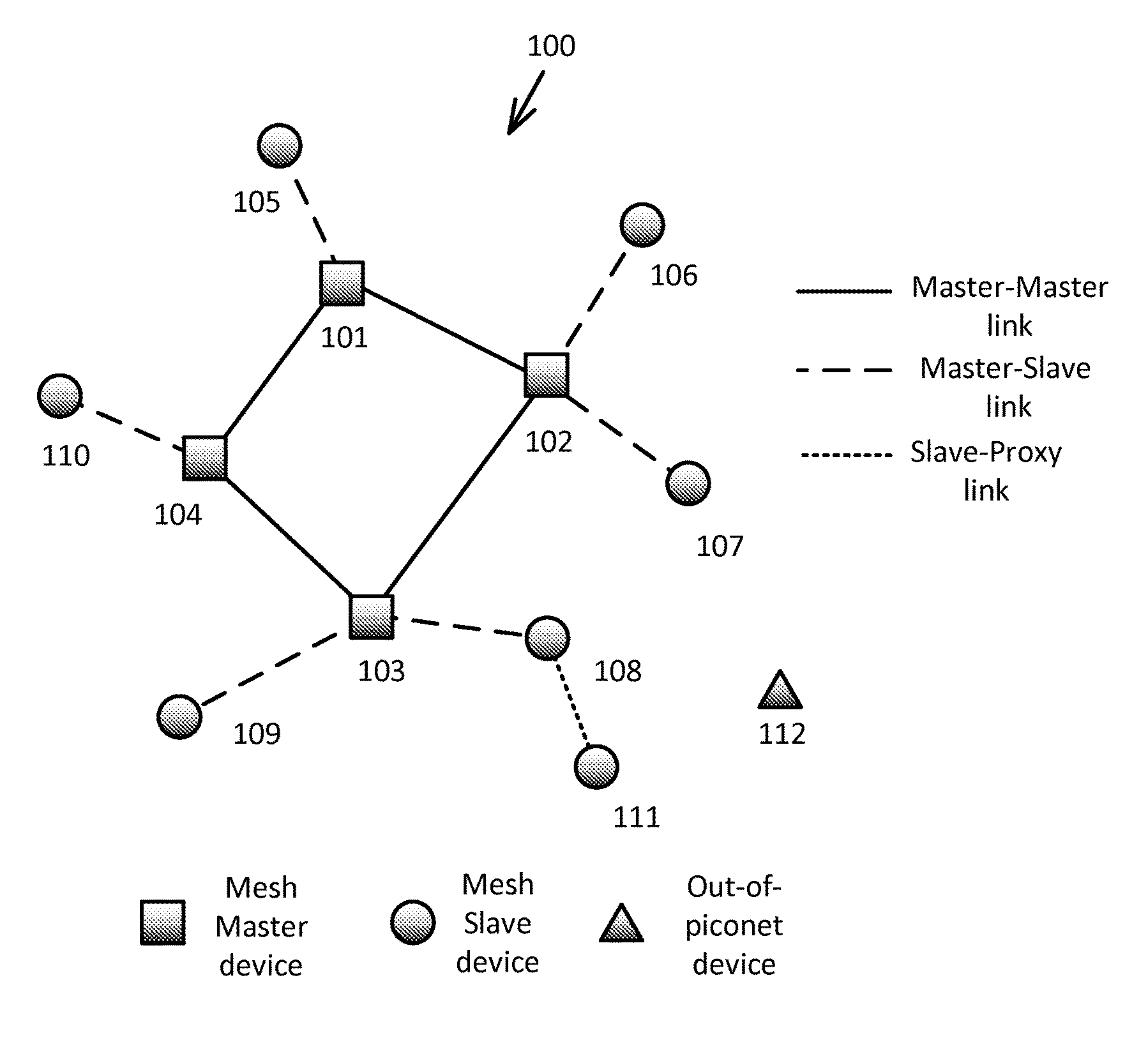
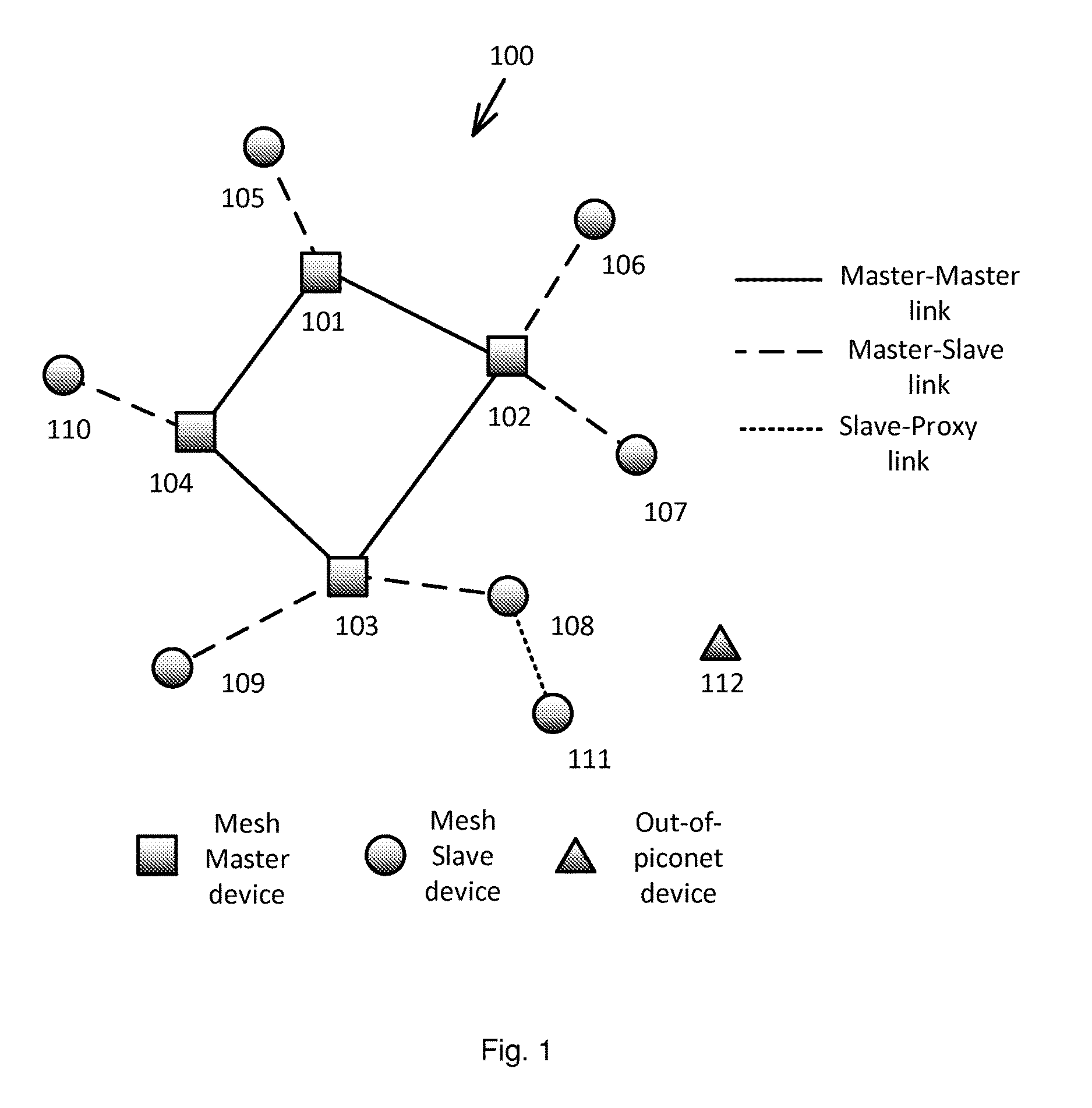
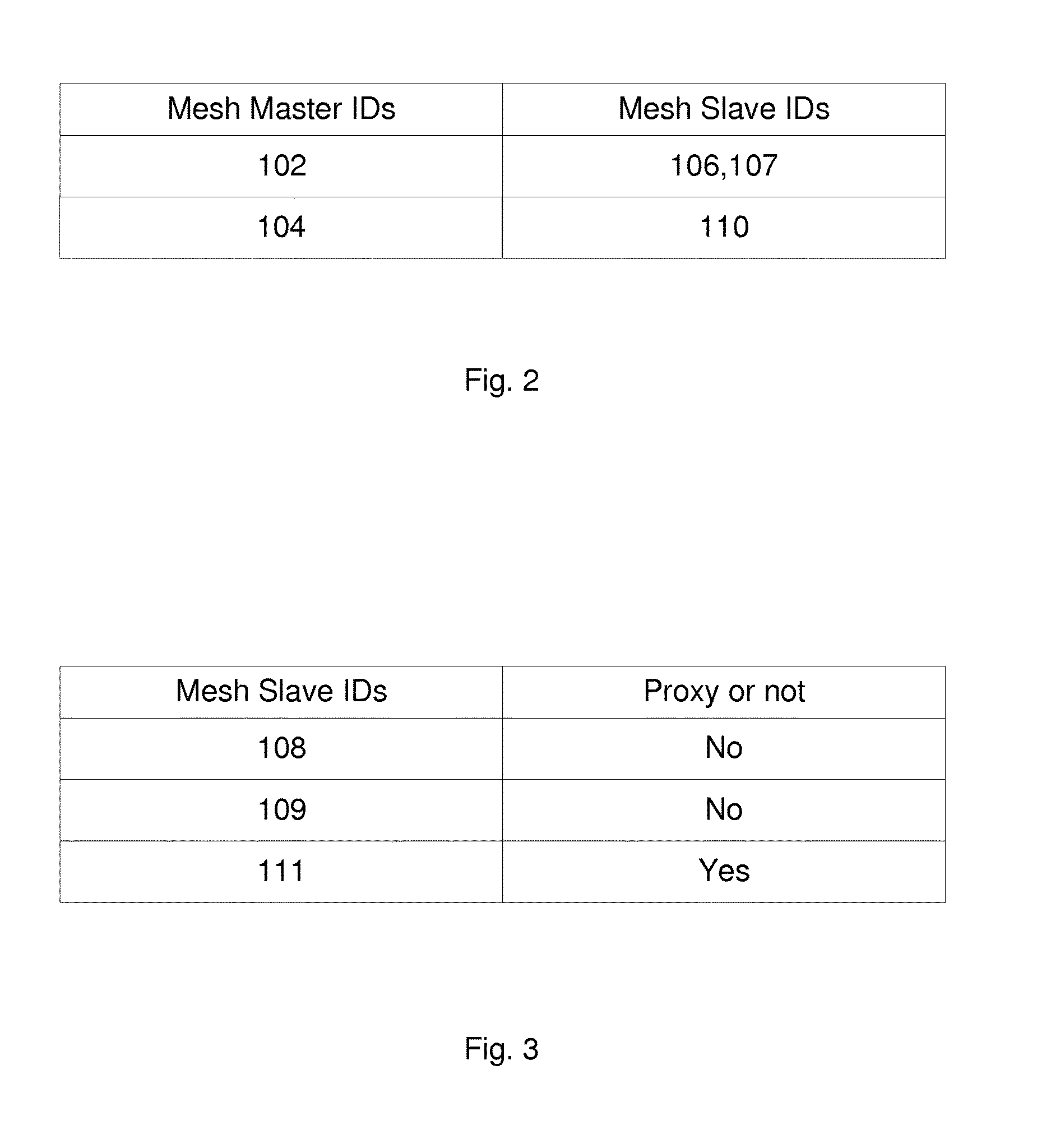
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
192results about How to "Improve network throughput" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Method of interference management for interference/collision prevention/avoidance and spatial reuse enhancement
InactiveUS20080144493A1Improve performanceImprove network throughputPower managementEnergy efficient ICTCollision preventionSingle hop
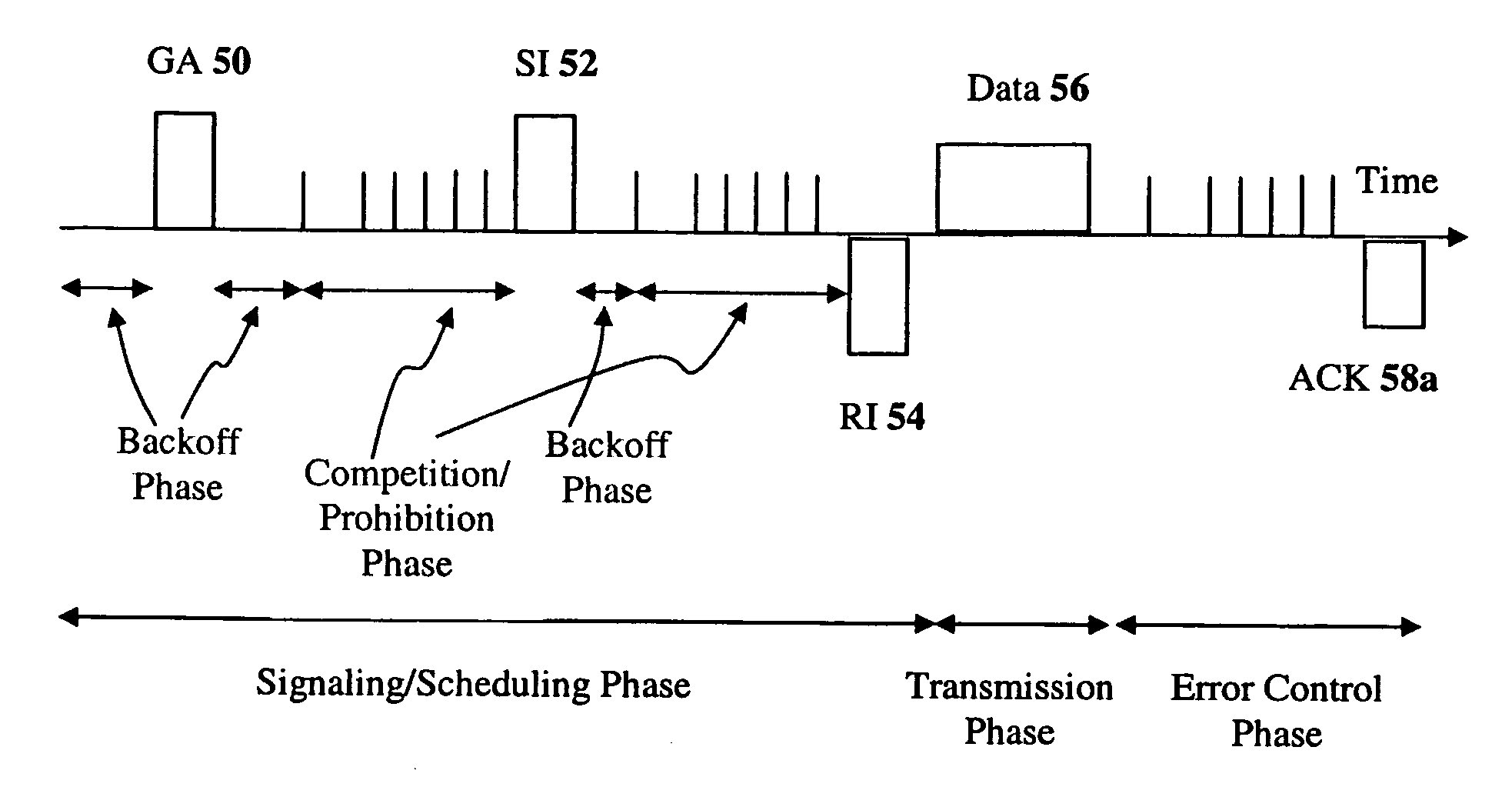
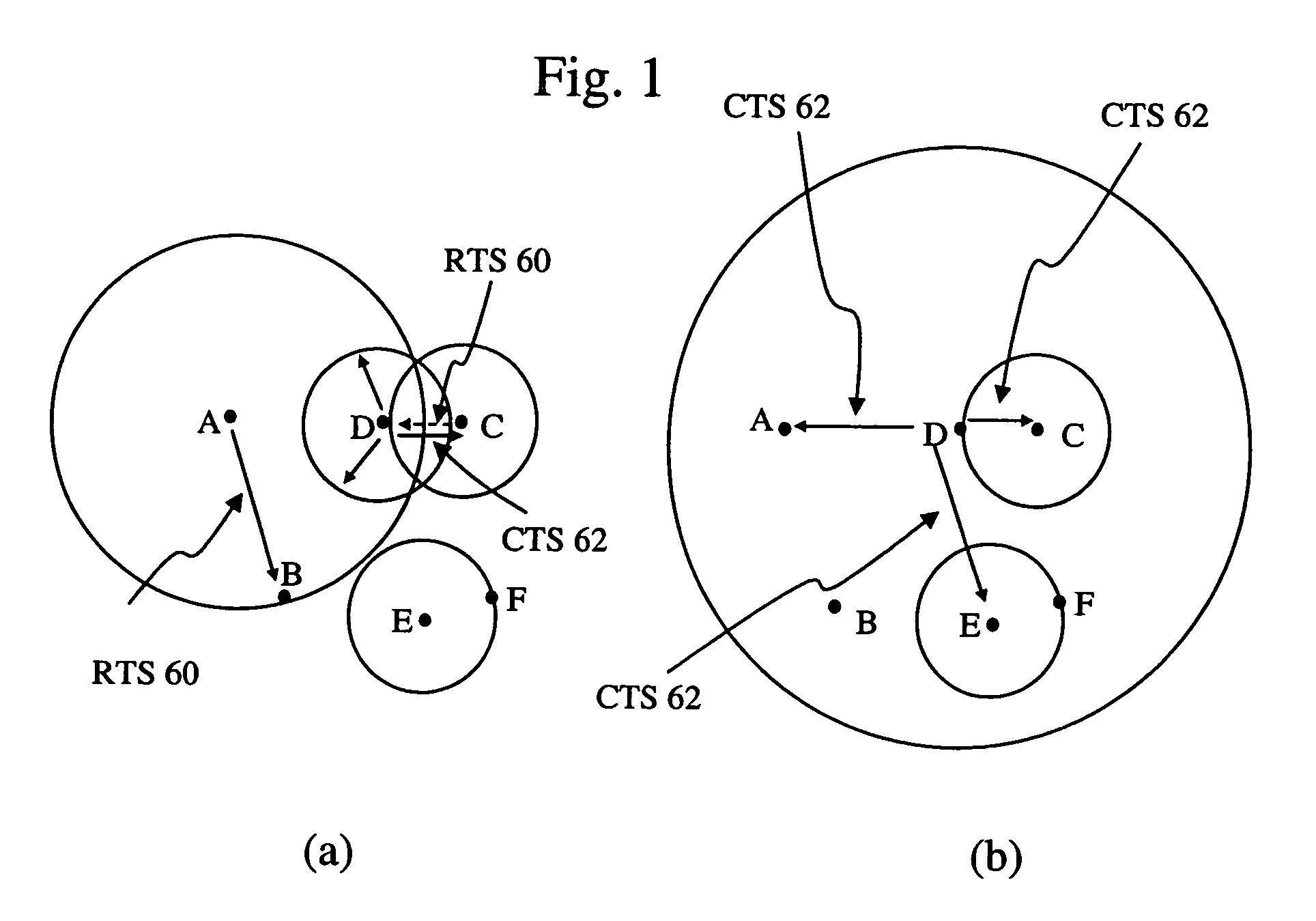
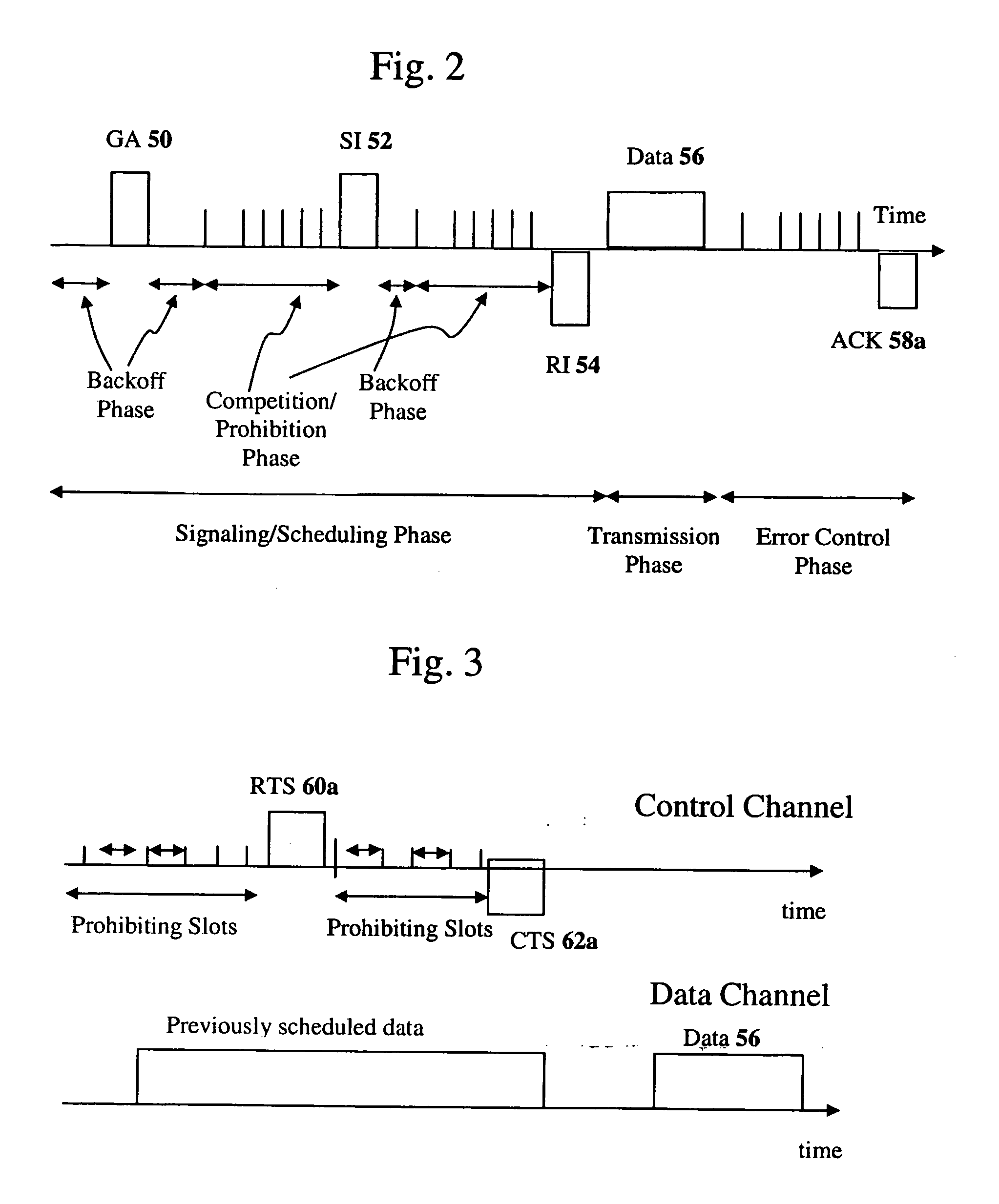
Interference, collisions, power control, and spatial reuse constitute important issues that need to be resolved urgently in multihop wireless networks such as ad hoc networks, single-hop / multihop wireless LANs, sensor networks, and mesh networks. A method called the evolvable interference management (EIM) method is disclosed in this patent for avoiding / preventing interference and collision and increasing network throughput and energy efficiency in wireless networks. EIM employs sensitive CSMA / CA, patching approaches, interference engineering, differentiated multichannel, detached dialogues, and / or spread spectrum techniques to solve the interference and QoS problems. Also, EIM embodiments based on collision prevention without dialogues are capable of collision reduction / control and can resolve several important problems encountered in previous MACP or RTS / CTS-based protocols, while improving / retaining their important advantages.
