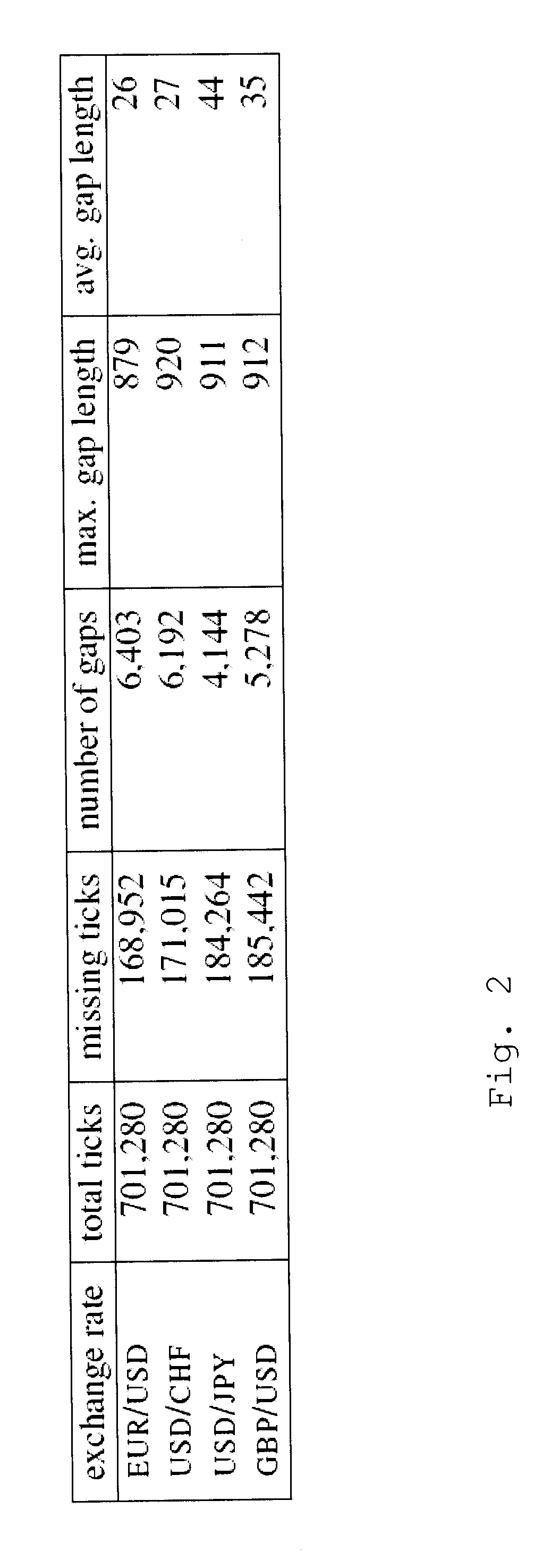
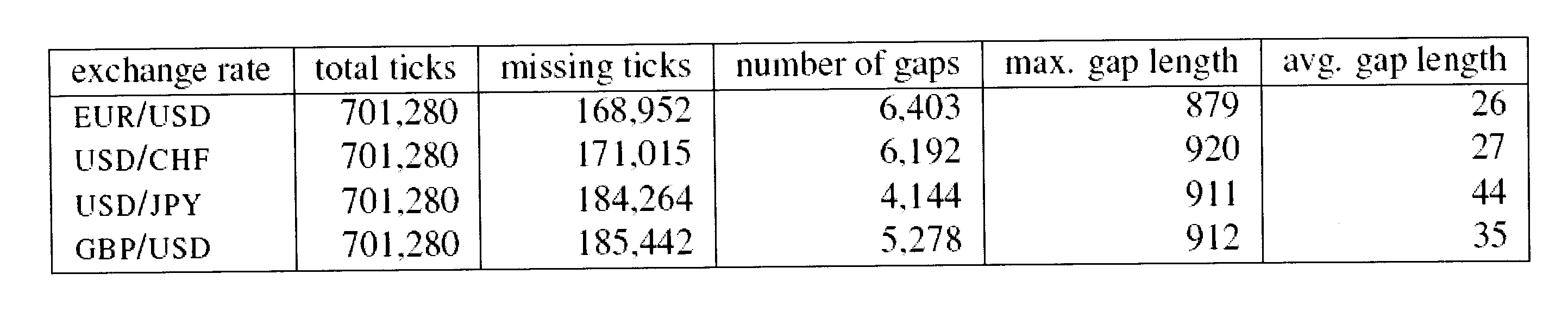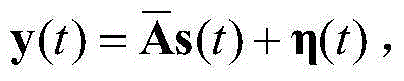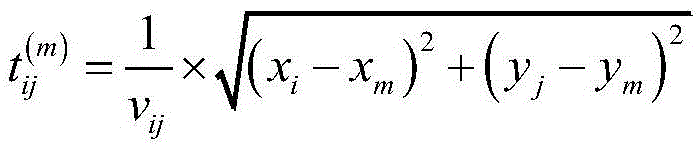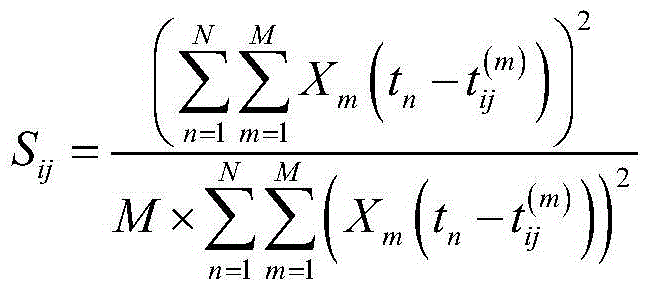Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
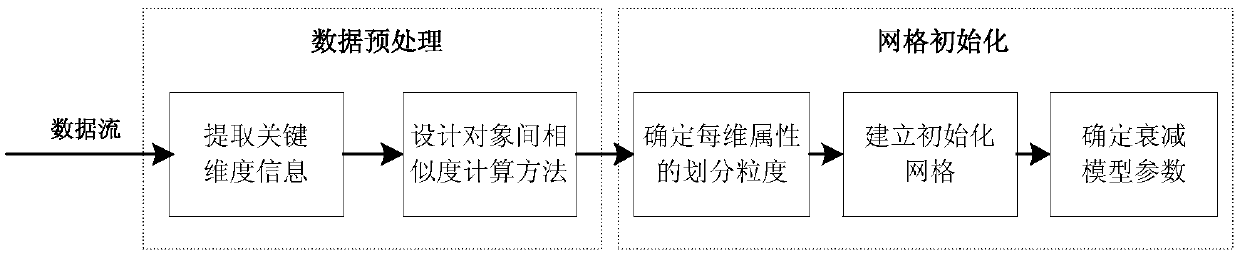
77 results about "Sparse grid" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Sparse grids are numerical techniques to represent, integrate or interpolate high dimensional functions. They were originally developed by the Russian mathematician Sergey A. Smolyak, a student of Lazar Lyusternik, and are based on a sparse tensor product construction. Computer algorithms for efficient implementations of such grids were later developed by Michael Griebel and Christoph Zenger.
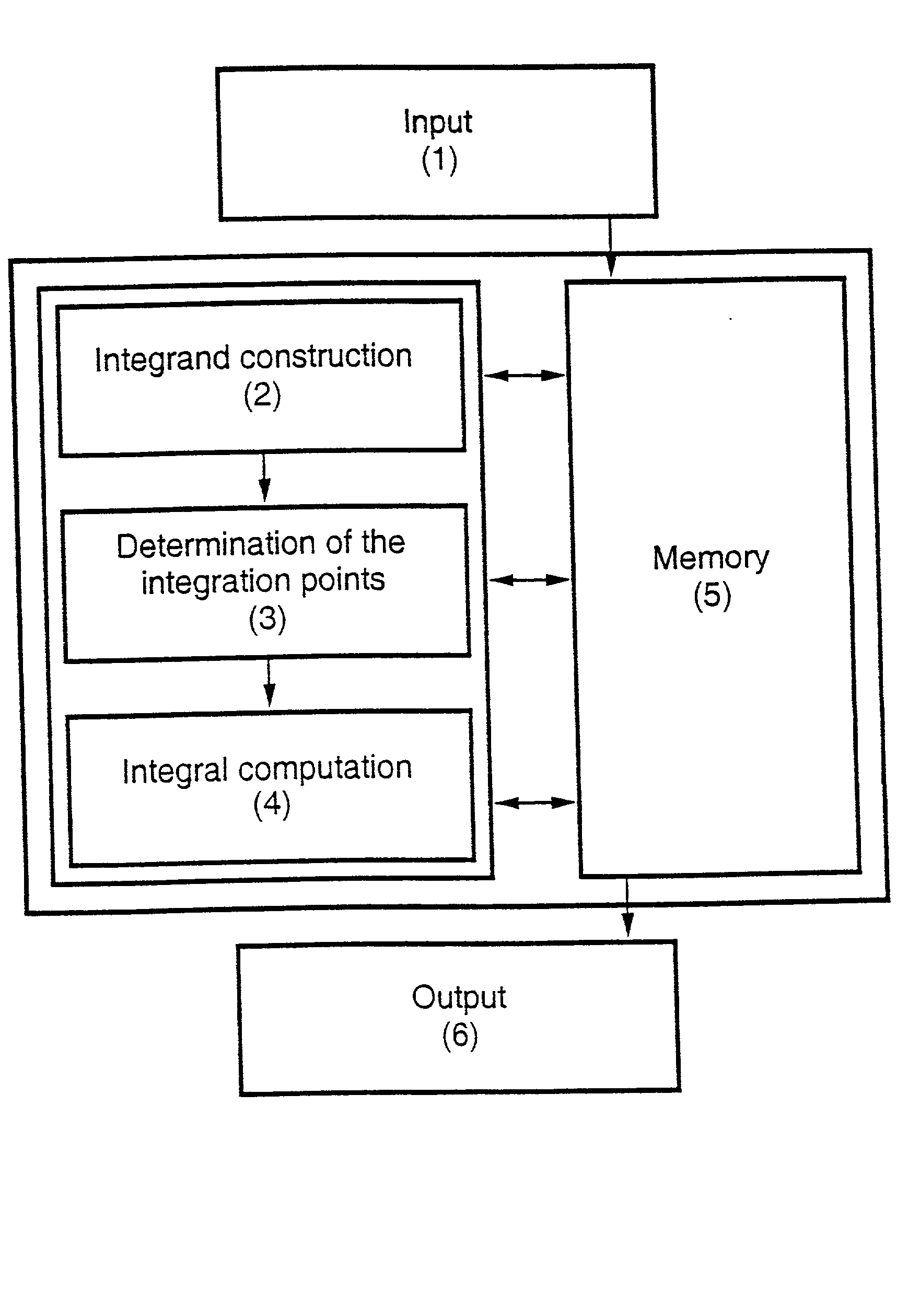
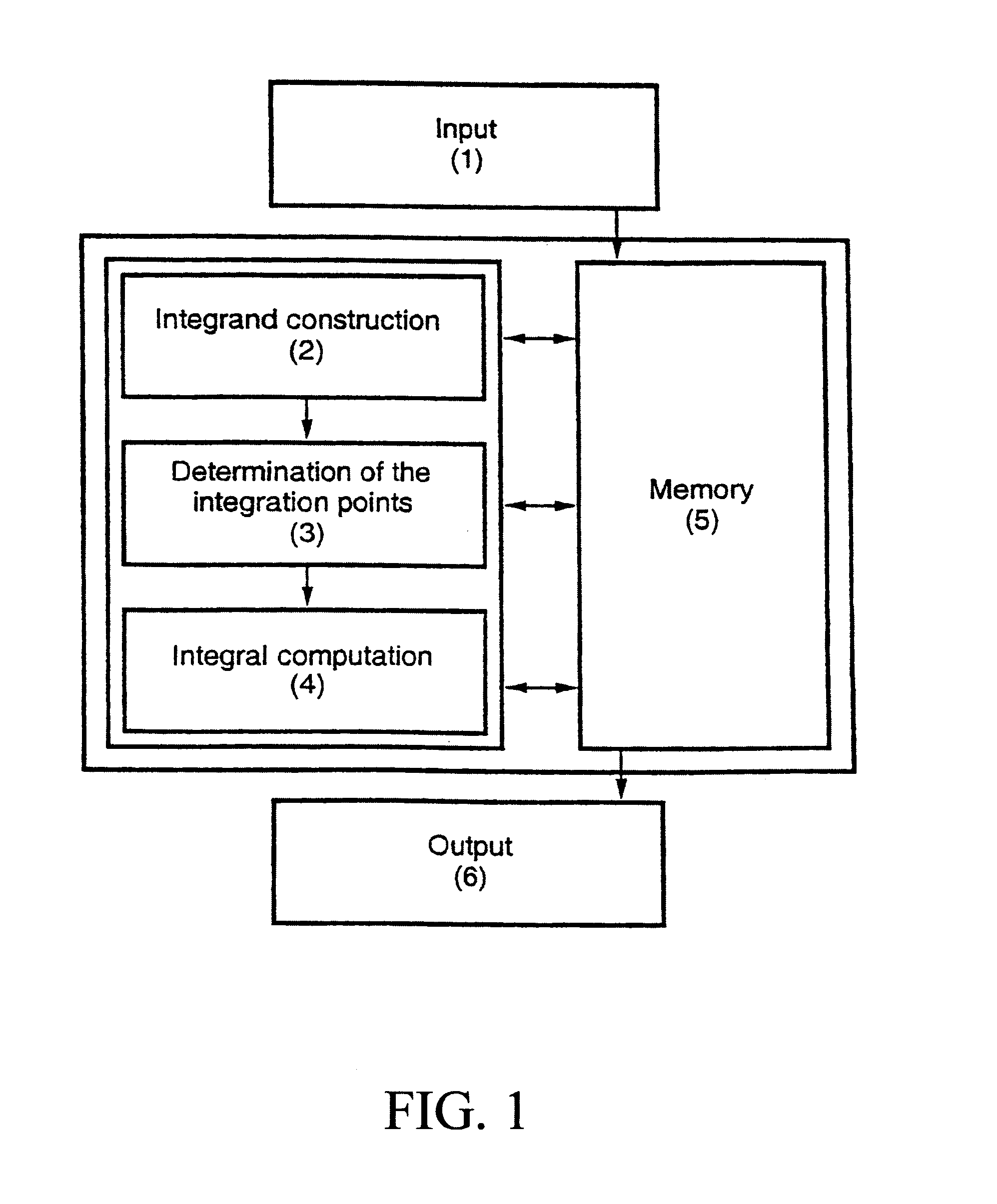
Method and device for evaluation of financial derivatives using sparse grids
A method and device for valuation of financial derivatives, wherein a value of a derivative is computed by a determination of an expectation. Input parameters are communicated by an input unit to a computer, such as at least one processor, to establish an integrand as a function of the input parameters. A multivariate integration domain is computed. A sparse grid method is used to determine integration points and integration weights as a function of the input parameters. The integrand is integrated with an integration domain at the integration points to determine integrand values. One or more expectation parameters are computed by combining the integrand values and the integration weights. A value of the derivative is communicated through an output unit, for example to a display monitor or another display device.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
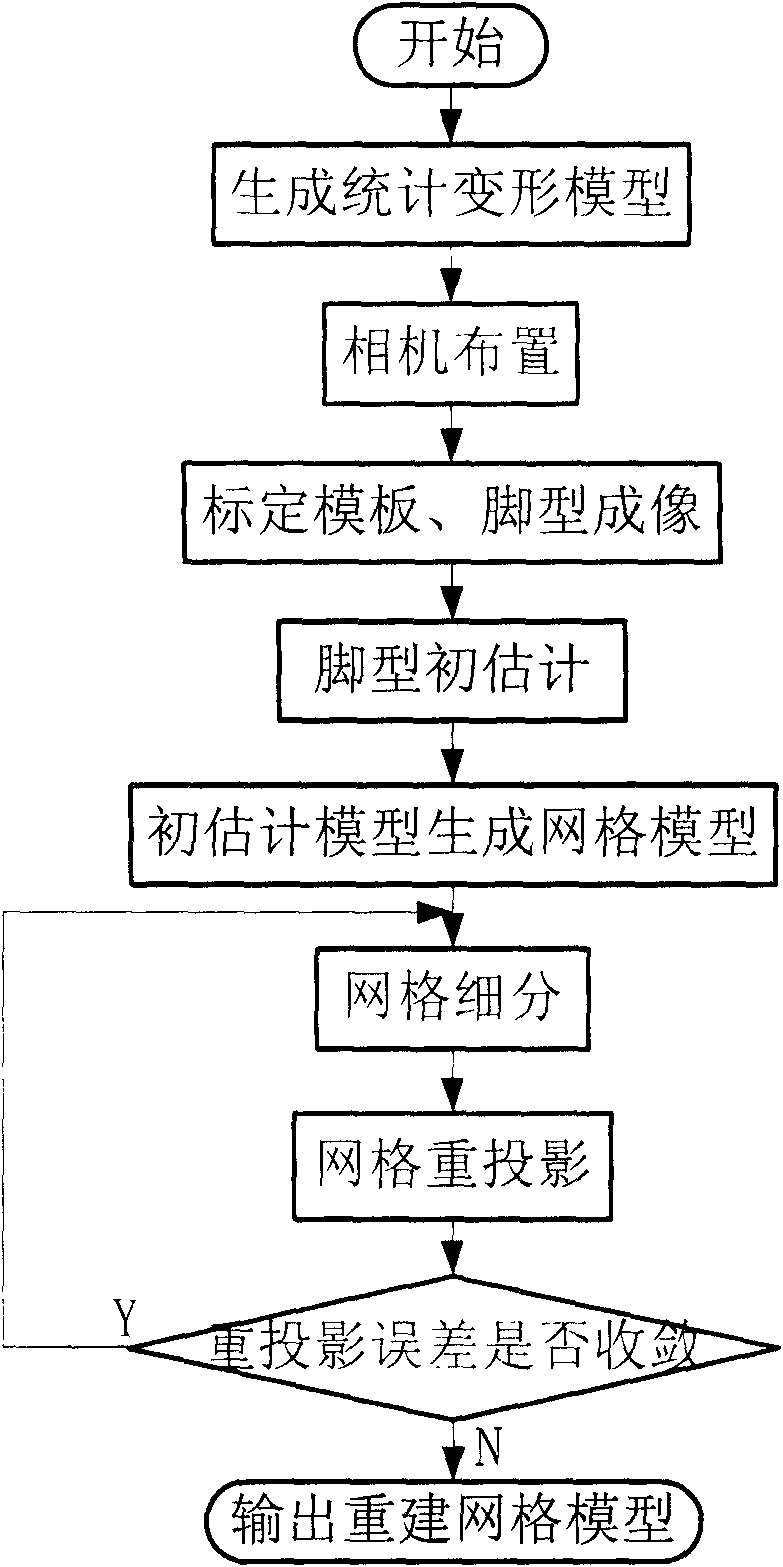
System for fully automatically reconstructing foot-type three-dimensional surface from a plurality of images captured by a plurality of cameras simultaneously
InactiveCN102157013AEasy to useLow costFoot measurement devices3D modellingMeasurement deviceSparse grid
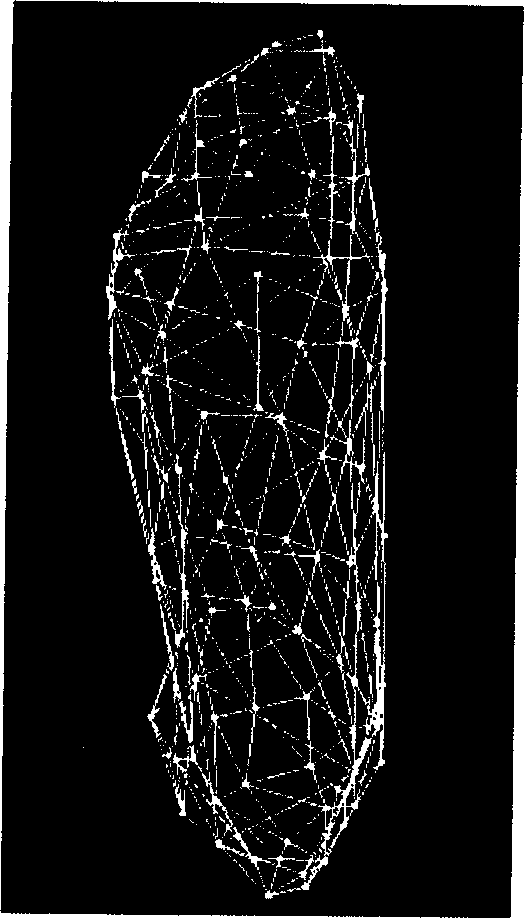
The name of the invention is 'system for fully automatically reconstructing foot-type three-dimensional surface from a plurality of images captured by a plurality of cameras simultaneously'. The invention relates to a system for fully automatically reconstructing foot-type three-dimensional surface from a plurality of images, comprising the following main steps of: firstly carrying out statistical analysis on a shoe-tree sample set so as to obtain the statistical deformation model; arranging the imaging environment; obtaining the calibrated template and the image of the human foot by a plurality of cameras; deforming statistical model, and fitting the foot type image so as to obtain the initially estimated model and generate the sparse grid model; and iterating to finely divide the grid model, wherein the image characteristic points from each image are divided in each turn of iteration, the plane characteristic point is matched with the space point, and the grid model is subdivided by using the spatial characteristic point; and finally obtaining the foot type model consistent with the target object. In the invention, a mark point is unnecessary to be set on the foot, and a high-precision laser measurement device is unnecessary; the camera and the computer are only used, and the shutter imaging time and the calculation processing time are only required. The system has fast speed, and can be widely applied to the condition for the three-dimensional reconstruction of the biological skin with relatively low precision request.
