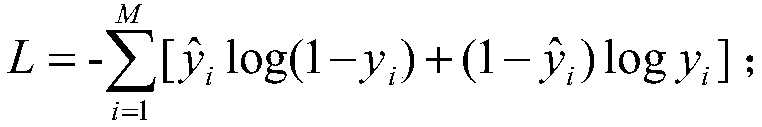Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
79results about How to "Avoid nuisance" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
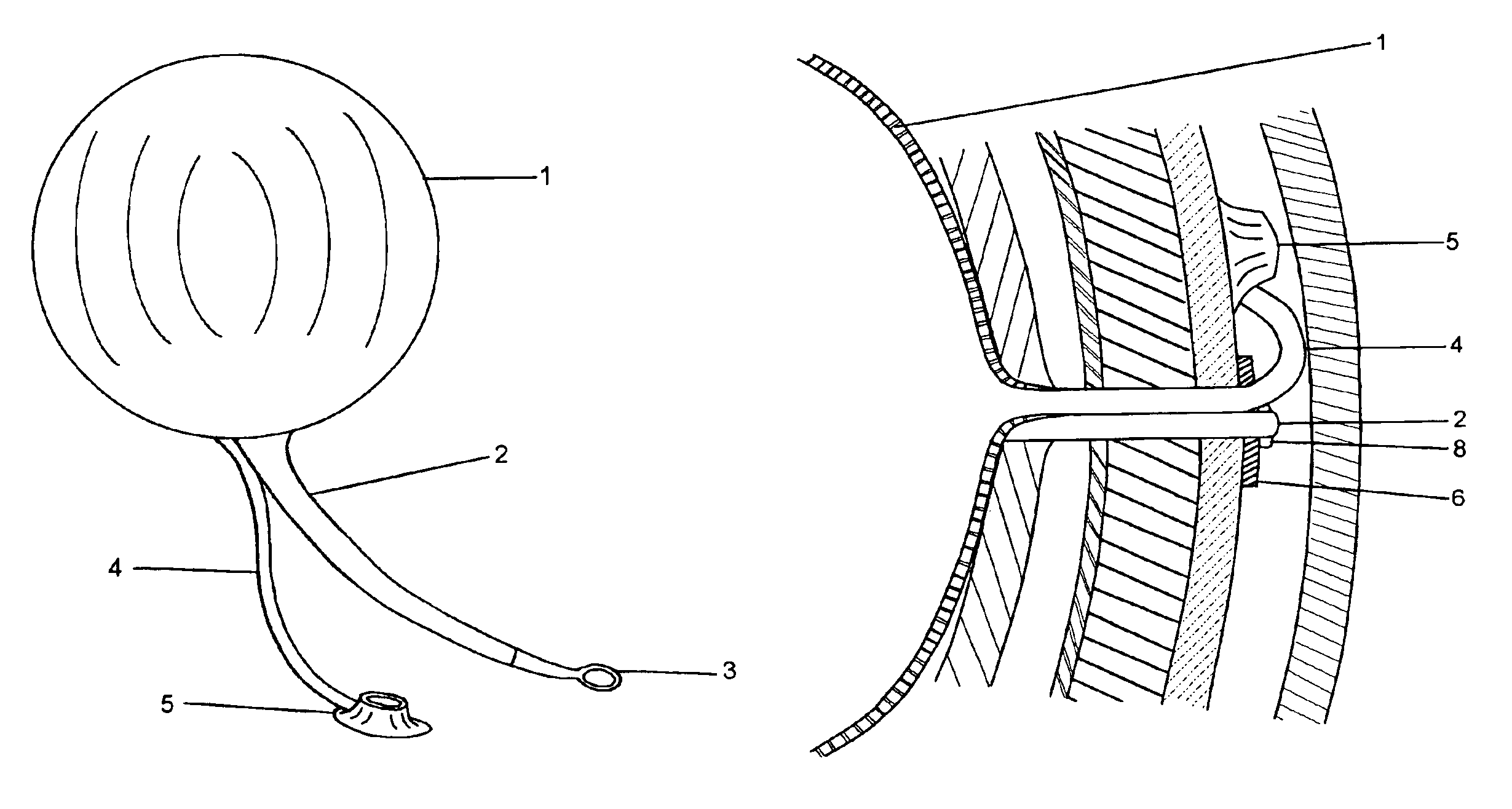
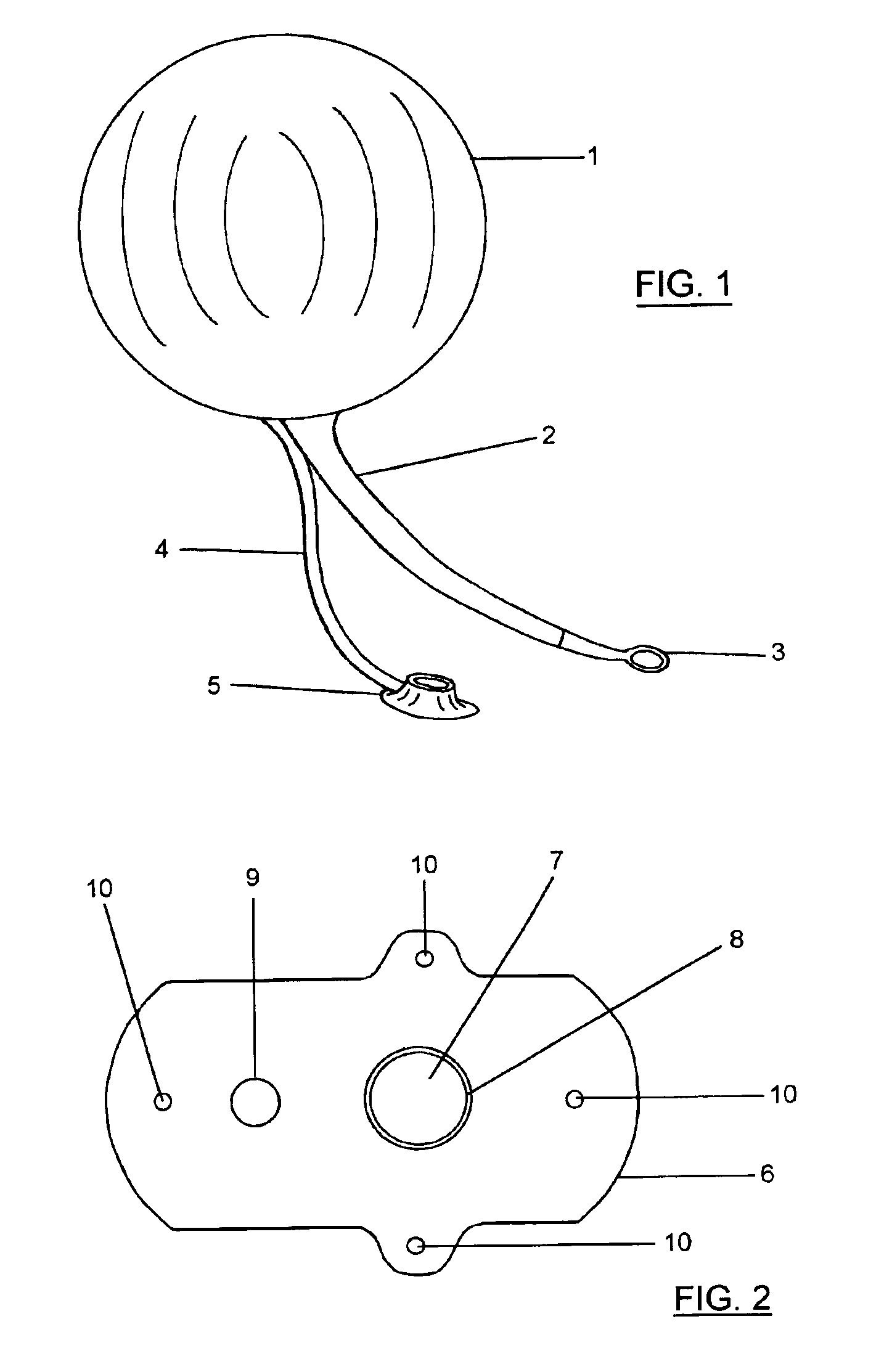
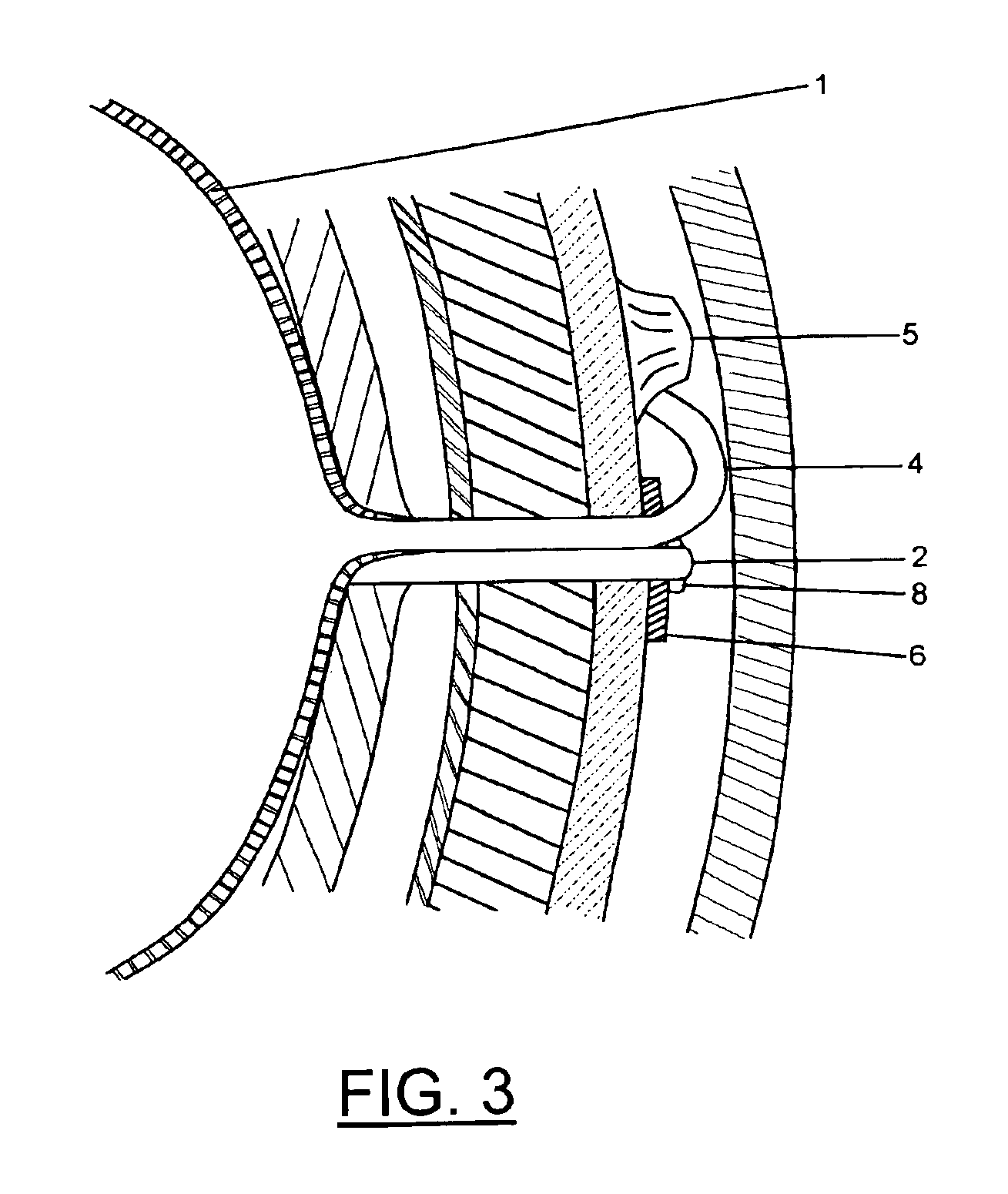
Intragastric balloon assembly
InactiveUS7056305B2Avoiding movement and migrationAvoid nuisanceDilatorsIntravenous devicesEndoscopeGuide tube
This invention combines three medical-surgical elements such as an intragastric balloon, a valve to control the postoperatory inflating and the technique of percutaneous gastronomy with endoscopic control, as well as a new mean to fix the assembly that avoids the balloon migration. The intragastric balloon assembly of the invention comprises the silicone balloon with an inflating catheter and a device consisting in a silicone bar, which will be used as a tension support and for fixation to the aponeurosis by means of an adjustable plate, according to the needs, that may be secured with suture points or with metallic staples to the aponeurosis. Once such elements have been secured, the support is cut and the catheter is connected to an inflating valve, which in a preferred embodiment is placed in subcutaneously and held in place with suture points or staples to the aponeurosis.
