Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
41results about How to "Softer characteristic" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
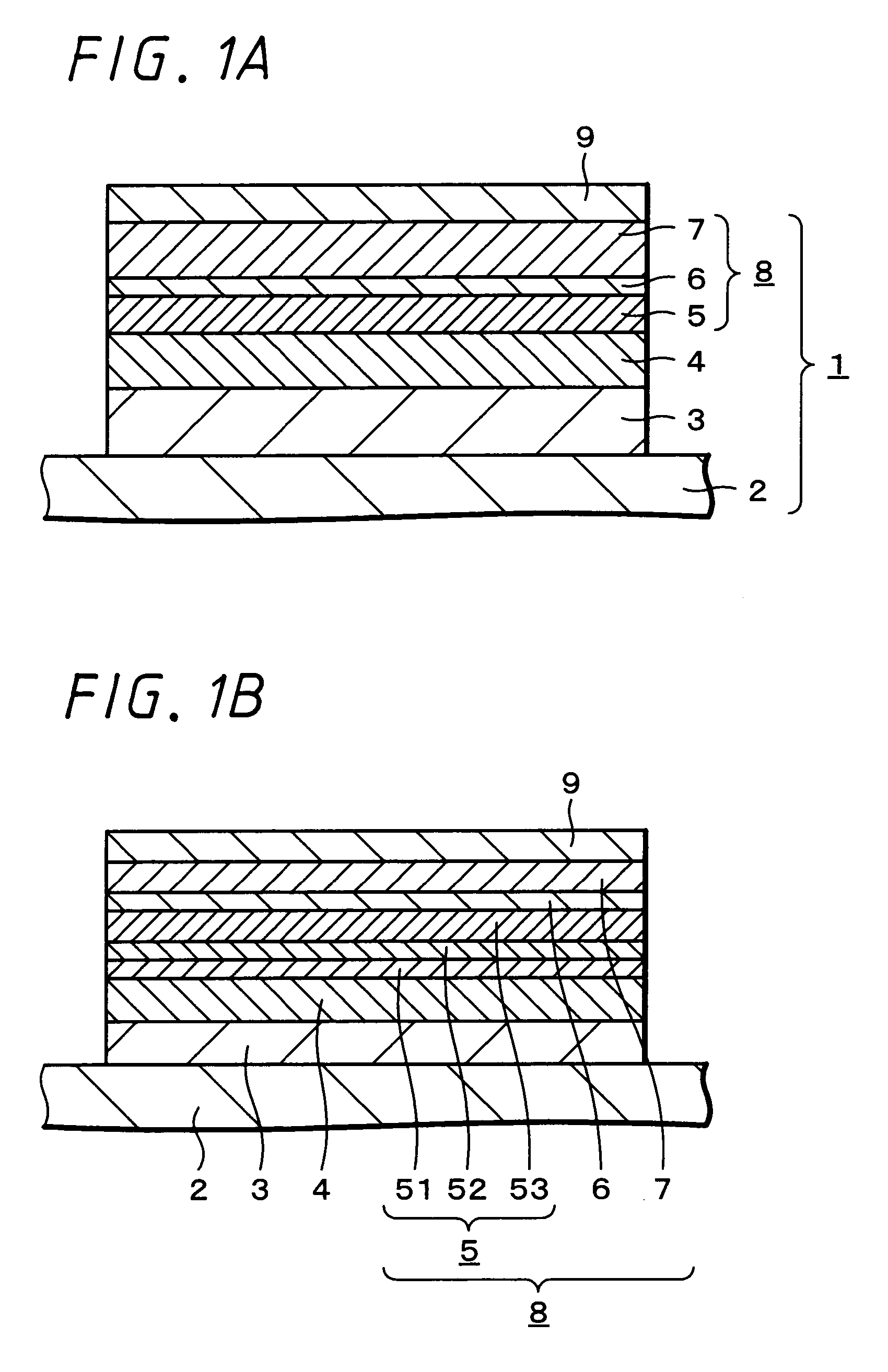
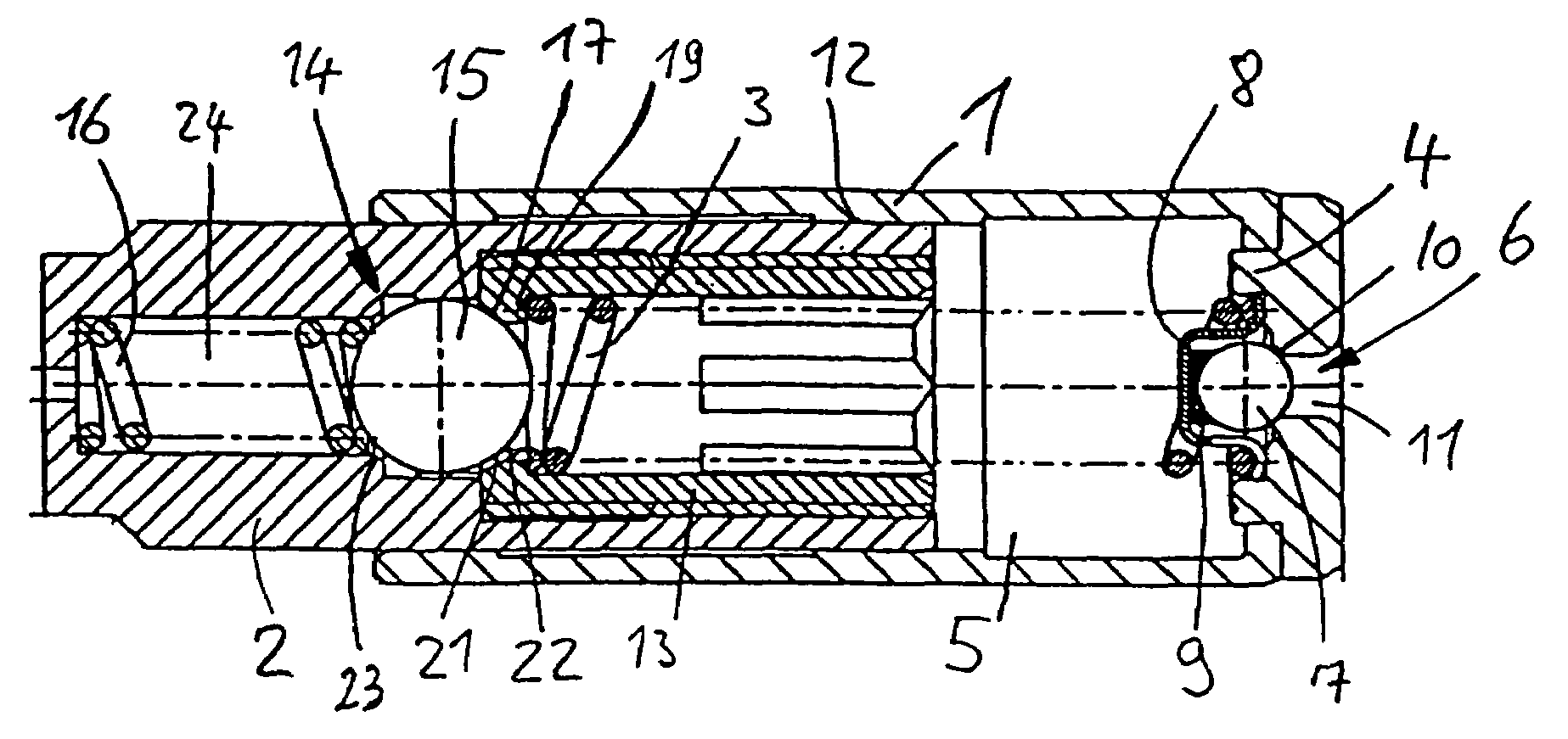
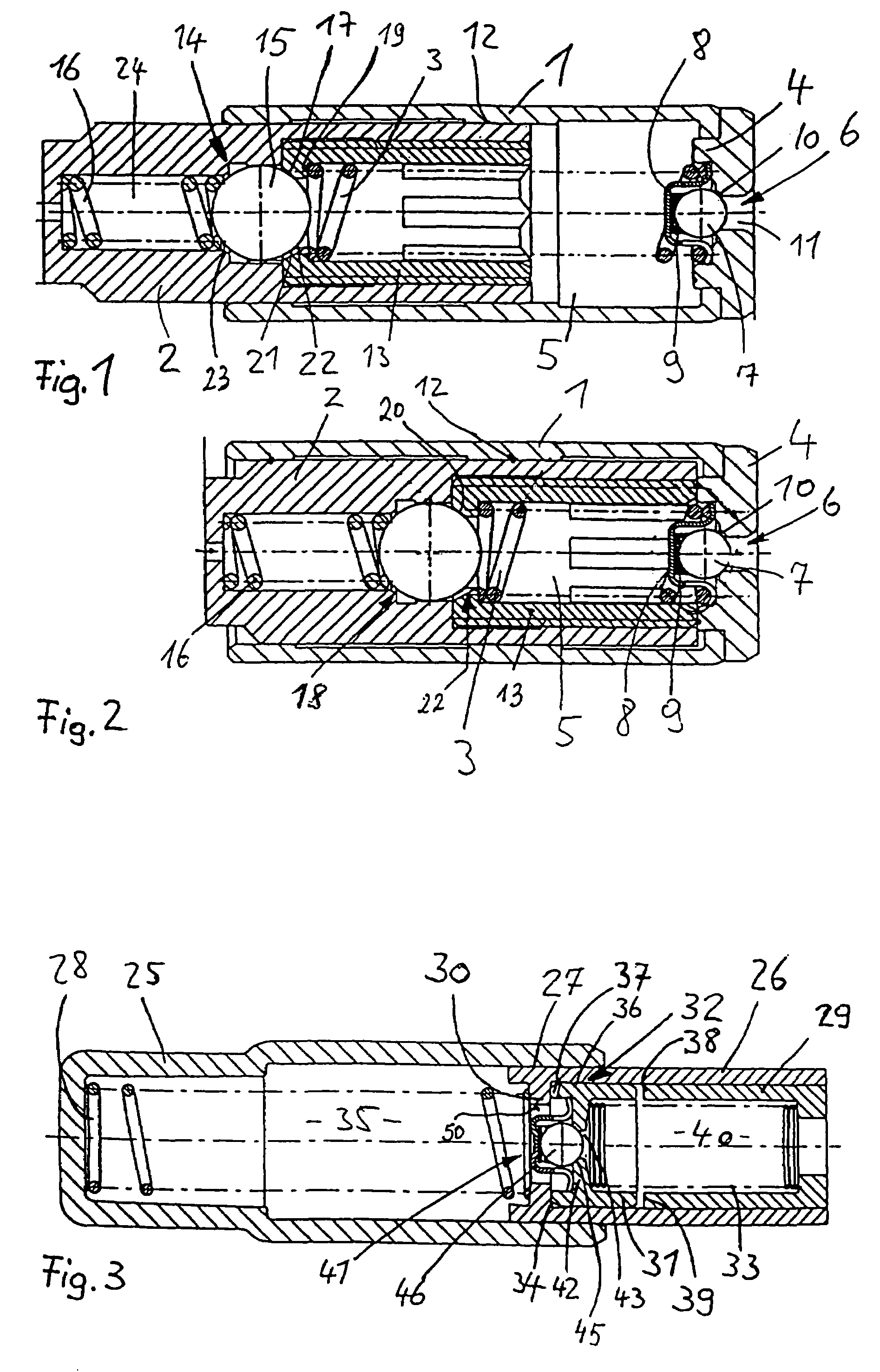
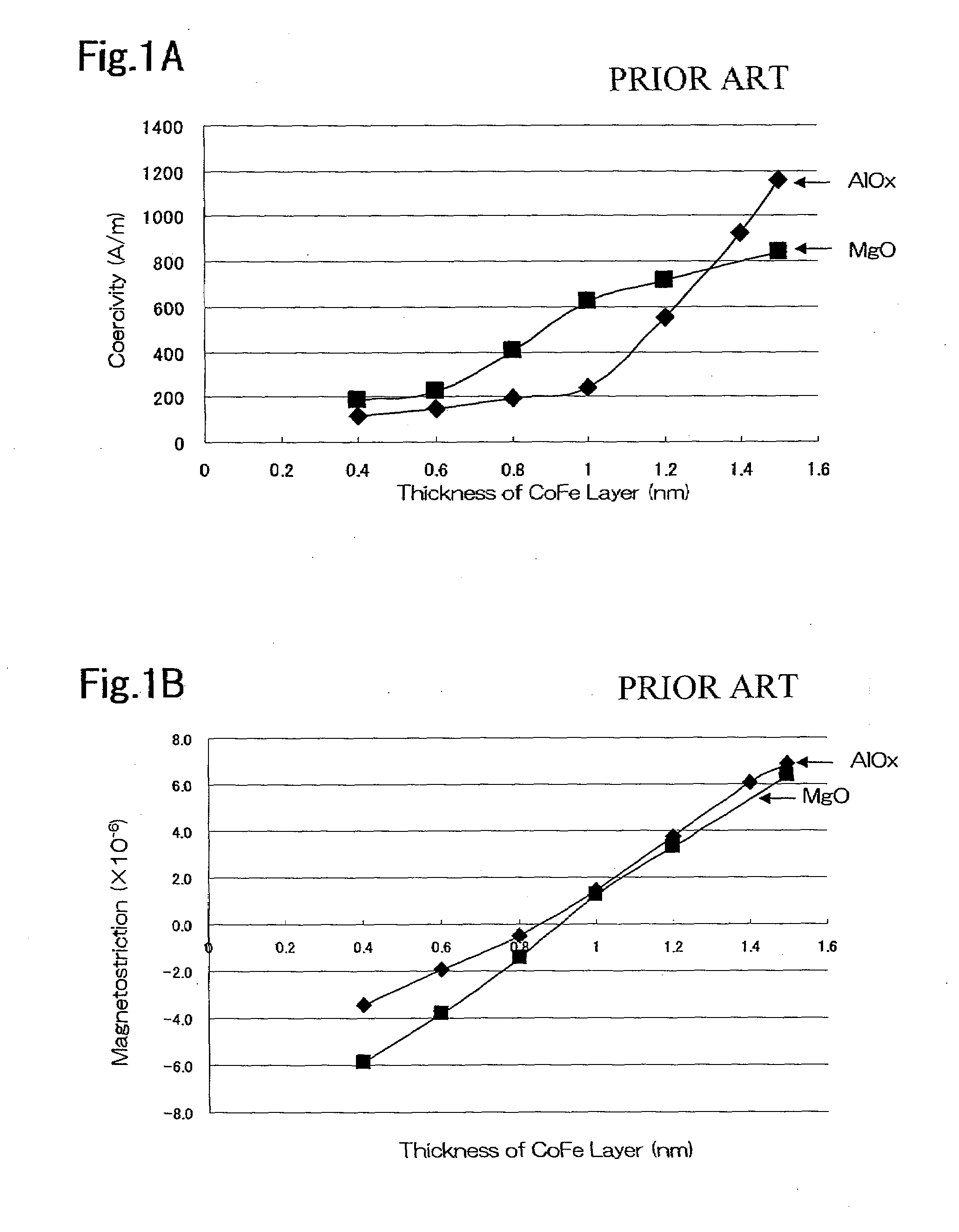
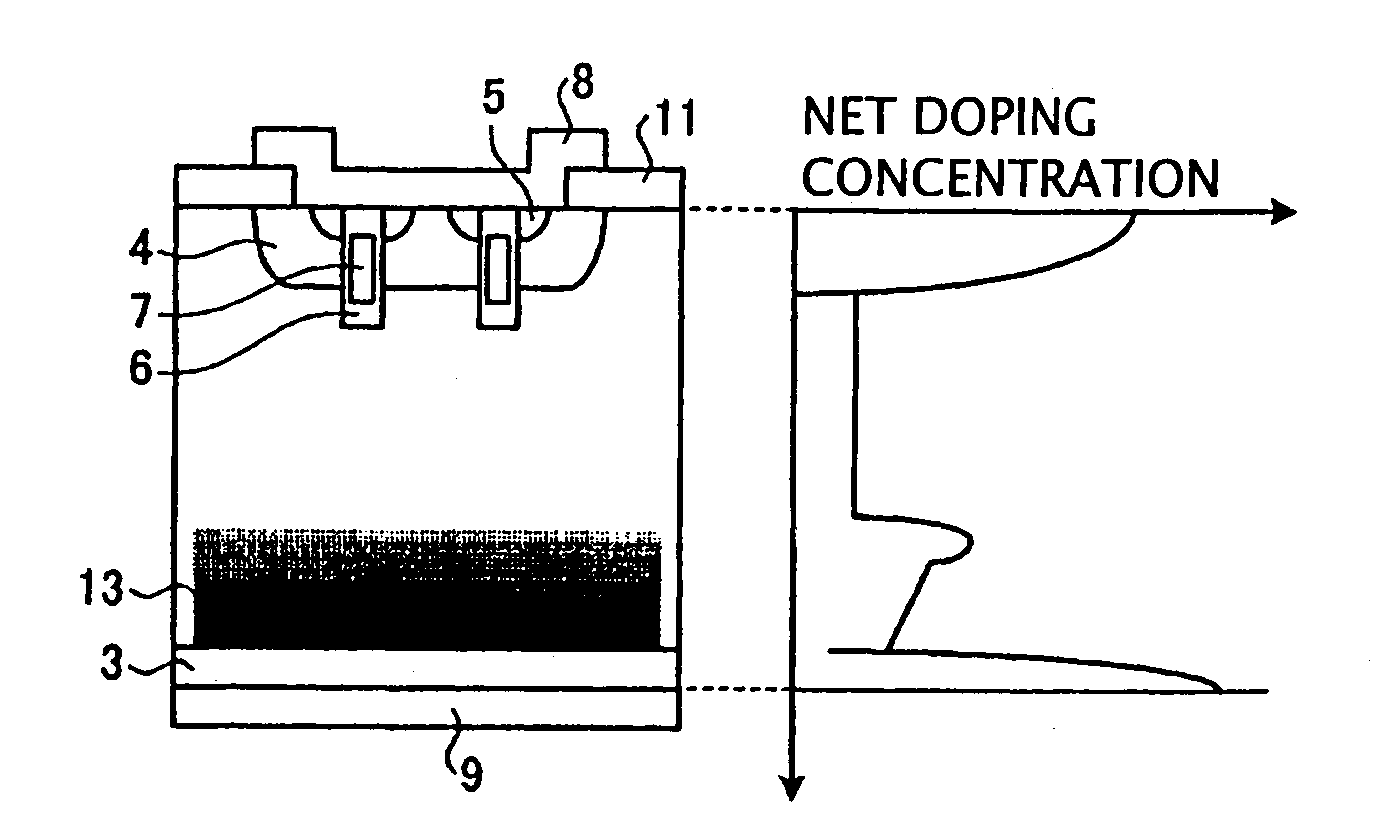
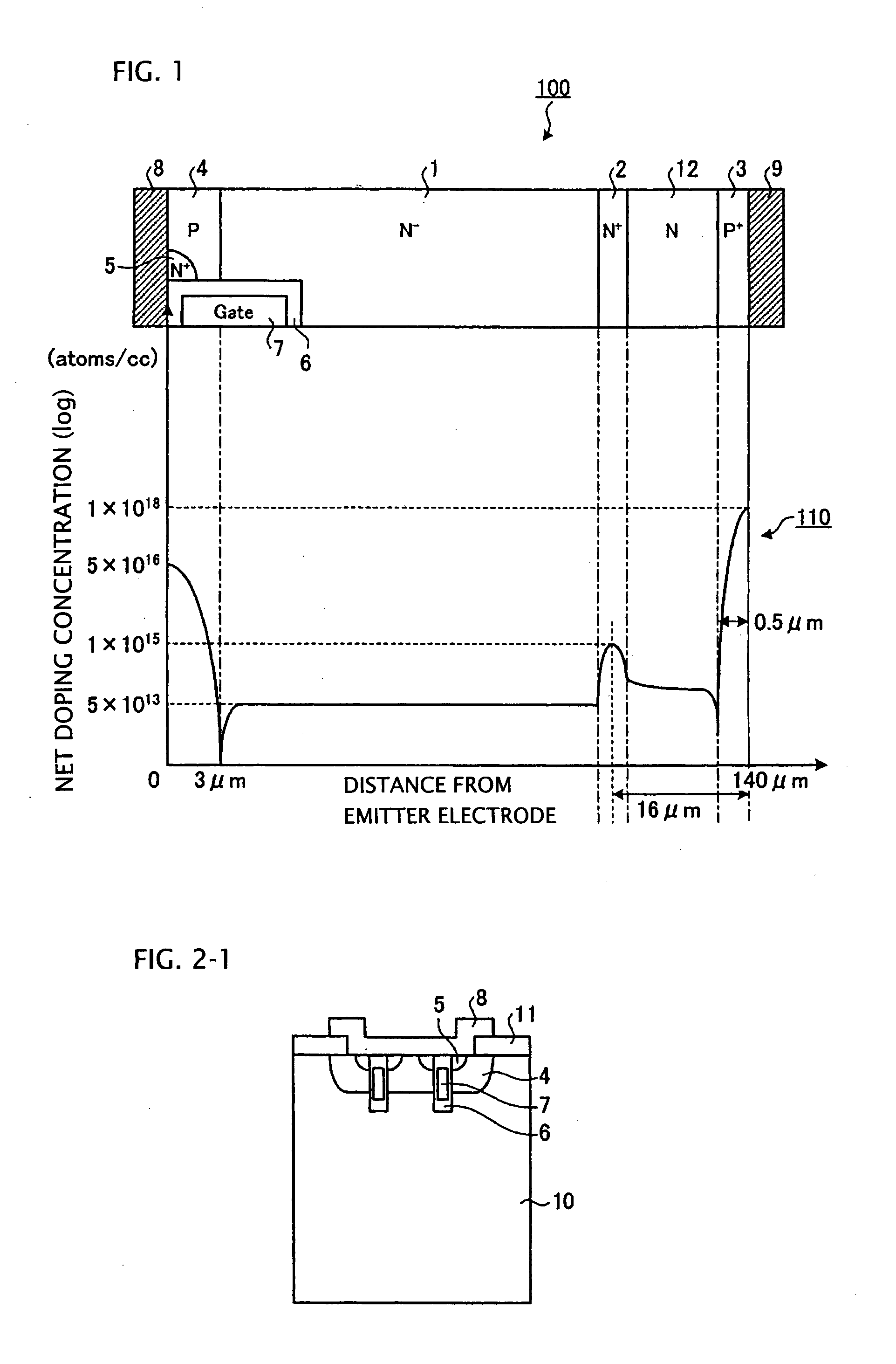
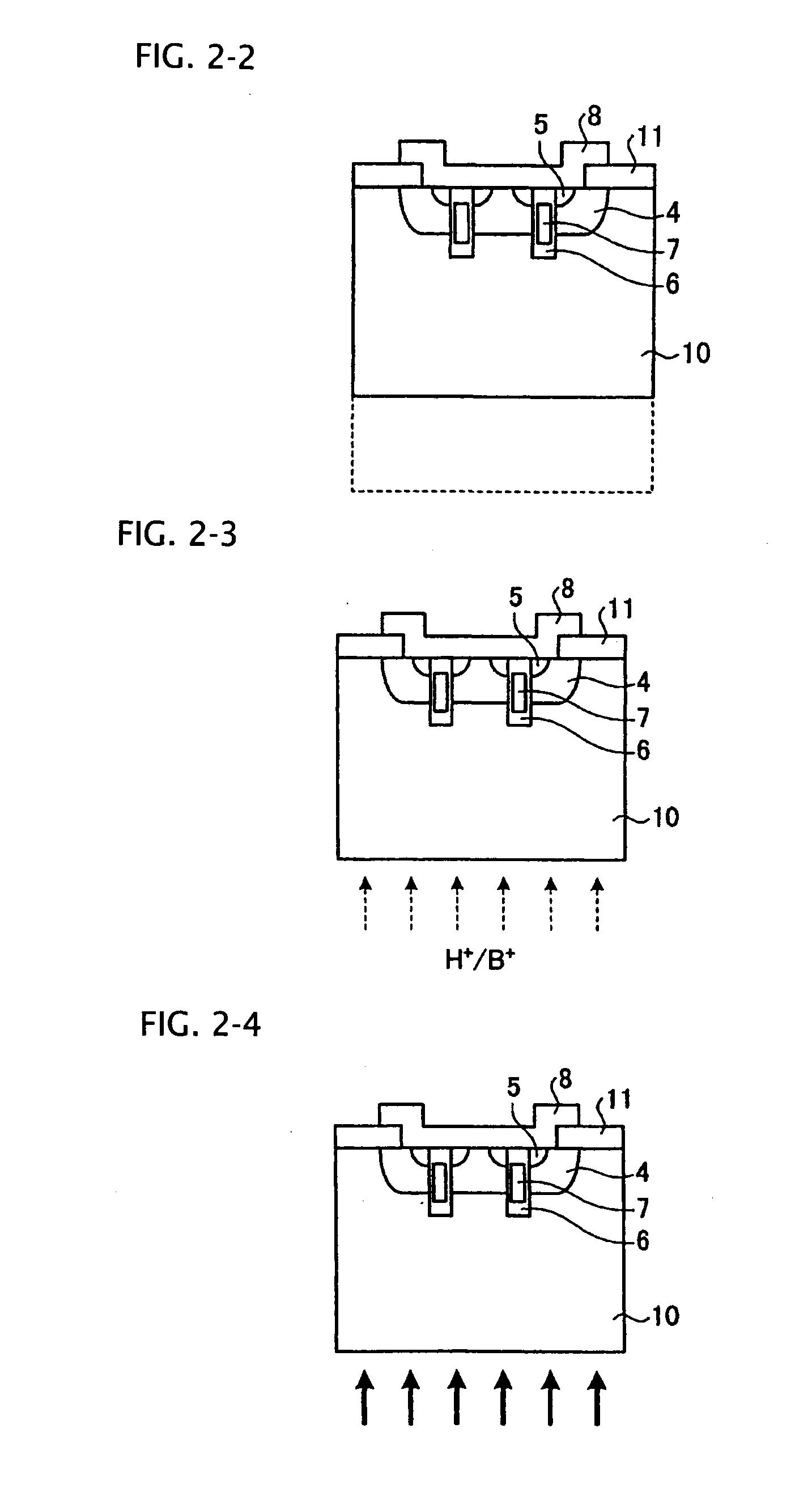
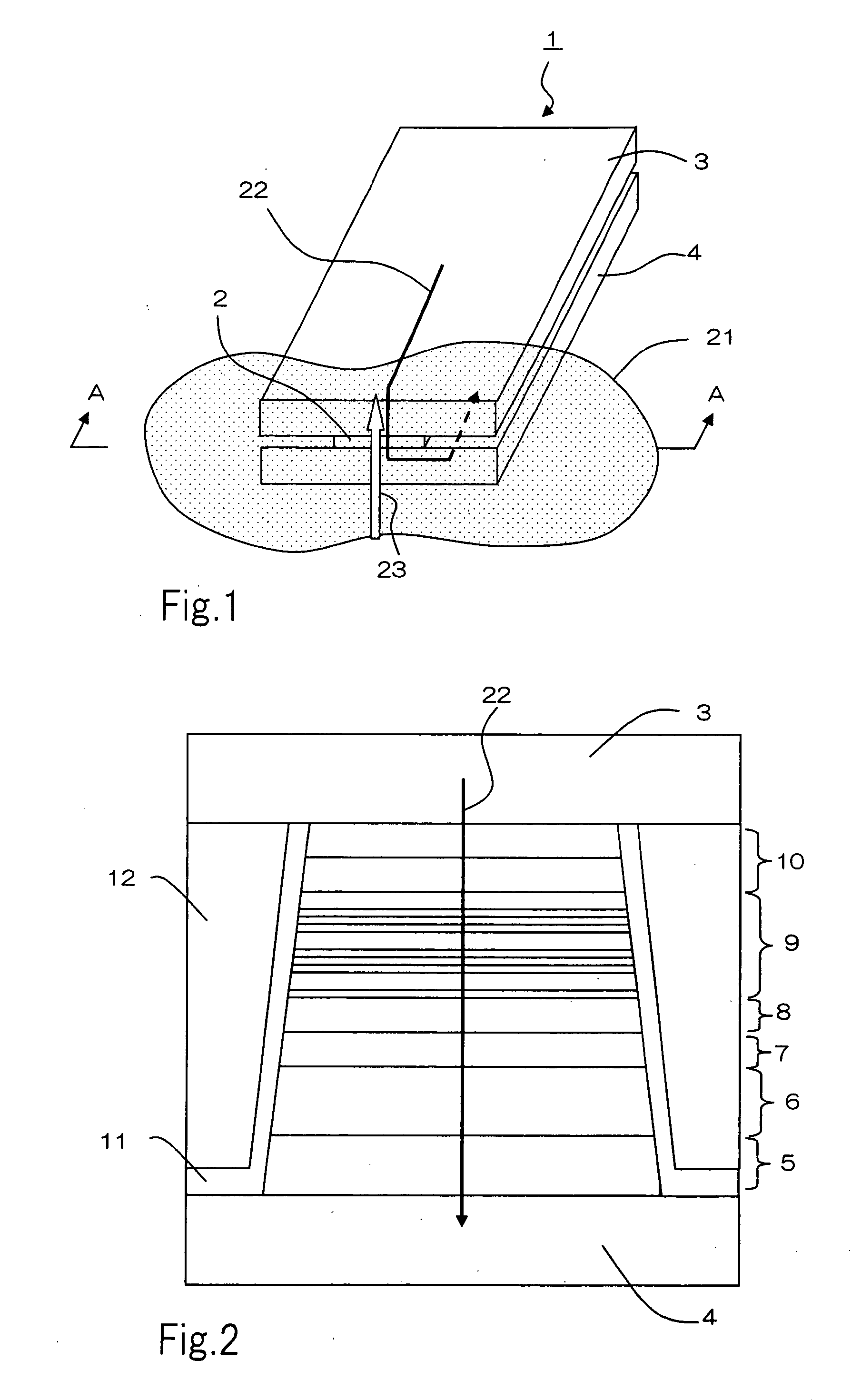
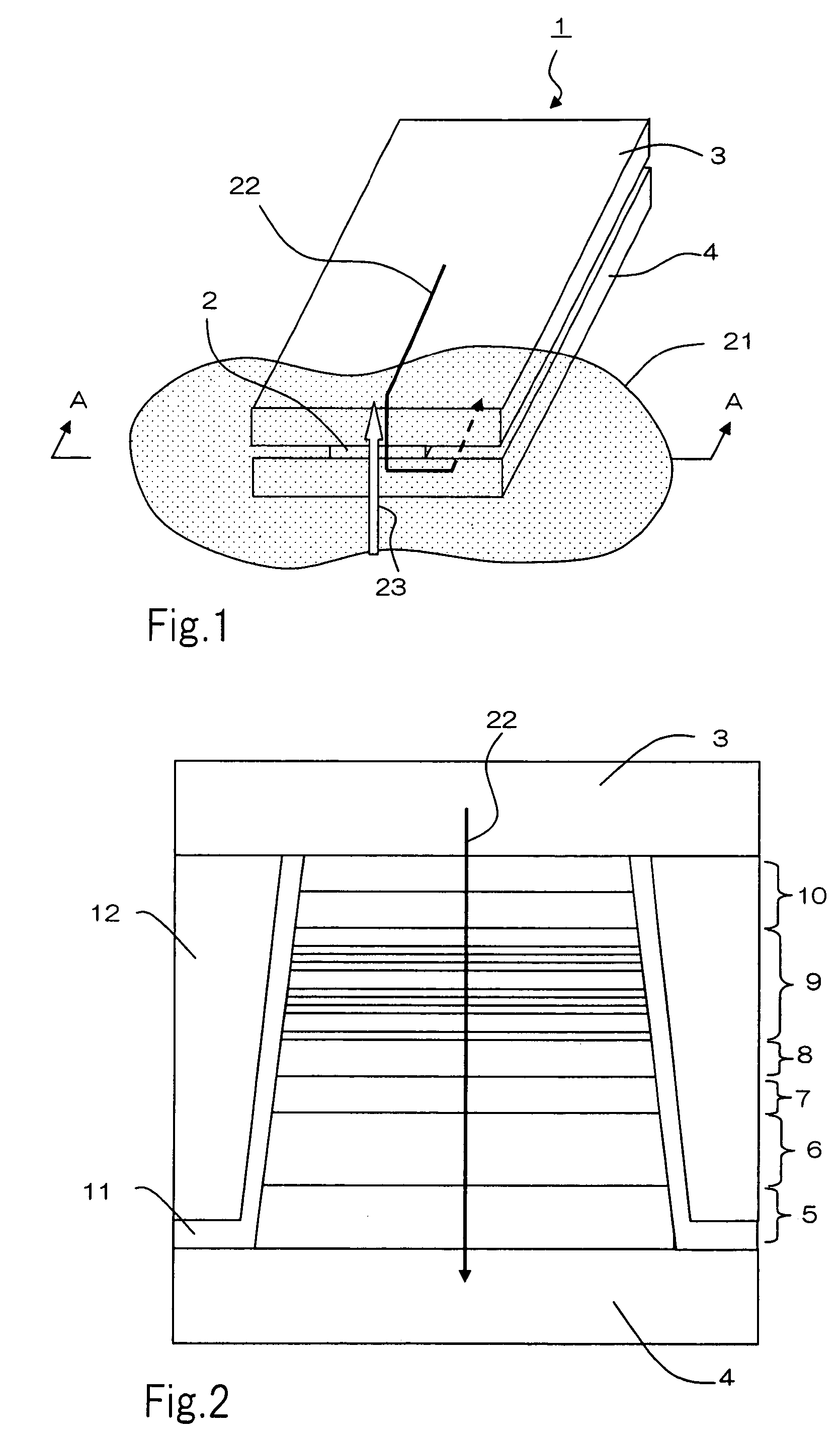
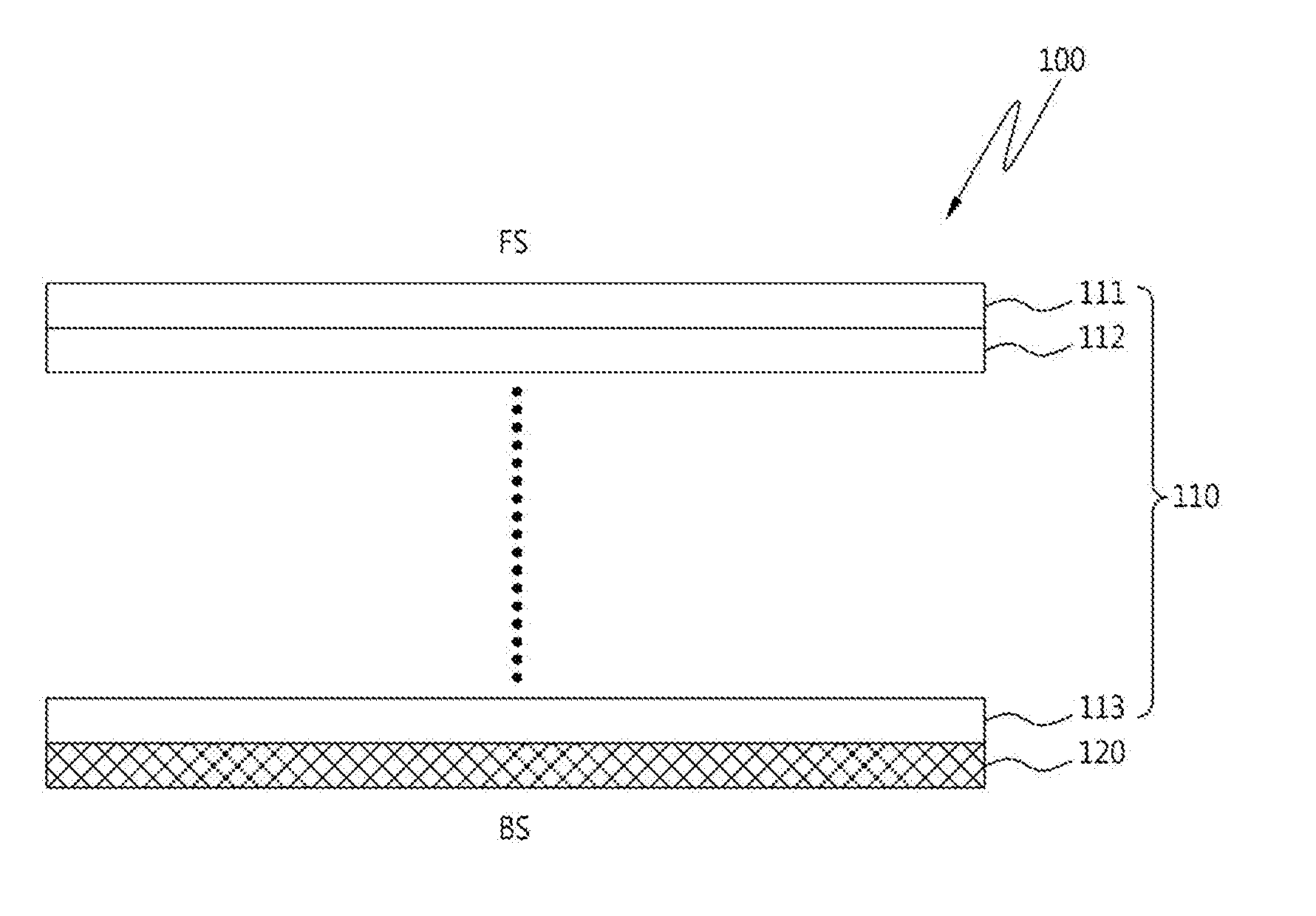
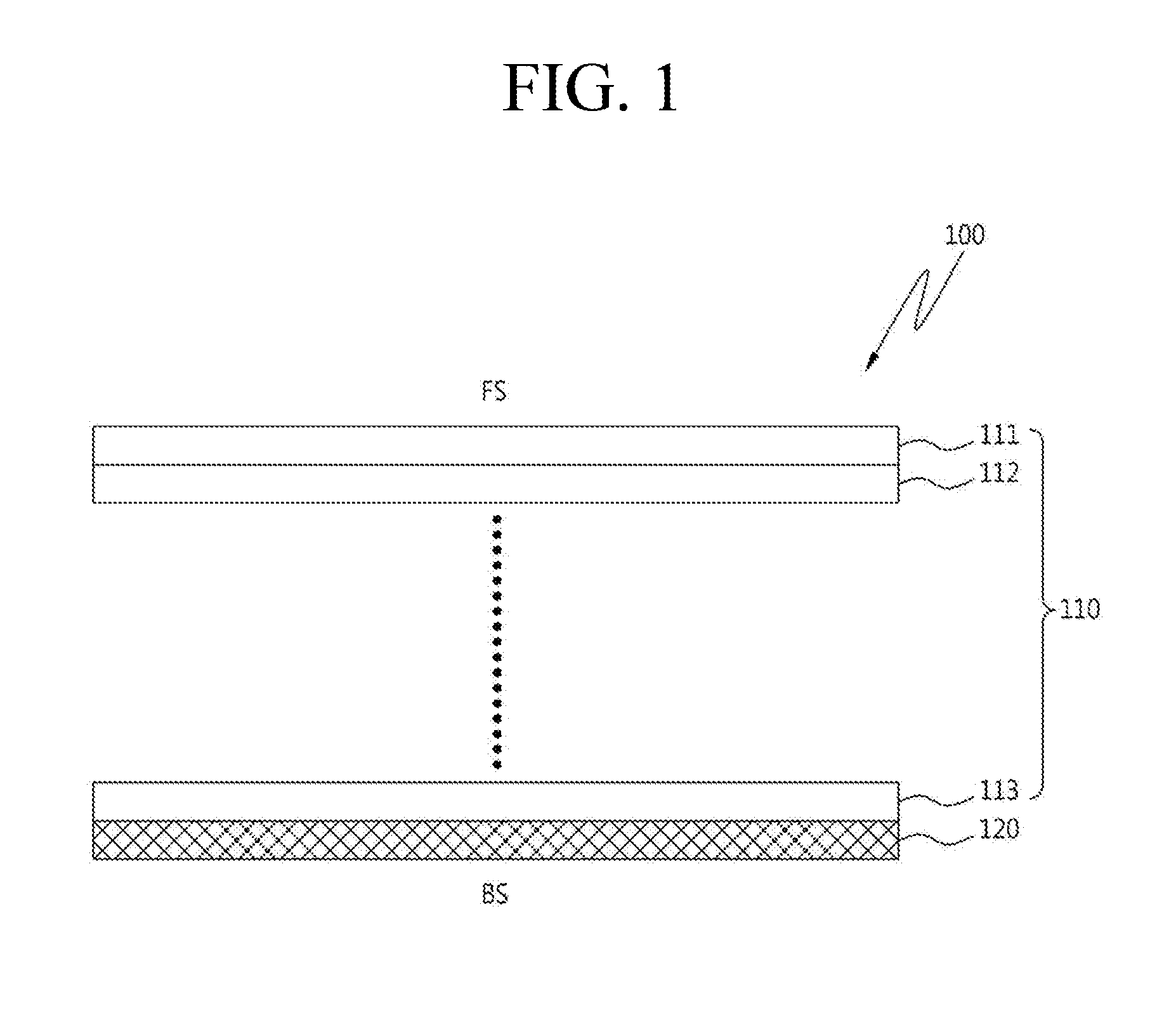
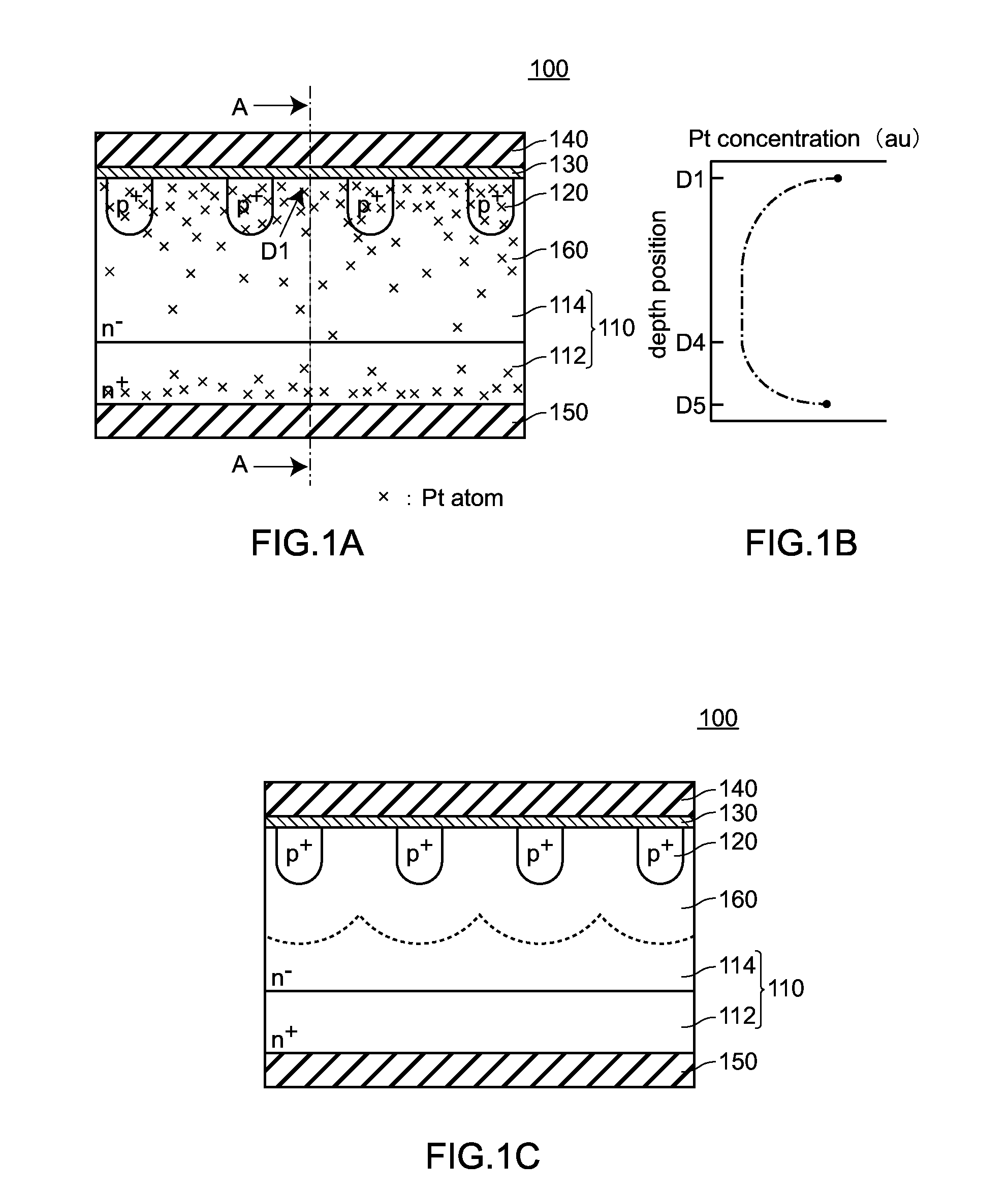
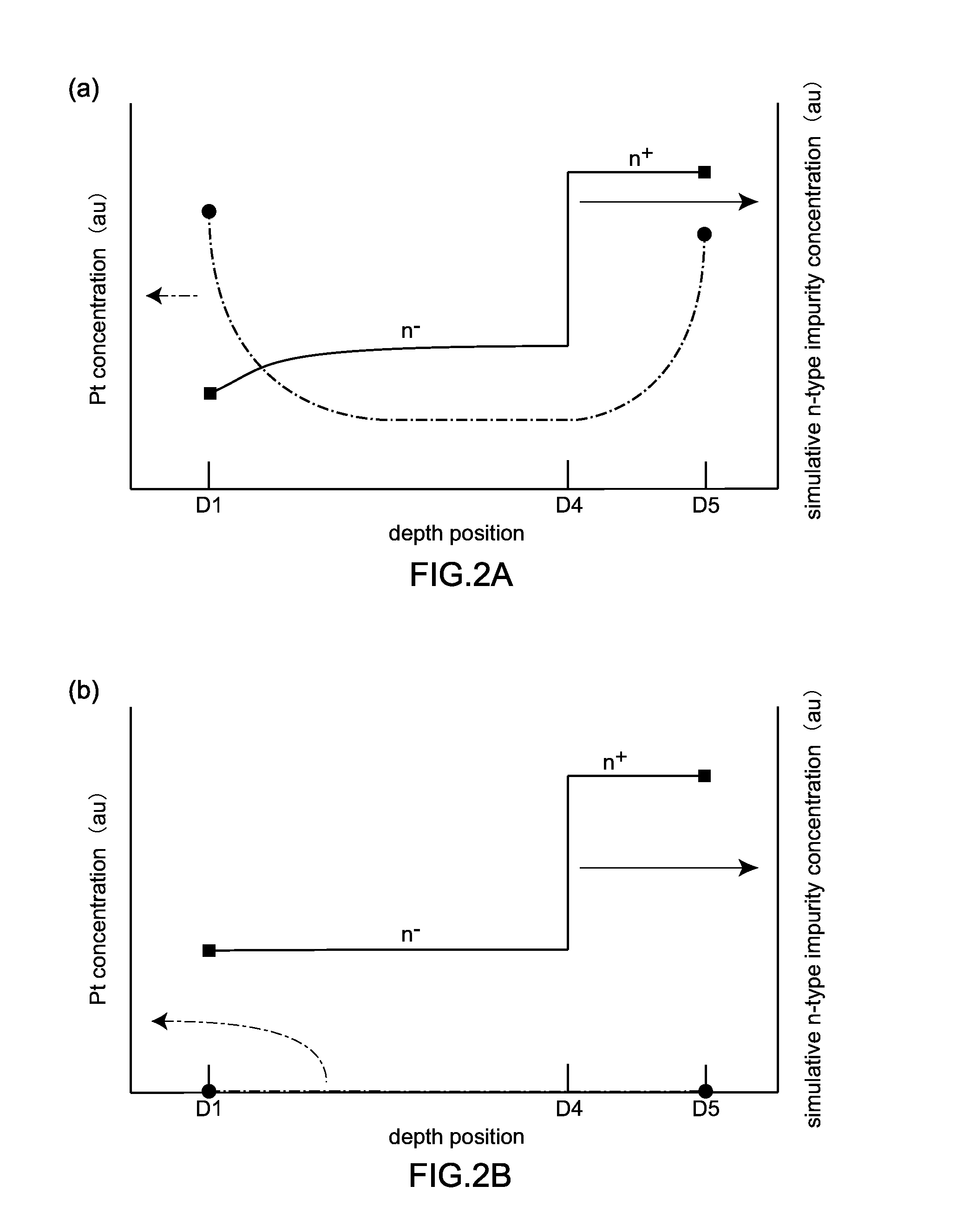
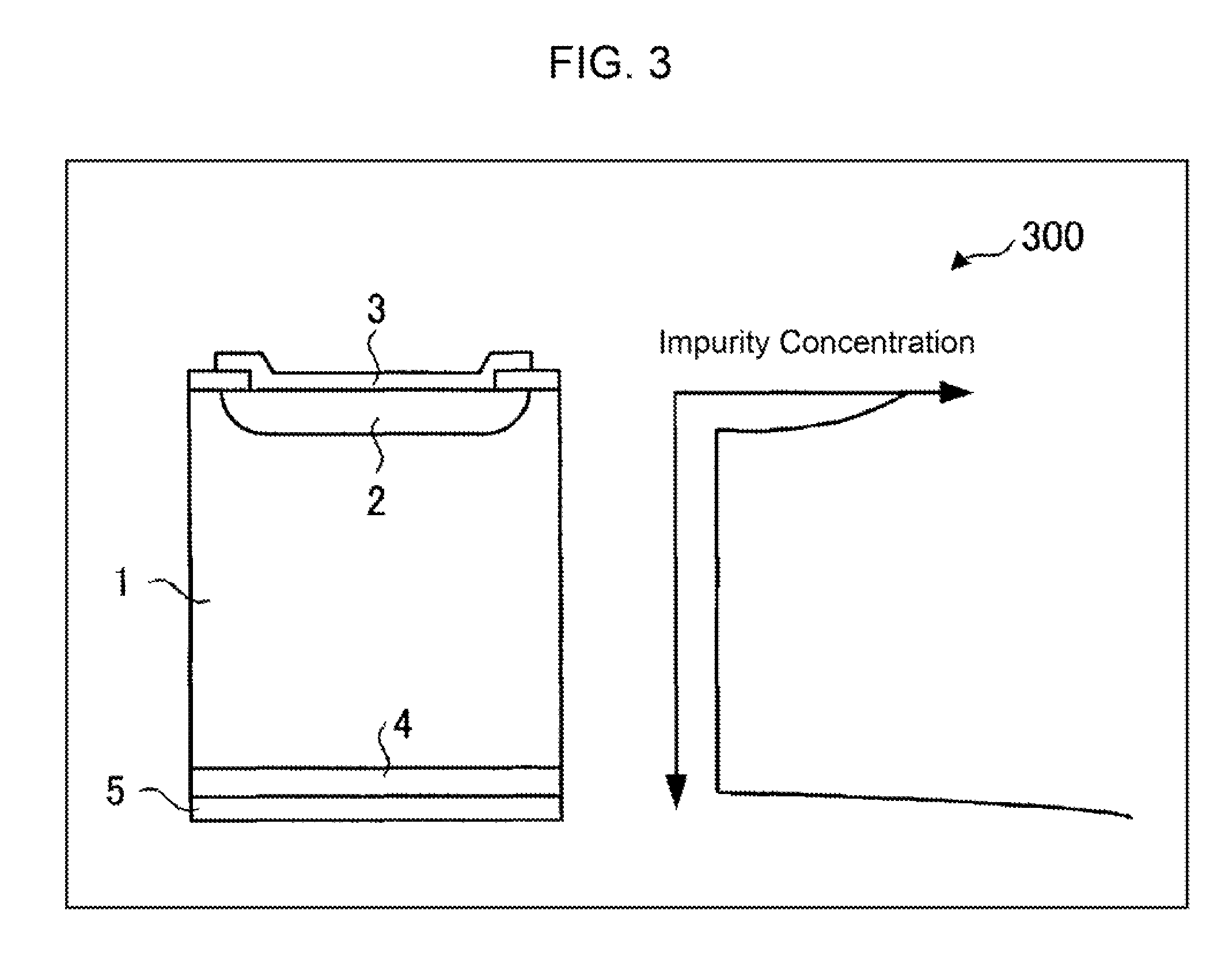
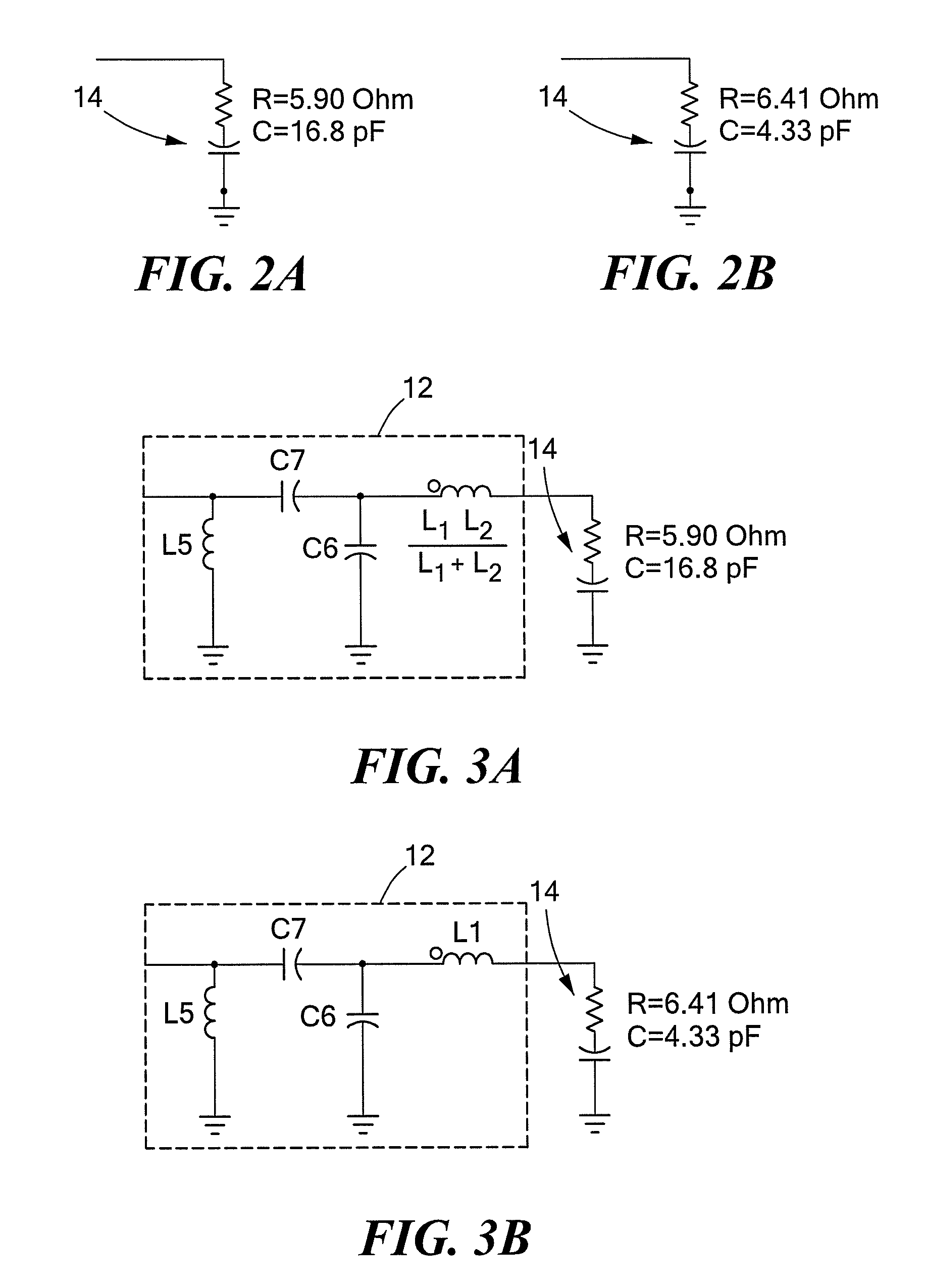
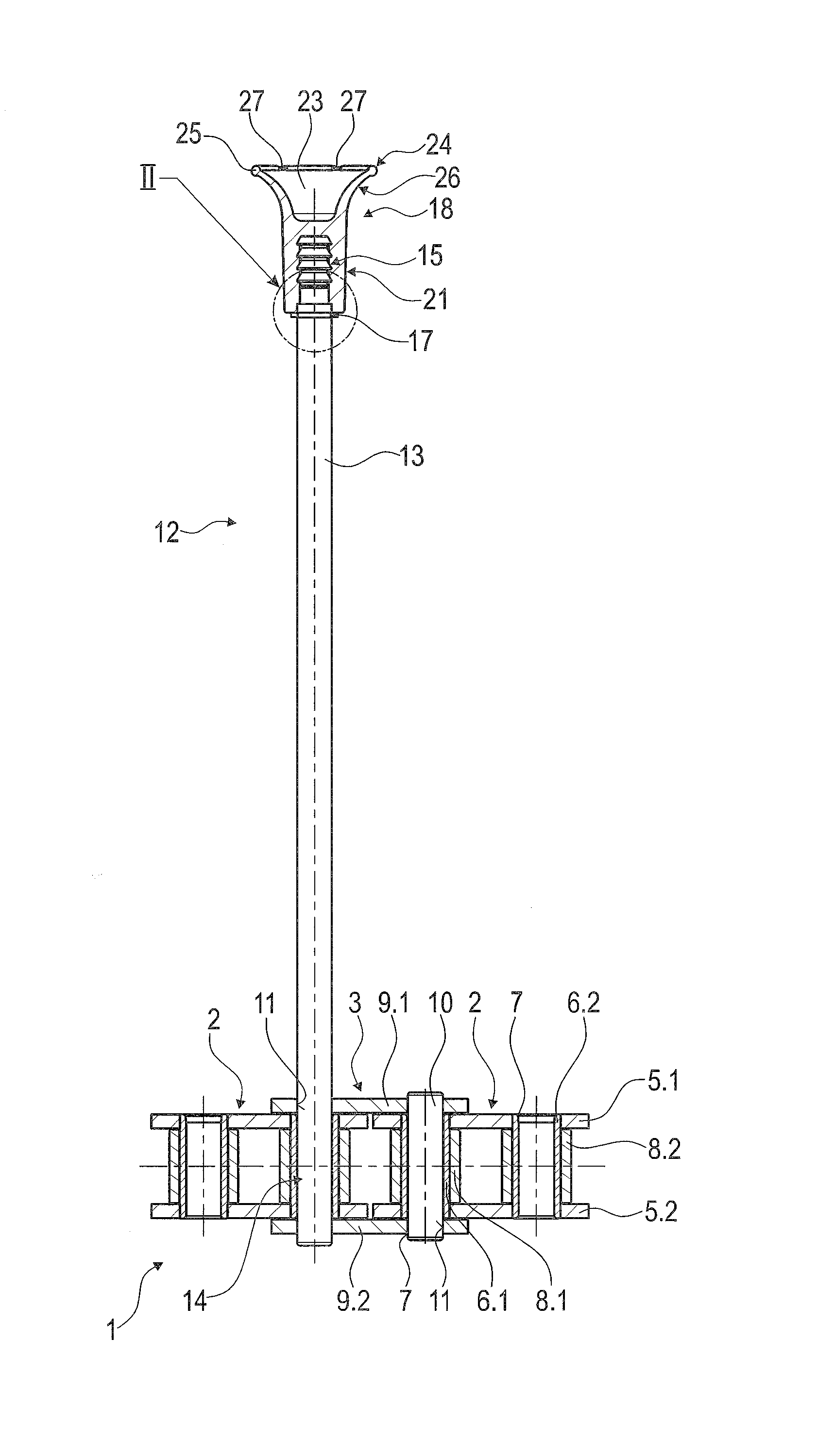
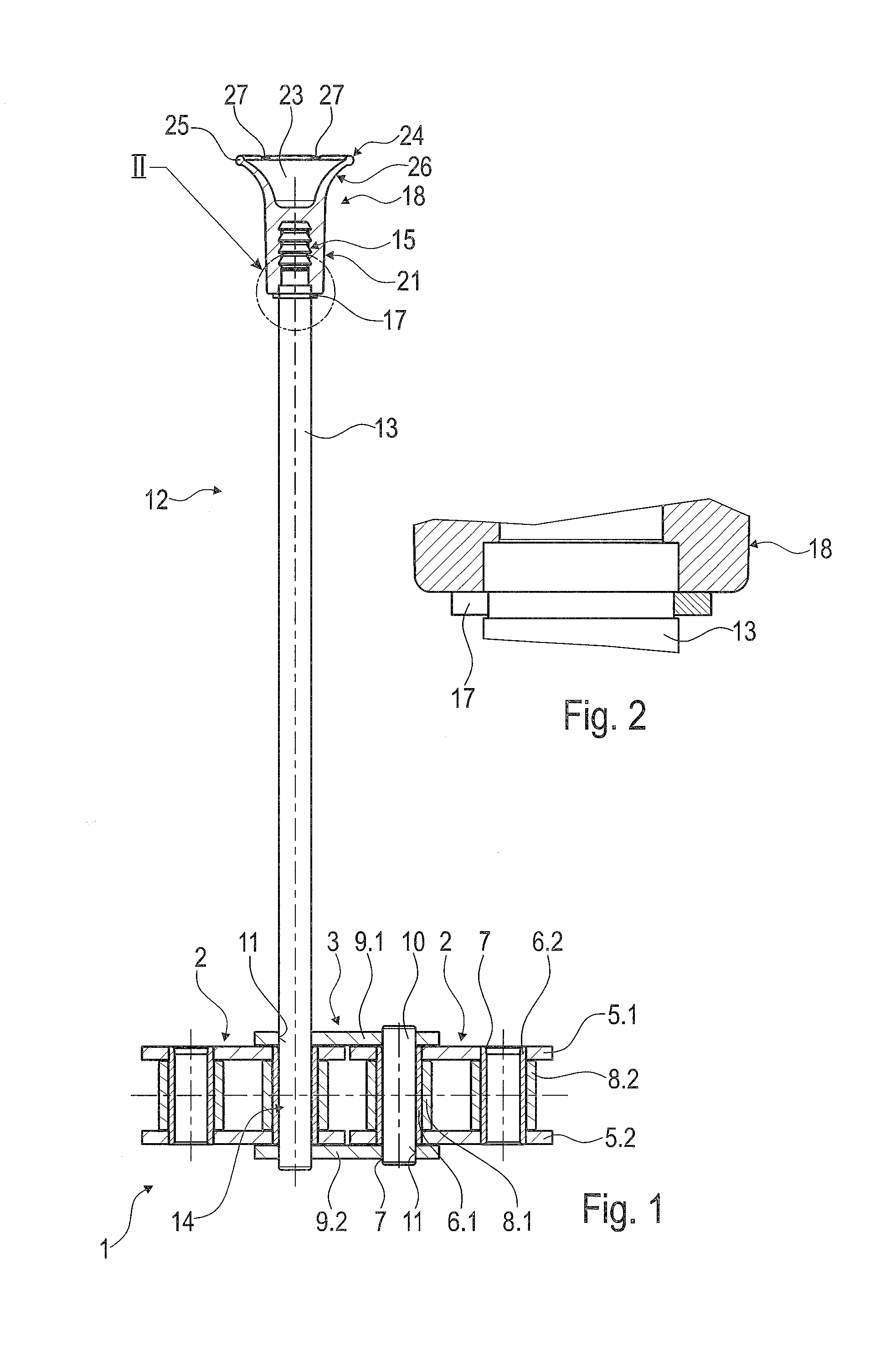
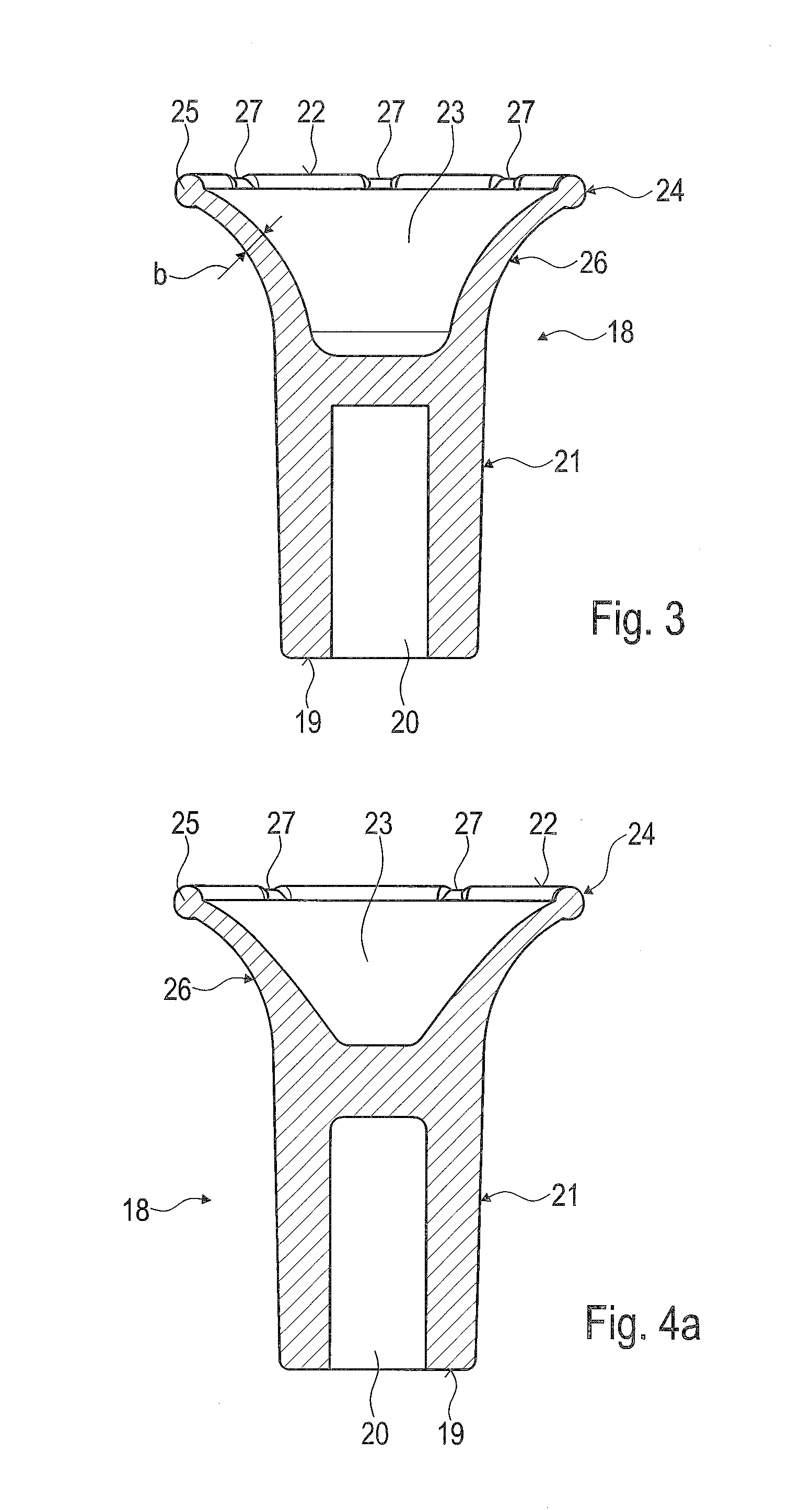
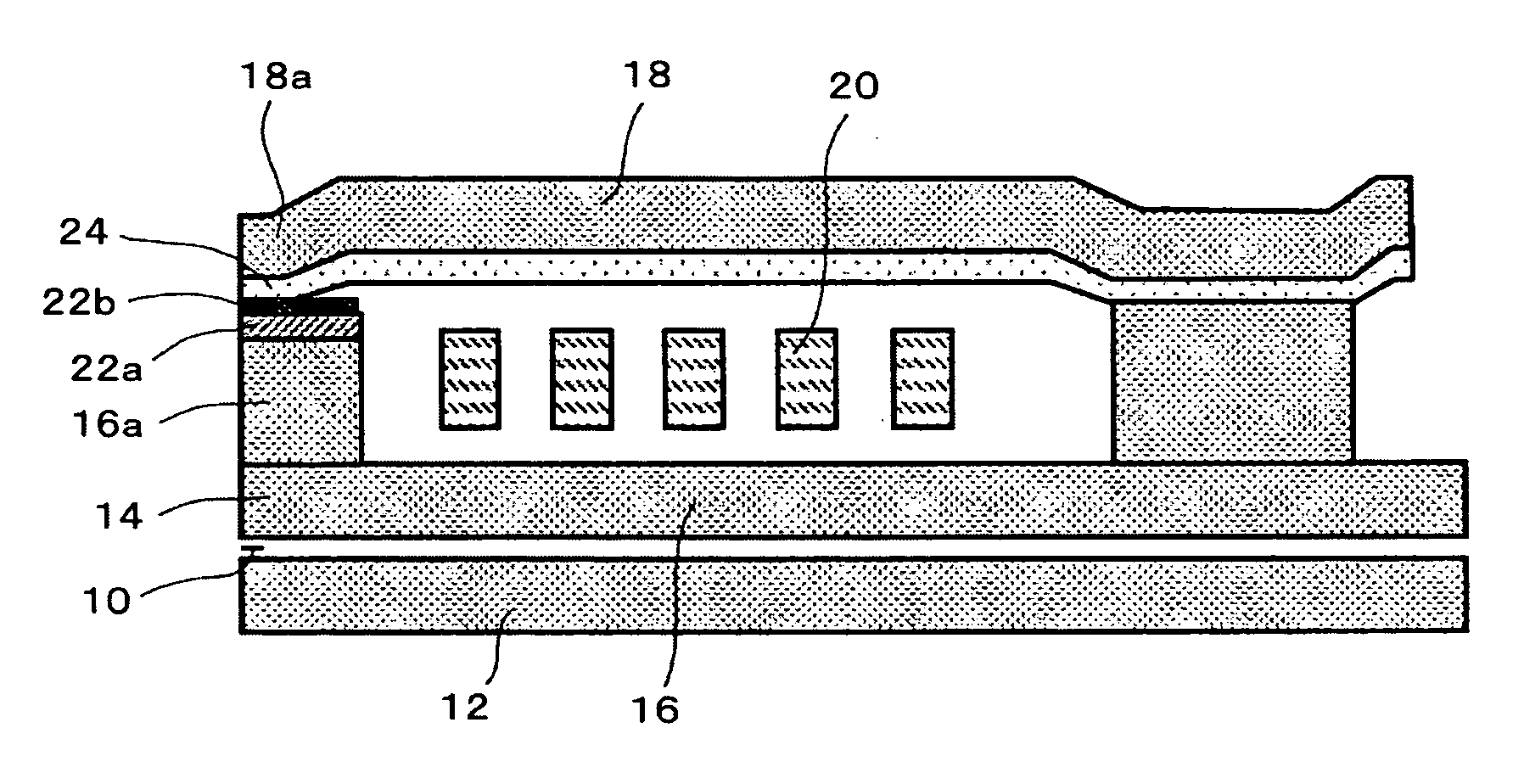
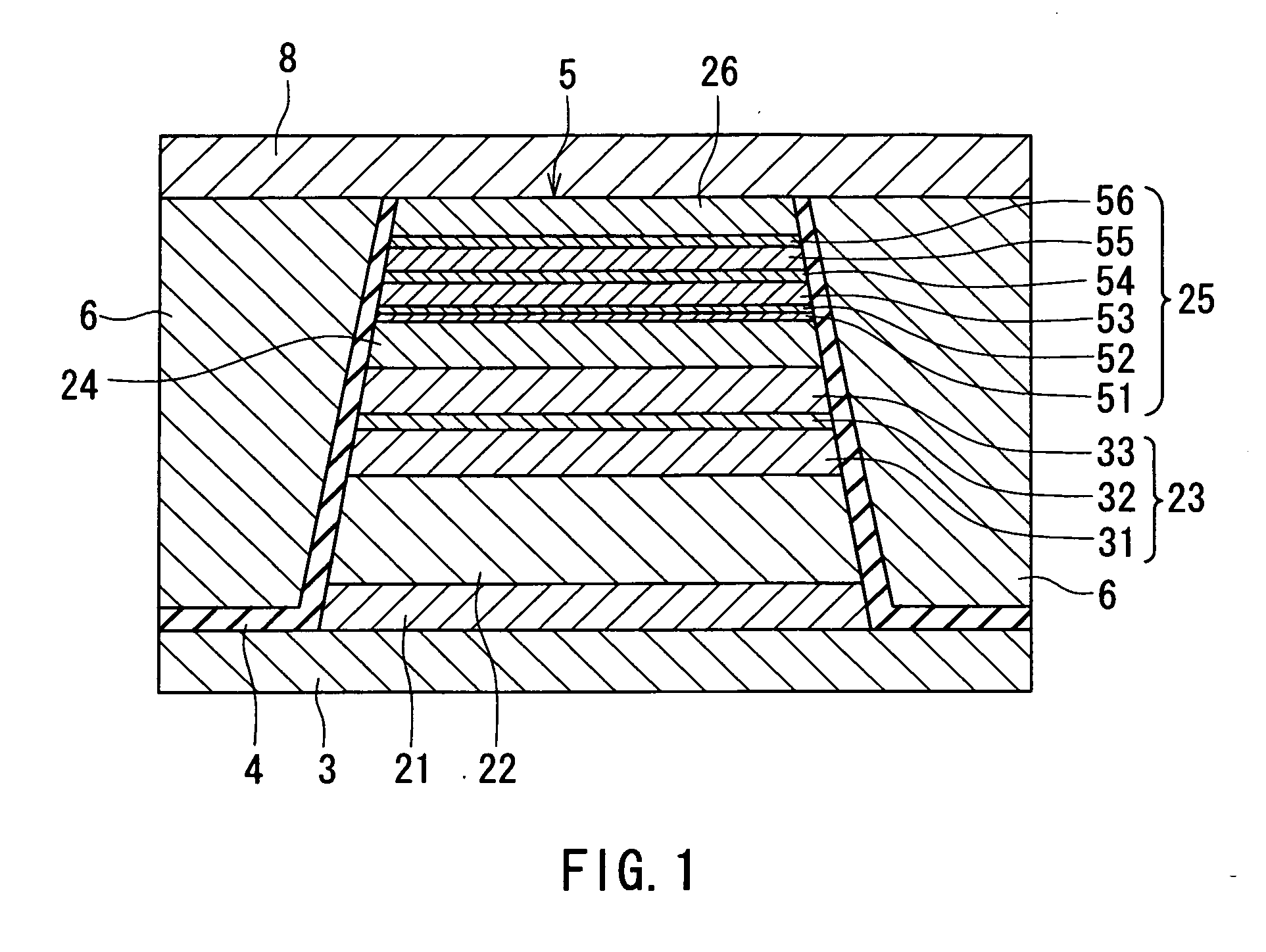
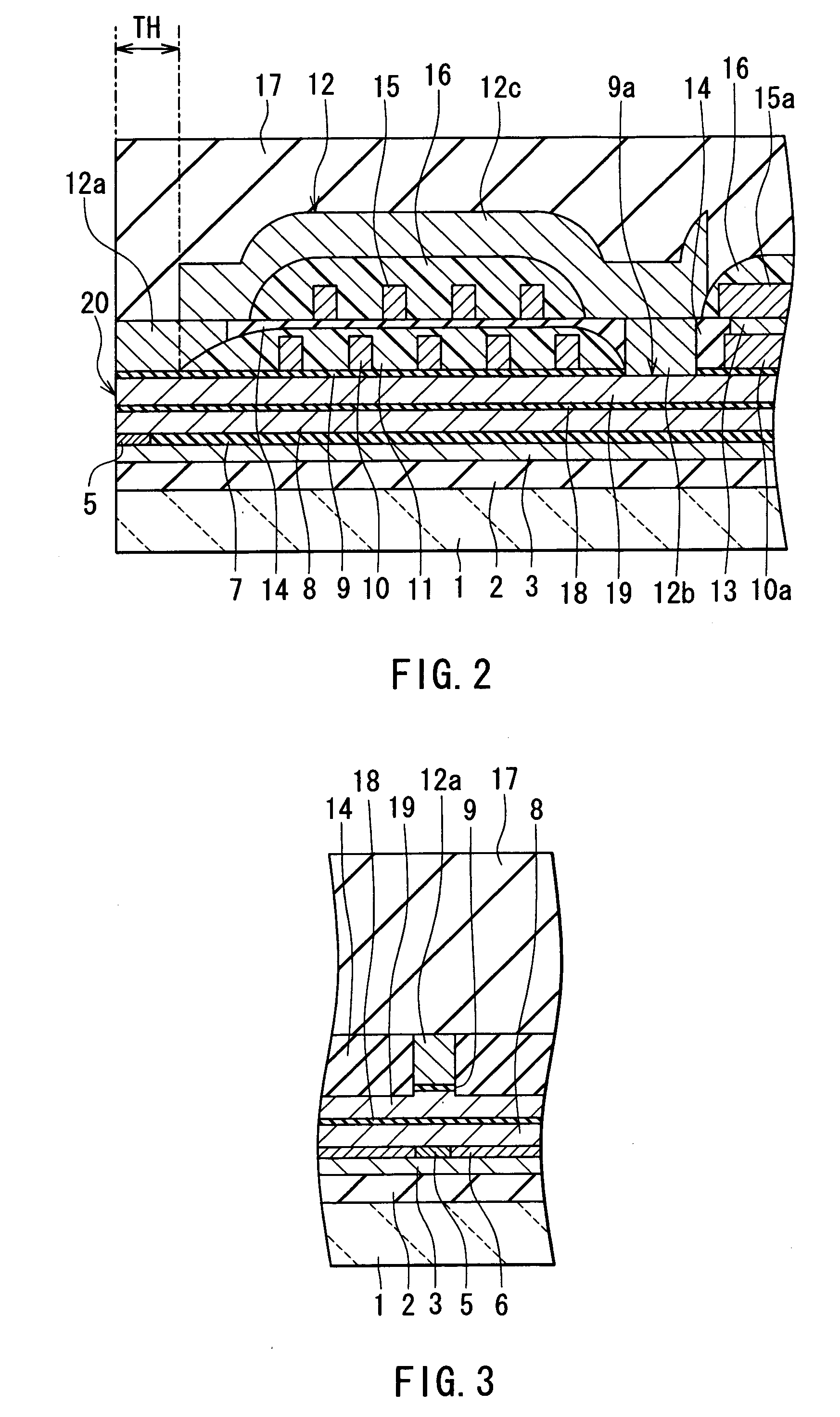
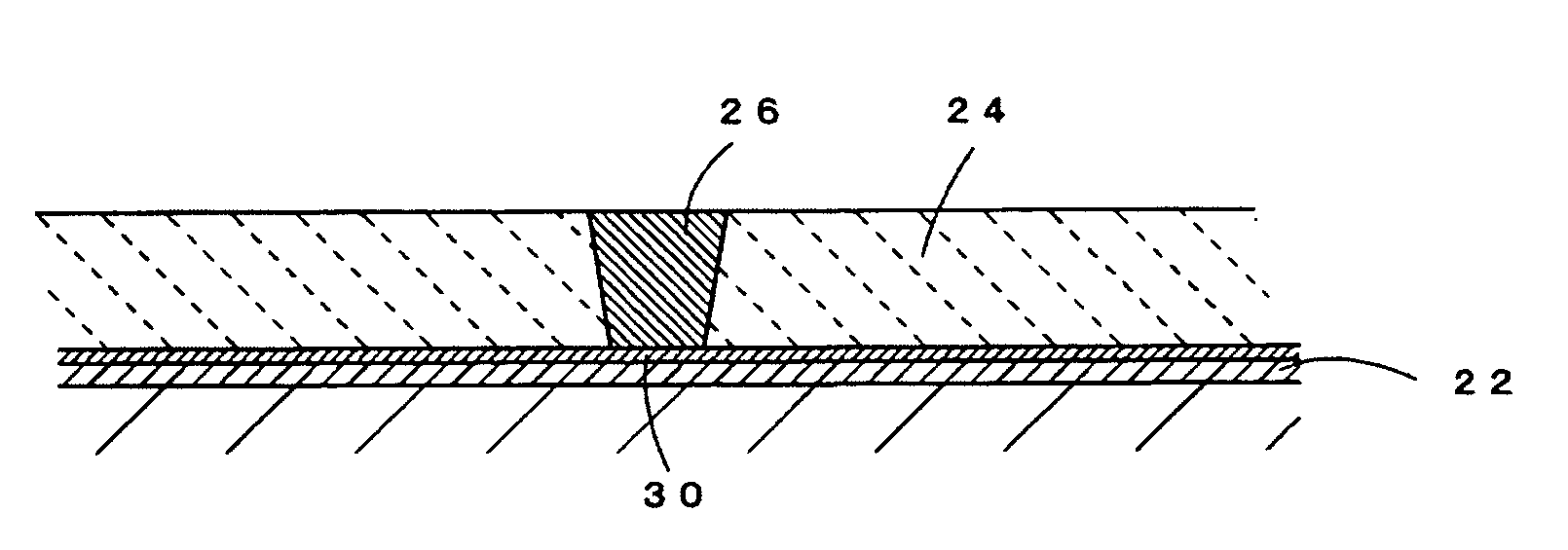
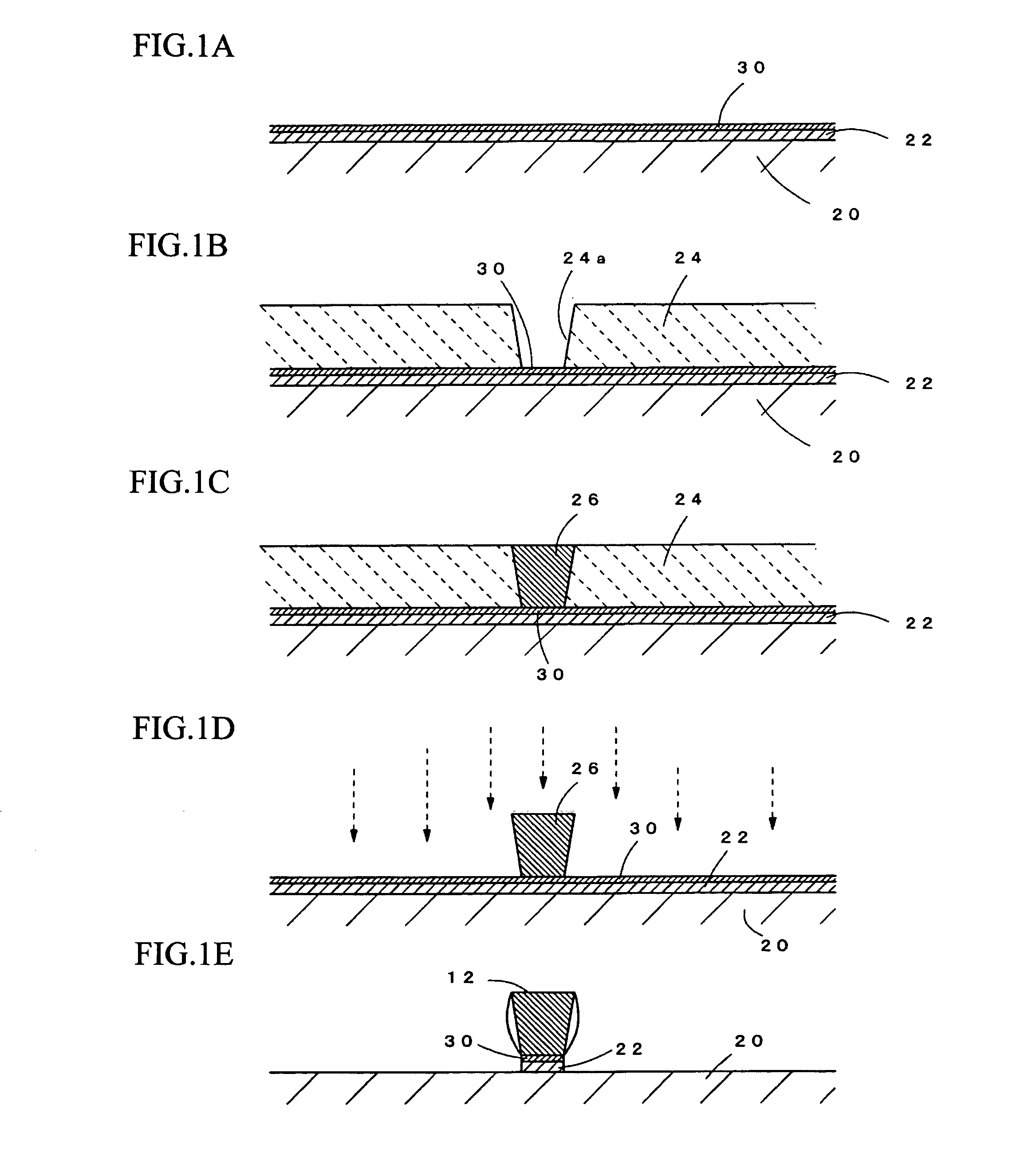
Semiconductor device and method of producing the same
ActiveUS20090184340A1Avoid damageSofter characteristicSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesProtonLength wave
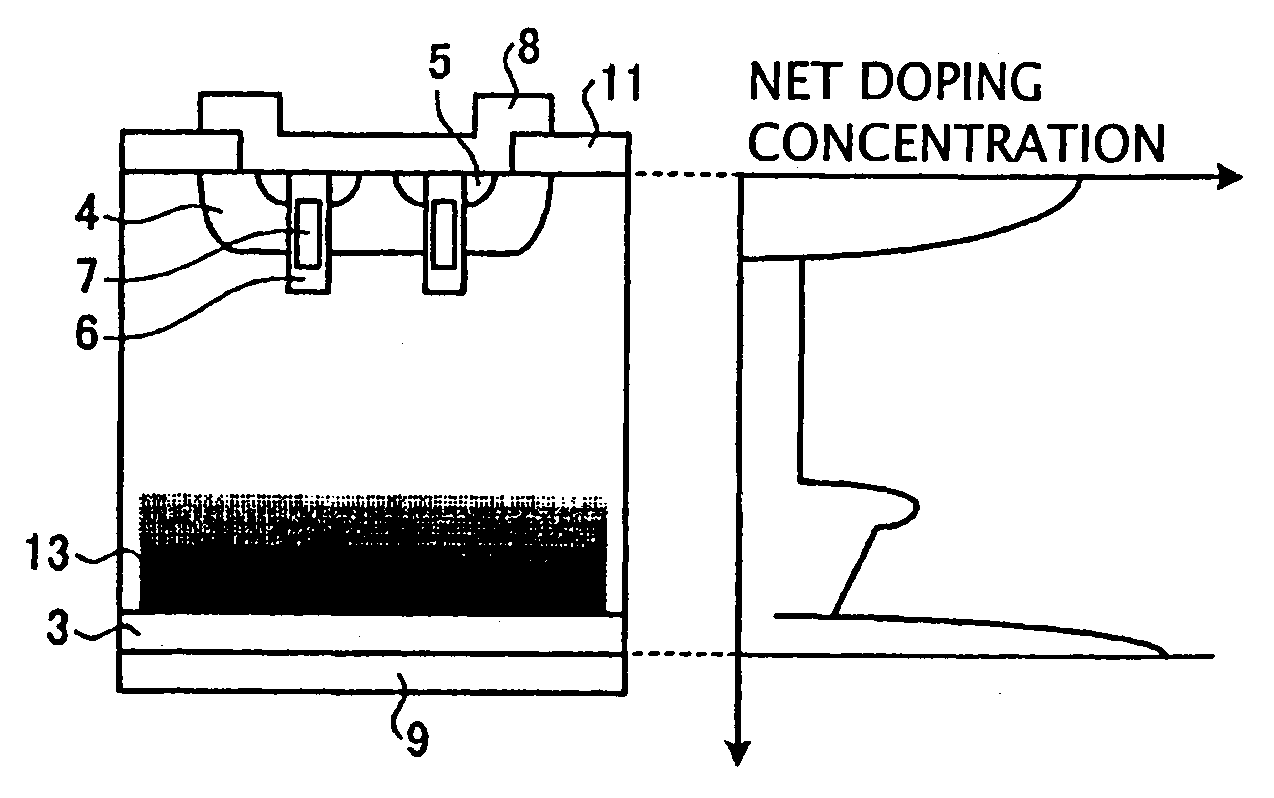
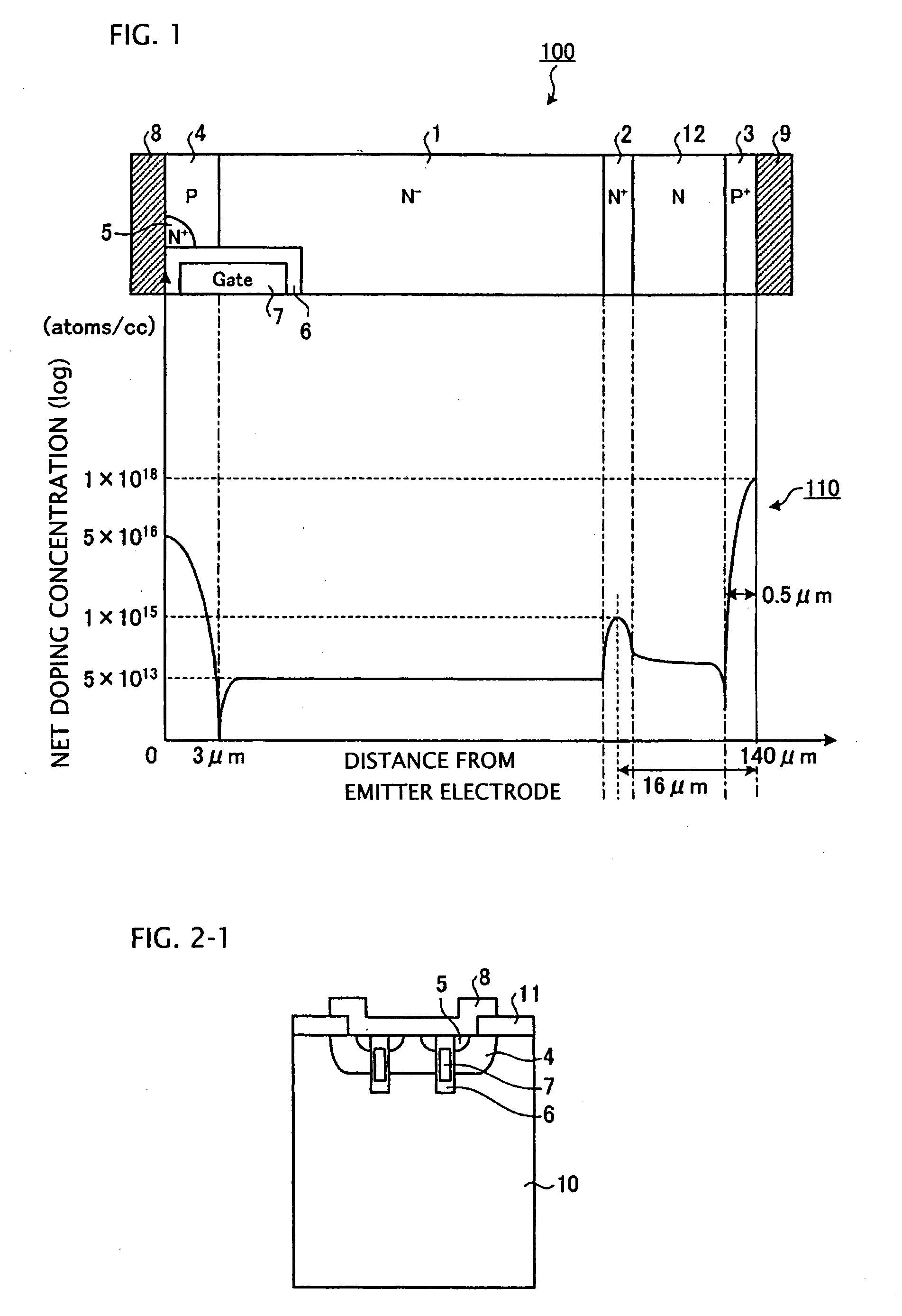
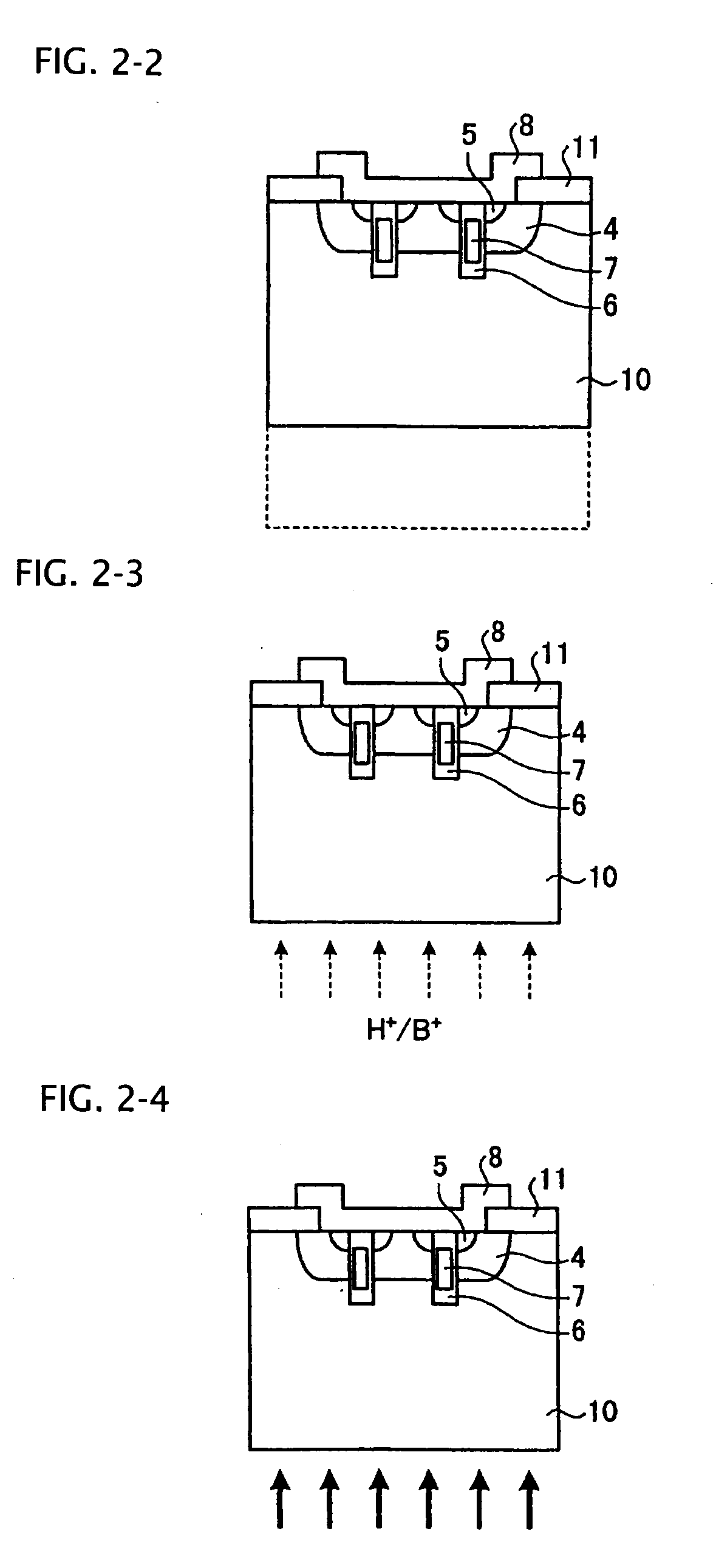
