Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
69results about How to "Simple correction" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
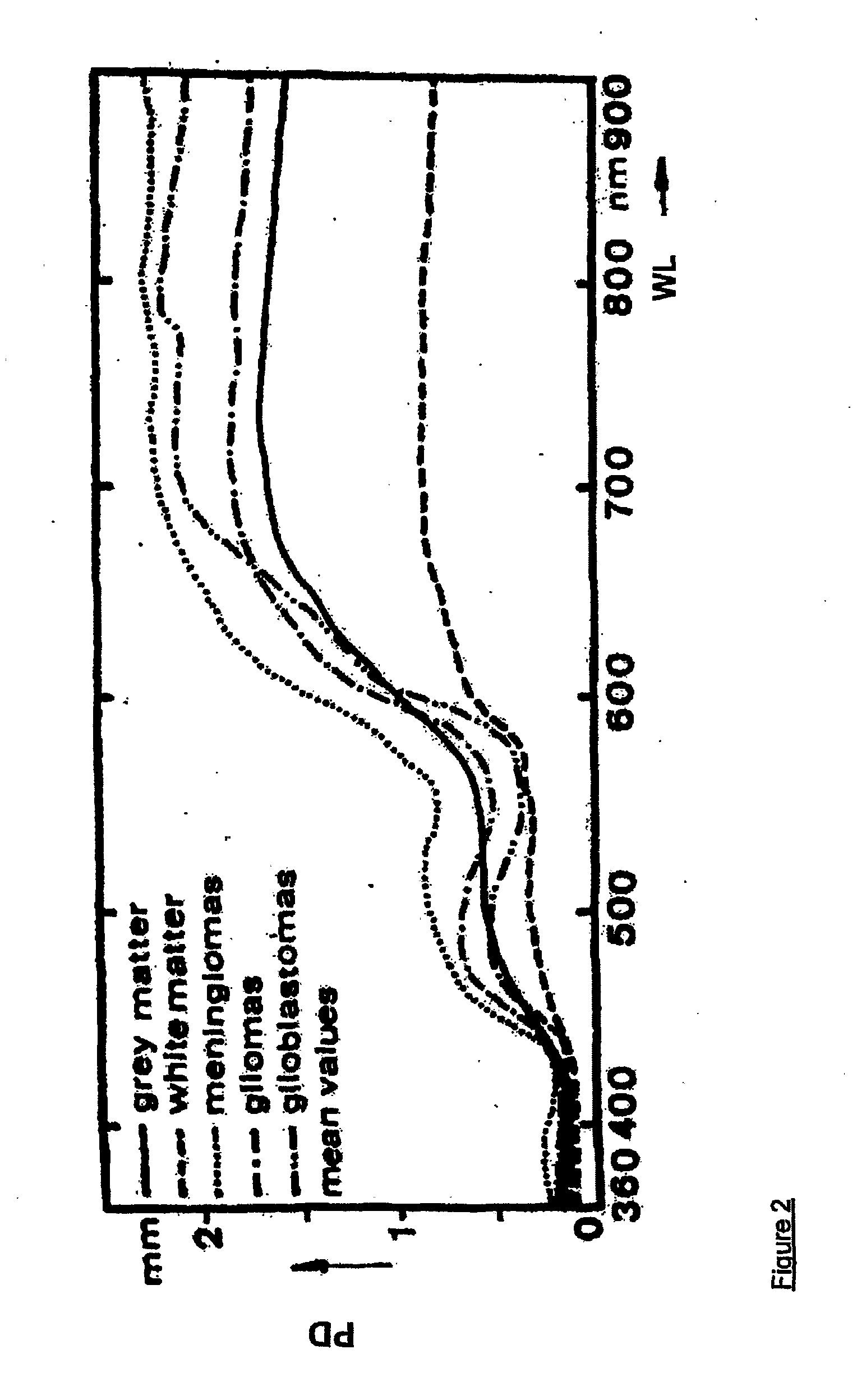
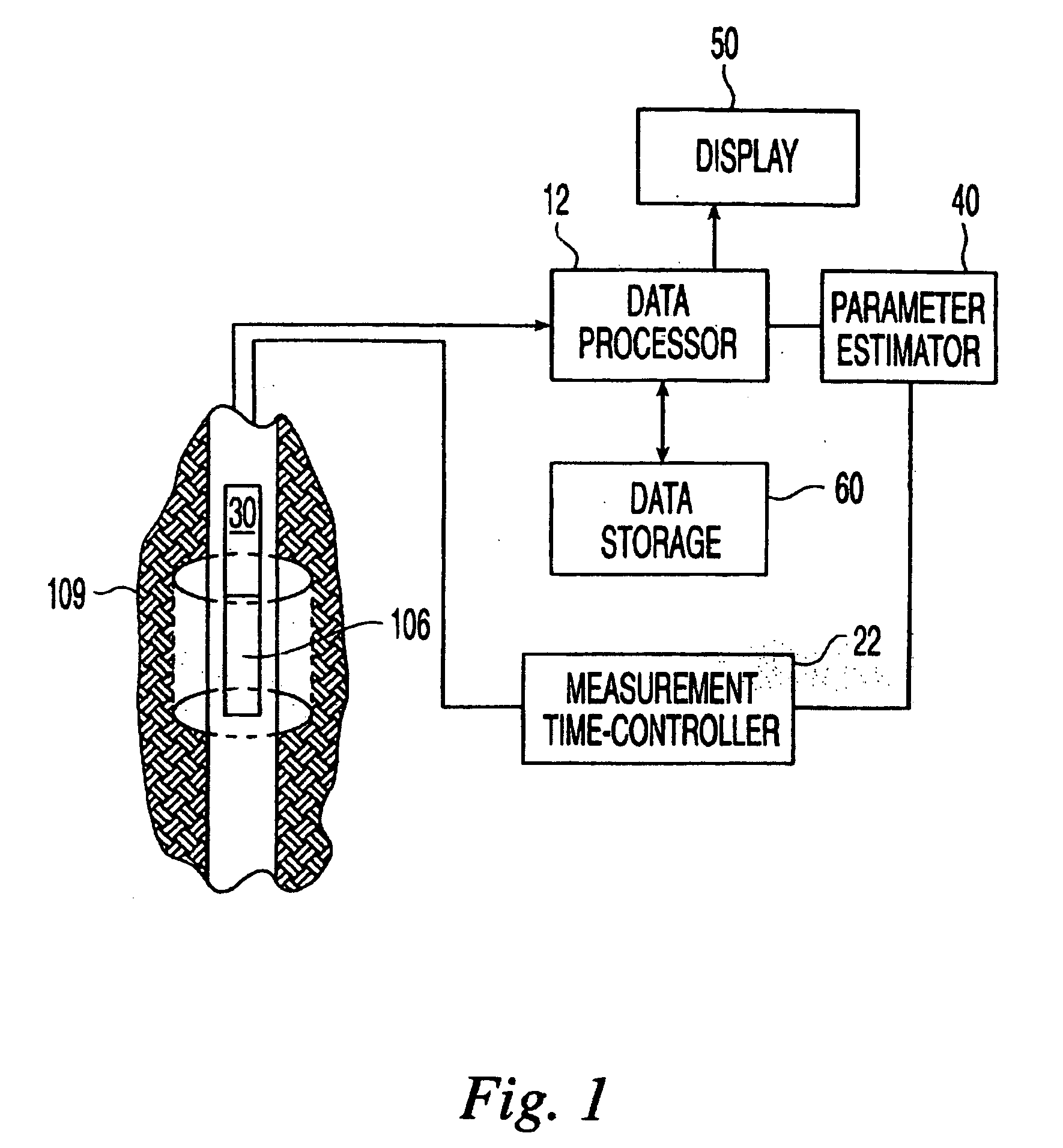
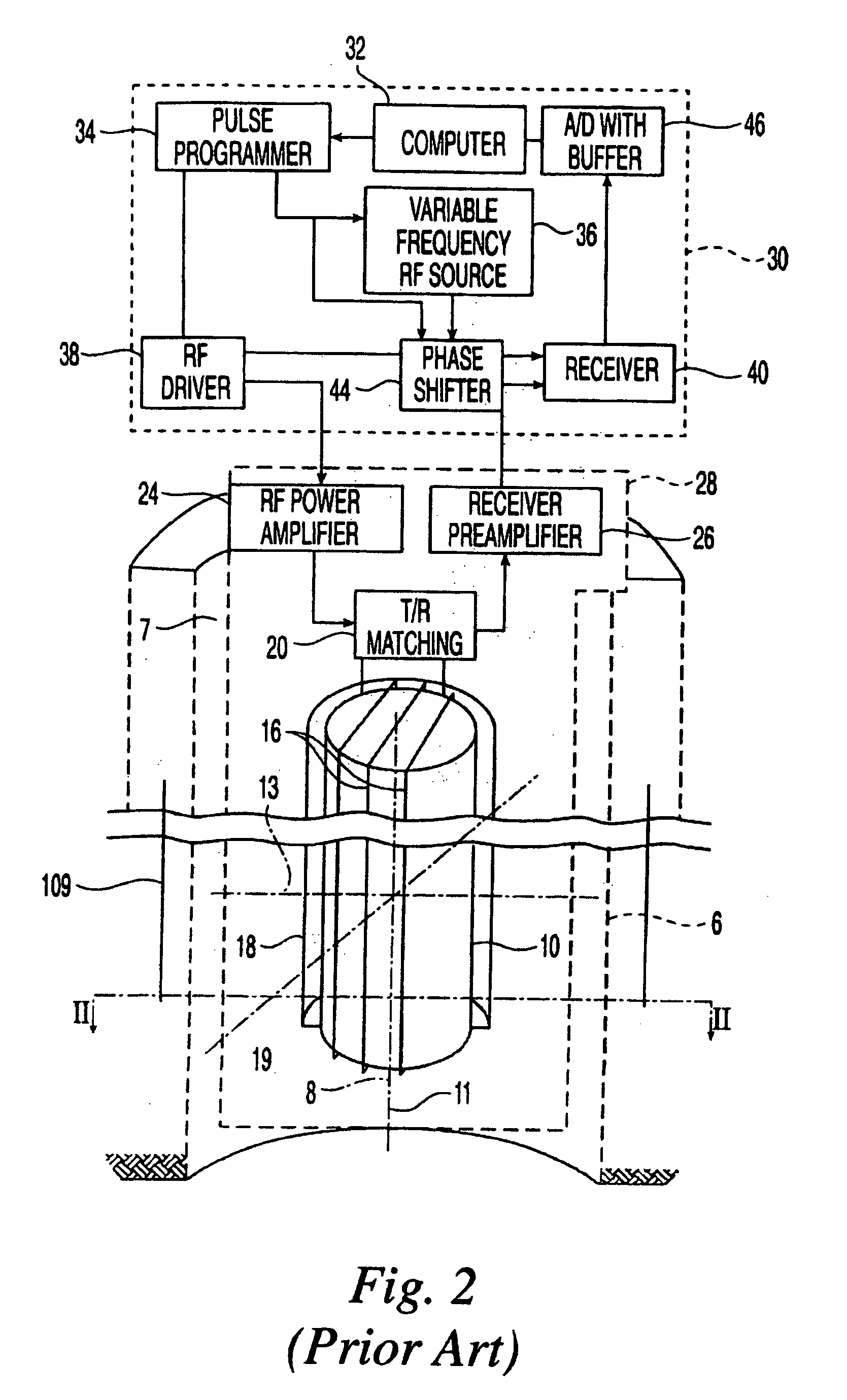
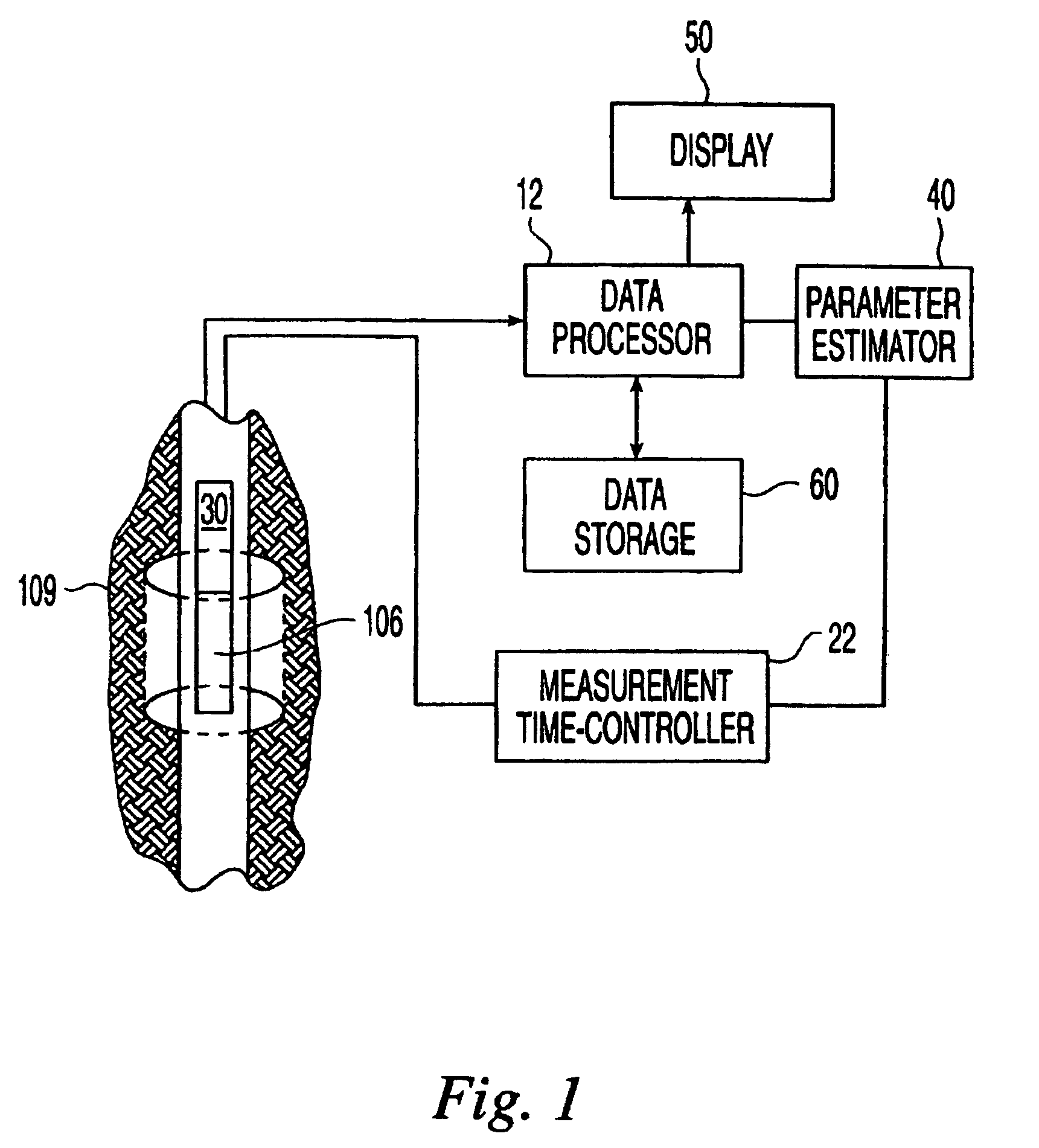
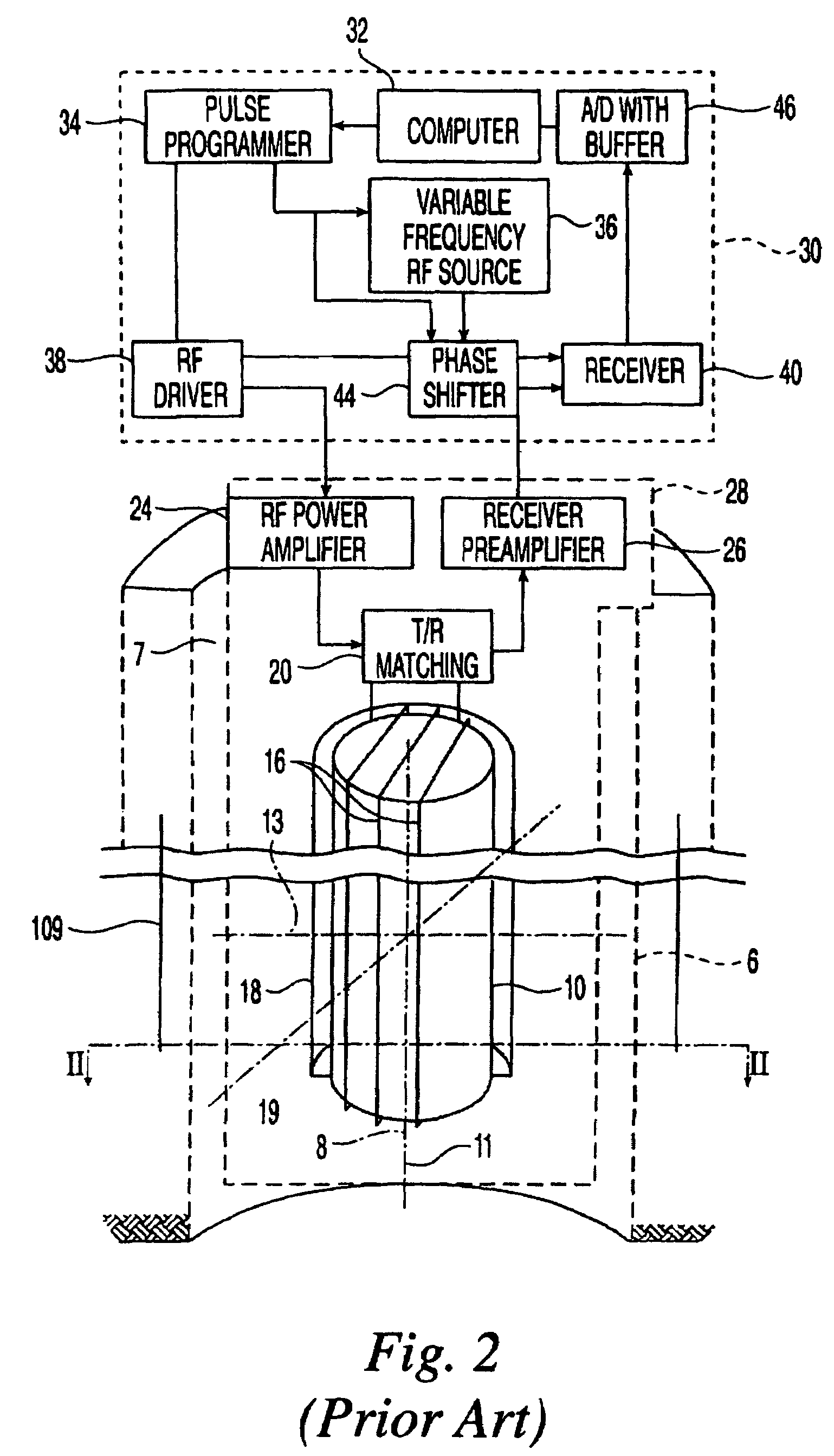
Apparatus and method for monitoring tissue vitality parameters
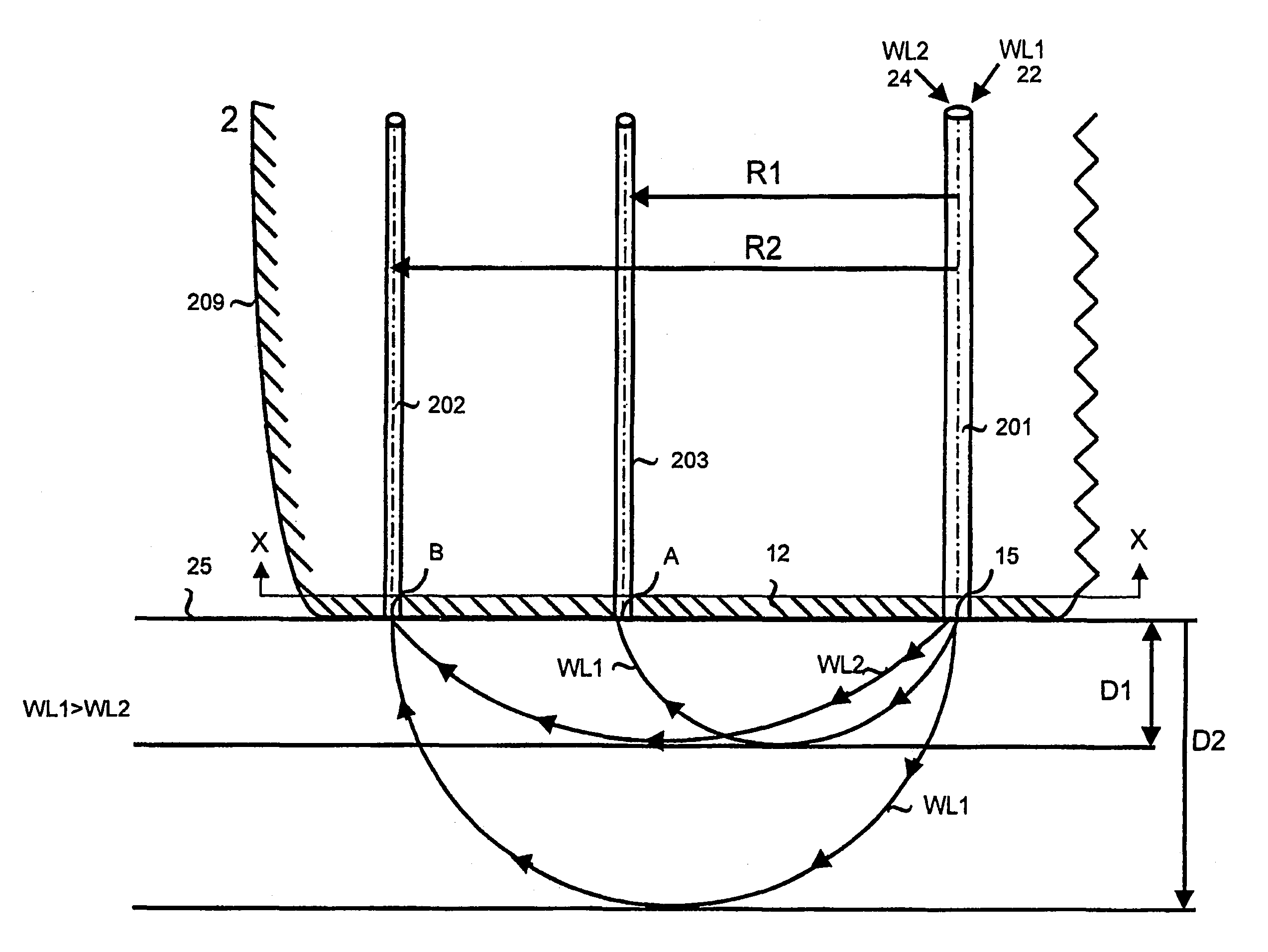
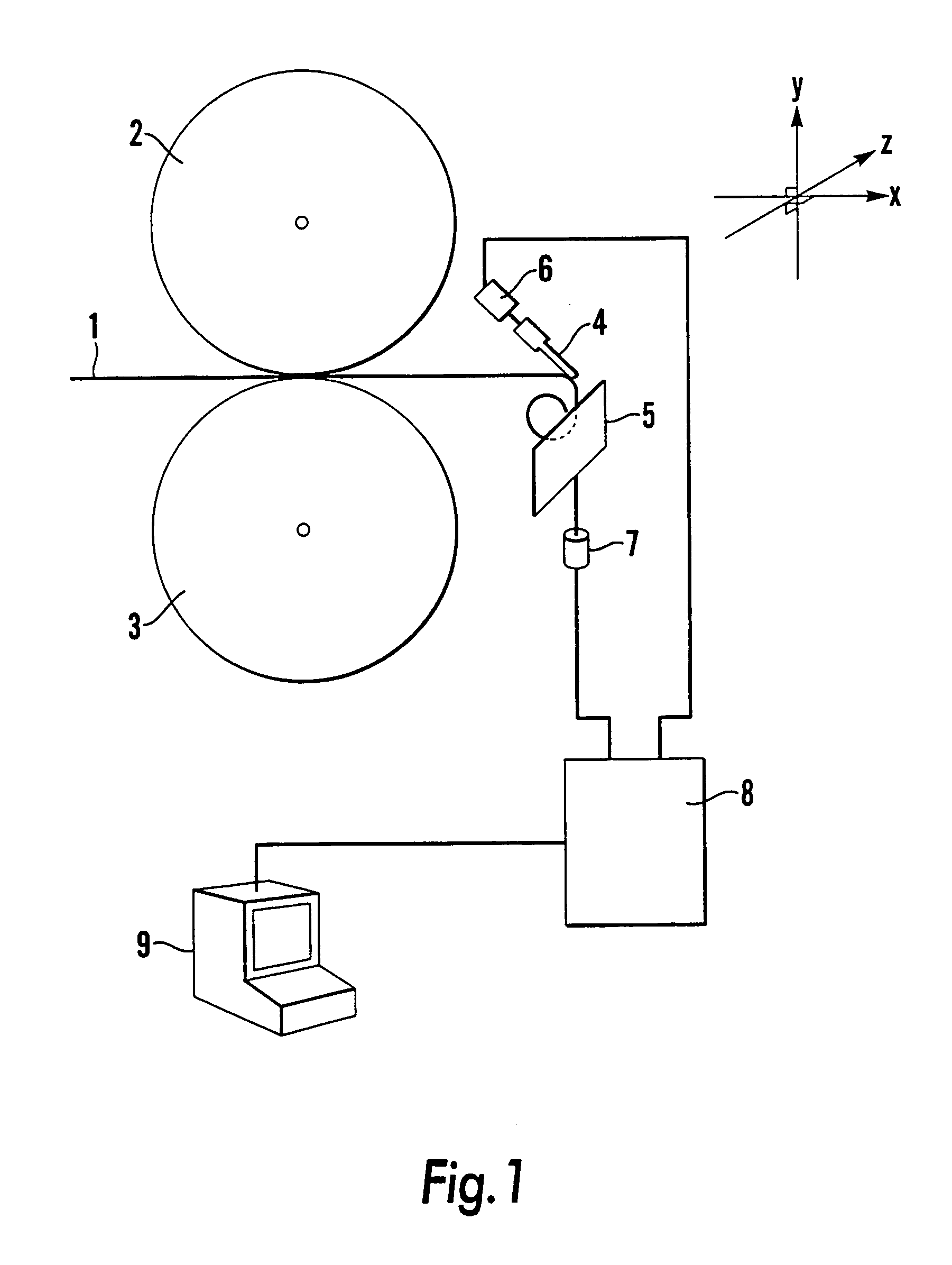
Apparatus for monitoring a plurality of tissue viability parameters of a tissue layer element, in which two different illumination sources are used via a common illumination element in contact with the tissue. One illumination source is used for monitoring blood flow rate and optionally flavoprotein concentration, and collection fibers are provided to receive the appropriate radiation from the tissue. The other illuminating radiation is used for monitoring any one of and preferably all of NADH, blood volume and blood oxygenation state of the tissue element, and collection fibers are provided to receive the appropriate radiation from the tissue. In one embodiment, the wavelengths of the two illumination sources are similar, and common collection fibers for the two illuminating radiations are used. In another embodiment, the respective collection fibers are distanced from the illumination point at different distances correlated to the ratio of the first and second illuminating wavelengths.
