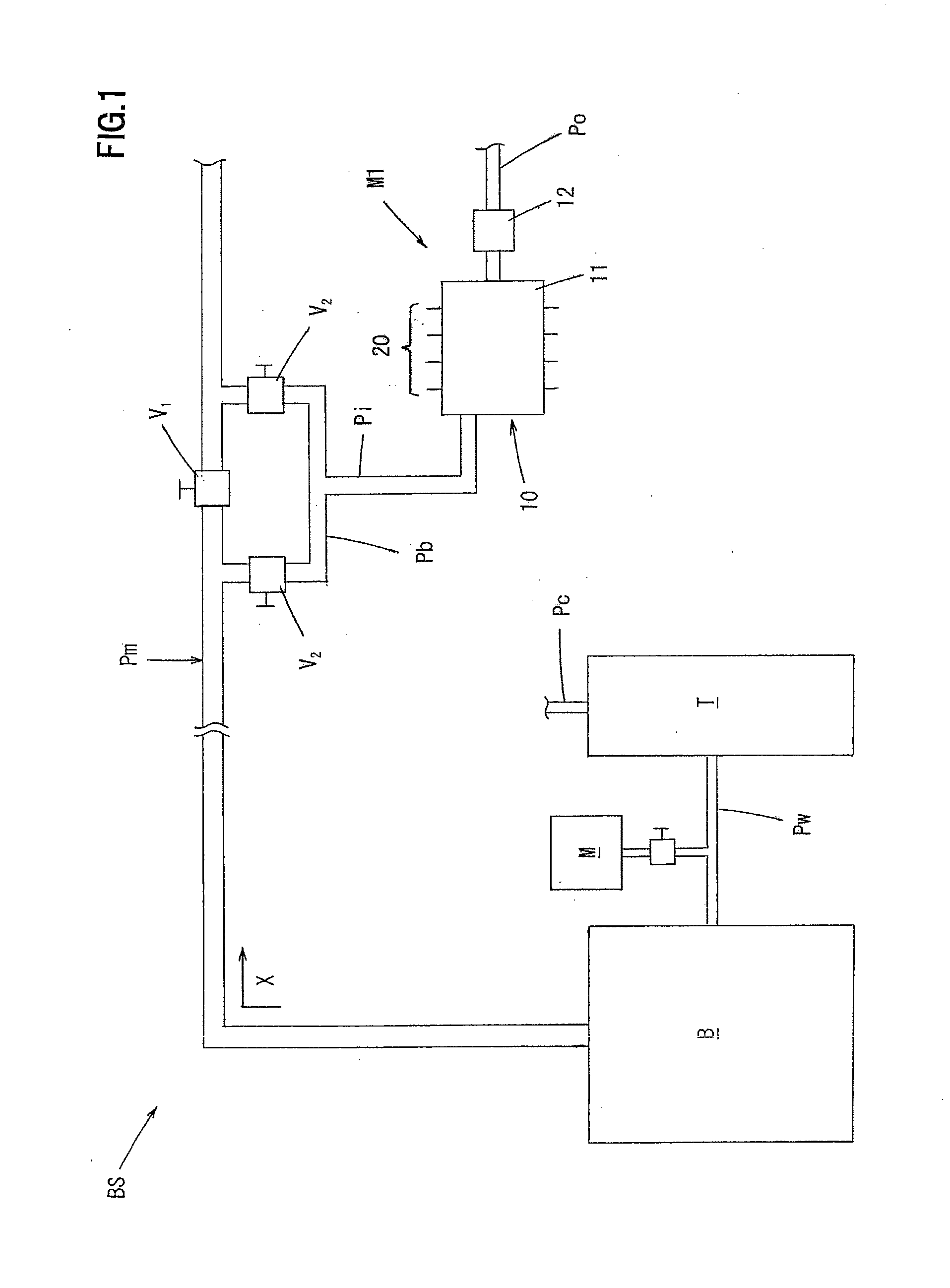Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
170results about How to "Stable reproduction" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
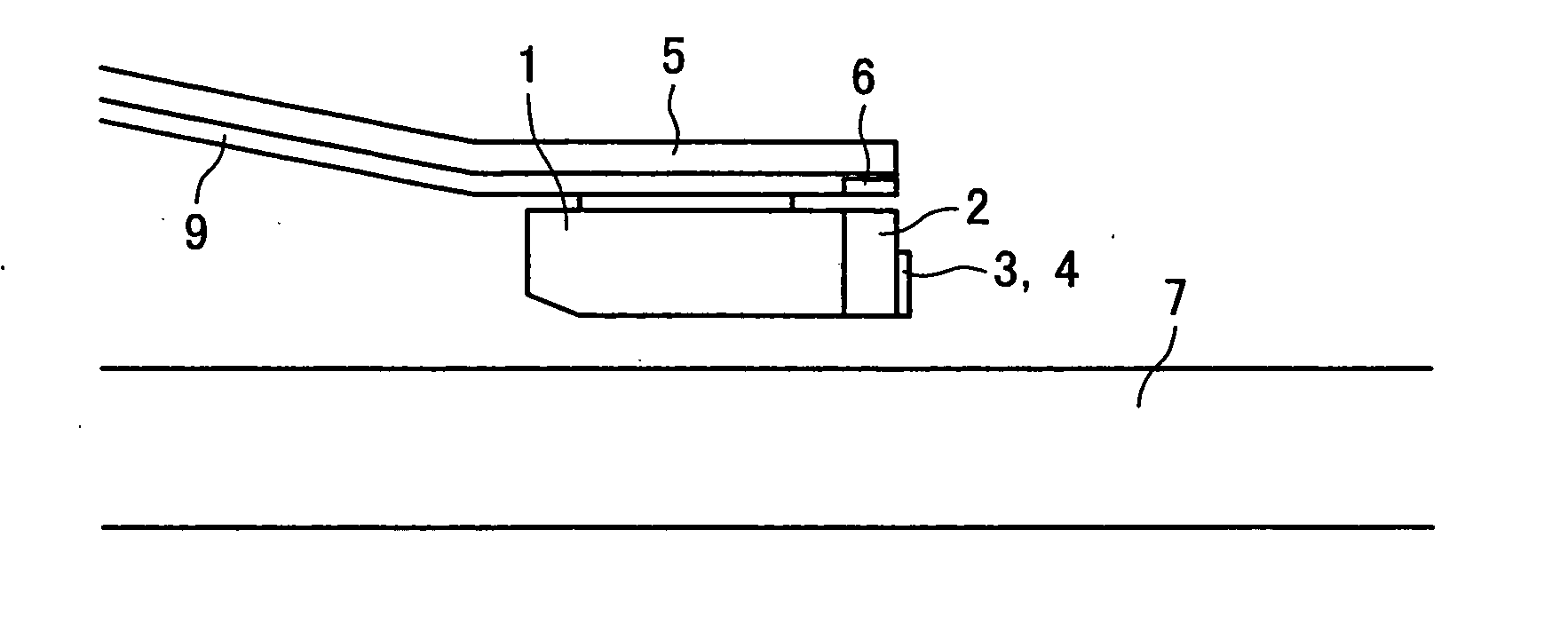
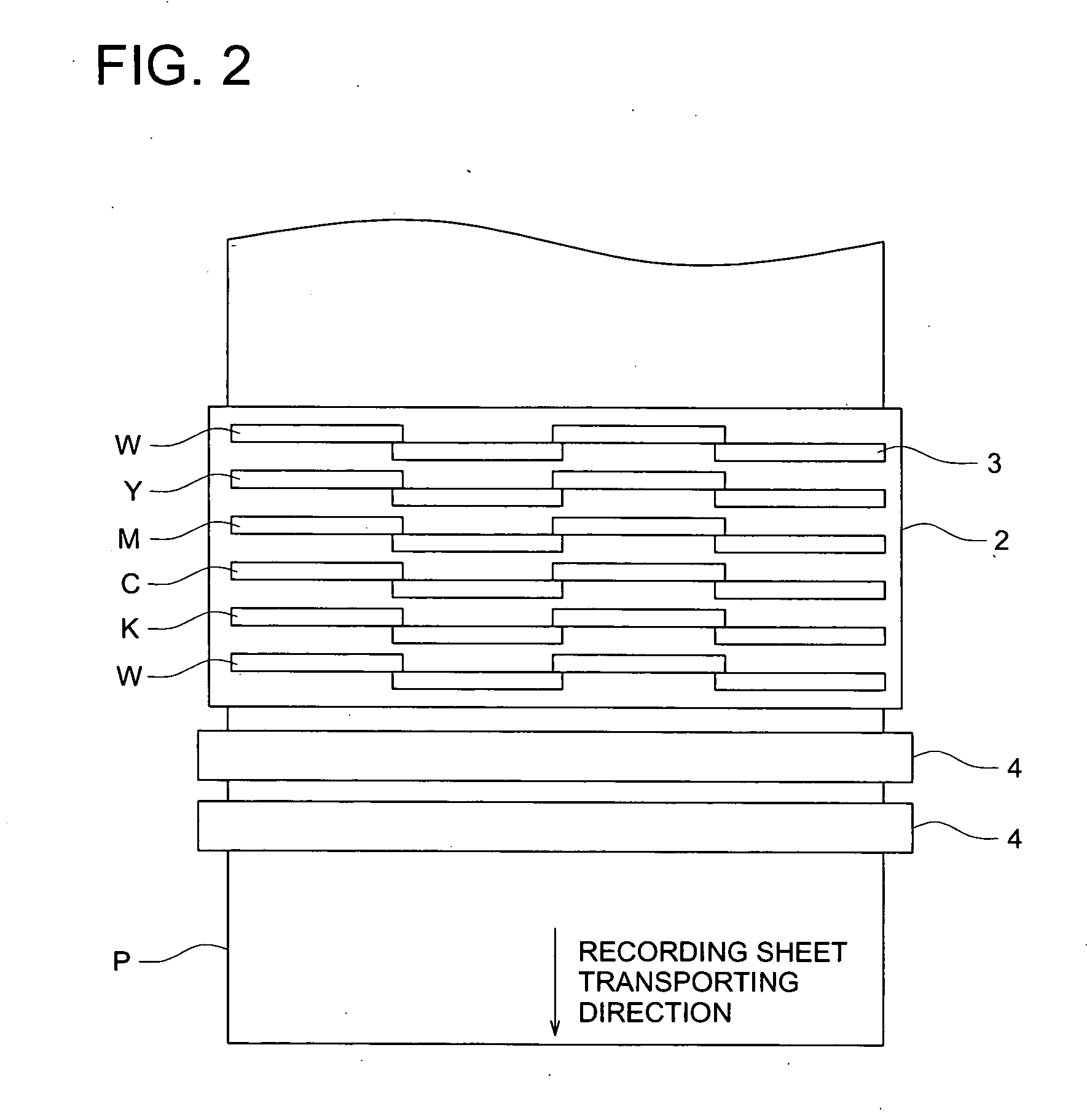
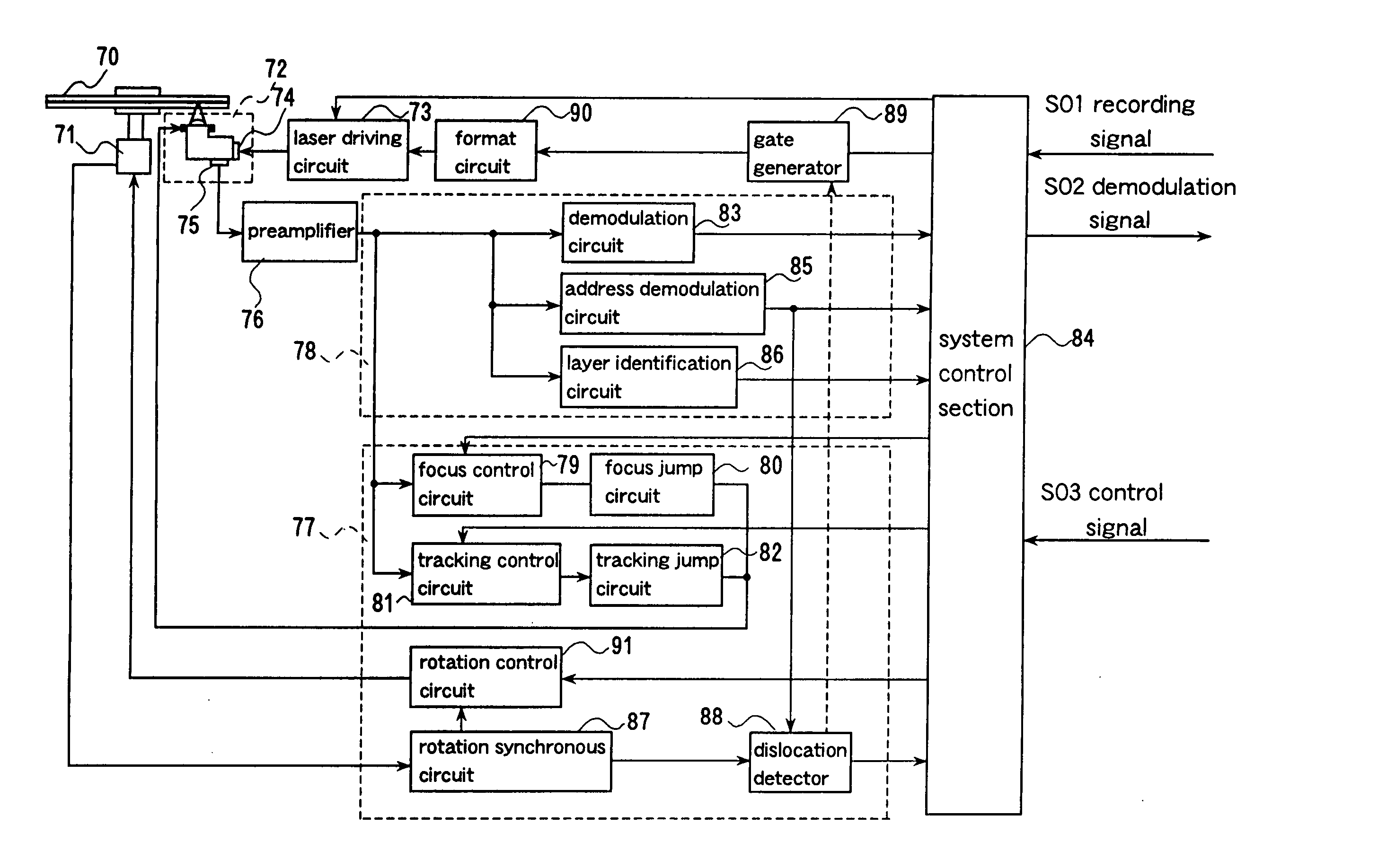
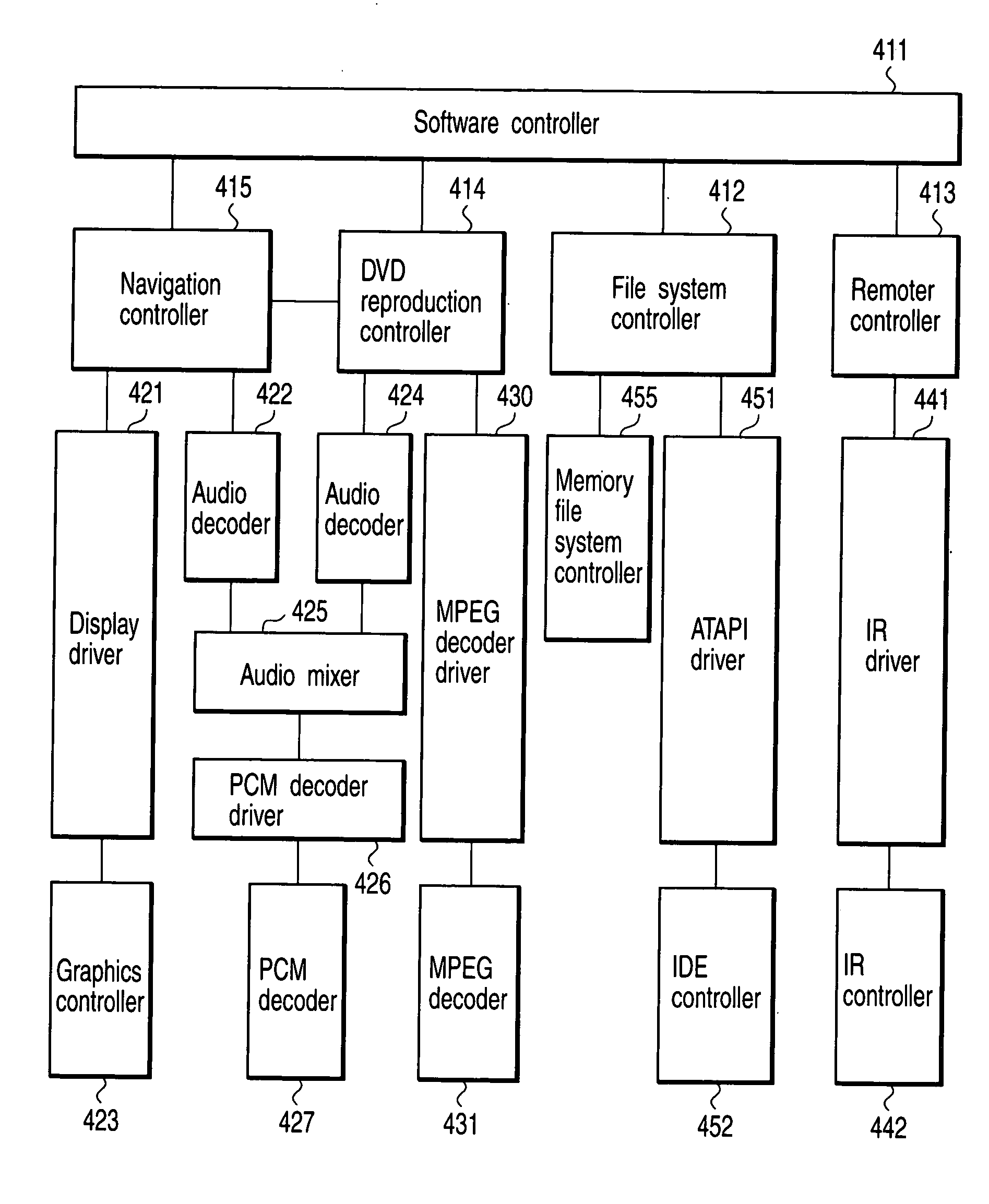
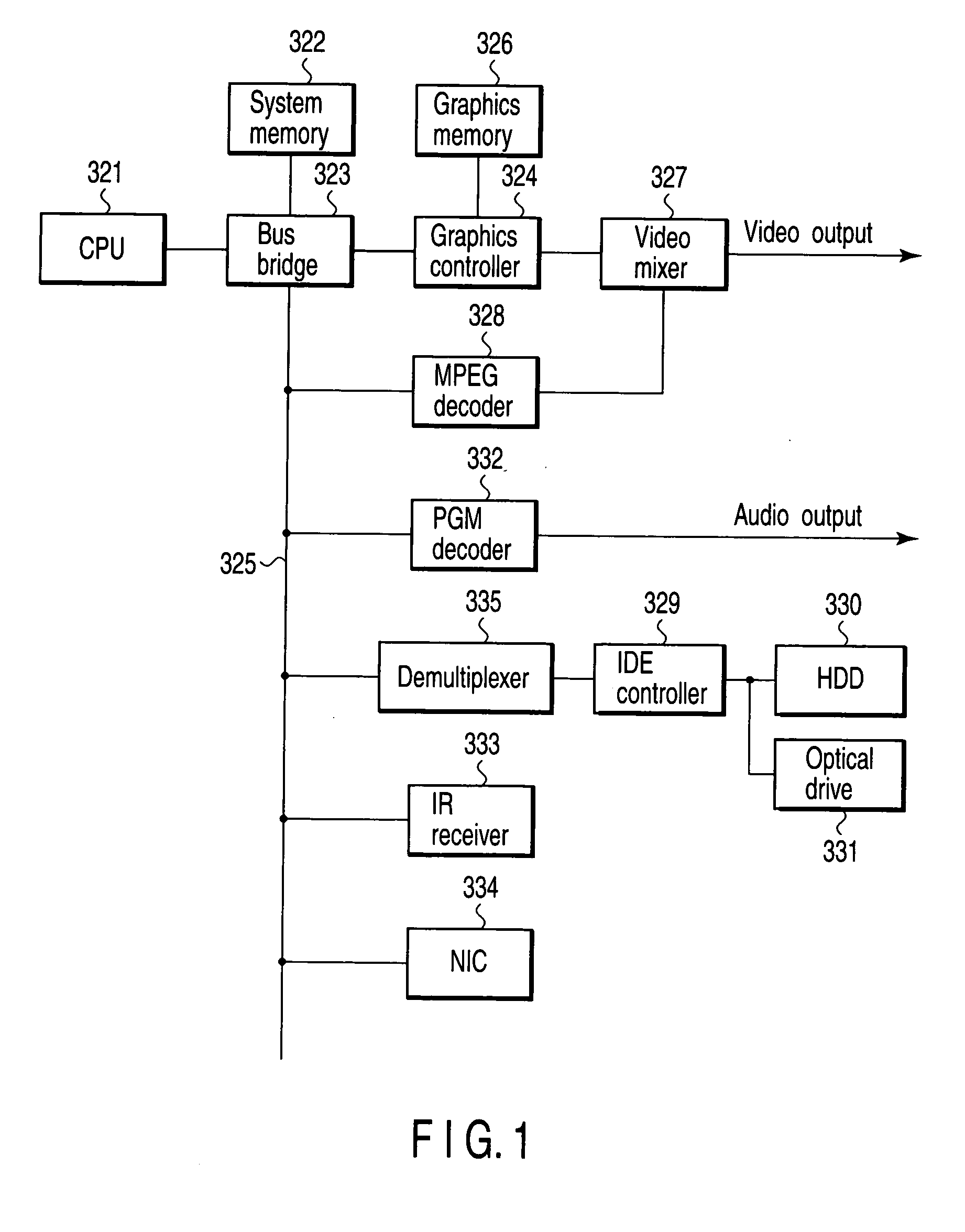
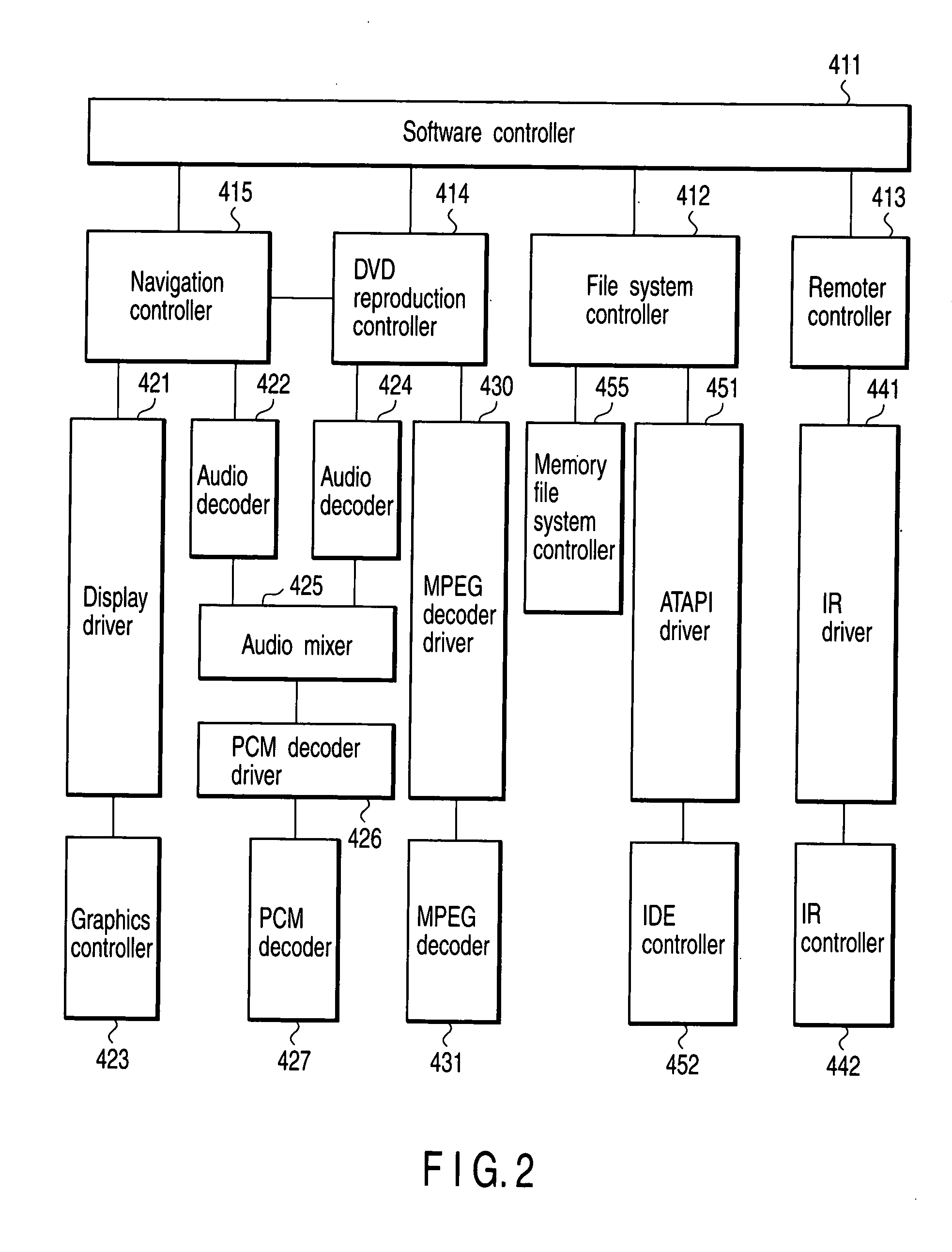
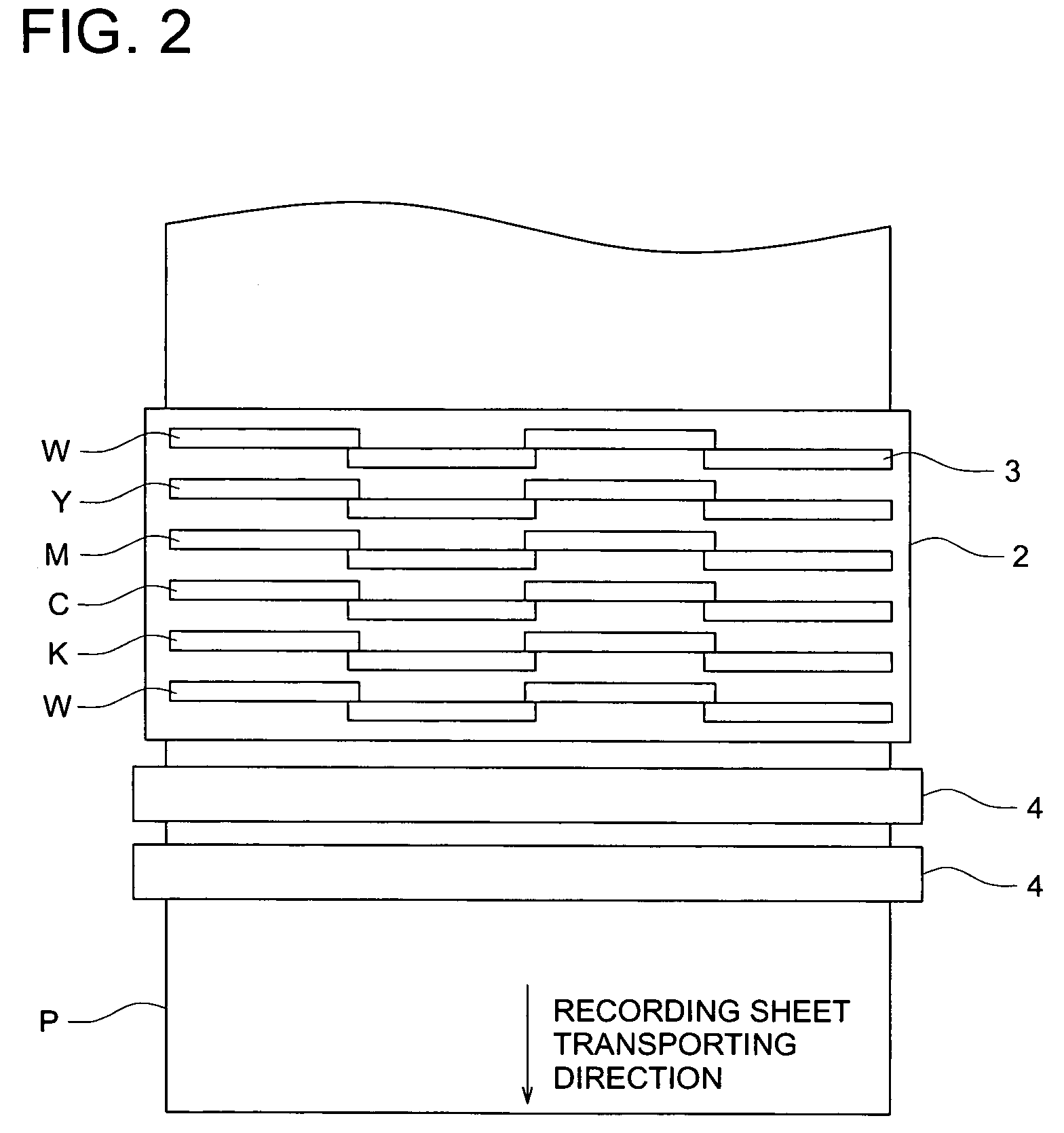
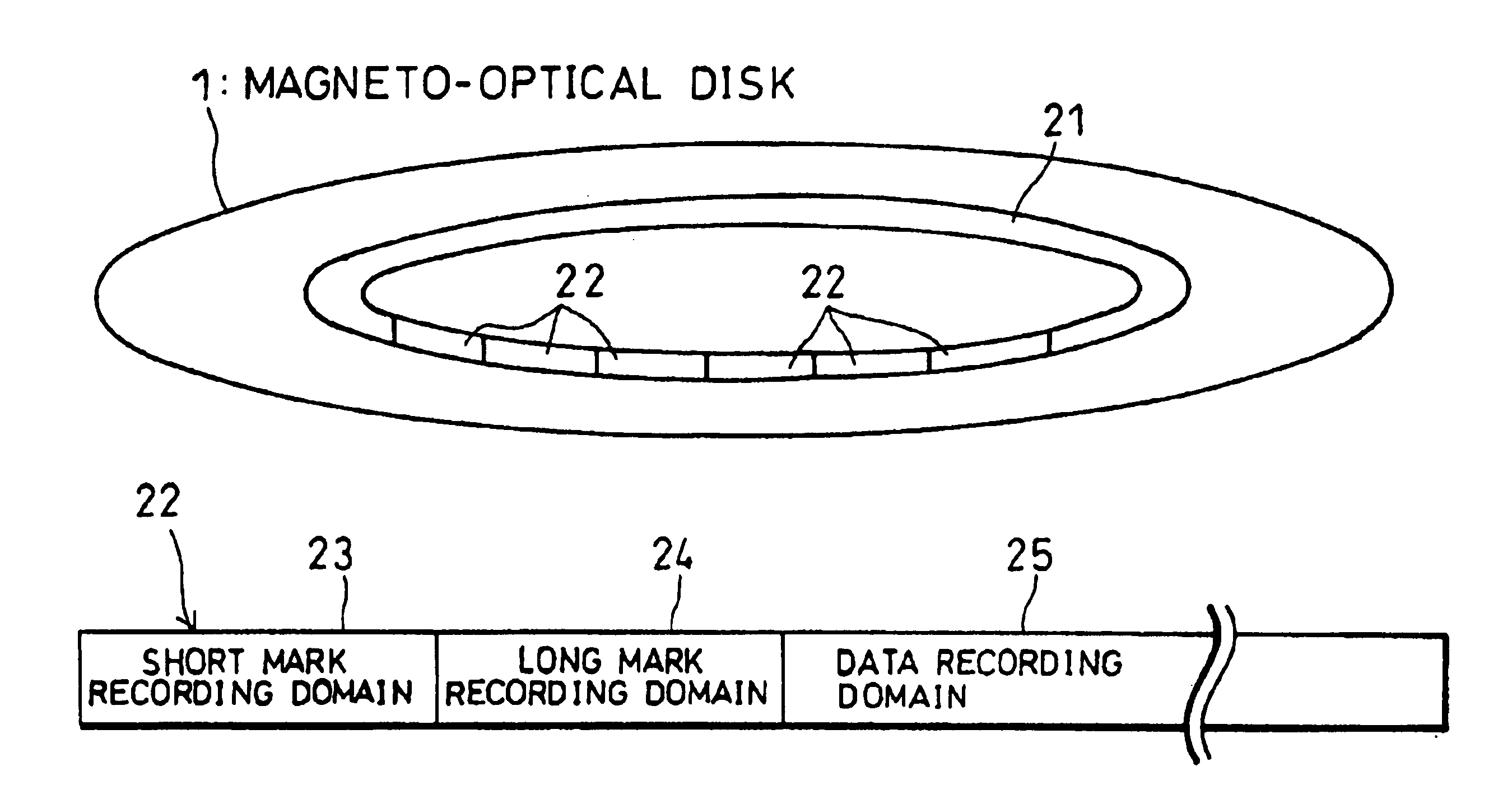
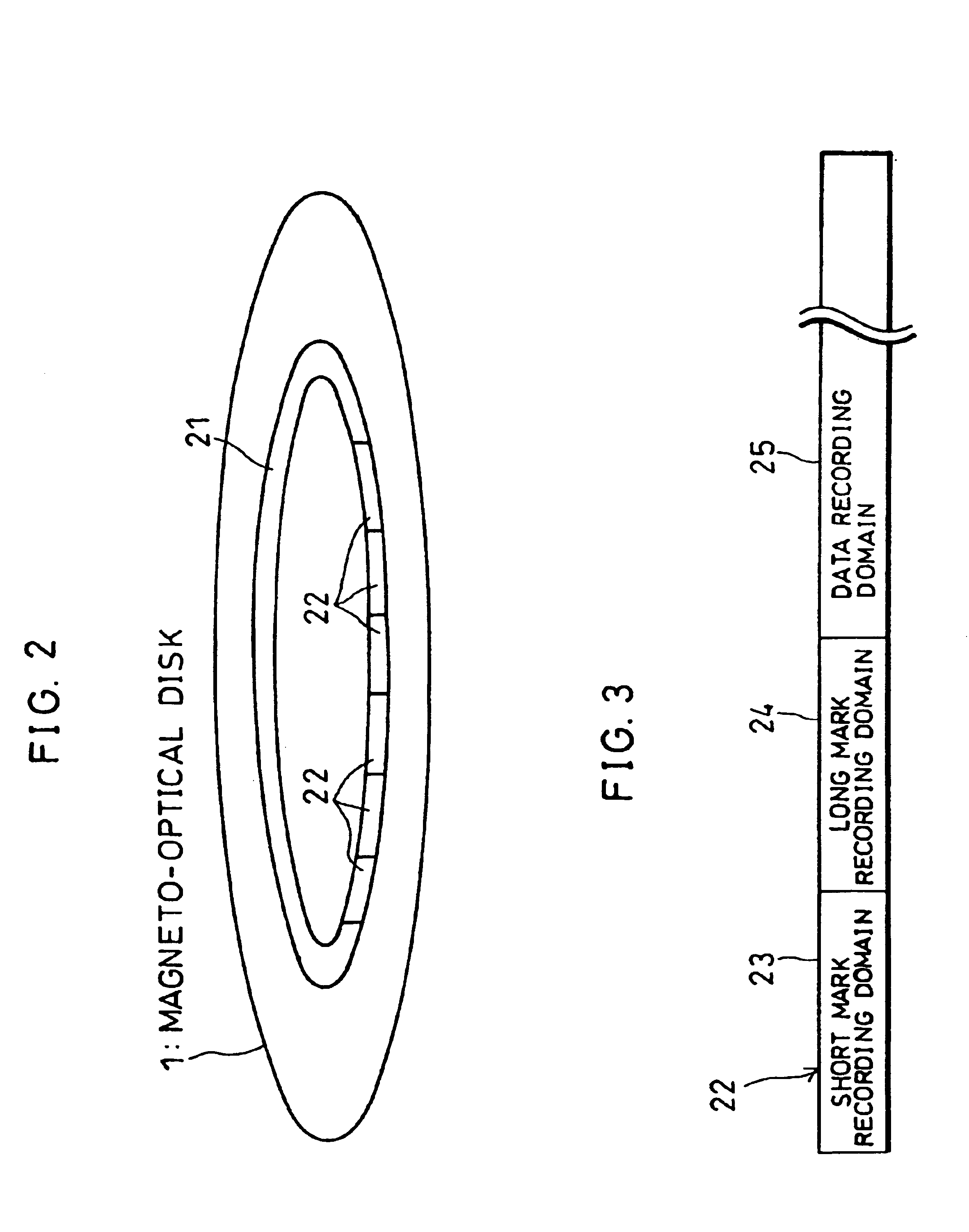
Read/write device, storage medium, driving method of read/write device, semiconductor laser life estimation method, program, program storage medium, and semiconductor laser
InactiveUS20050213436A1Shorten access timeDrive stabilityApparatus for flat record carriersHeads using thin filmsHeat-assisted magnetic recordingEstimation methods
In a read / write device for writing and reading a storage medium by way of a heat assisted magnetic recording / reproduction scheme, the read / write device including an elevated slider provided with a semiconductor laser, provided is a heat dissipation mechanism for dissipating heat generated in the elevated slider to an outside of a housing of the read / write device. Further, the storage medium has a second heatsink layer formed of an Al film having a thickness of 50 μm, a backing layer, a heat barrier layer, a first heatsink layer, a magnetic recording layer, and a protection film on a glass substrate. With this arrangement, in a read / write device which performs a heat assisted magnetic recording and reproduction by a semiconductor laser provided on the elevated slider, the occurrence of malfunction due to temperature rises in the storage medium is prevented.
Owner:SHARP KK
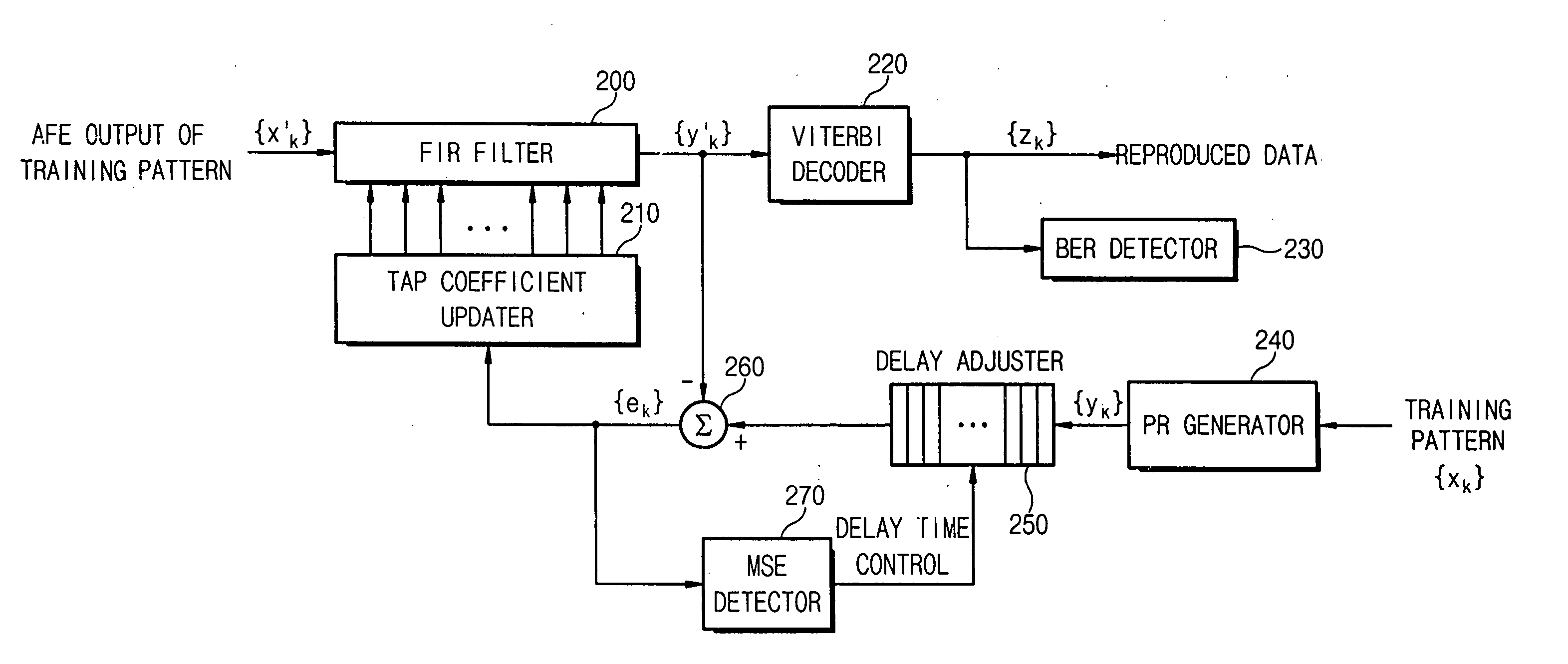
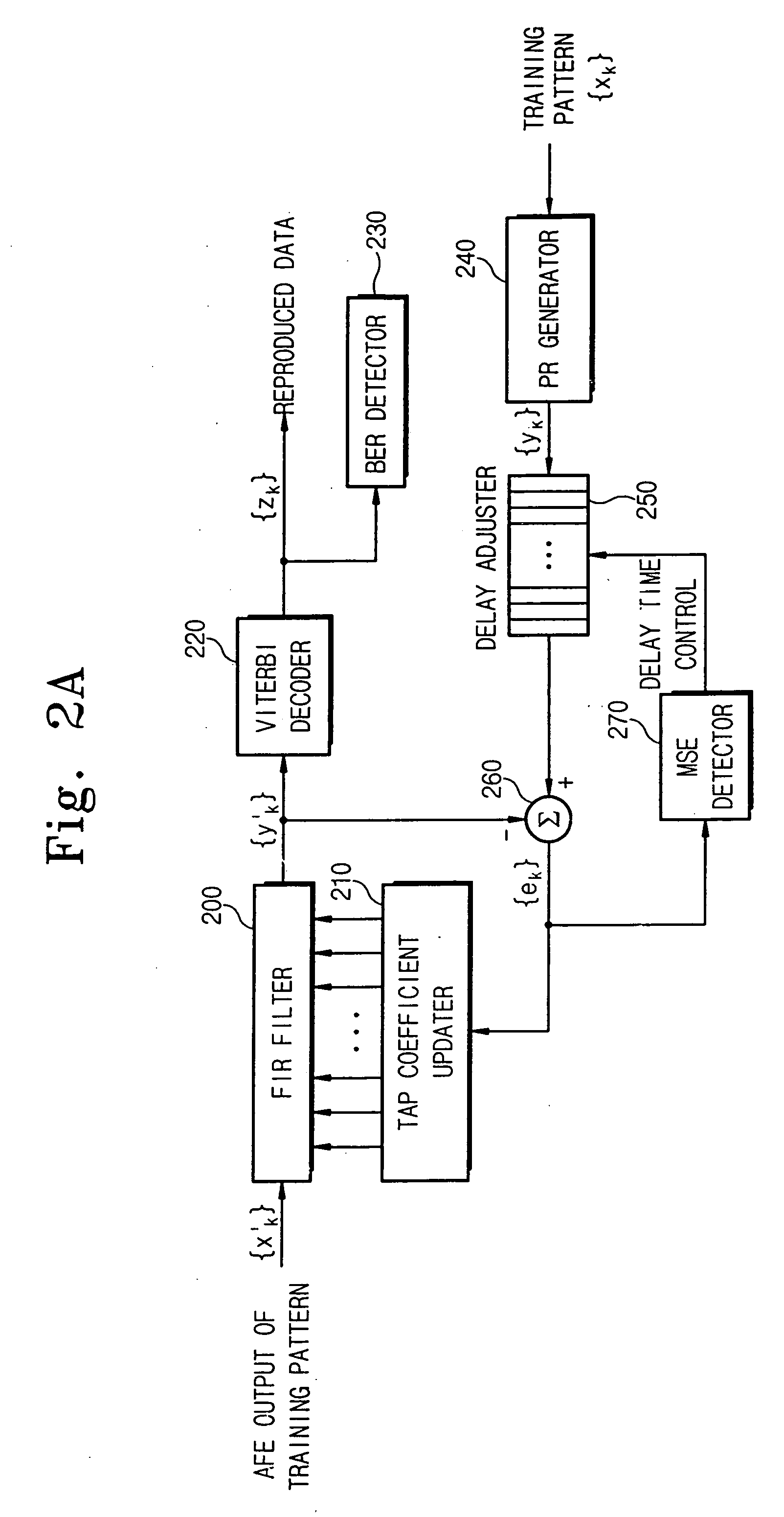
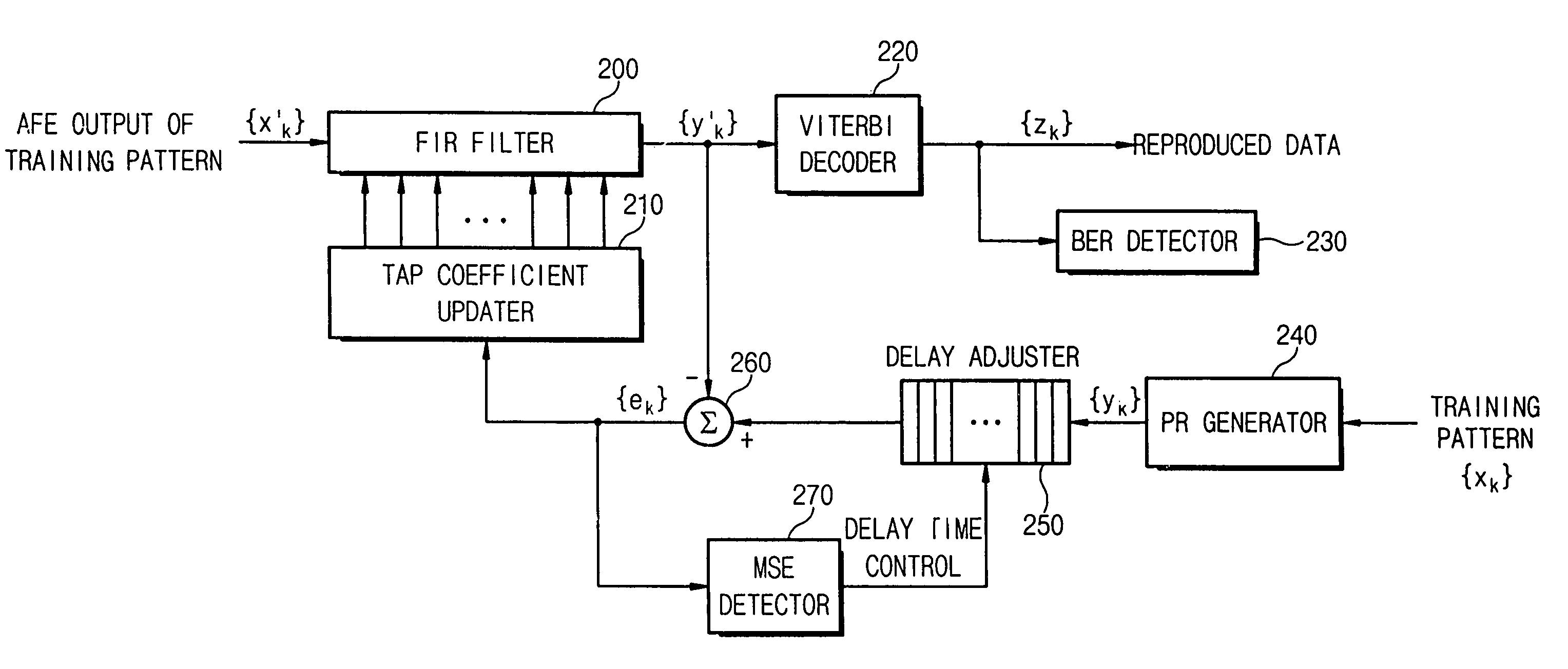
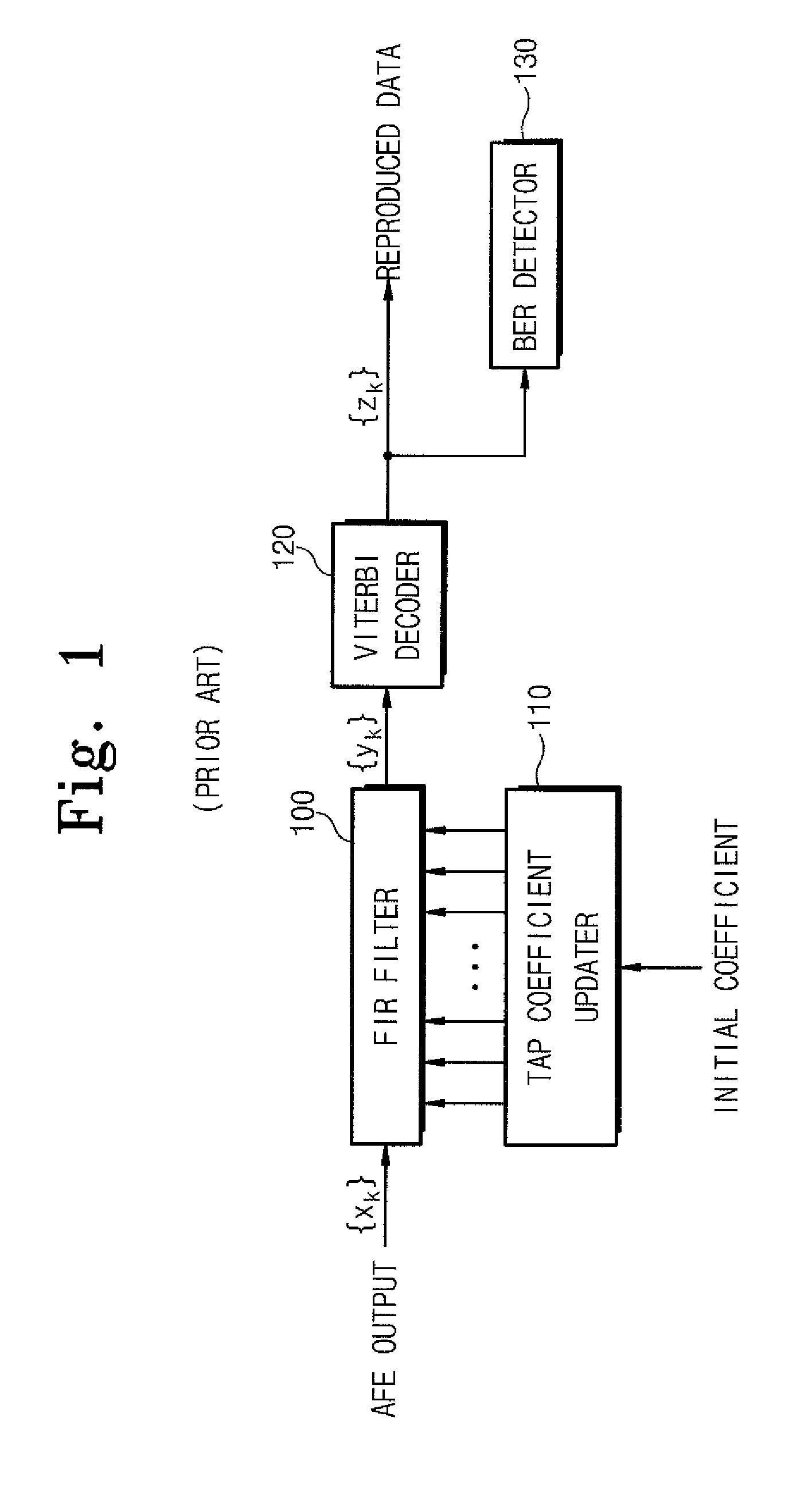
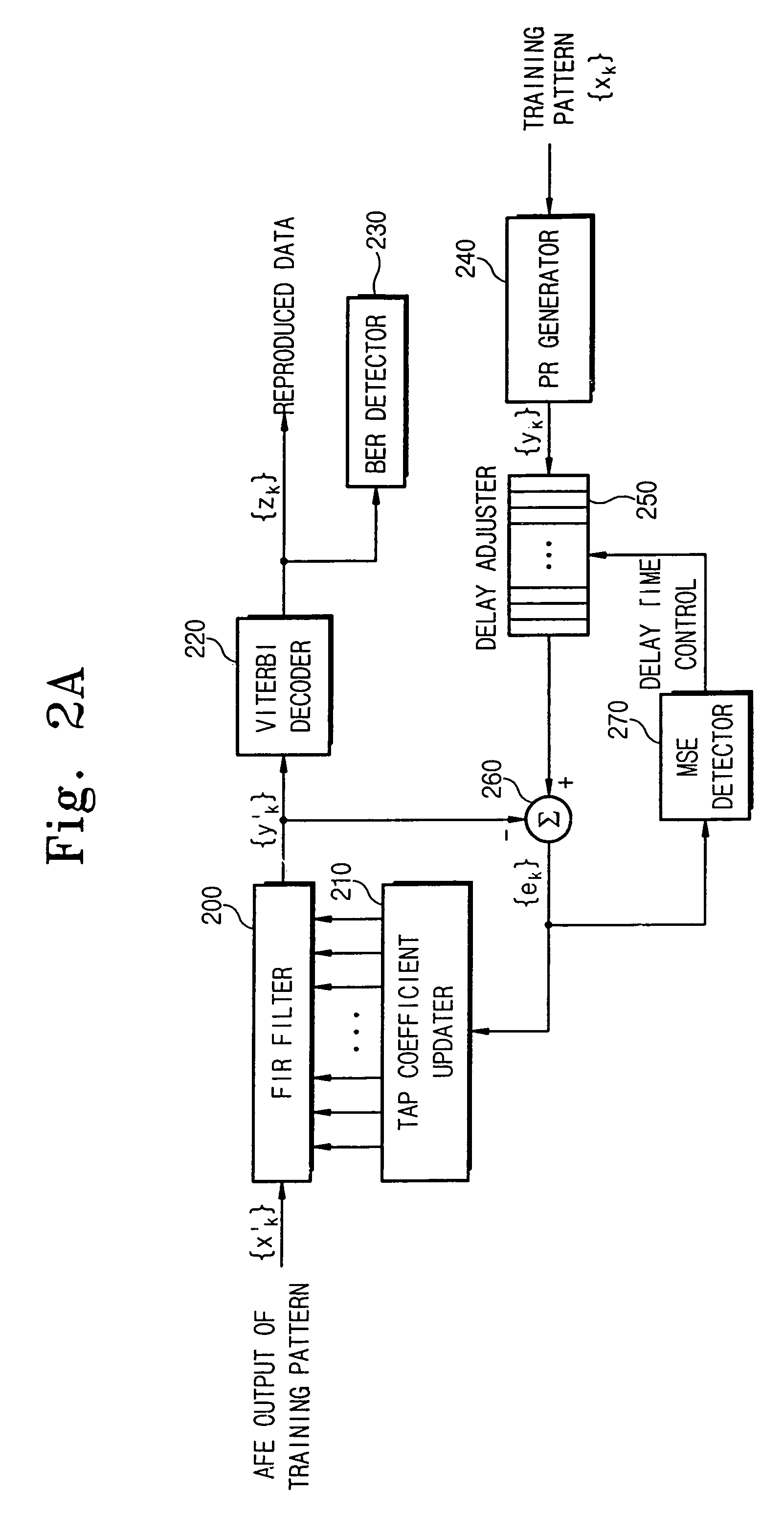
Apparatus and method for setting tap coefficient of adaptive equalizer
InactiveUS20060176947A1Wrong levelStable reproductionMultiple-port networksError preventionViterbi decoderOperation mode
There is provided an apparatus and method for initializing a tap coefficient of an adaptive equalizer constituting a read path for a storage medium, where the apparatus includes an FIR filter, a Viterbi decoder, a level error detector, and a tap coefficient updater, the FIR filter receives a first signal stream and outputs the first signal stream in the form of a second signal stream, the Viterbi decoder corrects a bit error of the second signal stream, the level error detector detects a level error between the second signal stream and a third signal stream that is an ideal output signal corresponding to the second signal stream, the tap coefficient updater selects a tap coefficient minimizing the level error and provides the selected tap coefficient as a tap coefficient of the FIR filter, the tap coefficient minimizing the level error is determined as an initial value in a system initialization mode, and the determined initial value is used as an initial value of the tap coefficient of the FIR filter in a normal operation mode.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
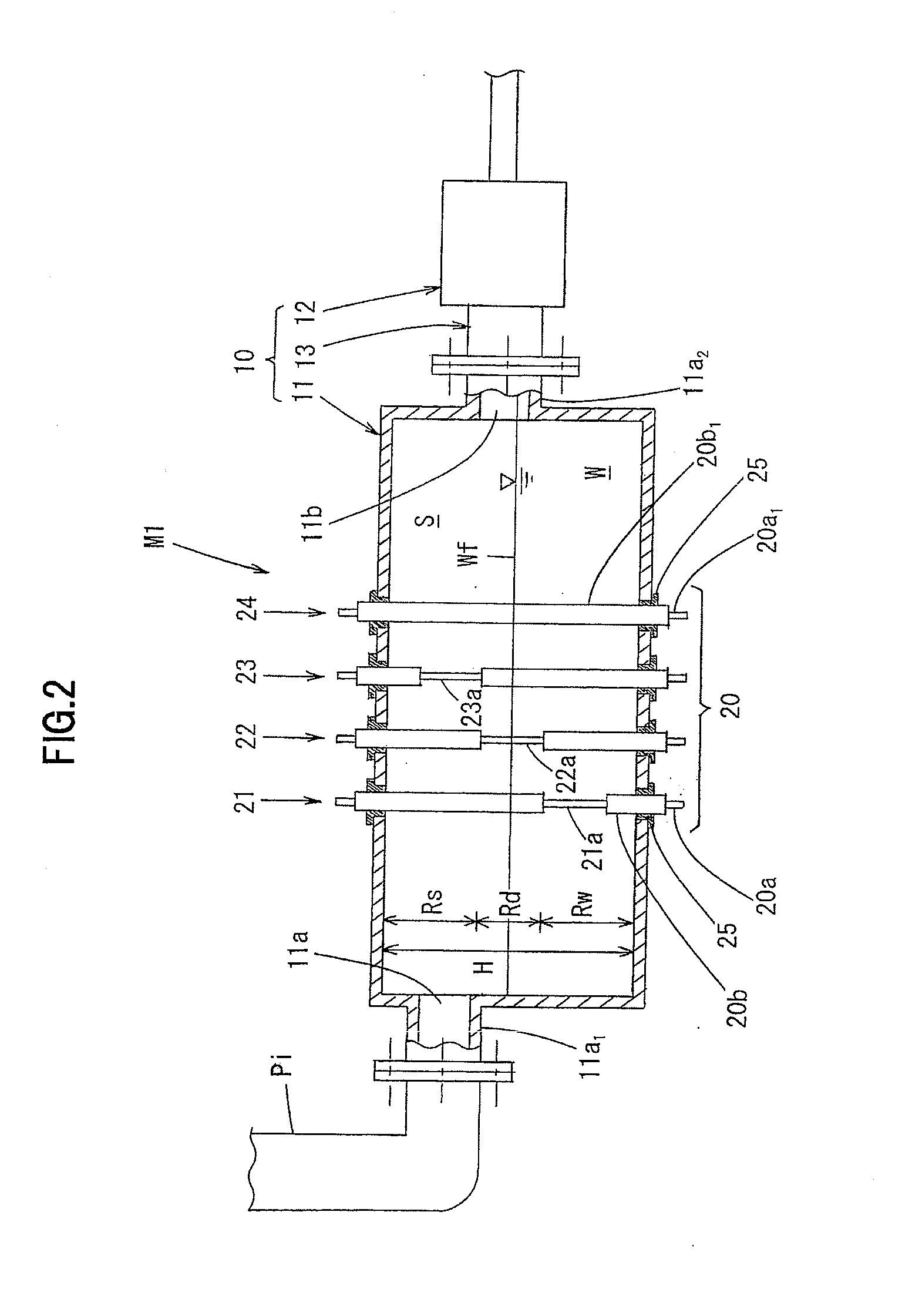
Three-dimensional recording and reproducing apparatus
ActiveUS7286153B1Information stabilityStable reproductionRecording apparatusInking apparatusHigh densityOptical axis
