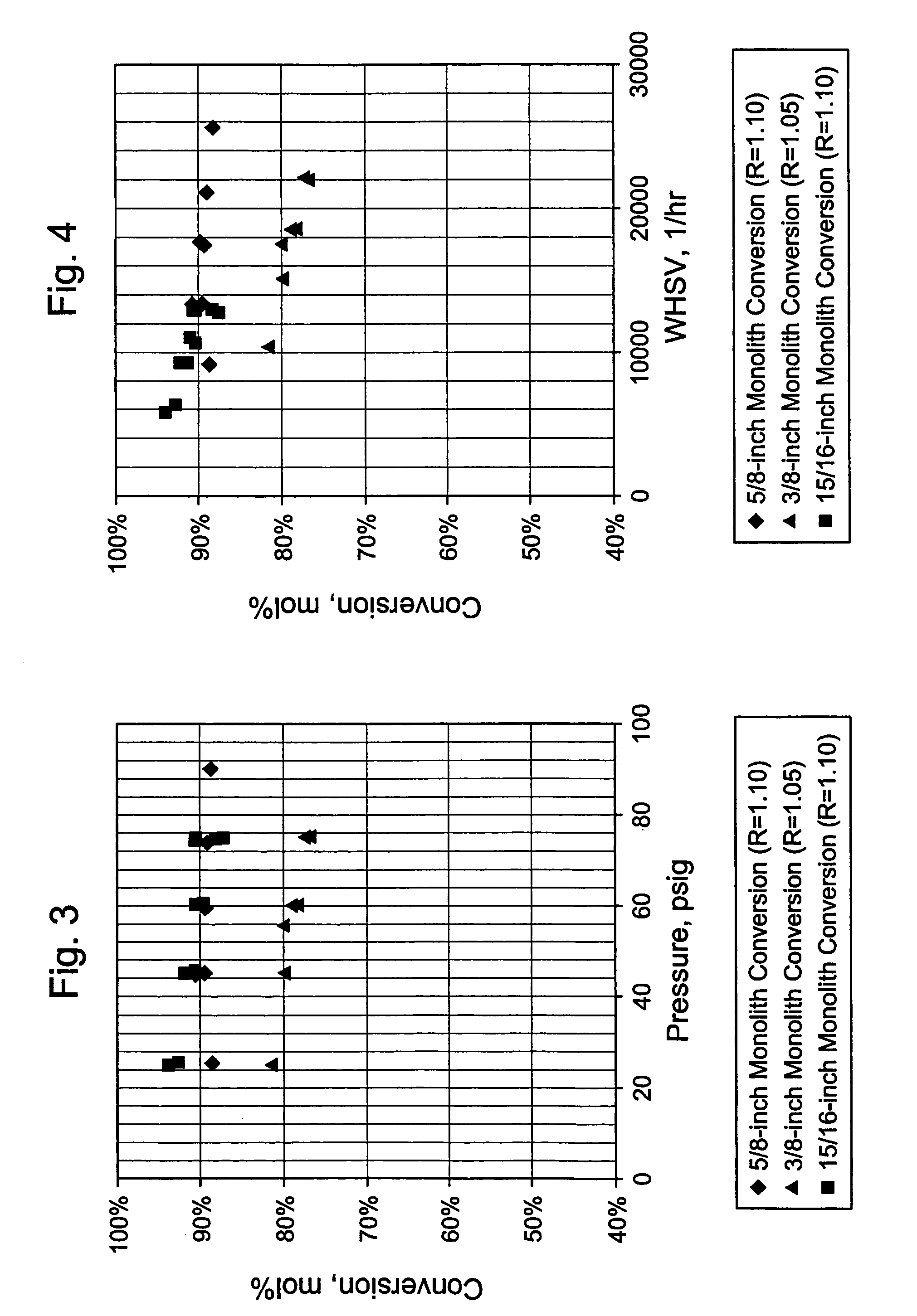
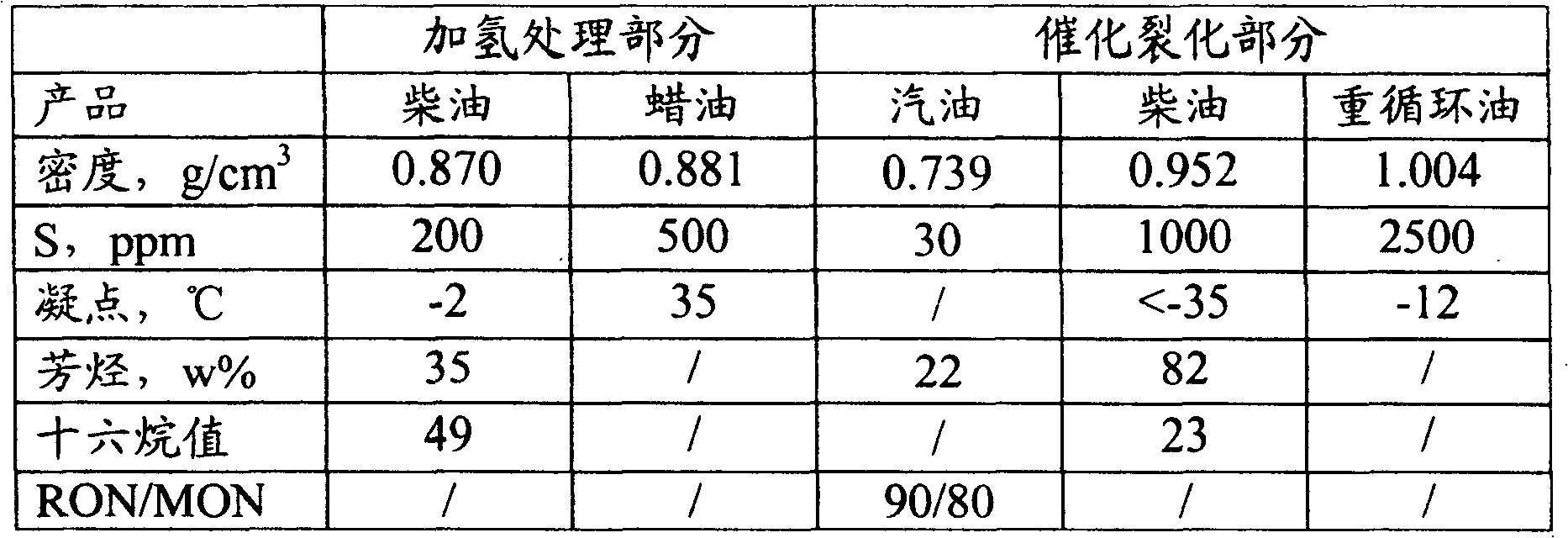
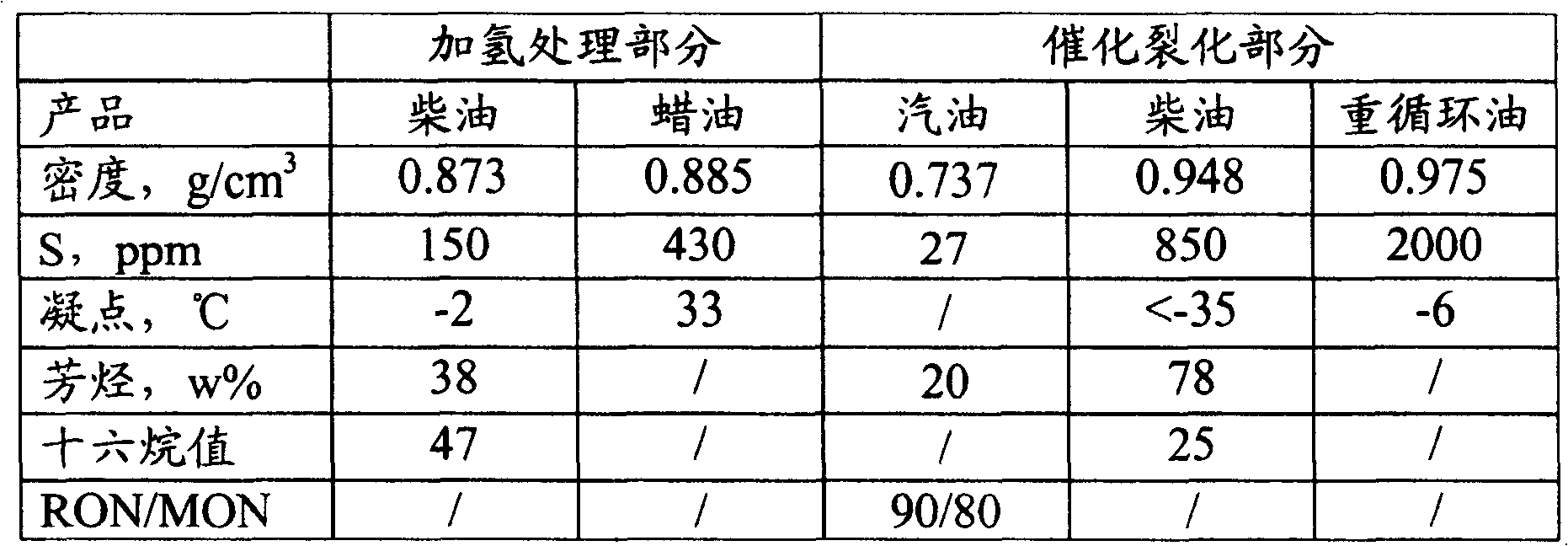
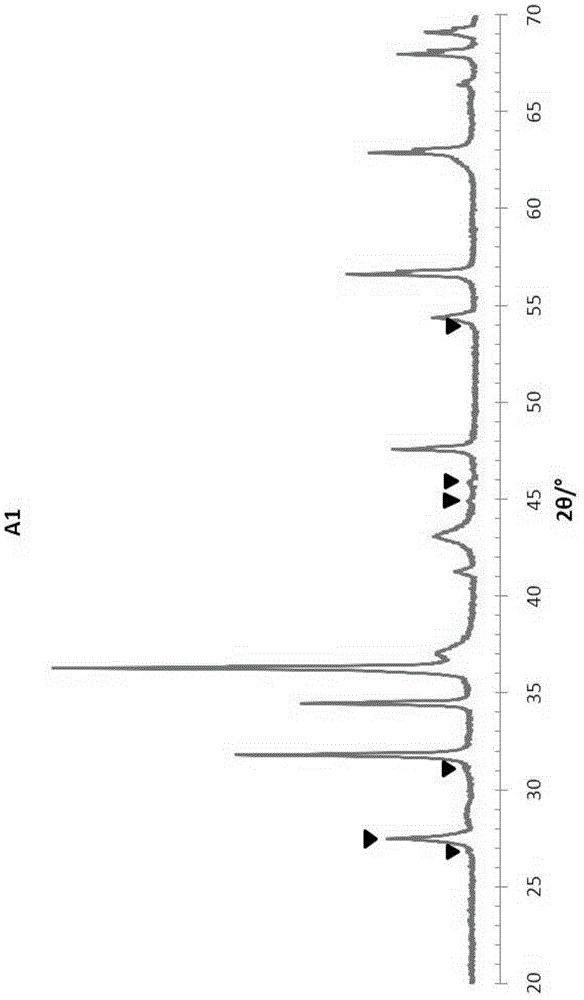
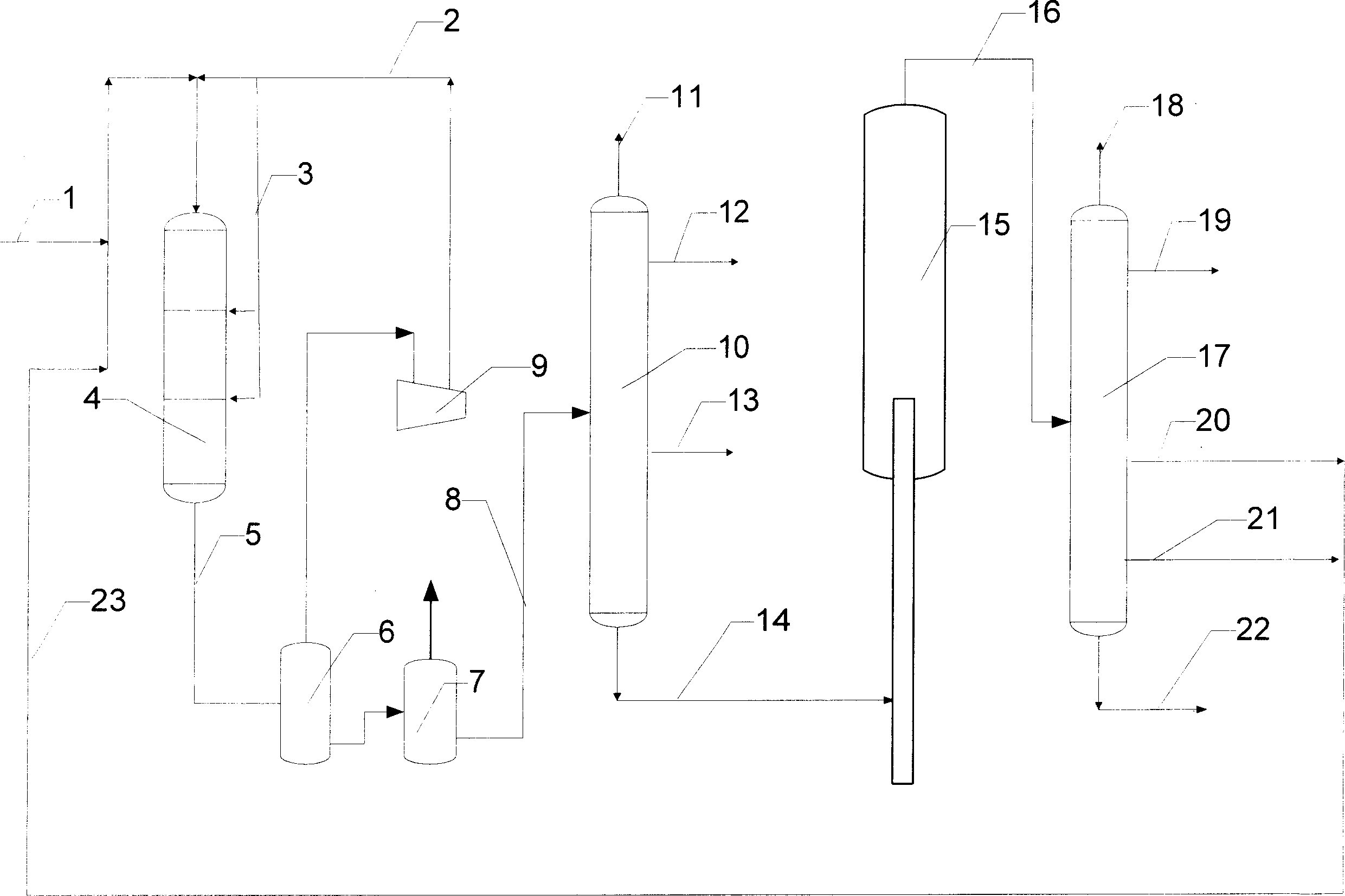Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
70results about How to "Less coke" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Two-way combined process of wax-oil hydrogenation treatment and catalytic cracking
A two-way combined process of wax oil hydro-process and catalytic crack is carried out by entering wax oil, catalytic cracking re-circulating oil and catalytic cracking diesel oil into hydro-processor, hydrogenation reacting under existence of hydrogen and hydrogenation catalyst, separating for reactant to obtain gas, hydrogenation naphtha oil, hydrogenation diesel oil and hydrogenation tail oil, entering hydrogenation tail oil into catalytic cracker, crack reacting under existence of catalytic cracking agent, separating to obtain dry gas, liquefied gas, catalytic cracking gasoline, catalytic cracking diesel oil and catalytic cracking re-circulating oil and oil slurry, and circulating for catalytic cracking diesel oil and catalytic cracking re-circulating oil to hydro-processor. It has higher recovery rate and cetyl value, less sulfur content, arene content and coke output.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Prepn process of catalyst for residual oil hydrocracking in suspension bed
The catalyst for residual oil hydrocracking in suspension bed is prepared with molybdenum ore dressing tailing or slag as material, and through wet oxidation and leaching with chemical reagent, filtering and other processing steps to obtain solution being used as the catalyst for hydrocracking in suspension bed. The catalyst is dispersed in heavy oil or residual oil, and in the presence of hydrogen, the inferior heavy oil or residual oil containing the catalyst is hydrocracked into light product. The catalyst has the features of low cost, environment friendship, high light product yield and others.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
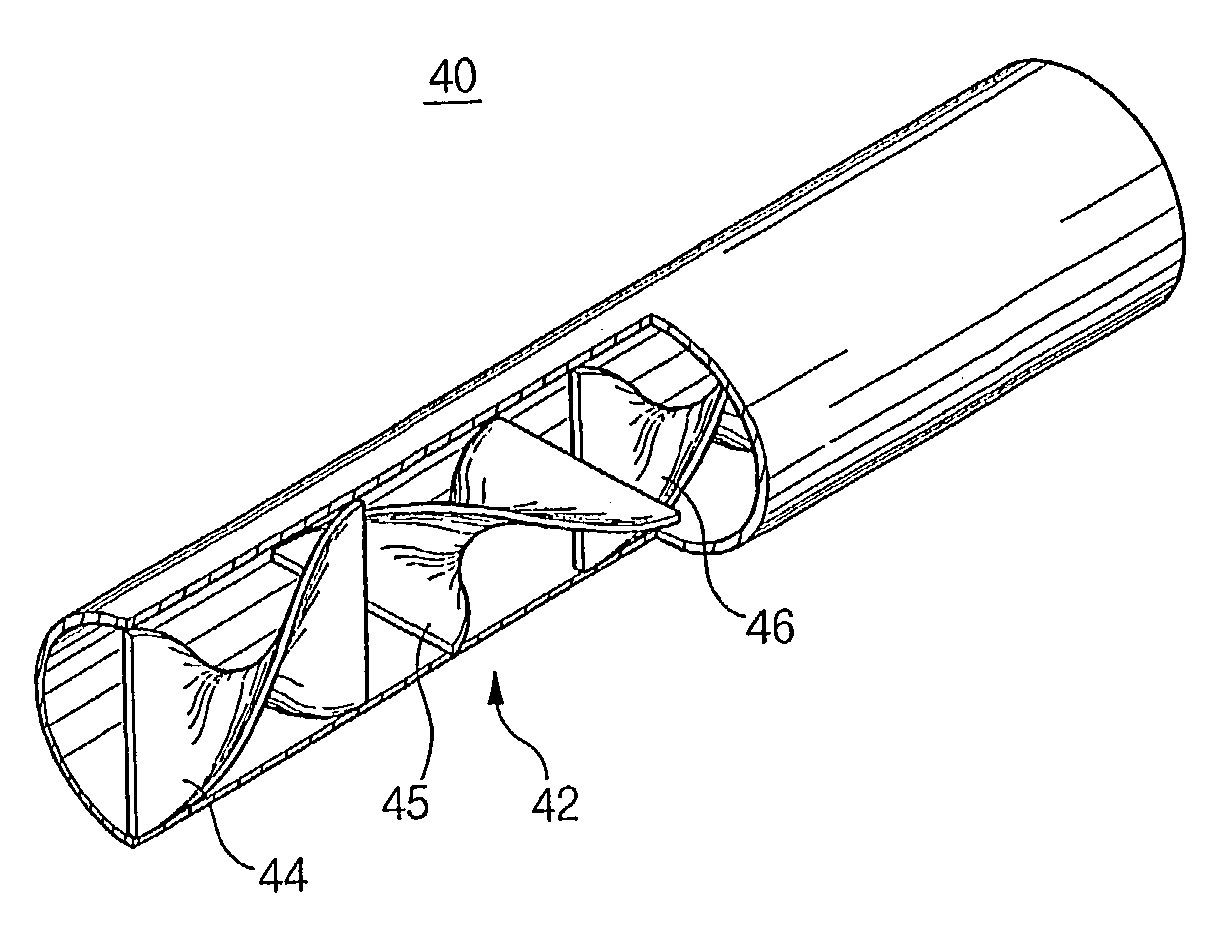
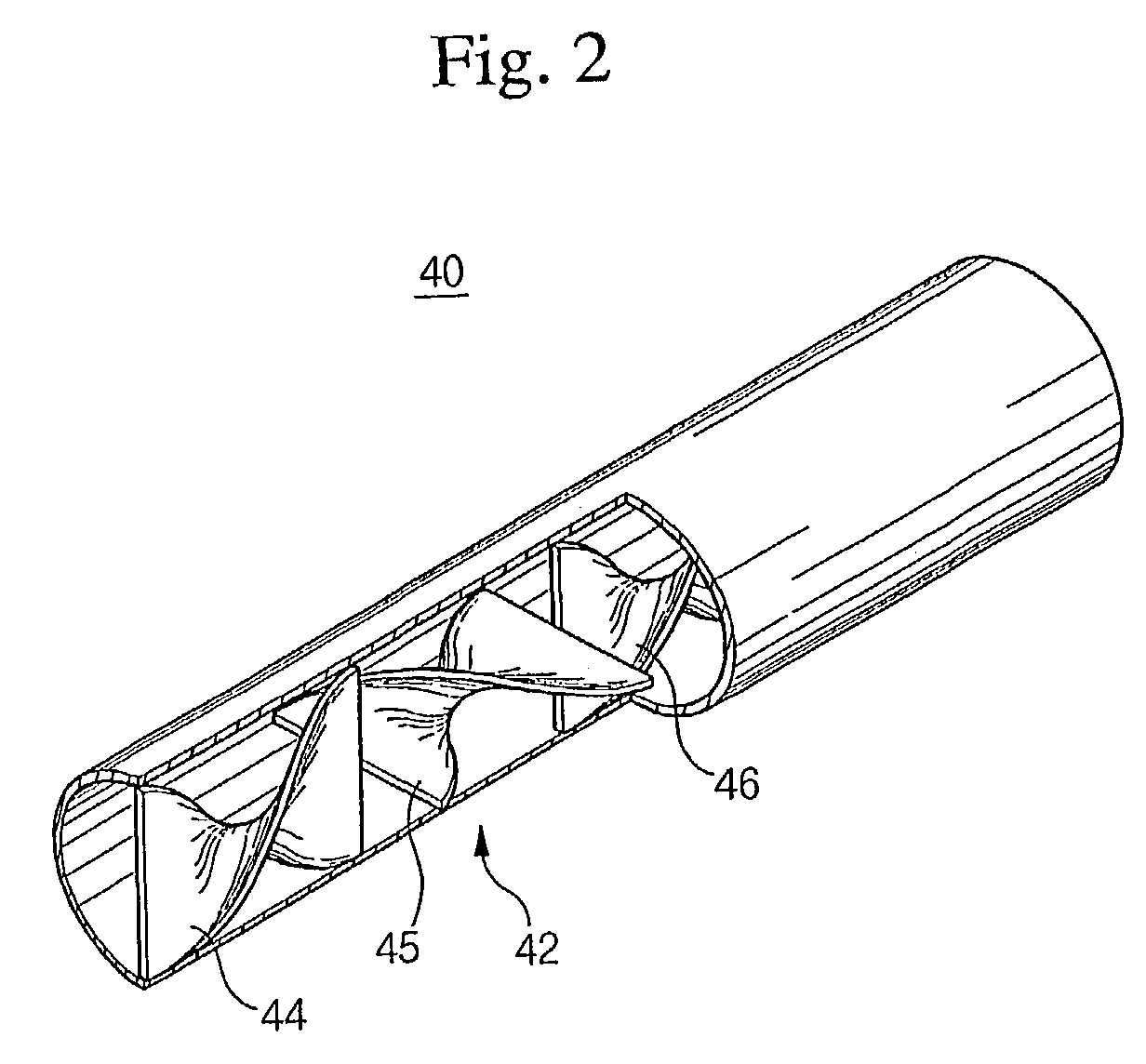
Pyrolysis tube and pyrolysis method for using the same
InactiveUS7169292B2More ethyleneLess cokeThermal non-catalytic crackingFluid heatersEngineeringResidence time
The present invention provides a pyrolysis tube for enhancing the yield of olefins and reducing a coking tendency in steam cracking of hydrocarbons. According to the present invention, the pyrolysis tube is characterized in that a plurality of mixing blades made by twisting two ends of a plate in opposite directions are included therein. The yield of ethylene is thereby improved and the coking tendency is reduced by mixing a fluid flow, improving a heat transfer rate and shortening a residence time of the reactants therein.
Owner:LG CHEM LTD
Poor residuum hydroconversion method
InactiveCN1488727AImprove conversion rateLow yieldHydrocarbon oil crackingHydrogenVapor–liquid separator
