Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
168results about "Coding theory basic assumptions" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Method and system for providing low density parity check (LDPC) encoding
ActiveUS7191378B2Readily apparentInterconnection arrangementsError correction/detection using LDPC codesAlgorithmParity-check matrix
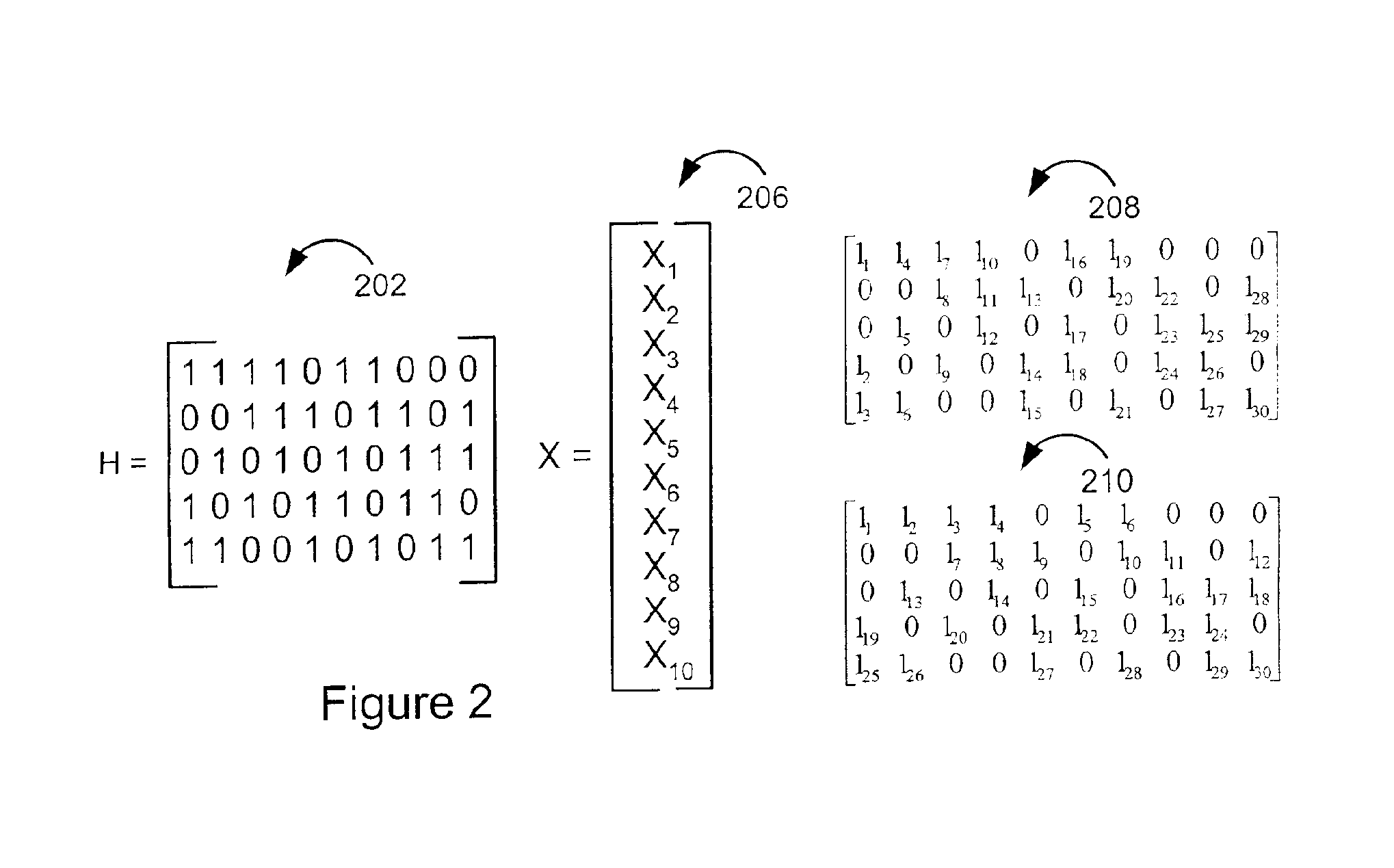
An approach is provided for a method of encoding structure Low Density Parity Check (LDPC) codes. Memory storing information representing a structured parity check matrix of Low Density Parity Check (LDPC) codes is accessed during the encoding process. The information is organized in tabular form, wherein each row represents occurrences of one values within a first column of a group of columns of the parity check matrix. The rows correspond to groups of columns of the parity check matrix, wherein subsequent columns within each of the groups are derived according to a predetermined operation. An LDPC coded signal is output based on the stored information representing the parity check matrix.
Owner:DTVG LICENSING INC
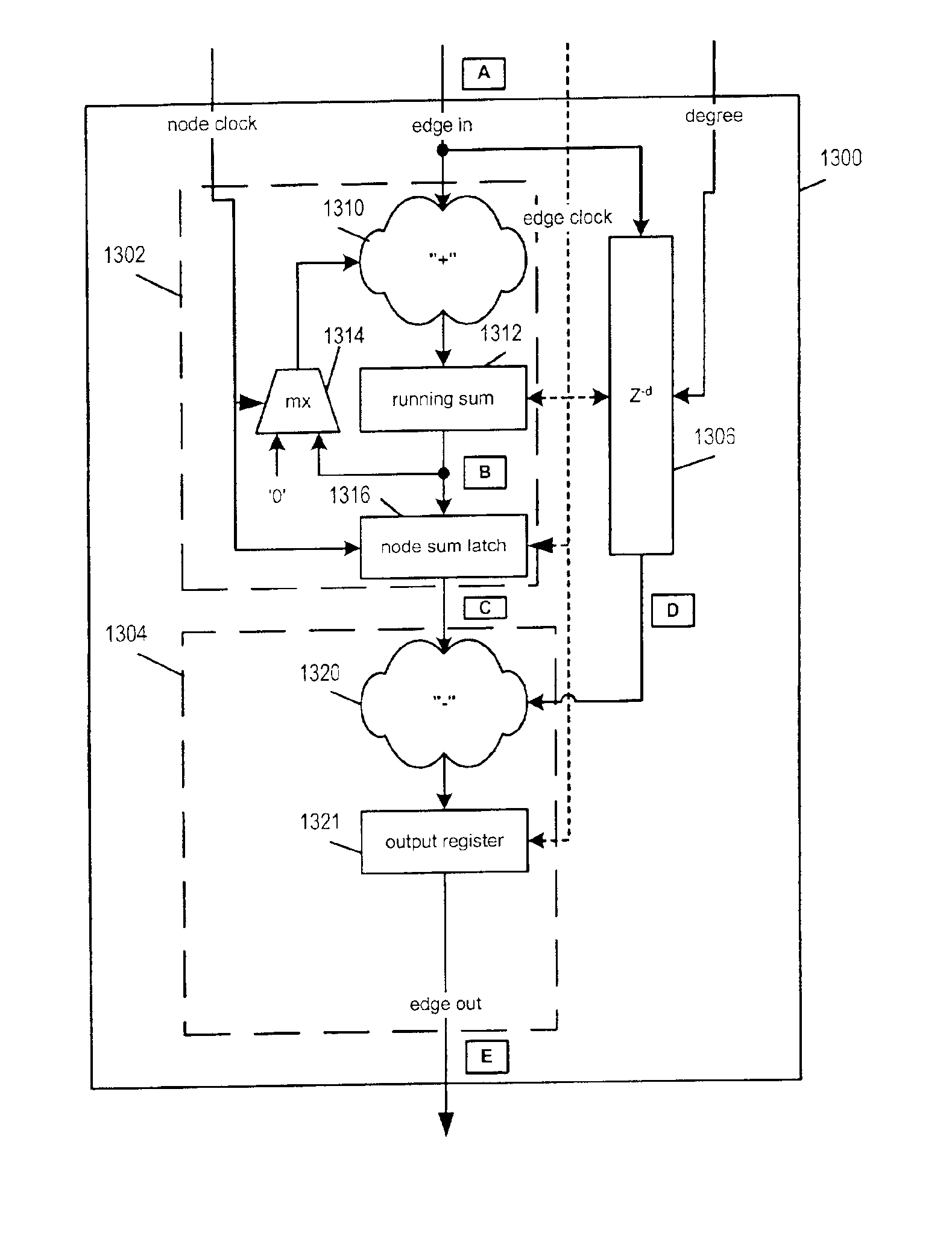
Node processors for use in parity check decoders
InactiveUS6938196B2Big errorCompensating for such errorError prevention/detection by using return channelOther decoding techniquesComputer moduleMessage processing
Techniques for implementing message passing decoders, e.g., LDPC decoders, are described. To facilitate hardware implementation messages are quantized to integer multiples of ½ ln2. Messages are transformed between more compact variable and less compact constraint node message representation formats. The variable node message format allows variable node message operations to be performed through simple additions and subtractions while the constraint node representation allows constraint node message processing to be performed through simple additions and subtractions. Variable and constraint nodes are implemented using an accumulator module, subtractor module and delay pipeline. The accumulator module generates an accumulated message sum. The accumulated message sum for a node is stored and then delayed input messages from the delay pipeline are subtracted there from to generate output messages. The delay pipeline includes a variable delay element making it possible to sequentially perform processing operations corresponding to nodes of different degrees.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Bit labeling for amplitude phase shift constellation used with low density parity check (LDPC) codes
InactiveUS6963622B2Improve performanceError correction/detection using LDPC codesCode conversionParity-check matrixEngineering
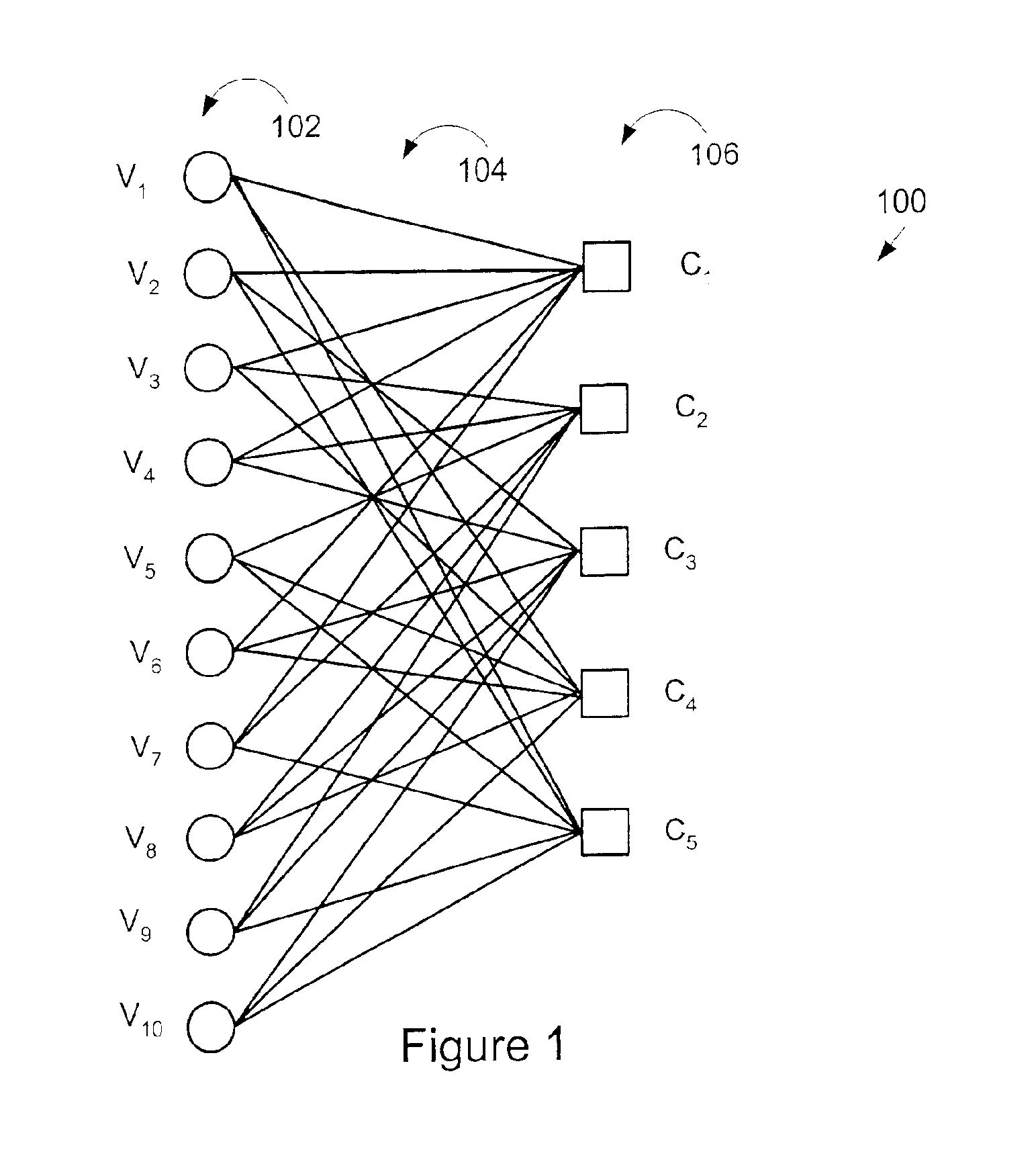
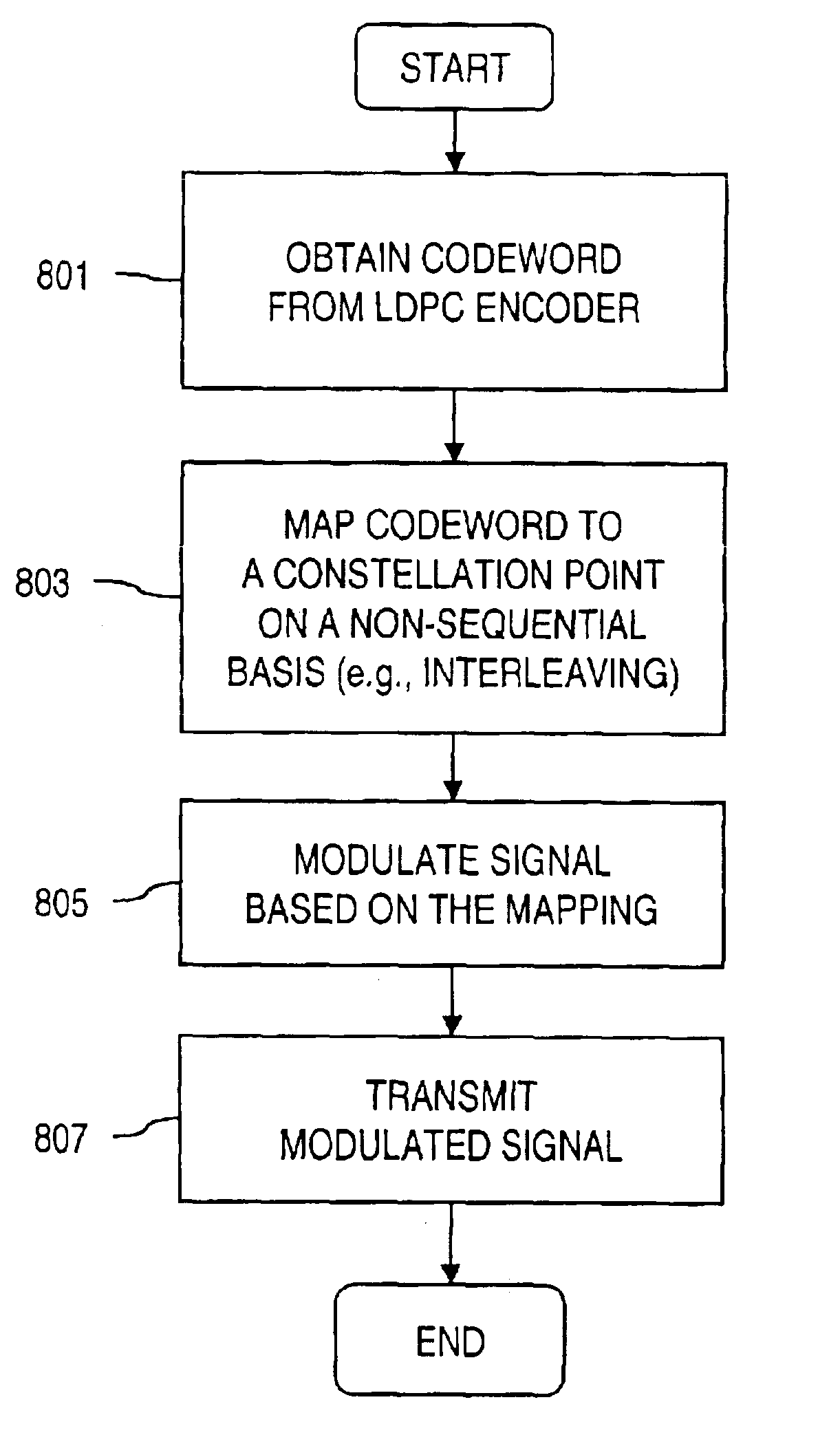
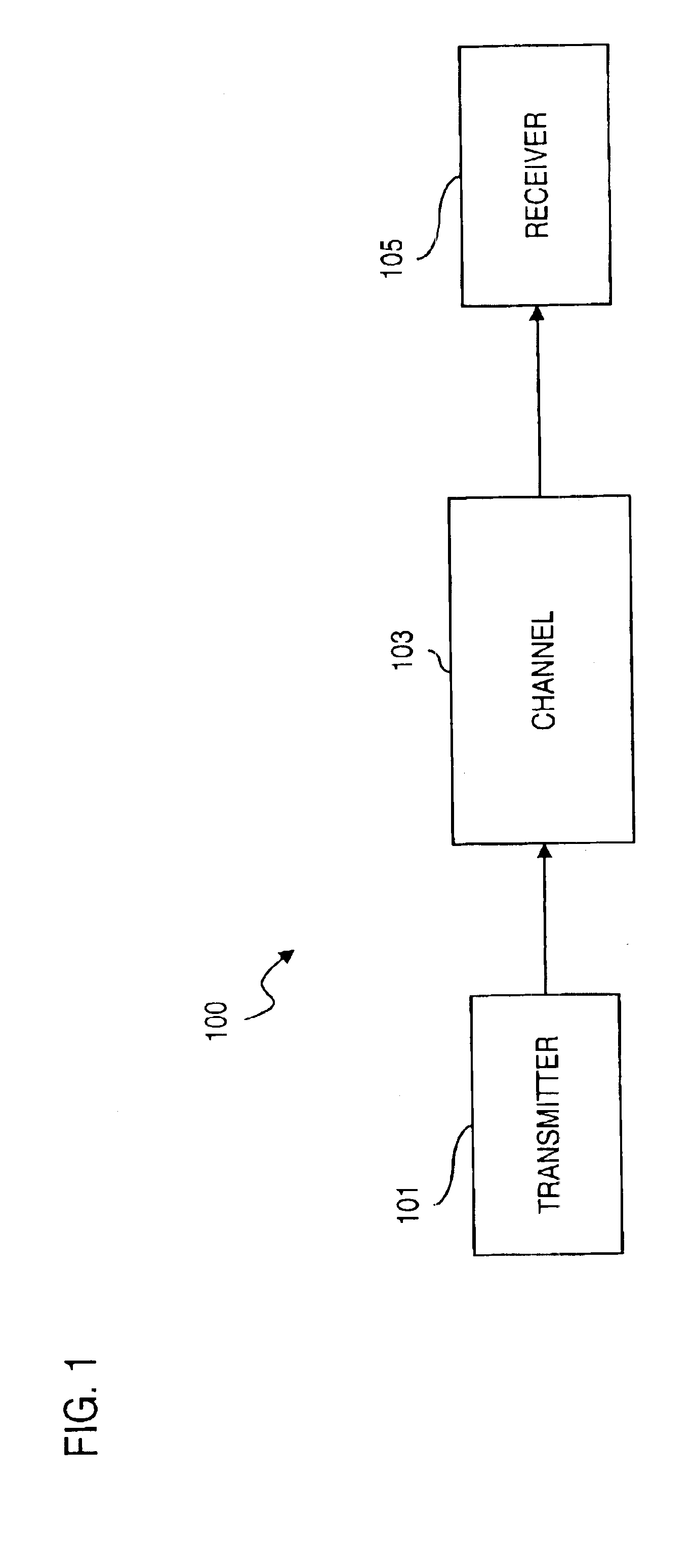
An approach is provided for bit labeling of a signal constellation. A transmitter generates encoded signals using, according to one embodiment, a structured parity check matrix of a Low Density Parity Check (LDPC) code. The transmitter includes an encoder for transforming an input message into a codeword represented by a plurality of set of bits. The transmitter includes logic for mapping non-sequentially (e.g., interleaving) one set of bits into a higher order constellation (Quadrature Phase Shift Keying (QPSK), 8-PSK, 16-APSK (Amplitude Phase Shift Keying), 32-APSK, etc.), wherein a symbol of the higher order constellation corresponding to the one set of bits is output based on the mapping.
