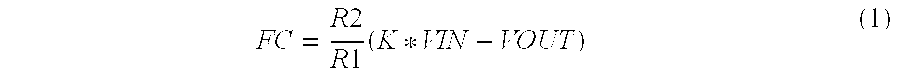Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
550 results about "Voltage droop" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
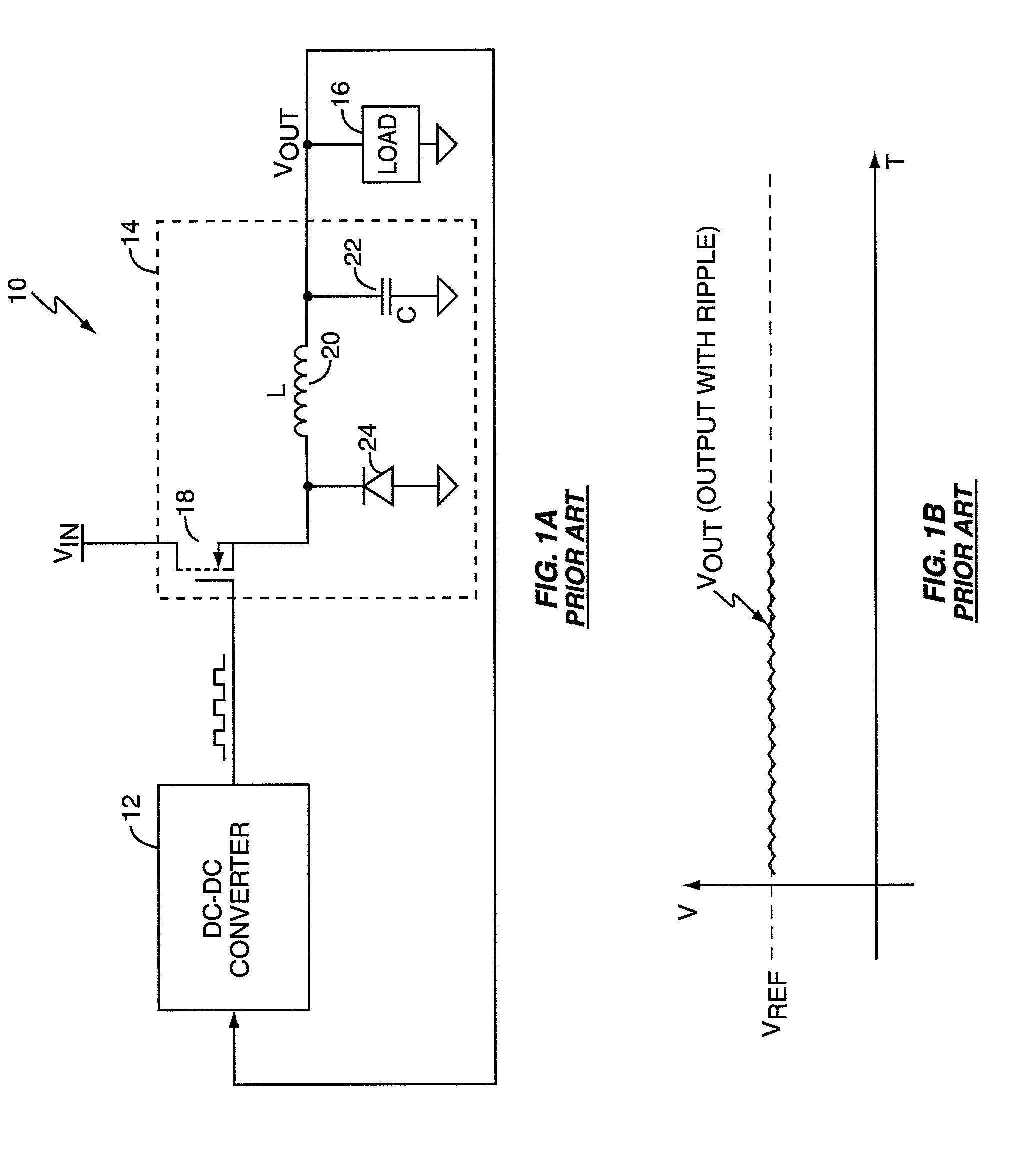
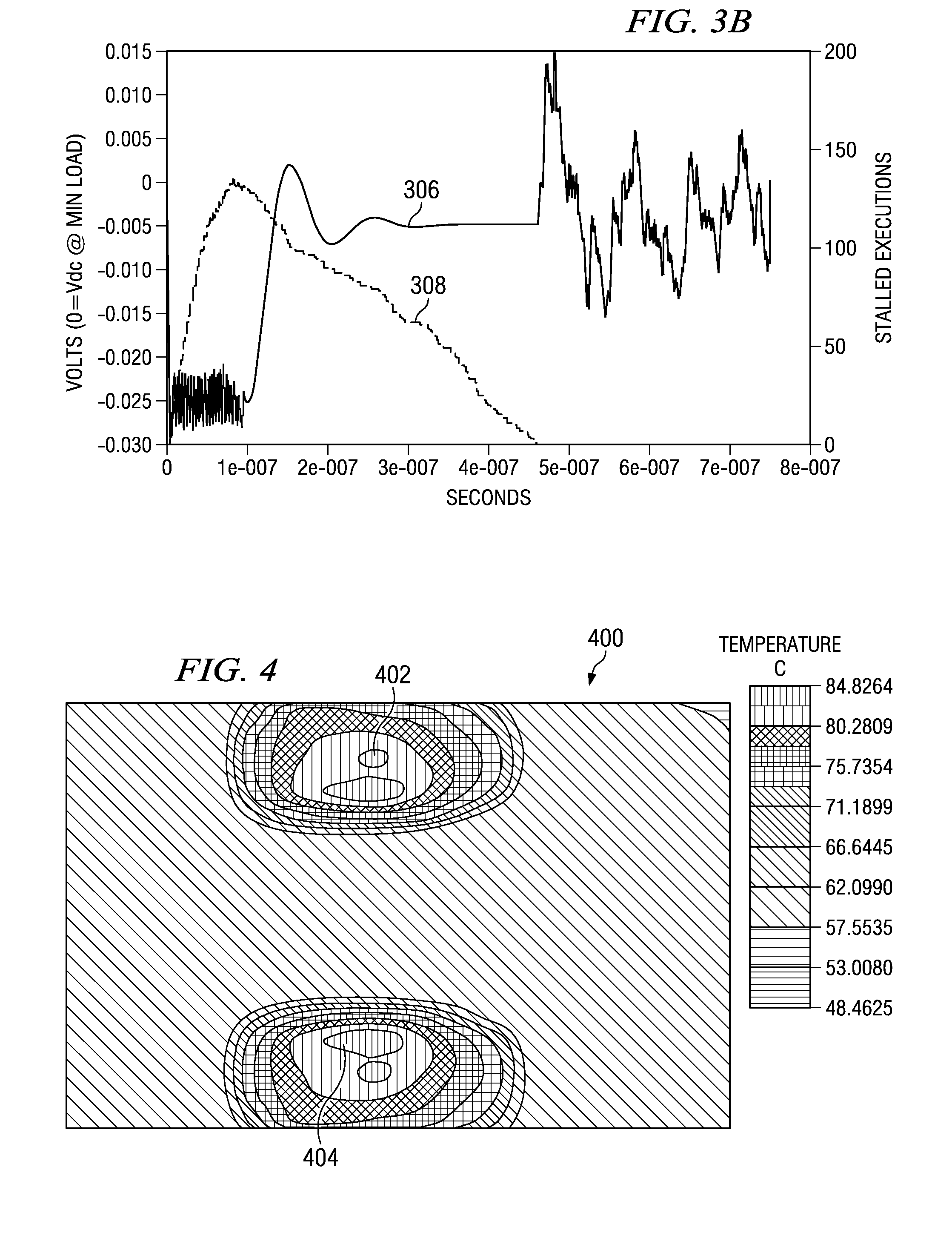
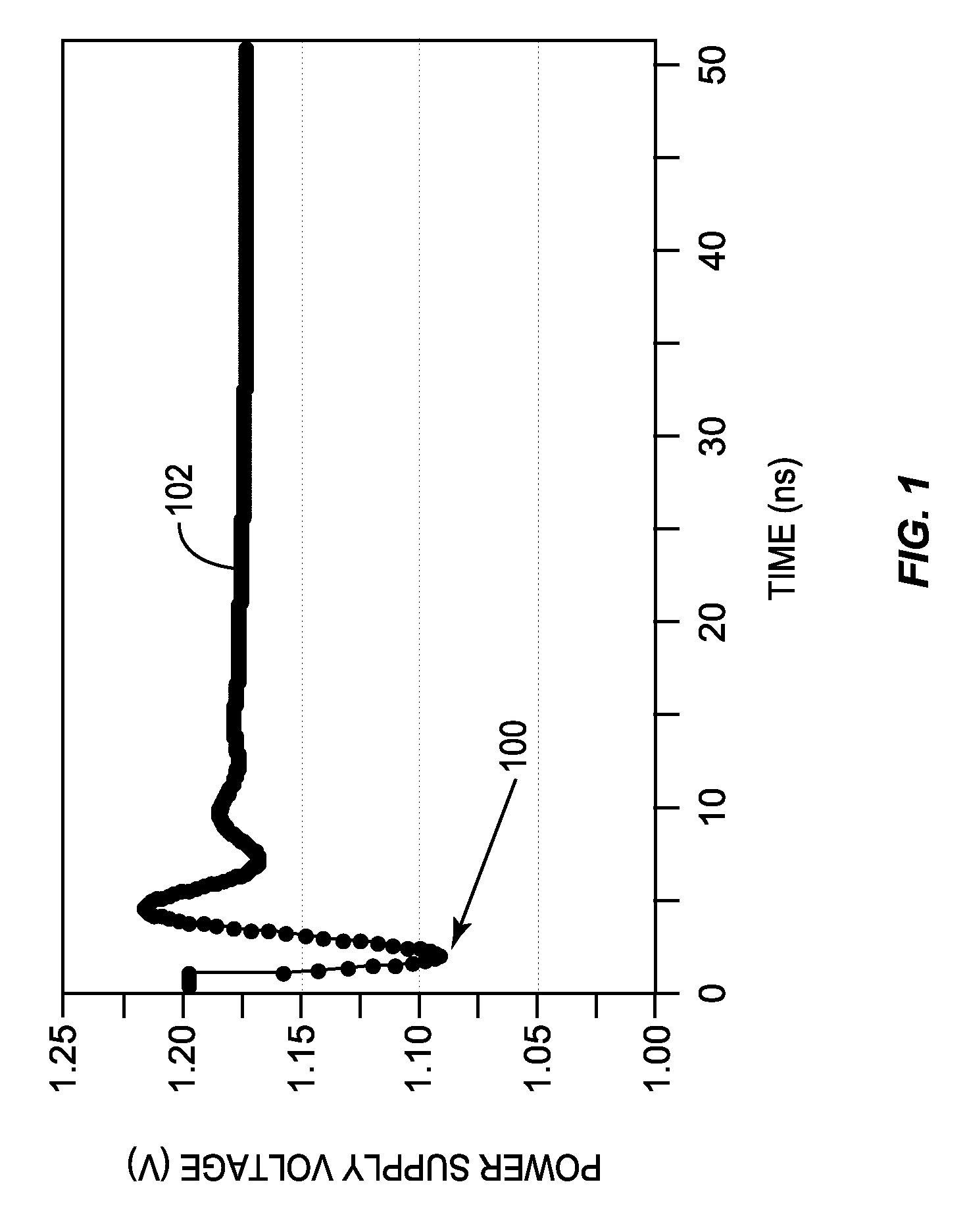
Voltage droop is the intentional loss in output voltage from a device as it drives a load. Adding droop in a voltage regulation circuit increases the headroom for load transients. Although it may seem counterproductive, a series resistor is included between the regulator output and the load. The resistance needs to be chosen so that at maximum output current, the output voltage at the load is the minimum acceptable.
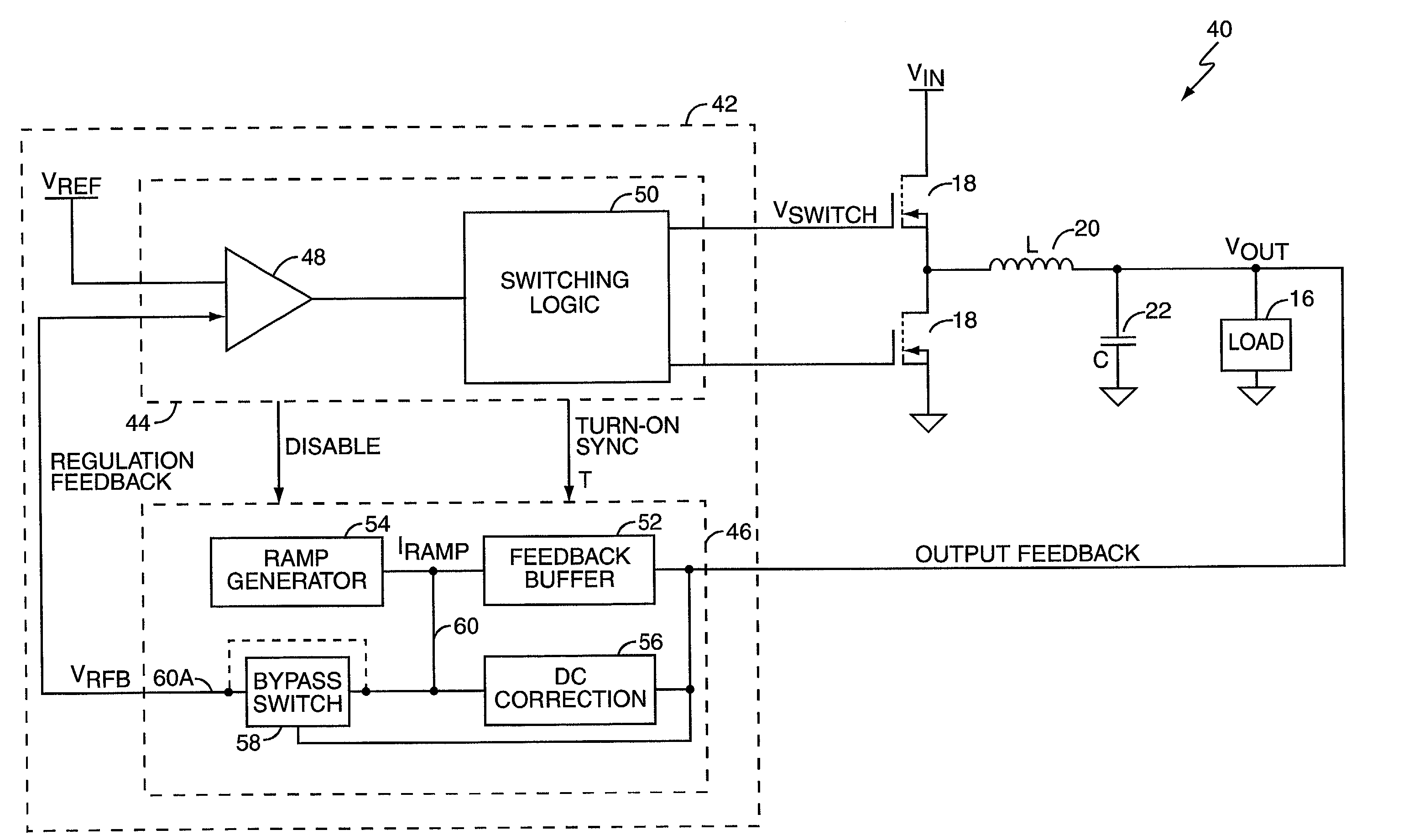
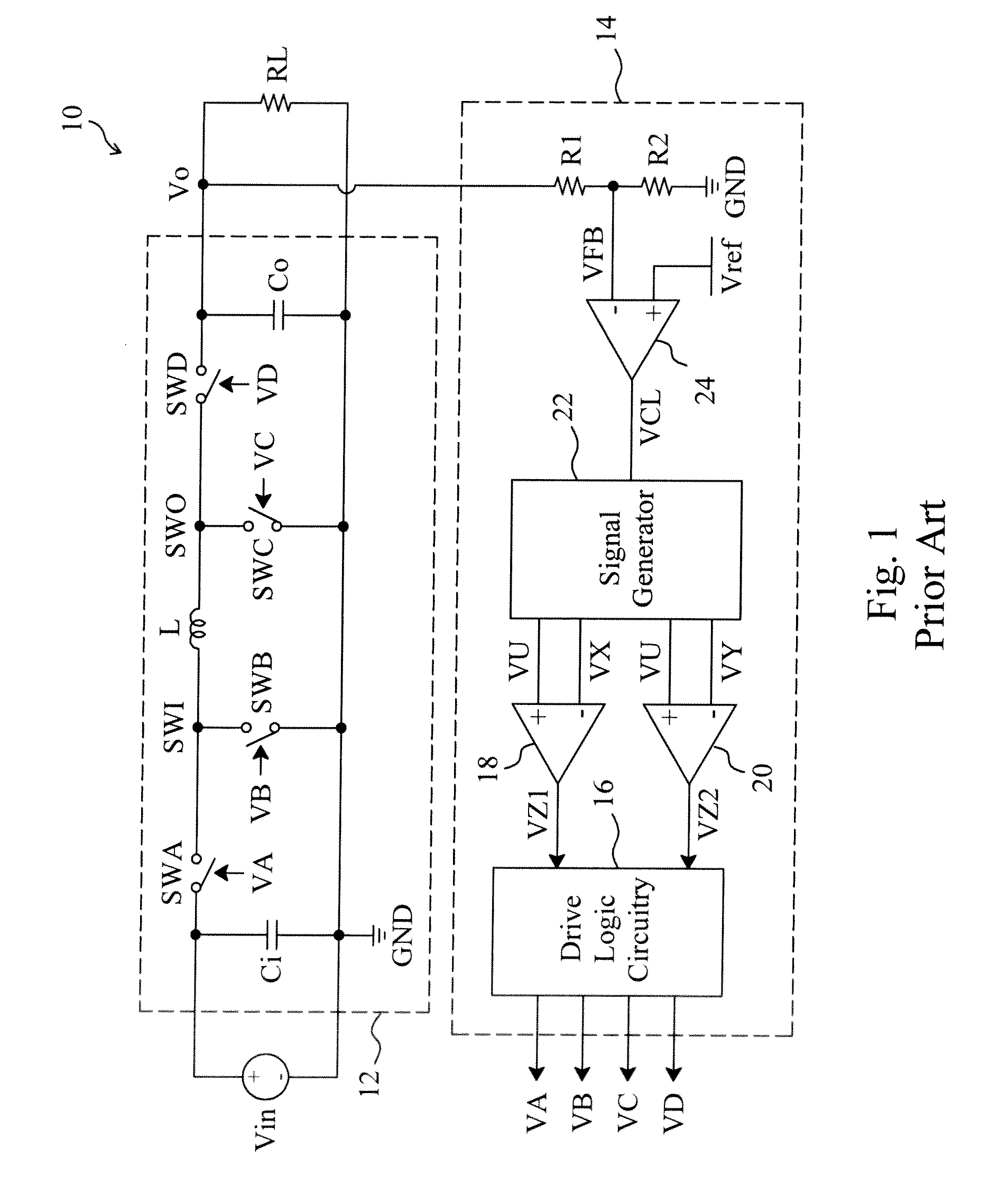
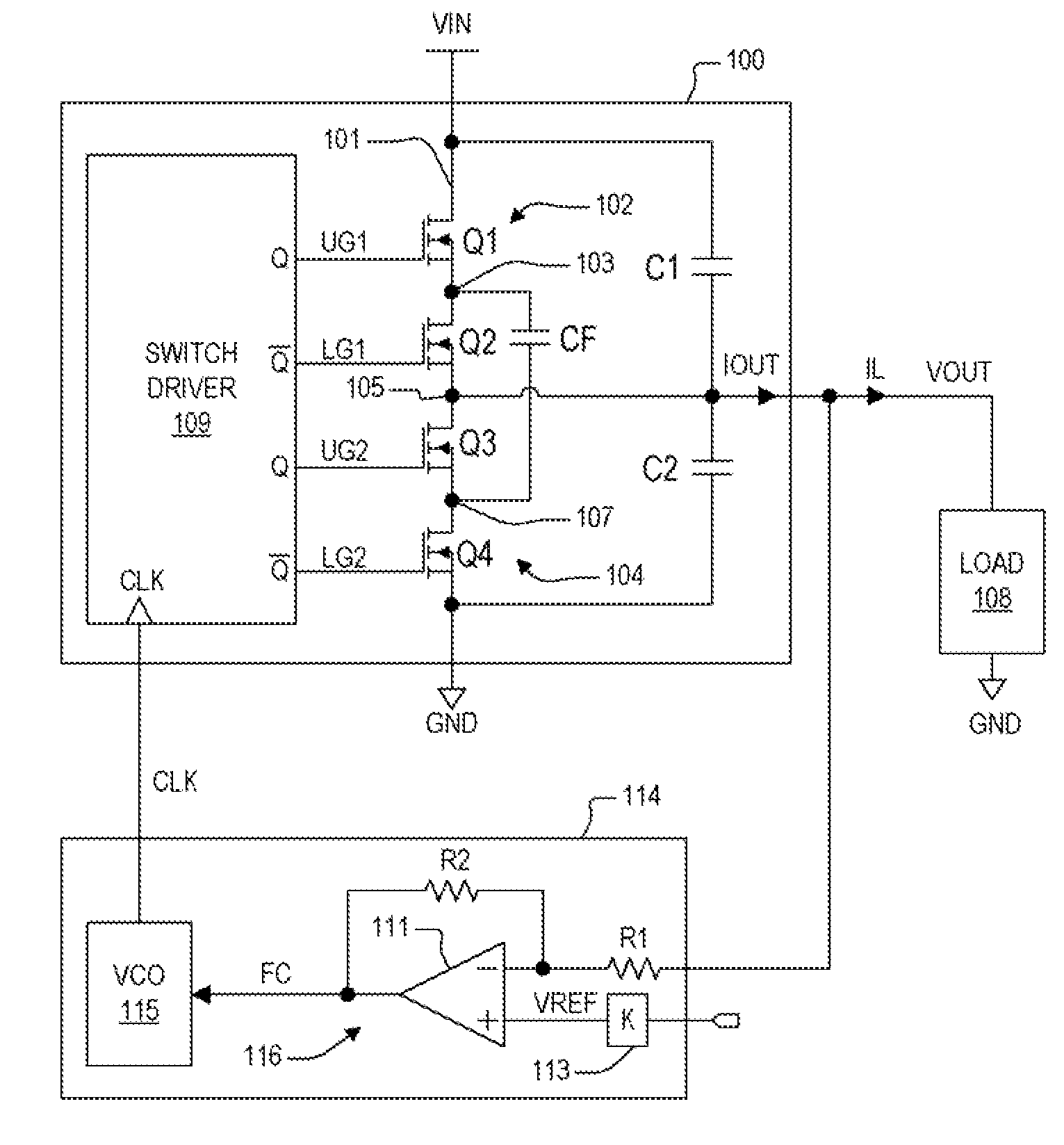
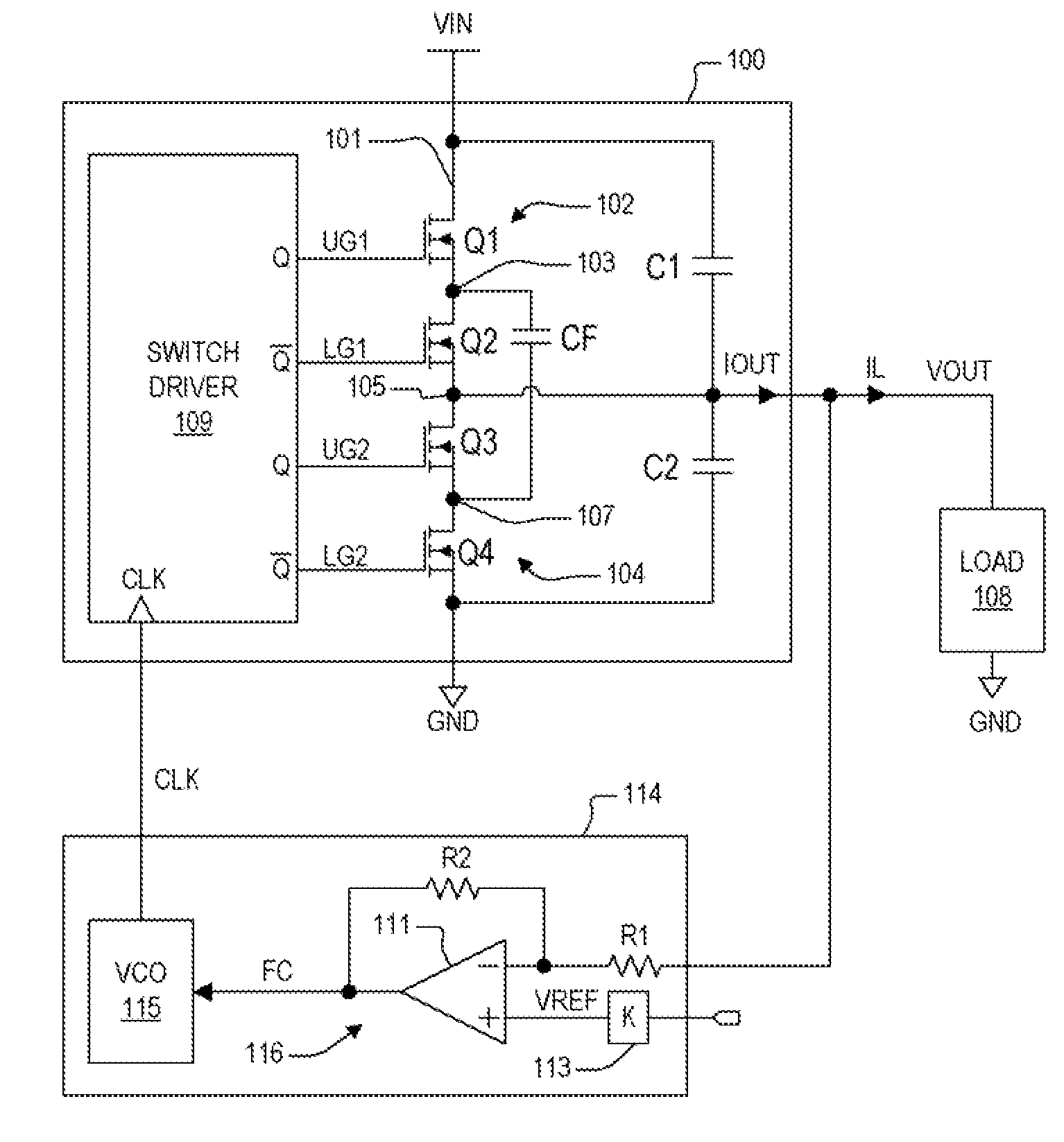
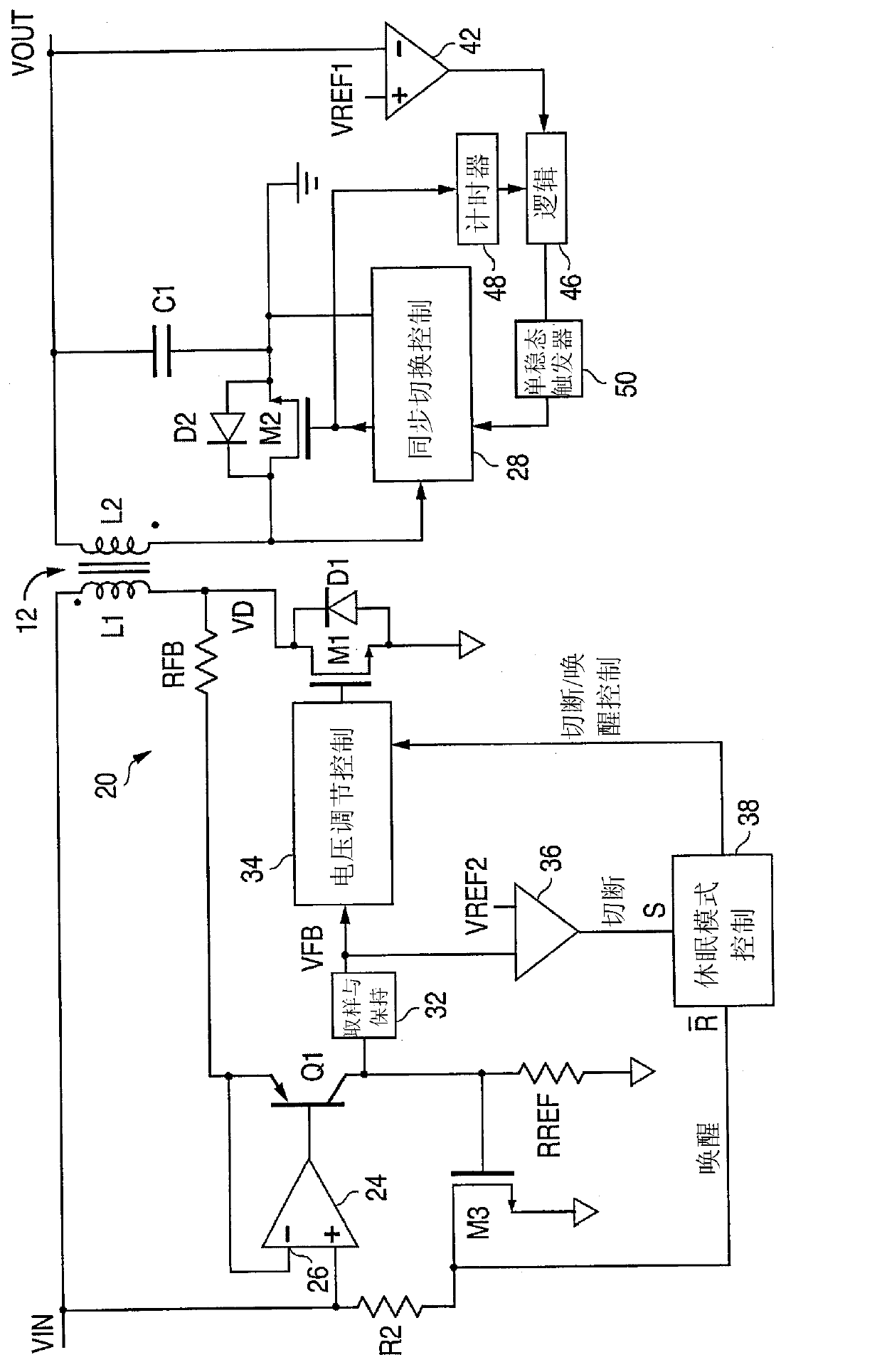
Virtual ripple generation in switch-mode power supplies
InactiveUS20020125872A1Prevent undesirable voltage overshootDroop compensationDc-dc conversionElectric variable regulationCapacitanceVoltage regulation
A system and method provides virtual ripple signal generation for use in voltage regulation applications. Some switch-mode power converters or voltage regulators use output signal ripple to effect voltage regulation. A virtual ripple generator provides this type of voltage regulator with a virtual ripple signal comprising an offset component responsive to actual load voltage, but with a generated AC ripple component of arbitrary magnitude that is independent of actual output signal ripple. Unlike the actual output ripple signal, the generated AC ripple component is not dependent on implementation specifics, such as circuit board layout or output capacitor ESR, and may have its gain set independent of the offset component. The generated AC ripple component is synchronized to the inductor switching actions of the voltage regulator and thus reflects actual inductor phase switching in single and multi-phase regulation applications. Virtual ripple signal generation can include output (load) voltage droop compensation.
