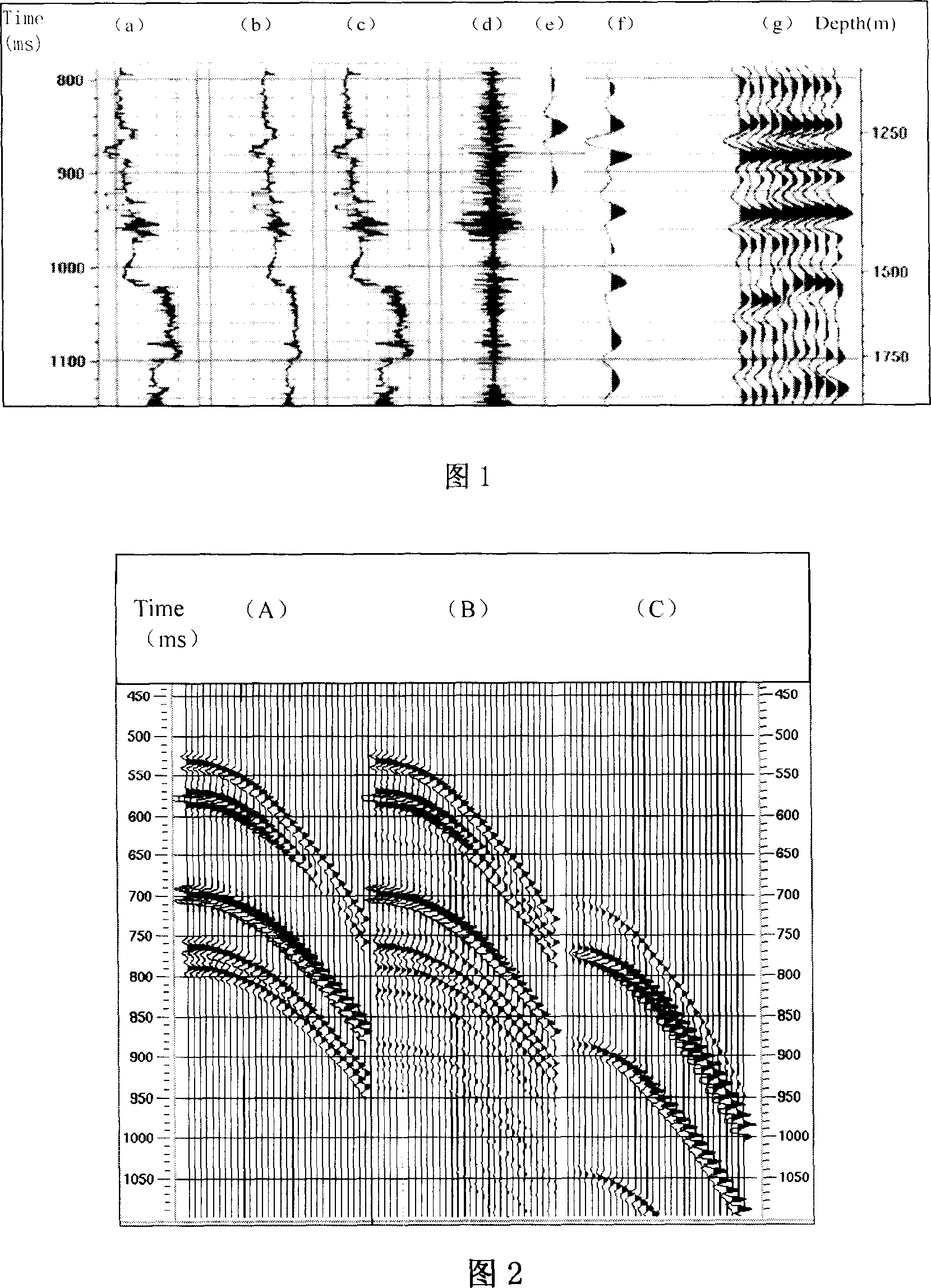
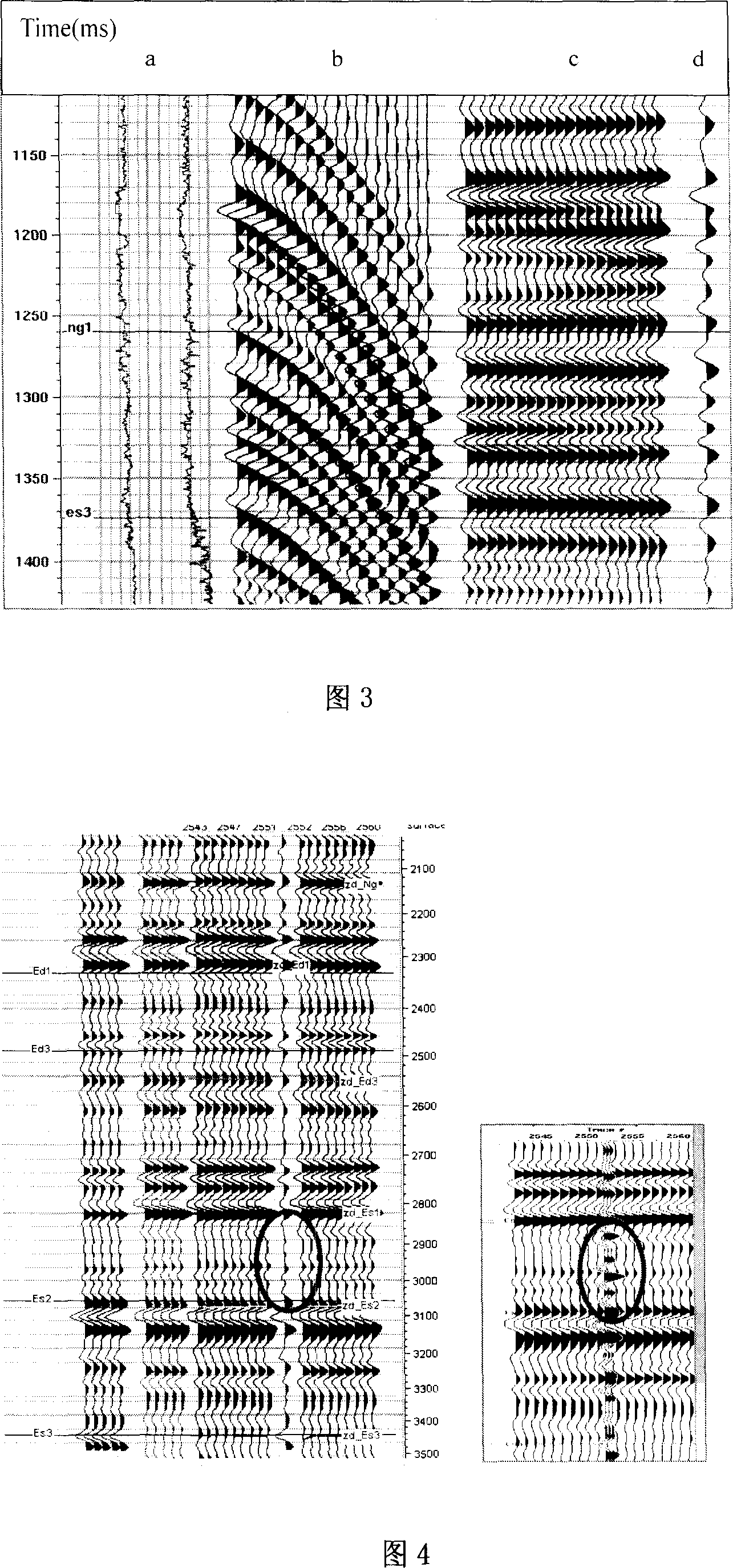
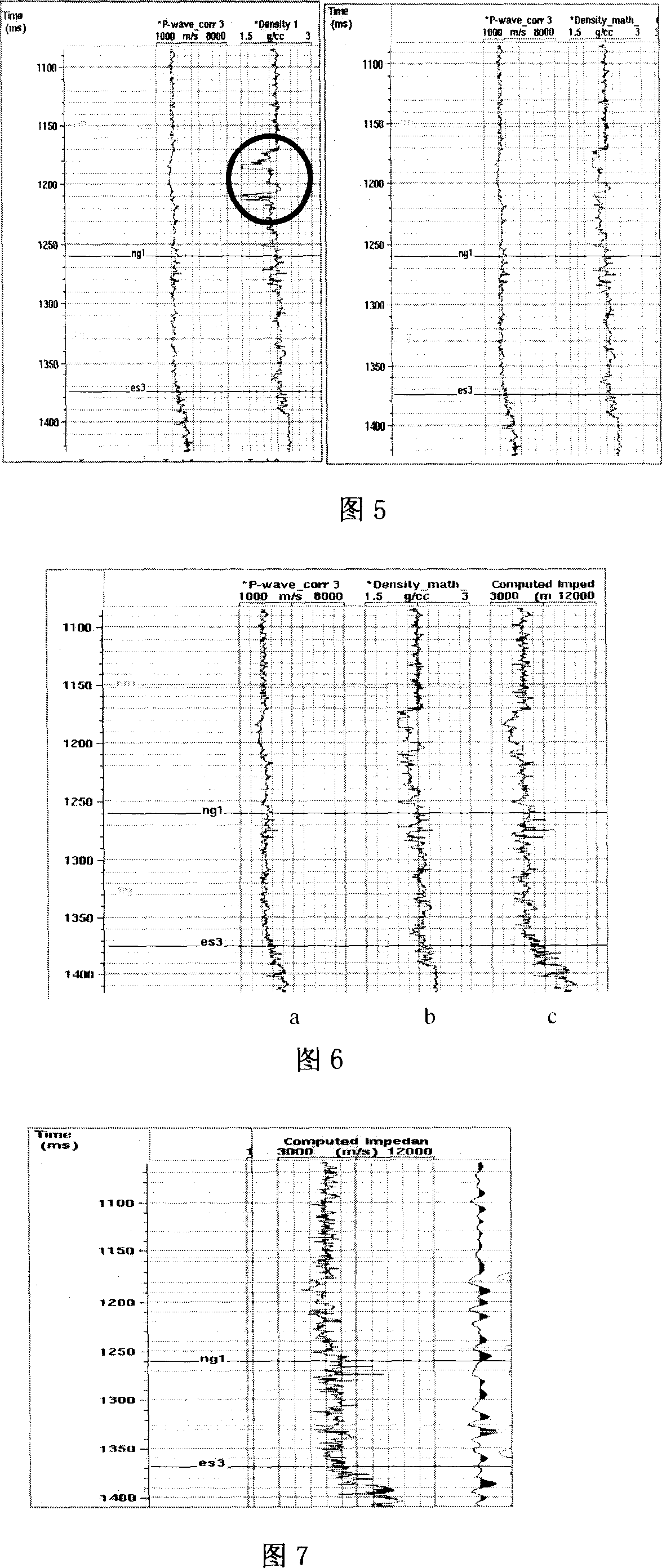
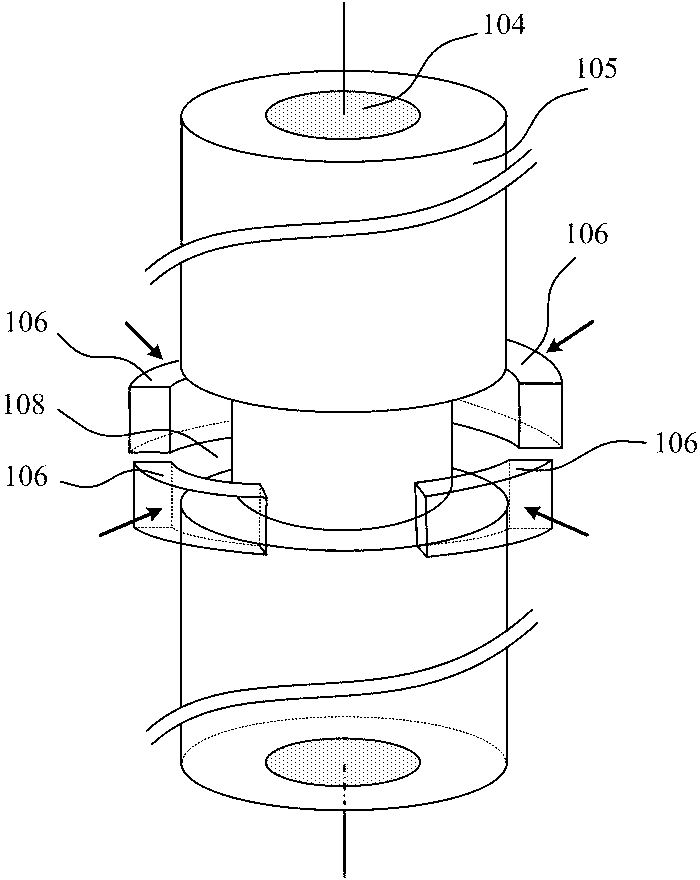
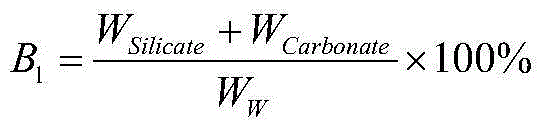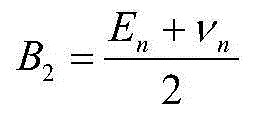Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
344 results about "Sonic logging" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
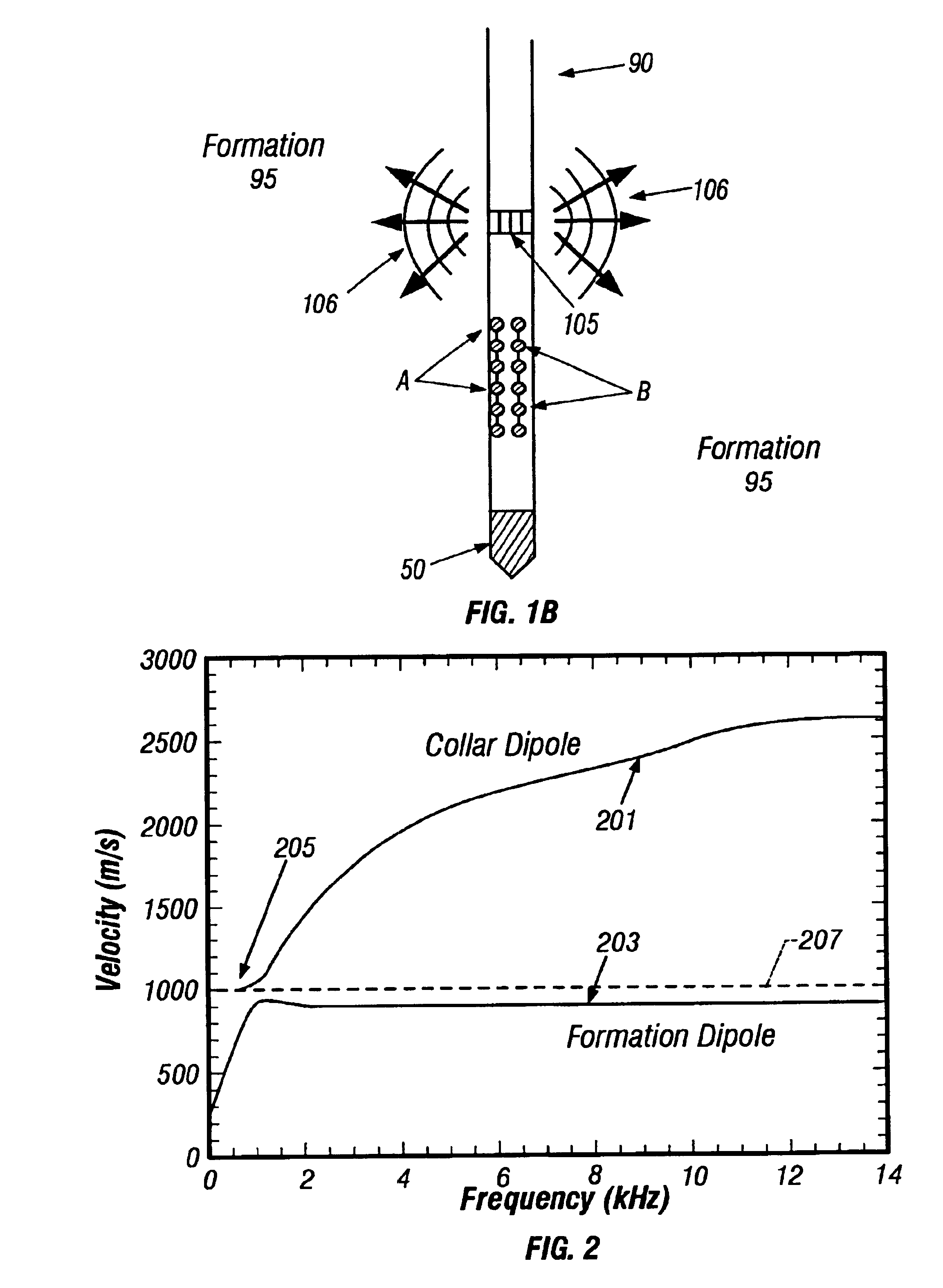
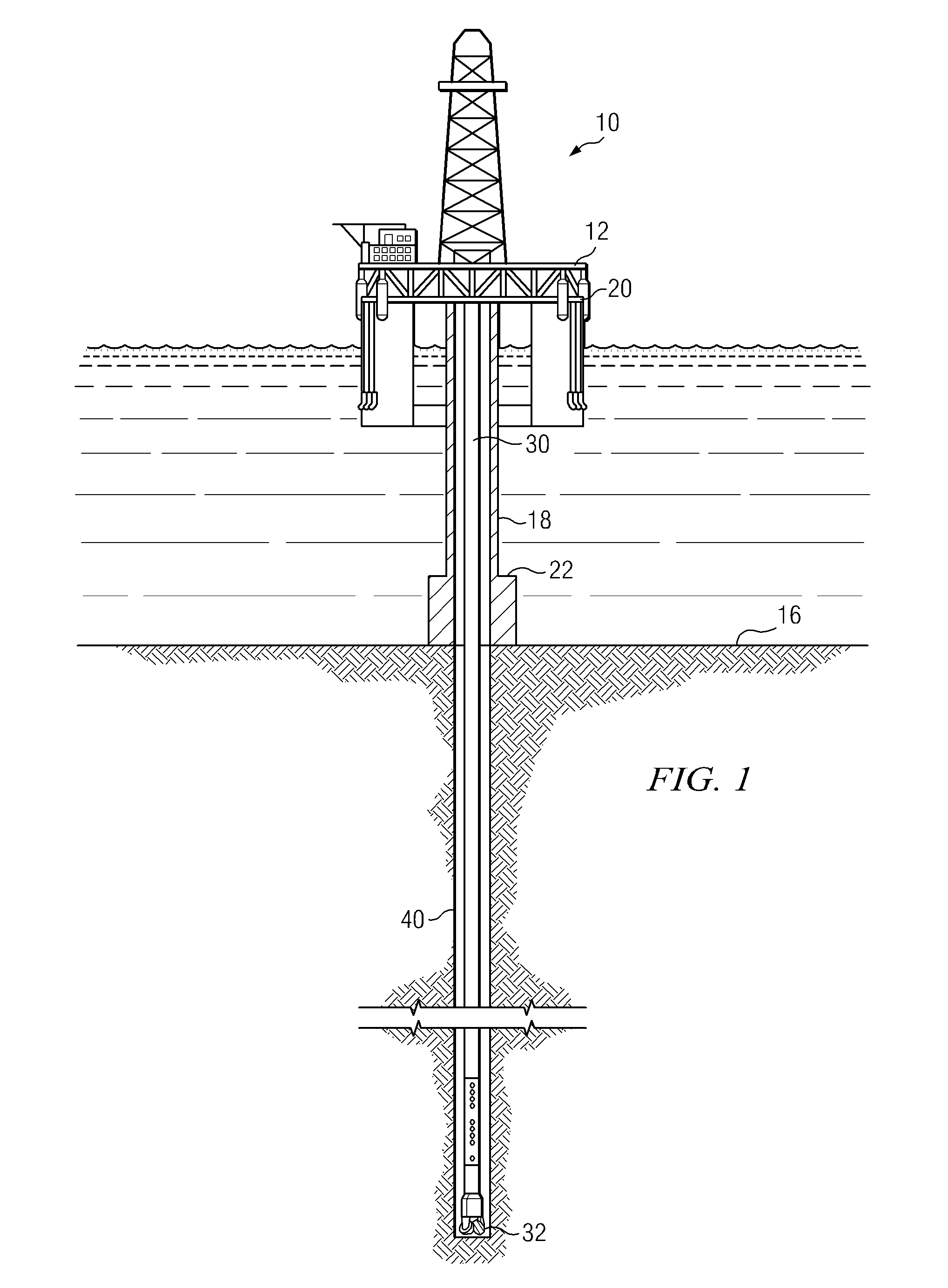
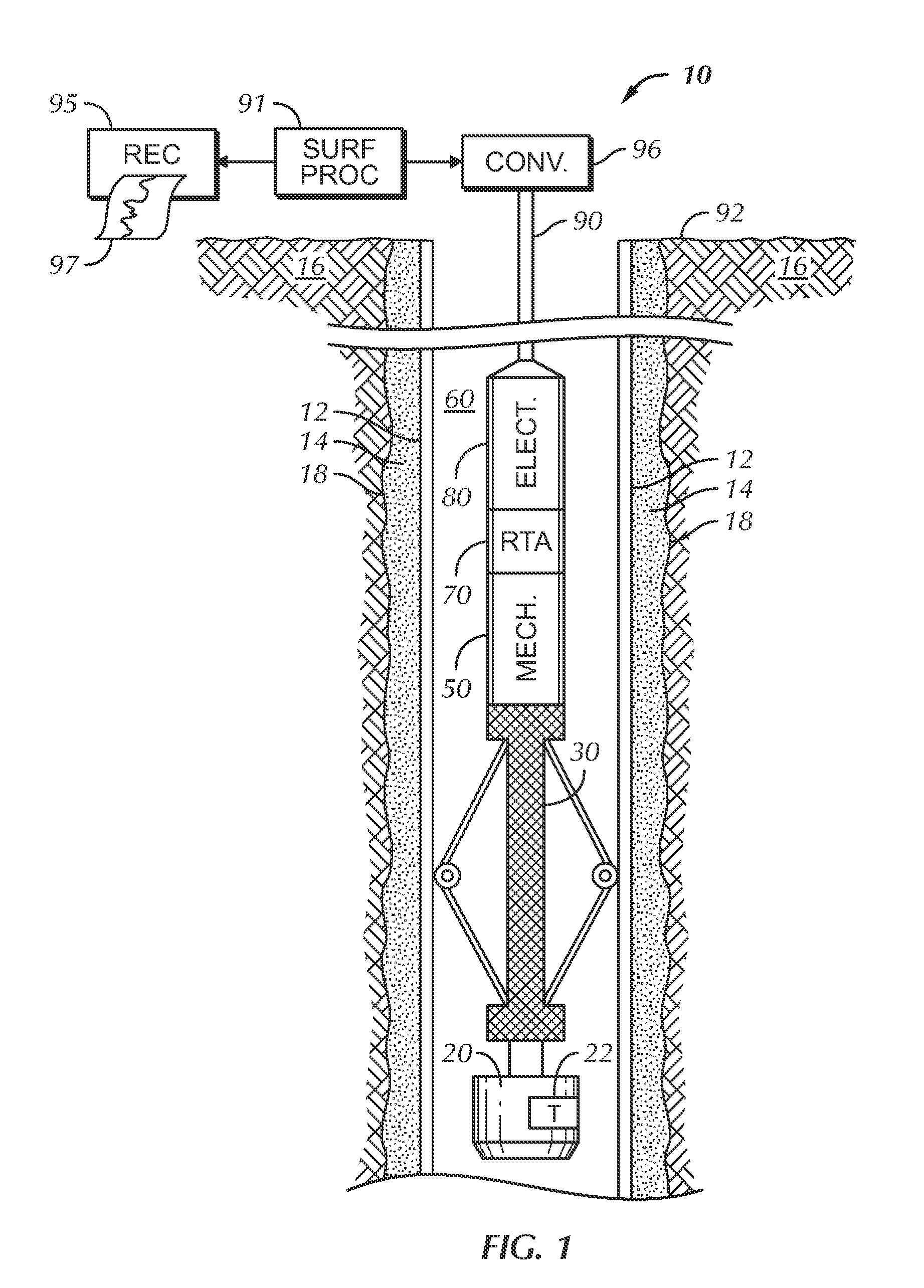
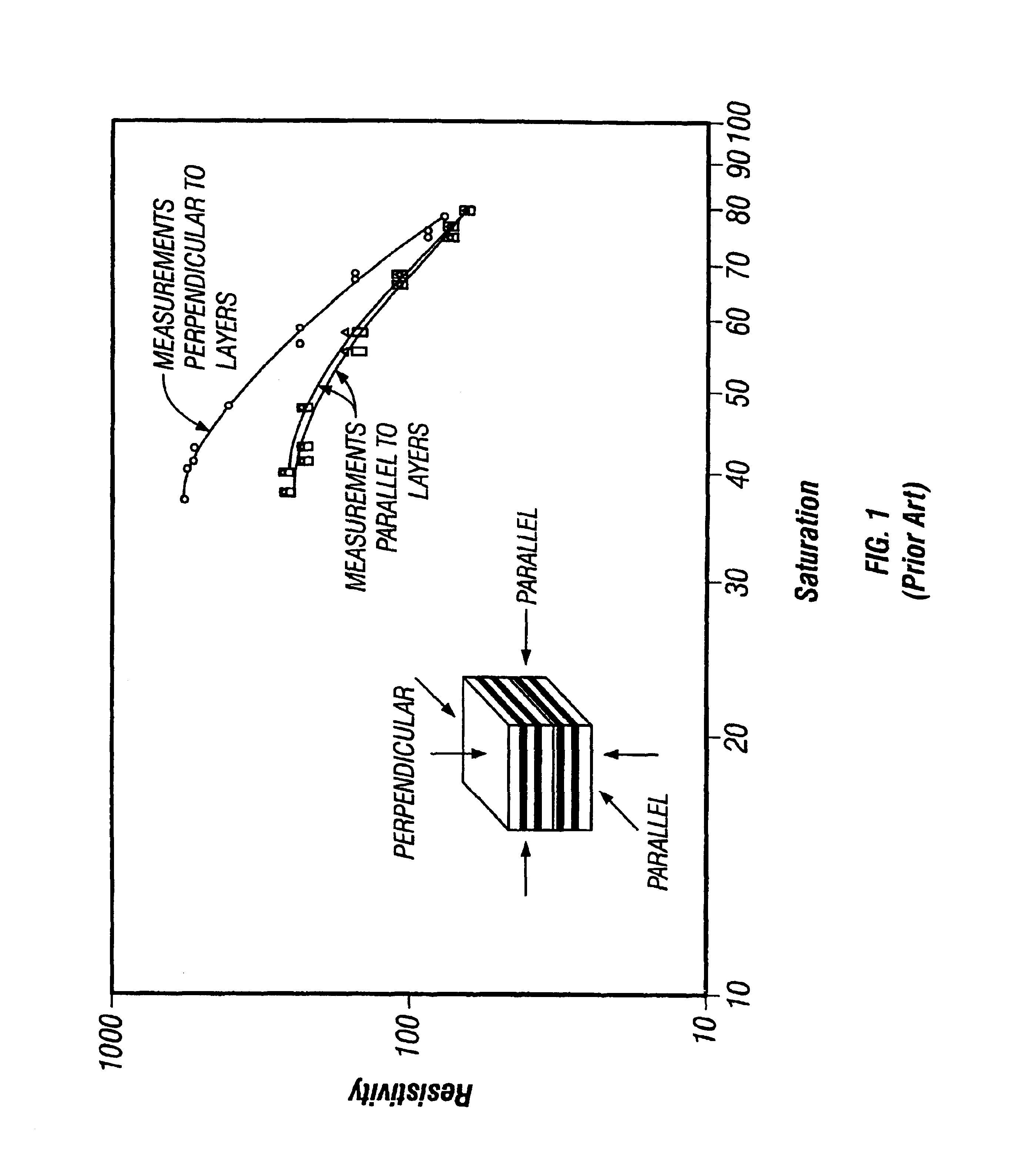
Sonic logging is a well logging tool that provides a formation’s interval transit time, designated as Δt, which is a measure of a formation’s capacity to transmit seismic waves. Geologically, this capacity varies with lithology and rock textures, most notably decreasing with an increasing effective porosity. This means that a sonic log can be used to calculate the porosity of a formation if the seismic velocity of the rock matrix, Vₘₐₜ, and pore fluid, Vₗ, are known, which is very useful for hydrocarbon exploration.