The present invention provides a residuum hydrocracking method, which adopts a pipe-in-pipe tye reactor, the top of internal pipe is equipped with gas-liquid separator, firstly, the raw material and hydrogen gas are fed into internal pipe reaction section in the upward-flowing mode, then they are separated at the upper gas-liquid separator place, the gas phase can be discharged from the reactor, and the liquid phase can be fed into the ring pipe reaction section together with added hydrocarbon oil containing more heavy aromatics, at the same time the hydrogen gas is added in the bottom of ring pipe reaction section. Said invention is mainly applicable to the hydrogenation cracking reaction of the heavy oil and residuum, specially applicable to the hydrogenation cracking reaction of poor heavy oil and residuum.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
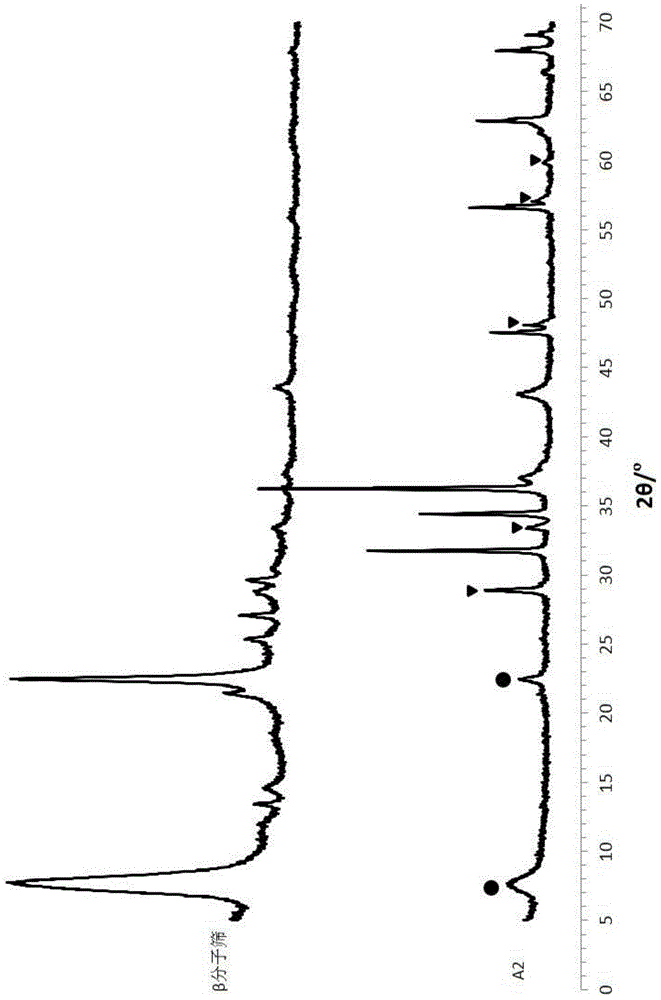
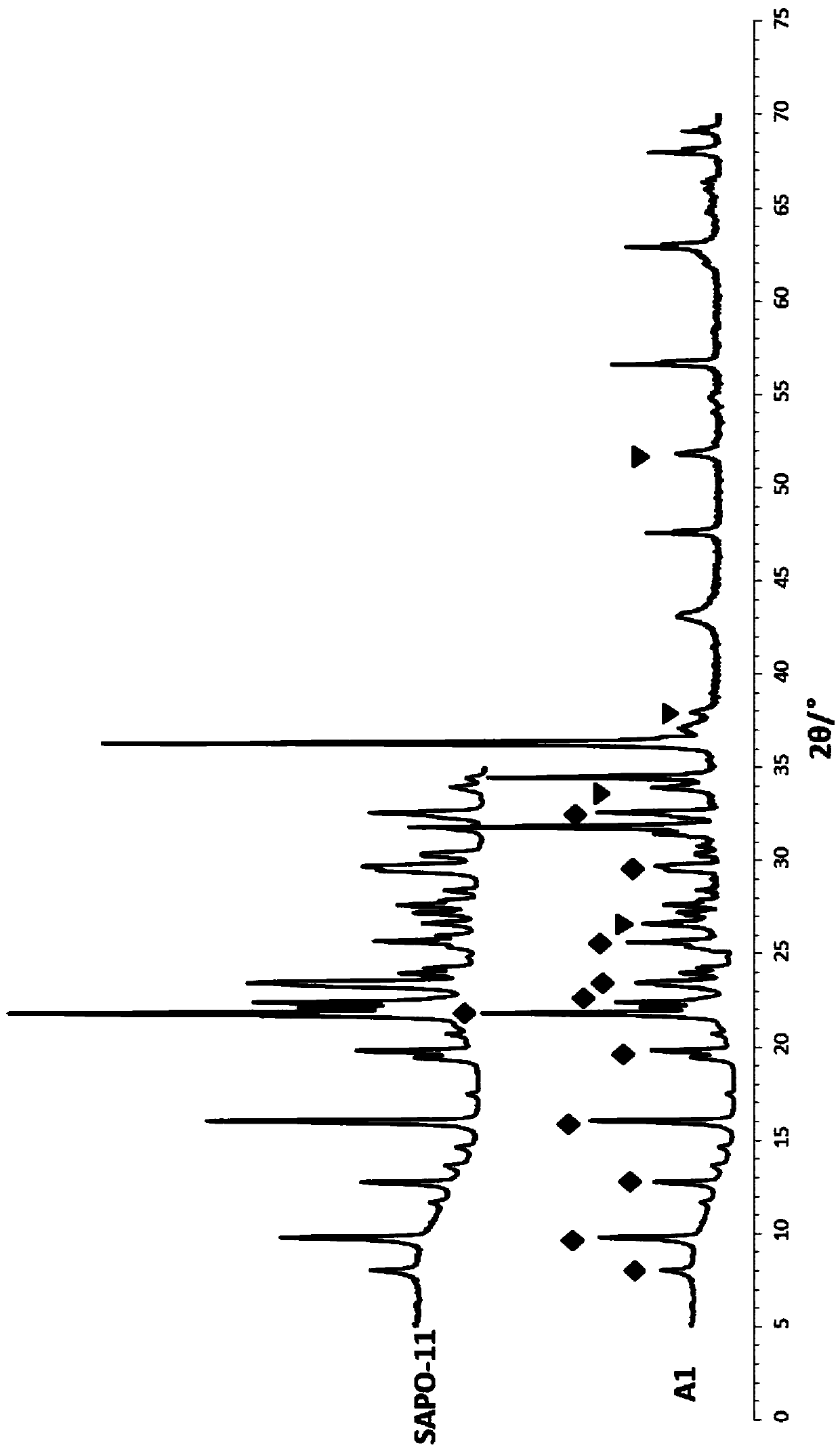
Desulphurization catalyst and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN104415775AHigh desulfurization activityGood desulfurization stabilityMolecular sieve catalystsHydrocarbon oils refiningRare-earth elementSilicon oxide
The invention discloses a desulphurization catalyst, and also discloses a preparation method of the desulphurization catalyst and the desulphurization catalyst prepared by the method, and an application of the desulphurization catalyst in desulphurization of sulfur-containing hydrocarbon oil. The desulphurization catalyst contains an aluminosilicate molecular sieve with a duodenary-ring pore-channel structure, rare earth oxide, titanium dioxide, a silicon oxide source, zinc oxide and active metal; the rare earth element content in the aluminosilicate molecular sieve with the duodenary-ring pore-channel structure is 0 mumg / g; and the characteristic peak of a tetragonal system of a rare earth-zirconiu composite oxide can be existed in a XRD spectrogram of the desulphurization catalyst. The desulphurization catalyst has better desulphurization activity and desulphurization stability.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Hydrocracking catalyst and method of hydrocracking heavy oil
InactiveUS20050115870A1Less deteriorationLess cokeCarbon compoundsCatalyst activation/preparationActivated carbonPetroleum
In a process of hydrocracking heavy oil with a catalyst in petroleum refining, asphaltene contained in heavy oil, and impurities including heavy metals such as nickel and vanadium, are efficiently removed with activated carbon, whereby the reduction in catalyst activity or formation of coke by the impurities can be prevented. The invention provides a hydrocracking catalyst comprising activated carbon extrudate as a carrier activated with steam and having a high distribution of pores having pore sizes in the range of 20 to 200 nm.
Owner:TOYO ENG CORP
Process for preparing ethylene and/or propylene
InactiveUS20140148631A1Good choiceLess cokeHydrocarbon from oxygen organic compoundsEthylene productionReaction systemEthylene