Owner:DTVG LICENSING INC
Digital telecommunication system with selected combination of coding schemes and designated resources for packet transmission based on estimated transmission time
InactiveUS6363425B1Quantity minimizationAir interface efficientlyError prevention/detection by using return channelCode conversionForward error correctionMajorization minimization
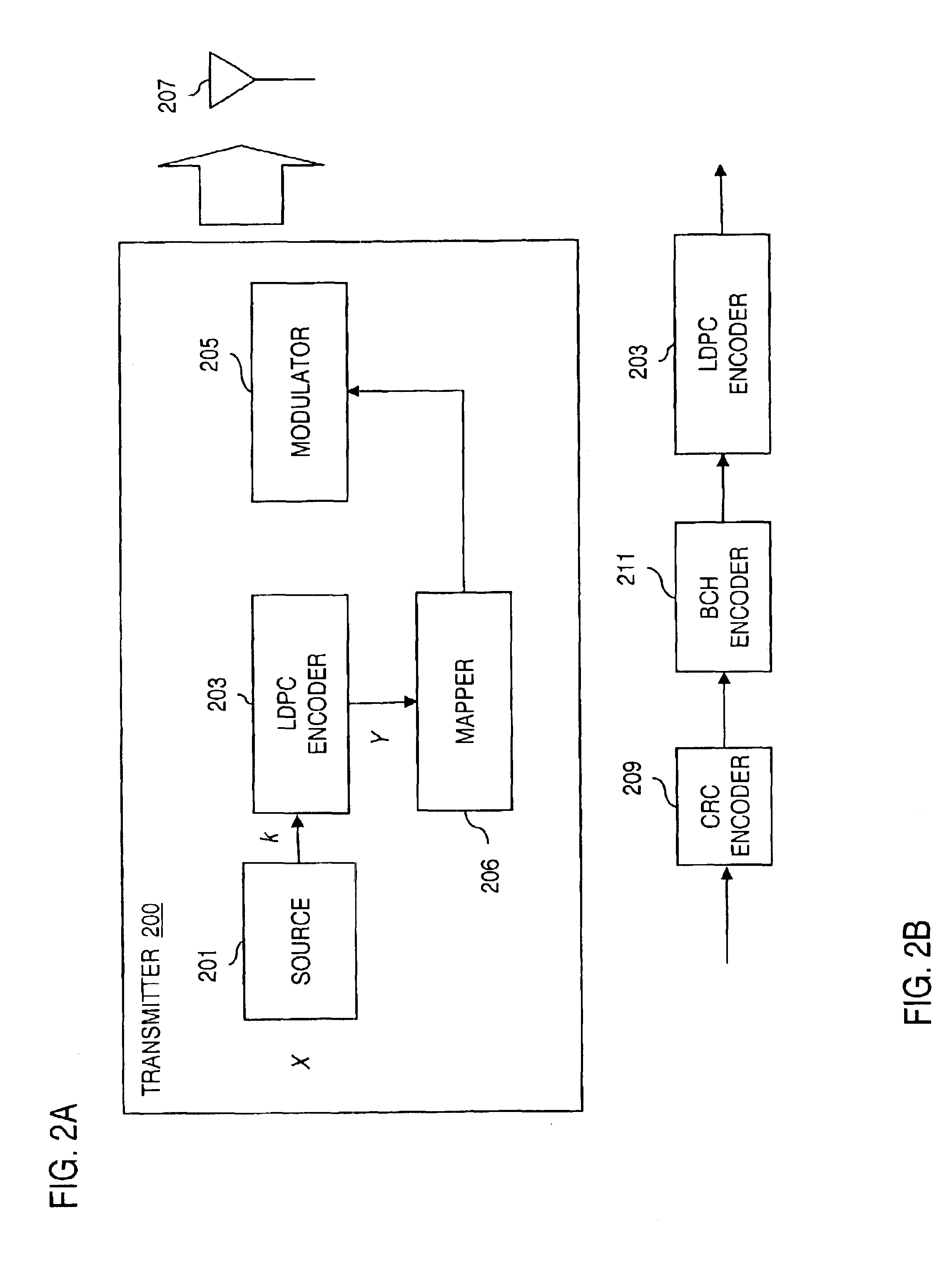
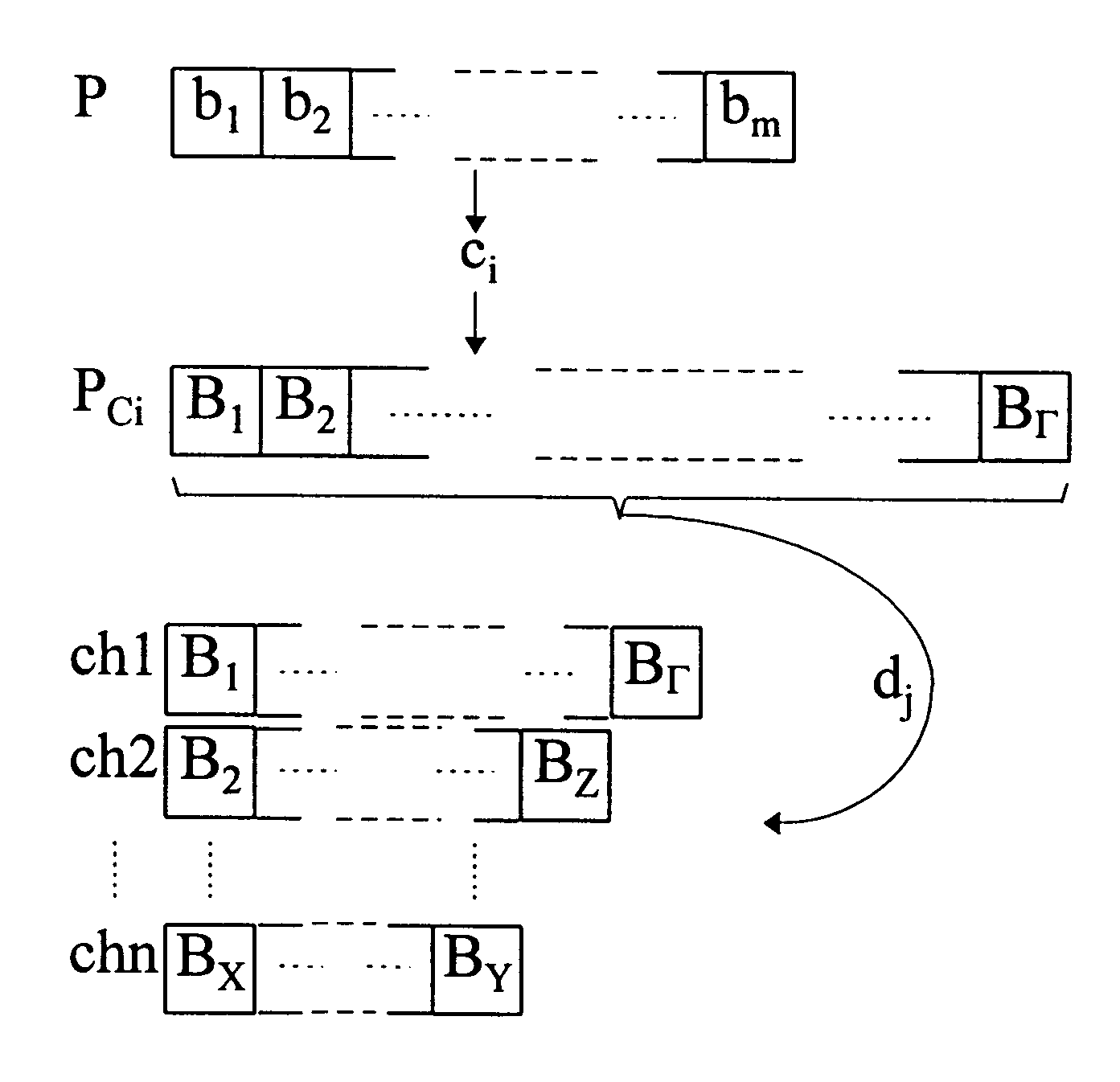
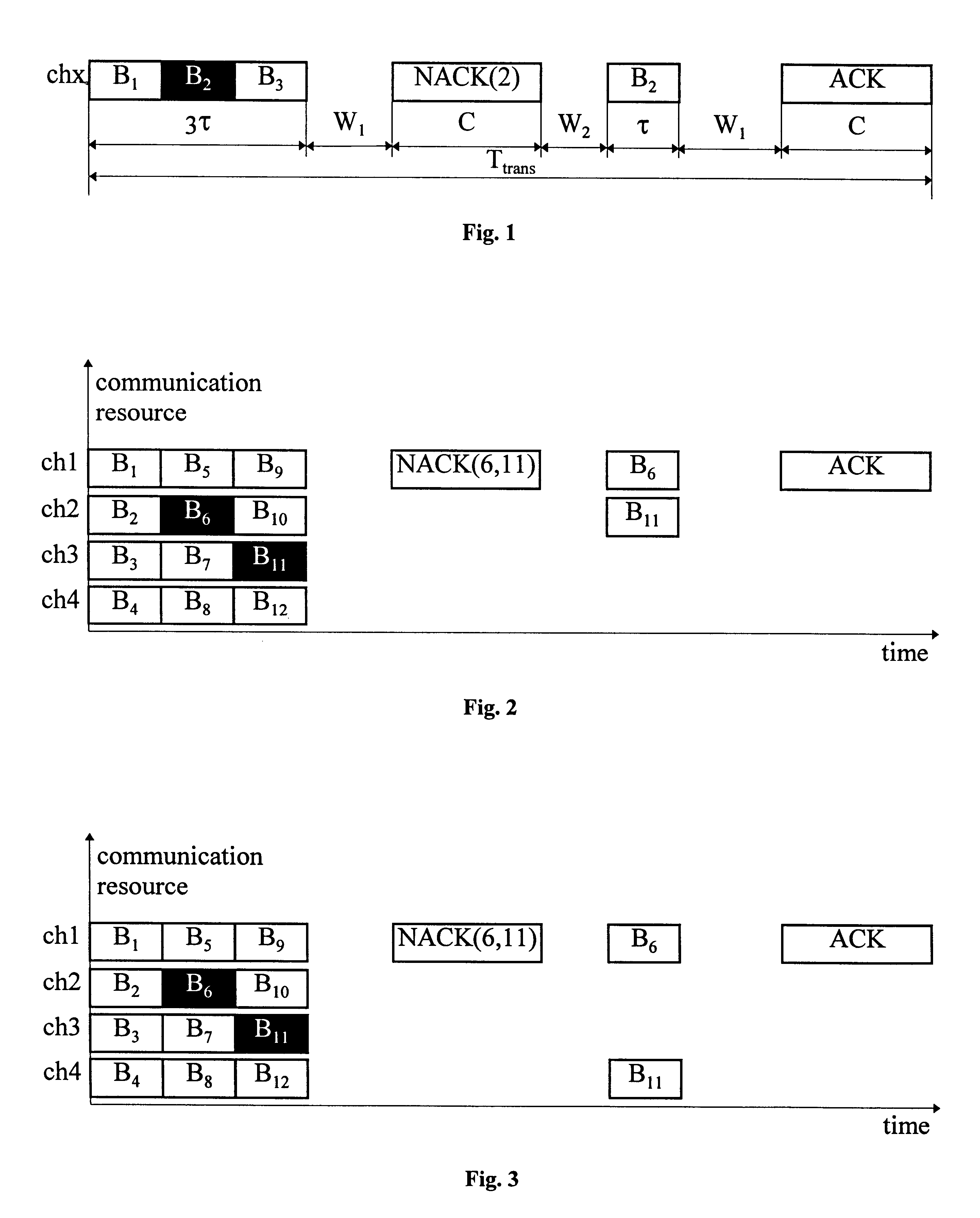
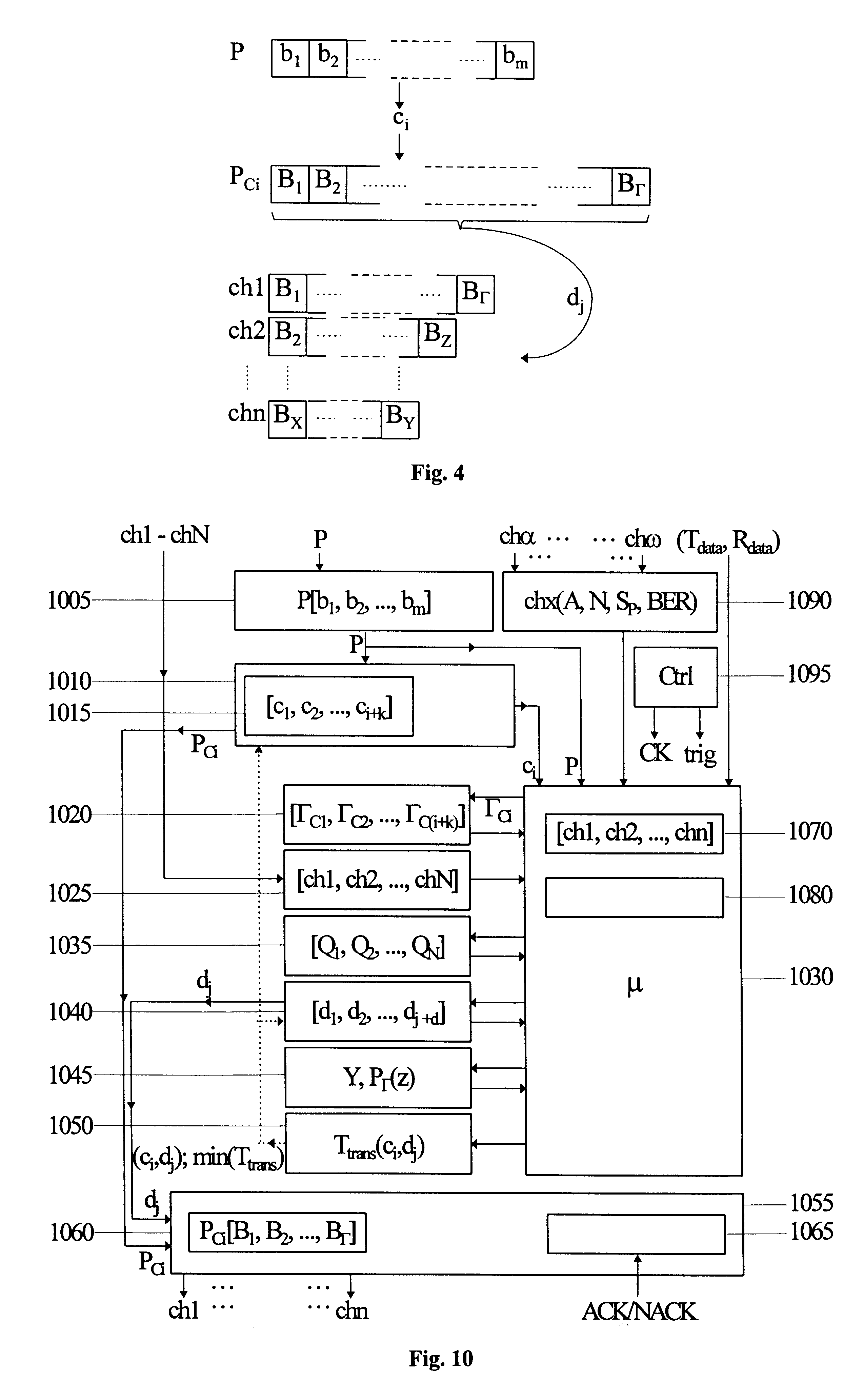
The present invention relates to a method and an arrangement for communicating packet information in a digital telecommunications system. Through the invention is selected a set of designated communication resources (ch1-chn) from an available amount of resources. Every packet (P) is forward error correction encoded into an encoded packet (Pci), via one of at least two different coding schemes (ci), prior to being transmitted to a receiving party, over the designated communication resources (ch1-chn). An estimated transmission time is calculated for all combinations of coding scheme (ci) and relevant distribution (dj) of the encoded data blocks (B1-BΓ), in the encoded packet (Pci) over the set of designated communication resources (ch1-chn), and the combination (ci,dj) is selected, which minimises the estimated transmission time.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
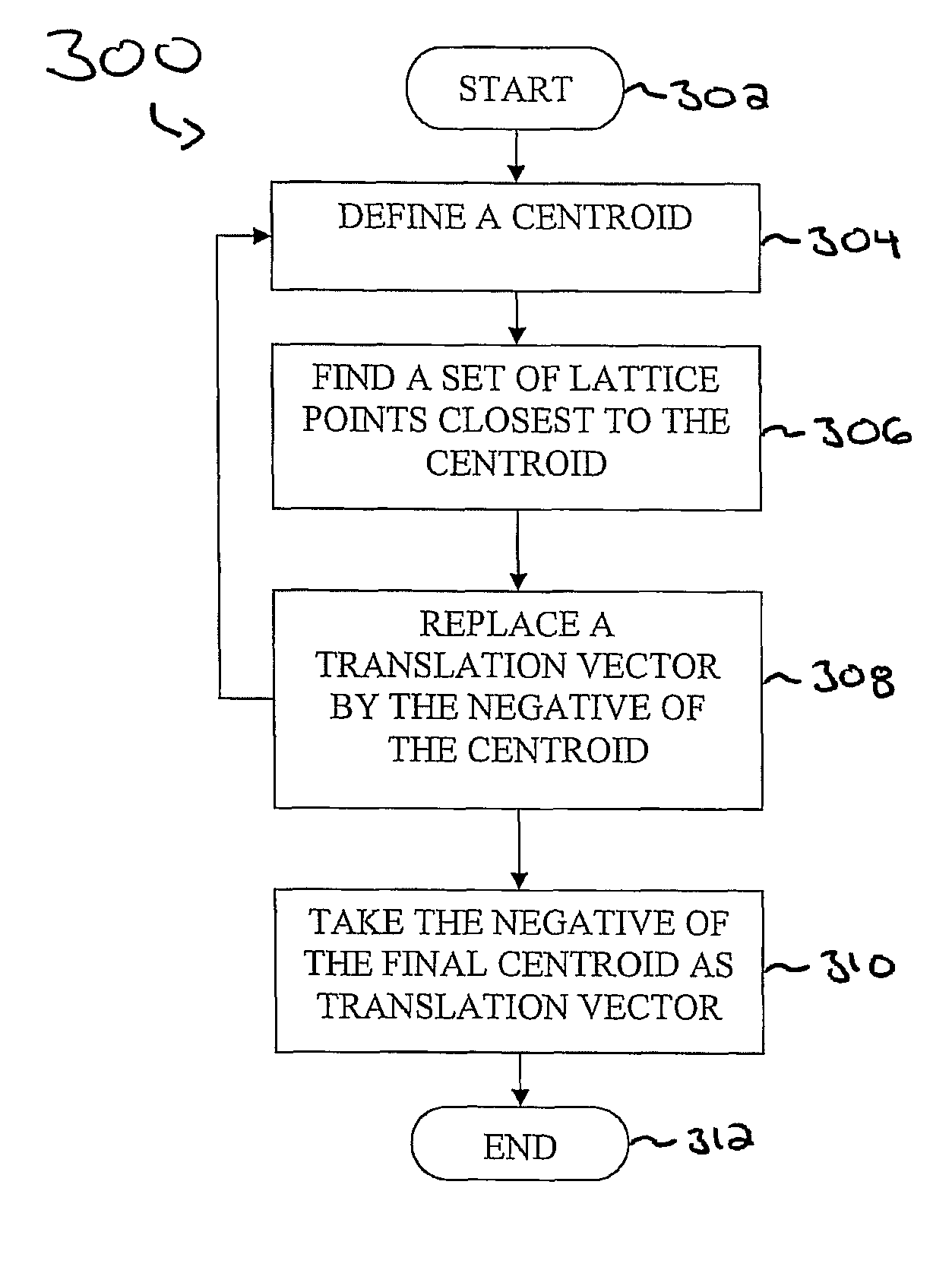
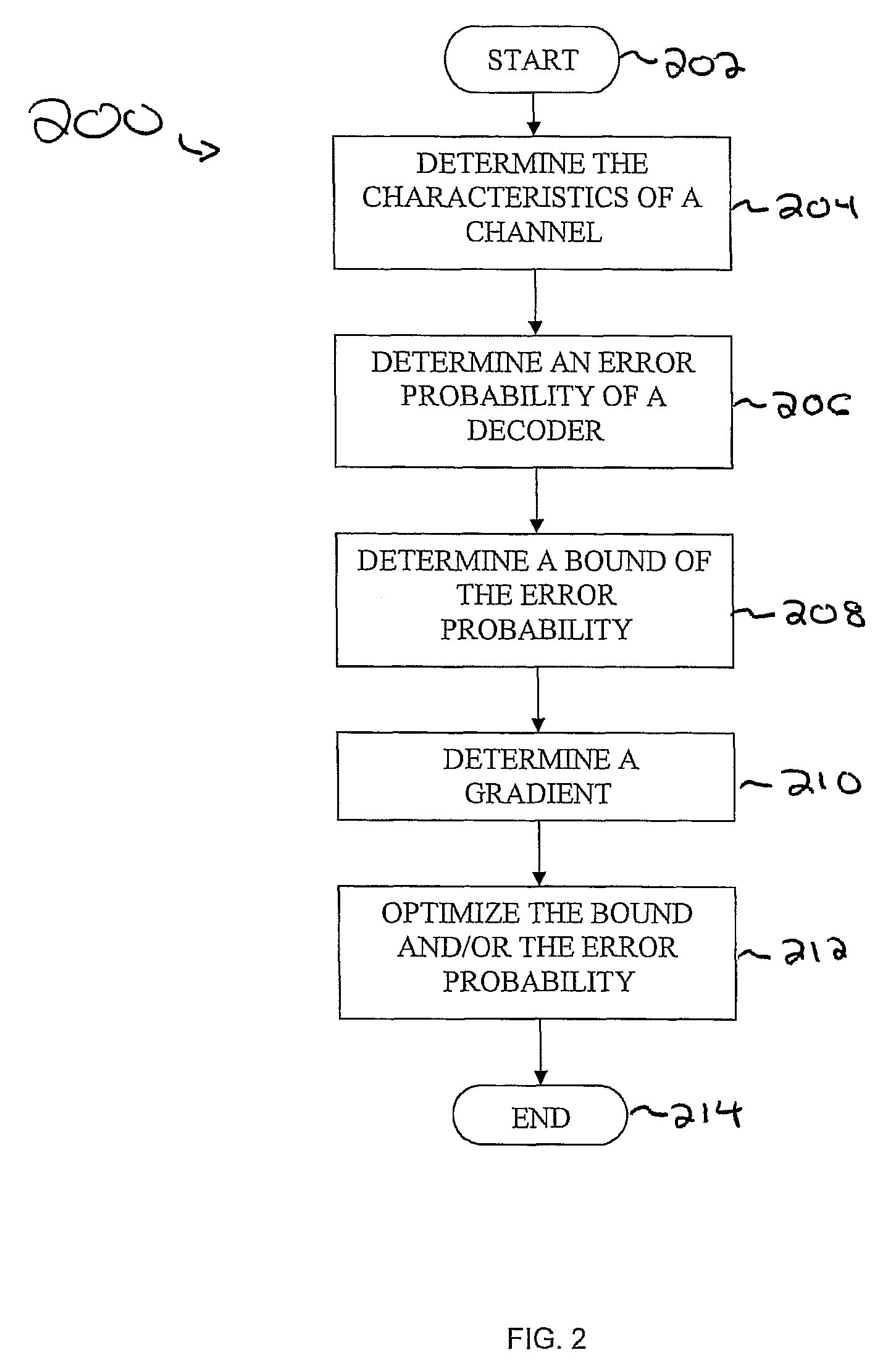
Spherical lattice codes for lattice and lattice-reduction-aided decoders
Methods and apparatus for designing spherical lattice codebooks for use in data transmission systems are provided. A spherical lattice codebook is constructed by determining the channel statistics of one or more channels, which can be accomplished by observing a sufficiently large set of channel realizations. After determining the channel statistics, an expression for the error probability of the decoder or expressions for bounds on the error probability and expressions for the corresponding gradients are determined. The gradient is then used in an optimization technique to produce a spherical lattice codebook which is subsequently used for transmission.