Owner:CRITISENSE
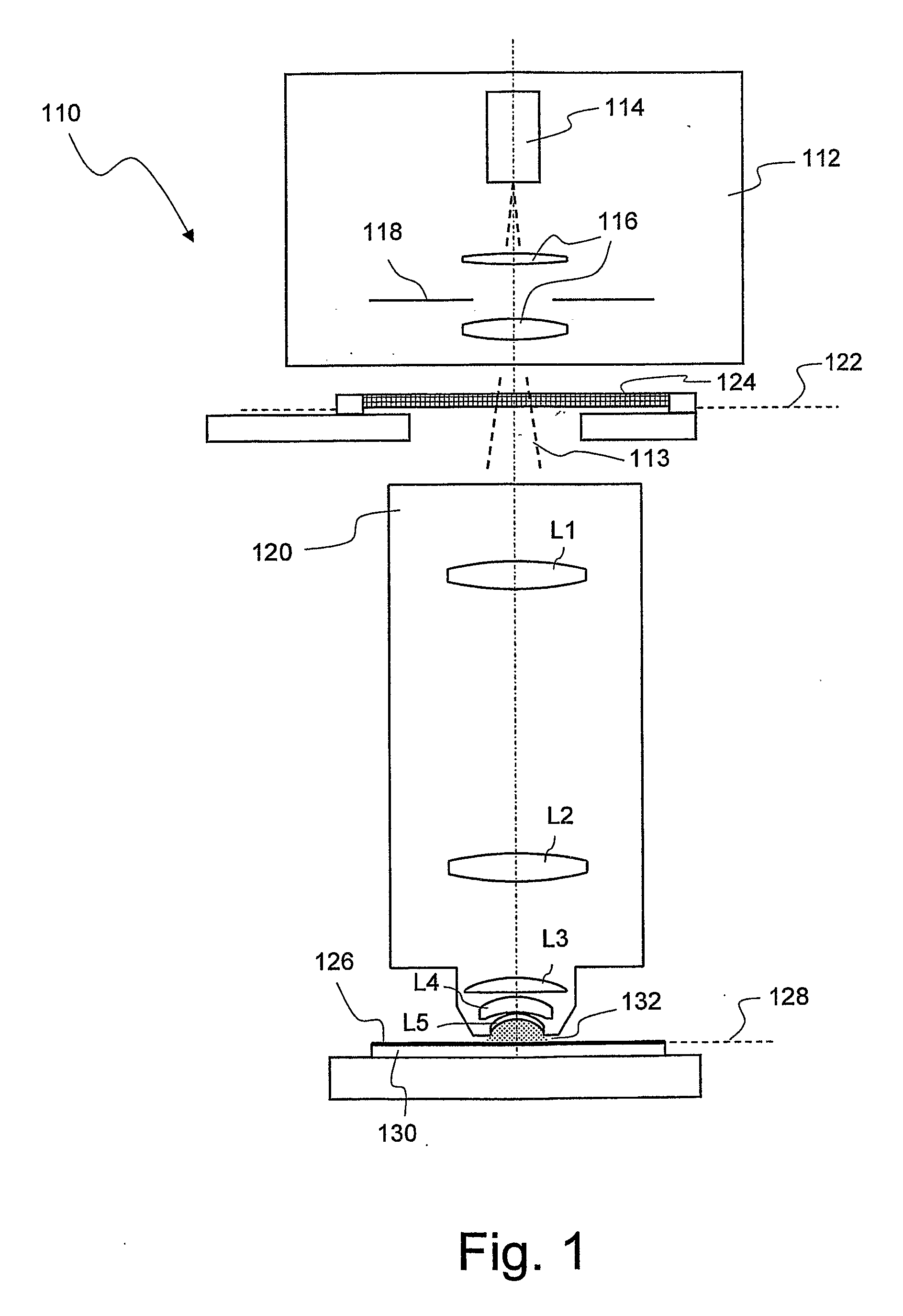
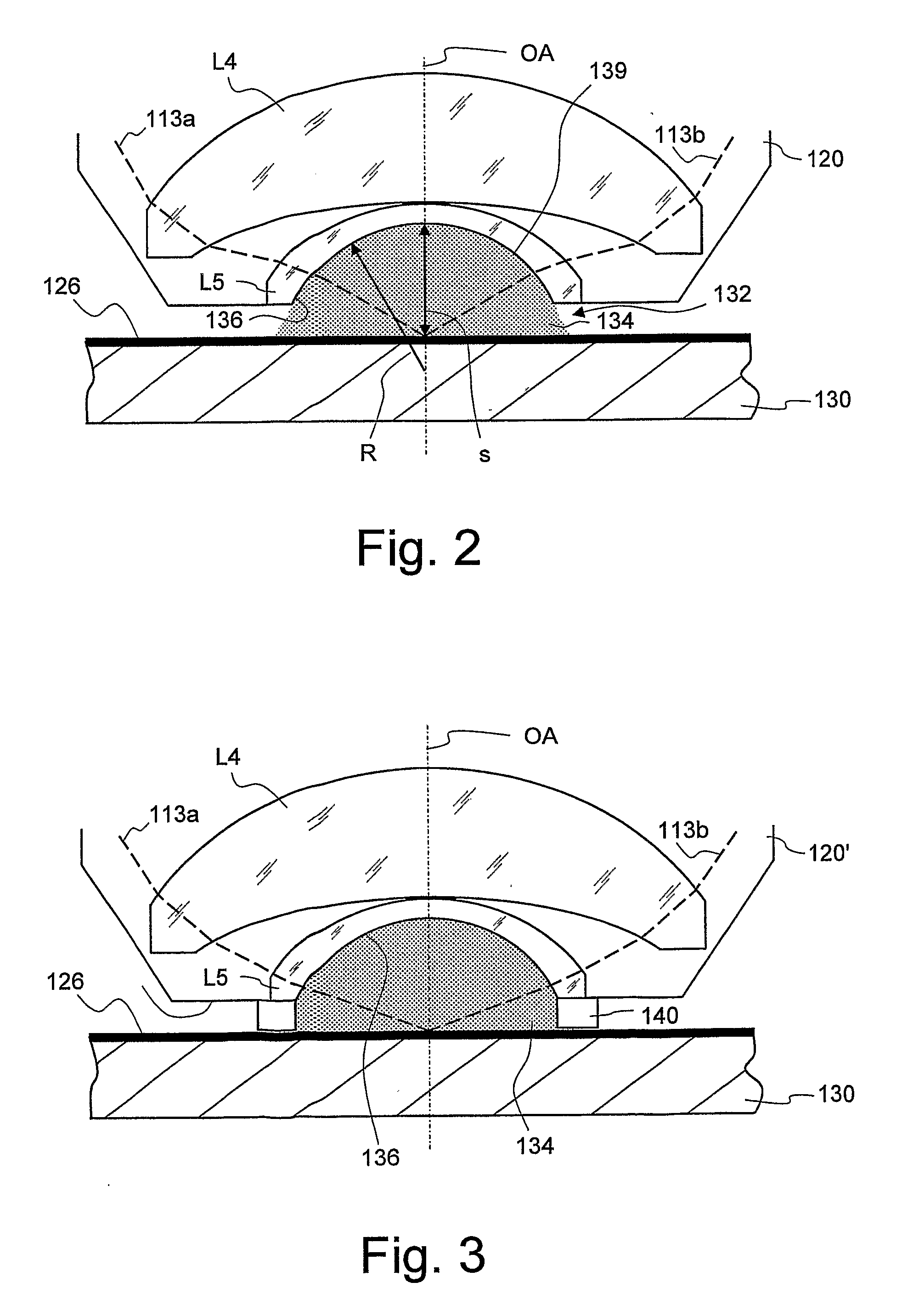
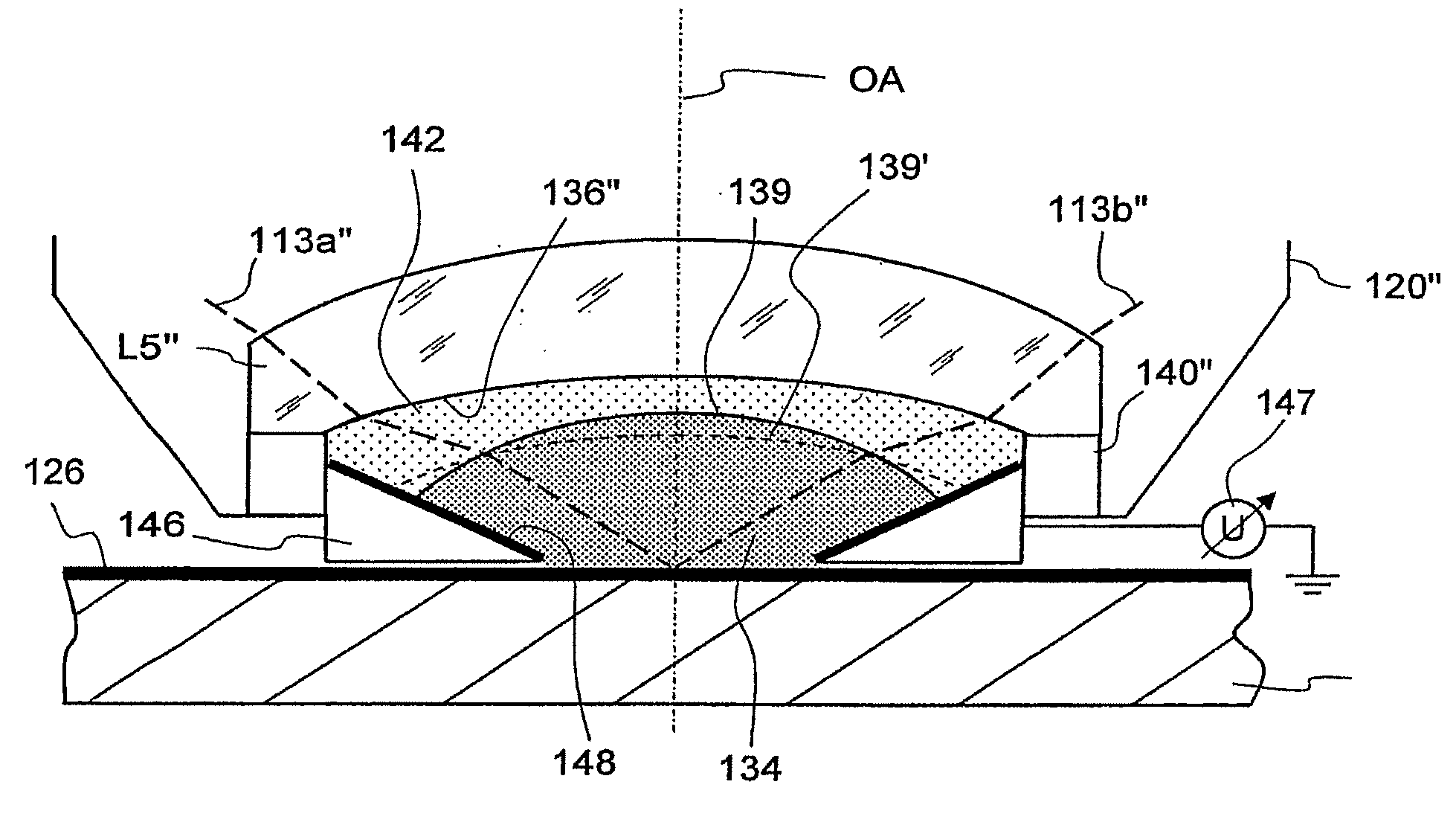
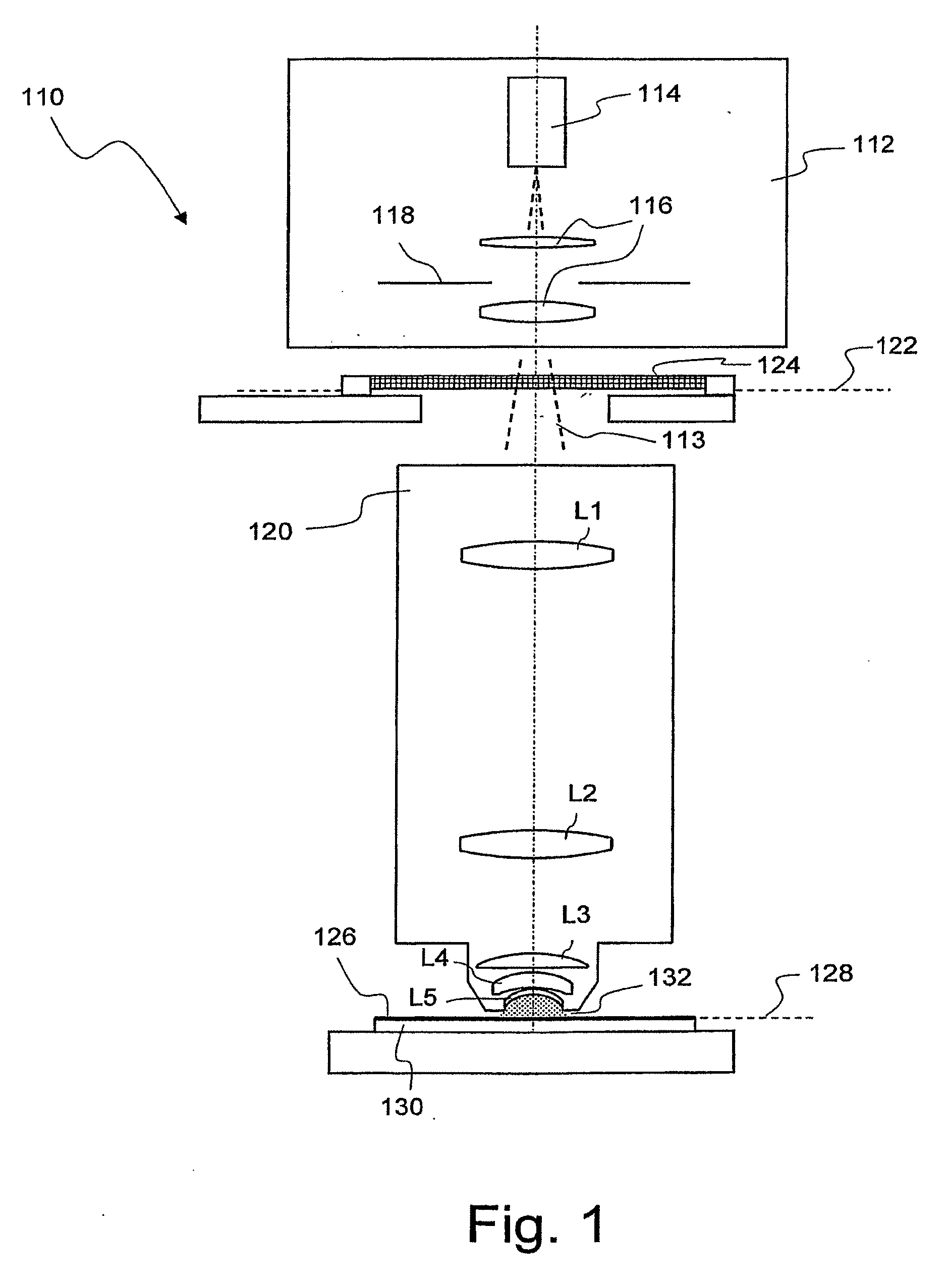
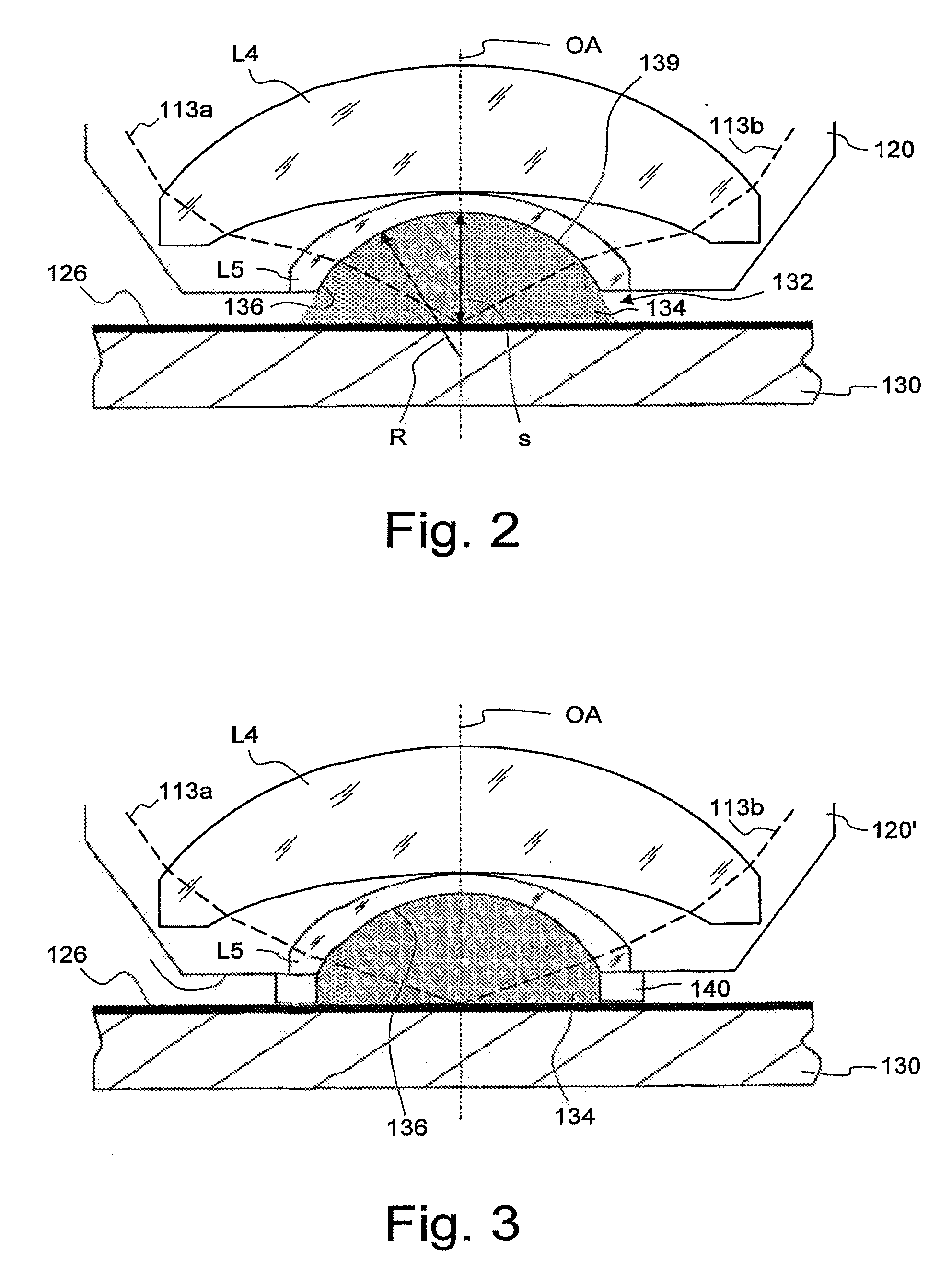
Projection objective for a microlithographic projection exposure apparatus
InactiveUS20070165198A1Reduce immersionIncrease the number ofPhotomechanical exposure apparatusMicrolithography exposure apparatusRefractive indexOphthalmology
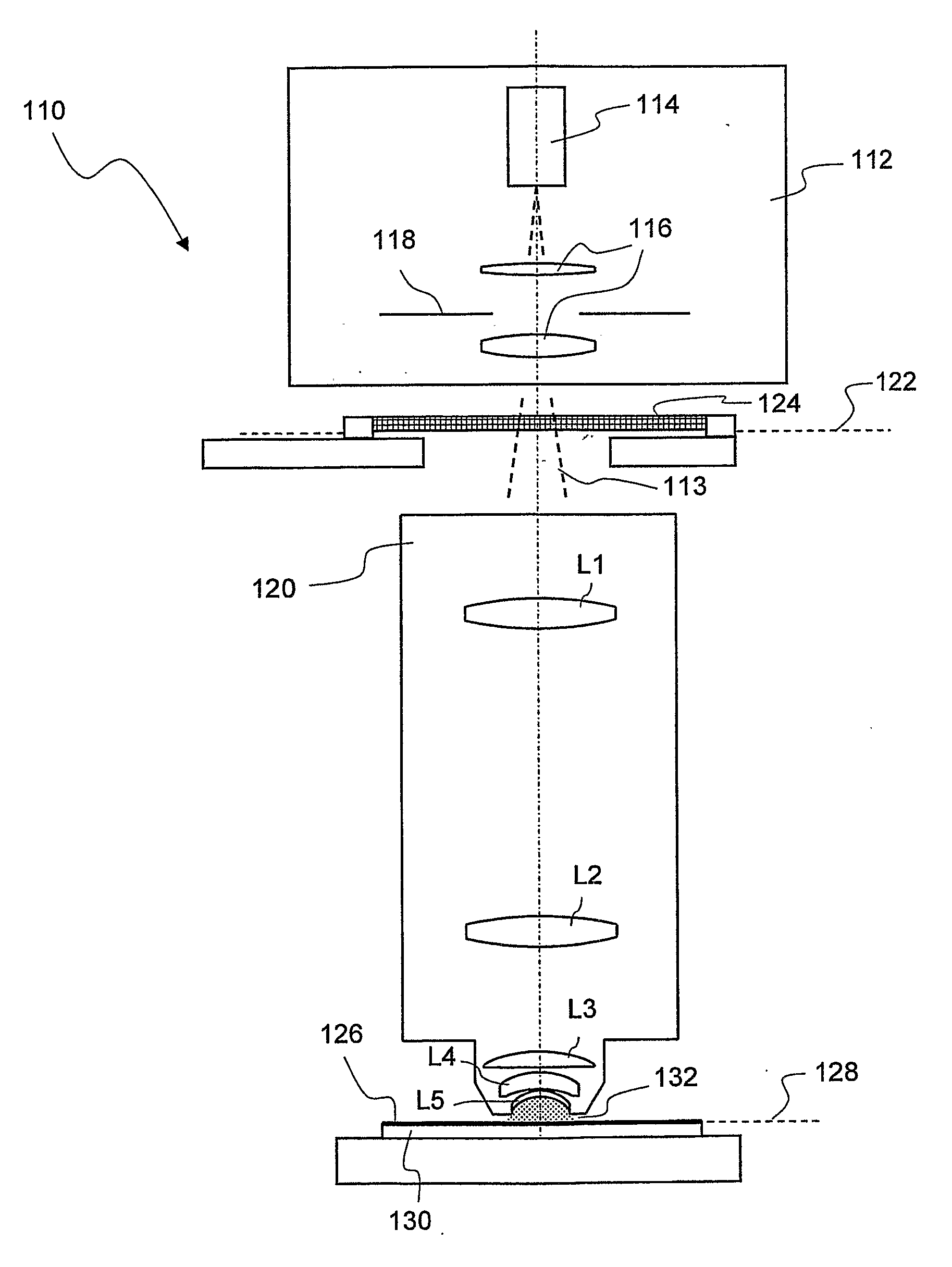
A projection objective of a microlithographic projection exposure apparatus (110) is designed for immersion operation in which an immersion liquid (134) adjoins a photosensitive layer (126). The refractive index of the immersion liquid is greater than the refractive index of a medium (L5; 142; L205; LL7; LL8; LL9). that adjoins the immersion liquid on the object side of the projection objective (120; 120′; 120″). The projection objective is designed such that the immersion liquid (134) is convexly curved towards the object plane (122) during immersion operation.
Owner:CARL ZEISS SMT GMBH
Apparatus and Method for Monitoring Tissue Vitality Parameters
InactiveUS20070179366A1Correction of artifactThe effect is accurateOptical sensorsBlood flow measurementTissue viabilityLength wave
Apparatus for determining the oxygenation state of at least one tissue element, comprising: a) illumination means for illuminating said tissue element with an illuminating radiation at a predetermined wavelength via at least one illumination location with respect to said tissue element, said illuminating radiation being at a wavelength within the NADH excitation spectrum or the Fp excitation spectrum; b) radiation receiving means and detection means for measuring the intensity of the corresponding NADH fluorescence or Fp fluorescence emitted by the tissue element at at least two predetermined wavelengths within the range of wavelengths comprised within the corresponding fluorescence emission spectrum.
