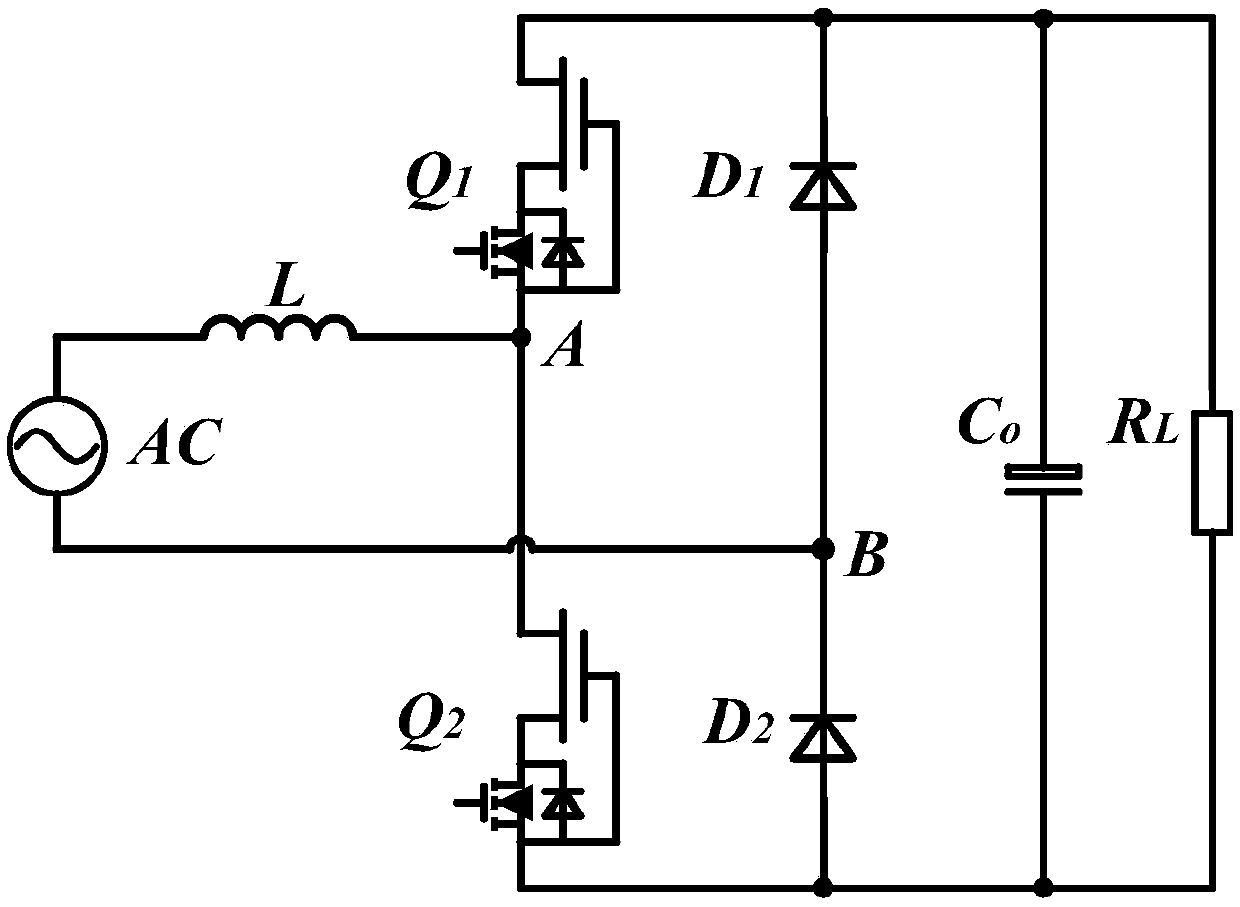
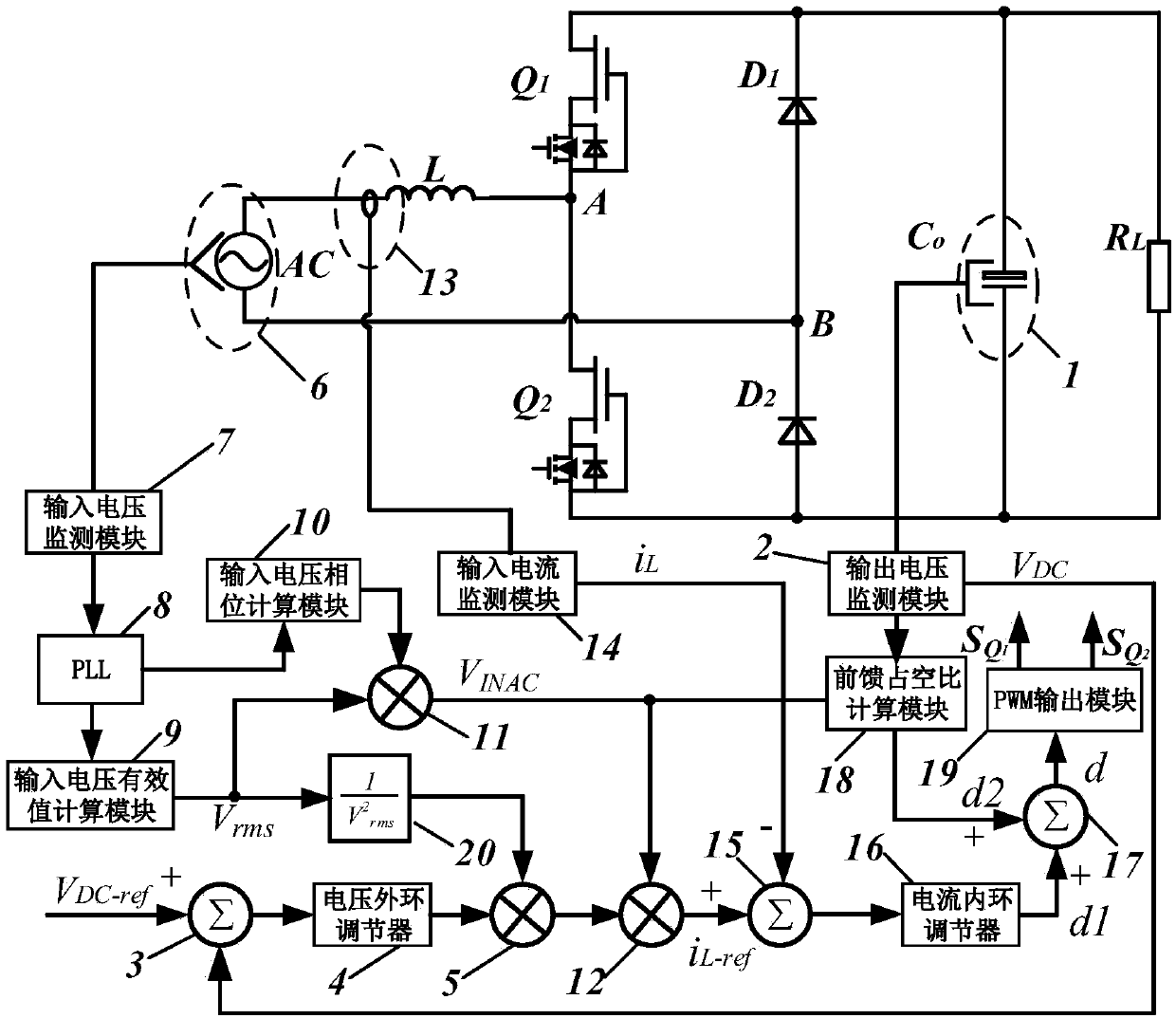
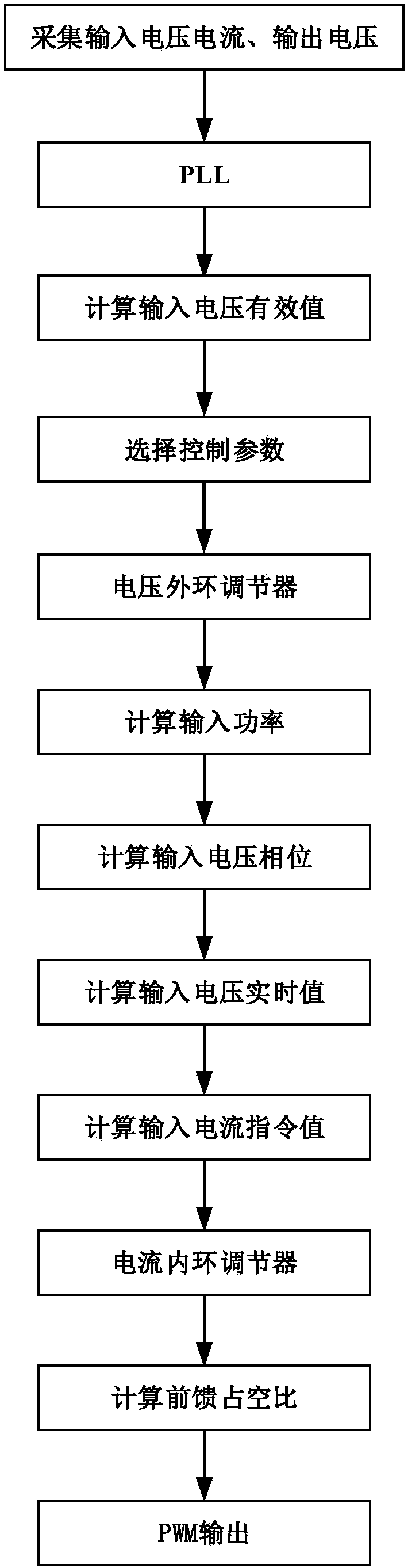
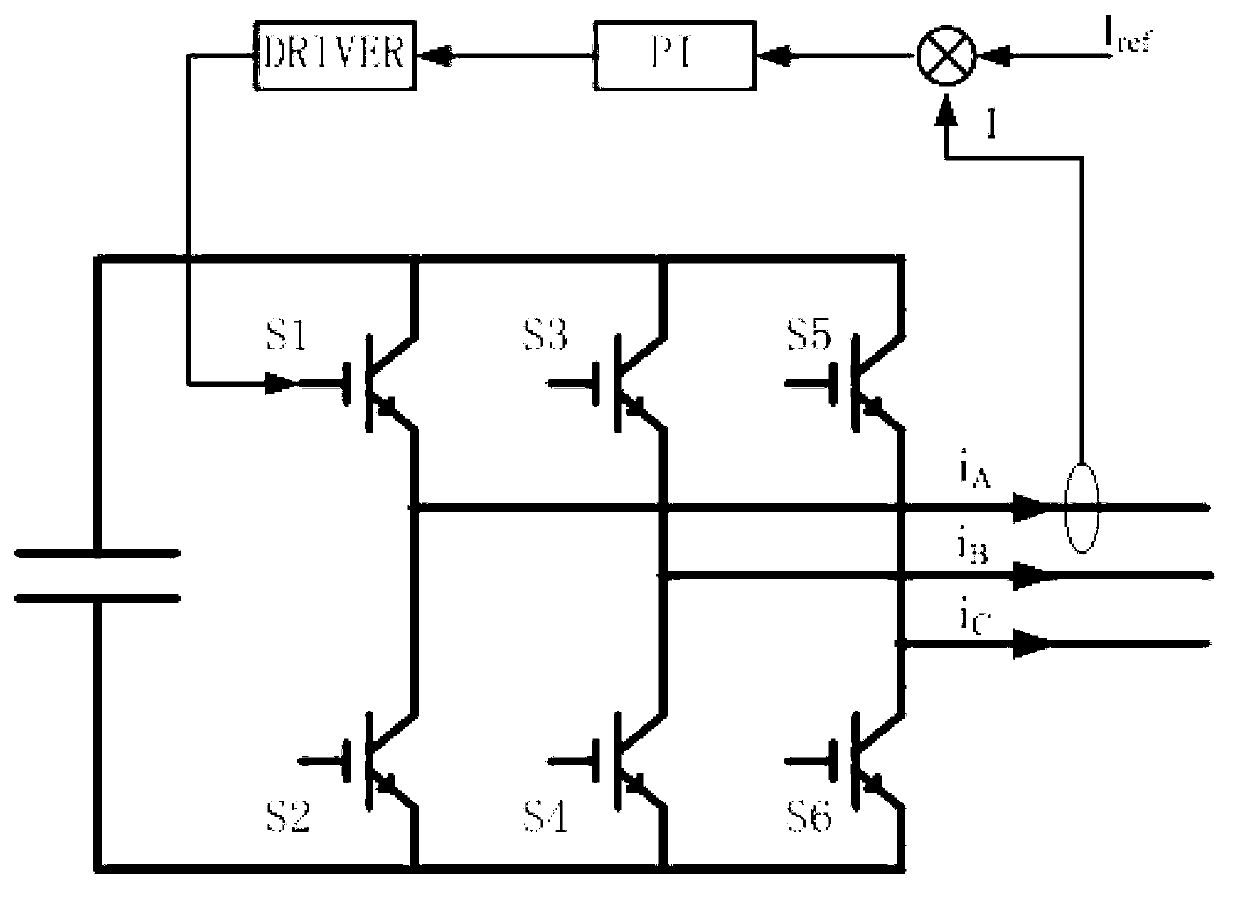
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
359 results about "Sinusoidal current" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A sinusoid is a signal which has the form of the sine or cosine function. A sinusoidal current is usually referred to as alternating current (AC) such a current reverses at regular time intervals and has alternately positive and negative values. Circuits driven by sinusoidal current or voltage sources are called AC circuits.