Owner:YEH CHI HSIANG
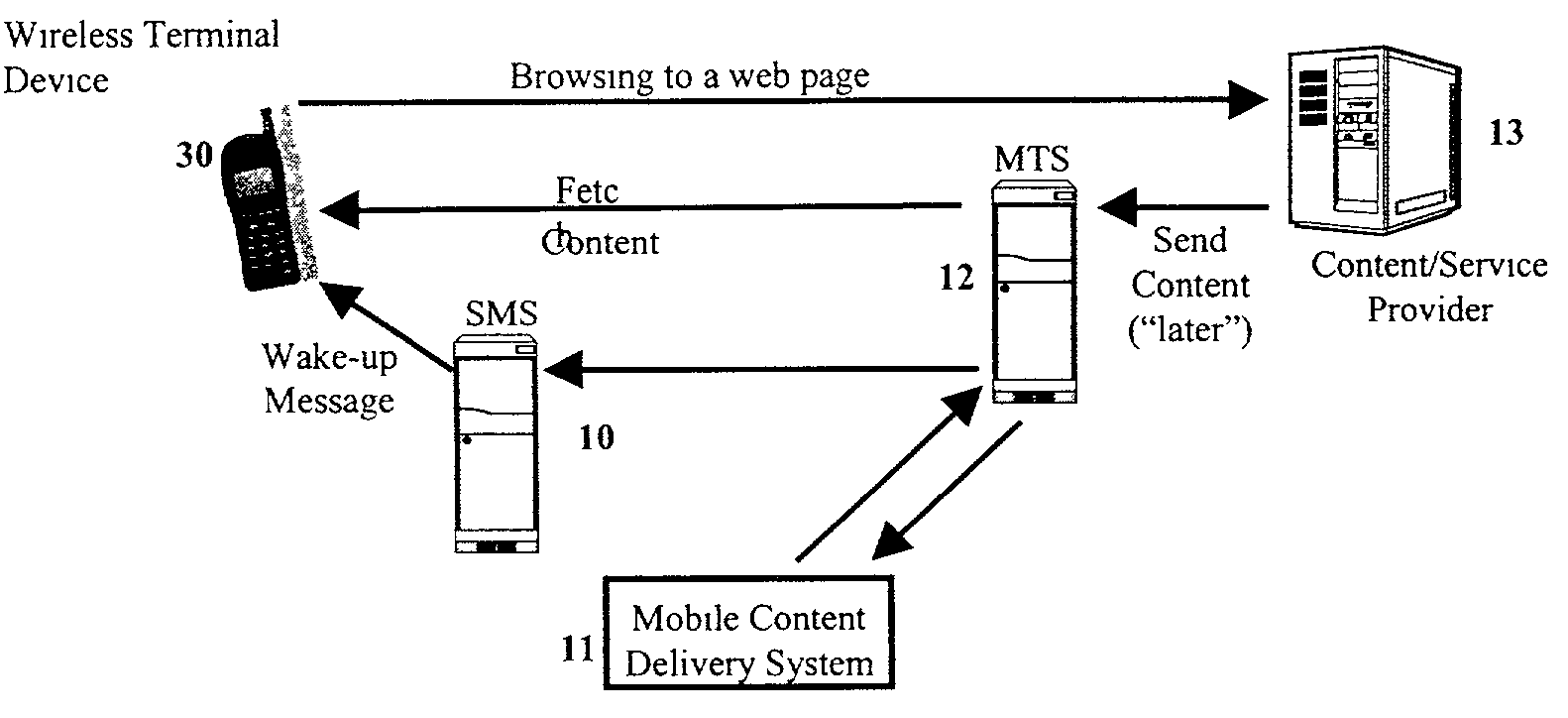
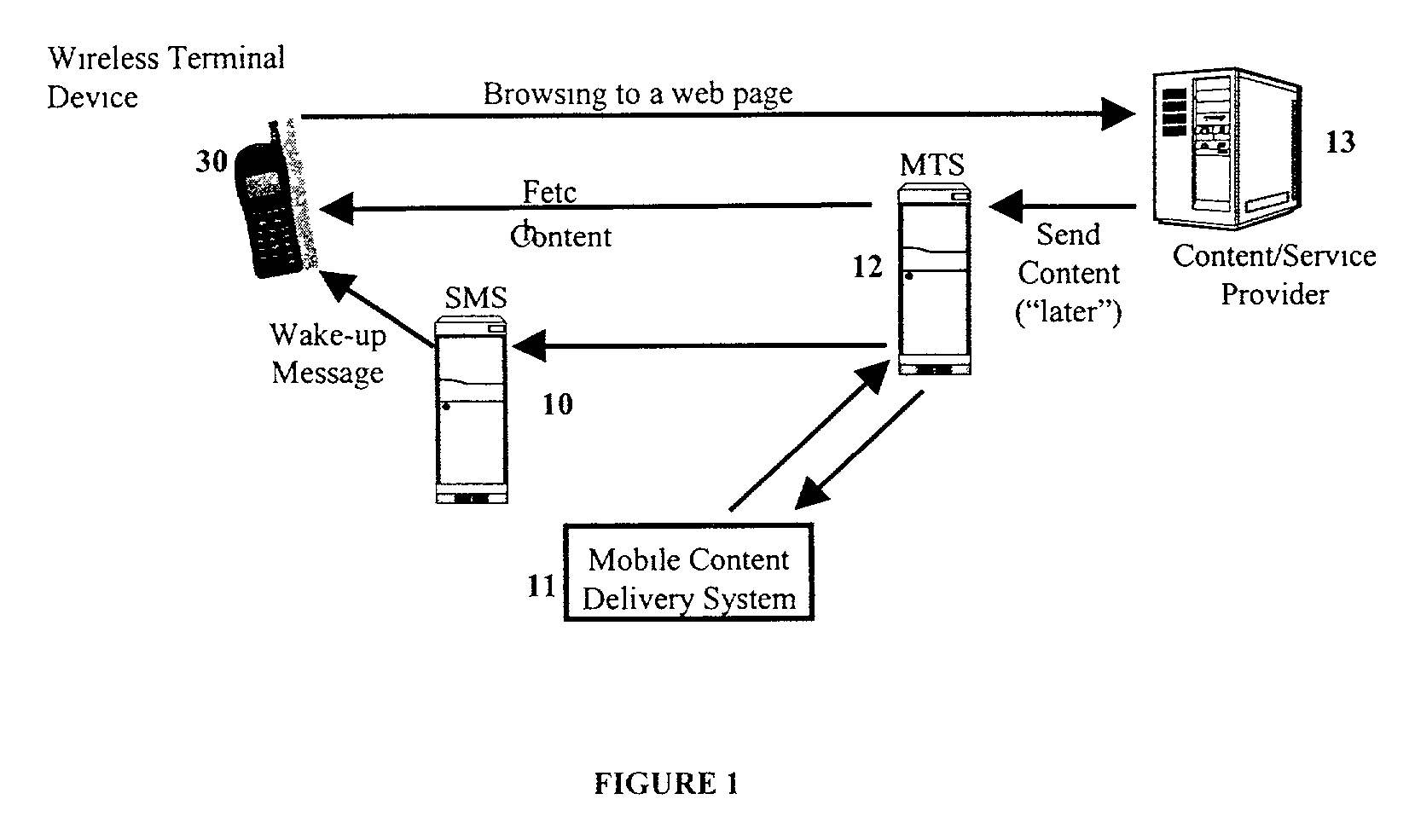
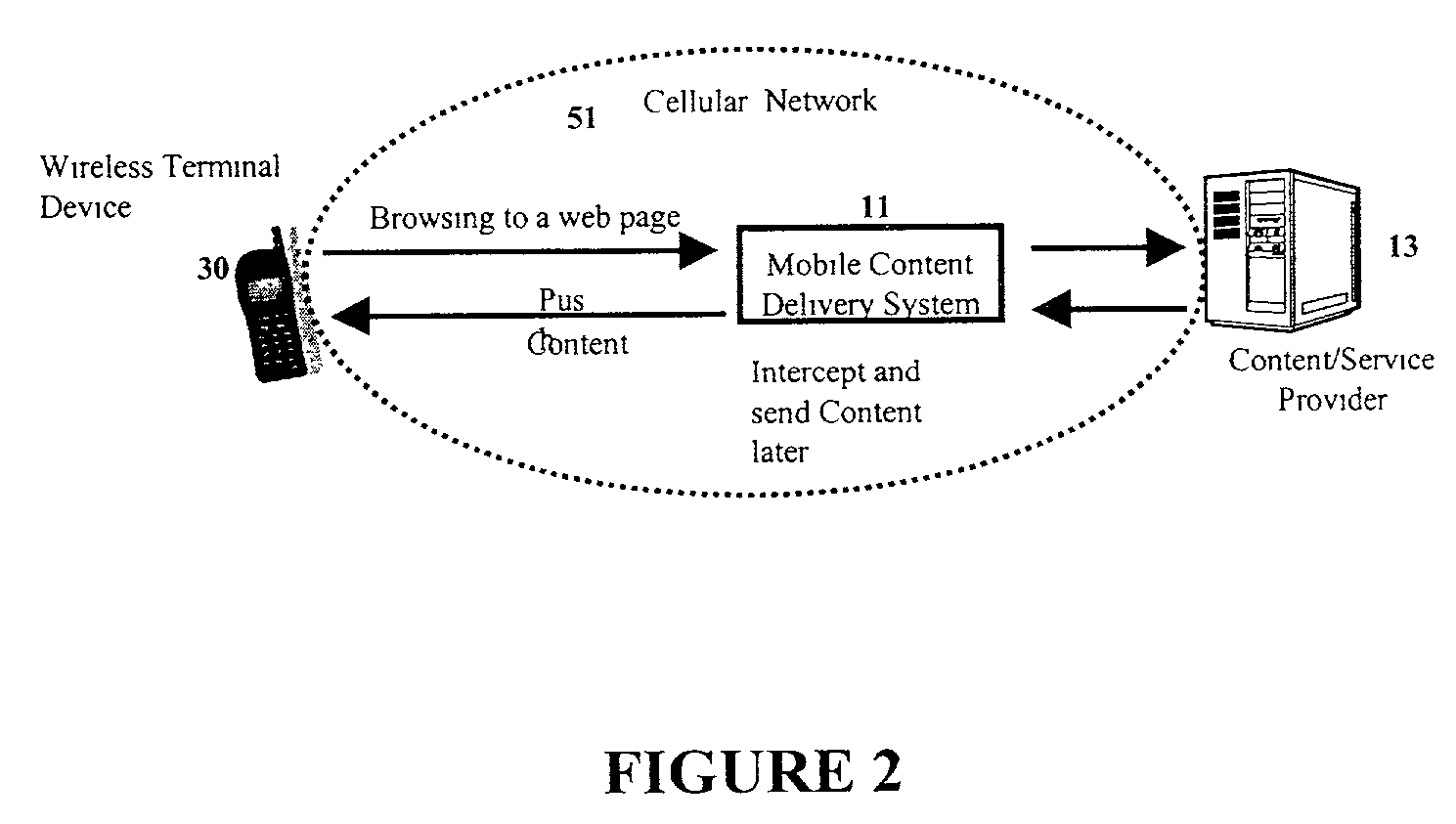
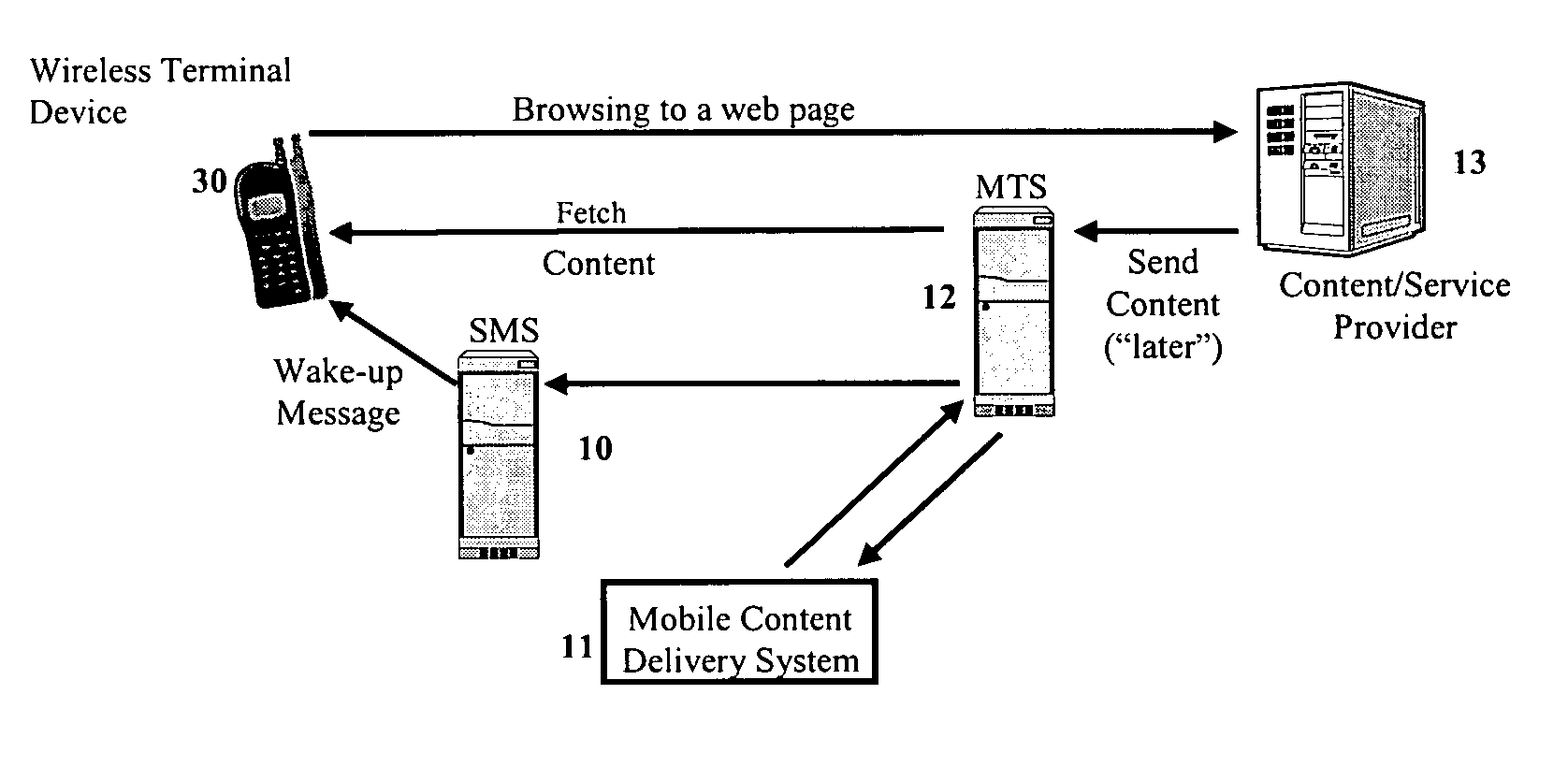
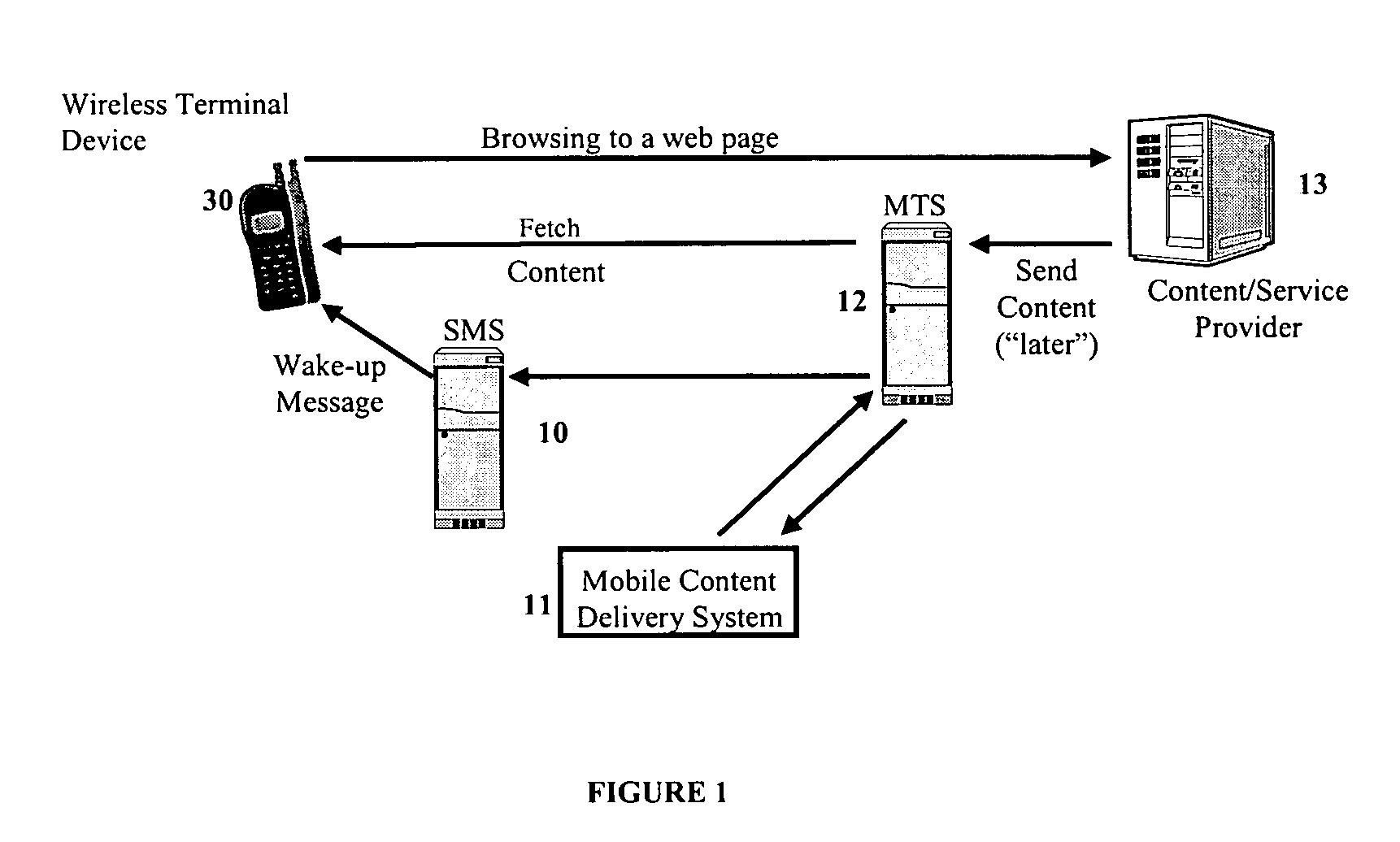
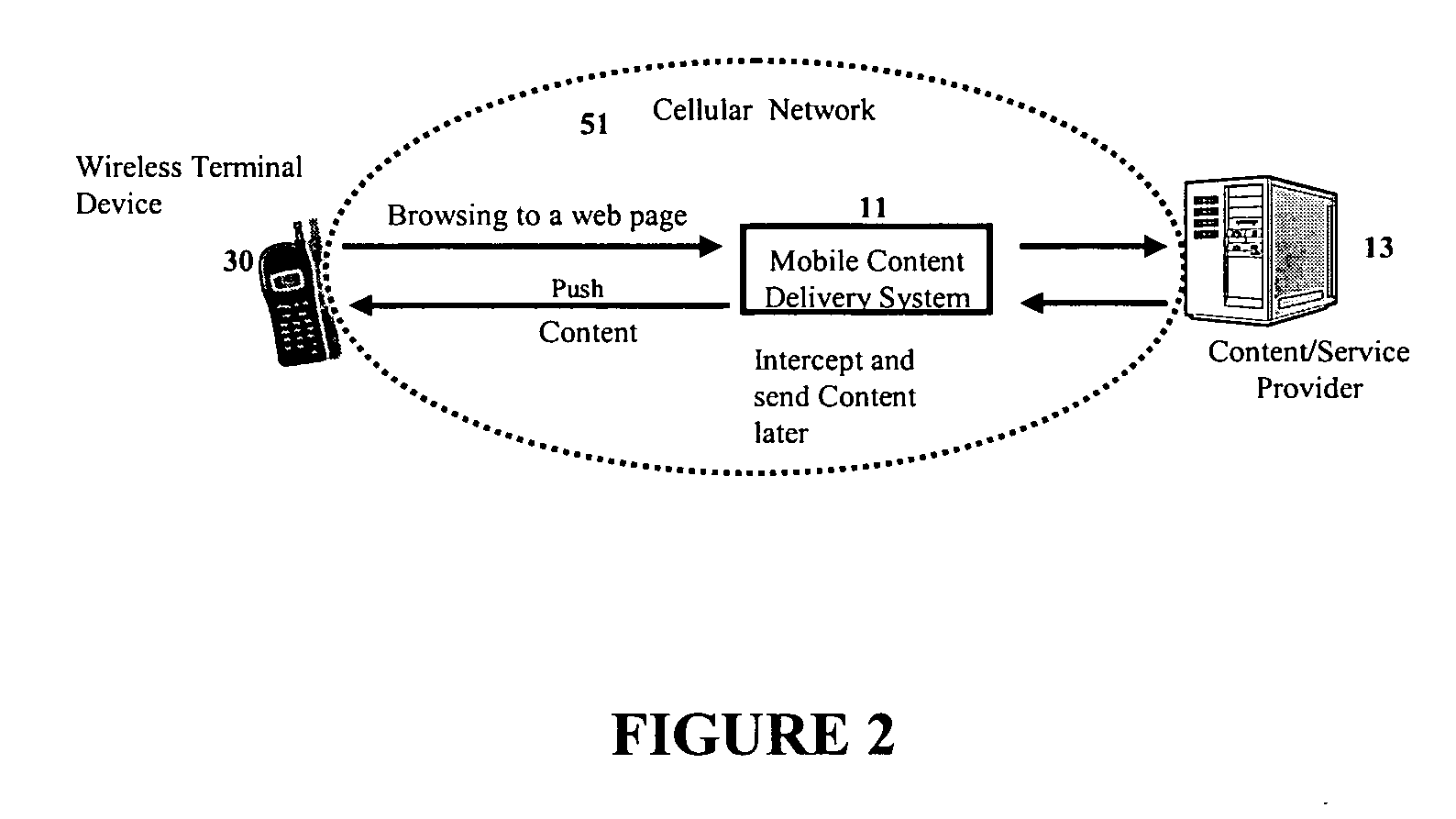
Mobile content delivery system
InactiveUS6996393B2Attracting more userImprove network throughputMetering/charging/biilling arrangementsSpecial service for subscribersRadio networksMobile content
A mobile content delivery system that optimizes the delivery of especially bandwidth-consuming content (or the flow of any peak-hour data traffic) in a way that best utilizes the free capacity in the radio network, thus enabling considerably more efficient usage of the radio capacity. It also allows new services and pricing structures to be used in the cellular network, that otherwise would not be possible. The class of delivery of message content can be selected by the user on a transaction basis, or subscription-based and pre-defined in a user profile. By choosing a scheduled delivery the user can receive the content at a fraction of the price compared to instant delivery, since the content is sent at a time when the network is least utilized.
Owner:NOKIA CORP
Mobile content delivery system
InactiveUS20060073810A1New data serviceMore serviceMetering/charging/biilling arrangementsSpecial service for subscribersRadio networksMobile content
Owner:NOKIA CORP
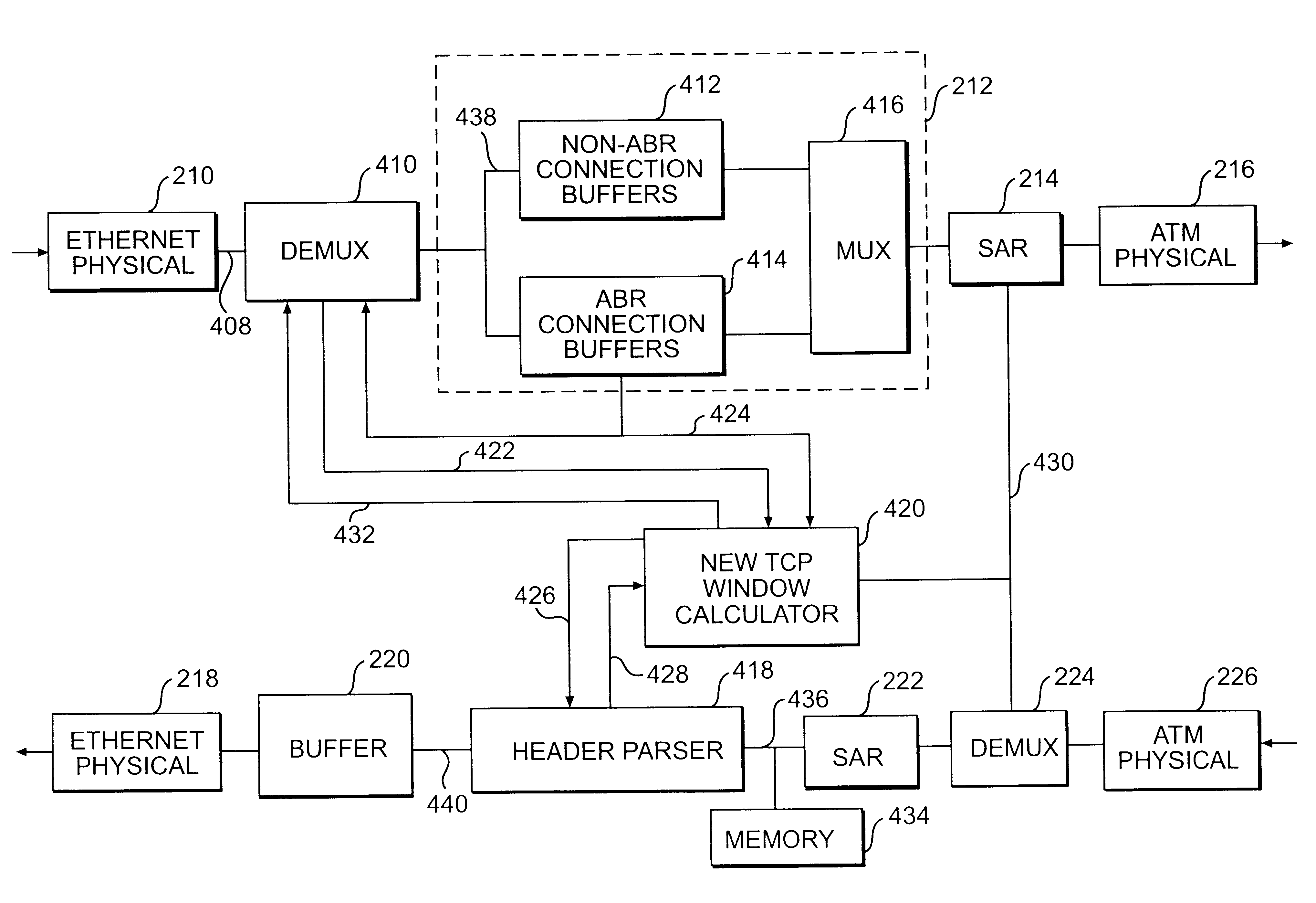
Apparatus and method for optimizing congestion control information in a multi-protocol network
InactiveUS6370114B1Improve network throughputStrengthen connectionError preventionTransmission systemsNetwork congestionTransport control protocol
The benefits of Transport Control Protocol (TCP) over Available Bit Rate (ABR) Service of an Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM) network is extended to the entire TCP connection by intercepting and modifying TCP congestion control information in accordance with resource information associated with the TCP connection. An algorithm calculates a new advertised window size based on various network resource parameters, such as ABR. The advertised window is adjusted if the newly calculated window size is smaller than the advertised window size. By adjusting the TCP window, the normal extreme fluctuations of the TCP window are avoided.
