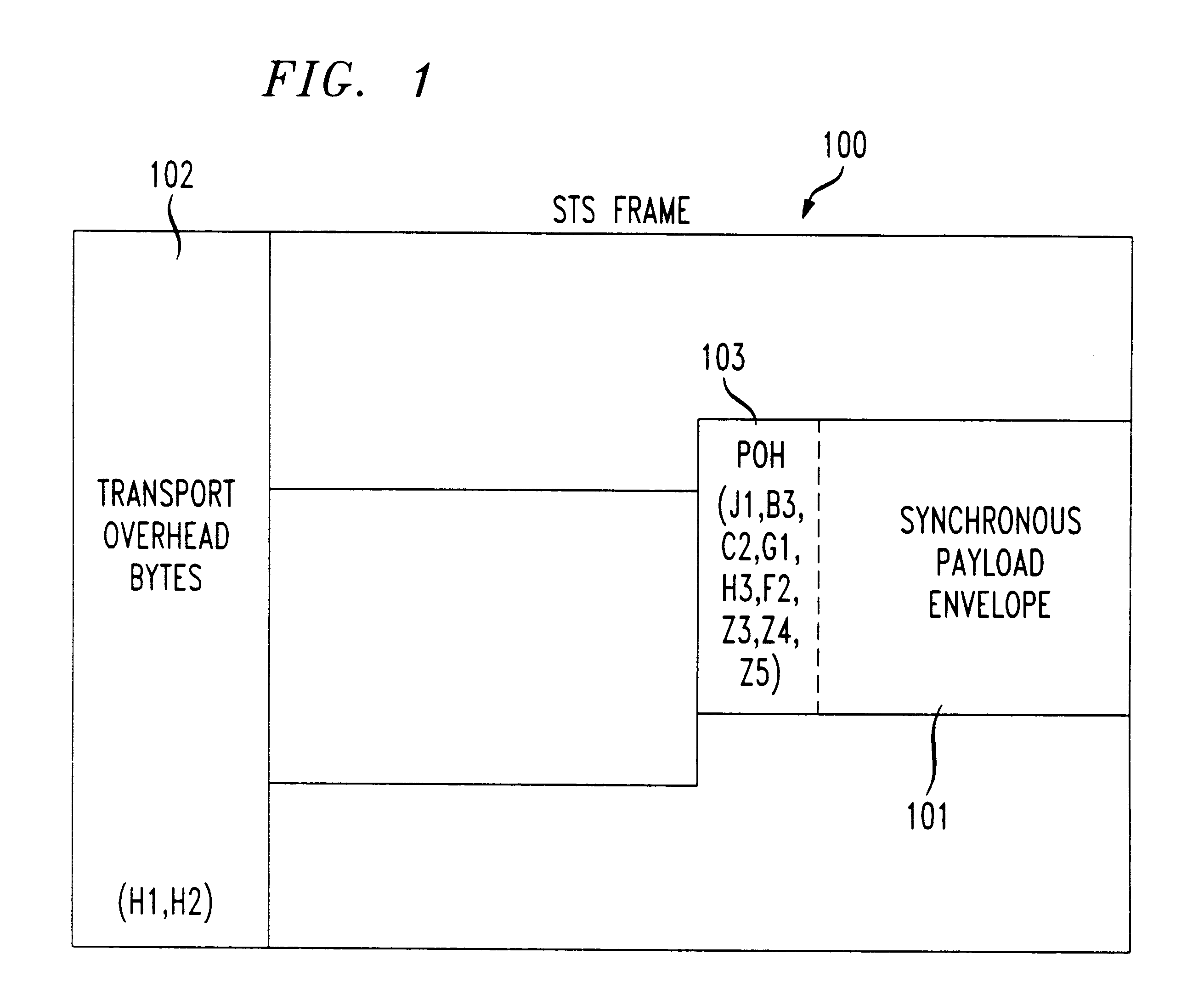
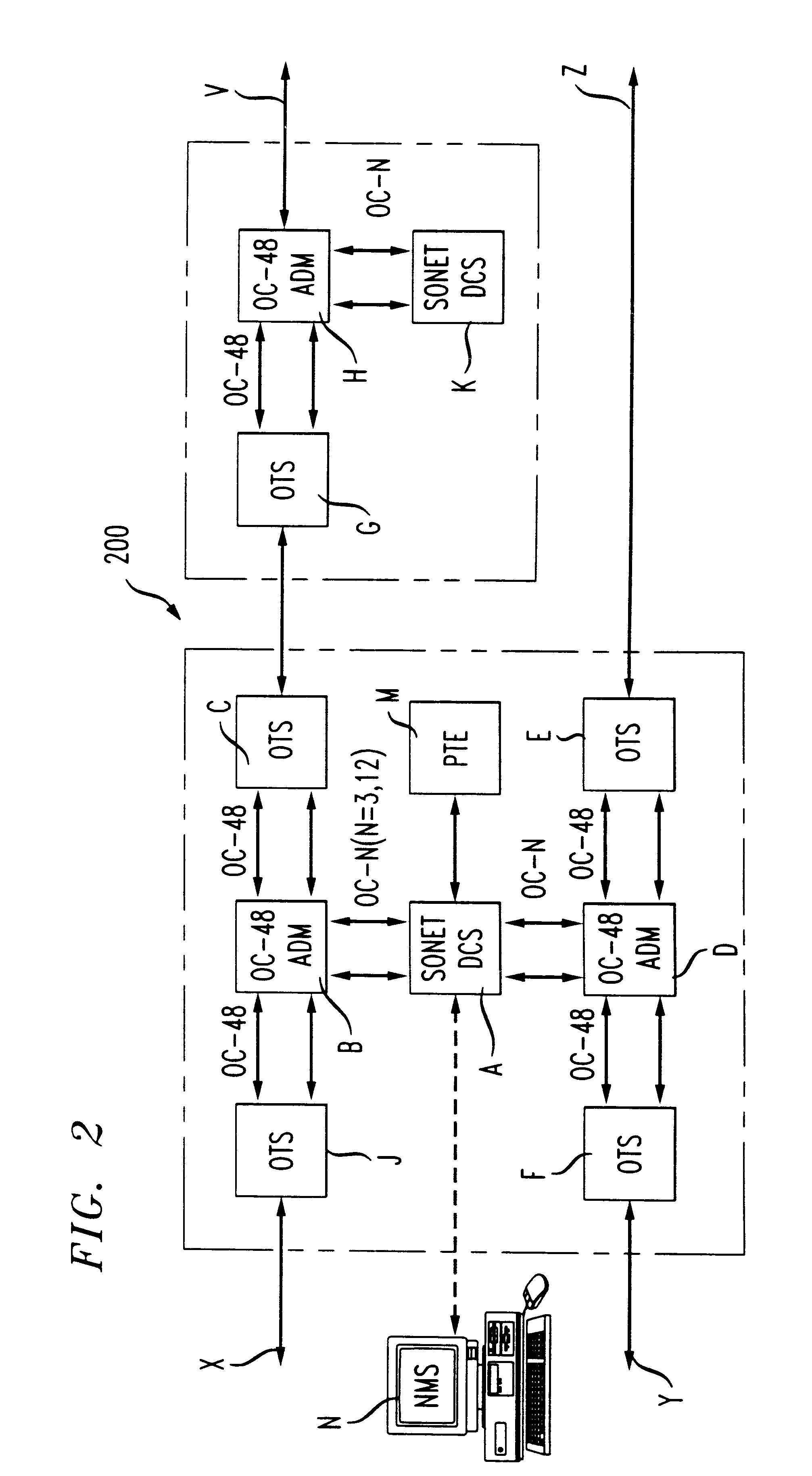
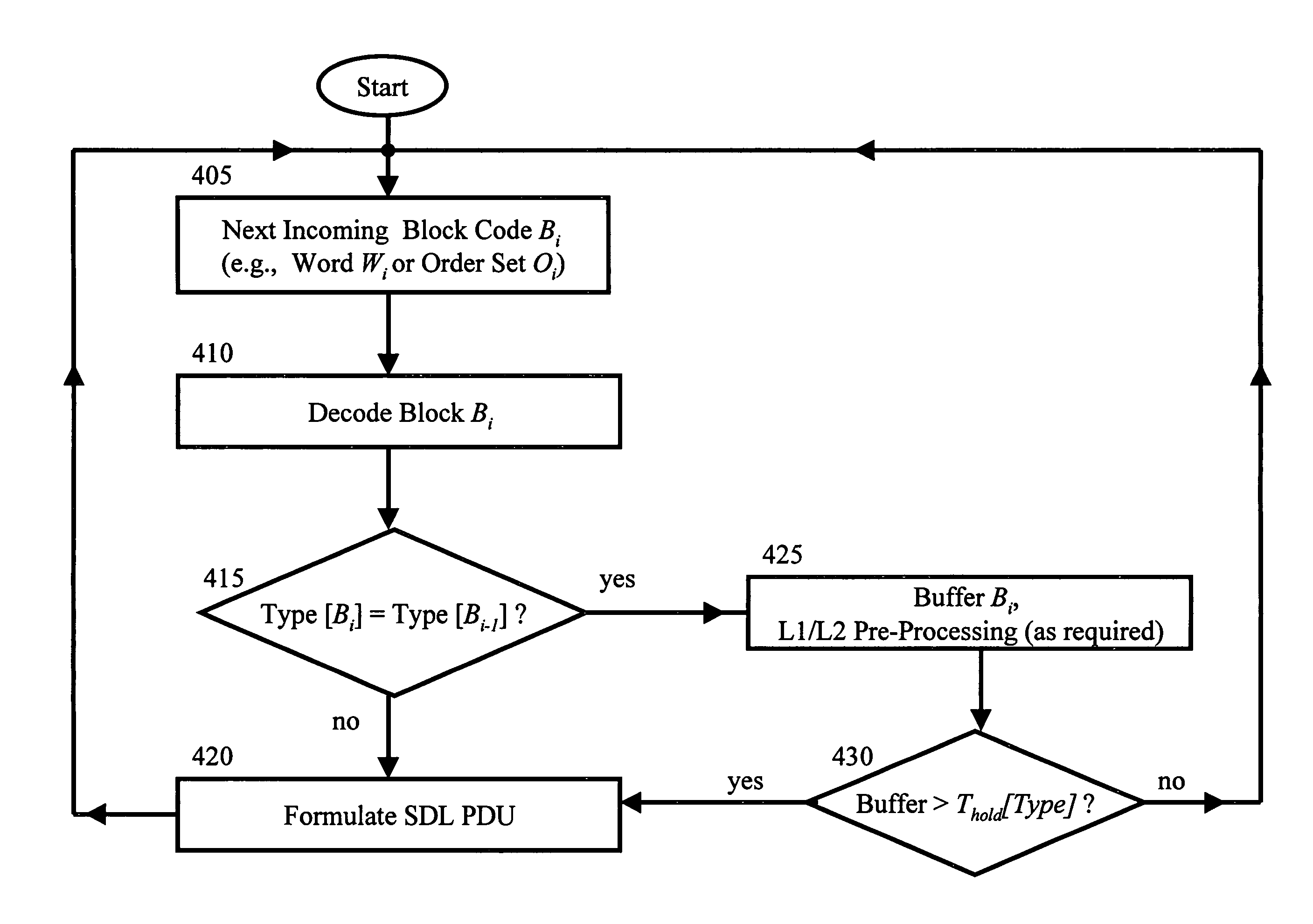
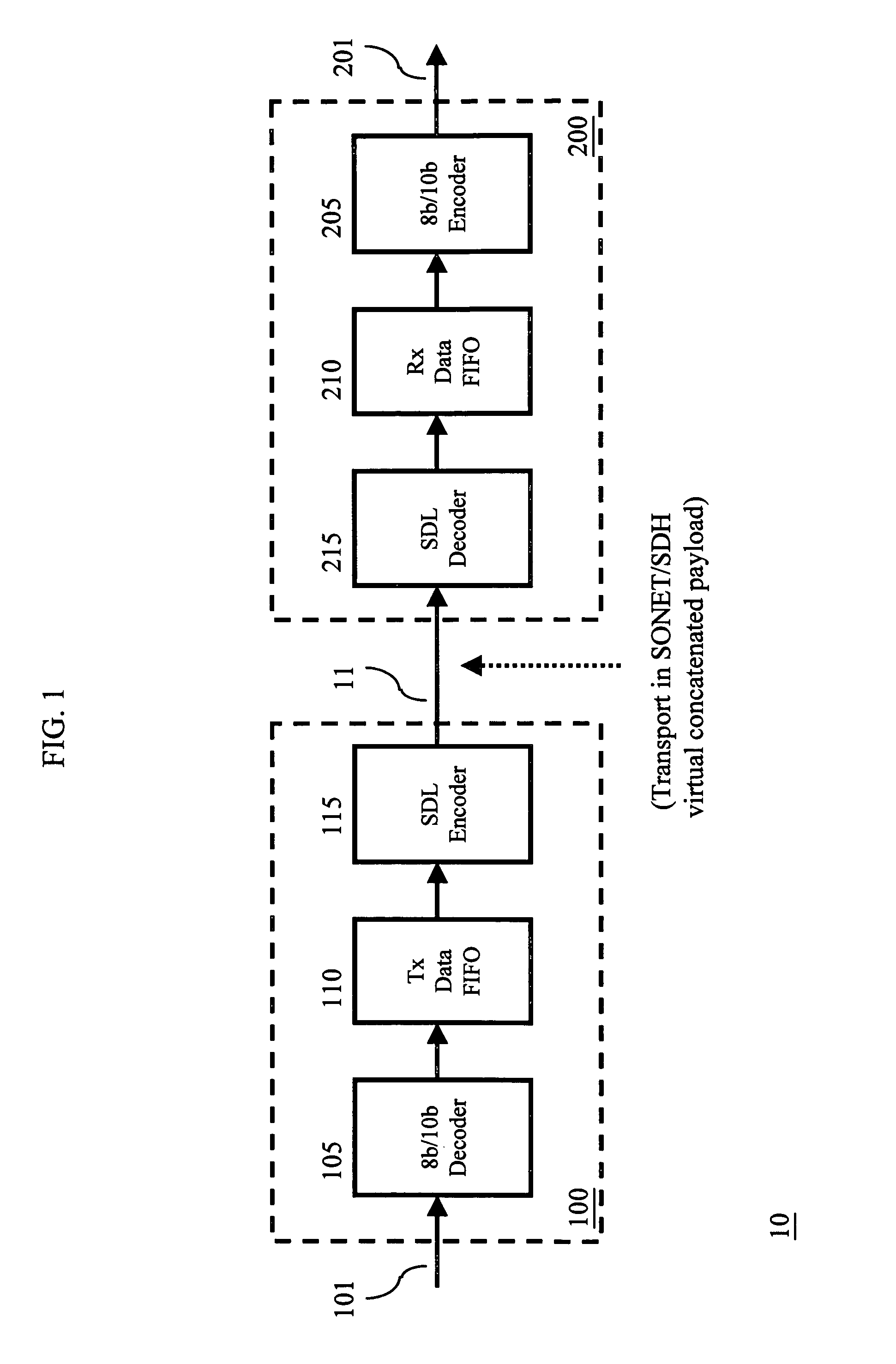
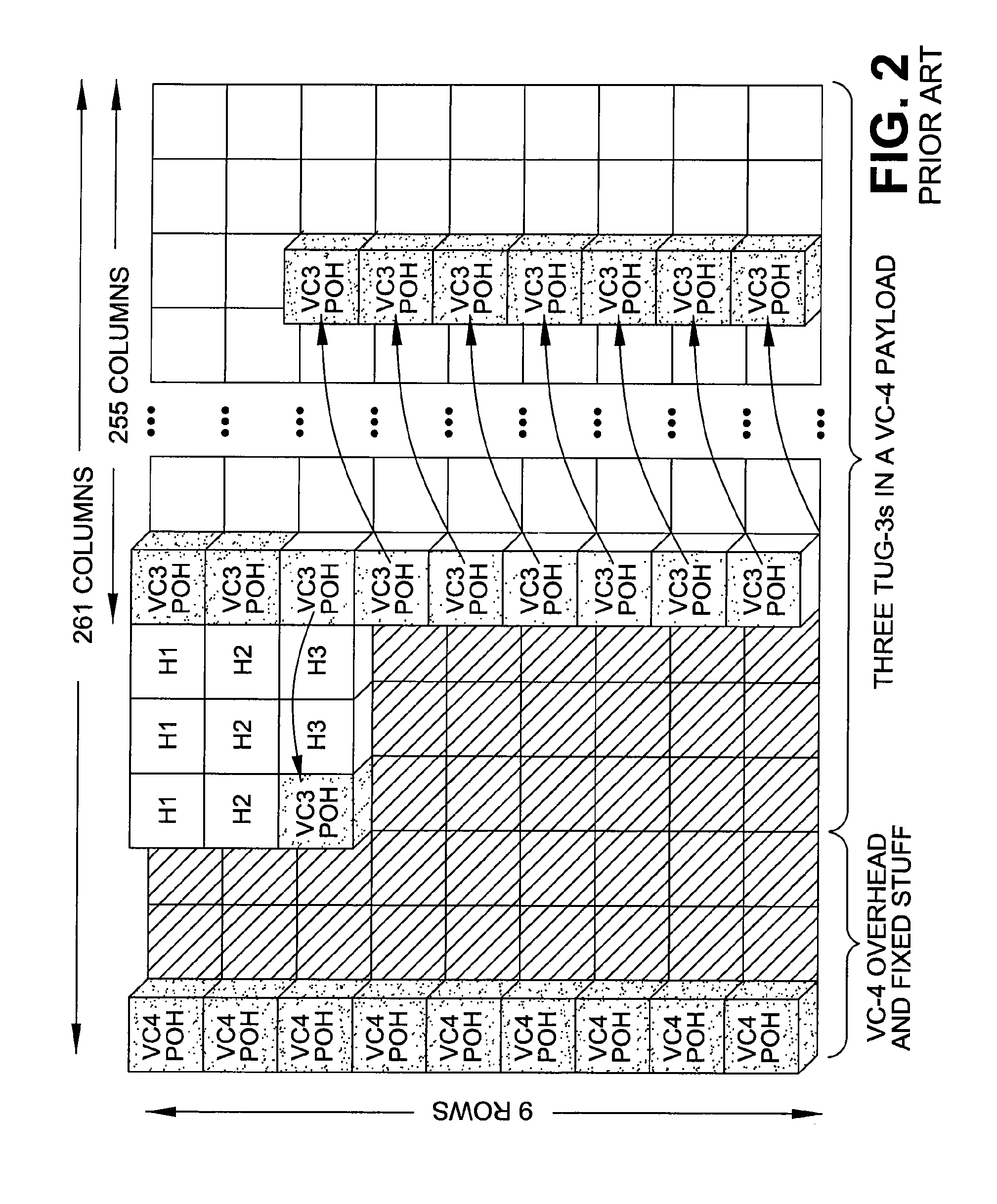
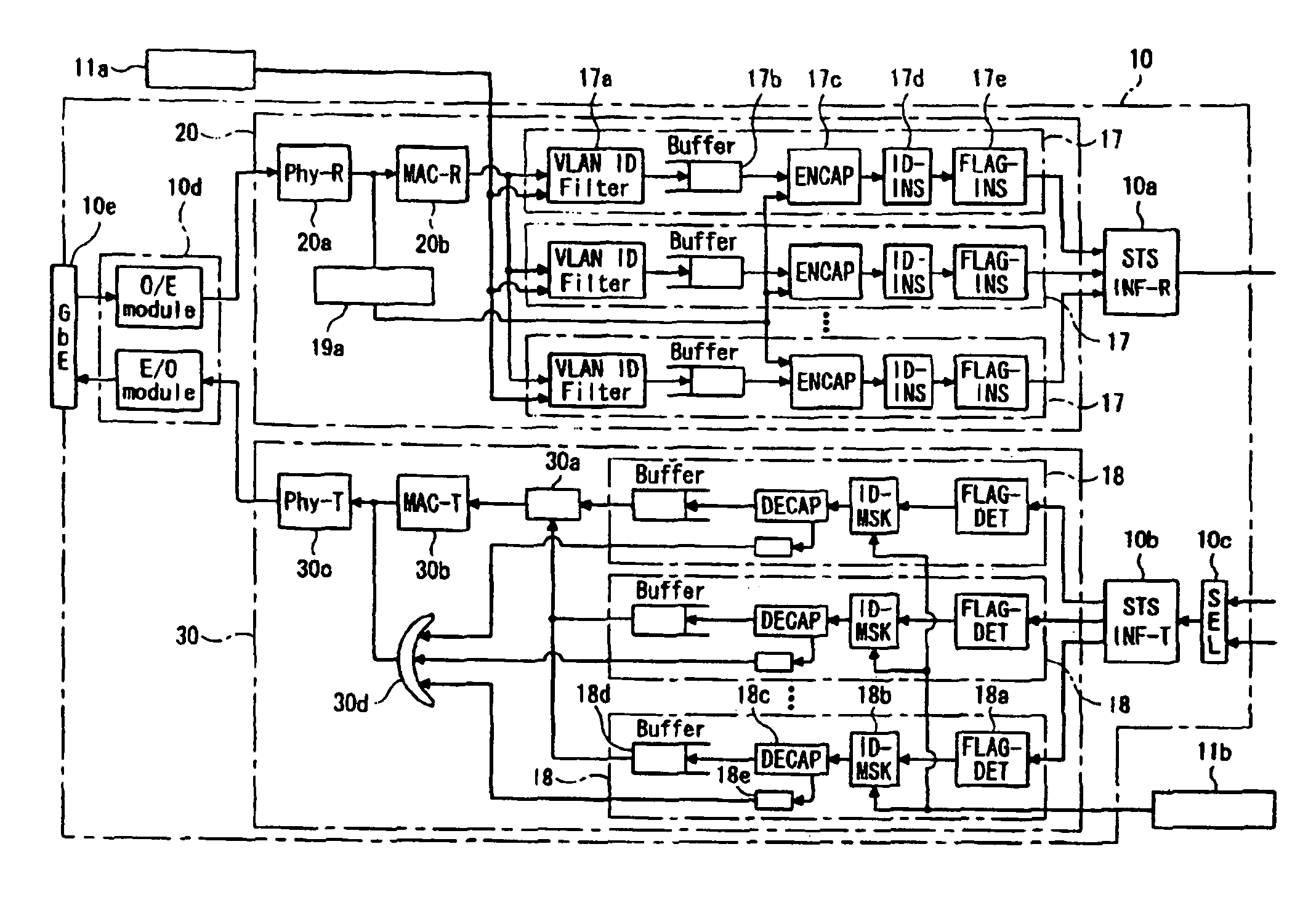
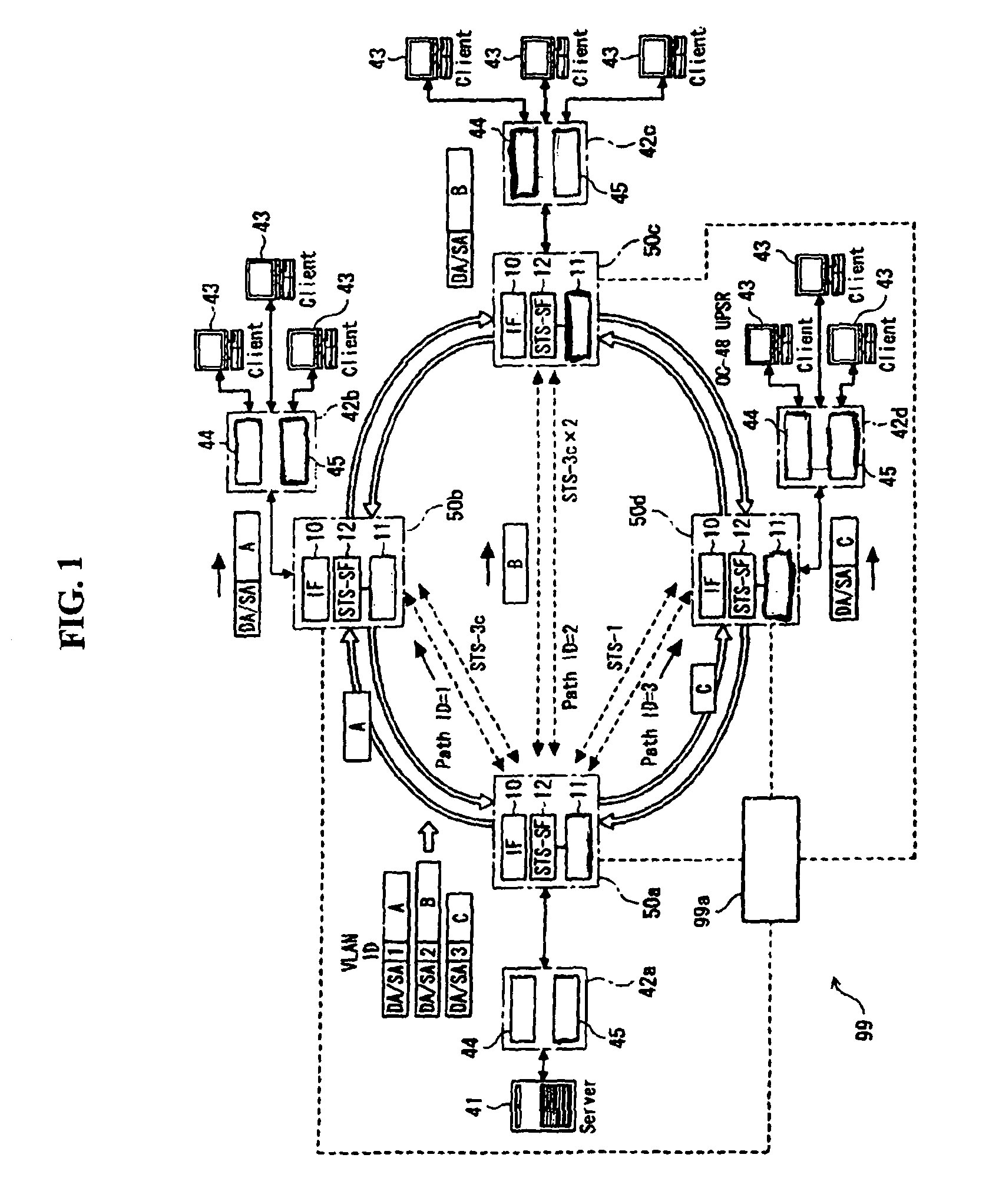
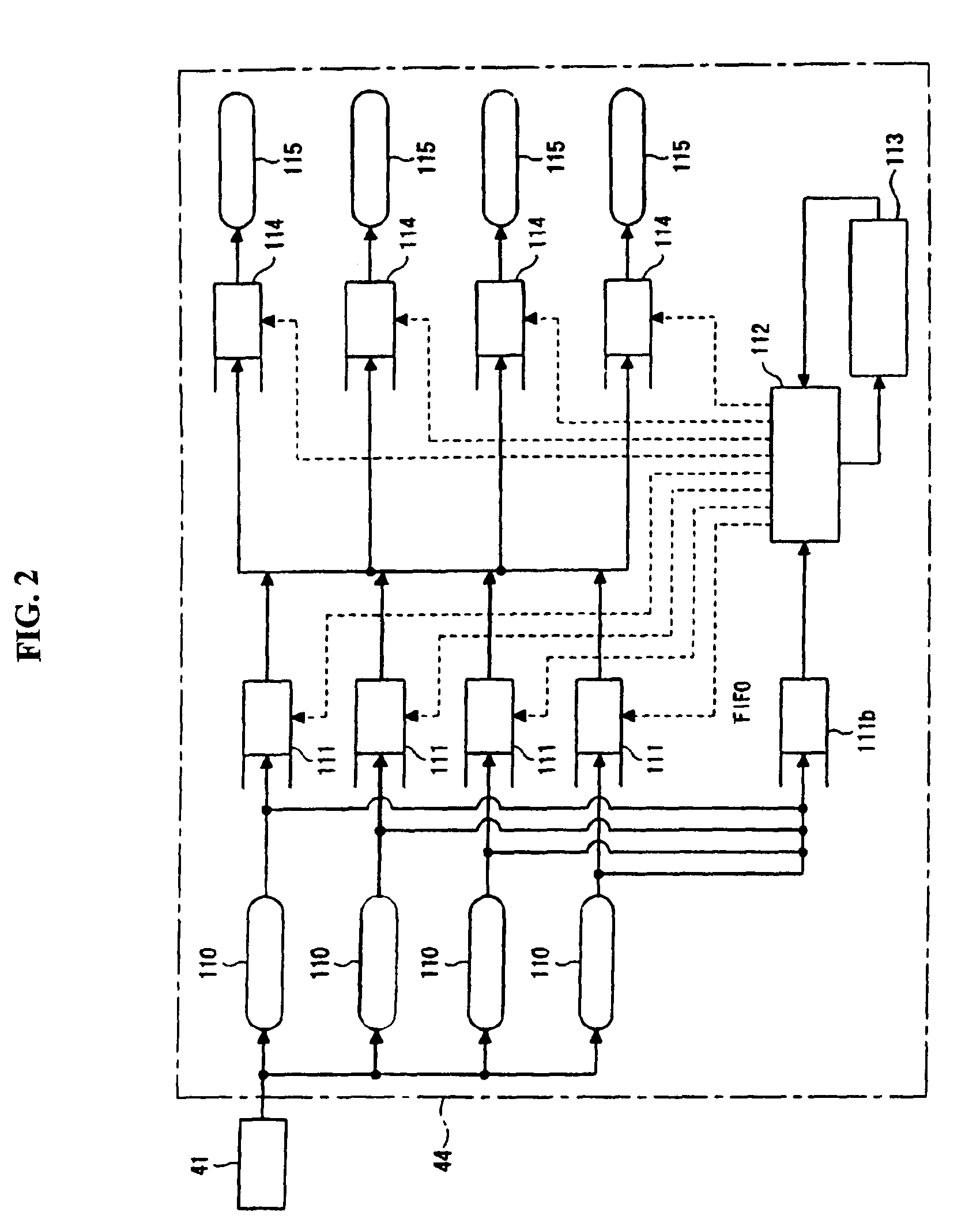
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
59 results about "Synchronous optical networking" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
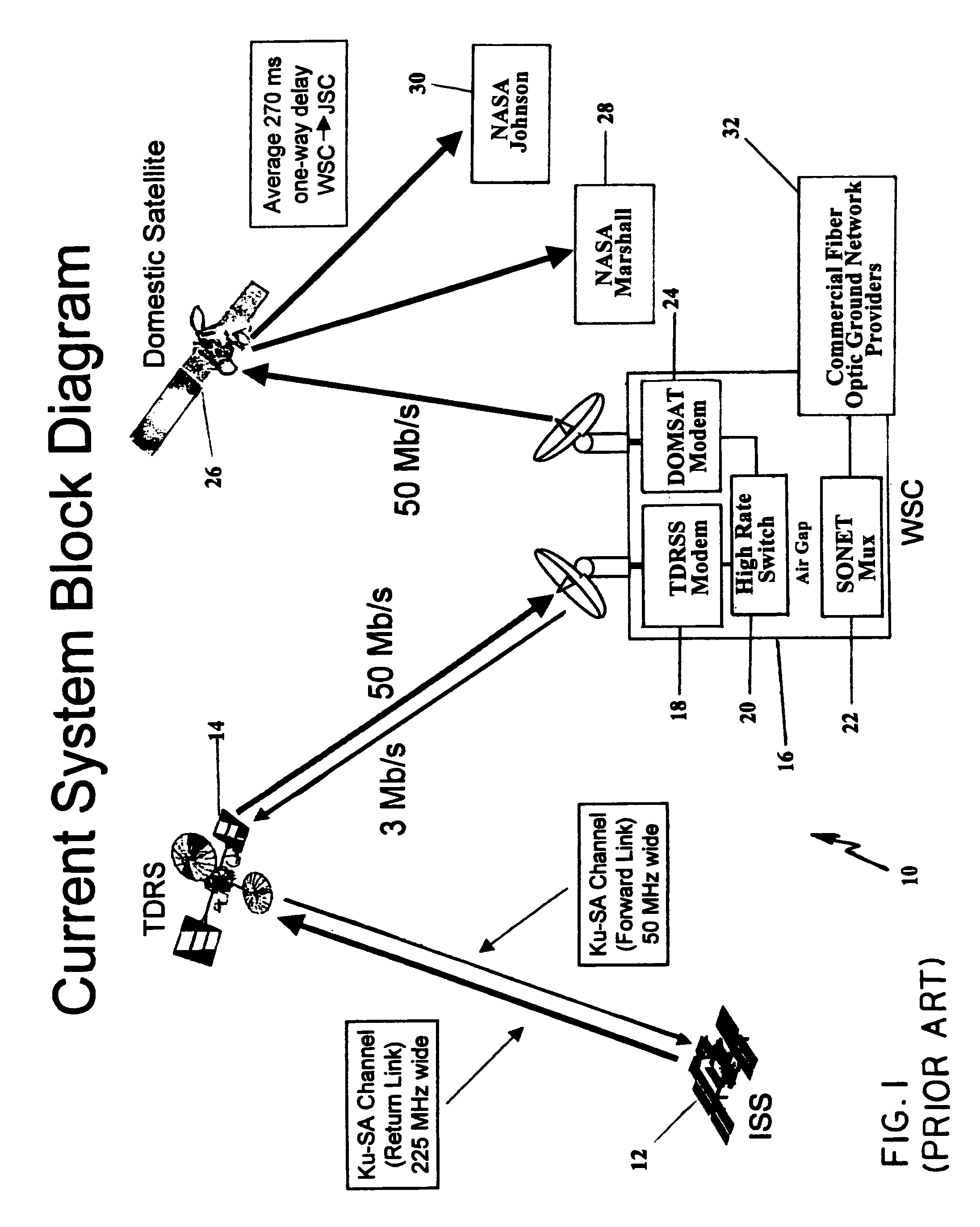
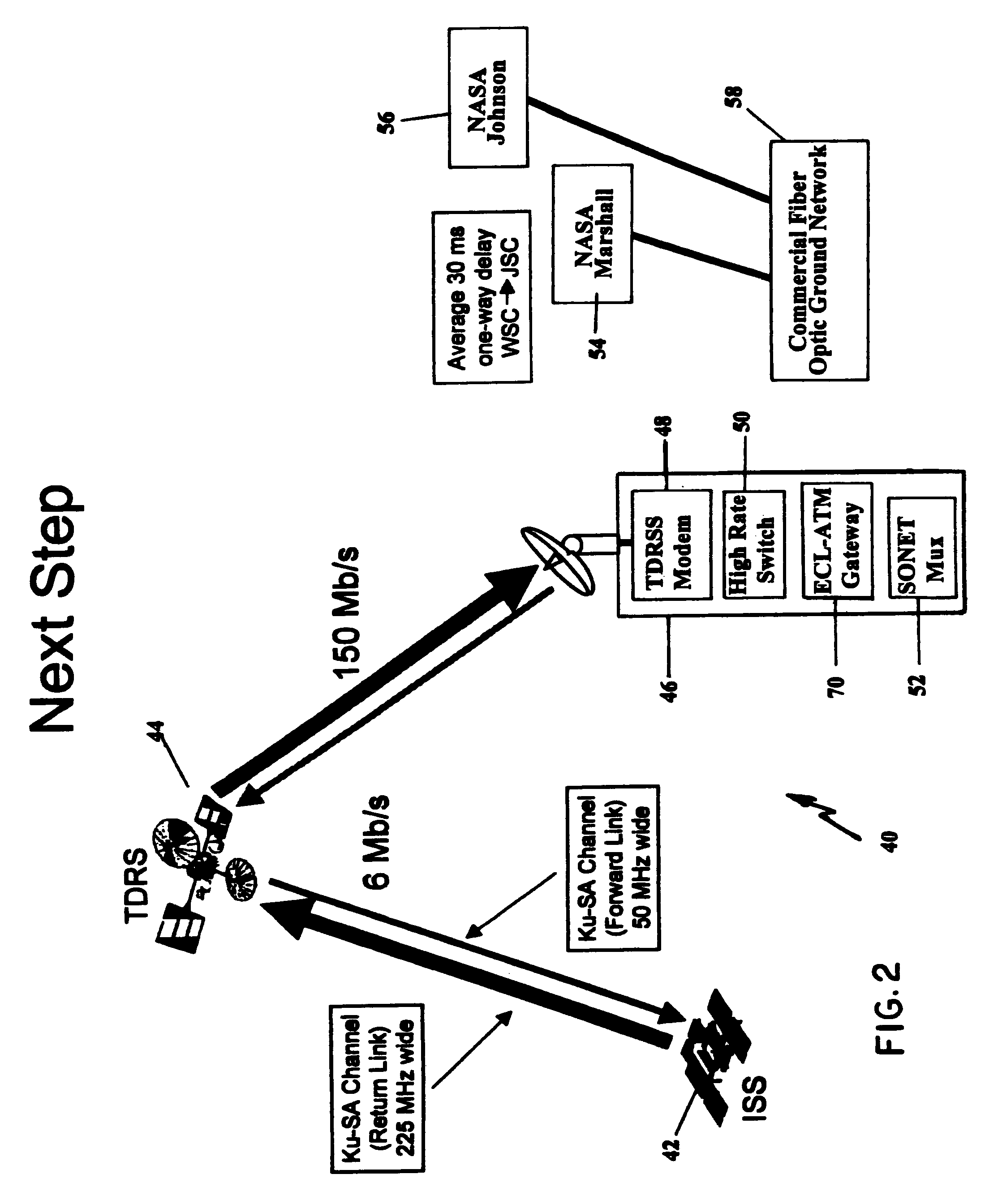
Synchronous optical networking (SONET) and synchronous digital hierarchy (SDH) are standardized protocols that transfer multiple digital bit streams synchronously over optical fiber using lasers or highly coherent light from light-emitting diodes (LEDs). At low transmission rates data can also be transferred via an electrical interface. The method was developed to replace the plesiochronous digital hierarchy (PDH) system for transporting large amounts of telephone calls and data traffic over the same fiber without the problems of synchronization.