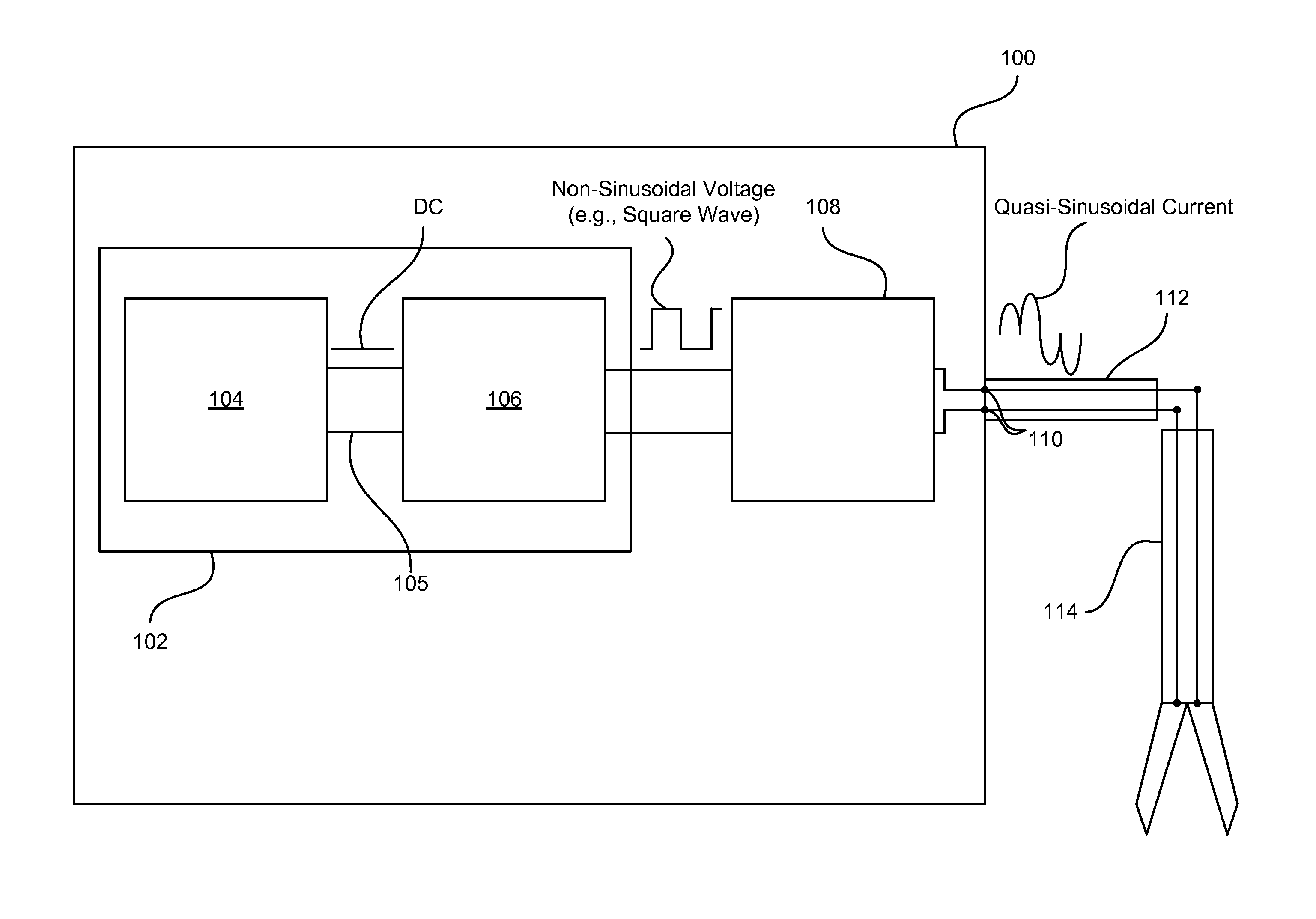
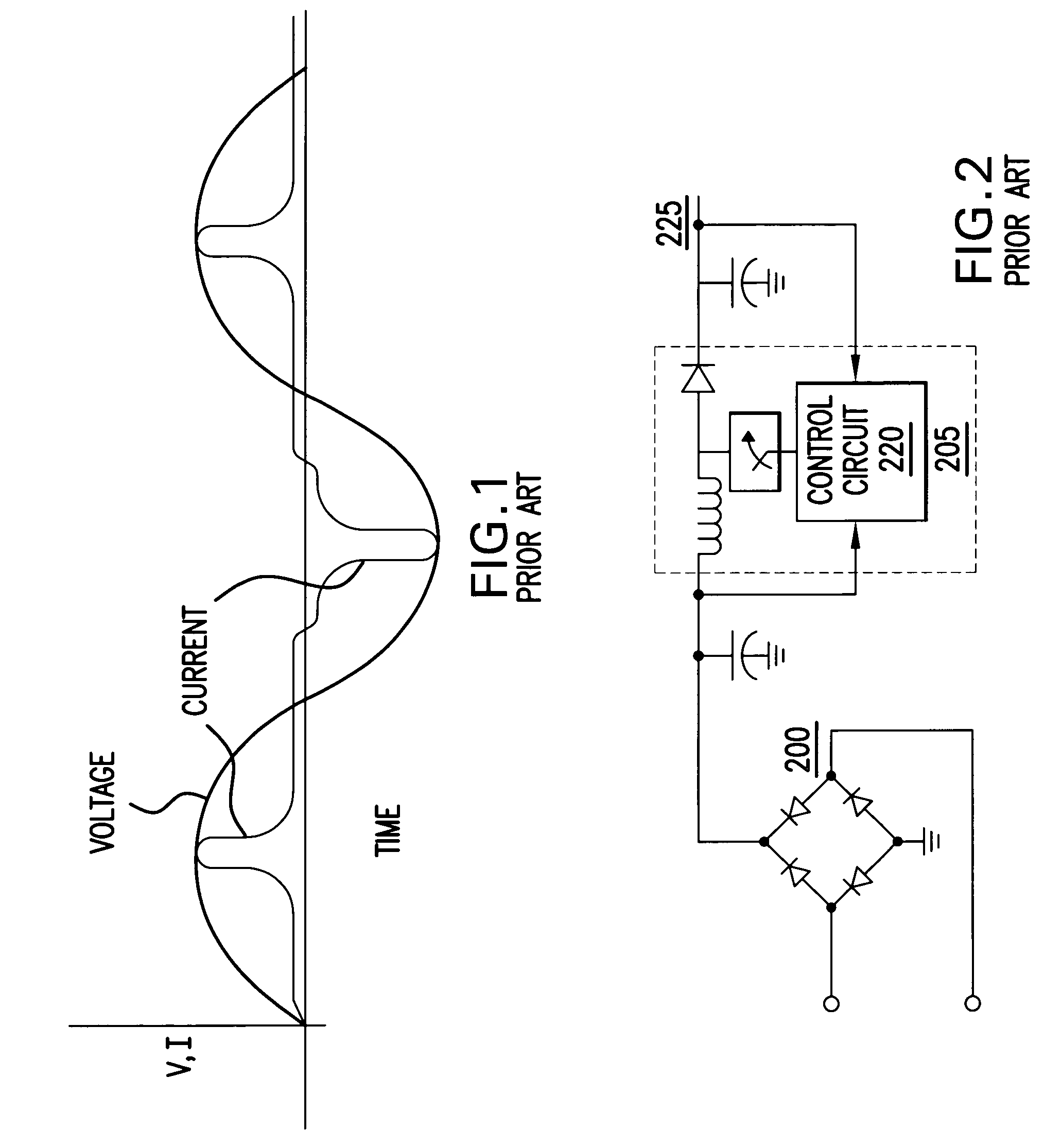
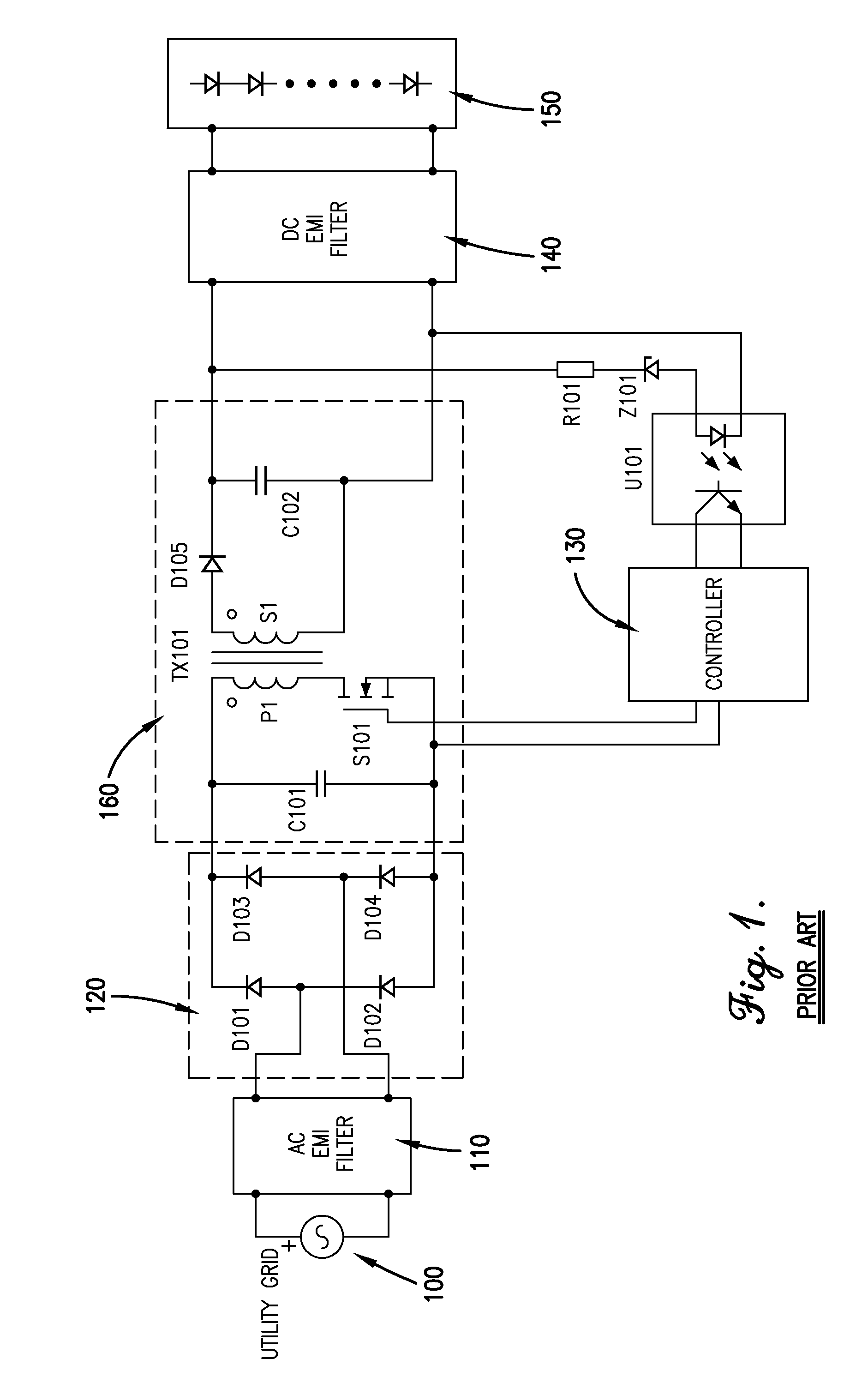
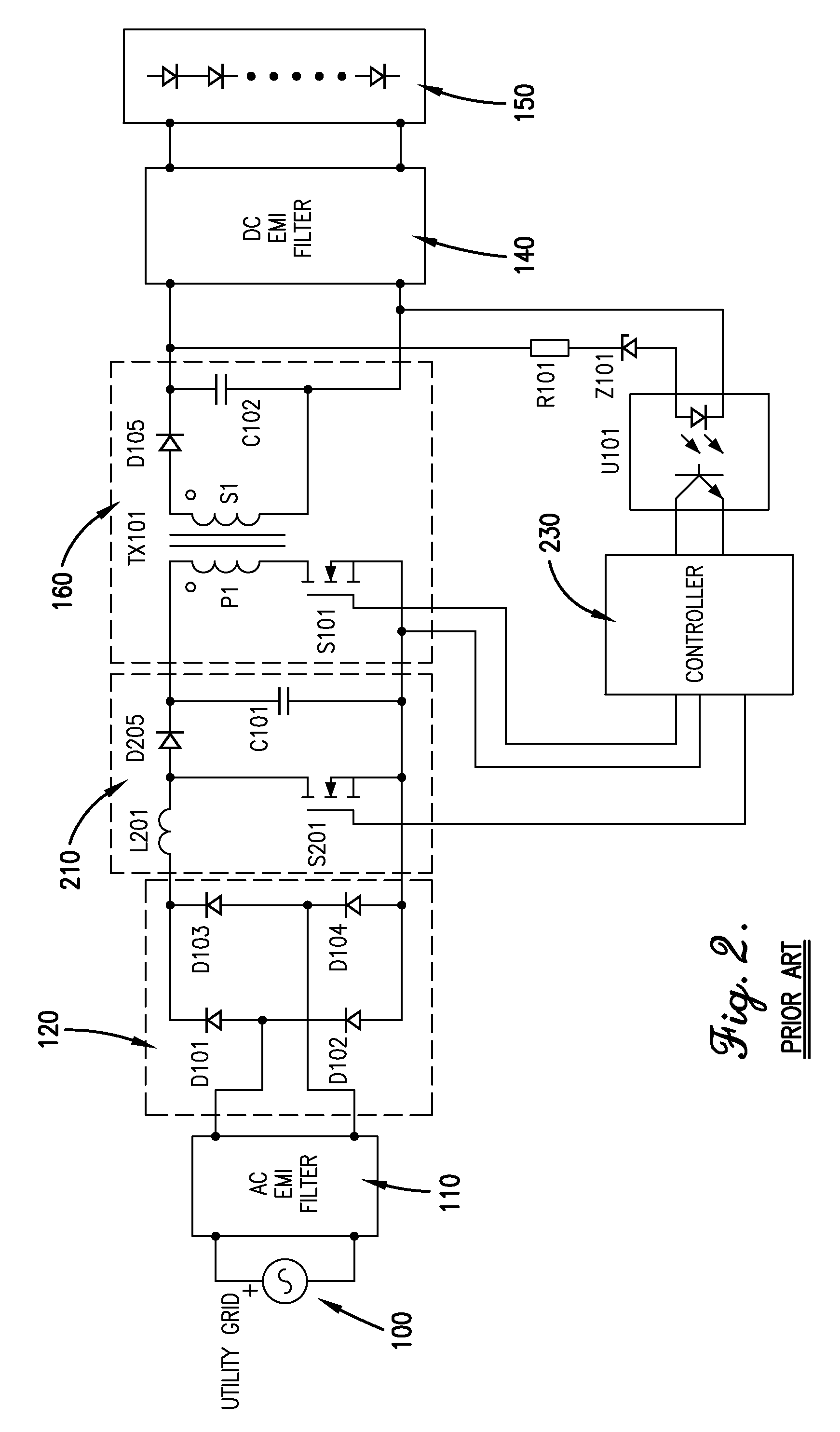
RF generator system for surgical vessel sealing
ActiveUS9039694B2Efficient power electronics conversionSurgical instruments for heatingConstant frequencyVessel sealing
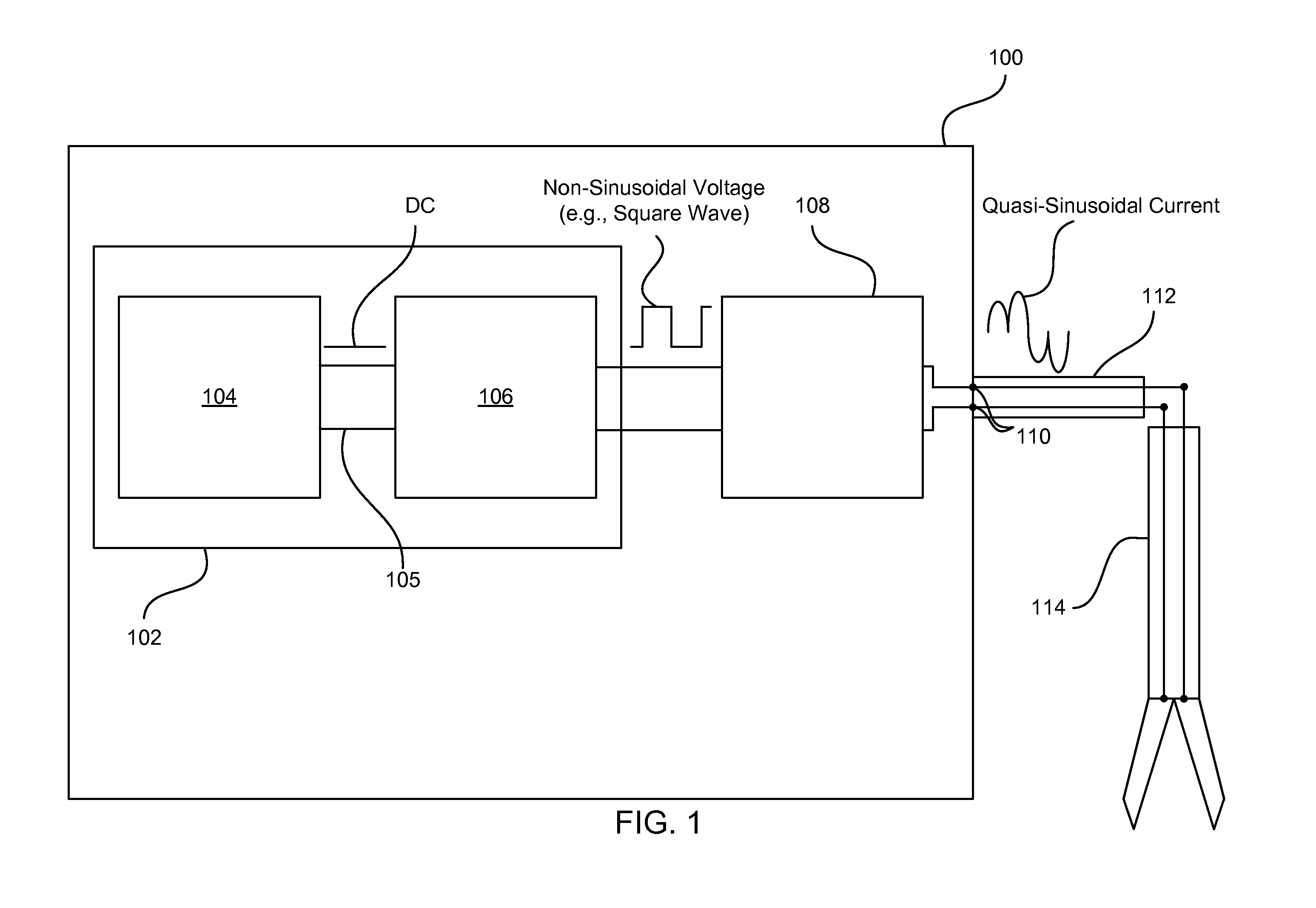
Systems, methods, and apparatus for providing power to an electrosurgical instrument. In particular, a power supply is disclosed in which non-sinusoidal (e.g., pulsed) constant frequency voltage having a variable amplitude is passed to an LC circuit to produce a quasi-sinusoidal current in the LC circuit. The constant driving frequency can be one half the resonant frequency of the LC circuit allowing the LC circuit to operate as an impedance, and thus limit current spikes and arcing. The frequency and phasing of the driving voltage also enables the LC circuit to discharge energy back into a power provider of the power supply so that energy does not build up in the LC circuit. These features result in less severe current spikes and arcing, as well as reduced cutoff times.