Owner:JOSE RAFAEL GARZA ALVAREZ
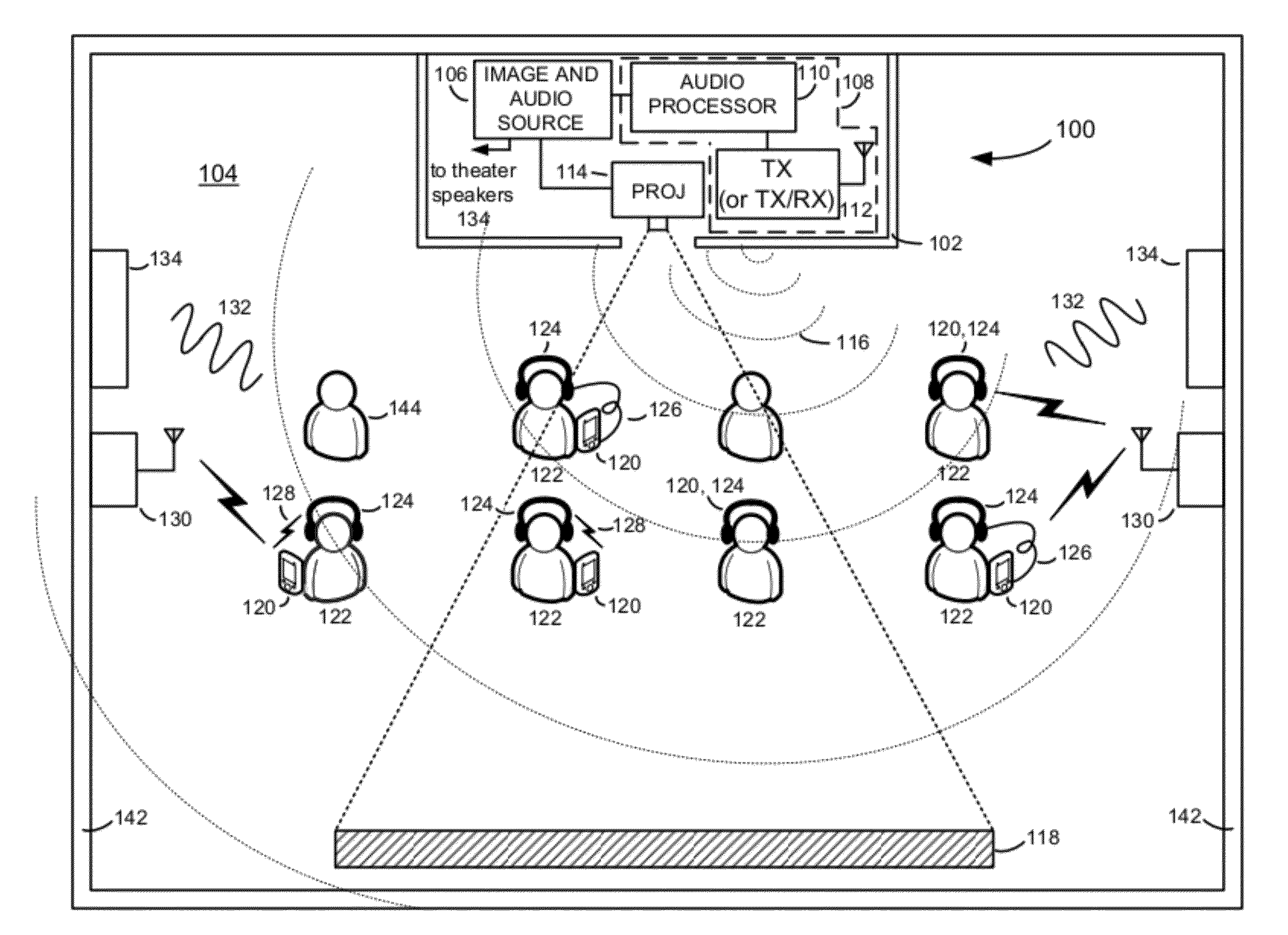
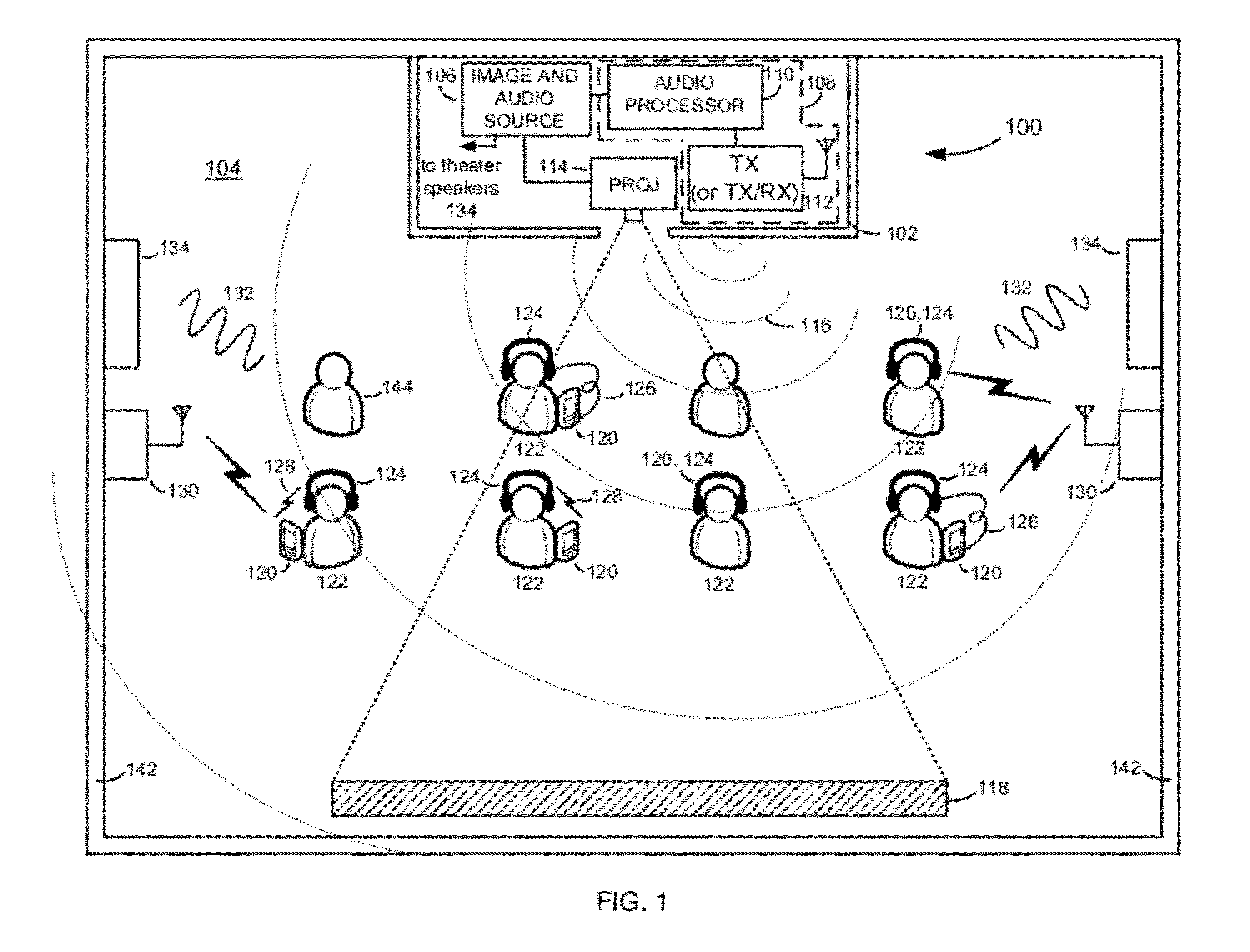
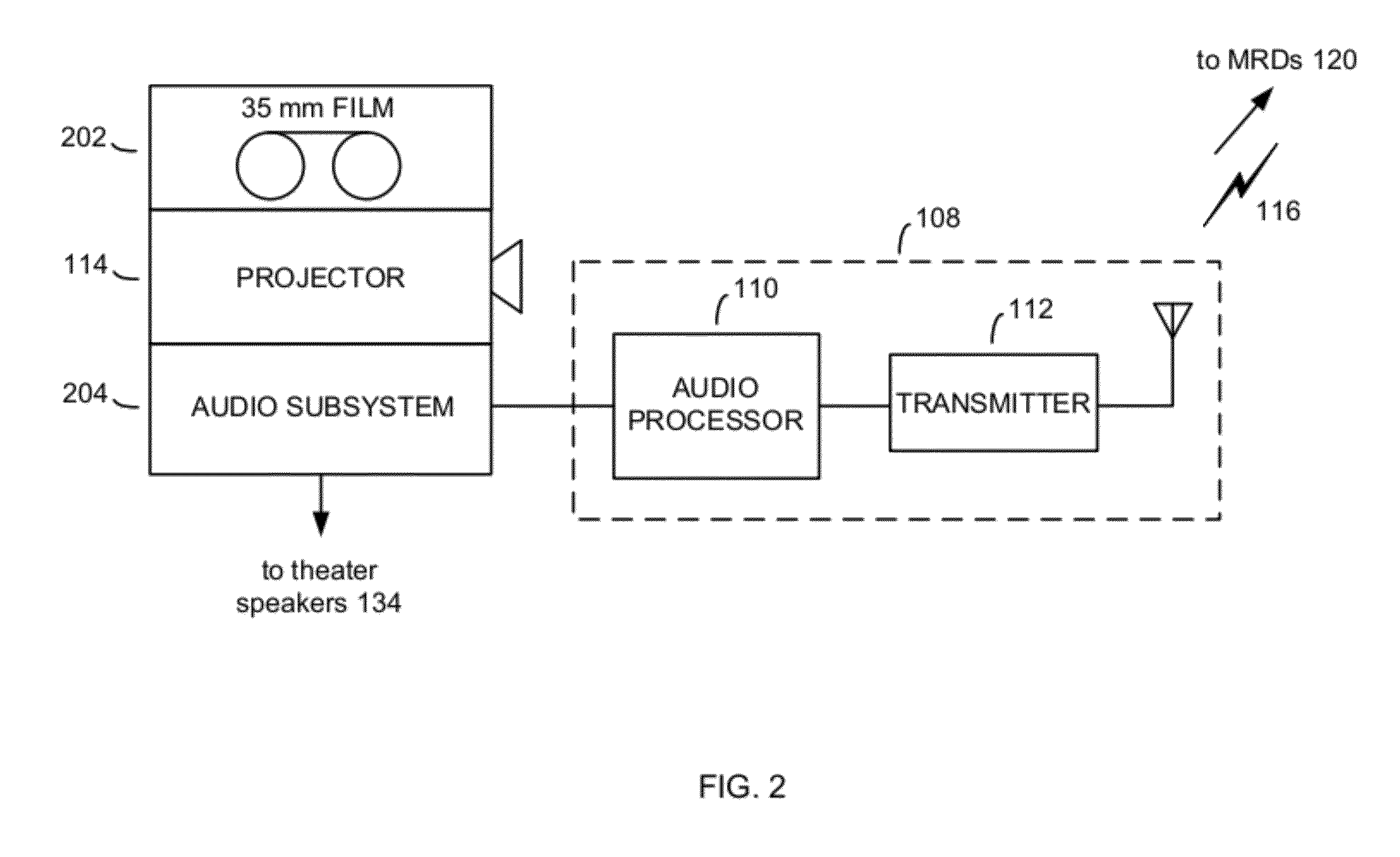
Multi-functional audio distribution system and method for movie theaters and other public and private venues
InactiveUS20120095749A1Avoid nuisanceImprove soundBroadcast specific applicationsSpeech analysisDistribution systemHeadphones
Audiovisual presentation methods, systems and apparatus for improving and enhancing the listening experience of attendees of audiovisual presentations. An exemplary audiovisual presentation system includes an audio processing and distribution unit (APDU) configured to generate and broadcast a wireless audio service containing audio of an audiovisual presentation (e.g., soundtrack and dialogue audio of a movie, in the case of a movie presentation) throughout an audiovisual presentation room or space (e.g., a movie theater, in the case of a movie presentation). The wireless audio service is received by mobile receiving devices (MRDs) having or comprising headsets, headphones or earbuds, through which MRD users listen to the audio of the audiovisual presentation provided by the wireless audio service while viewing images of the audiovisual presentation.
Owner:CAPRETTA ANTONIO
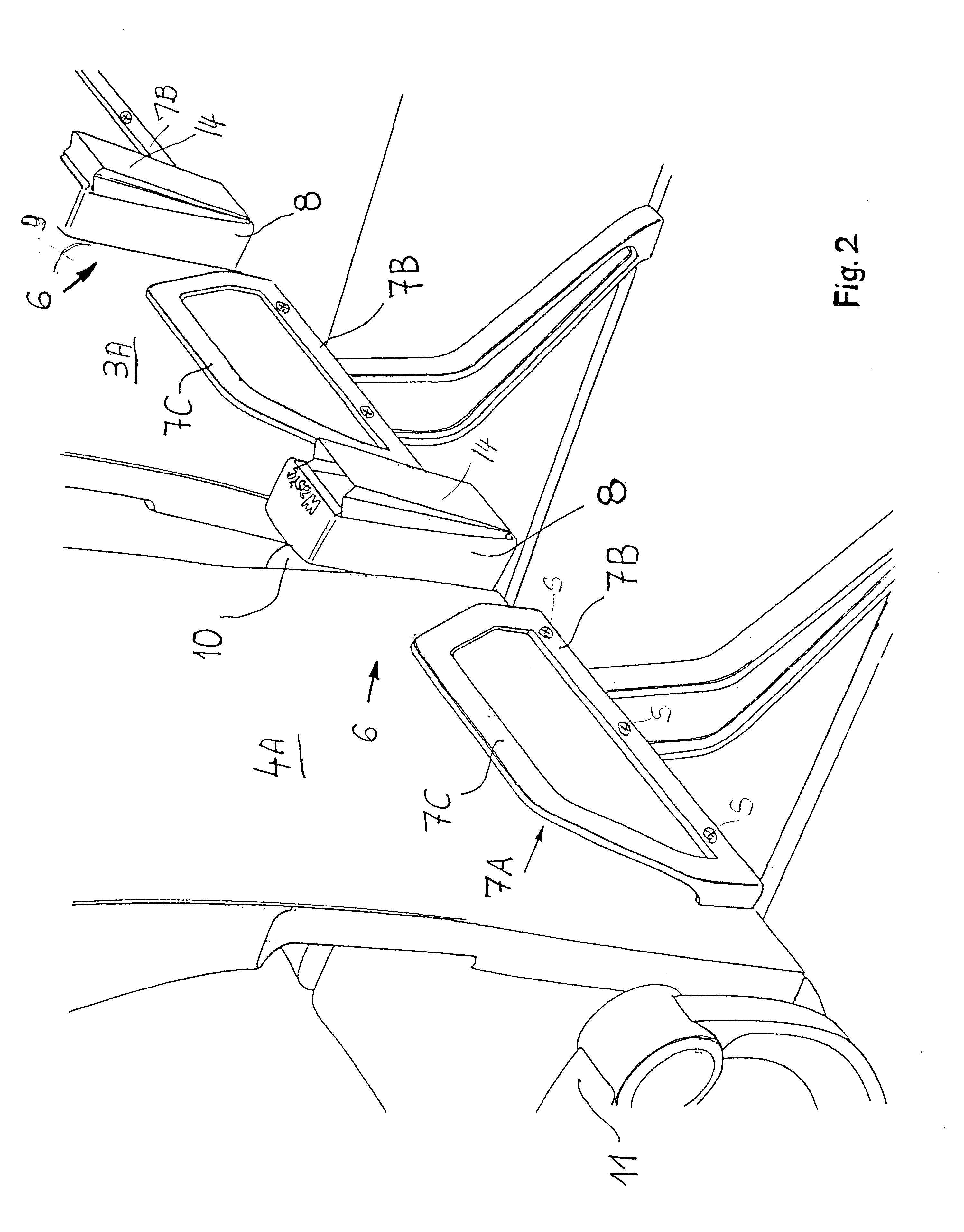
Passenger chair with a convenience device
InactiveUS20010024056A1Reduce usageShorten the timeVehicle seatsSeating arrangementsWaste materialAirplane
A passenger chair or a group of passenger chairs, particularly in an aircraft cabin, is equipped with a convenience device that includes an open storage bail which can hold only flat articles but not waste material, and a waste container for holding waste material but not flat articles. The storage bail and waste container form either a mounting unit or retrofit kit or are separate components. In both instances the mounting unit and the separate components are secured to a back facing area of a chair or group of chairs. The separate components are preferably so constructed that individual retrofit kits are provided.