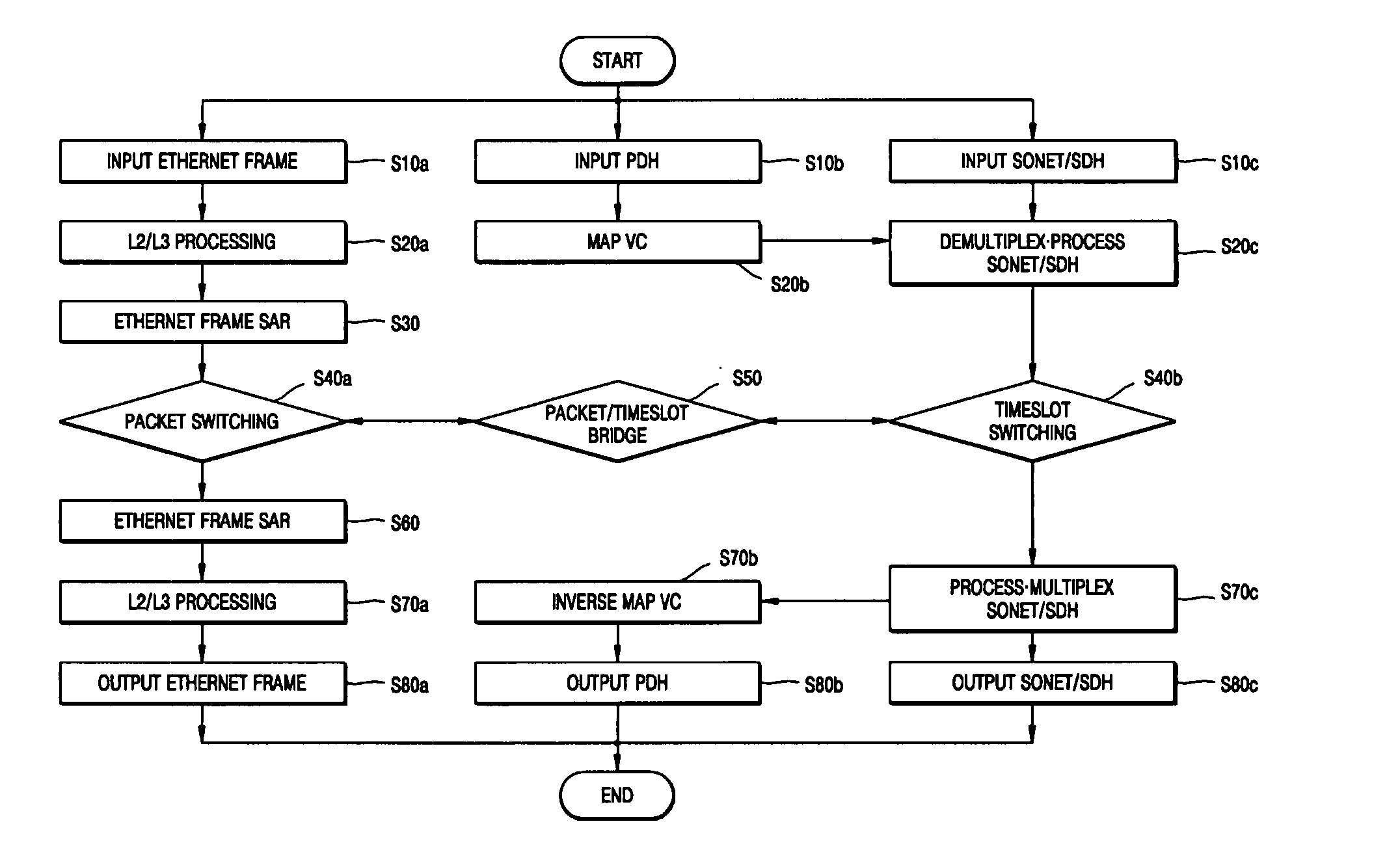
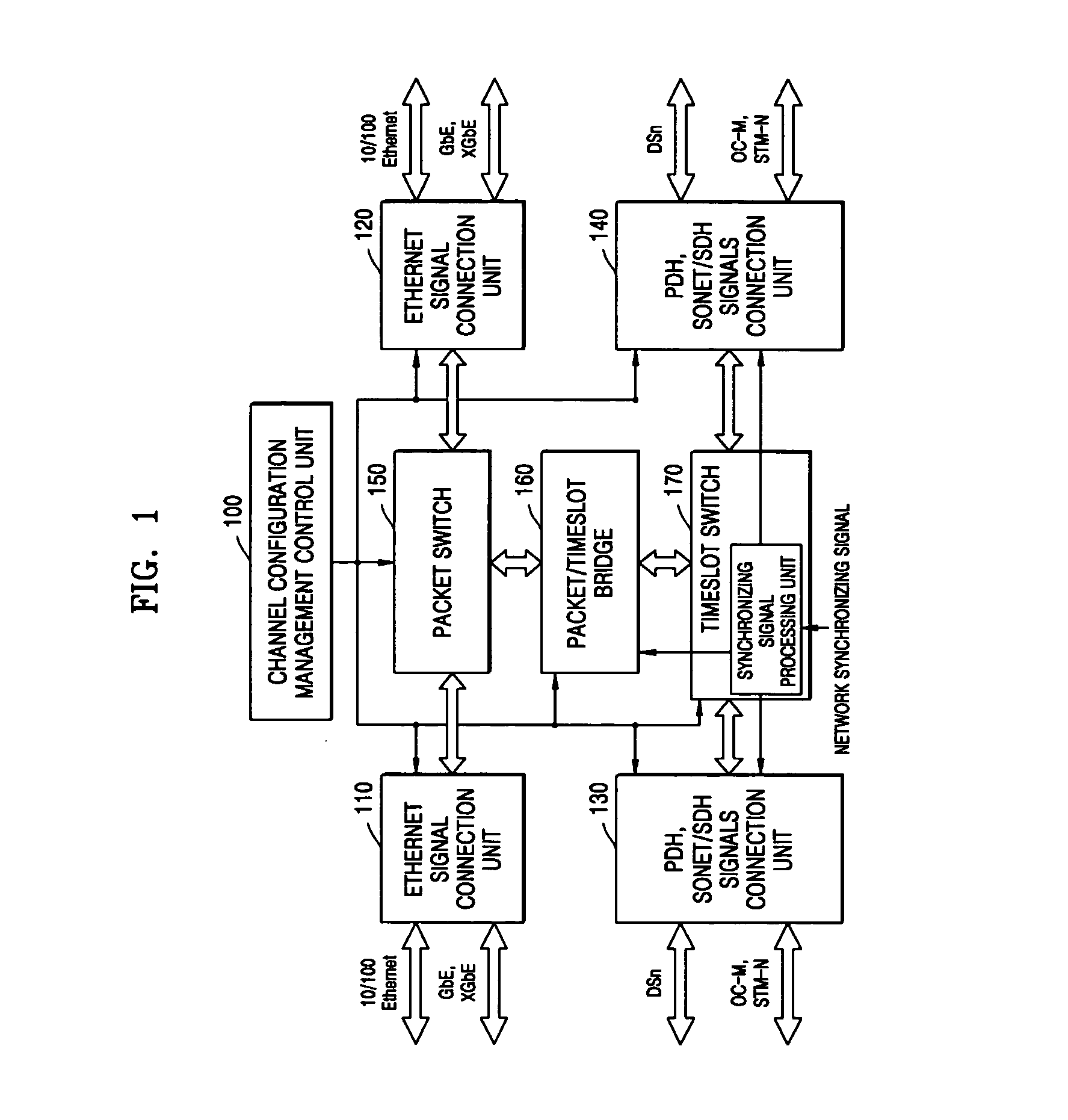
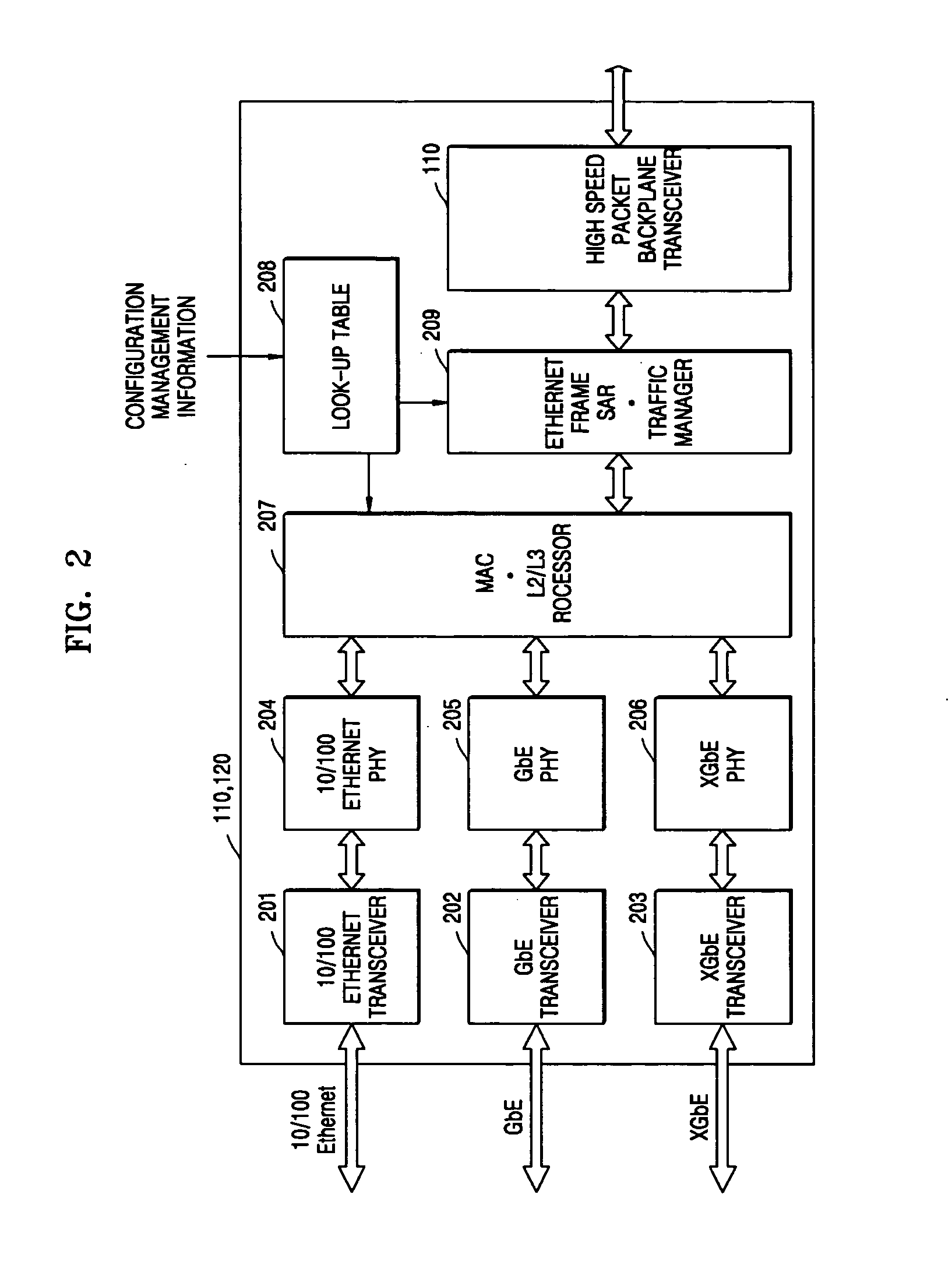
Apparatus for and method of integrating switching and transferring of SONET/SDH, PDH, and Ethernet signals
ActiveUS20050141568A1Low investment costDecreased maintenance feeTime-division multiplexData switching by path configurationPlesiochronous digital hierarchyEthernet
An apparatus for and a method of integrating switching and transferring of synchronous optical network / synchronous digital hierarchy (SONET / SDH), plesiochronous digital hierarchy (PDH), and Ethernet signals, which integrate and provide connection of synchronous digital (SONET / SDH) signals, plesiochronous digital (PDH) signals, and Ethernet signals, mutually change the synchronous digital (SONET / SDH) signals, the plesiochronous digital (PDH) signals, and the Ethernet signals, packet switching, synchronous timeslot switching, and channel configuration management and control functions in one system. Thus, packet switching capacity, timeslot switching capacity, and packet / timeslot bridging capacity can be enlarged and configured according to corresponding application. Also, a distinctive service compared to a service provided by a separate Ethernet device or a SONET / SDH network device can be provided through a packet / timeslot bridge. In addition, varied and reliable communication service at a moderate price can be provided to service users, and decreased investment and maintenance fee can be provided to carrier service providers.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Method for dynamic lossless adjustment of bandwidth of an embedded resilient packet ring network
InactiveUS20060062161A1Avoid wasting resourcesError preventionTransmission systemsLink Capacity Adjustment SchemeResilient Packet Ring
Disclosed is a method for dynamically and losslessly adjusting bandwidth of an embedded Resilient Packet Ring (RPR) ring network, in which dynamic and lossless bandwidth adjustment for an RPR ring network embedded in a Synchronous Digital Hierarchy (SDH) / Synchronous Optical Network (SONET) can be realized through adding a Link Capacity Adjustment Scheme (LCAS) system in the SDH / SONET processing layer. When it is required to increase ring network bandwidth, the bandwidth of the link section between sites on the SDH / SONET processing layer is first increased. Then the LCAS system in the SDH / SONET processing layer is started, and the actual bandwidth of the link on the SDH / SONET processing layer is increased losslessly with the LCAS system. Finally the bandwidth of the ring network on the RPR processing layer is increased. When it is required to decrease ring network bandwidth, the bandwidth of the ring network on the RPR processing layer is first decreased. Then the LCAS system in the SDH / SONET processing layer is started, and the actual bandwidth of the link on the SDH / SONET processing layer is decreased losslessly with the LCAS system. Finally the bandwidth of the link section between sites on the SDH / SONET processing layer is decreased. With the disclosed method, dynamic and lossless bandwidth adjustment for an embedded RPR ring network in SDH / SONET can be realized.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
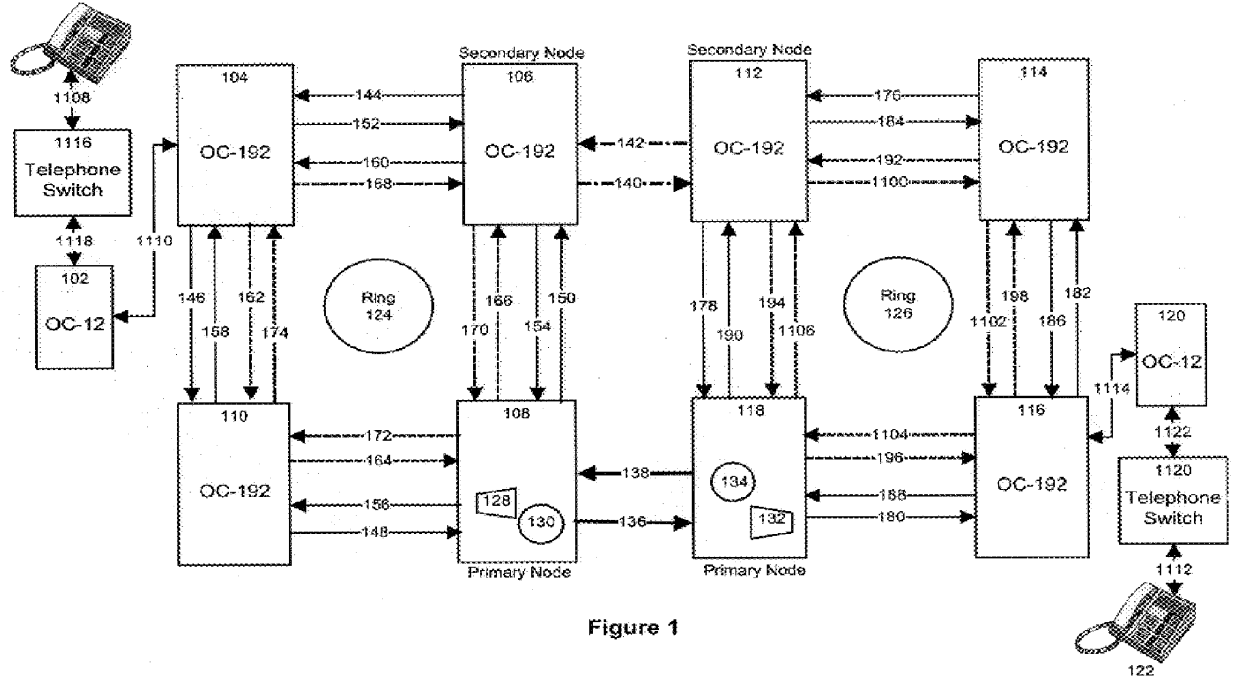
Method and apparatus for data transmission in synchronous optical networks
InactiveUS6147968AImproving quality and durationData augmentationError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsMaster controllerData transmission
The present invention relates to a switching node for use in a synchronous optical network ring, where the ring is transporting data divided into first size blocks, for example OC-192 optical signals, characterized by data blocks of size 192. The switching node includes several primary receive and send connections, for receiving and transmitting inter-ring optical signals divided into second size blocks, for example OC-48 optical signals, characterized by data blocks of size 48. The switching node further includes a secondary receive and send connection for receiving and transmitting intra-ring optical signals divided into first size blocks. A critical component of the switching node is the main controller, responsible for routing incoming intra-ring first size blocks towards a primary send connection. The main controller divides a first size block into smaller second size blocks, observes the second size blocks for the presence of concatenated data and, in the case where there is presence of concatenated data, routes the second size block as a single unit towards the adjacent network ring. In the case where there is absence of concatenated data, the routing controller routes the group of data forming the second size block as independent data elements towards the adjacent network ring.
