Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
50 results about "Synechocystis sp." patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Method for modeling production of fusion protein by utilizing trans-splicing of intein
InactiveCN101899489AShorten the lengthEasy to operatePeptide preparation methodsAlgae/lichens peptidesGeneral functionProtein target
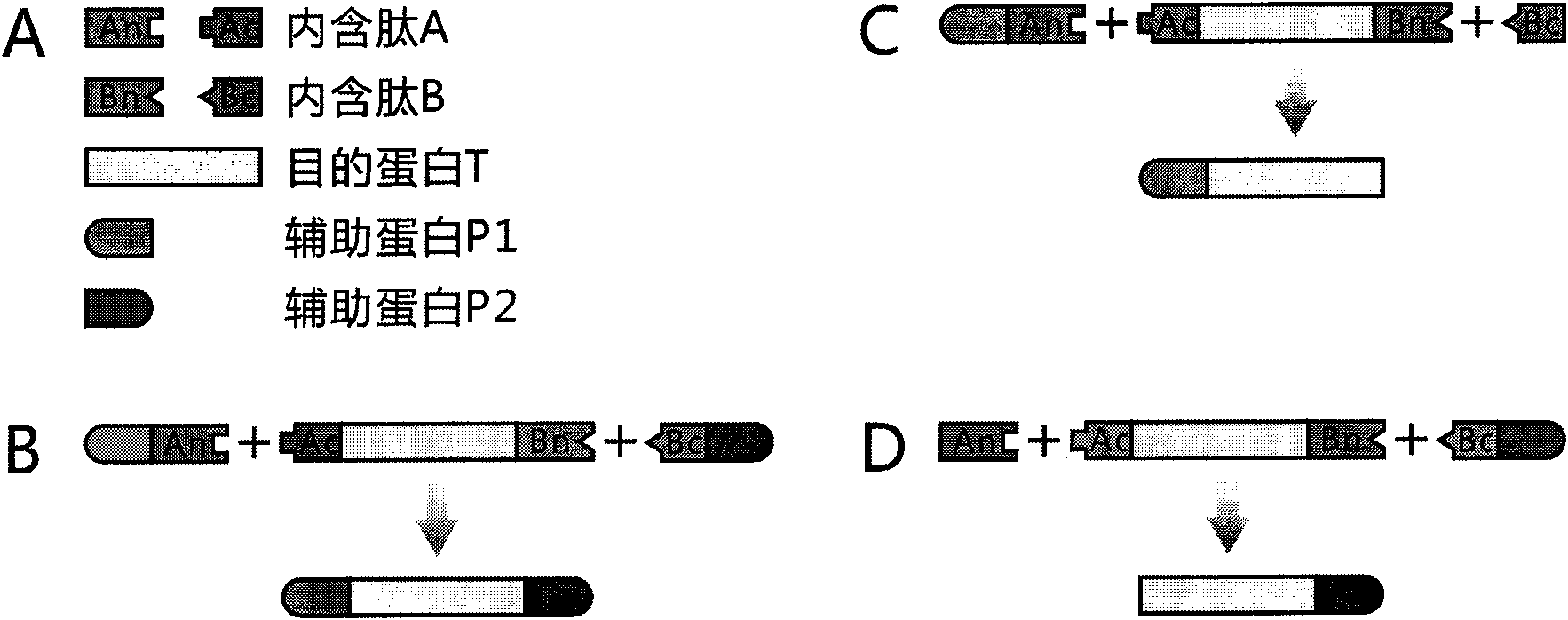
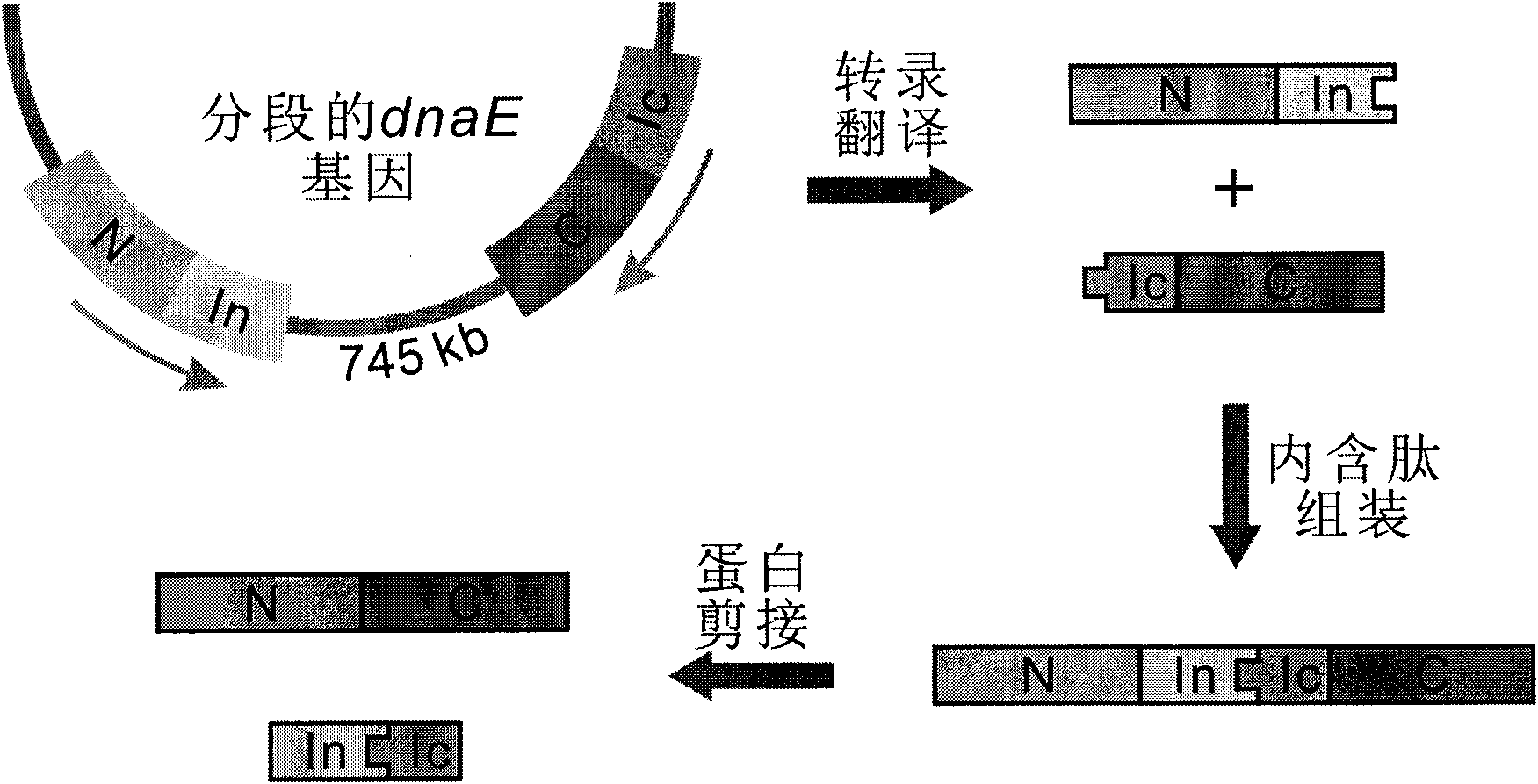
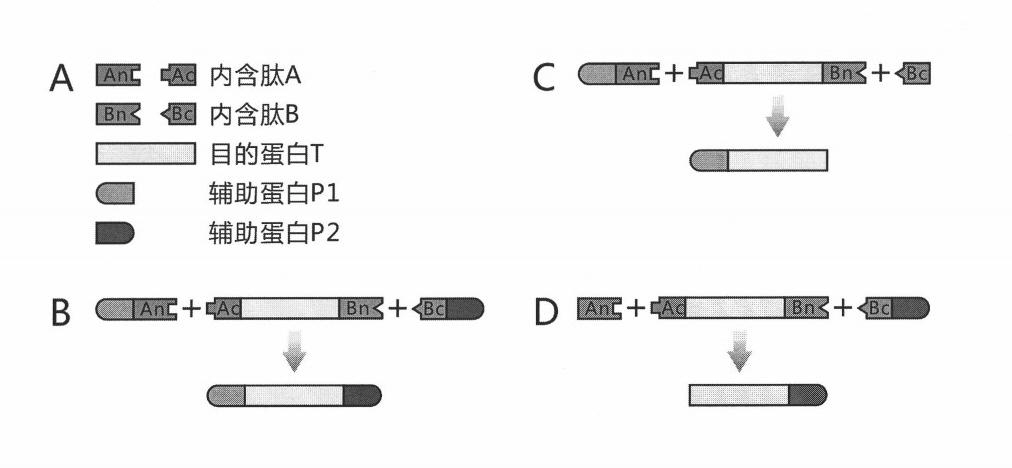
The invention discloses a method for the modeling production of fusion protein by utilizing the trans-splicing of intein, which can be used in fields, such as gene engineering, enzyme production, medicine production, food industry, farming and animal industry, and the like. In the invention, A target protein part with special biological functions and auxiliary protein with general functions are mainly connected together by utilizing the trans-splicing of the intein so as to obtain the fusion protein; the target protein T, the auxiliary protein P1 and P2, the intein A and the intein B which are mutually incompatible (such as blue algae: DnaE and DnaB of Synechocystis sp. PCC6803) are selected; the intein A and intein B are respectively decomposed into an amino terminal (N terminal) and a carboxyl terminal (C terminal), i.e. An, Ac, Bn and Bc; after different carrier systems are constructed; protein segments Ac-T-Bn, P1-An, Bc-P2, An and Bc are respectively obtained through host expression; the obtained protein segments are mixed; and the trans-splicing of the intein is carried out to generate the fusion protein P1-T-P2, P1-T or T-P2.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Process for the removal of calcium ions from the brine by marine cyanobacteria
InactiveUS6812011B2Economical simplePractical and convenientFungiBacteriaMicrobiologySynechocystis sp.
Owner:COUNCIL OF SCI & IND RES
Method and strain for remediating arsenic polluted high-salinity alkaline water through Synechocystis sp. in situ
ActiveCN110078220AImprove environmental adaptabilityLow costBacteriaWater contaminantsAlkaline waterTreatment effect
The invention discloses a method and a strain for remediating arsenic polluted high-salinity alkaline water through Synechocystis sp. in situ. The Synechocystis sp. can survive in the environment withthe highest salinity of 45 permillage, the rate of average growth biomass of 4 days is 0.104965 per day on the basis of absorbance value of OD685, the average photosystem activity Fv / Fm value of 4 days is 0.3355, the Synechocystis sp. can grow in the environment with the highest arsenic content of 50 mg / L at the average growth rate of 0.134 per day, and the average photosystem activity Fv / Fm value of 4 days is 0.3241675. The arsenic-containing high-salinity wastewater is treated by Synechocystis sp. without heterotopia, the method is convenient, low in cost and more ideal in treatment effect,the removal rate of arsenic can reach 70% or above, and secondary release is not easily caused. The Synechocystis sp. used in the method has the characteristics of high environment adaptability and capability of surviving in the severe environment. Therefore, the remediation technology is stable and environmentally friendly.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Synechococcus engineering bacterium capable of improving yield of cellulose, and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN102242065AShorten the growth cycleNo pollution problemUnicellular algaeBiofuelsDry weightSynechococcus sp.
