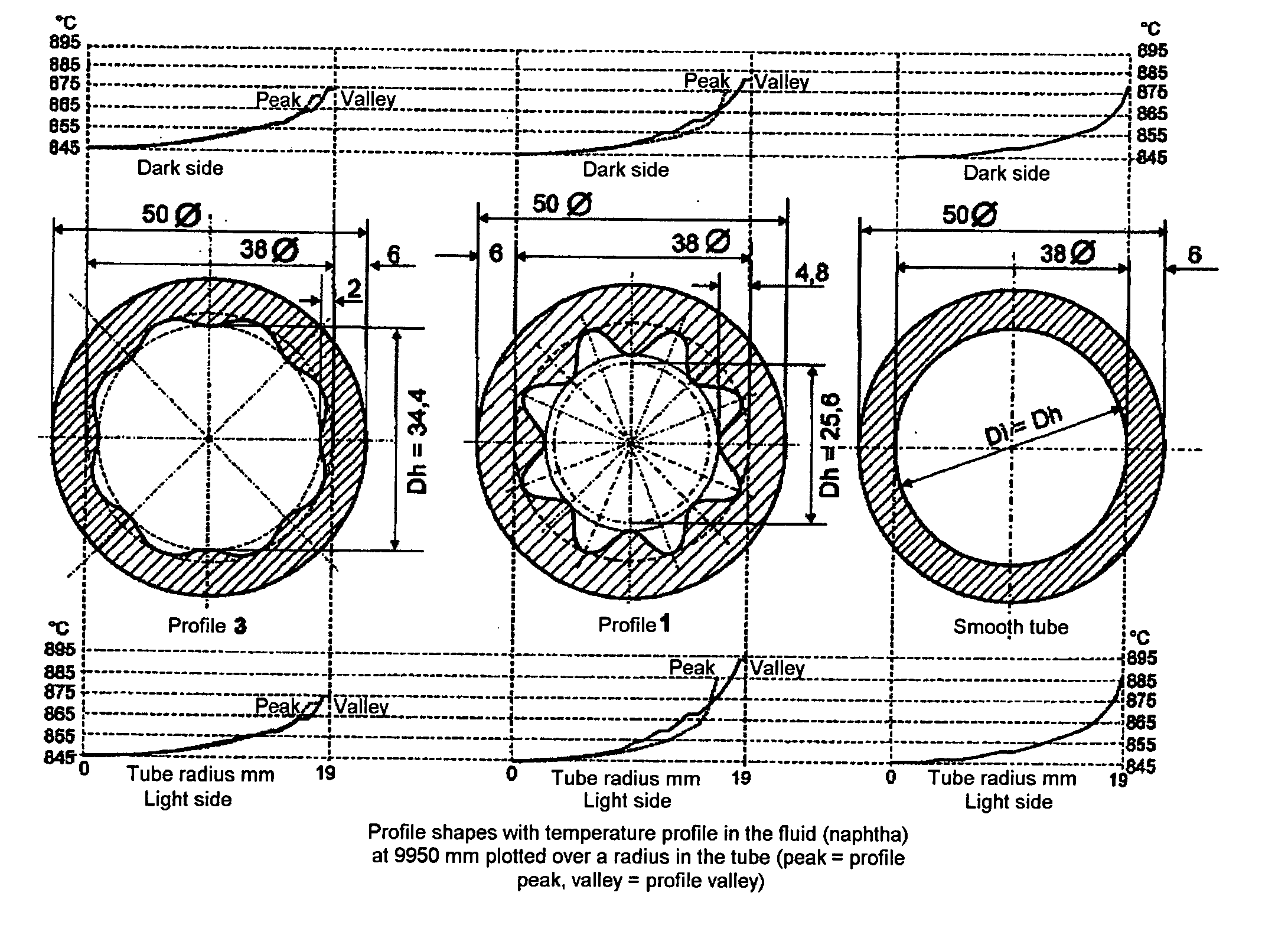
Process and finned tube for the thermal cracking of hydrocarbons
InactiveUS20050131263A1Tube densityHeating fastThermal non-catalytic crackingFluid dynamicsEngineeringHydrocarbon
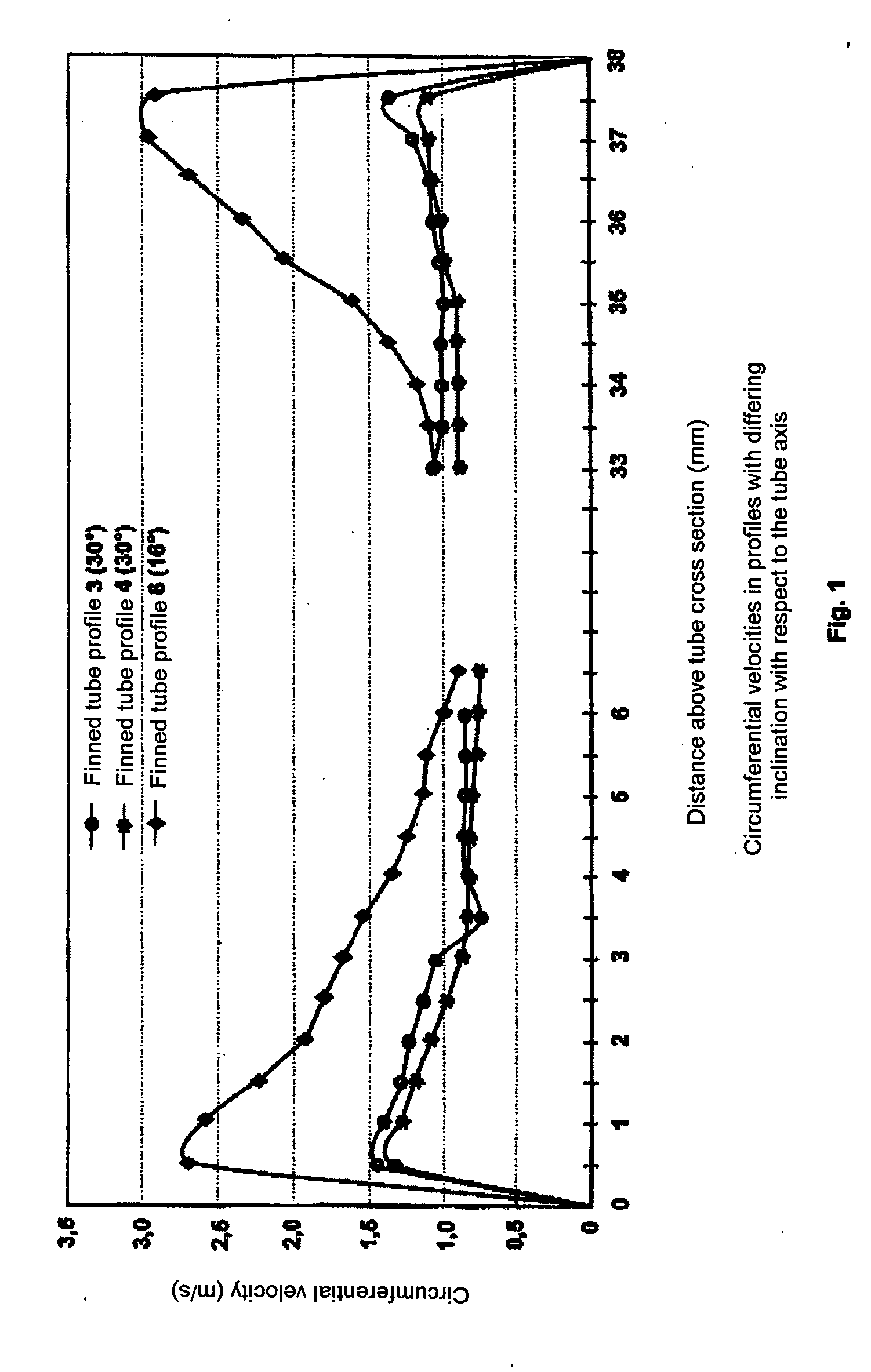
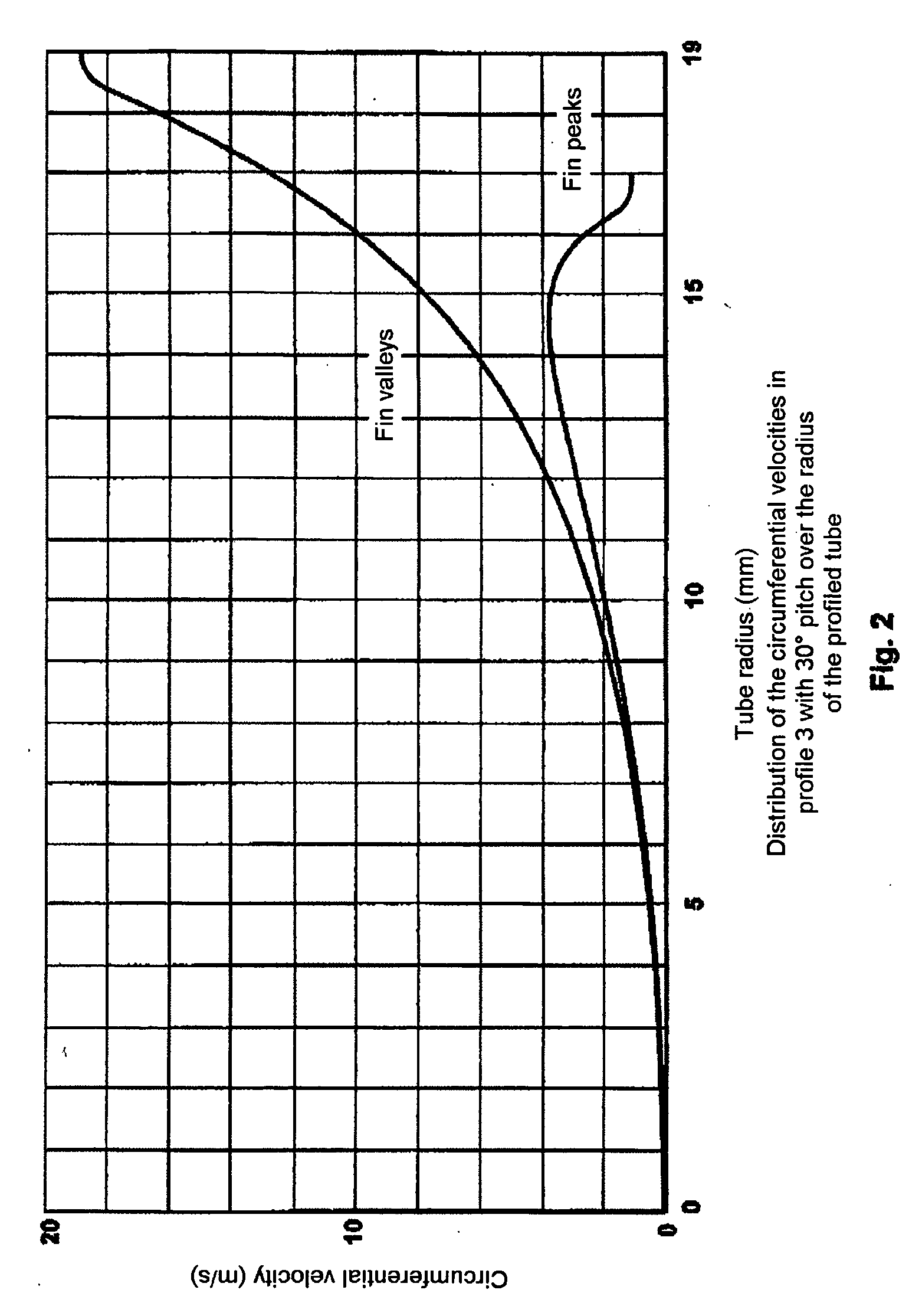
In a process for the thermal cracking of hydrocarbons in the presence of steam, the charge mixture is passed through externally heated tubes with helical inner fins, and to make the temperature in the tube wall and over the tube cross section more uniform, as well as to reduce the deposition of pyrolysis coke on the tube inner wall, a swirling flow is generated in the gas mixture and is gradually merged into a core zone with a predominantly axial flow at increasing radial distance from the fins.