Owner:CRITISENSE
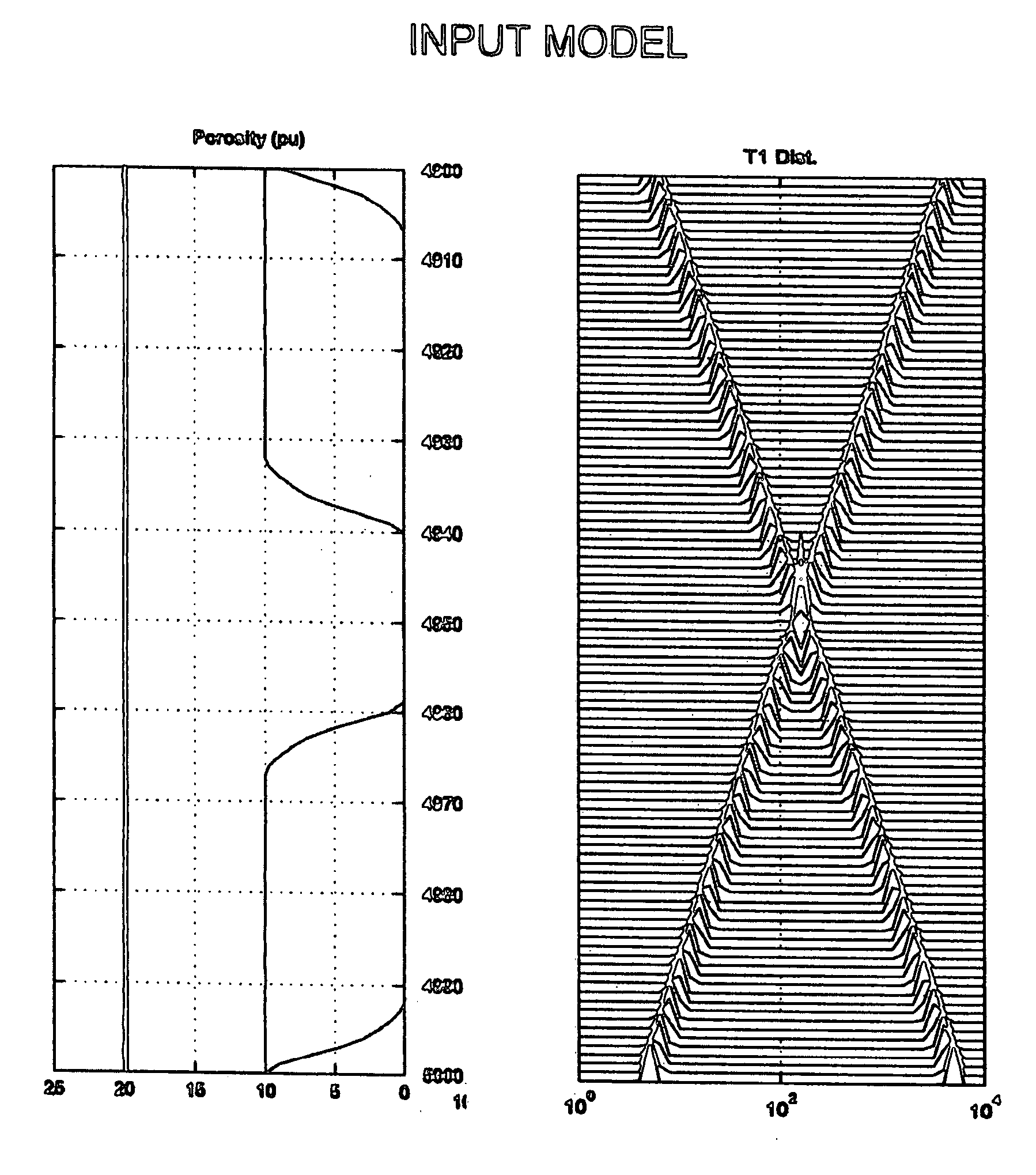
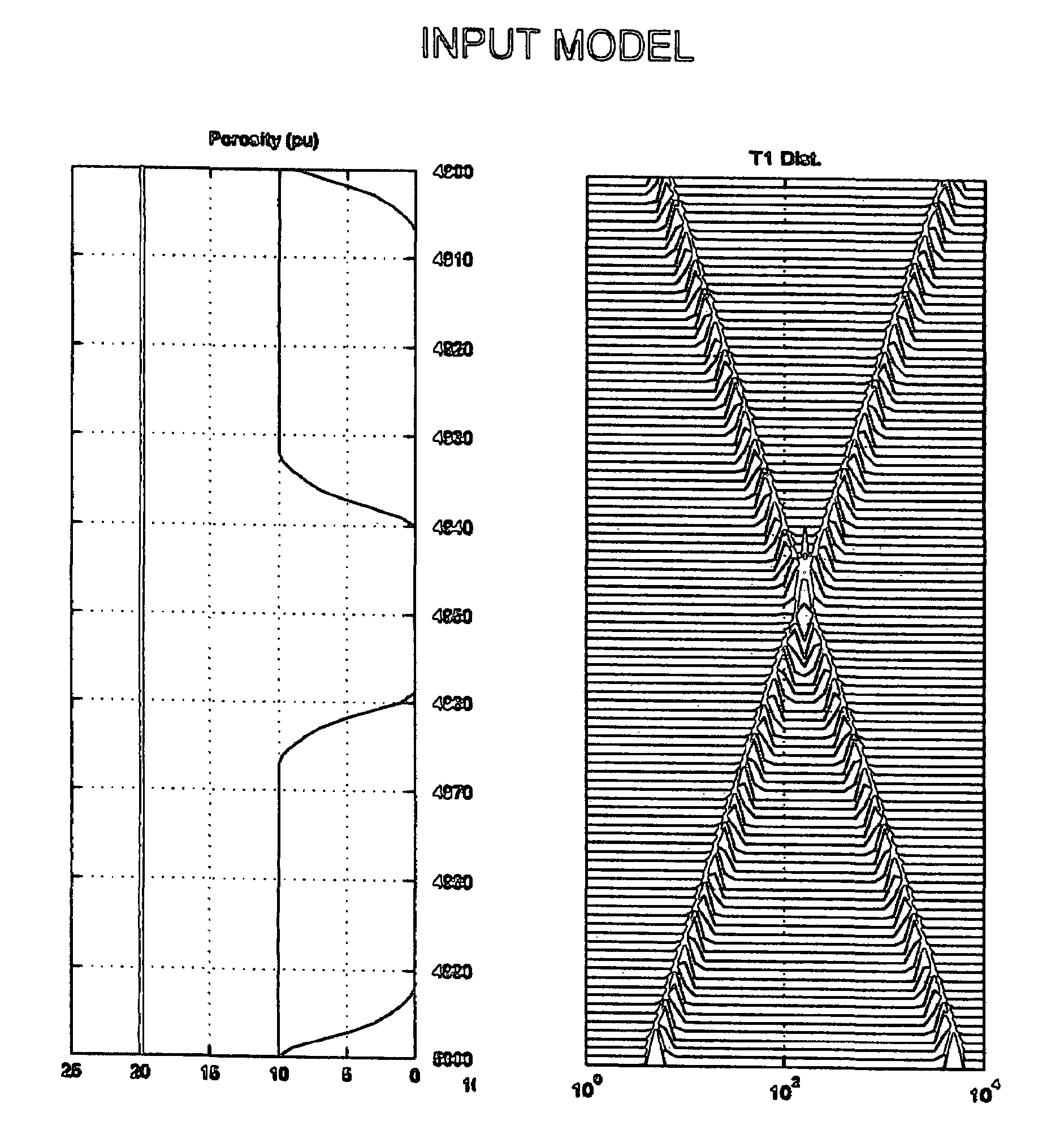
System and methods for T1-based logging
ActiveUS20050104587A1Efficient Data AcquisitionCompact and robust data setElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonanceData set
System and methods for using nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) T1 measurements for wireline, LWD and MWD applications and down-hole NMR fluid analyzers. The T1 measurements are characterized by insensitivity to motion, as the detrimental effects arising from tool motion or fluid flow are effectively reduced or eliminated. T1 measurements alone or in combination with other standard oil field measurements are shown to provide efficient data acquisition resulting in compact and robust data sets, the potential for substantially increased logging speeds, and simple methods for fluid typing, including direct and robust identification of gas.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
Magnetic sensor, magnetic direction sensor, method of detecting magnetic field and method of detecting magnetic direction
ActiveUS20080204011A1Uniform resistanceBig errorNanomagnetismMagnitude/direction of magnetic fieldsElectrical resistance and conductanceMagnetization
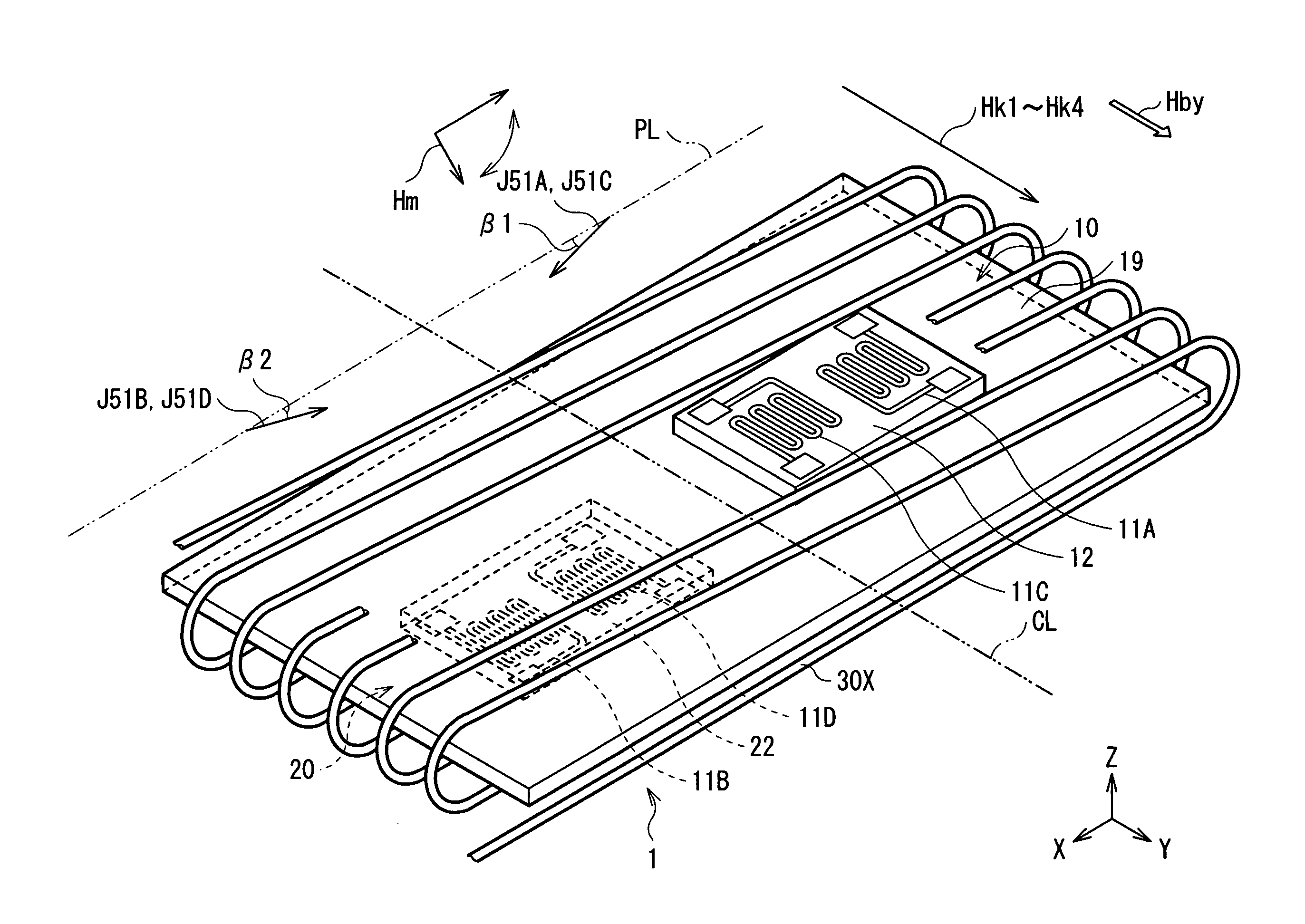
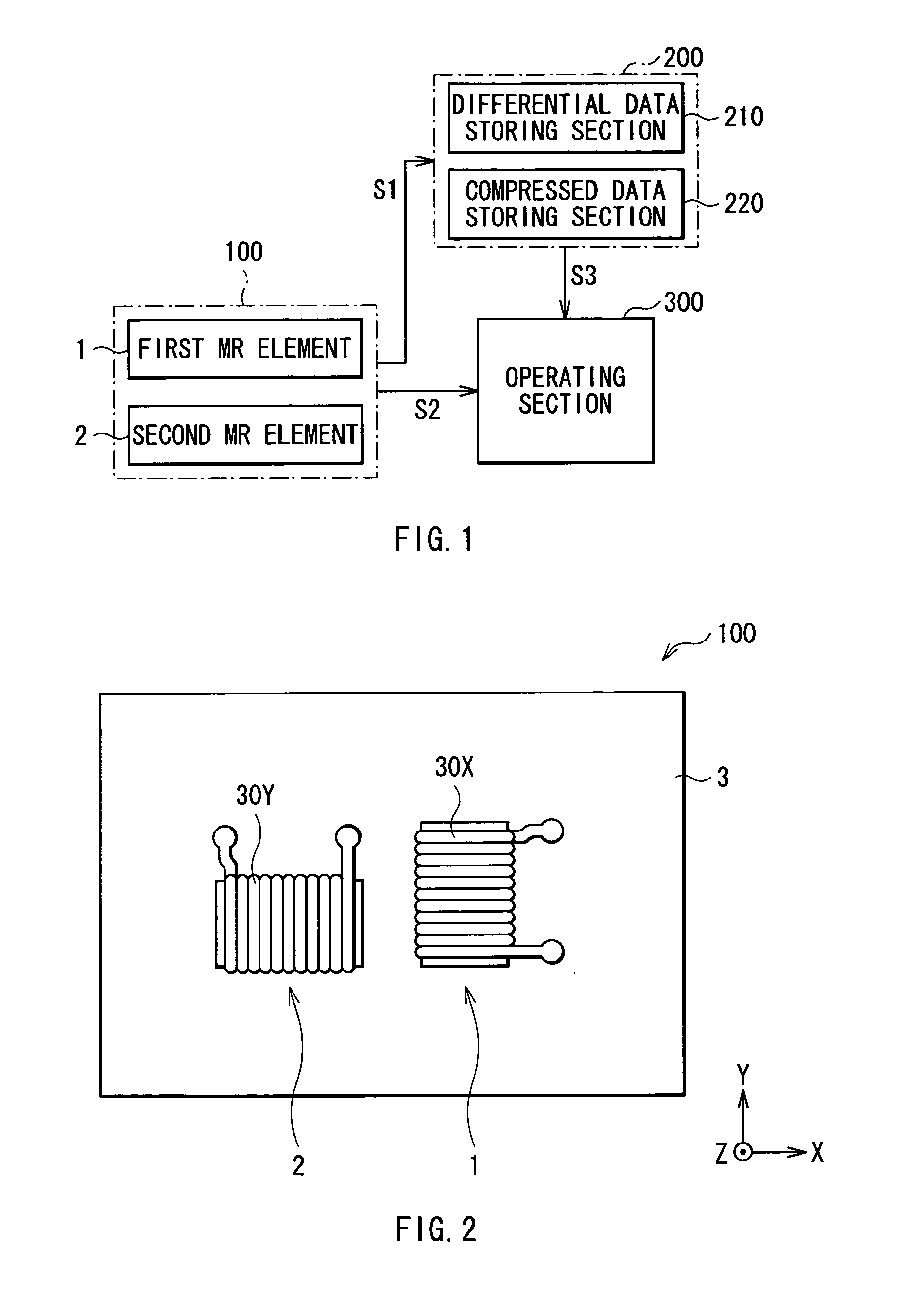
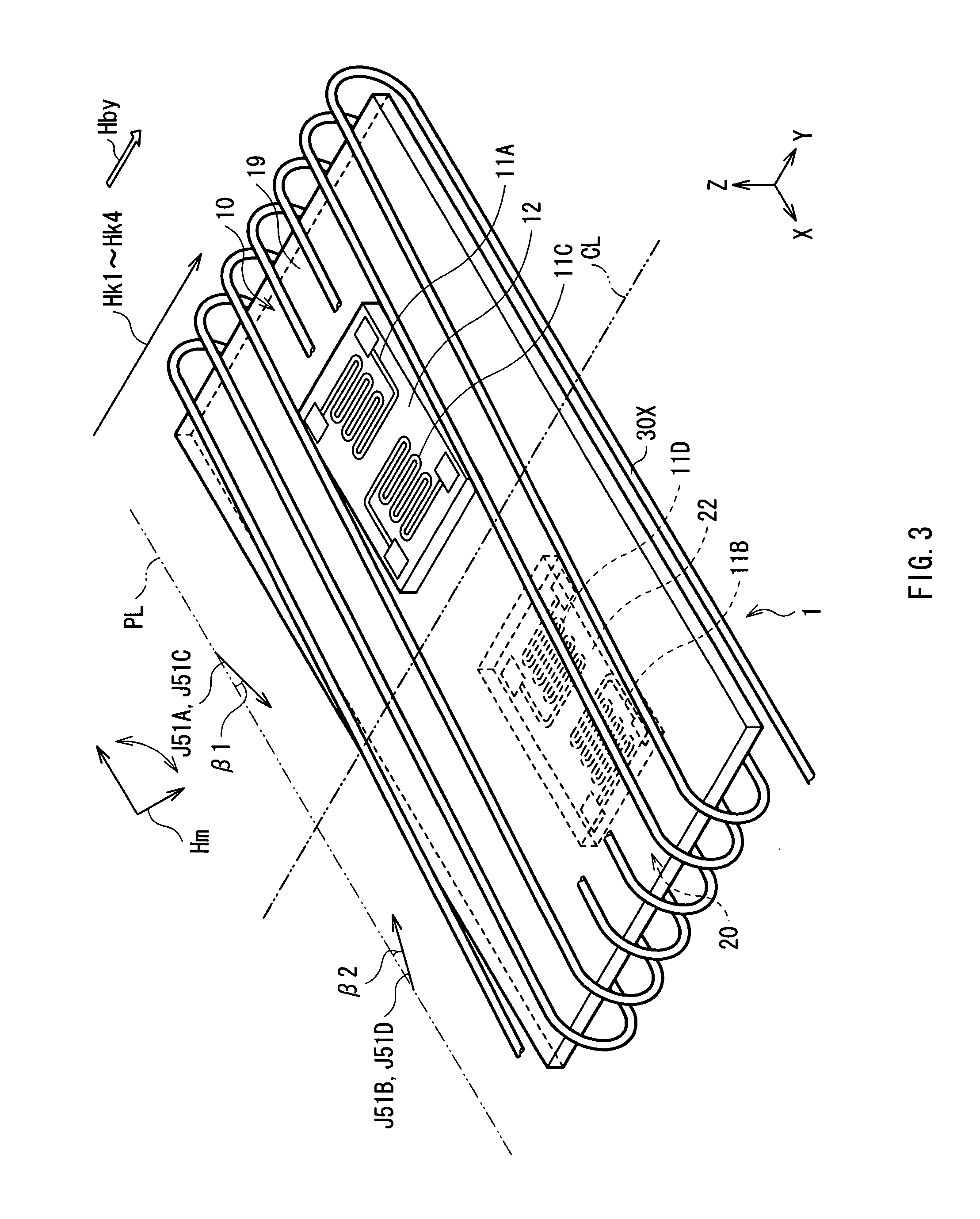
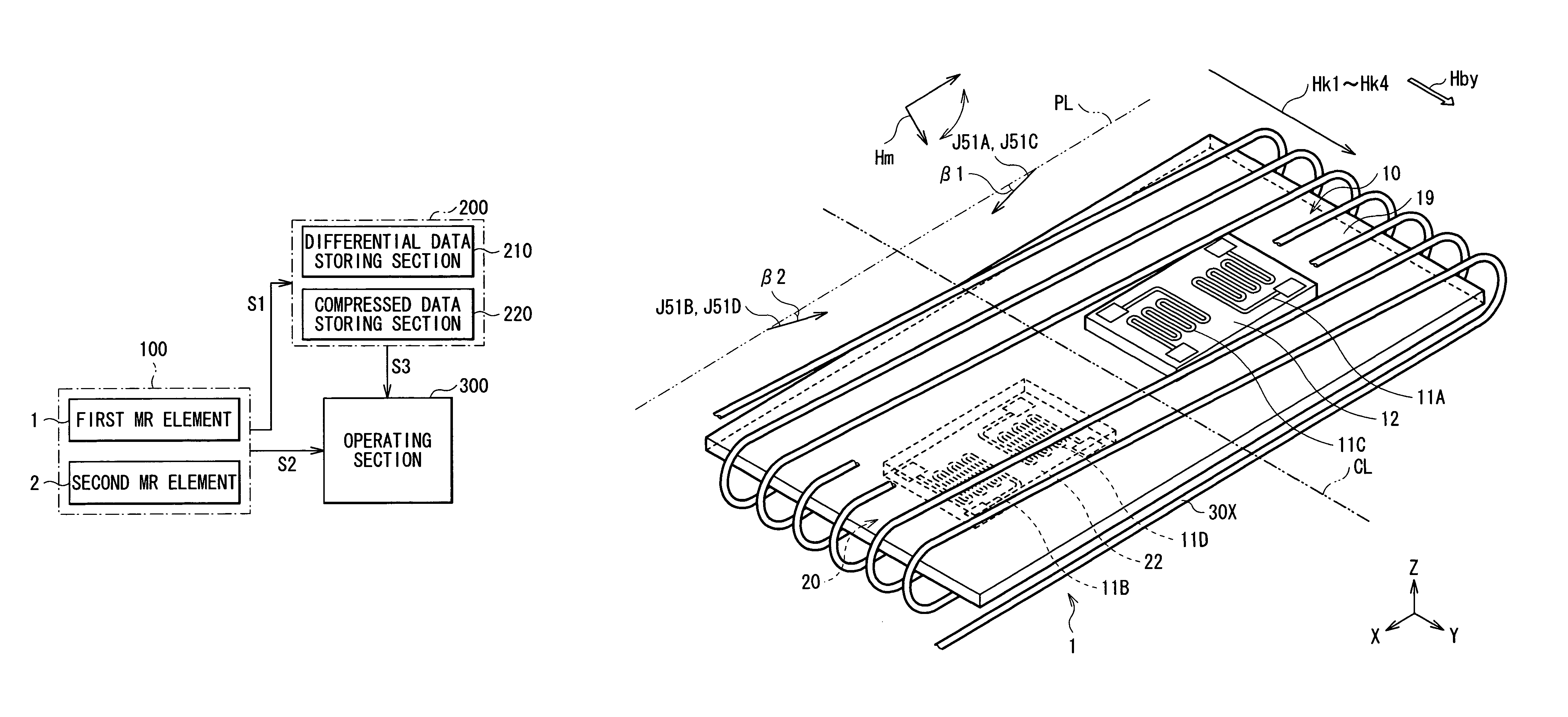
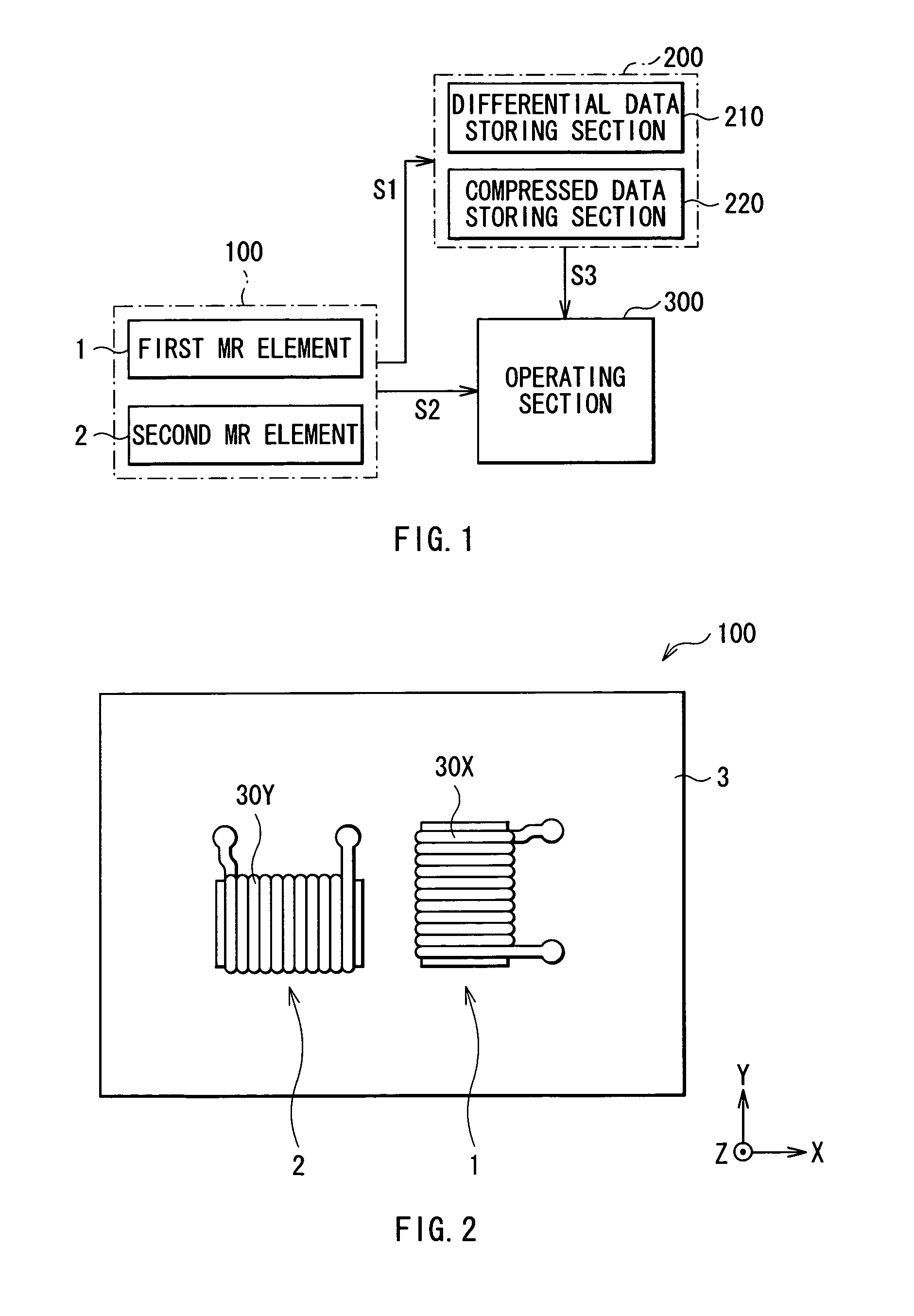
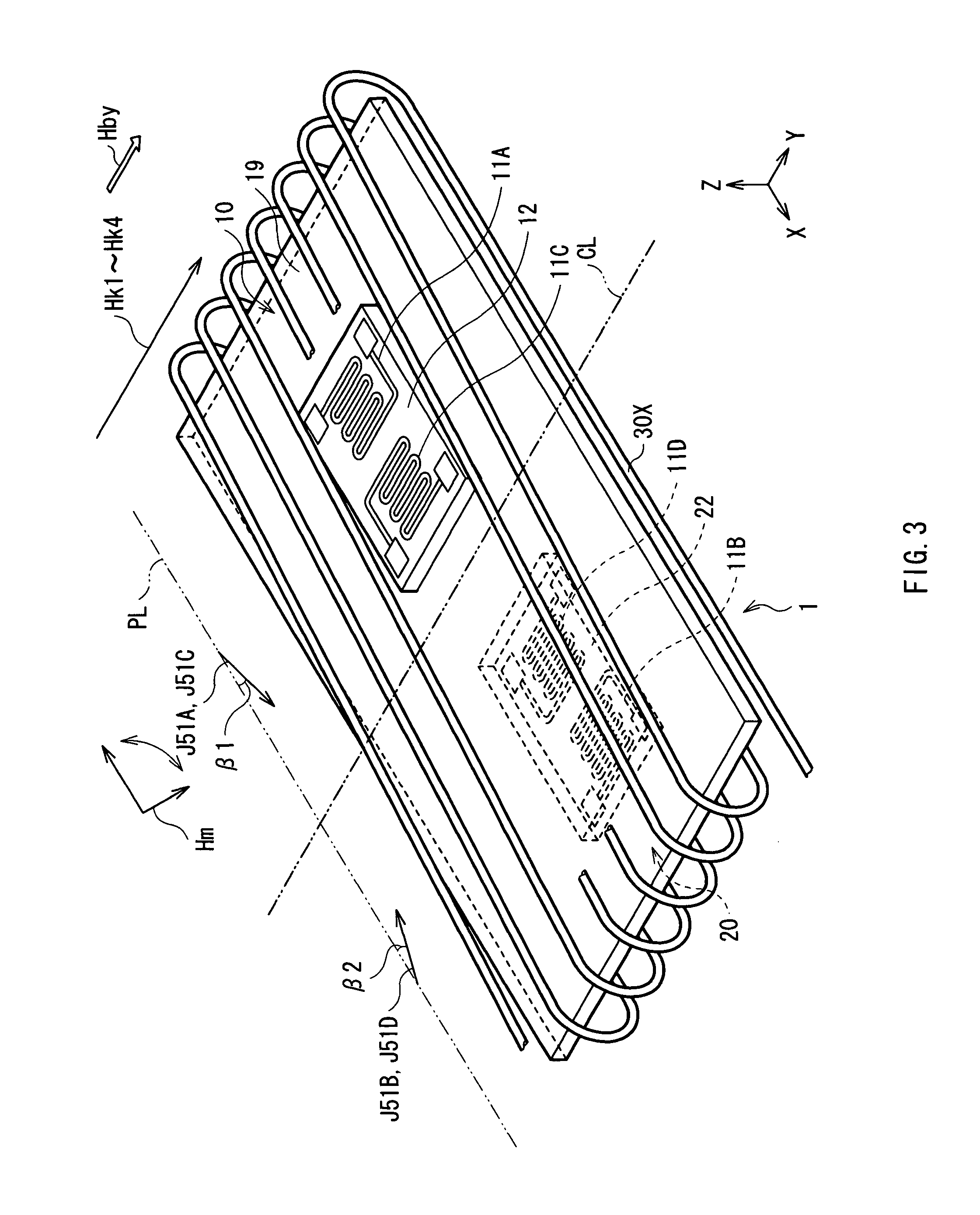
A magnetic direction sensor can detect at higher precision the magnitude and direction of a detected magnetic field. The magnetic direction sensor has a measuring section, a storage section and an operating section. The measuring section has first and second MR elements, and detects resistance values of these elements in accordance with an attitude change of the sensor and the presence or absence of a bias magnetic field to be applied through a coil in a direction orthogonal to a magnetization direction of each pinned layer in the first and second MR elements. The storage section stores fixed data invariable in response to a detected magnetic field direction, in resistance values of these elements measured by the measuring section. The operating section calculates a detected magnetic field vector from variable data of resistance values of these elements measured by the measuring section, and fixed data stored in the storage section.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Apparatus for the production of pocketed coil springs
InactiveUS6922895B1Easy to createEasy to modifyStuffed mattressesSpring mattressesCoil springEngineering
Owner:SPRINGFORM TECH
Trilateral poly-dimensional bar code easy for omnibearing recognition and reading method thereof
InactiveCN1908955ASimple correctionFast recognitionCharacter and pattern recognitionSensing record carriersGraphicsComputer vision
The trilateral multiple-dimension strap code convenient to omnibearing recognition comprises: three positioning images every with one positioning point on three angles respectively, and information area with multiple modules with chroma value corresponding to data value. When recognizing, scanning and searching globally to match three images and obtain positioning point coordinate; solving 6 affine transformation coefficients and the information area module size; obtaining the corresponding position of different module in image; finally, acquiring pixel chroma value for module data. This invention is simple and efficient.