Owner:AIRBUS OPERATIONS GMBH
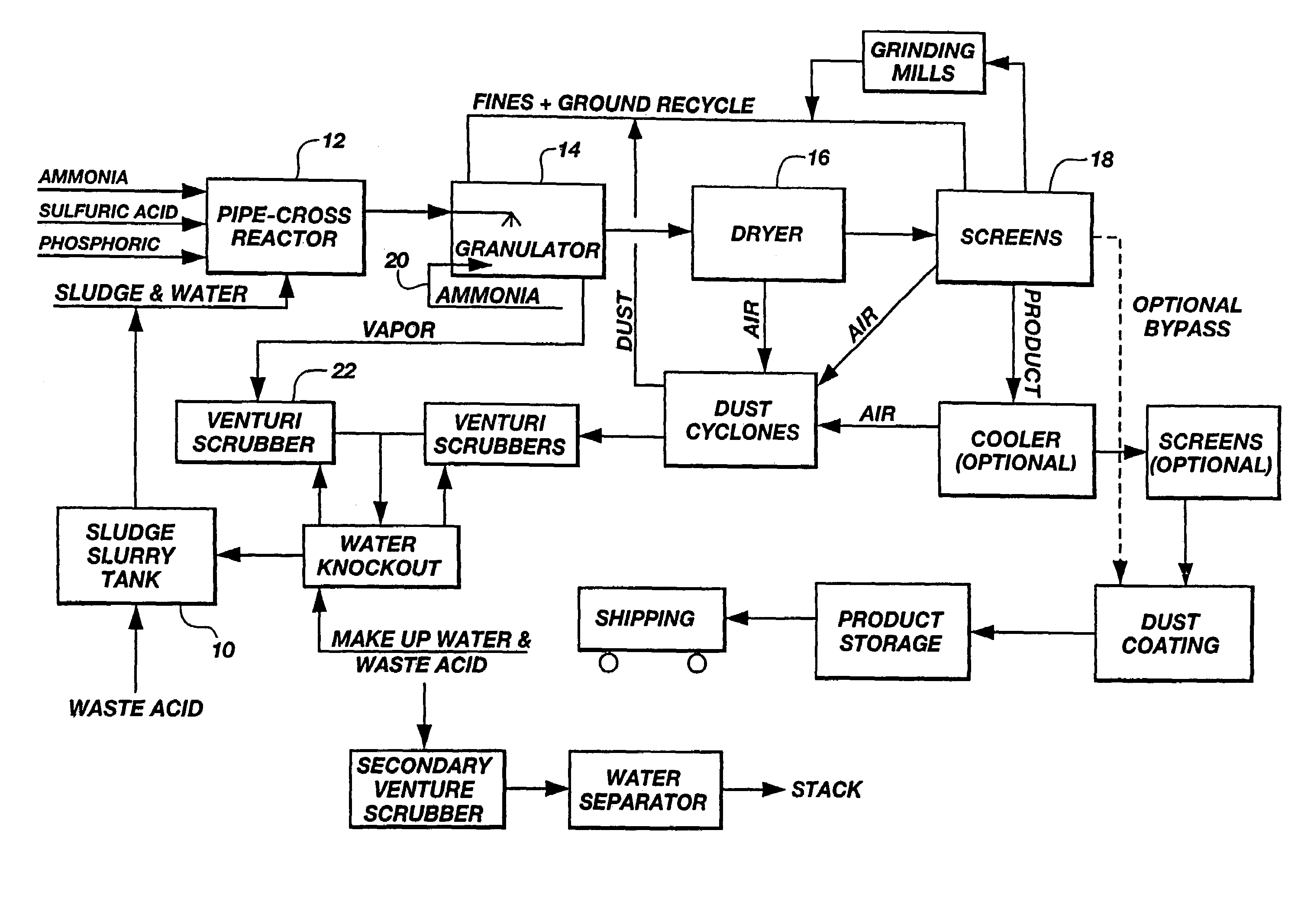
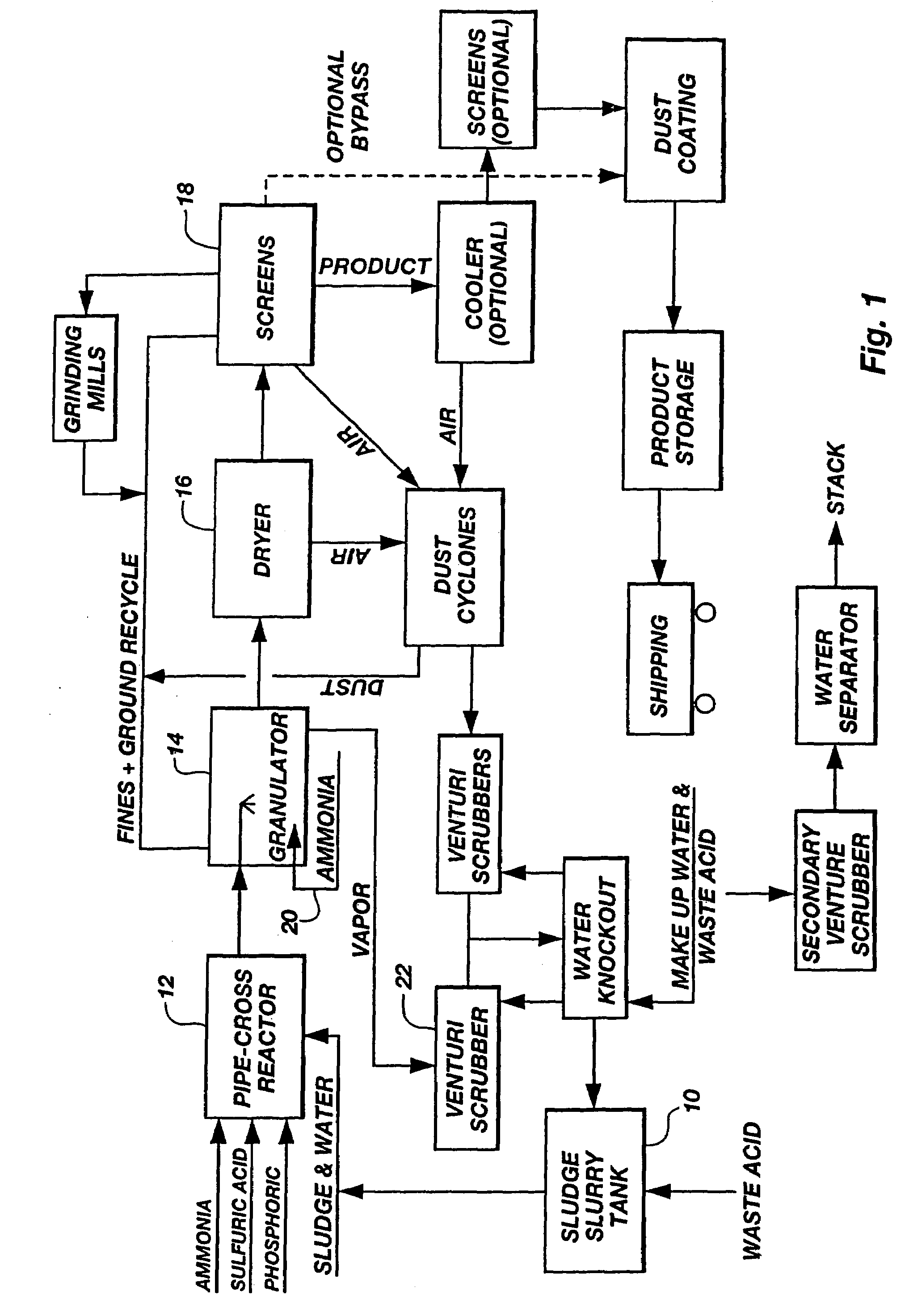
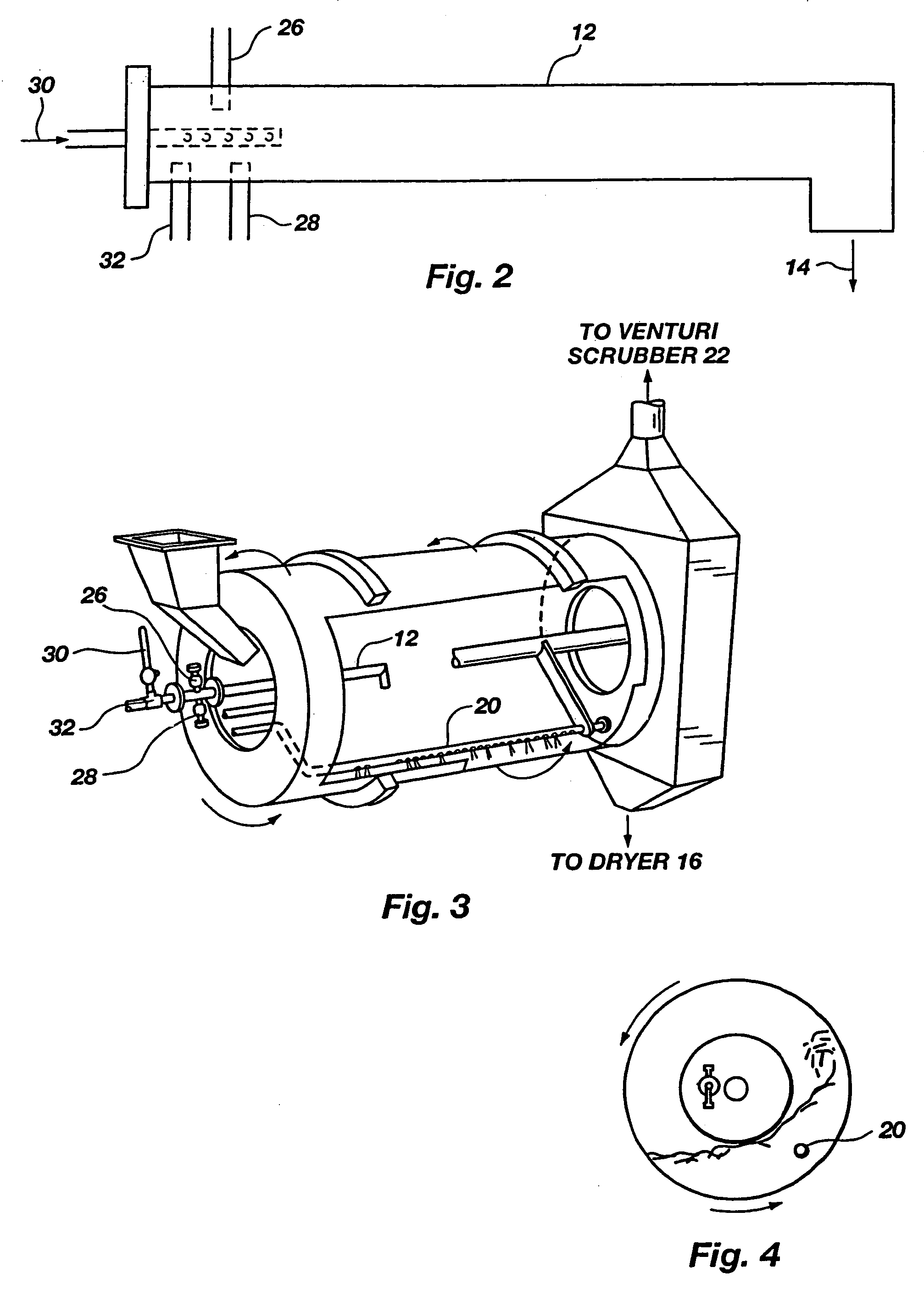
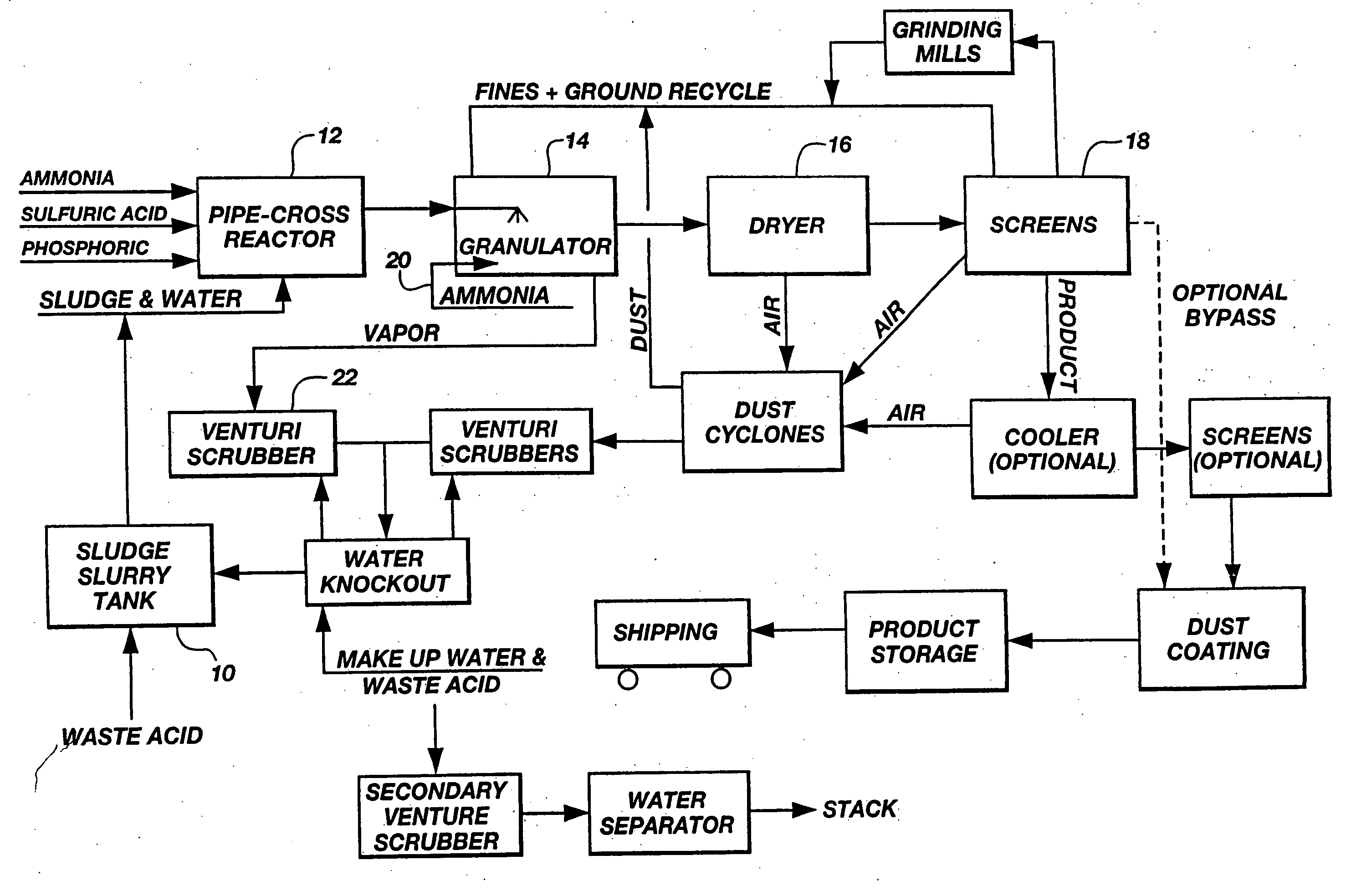
Sewage sludge recycling with a pipe cross-reactor
InactiveUS7169204B2Increase valueReduce moisture contentBio-organic fraction processingSludge treatmentSludgeVolumetric Mass Density
An improved process for enhancing the plant nutrient value of relatively low analysis organic waste material (e.g., sewage sludge) involves treating the waste material with an acid and base in a pipe-cross reactor. The process more particularly involves mixing the waste material with water to form a slurry (or initially taking the waste material as a slurry); pumping the slurry to a pipe-cross reactor for reaction with a base, acid, and water to form a melt; spraying the melt onto a recycling bed of fines in a granulator, and flashing off the water contained in the melt as steam; rolling the melt onto recycled fine particles in a granulator to form granulated particles; and drying these granulated particles to form an enhanced plant nutrient value composition (e.g., a fertilizer or soil conditioner having a greater “NPK” value than the original relatively low analysis organic waste material). The invention also includes fertilizers produced according to the improved process, which fertilizers are of the same size and shape and density of commonly used fertilizers. The method advantageously utilizes the heat generated by the exothermic acid-base reaction in the pipe-cross reactor to remove the approximately 80% water from sludge, thus saving large amounts of energy normally used in conventional drying or burning methods, while, at the same time, conserving the intrinsic values of the nutrients and humates contained in the sludge. In one embodiment, the process includes a method of disposing of spent acid from a hot dip galvanizing process or a steel pickling process involving incorporating the spent acid to maintain the low pH of a venturi scrubber used in the improved process.
