Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
143results about How to "Improve transmission loss" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
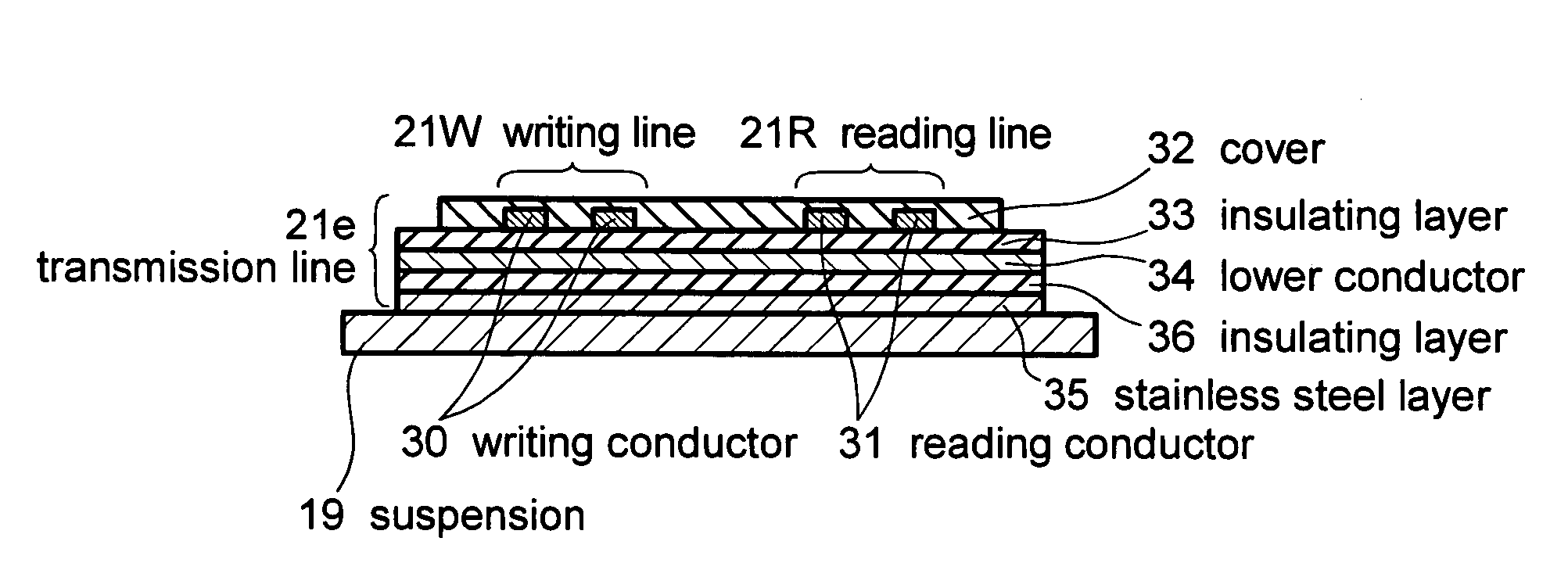
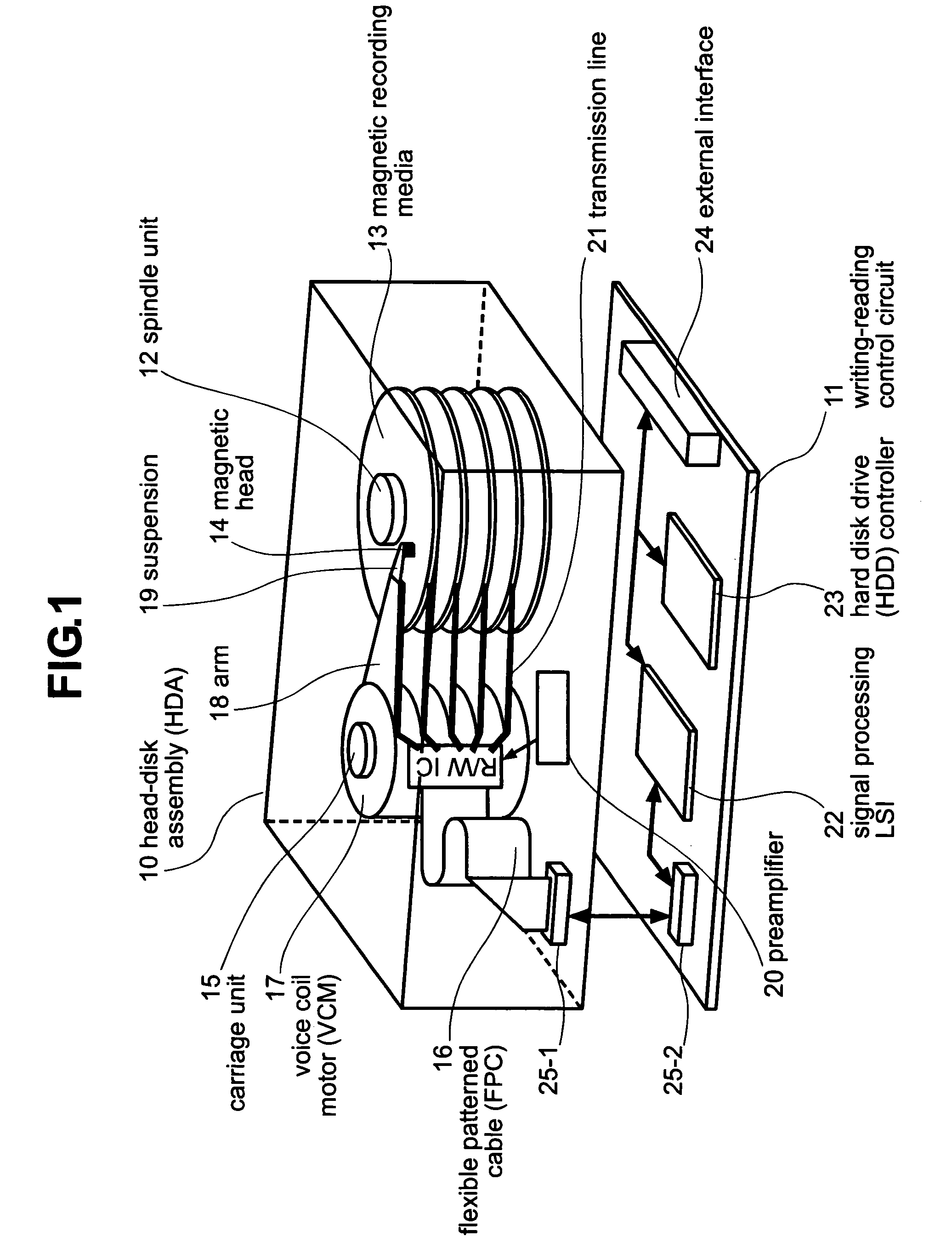
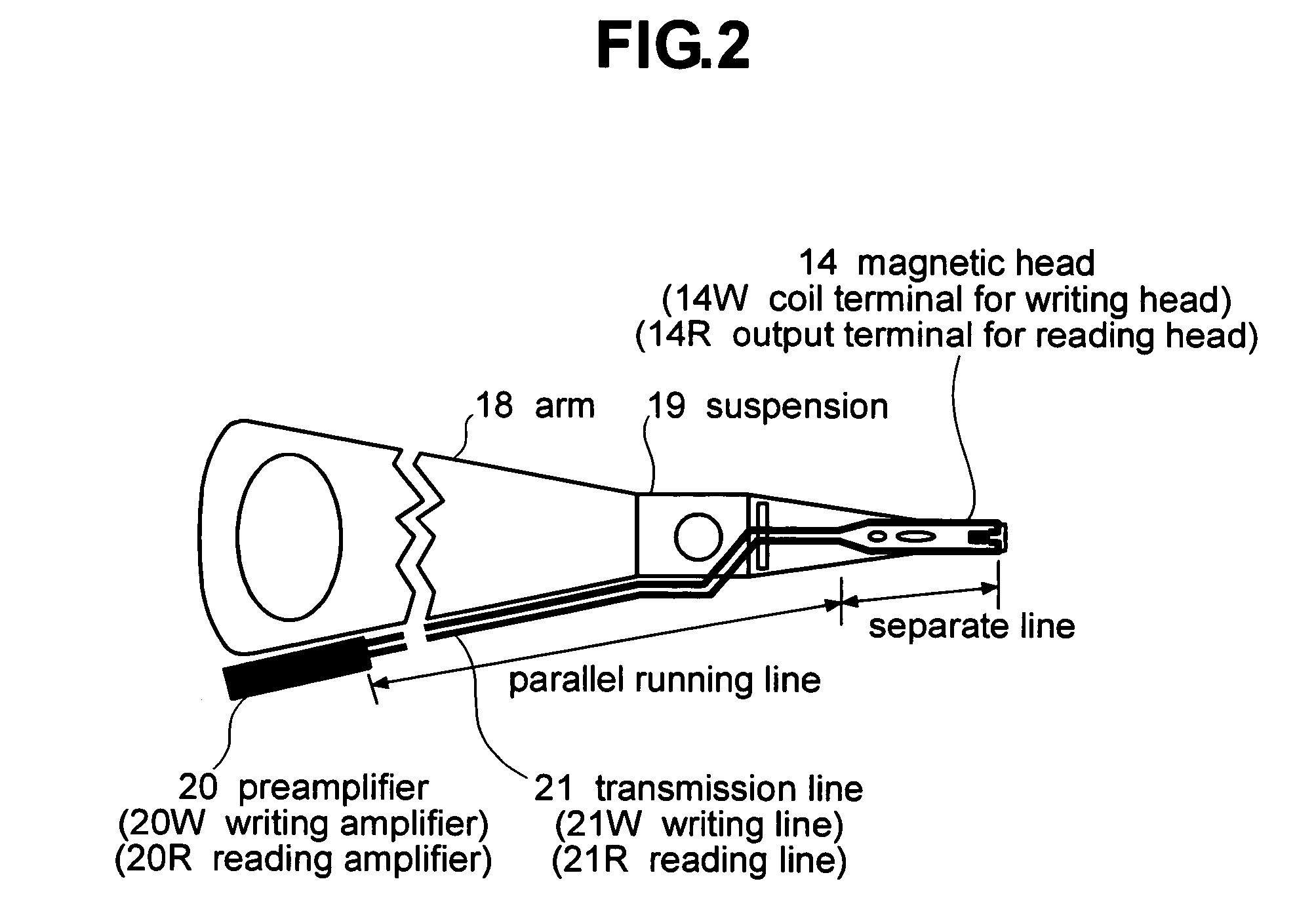
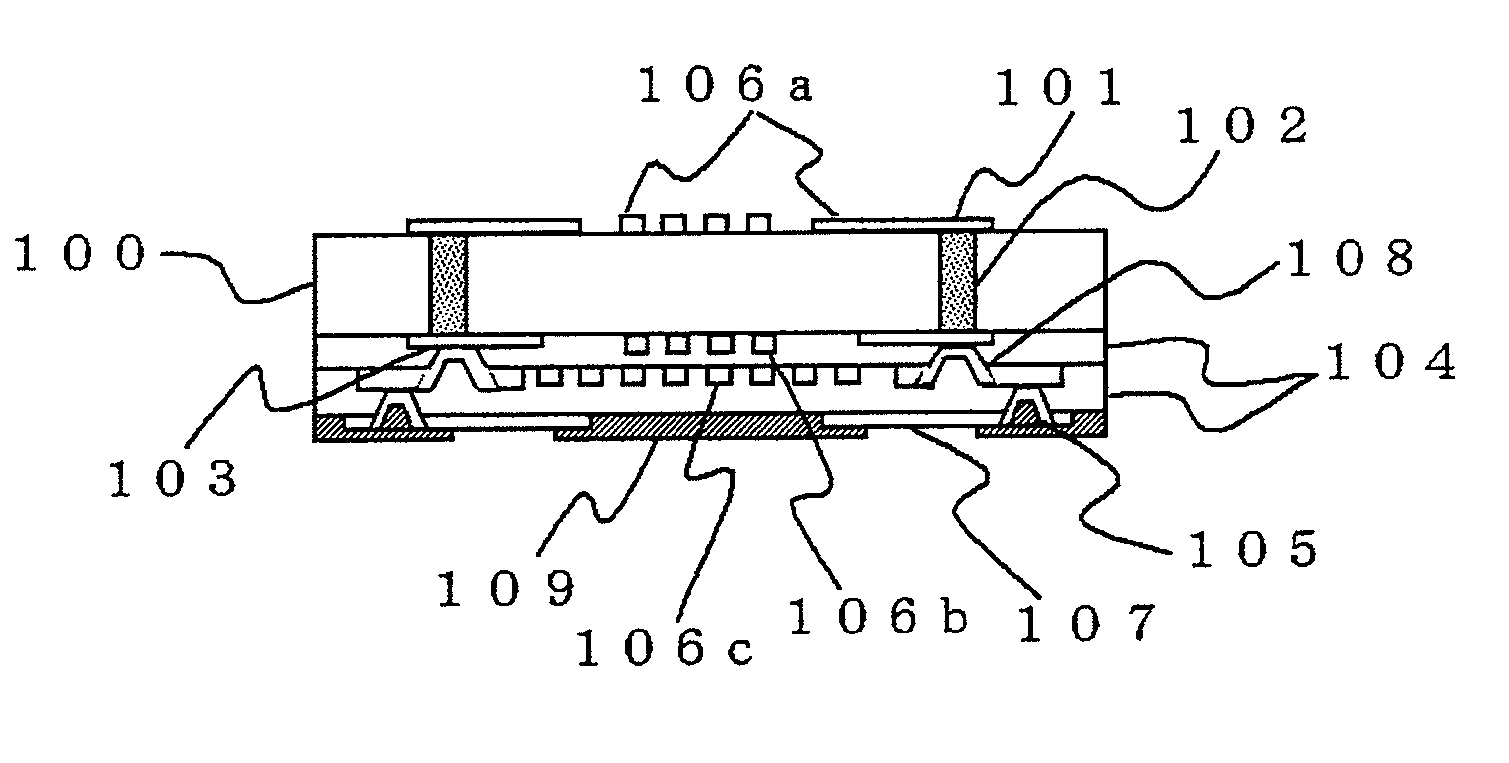
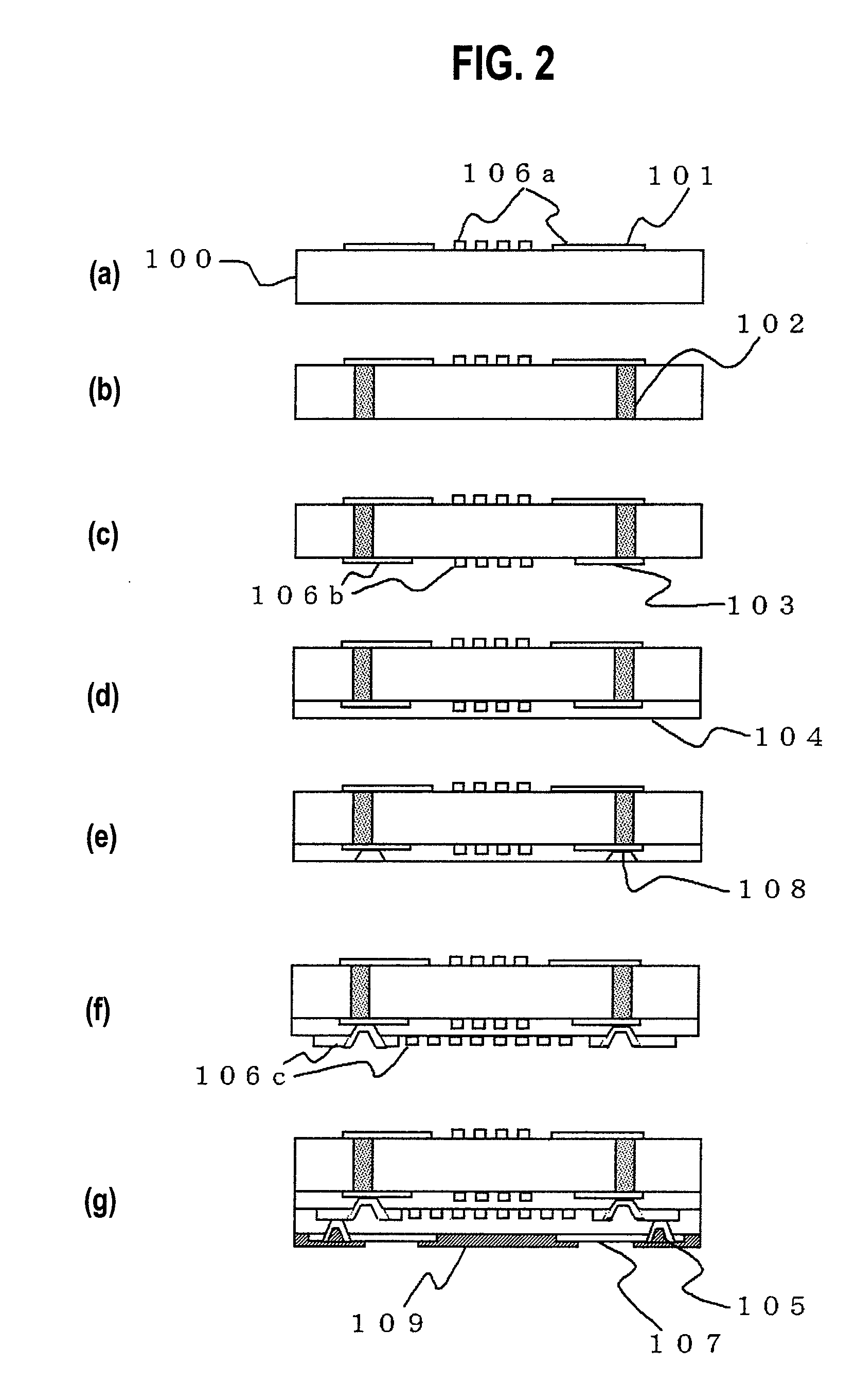
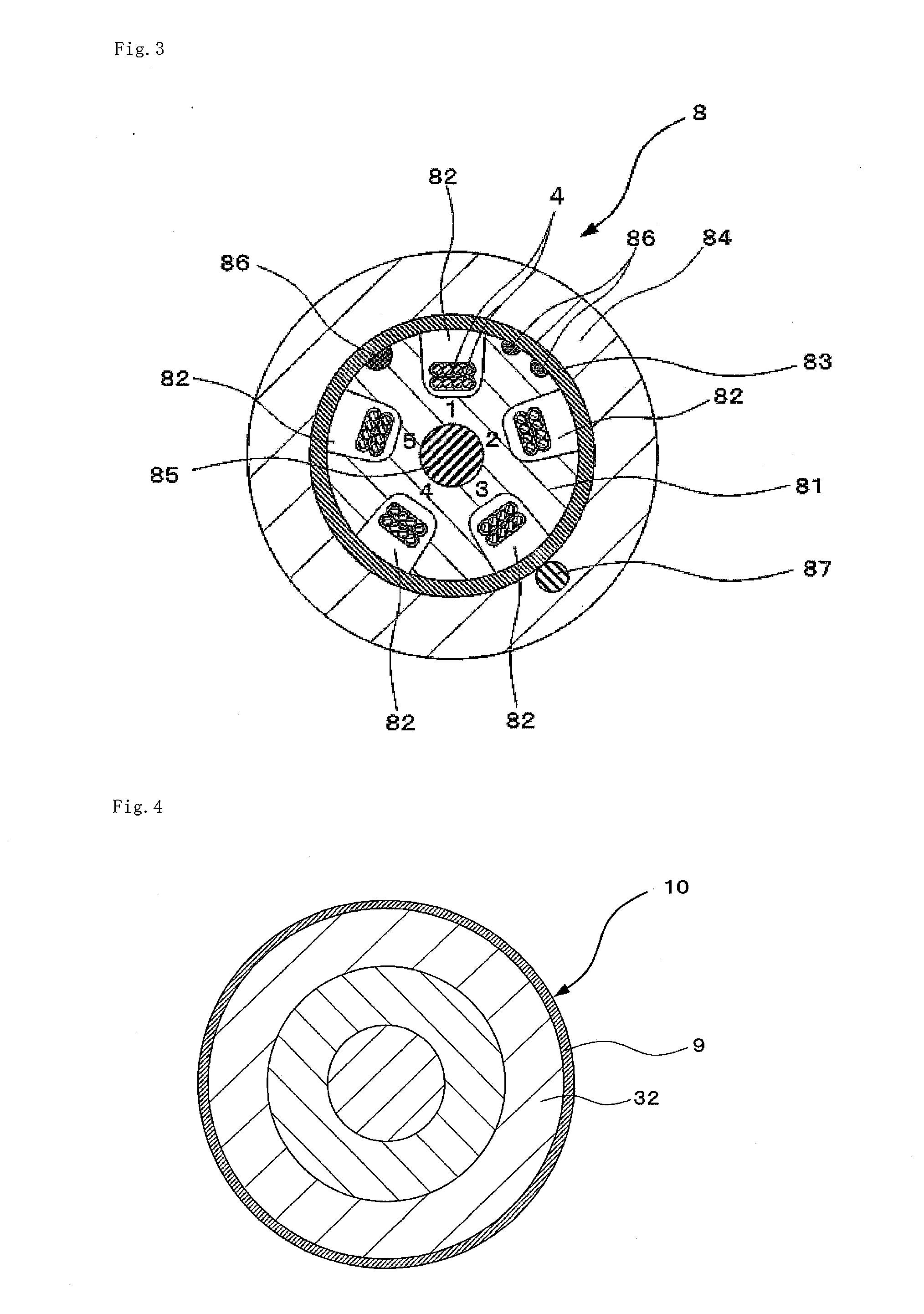
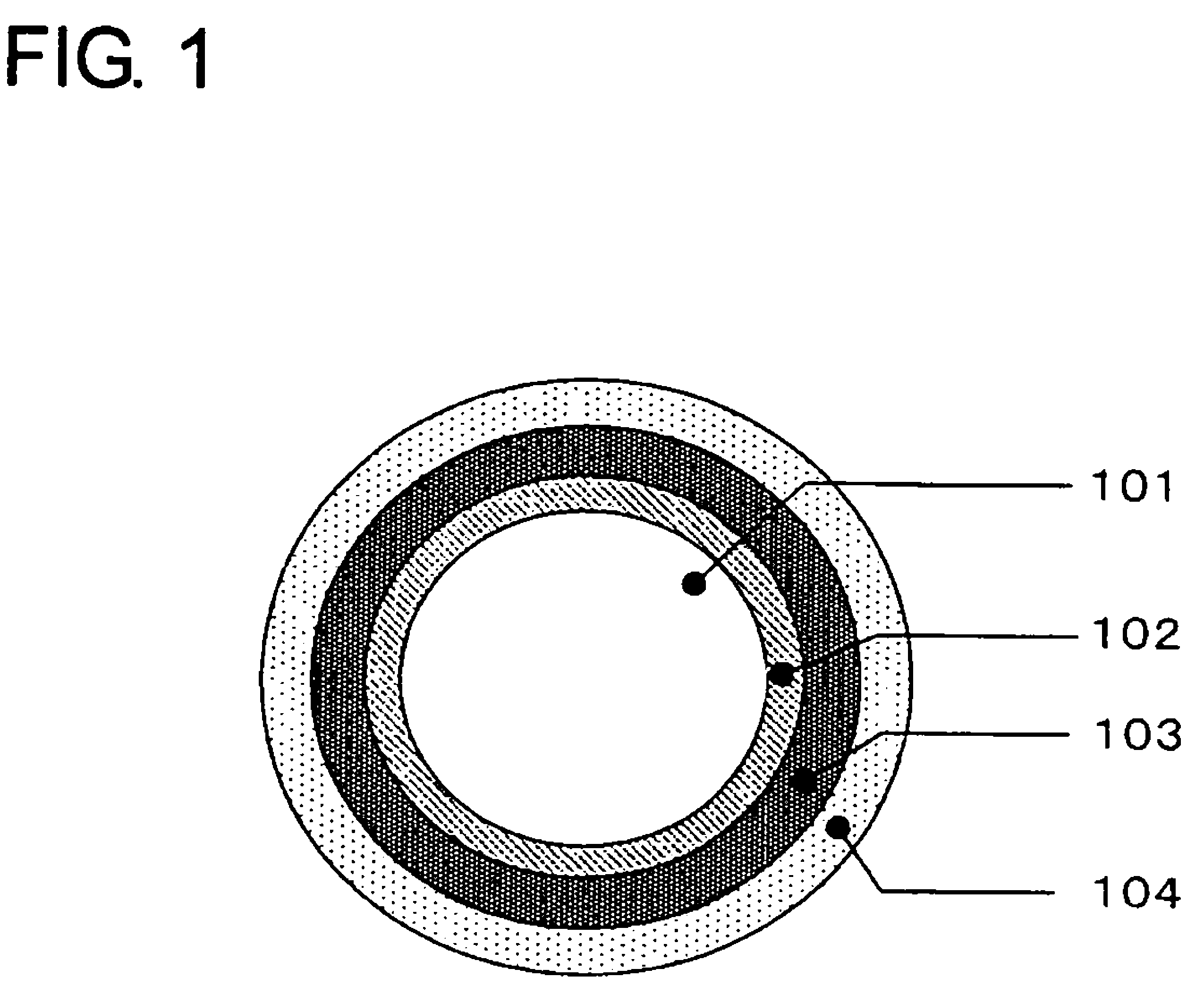
Magnetic disk drive having a suspension mounted transmission line including read and write conductors and a lower conductor
InactiveUS7319573B2Improve electrical performanceReduce transmission lossElectrotherapyMagnetotherapy using coils/electromagnetsElectrical conductorAlloy
Embodiments of the invention provide a magnetic disk drive which has improved electrical properties owing to a reduction in the loss of transmission line, improved vibration properties owing to a reduction in the stiffness of wiring around the head, and a flat impedance in the transmission line. In one embodiment, a magnetic disk drive comprises a suspension; a magnetic head coupled with the suspension and configured to write and read information to and from a magnetic recording medium; and a transmission line disposed on the suspension to transmit writing and reading information to and from the magnetic head. The transmission line includes a writing line and a reading line, a lower conductor disposed underneath the writing line and the reading line, and an insulating layer interposed between the lower conductor and the writing and reading lines. The lower conductor comprises copper or copper-based alloy and has a thickness of substantially less than 25 μm, desirably about 2-12 μm, and more desirably about 5 μm.