Owner:SCHMIDT CLEMENS
Wind powered turbine
InactiveUS20060210389A1Simple blade configurationRevolution speed be lowWind motor controlWind energy with electric storageTrailing edgeWind force
A blade for use with a vertical-axis wind turbine rotates about a vertical axis thereof along a circular blade path of travel. The blade includes a structural frame connecting to a blade support member of the wind turbine and supports loads acting on the blade. A semi-rigid skin at least partially covers the structural frame and connects thereto with a connector. The skin forms a longitudinally cross-section of the blade that has a water droplet shape-like contour defining a symmetry axis thereof, and extends between a wide convex leading edge of the blade and a narrow trailing edge thereof. The present invention also refers to the wind turbine and to a wind turbine assembly.
Owner:LES SYST ANDRO
A method for preparing polyacrylonitrile carbon fiber precursors by dry jet wet spinning
ActiveCN102277629AFull and even contactInhibition formationArtificial filament heat treatmentMonocomponent synthetic polymer artificial filamentYarnGas liquid reaction
The invention relates to a method for preparing a polyacrylonitrile carbon fiber precursor. The method comprises the following steps of: copolymerizing acrylonitrile and copolymerization components in multicomponent solution so as to form polymer spinning stock solution which has a relatively uniform and controllable molecular structure, performing demonomerization on the spinning stock solution,defoaming, filtering, and preparing the polyacrylonitrile carbon fiber precursor by a dry-jet wet-spinning process. The key technology of the method is that: a gas storage box is arranged on a dry wet spinning pack, the gas storage box and the liquid level of coagulating bath fluid form a dry-jet wet-spinning air layer into a confined space, and ammonia is persistently aerated into the space to carry out gas-liquid reaction with spinning solution trickle in the air layer. The polyacrylonitrile precursor prepared by the method has regular sections and few defects, the density is not less than 1.187g / cm<3>, the density after carbonization is not less than 1.79g / cm<3>, the strength is not less than 5.1GPa, and the modulus of elasticity is 280 to 300GPa.
Owner:KINGFA SCI & TECH CO LTD +1
Fixation apparatus for a medical device
InactiveUS7799000B2Easy to installEasy to removeCatheterInfusion needlesSurgical stapleSurgical department
A fixation apparatus for attaching a medical device to a patient includes an attachment feature attached to the medical device and configured to cooperate with one or more surgical staples to facilitate stapling of the medical device to the patient. The attachment feature includes a staple receiving portion including two ends, each of which has a staple retaining end disposed adjacent thereto. The staple receiving portion is configured to receive surgical staples, and the staple retaining ends are configured to inhibit the staple receiving portion from dislodging from the surgical staples.
Owner:HENRY FORD HEALTH SYST
Unconventional Bolt and a Fastening Device Using the Unconventional Bolt Thereof
An unconventional bolt includes a main body having two heads, and two threaded rods respectively formed at the external surface of each head coaxially with the main body, wherein the cross section of each head has a noncircular shape, and the axial projection of the cross section of the middle of the main body is located in the noncircular axial projection of each head of the main body. The unconventional bolt has a simple structure and a convenient assembly, and can improve the strength and rigidity of the nested profiled components after the connection; and the fastening device using the unconventional bolt can not only support the component but also reinforce it, thus effectively preventing the nested profiled components from transforming.
Owner:NINGBO BANGDA INDAL
System and method for continuous extrusion production of fine-grain magnesium alloy strip
ActiveCN102688907AShort processIncrease productivityExtrusion control devicesProduction lineLine heating
The invention discloses a system and a method for continuous extrusion production of a fine-grain magnesium alloy strip. The system comprises a decoiling emptying device, an on-line straightening device, an on-line heating device, a continuous extrusion device, a cooling device and a winding displacement collection device. Through control of a temperature of a rod, a good extrusion driving force is produced between the rod and an extrusion wheel groove. Through an expansion mold cavity and a flow-blocking mold, magnesium alloy expansion flowing in a width direction is realized. In order to extrude a plate having larger width, the system adopts a two / three rod feeding-type extrusion mode so that joining and intermetallic welding of multiple rods in a corresponding multi-rod mold cavity are realized. The system and the method have the advantages that a process route is short; production efficiency is high; a grain refinement degree of a product microstructure is high; plate formability is good; and a continuous production line provided by the invention is suitable for industrial application.