Owner:NORTEL NETWORKS LTD
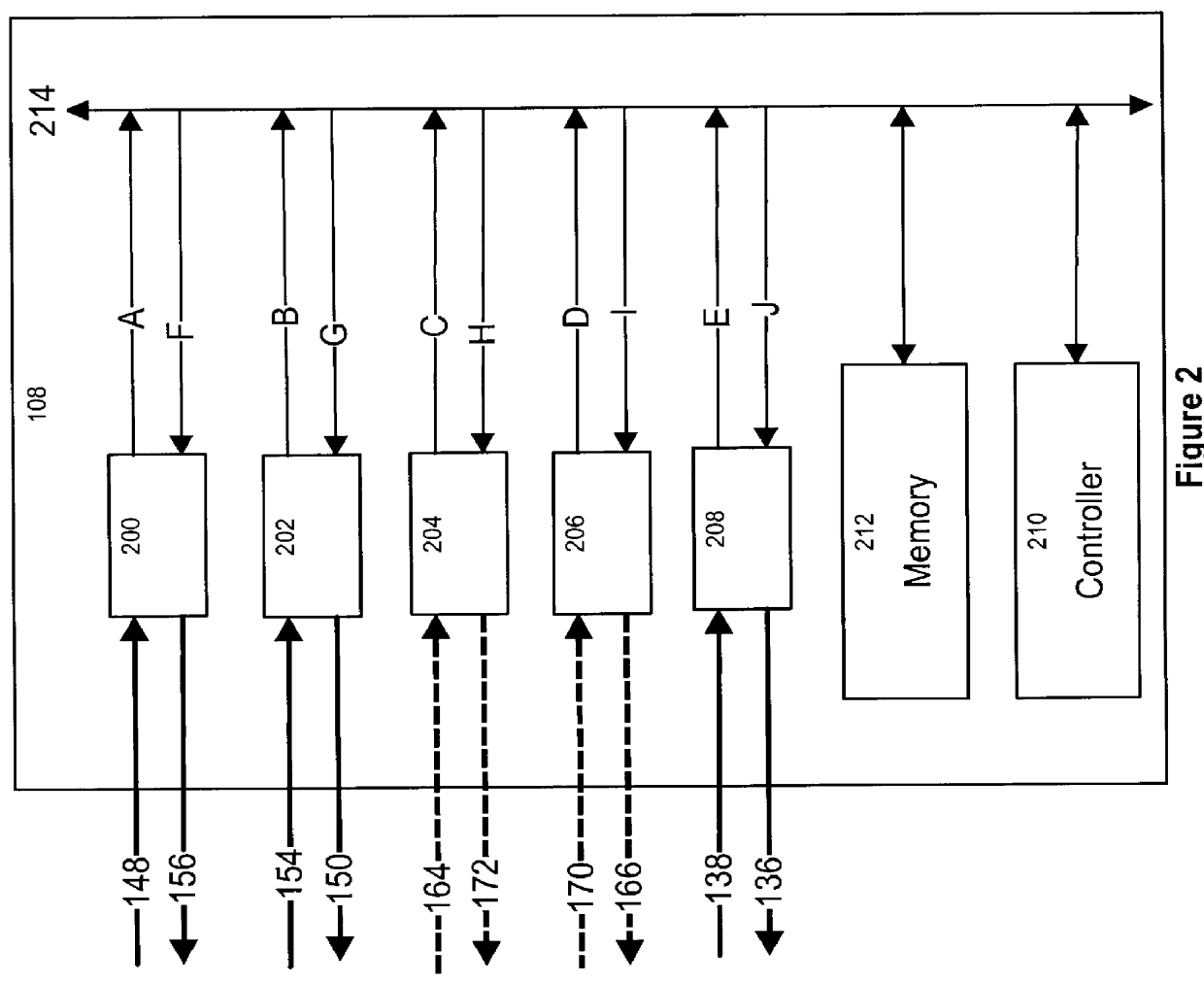
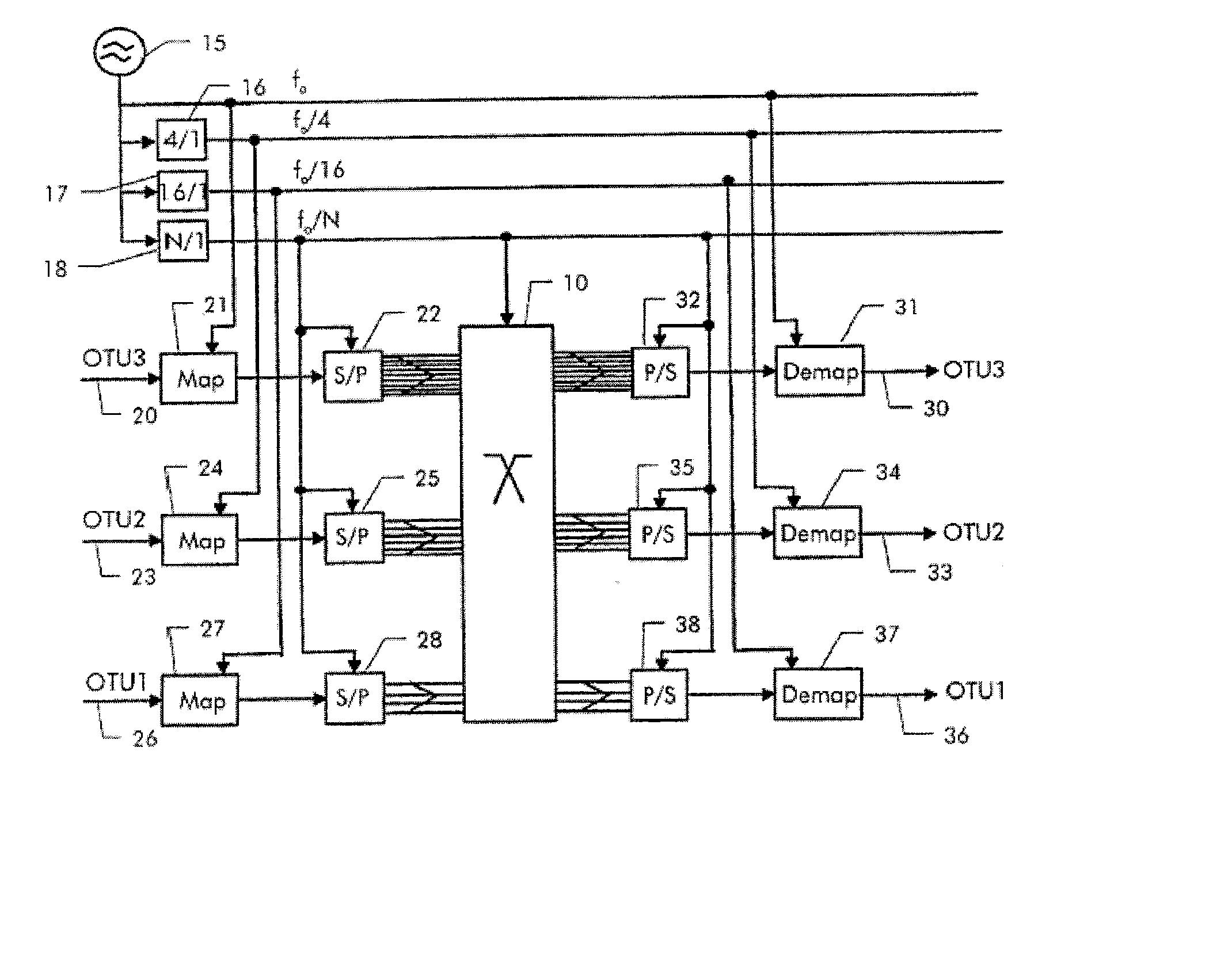
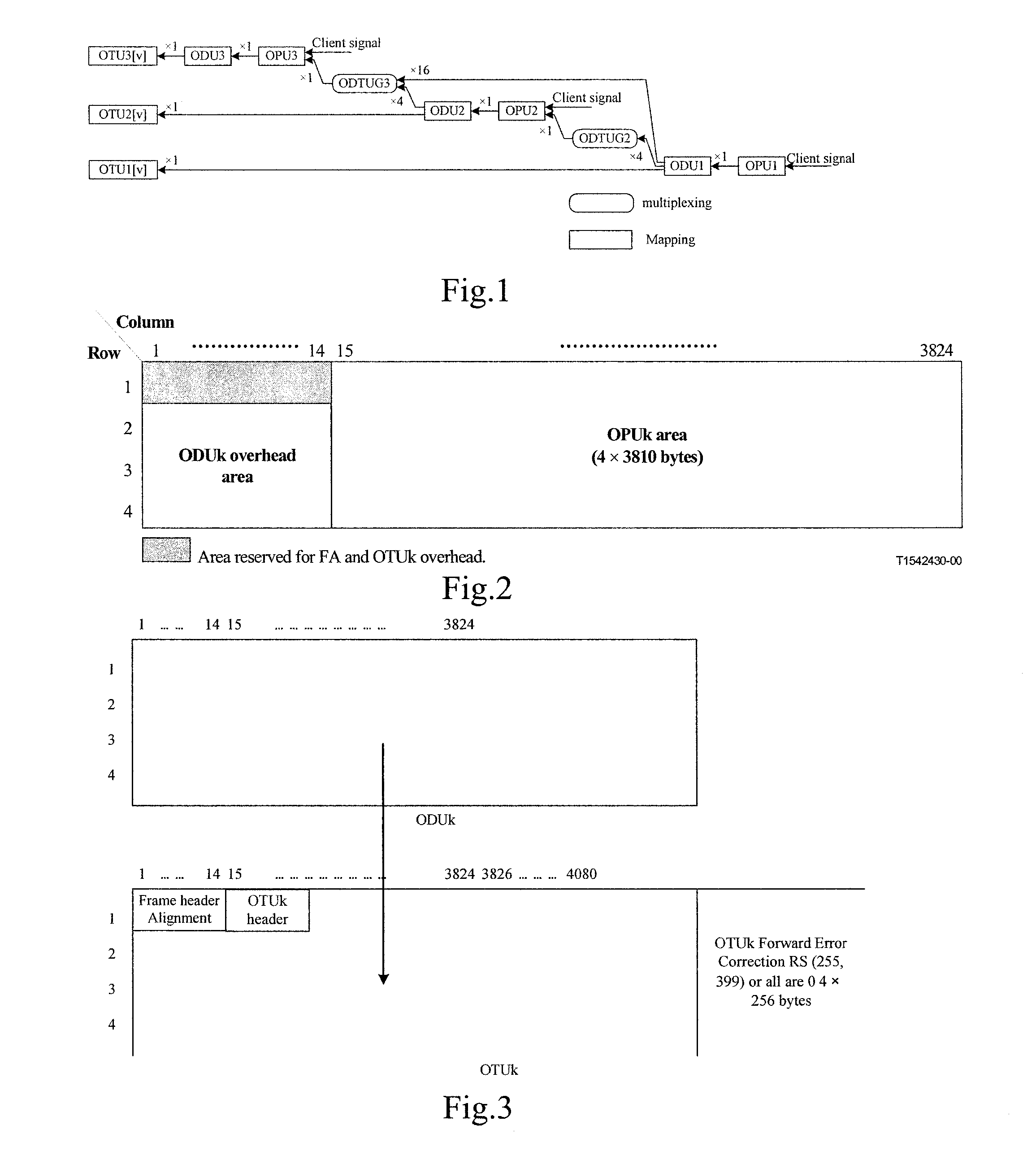
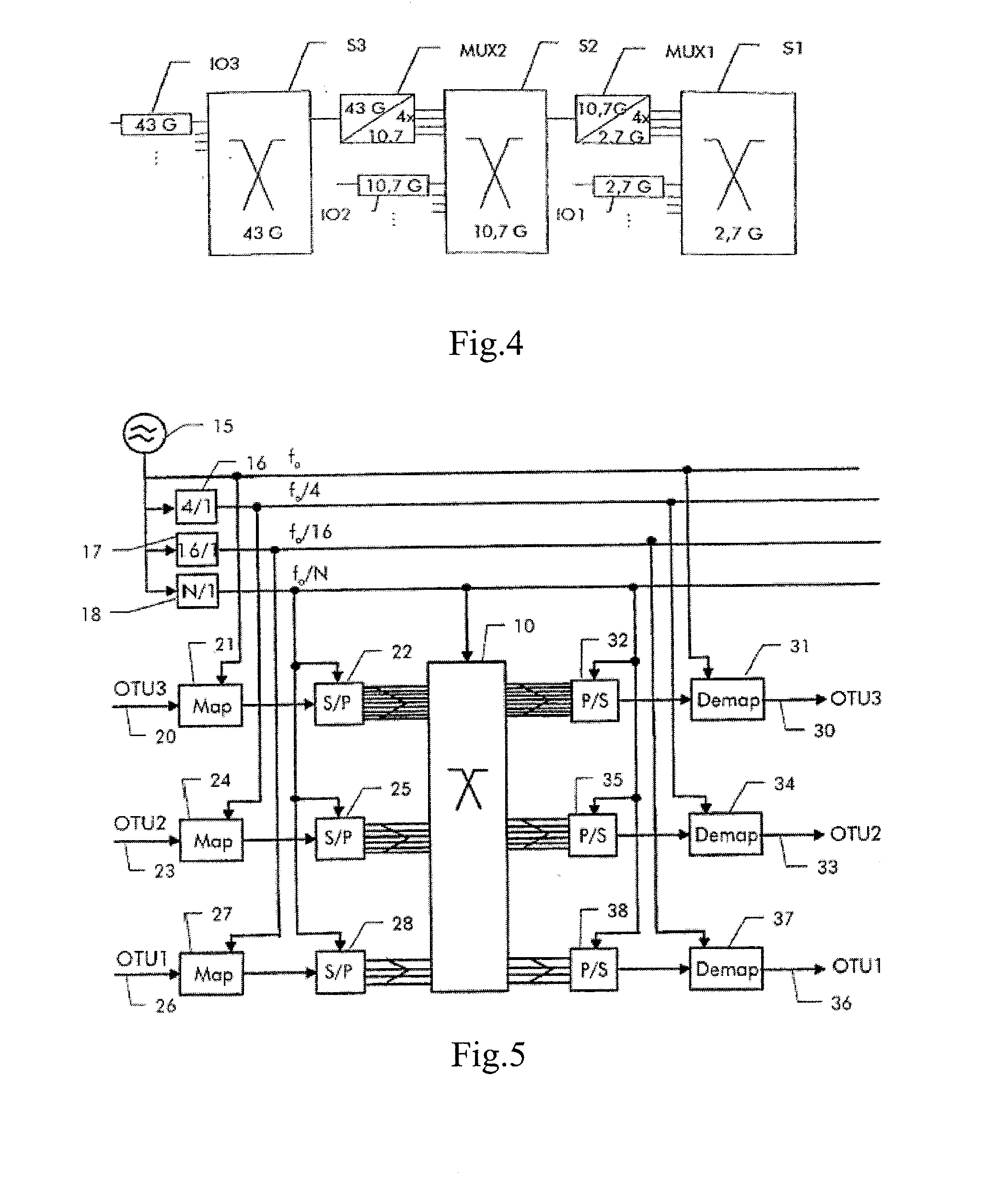
Uniform Switching System and Method for Synchronous Optical Network and Optical Transport Network
InactiveUS20070264015A1Easy to implementImprove switching performanceTime-division multiplexOptical multiplexCross connectionTransfer mode
Embodiments of the invention provide a method and a system for switching an OTN signal using the SDH. The system includes a system clock unit for providing a system clock signal and a frame header indication signal, a cross-connection unit for performing signal cross-connection at a uniform level of synchronous transfer mode rate, and an OTN signal interface processing unit for mapping, based on the system clock signal and frame header indication signal provided by the system clock unit, an OTN signal received from the circuit side into a synchronous transfer mode bus to be sent to the cross-connection unit, and de-mapping a signal output by the cross-connection unit through the synchronous transfer mode bus to an OTN signal to be output to the circuit side. An OTN signal may be switched in the SDH and the service interworking between an SDH network and an OTN may be achieved.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Adaptation method in use for syncretizing Ethernet and SHD or synchronous optical network
InactiveCN1728720AIncreased complexityAchieve teleportationTransmissionNetwork ConvergenceDigital video
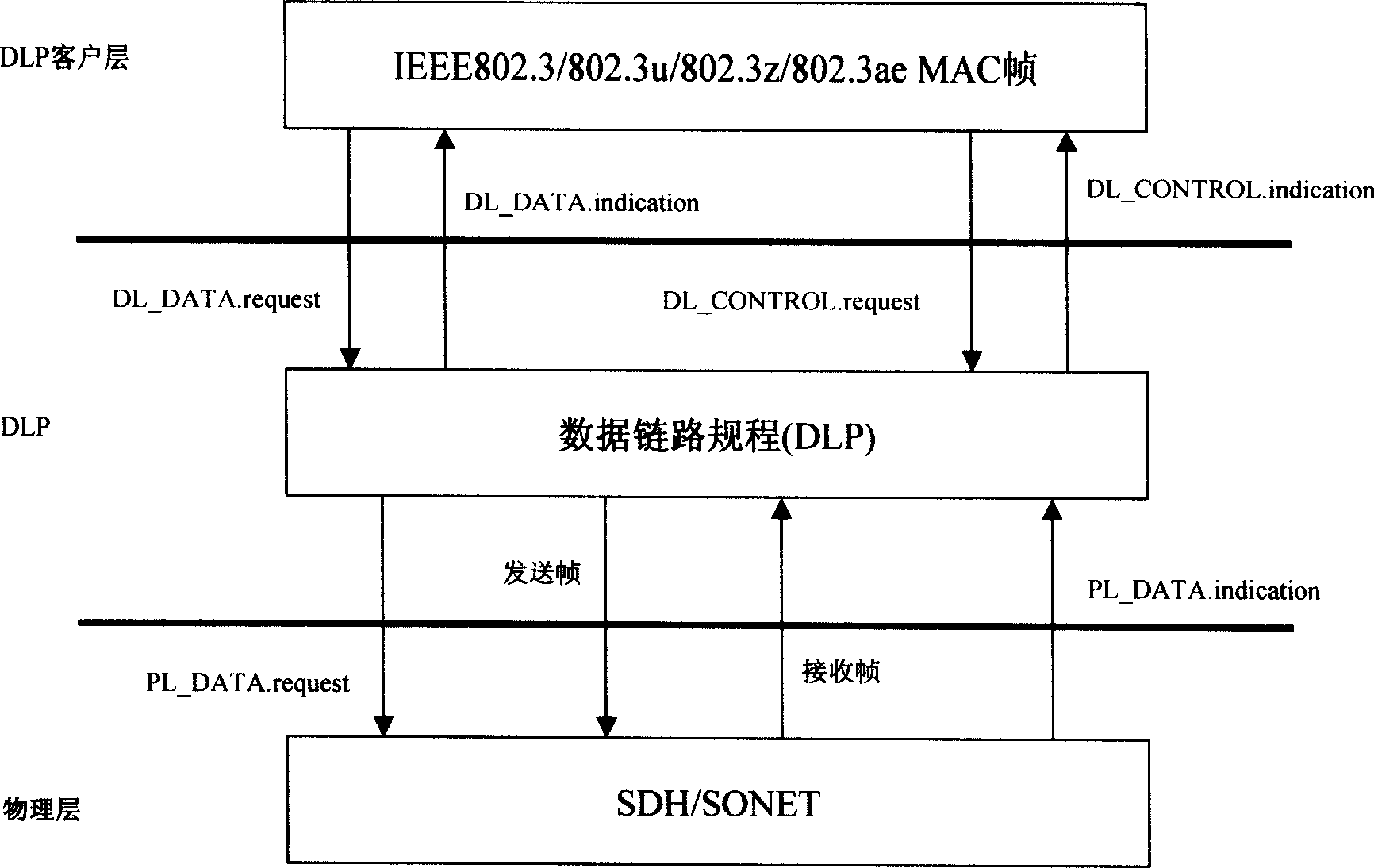
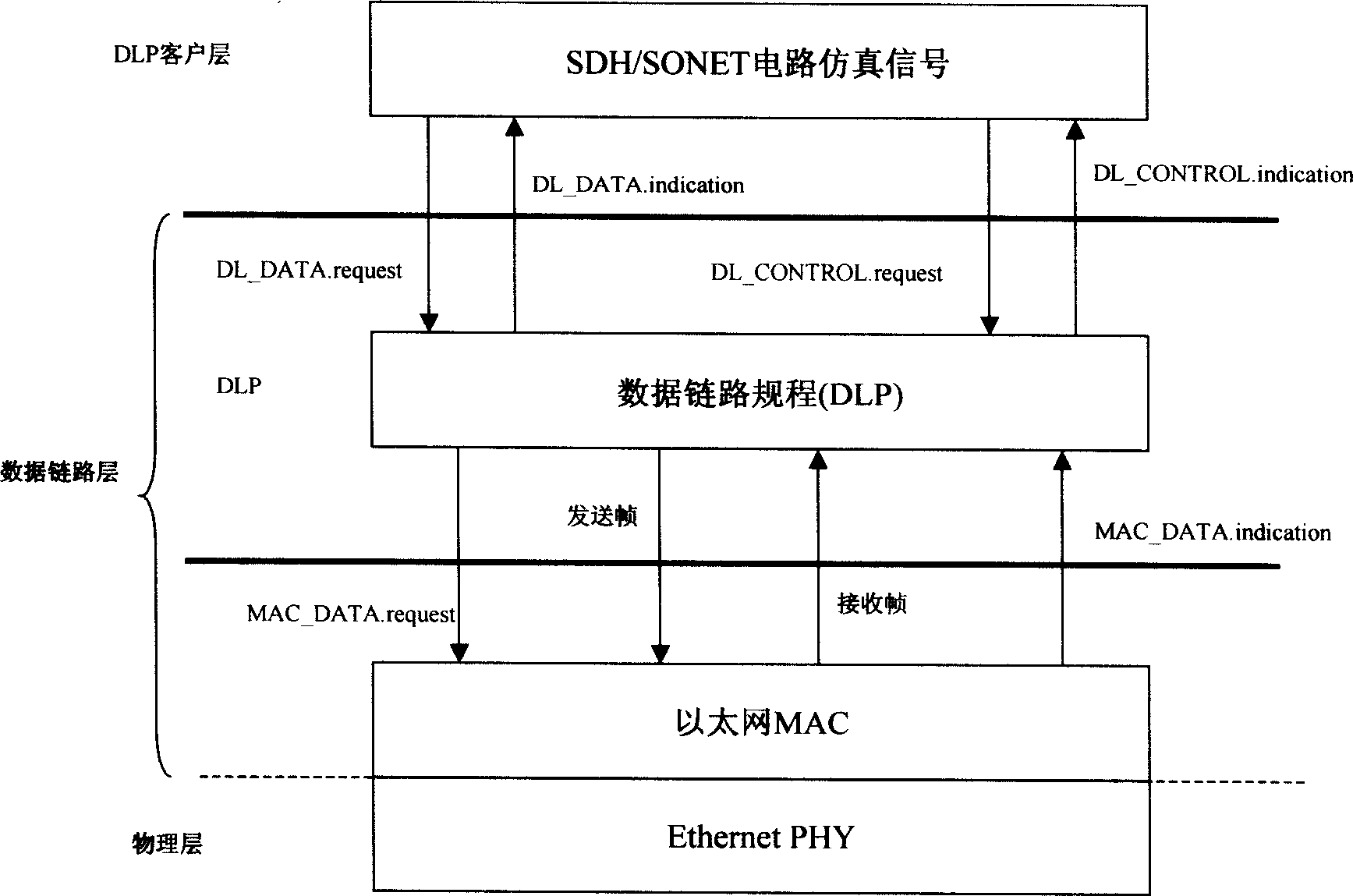
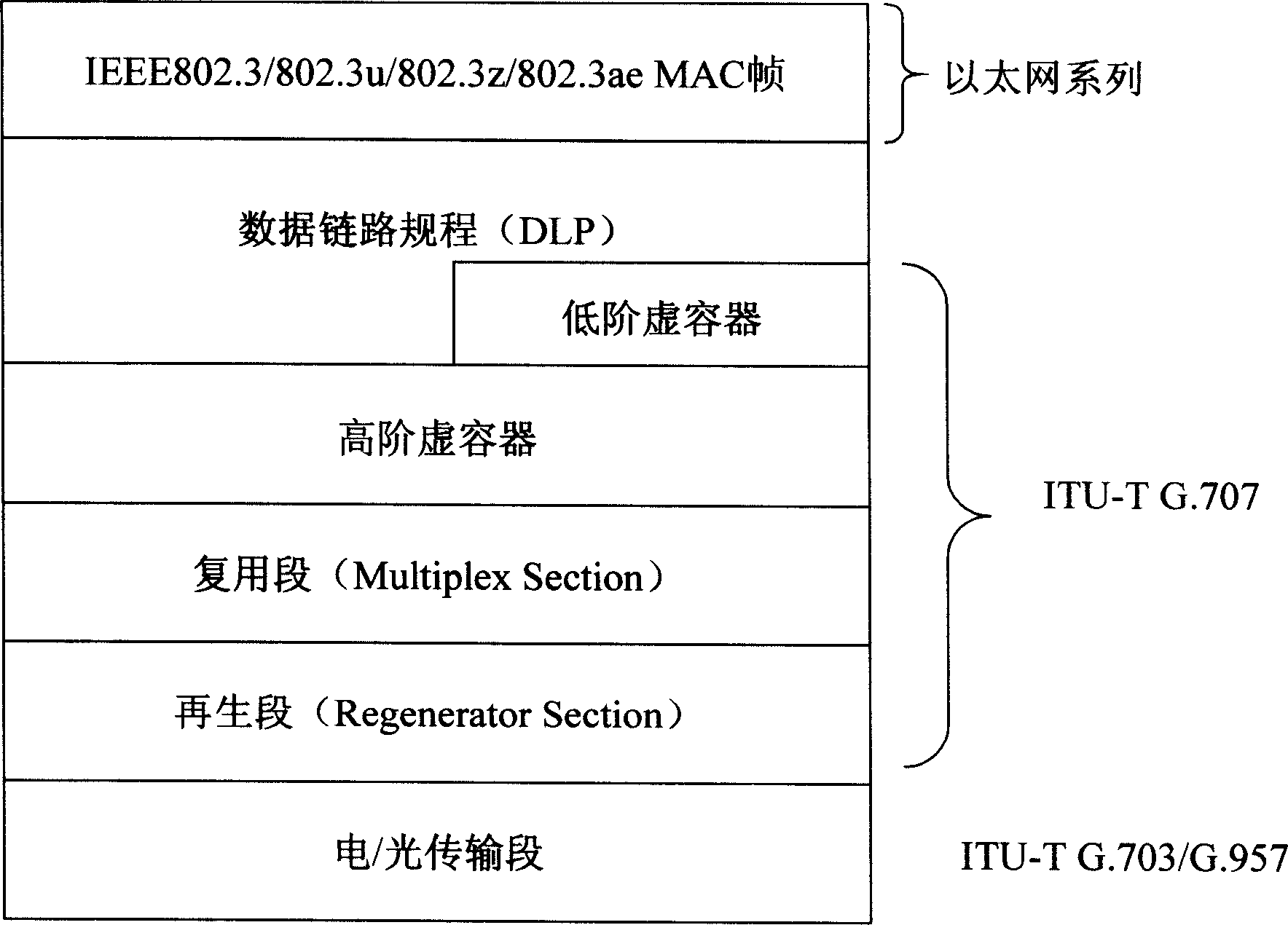
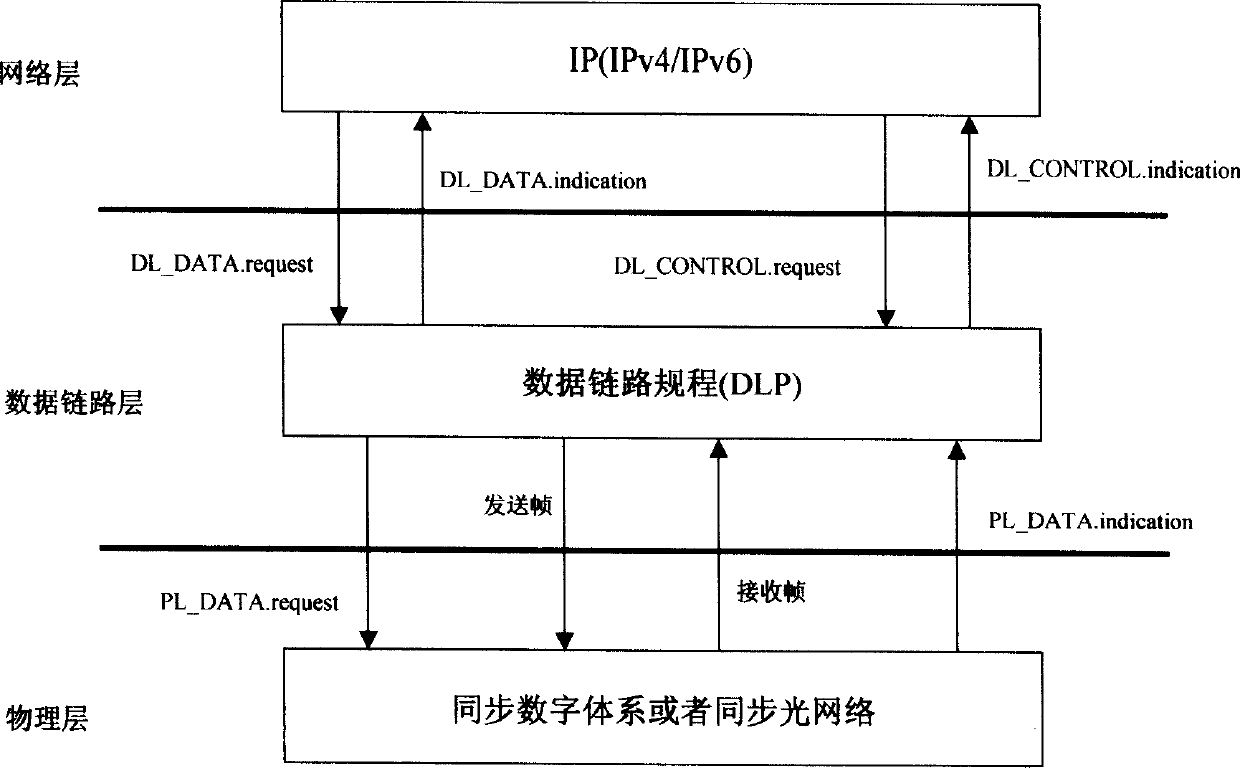
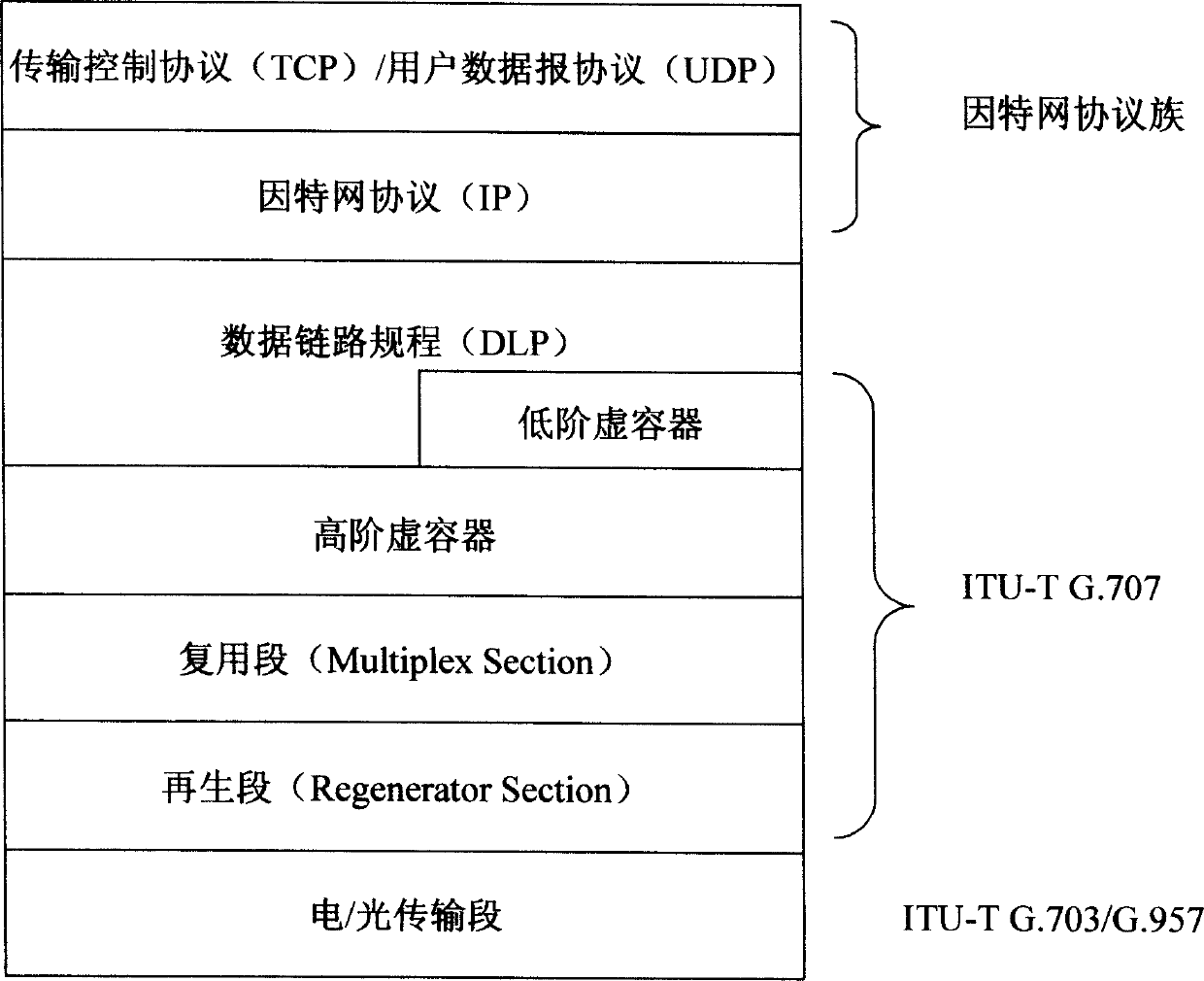
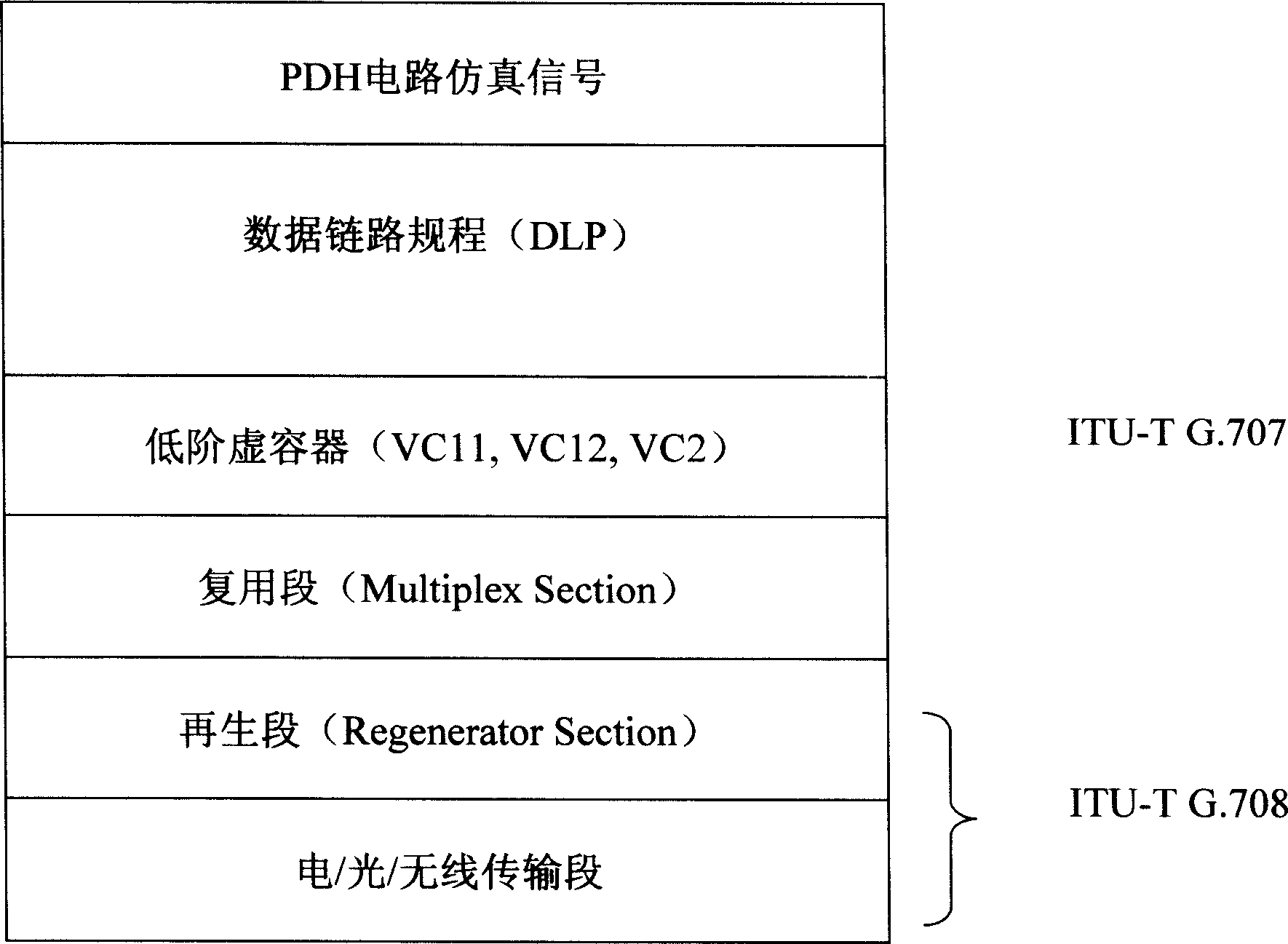
New layer of data link layer protocol - data link procedure (DLP) is introduced in the invention to realize syncretizing adaptation between Ethernet and SDH / SONET in order to overcome shortage of current adaptation technique including not matched interface speed, not supporting dynamic bandwidth allocation based on packets, and not possible to transmit SDH / SONET on Ethernet, not compatible to IP and packet voice service etc. The method realizes direct transmission of Ethernet on SDH / SONET, and SDH / SONET on Ethernet as well as realizes compatibility to IP network and packet voice network. Using safety mechanism, network control management mechanism, flow management mechanism provided by DLP realizes network management control function such as two layer protected rearrangement, performance management, fault management etc. The method makes current communication network transits to united public network in next generation of using packet switching technology smoothly.