Seismic exploration position calibration method based on prestack wave field simulation
InactiveCN101013161AImprove consistencyHigh precisionSeismic signal processingSeismology for water-loggingWave fieldReflected waves
The invention relates to the earthquake exploration position calibration technology based on the pre-stack wave field simulation, belonging to the seismic data processing and interpretation technology field in oil exploration. The invention considers the seismic information acquisition and processing impact, considers multiple waves and conversion waves action in the reflection waves, enhances the accuracy of integrated seismic records, and enhances the consistency of integrated seismic records and real seismic records, this approach including the following eight steps: filtering and editing of density and acoustic logging well curve; using density and acoustic logging well curve to calculate the wave impedance curve; using statistics sub wave to integrate the seismic records; comparing the integrated seismic records and well-side seismic road, properly stretching the logging well curve; using well-side seismic road and logging well reflection coefficient curve to extract certainty sub wave; using the reflection rate method to simulate the pre-stack common reflection points roads set; simulating the real seismic data processing, and obtaining the final integrated seismic records; using the final integrated seismic records and comparing with the well-side seismic road, to process seismic exploration position calibration.
Owner:DAGANG OIL FIELD OF CNPC
Acoustic logging-while-drilling device and acoustic logging-while-drilling method
InactiveCN103147747AThe control circuit is easy to implementWide applicabilitySurveyControl systemTransducer
The invention relates to an acoustic logging-while-drilling device and an acoustic logging-while-drilling method. The device comprises a drill collar, an acoustic wave transmitting transducer, a near-spacing acoustic wave receiving transducer, a sound insulator, far-spacing acoustic wave receiving transducer arrays and a control system, wherein acoustic wave signals radiated by the acoustic wave transmitting transducer are propagated in a well wall stratum at which the drill collar is positioned and outside a well; The near-spacing acoustic wave receiving transducer is used for receiving reflected wave signals reflected into the well by a stratum interface beside the well; and the first and second far-spacing acoustic wave receiving transducer arrays are used for receiving acoustic wave signals reflected into the well by the stratum interface beside the well and slide wave signals propagated along the well wall stratum; and the control system controls the acoustic wave transmitting transducer to transmit the acoustic wave signals and performs data processing on the acoustic wave signals of the near-spacing acoustic wave receiving transducer and the far-spacing acoustic wave receiving transducer arrays so as to obtain the lateral distance and azimuth from a well shaft to the stratum interface beside the well. The acoustic logging-while-drilling device is easy for realization of a control circuit, can be used for evaluating the distance and azimuth from a geologic structure body beside the well to the well shaft and is high in engineering application value.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (EAST CHINA)
Acoustic logging apparatus and method
InactiveUS6188961B1Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingSeismic signal processingAmbiguityTransducer
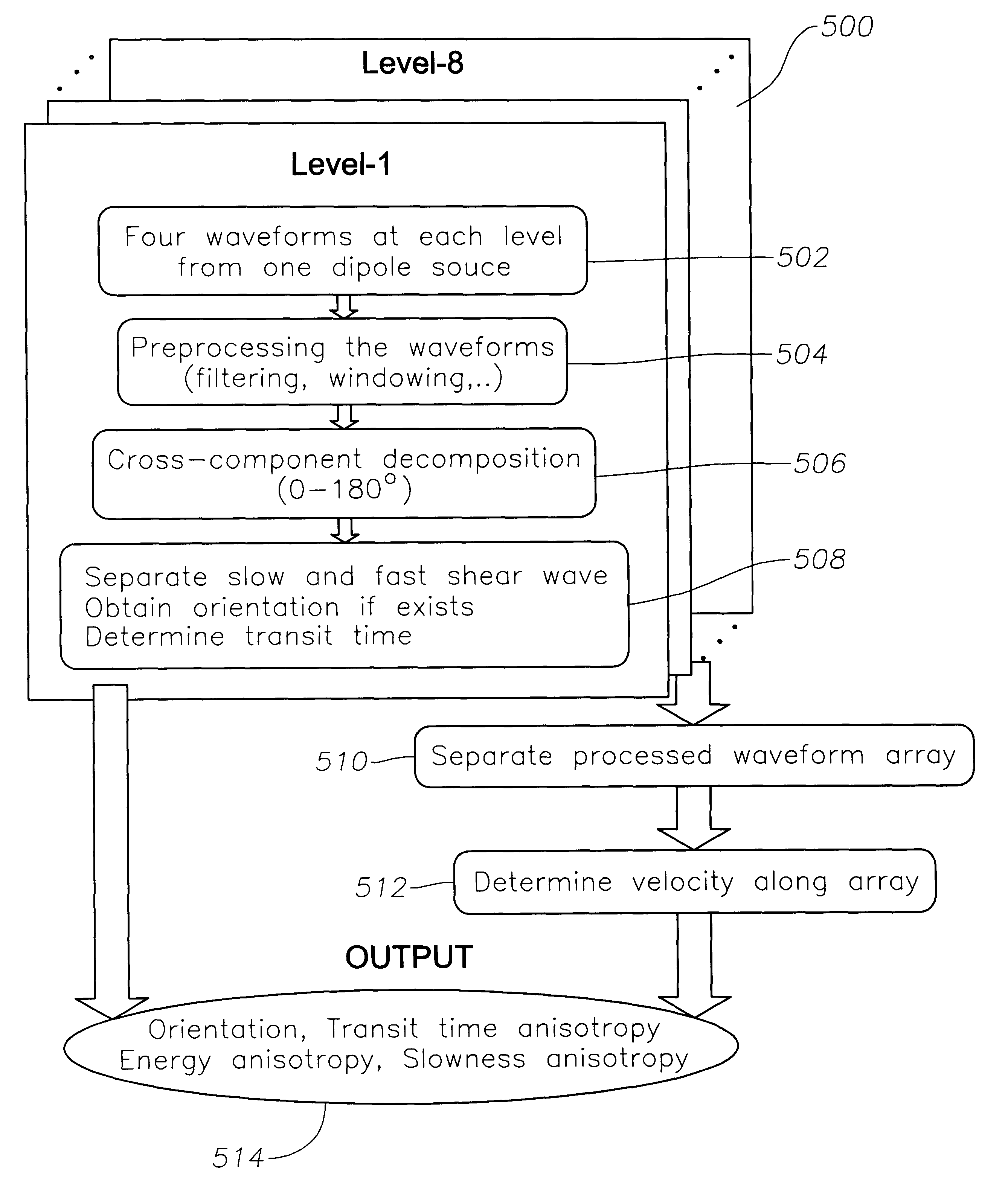
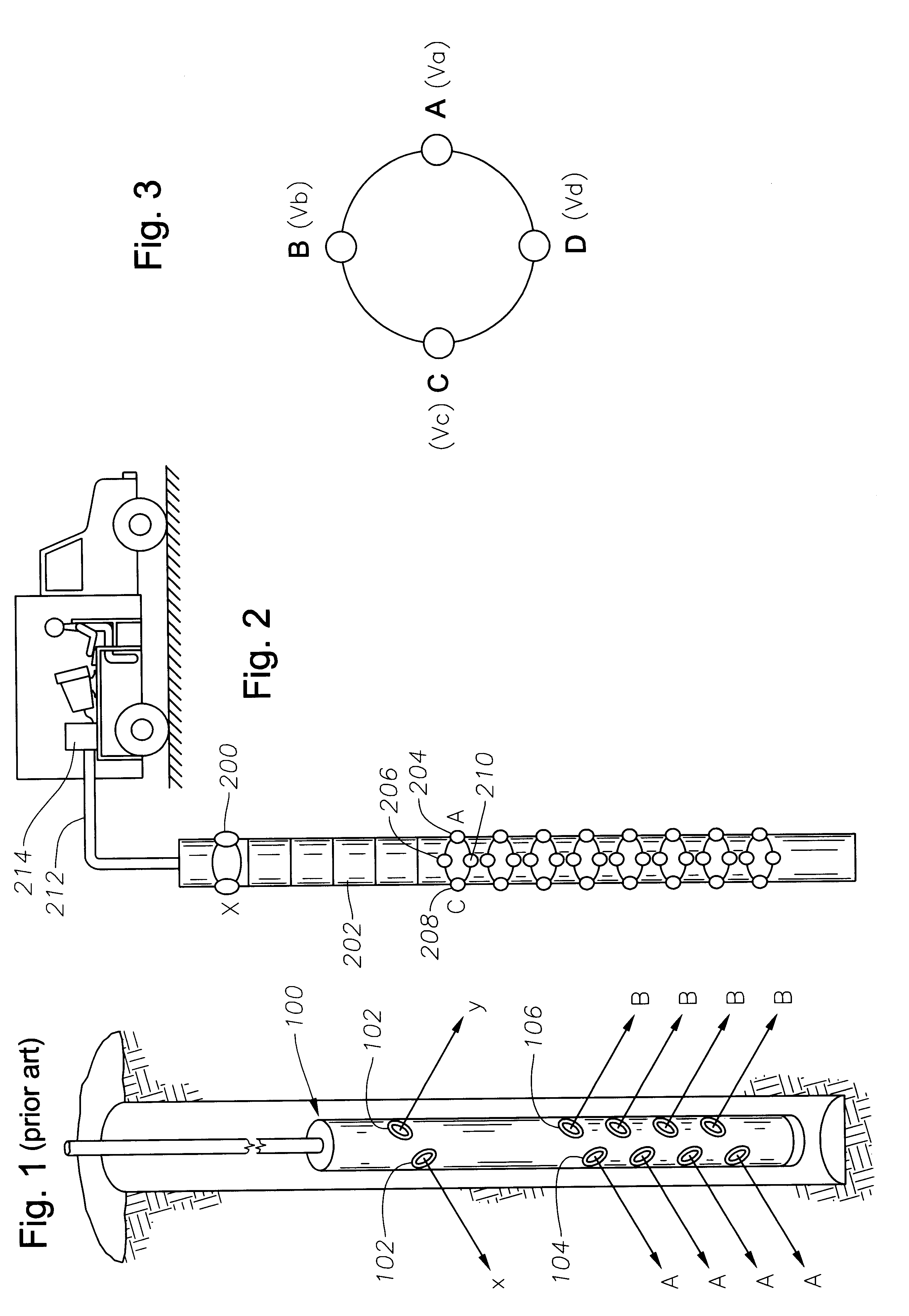
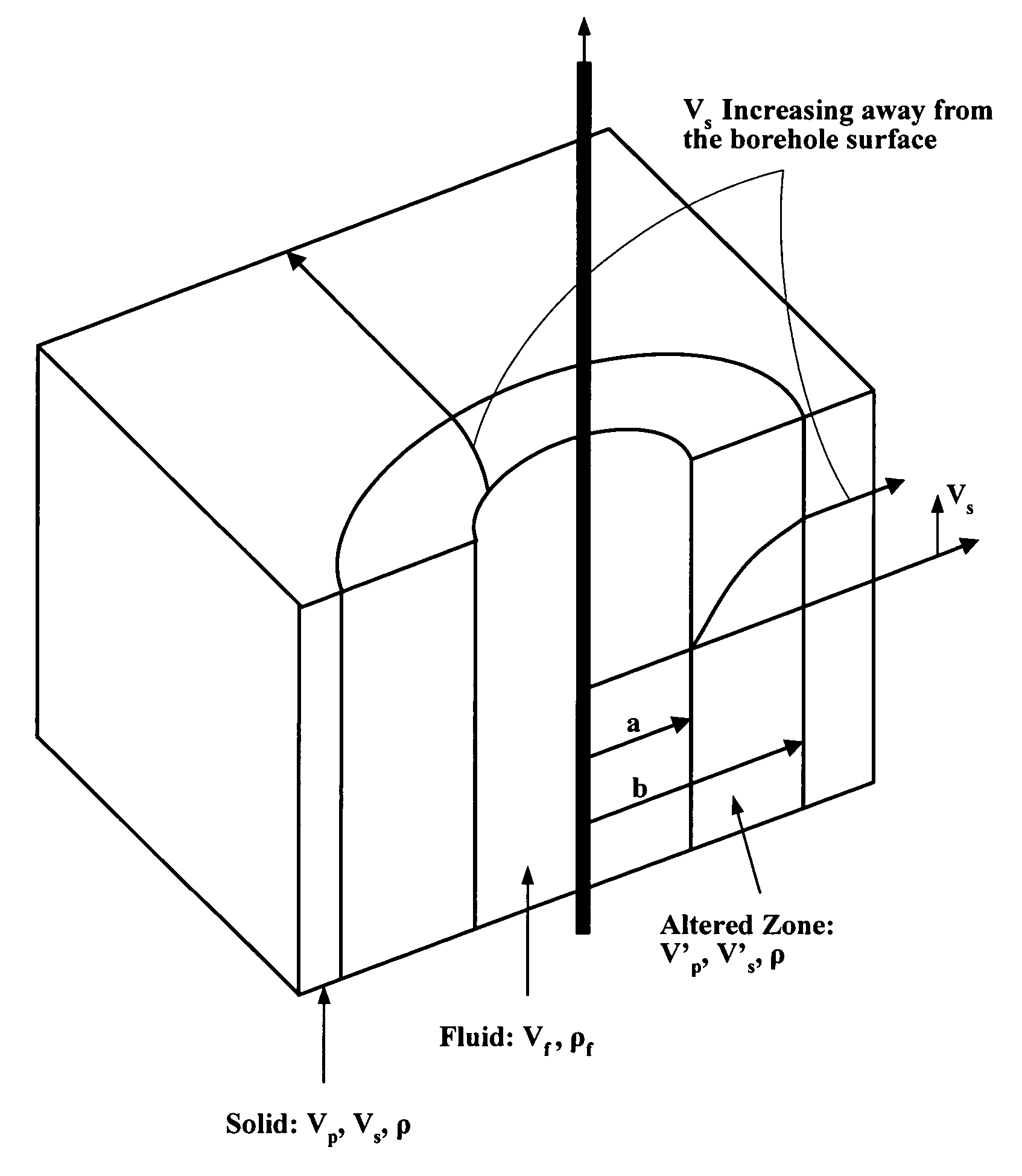
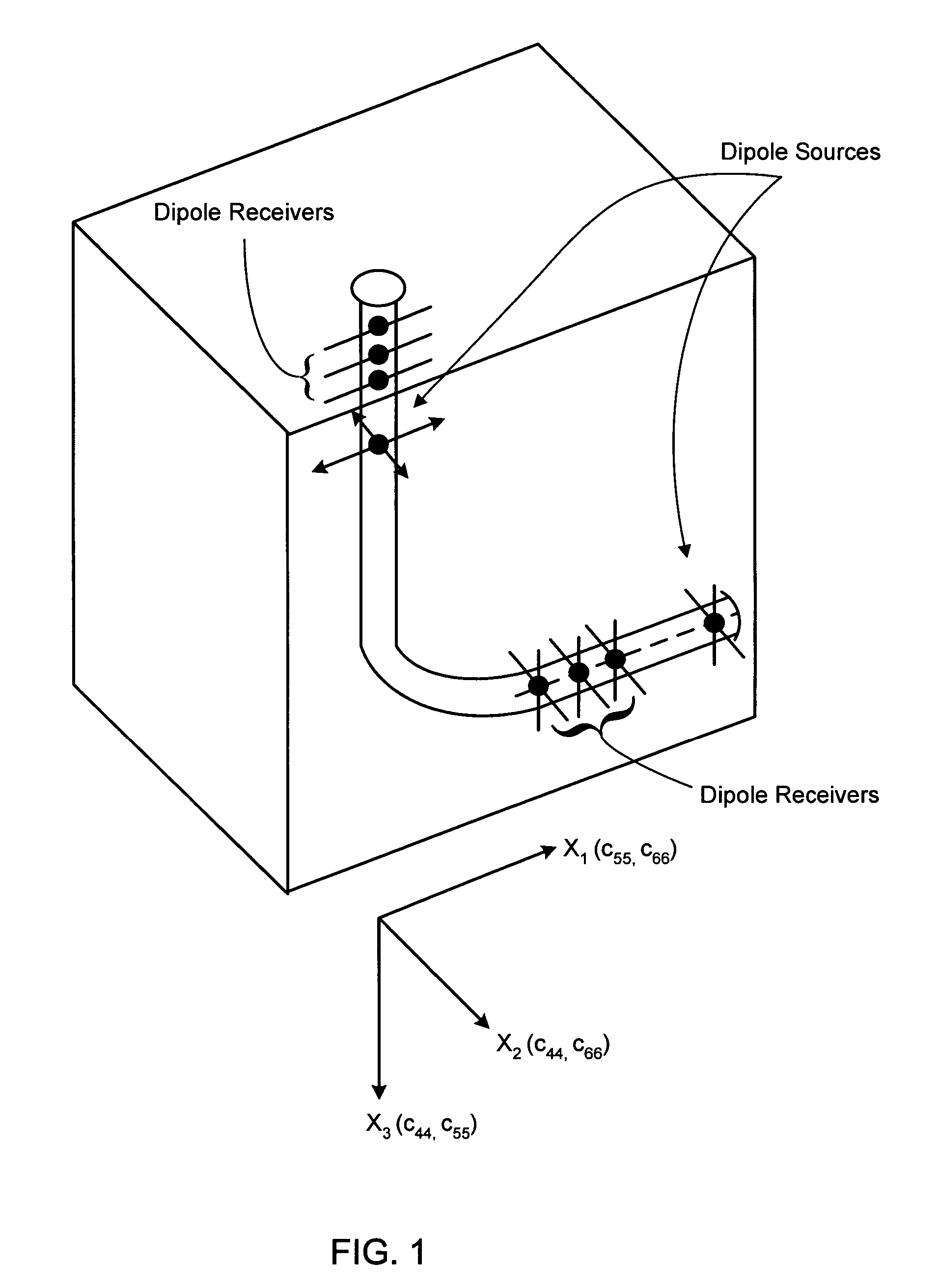
An apparatus and method for determining fast and slow shear wave velocities and orientations in an anisotropic earth formation that reduces the error and ambiguity in calculating these parameters and eliminates the need for dipole receivers and multiple dipole sources. The apparatus generally includes a single dipole source capable of generating an acoustic signal within a borehole. The acoustic logging tool contains multiple levels of receivers. At each level, four receivers, which may be conventional pressure transducers, receive shear / flexural wave signals which propagate along the borehole earth formation. These receivers measure the pressure fields from the wave signals. A processing device, preferably a UNIX(TM) based computer, interpolates the measured pressure fields between any two adjacent receivers. The processing device performs cross-component decomposition on the pressure field to determine shear wave orientation and velocity. Using the shear wave orientation and velocity the processing device determines transit time anisotropy, energy anisotropy, and slowness anisotropy.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
Method and apparatus for generating acoustic signals for LWD shear velocity measurement
InactiveUS6909666B2Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingSurveyMagnetostrictive actuatorAcoustic wave
An acoustic logging apparatus comprises a drill collar conveyed on a drilling tubular in a borehole within a formation. At least one transmitter is disposed in the drill collar. The transmitter includes at least one magnetostrictive actuator cooperatively coupled by a flexure ring to a piston for converting a magnetostrictive actuator displacement into a related piston displacement for transmitting an acoustic signal in the formation.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
Reservoir stratum identification method
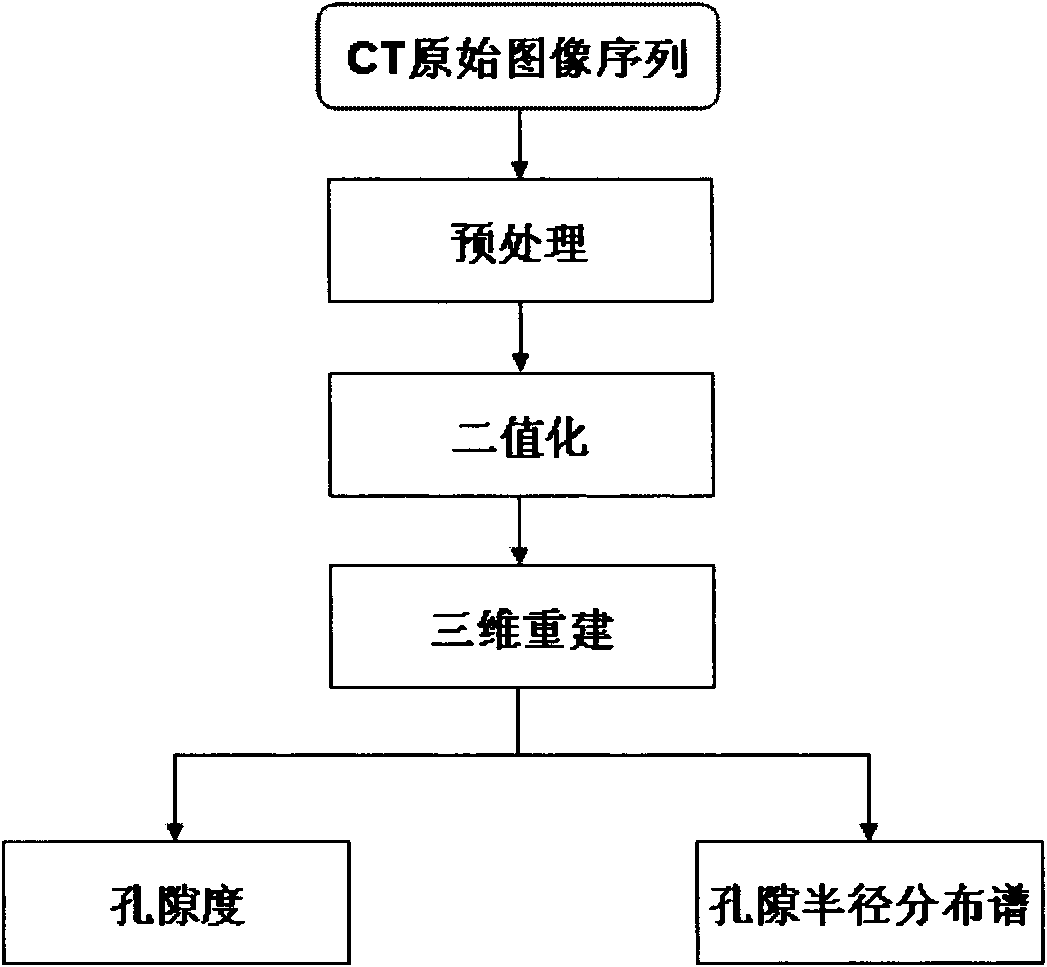
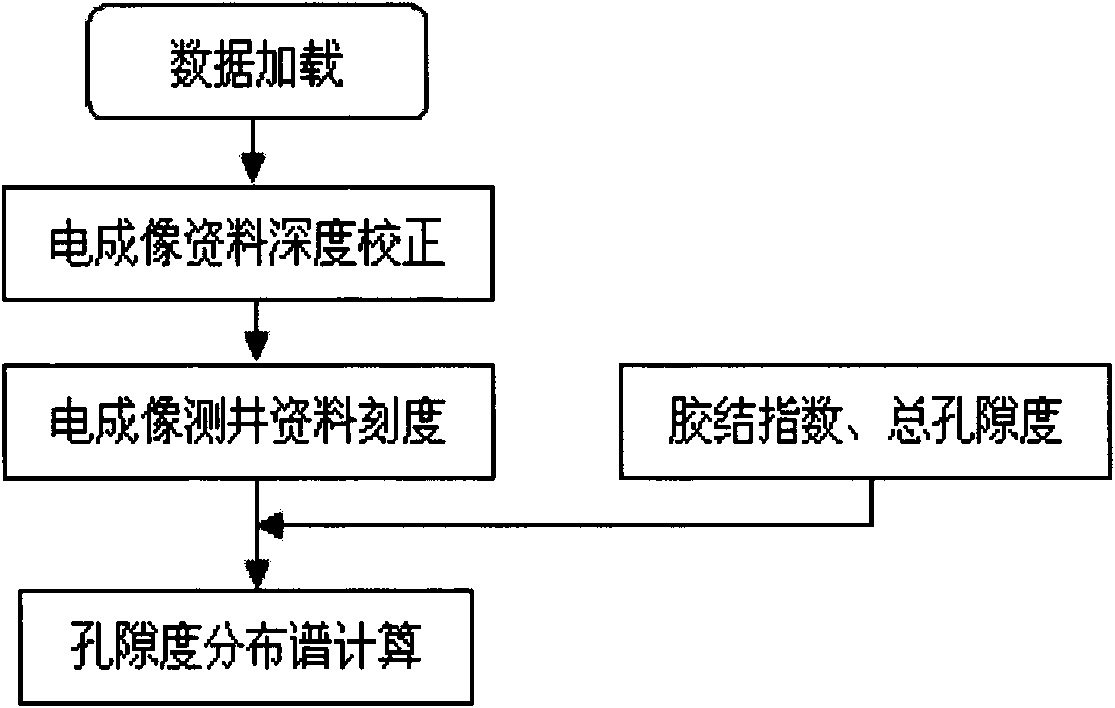
ActiveCN102373923AEasy to realize engineering applicationConstructionsBorehole/well accessoriesPorosityChannel data
The invention relates to a reservoir stratum identification method, which comprises the following steps of: separating out a contact well wall zone, a near well wall zone, a far well wall zone and an ultra far well wall zone according to the detection depth properties of different logging instruments; extracting the stratum seam hole development information of the contact well wall zone by using a micro computed tomography (CT) porosity analysis or electric imaging spectrum resolving technology; acquiring the stratum seam hole development condition of the near well wall zone based on dipolar sound wave logging data; acquiring the stratum seam hole development condition of the far well wall zone based on small-angle nearly perpendicular azimuth reflecting sound wave logging data; discovering a seam hole development belt in the stratum of the ultra far well wall zone based on well side seismic channel data; and judging whether the reservoir stratum has industrial capacity based on seam hole information extraction of the four detection depth zones. By establishing the effective reservoir stratum identification method with depth detection gradient and azimuth directing capacity, the identification coincidence rate of the effective reservoir stratum is improved, and a powerful technical support is provided for implementing the strategic goals of 'high yield in rare wells and high efficiency in sparse wells' in Chinese major oilfields.