The invention discloses a synechococcus engineering bacterium and a preparation method and application thereof. The synechococcus engineering bacterium is a cesA gene-deficient Synechococcus sp. PCC 7002 mutant; the plasmid or genome of the mutant is integrated with 7 cellulose synthesis related genes (cmcase, ccp, acsA, acsB, acsC, acsD and bglxA) of Gluconacetobacter xylinum ATCC 53582; and the 7 genes are started and expressed by a promoter PcpcBA of a cpcBA gene of Synechococcus sp. PCC 7002 or Synechocystis sp. PCC6803. The cellulose content of the engineering bacterium accounts for about 13% of the dry weight of the cell wall; and simultaneously, the cellulose produced by the synechococcus engineering bacterium has a short growth cycle and does not have the pollution problem of lignin in wood, the extraction and purification processes can be greatly simplified, and the degree of pollution to the environment can also be greatly reduced correspondingly, thus the synechococcus engineering bacterium is an ideal biological engineering bacterium for producing cellulose and is further used as a raw material for producing biological ethanol.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Synechocystis-6803 genetically engineered bacterium capable of producing 3-hydroxypropionic acid, and construction method and application thereof
InactiveCN104789516ABacteriaMicroorganism based processes3-Hydroxypropionic acidMalonyl-coenzyme A reductase
The invention discloses a synechocystis-6803 genetically engineered bacterium capable of producing 3-hydroxypropionic acid, and a construction method and application thereof. The construction method is as follows: a malonyl coenzyme A reductase gene in orange chloroflexus is cloned into synechocystis 6803; and acetylcoenzyme A carboxylase, biotin acylase and an NAD(P) transhydrogenase gene in the synechocystis 6803 are expressed. The synechocystis 6803 is transformed through a synthetic biology method to obtain the synechocystis-6803 genetically engineered bacterium capable of producing the 3-hydroxypropionic acid. The experiments prove that the final yield of the 3-HP (3-hydroxypropionic acid) of the genetically engineered bacterium is up to 837.18mg / L, which is of great theoretical and practical significances for the production of the 3-HP through photosynthetic microorganisms.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Biological mothballing system suitable for synechococcus elongatus, and construction method and application of biological mothballing system
ActiveCN110438053AAvoid Biosafety ConcernsBacteriaMicroorganism based processesPhylum CyanobacteriaSynechococcus elongatus
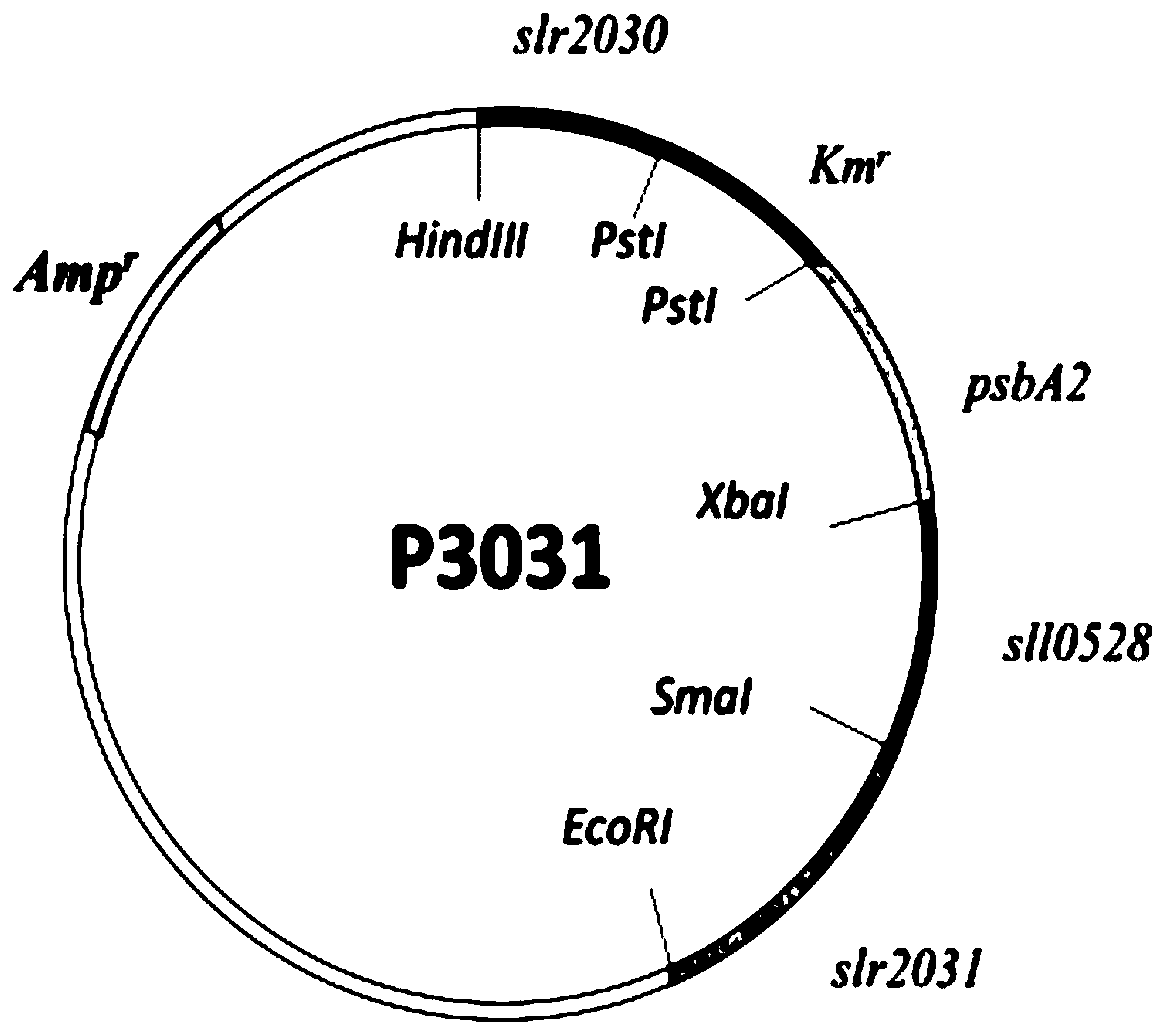
The invention discloses a biological mothballing system suitable for synechococcus elongatus, and a construction method and application of the biological mothballing system. The construction method comprises the steps that a virulent gene sepT2, an antitoxic gene sepA2 and an iron-deficiency inducible promoter PisiAB are obtained from the synechococcus elongatus 7942, and a promoter PpsbA2 is obtained from synechocystis 6803; a terminator Trbcl is obtained from integrative plasmid pBA3031 through amplification; pBR322 is taken as a carrier, the virulent gene sepT2 is expressed with the iron-deficiency inducible promoter PisiAB, and the terminator Trbcl is used for terminating transcription; and the antitoxic gene sepA2 is expressed with the promoter PpsbA2, and plasmid is constructed and transferred into the synechococcus elongatus. According to the system, the synechococcus elongatus grows normally under the non-inducing situation and rapidly dies after being induced. The important theoretical and practical significance for development and optimization of the biological mothballing system of the synechococcus elongatus is achieved, and reference is also provided for solving the bio-safety problem of other cyanobacteria.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
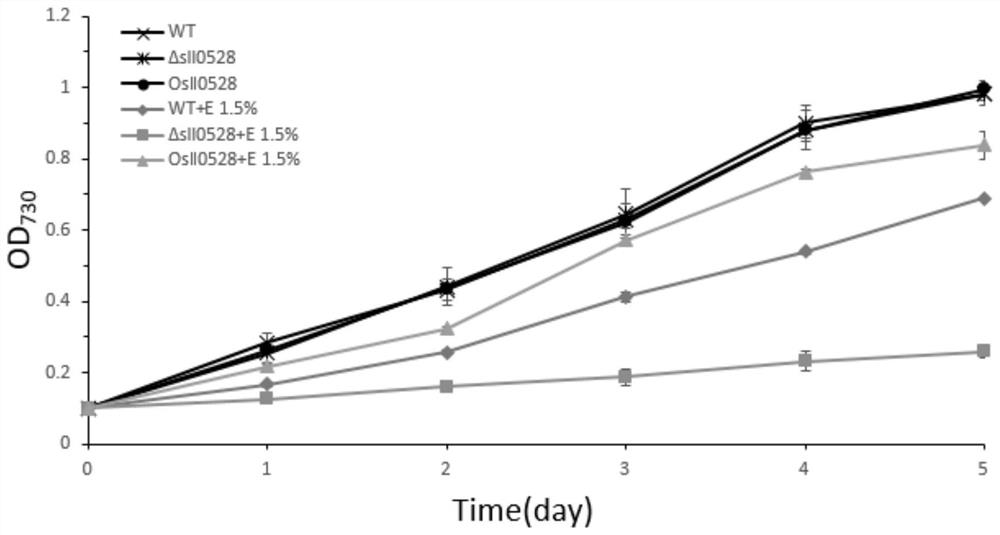
Application of sll0528 genes to improvement of ethanol tolerance of synechocystis PCC6803
The invention discloses an application of sll0528 genes to improvement of ethanol tolerance of synechocystis PCC6803, and belongs to the field of industrial microorganisms. Through a homologous reorganization method, the sll0528 genes in the synechocystis PCC6803 are knocked out and overexpressed, so that a synechocystis PCC6803 algae strain Osll0528 with notable improvement of ethanol tolerance is obtained. In a BG11 culture medium of ethanol of different concentrations (1.5%, 2.0%, 2.5% and 3.0%v / v), the growth state of the algae strain is obviously higher than that of wild algae strains. The obtained algae strains being tolerant to ethanol have important theory and actual significance in genetic engineering bacteria for producing ethanol as fuel, and have broad application prospects.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Synechocystis PCC6803 alga for achieving remarkable improvement of tolerance to ethyl alcohol and construction method thereof
ActiveCN106086055APromote growthHigh ethanol toleranceBacteriaMicroorganism based processesMicroorganismAlcohol
The invention discloses synechocystis PCC6803 alga for achieving remarkable improvement of tolerance to ethyl alcohol and a construction method thereof and belongs to the field of industrial microorganisms. Sll0687 genes in synechocystis PCC6803 are knocked out through a homologous recombination method, and the synechocystis PCC6803 alga ISm5 for remarkably improving tolerance to ethyl alcohol is obtained. Under stress of 1.5% (v / v) ethyl alcohol, the growth state of the alga is obviously superior to that of wild alga. The obtained ethyl-alcohol-tolerant alga has important theoretical and practical significance for constructing genetically engineered bacteria for producing fuel ethanol and has wide application prospects.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Mutant strain of synechocystis PCC6803 and application thereof
Belonging to the field of industrial microorganisms, the invention in particular relates to a synechocystis PCC6803 mutant strain with significantly improved ethanol tolerance and application thereof. The ethanol tolerance related gene is slr0599, and the base sequence is shown as SEQ ID No.7. The mutant strain PCC 6803Deltaslr0599 is preserved on August 4, 2017 in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center (CGMCC) located at No.3, 1st yard, Beichen west road, Chaoyang District, Beijing, the preservation number is CGMCC14333, and the strain is named as Synechocystis sp. by taxonomy. The synechocystis mutant strain is an ethanol tolerant mutant strain, and under 1.5% (v / v) ethanol stress, the growth state of the algal strain is obviously superior to that of wild algal strains. The ethanol tolerant algal strain obtained by the invention has important application value and referential significance for production of biofuel ethanol with synechocystis, and has wide application prospect.
Owner:YANTAI INST OF COASTAL ZONE RES CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
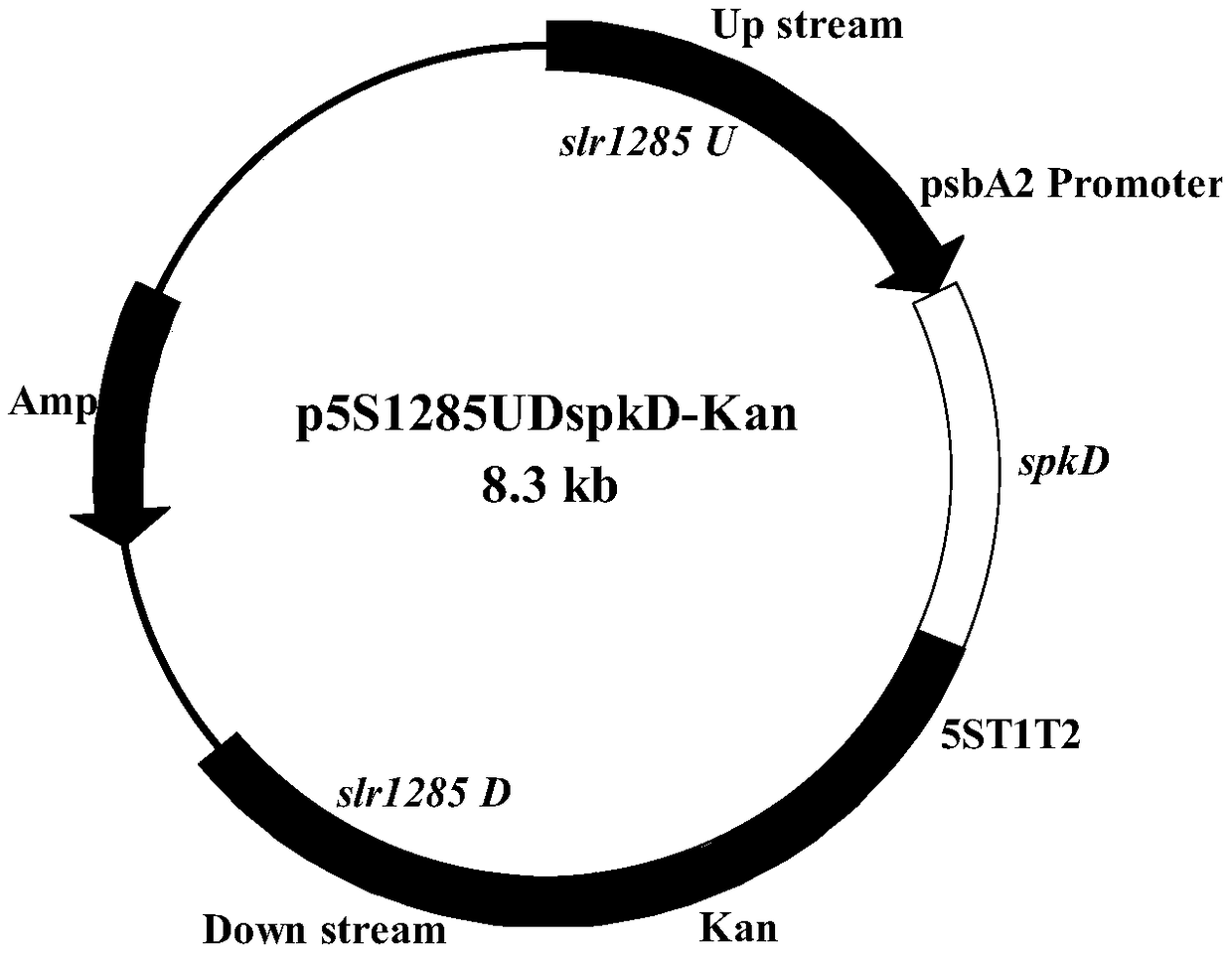
Application of gene spkD for regulating growth rate of Synechocystis
ActiveCN109234300AIncrease growth rateIncrease specific growth rateBacteria peptidesFermentationWild typeRecovery stage
The invention relates to the application of a gene spkD for regulating growth rate of Synechocystis. Application of the gene spkD regulating the growth rate of Synechocystis in increasing the growth rate of Synechocystis and / or restoring the growth rate after light stress; The nucleotide sequence of the gene spkD is shown in SEQ ID NO. 1. The invention discloses for the first time the important role of spkD gene of Microcystis aeruginosa PCC7806 in improving the growth rate of Synechocystis. The average specific growth rate of the transgenic Synechocystis sp. Increased by 13.97% compared withthe wild type in 6 days under normal culture conditions, However, both mutants overexpressing spkD gene and wild type exhibited overcompensatory growth performance in the light recovery stage (6 daysculture stage) after light limitation stress, and the specific growth rate of mutants increased by 7.13% compared with wild type in the overcompensatory growth stage.
Owner:TIANJIN AGRICULTURE COLLEGE +1
Genetically engineered algae strain of synechocystisPCC6803 producing cellulase and construction method thereof
InactiveCN110684704AA method for realizing the expression of exogenous cellulaseIncrease enzyme activityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyMicroorganism
The invention discloses a genetically engineered algae strain of synechocystisPCC6803 producing cellulase and a construction method thereof, and belongs to the field of industrial microorganisms. According to the genetically engineered algae strain of synechocystisPCC6803 producing cellulase and the construction method thereof, through the method of homologous recombination, an exogenous cellulaseexcision enzyme CBHII gene is integrated into the genome of the synechocyst is PCC6803 to obtain an algae strain SPSNCII of the synechocystisPCC6803.Under the same culture condition, the activity ofthe produced cellulase is significantly better than that of the wild synechocystis strain. According to the genetically engineered algae strain of the synechocystisPCC6803 producing the cellulase andthe construction method thereof, a novel way of obtaining the cellulase by using inorganic salt and carbon dioxide through photosynthetic organism-synechocystis is opened up, the genetically engineered algae strain of the synechocystisPCC6803 producing the cellulase and the construction method thereof are of great significance to reducing the consumption of an organic carbon source in the processof enzyme production and reducing the release of the greenhouse gases in the process of producing the cellulase, and the application prospect is broad.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV OF SCI & TECH +1
Chromone-containing benzoyl hydrazone compound with inhibiting effect on growth of synechocystis PCC6803 and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN111548338AEnhanced inhibitory effectHigh activityBiocideOrganic chemistryCarboxyl radicalChromone
The invention provides a chromone-containing benzoyl hydrazone compound with an inhibiting effect on growth of synechocystis PCC6803 and a preparation method thereof. The molecular structure of the compound is shown as a formula I, wherein R1 is selected from hydrogen, halogen, nitro, hydroxyl, carboxyl and C1-C4 alkyl; R2 is selected from hydrogen, bromine, hydroxyl or nitro; R3 is selected fromhydrogen or hydroxyl; R4 is selected from hydrogen, halogen, nitro, trifluoromethyl or hydroxyl; and R5 is selected from hydrogen or hydroxyl. The invention further provides a preparation method of the compound. According to the preparation method, benzoyl hydrazine or a substituent thereof reacts with 3-formyl chromone or a substituent thereof in an ethanol environment containing acetic acid to generate the compound. The compound has a good effect on inhibiting the growth of synechocystis PCC6803, the EC50 value is within a range of 0.8-29.8 [mu]M, and the compound can be used for preparing related algistat products.
Owner:JIANGXI SCI & TECH NORMAL UNIV
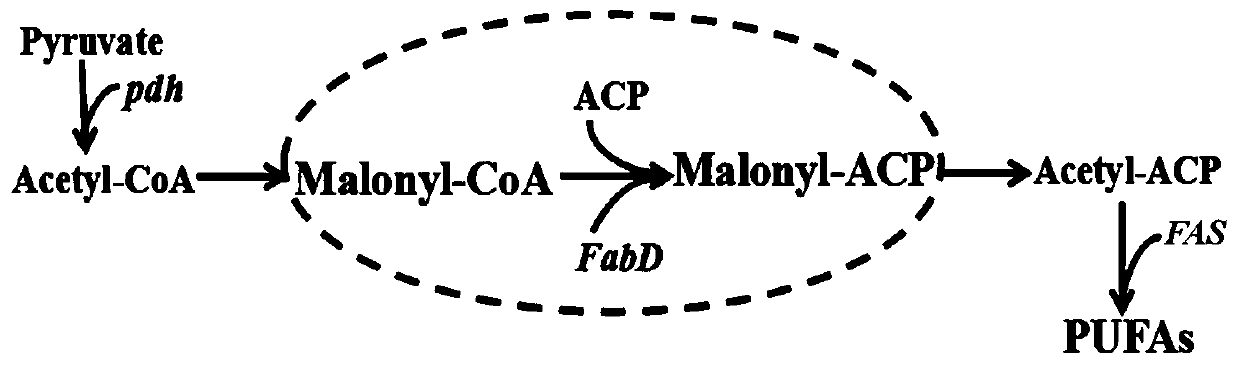
Application of ssl2084 gene in synthesis of medium and long chain fatty acids
ActiveCN110950941AIncrease contentUnicellular algaeMicroorganism based processesLong chain fatty acidProteinogenic amino acid
The invention relates to application of ssl2084 gene in synthesis of medium and long chain fatty acids. The ssl2084 is a protein capable of promoting synthesis of the medium and long chain fatty acidsin synechocystis, and has an amino acid sequence shown as SEQ ID NO. 2. The invention further relates to application of the ssl2084 gene in synthesis of medium and long chain saturated fatty acids ofthe synechocystis. For the first time, the invention discloses an important role of the ssl2084 gene of the synechocystis sp. PCC 6803 in synthesis of the medium and long chain saturated fatty acidsat low temperature. By increasing expression of the ssl2084 gene in the synechocystis sp. PCC 6803 by utilizing an overexpression method, contents of C12:0, C16:0 and C18:0 in mutant strains are significantly increased; and moreover, the contents of the C12:0, the C16:0 and the C18:0 in the mutant strains are further increased after low-temperature treatment, so that the recognition that it is easy to synthesize unsaturated fatty acids at low temperature in the field is changed.
