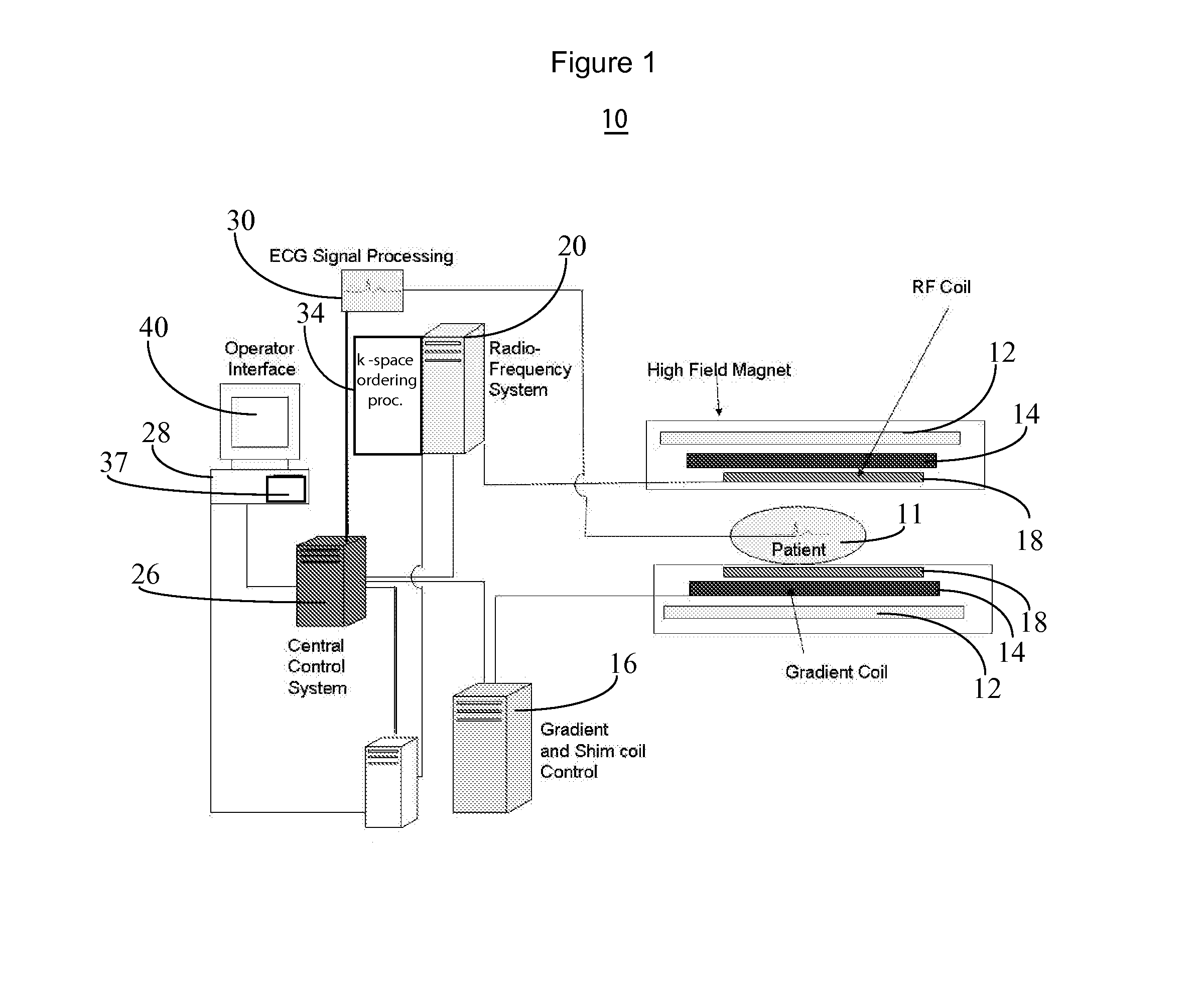
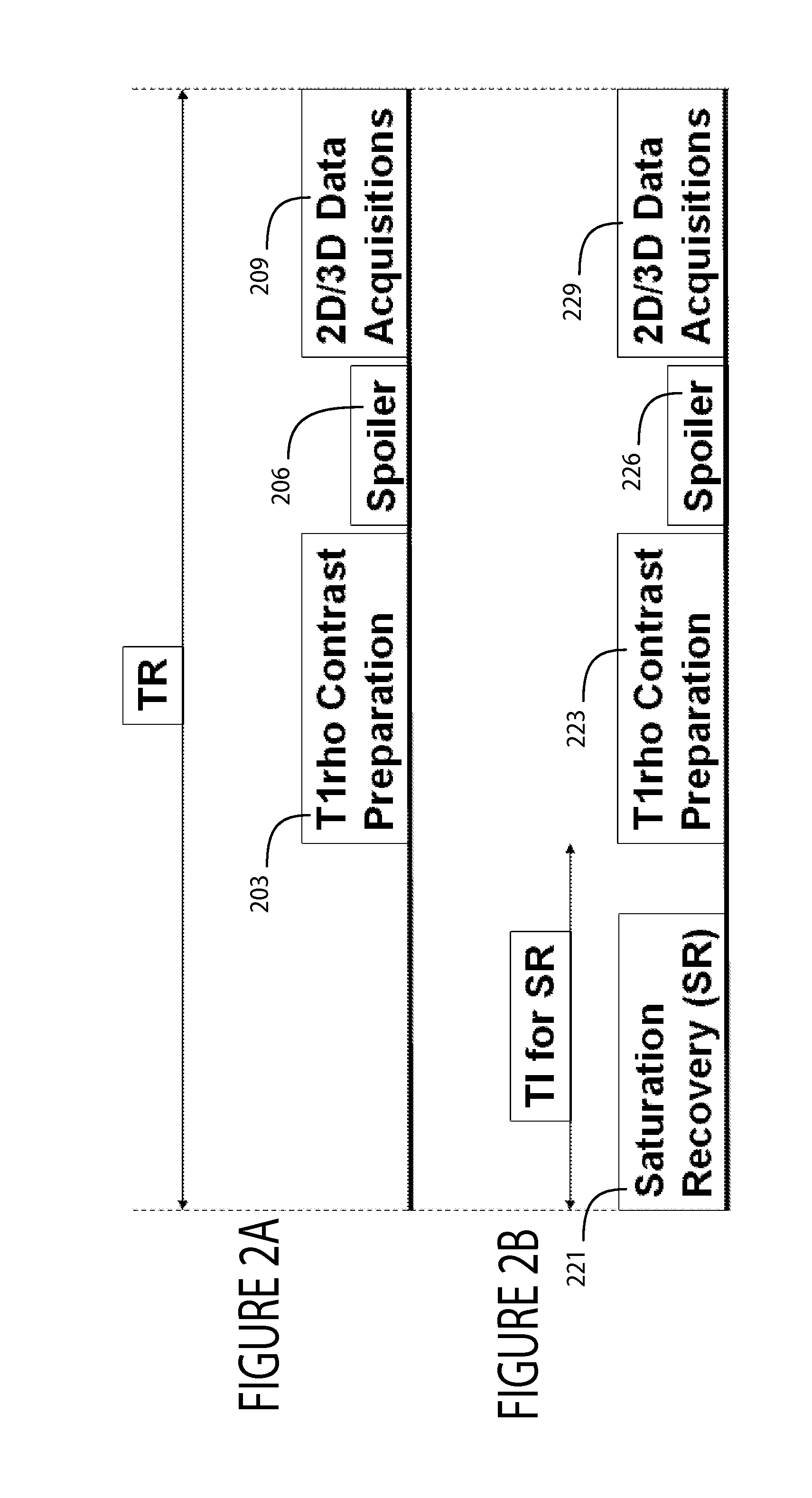
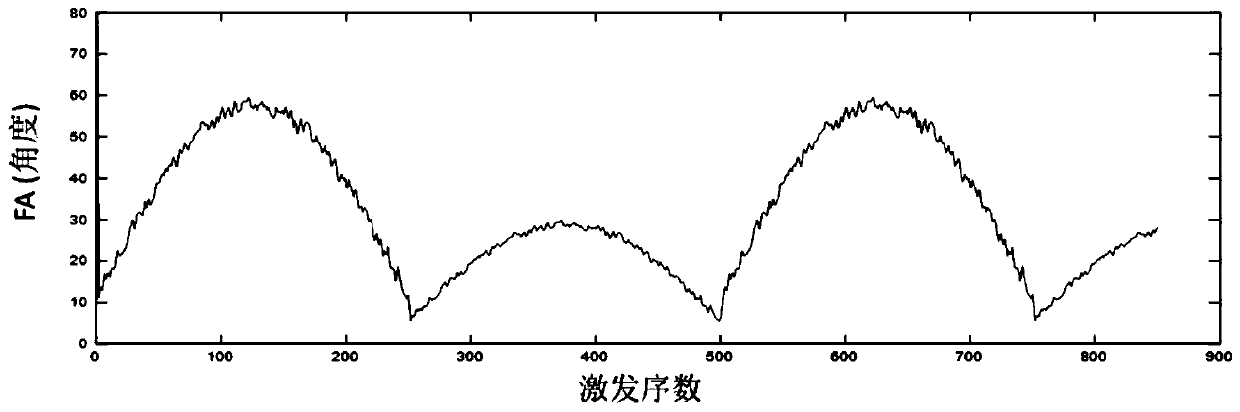
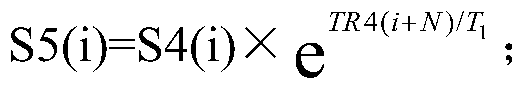Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
80 results about "Spin–lattice relaxation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In nuclear magnetic resonance, Spin–lattice relaxation is the mechanism by which the component of the total nuclear magnetic moment vector which is parallel to the constant magnetic field relaxes from a higher energy, non-equilibrium state to thermodynamic equilibrium with its surroundings (the "lattice"). It is characterized by the spin–lattice relaxation time, a time constant known as T₁.
Non-Aqueous Electrolyte Battery and Method of Manufacturing the Same
InactiveUS20090286160A1Extended service lifeImprove featuresFinal product manufactureElectrode carriers/collectorsElectrode potentialSolvent
Gas generation of a non-aqueous electrolyte battery having a negative active material that intercalates / deintercalates lithium ions at a potential not lower than 1.2 V relative to the potential of lithium as negative electrode is suppressed.A non-aqueous electrolyte battery comprising a non-aqueous electrolyte containing an electrolyte salt and a non-aqueous solvent, a positive electrode and a negative electrode is characterized in that the main active material of said negative electrode is an active material that intercalates / deintercalates lithium ions at a potential not lower than 1.2 V relative to the potential of lithium and the auxiliary active material of said negative electrode is an active material that at least intercalates lithium ions at a potential lower than 1.2 V relative to the potential of lithium and that there exists lithium showing a spin-lattice relaxation time (T1) of not less than 1 second as determined by a solid-state Li—NMR measurement in