Owner:PETROCHINA CO LTD
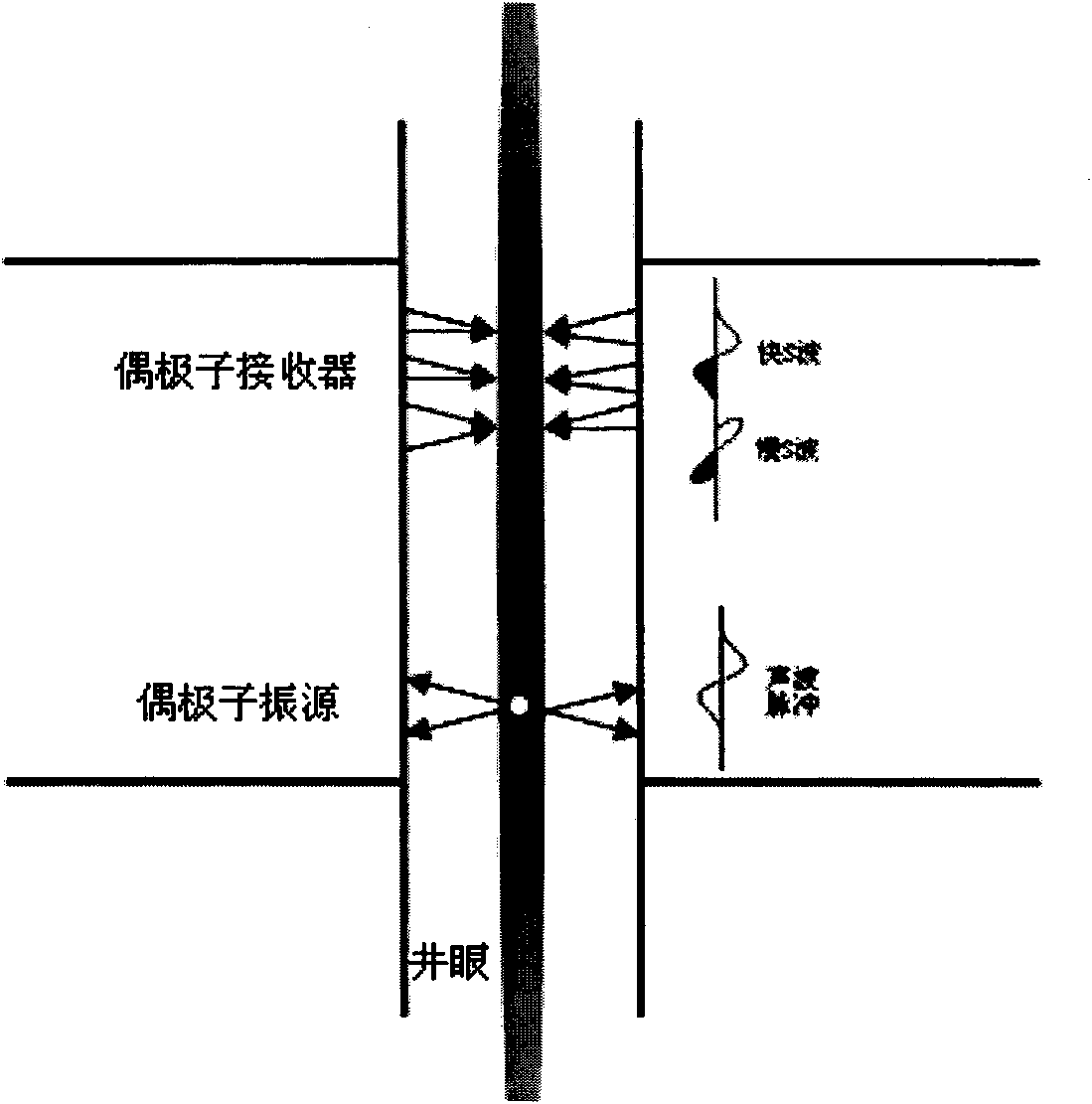
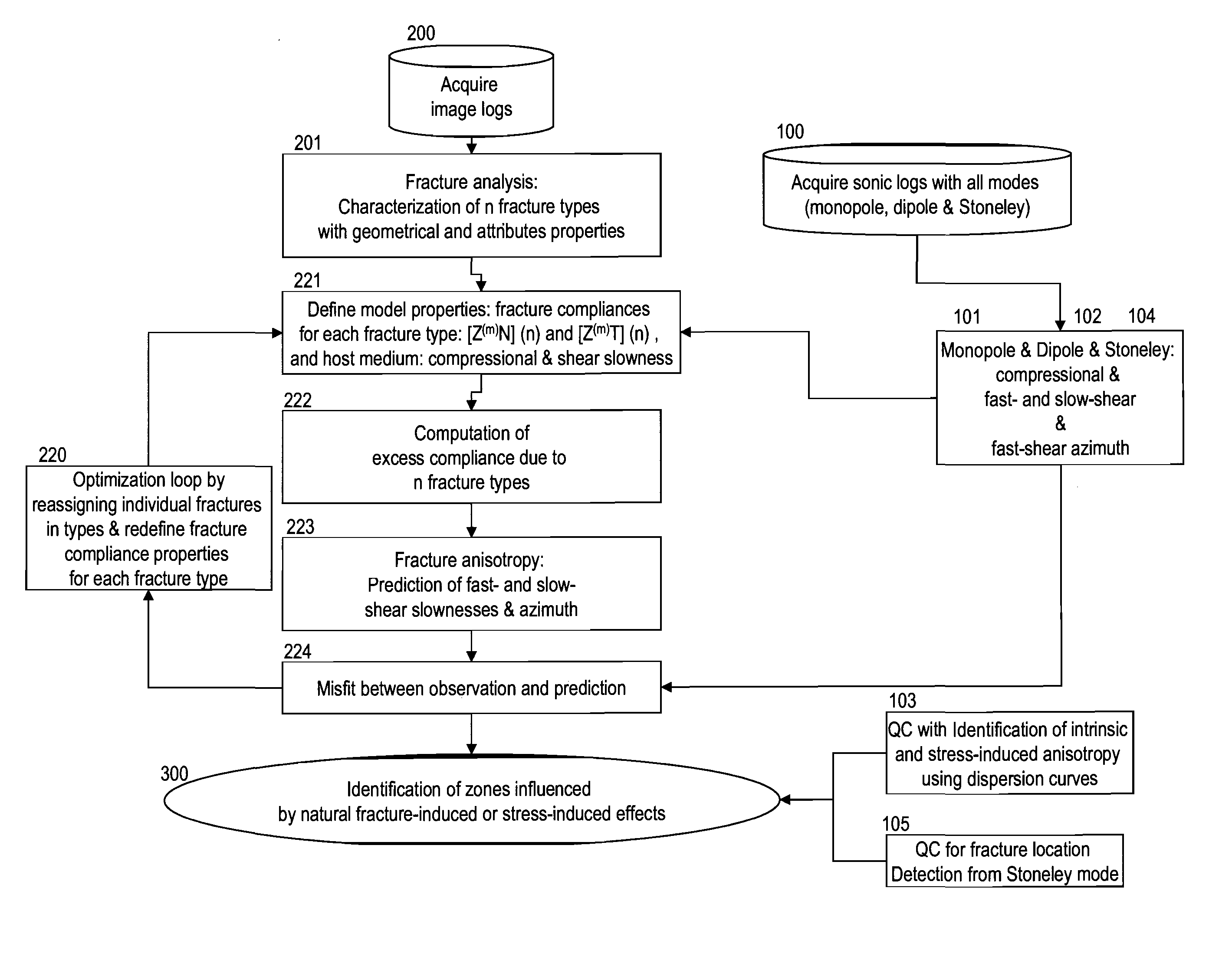
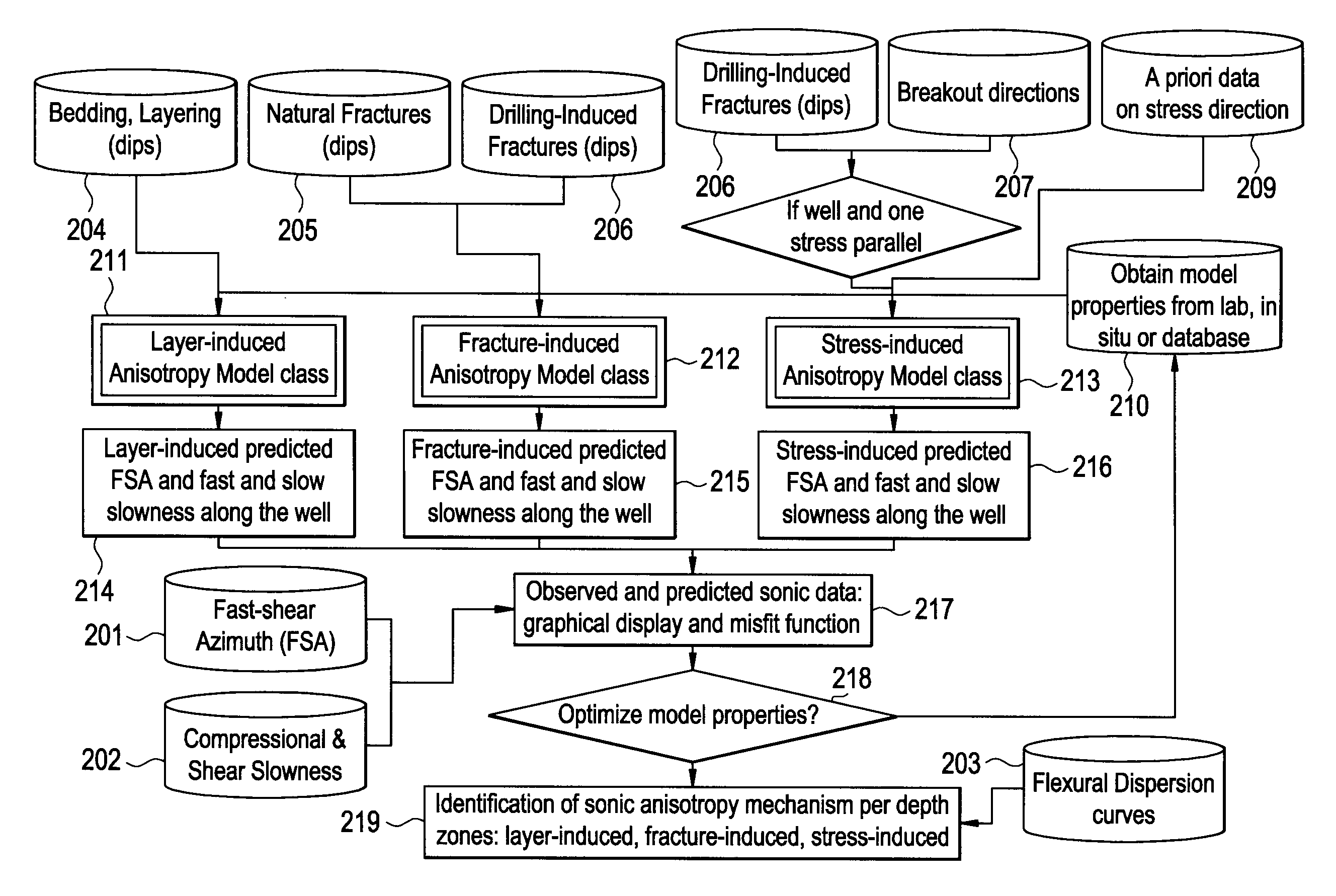
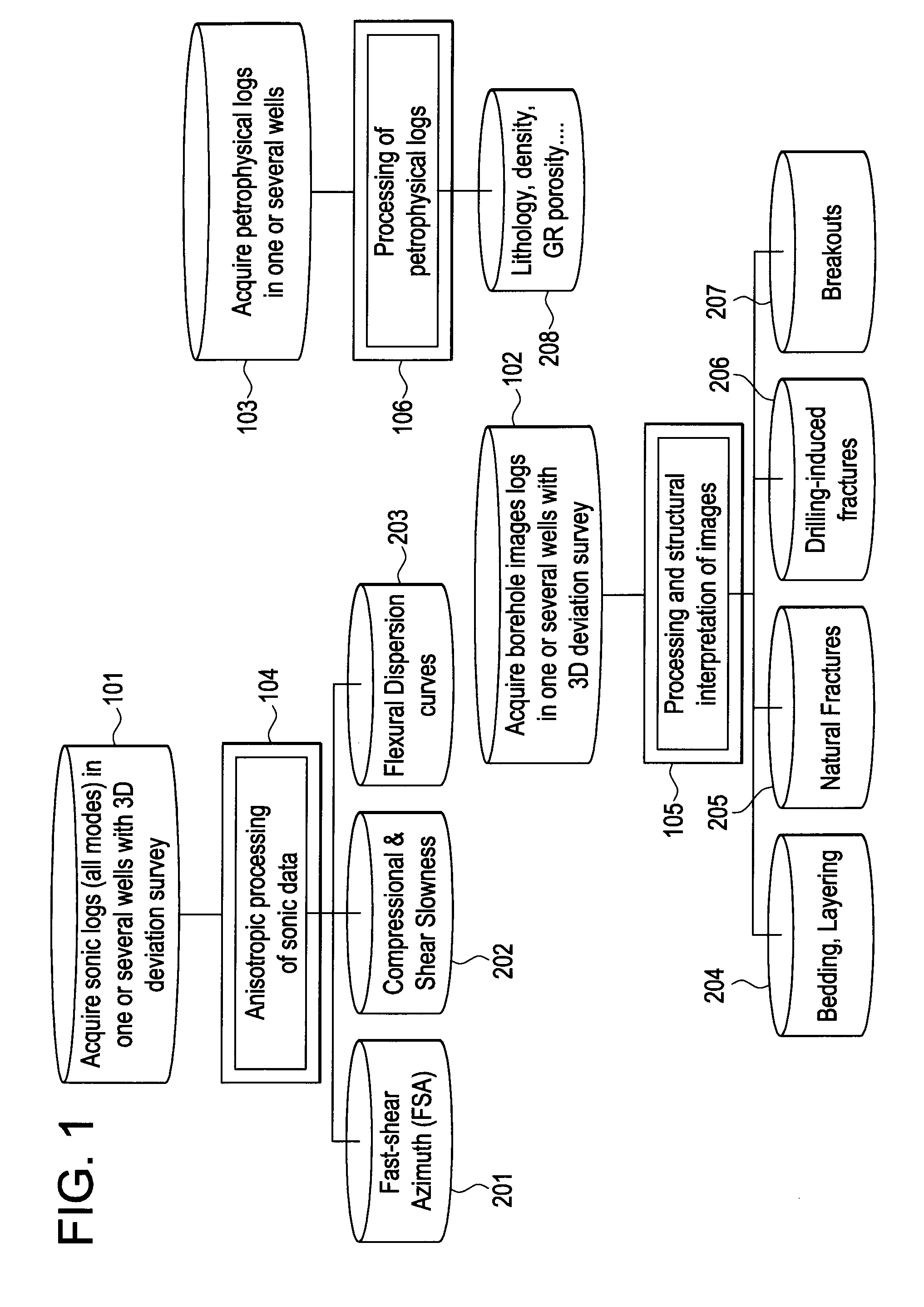
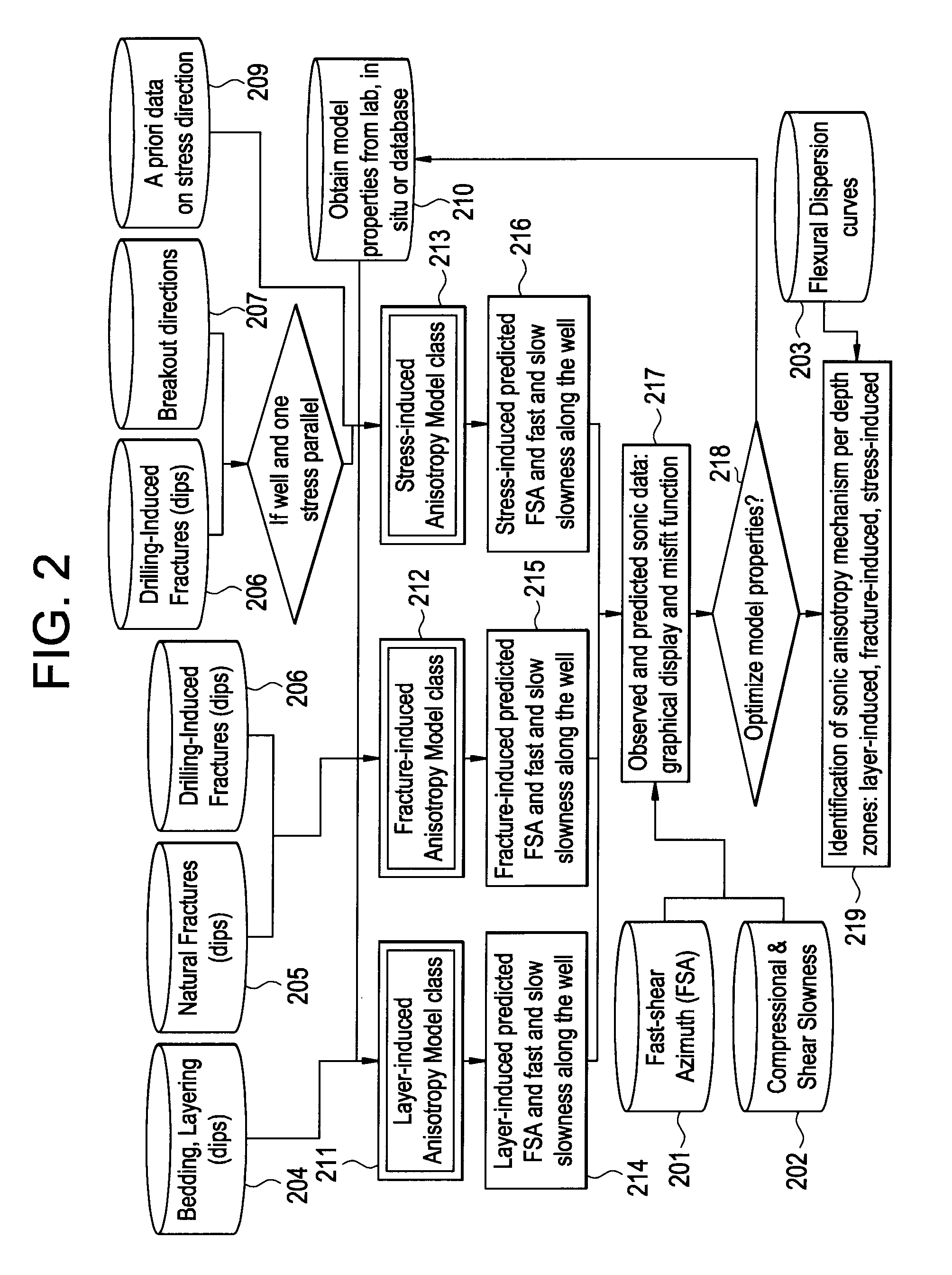
Discriminating natural fracture- and stress-induced sonic anisotropy using a combination of image and sonic logs
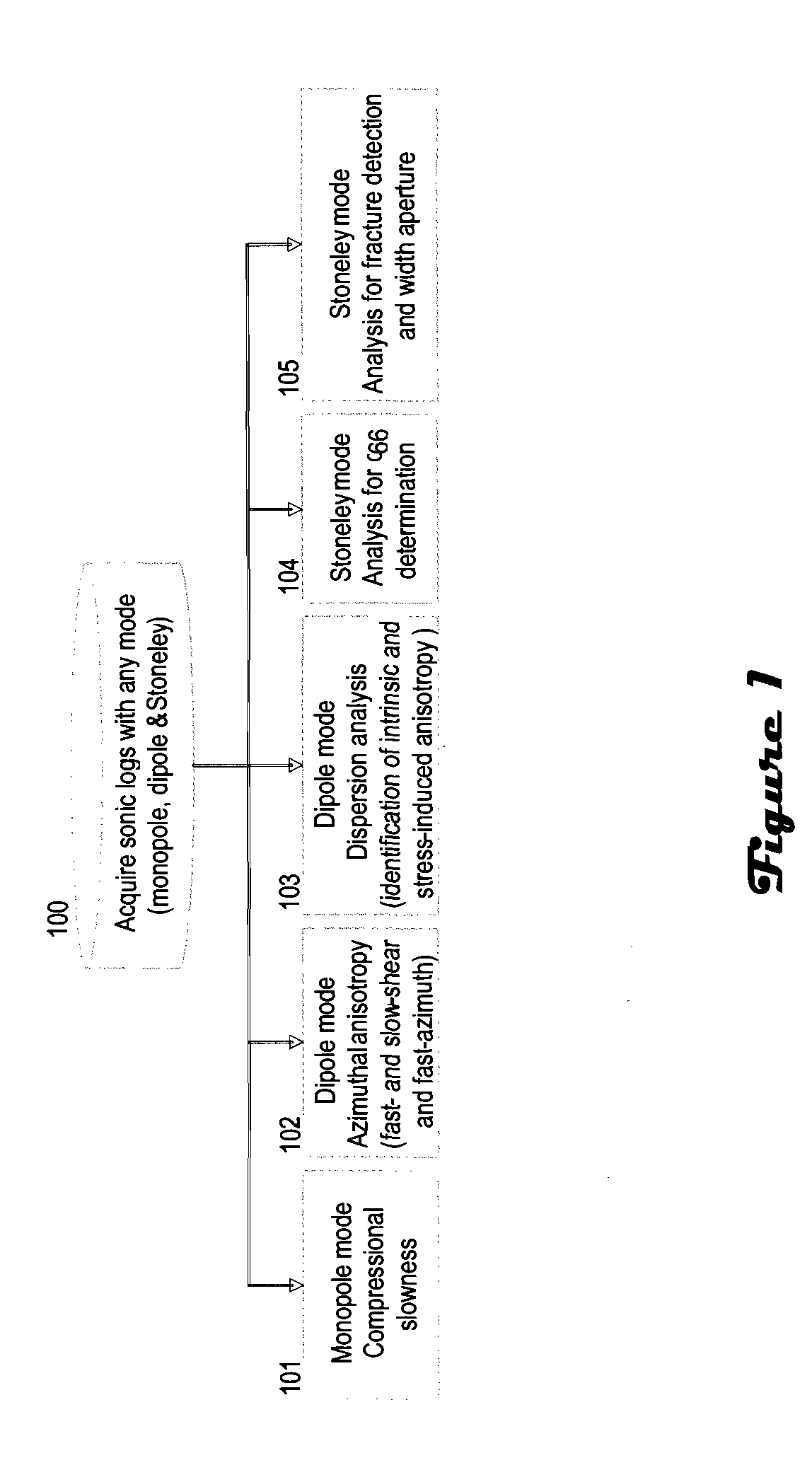
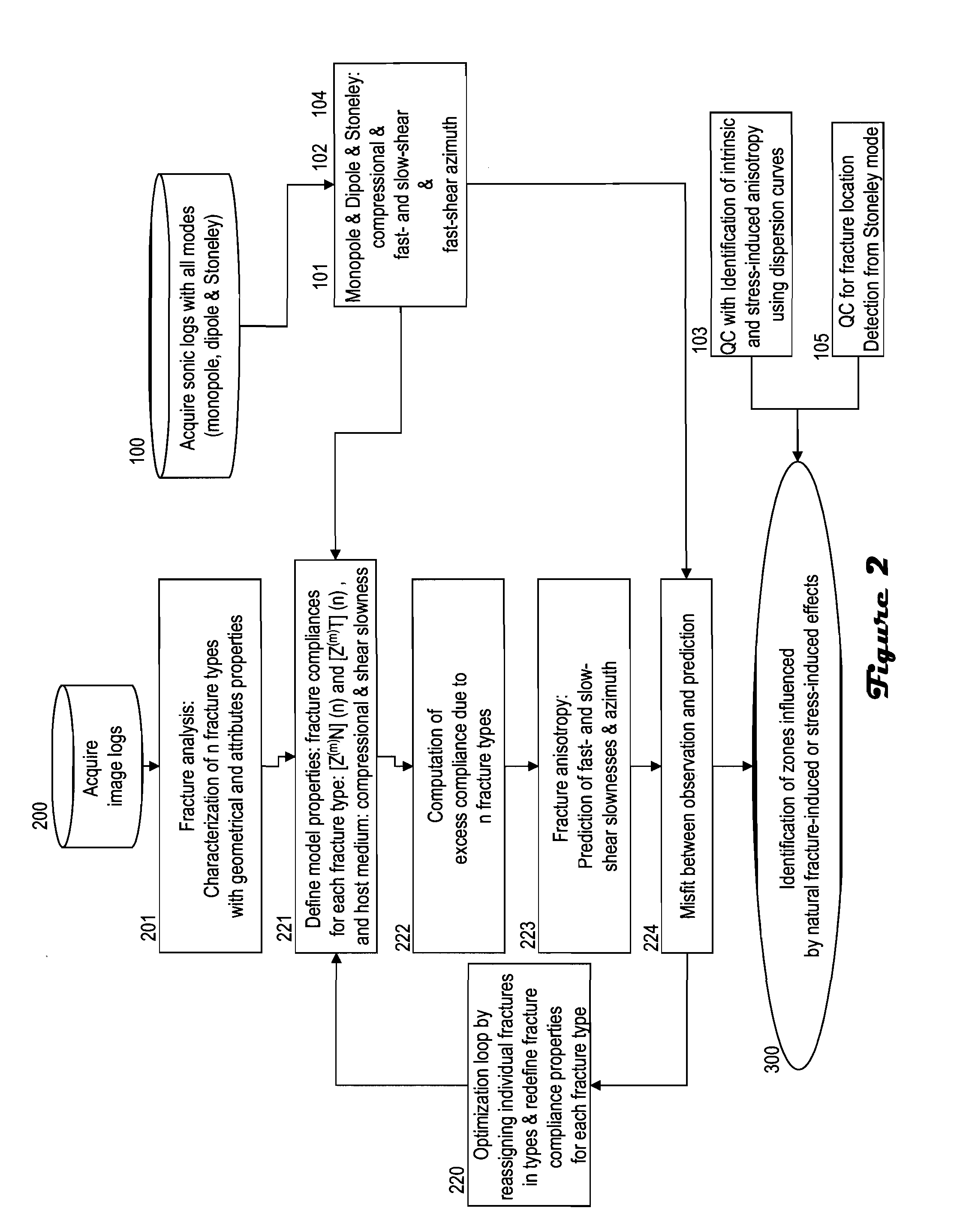
Fracture- and stress-induced sonic anisotropy is distinguished using a combination of image and sonic logs. Borehole image and sonic logs are acquired via known techniques. Analysis of sonic data from monopole P- and S-waves, monopole Stoneley and cross-dipole shear sonic data in an anisotropic formation are used to estimate at least one compressional and two shear moduli, and the dipole fast shear direction. Fracture analysis of image logs enables determination of fracture types and geometrical properties. Geological and geomechanical analysis from image logs provide a priori discrimination of natural fractures and stress-induced fractures. A forward quantitative model of natural fracture- and stress-induced sonic anisotropy based on the knowledge of fracture properties interpreted from image logs allows the computation of the fast-shear azimuth and the difference in slowness between the fast- and slow-shear. The misfit between predicted and observed sonic measurements (i.e. fast-shear azimuth and slownesses) is then optimized in order to discriminate depth zones with an elastic medium as being influenced by the presence of open natural fractures, closed natural fractures and fractures induced by non-equal principal stress effects.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
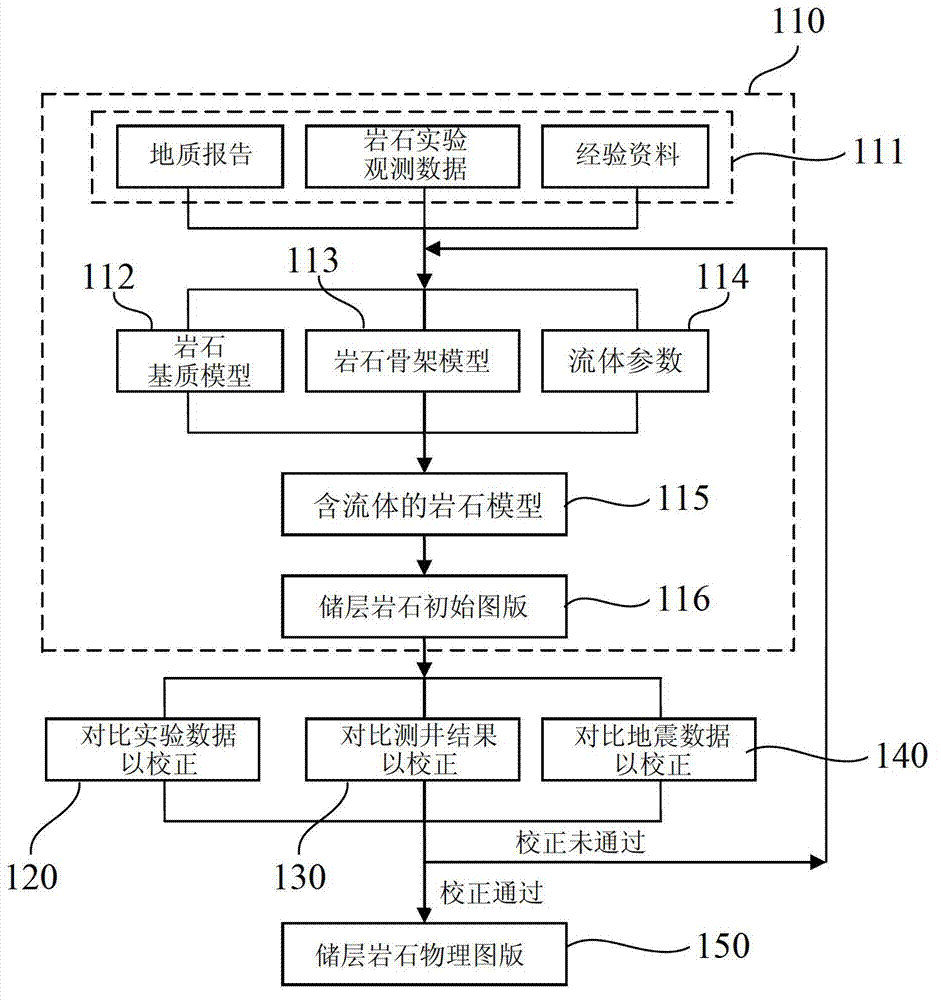
Multi-scale rock physical charting method and device for detecting reservoir hydrocarbon
The invention provides a multi-scale rock physical charting method and device for detecting reservoir hydrocarbon. The method comprises the steps as follows: obtaining a reservoir rock matrix model and a reservoir rock framework model; acquiring a liquid-containing rock model according to the reservoir rock matrix model, the reservoir rock framework model and liquid parameters; obtaining a multi-scale initial reservoir rock physical chart according to the liquid-containing rock model; correcting the initial reservoir rock physical chart under a plurality of frequency bands according to the rock physical experimental data: correcting the initial reservoir rock physical chart under an acoustic logging frequency band based on the logging interpretation result; correcting the initial reservoir rock physical chart based on the seismic interpretation result; and outputting the final reservoir rock physical chart after the correction, so as to carry out inversion of a reservoir rock physical parameter. With the adoption of the method provided by the invention, the precision of the rock physical chart can be increased, and the quantitative inversion of the rock parameter and the saturation of the liquid can be realized.
Owner:PETROCHINA CO LTD
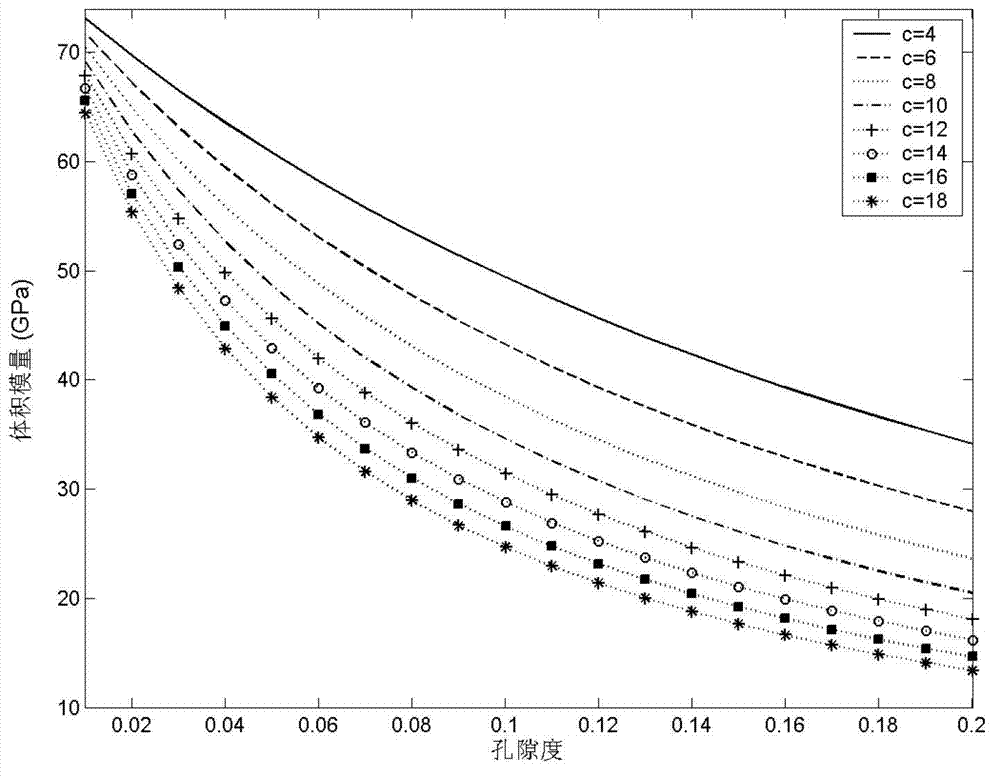