Owner:BIOTECH RES CENT SHANDONG ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
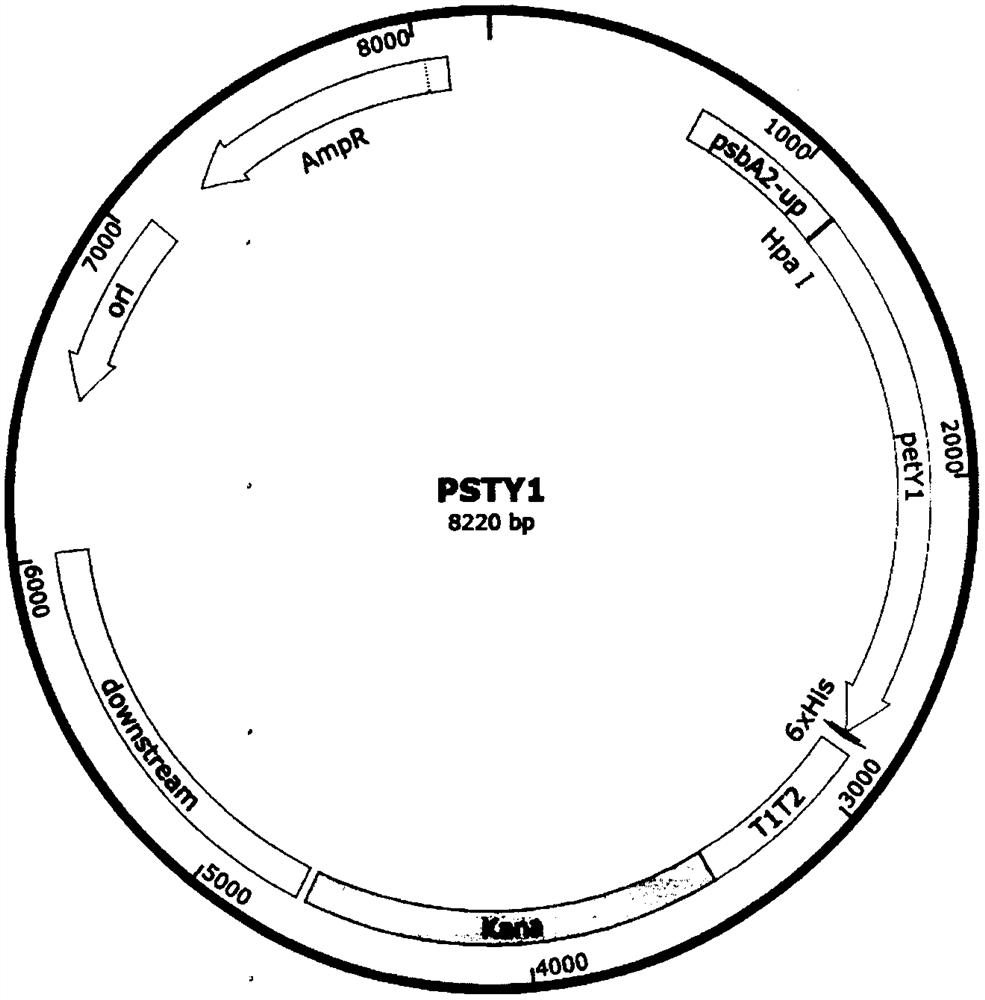
Synechocystis PCC6803 strain for producing alkaline pectate lyase and construction method of synechocystis PCC6803 strain
The invention discloses a synechocystis PCC6803 strain for producing alkaline pectate lyase and a construction method of the synechocystis PCC6803 strain, and belongs to the field of industrial microorganisms. An alkaline pectate lyase gene petyl derived from Klebsiella sp.Y1 is recombined into a synechocystis PCC6803 genome through a homologous recombination method, and a synechocystis PCC6803 genetic engineering strain PSY1 for producing the alkaline pectate lyase petyl is constructed, so that a method for producing pectinase by utilizing photosynthetic organisms is realized, a new way for producing the pectinase by using inorganic salt and carbon dioxide is obtained, and the consumption of energy (mainly carbon source) in a biomass conversion process is reduced.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
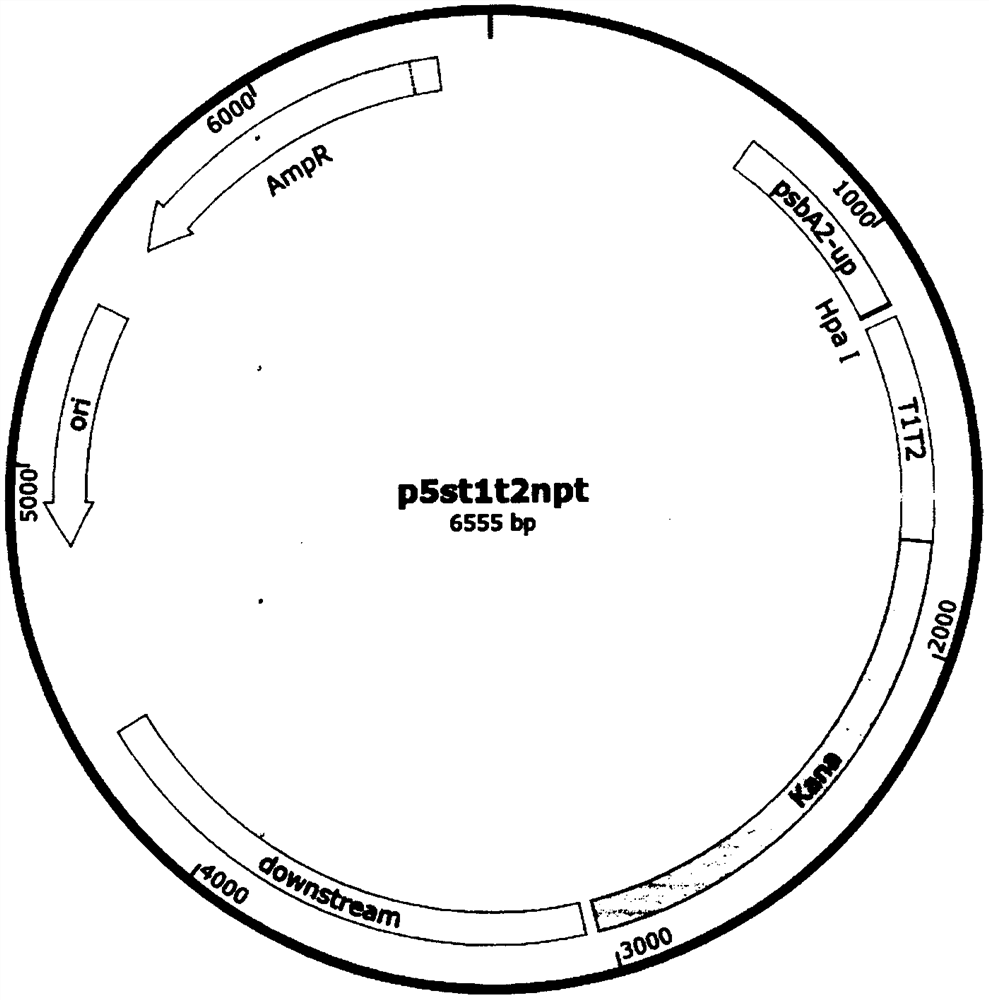
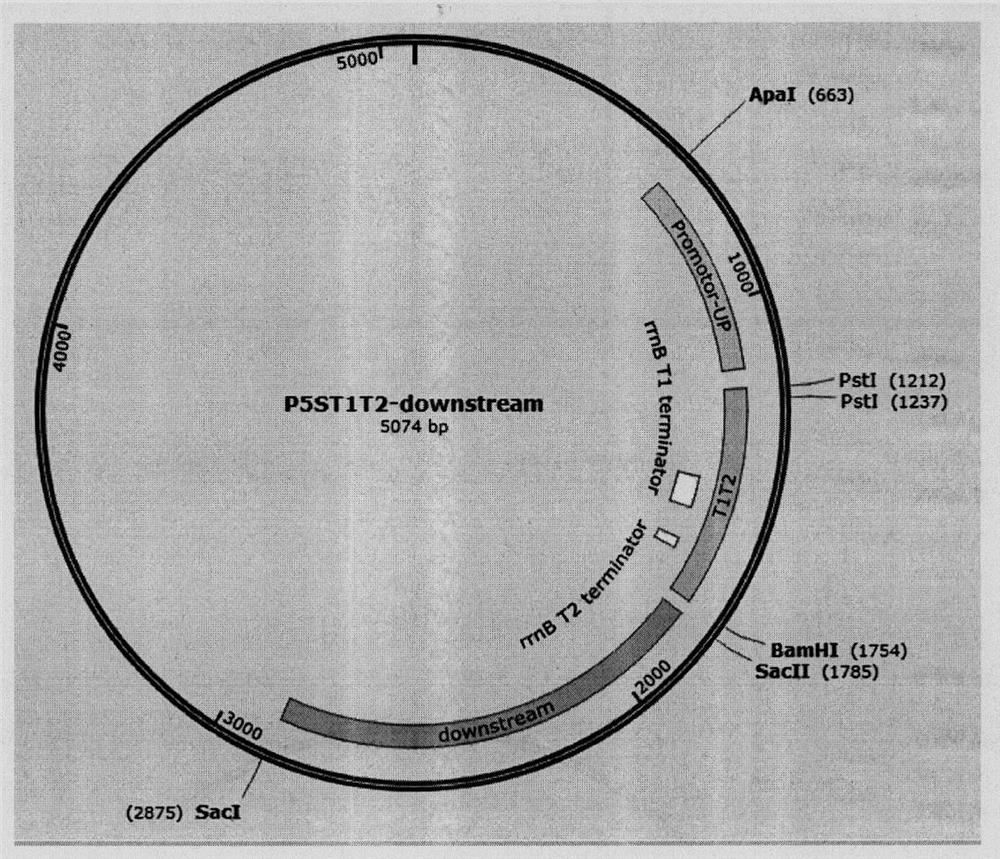
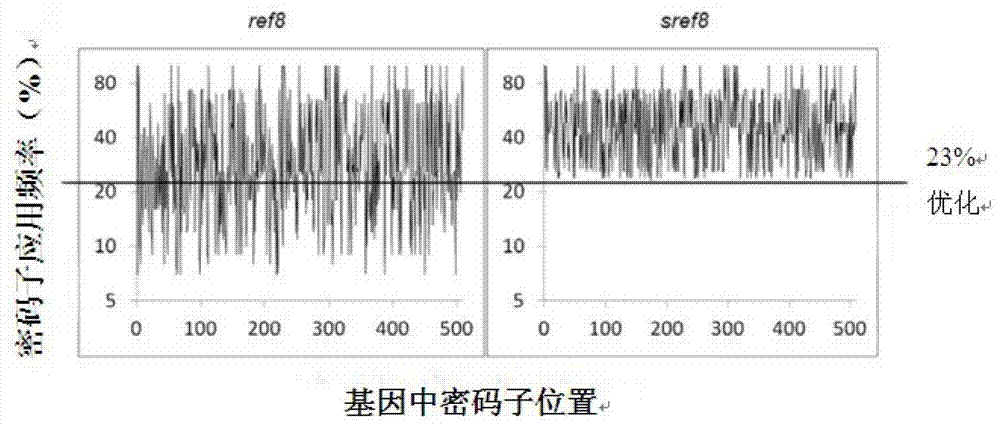
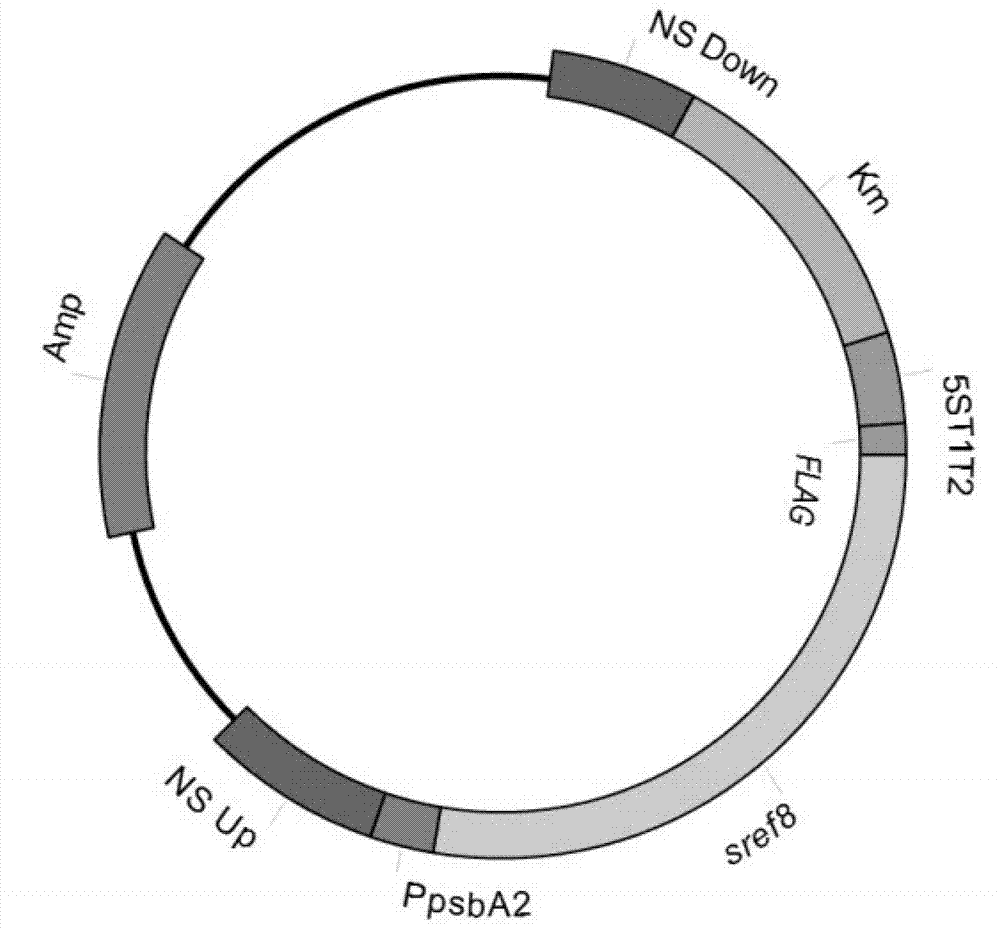
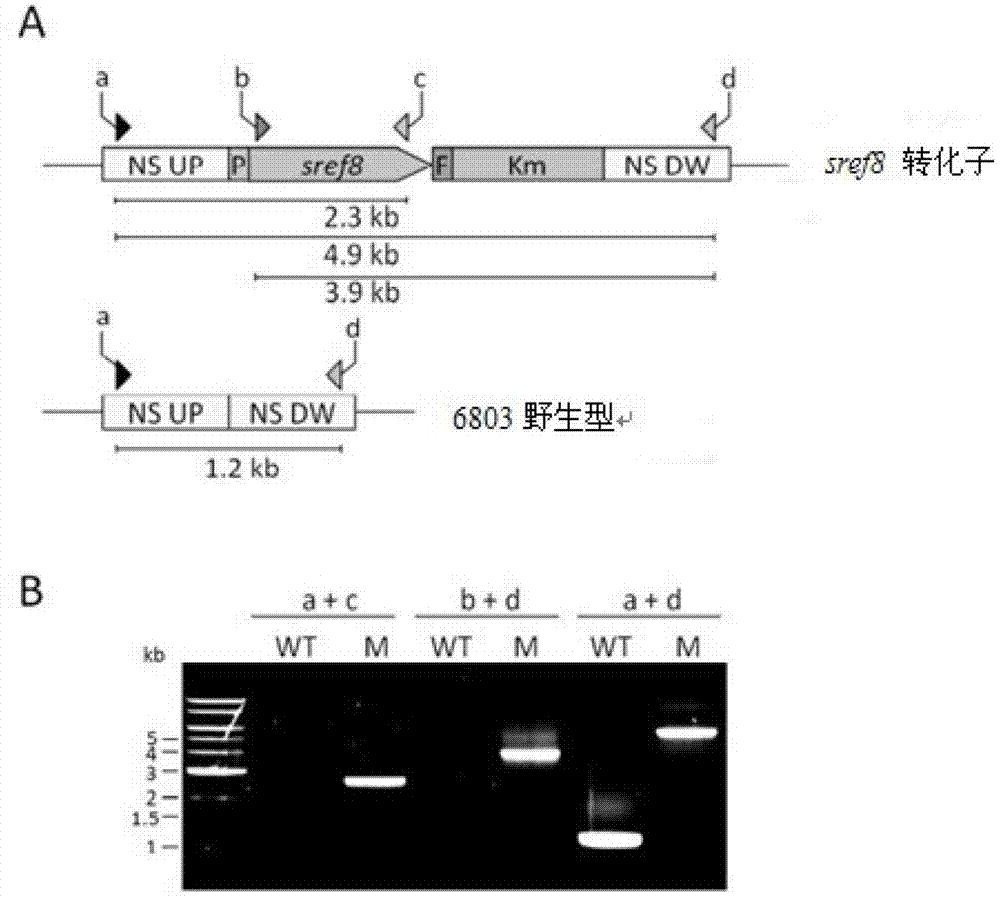
Universal plasmid, construction method of universal plasmid and novel method for expressing exogenous genes by synechocystis
PendingCN112646830ARealize new method of photosynthetic organism productionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesSynechocystis sp.Genetic engineering
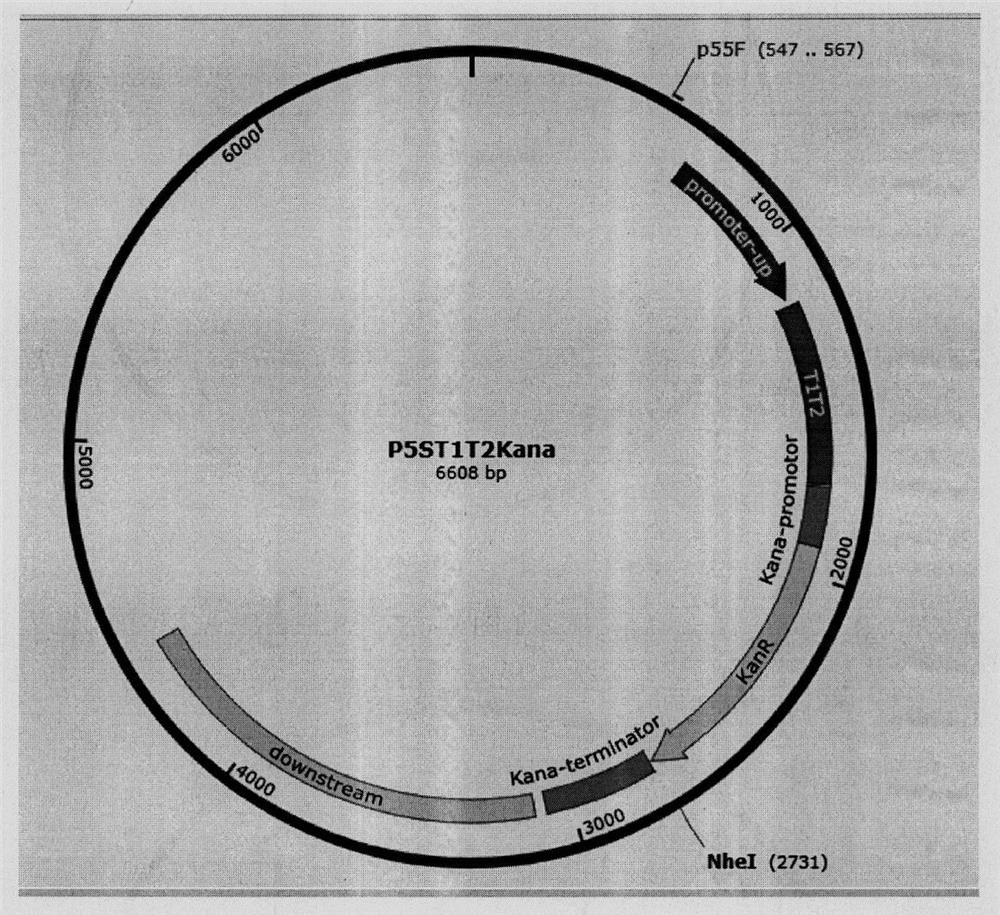
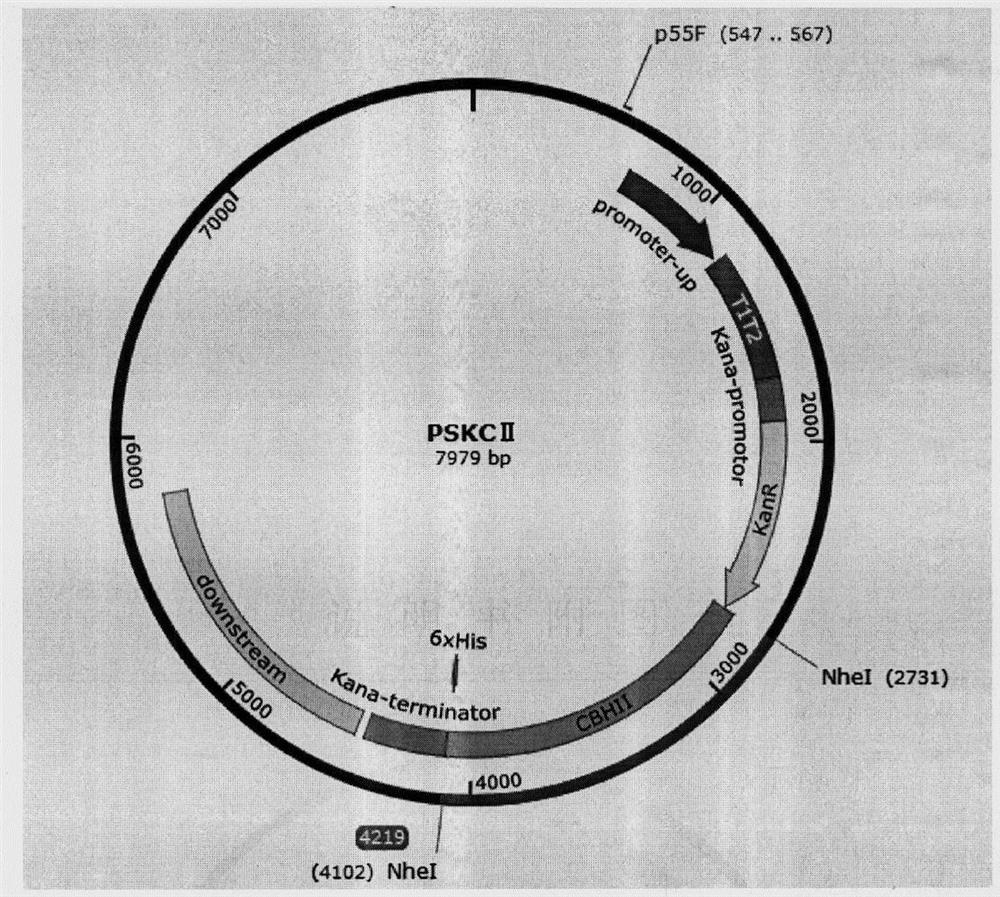