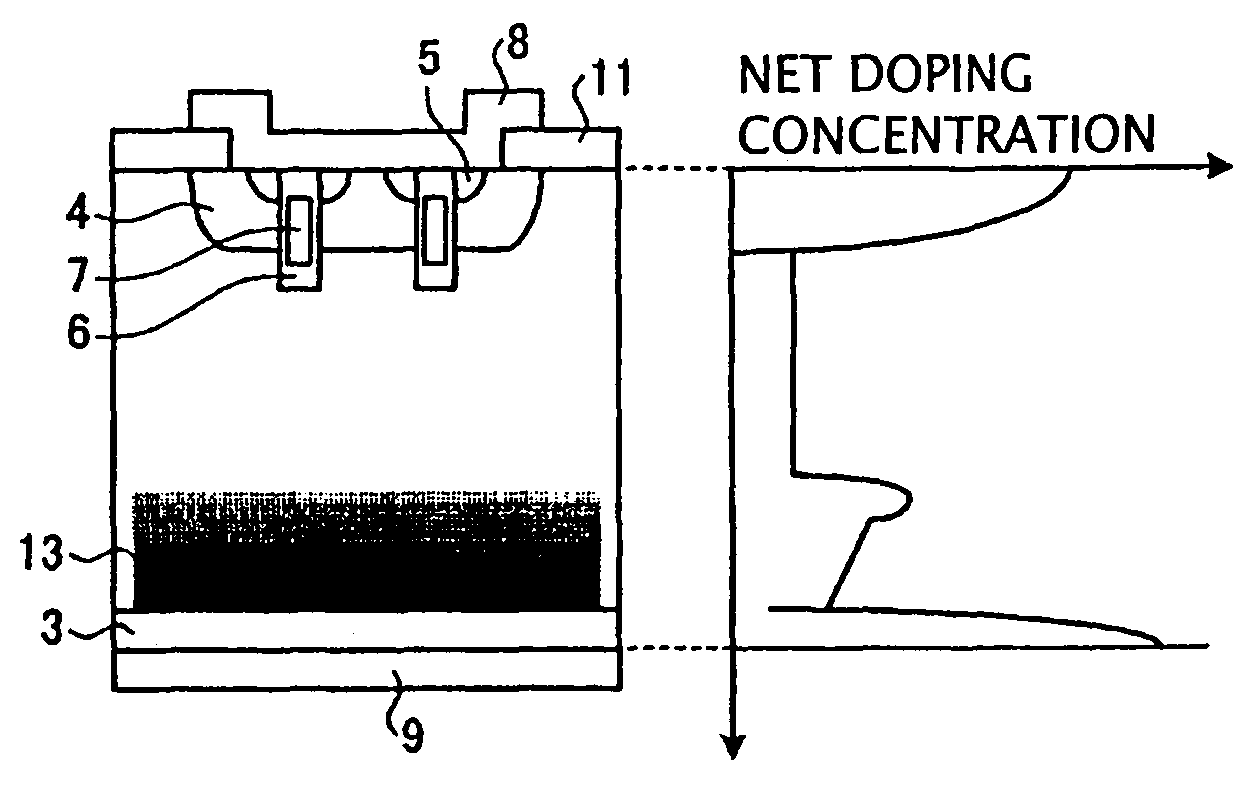
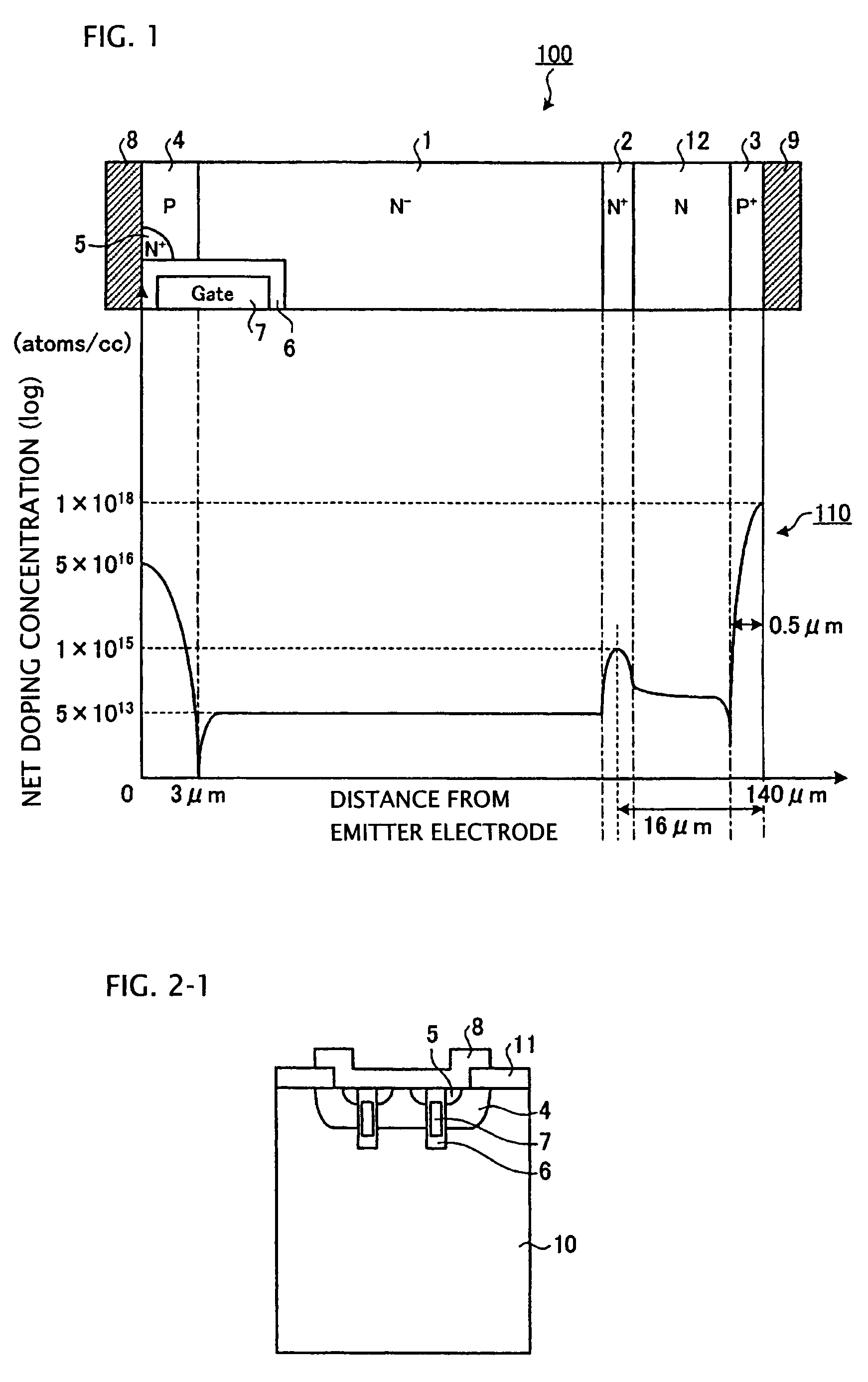
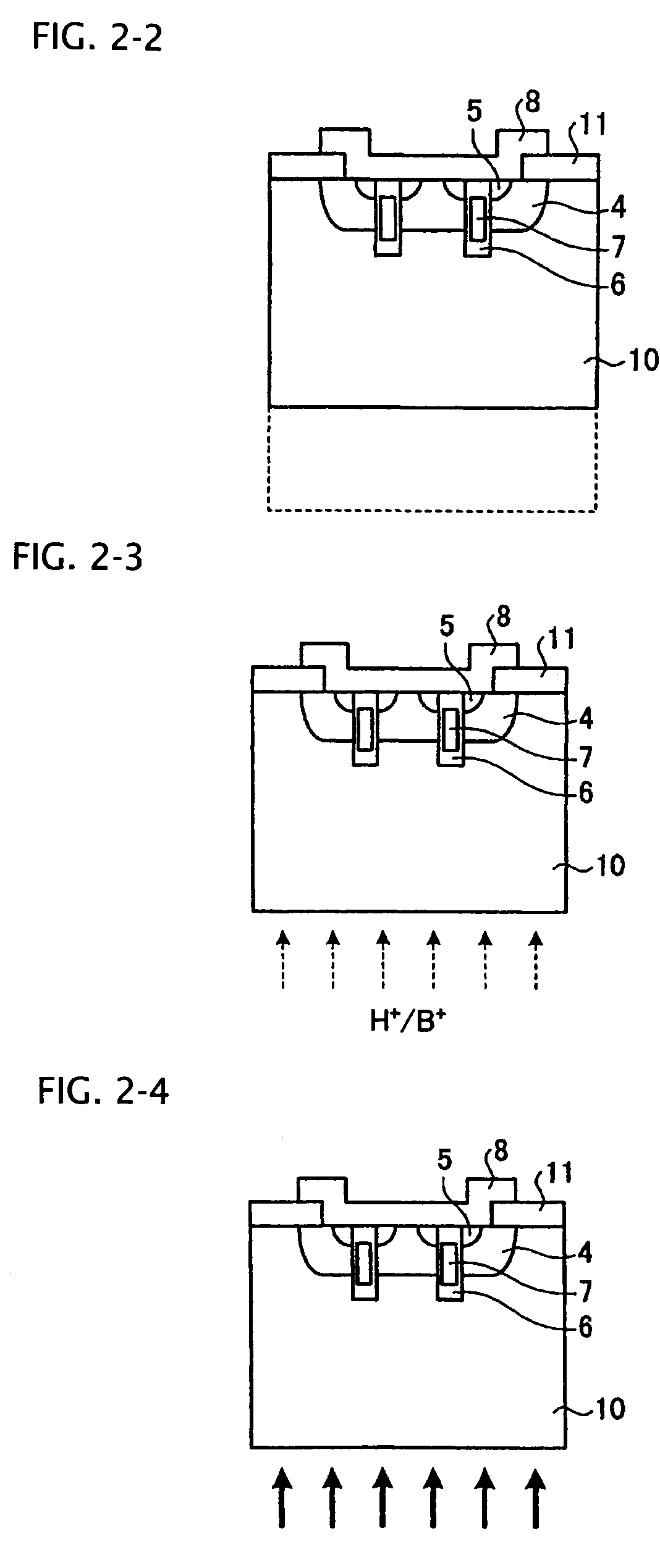
A semiconductor device is provided in which a semiconductor substrate can be prevented from being broken while elements can be prevented from being destroyed by a snap-back phenomenon. After an MOS gate structure is formed in a front surface of an FZ wafer, a rear surface of the FZ wafer is ground. Then, the ground surface is irradiated with protons and irradiated with two kinds of laser beams different in wavelength simultaneously to thereby form an N+ first buffer layer and an N second buffer layer. Then, a P+ collector layer and a collector electrode are formed on the proton-irradiated surface. The distance from a position where the net doping concentration of the N+ first buffer layer is locally maximized to the interface between the P+ collector layer and the N second buffer layer is set to be in a range of 5 μm to 30 μm, both inclusively.
Owner:FUJI ELECTRIC CO LTD
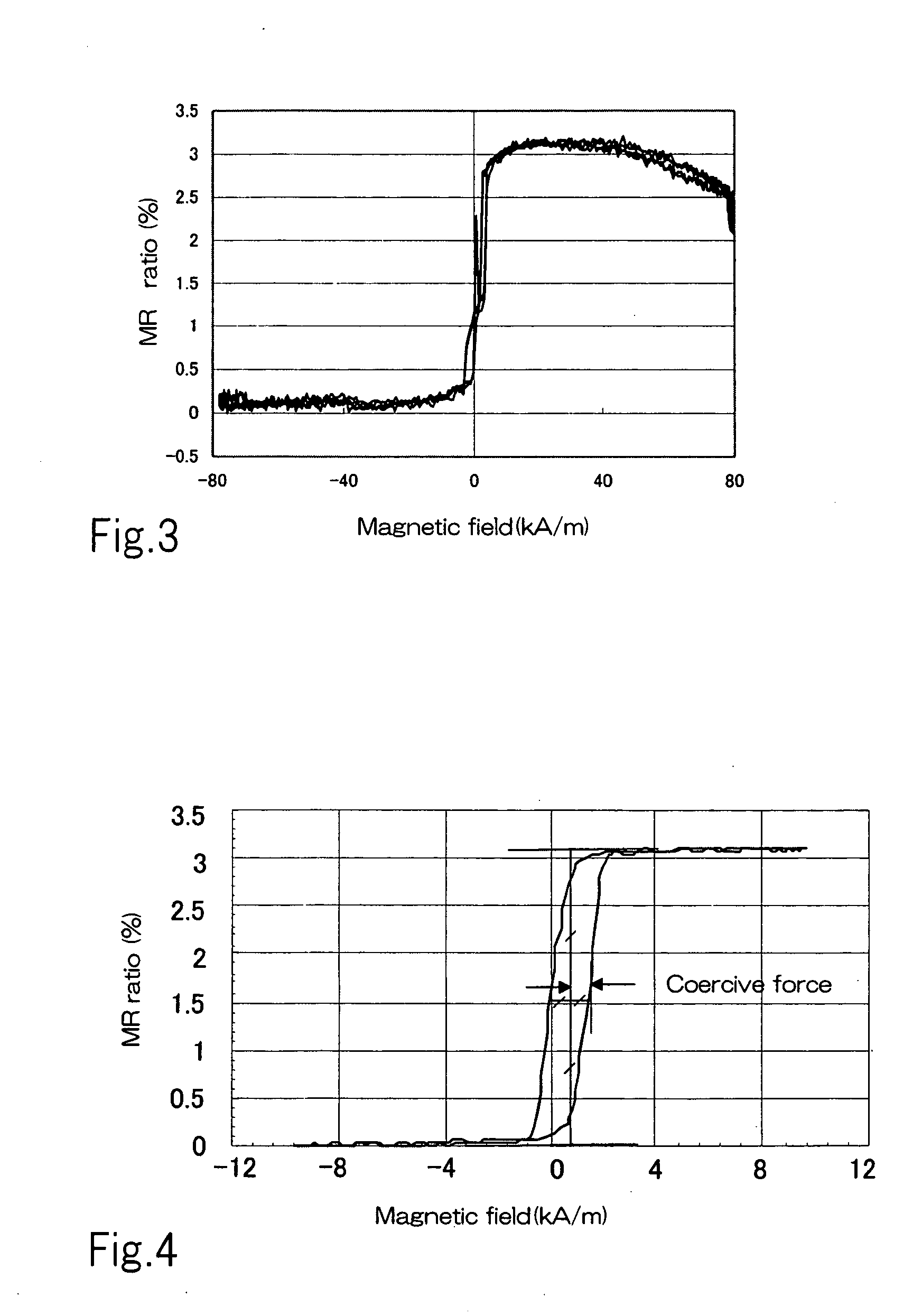
Magnetoresistive effect element, magnetic memory element magnetic memory device and manufacturing methods thereof
InactiveUS7262064B2Low coercivityBarkhausen noise increaseNanostructure applicationNanomagnetismMagnetic memoryTunnel junction
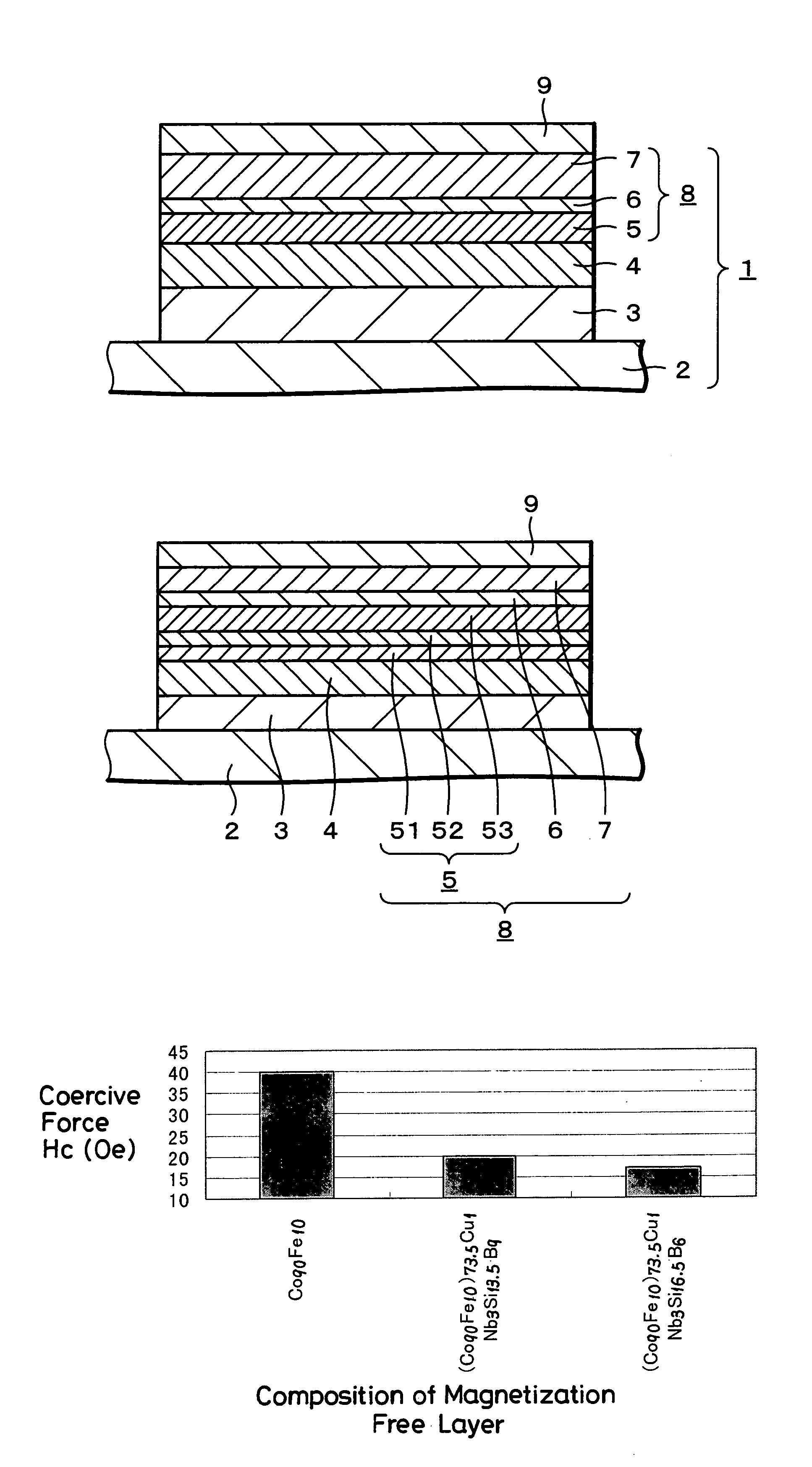