Owner:NEC CORP
Design of Spherical Lattice Codes for Lattice and Lattice-Reduction-Aided Decoders
ActiveUS20070283210A1Reduce transmit energyCode conversionDiversity/multi-antenna systemsChannel statisticsLattice reduction
Methods and apparatus for designing spherical lattice codebooks for use in data transmission systems are provided. A spherical lattice codebook is constructed by determining the channel statistics of one or more channels, which can be accomplished by observing a sufficiently large set of channel realizations. After determining the channel statistics, an expression for the error probability of the decoder or expressions for bounds on the error probability and expressions for the corresponding gradients are determined. The gradient is then used in an optimization technique to produce a spherical lattice codebook which is subsequently used for transmission.
Owner:NEC CORP
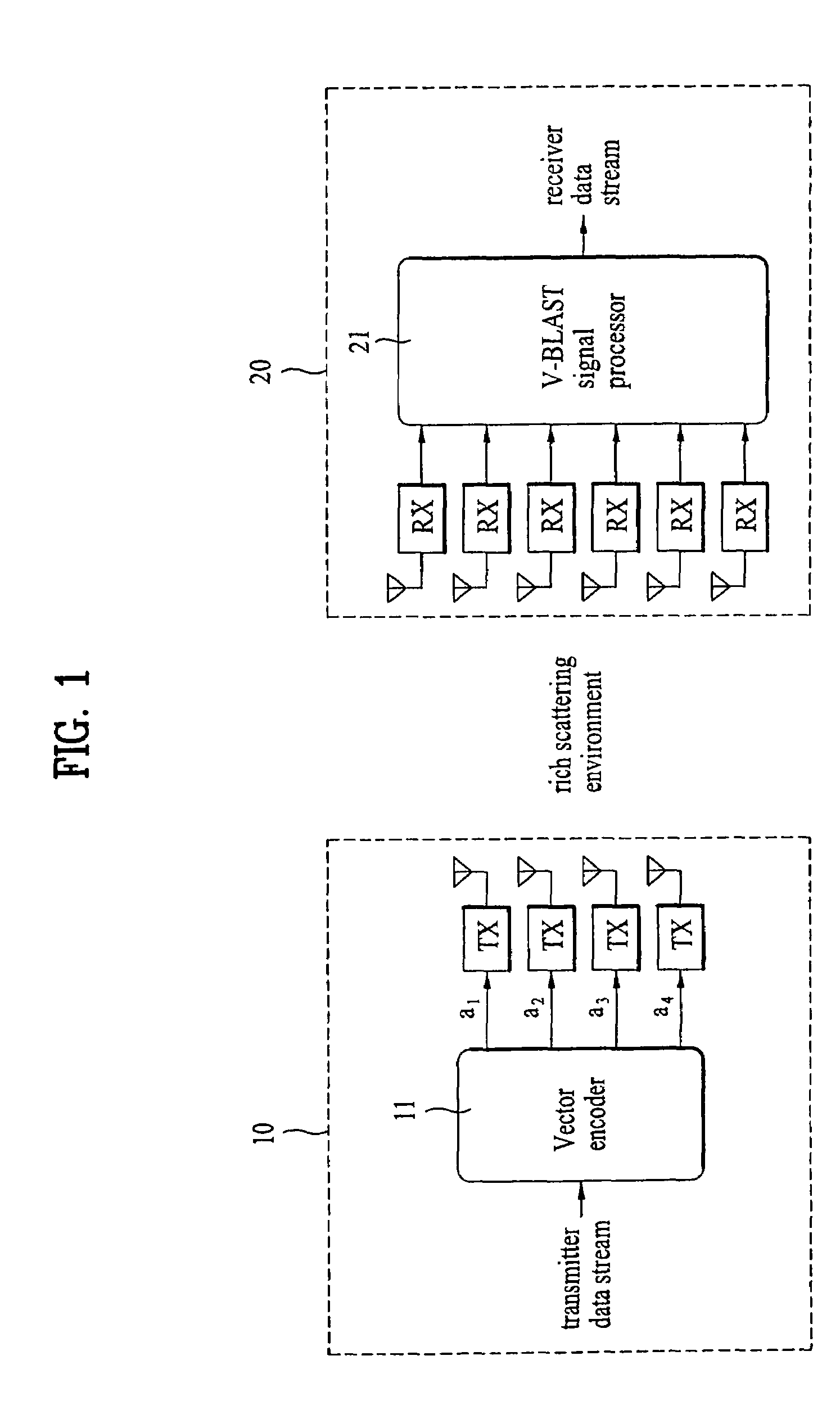
Mobile communication system and signal processing method thereof
ActiveUS7392460B2Preserve integrityError prevention/detection by using return channelSpatial transmit diversityMobile communication systemsComputer science
Owner:AEGIS 11 SA
Bit error rate tester
The present invention is a bit error rate tester that may operate on network paths having devices that add or drop idles within a transmitted bit sequence. In particular, the bit sequence determines whether a received bit sequence is synchronized. If the received sequence is not synchronized or if a certain event / threshold is reached, then the bit error rate tester re-synchronizes the sequence prior to analysis. Also, the bit error rate detector is able to operate on high-speed networks and provide bit granularity measurements.