According to the invention, a universal plasmid for promoting expression of a target gene in synechocystis PCC 6803 by using a Kana resistance gene promoter is constructed through a genetic engineering method; on the basis that the plasmid uses a psbA2 gene initiation codon ATG first 510 bp fragment of the synechocystis PCC 6803 as a homologous recombination upstream arm and a psbA2 gene ORF fragment as a downstream arm, the target gene is inserted between the Kana resistance gene and a terminator to obtain the universal plasmid P5ST1T2Kana; and the Kana resistance gene promoter is used for promoting the tandem expression of the kana resistance gene and the target gene in the synechocystis. Meanwhile, a synechocystis PCC 6803 engineering algal strain PSKC II capable of promoting the tandem expression of the Kana resistance gene and a cellulase CBHII gene by the Kana gene promoter is constructed by taking the universal plasmid as a vector, and a new means of heterologous expression of cellulase in the synechocystis is realized.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
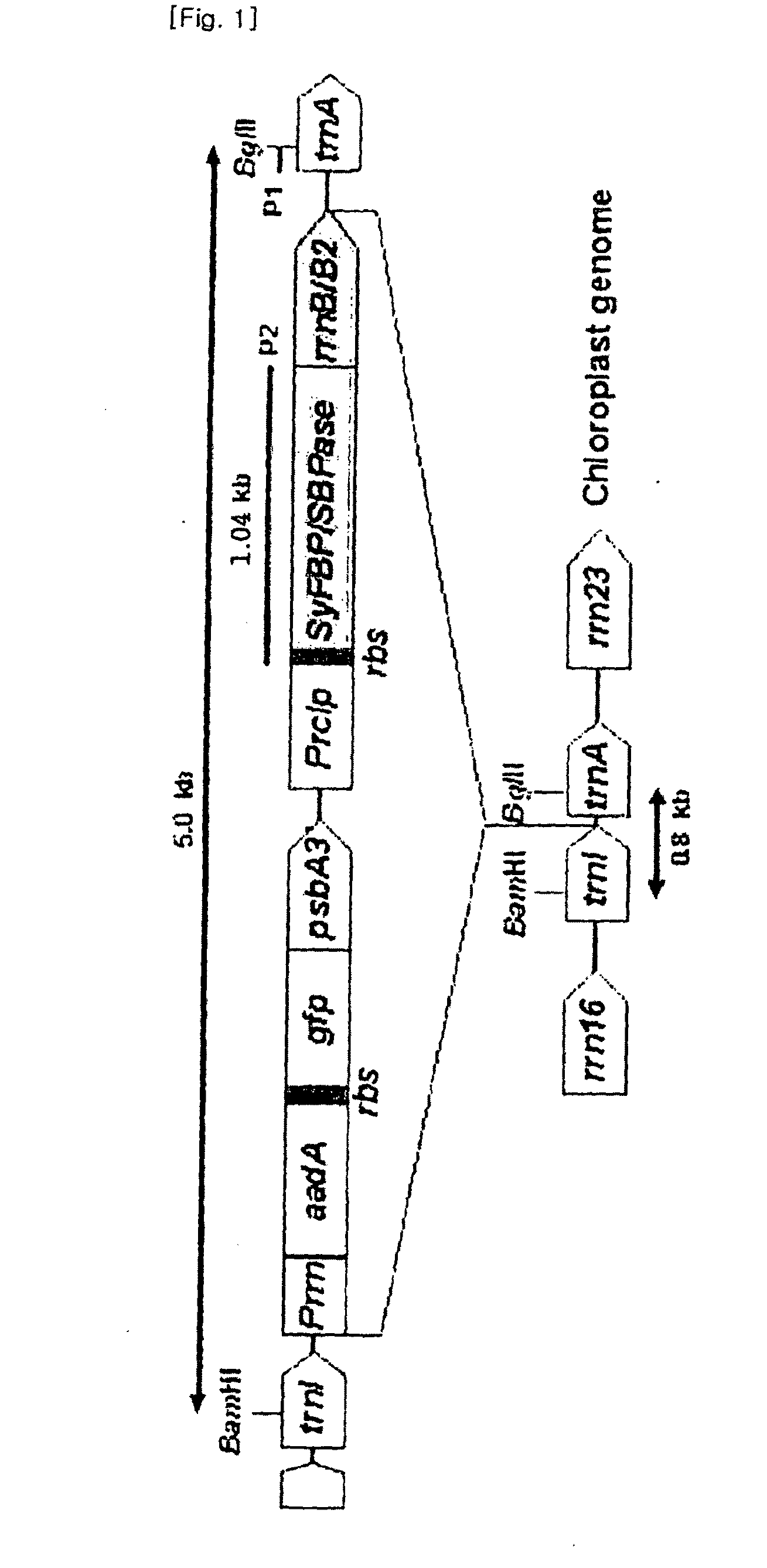
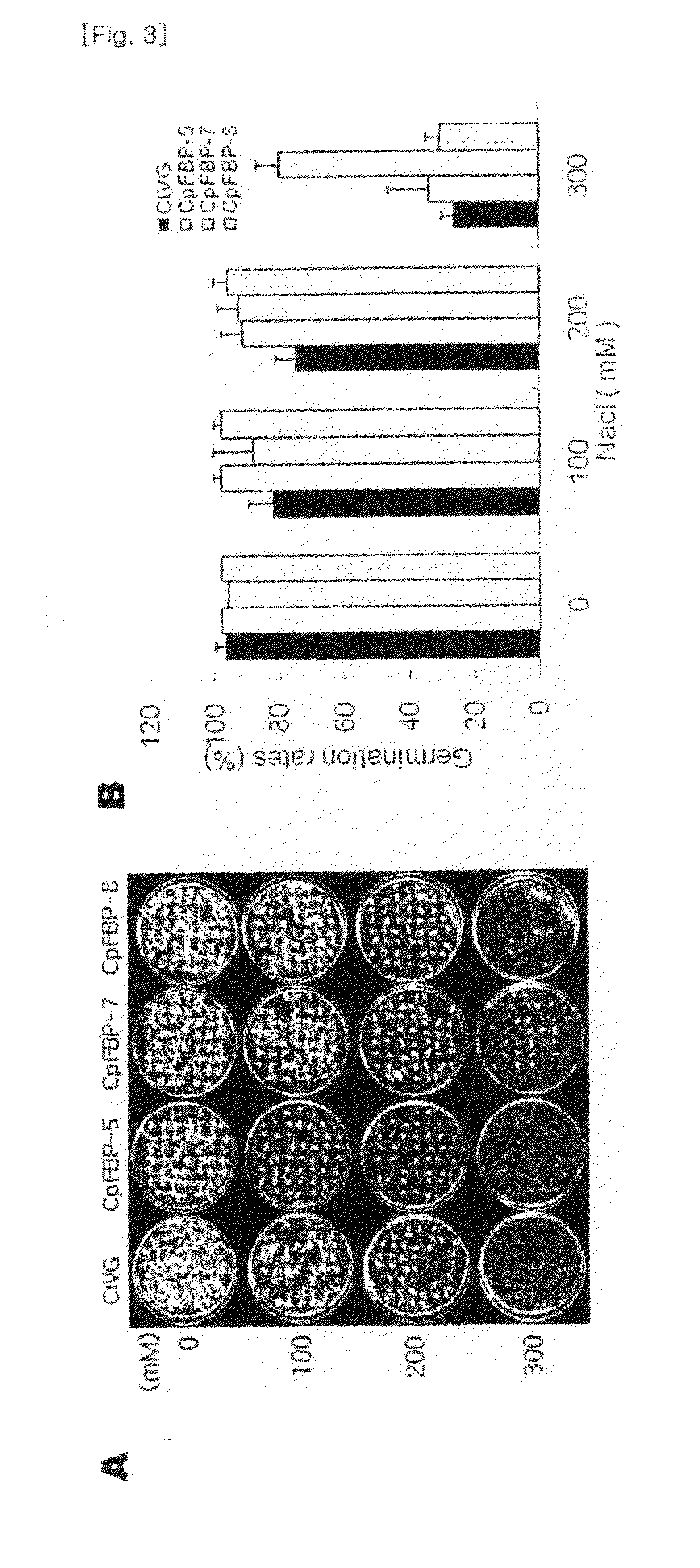
Method for increasing salt tolerance of plant by overexpressing syfbp/sbpase gene isolated from synechocystis and plant produced by the same
The present invention relates to a method for increasing salt tolerance of a plant by overexpressing SyFBP / SBPase gene isolated from Synechocystis, a plant and seed having increased salt tolerance ability that is produced by the same method, a composition for increasing salt tolerance of a plant in which gene encoding SyFBP / SBPase is comprised, and a recombinant vector for the transformation of chloroplasts in which gene encoding SyFBP / SBPase is comprised.