The present invention provides a process for preparing ethylene and / or propylene, wherein an oxygenate feedstock is contacted with a zeolite-comprising catalyst at a temperature in the range of from 500 to 700° C. to obtain a reactor effluent comprising ethylene and / or propylene and the oxygenate feedstock is contacted with the catalyst in a riser reactor having a reactor wall defining a flow trajectory towards a downstream outlet for reactor effluent, wherein at least oxygenate feedstock and catalyst are provided at one or more upstream inlets of the riser reactor and wherein C5 olefins are admitted to the riser reactor at one or more of locations along the length of the flow trajectory. The invention further provides a reaction system suitable for preparing ethylene and propylene.
Owner:SHELL OIL CO
Biomass hydrogen-donating pyrolysis technique of naphthenic base oil in presence of hydrogen-donating distillate oil
ActiveCN103254923AReduce oxygen contentImprove qualityBiofuelsLiquid hydrocarbon mixture productionDistillates petroleumHydrogen
The invention discloses a technical process of biomass hydrogen-donating pyrolysis in the presence of hydrogen-donating distillate oil. The technique adopts a naphthenic base oil fraction as the hydrogen-donating fraction, proportionally mixes the biomass and the naphthenic base oil hydrogen-donating distillate oil, and carries out hydrogen-donating pyrolysis at 350-400 DEG C. The hydrogen-donating distillate oil is selected from one or more sections of 400-520 DEG C fraction of the naphthene base crude oil. In the hydrogen-donating pyrolysis process, the biomass carries out sufficient chemical conversion and redistribution of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen, thereby being beneficial to enhancing the light oil yield and lowering the coke yield in the pyrolysis process; and besides, more oxygen element in the biomass is distributed in water molecules, thereby enhancing the quality of bio-oil, and being beneficial to deep processing and utilization of bio-oil.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (EAST CHINA)
Prepn process of catalyst for residual oil hydrocracking in suspension bed
The catalyst for residual oil hydrocracking in suspension bed is prepared with molybdenum ore dressing tailing or slag as material, and through wet oxidation and leaching with chemical reagent, filtering and other processing steps to obtain solution being used as the catalyst for hydrocracking in suspension bed. The catalyst is dispersed in heavy oil or residual oil, and in the presence of hydrogen, the inferior heavy oil or residual oil containing the catalyst is hydrocracked into light product. The catalyst has the features of low cost, environment friendship, high light product yield and others.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Catalyst system for enhanced flow syngas production
ActiveUS20050181939A1Increase conversionsHigh selectivityCatalytic gas-gas reactionHydrogenSyngasOxygen