Owner:HITACHI GLOBAL STORAGE TECH JAPAN LTD
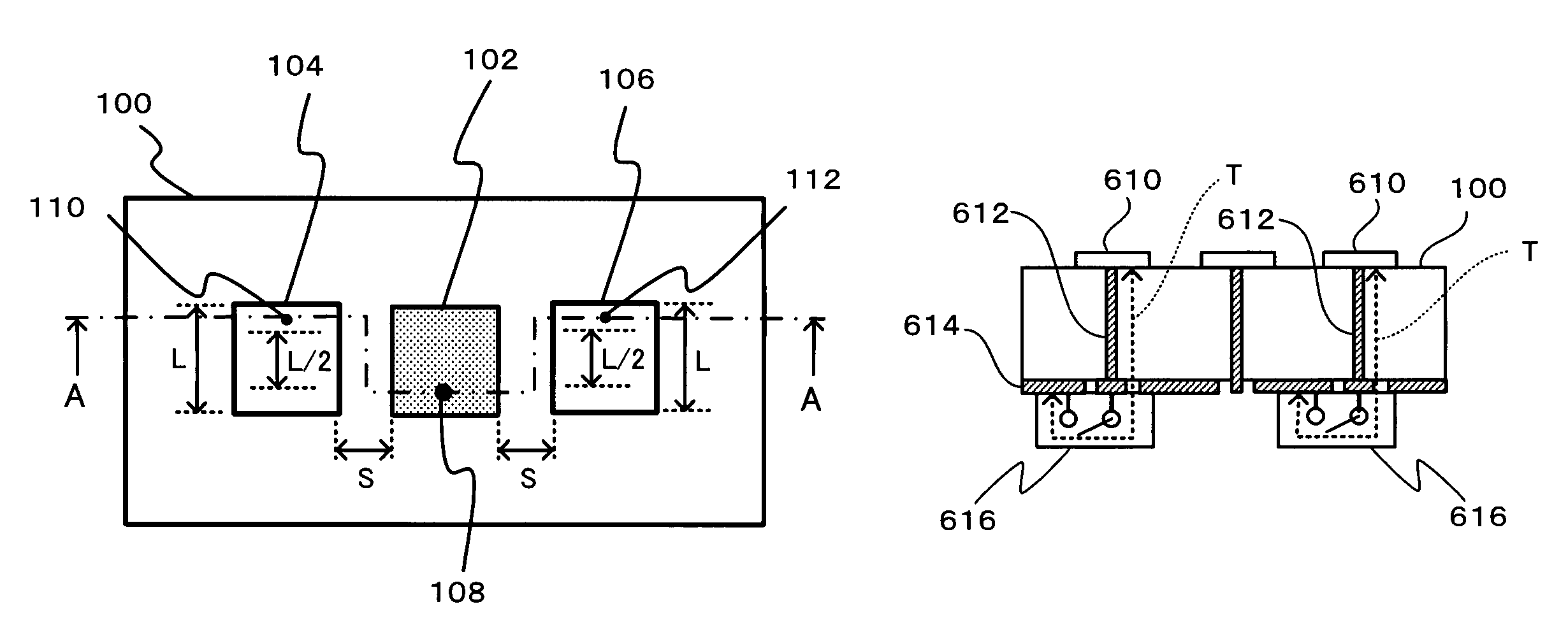
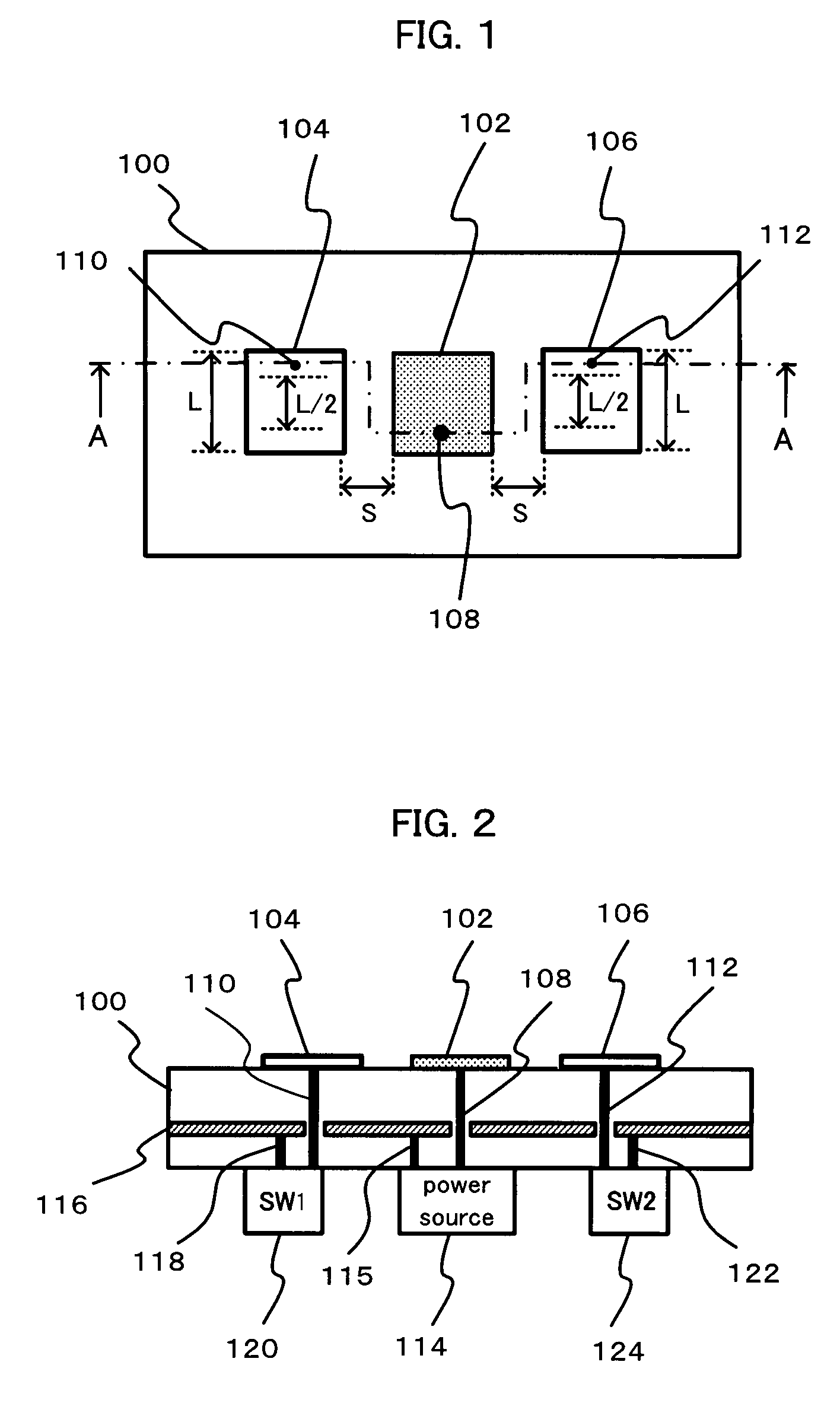
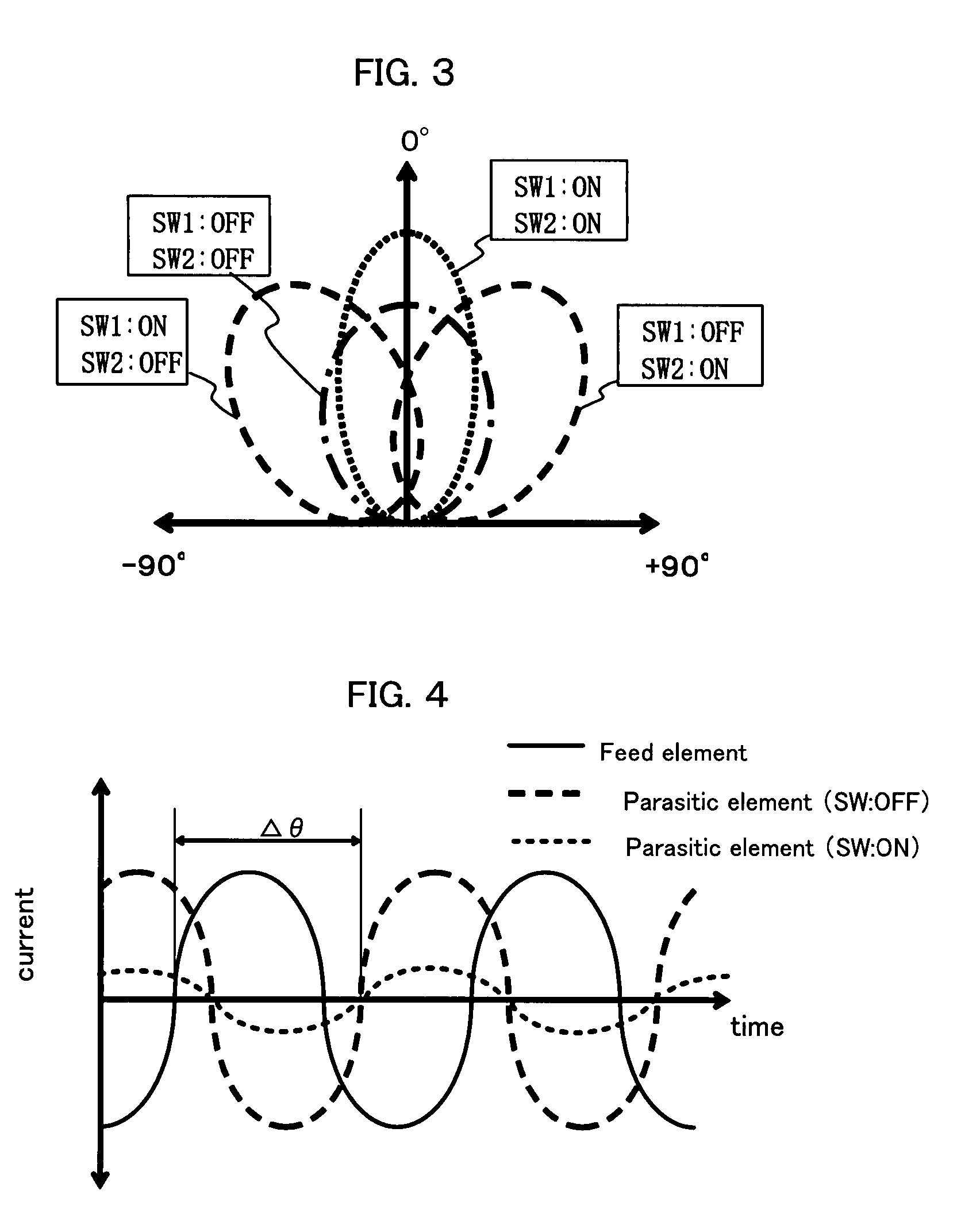
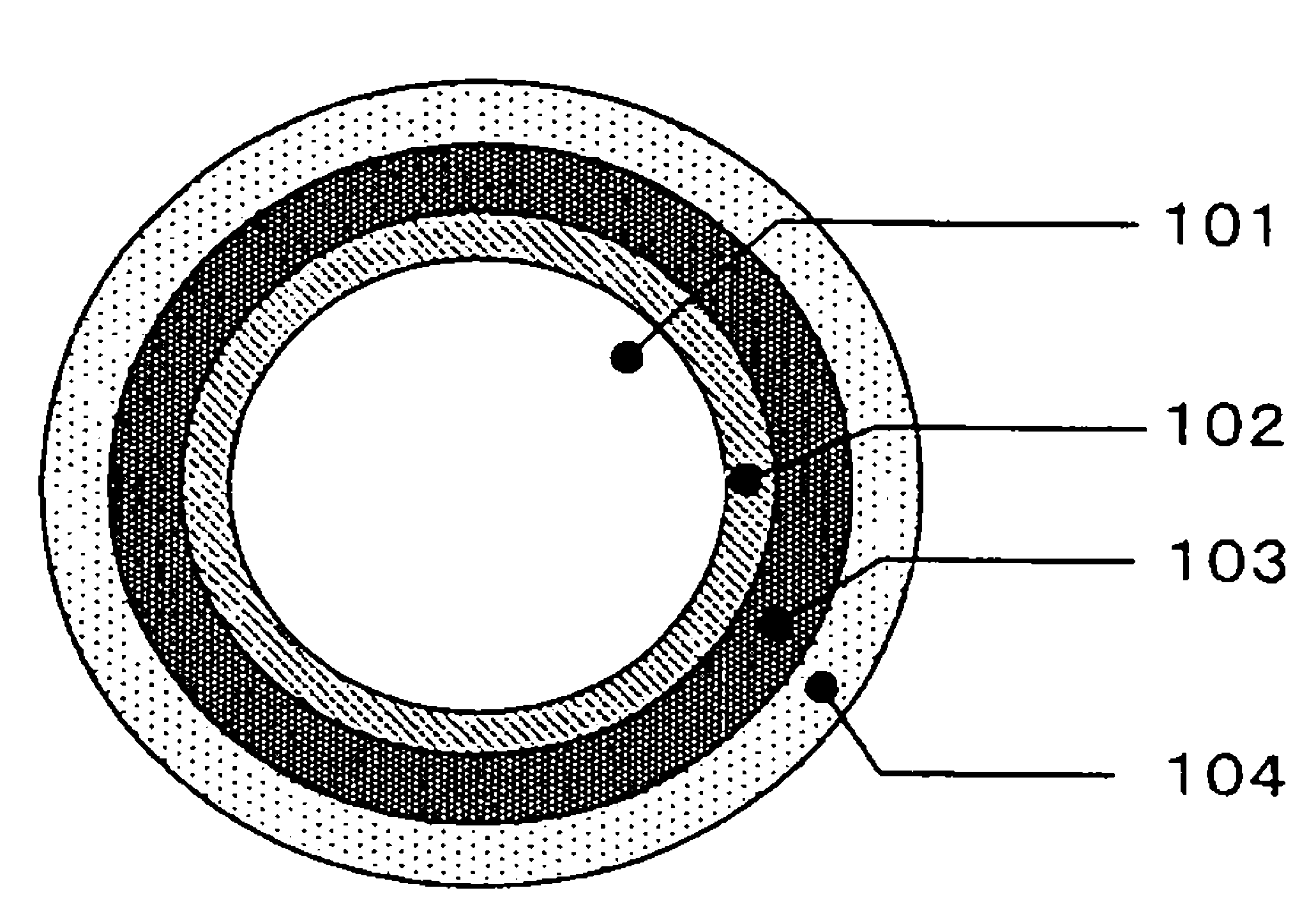
Microstrip Antenna And High Frequency Sensor Using Microstrip Antenna
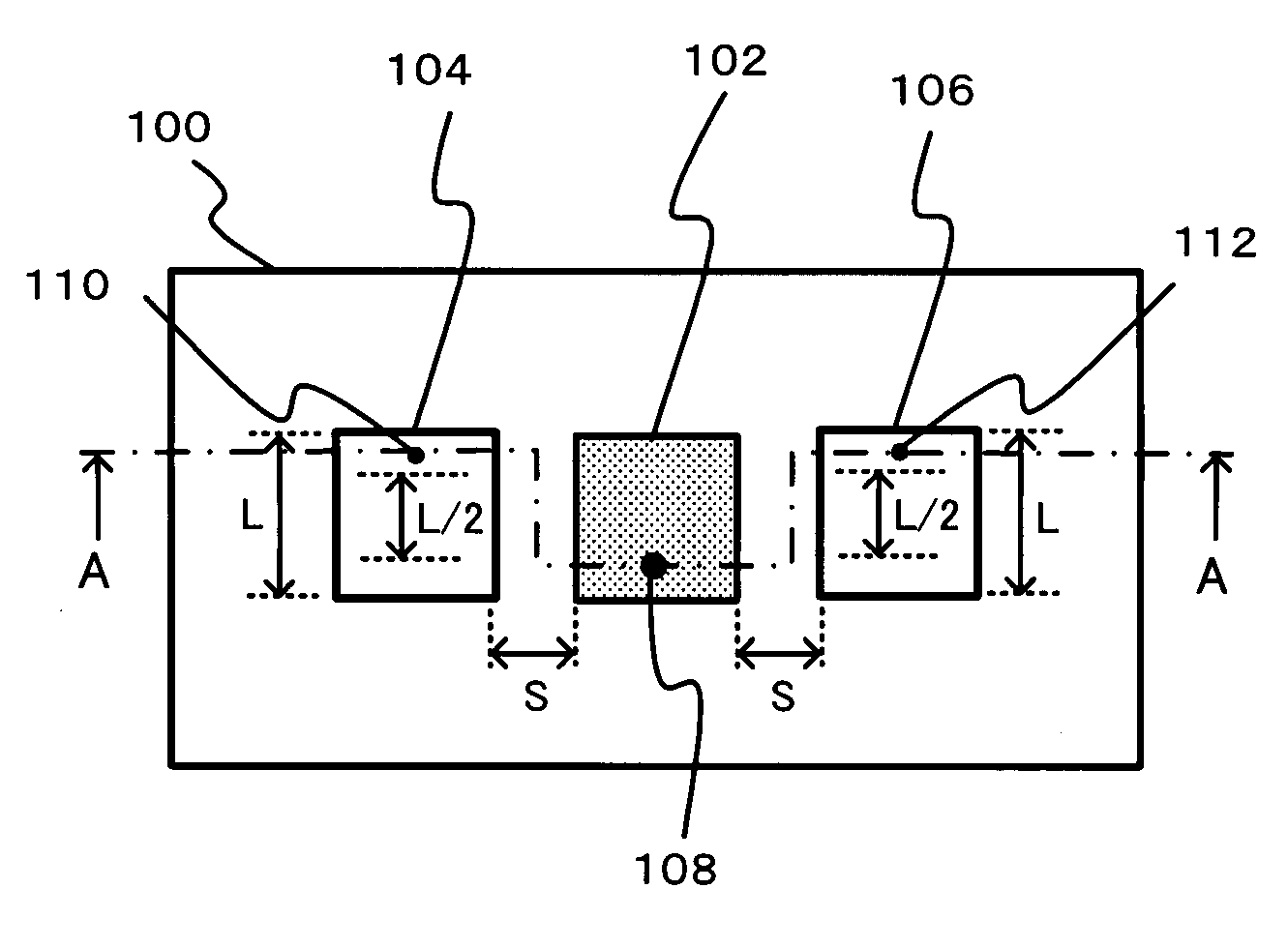
InactiveUS20080088510A1Simple structureAvoid inefficiencySimultaneous aerial operationsAntenna supports/mountingsEngineeringTransmission loss
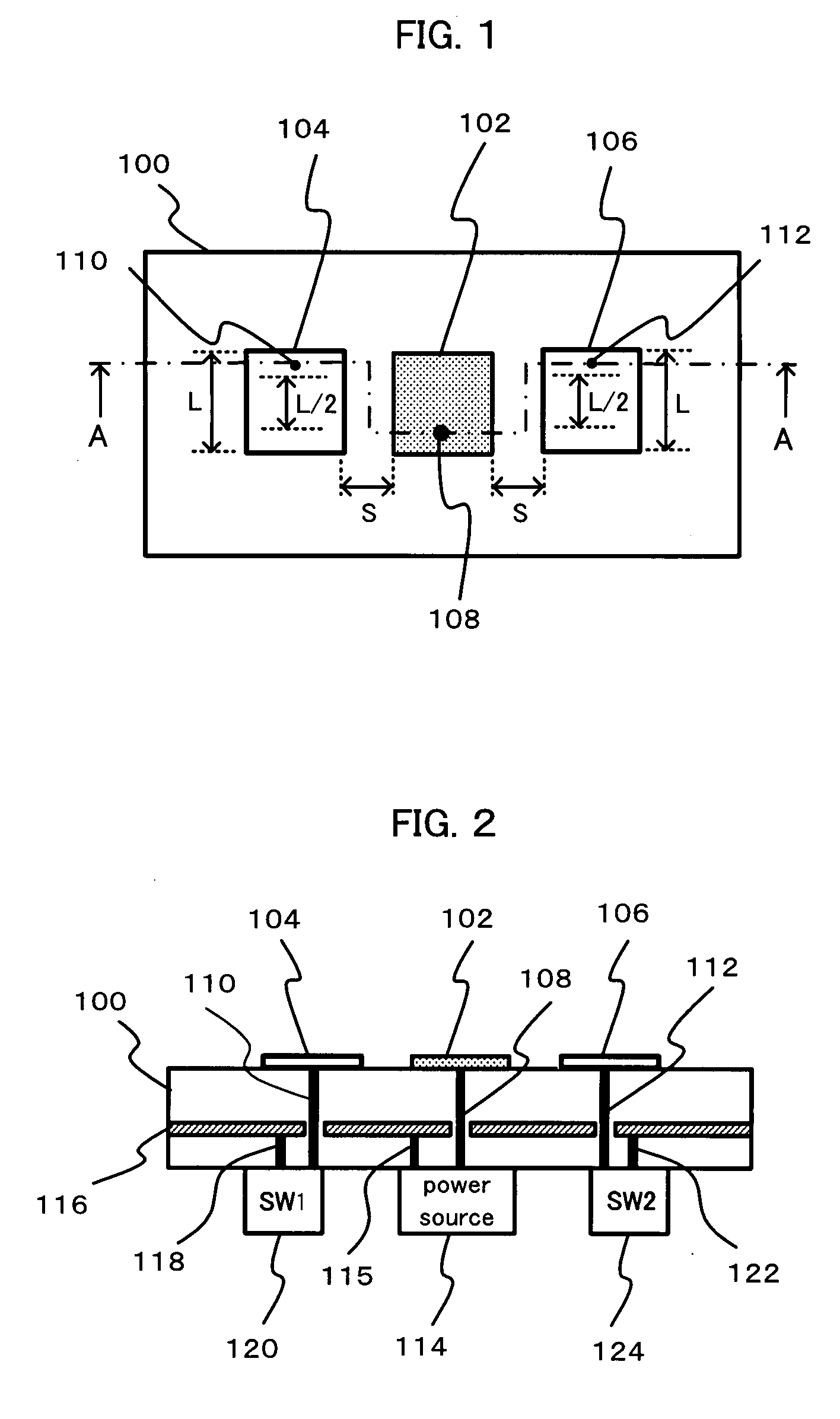
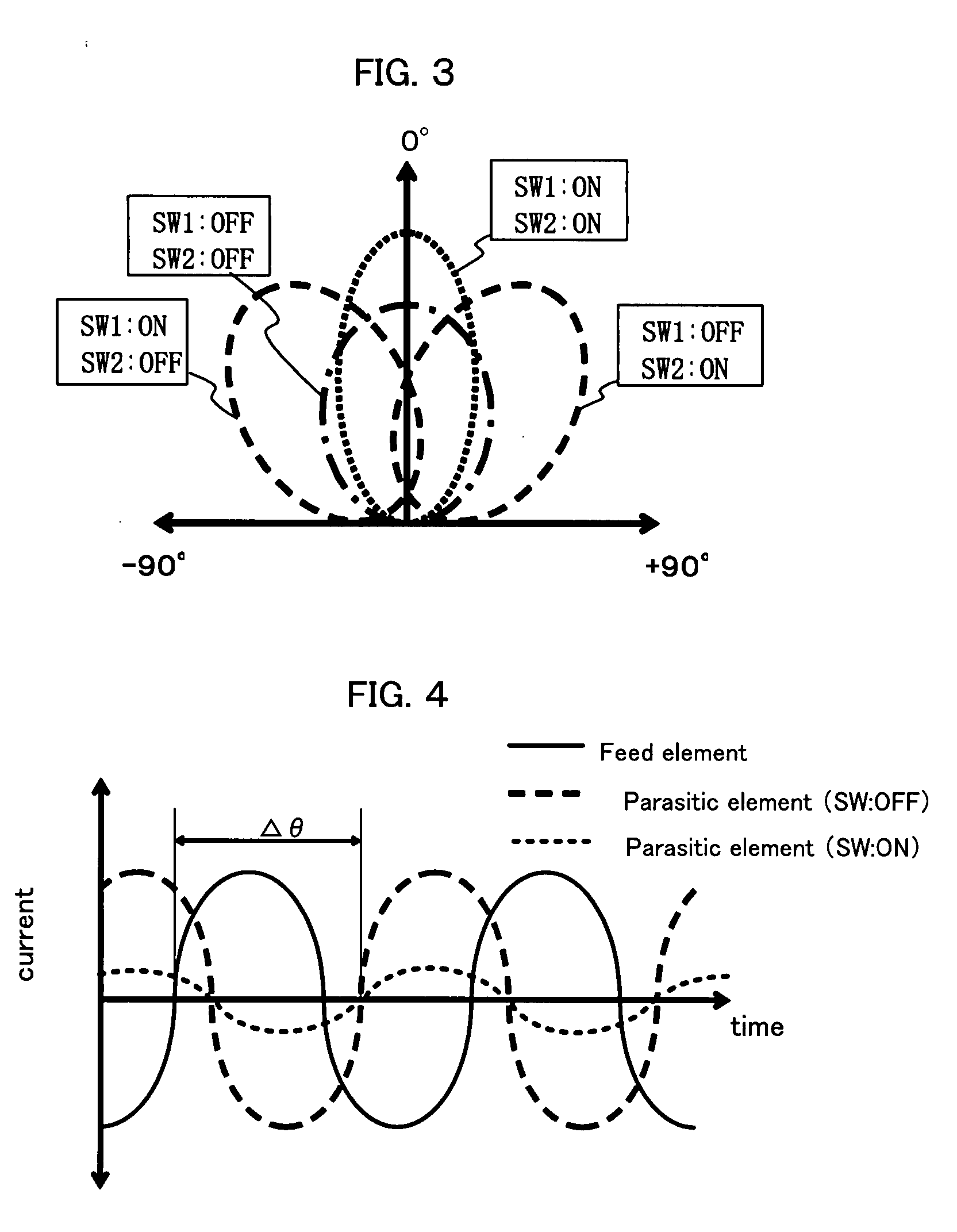
A microstrip antenna has feed element 102 and parasitic elements 104, 106 on the front surface of substrate 1. Microwave electrical power is applied to feed element 102. Parasitic elements 104, 106 are connected via through hole type leads passing through substrate 1, to switches upon the rear surface of substrate 1, respectively. By actuating the switches individually, parasitic elements 104, 106 are individually switched between a grounded state and a float state. The direction of the radio beam emitted from the microstrip antenna is varied by selecting which of parasitic elements 104, 106 is grounded and floated. A microwave signal source connects to feed element 102 via an feed line 108 very much shorter than the wavelength, accordingly the transmission losses being low and the efficiency being excellent.