In a magnetoresistive effect element using a ferromagnetic tunnel junction having a tunnel barrier layer sandwiched between at least a pair of ferromagnetic layers, a magnetization free layer comprising one of the ferromagnetic layers is composed of a single layer of a material having an amorphous or microcrystal structure or a material layer the main portion of which has an amorphous or microcrystal structure. The magnetoresistive effect element can produce excellent magnetic-resistance characteristics, and a magnetic memory element and a magnetic memory device using the magnetoresistive effect element as a memory element thereof can improve both of write and read characteristics at the same time.
Owner:SONY CORP
Modular furniture assembly with dual coupling mechanisms
InactiveUS20160174715A1Reduce minimize prevent tentingReduce and eliminate slackBenchesDismountable chairsRigid coreCoupling
A modular furniture assembly comprising first and second members (e.g., base and transverse member) may have convenient dual coupling mechanisms, for example, a magnetic coupling mechanism and a mechanical (e.g., hook and loop) coupling mechanism. The first member and / or second member may include a fabric or other cover over a foam or other body (e.g., fabric over foam, or other cover over a skeleton). Either or both members may include a rigid core (e.g., a board, skeleton, etc.). The coupling mechanisms may be such as to not detract from any soft, cushioned characteristics of a fabric over foam construction, if such is provided. The coupling structure in the first member and / or the second member may be tethered to the rigid core of the particular member to reduce tenting of the fabric or other cover of the first member and / or the second member as the tethered coupling structure is pulled.
Owner:THE LOVESAC CORP
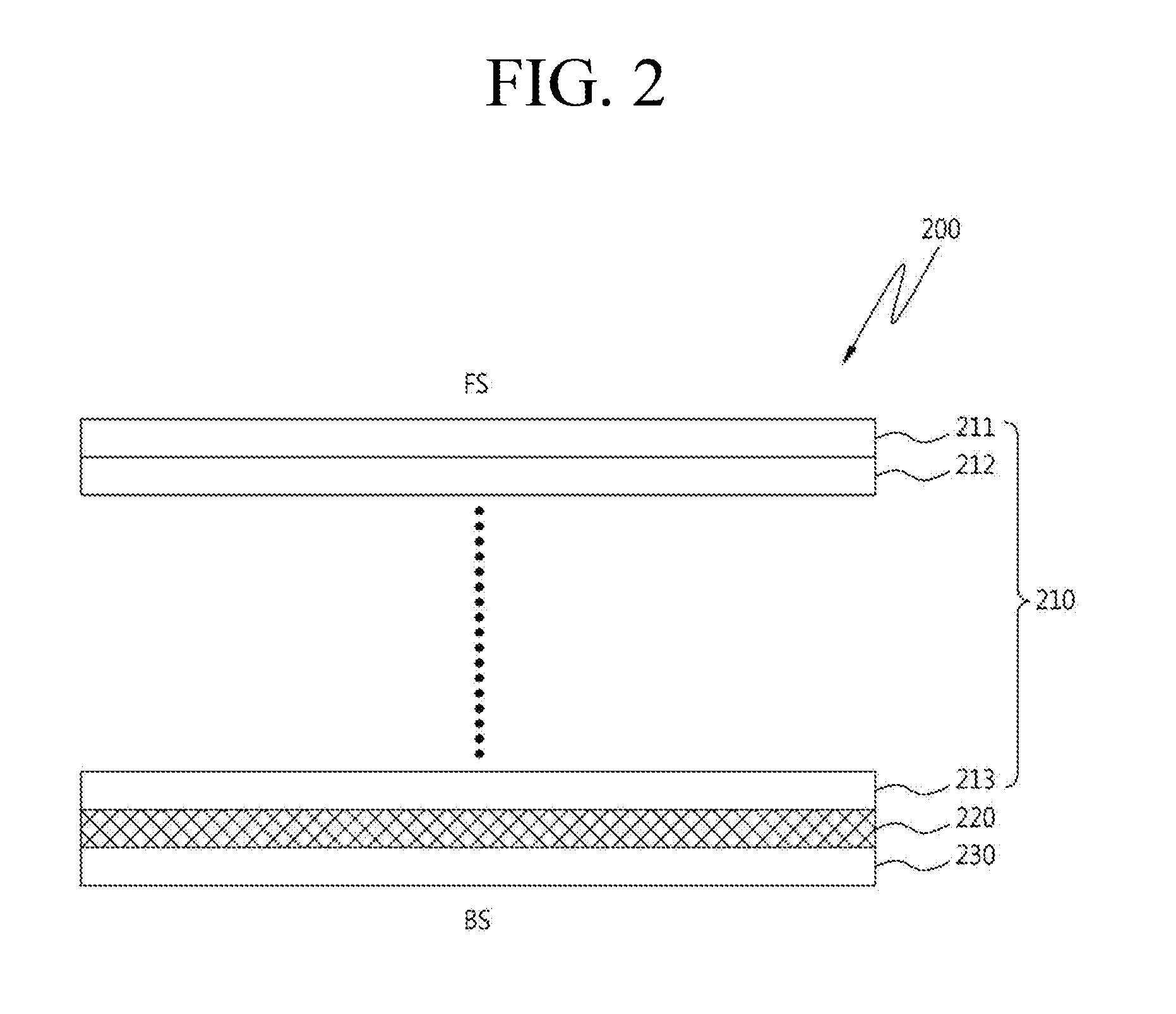
Semiconductor device and method of producing the same
ActiveUS8084814B2Avoid damageSofter characteristicSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesProtonLength wave
A semiconductor device is provided in which a semiconductor substrate can be prevented from being broken while elements can be prevented from being destroyed by a snap-back phenomenon. After an MOS gate structure is formed in a front surface of an FZ wafer, a rear surface of the FZ wafer is ground. Then, the ground surface is irradiated with protons and irradiated with two kinds of laser beams different in wavelength simultaneously to thereby form an N+ first buffer layer and an N second buffer layer. Then, a P+ collector layer and a collector electrode are formed on the proton-irradiated surface. The distance from a position where the net doping concentration of the N+ first buffer layer is locally maximized to the interface between the P+ collector layer and the N second buffer layer is set to be in a range of 5 μm to 30 μm, both inclusively.