Owner:WENZHOU UNIVERSITY +1
Image splicing method based on grid deformation
InactiveCN107067370APreserve shape featuresImprove efficiencyGeometric image transformationGrid deformationGrid based
The invention discloses an image splicing method based on grid deformation, relating to the technical field of image splicing. The method includes the following steps of S1 respectively extracting SIFT characteristics of two space adjacent images, and matching the characteristics; S2 performing iterative computation by means of an RANSAC algorithm and screening characteristic point pairs; S3 estimating the global projective matrix and performing global projective transformation; S4 by means of Delaunay triangulation, constructing a dense triangular grid for an overlapping region and constructing a sparse grid for a non-overlapping region; S5 establishing the grid deformation energy function and optimizing the global projective registration; and S6 fusing the images to produce a wide-view-field image. The dense triangular grid represents the overlapping region and the sparse triangular grid represents the non-overlapping region of the image, so that compared with the APAP method, the whole image uses dense and same matrix grids, the algorithm efficiency is greatly improved. Meanwhile, the grid deformation can make full use of the parallel and high-speed operation performance of the CPU, and the splicing speed can be greatly improved.
Owner:CHANGSHA PANODUX TECH CO LTD
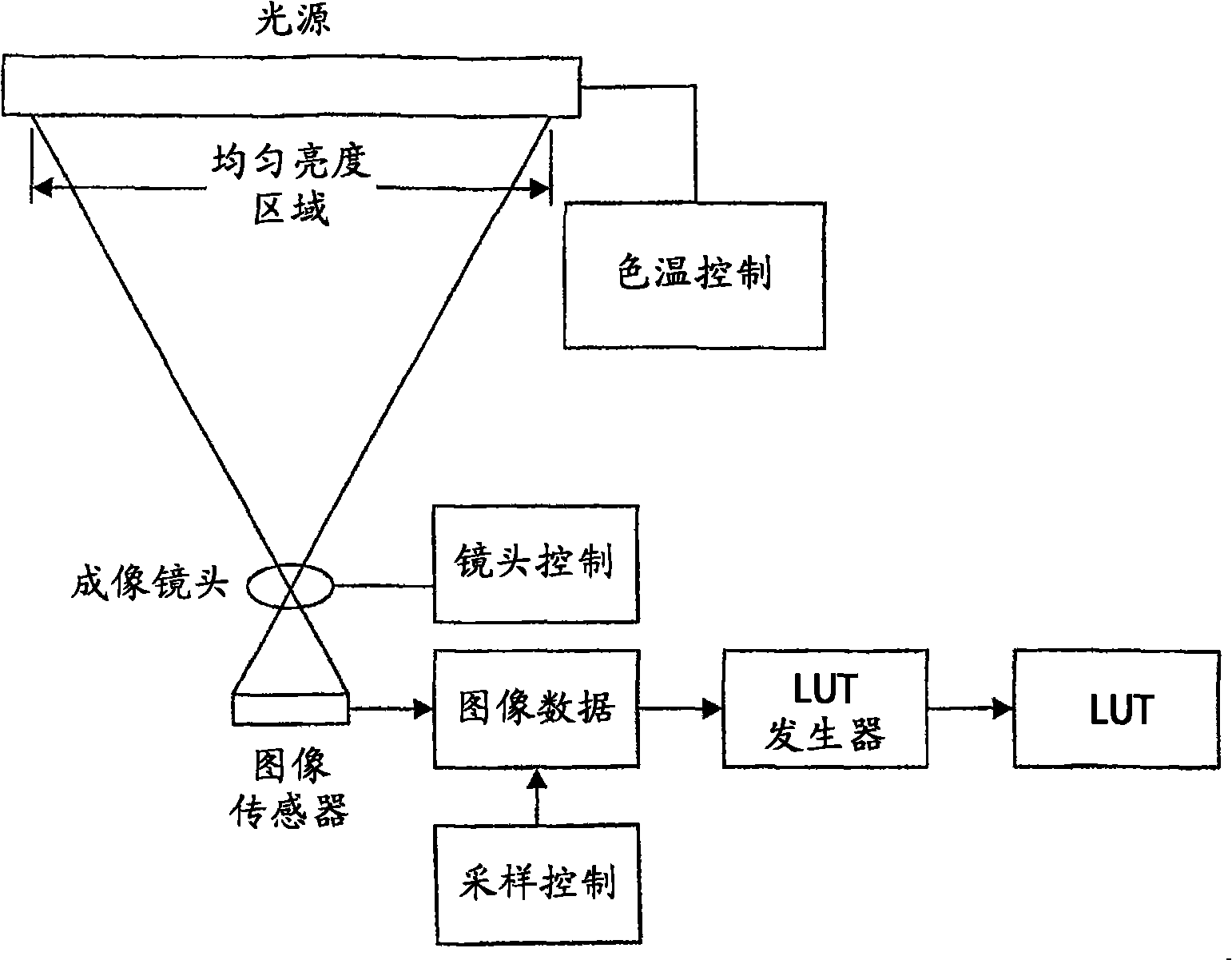
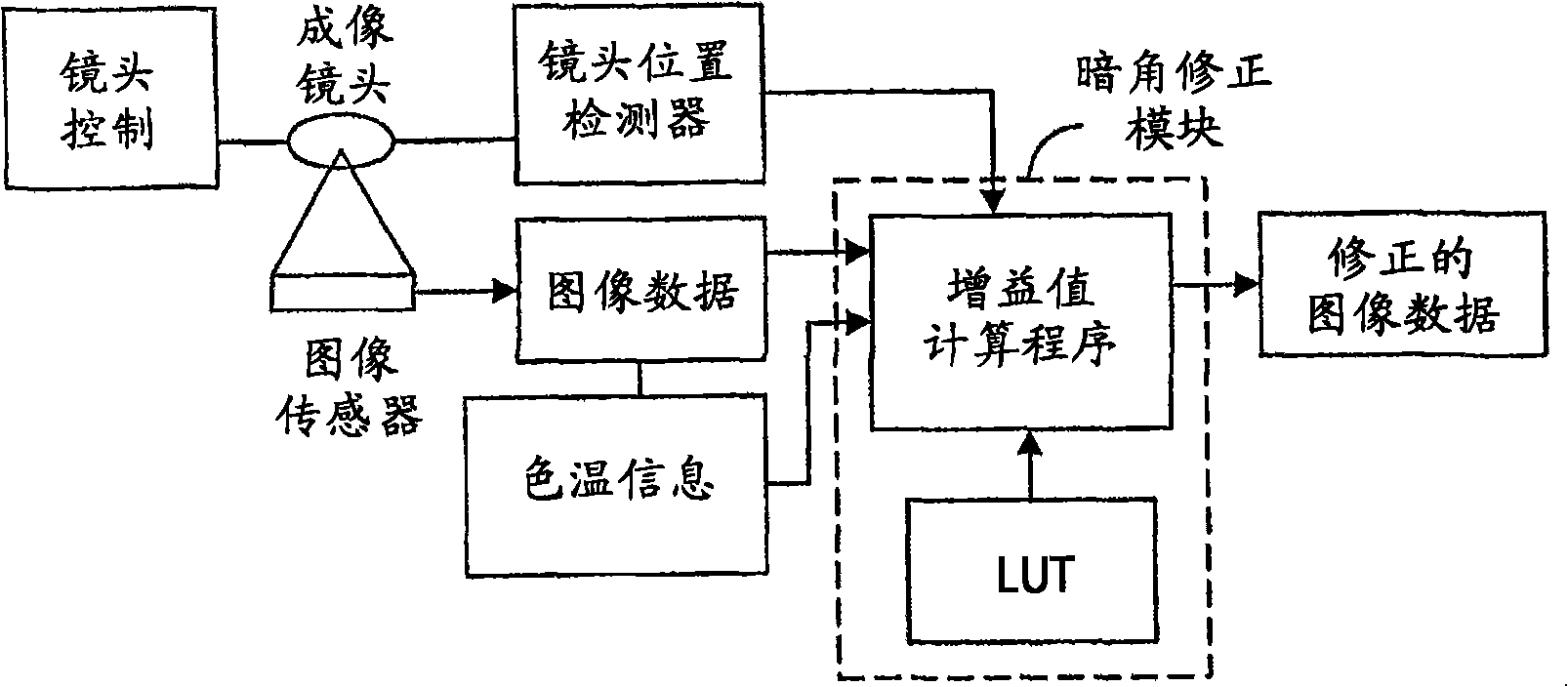
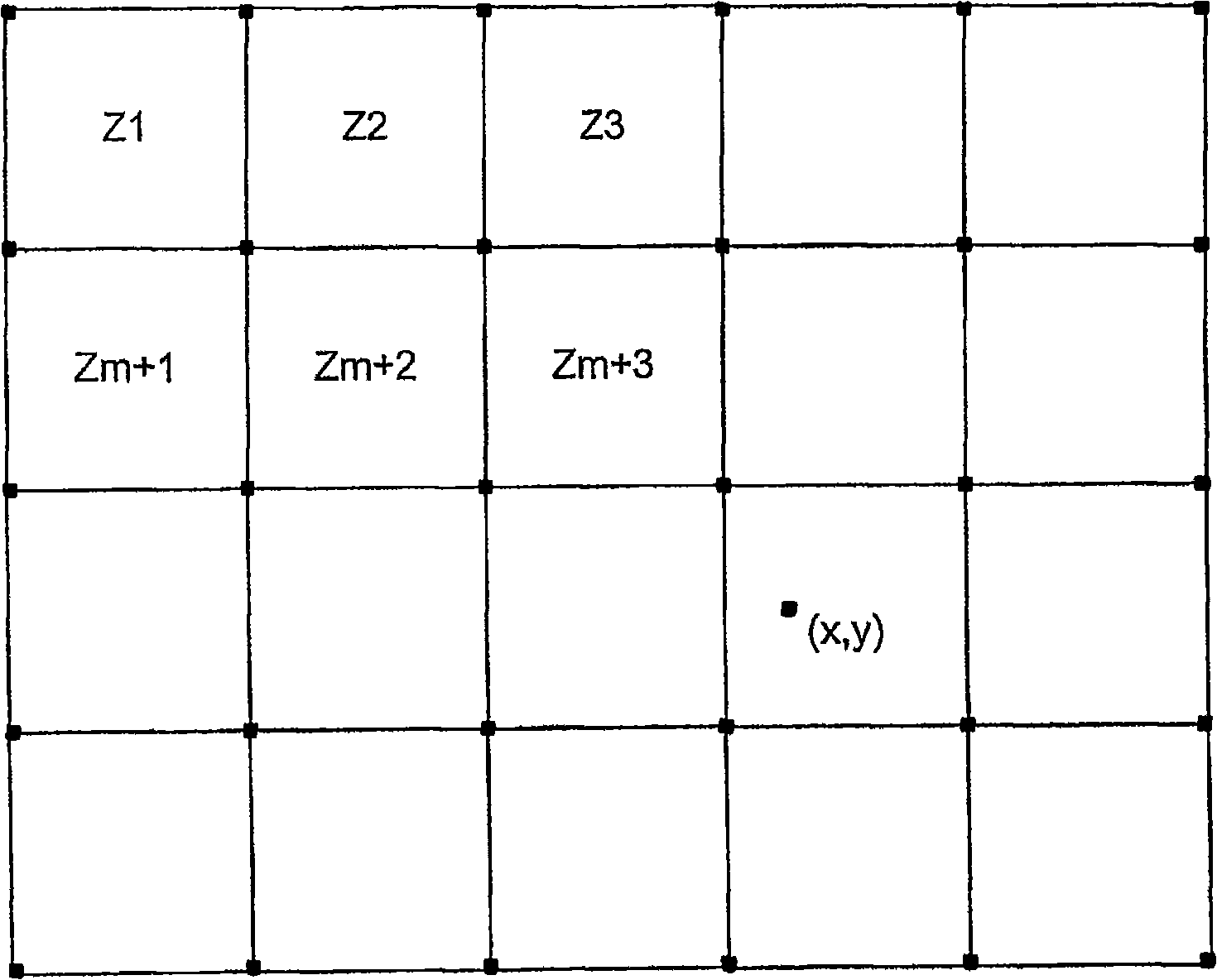
Dark corner eliminating method and system in digital image
InactiveCN101292519ATelevision system detailsSolid-state device signal generatorsSparse gridDigital image
An imaging system having one or more look-up tables to compensate for vignetting effect on an image sensor by a lens. An image of a test target formed by the lens is captured by the image sensor and sampling is carried out at discrete locations distributed on a sparse grid throughout the image area. The look-up table is generated according to gain values at sampling grid locations. Two or more look-up tables may be generated for different color temperatures and different lens positions. Image area is effectively divided into a plurality of image zones, each zone defined by four grid locations. The correction gain for each pixel within a zone is calculated in run time by interpolating a gain value on the basis of the correction gain values at those four grid locations, taken into account the distance of the pixel from each of those grid locations.