Owner:AVAYA INC
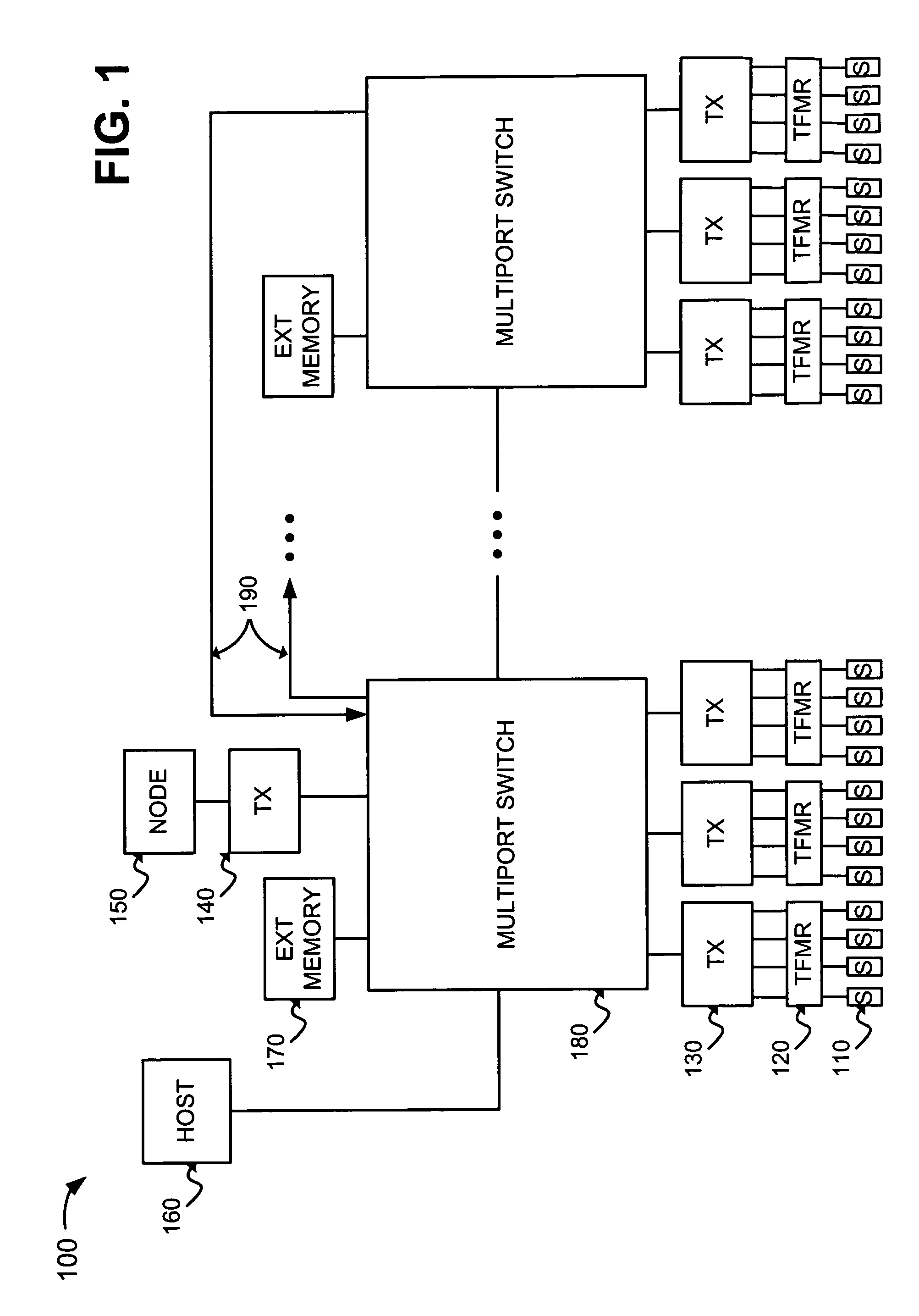
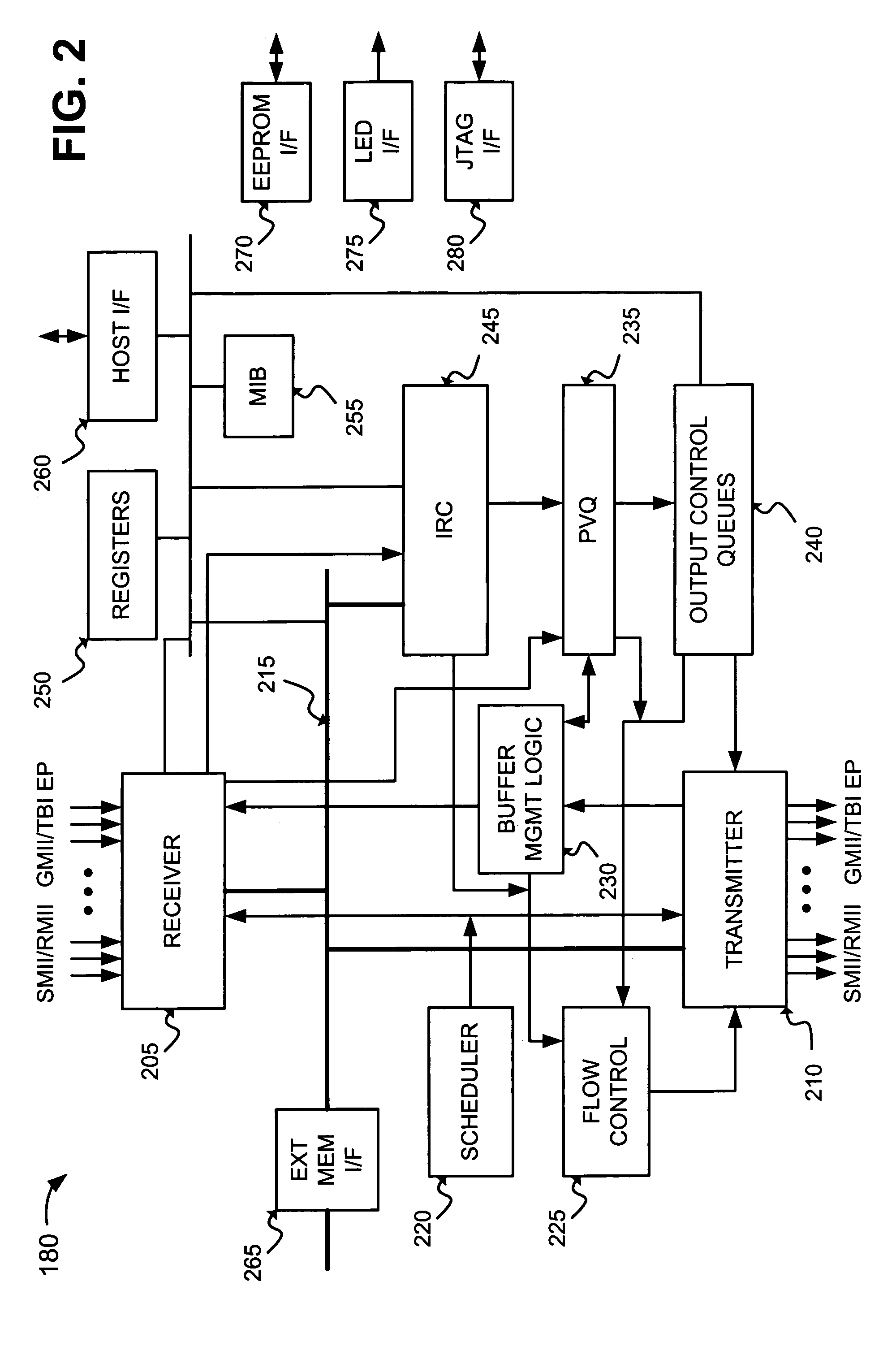
Method and apparatus for adjusting overflow buffers and flow control watermark levels
InactiveUS6084856AReduce congestionHigh trafficError prevention/detection by using return channelTransmission systemsShared memory architectureTraffic capacity
A network switch having a shared memory architecture for storing data frames includes configuration registers that are programmable by a host processor to adaptively adjust overflow buffer locations and flow control watermark levels based on monitored network traffic. The host processor allocates shared resources by setting memory configuration registers corresponding to an external memory, where the network switch uses the external memory for storing received data frames, Management Information Base (MIB) counter values, and output port overflow data. The host processor periodically reads the MIB counter values from the external memory, and adjusts flow control watermark levels or the memory configuration registers in the network switch based on rate-based network traffic derived from the MIB counter values. PCI burst transfers between the host processor and the external memory via the network switch ensure that stored data is not lost during reconfiguration of the external memory. The disclosed arrangement enables resources used by the network switch to be adjusted to minimize congestion by borrowing resources from network ports serving idle stations.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
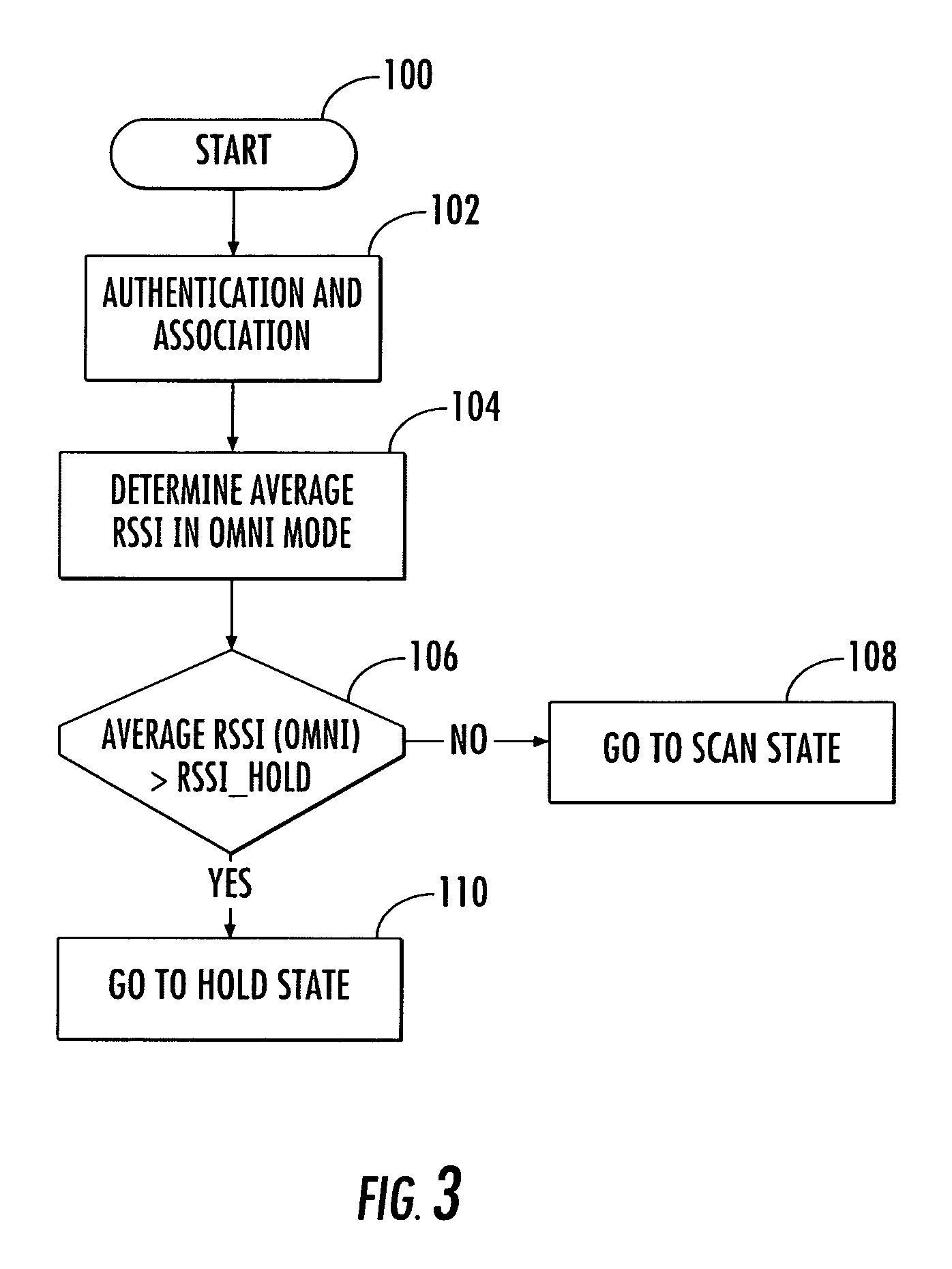
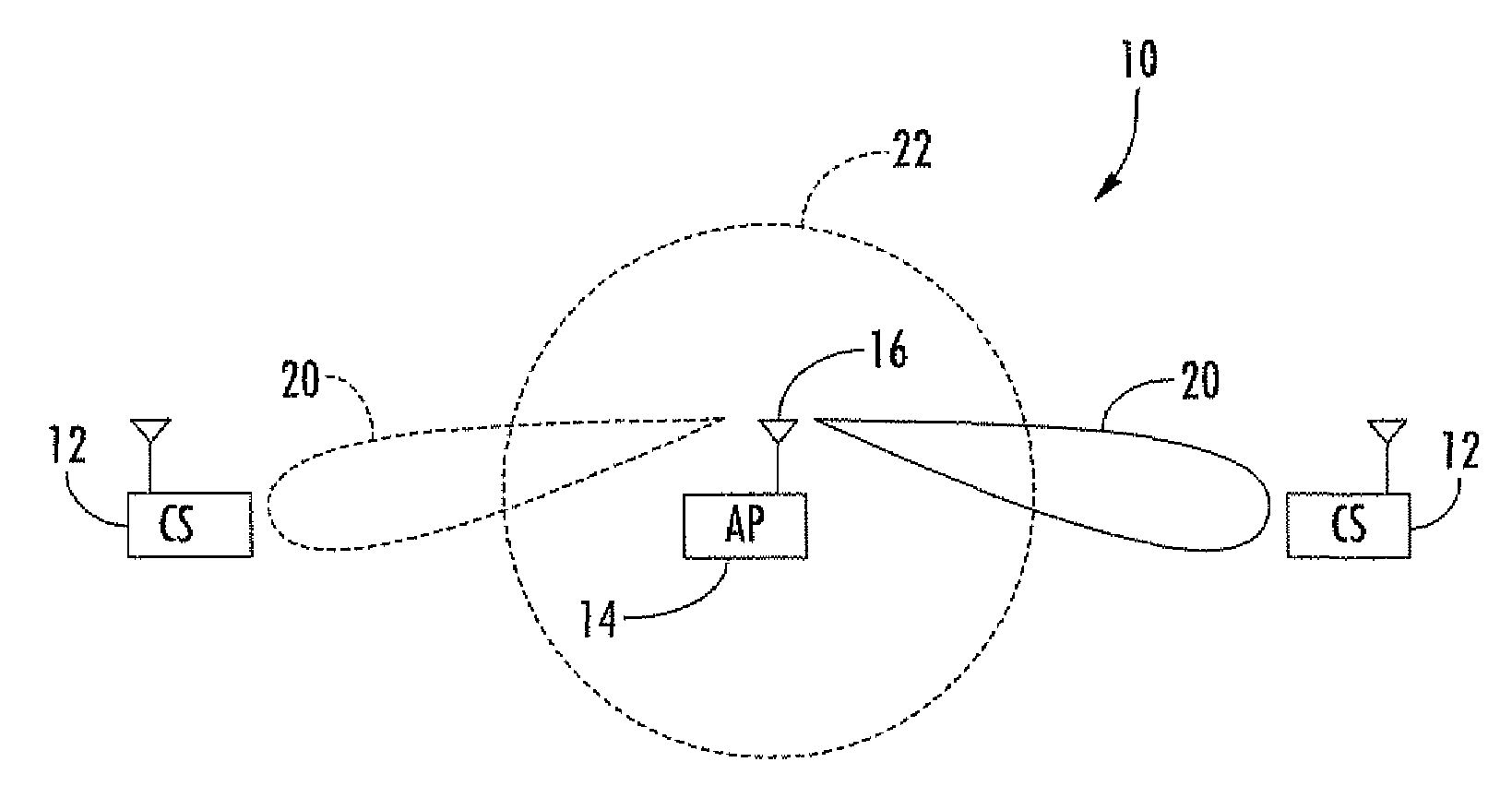
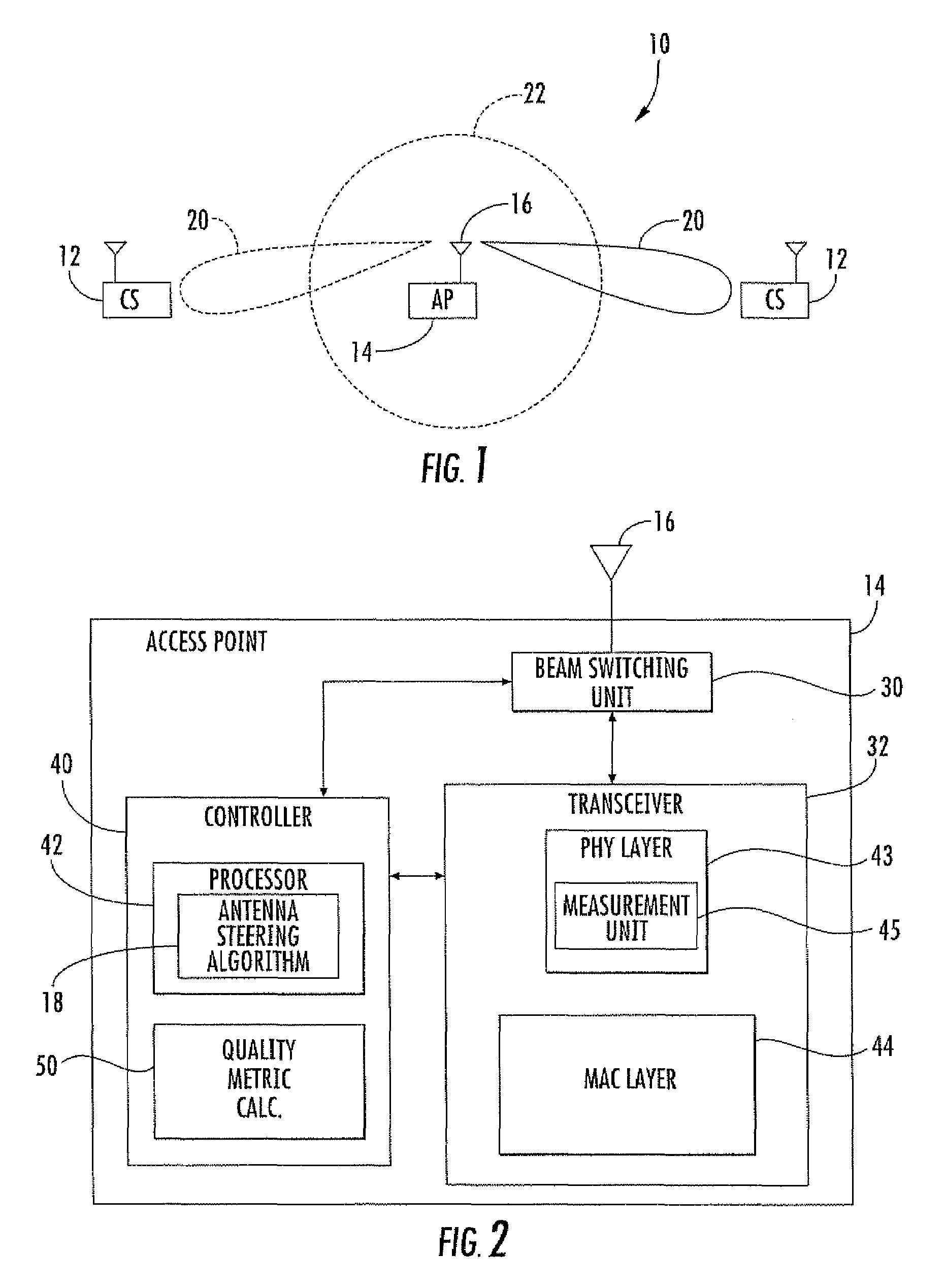
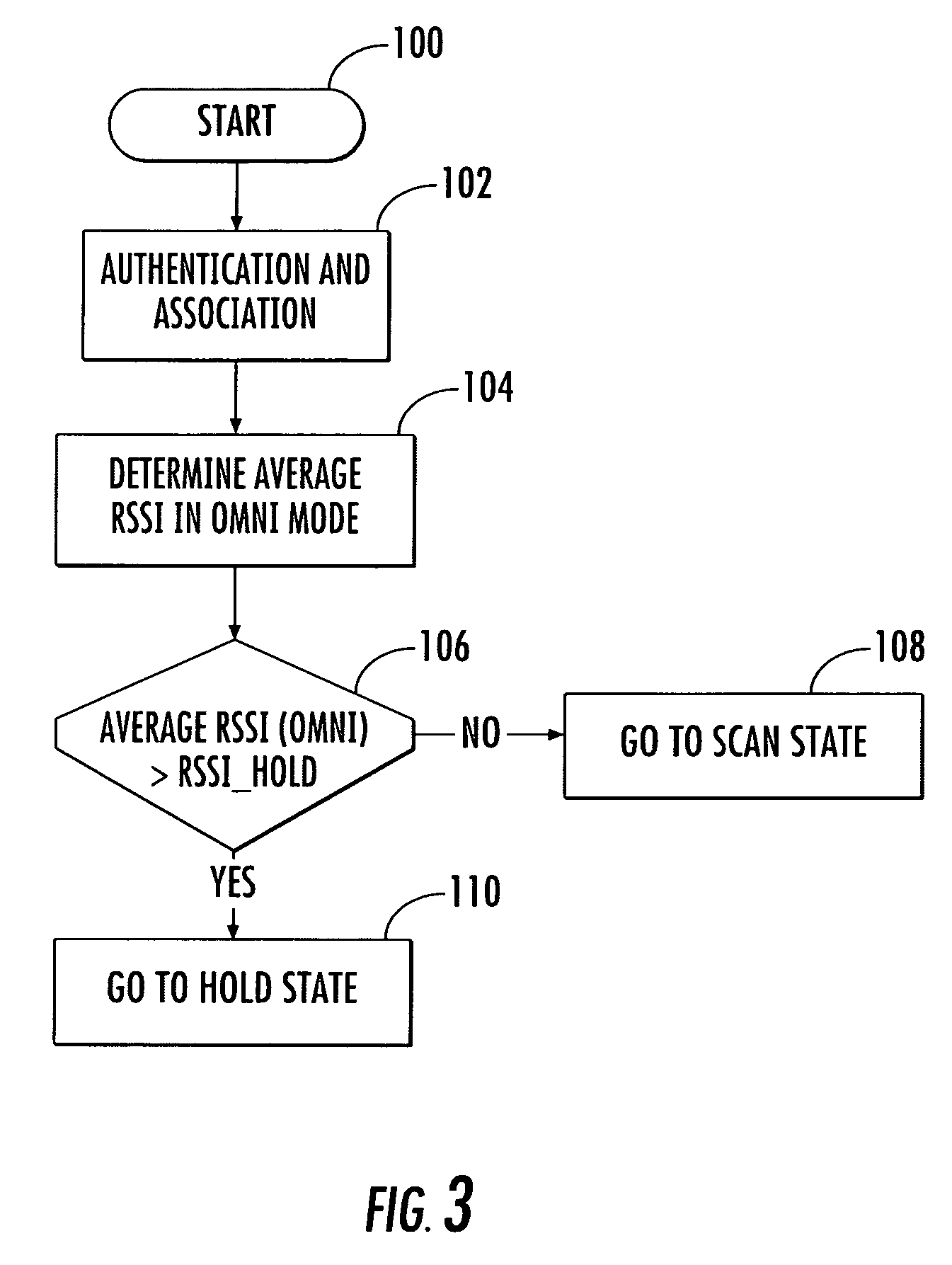
Access point operating with a smart antenna in a WLAN and associated methods
InactiveUS20050285803A1Increase rangeImprove network throughputAntenna supports/mountingsSubstation equipmentOmnidirectional antennaSmart antenna
An access point operates in an 802.11 wireless communication network communicating with a client station, and includes a smart antenna for generating directional antenna beams and an omni-directional antenna beam. An antenna steering algorithm scans the directional antenna beams and the omni-directional antenna beam for receiving signals from the client station. The signals received via each scanned antenna beam are measured, and one of the antenna beams is selected based upon the measuring for communicating with the client station. The selected antenna beam is preferably a directional antenna beam. Once the directional antenna beam has been selected, there are several usage rules for exchanging data with the client station. The usage rules are directed to an active state of the access point, which includes a data transmission mode and a data reception mode.
Owner:INTERDIGITAL TECH CORP
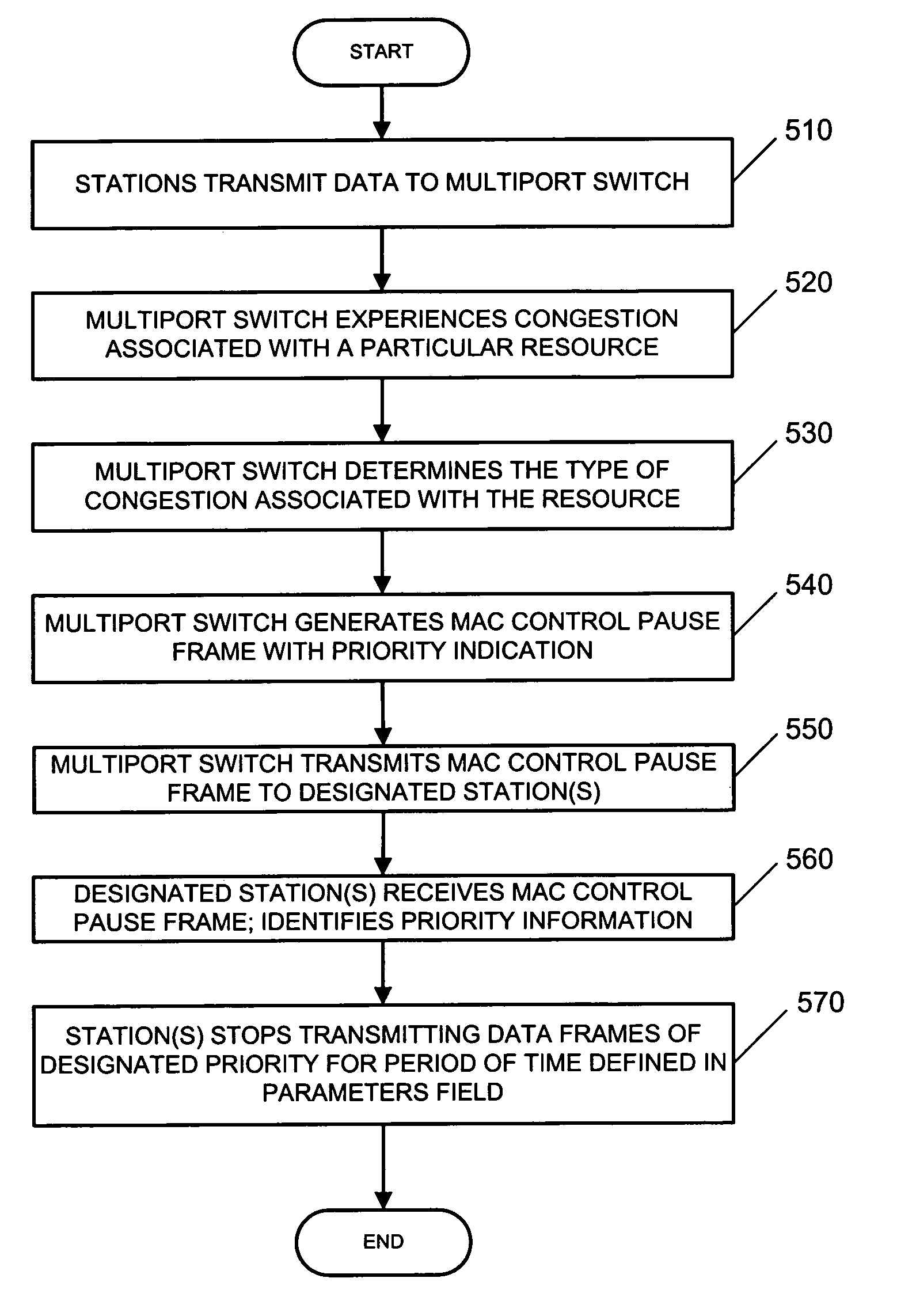
Method and apparatus for performing priority-based flow control
InactiveUS6957269B2Improve network throughputError preventionTransmission systemsFrame basedComputer science
A network device that controls the communication of data frames between stations receives data frames having different levels of priority. The network device identifies the levels of priority and processes the frames based on the priority level. When a congestion condition associated with a resource on the network device occurs, the network device generates a pause frame that includes a priority indicator and transmits the pause frame to at least one station. When a receiving station receives the pause frame, the receiving station suspends transmission of data frames having a priority corresponding to the priority indicator and continues transmitting frames having other priorities.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
High performance wireless networks using distributed control
ActiveUS20090040989A1Cost effectiveLower latencyNetwork traffic/resource managementNetwork topologiesSecure communicationOperational system
A design and proof of concept of a new type of WLAN, complete with simulation and results from the simulation has been described. Each AP Node is implemented as a self-contained embedded OS unit, with all algorithms resident in its Operating system. The normal day-to-day functioning of the AP node is based entirely on resident control algorithms. Upgrades are possible through a simple secure communications interface supported by the OS kernel for each AP node. Benefits provided by a wireless network, as proposed in this invention, are that: it installs out of the box; the network is self-configuring; the network is redundant in that mesh network formalism is supported, ensuring multiple paths; load balancing is supported; there is no single point of failure; allows for decentralized execution; there is a central control; it is network application aware; there is application awareness; there is automatic channel allocation to manage and curtail RF interference, maximize non interference bandwidth and enable seamless roaming between adjoining wireless sub networks (BSS) and it supports the wireless equivalent for switching—for seamless roaming requirements.