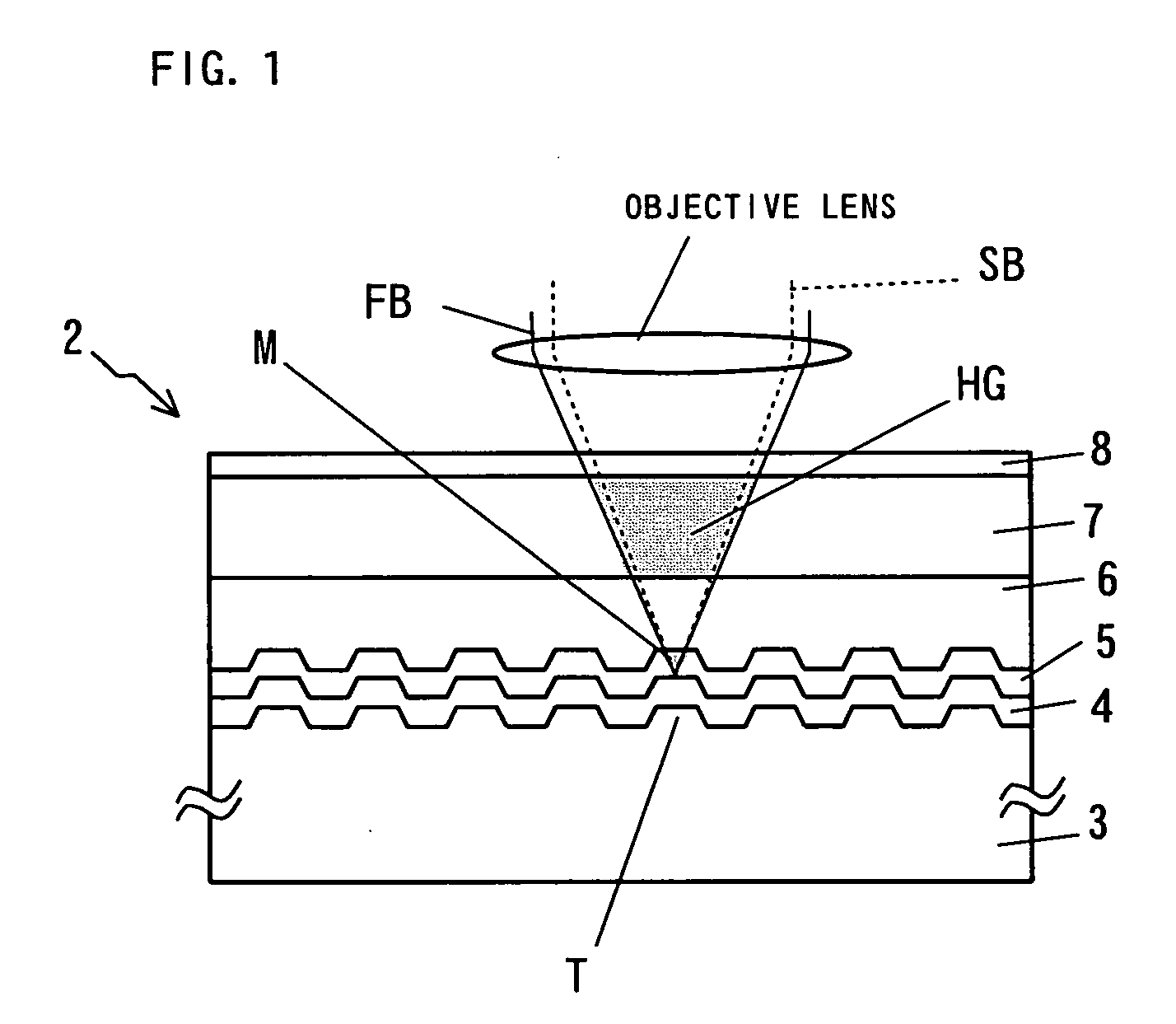
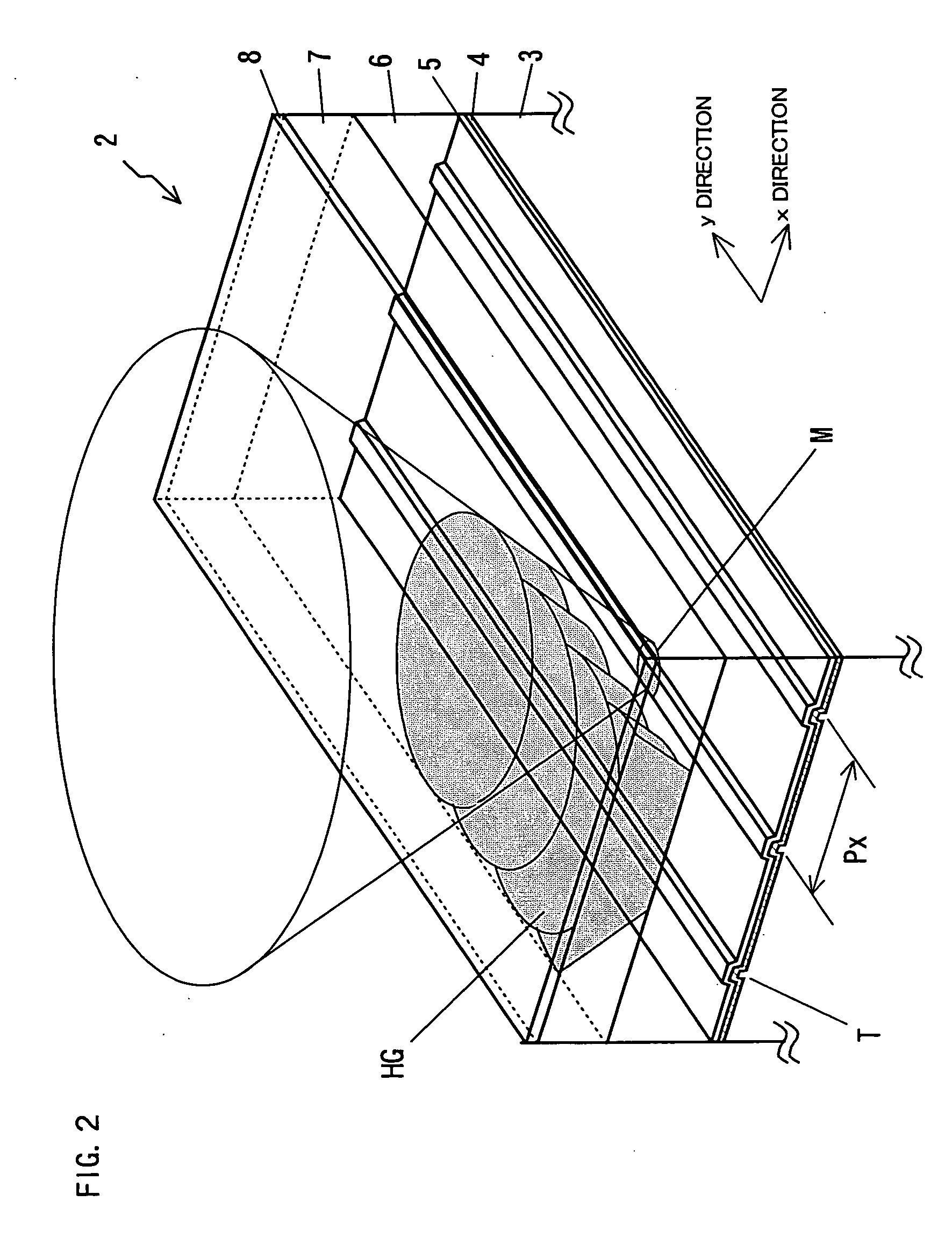
In a three-dimensional recording and reproducing apparatus having a recording medium including a plurality of recording layers stacked on a substrate and an optical system for converging a light irradiated from the substrate side on each of the plurality of recording layers to three-dimensionally record and reproduce information, the following equation is satisfied:λ / 4≦(1 / 8NB)(1 / NB2−1)NAF4Δd whereλ: Wavelength of the light;NB: Refractivity of the substrate 3; NAF: Numerical aperture of a focus lens 8 for converging a light;Δd: Positional range in the optical axis direction in which exists a recording layer on which the light is to be converged.A light spot is focused on each layer of the multi-layer structured disc to record and reproduce highly reliable data in a high density.
Owner:HITACHI CONSUMER ELECTRONICS CORP
Remote reproduction system and remote reproduction method
InactiveUS20060128370A1Stable reproductionMaintain continuityInstruments for road network navigationFrequency-division multiplex detailsReproductionEstimation result
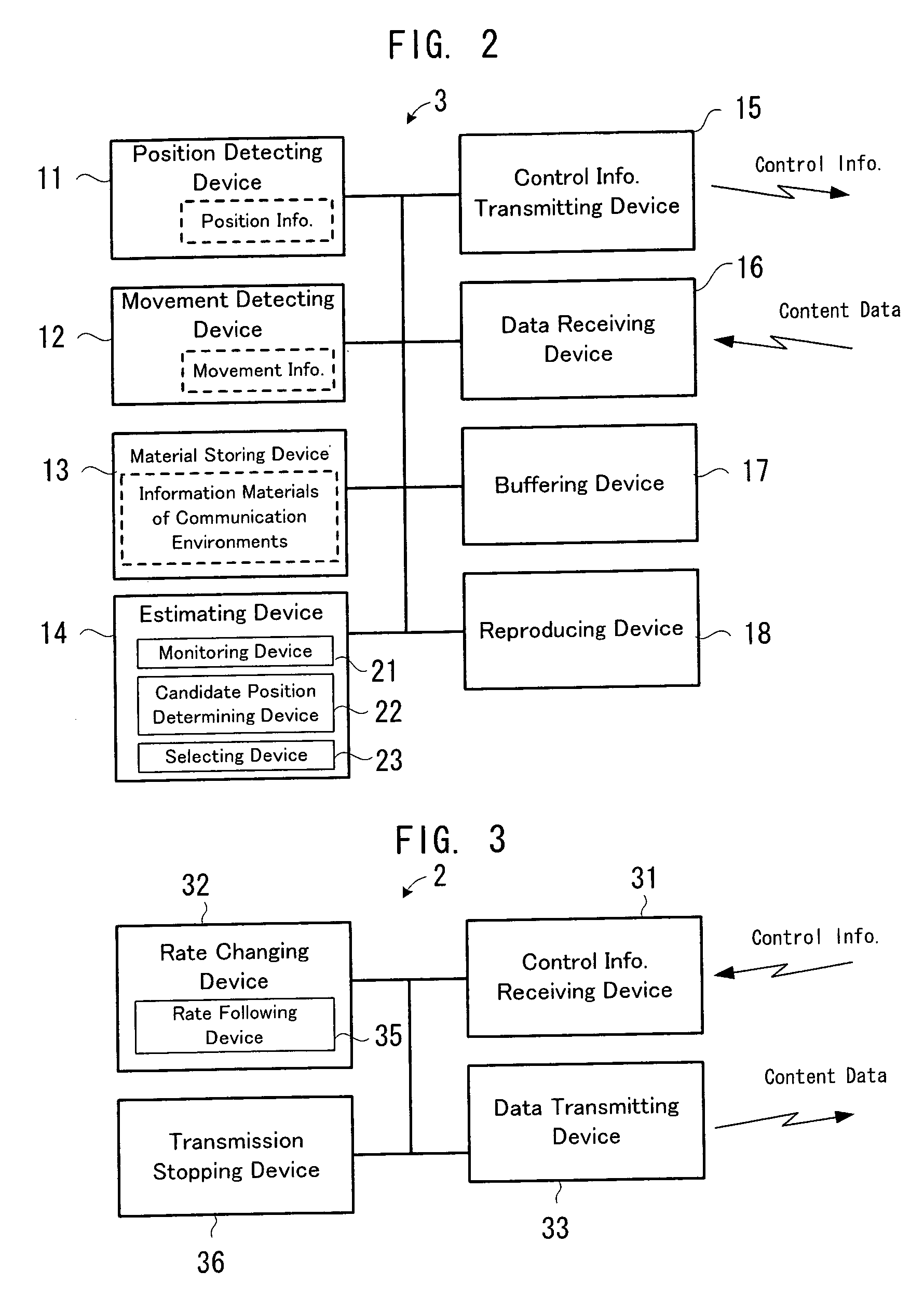
A communication condition between the transmitting apparatus and the mobile receiving apparatus at a future position of the mobile receiving apparatus is estimated on the basis of the position information and the information materials of communication environments. A transmission rate which is related to the transmission of the content data from the transmitting apparatus to the mobile receiving apparatus, is changed on the basis of the estimation result. Alternatively, the transmission of the content data from the transmitting apparatus to the mobile receiving apparatus is temporarily stopped, on the basis of the estimation result.
Owner:PIONEER CORP
Sea cucumber microecological water quality conditioning agent and method for preparing same
InactiveCN102616941AReduce stressPrevent diseaseClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaDiseaseWater quality
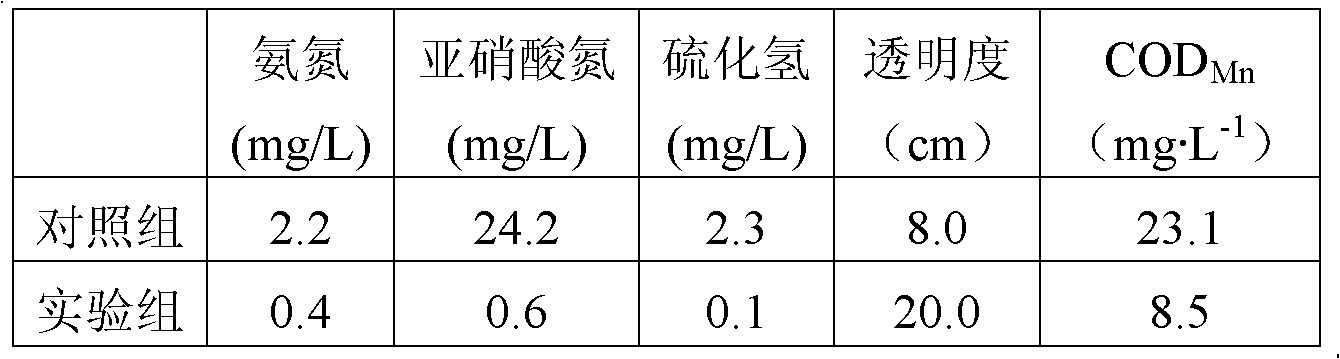
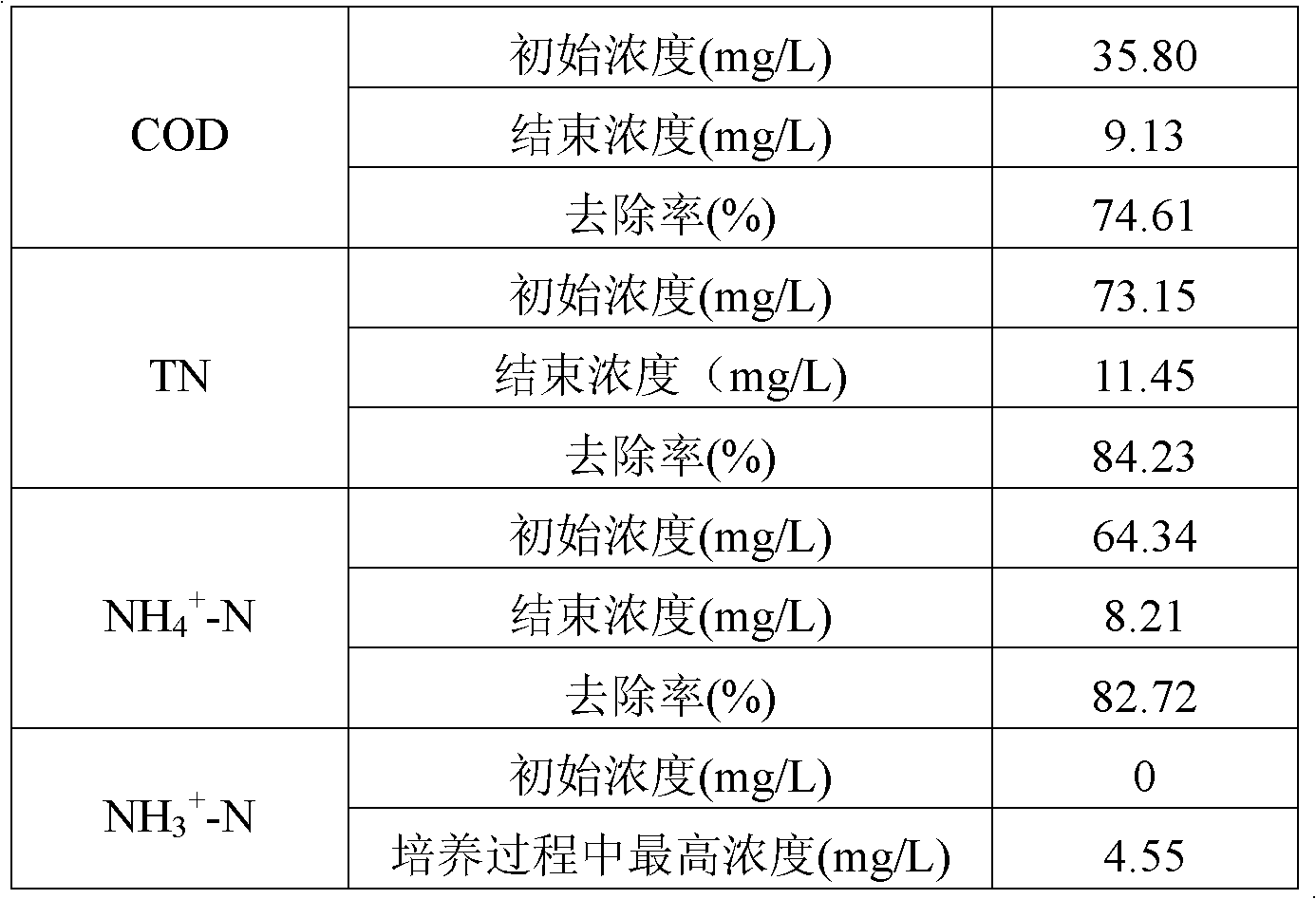
A microecological water quality conditioning agent applicable to restoring of sea cucumber culture water body and a method for preparing the microecological water quality conditioning agent belong to the technical field of aquaculture and microorganisms. By aiming at physiological habits and culturing characteristics of sea cucumbers and applying modern biological technique, the microecological water quality conditioning agent is made of bacillus flexus CGMCC (China general microbiological culture collection center) No.5115, bacillus subtilis CGMCC No.5116 and bacillus cereus CGMCC No.5117, which are separated and sieved from a sea cucumber culturing environment and prepared by steps: using corn starch and soybean cake powder as main culturing materials, fermentating for 24-48h at 25-40 DEG C, and using zeolite and wheat bran as adsorption carriers for processing to obtain the microecological water quality conditioning agent. The microecological water quality conditioning agent is less susceptible to environment conditions, has remarkable purifying effect on sea cucumber culturing water body, and is capable of greatly reducing content of harmful substances such as ammonia nitrogen, nitrite, hydrogen sulfide and the like, deodorizing and effectively restraining pathogenic bacteria so as to prevent sea cucumber diseases and improve yield and quality of cultured sea cucumbers.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Projector color correcting method