Owner:NOKIA CORP
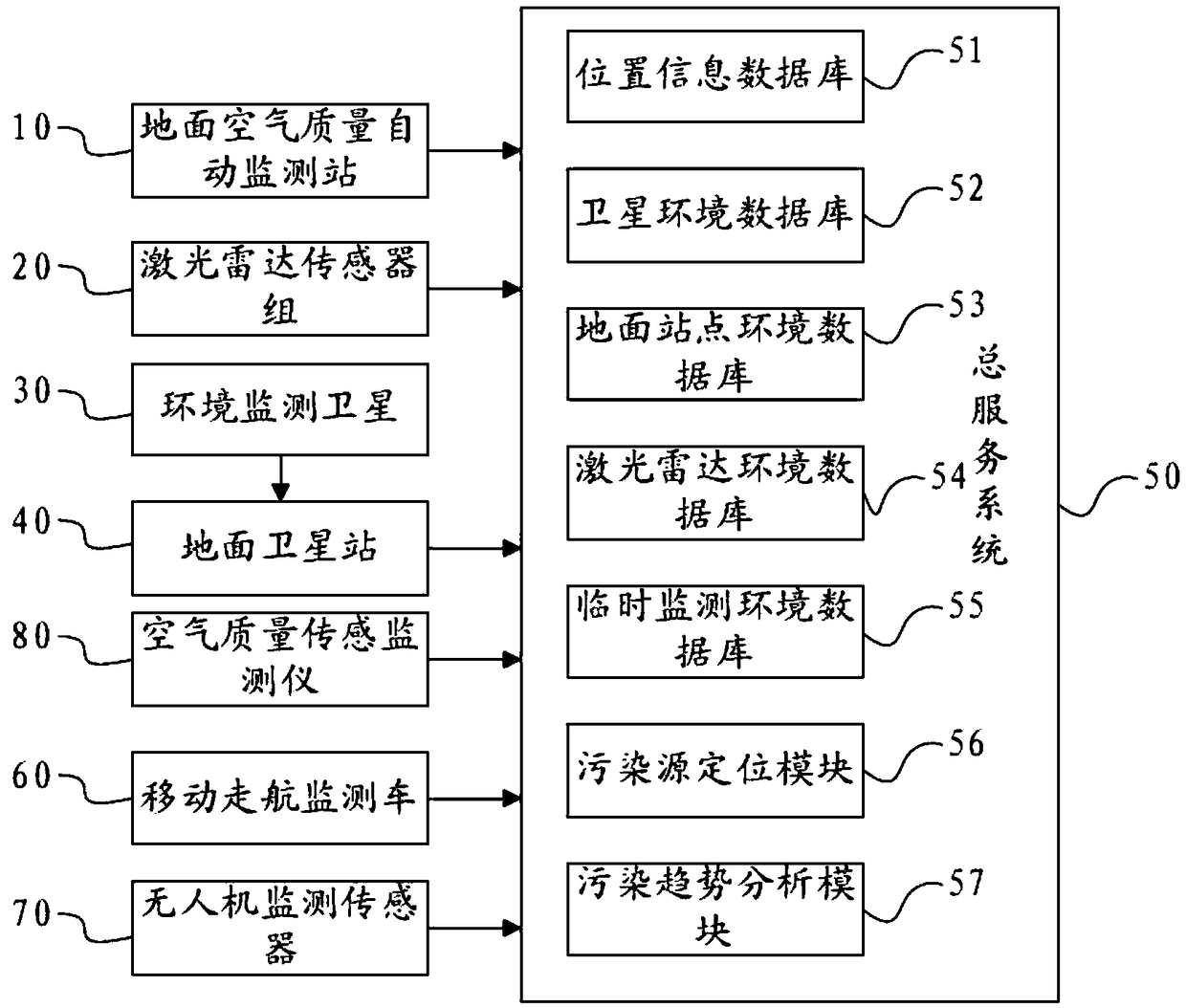
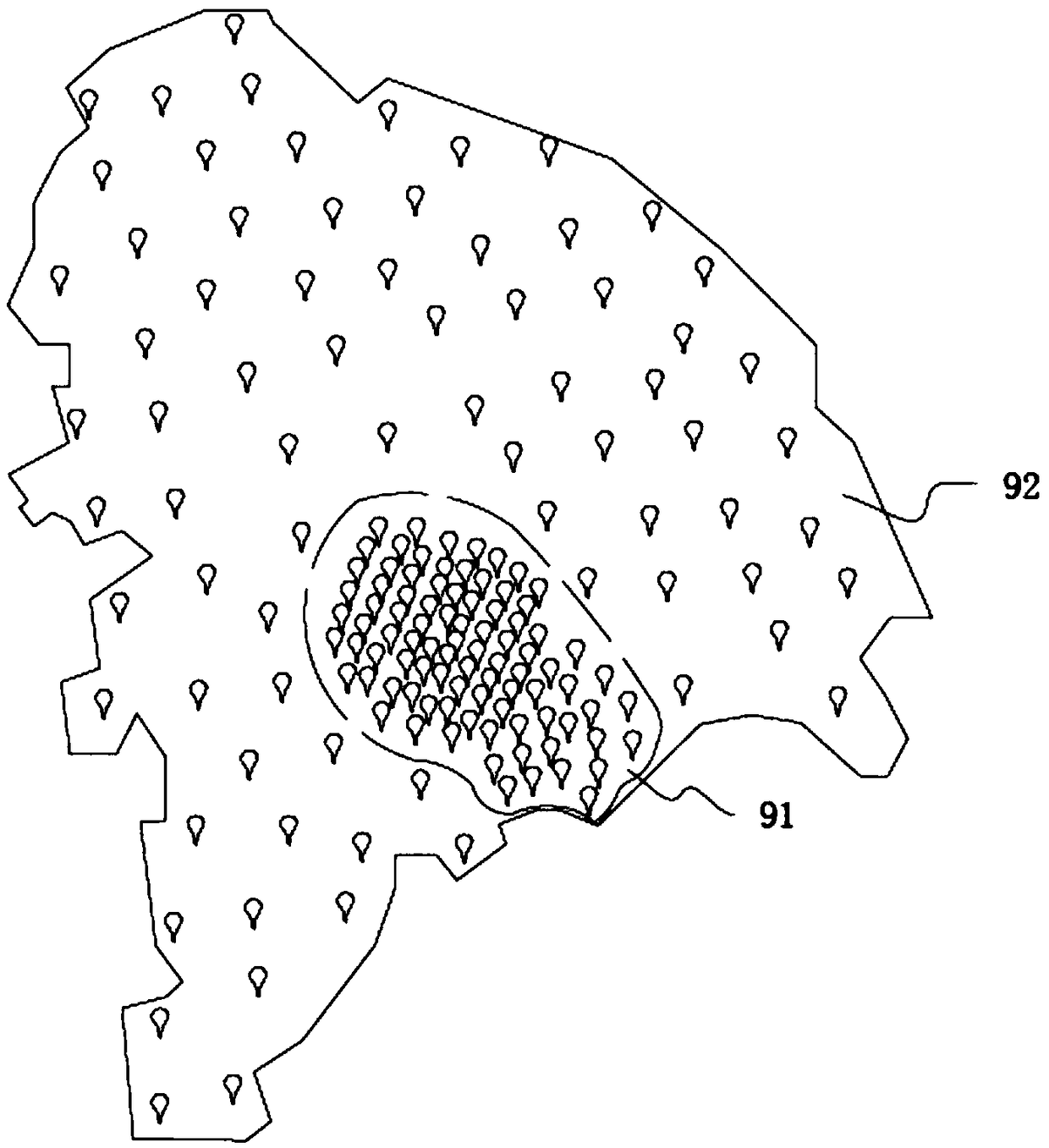
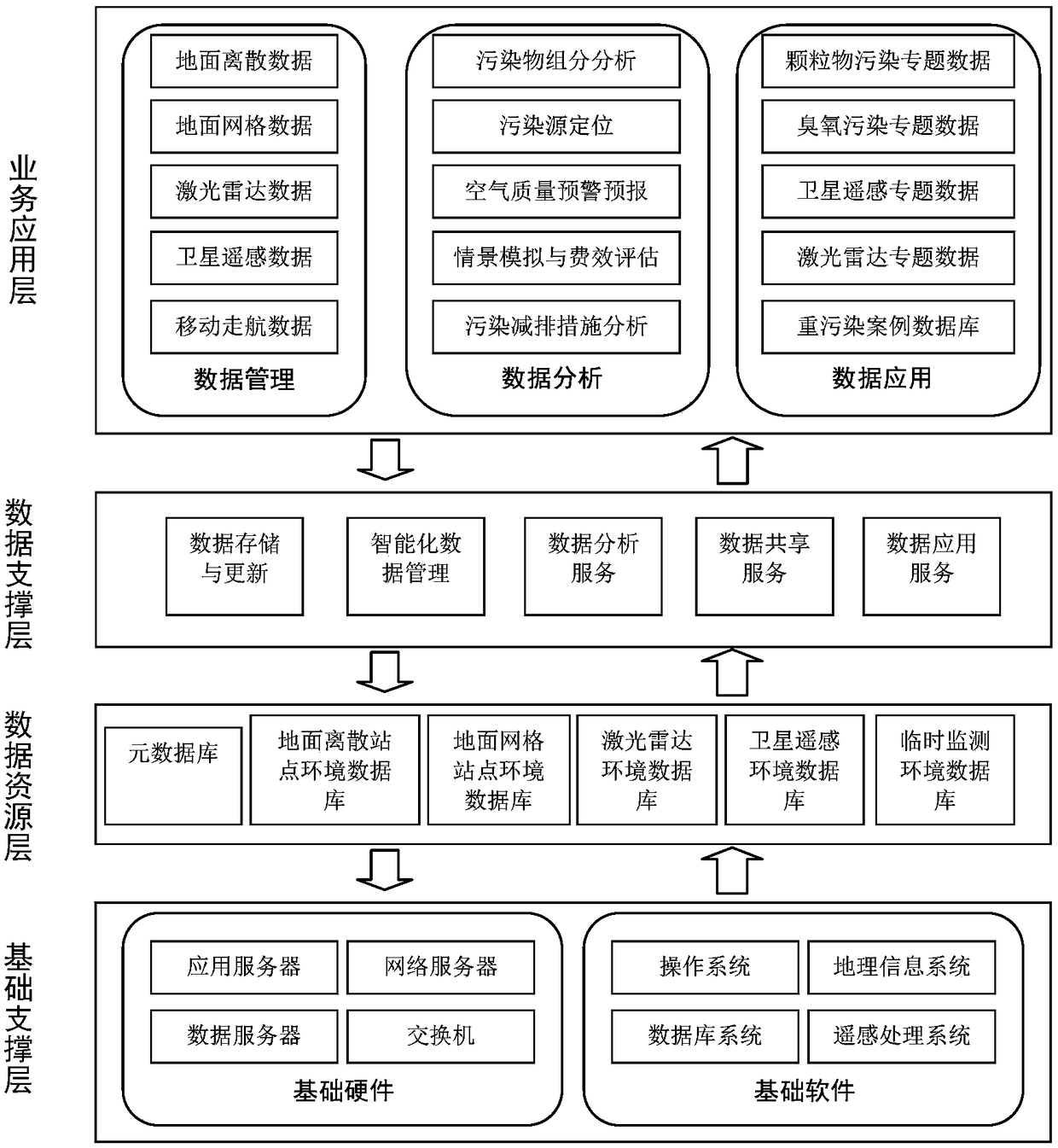
Atmospheric environment intelligent management system based on integration of space and air and earth
PendingCN108805368AAchieve integrationAchieving processing powerMeasurement devicesForecastingMobile navigationSparse grid
The invention discloses an atmospheric environment intelligent management system based on integration of space and air and earth. The atmospheric environment intelligent management system comprises multiple discrete ground air quality automatic monitoring stations, multiple environment monitoring satellites and ground satellite stations, laser radar sensor groups which are networked and arranged according to the pollution transmission characteristics, air quality sensing monitors which are distributed in the key pollution area according to the dense grid and distributed in the sub-key pollution area according to the sparse grid, mobile navigation monitoring vehicles which are organized according to the heavy pollution event and unmanned aerial vehicle monitoring sensors. The monitoring data of the ground air quality automatic monitoring stations, the ground satellite stations, the laser radar sensor groups, the air quality sensing monitors, the mobile navigation monitoring vehicles andthe unmanned aerial vehicle monitoring sensors are summarized to form an overall service system of the pollution layout. The mode of combination of the present ground monitoring network and network monitoring is used so that the disadvantage of the conventional ground monitoring network random distribution can be further improved and the data support can be provided for accurate haze treatment.
Owner:天津珞雍空间信息研究院有限公司
Foot-shaped three-dimensional surface reconstruction method based on image segmentation and grid subdivision
The invention relates to a foot-shaped three-dimensional surface reconstruction method based on image segmentation and grid subdivision, comprising the steps of: carrying out statistics and analysis on a shoe last sample set to obtain a statistic deformation model, using a plurality of cameras to obtain images of a foot, then using the statistic model to fit the foot-shaped images, obtaining a sparse grid model, then segmenting image characteristic points from all the images, reducing the planar characteristic points into spatial points, finally using the spatial characteristic points subdivide the grid model and carrying out the subdivision iteratively, thus obtaining a foot-shaped model consistent to a target object. In the foot-shaped three-dimensional surface reconstruction method, marking points do not need to be arranged on the foot, high-accuracy laser measurement equipment is also not needed, artificial participation is not needed, only the cameras and a computer and other devices are used, and the reconstruction risk is finished by software in a full-automatic manner. A reconstruction network can be consistent to a target foot shape automatically, can capture the detail characteristics in the images automatically and can adapt to information provided by the images automatically.
Owner:WENZHOU UNIVERSITY
Method and device for valuation of a traded commodity
A method and device for valuation of a traded commodityAn embodiment of the invention relates to a method for valuation of a traded commodity by a data processor, wherein a relative or absolute future value of the traded commodity is computed by a determination of an expectation by the data processor, the method comprising the steps of:receiving an historical time series indicating the commodity's value over time in the data processor;transferring the historical time series of the commodity's value into attribute values of at least one attribute representative for internal features of the historical time series; andconstructing a function predicting the future value of the commodity based on a sparse grid regression method which takes said attribute values into account.
Owner:TECH UNIV BERLIN +1
Target direction-finding method based on acoustic vector two-dimensional nested array
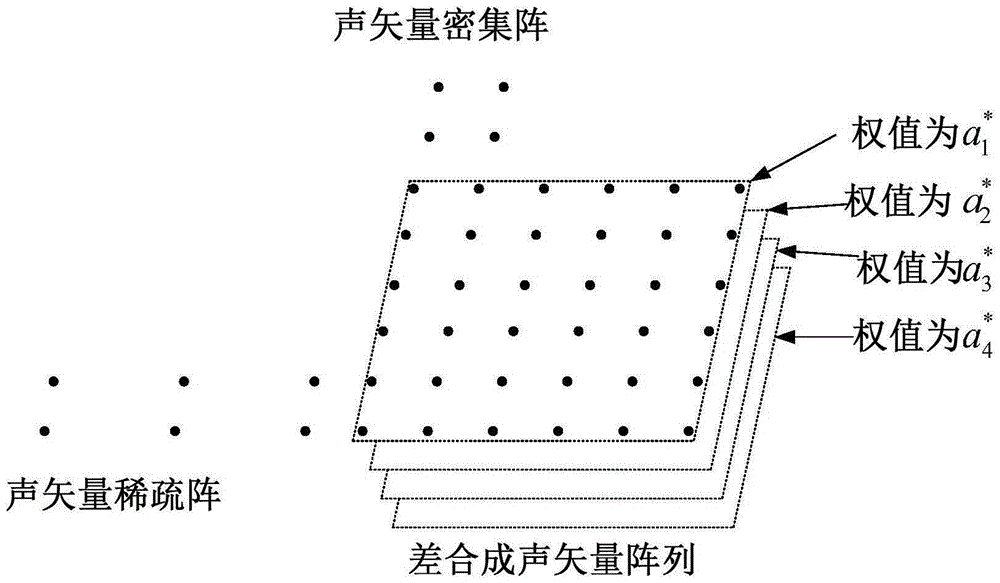
InactiveCN105182285AIncrease freedomRealize high precision direction findingDirection finders using ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic wavesNested arraysSparse grid
The invention discloses a target direction-finding method based on an acoustic vector two-dimensional nested array, and is used for direction and pitching measurement of an underwater target. The method includes building a new acoustic vector two-dimensional nested array which is formed by two two-dimensional acoustic vector subarrays nested in geometric position, array elements of the subarray 1 are distributed in sparse grids, array elements of the subarray 2 are distributed in dense grids, two grids can be selected arbitrarily, that a matrix that associate the grids is an integer matrix is required only, the integer matrix can also be selected freely, then an autocorrelation matrix of signals output by the array are utilized to build a difference synthesis acoustic vector two-dimensional array, and finally a three-dimensional smooth DOA algorithm is utilized to obtain second-order statistics of received signals of the difference synthesis acoustic vector array.