Owner:TOTO LTD
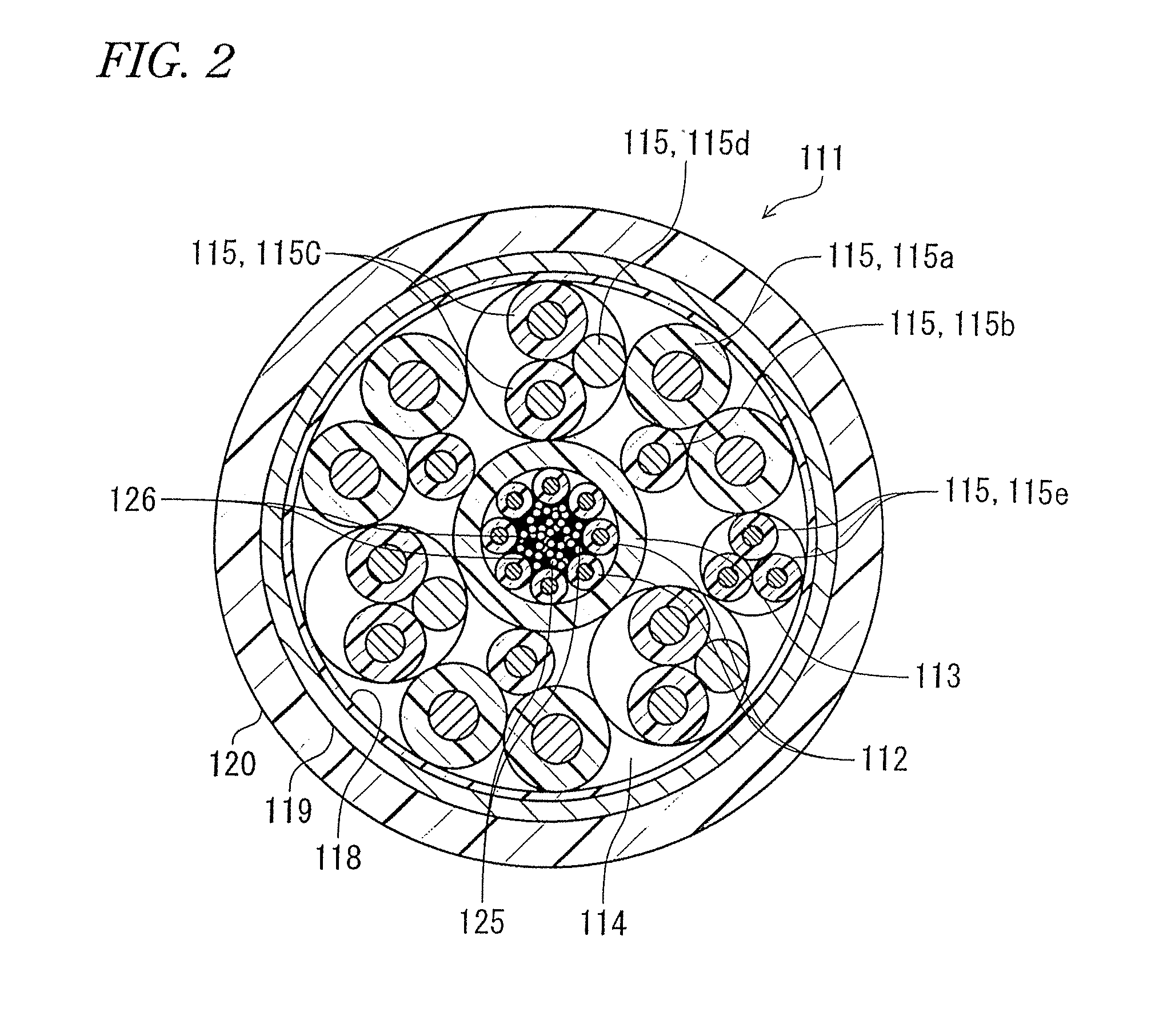
Opto-electro hybrid cable
ActiveUS20110311191A1Prevent lateral pressureHigh tensile strengthFibre mechanical structuresOpto electronicElectric cables
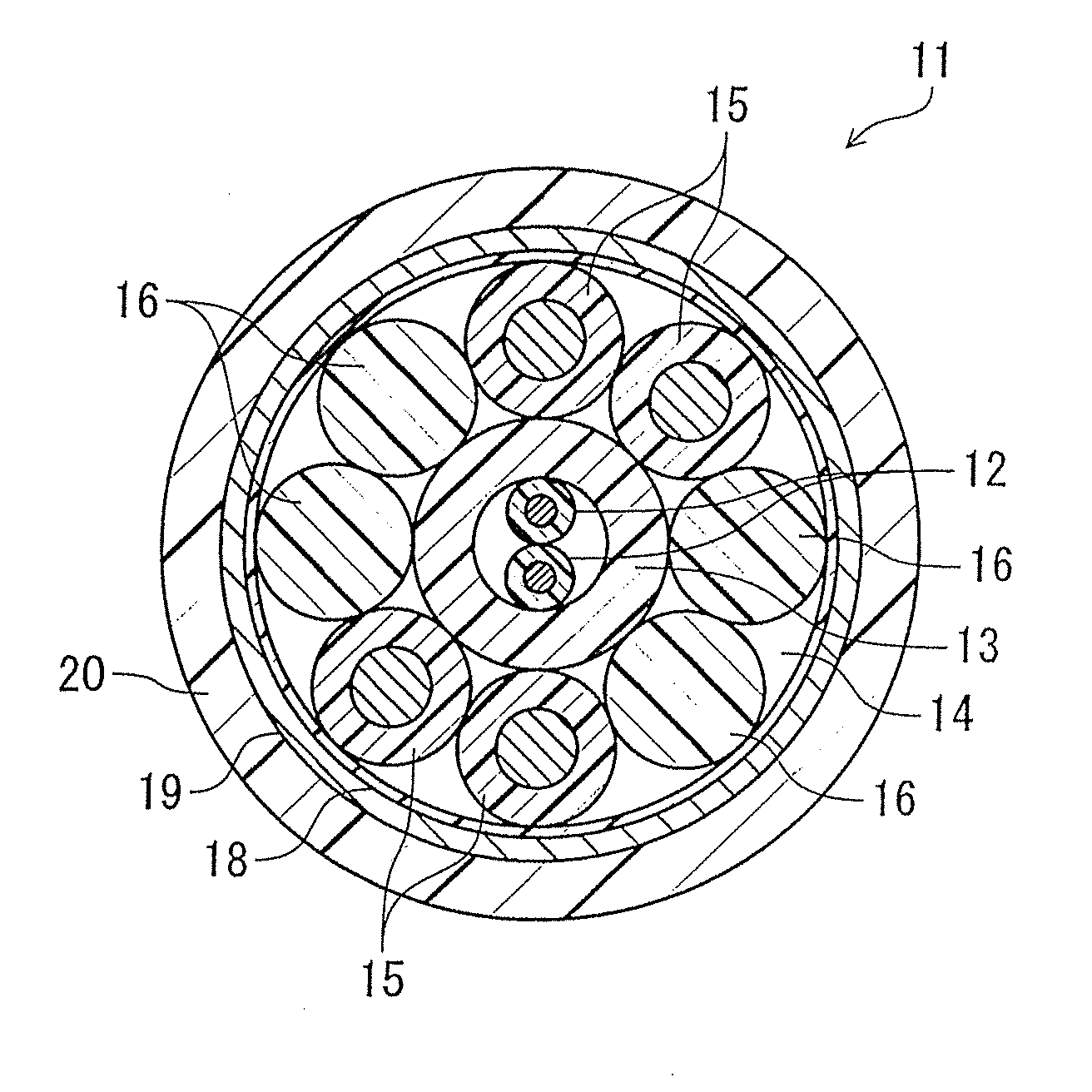
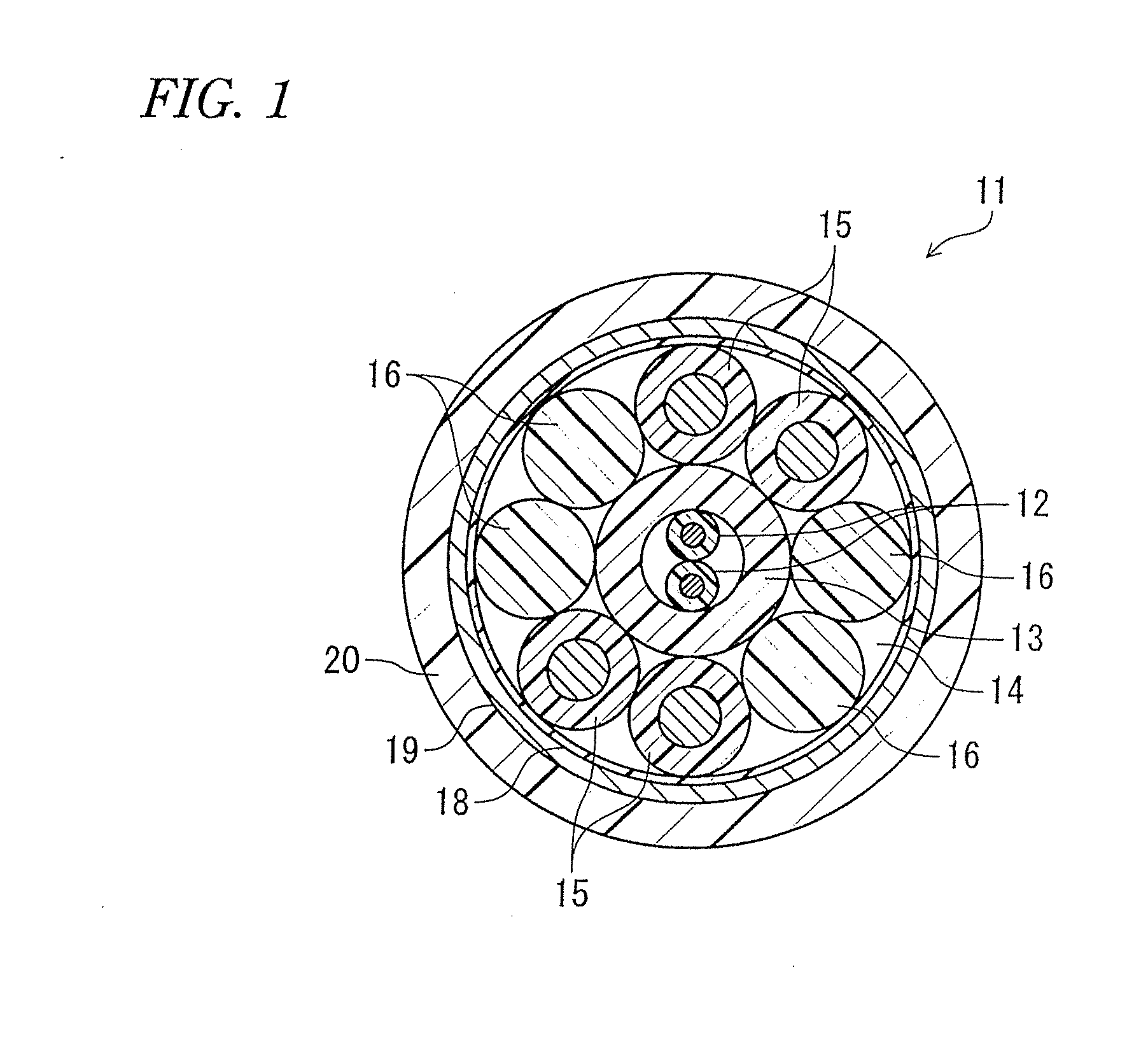
An opto-electro hybrid cable is an opto-electro hybrid cable that has a plurality of optical fibers and a plurality of electronic wires inside a sheath. The plurality of optical fibers are accommodated in a tube having Shore D hardness of 65 or greater, the plurality of optical fibers are circumferentially disposed to abut on an inner circumference of the tube, and the plurality of electronic wires are disposed around the plurality of optical fibers.
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC IND LTD +1
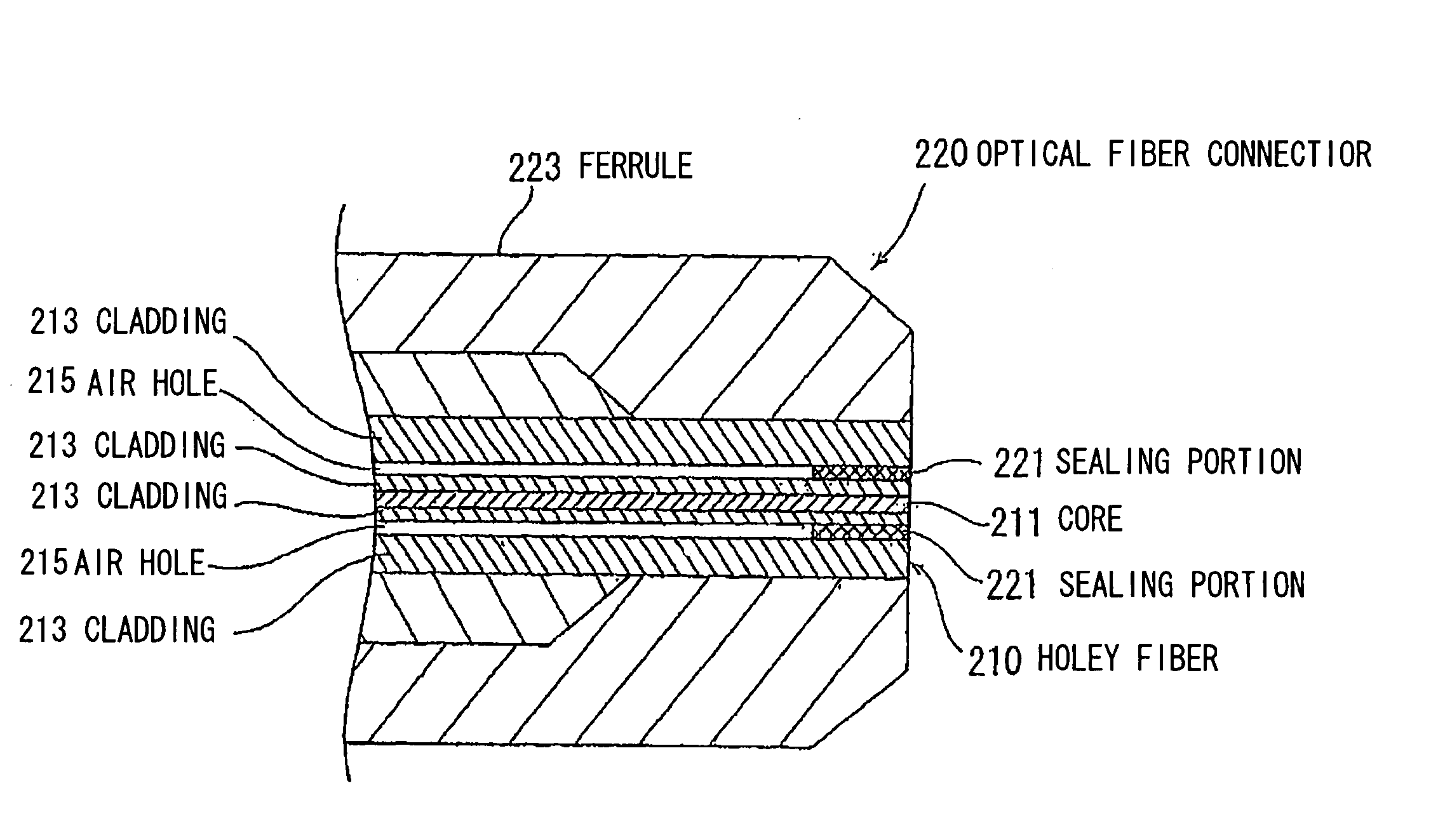
Optical fiber, optical fiber connecting method, and optical connector
InactiveUS20060204195A1Small connection loss and reflection amountSmall temperature characteristic variationOptical fibre with graded refractive index core/claddingOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingOptical fiber connectorEngineering
An optical fiber which, at an optical fiber connecting end having a plurality of voids around the periphery of a core, has a light-permeable substance, such as a resin or glass whose refractive index is lower than that of quartz type substances, filled in the voids adjacent to the connecting end. An optical fiber connecting section where an optical fiber having a plurality of voids in a clad around the periphery of a core is connected to another optical fiber, wherein the optical fiber is connected end-to-end to aforesaid another optical fiber through a refractive index matching agent whose refractive index at the minimum temperature in actual use is lower than that of the core.
Owner:HITACHI CABLE +1
Method Of Treating The Surface Of Copper And Copper
ActiveUS20080096046A1Easily deterioratedVariation in the height of the irregularitiesDecorative surface effectsPrinted circuit aspectsCopperOxidizing agent
A method of treating the surface of copper is provided to ensure adhesive strength between the surface of copper and an insulating layer without forming irregularities exceeding 1 μm on the surface of copper and to improve insulation reliability between wirings. A copper whose surface is treated by the above surface treating method is also provided. The method of treating the surface of copper comprises the surface of copper comprising the steps of: forming a metal nobler than copper discretely on the surface of copper; and subsequently oxidizing the surface of copper by using an alkaline solution containing an oxidant.
Owner:RESONAC CORP
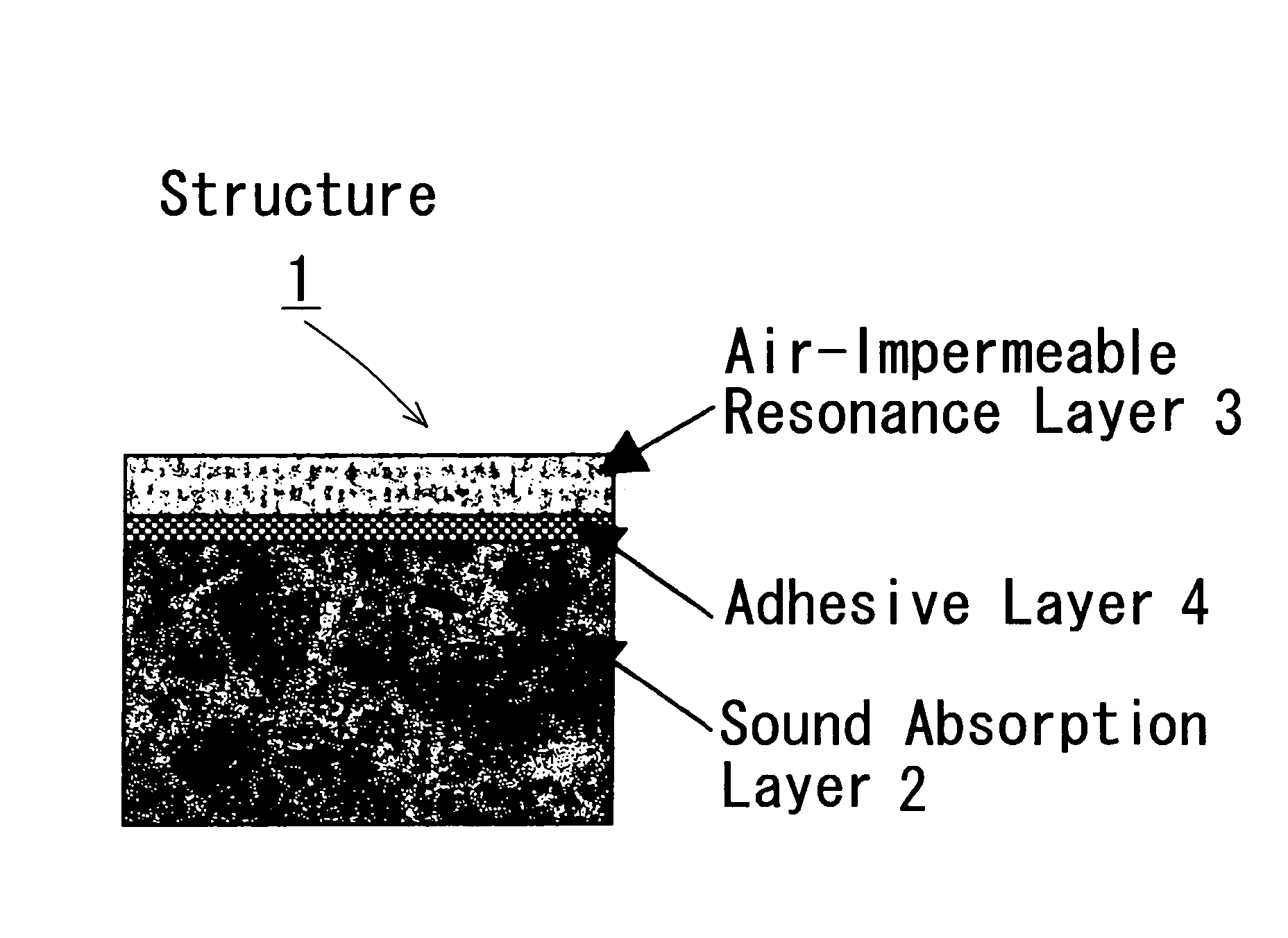
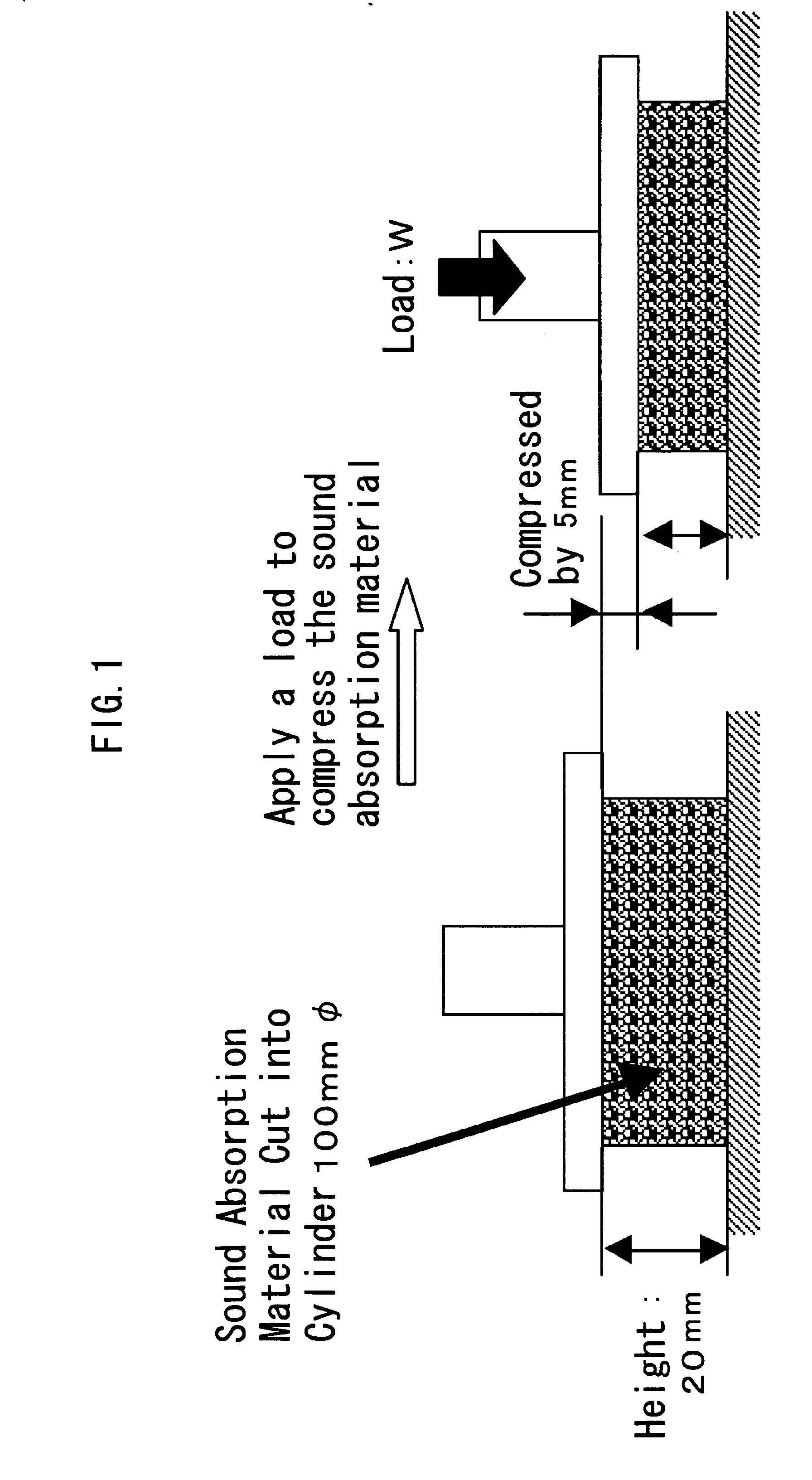
Ultralight soundproof material
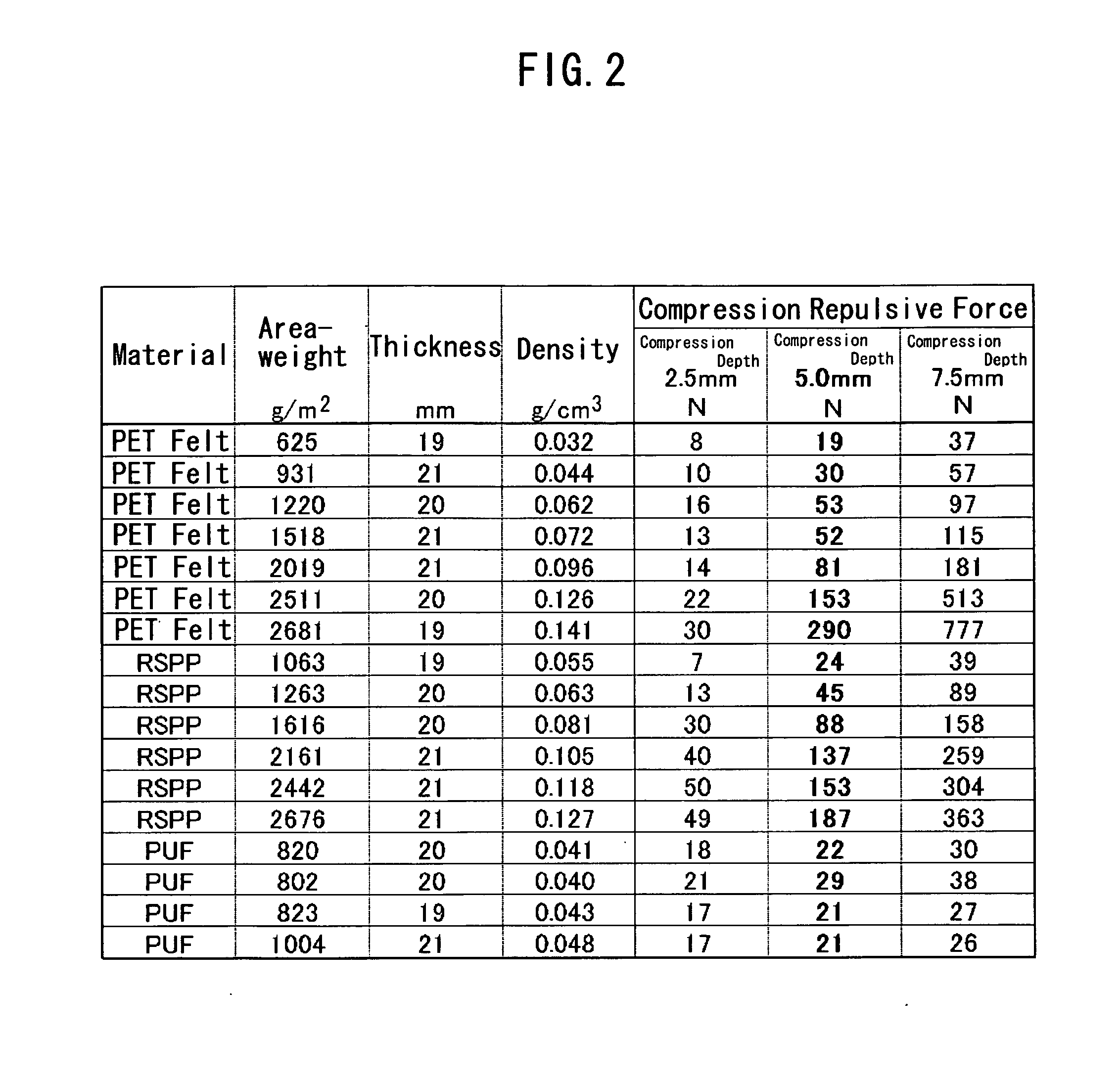
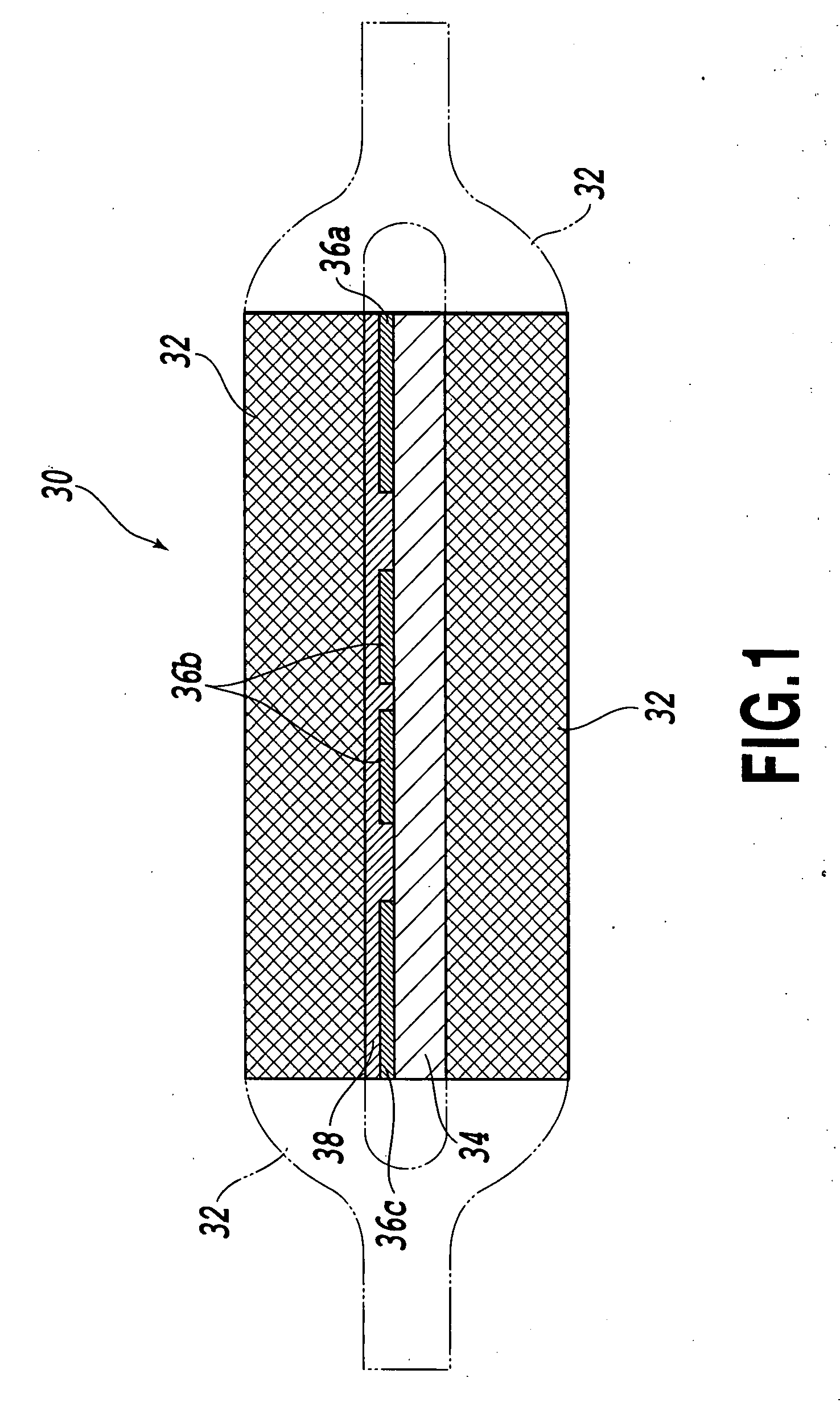
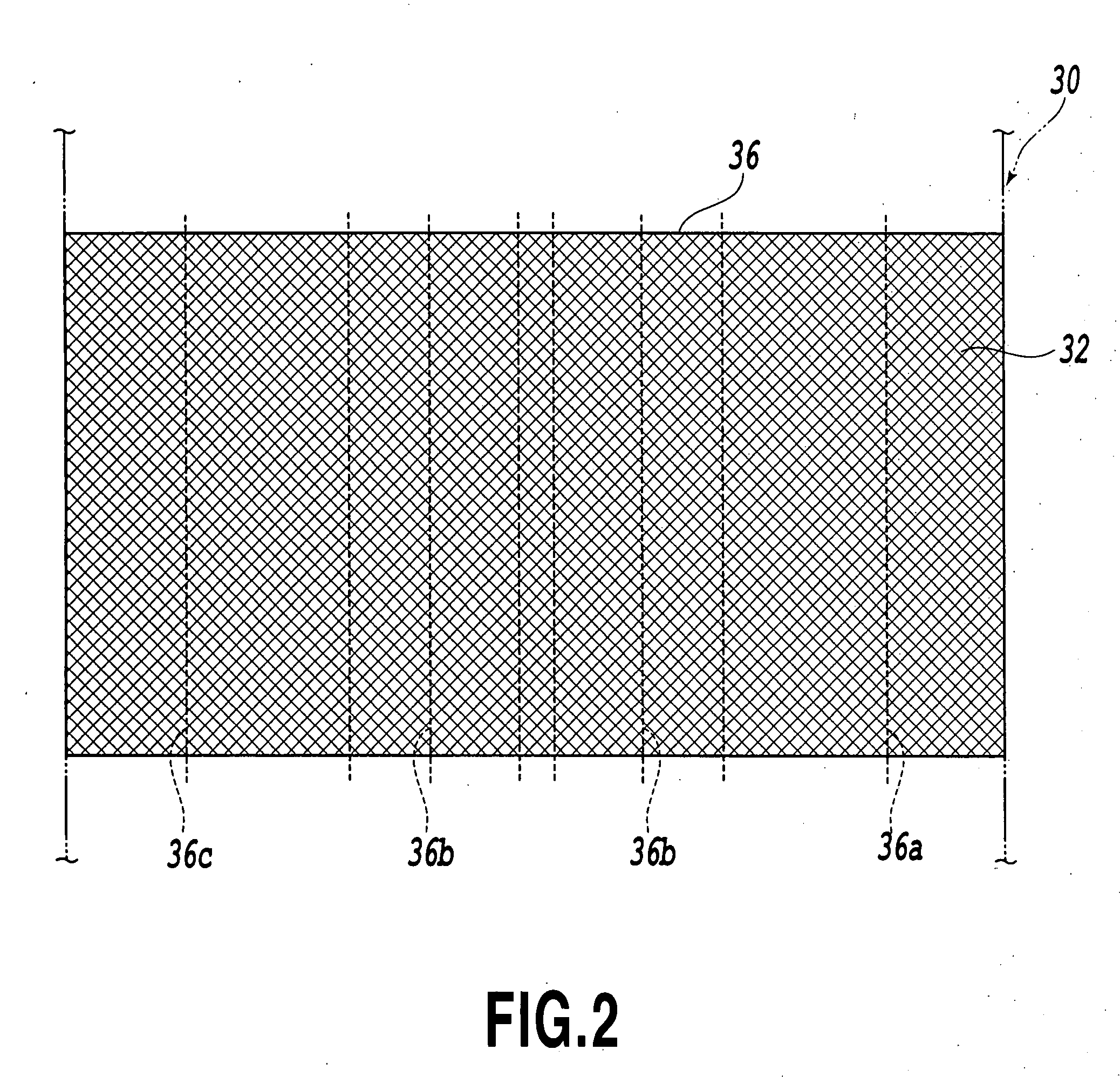
InactiveUS20060201741A1Improve sound insulationIncrease in transmission lossLayered productsMachines/enginesPhysicsFrequency band