Owner:PHILLIPS 66 CO
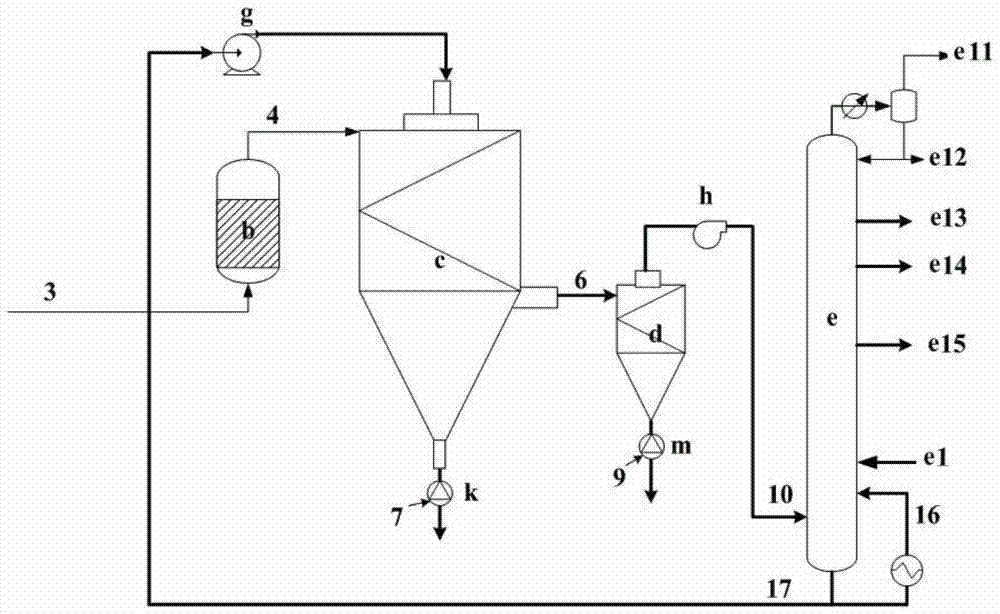
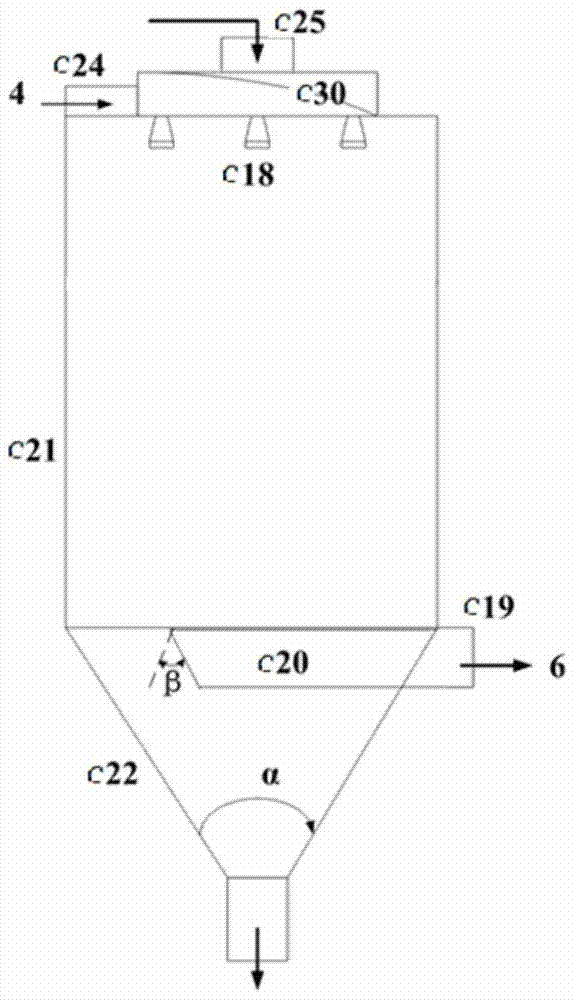
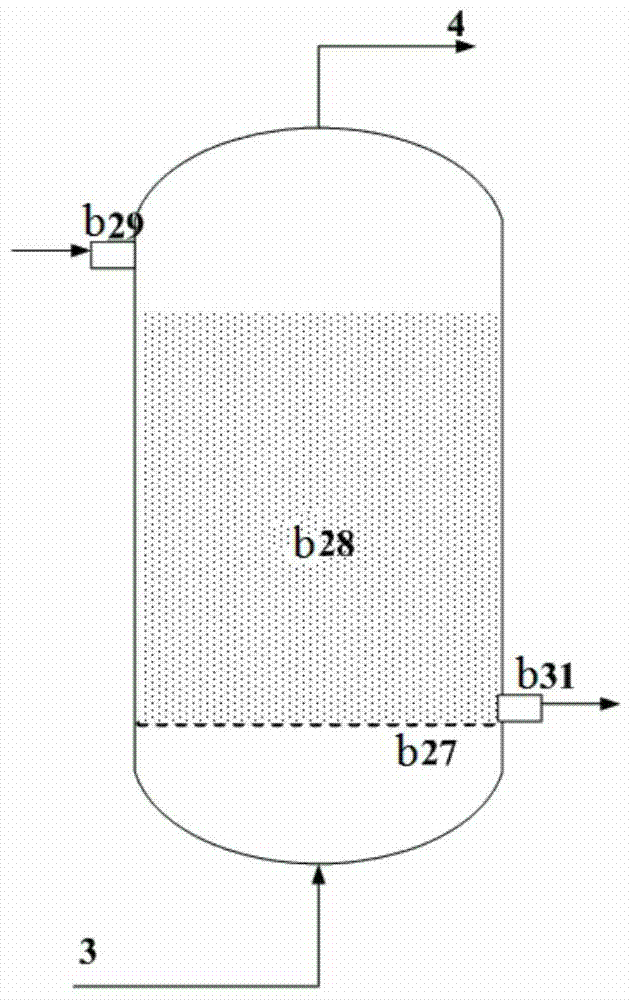
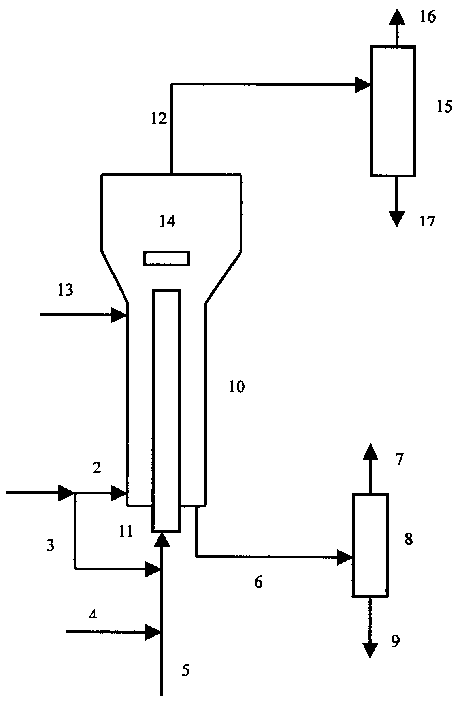
A heavy oil coking equipment
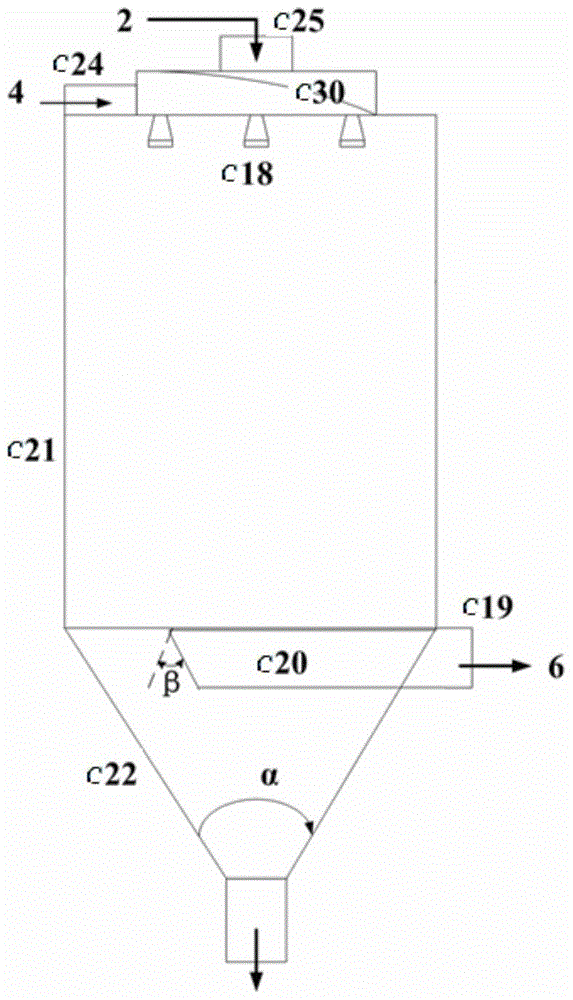
ActiveCN105586077BImprove coking performanceLower oxygen levelsTreatment with plural serial stages onlyCycloneFractionation
The invention provides heavy oil coking equipment, which includes a heating furnace (a), a coke reactor (b), a spray coking tower (c), a cyclone separator (d) and a fractionating tower (e). A coking raw material is preheated in a heating furnace (a) and then atomized by an atomizing nozzle (c18) of the spray coking tower (c), oxygen-containing high temperature gas from the heating furnace (a) is deoxidized by the coke reactor (b) and then contacts the atomized state coking raw material in the spray coking tower (c) to carry out coking reaction, the coarse coke powder in the coking reaction product is collected from a lower cone collection area (c22), oil gas and coke fine powder in the coking reaction product are separated by the cyclone separator (d), and oil gas is introduced into the fractionating tower (e) to perform fraction separation. Belonging to direct heating type coking equipment, the heavy oil coking equipment can greatly reduce coking in a heating furnace tube and improve the liquid yield, also the obtained coke powder and the dry gas from the fractionation tower can be burnt to serve as the heat source of the heavy oil coking equipment.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
A kind of heavy oil coking method
ActiveCN105586078BImprove coking performanceAvoid cokingTreatment with plural serial stages onlyFlue gasFuel oil
The invention provides a heavy oil coking method including the steps of: 1) atomizing a heavy oil coking raw material at 50-400 DEG C; 2) contacting the atomized heavy oil coking raw material with deoxidized flue gas at 490-750 DEG C to enable the atomized heavy oil coking raw material to reach a coking temperature, so that a coking reaction can be carried out; 3) separating coke coarse powder, coke fine powder and oil gas from a coking reaction product; and 4) performing fraction separation to the oil gas. The heavy oil coking method not only reduces, even completely avoids coking in a furnace tube of a heating furnace and increases liquid yield, but also is free of steps of desulfurization, denitrification and dust removal to the flue gas, so that the method is free of a large quantity of decoking waste water generated in coking and has a great industrial application prospect.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Poor residual hydroconversion method
InactiveCN1205318CImprove conversion rateLow yieldHydrocarbon oil crackingVapor–liquid separatorHydrogen