Owner:THE 28TH RES INST OF CHINA ELECTRONICS TECH GROUP CORP
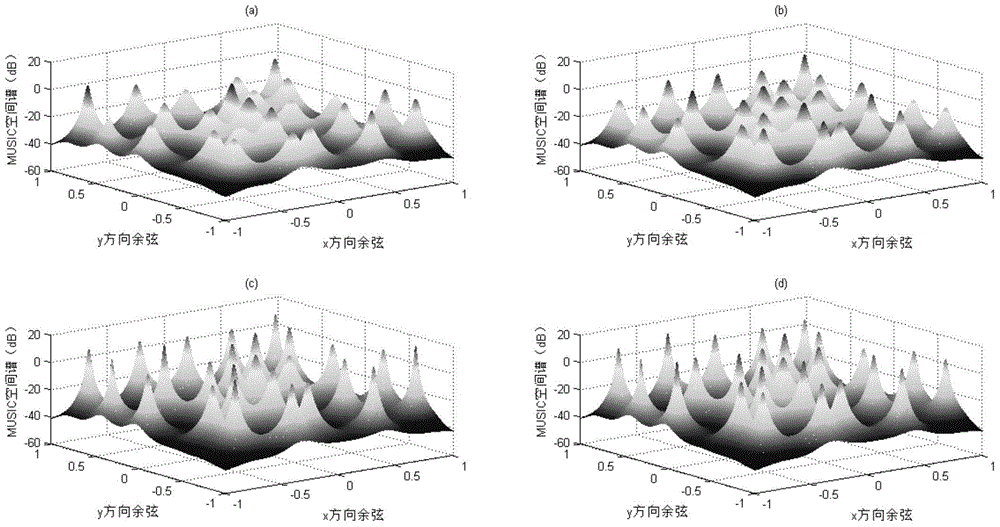
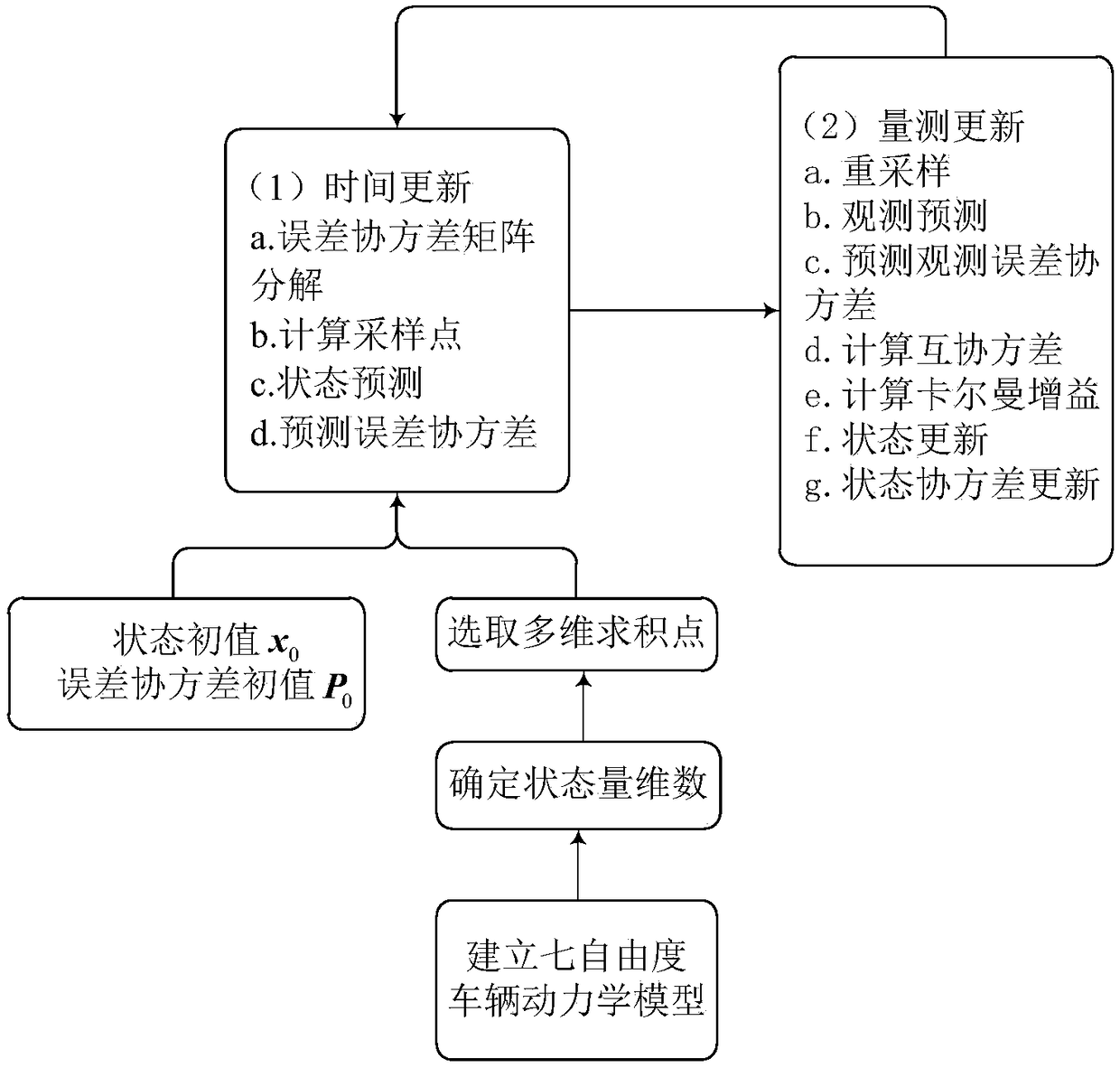
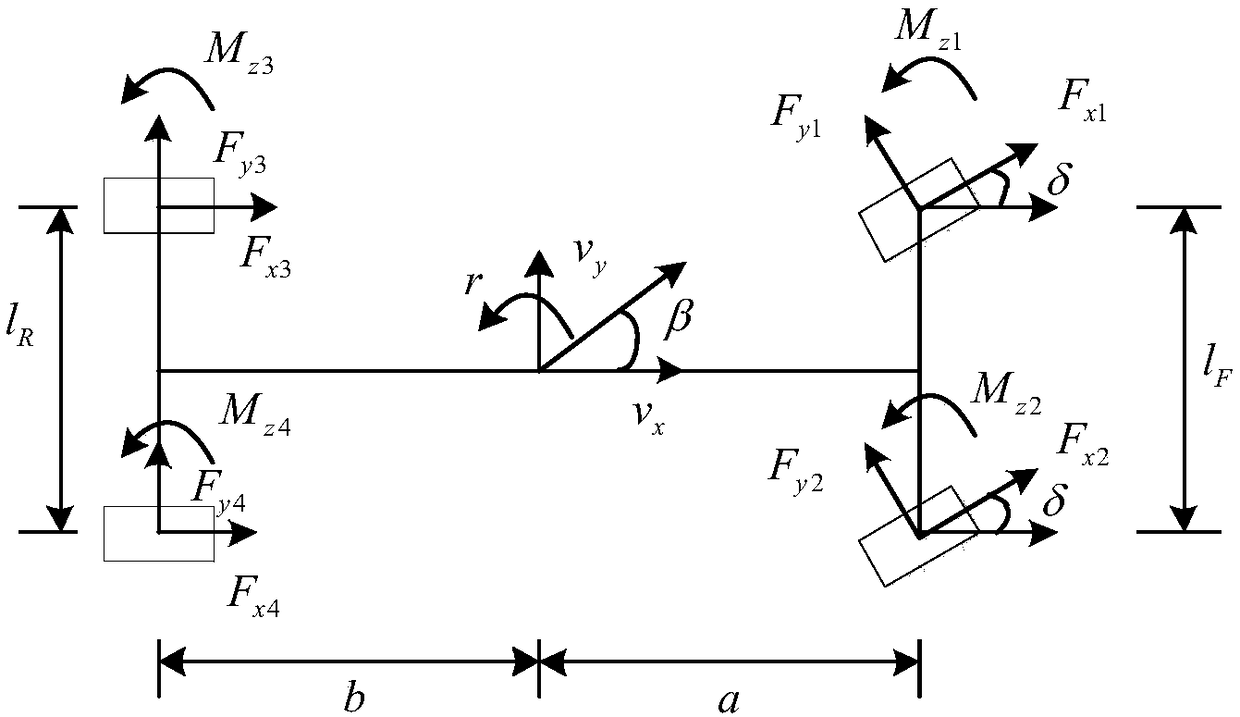
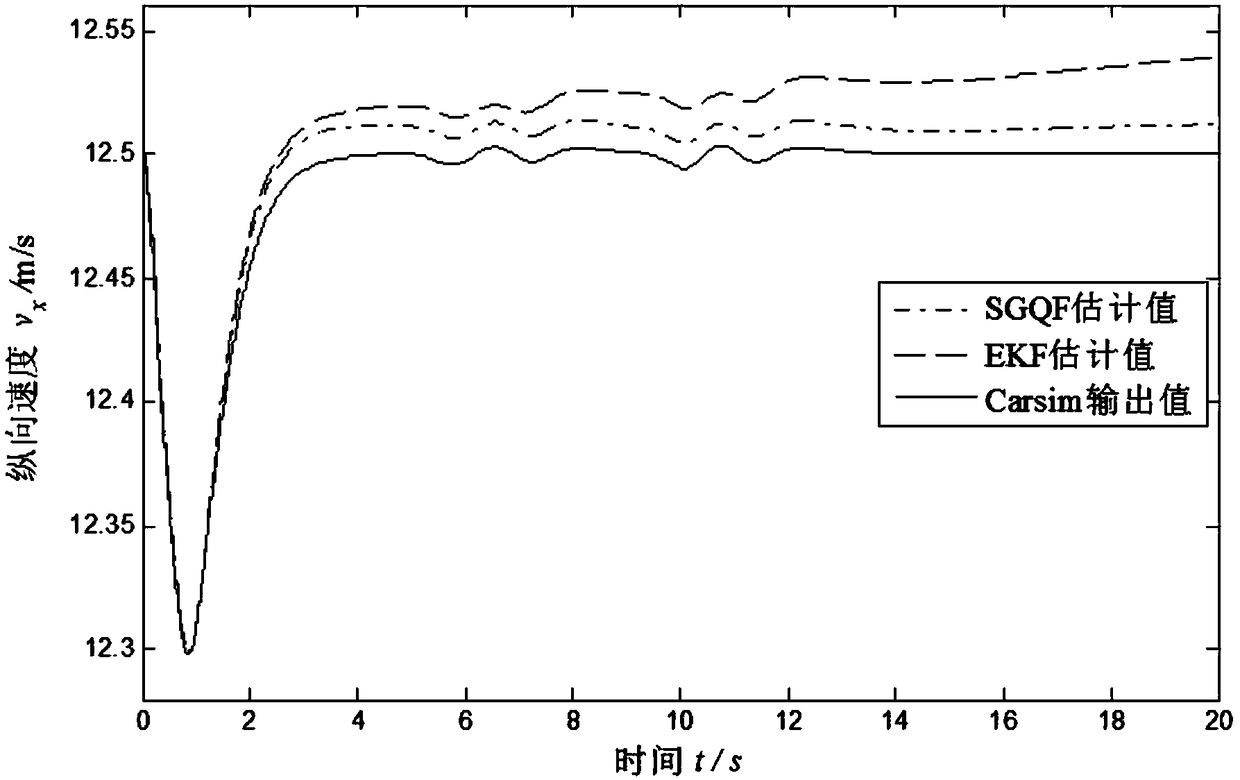
Vehicle traveling state estimation method based on sparse grid integrating Kalman filtering
InactiveCN108162976AImprove State Estimation AccuracyImprove real-time performanceGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationEstimation methodsState parameter
The invention discloses a vehicle traveling state estimation method based on sparse grid integrating Kalman filtering. Through a selected seven-degree-of-freedom vehicle motion module, on the basis ofan integrating Kalman filtering method combining with a sparse grid theory, multidimensional integration points are selected, time upgrading and measurement upgrading are conducted, and the longitudinal vehicle speed, the lateral vehicle speed and the side slip angle of a vehicle are estimated. The vehicle traveling state parameter estimation method has the characteristic of high precision, and the real-time performance of state parameter estimation can be effectively improved while the state estimation precision is improved.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
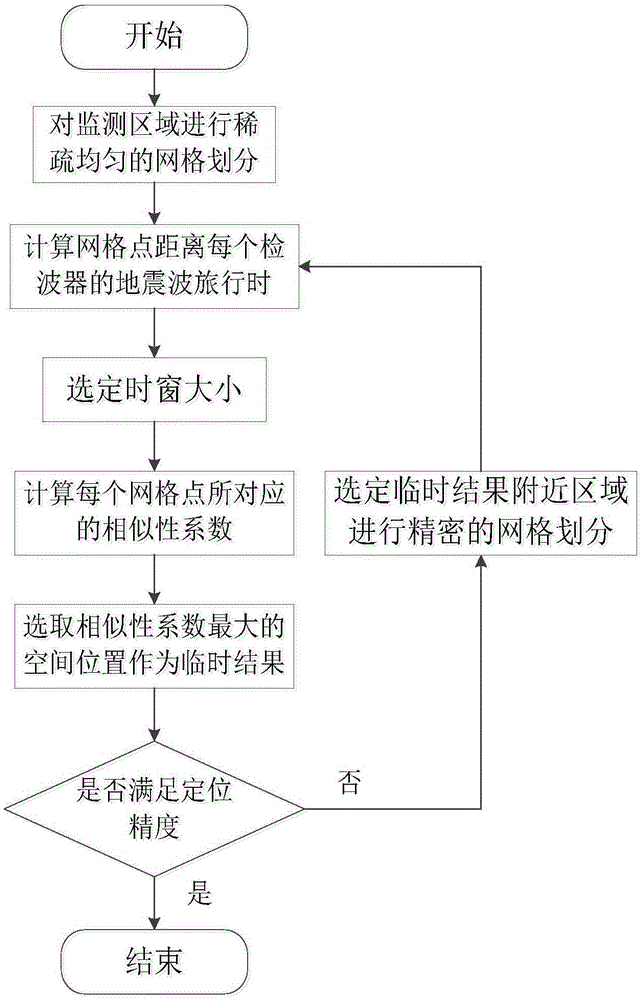
Micro-earthquake epicenter positioning method calculated based on multilevel multi-scale grid similarity coefficient
InactiveCN105549077AEffective positioningAvoid the disadvantage of long calculation timeSeismic signal processingMesh gridSparse grid
The invention discloses a micro-earthquake epicenter positioning method, belongs to the field of earth physics inversion algorithms. The positioning method comprises the following steps that a monitoring area is divided into uniform grids; the earthquake amplitude similarity coefficient corresponding to each grid division point is calculated; the grid position corresponding to the maximal similarity coefficient is selected as an epicenter positioning result; and the grid corresponding to the positioning result is further divided into grids uniformly, the similarity coefficients are calculated, and the grid position corresponding to the maximal similarity coefficient to update the epicenter positioning result till the positioning precision satisfies requirements. Compared with a traditional similarity coefficient positioning method, multilevel multi-scale grid division is carried out on the monitoring area, the disadvantage that the calculation time is too long caused by wholly dense grid division of the monitoring area is overcome, and the defect that the positioning precision is too low due to wholly sparse grid division of the monitoring area is also overcome.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF MINING & TECH (BEIJING)
Three-dimensional feet data measuring method to sparse grid based on curve subdivision
InactiveCN1895168ASave human effortSave moneyDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsSparse gridComputer vision
A sparse lattice-oriented method based on the fine division of curved surface for measuring the data about 3D foot type includes such steps as reading the 3D foot model on sparse lattice, setting up the iterative parameters for fine division, finely dividing the 3D foot model on sparse lattice, smoothing the generated 3D foot model, examining the terminating conditions of said model, 2D projection of generated 3D foot model, choosing the characteristic dots on the 2D profile of 3D foot model, obtaining the peripheral length of foot type, and outputting the characteristic parameters about foot type.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Sparse grid-oriented three-dimensional foot type fast acquiring method based on standard foot deformation
A method for obtaining 3D foot shape quickly based on standard foot variant by utilizing sparse grid includes setting up, standard foot shape library, setting up 3D coordinate for structuring foot length vector, rotating sparse grid foot model to let said vector be parallel to Y axle, selecting foot length and width information from said library, adjusting posture and position of sparse grid foot model to let it distribute uniformly around standard foot model, finding out corresponding points of two models, revising control top point of sparse grid foot model and using revised point to rebuild sparse grid foot model for obtaining 3D foot shape data.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
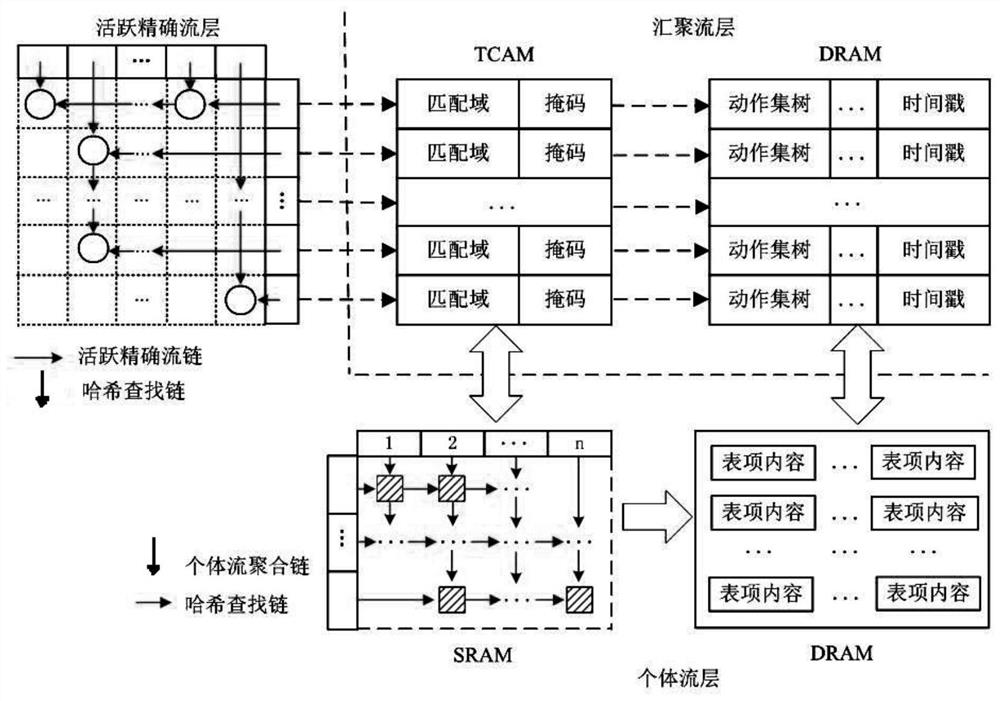
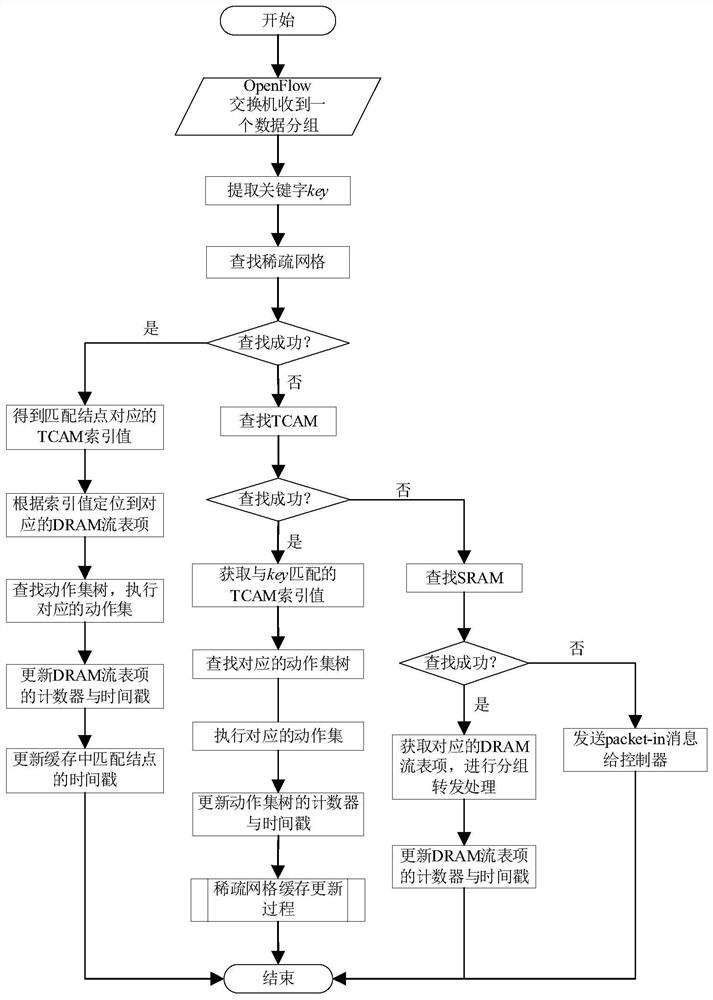
OpenFlow large-scale flow table elastic energy-saving and high-efficiency search framework and OpenFlow large-scale flow table elastic energy-saving and high-efficiency search method
ActiveCN111966284AImprove space utilizationImprove caching efficiencyInput/output to record carriersHigh level techniquesComputer networkInternet traffic
The invention discloses an OpenFlow large-scale flow table elastic energy-saving and efficient search architecture and method, and the architecture comprises an active precise flow layer which is usedfor caching active precise flow table entries in a network, and achieving the high-speed and low-power flow table cache search; a convergent flow layer which is used for storing universal flow tableentries so as to relieve the problem of insufficient TCAM storage capacity and improve the TCAM cache hit rate; wherein the convergent flow layer comprises a TCAM and a DRAM; the individual flow layeris used for storing accurate flow table entries which do not meet the aggregation condition temporarily so as to improve the packet forwarding capability of the OpenFlow switch; the bulk flow layer includes an SRAM and a DRAM. According to the method, the sparse grid is constructed by using the cross linked list, the cache space is dynamically applied, all accurate flows meeting conditions can bestored, no empty table item exists, the space utilization rate is very high, and the method can adapt to dynamic change of network flow and is rich in elasticity.