A sound insulator of the invention includes a sound absorption layer 202 and an air-impermeable resonance layer 203, which are bonded to each other via an adhesive layer 204. The sound absorption layer 202 has a thickness in a range of 5 to 50 mm and an area-weight of not greater than 2000 g / m2. The sound absorption layer 202 has a two-layer structure of a high-density sound absorption layer 202a and a low-density sound absorption layer 202b, which have different densities. The high-density sound absorption layer 202a is bonded to the air-impermeable resonance layer 203 via the adhesive layer 204 and has a density in a range of 0.05 to 0.20 g / cm3 and a thickness in a range of 2 to 30 mm. The low-density sound absorption layer 202b is bonded to the other face of the high-density sound absorption layer 202a, which is opposite to the air-impermeable resonance layer 203, via an adhesive layer 202c and has a density in a range of 0.01 to 0.10 g / cm3 and a thickness in a range of 2 to 30 mm. The structure of this sound insulator effectively reduces a noise level in a voice-tone frequency band, especially in a high frequency domain, thereby efficiently enhancing the clarity of conversion in a vehicle interior.
Owner:TAKEHIRO CO LTD +1
Split type ribbon optical fiber core cable
In a split type ribbon optical fiber core cable capable of being split into cables, there are a plurality of ribbon optical fiber core cable units, each of which are constituted by a plurality of colored optical fiber core cables arranged in a row; a coating resin of an ultraviolet curable resin wholly coats the plurality of colored optical fiber core cables; and a bonding resin of an ultraviolet curable resin bonds the ribbon optical fiber core cable units arranged in a row. In this cable, an adhesion strength between the coating resin and the bonding resin is in the range of 1 to 100 g / cm. Further, the bonding resin after curing has a Young's modulus of from 5 to 100 kg / mm2. The bonding resin after curing has an elongation coefficient of from 5 to 80%.
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC IND LTD
Diffraction grating type band-pass filter and method of making the same
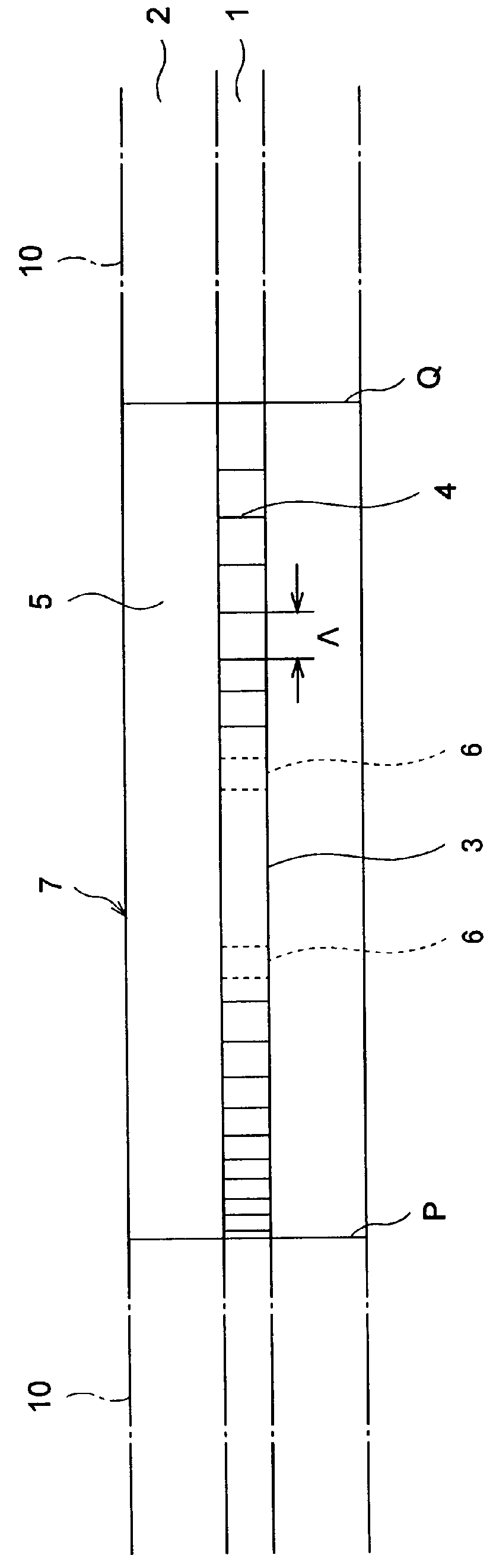
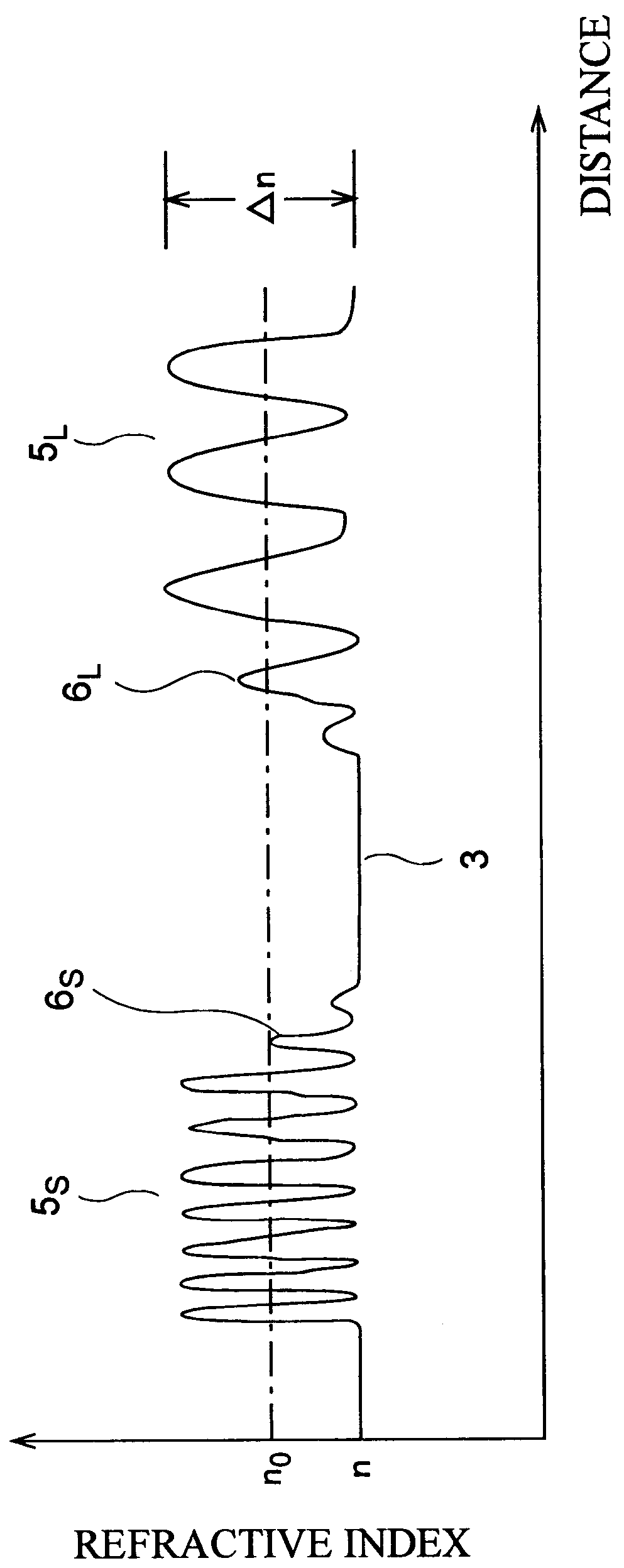
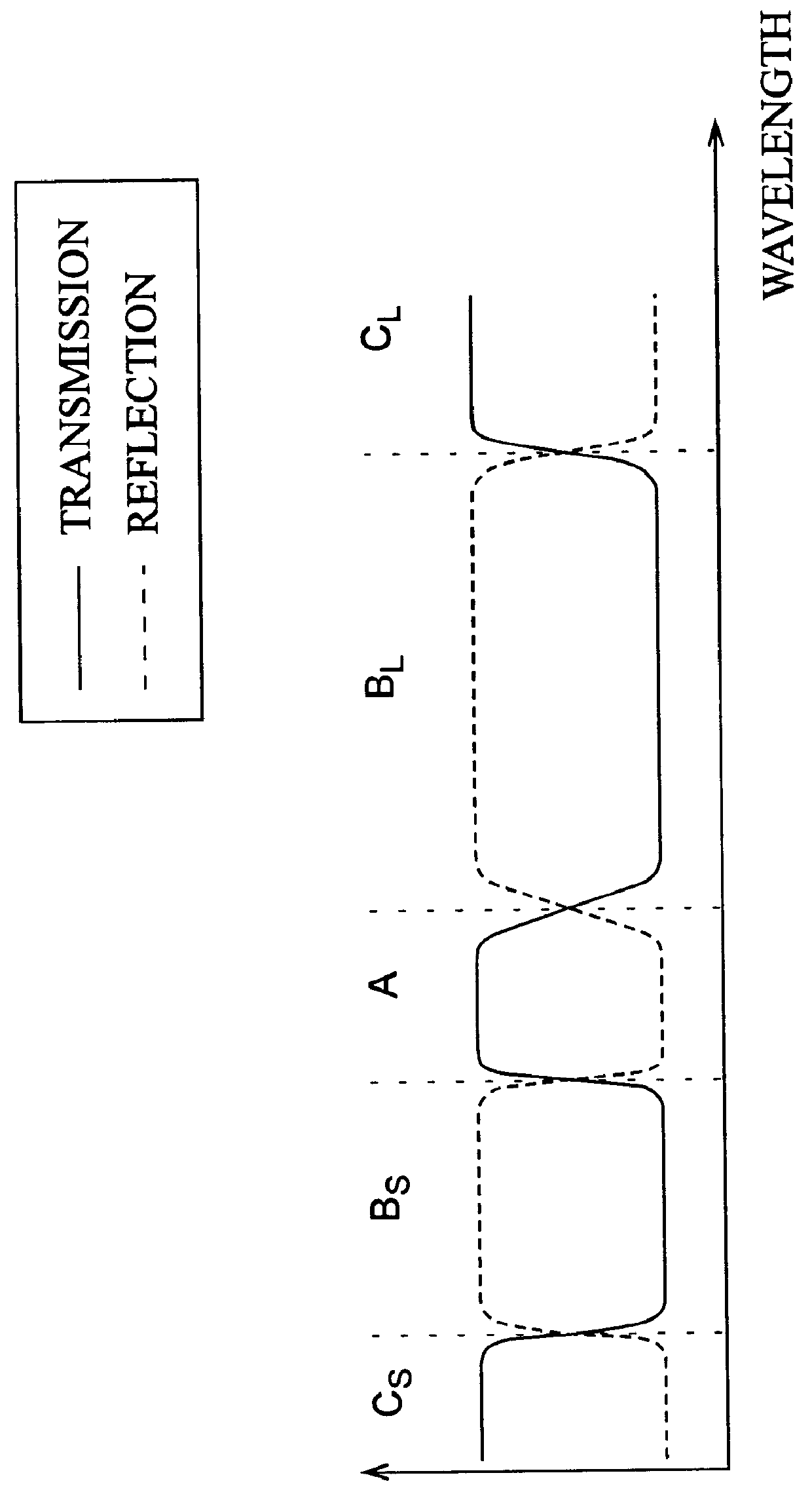
InactiveUS6021242AImprove transmission lossSpread the wordCladded optical fibreOptical filtersBand-pass filterRefractive index
A band-pass filter formed in an optical waveguide, provided with a diffraction grating group having a period LAMBDA of refractive index fluctuation changing in an axial direction with substantially a constant changing width DELTA n, comprises two periodic refractive index variable areas having periodes LAMBDA different from each other; a zero area, disposed therebetween, having substantially a constant refractive index; and boundary areas, disposed between the zero area and the respective periodic refractive index variable areas, in which the changing width of refractive index monotonously changes between 0 and DELTA n.
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC IND LTD
Phase element for introducing a phase shift pattern into an electromagnetic wave
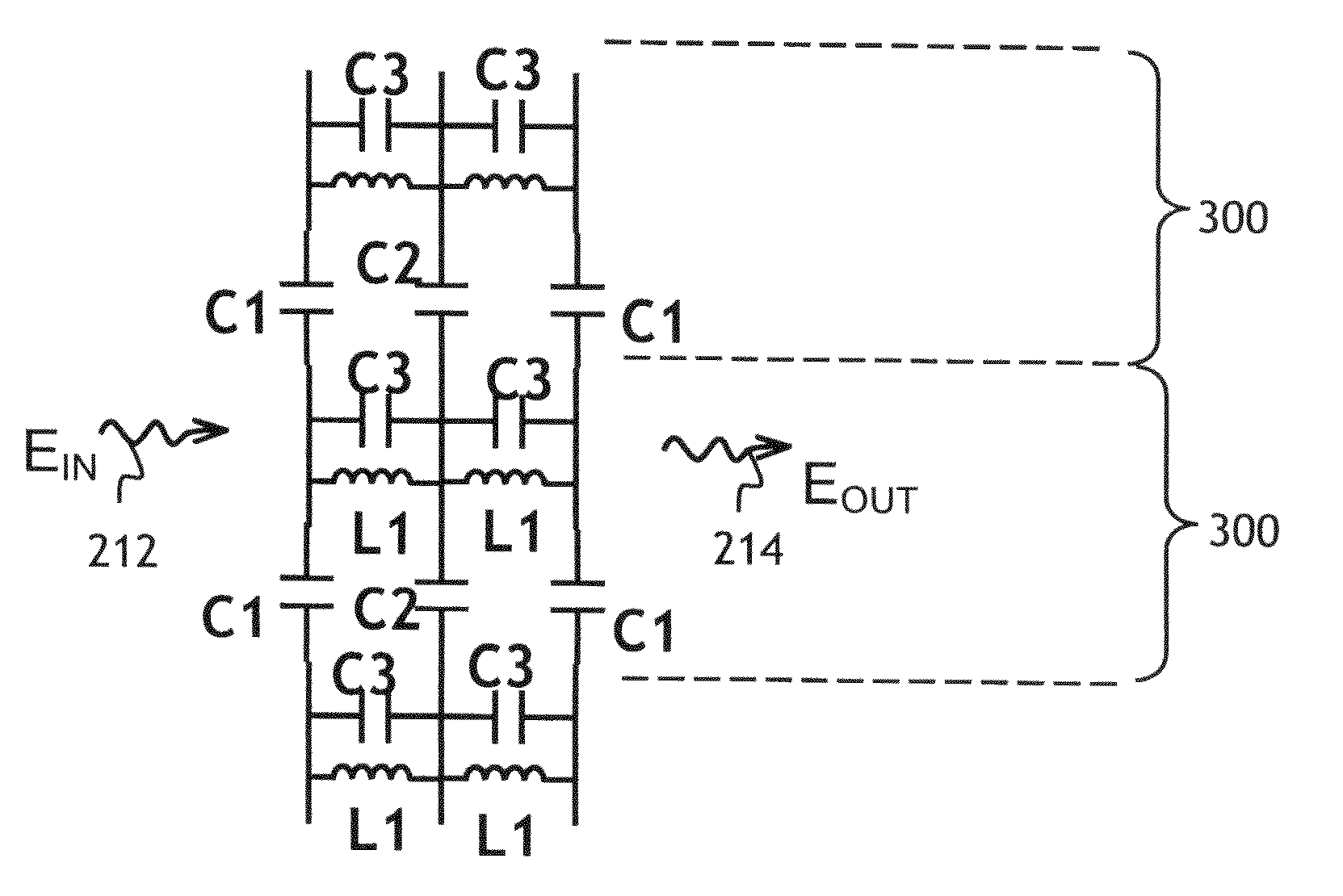
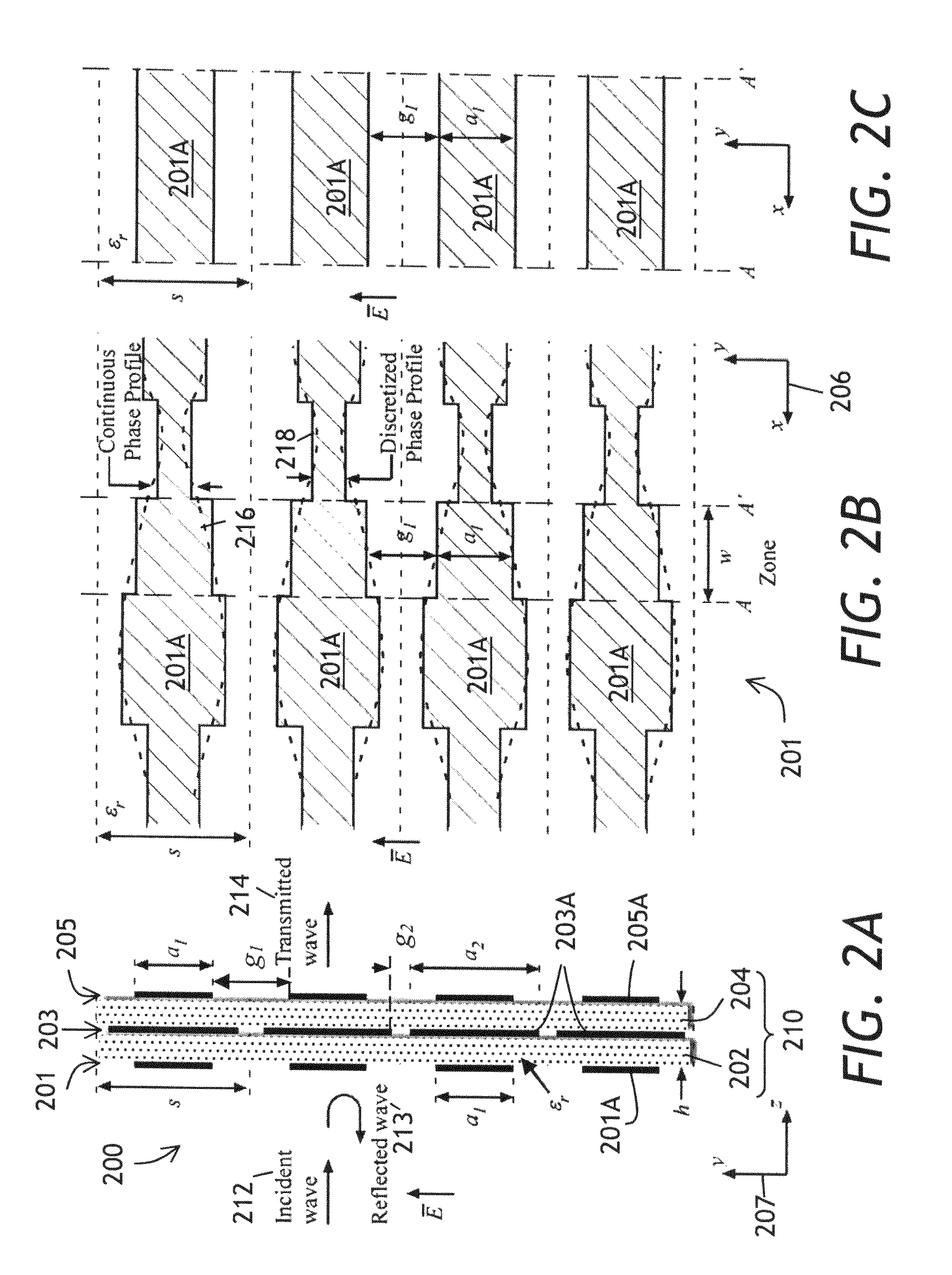
InactiveUS20110025432A1Increased transmission lossLow amplitude shiftOptical articlesDelay linesPhase shiftedMicrowave
A thin electromagnetic phase shifting element, named phase and amplitude shifting surface (PASS), is disclosed. The PASS is capable of independently altering both the phase and the amplitude distribution of the electromagnetic fields propagating through the structure. The element comprises a few patterned metallic layers separated by dielectric layers. The patterns of the metallic layers are tuned to locally alter the phase and / or the amplitude of an incoming electromagnetic wave to a prescribed set of desired values for the outgoing electromagnetic wave. The PASS can be applied to design components such as gratings, lenses, holograms, and various types of antennas in the microwave, millimetre wave and sub-millimetre wave.