Owner:DYNAMIC MESH NETWORKS
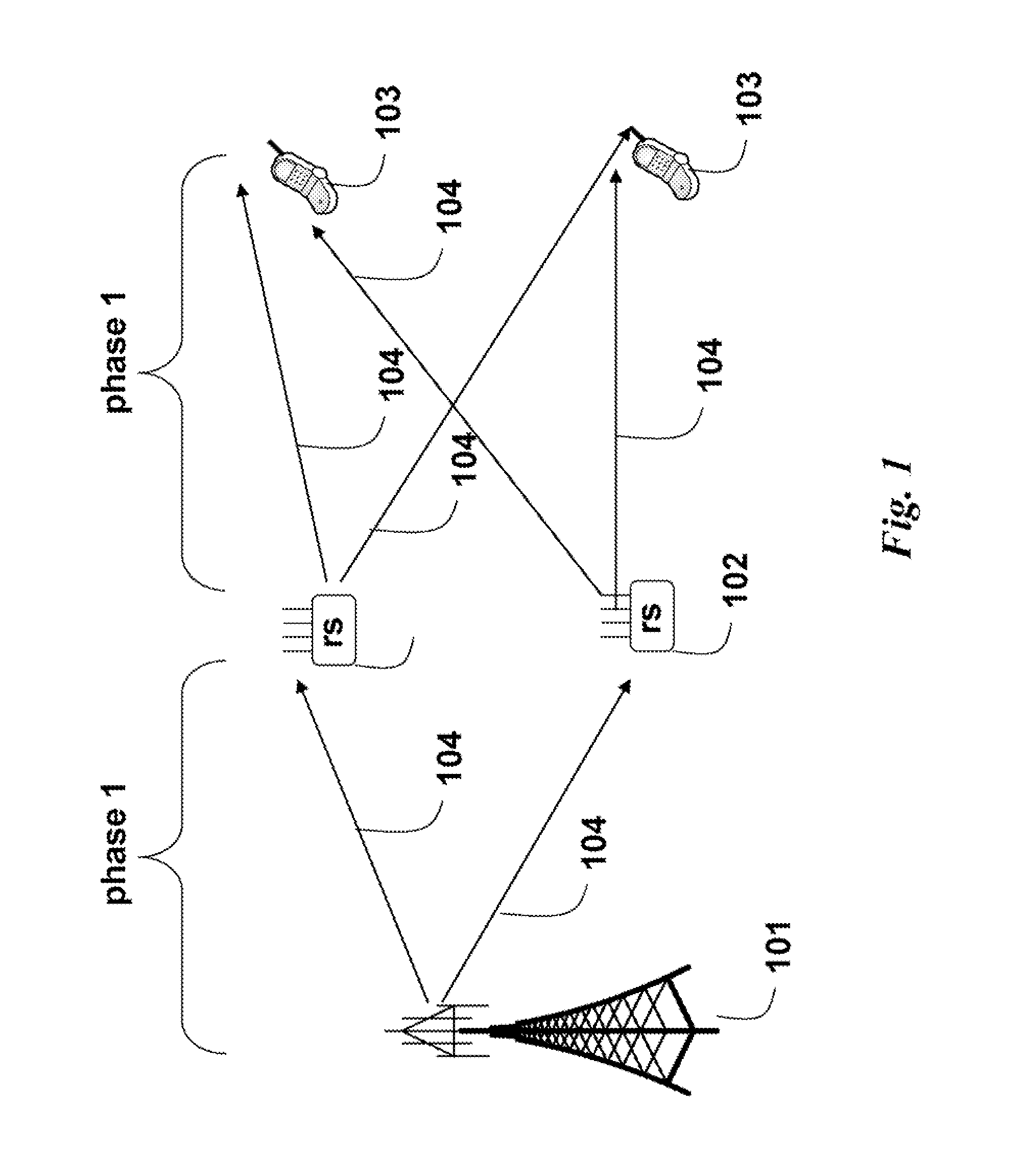
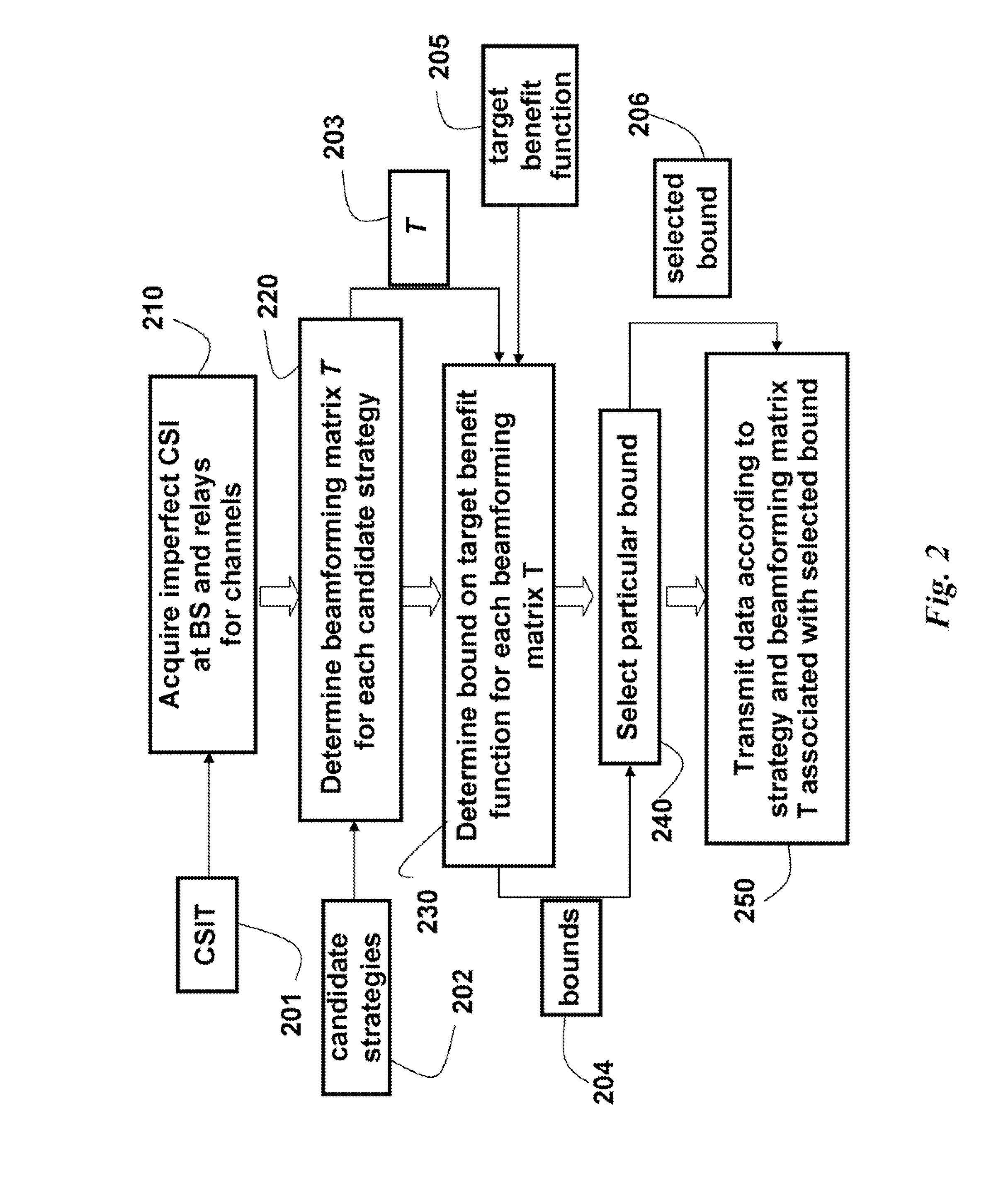
Wireless Cooperative Relay Network Transmitting Data using Imperfect CSI
InactiveUS20090147728A1Improve network throughputAssess restrictionRadio transmissionChannel state informationEngineering
A method, system and network transmit data from a base station, via relay stations, to user stations. Imperfect channel state information (CSI) for downlink channels from the base station and the relay stations to the user stations is acquired. For each candidate transmission strategy of a set of candidate transmission strategies, a corresponding beamforming matrix is determined according the imperfect CSI. For each beamforming matrix, a bound on an expected target benefit function is determined, and a particular one of the bounds is selected. The data are then transmitted from the base station, via the relay stations, to the user stations according to the beamforming matrix associated and the candidate strategy associated with the selected bound.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC RES LAB INC
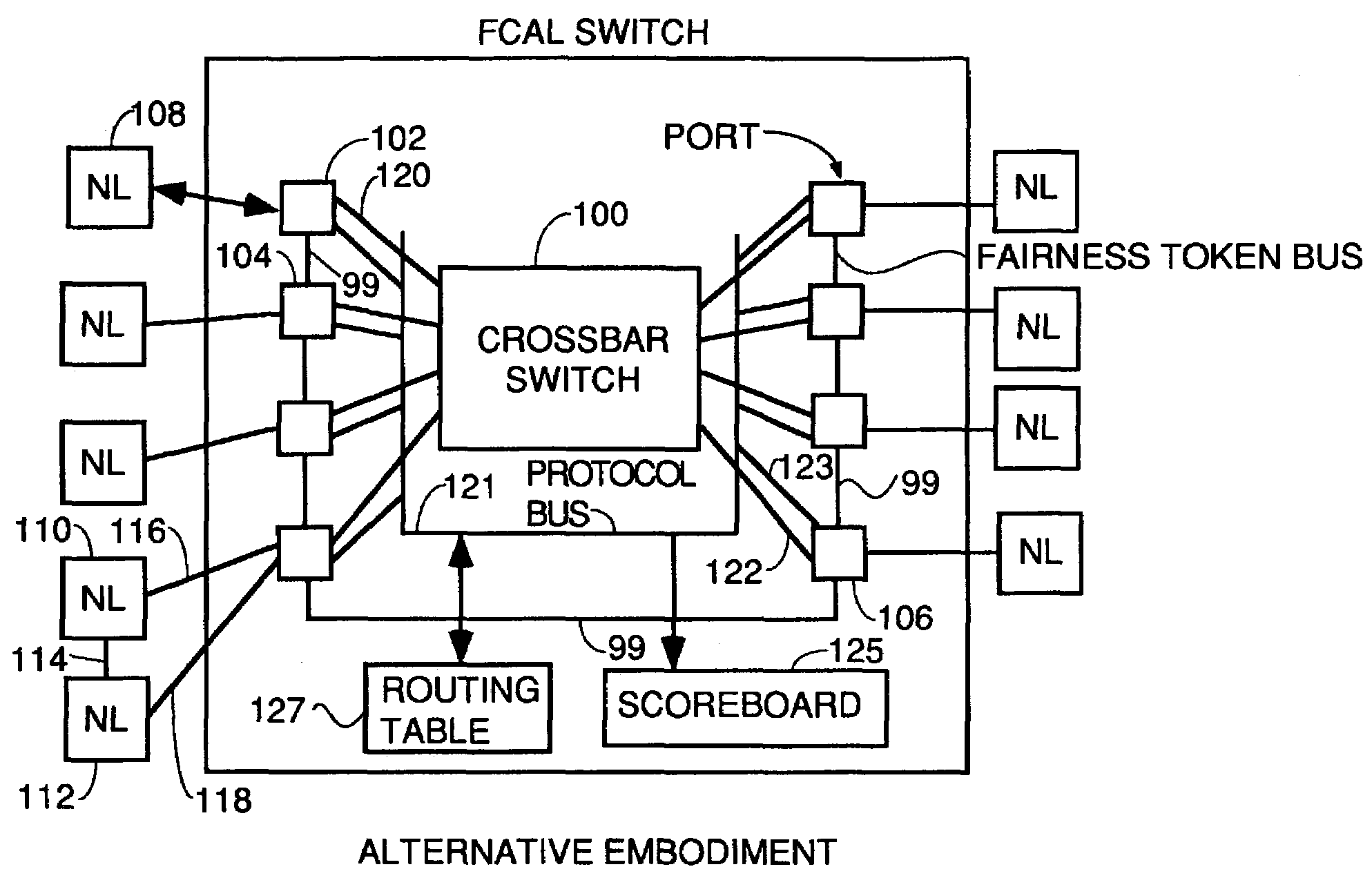
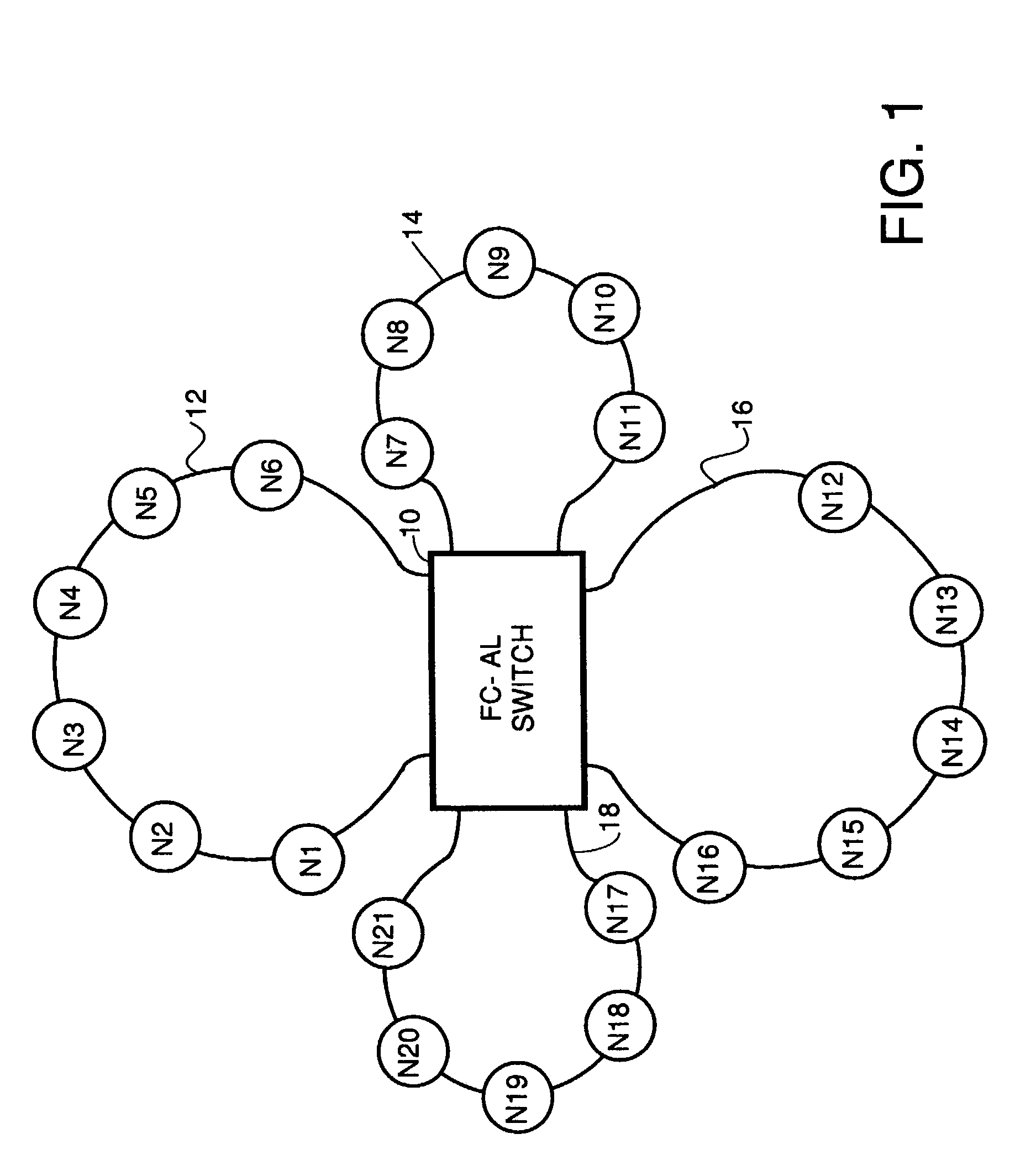
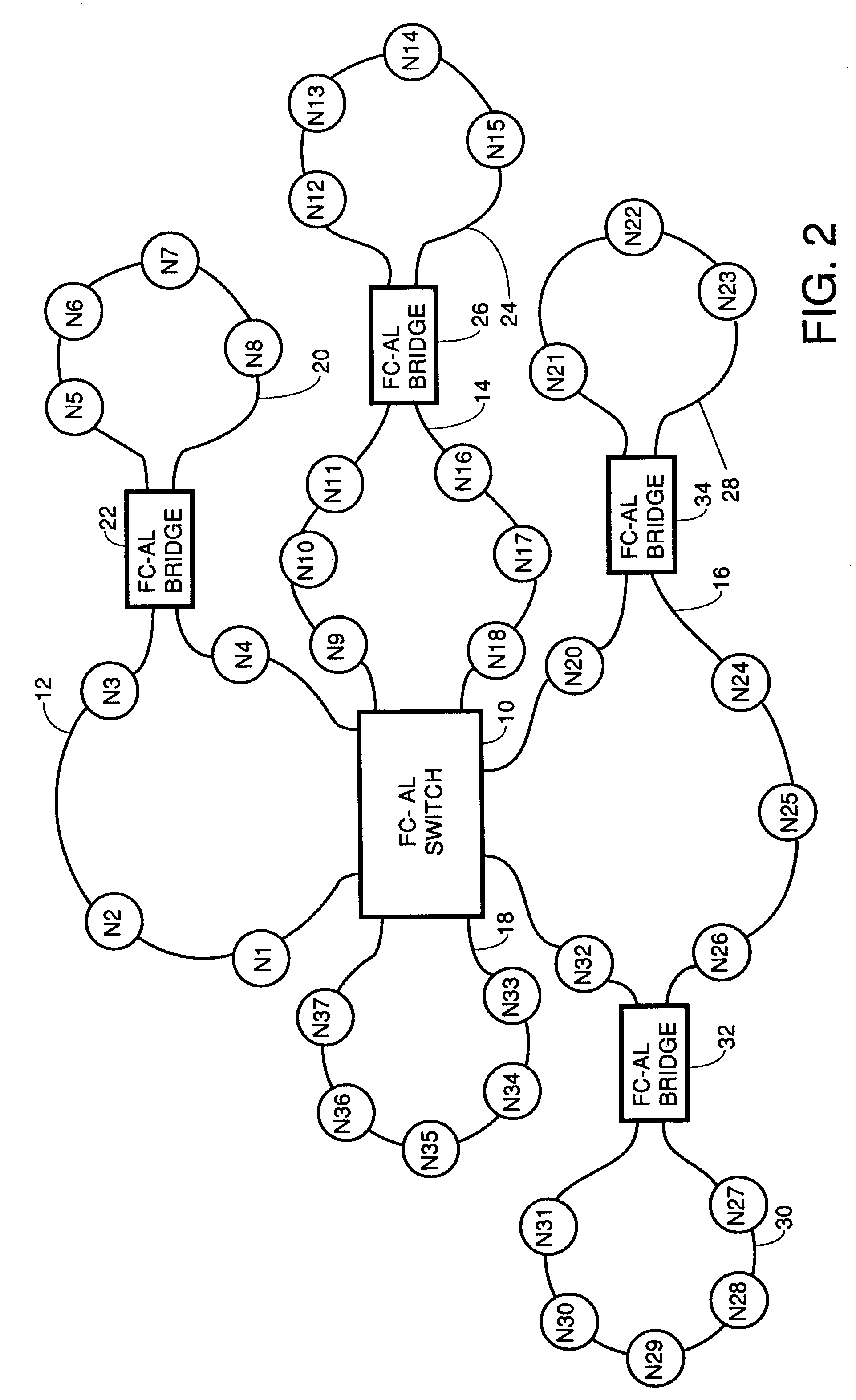
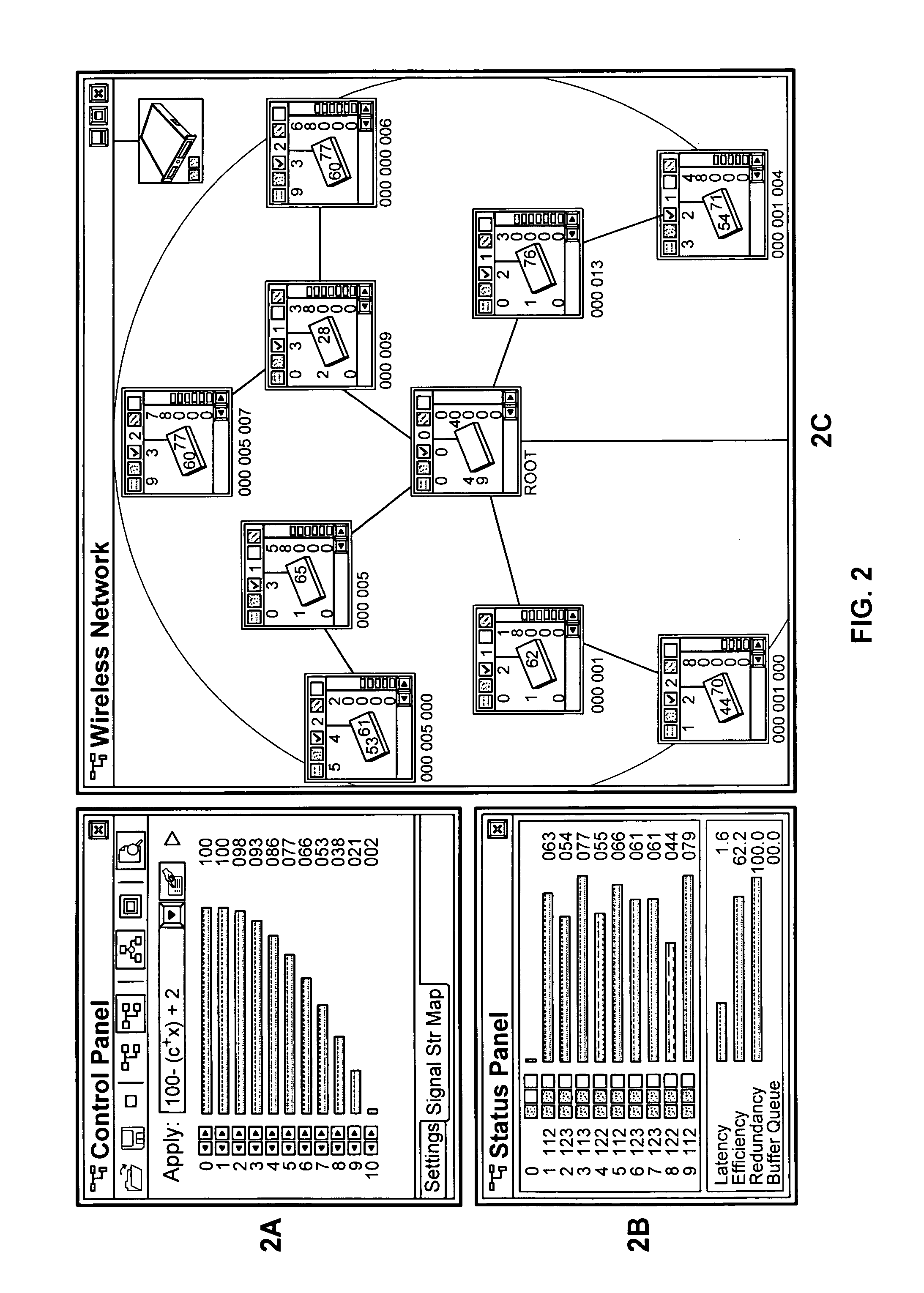
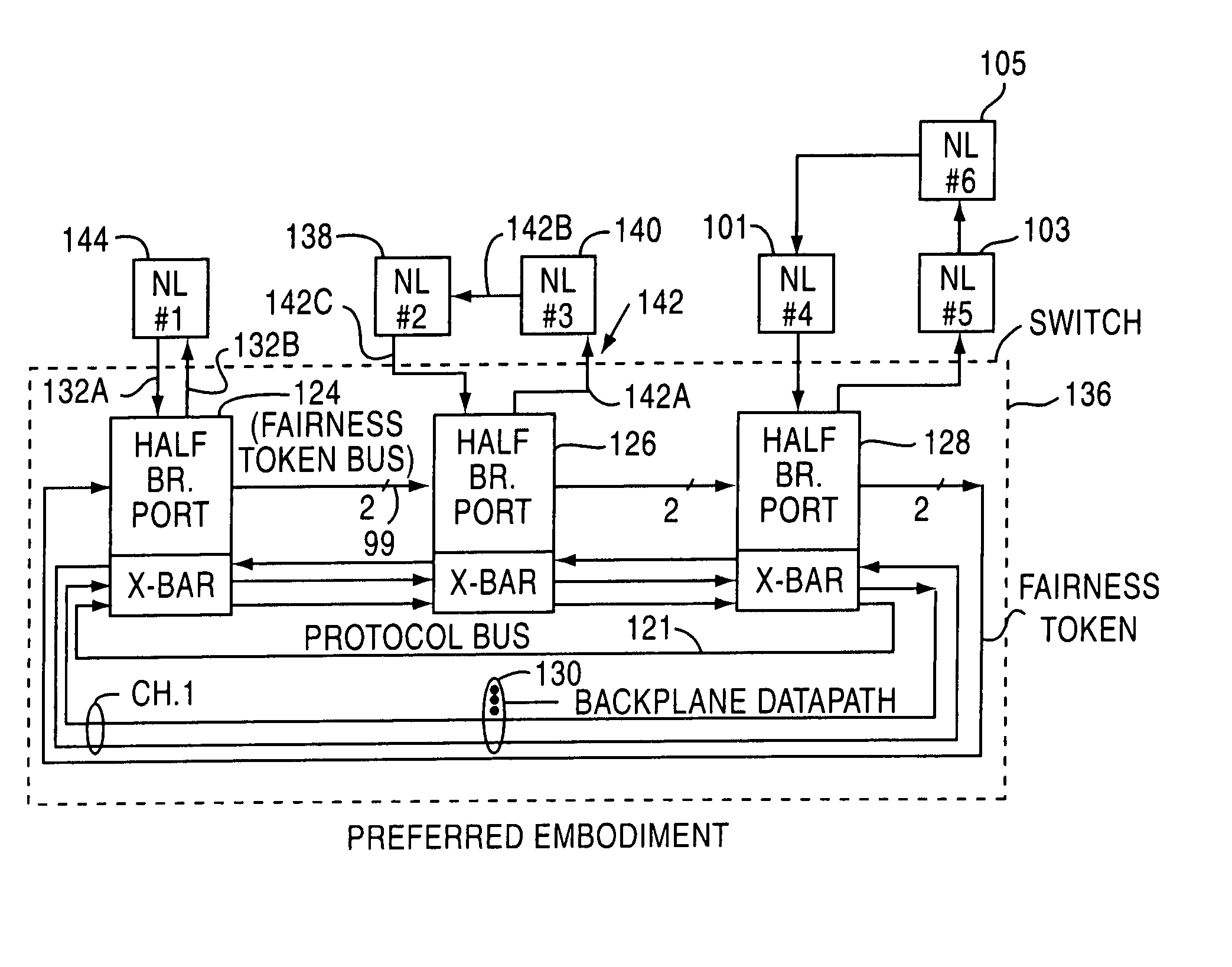
Fibre channel arbitrated loop bufferless switch circuitry to increase bandwidth without significant increase in cost
InactiveUS7009985B2Saving substantial expenseImprove network throughputNetworks interconnectionSelective content distributionBackplaneCrossbar switch
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
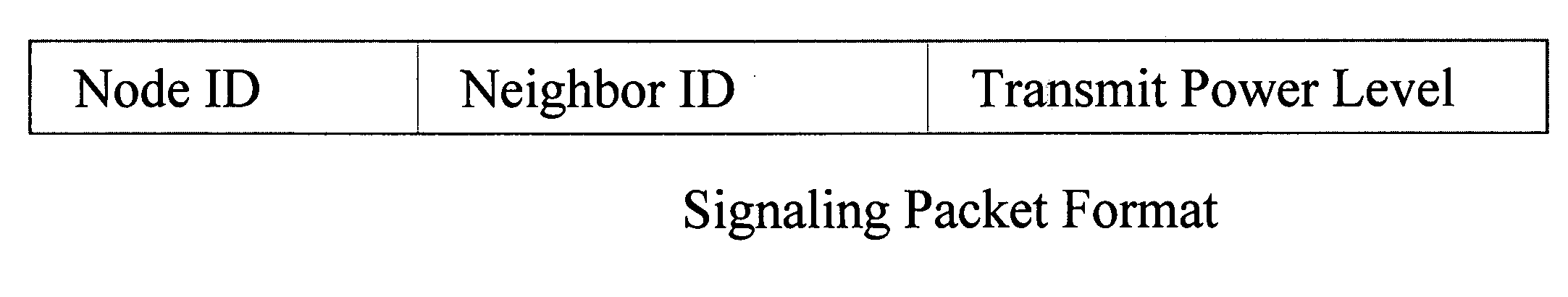
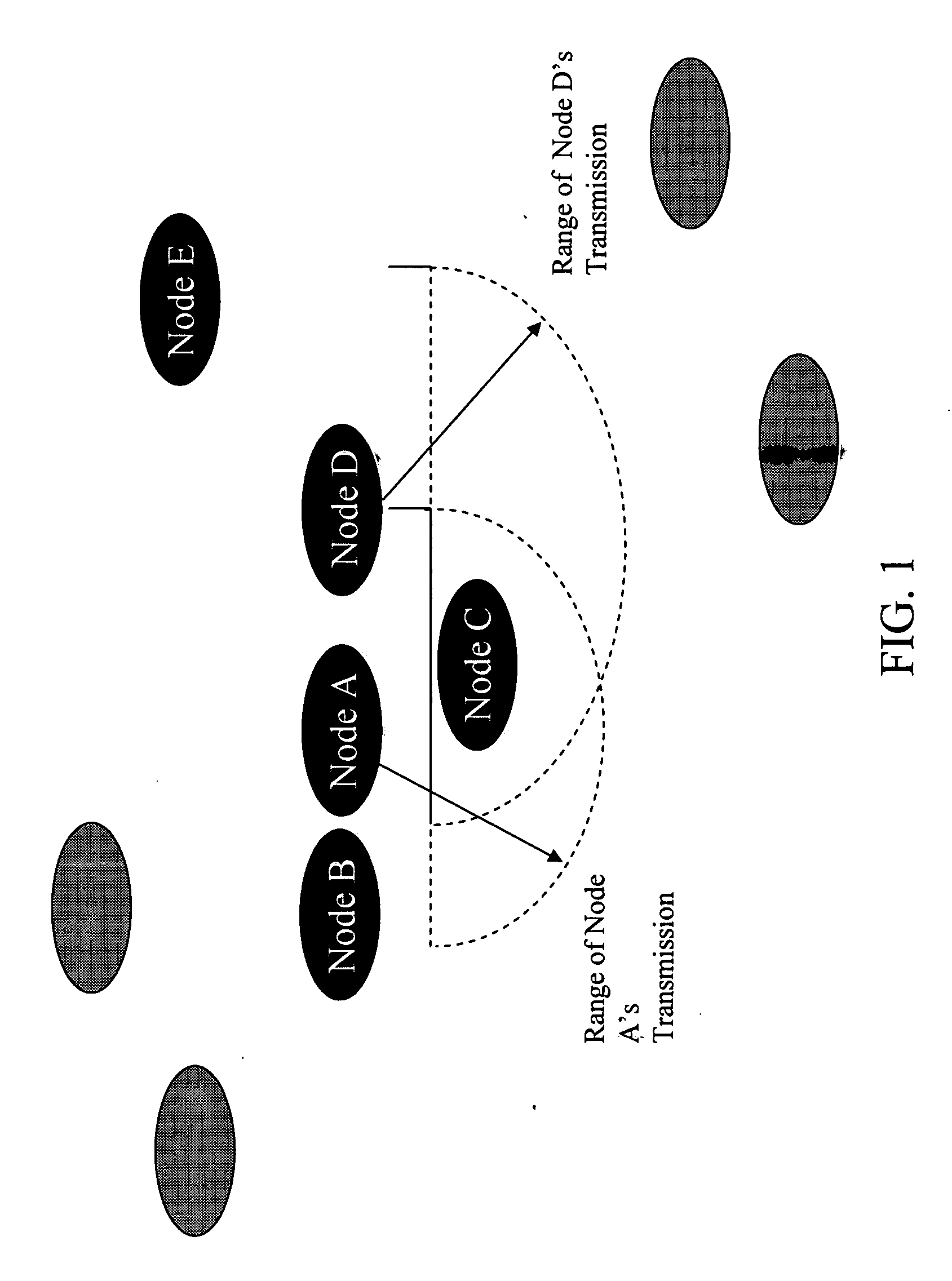
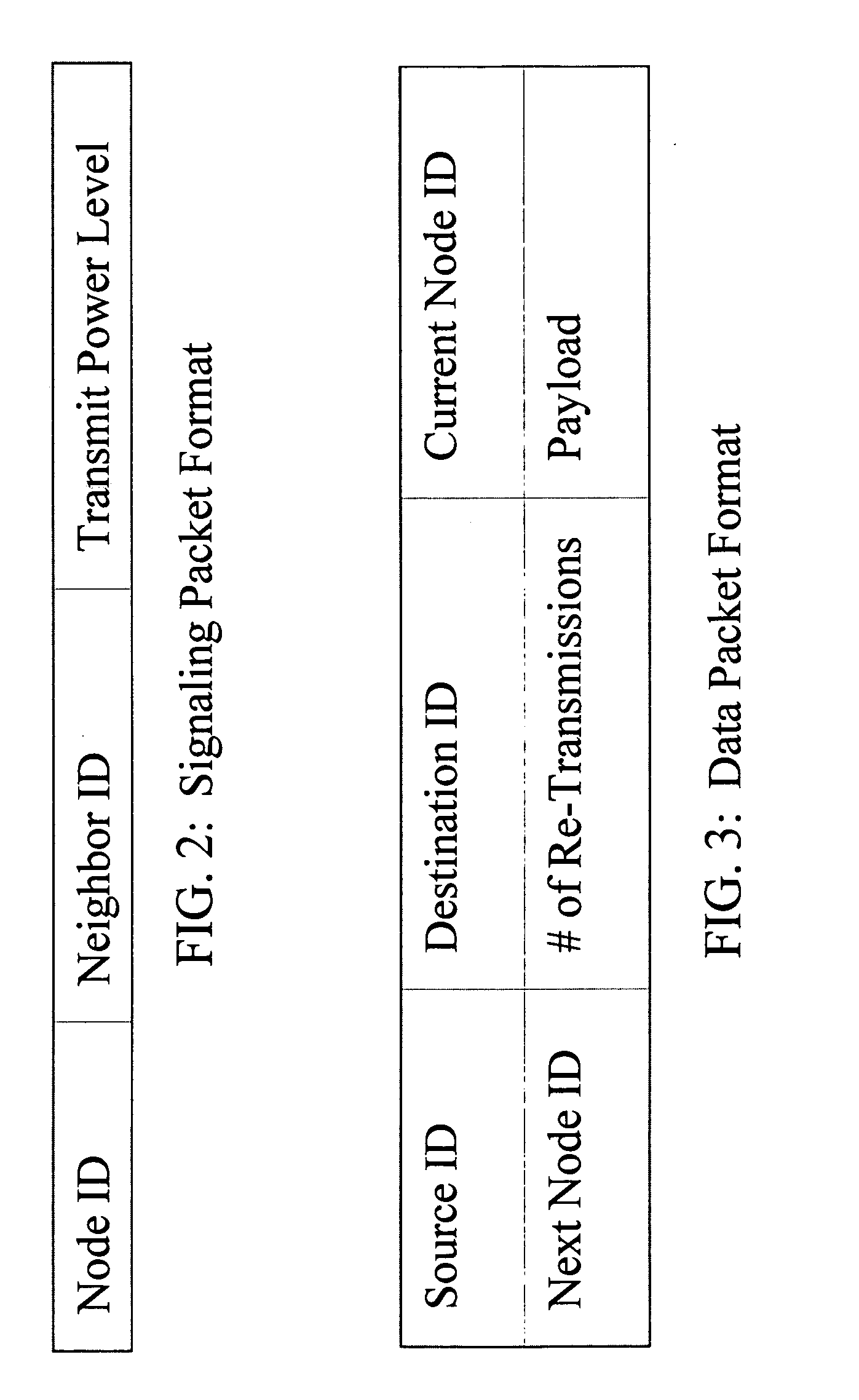
Power management for throughput enhancement in wireless ad-hoc networks
InactiveUS20080132264A1Reduce power consumptionExpand the transmission rangeEnergy efficient ICTFrequency-division multiplex detailsTelecommunicationsTransmitted power
The present invention relates to power management within the context of wireless ad-hoc networks. More specifically to the effects of using different transmit powers on the average power consumption and end-to-end network throughput in a wireless ad-hoc environment. This power management approach reduces the system power consumption and thereby prolongs the battery life of mobile nodes. Furthermore, the invention improves the end-to-end network throughput as compared to other ad-hoc networks in which all mobile nodes use the same transmit power. The improvement is due to the achievement of a tradeoff between minimizing interference ranges, reduction in the average number of hops to reach a destination, reducing the probability of having isolated clusters, and reducing the average number of transmissions including retransmissions due to collisions. The present invention provides a network with enhanced end-to-end throughput performance, and lower transmit power.