Owner:JUST RIGHT SURGICAL
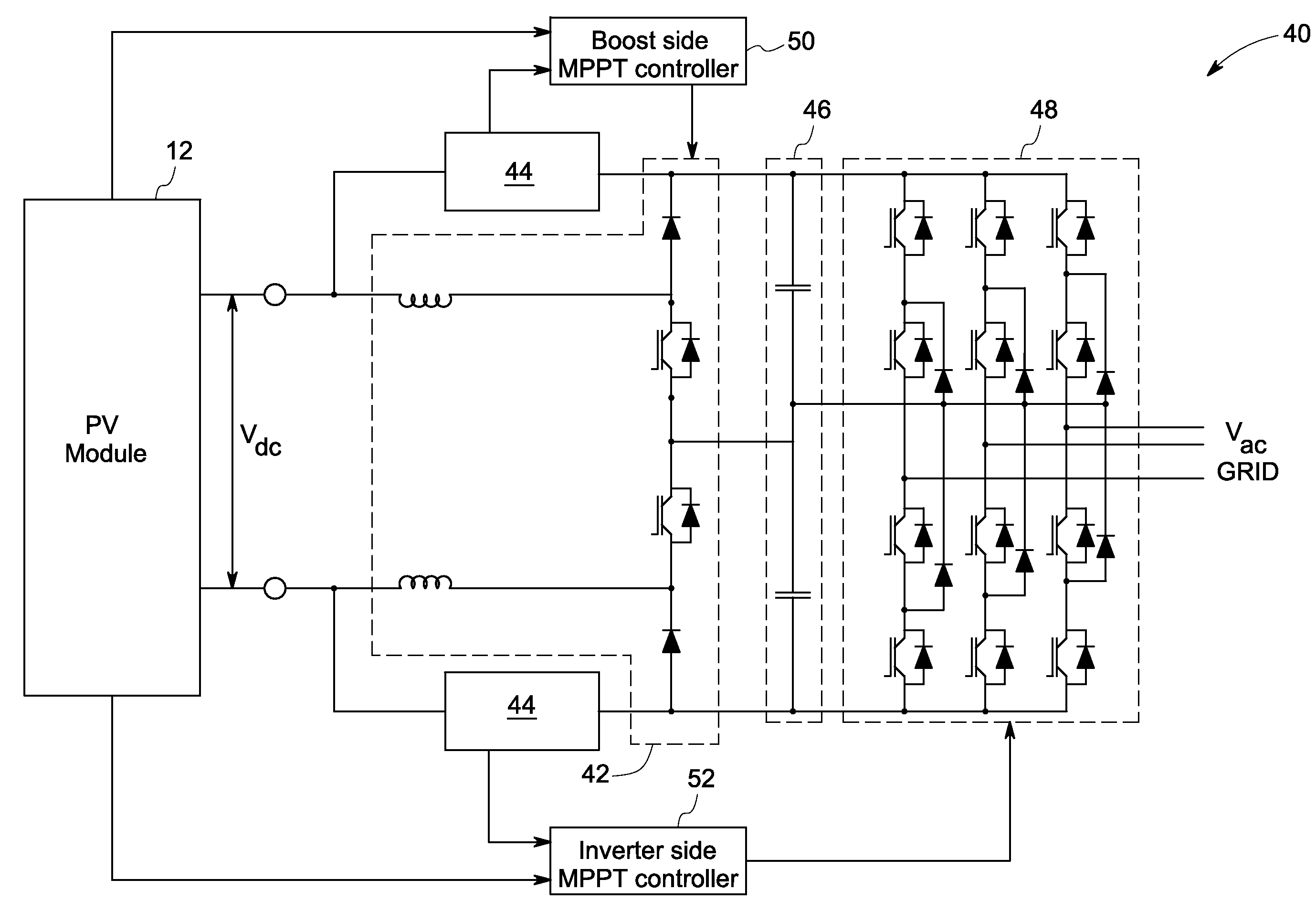
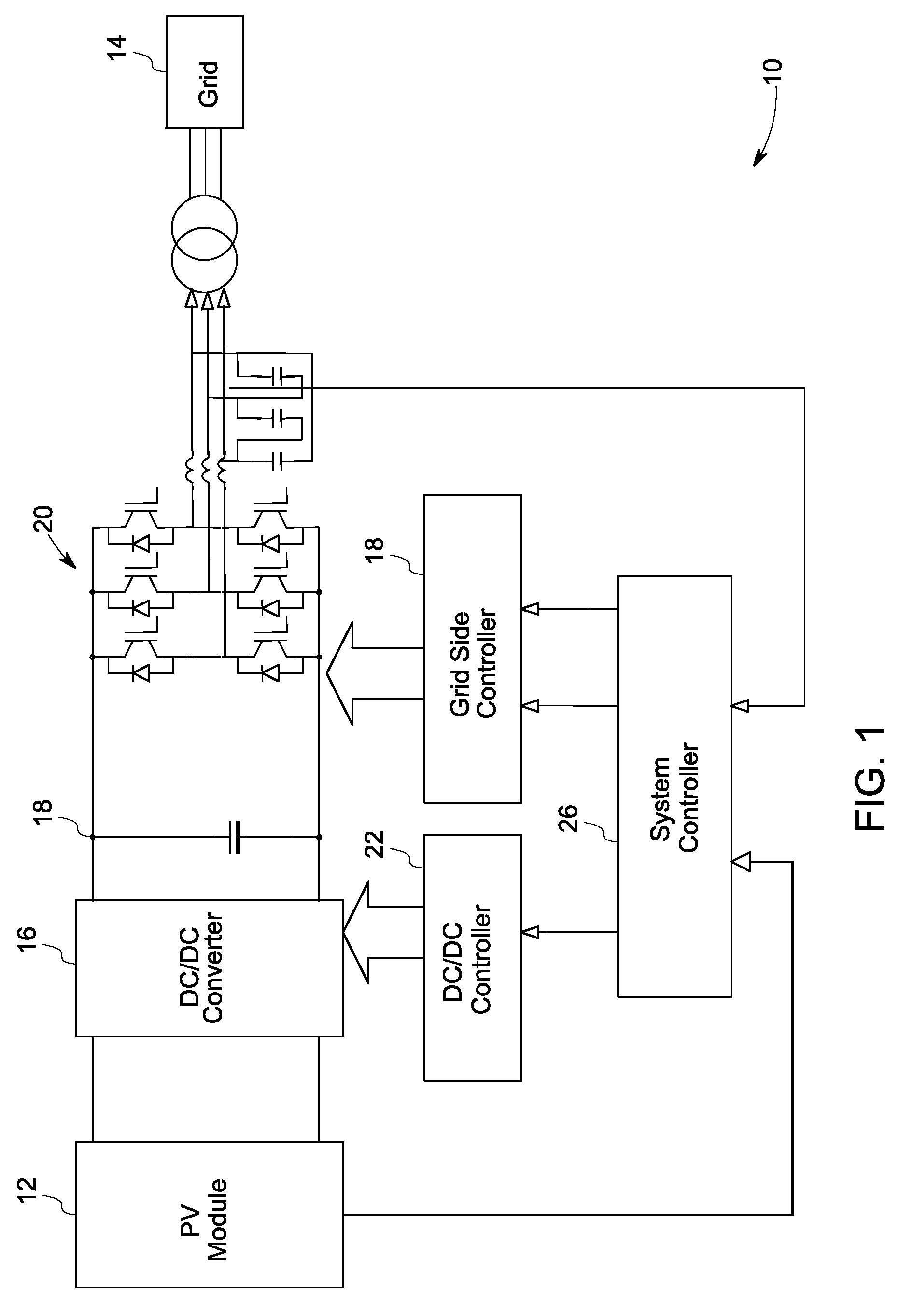
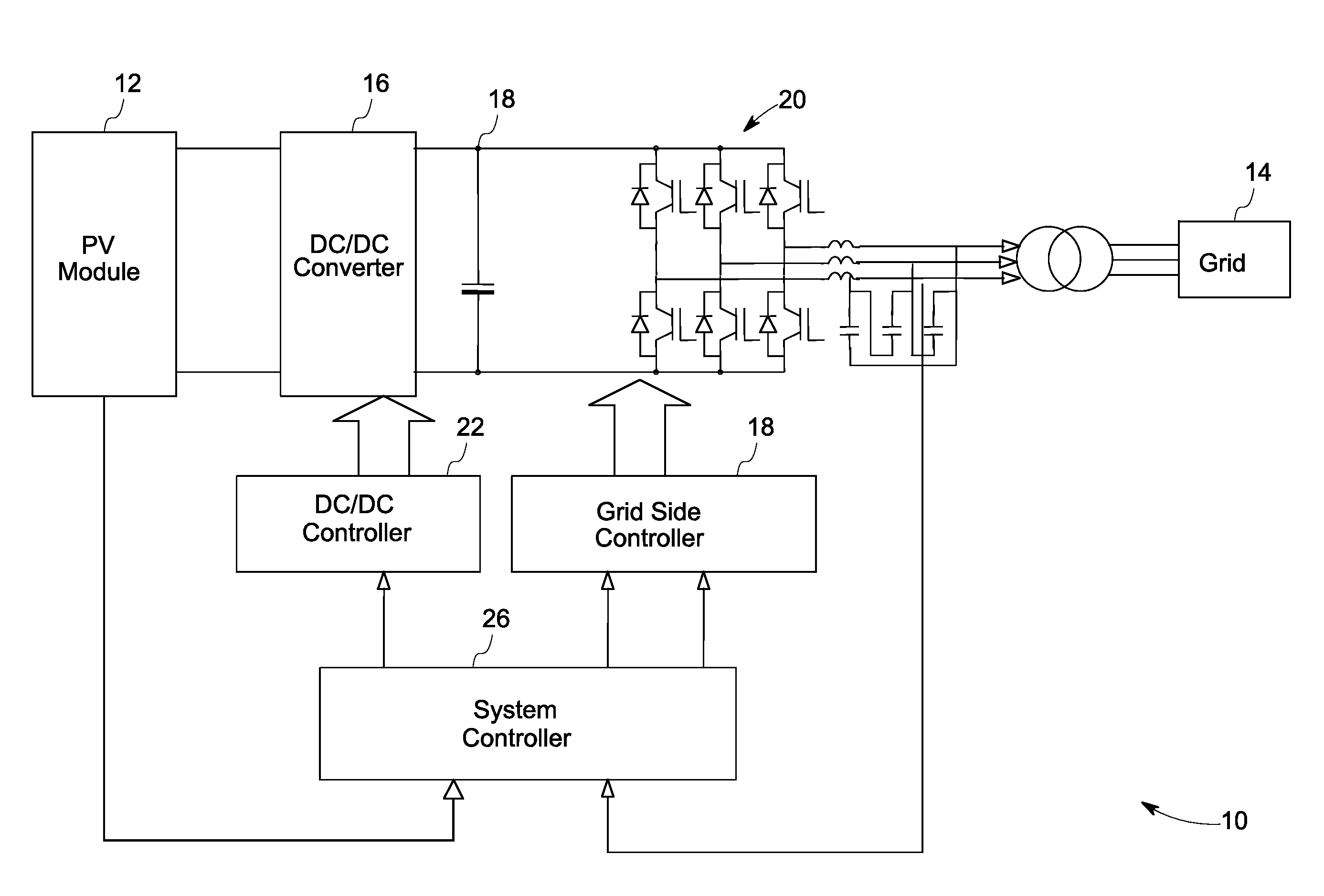
Solar inverter and control method
ActiveUS8184460B2Conversion with intermediate conversion to dcDc-dc conversionControl signalEngineering
A power generation system including a photovoltaic (PV) module to generate direct current (DC) power is provided. The system includes a controller to determine a maximum power point for the power generation system and a boost converter for receiving control signals from the controller to boost the power from the PV module to a threshold voltage required to inject sinusoidal currents into the grid. A DC to alternating current (AC) multilevel inverter is provided in the system to supply the power from the PV module to a power grid. The system also includes a bypass circuit to bypass the boost converter when an input voltage of the DC to AC multilevel inverter is higher than or equal to the threshold voltage.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
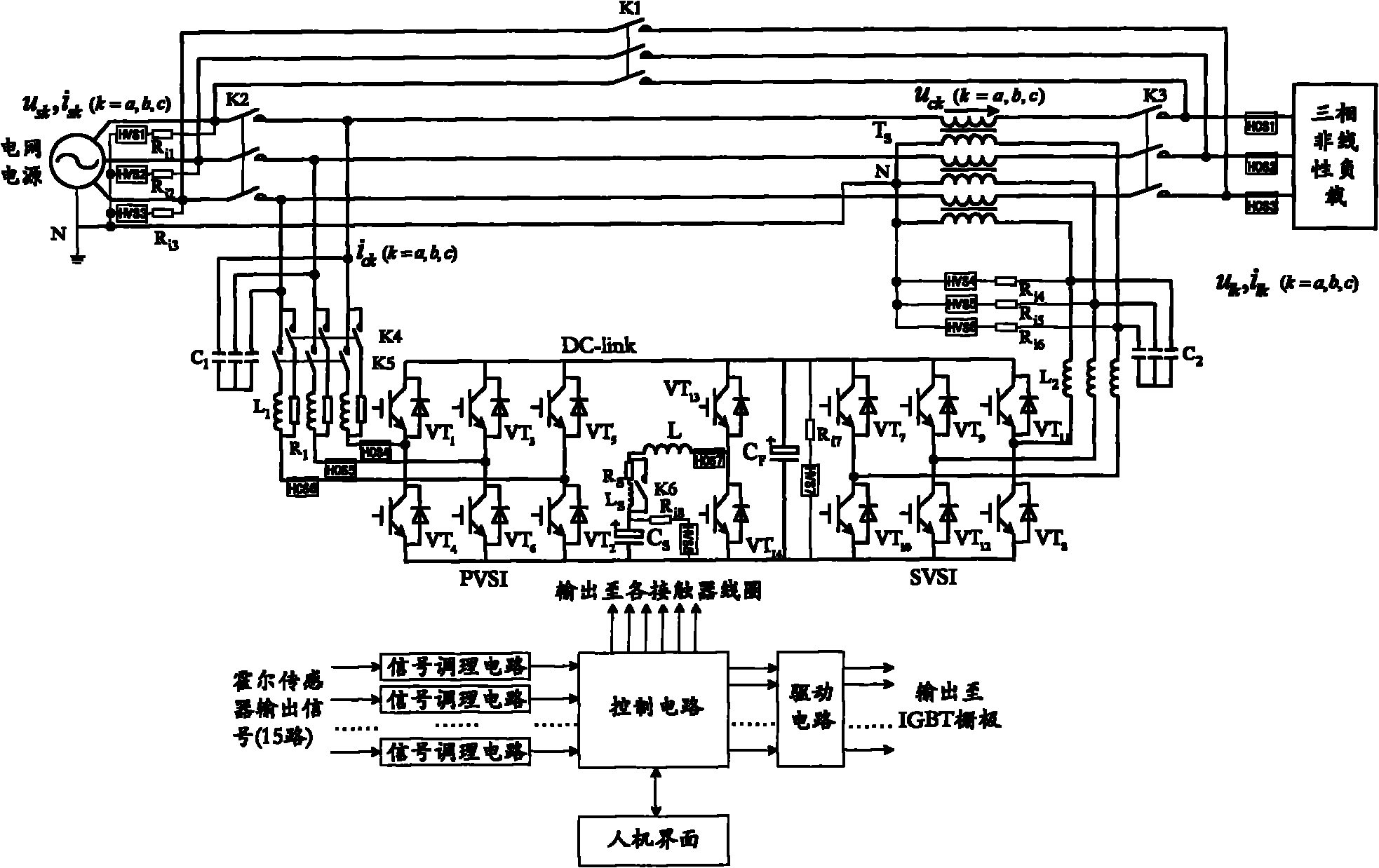
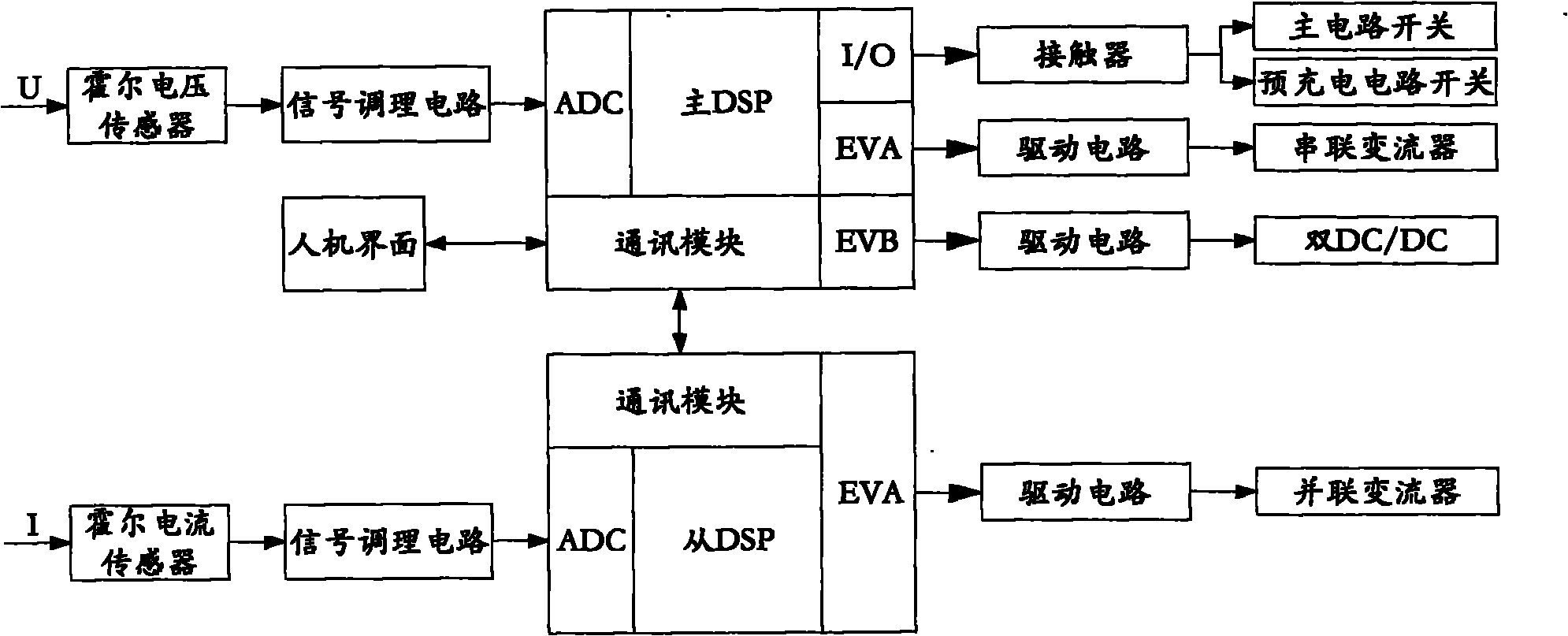
Super capacitor energy storage type power quality compensator
InactiveCN101807799AAvoid pollutionPrevent sensitive loads from working abnormallyElectrical storage systemReactive power adjustment/elimination/compensationPower qualityCapacitance
The invention relates to a super capacitor energy storage type power quality compensator. A system structure comprises a compensation transformer, a series compensator, a parallel compensator, a super capacitor group, a current foldback circuit, a bidirectional DC / DC chopper circuit, a signal sampling circuit, a control circuit, a drive circuit, a human-computer interface and corresponding auxiliary circuits, which form a three-phase three-wire system topological structure. By utilizing the excellent characteristics of great power density, high charging and discharging speed and long cycle life of a super capacitor, the super capacitor energy storage type power quality compensator is matched with the DC / DC chopper circuit to form an energy storage control system which plays the roles of adjusting power and stabilizing the voltage of a direct current bus in work. The invention also has the functions of dynamic voltage recovery, active filter and reactive compensation and can ensure that a load can obtain rated sine voltage and the current of a grid is sine current with the same direction (unit power factor) with that of a voltage fundamental wave positive sequence active component, thereby comprehensively improving the quality of power. The invention has positive generalization and application value for both the public grid and users.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
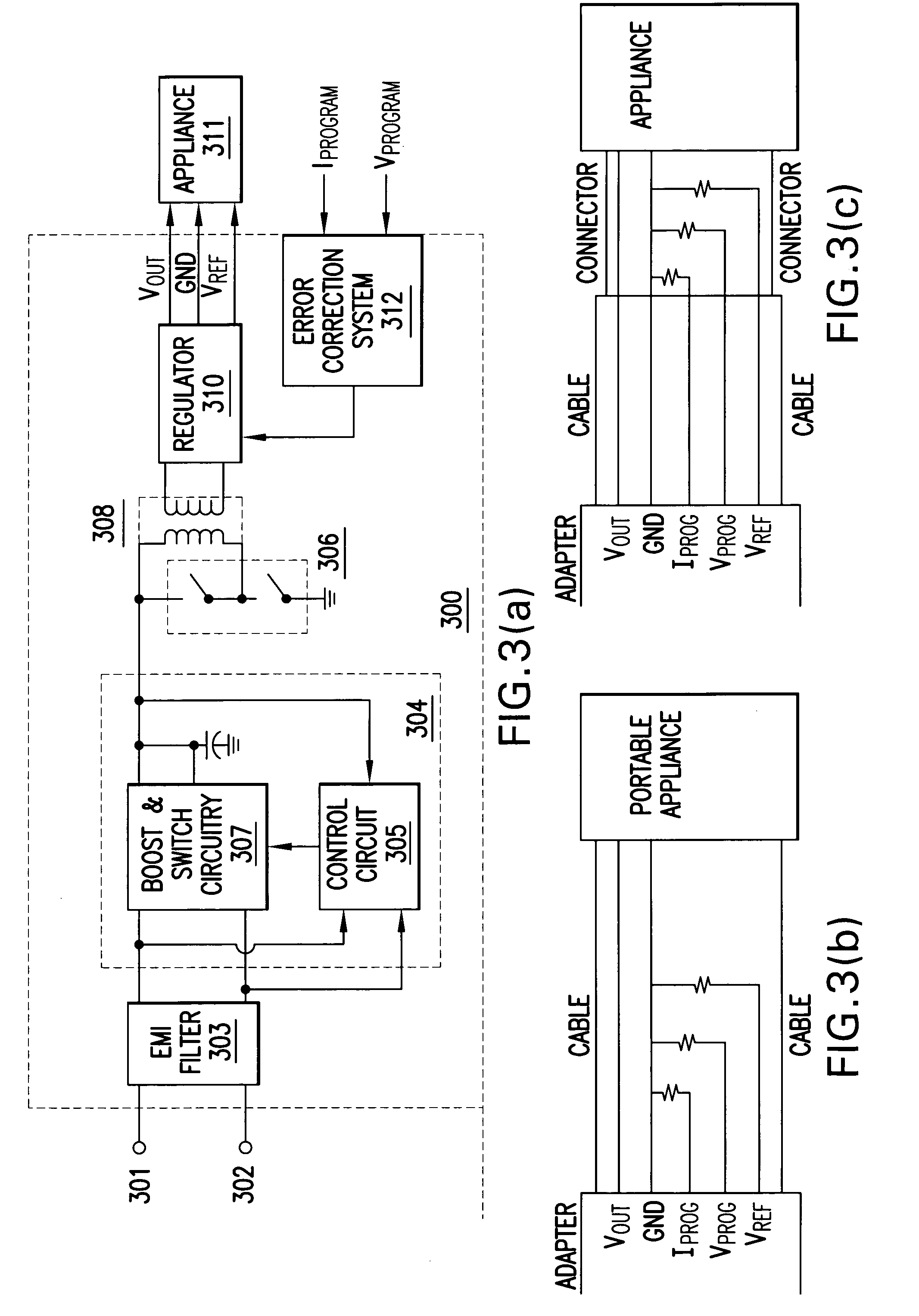
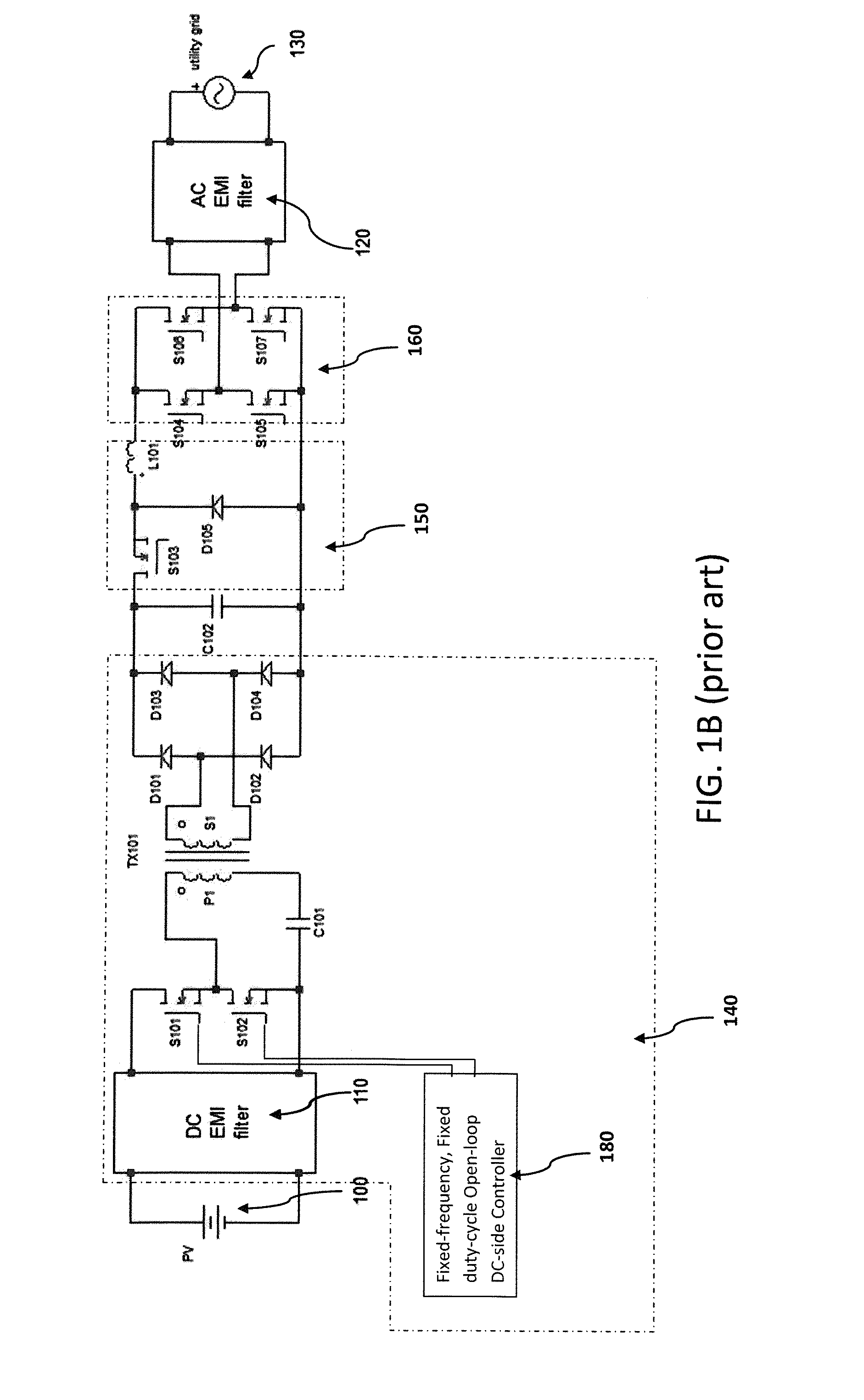
Control method applied to active-clamp flyback miniature photovoltaic grid-connected inverter device
ActiveCN102307017AImprove EMI characteristicsImprove efficiencyDc-dc conversionPhotovoltaic energy generationConstant frequencyPeak value
The invention relates to a control method which can be applied to an active-clamp flyback miniature photovoltaic grid-connected inverter device. The active-clamp flyback miniature photovoltaic grid-connected inverter device comprises a flyback converter and a power frequency polarity conversion circuit. In the device, a current reference is used for controlling a flyback primary-side current peak value so that the device can output a half-wave sinusoidal current, and the output voltage is clamped by a grid voltage. When the instantaneous power is lower, a constant frequency current discontinuous mode in combined with a variable frequency current critical continuous mode is adopted in the flyback control method. When the flyback converter works in a variable frequency current critical discontinuous mode, an auxiliary switching tube can be conducted for a period of time when the secondary-side current of the flyback converter reaches zero, the conduction time can be accurately controlled by a digital chip, thus realizing the leakage inductance energy feedback and the soft switch of a master switching tube under the condition of wide-range output voltages and different instantaneous powers and greatly improving the efficiency under the condition of full loads.