Owner:HER MAJESTY THE QUEEN & RIGHT OF CANADA REPRESENTED BY THE MIN OF IND THROUGH THE COMM RES CENT
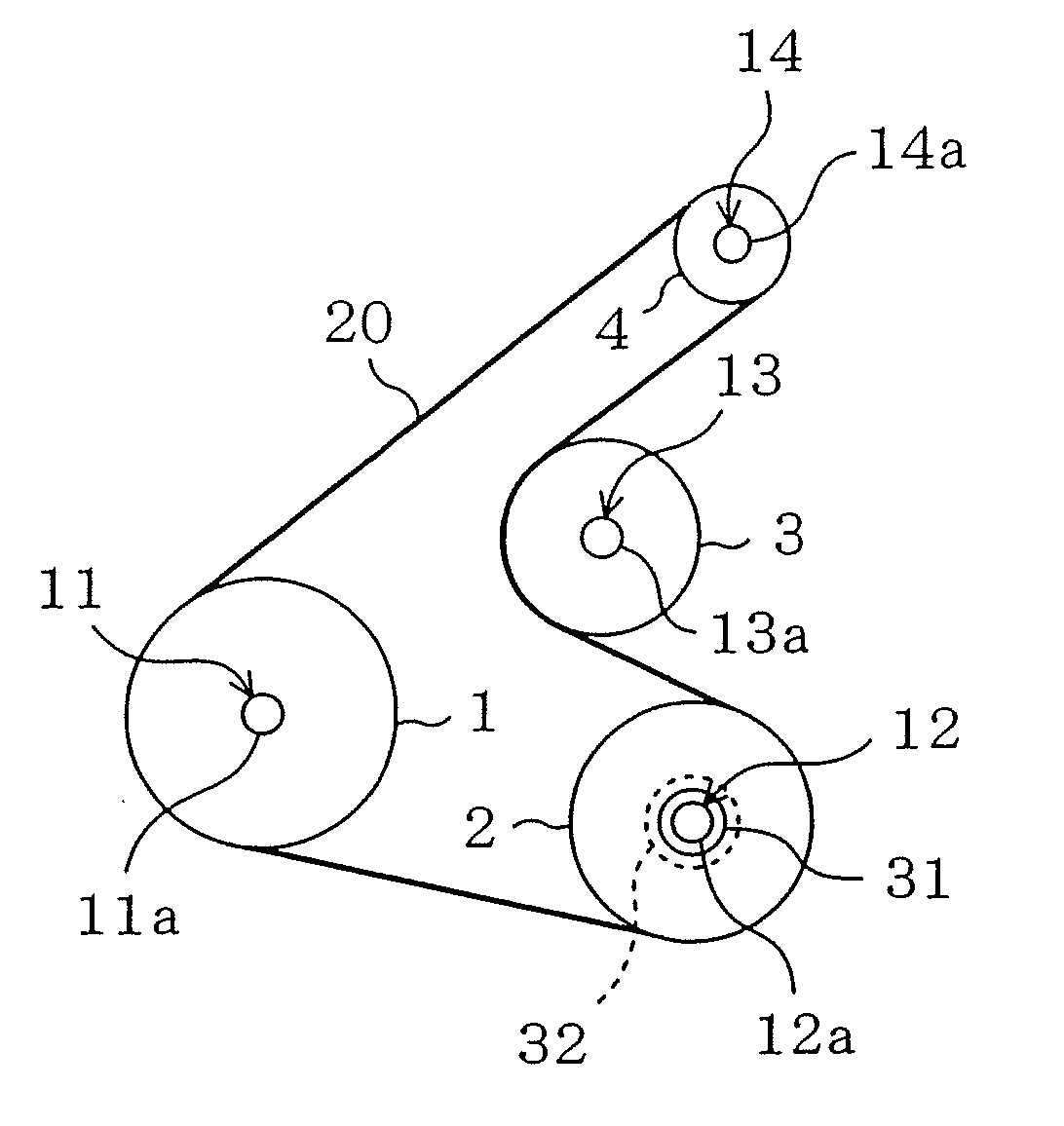
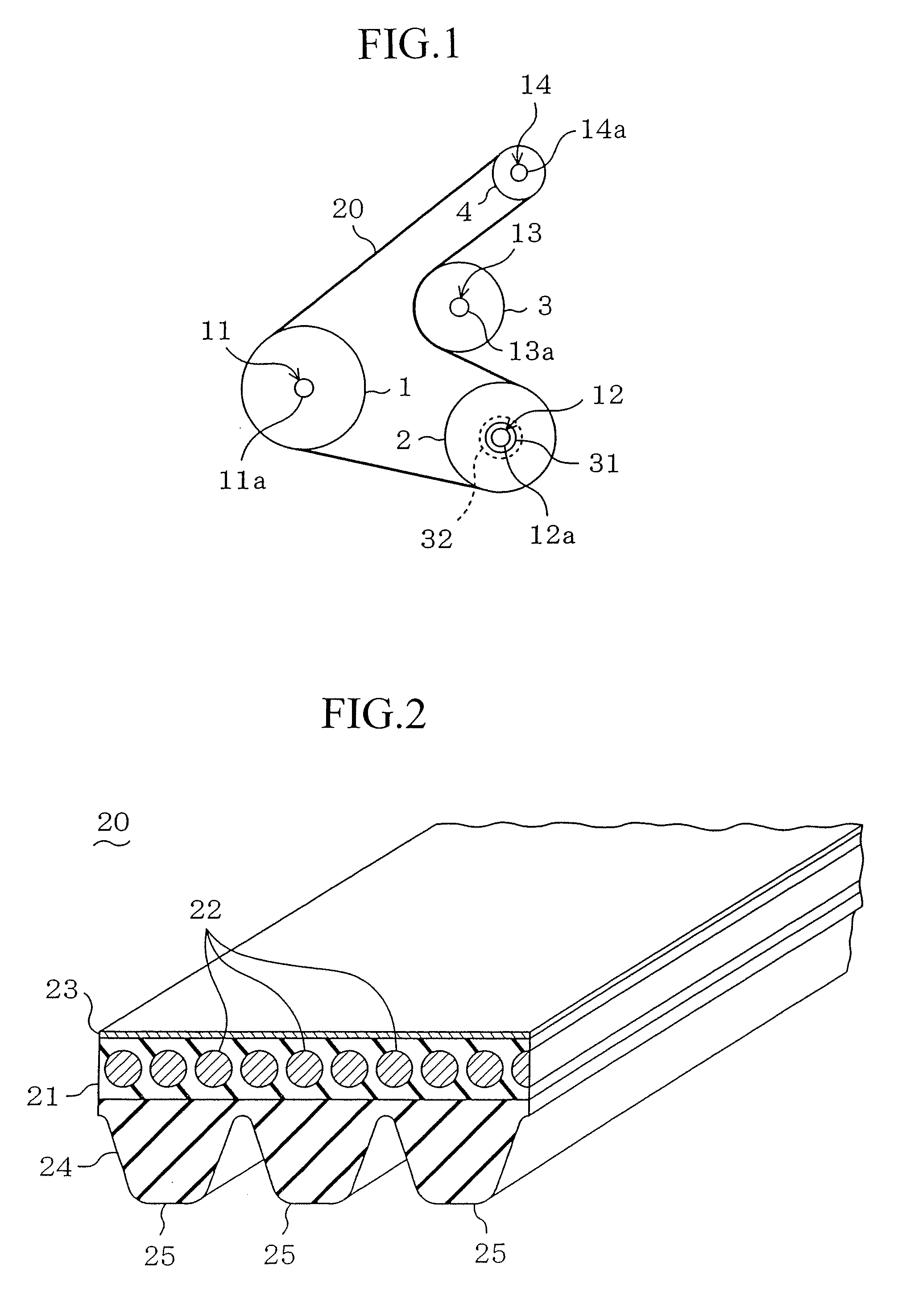
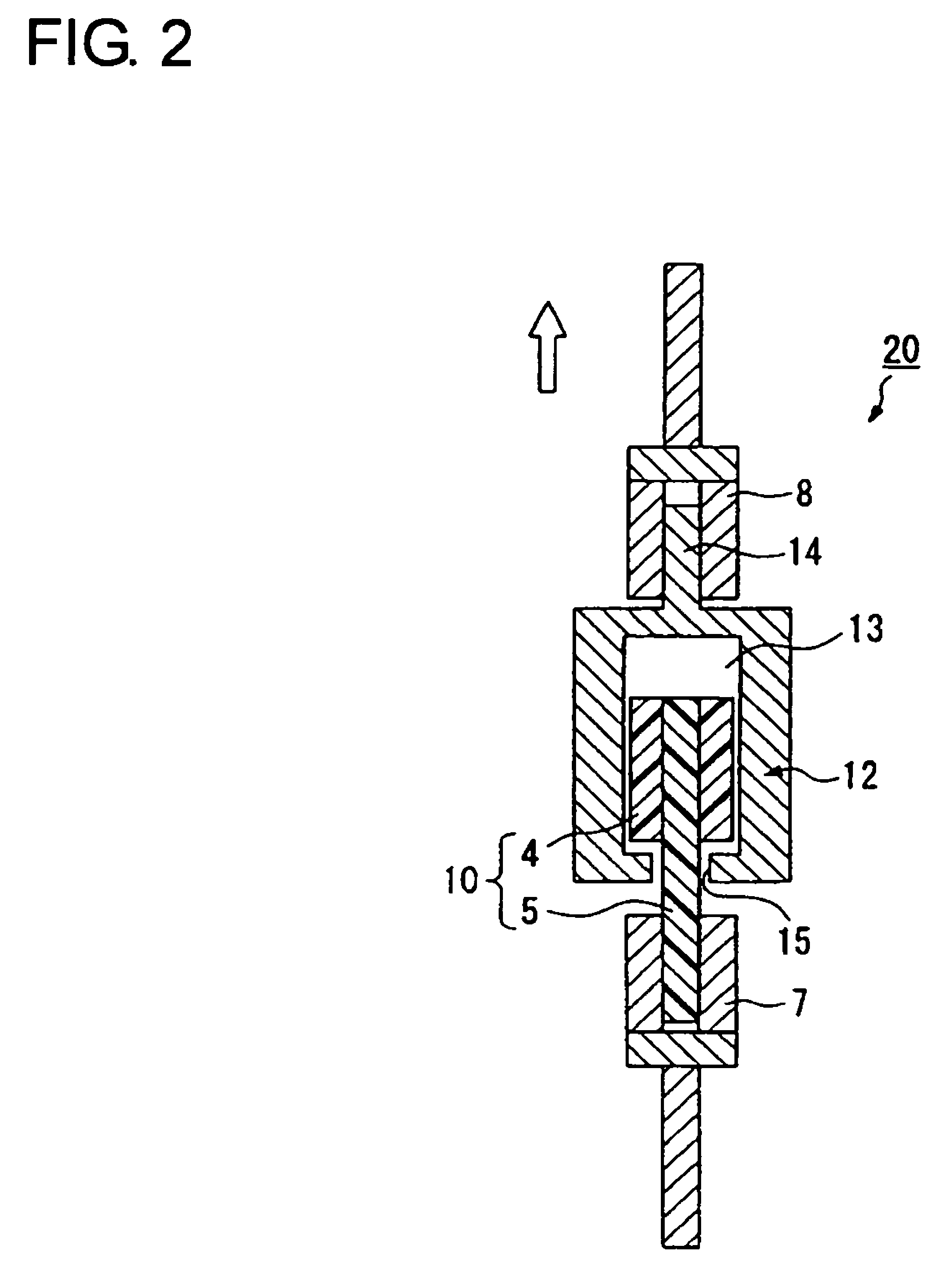
Belt transmission device
ActiveUS20090062050A1Increased transmission lossCoefficient of frictionV-beltsRopes and cables for vehicles/pulleyTorque transmissionFriction force
[Purpose] A belt drive system, in which a drive belt 20 is wrapped between a drive pulley 1 drivingly connected to a drive source 11 and a driven pulley 2 connected to an driven unit 12 via a joint 32 provided to stop torque transmission when receiving a load equal to or over a predetermined value and torque is transmitted via the drive belt 20 from the drive pulley 1 to the driven pulley 2, ensures that when the driven unit 12 malfunctions, the joint 32 stops the torque transmission without unnecessarily increasing the coefficient of friction against the driven pulley 2 or the belt tension.[Solution] The belt drive system is configured so that when a slip corresponding to the load on the joint 32 equal to or over the predetermined value occurs between the drive belt 20 and the driven pulley 2, the coefficient of friction between the drive belt 20 and the driven pulley 2 becomes higher than that before the slip occurs.
Owner:BANDO CHEM IND LTD
Optical fiber and optical fiber ribbon
ActiveUS20090232461A1Restrain delaminationIncrease in transmission lossGlass optical fibreOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingOperating environmentEngineering
The present invention relates to an optical fiber accommodated in an optical fiber cable, and more particularly, to an optical fiber which optimizes optical fiber coating resin and color resin and restrains an increase in transmission loss of the optical fiber due to an operating environment and aged deterioration and provides an optical fiber and optical fiber ribbon without any increase of transmission loss irrespective of the operating environment and aged deterioration, and especially when exposed to water or high humidity.The optical fiber is an optical fiber coated with at least two layers of coating resin, wherein the outermost coated coating resin is a colored layer made of color resin and when the optical fiber is immersed in water which is heated to 60° C. for 168 hours, an extraction rate of the coating resin of the optical fiber is set to 1.5 mass percent or below.
Owner:FURUKAWA ELECTRIC CO LTD
Colored optical fiber, optical fiber ribbon, and optical fiber cable
InactiveUS20140226941A1Good anti-microbend propertyIncreased transmission lossGlass optical fibreFibre mechanical structuresRelaxation modulusOptical fiber cable
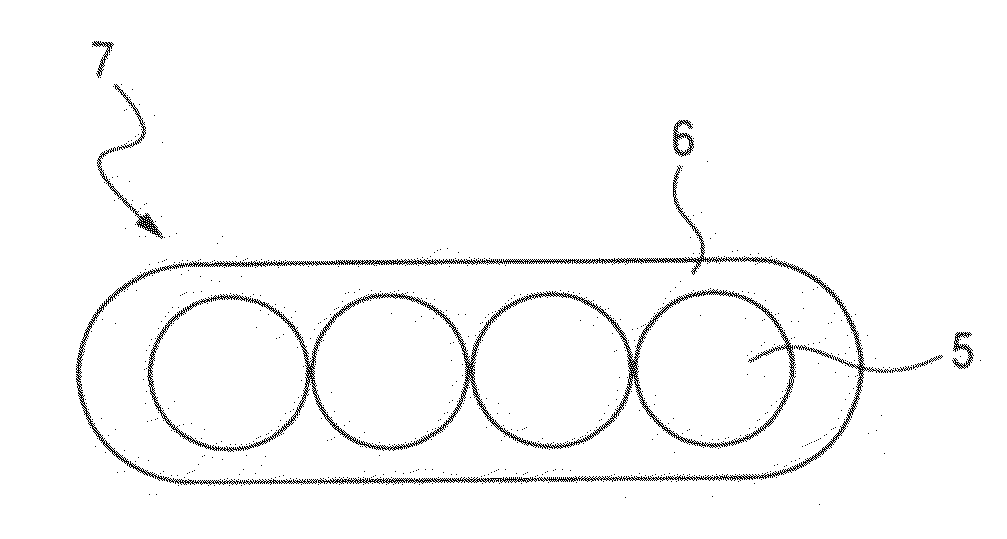
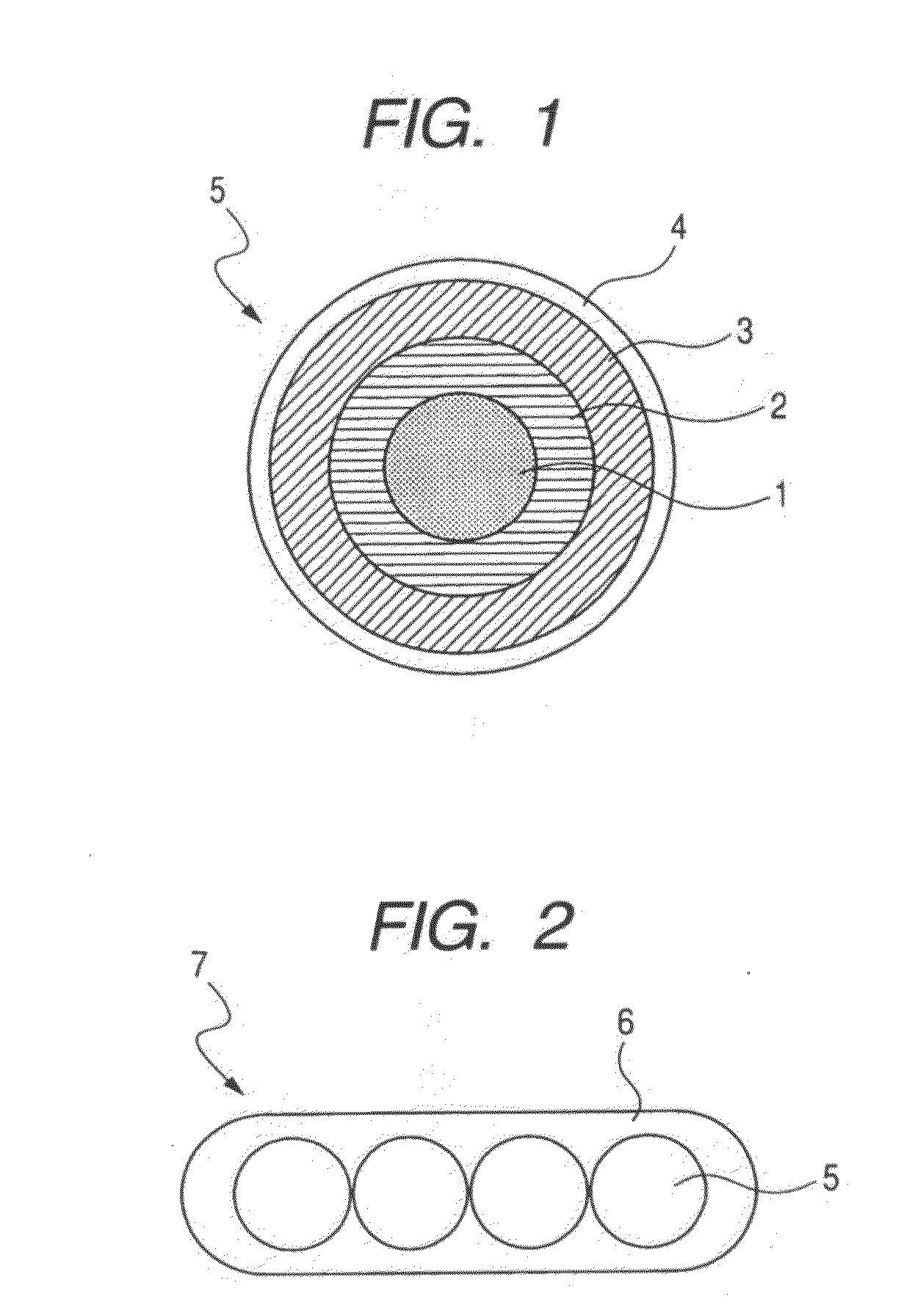
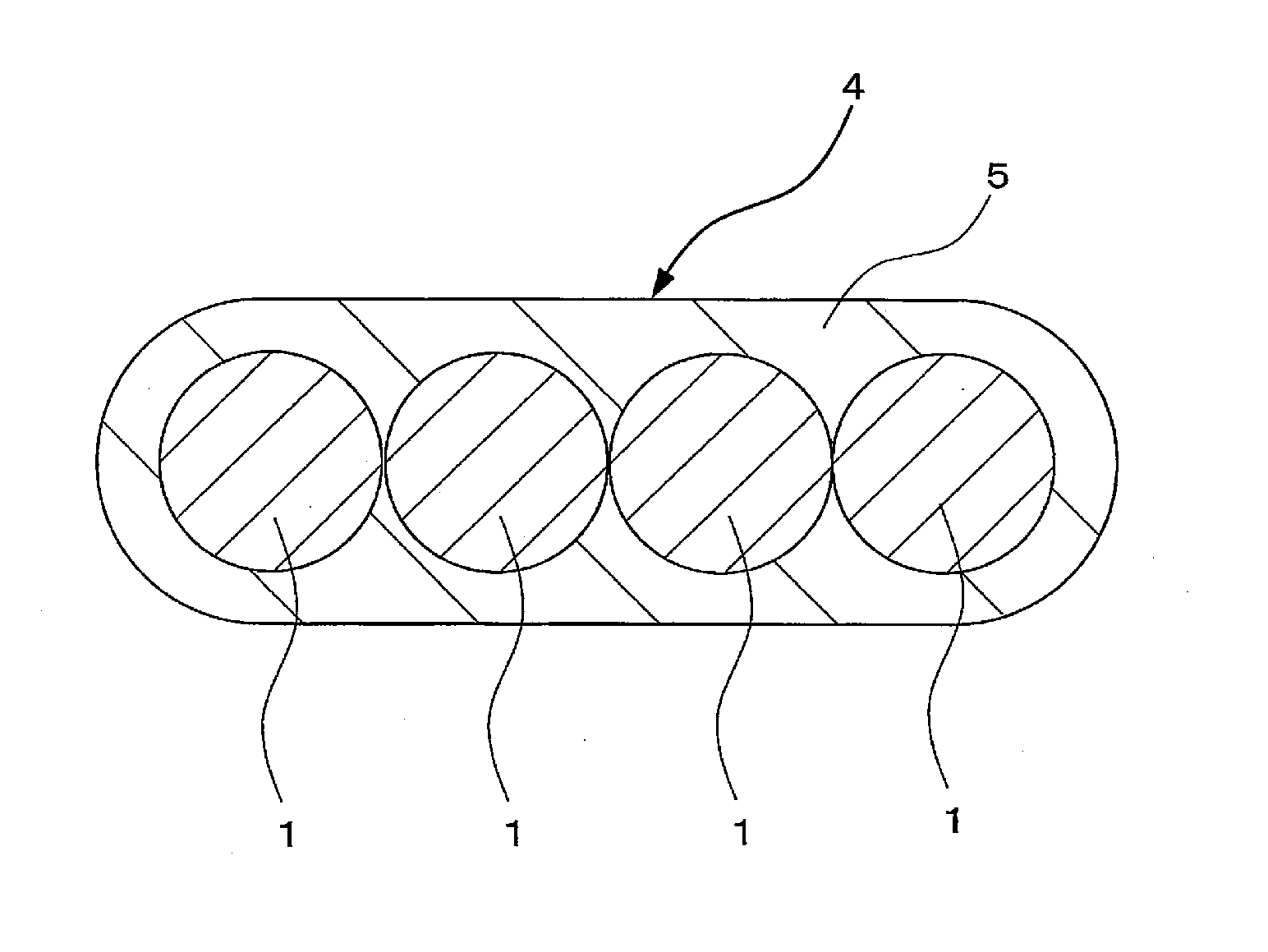
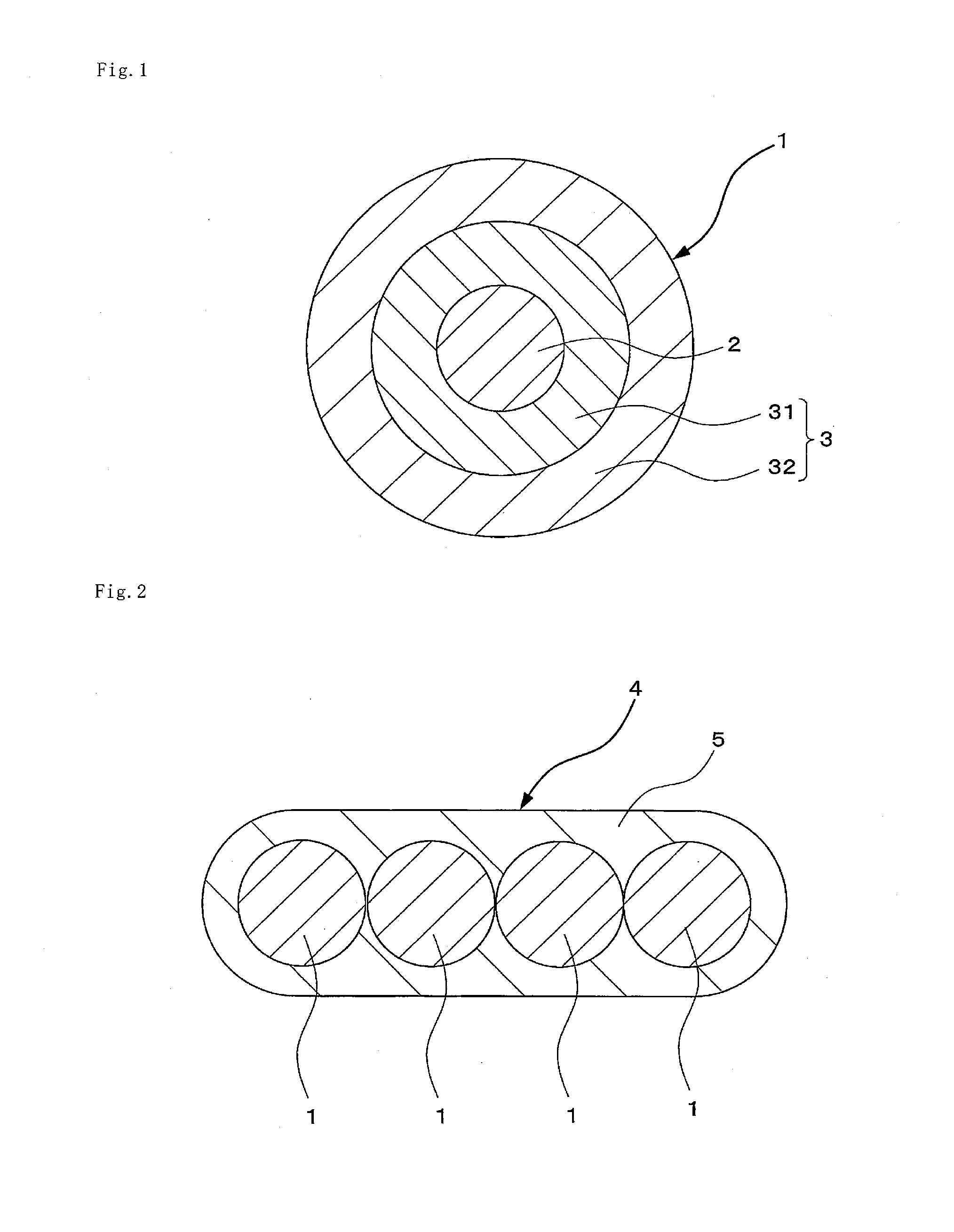
The present invention provides a colored optical fiber that shows anti-microbend property and hot-water resistance, an optical fiber ribbon that utilizes the same, and an optical fiber cable.It is a colored optical fiber 1, which comprises two coating layers of a primary coating layer 31 and a secondary coating layer 32, wherein either one of the primary coating layer 31 or the secondary coating layer 32 is colored, both coating layers have equilibrium elastic moduli of 60 MPa or less, and the secondary coating layer 32 has a relaxation modulus of 410 MPa or more, an optical fiber ribbon 4 that utilizes it, and an optical fiber cable 8.