Owner:HRL LAB
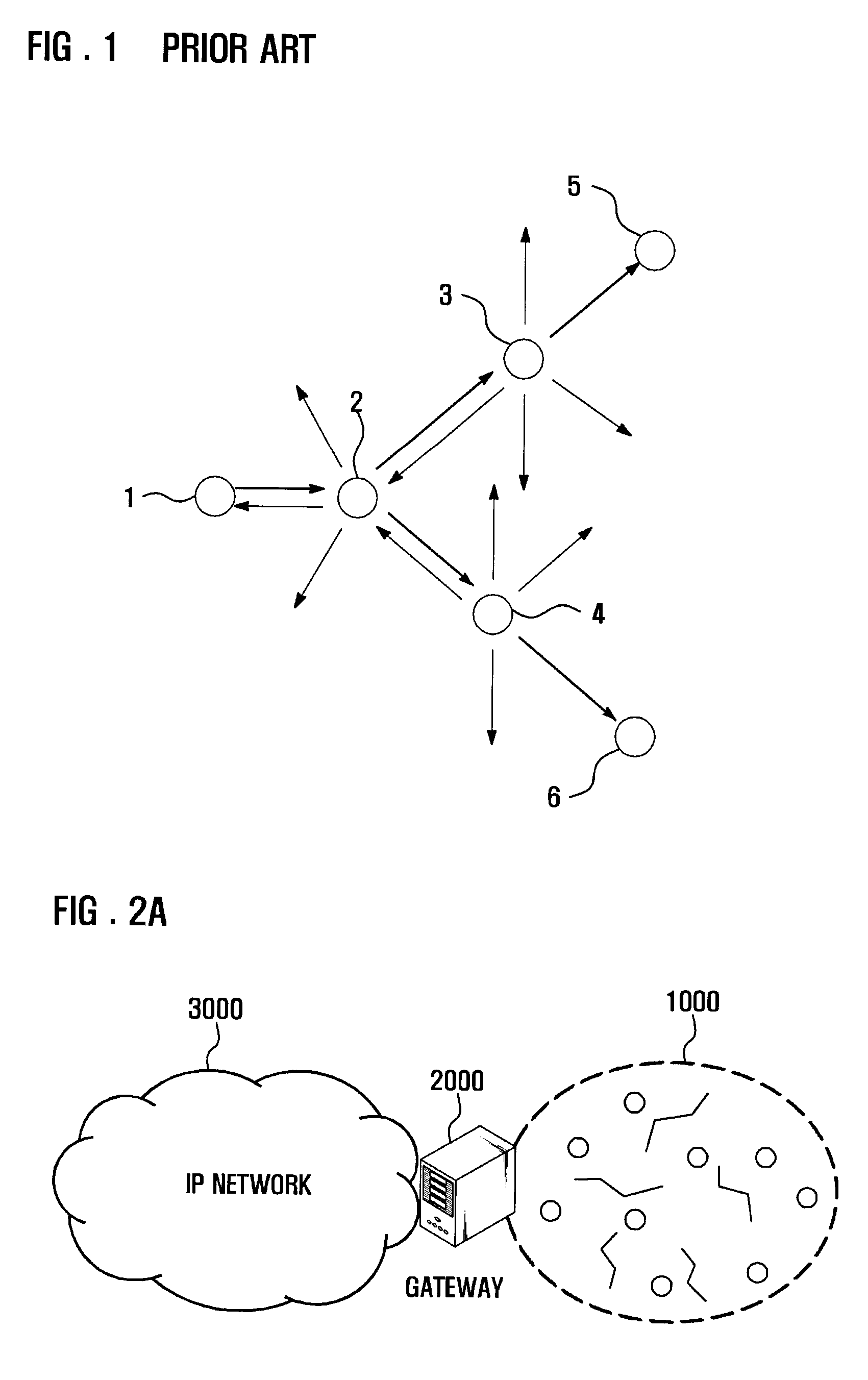
Tree based wireless mesh for an ospf network with intra-tree communication optimization
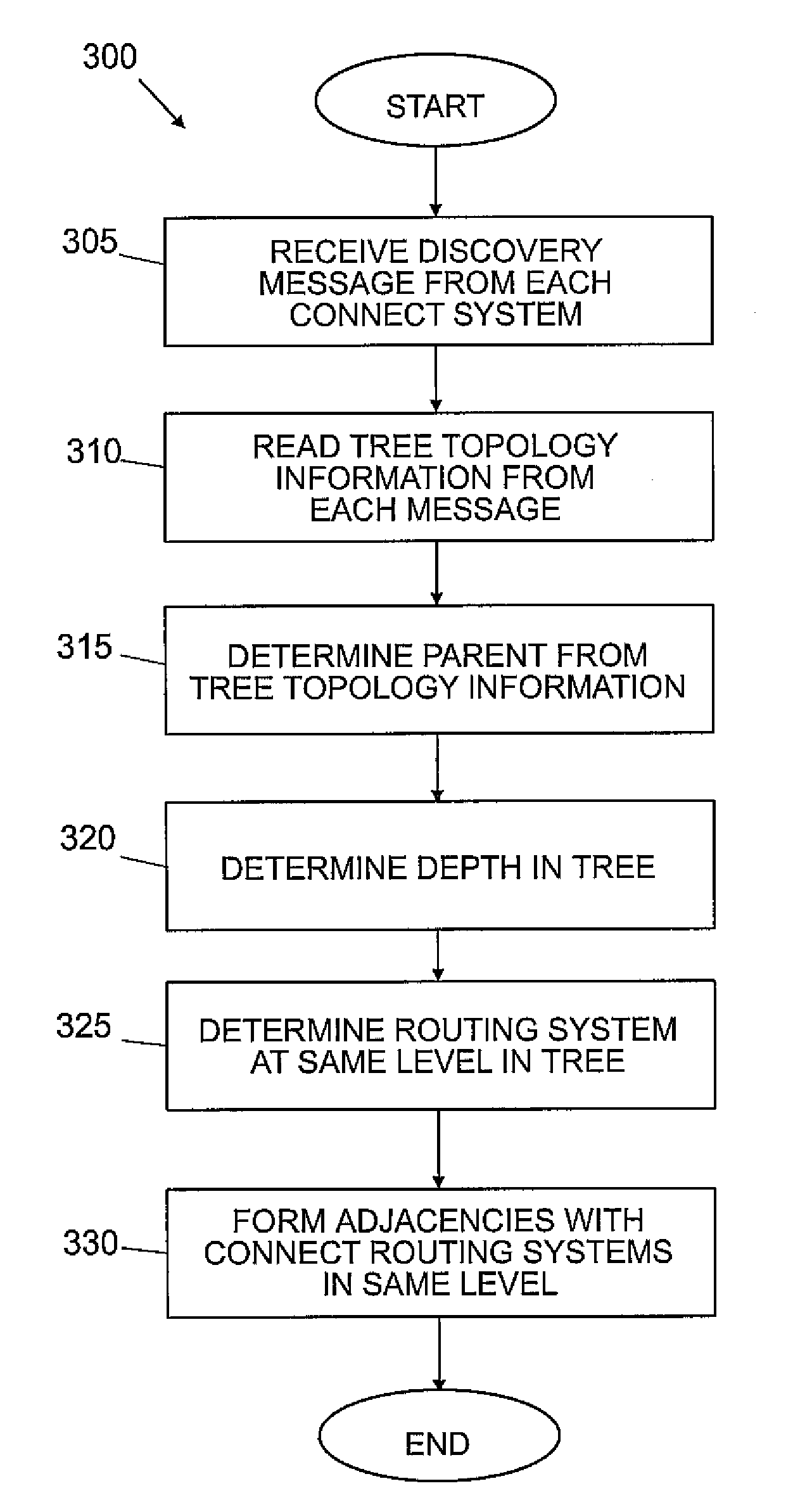
ActiveUS20080080401A1Shorten convergence timeReduce floodingAssess restrictionConnection managementTopology informationDevice Grid
A system for providing a tree topology for a network having an interior gateway protocol. A first router receives a hello message from all connected routers in the network. The hello messages include tree topology information. The first router then uses the tree topology information to determine a parent of the router. The first router then establishes connections with directly connected routers at the same level in the tree topology. The first router also generates link messages that include all of the prefixes for children of the first router and broadcasts the link messages.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
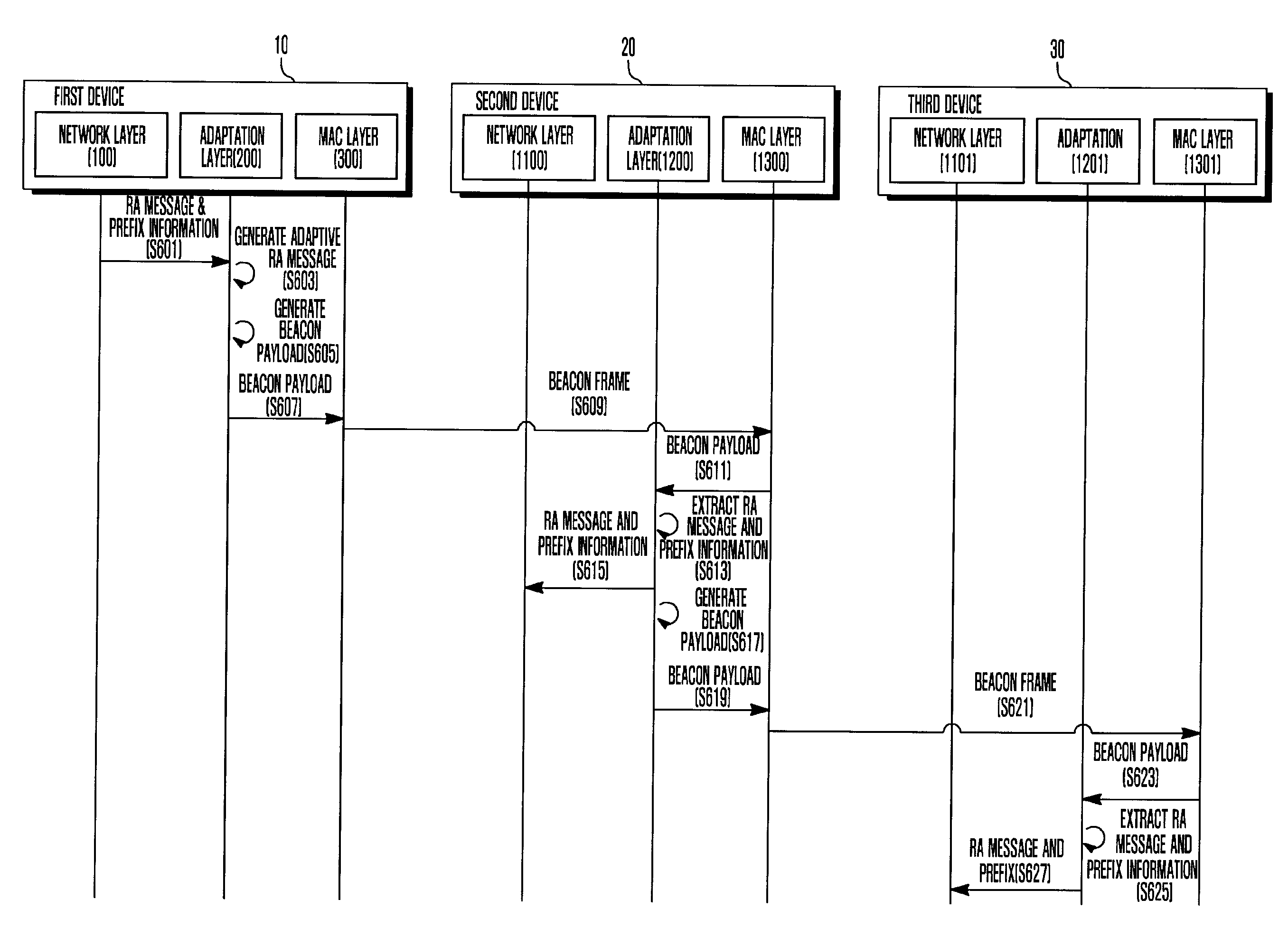
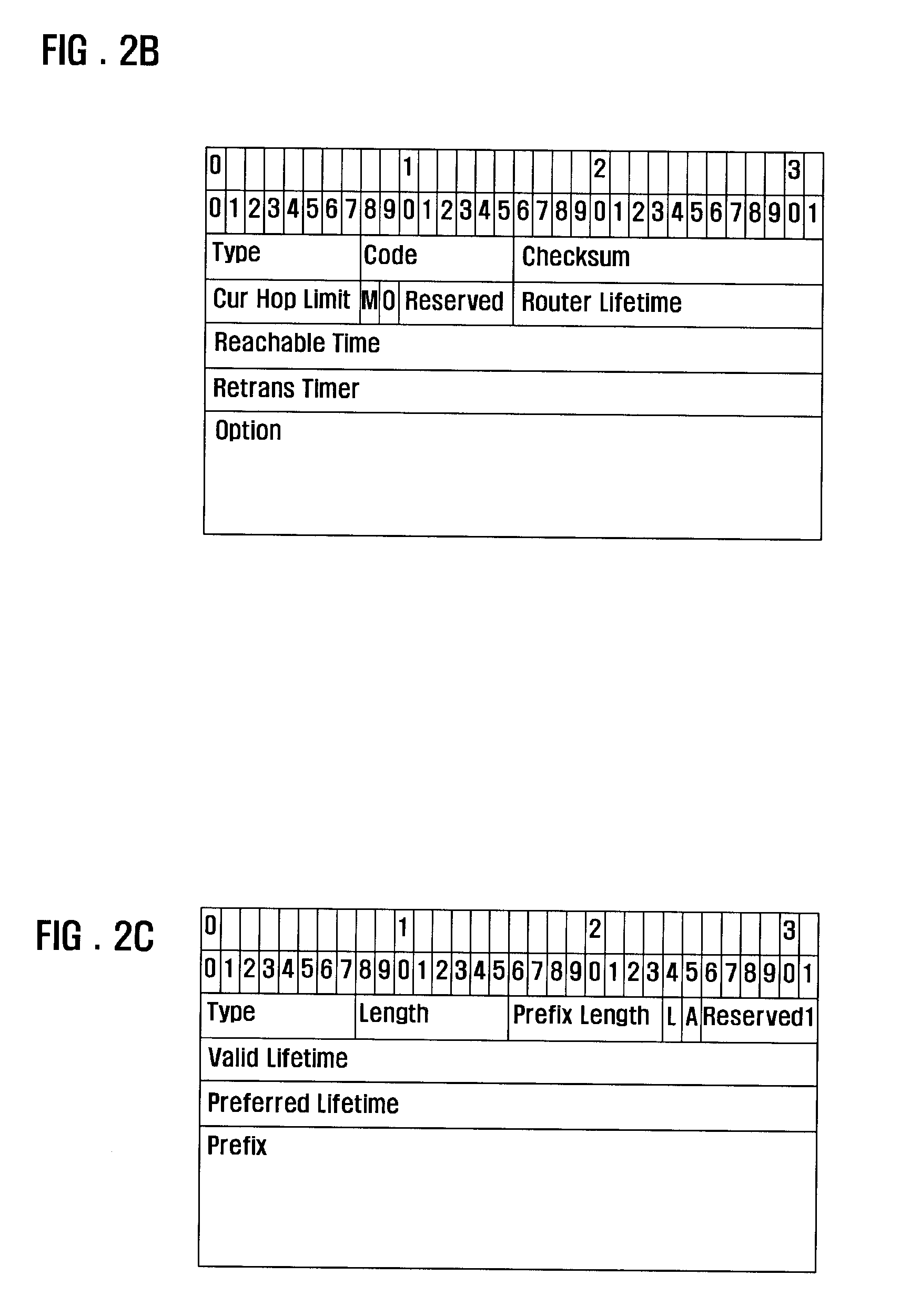
ADDRESS AUTOCONFIGURATION METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR IPv6-BASED LOW-POWER WIRELESS PERSONAL AREA NETWORK
InactiveUS20090161581A1Avoid trafficReduce network trafficPower managementAssess restrictionAuto-configurationIp address
An IP address autoconfiguration method and system of an IPv6-based Low Power WPAN for reducing network traffics is applicable for an Internet Protocol (IP) based network including a plurality of devices. The address autoconfiguration method generates and broadcasts, at a first device, a beacon frame containing an adaptive router advertisement (RA) message having prefix information, and configures, at a second device received the beacon frame, an IP address using the prefix information extracted from the adaptive RA message carried by the beacon frame and a physical address of the second device. The system includes a first type device which broadcasts a beacon frame carrying a prefix; at least one second type device which relays the prefix using a beacon frame; and at least one terminal device which configures an IP address using the prefix in the beacon frame and a physical address of the terminal device.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
High performance wireless networks using distributed control
ActiveUS7420952B2Cost-effective distributed sensingCost-effective controlError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsWireless mesh networkOperational system
A design and proof of concept of a new type of WLAN, complete with simulation and results from the simulation has been described. Each AP Node is implemented as a self-contained embedded OS unit, with all algorithms resident in its Operating system. The normal day-to-day functioning of the AP node is based entirely on resident control algorithms. Upgrades are possible through a simple secure communications interface supported by the OS kernel for each AP node. Benefits provided by a wireless network, as proposed in this invention, are that: it installs out of the box; the network is self-configuring; the network is redundant in that mesh network formalism is supported, ensuring multiple paths; load balancing is supported; there is no single point of failure; allows for decentralized execution; there is a central control; it is network application aware; there is application awareness; there is automatic channel allocation to manage and curtail RF interference, maximize non interference bandwidth and enable seamless roaming between adjoining wireless sub networks (BSS) and it supports the wireless equivalent for switching—for seamless roaming requirements.