Owner:BMC MEDICAL
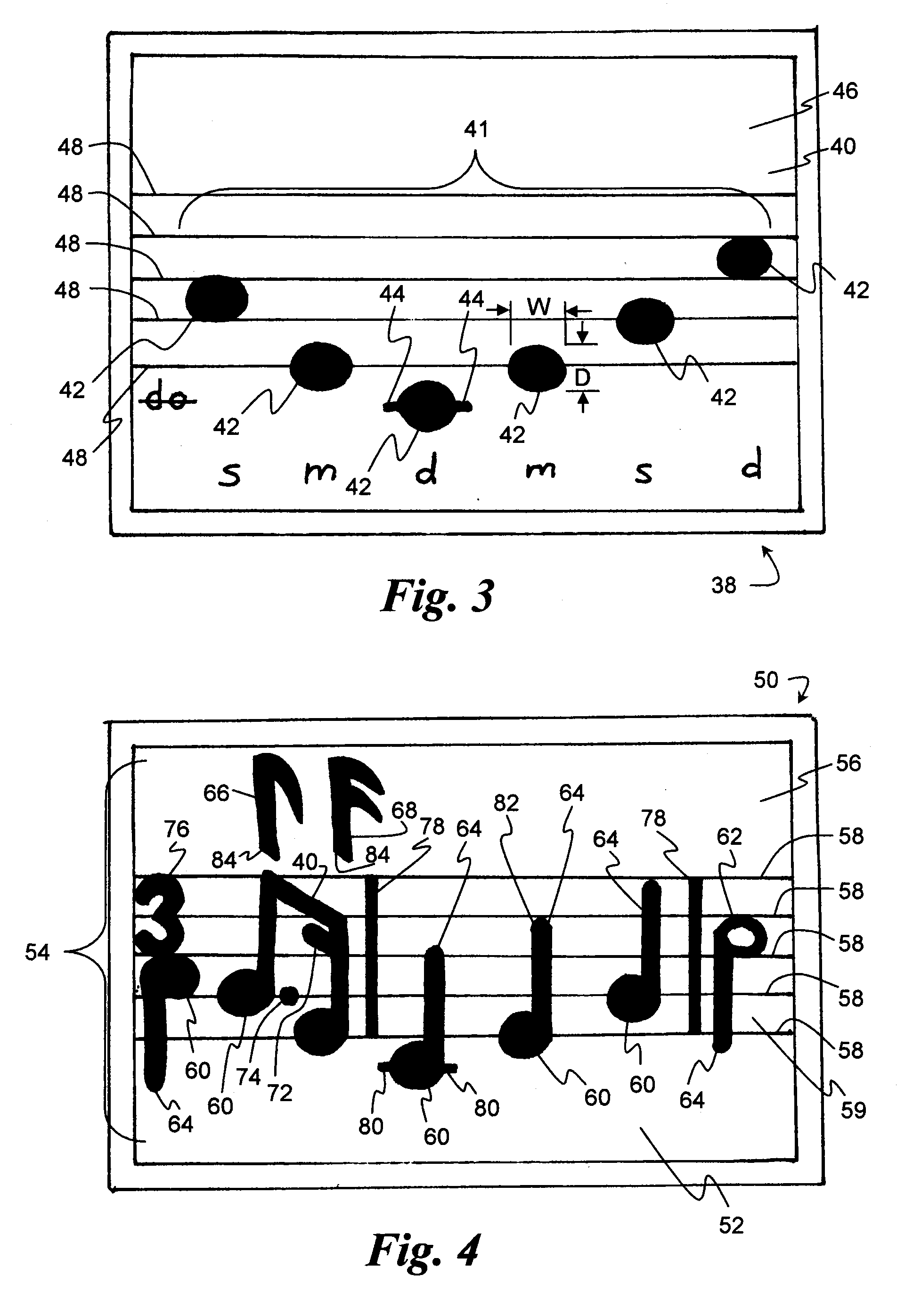
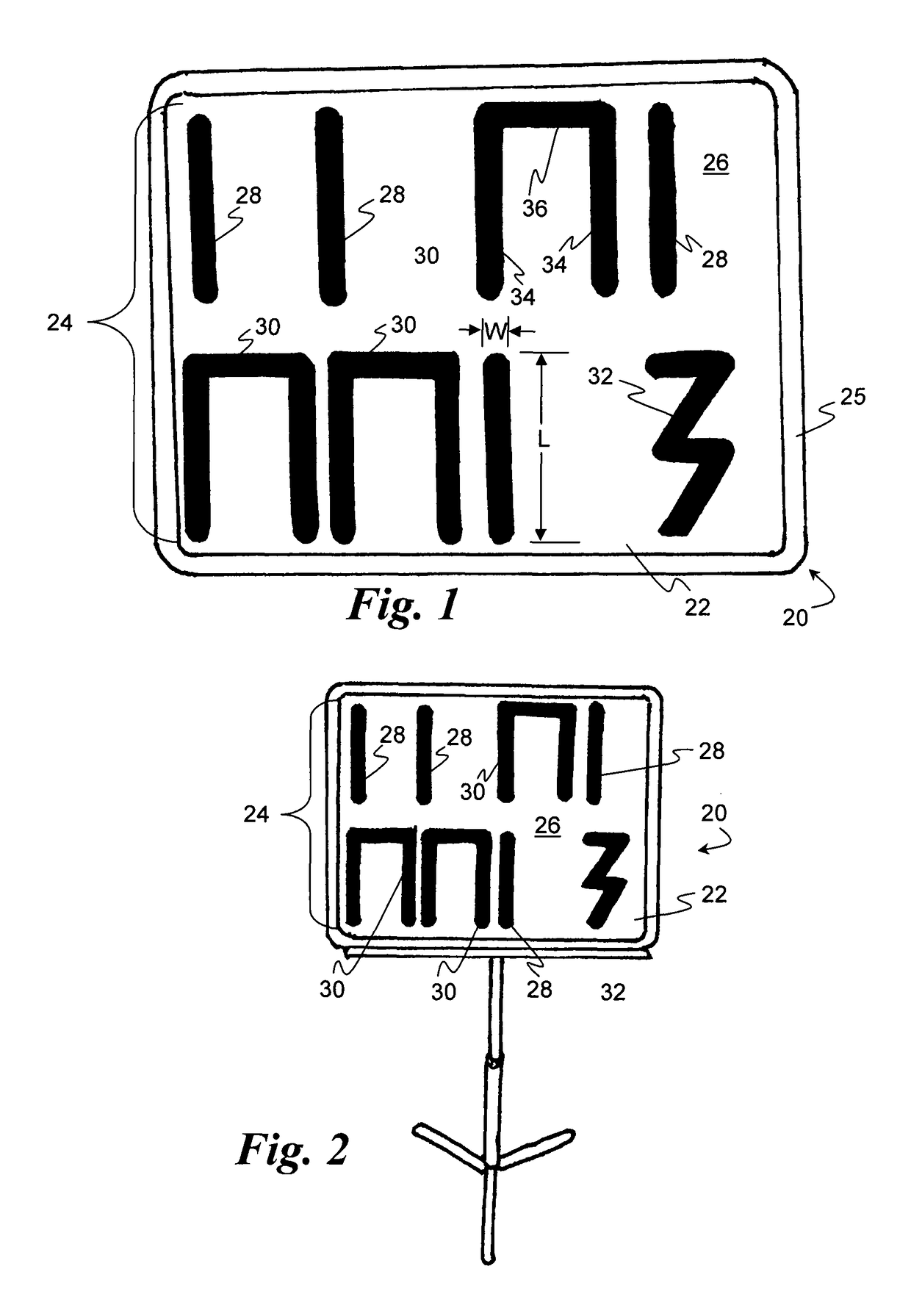
Manipulative system for teaching musical notation
Progressive systems and methods for enabling music students to easily notate the pitch and / or rhythm of musical compositions using three-dimensional manipulative members representing musical notation symbols. The members are adapted to removably affix to a workspace, such as a magnetic white board surface to notate a musical composition.
Owner:ARMSTRONG ROBIN ELIZABETH
Electro-optical device and electronic instrument
ActiveUS20160109752A1Suppression of uneven brightnessEasy to correctProjectorsColor television detailsElectronic instrumentEngineering
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
A method of eliminating deformation of a wax mould for an ultrathin elongated working blade of a turbine
ActiveCN104525853AEffective control of deformationSimple correctionFoundry mouldsFoundry coresWaxAviation
The invention relates to a method of eliminating deformation of a wax mould for an ultrathin elongated working blade of a turbine, and belongs to the technical field of manufacturing of blades of aviation engines. The method overcomes disadvantages in the prior art, provides a scheme of carrying and installing the blade wax mould by utilizing a wax mould clamping fixture, and discloses a design scheme of the wax mould clamping fixture. In an actual development and production process of a turbine working blade, because the wax mould clamping fixture is utilized to carry and install the blade wax mould, deformation of the blade wax mould is effectively controlled, and the deformation amount of the turbine working blade manufactured by utilization of the blade wax mould is reduced from original about 1 mm to now about 0.3 mm. Because the deformation amount is reduced, blade correction becomes relatively easy, thus avoiding generation of correction cracks, increasing the yield of precision casting of the turbine working blade by about 20%, largely reducing the rejection rate of the blade and largely saving the production cost.
Owner:SHENYANG LIMING AERO-ENGINE GROUP CORPORATION
Circuit arrangement and method for determining a frequency drift in a phase locked loop
InactiveUS20060067454A1Increase accuracyAvoid errorPulse automatic controlAngle demodulation by phase difference detectionEngineeringCharge pump
A circuit arrangement for determining a frequency drift in a phase locked loop includes a type I phase locked loop having a phase comparator, a charge pump, a loop filter, an oscillator and also a frequency divider in a feedback path of the control loop. A device is coupled to the phase locked loop for the purpose of determining a pulse length of the actuating voltage signal at at least two different times during an operation of the control loop. Furthermore, a computing unit is connected to an output of the device. It is designed for forming a difference between the pulse lengths at the at least two different times, as a result of which a phase and frequency drift of an output signal of the control loop can be determined.
Owner:INTEL CORP +1
Immunoassay and immunoassay apparatus
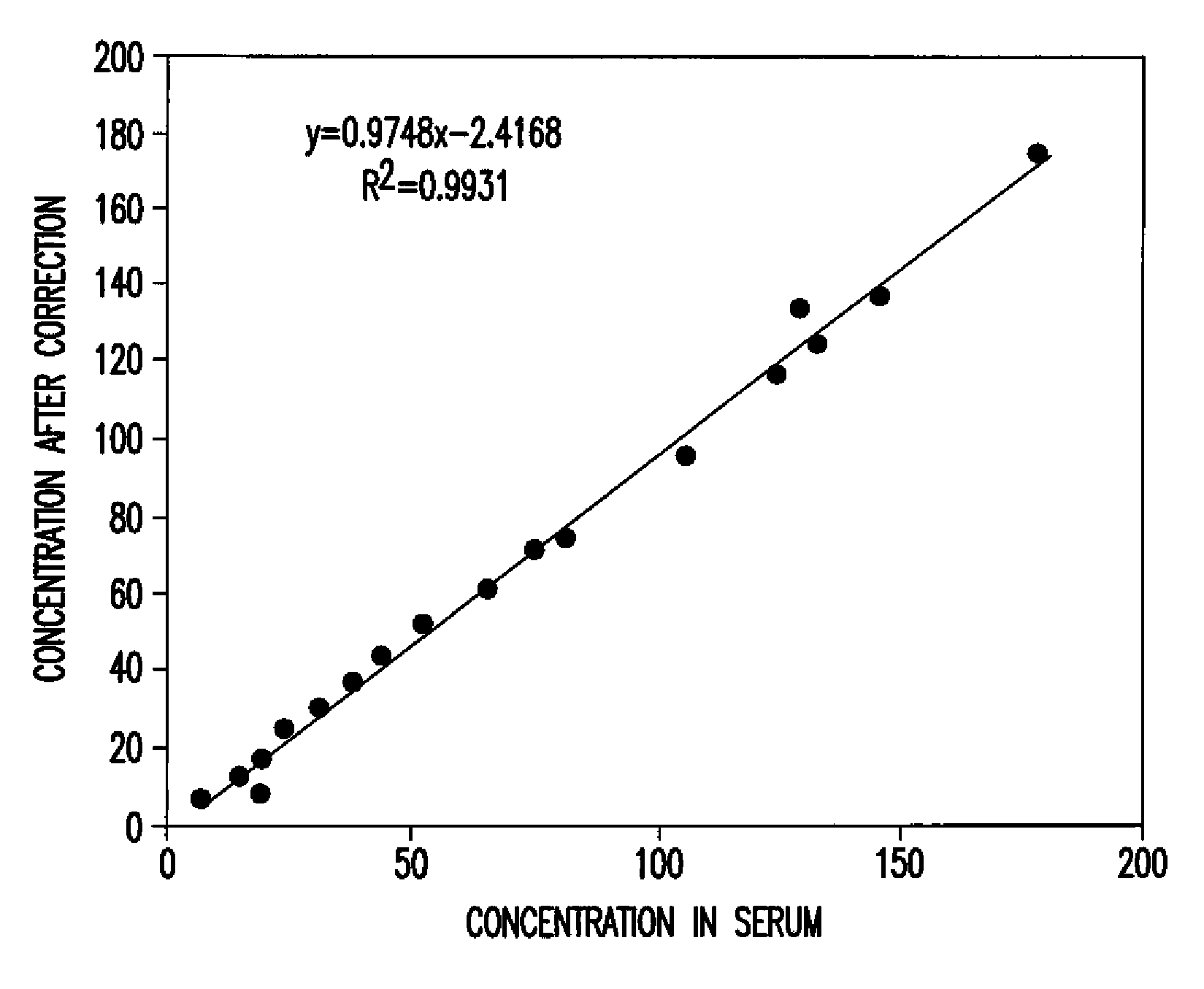
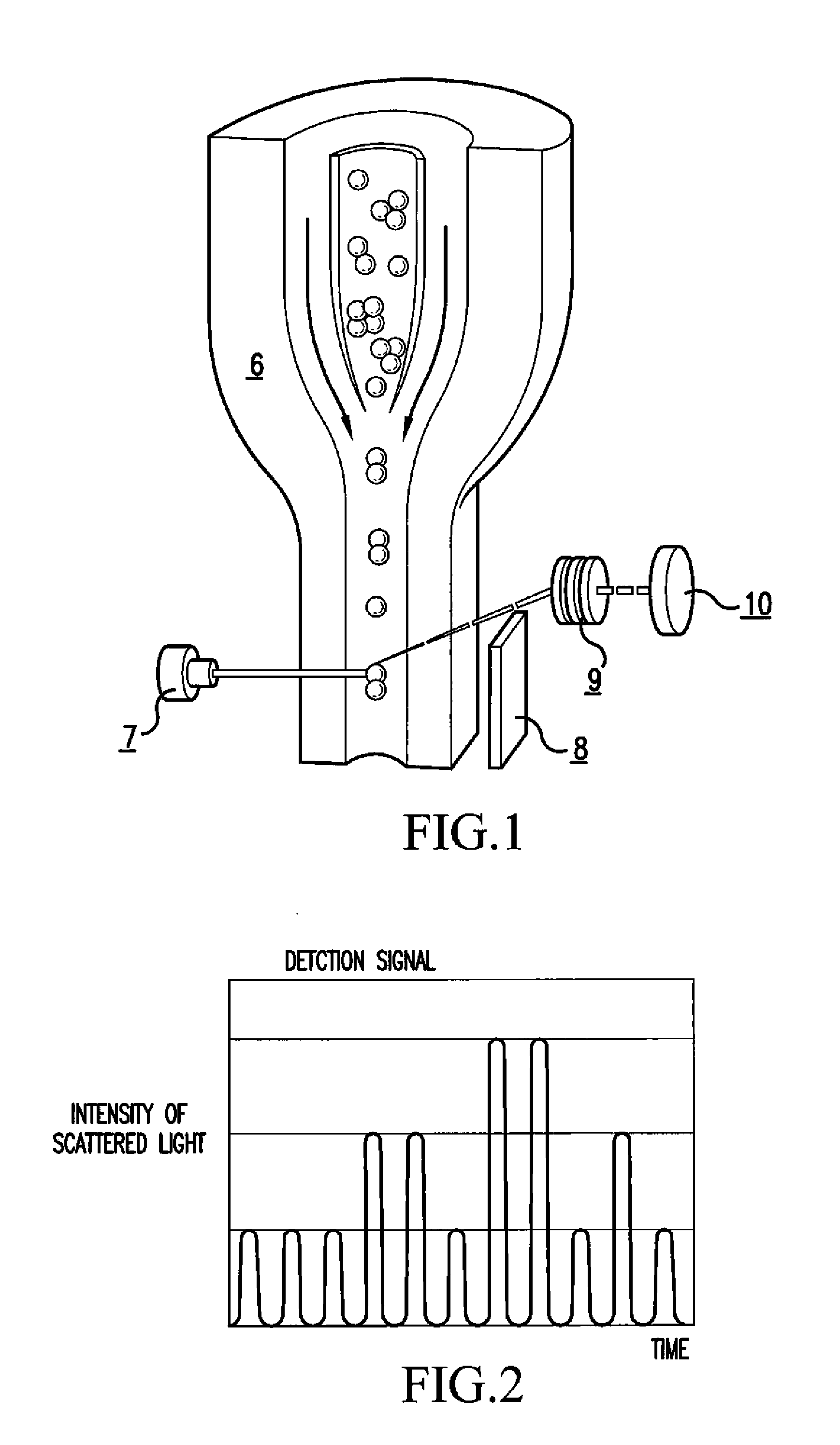
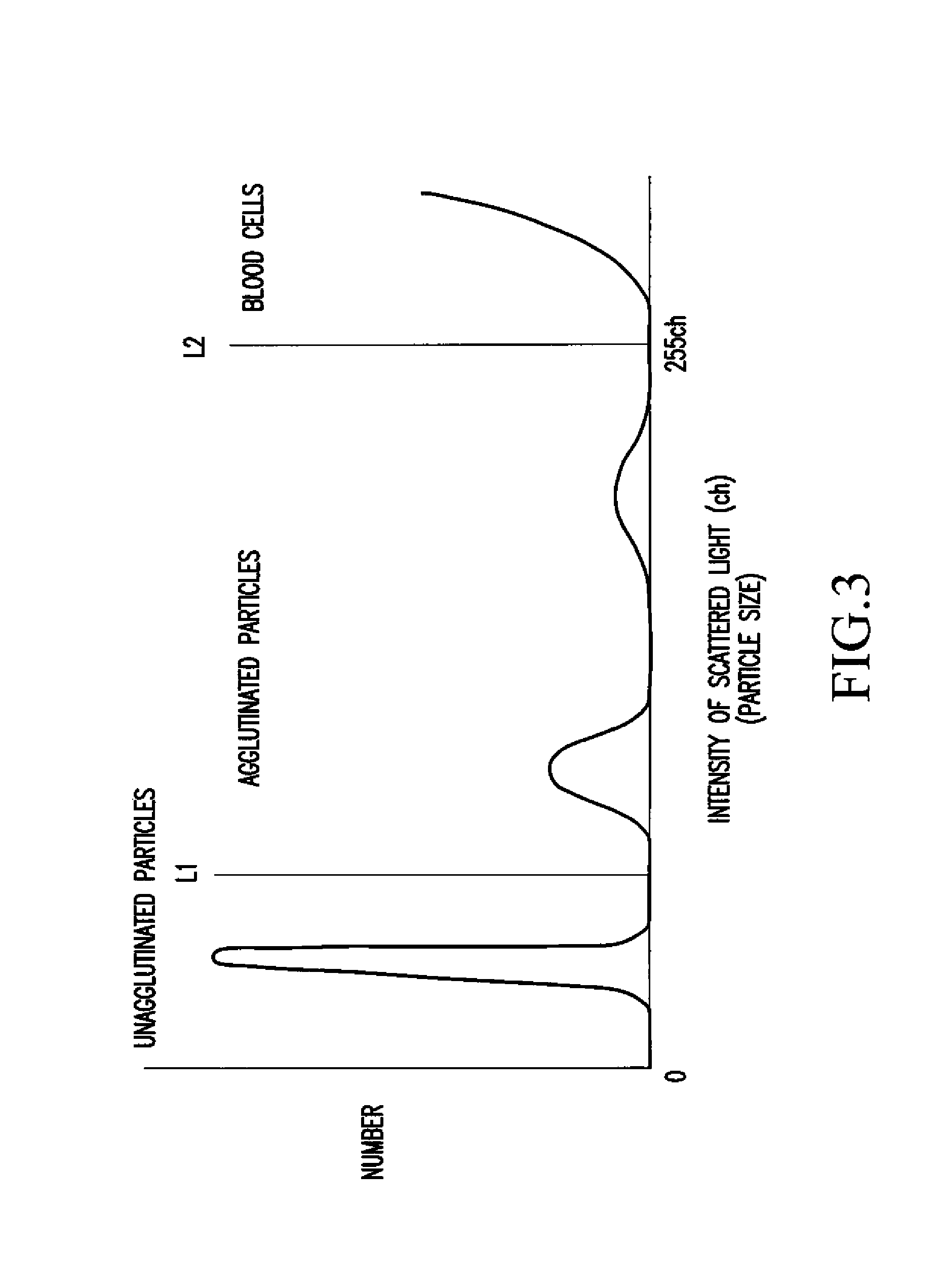
InactiveUS7390677B2Highly accurate immunoassaySimple correctionBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsValue setLaser light
An immunoassay comprises the steps of: (a) mixing a whole blood sample with sensitized insoluble carrier particles smaller than erythrocytes to cause an immune agglutination reaction; (b) introducing the resulting immune agglutination reaction mixture including agglutinated particles and unagglutinated particles to a flow cell, irradiating the particles passing through the flow cell with laser light, and detecting scattered lights generated thereby; (c) setting a threshold value for distinguishing unagglutinated particles from agglutinated particles and a threshold value for distinguishing the agglutinated particles from blood cells with regard to intensity of the scattered light; and (d) distinguishing and counting the unagglutinated particles, the agglutinated particles and the blood cells from the scattered lights detected in the step (b), in reference to the threshold values set in the step (c).
Owner:SYSMEX CORP
Zoom lens
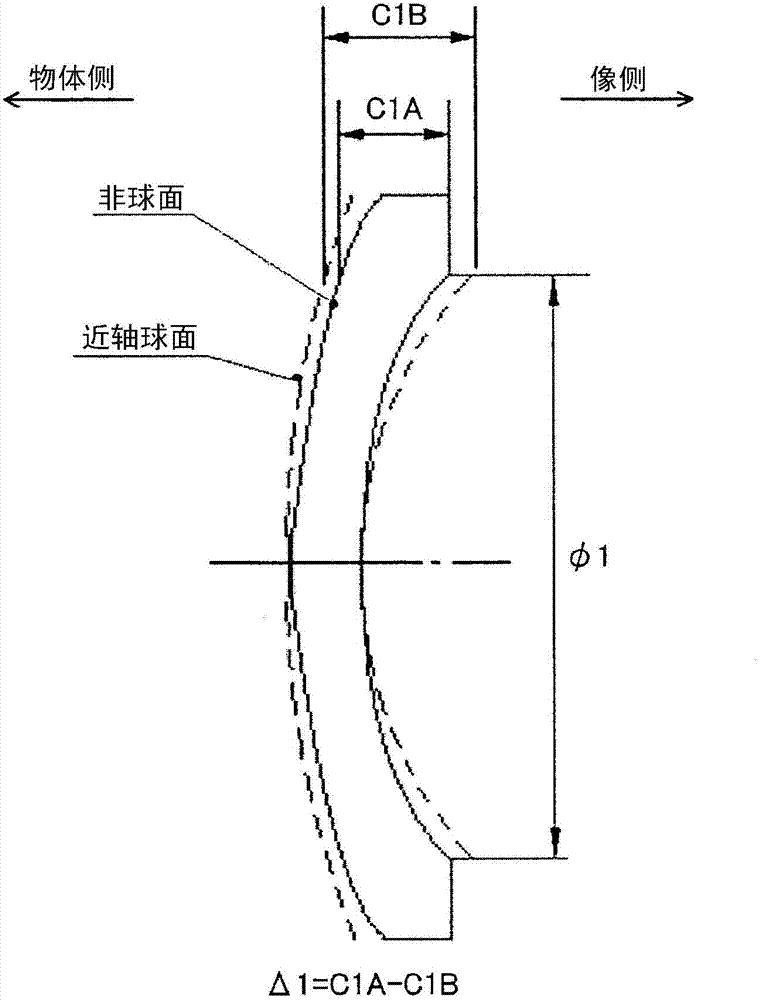
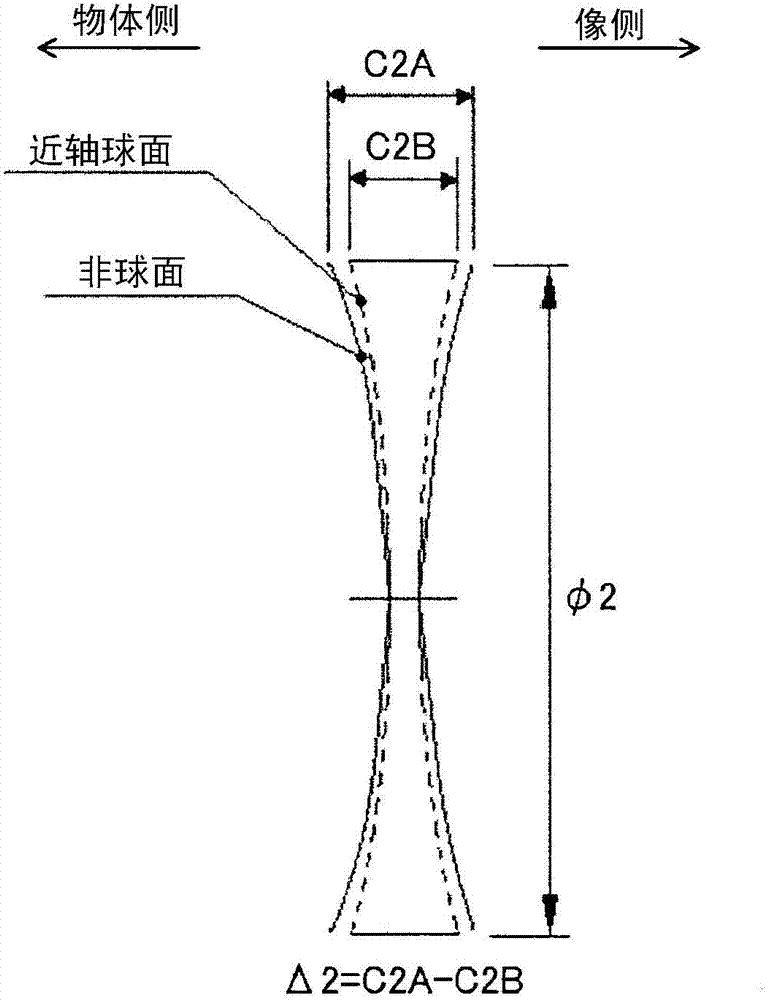
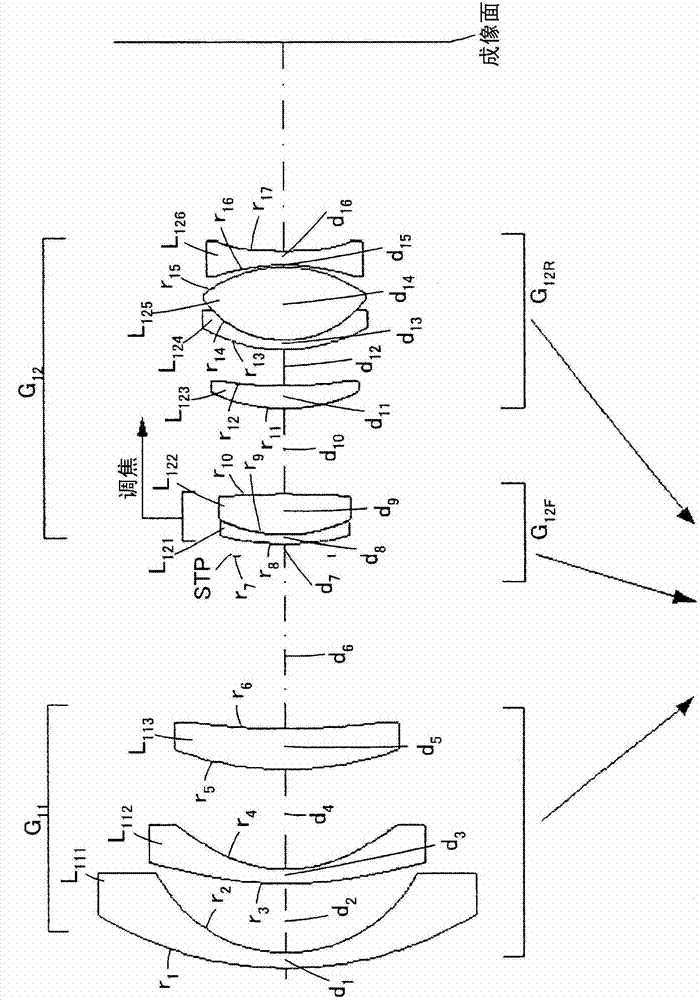
ActiveCN102955233ASimple correctionImprove imaging effectOptical elementsMiniaturizationImage formation
The present invention provides a zoom lens, which has a field angle more than 100 DEG, and is excellent in image formation performance, low in cost and small in shape. The zoom lens includes sequentially from an object side, a first lens section G11 having a negative refractive power and a second lens section G12 having a positive refractive power. The first lens section G11 includes sequentially from the object side, a negative lens L111, a negative lens L112, and a positive lens L113. Both surface of the negative lens L112 are aspheric. The second lens section G12 includes sequentially from the object side, a front group G12F having a positive refractive power and a rear group G12R having a positive refractive power. Both surfaces of a negative lens L126 included in the rear group G12R are aspheric. The zoom lens can maintain high imaging performance while achieving size reductions and wide angle views by satisfying given conditions.
