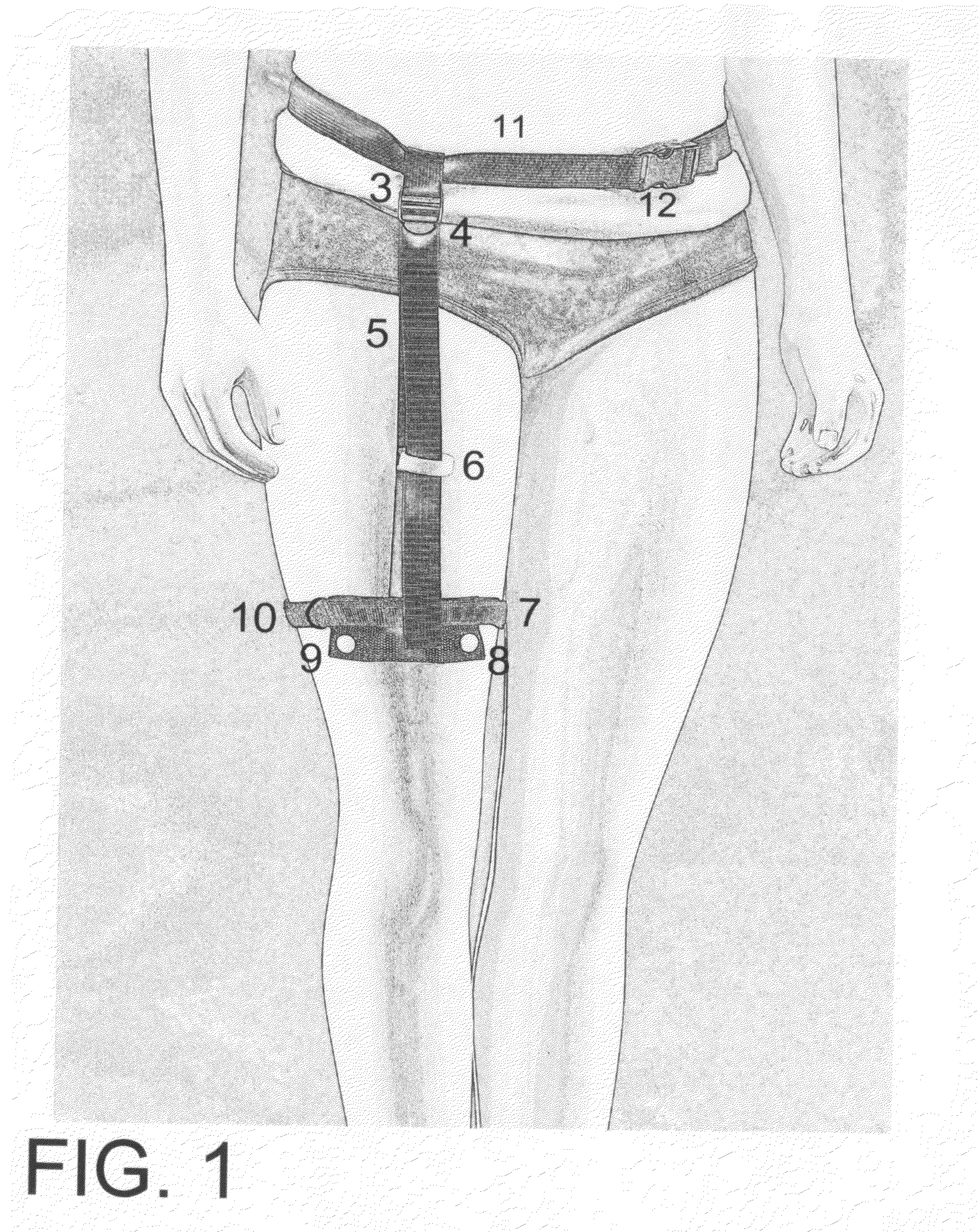Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
117results about How to "Issue can be solved" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
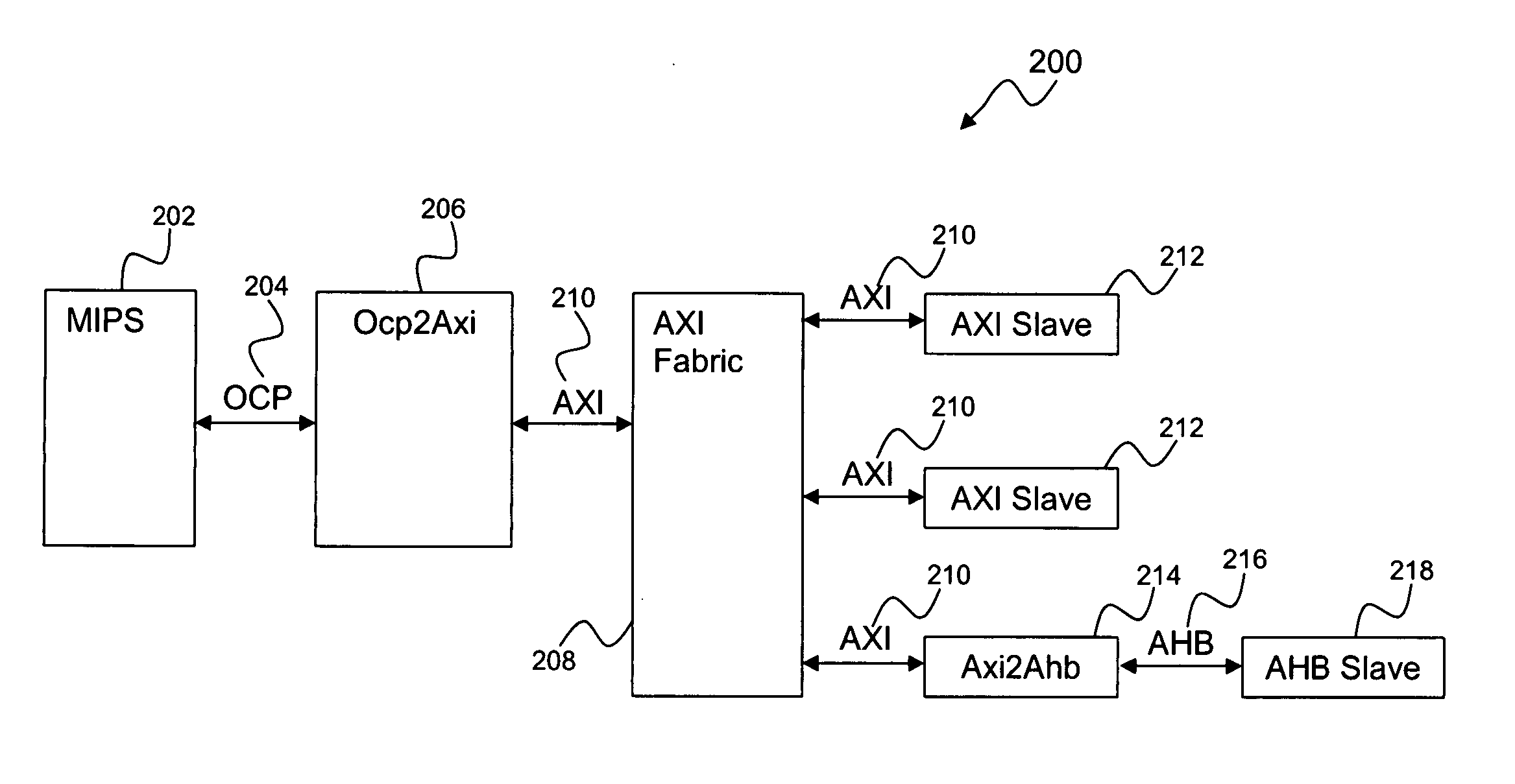
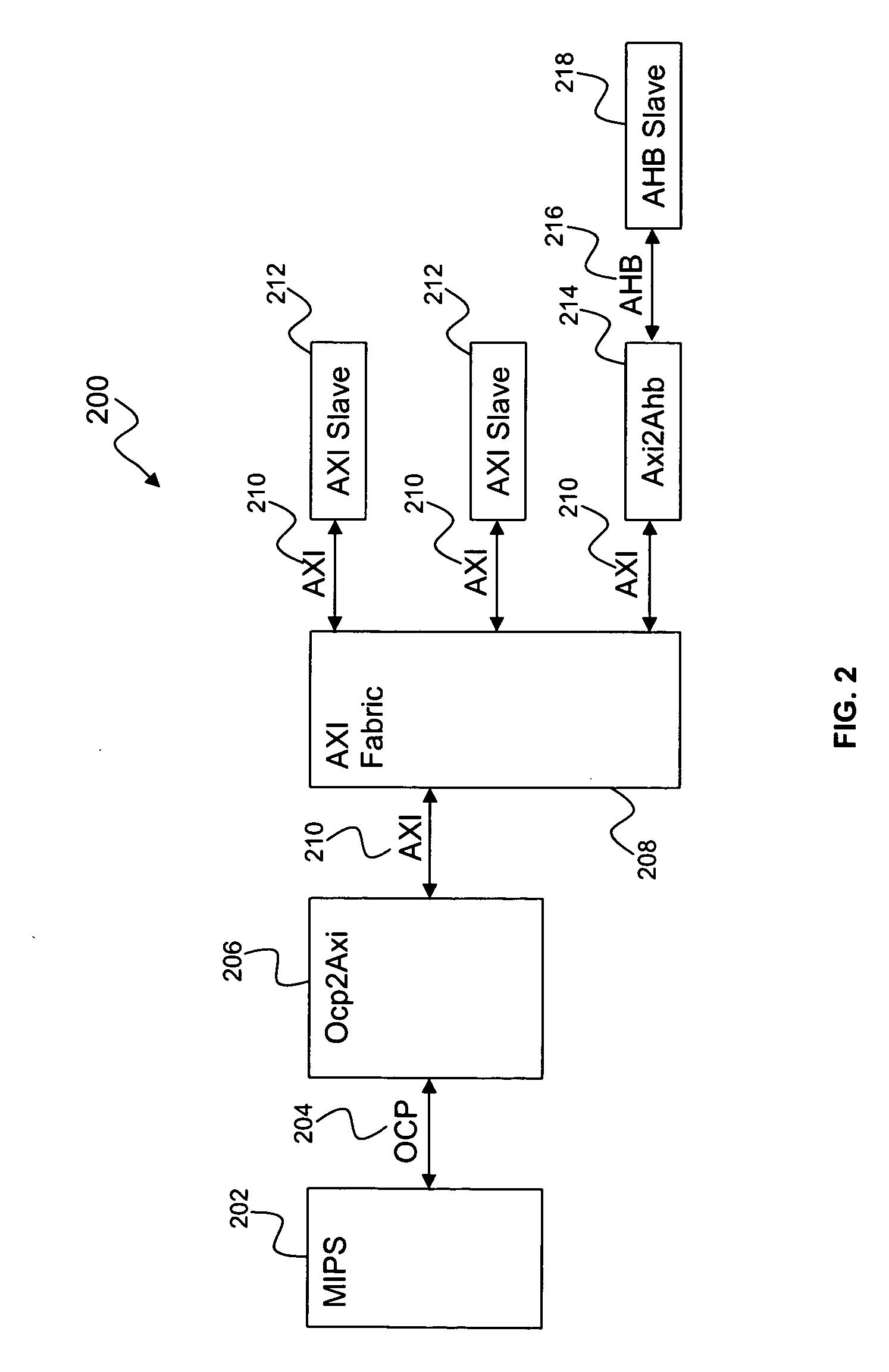
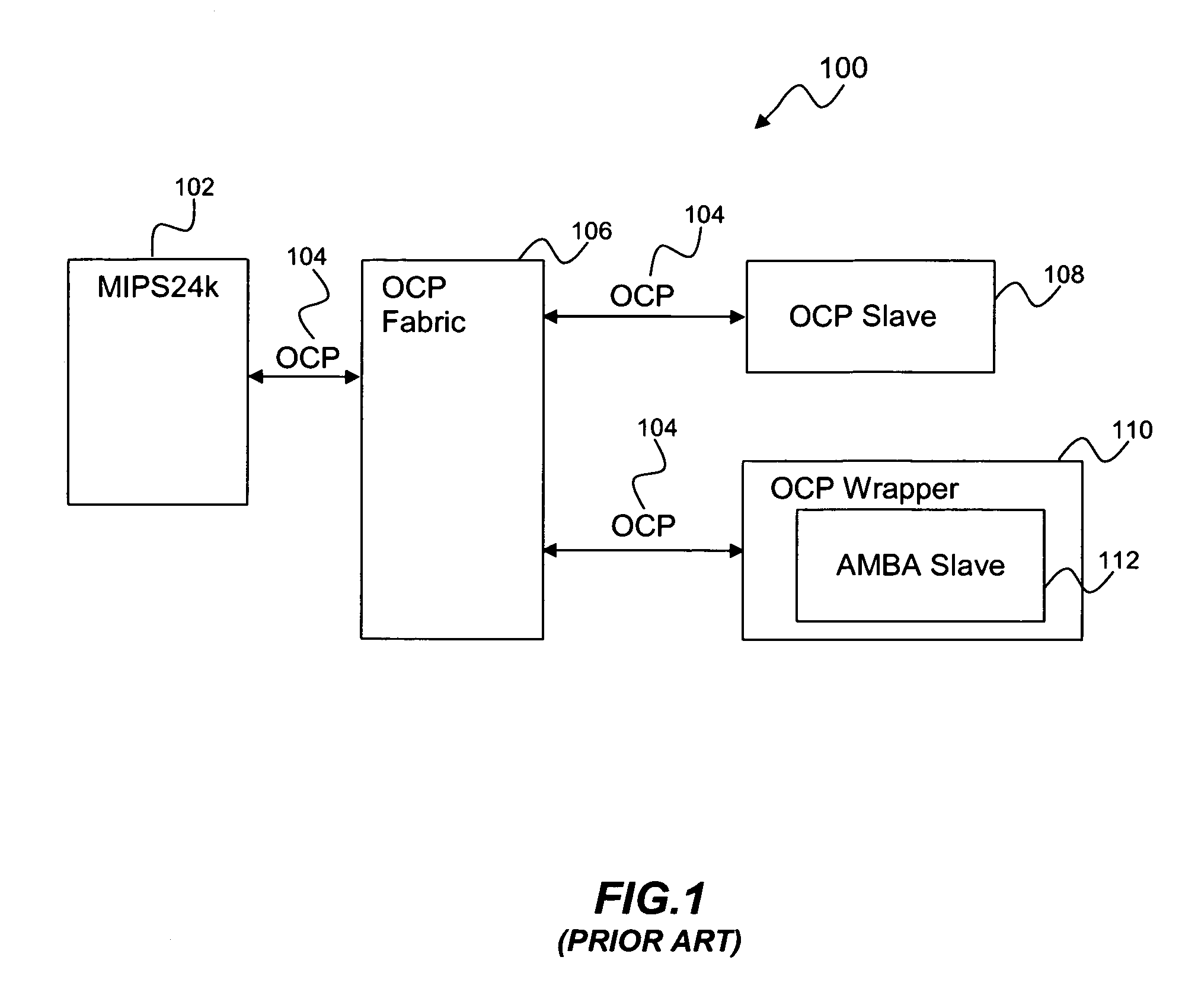
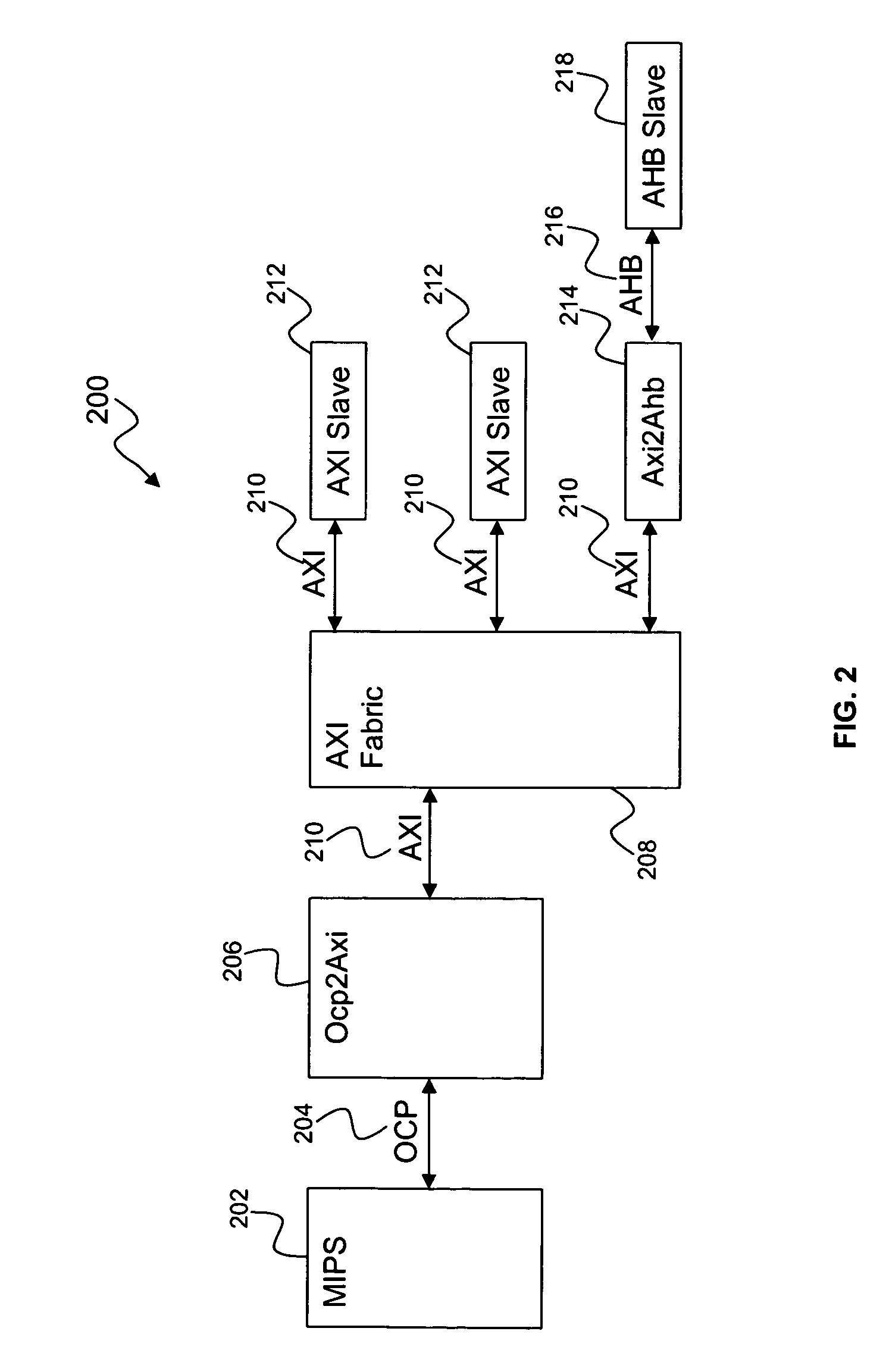
Method for request transaction ordering in OCP bus to AXI bus bridge design
ActiveUS20070067549A1Improve processor performanceImprove performanceData switching networksElectric digital data processingEmbedded systemComparator
A request transaction ordering method and system includes designing of the Open Core Protocol (OCP) bus to an Advanced extensible Interface (AXI) bus bridge. The general flow of the bridge is to accept a plurality of read and write requests from the OCP bus and convert them to a plurality of AXI read and write requests. Control logic is set for each first in first out policy of push and pop control and for a plurality of handshake signals in OCP and in the AXI. The request ordering part of the bridge performs hazard checking to preserve required order policies for both OCP and AXI bus protocols by using a FIFO (first in first out) policy to hold the outstanding writes, a plurality of comparators, a first in first out policy to hold OCP identities for a plurality of read requests.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Method for request transaction ordering in OCP bus to AXI bus bridge design
ActiveUS7457905B2Improve processor performanceImprove performanceData switching networksElectric digital data processingControl logicComparator
A request transaction ordering method and system includes designing of the Open Core Protocol (OCP) bus to an Advanced extensible Interface (AXI) bus bridge. The general flow of the bridge is to accept a plurality of read and write requests from the OCP bus and convert them to a plurality of AXI read and write requests. Control logic is set for each first in first out policy of push and pop control and for a plurality of handshake signals in OCP and in the AXI. The request ordering part of the bridge performs hazard checking to preserve required order policies for both OCP and AXI bus protocols by using a FIFO (first in first out) policy to hold the outstanding writes, a plurality of comparators, a first in first out policy to hold OCP identities for a plurality of read requests.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
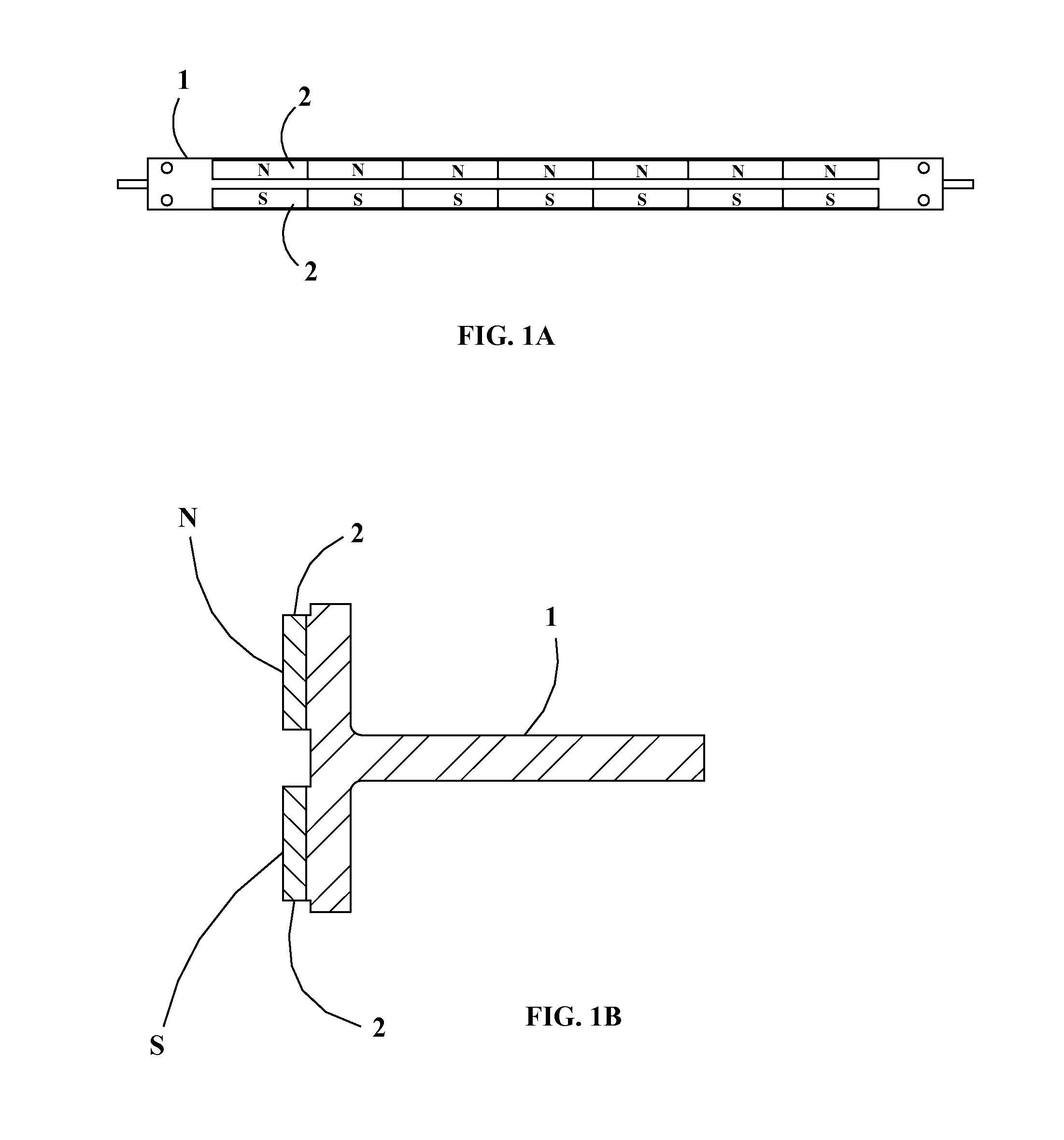
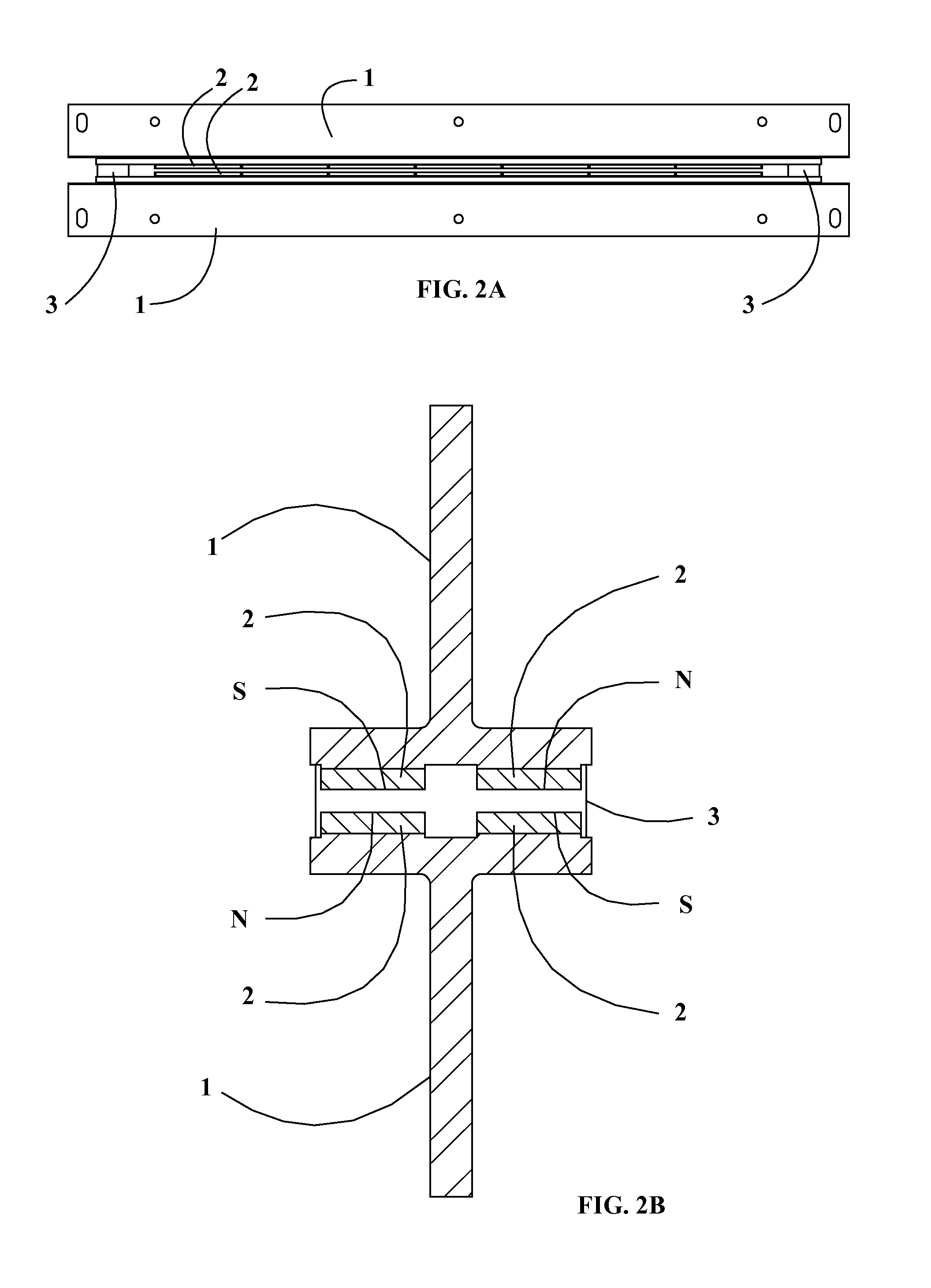
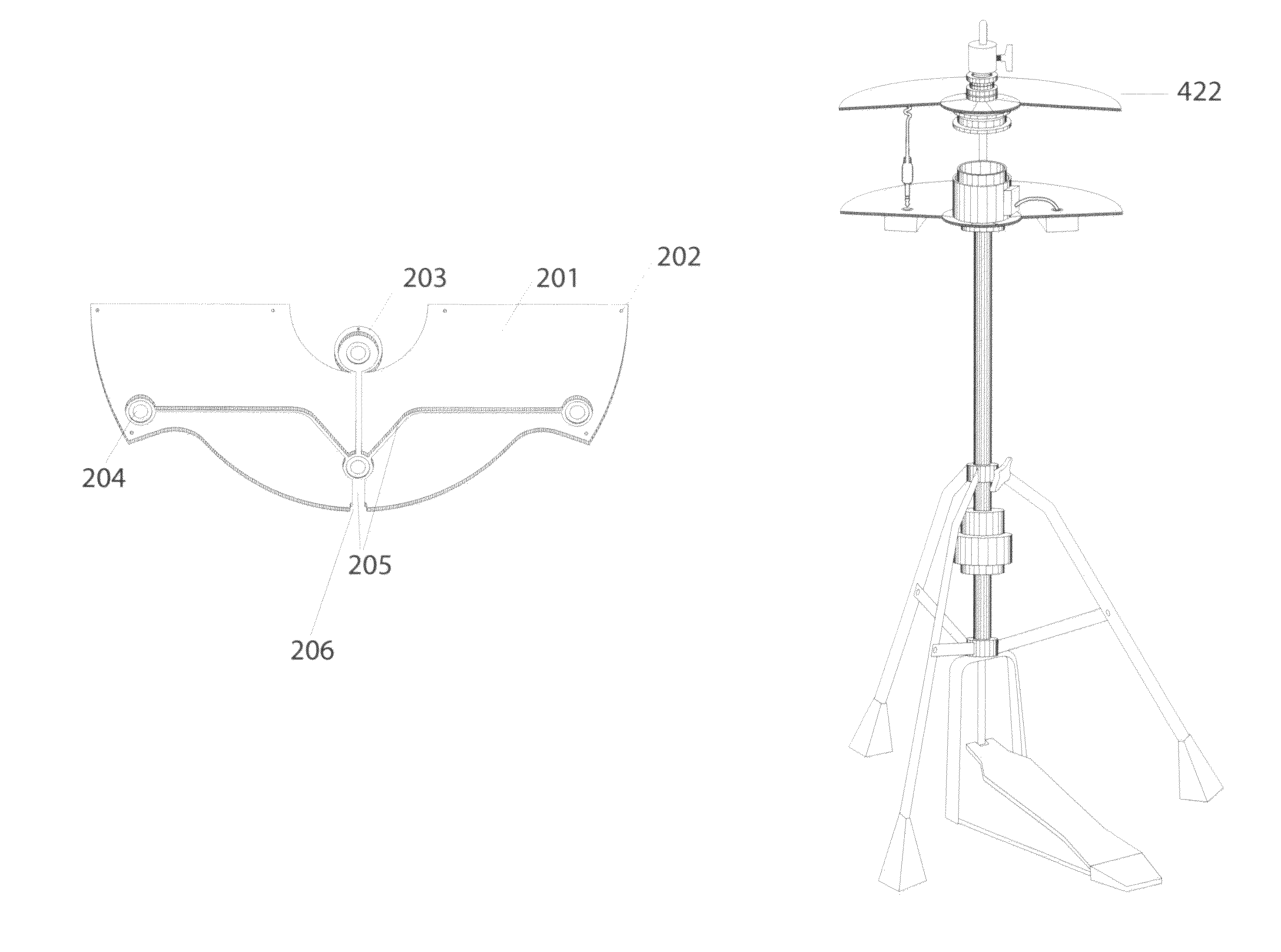
Electronic cymbal assembly with modular self-dampening triggering system
ActiveUS20120118130A1Easy maintenanceHighly accurate conversionElectrophonic musical instrumentsPercussion musical instrumentsThreaded rodClutch
The present invention includes an electronic cymbal assembly including a hi-hat clutch for mounting a hi-hat to a hi-hat stand post; a top cymbal; a self dampening trigger system attached to the underside of the top cymbal; a bottom cymbal; an input jack box mounted to the underside of the bottom cymbal; and a hi-hat cymbal mounting post. The cymbal assembly may be mounted using a magnetic ring configuration or a threaded pole configuration.