Owner:KOREA RES INST OF BIOSCI & BIOTECH
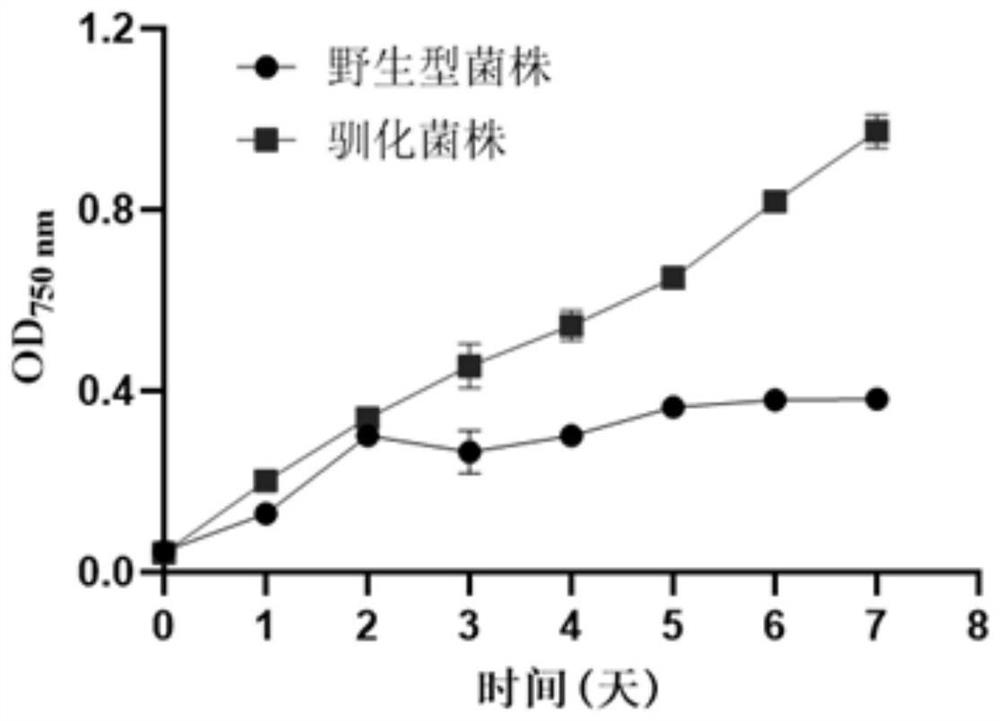
Domestication method of synechocystis domestication strain capable of tolerating high light intensity
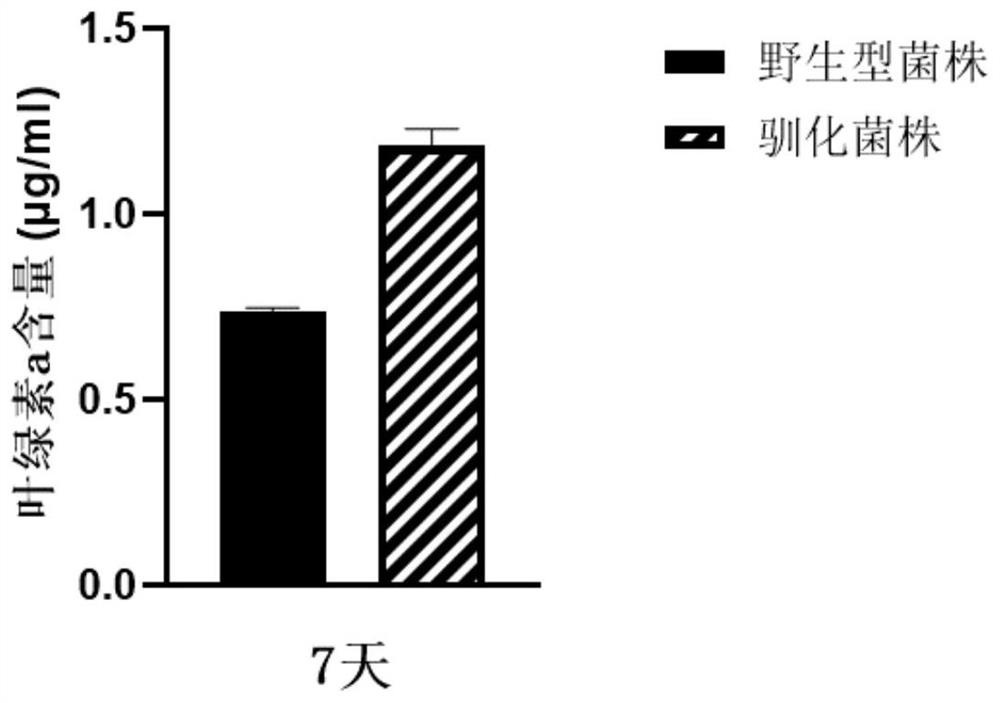
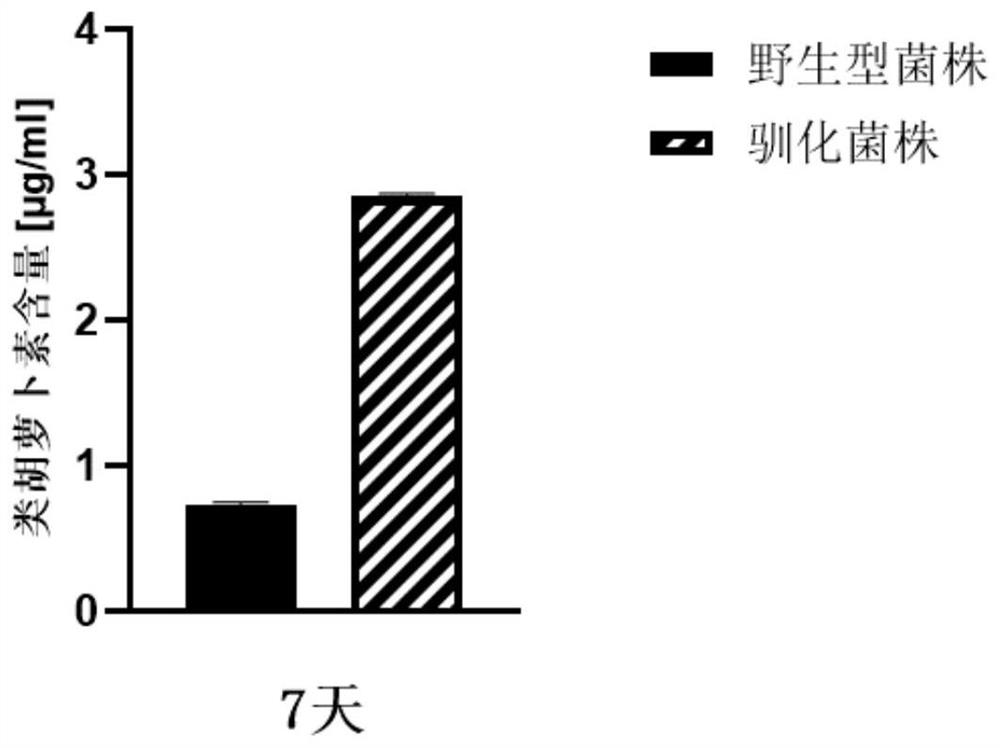
The invention discloses a directional domestication method for obtaining a high-light-intensity-tolerant synechocystis strain. The method comprises the following steps: determining the initial sensitive illumination intensity of a wild synechocystis strain; inoculating synechocystis wild-type bacterial liquid into the culture medium to enable OD750nm measured by a microplate reader to be 0.04, and culturing to a plateau phase under initial sensitive illumination intensity; transferring the synechocystis into a culture medium, continuously domesticating, and continuously subculturing until the OD750nm measured by a microplate reader at a plateau phase of the synechocystis is greater than or equal to 0.8; the illumination condition is gradually improved, domestication is continued, continuous subculture is carried out until the illumination intensity reaches 2000 [mu] mol photon m <-2 > s <-1 >, and it is determined that OD750nm of synechocystis is larger than or equal to 0.8 through a microplate reader of the synechocystis in the platform phase. The domesticated strain obtained through the method can grow for 7 days under the highlight condition of 2000 [mu] mol photon m <-2 > s <-1 >, and the content of OD750nm, chlorophyll a, carotenoid, dry weight and glycogen is higher than that of a wild strain.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Photo-enhanced chemical algaecide
InactiveCN109179563AWater/sewage treatment by irradiationWater/sewage treatment using germicide/oligodynamic-processSynechocystis sp.Anabaena
The invention discloses a photo-enhanced chemical algaecide. The photo-enhanced chemical algaecide is obtained by dissolving an allelopathic substance in dimethyl sulfoxide, and has a remarkable effect under an illumination condition, wherein the allelopathic substance is one of or a mixture of p-hydroxybenzoic acid and p-hydroxybenzaldehyde, and the concentration range of the allelopathic substance in the dimethyl sulfoxide is 0.2-50%. When the photo-enhanced chemical algaecide is applied to removal of algae in water, the algae in the water are bleached and killed under a condition of naturaloutdoor illumination or irradiation with an artificial light source having a light intensity of 500-30000 Lux by adding 0.05-10 kg to every ton of an alga solution. The photo-enhanced chemical algaecide can effectively aim at Synechocystis sp., Dunaliella salina, Nostoc flagelliforme, chlorella, Anabaena, Microcystis aeruginosa and various other algae in water, has the advantages of rapid alga removal, long acting time, elimination of the advantages of the algaecide dependence, no pollution, odorlessness and no pollution to the environment, and is a green algaecide.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
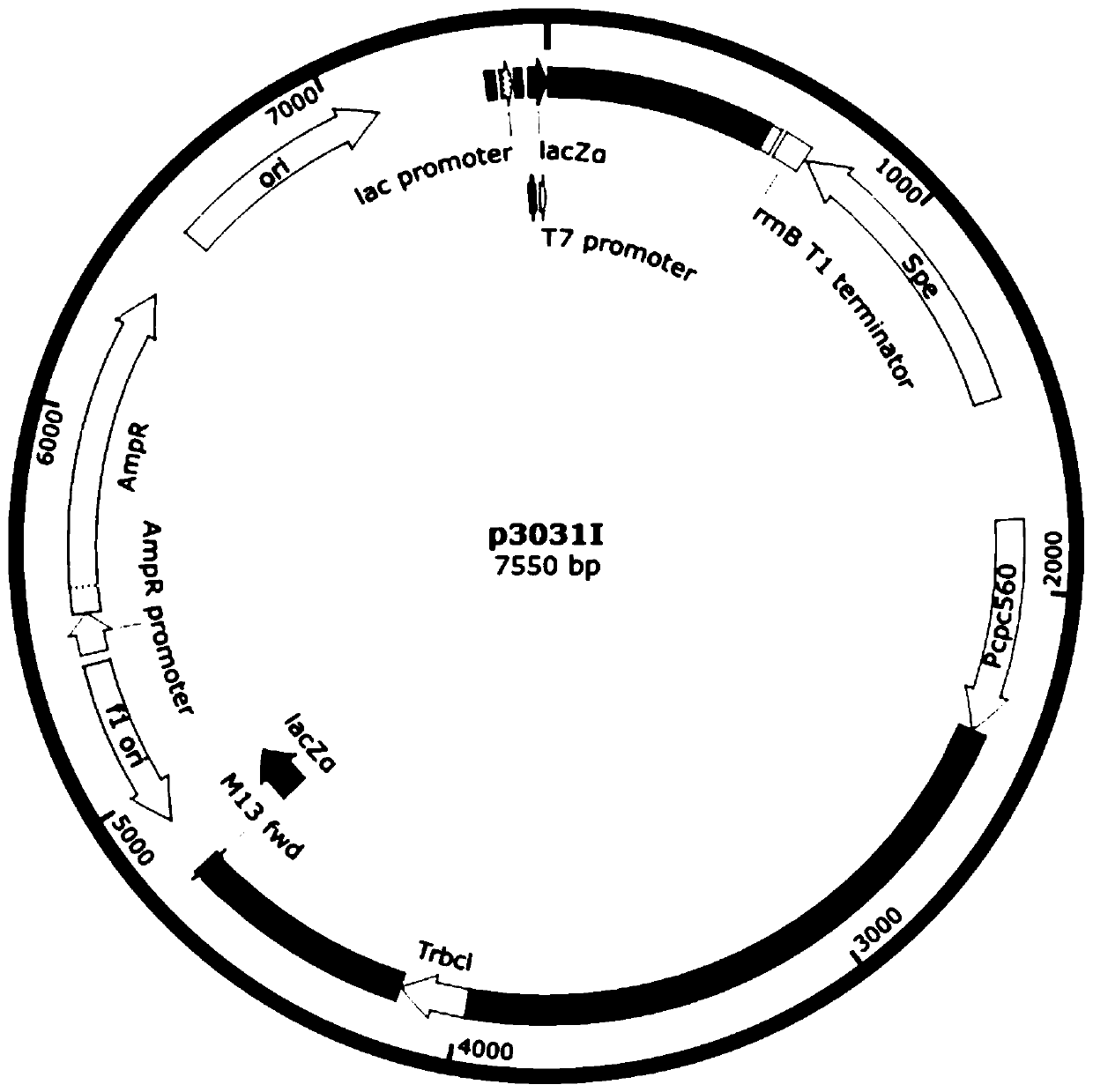
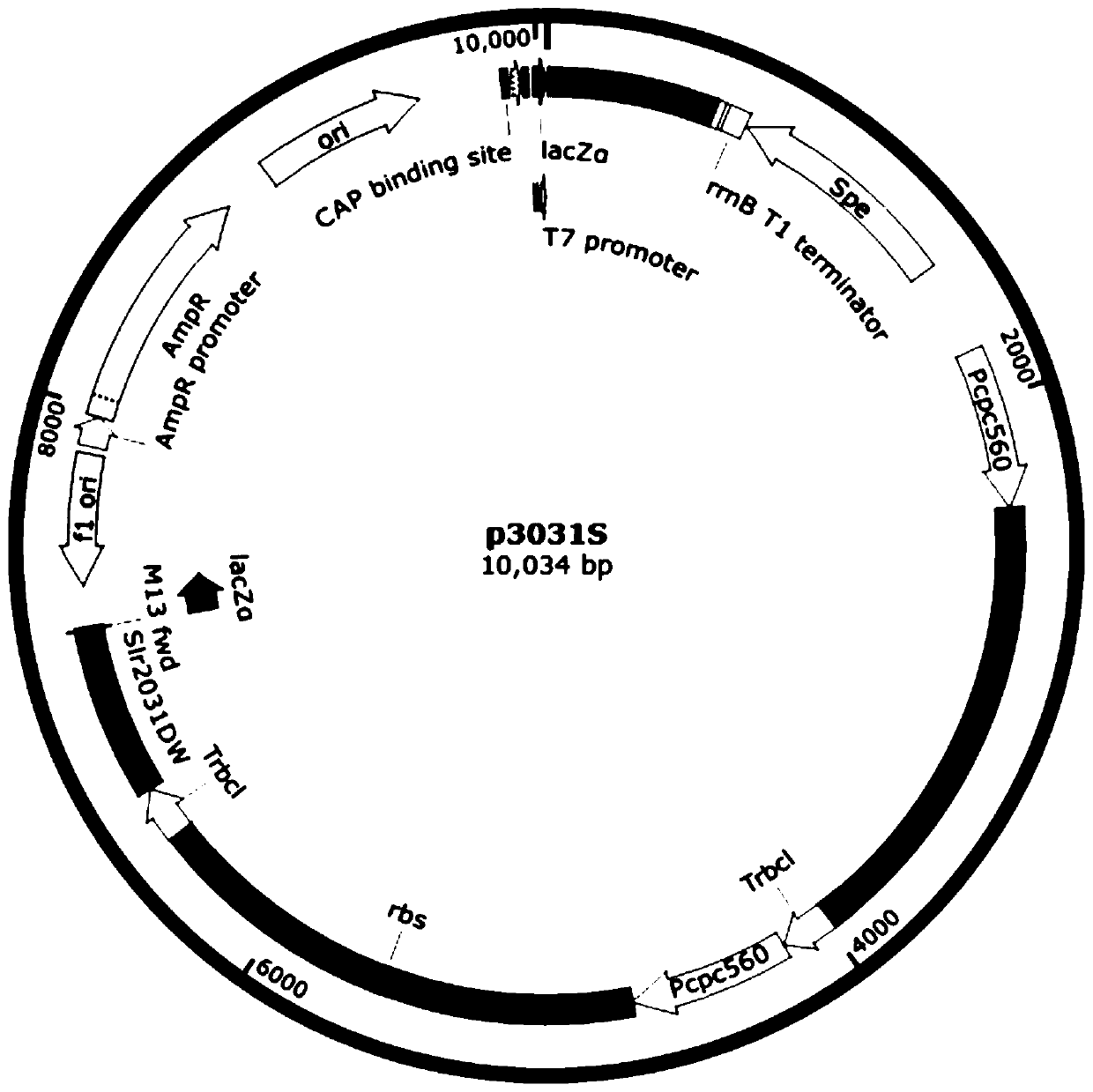
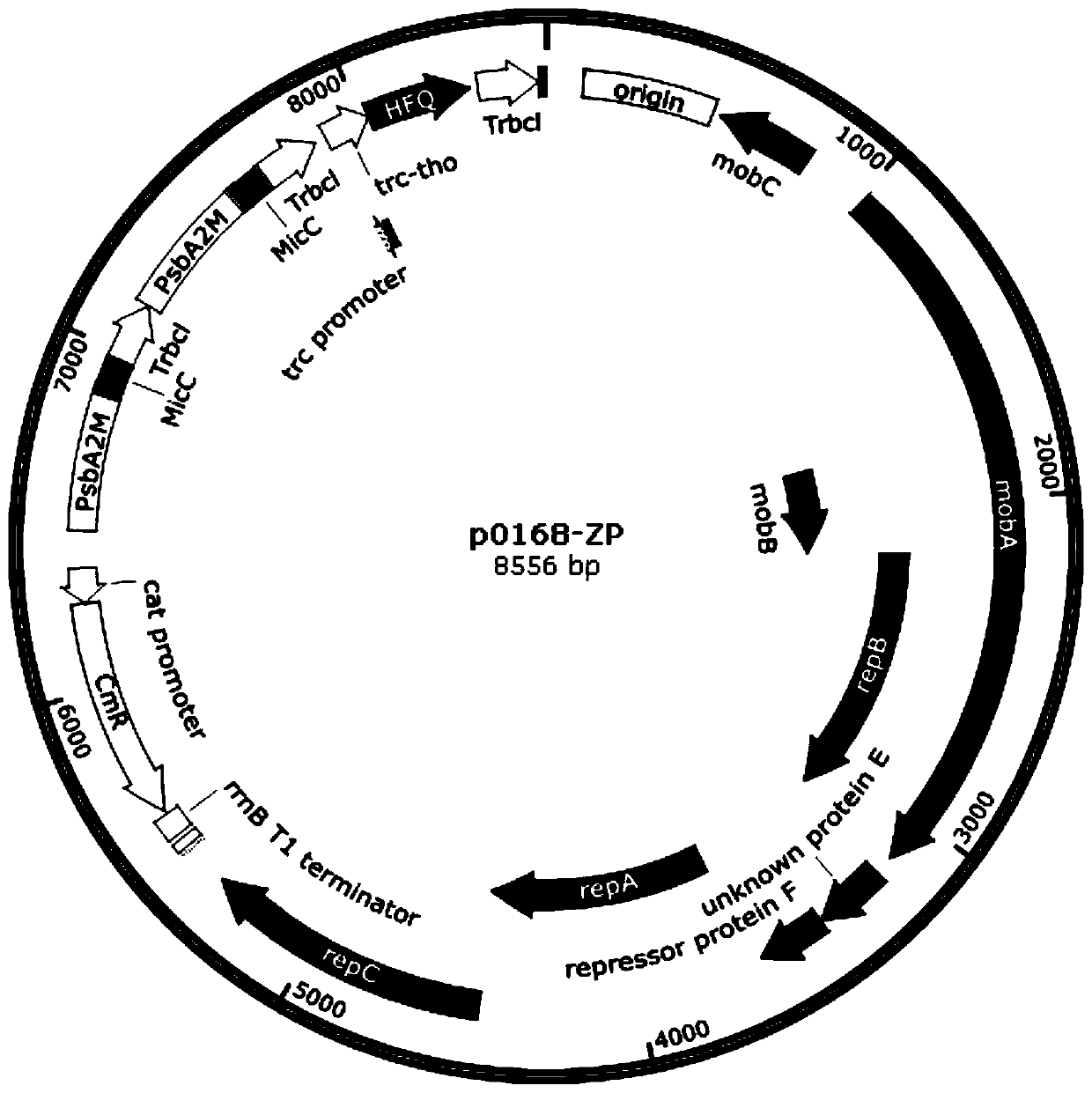
Synechocystis genetically engineered bacterium for biosynthesizing inositol as well as construction method and application thereof
The invention discloses synechocystis genetically engineered bacterium for biosynthesizing inositol as well as a construction method and application of the synechocystis genetically engineered bacterium. The construction method comprises the following steps: obtaining an inositol-1-phosphate synthase gene from saccharomyces cerevisiae, integrating the inositol-1-phosphate synthase gene and an inositol-1-monophosphase gene obtained from synechocystis 6803 onto a plasmid pCP3031, and constructing p3031S to obtain the recombinant synechocystis 6803 engineering bacterium WT-INO1SS. The recombinantsynechocystis 6803 engineering bacterium WT-INO1SSZP is obtained by taking plasmid pBA3031-HM (the *) as a template, constructing P0168-ZP, and transferring the P0168-ZP into the engineering bacterium WT-INO1SS. Experiments prove that the yield of final inositol of the genetically engineered bacterium is 21.74 mg / L <-1 >. Biosynthesis of inositol is successfully realized in synechocystis 6803, and the blank that no cyanobacteria is used as a chassis for producing inositol at present is filled up. The important significance is realized on the production of inositol by utilizing photosyntheticmicroorganisms.