Owner:TAMRON
Lens distortion correcting method and system used for automatic optical detection
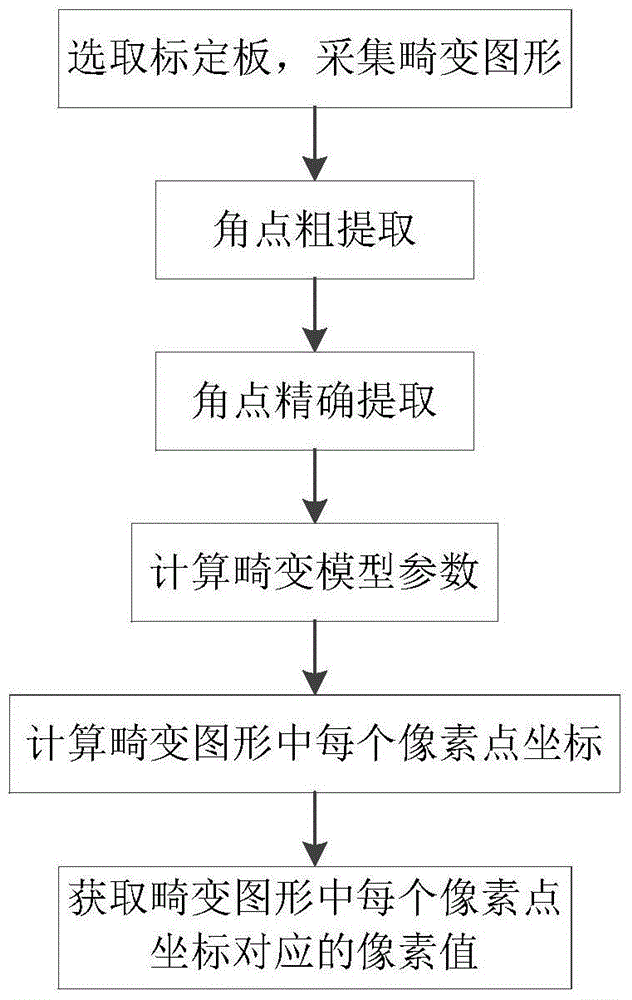
ActiveCN105701776AAccurate extractionImprove extraction accuracyImage enhancementImage analysisAngular pointModel parameters
The present invention discloses a lens distortion correcting method and system used for automatic optical detection. The method comprises the processes of selecting an uneven checkerboard as a calibration board, and obtaining a distorted figure; carrying out the angular point rough extraction on the distorted figure; carrying out the accurate angular point extraction on the roughly extracted dense angular points via the erosion and dilation and the blob analysis to obtain the real angular points; calculating a distortion model parameter between the coordinates of the real angular points and the ideal diagram angular point coordinates; according to the distortion model parameter and the coordinate of each pixel point in an ideal diagram, calculating the coordinate of each pixel point in the distorted figure; obtaining a pixel value corresponding to the coordinate of each pixel point in the distorted figure according to the coordinate of each pixel point in the distorted figure. According to the present invention, with the usage of the uneven checkerboard, the edge feature points are more and denser, so that the actual situation is approached better, and the calculated distortion model parameter is more reasonable. By the erosion and dilation and the blob analysis, the real angular points are extracted, the angular point extraction precision is high, and a distortion correction effect is good.
Owner:WUHAN JINGCE ELECTRONICS GRP CO LTD
Projection objective for a microlithographic projection exposure apparatus
InactiveUS20080304033A1Reduce immersionIncrease the number ofPhotomechanical exposure apparatusMicrolithography exposure apparatusResistImage resolution
Another approach to decrease the resolution is to introduce an immersion liquid having high refractive index into the gap that remains between a final lens element on the image side of the projection objective and the photoresist or another photosensitive layer to be exposed. Projection objectives that are designed for immersion operation and are therefore also referred to as immersion objective may reach numerical apertures of more than 1, for example 1.3 or 1.4. The term “immersion liquid” shall, in the context of this application, relate also to what is commonly referred to as “solid immersion”. In the case of solid immersion, the immersion liquid is in fact a solid medium that, however, does not get in direct contact with the photoresist but is spaced apart from it by a distance that is only a fraction of the wavelength used. This ensures that the laws of geometrical optics do not apply such that no total reflection occurs.
Owner:CARL ZEISS SMT GMBH
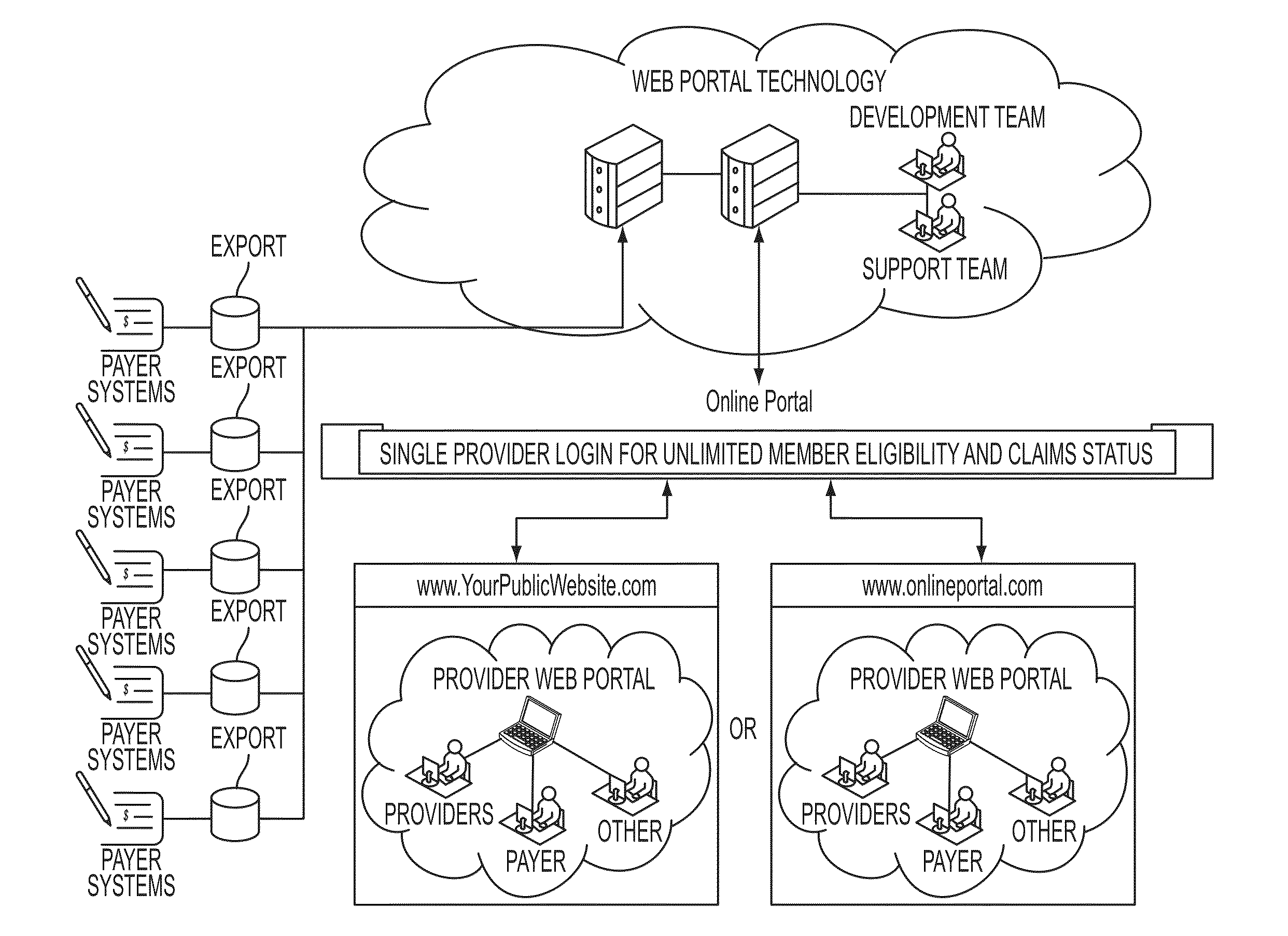
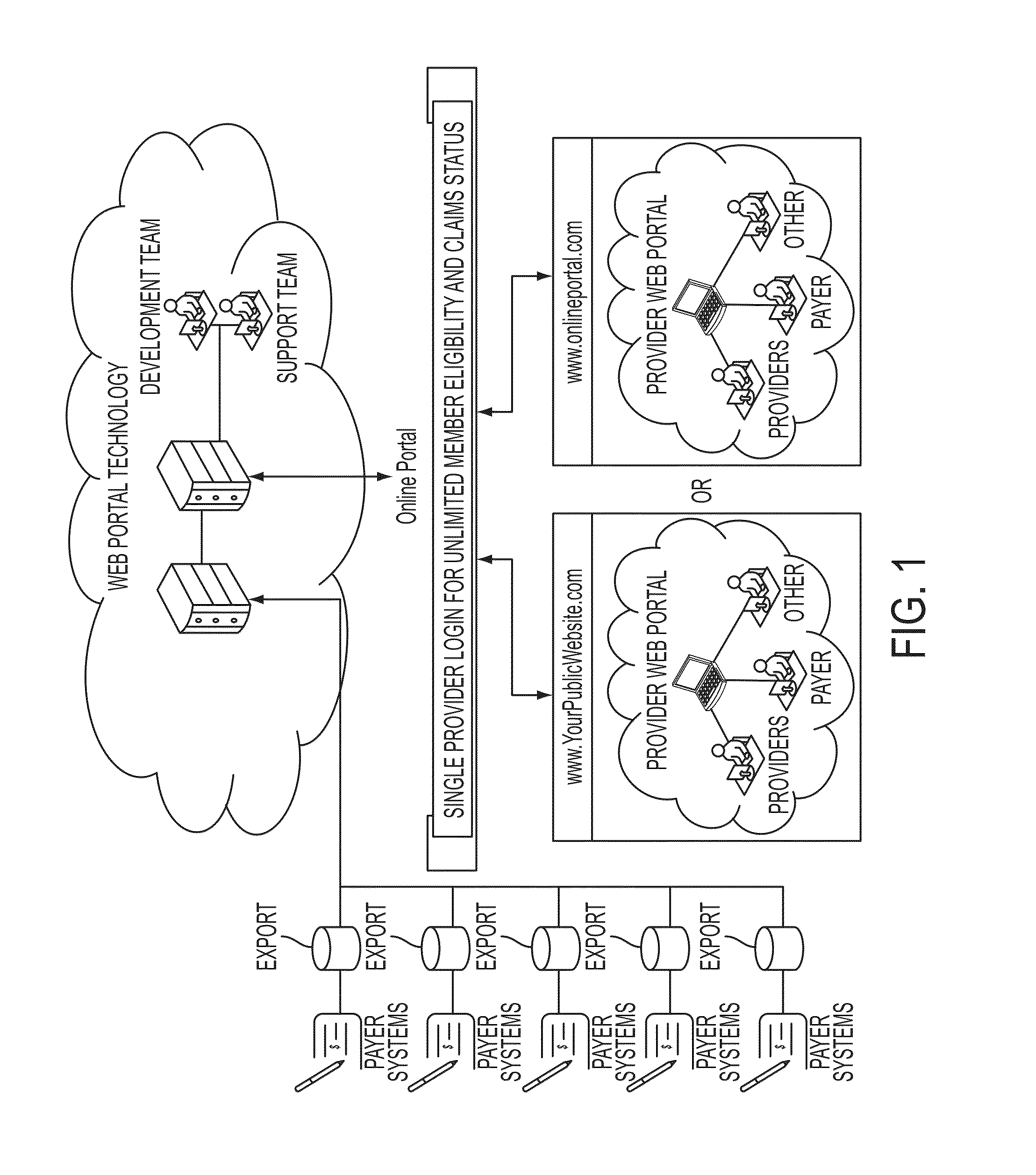
Method and system for verifying a user's healthcare benefits
InactiveUS20130159017A1Avoid mistakesCorrection of any claim errors much simplerFinanceOffice automationService provisionMedicine
The present invention provides a method and system by which a service provider is able to verify the benefit eligibility of a patient. Methods and systems of the claimed invention are used to create one or more queries to verify a patient's insurance benefits in a database to determine the eligibility of the claim. Embodiments of the invention are also used to verify a patient's claims history.
Owner:TPABENEFITS
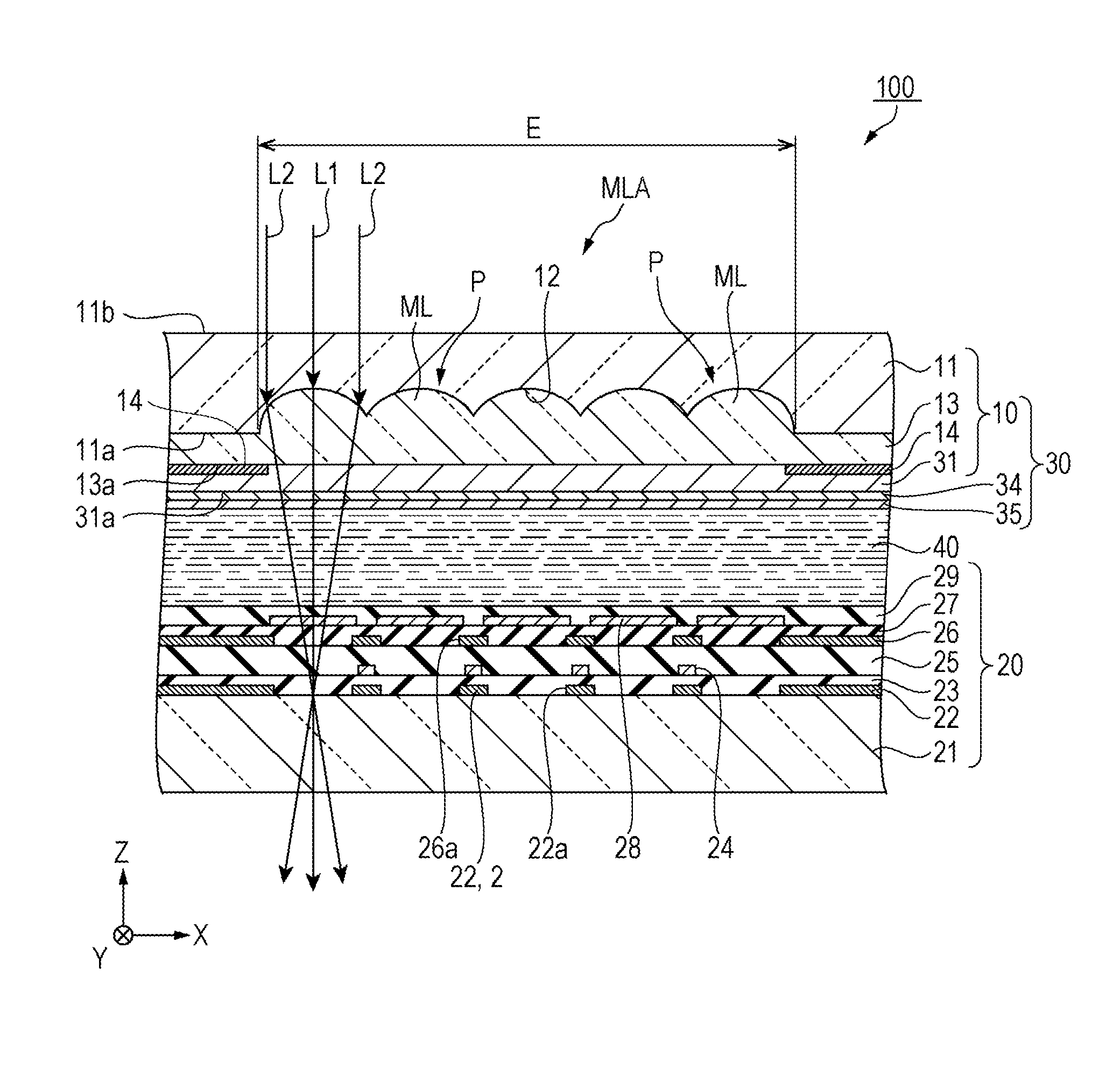
Colour Measurement Method and Colour Measurement Device
ActiveUS20160327431A1Simple correctionUniformity in useRadiation pyrometryColor measuring devicesMeasurement deviceMeasurement point
A colour measurement device includes a measurement array (MA) which includes: a plurality of illumination arrays (20, 30, 40) for exposing a measurement spot (MS) on a measurement object (MO) to illumination light in an actual illumination direction (2, 3, 4) in each case, and a pick-up array (50) for detecting the measurement light reflected by the measurement spot (MS) in an actual observation direction (5) and for converting it into preferably spectral reflection factors; and a controller for the illumination arrays and the pick-up array and for processing the electrical signals produced by the pick-up array. The controller is embodied to process the measured reflection factors on the basis of a correction model, such that distortions in the measurement values as compared to nominal illumination and / or observation directions, caused by angular errors in the illumination arrays and / or the pick-up array, are corrected.
Owner:X RITE SWITZERLAND
Fisheye image correction method and device and computer equipment
ActiveCN107749050ASimple correctionFlexible correctionImage enhancementImage correctionComputer vision
The invention relates to a fisheye image correction method and device. The fisheye image correction method comprises the steps of acquiring an optical imaging center of an initial fisheye image to becorrected, and converting image coordinates of the initial fisheye image into image physical coordinates; performing correction on the initial fisheye image according to a preset mapping relation to obtain a longitudinal repair image of the initial fisheye image; performing a primary rotation operation on the longitudinal repair image to obtain a rotated image, wherein the rotating angle of the primary rotation operation is odd times of 90 degrees; performing correction of the rotated image according to the mapping relation to obtain a preliminary repair image of the initial fisheye image; andperforming a secondary rotation operation on the preliminary repair image to obtain a target corrected image of the initial fisheye image, wherein the secondary rotation operation and the primary rotation operation are identical in angle and opposite in direction. According to the invention, the reading and writing efficiency of a memory in the image correcting process is improved, and the correcting process is simple and flexible.
Owner:ZHUHAI JIELI TECH
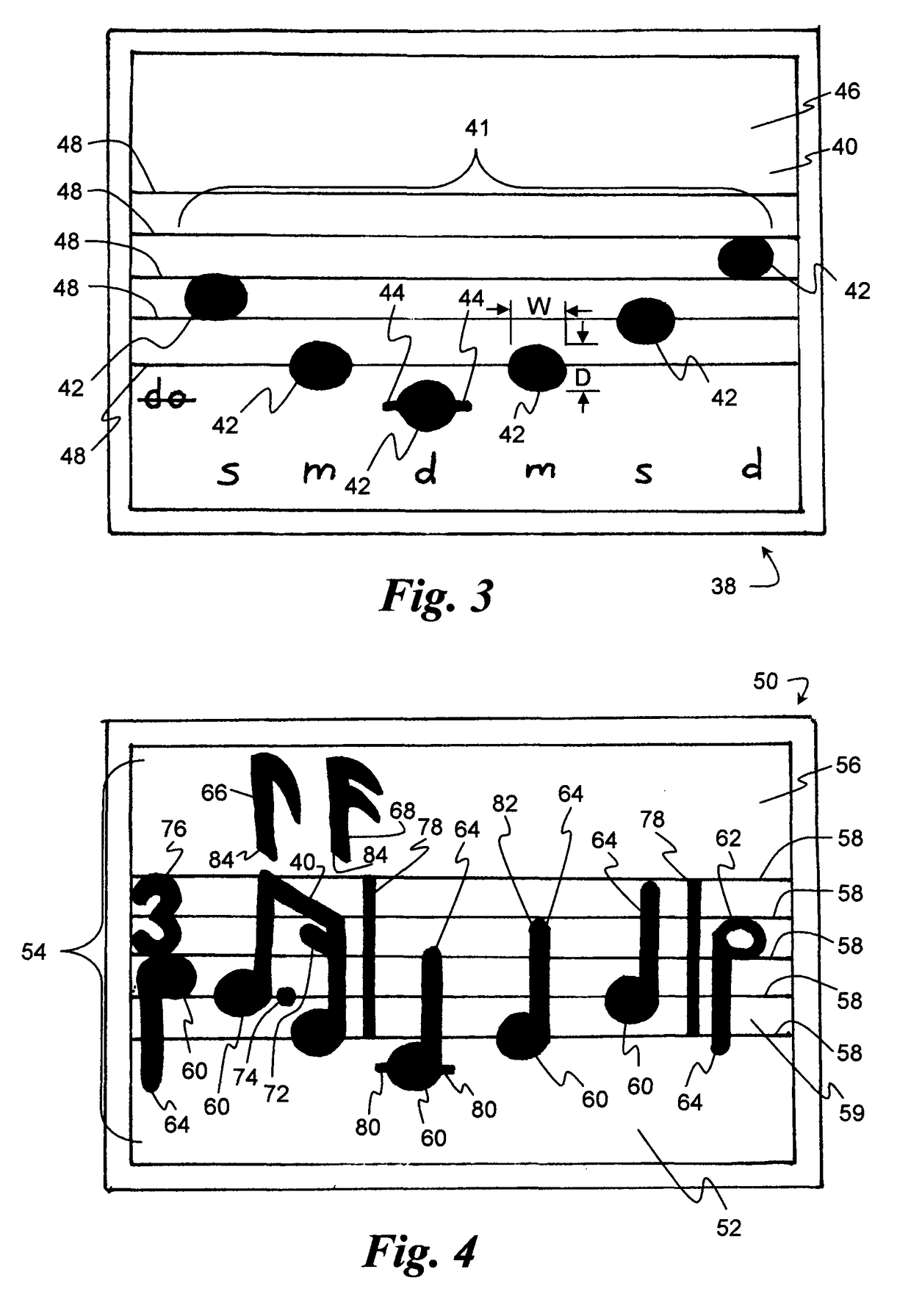
Manipulative system for teaching musical notation
Progressive systems and methods for enabling music students to easily notate the pitch and / or rhythm of musical compositions using three-dimensional manipulative members representing musical notation symbols. The members are adapted to removably affix to a workspace, such as a magnetic white board surface to notate a musical composition.