Owner:FIELD ELECTRONICS DRUMS
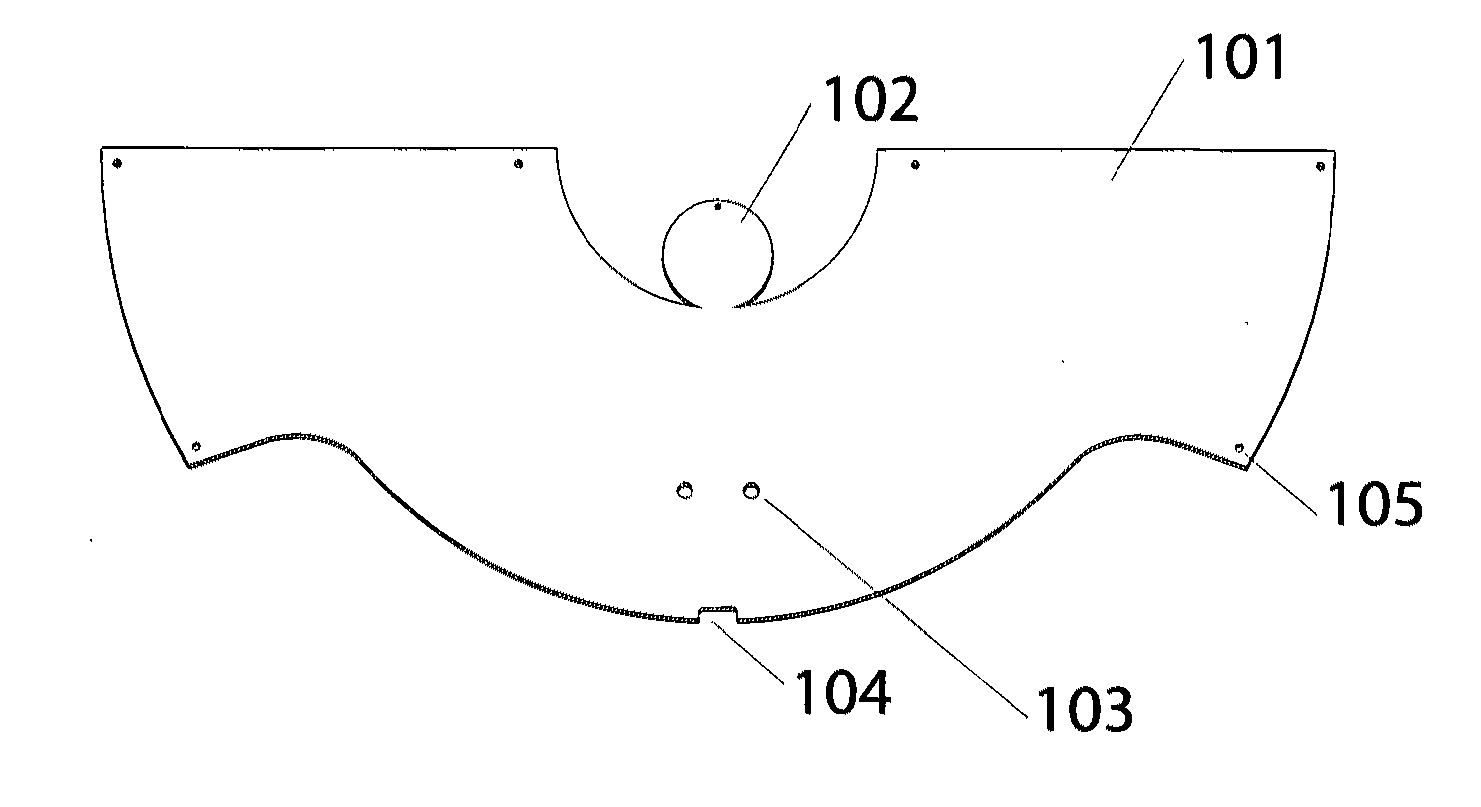
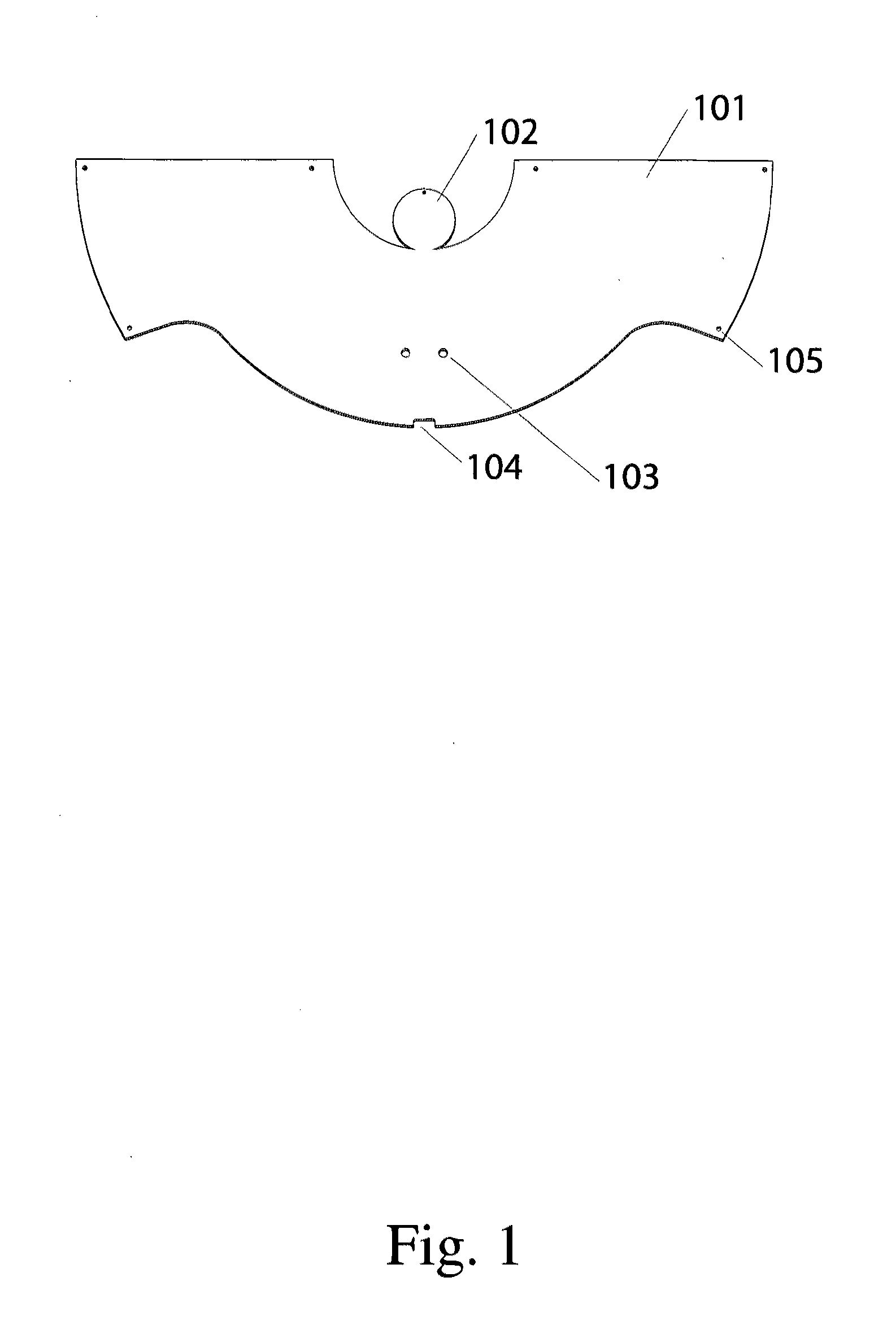
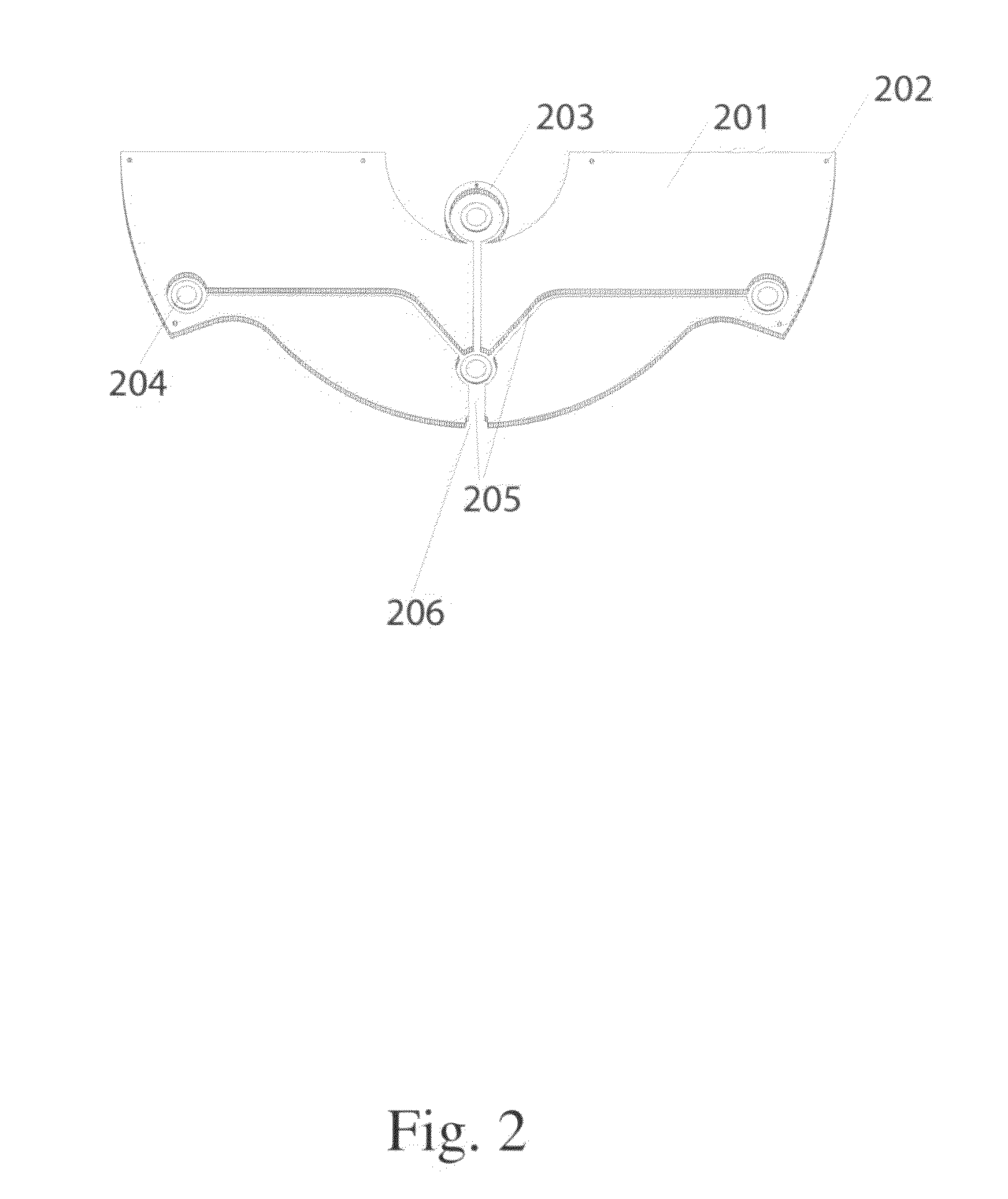
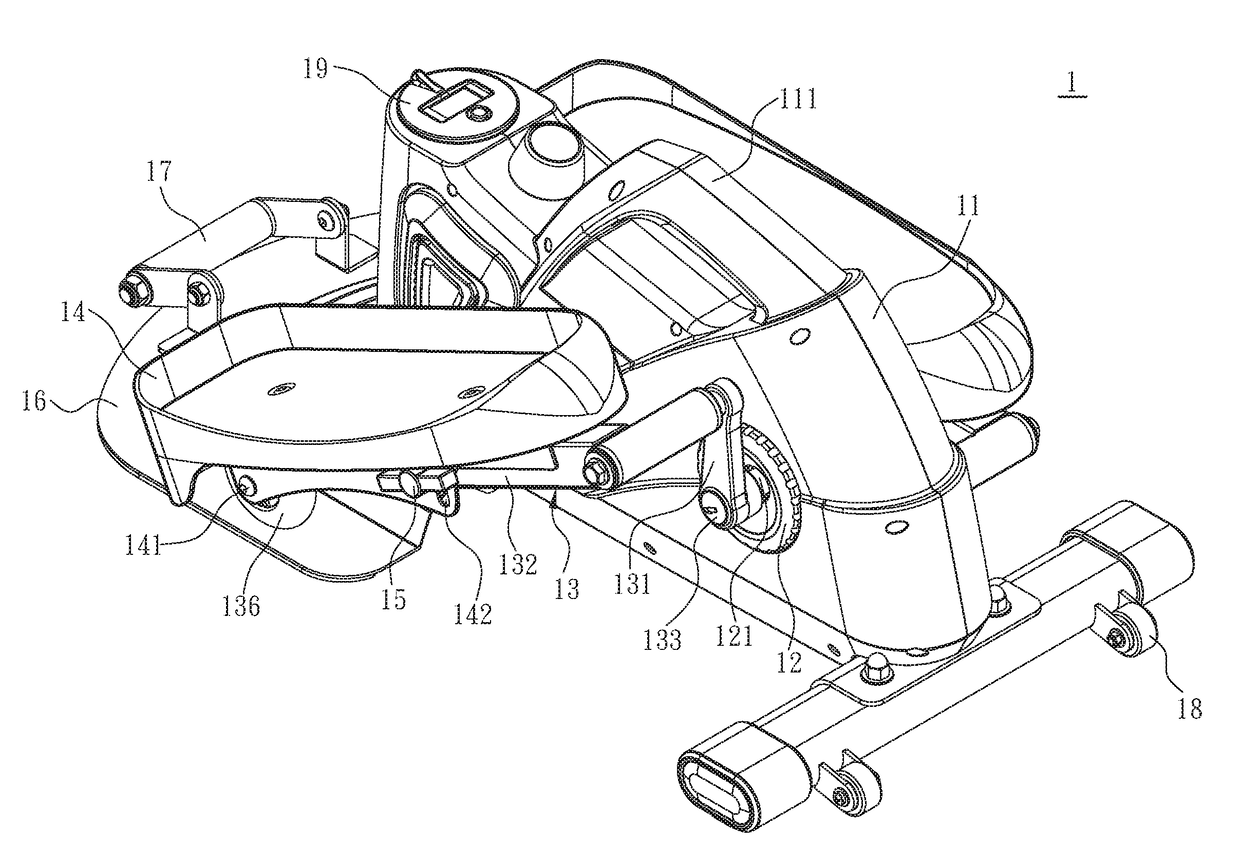
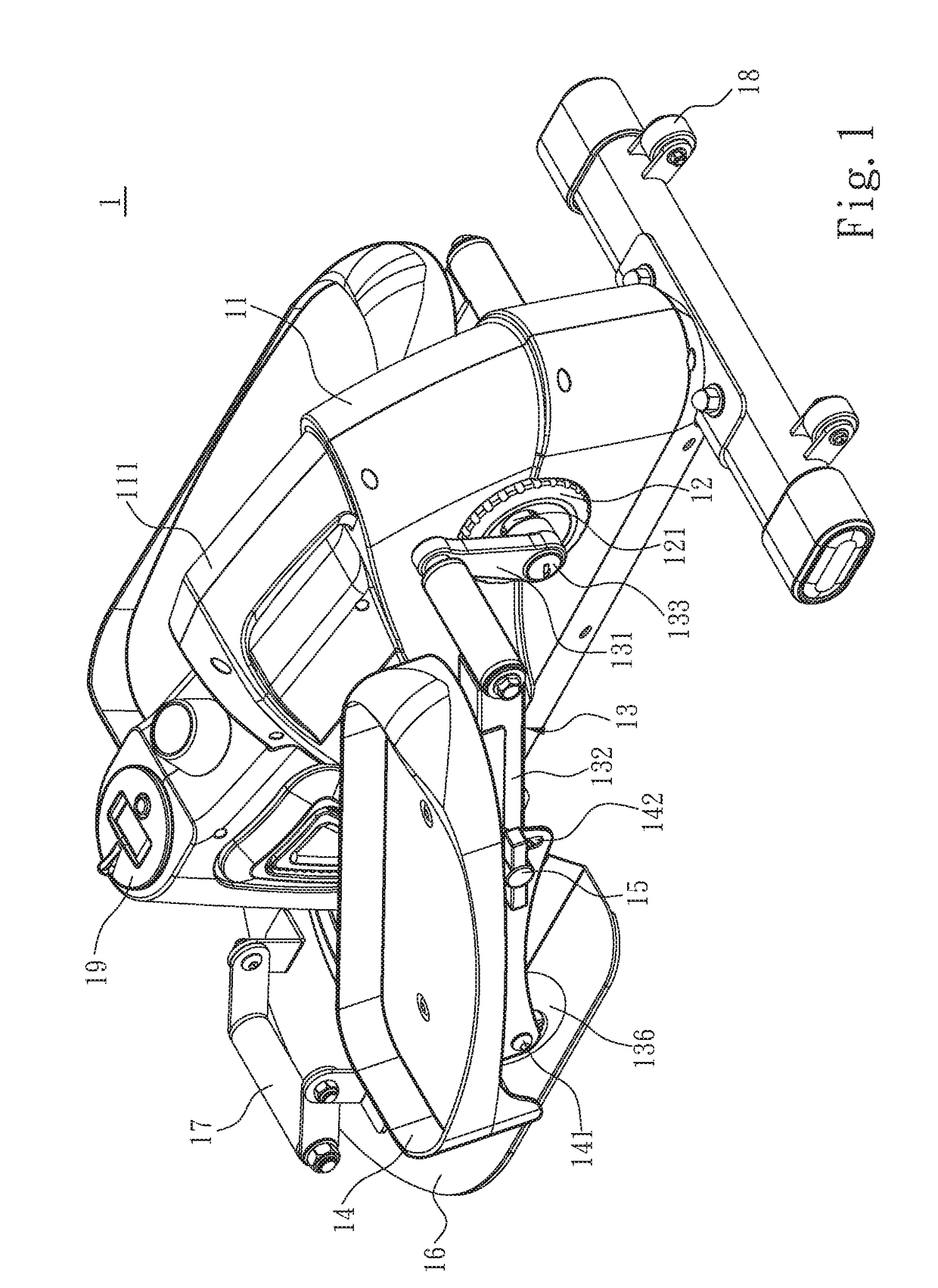
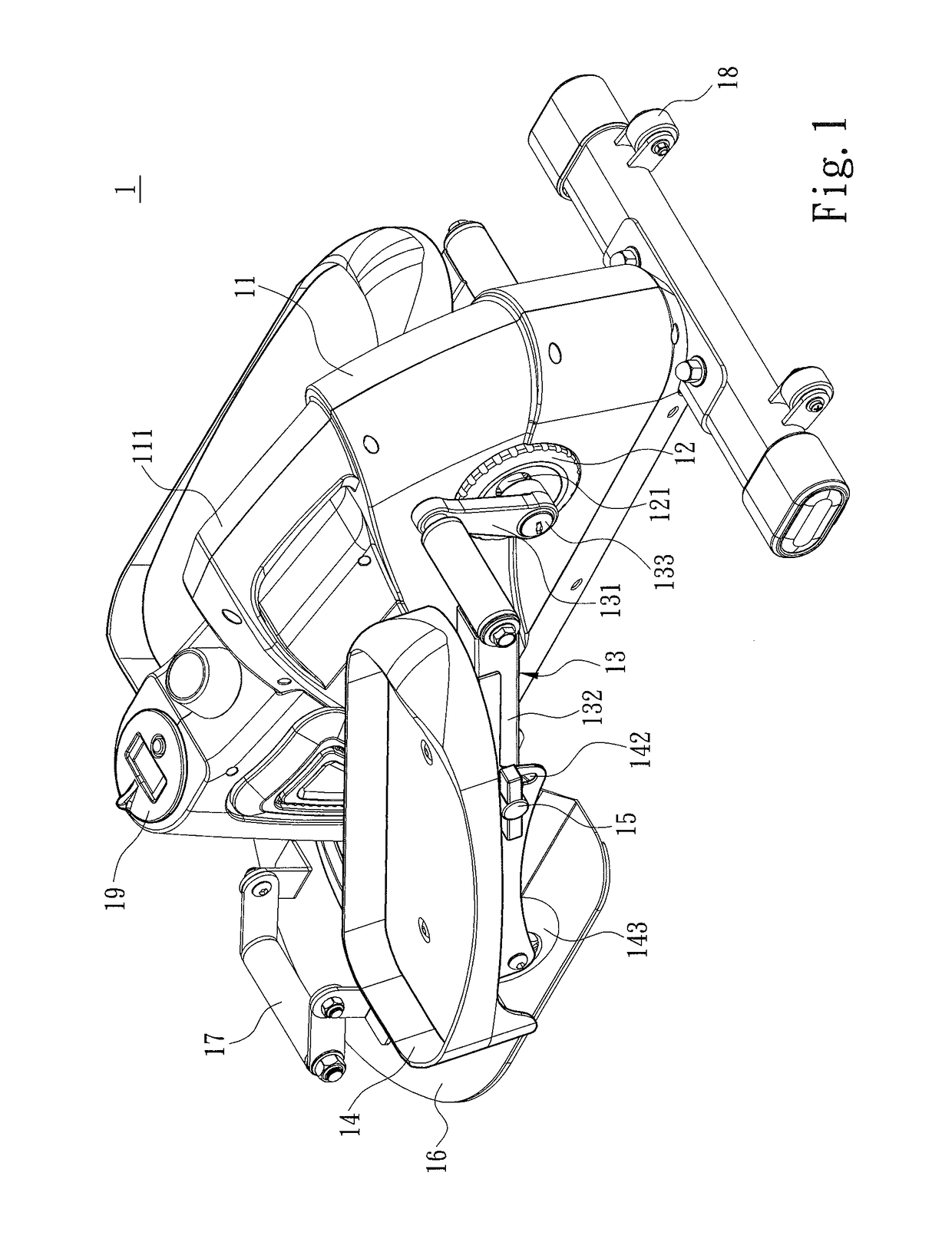
Portable sit-stand elliptical exercise machine
ActiveUS20170216660A1Improve utilizationIssue can be solvedSpace saving gamesMovement coordination devicesSitting PositionsFootplate
A portable sit-stand elliptical exercise machine includes a seat, a transmission wheel installed at the seat, two linkage mechanisms installed at the transmission wheel, and two mobile pedals respectively installed at the linkage mechanisms. Each linkage mechanism includes a driving portion connected to the transmission wheel, an axle portion disposed at one side away from the transmission wheel, and an adjustment portion disposed between the axle portion and the driving portion. Each mobile pedal is pivotally connected to the axle portion and includes a plurality of assembly portions. Thus, an angle is formed between each mobile pedal assembled to one of the assembly portions and the linkage mechanism to facilitate a user to utilize the portable sit-stand elliptical exercise machine in either a sitting or standing posture, thereby solving issue of a conventional solution that cannot be applied for a dual use of both sitting and standing postures.
Owner:LERNIHAN JODY NEWGARD
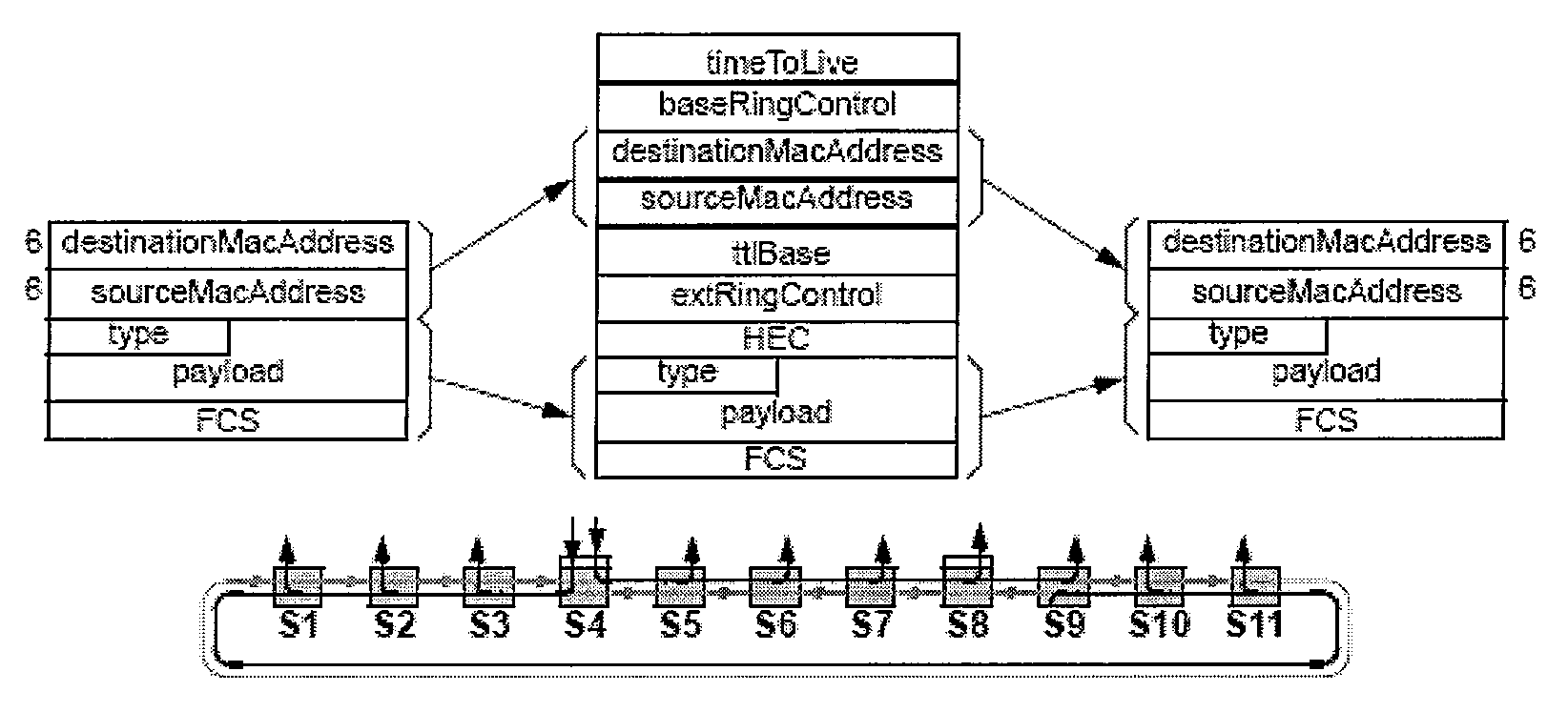
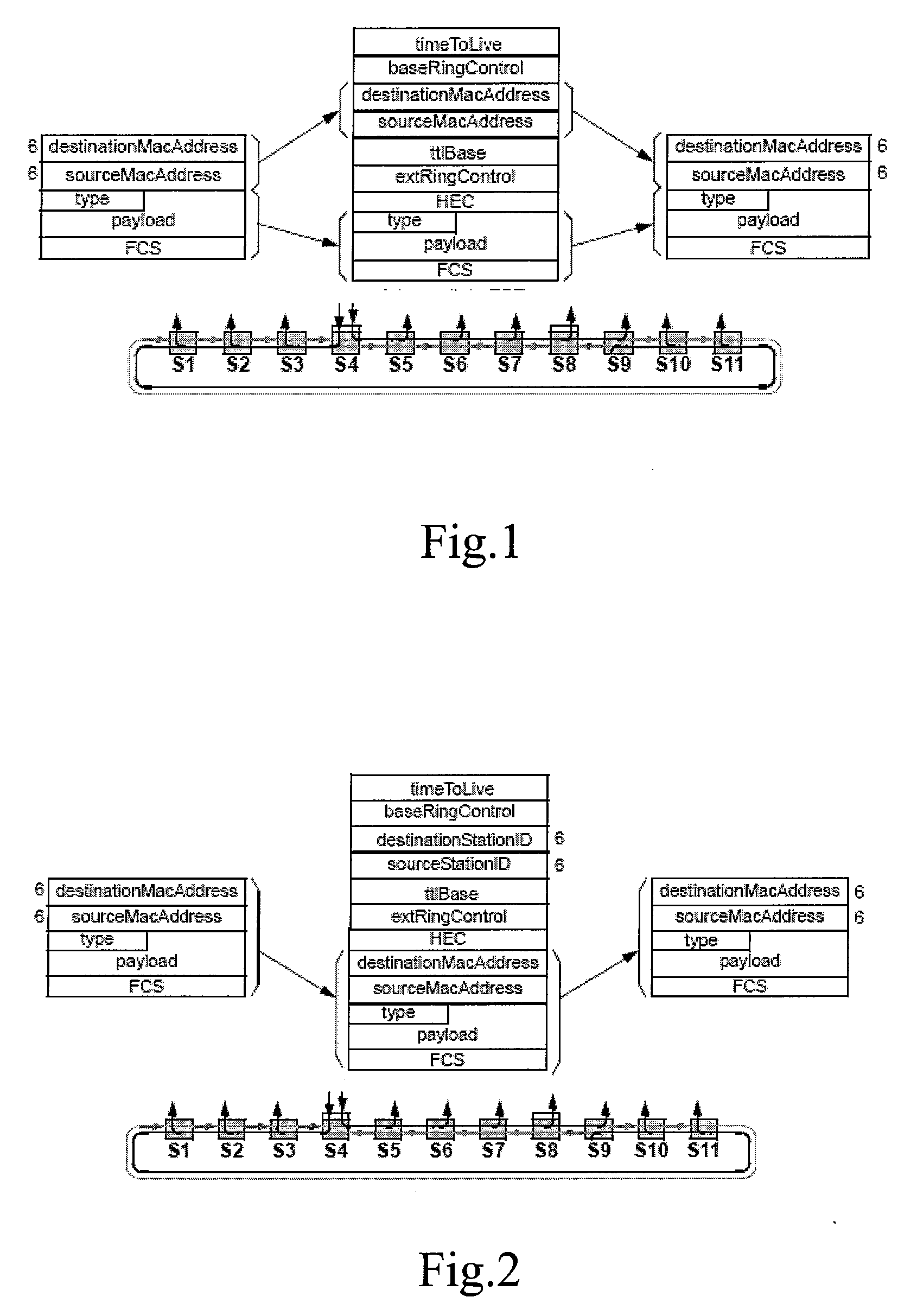
Method For Implementing on-Ring Process, Off-Ring Process and Data Forwarding in Resilience Packet Data Ringnet and a Network Device Thereof
InactiveUS20080130490A1Issue can be solvedEfficiently provideError preventionTransmission systemsStationEngineering
An inserting and copying processing method for implementing an L2 / L3 compatible RPR network is provided. The inserting processing method includes: encapsulating an Ethernet data frame with local mode or remote mode according to whether the source and destination MAC addresses of the Ethernet data frame may be found in the ring station MAC address table or in the correspondence table of host MAC address and RPR station, and whether the destination address of the Ethernet data frame is a unicast address or a non-unicast address. The copying processing method includes: recombining the RPR data frame into an Ethernet data frame according to the forwarding mode of the RPR data frame, and learning the correspondence relationship between source host address and RPR station address according to the Flooding flag and the forwarding mode of the RPR data frame. This invention also provides a data forwarding method and a network apparatus.