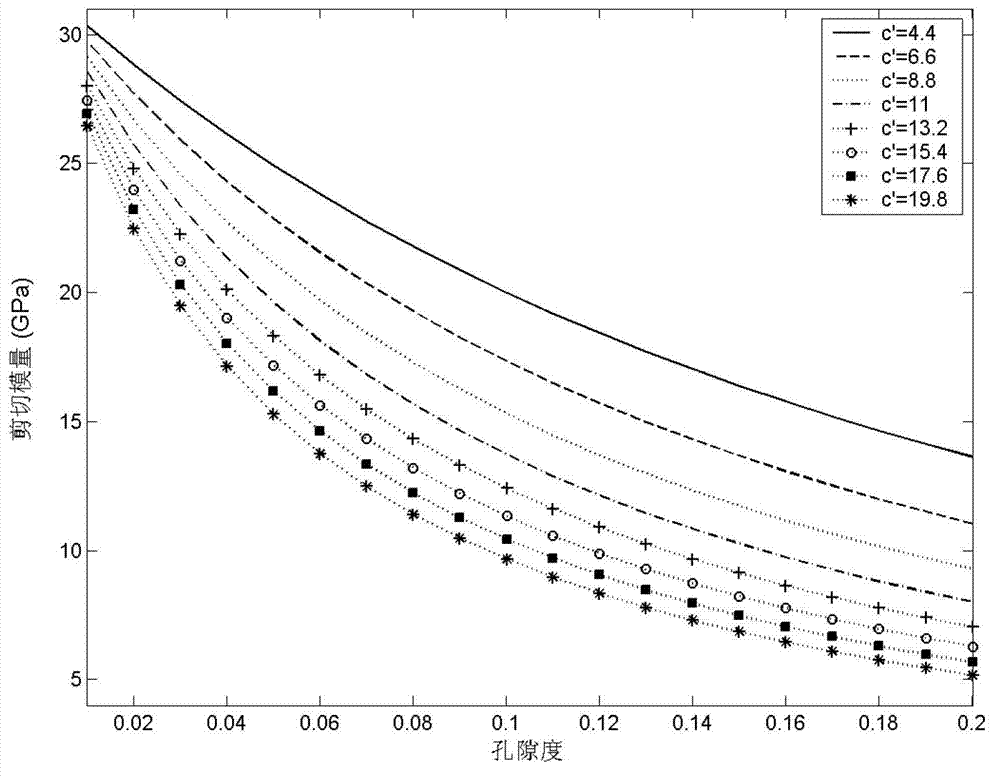
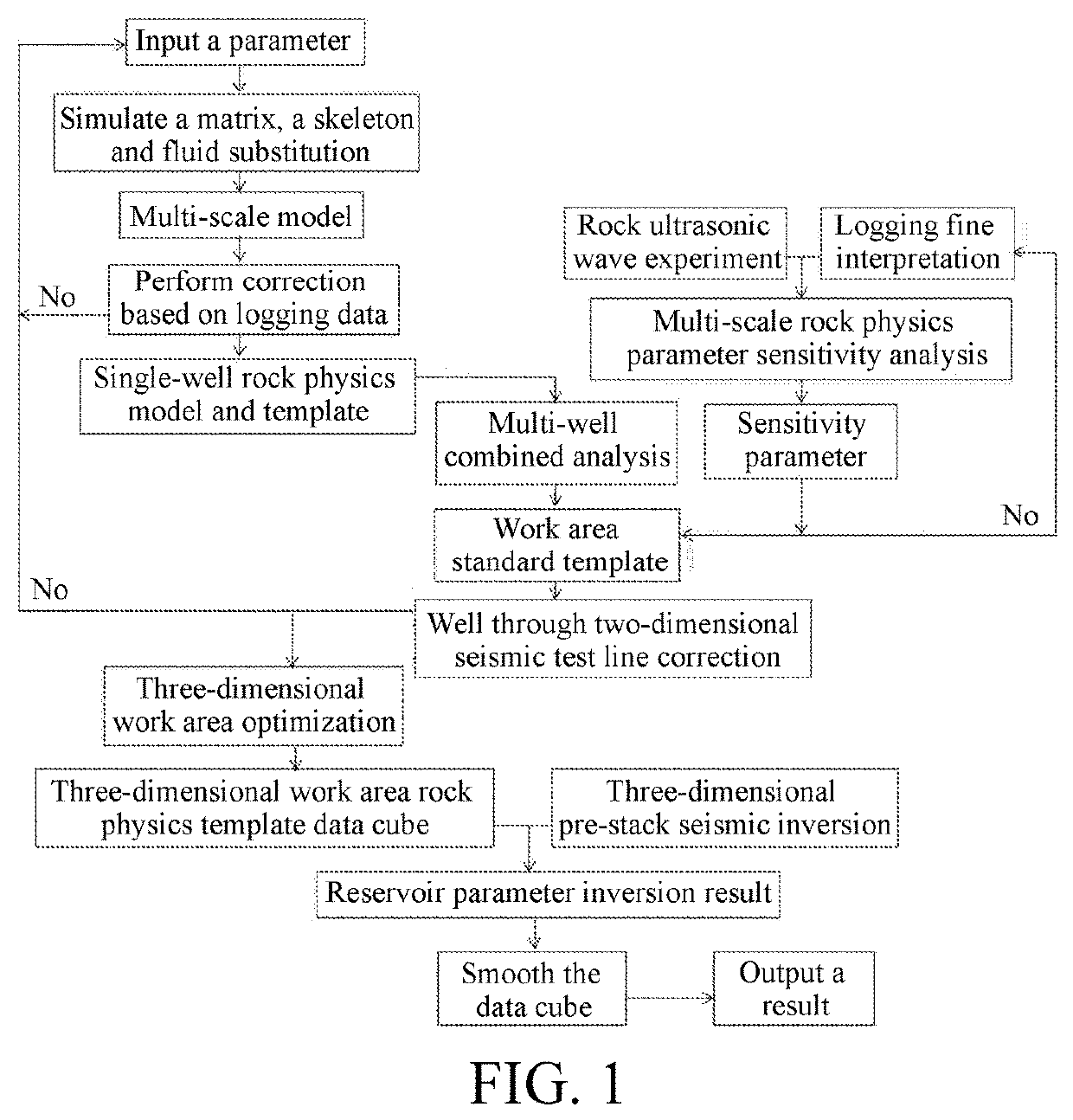
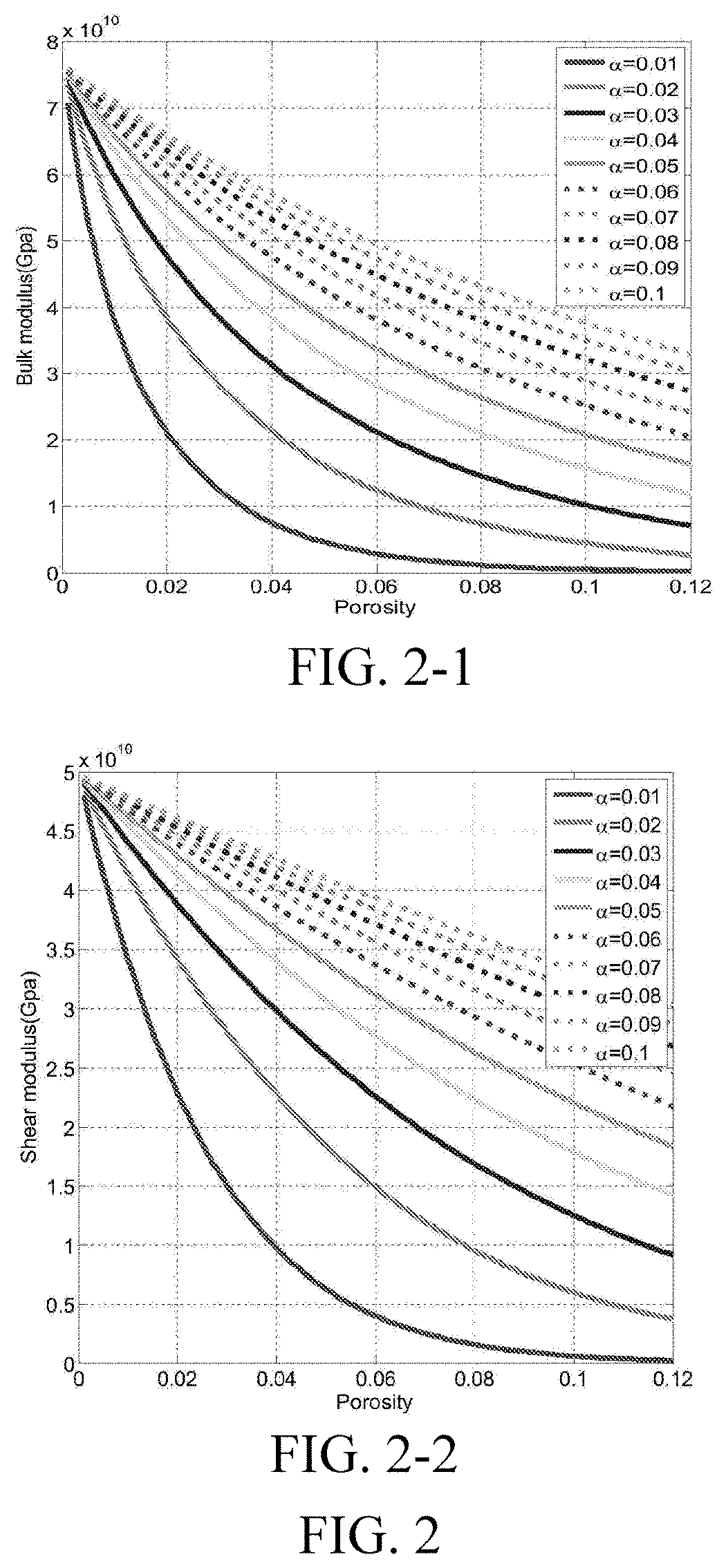
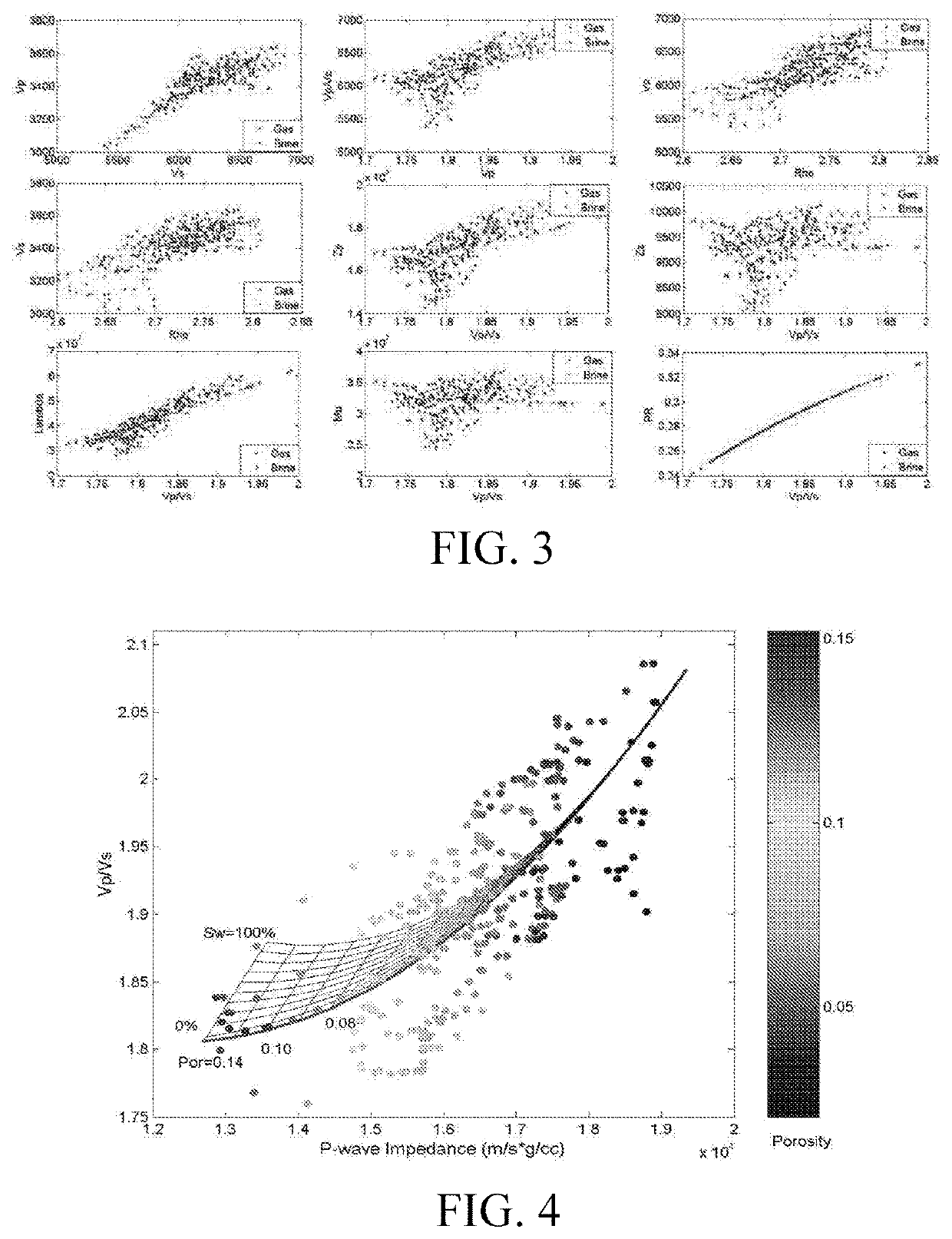
Seismic rock physics inversion method based on large area tight reservoir
A seismic rock physics inversion method based on a large area tight reservoir includes steps: building a multi-scale rock physics model; analyzing fluid sensitivities of rock physics parameters in two scales of acoustic logging and ultrasonic wave, and sifting the rock physics parameters that are most sensitive to a porosity and a gas saturation in a plurality of observation scales; building a single-well rock physics template, preferably a standard template; considering lateral variations and heterogeneity of reservoir geological features, fine-tuning input parameters of the rock physics template according to gas testing situations of all wells in a large work area, optimizing the whole work area and building a three-dimensional work area rock physics template data volume, and combining the data volume with pre-stack seismic inversion to calculate a porosity and a saturation of a target layer; and smoothing a result and finally outputting a reservoir parameter inversion data volume.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
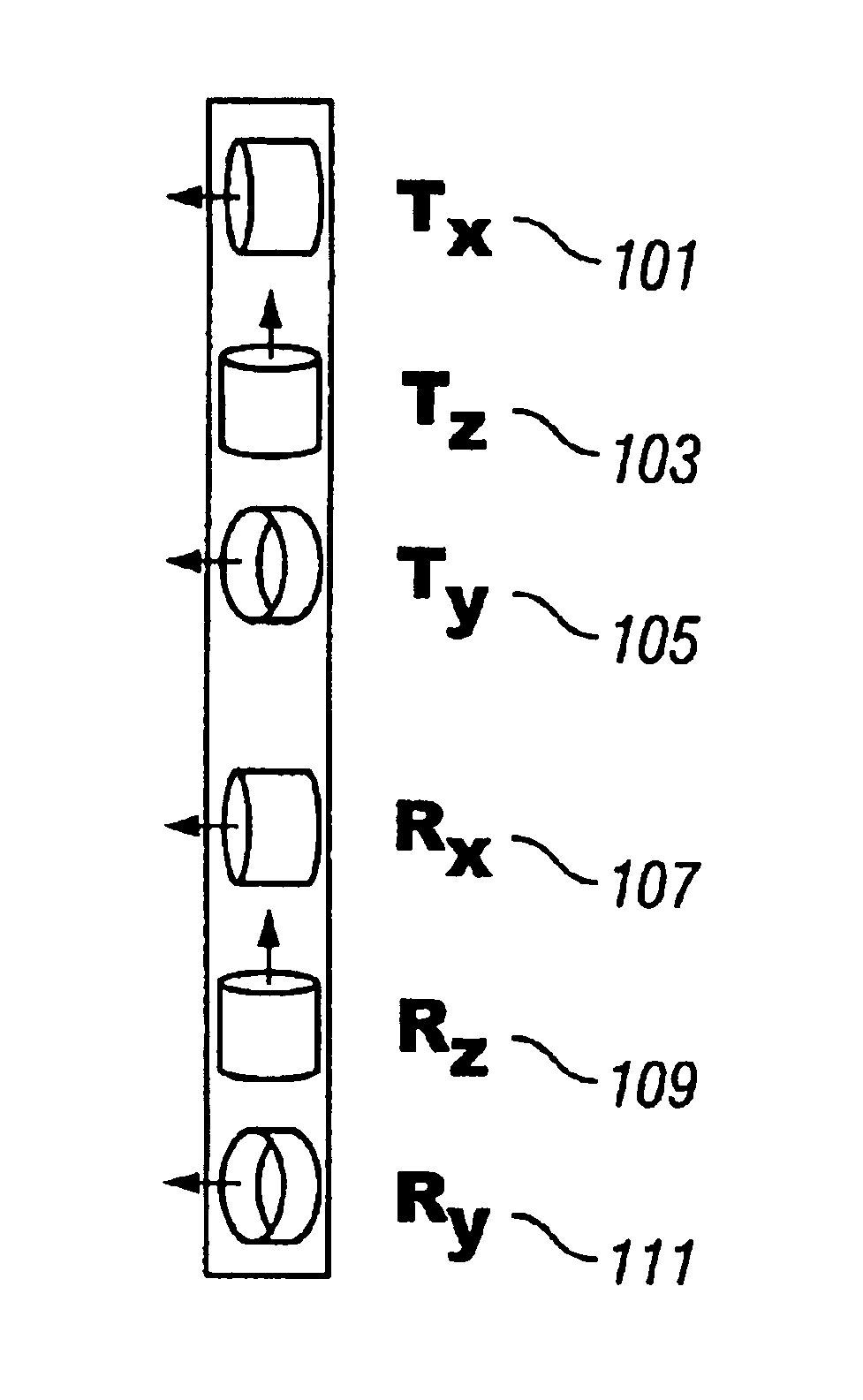
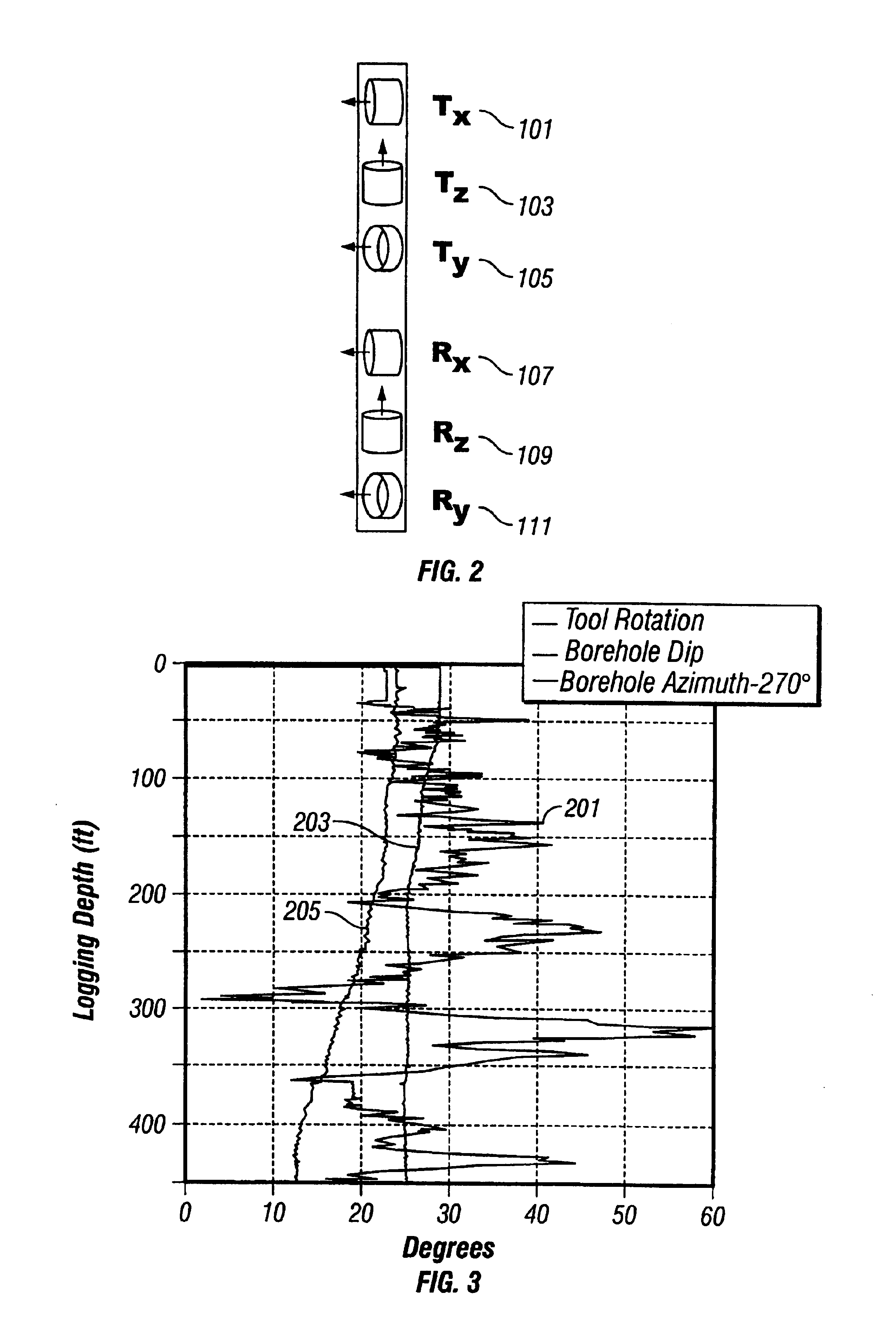
Downhole Sonic Logging Tool Including Irregularly Spaced Receivers
InactiveUS20110188345A1Reduces (or even substantially eliminates) aliasingReducing aliasing effectSeismology for water-loggingAcousticsMechanical engineering
A downhole acoustic measurement tool includes at least one transmitter longitudinally spaced apart from a non-uniformly spaced longitudinal array of acoustic receivers. The array has a non-uniform spacing such that a first spacing between a first pair of consecutive acoustic receivers in the array is not equal to a second spacing between a second pair of consecutive acoustic receivers in the array. Non-uniform spacing of the receivers in the array reduces aliasing when the received waveforms are processed, for example, to obtain semblance data.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Method for building stratum velocity model
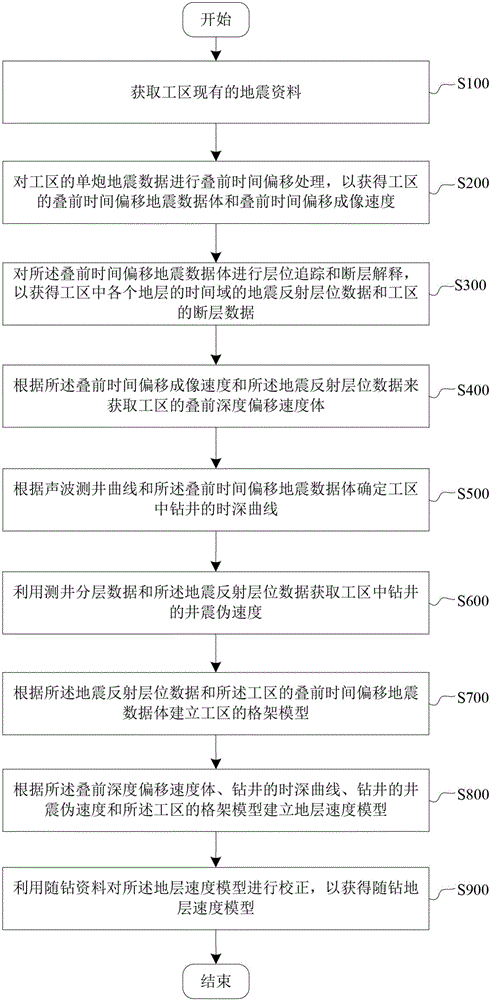
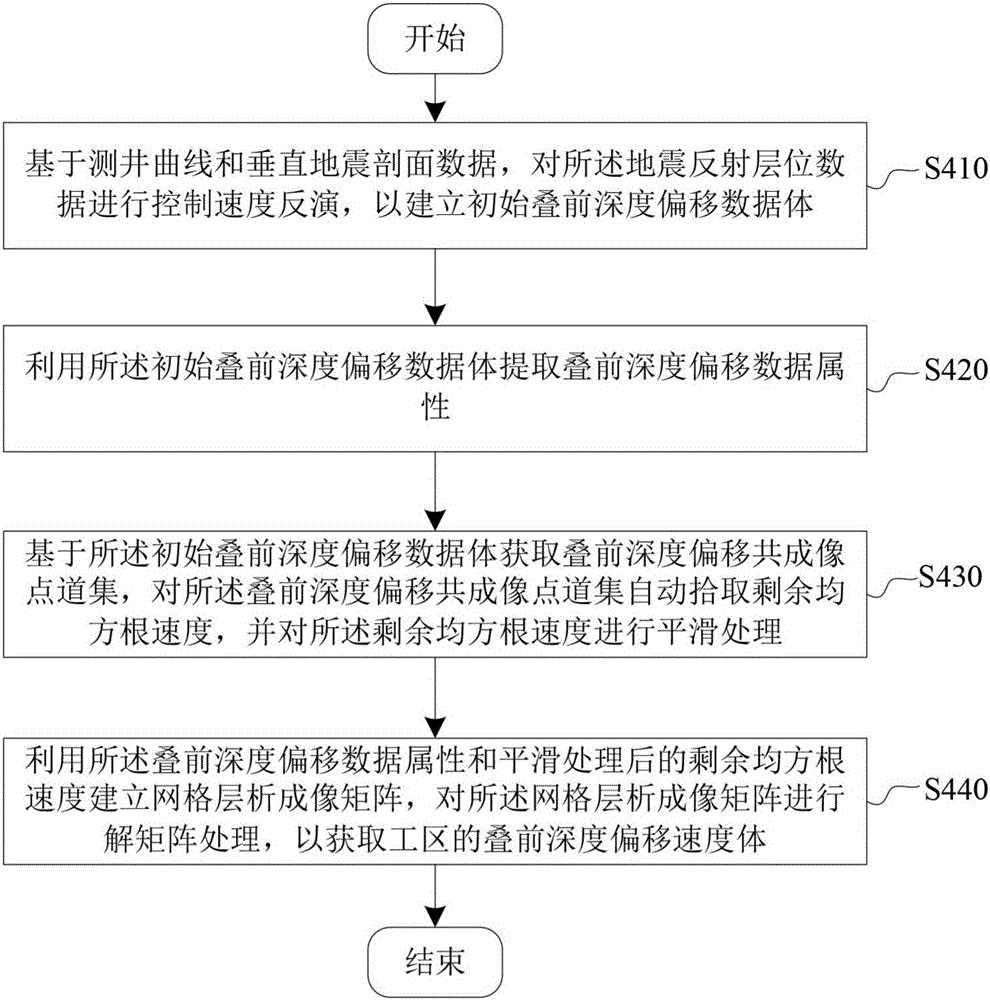
The invention provides a method for building a stratum velocity model, which comprises the steps of (A) acquiring existing seismic data of a work area, (B) acquiring pre-stack time migration seismic data volume and pre-stack time migration imaging velocity of the work area, (C) acquiring seismic reflection stratum data of the time domain of each stratum in the work area and fault data of the work area, (D) acquiring pre-stack depth migration velocity volume of the work area, (E) determining a time-depth curve of well drilling in the work area according to an acoustic logging curve and the pre-stack time migration seismic data volume, (F) acquiring well seismic pseudo velocity of well drilling in the work area, (G) establishing a framework model of the work area, (H) establishing a stratum velocity