Owner:ARMSTRONG ROBIN ELIZABETH
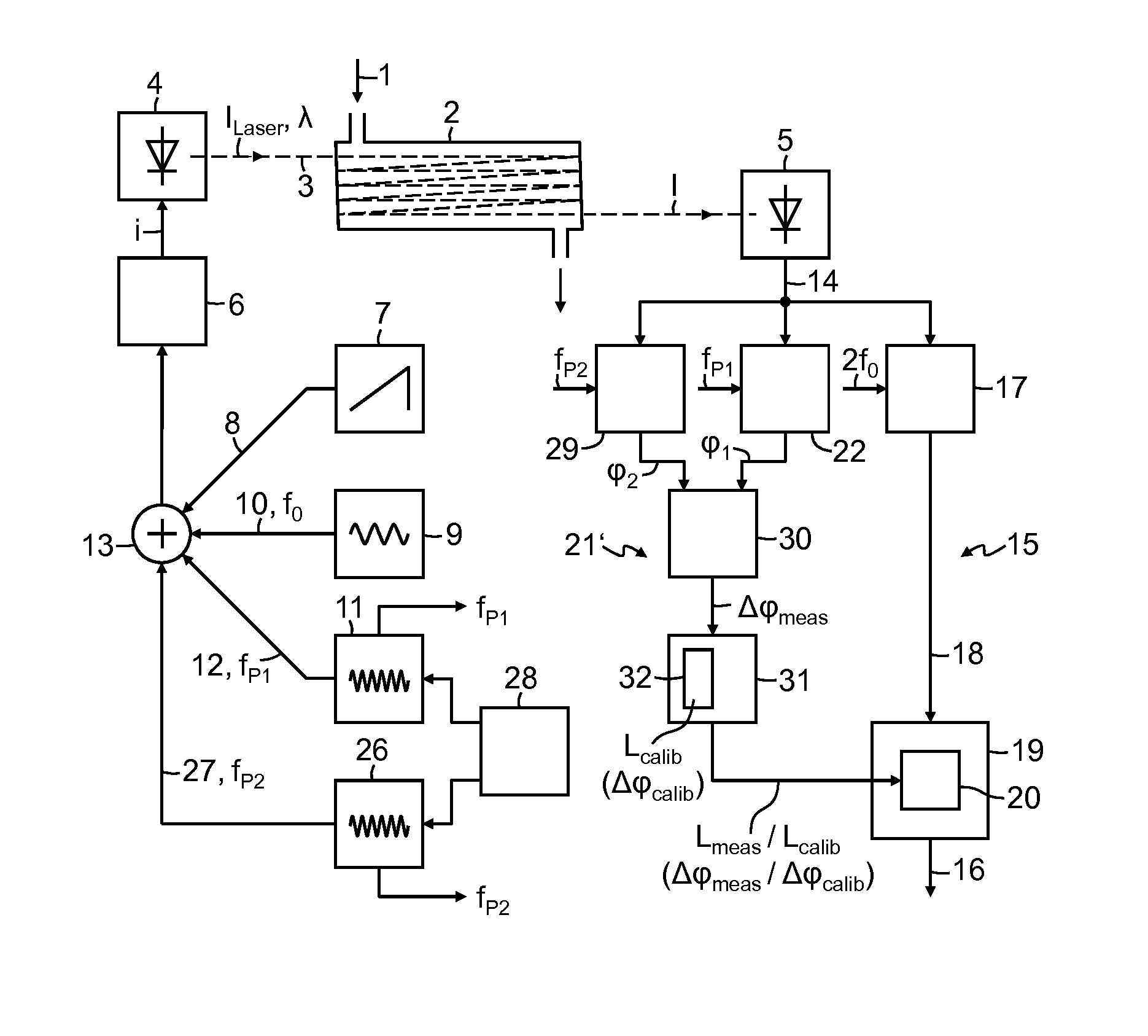
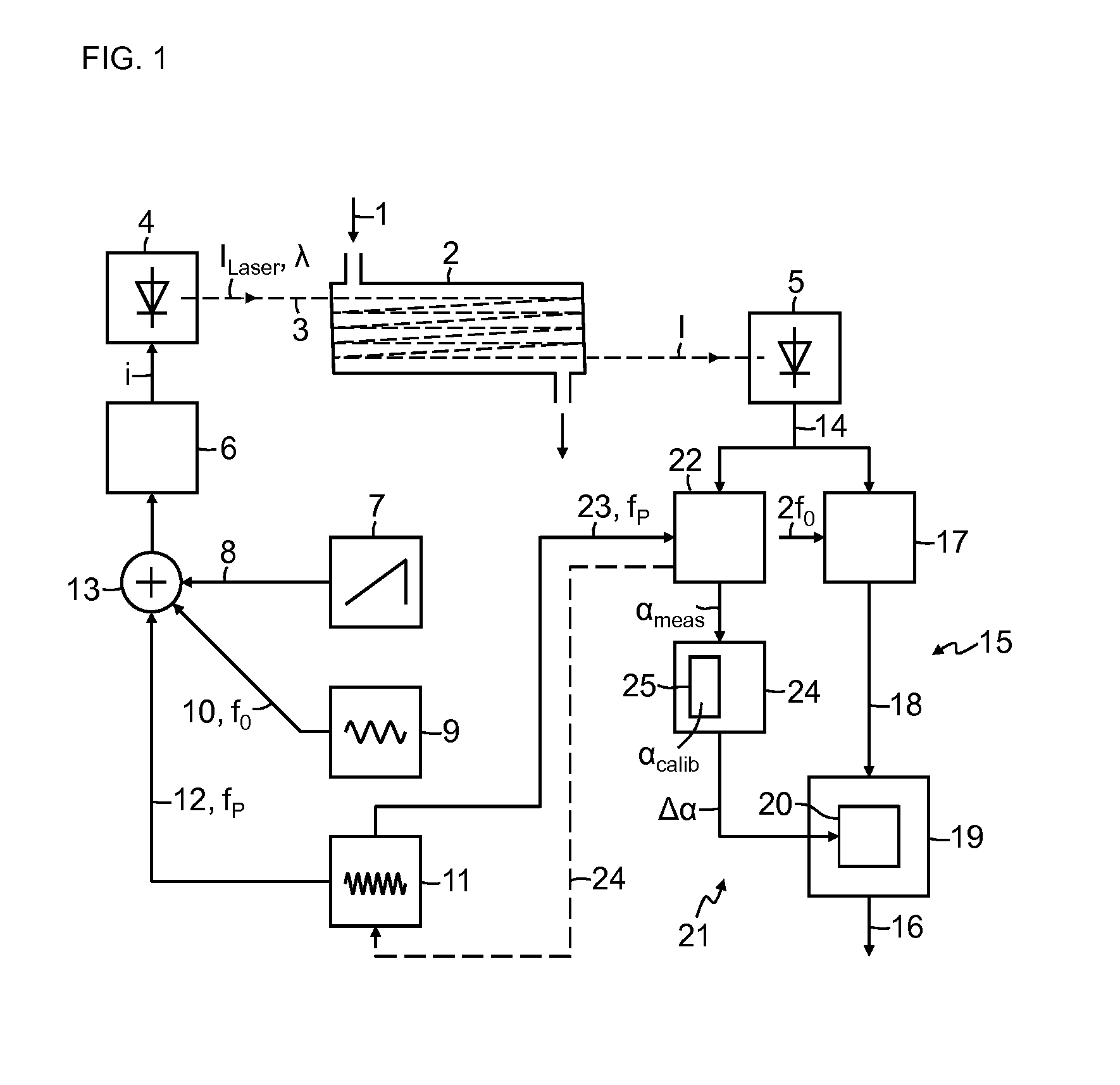
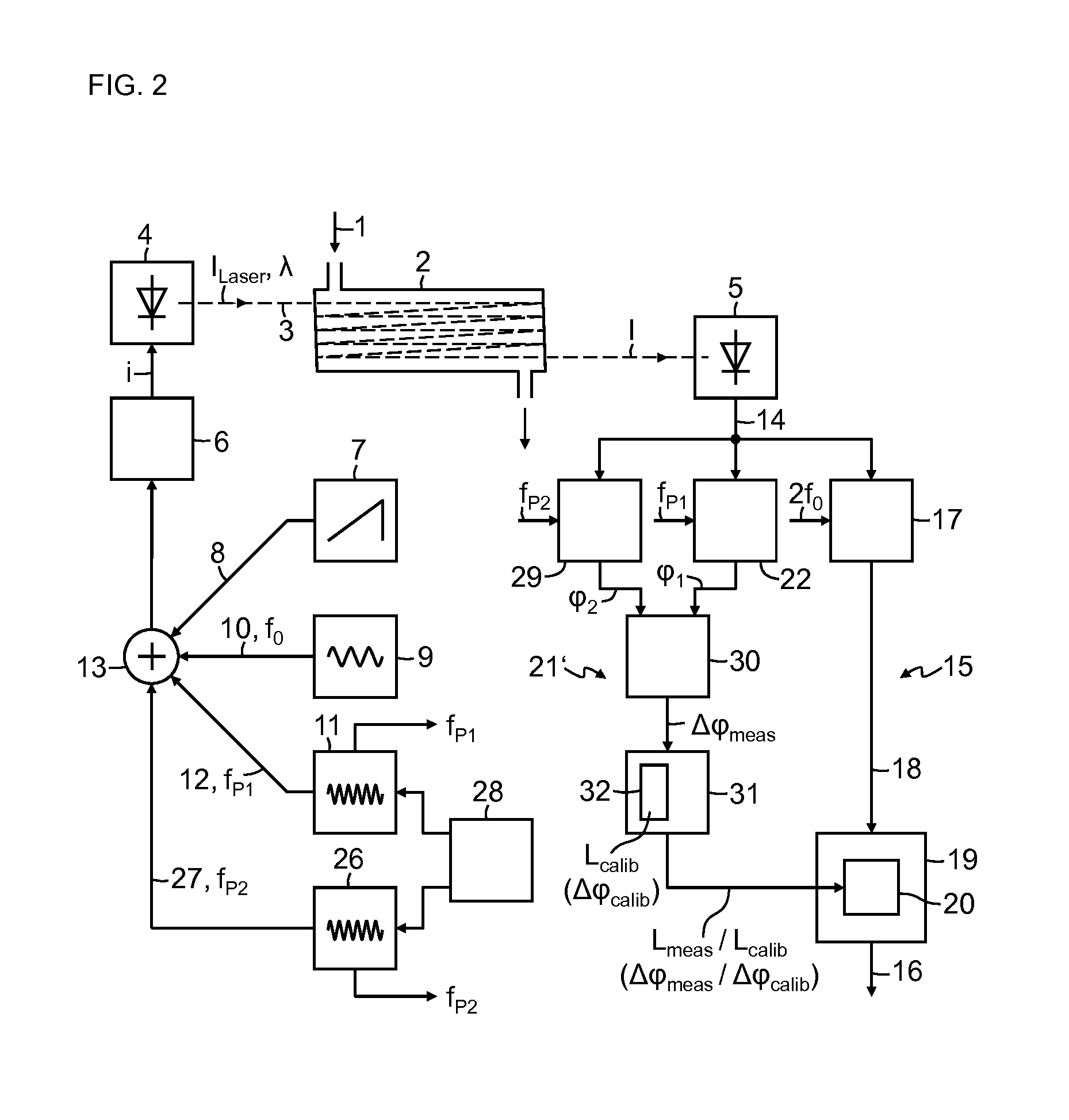
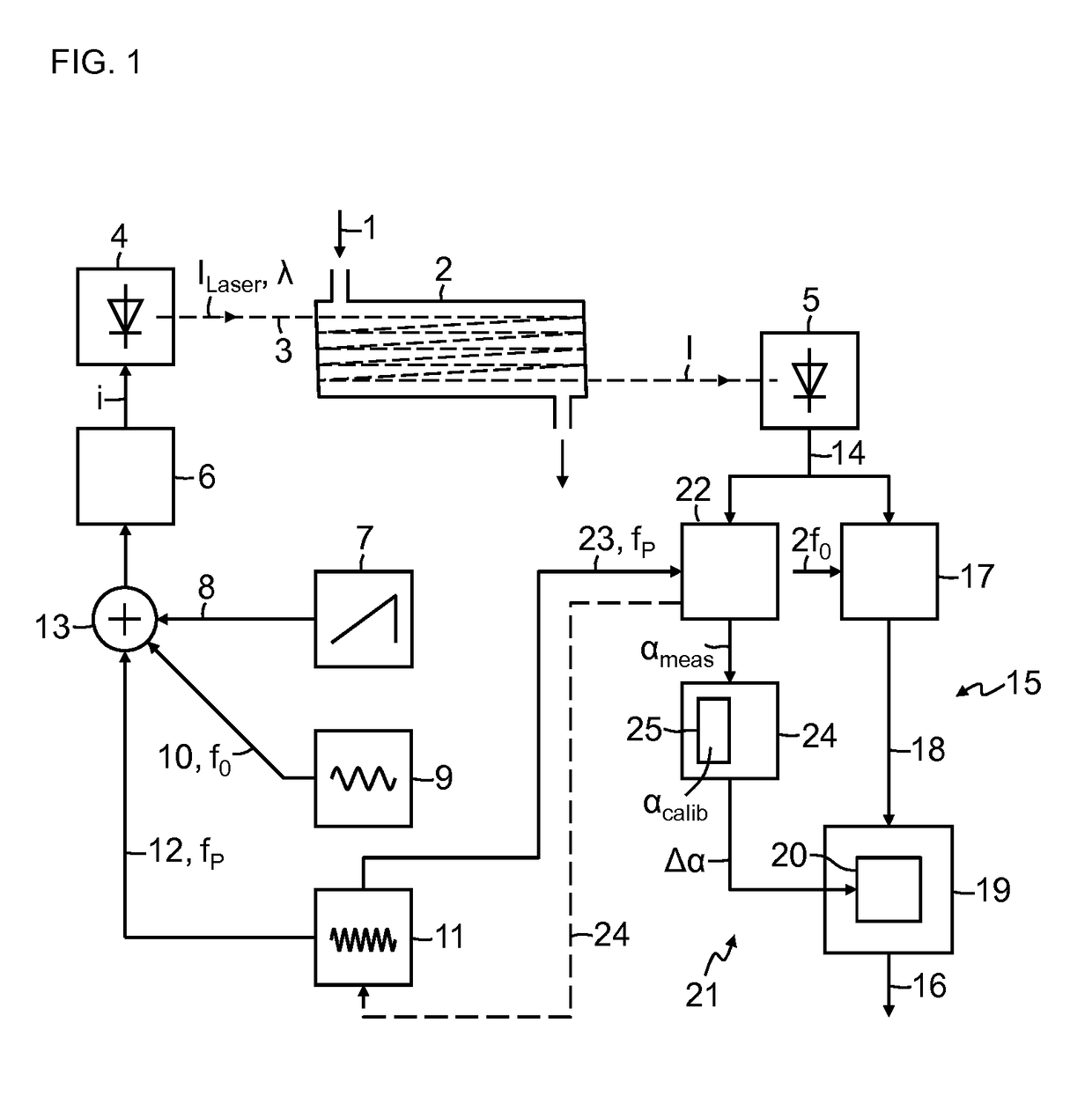
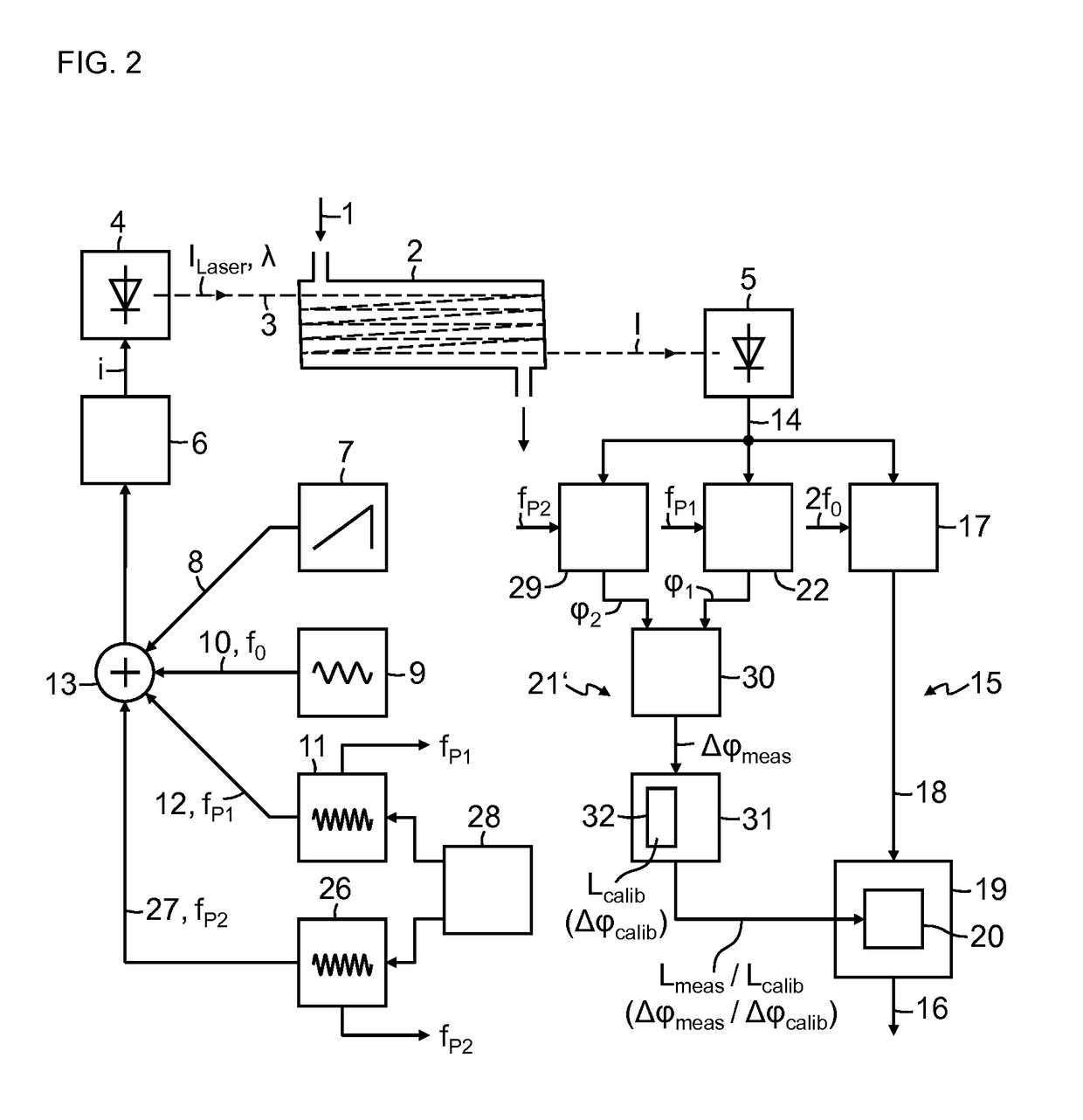
Absorption spectrometer and method for measuring the concentration of a gaseous component of interest in a measurement gas
ActiveUS20160047739A1High resolutionReduce selection requirementsRadiation pyrometryColor measuring devicesPhase sensitiveFrequency modulation
Owner:SIEMENS AG
System and methods for T1-based logging
ActiveUS7199580B2Efficient Data AcquisitionCompact and robust data setElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonanceData set
System and methods for using nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) T1 measurements for wireline, LWD and MWD applications and down-hole NMR fluid analyzers. The T1 measurements are characterized by insensitivity to motion, as the detrimental effects arising from tool motion or fluid flow are effectively reduced or eliminated. T1 measurements alone or in combination with other standard oil field measurements are shown to provide efficient data acquisition resulting in compact and robust data sets, the potential for substantially increased logging speeds, and simple methods for fluid typing, including direct and robust identification of gas.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
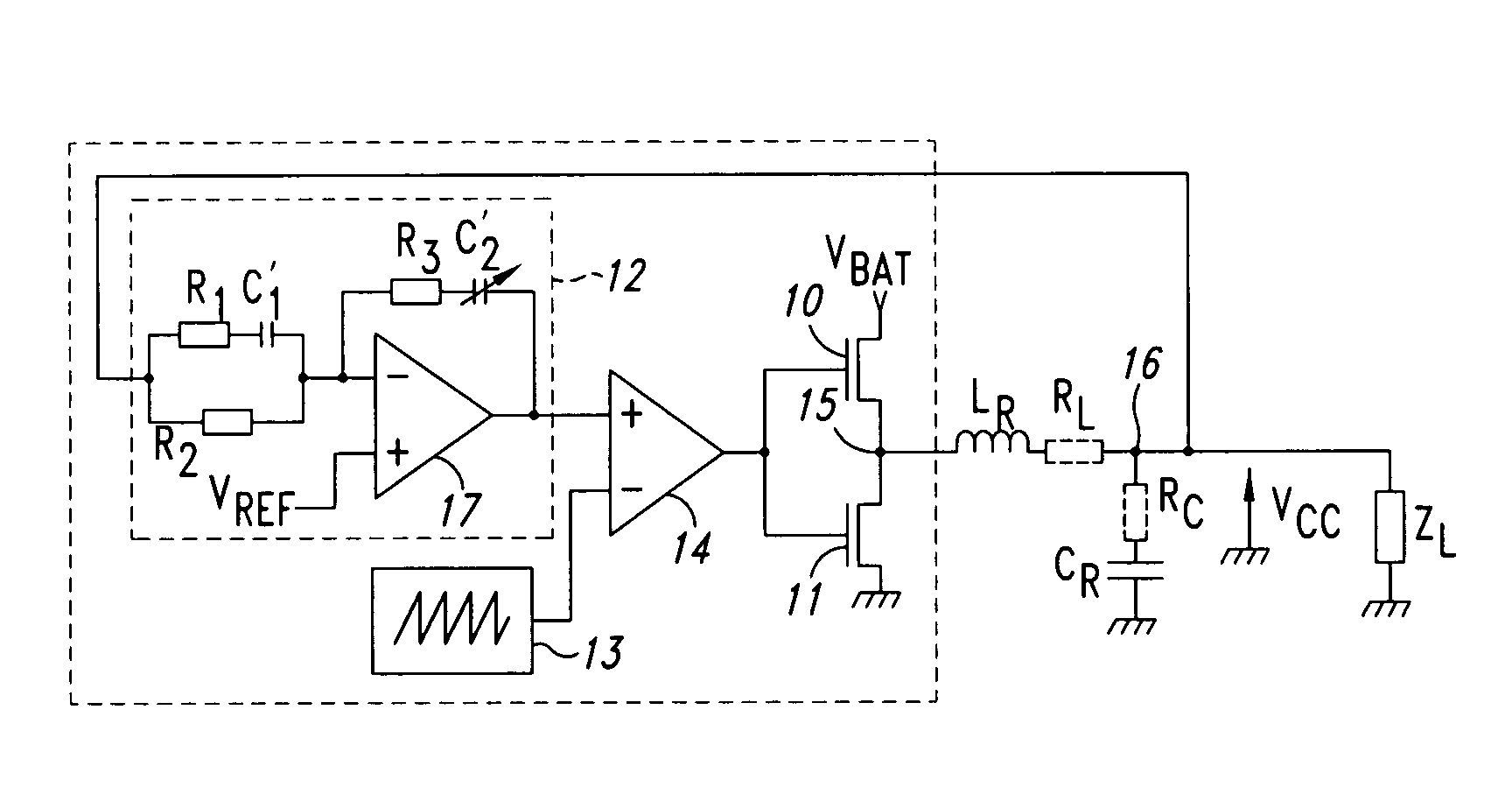
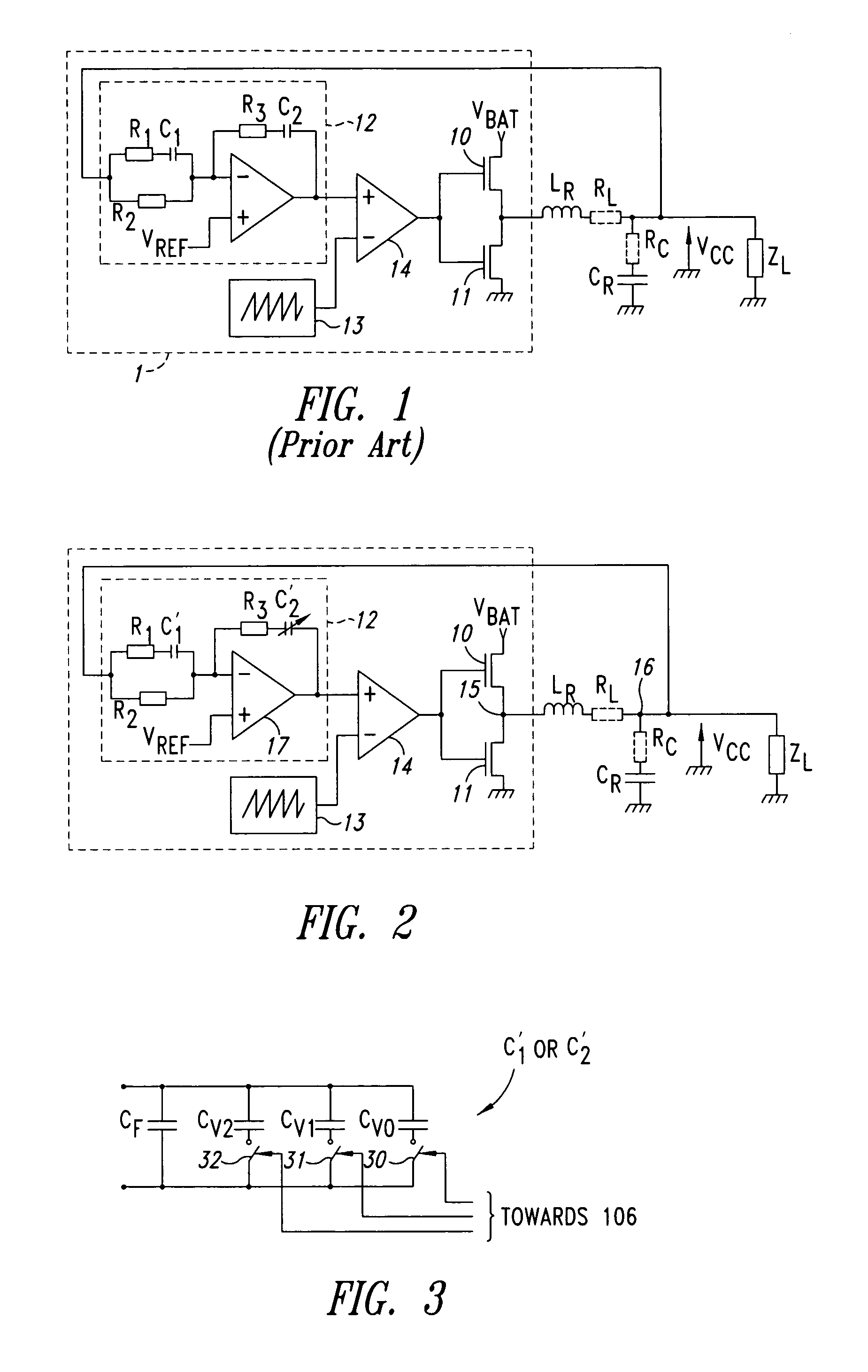
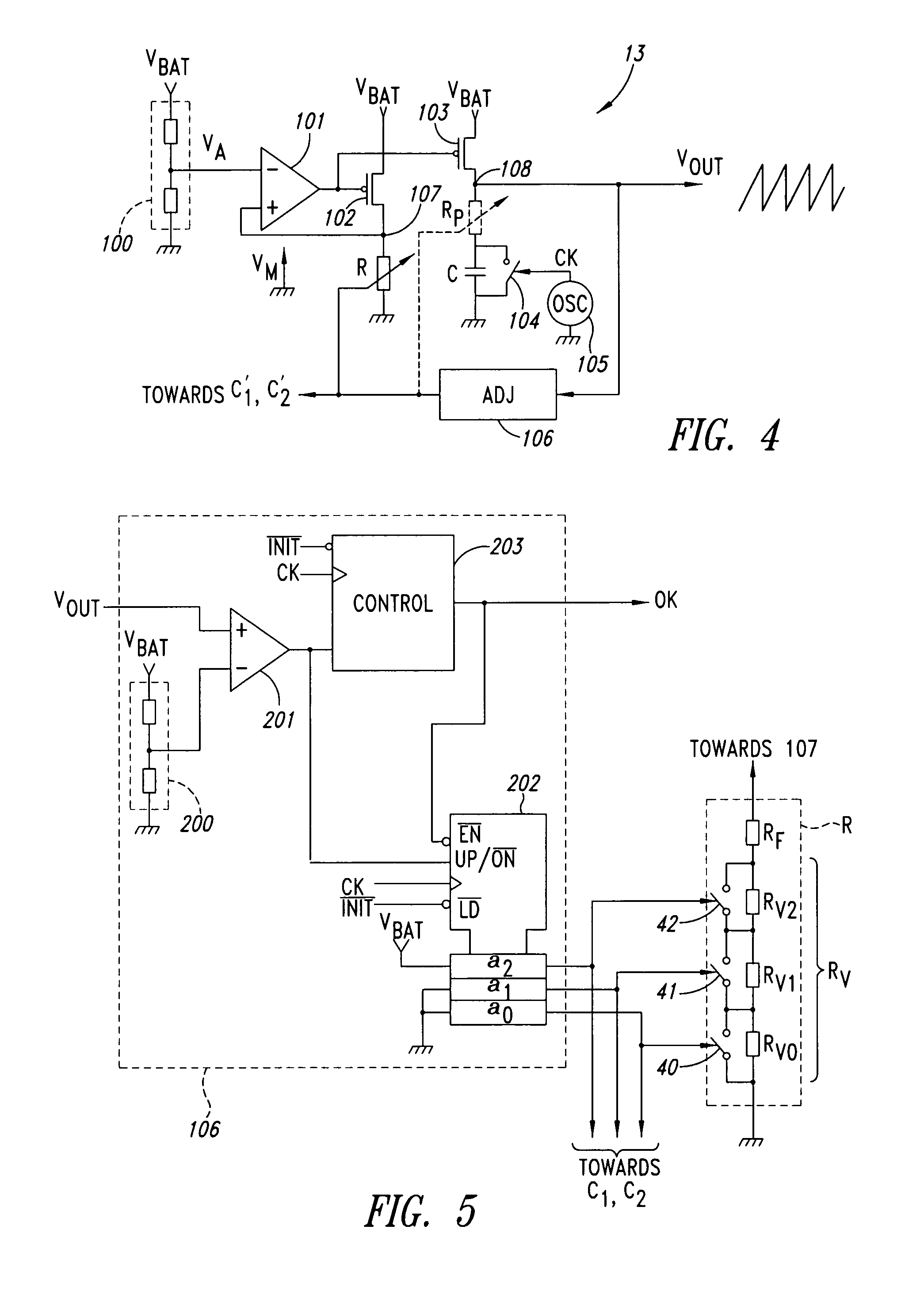
Auto-adjustment of RC cells within a circuit
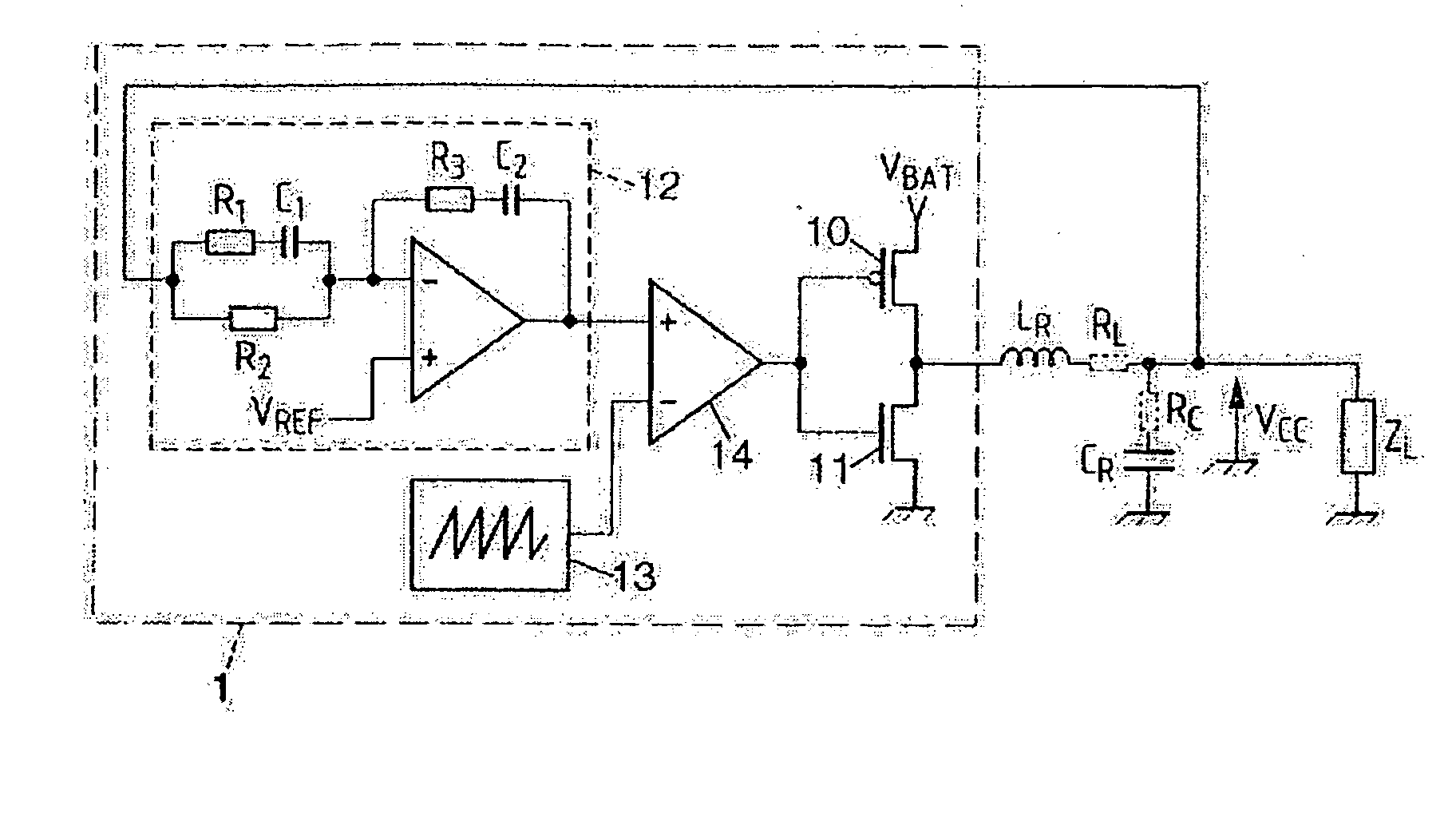
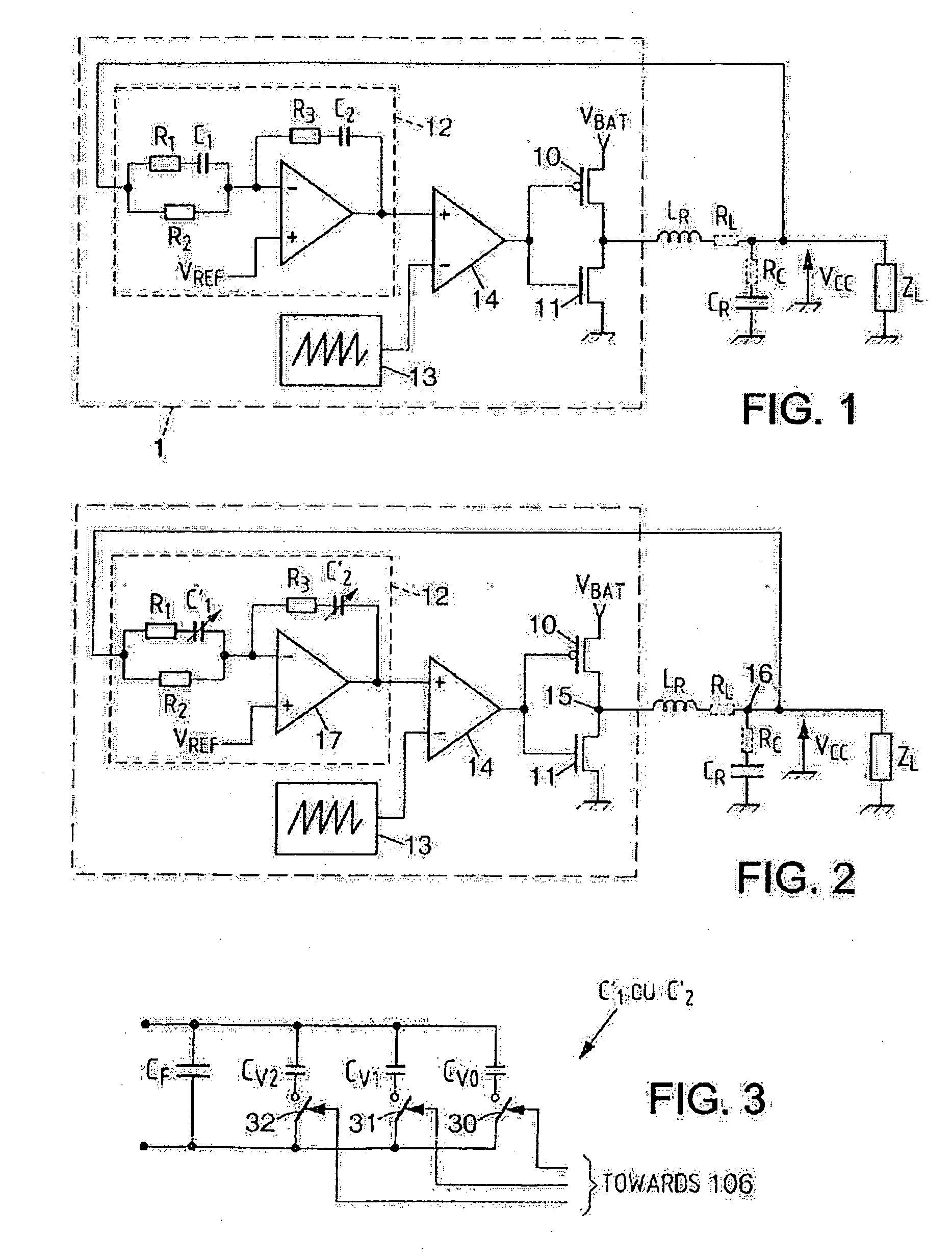
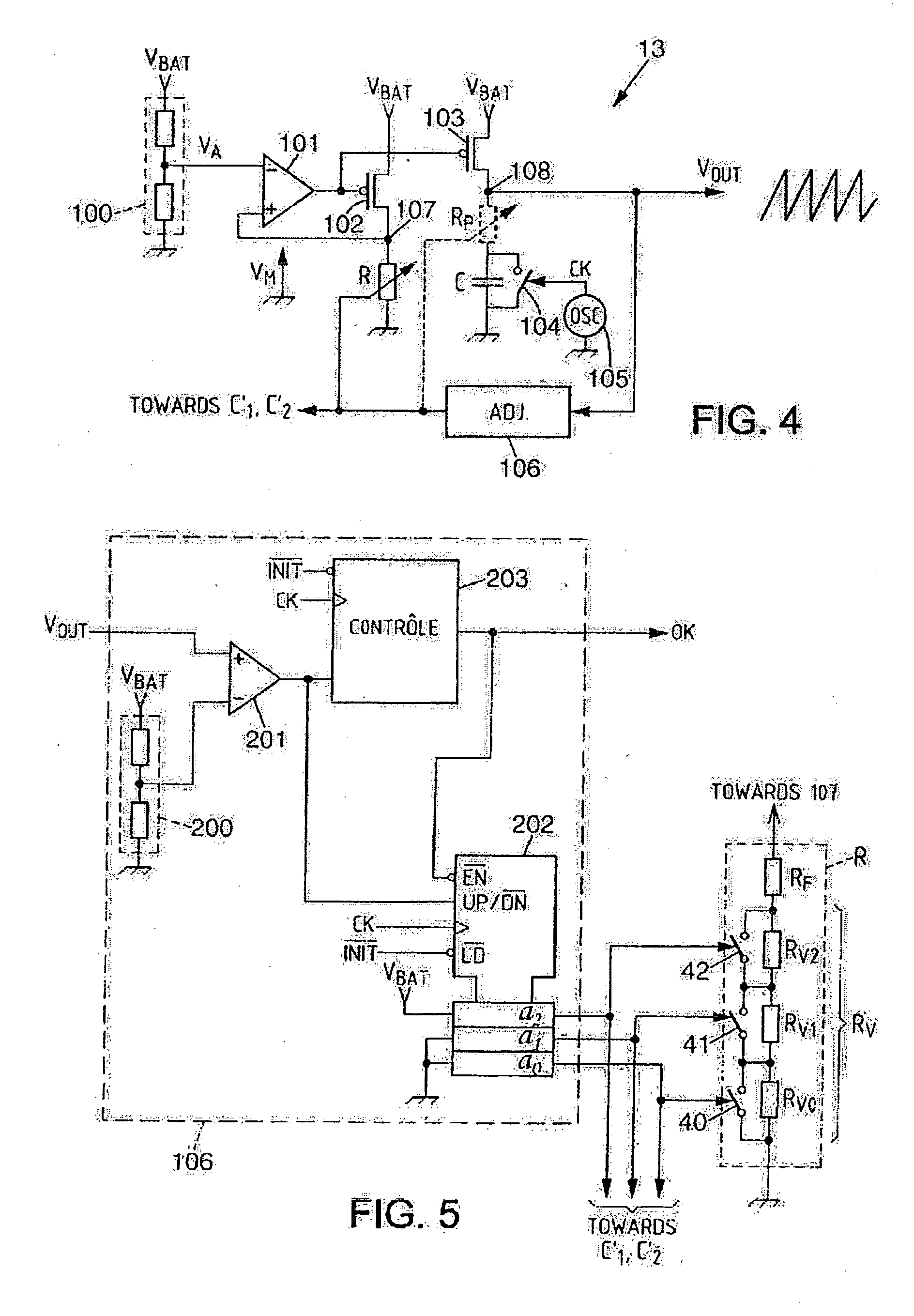
InactiveUS7176699B2Simple correctionMultiple-port networksResistance/reactance/impedenceEngineeringIntegrated circuit
An integrated circuit having a first couple of components R and C, at least a second couple of components R1–R3 and C′1–C′2 and a calibration circuit. The couple of componets form an RC cell of which one component is adjustable, and the calibration circuit. The invention corrects the errors in the values of the components of RC cells of the same nature. The calibration circuit performs the adjustment of an RC cell and then applies the same correction to the components of the other RC cells of the same nature.