Owner:ALTENERGY POWER SYST
Power factor correction circuits
InactiveUS7279868B2Efficient power electronics conversionAc-dc conversionPower factor controlEngineering
A bi-directional boost circuit for power factor correction includes a power factor control circuit and a pair of diodes, a pair of inductors, and a pair of switches. A first diode, a second diode, a first inductor, a second inductor, a first switch, and a second switch convert the AC input voltage, rectify the AC input voltage, and output an intermediate DC voltage. The power factor control circuit receives the AC input voltage and receives the intermediate DC voltage. The power factor control circuit regulates the DC output voltage. Based on the AC input voltage and the intermediate DC output voltage, the power factor control circuit controls an inductor current waveform by driving the first switch and the second switch to create a substantially sinusoidal current as seen by the power source that is in phase with the AC input voltage.
Owner:COMARCO WIRELESS TECH
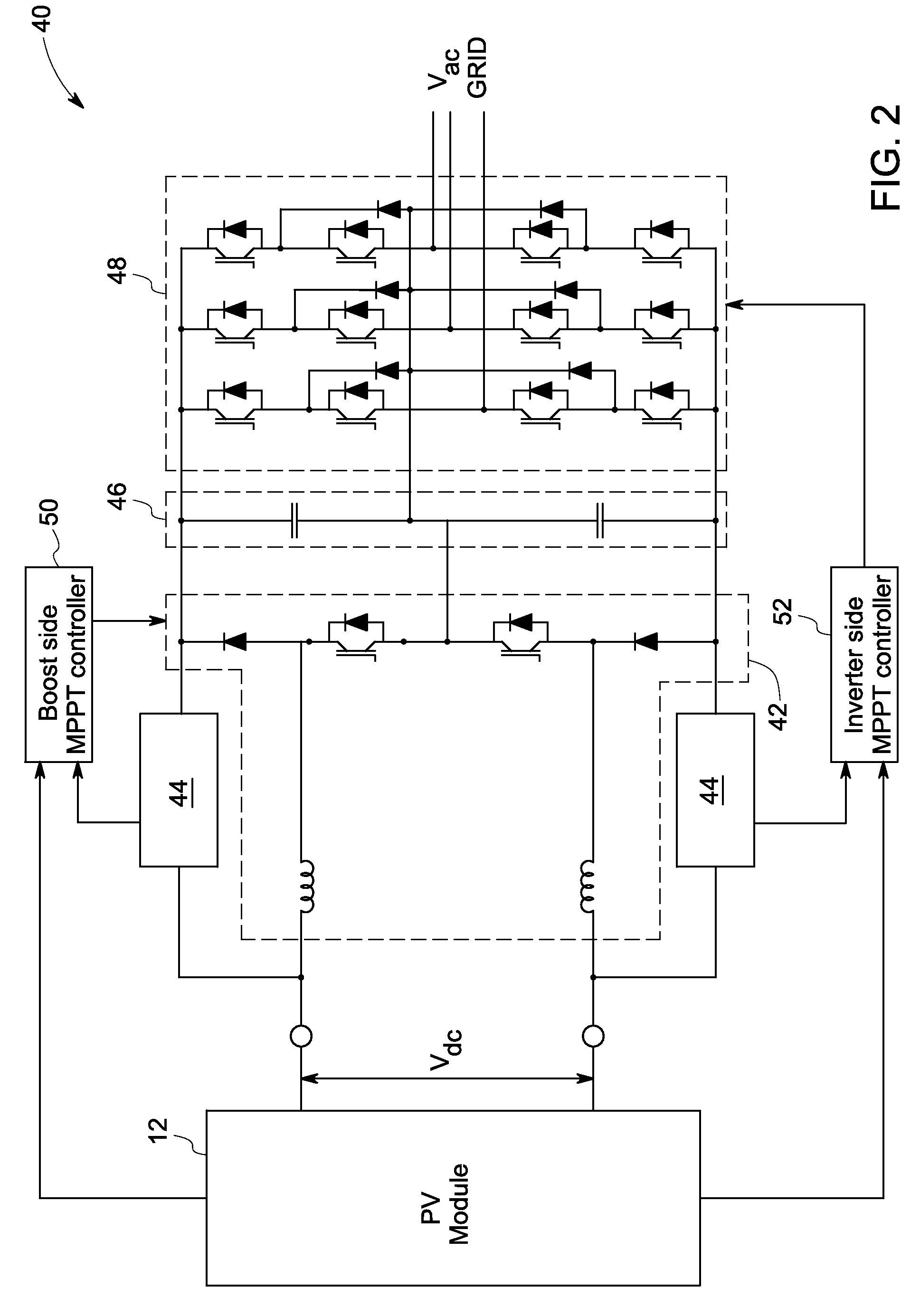
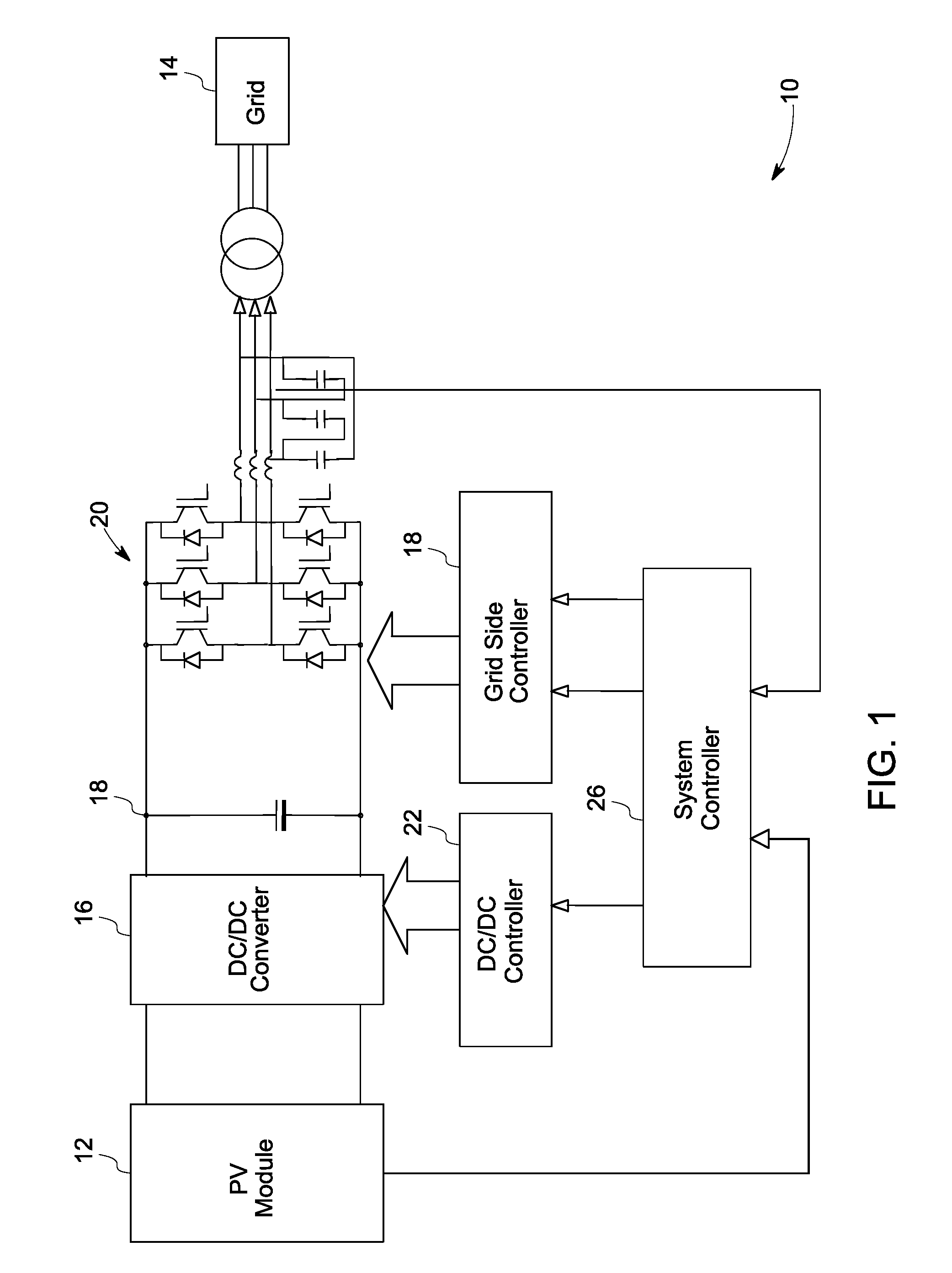
Solar inverter and control method
ActiveUS20100302819A1High strengthConversion with intermediate conversion to dcDc-dc conversionControl signalPower grid
A power generation system including a photovoltaic (PV) module to generate direct current (DC) power is provided. The system includes a controller to determine a maximum power point for the power generation system and a boost converter for receiving control signals from the controller to boost the power from the PV module to a threshold voltage required to inject sinusoidal currents into the grid. A DC to alternating current (AC) multilevel inverter is provided in the system to supply the power from the PV module to a power grid. The system also includes a bypass circuit to bypass the boost converter when an input voltage of the DC to AC multilevel inverter is higher than or equal to the threshold voltage.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Control structure of double-fed AC-DC-AC converter for wind power generation
ActiveCN1992496AIncrease speedImprove robustnessConversion with intermediate conversion to dcSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsPower factorFuzzy pi
This invention discloses a dual-feed AC-DC-AC converter control structure for wind power generation, and the rotor exciting magnetic converter using the fuzzy PI adaptive control strategy of current inner loop. When the generator no-load networking, the current inner loop uses the conventional PI regulator, and after networking, as to three modes, sub-synchronization, synchronization, super-synchronous, it uses fuzzy adaptive PI control. The network-side converter uses SPWM control strategy which fixed switching frequency and combining electric network electromotive front-feed. In the invention, both converting processes use four-quadrant operation PWM converters based on full-controlled devices, so it can not only improve the system dynamic response, reduce wastage and impact, achieve the two-way electric transmission, but also it can achieve wind power generation network side unit power factor sinusoidal current networking power generation operating.