model according to the pre-stack depth migration velocity volume, the time-depth curve of well drilling, the well seismic pseudo velocity of well drilling and the framework model of the work area, and (I) carrying out correction on the stratum velocity model by using while-drilling materials so as to acquire a while-drilling stratum velocity model. The precision of the stratum velocity model can be effectively improved according to the method provided by the invention.
Owner:BC P INC CHINA NAT PETROLEUM CORP +1
Methods to estimate subsurface deviatoric stress characteristics from borehole sonic log anisotropy directions and image log failure directions
InactiveUS20100250214A1Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingComputation using non-denominational number representationAcousticsImaging data
Methods and apparatus for estimating stress characteristics of formations. The method comprises: (a) acquiring sonic anisotropy data, image data or both associated with at least one borehole (b) employing sonic anisotropy data to estimate fast shear direction (FSA) to extract FSA observed data; (c) computing FSA from forward modeling, forward modeling utilizes a first deviatoric stress tensor to extract FSA predicted data; (d) computing FSA misfit from difference between FSA observed data and FSA predicted data to obtain computed FSA misfit relating to first deviatoric stress tensor; (e) if computed FSA misfit is equal to or less than a defined value, then store computed FSA misfit, otherwise repeat steps (d)-(h) using another deviatoric stress tensor so a different deviatoric stress tensor is used for each repeat; (f) selecting smallest stored computed misfit from group consisting of stored computed FSA misfit, at least one other stored computed misfit or combination thereof.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Complex lithology natural gas reservoir interval transit time discriminating method
InactiveCN103867197ASolve the discrimination problemImprove discriminationSurveyLithologyIgneous rock
The invention discloses a complex lithology natural gas reservoir interval transit time discriminating method, and belongs to the technical field of acoustic logging information application. Formation lithology mineral composition, porosity, water saturation and formation water electrical resistivity factors are utilized to calculate an interval transit time theoretical value curve, the interval transit time theoretical value curve obtained through calculation is compared with an interval transit time curve measured actually, and a natural gas reservoir is discriminated according to the different features of the interval transit time theoretical value curve obtained through the calculation and the interval transit time curve measured actually. The complex lithology natural gas reservoir interval transit time discriminating method is especially suitable for being used in discrimination of natural gas reservoirs of clastic rock, carbonate rock, igneous rock and the like, good in application prospect and capable of improving discriminating effect of the natural gas reservoirs.