Owner:SEMTECH CORP
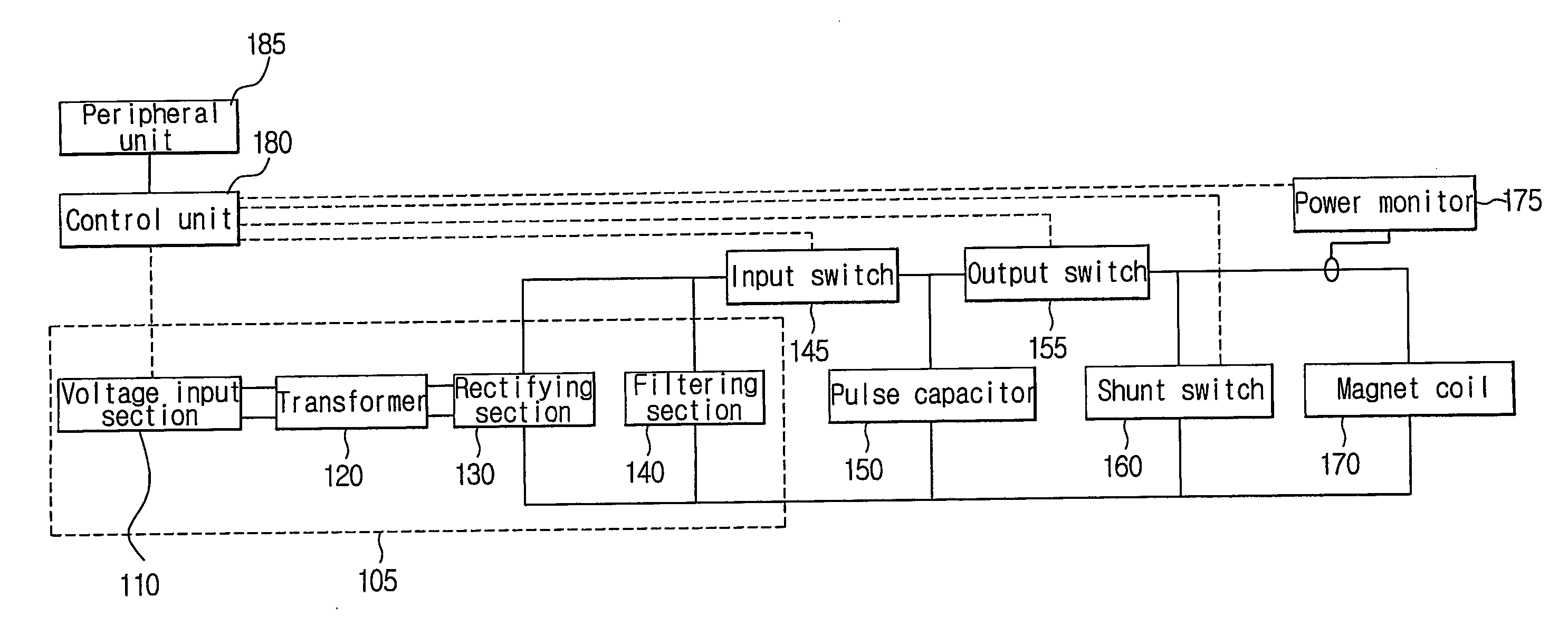
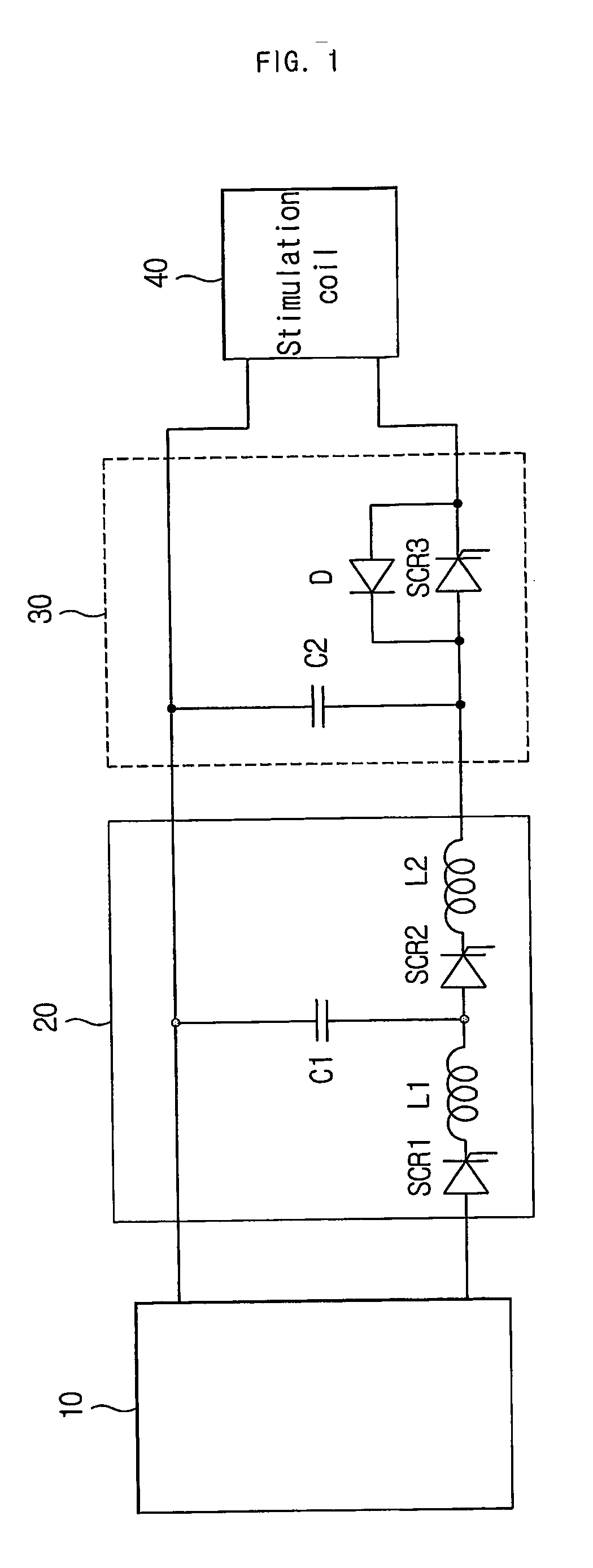
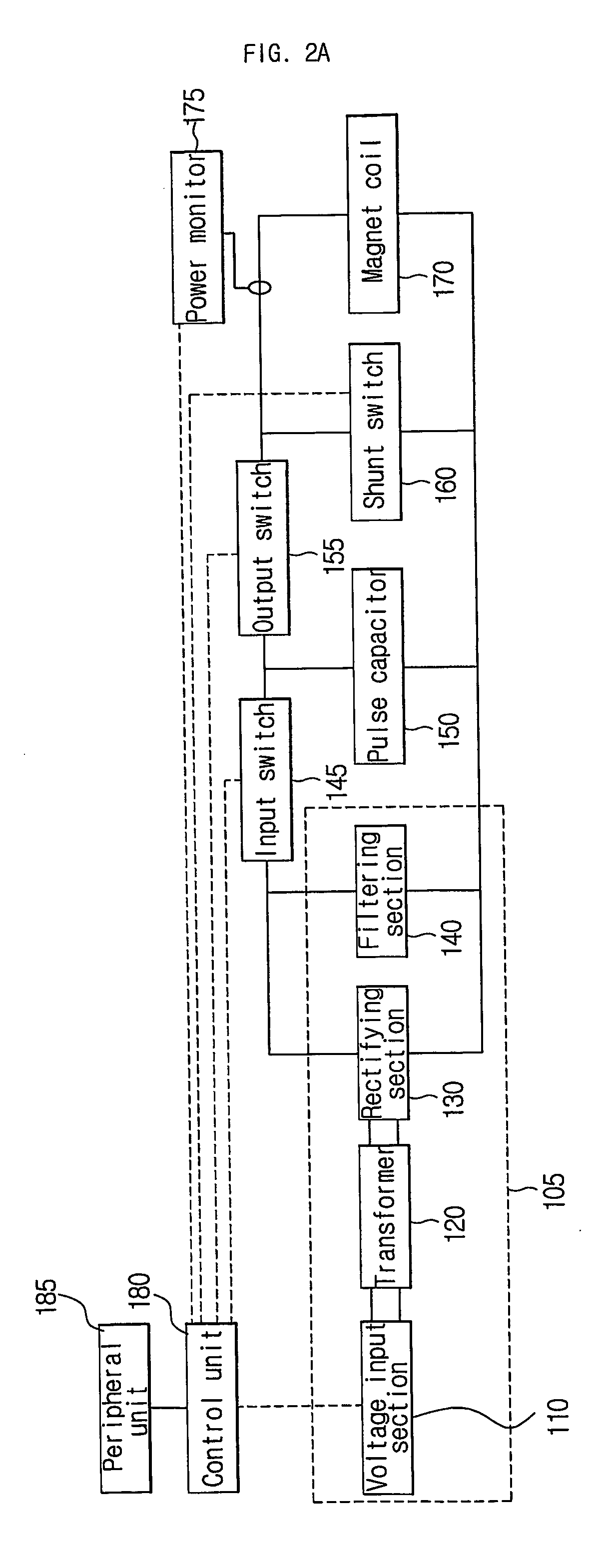
Apparatus and method for creating pulse magnetic stimulation having modulation function
InactiveUS20060187607A1Efficiently transferring energyEnergy efficiencyElectrotherapyMagnetotherapy using coils/electromagnetsModulation functionVoltage source
An apparatus for creating pulse magnetic stimulation, having a modulation function, according to the present invention, comprises: a driving voltage supplying section for converting AC voltage input from a voltage source into DC voltage having a predetermined magnitude; a capacitor section for accumulating electric charge in accordance with the DC voltage; an input switch section for controlling the accumulation of electric charge in the capacitor section; a coil for generating magnetic flux in accordance with current generated by both-end voltage corresponding to the electric charge accumulated in the capacitor section; an output switch section for controlling discharge of the electric charge accumulated in the capacitor section through the coil; and a shunt switch section for lowering magnetic energy stored in the coil and voltage stored in the capacitor section into a ground level to obtain a pulse magnetic field. In this pulse-magnetic-stimulation creating apparatus having a modulation function according to the present invention, it is possible to efficiently transfer energy on the basis of current compliance of a patient and impedance of biologic tissue for therapeutic applications.
Owner:MO SEUNG KEE
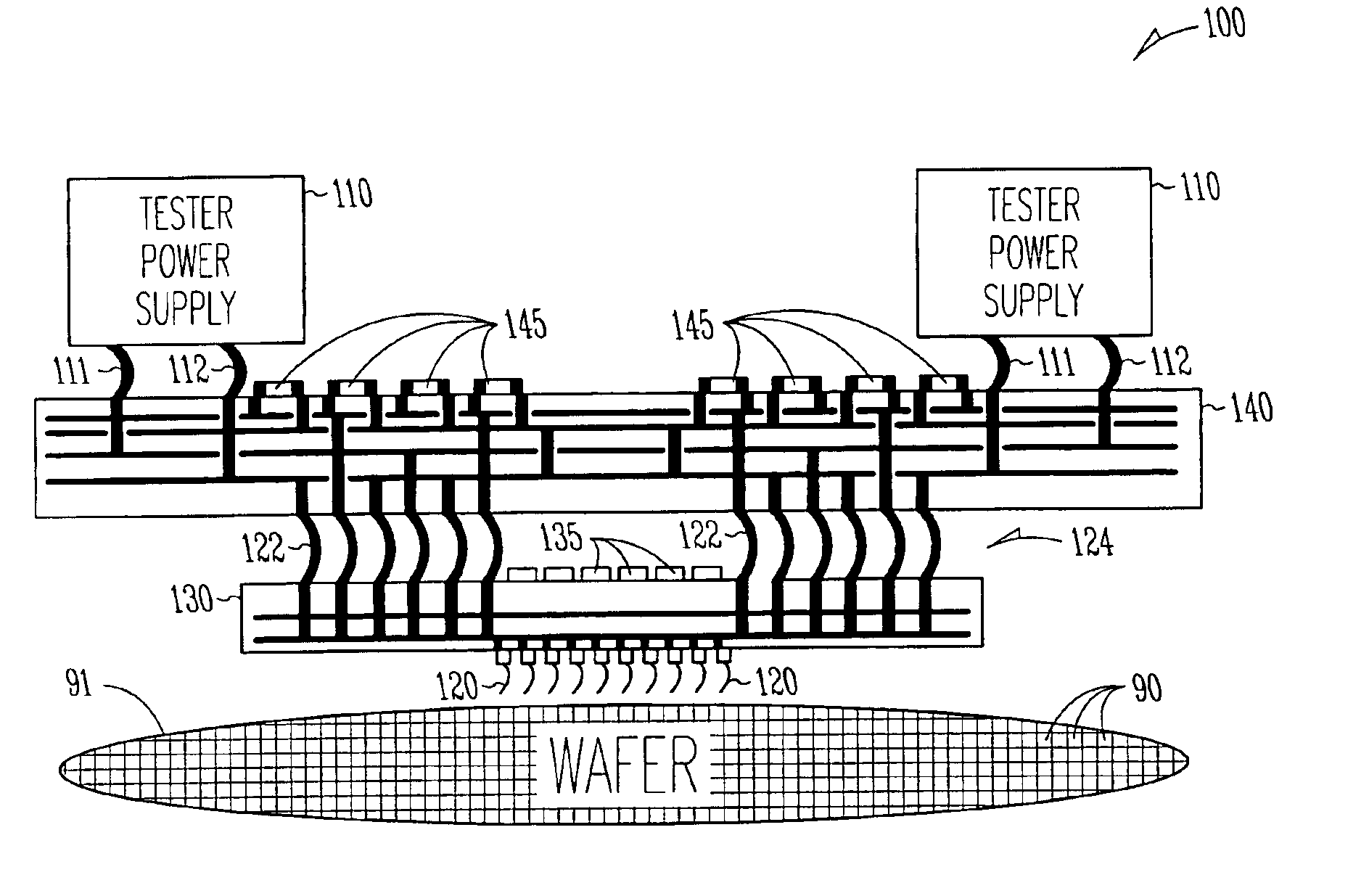
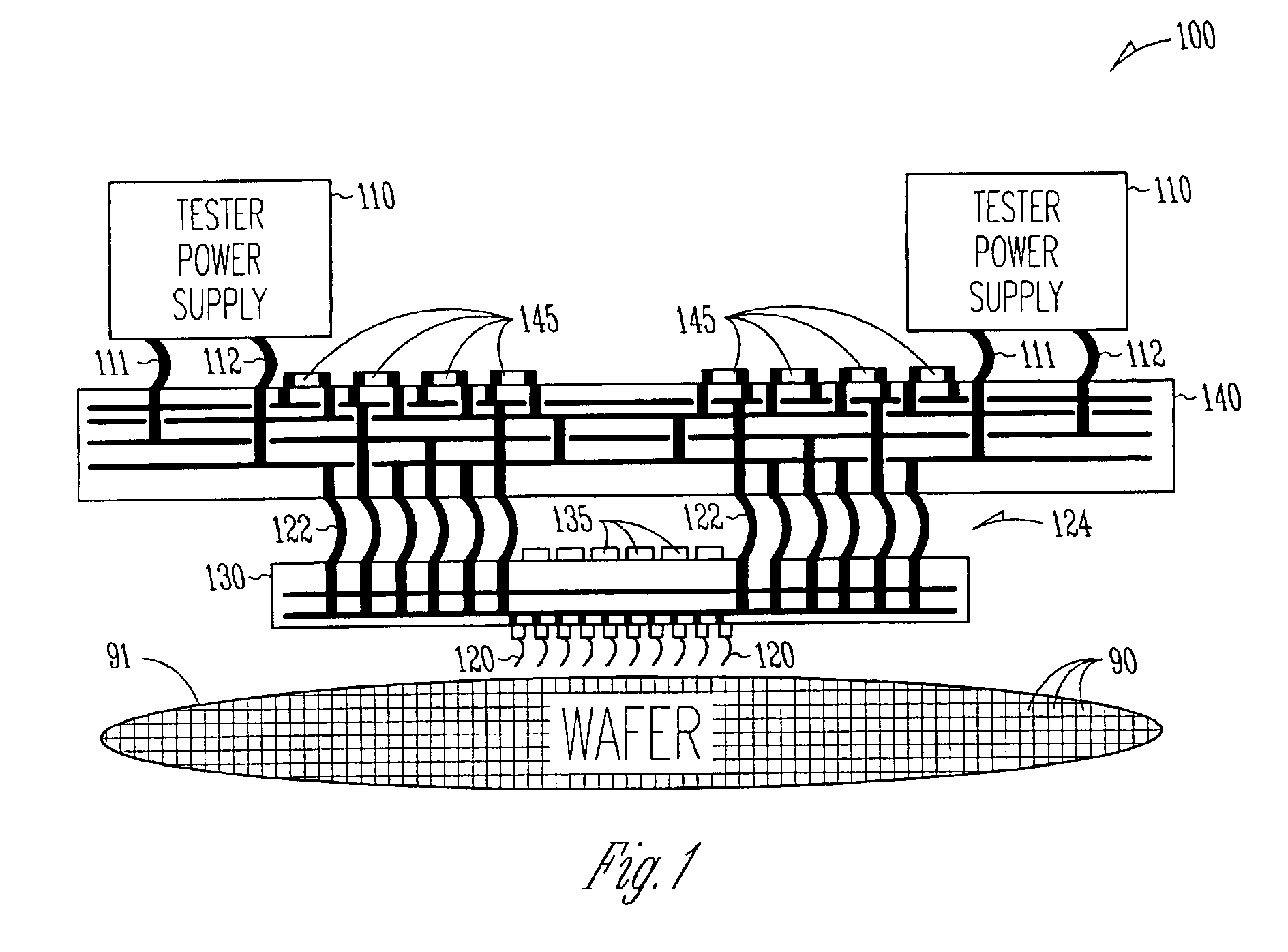
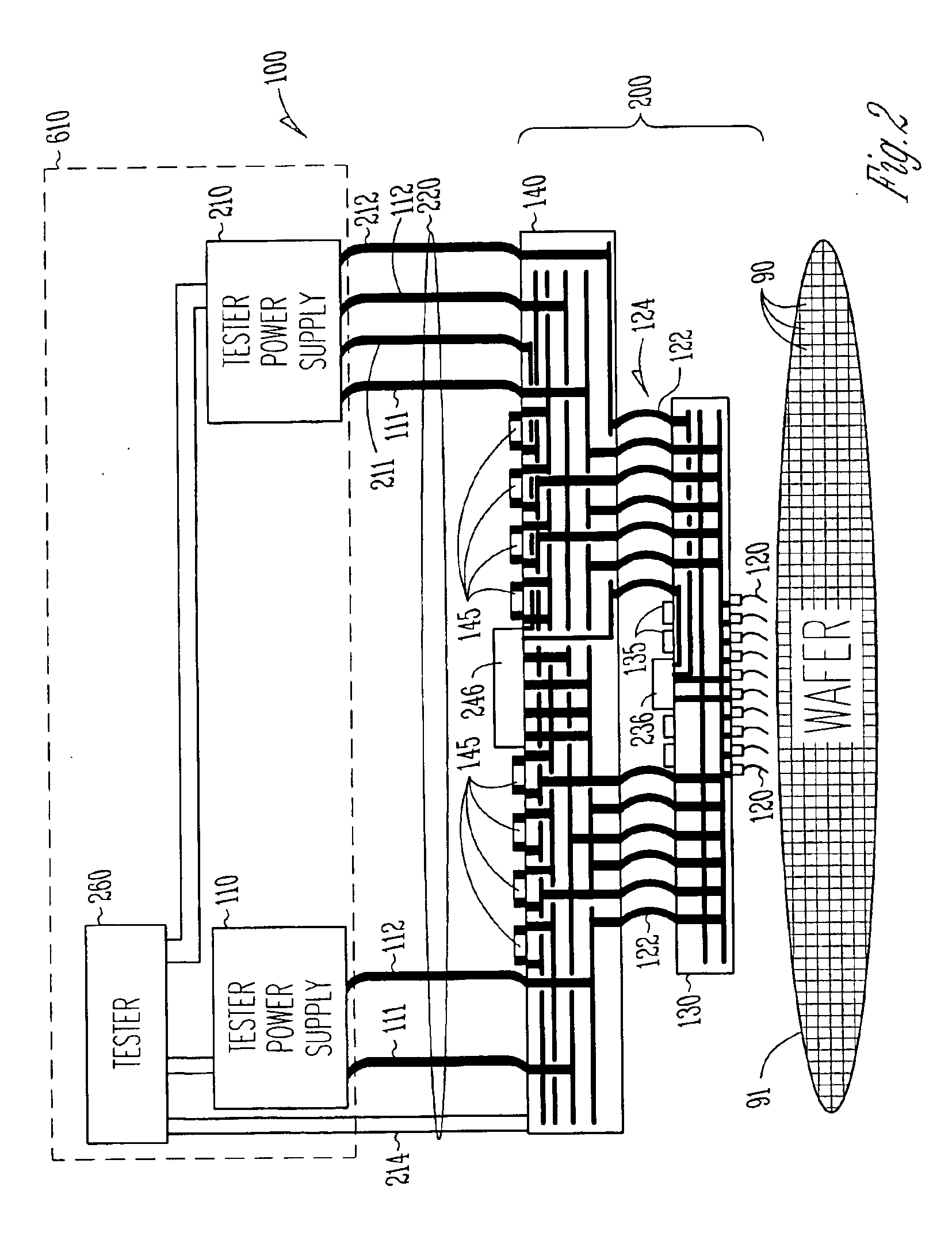
Embedded voltage regulator and active transient control device in probe head for improved power delivery and method
InactiveUS6897666B2Electrical measurement instrument detailsIndividual semiconductor device testingElectricityElectrical conductor
A method and apparatus for making a probe head that has reduced voltage droop and improved transient response. One embodiment a cable providing a plurality of signal conductors and a plurality of power conductors including a first power conductor and a second power conductor, a probe head wired to the cable, a plurality of electrical contacts including a first electrical contact and a second electrical contact, wherein each one of the plurality of electrical contacts is fixed to the probe head and wherein the first power conductor is connected to the first electrical contact, and a first regulatory device physically residing in the probe head and wired between the second power conductor and the first electrical contact. In some embodiments, the first regulatory device includes an active transient control device that senses an output voltage and sources or sinks an appropriate supplemental amount of current to improve transient response.