Owner:FURUKAWA ELECTRIC CO LTD
Microstrip antenna and high frequency sensor using microstrip antenna
InactiveUS7773035B2Avoid inefficiencyReduce manufacturing costSimultaneous aerial operationsAntenna supports/mountingsTransmission lossLength wave
A microstrip antenna has feed element 102 and parasitic elements 104, 106 on the front surface of substrate 1. Microwave electrical power is applied to feed element 102. Parasitic elements 104, 106 are connected via through hole type leads passing through substrate 1, to switches upon the rear surface of substrate 1, respectively. By actuating the switches individually, parasitic elements 104, 106 are individually switched between a grounded state and a float state. The direction of the radio beam emitted from the microstrip antenna is varied by selecting which of parasitic elements 104, 106 is grounded and floated. A microwave signal source connects to feed element 102 via an feed line 108 very much shorter than the wavelength, accordingly the transmission losses being low and the efficiency being excellent.
Owner:TOTO LTD
Thermal-acoustic sections for an aircraft
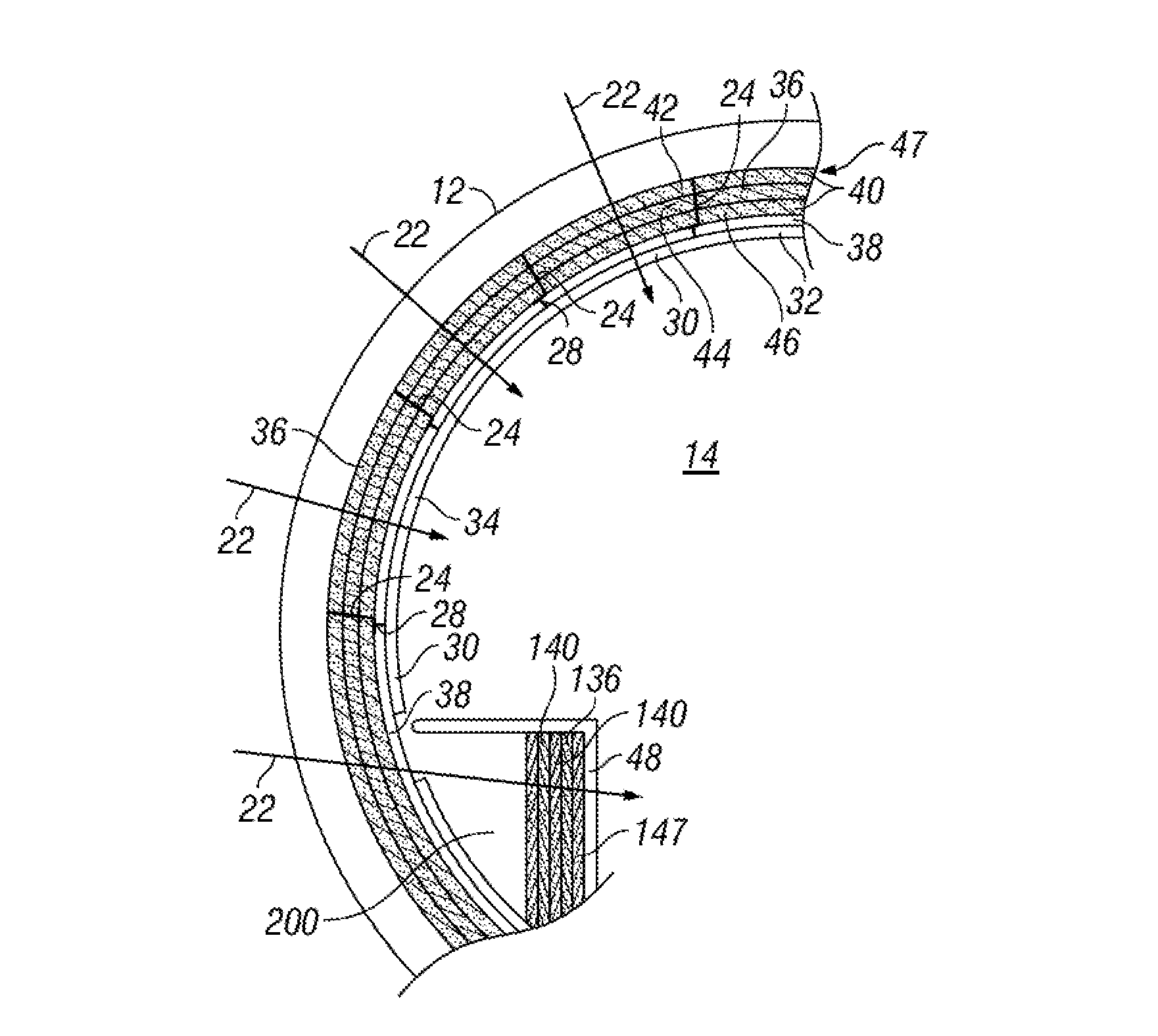
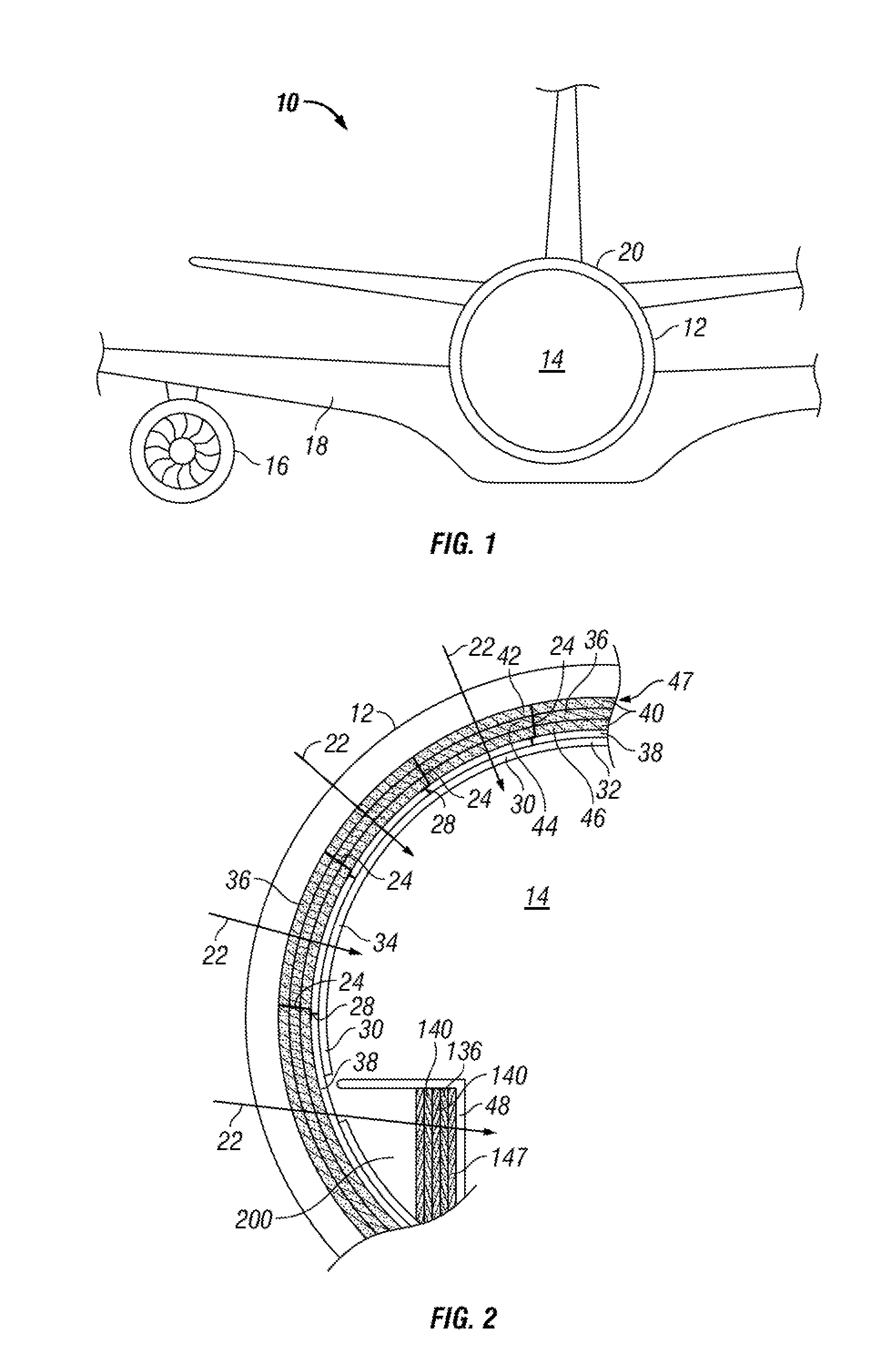
ActiveUS8413762B1Reduce noiseImprove transmission lossPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesWallsPorous layerAcoustics
Embodiments of thermal-acoustic sections for an aircraft for reducing noise along an acoustic path produced from an acoustic source are provided herein. The thermal-acoustic section comprises a first porous layer having a first characteristic acoustic impedance. A second porous layer is disposed adjacent to the first porous layer and has a second characteristic acoustic impedance that is greater than the first characteristic acoustic impedance. The thermal-acoustic section is configured to be positioned along the acoustic path such that at least a portion of the noise from the acoustic source is directed through the first porous layer to the second porous layer to promote absorption of the noise.
Owner:GULFSTREAM AEROSPACE CORP
Flexible printed circuit board
InactiveUS20080083559A1Facilitate conductionImprove transmission lossPorous dielectricsMagnetic/electric field screeningEngineeringFlexible electronics
A flexible printed circuit board wherein the insulative substrate 34 having a plurality of conductive layers 36b covered with a protective layer 38 is encircled by a mesh-cloth member 32.
Owner:YAMAICHI ELECTRONICS
Sound attenuation
InactiveUS20170132999A1Reduce decreaseLower performance requirementsSound proofingSound producing devicesUltrasound attenuationEngineering
Owner:CARBON AIR
Heat insulating acoustical structure and carbody shell structure using the same
To obtain a wide passenger compartment space, the thickness of a heat insulating acoustical layer is reduced, and for this purpose, a comfortable in-car environment is obtained by using a vacuum insulating panel which combines high heat insulating performance and sound insulating performance. A heat insulating acoustical layer 20 is formed on one surface of a lightweight alloy structure 10 of double skin construction by using a vacuum insulating panel 21 as a middle member and sandwiching two surfaces of the panel with elastic sound absorbing materials 22, 23 made of a nonwoven fabric or a foamed body, and the heat insulating acoustical layer is covered with an interior material 24. Owing to this construction, the transmission loss of a noise which transmits from the double skin structure side is improved by the mutual actions of the elasticity of the sound absorbing material and the rigidity of the vacuum heat insulating panel.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Plastic optical fiber cable and method of signal transmission using the same
ActiveUS20090279837A1Improve transmission lossExcellent long-term heat resistanceOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingFibre mechanical structuresBare fiberPolymethyl methacrylate
A plastic optical fiber cable includes: a bare optical fiber including a core made of a poly(methyl methacrylate) or a copolymer including methyl methacrylate as a major component and a cladding layer including, at least in the outermost layer, a layer made of a certain fluorine-containing olefin-based resin; and a coating layer provided on the outer surface thereof. The coating layer includes a protective coating layer, a light blocking coating layer, and a functional coating layer, the layers being provided in the order mentioned from inner side. The protective coating layer is made of a certain resin material. The light blocking coating layer is made of a nylon-based resin including, as a major component, nylon 11 or nylon 12, the nylon-based resin containing monomer and oligomer compounds derived from the nylon-based resin in an amount of a certain range. The functional coating layer is made of a nylon-based resin composition having a crystalline melting point within a certain range, the nylon-based resin composition containing a certain amount of melamine cyanurate or bromine atoms and further containing a certain amount of inorganic chromatic pigments, or the layer is made of a nylon-based resin composition having a crystalline melting point of within a certain range and an oxygen transmission rate within a certain range.
Owner:MITSUBISHI CHEM CORP
Anti-resonant hollow core optical fiber having multiple resonant layers
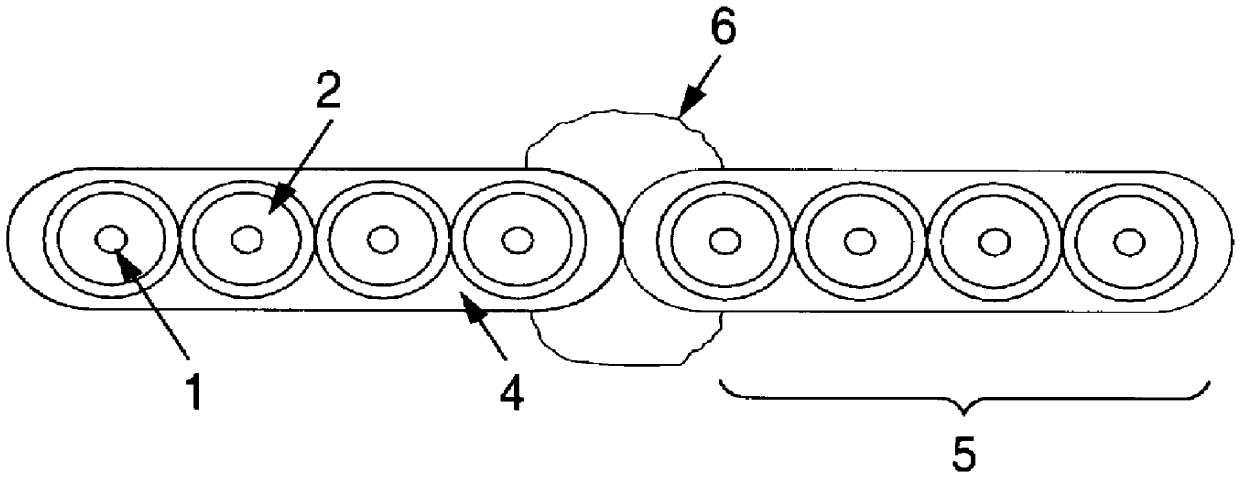
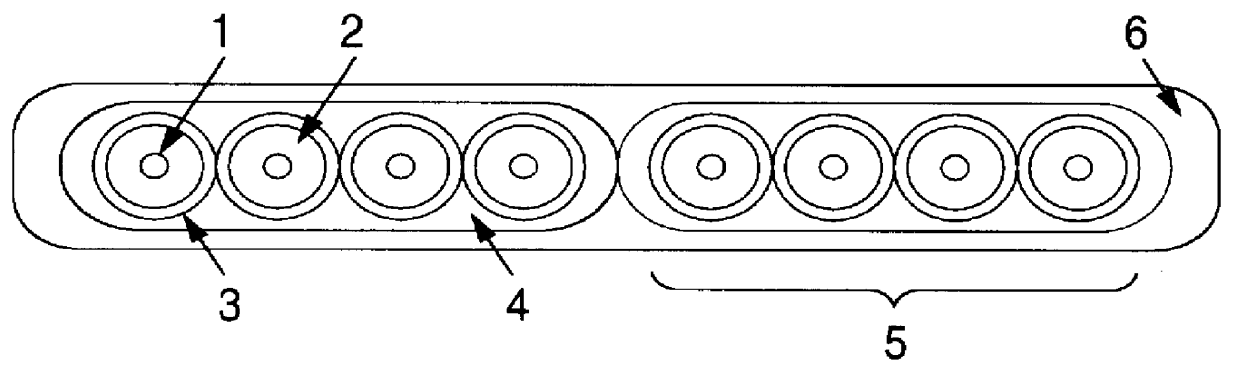
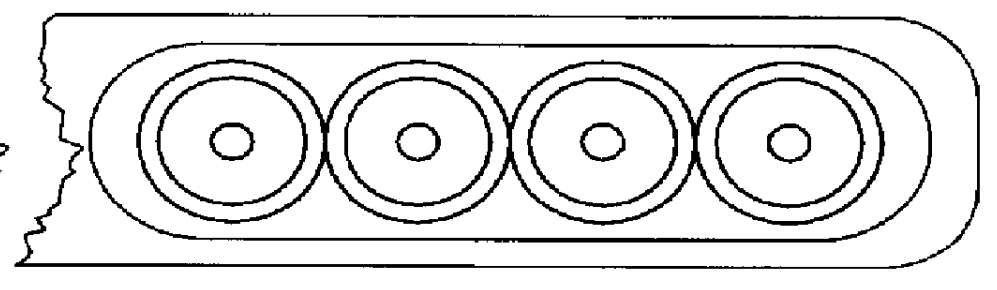
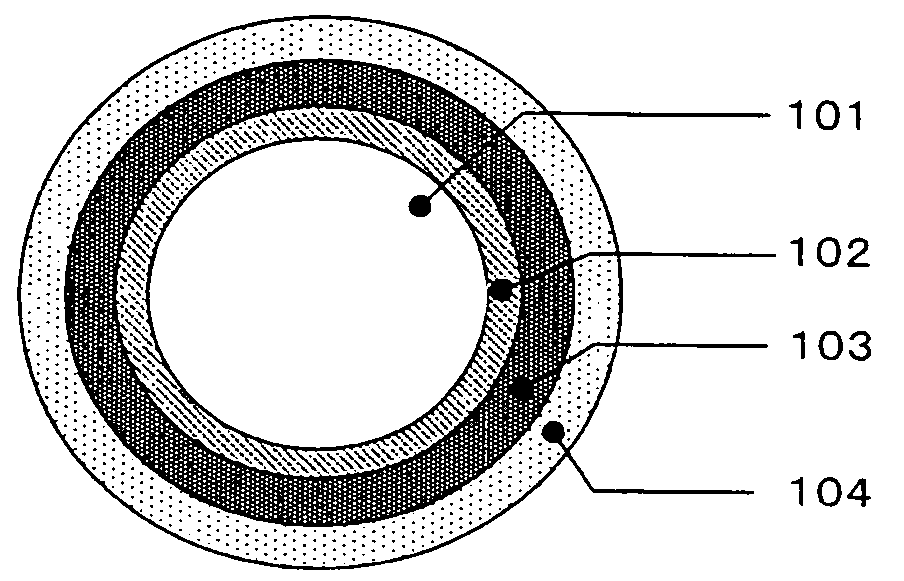
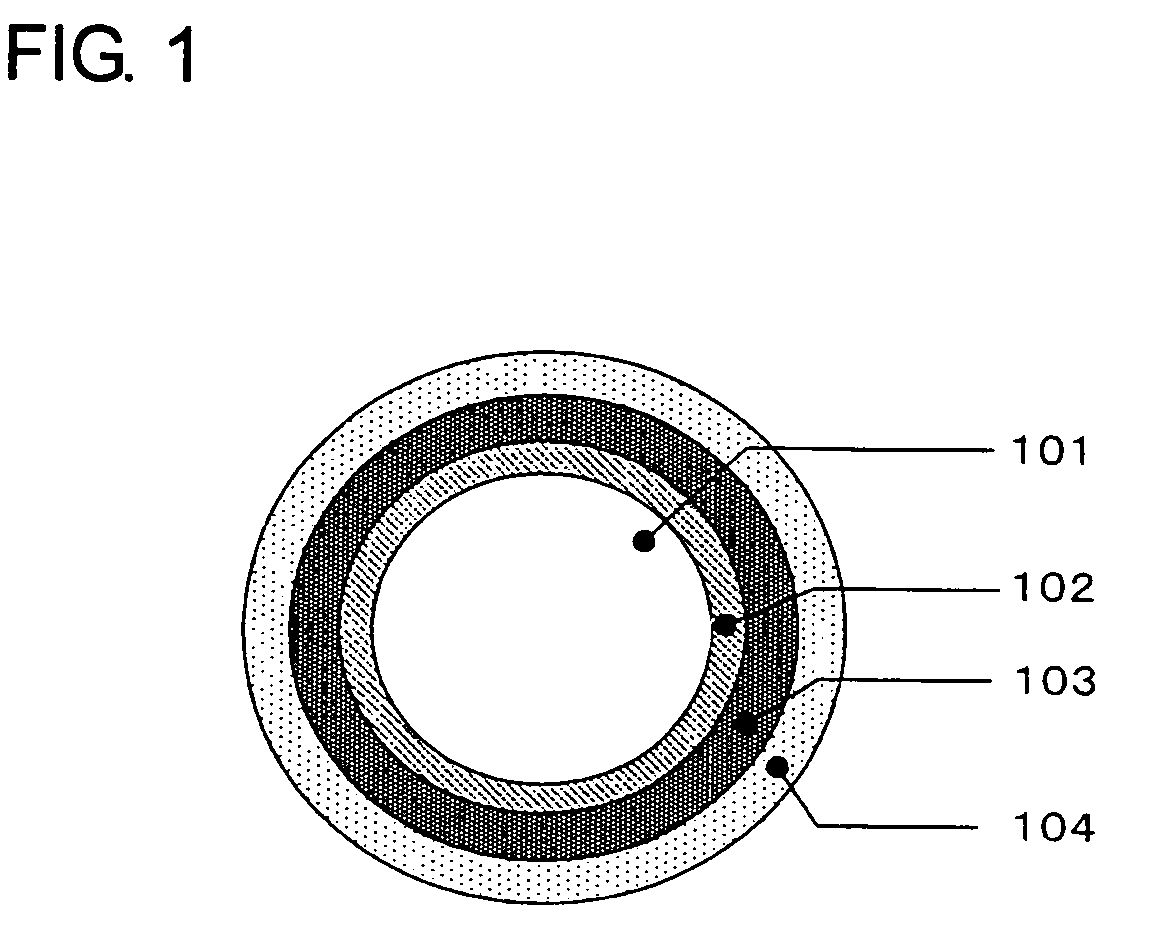
ActiveUS20200241200A1Narrow bandwidthLow efficiencyOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingNanoopticsTransmission lossMaterials science
An anti-resonant hollow core optical fiber having multiple resonant layers. The optical fiber comprises a low-refractive index core region (1) and a high-refractive index cladding region. The high-refractive index cladding region comprises an inner cladding region (4) and an outer cladding region (5). The outer cladding region (5) clads the inner cladding region (4) and the core region (1). The inner cladding region (4) comprises a first anti-resonant layer (2) and a second anti-resonant layer (3), and the first anti-resonant layer (2) and the second anti-resonant layer (3) surround the core region (1); and the first anti-resonant layer (2) comprises several layers of microcapillary tubes, and the second anti-resonant layer (3) supports the first anti-resonant layer (2). The optical fiber adopts a double-cladding structure and uses two or more anti-resonant layers such that theoretically simulated loss is reduced to 0.1 dB / km, and has the features of ultralow transmission loss, wide spectral bandwidth, low bending loss, low transmission loss, high damage threshold and single-mode transmission.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Optical Fiber
InactiveUS20100046900A1Increase stickinessIncrease valueOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingOptical waveguide light guideFiberPlastic optical fiber
The present invention provides an optical fiber in which composites constructing its coating are not complicated, so, there is also little constraint in view of production, and, moreover, delamination between a glass optical fiber and a primary layer, and a bubble in the primary layer hardly arise. The optical fiber of the present invention is an optical fiber which has a glass optical fiber which has a core 1, which passes an optical signal, in a center portion, and a cladding 2 surrounding this, a primary protective layer 3 made to coat the glass optical fiber, a secondary protective layer 4 applied on this primary protective layer 3, and a third protective layer 5 applied to an outer periphery of this secondary protective layer 4, wherein glass transition temperature of the primary protective layer 3 is made to be higher than −20° C. and 10° C. or lower, glass transition temperature of the secondary protective layer 4 is made to be −10° C. or less, and the glass transition temperature of the primary protective layer 3 is set higher than that of the secondary protective layer 4.