Owner:CHANGSHA UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Apparatus for and method of analyzing transmission characteristics of a circuit apparatus
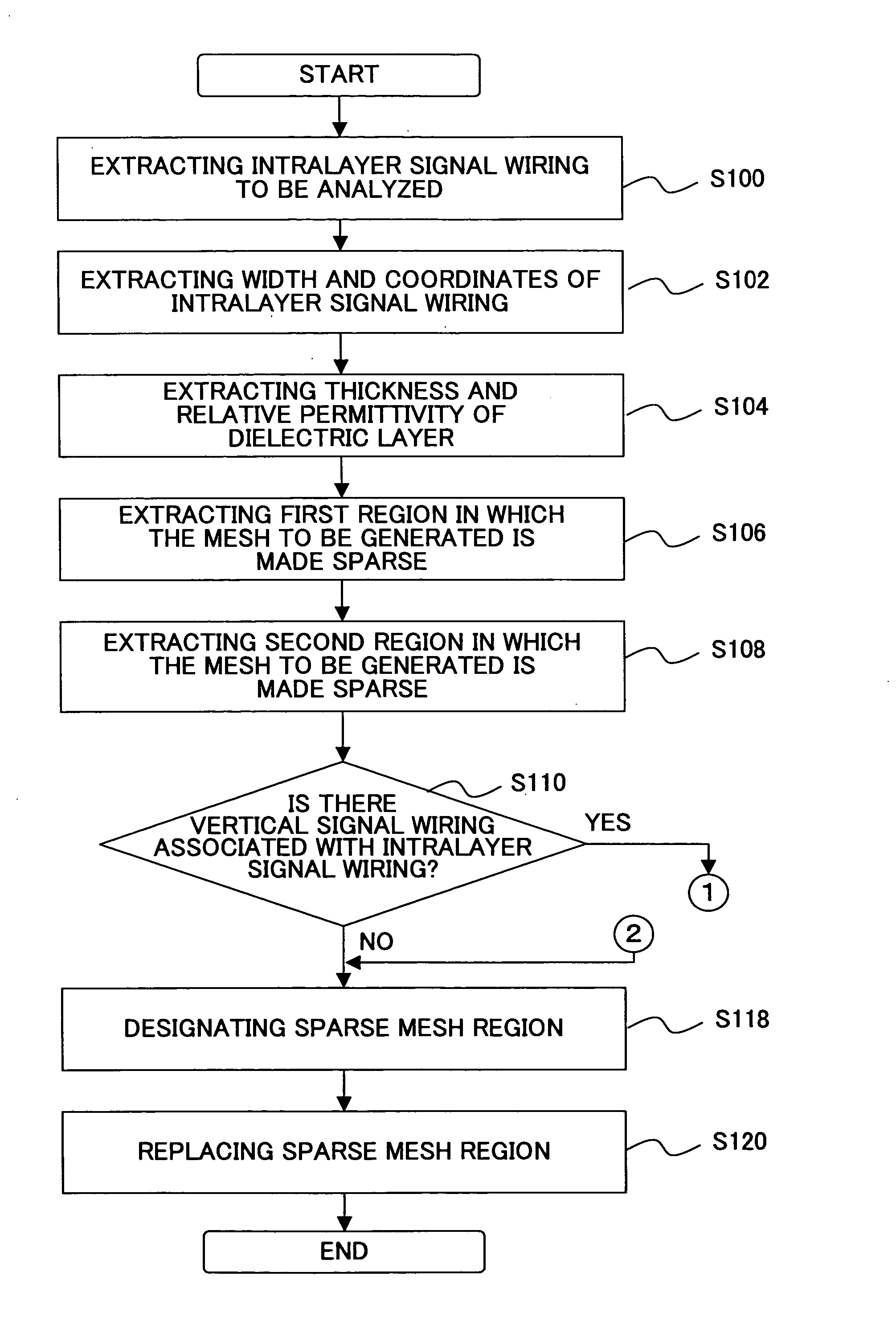
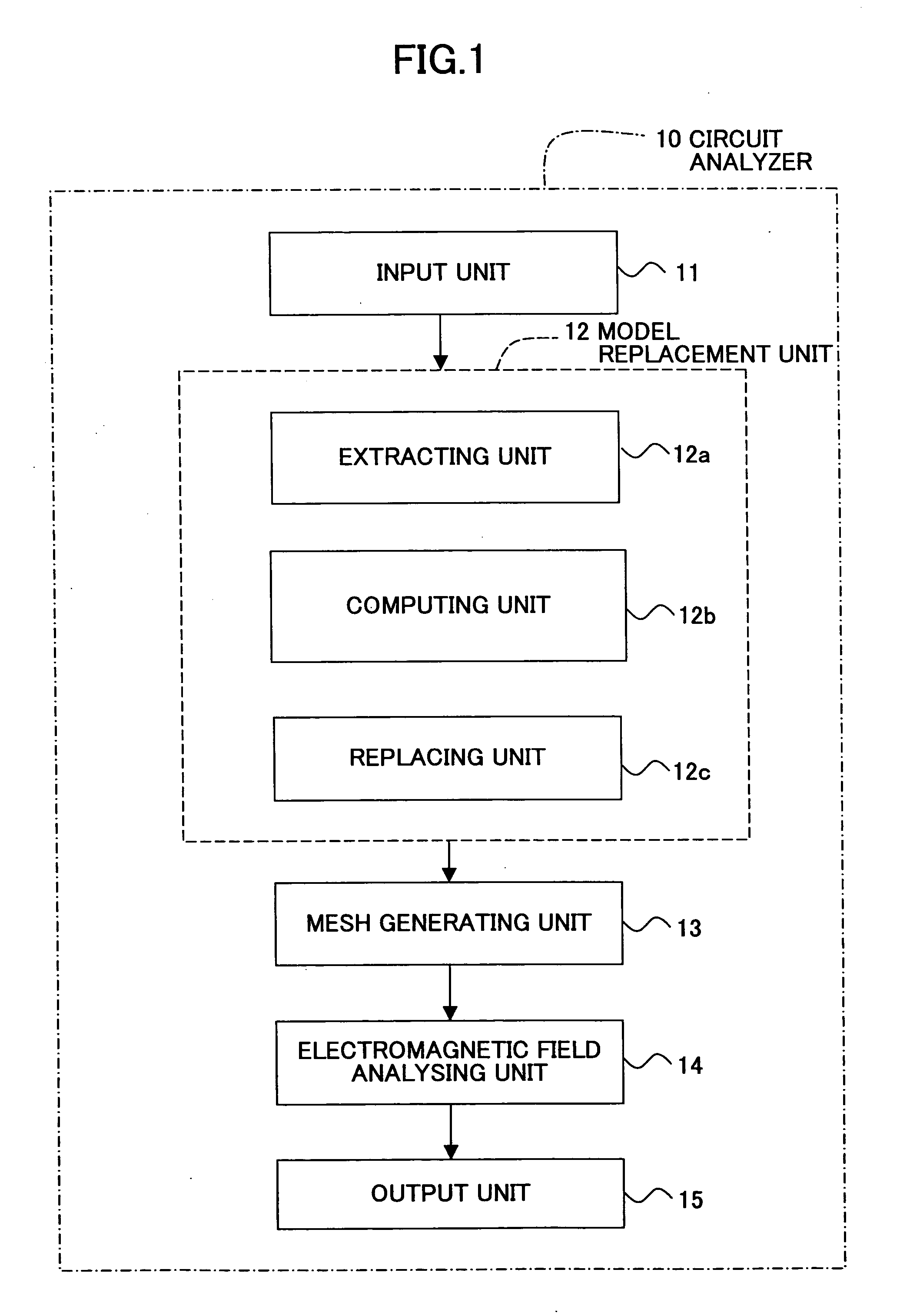
InactiveUS20050246669A1Shorten the timeReduce the numberDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsEngineeringAnalysis method
A method of analyzing transmission characteristics of signal wiring in a circuit apparatus including the signal wiring and insulative layer is disclosed. The transmission characteristics are analyzed by dividing the circuit apparatus with a mesh and applying electromagnetic analysis method to each unit of the mesh. The method includes the steps of: extracting signal wiring data from 3 dimensional data of the circuit apparatus; designating a sparse mesh region in which the mesh can be made sparse based on the extracted signal wiring data and the 3 dimensional data; and generating sparse mesh in the sparse mesh region. Since the sparse mesh region is designated based on the sizes of the signal wiring and the insulative layer and on the electric properties of the insulative layer, a region that affects the transmission characteristics of the signal wiring only to a small extent can be designated as the sparse mesh region.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Image restoration method and device based on Shannon-Nuttall wavelet multi-scale expression
ActiveCN104574294AHigh-resolutionReduce resolutionImage enhancementSparse gridInterpolating wavelets
The invention discloses an image restoration method and device based on a Shannon-Nuttall wavelet multi-scale expression. The method comprises the following steps: obtaining a to-be-restored image; shielding a to-be-restored area in the to-be-restored image; constructing a multi-scale interpolation operator based on a Shannon-Nuttall interpolating wavelet and realizing the geometric description of the to-be-restored image under an interpolating wavelet framework; constructing an image restoration variational model under the interpolating wavelet framework according to the geometric description of the to-be-restored image under the interpolating wavelet framework; solving the image restoration variational model under the interpolating wavelet framework and obtaining a sharp image. According to the image restoration method and device disclosed by the invention, the image is reconstructed through the multi-scale interpolation operator, the image restoration variational model is constructed under the interpolating wavelet framework, and the image is solved through a sparse grid algorithm to obtain the restored image, so that the efficiency and the precision of image restoration are improved.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Method and device for evaluation of financial derivatives using sparse grids
ActiveUS7536327B2Fast and accurate valuationImprove accuracyFinanceComplex mathematical operationsIntegration pointSparse grid
A method and device for valuation of financial derivatives, wherein a value of a derivative is computed by a determination of an expectation. Input parameters are communicated by an input unit to a computer, such as at least one processor, to establish an integrand as a function of the input parameters. A multivariate integration domain is computed. A sparse grid method is used to determine integration points and integration weights as a function of the input parameters. The integrand is integrated with an integration domain at the integration points to determine integrand values. One or more expectation parameters are computed by combining the integrand values and the integration weights. A value of the derivative is communicated through an output unit, for example to a display monitor or another display device.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
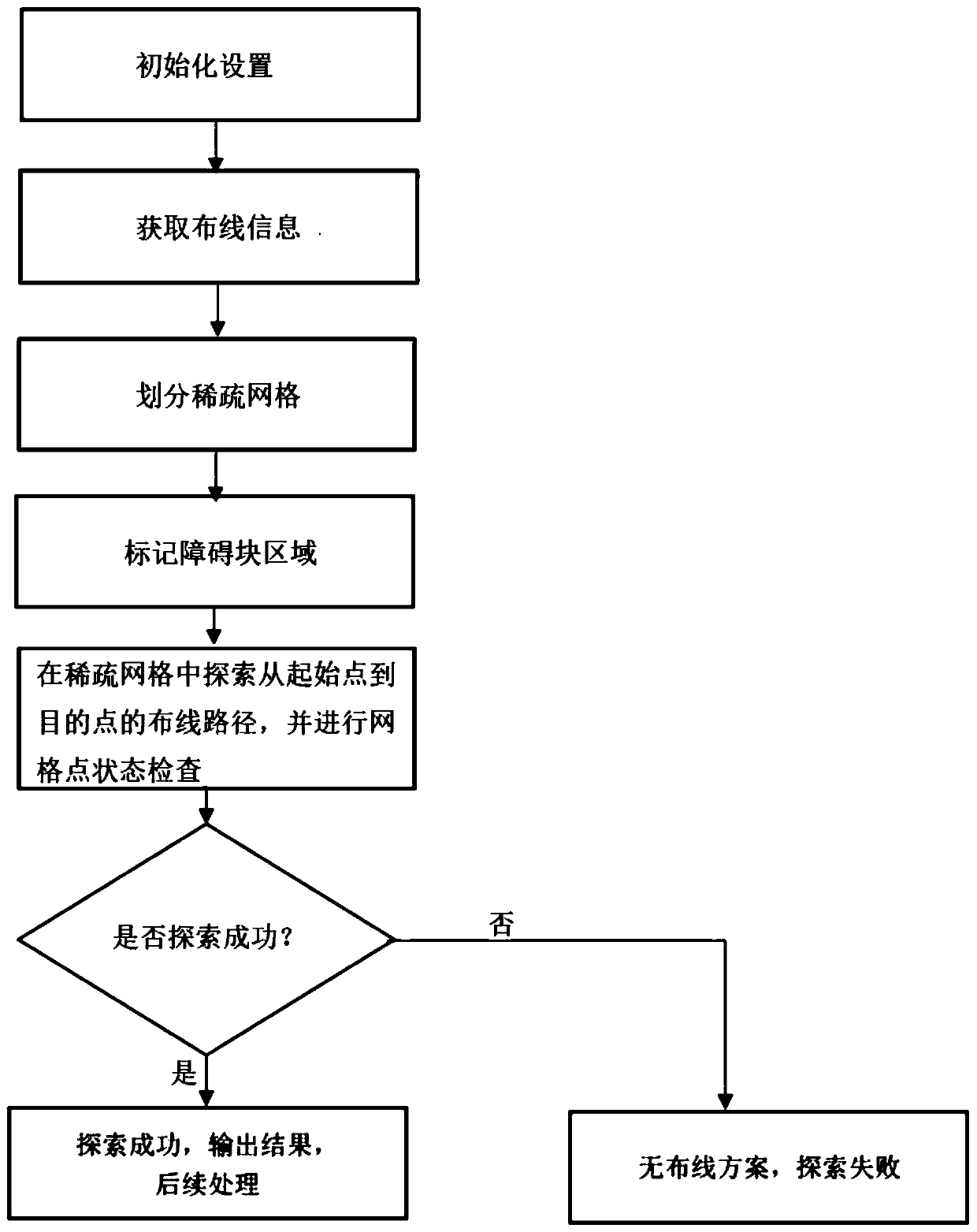
Automatic layout wiring generation method based on sparse grids
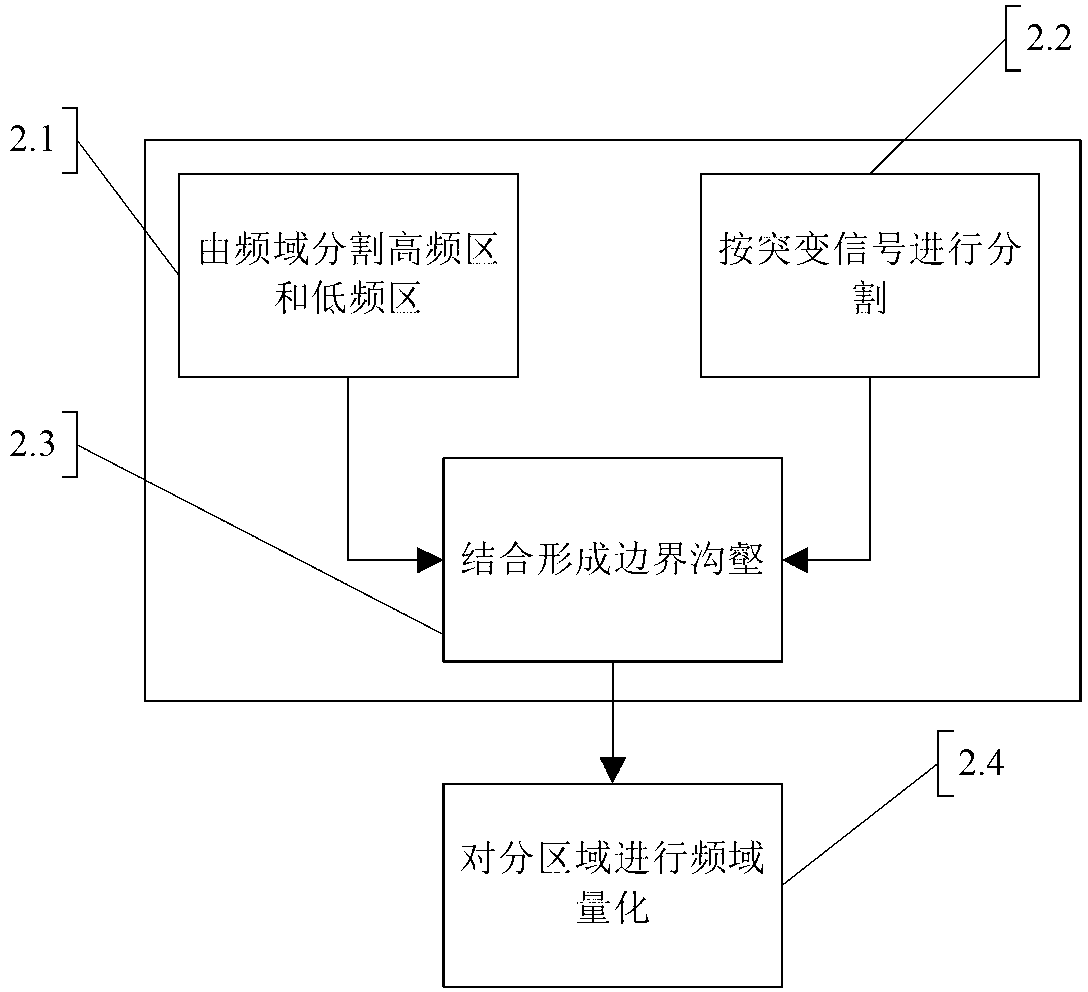
ActiveCN111368493AReduced effectivenessImprove efficiencyComputer aided designSpecial data processing applicationsSparse gridLayout
The invention relates to an automatic layout wiring generation method based on sparse grids. The method comprises the following steps: 1, initialization setting; 2, acquiring wiring information; 3, dividing grids; 4, marking a grid state; 5, wiring; and 6, inquiring whether components to be wired exist or not, and if yes, repeating the step (2) until wiring of all layouts is completed. According to the invention, design requirements can be met according to different devices and layouts; according to the method and the system, the wiring grids are adaptively and reasonably divided to obtain thedata of the related grids, and then the grids are explored by adopting the algorithm, so that the defect of large storage space caused by uniform grid division can be greatly reduced, the space effectiveness is favorably reduced, and the space use efficiency is improved.