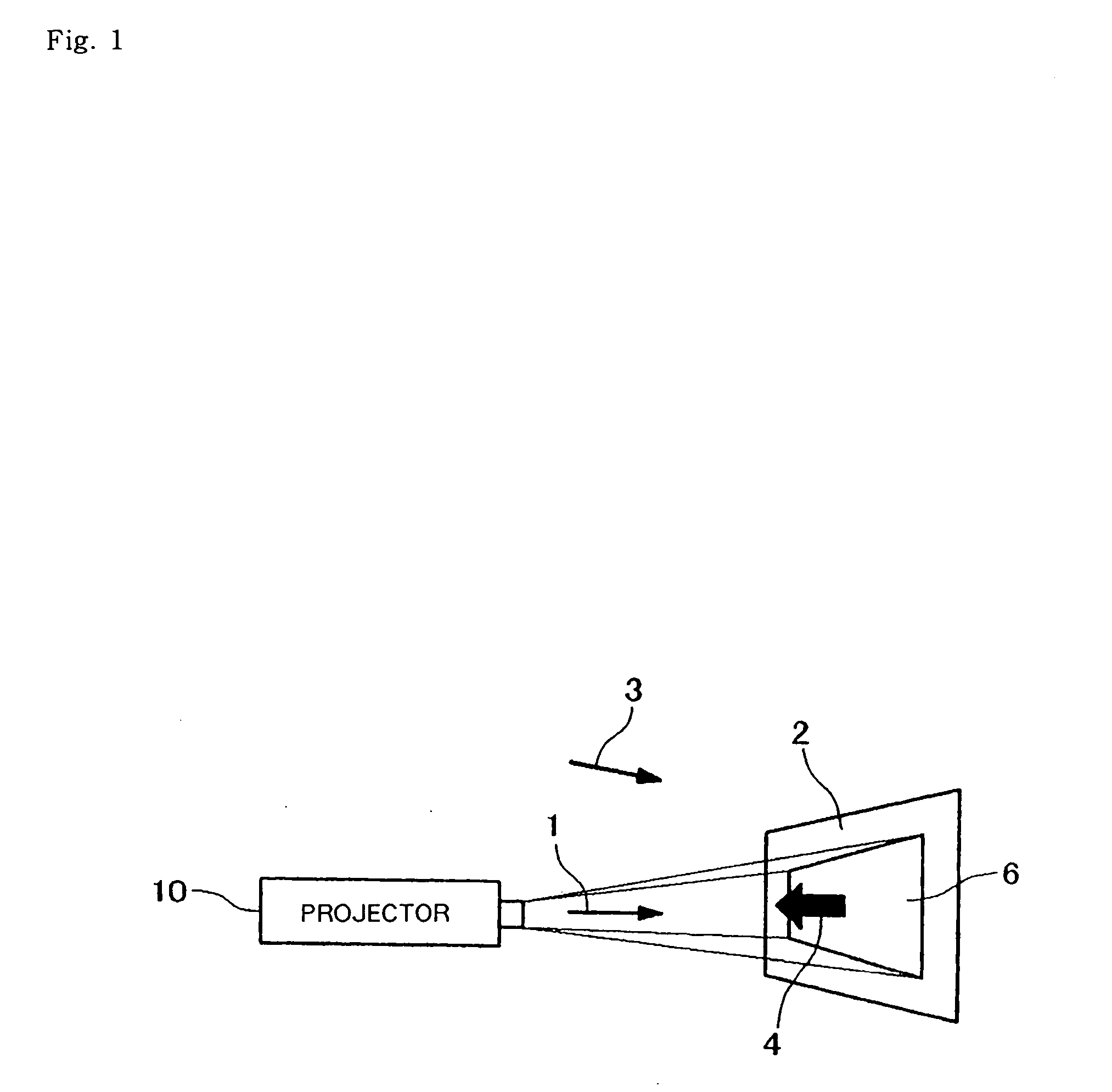
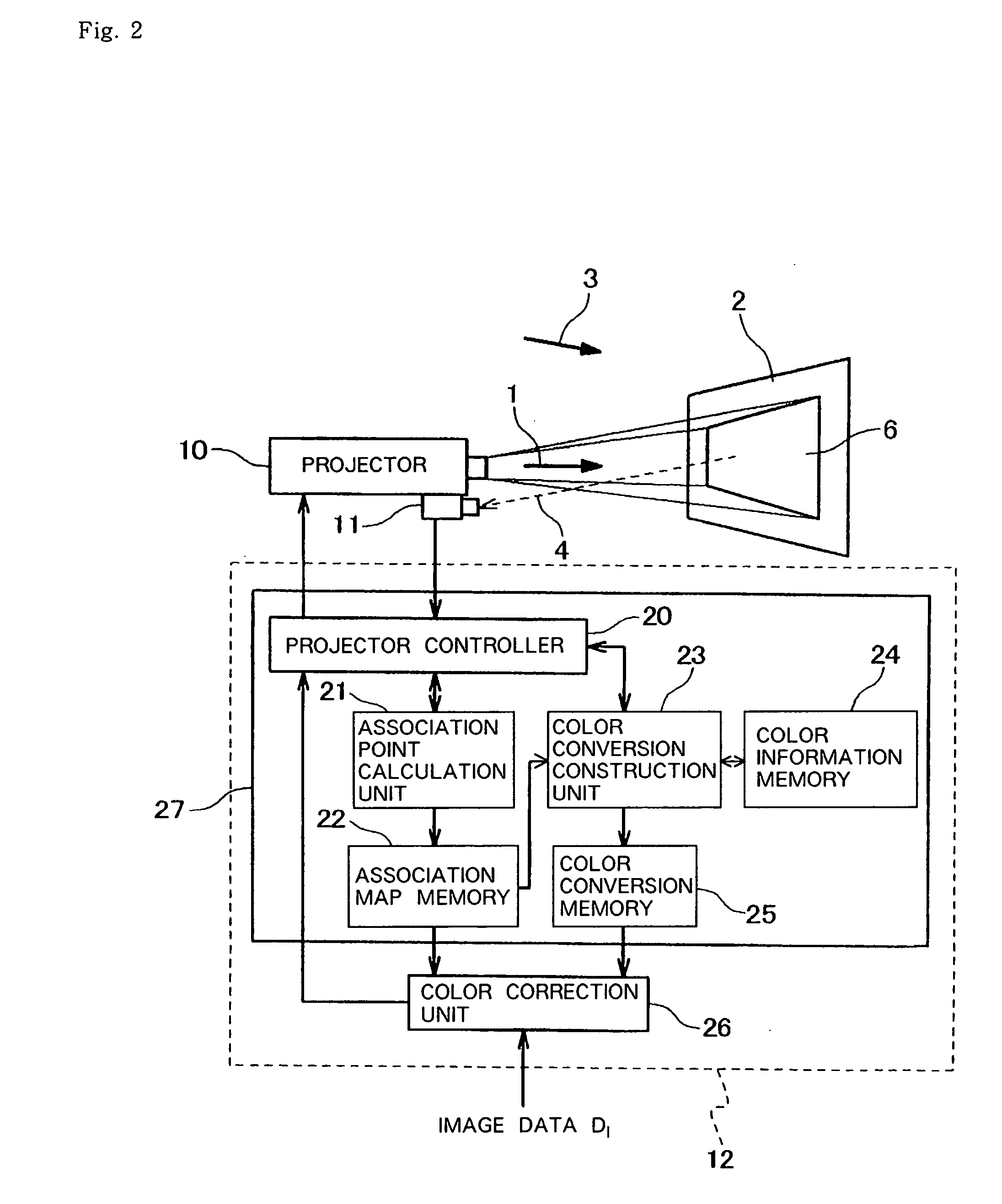
InactiveUS20070110304A1Stable color reproductionAlleviating influence of lacking of uniformity in colorColor signal processing circuitsProjectorsColor correctionProjection plane
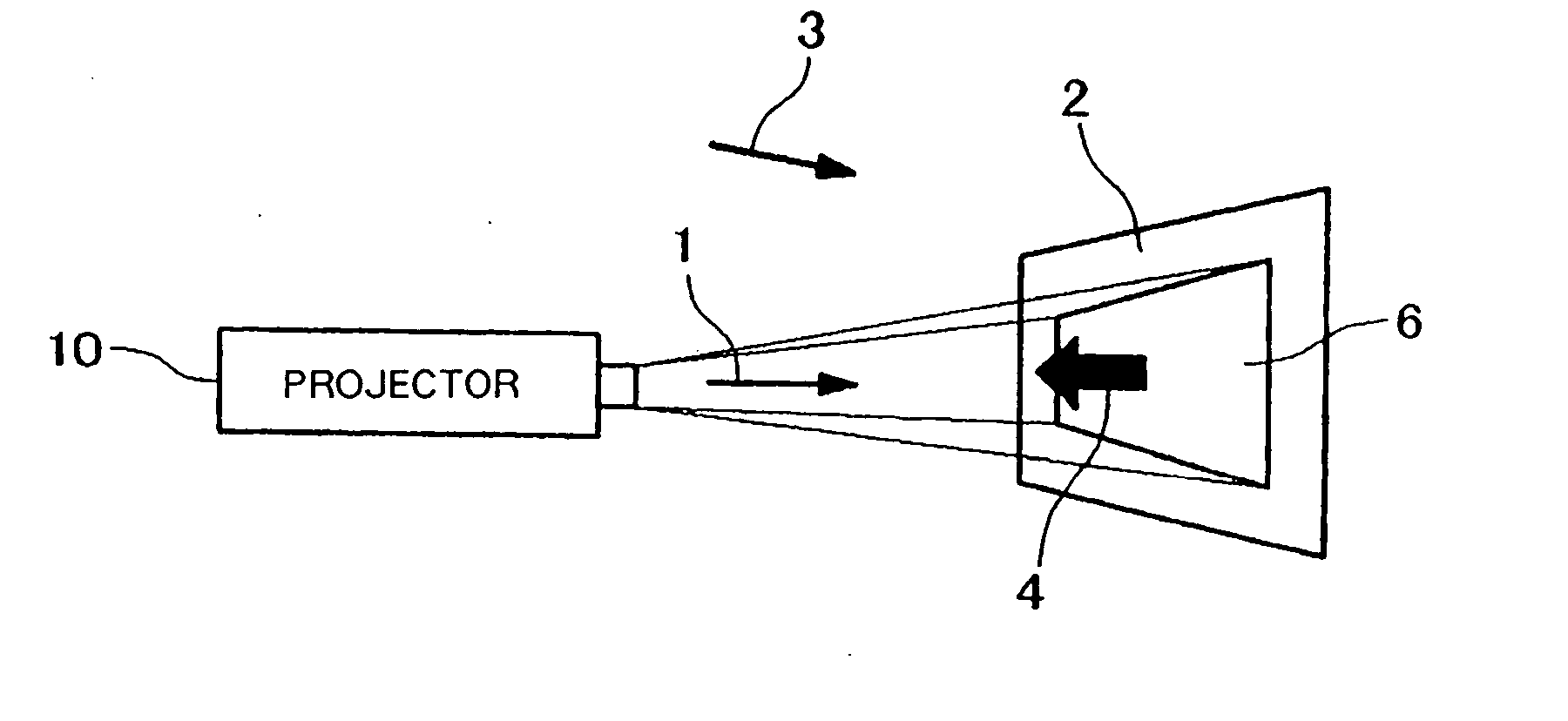
When a projection plane is not uniform due to colors and patterns on the projection plane and ambient environmental light, a reproduced image projected by a projector is made to appear in desired colors. A color correcting apparatus is used, comprising association unit (21), association storage memory 22, color information acquisition unit (23), color conversion calculation unit (23), color conversion storage memory (25), and color correction unit (26). Association unit (21) acquires captured image (7) generated by capturing image (5) projected onto projection plane (2) to establish an association between pixels of image (5) and pixels of captured image (7). Association storage memory (22) records the association. Color information acquisition unit (23) acquires second color information as color information for each pixel of the captured image. Color conversion calculation unit (23) calculates a color conversion for each pixel of the image based on first color information, second color information, and the association. Color conversion storage memory (25) records the color conversion. Color correction unit (26) corrects the input image for colors on a pixel-by-pixel basis using the color conversion.
Owner:NEC CORP
Photocurable ink-jet ink, ink-jet image forming method and ink-jet recording apparatus using the same
A photocurable ink for ink-jet printing, including: a photopolymerizable compound; a pigment; and a dispersing agent, wherein the photopolymerizable compound is a radical polymerizable compound; an amine value of the pigment (AMp) is larger than an acid value of the pigment (ACp); and an acid value of the dispersing agent (ACd) is larger than an amine value of the dispersing agent (AMd).
Owner:KONICA MINOLTA MEDICAL & GRAPHICS INC
Colorful haze image defogging and illumination compensation restoration method
InactiveCN103914813AFully describe the physical causesDescribe the physical causesImage enhancementPattern recognitionRestoration method
The invention discloses a colorful haze image defogging and illumination compensation restoration method. The method mainly solves the problems of restoration result color distortion, halo artifacts and darker halos existing in the prior art. The method comprises the steps of using a dark channel image D (x, y) of a haze image I (x, y) for initially estimating air curtain images, conducting gray opening operation on the dark channel image, and obtaining an air curtain image rough estimation image D' (x, y); taking the dark channel image as a guide image, conducting guide filtering on the air curtain image rough estimation image, and obtaining an air curtain image V (x, y); conducting difference on the haze image and the air curtain image, and obtaining a residual image E (x, y); conducting gray closing operation on a bright channel image B (x, y) of the residual image, and obtaining an illumination component image rough estimation image B' (x, y); taking the bright channel image as a guide image, conducting guide filtering on the illumination component image rough estimation image, and obtaining an illumination component image L (x, y); substituting the illumination component image into an illumination-reflection imaging model, and conducting solving to obtain a restoration result. According to the method, a clear image can be stably restored without calculating ambient light and transmissivity.