Owner:SUNGROW POWER SUPPLY CO LTD
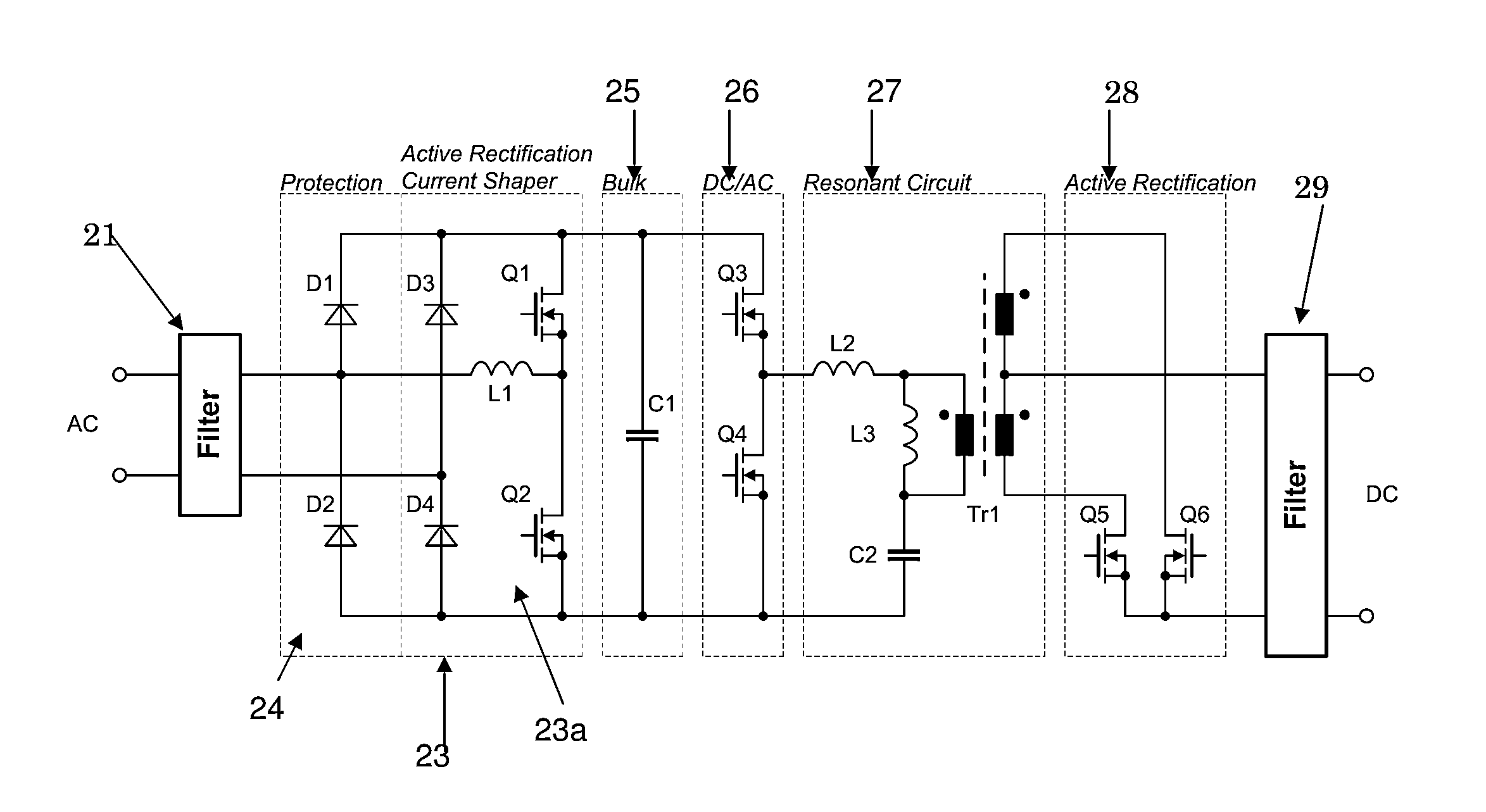
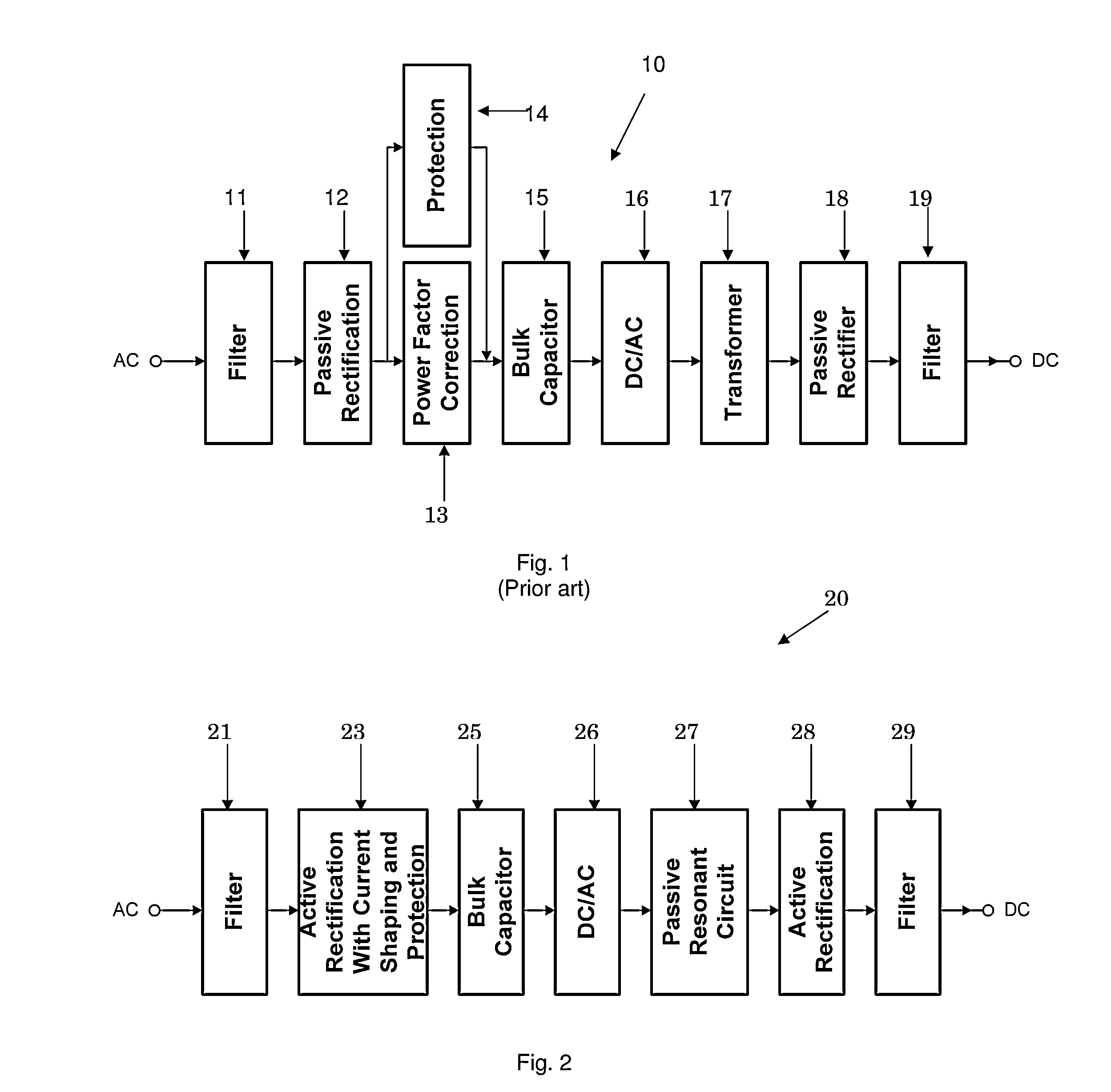
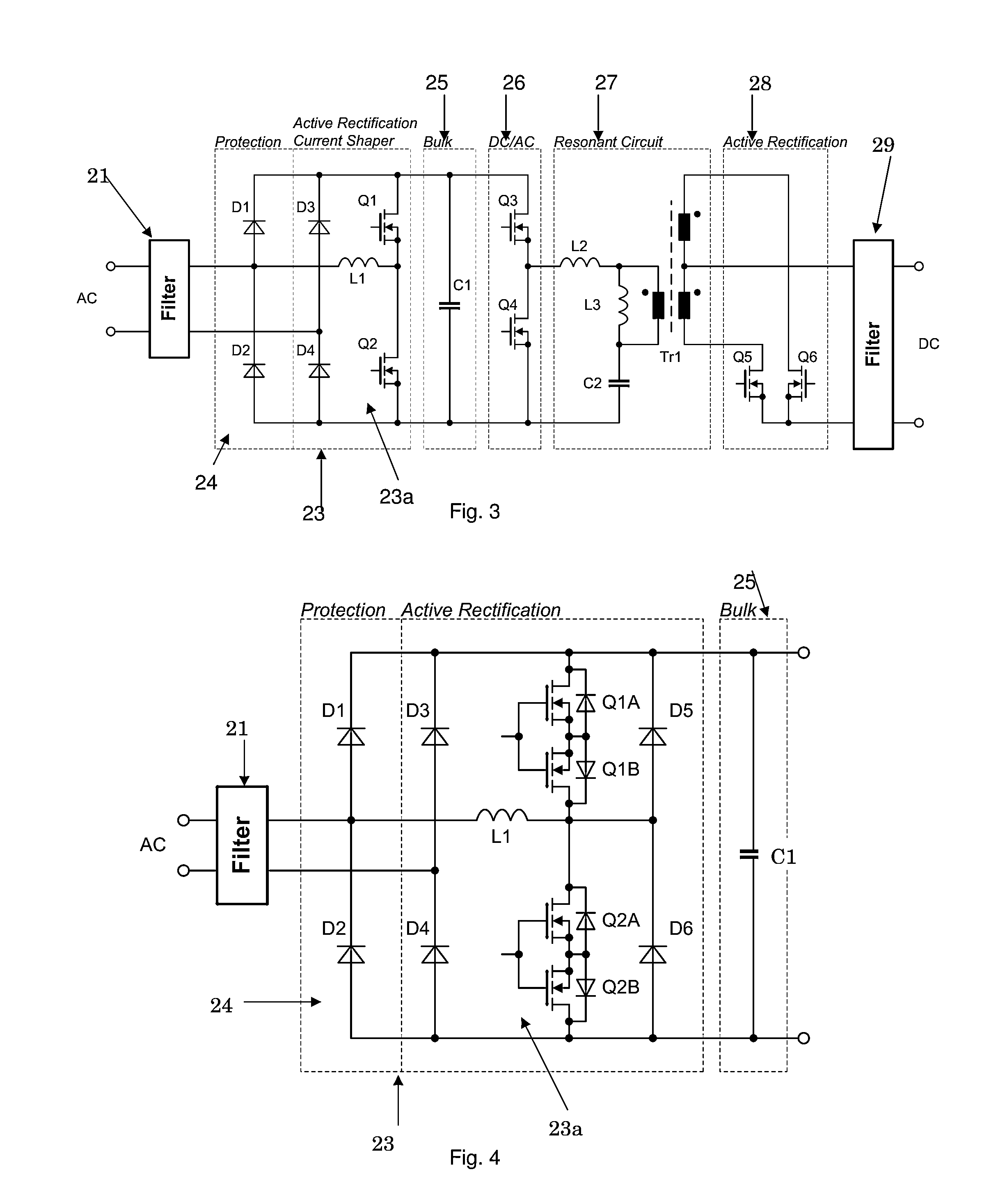
AC/DC power converter with active rectification and input current shaping
ActiveUS8503199B1Improve efficiencyReduce lossesEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionEngineeringCapacitor
An AC / DC power converter has an AC input and a DC output, with an input rectifier circuit coupled to the AC input. The input rectifier circuit includes a passive half-bridge rectifier circuit functional to provide passive rectification of an AC input power sign and at least one current shaper circuit. The current shaper circuit includes an input inductor coupled between the AC input and a switch node in the input active rectifier circuit. The input current shaper circuit is functional to shape an AC input current signal associated with an AC input power signal to a substantially sinusoidal current signal. A bulk capacitor circuit is coupled to the input active rectifier circuit. A DC / AC converter circuit is coupled to the bulk capacitor circuit. A resonant circuit is coupled to the DC / AC converter circuit and an output rectifier circuit may be coupled between the resonant circuit and the DC output.
Owner:BEL POWER SOLUTIONS INC
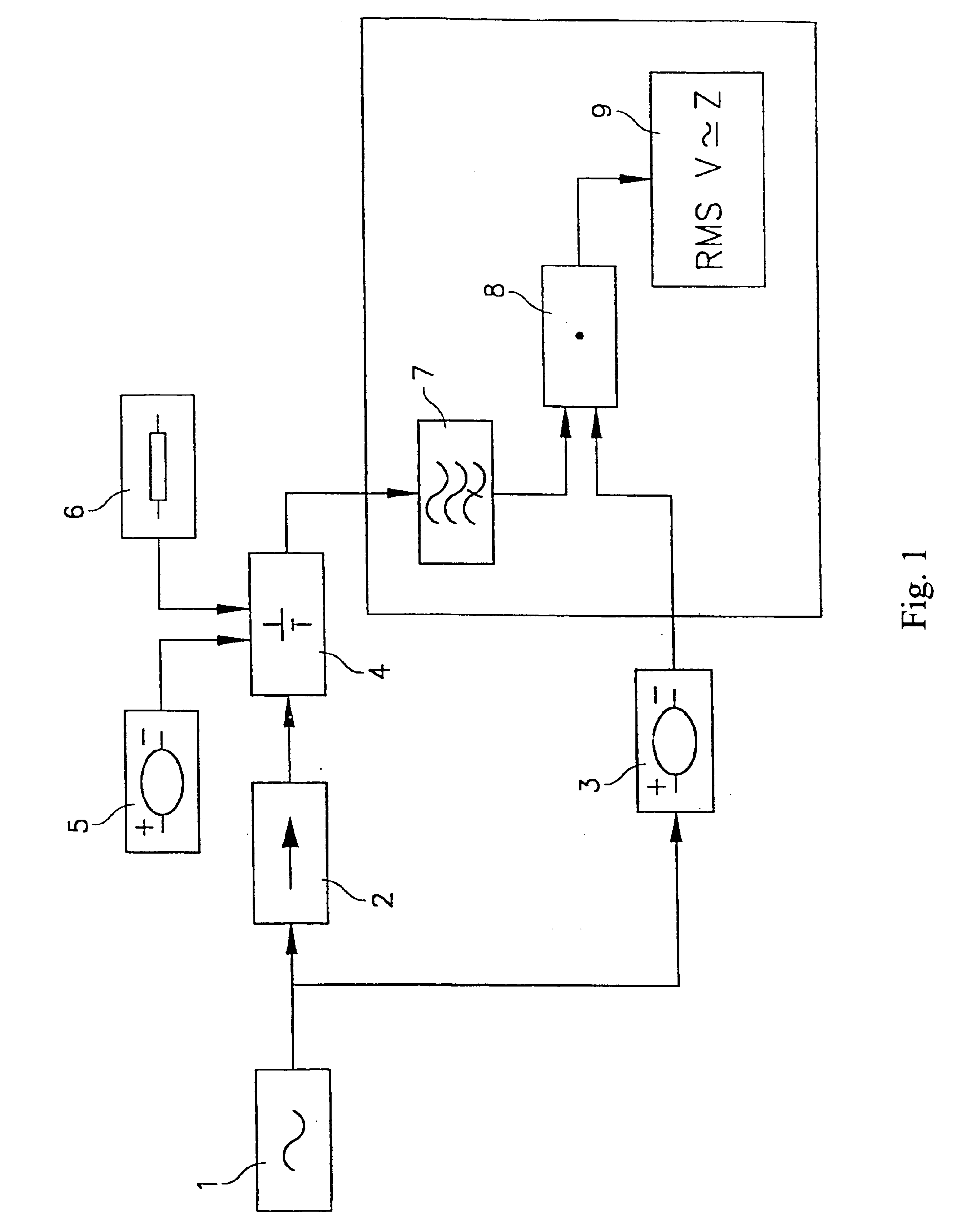
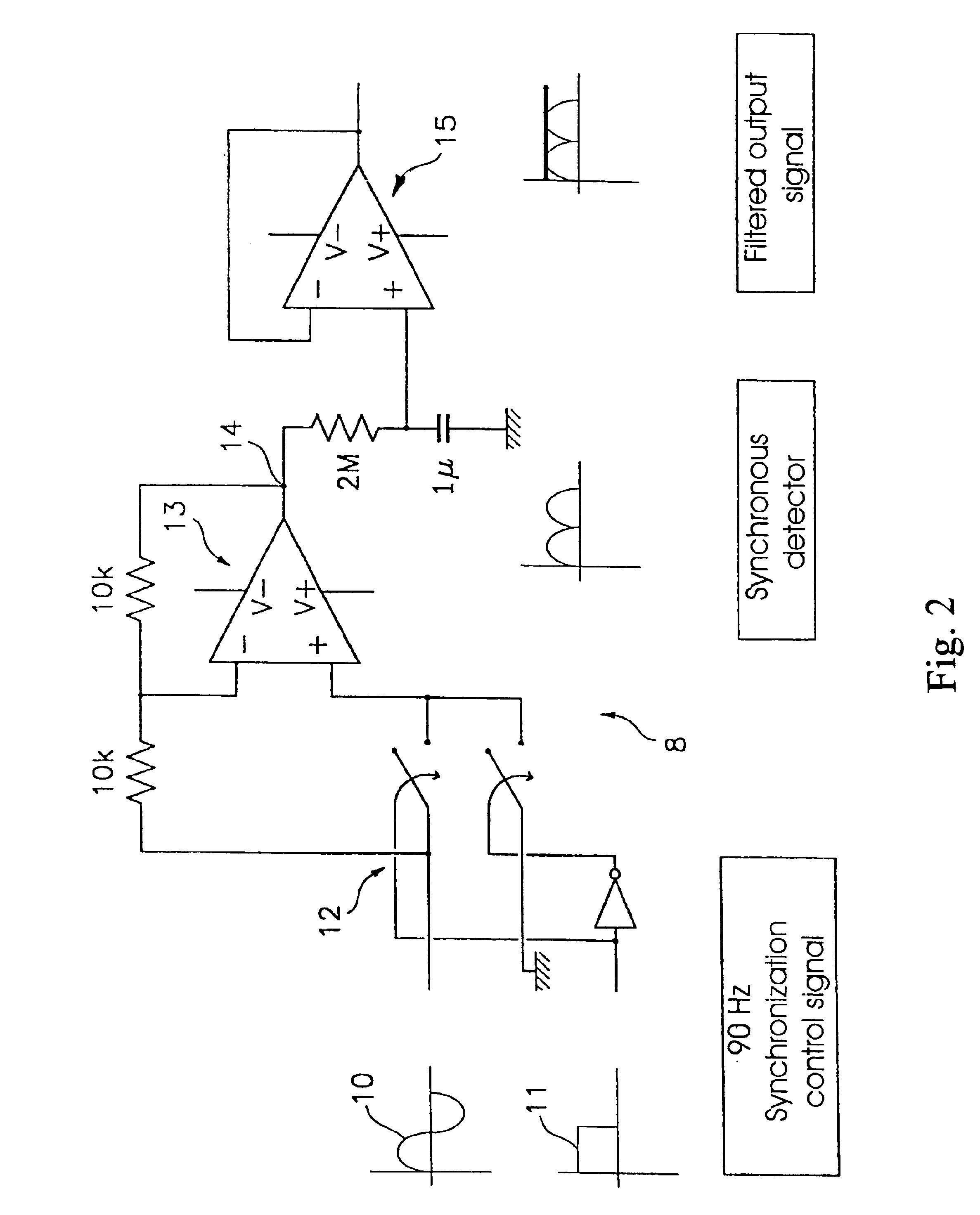
Method for dynamically measuring the state of health and charge of a car battery and device for implementing said method
InactiveUS6876174B1Batteries circuit arrangementsElectrical testingAutomotive batteryElectrical battery
Based on the measurement of the increase of sinusoidal voltage ΔV=Vmaxsine(2πft) on adding a sinusoidal current ΔI=Imaxsine(2πft+φ) to the battery current, where f is the frequency and Imax, the amplitude of the superimposed current, with whose magnitudes the electrochemical impedance of the battery Z(f)=Vmax / Imaxejφ is calculated, comprising the application of a first sinusoidal signal of prefixed frequency to the battery which generates an alternate voltage component superimposed over the direct one; eliminating the direct component of the response signal; applying a second periodic voltage signal with a frequency identical to that of said first signal and carrying out a synchronous detection of the alternate component generated by the application of said first signal to obtain the voltage proportional to the electrochemical impedance and evaluate the state of health and charge of the battery.