Owner:VIAVI SOLUTIONS INC
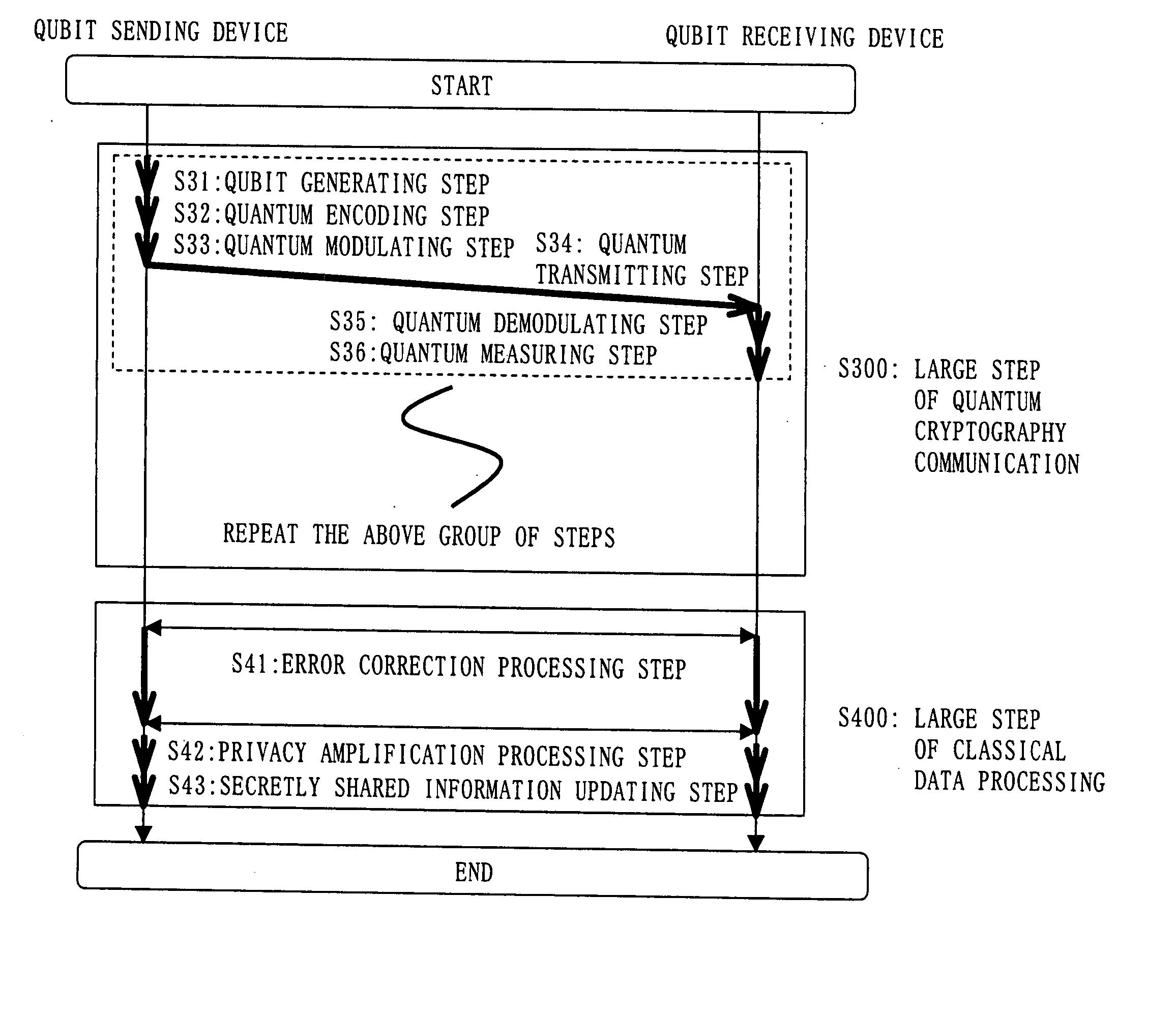
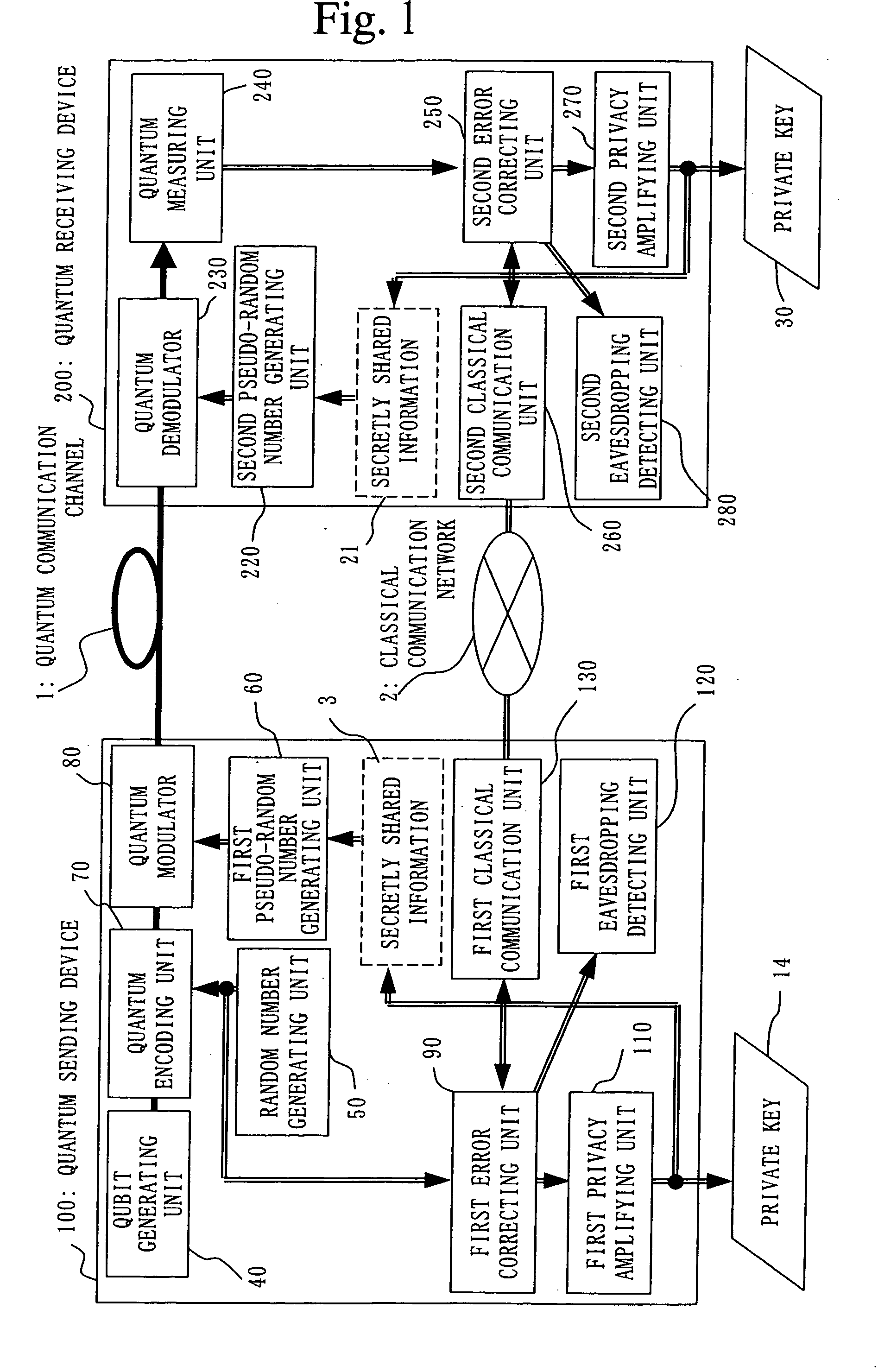
Crytographic communication apparatus
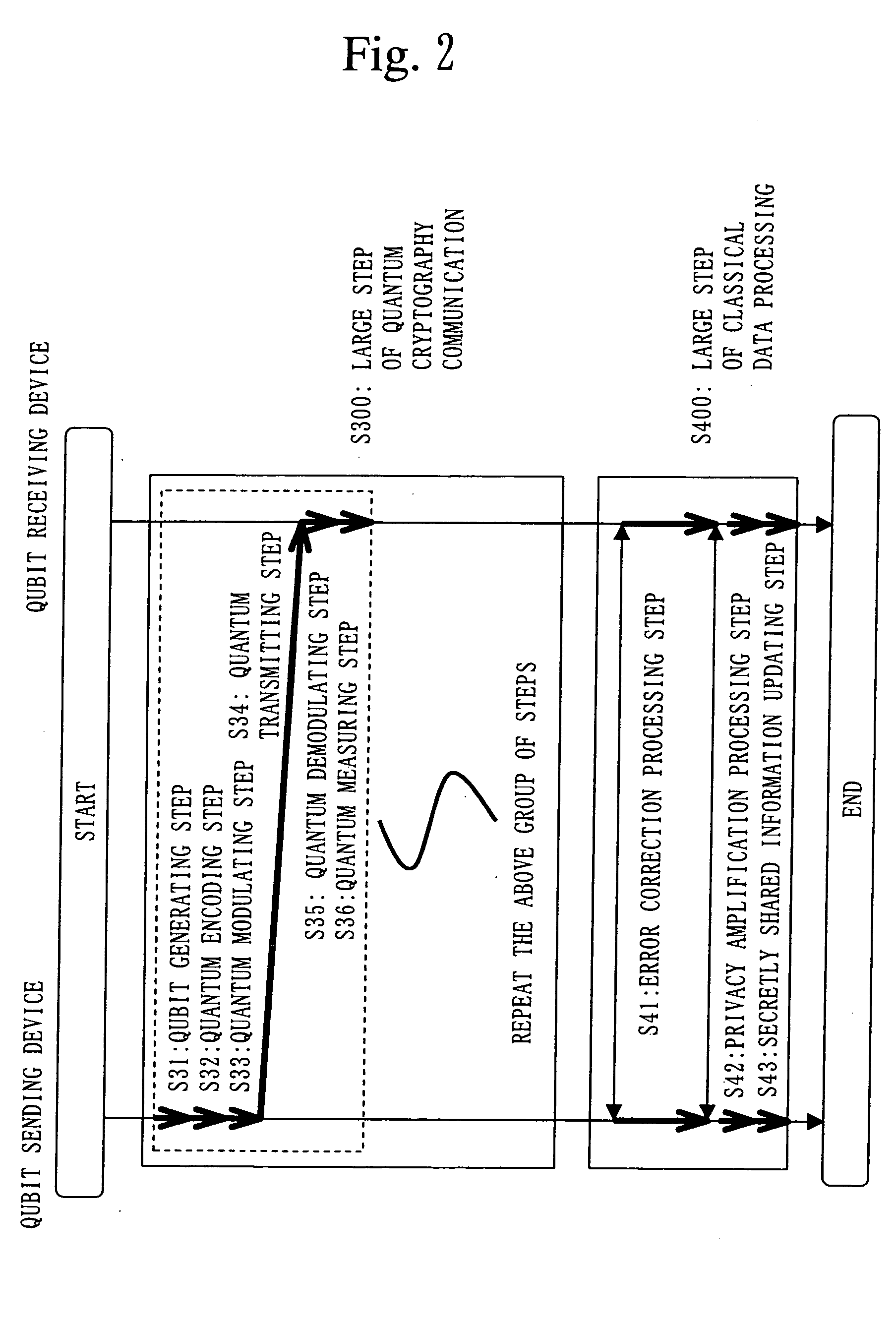
InactiveUS20050157875A1Key distribution for secure communicationSynchronising transmission/receiving encryption devicesPseudo random number generationQuantum electrodynamics
A qubit generating unit 40 generates a qubit having a predetermined quantum state. A qubit encoding unit 70 performs quantum encoding of the generated qubit. A first pseudo-random number generating unit 60 generates a first pseudo-random number from secretly shared information 3 which has been secretly shared with the quantum receiving device 200 in advance. A quantum modulator 80 performs quantum modulation of the qubit on which quantum encoding has been performed based on the first pseudo-random number and sends the modulated qubit to the quantum receiving device 200. A second pseudo-random number generating unit 220 generates a second pseudo-random number from secretly shared information 21 which has been secretly shared with the above quantum sending device 100 in advance synchronously with generation of the above first pseudo-random number. A qubit demodulator 230 performs quantum demodulation of the qubit which has been received from the quantum demodulator 80 based on the second pseudo-random number.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
DTV transmitting system and receiving system and method of processing television signal
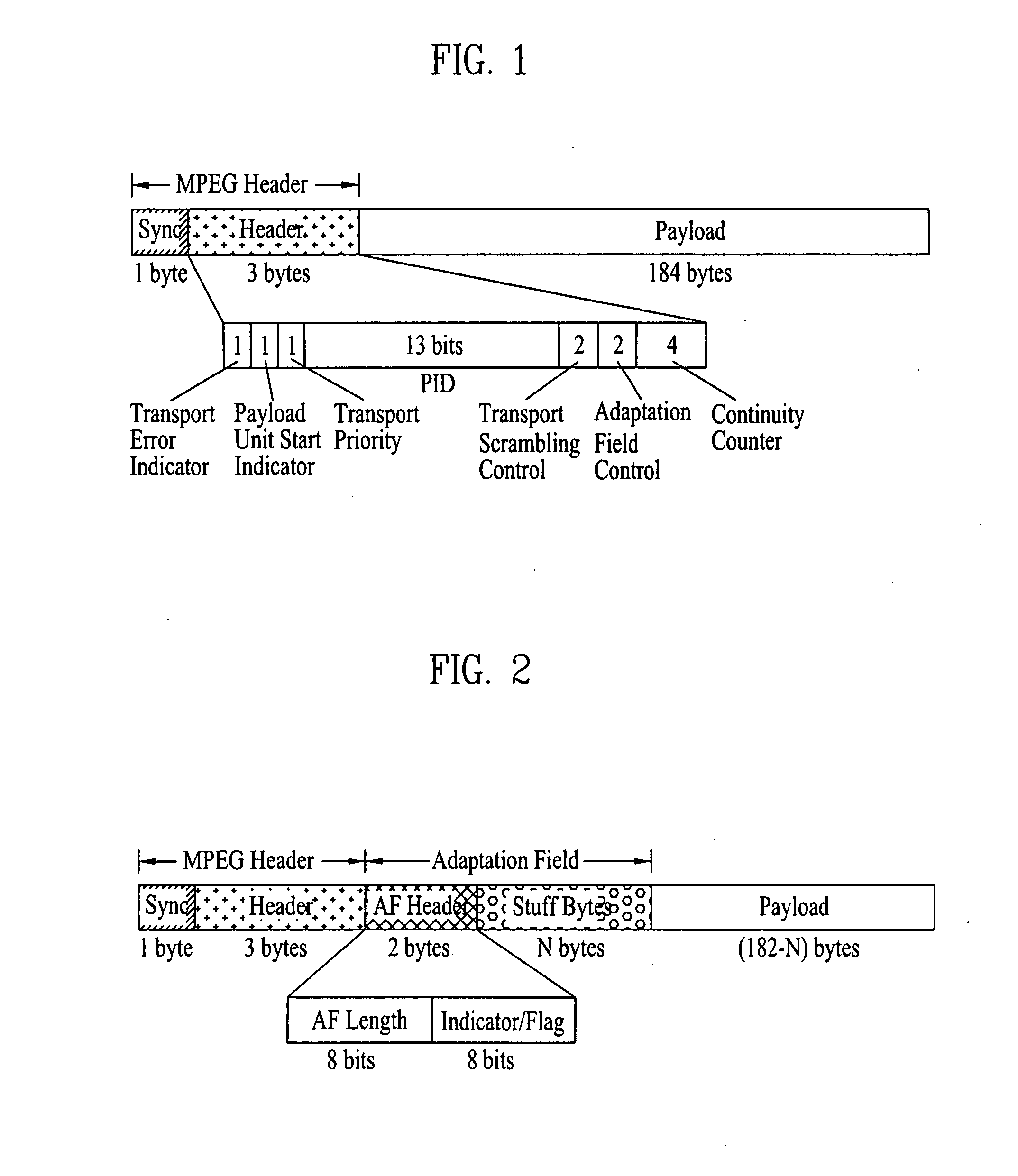
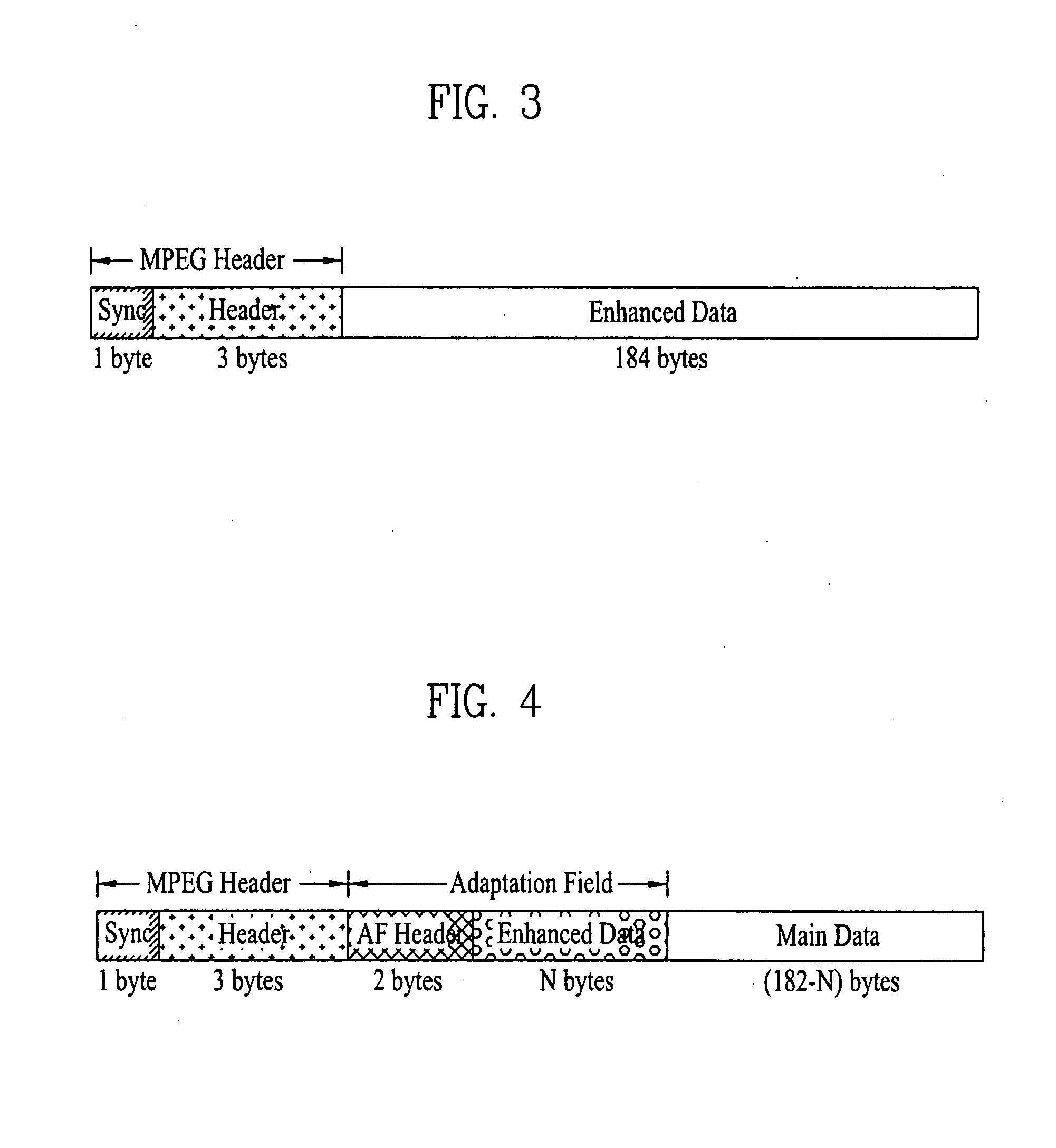
InactiveUS20080002765A1Eliminate the problemError correction/detection using convolutional codesOther decoding techniquesComputer hardwarePacket generator
A digital television transmitting system includes a pre-processor, a packet generator, an RS encoder, and a trellis encoder. The pre-processor pre-processes enhanced data by coding the enhanced data for first forward error correction (FEC) and expanding the FEC-coded enhanced data. The packet generator generates first and second enhanced data packets including the pre-processed enhanced data and main data packets and multiplexes the enhanced and main data packets. The first enhanced data packet includes an adaptation field including the pre-processed enhanced data and second enhanced data packet includes a payload region including the pre-processed enhanced data. The RS encoder performs RS encoding on the multiplexed data packets for second forward error correction (FEC), and the trellis encoder performs trellis encoding on the RS-coded data packets.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Evaluating and optimizing error-correcting codes using a renormalization group transformation