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AUSTRIA AG +1
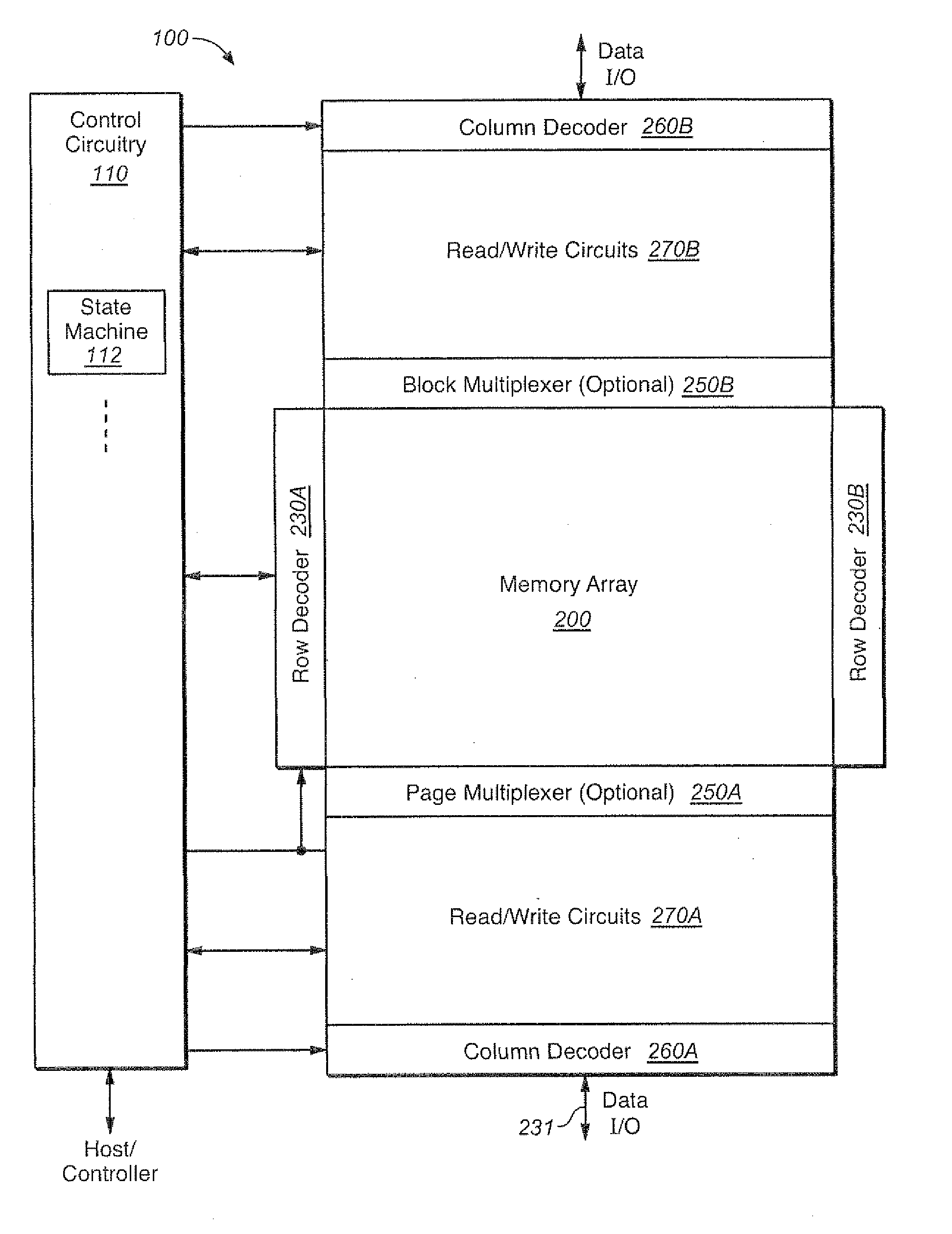
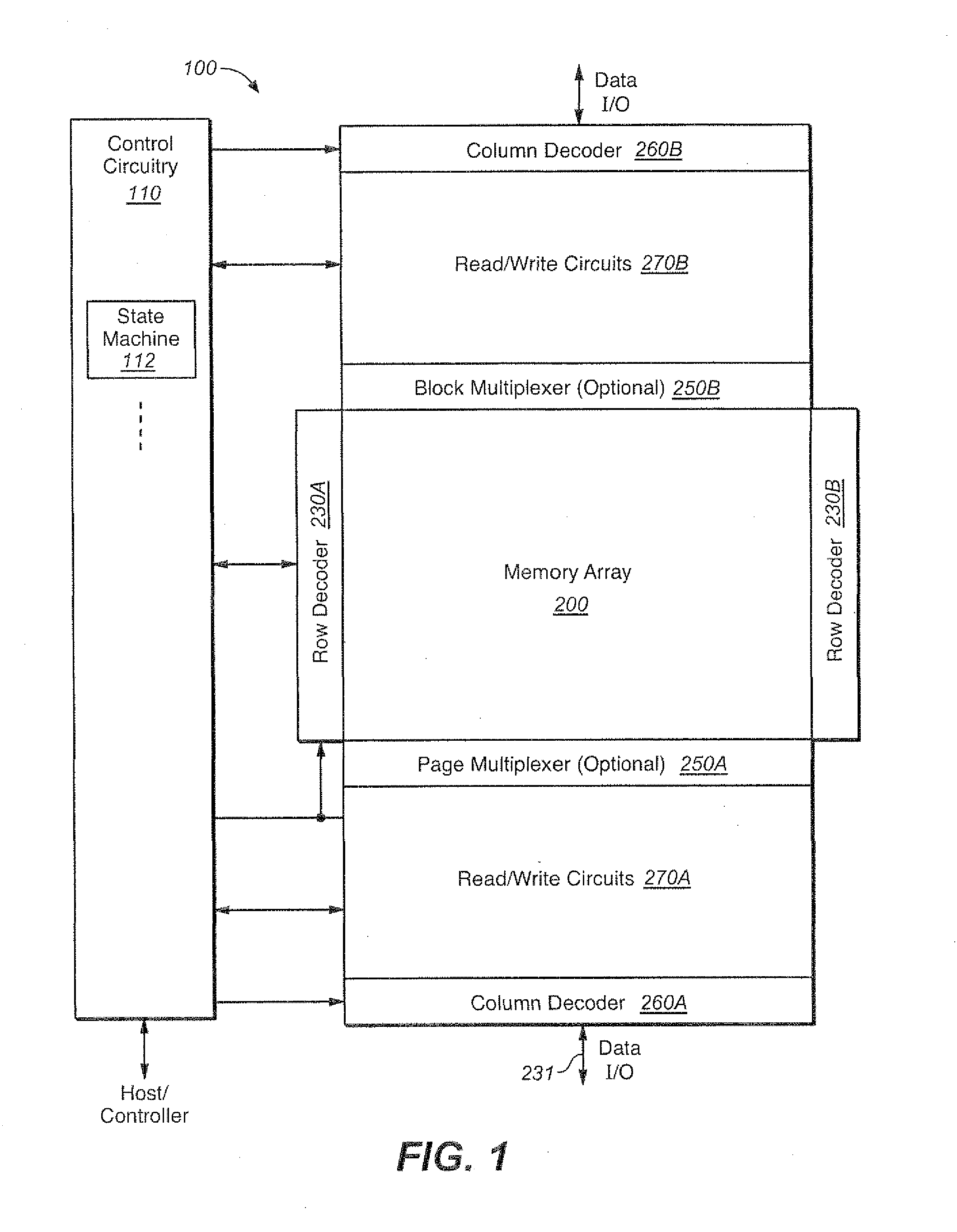
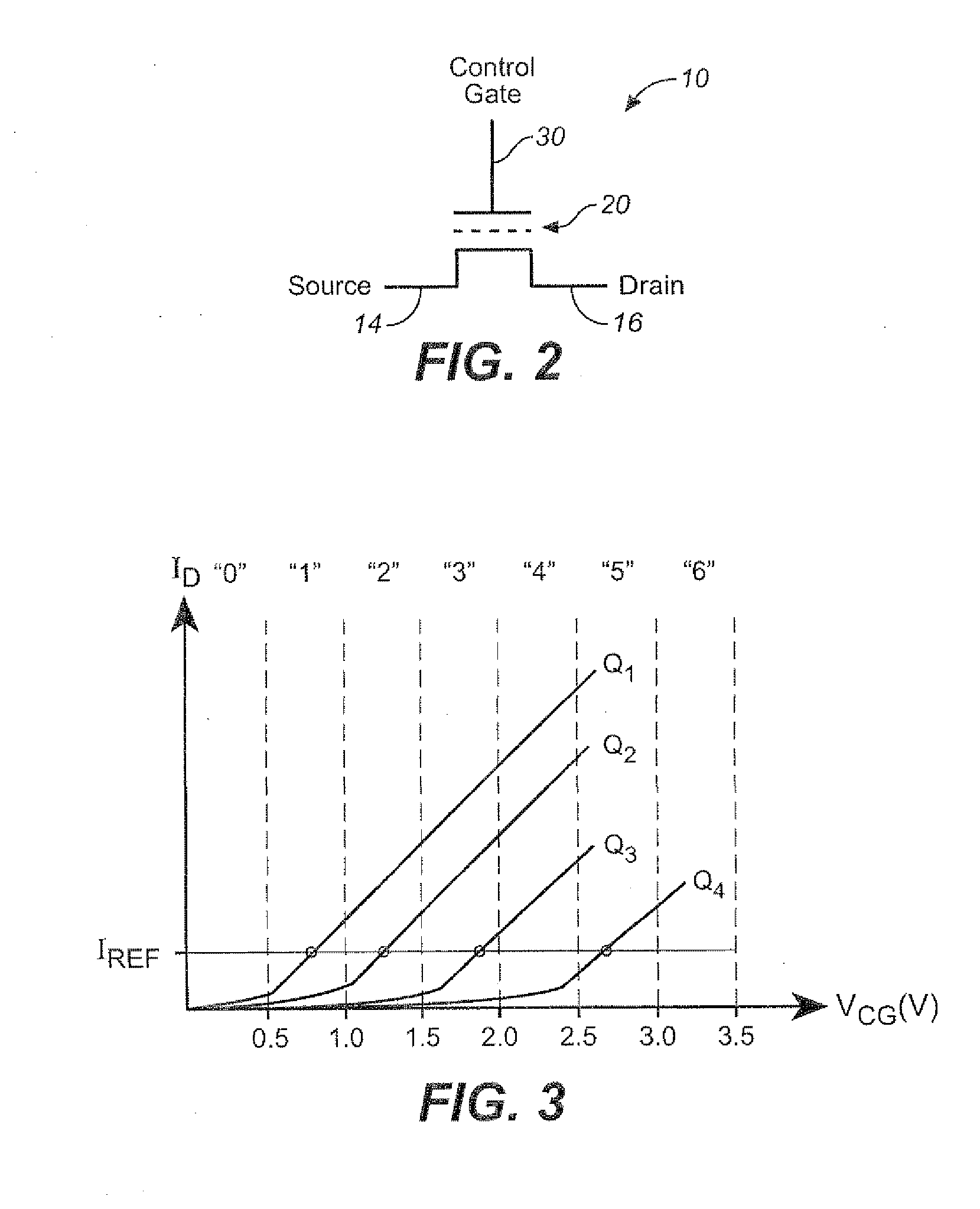
Detection of Word-Line Leakage in Memory Arrays
Techniques and corresponding circuitry are presented for the detection of wordline leakage in a memory array. In an exemplary embodiment, a capacitive voltage divider is used to translate the high voltage drop to low voltage drop that can be compared with a reference voltage to determine the voltage drop due to leakage. An on-chip self calibration method can help assure the accuracy of this technique for detecting leakage limit.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
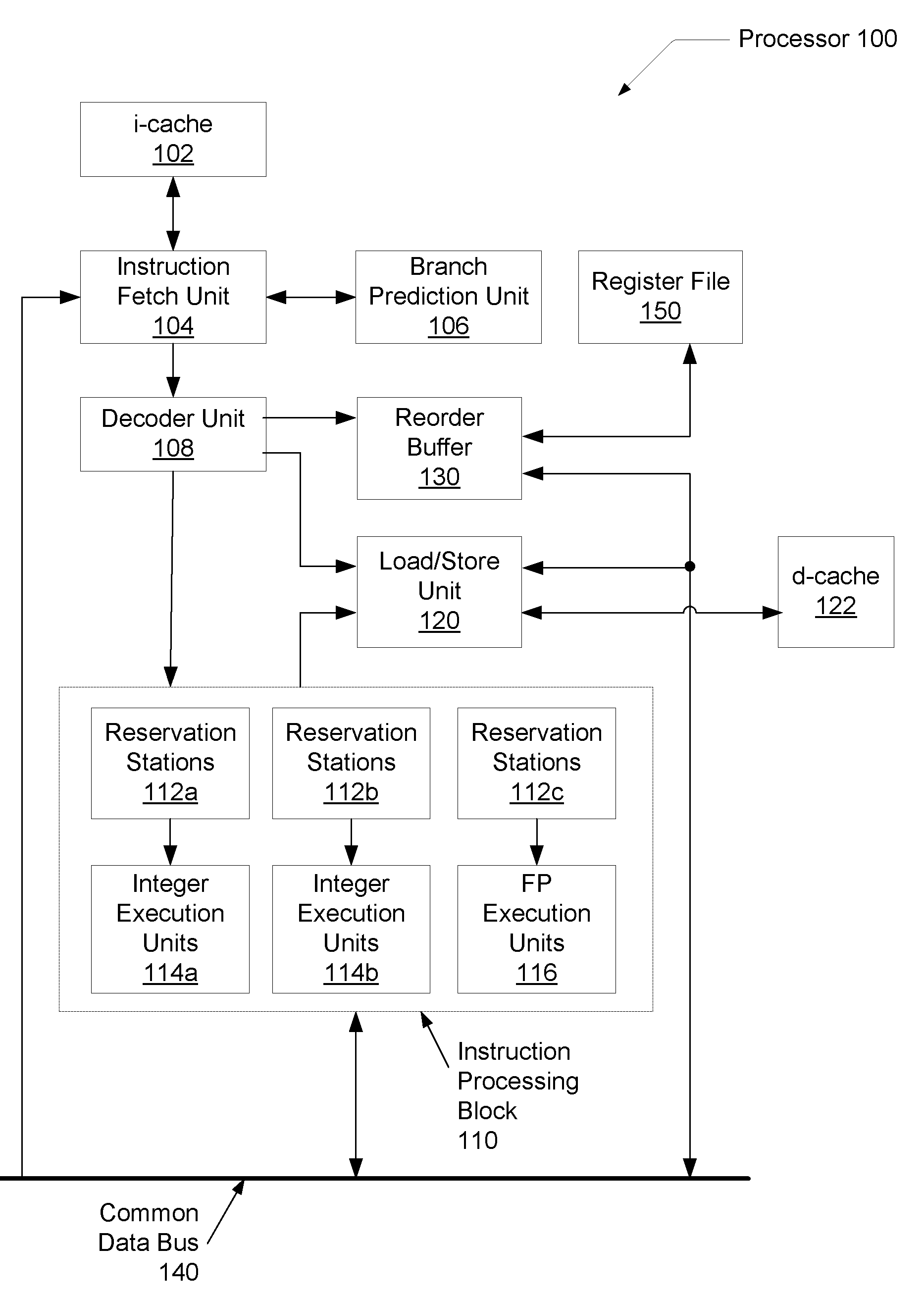
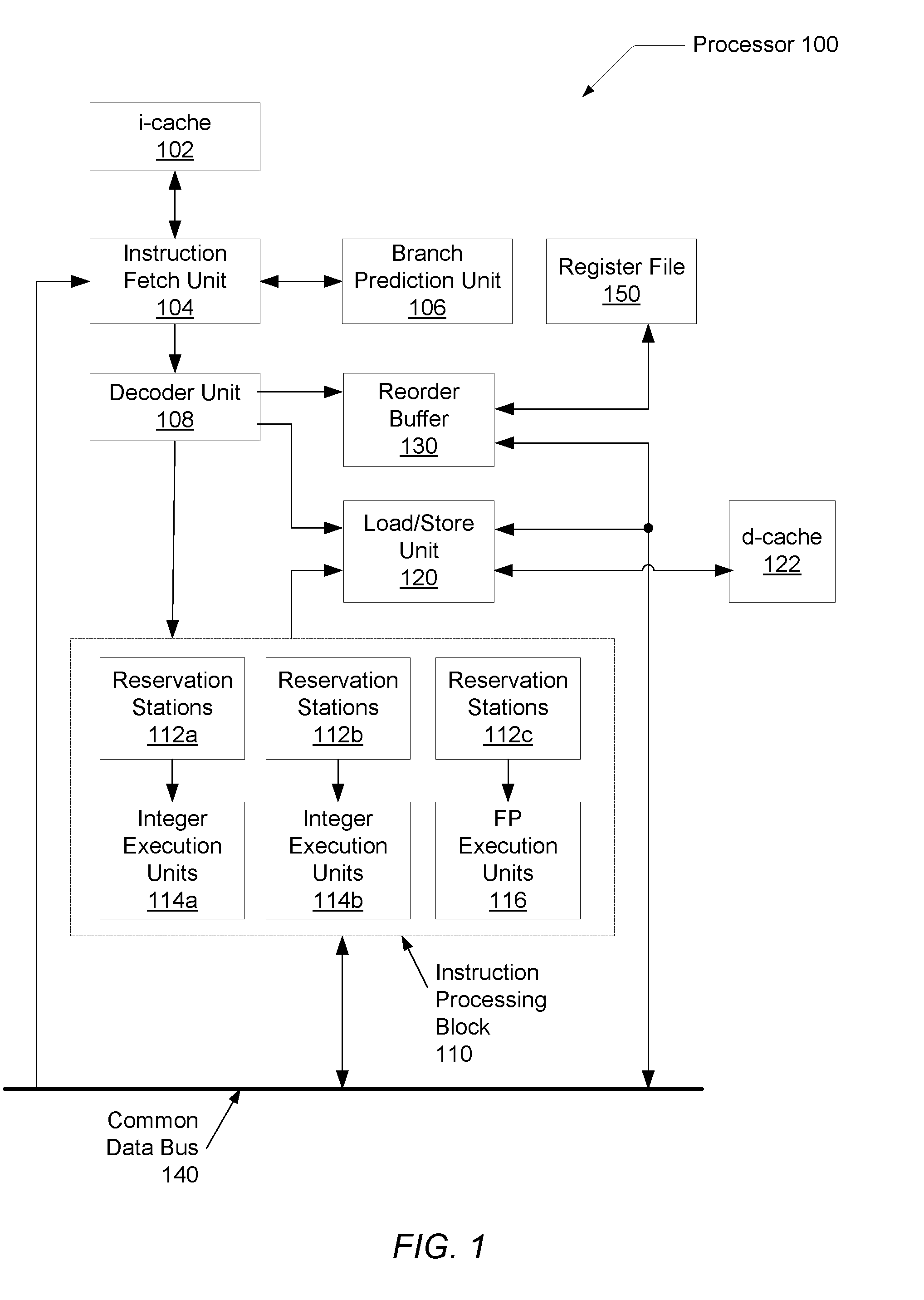
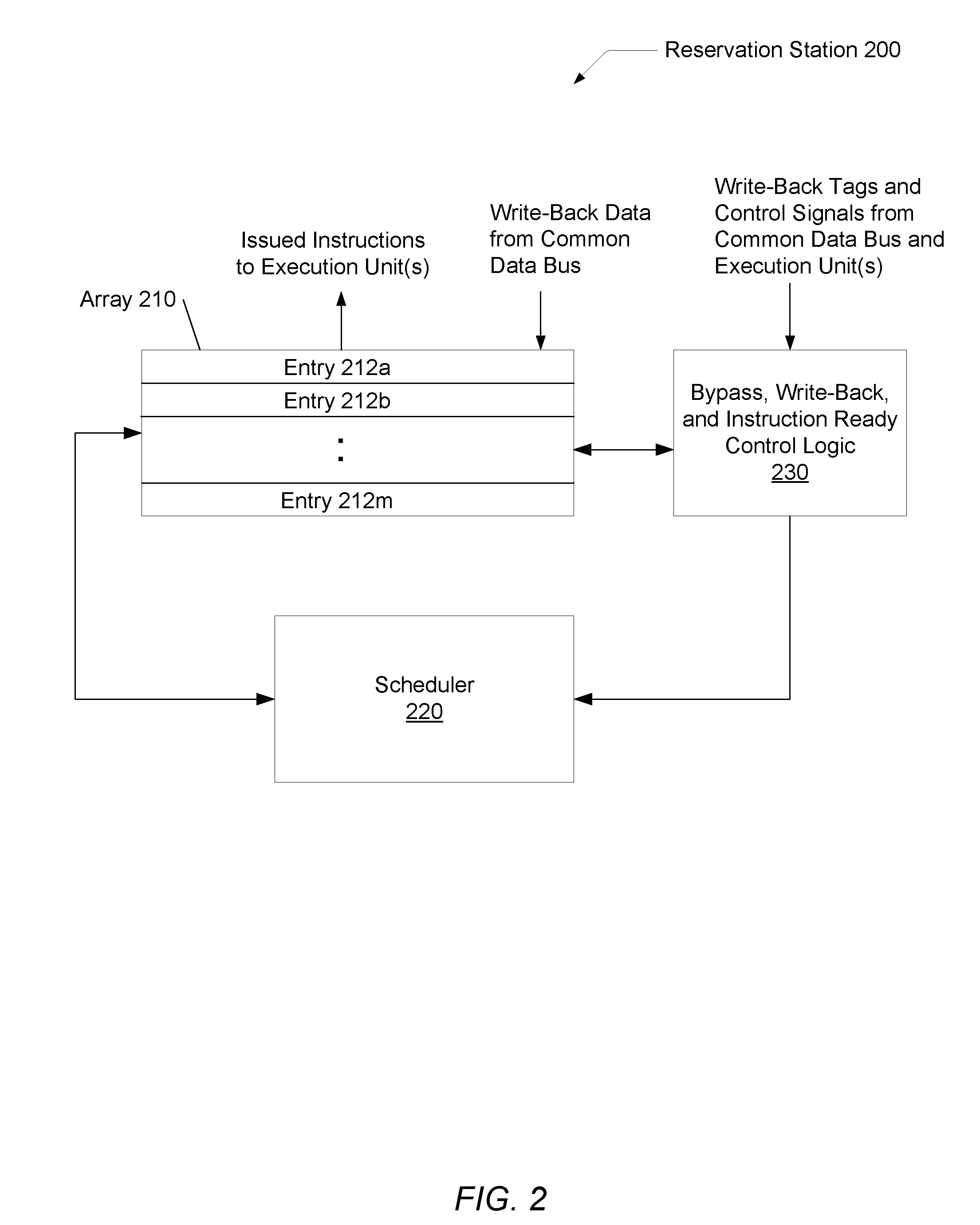
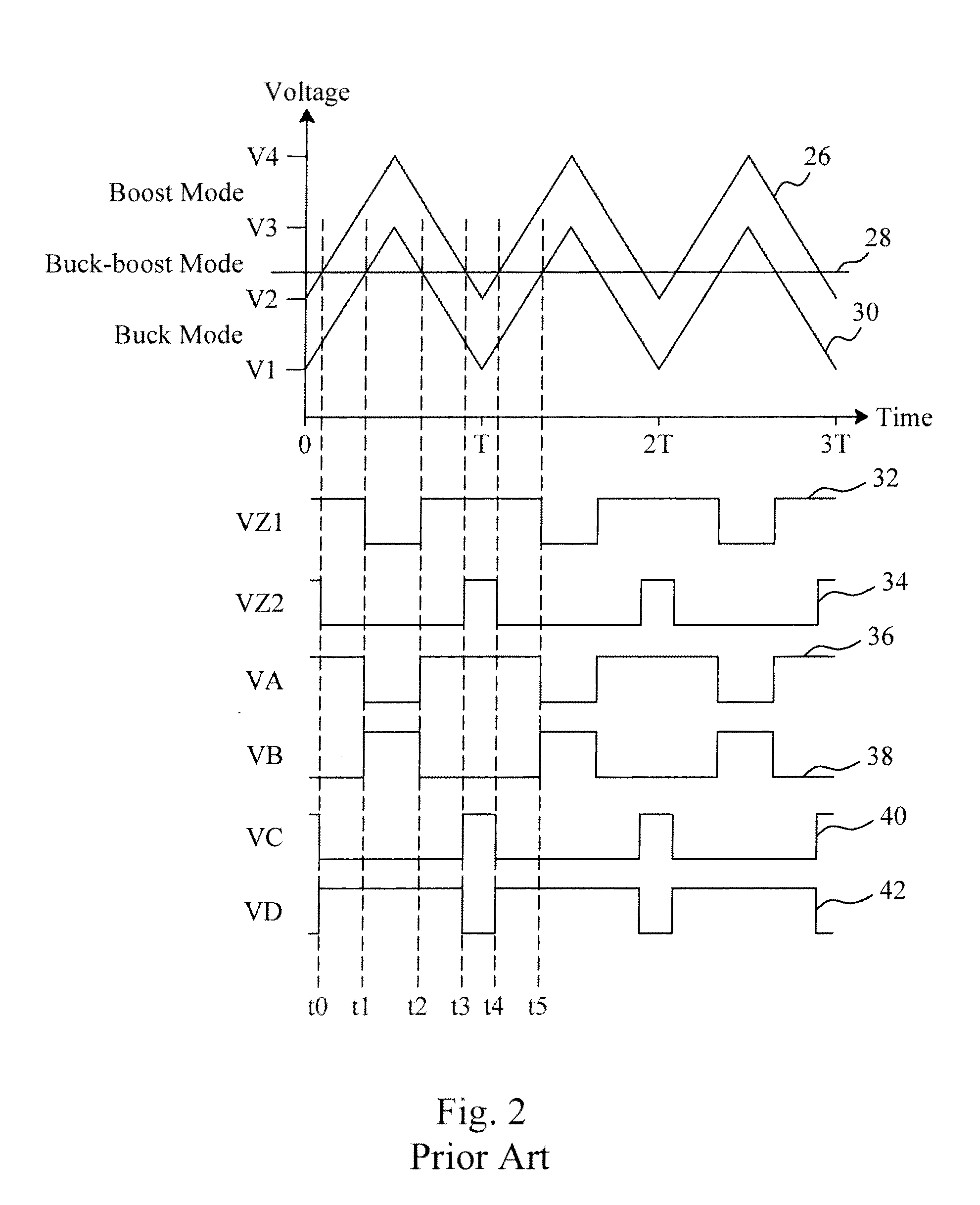
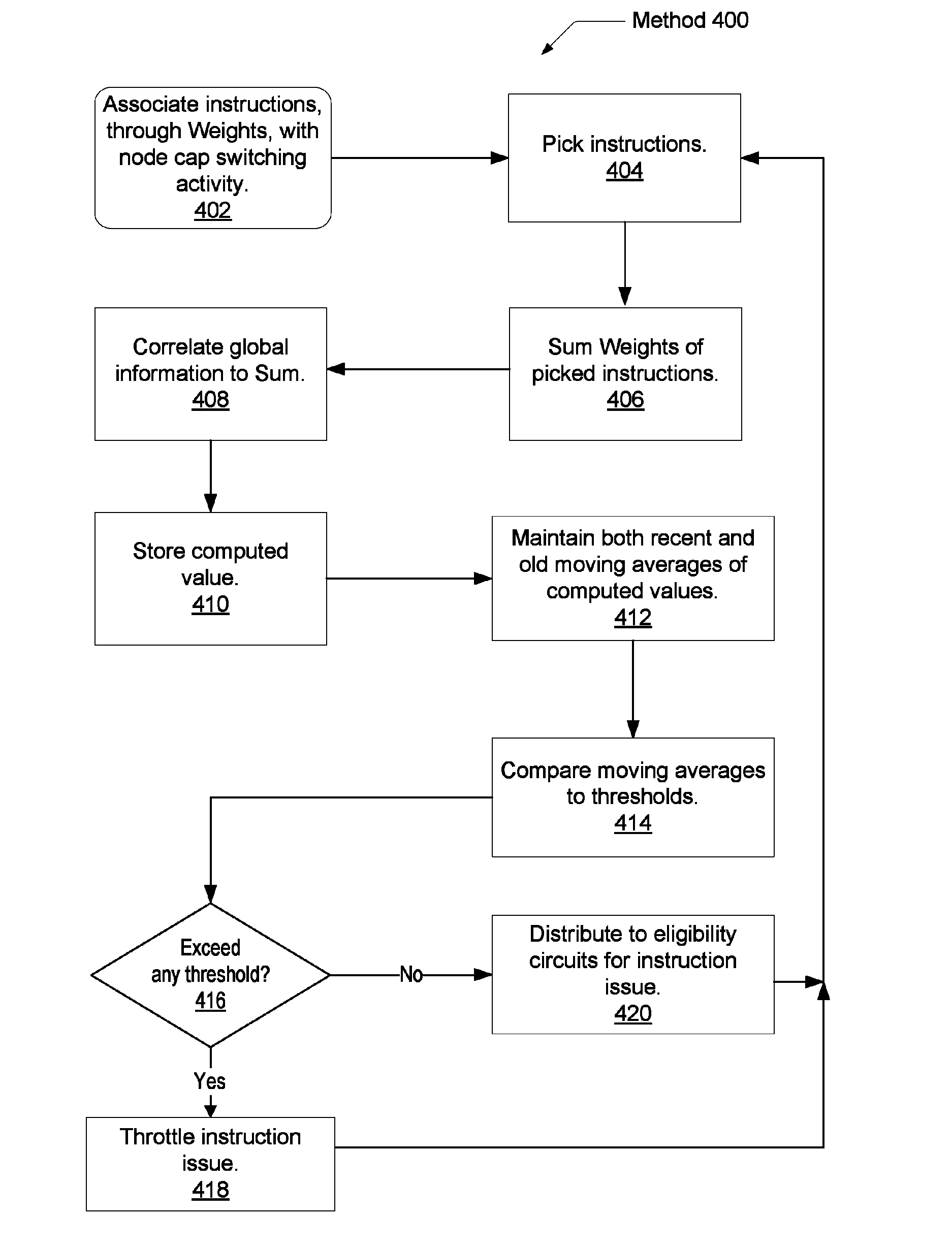
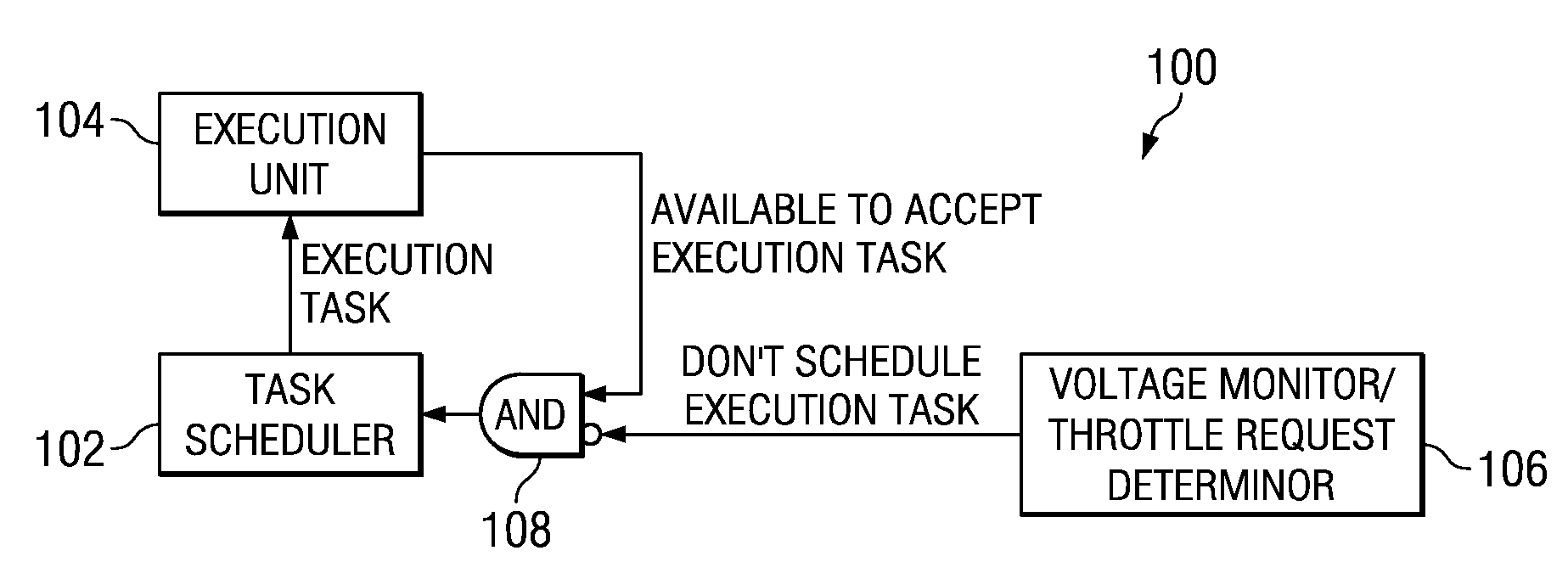
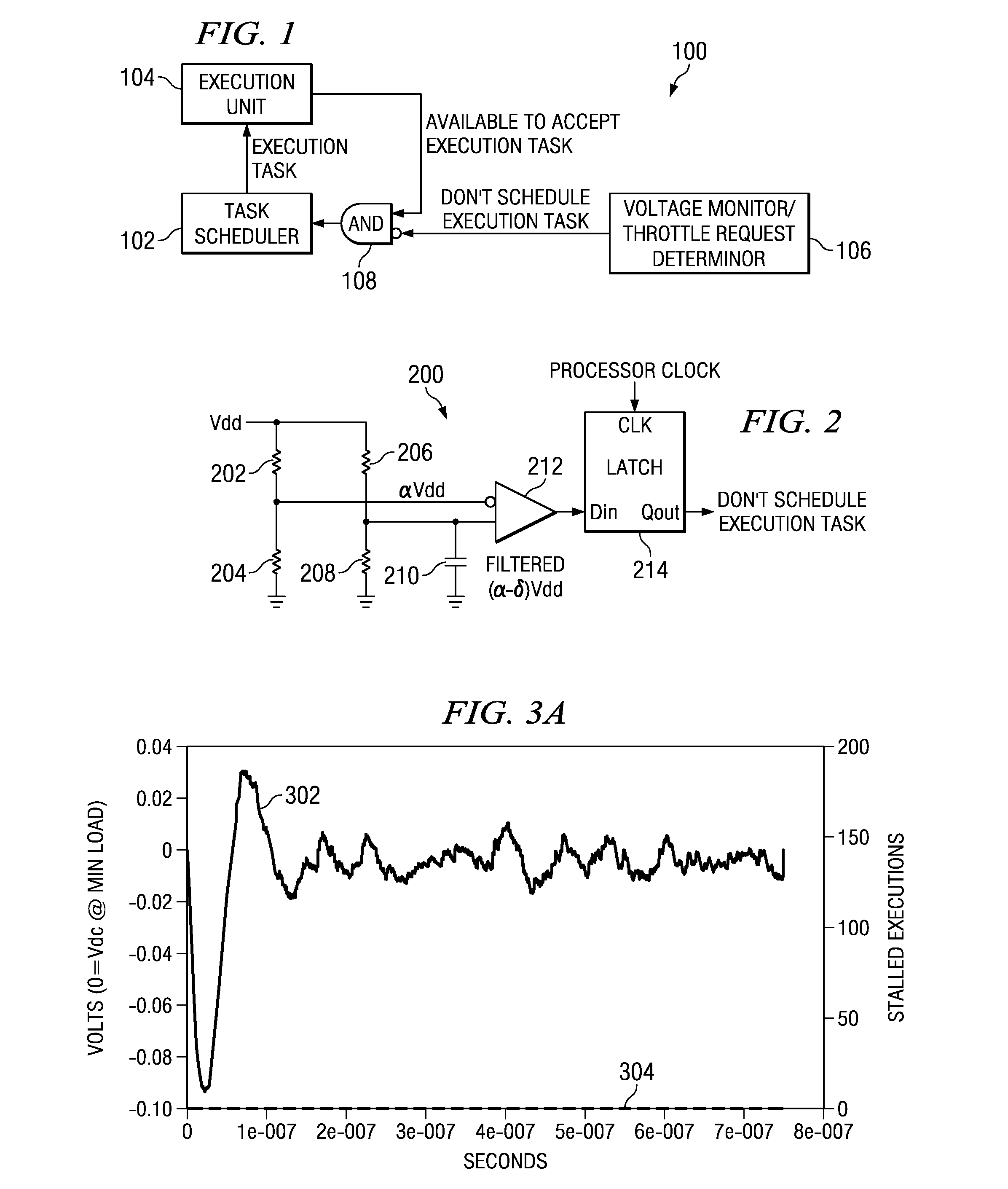
Voltage droop mitigation through instruction issue throttling
ActiveUS20090300329A1Reduce voltage dropVolume/mass flow measurementDigital computer detailsCapacitanceHash function
A system and method for providing a digital real-time voltage droop detection and subsequent voltage droop reduction. A scheduler within a reservation station may store a weight value for each instruction corresponding to node capacitance switching activity for the instruction derived from pre-silicon power modeling analysis. For instructions picked with available source data, the corresponding weight values are summed together to produce a local current consumption value and this value is summed with any existing global current consumption values from corresponding schedulers of other processor cores yielding an activity event. The activity event is stored. Hashing functions within the scheduler are used to determine both a recent and an old activity average using the calculated activity event and stored older activity events. Instruction issue throttling occurs if either a difference between the old activity average and the recent activity average exceed a first threshold or the recent activity average exceeds a second threshold.