Owner:DALIAN JIAOTONG UNIVERSITY
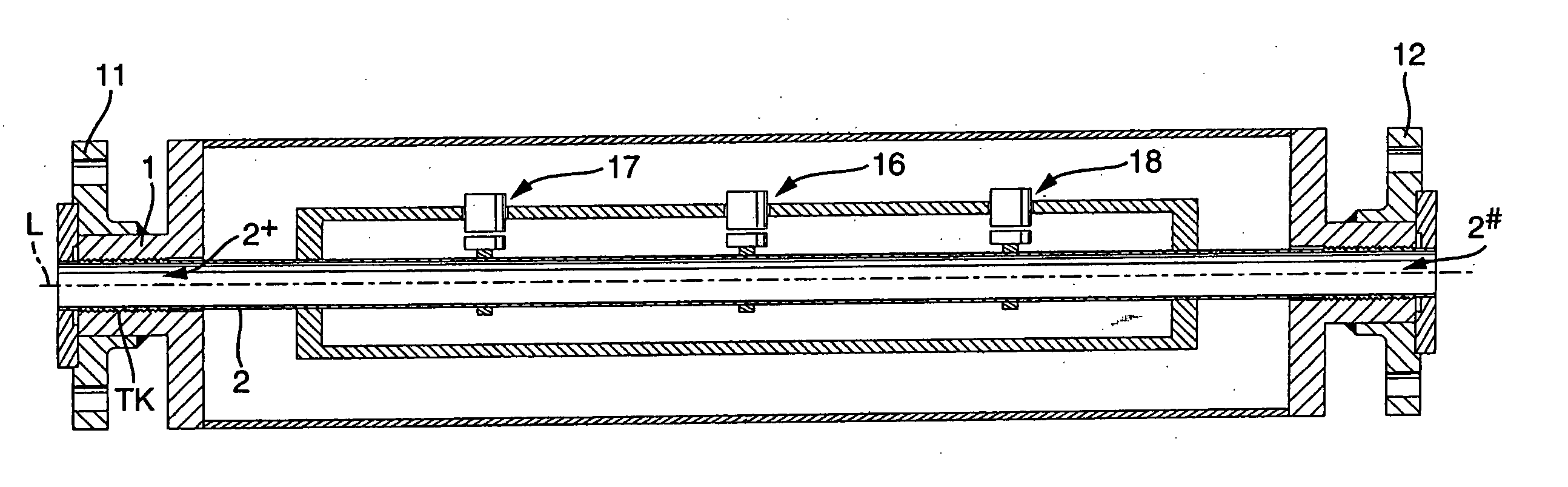
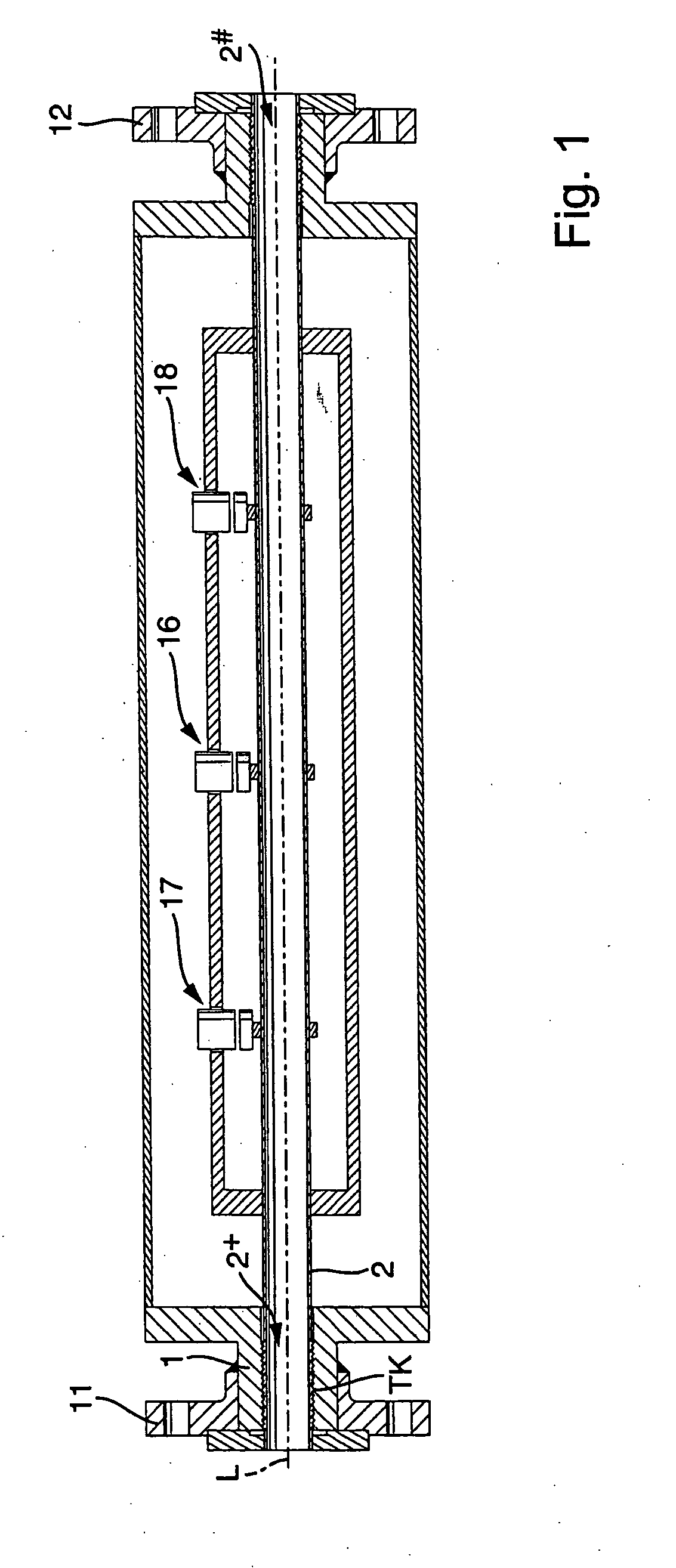
Thruster pig
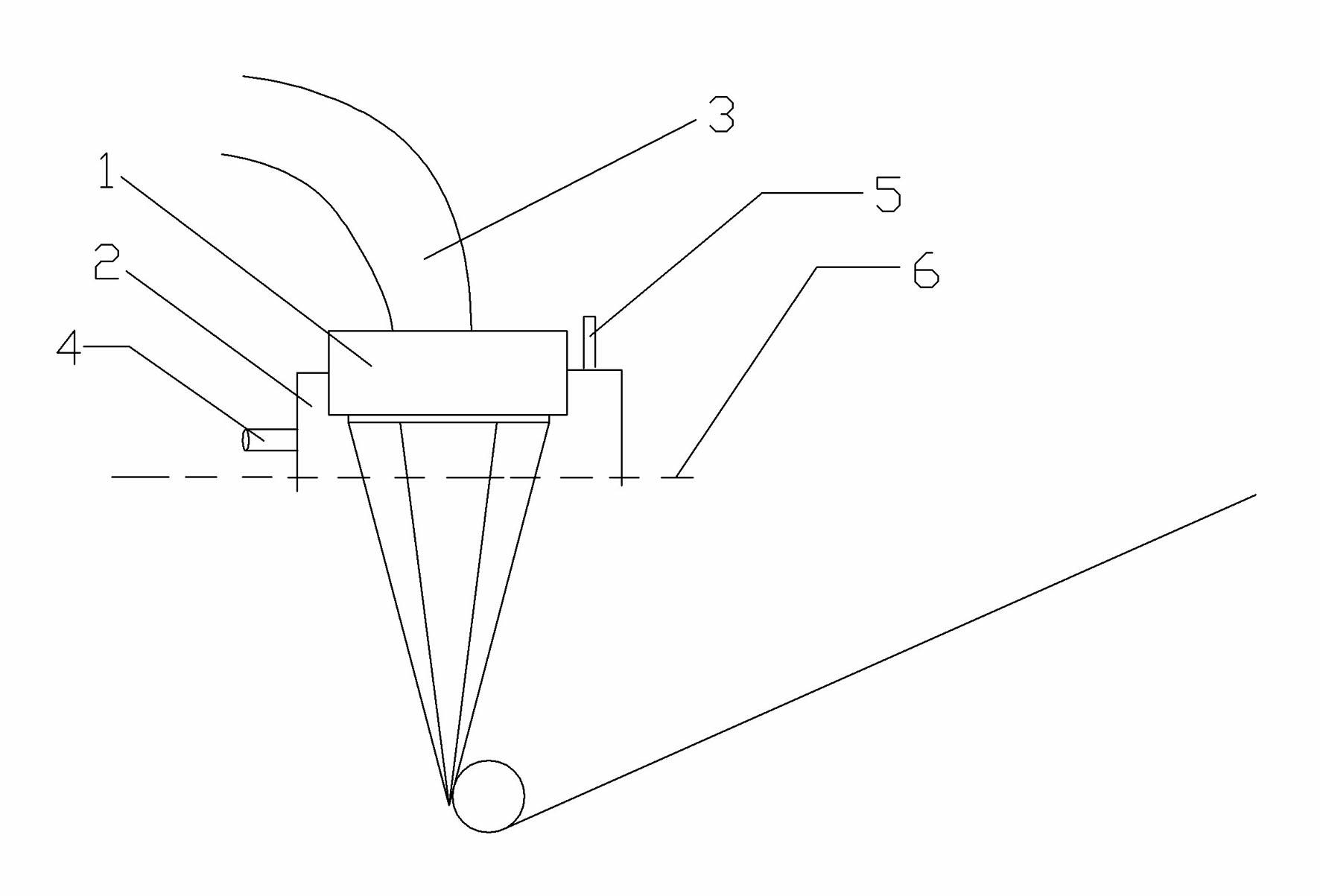
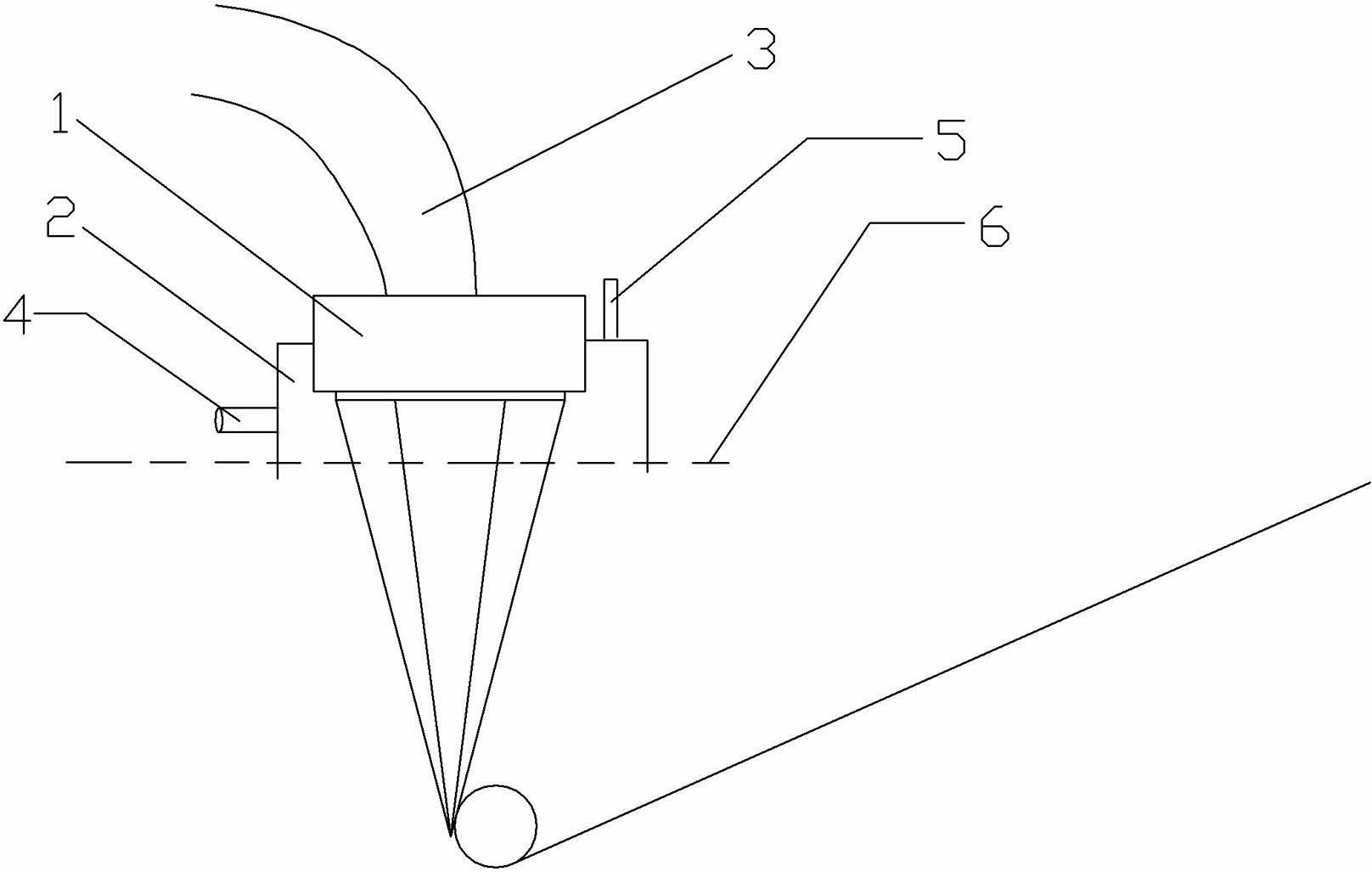
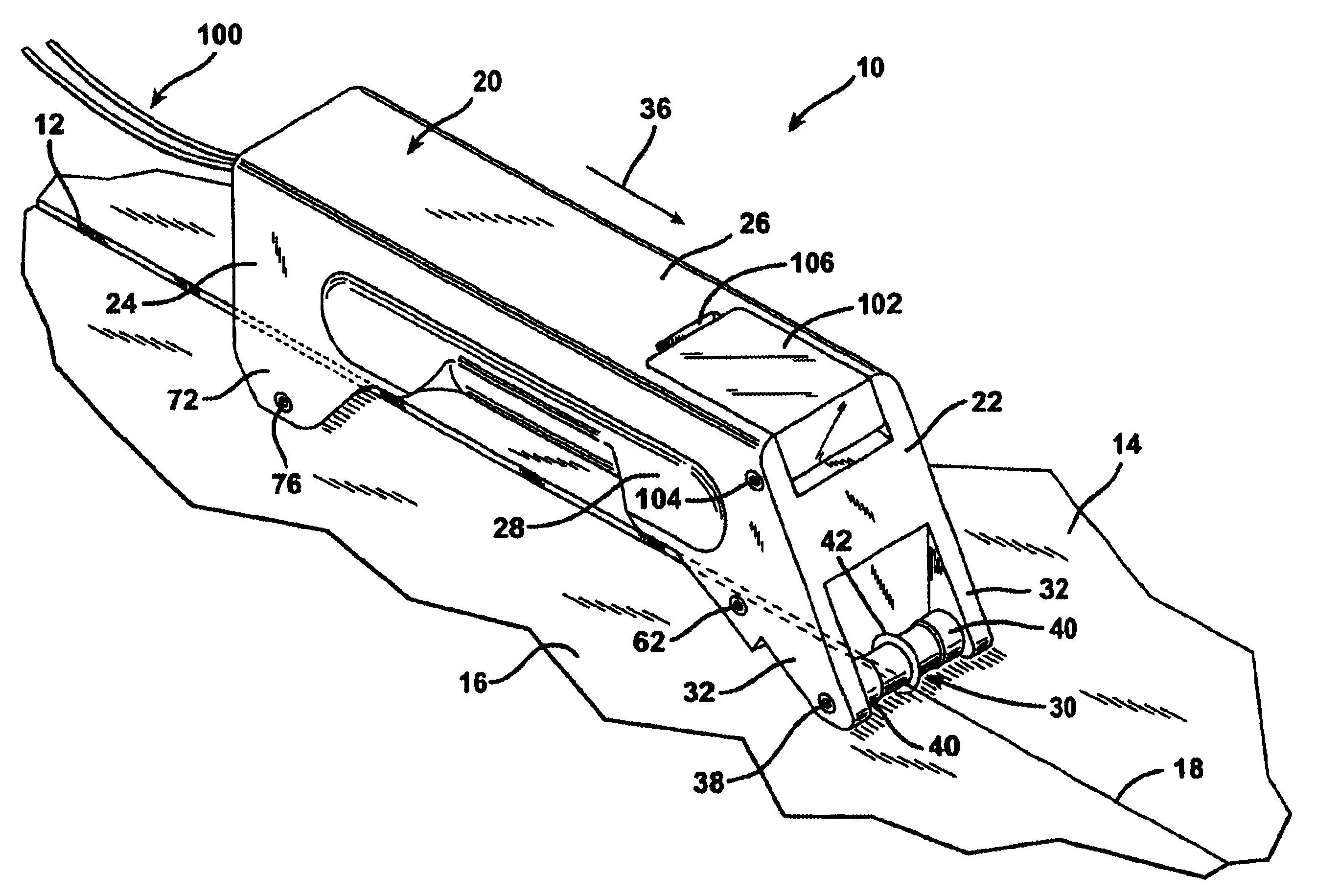
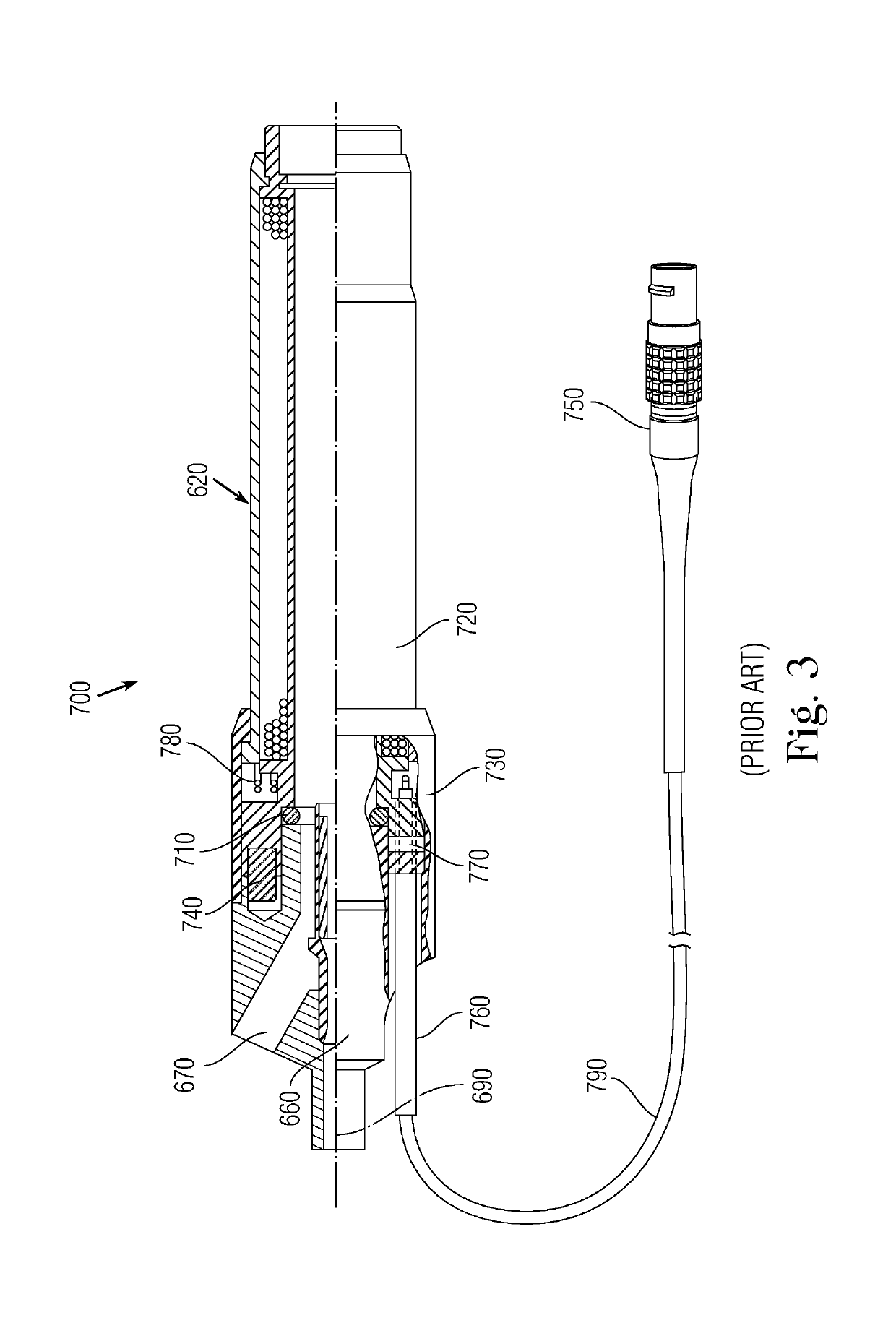
ActiveUS20050283927A1Uniform sectionCable can be longHollow article cleaningPipe elementsLine tubingDifferential pressure
A thruster pig for sending through a pipe from an entrance facility to a receiving location, for servicing or monitoring, by pumping a thrusting fluid into the pipe to force the pig forward is disclosed. The thruster pig includes a body having a front end and a back end, where the back end includes a reaction surface to which said the thrusting fluid applies a motive force. The body is slightly smaller in diameter than the inner diameter of the pipe. The pig also includes a seal circumferentially arranged on the pig to seal between said body and said pipe. A desired differential pressure is maintained over the pig to urge said pig forward through the pipe by pumping a fluid into the annulus between the pipe and the return flow line while returning fluid through said return flow line utilizing connected servicing or monitoring equipment. A connector releasably connects a return flow line to the pig. The connector includes a shifting mandrel that may be activated to open the connector by a ball pumped through the return flow line, where the ball is retained in the return flow line after releasing the connector. A blanking device is then provided to blank the bore within the pig that is left after the return flow line is disconnected.