Owner:LEAR AUTOMOTIVE (EEDS) SPAIN SL
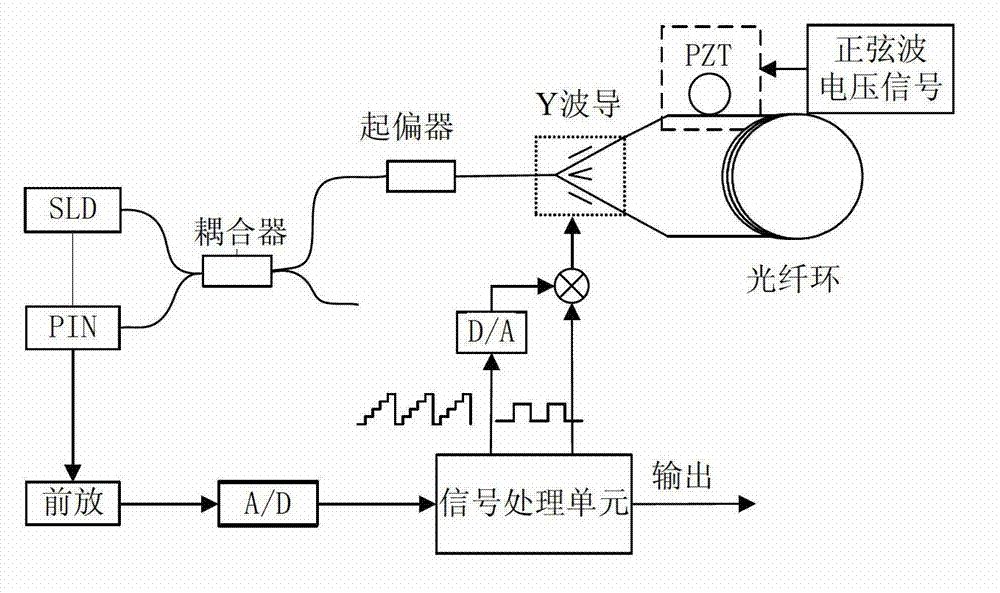
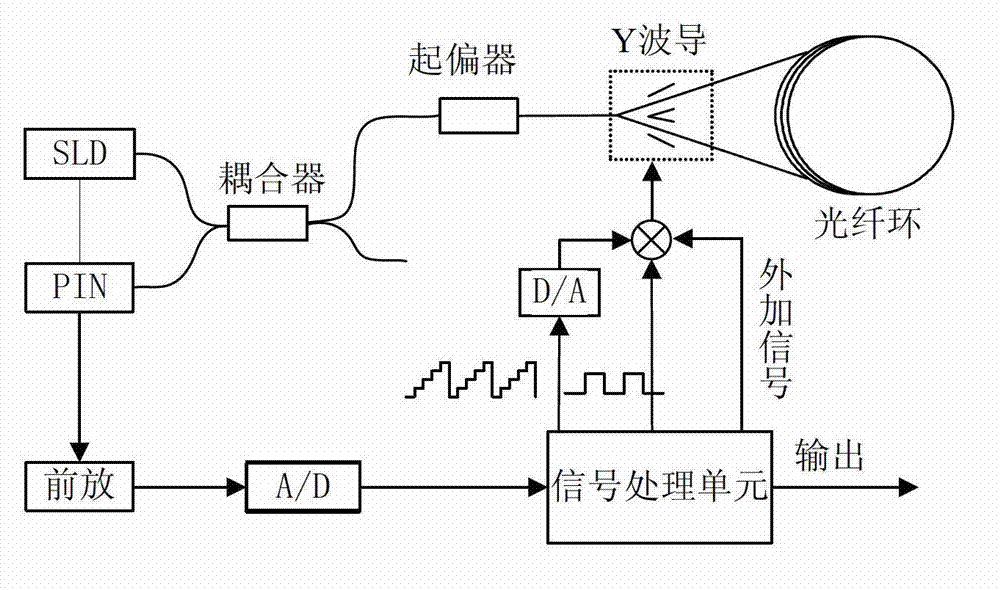
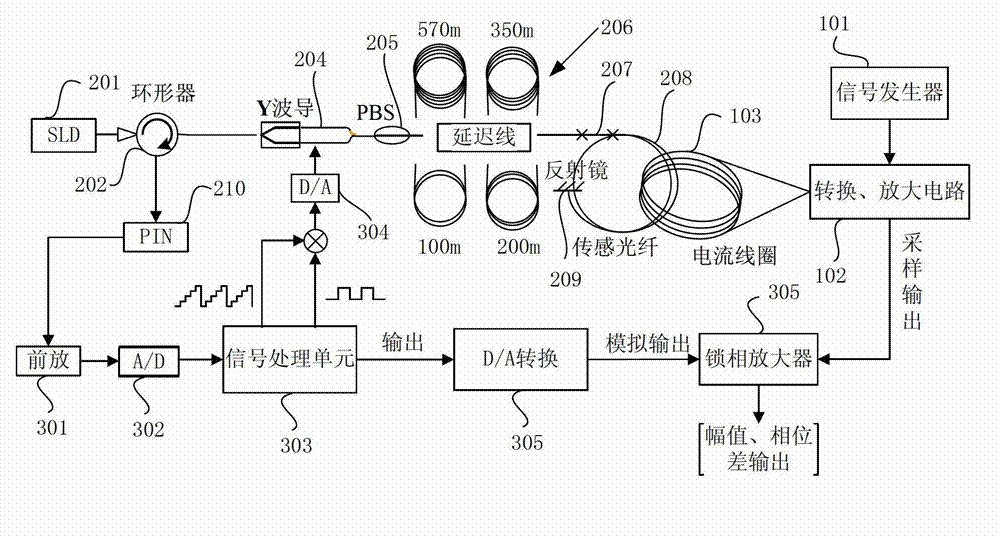
Optical fiber gyroscope frequency characteristic elevating method and device based on Faraday effect
InactiveCN102788595ASolve the problem of limited output frequencyHigh frequency outputMeasurement devicesDigital signal processingGyroscope
The invention discloses an optical fiber gyroscope frequency characteristic elevating device based on a Faraday effect. An excitation current source comprises a signal generator, a conversion amplifying circuit and a current coil, wherein a sensitive light path comprises a light source, a circulator, a Y waveguide phase regulator, a polarization beam splitter, a polarization-maintaining fiber coil, a gamma / 4 wave plate, a sensing optical fiber, a reflecting mirror and a detector; and an analog optical fiber gyroscope signal processing detection circuit comprises a front amplifying circuit, an A / D (Analog to Digital) converting circuit, a digital signal processing unit, a first D / A (Digital to Analog) converting unit, a second D / A converting circuit and a phase-locked amplifier. The Faraday effect applied in the invention is generated by exciting the sensitive light path with sinusoidal current, and a sinusoidal signal serving as an exciting signal can be output at a high frequency, so that the problem of limitation on the excitation signal output frequency during frequency characteristic test of an optical fiber gyroscope is solved, and evaluation of high bandwidth can be realized.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
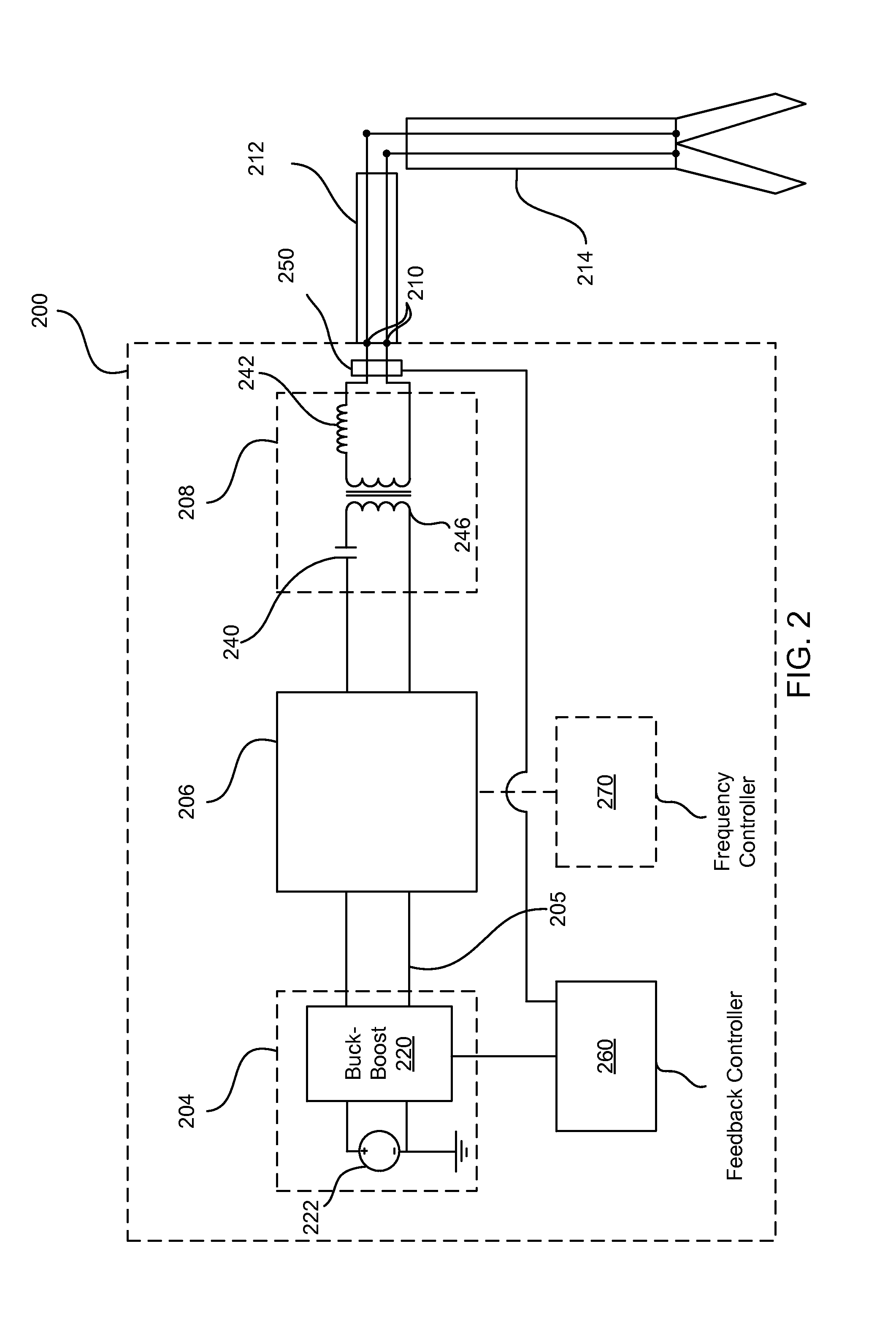
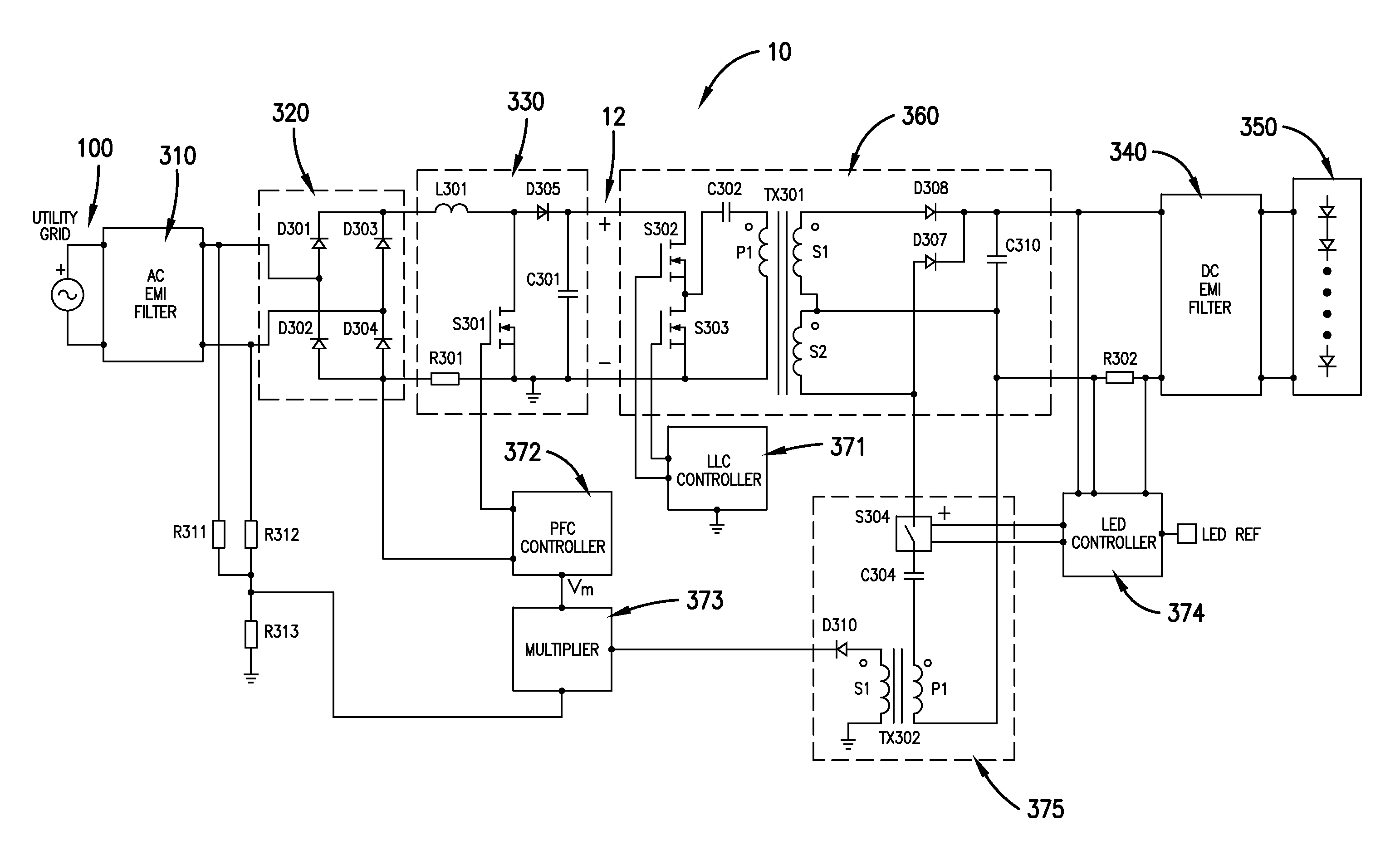
LED driver
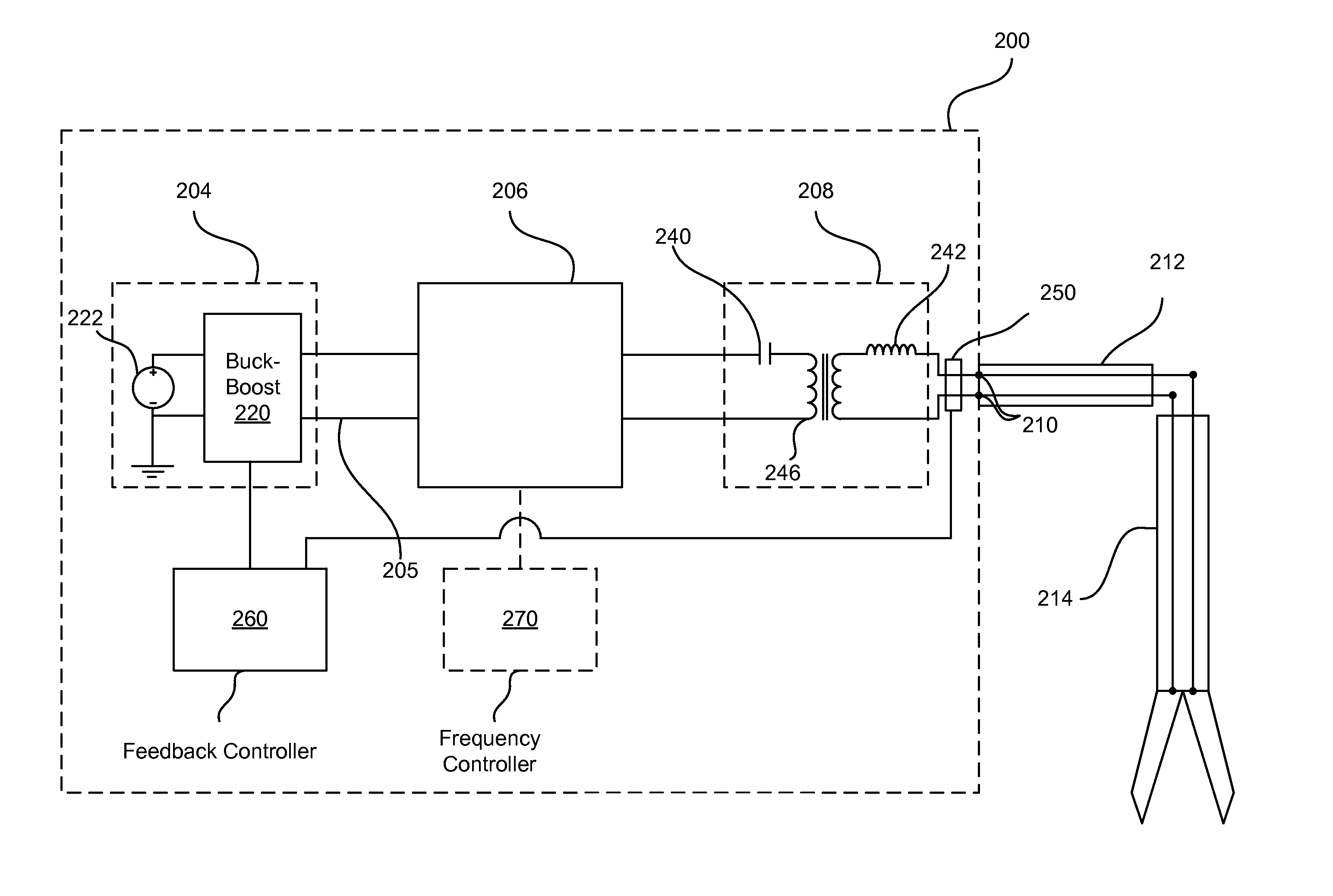
ActiveUS20150195878A1Extend your lifeEasily trade switching lossElectrical apparatusElectroluminescent light sourcesConstant powerAverage current
An LED driver having an input to receive AC power from an AC power source, a semiconductor switch and an inductor controlled to produce a sinusoidal current drawn from the AC power source, and a large non-electrolytic (e.g. film) capacitor energy storage component. The semiconductor switch operates with a varying pulse-width-modulation frequency to regulate the voltage across the non-electrolytic capacitor energy storage component in such a way that a ripple current through the inductor is substantially smaller than a pulse-width-modulation cycle average current through the inductor. A DC-to-DC converter couples the energy from the non-electrolytic energy-storage capacitor to an LED string. A feedback loop allows the LED string to be regulated in either constant current mode or constant power mode and information for the feedback regulation is fed back across a high-voltage boundary using a low-cost signal transformer.