the main active material of said negative electrode. A method of manufacturing a non-aqueous electrolyte battery containing a non-aqueous electrolyte, a positive electrode and a negative electrode (a main active material and an auxiliary active material of the negative electrode) is characterized in that the negative electrode potential is lowered to not higher than 0.8 V relative to the potential of lithium at least once in the initial cycle.
Owner:GS YUASA INT LTD
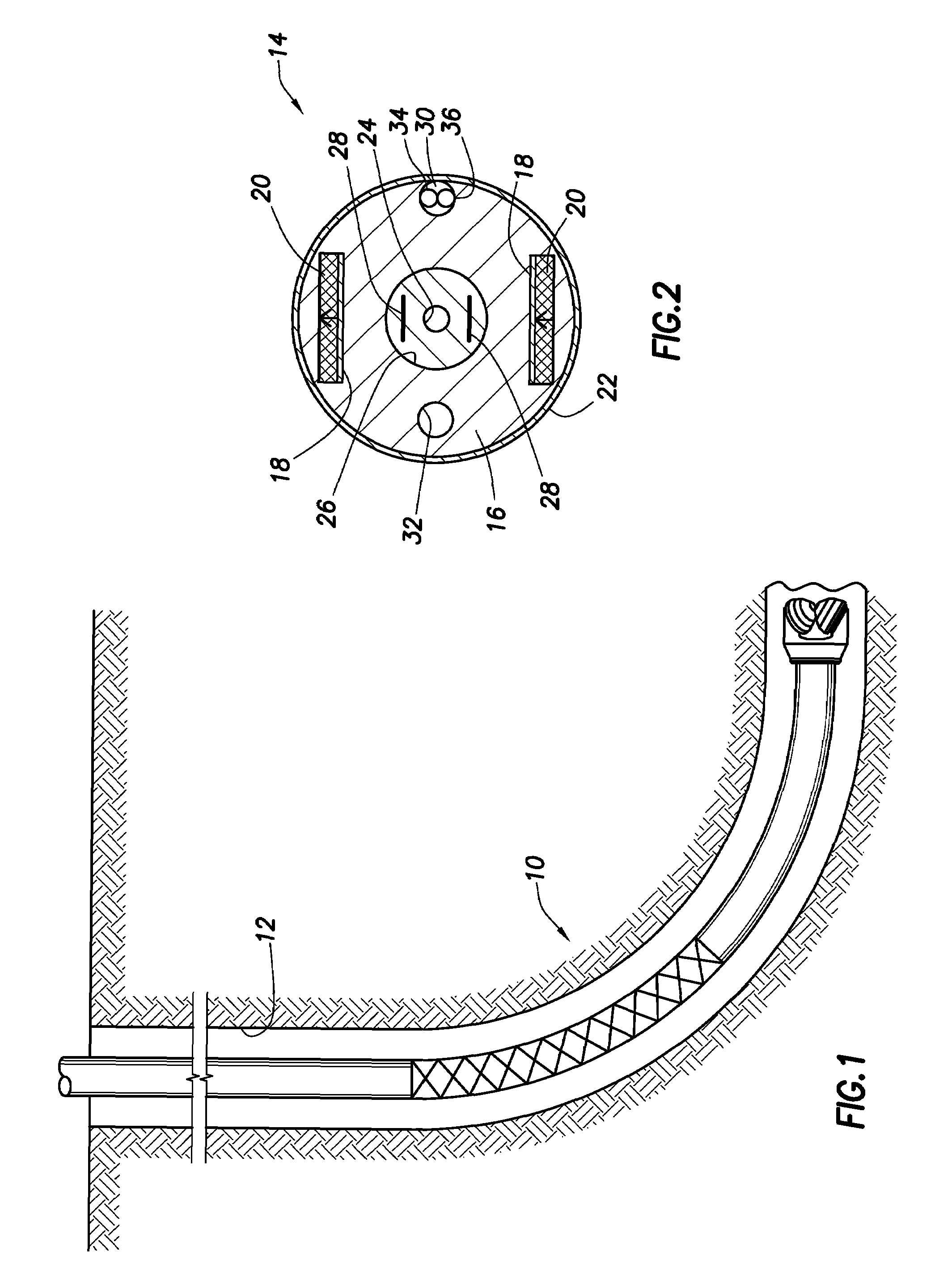
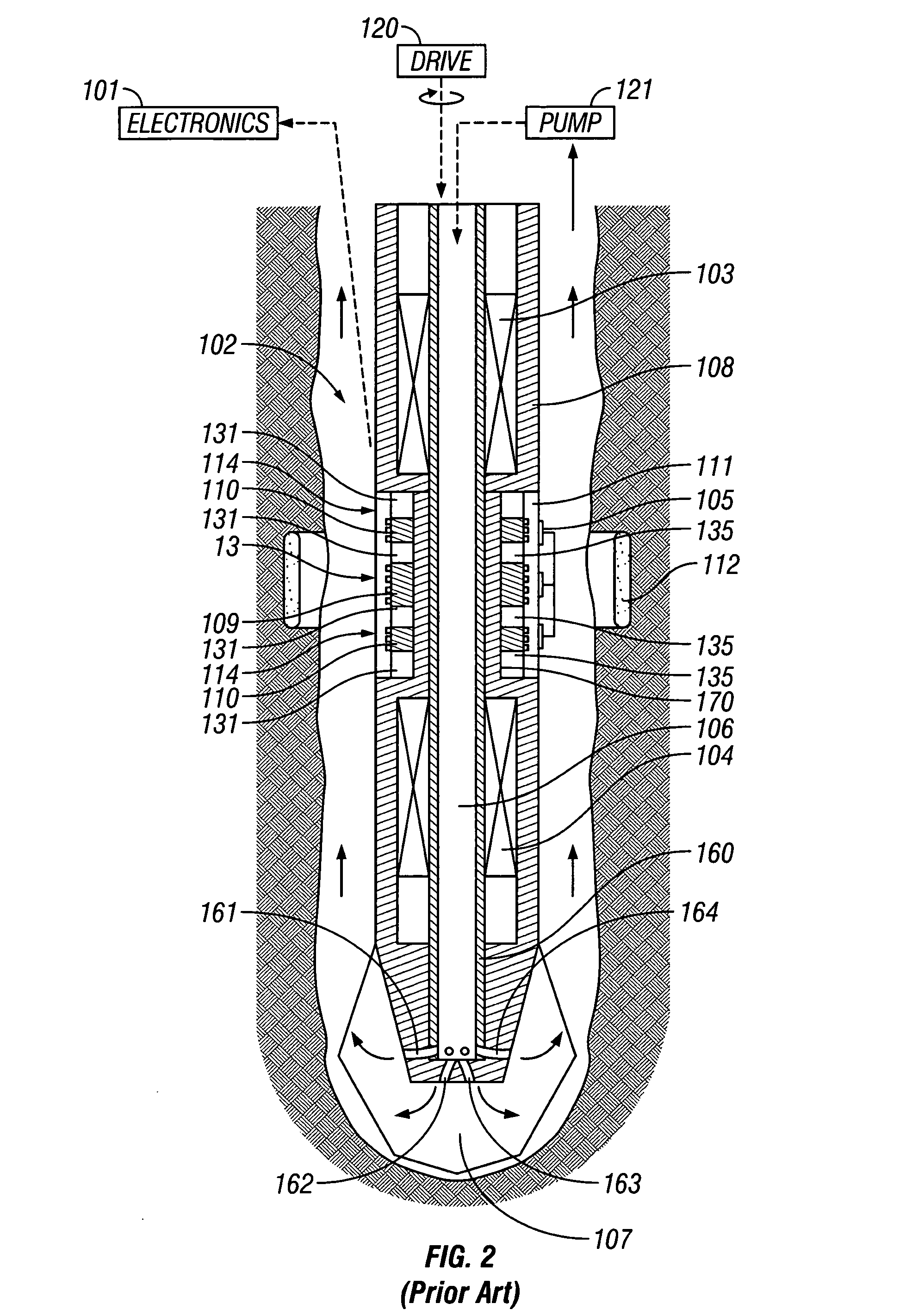
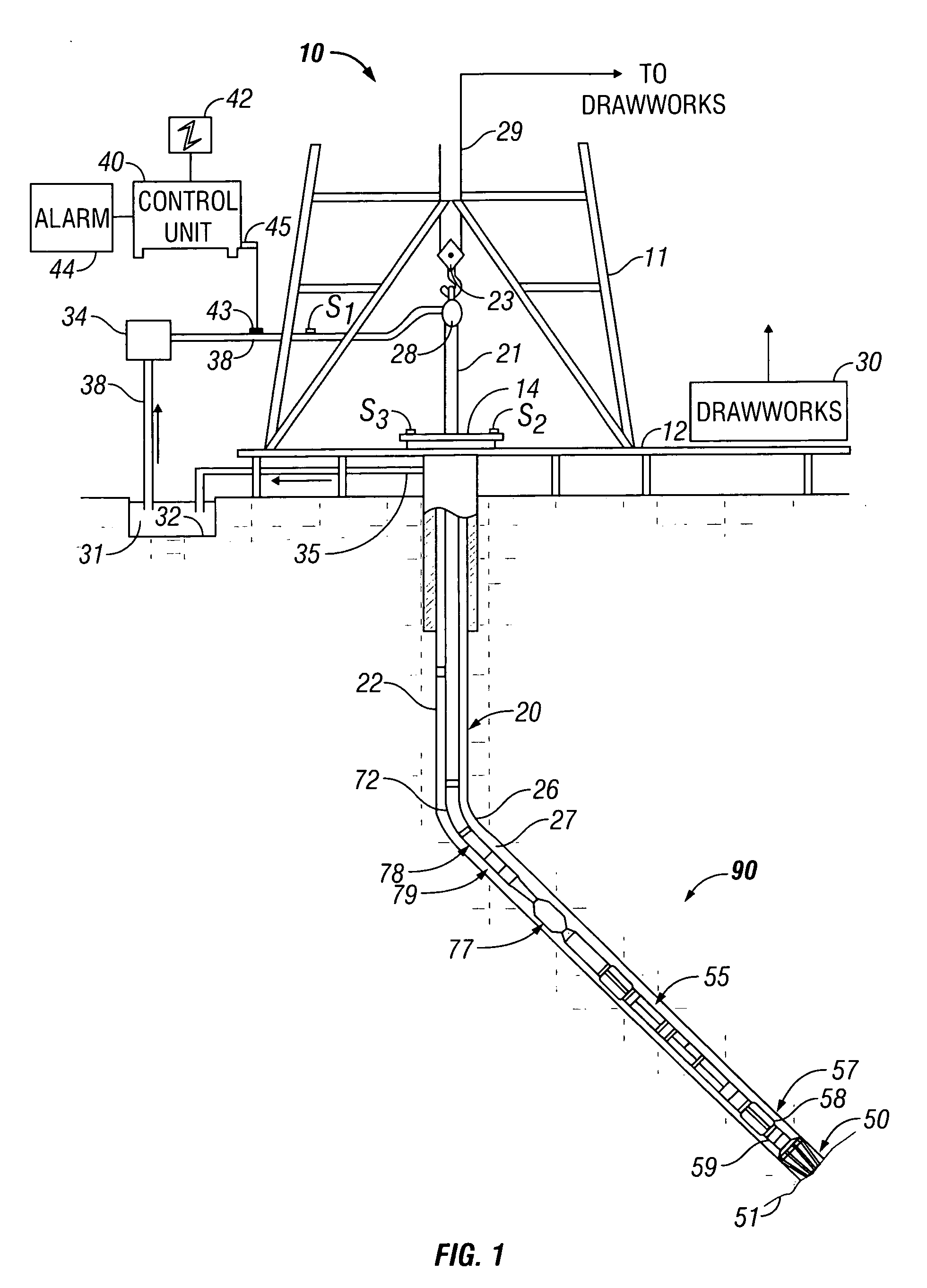
High pressure/high temperature magnetic resonance tool
InactiveUS7683613B2Easy to useMeasurements using electron paramagnetic resonanceMaterial analysis by using resonanceResonance measurementHigh pressure
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
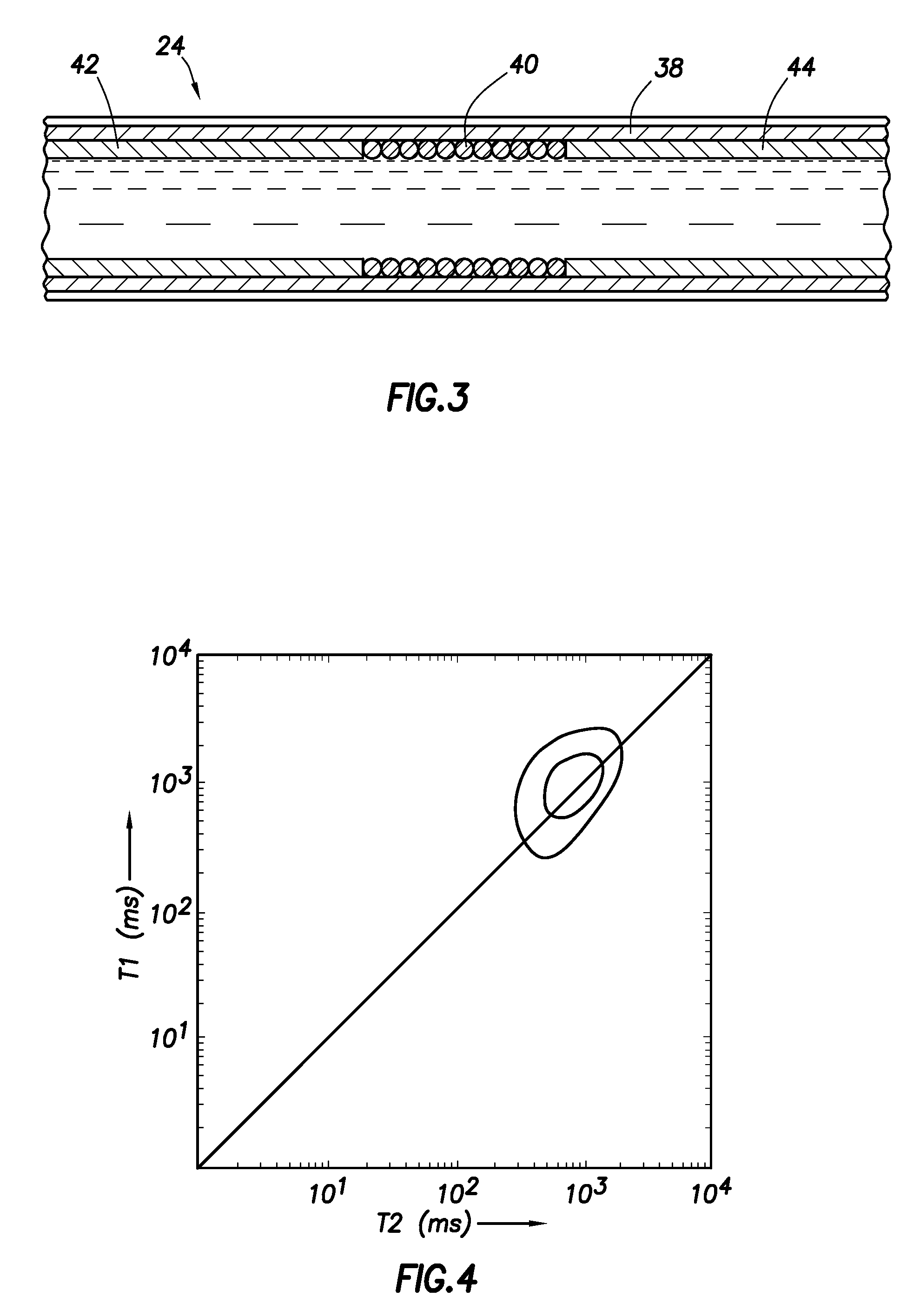
Correction of NMR artifacts due to constant-velocity axial motion and spin-lattice relaxation
ActiveUS20060033491A1Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingMagnetic measurementsSpinsPulse sequence
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
Non-invasive blood glucose sensors using a magneto-resonance absorption method and measurement methods thereof
InactiveUS7635331B2Easy to detectImproving a uniformity of the constant magnetic fieldDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsGlucose sensorsBlood Glucose Measurement
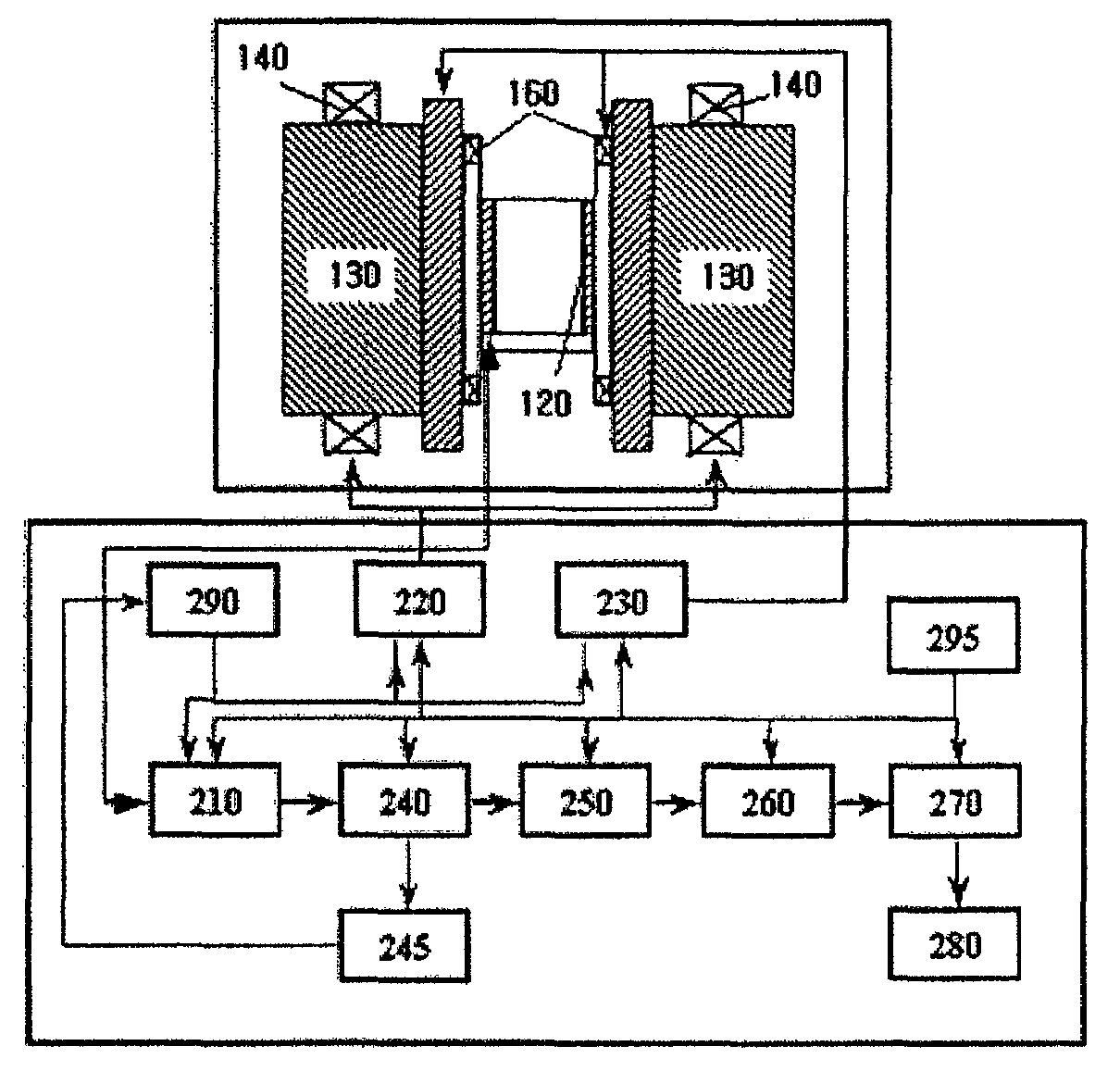
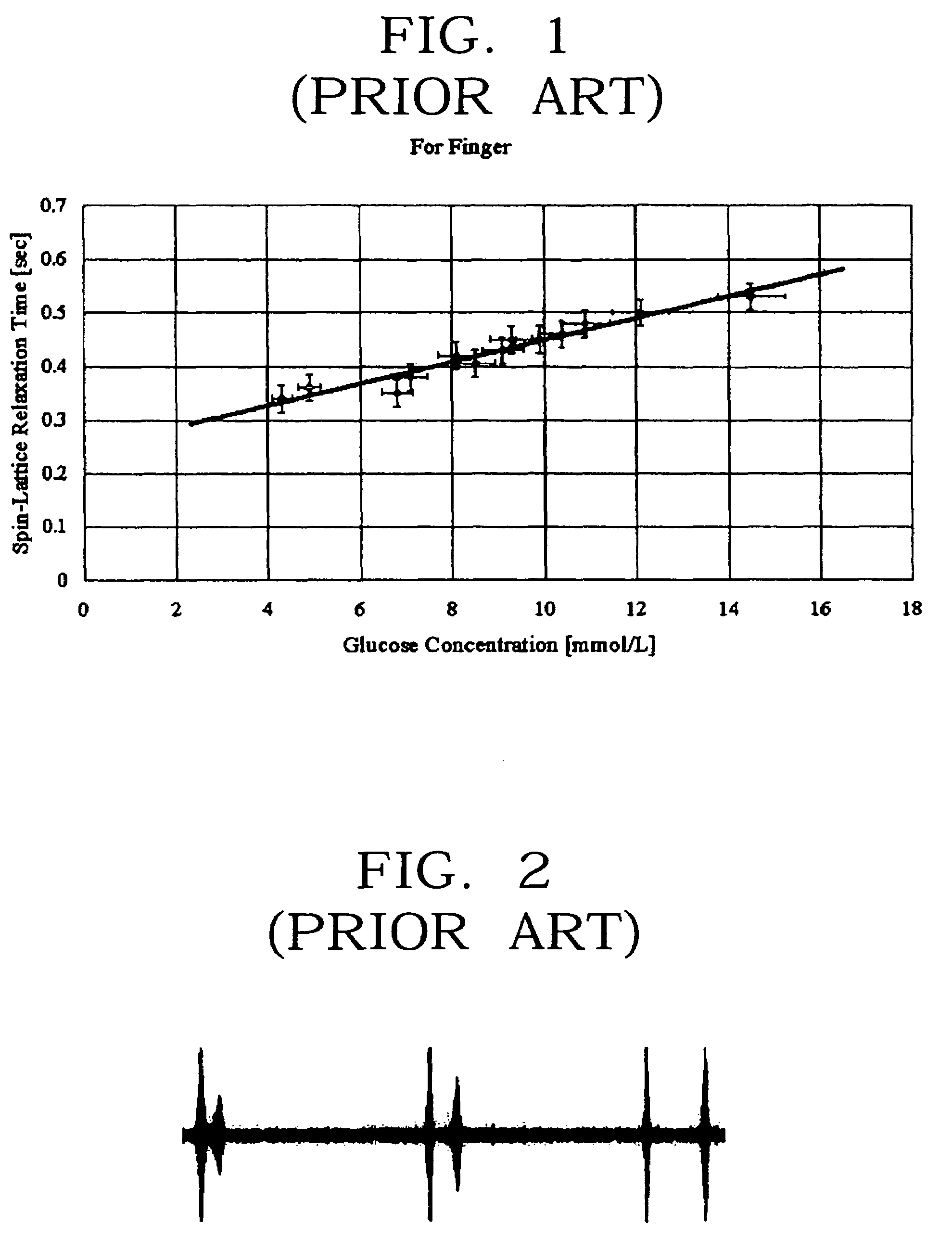
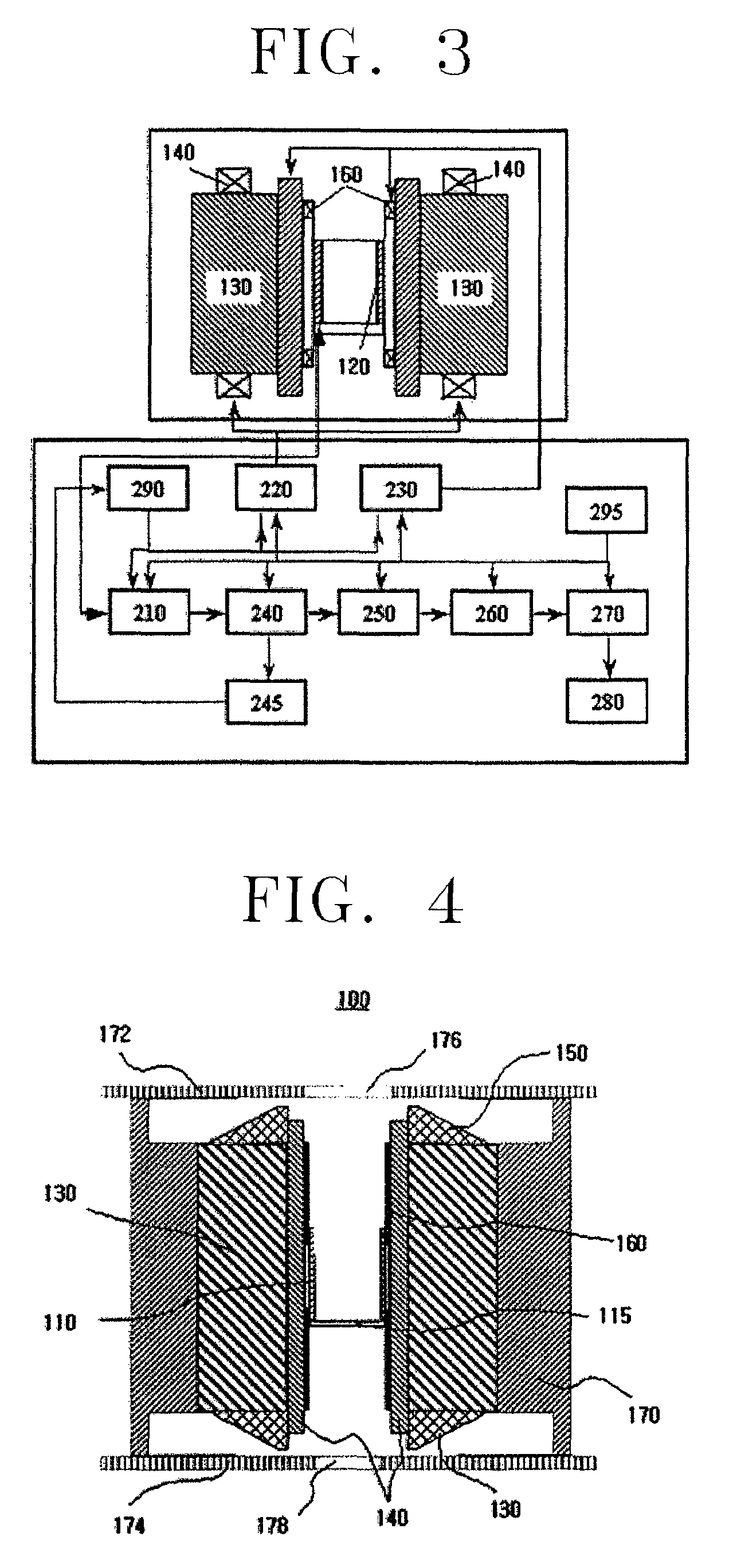
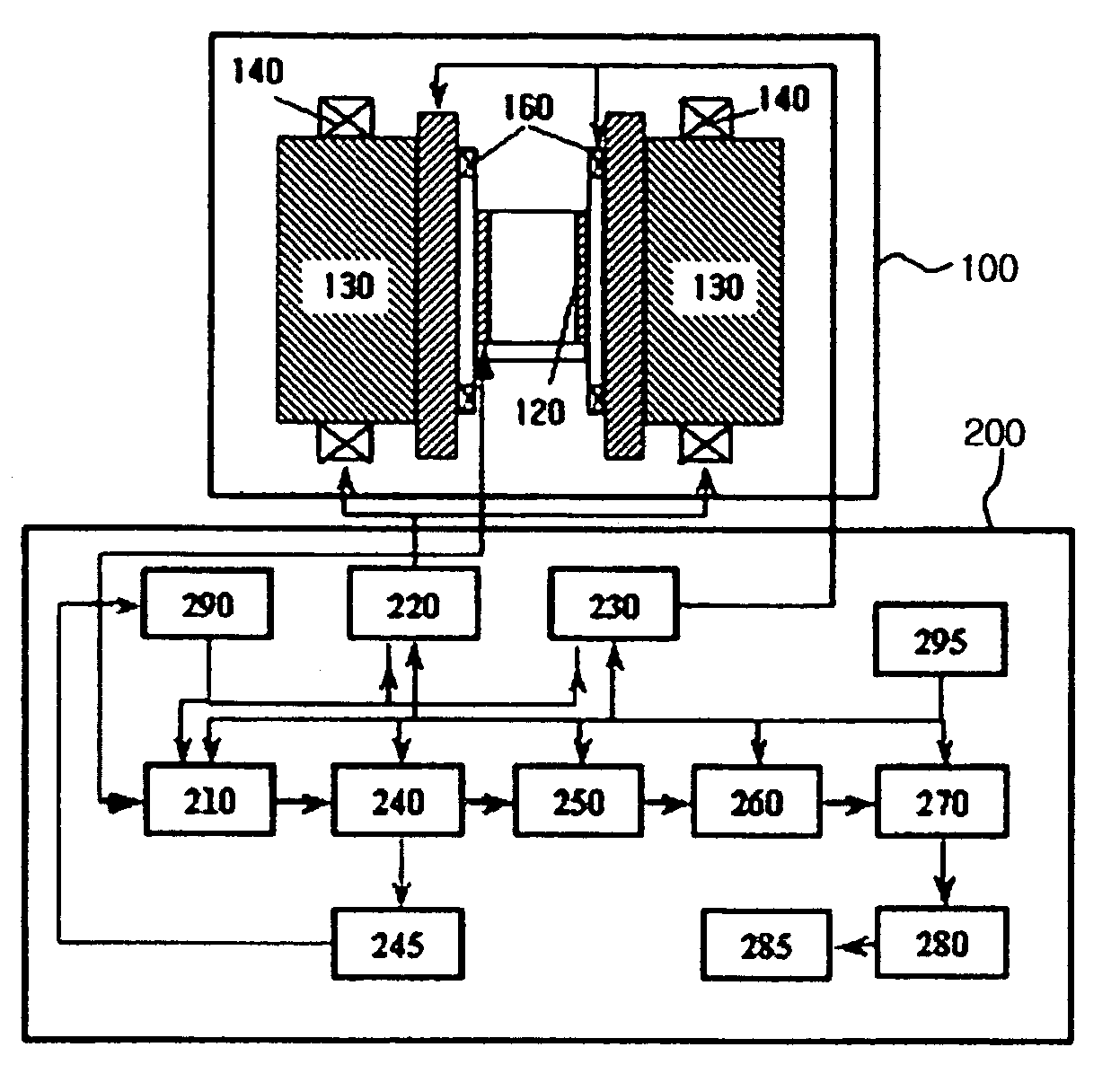
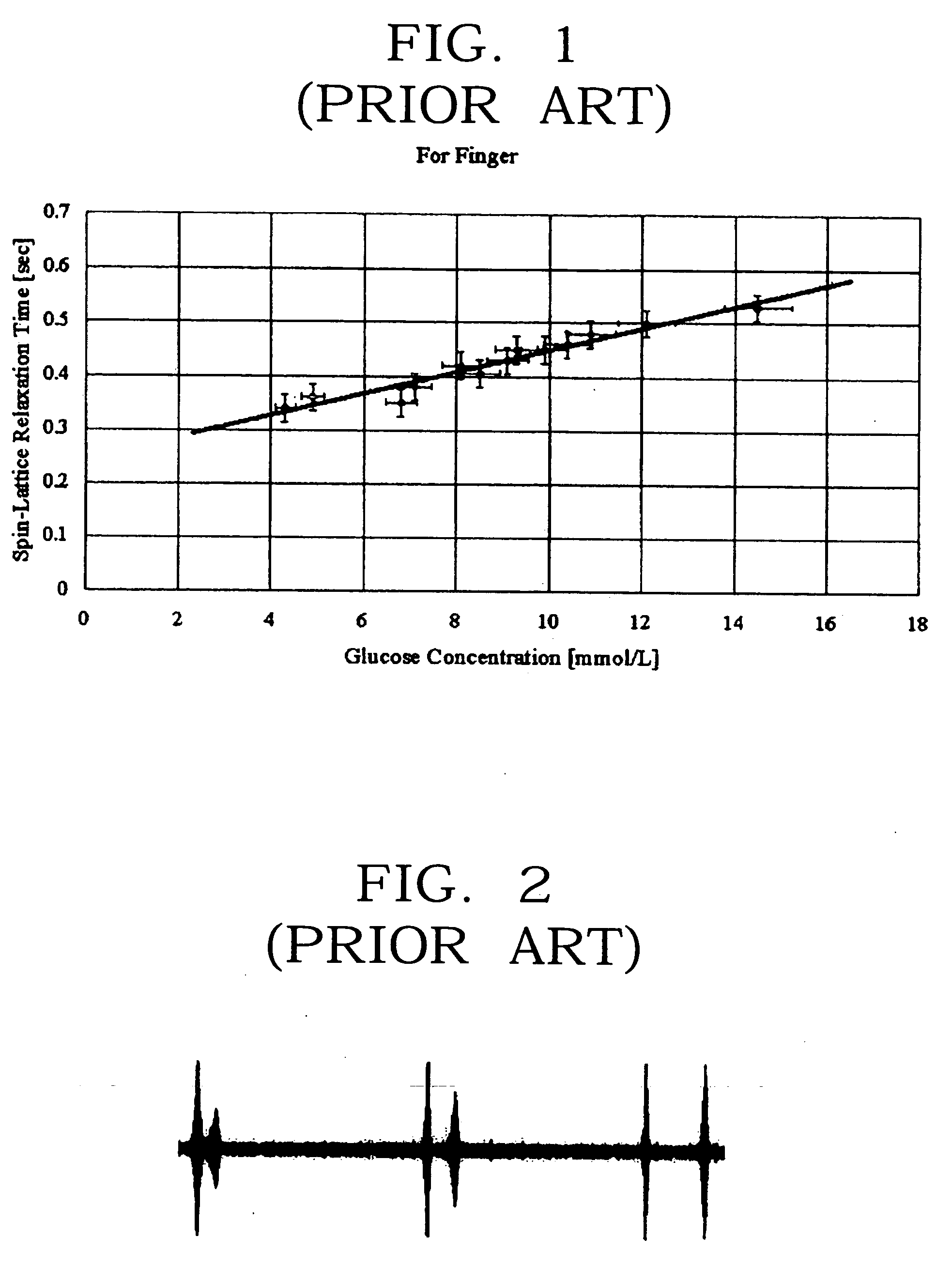
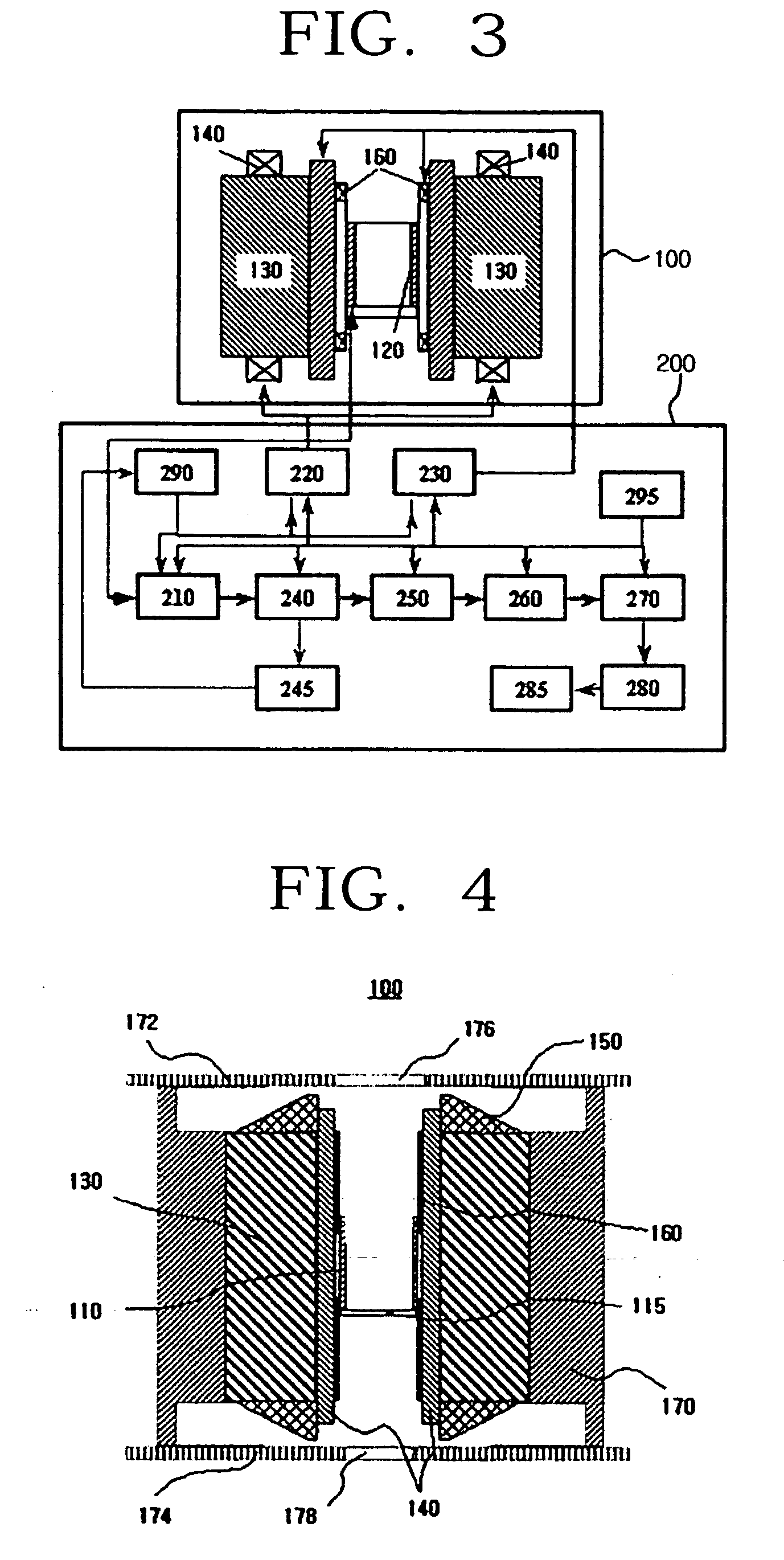