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Mach-zehnder interferometer type optical modulator
InactiveUS20110243491A1Reduce adverse effectsSuppress lightNon-linear opticsMach–Zehnder interferometerOptical coupler
A Mach-Zehnder interferometer type optical modulator includes a first end facet and a reflecting portion opposing the first end facet; a single optical coupler including input and output ports, the optical coupler being disposed between the first end facet and the reflecting portion; first and second optical waveguides that are connected to the input ports of the optical coupler; third and fourth optical waveguides that are connected to the output ports of the optical coupler; and a phase shifting section disposed between the optical coupler and the reflecting portion. The phase shifting section includes a first optical waveguide structure constituting part of the third optical waveguide; a first upper electrode on the first optical waveguide structure; a second optical waveguide structure constituting part of the fourth optical waveguide; and a second upper electrode on the second optical waveguide structure.
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC IND LTD
Voice coil assembly, loudspeaker using the same, and method for producing the same
InactiveUS20090116681A1Reduced divided vibrationIncrease bobbin rigidityTransducer detailsElectromagnetsBobbinEngineering
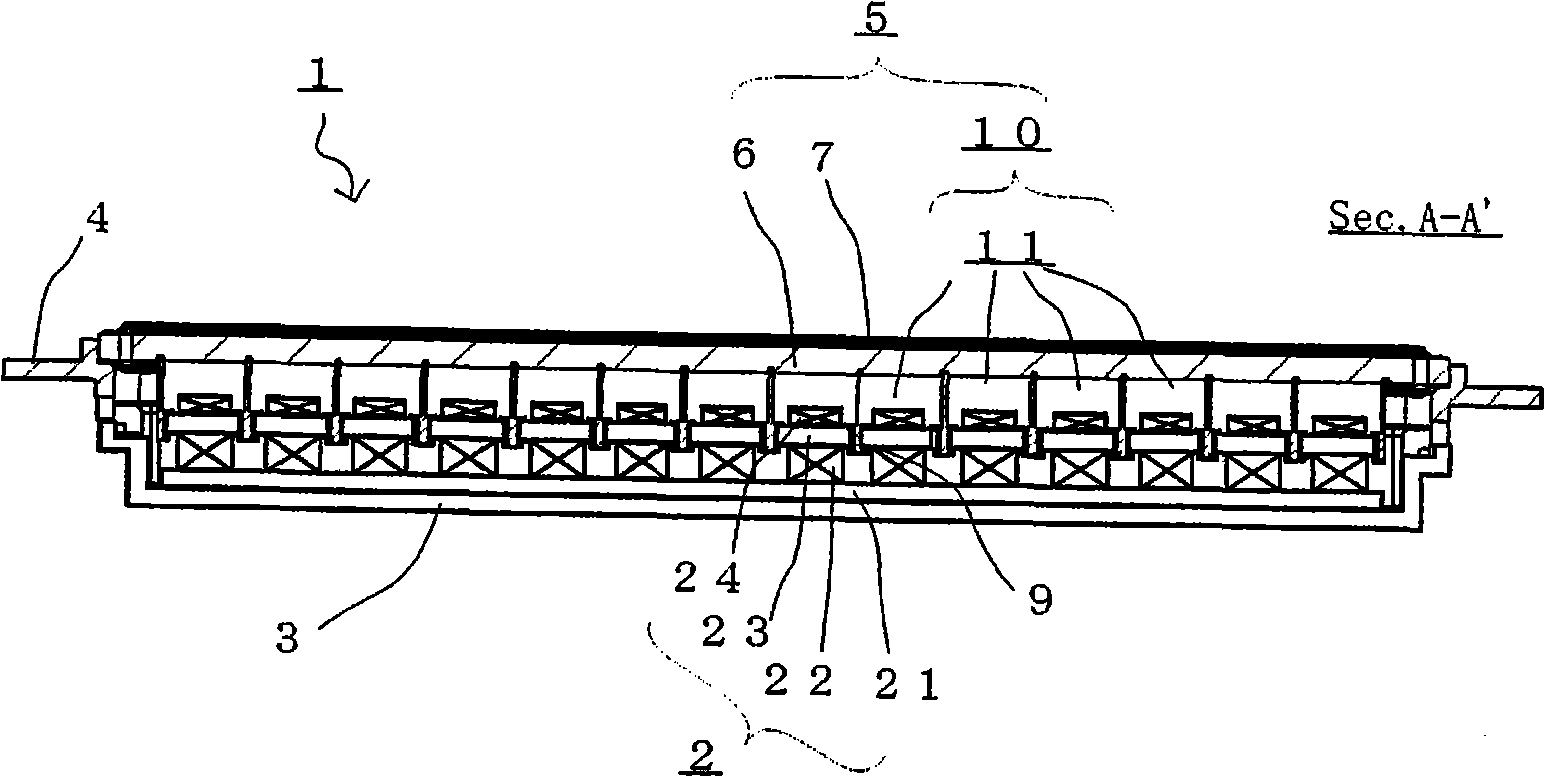
A voice coil assembly capable of realizing a flat thin loudspeaker having a high efficiency, reduced divided vibrations, a flat frequency response, and reduced operation defects. The voice coil assembly includes a plurality of internal-winding voice coils, each including a rectangular bobbin having a rectangular cross section and defining a rectangular space therein and an internal rectangular coil fixed to an inner wall surface of the rectangular bobbin defining the rectangular space, wherein an outer wall surface of the rectangular bobbin of one internal-winding voice coil is adhered and fixed to an outer wall surface of the rectangular bobbin of another internal-winding voice coil.
Owner:ONKYO KK
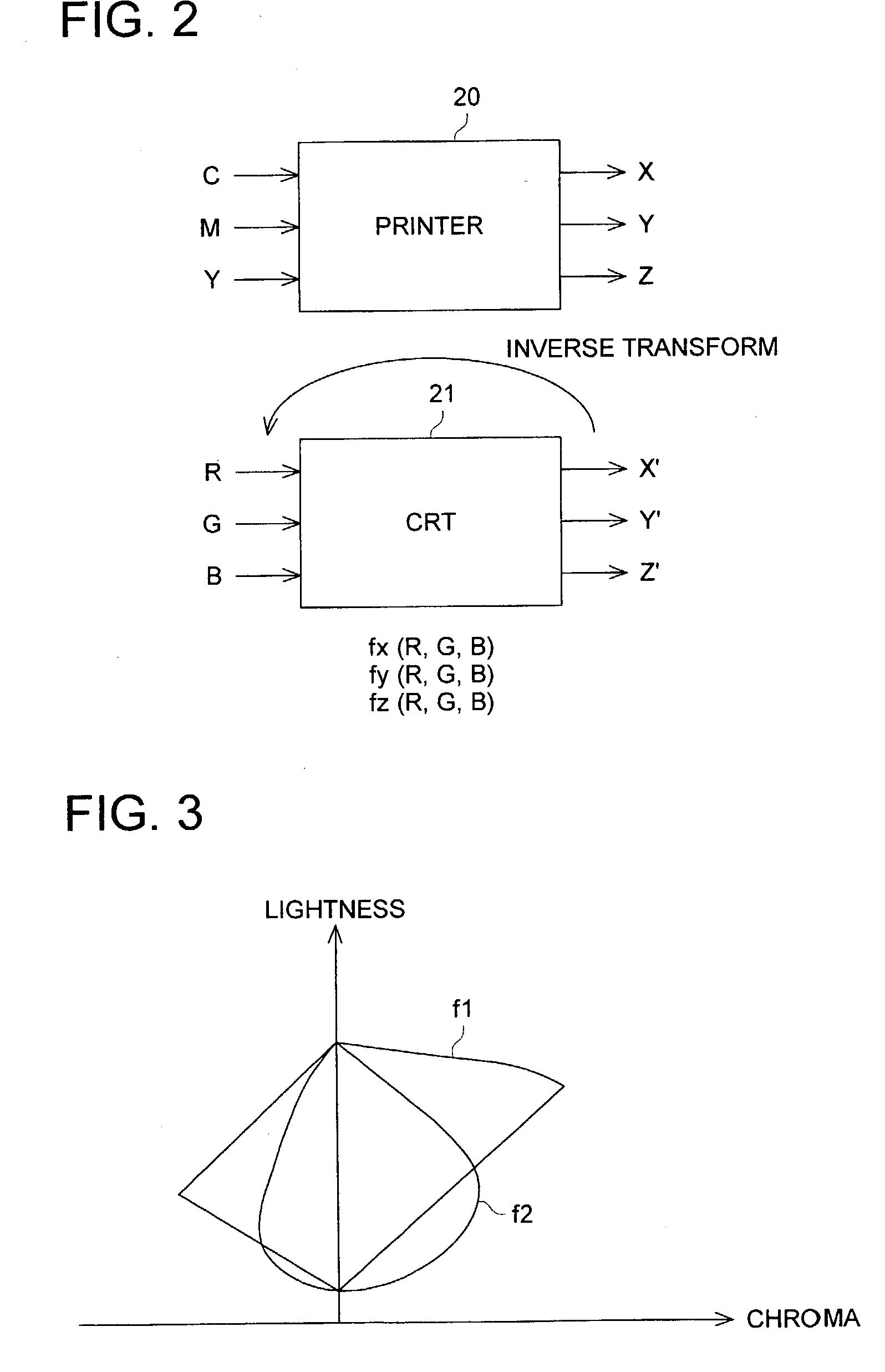
Color image processing method and color image processing apparatus
ActiveUS7142710B2Stable reproductionEasy to giveCharacter and pattern recognitionImage data processing detailsImaging processingImage signal
An image processing method for subjecting image signals from an image input apparatus to a color transform and an image processing for an output apparatus, including the steps of conducting a first color transform process to practice color transform from data for a first image medium into data for a second image medium; and conducting a second color transform process to practice a color transform from data for the second image medium to data for the first image medium, wherein the first color transform process and the second color transform process are in an approximately inverse relation with each other.