Owner:邓里文
Fault detection and isolation in a synchronous optical network (SONET) and in a synchronous digital hierarchy (SDH) network
InactiveUS6452906B1Reducing and/or eliminating any difference in the behavior of the PTEsError preventionTransmission systemsCross connectionMultiplexer
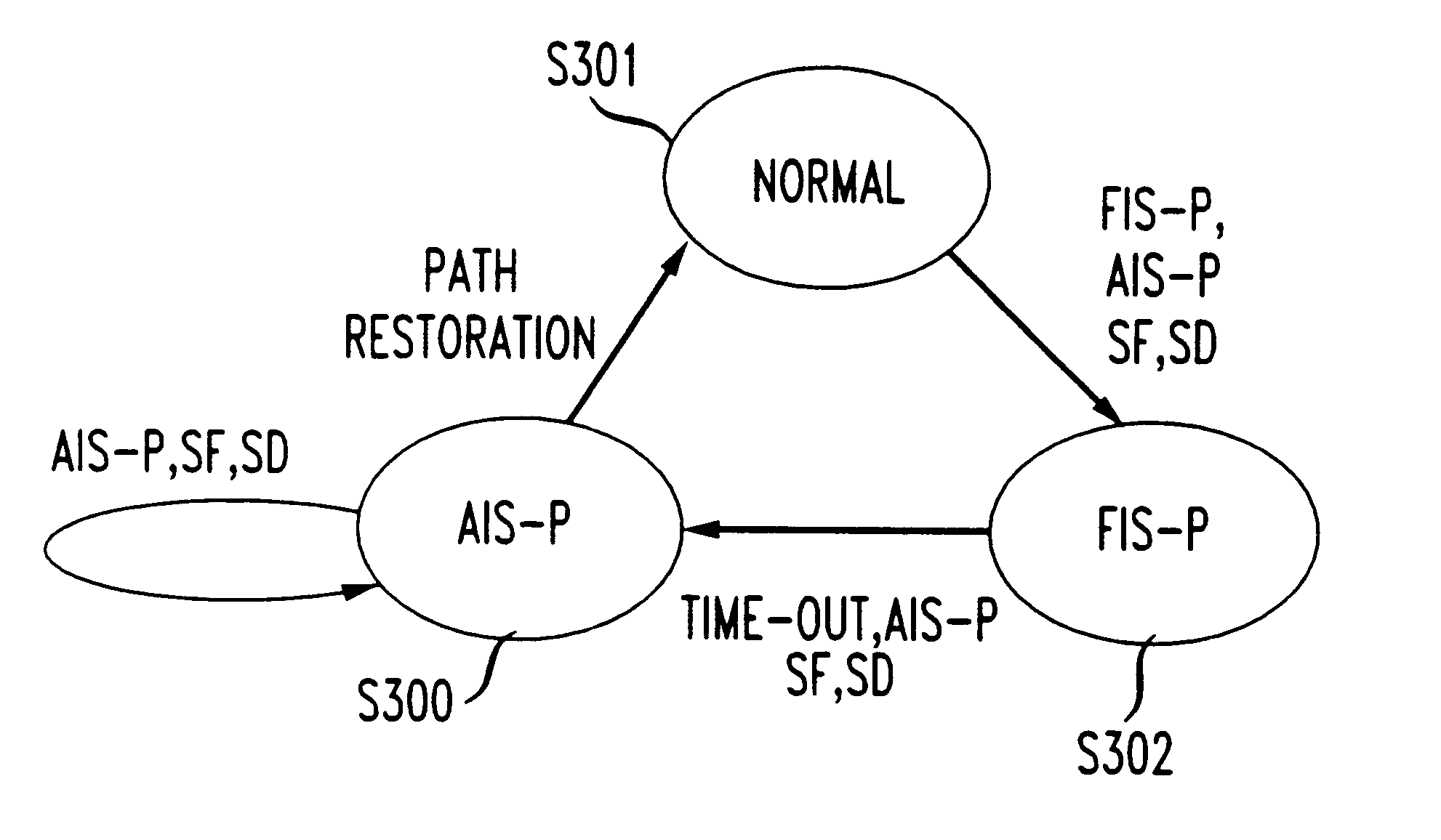
An in-band fault detection and isolation system and method for networks such as Synchronous Optical Network / Synchronous Digital Hierarchy (SONET / SDH) networks. Fault detection may be quickly and efficiently performed by a network without requiring modification to any add / drop multiplexers (ADMs) and / or without the involvement of an external network management system (NMS). To accomplish this without violating SONET / SDH standards, a new signal, called a fault isolation signal in the path (FIS-P), is proposed. The FIS-P may be used in lieu of an AIS-P to support special applications on certain digital cross connect (DCS)-to-DCS path segments. Moreover, the present invention may be implemented such that the behavior, of path terminating equipment (PTE) is unaffected.
Owner:AMERICAN TELEPHONE & TELEGRAPH CO
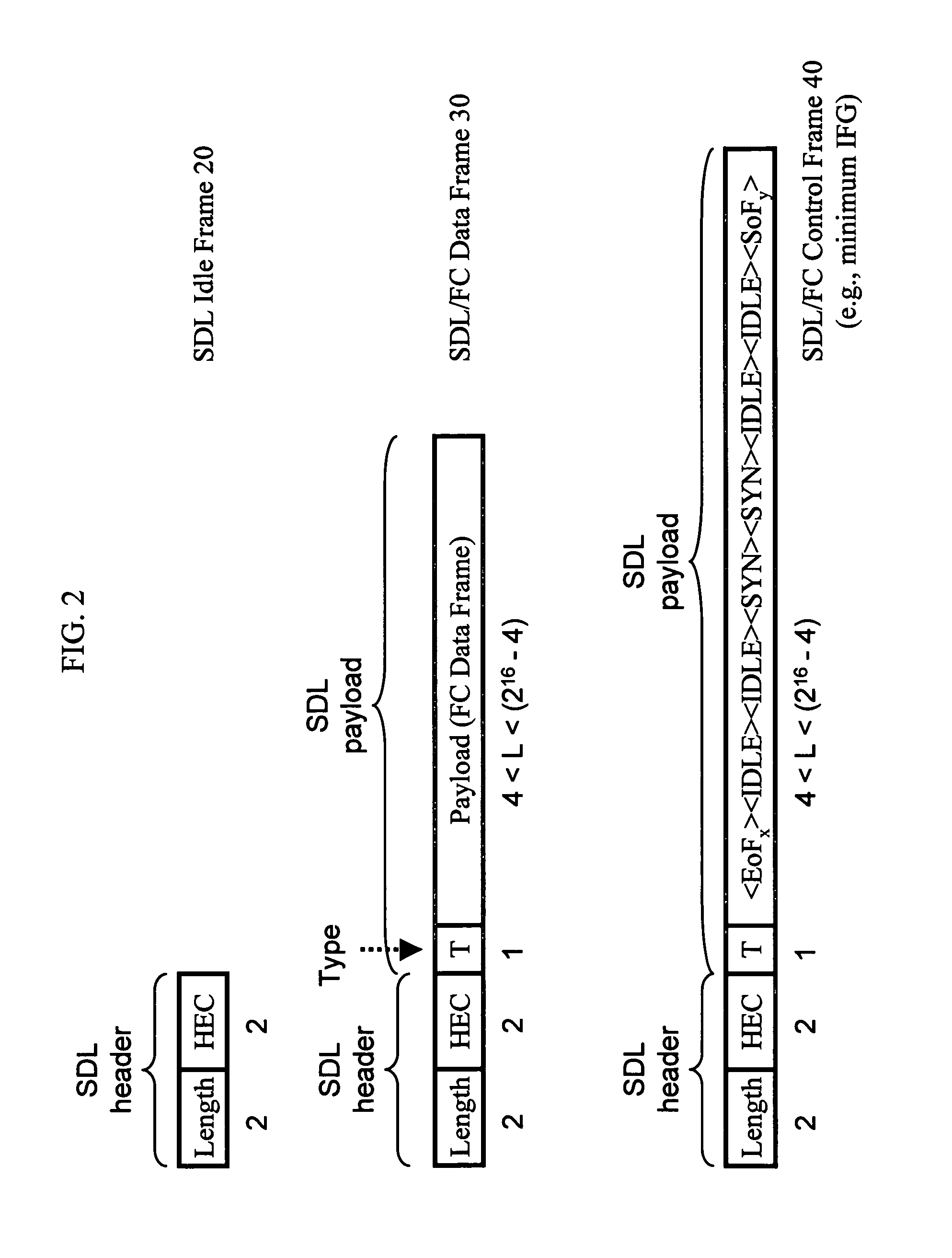
Mapping of block-encoded data formats onto a bit/byte synchronous transport medium
InactiveUS6993046B1Highly inefficientEfficient codingSimultaneous amplitude and angle modulationTime-division multiplexTransport mediumByte
A fibre channel (FC) signal representing block encoded data is applied to a block decoder, which removes the block encoding from the data. The data is then applied to a simplified data link (SDL) protocol encoder, which maps the data into an SDL protocol packet for transmission over a SONET (Synchronous Optical Network)-based transport medium.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
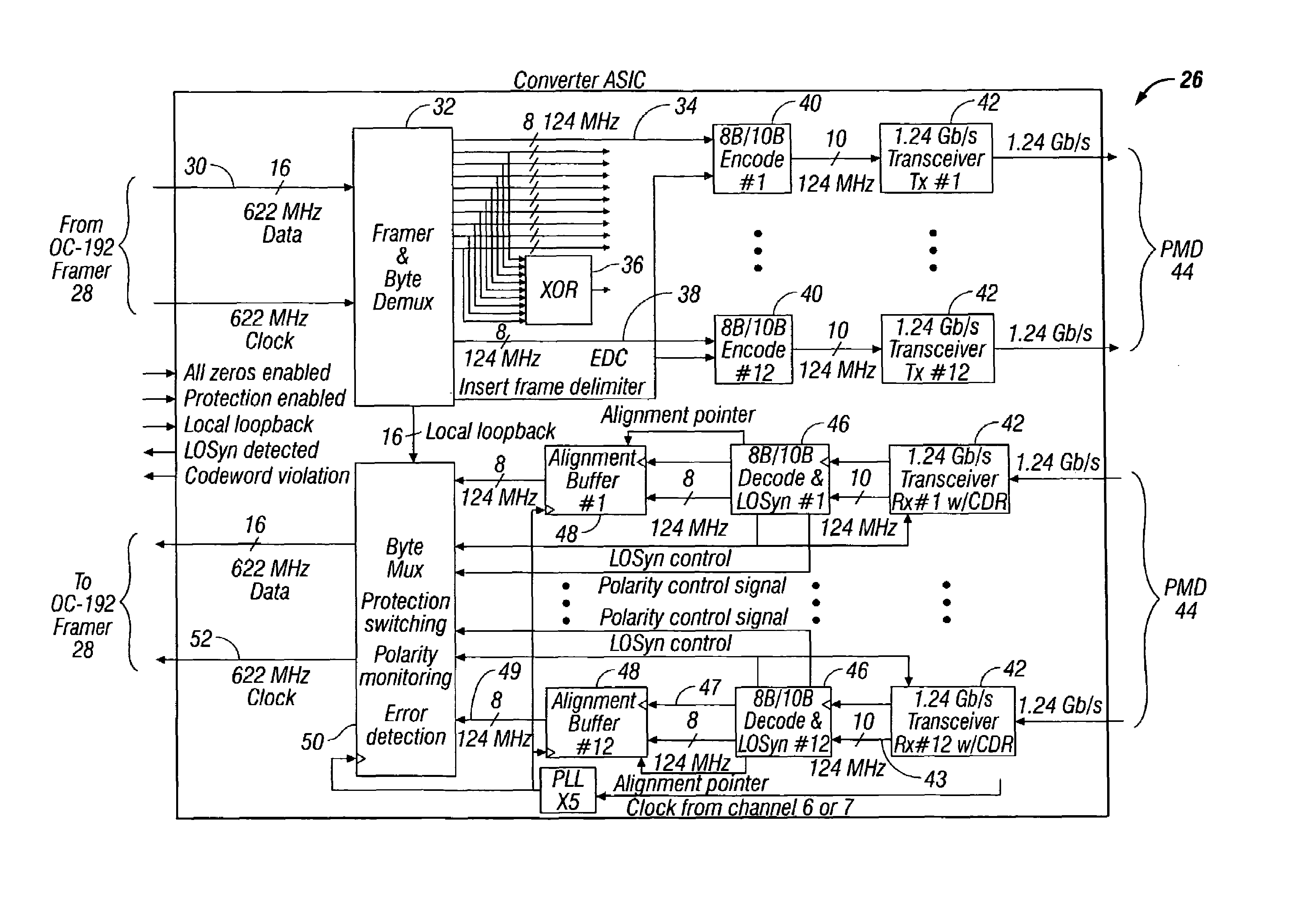
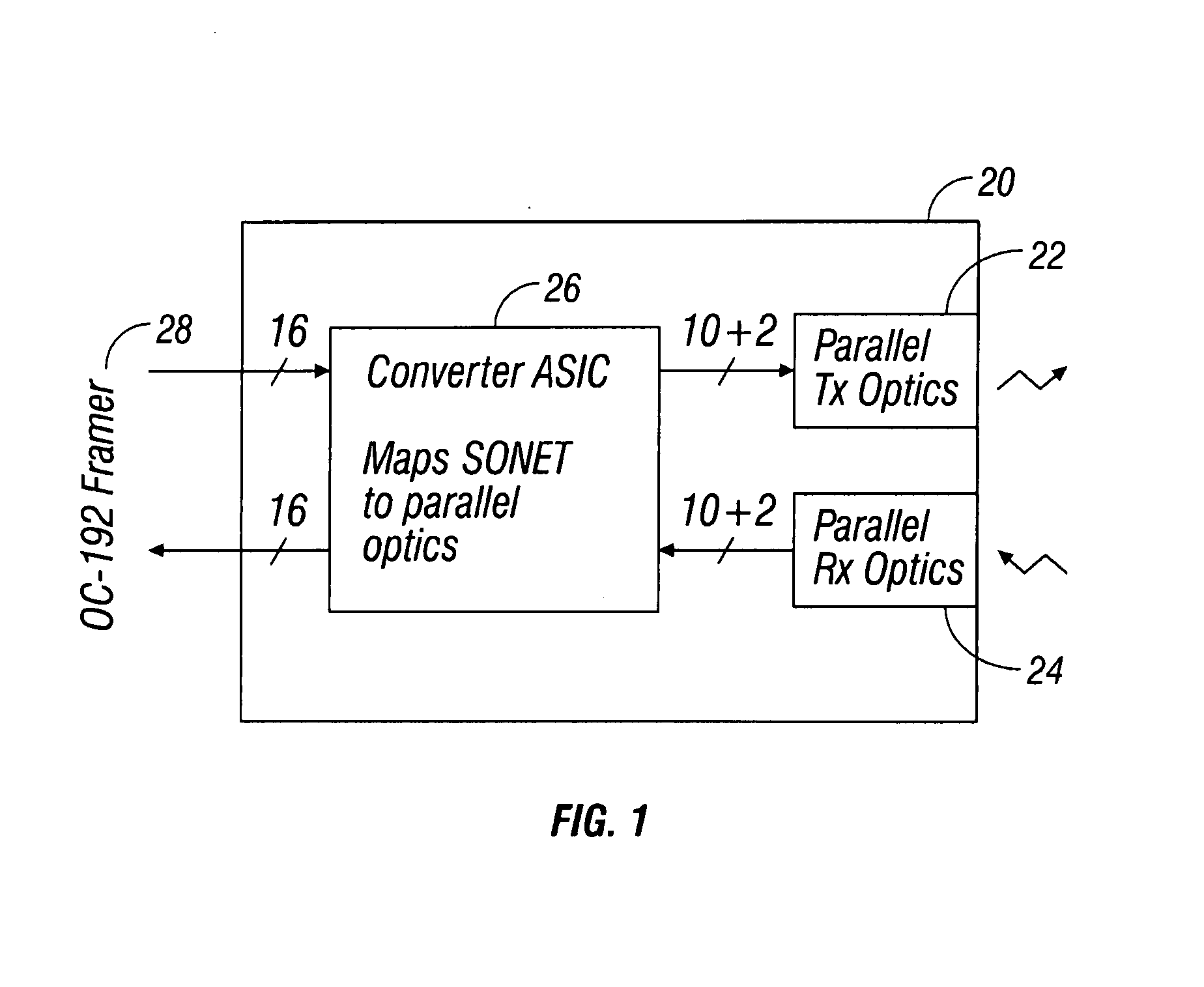
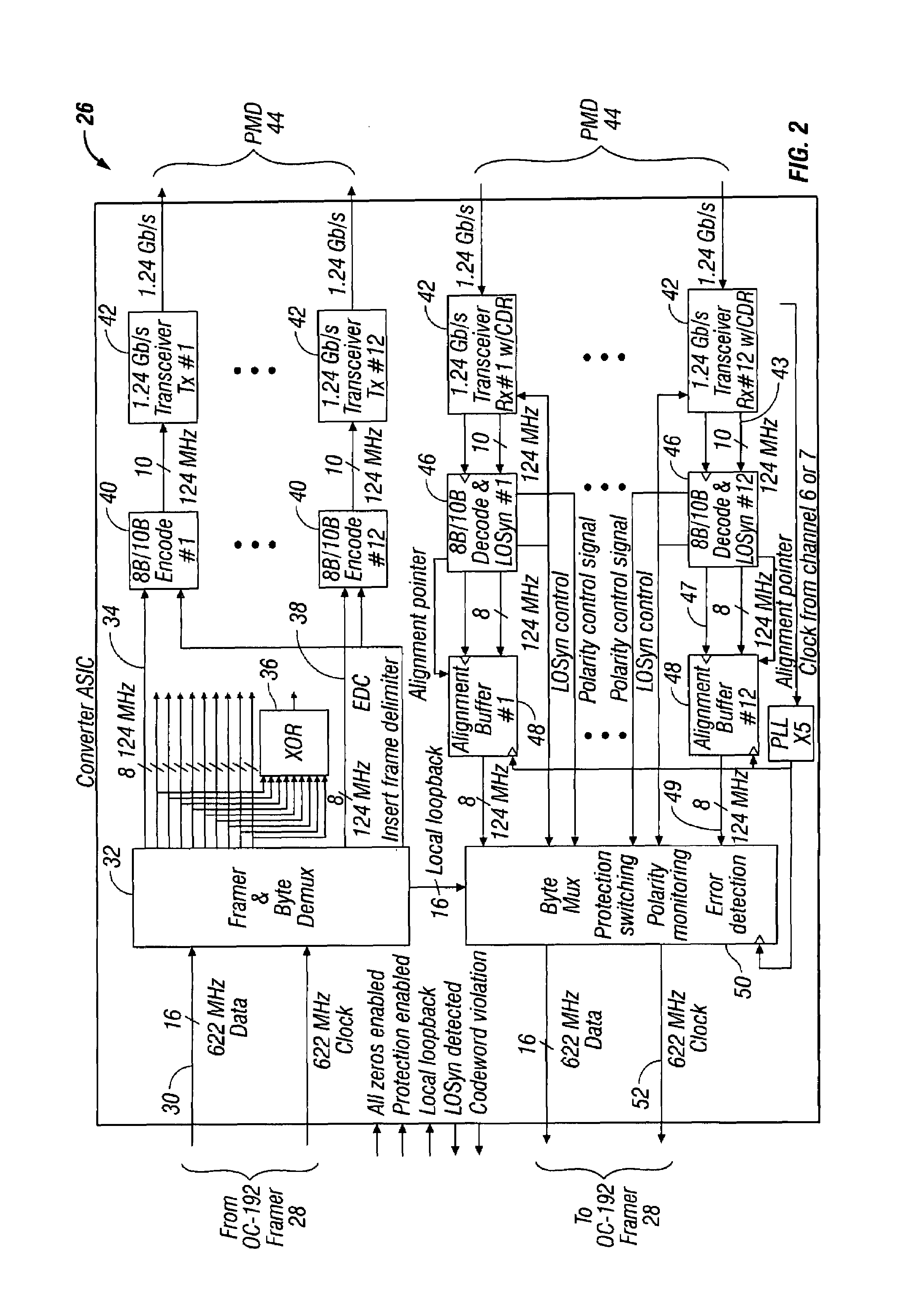
Method and apparatus for transferring synchronous optical network/synchronous digital hierarchy(SONET/SDH) frames on parallel transmission links
The present invention relates to methods and systems for transferring SONET / SDH frames between nodes by mapping the SONET / SDH frames onto individual channels of data and transferring the SONET / SDH frames over parallel transmission links. More particularly, the methods for transferring SONET / SDH frames includes transmitting SONET / SDH frames and receiving SONET / SDH frames using a transceiver module.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Methods, systems, and storage media for data encapsulation in networks
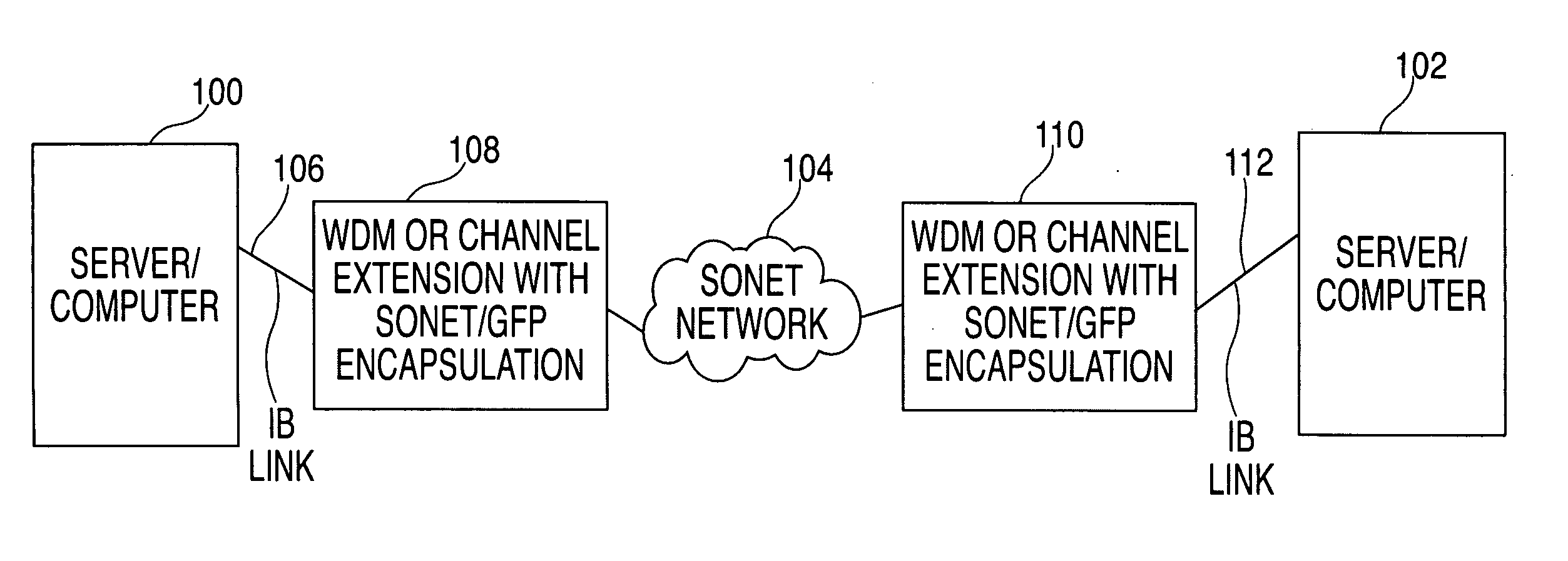
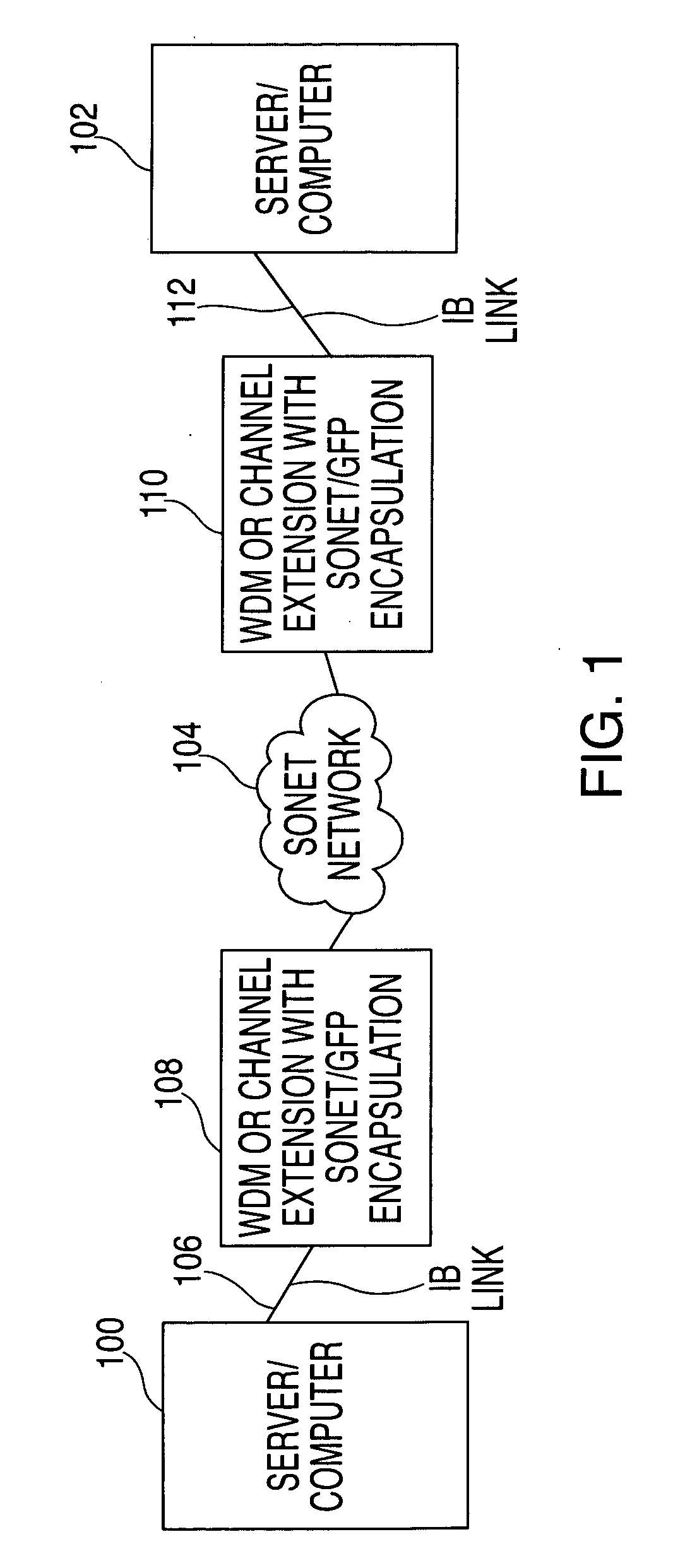
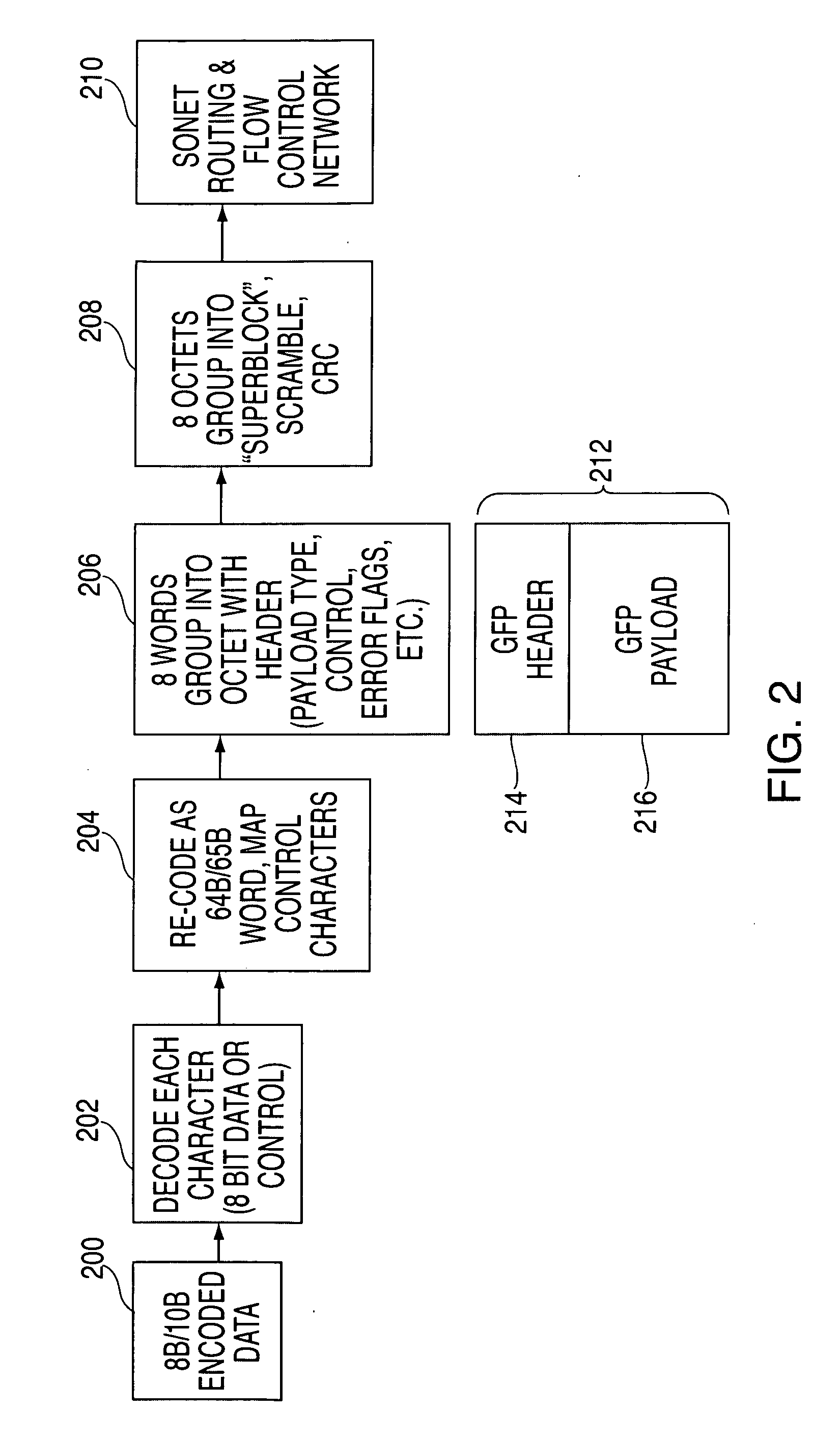
Methods, systems, and storage media enable the transport of InfiniBand (IB) data over a synchronous optical network (SONET) using generic frame procedure (GFP) encapsulation. User protocol identifiers for IB data in a GFP-SONET frame are defined. A process for maintaining running disparity of data during GFP encapsulation of IB data is provided. Data rate adaptation for this encapsulation is also provided. A simple, cost-effective scheme for data rate compression ensures that IB data is contained within a minimum SONET data rate traffic.