A non-invasive blood glucose measurement method using a magneto-resonance absorption method. A constant magnetic field is applied using a pair of permanent magnets, the magnetic field having a uniform strength. A triangular waveform low frequency modulation magnetic field is applied using a low frequency generator and a pair of low frequency coils, the low frequency modulation magnetic field having a uniform strength. A weak acoustic wave modulation magnetic field is applied using an acoustic wave generator and a pair of acoustic wave coils. Electromagnetic waves are applied to a detector in which a finger is positioned to produce a nuclear magneto-resonance, the electromagnetic waves having a frequency varying in a specific frequency band step by step, the applying being done using a high frequency generator and a sensor coil. A magneto-resonance absorption signal produced by spin-lattice relaxation of protons in a tissue of the finger because of the nuclear magneto-resonance is detected. A magneto-resonance spin-lattice relaxation time of the finger from the magneto-resonance absorption signal is determined. A blood glucose concentration in a human body is determined from a correlation between a pre-determined blood glucose concentration in the human body and the determined magneto-resonance spin-lattice relaxation time.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Organic Spintronic Devices and Methods for Making the Same
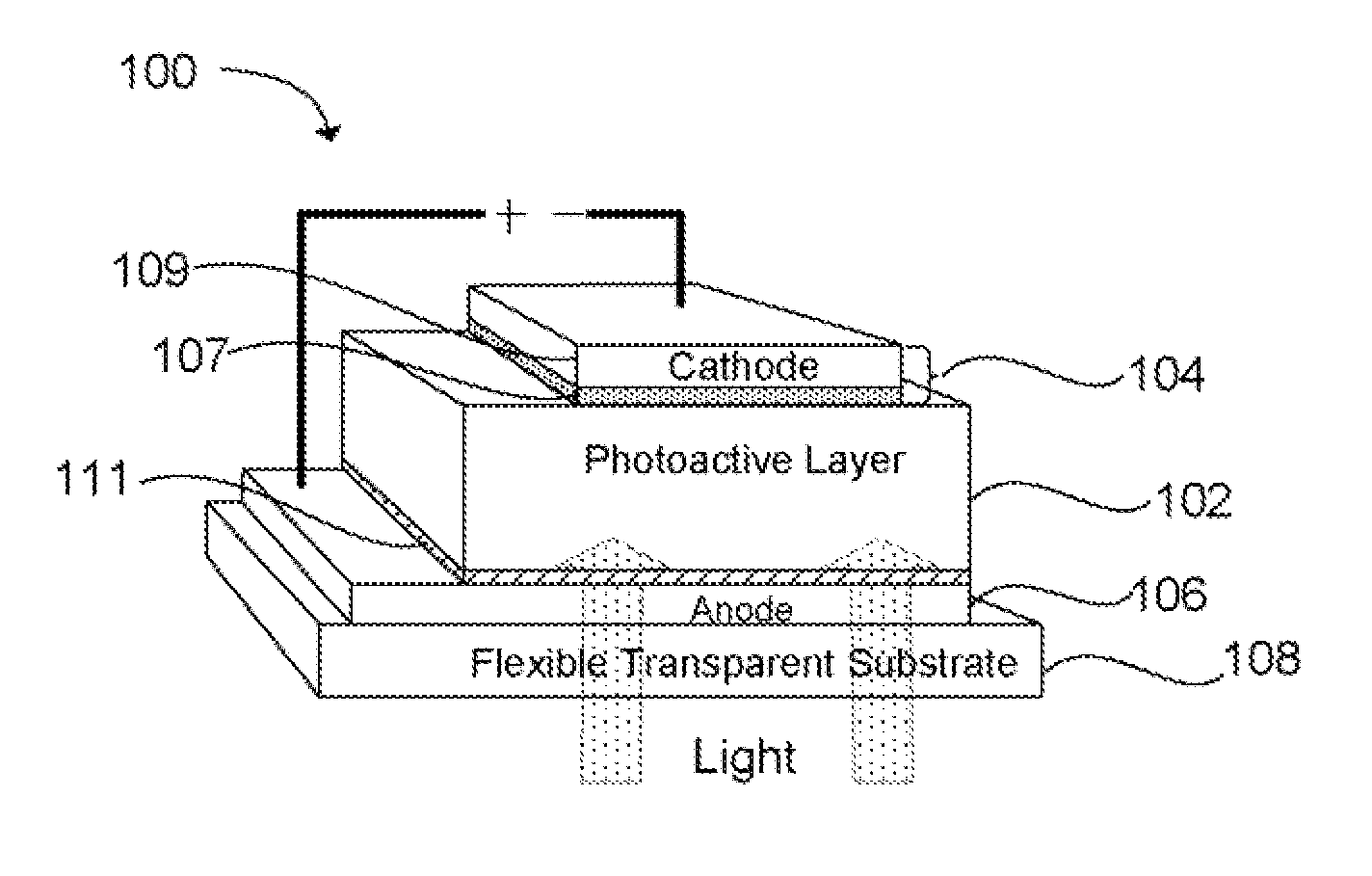
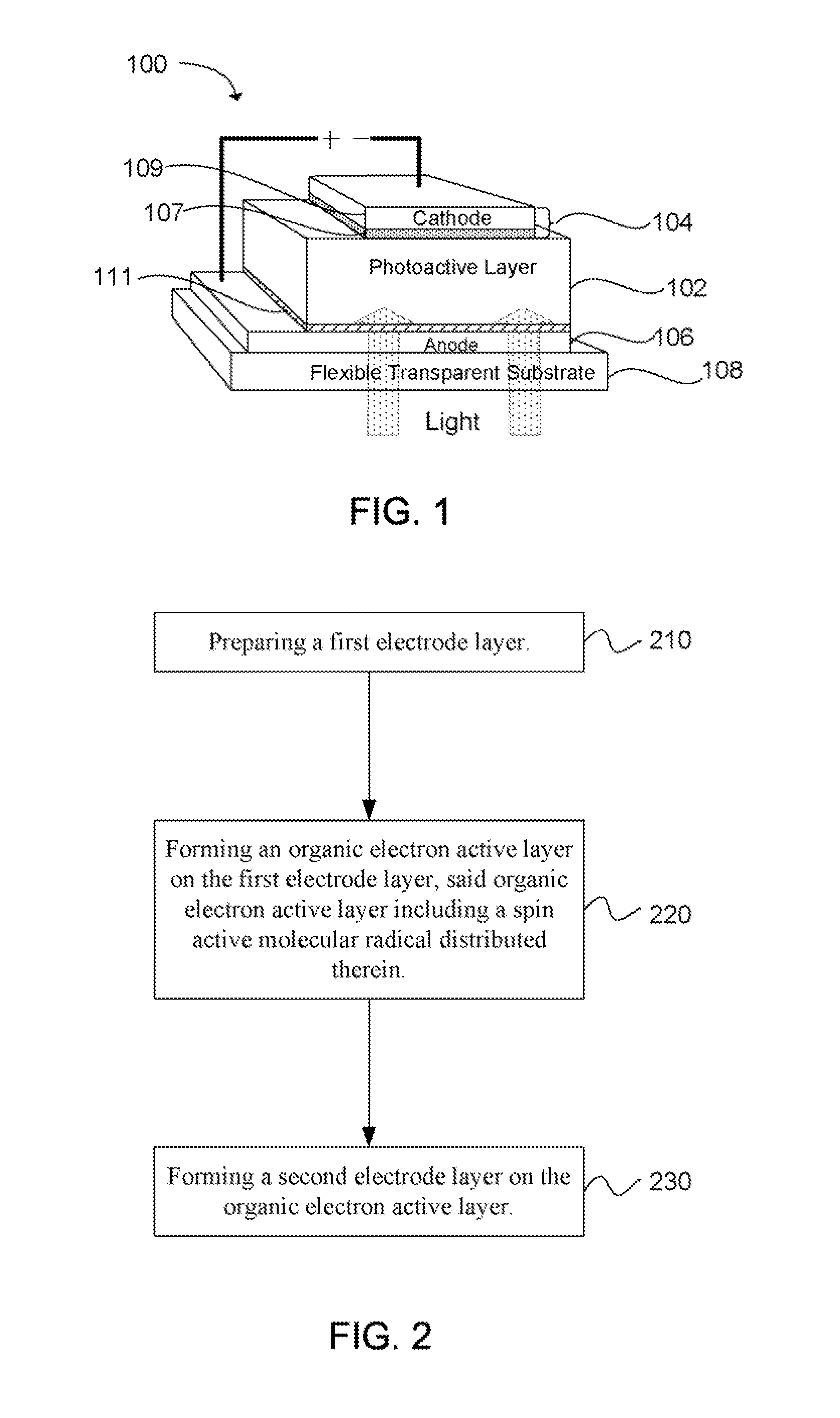
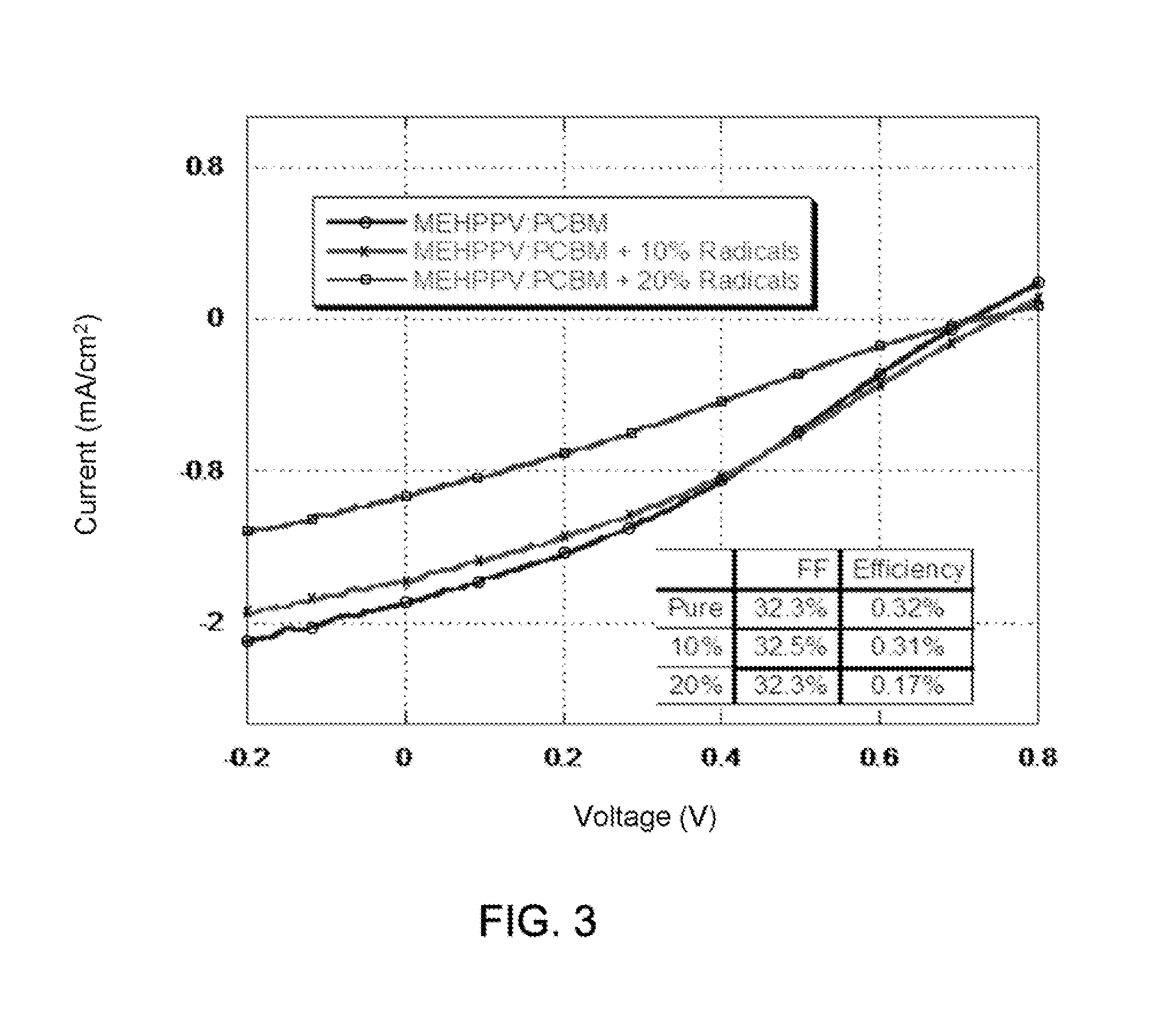
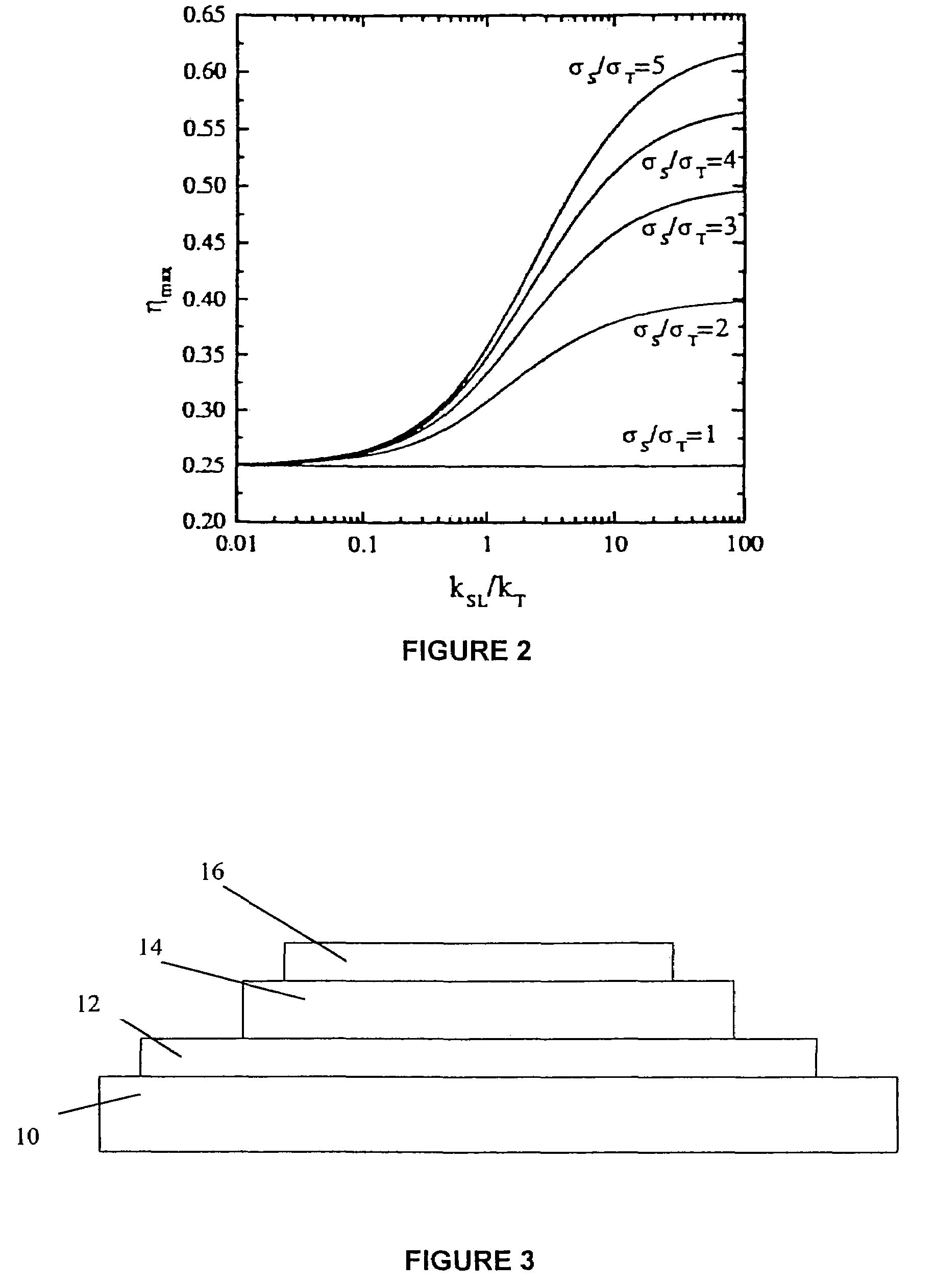
An organic spintronic photovoltaic device (100) having an organic electron active layer (102) functionally associated with a pair of electrodes (104, 106). The organic electron active layer (102) can include a spin active molecular radical distributed in the active layer (102) which increases spin-lattice relaxation rates within the active layer (102). The increased spin lattice relaxation rate can also influence the efficiency of OLED and charge mobility in FET devices.