Owner:DYNAMIC MESH NETWORKS
Fibre channel arbitrated loop bufferless switch circuitry to increase bandwidth without significant increase in cost
InactiveUS7362769B2Good saveImprove network throughputTime-division multiplexLoop networksBackplaneCrossbar switch
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
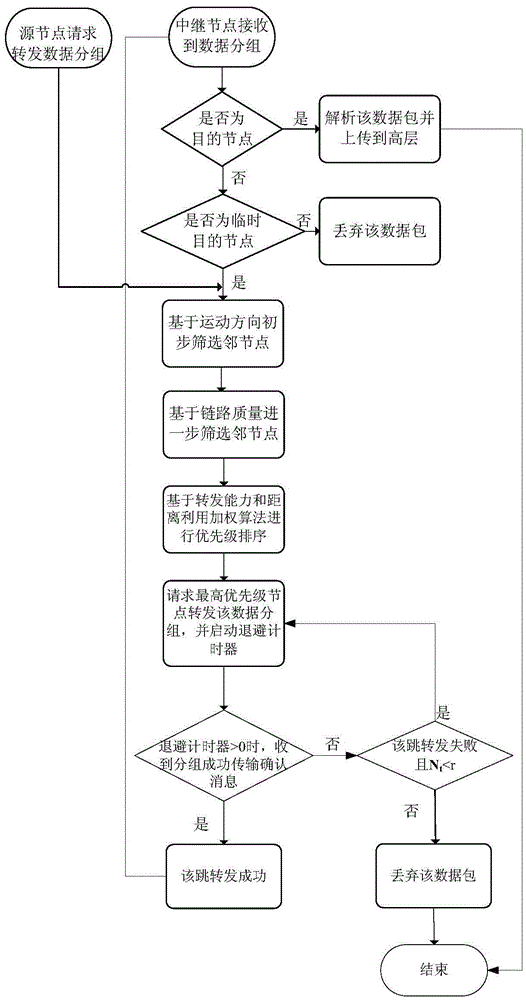
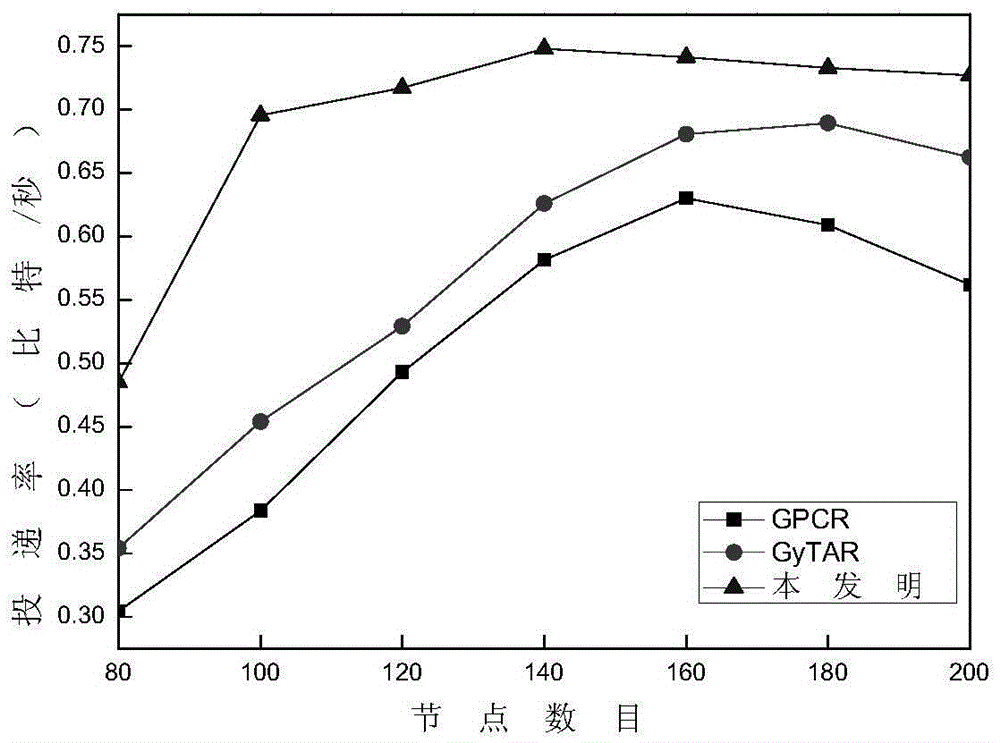
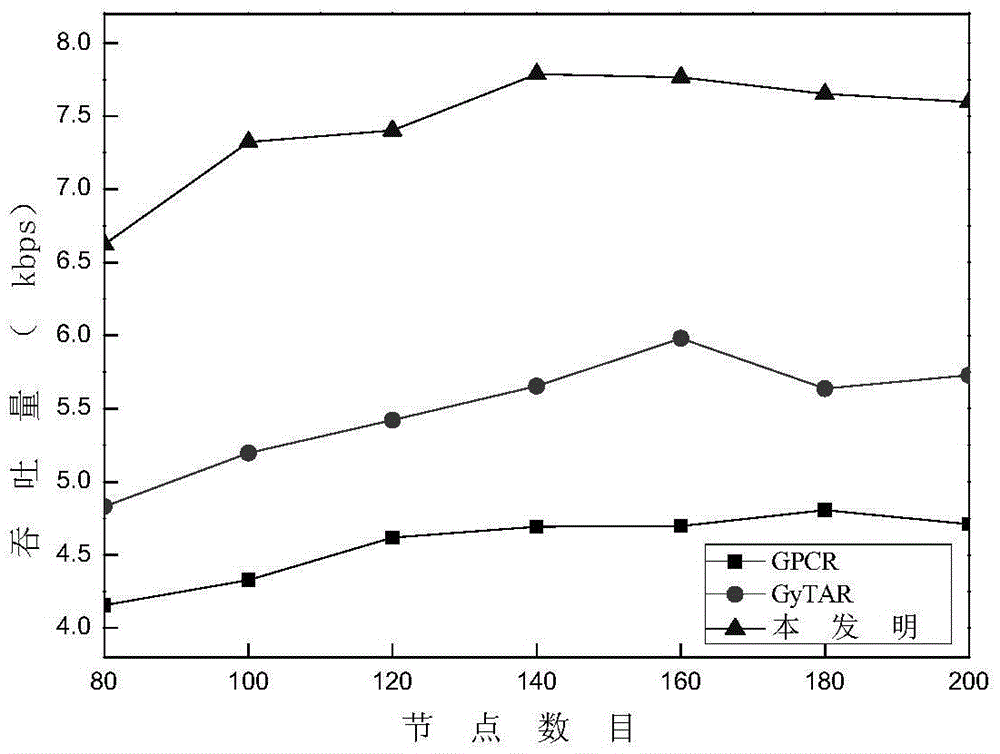
Routing protocol design method based on link quality and node forwarding capacity
ActiveCN105657777AComprehensive assessmentAccurate and reliable reflectionNetwork topologiesNetwork packetRanking
The invention discloses a routing protocol design method based on link quality and node forwarding capacity. The problems that in an existing routing protocol based on the geographic position, data grouping end-to-end transmission path selection is low in efficiency, consequently, the data grouping delivery rate is small, and network throughput is small are solved. The realizing scheme includes the steps that parameters which are related to node quality and include the motion direction, the distance, the link quality and internal forwarding capacity are calculated; then, candidate adjacent node set selection and node priority ranking are conducted through a screening mechanism and a weighting algorithm; based on a candidate adjacent node set and node priority information, an opportunity forwarding strategy is executed on data grouping. On the premise of ensuring acceptable data grouping end-to-end delay, the delivery rate of data packages and the network throughput are increased. The routing protocol design method can be applied to communication among vehicles in car networking, effective information exchange among the vehicles is achieved, and safety and efficiency of vehicle traffic are improved.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
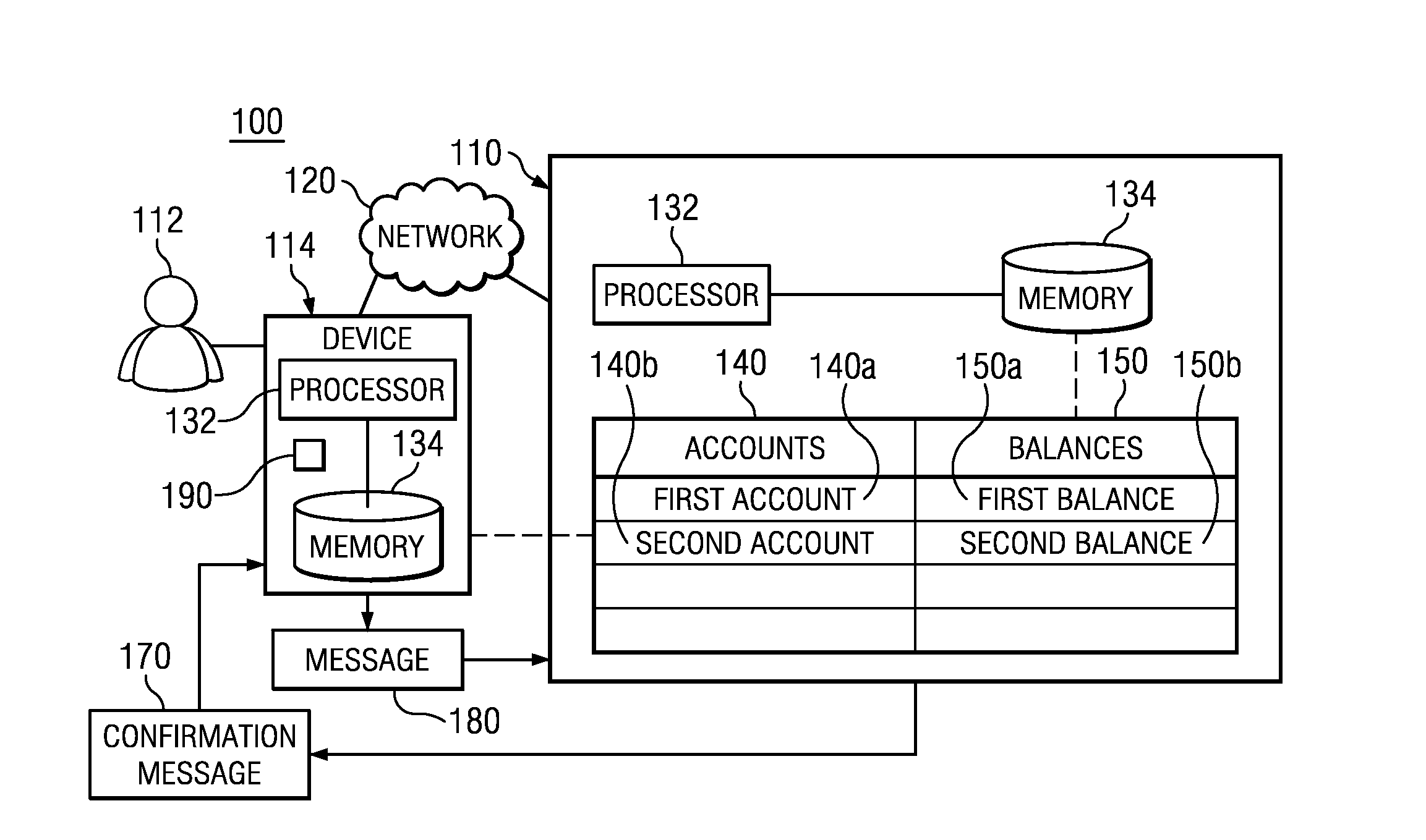
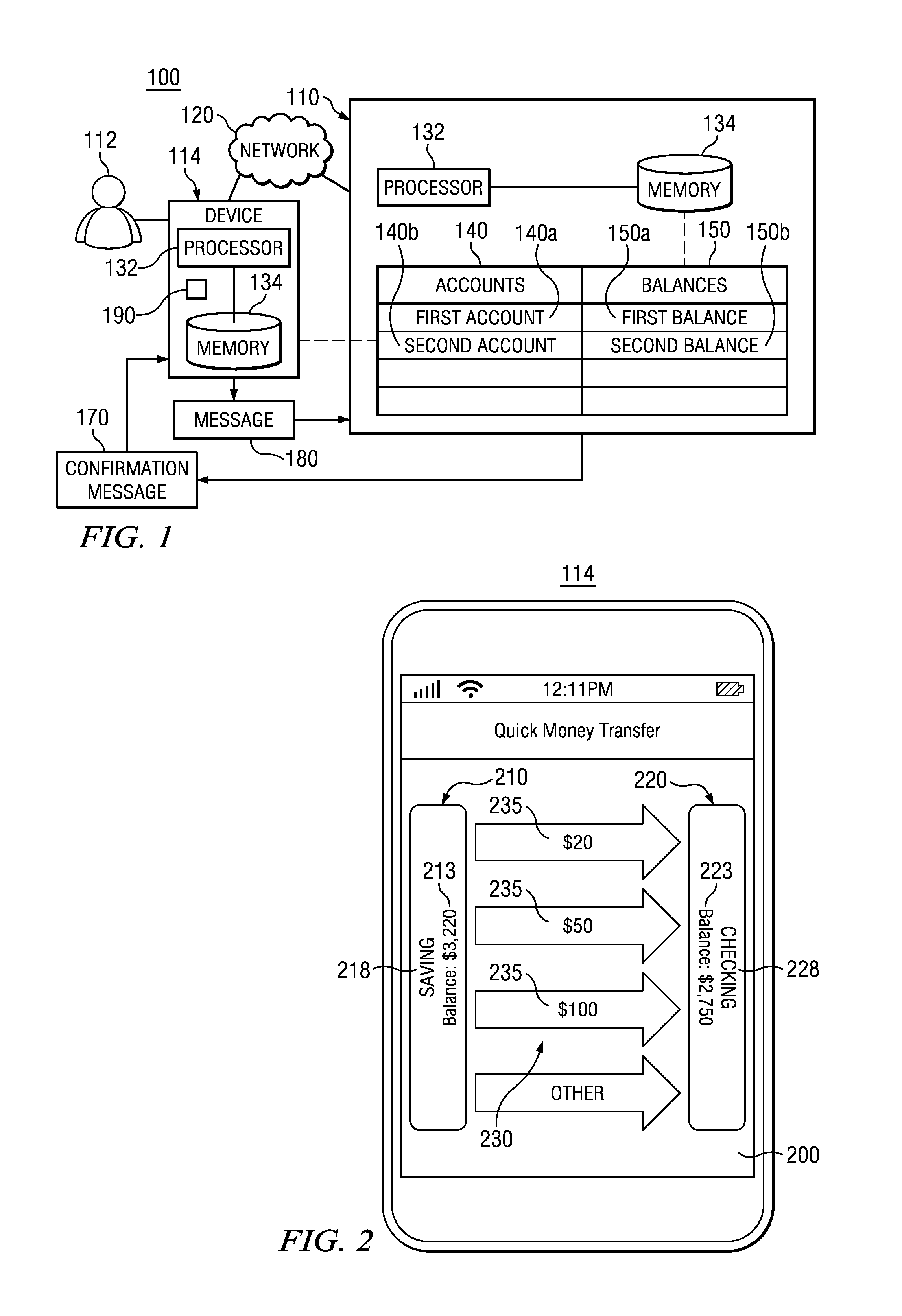
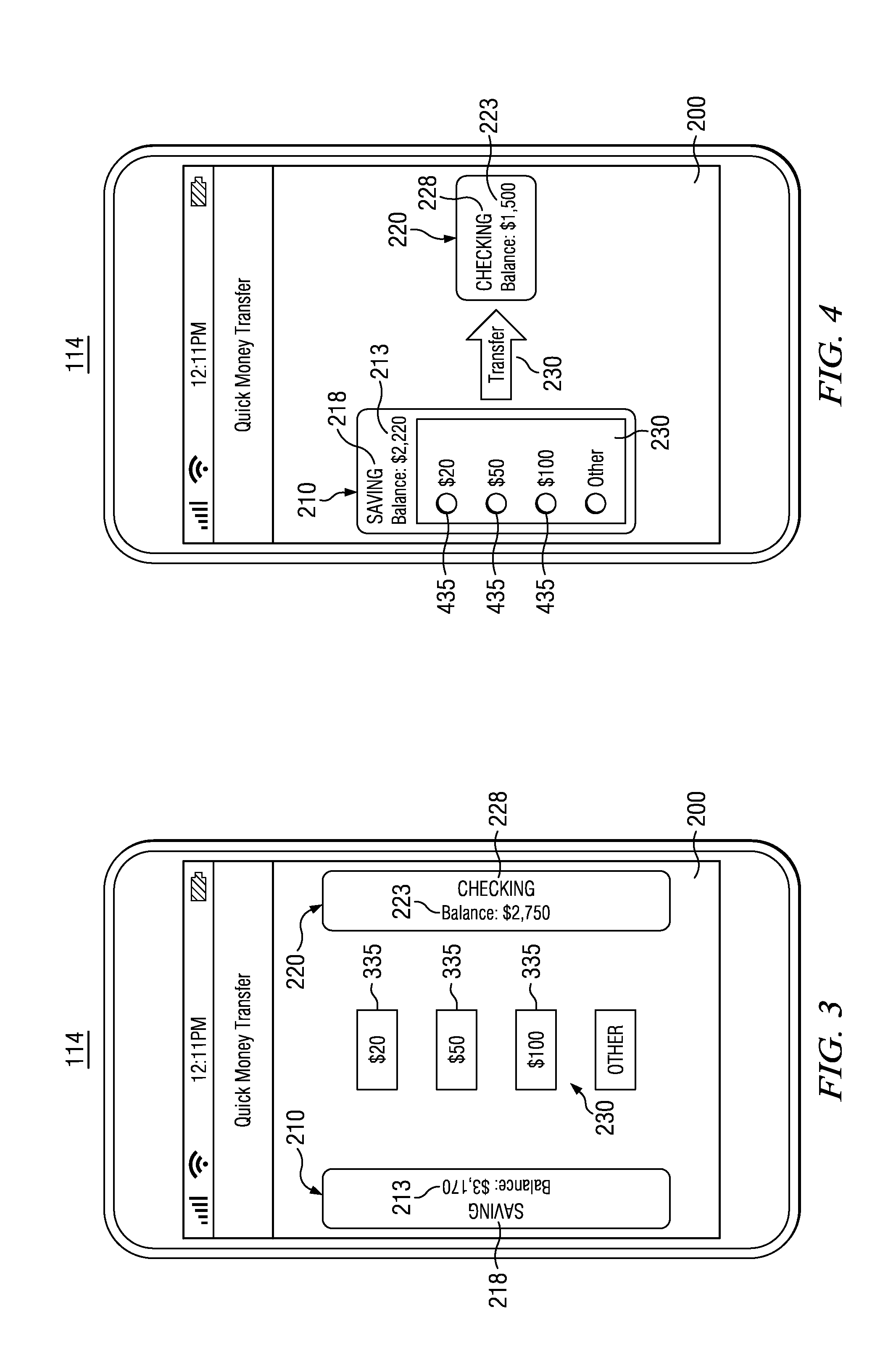
Apparatus and Method for the Electronic Transfer of Balances Between Accounts
InactiveUS20140067654A1Easy to handleImprove network throughputFinancePayment architectureDisplay deviceComputer science
Owner:BANK OF AMERICA CORP
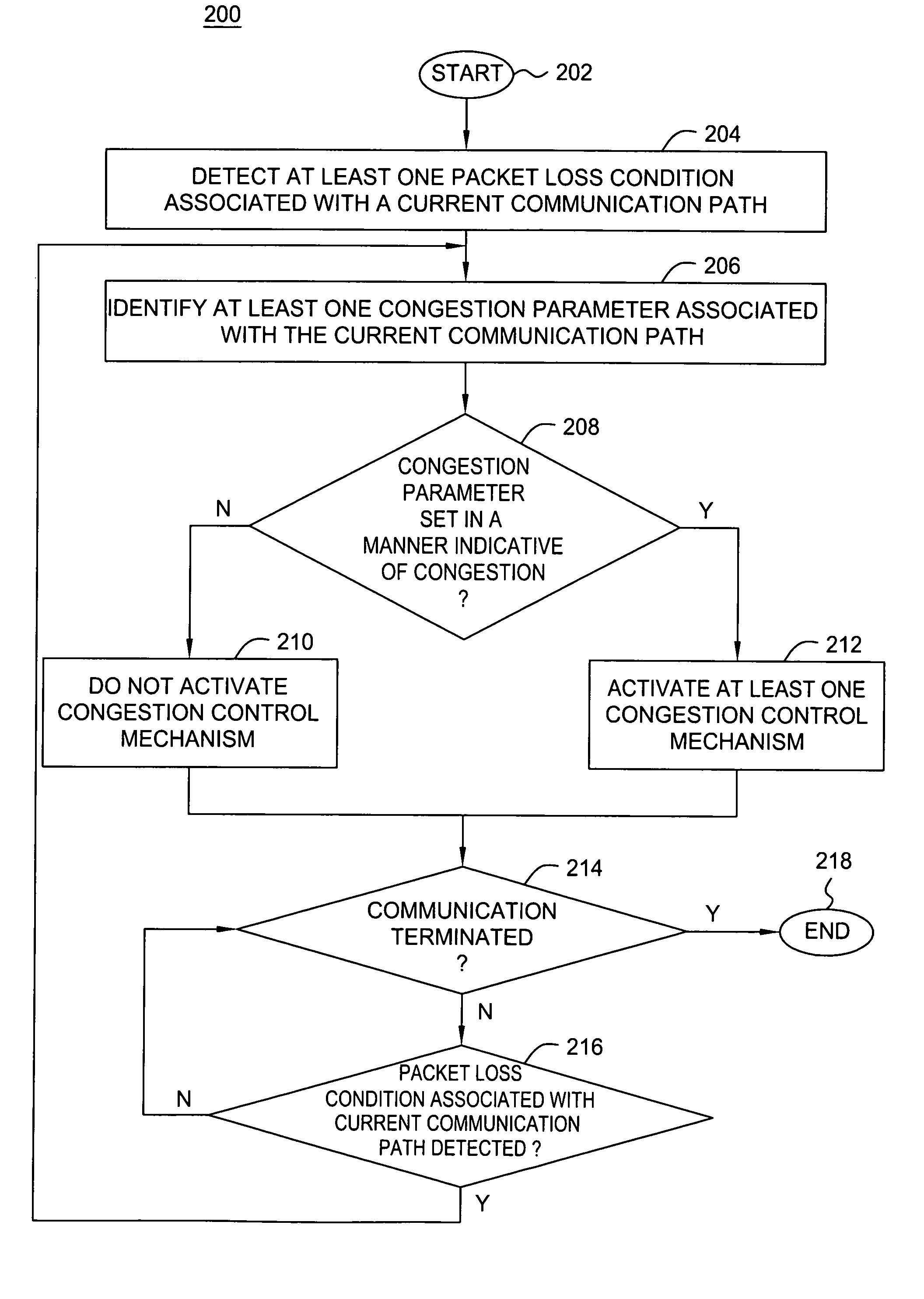
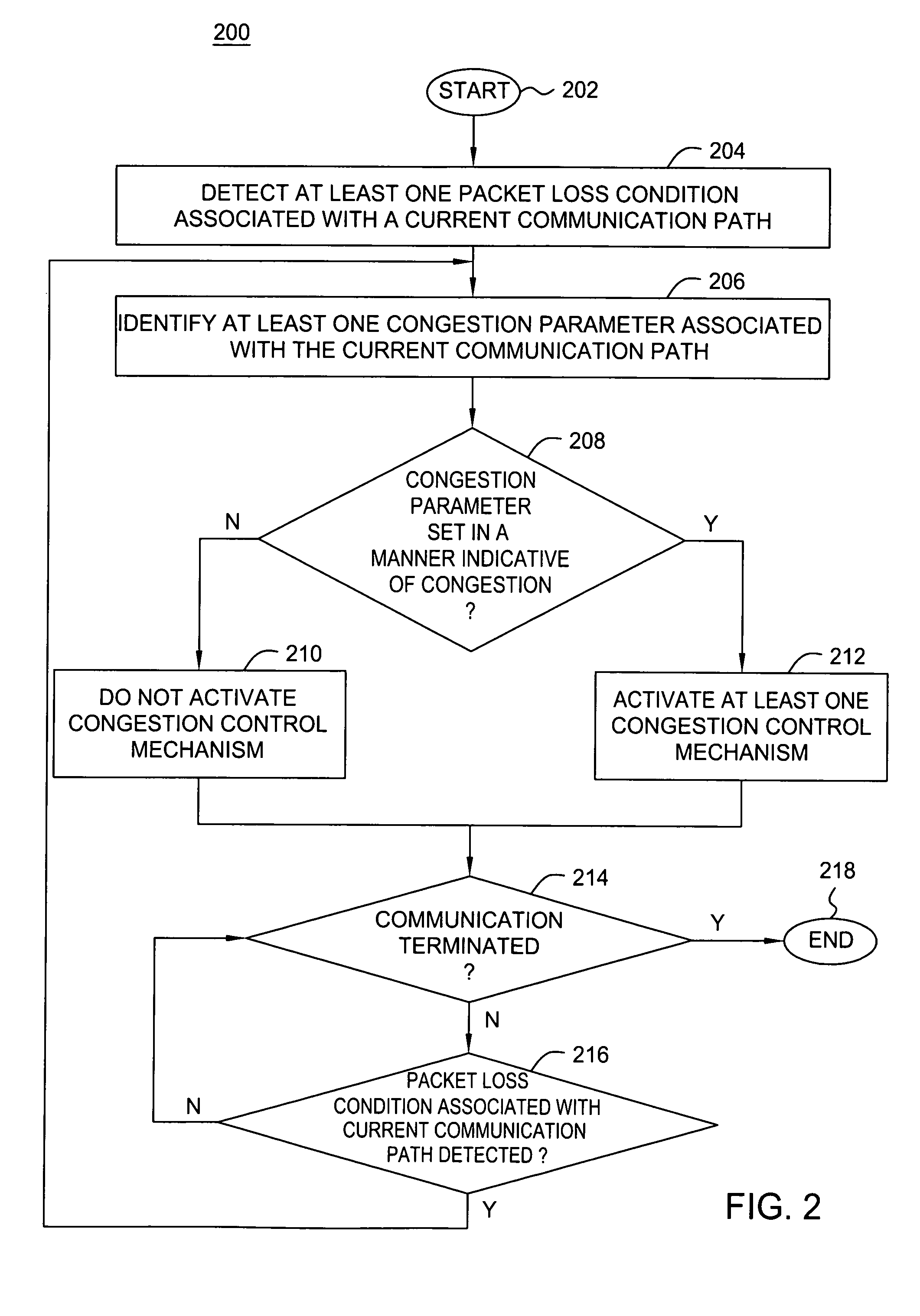
Method and apparatus for preventing activation of a congestion control process
ActiveUS20070076598A1Improve network throughputImprove network utilizationError preventionTransmission systemsPacket lossBiological activation
The invention comprises a method and apparatus that prevents the activation of a congestion controlling process that would otherwise be activated in response any packet loss condition. The congestion controlling process is inhibited when a congestion parameter associated indicates that the packet loss condition is not caused by congestion.
Owner:RPX CORP
Radio resource managment
ActiveUS20140269526A1Improve radio resource (Maximize aggregate user quality of experienceTelephonic communicationInter user/terminal allocationHuman resource managementService provider
Methods and systems described herein relate to more optimally allocating and scheduling radio resources simultaneously in space, time and frequency to enhance user quality of experience (QoE) according to use context within the constraints of maximizing long term service provider revenue expectation for a given investment in radio access network infrastructure for improved radio resource management, such methods optionally including use of heat maps of user trajectories as a factor in a process for resource allocation.