Owner:FURUKAWA ELECTRIC CO LTD
Plastic optical fiber cable and method of signal transmission using the same
ActiveUS8023789B2Improve transmission lossExcellent long-term heat resistanceOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingFibre mechanical structuresPoly(methyl methacrylate)Engineering
Owner:MITSUBISHI CHEM CORP
Method of treating the surface of copper and copper
ActiveUS7588835B2Easily deterioratedVariation in the height of the irregularitiesDecorative surface effectsPrinted circuit aspectsCopper oxideOxidizing agent
A method of treating the surface of copper is provided to ensure adhesive strength between the surface of copper and an insulating layer without forming irregularities exceeding 1 μm on the surface of copper and to improve insulation reliability between wirings. A copper whose surface is treated by the above surface treating method is also provided. The method of treating the surface of copper comprises the surface of copper comprising the steps of: forming a metal nobler than copper discretely on the surface of copper; and subsequently oxidizing the surface of copper by using an alkaline solution containing an oxidant.
Owner:RESONAC CORPORATION
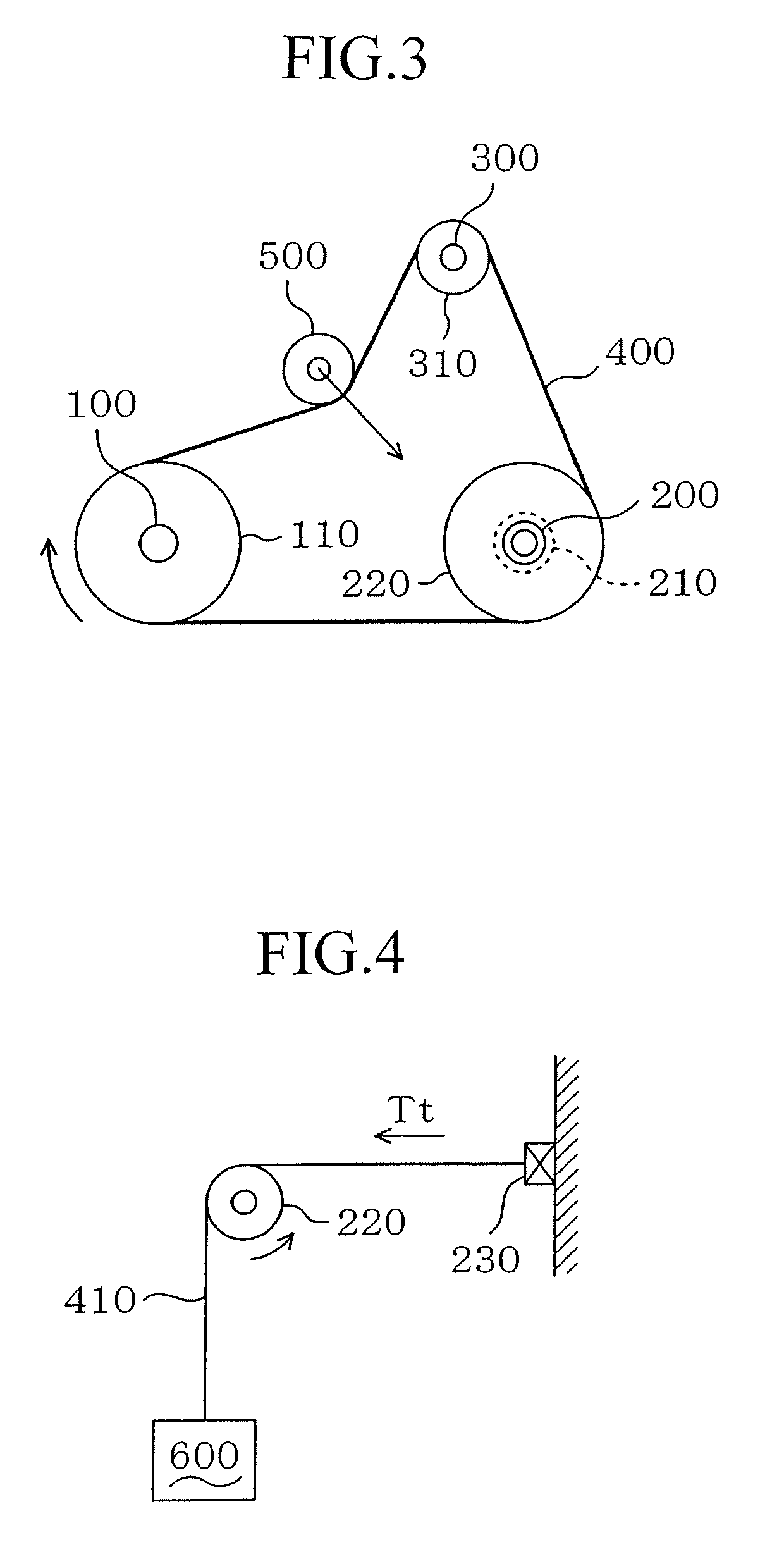
Method and system for identifying the degree of a slip of a belt part of a belt transmission
InactiveUS7174245B2Easy to wearImprove transmission lossDigital data processing detailsGearingConveyor beltIndustrial engineering
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
Optical cable
InactiveUS20130129288A1Reduced flexibilityNot easy to bendFibre mechanical structuresEngineeringTension member
An optical cable comprises an optical fiber ribbon, a tension member and a sheath. The optical fiber ribbon is constructed by integrating a plurality of optical fibers arranged in parallel. The sheath is provided so as to surround the optical fiber ribbon. The sheath is used for protecting the optical cable. One optical fiber ribbon is arranged twistably within an inner space surrounded by the sheath.
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC IND LTD
Optical fiber cable
InactiveUS20090034922A1Avoid transmission lossImprove transmission lossFibre mechanical structuresTension memberEngineering
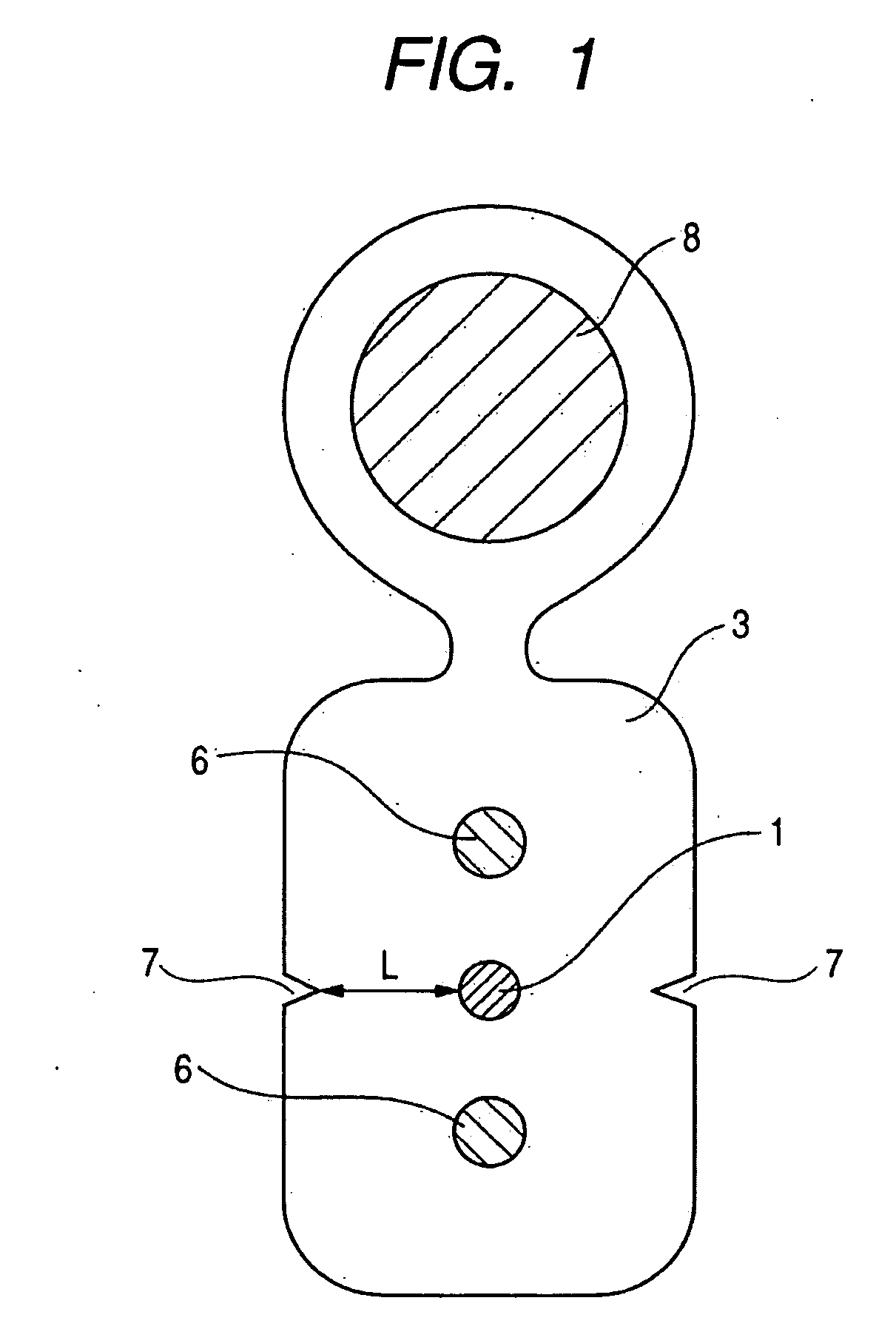
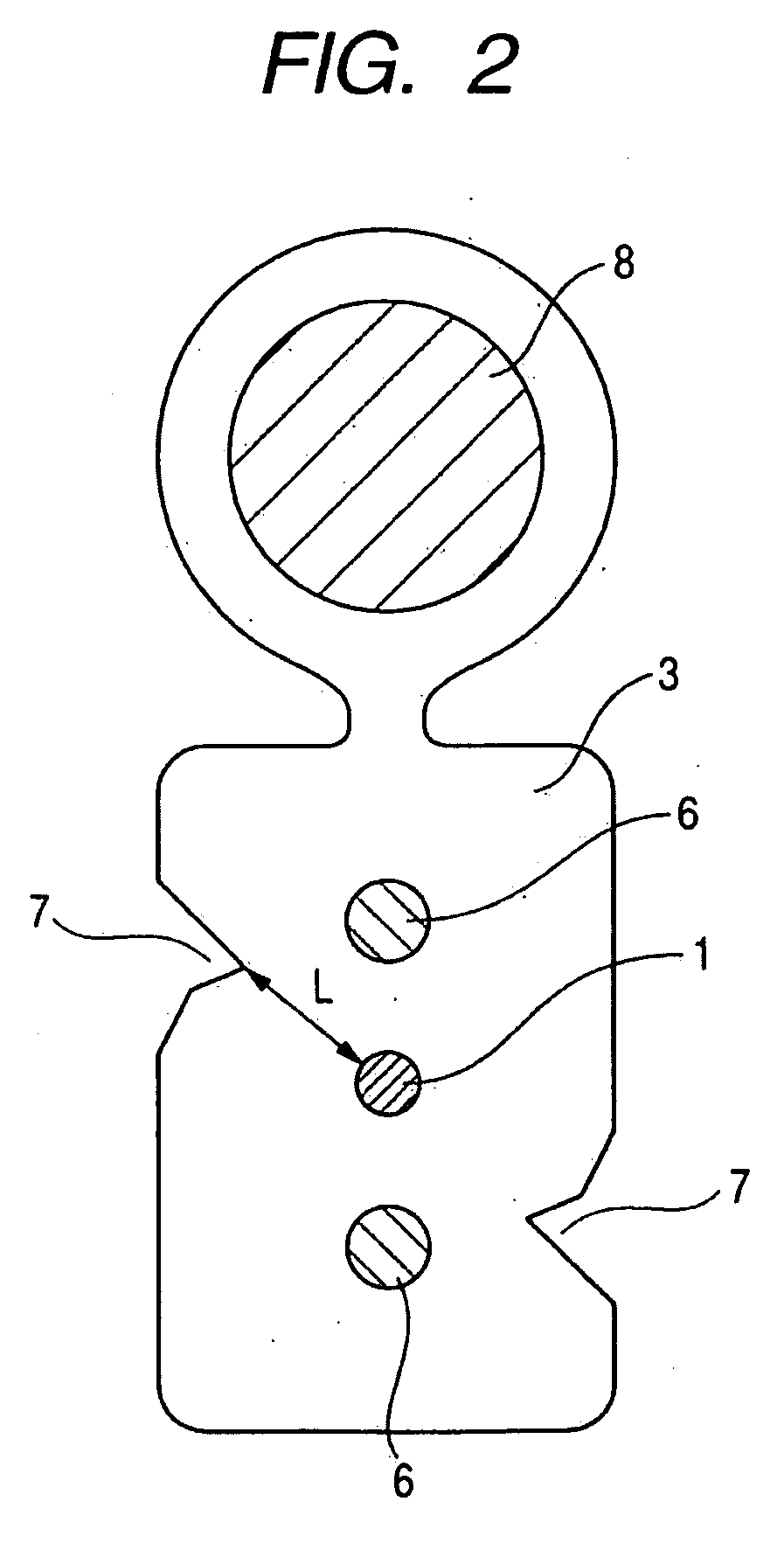
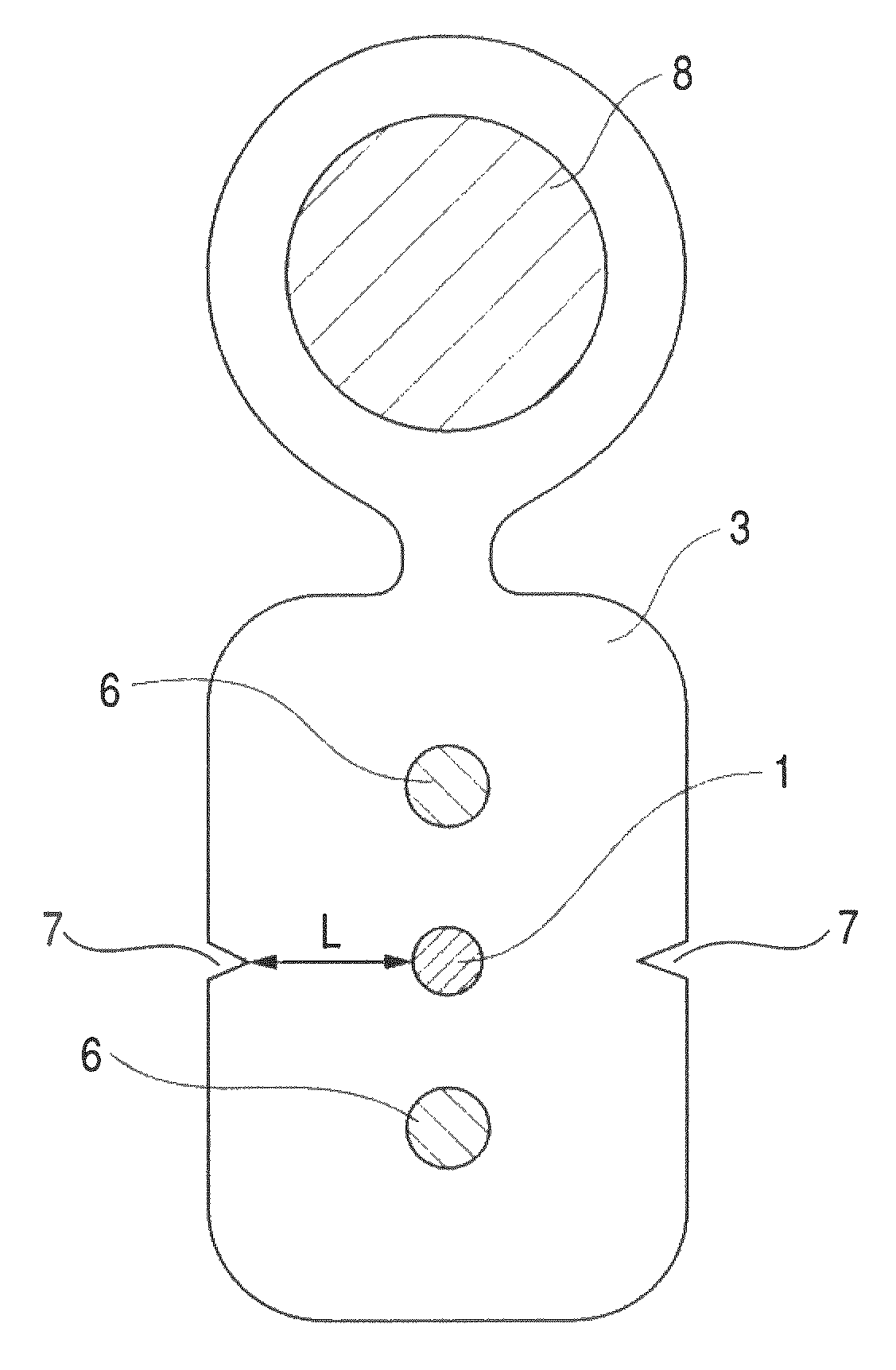
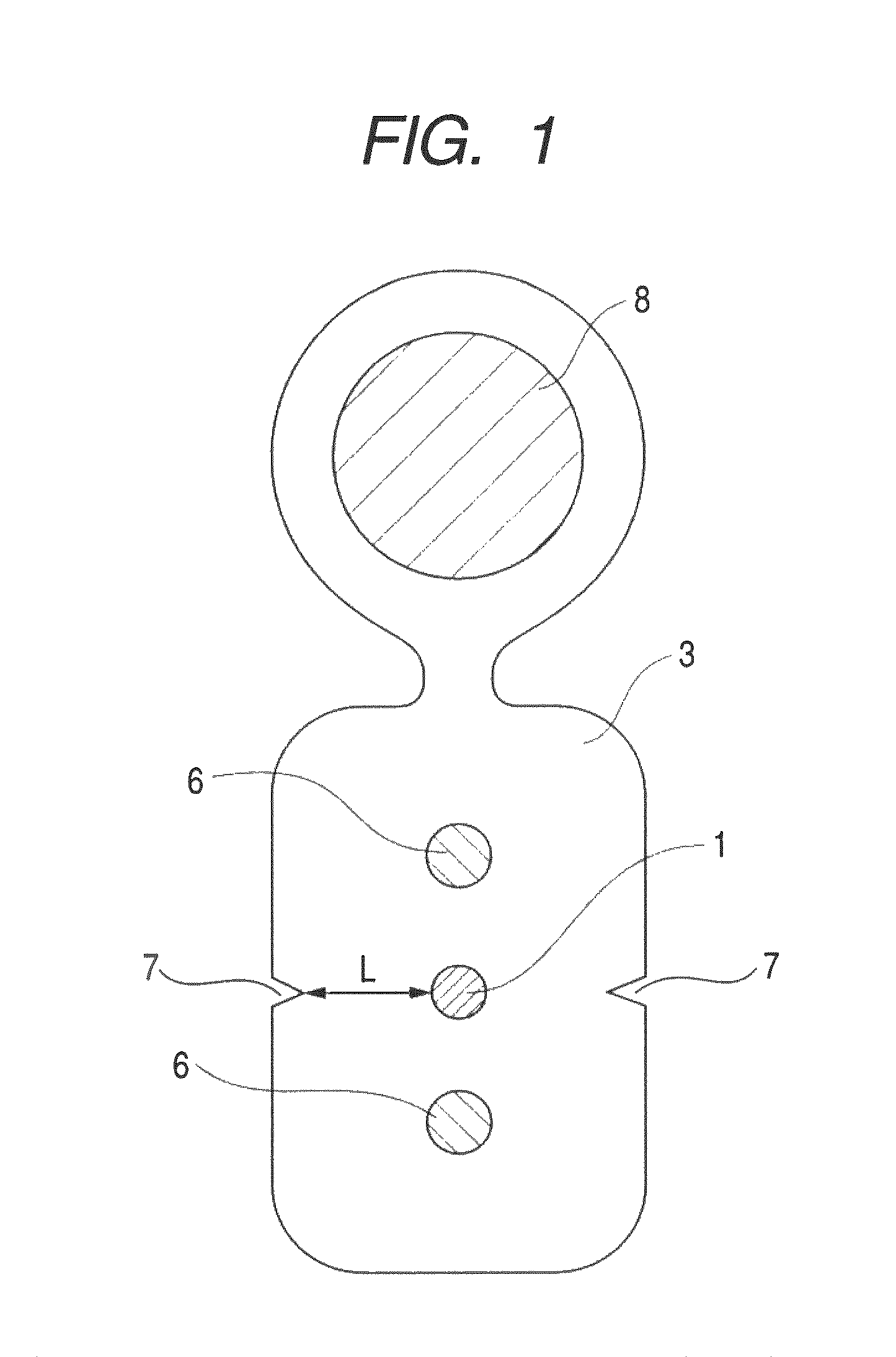
It is an object of the present invention to provide an optical fiber cable which can reliably prevent increased transmission loss due to damage of the optical fiber as a result of the egg-laying behavior of cicadas. The cable includes at least an optical fiber 1, tension members 6 and a sheath 3. The sheath 3 has a shore D hardness of 55 or more and a minimum distance L from a surface of the optical fiber 1 to an outer surface of the sheath 3 of greater than 0.3 mm. Further, in the cable, the surface of sheath 3 has a coefficient of friction of 0.45 or less and the sheath 3 has a shore D hardness of 57 or more. In addition, the cable is made by using a specific flame retardant composition (P) as the sheath material.
Owner:FURUKAWA ELECTRIC CO LTD
Optical fiber
ActiveUS20170003446A1Modulus is reducedResistance to deteriorationGlass optical fibreOptical fibre with graded refractive index core/claddingGlass fiberFiber
An optical fiber comprises a glass fiber which comprises a core and a cladding, a primary resin coating layer which covers the periphery of the glass fiber, and a secondary resin coating layer which covers the periphery of the primary resin coating layer. The glass fiber is a multimode fiber having a core diameter of 40-60 μm and a cladding diameter of 90-110 μm, and the primary resin coating layer is a layer formed by curing a curable resin composition which comprises oligomers, monomers, and a reaction initiator, the curable resin composition containing a one-end-capped oligomer in an amount of 30% by mass or larger based on all the oligomers.