Owner:ST ERICSSON SA
Nuclear magnetic resonance analysis method
ActiveUS20170052238A1Simple correctionEfficient simple correctionMeasurements using NMR spectroscopyNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonanceFrequency spectrum
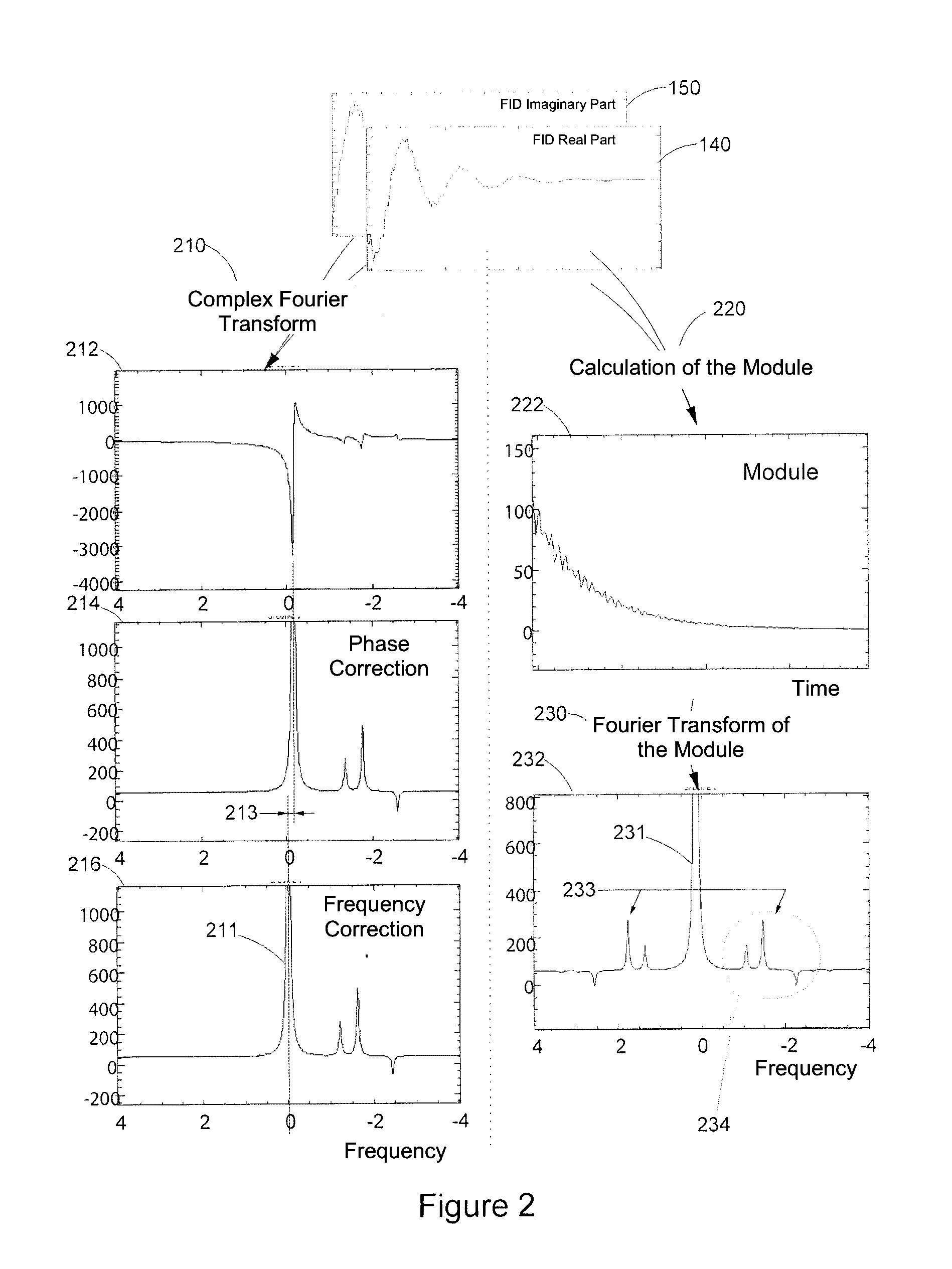
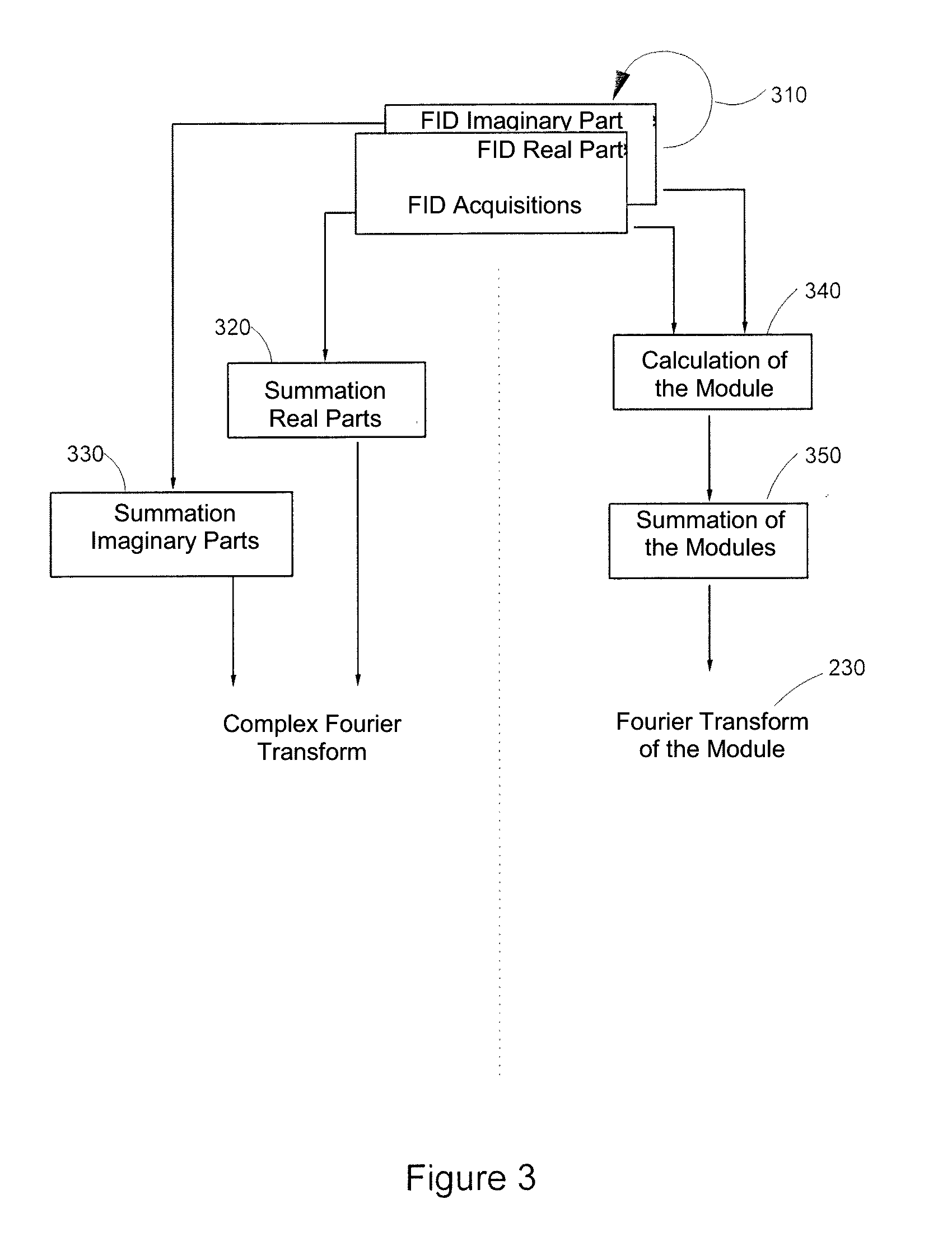
Method for analyzing a sample including a species to be characterized and a reference species, includes:acquiring one or more complex free induction decay (FID) signal(s) (S(t)),obtaining a FID spectrum S(ω) by applying a Fourier transform to the signal S(t), with the FID spectrum obtained including two portions, each extending from the resonance frequency of the reference species (F0ref) and respectively on either side of F0Ref, with the frequency of the species to be characterized located on a portion of the spectrum;modeling the signal of the reference species from the real and complex parts of the at least one complex FID signal;obtaining a spectrum Sref(ω) of the reference species including the reference species only,obtaining a modified FID {tilde over (S)}(ω) spectrum;applying a reverse Fourier transform to {tilde over (S)}(ω) to obtain a modified signal {tilde over (s)}(t);calculating the module of the {tilde over (s)}(t) modified FID signal.
Owner:UNIV DE PROVENCE D AIX MARSEILLE I +1
Auto-adjustment of RC cells within a circuit
InactiveUS20060145681A1Simple correctionMultiple-port networksResistance/reactance/impedenceEngineeringIntegrated circuit
The invention is an integrated circuit comprising a first component couple R and C, at least a second component couple R1—R3 and C′1-C′2 and a calibration circuit 106. The component couples are RC cells. The invention corrects the errors in the values of the components of the RC cells of the same nature. Each RC cell comprises a component R, C′1 and C′2 having an adjustable value. The calibration circuit 106 performs the adjustment of an RC cell, then applies the same correction to the components of the other cells of the same nature.