Owner:NEW H3C TECH CO LTD
Contiguous microlens array, method of fabricating the same and photomask for defining the same
ActiveUS20090174945A1Issue can be solvedAccurate recordOptical articlesPhotosensitive material processingMicro lens array
A contiguous microlens array including a plurality of contiguous microlenses is described. Each microlens has substantially circular contours at the heights higher than the connection sections of the microlens with neighboring microlenses, and has substantially partially circular contours at the heights on the connection sections adjacent to the neighboring microlenses. The shape of the curved surface of a microlens in the microlens array is selectively adjusted according to its position in the array and the incident angle of light incident thereto.
Owner:MARLIN SEMICON LTD
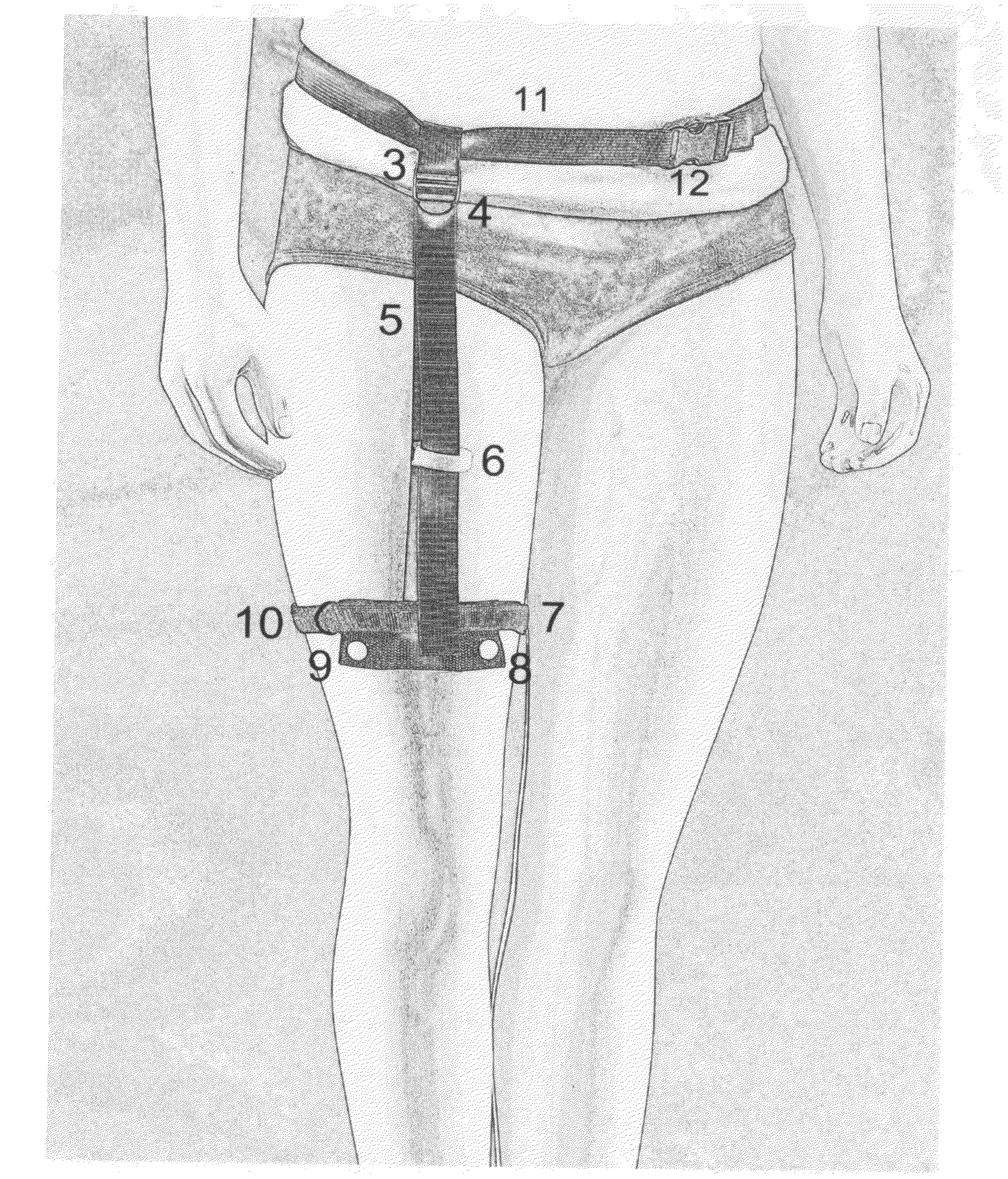
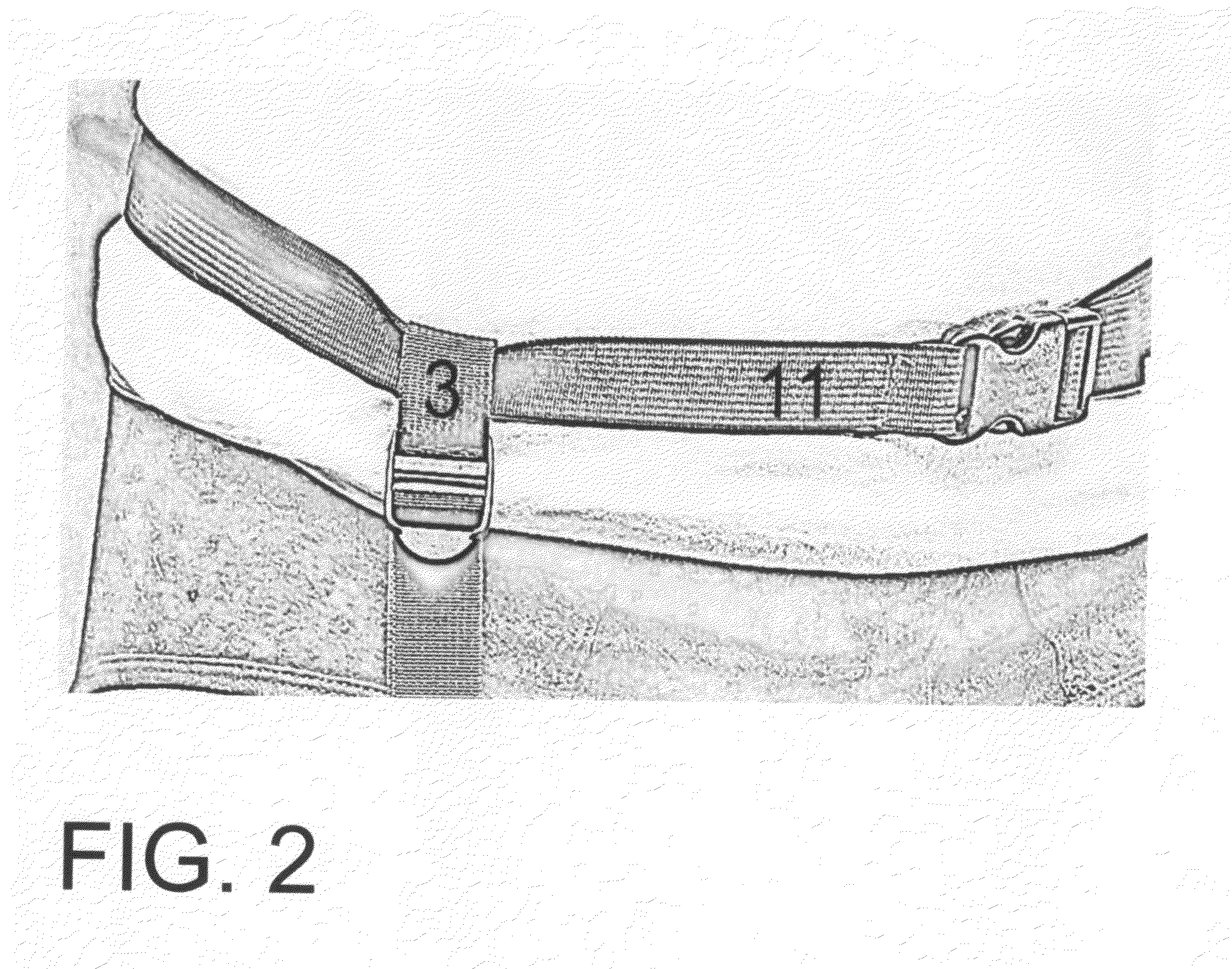
Catheter Leg Bag Support Device
InactiveUS20110202024A1Issue can be solvedFacilitated releaseColostomySuction devicesSupporting systemSupport system
A catheter leg bag support system is provided for supporting and holding in place a catheter bag. An adjustable belt is secured around a user's waist, with a drop down strap having an adjustable length attached to the belt. A hook and loop fastener wrap is provided on the drop down strap to attach to excessive catheter tubing in order to keep the tubing in a desired position. A reinforced stabilizer member is attached to the drop down strap to support a catheter bag, and can keep the catheter bag flat. Button posts attached to the reinforced member can quickly and easily connect to a conventional catheter leg bag. The catheter bag is secured in place along a user's leg using a soft and stretchable band that can be adjusted as loose or tight as desired.
Owner:COZZENS DEIRDRE LISA
Bag tossing game
Owner:DRIVEWAY GAMES COMPANY
Temperature conditioning radiant wall system for buildings
InactiveUS20070108307A1Reduce pipingReduce in quantityFluid heatersHot-air central heatingTemperature conditioningEngineering
Owner:CREATIVE ENERGY SOLUTIONS
Method and Apparatus for Maintaining Traffic Continuity
ActiveUS20120224476A1Maintain continuityIssue can be solvedError preventionTransmission systemsTraffic capacityNetwork packet
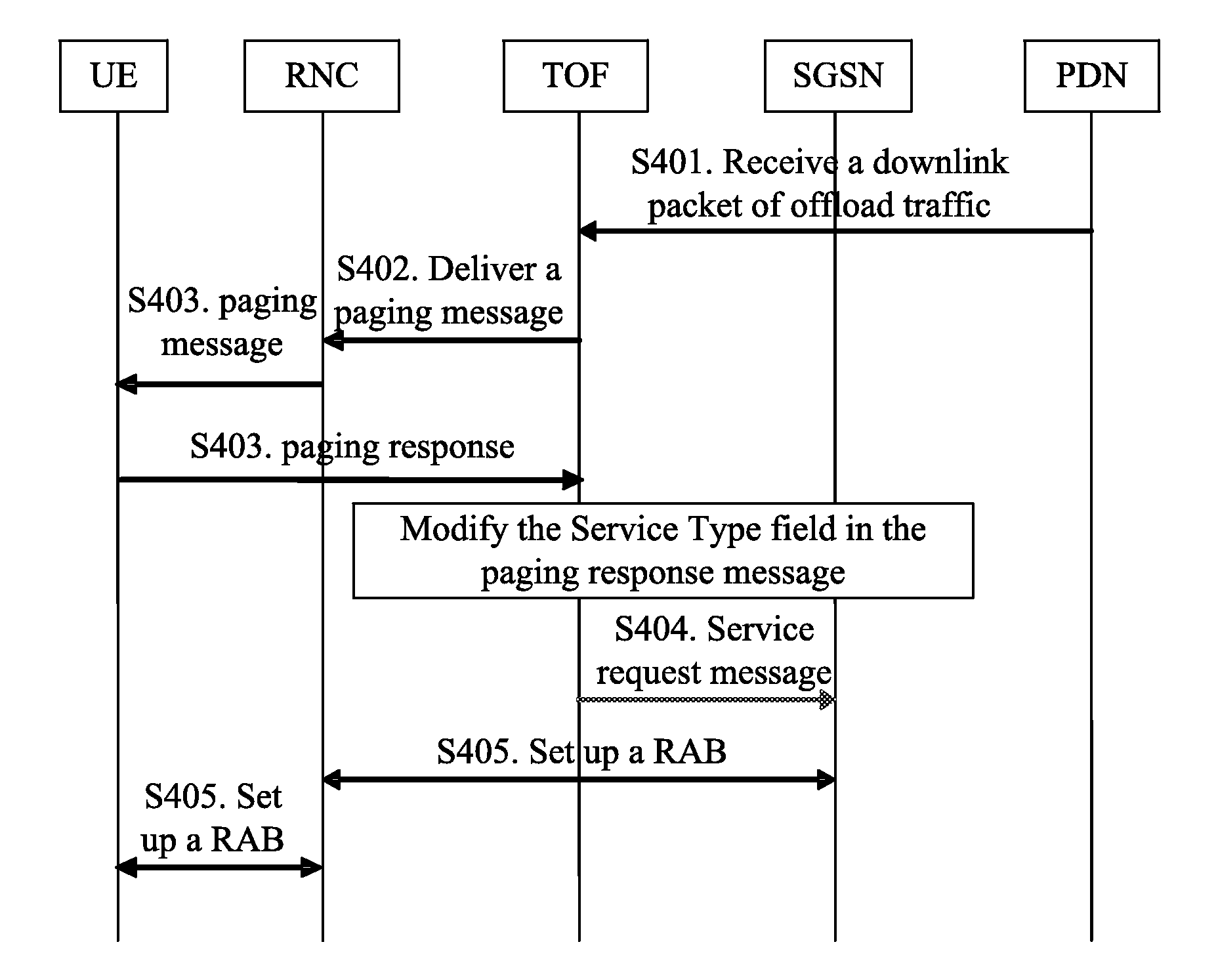
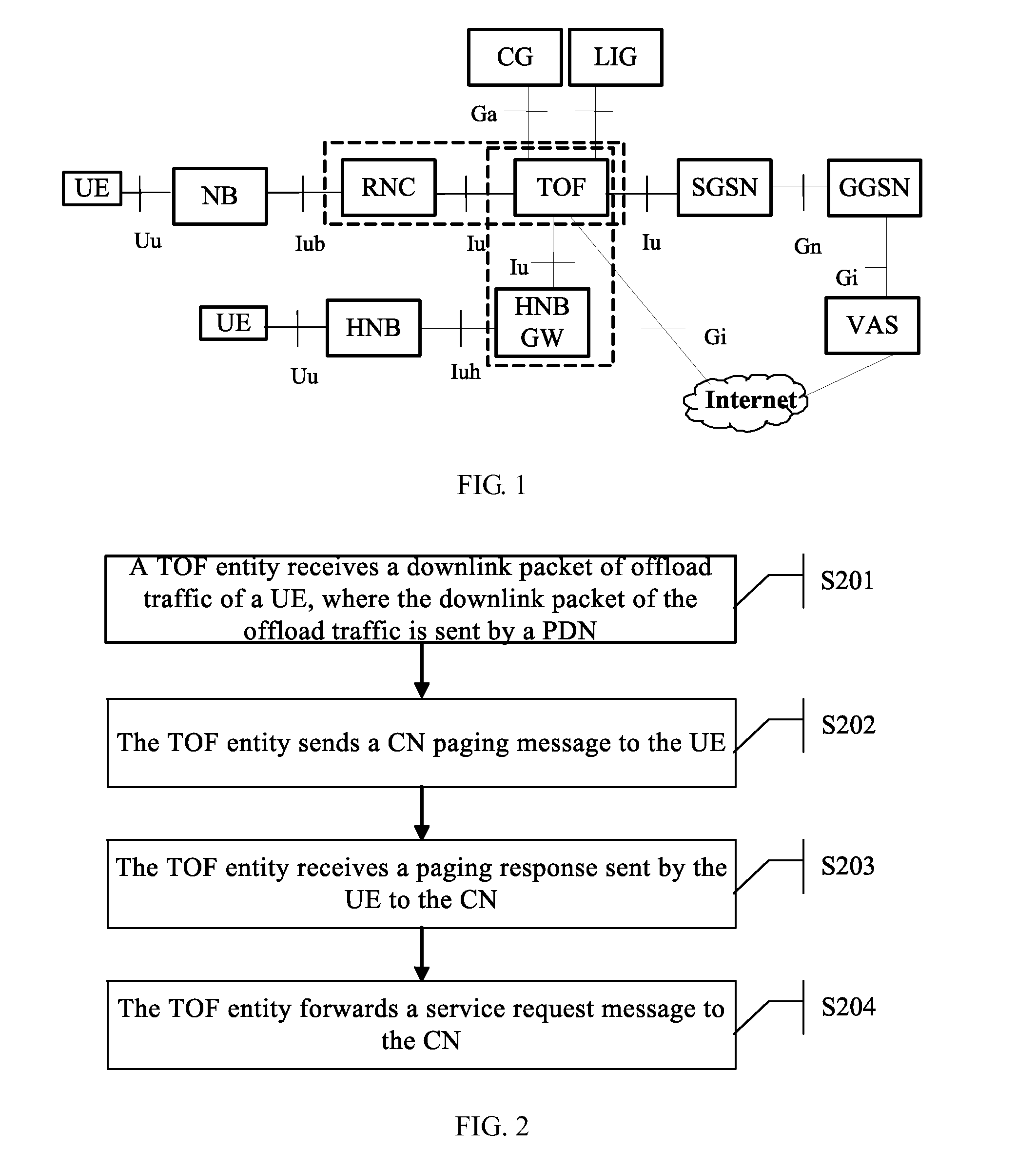
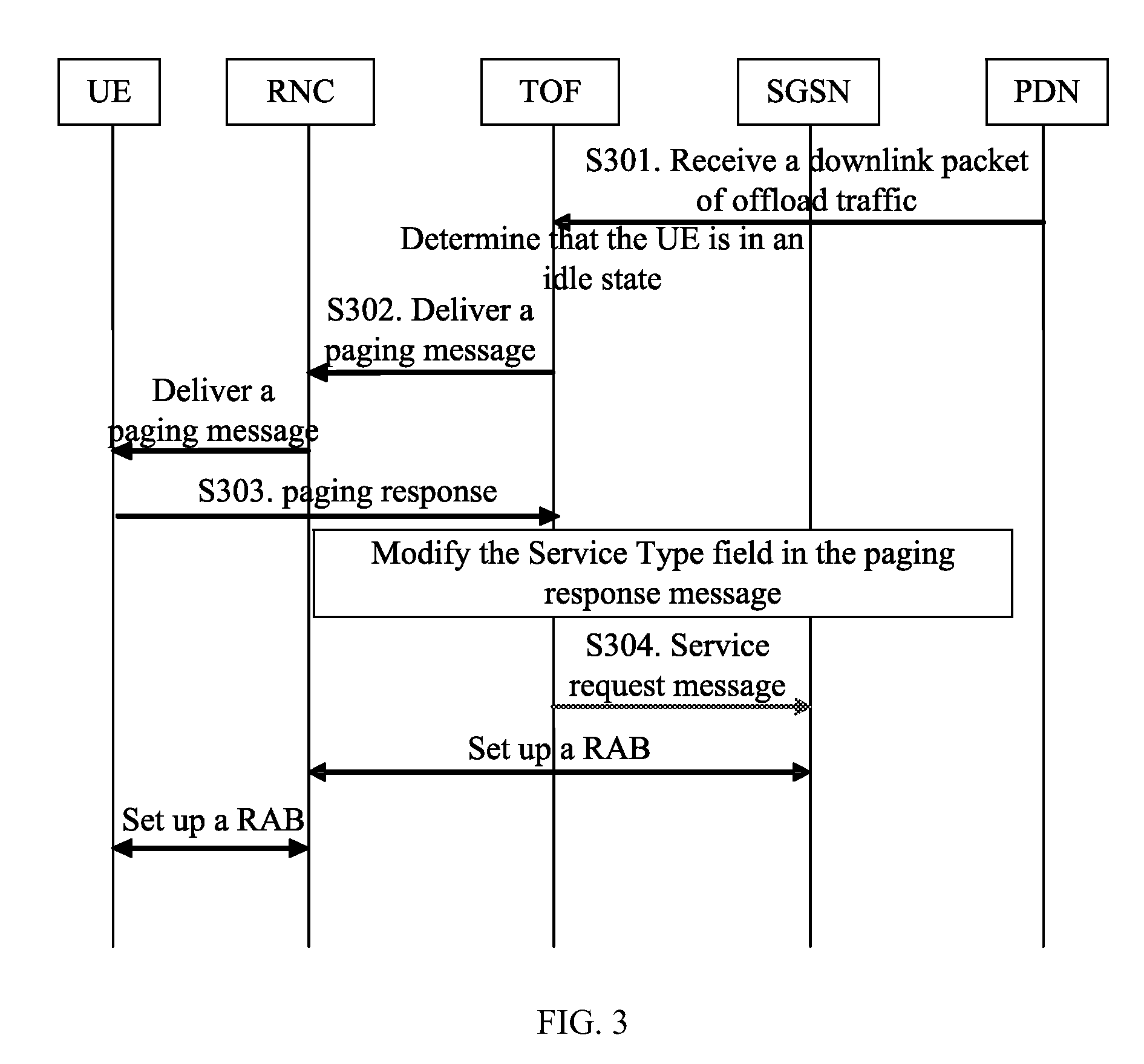
A method for maintaining traffic continuity through a Traffic Offload Function (TOF) entity includes the following steps: the TOF entity receives a downlink packet of offload traffic of a User Equipment (UE), where the downlink packet of the offload traffic is sent by a Packet Data Network (PDN); the TOF entity sends a Core Network (CN) paging message to the UE; the TOF entity receives a paging response sent by the UE to the CN, where the paging response includes a service request message of the UE; and the TOF entity forwards the service request message to the CN so that the CN sets up a Radio Access Bearer (RAB) after the service request message is received. With the method, the communication between the CN and the UE can be restored to guarantee the transmission of traffic. Accordingly, a TOF entity is also disclosed according to the present invention.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
High performance linear moving coil magnetic drive system
ActiveUS20150195655A1Minimal and reduced separationNew level of acousticLoudspeaker screensPlane diaphragmsVoltage amplitudeFiber
A linear moving coil magnetic drive system includes a continuous loop coil of flat, thin, rigid construction which levitates inside a quadrupole permanent magnet assembly with minimum gap. The linear coil may be a flat, racetrack-shaped, continuous loop, which may be constructed with single or multilayers PCB, flex-circuit, or other membrane process. The linear coil may include a coating of permeable magnetic material along the insulated conductor traces. The linear coil may be sandwiched between carbon fiber fabrics and cured to create a long, flat, thin and perfectly straight, extremely stiff, light-weight, load-bearing tee-shaped structure. This structure is levitated inside a quadrupole permanent magnetic assembly with minimum air gap between the high gauss magnets. In additional to the bare conductor traces inside this coil, also integrated into this PCB structure, is simple second-order equalizer electronic circuitry, comprised of surface-mounted resistors, capacitors, and IC chips. Either a close loop or open loop control may be included to tune the voltage amplitude at the resonance frequency of this magnetic drive system.
Owner:WALL AUDIO
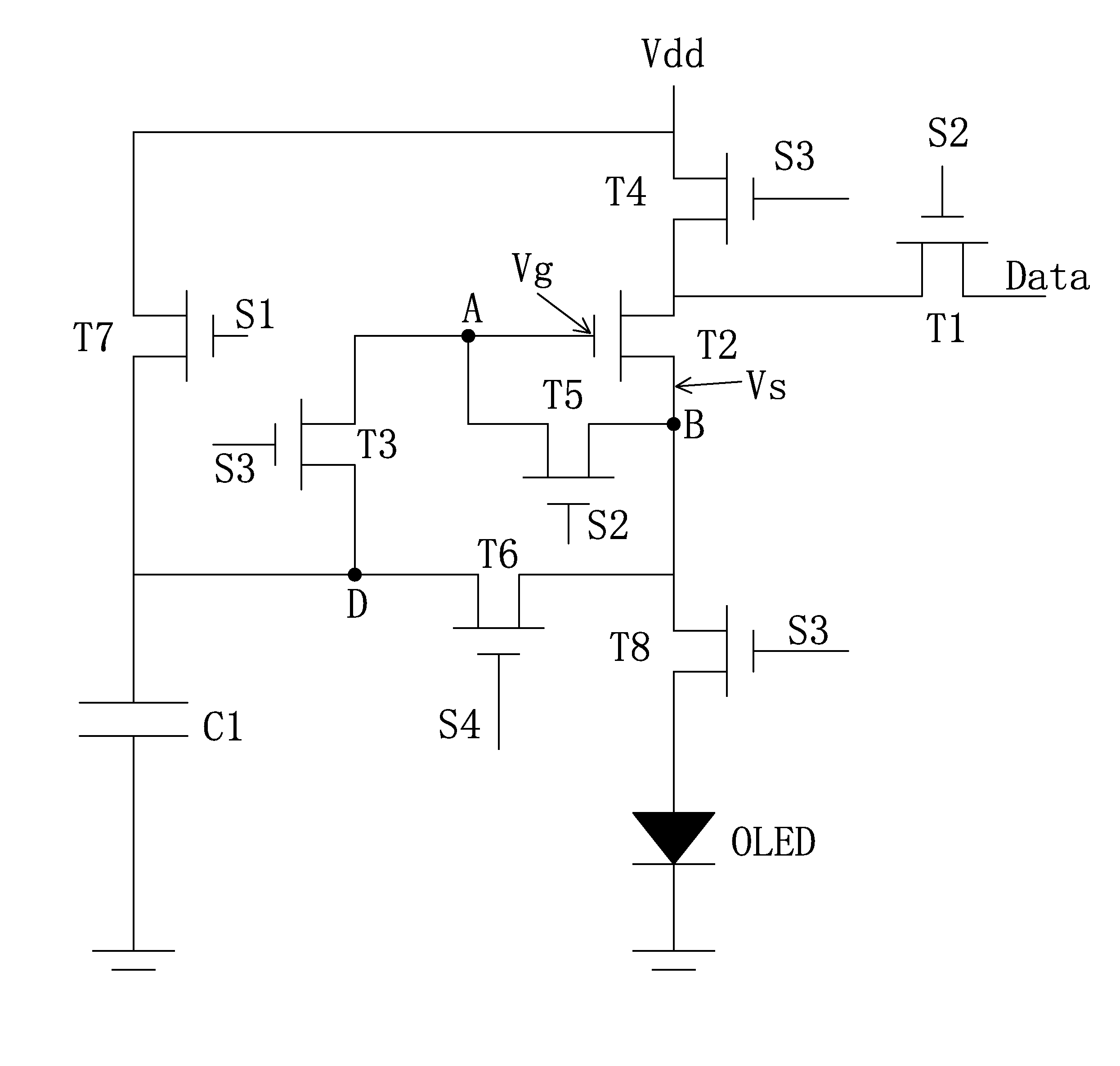
Amoled pixel driving circuit and pixel driving method
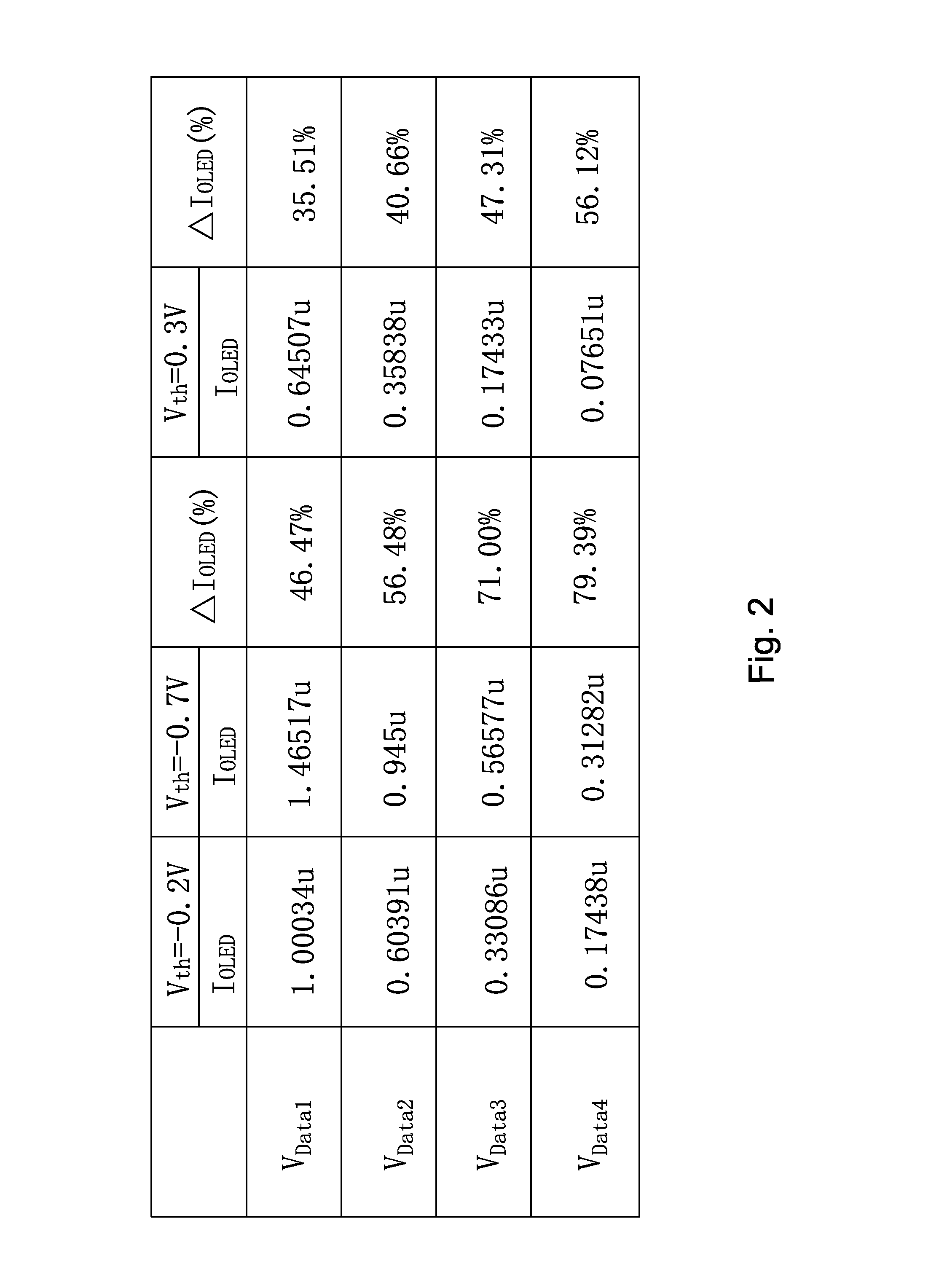
ActiveUS20160365030A1Improve the display effectCompensation Threshold VoltageStatic indicating devicesHemt circuitsEngineering
The present invention provides an AMOLED pixel driving circuit and a pixel driving method. The AMOLED pixel driving circuit utilizes a 8T1C structure, comprising a first, a second, a third, a fourth, a fifth and a sixth, a seventh and an eighth thin film transistors (T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8), a capacitor (C1) and an organic light emitting diode (OLED). The AMOLED pixel driving circuit, by directly gaining the second thin film transistor (T2), i.e. the drive thin film transistor, can effectively compensate the threshold voltage of the drive thin film transistor and stabilize the current flowing through the organic light emitting diode (OLED) to ensure the uniform brightness of the organic light emitting diode (OLED) and improve the display effect of the pictures. The unnecessary irradiance of the organic light emitting diode (OLED) can be avoided to reduce the electrical power consumption.