Owner:SEMITRONIX
Cognitive radio frequency spectrum sensing method based on circulation symmetry
InactiveCN102111228AImprove accuracyProof of accuracyTransmission monitoringFrequency spectrumSparse grid
The invention relates to a cognitive radio frequency spectrum sensing method based on circulation symmetry, belonging to the field of communication. The invention aims at solving the problems that the calculated quantity is high, the operation is complex and the accuracy of frequency spectrum sensing is low under the condition of low signal to noise ratio in the traditional method for realizing radio frequency spectrum sensing by judging whether cyclic spectrum of a received signal has symmetry. The method provided by the invention comprises the following steps of: 1, sampling a radio signal,and acquiring the cyclic spectrum of the radio signal by adopting an SSCA (stochastic sparse-grid collocation algorithm) algorithm; 2, selecting 15 pairs of symmetric points on the cyclic spectrum acquired in the step 1; 3, calculating the sum of the amplitude differences of the 15 pairs of symmetrical points selected in the step 2; and 4, judging whether the sum of the amplitudes differences of the 15 pairs of symmetrical points is less than a symmetry decision threshold, if the sum is less than the symmetry decision threshold, judging that a master user signal is existed in a channel; and if the sum is not less than the symmetry threshold, judging that no master user signal is existed in the channel. The accuracy of spectrum sensing under the condition of low signal-to-noise ratio is obviously improved.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
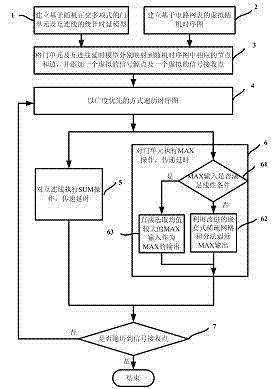
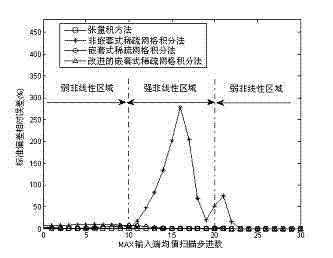
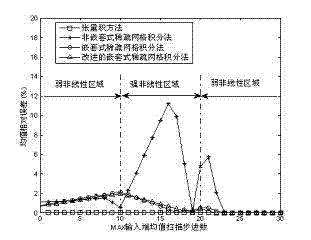
Statistical timing analysis method and device based on improved adaptive random configuration method
InactiveCN102054090AReduce calculation precisionImprove calculation accuracySpecial data processing applicationsIntegration pointTheoretical computer science
The invention relates to a statistical static timing analysis method. In the method, the MAX approximation problem in the statistical static timing analysis method is solved through an adaptive random configuration method (MASCM) based on an improved nested sparse grid integration method. In the MASCM, the MAX approximation is divided into two classes according to input end conditions, namely a linear input condition and a nonlinear input condition, wherein under the linear input condition, an input end with the maximum mean value is selected as output of the MAX; and under the nonlinear input condition, the orthogonal multinomial expansion coefficient is calculated by the improved nested sparse grid integration method. The improved nested sparse grid integration method improves the utilization rate of integration points in the random configuration method, guarantees the integration accuracy, reduces the number of configuration points and reduces the calculation time for statistical static timing analysis. Compared with the conventional methods, the provided MASCM has the equivalent calculation accuracy, while the needed number of integration points and calculation time are greatly reduced.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
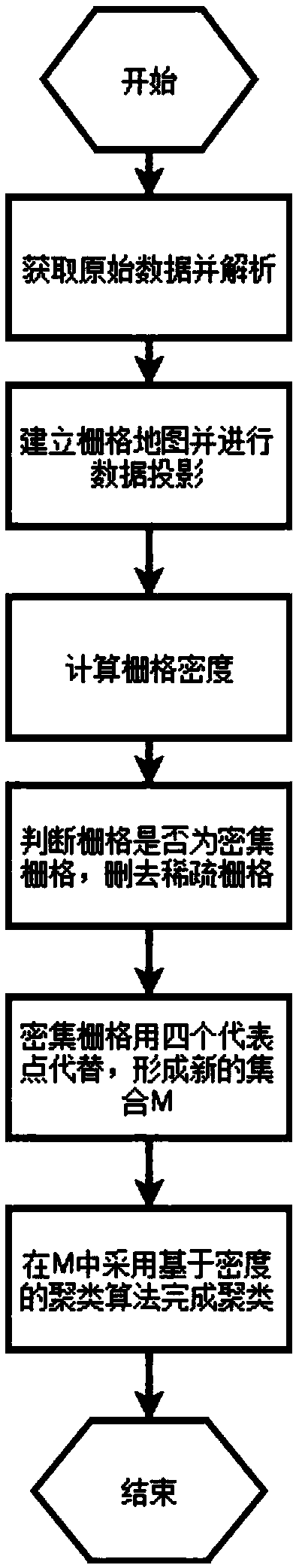
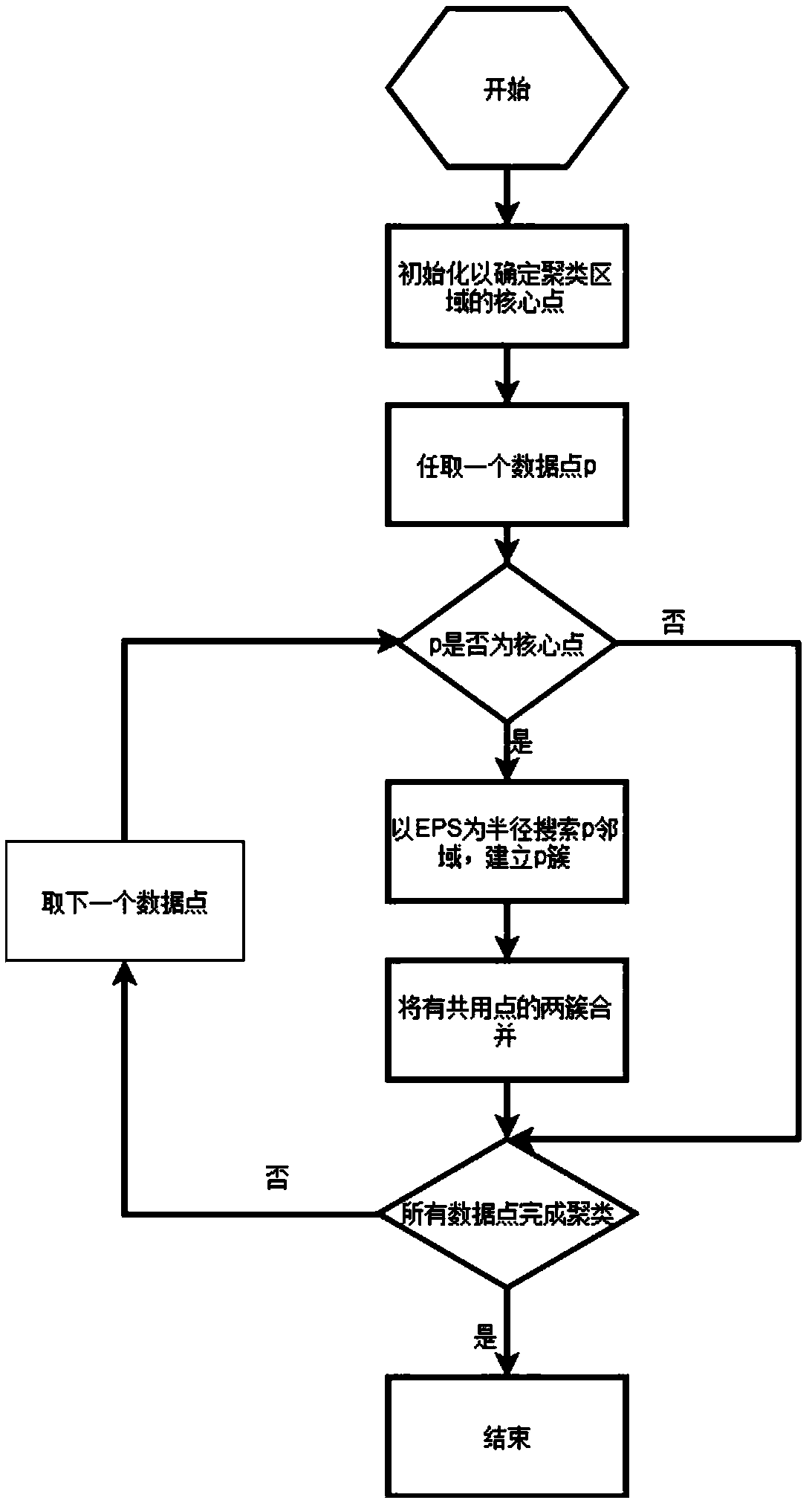
Lidar target detection method based on grid and density clustering algorithm
ActiveCN109101892ASolve the shortcomings of large amount of point cloud dataReduce search timeImage enhancementImage analysisCluster algorithmGrid density
The invention discloses a laser radar target detection method based on grid and density clustering algorithm, which comprises the following steps: 1, obtaining the original data of the laser radar andanalyzing; 2, establishing a grid map and projecting data; 3, calculating the grid density, judging whether the grid is a dense grid or not, and deleting the sparse grid; 4, replacing the dense gridwith four representative points to generate a new set; 5, adopting a density-based clustering algorithm to complete clustering in the new set. The detection method combines the grid algorithm and density clustering algorithm to solve the problem of large amount of point cloud data in an lidar object detection algorithm, reduce the search time of traditional clustering algorithm, and has the characteristics of fast and efficient.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
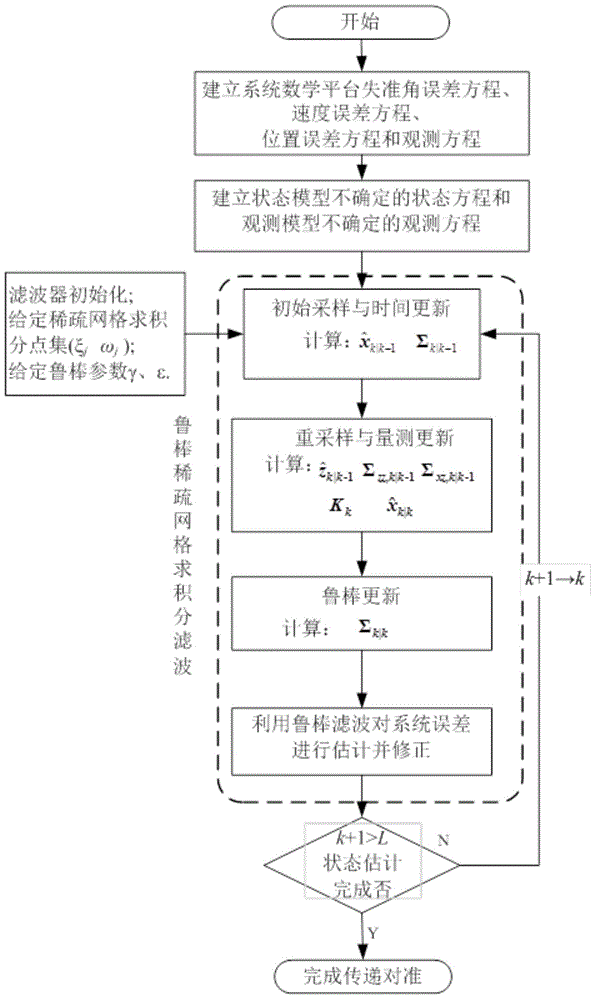
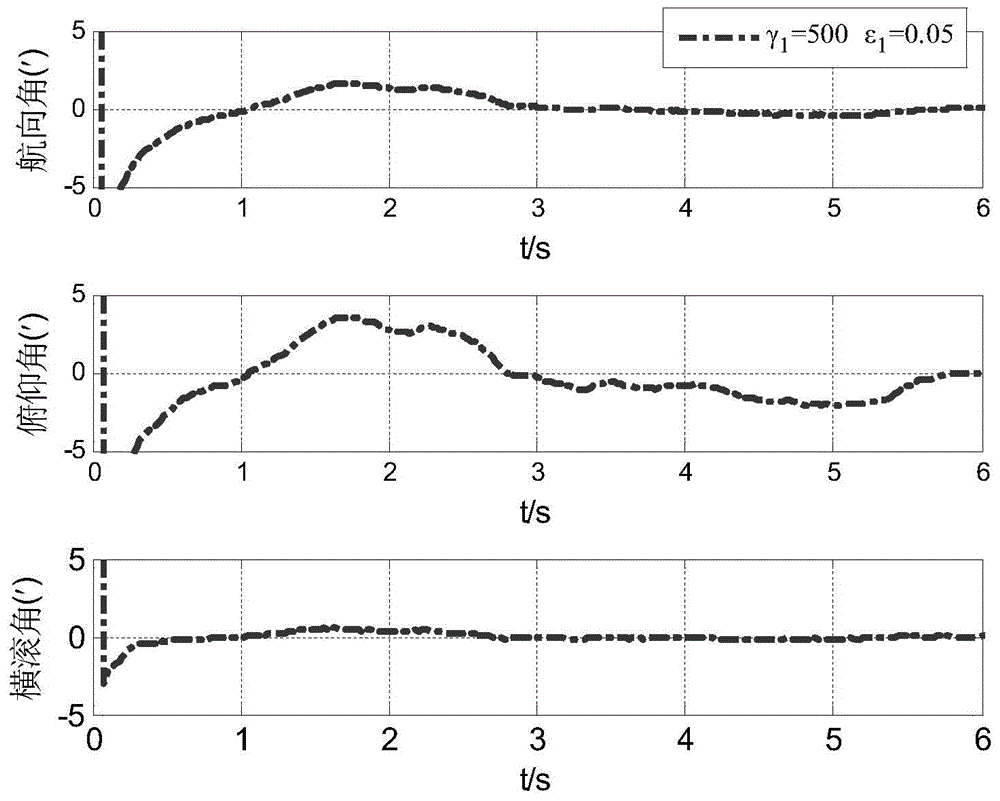
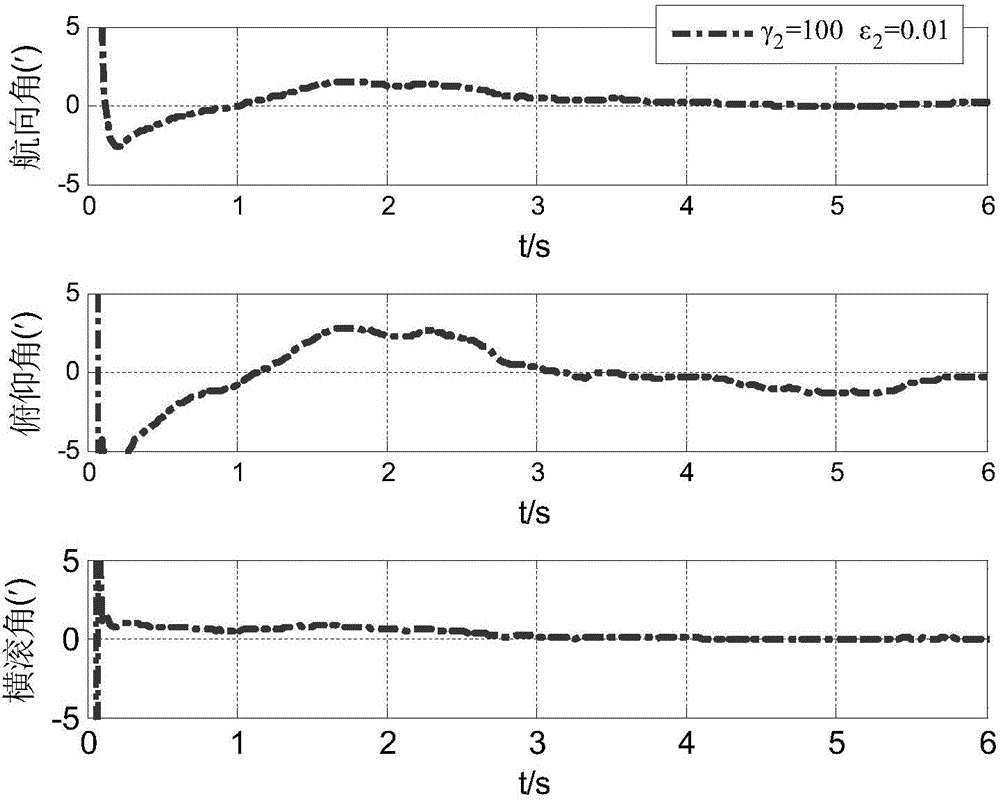
Robust filtering method of near space aerocraft transfer alignment model uncertainty
ActiveCN104613984AHigh precisionImprove robustnessNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsSparse gridEquation of state
The invention discloses a robust filtering method of near space aerocraft transfer alignment model uncertainty. The method comprises the following four steps: step 1, based on working principle and characteristics of a near space aerocraft transfer alignment system, establishing a math platform misalignment angle error equation, a velocity error equation, a position error equation and an observation equation of the system; step 2, establishing a state equation and the observation equation of model uncertainty according to the error equation of the system; step 3, providing a state variable initial value (x0) and a forecast error variance matrix initial value (sigma 0|0), providing a sparse grid quadrature point set (zeta j, epsilon j; j=1, 2,... Np), and providing robust filtering parameters gamma and epsilon; and step 4, estimating system state by robust filtering, performing error correction for a secondary inertial navigation system, and finishing the transfer alignment process. The method provided by the invention is applicable for transfer alignment in the case that primary and secondary inertial navigation systems have model uncertainty when the near space aerocraft is in dynamic state.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Cancer subtype precise discovery and evolution analysis method based on data stream clustering