Owner:IBM CORP
Multi-protocol link encapsulation technique based POS (packet over synchronous optical network/internet protocol) frame decoding and framing device and method thereof
ActiveCN104580031ASolve heterogeneous problemsLow costTime-division multiplexData switching networksNetwork packetMulti protocol
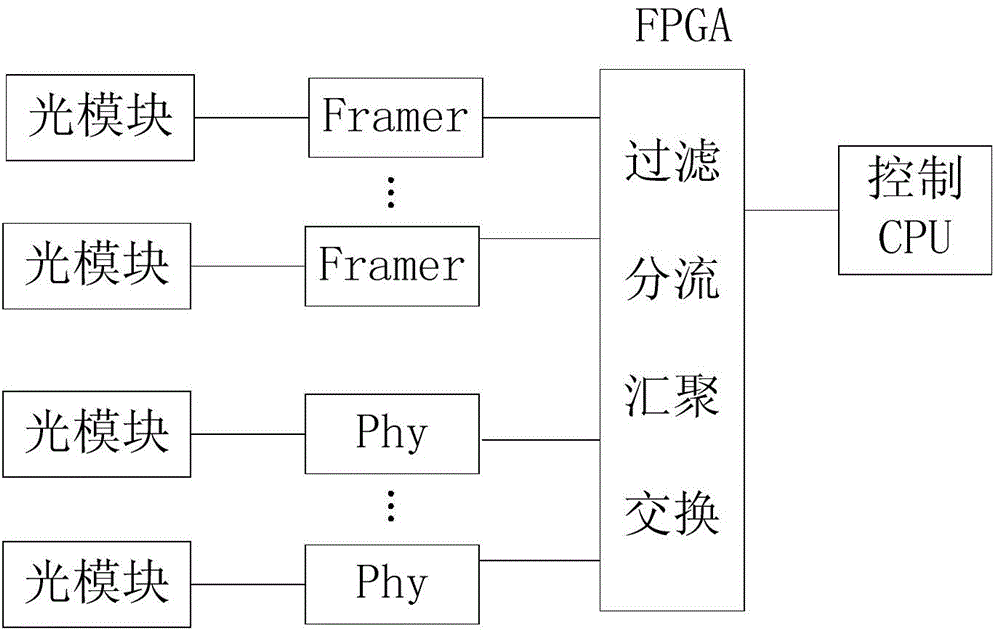
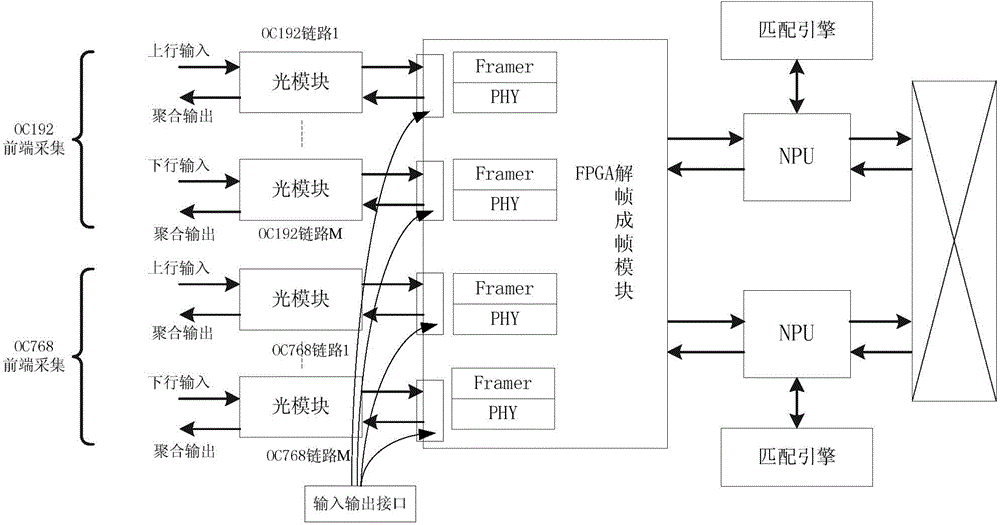
The invention discloses a multi-protocol link encapsulation technique based POS (packet over synchronous optical network / internet protocol) frame decoding and framing device and a method thereof. The device comprises an FPGA (field programmable gate array) frame decoding and framing module and a plurality of input and output interfaces arranged on a port of the FPGA frame decoding and framing module. The FPGA frame decoding and framing module comprises an FPGA chip unit, a POS message is subjected to frame decoding through the FPGA chip to acquire an IP (internet protocol) data packet, and the IP data packet is encapsulated into a Ethernet format to acquire Ethernet data; each input and output interface is used for outputting the POS message accessing to a link to the FPGA frame decoding and framing module and outputting the Ethernet data acquired after frame decoding of the POS message by the FPGA frame decoding and framing module. The method refers to a POS frame decoding and framing method utilizing the device. Frame decoding and framing of the POS message can be realized without utilization of special POS frame decoding and framing chips, and the device and the method have the advantages of high efficiency, low power consumption and low required cost.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
Utilizing the protecting bandwidth in a SONET network
InactiveUS20050147409A1Increase network capacityUtilize bandwidthLaser detailsTime-division multiplexOptical line terminationDistributed computing
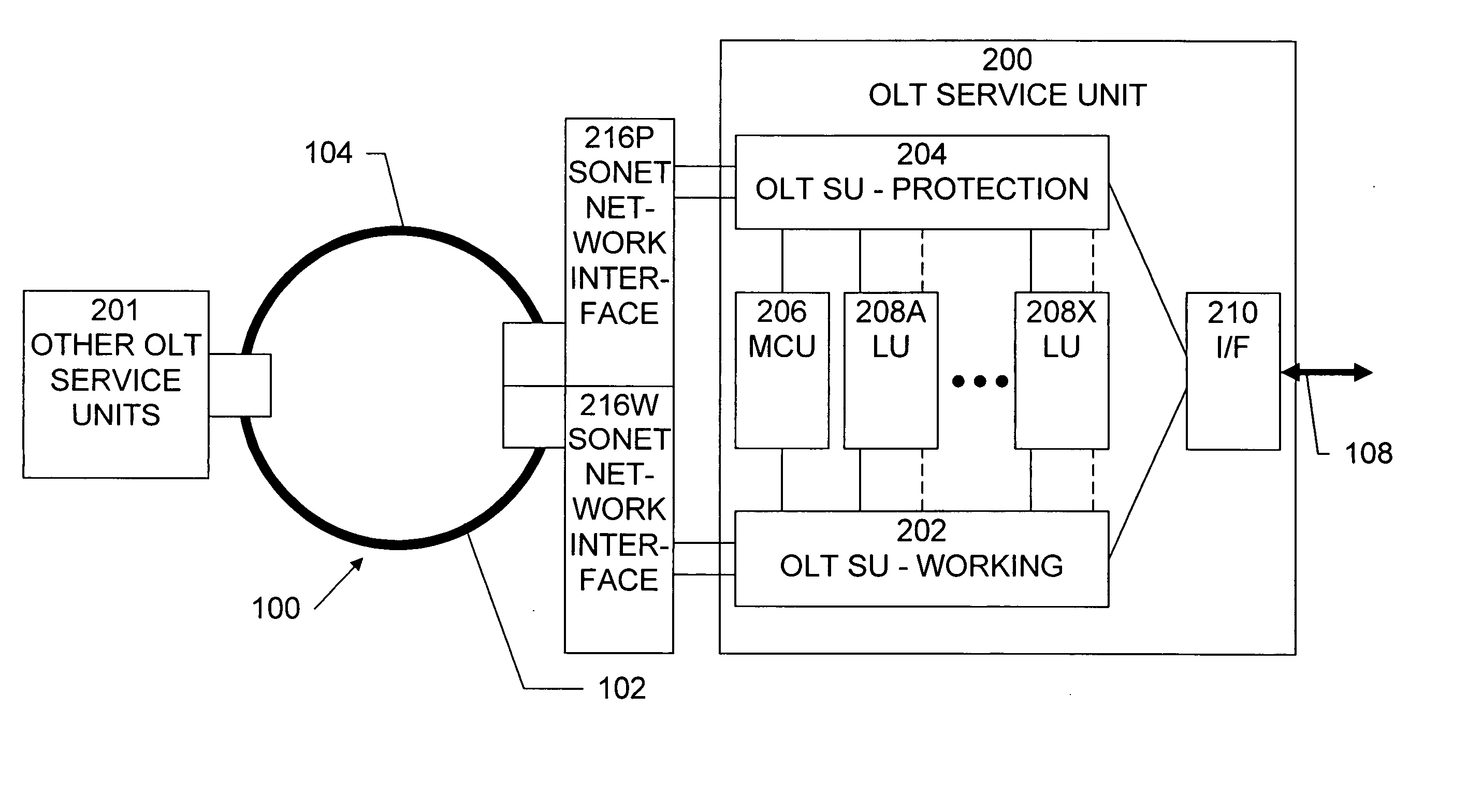
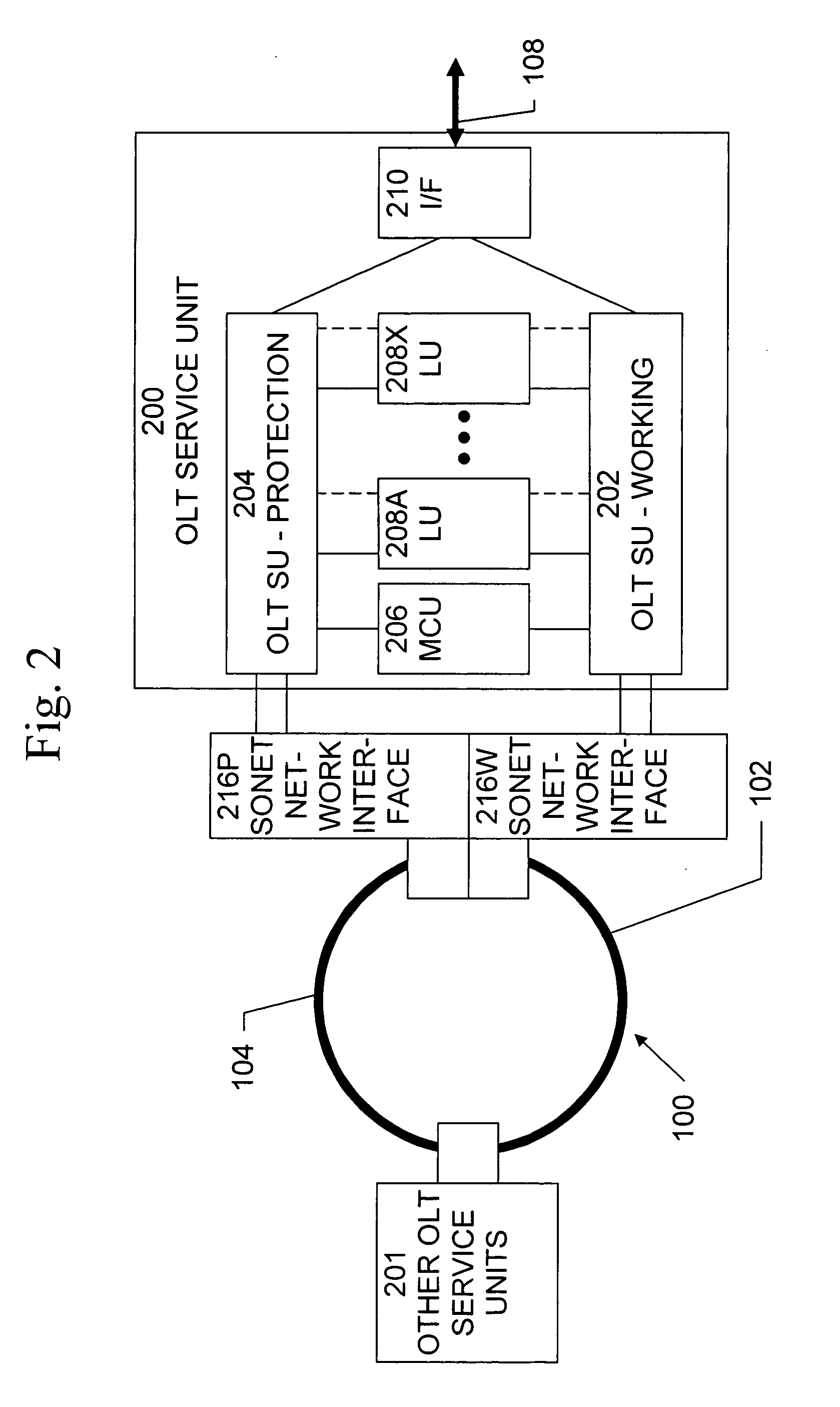
A system provides more cost and bandwidth efficient utilization of a SONET network having both a Working path and a Protection path by using both communication paths to carry data. A system for communicating data over a Synchronous Optical Network / Synchronous Digital Hierarchy, the system comprises an Optical Line Termination unit operable to interface with a plurality of Synchronous Optical Network / Synchronous Digital Hierarchy communication paths, and communicate different data on each of the plurality of Synchronous Optical Network / Synchronous Digital Hierarchy communication paths.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
System for bidirectional free-space laser communication of gigabit Ethernet telemetry data
ActiveUS9438338B1Reduce the impactLow costTime-division multiplexLine-of-sight transmissionCorrection algorithmTelecommunications link
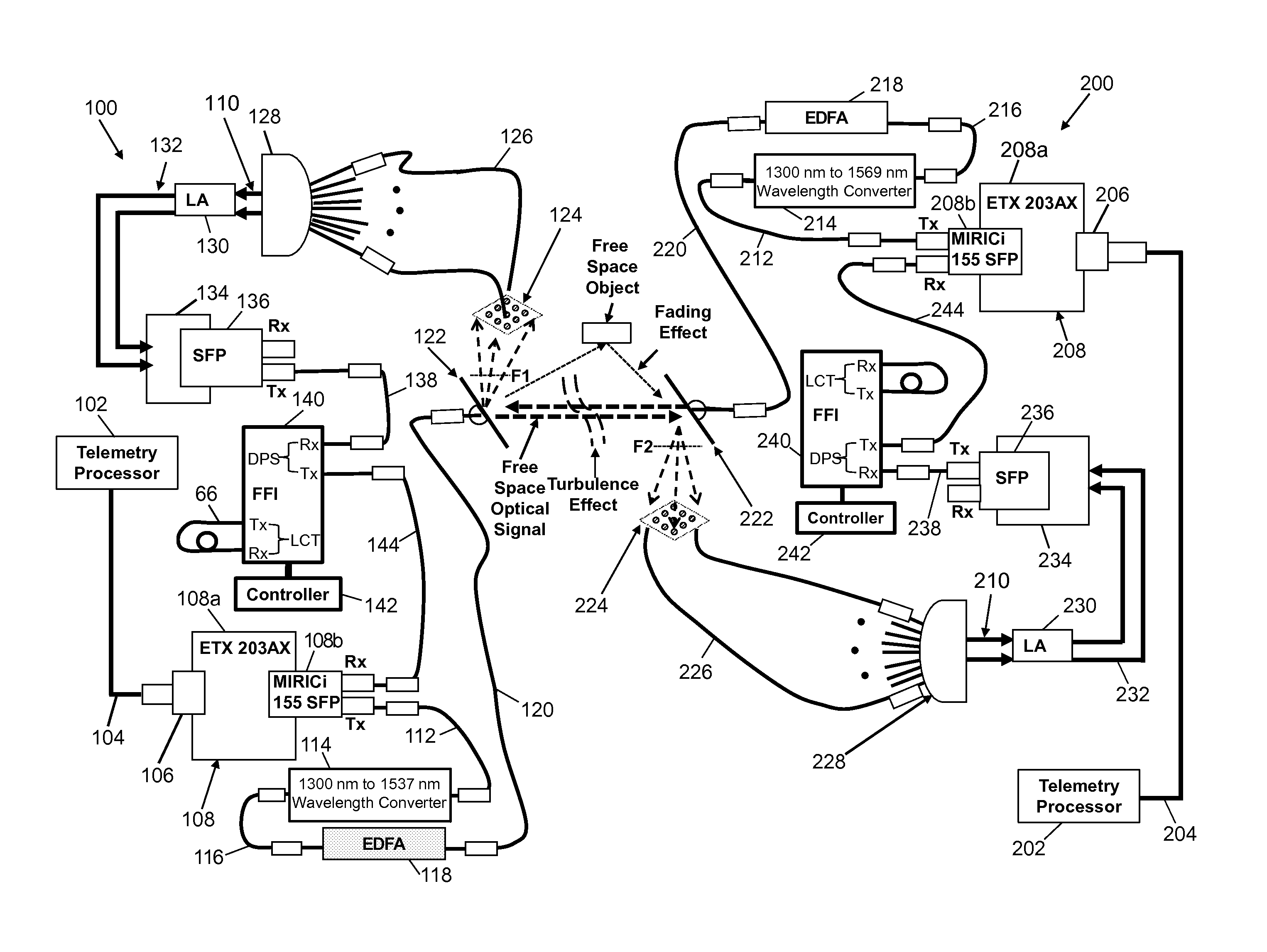
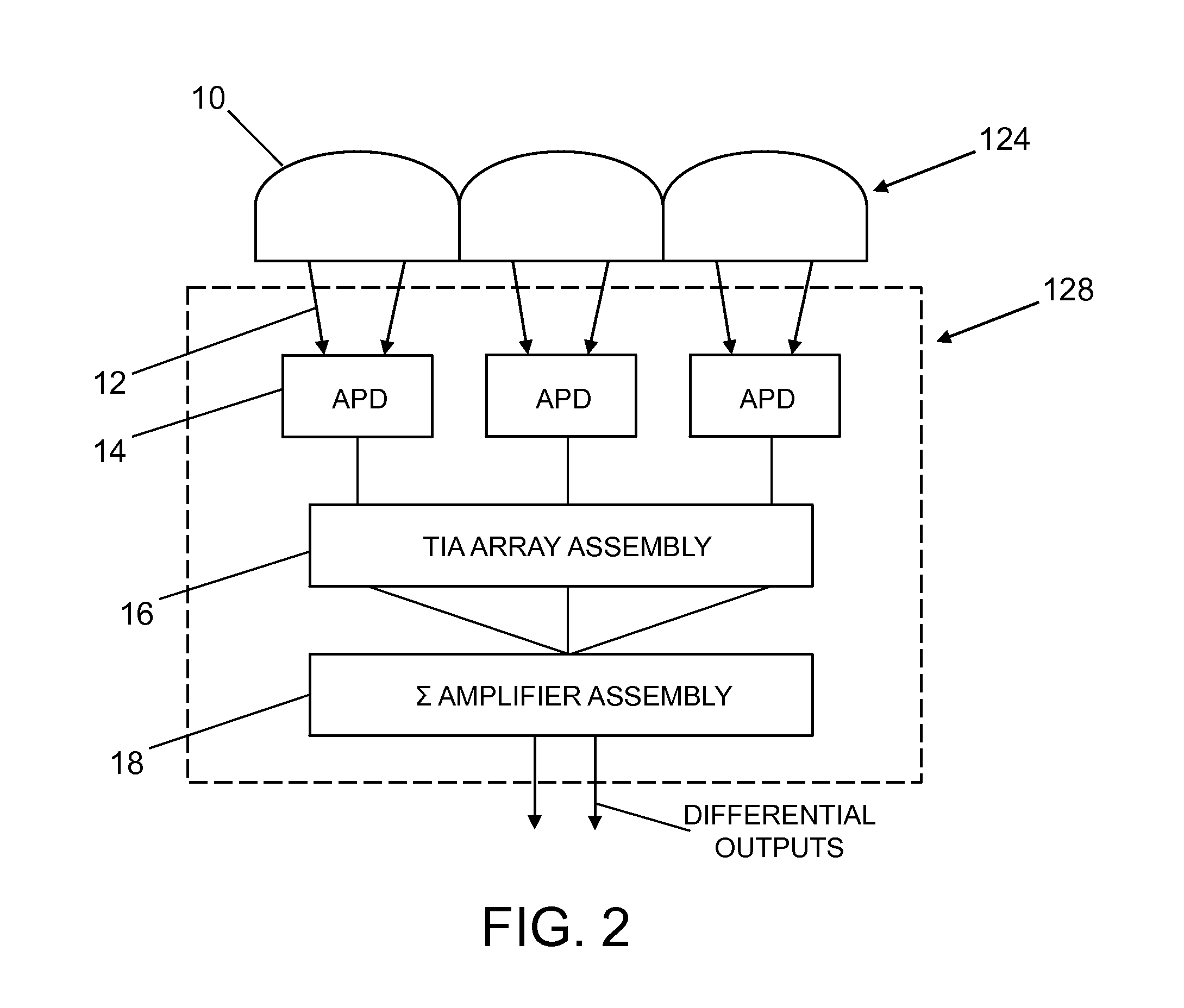
A free-space laser communication system for bidirectional transmission of telemetry data in Gigabit Ethernet (GBE) protocol using a dual atmospheric effect mitigation approach. This free-space bidirectional GBE laser communication system utilizes an Optical Combining Receiver Array and a Framer / Forward Error Correction / Interleaver (FFI) device to mitigate the combined effects of atmospheric turbulence and channel fading. Since the FFI device is designed for Synchronous Optical Network (SONET) protocol, an intelligent (or smart) media converter is used to convert GBE telemetry data to SONET frames, which enables the FFI device to perform an error correction algorithm and provide a seamless error-free GBE laser communication link for distance over a kilometer. This bidirectional laser communication system can be implemented with low-cost commercially available components.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
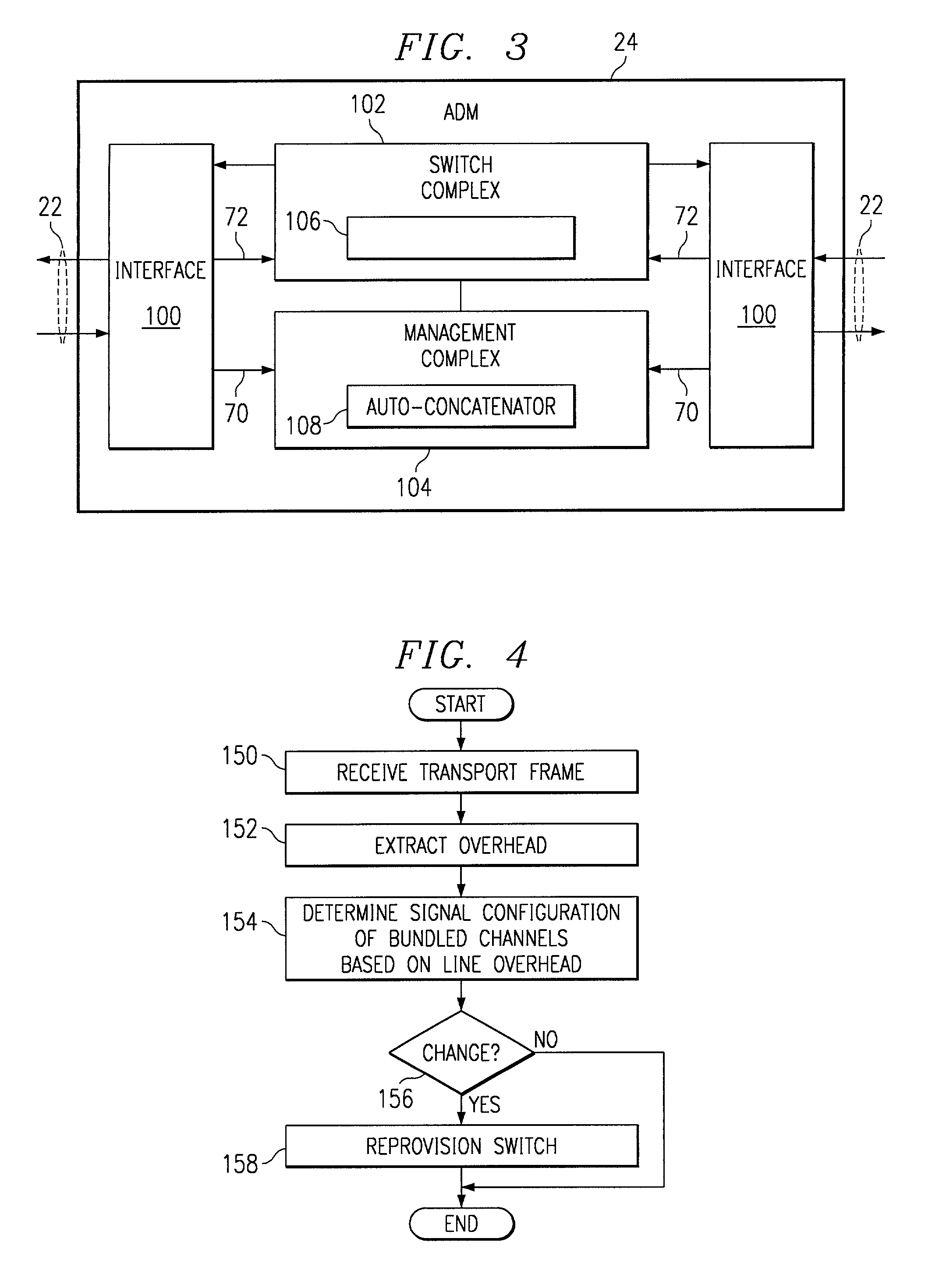
Method and system for automatic concatenation detection of synchronous optical network (SONET) channels
InactiveUS6956874B1Reduce eliminateMinimization of expenseTime-division multiplexOptical multiplexCross connectionComputer science
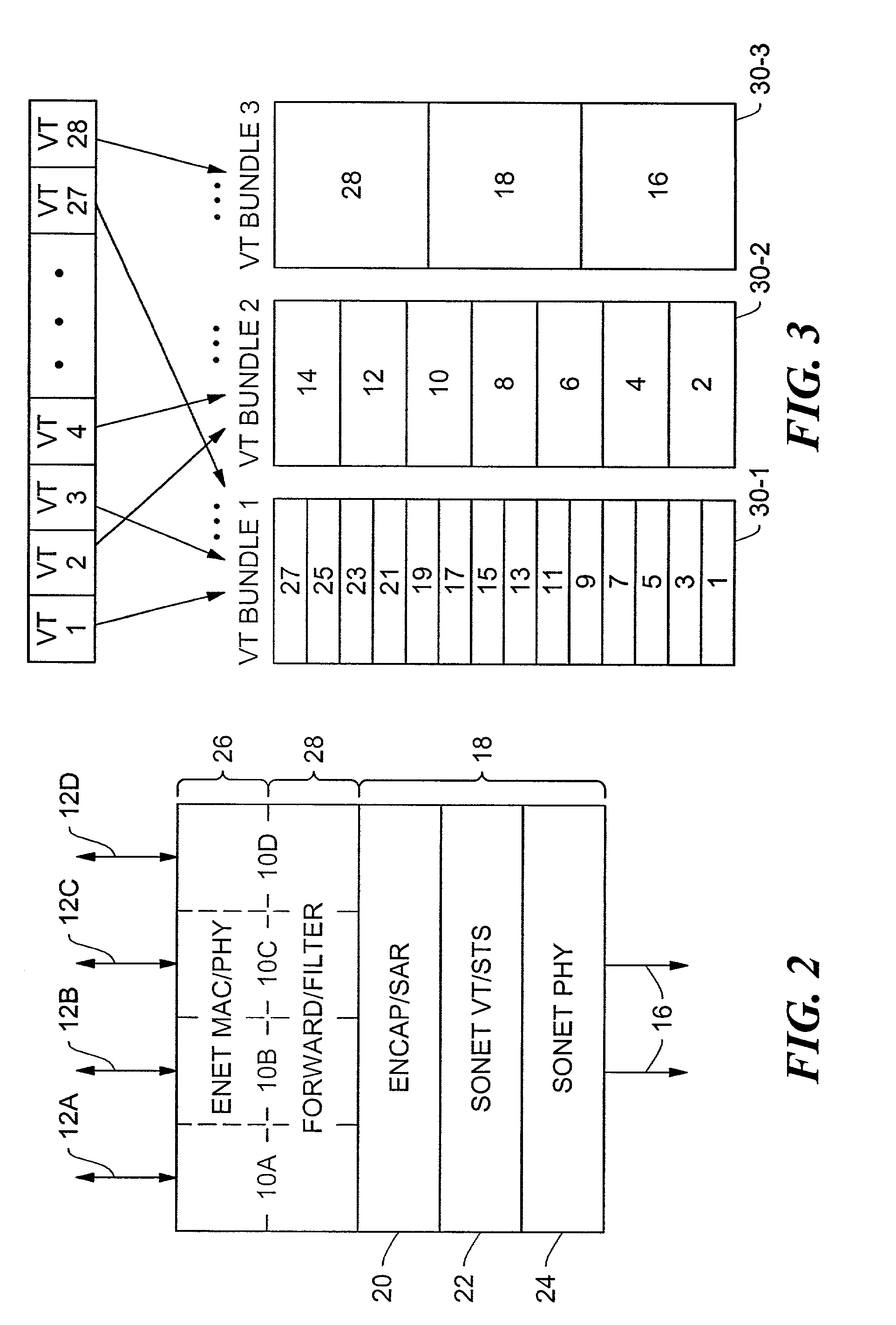
A method and system for automatic concatenation of synchronous optical network (SONET) channels includes receiving at a network element a SONET frame including a mandatory overhead and a plurality of channels for a bundled connection. A signal configuration of the channels in the bundled connection is automatically determined based on the mandatory overhead. The network element is automatically provisioned to cross-connect the channels in the bundled connection based on the signal configuration determined from the mandatory overhead.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
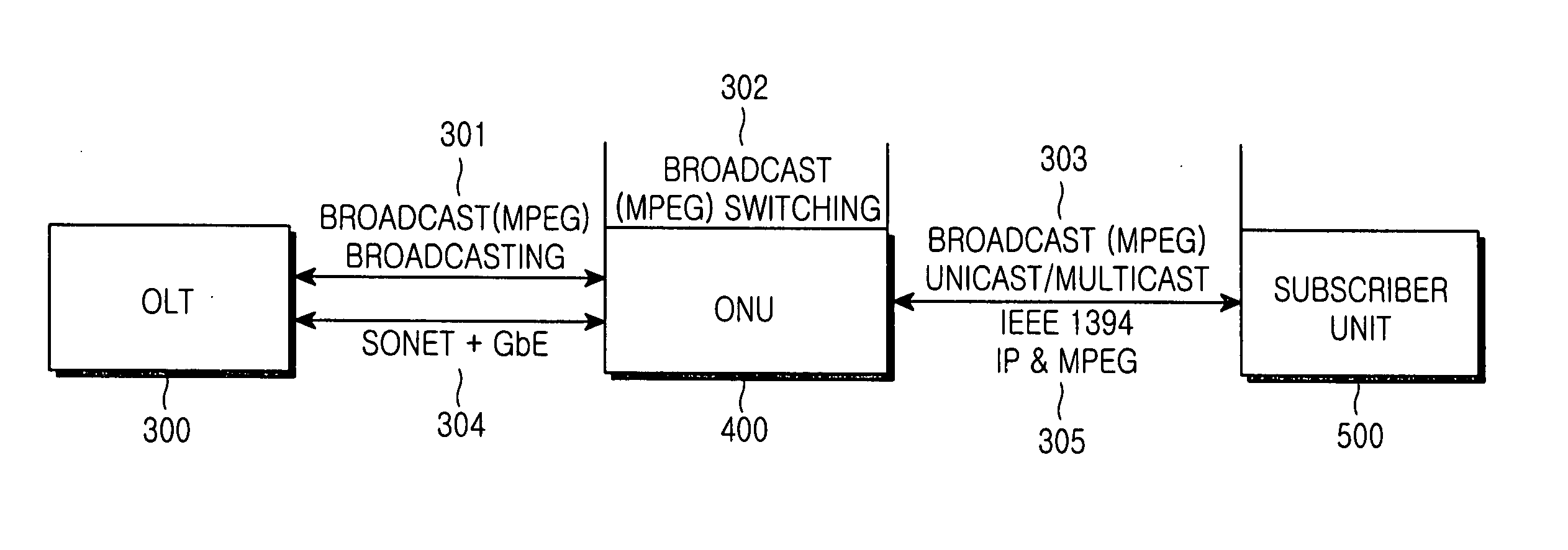
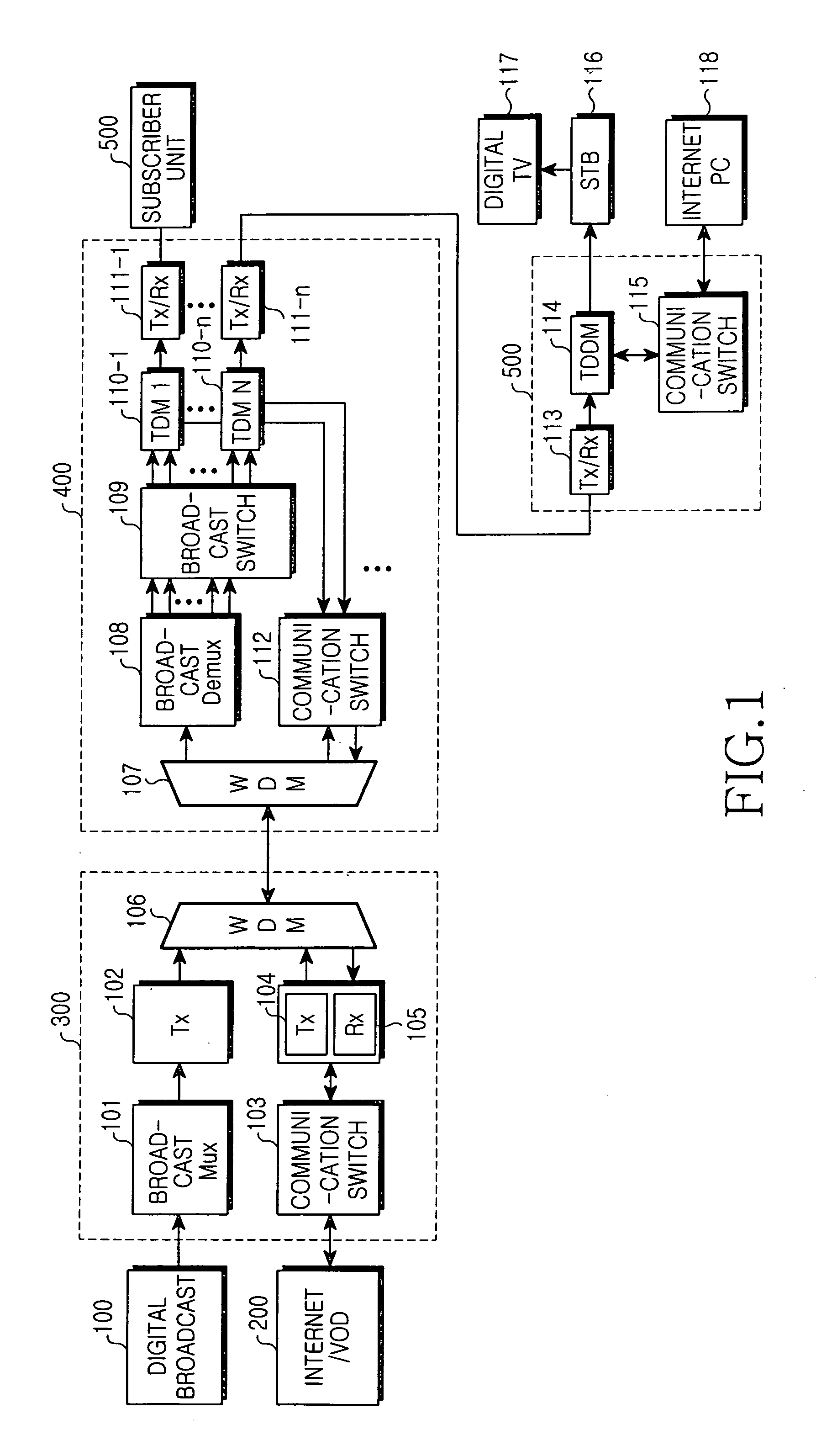
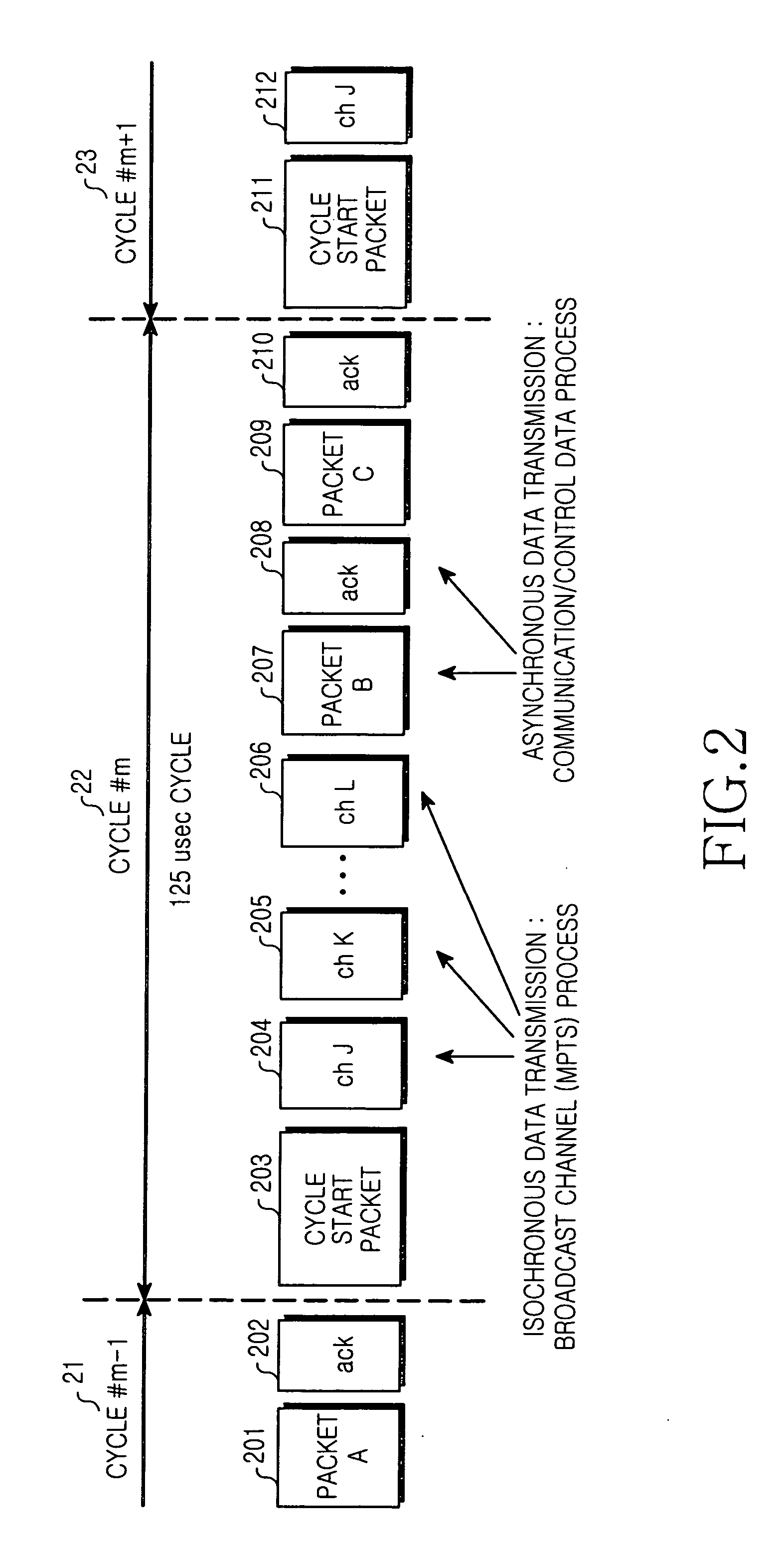
Optical network unit for an access network employing IEEE1394
InactiveUS20050207398A1Increase switching capacityMultiplex system selection arrangementsCarpet cleanersBroadcast channelsOptical line termination