Owner:KONICA CORP
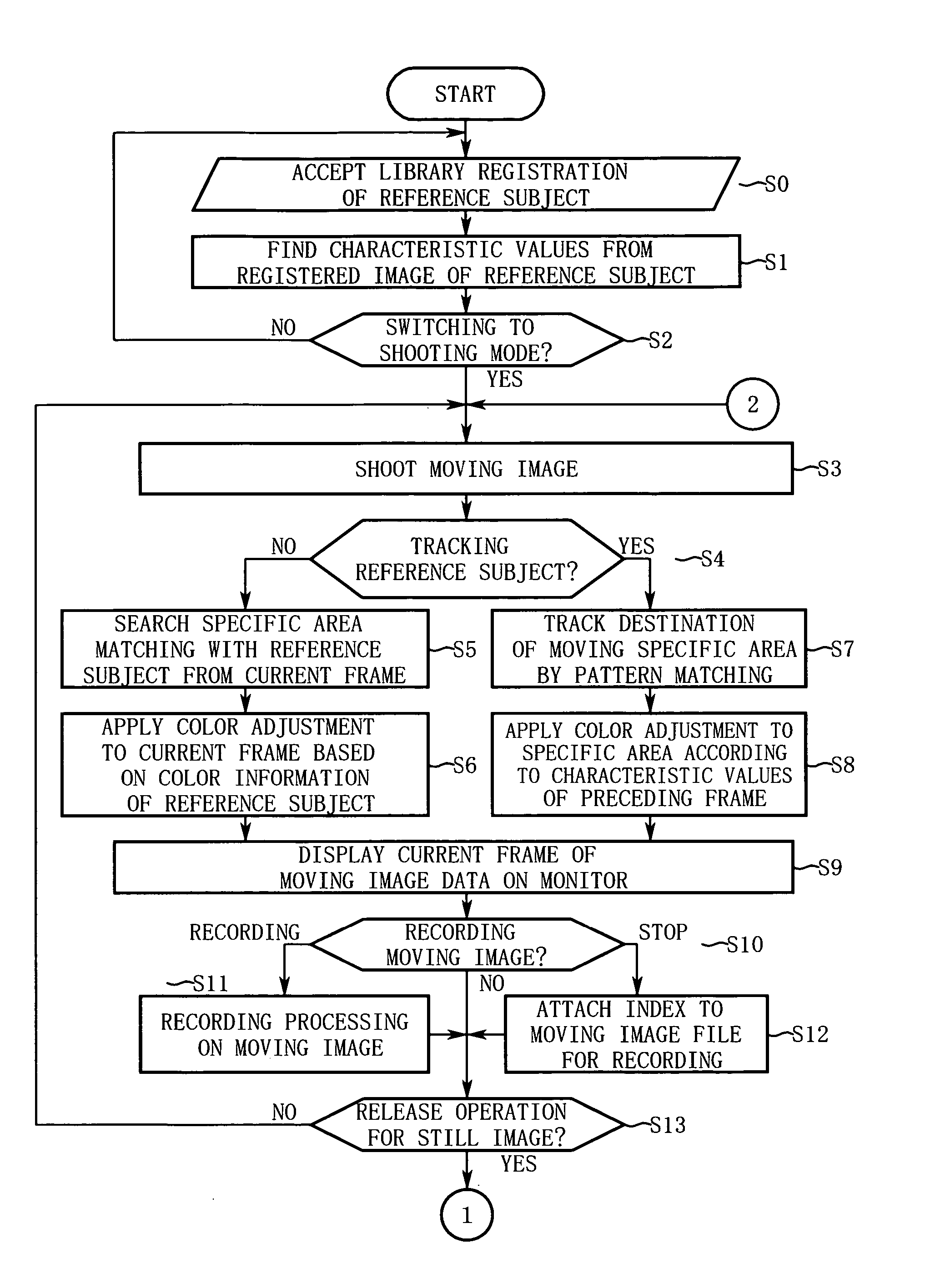
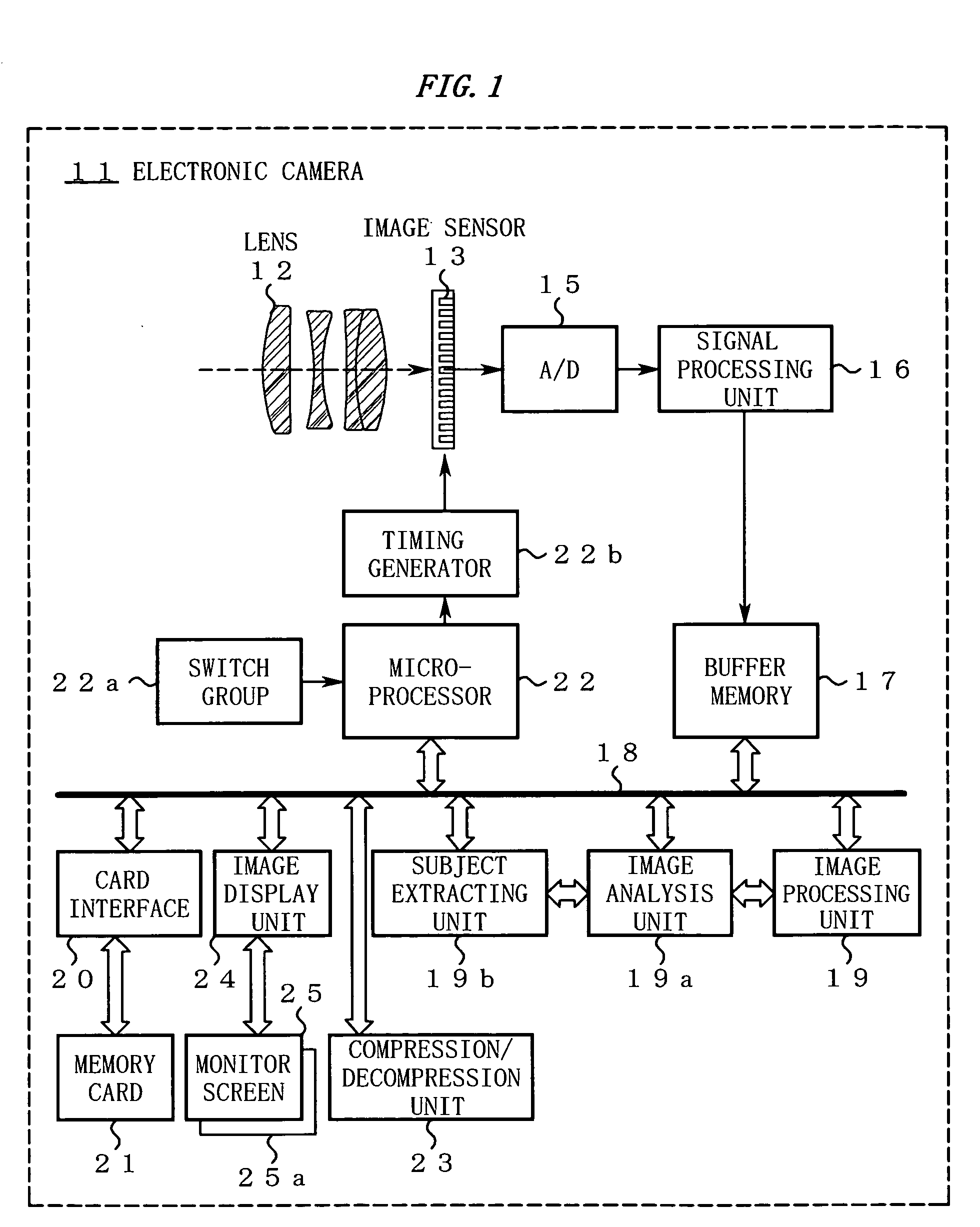
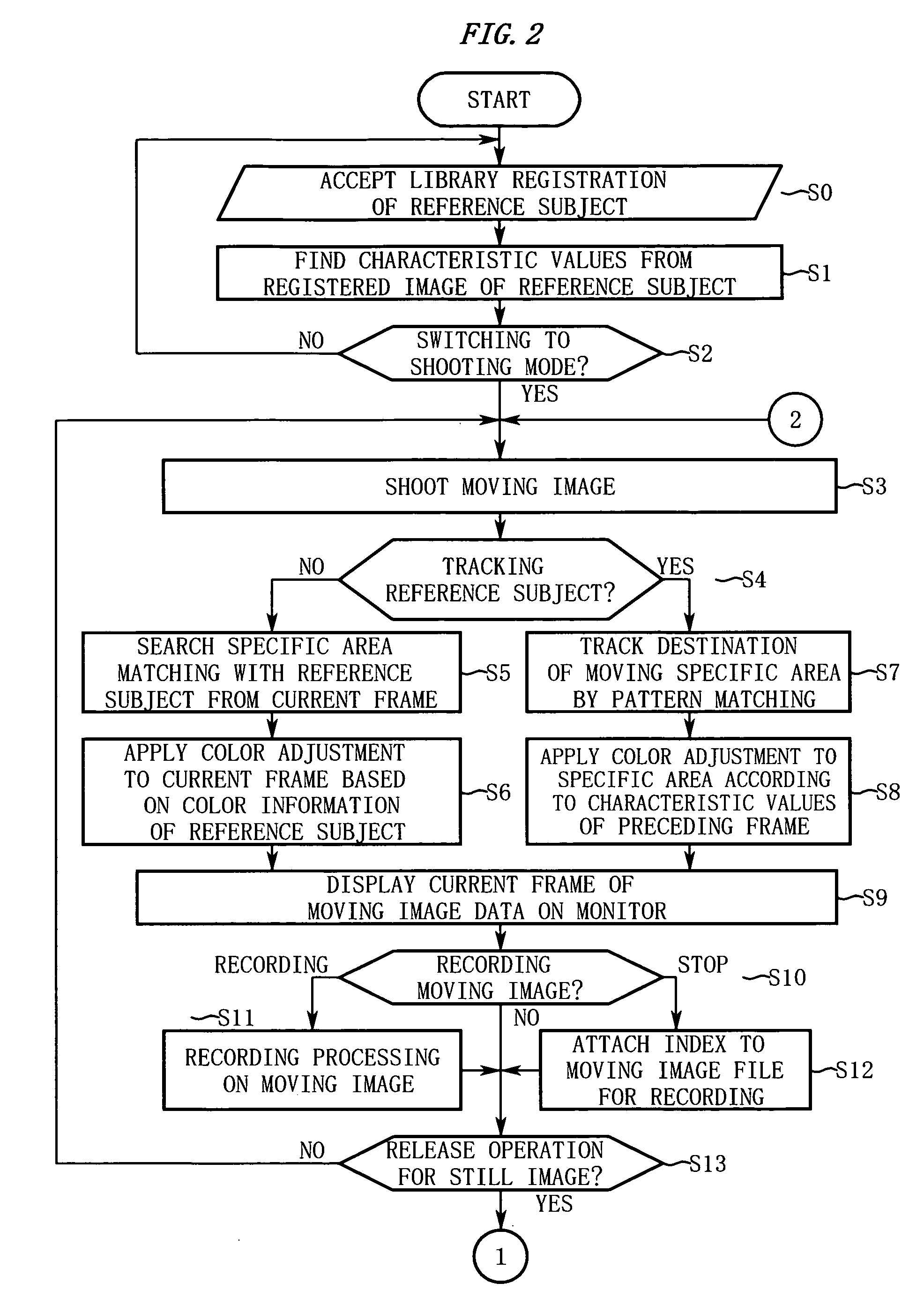
Imaging device having image color adjustment function
InactiveUS20060055784A1Stable color reproductionInhibition effectTelevision system detailsPicture signal generatorsImaging dataImage area
An imaging device according to the present invention includes a registration unit, an imaging unit, a searching unit, and a color adjustment unit. The registration unit registers a reference subject. The imaging unit shoots a subject and outputs image data. The searching unit searches a specific area matching with the reference subject from an image area of the image data. The color adjustment unit performs color adjustment such that color information of the specific area approximates to the color information of the registered reference subject.
Owner:NIKON CORP
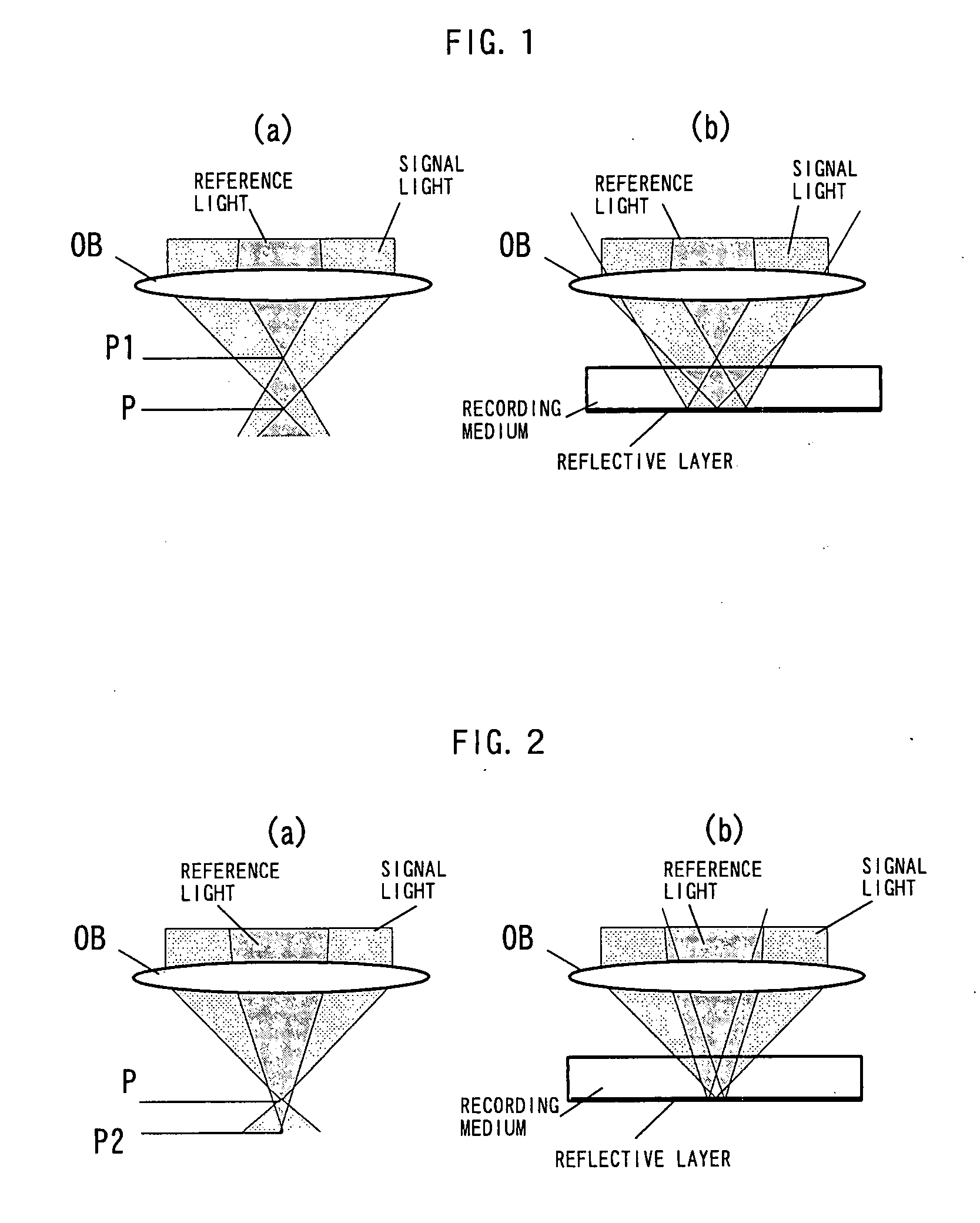
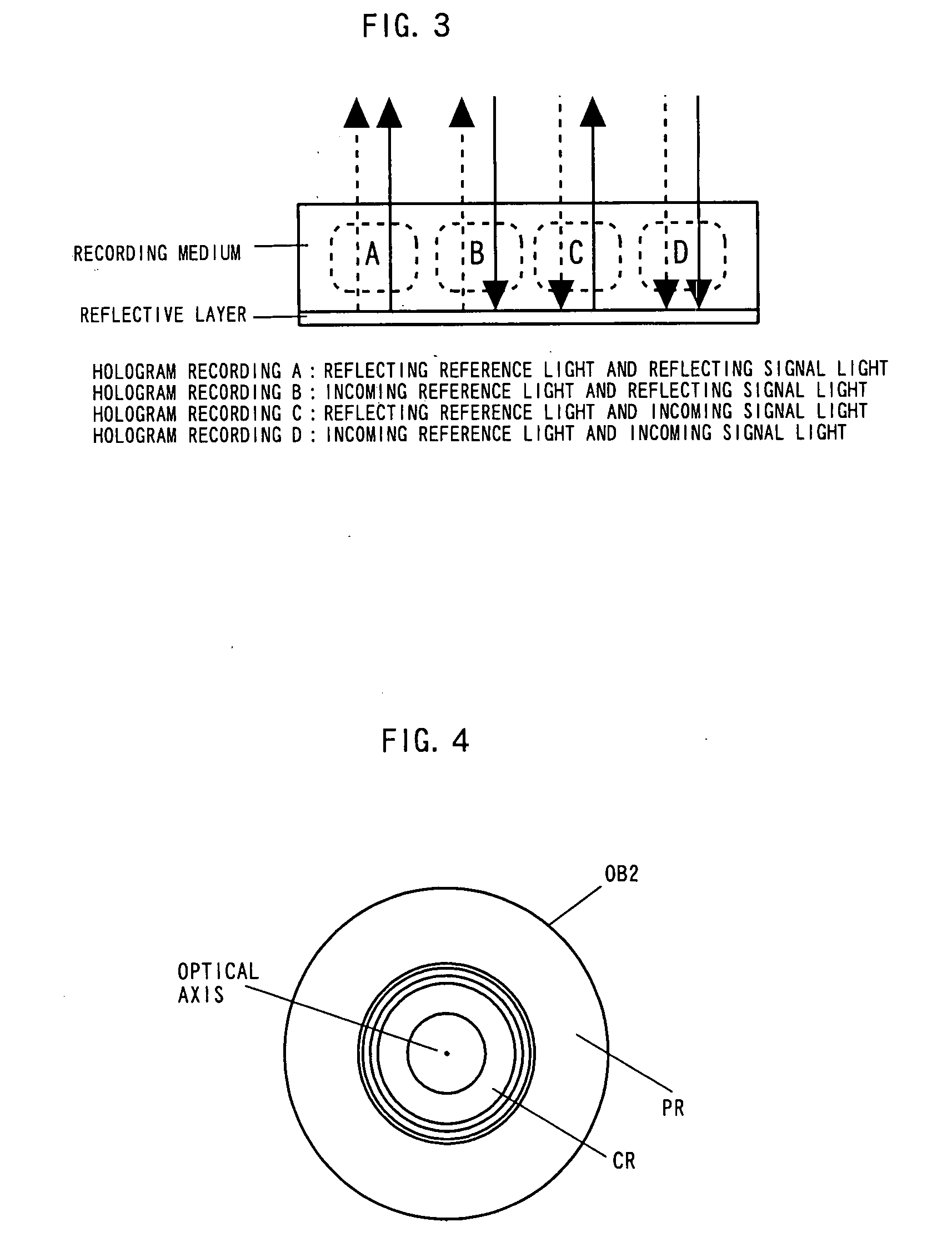
Hologram recording medium and recording and reproducing system
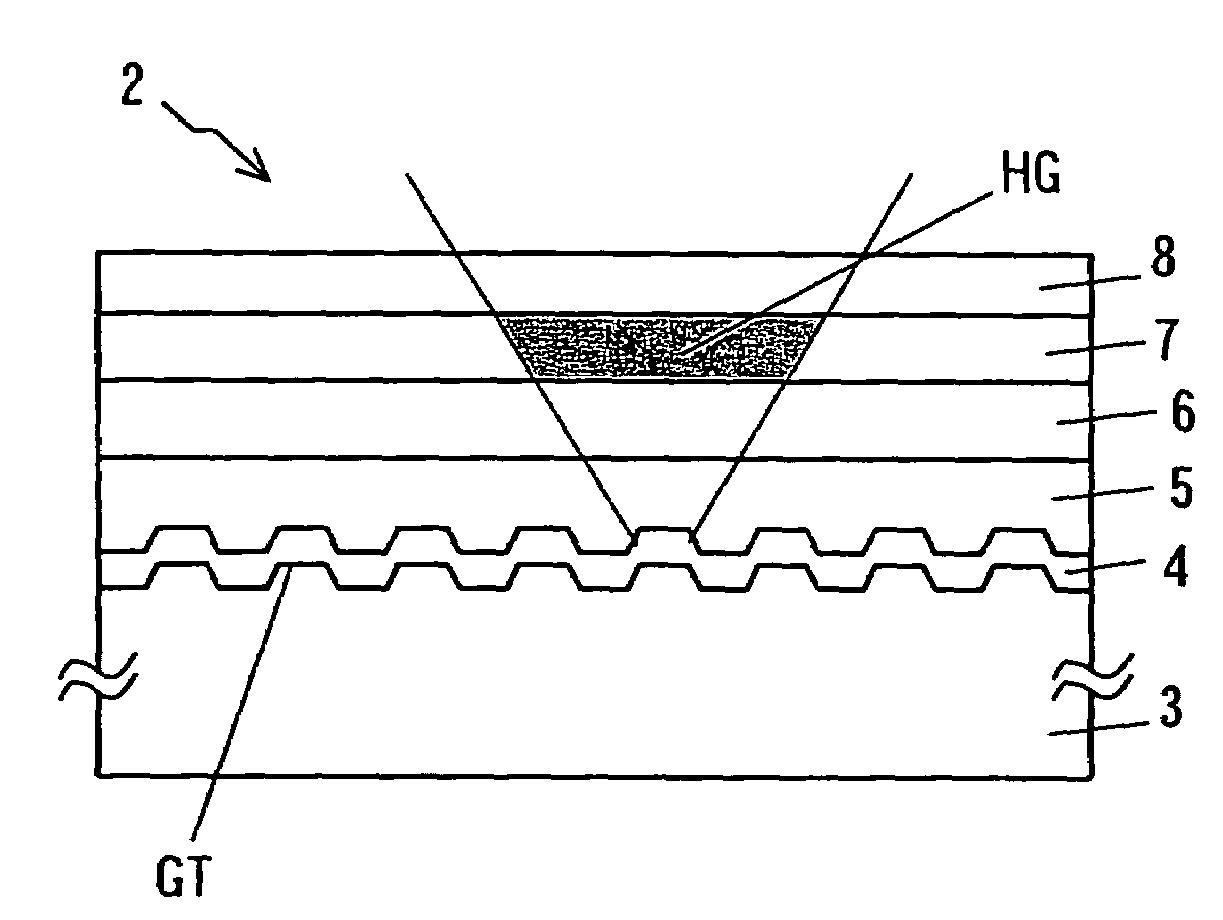
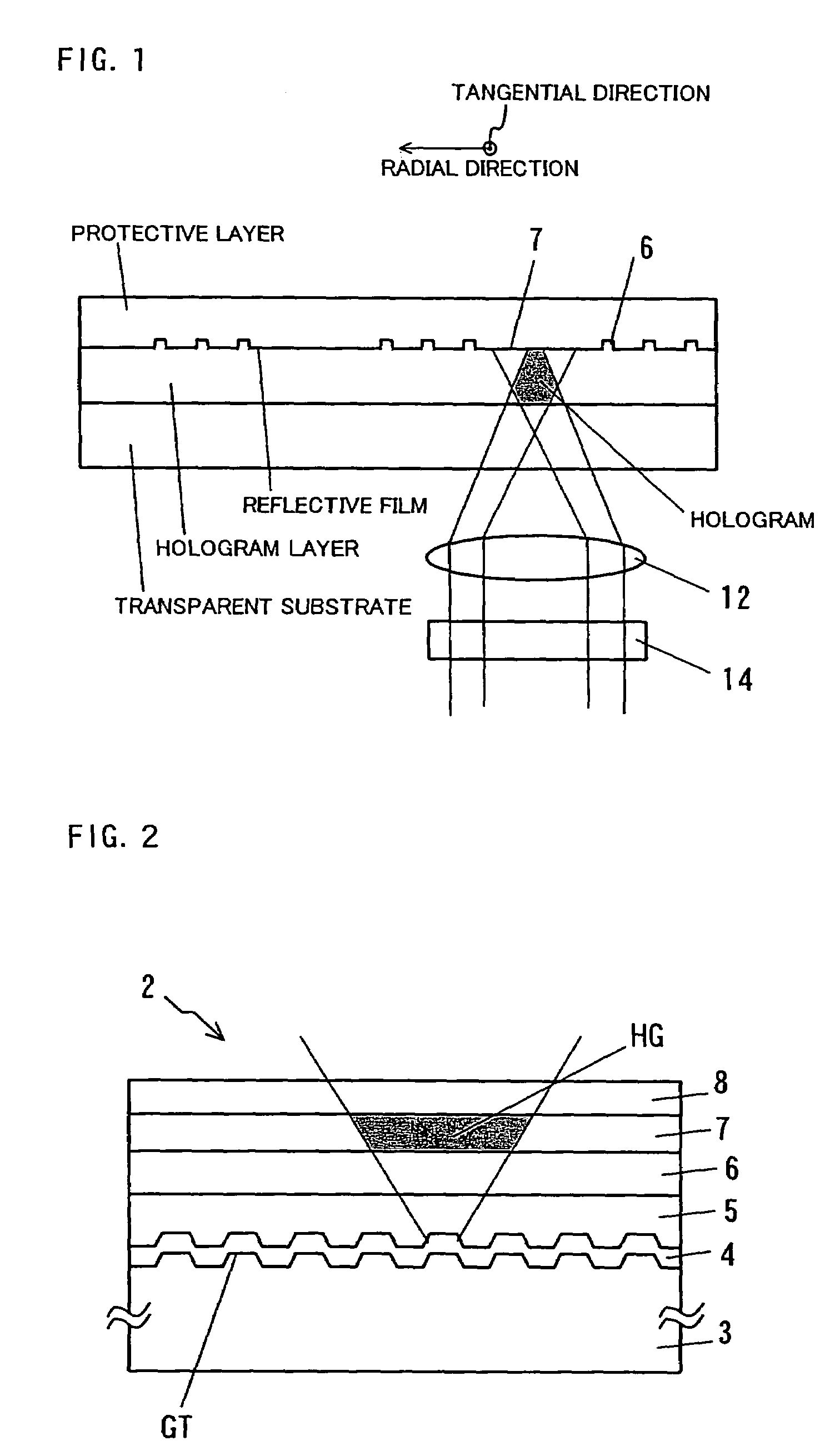
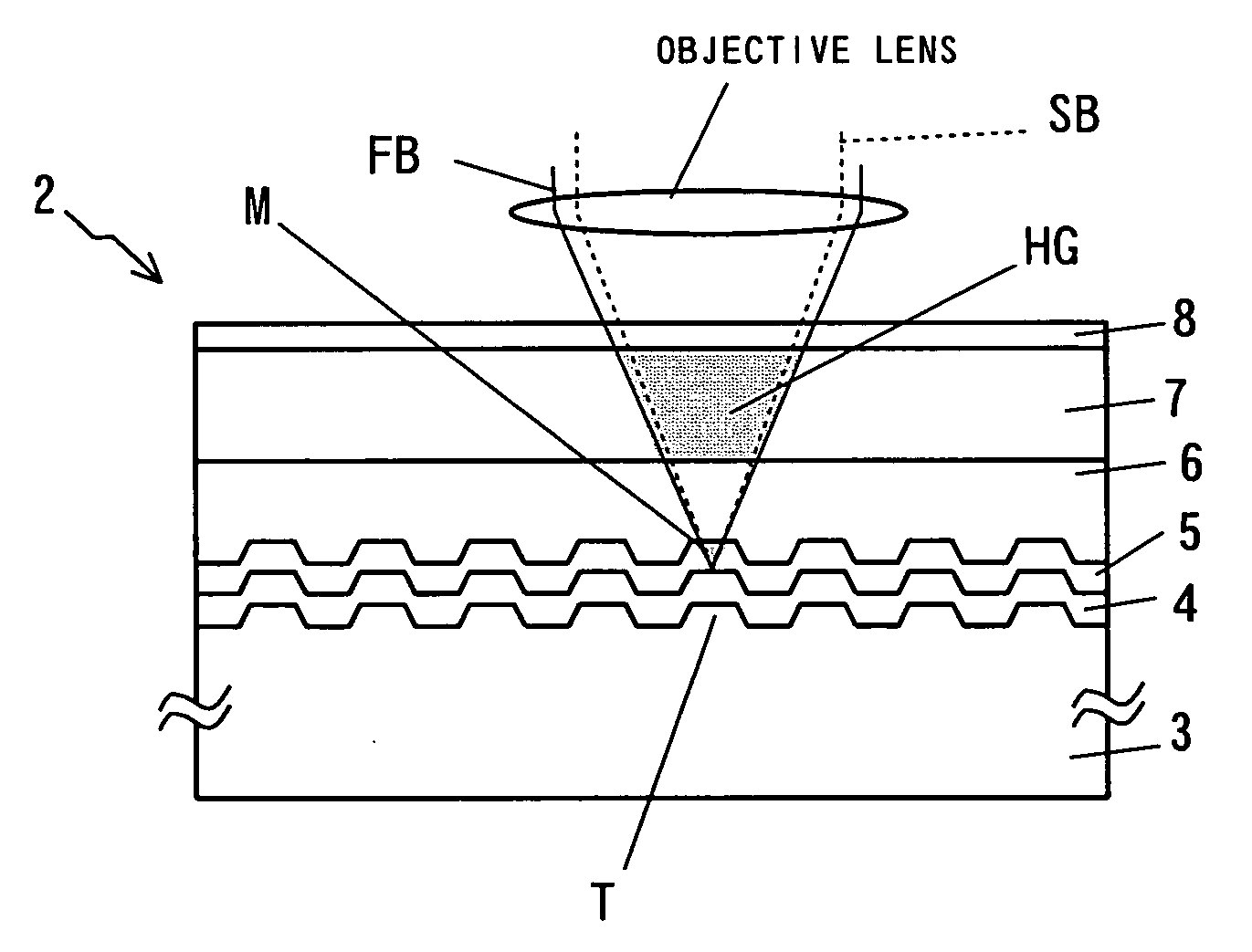
InactiveUS7170661B2Stable reproductionOptical beam sourcesRecord information storageLight beamRecording layer
Owner:PIONEER CORP
Hologram Recording Carrier and Recording/Reproduction Method and Device
InactiveUS20080037083A1Stable recordStable reproductionRecord information storageOptical beam guiding meansLight irradiationSignal light
A hologram record carrier has a substrate and a reflective layer, wherein recording or reproducing of information is performed by light irradiation. The hologram record carrier further comprises a holographic recording layer that reserves an optical interference pattern comprising components of coherent reference light and signal light as a diffractive grating therein, and a two-dimensional recording layer that is laminated in a film thickness direction of the holographic recording layer and whose physical property changes in response to light intensity.