Owner:SHENZHEN CHINA STAR OPTOELECTRONICS TECH CO LTD
Tonneau cover access panel
ActiveUS20170120736A1Issue can be solvedEasy to implementEngine sealsVehicle sealing arrangementsEngineeringMechanical engineering
A tonneau cover access panel assembly connectable to a tonneau cover assembly that eliminates the need for side rails to both locate and tension the top cover. The tension works to seal out environmental elements and holds the tonneau cover and locating bows of the tonneau cover in place. The tonneau cover access panel holds the rear of the tonneau in the closed tension state keeping the tonneau secured and tight until the cover is opened by an operator. The tonneau cover access panel assembly is movable between a closed position and a fully open position, and, is movable between at least a first open position and the closed position for more limiting access to the cargo bed of the vehicle when desired. The tonneau cover access panel assembly also reduces weight and complexity.
Owner:BESTOP
S.a.c. degradable bags for discreet disposal of used or soiled personal care products
InactiveUS20110229059A1Convenient easy dispensingReadily and consistently availableFlexible coversWrappersPurchasingPersonal Care Product
A packaging system for the disposal of any manner of used or soiled personal care products includes a package member configured for the receipt of the used personal care products therein. The unique packaging disposal system member is comprised of a biodegradable, degradable, opaque, sealable, generally a soft-side bag like structure which is part of common element consisting of multiple packaging systems which are connected together or to a common element. The package member includes an opaque external surface having a desired nondescript aesthetic configuration or appearance for the purpose of discreet disposal of used or soiled personal care products. The aesthetic configuration of the said invention may include any manner of print, color, etc., for the purpose of disposal instructions, warnings or purchasing indicia. In other words, one viewing the package from the outside is not given obvious, noticeable indication that the package contains used or soiled personal care products nor are the items contained therein visible through the packaging system member.
Owner:GOLDEN GROUP INT
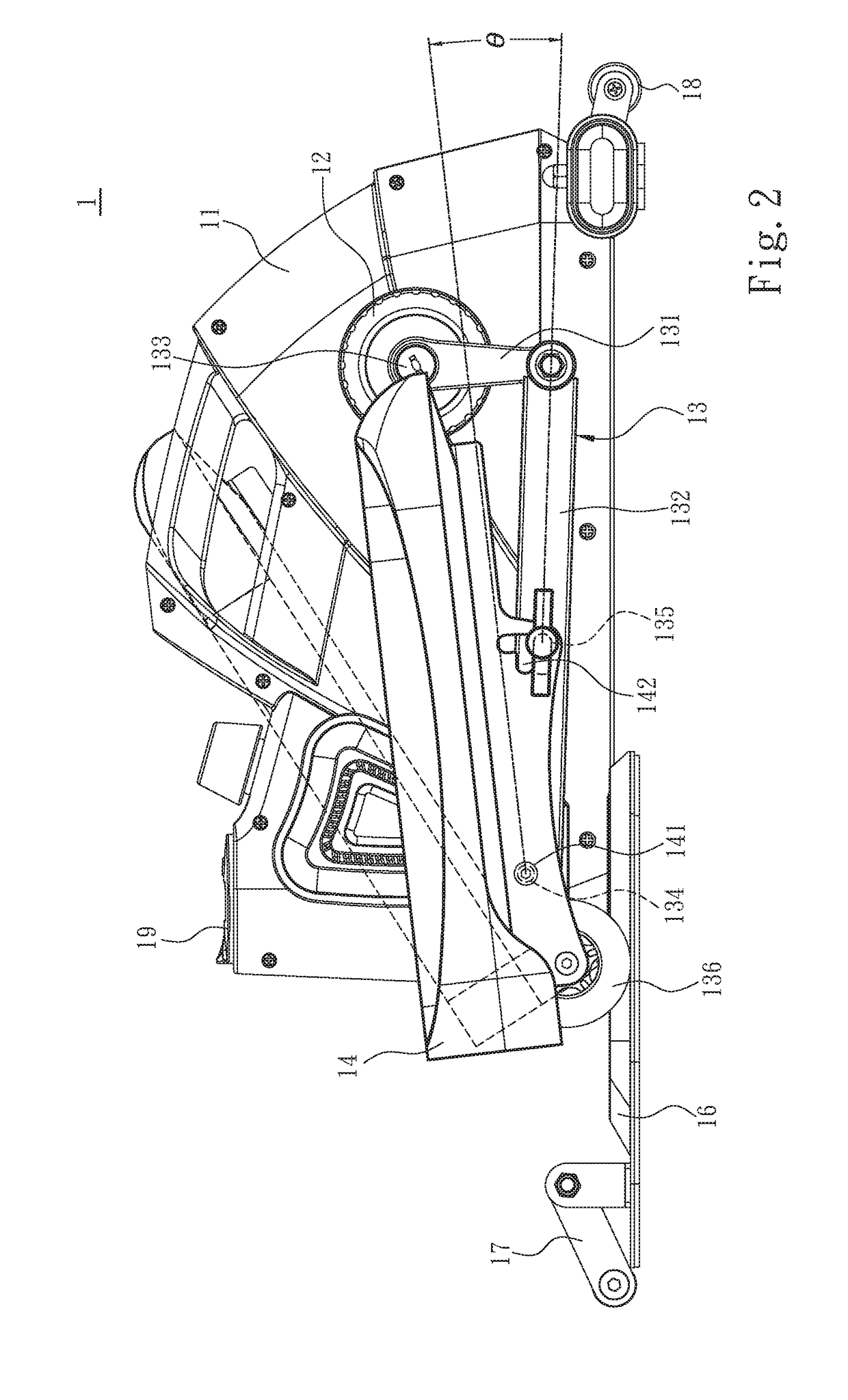
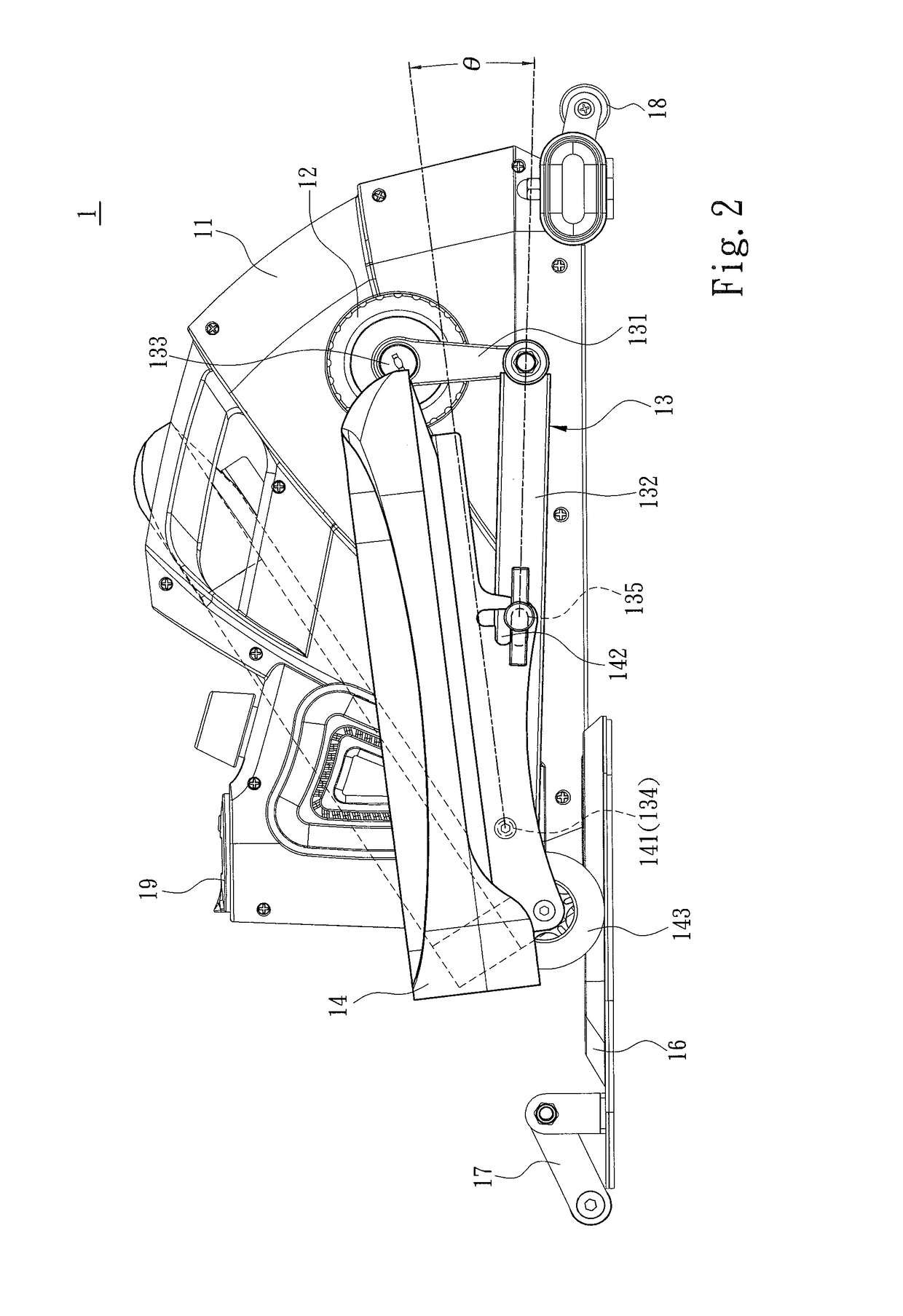
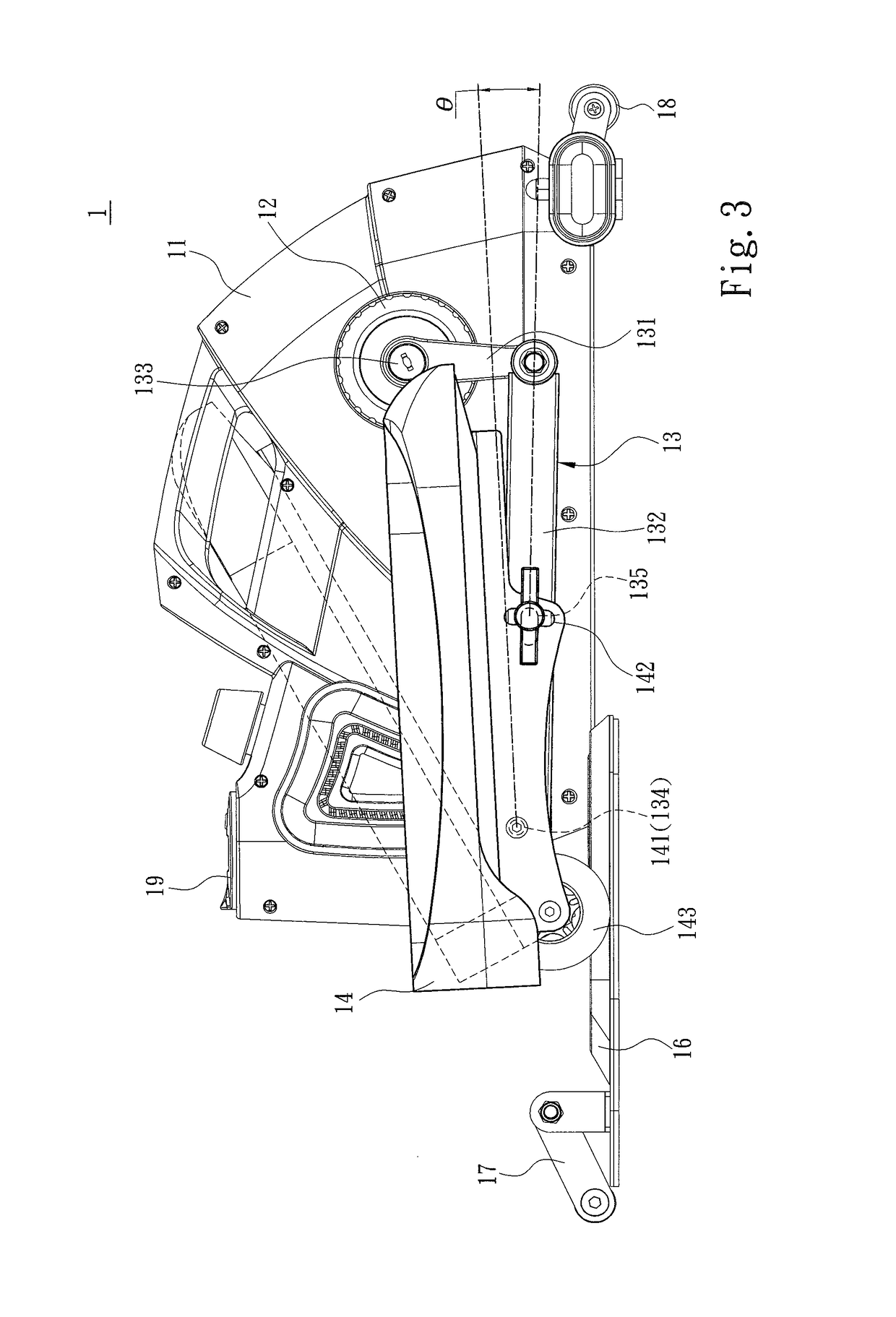
Portable sit-stand elliptical exercise machine
ActiveUS10220246B2Improve utilizationIssue can be solvedSpace saving gamesMuscle exercising devicesExercise machineSitting Positions
A portable sit-stand elliptical exercise machine includes a seat, a transmission wheel installed at the seat, two linkage mechanisms installed at the transmission wheel, and two mobile pedals respectively installed at the linkage mechanisms. Each linkage mechanism includes a driving portion connected to the transmission wheel, an axle portion disposed at one side away from the transmission wheel, and an adjustment portion disposed between the axle portion and the driving portion. Each mobile pedal is pivotally connected to the axle portion and includes a plurality of assembly portions. Thus, an angle is formed between each mobile pedal assembled to one of the assembly portions and the linkage mechanism to facilitate a user to utilize the portable sit-stand elliptical exercise machine in either a sitting or standing posture, thereby solving issue of a conventional solution that cannot be applied for a dual use of both sitting and standing postures.
Owner:LERNIHAN JODY NEWGARD
Integrated circuit (IC) design method with enhanced circuit extraction models
ActiveUS20140351779A1Improve reliabilityCareful calibrationDesign optimisation/simulationCAD circuit designCircuit extractionEngineering
A method is provided for designing an IC chip. The method includes receiving data from a pre-layout design process for the IC chip, routing a plurality of interconnecting wires to connect various devices of the IC chip, and extracting various circuit parameters. The method also includes simulating the IC chip using the extracted various circuit parameters to detect logic or timing error in the IC chip. The extracting the various circuit parameters includes establishing a statistical interconnect technology profile (ITP) file containing at least interconnect parasitic parameters based on correlations of interconnect layer geometric parameter variations.
Owner:SHANGHAI INTEGRATED CIRCUIT RES & DEV CENT
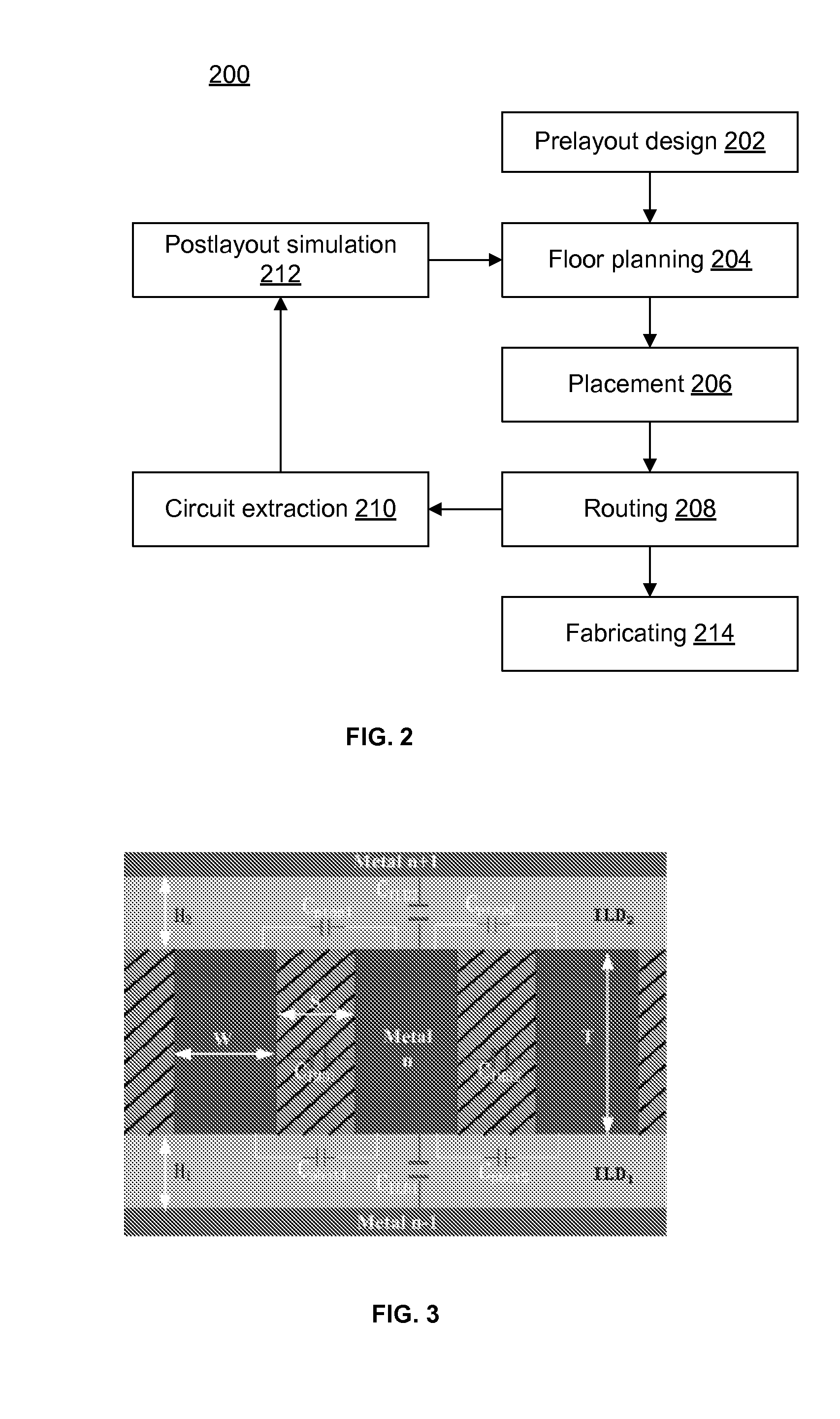
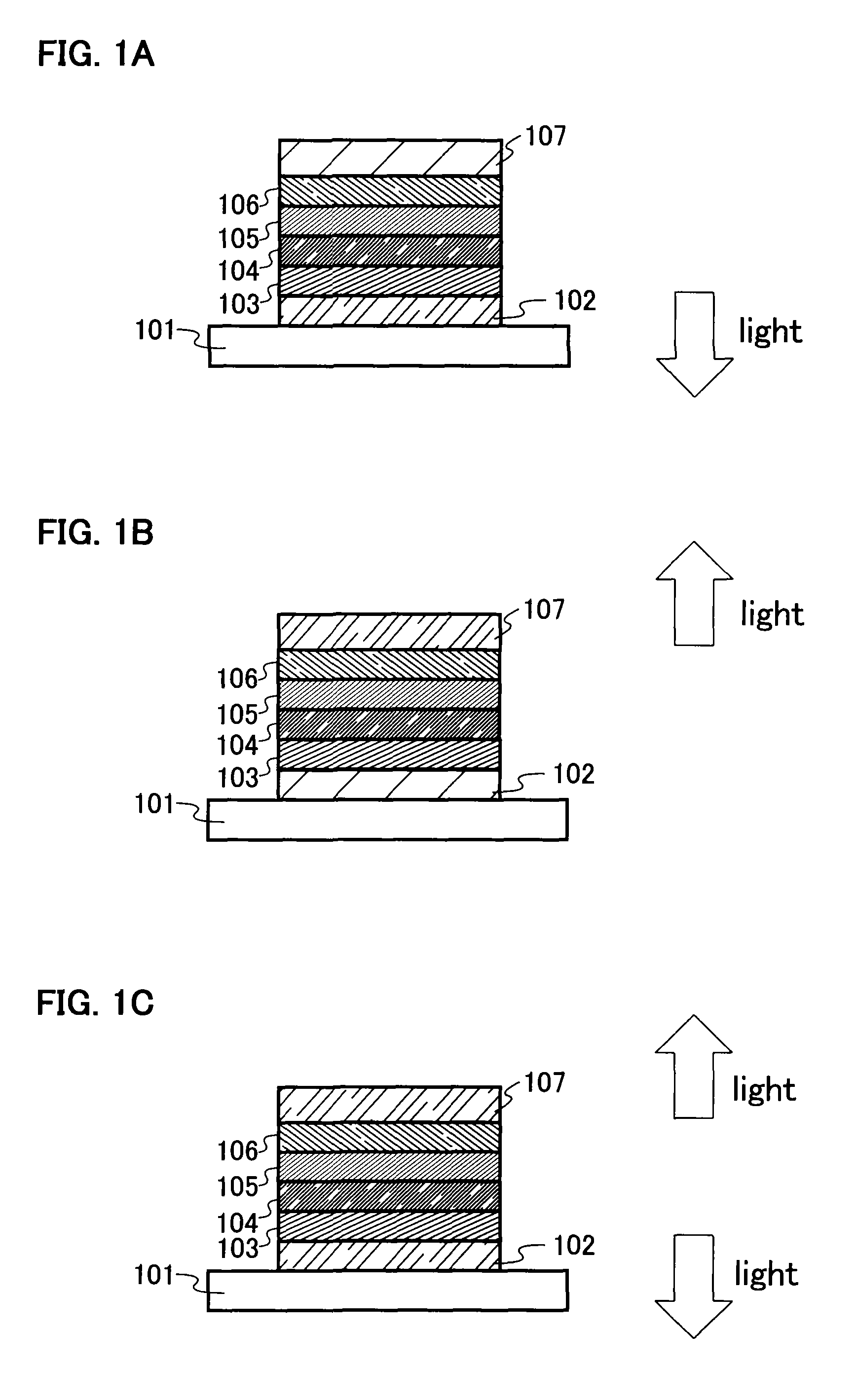
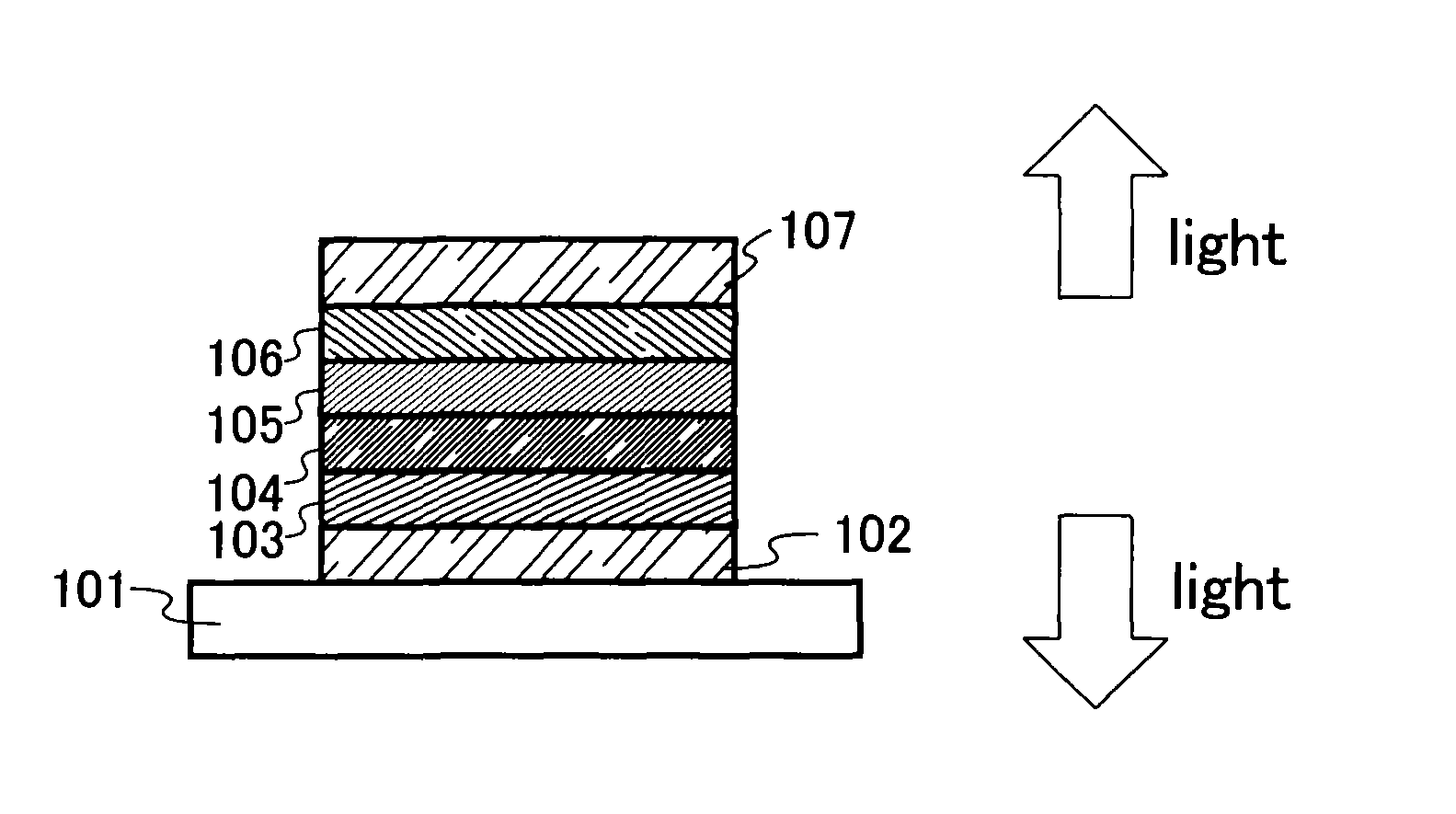
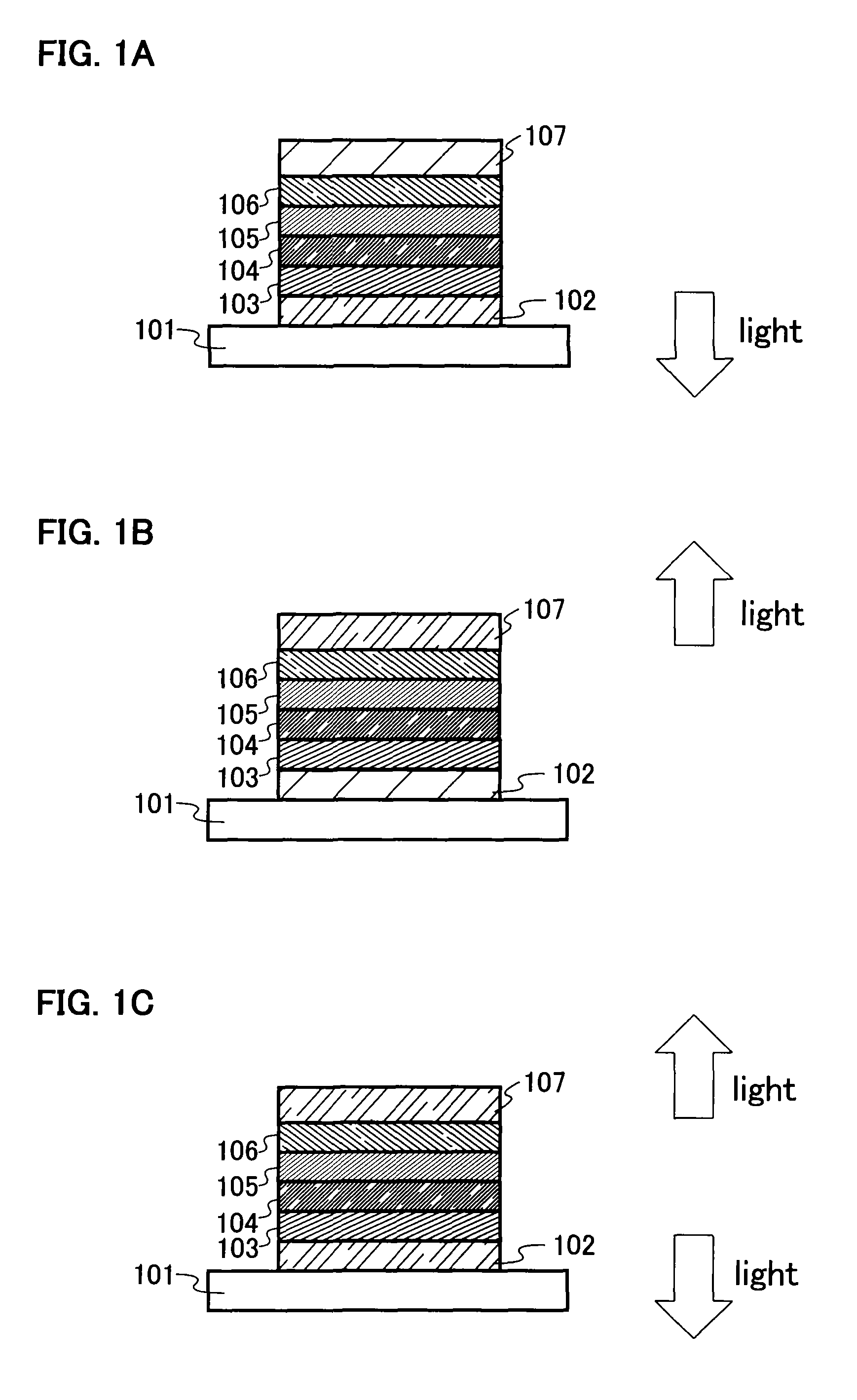
Light emitting element, light emitting device and manufacturing method of light emitting element
InactiveUS7511418B2High luminous efficiencyIssue can be solvedDischarge tube luminescnet screensLamp detailsMulti materialQuantum yield