Disclosed is an optical network unit of an access network for converging broadcast / telecommunication by employing IEEE 1394. The optical network unit processes the broadcast data and the communication data delivered from the optical line terminal according to each corresponding subscriber and delivering the broadcast data and the communication data to each corresponding subscriber. Furthermore, the optical network unit includes a synchronous optical network (SONET) demultiplexer for receiving the broadcast data from the optical line terminal to demultiplex the broadcast data according to each broadcast channel, a broadcast switch part for switching data of each broadcast channel, demultiplexed by the synchronous optical network (SONET) demultiplexer, according to each subscriber unit to deliver the data to each subscriber unit, an Internet protocol (IP) control part for receiving the communication data from the optical line terminal, a main control part for controlling switching with respect to the data according to each channel of each subscriber unit in the broadcast switch part and delivering the communication data from the IP control part to each subscriber unit, a 1394 link layer controller / physical layer controller for converting the data of each broadcast channel delivered from the broadcast switch part and the communication data from the main control part into data of an IEEE 1394 format to deliver the data of the IEEE 1394 format, and an optical transmitting / receiving part for performing optical transmission together with the subscriber units.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
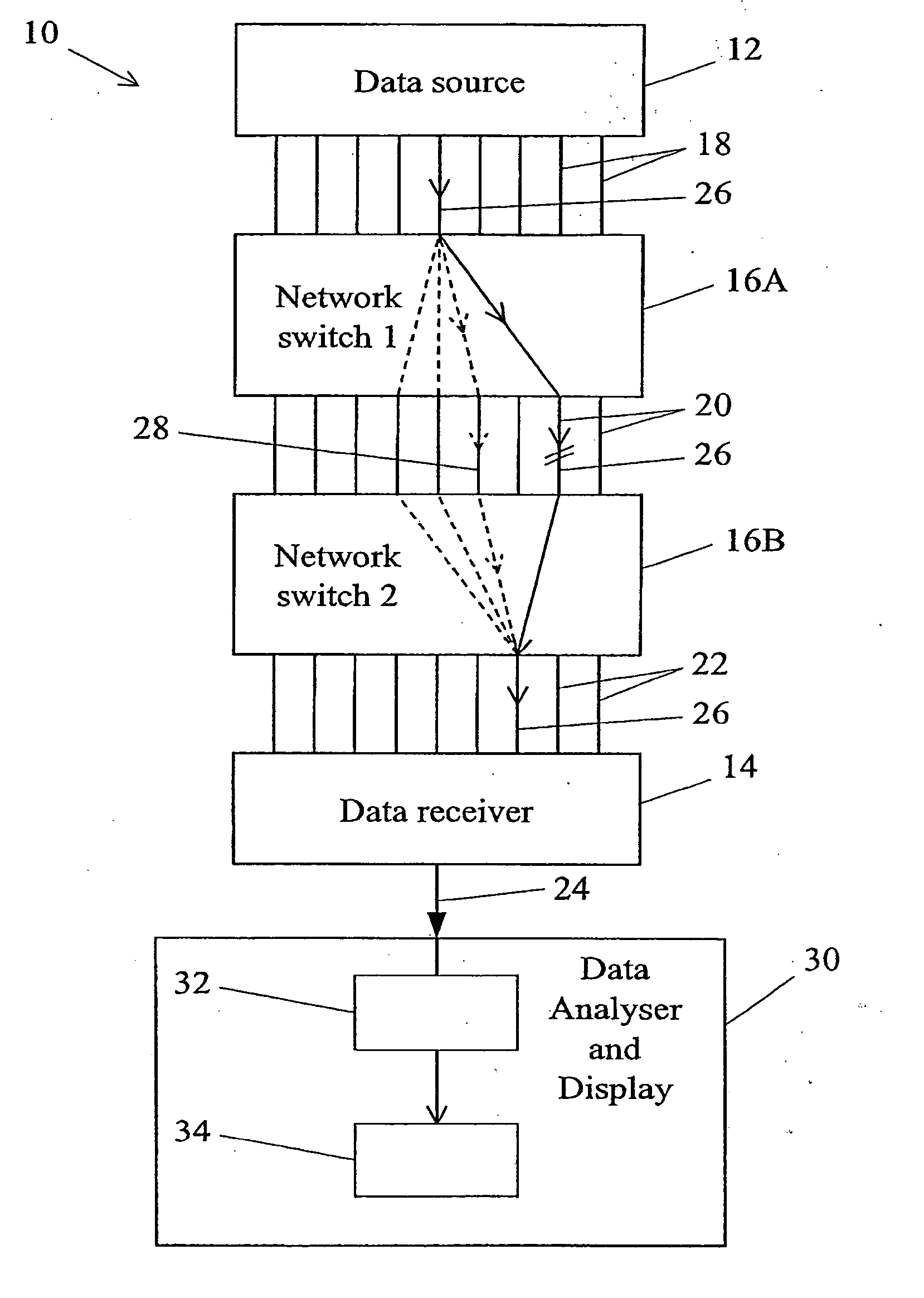
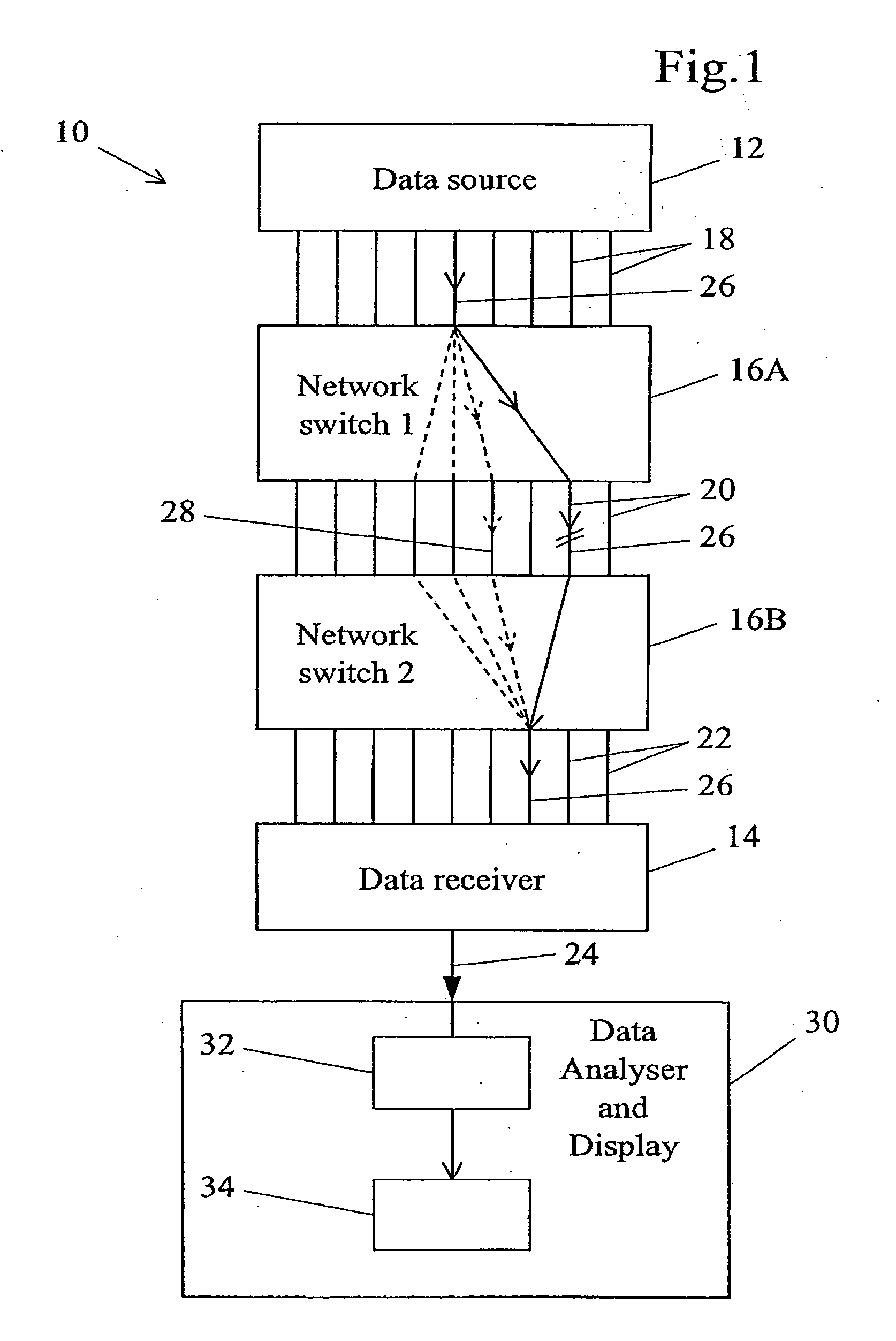
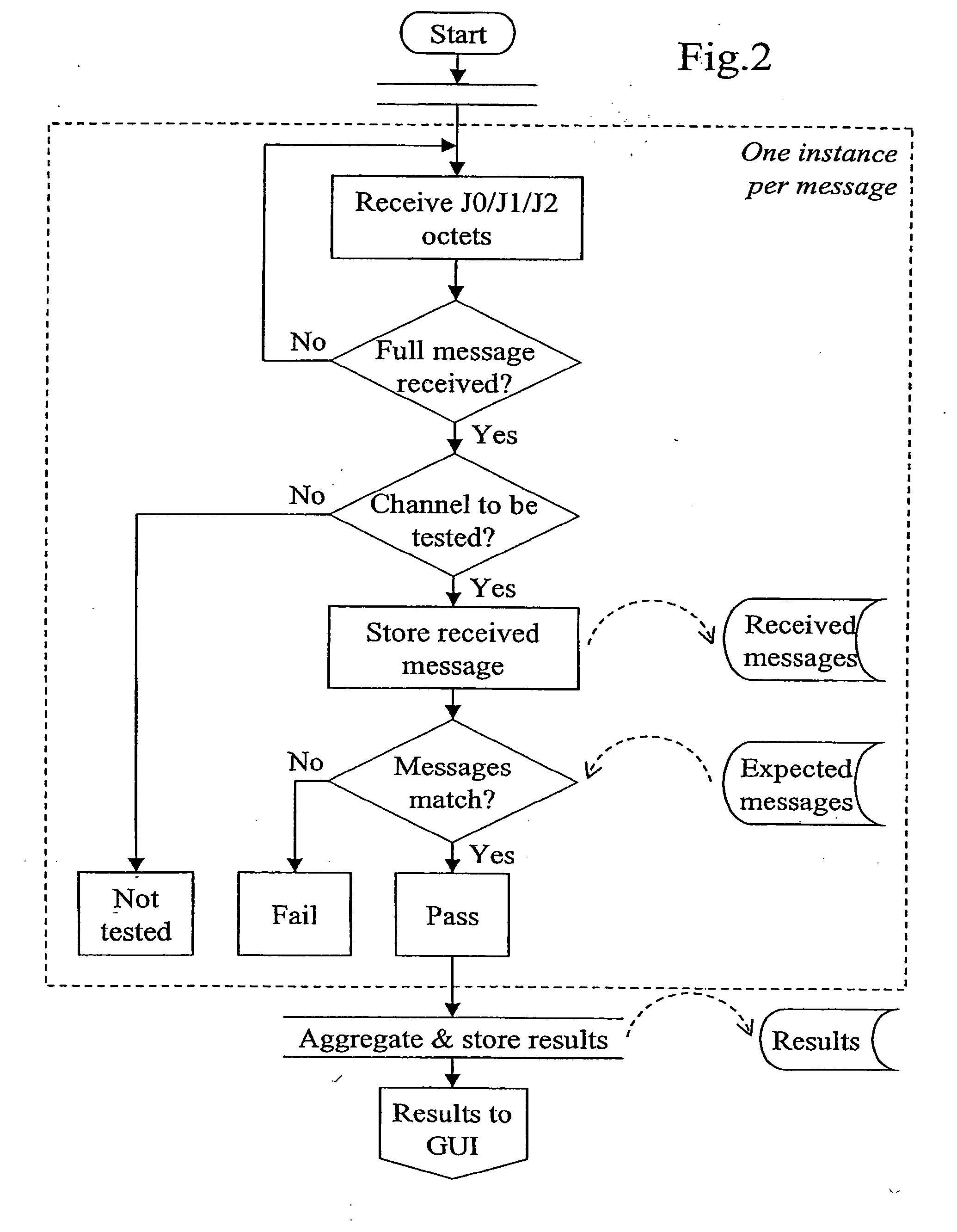
Methods and apparatus for testing automatic path protection switching
Automatic path protection switching in a synchronous optical network is tested by reference to test messages carried in section trace (J0), path trace (J1) and / or lower-order path trace (J2) sequences.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
Adaptation method in use for syncretizing Internet and synchronous digital hierarchy (SHD) or synchronous optical network
InactiveCN1728716AFast protection switchingFast Protection Switching FunctionTransmissionNetwork ConvergenceData link layer
New layer of data link layer protocol - data link procedure (DLP) is introduced between IP of network layer and SDH / SONET in physical layer in the invention to realize syncretizing adaptation between Internet and SDH / SONET in order to overcome shortage of current adaptation technique. The method possesses features are: high efficiency of forwarding IP packets, safety and reliability, flux engineering capability, 50 ms protected rearrangement function, realizing exchange between SDH / SONET circuit of virtual container and optical wavelength directly, and realizing compatibility between 1Pv4 and IPv6 networks and compatibility to packet voice network. Using safety mechanism, network control management mechanism, flow management mechanism provided by DLP realizes safety management, control management and flow management for IP network. The method makes current IP network transits to united public network in next generation smoothly.
Owner:邓里文
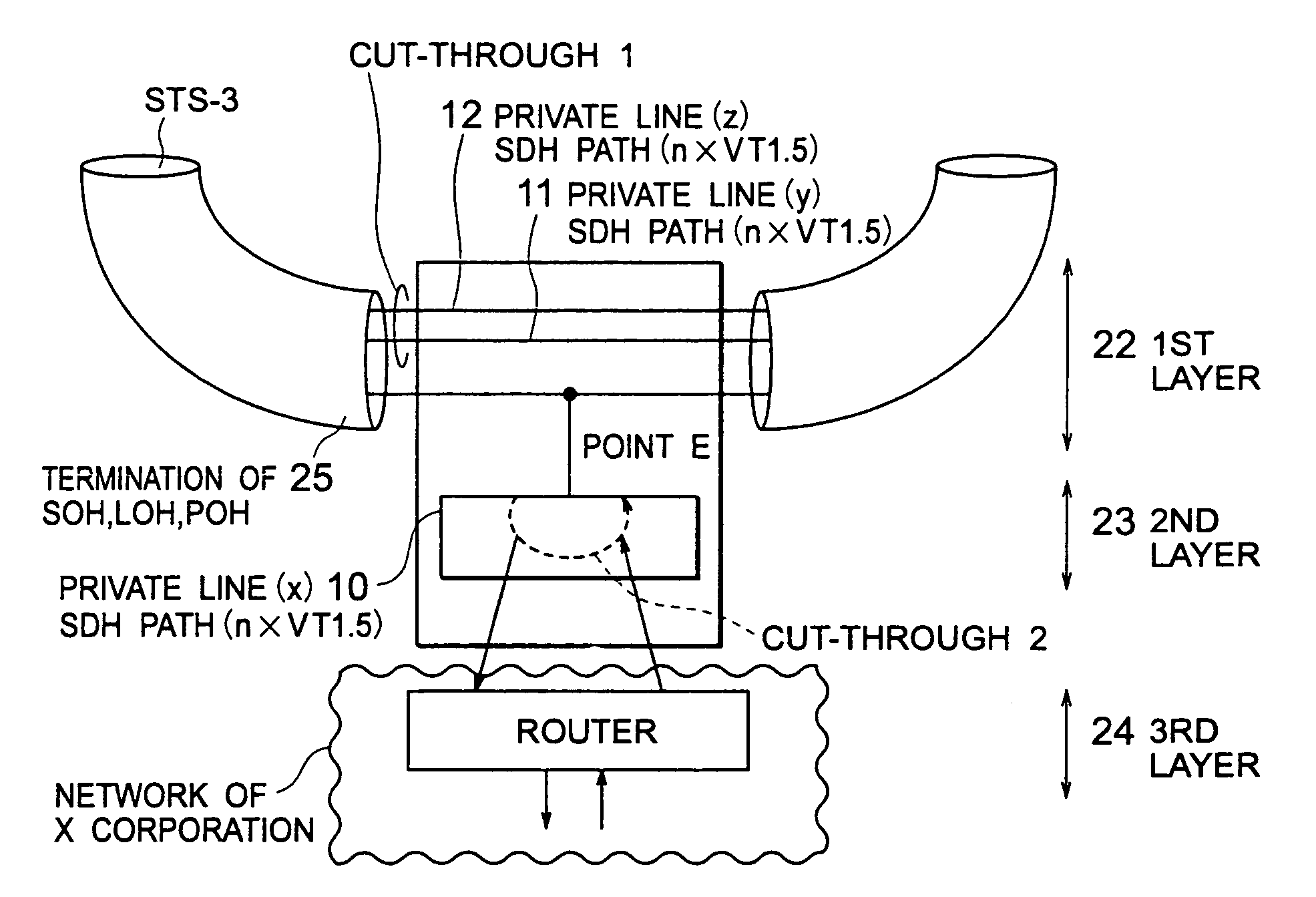
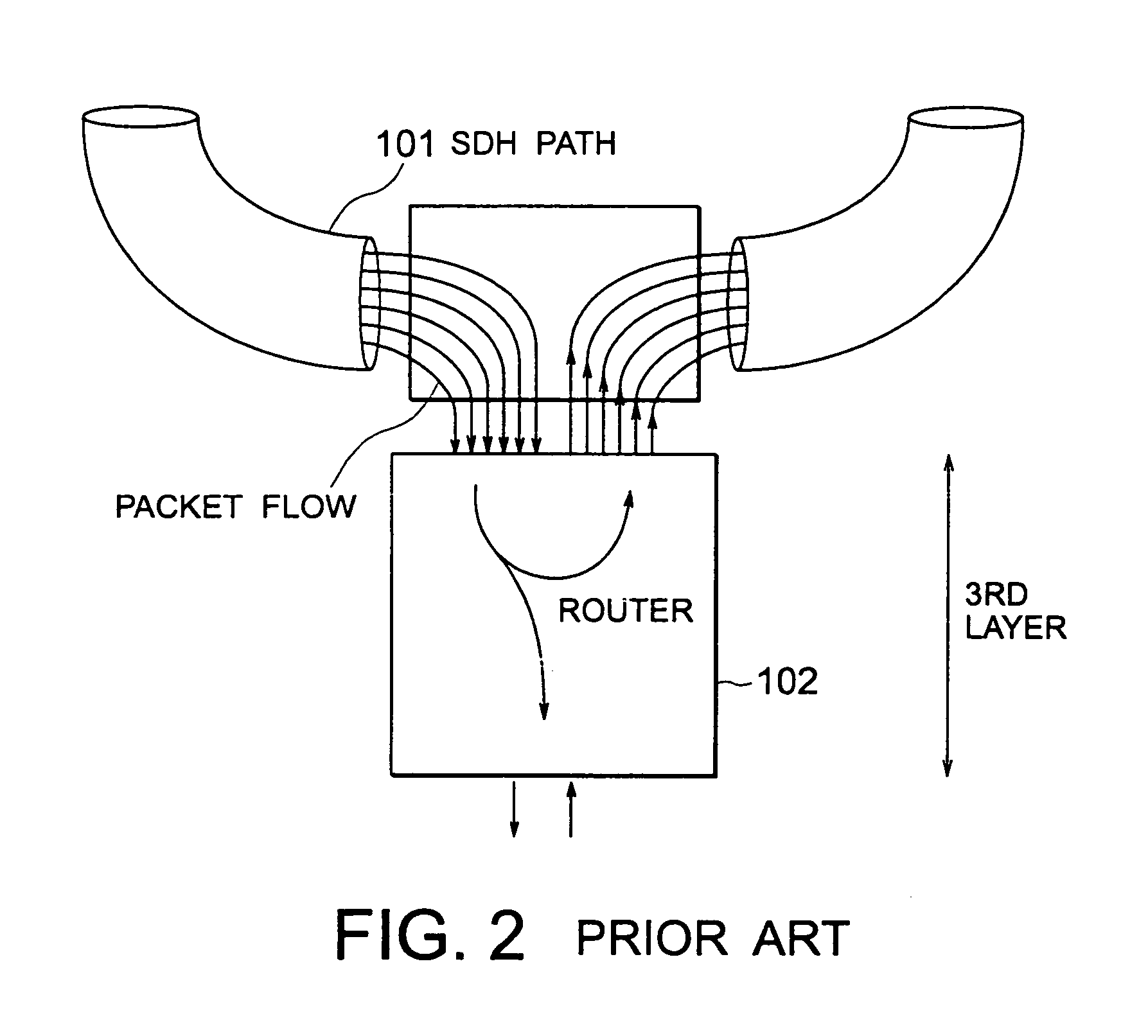
Node capable of saving a third layer packet handling operation in a synchronous optical network
InactiveUS6957271B1Operational savingTime-division multiplexMultiple digital computer combinationsComputer scienceDistributed computing
In a node having first, second, and third layers, a packet (or a cell) is mapped in the first layer. The first layer judges whether the packet (or the cell) is to be dropped at the node or to be hopped to a next node. The first layer transmits the packet to the third layer through the second layer when the first layer judges that the packet is to be dropped at the node. The first layer transmits, when the first layer judges that the packet is to be hopped to the next node, the packet to the next node by making the packet cut through the first layer.
Owner:NEC CORP
Device for transmitting data packet on synchronous optical network
ActiveCN101699779AReduce usageLow costTime-division multiplexTransmissionPoint-to-Point ProtocolOptical Module
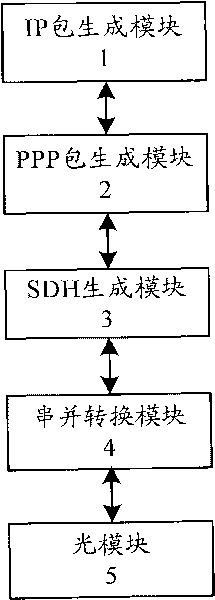
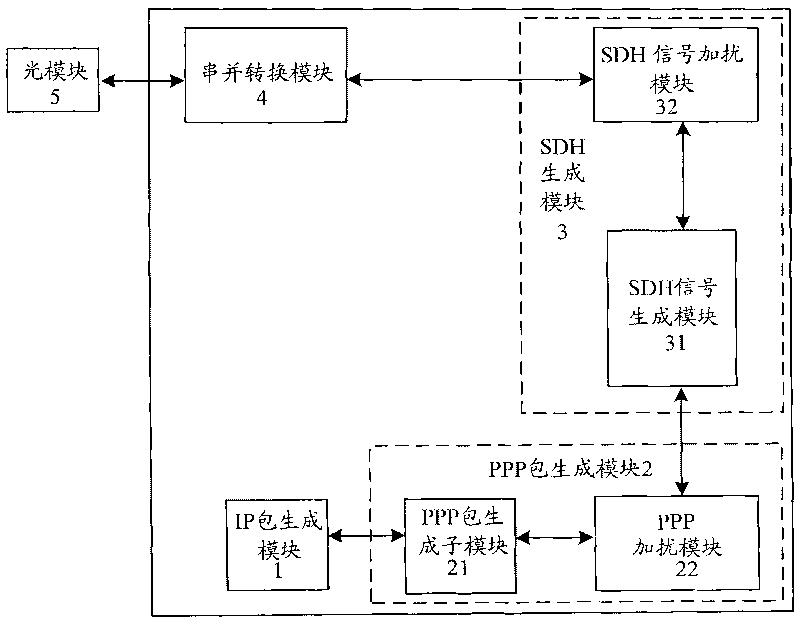
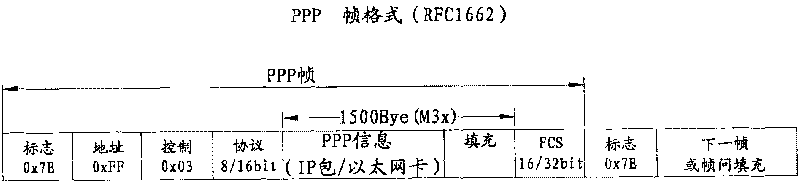
The invention provides a device for transmitting data packets on a synchronous optical network. The device comprises an IP packet generating module for generating IP packets, a point-to-point protocol (PPP) packet generating module for adding protocol domain bytes to the IP packets and performing byte escape filling and byte addition to the IP packets according to the protocol requirements to obtain PPP frame format data, an SDH generating module for adding format expense to the PPP frame format data in accordance with an SDH protocol to obtain the data packets (namely, POS data packets)on the synchronous optical network, a serial parallel converting module for converting parallel 16-bit POS data packets into a serial 1-bit datum, an optical module for transmitting the serial POS data packets. The device for transmitting data packets realizes the generation and transmission of the POS data packet through an FPGA with low cost, avoids the use of an expensive and bulk special packet transmitter and reduces cost and energy consumption.