Owner:FEDERATED WIRELESS
Dynamic allocation of a pool of threads
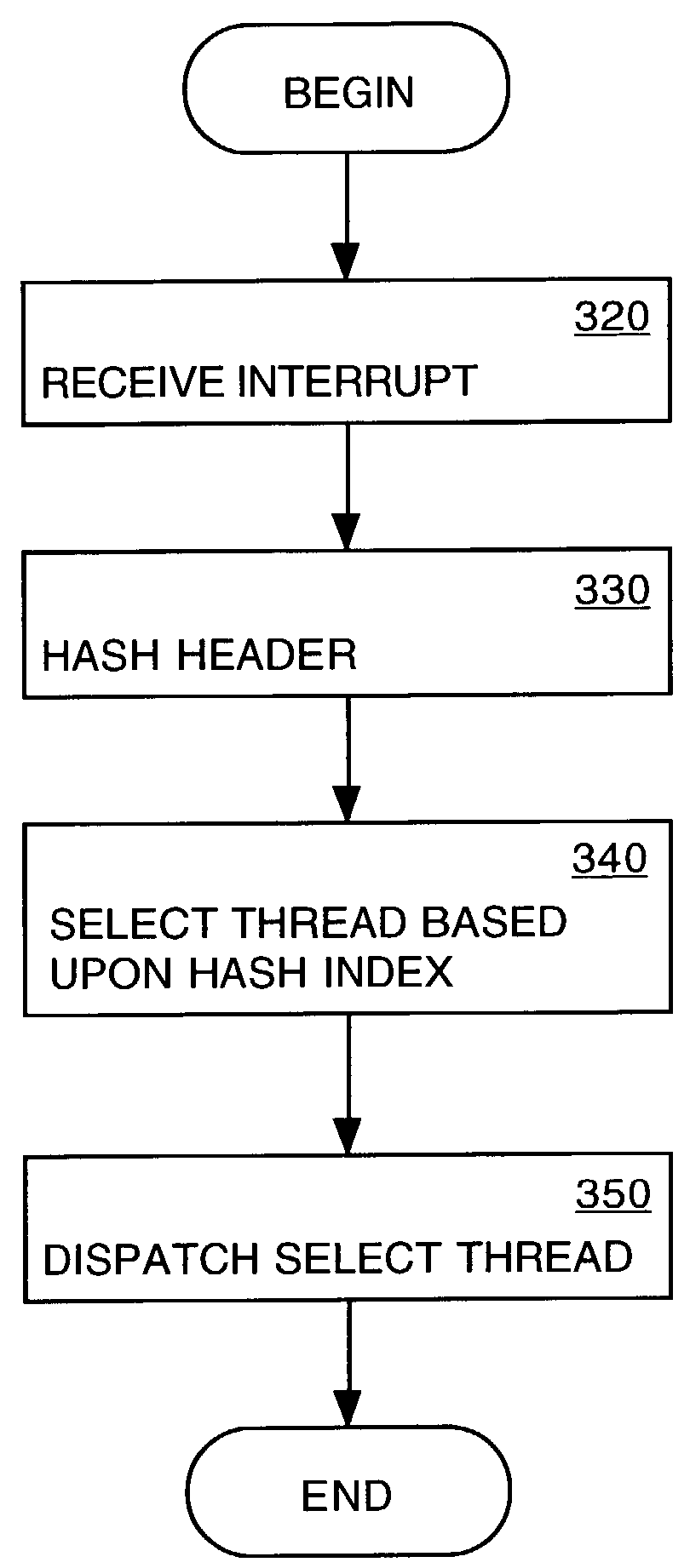
ActiveUS7257633B2Improve data localityEfficient comprehensive utilizationProgram initiation/switchingResource allocationMulti processorHash table
Embodiments of the present invention provide for execution of a protocol in a multi-processor network device. In one embodiment, a hash function is applied to one or more fields of the data packet header to determine a unique index. A hash table is then queried, whereby data indicating one or more threads corresponding to said unique index is extracted. An available thread of execution, which has previously handled packet in the same receive stream, may thus be selected from a pool of threads. The selected thread of execution is then dispatched to provide for receive processing of the present data packet.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
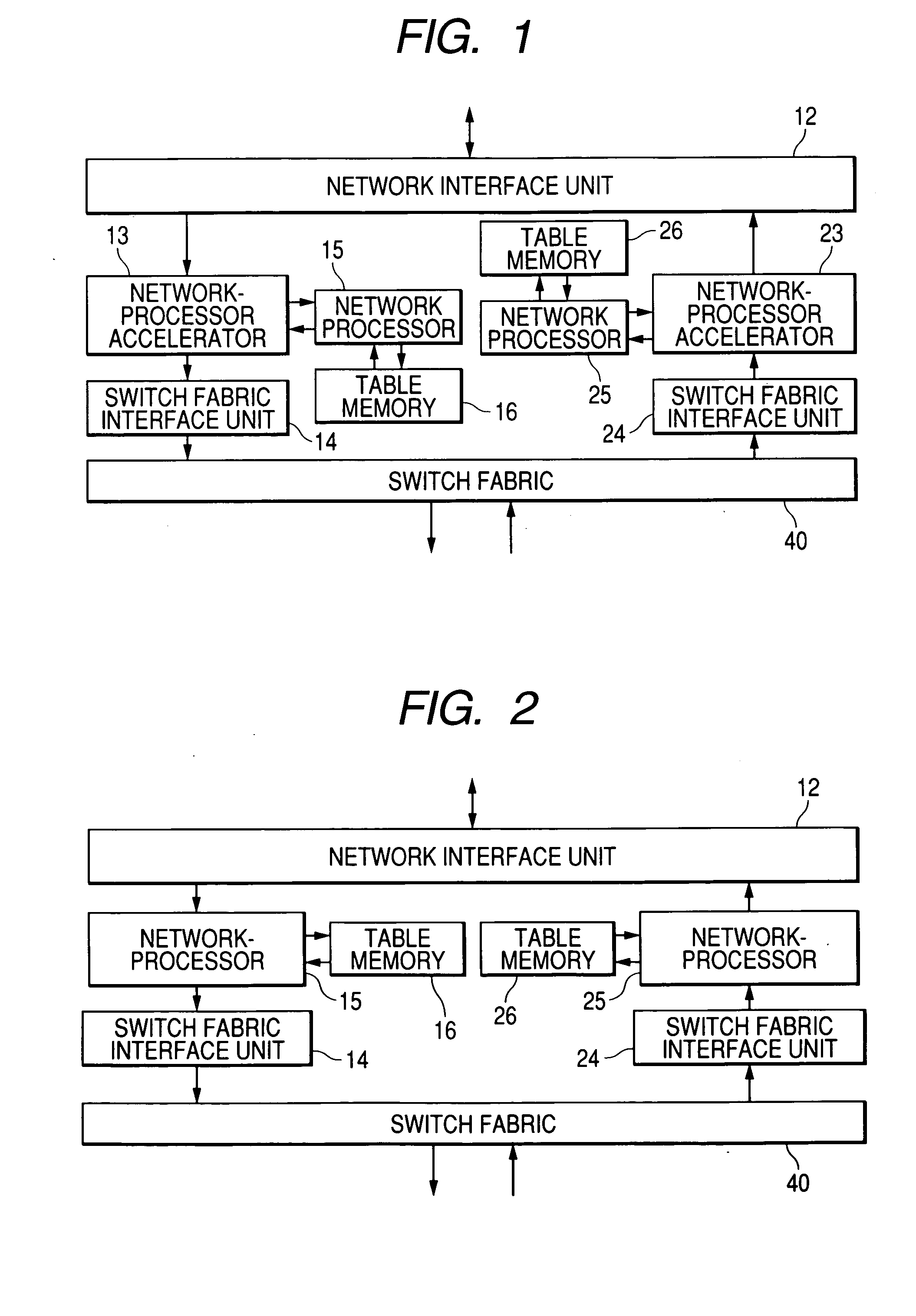
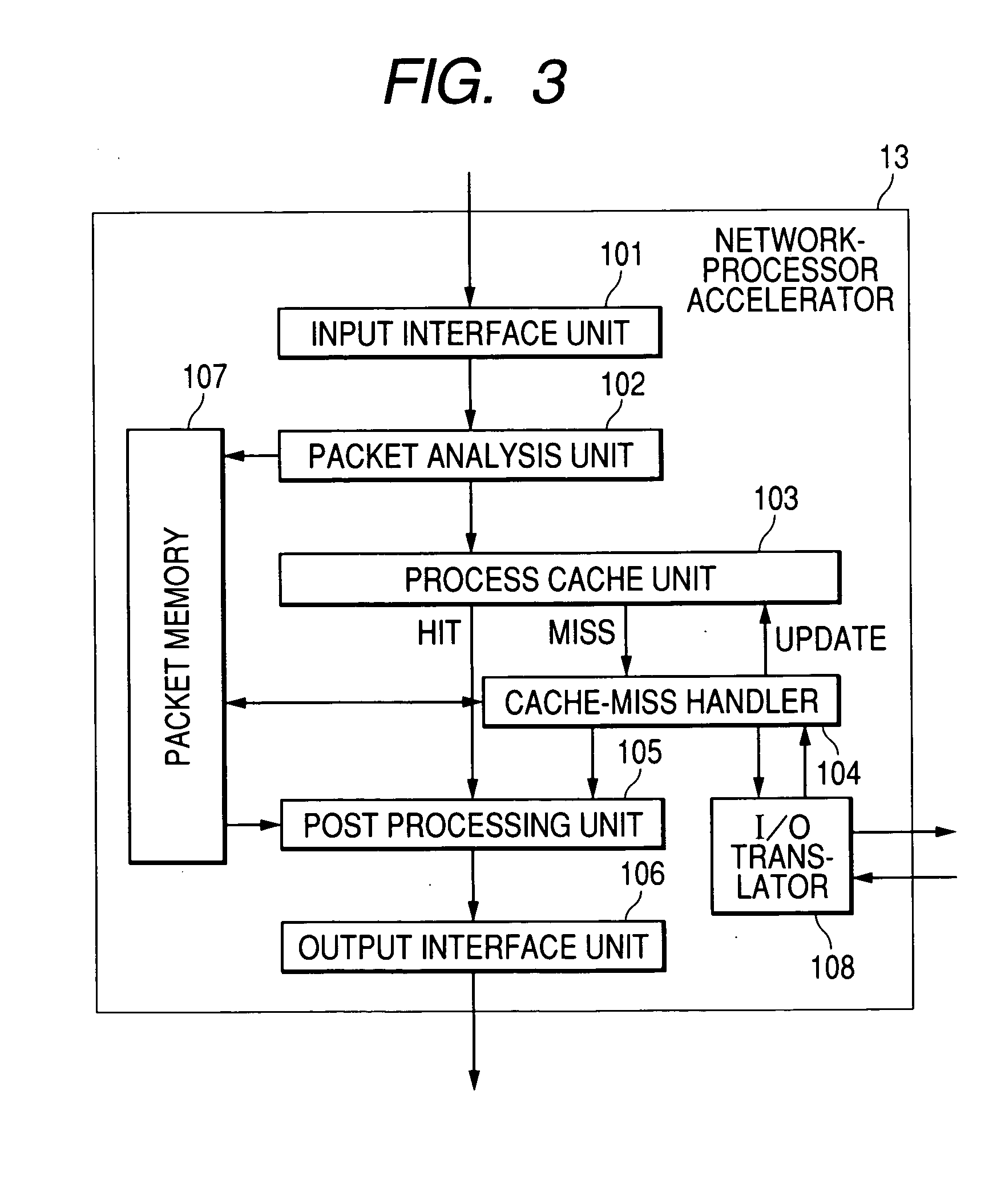
Network-processor accelerator
InactiveUS20050074005A1Increase in sizeImprove throughputData switching by path configurationDigital storagePacket processingExternal connection
In order to perform cache processing for the received packets, a network apparatus is provided with a network-processor accelerator for caching the process result of a network processor. Accordingly, the network apparatus of the present invention ensuring higher packet-processing throughput can be realized by improving the packet-processing throughput without increase in the chip area, increase in the power consumption, and shortage in an external connected memory bandwidth.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Apparatus, method, and computer readable medium for transmitting data via a plurality of network interfaces
InactiveUS20080125163A1BandwidthAvoid problemsNetwork traffic/resource managementSubstation equipmentMobile deviceThroughput
An apparatus, a method, a computer program, and a computer readable medium for transmitting data via a plurality of network interfaces are provided. The apparatus derives statuses of transmission media and then transmits data based on the statuses. In addition, each base station adopts tunneling technique by adding a tunnel header to each of the transmitted packets. By the aforementioned arrangement, a mobile device is capable of adjusting the data amount for each of the network interfaces. Thus, the throughput of mobile host can be increased and connection can be dependable.
Owner:INSTITUTE FOR INFORMATION INDUSTRY
Wireless communication method and device
ActiveUS20150296528A1Improve network throughputNetwork topologiesWireless commuication servicesTransfer procedureChannel assessment
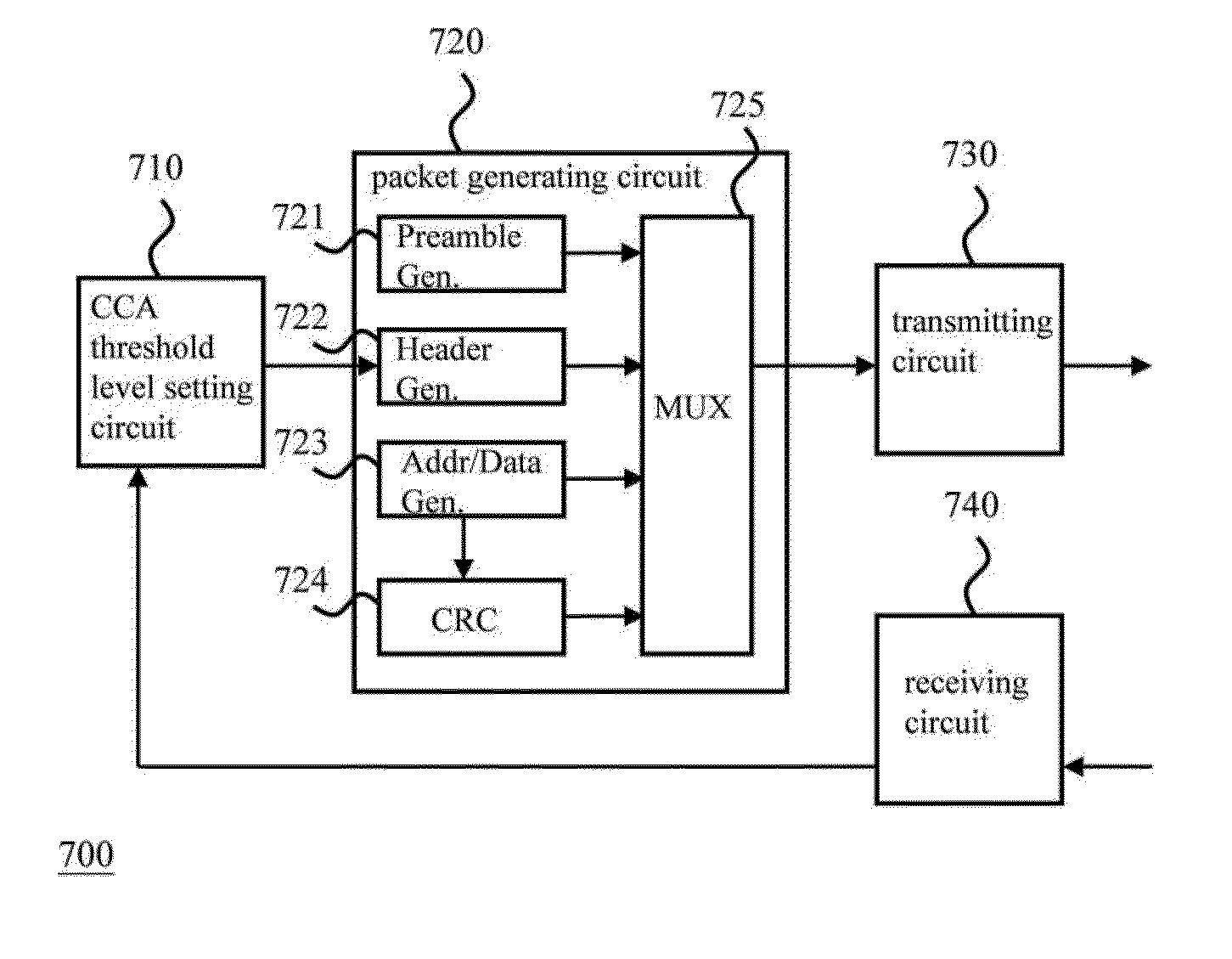
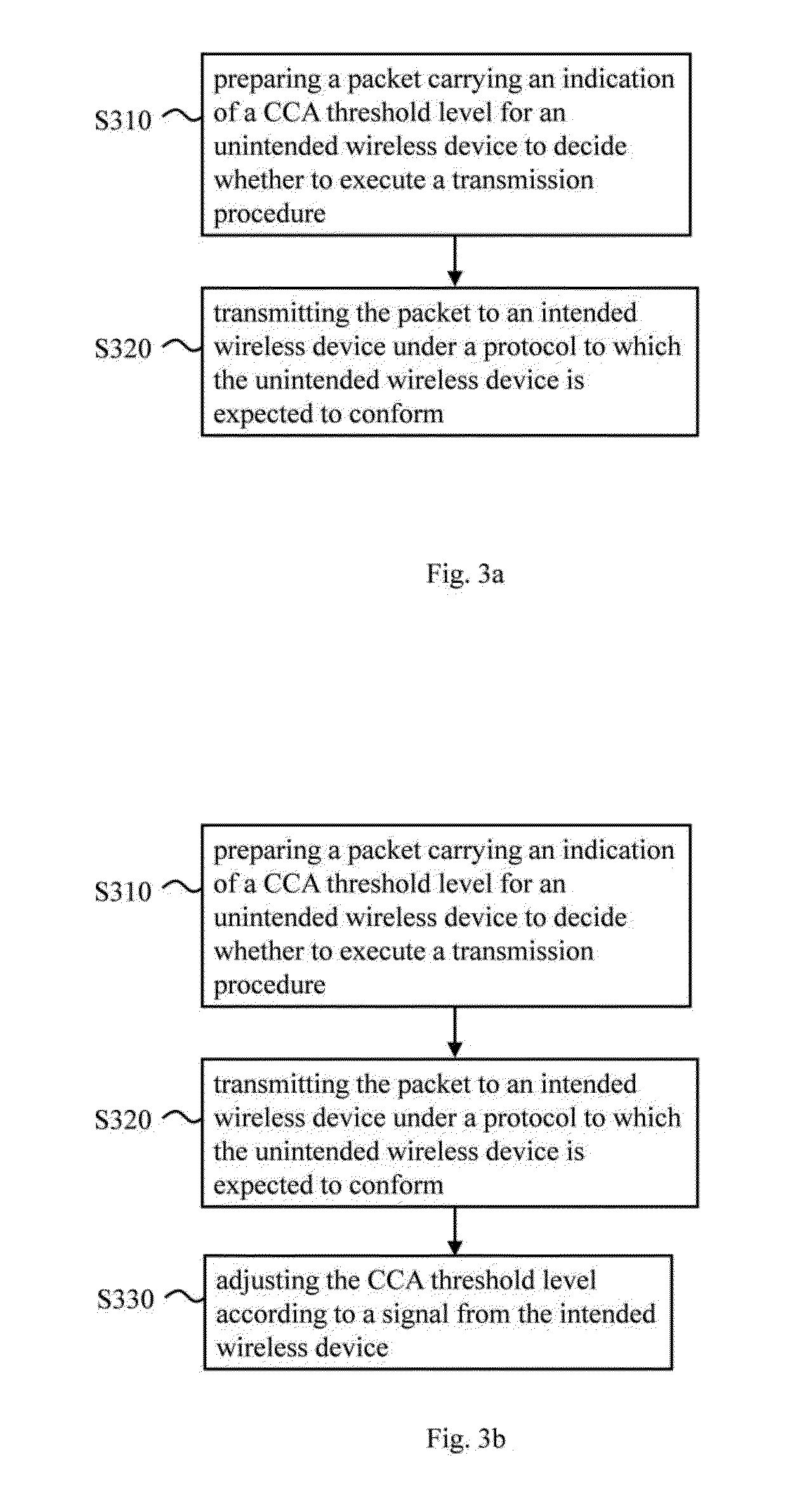
The present invention discloses a wireless communication method carried out by a wireless transmitter capable of offering an unintended wireless device a chance of starting or proceeding with a transmission procedure during a transmission duration of the wireless transmitter. An embodiment of said wireless communication method comprises the following steps: preparing a packet carrying an indication of a clear channel assessment (CCA) threshold level for an unintended wireless device to decide whether to execute a transmission procedure; and transmitting the packet to an intended wireless device under a protocol by which the unintended wireless device is expected to abide.
Owner:REALTEK SEMICON CORP
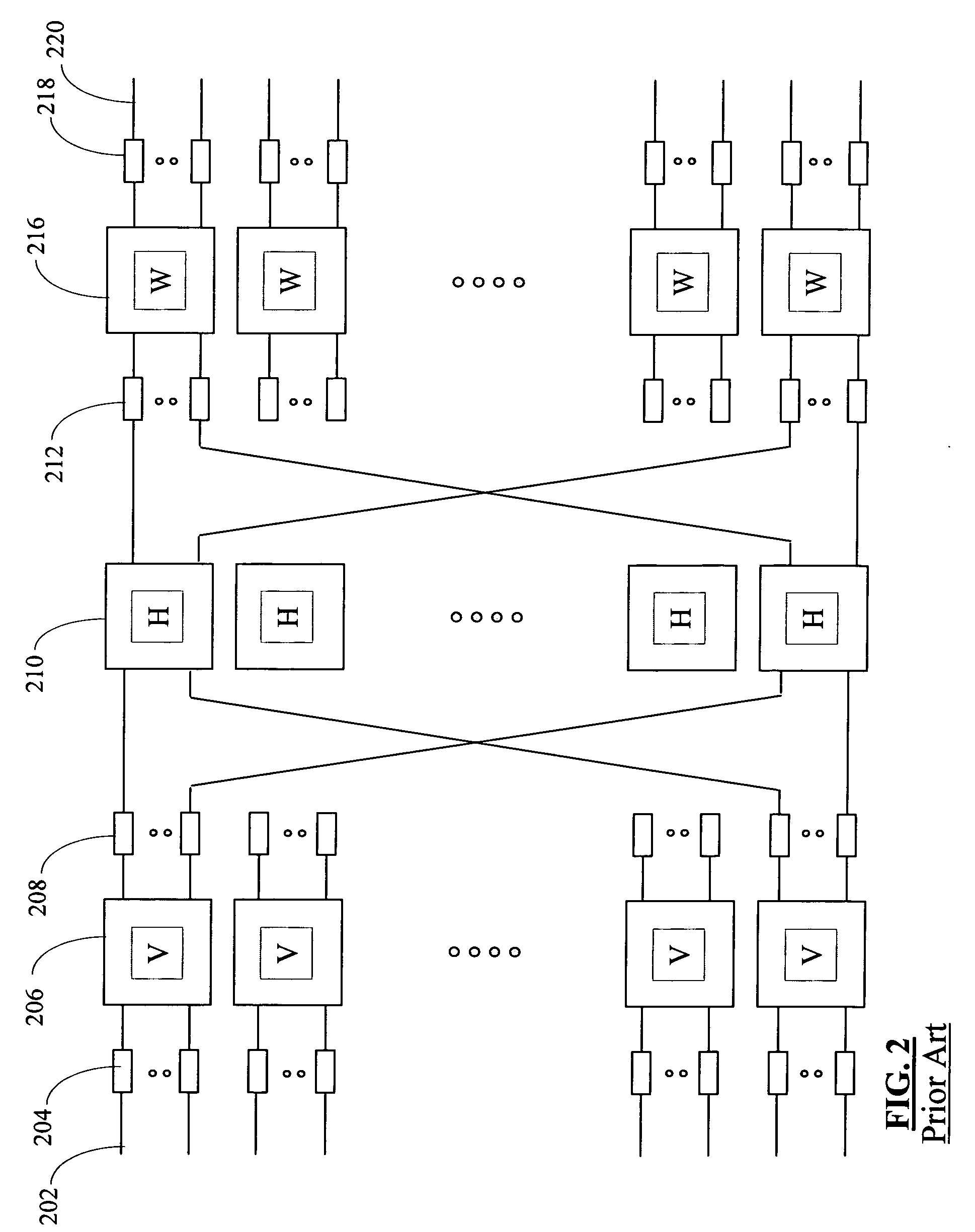
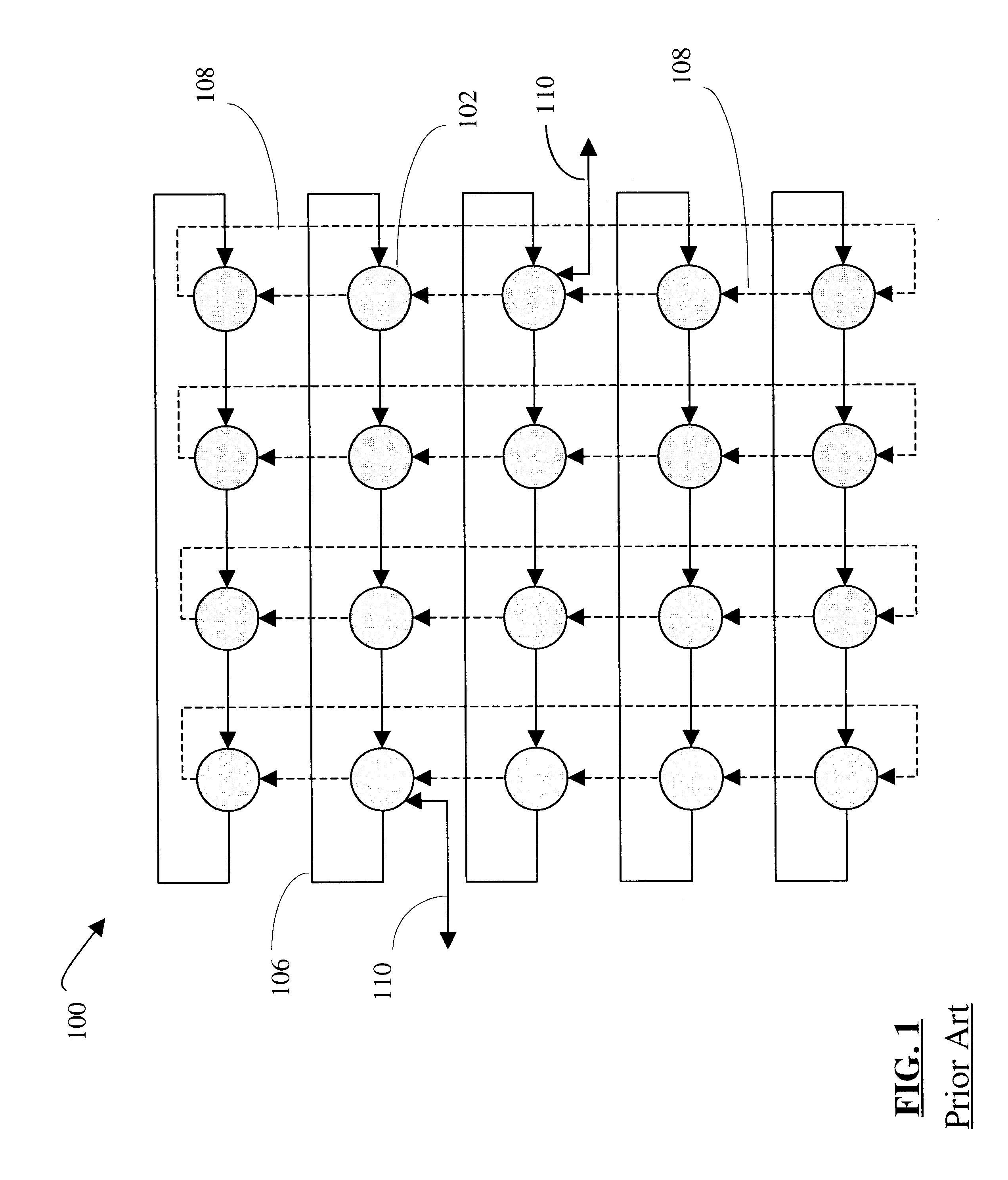
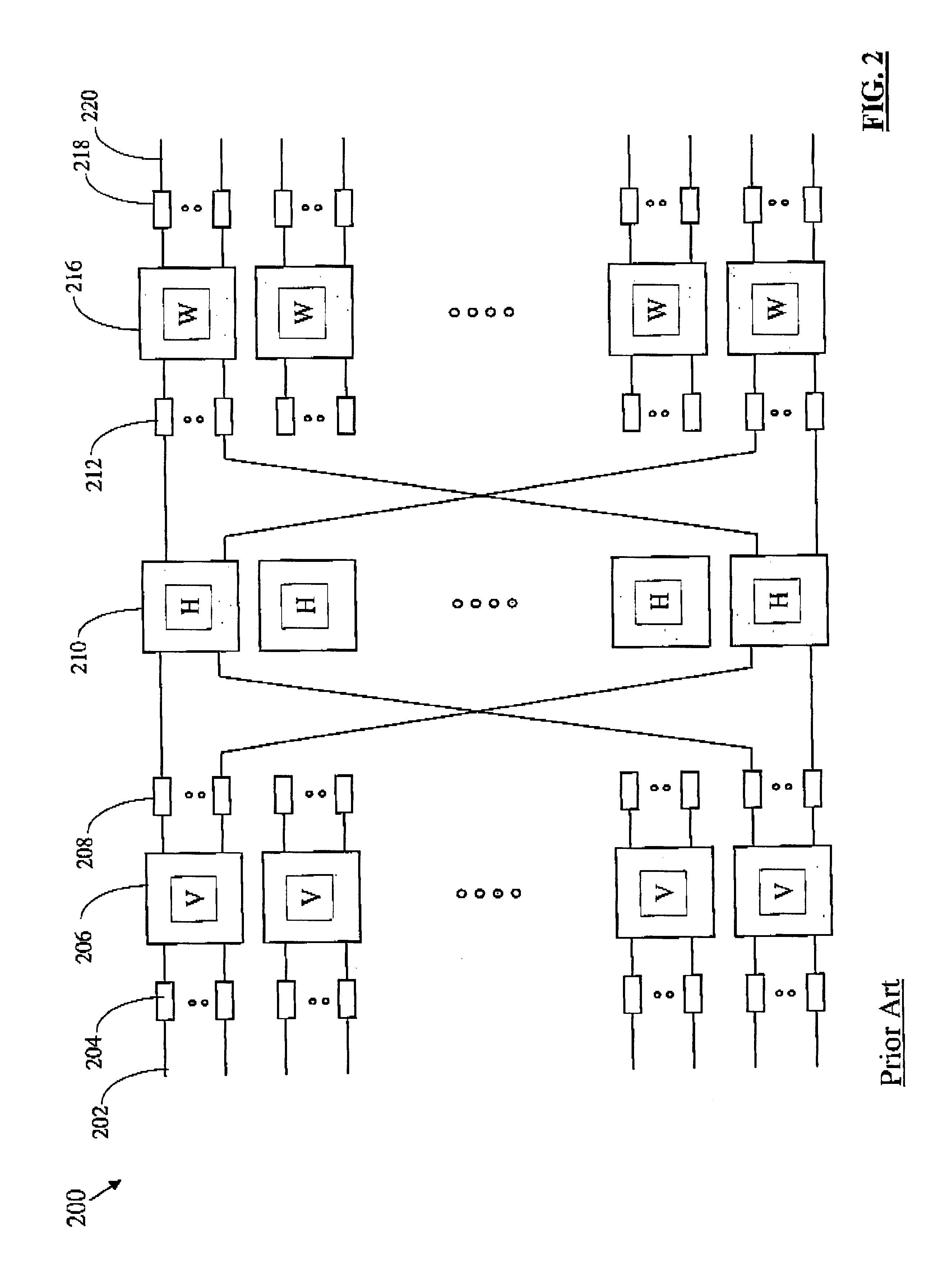
Multi-dimensional lattice network
InactiveUS20050068946A1Increase the number ofImprove transmission performanceMultiplex system selection arrangementsDigital computer detailsRouting tableDot matrix
Owner:RPX CLEARINGHOUSE
Multi-dimensional lattice network
InactiveUS6853635B1Increase the number ofImprove transmission performanceData switching by path configurationMultiple digital computer combinationsRouting tableGrid network
Owner:ROCKSTAR CONSORTIUM INC
A Master Device and Methods Therein
InactiveUS20160380778A1Optimize networkExtended service lifeSpecial service provision for substationNetwork traffic/resource managementComputer hardwareUnicast
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
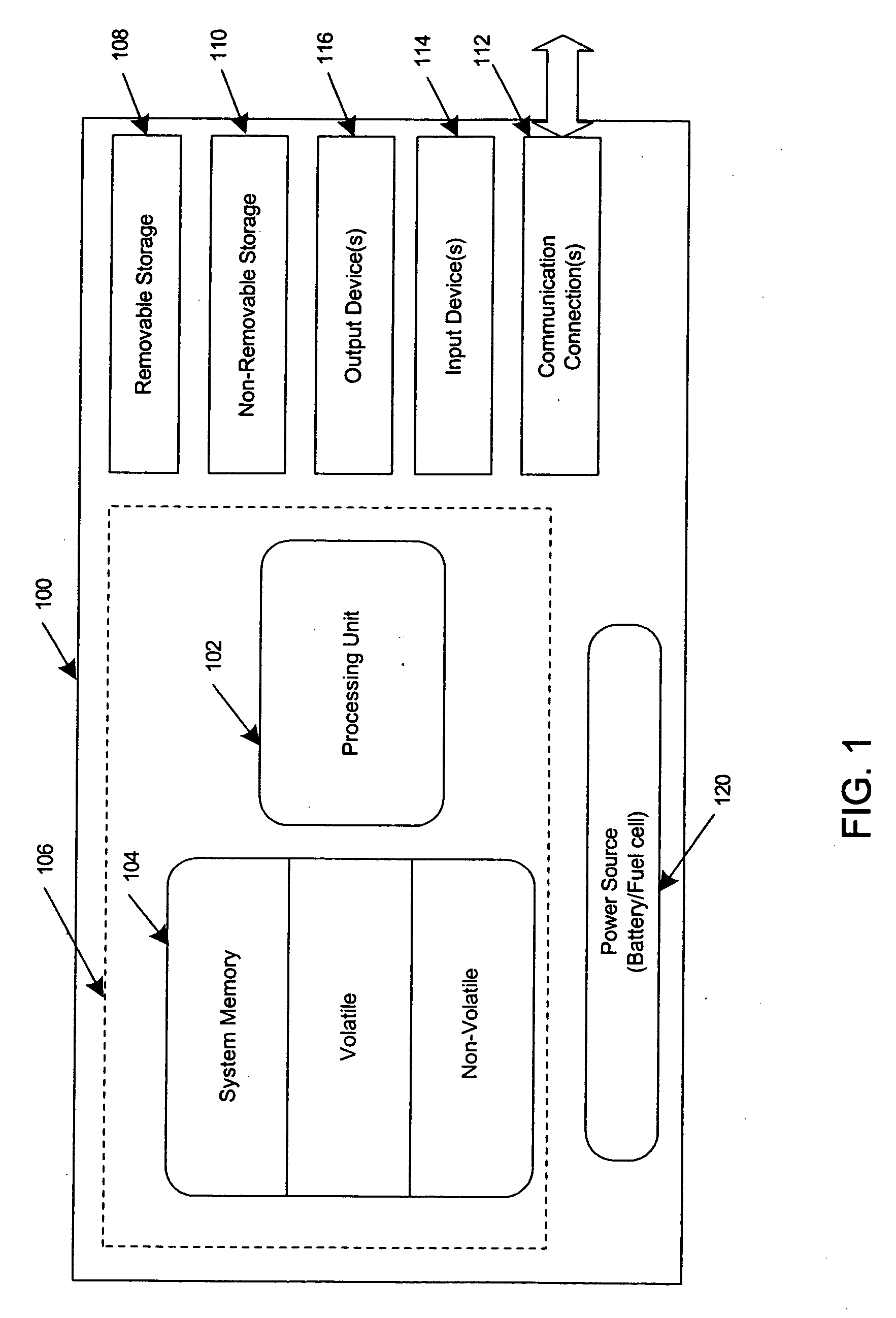
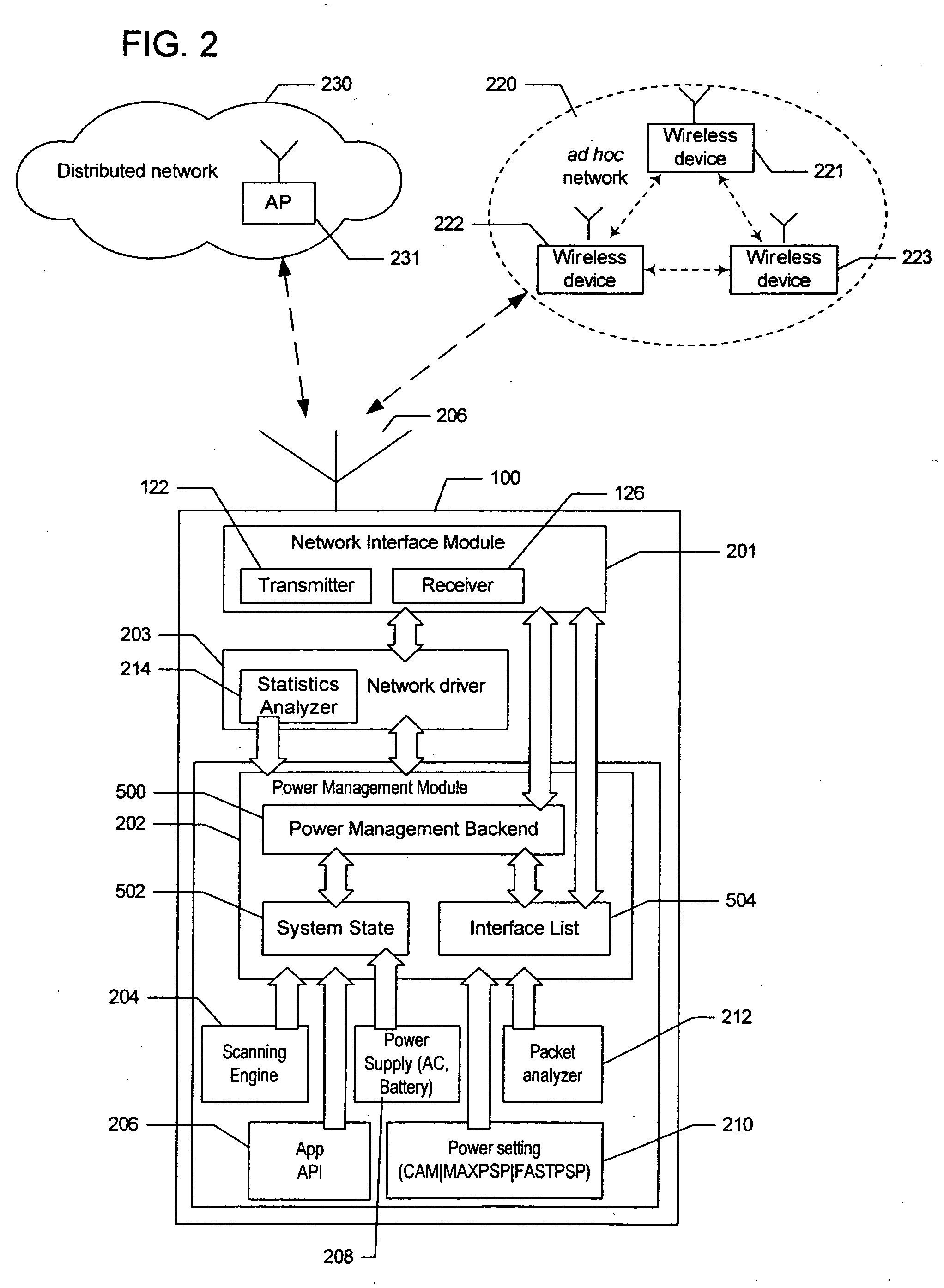
Method and apparatus for managing power in network interface modules
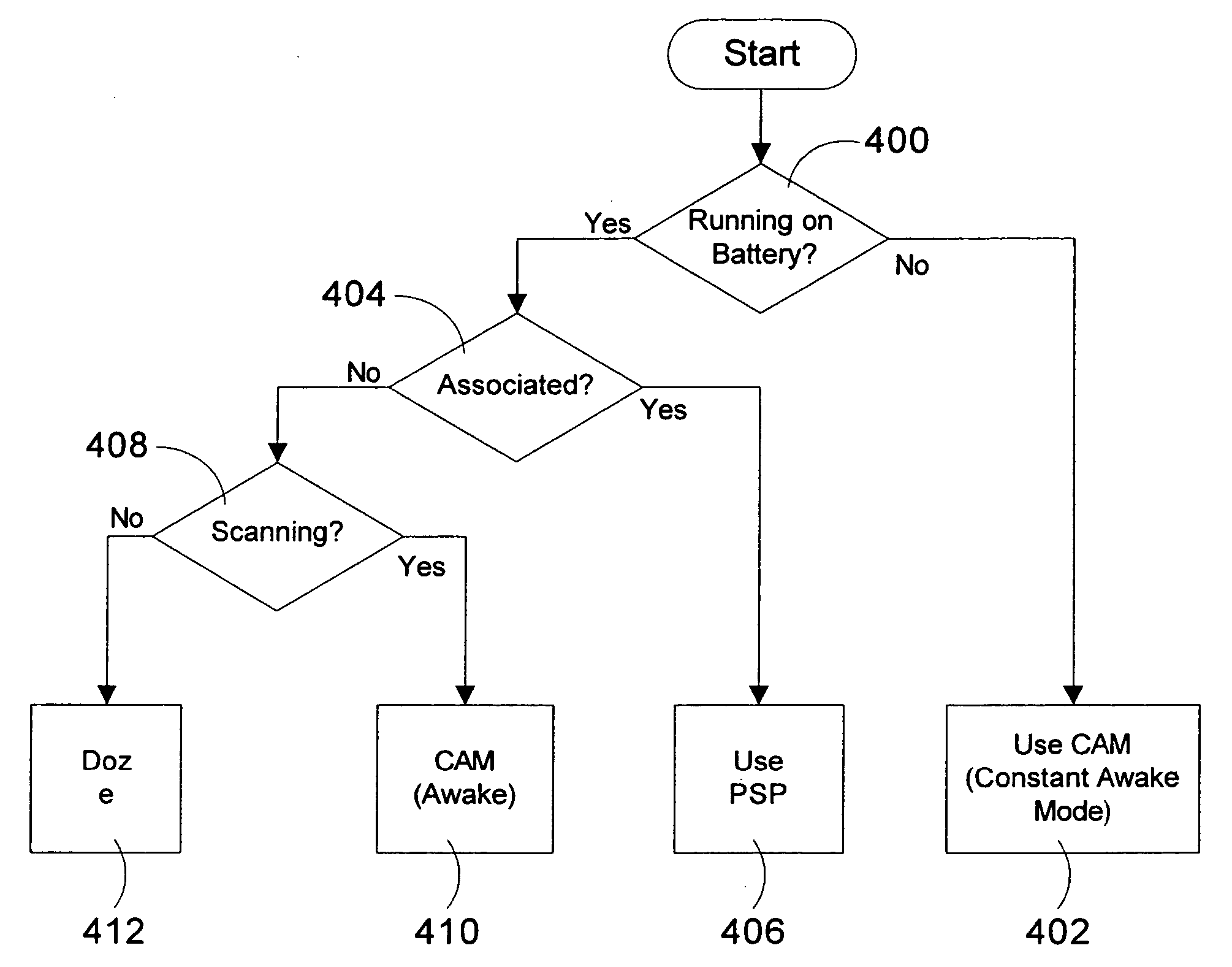
InactiveUS20060107081A1Improve network throughputPower managementVehicle seatsTraffic capacitySleep time