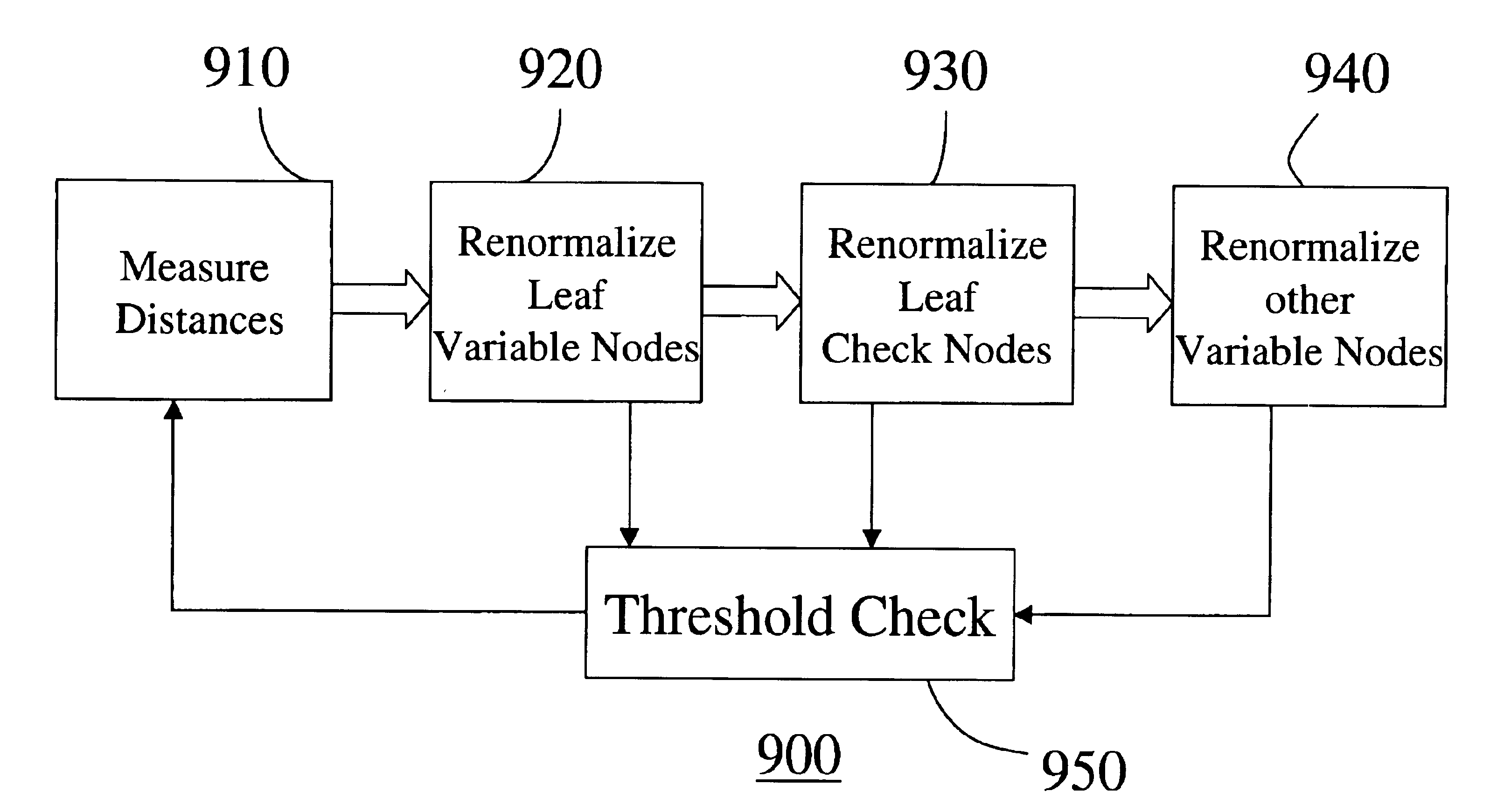
InactiveUS6857097B2Improve performanceCorrect operation testingOther decoding techniquesRenormalizationParity-check matrix
A method evaluates an error-correcting code for a data block of a finite size. An error-correcting code is defined by a parity check matrix, wherein columns represent variable bits and rows represent parity bits. The parity check matrix is represented as a bipartite graph. A single node in the bipartite graph is iteratively renormalized until the number of nodes in the bipartite graph is less than a predetermine threshold. During the iterative renormalization, a particular variable node is selected as a target node, and a distance between the target node and every other node in the bipartite graph is measured. Then, if there is at least one leaf variable node, renormalize the leaf variable node farthest from the target node, otherwise, renormalize a leaf check node farthest from the target node, and otherwise renormalize a variable node farthest from the target node and having fewest directly connected check nodes. By evaluating many error-correcting codes according to the method, an optimal code according to selected criteria can be obtained.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC RES LAB INC
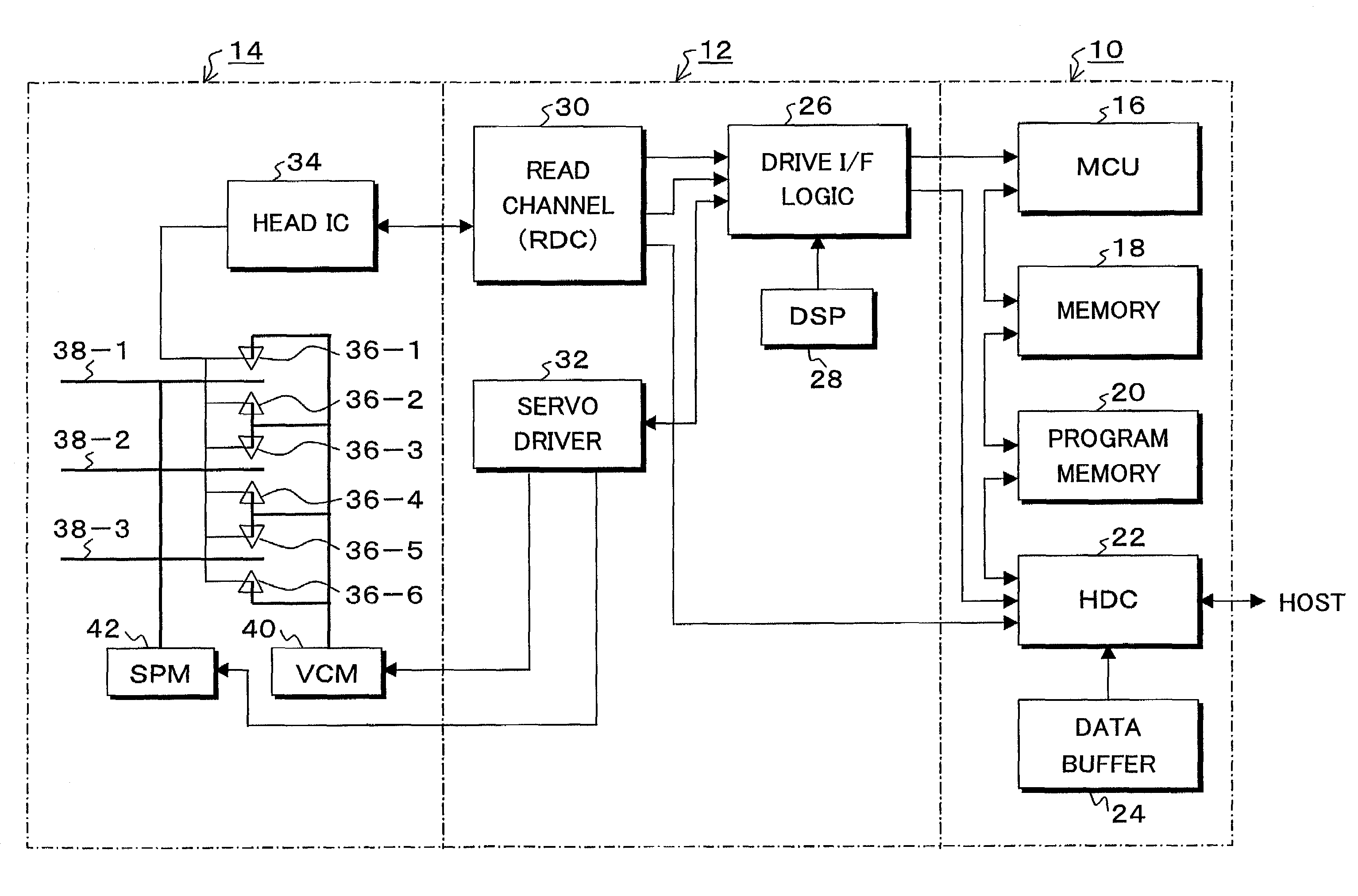
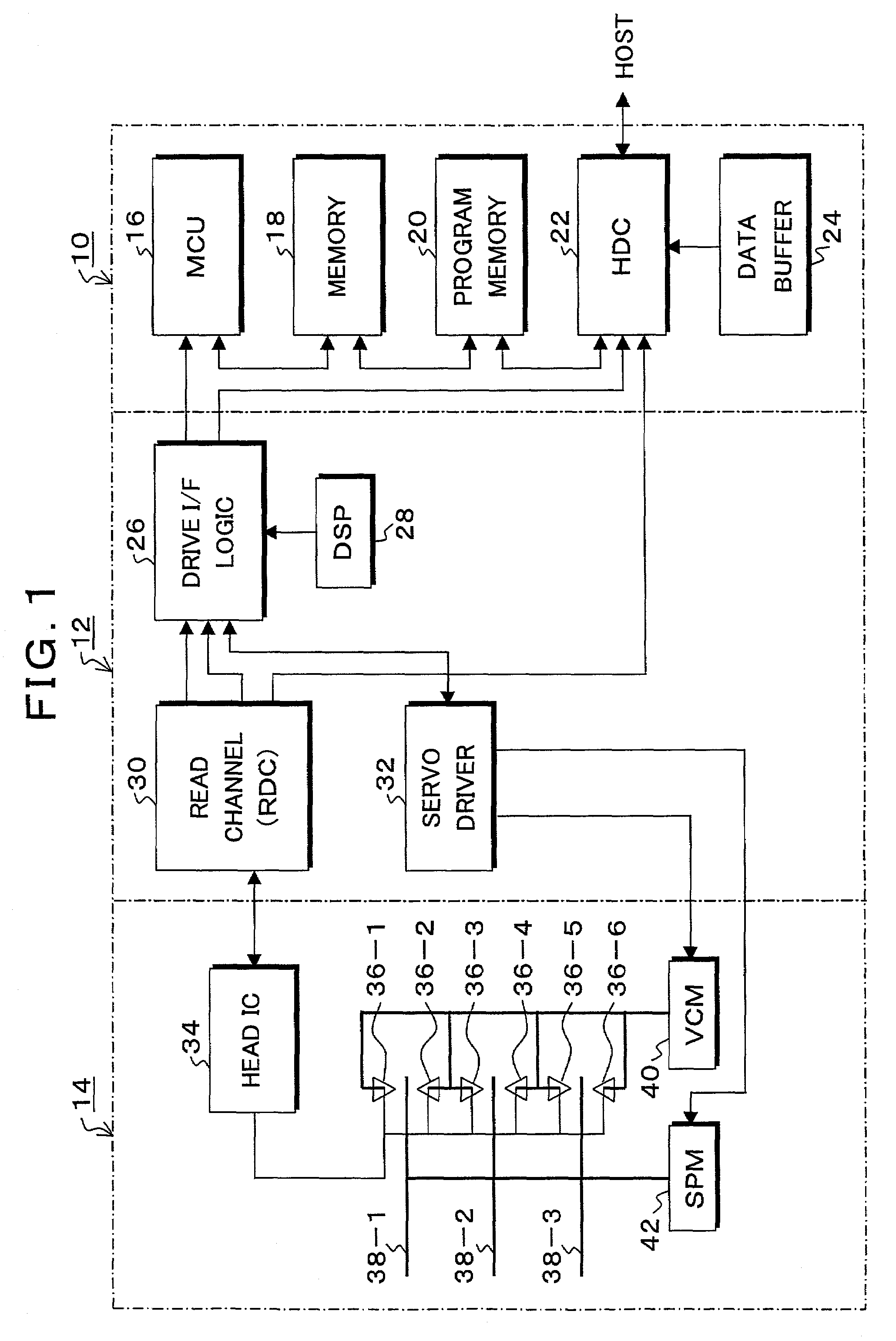
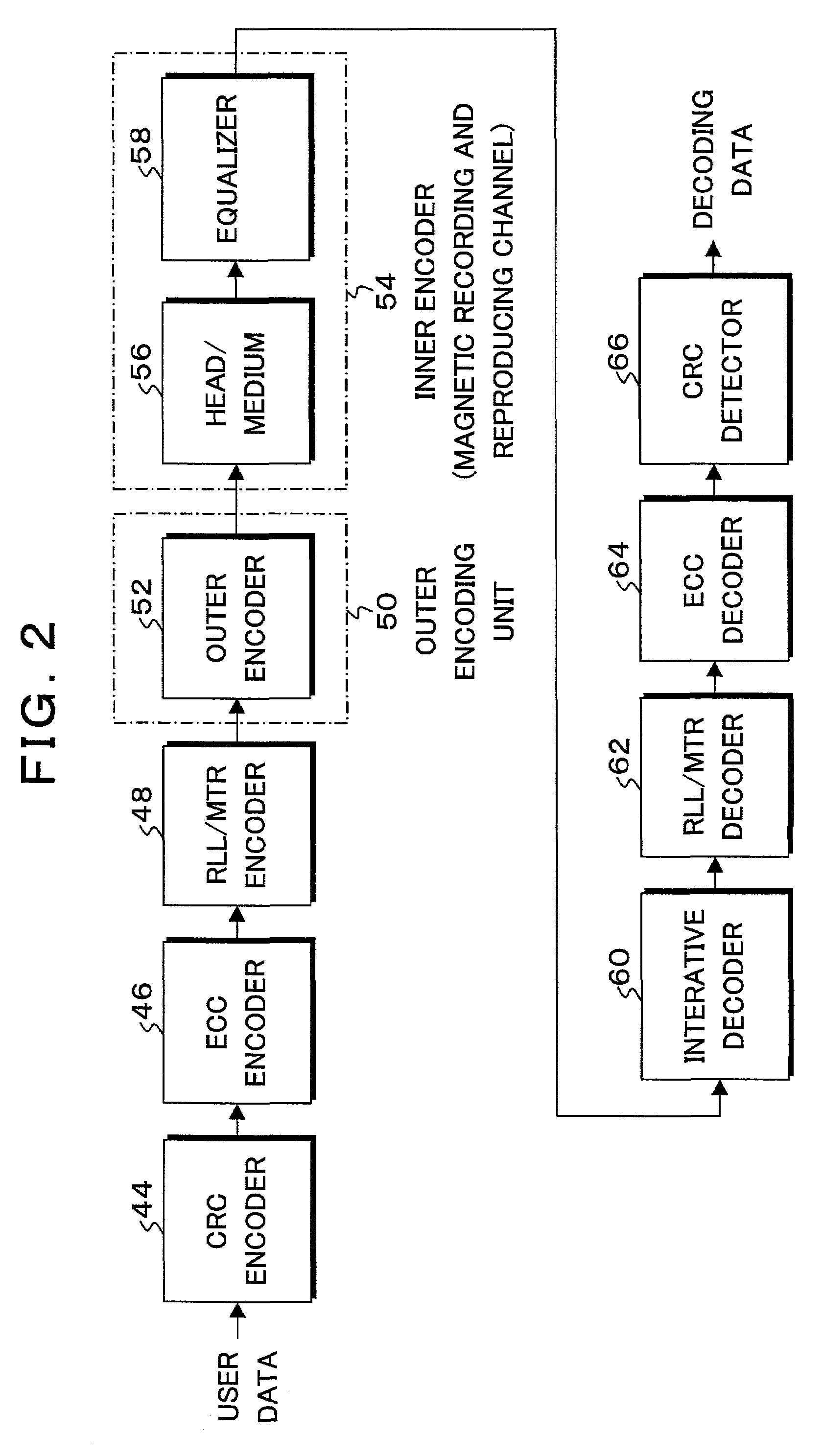
Information recording and reproducing apparatus and method and signal decoding circuit having improved noise processing characteristics
InactiveUS7031090B2Effective applicationImprove decoding performanceModification of read/write signalsOther decoding techniquesMaximum a posteriori estimationComputer science
In a Maximum A posteriori Probability decoding (MAP decoding), a correlation and a deviation of noises for past and future states which depend on input signal patterns in past N bits and future Q bits are calculated by training by a noise correlation arithmetic operating unit 84 and they are stored. Upon reproduction, in a white noise arithmetic operating unit 91, white noise values for the past and future states in which colored noises are converted into white noises are obtained by using the stored correlation and deviation of the noises. In an input signal arithmetic operating unit 92, an input signal (channel information) Λc(yk|Smk) of the MAP decoding is calculated from the white noise values and the deviation for the past and future states. A likelihood in the MAP decoding is obtained from the input signal.