Owner:ADVANCED MICRO DEVICES INC
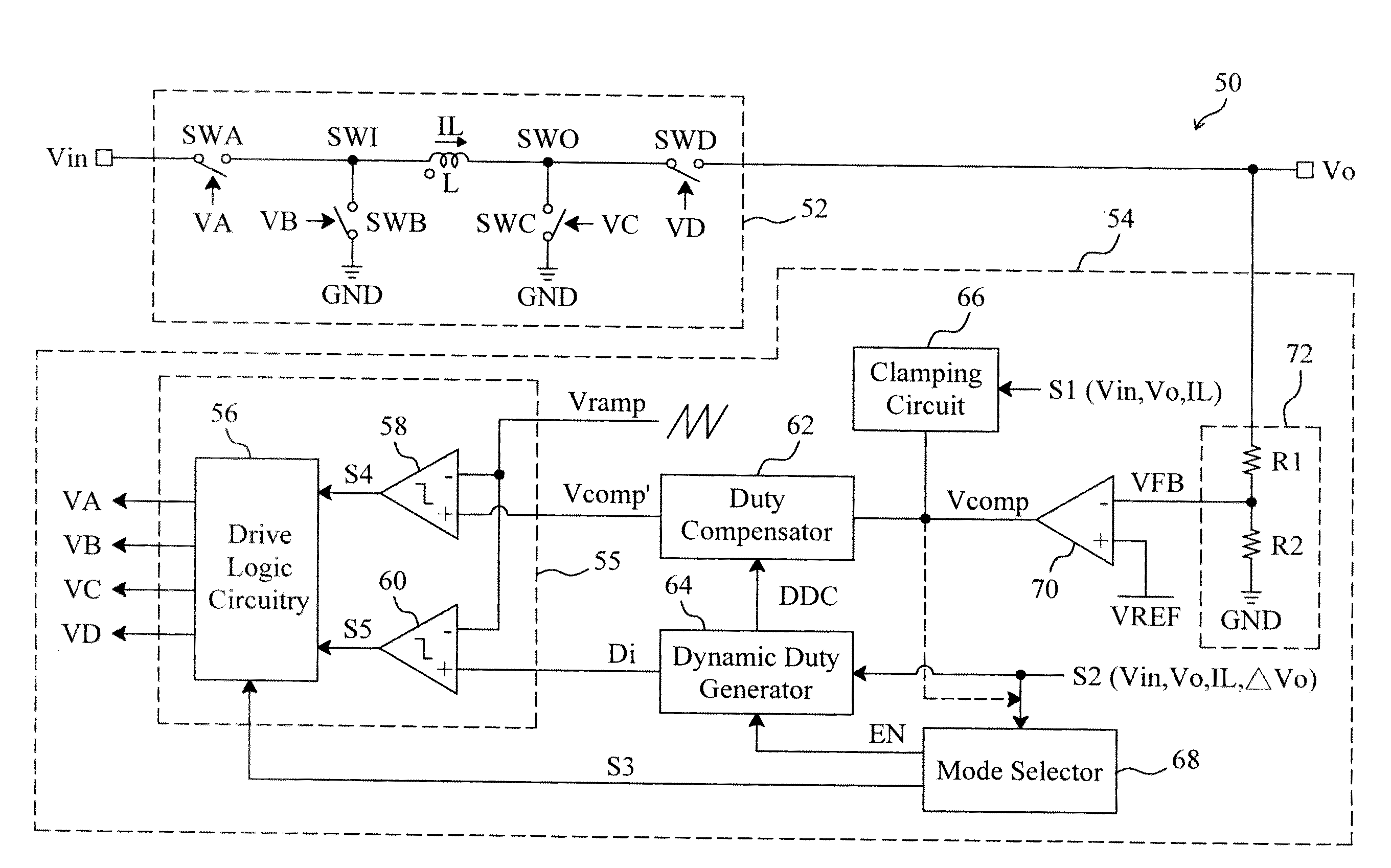
Control circuit and method for a buck-boost power converter
ActiveUS20110074373A1Improve efficiencyMinimize output rippleDc-dc conversionElectric variable regulationEngineeringControl circuit
Control signals are generated for a buck-boost power stage of a buck-boost power converter to convert an input voltage to an output voltage. The buck-boost power stage includes an inductor and at least two power switches connected thereto. The output voltage is monitored to generate an error signal having clamped level according to a first detecting signal related to at least one of the input voltage, output voltage and inductor current. In a buck-boost mode, a compensation signal and a duty insertion signal are generated according to a second detecting signal related to at least one of the input voltage, output voltage, inductor current and variation of the output voltage, the error signal is compensated with the compensation signal to generate a compensated error signal, and the control signals are determined upon the combination of the compensated error signal, the duty insertion signal and a ramp signal.
Owner:RICHTEK TECH
Voltage droop mitigation through instruction issue throttling
A system and method for providing a digital real-time voltage droop detection and subsequent voltage droop reduction. A scheduler within a reservation station may store a weight value for each instruction corresponding to node capacitance switching activity for the instruction derived from pre-silicon power modeling analysis. For instructions picked with available source data, the corresponding weight values are summed together to produce a local current consumption value and this value is summed with any existing global current consumption values from corresponding schedulers of other processor cores yielding an activity event. The activity event is stored. Hashing functions within the scheduler are used to determine both a recent and an old activity average using the calculated activity event and stored older activity events. Instruction issue throttling occurs if either a difference between the old activity average and the recent activity average exceed a first threshold or the recent activity average exceeds a second threshold.
Owner:ADVANCED MICRO DEVICES INC
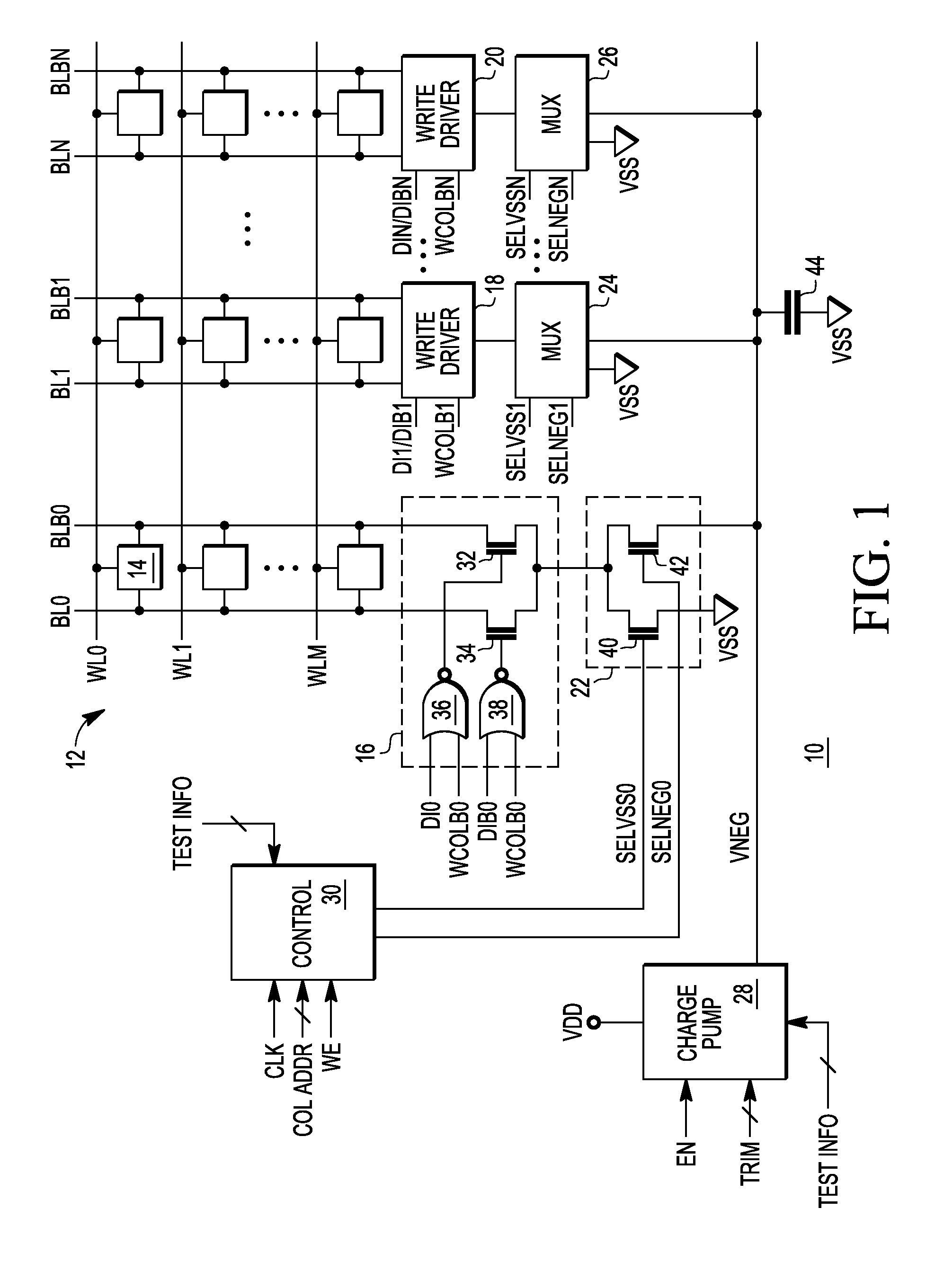
Memory having negative voltage write assist circuit and method therefor
A method of writing data to a selected column of a memory includes selecting a first column. The data writing is initiated by applying a logic high to a first bit line of the first column and a first potential to a second bit line of the first column that is lower than the logic high. The first potential is removed and a second potential is applied to the second bit line. The second potential is less than the first potential. The first potential may be ground, and the second potential may be a negative voltage. Reducing the write voltage for the bit line that is receiving a logic low improves its ability to be written. By first bringing the logic low to the first potential, which may be ground, and then further reducing the applied voltage, the requirements on the source of the second potential are reduced.
Owner:NXP USA INC
Switching frequency control of switched capacitor circuit using output voltage droop
A frequency control circuit including a controlled oscillator and an amplifier circuit is disclosed for providing a clock signal to a switched capacitor circuit which divides an input voltage to provide an output voltage. The controlled oscillator has a frequency control input receiving a frequency control signal and an output for providing the clock signal at a frequency based on the frequency control signal. The amplifier circuit has an input for receiving the output voltage and an output providing the frequency control signal based on droop of the output voltage. In one embodiment, the amplifier circuit adjusts the frequency control signal to optimize efficiency of the switched capacitor circuit over a voltage range of the output voltage, which changes based on load level.
Owner:INTERSIL INC
Automatic voltage selection in a DC power distribution apparatus
InactiveUS20030222503A1Volume/mass flow measurementCoupling device detailsElectricityElectrical resistance and conductance
Provision is made in the housing of a host to provide a socket, or sockets, to which a peripheral piece of equipment can be connected for receiving directly from the host the low voltage DC power it requires. The socket(s) are connected electrically to the outputs of a power supply (or regulator) of a host for providing the low voltage needed to power the peripheral. The power supply may be mounted on the rear face of a computer. The principal feature of the invention resides in the use of a connector for connecting the host DC power to the peripheral DC power usage device. The connector comprises pins connected to a selected resistor in the power supply. The resistor value (i.e., resistance) is selected to produce a pre-determined control voltage which is fed back to a DC to DC converter in the host's internal power supply. The converter comprises a pulse width modulation control device. The control voltage determines the duty cycle (i.e., pulse width) of the modulation to reduce the output from a maximum voltage to an appropriate voltage suitable for the particular peripheral power usage device. Thus, by simply selecting the appropriate connector (or cable) having the proper pins correlated to a selected resistor previously installed in the power supply, the voltage level for the corresponding peripheral device is automatically selected. In an alternative embodiment, the DC power distribution apparatus of the present invention comprises a stand-alone unit having one or more universal ports for receiving a cable with a connector containing the appropriate pins for a selected DC power usage device.
Owner:AM GROUP
Dead-time compensation algorithm for 3-phase inverter using svpwm
InactiveUS20130088905A1Minimizing distortion of output voltageReduce voltageDc-ac conversion without reversalPhase currentsSwitching signal
Disclosed is a dead-time compensation method of a 3-phase inverter using an SVPWM scheme. The dead-time compensation method includes generating a switching signal having dead-time with respect to the power semiconductor switches of the upper and lower arms in order to obtain a predetermined output through the SVPWM scheme, detecting medium phase current from each phase current output through the switching signal, determining polarity of the medium phase current, and generating a switching signal by calculating switching time in order to compensate for time to apply effective voltage according to the polarity of the medium phase current. Through the dead-time compensation method, the distortion of the output voltage and the reduction of voltage having a fundamental wave in the output voltage, which are caused by the dead-time, are minimized through the switching of compensating for the time to apply effective voltage based on the polarity of the load current.
Owner:KYUNGPOOK NAT UNIV IND ACADEMIC COOP FOUND +1
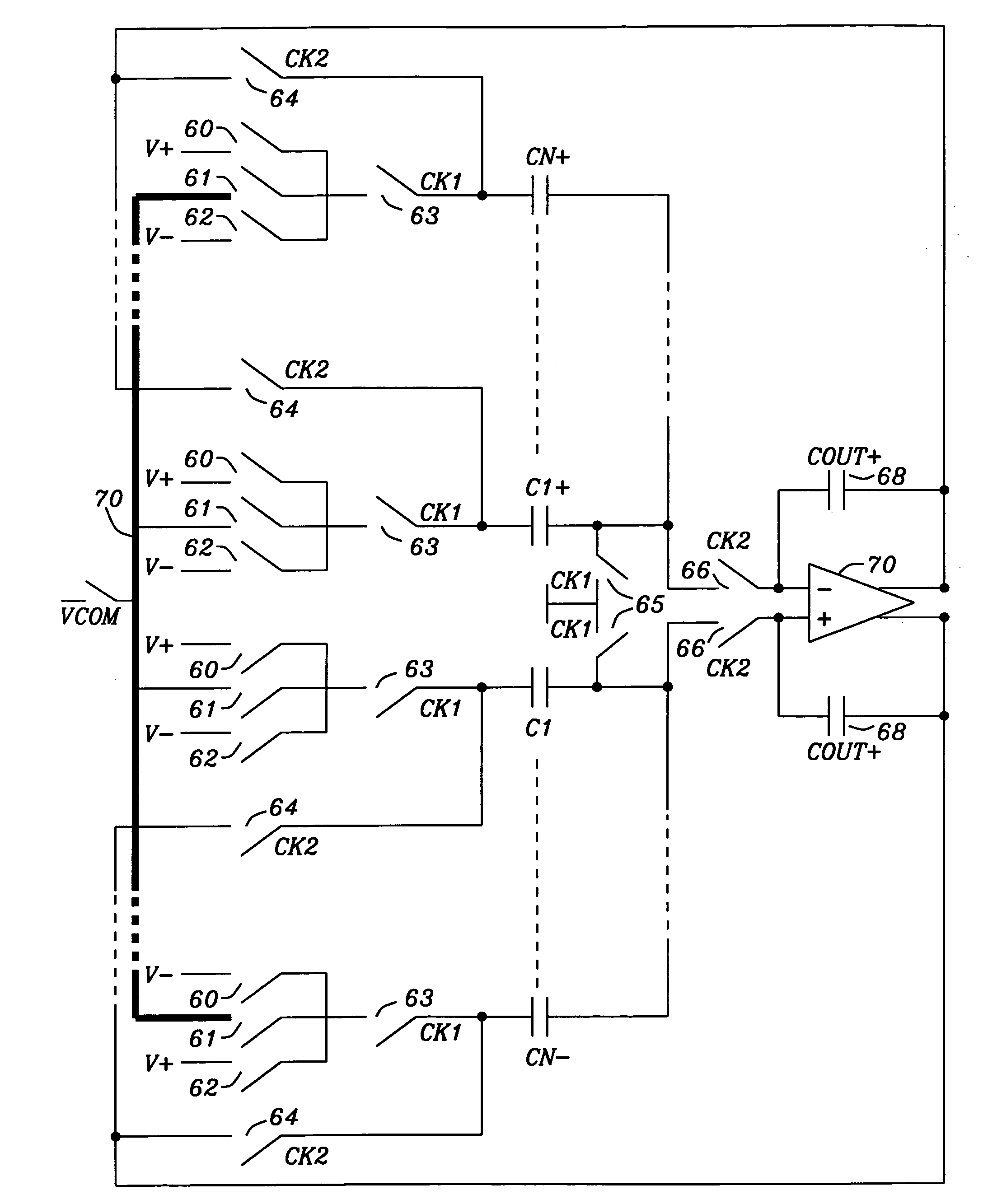
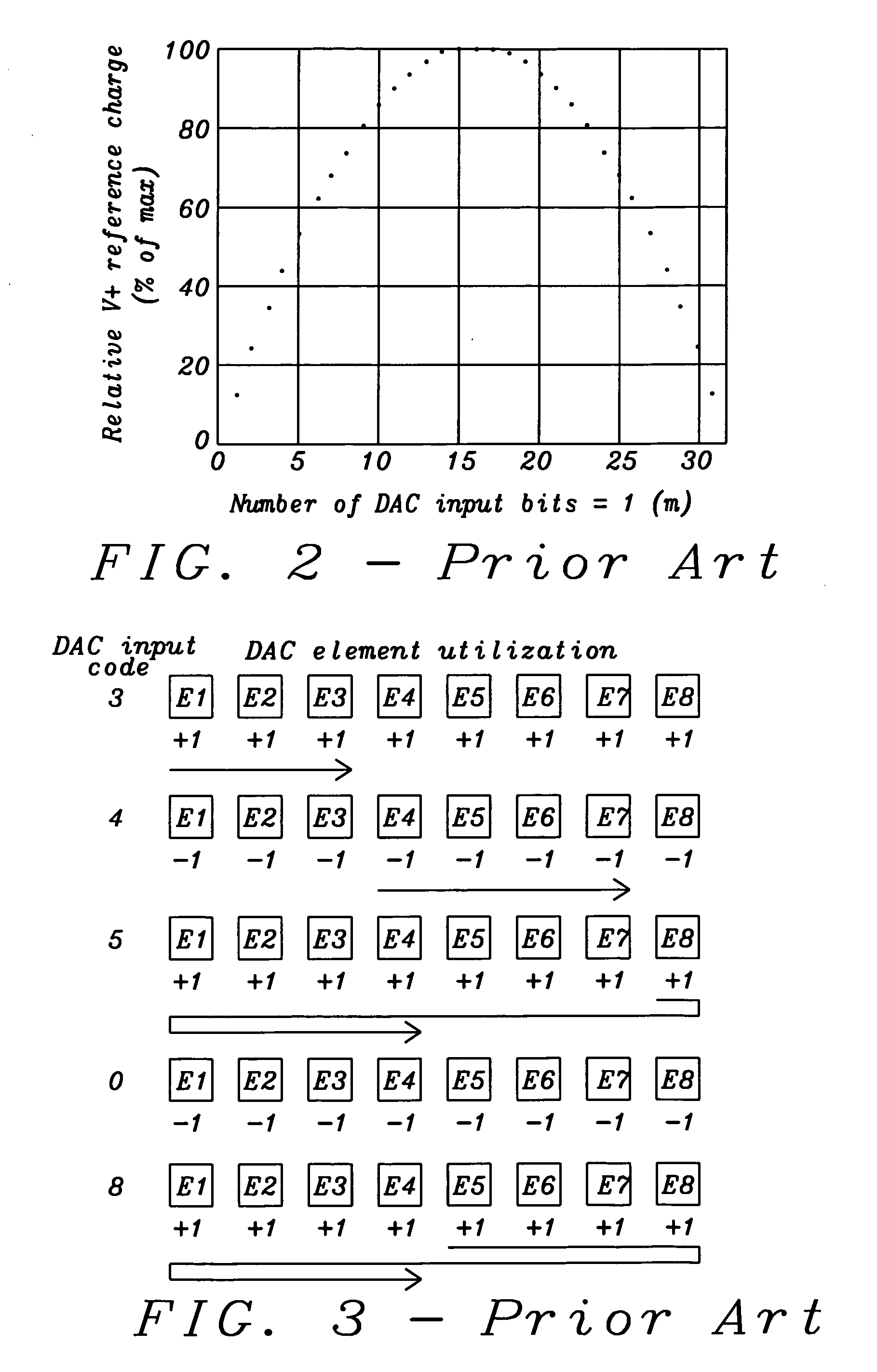
Tri-level dynamic element matcher allowing reduced reference loading and dac element reduction
ActiveUS20100245142A1Reduce power consumptionTotal current dropElectric signal transmission systemsAnalogue conversionCircuit complexityNoise shaping
Systems and methods using the same to achieve a tri-level multi-bit delta-sigma DAC having reduced power consumption and voltage droop have been achieved. A new rotation-based first order noise-shaping Dynamic Element Matcher (DEM) technique for use with 3-level unit elements have been disclosed. Reduced reference loading has been achieved when the tri-level DEM scheme is applied to switched capacitor implementations in particular. Furthermore a differential switched-capacitor DAC implementation, which enables use of the DEM technique is disclosed. The invention allows reduced circuit complexity required to implement a N-bit DAC when constructed using 3-level unit elements.