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Application of sll0528 Gene in Improving Ethanol Tolerance of Synechocystis pcc6803
The invention discloses an application of sll0528 gene in improving ethanol tolerance of Synechocystis sp. PCC6803, which belongs to the field of industrial microbes. The present invention knocks out and overexpresses the s110528 gene in Synechocystis PCC6803 through the homologous recombination method to obtain a Synechocystis PCC6803 strain Os110528 with significantly improved ethanol tolerance. In the BG11 medium with different concentrations (1.5%, 2.0%, 2.5%, 3.0% v / v) of ethanol, the growth state of the algae strain is obviously better than that of the wild type algae strain. The ethanol-tolerant algae strain obtained by the invention has important theoretical and practical significance for the construction of genetically engineered bacteria for producing fuel ethanol, and has broad application prospects.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Method for producing caffeic acid by using blue algae
InactiveCN103243124BEfficient synthesisMicroorganism based processesFermentationNucleotideCaffeic acid
The invention relates to a method for producing caffeic acid by using blue algae, which comprises the following steps of 1) inserting relevant gene segments in plasmid pBluescript II SK+ to obtain recombined blank plasmids; 2) inserting gene segments of nucleotide sequences such as SEQ ID NO.1 among enzyme cutting sites of the EcoRI-PstI incision enzymes of the recombined blank plasmids obtained in the step 1 to obtain recombined plasmids; 3) transforming the recombined plasmids into Synechocystis sp. PCC6803 to obtain transgenic synechocystis; and 4) conducting enlarging cultivation on the transgenic synechocystis obtained in the step 3 and then conducting extraction to obtain the caffeic acid. By constructing homologous recombination carriers for Synechocystis sp. PCC6803 transformation, algal strains capable of producing the caffeic acid under the condition that precursor substance p-coumaric acid is added are obtained through synechocystis transformation, and a new means is provided for the production of the caffeic acid.
Owner:山东省农业科学院高新技术研究中心
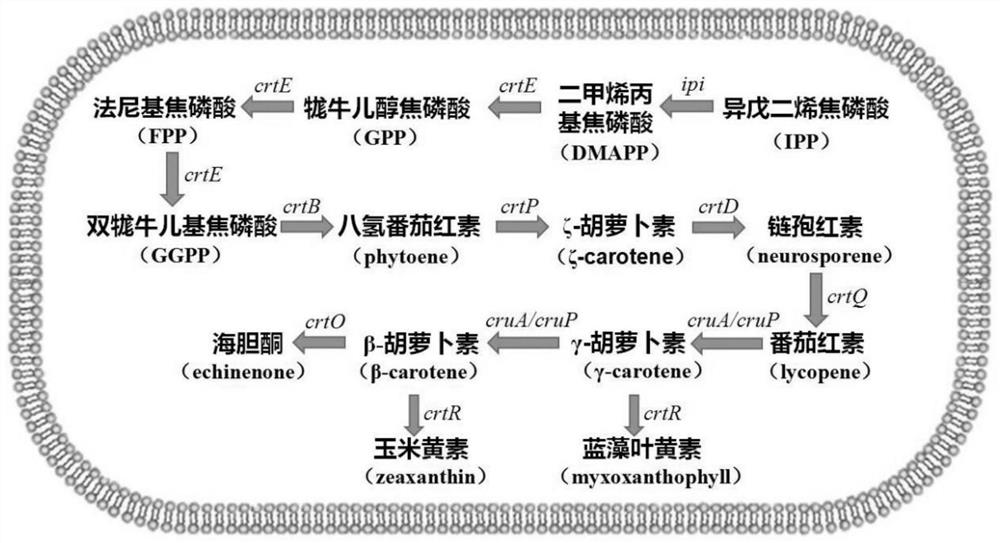
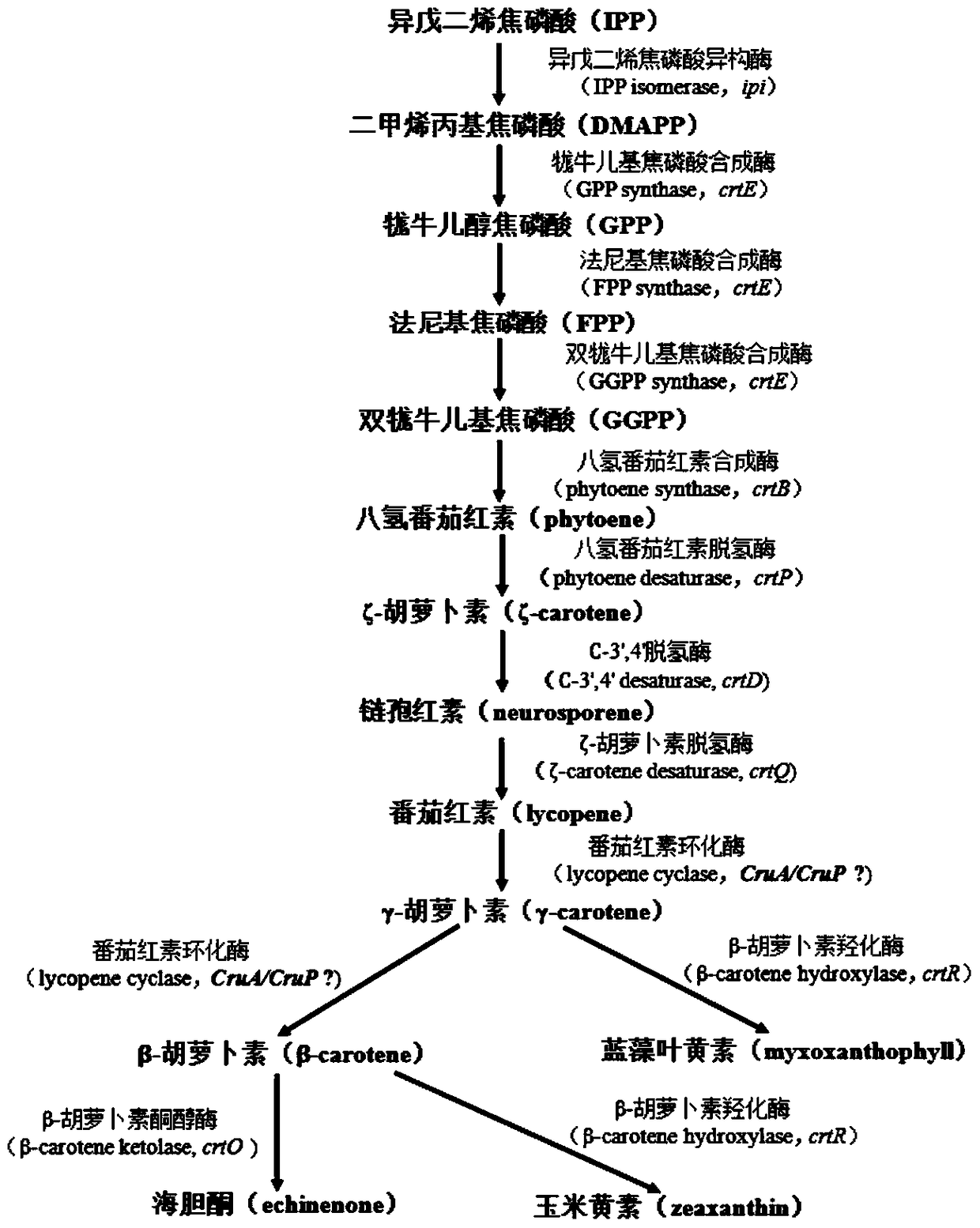
Application of slr0681 gene in synthesis of synechocystis carotene
ActiveCN113817752AGrowth impactIncrease contentBacteriaMicroorganism based processesWild typeSynechocystis sp.
The invention relates to application of an slr0681 gene in synthesis of synechocystis carotene. The invention discloses that the slr0681 gene of synechocystis PCC6803 has obvious influence on carotenoid synthesis in a high-salt environment for the first time, an slr0681 gene knockout mutant strain delta slr0681 is constructed by utilizing a homologous recombination method, and a result shows that the growth condition of the delta slr0681 has obvious advantages under a high-salt stress condition, the content of total carotenoid and chlorophyll a is increased, HPLC analysis shows that the content of myxoxanthophyll, zeaxanthine, echinenone and beta-carotene is increased by 1.2 times, 1.1 times, 1.7 times and 1.05 times respectively compared with the content of wild type counterparts, and the expression of psaA, psaB and psaL in PSI and the expression of psbB and psbD genes in PSII are increased to some extent.