Owner:CHINA NAT PETROLEUM CORP CHUANQING DRILLING ENG CO LTD
Acoustic logging apparatus and method
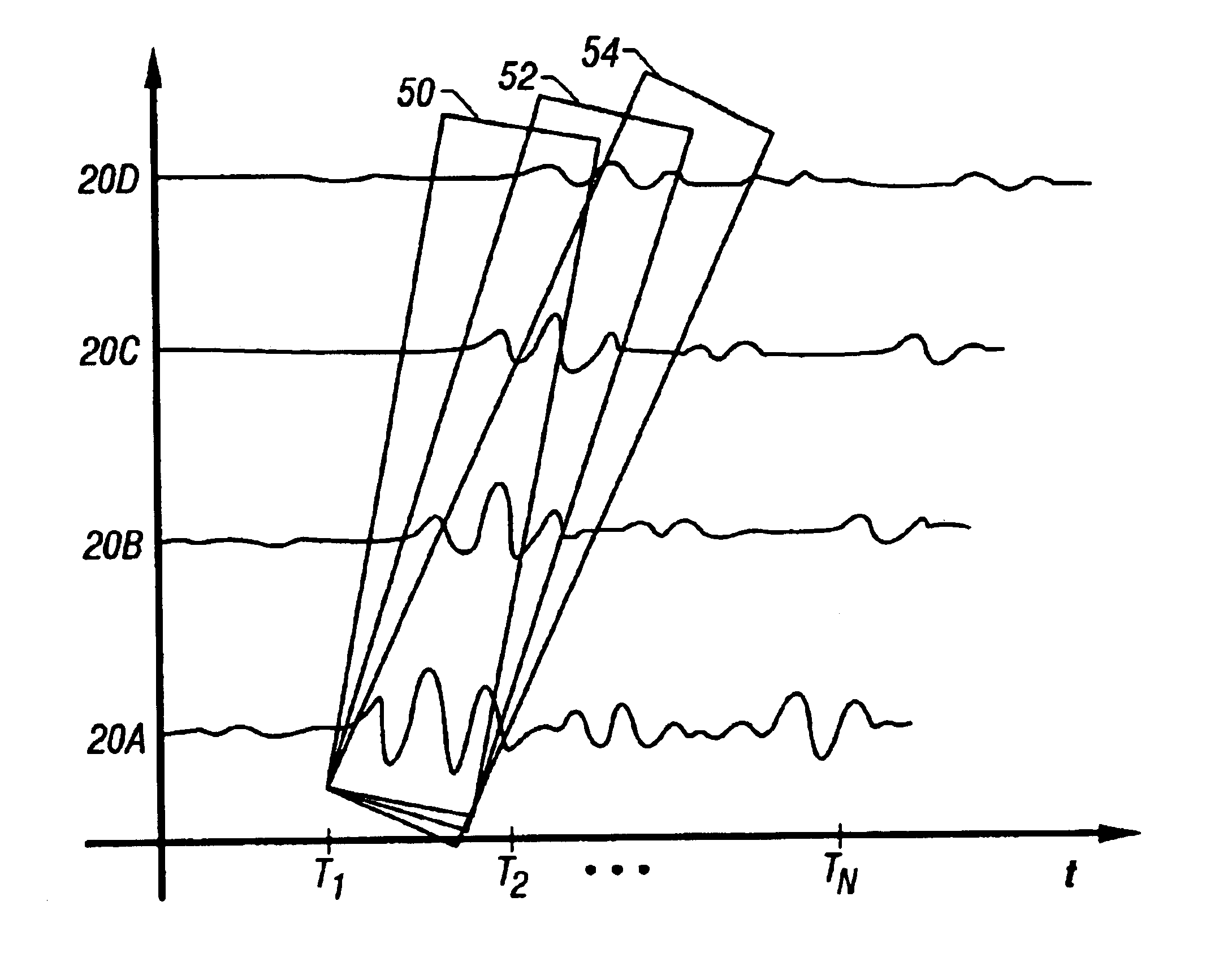
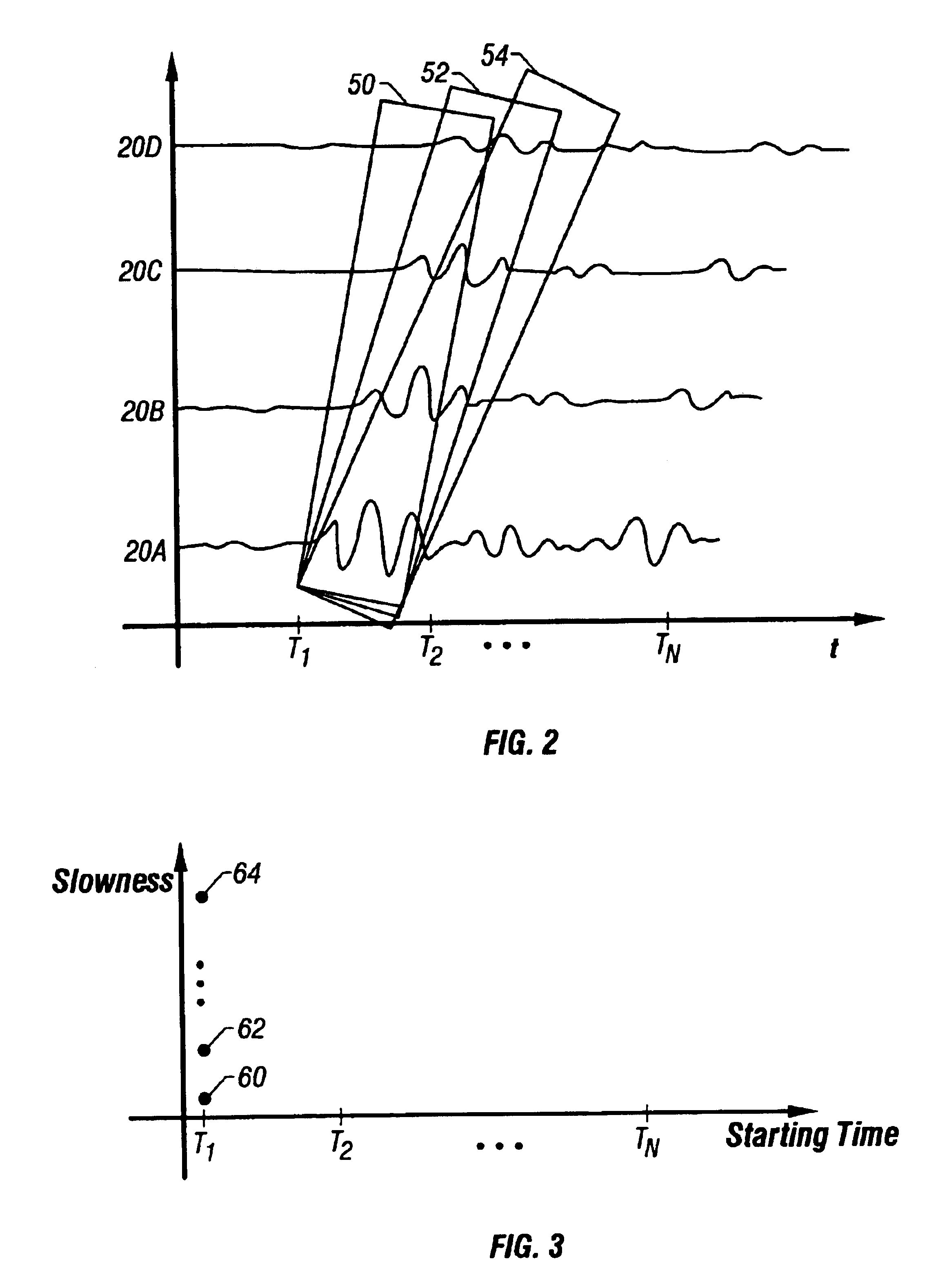
InactiveUS6842400B2Accurate valueSolve excessive overheadElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingSurveyStart timeAcoustic energy
The specification discloses a system and related method for determining characteristics of earth formations traversed by a borehole. An acoustic transmitter mounted on a tool, whether that tool is a wireline tool or a logging-while-drilling tool, imparts acoustic energy into the formation, and a plurality of receivers spaced apart from the transmitter and from each other receive acoustic energy responsive to the transmitter firing. Portions, or all, of each received signal are used to estimate source signals using an assumed transfer function. Each of those estimated source signals are then compared in some way to determine an objective function. This process is repeated for multiple assumed transfer functions, and at multiple starting times within the received signals. By searching for minimas of a plot of the objective function, characteristics of the earth formation may be determined.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
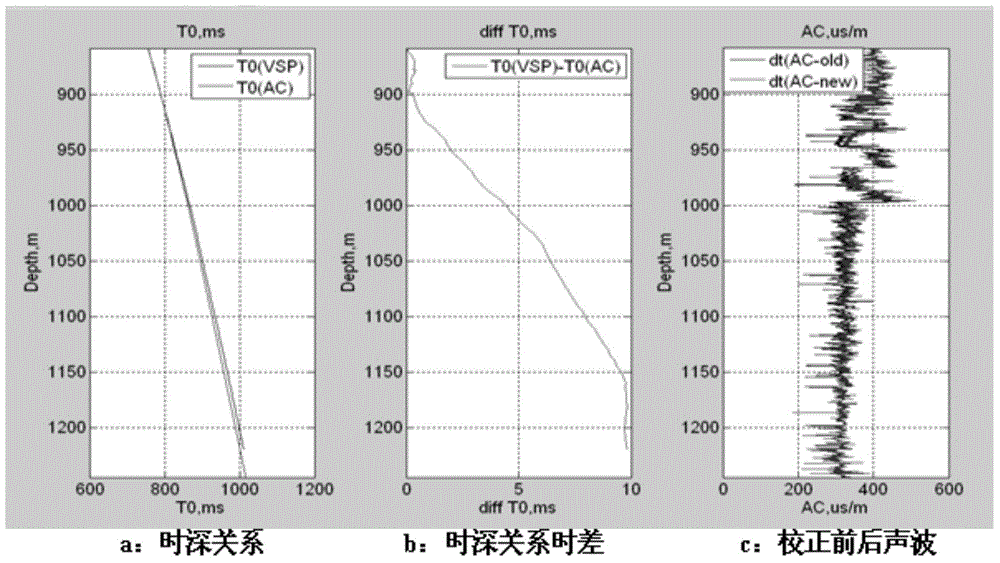
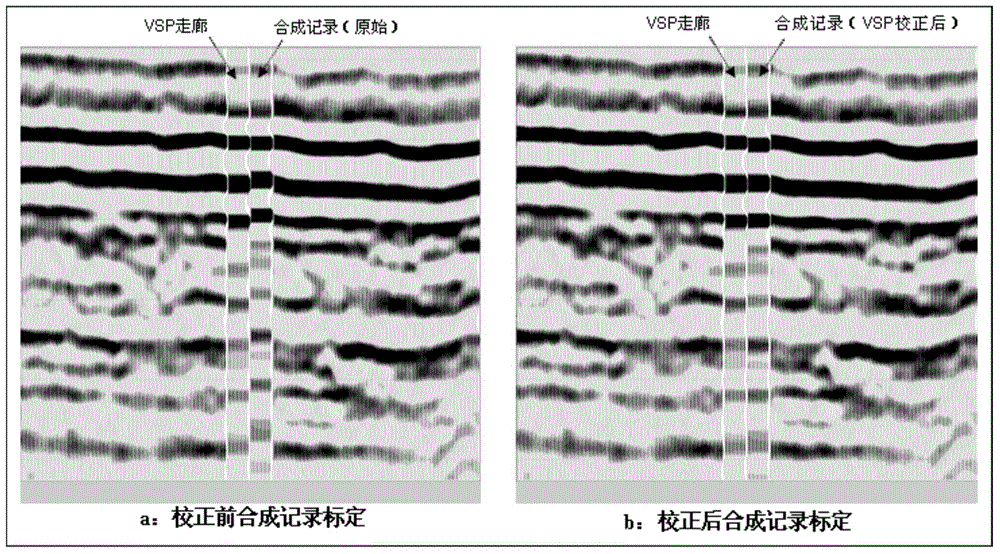
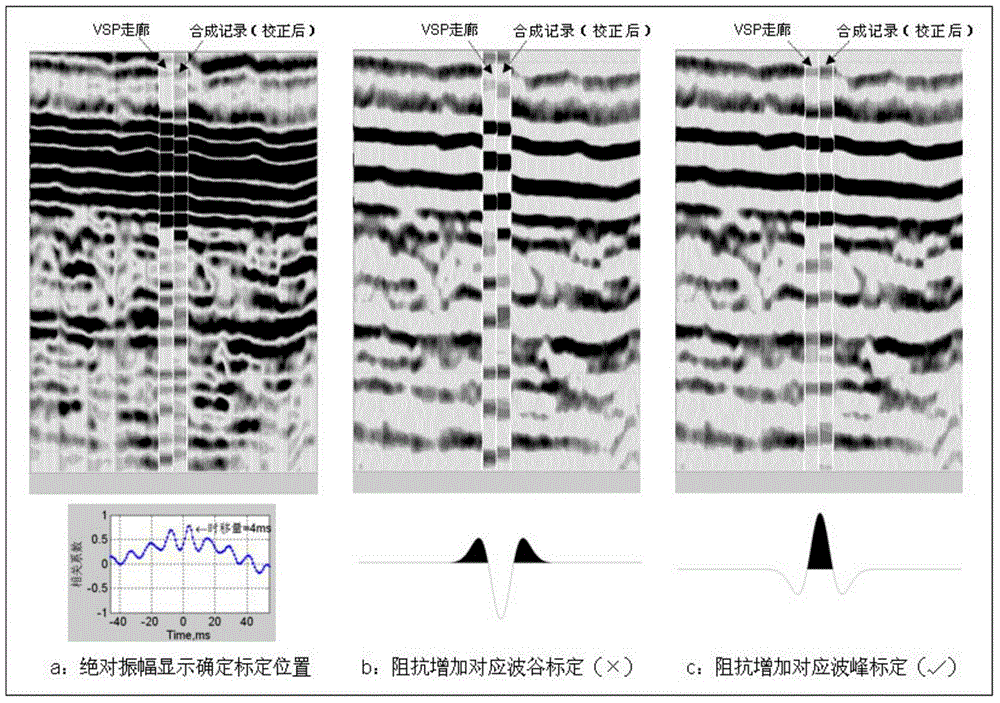
Seismic horizon calibration method utilizing vertical seismic profiling (VSP) and well-logging combination
The invention relates to a seismic horizon calibration method utilizing a vertical seismic profiling (VSP) and well-logging combination. The seismic horizon calibration method comprises the following steps: measuring and obtaining a longitudinal wave time-depth relationship and a corridor stacking profile according to zero offset data, performing well logging and obtaining acoustic well logging and density well logging data, calculating an acoustic wave time-depth relationship and a VSP time-depth relationship to get time difference, correcting an acoustic wave curve, obtaining a synthetic record through corrected well-logging curve and seismic wavelet convolution, making a horizon calibration chart after the time shift quantity of a VSP corridor and the correct polarity are determined and performing horizon calibration on a ground seismic profile according to known drilling geological stratification. According to the seismic horizon calibration method, the acoustic well logging error and the frequency dispersion effect are eliminated, the synthetic record making precision is improved, human factors in the calibration are reduced, and the calibration accuracy is improved.
Owner:BC P INC CHINA NAT PETROLEUM CORP +1
Use of an effective tool model in sonic logging data processing
Methods and apparatus facilitating radial profiling of shear slowness are disclosed. According to some aspects of the invention, acoustic tool bias is accounted for in the calculation of radial profiles. According so some aspects, acoustic tool bias is accounted for by replacing acoustic tool structure with a resonance-impedance model. The resonance-impedance modeling according to principles of the present invention is applicable to vertical, deviated, and horizontal boreholes.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Acoustic logging while drilling tool having raised transducers
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Identification of Stress in Formations Using Angles of Fast and Slow Dipole Waves in Borehole Acoustic Logging
InactiveUS20090185446A1Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingSeismology for water-loggingAcousticsShear mode
Cross-dipole measurements are obtained in a borehole. By estimating a direction of polarization of the fast shear mode at low and high frequencies and comparing the estimated distances, a cause of anisotropy is established. Formation stresses and directions may be estimated.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
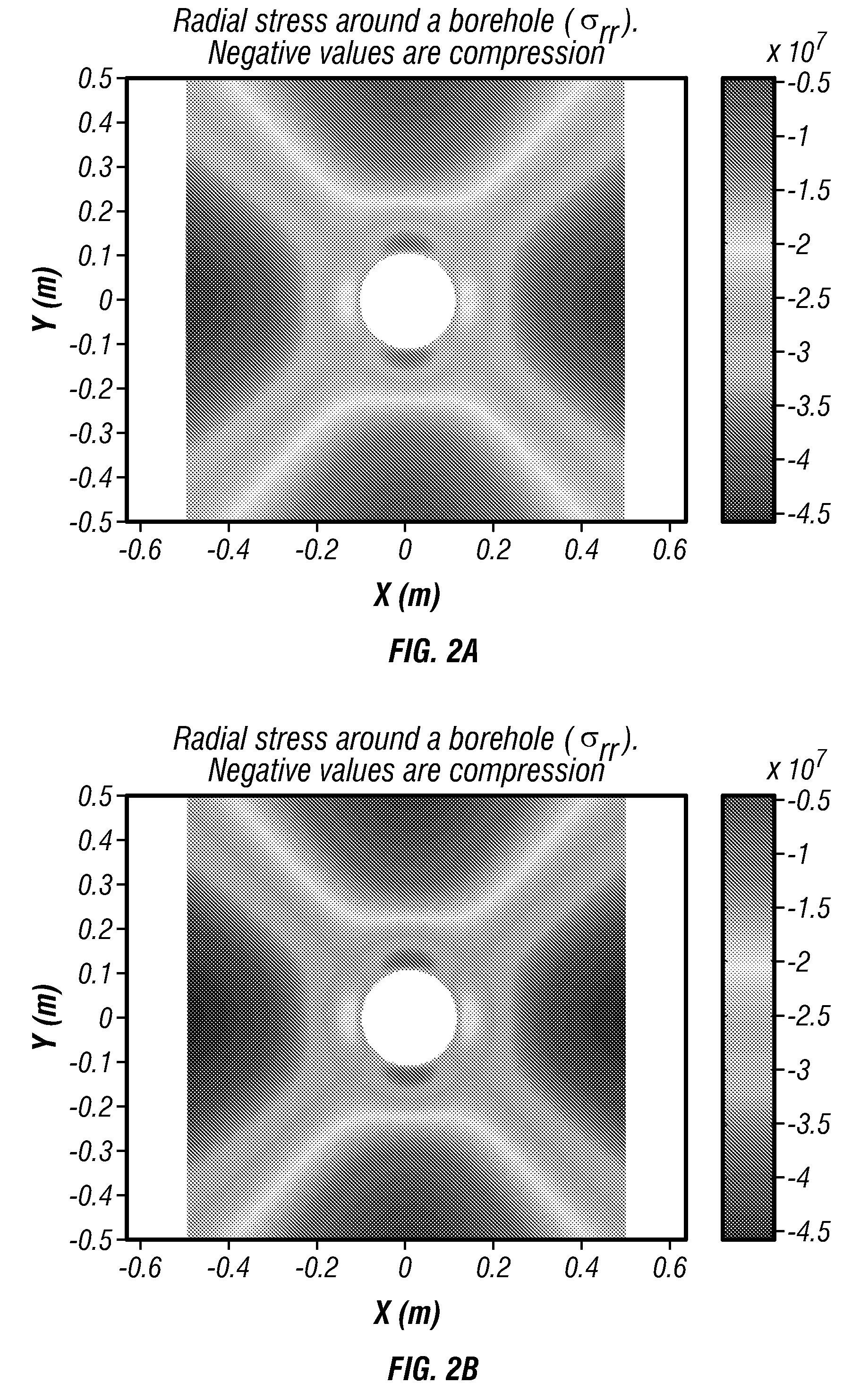
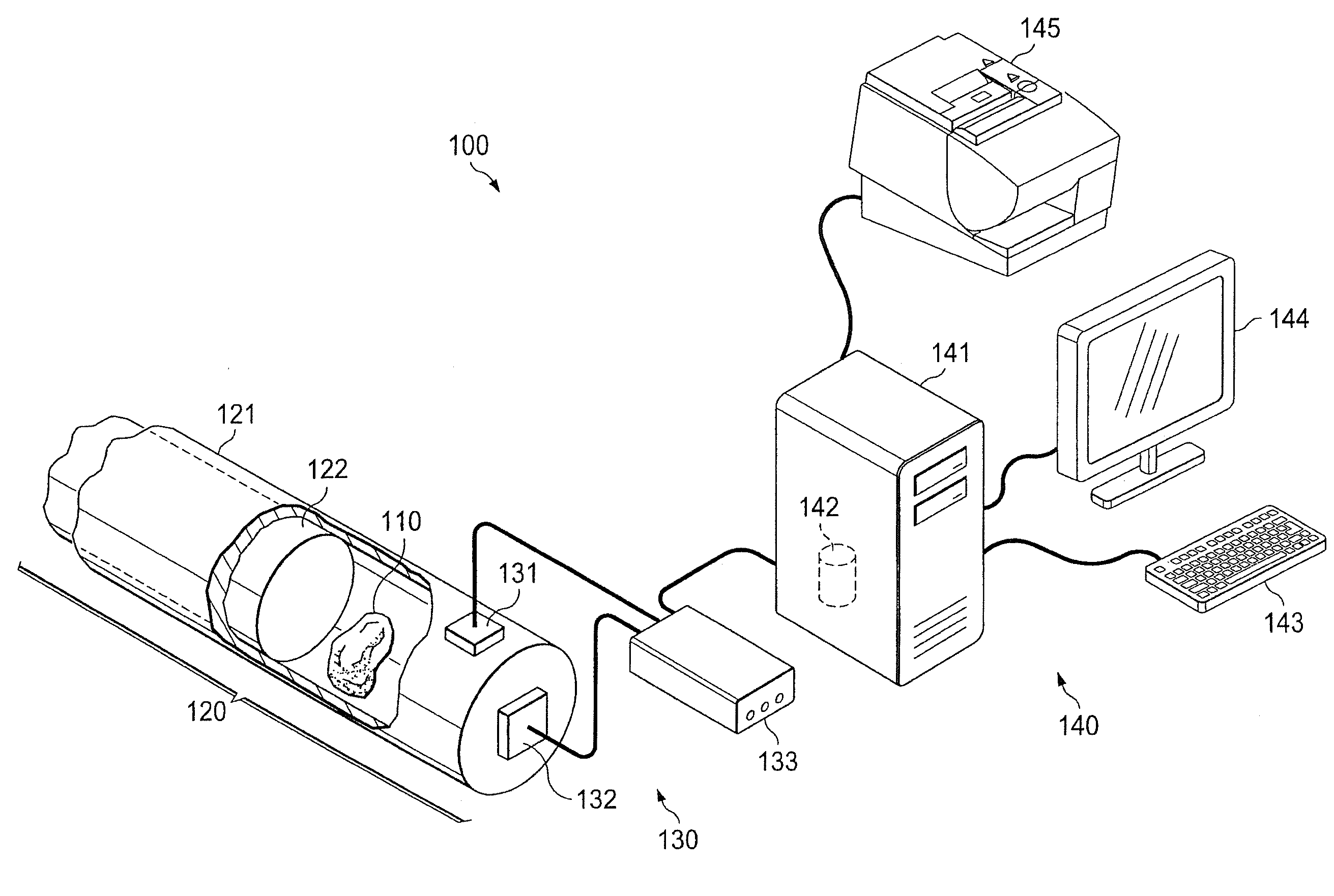
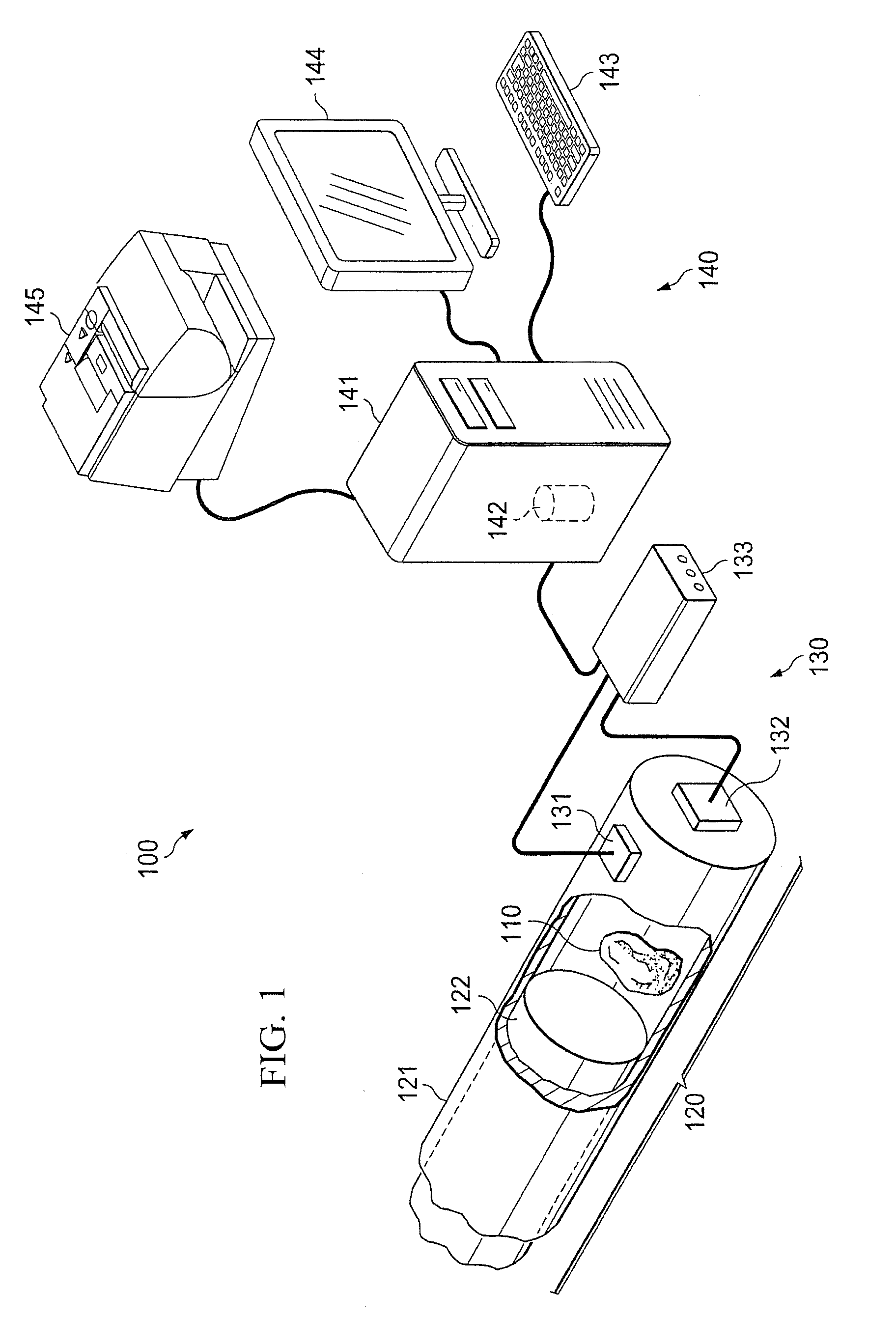
Systems and Methods For Determining Geologic Properties Using Acoustic Analysis
ActiveUS20110066390A1Increase the number ofFast analysisMaterial analysis using acoustic emission techniquesFlow propertiesTime informationLithology
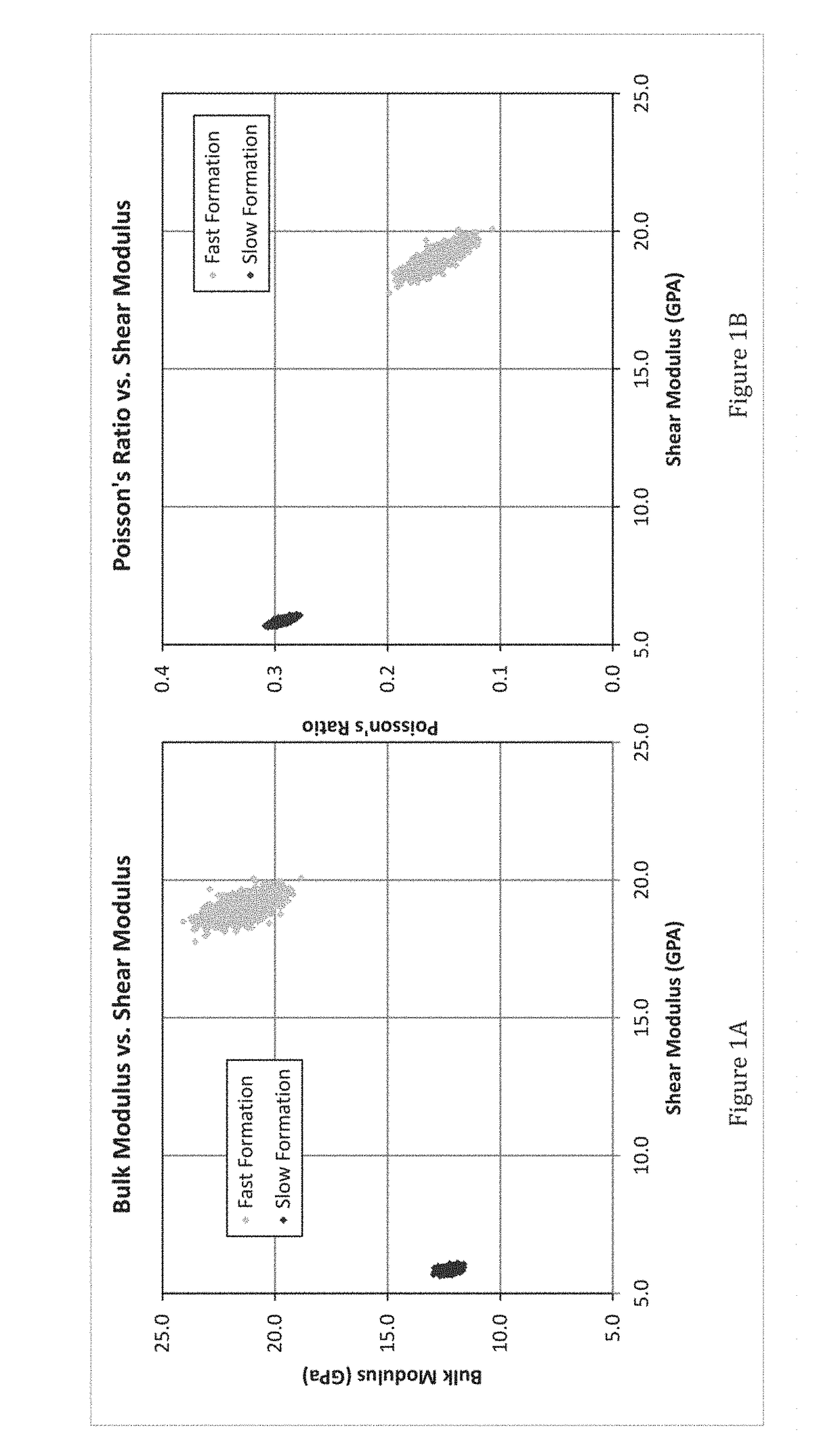
Systems and methods which determine geologic properties using acoustic analysis are shown. Acoustic signals are collected during processing (e.g., crushing, shearing, striking, compressing, etc.) of geologic media, such as rock samples, for determining geologic properties according to embodiments. The acoustic signals collected may include frequency information, amplitude information, time information, etc. which may be utilized in determining geologic properties, such as geologic media properties (e.g., mineralogy, porosity, permeability, sealing capacity, fracability, compressive strength, compressibility, Poisson's Ratio, Youngs Modulus, Bulk Modulus, Shear Modulus), geologic structure properties (e.g., lithology, seal quality, reservoir quality), geologic acoustic properties (e.g., acoustic logging effectiveness, acoustic response, natural or harmonic frequencies, etc.). Embodiments may be used to provide determination of geologic properties from a variety of geologic media samples, such as cuttings, core samples, etc.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL UPSTREAM RES CO
Inversion method of stratum shear wave velocity radial sections
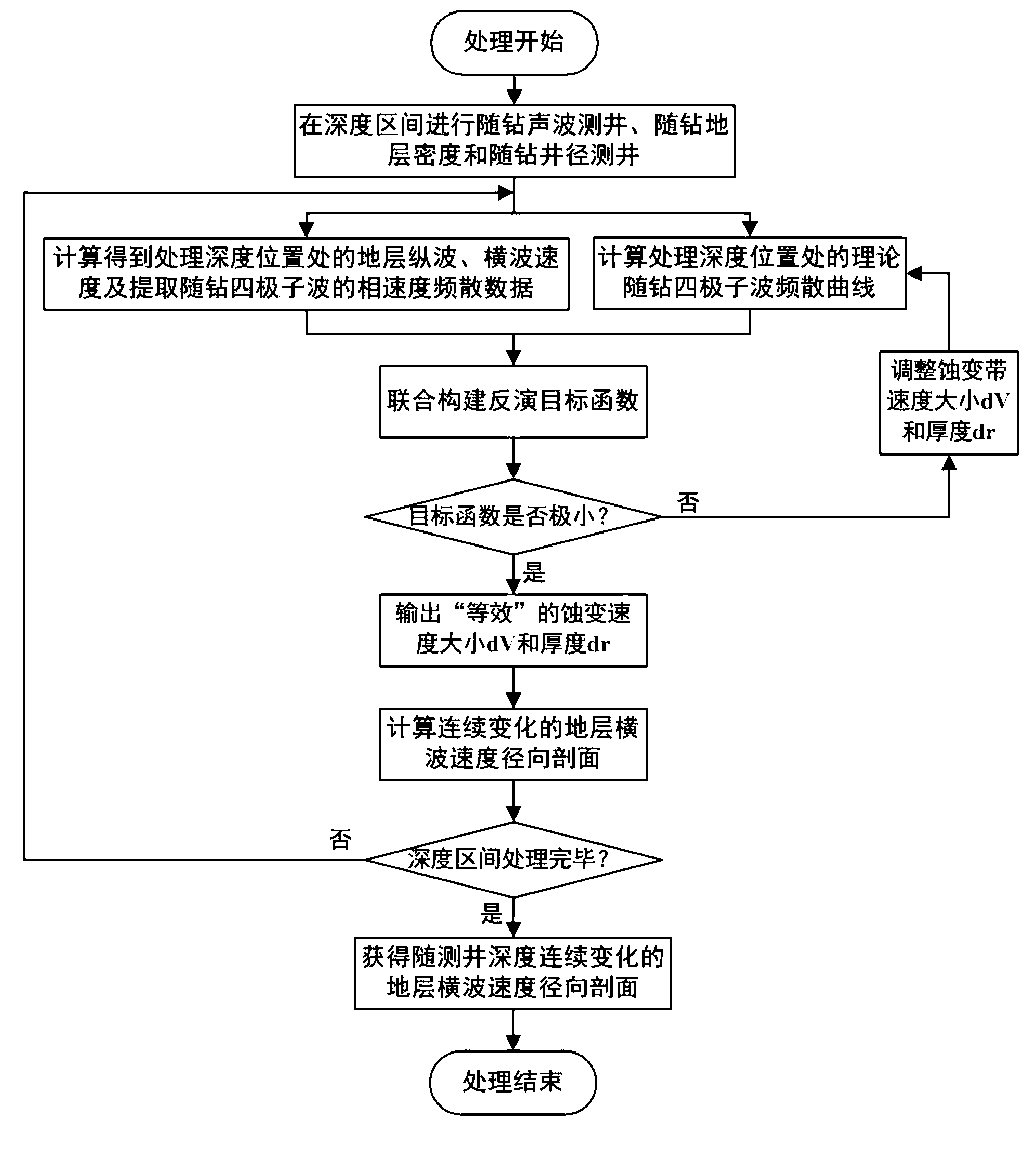
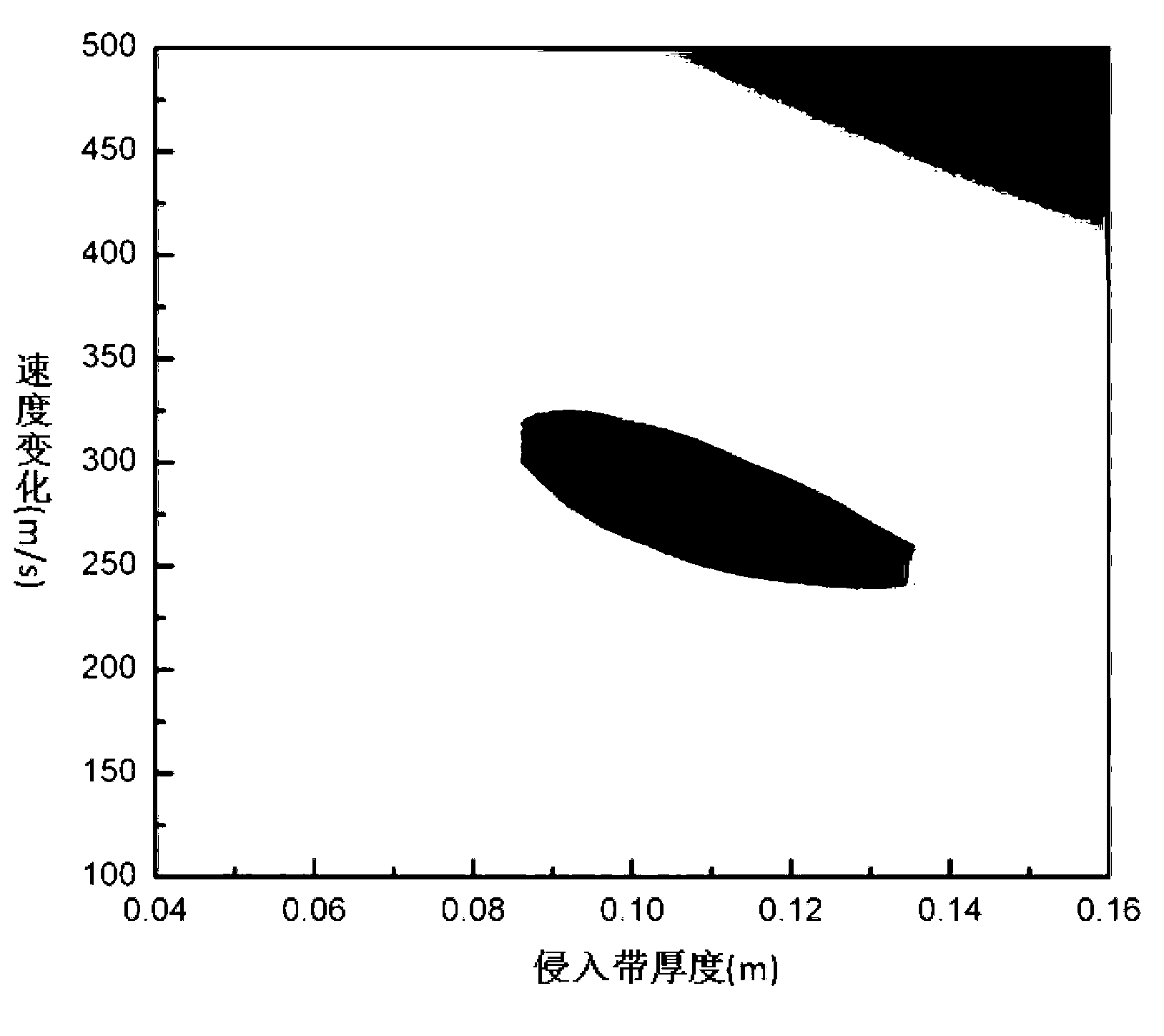
ActiveCN103233727AObtain changes in mechanical/acoustic parameters in real timeObtain real-time changes in mechanical/acoustic parameters of the dominant mechanical/acoustic parameters near the wellBorehole/well accessoriesFull waveQuadrupole
The invention relates to an inversion method of stratum shear wave velocity radial sections. The inversion method includes: performing acoustic logging while drilling and while drilling stratum density and well diameter logging in a depth interval, and obtaining while drilling monopole and quadrupole array acoustic full wave train data, a while drilling stratum density logging curve and a while drilling well diameter logging curve; obtaining stratum longitudinal wave velocity and shear wave velocity at the position of processing depth through calculation, and extracting phase velocity frequency dispersion data of while drilling quadrupole wave; calculating a theoretical while drilling quadrupole wave frequency dispersion curve at the position of the processing depth; constructing an inversion objective function in a combined mode; outputting equivalent alteration velocity and thickness; calculating continuously variable stratum shear wave velocity radial sections; and repeating the steps until processing of the whole depth interval is finished, and obtaining the stratum shear wave velocity radial sections changing continuously along with logging depth. The inversion method of stratum shear wave velocity radial sections has the advantages of obtaining changes of mechanics / acoustic parameters nearby a well in real time, solving the problem of ununiqueness of inversion, and improving reliability of inversion results.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (EAST CHINA)
Method utilizing logging information for determining optimal perforation layer for SRV fracturing
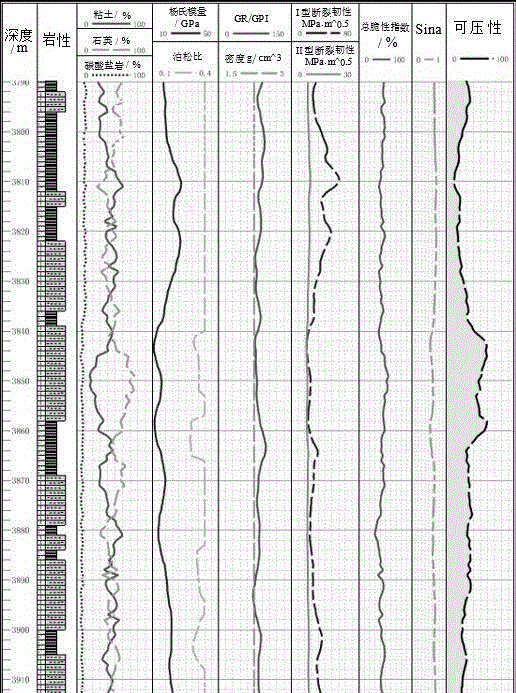
InactiveCN105114047AConvenient and efficient calculationComputationally efficientFluid removalType fractureReservoir volume