The invention provides a residual oil hydrocracking method, which adopts a tube-in-tube reactor, and a gas-liquid separator is arranged on the top of the inner tube. The separator is separated, the gas phase is discharged from the reactor, and the liquid phase enters the loop reaction section together with the added hydrocarbon oil containing more heavy aromatics, and at the same time hydrogen is added at the bottom of the loop reaction section. Compared with the prior art, the method of the invention has the advantages of uniform reactor temperature, less coke deposition, reduced dry gas output and the like. The method of the invention is mainly applicable to the hydrocracking reaction of heavy and residual oil, especially the hydrocracking reaction of inferior heavy and residual oil.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Heavy oil coking method
ActiveCN105586079AReduce cokingHigh yieldTreatment with plural serial stages onlyCombustion chamberProcess engineering
The invention provides a heavy oil coking method. The method comprises the following steps: heavy oil coking raw materials are preheated in a radiation heating zone of a heating furnace to 50-400 DEG C; the materials are introduced into a spraying and coking tower for atomization, and oxygen-containing high-temperature gas generated in a combustion chamber of the heating furnace is deoxidized; after deoxidation, deoxidized high-temperature gas and heavy oil coking raw materials in atomized state are contacted in the spraying and coking tower, the heavy oil coking raw materials in atomized state reach a coking temperature, and a coking reaction is carried out; rough coke powder, fine coke powder and oil gas are separated from coking reaction products, and fraction separation is carried out for the oil gas. The heavy oil coking method can reduce coking in a furnace tube of the heating furnace and increase liquid yield, and the method has an industrial application prospect.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Desulfurization catalyst, method for preparing desulfurization catalyst and hydrocarbon oil desulfurization method
ActiveCN104549488AHigh desulfurization activityGood desulfurization stabilityMolecular sieve catalystsOther chemical processesMolecular sieveTin dioxide
The invention discloses a desulfurization catalyst, a method for preparing the desulfurization catalyst, the desulfurization catalyst prepared by the method and a hydrocarbon oil desulfurization method. The desulfurization catalyst contains an SAPO molecular sieve, rare earth oxide, tin dioxide, silicon oxide, zinc oxide and active metals, and has good desulfurization activity and desulfurization stability.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Catalyst system for enhanced flow syngas production
ActiveUS7922977B2Increase conversionsHigh selectivityCombination devicesExhaust apparatusSyngasProduct gas
A method and apparatus for converting a hydrocarbon and oxygen containing gas feed stream to a product stream, such as syngas, including catalytically partially oxidizing the hydrocarbon feed stream over a catalyst bed. The catalyst bed has a downstream zone which is less resistant to flow than the upstream zone.