Owner:TOSHIBA STORAGE DEVICE CORP
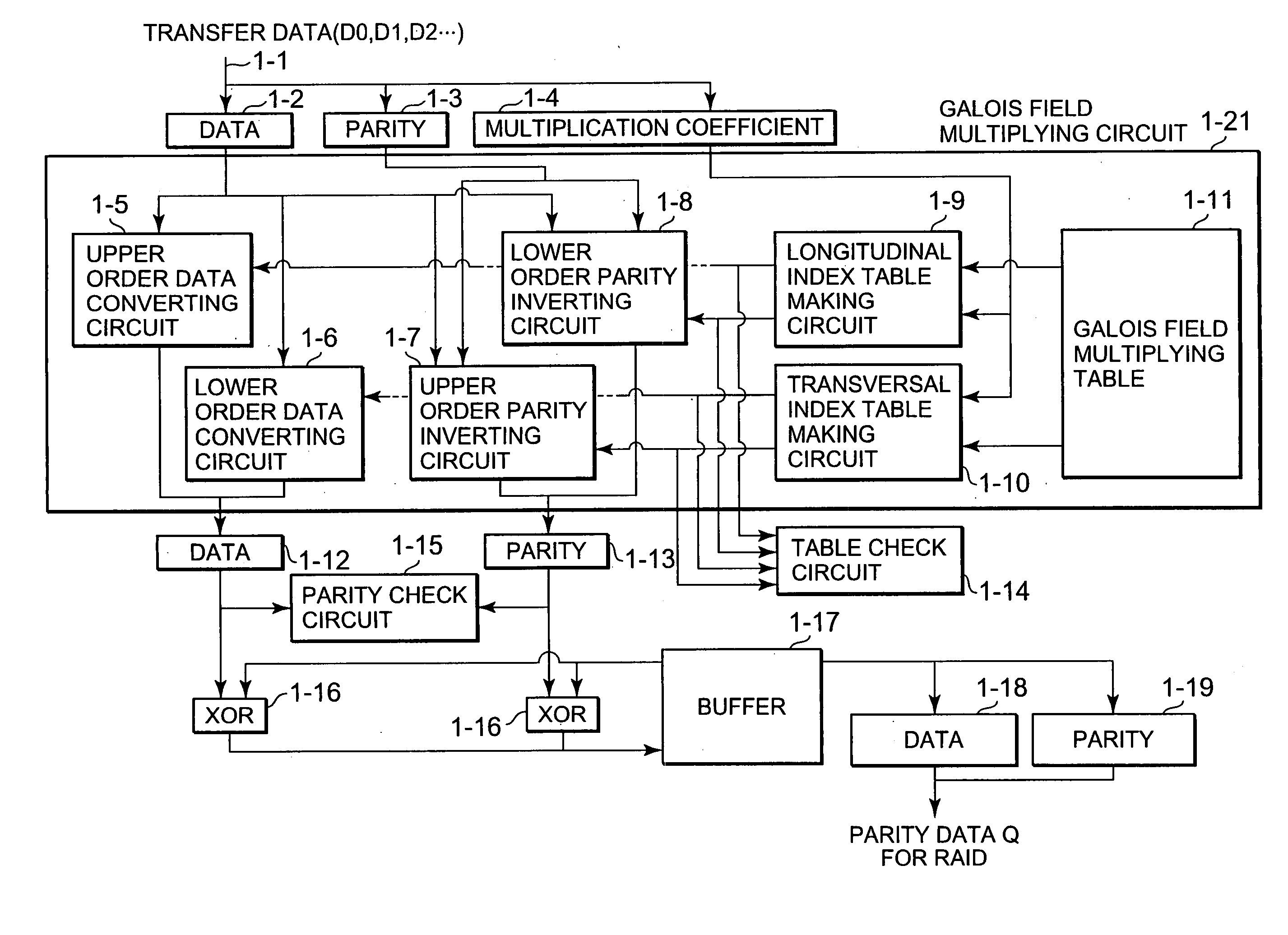
Disk array device, parity data generating circuit for raid and galois field multiplying circuit
ActiveUS20050108613A1Reliably guaranteeing data by parityImprove reliabilityInput/output to record carriersCode conversionRAIDTheoretical computer science
In this parity data generating circuit, a Galois field multiplying calculation is realized by performing data conversion by index table information generated from a Galois field multiplying table so that data for RAID6 are generated. A table check circuit inspects nonconformity of the index table information in advance by using results in which the Galois field multiplying table is indexed from different directions constructed by the longitudinal direction and the transversal direction. Data and parity for making the multiplying calculation are decomposed into plural data and parities by using this table check circuit, and index table information different from each other are allocated to these data and parities. Thus, a longitudinal index table making circuit and a transversal index table making circuit themselves are checked.
Owner:NEC CORP
Method and apparatus for generating bit errors in a forward error correction (FEC) system to estimate power dissipation characteristics of the system
ActiveUS7073117B1Precision productionPower dissipationData representation error detection/correctionCode conversionFir systemForward error correction
A method and apparatus for generating and inserting bit errors in data words that have been encoded in a forward error correction (FEC) system in order to estimate power dissipation. In accordance with the present invention, it has been determined that a burst error generator that is capable of erroring the maximum number of correctable data bits in every FEC encoded frame, which allows the designer to accurately produce test vectors that are suitable for use in commercially available power estimation tools. In addition, after the IC is produced, the burst error generator of the present invention can be enabled to provide real-time FEC power dissipation data for use in system thermal modeling, thus obviating the need to use costly external devices that emulate a given error rate. Furthermore, the power dissipation data obtained in real-time may be used to refine the initial design power estimate, which will then allow the designer to develop a more accurate prediction of power consumption for future IC designs. Thus, the burst error generator of the present invention is capable of reducing iterations of IC designs by accurately estimating the worst-case power dissipation of FEC decoders.
Owner:CIENA
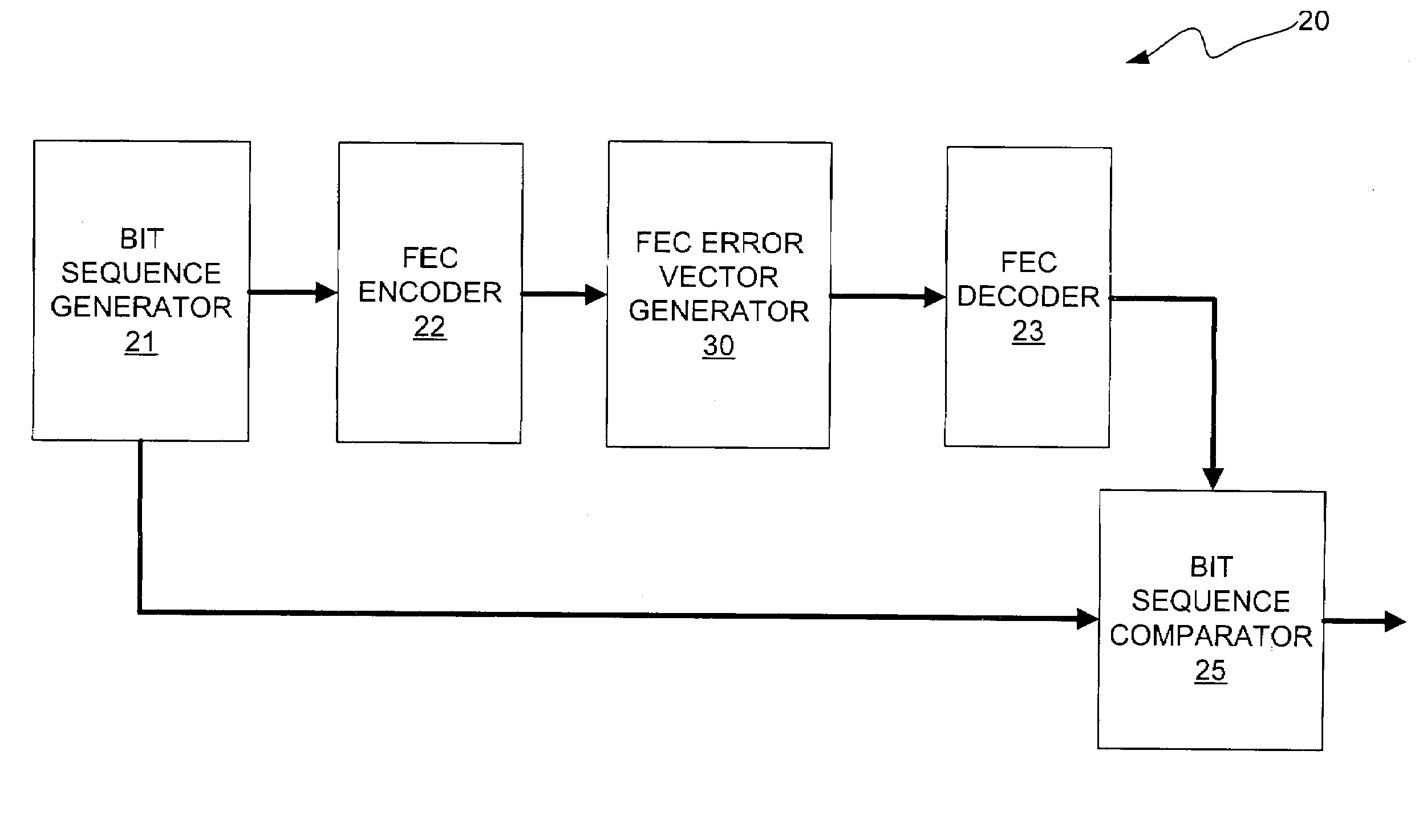
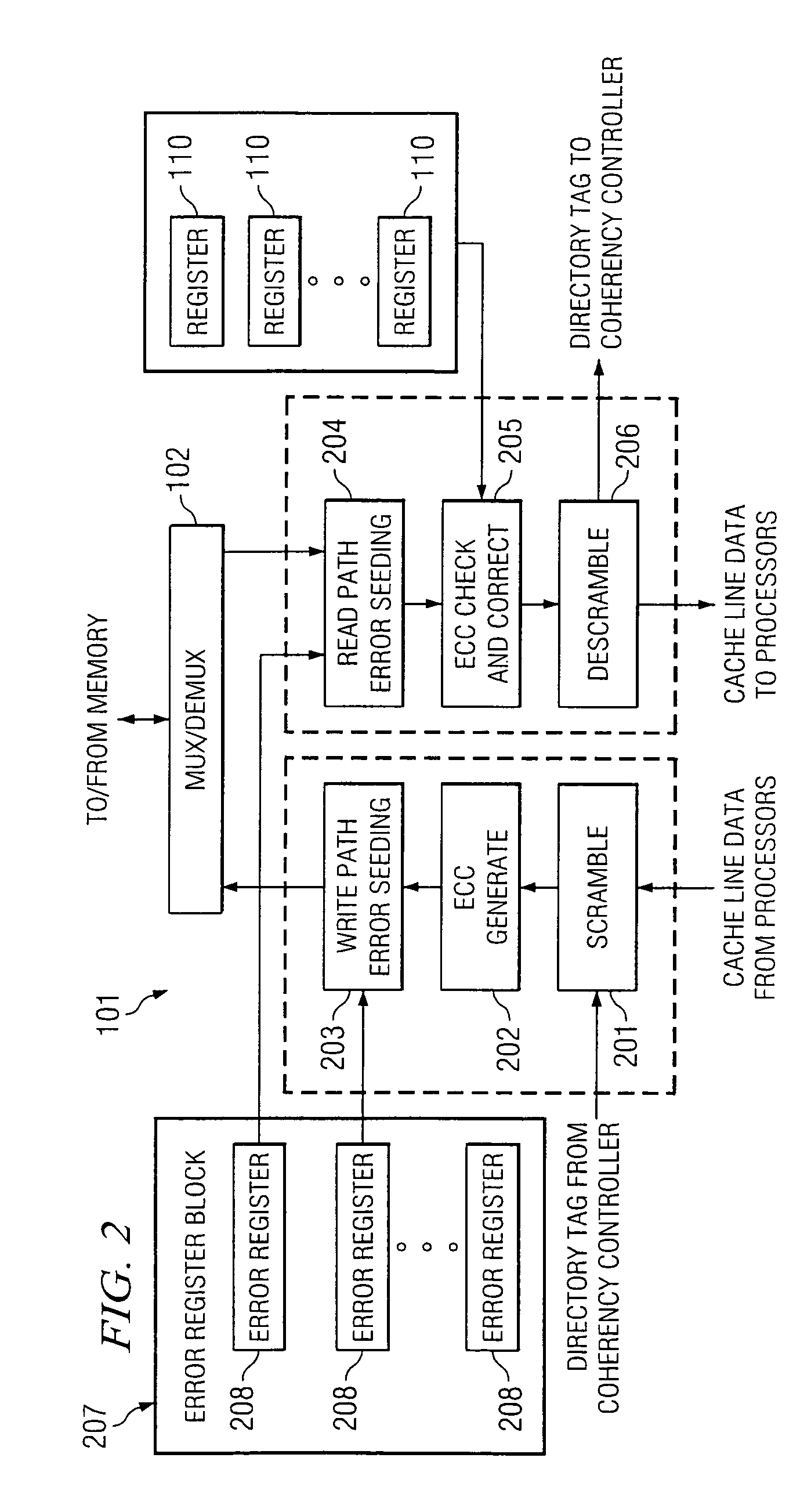
Systems and methods for providing error correction code testing functionality
In one embodiment, a memory controller comprises a cache line processing block for processing a cache line into a plurality of segments, an error correction code (ECC) generation block that forms ECC code words for each of the plurality of segments for storage in a plurality of memory components, an ECC correction block for correcting at least one single-byte erasure error in each erasure corrupted ECC code word retrieved from the plurality of memory components, and an error seeding block that enables a respective error to be inserted into each ECC code word of the cache line in response to a plurality of error registers.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP +1
Cryptographic communication apparatus
InactiveUS7649996B2Key distribution for secure communicationSynchronising transmission/receiving encryption devicesQuantum gatePseudo random number generation
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Method and system for optimizing forward error correction of multimedia streaming over wireless networks
The loss of packets in a communication system can be minimized in an optimal manner by adapting a set of error correction (EC) parameters in response to a calculated probability of packet loss. The calculated probability is obtained from derived algorithms that are applied to a set of communication parameters. Algorithms are derived from Bernoulli-distributed traffic models and constant bit rate (CBR) traffic models of the communication system. A collapsed-state model is used to derive a very efficient algorithm that calculates an approximate probability of packet loss. Alternate applications for the algorithms are also disclosed.
Owner:DOLBY LAB LICENSING CORP
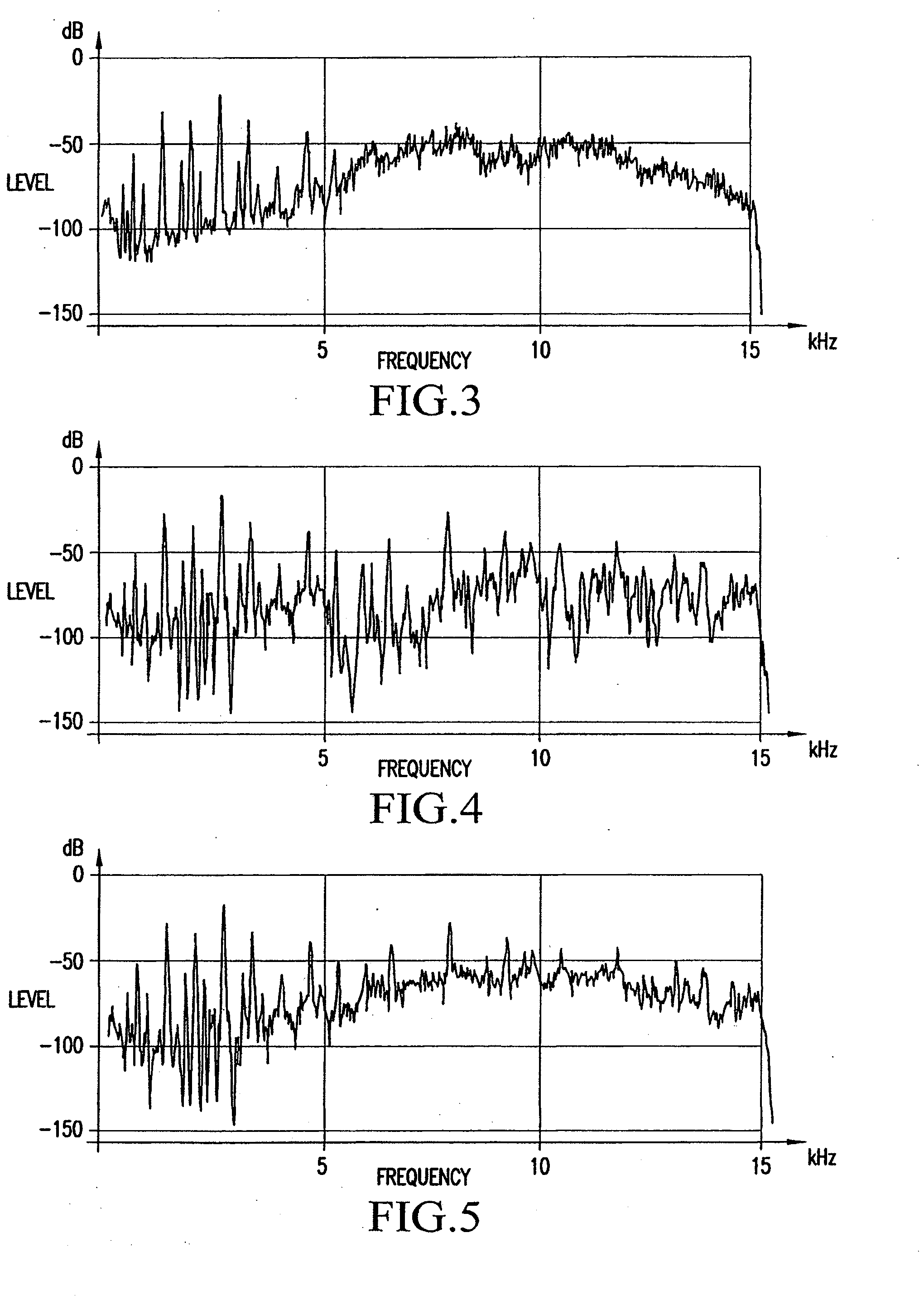
Semiconductor device and testing method for same
A test method for a semiconductor device that is provided with an ECC circuit that uses product code that is composed of a first code and a second code for implementing error correction of a memory, the test method includes steps of: obtaining first pass / fail determination results and second pass / fail determination results that are realized by independent correction operations based on the first code and the second code, respectively; recording the results in a first fail memory and a second fail memory, respectively; executing a prescribed logical operation such as an AND operation relating to the contents of the first fail memory and the contents of the second fail memory; and based on the results of the logical operation, remedying both fail bits and potential fail bits.