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC IND LTD
Control device for vehicle drive device
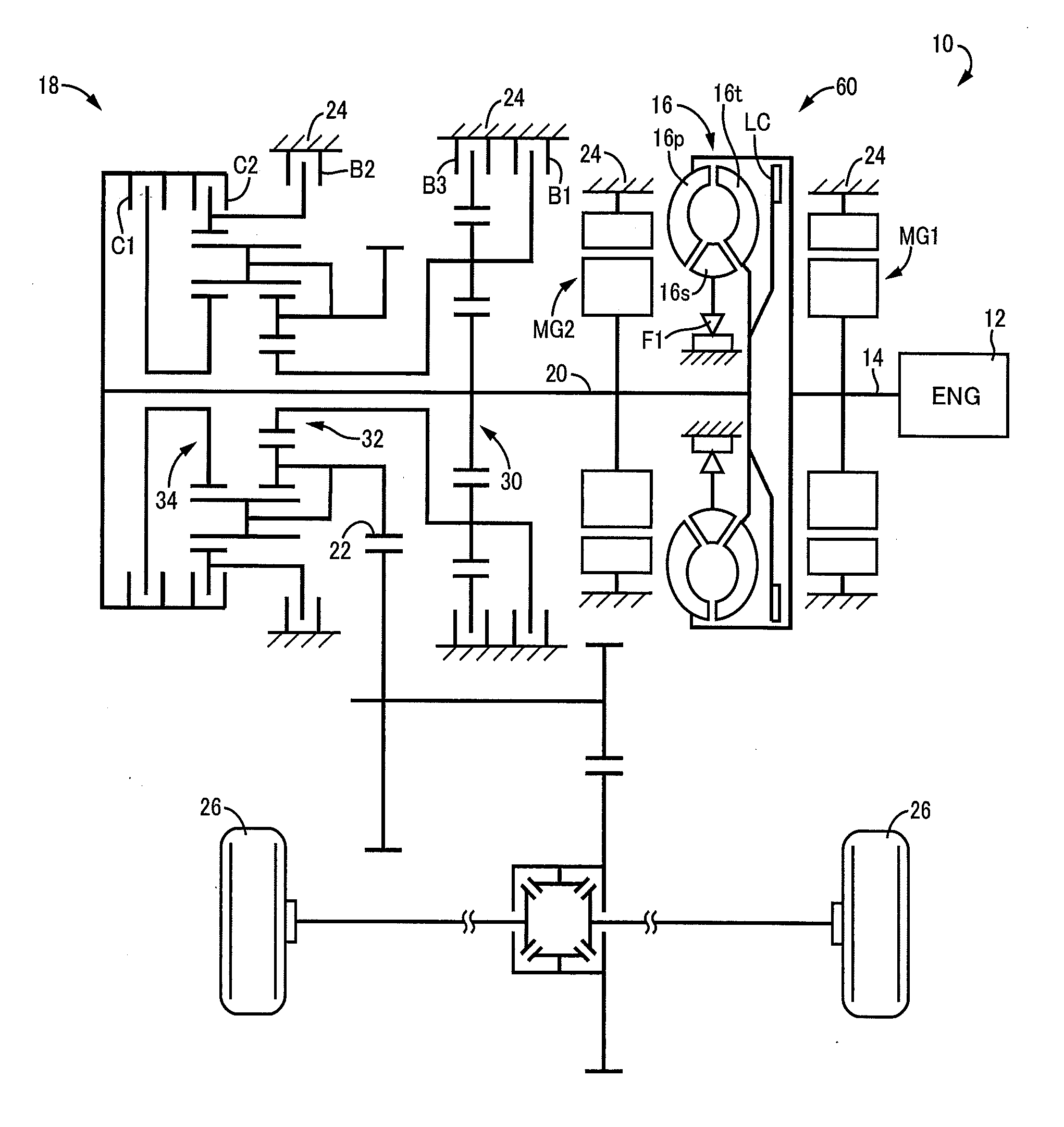
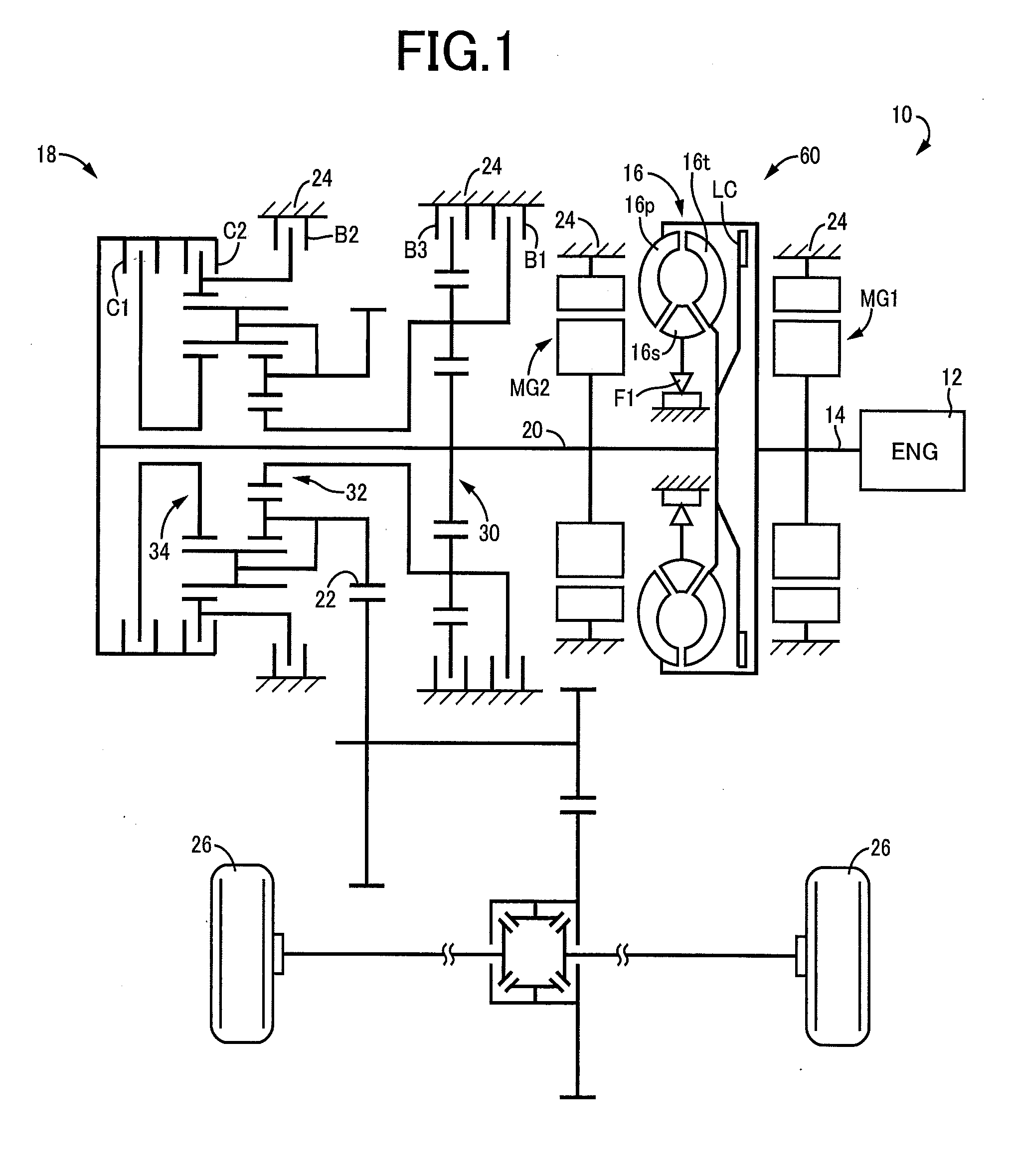
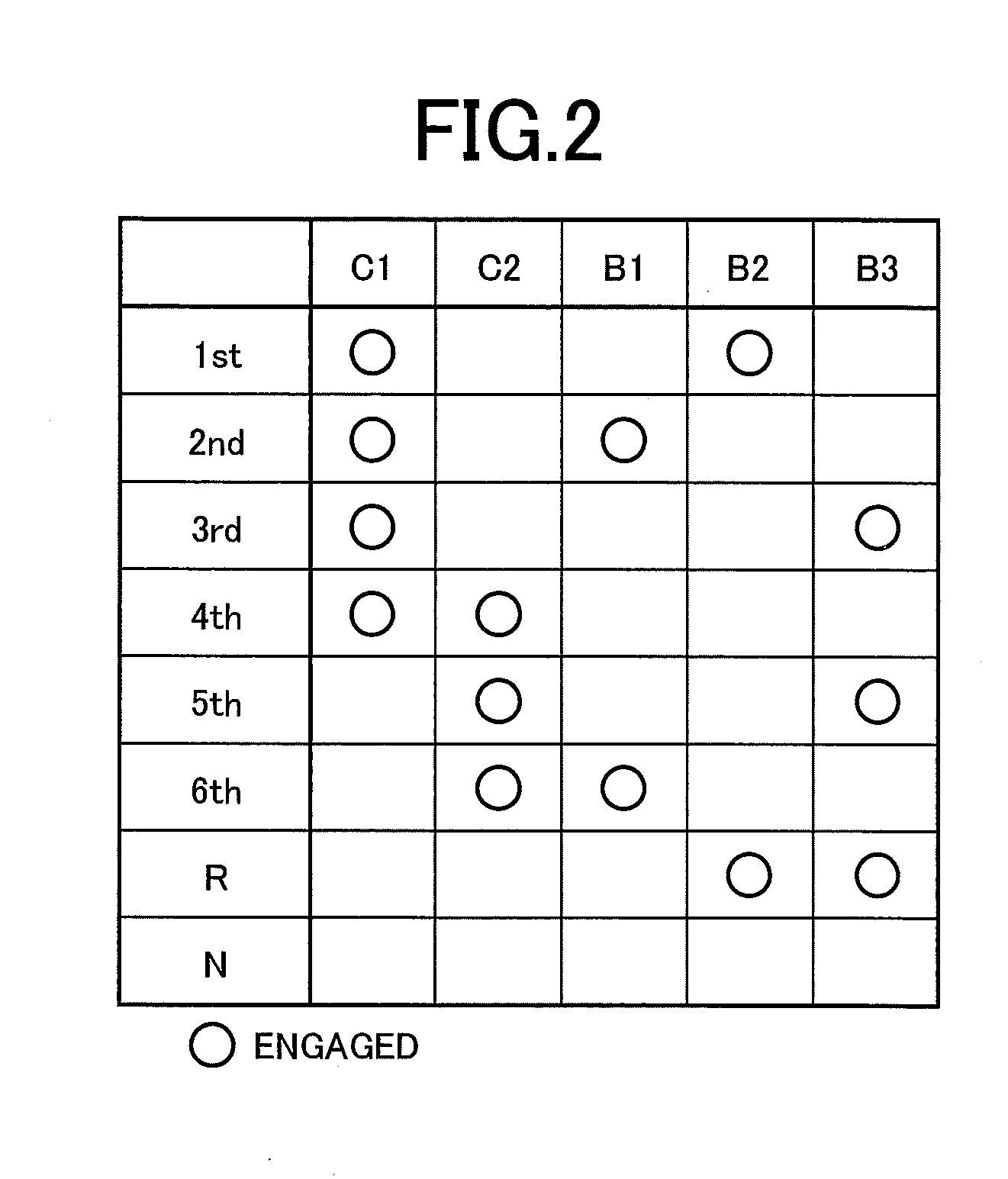
ActiveUS20140309079A1Improve fuel efficiencyReduced speed ratioHybrid vehiclesElectric propulsion mountingElectric power transmissionOperating point
A control device of a vehicle drive device includes a fluid transmission device having an input-side rotating element to which power from an engine is input and an output-side rotating element outputting power to drive wheels, a first electric motor directly or indirectly coupled to the input-side rotating element, and a second electric motor directly or indirectly coupled to the drive wheels, the control device of a vehicle drive device having an electric path through which power is electrically transmitted by giving / receiving electric power between the first electric motor and the second electric motor and a mechanical path through which power is mechanically transmitted via the fluid transmission device, the control device of a vehicle drive device being configured to control an operating point of the engine by adjusting a torque of the first electric motor, the torque of the first electric motor being adjusted such that a sum of an engine torque and the torque of the first electric motor is balanced with an input-side load torque generated in the input-side rotating element depending on a speed ratio of the fluid transmission device, the input-side load torque being obtained based on an engine rotation speed indicated by a target engine operating point, and the torque of the first electric motor being determined based on the input-side load torque and the engine torque indicated by the target engine operating point, and the control device of a vehicle drive device adjusting a torque of the first electric motor while giving / receiving electric power between the first electric motor and the second electric motor to reduce a speed ratio of the fluid transmission device when a temperature of operating oil for actuating the fluid transmission device is lower as compared to when the temperature is higher.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Manufacture method of optical printed wiring board
InactiveCN102928936AImprove transmission lossLow transfer data ratePrinted circuit detailsCoupling light guidesElectricityEngineering
The invention provides a manufacture method of an optical printed wiring board. The manufacture method of the optical printed wiring board includes the following steps: a step of opening a groove, a step of pressing a plate, a step of cutting out an angle, a step of polishing a laser surface and a step of drilling a hole on the back. The manufacture method of the optical printed wiring board has the advantages that a bottleneck of electric mutual connection broadcasting brand width on a conventional printed wiring board is broken through and signal broadcasting brand width can be higher than 10 gigabytes / second. Besides, conventional optical components such as a vertical cavity face emitting laser device. An optical sensor and the like can be also inserted on a wiring board face. The wiring board face is compatible with an existing surface mount technology and the development potential for mass production.
Owner:ELEC & ELTEK GUANGZHOU ELECTRONICS +1
Optical fiber cable
InactiveUS7813606B2Improve transmission lossAvoid transmission lossFibre mechanical structuresEngineeringTransmission loss
It is an object of the present invention to provide an optical fiber cable which can reliably prevent increased transmission loss due to damage of the optical fiber as a result of the egg-laying behavior of cicadas. The cable includes at least an optical fiber 1, tension members 6 and a sheath 3. The sheath 3 has a shore D hardness of 55 or more and a minimum distance L from a surface of the optical fiber 1 to an outer surface of the sheath 3 of greater than 0.3 mm. Further, in the cable, the surface of sheath 3 has a coefficient of friction of 0.45 or less and the sheath 3 has a shore D hardness of 57 or more. In addition, the cable is made by using a specific flame retardant composition (P) as the sheath material.
Owner:FURUKAWA ELECTRIC CO LTD
Optical fiber cable and method of mid-span access thereof
InactiveUS20110002588A1Increased transmission lossAvoid damageFibre mechanical structuresEngineeringUltimate tensile strength
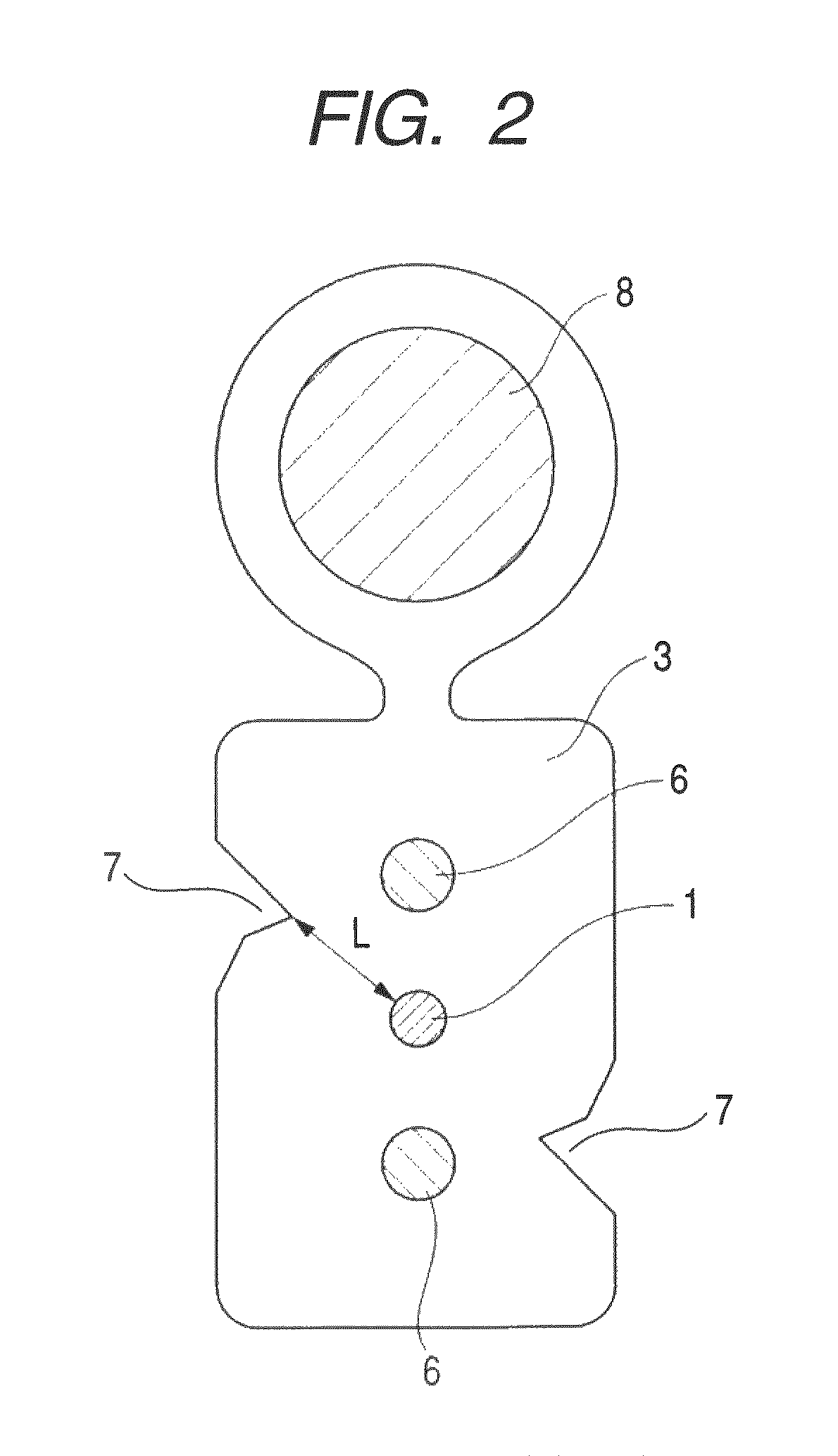
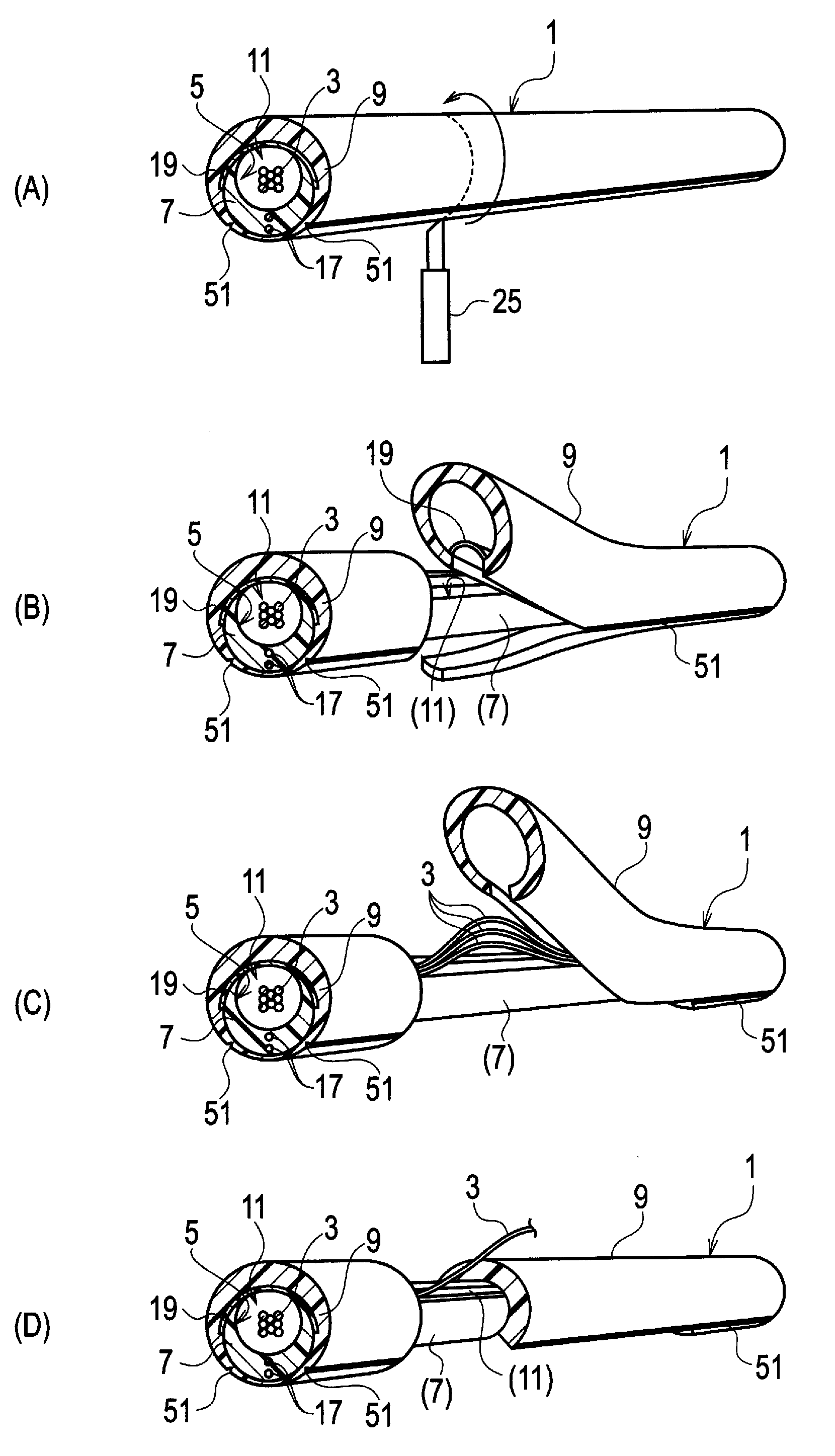
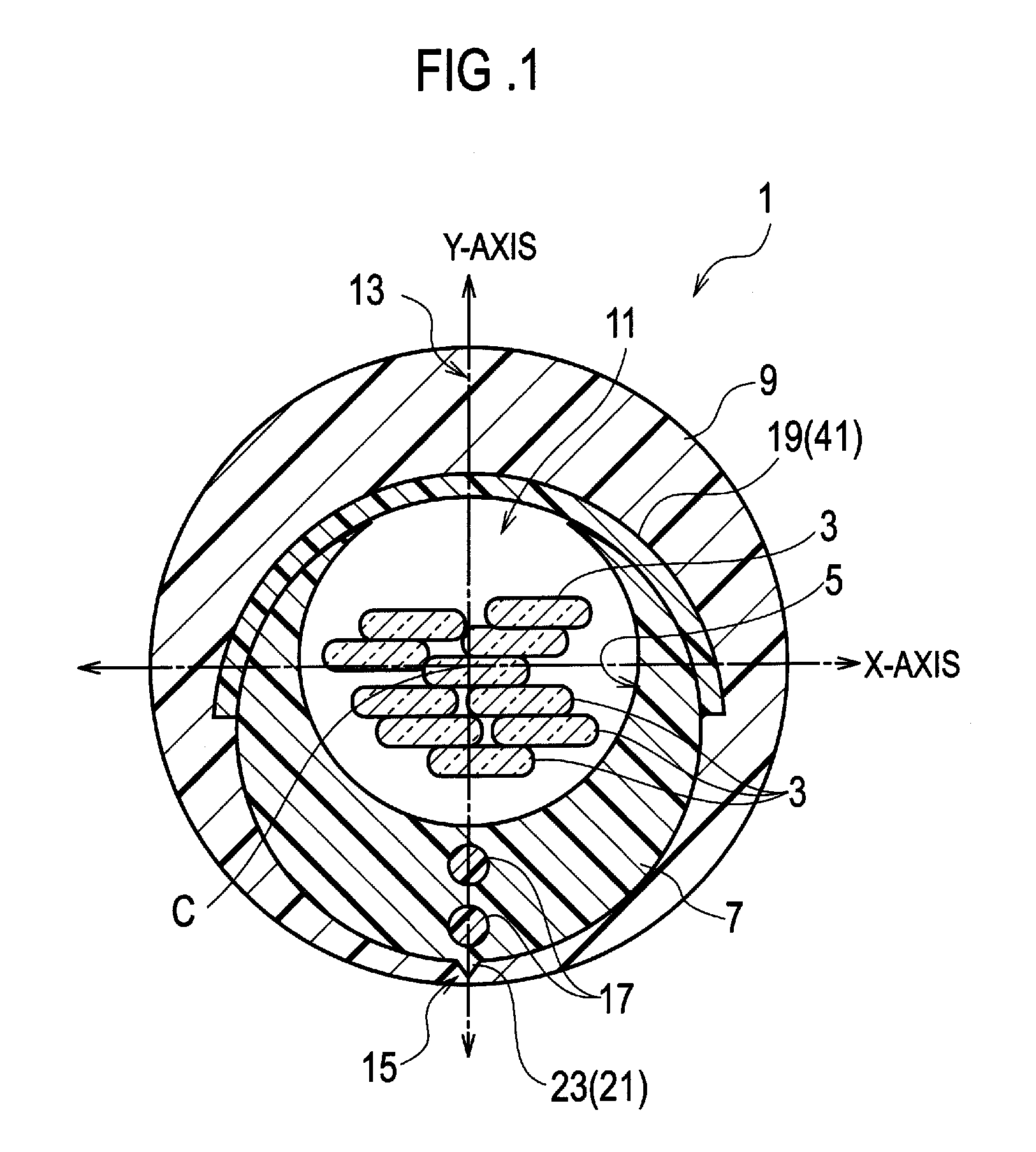
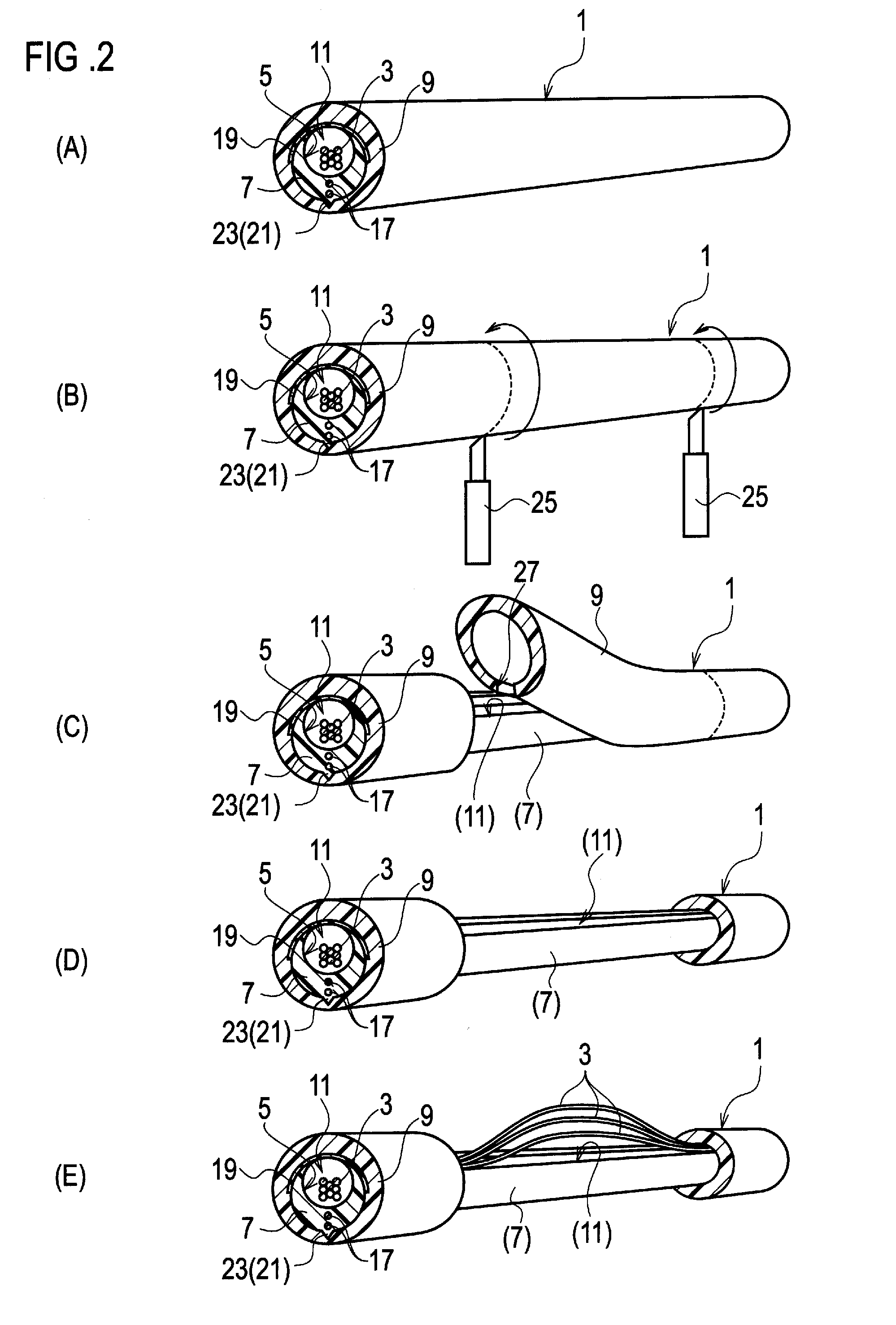
An optical fiber cable is comprised of: a slotted core (7) elongated along an axis of the optical fiber cable, the slotted core including a slot (11) running in parallel with the axis and a groove (5) accessible through the slot; one or more optical fibers (3) placed in the groove; a sheath (9) enclosing the slotted core and the optical fibers; a bonding portion (15) where the slotted core is bonded with the sheath; and two or more strength members (17) embedded in the slotted core, the strength member running in parallel with the axis, and being aligned on a plane including the axis.
Owner:THE FUJIKURA CABLE WORKS LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com