It is an object of the present invention to provide a light emitting element and a light emitting device having high luminous efficiency. It is a further object of the present invention to provide a method for manufacturing the light emitting element using a simplified method compared with the conventional method. A light emitting element having a light emitting region which includes plural kinds of materials with a high luminous quantum yield, and one or plural kinds of materials with a high carrier transporting property and which has a structure where regions in which the material with a high luminous quantum efficiency is dispersed in a material with a high carrier transporting property and regions in which the concentration of the material with a high carrier transporting property is high are laminated alternately, between a pair of electrodes, is provided.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Multi-table based grant generator for improved granularity in an ATM-PON
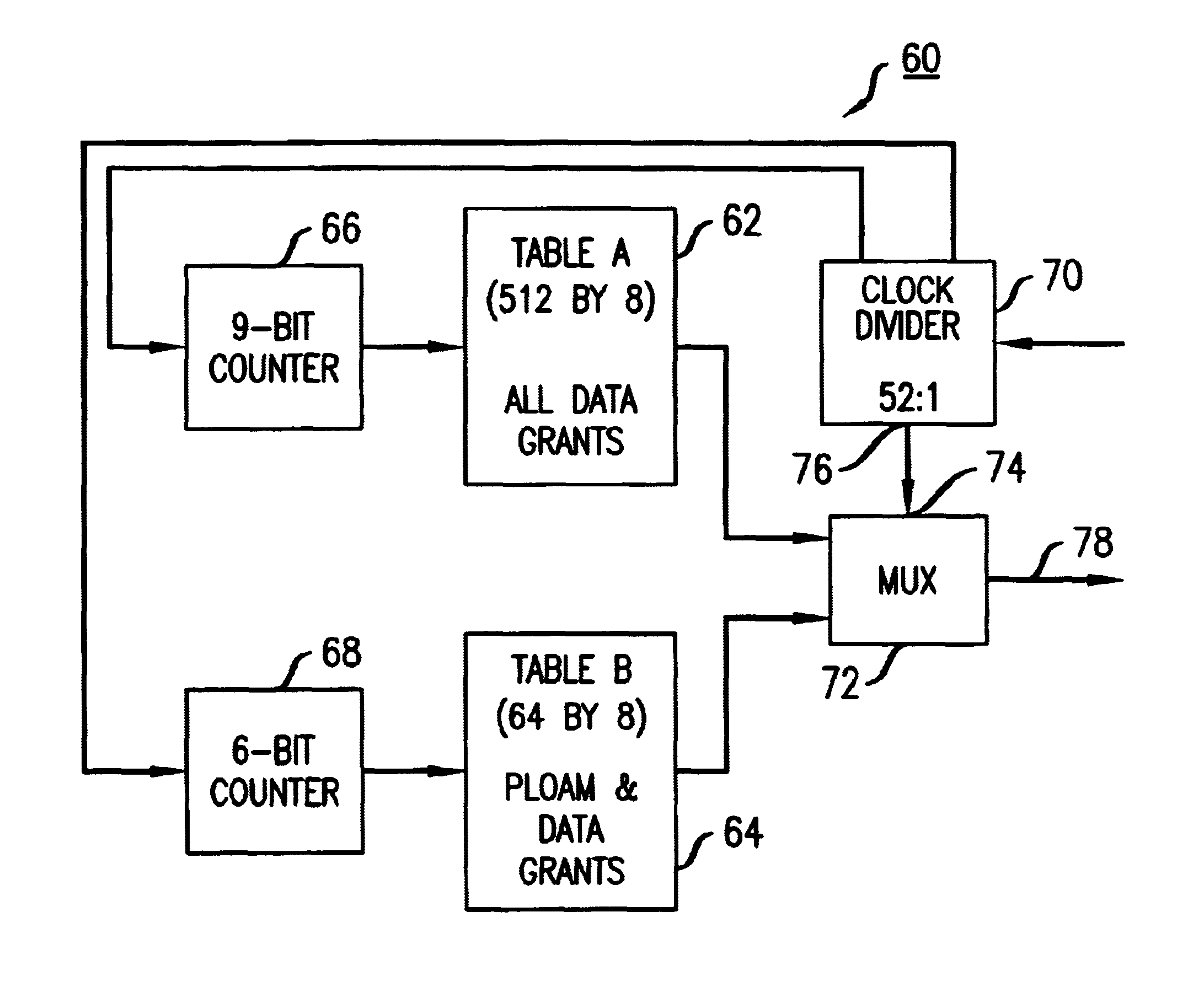
InactiveUS6980519B1Issue can be solvedLarge and small bandwidthMultiplex system selection arrangementsError preventionMultiplexerGranularity
A multi-table-based grant generator in accordance with the present invention solves the issue of bandwidth granularity, while maintaining the simplicity of a table approach. The present invention grant generator provides grants of fine granularity for regulation of upstream transmission of cells in an ATM PON. Multiple grant tables having differing bandwidth granularities are linked together through a simple grant distribution mechanism. The grant tables and grant distribution mechanisms can be recursively linked to achieve a number of different granularities. The grant generator of the present invention is based on multiple grant tables with a combination of multiplexers, dividers, and address counters. The grant generator provides both larger and smaller bandwidths for data grants as well as PLOAM grants without large size grant tables. In one exemplary embodiment of the present invention, improved granularity is achieved, where a first grant table is used for one size of bandwidth grant, e.g., data grants, and the second grant table is used for another size of bandwidth grant, e.g., low bandwidth data grants as well as PLOAM grants. A simple clock divider couples to each of the grant tables through corresponding address counters. The clock divider provides a set number of bandwidth grants from each table over a complete cycle. The clock divider also selects an appropriate input port of a multiplexer through which the grants from each grant table are respectively transmitted. By having the ability to issue variable sized bandwidth grants, the granularity is significantly improved, thereby translating to a more efficient use of the bandwidth. More specifically, grants of a finer granularity can be issued without the need for an excessively large grant table usually thought to be necessary to produce fine granularities.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
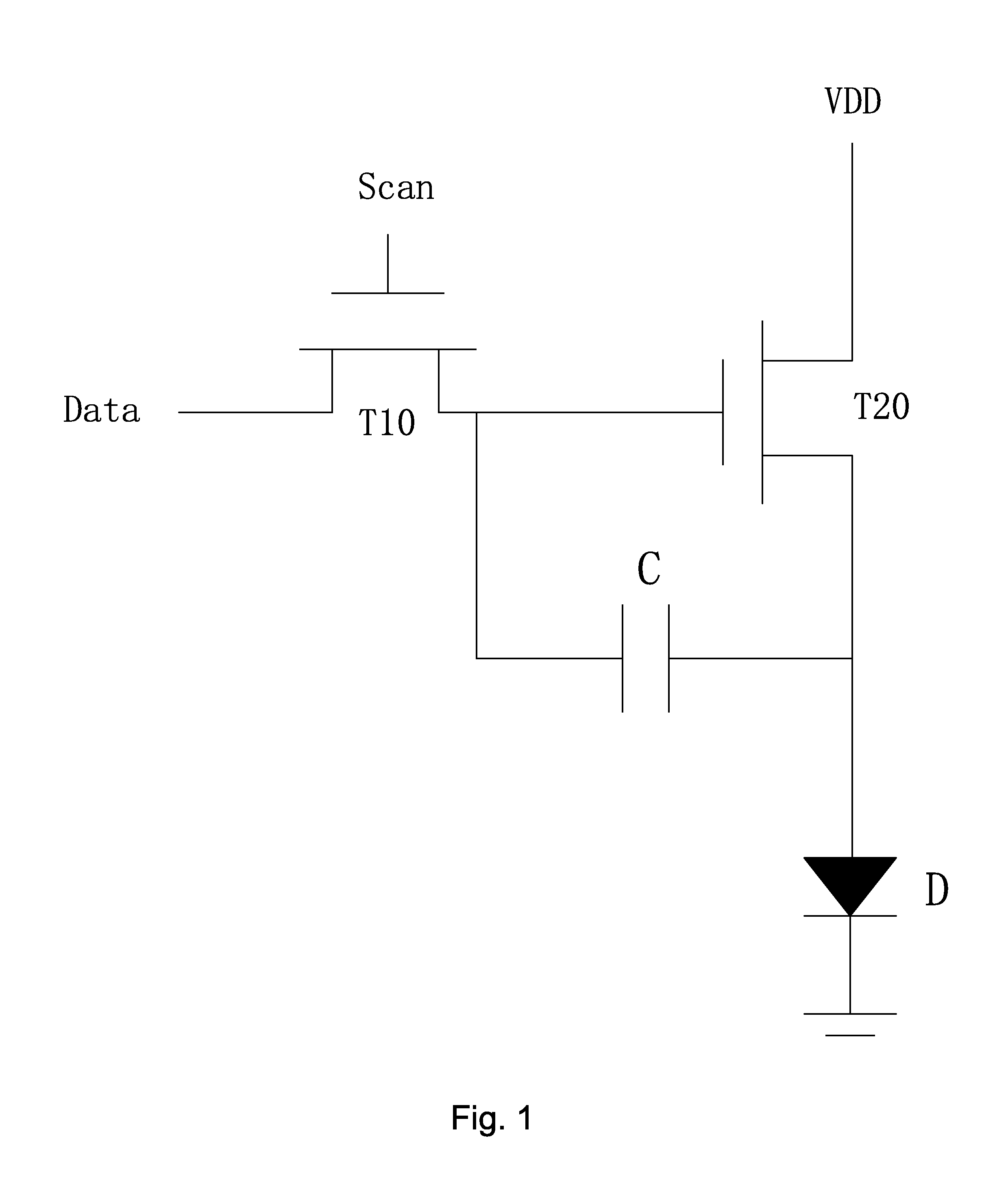
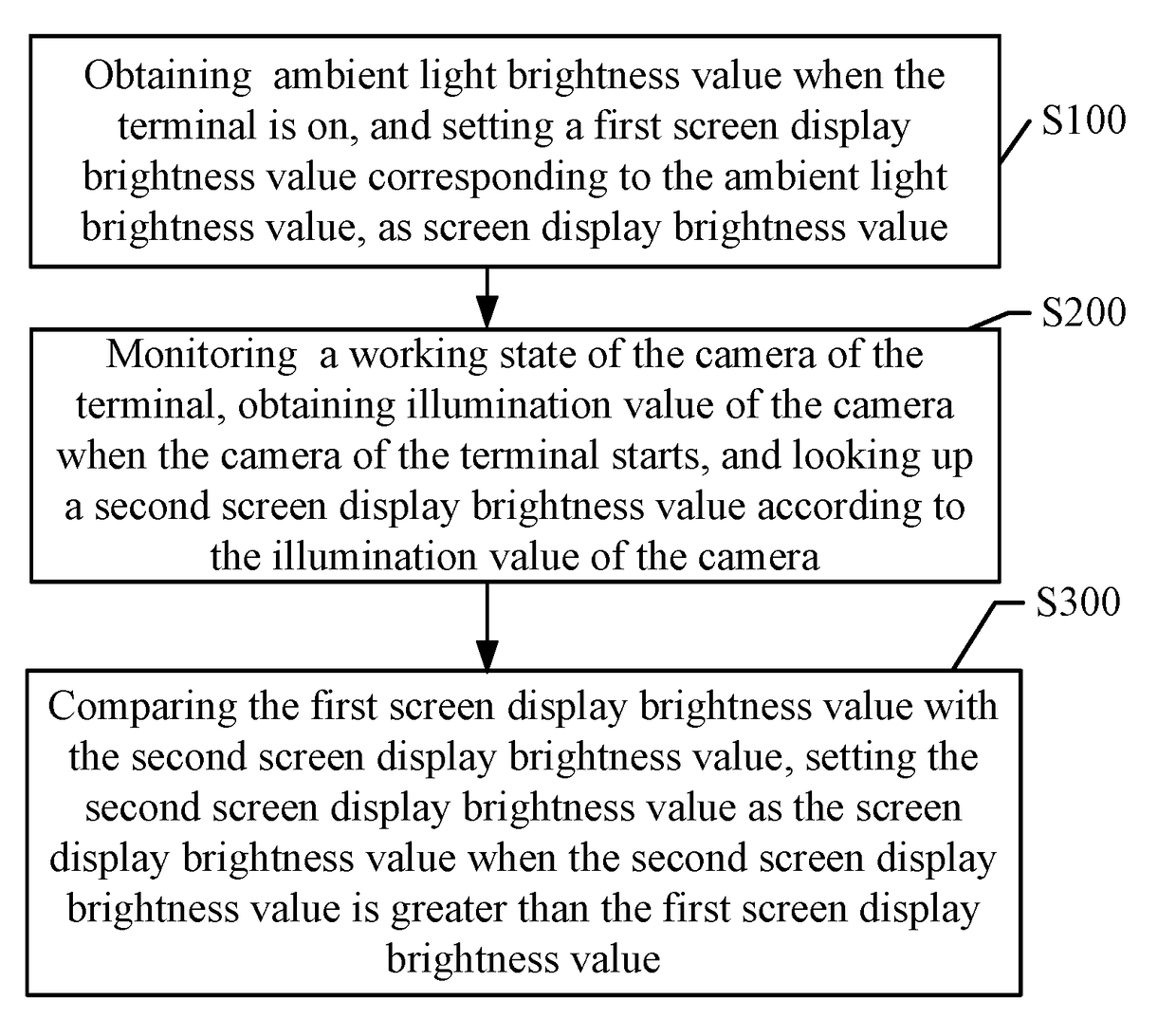
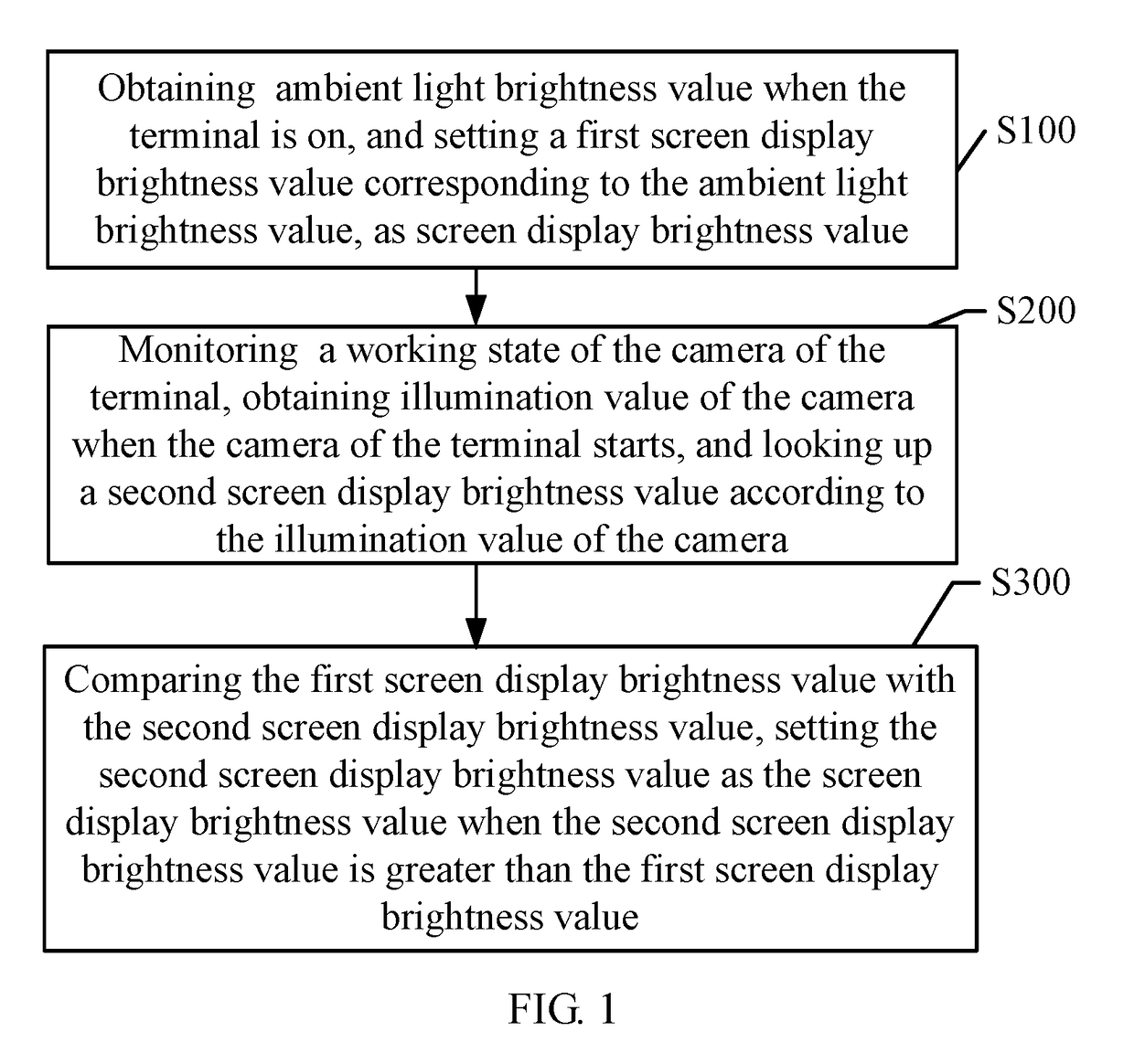
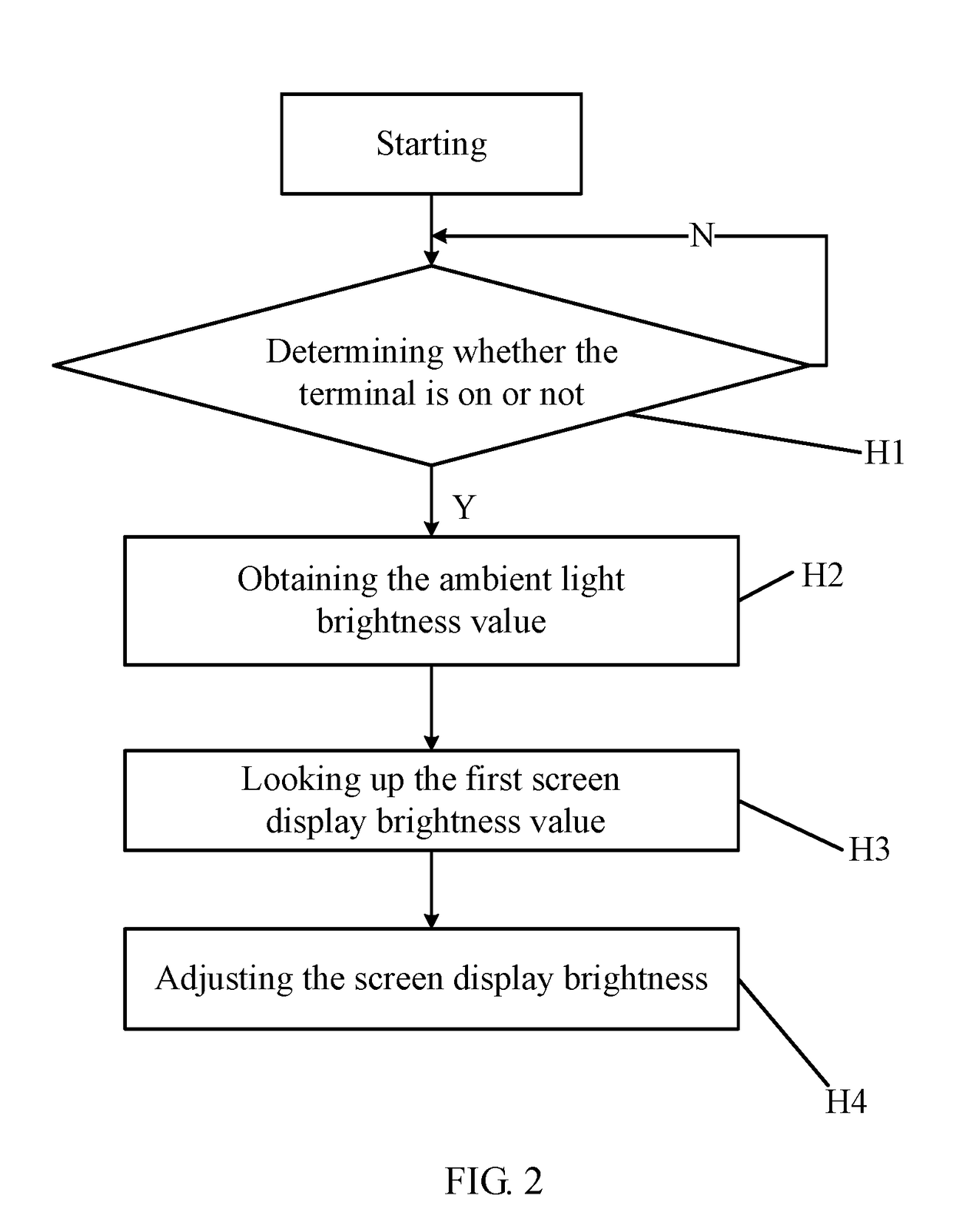
Method, system, and terminal for adjusting screen brightness of terminal
ActiveUS20180122335A1Issue can be solvedIncreasing image displaying detailTelevision system detailsCurrent supply arrangementsComputer graphics (images)Display device
A method, a system, and a terminal for adjusting screen brightness of the terminal includes the steps of obtaining a first screen display brightness value corresponding to ambient light brightness value, and obtaining illumination value of a camera and looking up a second screen display brightness value. When the second screen display brightness value is greater than the first screen display brightness value, the second screen display brightness value is set as the screen display brightness value. Namely, the display brightness is controlled by an Automatic Exposure Control (AEC) system, which increases displaying detail of image on the display.
Owner:JRD COMM INC
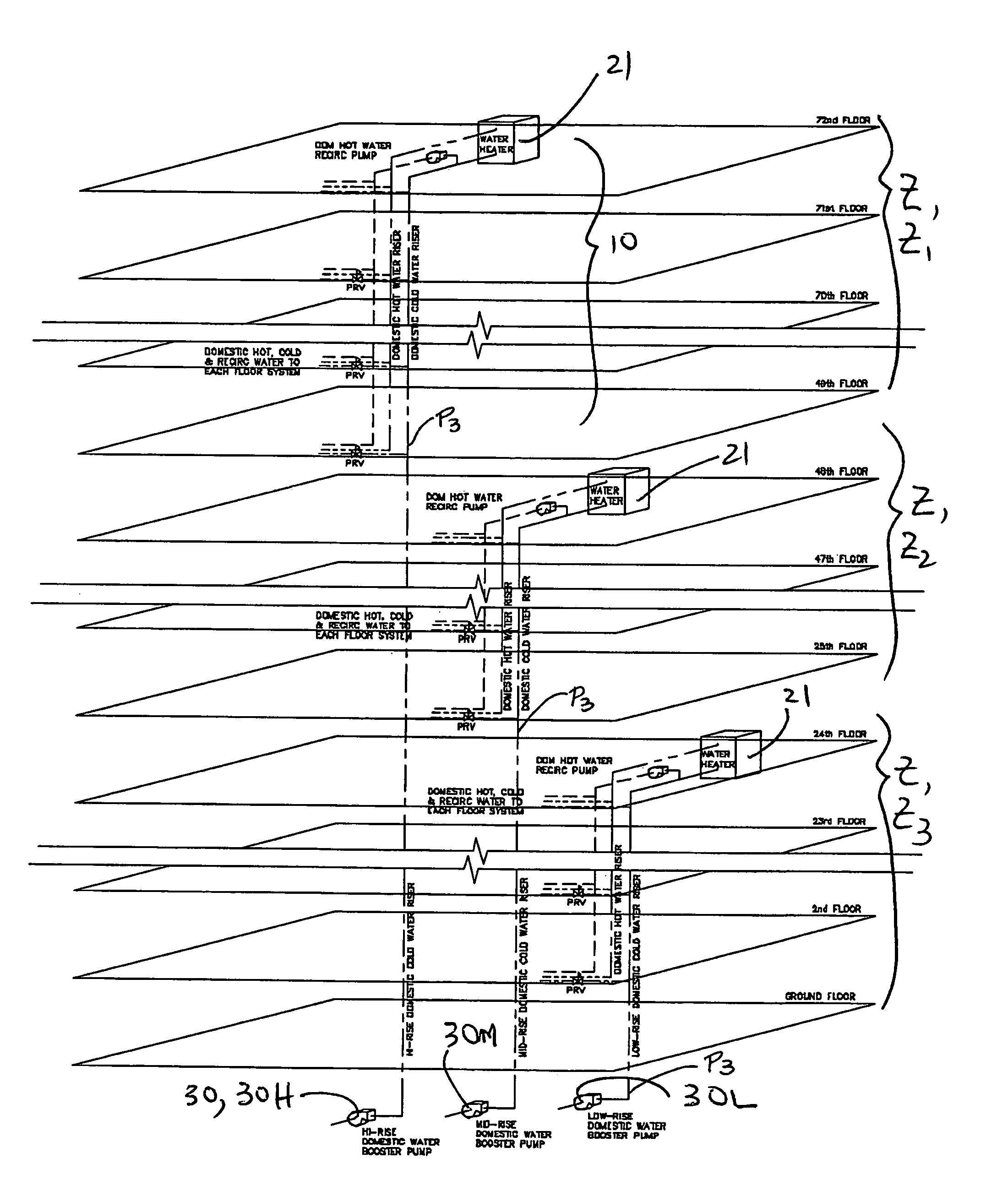
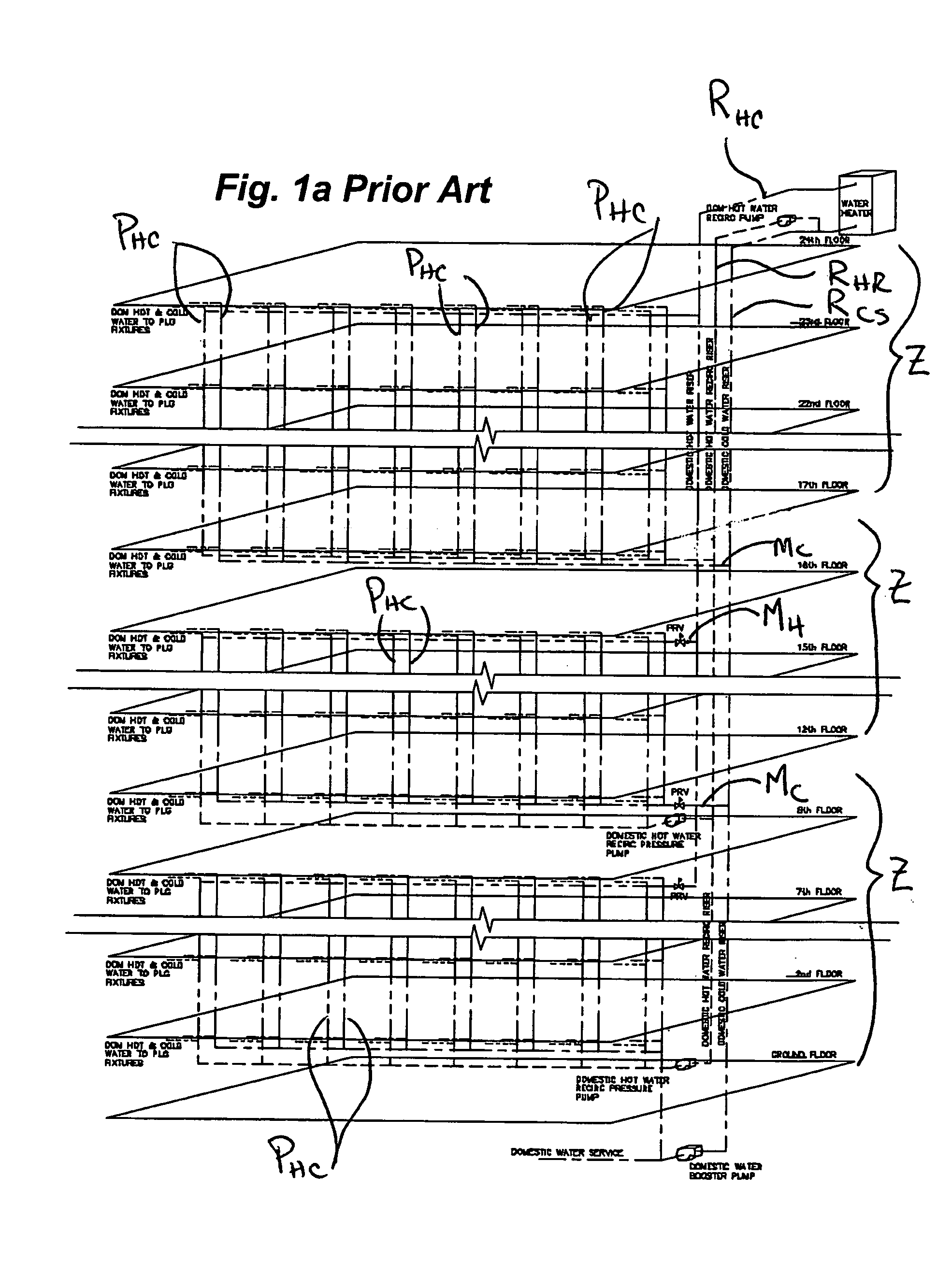
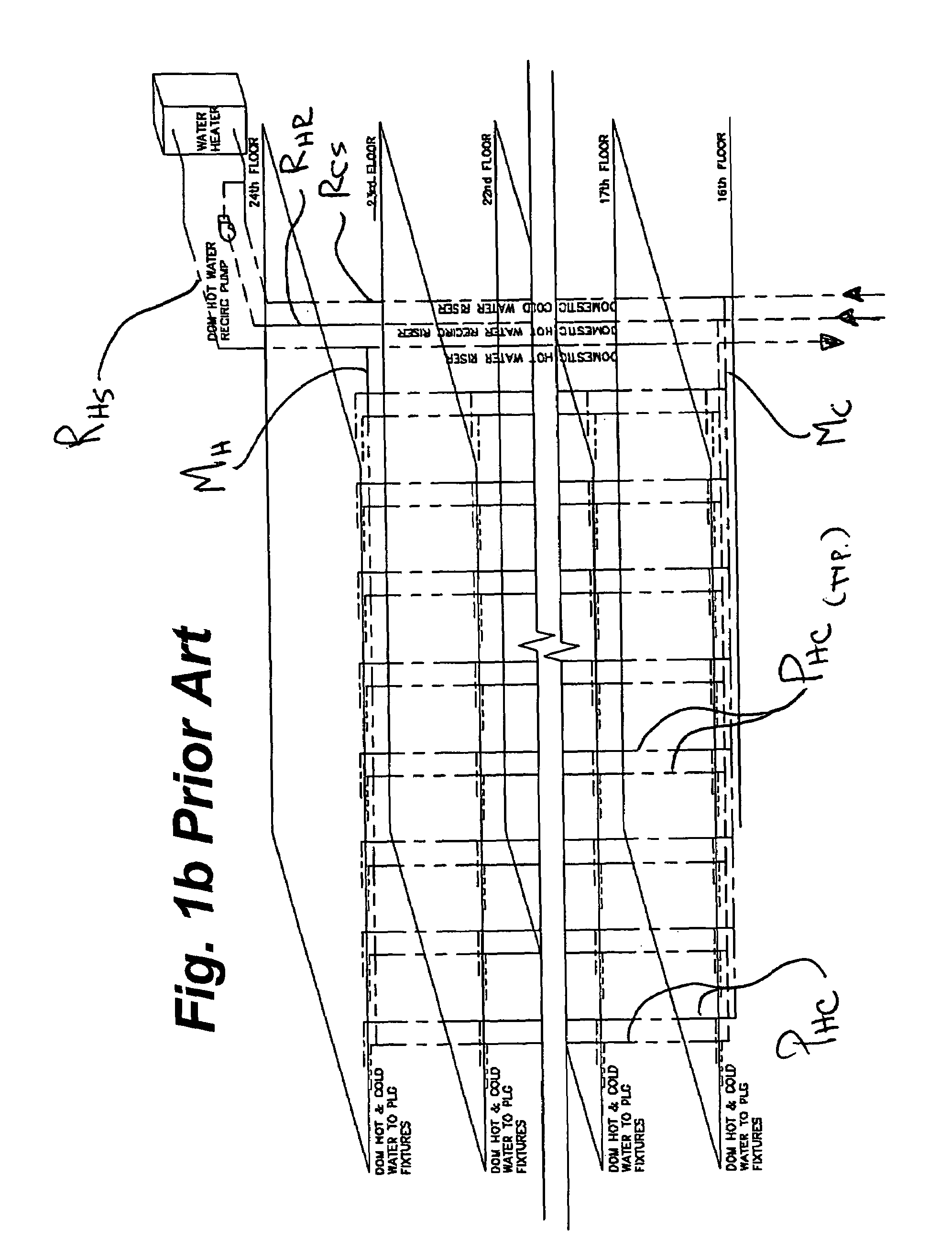
Multi-story water distribution system
InactiveUS7308906B2Reduce pipingReduce in quantityLighting and heating apparatusPipesWater useDecreased pressure
A method and system for the distribution of water in a high rise building is provided using a minimum number of piping risers. The system has a domestic cold water riser, and a domestic hot water supply riser and a return riser. At each serviced floor, a cold water supply main extends from the domestic cold water riser and a hot water supply main extends from the domestic hot water supply riser. On each floor at which riser pressure is higher than domestic use pressures, a valve reduces the pressure of the entire cold water supply main to domestic use pressures. One or more valves at each of one or more suites on the floor reduce the pressure of the hot water to each suite, leaving the hot water supply main for the floor at full riser pressure. Coupling fan-coils with chilled water supply and the full pressure domestic hot water provides an efficient piping system for both environmental controls and domestic hot water use. Regular and periodic circulation through fan-coils avoid stagnation of the domestic hot water supply.