Owner:FUJI ELECTRIC CO LTD
Modular furniture assembly with dual coupling mechanisms
ActiveUS20160206100A1Firmly connectedReduces and minimizes and prevents tentingBenchesDismountable chairsRigid coreStructural engineering
A modular furniture assembly comprising first and second members (e.g., base and transverse member) may have convenient dual coupling mechanisms, for example, a magnetic coupling mechanism and a mechanical (e.g., hook and loop) coupling mechanism. The first member and / or second member may include a fabric or other cover over a foam or other body (e.g., fabric over foam, or other cover over a skeleton). Either or both members may include a rigid core (e.g., a board, skeleton, etc.). The coupling mechanisms may be such as to not detract from any soft, cushioned characteristics of a fabric over foam construction, if such is provided. The coupling structure in the first member and / or the second member may be tethered to the rigid core of the particular member to reduce tenting of the fabric or other cover of the first member and / or the second member as the tethered coupling structure is pulled.
Owner:THE LOVESAC CORP
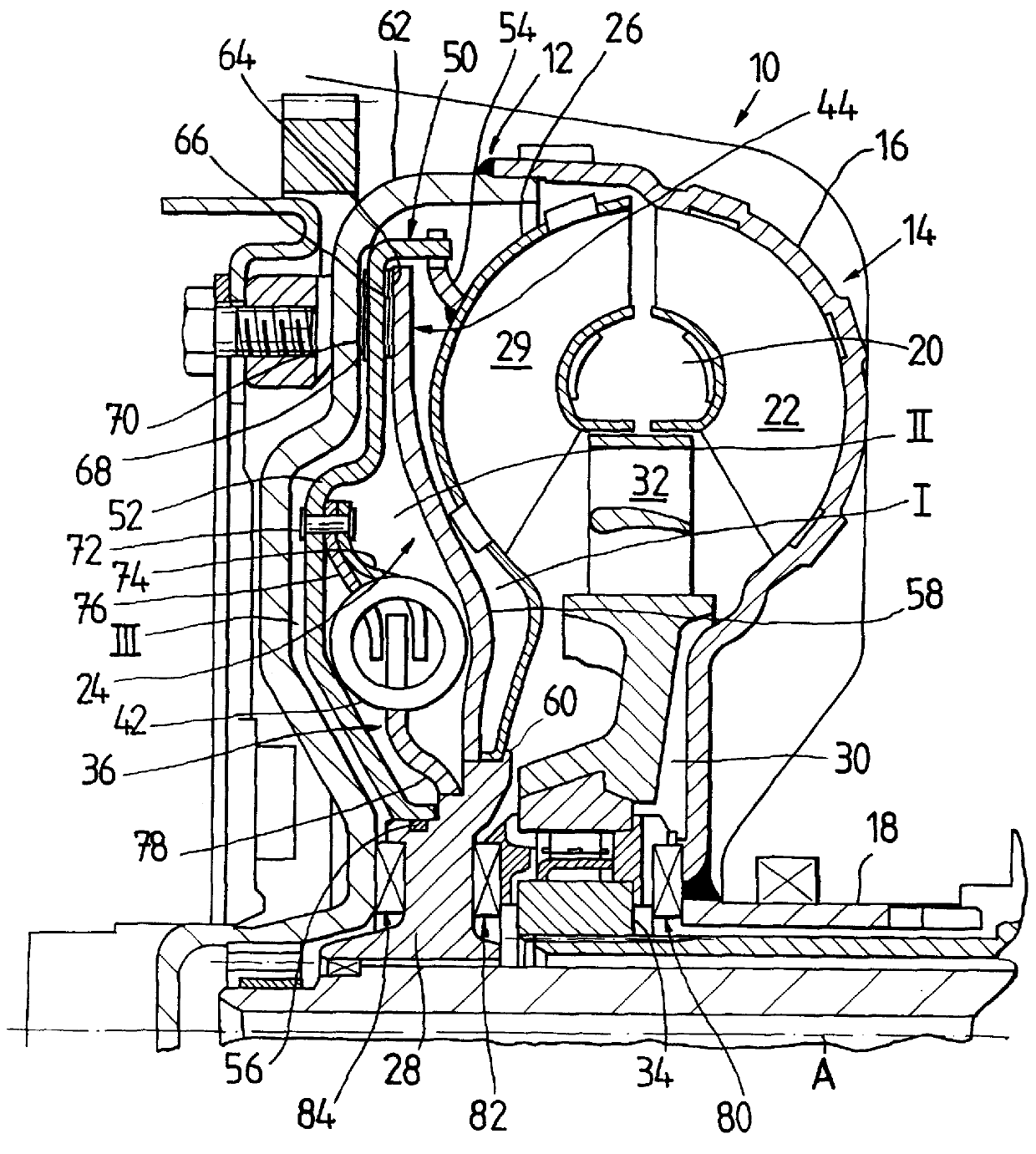
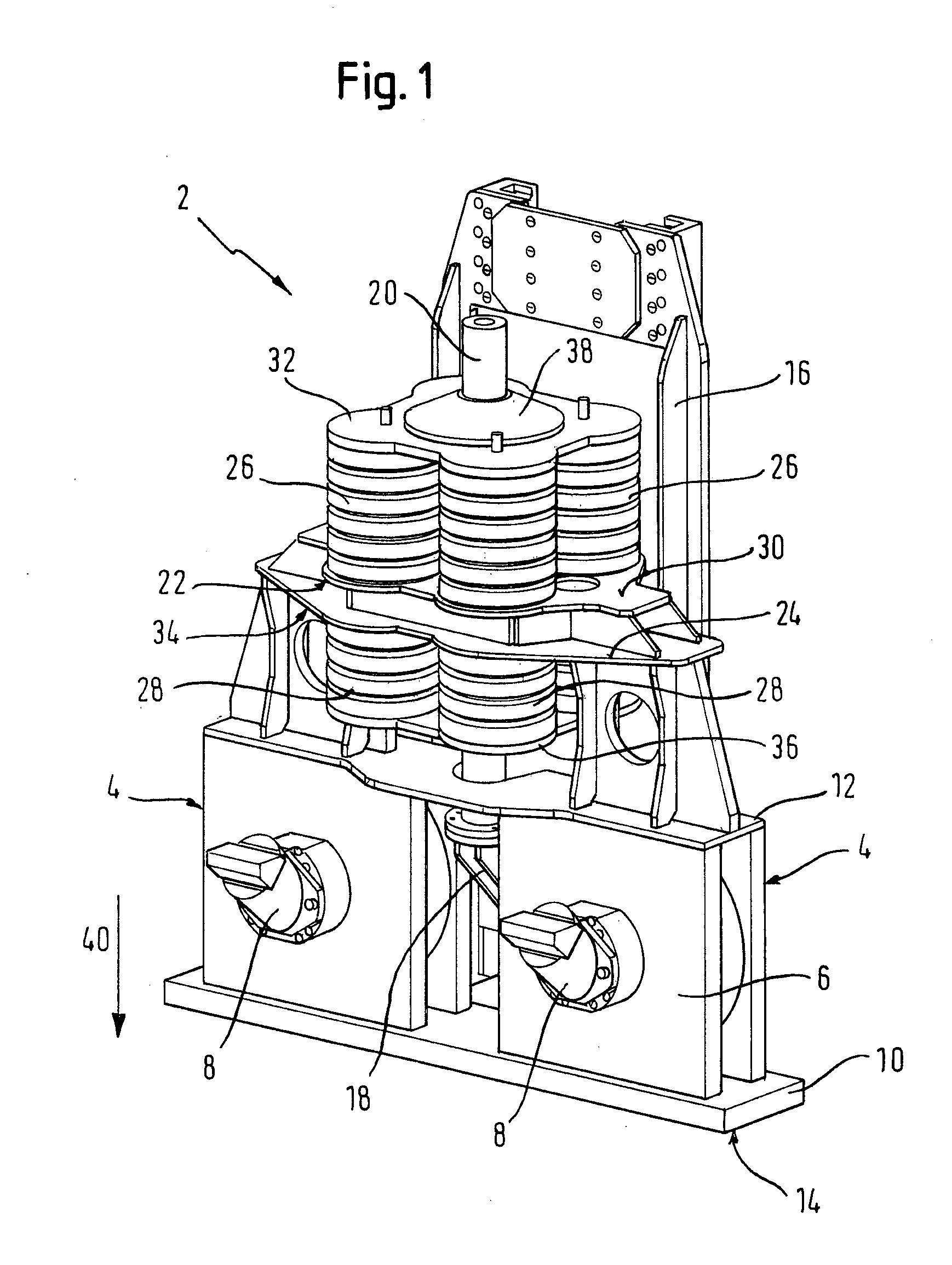
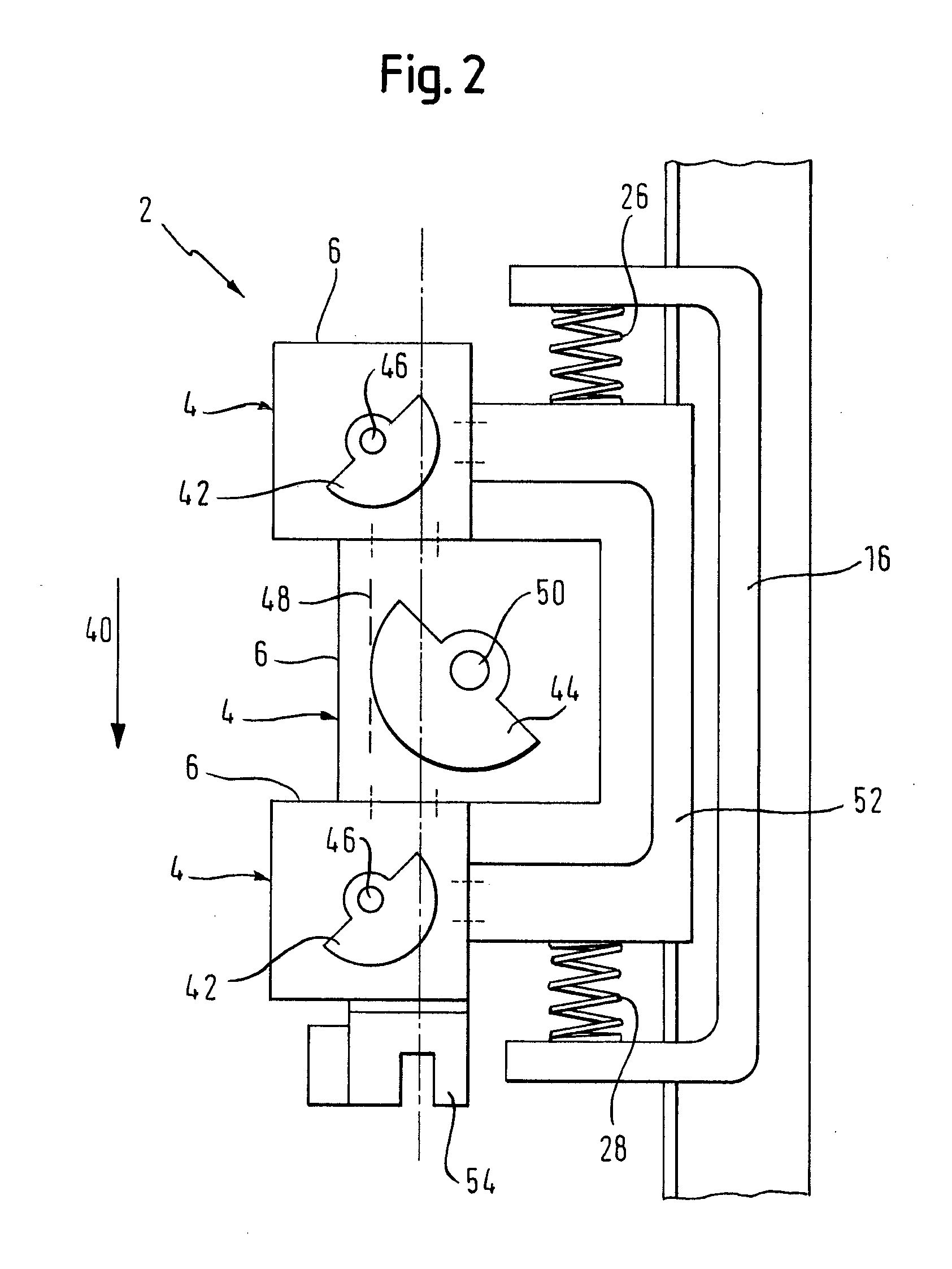
Torque converter
InactiveUS6070704APrevent slippingSmall frictional forceRotary clutchesFluid gearingsImpellerTurbine wheel
A torque converter having a converter housing which is coupled to a driving unit, a turbine wheel which is arranged in the converter housing and is rotatable with respect to the converter housing about an axis of rotation and has a turbine wheel shell and a turbine wheel hub which is connected with the turbine wheel shell and which can be coupled with or is coupled with a converter driven shaft. A lockup clutch provides selectable rotational coupling of the converter housing with the turbine wheel, and a torsional vibration damper arrangement is provided in the power transmission path between the converter housing and the turbine wheel hub and / or between the turbine wheel shell and the turbine wheel hub. A friction device is connected parallel to the torsional vibration damper arrangement in the power transmission path for generating a frictional force which may be changed in a selected manner.
Owner:ZF FRIEDRICHSHAFEN AG
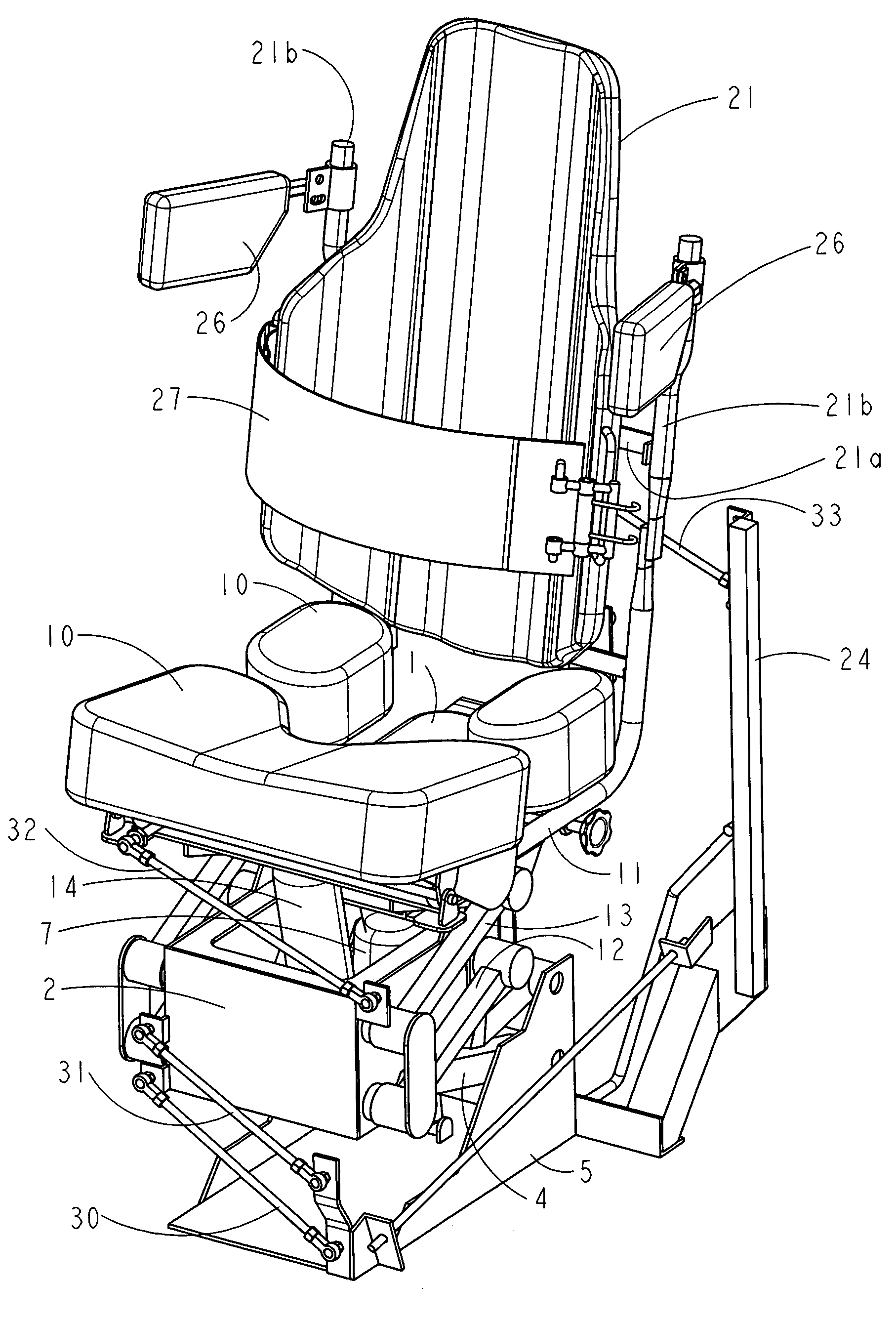
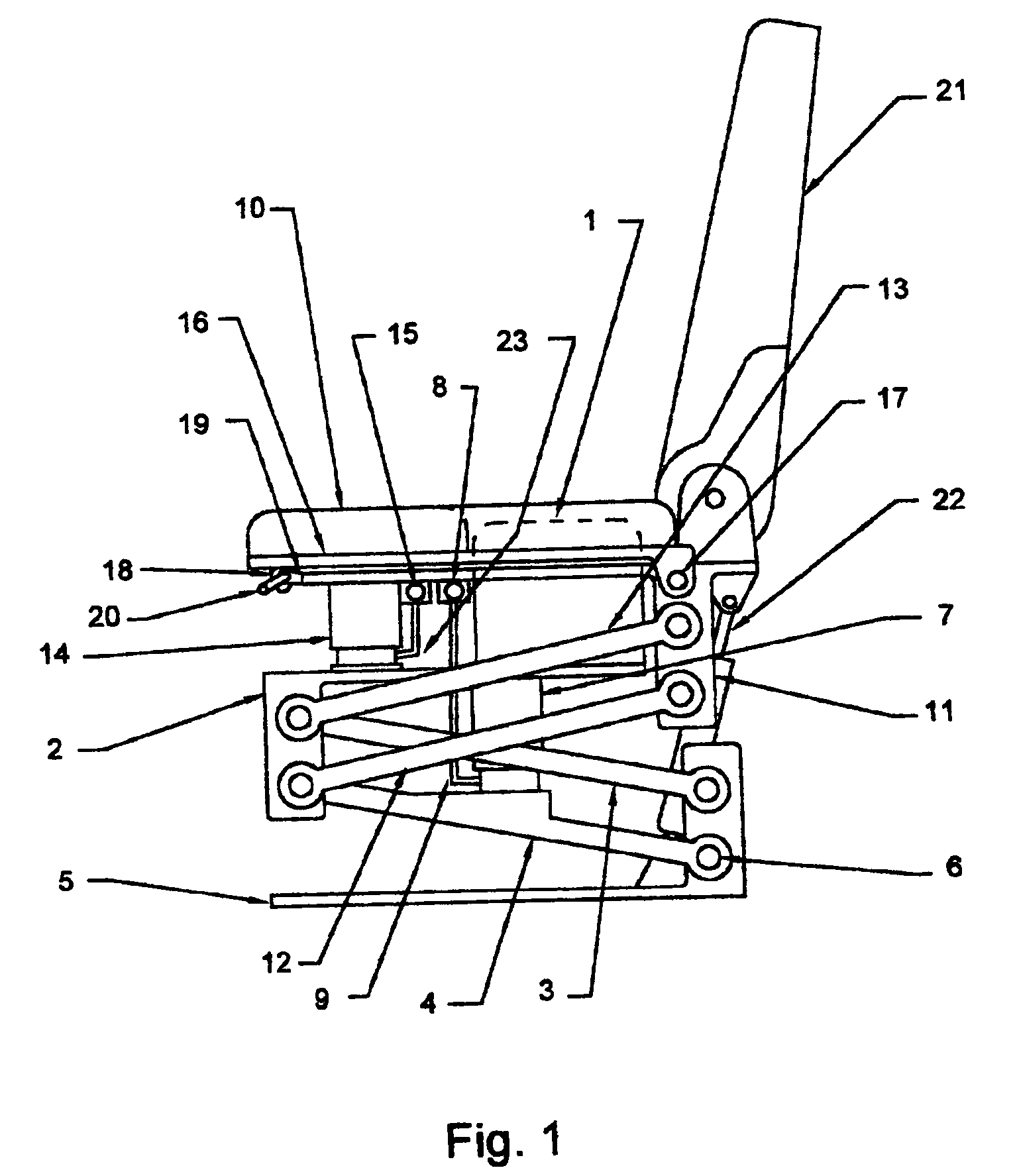
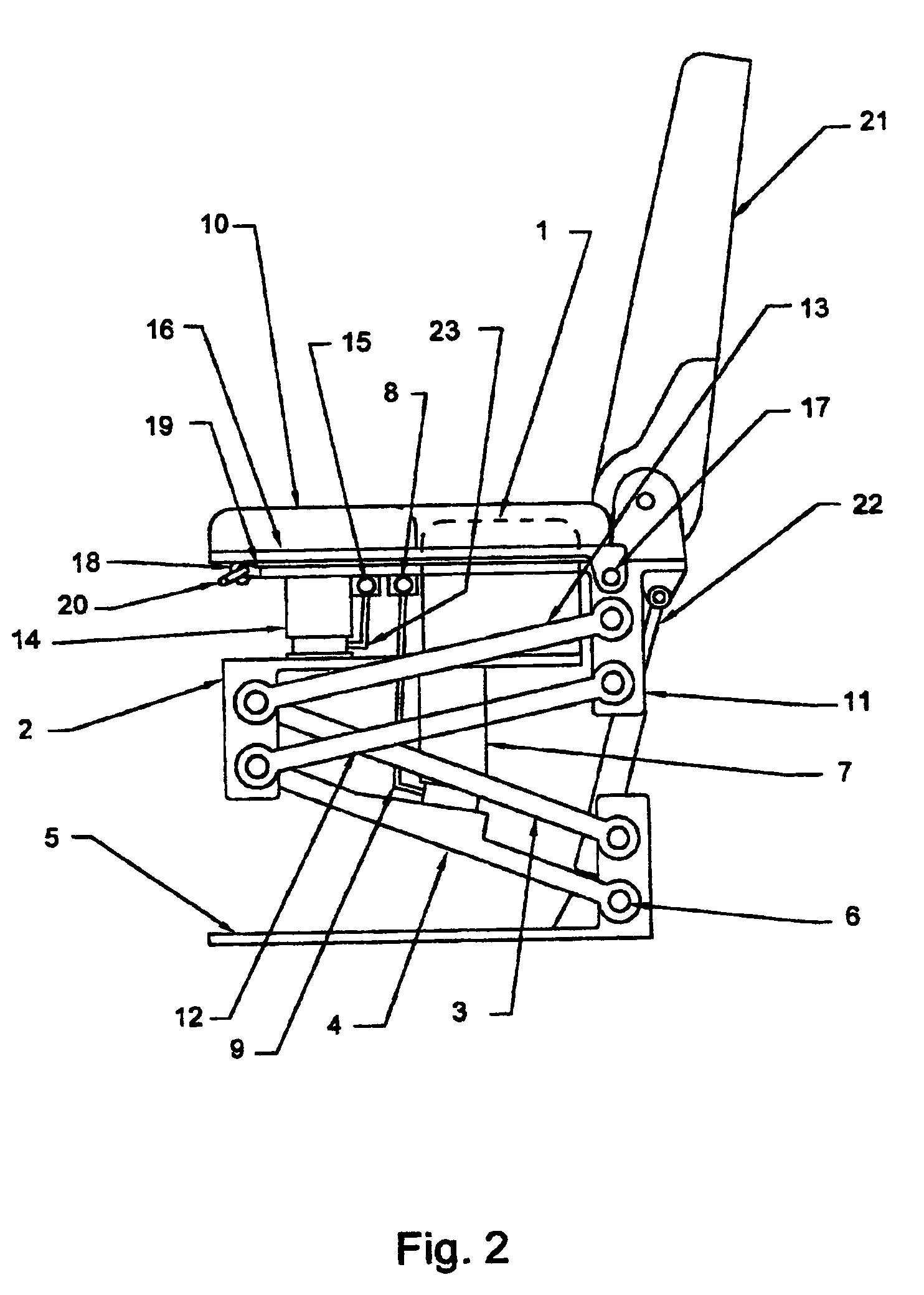
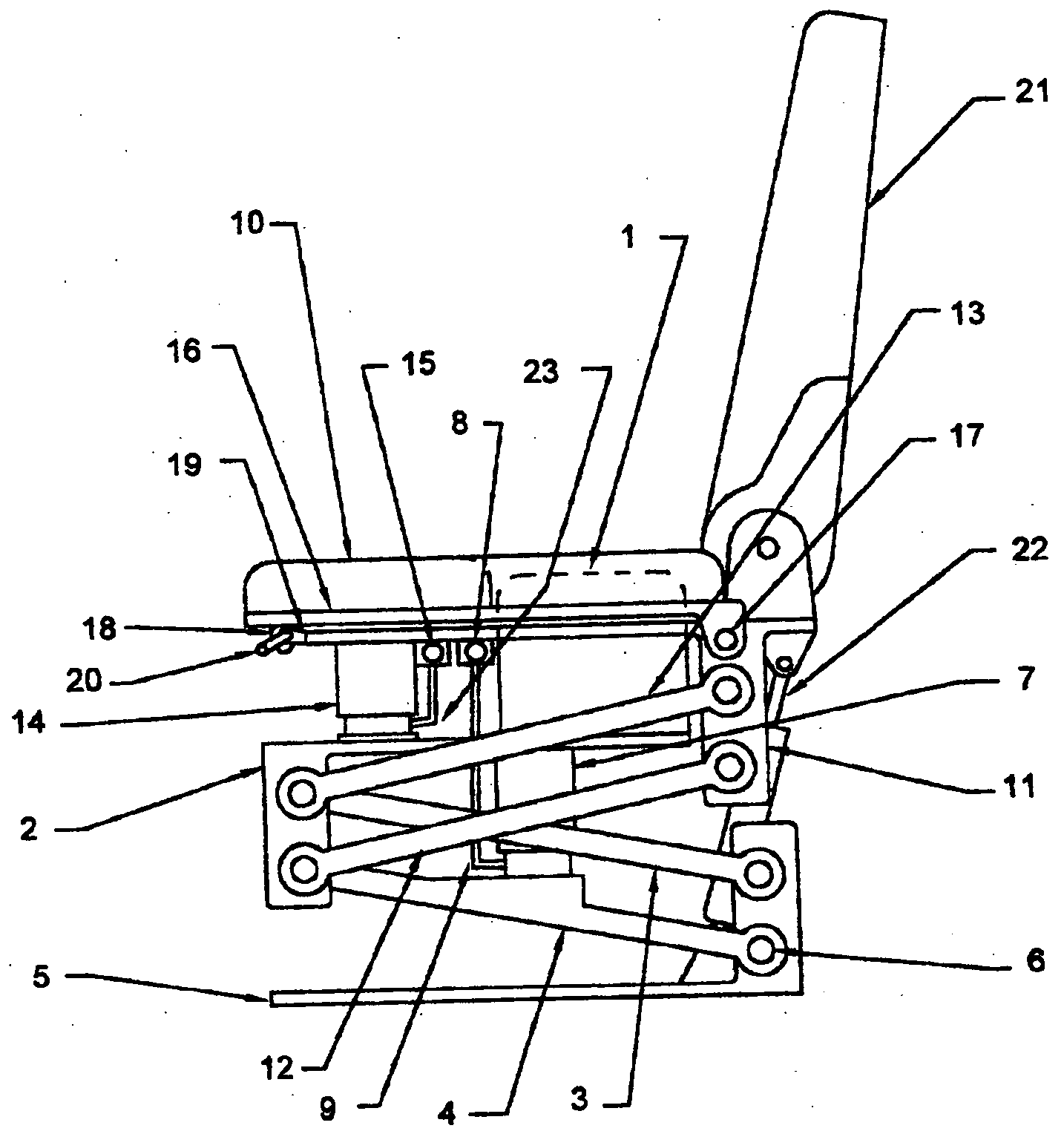
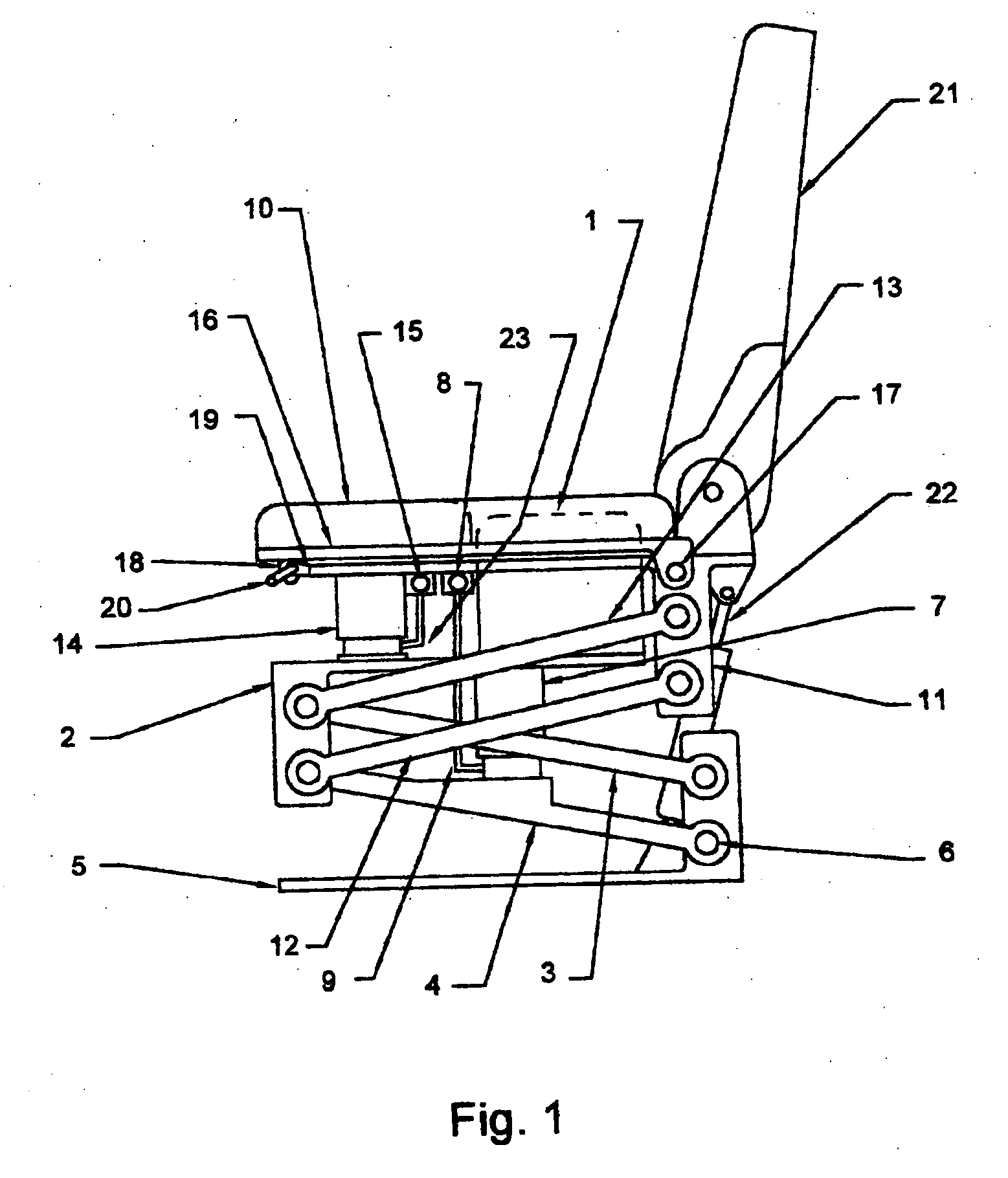
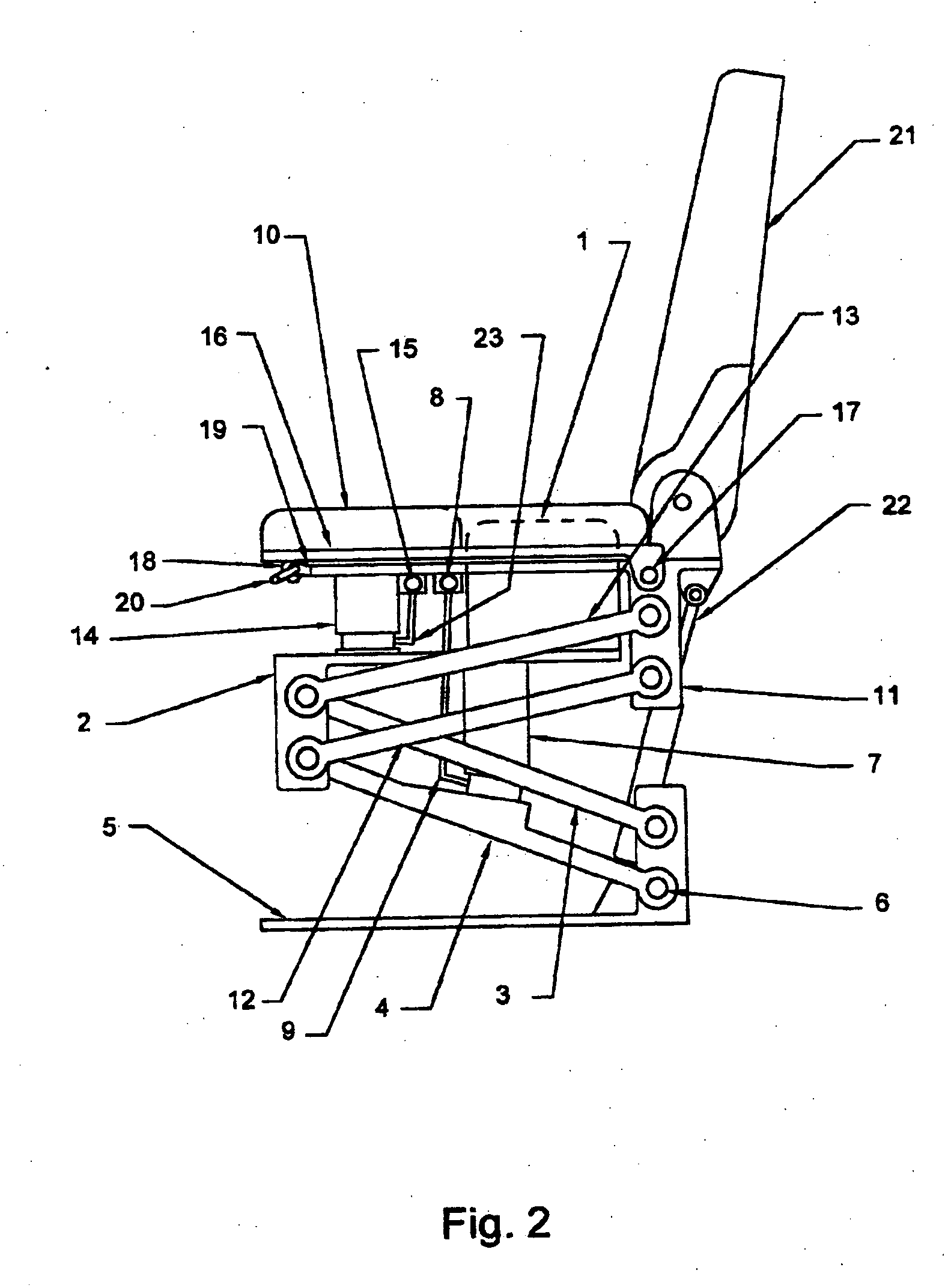
Vehicle seat with dual independently adjustable supports
InactiveUS7134721B2Softer characteristicDampen repetitive oscillationPedestrian/occupant safety arrangementStoolsTerrainRide height
Owner:ROBINSON GARRY
Modular furniture assembly with dual coupling mechanisms
ActiveUS10070725B2Firmly connectedReduces and minimizes and prevents tentingBenchesDismountable chairsRigid coreStructural engineering
A modular furniture assembly comprising first and second members (e.g., base and transverse member) may have convenient dual coupling mechanisms, for example, a magnetic coupling mechanism and a mechanical (e.g., hook and loop) coupling mechanism. The first member and / or second member may include a fabric or other cover over a foam or other body (e.g., fabric over foam, or other cover over a skeleton). Either or both members may include a rigid core (e.g., a board, skeleton, etc.). The coupling mechanisms may be such as to not detract from any soft, cushioned characteristics of a fabric over foam construction, if such is provided. The coupling structure in the first member and / or the second member may be tethered to the rigid core of the particular member to reduce tenting of the fabric or other cover of the first member and / or the second member as the tethered coupling structure is pulled.