Owner:UNIV OF UTAH RES FOUND
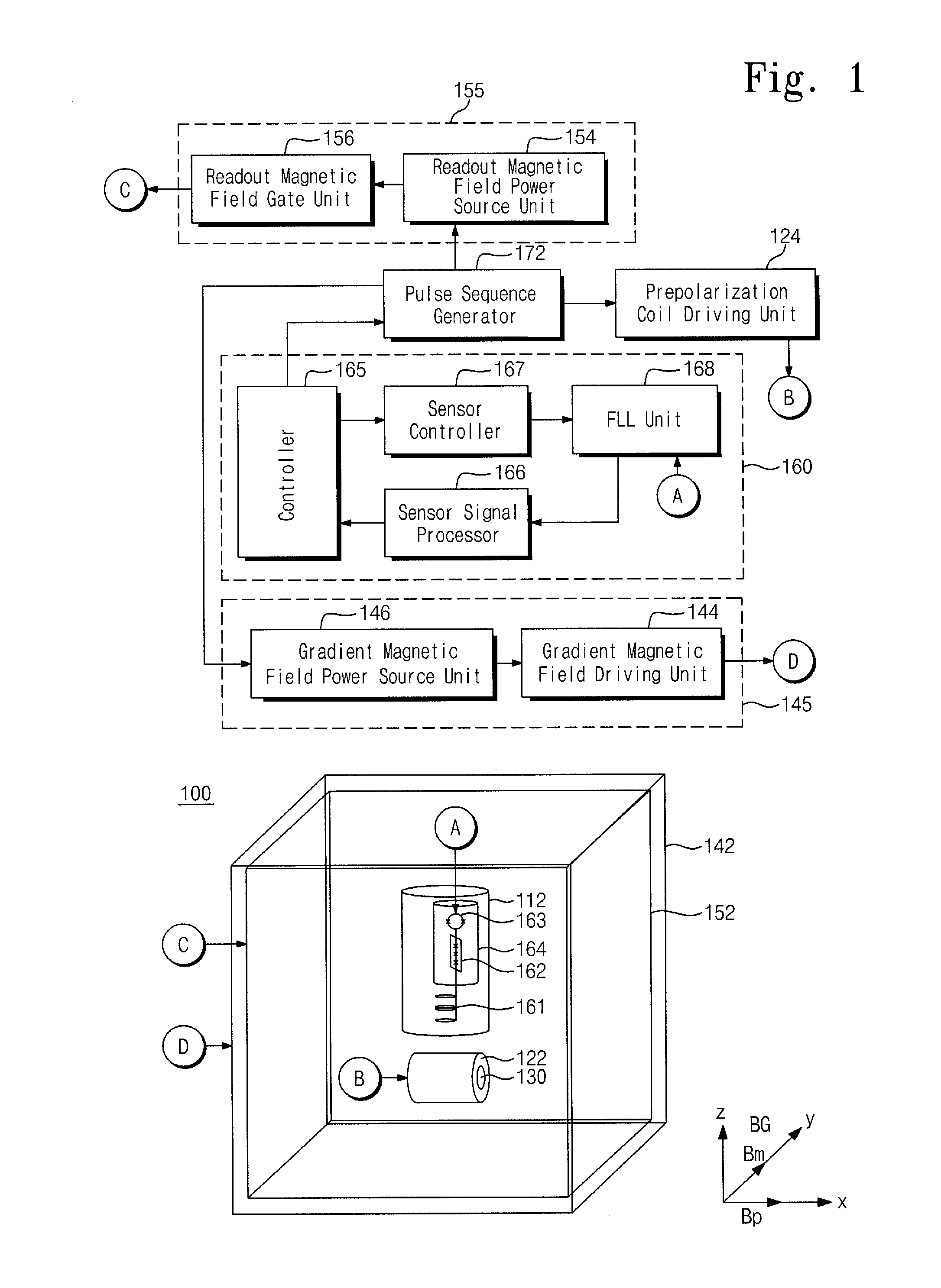
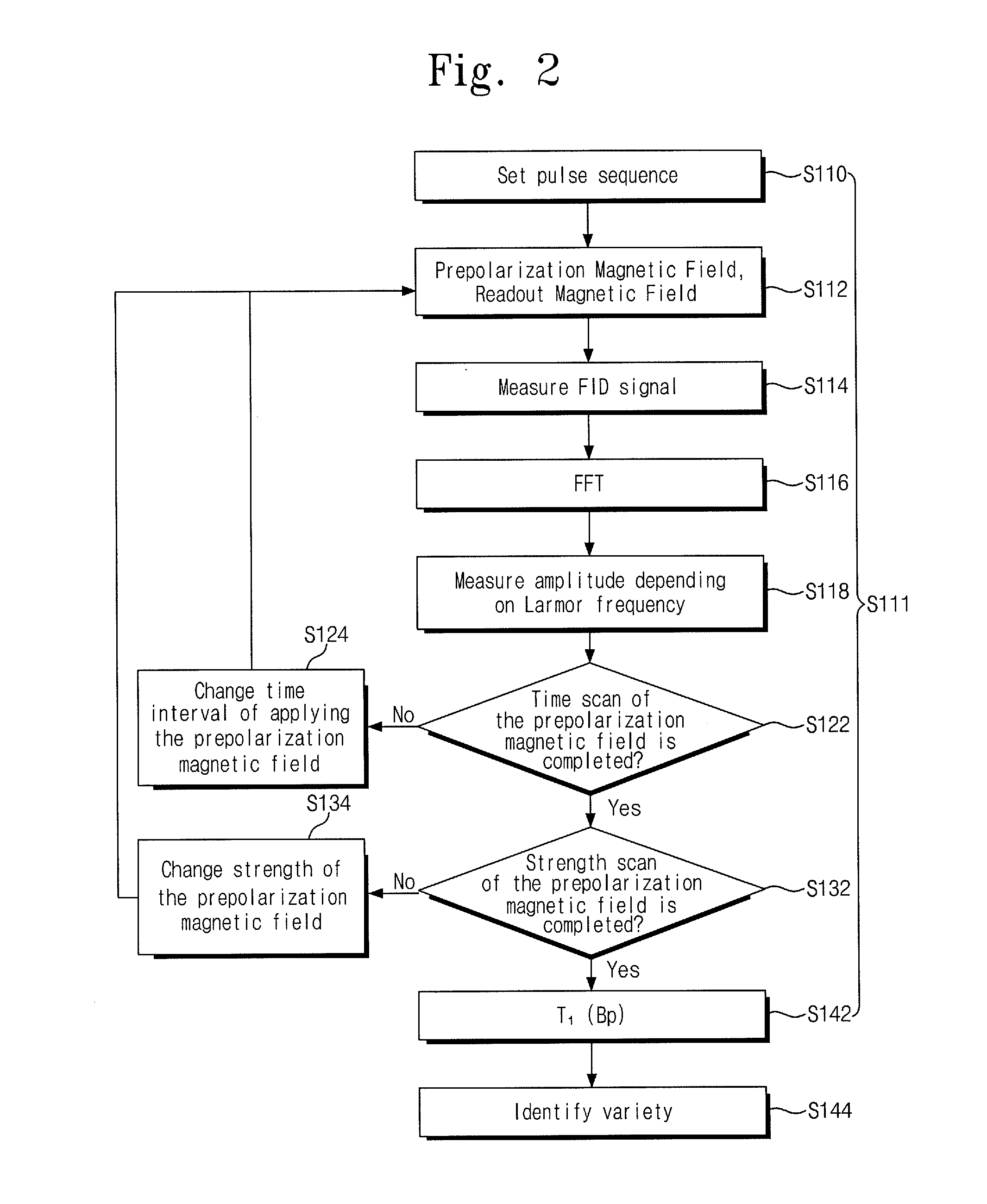
Object discrimination method using ultra-low magnetic field nuclear magnetic resonance and an object discrimination apparatus of the same
ActiveUS20140232400A1Analysis using nuclear magnetic resonanceElectric/magnetic detectionNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonanceLow field nuclear magnetic resonance
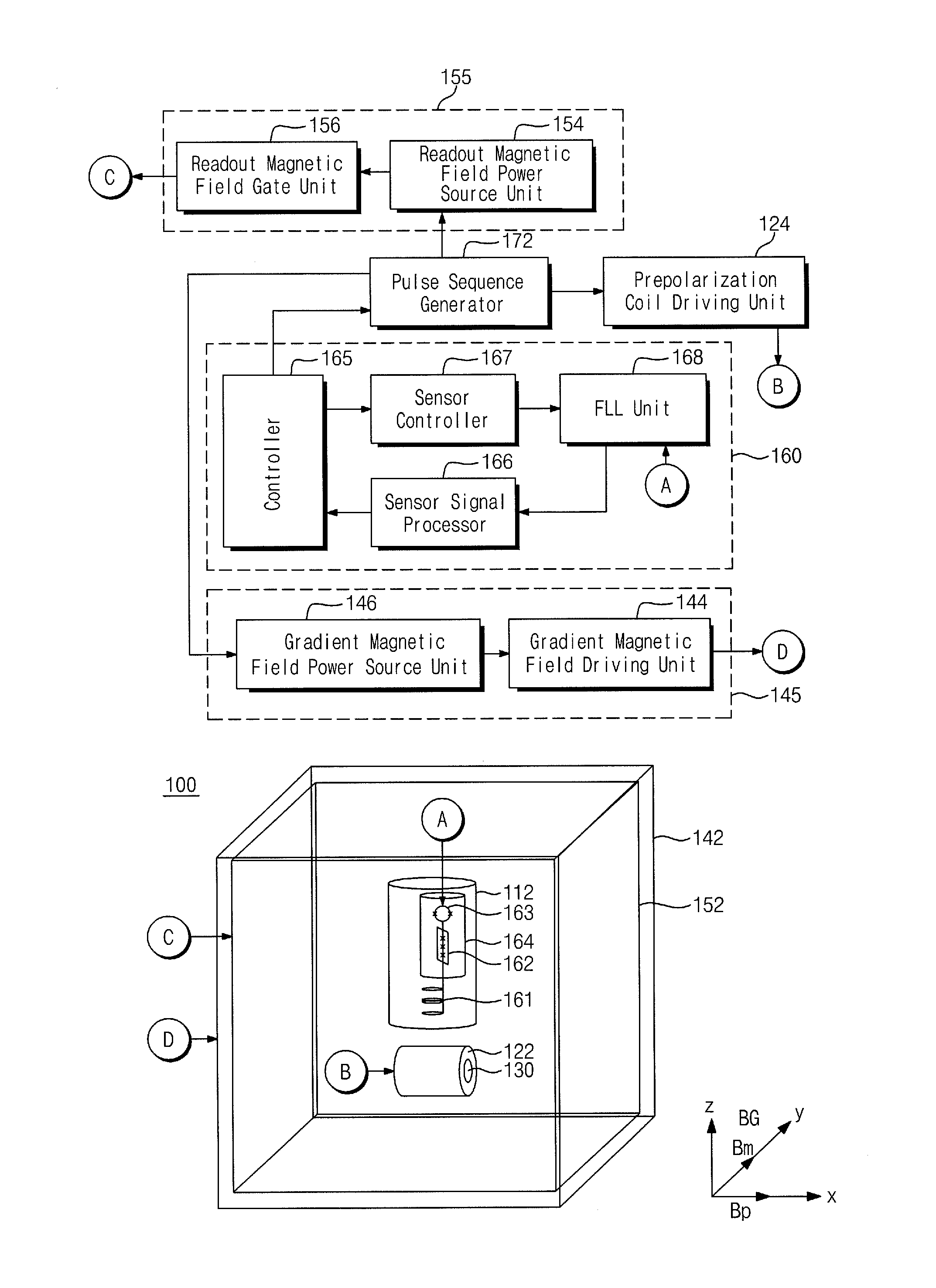
Provided are an object discrimination method and an object discrimination apparatus using an ultra-low magnetic field nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR). The method includes measuring the respective spin-lattice relaxation times at a plurality of strengths of prepolarization magnetic fields with respect to a measurement target and classifying the measurement target using the spin-lattice relaxation times.
Owner:KOREA RES INST OF STANDARDS & SCI
Golf ball resin composition and golf ball
ActiveUS20130172110A1Increase elasticityFeel goodGolf ballsSolid ballsIonomerSolid-state nuclear magnetic resonance
An object of the present invention is to provide a golf ball excellent in a shot feeling and resilience. The present invention provides a golf ball resin composition comprising (A) at least one resin component selected from the group consisting of (a-1) a binary copolymer composed of an olefin and an α,β-unsaturated carboxylic acid having 3 to 8 carbon atoms, (a-2) an ionomer resin consisting of a metal ion-neutralized product of the binary copolymer, (a-3) a ternary copolymer composed of the binary copolymer components and an α,β-unsaturated carboxylic acid ester, and (a-4) an ionomer resin consisting of a metal ion-neutralized product of the ternary copolymer components; and (B) a basic metal salt of a fatty acid, and having a spin-lattice relaxation time (T1) of 13C nucleus of 5.56 seconds or shorter measured by a High resolution solid state nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) method.
Owner:SUMITOMO RUBBER IND LTD
Correction of NMR artifacts due to axial motion and spin-lattice relaxation
InactiveUS20060273787A1Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingMagnetic measurementsSpinsPulse sequence
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
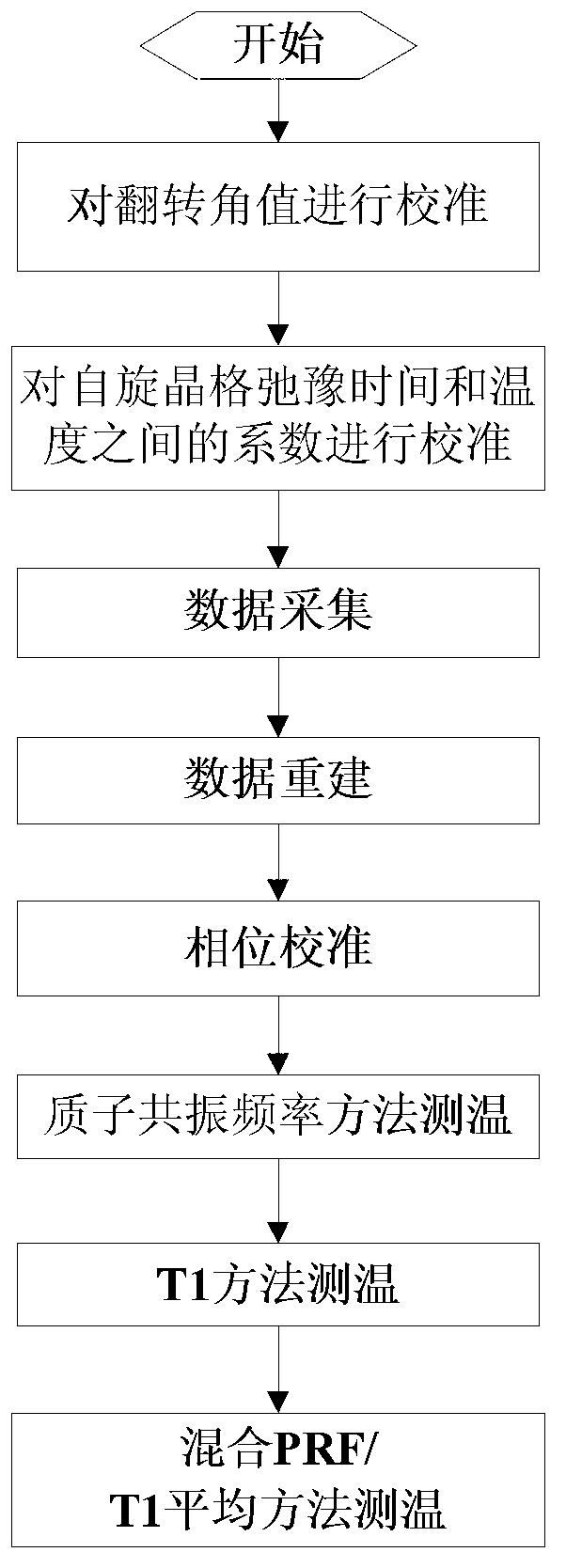
Temperature measurement method of permanent-magnet MRI system
ActiveCN103284722AAccurate and stable temperature measurementDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsProton resonance frequencyData acquisition
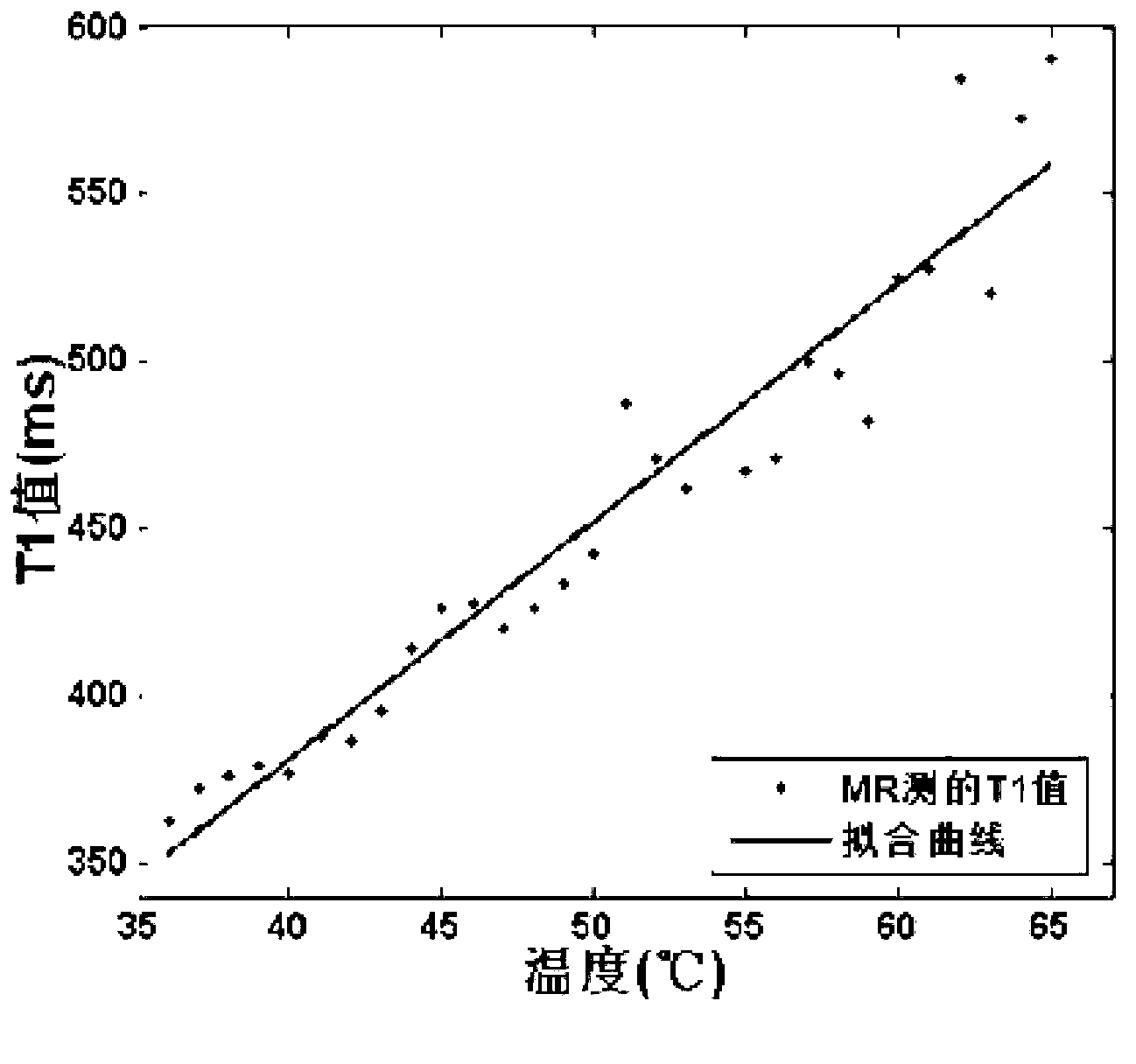
The invention relates to a temperature measurement method of a permanent-magnet MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) system. The method comprises the steps that a flip angle value is calibrated; a coefficient between the spin lattice relaxation time and the temperature is calibrated; two groups of temperature measurement results by a proton resonance frequency method are obtained after data acquisition, data reconstruction and phase calibration; a group of temperature measurement results are obtained by a spin lattice relaxation time method; the temperature measurement results by the proton resonance frequency method and the temperature measurement results by the spin lattice relaxation time method are mixed and averaged; and a final temperature measurement result is obtained. The method is applied to a temperature measurement process of the permanent-magnet MRI system, and can effectively improve the temperature measurement accuracy and the temperature measurement stability.