Owner:SINCLAIRE ROSS
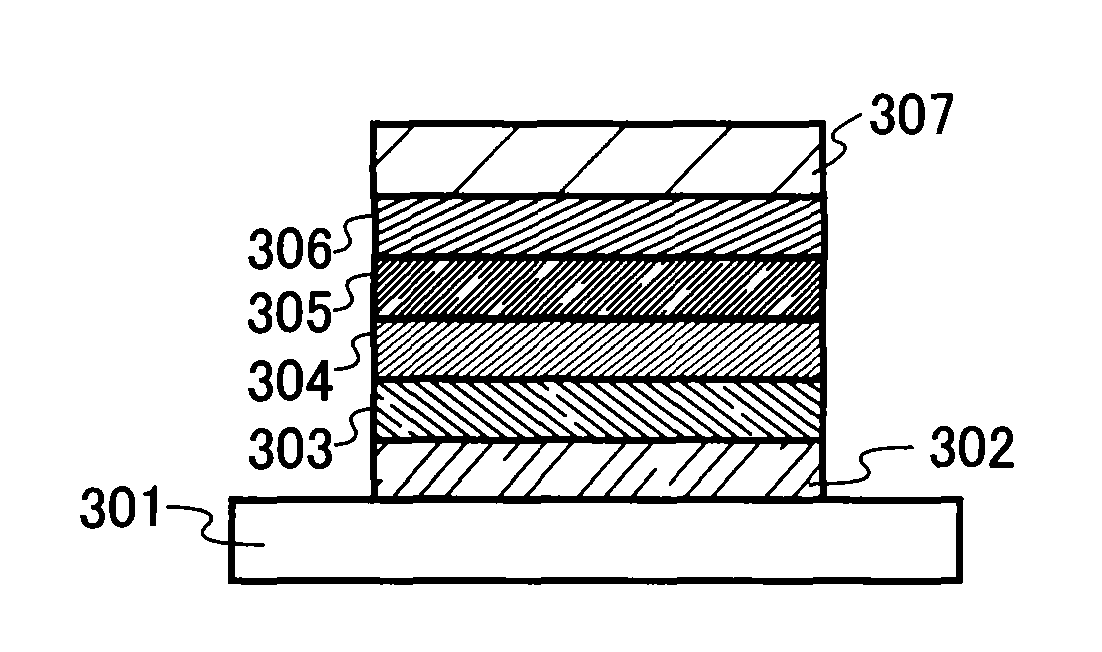
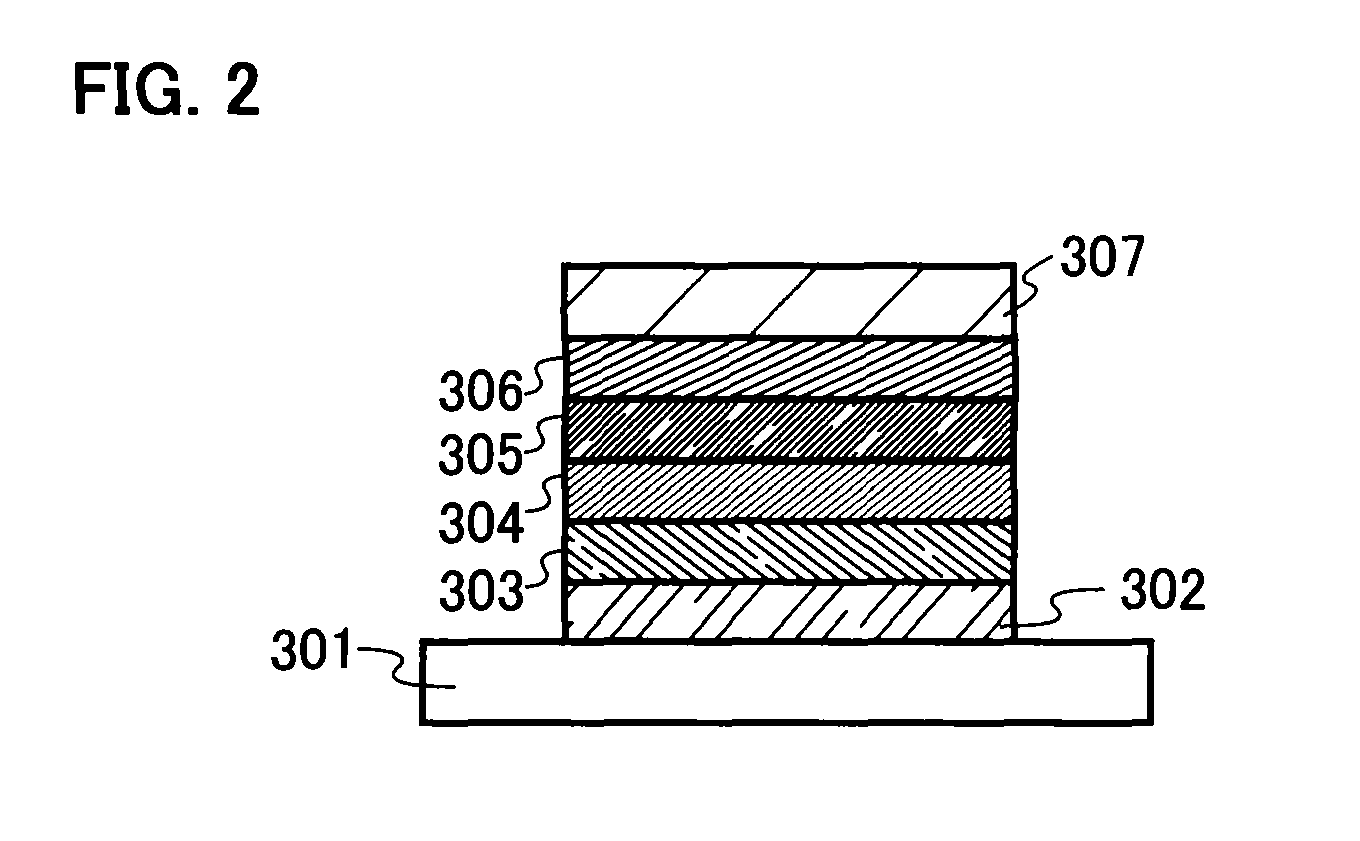
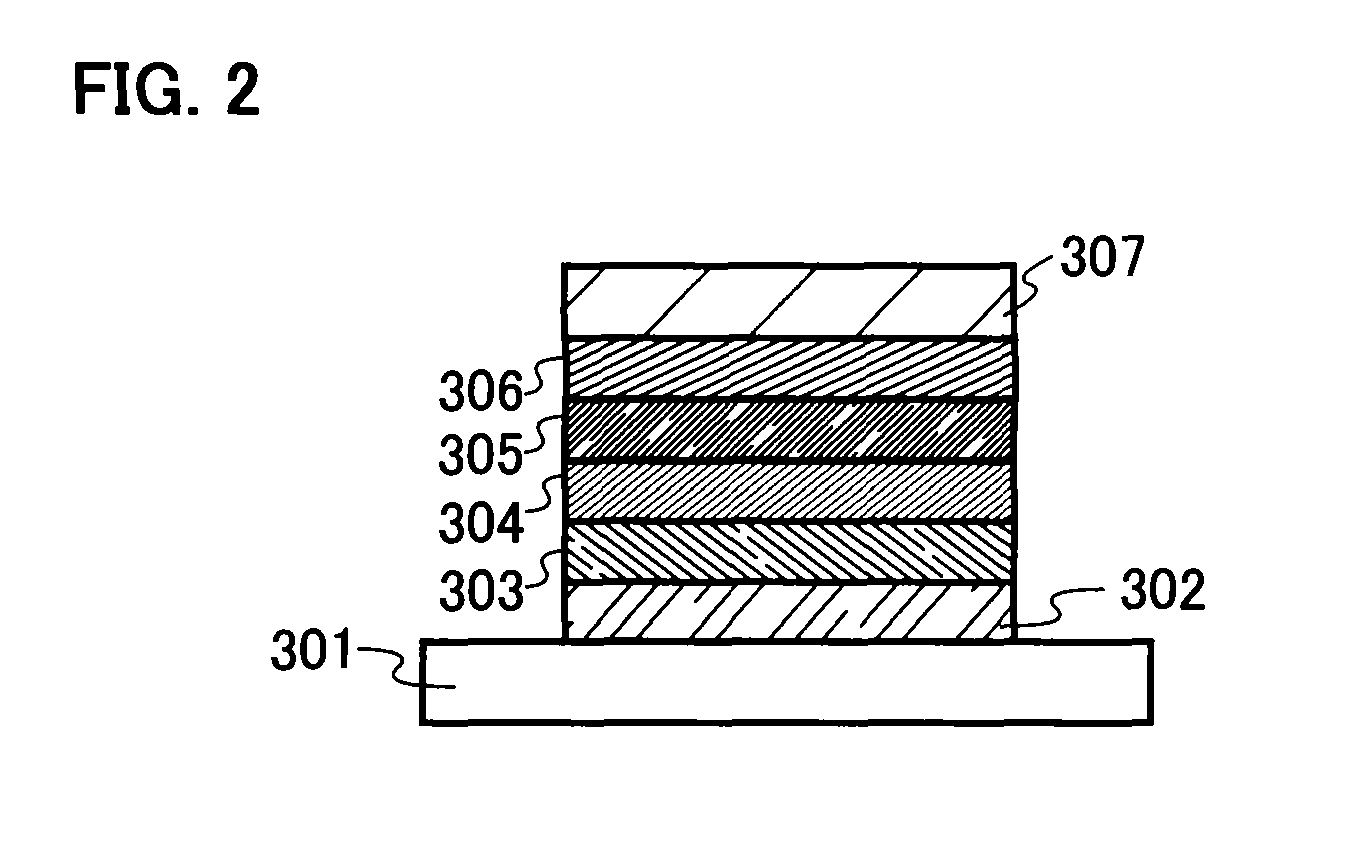
Light emitting element, light emitting device and manufacturing method of light emitting element
InactiveUS20060261728A1Solve low luminous efficiencyHigh quantum yieldDischarge tube luminescnet screensElectroluminescent light sourcesQuantum efficiencyLuminescence quantum yield
It is an object of the present invention to provide a light emitting element and a light emitting device having high luminous efficiency. It is a further object of the present invention to provide a method for manufacturing the light emitting element using a simplified method compared with the conventional method. A light emitting element having a light emitting region which includes plural kinds of materials with a high luminous quantum yield, and one or plural kinds of materials with a high carrier transporting property and which has a structure where regions in which the material with a high luminous quantum efficiency is dispersed in a material with a high carrier transporting property and regions in which the concentration of the material with a high carrier transporting property is high are laminated alternately, between a pair of electrodes, is provided.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Vehicle extrication preparatory tool
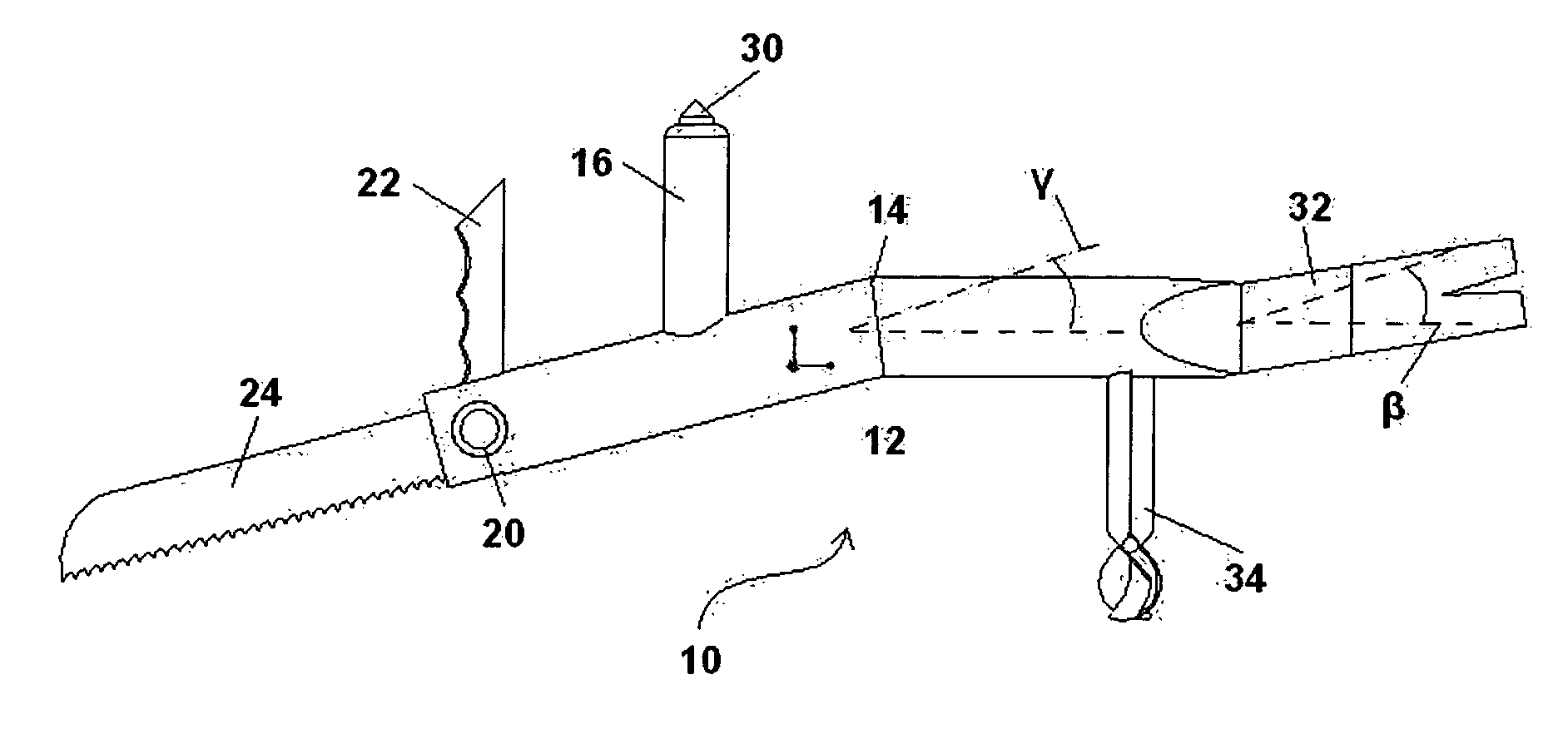
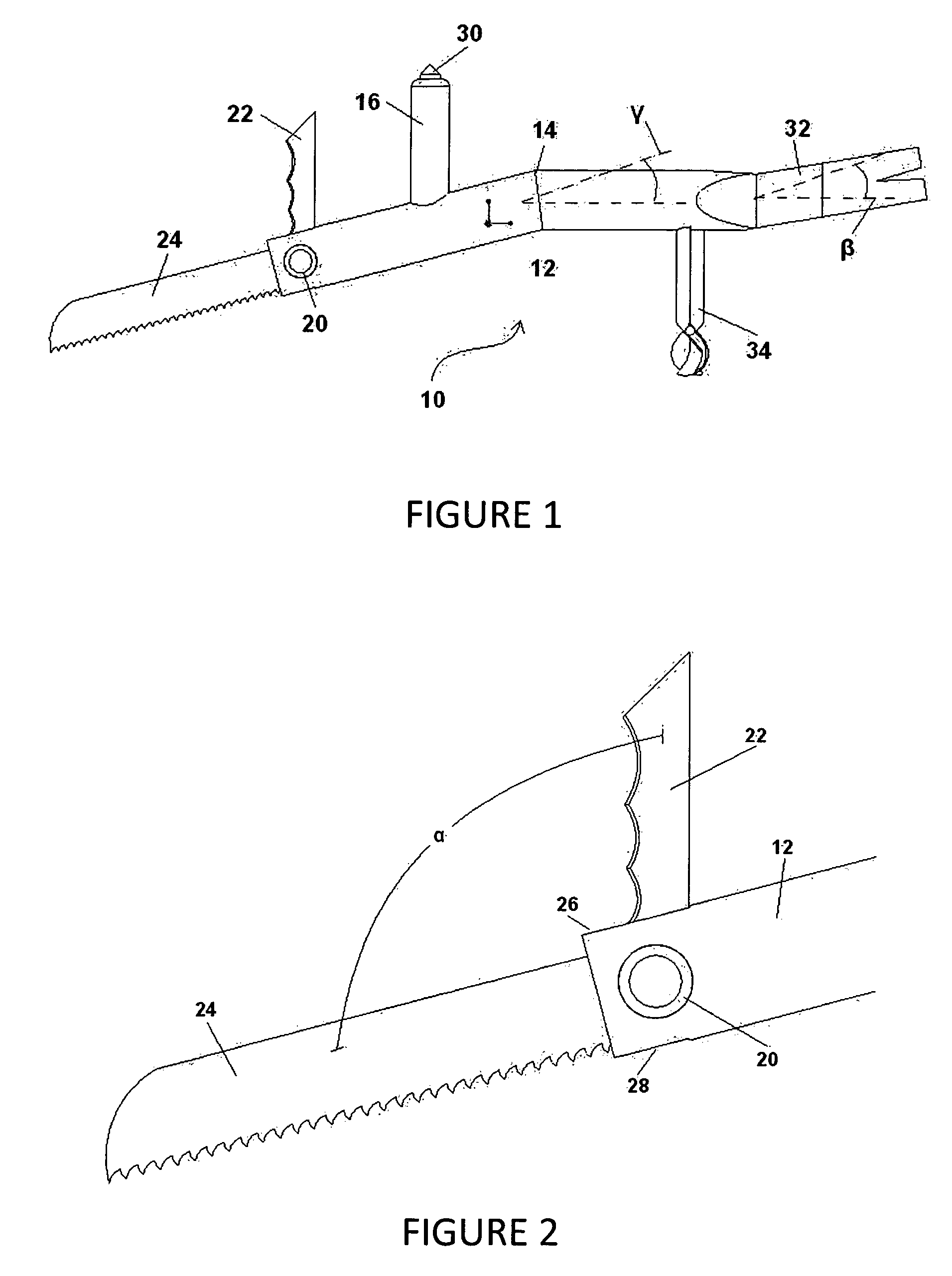
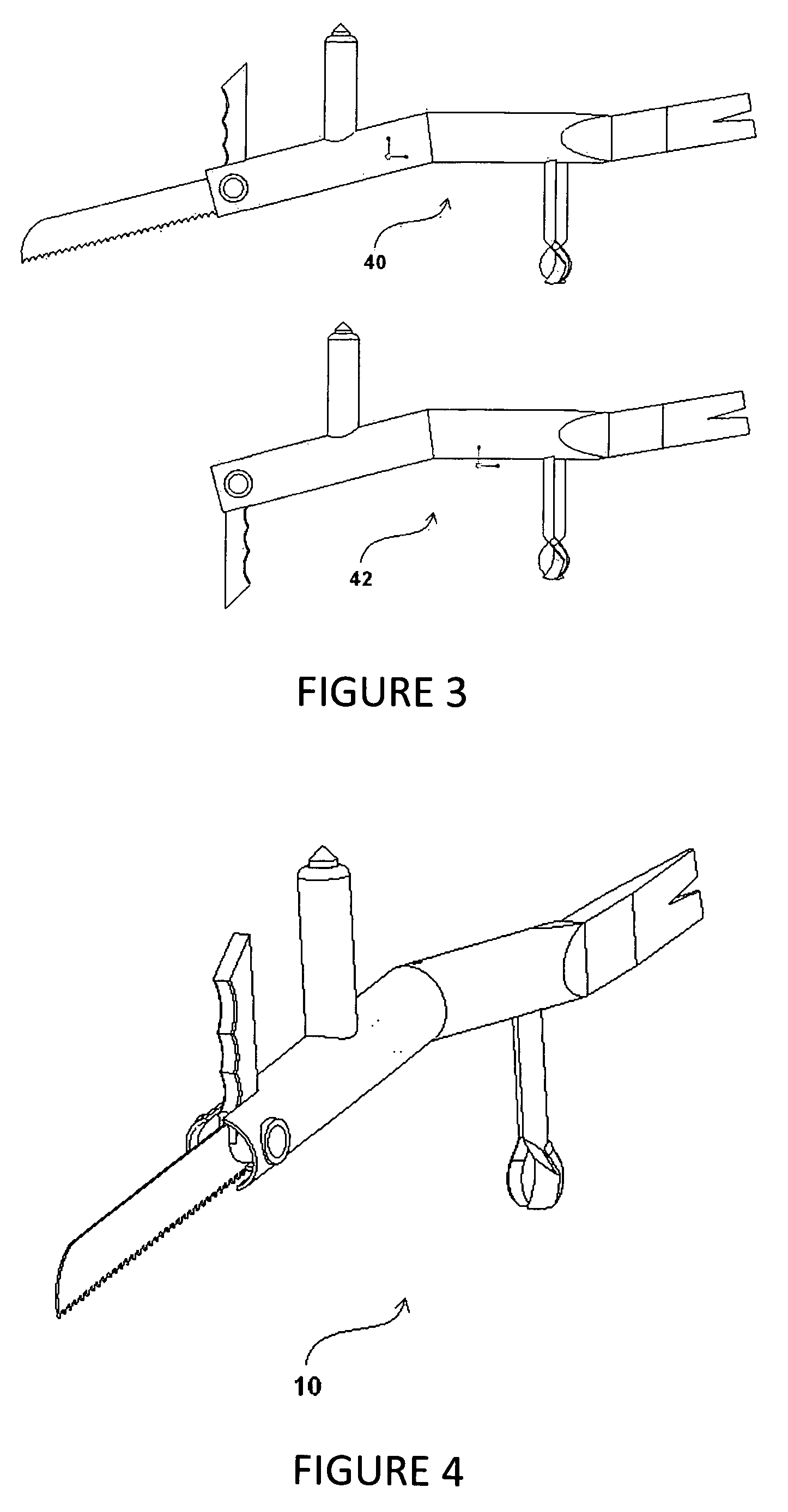
InactiveUS7703161B1Safe wayFast and reliableThrusting weaponsPortable percussive toolsEngineeringWindshield
A vehicle extrication preparatory tool includes an elongated body portion with an ergonomic bend in the middle. A handle is provided forward of the bend extending in an upward direction perpendicularly to the rear section of the body. Incorporated into the upward end of the handle is a window punch. A pry bar is attached to the rearward end of the body portion. Incorporated into the forward end of the tool is a swivel segment. The swivel segment incorporates both a windshield spike and a windshield saw blade. In the open position, the saw blade extends from the swivel segment, running parallel with the front section of the body and the spike extends upward from the swivel segment perpendicular to the rear section of the body. When closed, the saw blade fits inside a slot in the body portion extending from the swivel segment inline with the front section of the body and the spike extends downward perpendicular to the rear section of the body from the swivel segment.
Owner:HANDSHAW DARRAN MICHAEL
Electronic cymbal assembly with modular self-dampening triggering system
ActiveUS8946536B2Highly accurate conversionIssue can be solvedElectrophonic musical instrumentsPercussion musical instrumentsElectricityComputer module
The present invention includes a method and apparatus for temporary dampening and temporary conversion of a wide range of an analog percussion surfaces into electronic percussive surfaces by means of a modular self-dampening trigger system attachable in an openly modular configuration to the underside of said analog percussive surfaces in a manner that allows physical variations to traverse different media and span distance and time and allowing for discrete detection and manipulation of said variations. A trigger system that is releasably attachable to an acoustic percussion element has a metal cover plate releasably affixable to an undersurface of the acoustic percussion element, the metal cover plate partially covering less than half of the undersurface. A plurality of piezo sensors are releasably affixable to the undersurface of the acoustic percussion element. A rubber dampening element with a footprint substantially similar to a footprint of the metal cover plate is formed from a flexible thin sheet of rubber with an opening corresponding to and aligned with each of the piezo sensors, the openings each sized slightly larger than the piezo sensor. The rubber dampening element is sandwiched between the undersurface of the cymbal and the metal cover plate.