Owner:VEGETABLE RES INST OF SHANDONG ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Culture medium and culture method for promoting synechocystis sp. to secrete amino acids and algal strain
The invention relates to a culture medium for promoting synechocystis sp. PCC 6803 to secrete amino acids. The culture medium is a basal culture medium into which glucose with the concentration of 3.5-21g / L is added, and the concentration of the NaNO3 is 6-12 g / L. The invention further relates to a culture method for promoting the synechocystis sp. PCC 6803 to secrete the amino acids. The culture method comprises the step of using the culture medium for culturing the synechocystis sp. PCC 6803 so as to reach the condition of secreting the amino acids. The invention further relates to an algal strain obtained through genetic modification of the amino acid secreting synechocystis sp. PCC 6803. After use of the culture medium, the culture method and the algal strain, biological denitrationcan be performed by virtue of the synechocystis sp. PCC 6803, and inorganic nitrogen is converted into organic nitrogen so as to produce the amino acids. Under better conditions, after application of the synechocystis sp. PCC 6803 cultured by the culture method provided by the invention, the daily free amino acid output reaches 52.94 mg / L / d plus or minus 1.50 mg / L / d, and the daily sodium nitrate consumption reaches 0.51 g / L / d plus or minus 0.016 g / L / d.
Owner:INST OF AQUATIC LIFE ACAD SINICA
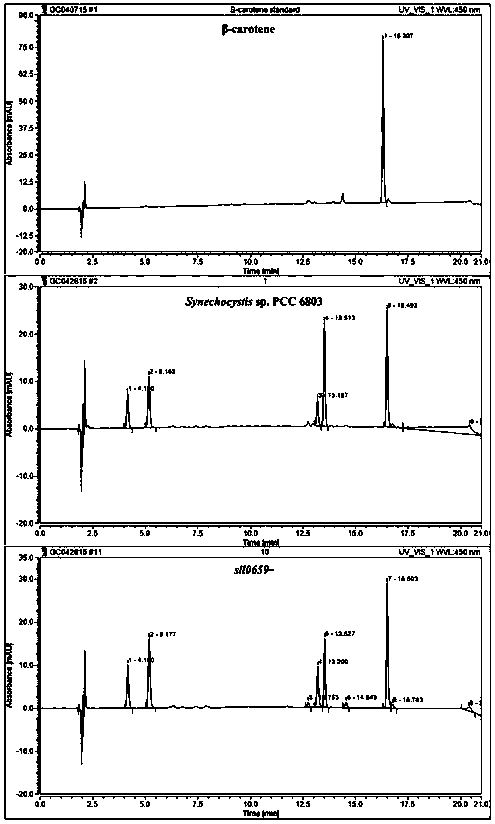
Application of a sll0659 gene in synthesizing Synechocystis carotenoids
ActiveCN105087627BIncrease Lutein ContentReduce percentageBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBeta-CaroteneAlpha-Carotene
The invention relates to application of a sll0659 gene to synthesis of synechocystis carotenoids. The nucleotide sequence of the sll0659 gene is shown in SEQ ID No.1. The invention provides application of the sll0659 gene in synechocystis PCC6803, which has an important effect on synthesis of synechocystis PCC6803 beta-carotene. By knocking out the sll0659 gene in synechocystis PCC6803, the lutein content of the synechocystis PCC6803 is increased by 22.3%, zeaxanthin content is increased by 31.3%, the echinenone content is reduced by 34.3%, and the percentage content of beta-carotene is reduced by 1.3%. Meanwhile, HPLC detection results show when synechocystis PCC6803 involved in the invention is compared with wild synechocystis PCC6803, an obvious peak exists in the carotenoid components in the sll0659 gene knockout mutant, and the obvious peak is determined to be alpha-carotene by contrasting the obvious peak with a standard product and detecting.
Owner:BIOTECH RES CENT SHANDONG ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
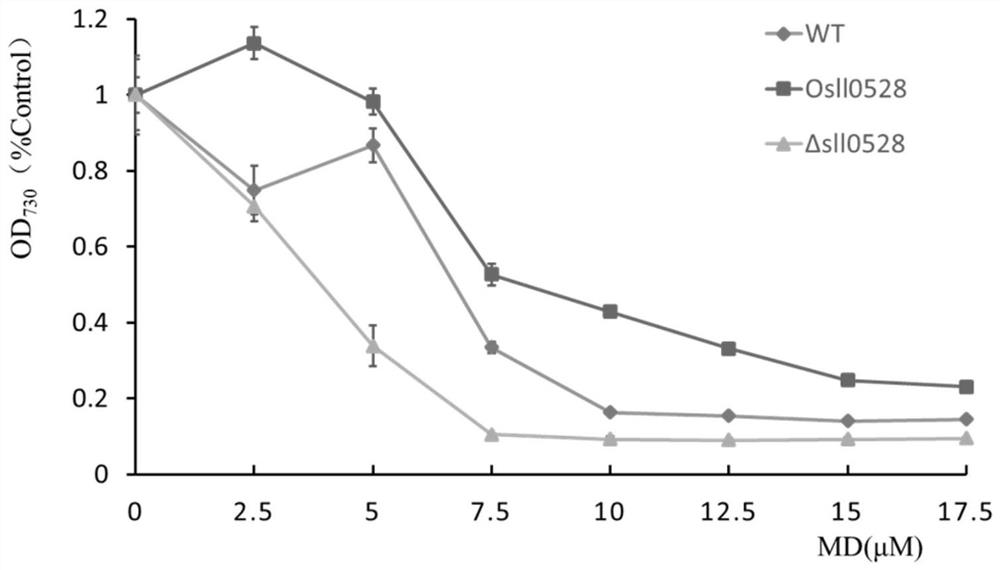
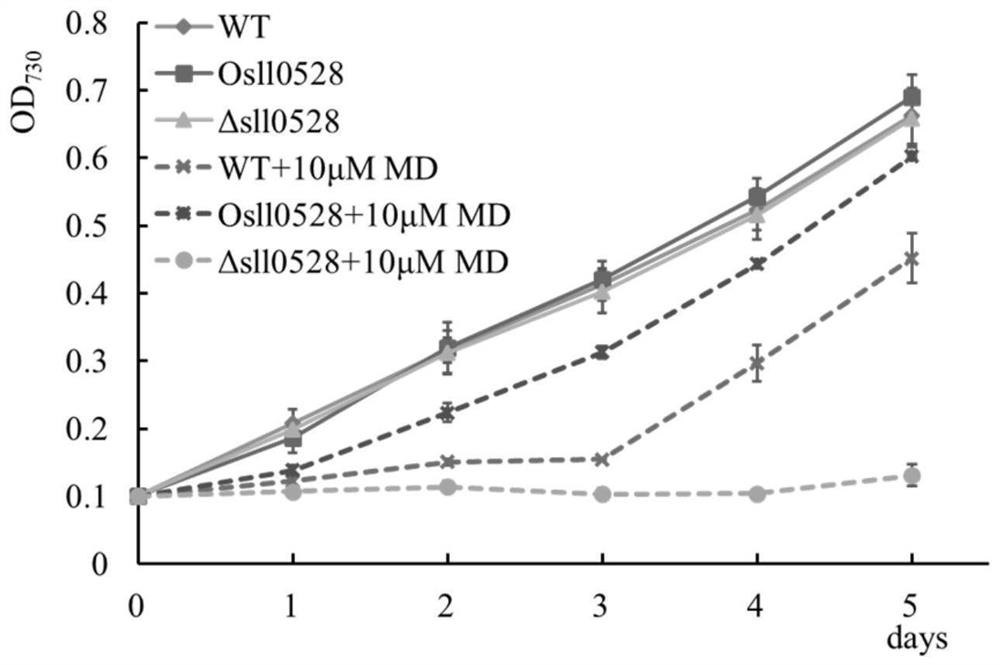
Application of sll0528 gene in improving oxidative stress tolerance of Synechocystis pcc6803
ActiveCN111172092BIncreased tolerance to oxidative stressPromote growthBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyMicroorganism
The invention discloses the application of a sll0528 gene in improving the oxidative stress tolerance of Synechocystis sp. PCC6803, which belongs to the field of industrial microbes. The present invention overexpresses the s110528 gene in Synechocystis PCC6803 through homologous recombination, and obtains a Synechocystis PCC6803 strain Os110528 with significantly improved tolerance to oxidative stress. In the BG11 medium supplemented with different concentrations (2.5μM-15μM) of menadione or different concentrations (1mM-3mM) of hydrogen peroxide, the growth state of Osll0528 was significantly better than that of the wild-type strain. The oxidative stress-tolerant algae strain obtained by the invention has important theoretical and practical significance and broad application prospects for constructing genetically engineered bacteria tolerant to high oxidative stress and genetically engineered algal strain chassis tolerant to various environmental stresses.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
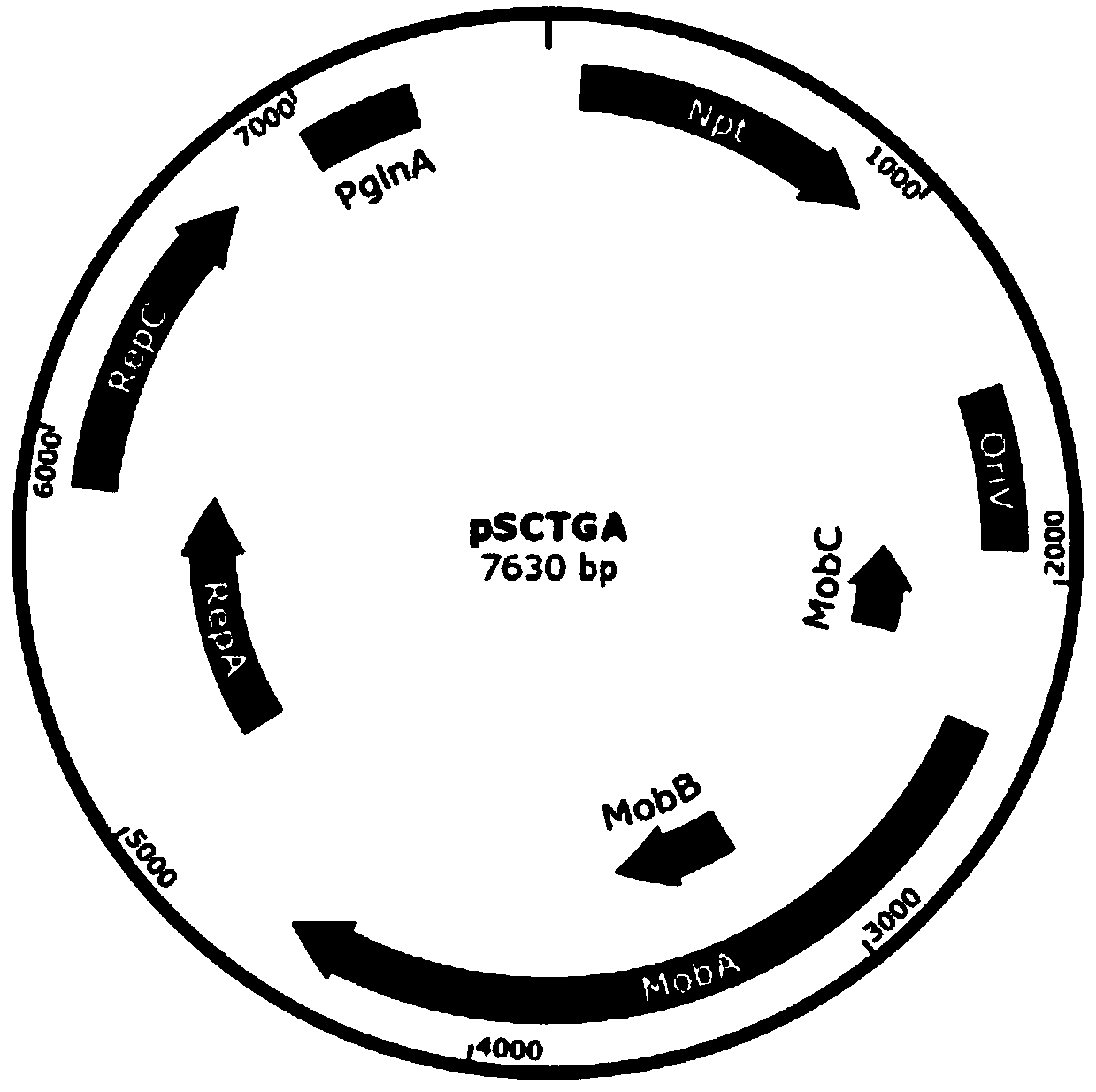
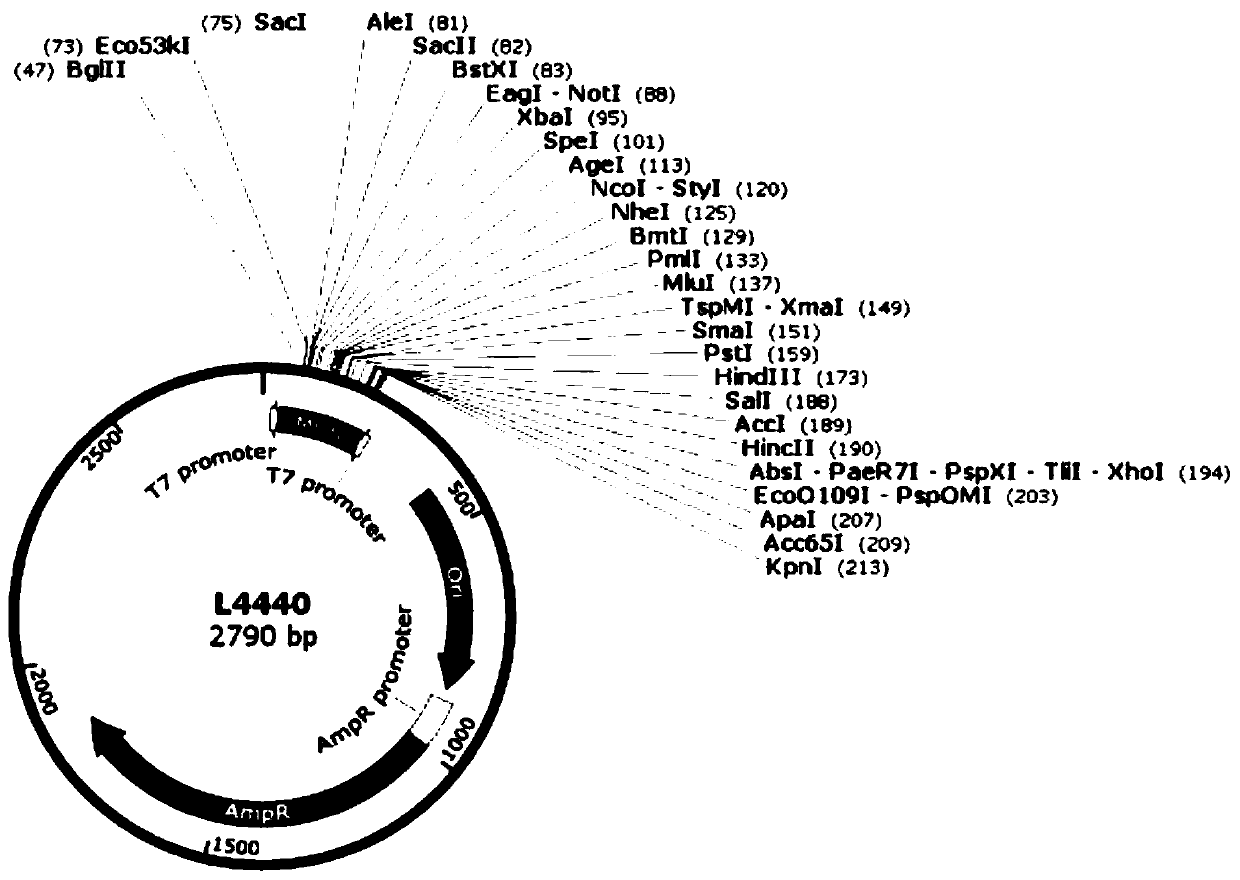
Stentor coeruleus RNA interference expression vector as well as construction method and application thereof
ActiveCN111471685APromote accumulationInhibit expressionBiocideAnimal repellantsA-DNASynechocystis sp.