Owner:UNITY FERTILIZER LLC
Preparing method for semen euryales and chrysanthemum instant tea with high blood pressure, lipid and glucose reducing effect
The invention provides a preparing method for semen euryales and chrysanthemum instant tea with a high blood pressure, lipid and glucose reducing effect and relates to the technical field of functional drinks. The instant tea is formed by preparing semen euryales extract spray-dried powder obtained by pretreating semen euryales and chrysanthemum extract freeze-dried powder obtained by pretreating chrysanthemum according to the proportion. The instant tea has the advantages that the semen euryales is smashed and fried, low-temperature reflux extraction is carried out on the semen euryales to obtain an effective ingredient, the effective ingredient is matched with the chrysanthemum with the synergistic effect, the mouthfeel is improved, the good mouthfeel of chrysanthemum faint scent and semen euryales wheat aftertaste is achieved, and spray drying is carried out to obtain the instant tea. In the production process, the effective ingredient is fully extracted, the original taste is retained, a membrane concentration method is used for isolating the small quantity of fat soluble pesticide ingredients possibly remaining in the raw materials, the instant tea has the high blood pressure, lipid and glucose reducing effect and has the fire clearing effect of the chrysanthemum, insect nuisance in traditional chrysanthemum tea drinking is avoided, the instant tea is very suitable for modern life pace, and the raw materials are homology of medicine and food and free from toxic and side effects.
Owner:TIANCHANG QIANNUO BIOTECH CO LTD
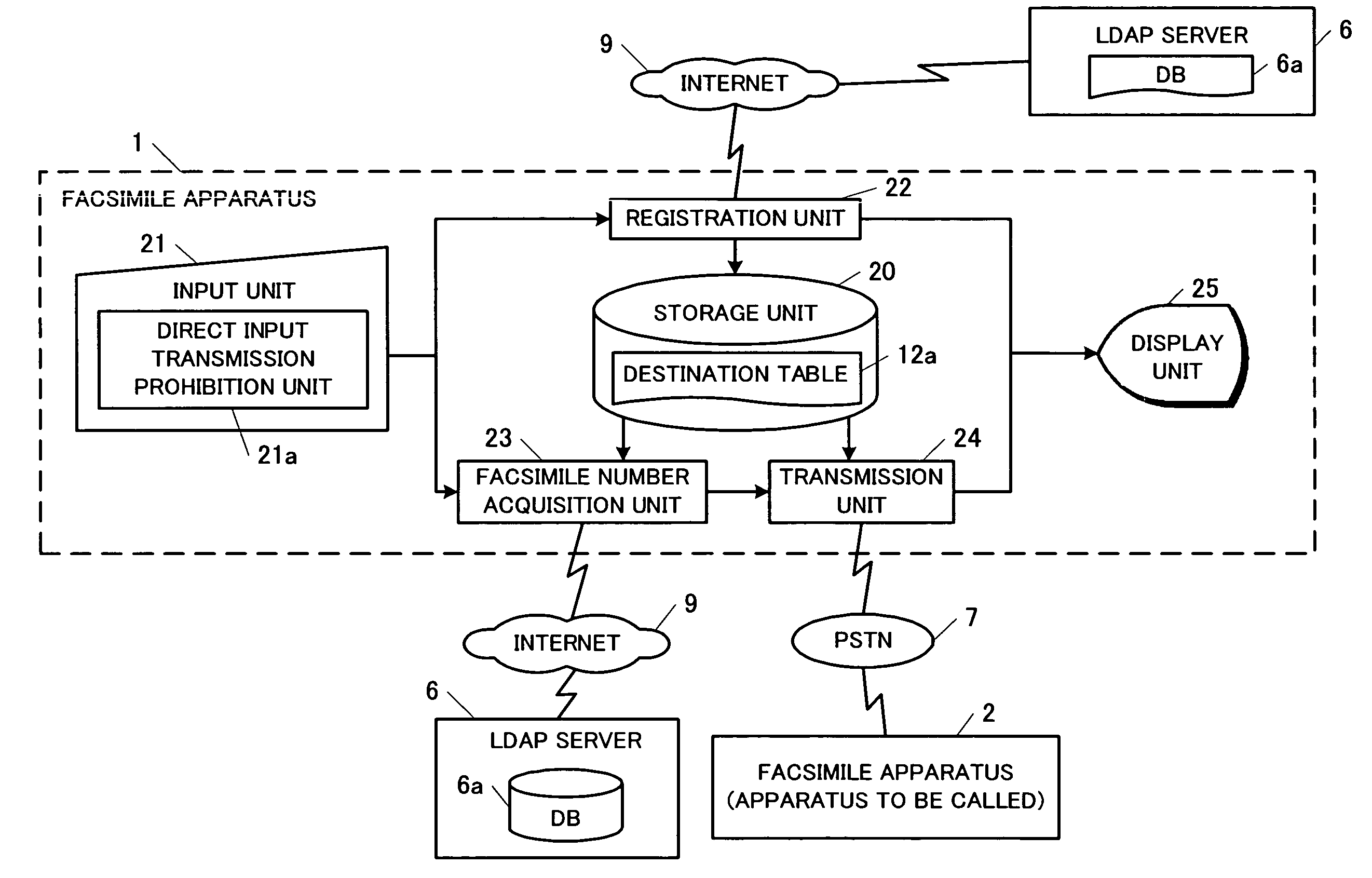
Facsimile apparatus, facsimile communication method, and facsimile communication system
ActiveUS20070247670A1Avoid nuisanceIncrease valuePictoral communicationDigital output to print unitsCommunications systemFacsimile transmission
A facsimile apparatus 1 is provided, which can access a latest database 6a associating facsimile numbers and destination names. The apparatus includes a storage unit 20 for storing a destination table 12a in which button information such as one-touch dial buttons, facsimile numbers, and destination names are associated, an input unit 21 for accepting an instruction for one-touch facsimile transmission, a facsimile number acquisition unit 23 for identifying a destination name associated with the transmission instruction by referring to the destination table 12a and searching the database 6a using the destination name as a search key to acquire a facsimile number associated therewith, and a transmission unit 24 for determining whether the acquired facsimile number agrees with a facsimile number associated with a one-touch dial button accepted by the input unit 21 and executing facsimile transmission only when the numbers agree.
Owner:MURATA MASCH LTD
Passenger chair with a convenience device
Owner:AIRBUS OPERATIONS GMBH
Mobile terminal and method for controlling flashlight
InactiveCN106303089ASave electricityAvoid nuisanceTelephone set constructionsComputer terminalFlashlight
The invention provides a mobile terminal and a method for controlling flashlight. The mobile terminal comprises a flashlight, a light detection module and a control module, wherein the light detection module is used for detecting the light intensity of the surrounding environment, the control module is used for judging whether the detected light intensity is smaller than first preset light intensity, and when the detected light intensity is smaller than first preset light intensity, automatically switching on the flashlight and gradually adjusting the light intensity of the flashlight to preset light intensity. According to the mobile terminal and the method for controlling flashlight, the flashlight can be automatically switched on according to the environment, and the light intensity of the flashlight is adjusted to corresponding light intensity by gradually increasing the light intensity to provide proper lighting light and avoid damage to the user eyes.
Owner:NUBIA TECHNOLOGY CO LTD
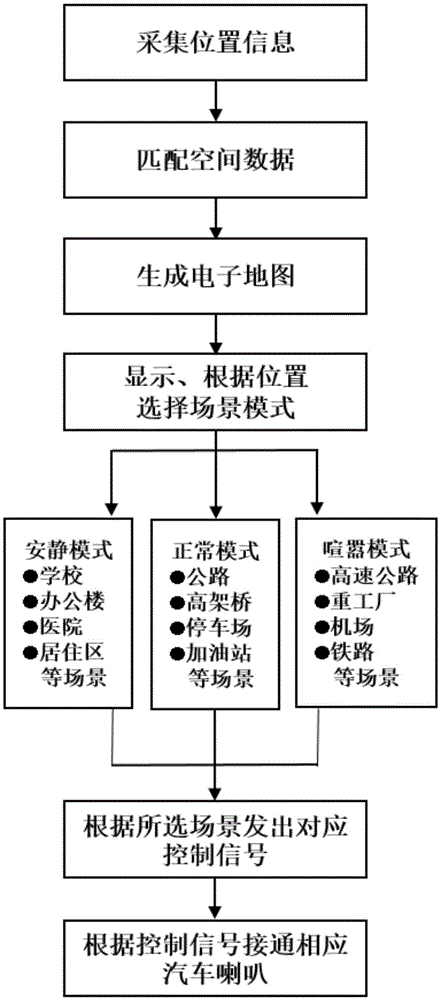
Car horn volume mode self-adaptive control method based on environmental identification