Owner:PHILLIPS 66 CO
Two-way combined process of wax-oil hydrogenation treatment and catalytic cracking
ActiveCN100434496CLow aromatic contentLow sulfur and nitrogen contentTreatment with hydrotreatment processesWaxNaphtha
A two-way combined process of wax oil hydro-process and catalytic crack is carried out by entering wax oil, catalytic cracking re-circulating oil and catalytic cracking diesel oil into hydro-processor, hydrogenation reacting under existence of hydrogen and hydrogenation catalyst, separating for reactant to obtain gas, hydrogenation naphtha oil, hydrogenation diesel oil and hydrogenation tail oil, entering hydrogenation tail oil into catalytic cracker, crack reacting under existence of catalytic cracking agent, separating to obtain dry gas, liquefied gas, catalytic cracking gasoline, catalytic cracking diesel oil and catalytic cracking re-circulating oil and oil slurry, and circulating for catalytic cracking diesel oil and catalytic cracking re-circulating oil to hydro-processor. It has higher recovery rate and cetyl value, less sulfur content, arene content and coke output.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
A kind of heavy oil hydrogen conversion method
ActiveCN104560170BLightweightImprove conversion rateTreatment with hydrotreatment processesHydrogenReaction temperature
The invention provides a heavy oil hydro-conversion method. The method comprises the following steps that: (1) heavy oil or heavy oil and hydrogen enter a first reactor to be subjected to a hydrogen-thermal cracking reaction in the presence or absence of a hydrogen-thermal cracking catalyst; (2) deoiled asphalt, a hydrogen-thermal cracking catalyst and hydrogen enter a second reactor, contact with the hydrogen-thermal cracking catalyst, and are subjected to a hydrogen-thermal cracking reaction at a relatively low temperature; (3) the reaction product in the first reactor and the reaction product of the second reactor are mixed and enter a separation unit, and are separated to obtain a distillate product and residual oil; and (4) the residual oil from the step (3) enters a solvent extraction tower to remove asphalt to obtain deasphalted oil and deoiled asphalt, and the deoiled asphalt is returned to the second reactor for further reacting, wherein the reacting temperature of the second reactor is 5-50 DEG C lower than that of the first reactor. Compared with the prior art, the method has the advantages of remarkably improving the heavy oil conversion rate and light oil yield, and improving the light rate of heavy oil.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
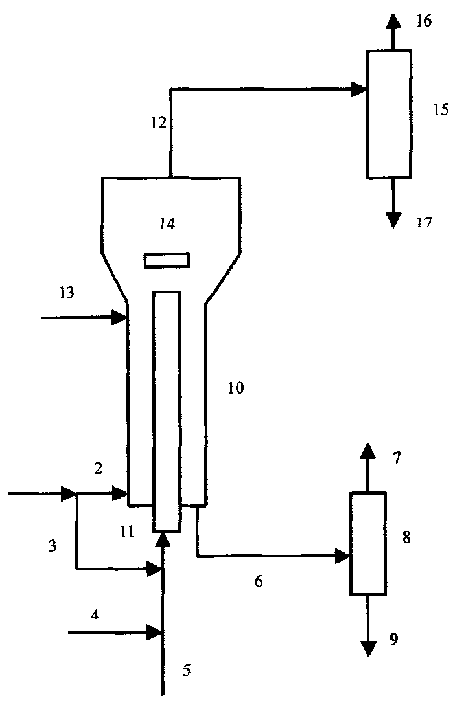
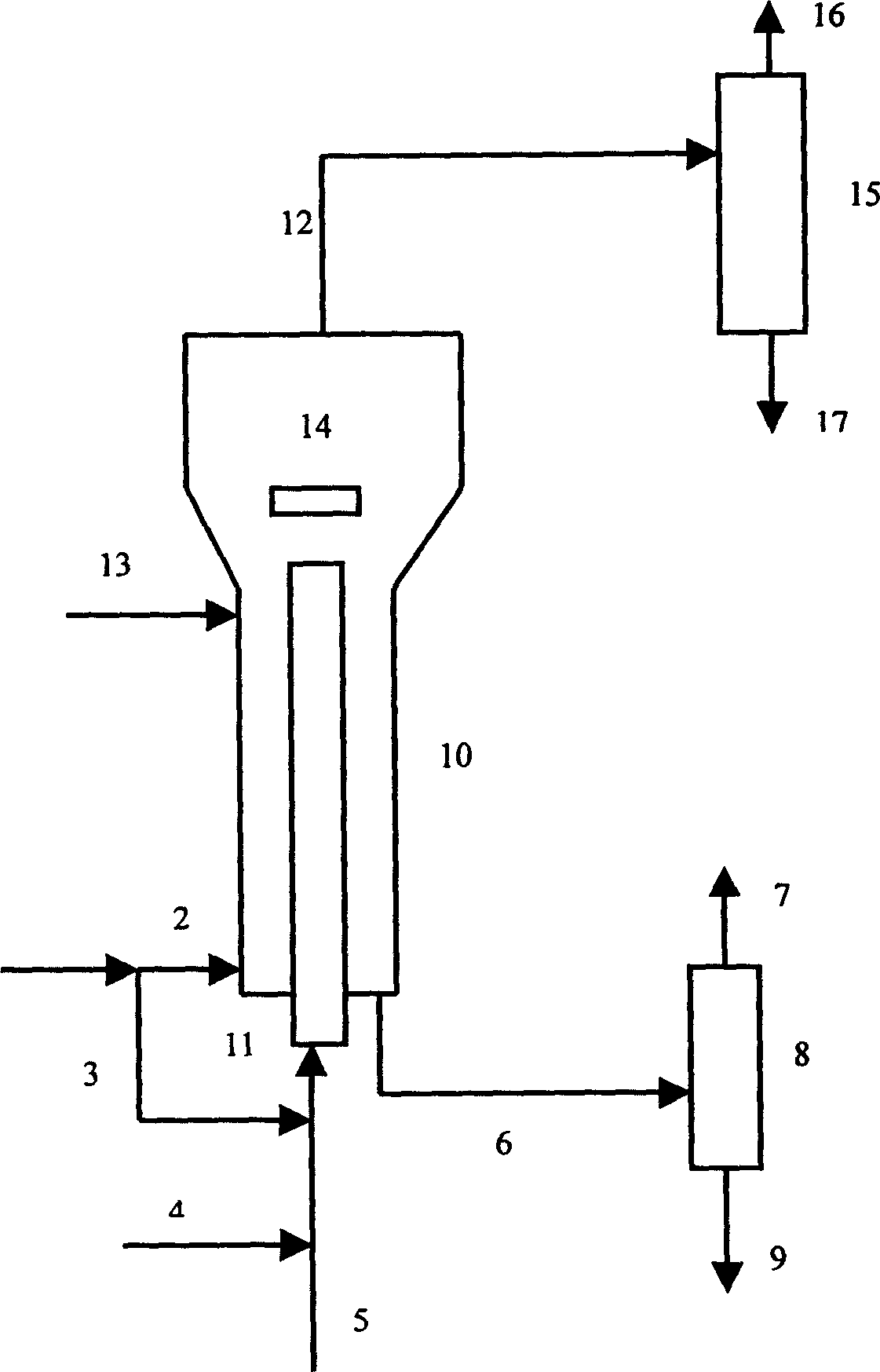
Efficient fluidized catalytic converting steam stripping device
InactiveCN1611288ALess cokeHigh yieldDistillation separationChemical/physical processesEngineeringYield rate
The present invention relates to a high-efficiency fluid catalytic conversion stripper. Said equipment comprises cylinder body, interior of said cylinder body is equipped with several layers of baffle plates, lower portion of the cylinder body is equipped with steam inlet, and its upper portion is equipped with waste gas outlet, the interior of said cylinder body is equipped with more tan two stages of stripping stages, the upper portion of said cylinder body is equipped with primary stripper, and the side of cylinder body of said primary stripper is equipped with inlet of catalyst with oil, its lower portion is equipped with steam inlet, and its upper portion is equipped with waste gas outlet, the upper end or lower end of cylinder body of primary stripper can be communicated with the cylinder body of stripper. Said invention can raise the yield rate of light oil.