Owner:DEN NORSKE STATS OLJESELSKAP AS +1
Composite system, method for its manufacture, and measurement pickup using such a composite system
ActiveUS20060083941A1Stable and high-strength and lasting and mechanical connectionIncreased pull-out strengthMaterial analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesPig casting plantsEngineeringCompound system
A composite system includes a first component, for instance of metal, and a second component extending at least partly through the first component along an imaginary longitudinal axis of the composite system. The second component contacts, with an at least partially curved, especially cylindrical, outer surface, an inner surface of the first component flushly such that the first component at least sectionally, at least partly, grips around the second component. Joining surfaces of the composite system, which are formed by the mutually contacting surfaces of the two components, are formed in such a manner that the two components exhibit contour portions in the area of these joining surfaces embodied as self-closing, peripheral surfaces. The contour portions fit at least partly into one another, to form a mechanical interference locking effective, at least in part, likewise in the direction of the longitudinal axis. Additionally, the second component, with its outer surface, contacts the inner surface of the first component flushly, such that the two components are mechanically tightly connected together also by means of a frictional locking effective at least partly in the direction of the longitudinal axis. Alternatively, or in supplementation thereof, at least one of the components is subjected at least partly to lastingly elastic, especially mixed plastic-elastic, deformations. The composite system is distinguished by a high pull-out strength, even in the presence of repeatedly arising vibrations in one of the components and is, therefore, especially suited also for use in a vibration-type measurement pickup.
Owner:ENDRESS HAUSER FLOWTEC AG
Technique for producing titanium-copper compound wire
ActiveCN101698206ARealize localizationFit tightlyTemperature control deviceSurface finishEconomic benefits
The invention relates to the field of a technique for producing a titanium-copper compound wire. The invention has the technical proposal that the technique comprises the following steps: selecting a titanium or titanium alloy pipe in proper dimensions meeting the national standard as a sleeve pipe (1); selecting a copper rod matching the dimensions of the titanium pipe as a rod material (2); penetrating the rod material (2) into the sleeve pipe (1), and attaching the rod material (2) to the sleeve pipe (1) by using an explosion compounding method to make a titanium-copper compound rod and form a titanium-base compound layer (3); and swaging the titanium-copper compound rod, and drawing to make the titanium-copper compound wire. The titanium-copper compound wire has the advantages of high bond strength, high surface smoothness and high quality of finished products. The invention changes the current unfavorable situation that the high-quality titanium-copper compound wire in China still highly depends on import, and enjoys favorable economic benefits.
Owner:宝鸡巨成钛业股份有限公司
Floor groover
InactiveUS6640446B2Uniform sectionUnique configurationCovering/liningsDomestic articlesEngineeringAbutment
A manually operated floor grooving tool is provided which has opposing front and rear ends with a seam-following roller at its front end and a groove-following roller at its rear end. The tool also employs a pair of grooving blades, one at the front end and one at the rear end. The front grooving blade is inclined upwardly and rearwardly with its cutting tip located just behind the forward axis of rotation of the seam-following guide. The rear-end grooving blade, on the other hand, projects rearwardly from the rear end of the tool and is inclined upwardly and forwardly and behind the groove-following roller. Since the rear-end grooving blade projects beyond the end of the tool in which it is secured, it can complete the formation of the groove all the way up to a vertical abutment. The groove is thereafter filled with sealant in a conventional manner.
Owner:MARTINEZ LEO
Porous acrylic fiber and fabric comprising the same, and method of producing the same
InactiveUS6821599B1Avoid decompositionImprove featuresLayered productsMonocomponent synthetic polymer artificial filamentSingle fiberThermal water
Porous acrylic fibers produced by a method comprising subjecting a spinning dope containing 0.3 to 20 parts by weight of poly(vinyl acetate) relative to 100 parts of an acrylic copolymer to a wet spinning to give fibers, crimping and cutting the fibers, subjecting the resultant fibers to a treatment by hot water at 90 to 100° C. for 30 to 120 minutes or by saturated steam at 90 to 130° C. for 10 to 90 minutes to thereby form porous fibers; and a pile fabric having pile portions which comprise the porous fibers in an amount of 3 wt % or more, and, in the pile fabric, respective single fibers are visible being separate and emphasized, and thus the pile fabric has an appearance being highly decorative and excellent in design characteristics.
Owner:KANEKA CORP
Watering mat for the large-area distribution of water
InactiveUS20100282859A1Improve water storage capacityEliminate disadvantagesSelf-acting watering devicesWatering devicesWater storageLandscaping
The disclosure relates to a watering mat for the large-area distribution of water, particularly in horticulture and landscaping as well as agriculture, comprising a first and a second carrier layer to accommodate elements of the watering mat, one or more connections for connecting the first and the second carrier layers, one or more water-feeding elements arranged between the first and the second carrier layers for feeding water into the watering mat and distributing water through the watering mat, an absorption layer for water storage arranged between the first and the second carrier layers and means for detecting the moisture level in the watering mat.
Owner:IGG INT GEOTEXTIL
Watering mat for the large-area distribution of water
InactiveUS8770888B2Cost-effectiveUniform sectionConstructionsSelf-acting watering devicesWater storageLandscaping
A watering mat is provided for the large-area distribution of water, particularly in horticulture and landscaping as well as agriculture. The watering mat includes a first and a second carrier layer to accommodate other elements of the watering mat, one or more connections for connecting the first and the second carrier layers, one or more water-feeding elements arranged between the first and the second carrier layers for feeding water into the watering mat and distributing water through the watering mat, an absorption layer for water storage arranged between the first and the second carrier layers and a moisture level detector in the watering mat.
Owner:IGG INT GEOTEXTIL
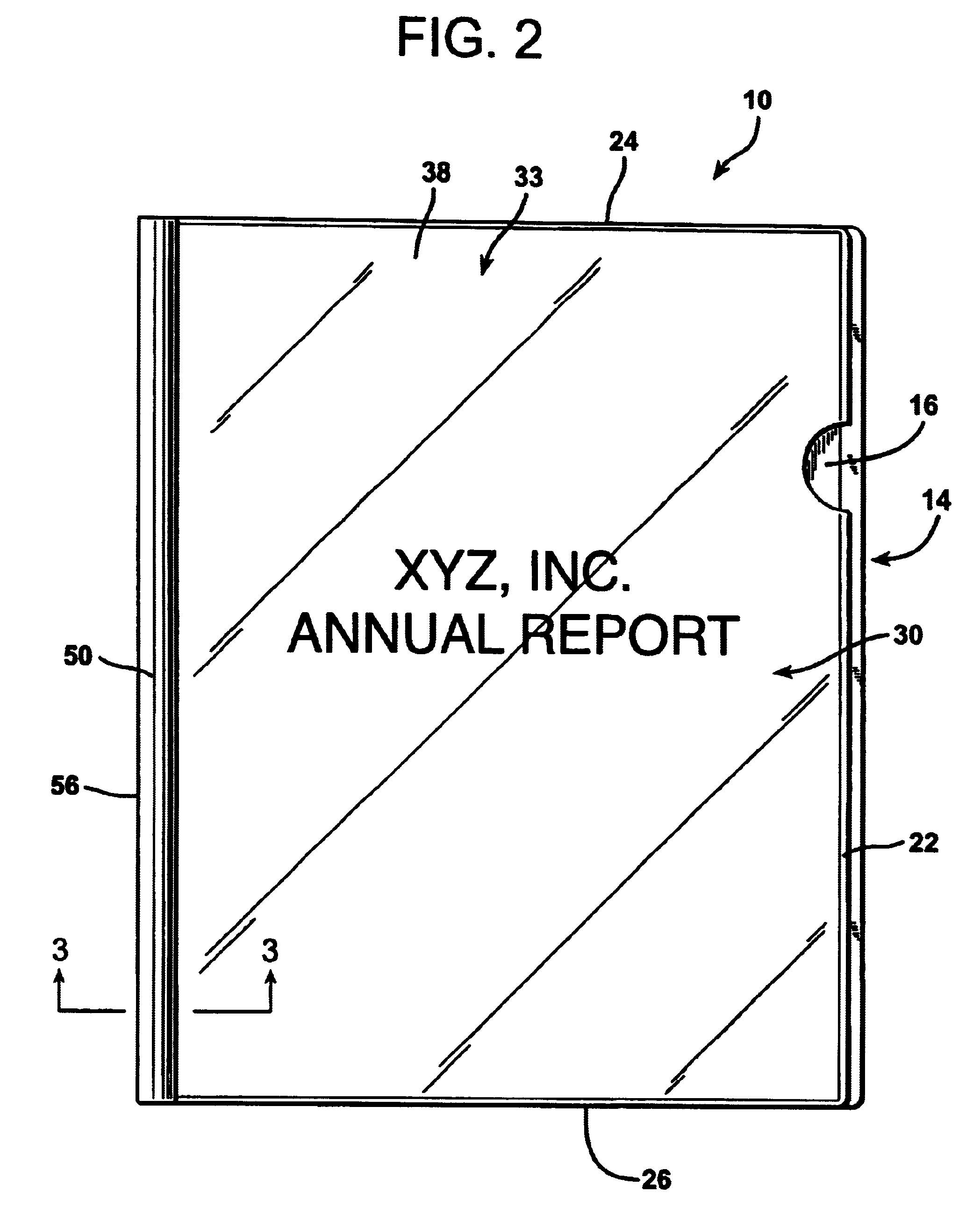
Report cover with clamping slide bar
A document formed of a stack of papers bound at the spine is equipped with a slide bar that achieves locking engagement with a document cover formed of a plurality of sheets of material. The sheets of document cover material are joined to each other at a binding margin. The sheet of cover material that passes around the spine of the cover forms a back cover beneath the stack of papers and a narrow, margin panel or strip that overlies the adjacent edge of the other sheet of binding material, which forms a front cover. The slide bar has a pair of jaws that terminate in distal tips that face each other at an angle of least forty-five degrees across a gap defined between the distal tips of the jaws. The slide bar is inserted onto the binding edge of the stack of papers and the cover encompassing them in a direction parallel to the binding edge from either the top or bottom end of the stack. The narrow margin panel atop the binding edge margin or the stack of papers fits within and is captured by the distal tip of one of the clasp jaws adjacent thereto throughout its length and throughout the length of the binding edge of the stack of papers. The capture of the narrow binding margin panel by the distal tip of the clasp jaw engaged at the junction between the sheets of the material forming the binder prevents the slide bar from being pulled laterally off of the binding edge of the stack.