InactiveCN105653235AImprove securityEffective warningAcoustic signal devicesSound input/outputDriver/operatorFace sheet
The invention discloses a car horn volume mode self-adaptive control method based on environmental identification. The method includes the following steps that in the driving process of a car, a GPS module positions the current driving state and the position coordinates of the car and meanwhile sends the positioned information to a GIS module and an electronic map generating module, the GIS module matches the position coordinates of the car with existing space data in the module to obtain the space position where the car is located currently, the space position is sent to the electronic map generating module which converts the information into a digital electronic map displayed on an interaction panel of a driver, and a car-mounted control unit analyzes the obtained space data, identifies the scene mode type which the current environment of the car belongs to and selects and sends volume mode signals to an execution unit. By means of the self-adaptive mode, safety of the car during driving in various environments is improved, and driving behaviors are more civilized.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
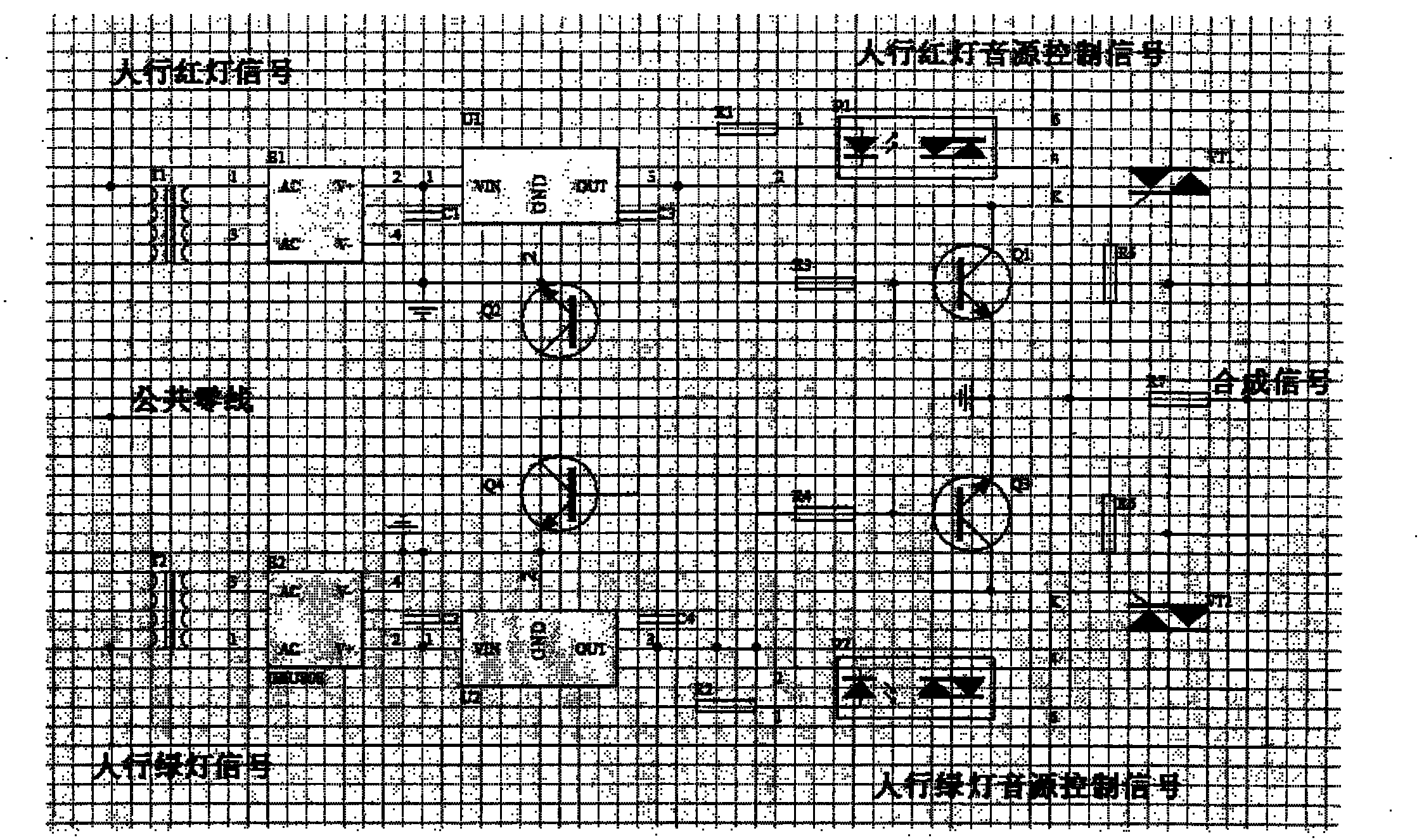
Intelligent pedestrian street crossing voice prompt device
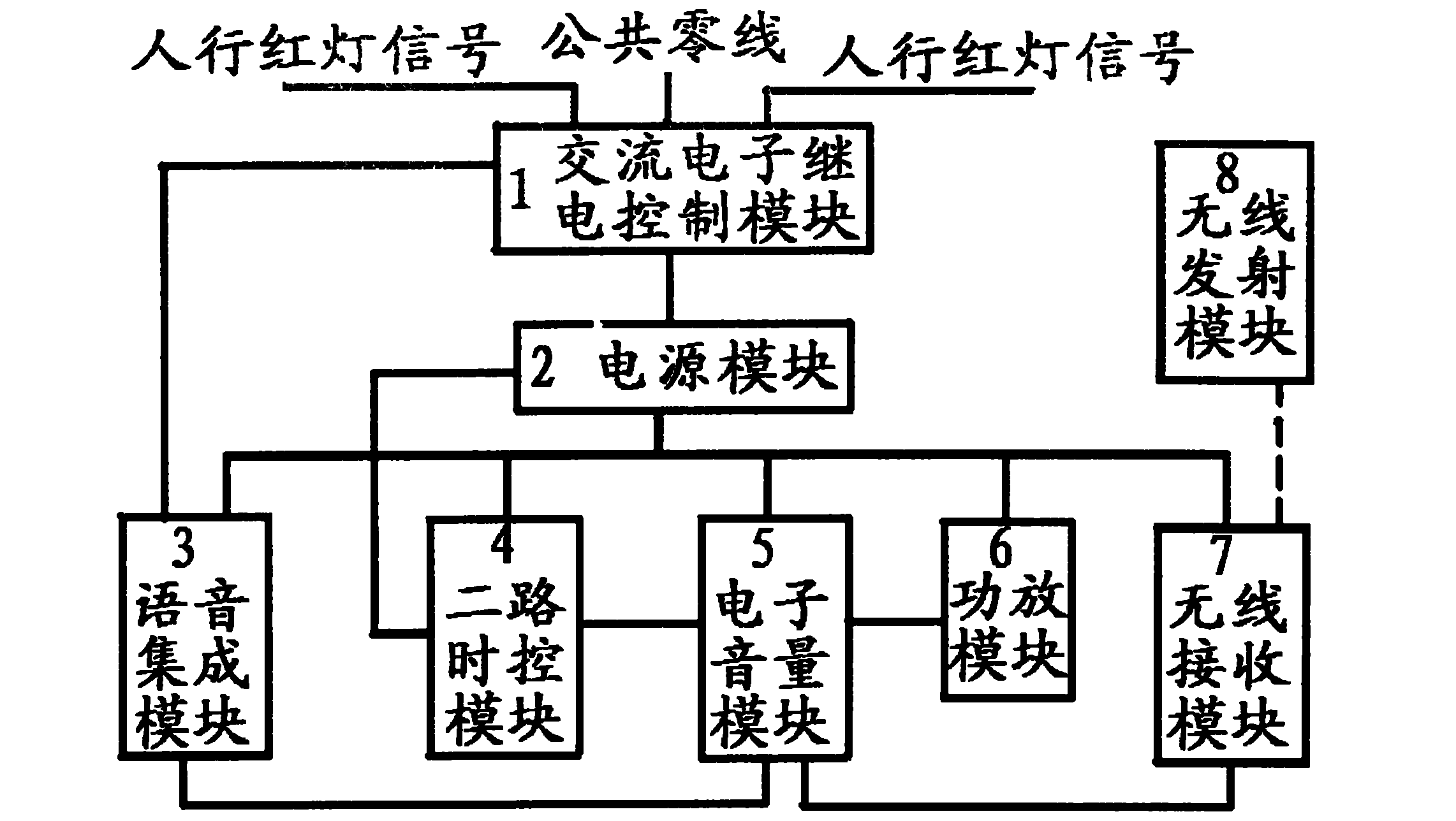
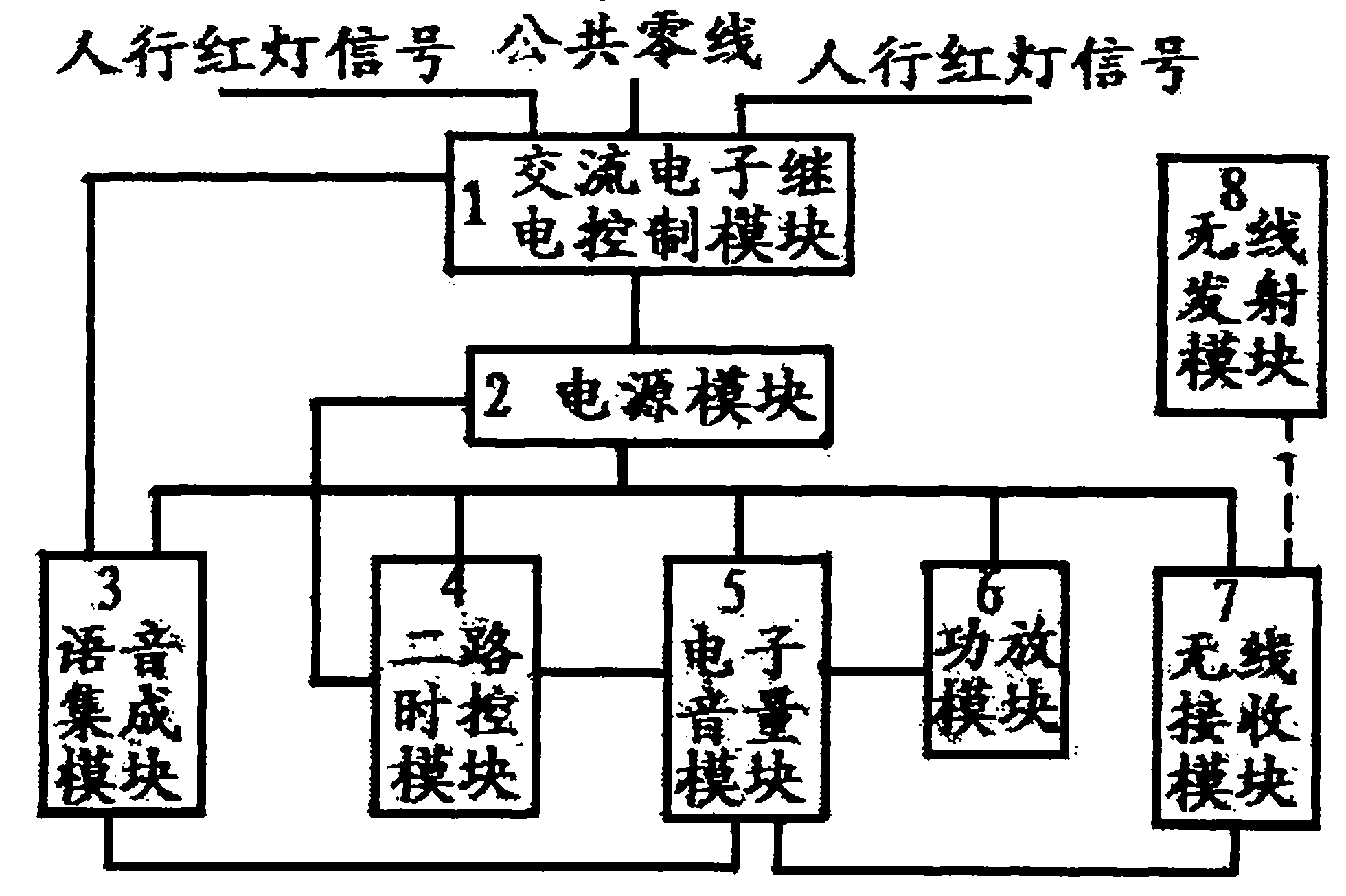
InactiveCN102254427ANo noiseNo sparkControl with pedestrian guidance indicatorEnvironmental noiseControl signal
The invention relates to an intelligent pedestrian street crossing voice prompt device, characterized by comprising an alternating current electronic relay control module (1), a power source module (2), a voice integrated module (3), a two-path time control module (4), an electronic voice volume module (5), a power amplification module (6), a wireless receiving module (7) and a wireless transmission module (8), wherein (1) receives pedestrian traffic light signals and provides a stable voltage for (2), and simultaneously provides voice source control signals for (3) and controls (3) to supply a voice source for (5); (2) provides power sources for (4), (5), (6) and (7); one path of (4) controls (2), namely the on and off and time, and the other path of (4) controls (5), namely the conversion of high voice and low voice and time; the voice volumes of a low voice section and a high voice section are respectively manually set through a common potentiometer in (5) and remotely set through an electronic potentiometer; (8) can transmit wireless signals at the high voice section; (7) can receive wireless signals and decode the wireless signals, and controls (6) by (5) to realize voice volume control when pedestrian traffic lights work; and the system voice volume can be changed by 0-20dB along with external environmental noises via the automatic voice volume circuit in (5).
Owner:张驰
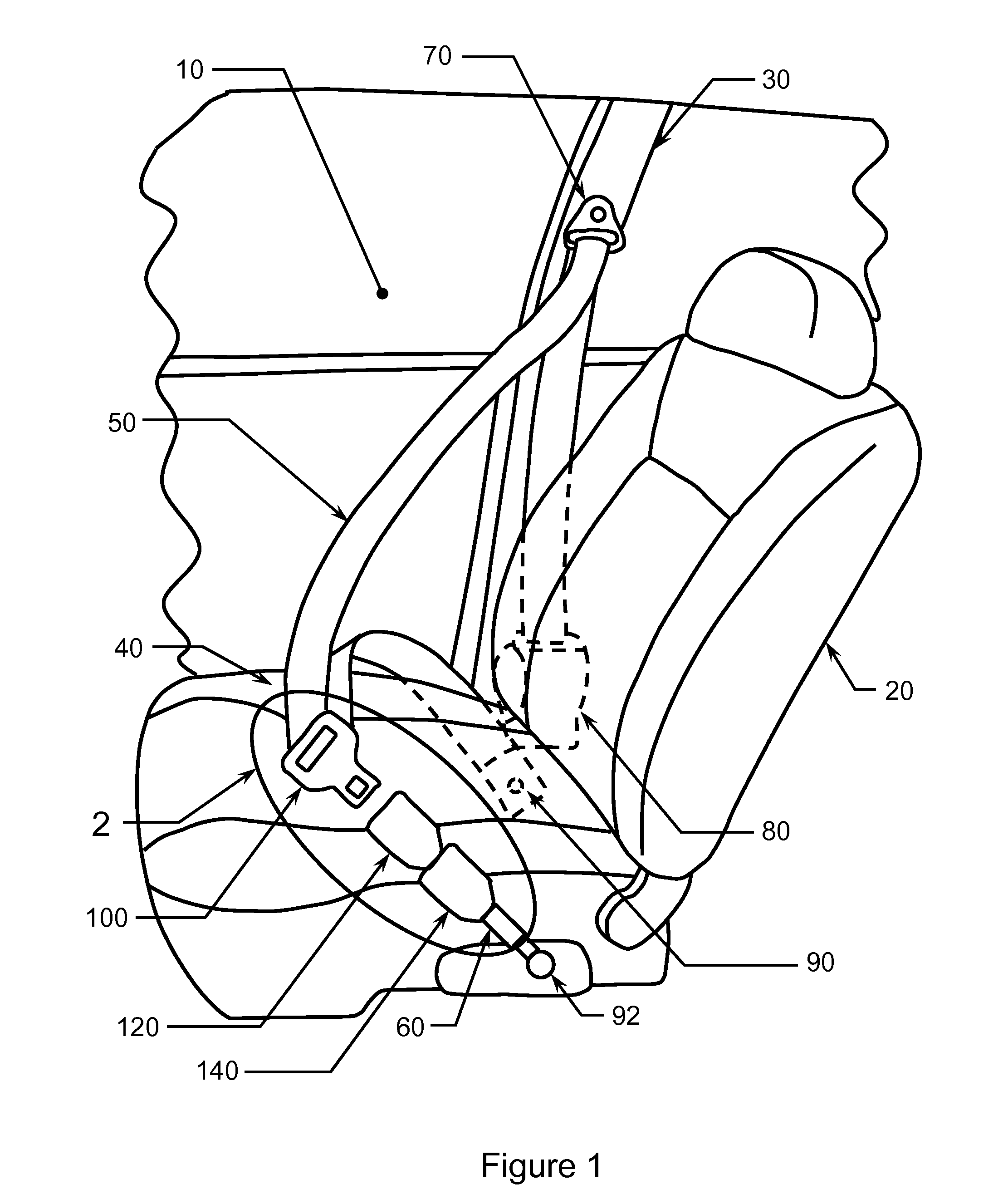
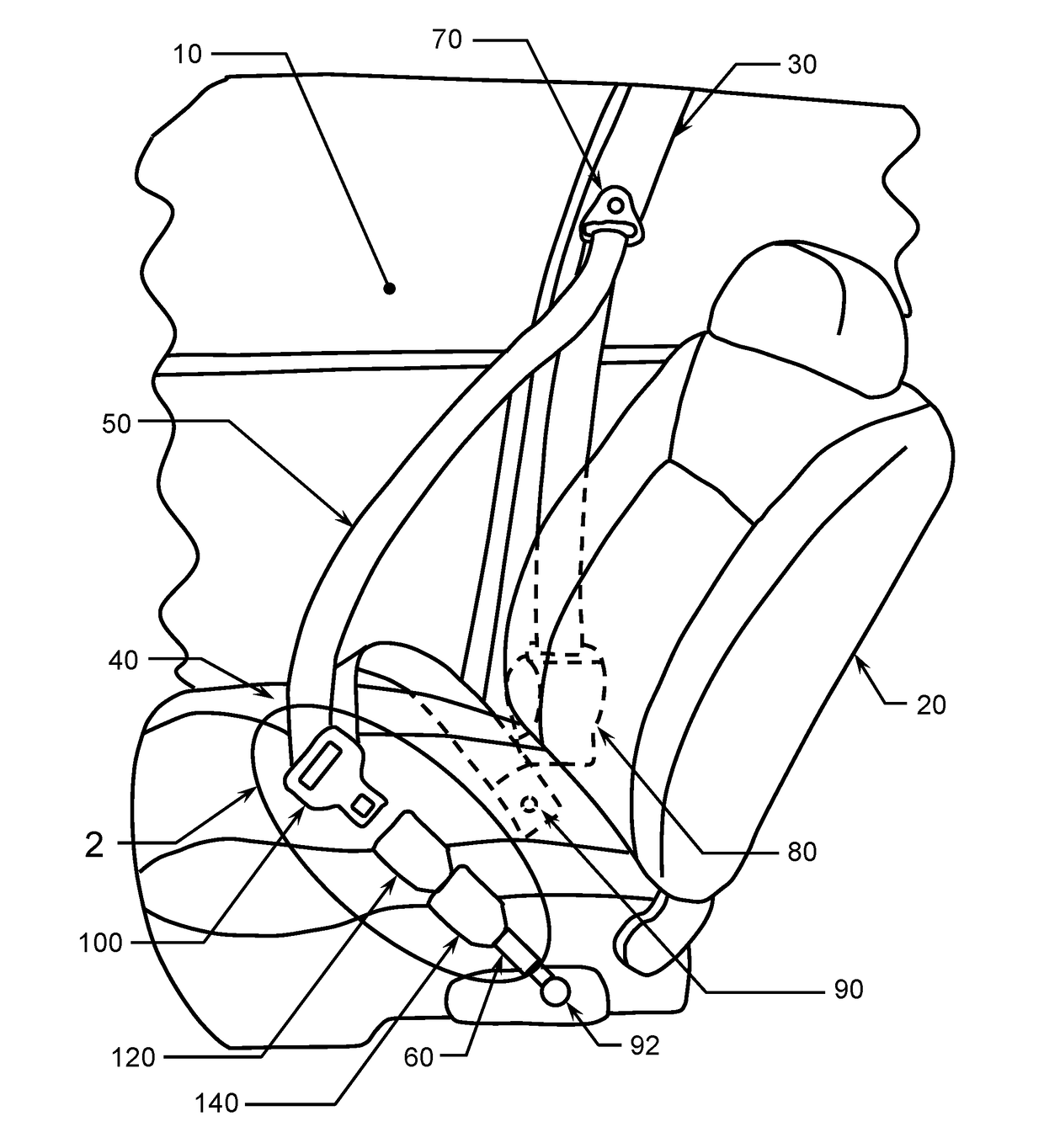
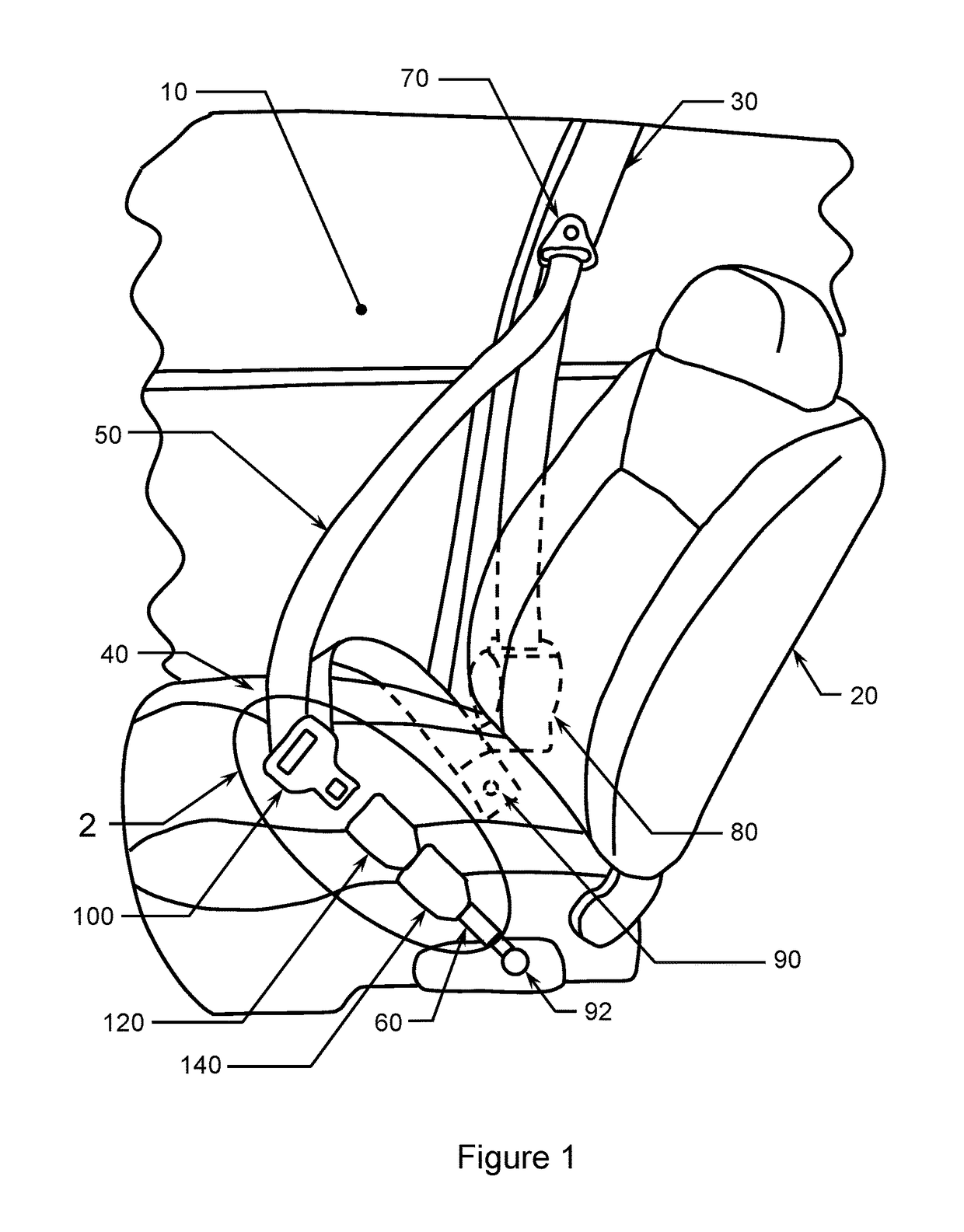
Adaptive Seatbelt Apparatus
InactiveUS20100162530A1Avoids nuisanceRending the seatbelt easily releasable or extractableSnap fastenersFastening devicesAdaptive securitySafety harness
Owner:SCHRAMM MICHAEL R
Client side, server and friend feed prompting system and friend feed prompting method in SNS (social network service) network
InactiveCN102957727AIncrease stickinessHigh activityServices signallingMobile application execution environmentsSocial network serviceClient-side
An embodiment of the invention discloses a friend feed prompting method in an SNS (social network service) network. The method includes: when a user enters an application store, an SNS network client side acquires user information of the user; the SNS network client side acquires friend feed of the user from an SNS network server according to the user information, wherein the friend feed comprises at least one App news feed; and the SNS network client side prompts the friend feed. The embodiment of the invention further discloses the client side, the server and the friend feed prompting system in the SNS network. By the aid of the client side, the server, the method and the system, user adhesiveness and activeness of users are improved beneficially, and SNS is given to full play.