Owner:THE LOVESAC CORP
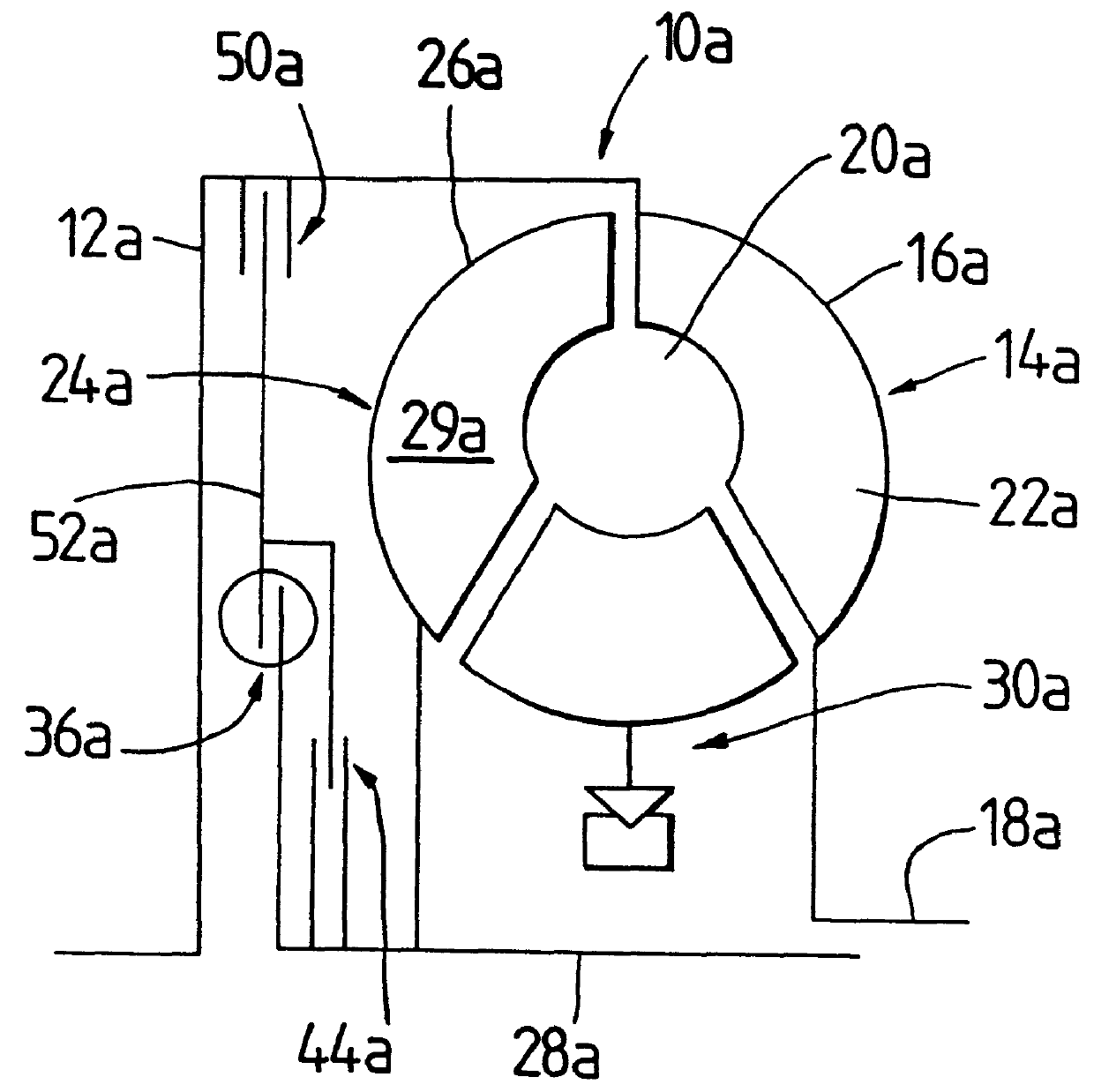
Chain tensioner
A tensioner for a chain, includes a tensioner piston bearing upon a chain and guided by a cylinder for movement in the direction of the chain. The cylinder and the piston define a pressure chamber for receiving hydraulic fluid, wherein hydraulic fluid is able to escape from the pressure chamber via a leakage gap. A control member is provided to at least reduce the leakage gap in size, when a pressure in the pressure chamber increases.
Owner:INA WALZLAGER SCHAEFFLER KG
Vehicle seat with dual independently adjustable supports
InactiveUS20050116516A1Softer characteristicDampen repetitive oscillationPedestrian/occupant safety arrangementChildren furnitureSitting PositionsTerrain
A vehicle seat, which provides an enhanced level of comfort, by means of dual independently supported seat cushions is disclosed. The apparatus comprises an inner seat cushion and an outer seat cushion, each of which is independently supported by a compressed air pneumatic device to control vertical movement, and by parallelogram linkages control lateral movement, and allow for vertical transition of the seats while maintaining them horizontal. The occupant of this vehicle seat can independently adjust the distribution of body weight shared by the inner seat cushion and the outer seat cushion from time to time, in order to change the pressure pattern against body parts and to provide optimum ergonomic seating posture. Furthermore, by adjusting the air supply, the occupant can increase or decrease the seat's effective spring rate, thus controlling the ride height and the seat's compliance for travel on both rough terrain and smooth roadways.
Owner:ROBINSON GARRY
Fe-based amorphous alloy ribbon and magnetic core formed thereby
InactiveUS20060000525A1Improve saturation magnetic flux densityStress be relaxMagnetic materialsCores/yokesMagnetic coreTransformer
A magnetic core provided with a shape for a transformer by a cut-lap or step-lap method, which is constituted by an Fe-based amorphous alloy ribbon having excellent magnetic characteristics, which is represented by the general formula: FeaSibBcMx or FeaSibBcCdMx wherein M is Cr and / or Ni, a is 78 to 86 atomic %, b is 0.001 to 5 atomic %, c is 7 to 20 atomic %, x is 0.01 to 5 atomic %, and d is 0.001 to 4 atomic %, (a+b+c+x) or (a+b+c+d+x) being 100.
Owner:HITACHI METALS LTD
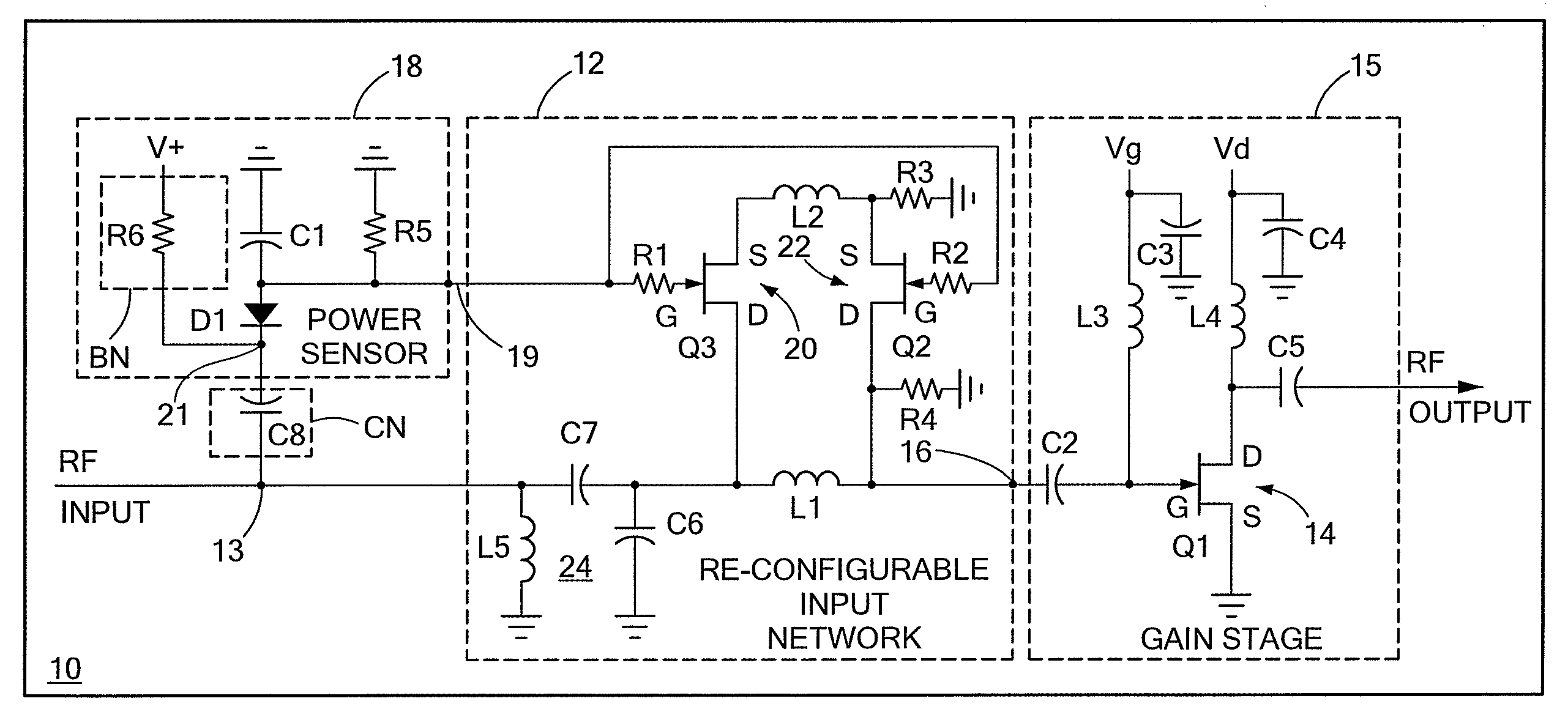
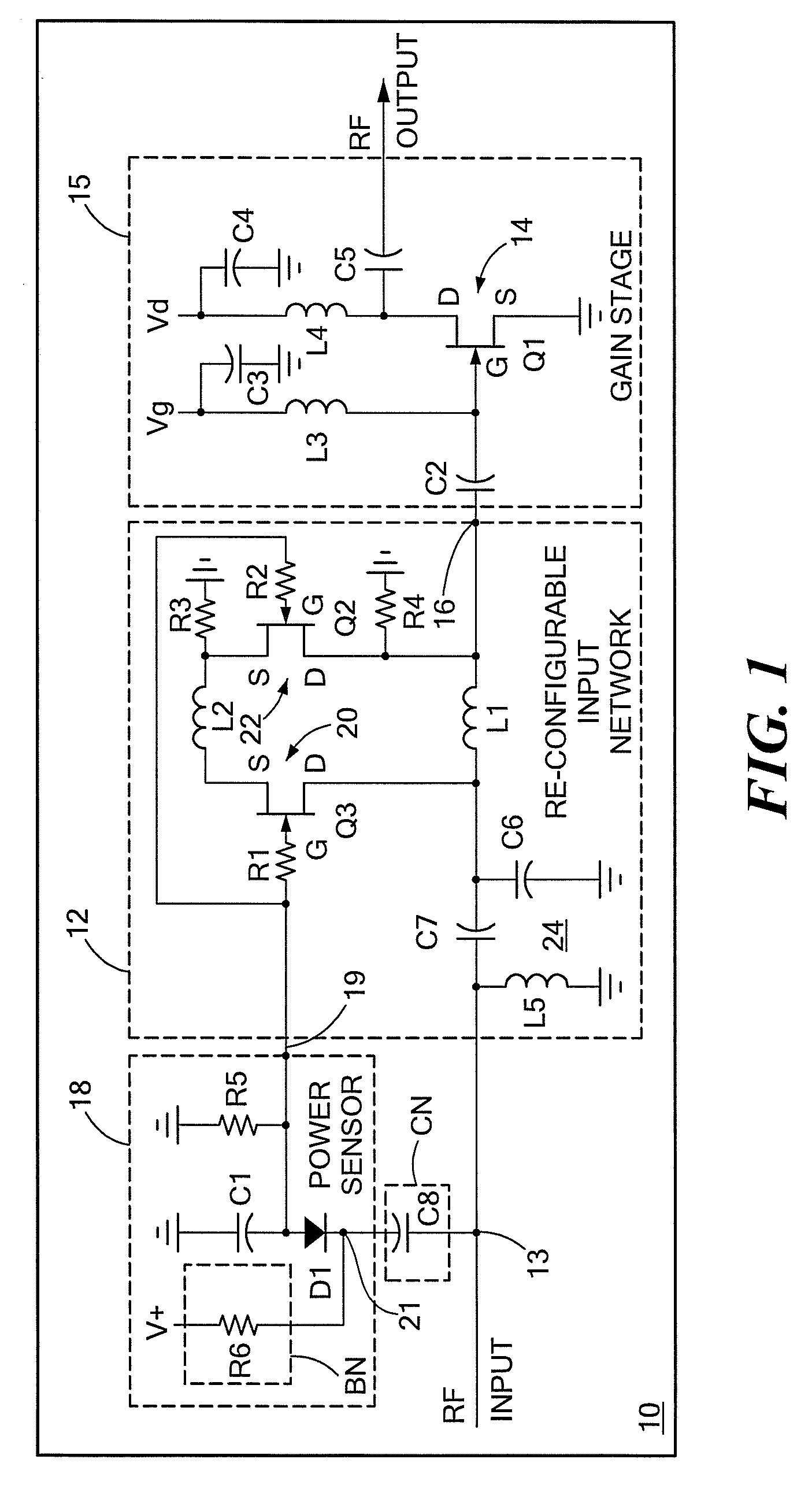
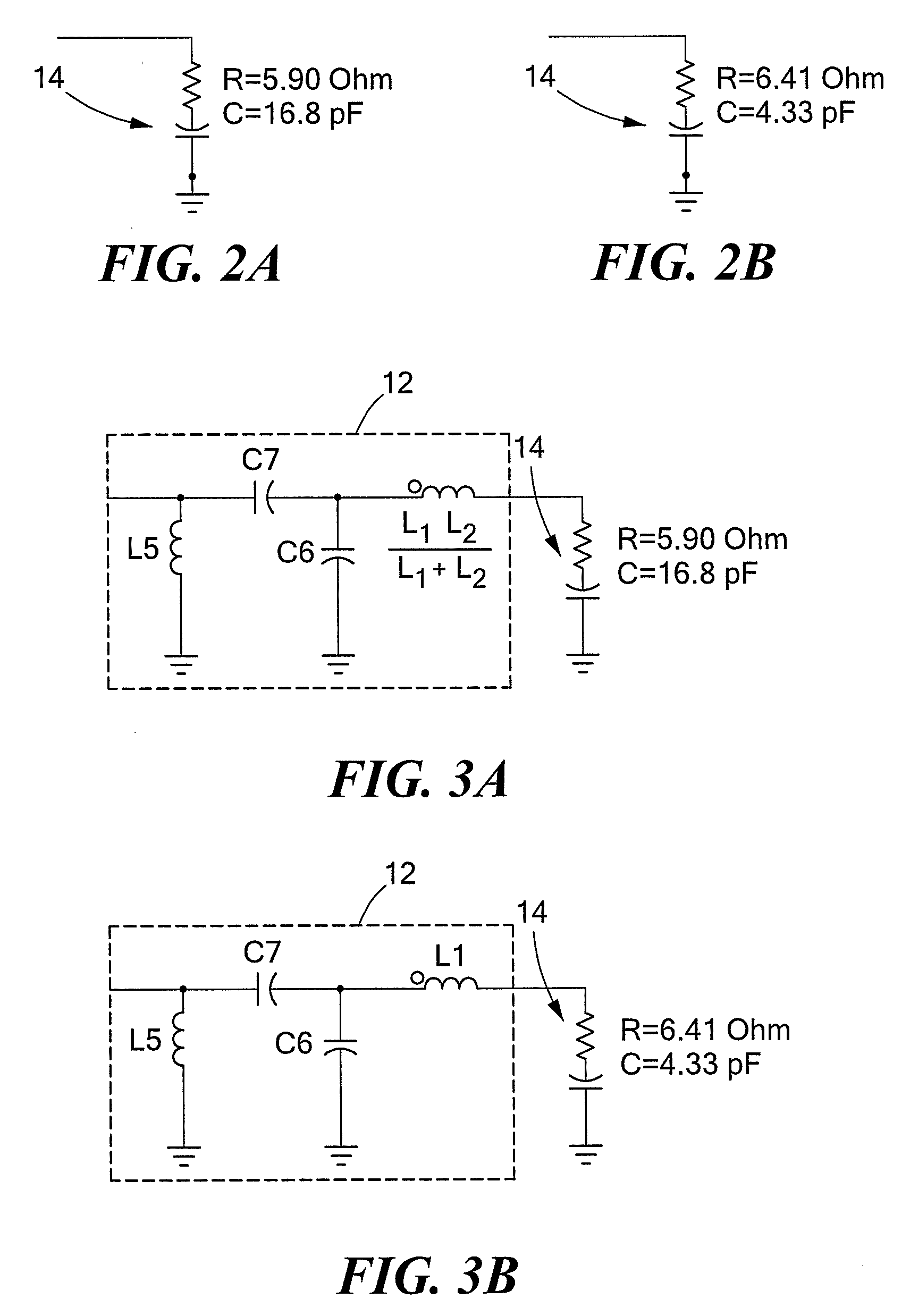
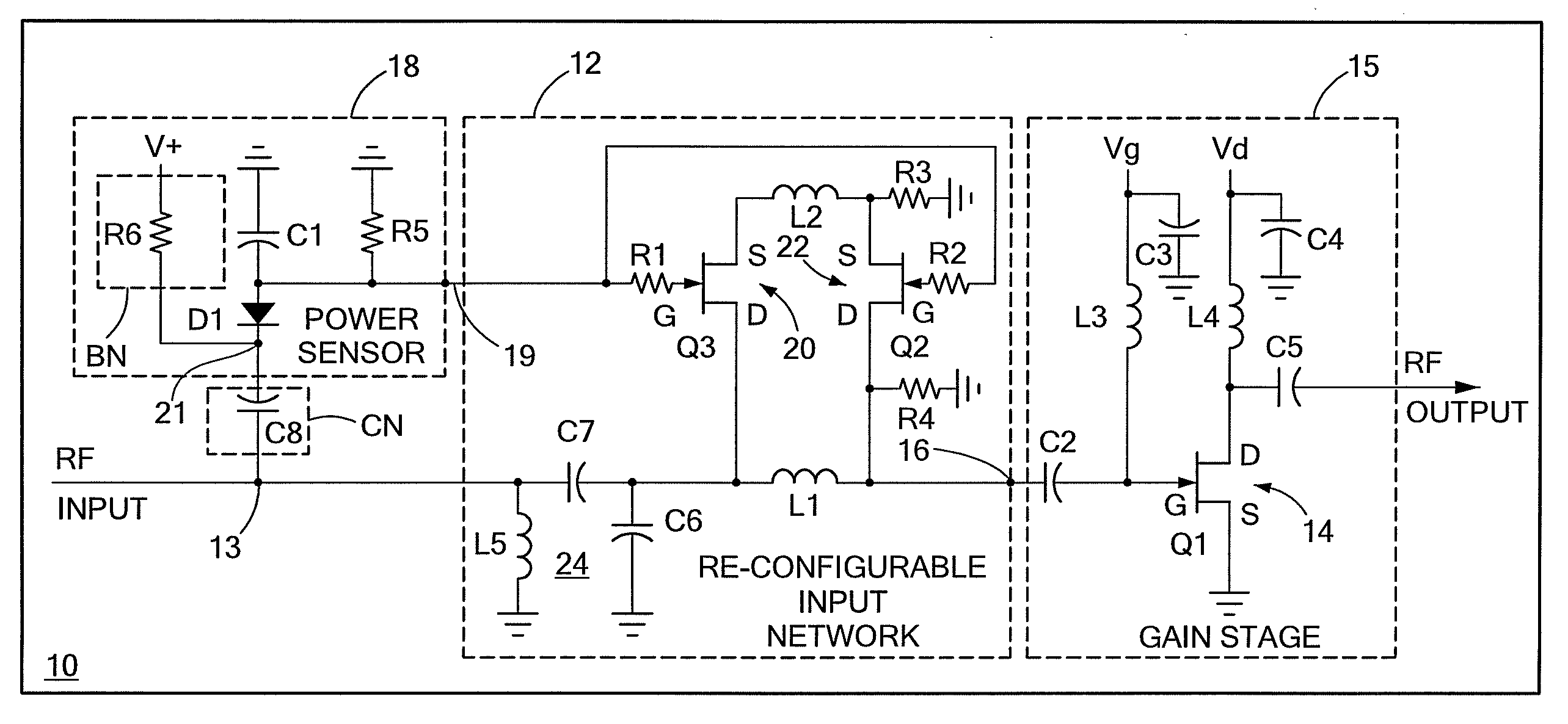
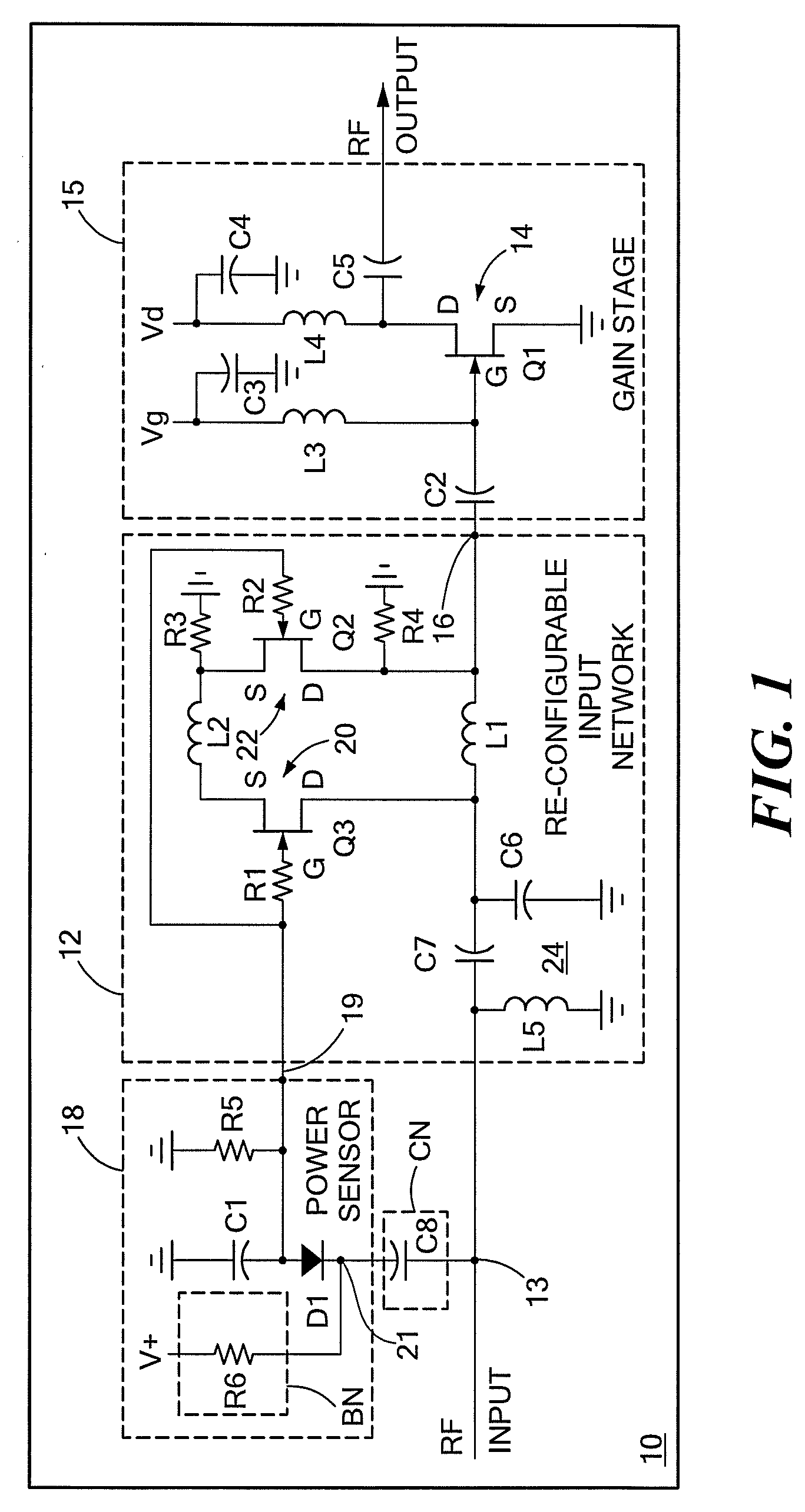
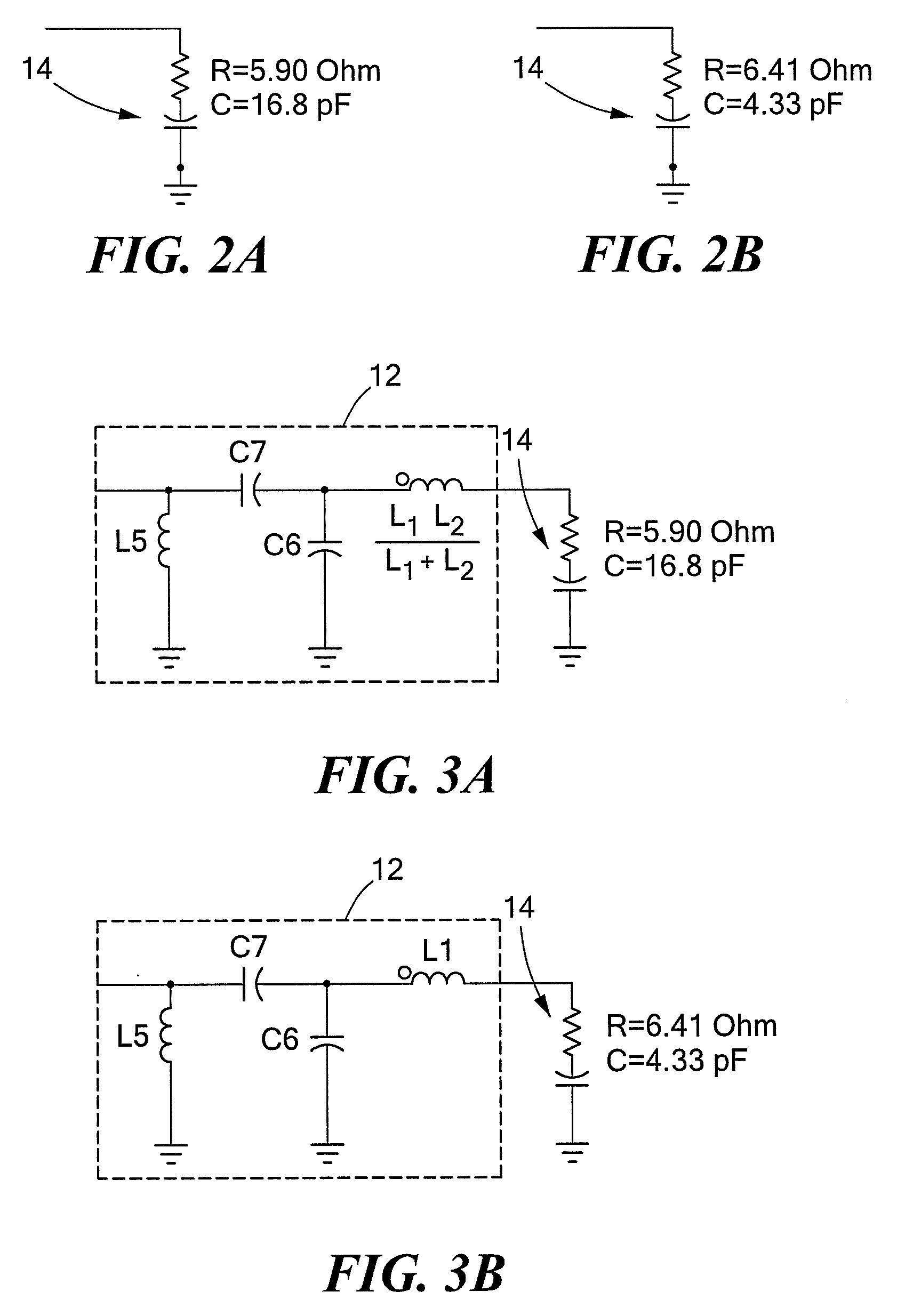
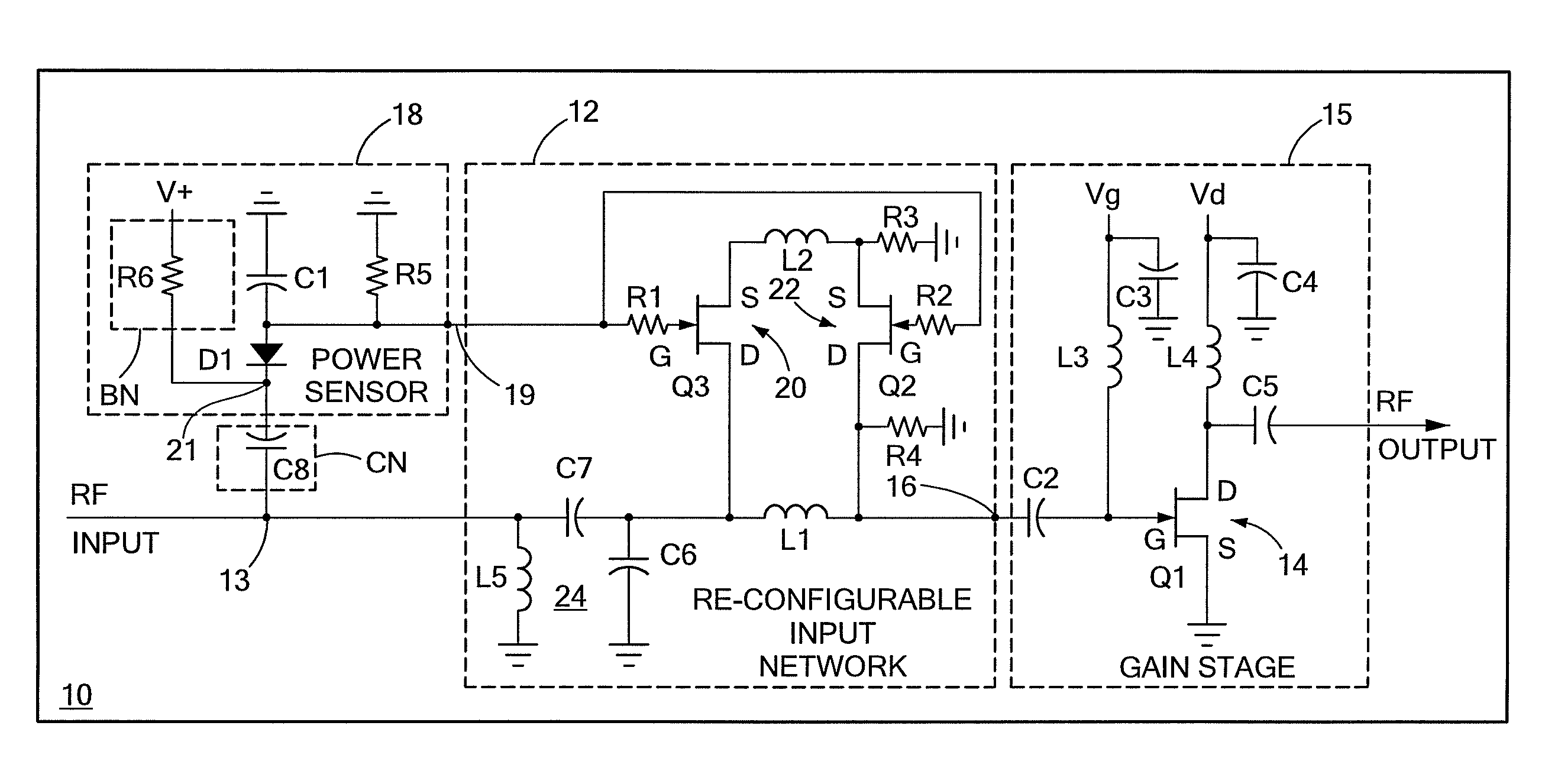
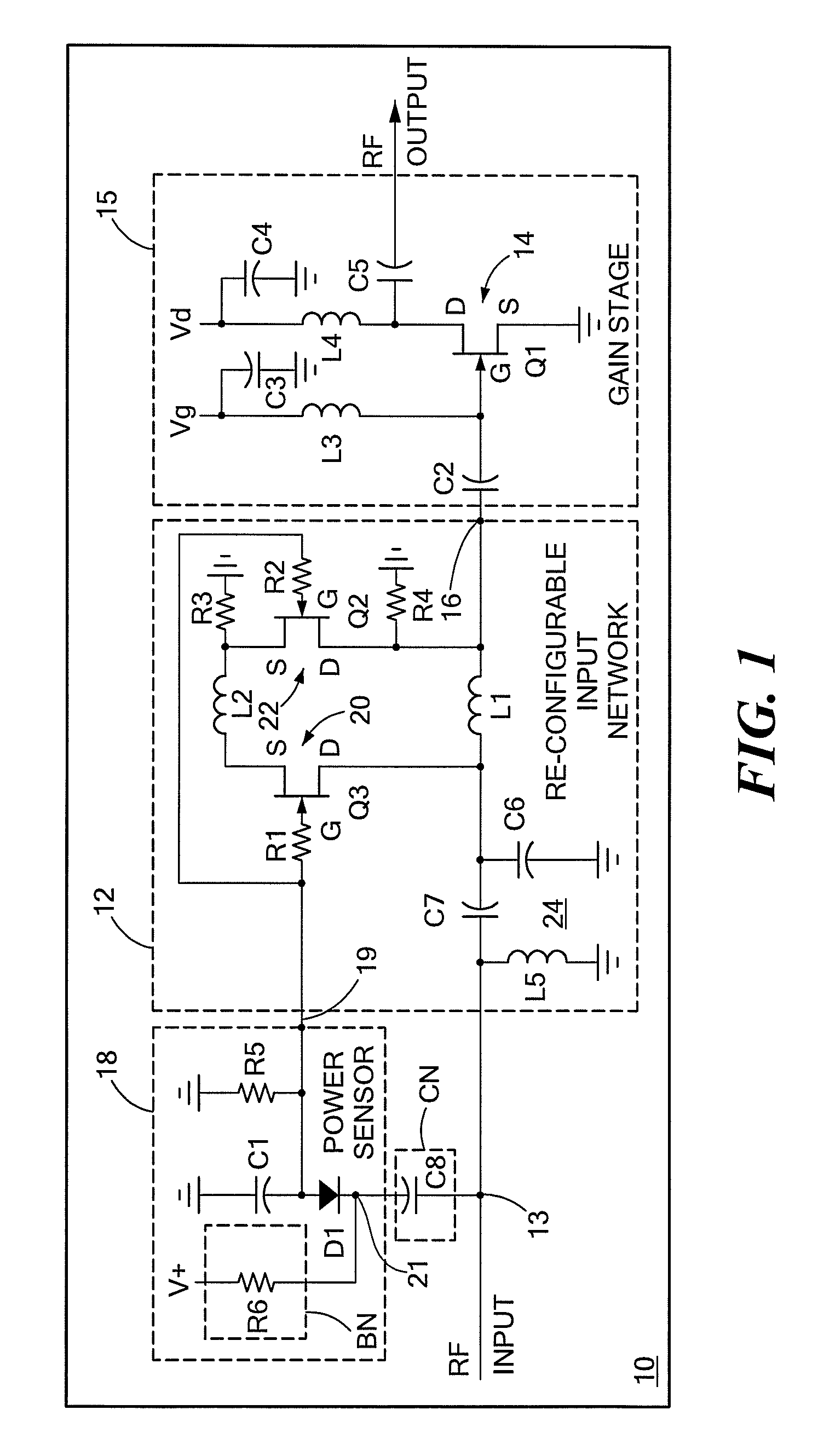
Input circuitry for transistor power amplifier and method for designing such circuitry
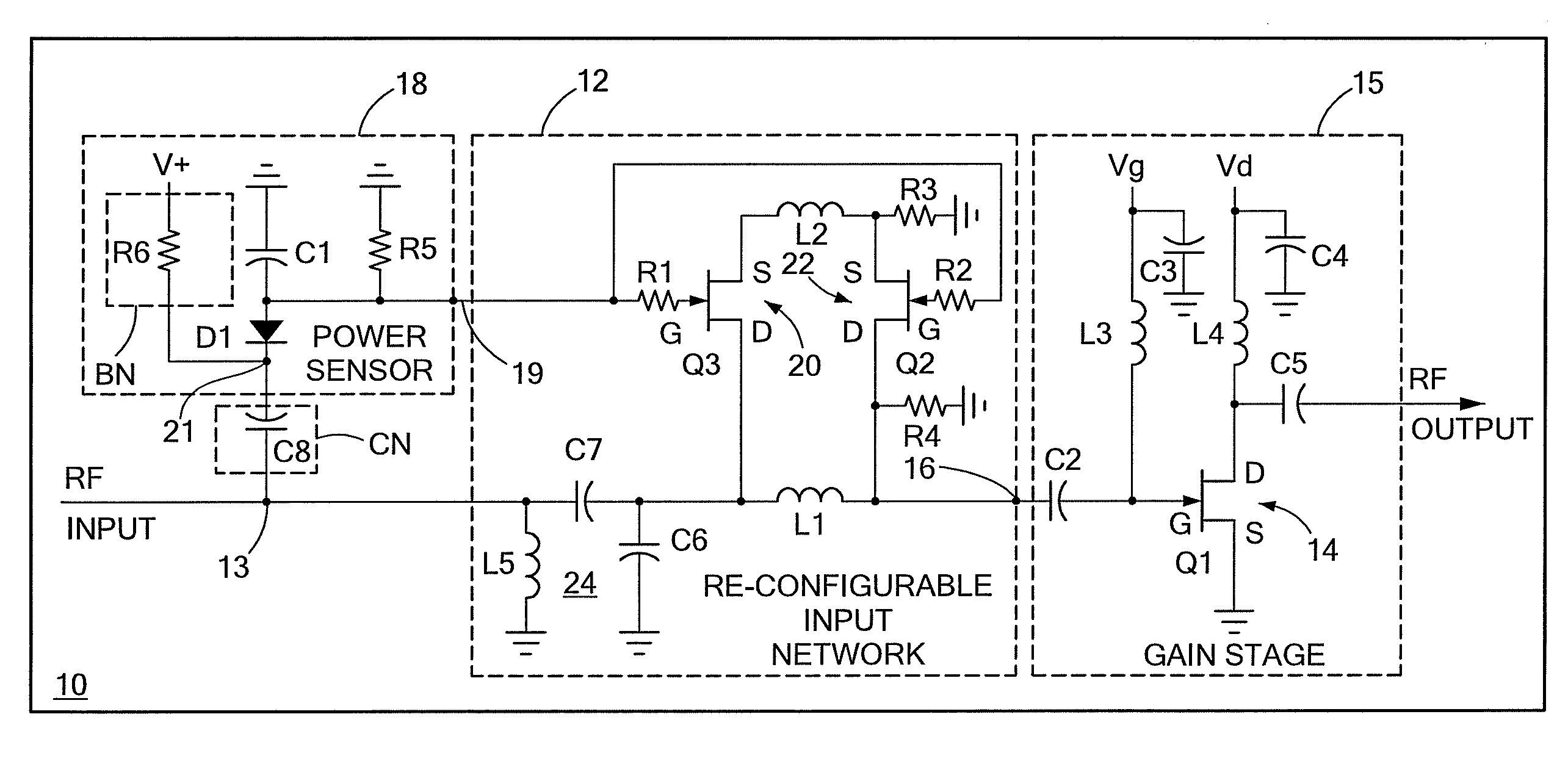
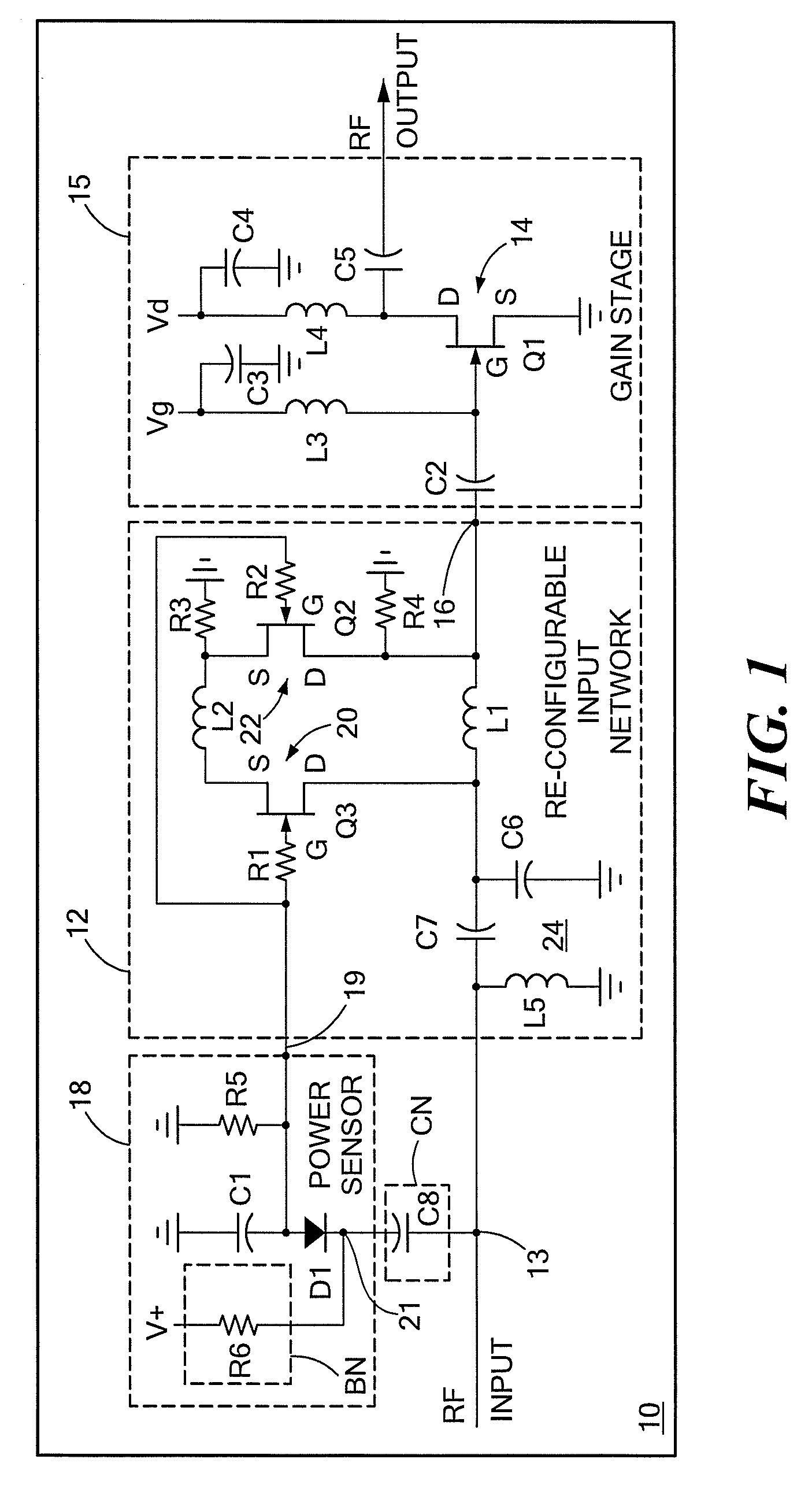
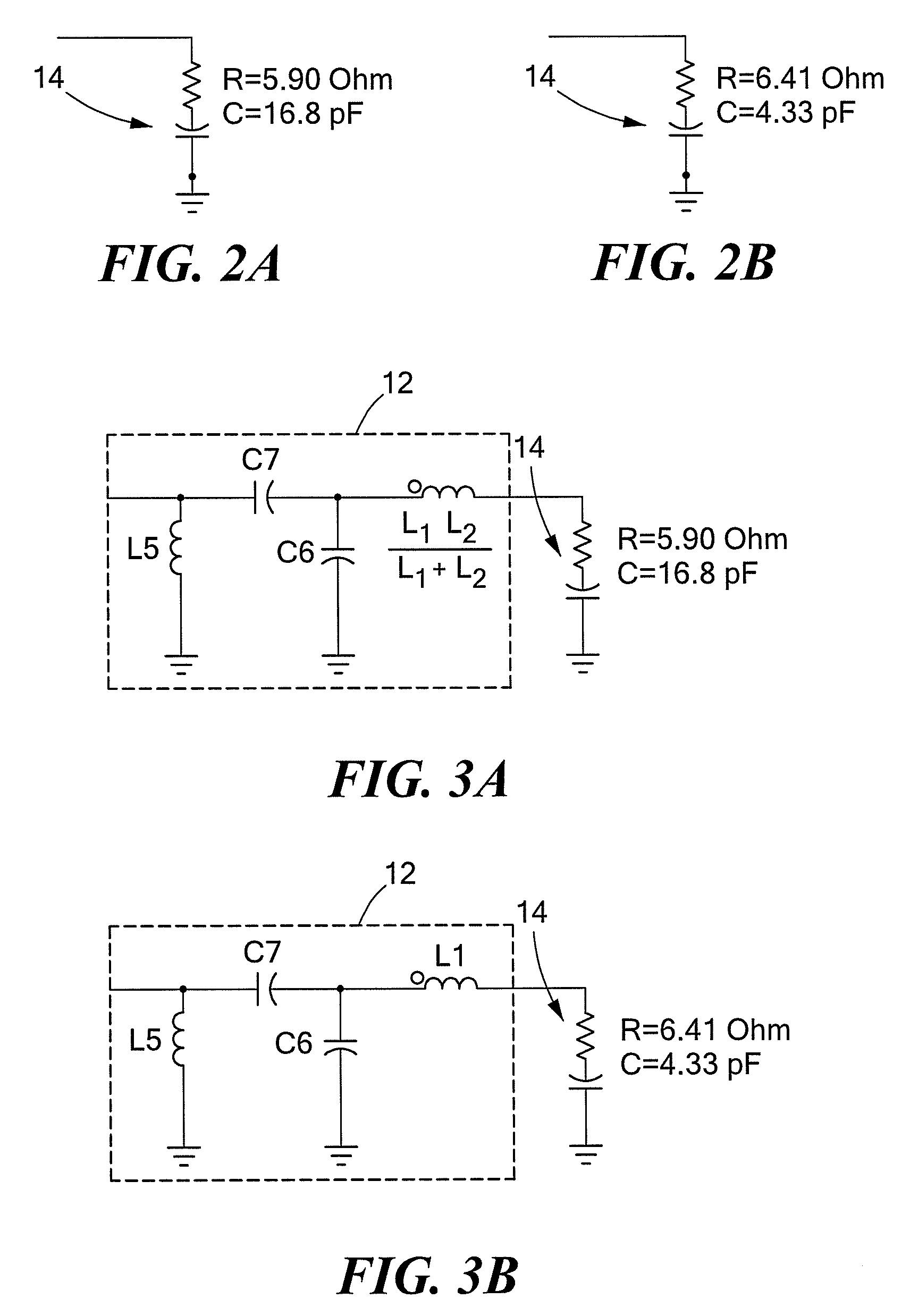
ActiveUS20090066439A1Improve stabilityLower performance requirementsMultiple-port networksRF amplifierAudio power amplifierInput impedance
A circuit having: an input matching network; a transistor coupled to an output of the input matching network; and wherein the input matching network has a first input impedance when such input matching network is fed with an input signal having a relatively low power level and wherein the input matching network has an input impedance different from the first input impedance when such input matching network is fed with an input signal having a relatively high power level.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
Cpp-type magneto resistive effect element having a pair of magnetic layers
InactiveUS20090174971A1High magneto-resistive ratioSoft magnetic characteristicNanomagnetismNanoinformaticsCrystalline oxideFilm plane
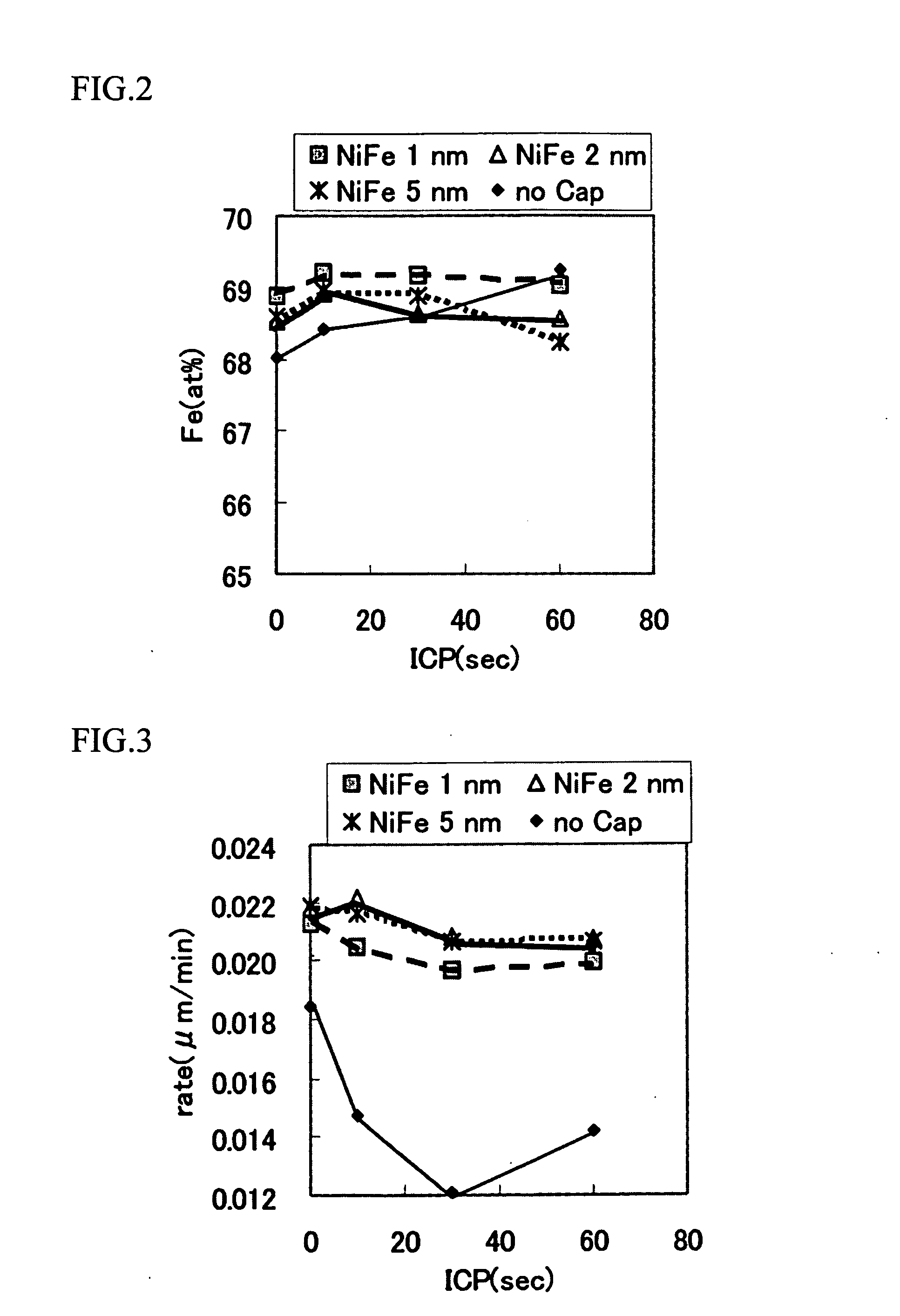
A magnetoresistance effect element comprises: a pair of magnetic layers whose magnetization directions form a relative angle therebetween that is variable depending on an external magnetic field; and a crystalline spacer layer sandwiched between the pair of magnetic layers; wherein sense current may flow in a direction that is perpendicular to a film plane of the pair of magnetic layers and the spacer layer. The spacer layer includes a crystalline oxide, and either or both magnetic layers whose magnetization direction is variable depending on the external magnetic field has a layer configuration in which a CoFeB layer is sandwiched between a CoFe layer and a NiFe layer and is positioned between the spacer layer and the NiFe layer.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Semicondcutor device and method of producing the same