Owner:ST ERICSSON SA
Method for operating an internal combustion engine and electronic control unit for an internal combustion engine
ActiveUS20190093594A1Simple correctionEasy to carryElectrical controlMachines/enginesFrequency spectrumExternal combustion engine
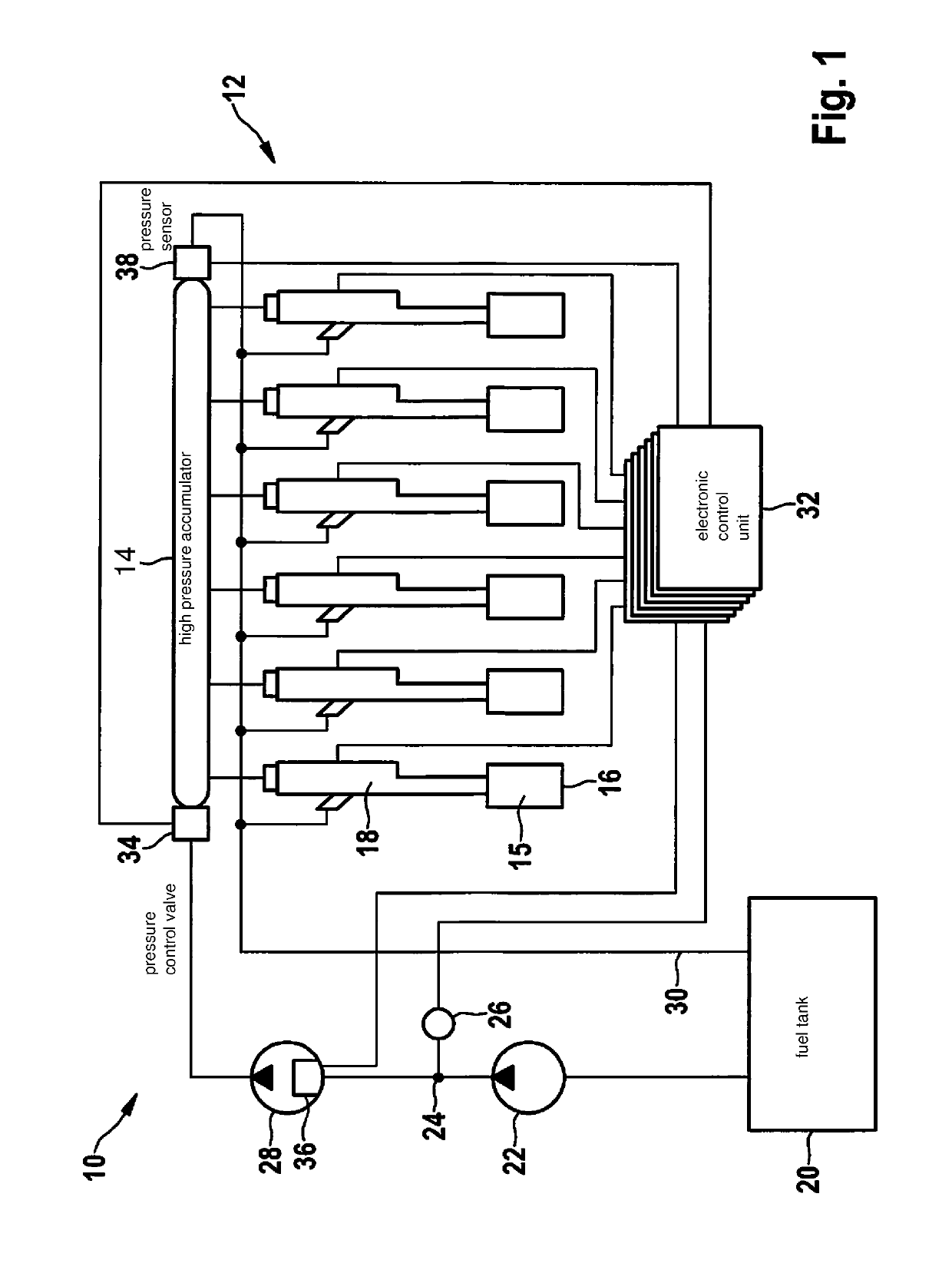
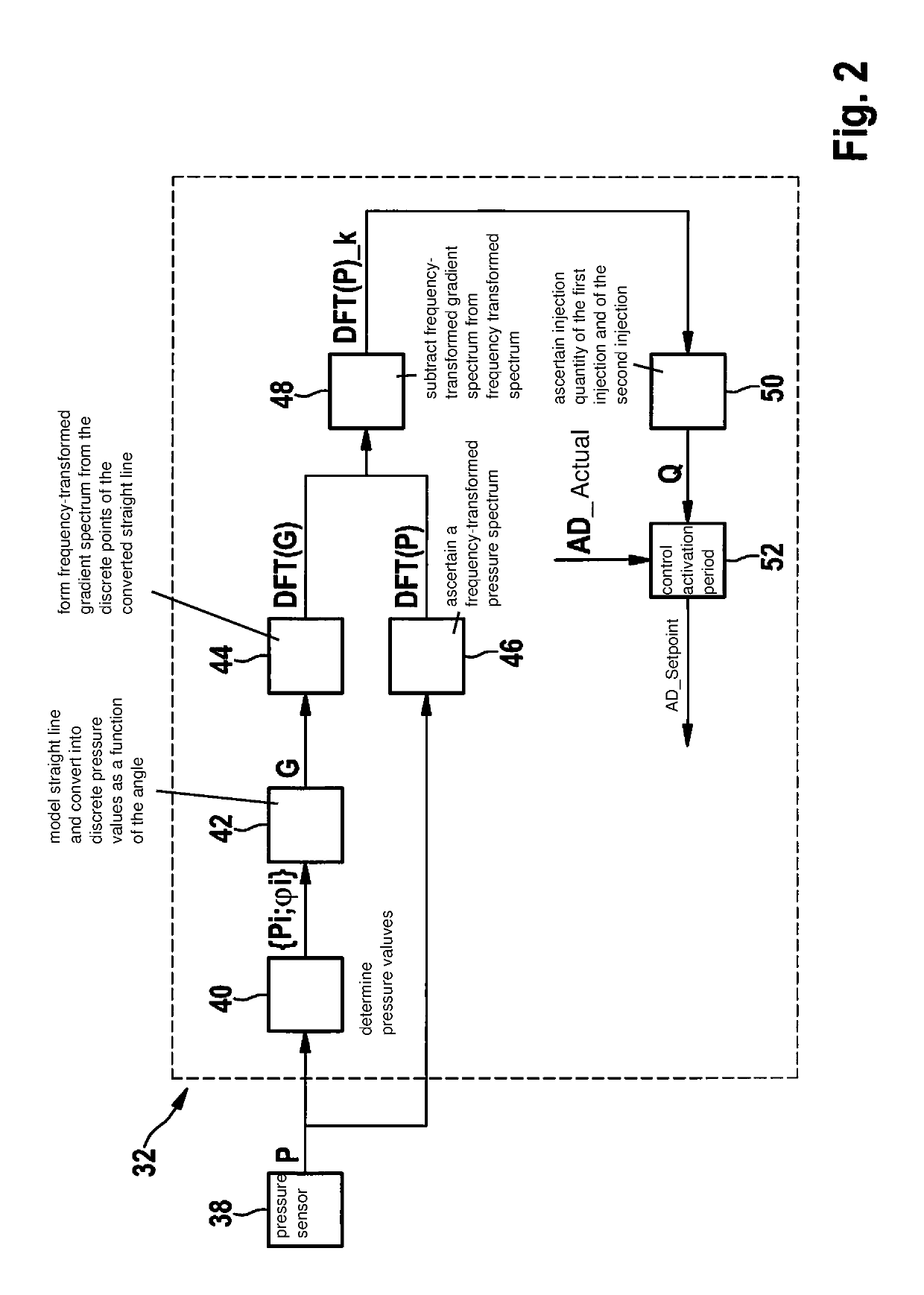
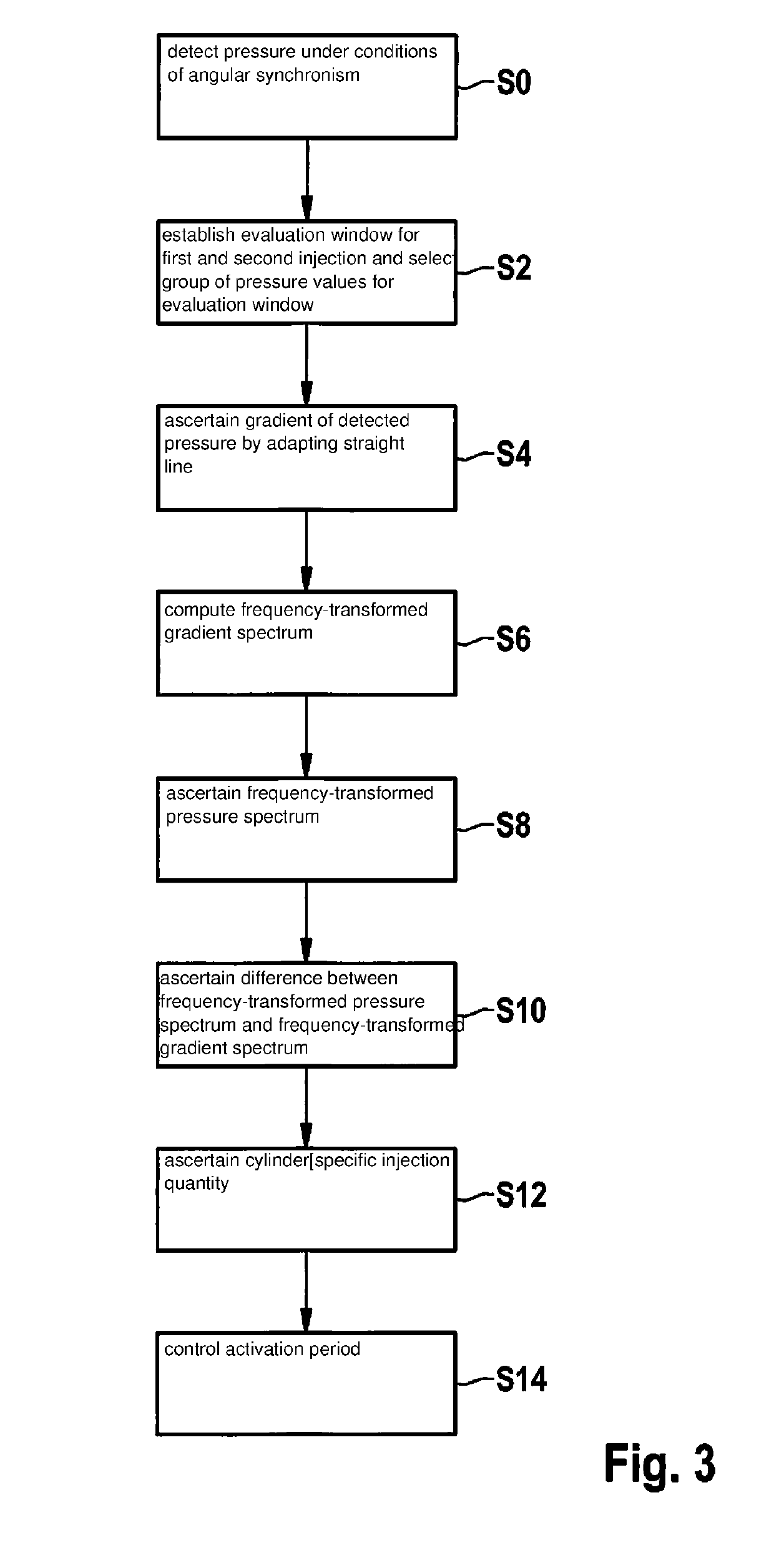
A method for operating an internal combustion engine is provided in which fuel is withdrawn from a high-pressure accumulator and injected into a combustion chamber of at least one cylinder of the internal combustion engine, the method including the steps of detecting under conditions of angular synchronism a pressure of the fuel in the high-pressure accumulator during a first injection into the at least one cylinder and during a later, second injection into the at least one cylinder; ascertaining a gradient of the detected pressure; ascertaining a frequency-transformed spectrum of the detected pressure and a frequency-transformed spectrum of the ascertained gradient; correcting the frequency-transformed spectrum of the detected pressure by the frequency-transformed spectrum of the ascertained gradient; and ascertaining a cylinder-individual injection quantity of fuel, which was injected into the at least one cylinder, from the corrected frequency-transformed spectrum of the detected pressure.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
Magnetic sensor, magnetic direction sensor, method of detecting magnetic field and method of detecting magnetic direction
ActiveUS7969149B2Big errorImprove accuracyNanomagnetismMagnitude/direction of magnetic fieldsElectrical resistance and conductanceMagnetization
A magnetic direction sensor can detect at higher precision the magnitude and direction of a detected magnetic field. The magnetic direction sensor has a measuring section, a storage section and an operating section. The measuring section has first and second MR elements, and detects resistance values of these elements in accordance with an attitude change of the sensor and the presence or absence of a bias magnetic field to be applied through a coil in a direction orthogonal to a magnetization direction of each pinned layer in the first and second MR elements. The storage section stores fixed data invariable in response to a detected magnetic field direction, in resistance values of these elements measured by the measuring section. The operating section calculates a detected magnetic field vector from variable data of resistance values of these elements measured by the measuring section, and fixed data stored in the storage section.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Absorption spectrometer and method for measuring the concentration of a gaseous component of interest in a measurement gas
ActiveUS9869632B2Correction of the measured result becomes more accurate or more robustGreat freedomRadiation pyrometryColor/spectral properties measurementsPhase sensitiveFrequency modulation
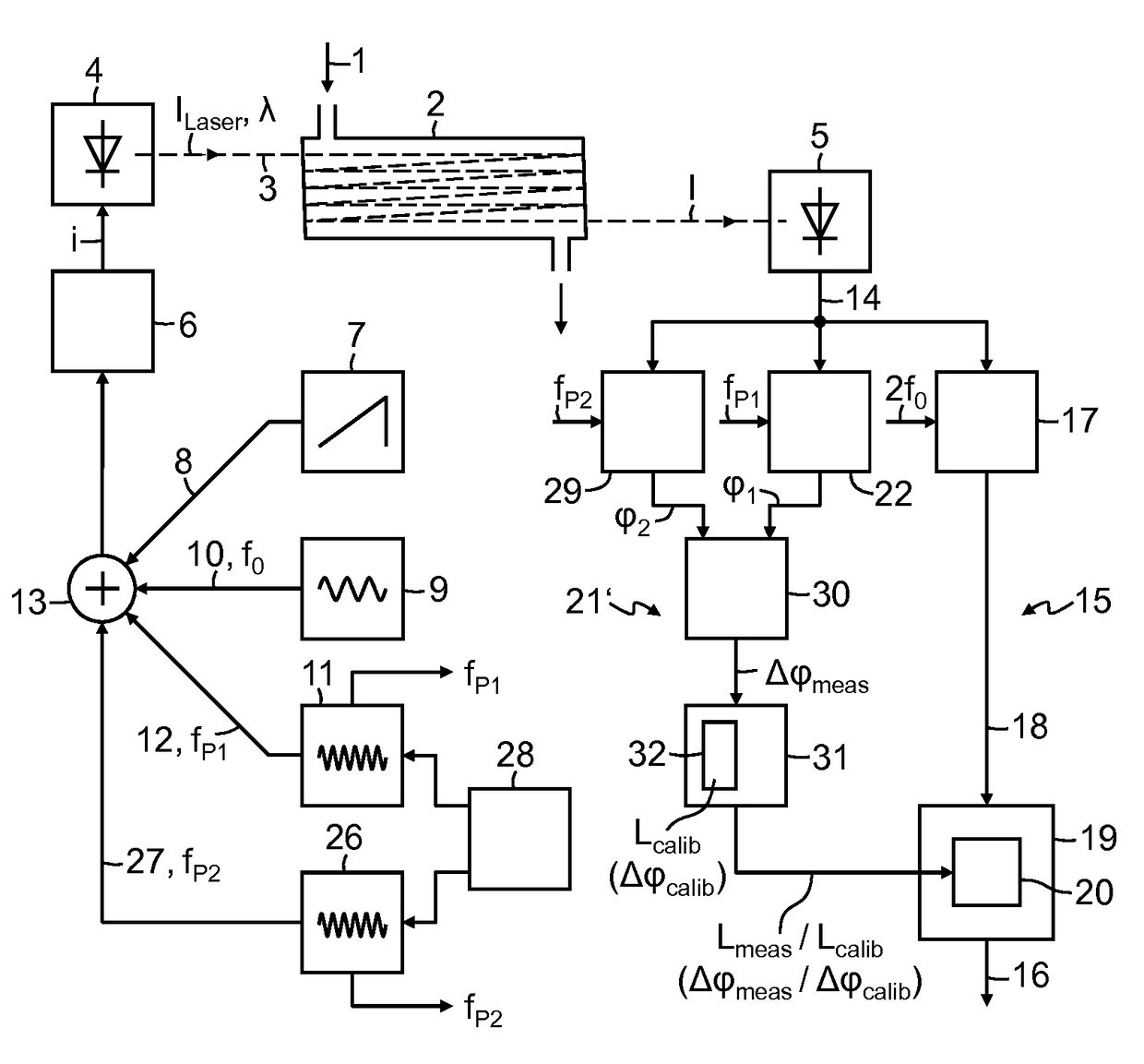
Absorption spectrometer and method for measuring the concentration of a gaseous component of interest in a measurement gas, wherein to compensate influence of changes in an optical path length in the absorption spectrometer on a measured result, light from the laser is modulated with at least one pilot frequency in the MHz range, the measurement signal is analyzed in a phase-sensitive manner for the pilot frequency, phase information obtained during this analysis is compared with phase information obtained during calibration of the absorption spectrometer, where the measured result is corrected as a function of the difference between the two items of phase information. Alternatively, light from the laser is modulated with two pilot frequencies, where signal components contained in the measurement signal with the pilot frequencies are detected in a phase-sensitive manner and the difference between the phase information of the two signal components obtained in this operation is analyzed.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
Thermal Material-Processing Method
ActiveUS20110095001A1Simple correctionElectric discharge tubesElectron beam welding apparatusEngineeringRelative motion
A thermal material-processing method wherein between the working spot of an electron beam and a workpiece a relative motion is brought about. Prior to the actual thermal treatment an effective processing contour is ascertained, in that the working spot of the electron beam executes, in accordance with the stored data of an ideal processing contour, a relative motion in relation to the workpiece, and on this relative motion a scan motion is superimposed which is directed transversely to the ideal processing contour. In this manner, both geometrical and magnetically conditioned deviations of the points of incidence of the electron beam on the workpiece can be compensated.
Owner:PROBEAM AG & CO KGAA
Hydraulic expansion assembled combination die for quenching ferrules
ActiveCN102776342ASolve the deformationSolve the difficulty of demouldingFurnace typesHeat treatment furnacesQuenchingMaterials science
The invention relates to a heat treatment quenching die, and in particular relates to a hydraulic expansion assembled combination die for quenching ferrules. The hydraulic expansion assembled combination die comprises a quenching working table, a quenching disc which is installed on the quenching working table, a die holder and a quenching die. The hydraulic expansion assembled combination die is characterized in that the quenching die consists of a central conical body and 4-12 quenching working blocks which are installed on the external conical surface of the central conical body, the quenching working blocks are wrapped on the external conical surface of the central conical body through annular tension springs, and a hydraulic rod of the quenching die is connected with the central conical body. The hydraulic expansion assembled combination die is used for solving the problems that a quenching workpiece deforms and is difficult to demould; the volume and the number of the die are greatly decreased, the problems of die processing difficulty and die storage space are solved, and the production period and the production cost of the die are also greatly reduced; one set of die can be suitable for quenching the workpieces within one dimension range; and a quenched workpiece has a stable size and small deformation, is easy to correct and has stable quenching quality.
Owner:NINGXIA MACHINERY RES INST
Non-redundant multi-error correcting binary differential demodulator
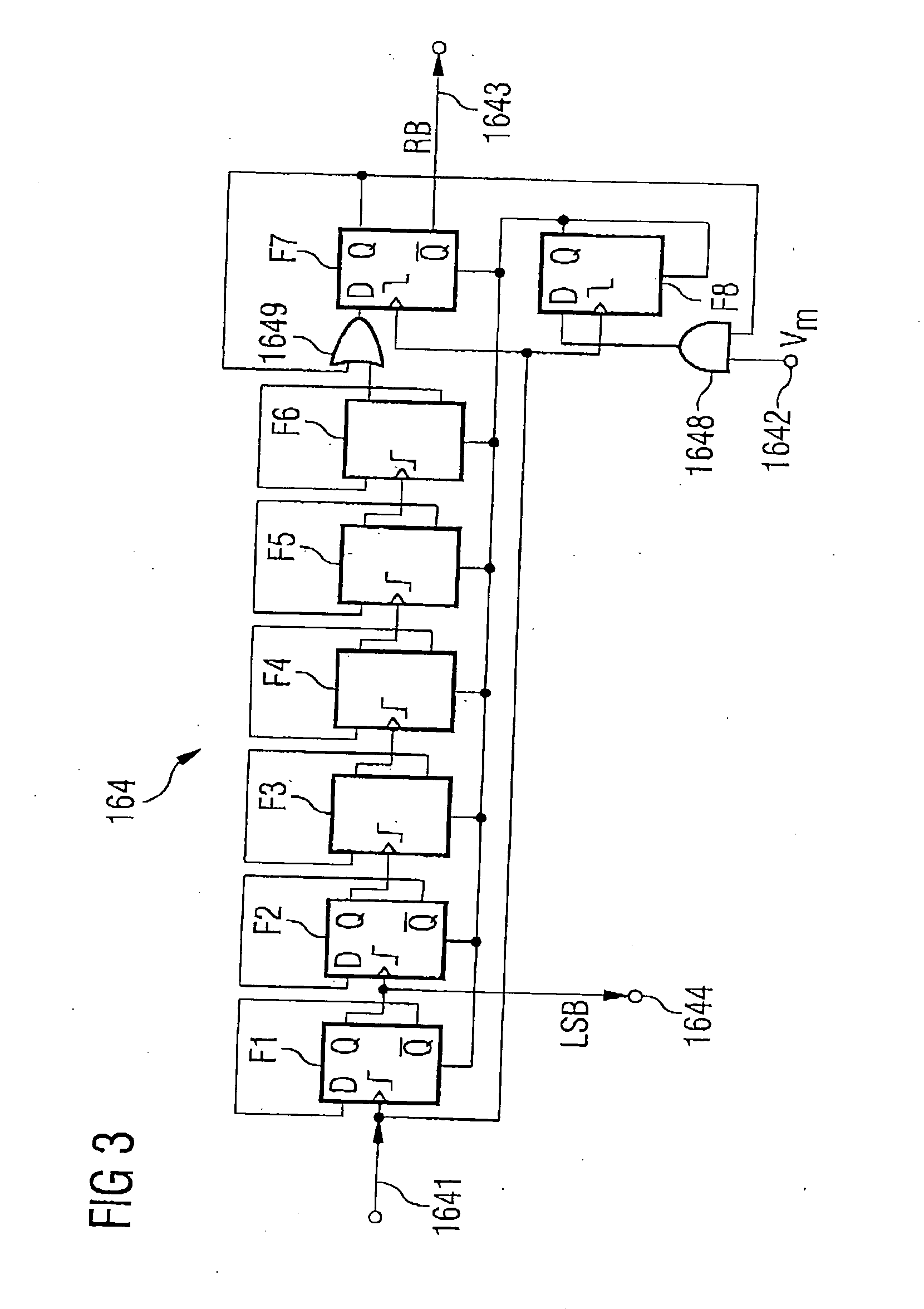
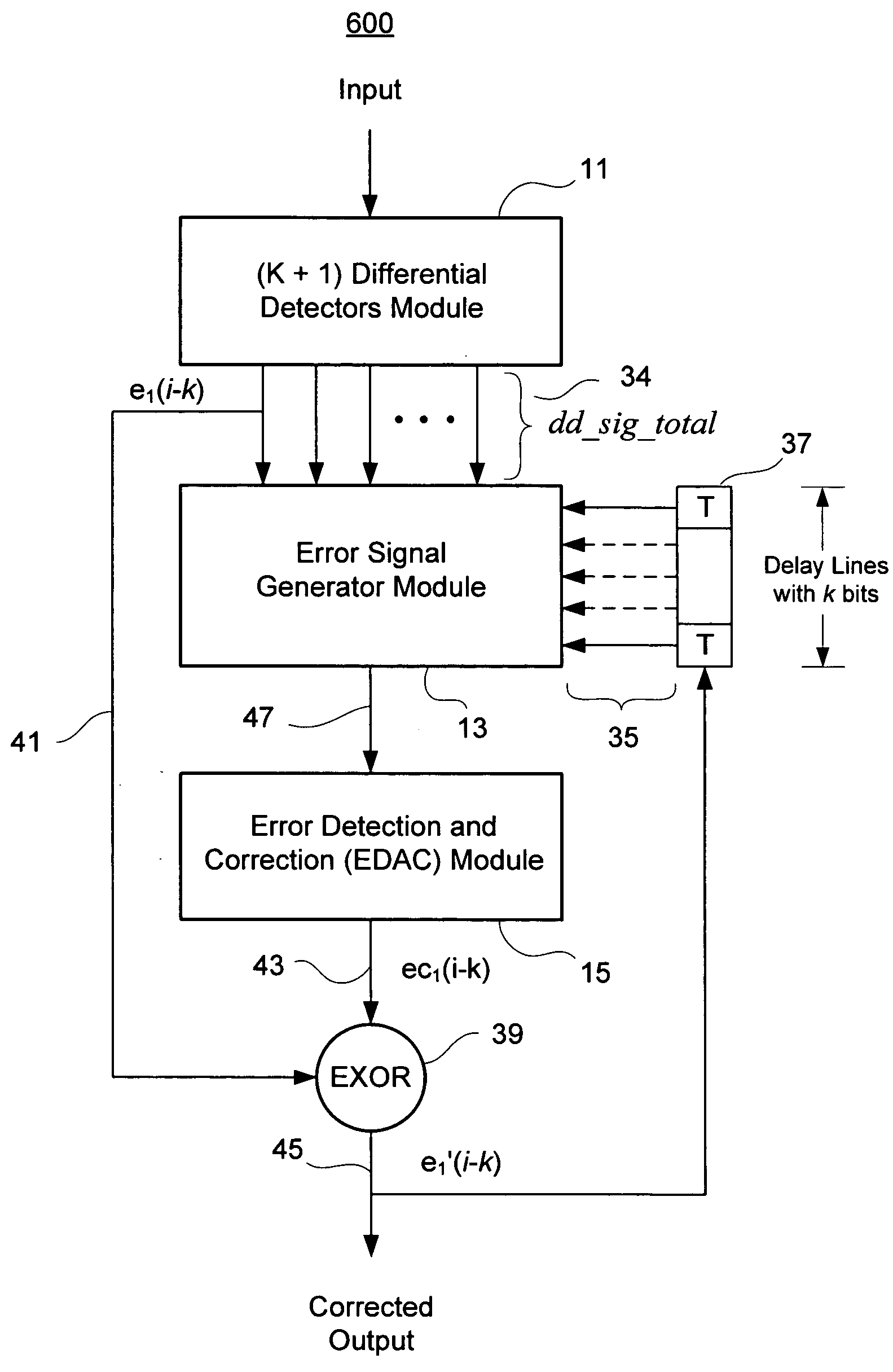
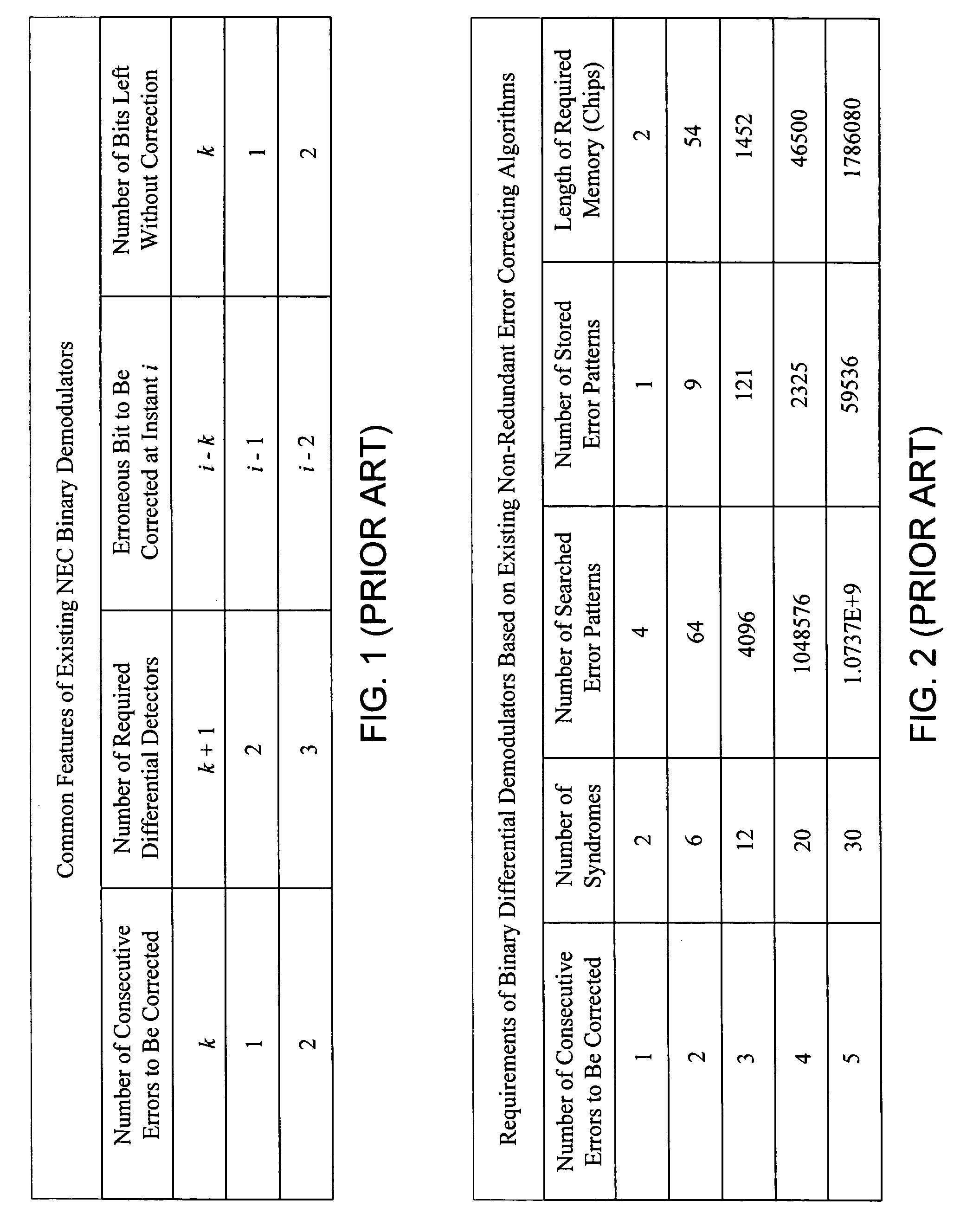
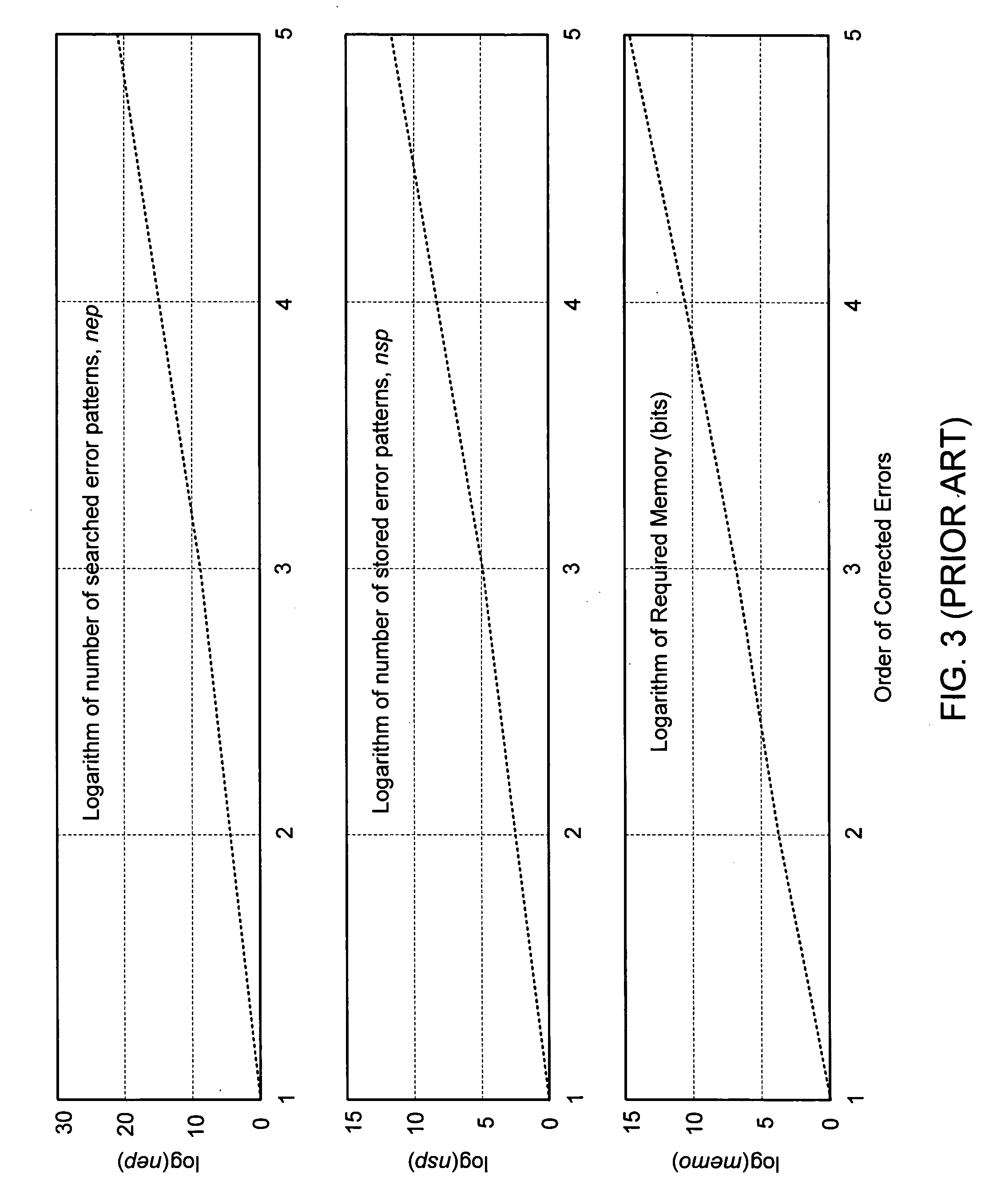
ActiveUS20080092022A1Simplifies error detectionSimple correctionData representation error detection/correctionCode conversionComputer scienceError correcting
An algorithm for a non-redundant multi-error correcting binary differential demodulator simplifies error detection and reduces memory requirements in circuits embodying the same. The demodulator includes a differential detectors (DD) module, an error signal generator (ESG) module, and an error detection-and-correction (EDAC) module. The DD module receives modulated binary input at each of (k+1) differential detectors, each producing (k+1) outputs. The ESG module combines the (k+1)2 output signals with k corrected feedback signals to derive syndromes orthogonal to an erroneous bit to be corrected and generates 2k error signals from the syndromes. The EDAC module generates a correction factor from the 2k error signals and combines the factor with the output of the first order detector delayed by k bits to correct an erroneous bit. The k corrected feedback signals may be derived by successively delaying the corrected erroneous bit. Simplified higher order demodulators may be constructed using a nested hierarchy of lower order demodulators based on the algorithm.
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMMAN SYST CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com