Owner:FIELD ELECTRONICS DRUMS
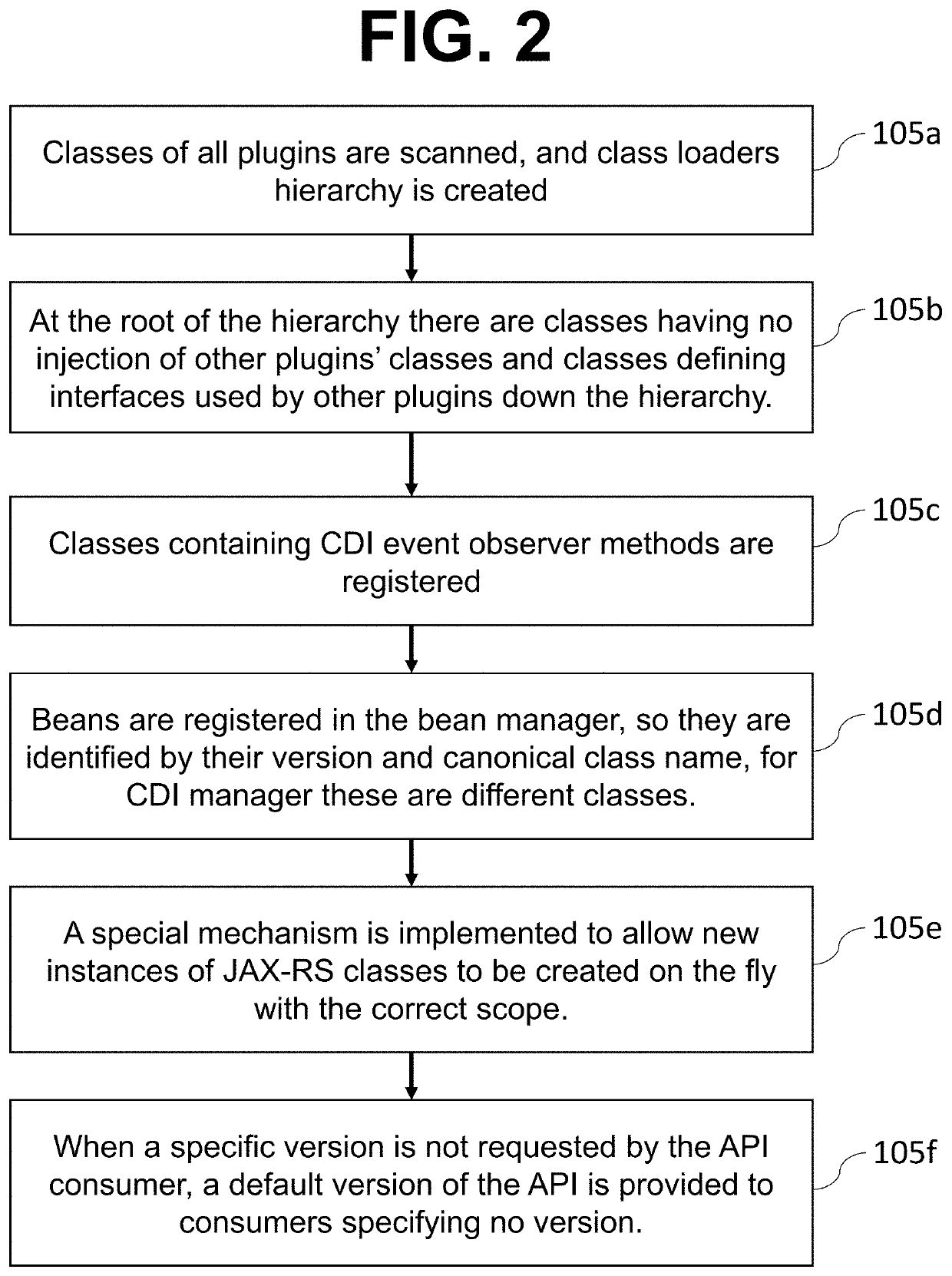
Performance of Concurrent Data Inserting
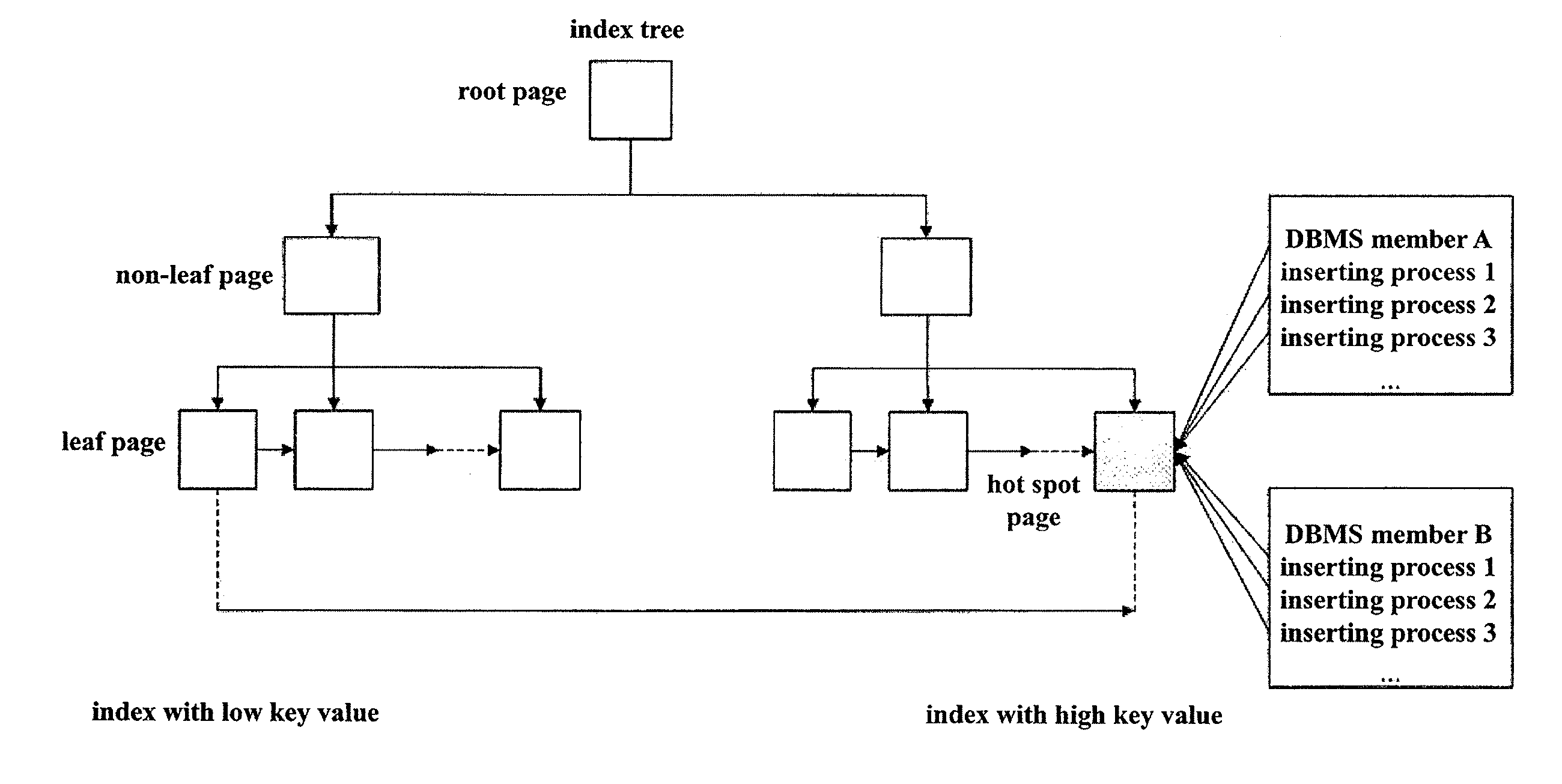
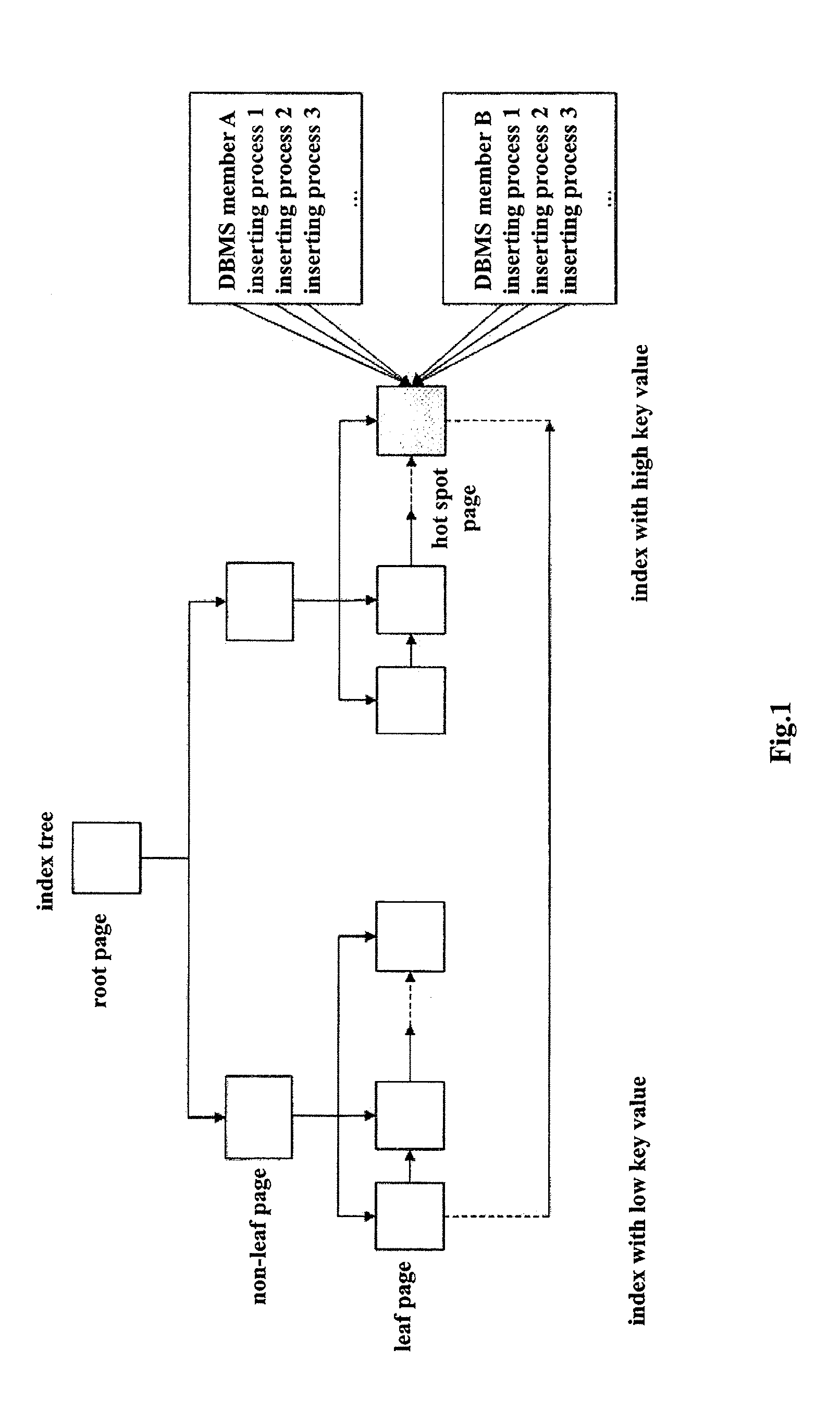
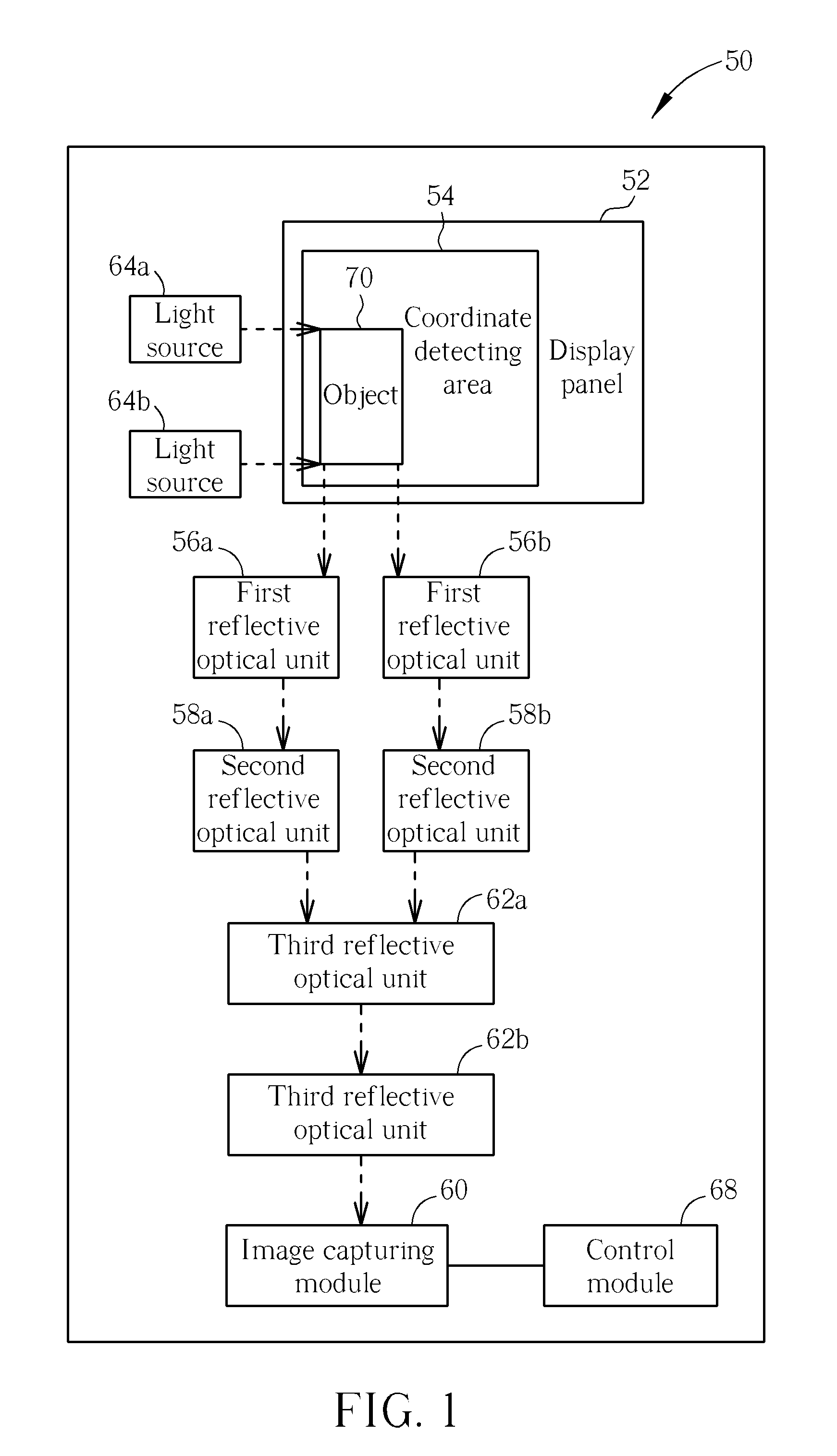
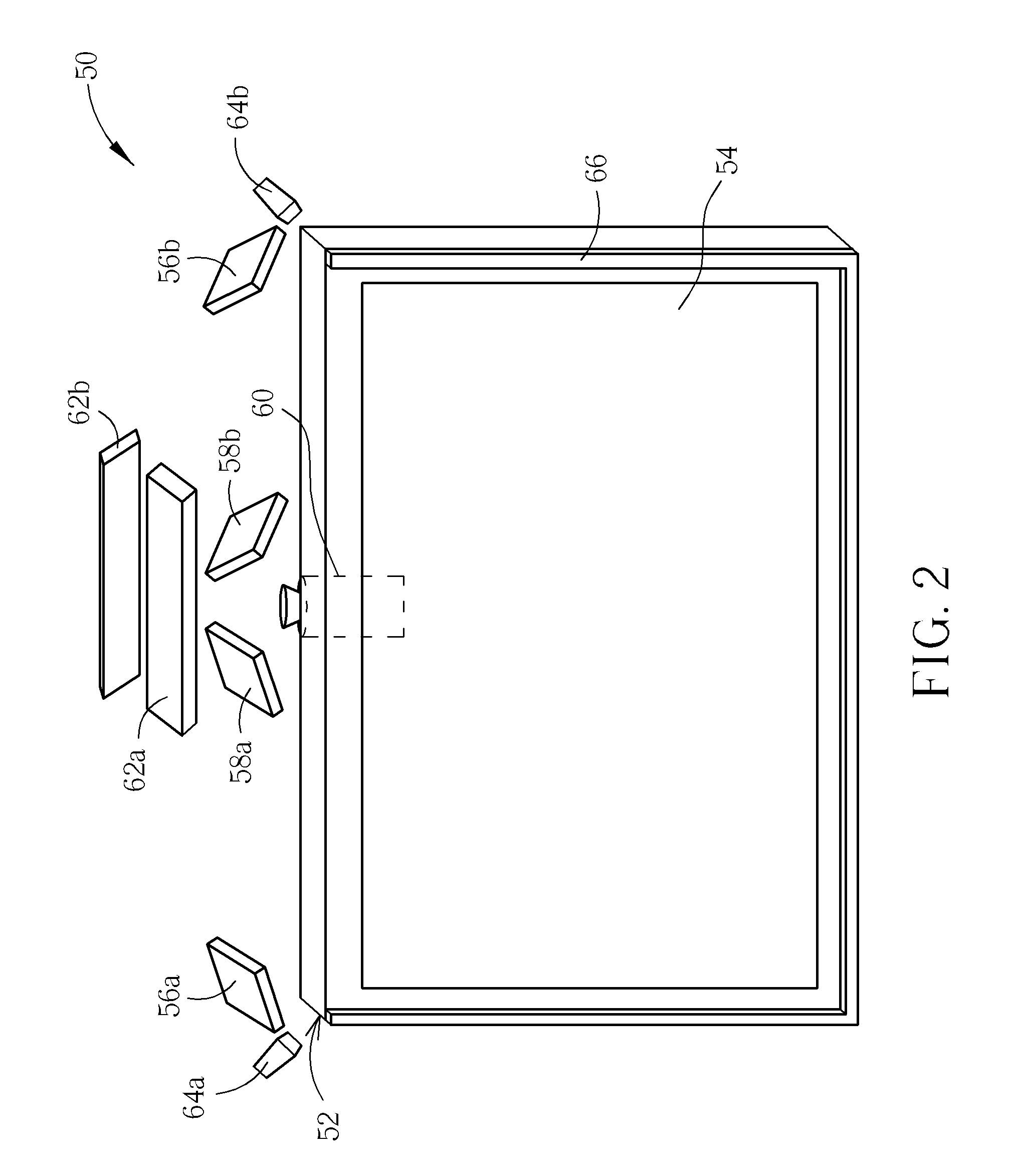
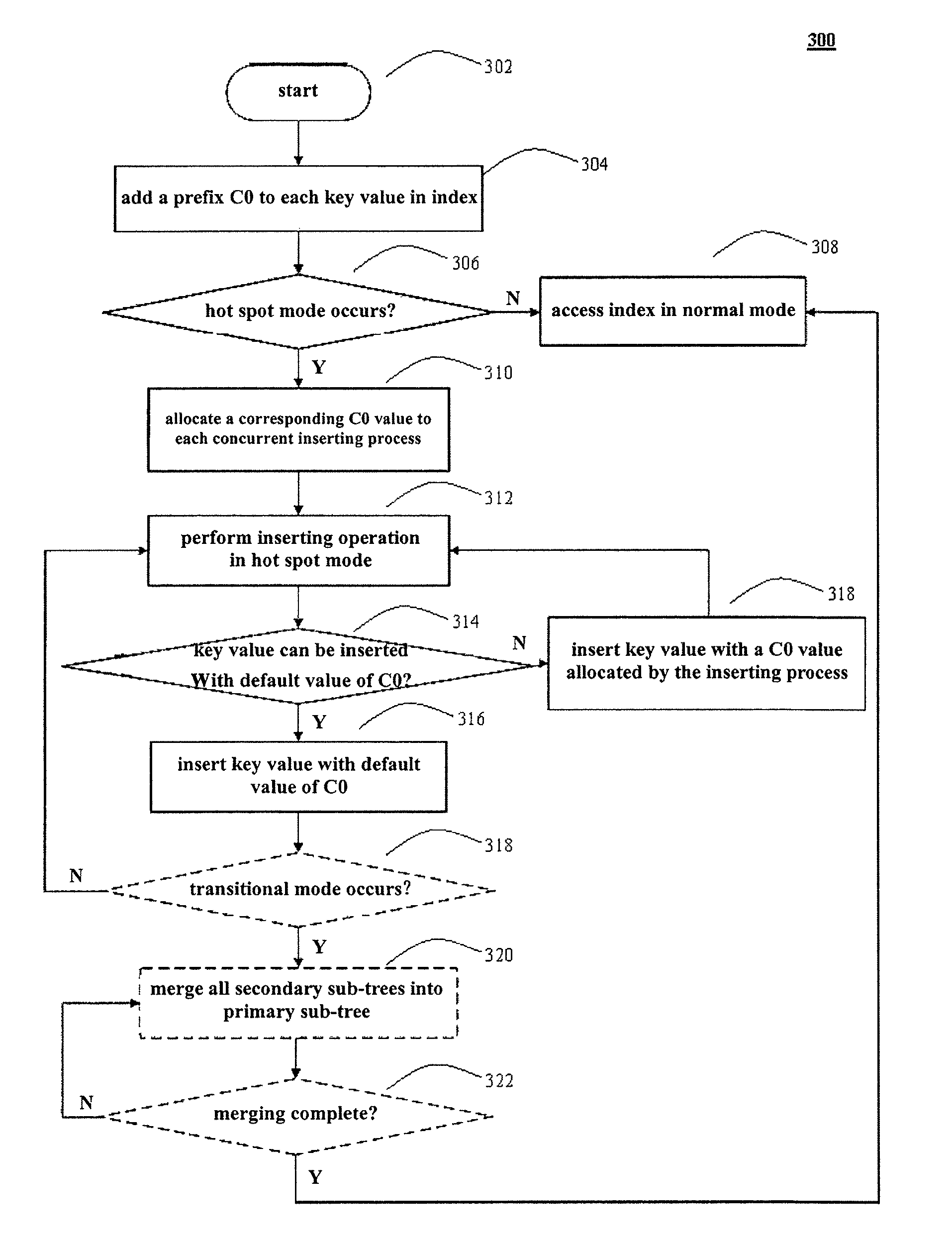
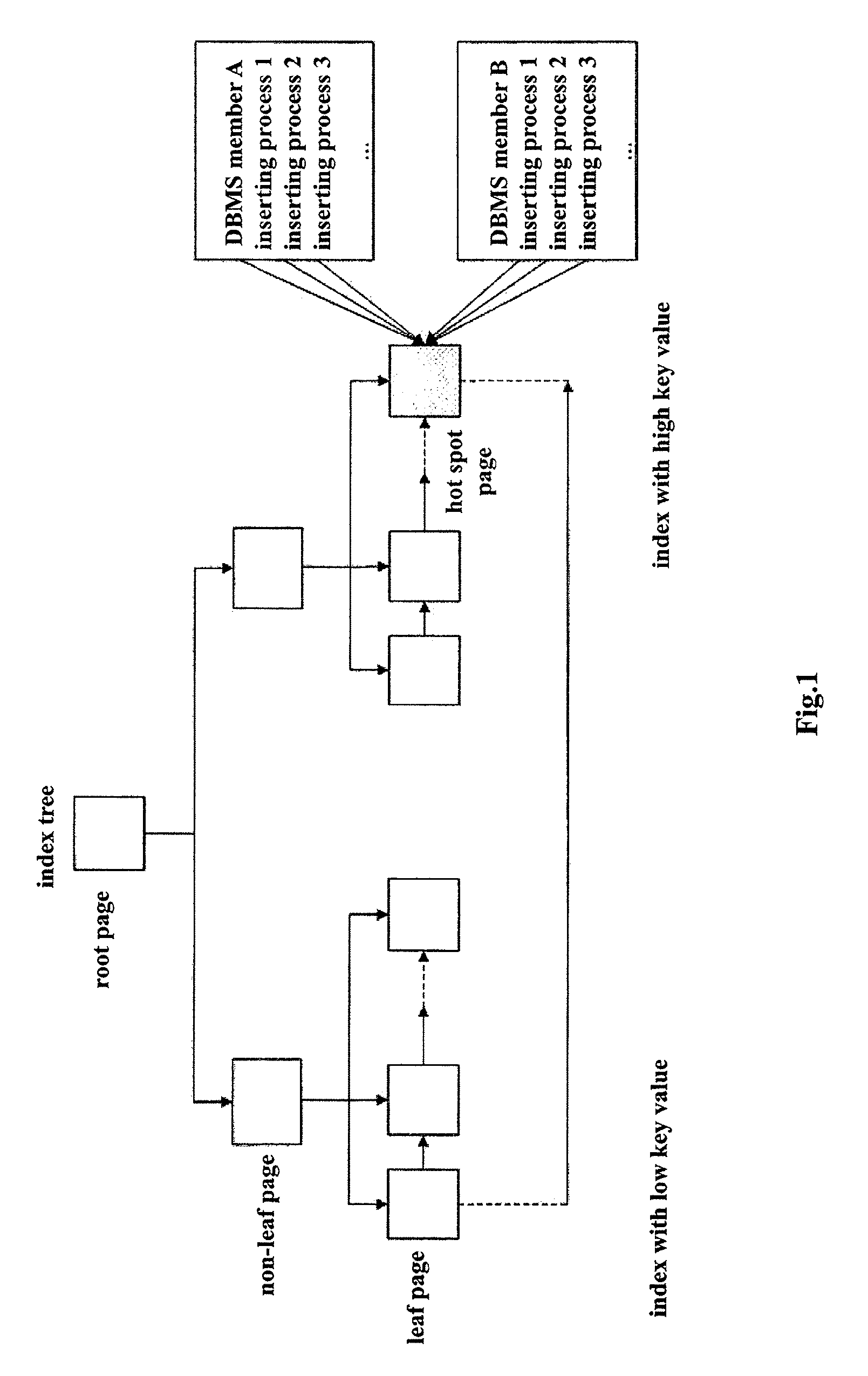
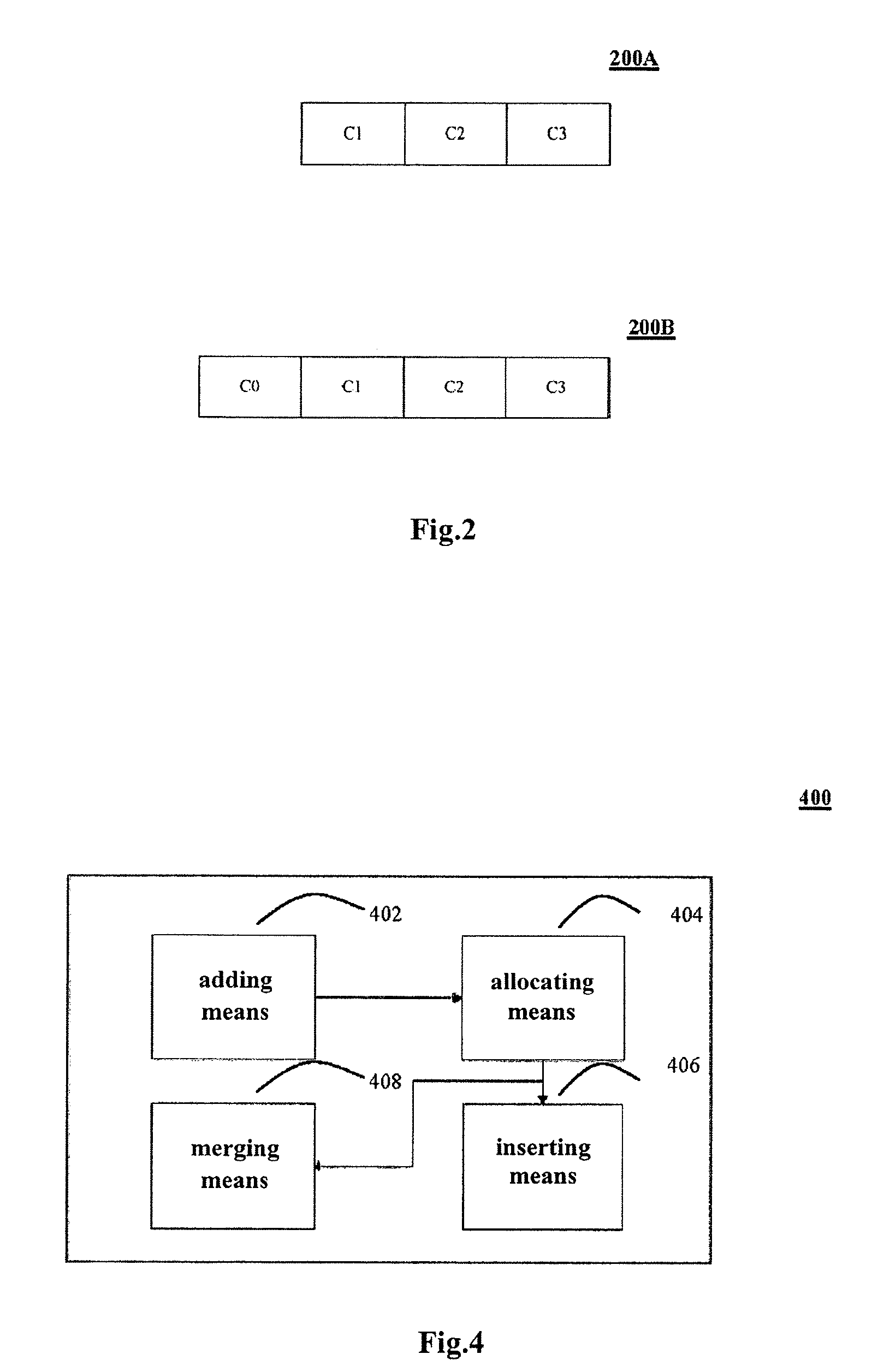
ActiveUS20120054159A1Improve performanceConflict among the multiple inserting processes are reducedDigital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsTheoretical computer scienceComputer program
A method, system and computer program product for improving performance of concurrent data inserting provide the features of adding a prefix to each key value in an index, wherein the prefix has a default value, allocating a corresponding prefix to each concurrent inserting process in response to an occurrence of a hot spot mode being detected, wherein each allocated prefix is different from the default value, performing an inserting operation in the hot spot mode, wherein the inserting operation includes deciding whether a key value can be inserted with the default value of the prefix, in response to a determination that an insertion of a key value with the default value of the prefix can be performed, inserting the key value with the default value of the prefix, and in response to a determination that an insertion of a key value with the default value of the prefix cannot be performed, inserting the key value with another prefix allocated by the inserting process.