Owner:DIALOG SEMICONDUCTOR GMBH
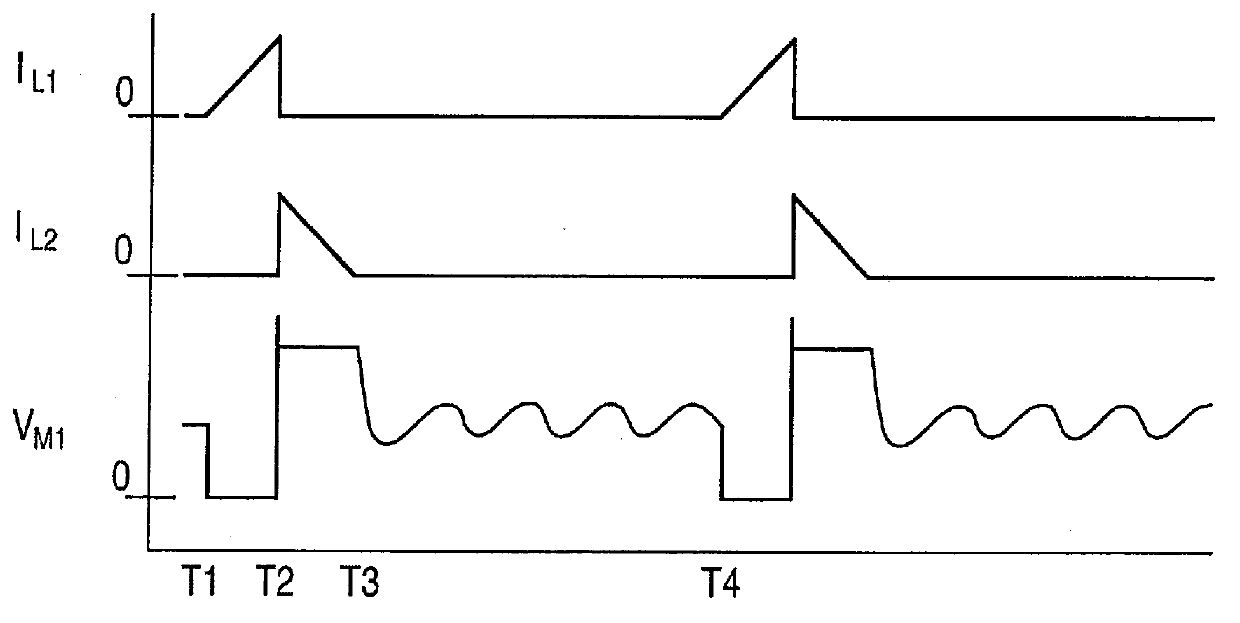
Isolated flyback converter with sleep mode for light load operation
In a flyback converter using primary side sensing to sense the output voltage for regulation feedback a comparator on the primary side detects whether the output voltage has exceeded a predetermined regulated voltage by a first threshold to detect an over-voltage condition, resulting from a current generated by the converter exceeding the load current. Triggering of the comparator causes the converter to enter a non-switching sleep mode, whereby the output voltage droops over a period of time. When the output voltage has dropped below the predetermined regulated voltage by a second threshold, a synchronous rectifier is controlled to turn on, then off, to generate a pulse in the primary winding. Upon detection of the pulse, the sleep mode is terminated, and normal operation resumes until a regulated voltage is achieved or until the first threshold is again exceeded by the output voltage.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INT UNLTD
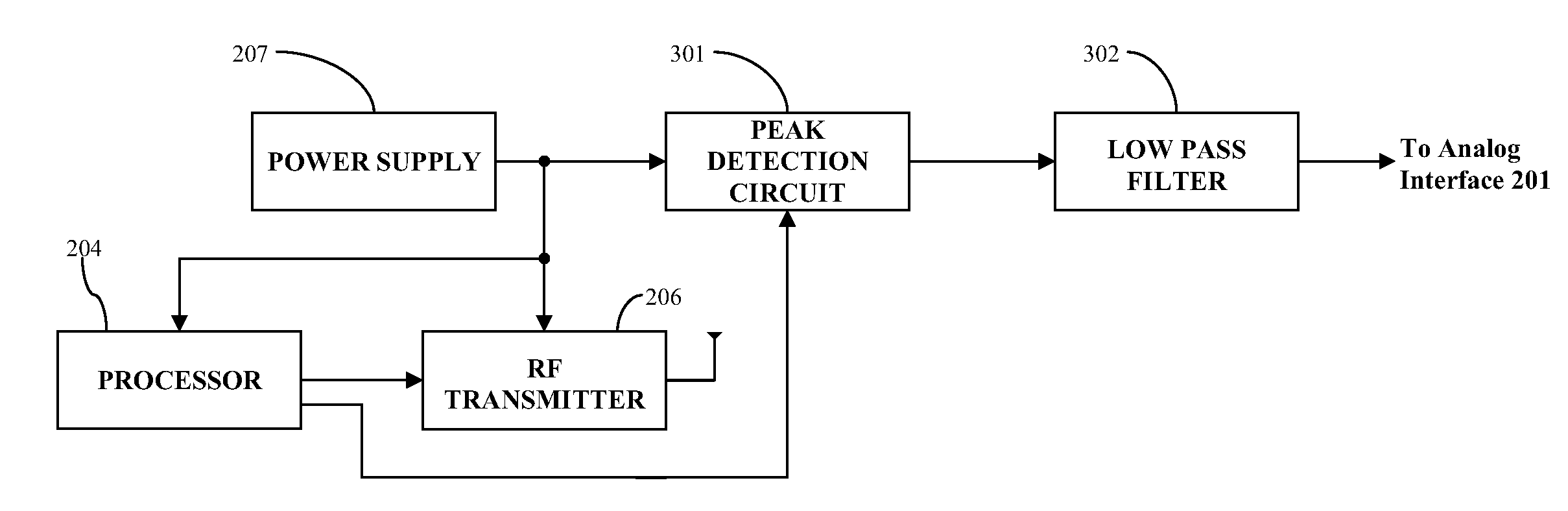
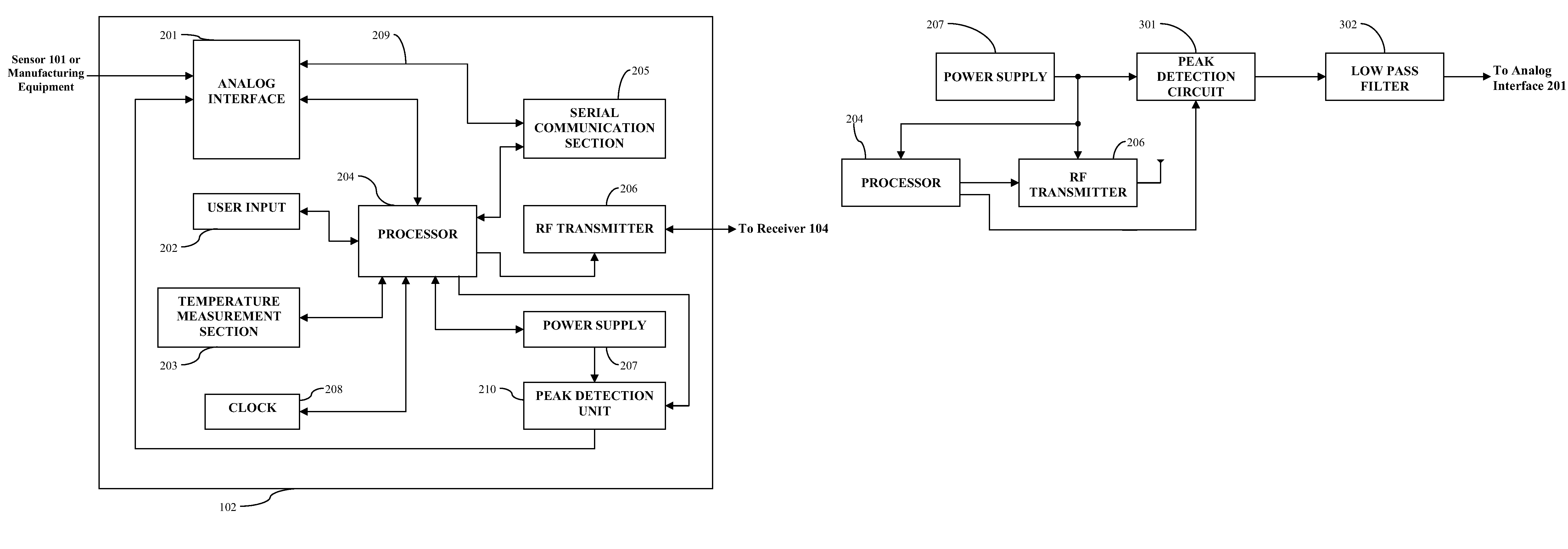
Method and apparatus for providing peak detection circuitry for data communication systems
ActiveUS20090083003A1Effective and low cost and low noise approachEffective and low cost and lowTariff metering apparatusCurrent/voltage measurementCommunications systemPeak value
Method and apparatus for providing a peak detection circuit comprising a diode including an input terminal and an output terminal the input terminal of the diode configured to receive an input signal, a capacitor operatively coupled to the output terminal of the diode, an output terminal operatively coupled to the capacitor and the output terminal of the diode for outputting an output signal is provided. Other equivalent switching configuration is further provided to effectively detect and compensate for a voltage droop from a power supply signal, as well as to electrically isolate the voltage droop from the system circuitry.
Owner:ABBOTT DIABETES CARE INC
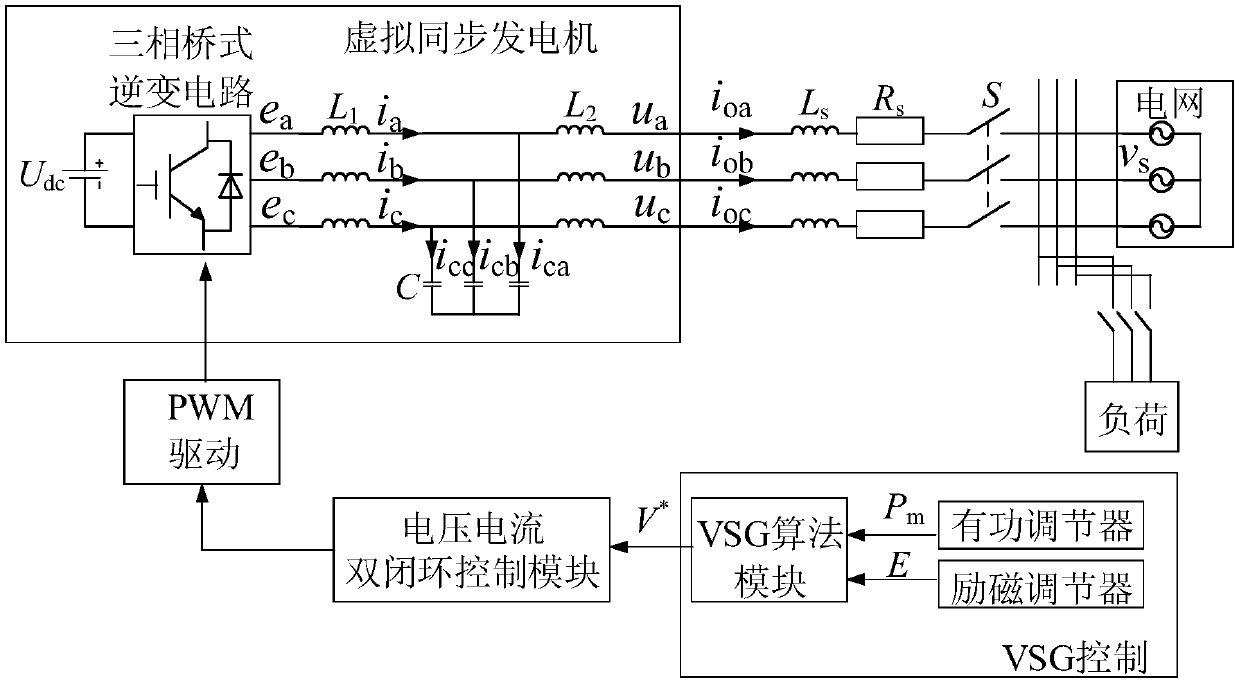
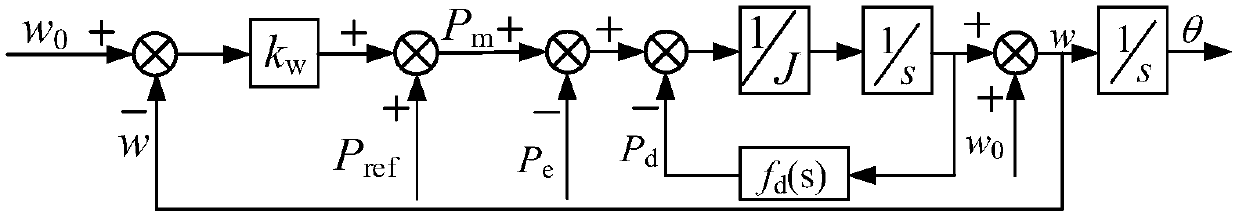
Inverter secondary-frequency-regulation control circuit based on virtual synchronous generator
ActiveCN106684921ALarge capacityGood for total FM capacitySingle network parallel feeding arrangementsPower oscillations reduction/preventionVirtual synchronous generatorVoltage droop
The invention discloses an inverter secondary-frequency-regulation control circuit based on a virtual synchronous generator. The inverter secondary-frequency-regulation control circuit comprises an inverter, an LC filter and a power measurement module, and also comprises a voltage loop and a VSG controller. The input end of the VSG controller is connected with the output end of the power measurement module, the output end of the VSG controller is connected with the input end of the voltage loop, and the output end of the voltage loop is connected with the inverter; the VSG controller comprises a power frequency controller and an excitation controller, the power frequency controller is used for simulating a rotor motion equation of the synchronous generator, the excitation controller is used for reactive-voltage droop control, the amplitude information of command voltage generated by the excitation controller and the phase information of command voltage generated by the power frequency controller are synthesized, and an input command signal em of the voltage loop cam be obtained. According to the inverter secondary-frequency-regulation control circuit, the VSG control strategy can automatically track load fluctuation and change output force of inverter secondary-frequency-regulation control circuit under the island model, and frequency support is provided for a micro grid.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
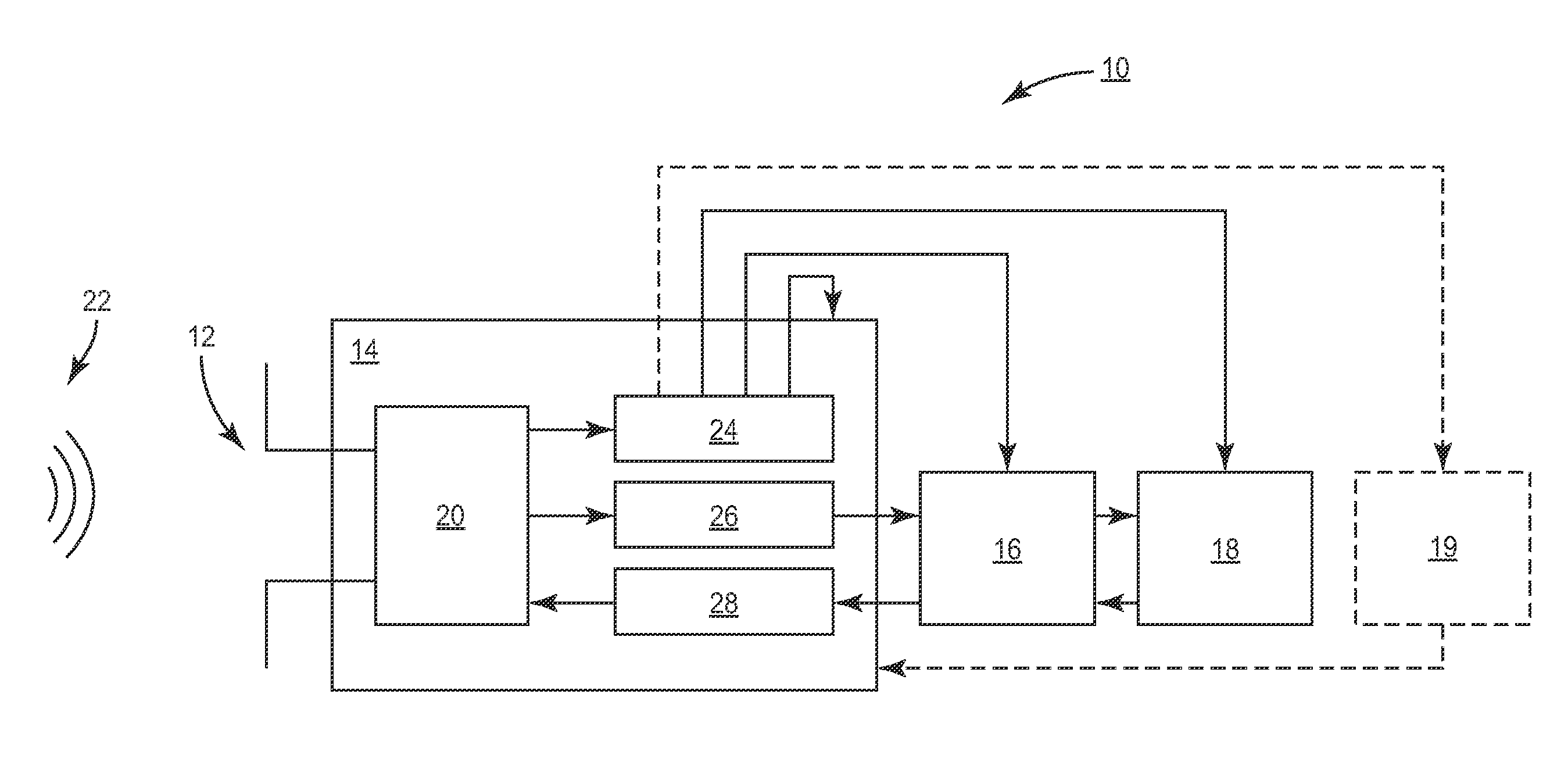
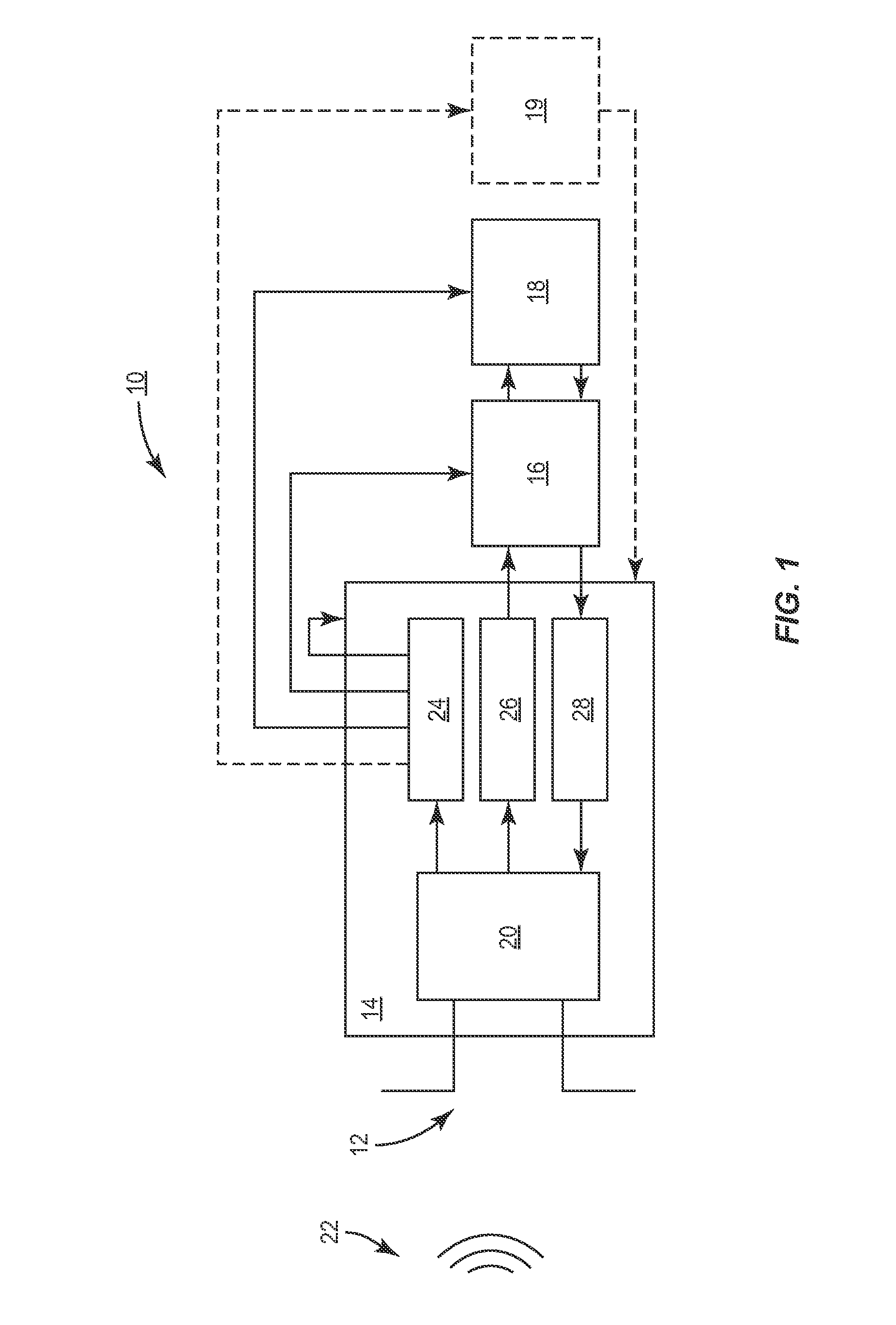
Application of Multiple Voltage Droop Detection and Instruction Throttling Instances with Customized Thresholds Across a Semiconductor Chip
InactiveUS20090063065A1Energy efficient ICTCurrent/voltage measurementTiming marginSemiconductor chip
A method and system for applying multiple voltage droop detection and instruction throttling instances with customized thresholds across semiconductor chips. Environmental parameters are detected for various locations on a chip, and timing margins are determined for each location on the chip. An acceptable voltage droop for each location is determined based on the environmental parameters and the timing margins for the corresponding location. A droop threshold is then determined for each location based on the corresponding acceptable voltage droop determined for the corresponding location.
Owner:IBM CORP
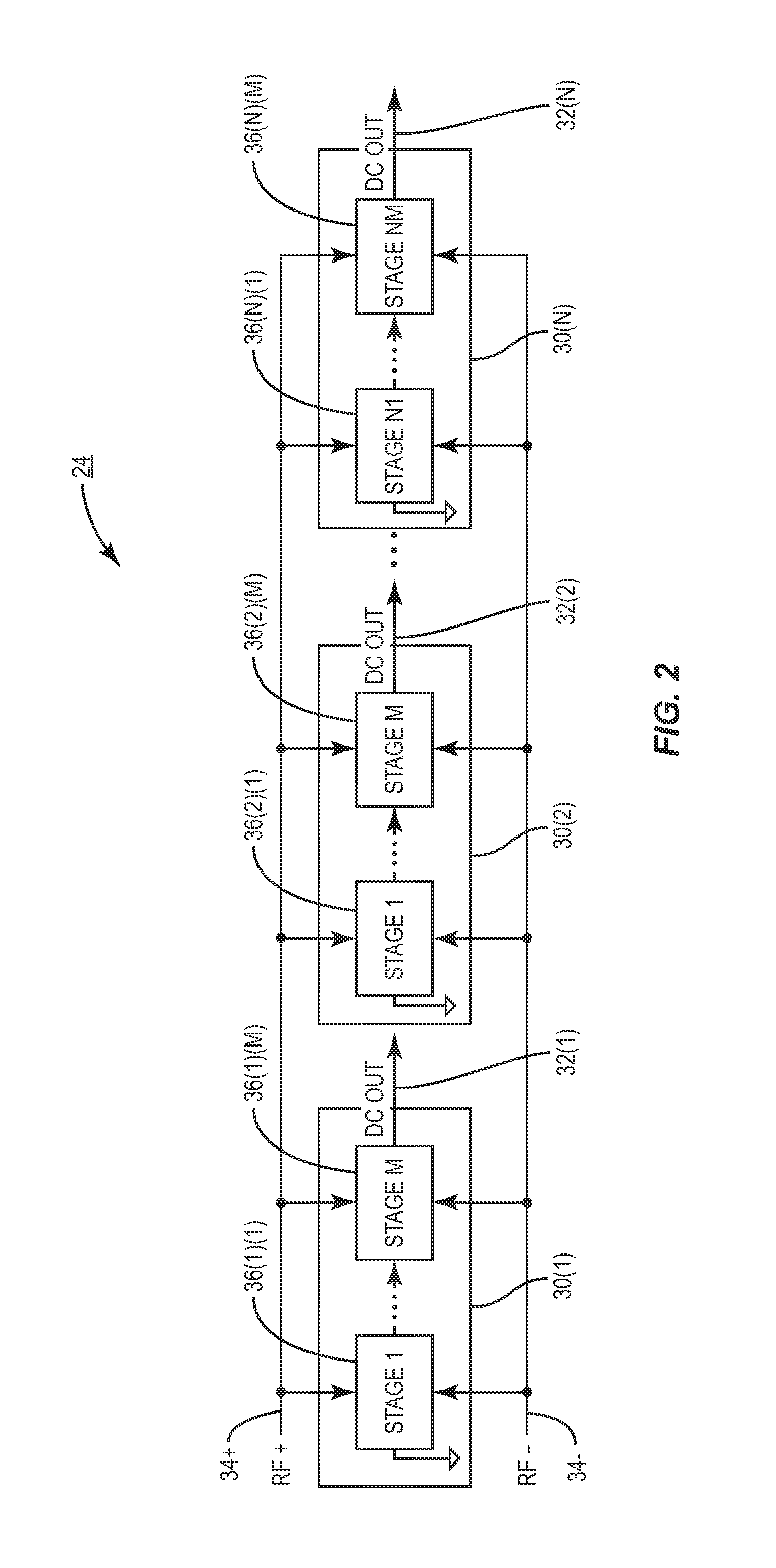
Parallel stage power output rectifier for radio-frequency identification (RFID) devices, and related components and methods
InactiveUS20130299593A1Easy to useImprove voltage dropAc-dc conversion without reversalRecord carriers used with machinesPower flowEngineering
Parallel stage power output rectifiers for radio-frequency identification (RFID) devices and related components and methods are disclosed. An RFID tag receives a radio-frequency (RF) signal comprising RF input energy through an input such as an antenna. The RF input energy provided to a rectifier splits the RF input energy into two or more stages having parallel electrical outputs. The parallel electrical outputs allow for a more efficient use of the input energy in terms of current draw and improves voltage droop, thus improving the range and operation of the RFID tag.
Owner:CORNING INC
Application of Multiple Voltage Droop Detection and Instruction Throttling Instances with Customized Thresholds Across a Semiconductor Chip
InactiveUS20090063884A1Energy efficient ICTElectronic circuit testingTiming marginSemiconductor chip
A method and system for applying multiple voltage droop detection and instruction throttling instances with customized thresholds across semiconductor chips. Environmental parameters are detected for various locations on a chip, and timing margins are determined for each location on the chip. An acceptable voltage droop for each location is determined based on the environmental parameters and the timing margins for the corresponding location. A droop threshold is then determined for each location based on the corresponding acceptable voltage droop determined for the corresponding location.