Owner:DAWNING INFORMATION IND BEIJING +1
Adaptation method in use for syncretizing plesiochronous digital hierarchy or synchronous optical network
InactiveCN1728719AEasy to handleSimplified processing hierarchyTransmissionNetwork ConvergenceLow speed
New layer of data link layer protocol - data link procedure (DLP) is introduced in the invention to realize syncretizing adaptation between PDH and SDH / SONET in order to overcome shortage of current adaptation technique including too many process layers, not matched interface speed, not supporting dynamic bandwidth allocation based on packets, and not compatible to IP and packet voice service etc. The method realizes interconnection of interfaces between PDH interfaces in low speed and SDH / SONET interfaces in high speed directly, and dynamic bandwidth allocation, and realizes compatibilities as described above. Using safety mechanism, network control management mechanism, flow management mechanism provided by DLP realizes security management, control management and flow management, and realizes united transmission and exchange. The method makes current communication network transits to united telecom public network in next generation smoothly.
Owner:邓里文
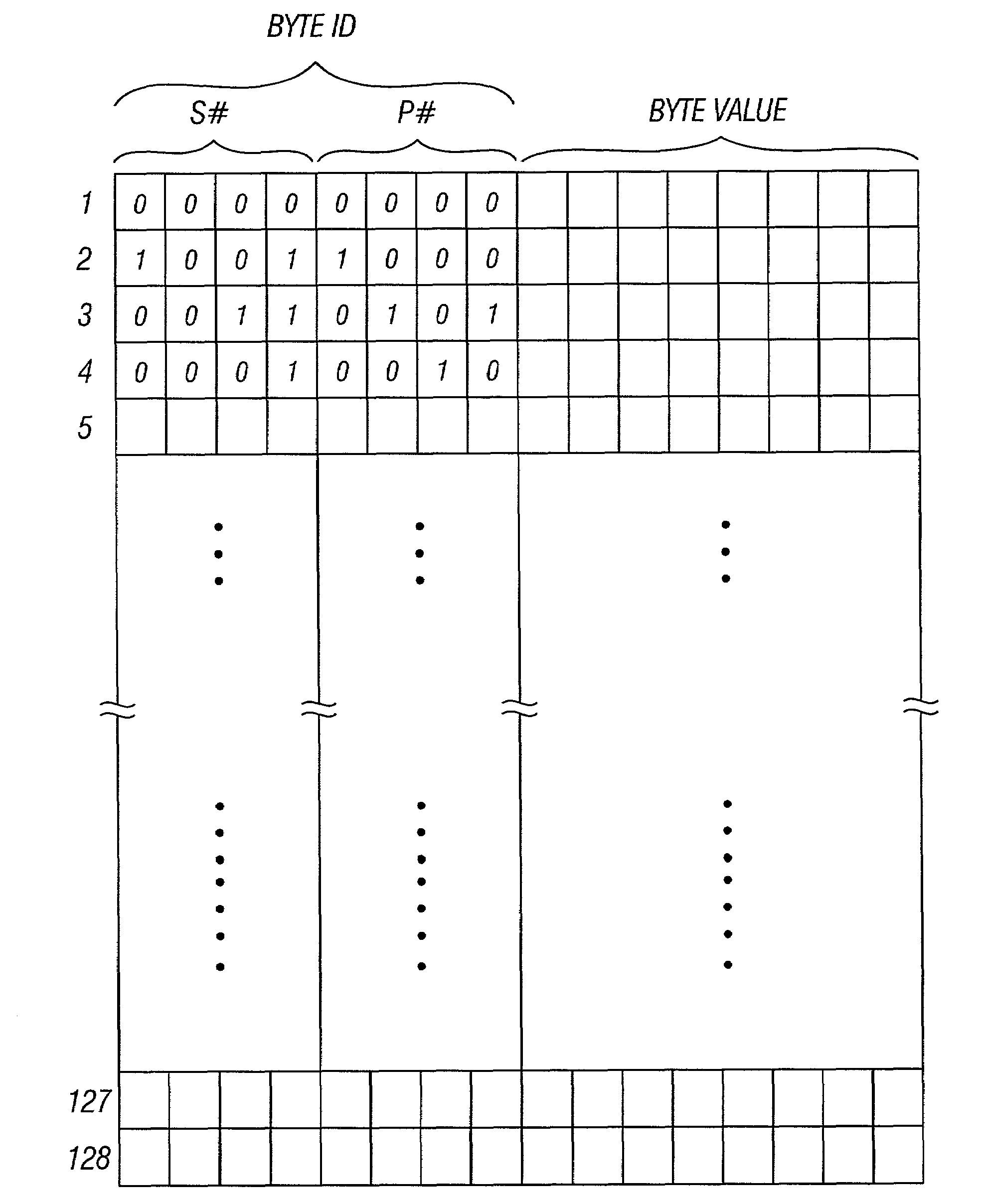
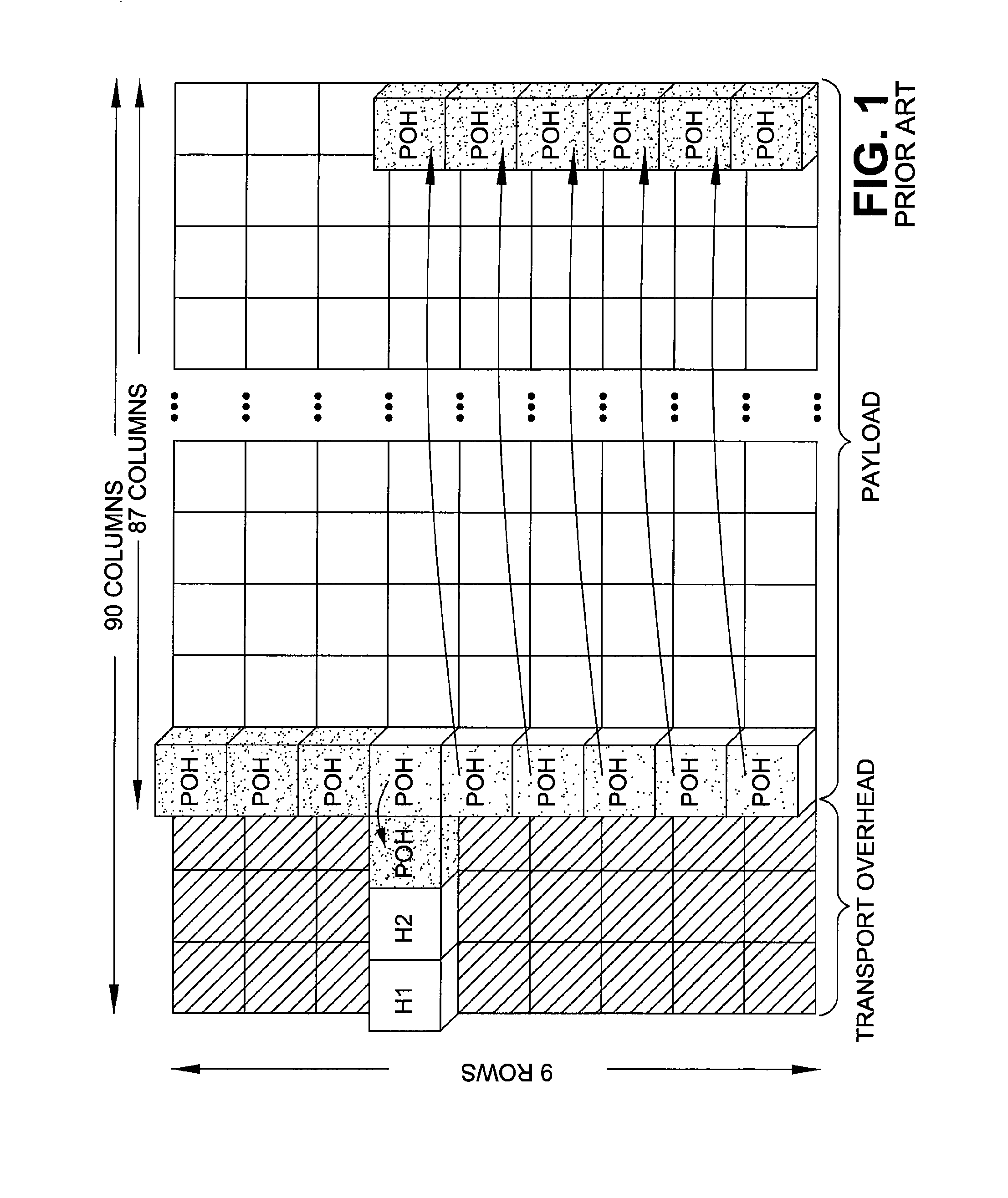
Onboard RAM based FIFO with pointers to buffer overhead bytes of synchronous payload envelopes in synchronous optical networks
InactiveUS7277447B2Less-expensiveLess hardwareTime-division multiplexData switching by path configurationByteComputer science
An on-chip RAM FIFO (first-in-first-out) buffer for storing SPE overhead bytes wherein each entry of the RAM FIFO stores (1) a byte of the SPE overhead; (2) an indication of which byte of the SPE overhead is currently stored in that entry; and (3) an indication of which STS signal that byte was taken from.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
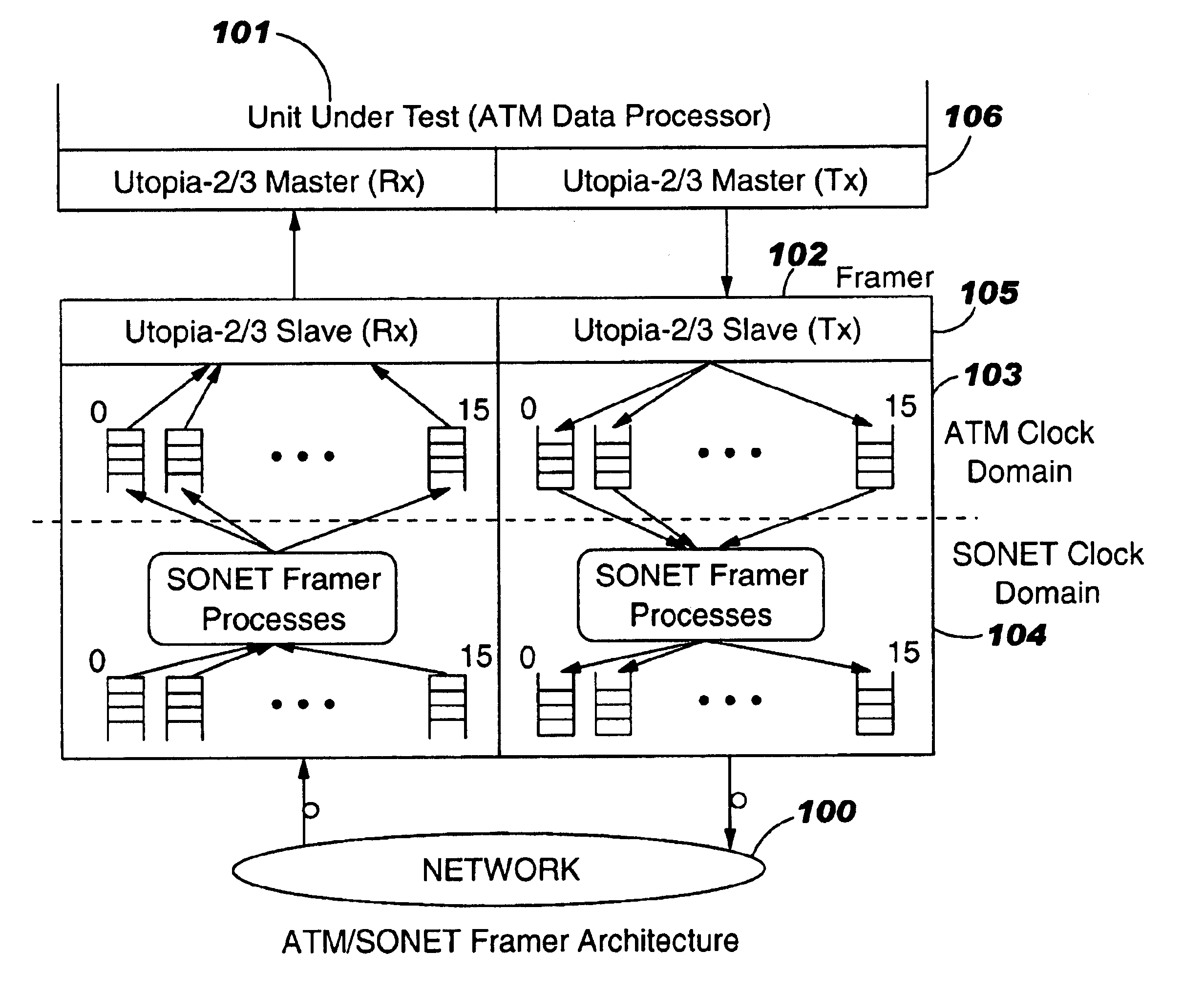
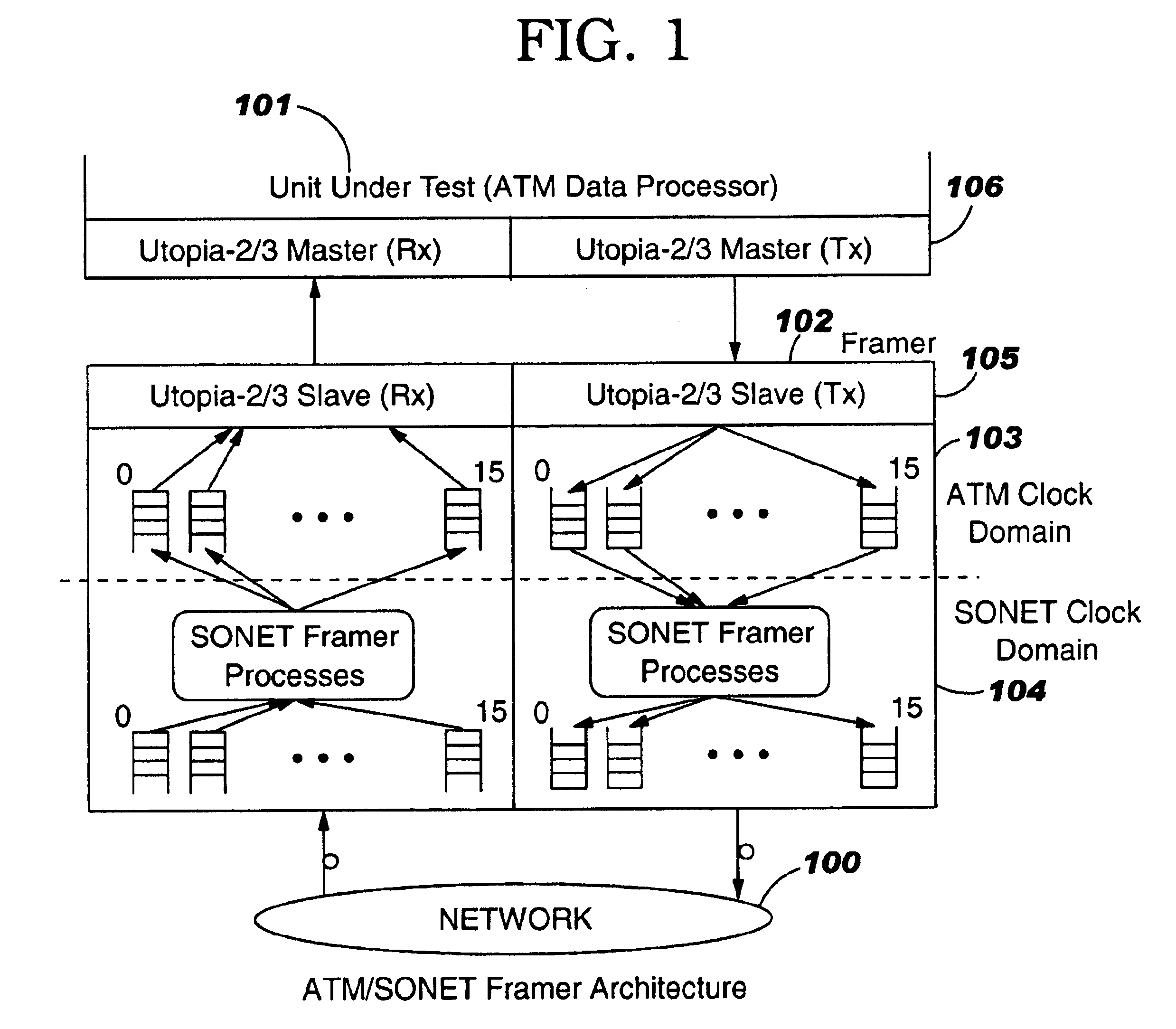
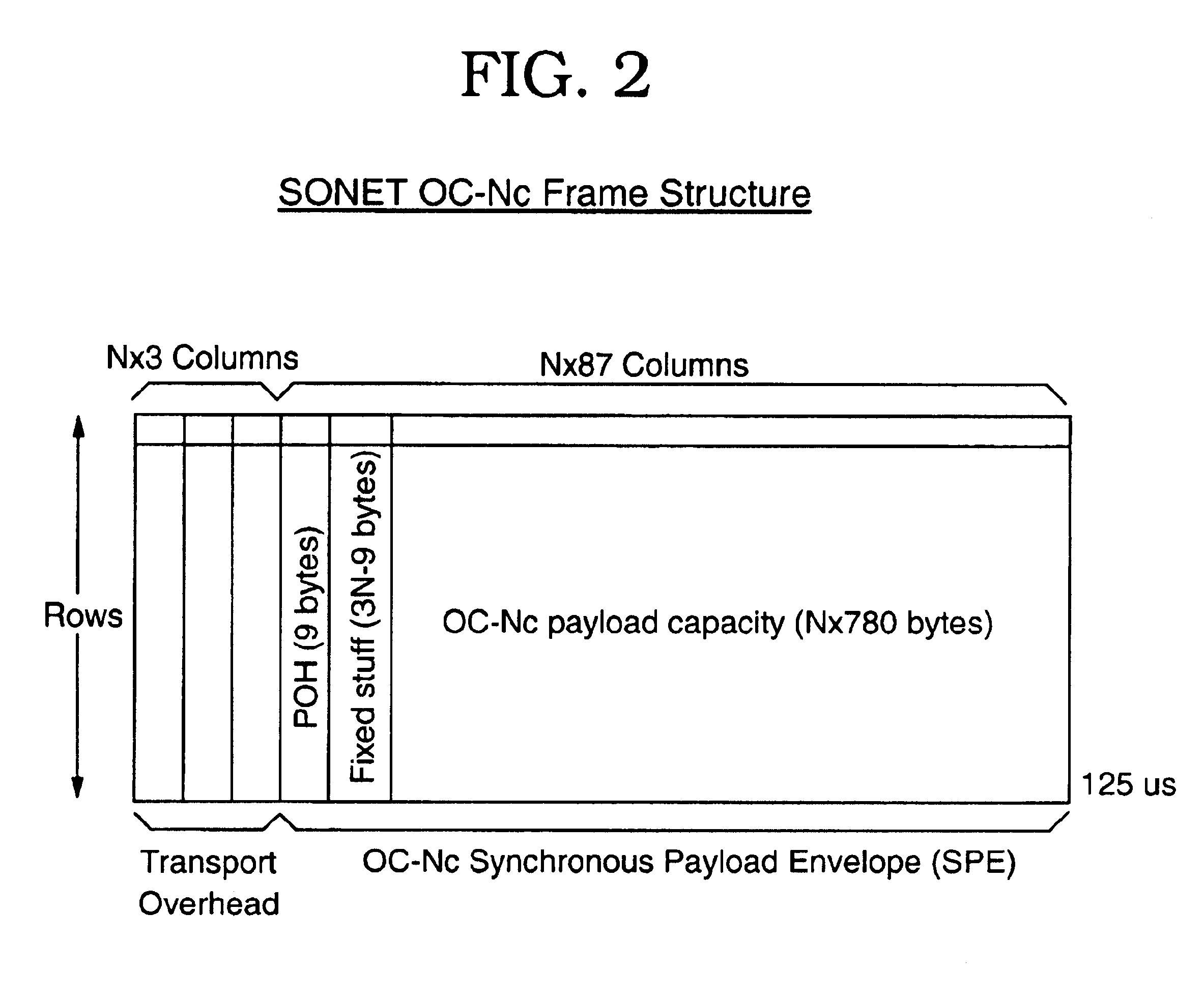
Customizable simulation model of an ATM/SONET framer for system level verification and performance characterization
This system represents a customizable simulation model of an ATM / SONET Framer for System Level Verification and Performance-Characterization. An Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM) data processing ASIC interfaces with a Media Access Control (MAC) device that presents an electrical data path interface, called Universal Test & Operations PHY Interface for ATM (UTOPIA), using ATM protocol on the ASIC side and simplex optical interfaces using Synchronous Optical Network (SONET) protocol on the network side. Such a MAC device, commonly referred to as ATM / SONET Framer, provides one Receive and one Transmit interface to the network at various SONET line rates such as 155.52 Mbps (OC-3), 622.08 Mbps (OC-12), 2488.32 Mbps (OC-48), etc. The ATM and the SONET interfaces operate on different clock frequencies and thus represent two distinct clocking domains. The data interchange between the two clocking domains is achieved via FIFO buffer elements and associated control and status signals.
Owner:IBM CORP
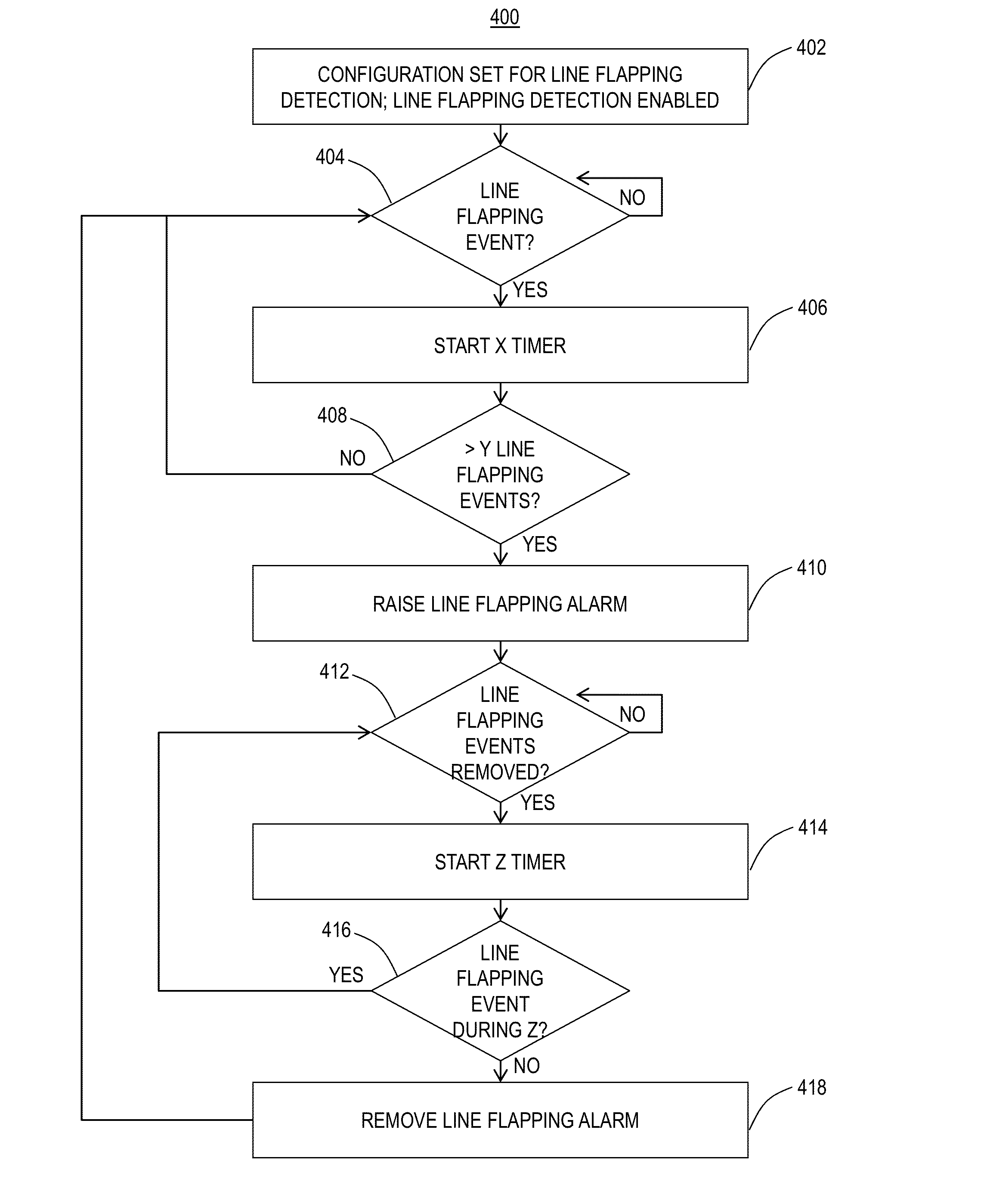
Systems and methods for detecting line flapping in optical networks
ActiveUS20130051792A1Time-division multiplexTransmission monitoringFlappingOptical Transport Network
The present disclosure provides line flapping detection systems and methods for optical networks using, for example, Synchronous Optical Network (SONET), Synchronous Digital Hierarchy (SDH), Optical Transport Network (OTN), and the like. Line flapping includes conditions, failures, etc. on a particular line going in and out of failure without raising an alarm or the like. The line flapping detection systems and methods provide configurable settings to set an alarm when it has been determined that a line is indeed flapping. First, there is a two level hierarchical control mechanism used to determine whether to report the alarm. Additionally, the line flapping detection systems and methods are configured to correlate events to count as single line failures instead of a plurality of distinct events.