Owner:XINGAOYI MEDICAL EQUIP CO LTD
Golf ball polyurethane composition and golf ball
ActiveUS20130053176A1Increase elasticityFeel goodGolf ballsSolid ballsPolyurethane elastomerSolid-state nuclear magnetic resonance
An object of the present invention is to provide a golf ball polyurethane composition excellent in resilience. Another object of the present invention is to provide a golf ball excellent in a shot feeling and resilience. The present invention provides a golf ball polyurethane composition comprising, as a resin component, a polyurethane elastomer including a polyisocyanate with at least two alicyclic hydrocarbon structures having 3 or more carbon atoms as a constituting component, and having a spin-lattice relaxation time (T1) of 13C nucleus of 7.3 seconds or less measured by a High resolution solid state nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) method.
Owner:SUMITOMO RUBBER IND LTD
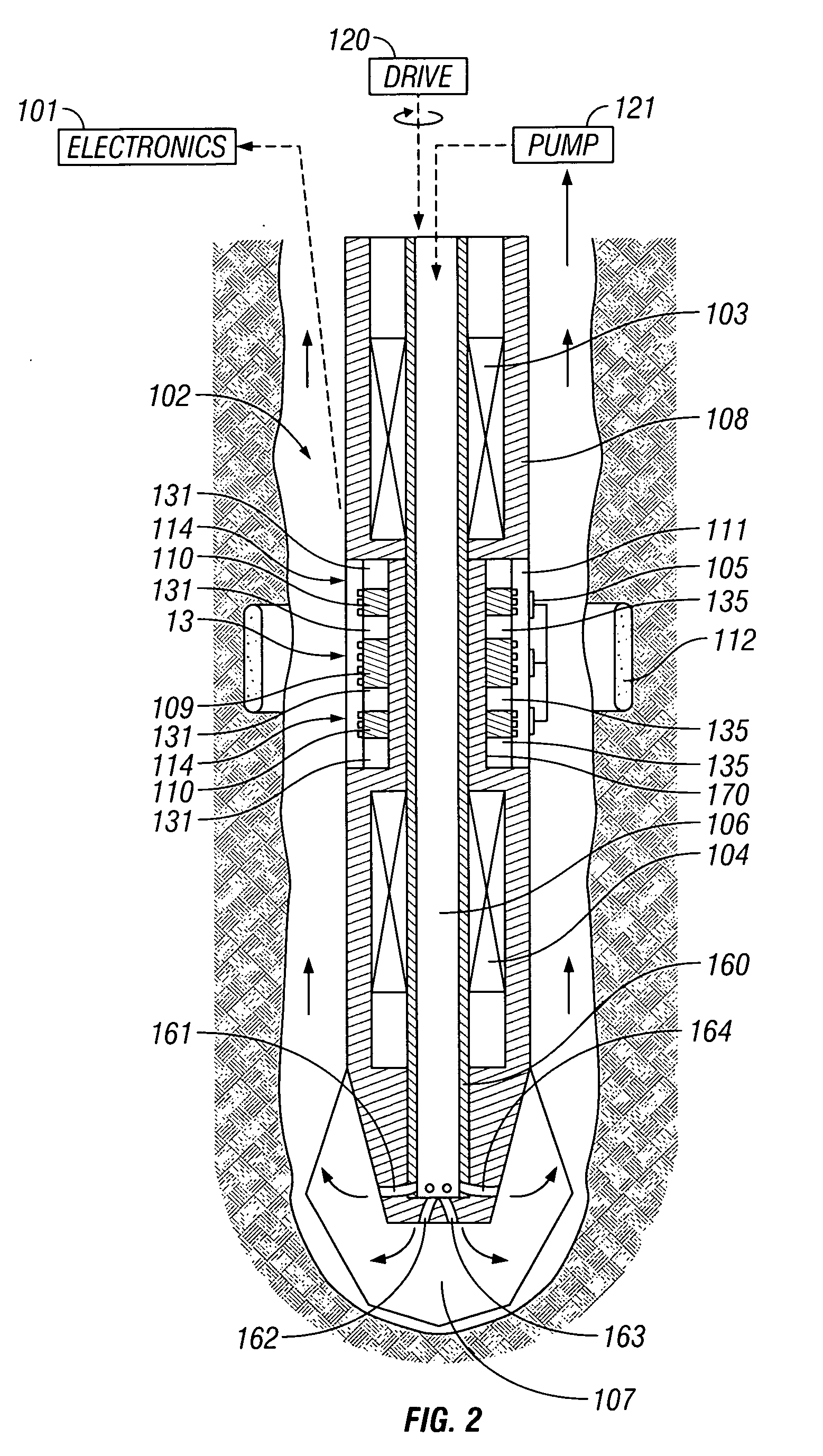
Detection of material within a region of the earth using nuclear magnetic resonance
InactiveUS20190107590A1Quick changeMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsMaterial analysis by using resonanceNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonanceMeasurement device
Provided are systems, methods, and apparatus for using nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) to detect a first material in the presence of a second material within a region of the Earth and within a static magnetic field (such as Earth's magnetic field). These inventions are uniquely suited to detect NMR signals from materials remotely located from a measurement device (e.g., below ice with the device above the ice). They are further useful in detecting first material having relatively short spin-lattice (T1) relaxation time in the presence of second material having longer T1 relaxation time (and therefore slower response to applied magnetic fields). Two pre-polarization currents are used to create pre-polarization magnetic fields stronger than the static magnetic field, each applied over a period of time between the first material's T1 relaxation time and the second material's T1 relaxation time, enabling different ways to null the NMR signal from the second material.
Owner:FUKUSHIMA EIICHI +3
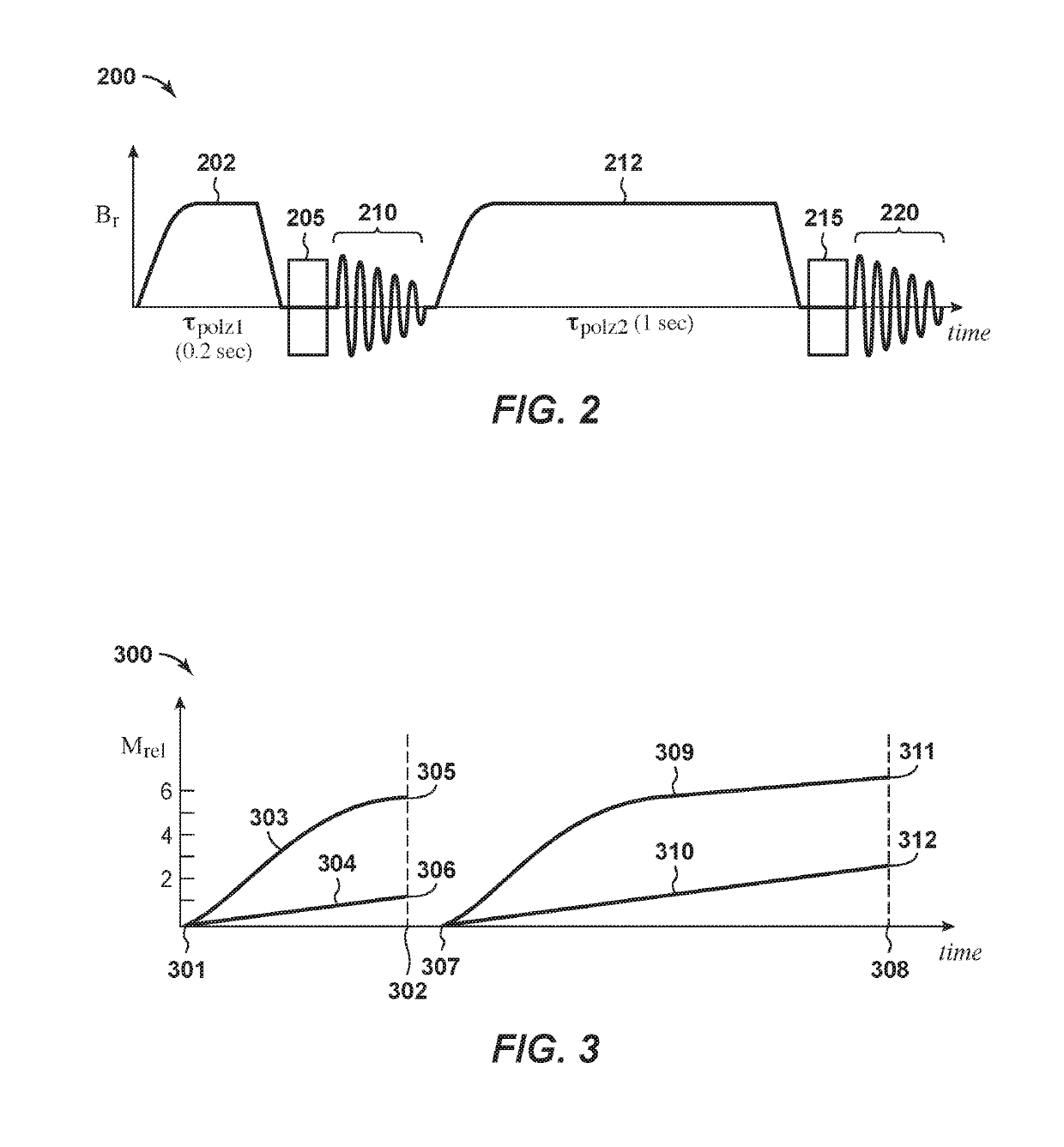
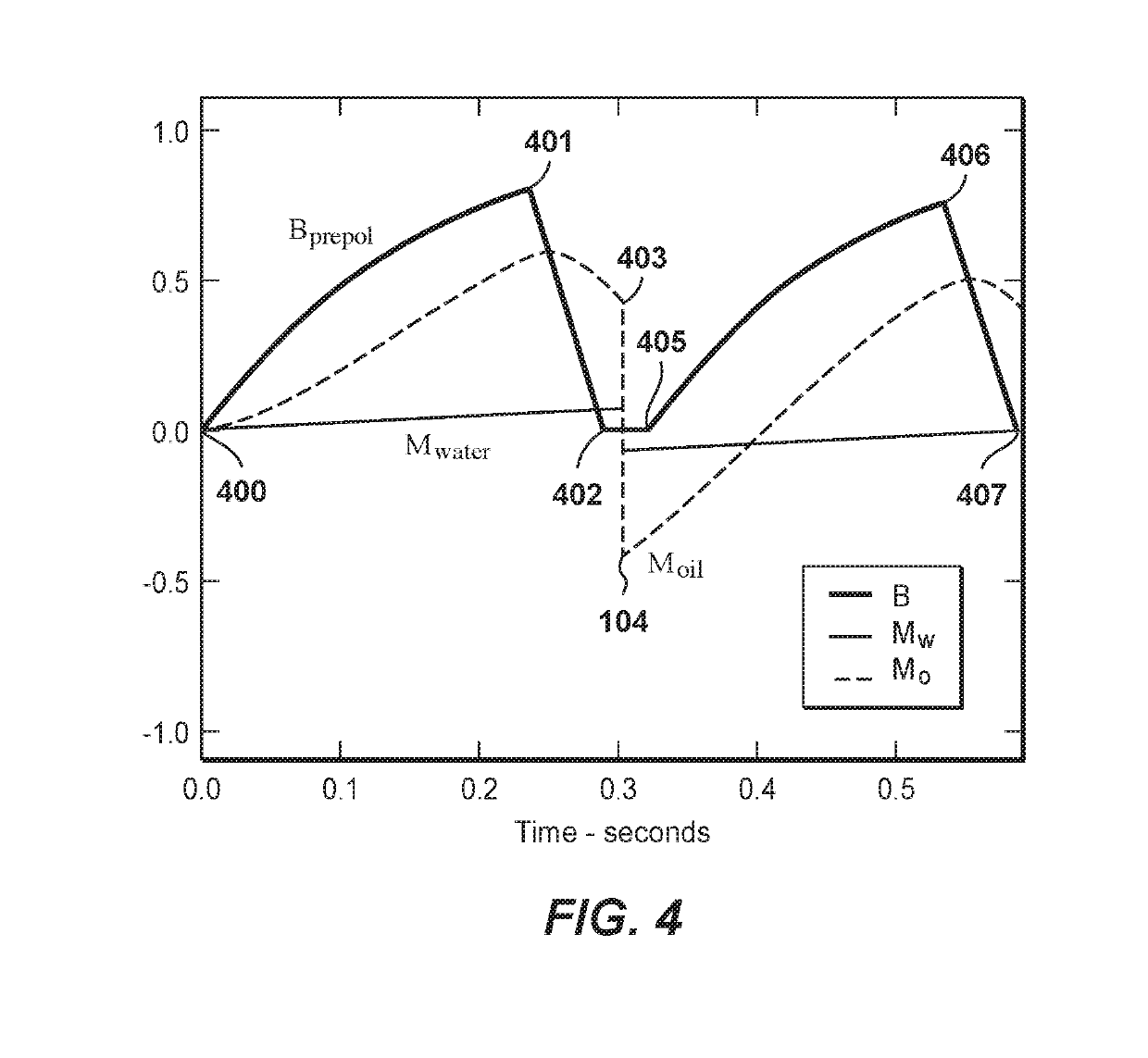
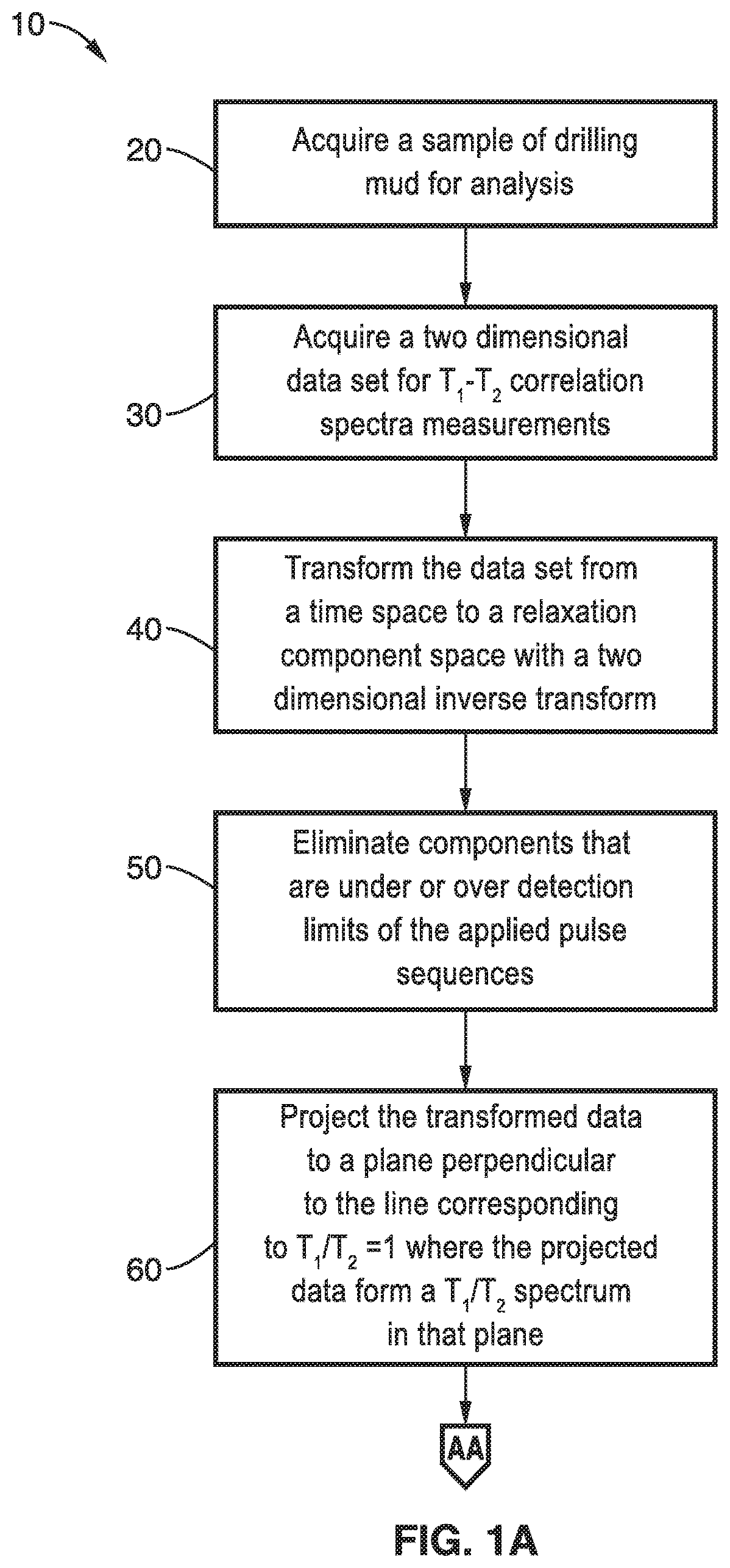
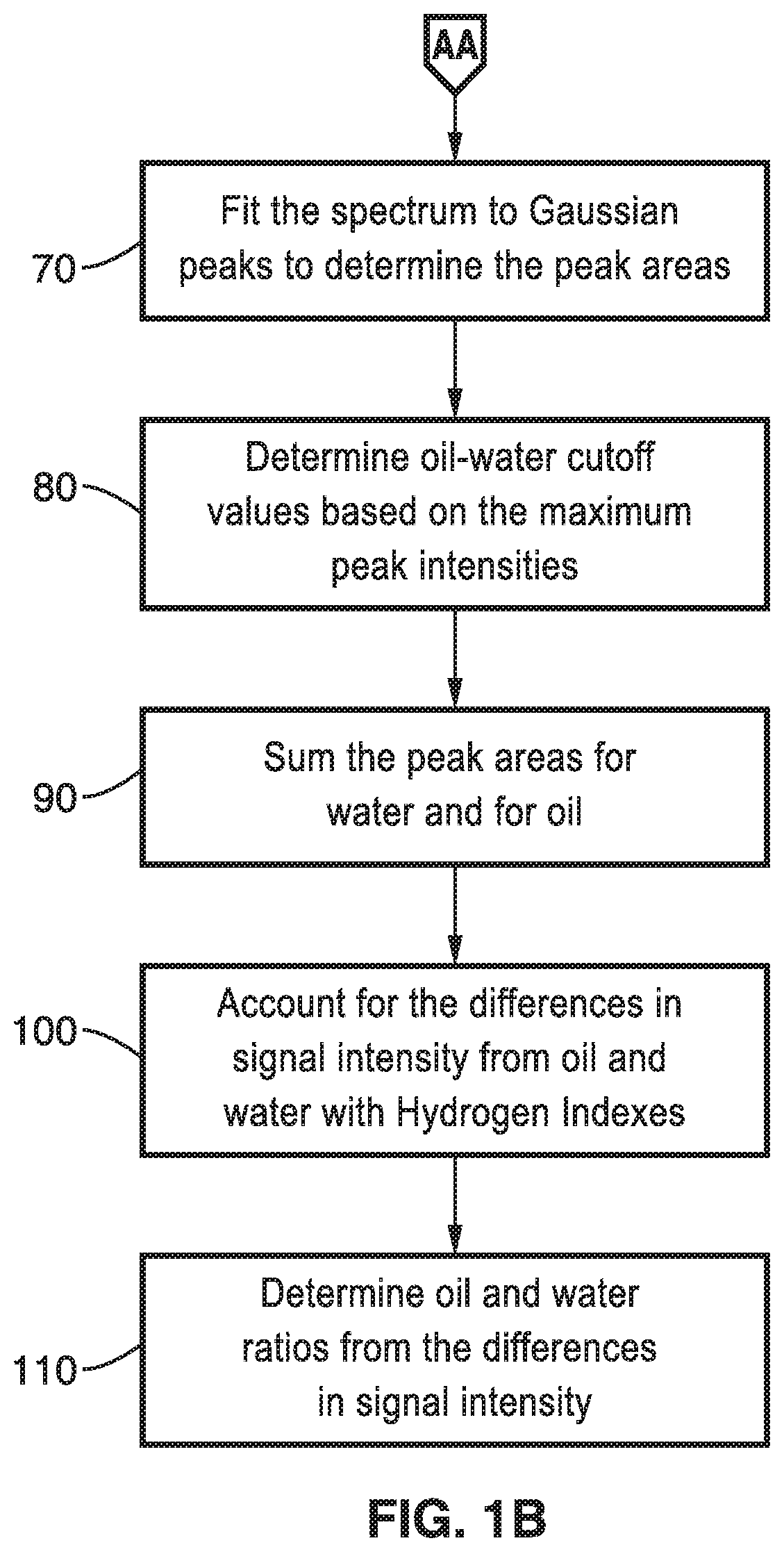
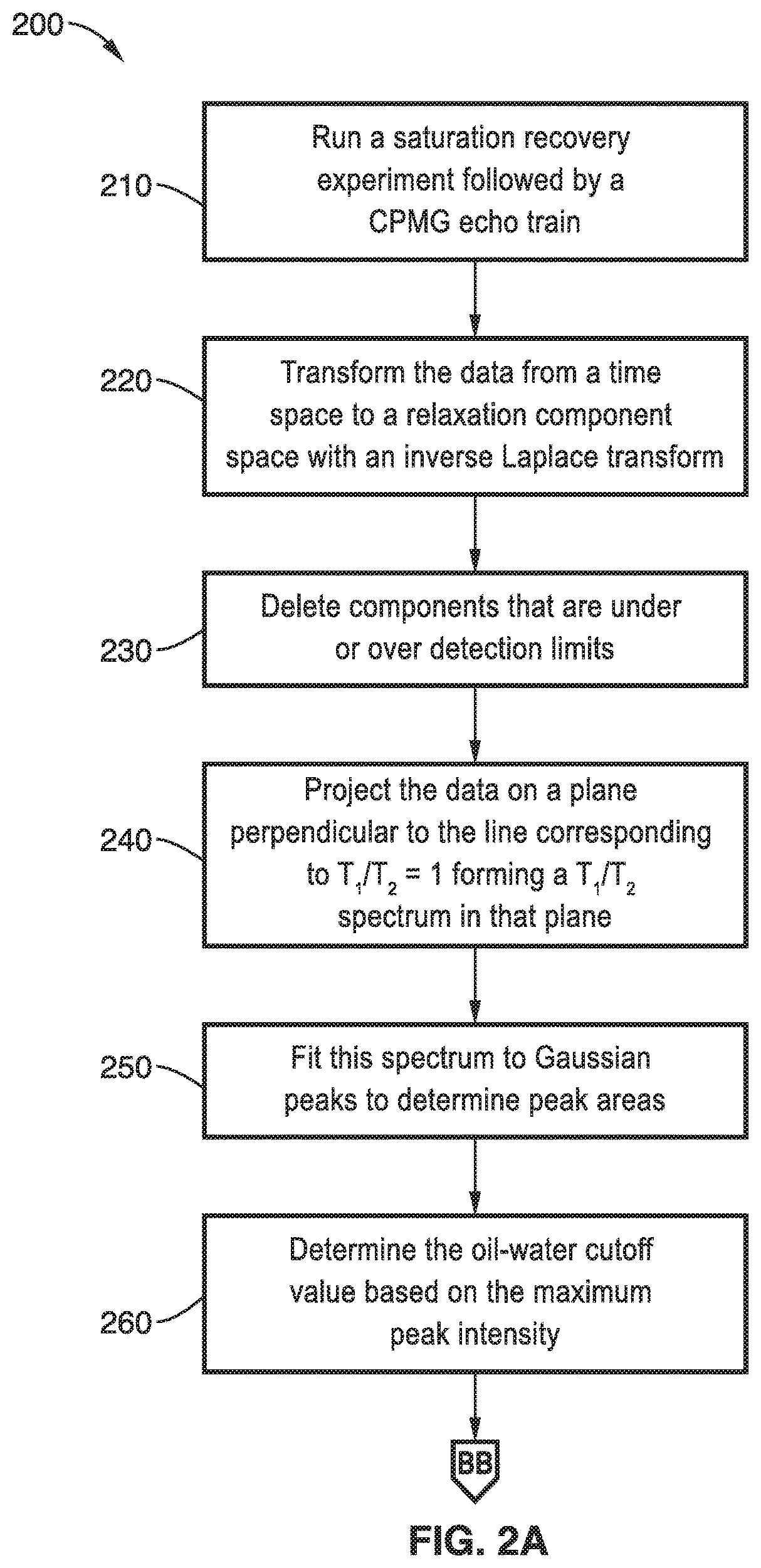
Methods for determining oil and water compositions in drilling muds
ActiveUS20170122891A1Short relaxation timeQuick analysisMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonanceTime distributionProton NMR
A nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) system and method for determining oil and water composition in drilling mud by separating out signals from oil and water in a two dimensional relaxation space wherein the oil and water ratio is a function of the separated out signals. The spin-lattice relaxation time distribution or a spin-spin relaxation time distribution of the sample is measured and a spin-lattice versus spin-spin or a spin-spin versus diffusion two-dimensional procedure is applied to separate the components of the drilling fluid. The signal intensities from the oil and water regions of the one-dimensional or two-dimensional NMR measurements are used to quantify the relative portion of the proton NMR signal from the oil and water and to determine the ratio of oil and water in the drilling mud.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
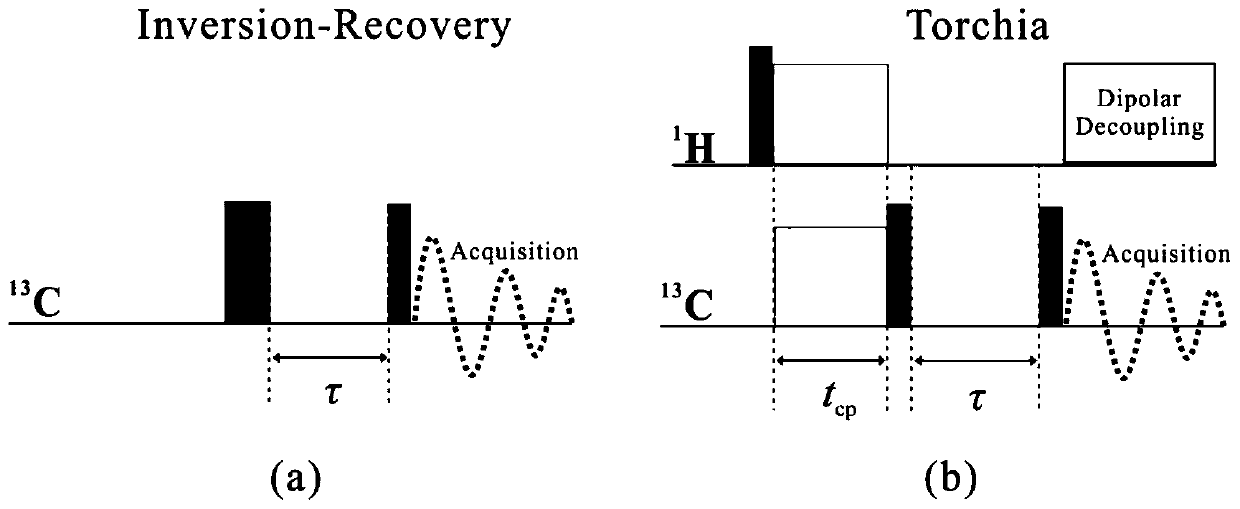
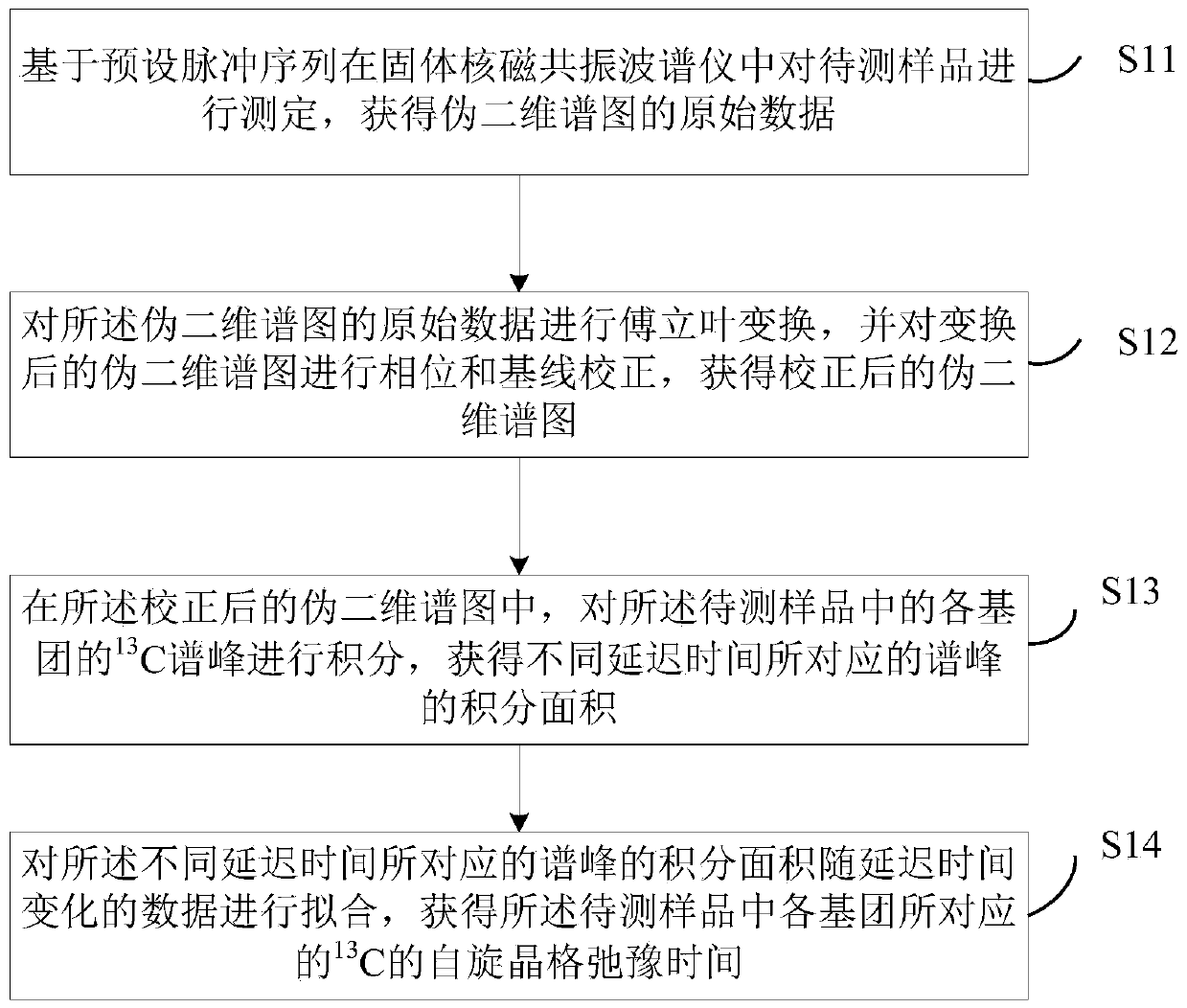
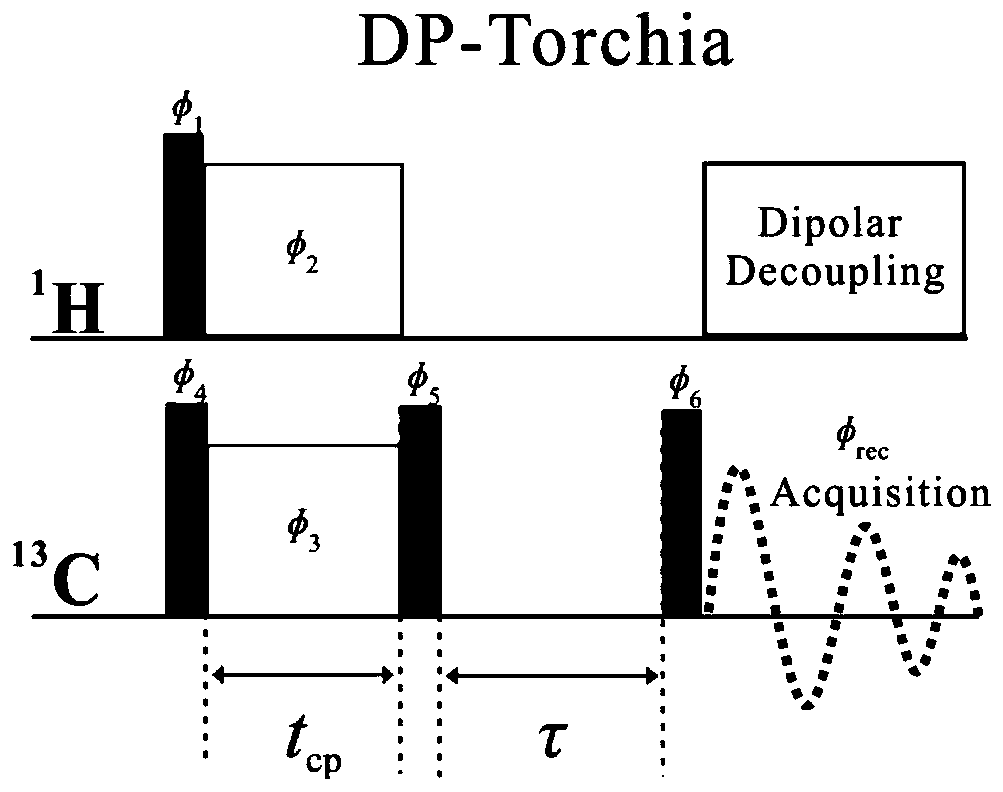
Method and device for measuring spin lattice relaxation time
ActiveCN109932381AImprove universalityAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonanceOriginal dataDelayed time
The invention discloses a method and a device for determining the spin lattice relaxation time. The method comprises the steps that a sample to be tested is determined based on a preset pulse sequenceto acquire the original data of a pseudo two-dimensional spectrum; phase and baseline correction is carried out on the pseudo two-dimensional spectrum after Fourier transform to acquire a corrected two-dimensional spectrum; in the corrected pseudo two-dimensional spectrum, the 13C peak of each group in a sample to be tested are integrated to acquire the integrated area of the peaks correspondingto different delay times; and the data, which change with the delay time, of the integrated area of the peaks corresponding to different delay times are fitted to acquire the spin lattice relaxation time of the sample to be tested. A predetermined pulse sequence includes the determination of the part with high molecule local mobility or the part without 1H in the sample to be tested, and the determination of the hydrogenous rigid part with weak molecule local mobility in the sample to be tested. The spin lattice relaxation time of 13C for each group in a blend system is determined based on onemeasurement.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
System for Reducing Artifacts in Imaging in the Presence of a Spin-lock Radio-Frequency Field