Owner:TELOS CORP +1
Method and apparatus for measuring quality parameters of optical transmission channel
ActiveUS9608722B2Conserve costEasy maintenanceDistortion/dispersion eliminationDigital signal processingPolarization multiplexed
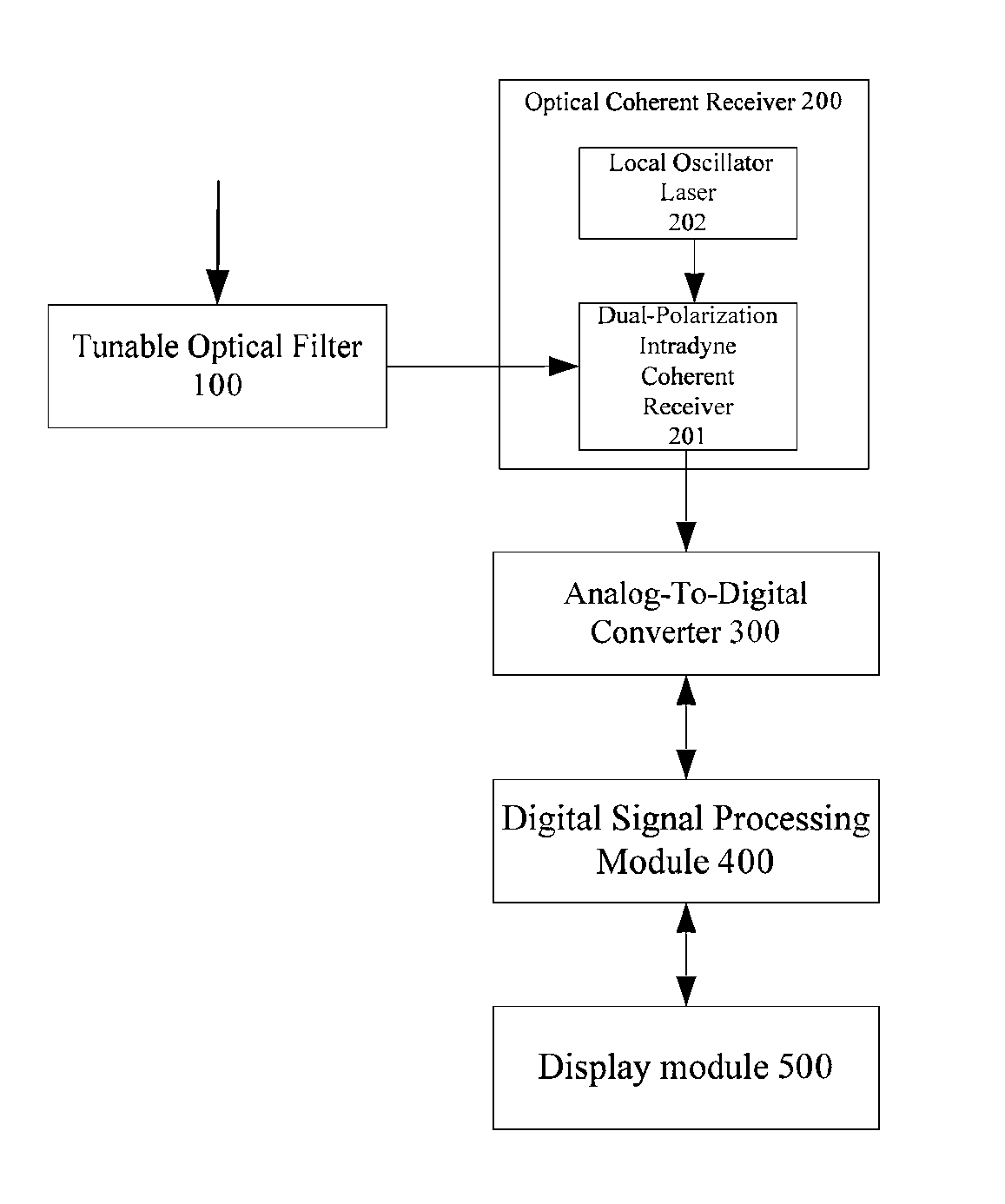
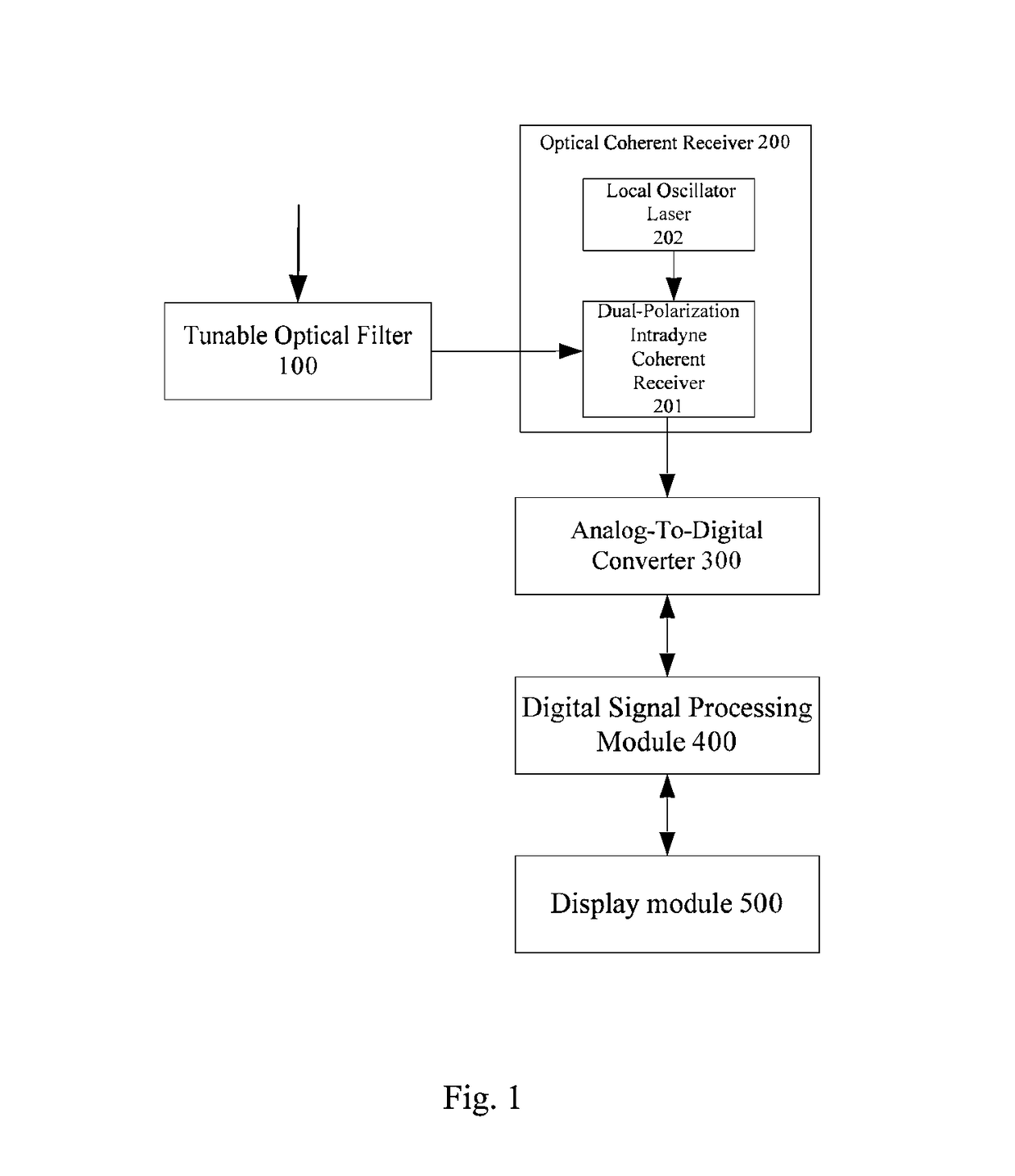
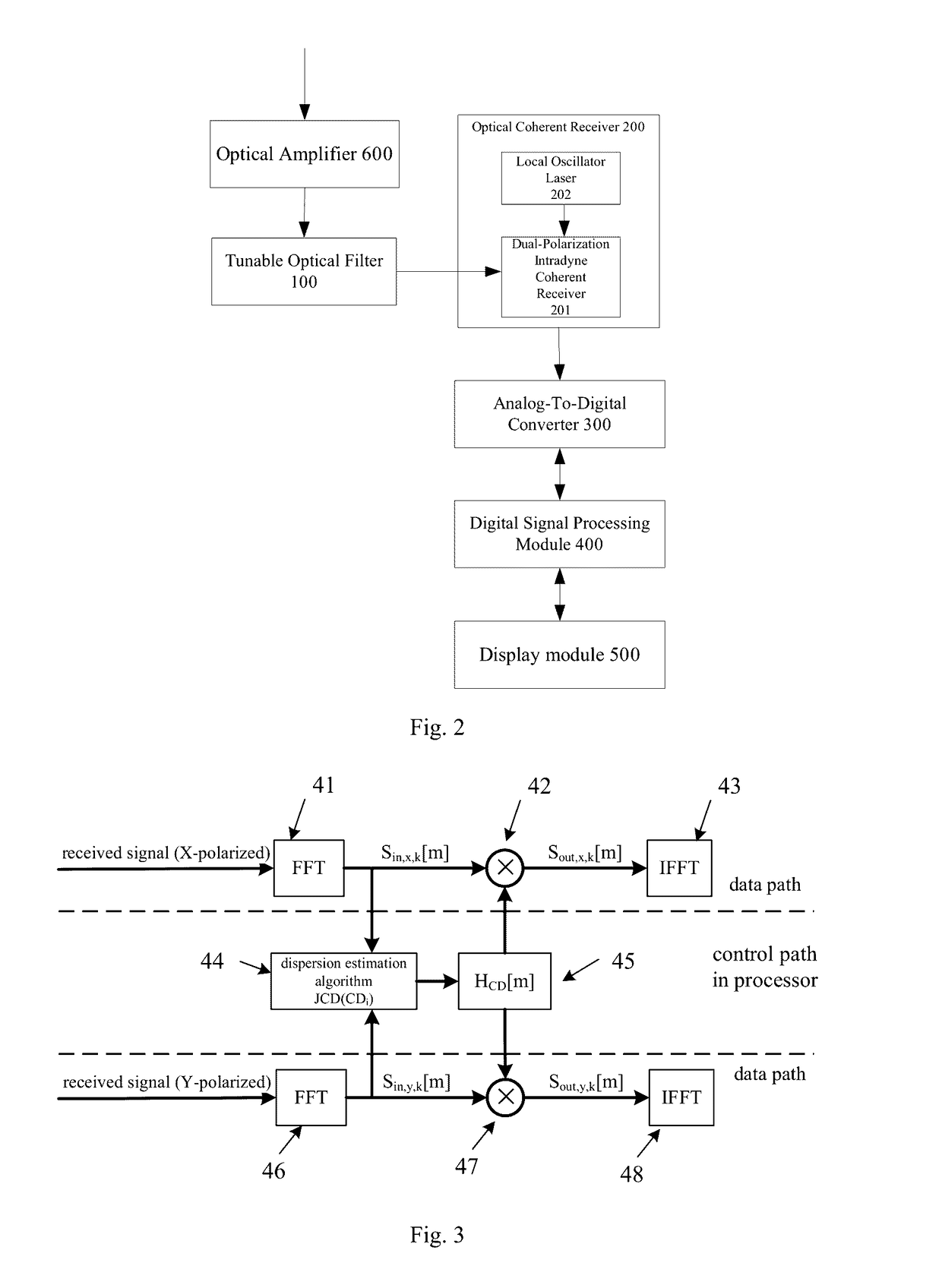
The present invention discloses a method and an apparatus for measuring quality parameters of optical transmission channels. The apparatus comprises: a tunable optical filter for receiving an optical signal, performing wavelength or optical carrier demultiplexing on the optical signal, and out-of-band ASE noise suppression; an optical coherent receiver connected to the tunable optical filter, for performing polarization- and phase-diversity detection on the filtered optical signal and converting it into multiple lane baseband electrical signals; analog-to-digital converters for sampling and quantizing the multiple lane baseband electrical signals so as to convert the them into multiple lane digital signals; a digital signal processing module for processing the multiple lane digital signals to obtain quality parameters; and an display module for displaying the quality parameters. By the device according to an embodiment of the invention, real-time measurement of various key performance parameters of the 40 Gbps, 100 Gbps and extra-100 Gbps (for example, 200 Gbps, 400 Gbps and 1 Tbps) coherent polarization-multiplexed system is achieved simultaneously, especially the issue of real-time measurement of the in-service in-band OSNR is solved. Therefore, the network operation and maintenance are facilitated and the cost of network operation and maintenance is saved.
Owner:LUSTER LIGHTWAVE CO LTD
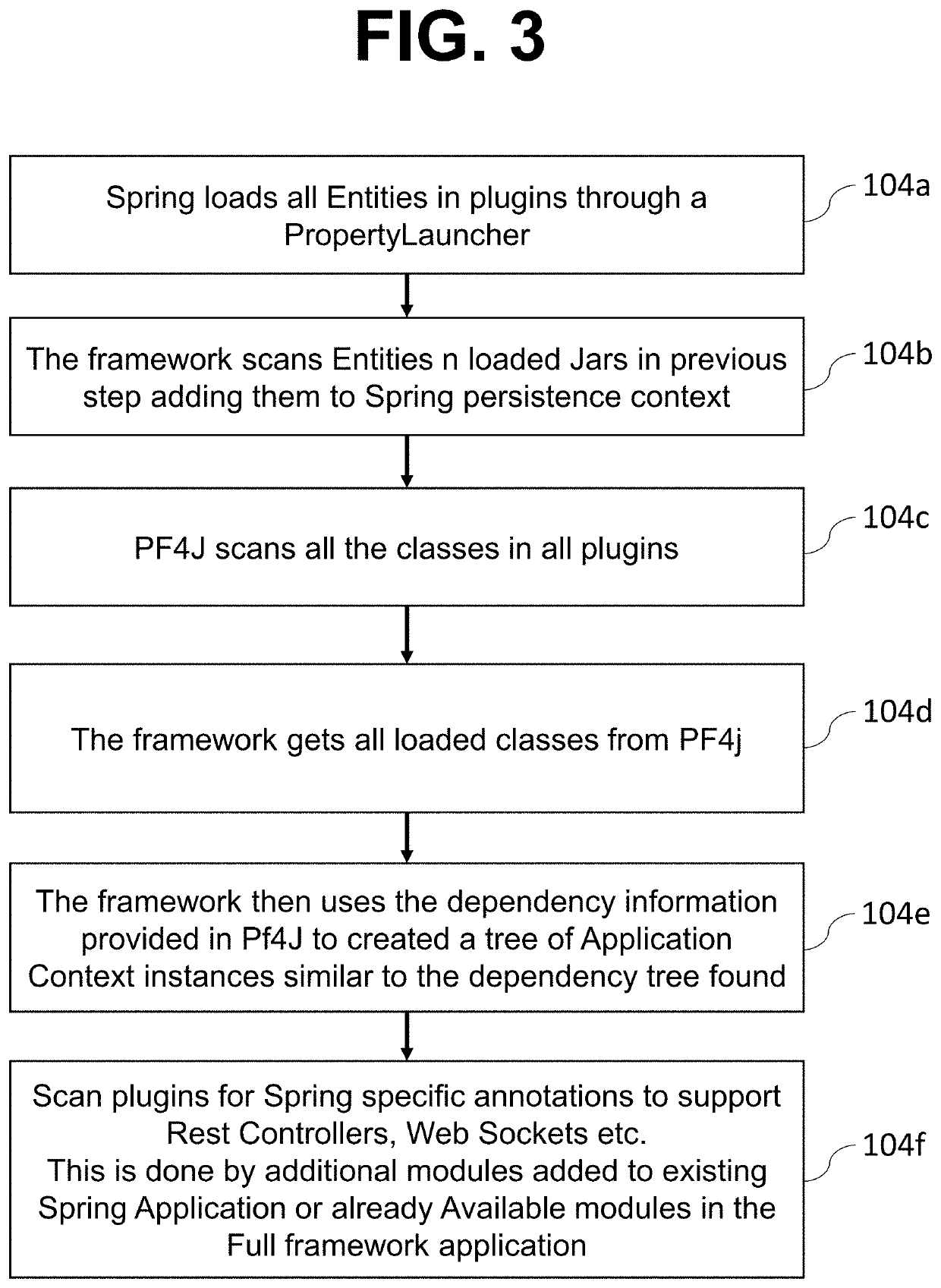
Method for componentization of enterprise applications using plugins
ActiveUS20210382731A1Issue can be solvedInterprogram communicationProgram loading/initiatingThird partyApplication server
The present invention relates to a software method for componentized enterprise applications for backend development based on Spring Boot and Java EE application server using plugins. The object of the present invention is to build back end servers and desktop applications from reusable plugins. Another object of the present invention is the benefits of a single process implementation and truly decupled parent child dependency. Moreover, the present invention is to build entire applications (deployment in application server or Spring Application) from separate and easy to maintain run time components. Finally, the present invention is that the invention can be used by almost any development team using Java EE and Spring for back end enterprise development. Moreover, the present invention is to allow plugins to provide their services either in the same process or on a remoter server in a transparent way to their services consumers. Moreover, the present invention is to allow front end clients and remote third party systems to consume backend services in a generic way allowing a properly built such said system to automatically adapt to changes in backends built using the present invention.
Owner:NATAN ASAF BEN +1
Optical imaging device
ActiveUS8797446B2Low costImprove stabilityTelevision system detailsColor television detailsComputer moduleImage capture
Owner:WISTRON CORP
Performance of concurrent data inserting
ActiveUS8832036B2Improve performanceConflict among the multiple inserting processes are reducedDigital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsTheoretical computer scienceComputer program
Owner:TELOS CORP +1
Modular crankset for bicycles
ActiveUS20190241233A1Easy to assembleEliminate lateral playVehicle cranksCouplings for rigid shaftsModularityEngineering
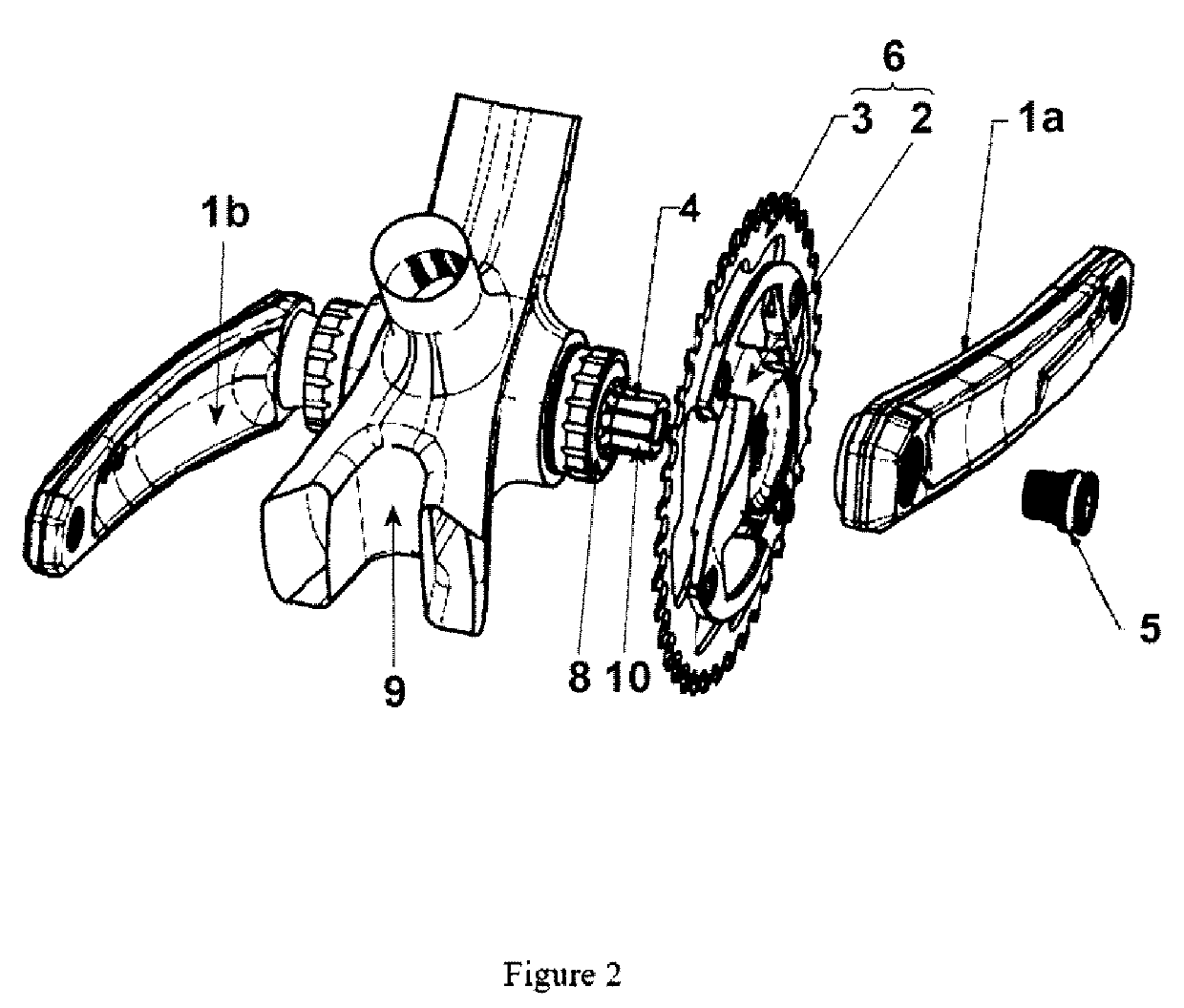
The present patent application describes a modular crankset for bicycles. The described modular crankset is useful for users, since it solves issues related to the speed of replacement of elements, the easiness of the replacement procedures and lowers the weight of the set without compromising the consistency and rigidity of the set. The current technology is applicable to any bicycle available in the market, including electrical bicycles, and it is especially interesting for competition bicycles, wherein the replacement of the constituent elements of the crankset should be made as quickly as possible.
Owner:MIRANDA & IRMAO LDA
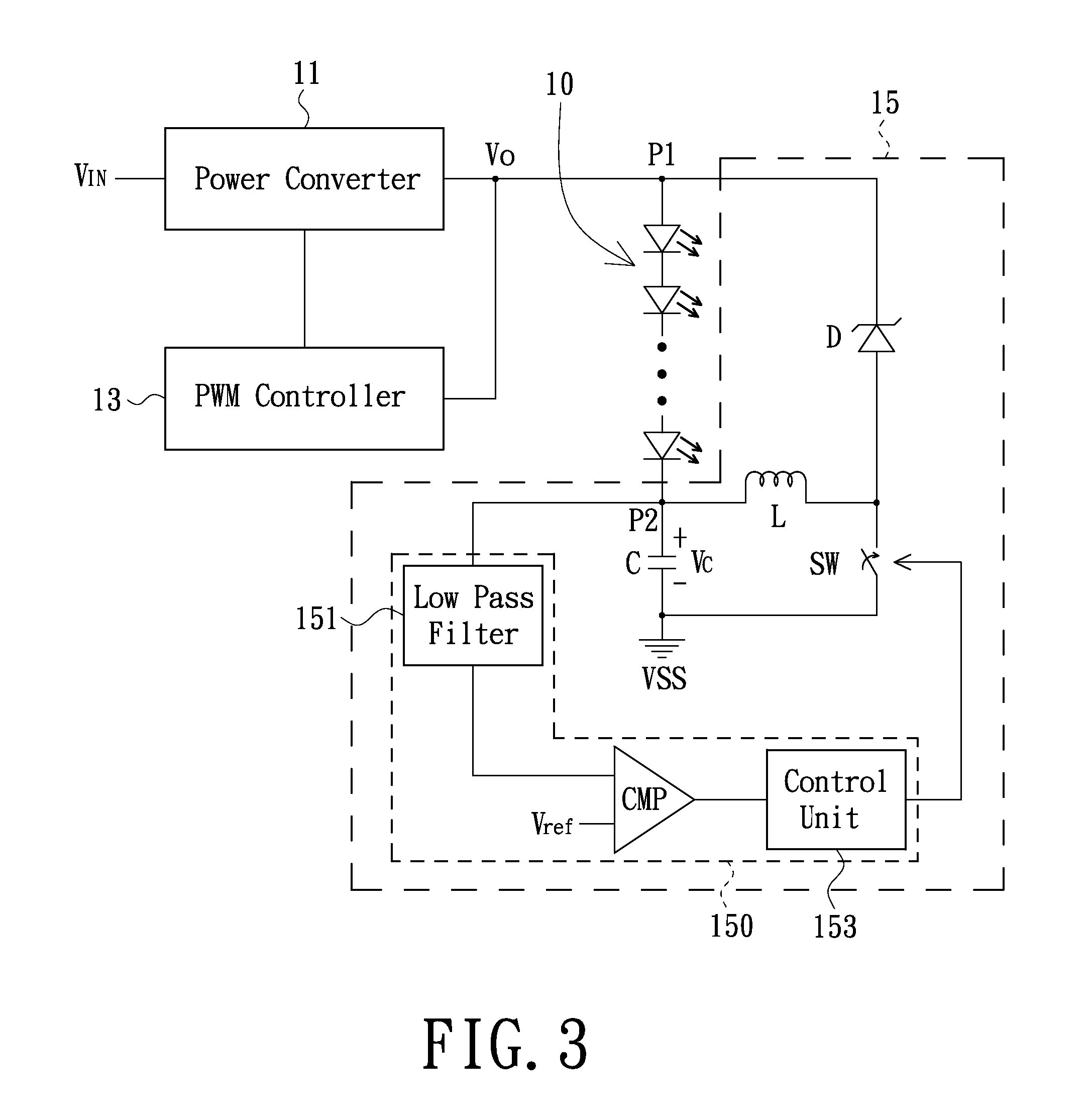
Current regulating circuit of light emitting diode (LED) string and LED illumination device
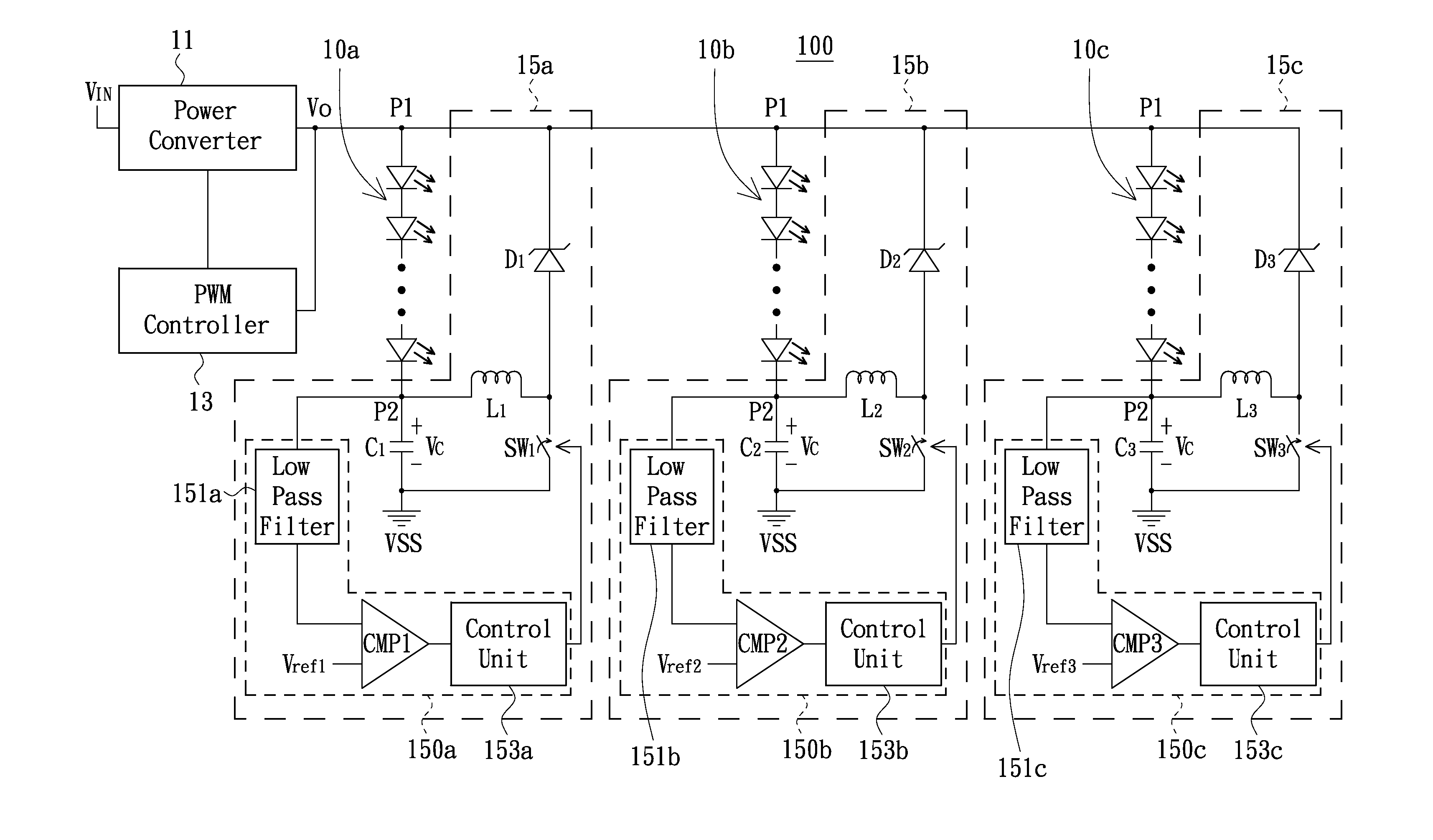
ActiveUS20120161648A1Facilitates can be recycledReduce power consumptionElectrical apparatusElectroluminescent light sourcesLow voltageInductor
An exemplary current regulating circuit of LED string includes a capacitor, an inductor, a diode, a switch and a detection circuit. First and second terminals of the capacitor respectively are connected to a low voltage and a preset voltage. A first terminal of the inductor is connected to the low voltage. Positive and negative terminals of the diode are respectively connected to a second terminal of the inductor and a high voltage. First and second terminals of the switch are respectively connected to the second terminal of the inductor and the preset voltage. The detection circuit detects the low voltage to thereby switch ON-OFF states of the switch in demand. Moreover, a LED illumination device using the current regulating circuit also is provided.
Owner:AU OPTRONICS CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com