Owner:PIONEER CORP
Optical disk unit for recording or reproducing information
InactiveUS6937544B2Stable reproductionOptical beam sourcesRecord information storageOptical pickupLight beam
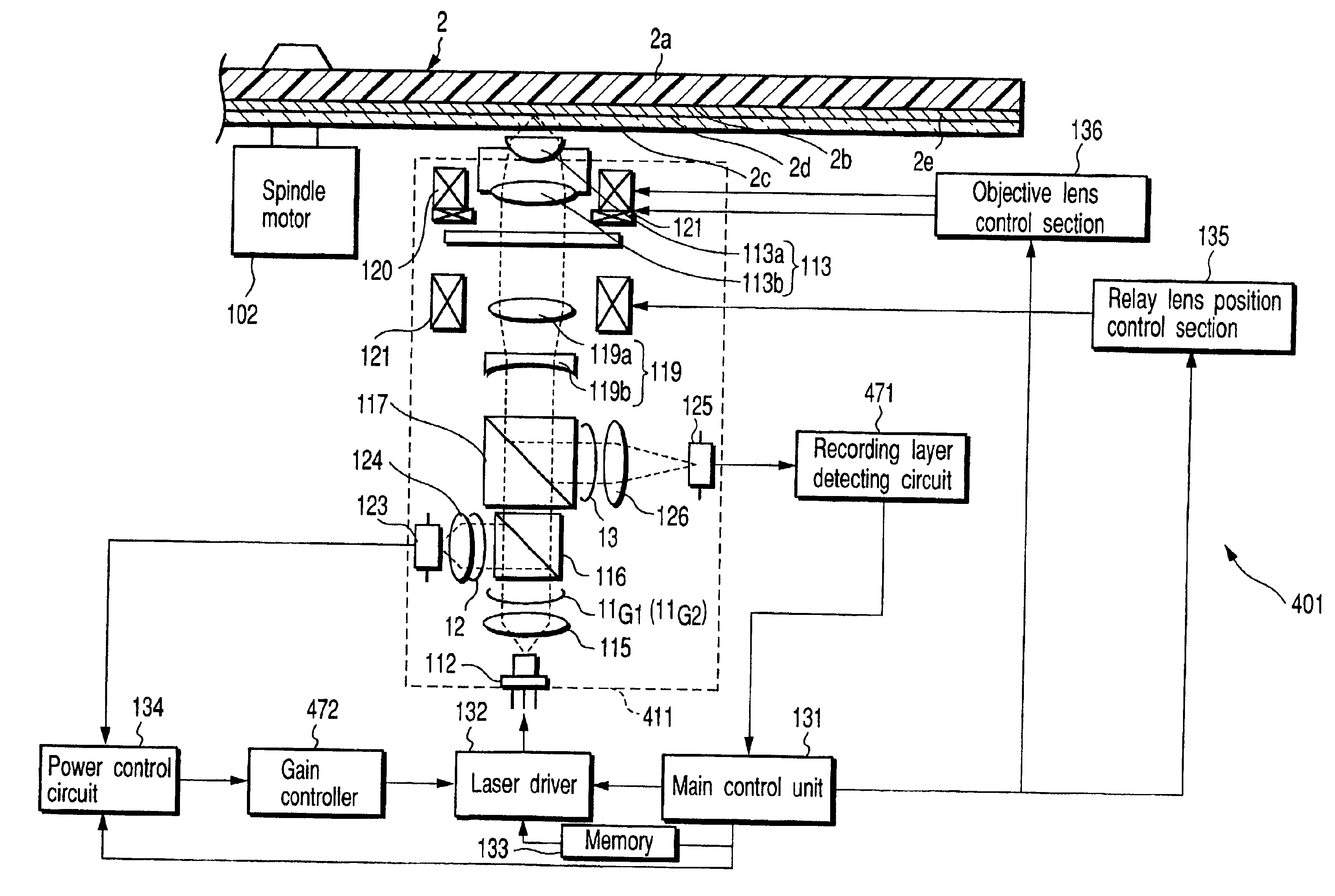
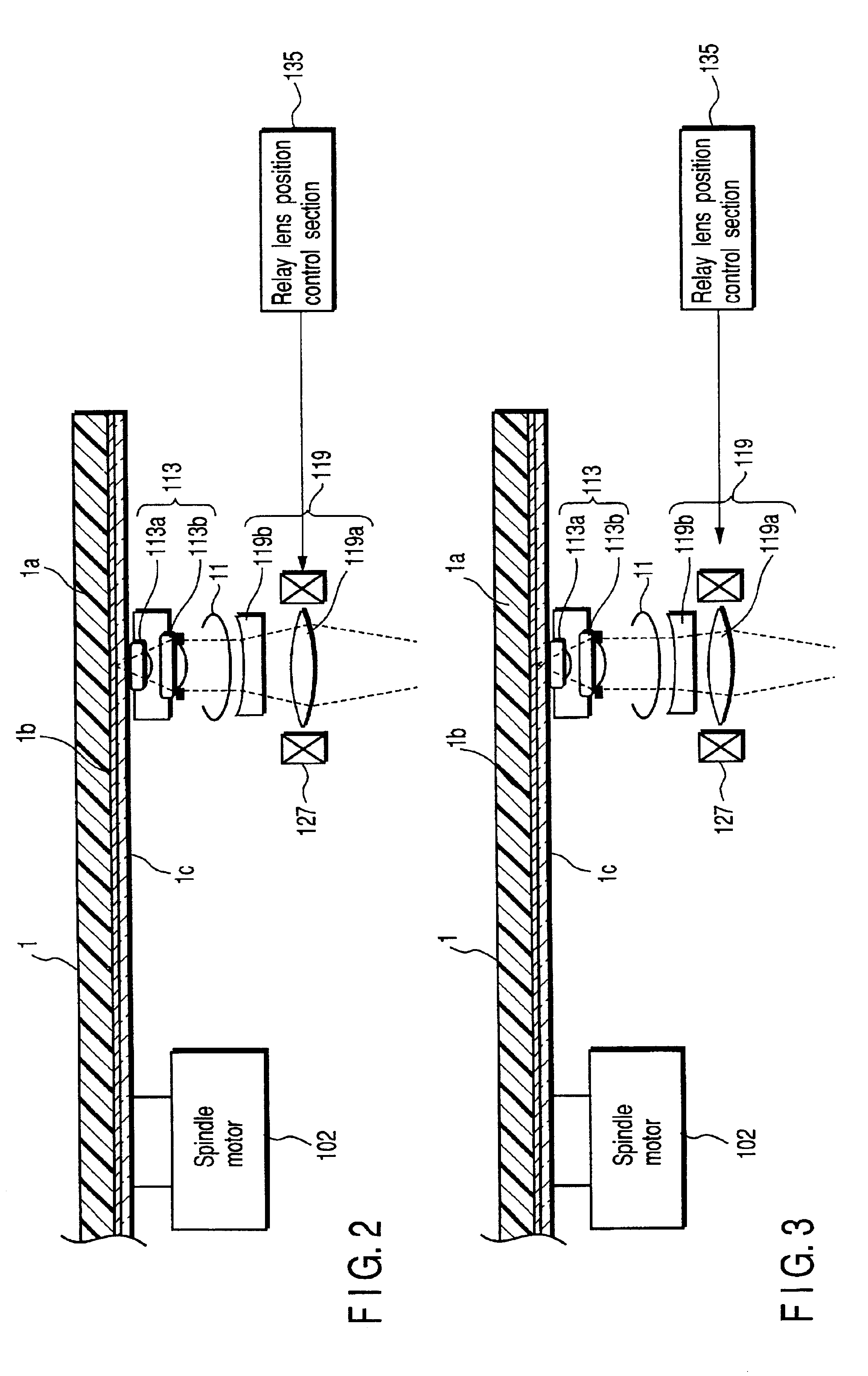
The present invention relates to an optical head device and an optical disk unit using the same. The optical head device includes a relay lens control unit to control at least one of lenses of a relay lens unit based on an output signal outputted from a first optical detector and a power control circuit to control an intensity of a light beam emits from a light source.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Recording medium, optical disk apparatus and writing method
InactiveUS20080037395A1Assure continuityHigh reproduction qualityRecording strategiesFilamentary/web record carriersEngineeringTime control
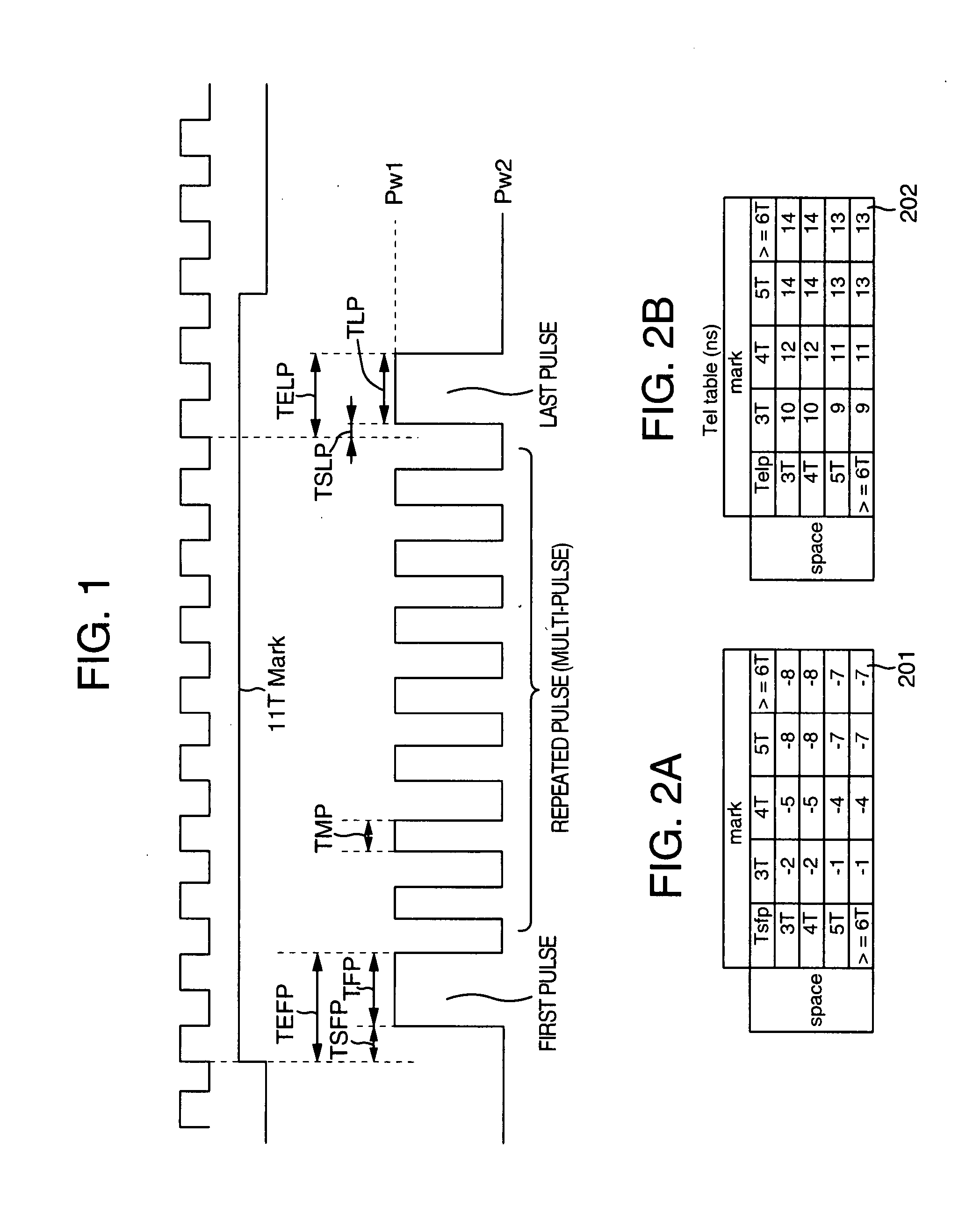
Recording parameters are decided so that the time control information on at least the front edge and the rear edge of a parameter forming a mark of twice size or above of the laser spot diameter focused on the recording medium is substantially proportional to the recording linear velocity. The mark is recorded and reproduced at a predetermined linear velocity to obtain an electric signal waveform having a time width Tm. A parameter is decided so as to control the laser pulse for recording information so that a voltage value change amount at two points at a distance Ts (Ts<Tm / 2) in the time axis direction before and after the time position Tm / 2 from the front edge of the waveform is substantially constant for the recording linear velocity change. Identification information indicating the parameter is described on the recording medium.
Owner:HITACHI CONSUMER ELECTRONICS CORP
Voice coil assembly, loudspeaker using the same, and method for producing the same
InactiveCN101472211AReduce separation vibrationIncrease reproduction efficiencyElectrical transducersBobbinEngineering
A voice coil assembly capable of realizing a flat thin loudspeaker having a high efficiency, reduced divided vibrations, a flat frequency response, and reduced operation defects. The voice coil assembly includes a plurality of internal-winding voice coils, each including a rectangular bobbin having a rectangular cross section and defining a rectangular space therein and an internal rectangular coil fixed to an inner wall surface of the rectangular bobbin defining the rectangular space, wherein an outer wall surface of the rectangular bobbin of one internal-winding voice coil is adhered and fixed to an outer wall surface of the rectangular bobbin of another internal-winding voice coil.
Owner:ONKYO KK +1
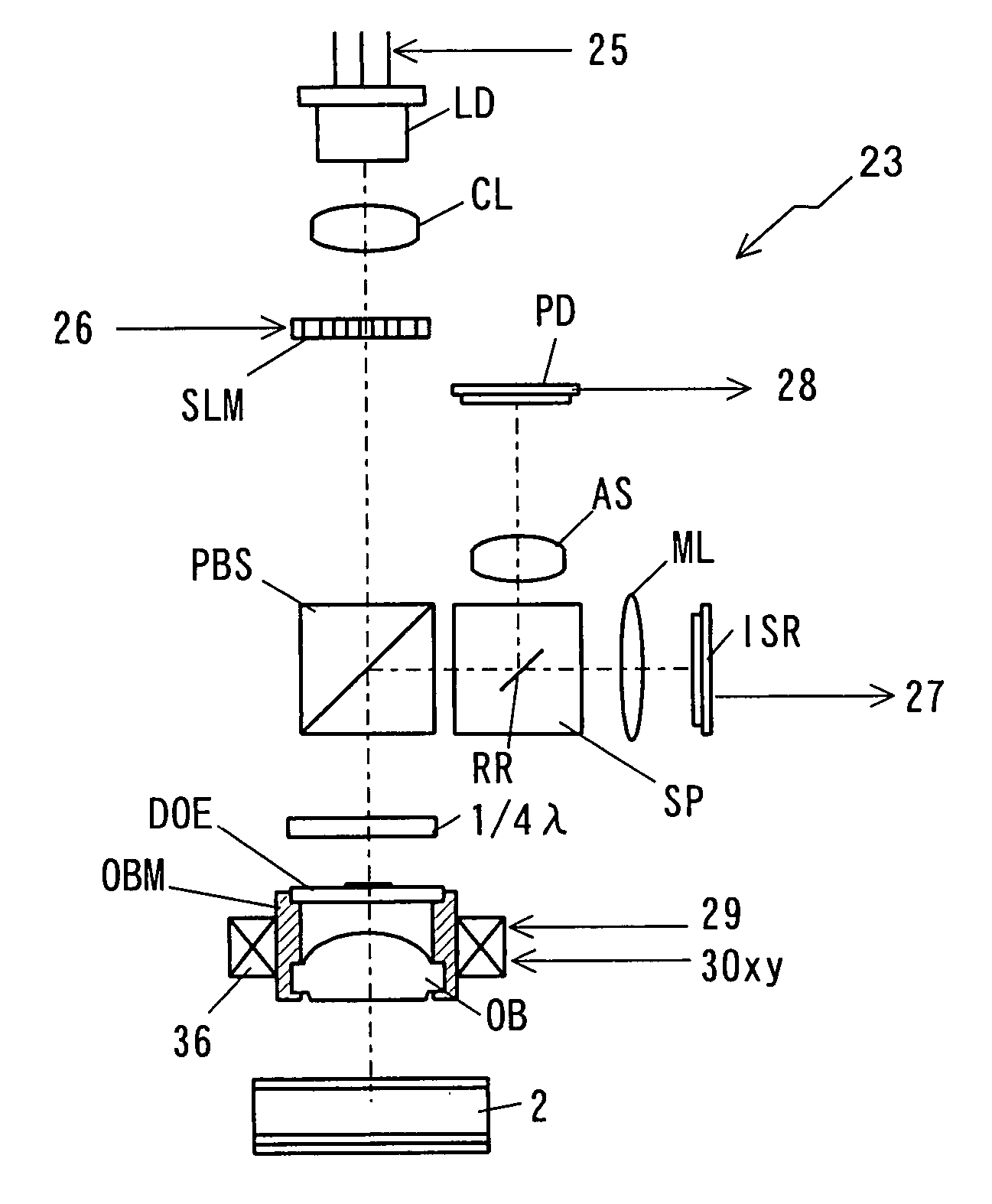
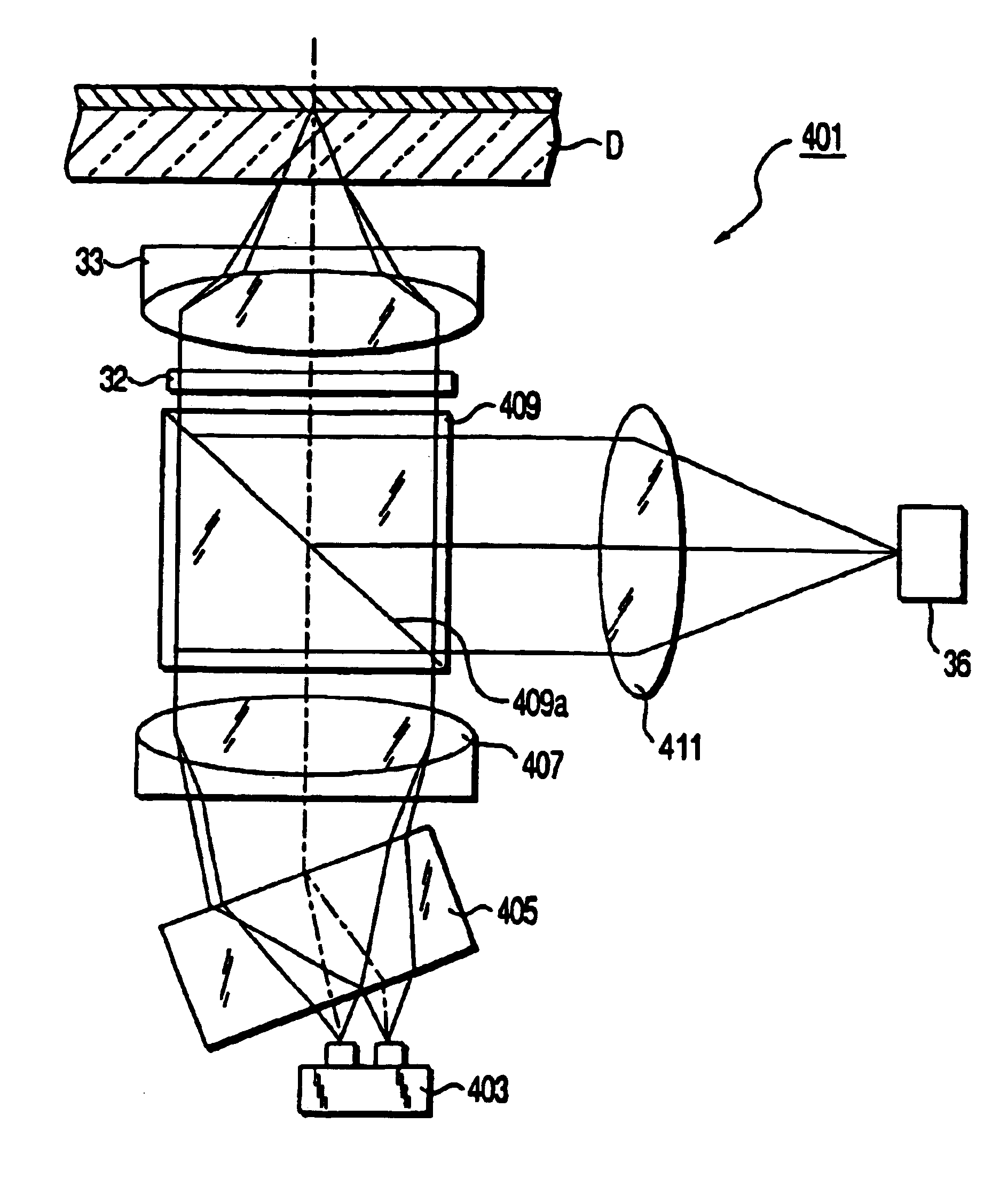
Hologram Recording and Reproducing Method, Device and System
InactiveUS20080007808A1Stable recordStable reproductionOptical beam sourcesHolographic optical componentsLight sourceOptical axis
A hologram device includes: a support section that keeps hold of, to be able to be attachable and removable, a hologram record carrier including a hologram recording layer stored therein with an optical interference pattern of a coherent signal light and a coherent reference light as a diffraction grating; a light source that generates the coherent reference light; a signal light generation section that is disposed on an optical axis, and generates the signal light by modulating the reference light in accordance with recording information; and an interference section that is disposed on the optical axis, and forms the diffraction grating being the optical interference pattern inside of the hologram recording layer by directing the signal light and the reference light toward the hologram recording layer. The signal light generation section is provided with a spatial light modulator, and the spatial light modulator is configured by a center are a disposed on the optical axis for passing through or reflecting the reference light with no modulation, and a spatial light modulation are a disposed around the center are a for generating the signal light by modulating the reference light in accordance with the recording information. The reference light is propagated on the optical axis, and the signal light is propagated around the reference light with spatial separation therefrom. The interference section includes an objective lens and an optical device, and the objective lens and the optical device gather the reference light at a first focal point, and the signal light at a second focal point being different from the first focal point.