Owner:IBM CORP
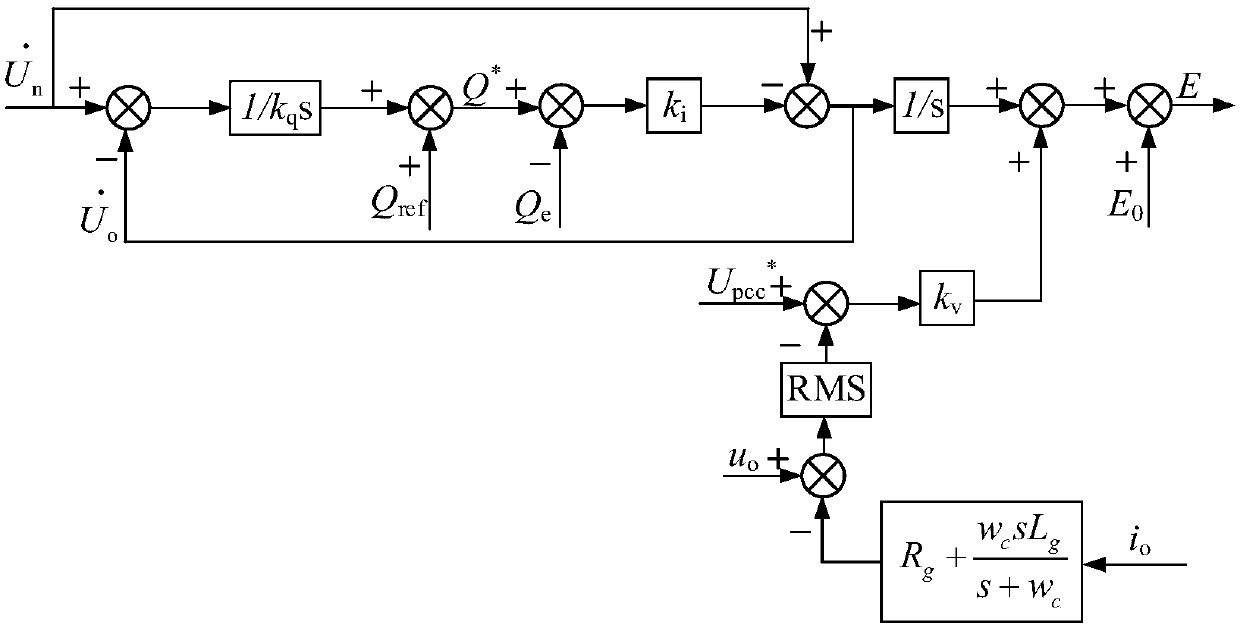
Inverter system based on improved power distribution policy of virtual synchronous generator
ActiveCN107732978AImprove receptivityImprove dynamic response performanceSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsDc-ac conversion without reversalVirtual synchronous generatorDamping factor
The invention discloses an inverter system based on the improved power distribution policy of a virtual synchronous generator. The inverter system comprises a grid-connected inverter system which is controlled by a virtual synchronous generator and is composed of a direct current voltage source, a three-phase bridge inverter circuit, an LCL filter, a public power grid, a load and a control drive circuit. The inverter system consists of an active regulator, an excitation regulator, a VSG algorithm module, and a voltage and current double closed-loop control module. The introduction of the control of the synchronous generator overcomes the problems of fast response and low inertia of a traditional grid-connected inverter. The permeability of renewable energy in a micro grid can be effectively improved. The dynamic characteristic of a synchronous generator rotor is introduced into a second-order transient model, which eliminates the influence of a traditional constant damping coefficienton droop control. In addition, by improving the reactive-voltage droop control, the influence of the inverter output filter impedance and the line impedance on reactive power distribution is reduced,and reasonable distribution of the inverter output power is ensured.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
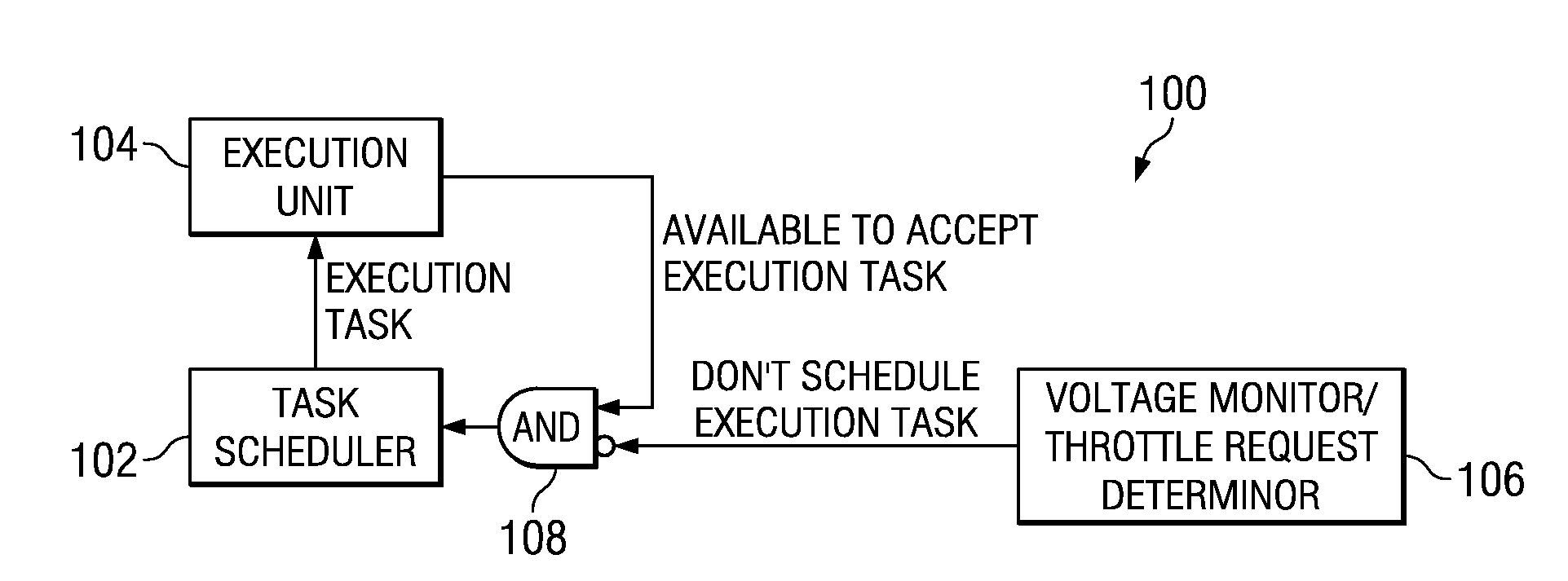
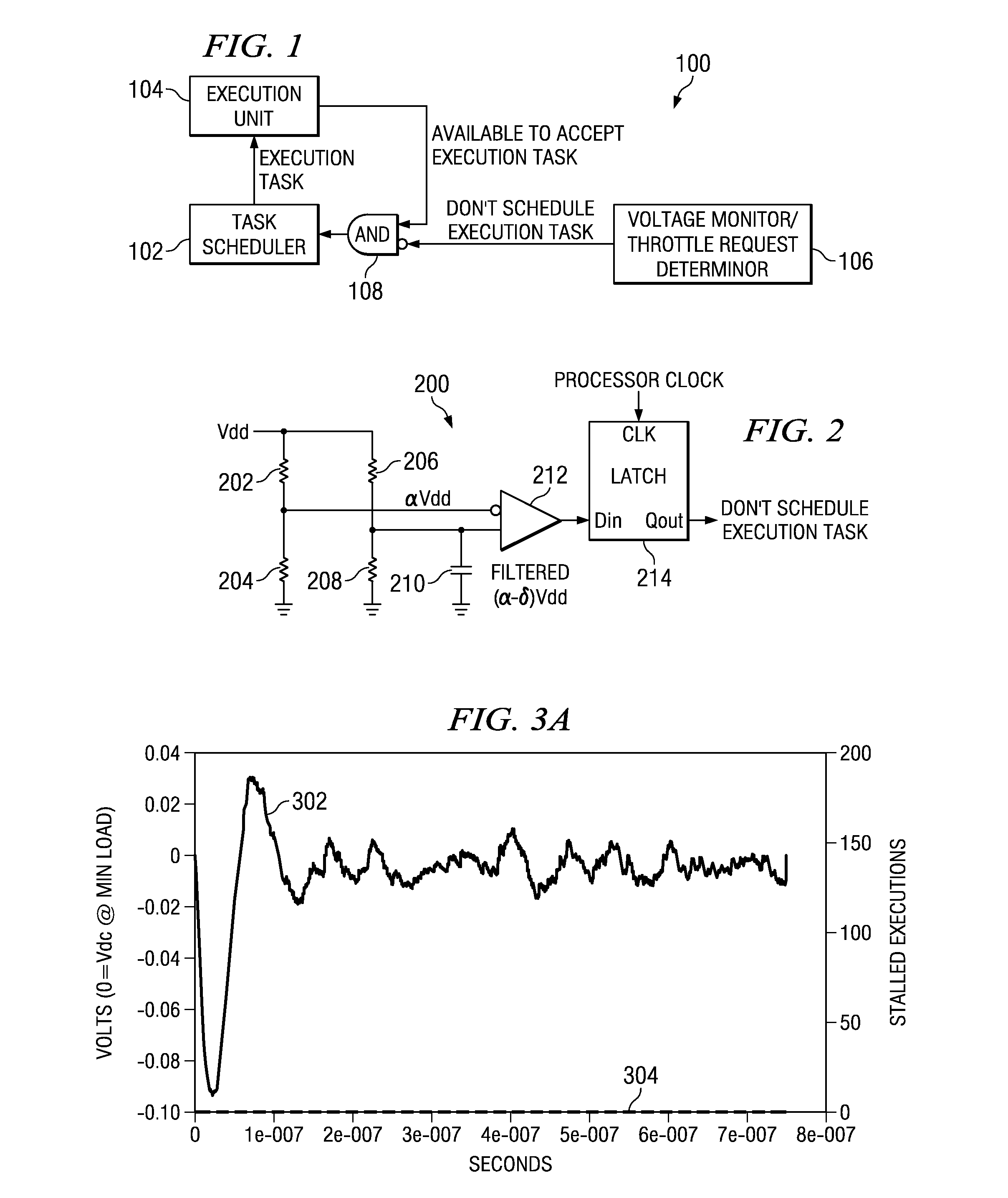
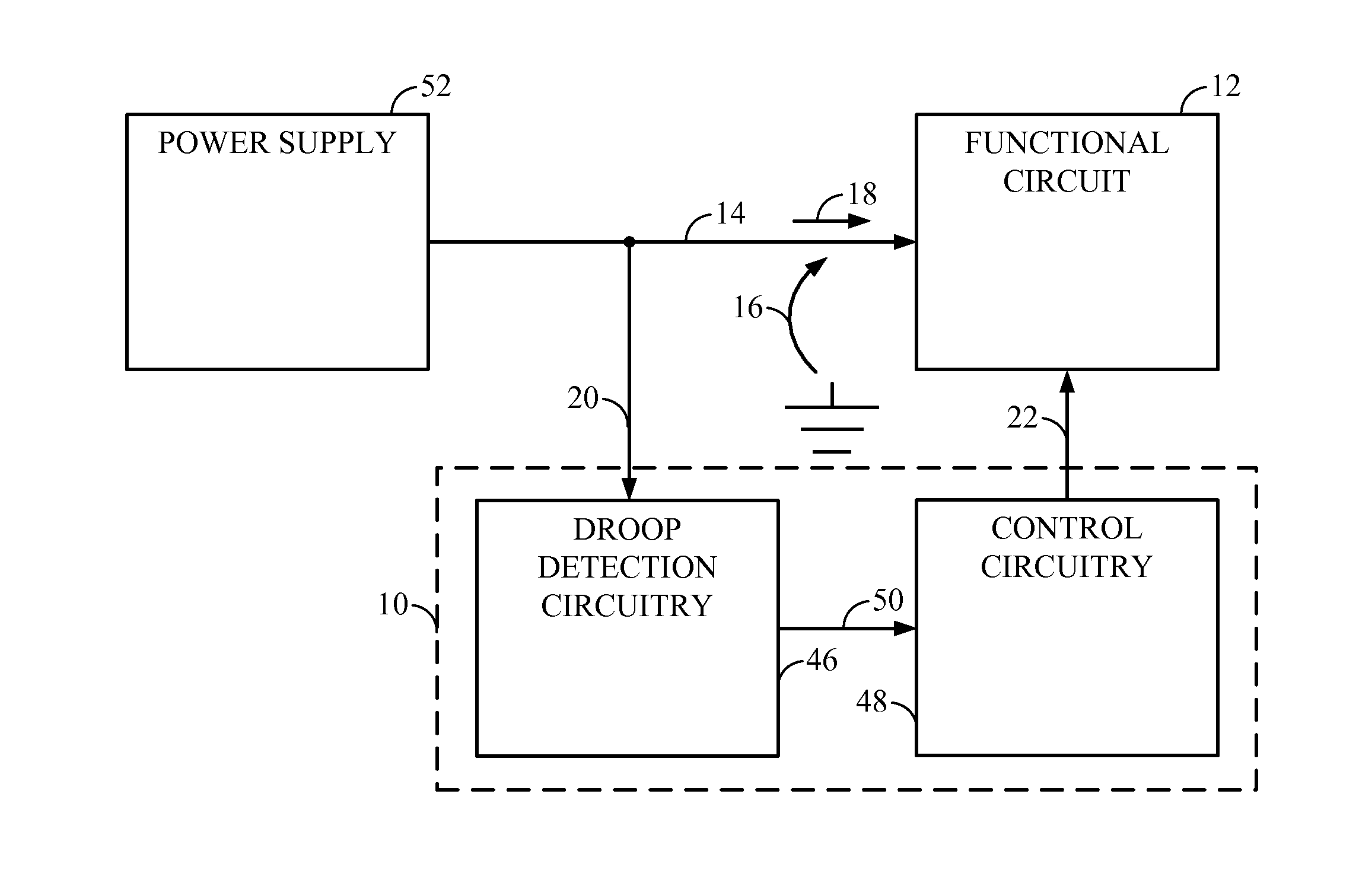
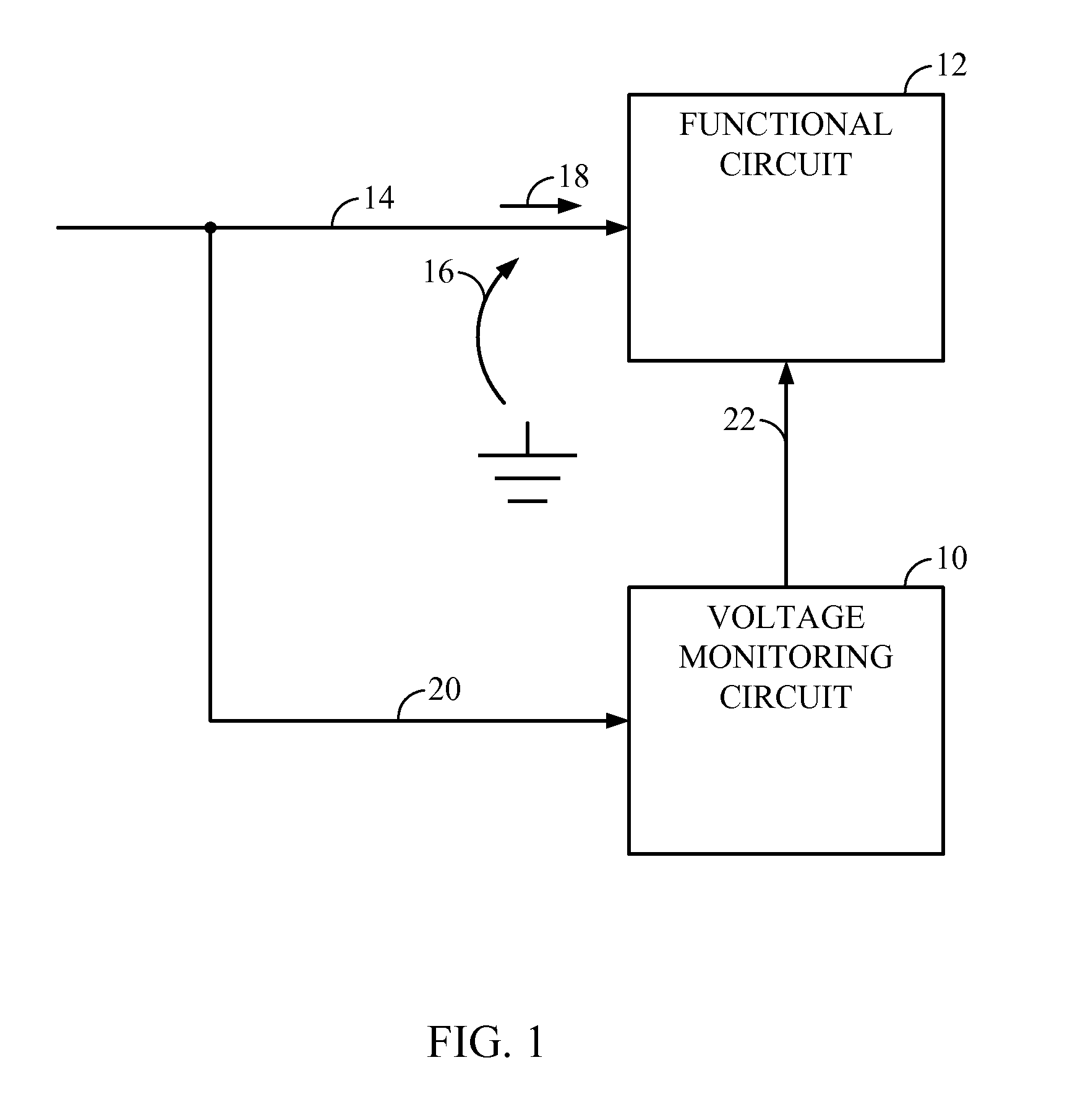
Circuits, Systems and Methods to Detect and Accommodate Power Supply Voltage Droop
ActiveUS20110241423A1Dc network circuit arrangementsDigital data processing detailsEngineeringVoltage droop
Circuits, systems, and methods for monitoring a power supply voltage and determining if the power supply voltage has drooped are disclosed. In one embodiment, a voltage monitoring circuit is provided and configured to determine if the power supply voltage supplied to a functional circuit has drooped. When no droop of the power supply voltage is detected, the voltage monitoring circuit is configured to provide an indication to the functional circuit to operate in a first mode. When droop of the power supply voltage is detected, the voltage monitoring circuit is configured to provide an indication to the functional circuit to operate in a second mode. In this manner, operating margin in the power supply may be reduced since the functional circuit may be configured to properly operate when a voltage droop of the power supply voltage occurs.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
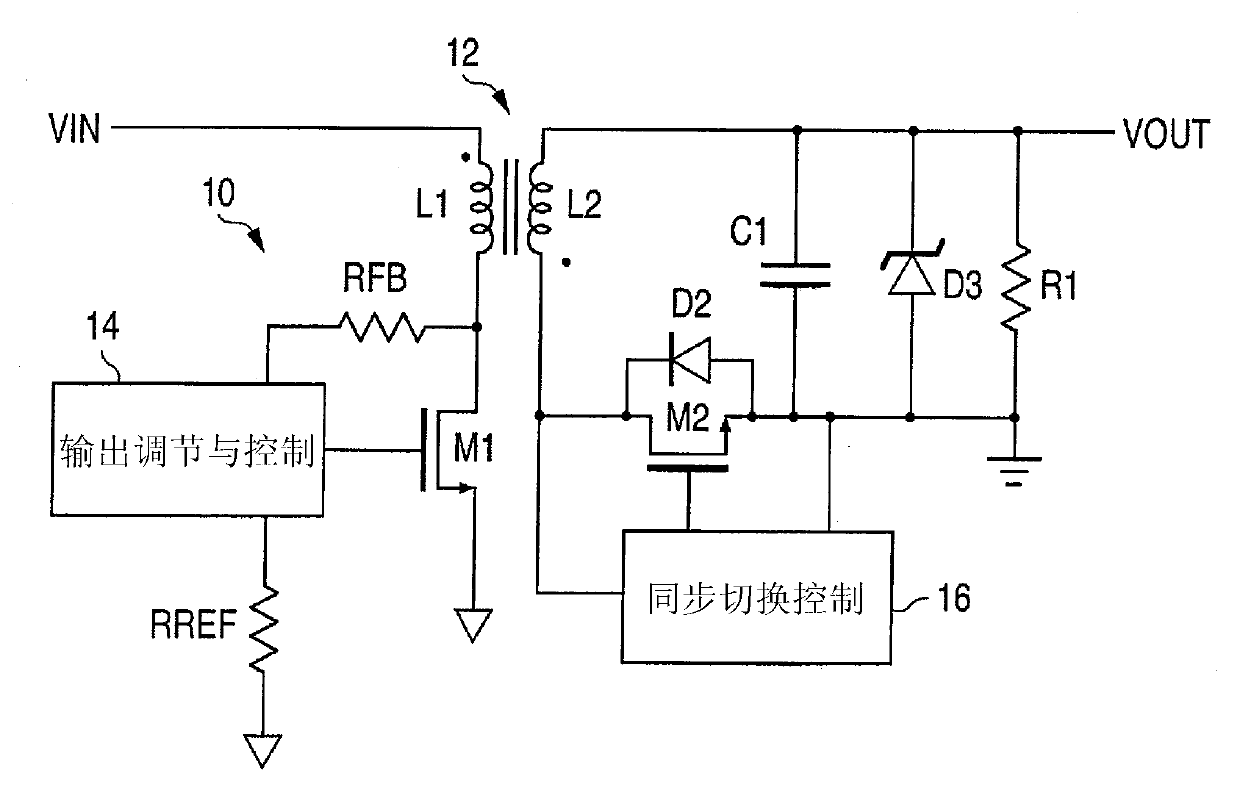
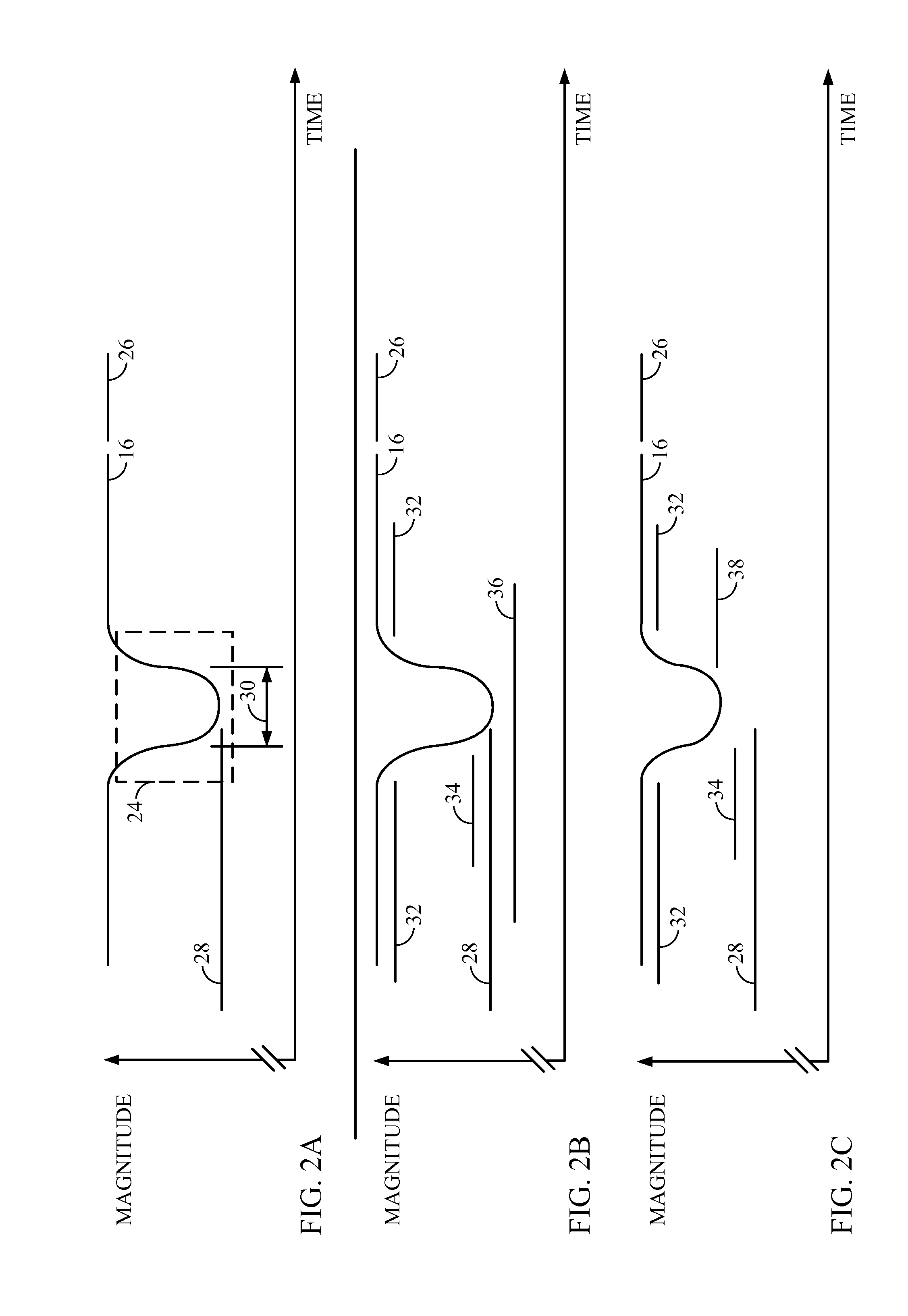
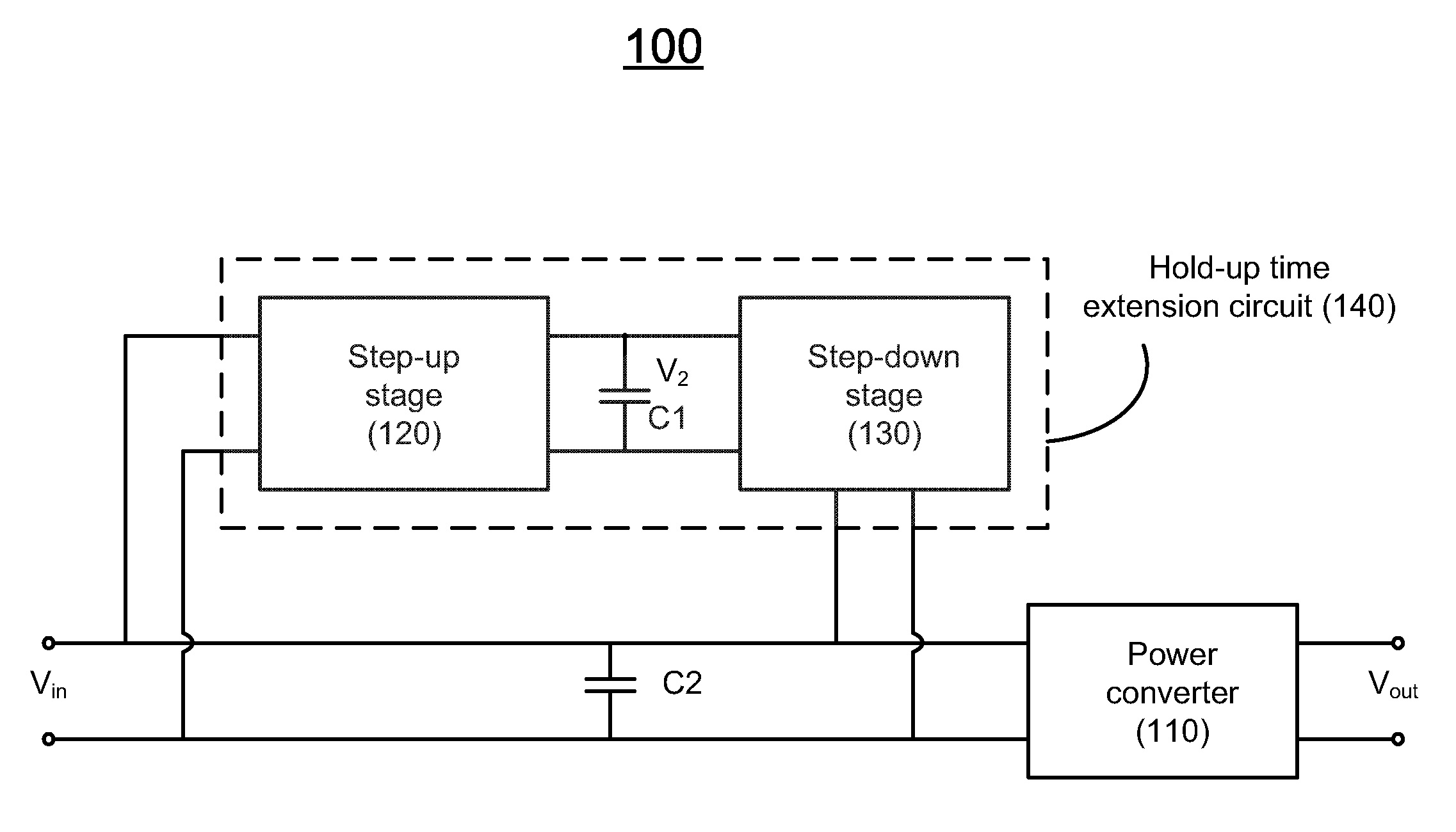
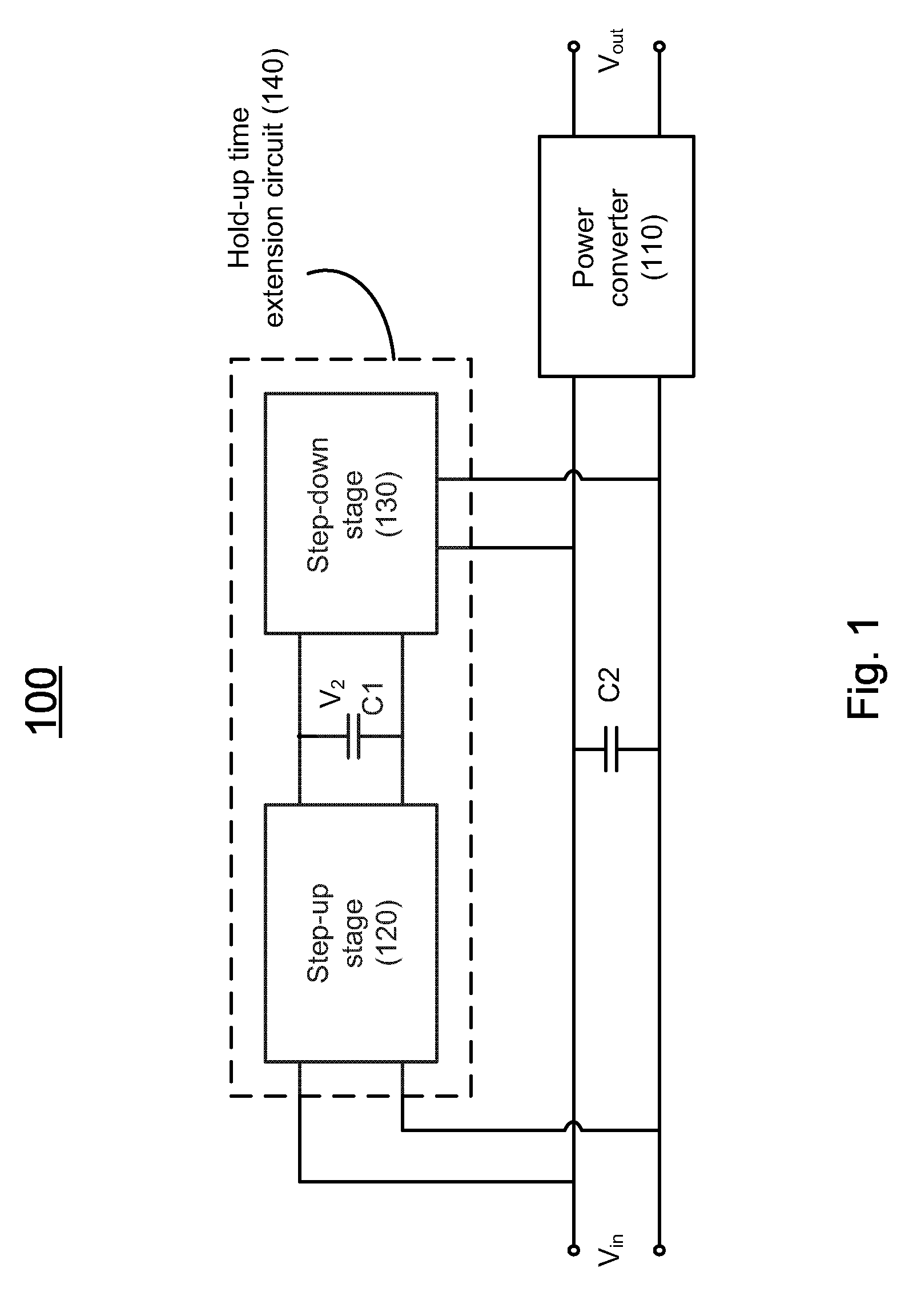
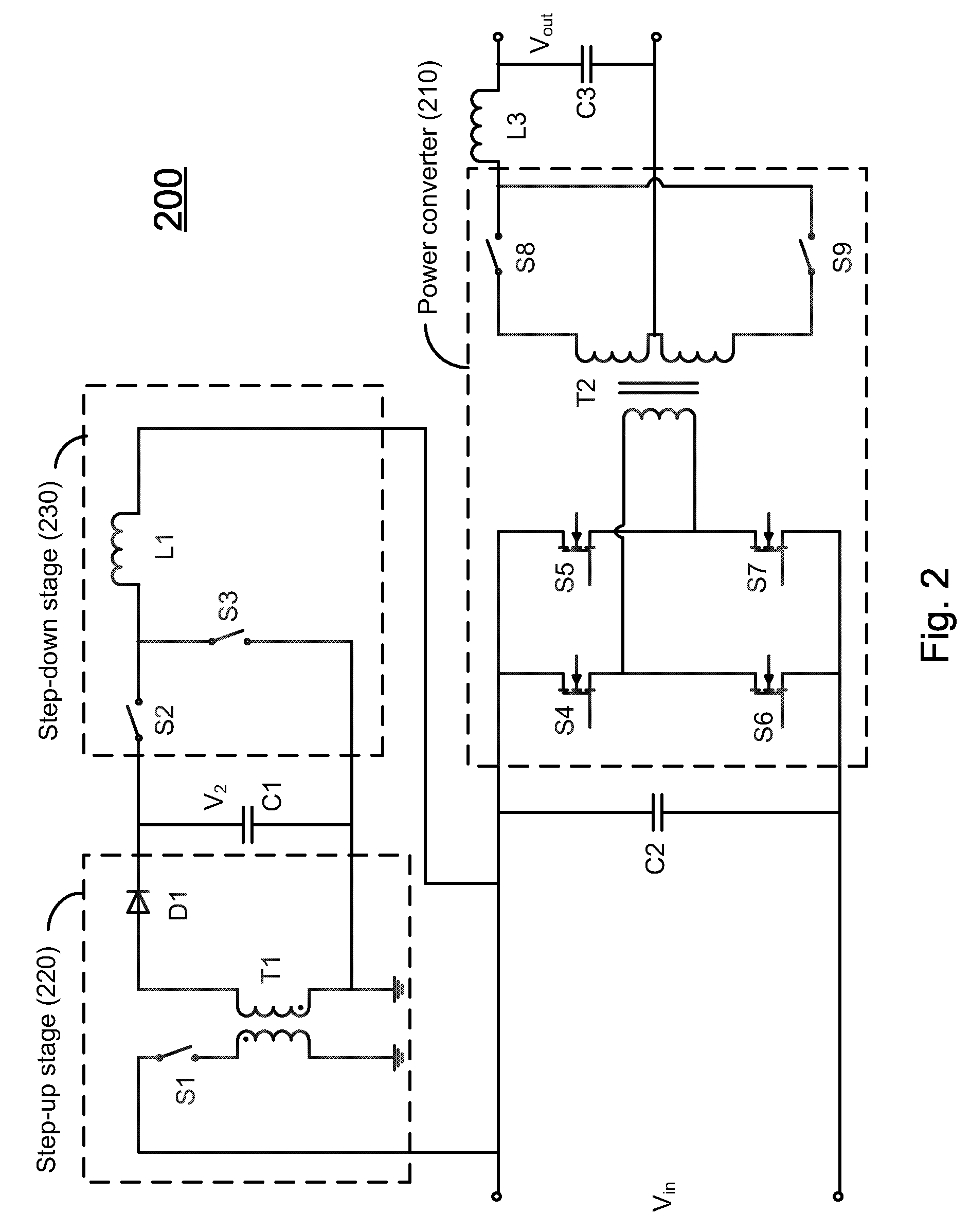
Hold-up time extension circuit for a power converter
InactiveUS8736240B2Electric signal transmission systemsElectric power transfer ac networkTime extensionEngineering
Owner:DELTA ELECTRONICS (SHANGHAI) CO LTD
Wind power dispersion and integration droop control method based on VSC-HVDC
InactiveCN104734189AImprove anti-interference abilityInhibition effectClimate change adaptationSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsEffective solutionElectricity
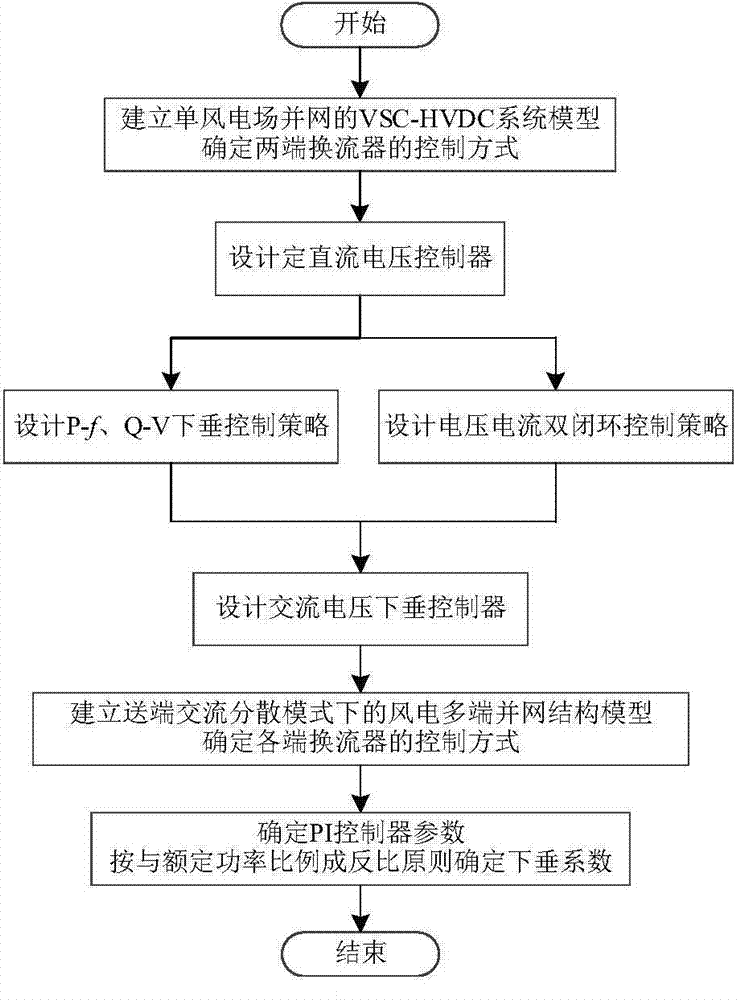
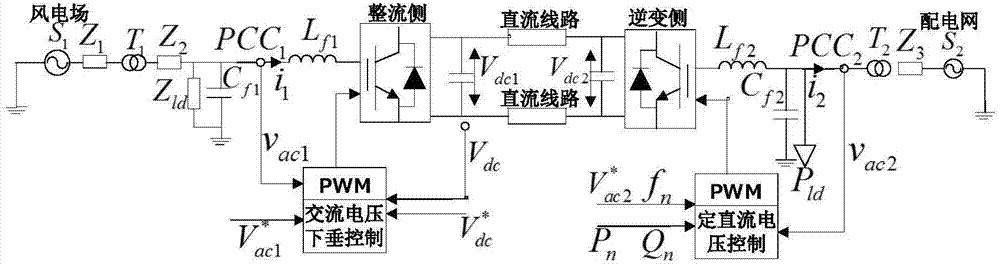
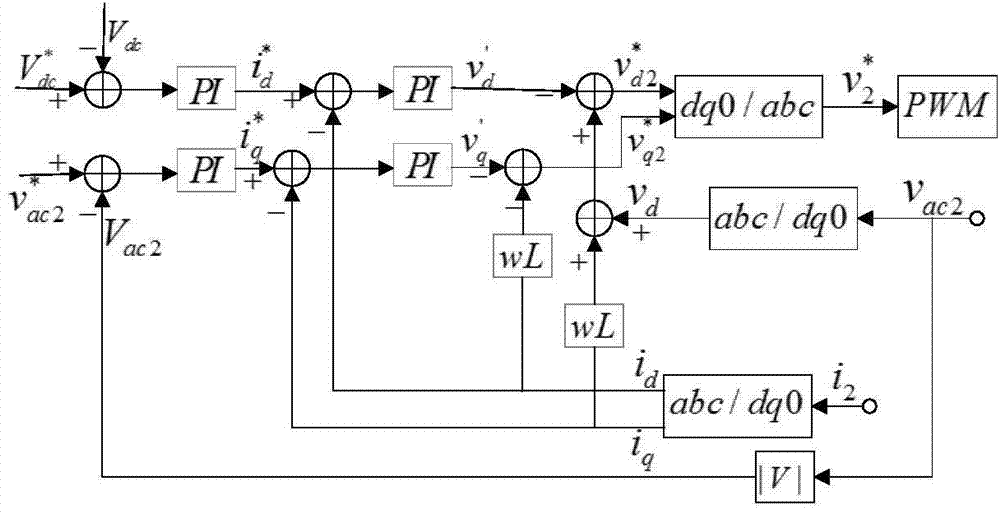
The invention discloses a wind power dispersion and integration droop control method based on the VSC-HVDC. The method includes the steps that first, a VSC-HVDC system structure model for single wind power plant integration is established; second, a constant DC voltage controller for a power distribution network side inverter of the VSC-HVDC system structure model is established; third, an AC voltage droop controller for a wind power plant side rectifier of the VSC-HVDC system structure model is established; fourth, the VSC-HVDC system structure model for multiple-wind-power-plant integration in an AC dispersion mode at the sending end is established according to power distribution network distribution, the power distribution network side inverter is controlled by the constant DC voltage controller, and the wind power plant side rectifier is controlled by the AC voltage droop controller. According to the wind power dispersion and integration droop control method based on the VSC-HVDC, an effective solution can be provided for dispersion wind power plant joint coordination operation in an AC converging mode at the receiving end, and the method is suitable for remote wind power plant integration control.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV +2