ActiveUS20120064706A1Avoid damageSofter characteristicSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesProtonLength wave
Owner:FUJI ELECTRIC CO LTD
Cosmetic wiper with wiper arms
ActiveUS10448725B2Improve balanceSofter characteristicPackaging toiletriesPackaging cosmeticsBiomedical engineeringWindscreen wiper
Owner:GEKA
Magnetoresistive sensor having cobalt-iron alloy layer in free layer
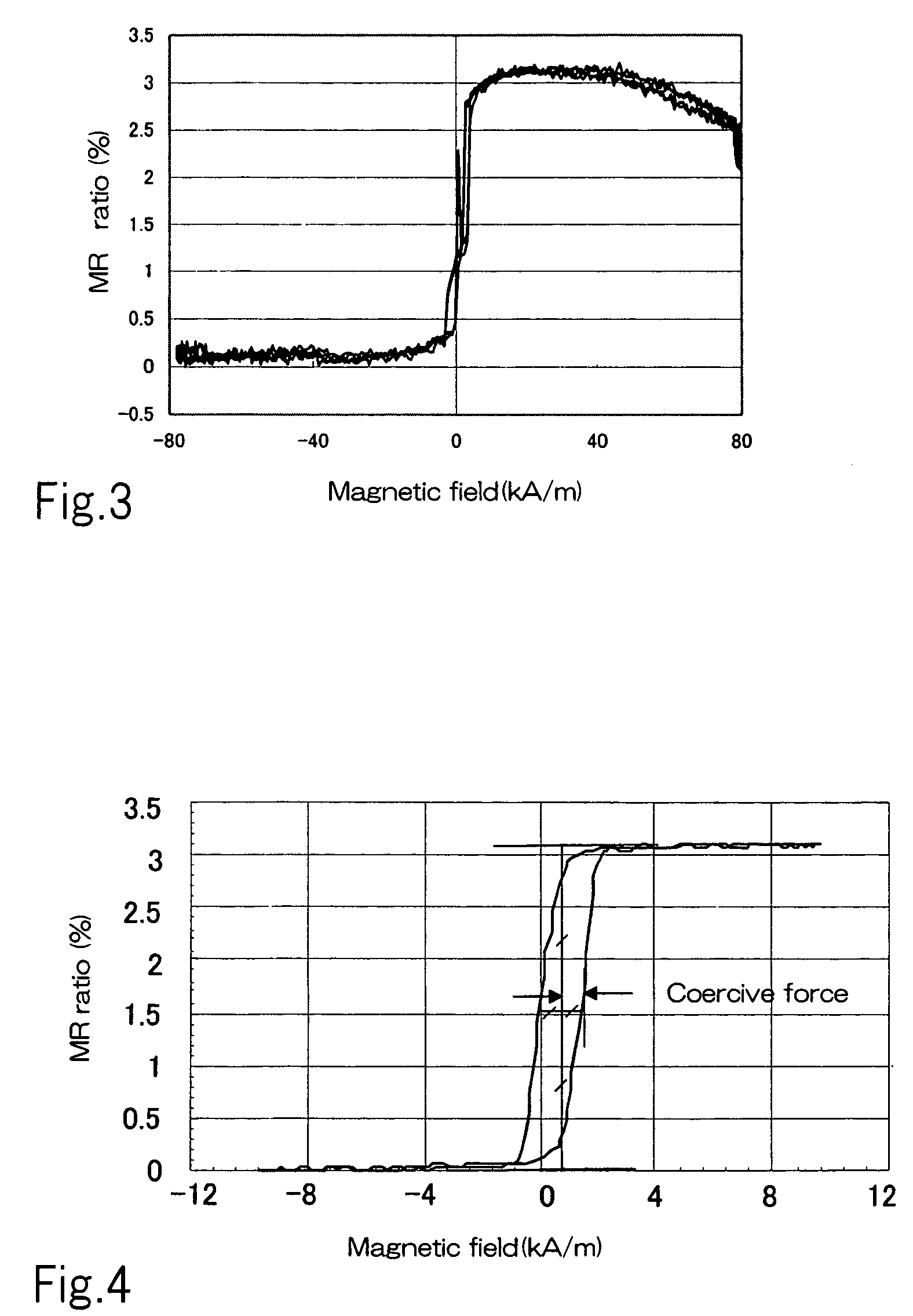
ActiveUS20050168888A1Softer characteristicSignificant changeNanomagnetismNanoinformaticsMagnetizationAlloy
A magnetoresistive sensor comprises a pinned layer having a magnetization direction fixed with respect to an external magnetic field, a free layer, having a magnetization direction variable in accordance with the external magnetic field, and a spacer layer mainly containing copper, sandwiched between the pinned layer and the free layer. A sense current flows through the pinned layer, the spacer layer, and the free layer substantially in a direction in which the layers are stacked. The free layer comprises at least one intermediate stack composed of a non-magnetic layer mainly containing copper, and a first cobalt iron layers made of a cobalt iron alloy and disposed on boundaries on both sides of the non-magnetic layer, a nickel iron alloy layers disposed on boundaries on both sides of the intermediate stack, and a second cobalt iron layer made of a cobalt iron alloy and formed in contact with the spacer layer on a boundary, opposing the spacer layer, of a stack composed of the intermediate stack and the nickel iron alloy layer.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Magnetoresistive sensor having cobalt-iron alloy layer in free layer
ActiveUS7310210B2Softer characteristicSignificant changeNanomagnetismNanoinformaticsContact formationMagnetization
A magnetoresistive sensor comprises a pinned layer having a magnetization direction fixed with respect to an external magnetic field, a free layer, having a magnetization direction variable in accordance with the external magnetic field, and a spacer layer mainly containing copper, sandwiched between the pinned layer and the free layer. A sense current flows through the pinned layer, the spacer layer, and the free layer substantially in a direction in which the layers are stacked. The free layer comprises at least one intermediate stack composed of a non-magnetic layer mainly containing copper, and a first cobalt iron layers made of a cobalt iron alloy and disposed on boundaries on both sides of the non-magnetic layer, a nickel iron alloy layers disposed on boundaries on both sides of the intermediate stack, and a second cobalt iron layer made of a cobalt iron alloy and formed in contact with the spacer layer on a boundary, opposing the spacer layer, of a stack composed of the intermediate stack and the nickel iron alloy layer.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Input circuitry for transistor power amplifier and method for designing such circuitry
ActiveUS7609115B2Softer characteristicHigh levelMultiple-port networksRF amplifierAudio power amplifierInput impedance
A circuit having: an input matching network; a transistor coupled to an output of the input matching network; and wherein the input matching network has a first input impedance when such input matching network is fed with an input signal having a relatively low power level and wherein the input matching network has an input impedance different from the first input impedance when such input matching network is fed with an input signal having a relatively high power level.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
Bulletproof material
InactiveUS20160116257A1Decrease back-side deformationSofter characteristicProtective equipmentLayered productsCarbon fibersFiber network
Disclosed is a bulletproof material having superior bulletproof performance and enhanced back-side deformation characteristics along with superior wearing sensation due to relatively light weight and soft texture. The bulletproof material according to the present invention includes a fibrous layer including a carbon fiber network at a back side or near a back side.