Owner:ONG BON S
Vegetation trimmer having a blowing function
The present invention provides a vegetation trimmer (10) comprising: a motor (20) having a motor output shaft (30); a cutting head (22) for cutting vegetation presented thereto; a gear mechanism (26, 34, 36, 38) for transmitting power from said motor output shaft (30) to said cutting head (22), the gear mechanism having a step-down gear ratio for reducing the rate of rotation of said cutting head (22) relative to the rate of rotation of said motor (20), said gear mechanism comprising a pinion wheel (34) mounted on the motor output shaft (30); and a fan (28) also mounted on the motor output shaft (30); wherein the gear mechanism (26, 34, 36, 38) further comprises an internal gear wheel (26) engaging with the pinion wheel (34) and connected to the cutting head (22), whereby the cutting head (22) rotates in the same direction (B) as the fan does (D) during operation of the motor (20).
Owner:BLACK & DECKER INC
Insulated log homes
InactiveUS20100043323A1Great thermal efficiencyUniform cross sectionWallsPretreated surfacesThermal ratingElectrical and Electronics engineering
A log for a log home has a plurality of pockets formed within the body of the log. The pockets are filled with foam to enhance the thermal rating of the log.
Owner:WRIGHTMAN RONALD A
Rear projection display apparatus
InactiveUS20070177063A1Reduce material thicknessIncrease stiffnessBuilt-on/built-in screen projectorsPicture reproducersEngineeringProjection lens
Disclosed herein is a rear projection display apparatus including, a screen, a projection mirror, a video apparatus for projecting a picture, an optical unit including a projection lens, a light source, a drive and control circuit, and a structure body for holding the screen, the structure body having, a frame body formed from an extruded metal member, and a reinforcement member formed from a sheet metal, the frame body including, a bottom frame constituting a bottom surface, left and right side frames erected at both ends on the front side of the structure body, of the bottom frame, and a top frame bridgingly disposed between the upper ends of the left and right side frames, and the reinforcement member including, at least a frame support for connecting between the bottom surface of the bottom frame and the right side frame, or connecting between the bottom surface of the bottom frame and the left side frame.
Owner:SONY CORP
Method for manufacturing a flow cell
InactiveUS7005090B2Stable and form-fitting connectionEliminate the effects ofWithdrawing sample devicesOptical articlesFlow cellOptical property
A method of manufacturing a flow cell with a cell housing having a bore for the passage of sample, and with an inner layer of a totally reflecting polymer material for guiding radiation through the bore for the analysis of the sample, comprises the steps of: a) providing a tube of the polymer material in the bore of the cell housing, and b) applying a force on the walls of the tube from the interior of the tube for pressing the walls of the tube against the cell housing. The force may be applied by any suitable means, for example by drawing a mandrel through the interior of the tube, or by using pressurized gas or liquid. The resulting flow cell has a smooth inner surface with improved optical properties.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