Owner:GARRITY POWER SERVICES
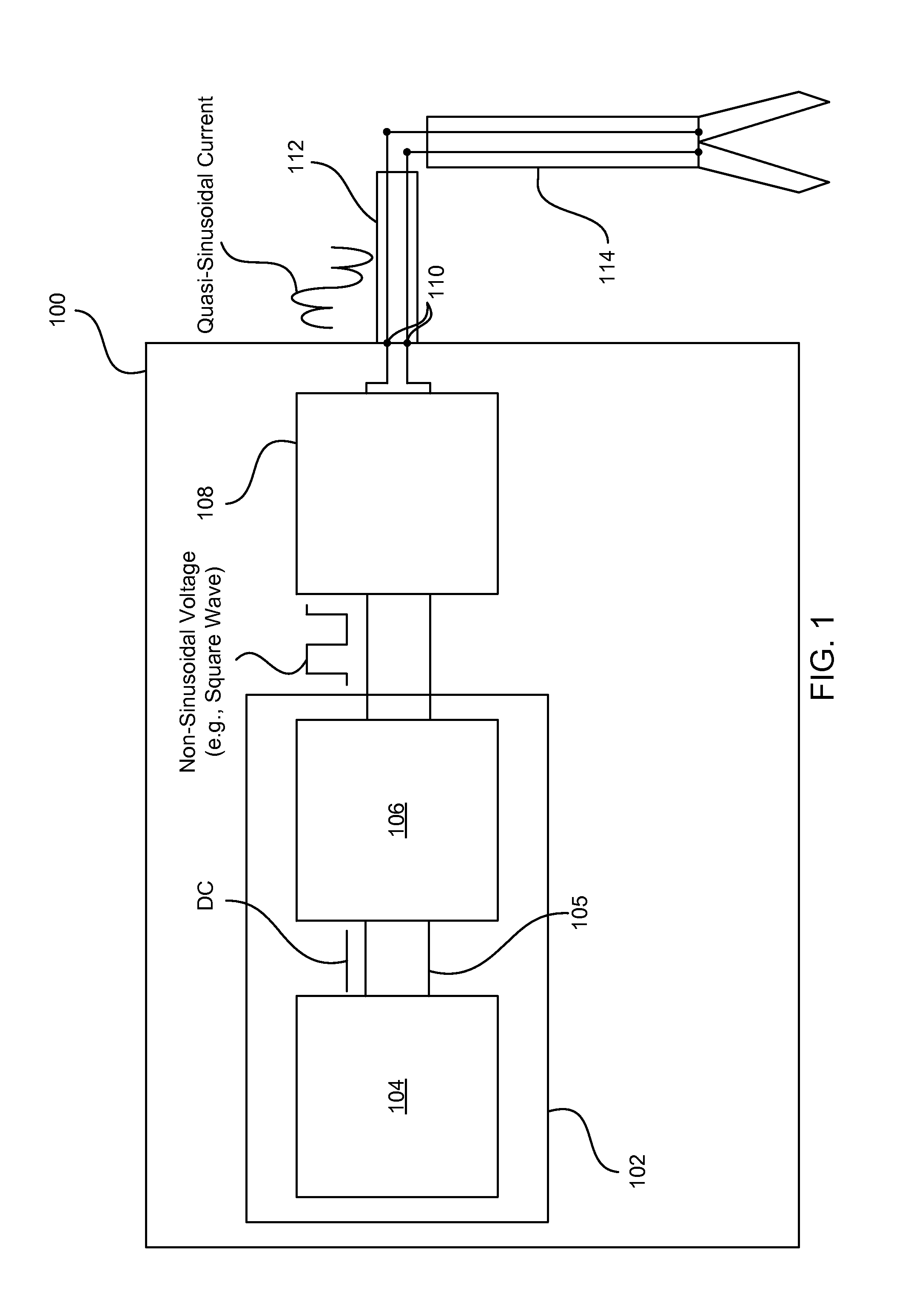
RF Generator System for Surgical Vessel Sealing
Systems, methods, and apparatus for providing power to an electrosurgical instrument. In particular, a power supply is disclosed in which non-sinusoidal (e.g., pulsed) constant frequency voltage having a variable amplitude is passed to an LC circuit to produce a quasi-sinusoidal current in the LC circuit. The constant driving frequency can be one half the resonant frequency of the LC circuit allowing the LC circuit to operate as an impedance, and thus limit current spikes and arcing. The frequency and phasing of the driving voltage also enables the LC circuit to discharge energy back into a power provider of the power supply so that energy does not build up in the LC circuit. These features result in less severe current spikes and arcing, as well as reduced cutoff times.
Owner:JUST RIGHT SURGICAL
Two-way DC-DC converter
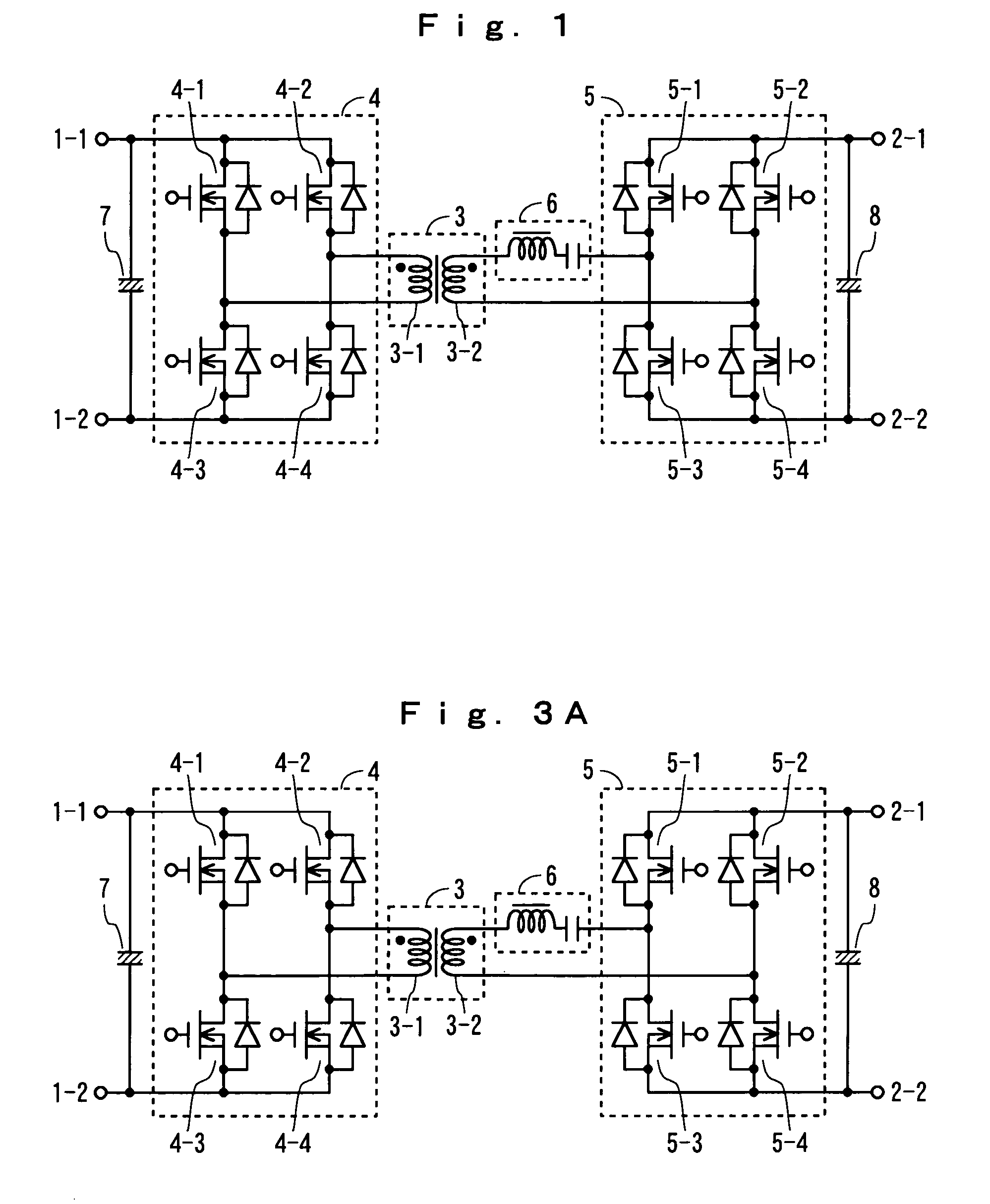
ActiveUS7177163B2Reduce switching lossesSimple configurationAc-dc conversion without reversalEfficient power electronics conversionDc dc converterLc resonant circuit
Rectifying elements are connected in parallel with switching elements 4-1 through 4-4 in a switching section 4 for the lower voltage side and rectifying elements are connected in parallel with switching elements 5-1 through 5-4 in a switching section 5 for the higher voltage side. An LC resonant circuit 6 is provided between the winding wire 3-2 for the high-voltage side in the transformer 3 and the switching section 5 for the higher voltage side; currents which flows on the primary side and the secondary side is changed into a sinusoidal one; and switching is executed in the vicinity of the zero crossing points of the currents.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
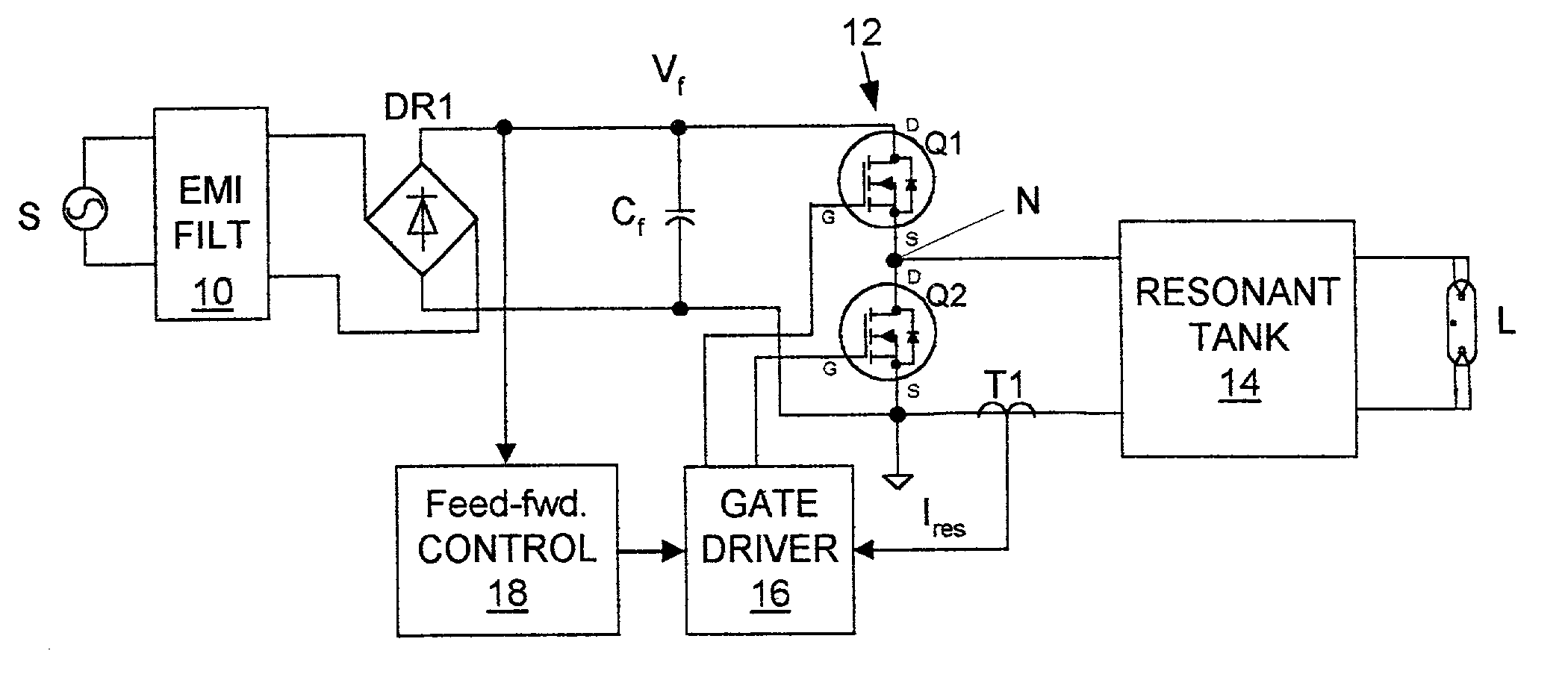
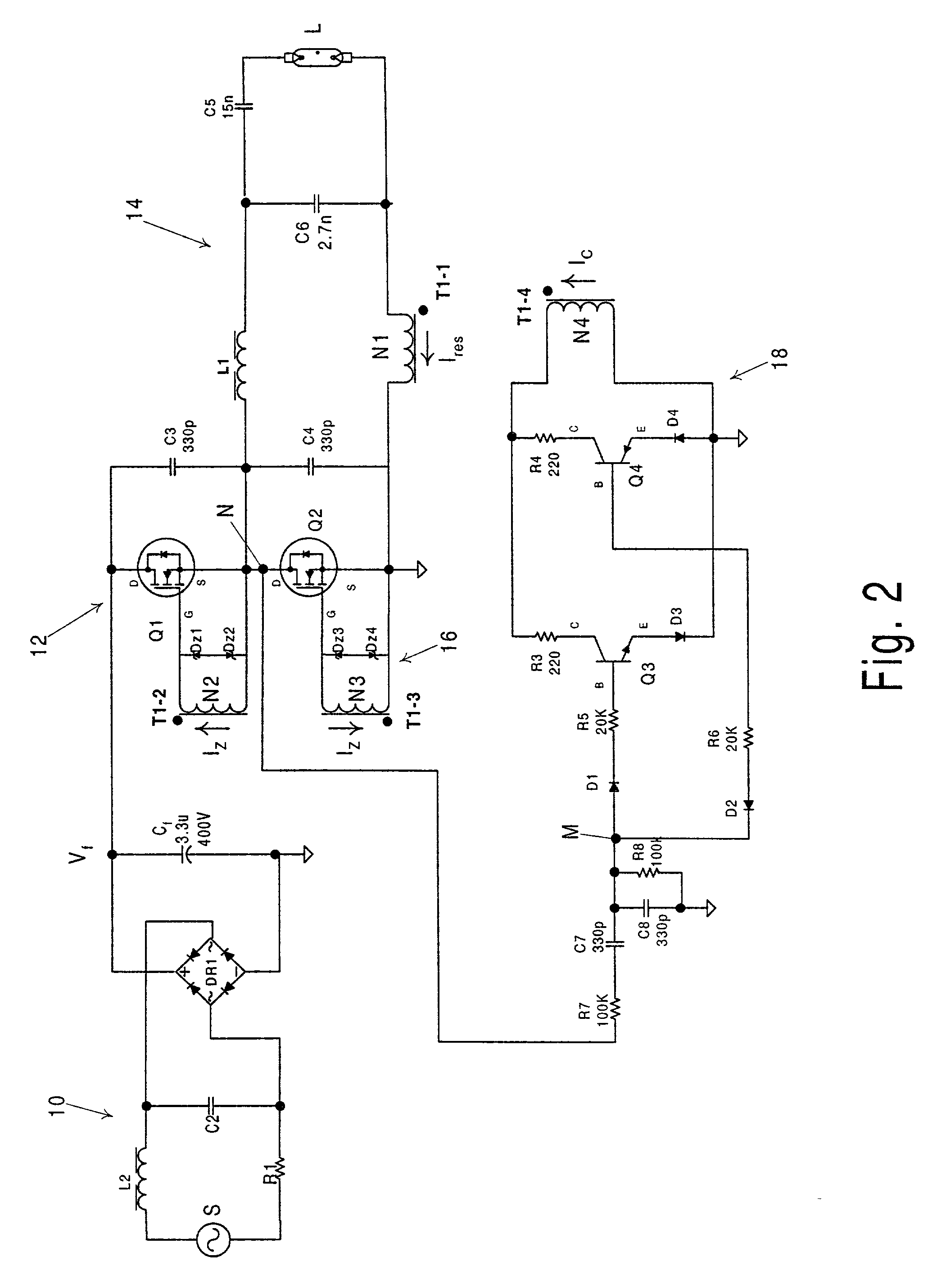
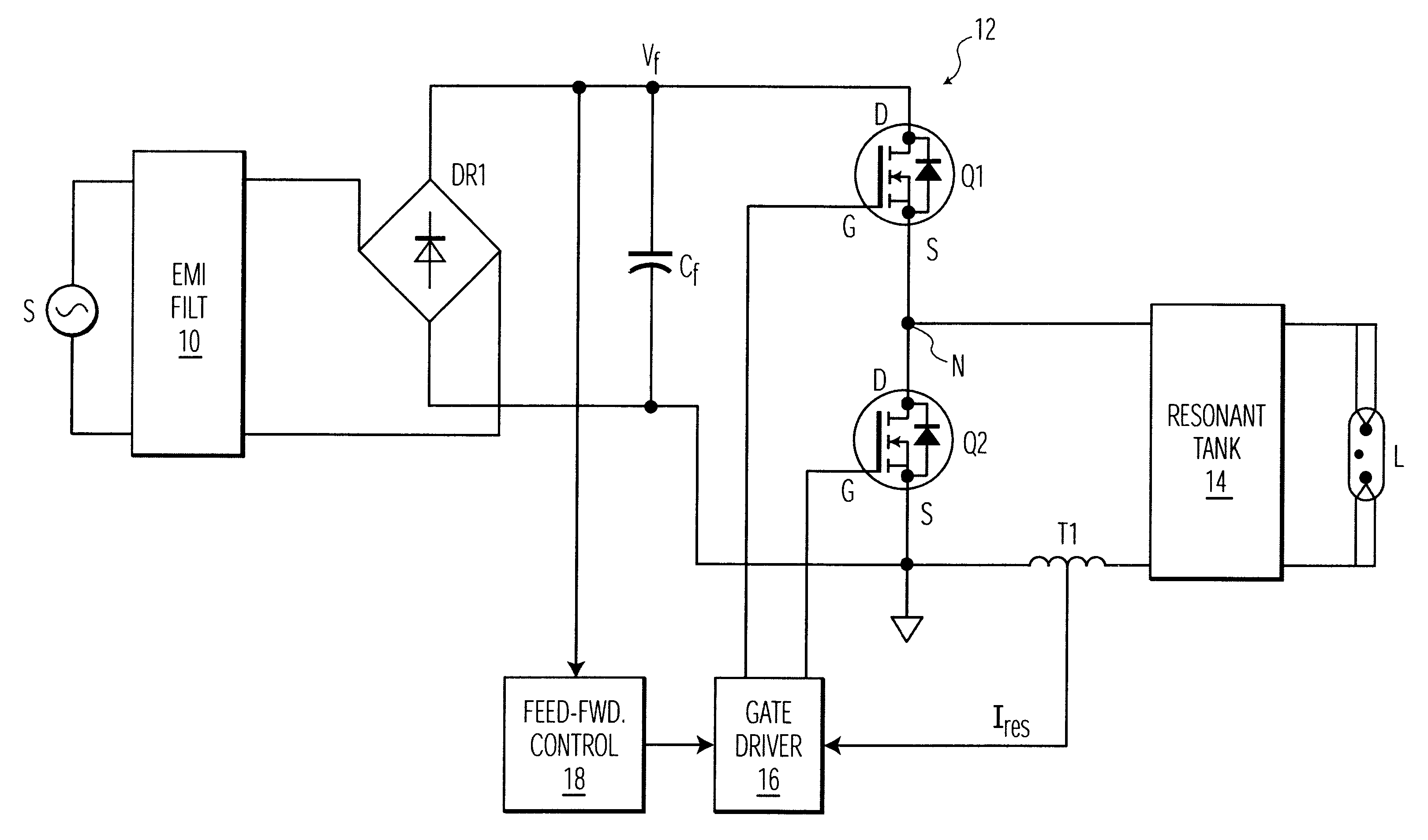
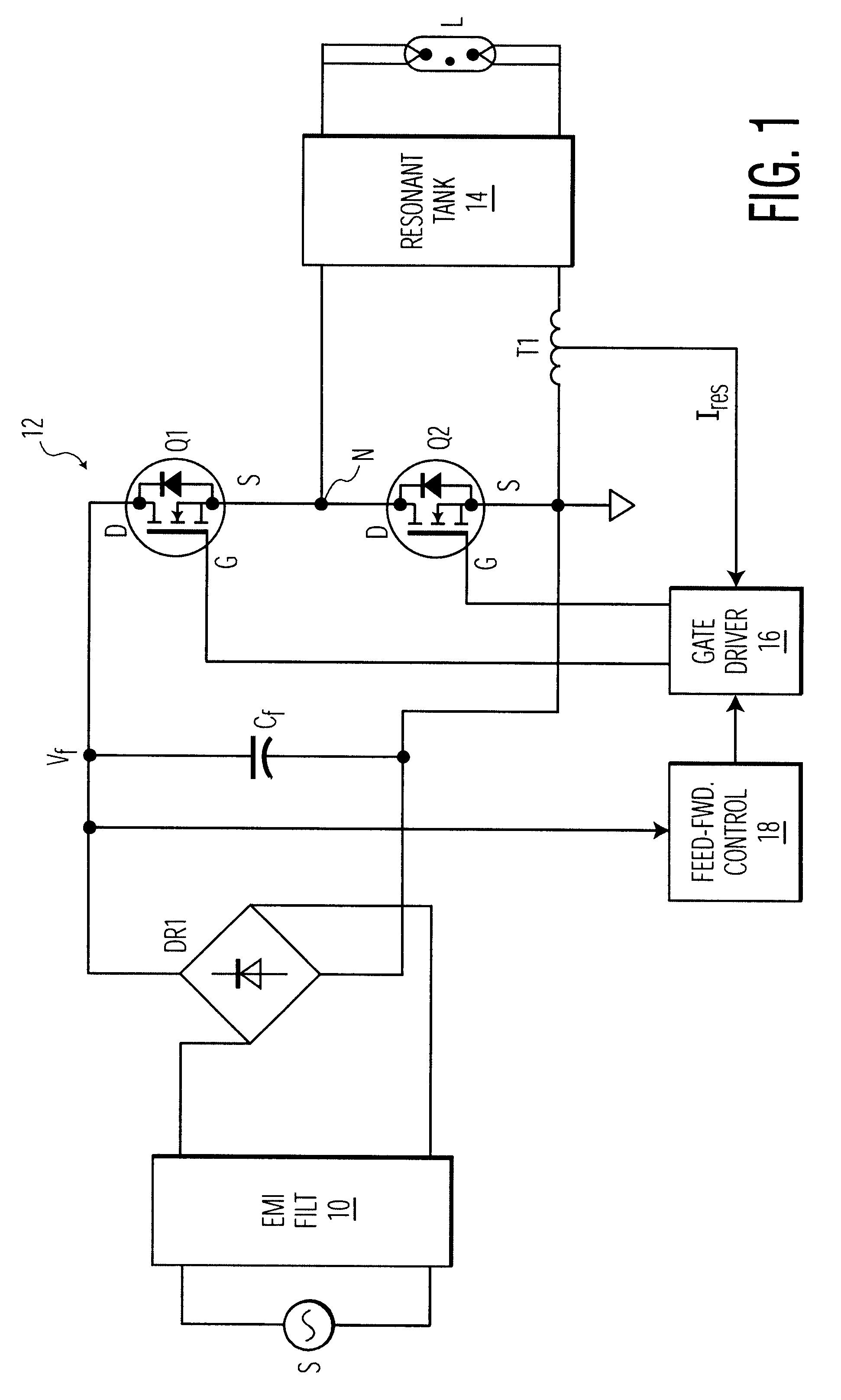
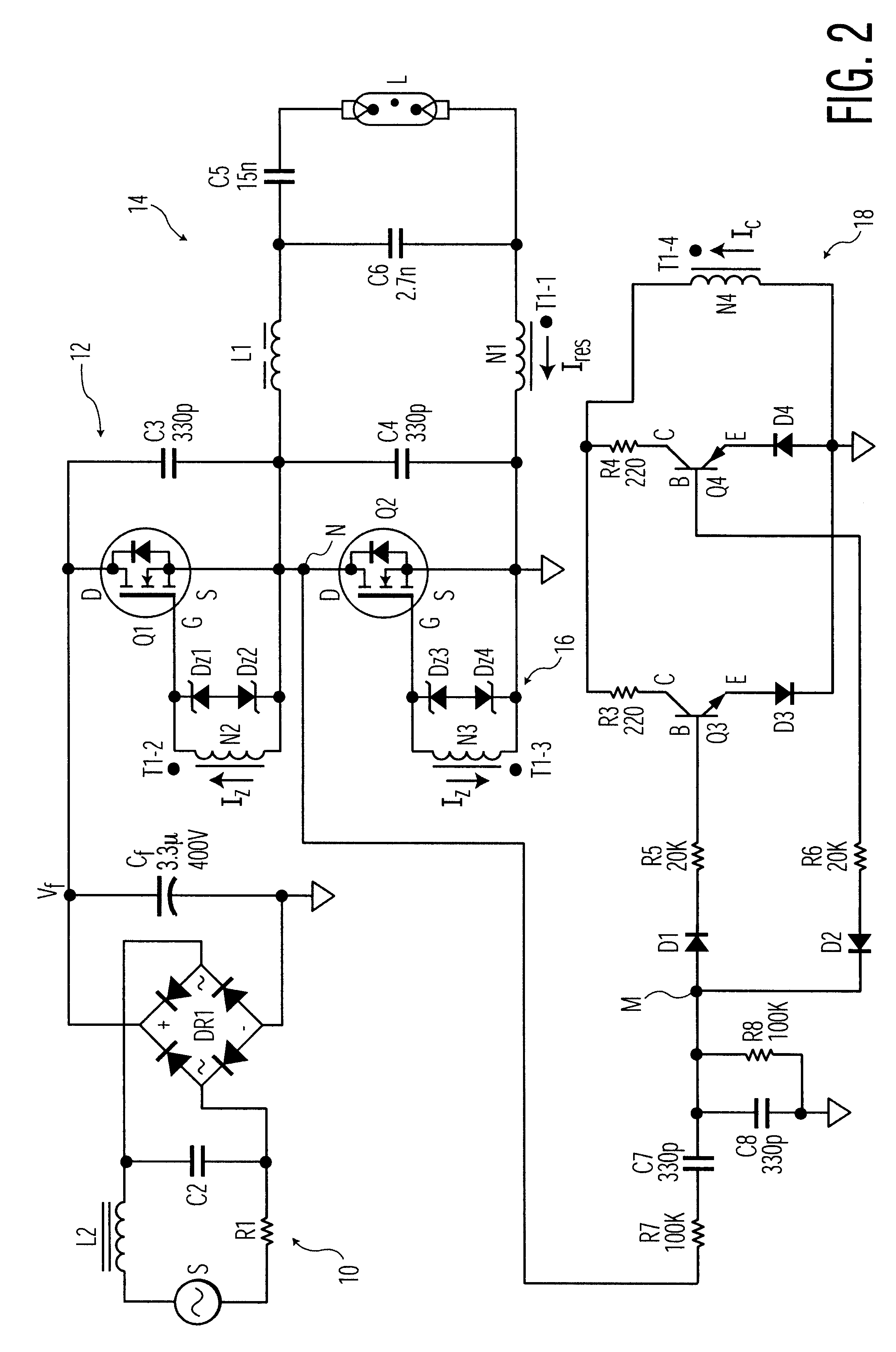
Electronic ballast with feed-forward control
InactiveUS20020067139A1Small sizeDecrease DC powerEfficient power electronics conversionAc-dc conversionVoltage dropOperating frequency