Owner:KOLON IND INC
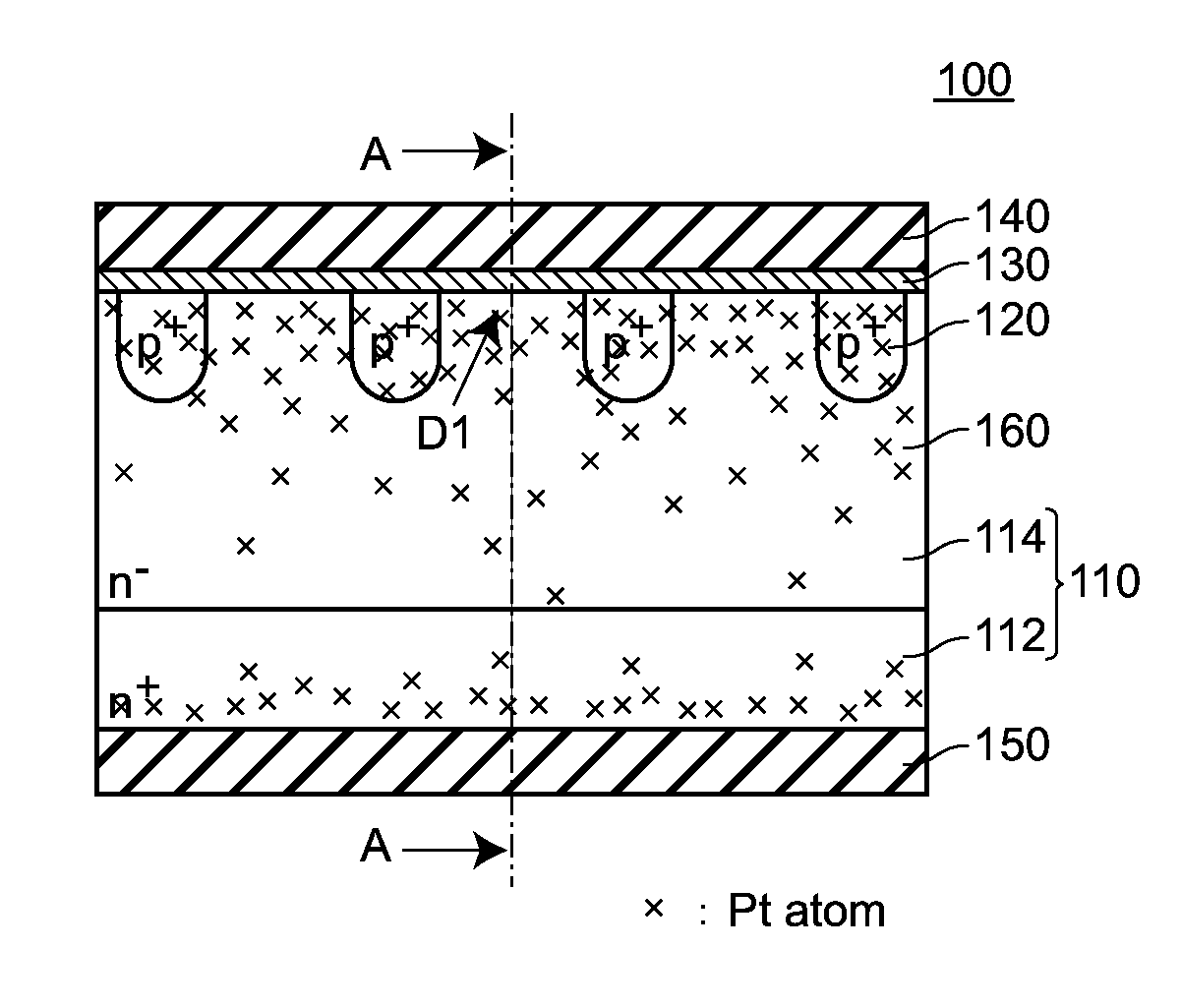
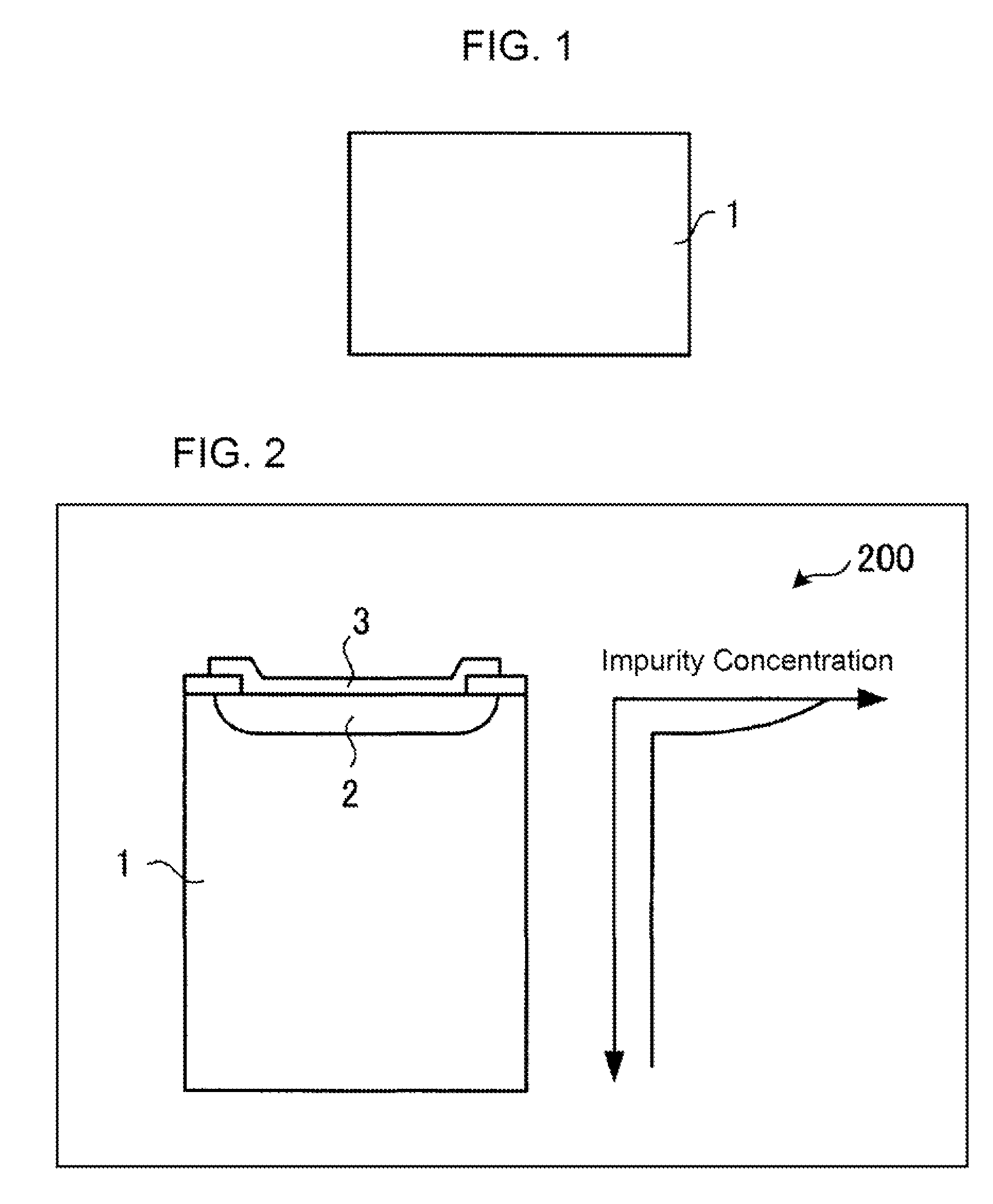
Semiconductor device
ActiveUS20150001667A1Total current dropImprove reverse withstand voltageSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesDevice materialOptoelectronics
A semiconductor device includes a semiconductor base body having an n+-type semiconductor layer and an n−-type semiconductor layer p+-type diffusion regions selectively formed on a surface of the n−-type semiconductor layer, and a barrier metal layer formed on a surface of the n−-type semiconductor layer and surfaces of p+-type diffusion regions. A Schottky junction is between the barrier metal layer and the n−-type semiconductor layer. An ohmic junction is between the barrier metal layer and the p+-type diffusion regions. Platinum is diffused into the semiconductor base body such that a concentration of platinum becomes maximum in a surface of the n−-type semiconductor layer.
Owner:SHINDENGEN ELECTRIC MFG CO LTD
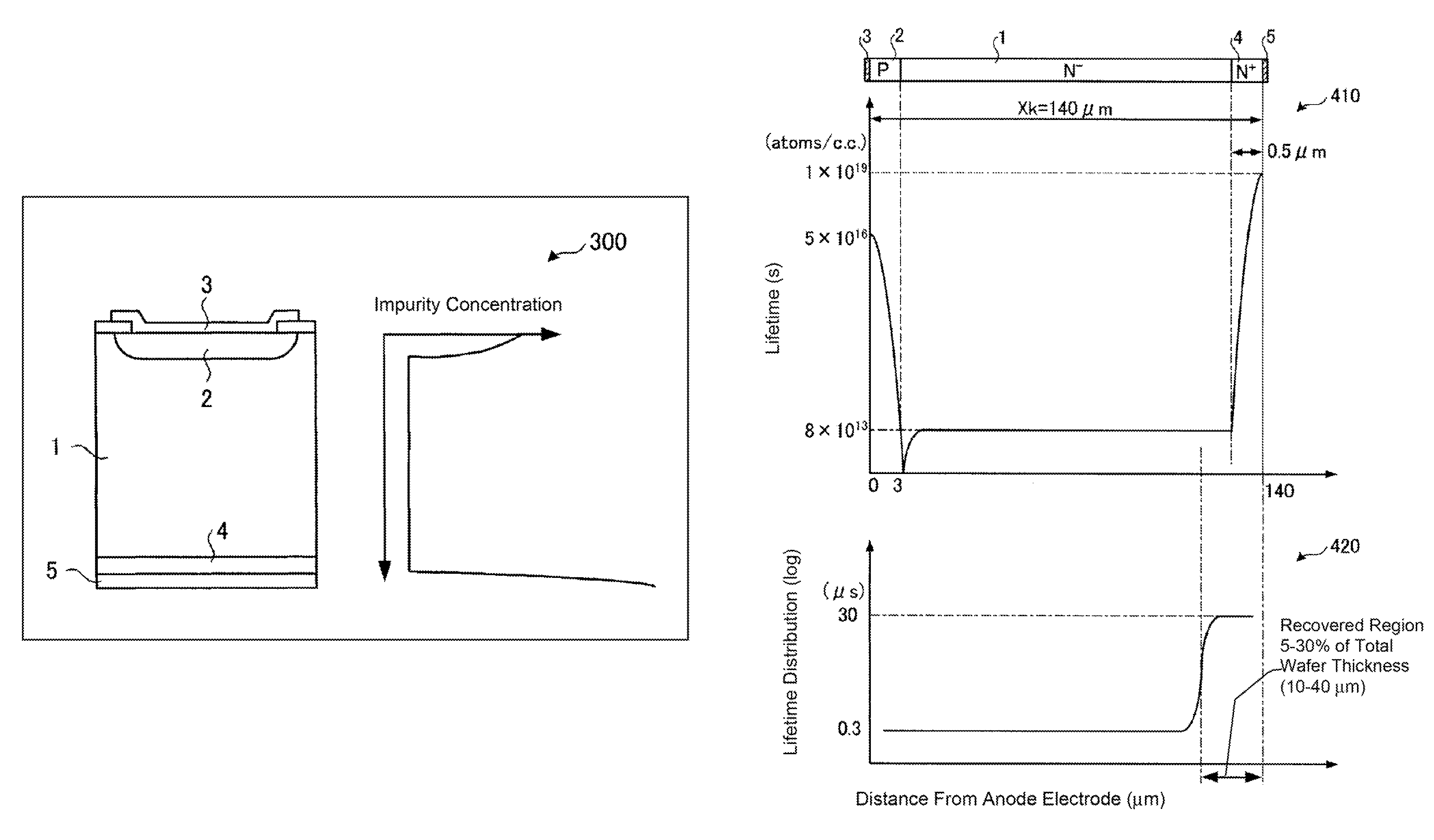
Method of manufacturing semiconductor device and semiconductor device formed by the method
ActiveUS7517777B2Improve featuresReduce manufacturing costSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesLight beamCrystallographic defect
The method of manufacturing a semiconductor device includes forming a p-type anode layer and an anode electrode on one major surface of an n-type semiconductor substrate, irradiating an electron beam to the semiconductor substrate to introduce crystal defects into the semiconductor substrate, grinding the other major surface of semiconductor substrate to reduce the thickness the semiconductor substrate, implanting phosphorus ions from the exposed surface of semiconductor substrate, and irradiating pulsed YAG laser beams by the double pulse technique to the exposed surface, from which the phosphorus ions have been implanted, to activate the implanted phosphorus atoms and to recover the region extending from the exposed surface irradiated with the YAG laser beams to the depth corresponding to 5 to 30% of the total wafer thickness from the defective state caused by the crystal defects introduced therein.
Owner:FUJI ELECTRIC CO LTD
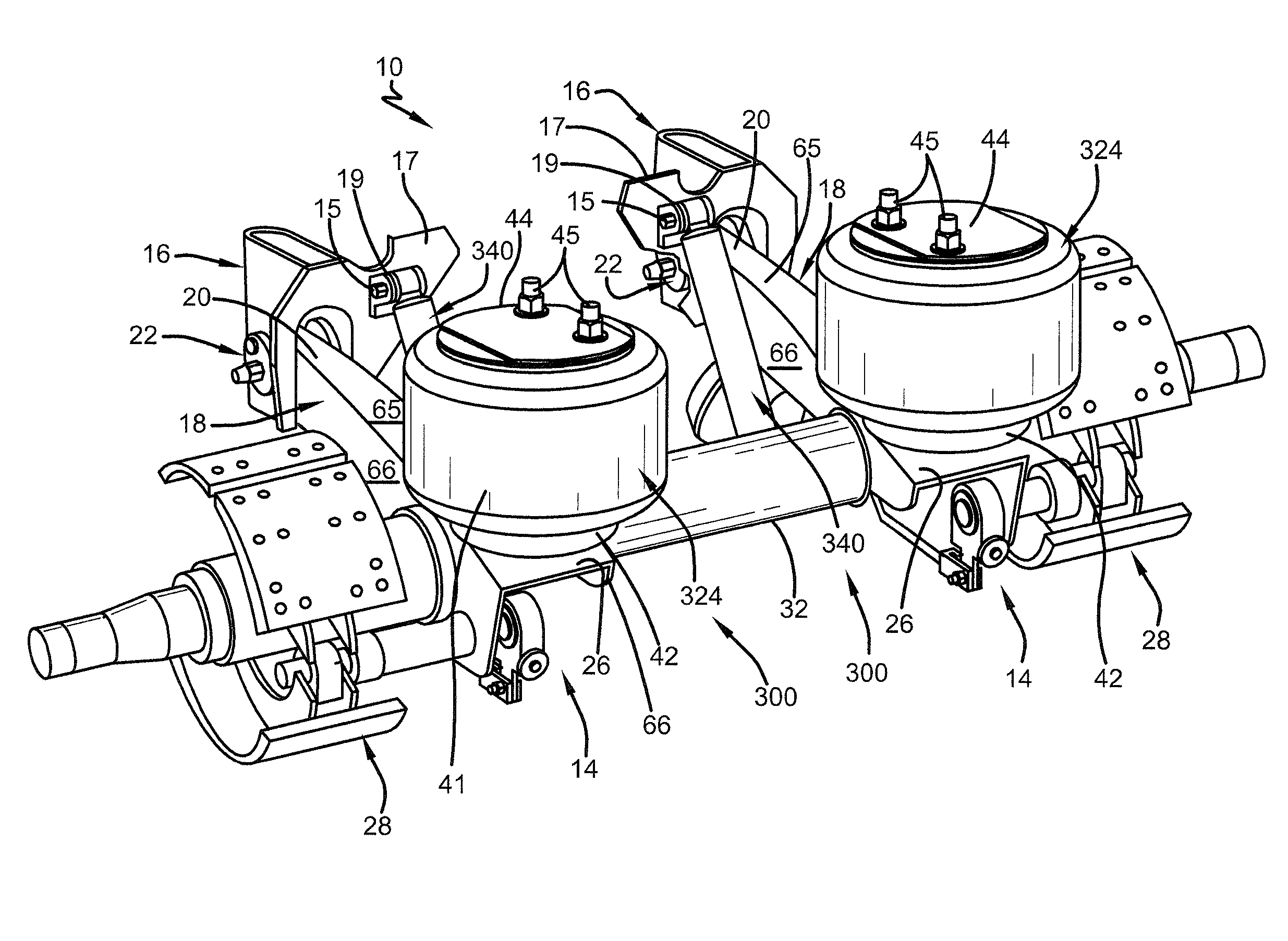
Damping air spring and shock absorber combination for heavy-duty vehicle axle/suspension systems
ActiveUS20160280033A1Increase dampingReduce transmission rateResilient suspensionsGas based dampersAir springAir suspension
A damping air spring and shock absorber combination for heavy-duty vehicle axle / suspension systems includes a damping air spring and a shock absorber both operatively attached to the axle / suspension system. The damping air spring primarily provides damping to the axle / suspension system over a first range of frequencies. The shock absorber primarily provides damping to the axle / suspension system over a second range of frequencies. The first range of frequencies is from about 0.0 Hz to about 6.0 Hz and the second range of frequencies is from about 0.0 Hz to about 13.0 Hz.
Owner:HENDRICKSON USA L L C
Method for designing input circuitry for transistor power amplifier
ActiveUS20090066411A1Improve stabilityLower performance requirementsMultiple-port networksElectric devicesAudio power amplifierInput impedance
A circuit having: an input matching network; a transistor coupled to an output of the input matching network; and wherein the input matching network has a first input impedance when such input matching network is fed with an input signal having a relatively low power level and wherein the input matching network has an input impedance different from the first input impedance when such input matching network is fed with an input signal having a relatively high power level.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
Device for a Vibration Generator
InactiveUS20100224016A1Reduce weightAvoid disadvantagesGearingMechanical vibrations separationSpring forceEngineering
A device for a vibrator, including at least one resilient element, with a force / travel curve having a first region, at least approximately given by an equation of formula K=a+b*W, where K is the spring force of the at least one resilient element, W is the spring travel and a and b are number greater than zero and a vibrator including such a device.
Owner:ABI ANLAGENTECHN BAUMASCHEN INDBEBEDARF
Method for designing input circuitry for transistor power amplifier
ActiveUS7528649B2Softer characteristicHigh levelMultiple-port networksElectric devicesAudio power amplifierInput impedance
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
Conveyor chain, in particular a can conveyor chain
ActiveUS9533829B2Good damping propertiesAvoid more failuresConveyorsPackagingElastomerPlastic materials
A conveyor chain, in particular a can conveyor chain, comprises chain links, which are interconnected by a respective chain hinge, and laterally projecting transport bars, which have a damping head made of a plastic material and provided for contact with the articles to be conveyed, the damping head comprising a fastening portion, a spring section arranged on said fastening portion and a contact portion connected to the spring section and adapted to contact the articles to be conveyed. A conveyor chain is provided of this type with a simpler and less failure-prone structural design. To this end, the damping head is provided with a front-side cavity of such a nature that the spring section has an elastically deformable wall portion whose wall thickness narrows, at least sectionwise, towards the contact portion, at least said spring section being made of an elastomer having a maximum shore hardness of A90.
Owner:IWIS ANTRIEBSSYST
Soft magnetic thin film, method of producing the same, and magnetic head
InactiveUS20070188916A1Increase internal stressImprove featuresLiquid applicationHeads using thin filmsAlloyMagnetic characteristic
The soft magnetic thin film has high saturation magnetic flux density and superior soft magnetic characteristics, and it can be suitably used as a magnetic film of a magnetic head of a magnetic disk drive unit. The soft magnetic thin film, which is made of an alloy including two or three elements selected from a group consisting of Fe, Co and Ni, is formed by an electrolytic plating process, and internal stress of the plated film is 400 MPa or more.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Magnetoresistive element and method of manufacturing same, magnetoresistive device, thin-film magnetic head, head gimbal assembly, head arm assembly and magnetic disk drive
InactiveUS20060240289A1Great magnetoresistance change amountExcellent soft magnetic propertiesNanoinformaticsRecord information storageMagnetic reluctanceAlloy
A free layer of an MR element incorporates a first layer, a second layer, a third layer, a fourth layer, a fifth layer and a sixth layer that are stacked in this order on a nonmagnetic conductive layer. The absolute value of magnetostriction constant of the free layer is 1×10−6 or smaller. The coercivity of the free layer is 20×79.6 A / m or smaller. The first layer is made of an alloy containing ‘a’ atomic percent cobalt and (100−a) atomic percent iron wherein ‘a’ falls within a range of 20 to 50 inclusive. The second layer is made of an alloy containing ‘b’ atomic percent cobalt and (100−b) atomic percent iron wherein ‘b’ falls within a range of 70 to 90 inclusive. In addition, oxidation treatment is given to a surface of the second layer farther from the first layer.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Method of producing magnetic head and magnetic head
InactiveUS20070217068A1Improving soft magnetic characteristic of magneticHigh density recordingElectrical transducersManufacture head surfaceMagnetic polesElectroplating
The a method of producing a magnetic head is capable of stabilizing deposition rate of a plated magnetic film forming a magnetic pole of a write-head. The method of producing a magnetic head, in which a magnetic pole of a write-head is constituted by a magnetic film, comprises the steps of: forming a seed layer made of Ru on a surface of a work piece; forming a cap layer on a surface of the seed layer so as to stabilize deposition rate of the magnetic film; and forming the magnetic film by electrolytic plating, and the seed layer and the cap layer are used as power feeding layers for the electrolytic plating.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Antenna core and antenna
InactiveUS8035569B2Efficient productionImprove performanceLoop antennas with ferromagnetic coreMagnetic materialsMetallurgyNanocrystal
An antenna core produced by shaping a soft magnetic metal powder with the use of a resin as a binder, wherein the soft magnetic metal powder is an amorphous soft magnetic metal powder or a nanocrystal-containing amorphous soft magnetic metal powder, of the general formula (1): (Fe1-x-yCoxNiy)100-a-b-cSiaBbMc (1), and wherein the resin as a binder is a thermosetting resin. In the formula, M is at least one element selected from the group consisting of Nb, Mo, Zr, W, Ta, Hf, Ti, V, Cr, Mn, Y, Pd, Ru, Ga, Ge, C, P, Al, Cu, Au, Ag, Sn and Sb. Each of x and y is an atomic ratio and each of a, b and c an atomic %, satisfying the relationships: 0≦x≦1.0, 0≦y≦0.5, 0≦x+y≦1.0, 0≦a≦24, 1≦b≦30, 0≦c≦30 and 2≦a+b≦30.
Owner:NAKAGAWA SPECIAL STEEL CO
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com