Wiper blade for cleaning vehicle windowa
InactiveUS20020148064A1Easy to installSimple to executeWindow cleanersVehicle cleaningEngineeringWindscreen wiper
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH CORP
Method and apparatus for protecting a substrate
A method and apparatus for capping and encapsulating a shaped wooden workpiece or substrate to protect against environmental elements and prevent splintering of the wooden substrate in the installed condition is disclosed. An inventive end cap having a melt ring integrally formed therewith is installed on a portion of the substrate, such as a terminus of the substrate. According to the invention, the wooden substrate is sheathed during a polymeric extrusion process with a substantially continuous, unbroken polyethylene or other polymeric layer extending from and continuous with the inventive end cap. During the extrusion process, the melt ring integrally formed along the annular walls of the end cap melt the encapsulant and form a substantially sealed configuration with the polymeric layer applied to the substrate. The melt ring is engineered to sealingly incorporate with the polymeric extrusion as the molten encapsulant is applied to the wooden substrate, to provide a substantially uniform sealed joint between the end cap and the polymeric layer while maintaining a substantially uniform cross-section along the length of the wooden substrate following completion of the encapsulation process.
Owner:WOODGUARD PARTNERS LLC
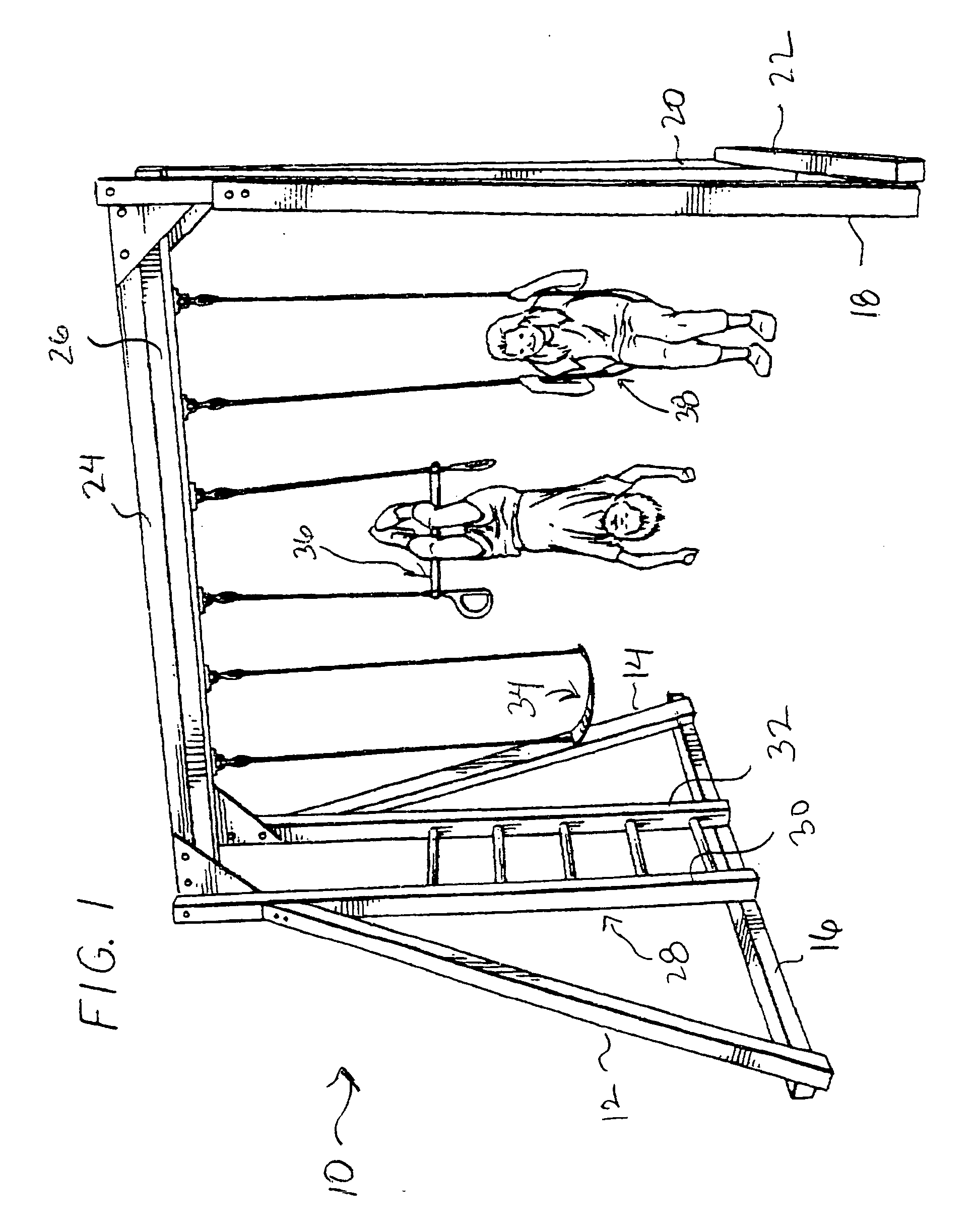
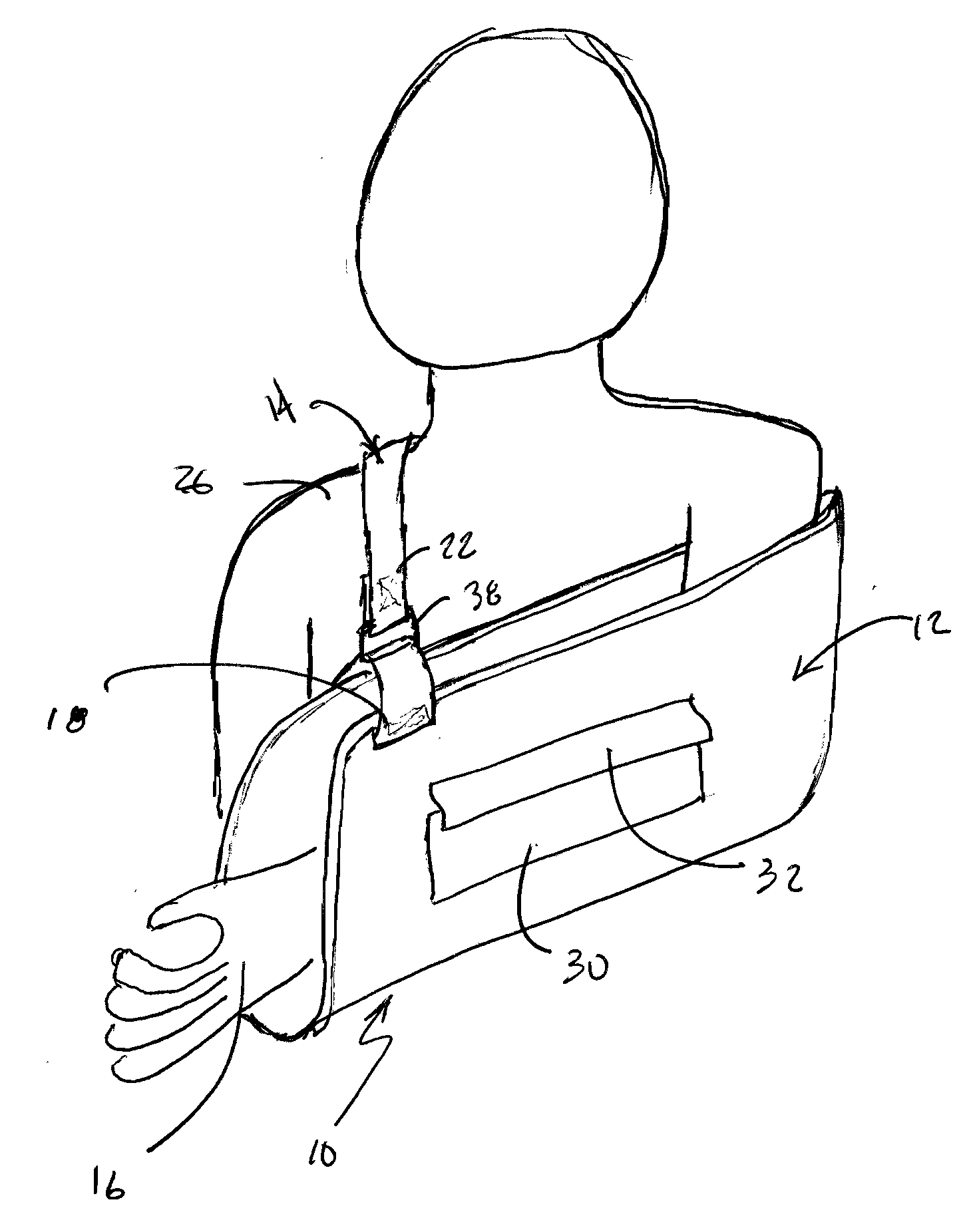
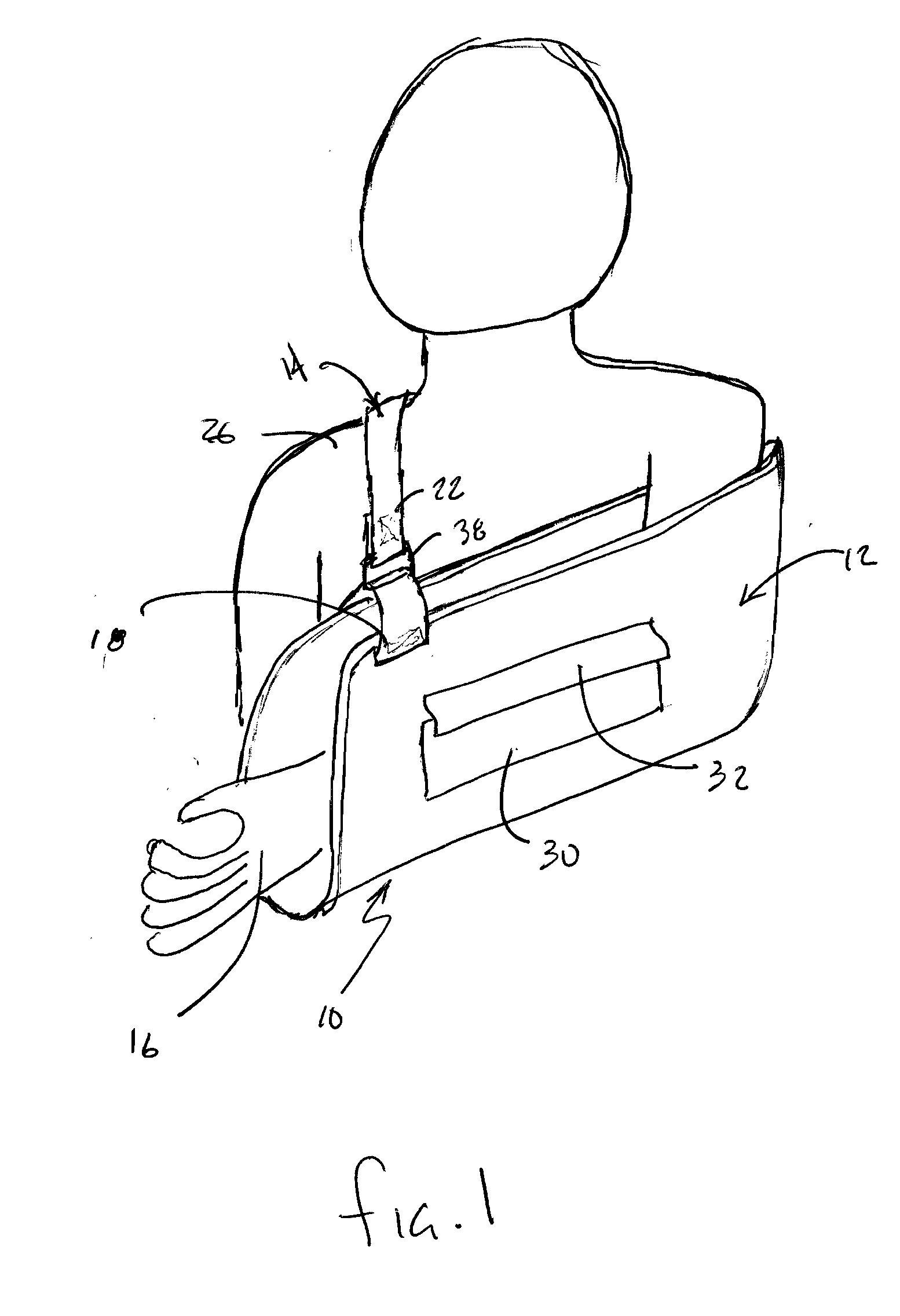
Sling design
InactiveUS20080015479A1Preventing strap bunchingPrevent creepRestraining devicesSuspensory bandagesModularityArchitectural engineering
A sling construction is provided that includes an improved support strap for more uniformly distributing the weight of the supported arm of the wearer's shoulder while preventing strap bunching and creep. The strap is preferably formed from an elastomer or a rubber that is relatively compliant yet has a low coefficient of elongation. This allows the strap to be highly supportive of the sling while also conforming to the contour of the wearer's neck and shoulders in a manner that makes the strap and sling comfortable to wear. The inner contact surface of the strap includes nubs or raised features that prevent the strap from sliding. Further, the improved strap support construction may be used in a modular fashion in conjunction with standard sling pouches or with an enhanced sling pouch in order to greatly improve the performance and appearance of the sling.