Owner:PS4 LUXCO SARL
Semiconductor device and testing method for same
Owner:PS4 LUXCO SARL
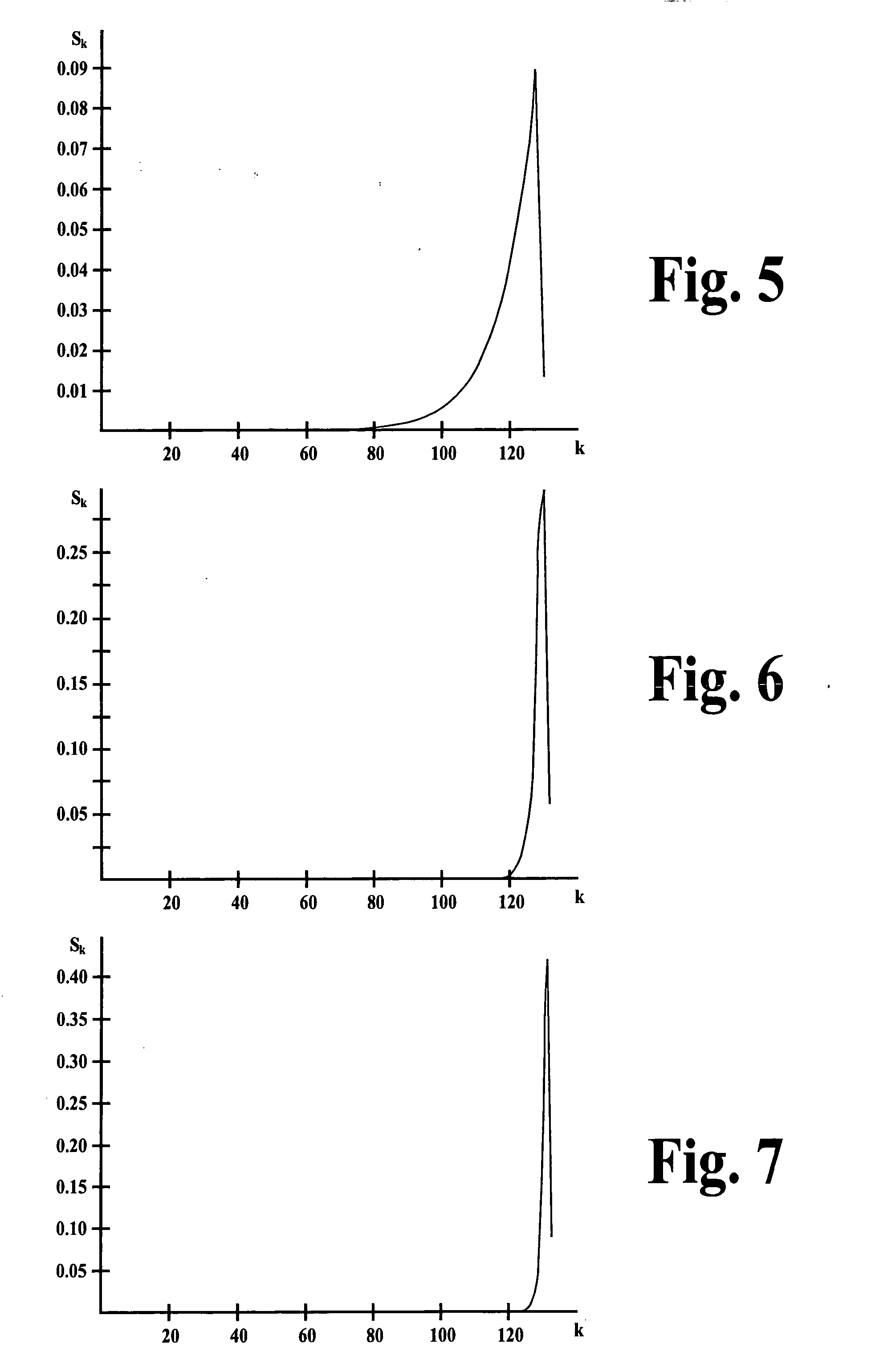
Soft output metrics generation for symbol detectors
InactiveUS6480552B1Other decoding techniquesDc level restoring means or bias distort correctionCommunications systemTransmitter
A method for calculating soft outputs of a detector used in a receiver that is part of a communication system having either memory introducing modulators or memoryless modulators. The output of a soft output detector, also known as reliability information, provides a probability that a certain symbol was transmitted by a transmitter of the communication system or the probability that a bit within a transmitted symbol was transmitted by a transmitter.
Owner:WSOU INVESTMENTS LLC +1
Method and system for optimizing forward error correction of multimedia streaming over wireless networks
InactiveUS7447977B2Minimize impactUnequal/adaptive error protectionCode conversionPacket lossCommunications system
The loss of packets in a communication system can be minimized in an optimal manner by adapting a set of error correction (EC) parameters in response to a calculated probability of packet loss. The calculated probability is obtained from derived algorithms that are applied to a set of communication parameters. Algorithms are derived from Bernoulli-distributed traffic models and constant bit rate (CBR) traffic models of the communication system. A collapsed-state model is used to derive a very efficient algorithm that calculates an approximate probability of packet loss. Alternate applications for the algorithms are also disclosed.
Owner:DOLBY LAB LICENSING CORP
Method and apparatus for watermarking with no perceptible trace
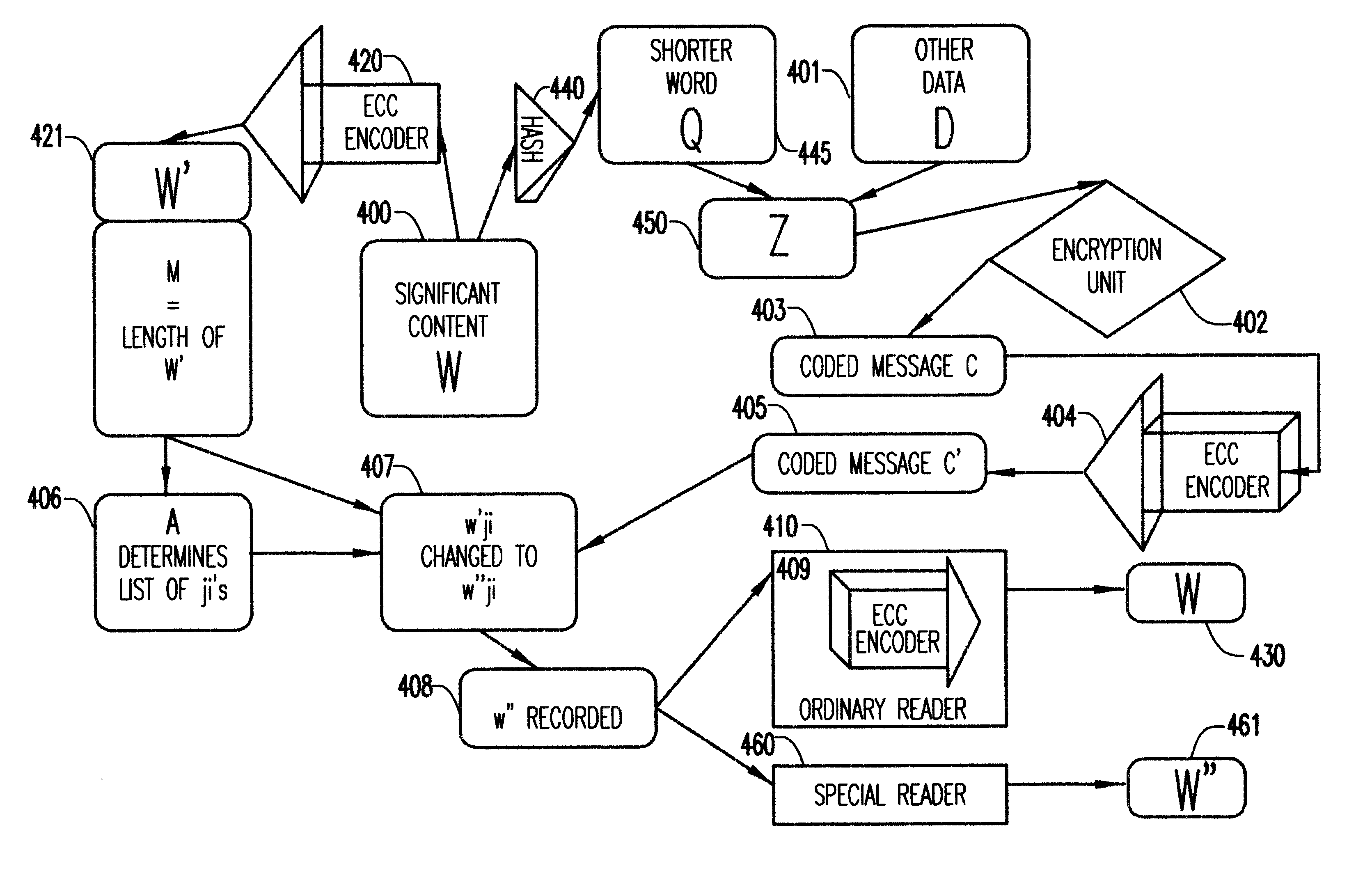
InactiveUS6564322B1Public key for secure communicationDigital data processing detailsDigital recordingDigital records
A watermark in the form of an added message is attached to a digital recording so that a significant content of the recording is completely unchanged by the process in the sense that any reader commonly used for such recording will extract from the recording exactly what would have been extracted in the case the added message had not been attached. This is done by hiding the added message in the error correcting code (ECC) for the significant content of the recording.
Owner:IBM CORP
Method for partitioning encoding block
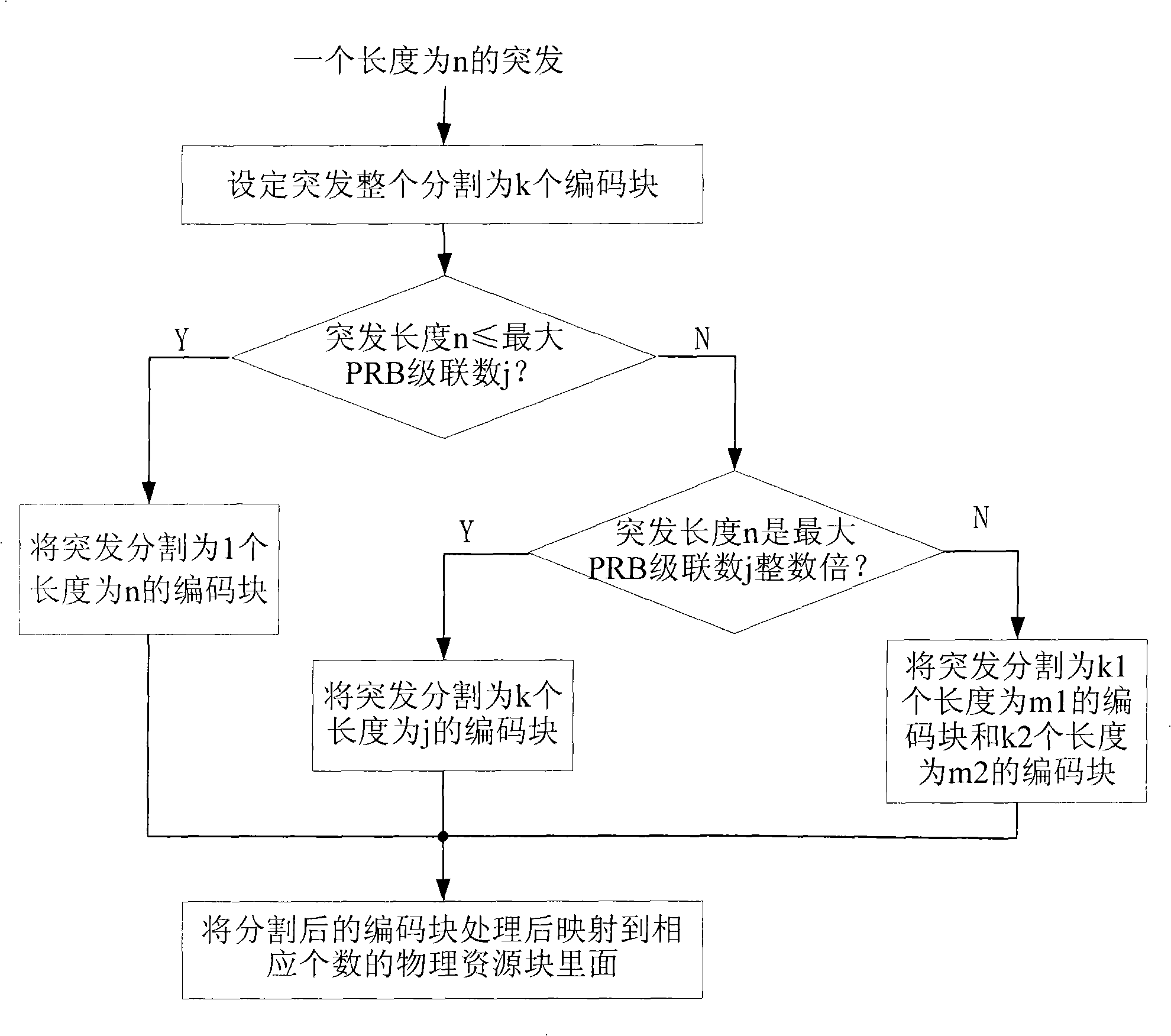
InactiveCN101282122AGuaranteed burst performanceHigh coding gainCodes simulation/testingCoding theory basic assumptionsCoding blockResource block
The present invention discloses a coding block dividing method. The device comprises a coding block dividing unit, a code modulation processing unit, a mapping unit, a first calculating unit and a second calculating unit. The method comprises the following steps: setting to divide the burst to k coding blocks in total; if the burst length n<=cascade connection number j of physical resource block of the maximum coding block, then taking the whole burst as a coding block with length for n; otherwise if the n is integer times of j, dividing the burst to k coding blocks with length for j; if the n is not integer times of j, dividing the burst to k1 coding blocks with length for m1 and k2 coding blocks with length for m2; and at last mapping the divided coding blocks to the physical resource blocks with a corresponding number after procession. The coding device according to the invention can reasonably divide the burst and guarantees that the smallest coding block generated by dividing is as large as possible thereby obtaining the purpose of guaranteeing the burst capability and obtaining larger coding gain and interweaving gain.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Enhancing Perceptual Performance of SBR and Related HFR Coding Methods by Adaptive Noise-Floor Addition and Noise Substitution Limiting
InactiveUS20090319259A1Prevents unwanted noise substitutionAvoid noiseDigital variable displayOther decoding techniquesAlgorithmPerceptual performance
Methods and an apparatus for enhancement of source coding systems utilizing high frequency reconstruction (HFR) are introduced. The problem of insufficient noise contents is addressed in a reconstructed highband, by using Adaptive Noise-floor Addition. New methods are also introduced for enhanced performance by means of limiting unwanted noise, interpolation and smoothing of envelope adjustment amplification factors. The methods and apparatus used are applicable to both speech coding and natural audio coding systems.