Owner:CIENA
Transmission of data frames using low-overhead encapsulation and multiple virtual tributaries in a synchronous optical network
InactiveUS6982989B2Easy to useFlexible processTime-division multiplexData switching by path configurationSynchronous networkVariable length
A network device transfers variable-length data frames across a synchronous network employing a multiple-channel synchronous transport signal. Encapsulation logic encapsulates each data frame in a point-to-point frame including a body portion of the data frame and a length value located in a beginning portion of the point-to-point frame. Segmentation logic divides each point-to-point frame into fixed-sized segments, a first segment carrying the beginning portion of the point-to-point frame. Transmitting circuitry transmits the frame segments as payloads of at least one channel of the synchronous transport signal, the payloads being marked so as to be identifiable. Receiving circuitry receives payloads of at least one channel of the synchronous transport signal and from each received set of payloads regenerates a corresponding point-to-point frame using the length value from the first segment thereof. De-capsulation logic de-capsulates each regenerated point-to-point frame to recover the corresponding data frame.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
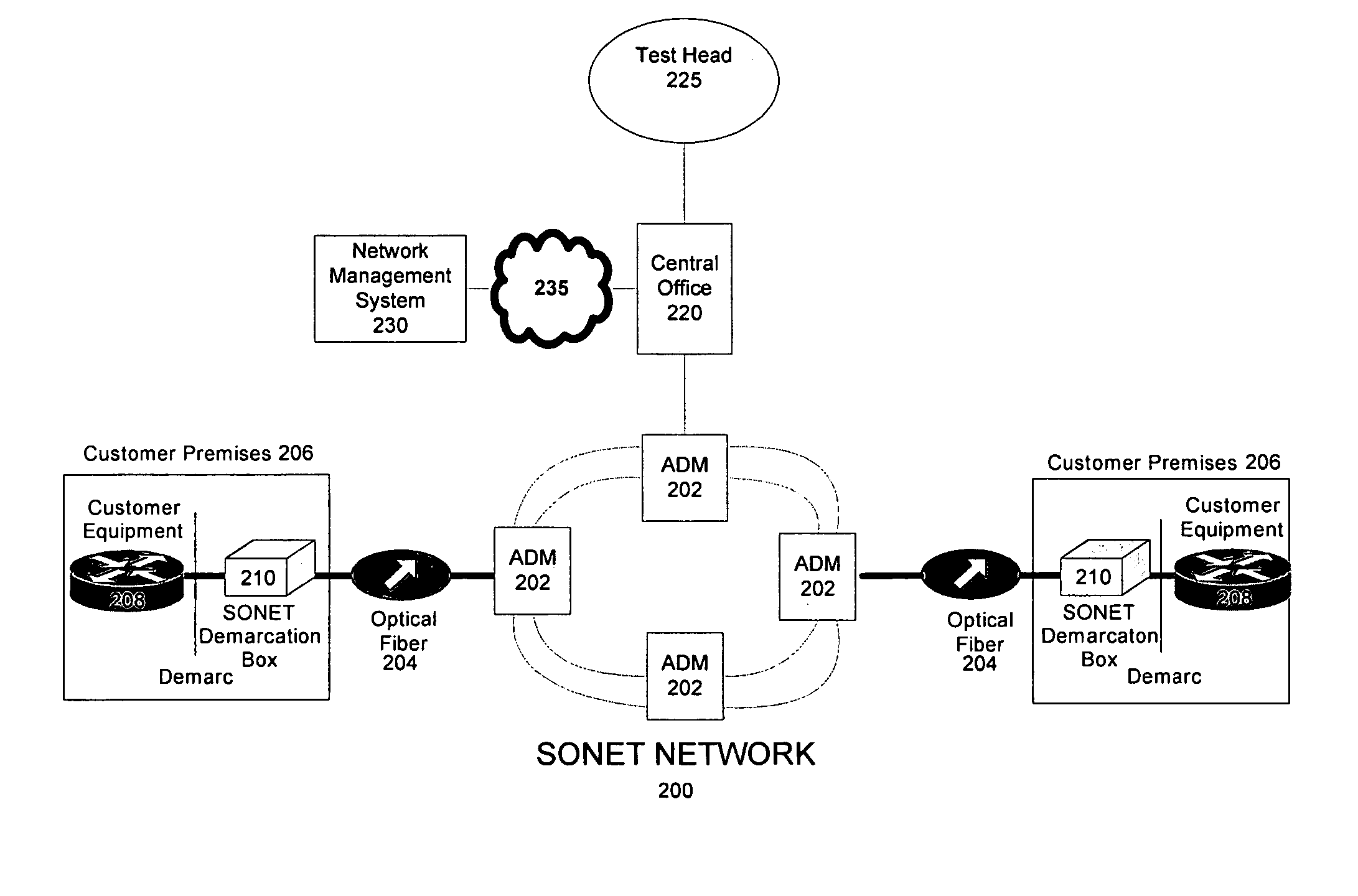
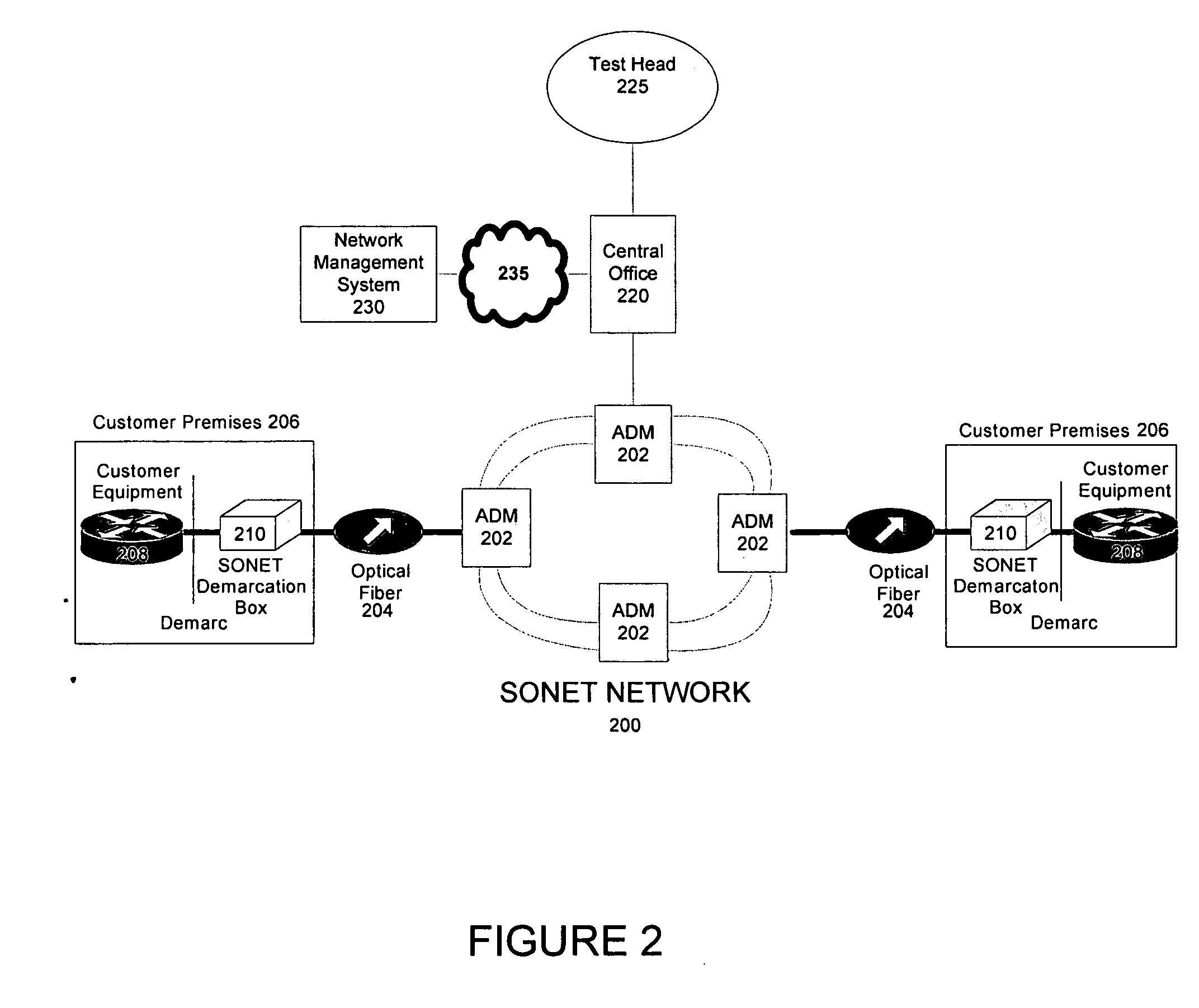
Synchronous optical network (SONET) demarcation device
InactiveUS20070147259A1Streamlining disclosureError preventionTransmission systemsMultiplexingMultiplexer
A synchronous optical network (SONET) demarcation device can be placed on a customer premises to enable remote testing and trouble shooting of customer premises equipment. The device includes a SONET signal analyzer that extracts SONET data, such as section, line and path overhead. The SONET demarcation device also includes a SONET fault condition, performance statistics, and alarm generator that generates fault conditions, performance statistics, and alarms based upon the extracted SONET data. The device also includes a transmitter that transmits the alarm and / or performance data to a remote site. The SONET demarcation device does not include ring functionality and / or multiplexing functionality, thus being lower in cost than a SONET multiplexer.
Owner:SBC KNOWLEDGE VENTURES LP
High performance ECL-to-ATM protocol network gateway
A network protocol translation device that allows serial data sent using the standard Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM) protocol to be used between two locations, using a satellite link or a terrestrial wireless link between the two locations. This is done by translating the standard ATM data to a standard satellite modem interface at one location, and translating the data back to the ATM format at the second (remote) location. The translation can occur at any data rate up to the available effective bandwidth of the ATM connection. The device is also capable of providing Forward Error Correction in the protocol translation. The device is functionally transparent to protocols above ATM, i.e., IP, UDP and TCP. It also interfaces with standard physical layers below ATM such as Synchronous Optical Network (SONET). At the satellite interface, the device is compatible with (but not limited to) Emitter Coupled Logic (ECL).
Owner:BEERING DAVID R
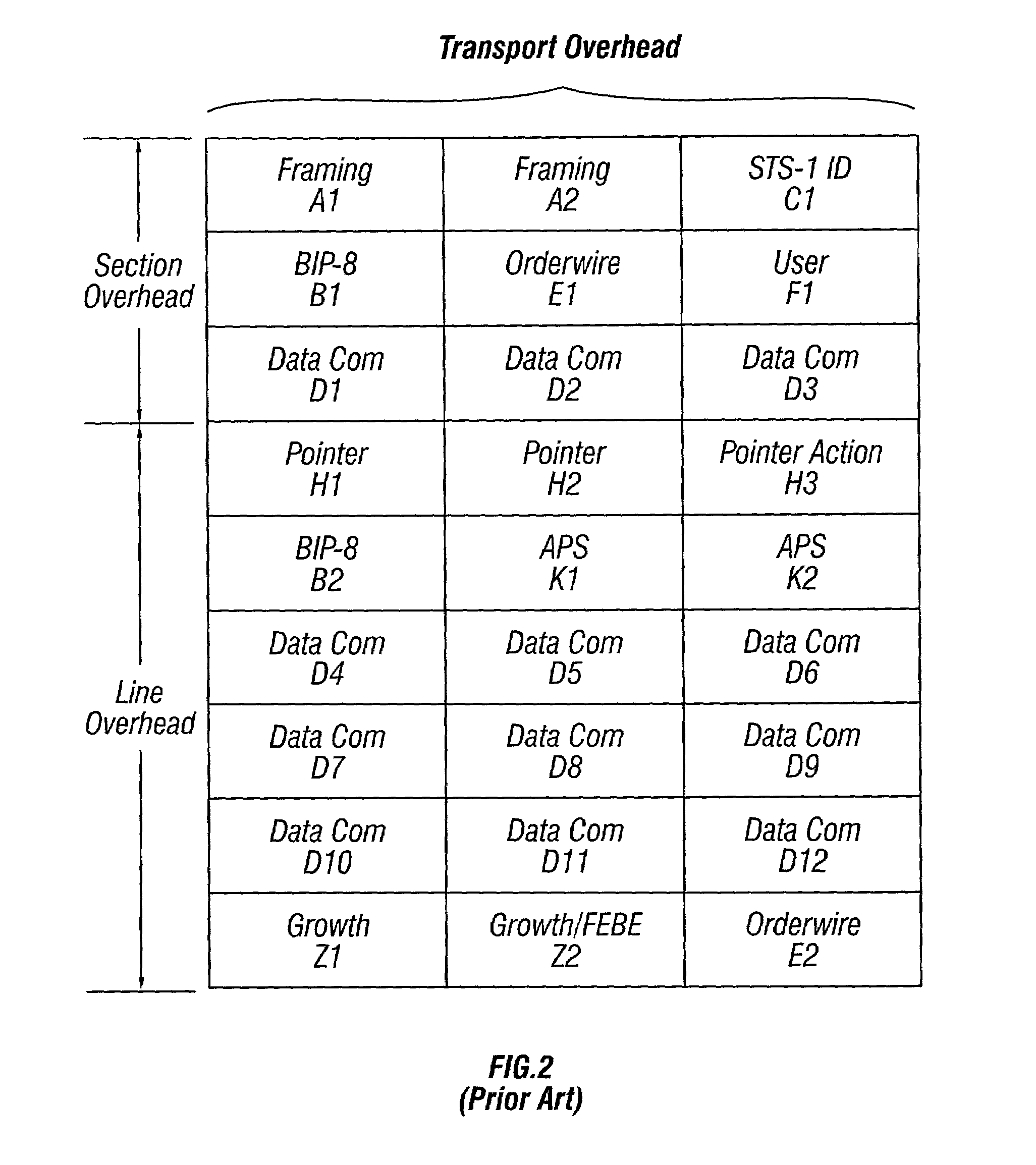
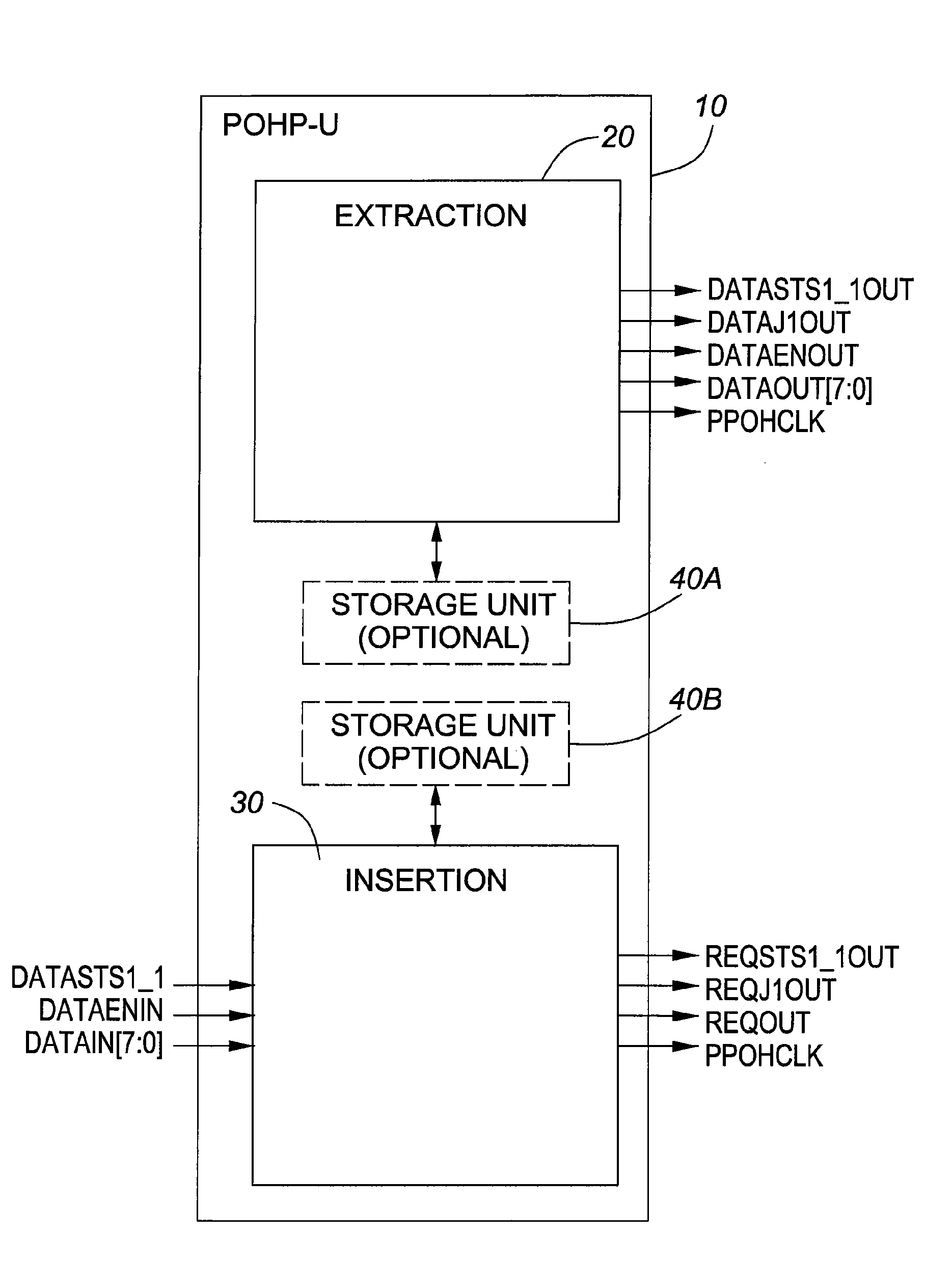
Method and architecture for the extraction and/or insertion of SONET or SDH path overhead data streams
InactiveUS7567587B1Minimizes amount of storageLow required frequency of operationTime-division multiplexInsertion timeData stream
A method and architecture for the extraction of data from or the insertion of data into Synchronous Optical Network (SONET) or Synchronous Digital Hierarchy (SDH) frames is disclosed. The method and architecture provides an interface that permits the time-multiplexed data streams being extracted or inserted to have variable data-rates and no fixed alignment with respect to each other. The extraction and insertion interface accommodates for variable POH data rates and alignment inconsistencies of POH bytes amongst different paths due to floating pointer positions. The interface operates at the lowest possible frequency that can still accommodate the minimum spacing between any two consecutive words of data for a given data stream. In the insertion case, the frequency of operation chosen also allows the pipelining of requests as well as the pipelining of the subsequent associated data in response. The implementation of the present invention minimizes the amount of storage and enables a relatively low required frequency of operation while maintaining a smooth clock. In addition, in the insertion case, the pipelined nature of the interface provides flexibility in meeting interface timing.
Owner:MICROSEMI STORAGE SOLUTIONS
Ethernet frame and synchronous optical network (SONET) frame convertible interface device and frame transmission method
InactiveUS7978727B2Improve equipment reliabilityInhibit outputHybrid switching fabricsTime-division multiplexMultiplexingThumb opposition
An apparatus for decreasing the hardware load from L2 switch MAC address learning for Ethernet-Over-SONET technology that uses VLAN, simplifying frame transmission between Ethernet and SONET, and improving the reliability of each device is disclosed. An Ethernet frame and SONET frame convertible interface part establishes a register that holds an Ethernet frame specific VLANID and SONET frame specific STS path ID in opposition, and a multiplexing part that multiplexes an Ethernet frame having a specific VLANID corresponding to a specific STS path ID that is held by a register among an input plurality of Ethernet frame VLAN ID's.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
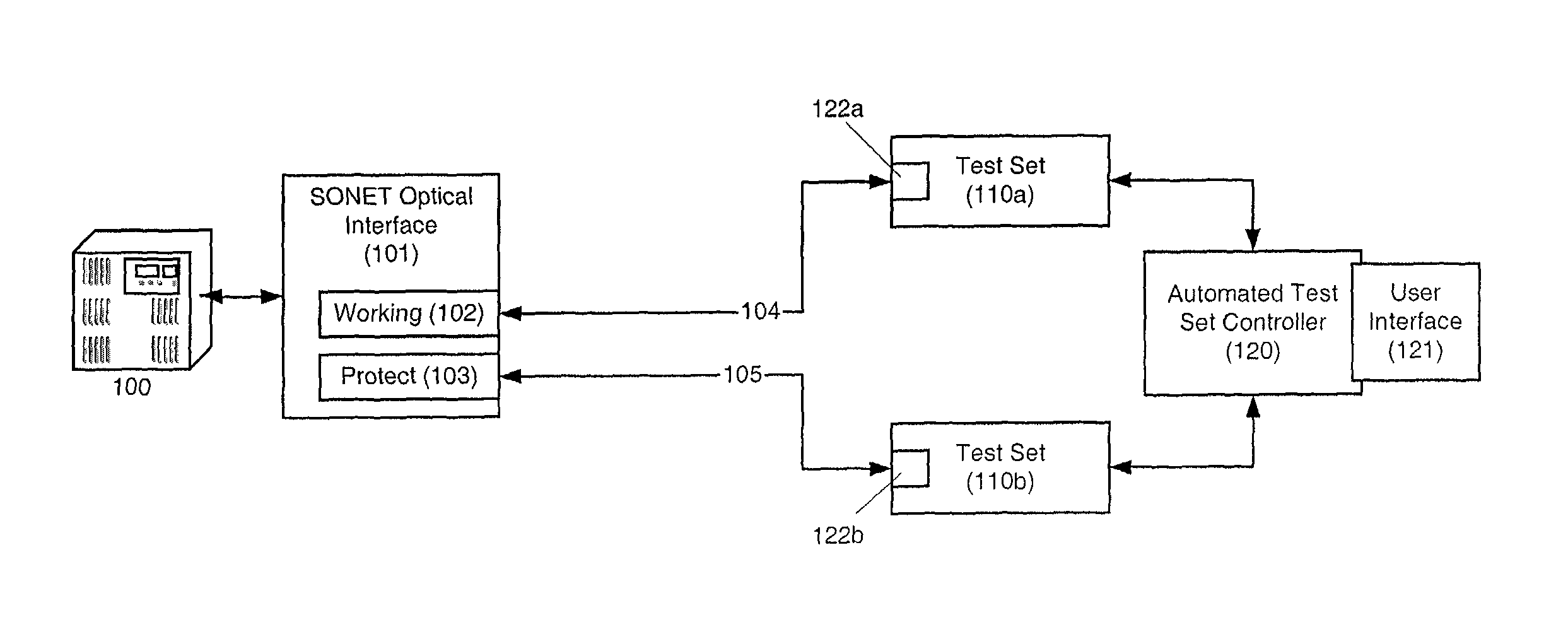
Method and systems for testing automatic protection switching protocol in optical interfaces for synchronous optical networks
ActiveUS8204375B1Time-division multiplexTransmission monitoringComputer hardwareAutomatic protection switching
A standard test device is used to test the interoperability of a Synchronized Optical Network (SONET) optical interface, e.g., a 1+1 protected SONET interface. In one embodiment, two test sets, under the common control of a master controller, can be connected respectively to the working and protect lines of an optical interface. The controller then operates the test sets to test the operation of the interface under the Automatic Protection Switching (APS) protocol to verify interoperability based on the standards incorporated in the test sets while requiring minimal operator intervention. Alternatively, a single test set can include two connections that are connected, respectively, to the working and protection lines of the interface being tested. The test set can then test the operation of the interface under the APS protocol to verify interoperability based on the standards incorporated in the test set.
Owner:VERIZON PATENT & LICENSING INC
RPR span BW protection scheme for RPR transported over SONET paths
InactiveUS20070091791A1Ring-type electromagnetic networksError preventionLink Capacity Adjustment SchemeCommunications system
A communication system and method provide fractional protection of Resilient Packet Ring (RPR) span bandwidth (BW) by provisioning the number of SONET paths in a given span to greater than the RPR ring BW. A communication system comprises a plurality of Synchronous Optical Network paths, a Resilient Packet Ring span implemented using the plurality of Synchronous Optical Network paths, and a Link Capacity Adjustment Scheme operable, in response to failure of a Synchronous Optical Network path implementing the Resilient Packet Ring span, to remove the failed Synchronous Optical Network path from implementing the Resilient Packet Ring span and to redistribute the Resilient Packet Ring traffic over the remaining Synchronous Optical Network paths.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Address resolution protocol (ARP) processing method for Ethernet matching
InactiveUS20070124486A1Reduce unnecessaryReduce trafficTime-division multiplexData switching by path configurationData packAddress Resolution Protocol
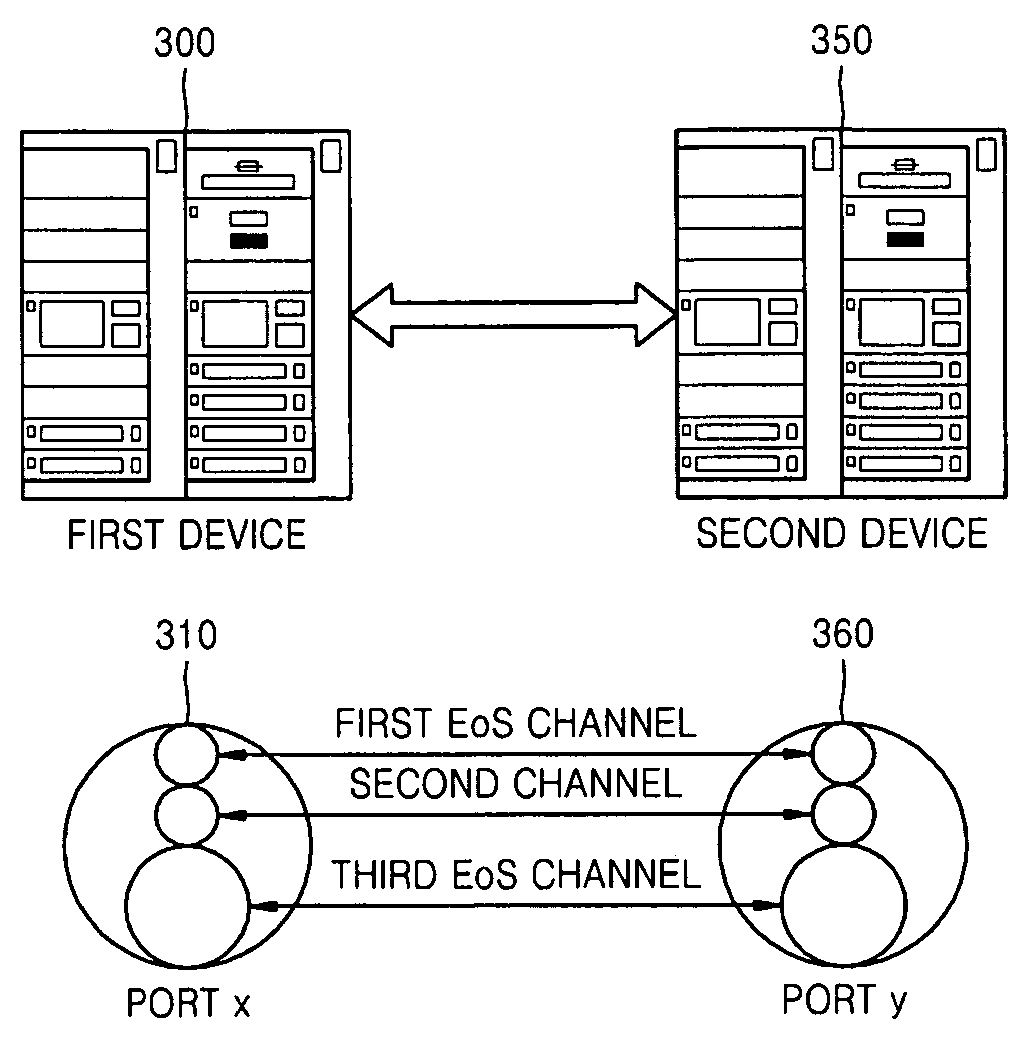
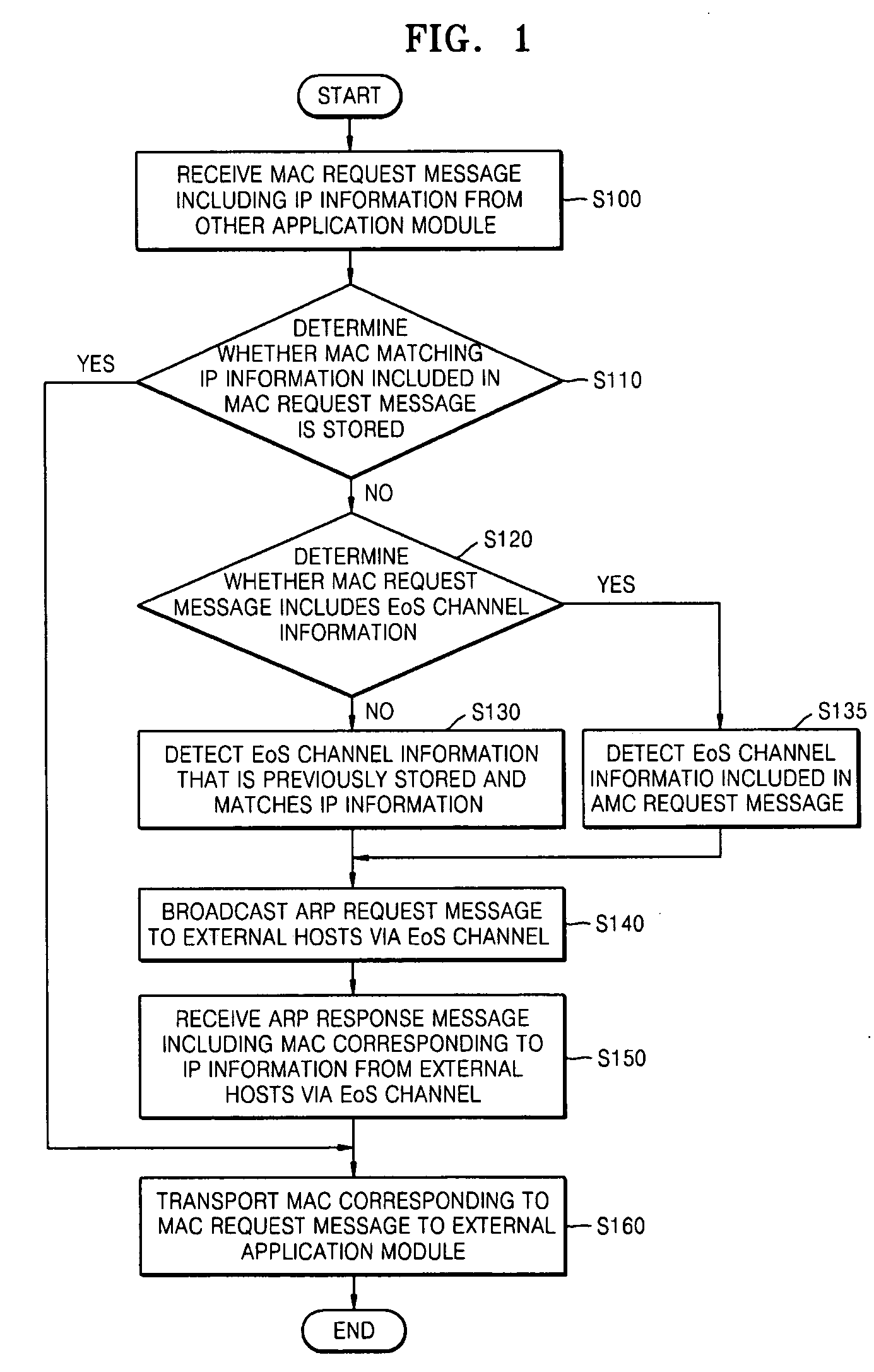
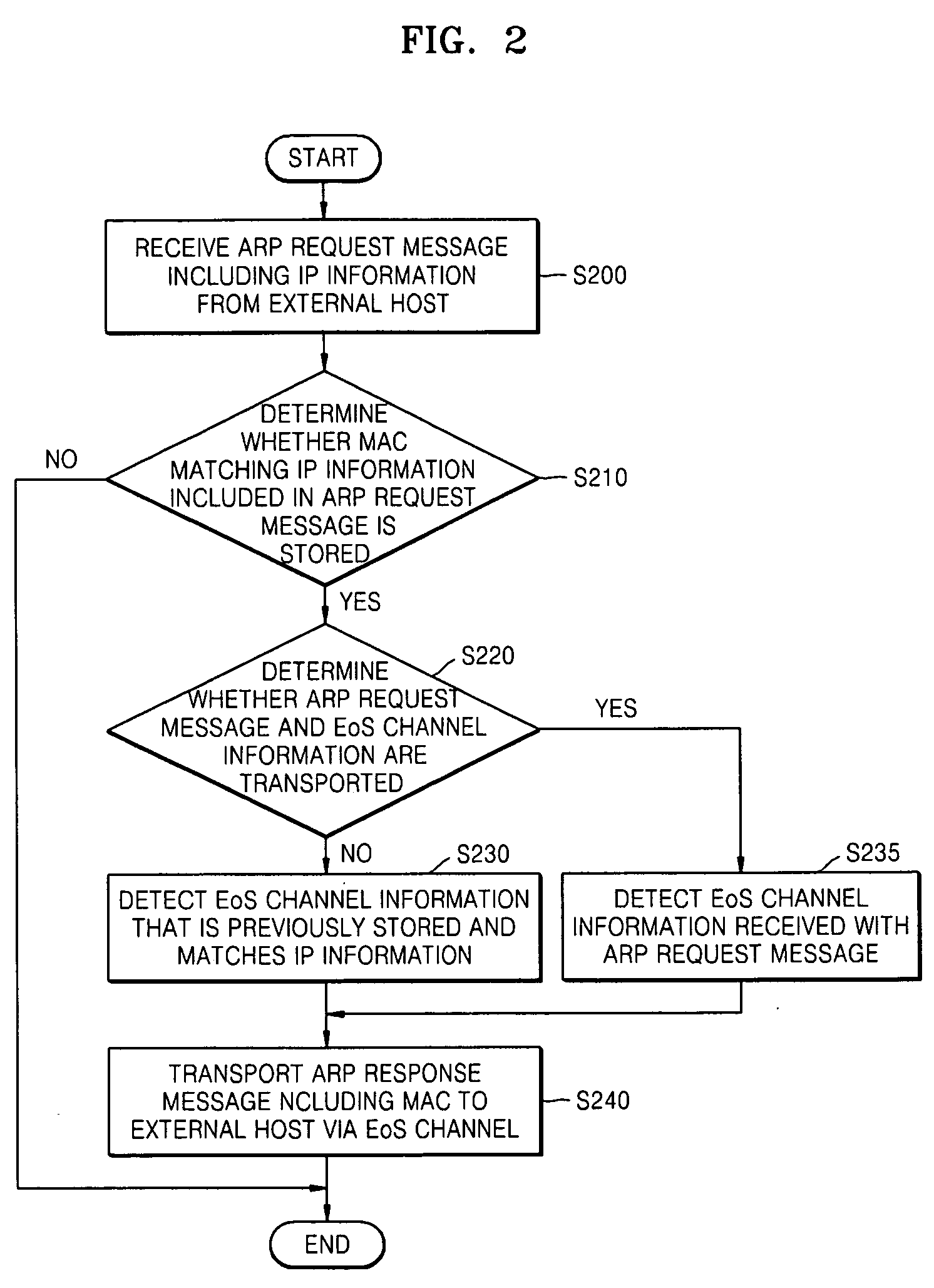
An address resolution protocol (ARP) processing method for Ethernet matching is provided in which a message authentication code (MAC) request message including IP information is received from another application module and provides a MAC corresponding to the MAC request message, the method including: determining whether a MAC matching the IP information included in the MAC request message is stored; determining whether the MAC request message includes Ethernet over synchronous optical network / synchronous digital hierarchy (SONET / SDH) (EoS) channel information; if it is determined that the MAC request message does not include EoS channel information, detecting EoS channel information that is previously stored and that matches the IP information; and broadcasting an ARP request message to an external host via an EoS channel. The ARP processing method is performed using the EoS channel, thereby reducing unnecessary broadcast traffic packets.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com