Owner:石宝珍
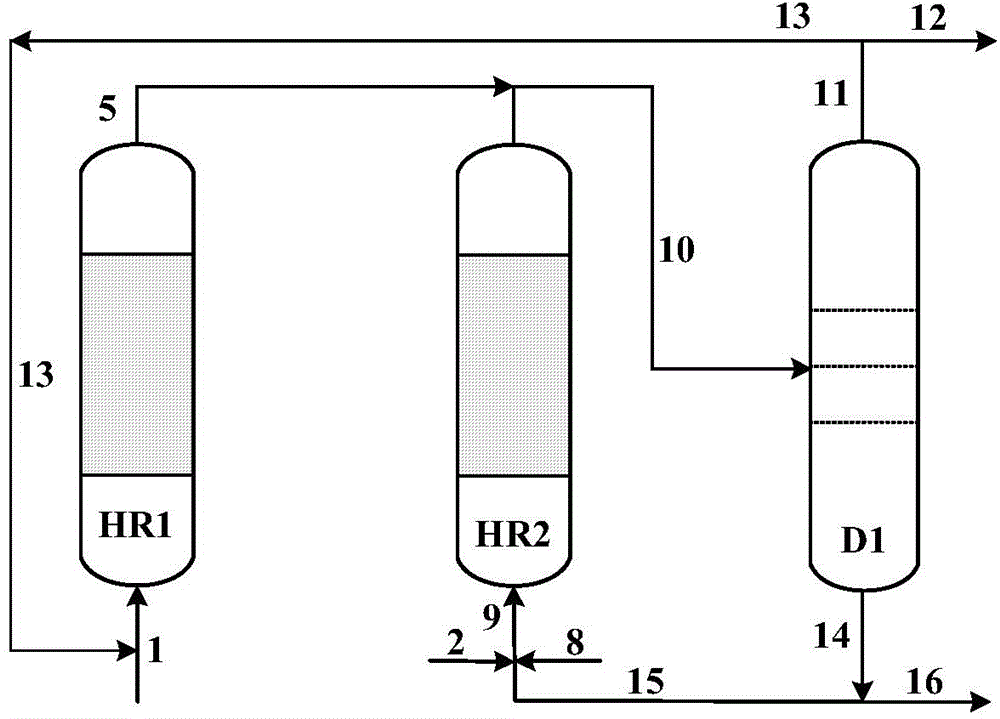
Hydrogenation coke method by adding coking distillate oil in residual oil
InactiveCN103421538AImprove burn cycle is shorterEfficient use ofHydrocarbon oil crackingCycloalkaneChemistry
The invention relates to a hydrogenation coking method by adding coking distillate oil in residual oil. According to the invention, coking distillate oil and the coking raw material residual oil are mixed according to a weight ratio of 0.2:0.4; the mixture is preheated in a heating furnace convection section, and is delivered into a buffering tank; the mixture is heated into a heating furnace radiation section and is heated to a coking temperature; the mixture is coked in a coking tower. A reaction tower inlet temperature is 480-520 DEG C, and a pressure is 0.1-1MPa. The coking distillate oil is selected from coking diesel, coking middle-section distillate, coking light gas oil, coking heavy gas oil, or a mixture thereof. According to the invention, because the coking distillate oil is rich in benzo cycloalkane ring, the coking distillate oil can be adopted as a hydrogen donor. Therefore, furnace pipe coking and production of shot coke can be inhibited, coke yield can be reduced, and liquid distillate oil product yield can be improved.
Owner:PETROCHINA CO LTD +1
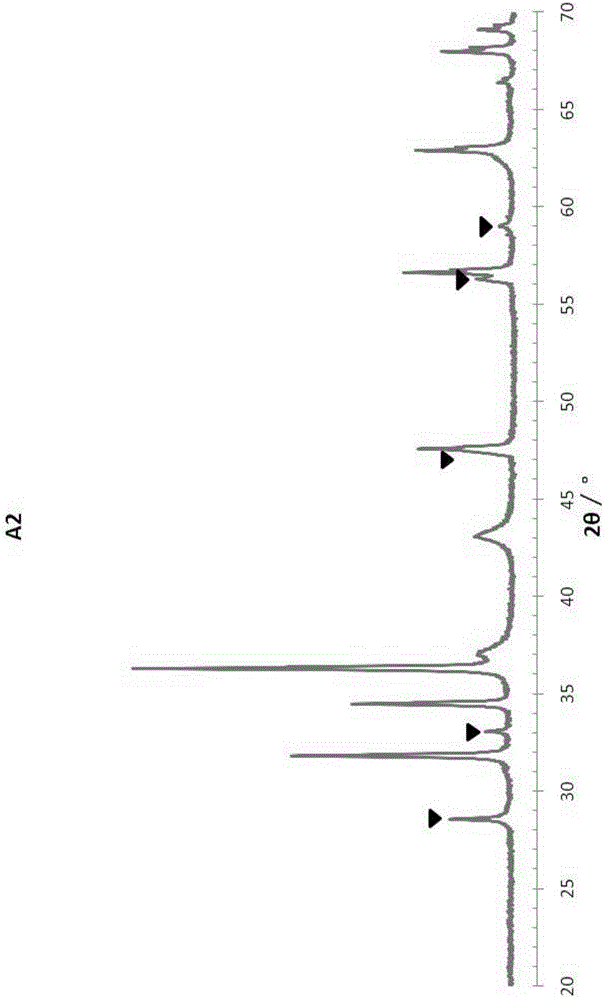
Desulphurization catalyst and preparation method thereof as well as hydrocarbon oil desulfurizing method
ActiveCN105582944AReduced effectSilicate reductionMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsRefining to eliminate hetero atomsRare earthSilicon oxide
The invention discloses a desulphurization catalyst, and discloses a preparation method of the desulphurization catalyst and the desulphurization catalyst obtained by the method, and an application of the desulphurization catalyst in sulfur-containing hydrocarbon oil desulphurization. The desulphurization catalyst contains a non-aluminum oxide, a silicon oxide source, a first metal oxide, bismuth oxide, a rare-earth metal oxide and active metal; and an XRD spectrum of the desulphurization catalyst has a characteristic peak of a rare earth-bismuth composite oxide. The desulphurization catalyst has better desulphurization activity and activity stability.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
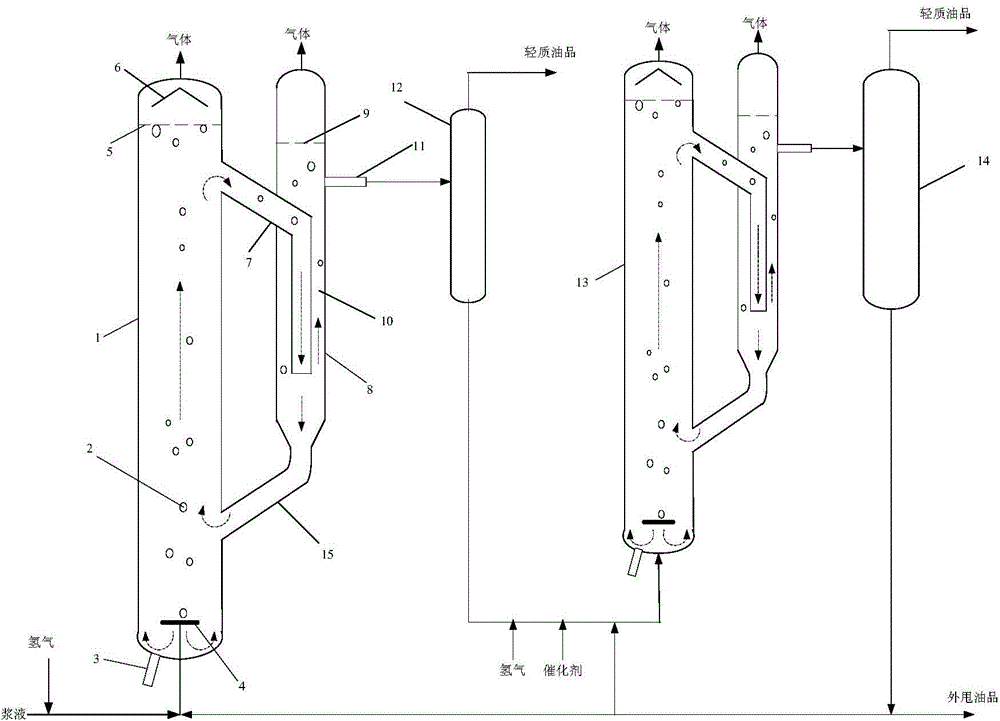
Two-stage heavy oil slurry-bed reactor hydrogenation equipment and application method
InactiveCN105623728AEfficient and lightweightHigh conversion rate of heavy oilTreatment with hydrotreatment processesProcess engineeringFuel oil
Two-stage heavy oil slurry-bed reactor hydrogenation equipment and an application method thereof are disclosed. The equipment comprises a first slurry-bed reactor, a first separating unit, a second slurry-bed reactor and a second separating unit. The slurry-bed reactor comprises a riser tube (1) and a downcomer (8). A splitter plate (10) is arranged inside the downcomer (8) to divide the internal space of the downcomer into two parts which are communicated up and down and separated in the middle. The upper part of the riser tube (1) and one side of the two space parts of the downcomer are communicated through an upper connecting pipe (7). The lower part of the riser tube (1) and the bottom of the downcomer (8) are communicated through a lower connecting pipe (15). The other side of the two space parts of the downcomer (8) is provided with a product outlet. The bottom of the riser tube (1) is provided with a raw material inlet. Tops of the riser tube (1) and the downcomer (8) are respectively provided with gas outlets. The two-stage heavy oil slurry-bed reactor hydrogenation equipment and the application method are convenient for long-term operation of the reactors, hydrogenation conversion rate of heavy oil is raised, and slurry processing of subsequent equipment is enhanced.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Two-stage heavy oil slurry-bed reactor hydrogenation equipment and method
InactiveCN105623729AImprove conversion rateImprove stabilityTreatment with hydrotreatment processesFuel oilProcess engineering
Two-stage heavy oil slurry-bed reactor hydrogenation equipment and a method thereof are disclosed. The equipment comprises a first slurry-bed reactor, a first separating unit communicated with the first slurry-bed reactor, a second slurry-bed reactor communicated with a discharge port of the first separating unit, and a second separating unit communicated with the second slurry-bed reactor. The first and second slurry-bed reactors comprise a riser tube (1) and a downcomer (8). Upper parts and lower parts of the riser tube (1) and the downcomer (8) are respectively communicated through connecting pipes. An opening of the upper connecting pipe (7) extends into the lower part of the downcomer (8). The bottom of the riser tube (1) is provided with a raw material inlet. Tops of the riser tube (1) and the downcomer (8) are respectively provided with gas outlets. The middle upper part of the downcomer (8) is provided with a product outlet. The two-stage heavy oil slurry-bed reactor hydrogenation equipment and the method are convenient for long-term operation of the reactors, hydrogenation conversion rate of heavy oil is raised, and slurry processing of subsequent equipment is enhanced.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Desulphurization catalyst and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN104415774AHigh desulfurization activityGood desulfurization stabilityMolecular sieve catalystsRefining with metal oxidesRare-earth elementSilicon oxide
The invention discloses a desulphurization catalyst, and also discloses a preparation method of the desulphurization catalyst and the desulphurization catalyst prepared by the method, and an application of the desulphurization catalyst in desulphurization of sulfur-containing hydrocarbon oil. The desulphurization catalyst contains an aluminosilicate molecular sieve with a duodenary-ring pore-channel structure, rare earth oxide, titanium dioxide, a silicon oxide source, zinc oxide and active metal; the rare earth element content in the aluminosilicate molecular sieve with the duodenary-ring pore-channel structure is 0 mumg / g; and the characteristic peaks of an tetragonal system of a rare earth-tin solid solution or an isometric system of a rare earth-tin composite oxide can be existed in a XRD spectrogram of the desulphurization catalyst. The desulphurization catalyst has better desulphurization activity and desulphurization stability.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
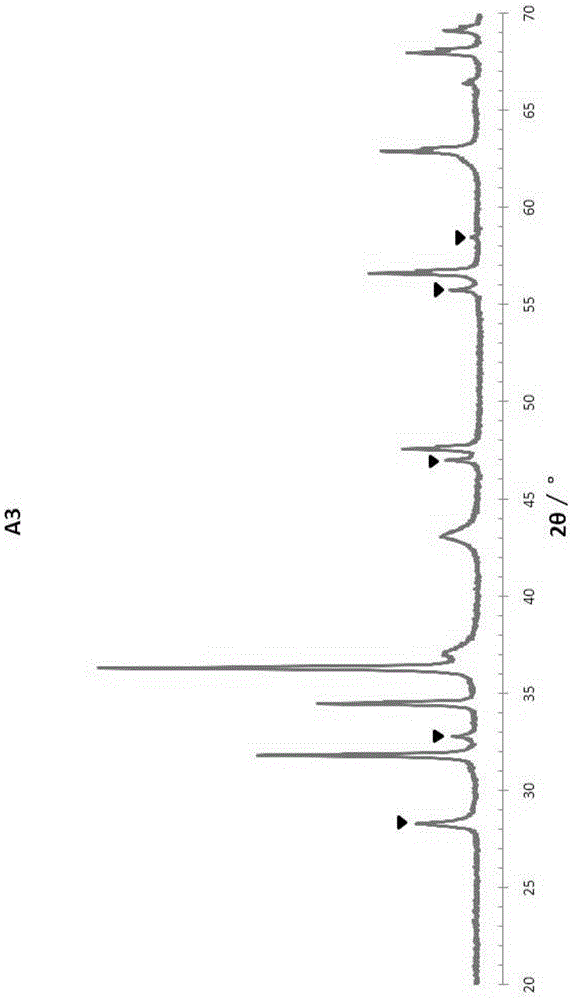
Desulphurization catalyst and preparation method thereof as well as hydrocarbon oil desulfurizing method