Owner:DOLBY INT AB
Apparatus and method for generating scrambling code in UMTS mobile communication system
InactiveUS7362867B1Minimize complexityIncrease the number ofMultiplex code generationSecret communicationCommunications systemMobile communication systems
A scrambling code generating apparatus of a downlink transmitter in a UMTS mobile communication system, which uses one primary scrambling code for separation of base stations and multiple secondary scrambling codes for channel separation. The apparatus includes a first m-sequence generator for generating a first m-sequence and a second m-sequence generator for generating a second m-sequence. A first summer adds the first and second m-sequences to generate the primary scrambling code. A plurality of first masking sections each shift the first m-sequence, and a plurality of second masking sections corresponding to the respective first masking sections each shifts the second m-sequence. A plurality of second summers each adds one of the first shifted m-sequences with the second m-sequence corresponding to the first m-sequence. The output of the second summers thus generates the multiple secondary scrambling codes.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
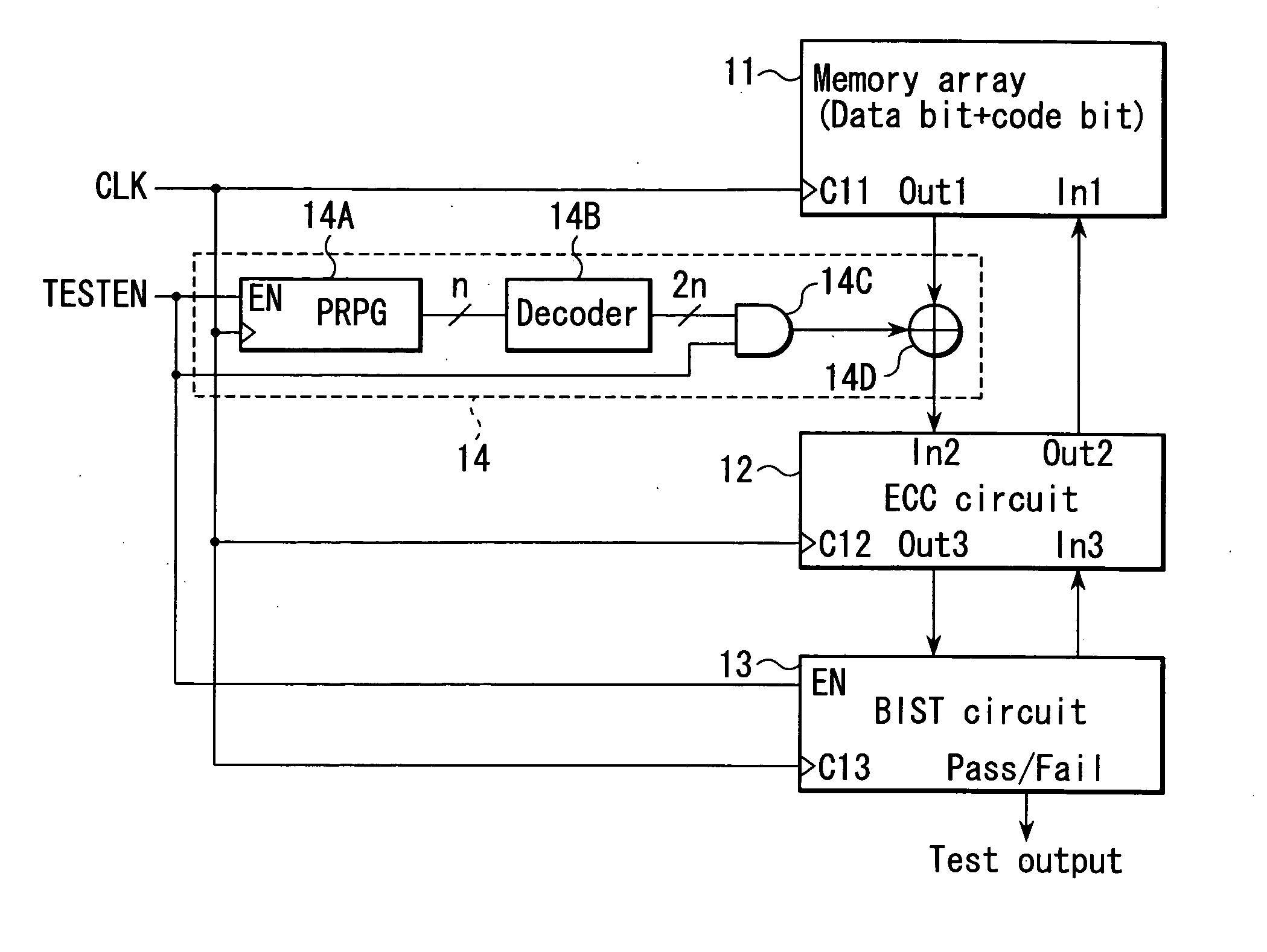
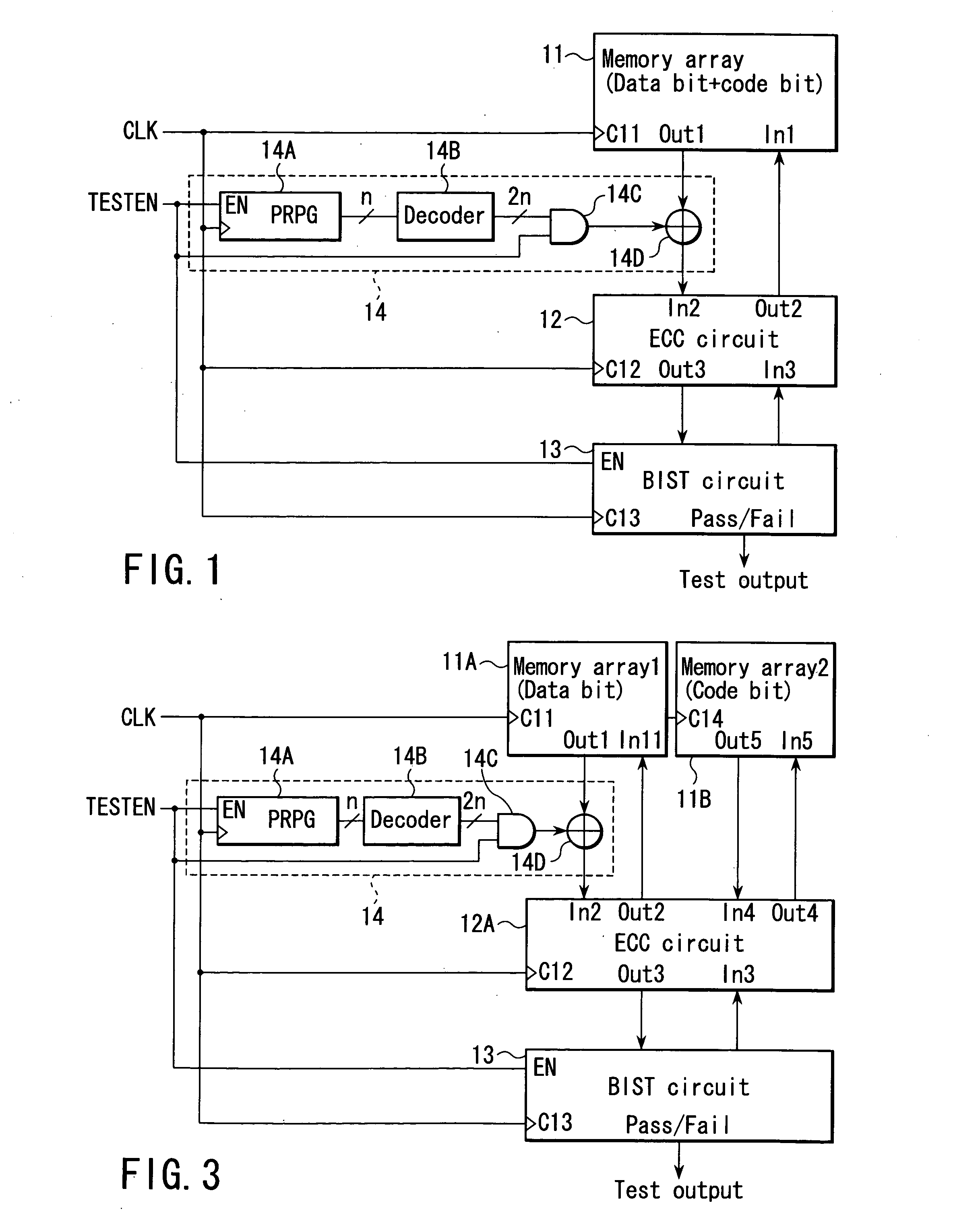
Semiconductor device having ECC circuit
InactiveUS20050086572A1Electronic circuit testingDetecting faulty computer hardwareComputer scienceSemiconductor device
A semiconductor device includes a memory which stores data, an ECC circuit which corrects a bit error of data read out from the memory and generates correction data, a BIST circuit which tests the correction data output from the ECC circuit, and a pseudo error generator circuit which generates a pseudo error for at least one bit configuring the data read out from the memory and supplies the pseudo error to the ECC circuit in a test mode.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Low-Complexity High-Performance Low-Rate Communications Codes
An encoder includes an outer repetition encoder, an interleaver for permuting encoding from said outer repetition encoder; and an inner encoder for encoding information from the interleaver to provide a repeat zigzag-Hadamard code. In an exemplary embodiment, a common bit of a zigzag-Hadamard segment of encoding from said inner encoder is a repetition of a last parity bit of a previous zigzag-Hadamard segment of encoding from said inner encoder and said common bit is punctured.
Owner:NEC CORP
Method and device for performance evaluation of forward error correction (fec) codes
InactiveCN104205647AError detection/correctionCode conversionCommunications systemTransmission channel
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Method of providing error protection for a data bit flow
InactiveUS6973610B1Error correction/detection using convolutional codesOther decoding techniquesTest error rateData stream
A method and device for providing error protection for a data bit stream in a digital telecommunications transmissions transmission system in order to reduce the bit error rate, characterized in that wherein, before channel coding, a multiplicity number of previously known dummy bits are inserted in a non-terminating fashion at predetermined bit positions in a primary data bit stream near to on both sides of information-carrying bits, in particular on both sides thereof.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
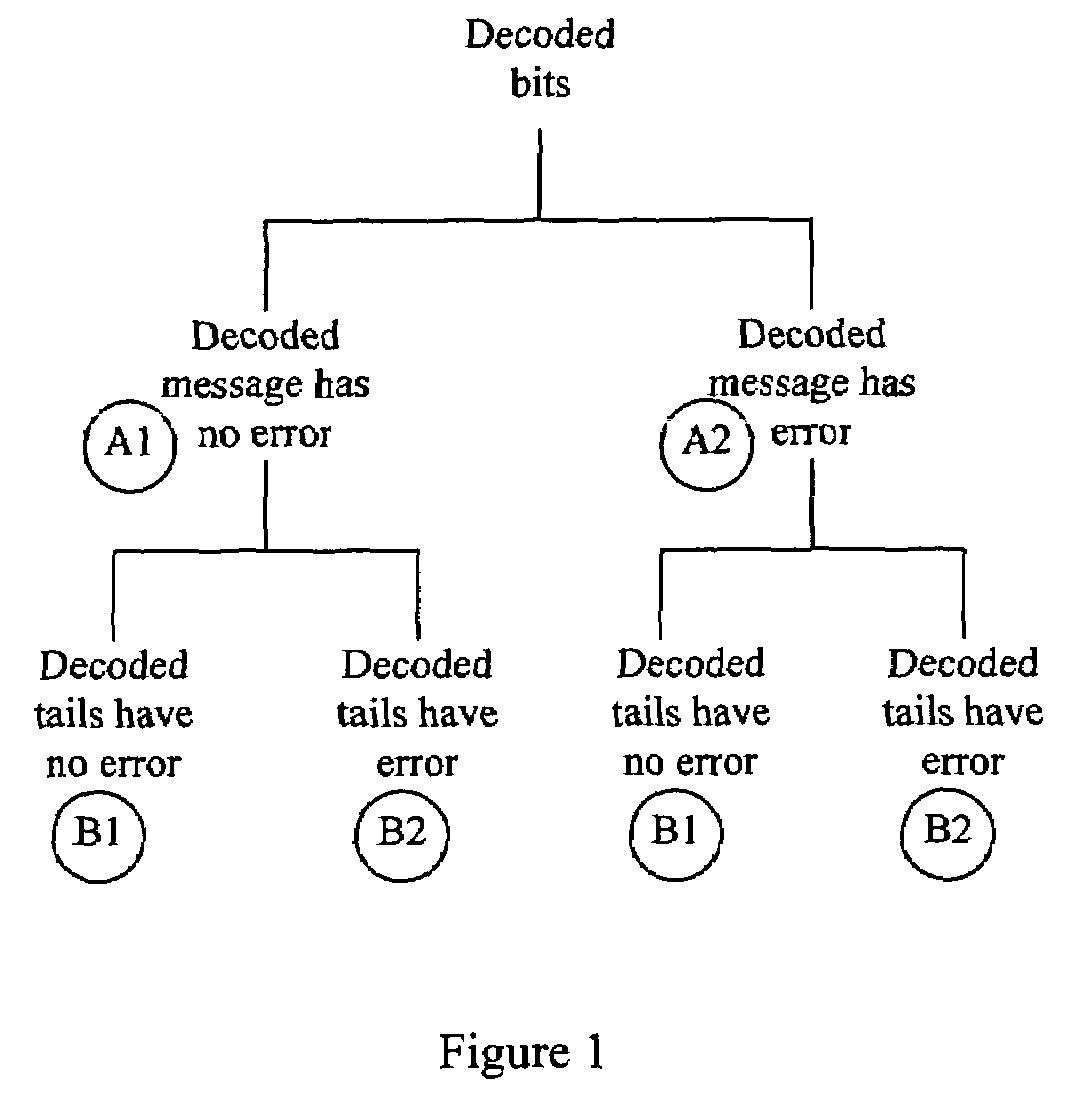
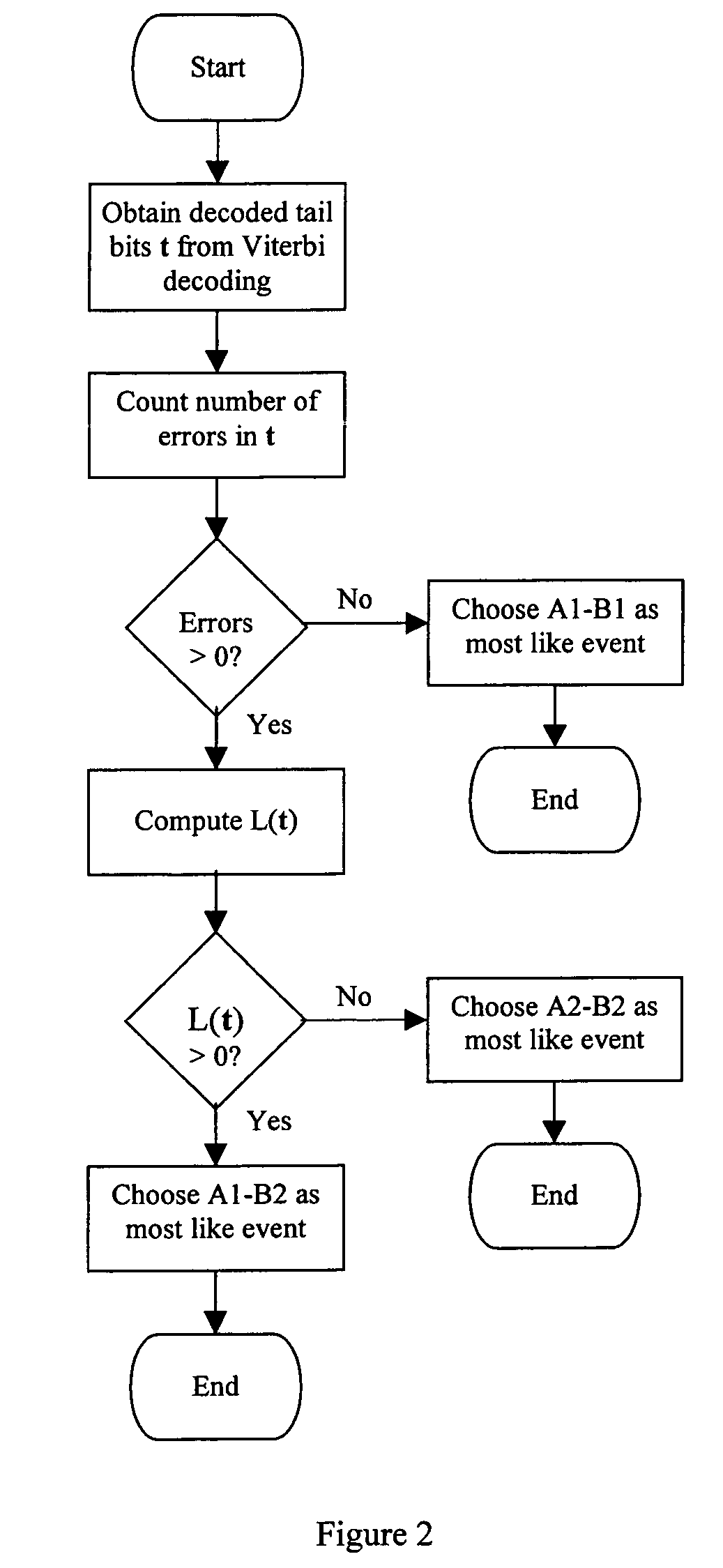
Method of estimating reliability of decoded message bits
InactiveUS7203894B2Less computation complexityImprove accuracyData representation error detection/correctionError preventionComputer hardwareCommunications system
A method of estimating the reliability of decoded message bits in a digital communications system is proposed. Message and tail bits are coded and transmitted across a communications channel. The coded message and tail bits are then decoded and it is determined that the decoded message bits have no error when the decoded tail bits have at least one error.
Owner:OKI TECHNO CENT SINGAPORE PTE
Popular searches
Error correction/detection by combining multiple code structures Substation equipment Error correction/detection using interleaving techniques Redundant data error correction Baseband systems Satellite broadcast receiving Error correction/detection using multiple parity bits Single error correction Cyclic codes Phase-modulated carrier systems
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com