Owner:PIONEER CORP
Method for recording information in optical information medium and reproducing information therefrom
InactiveUS7072269B2High speed recordingStable reproductionOptical beam sourcesRecord information storageBeam splitterPolarization beam splitter
An optical head apparatus is provided with a first laser element, a second laser element and a polarized beam splitter. The first laser element emits a laser beam having a first wavelength. The second laser element emits a laser beam having a second wavelength. The second wavelength may be equivalent to the first wavelength, alternatively, it may be different from the first wavelength. The polarized beam splitter enables the laser beams of the first and second laser elements to be simultaneously radiated to the recording layer of an optical disk. When information are recorded in the optical disk, the laser beams of the first and second laser elements are used at the same time. At least one of the laser elements emits a laser beam having such a wavelength as enables the recording layer of the optical disk to absorb the largest possible amount of energy.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
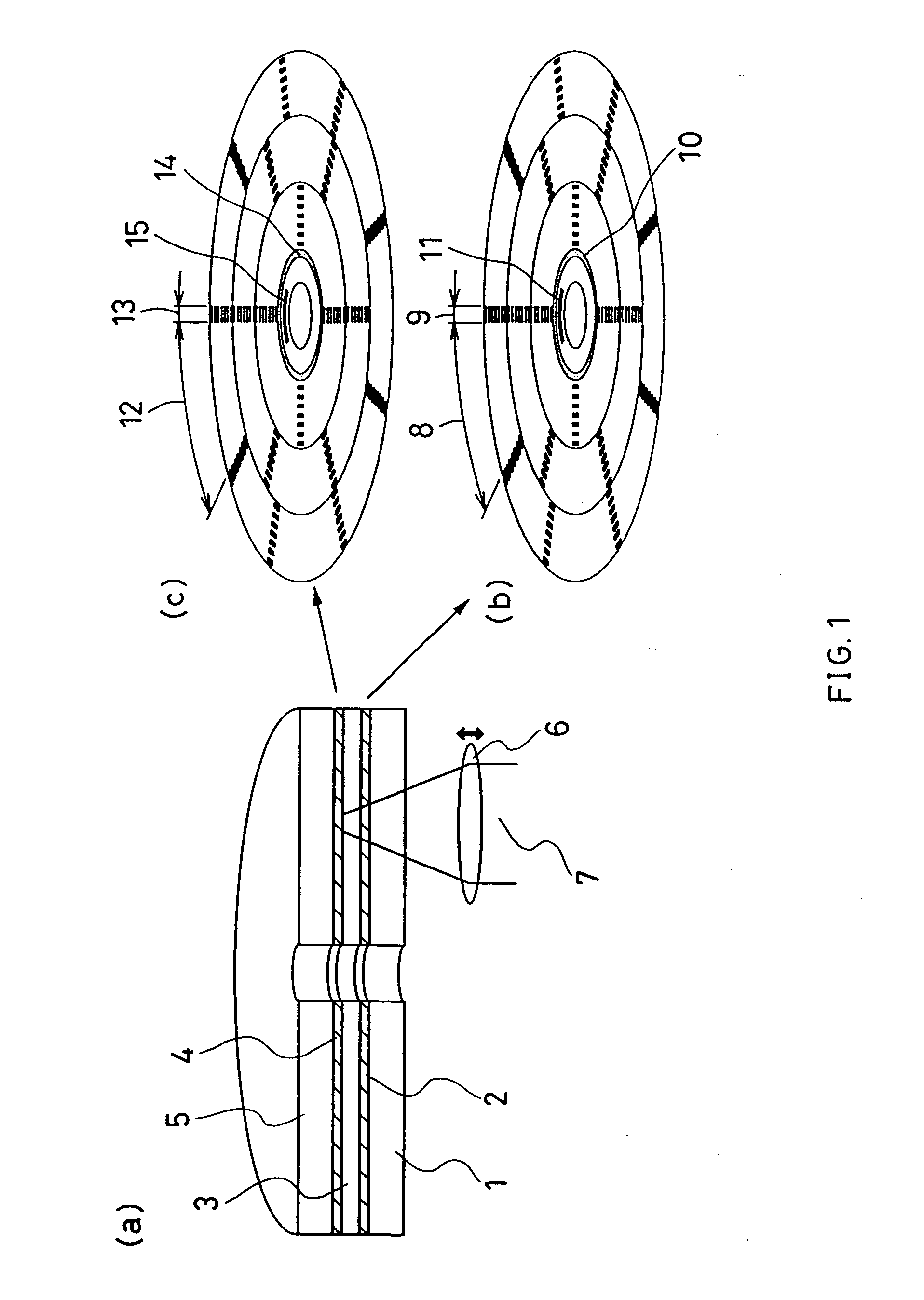
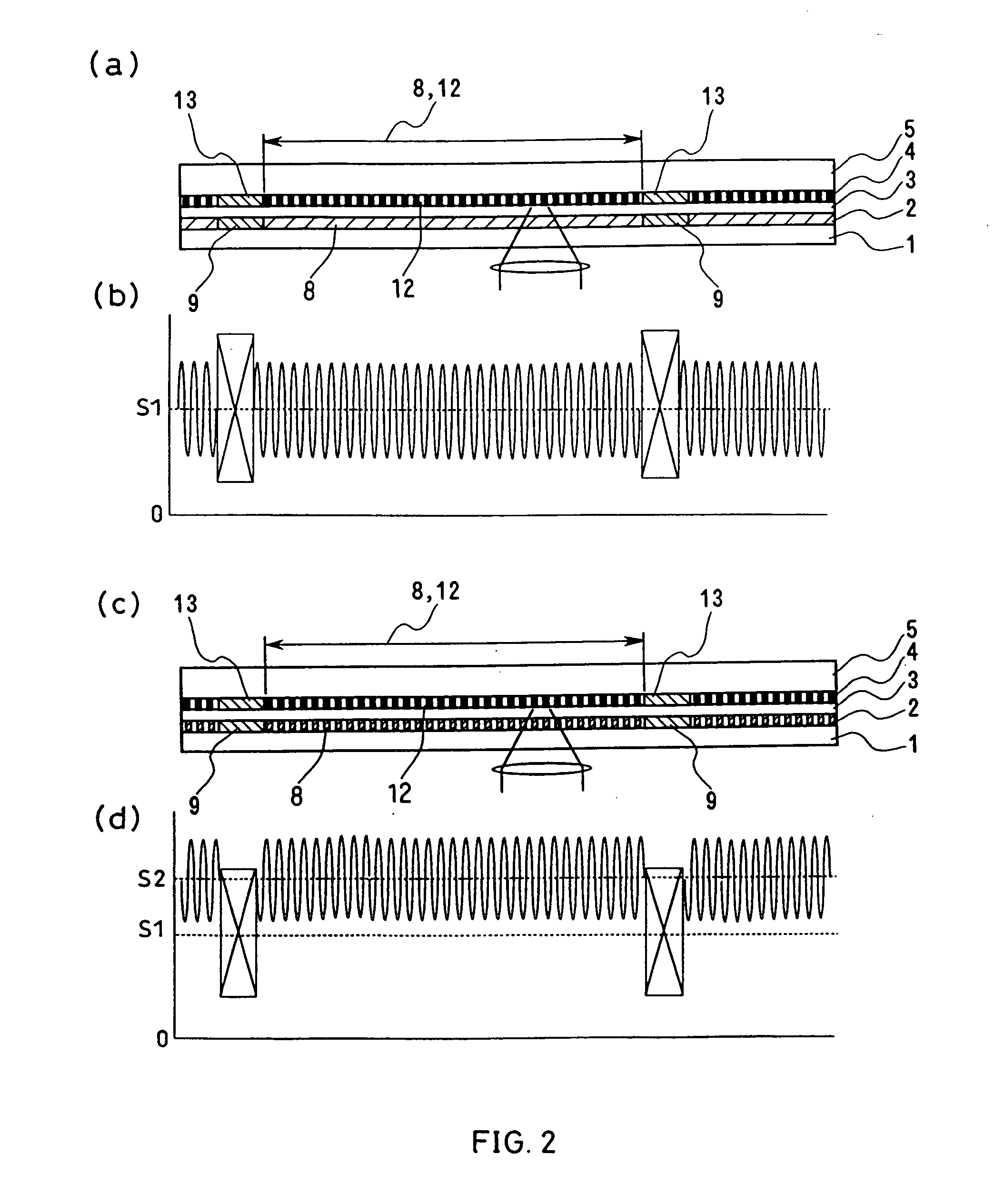
Optical information recording medium, method of manufacturing thereof, and method of recording and reproduction
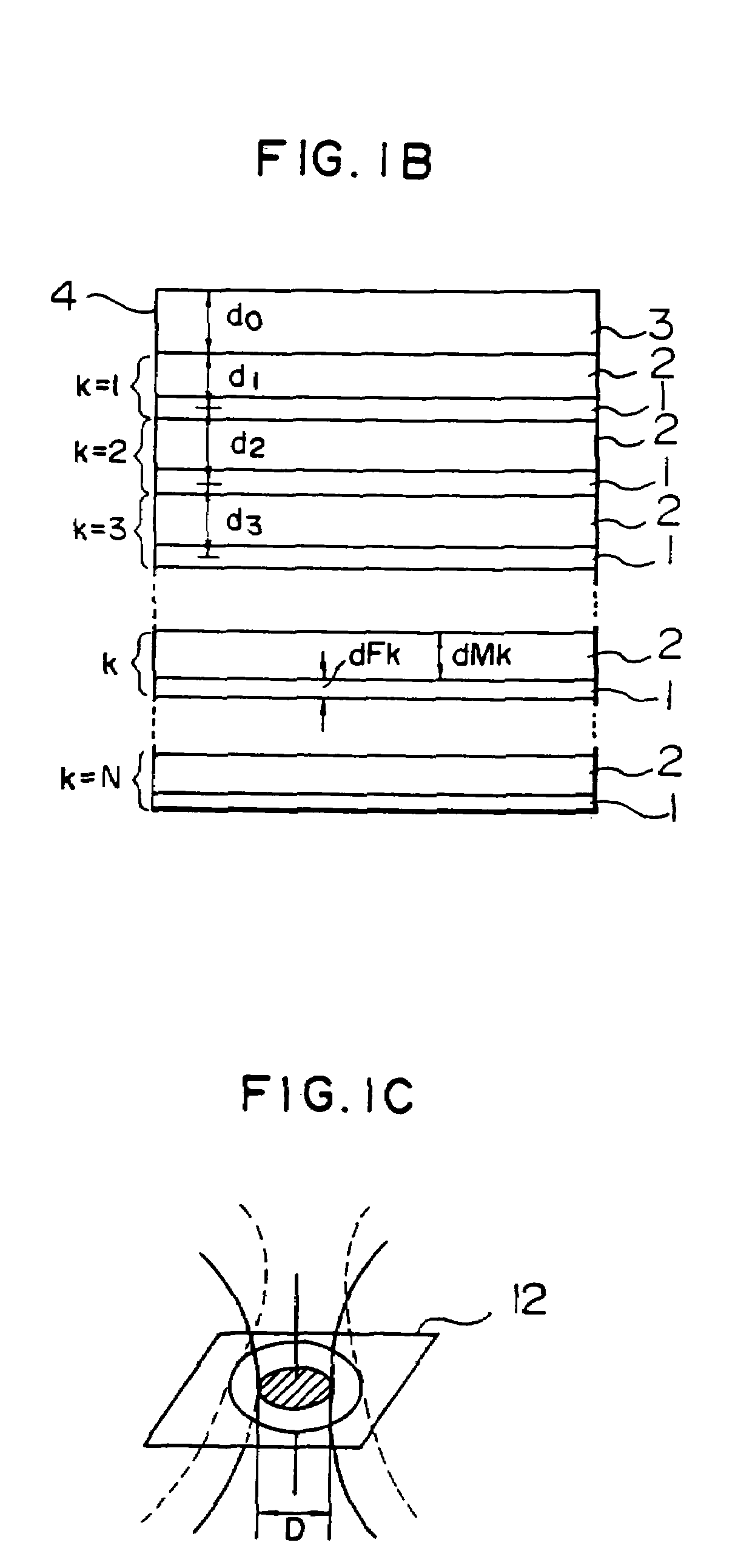
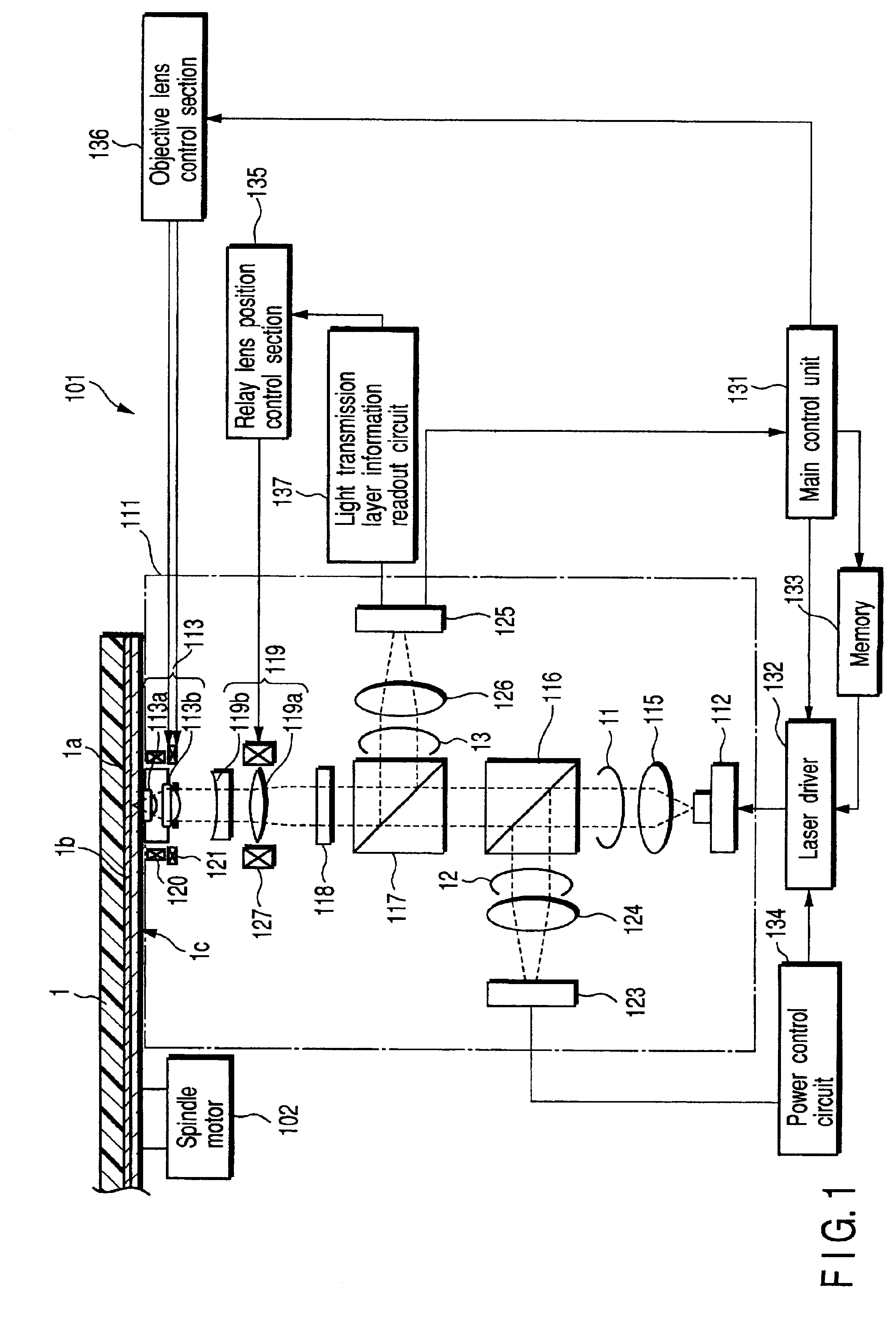
InactiveUS20050007924A1Easy to adjust the positionStable reproductionMechanical record carriersRecord information storageComputer hardwareRecording media
An optical information recording medium is provided with a plurality of information layers (2, 3), each of which has a sector structure in which a data area (8, 12) is divided in the circumferential direction by a sector address (9, 13). The positions of the sector addresses (9, 13) of the respective information layers (2, 3) coincide in the circumferential direction. This can prevent errors during reproduction caused by the effect of other information layers and stabilize recording characteristics, resulting in an increased recording capacity of a rewritable recording medium having a plurality of information layers with a sector structure.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
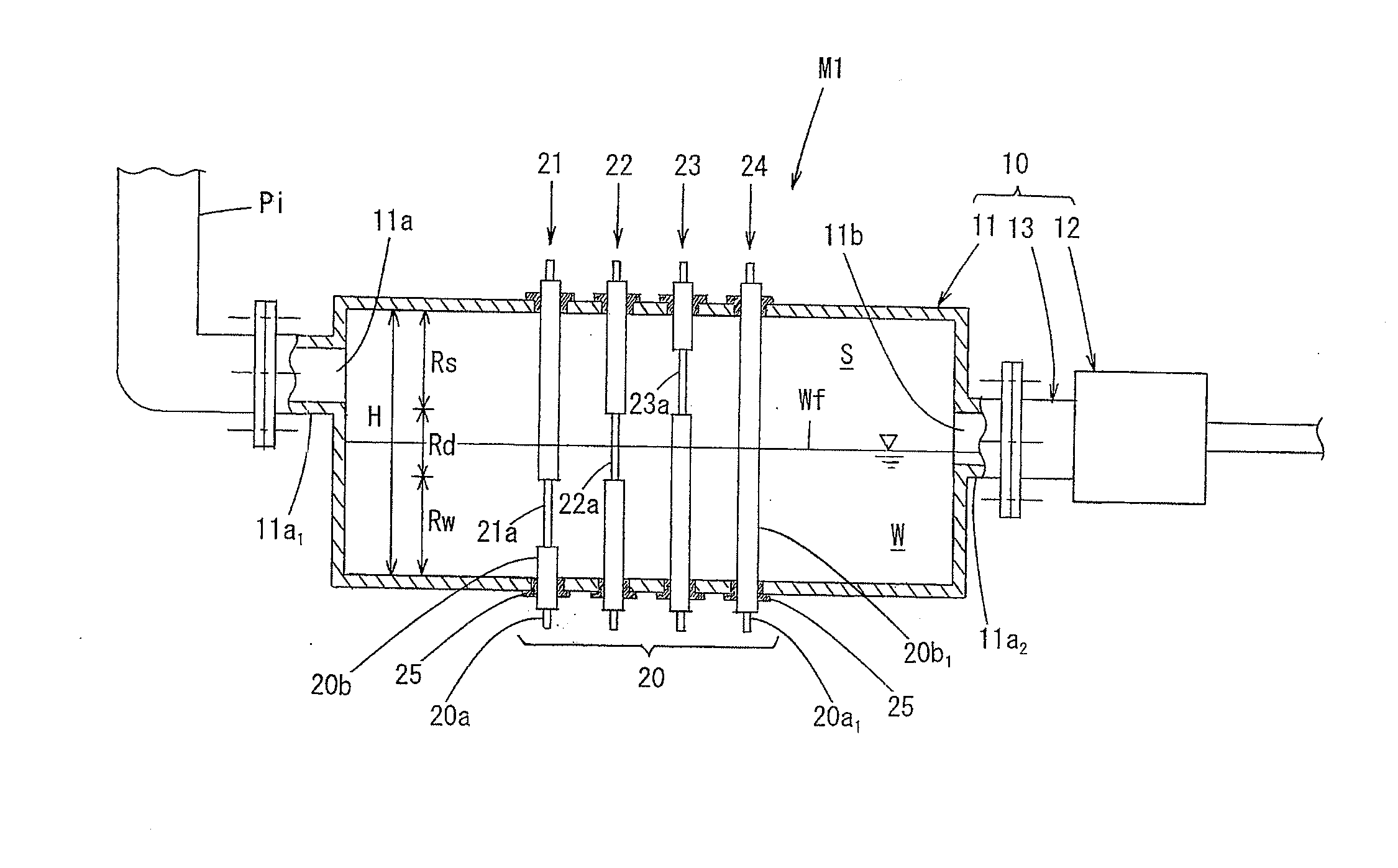
Metal pipe corrosion monitoring device and use thereof
ActiveUS20140306726A1Stable reproductionCorrosionWeather/light/corrosion resistanceResistance/reactance/impedenceCondensed waterVapor phase
A metal pipe corrosion monitoring device includes a steam introduction unit for introducing thereinto steam flowing through a metal pipe; and a corrosion testing unit provided in the steam introduction unit, characterized in that the steam introduction unit is configured to generate condensed water by condensing some of the steam to create a simulated environment similar to an actual environment in the metal pipe and discharge the condensed water above a predetermined water level to the outside. The corrosion testing unit has one or more contact members that contact with a water line region around a water surface of the condensed water in the steam introduction unit, a water phase region on a condensed water side and a vapor phase region on a steam side, and is configured to be able to measure an electric resistance of the one or more contact members.
Owner:NAIGAI KAGAKU SEIHIN
Optical recording/reproducing medium, stamper for manufacturing optical recording/reproducing medium, and optical recording/reproducing apparatus
InactiveUS7280461B2Degree of modulation to degradePractical problemRecord information storageOptical beam guiding meansEngineeringOptical recording
An optical recording and reproduction medium in which pits corresponding to recording information are formed along a recording track, wherein auxiliary pits are formed in at least a portion of the spaces between adjacent pits along the recording track direction; when the pit depth is d1 and the auxiliary pit depth is d2, then d1≧d2 is obtained; and both edges of the auxiliary pits along the recording track direction are shaped as simple convex curves.
Owner:SONY CORP
Information recording medium, information reproducing apparatus, information recording method and reproducing method
InactiveUS20060177199A1Stable controlUseless access operationTelevision system detailsRecording carrier detailsComputer hardwareMultiplexing
A design is made for recording and arrangement of application data so as to stably control the behavior of moving picture data based on application data and easily achieve special reproduction of moving picture data. Therefore, moving picture data encoded in a preset format is multiplexed with application data used to control the behavior of a reproduced picture of the moving picture data. Further, the basic process is provided to deal with a first file which contains a multiplexed stream separated by preset units and a second file containing the same data as the application data.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Photocurable ink-jet ink, ink-jet image forming method and ink-jet recording apparatus using the same
Owner:KONICA MINOLTA MEDICAL & GRAPHICS INC
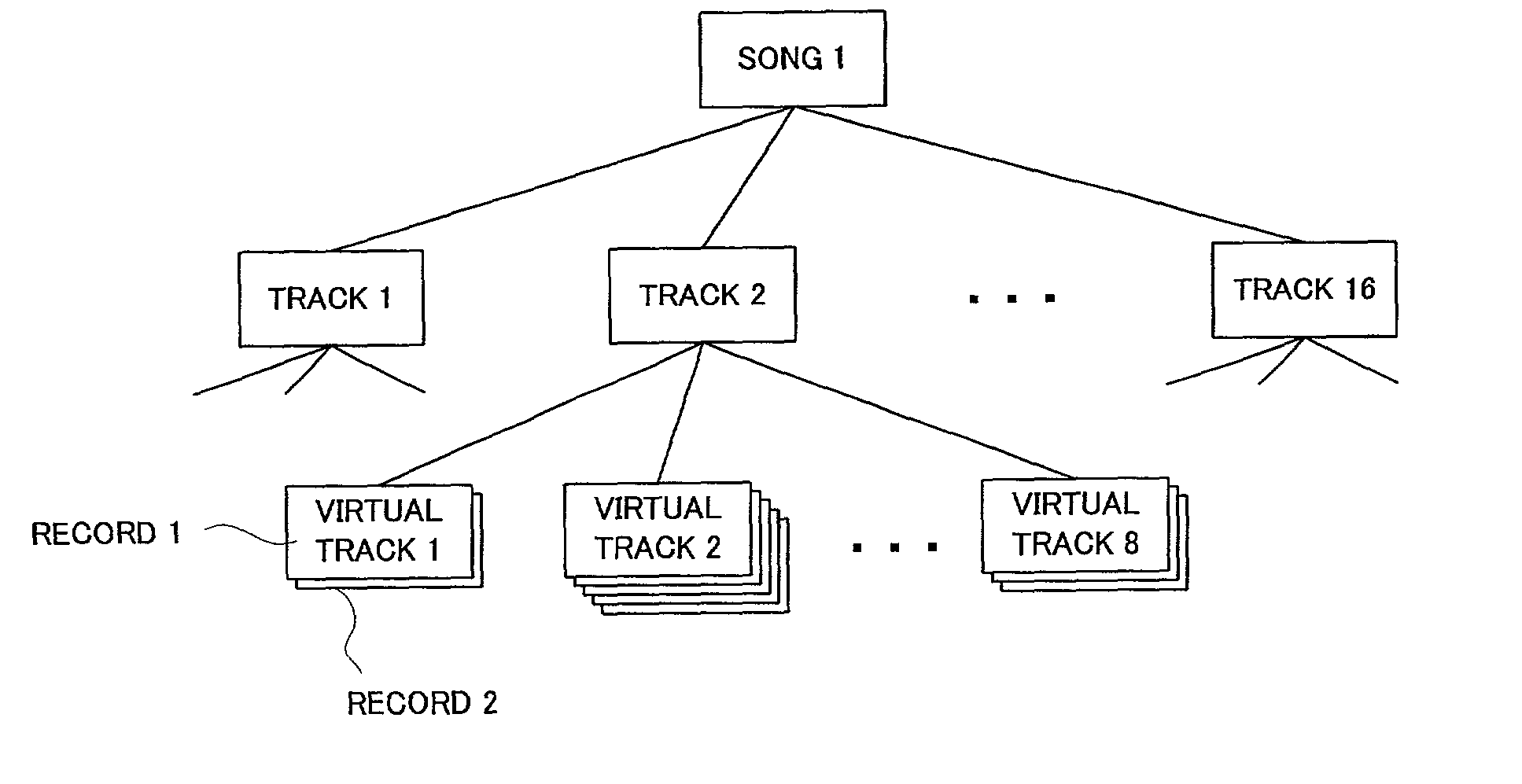
Audio data recording/reproducing apparatus and method
InactiveUS7058882B2Stable reproductionReduce the burden onElectrophonic musical instrumentsDisc-shaped record carriersComputer graphics (images)Data recording
Each track is made up of a linkage of regions, and each of the regions is made up of a linkage of nodes or clusters. Sound data are stored on a cluster-by-cluster basis, and reproduced by tracing such linkages. Each time editing is performed on a virtual track of the track, a track data of a corresponding leading region in the edited virtual track is stored in memory as a history record of the track. When an undoing instruction is given, desired record data is selected from the history records of the leading region. Where the sound data in the trailing-end cluster of a preceding region and leading-end cluster of a succeeding region amount to less than 50% of a predetermined total data quantity of sound data to be contained in a proper cluster, the sound data represented by a trailing-end offset and the sound data represented by a leading-end offset are combined together and then written into a reproducing cluster. In reproduction, the sound data written in the reproducing cluster are reproduced for a connecting portion between the preceding and succeeding regions.
Owner:YAMAHA CORP
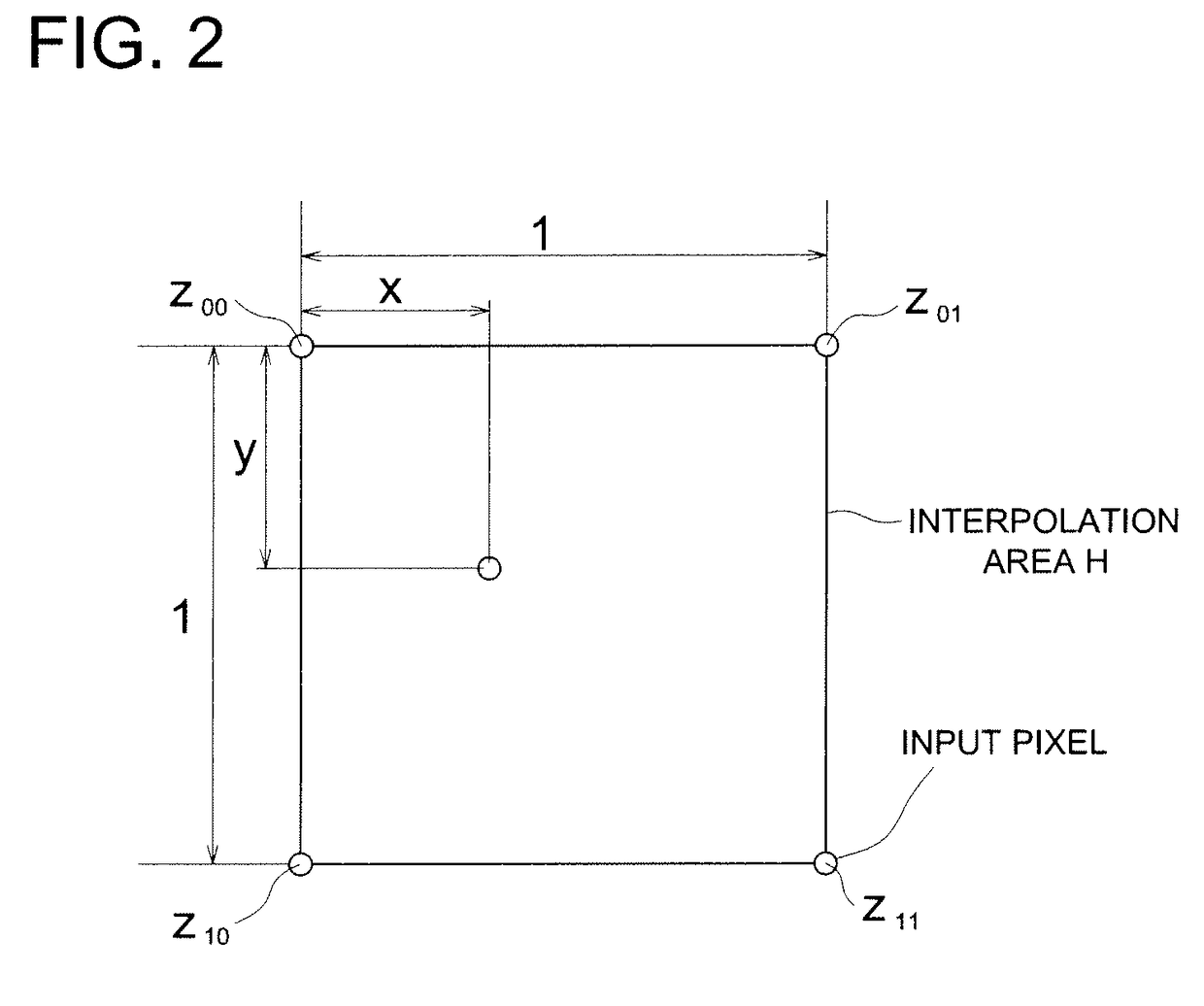
Resolution conversion method
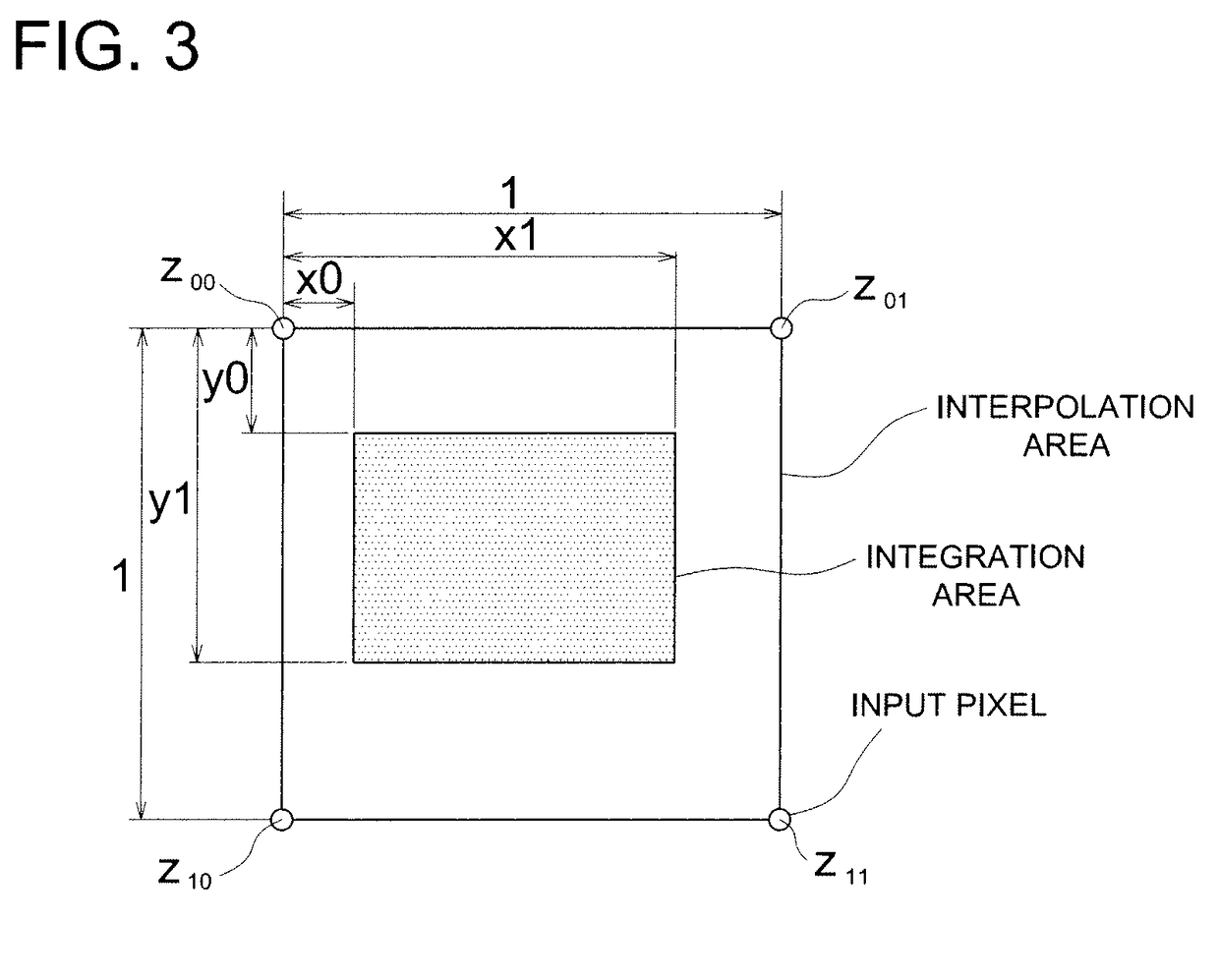
InactiveUS7907788B2Stable reproductionGeometric image transformationCharacter and pattern recognitionDot matrixImage resolution
Disclosed is a resolution conversion method, which makes it possible not only to acquire a diagonal edge that is smoothed without causing any unevenness all over the image, but also to stably reproduce a thin line having a thickness corresponding to its original thickness, irrespective of an integer multiple or a non-integer multiple of the magnification factor to be employed for enlarging an original image, when the high-resolution conversion processing is applied to a binary image represented in the dot-matrix format. An operation for integrating the interpolation value with respect to the area of the input pixel is implemented after the output pixel area is shifted in a horizontal direction and / or a vertical direction so as to make the output pixel area depart from a center of the interpolation area, when the output pixel area is included in a single interpolation area in the horizontal direction and / or a vertical direction.