ActiveUS20140021951A1Easy to prepareShorten the lengthMagnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionMagnetic field gradientData acquisition
A system acquires MR image data of a portion of patient anatomy associated with spin lattice relaxation time in a rotating frame using an RF (Radio Frequency) signal generator and a magnetic field gradient generator. The RF (Radio Frequency) signal generator generates RF excitation pulses in anatomy and enables subsequent acquisition of associated RF echo data. The magnetic field gradient generator generates anatomical volume select magnetic field gradients for phase encoding and readout RF data acquisition in a three dimensional (3D) anatomical volume. The RF signal generator and the gradient generator use in order, a saturation pulse, a T1 spin lattice relaxation rotating frame preparation pulse sequence and a spoiler gradient, in acquiring image data of the 3D volume showing luminance contrast associated with T1 spin lattice relaxation in a rotating frame.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Rapid magnetic resonance multi-parameter imaging method and device
ActiveCN111537931AImprove accuracyMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsPulse sequenceData reconstruction
The application is suitable for the technical field of magnetic resonance, and provides a rapid magnetic resonance multi-parameter imaging method and device. The method comprises the steps: collectingN groups of data through a pulse sequence, and carrying out the reconstruction based on the N groups of data to obtain N images, setting the N to be an integer greater than or equal to 1; generatinga dictionary from the parameters of the pulse sequence, a spin-lattice relaxation time constant T1 and a spin-spin relaxation time constant T2 through a fractional order Bloch model; and matching thesignal sequences of the corresponding pixels on the N images with the entries in the dictionary, and determining final R tissue characteristic parameter graphs as the output of fingerprint imaging according to the matching degree. According to the application, the accuracy of magnetic resonance fingerprint quantitative imaging can be improved.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH
Non-invasive blood glucose sensors using a magneto-resonance absorption method and measurement methods thereof
InactiveUS20060020193A1Improve accuracyImprove precisionDiagnostic recording/measuringAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonanceGlucose sensorsBlood Glucose Measurement
A non-invasive blood glucose measurement method using a magneto-resonance absorption method. A constant magnetic field is applied using a pair of permanent magnets, the magnetic field having a uniform strength. A triangular waveform low frequency modulation magnetic field is applied using a low frequency generator and a pair of low frequency coils, the low frequency modulation magnetic field having a uniform strength. A weak acoustic wave modulation magnetic field is applied using an acoustic wave generator and a pair of acoustic wave coils. Electromagnetic waves are applied to a detector in which a finger is positioned to produce a nuclear magneto-resonance, the electromagnetic waves having a frequency varying in a specific frequency band step by step, the applying being done using a high frequency generator and a sensor coil. A magneto-resonance absorption signal produced by spin-lattice relaxation of protons in a tissue of the finger because of the nuclear magneto-resonance is detected. A magneto-resonance spin-lattice relaxation time of the finger from the magneto-resonance absorption signal is determined. A blood glucose concentration in a human body is determined from a correlation between a pre-determined blood glucose concentration in the human body and the determined magneto-resonance spin-lattice relaxation time.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Organic light-emitting devices using spin-dependent processes
InactiveUS7682707B2Increase ratingsShorten the timeNanoinformaticsConductive materialStimulated emissionSingle crystal
The maximum luminous efficiency of organic light-emitting materials is increased through spin-dependent processing. The technique is applicable to all electro-luminescent processes in which light is produced by singlet exciton decay, and all devices which use such effects, including LEDs, super-radiant devices, amplified stimulated emission devices, lasers, other optical microcavity devices, electrically pumped optical amplifiers, and phosphorescence (Ph) based light emitting devices. In preferred embodiments, the emissive material is doped with an impurity, or otherwise modified, to increase the spin-lattice relaxation rate (i.e., decrease the spin-lattice time), and hence raise the efficiency of the device. The material may be a polymer, oligomer, small molecule, single crystal, molecular crystal, or fullerene. The impurity is preferably a magnetic or paramagnetic substance. The invention is applicable to IR, UV, and other electromagnetic radiation generation and is thus not limited to the visible region of the spectrum. The methods of the invention may also be combined with other techniques used to improve device performance.