Owner:TENCENT TECH (SHENZHEN) CO LTD
Sewage sludge recycling with a pipe cross-reactor
InactiveUS20050279146A1Enhance plant nutrient valueIncrease valueBio-organic fraction processingSludge treatmentSludgeSlurry
An improved process for enhancing the plant nutrient value of relatively low analysis organic waste material (e.g., sewage sludge) involves treating the waste material with an acid and base in a pipe-cross reactor. The process more particularly involves mixing the waste material with water to form a slurry (or initially taking the waste material as a slurry); pumping the slurry to a pipe-cross reactor for reaction with a base, acid, and water to form a melt; spraying the melt onto a recycling bed of fines in a granulator, and flashing off the water contained in the melt as steam; rolling the melt onto recycled fine particles in a granulator to form granulated particles; and drying these granulated particles to form an enhanced plant nutrient value composition (e.g., a fertilizer or soil conditioner having a greater “NPK” value than the original relatively low analysis organic waste material). The invention also includes fertilizers produced according to the improved process, which fertilizers are of the same size and shape and density of commonly used fertilizers. The method advantageously utilizes the heat generated by the exothermic acid-base reaction in the pipe-cross reactor to remove the approximately 80% water from sludge, thus saving large amounts of energy normally used in conventional drying or burning methods, while, at the same time, conserving the intrinsic values of the nutrients and humates contained in the sludge. In one embodiment, the process includes a method of disposing of spent acid from a hot dip galvanizing process or a steel pickling process involving incorporating the spent acid to maintain the low pH of a venturi scrubber used in the improved process.
Owner:UNITY FERTILIZER
Automobile intelligent anti-theft system
The invention discloses an automobile intelligent anti-theft system, which comprises a power supply module, a central controller, a door touch switch, an infrared detection module, a vibration sensor, an infrared camera, an alarm device and a mobile terminal; the power supply module is coupled to the central controller; the infrared camera is connected with a storage in the central controller; the vibration sensor, the door touch switch and the infrared detection module are connected with the infrared camera separately; the door touch switch and the infrared detection module are also connected with a microprocessor in the central controller; the central controller is also connected with an automobile starting system and the alarm device; and the mobile terminal is provided with a launcher matched with a communication module in the central controller. The automobile intelligent anti-theft system overcomes the problems that automobile theft resistance in the prior art mostly adopts an automobile starting lock and vibration alarm, so that the anti-theft function can be lost when an automobile key is lost, and the vibration sensor is more easily triggered by a non-theft vibration source to cause unnecessary environment noise.
Owner:ANHUI TECHN COLLEGE OF MECHANICAL & ELECTRICAL ENG
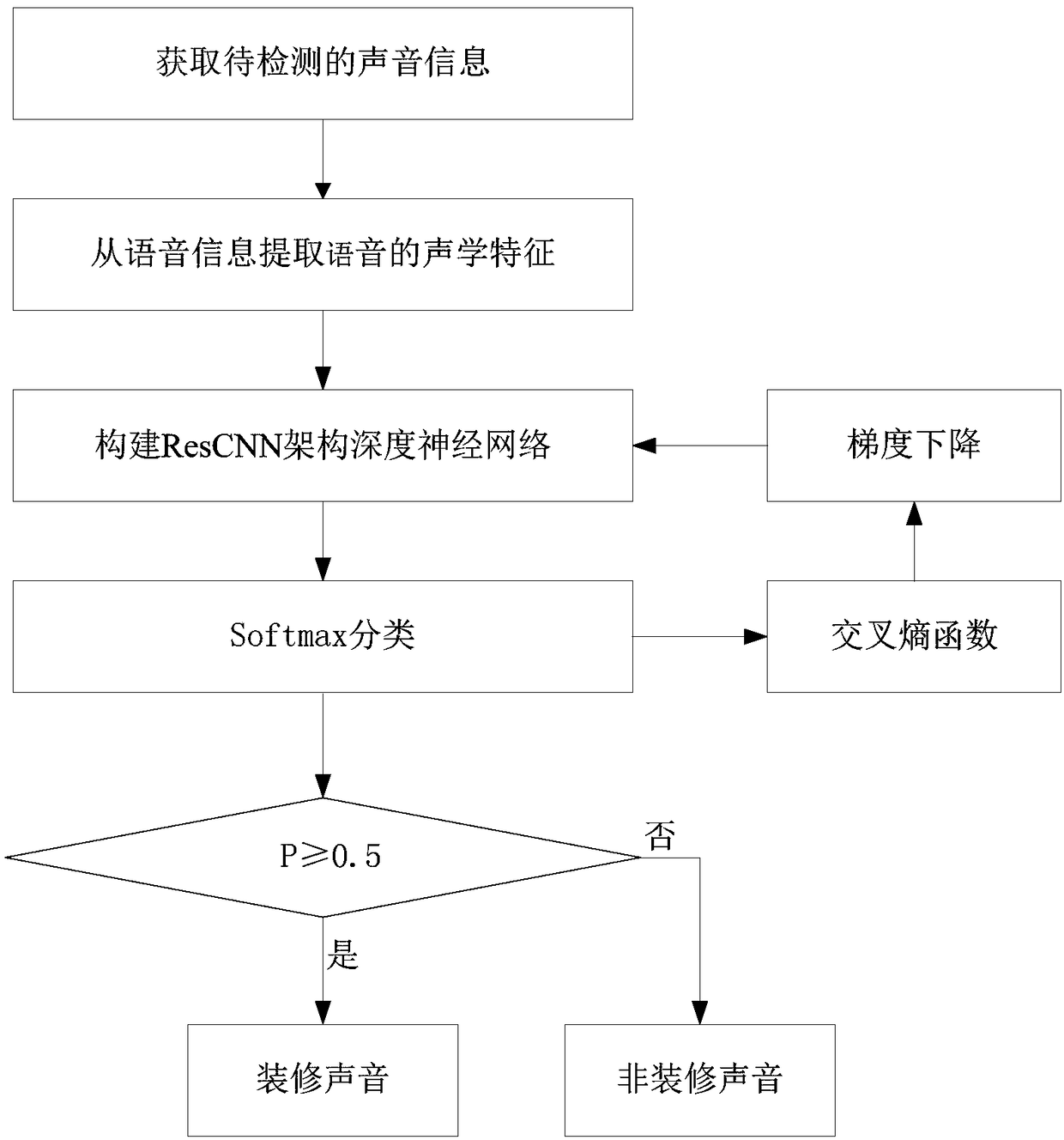
Decoration event detection method and device, computer device and medium
InactiveCN109102798AAvoid nuisanceImprove the recognition rate of decoration soundSpeech recognitionNetwork modelComputer science
The invention discloses a decoration event detection method and device, a computer device and a medium. The method comprises the sound is collected by a microphone or a microphone array in real time to obtain the to-be-detected sound information; acoustic characteristics of the sound information are extracted; a ResCNN neural network model is constructed; the acoustic characteristics are inputtedinto the ResCNN neural network model to obtain the decoration sound probability p; the acoustic probability p is compared with the actual result, and a cross entropy loss function is constructed; theResCNN neural network model is trained according to the cross entropy loss function; the trained ResCNN neural network model is utilized to perform decoration sound prediction, if the sound is determined to be the decoration sound, the location where a decoration event occurs is identified based on the device number of the microphone. The method is advantaged in that whether decoration occurs andidentification of the decoration location can be effectively determined, through combining the ResCNN neural network architecture and the cross entropy loss function, not only the decoration sound identification rate is improved, but also whether a certain sound is the decoration sound can be accurately identified, and the overall model size is reduced.
Owner:XIAMEN KUAISHANGTONG INFORMATION TECH CO LTD
Adaptive seatbelt apparatus
InactiveUS8336663B2Rending the seatbelt easily releasable or extractableAvoid nuisanceSnap fastenersFastening devicesEngineeringAdaptive security
Owner:SCHRAMM MICHAEL R
Resettable Load-Limiting Adaptive Seatbelt Apparatus
InactiveUS20180056934A1Rending the seatbelt easily releasable or extractableAvoid nuisanceBucklesEmergency release devicesAdaptive securitySelf adaptive
Owner:SCHRAMM MICHAEL R
Information pushing method and device, computer equipment and storage medium
ActiveCN112637282AImprove intelligenceReduce complaintsDigital data information retrievalAdvertisementsData feedBusiness Personnel
The invention relates to the field of artificial intelligence, and provides an information pushing method and device, computer equipment and a storage medium, and the method comprises the steps: carrying out the parameter verification of a received information pushing request, and obtaining a verification result; judging whether the information pushing request carries the identity information, the to-be-pushed information and the to-be-pushed number or not; if yes, obtaining questioning question data corresponding to the identity information, performing identity verification on the business personnel based on feedback answer voice data fed back by the business personnel, and judging whether identity verification is passed or not; if yes, extracting the to-be-pushed information, analyzing and processing the to-be-pushed information, and judging whether the type of the to-be-pushed information belongs to a marketing type or not; if yes, extracting a to-be-pushed number, and judging whether the to-be-pushed number exists in the shielding white list or not; and if yes, limiting sending of the to-be-pushed information to the client terminal corresponding to the to-be-pushed number. According to the invention, the intelligence of marketing information pushing is improved. The method can also be applied to the field of block chains, and the to-be-pushed information and other data can be stored on the block chains.
Owner:PINGAN PUHUI ENTERPRISE MANAGEMENT CO LTD
Prompt and alarm system used for walking of blind person
The invention discloses a prompt and alarm system used for walking of a blind person. The system includes a walking stick and an alarm device; the bottom of the walking stick is provided with thread teeth, anti-skidding glue is in threaded connection with the walking stick, the anti-skidding glue is internally provided with an upper magnet, and the lower end of the upper portion of the walking stick is provided with a handheld part. The alarm device is composed of a plastic blind-person brick and an alarm, the plastic blind-person brick is internally and fixedly provided with a lower metal elastic piece and an upper metal contact, the upper metal contact is arranged on the upper portion of the inner wall of the plastic blind-person brick, the lower metal elastic piece is arranged under the upper metal contact, and a lower magnet is fixedly embedded in the lower portion of the lower metal elastic piece; the alarm is composed of a voice player, an electronic assembly, a storage battery, a wire and a shell. The system can perform voice broadcasting at a traffic light crossing for prompting the blind person, after hearing the broadcast, the blind person lifts the walking stick, voice broadcasting work is automatically stopped, and the disturbing phenomenon is avoided.
Owner:刘建军
Compound microbe preparation and poultry fermenting bed padding
The invention discloses a compound microbe preparation which is mainly formed by mixing 4 fungicides and an auxiliary material, wherein the ratio of the 4 fungicides to the auxiliary material is (60:40) to (80:20); the 4 fungicides are a streptococcus lactis fermentation microbial agent, an aspergillus oryzae fermentation microbial agent, a thermo-actinomyces fermentation microbial agent and a beer yeast fermentation microbial agent; the ratio of the streptococcus lactis fermentation microbial agent to the aspergillus oryzae fermentation microbial agent, the thermo-actinomyces fermentation microbial agent and the beer yeast fermentation microbial agent is (0.8-1.2):(0.8-1.2):(0.8-1.2):(0.8-1.2) by mass in part. The invention further discloses a poultry fermenting bed padding containing the compound microbe preparation. The compound microbe preparation can radically decompose a great amount of un-digested substances of poultry manure, and can reduce the vast majority of odor in a poultry house. The padding is suitable for poultry culture, and can effectively reduce the generation of poultry epidemic diseases, reduce use of medicine, and improve the quality of poultry meat.