The invention discloses a method utilizing logging information for determining the optimal perforation position for SRV (Stimulated Reservoir Volume) fracturing. The method comprises the following steps: (A) calculating mineral friability index B1 by using conventional logging information, elemental capture spectroscopy logging information and natural gamma spectroscopy logging information; (B) calculating dynamic Young modulus E and dynamical poisson ratio v of each layer section by using acoustic logging information and calculating a mechanical friability index B2 of each layer section; (C) calculating total friability index BTot of the layer sections; (D) calculating confining pressure Pc; (E) calculating rock tensile strength St of the layer sections; (F) calculating an I type fracture toughness value KIC and an II type fracture toughness value KIIC of the each layer section; (G) calculating an inner friction angle of each layer section by using logging information; (H) calculating the reservoir compressibility index Frac of each layer section; and (I) selecting a layer section with a high reservoir compressibility index Frac as the optimal SRV fracturing perforation layer. The method is capable of conveniently and efficiently calculating the compressibility index of each layer section by directly using the logging information, so as to provide decision basis for selecting the optimal SRV fracturing perforation layer and promoting exploitation of shale reservoirs.
Owner:SOUTHWEST PETROLEUM UNIV
Real-time compression method of three-dimensional sonic logging data
InactiveCN102522999AReal-time compression implementationReduce storageCode conversionArray data structureAcoustic wave
The invention discloses a real-time compression method of three-dimensional sonic logging data, which comprises the following steps: dividing data to be compressed into data to be compressed, which have the length of m, by splitting original sonic data into retention data with a high n1 bit and the data to be compressed, which have a low n2 bit; then carrying out DCT (discrete cosine transformation) on the data to be compressed according to groups to obtain mapping data, quantifying the mapping data, i.e. retaining more bit numbers for the data with larger numerical value while retaining less bit numbers for the data with smaller numerical value, realizing the real-time compression of the data and coding the data after being quantified; and finally, merging the retention data with the high n1 bit in retention data number groups and the data after being coded so as to obtain compressed data. Therefore, the storage quantity and the transmission quantity of data are reduced, and the logging efficiency is enhanced.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
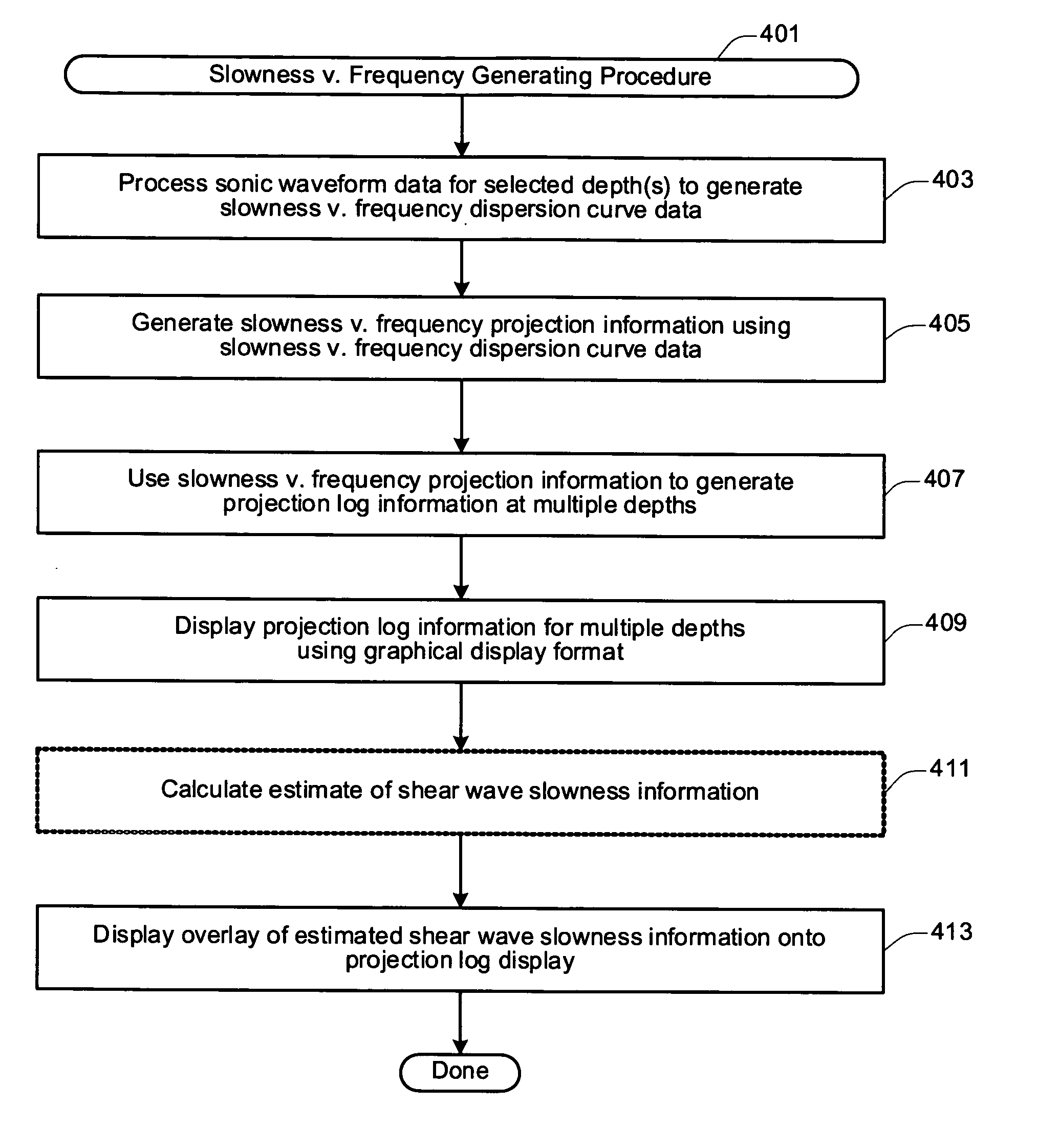
Slowness-frequency projection display and animation
InactiveUS20050190651A1Seismic signal processingSeismology for water-loggingAnimationQuality control
The present invention describes several techniques for displaying sonic logging data that provide highly reliable, visual quality-control (QC) indicators. One aspect of the present invention is directed to a novel display of sonic logging data corresponding to a slowness frequency analysis (SFA) projection log. One of the benefits of the SFA projection log display of the present invention is that the format of the information displayed may be used to visually confirm the accuracy / inaccuracy of the processed sonic logging data over selected depth intervals. The SFA projection log display may also be used to visually identify any potential problematic or inconsistent portions of the processed sonic logging information. An overlay of estimated wave slowness information may also be displayed onto the SFA log display in a manner which enables an observer of the SFA log display to visually assess the relative accuracy of the estimated wave slowness information over selected depth intervals. The SFA log display may also include a navigable pointer mechanism configured or designed to allow a user to navigate within the SFA log display in order to access depth specific sonic logging information associated with selected depths. In this way selected characteristics of depth specific sonic logging information may be accessed and displayed concurrently with log information for an entire depth interval.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Soundwave-while-drilling well logging device
The invention relates to a soundwave-while-drilling well logging device, which comprises a drill collar and a transmission energy converter arranged on the drill collar, wherein the transmission energy converter comprises a first end socket metal block and a second end socket metal block which are arranged at two ends of the transmission energy converter, a metal splint positioned in the middle of the transmission energy converter and a plurality of piezoelectric ceramic wafers which are positioned between the first end socket metal block, the second end socket metal block and the metal splint respectively; the number of the piezoelectric ceramic wafers is even, the direction of polarization of each piezoelectric ceramic wafer is the thickness direction, and the directions of polarizationof the adjacent piezoelectric ceramic wafers are opposite; and the length direction of the transmission energy converter is perpendicular to that of the drill collar. The soundwave-while-drilling well logging device can judge information such as the velocity of longitudinal waves and transverse waves, porosity, pore pressure and the like of formations, particularly soft formations (the velocity of the transverse waves of the formations is less than sound velocity of fluid in a well), the velocity of the transverse waves of the formations can be measured by a quadrapole mode to perform the analysis of terrestrial stress, and thus, the integral function of the energy converter is expanded.
Owner:INST OF ACOUSTICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method and apparatus for logging foam cement in cased boreholes
InactiveUS20090086575A1Minimizing telemetry band width requirementMinimization requirementsConstructionsSeismology for water-loggingFast Fourier transformTransducer
An acoustic logging system that measures distribution of foam cement and other material in a casing-borehole annulus. The distribution is preferably displayed as map. A borehole tool utilizes at least one acoustic transducer with a known frequency response and mounted on a rotating scanning head that is pointed essentially perpendicular to the borehole wall. The response of the transducer is used to measure an original impedance map of material within the borehole-casing annulus. A fast Fourier transform is used to generate a FFT map from the data comprising the original impedance map. The original impedance map is then combined with the FFT map using logic rules to obtain a final impedance map that is indicative of material within the casing-borehole annulus.
Owner:WEATHERFORD TECH HLDG LLC
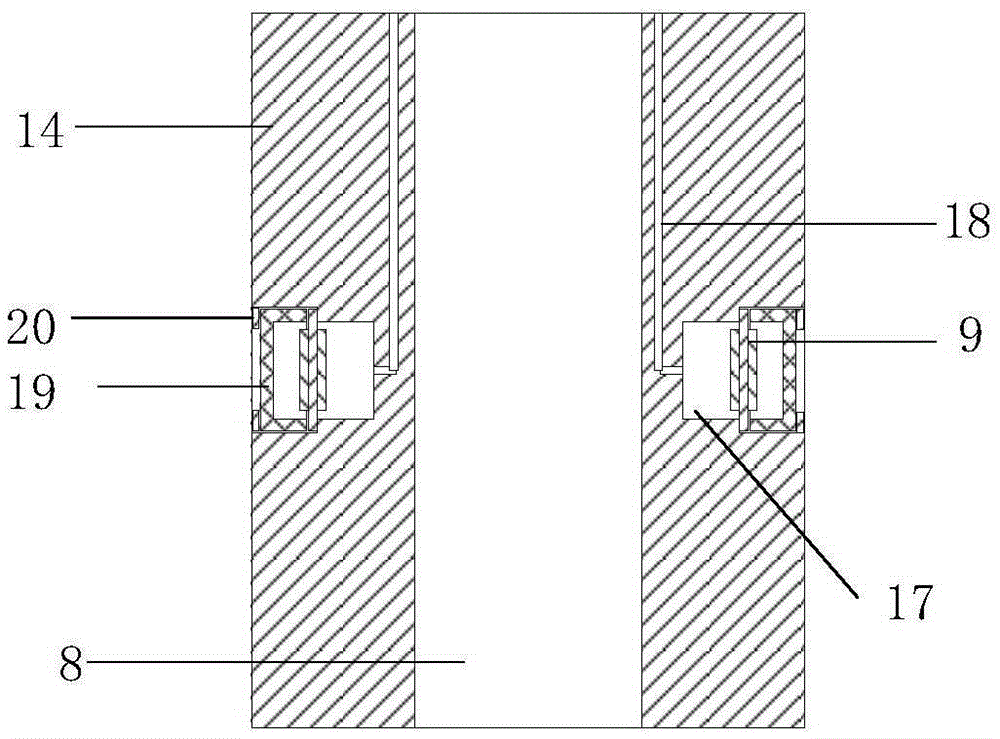
Acoustic logging-while-drilling transmitting unit and device thereof
InactiveCN105257282AWith high temperature resistanceWith high pressureSurveyDrilling rodsTransducerAcoustic wave
The invention relates to an acoustic logging-while-drilling transmitting unit and a device thereof. The transmitting unit comprises a drill collar chisel groove (17), a transmitting transducer (9) and an acoustic window (19), wherein the drill collar chisel groove (17) is provided with a step; the transmitting transducer (9) is arranged on the step and is used for generating acoustic waves; the acoustic window (19) is arranged on the transmitting transducer (9); the acoustic window (19) and the transmitting transducer (9) form a cavity; oil is injected into the cavity to form a liquid cavity; and the acoustic waves generated by the transmitting transducer (9) are transmitted outwards through the liquid cavity. The multi-pole acoustic logging-while-drilling transmitting device has the advantages of high temperature resistance, high pressure resistance, vibration resistance, small size, easiness in assembly, good insulation and sealing and the like.