Owner:THE UNIV OF UTAH
A KMnF4 nanoprobe-based NMR rapid detection method for food-borne allergens
InactiveCN105352987AQuick checkEfficient detectionAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonanceNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonanceFood borne
The invention discloses a KMnF4 nanoprobe-based NMR rapid detection method for food-borne allergens and belongs to the technical field of rapid detection of allergens in food safety. The method depends on an established nuclear magnetic resonance detection process used for allergens in food samples, and detects whether samples contain allergens or not by utilization of influences of paramagnetic characteristics of KMnF4 nanoprobes on nuclear magnetic resonance relaxation time. Specific corresponding relations are that a linear relation exists for the KMnF4 nanoprobes under certain conditions, namely the higher the content of the KMnF4 nanoprobes is, the smaller the spin-lattice relaxation time value of the samples is, so that quantitative detection of the allergens in a certain range can be achieved. The method can be used for rapid detection of specific allergens in food samples so that the method can be used for rapid screening of a large scale of samples to be detected.
Owner:NANCHANG UNIV
Crystalline polymer of higher alpha-olefin and process for producing the same
A crystalline higher (x-olefin polymer which is obtained from a C10 or more α-olefin and satisfies either (1) the melting point (Tm) as measured with a differential scanning calorimeter (DSC) is 20 to 100° C. or (2) in an examination of spin-lattice relaxation time (T1) by solid NMR analysis, a single T1 is observed at the temperatures not lower than the melting point; and a process for producing the α-olefin polymer with a specific metallocene catalyst. The crystalline higher α-olefin polymer is excellent in low-temperature characteristics, rigidity, heat resistance, compatibility with lubricating oils, mixability with inorganic fillers, and secondary processability.
Owner:IDEMITSU KOSAN CO LTD
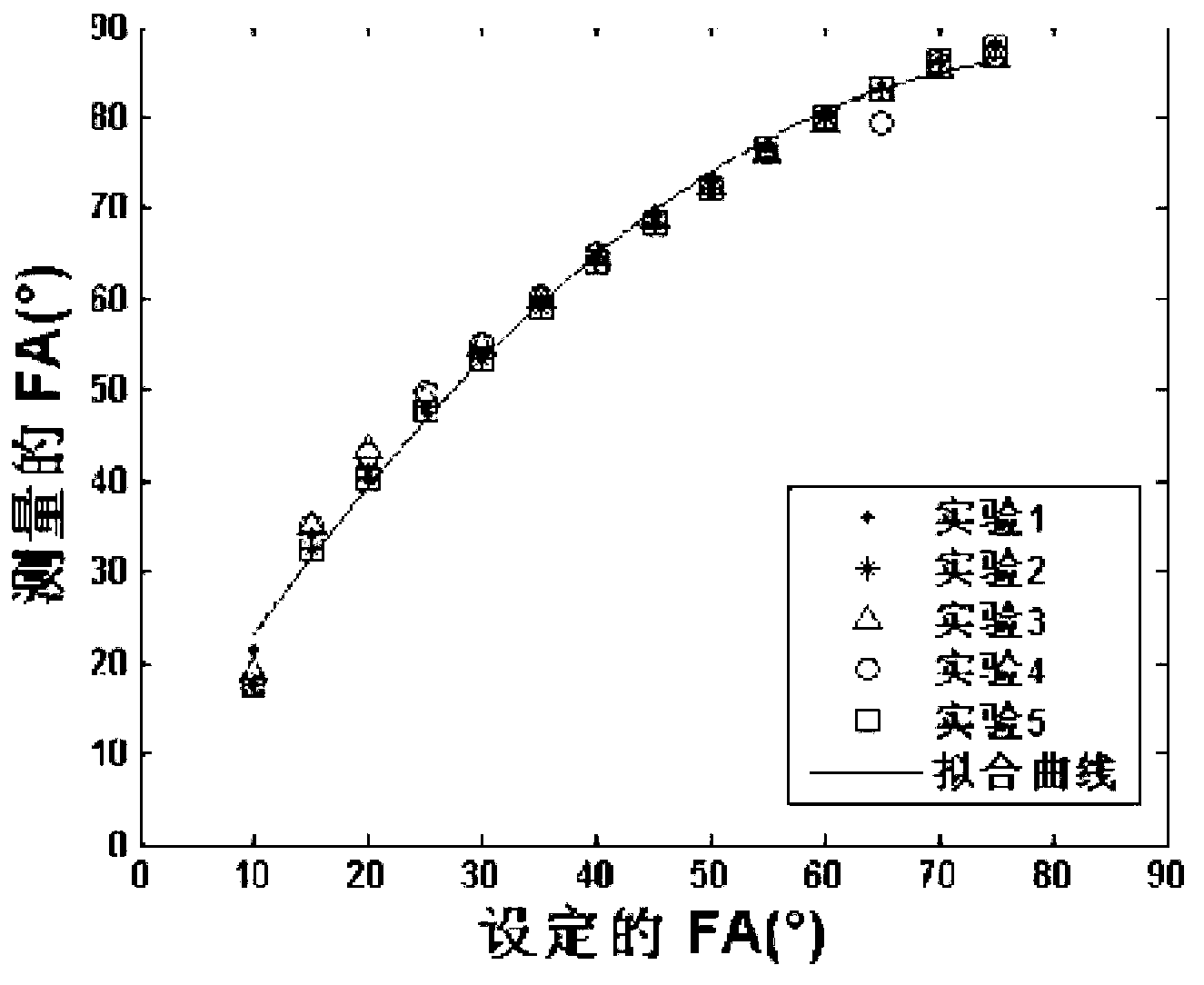
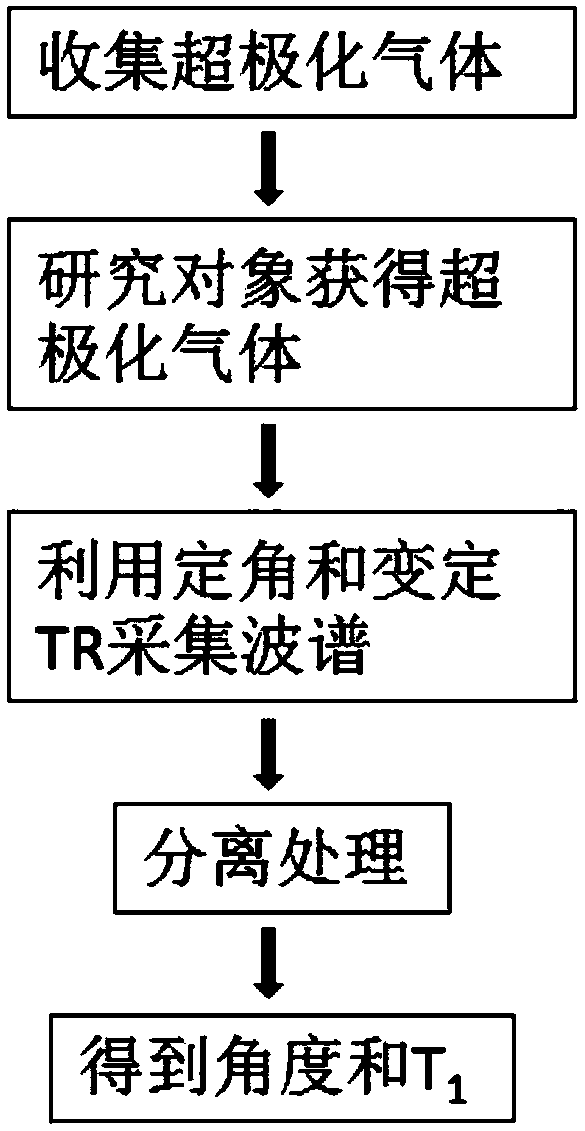
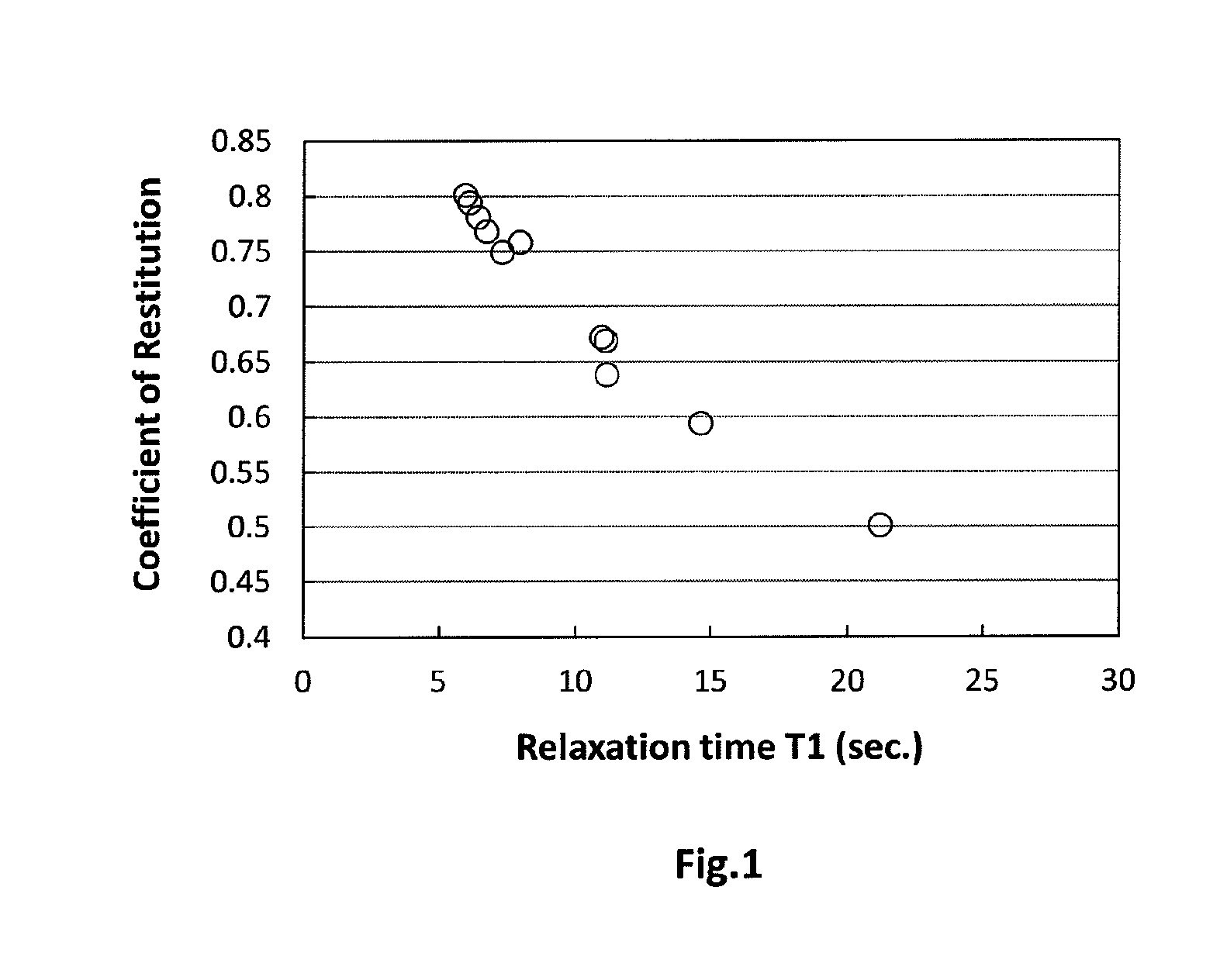
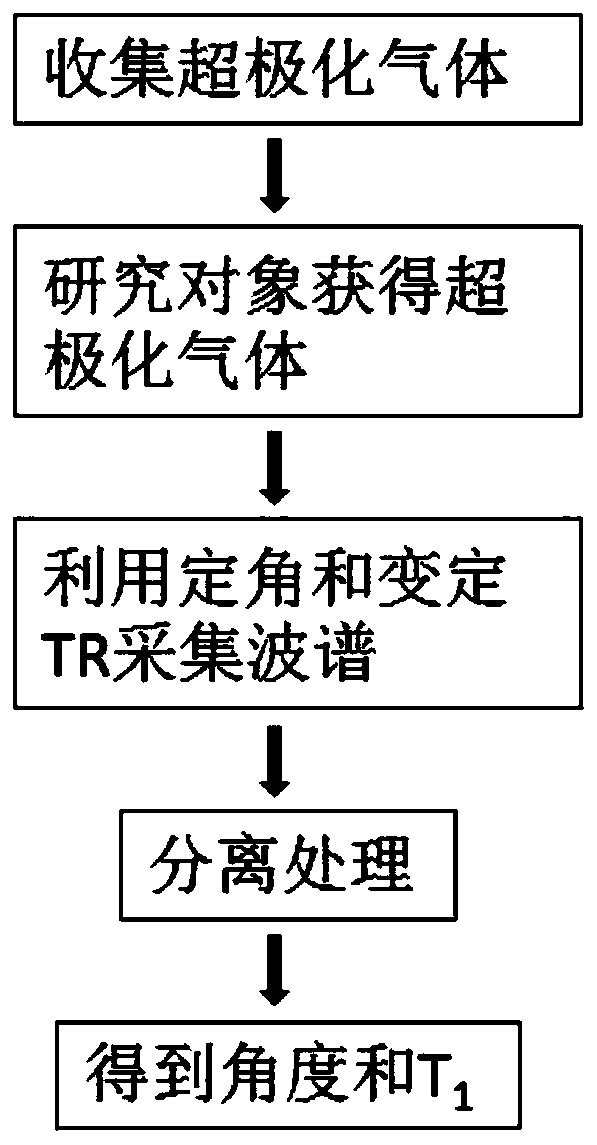
Angle and T1 simultaneous measurement method based on hyperpolarized gas spectrum
ActiveCN108152769AReduced sampling timeLower requirementMeasurements using NMR spectroscopyMagnetic resonance spectroscopicResearch Object
The invention discloses an angle and T1 simultaneous measurement method based on a hyperpolarized gas spectrum, and the method comprises the steps: collecting hyperpolarized gas; enabling a research object to obtain the hyperpolarized gas; fixing an excitation angle theta of a radio frequency pulse in one breath holding process, collecting a magnetic resonance spectrum of the hyperpolarized gas ofthe research object, and obtaining a free induction decay signal FID1 of the hyperpolarized gas of the research object in a variable repetition time TR1 and a free induction decay signal FID2 of thehyperpolarized gas of the research object in a fixed repetition time TR2; processing the FID1 and FID2 signals, and obtaining an actual excitation angle theta(r) of the radio frequency pulse and the spin-lattice relaxation time constant T1 of the hyperpolarized gas of the research object. According to the invention, the method can achieve the simultaneous obtaining of the angle and an analytical solution of T1, shortens the sampling time, reduces the requirements for hardware, is easy for engineering implementation, and is simple in data processing.
Owner:WUHAN INST OF PHYSICS & MATHEMATICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Method for screening anaerobe traditional Chinese medicine inhibitor on basis of ZnO nanoprobe
InactiveCN106841271AAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonanceNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonanceMedicine
The invention relates to a method for screening an anaerobe traditional Chinese medicine inhibitor on basis of a ZnO nanoprobe and belongs to the technical field of traditional Chinese medicine development and application. The method depends on establishment of a method based on the prepared ZnO nanoprobe and used for screening a traditional Chinese medicine formula for inhibiting anaerobes. Whether a sample contains target bacteria is detected by using the characteristic that the antibody-coated magnetic ZnO nanoprobe can perform specific combination on the target bacteria and by using the effect of the magnetic characteristic of ZnO on nuclear magnetic resonance relaxation time. The magnetic ZnO nanoprobe has a linear relation with the nuclear magnetic resonance relaxation time within a certain range, that is, the higher the nano ZnO content, the shorter the nuclear magnetic resonance spin-lattice relaxation time and spin-spin relaxation time of the sampler is, the target bacteria can be detected quantitatively in a certain range, and the antibacterial effect of the traditional Chinese medicine formula is indirectly evaluated. The method can be used for screening the traditional Chinese medicine formula having the inhibition effect on the anaerobes and increase the development speed of traditional Chinese medicine products.