Owner:胡小勇 +1
Airliner overhead meals delivery
Abundant space above an airliner's ceiling lends itself well for replacement of a single food cart blocking aisles with overhead conveyance of passengers' meals. A linear levitating motor for quaintness and easy controls, in fastened to airplane's structure track system, is a motive element. By movements of the motor's mover and attached to it elevator meals are delivered to passengers at several points simultaneously. Overhead moving trays holders are lowered over the center aisles for distribution of meal trays by attendants, and elevated to return to the galley for new load. Same system is used to collect discards.
Owner:BARANSKI GREGORY
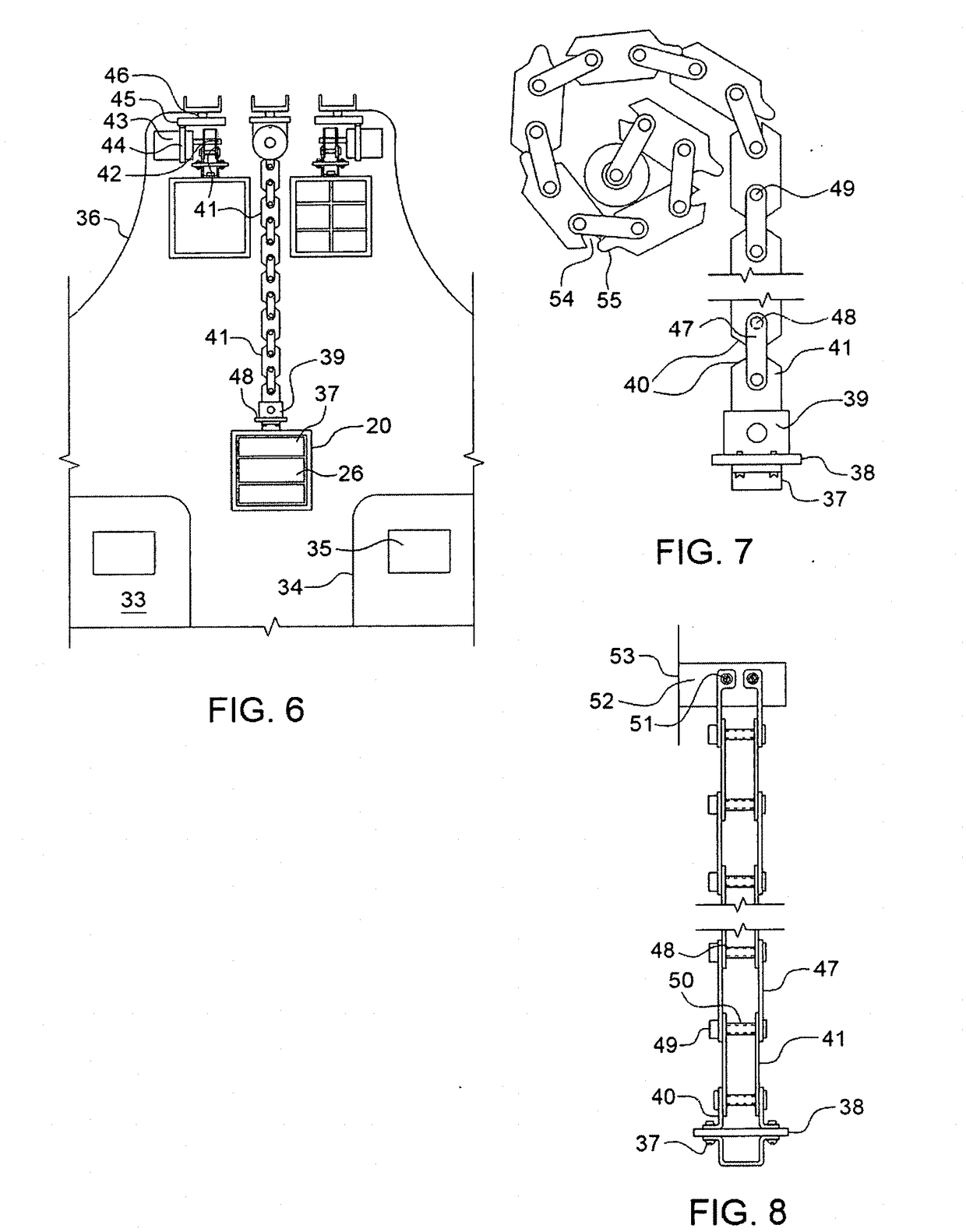
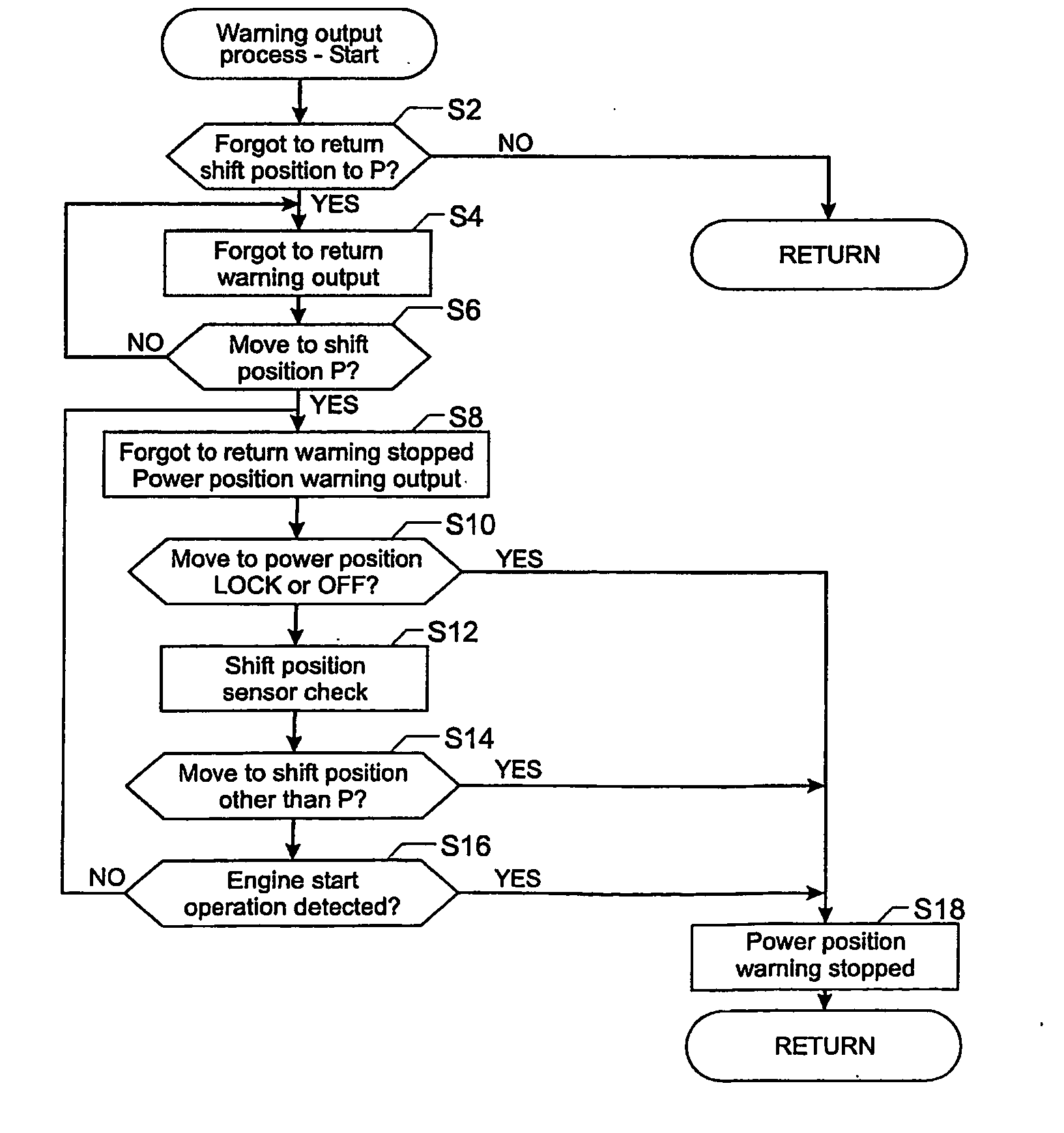
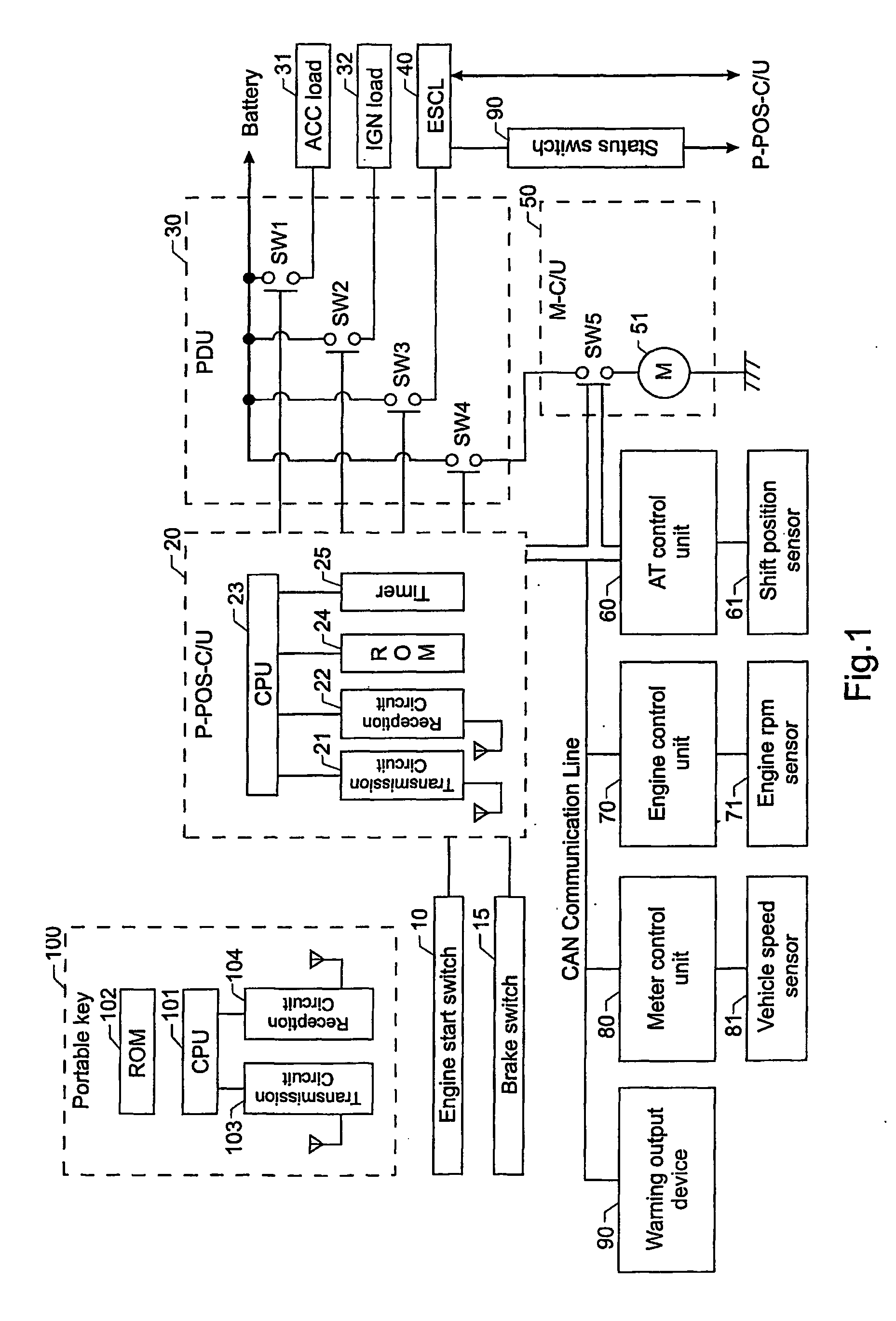
Warning System and Method of Providing a Warning
A warning system has a power position detection device, a gear shift position detection device, an alighting detection device, and a power position warning device. The device is operable to provide the power position warning indication when the power position detection device, the gear shift position detection device and the alighting detection device detect that there are preparations for alighting, that the gear shift position is in a P (Park) range and that the power position is in a position other than showing IGNITION OFF. In another aspect, the invention provides a gear shift position warning device. The power position warning device outputs a power position warning indication when the gear shift position detection device detects that the gear shift position has moved to the P range during output of the gear shift position warning indication.
Owner:NISSAN MOTOR CO LTD
Sound prompting method and equipment for low speed driving, and vehicle
InactiveCN108839613AAvoid nuisanceAvoid security-threatening issuesAcoustic signal devicesEnvironmental noiseEnvironmental sounds
The invention provides a sound prompting method and equipment for low speed driving, and a vehicle. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring the external environmental sound pressure levelof the vehicle; when the driving speed of the vehicle is smaller than a preset driving speed threshold value, determining a target sound pressure level according to the external environmental sound pressure level; and carrying out sound prompting according to the target sound pressure level. The method determines the sound pressure level of a prompt sound sent by the vehicle based on the externalenvironmental sound pressure level to achieve sound prompt which is adjusted actively based on change of environmental noises, so that the effect of sound prompting is improved in a relatively noisy environment is achieved and residents are prevented from being distributed in a relatively quiet environment.
Owner:AIWAYS AUTOMOBILE CO LTD
Smart city service recommendation method and device, computer equipment and storage medium
PendingCN111882398ARaise enthusiasm for participationEasy to findBuying/selling/leasing transactionsEngineeringSmart city
The invention relates to a smart city interactive service recommendation method and device, computer equipment and a storage medium, and the method comprises the steps: obtaining the related behaviordata of a user terminal for the checking of government affair propaganda information and participation in a city activity, so as to obtain behavior data; analyzing the behavior data to obtain a user portrait; obtaining service data to be recommended; dividing the to-be-recommended service data to obtain to-be-pushed content; and pushing the corresponding push content according to the user portraitso as to display the corresponding push content at the user terminal. According to the invention, the related behavior data of the user terminal for checking government affair propaganda informationand participating in urban activities is acquired and analyzed to obtain the corresponding user portrait, and the corresponding service data is pushed according to the user portrait, so that the information is pushed according to the own preference of the user, the resident disturbance phenomenon is avoided, and the participation enthusiasm of citizens can be improved, and the citizens can conveniently search urban service resources.
Owner:深圳市华云中盛科技股份有限公司
An incoming call number identification and control method
InactiveCN109698883AReduce nuisanceAvoid nuisanceSpecial service for subscribersCalling susbscriber number recording/indicationCloud computingBlack list
The invention discloses an incoming call number identification and management and control method, which comprises a mobile phone end program and a cloud computing center, the mobile phone end programis provided with a mobile phone end blacklist and a mobile phone end white list, and when an incoming call comes, the mobile phone end identifies the identity of an inbound person according to the mobile phone end blacklist and the mobile phone end white list; If the mobile phone end cannot identify the identity of the caller, auxiliary identification is performed on the identity of the caller through the cloud computing center; The mobile phone end program classifies and processes the identity recognition result of the caller according to the mobile phone end or the cloud computing center andexecutes one of the following operations: normally answering the incoming call; Hanging up the telephone; And the calling party is informed to reserve the call, and the reservation request of the calling party is authorized and agreed by the owner and then makes the call.