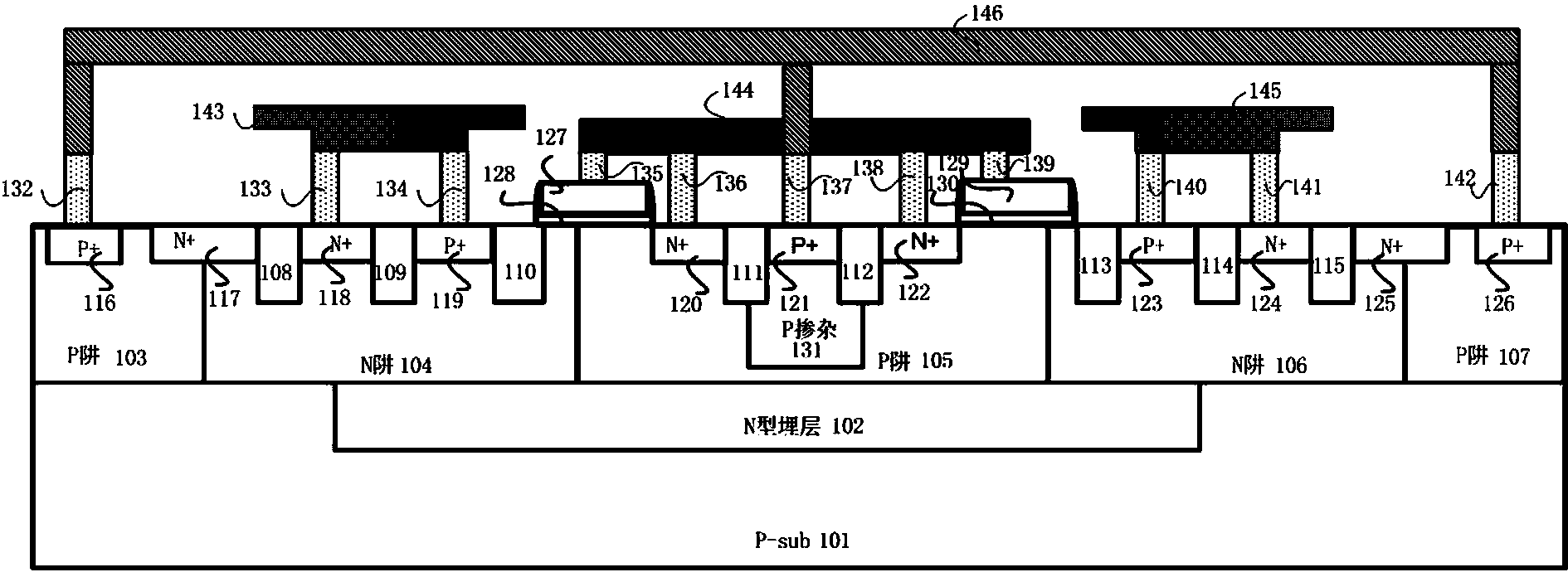
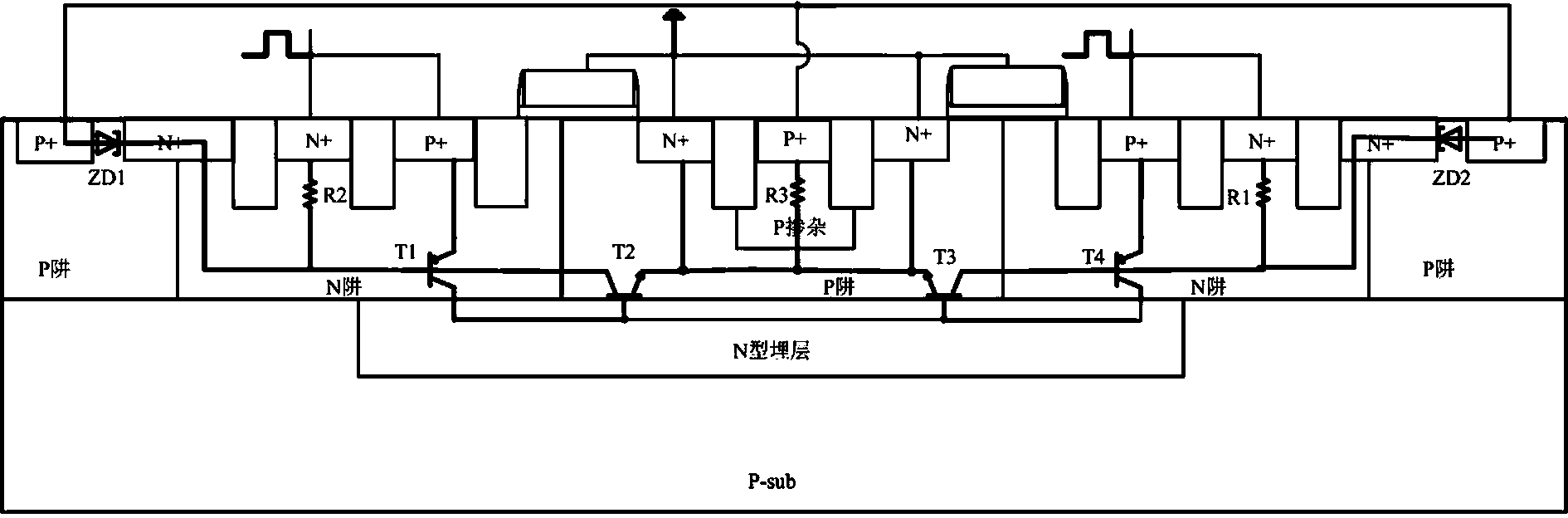
High-voltage ESD protective device with dual latch-up resistance and of annular LDMOS-SCR structure
ActiveCN103681660AImprove pressure resistanceLower on-resistanceSolid-state devicesSemiconductor devicesLDMOSHemt circuits
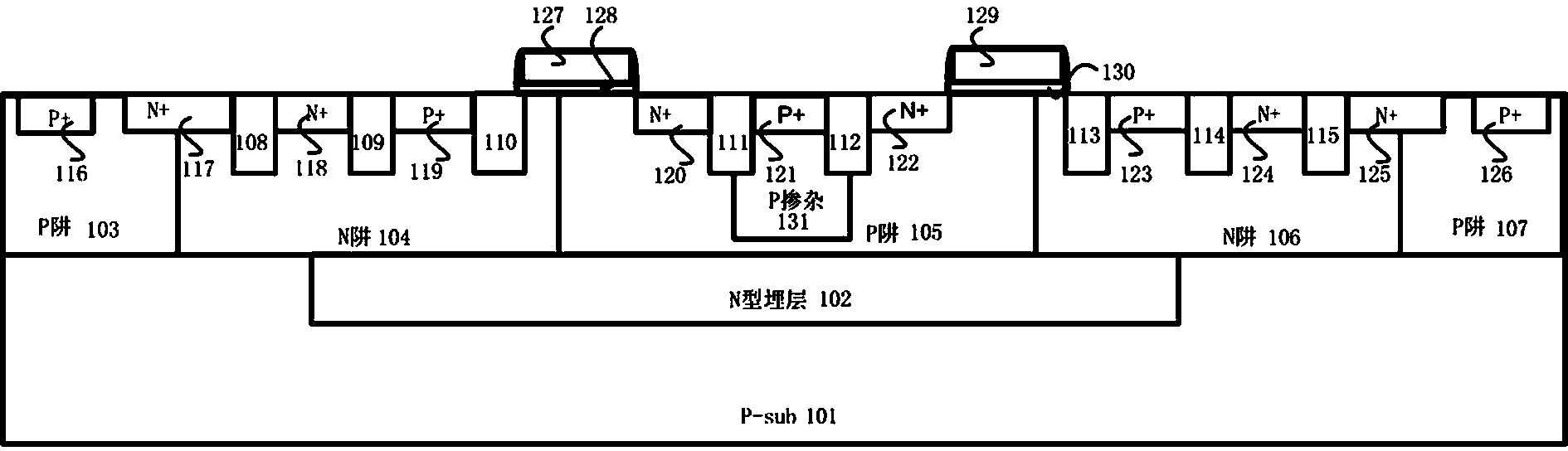
The invention discloses a high-voltage ESD protective device with dual latch-up resistance and of an annular LDMOS-SCR structure. The high-voltage ESD protective device with the dual latch-up resistance and of the annular LDMOS-SCR structure can be applied to an on-chip IC. The high-voltage ESD protective device with the dual latch-up resistance and of the annular LDMOS-SCR structure comprises a P type substrate, an N type buried layer, a first P trap, a first N trap, a second P trap, a P adulterant, a second N trap, a third P trap, an isolation area, a first P+, a first N+, a second N+, a second P+, a third N+, a third P+, a fourth N+, a fourth P+, a fifth N+, a sixth N+, a fifth P+, a metal anode and a metal cathode, wherein a Zener breakdown ESD current discharging path is formed by the second N+, the second P+, the first N+ and the first P+ or by the fourth P+, the fifth N+, the sixth N+ and the fifth P+. According to the high-voltage ESD protective device with the dual latch-up resistance and of an annular LDMOS-SCR structure, the ESD robustness of the device can be improved, the maintaining voltage can be improved, and the trigger voltage can be reduced; due to the design of the annular layout of the LDMOS-SCR structure, the on resistance can be reduced, and the maintaining current can be improved; the ESD protective capacity of the dual latch-up resistance is achieved.
Owner:NANTONG JIANGHUA MASCH CO LTD
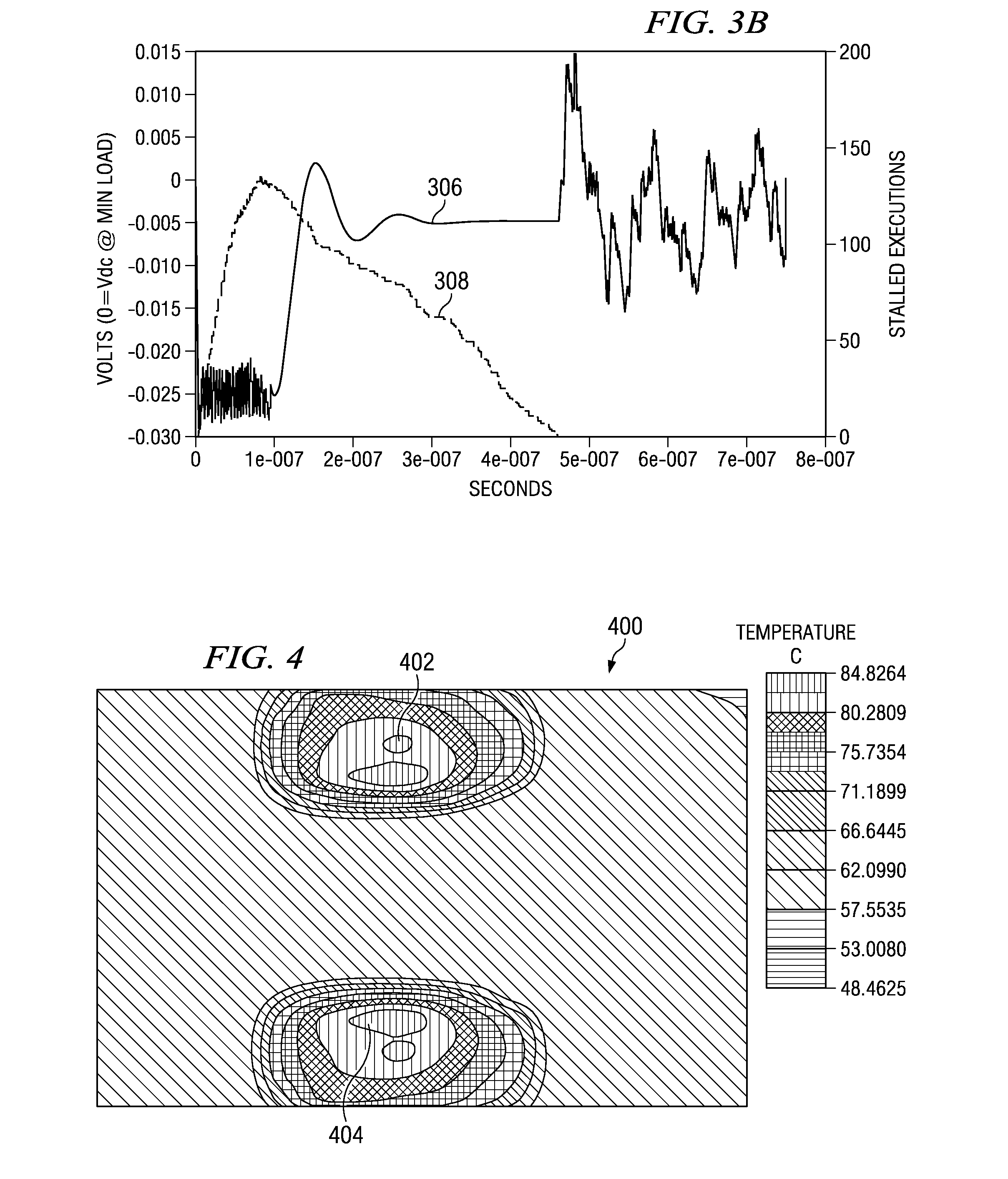
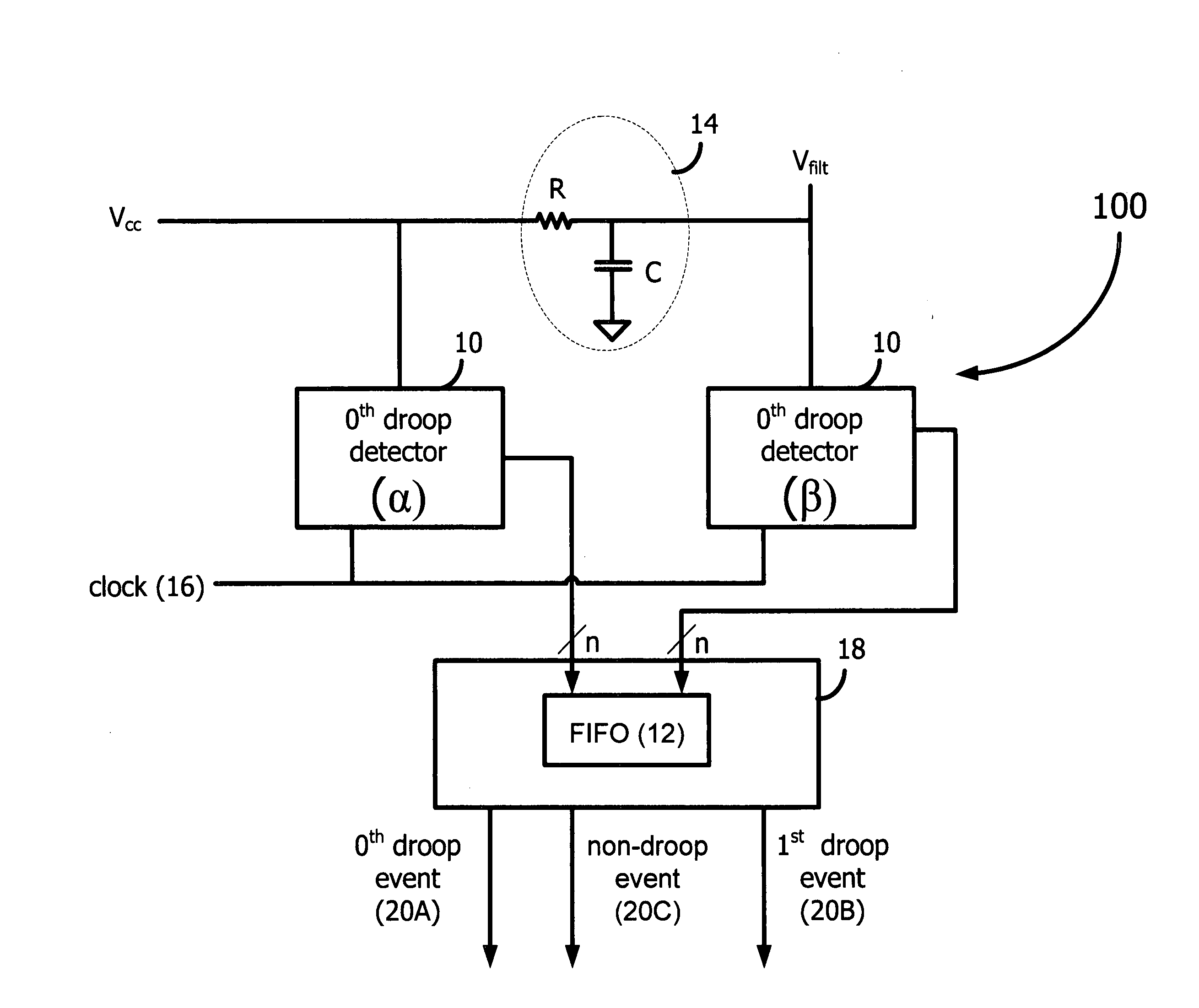
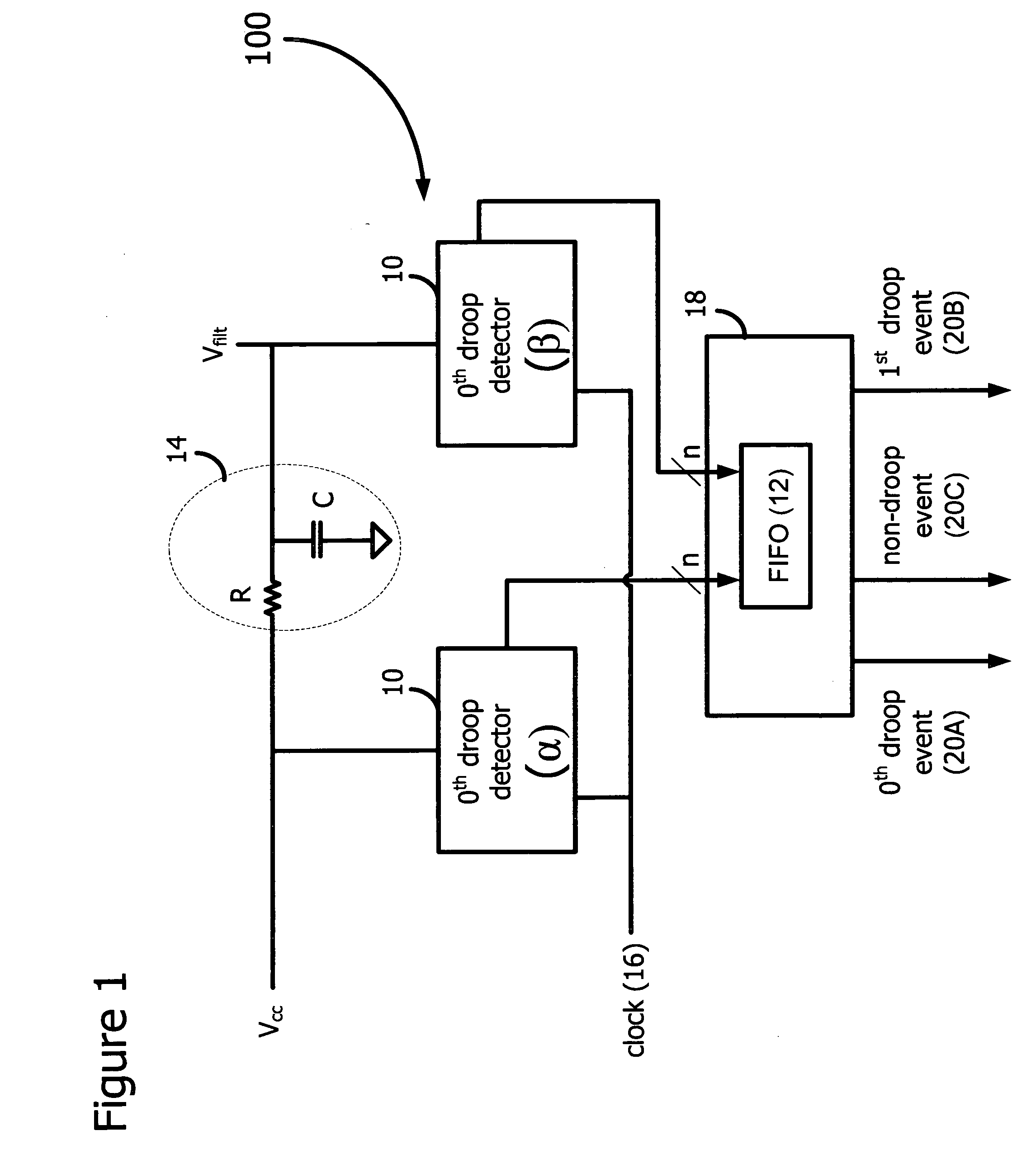
0th droop detector architecture and implementation
A voltage droop detector captures the very high-frequency noise on the power grid of a load, such as a microprocessor. The droop detector includes twin circuits, one of which receives the voltage from the power grid of the load, the other of which receives a filtered voltage. A 0th droop, as well as 1st droops, 2nd droops, and so on, are captured and stored for subsequent analysis. The circuits sample the voltages frequently enough to ensure that all droop events are captured. Other embodiments are described and claimed.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Microprocessor performance and power optimization through inductive voltage droop monitoring and correction
A voltage droop monitoring and correcting circuit for a microprocessor includes: a monitor circuit configured to monitor voltage droops of the microprocessor and perform a temporary clock-skipping technique to compensate for the voltage droops. A method for monitoring and correcting voltage droops of a microprocessor includes: monitoring voltage droops of the microprocessor; and performing a temporary clock-skipping technique to compensate for the voltage droops. A computer system includes memory; a processor operatively connected to the memory; and computer-readable instructions stored in the memory for causing the processor to: monitor voltage droops of the microprocessor; and perform a temporary clock-skipping technique to compensate for the voltage droops.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
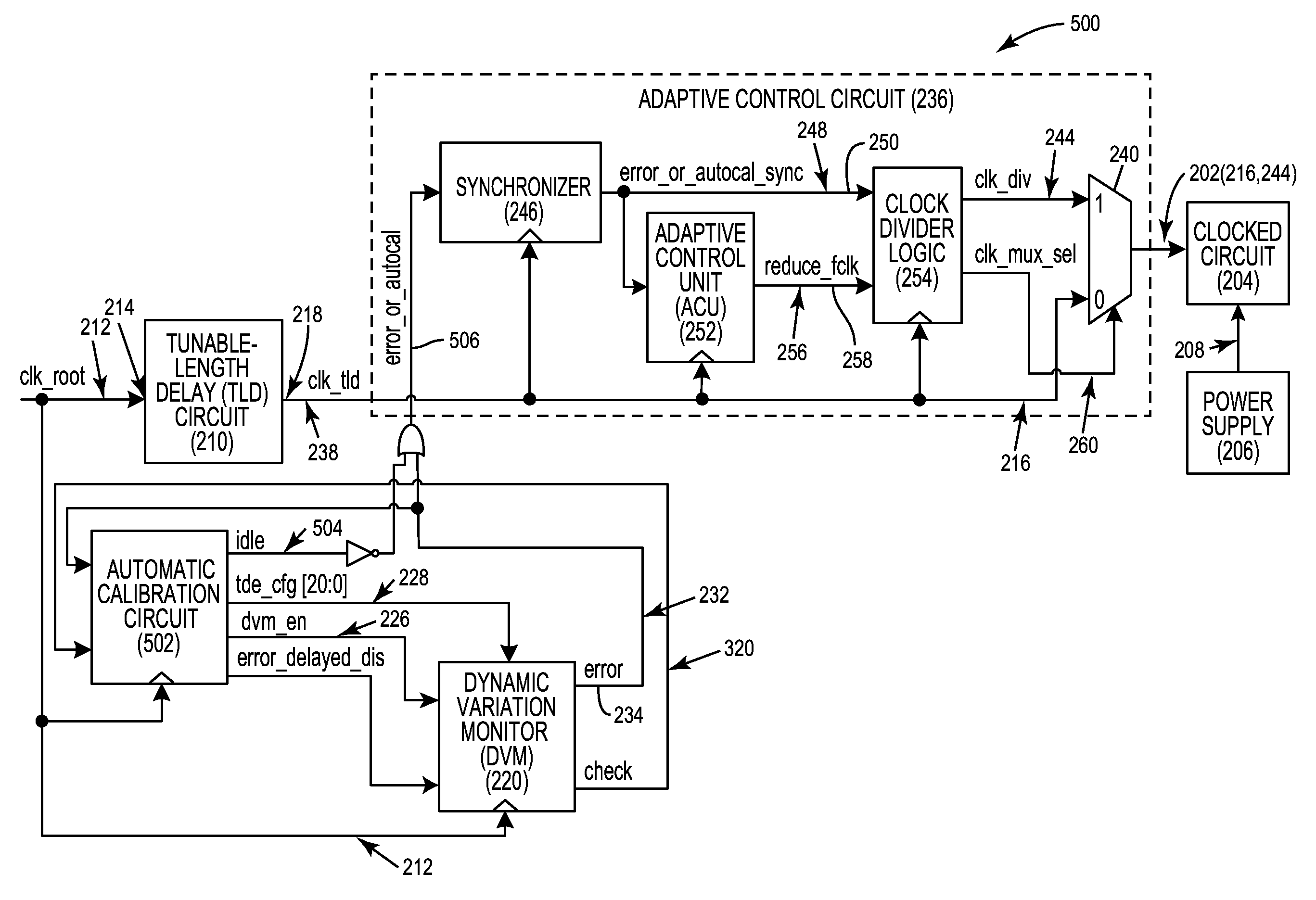
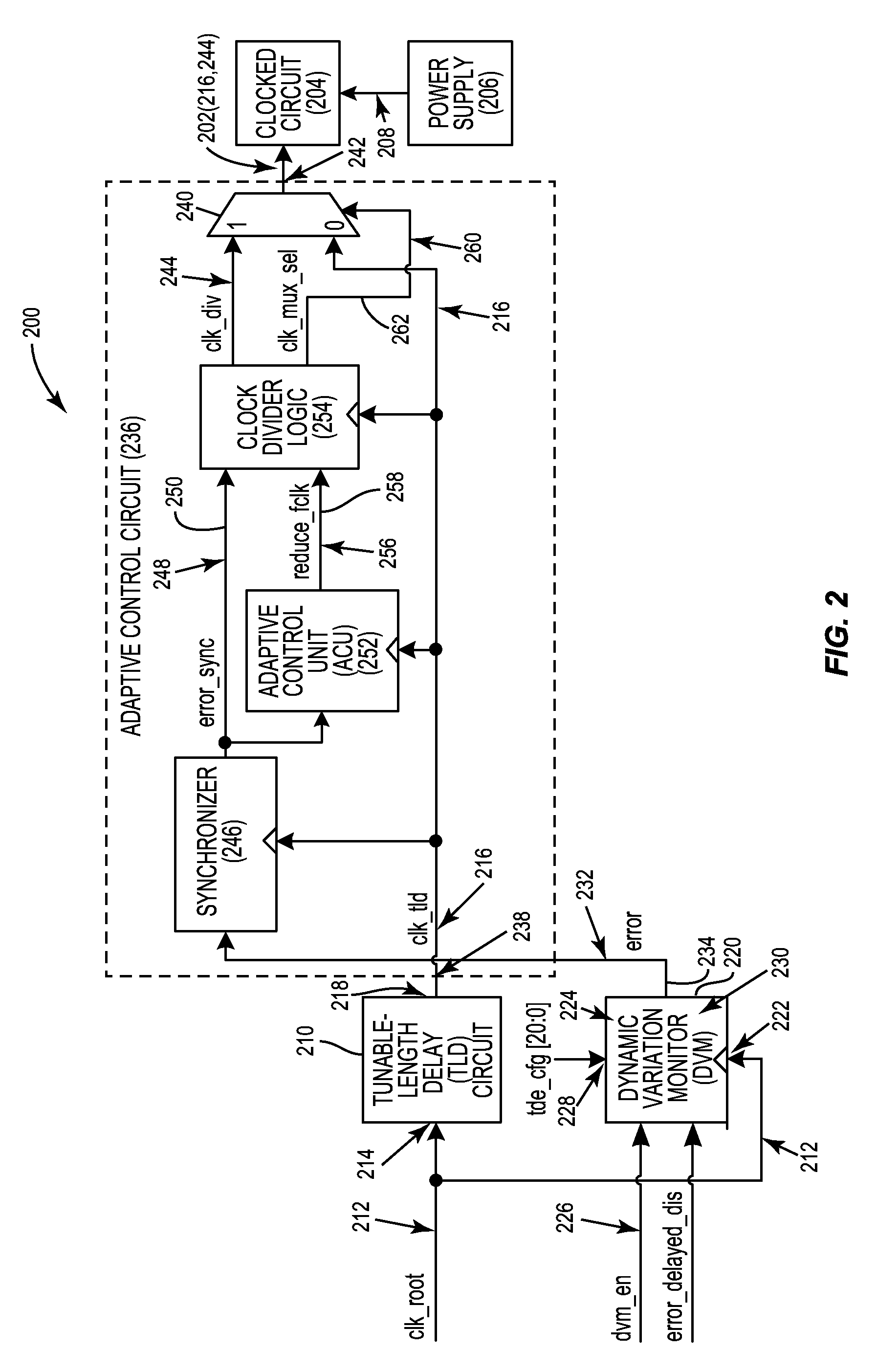
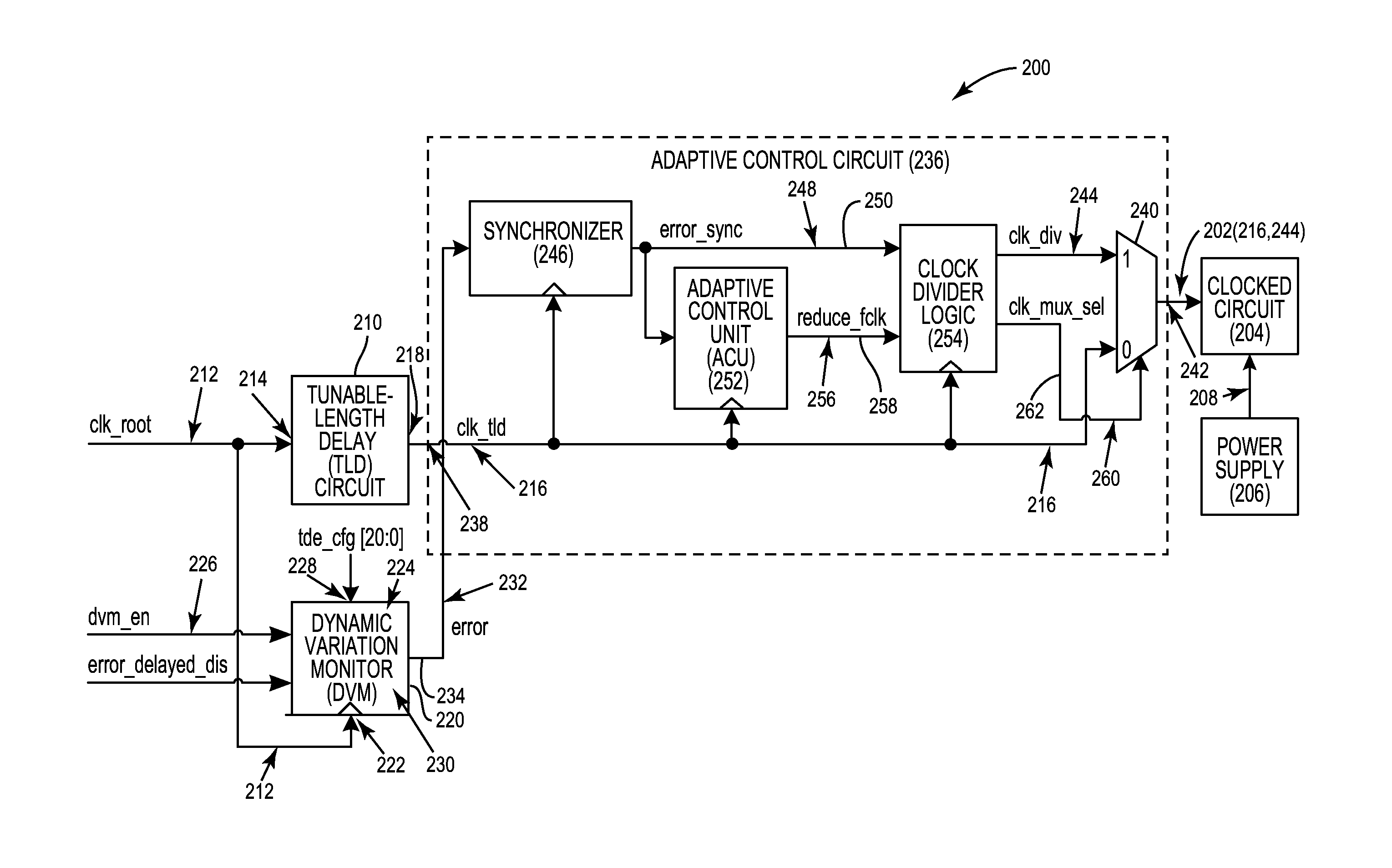
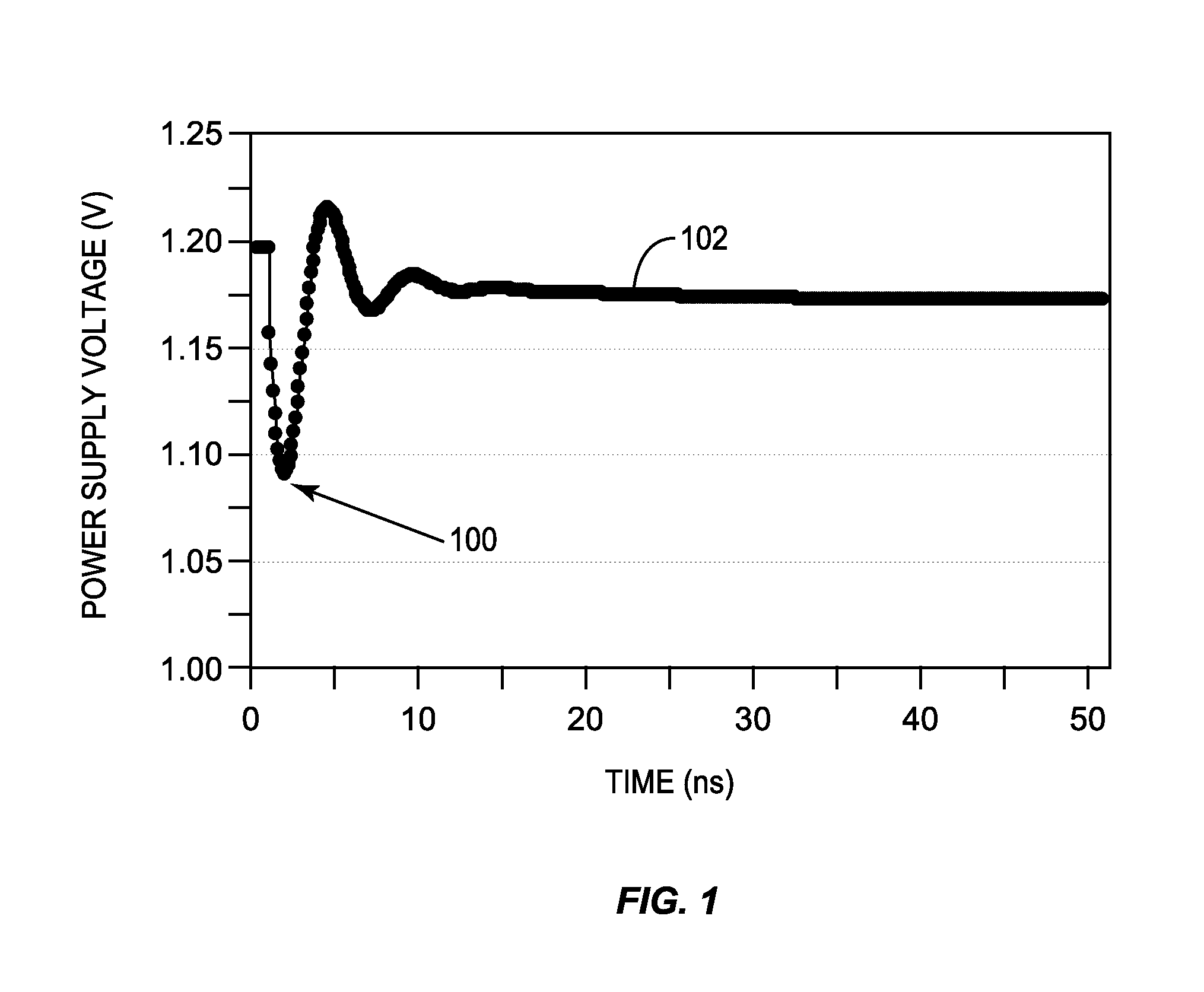
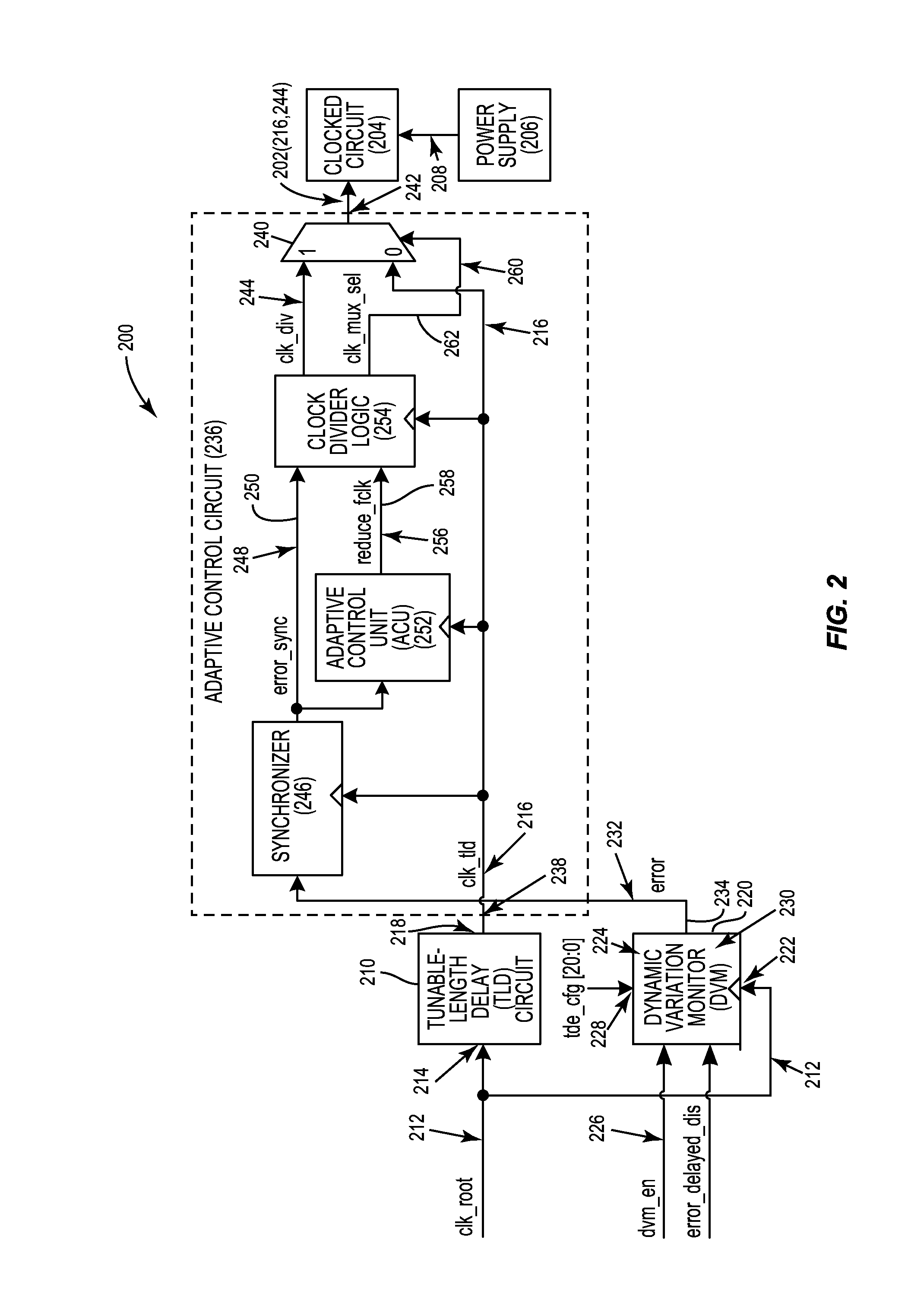
Automatic calibration circuits for operational calibration of critical-path time delays in adaptive clock distribution systems, and related methods and systems
ActiveUS9413344B2Costly overheadCostly timeContinuous to patterned pulse manipulationSingle output arrangementsTiming marginDistribution system