Owner:INST OF ACOUSTICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method of using electrical and acoustic anisotropy measurements for fracture identification
InactiveUS6925031B2Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingSeismic signal processingAcousticsElectric resistivity
Measurements made by a cross-dipole acoustic logging tool in a borehole are processed to determine the principal directions of azimuthal anisotropy of a subsurface formation. Measurements indicative of azimuthal resistivity variations are also made with a multicomponent induction logging tool. These electrical measurements are processed using the principal direction determined from acoustic measurements to give an estimate of azimuthal resistivity variations. Based on modeling results, azimuthal resistivity variations are interpreted to estimate a fracture depth in the rock for known fluids therein.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
System and method for modeling the effects of fluid changes in low porosity hydrocarbon reservoirs
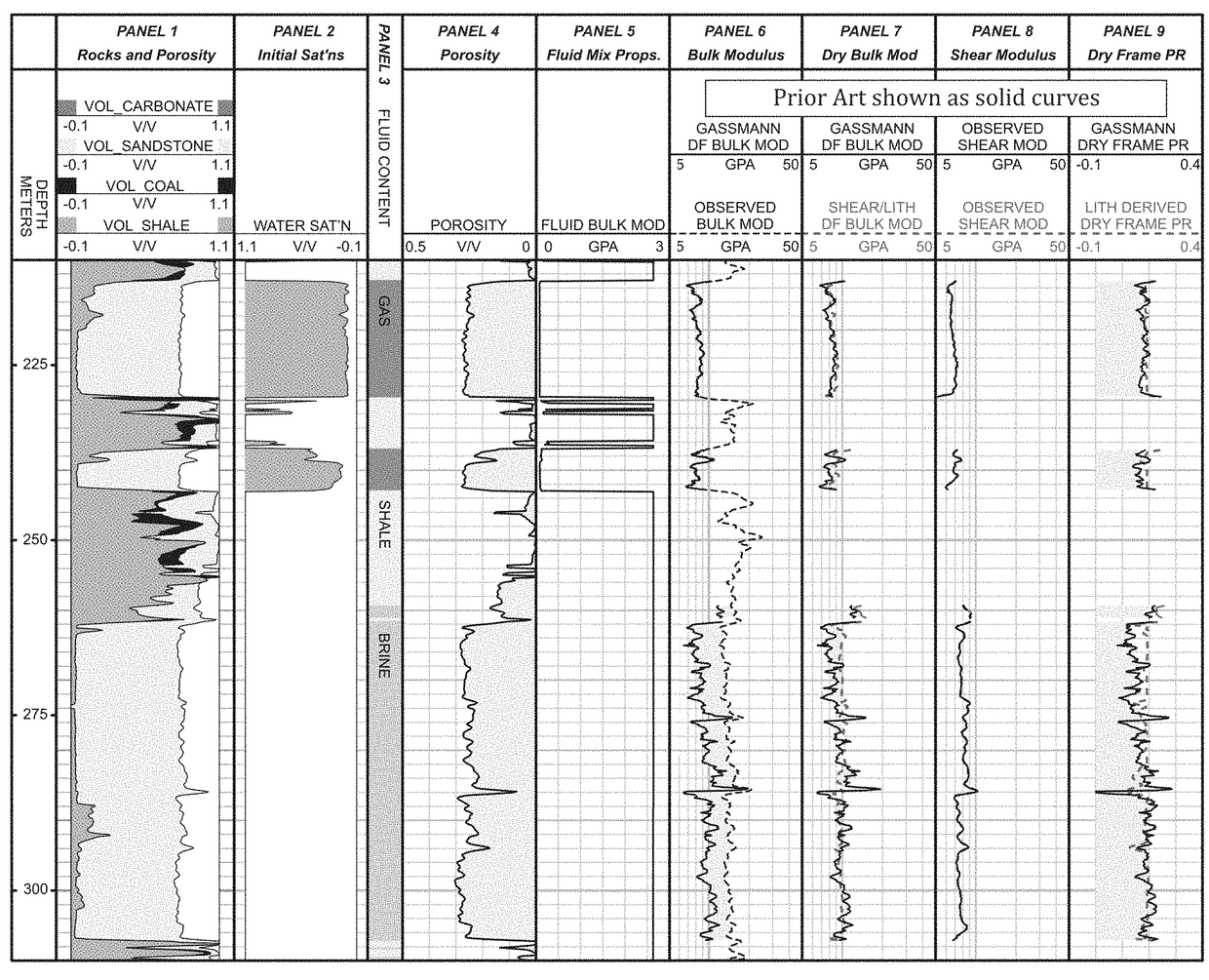
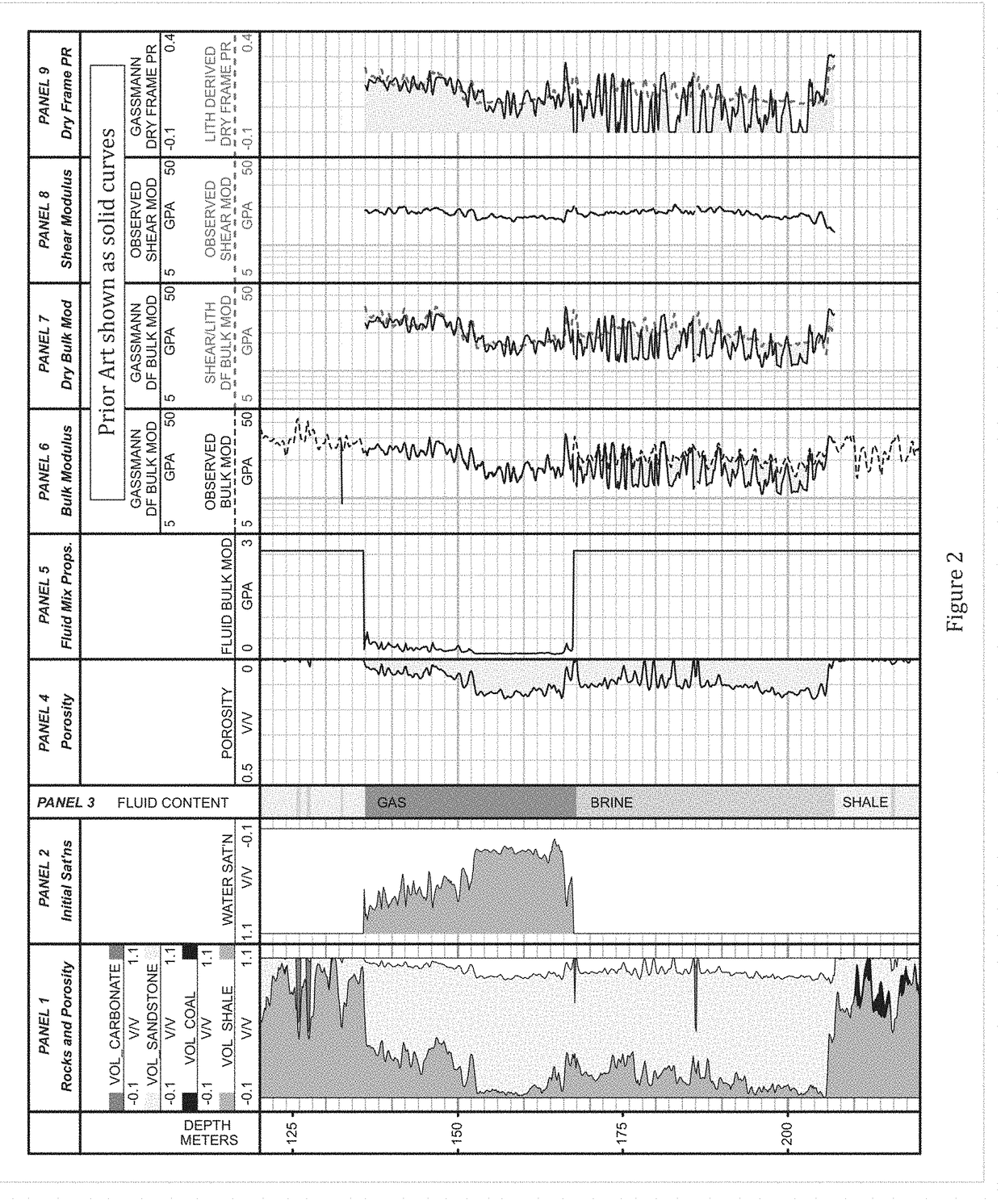
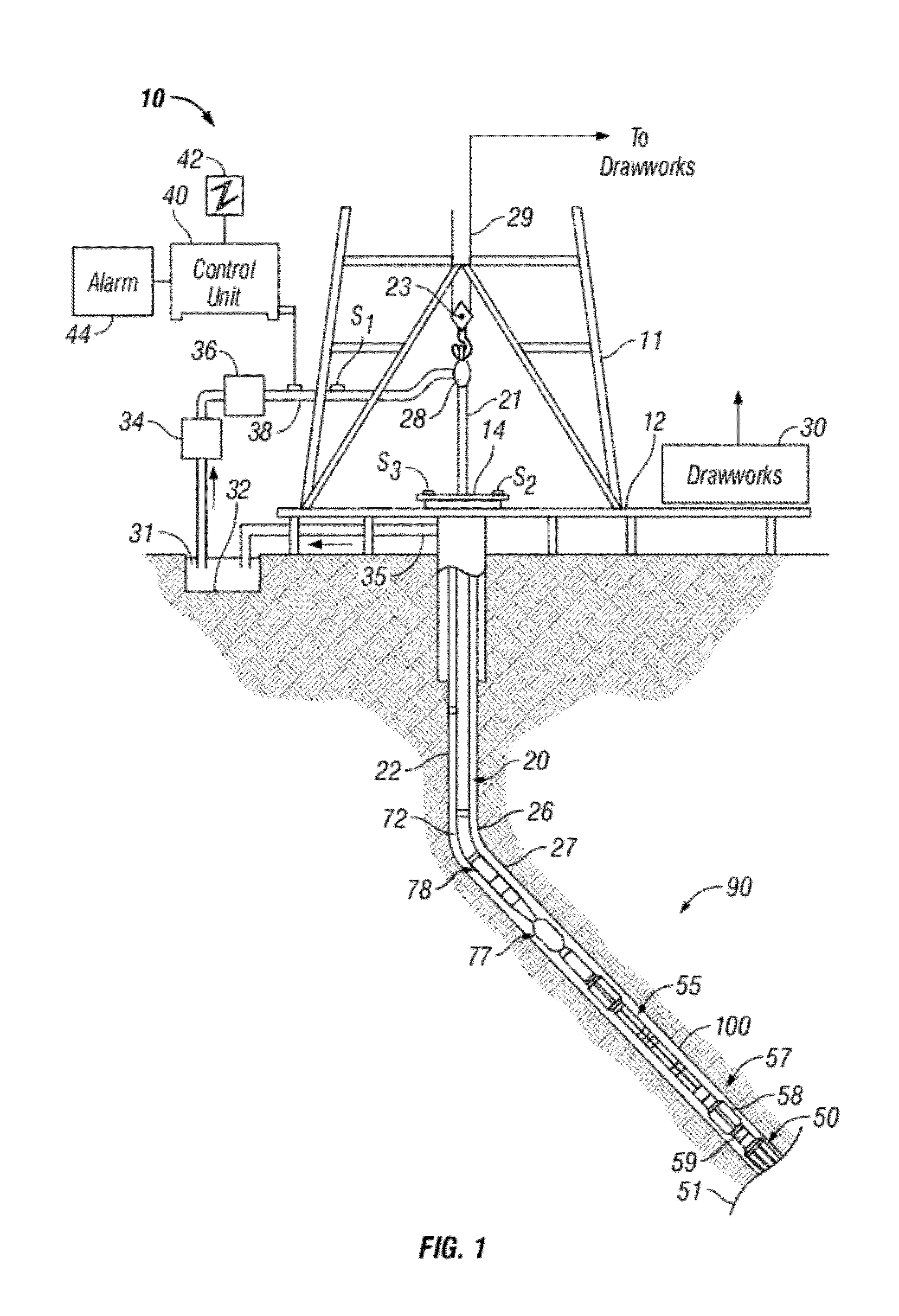
InactiveUS20170212275A1Overcome limitationsWell formedGeomodellingComputer aided designShear modulusLithology
A system and method for modeling fluid effects in a subsurface reservoir combines high quality shear modulus data from modern sonic logs with the inherent stability of VpVs ratio to derive more credible dry frame bulk modulus, in turn leading to improved fluid saturation modeling and improve fluid effect modeling. The system and model are designed primarily for low porosity and mixed lithology subsurface reservoirs although they may also be used with confidence in high porosity reservoirs.
Owner:CHEVROU USA INC
Optimal drilling trajectory prediction method of lateral well
PendingCN108442922ADetermine reliabilityVerify reliabilitySurveyData processing applicationsAcoustic emissionAcoustic wave
The invention relates to the technical field of exploration and development of oil and gas fields, in particular to an optimal drilling trajectory prediction method of a lateral well. The method includes the steps of acquiring a rock three-dimensional dynamics parameter field through conversion of dynamic static rock dynamics; determining natural fracture systems and occurrence distribution through core palaeomagnetic orientation, imaging logging and array acoustic logging; conducting present stress field simulation utilizing the rock three-dimensional dynamics parameter field; determining development probability of fractures of different periods utilizing acoustic emission experiments to simulate ancient stress field of different periods; simulating and determining present crustal stressvertical distribution through stress field simulation of well areas; and predicting fracturing fracture spreading directions utilizing crustal stress, fractures and vertical distribution of rock dynamics to establish an equivalent extending vertical zonation model of fracturing fractures. The optimal drilling trajectory prediction method of the lateral well verifies the reliability of fracturing fracture spreading directions by combining the drilling direction of the lateral well and dynamic materials of the lateral well, and realizes direction prediction of fracturing fractures of different blocks and optimal drilling trajectory design of the lateral well.
Owner:刘敬寿
Imaging of Formation Structure Ahead of the Drill-Bit
The present disclosure is related to apparatuses and methods for downhole acoustic logging. The tool may be used for generating a guided borehole wave that propagates into the formation as a body wave, reflects from an interface, and is converted back into a a guided borehole wave. Guided borehole waves resulting from reflection of the body wave are used to image a reflector. Methods may include processing of acoustic logging signals including: wavefield separation, auto-correlation of wavefield components, filtering using a dip filter, and estimating a distance to the reflective interface.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
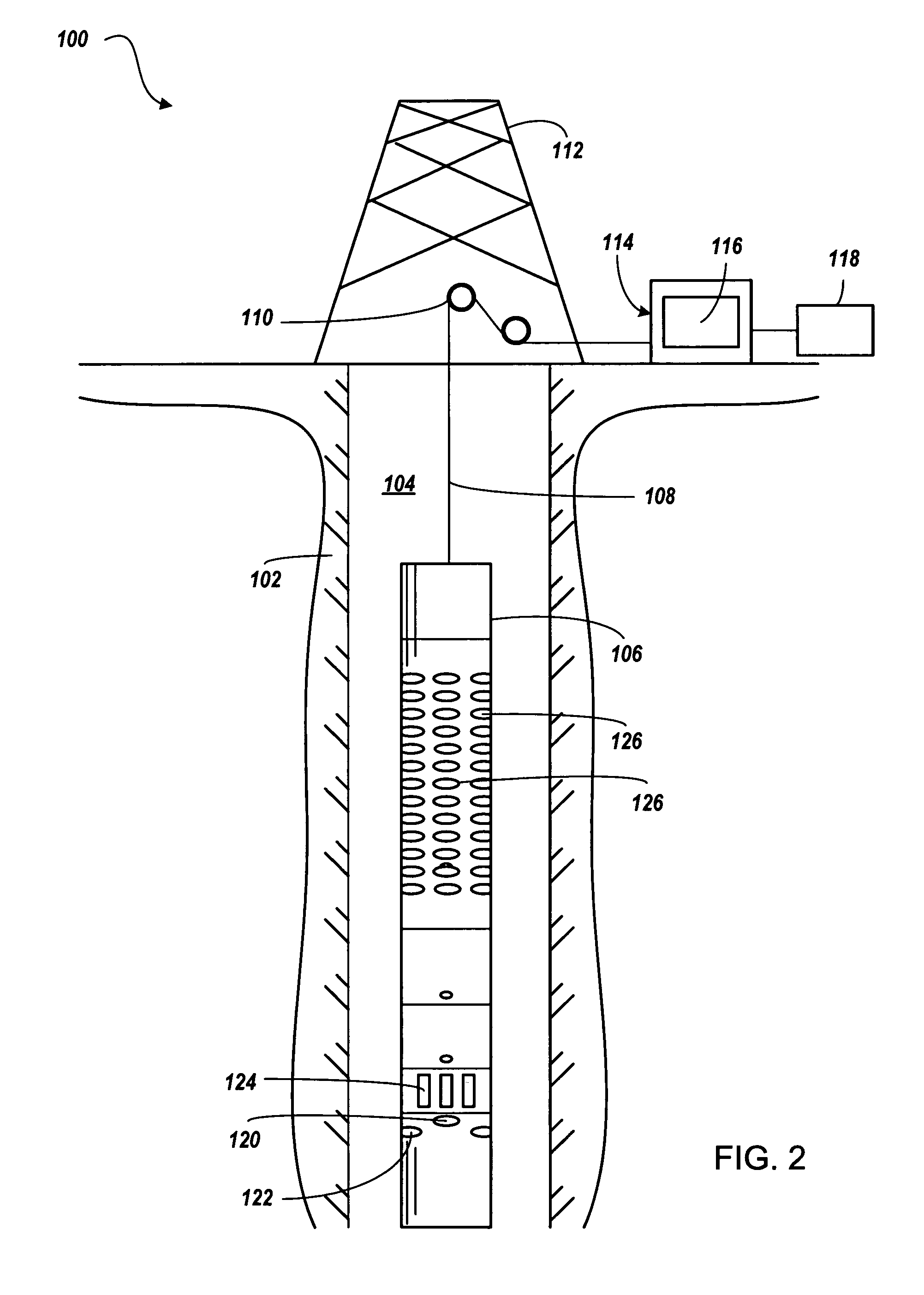
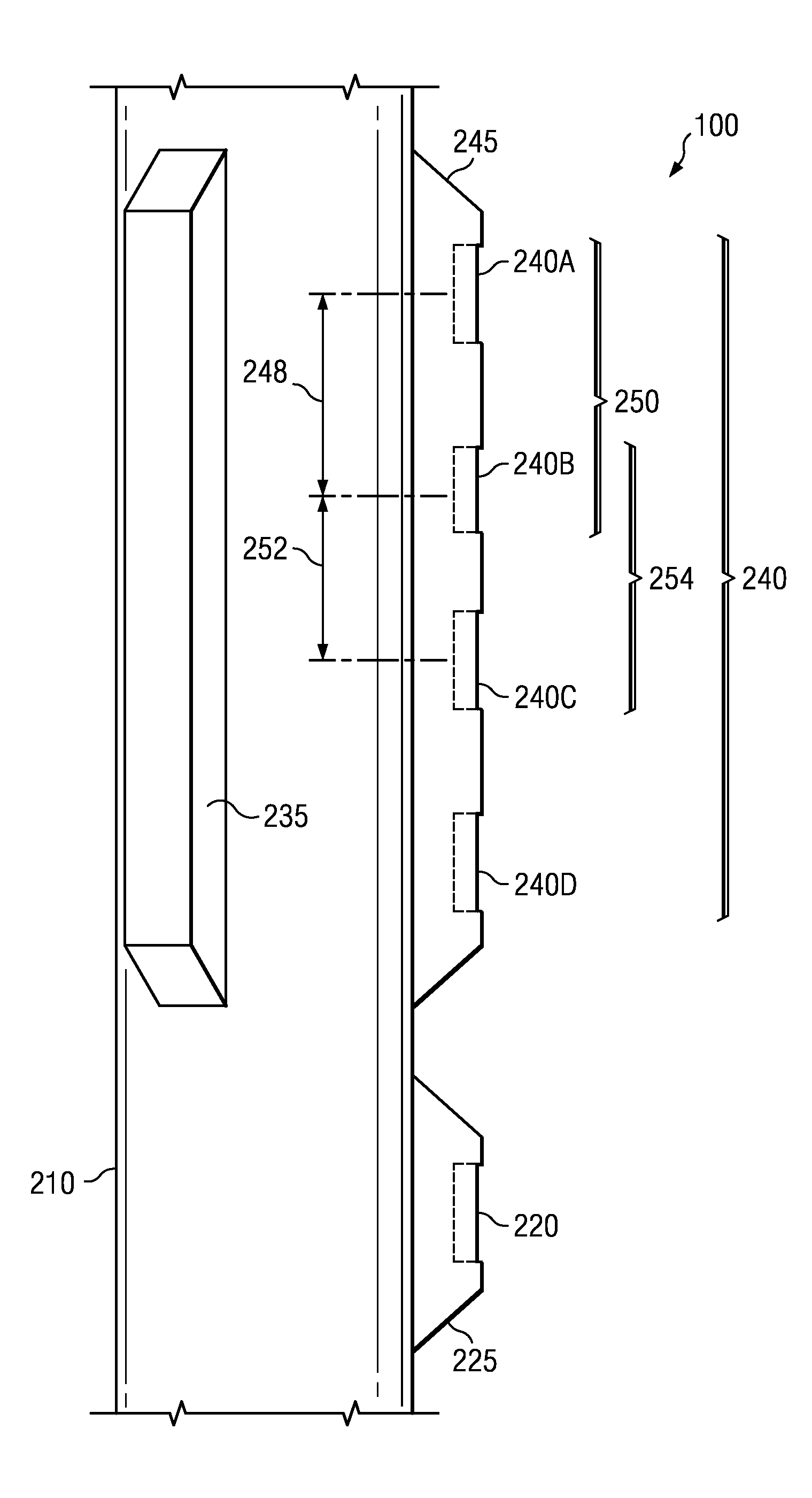
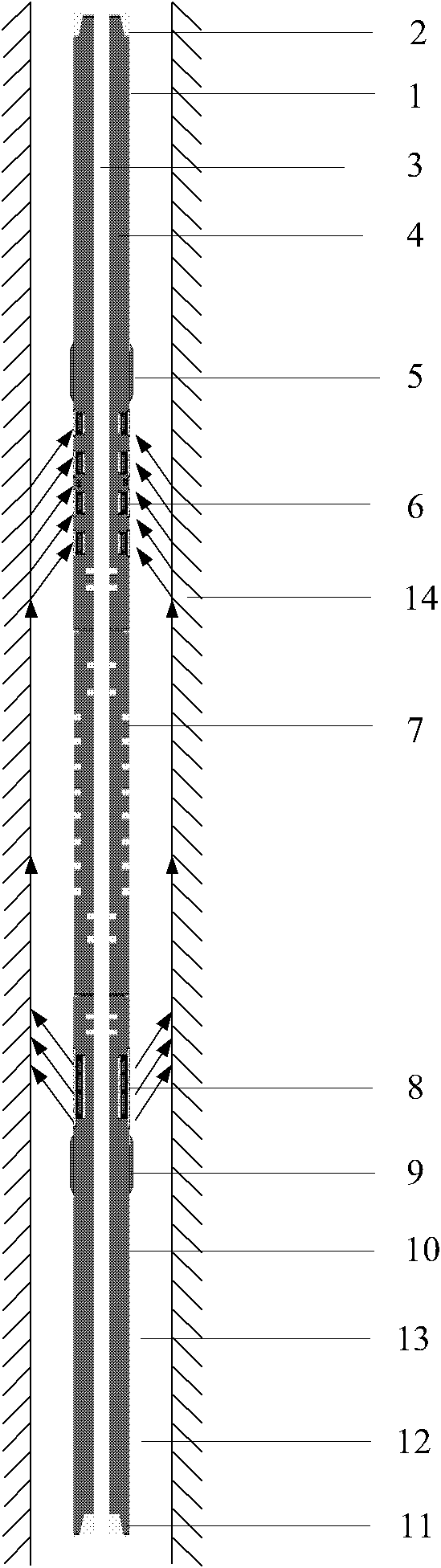
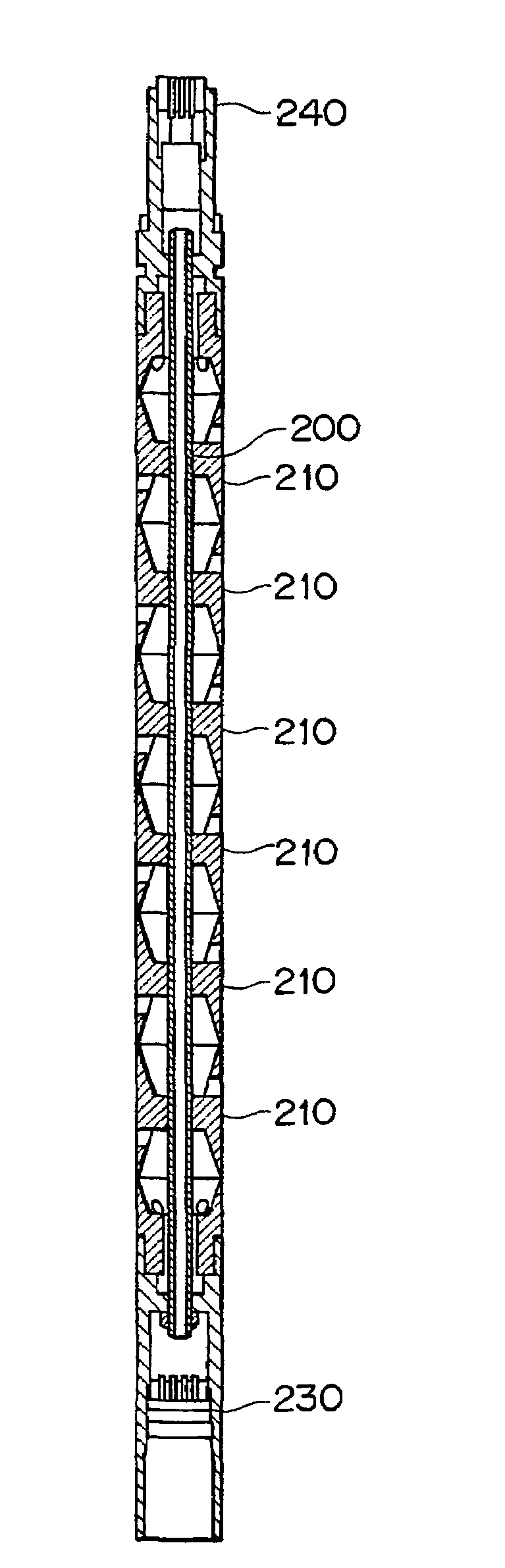
Sonic logging tool including receiver and spacer structure
InactiveUS7336562B1Prevent removalAchieve communicationSeismology for water-loggingAcoustic wave reradiationDispersion curveEngineering
A formation logging tool having a substantially continuous central mandrel with regularly spaced mass blocks disposed thereon, at least some of the mass blocks carrying sensors such as receivers. By adopting this structure, the tool can be made to behave as a mass-spring structure and its flexural and extensional behaviour controlled such that its dispersion curve does not extend into the dispersion curve of the formation to be logged. The structure can be applied to the whole of the logging tool or just to the receiver section and / or any spacer section between the receiver and the transmitter section.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com