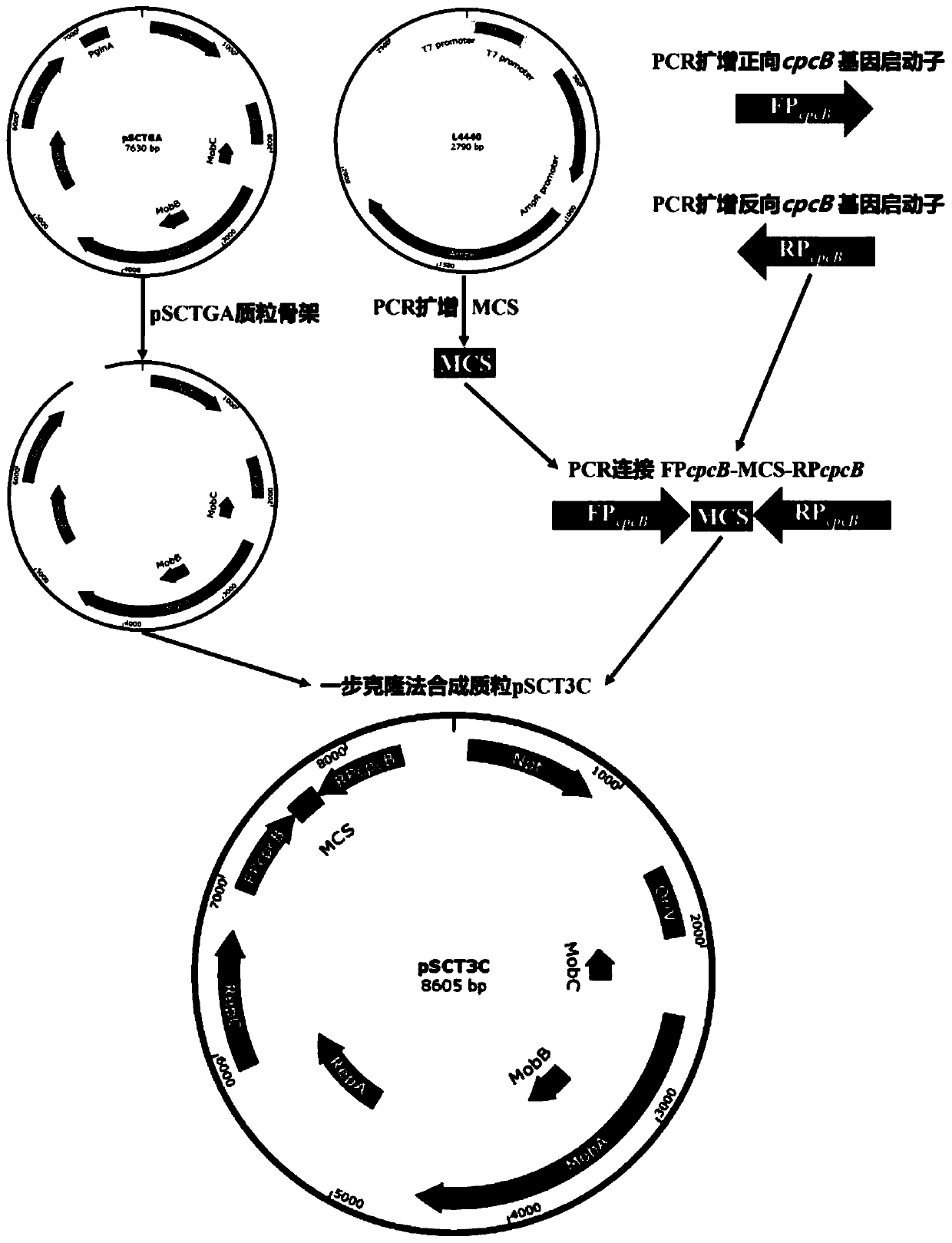
The invention discloses a Stentor coeruleus RNA interference expression vector as well as a construction method and application thereof. The method comprises the following steps of 1) obtaining a pSCTGA plasmid skeleton by using a known sequence of plasmid pSCTGA; (2) amplifying a promoter of a C-phycocyanin beta subunit through PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) by using synechocystis PCC6803 genomeDNA (Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid); 3) amplifying multiple cloning sites of the plasmid through PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) by using the plasmid L4440; and 4) finally constructing a RNAi expression vector pSCT3C by using a DNA fragment obtained by PCR amplification through homologous recombinant fusion PCR and a one-step cloning method. The method comprises the following steps of transfecting a RNAi expression vector containing a target gene into an Escherichia coli DH10B strain by using a calcium chloride method, and transfecting the Escherichia coli DH10B strain into synechocystis PCC6803 by using a conjugational transfer method to successfully obtain a positive monoclonal algae strain, and then interfering the expression of a target gene in the Stentor coendeus in a feeding mode. In conclusion, the method is easy to implement and convenient to operate, and has the feasibility of being applied to gene interference of other ciliates.
Owner:INST OF AQUATIC LIFE ACAD SINICA
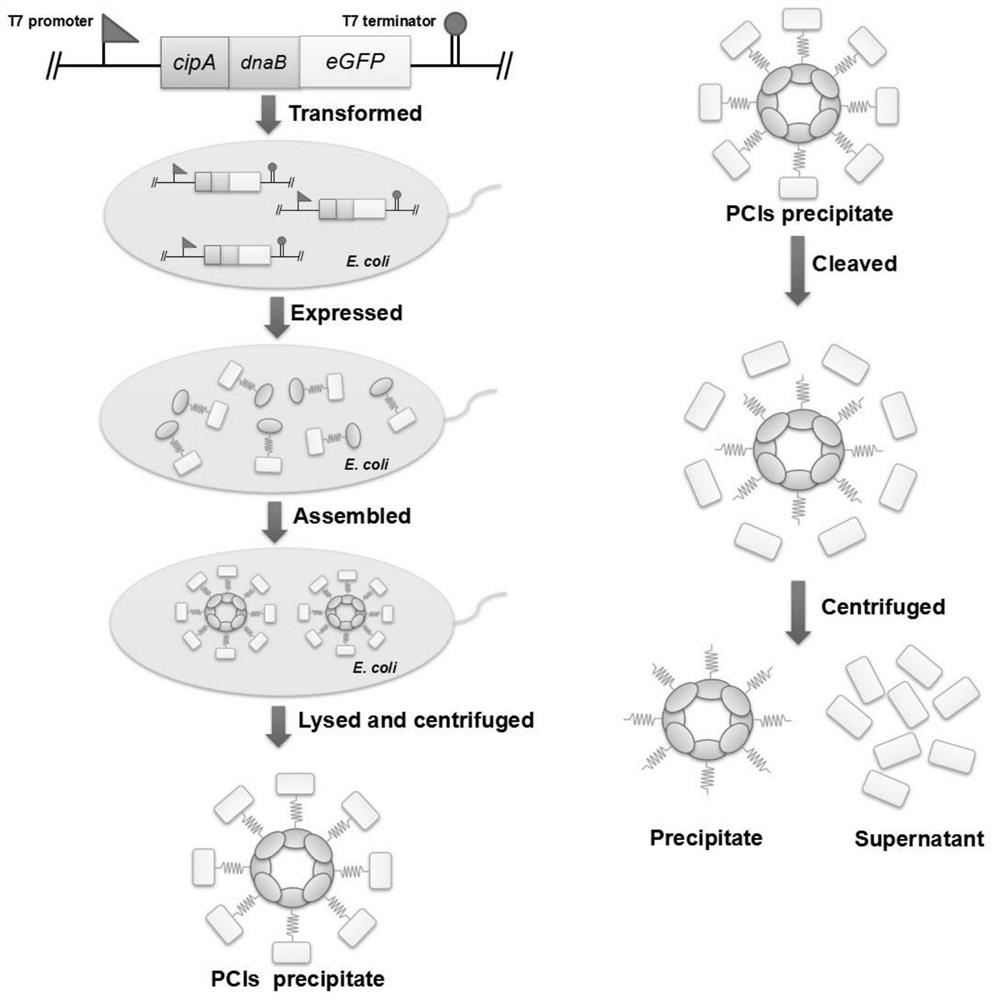
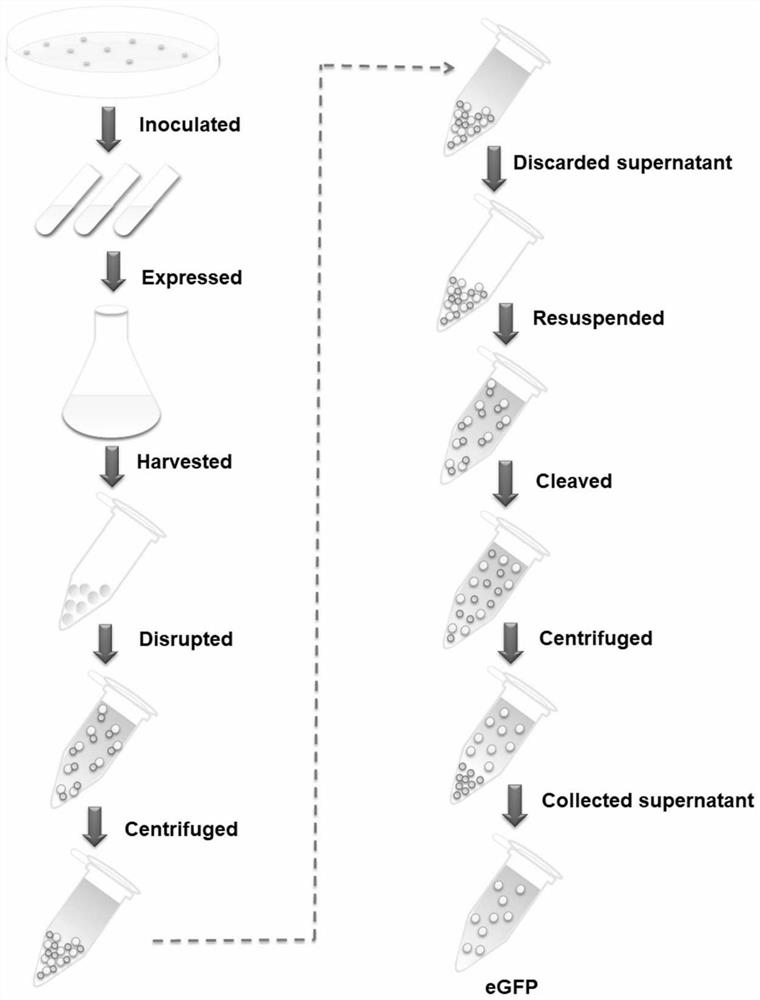
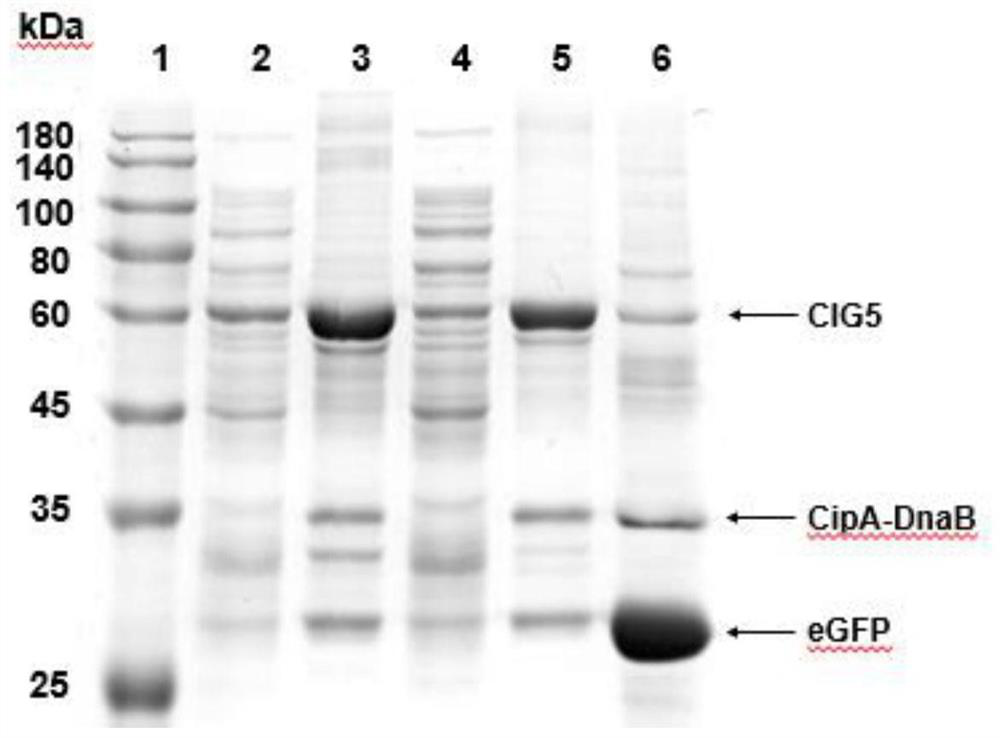
A simple and efficient method for protein purification
ActiveCN110714020BGood cracking effectEGFP-multipleBacteriaAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsBiotechnologyProtein target
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Synechococcus engineering bacterium capable of improving yield of cellulose, and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN102242065BShorten the growth cycleNo pollution problemUnicellular algaeBiofuelsDry weightSynechococcus sp.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
A method and application of improving ethanol tolerance of Synechocystis pcc6803
ActiveCN106399114BPromote growthImprove toleranceUnicellular algaeBiofuelsMicroorganismEthanol stress
The invention discloses a method for improving ethanol tolerance of synechocystis PCC6803 and an application, and belongs to the field of industrial microorganism. With the application of the method, a synechocystis PCC6803 strain with ethanol tolerance obviously improved is obtained, and the strain is applicable to the construction of genetically engineered bacteria for producing fuel ethanol. According to the method provided by the invention, an sll0687 gene in the synechocystis PCC6803 is knocked out through homologous recombination; and the ethanol tolerance of the synechocystis PCC6803 strain IK2 obtained through the application of the method is significantly improved. Under 1.5% (v / v) ethanol stress, the growth state of the strain is obviously better than that of a wild-type strain. The ethanol-tolerance strain prepared by the invention has important theoretical and practical significance for the construction of the genetically engineered bacteria for producing the fuel ethanol; and the strain has a broad application prospect.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Carotenoid metabolism gene function identification method
ActiveCN110484550AEasy identificationEasy to identifyComponent separationMicroorganism based processesCarotene metabolismPhylum Cyanobacteria
The invention discloses a carotenoid metabolism gene function identification method, which comprises the following steps: S1, cloning a selection marker element: cloning a kanamycin resistance gene Kanr driven by an Ampr promoter from a pGBK-T7 vector, and taking the element (pAmpr:: Kanr) as a subsequent selection marker; S2, cloning a promoter: cloning a promoter sequence of a RuBisCO large-subunit gene (rbcL) in the synechocystis sp. PCC6803 of the cyanobacteria, wherein the promoter is used for driving an enzyme gene to be detected; S3, cloning an enzyme gene: cloning a carotenoid metabolism-related enzyme gene X to be identified from different organisms to the downstream (rbcL:: X) of a rbcL promoter, and driving the carotenoid metabolism-related enzyme gene X by the promoter; and S4,constructing an expression cassette: a complete gene expression cassette comprises a pAmpr:: Kanr selection marker element and a rbcL:: X element for expressing zymoprotein which are arranged in sequence. Compared with a traditional identification method, the method is simpler and more convenient and more direct and can be adopted to clearly identify gene functions in a targeted mode.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com