Automatic calibration circuits for operational calibration of critical-path time delays in adaptive clock distribution systems, and related methods and systems, are disclosed. The adaptive clock distribution system includes a tunable-length delay circuit to delay distribution of a clock signal provided to a clocked circuit, to prevent timing margin degradation of the clocked circuit after a voltage droop occurs in a power supply supplying power to the clocked circuit. The adaptive clock distribution system also includes a dynamic variation monitor to reduce frequency of the delayed clock signal provided to the clocked circuit in response to the voltage droop in the power supply, so that the clocked circuit is not clocked beyond its performance limits during a voltage droop. An automatic calibration circuit is provided in the adaptive clock distribution system to calibrate the dynamic variation monitor during operation based on operational conditions and environmental conditions of the clocked circuit.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Automatic calibration circuits for operational calibration of critical-path time delays in adaptive clock distribution systems, and related methods and systems
ActiveUS20160072491A1Reduce calibration timeReduces delay variationContinuous to patterned pulse manipulationSingle output arrangementsTiming marginTime delays
Automatic calibration circuits for operational calibration of critical-path time delays in adaptive clock distribution systems, and related methods and systems, are disclosed. The adaptive clock distribution system includes a tunable-length delay circuit to delay distribution of a clock signal provided to a clocked circuit, to prevent timing margin degradation of the clocked circuit after a voltage droop occurs in a power supply supplying power to the clocked circuit. The adaptive clock distribution system also includes a dynamic variation monitor to reduce frequency of the delayed clock signal provided to the clocked circuit in response to the voltage droop in the power supply, so that the clocked circuit is not clocked beyond its performance limits during a voltage droop. An automatic calibration circuit is provided in the adaptive clock distribution system to calibrate the dynamic variation monitor during operation based on operational conditions and environmental conditions of the clocked circuit.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Tri-level dynamic element matcher allowing reduced reference loading and DAC element reduction
ActiveUS7812753B1Reduce power consumptionTotal current dropElectric signal transmission systemsAnalogue conversionCircuit complexityNoise shaping
Owner:DIALOG SEMICONDUCTOR GMBH
Method and apparatus for providing peak detection circuitry for data communication systems
ActiveUS7679407B2Effective and low cost and lowEffective and low and low noiseTariff metering apparatusCurrent/voltage measurementElectricityCommunications system
Method and apparatus for providing a peak detection circuit comprising a diode including an input terminal and an output terminal the input terminal of the diode configured to receive an input signal, a capacitor operatively coupled to the output terminal of the diode, an output terminal operatively coupled to the capacitor and the output terminal of the diode for outputting an output signal is provided. Other equivalent switching configuration is further provided to effectively detect and compensate for a voltage droop from a power supply signal, as well as to electrically isolate the voltage droop from the system circuitry.
Owner:ABBOTT DIABETES CARE INC
Light emitting panel and light emitting apparatus having the same
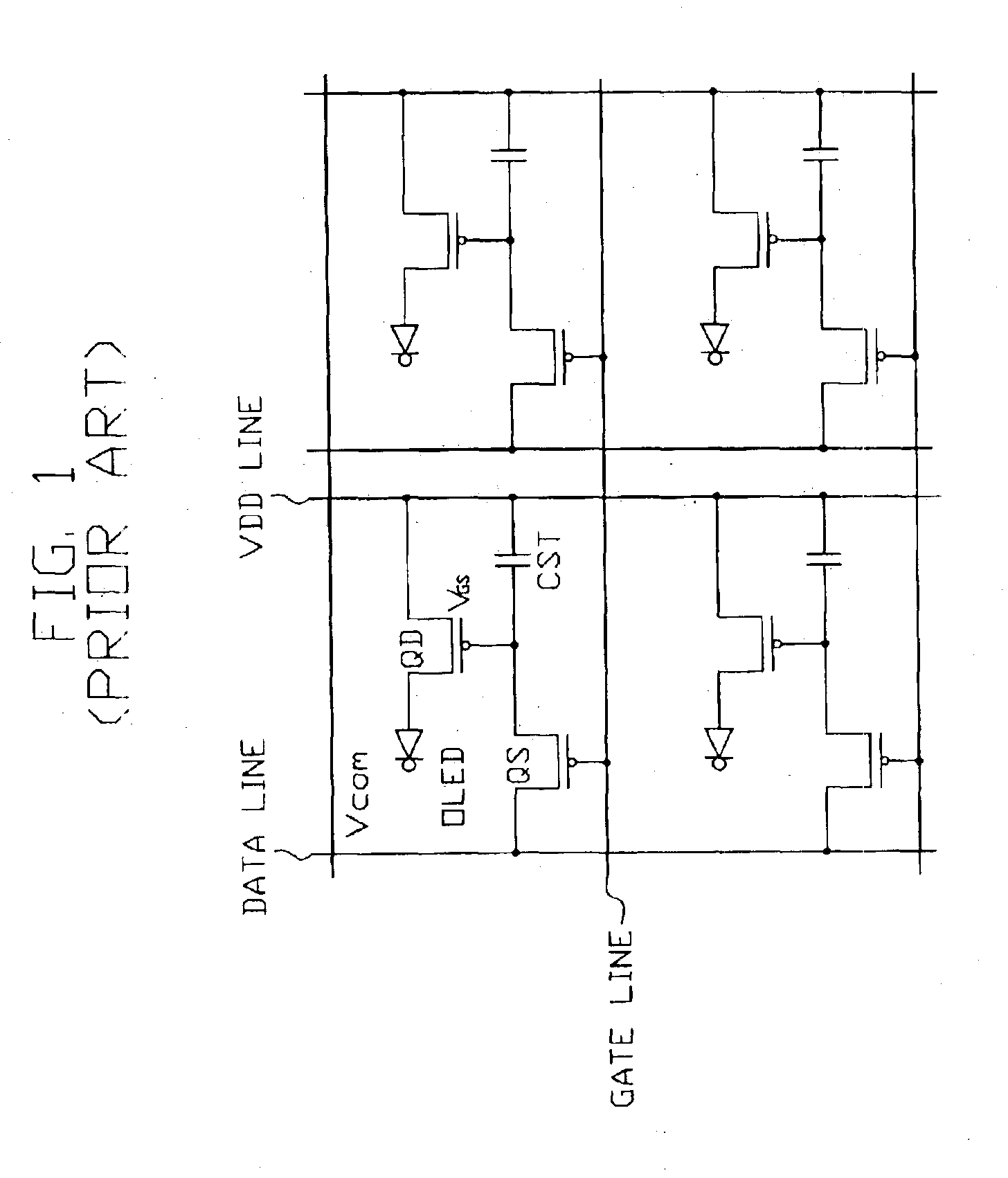
InactiveUS6903513B2Reduce voltage dropCross talk decreasesStatic indicating devicesSolid-state devicesOrganic light emitting deviceScan line
An organic light-emitting panel includes a data line, a scan line, a voltage applying line, a switching device, an organic light emitting device and a driving device. The voltage applying line satisfies a condition expressed as ¡a^V(max)n<A¡a^VdataGSn [Volt],wherein ΔVmax is a maximum voltage drop, ‘n’ is a number of pixels those are electrically connected to the voltage applying line, ‘A’ is a correction coefficient that is in a range from about 1 to about 2, ΔVdata is a voltage difference between the gray scales, and GS is a number of gray scale. According to the organic light-emitting panel, the voltage drop of the voltage applying line is reduced.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com