Owner:NANCHANG UNIV
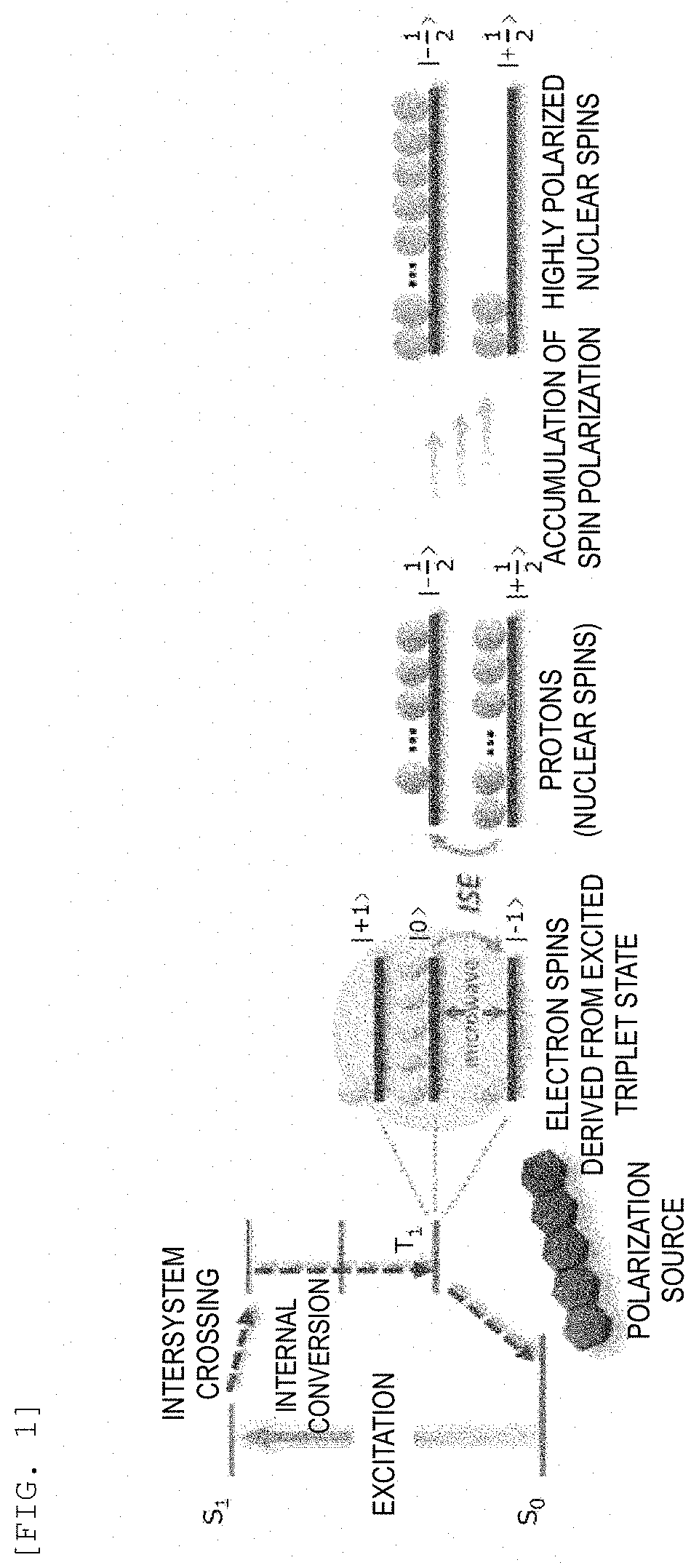
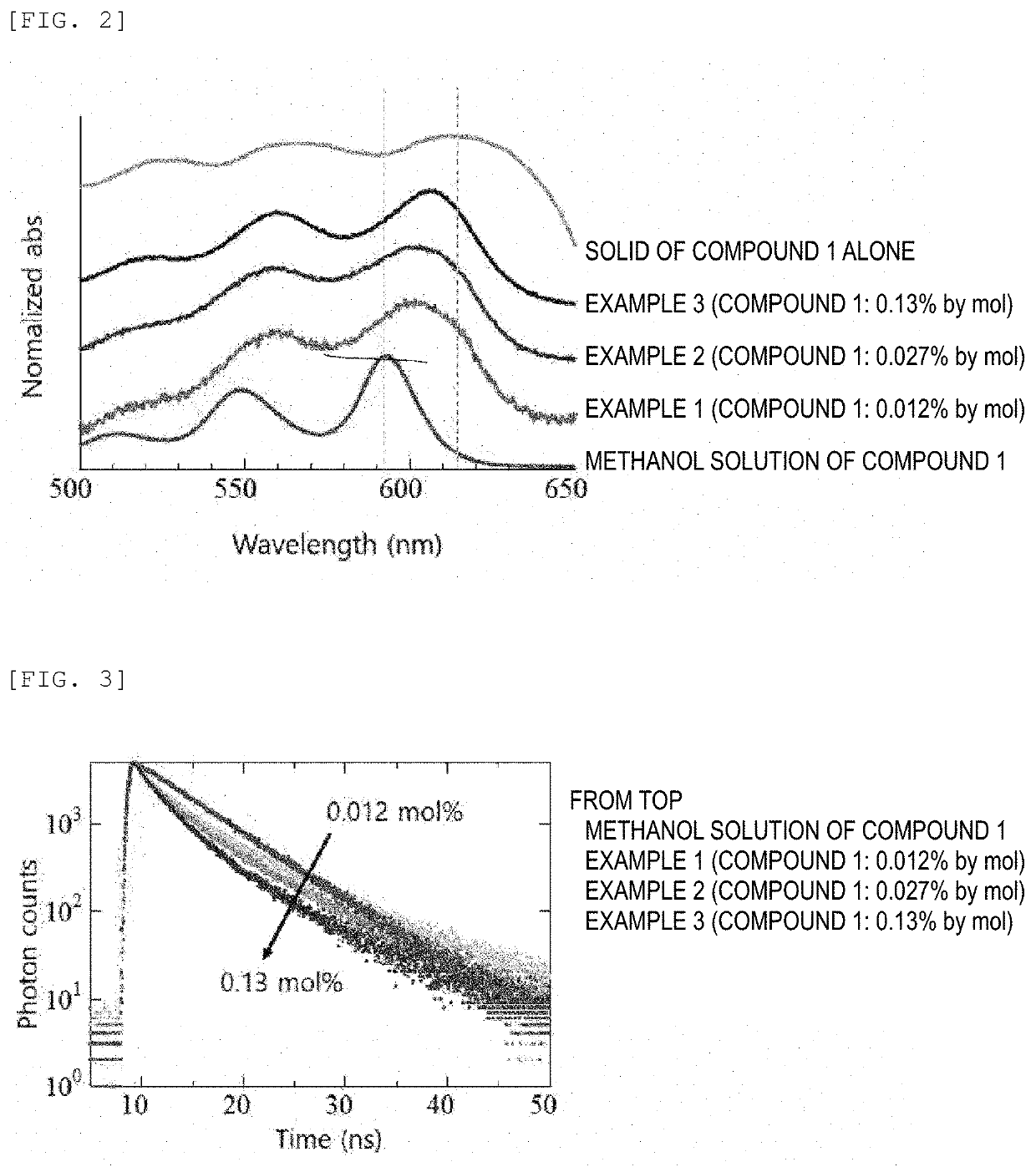
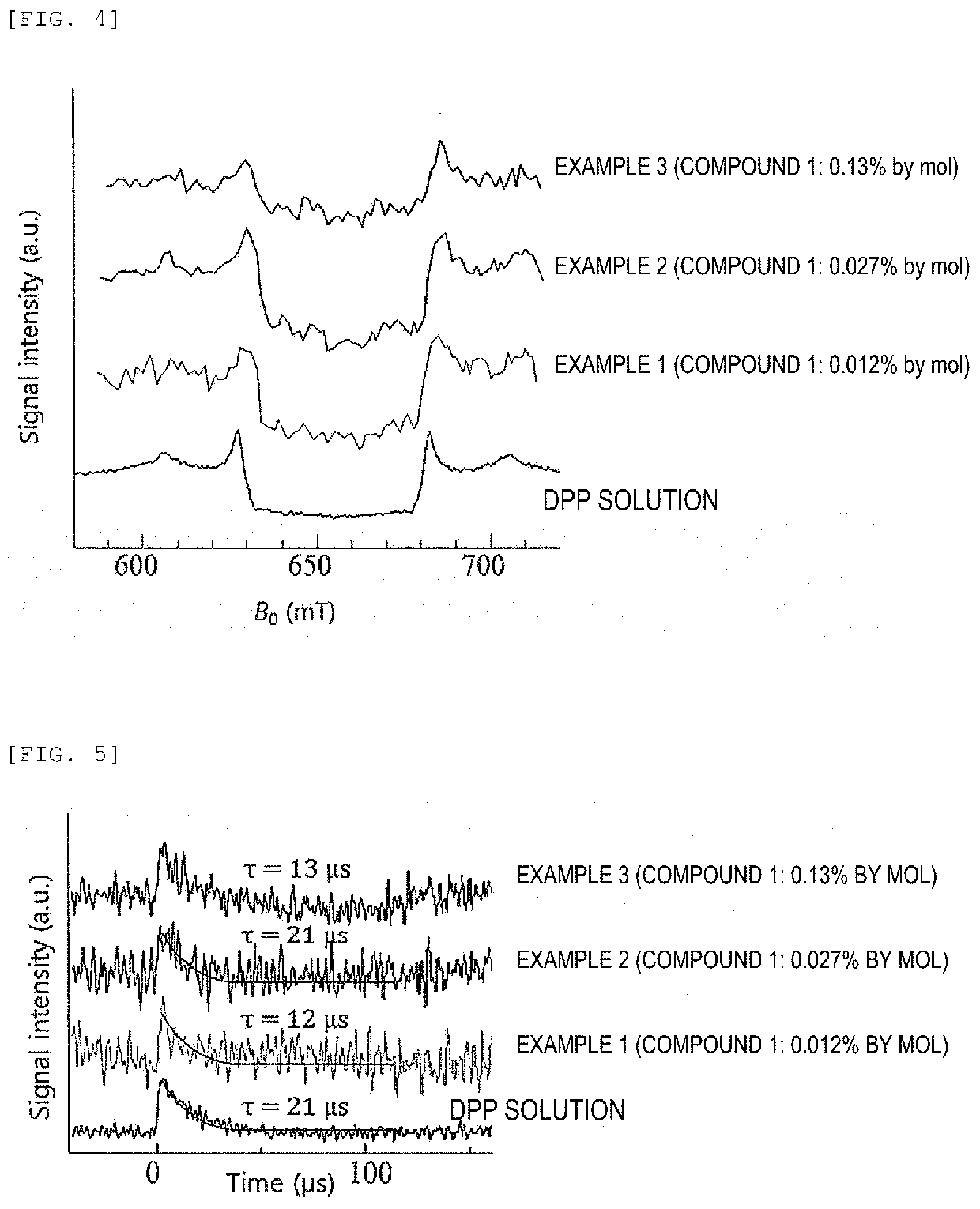
Composition, composition for dynamic nuclear polarization, polarization enhancing method, highly polarized substance, and nmr measurement method
InactiveUS20200289678A1Long spin-lattice relaxation timeEasy to introduceMeasurements using double resonanceDiagnostic recording/measuringNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonanceDynamic nuclear polarisation
A composition containing (1) a porous material and (2) a polarization source for dynamic nuclear polarization containing a molecule capable of being in an excited triplet state. According to the composition, a dynamic nuclear polarization system that has a long spin-lattice relaxation time and can readily introduce the polarization object thereto can be provided.
Owner:KYUSHU UNIV +1
Methods for determining oil and water compositions in drilling muds
ActiveUS10527566B2Quick analysisAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonanceMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsEngineeringProton NMR
A nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) system and method for determining oil and water composition in drilling mud by separating out signals from oil and water in a two dimensional relaxation space wherein the oil and water ratio is a function of the separated out signals. The spin-lattice relaxation time distribution or a spin-spin relaxation time distribution of the sample is measured and a spin-lattice versus spin-spin or a spin-spin versus diffusion two-dimensional procedure is applied to separate the components of the drilling fluid. The signal intensities from the oil and water regions of the one-dimensional or two-dimensional NMR measurements are used to quantify the relative portion of the proton NMR signal from the oil and water and to determine the ratio of oil and water in the drilling mud.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
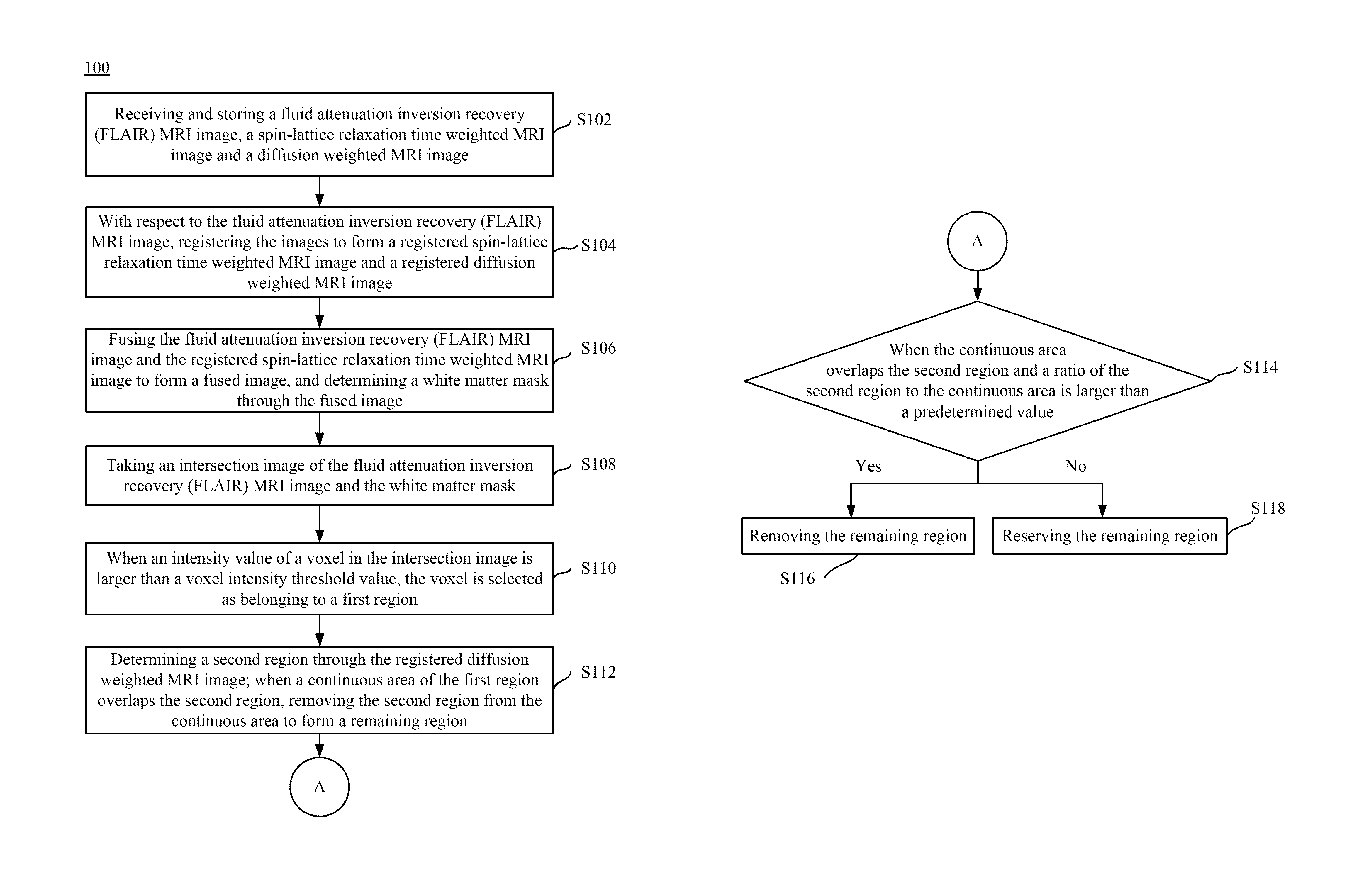
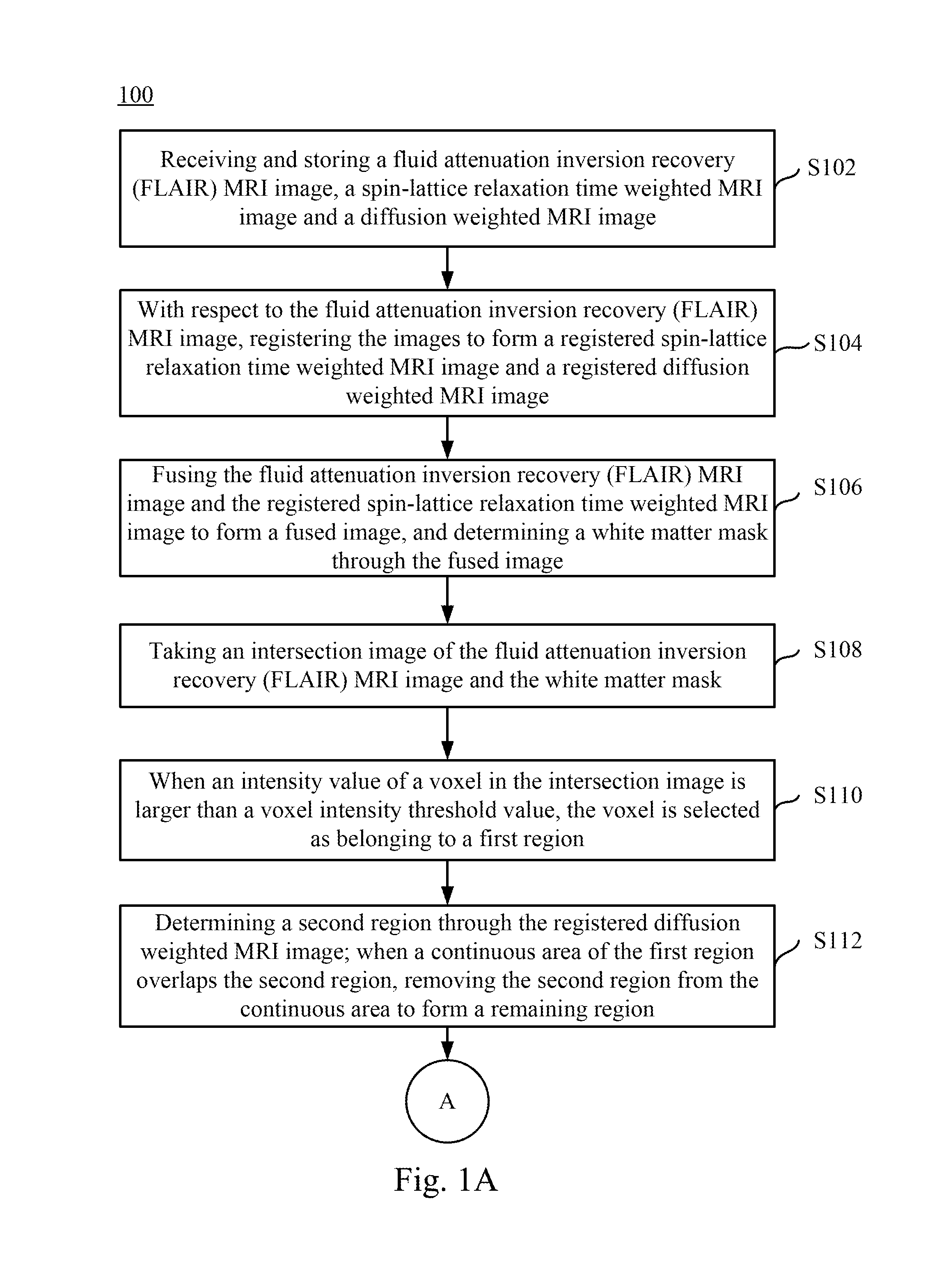
Magnetic resonance imaging white matter hyperintensities region recognizing method and system
ActiveUS9466105B2Remove the burdenImprove efficiencyImage enhancementImage analysisDiffusionResonance
Owner:NAT CENT UNIV +1
A rapid NMR method for the detection of foodborne pathogens based on a paramagnetic nanofe-ni-co alloy probe
ActiveCN103217451BQuick filterThe detection is objective and effectiveAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonanceFood safetyPhysical chemistry
The invention discloses an NMR rapid detection method for food-borne pathogenic bacteria based on a paramagnetic nanometer Fe-Ni-Co alloy probe, belonging to the technical field of rapid detection of food-safe pathogenic bacteria. The present invention relies on the established NMR detection method that can be used for pathogenic bacteria in food samples, utilizes the influence of the paramagnetic properties of the paramagnetic nanometer Fe-Ni-Co alloy probe on the relaxation time of the NMR attenuation signal, and detects Determine whether the target bacteria are present in the sample. The different specific correspondences are: the paramagnetic nano-Fe-Ni-Co alloy probe shows a linear relationship under certain conditions, that is, the content of the nano-Fe-Ni-Co alloy is large, and the spin-lattice relaxation time of the sample The smaller the value of spin-spin relaxation time and spin-spin relaxation time, the target bacteria can be quantitatively detected in a certain range. The method can be used for rapid detection of harmful pathogenic bacteria in food samples, and thus can be used as a rapid screening of a large number of samples to be tested.
Owner:苏州辅测技术服务有限公司
NMR virus rapid detection method based on KMnF4 nanoprobes
InactiveCN105424938AQuick filterThe detection is objective and effectiveMaterial analysisNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonanceFood safety
The invention discloses an NMR virus rapid detection method based on KMnF4 nanoprobes, and belongs to the technical field of food safety rapid detection. The method relies on an established nuclear magnetic resonance detection method capable of being applied to viruses in samples, and whether the samples contain viruses or not is detected by utilizing the influences of the paramagnetic property of the KMnF4 nanoprobes on nuclear magnetic resonance relaxation time. According to different specific corresponding relations, the KMnF4 nanoprobes show a linear relation under certain conditions, namely, the larger the content of the KMnF4 nanoprobes is, the smaller the spin-lattice relaxation time value of the samples will be, and therefore viruses can be quantitatively detected within a certain range. The method can be applied to rapid detection of viruses in the samples, and therefore the method can be applied to rapid screening of a large batch of samples to be detected.
Owner:NANCHANG UNIV
Non-aqueous electrolyte battery and method of manufacturing the same
InactiveUS8163423B2Extended service lifeImprove featuresFinal product manufactureElectrode carriers/collectorsElectrode potentialPhysical chemistry
Owner:GS YUASA INT LTD
Golf ball resin composition and golf ball
ActiveUS20120165120A1Increase elasticityFeel goodFibre treatmentSynthetic resin layered productsNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonanceEngineering
An object of the present invention is to provide a golf ball resin composition excellent in resilience. Another object of the present invention is to provide a golf ball excellent in a shot feeling and resilience. The present invention provides a golf ball resin composition having the spin-lattice relaxation time (T1) of 13C nucleus measured by a High resolution solid state carbon nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) method of 7.3 seconds or shorter.
Owner:SUMITOMO RUBBER IND LTD
Method for screening anaerobion traditional Chinese medicine inhibitor based on Fe-Ta-Cu-B nanoprobe
InactiveCN107144590AAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonanceNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonanceMedicine
The invention provides a method for screening an anaerobion traditional Chinese medicine inhibitor based on a Fe-Ta-Cu-B nanoprobe, and belongs to the technical field of development and application of traditional Chinese medicine. The method is characterized in that the Fe-Ta-Cu-B nanoprobenanoprobe is prepared and used as the basis for screening an anaerobion traditional Chinese medicine formula; the property that a paramagnetic Fe-Ta-Cu-B nanoprobenanoprobe prepared by antibody-coating is capable of performing specific binding with target bacteria and the influence of the paramagnetic property of Fe-Ta-Cu-B on nuclear magnetic resonance relaxation time are utilized for detecting whether a sample contains the target bacteria. The paramagnetic Fe-Ta-Cu-B nanoprobe shows a linear relation with the nuclear magnetic resonance relaxation time within a certain range, that is, if the nano Fe-Ta-Cu-B content is high, the nuclear magnetic resonance spin-lattice relaxation time and spin-spin relaxation time of the sample are small, and the target bacteria can be quantitatively detected within a certain range, and as a result, the bacteria inhibition effect of the traditional Chinese medicine formula can be indirectly assessed. The method is applicable to the screening of the traditional Chinse medicine formula capable of inhibiting anaerobion; and the development of a traditional Chinese medicine product is sped up.
Owner:NANCHANG UNIV
A Simultaneous Measurement Method of Angle and Relaxation Time Constant t1 of Gas Spectrum
ActiveCN108152769BReduced sampling timeLower requirementMeasurements using NMR spectroscopyMagnetic resonance spectroscopicResearch Object
The invention discloses an angle and T1 simultaneous measurement method based on a hyperpolarized gas spectrum, and the method comprises the steps: collecting hyperpolarized gas; enabling a research object to obtain the hyperpolarized gas; fixing an excitation angle theta of a radio frequency pulse in one breath holding process, collecting a magnetic resonance spectrum of the hyperpolarized gas ofthe research object, and obtaining a free induction decay signal FID1 of the hyperpolarized gas of the research object in a variable repetition time TR1 and a free induction decay signal FID2 of thehyperpolarized gas of the research object in a fixed repetition time TR2; processing the FID1 and FID2 signals, and obtaining an actual excitation angle theta(r) of the radio frequency pulse and the spin-lattice relaxation time constant T1 of the hyperpolarized gas of the research object. According to the invention, the method can achieve the simultaneous obtaining of the angle and an analytical solution of T1, shortens the sampling time, reduces the requirements for hardware, is easy for engineering implementation, and is simple in data processing.
Owner:WUHAN INST OF PHYSICS & MATHEMATICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com