ActiveCN105582941AReduced effectSilicate reductionMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsRefining to eliminate hetero atomsRare earthLead oxide
The invention discloses a desulphurization catalyst, a preparation method of the desulphurization catalyst and the desulphurization catalyst obtained by the method, and an application of the desulphurization catalyst in sulfur-containing hydrocarbon oil desulphurization. The desulphurization catalyst contains alumina, a silicon oxide source, a first metal oxide, lead oxide, a rare-earth metal oxide and active metal; and an XRD spectrum of the desulphurization catalyst has a characteristic peak of a rare earth-lead composite oxide. The desulphurization catalyst has better desulphurization activity and activity stability.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Heavy oil hydro-conversion method
ActiveCN104560163AImprove light oil yieldKeep catalyst activeTreatment with hydrotreatment processesWaxChemistry
The invention provides a heavy oil hydro-conversion method. The method comprises the following steps: (1) a heavy oil raw material and heavy wax oil enter a first reactor in the presence of hydrogen and in the presence or absence of a hydrogen-thermal cracking catalyst to be subjected to a hydrogen-thermal cracking reaction; (2) the reaction product in the first reactor is separated into light distillate, heavy wax oil and residual oil; (3) the residual oil and hydrogen enter a second reactor, and contact with the hydrogen-thermal cracking catalyst to be subjected to a hydrogen-thermal cracking reaction at a relatively low temperature; (4) the reaction product in the second reactor is separated into light distillate, heavy wax oil and residual oil, the separated heavy wax oil is returned to the first reactor, and the separated residual oil part is respectively returned to the two reactors for further reacting according to a proportion; and the reacting temperature in the second reactor is 5-50 DEG C lower than that in the first reactor. Compared with the prior art, the method has the advantages of remarkably improving the heavy oil conversion rate and light oil yield, and improving the light rate of heavy distillate.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
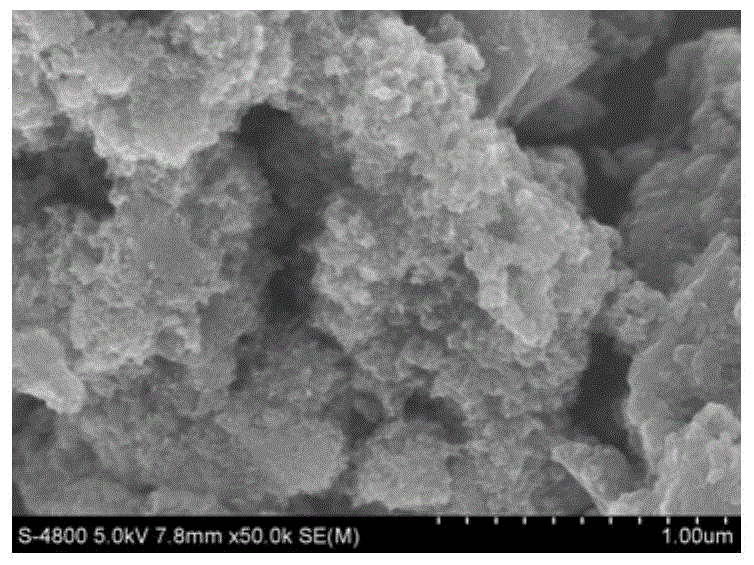
Catalytic hydroprocessing thermal cracking catalyst, preparation method thereof and composite catalyst
ActiveCN107282073AHigh molybdenum utilizationFacilitate depositionMolecular sieve catalystsHydrocarbon oil crackingFixed bedHydroxylamine Hydrochloride
The invention provides a catalytic hydroprocessing thermal cracking catalyst, a preparation method thereof and a composite catalyst for producing high-density fuel blending components by inferior heavy oil hydroprocessing. The catalyst takes silicon dioxide as an inner core, and molybdenum disulfide is coated outside the inner core to serve as a shell; and the catalyst is prepared by enabling an ethanol dispersion solution of ammonium tetrathiomolybdate and silicon dioxide, serving as a raw material, to react with an amphipathic molecule modifying agent under the participation of hydroxylamine hydrochloride serving as a reducing agent. The composite catalyst comprises the catalytic hydroprocessing thermal cracking catalyst and a fixed-bed hydrogenation catalyst. The catalyst is applied to the slurry-bed hydrocracking technology of inferior residual oil, the addition amount of the catalyst can be reduced, and the processing cost of the residual oil can be lowered.
Owner:INNER MONGOLIA SHENGYUAN TECH CO LTD +1
Desulphurization catalyst and preparation method thereof as well as hydrocarbon oil desulfurizing method
ActiveCN105582943AReduced effectHigh desulfurization activityMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsRefining to eliminate hetero atomsMischmetalRare earth
The invention discloses a desulphurization catalyst, a preparation method of the desulphurization catalyst and the desulphurization catalyst obtained by the method, and an application of the desulphurization catalyst in sulfur-containing hydrocarbon oil desulphurization. The desulphurization catalyst contains alumina, a silicon oxide source, a first metal oxide, antimony oxide, a rare-earth metal oxide and active metal; and an XRD spectrum of the desulphurization catalyst has a characteristic peak of a rare earth-antimony composite oxide. The desulphurization catalyst has better desulphurization activity and activity stability.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Desulfurization catalyst, preparation method thereof and method for desulfurizing hydrocarbon oil by employing same
ActiveCN105498831AReduced effectSilicate reductionMolecular sieve catalystsHydrocarbon oils refiningRare earthSilicon oxide
The invention discloses a desulfurization catalyst, a preparation method thereof and application of the desulfurization catalyst to desulfurize sulfur-containing hydrocarbon oil. The desulfurization catalyst contains a non-aluminium oxide, a silicon oxide source, a first metal oxide, antimony oxide, a rare earth metal oxide, a phosphorus-aluminium molecular sieve and an active metal. The XRD spectrum of the desulfurization catalyst possesses the characteristic peak of a rare earth-antimony composite oxide. The desulfurization catalyst possesses relatively good desulfurization activity and desulfurization stability.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
A kind of heavy oil hydrogen conversion method
ActiveCN104560163BImprove conversion rateImprove stabilityTreatment with hydrotreatment processesHydrogenReaction temperature
The invention provides a heavy oil hydro-conversion method. The method comprises the following steps: (1) a heavy oil raw material and heavy wax oil enter a first reactor in the presence of hydrogen and in the presence or absence of a hydrogen-thermal cracking catalyst to be subjected to a hydrogen-thermal cracking reaction; (2) the reaction product in the first reactor is separated into light distillate, heavy wax oil and residual oil; (3) the residual oil and hydrogen enter a second reactor, and contact with the hydrogen-thermal cracking catalyst to be subjected to a hydrogen-thermal cracking reaction at a relatively low temperature; (4) the reaction product in the second reactor is separated into light distillate, heavy wax oil and residual oil, the separated heavy wax oil is returned to the first reactor, and the separated residual oil part is respectively returned to the two reactors for further reacting according to a proportion; and the reacting temperature in the second reactor is 5-50 DEG C lower than that in the first reactor. Compared with the prior art, the method has the advantages of remarkably improving the heavy oil conversion rate and light oil yield, and improving the light rate of heavy distillate.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com