The invention provides a cancer subtype precise discovery and evolution analysis method based on data stream clustering. The method comprises the following steps of (a) initialization of gene expression data stream; (b) online real-time clustering of the gene expression data stream: putting each reachable data point into a corresponding grid cell; performing online grid maintenance; and when the specific time node is reached, deleting a sparse grid according to the grid density information; (c) offline precise clustering of the gene expression data stream: regarding the grid as a virtual data point with the density information; clustering the virtual data point by using a clustering method based on density-distance distribution; performing fast clustering division on other data points according to the density information of the determined clustering center points; and finally outputting a clustering result; and (d) class cluster evolution migration analysis. The invention provides the cancer subtype precise discovery and evolution analysis method based on data stream clustering with high precision.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
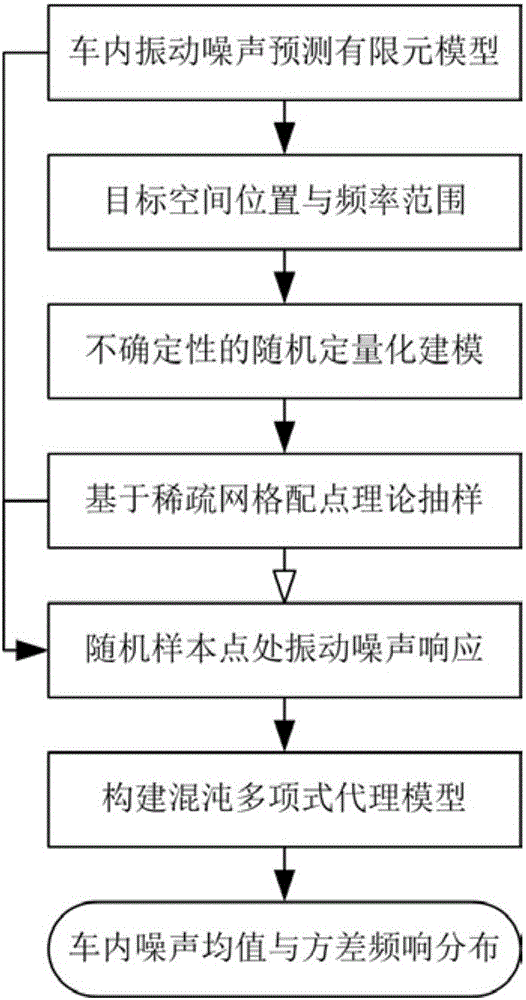
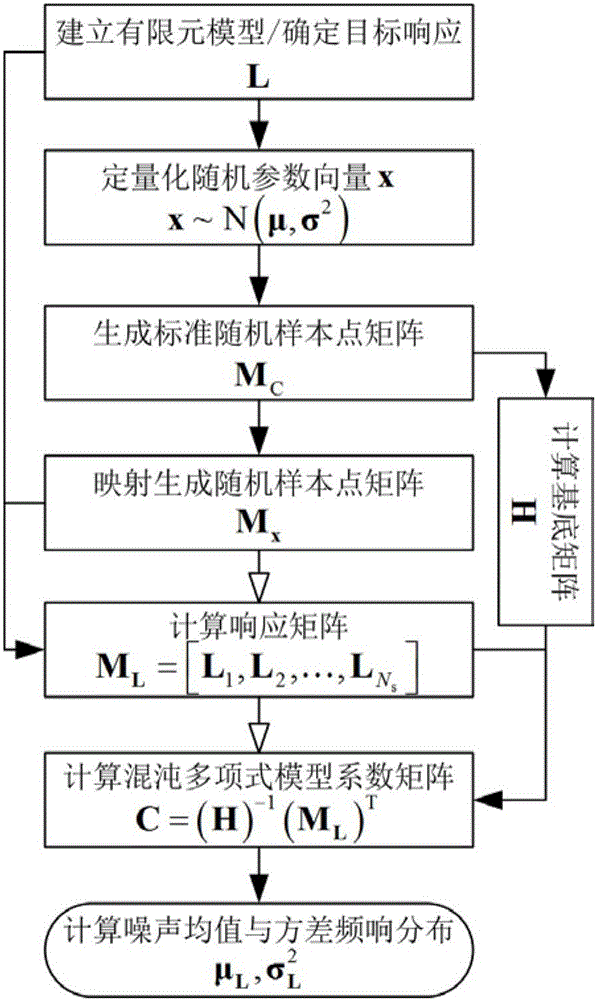
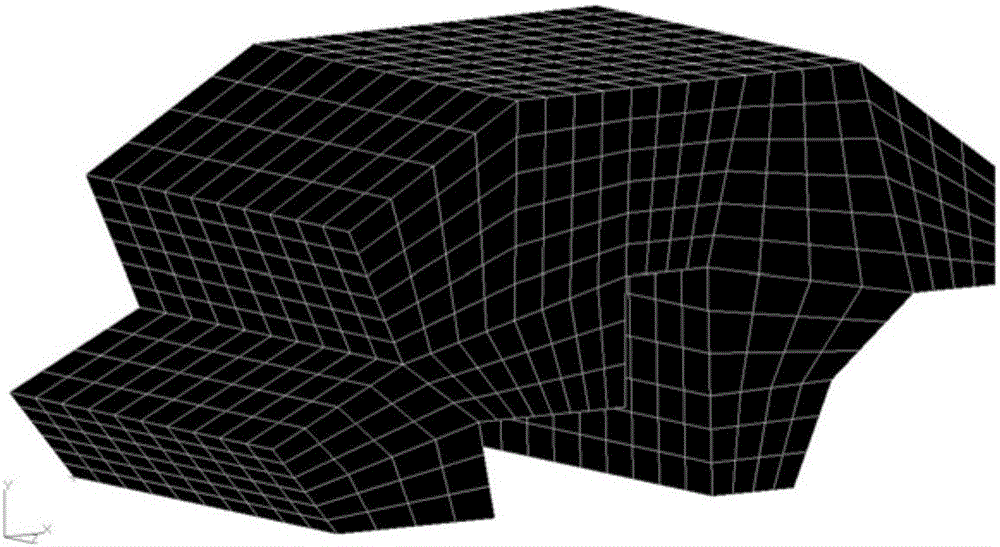
In-car random vibration noise prediction method based on sparse grid point collocation theory
InactiveCN105956283AImprove calculation accuracySustainable transportationDesign optimisation/simulationDielectricElement model
The invention discloses an in-car random vibration noise prediction method based on a sparse grid point collocation theory. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, according to the practical requirements of an engineering field, establishing a finite element model for in-car random vibration noise prediction, and determining a target spatial position and a target frequency range; secondly, after a random model realizes the quantification of relevant uncertainty, sampling random parameters on the basis of the sparse grid point collocation theory, and utilizing the finite element model for the in-car random vibration noise prediction to calculate a response value on each random parameter sample point; and finally, according to a discrete scheme response value, calculating to obtain the coefficient matrix of a polynomial chaos expansion agent model responded by the in-car random vibration noise, and furthermore, calculating to obtain the mean value frequency response distribution and the variance frequency response distribution of the in-car random vibration noise on the basis of the coefficient matrix. The method simultaneously considers the random effect on the in-car random vibration noise by external load and structure material parameters and air dielectric characteristic parameters, and provides a basis for formulating noise reduction measures including in-car noise optimization and control and the like.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
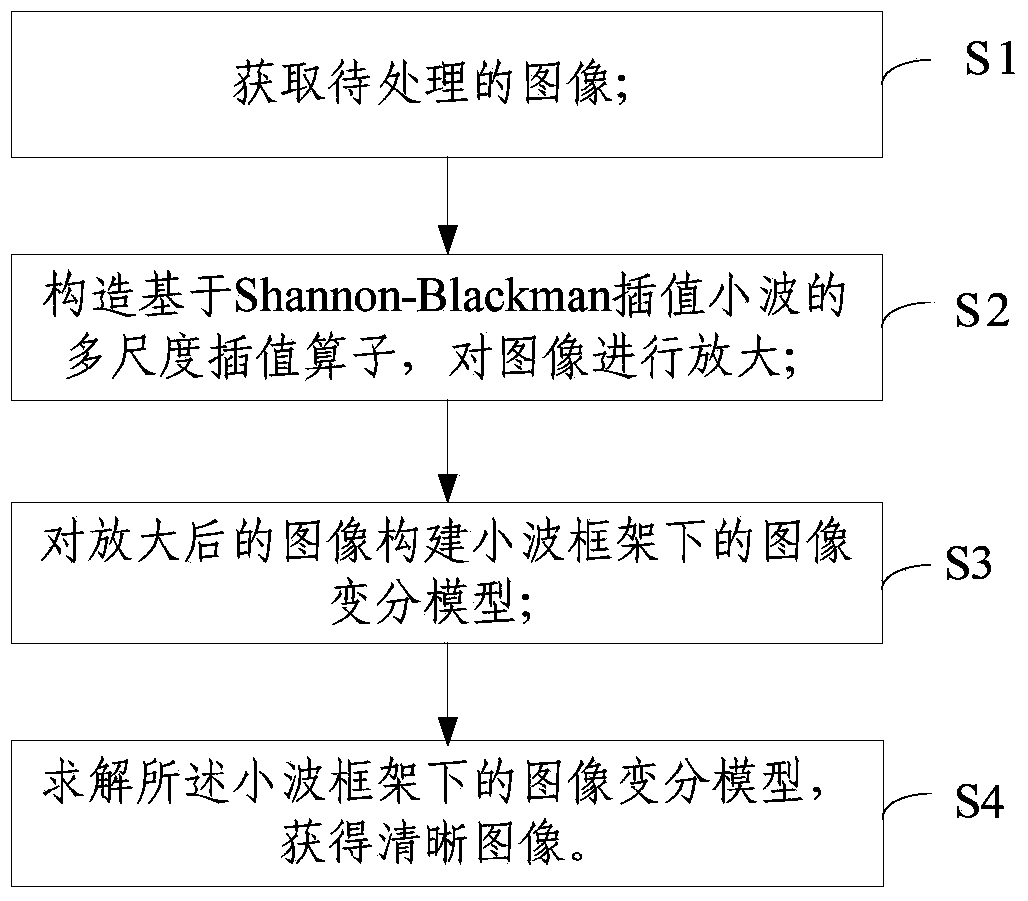
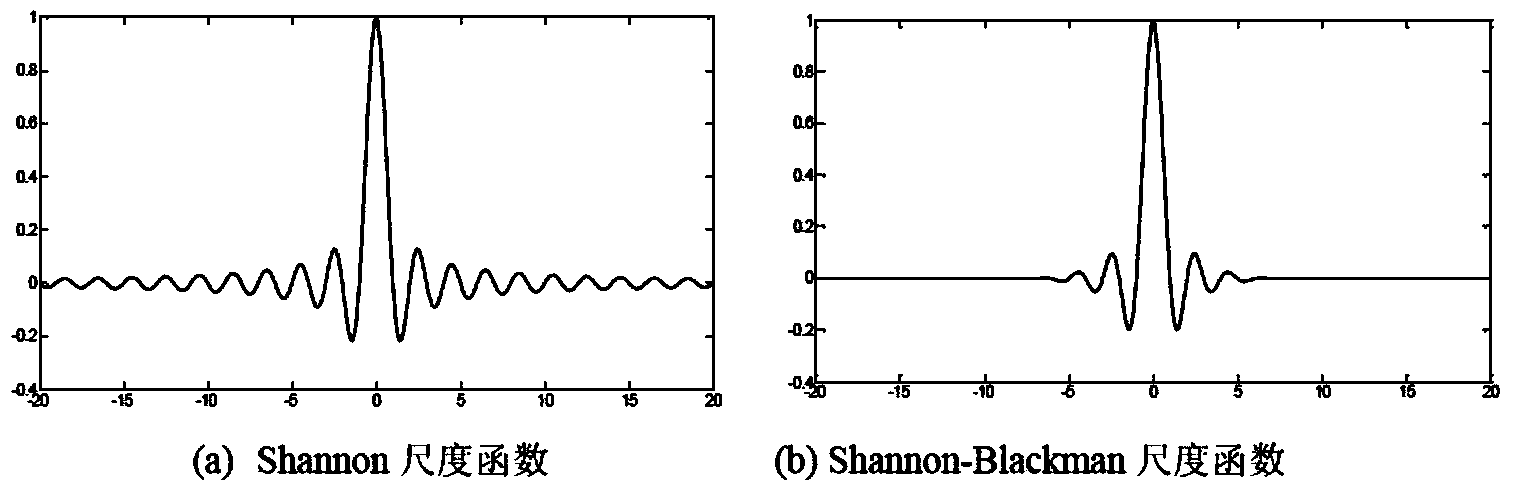
Image processing method and device based on Shannon-Blackman wavelet sparse representation
ActiveCN104392411AImprove super resolutionImplement adaptive configurationGeometric image transformationImaging processingSparse grid
The invention discloses an image processing method and device based on Shannon-Blackman wavelet sparse representation. The method comprises steps as follows: a to-be-processed image is acquired; a multi-scale interpolation operator based on Shannon-Blackman interpolating wavelets is established, and the image is amplified; an image variation model for the amplified image under a wavelet frame is established; and the image variation model under the wavelet frame is solved to obtain a sharp image. According to the Shannon-Blackman wavelet sparse representation based image processing method and device, the image is amplified through the multi-scale interpolation operator, the image variation model under the wavelet frame is established, the image is solved through a sparse grid algorithm to obtain a super-resolution image, and the image processing efficiency and accuracy are improved.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
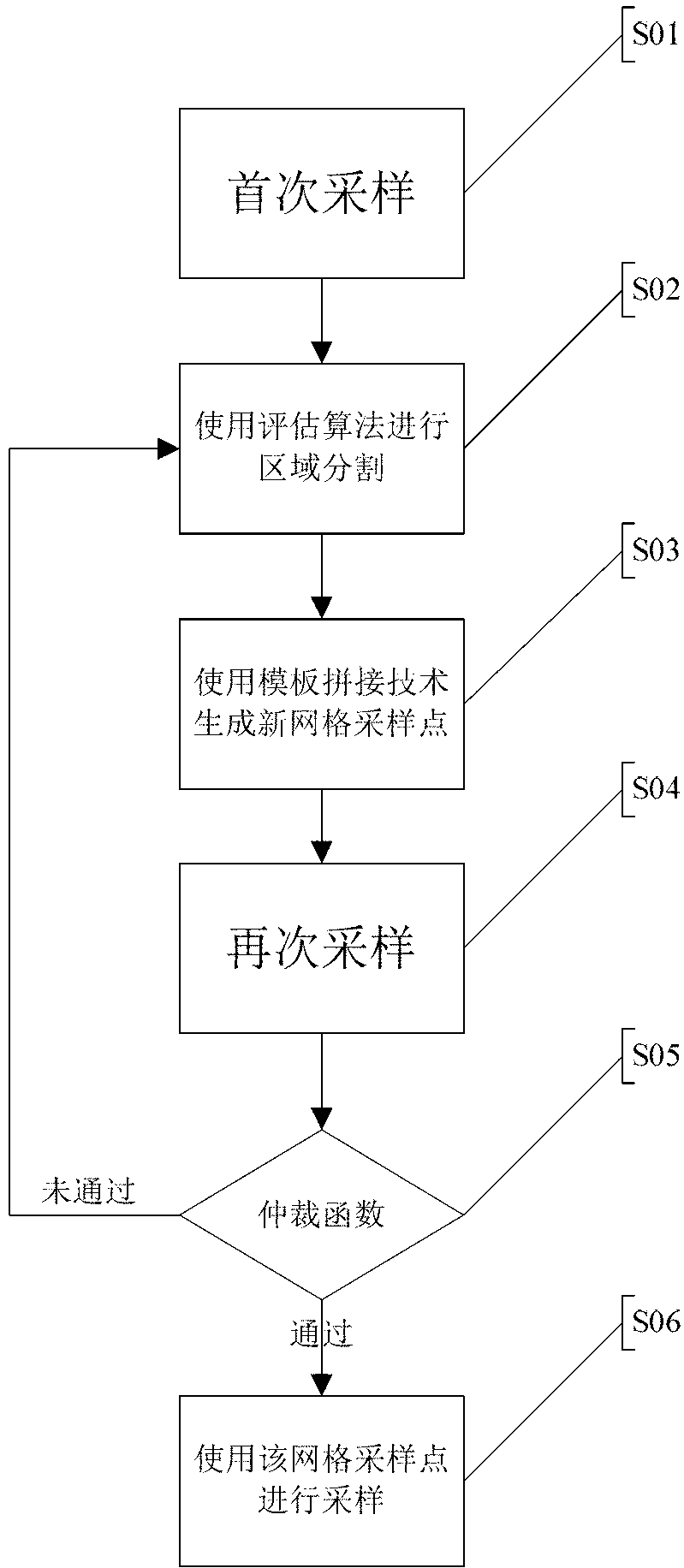
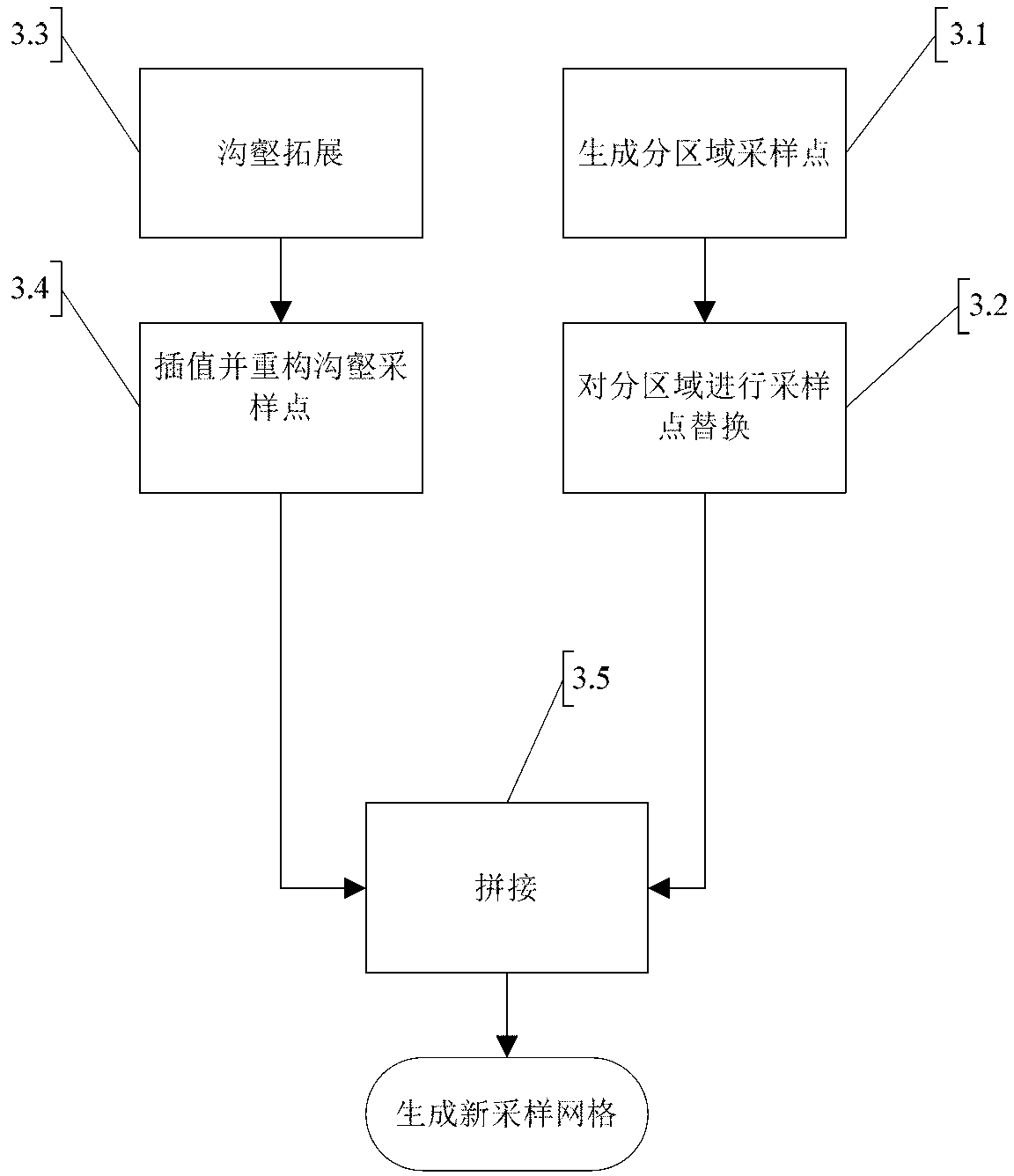
Adaptive technology based two-dimensional plane sampling method
InactiveCN103310447ARealize regional samplingThe number of sampling points is smallImage analysisSparse gridSelf adaptive
The invention relates to an adaptive technology based two-dimensional plane sampling method. The method includes firstly, using a uniform sparse grid for performing first sampling, evaluating sampling results by the aid of an evaluation algorithm to obtain sub-regions of different frequency ranges, and replacing grid measuring points of each sub-region; secondly, using a newly generated grid for performing second sampling on the surface of a sampled object, using the evaluation algorithm for evaluating measuring results again, and modifying the gird according to frequency magnitude; thirdly, modifying repeatedly in the way until the grid passes the evaluation algorithm; and finally sampling the surface of an object needing sampling by a measuring system according to the measuring grid. By the method, the number of sampling points can be guaranteed to be minimized, and sampling effect can be guaranteed to be optimal under the condition of the same number of sampling points.