A method and system for managing power consumption in a portable computing device having a network interface module is presented. A power management module receives inputs from other modules and determines when the network interface module is to be put in a doze state for a predetermined number of beacon intervals to conserve power consumption in the network interface module. The network interface module in a device that is associated with a network is put in the doze state after an event has occurred including when a scan has been performed, after a delayed sleep timer has expired, and after a beacon transmission has been completed and no traffic is buffered for the device. The delayed sleep time is set based on the estimated round trip time of a packet.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
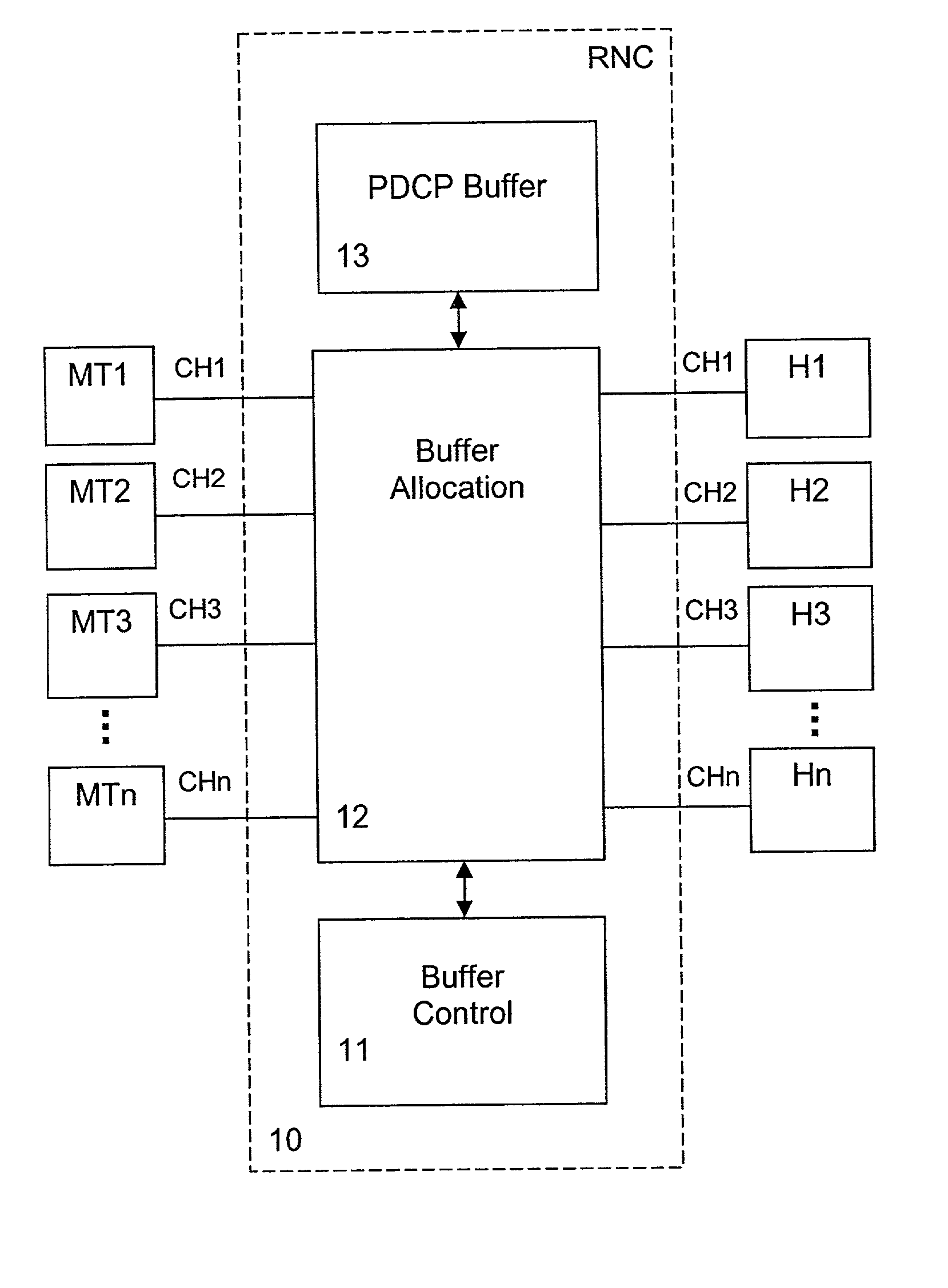
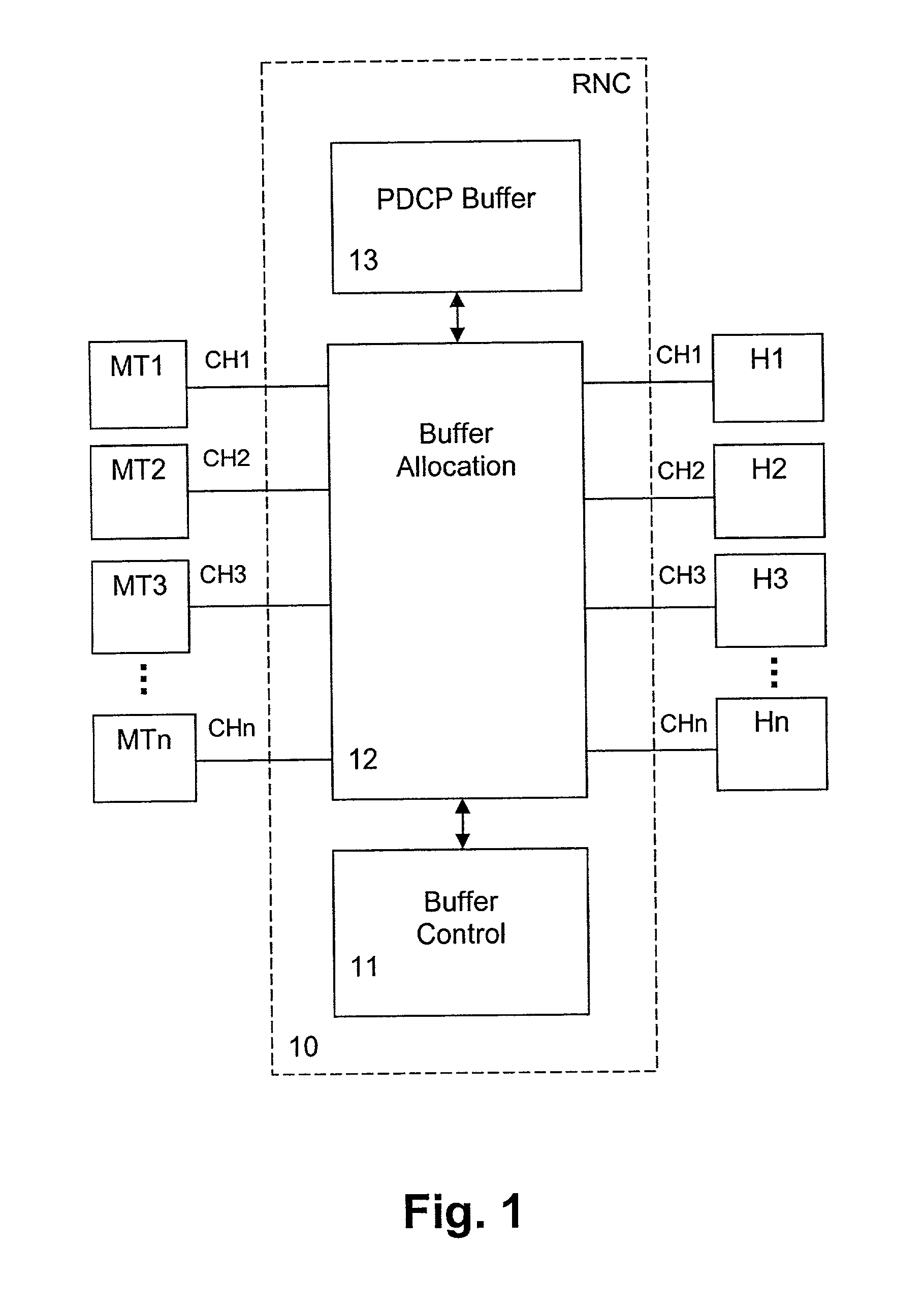
Packet flow control method and device
InactiveUS7039013B2Reduces packet-dropsImproves overall packet-throughputError preventionTransmission systemsData connectionTraffic capacity
The present invention relates to a method and network node for controlling packet flow in a buffer means (13; 14) of a network node of a data network, wherein a nominal capacity is assigned to each data flow, and an additional or free capacity is shifted from a first flow portion to a second flow portion when a new data packet of said second flow portion has been received and said nominal capacity has been exceeded. The nominal capacity may be an upper buffer memory limit used for controlling queuing of data packets in a buffer memory (13) of said buffer means, wherein the memory space of the buffer memory (13) is shared between a plurality of channels allocated to respective packet data connections. Then, the free capacity corresponds to a memory space shifted from a first channel to a second channel, when a new data packet of the second channel has been received and not enough memory space is available for the second channel. Thus, a dynamic buffer-sharing mechanism is provided which reduces the number of packet drops in the buffer memory (13) during congestion and improves network throughput. Alternatively, the nominal capacity may be a nominal flow rate at which data flow traffic is guaranteed in a QoS scheduling algorithm. Then, a residual rate corresponding to the difference between the nominal flow rate and an instantaneous traffic is shifted between flow portions of a buffer means controlled by the scheduling algorithm to maximize total system throughput.
Owner:NOKIA SOLUTIONS & NETWORKS OY
Access point operating with a smart antenna in a WLAN and associated methods
InactiveUS7366464B2Increase rangeImprove network throughputSubstation equipmentTransmission monitoringOmnidirectional antennaDirectional antenna
An access point operates in an 802.11 wireless communication network communicating with a client station, and includes a smart antenna for generating directional antenna beams and an omni-directional antenna beam. An antenna steering algorithm scans the directional antenna beams and the omni-directional antenna beam for receiving signals from the client station. The signals received via each scanned antenna beam are measured, and one of the antenna beams is selected based upon the measuring for communicating with the client station. The selected antenna beam is preferably a directional antenna beam. Once the directional antenna beam has been selected, there are several usage rules for exchanging data with the client station. The usage rules are directed to an active state of the access point, which includes a data transmission mode and a data reception mode.
Owner:INTERDIGITAL TECH CORP
Method and system for p2p communications and decentralized spatial sharing in wireless networks with directional transmissions
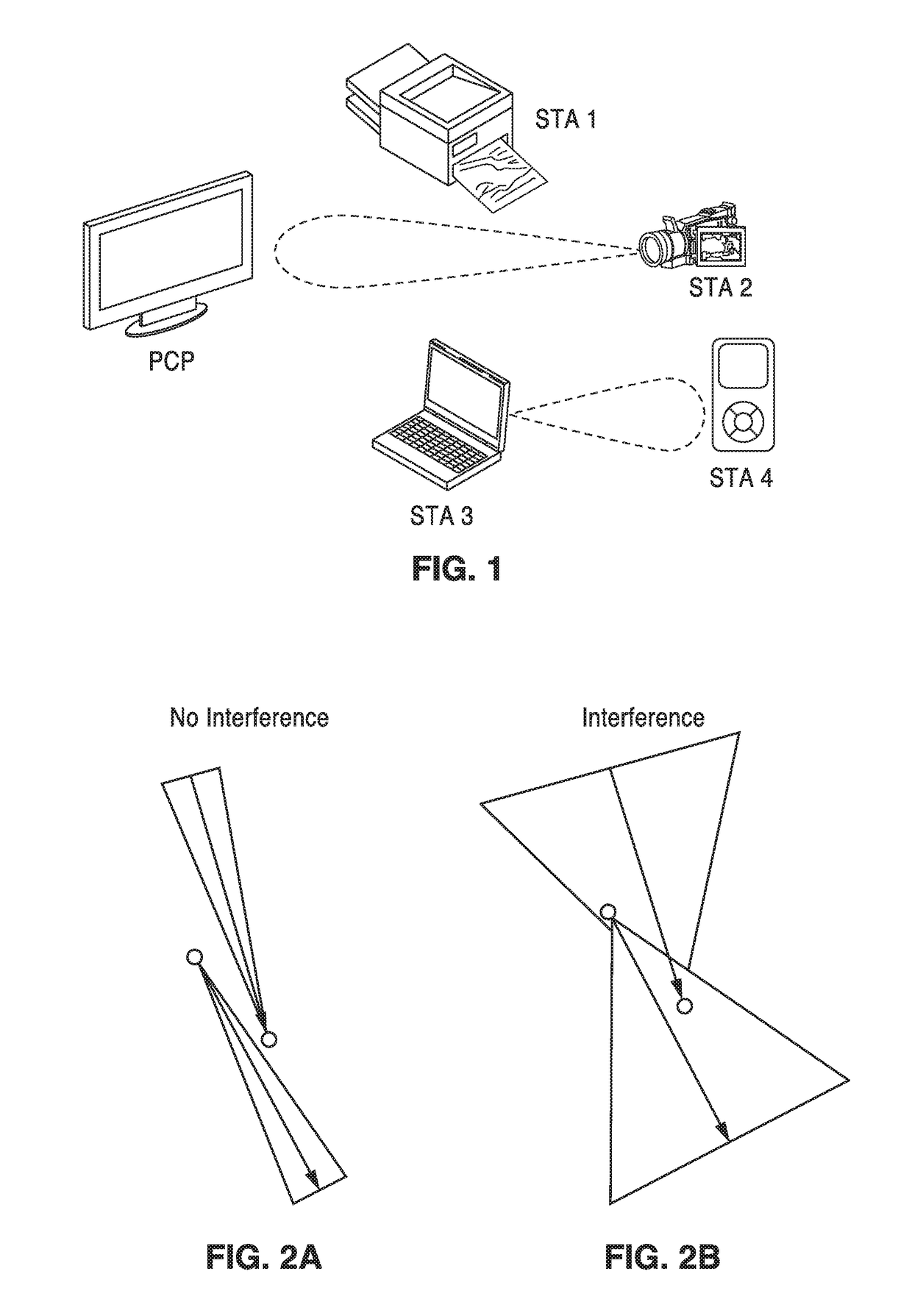
ActiveUS20170353984A1Enhanced spatial re-useImprove network throughputCriteria allocationSignal allocationComputer networkStation
Beamformed directional wireless communications are described that provide for spatial re-use that allows multiple pairs of peer-to-peer (P2P) links to communicate simultaneously over the same channel in the same spatial vicinity, without contention, and independent of centralized control. The spatial re-use improves network throughput by sharing spectrum resource among multiple links. Beamformed training includes obtaining best sector and least sector information by all stations. Prior to performing an independent P2P communication, antenna array sector information is checked, to assure that the sector to be selected is not impinging interference on other P2P interactions, then a request is made to a target station. The target station also refers to its sector information, and if no conflict is found it accepts and acknowledges the request, upon which it receives the P2P communication.
Owner:SONY CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com