Owner:SOSCIA SUSAN
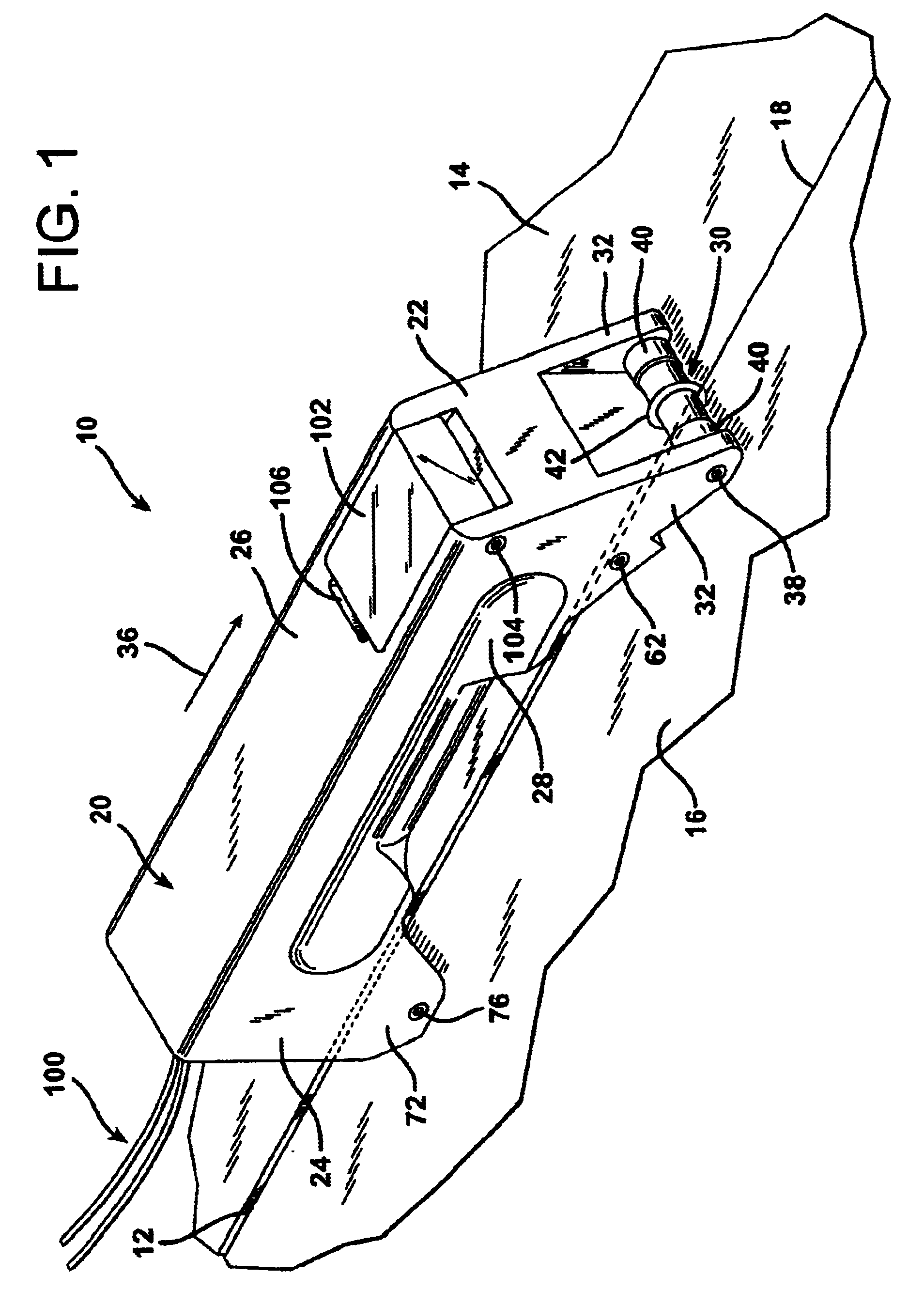
Thruster pig
ActiveUS7406738B2Uniform sectionCable can be longHollow article cleaningCleaning using toolsLine tubingDifferential pressure
A thruster pig for sending through a pipe from an entrance facility to a receiving location, for servicing or monitoring, by pumping a thrusting fluid into the pipe to force the pig forward is disclosed. The thruster pig includes a body having a front end and a back end, where the back end includes a reaction surface to which said the thrusting fluid applies a motive force. The body is slightly smaller in diameter than the inner diameter of the pipe. The pig also includes a seal circumferentially arranged on the pig to seal between said body and said pipe. A desired differential pressure is maintained over the pig to urge said pig forward through the pipe by pumping a fluid into the annulus between the pipe and the return flow line while returning fluid through said return flow line utilizing connected servicing or monitoring equipment. A connector releasably connects a return flow line to the pig. The connector includes a shifting mandrel that may be activated to open the connector by a ball pumped through the return flow line, where the ball is retained in the return flow line after releasing the connector. A blanking device is then provided to blank the bore within the pig that is left after the return flow line is disconnected.
Owner:DEN NORSKE STATS OLJESELSKAP AS +1
Lithographic apparatus and device manufacturing method
InactiveUS20050179884A1Small sizeReduce the impactPillowsDismountable chairsDistribution systemPhysics
Provided is a radiation distribution system for distributing the radiation from an illumination system to two or more patterning means, each for patterning beams of radiation, which are subsequently projected onto a substrate.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
Low-cost disposable ultrasonic surgical handpiece
ActiveUS20190133823A1Improve efficiencyReduce manufacturing costsSurgical furnitureEye surgerySurgical bladeTransducer
A disposable ultrasonic handpiece that contains a transducer and a connecting body that tapers to a surgical blade in a single piece. The housing that surrounds the ultrasonic transducer does not require waterproofing for repeated autoclaving. Also, the electrical cord that provides power to the transducer is made of very inexpensive wire, along with a low-cost electrical connector. By making the blade, connecting body with a protective sheet and transducer as a unit with an electrical terminal at the proximal end, they can be plugged and unplugged from a socket and electrical cord in the housing of the handpiece. Thus, only the unit needs to be disposed of after a procedure, making the disposable part of the handpiece even less expensive. The low-cost, disposable handpiece can be packaged along with additional disposable items that are required for one of several types surgeries.
Owner:SURGICAL DESIGN
Apparatus in spinning preparation for separating foreign objects at conveying equipment for fibre material
InactiveUS20080178432A1Reduce proportionReduce the ratioSafety devices for fibre treatmentSpray nozzlesAirflowForeign body
In an apparatus in spinning preparation for separating foreign objects at conveying equipment for fibre material, at least one separation device is associated with the conveying equipment. The separation device comprises an arrangement for producing a blast of air that flows in the direction onto the conveying equipment and generates an air flow that detaches the foreign objects from the conveyed fibres and carries them away. The arrangement comprises a plurality of blast nozzles arranged across the width of the conveying equipment and connected to a compressed air pipe and to valves. To reduce the proportion of good fibres in the waste in a simple manner, and to allow a more selective action of the blast air current, a bar member for mounting the blast nozzles is present and the nozzles are integrated in the bar member.
Owner:TRUETZSCHLER GMBH & CO KG
Methods and apparatus for forming a composite component
A mould for a composite component having a fillet joint, the mould including a mould body having a cavity within which the component is formed, and an insert mating with the mould body and including a forming surface against which, in use, the fillet of the component fillet joint is formed. The insert may be thermally insulating and highly rigid. A method of forming a composite component having a fillet joint using a mould, the method including forcing a surface of the fillet region of the component to adopt a non constant radius of curvature while the component is inside the mould during the cure process is also provided. Additionally, a method of forming a composite component having a fillet joint that is defined between first and second legs the method including placing the legs of the component in bending during cure of the component is described.
Owner:ROLLS ROYCE PLC
Vegetation trimmer having a blowing function
A vegetation trimmer (10) having a motor (20) with a motor output shaft (30), a cutting head (22) for cutting vegetation, and a gear mechanism (26, 34, 36, 38) for transmitting power from said motor output shaft (30) to the cutting head (22). The motor output shaft (30) has a gear mechanism with a pinion wheel and a fan (28) mounted thereon. The gear mechanism (26, 34, 36, 38) further comprises an internal gear wheel (26) engaging with the pinion wheel (34) and connected to the cutting head (22), whereby the cutting head (22) rotates in the same direction (B) as the fan does (D) during operation of the motor (20).
Owner:BLACK & DECKER INC
Ampoule bottle opener
ActiveCN111977590ASolve pollutionEasy to operateBottle/container closurePower operated devicesBottle neckControl circuit
The invention discloses an ampoule bottle opener. The ampoule bottle opener comprises an upper box body and a lower box body which can be opened and closed through hinging, wherein a supporting platform is arranged in the lower box body; accommodating holes with various dimensions and used for placing ampoule bottles are formed in the supporting platform; a tray capable of freely rotating, a control circuit board, a lithium battery electrically connected with the control circuit board and a power supply port used for charging are arranged on the bottom of any accommodating hole; a cutting mechanism for forming physical scratches on bottle necks of the ampoule bottles and a heating mechanism are arranged in the upper box body; and the heating mechanism is powered and heated through the control circuit board. According to the ampoule bottle opener disclosed by the invention, tensile stress is formed on a specified position of each ampoule bottle through cutting, heating and cooling, so that the ampoule bottles can be broken by applying relatively small shearing stress by hands, and broken sections are flat, uniform and smooth; and the problems that medicament and liquid medicine arewasted as the whole ampoule bottles are broken, and potential safety hazards are caused to medical staff are fundamentally solved.
Owner:WEST CHINA HOSPITAL SICHUAN UNIV
Airless pump dispensing system with multi-lobe ring seal
InactiveUS20120067924A1Improve sealingUniform sectionOpening closed containersBottle/container closureAir pumpEngineering
Method and apparatus for dispensing a fluid using a dispensing container employing an airless pump, which may employ abstract or non-cylindrical shapes. The airless pump uses a chamber enclosing a fluid with a piston comprising a surface of the chamber. The chamber has an interior volume with a substantially uniform cross section along a height of the chamber, to which the piston is conformed allowing the piston to transverse the height of the chamber. The gaps between the piston and the interior of the chamber are sealed with a multi-lobe ring seal.
Owner:ROBERTS CONTAINER CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com