Owner:KONICA MINOLTA BUSINESS TECH INC
Apparatus and method for setting tap coefficient of adaptive equalizer
InactiveUS7606300B2Stable reproductionImprove efficiencyMultiple-port networksError preventionViterbi decoderOperation mode
There is provided an apparatus and method for initializing a tap coefficient of an adaptive equalizer constituting a read path for a storage medium, where the apparatus includes an FIR filter, a Viterbi decoder, a level error detector, and a tap coefficient updater, the FIR filter receives a first signal stream and outputs the first signal stream in the form of a second signal stream, the Viterbi decoder corrects a bit error of the second signal stream, the level error detector detects a level error between the second signal stream and a third signal stream that is an ideal output signal corresponding to the second signal stream, the tap coefficient updater selects a tap coefficient minimizing the level error and provides the selected tap coefficient as a tap coefficient of the FIR filter, the tap coefficient minimizing the level error is determined as an initial value in a system initialization mode, and the determined initial value is used as an initial value of the tap coefficient of the FIR filter in a normal operation mode.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Optical reproducing device and optical memory medium
InactiveUS6847592B2Easy to controlReduce read frequencyTelevision system detailsFilamentary/web record carriersEngineeringOptical memory
An optical reproducing device according to the present invention detects mean amplitude values of short marks and long marks, which are recorded marks for reproducing power control, by means of a short mark level detecting circuit and a long mark level detecting circuit. Then a differential amplifier compares a ratio between these two mean amplitude values with a standard value, and outputs the result of this comparison. Thereafter, a reproducing power control circuit controls reproducing power of a semiconductor laser such that the absolute value of this comparison result is reduced. Since mean values of the amplitude values of the short marks and long marks are detected, the detection results are very accurate, and the precision of control of reproducing power can be greatly improved.
Owner:SHARP KK
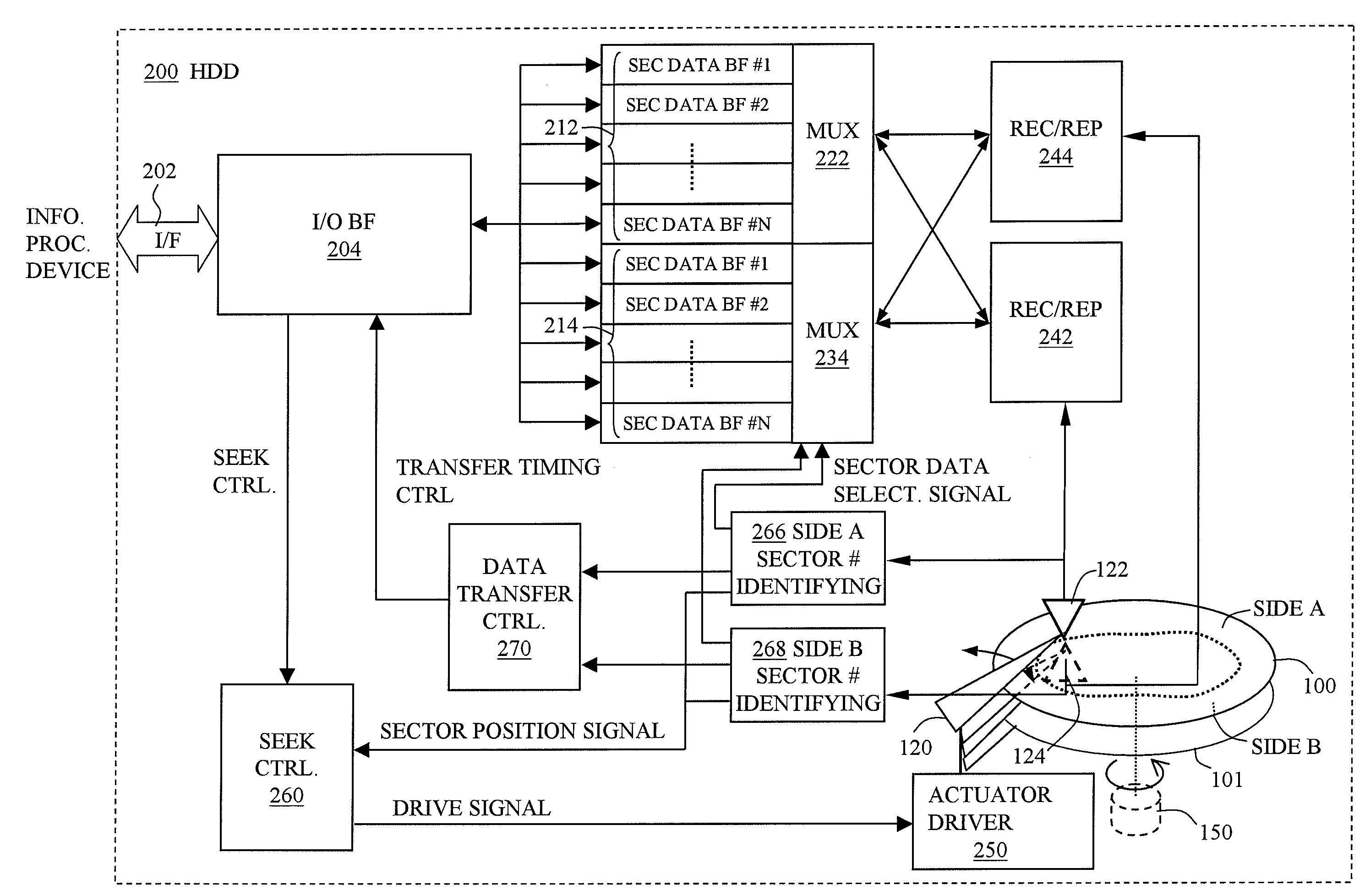
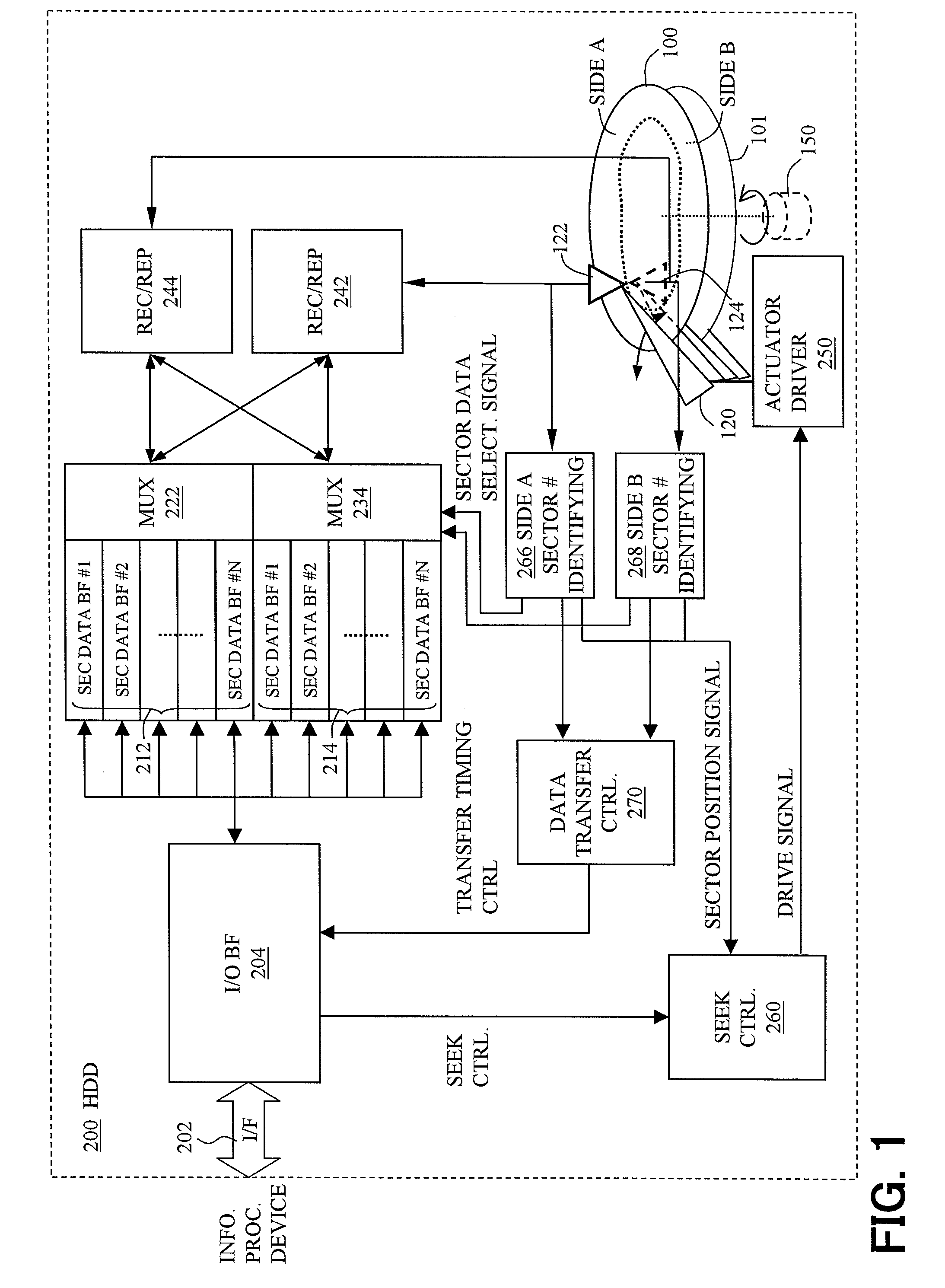
Hard disk drive
InactiveUS20080186616A1Stably reproduceStable recordDriving/moving recording headsData buffering arrangementsMagnetic disksHard disc drive
Stable recording and reproduction of data onto and from a recording medium that requires precise tracking is provided by using a simple head tracking mechanism. In a hard disk drive (200), a piece of sector data to be written or read is pre-associated with a sector number of a sector where the piece of sector data is to be written or read. A seek control unit (260) corrects first-order run-out relative to a revolution axis of a DTM magnetic disk (100) and permits second-and-higher order run-out relative to the revolution axis, and moves a read / write head (122, 124) gradually in one radial direction of the DTM magnetic disk at a shift pitch smaller than the track pitch for each revolution in accordance with the sector numbers of the sectors where pieces of sector data are to be written or read, within a range of tracks containing the sector numbers of the sectors where the pieces of sector data are to be written or read. A recording / reproducing unit (266, 268) writes or reads, in accordance with a present sector number of a sector where the write / read head is located, a corresponding piece of sector data onto or from the DTM magnetic disk, independently of the order of the sector numbers.
Owner:TOSHIBA STORAGE DEVICE CORP
Method of controlling an optical disk apparatus
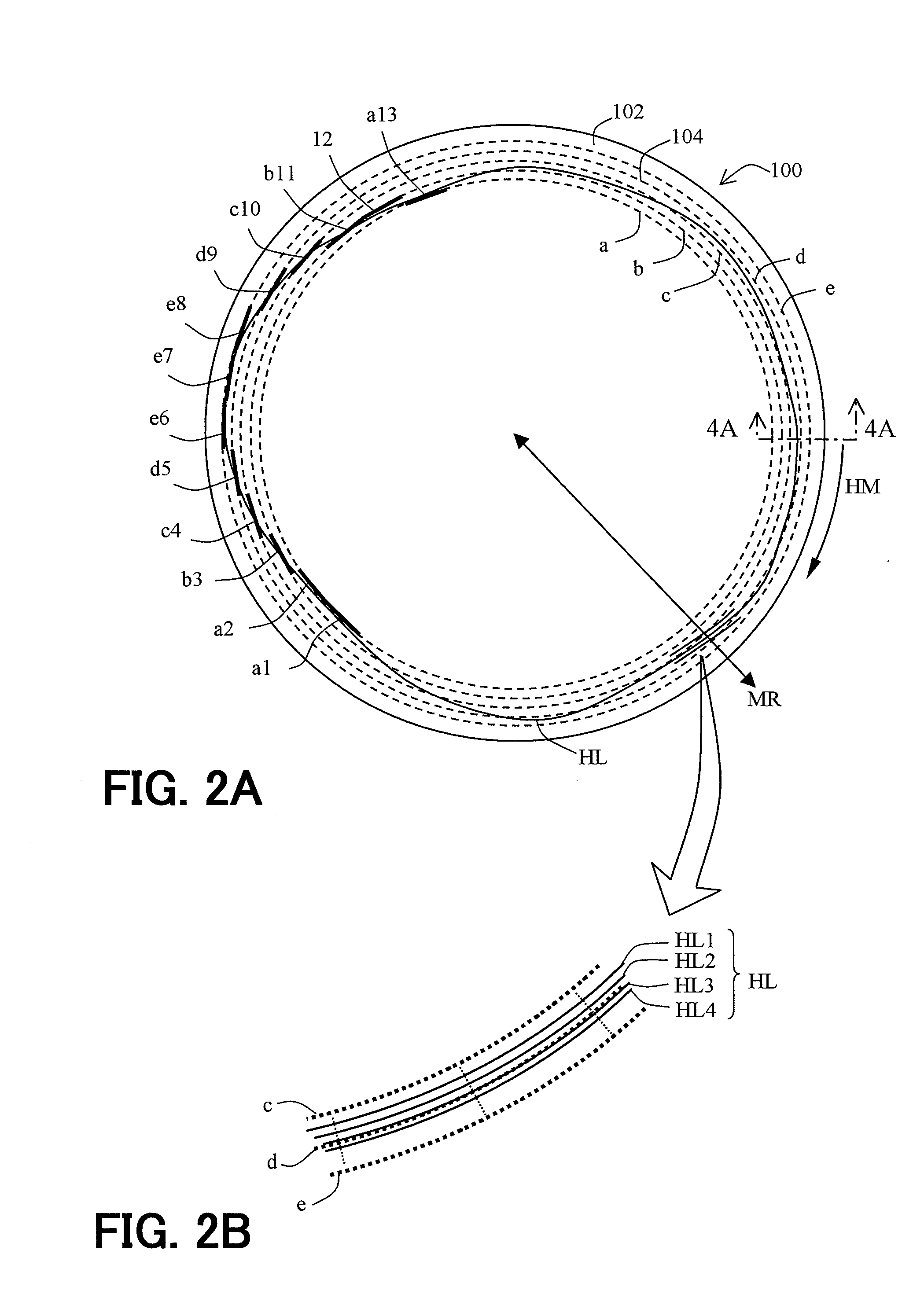
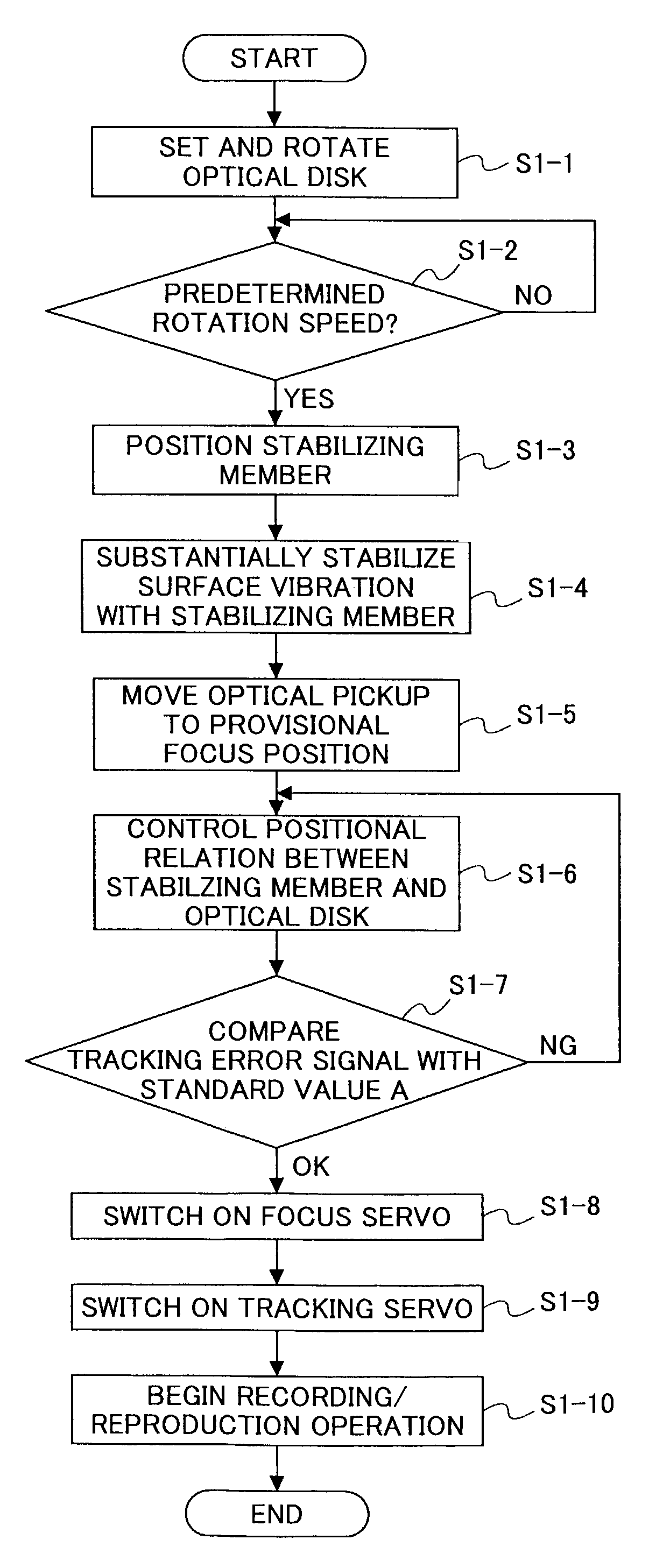
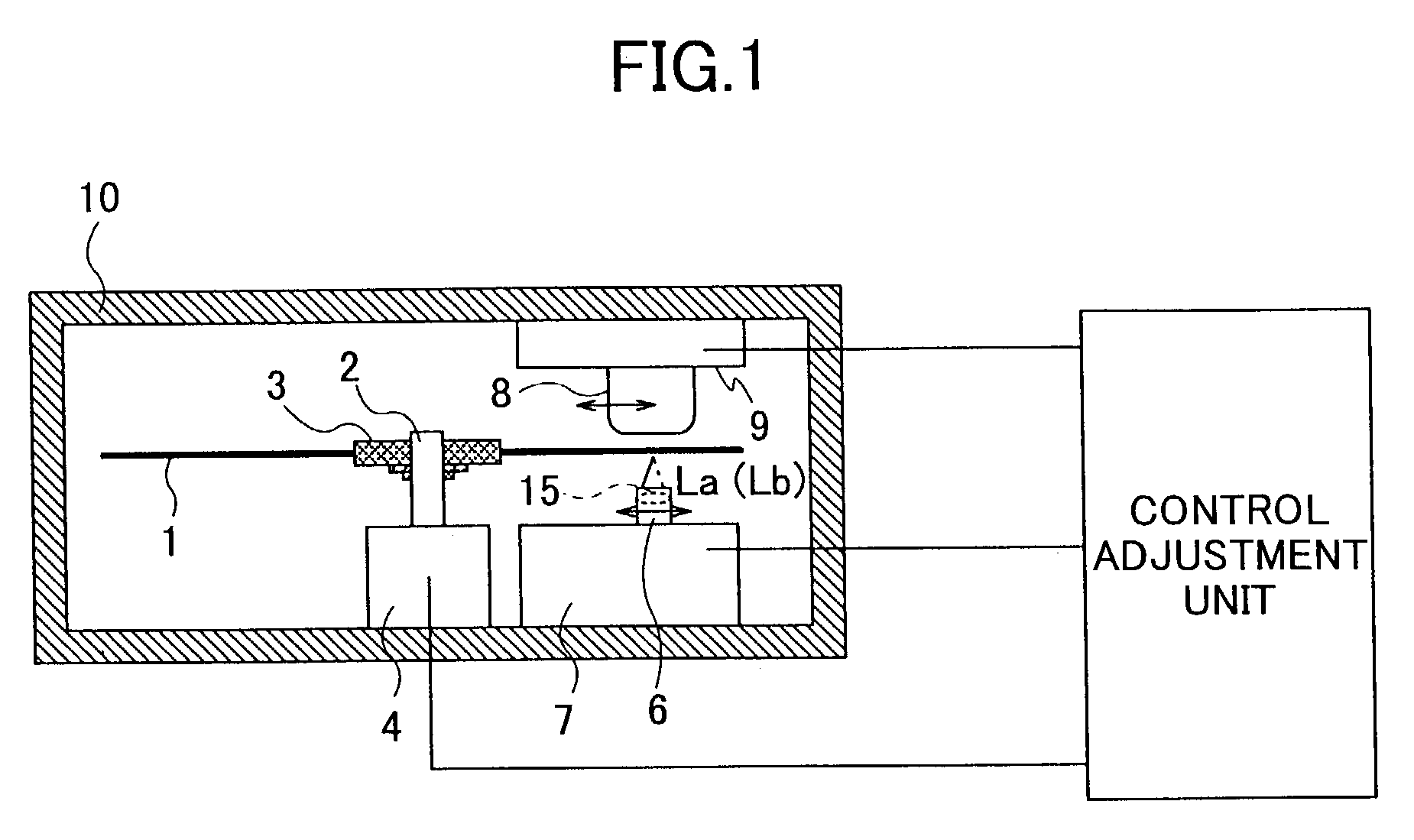
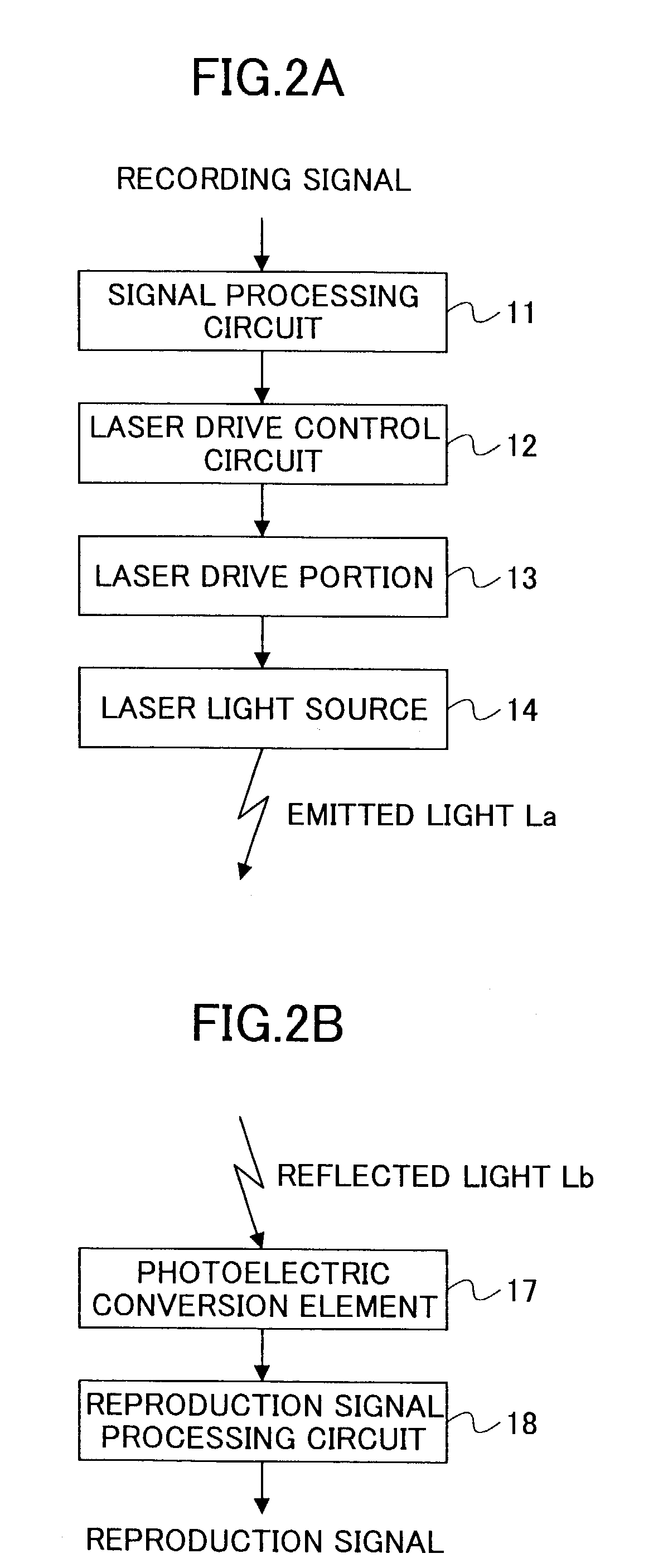
InactiveUS7164629B2Stable reproductionStable recordCombination recordingDisposition/mounting of recording headsOptical pickupThree-dimensional space
An optical disk apparatus includes a rotary driving unit rotating an optical disk which is flexible, an optical pickup irradiating light upon a recording surface of the optical disk on which writing / reading of information is performed, a stabilizing unit stabilizing vibration of the optical disk in a rotary axial direction by using pressure difference of air flow at least on a portion where writing / reading is performed, and being disposed on a side of the optical disk opposite to a side on which the recording surface is provided, and a control-adjustment unit analyzing a value of a tracking error signal of the optical disk obtained by scanning along a groove of the optical disk with use of the optical pickup, comparing the analyzed value of the tracking error signal of the optical disk and a value priorly obtained by scanning along a groove of a standard disk prepared beforehand, and adjusting a positional relation between the optical disk and the stabilizing member in a three dimensional space according to the result of the comparison.
Owner:RICOH KK
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com