Owner:INST OF OPTICS & ELECTRONICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Automatic layout winding method based on pre-winding, storage device and system
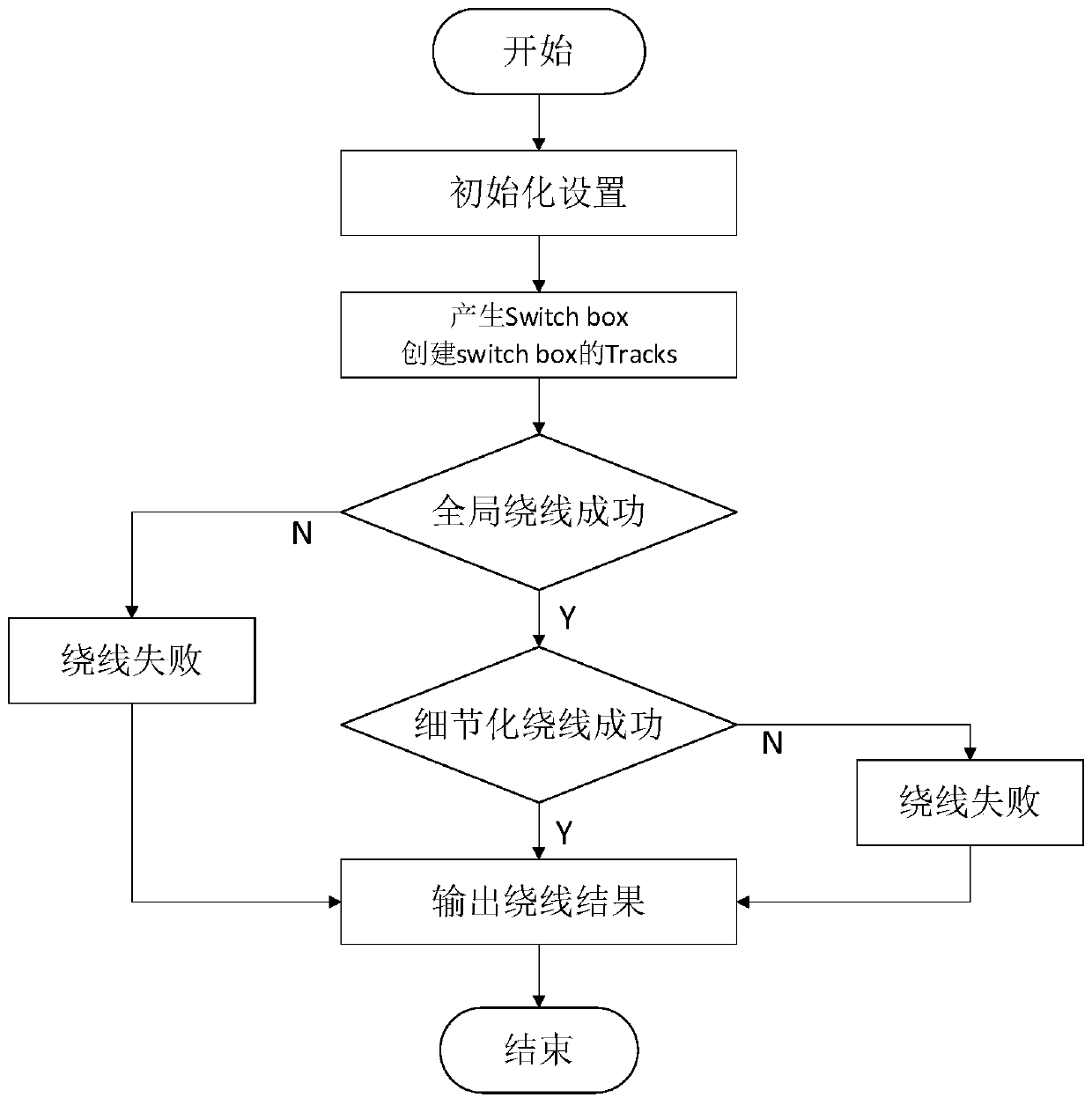
ActiveCN111027273AImprove efficiencyImprove exploration efficiencyComputer aided designSpecial data processing applicationsSwitch boxControl engineering
The invention relates to an automatic layout winding method and system based on pre-winding, and a storage equipment. The automatic layout winding method specifically comprises the following steps: (1) initializing winding information; (2) creating a switch box; (3) creating a winding track and nodes; creating a winding track to perform grid division on the winding area, and setting intersection points of the winding track as nodes; (4) carrying out global winding; (5) carrying out detailed winding; and carrying out detailed winding processing on all the networks to be wound passing the globalwinding to obtain a winding result. According to the invention, during detailed winding, sparse grids are divided according to winding tracks created by a switch box and pins, the node path exploration efficiency is improved, penalty values of related nodes are increased according to the pins to be wound in a subsequent network to be wound, certain windings are reserved for subsequent winding, and the problem of winding conflicts generated in the winding process can be well solved.
Owner:SEMITRONIX
Local grid and photon encryption method in radiation energy propagation Monte-Carlo algorithm
ActiveCN104699993AImprove computing efficiencySpecial data processing applicationsOptical propagationVoxel
Owner:上海积鼎信息科技有限公司
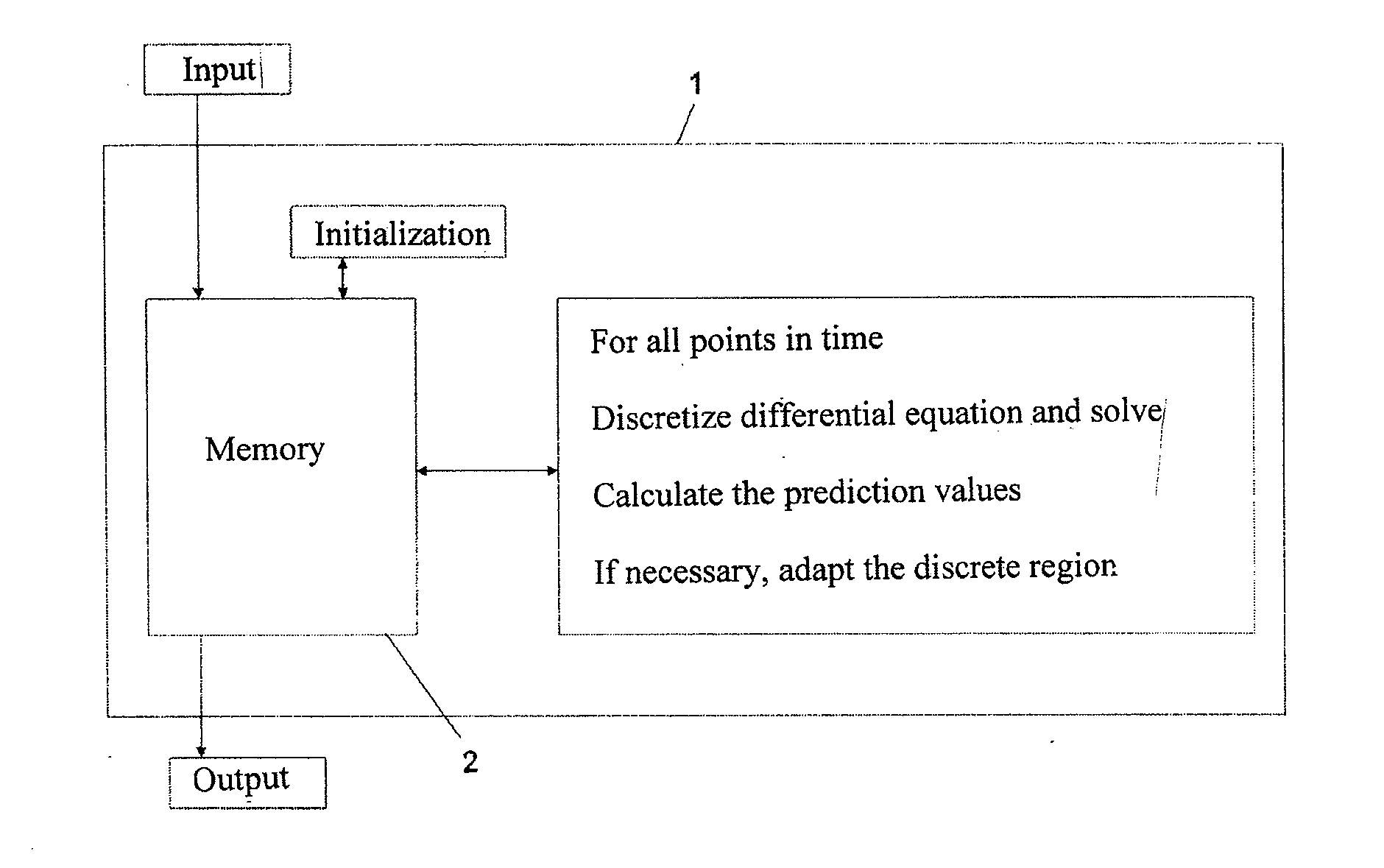
Method and device for tracking the path of motion of a moving object as well as computer program and data storage media
ActiveUS20110270592A1Efficient executionComputation using non-denominational number representationComplex mathematical operationsComputational probabilityPathPing
Method, device, computer program and computer program product for tracking the path of motion of a moving object. The method includes a) providing data of at least one state variable to be determined, which influences the movement of the moving object, at a first point in time; b) initializing the probability density (p) of the at least one state variable to be determined at the first point in time; c) predicting of the probability density (p) of the at least one state variable to be determined at a next point in time after the first point in time; d) verifying of whether measurement data are available that can be used for a calculation of the probability density (p) of the at least one state variable to be determined, and d′) recalculating the probability density (p) with these measurement data when such data is available; e) calculating the prediction values of the state variable(s) to be determined from the probability density (p); f) outputting the calculated prediction values to a downstream data processing device; and g) repeating the steps c) through f). The steps of initializing the probability density (p) of step b); predicting the probability density (p) of step c); recalculating the probability density (p) of step d′); and calculating the prediction values of step e) are performed by discretizing the probability density (p) on sparse grids.
Owner:MBDA DEUTSCHLAND GMBH
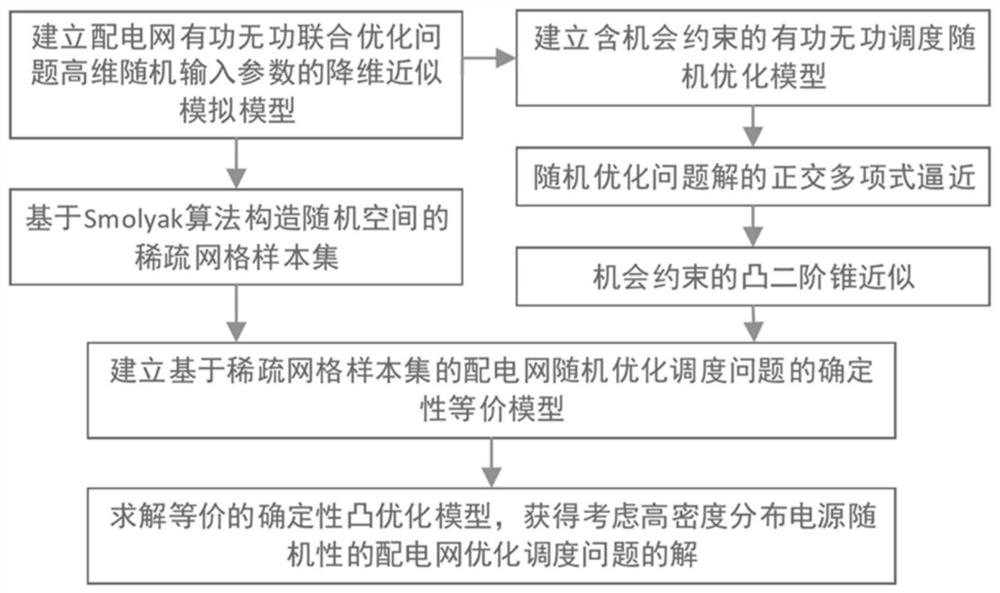
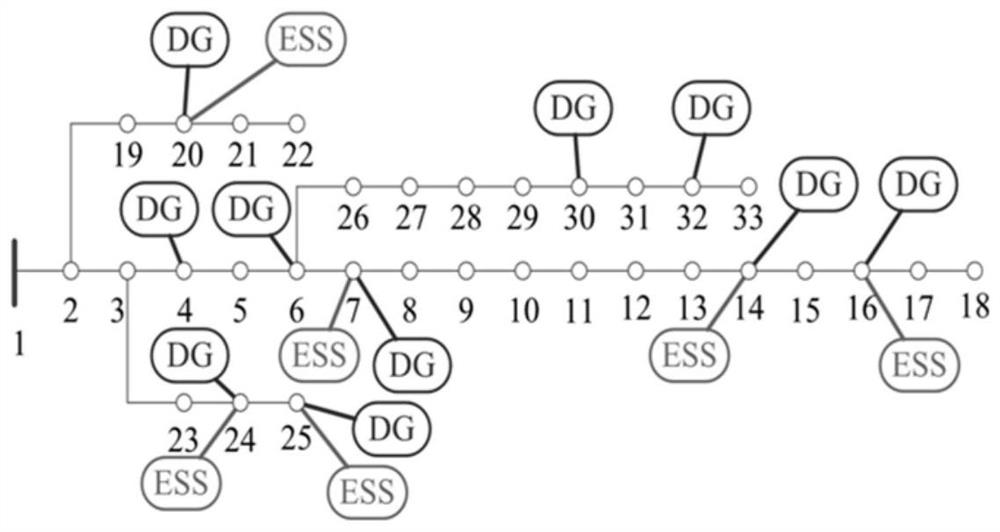
Power distribution network optimization scheduling method considering random output of high-density distributed power supply
ActiveCN111900715AMeet actual operating needsGuaranteed feasibilityLoad forecast in ac networkSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsHigh densityPower flow
The invention discloses a power distribution network optimization scheduling method considering random output of a high-density distributed power supply. The method comprises the steps ofcarrying outthe modeling of the random time sequence characteristics of the injection power of a wind and light distributed power supply at a power grid node, and carrying out the sampling of a random power flowspace based on a sparse grid point distribution theory,aiming at reducing active loss and node voltage deviation of the power distribution network, establishing a power distribution network active andreactive joint random optimization model containing power flow balance and opportunity constraints,and finally, conducting orthogonal polynomial approximation on a random space in the active and reactive power scheduling problem based on a spectral decomposition method. A convex approximate deterministic optimization model equivalent to a random optimization model is established, and a sample setcomposed of sparse nodes is utilized to approximate a random space optimal solution, so that the approximation precision of the solution is ensured, and the dimensionality disaster of the active andreactive joint optimization scheduling model of the power distribution network in a high-dimensional random parameter space is avoided. The method can be widely applied to power distribution network optimization scheduling under the influence of high-dimensional random factors, and improves the power distribution network power quality.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV CITY COLLEGE
Two-dimensional unwrapping method based on time sequence differential interference synthetic aperture radar data
ActiveCN111598929ASolve the difficulty that it is not suitable for data with large interferometric phase errorSuppress interferenceImage enhancementImage analysisRegular gridData set
The invention provides a two-dimensional unwrapping method based on time sequence differential interference synthetic aperture radar data. The method comprises the following steps: generating a time sequence SAR image data set; registering the time sequence SAR images; extracting high-coherence points of the registered time sequence SAR image data set; carrying out differential interference processing on the SAR images after time sequence registration; performing nearest neighbor interpolation on the interferometric phase diagram; performing phase unwrapping on each interpolation differentialinterferometric phase diagram; and extracting a high-coherence point unwrapping result. According to the method, phase data on high-coherence points in the differential interferogram are utilized instead of all phases, interference of points with large phase errors on the whole unwrapping process is eliminated, and therefore the phase unwrapping errors are reduced; sparse grid data and regular grid data are associated by adopting a nearest neighbor interpolation method, so that an original regular grid unwrapping method is suitable for sparse grids, only an original data processing flow needsto be slightly changed, and the method has a relatively high integration level.
Owner:YUNNAN POWER GRID CO LTD ELECTRIC POWER RES INST
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com