Owner:广州市众禾信息科技有限公司
ZigBee remote controller based on smart home
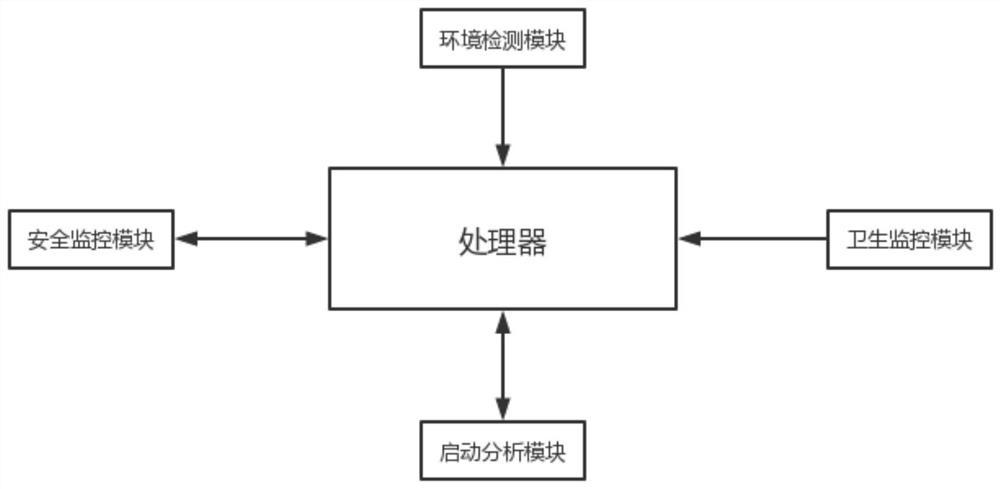
PendingCN114326422AImprove comfortImprove cleaning efficiencyComputer controlTotal factory controlRemote controlEngineering
The invention belongs to the field of smart home, relates to a remote control technology, and is used for solving the problem that an existing smart home remote controller does not have the function of automatically controlling on and off of electric appliances in a time-phased manner, in particular to a ZigBee remote controller based on smart home. The processor is in communication connection with an environment detection module, a safety monitoring module, a health monitoring module and a starting analysis module; the environment detection module is used for detecting and analyzing the indoor environment through temperature data and humidity data and sending an environment adjusting signal to the processor when the environment is abnormal, the temperature data is the average value of the indoor air temperature value and the floor temperature value, and the humidity data is the average value of the indoor air humidity value and the floor humidity value. According to the invention, the analysis module is started to analyze and control the time of environment adjustment and floor cleaning, so that the phenomenon of disturbing residents caused by late-night cleaning is avoided, science and technology are humanized, and the user experience of smart home is improved.
Owner:SHENZHEN SHYUGJ TECH CO LTD
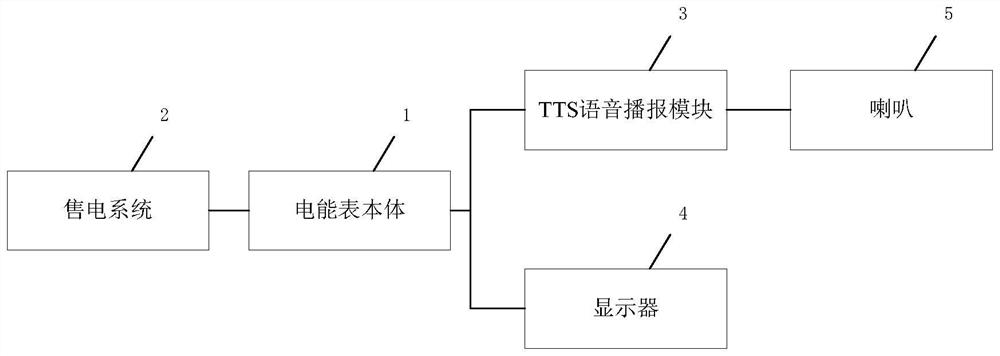
Electric energy meter with arrearage reminding function and reminding method
The invention discloses an electric energy meter with an arrearage reminding function, and the electric energy meter comprises an electric energy meter body which is electrically connected with an electricity selling system; the electric energy meter also comprises a TTS voice broadcast module, and the TTS voice broadcast module is electrically connected with the electric energy meter body. And the loudspeaker is arranged on the electric energy meter body, and the loudspeaker is electrically connected with the TTS voice broadcast module. The problems that in the prior art, when branches are too high and a lifting platform cannot be used, the branches close to an electric wire are trimmed, falling is likely to happen, the working efficiency is low, and the probability of electric shock accidents is increased are solved.
Owner:GUIZHOU POWER GRID CO LTD
Novel fan
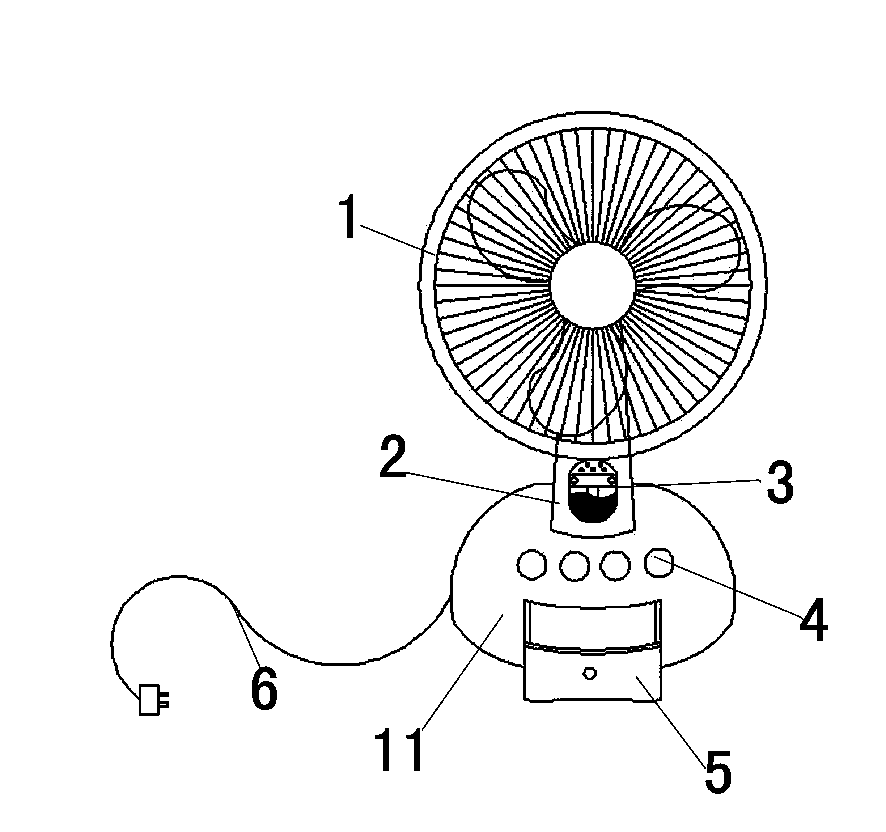
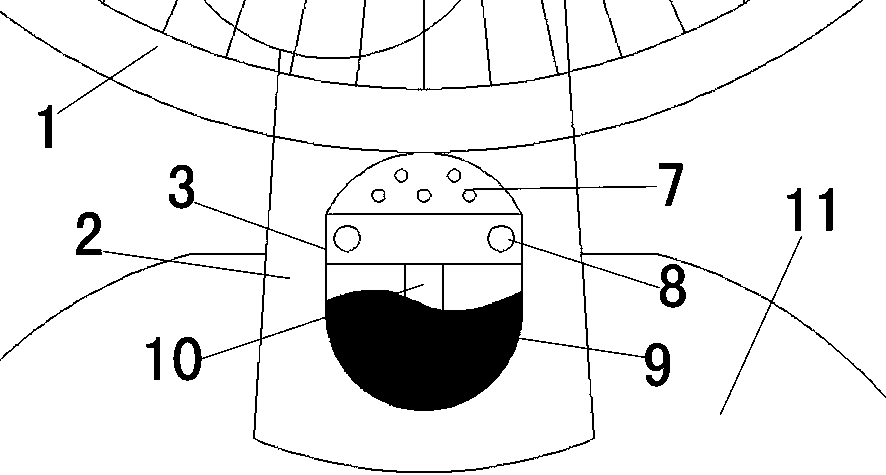
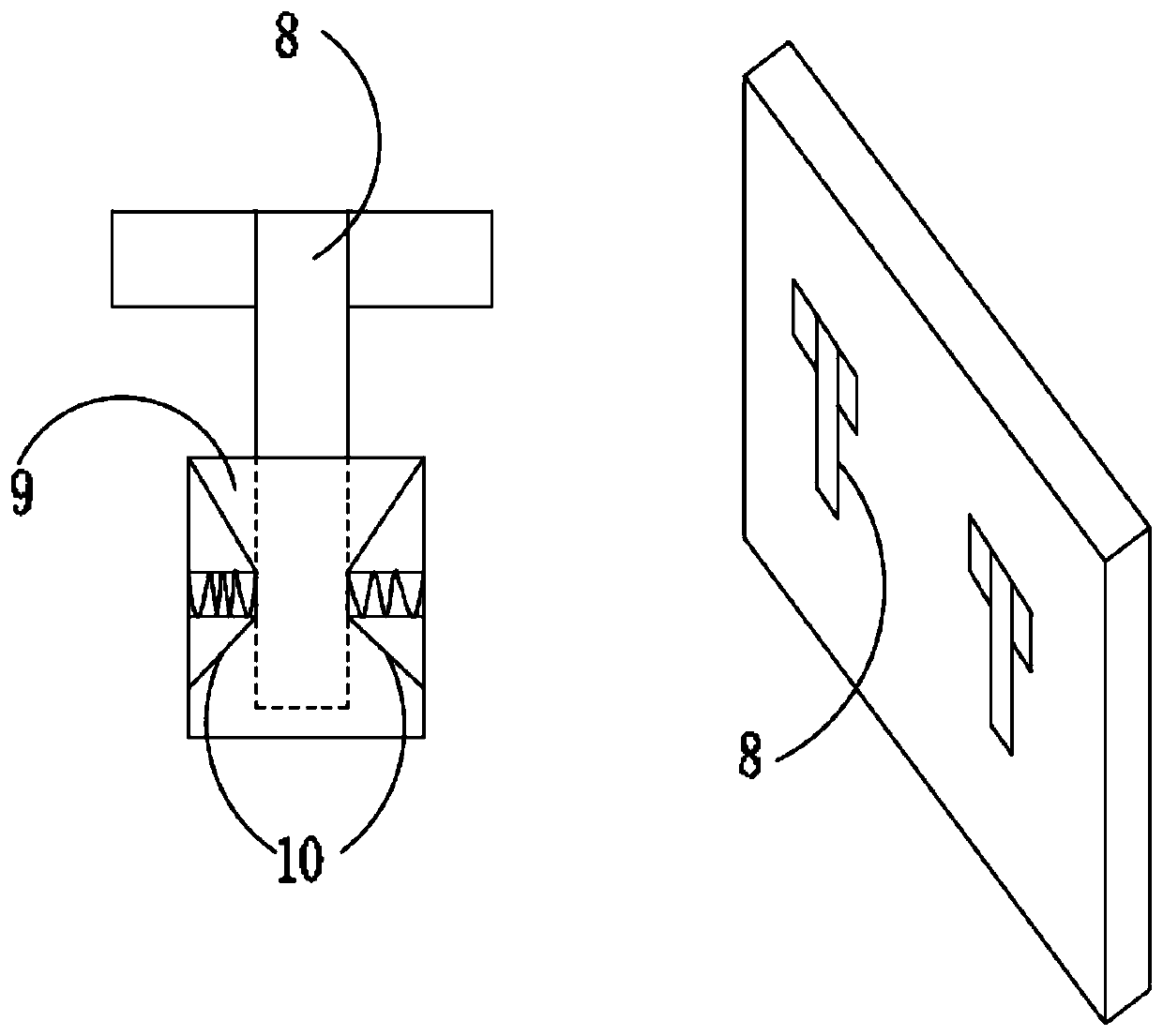
InactiveCN103850950APrevent the nuisance of mosquitoesImprove mosquito repellent effectPump controlAnimal repellantsEngineeringLower half
The invention relates to the technical field of domestic small appliances, in particular to a novel fan. The novel fan mainly comprises a fan head, a support post, an electric warming mosquito killer, a pedestal and a storage drawer, wherein the storage drawer is mounted at the lower half of the front of the pedestal, a speed regulating button is mounted above the storage drawer, the support post is mounted at the upper half of the pedestal, the top end of the support post is connected with the fan head, and the position between the lower half of the support post and the pedestal is provided with the electric warming mosquito killer. According to the novel fan, the storage drawer can be used for storing such small objects as tissue, extension sockets and electric mosquito incense liquor; the support post is provided with the electric warming mosquito killer, so that people can simultaneously enjoy cool wind and be protected from mosquitoes in the hot summer, the electric warming mosquito killer is used with the fan head so that mosquito repellent gas can be blown to each corner of a room more effectively, and the mosquito repellent effect of the electric warming mosquito killer is improved; the electric warming mosquito killer can be opened or closed according to the need, so that the electric warming mosquito killer is more friendly to users.
Owner:张培芝
Multifunctional combined rod for urban road and design method of multifunctional combined rod
PendingCN111519559AReduce in quantityAvoid wastingTraffic signalsRoad signsLight equipmentStructural engineering
The invention provides a multifunctional combined rod for an urban road. The multifunctional combined rod comprises a rod main body, a rod head, a first connecting rod, a second connecting rod and a cross arm; the rod head is used for carrying lighting equipment; the rod head is connected with the rod main body; the rod main body is connected with the cross arm; mounting guide rails are arranged on four sides of the rod main body; and the mounting guide rails are used for mounting functional facilities; the cross arm is provided with a plurality of first installation positions, a plurality ofsecond installation positions and a plurality of third installation positions. According to the multifunctional combined rod of the invention, the problem that main rod pieces arranged on municipal roads are generally single-purpose single-rods is solved; various rod lines and road landscapes on urban roads are messy and unsystematic, function independently and are mutually shielded; repeated construction may disturb residents and waste resources; and the various messy and clustered rod pieces and cases matched with the rod pieces severely destroy the urban appearance and influence traffic, and construction and operation cost is increased. With the multifunctional combined rod adopted, the above problem can be solved.
Owner:四川城乡发展工程设计有限公司
NRF2401-based wireless meter reading device
InactiveCN102568176AReduce frequency offsetAccurate measurementTransmission systemsData acquisitionComputer terminal
The invention discloses an NRF2401-based wireless meter reading device and relates to the technical field of wireless data transmission. The device comprises a data acquisition module and a handheld terminal, wherein the data acquisition module is arranged in an electric meter box, is connected with each electric meter, reads the numerical value of the electric meter and transmits the numerical value to the handheld terminal; and the handheld terminal consists of keys, a display module, a storage module, a microprocessor and a printer interface, displays the numerical value on a screen and stores the numerical value in a secure digital (SD) card simultaneously after receiving the numerical value of the electric meters through a wireless module. The device has the characteristics of high data transmission rate, simple mounting, convenience in maintenance and the like. The meter reading time is greatly reduced, and the meter reading efficiency is improved.
Owner:HARBIN FEIYU TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com