An electronic ballast is provided which is capable of compactly powering a discharge lamp from a source of rectified, but unregulated, power having a varying DC voltage. The ballast includes a self-oscillating converter powered by the DC voltage for producing pulses at a nominal operating frequency which is determined by a resonant tank. The resonant tank converts the pulses to a sinusoidal current for powering the discharge lamp and includes an inductive impedance in series with the lamp for providing a voltage drop which varies with the operating frequency. A feed-forward control circuit is coupled to the converter for varying the operating frequency directly with variations in the DC source voltage. The voltage drop across the inductive impedance is substantially proportional to the magnitude of the DC source voltage. This enables regulation of the voltage supplied to the discharge lamp by the ballast without sensing the lamp voltage itself.
Owner:PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NORTH AMERICA
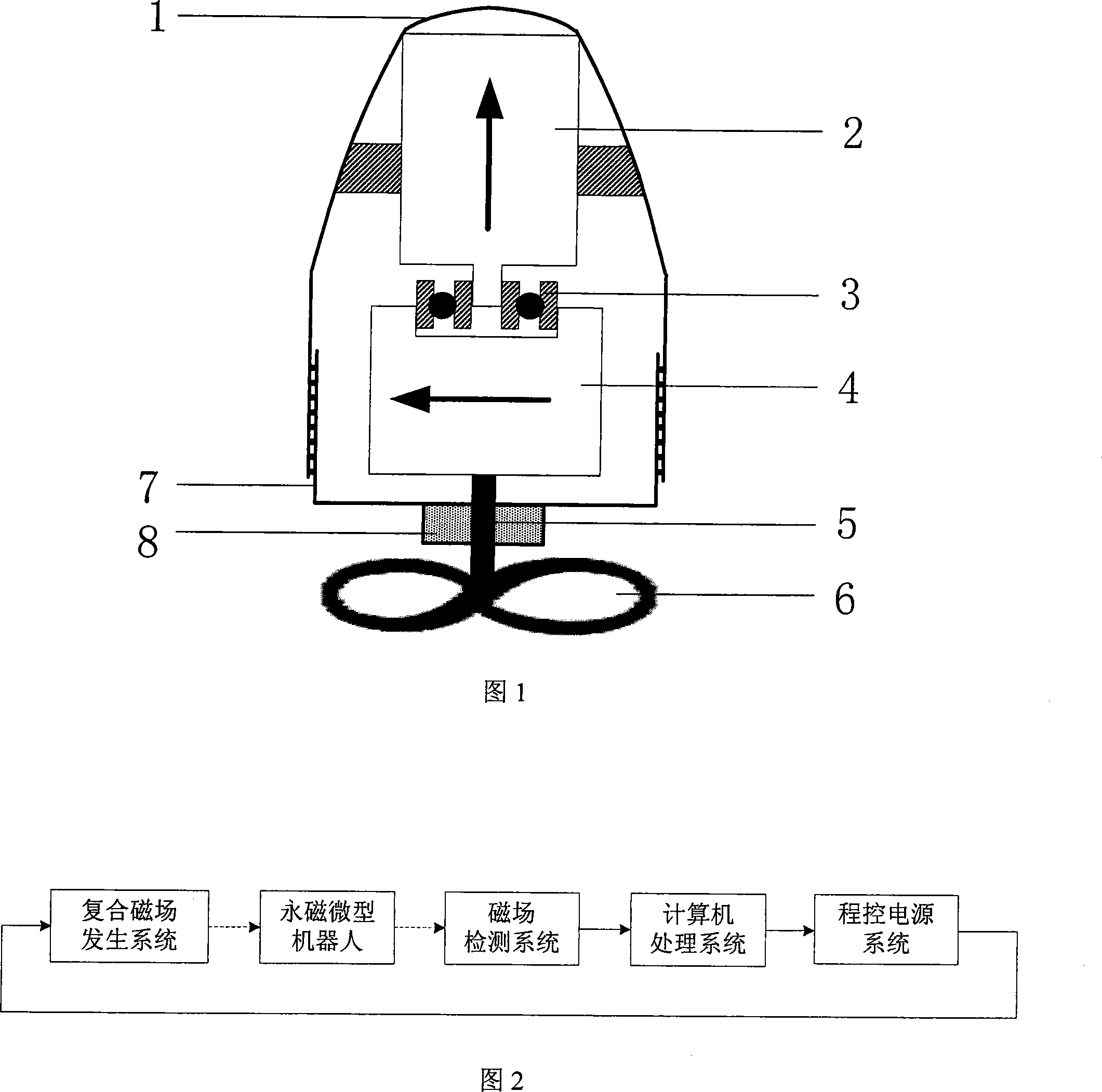
Permanent magnetism minisize robot
InactiveCN101169212ARealize external wireless driver controlReduce volumePigs/molesHelmholtz coilDc current
A permanent-magnet micro-robot consists of a casing (5), an axially magnetized permanent magnet (1), a radially magnetized permanent magnet (2), a non-magnetic miniature bearing (3) and a propeller (4), wherein, the head of the casing (5) is round and smooth, and a bottom (6) has a cavity (7) which is filled with lubricating grease; the axially magnetized permanent magnet (1) and the radially magnetized permanent magnet (2) are connected by the non-magnetic miniature bearing (3); the radially magnetized permanent magnet (2) and the propeller (4) are fixed via an axle (8) of the propeller. An outside magnetic field is generated by a rotation magnetic field device and a uniform magnetic field device, wherein, the rotation magnetic field consists of three groups of perpendicular Helmholtz coils, a sinusoidal current source and a phaser; the uniform magnetic field device consists of three groups of perpendicular Helmholtz coils and three groups of direct current sources. Under the effect of the rotation magnetic field, the robot rotates with the radially magnetized permanent magnet (2) and produces the axial driving force to drive; at the same time, under the deflecting guidance of the uniform magnetic field, the robot realizes flexible steering and moves along an expected locus.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRICAL ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
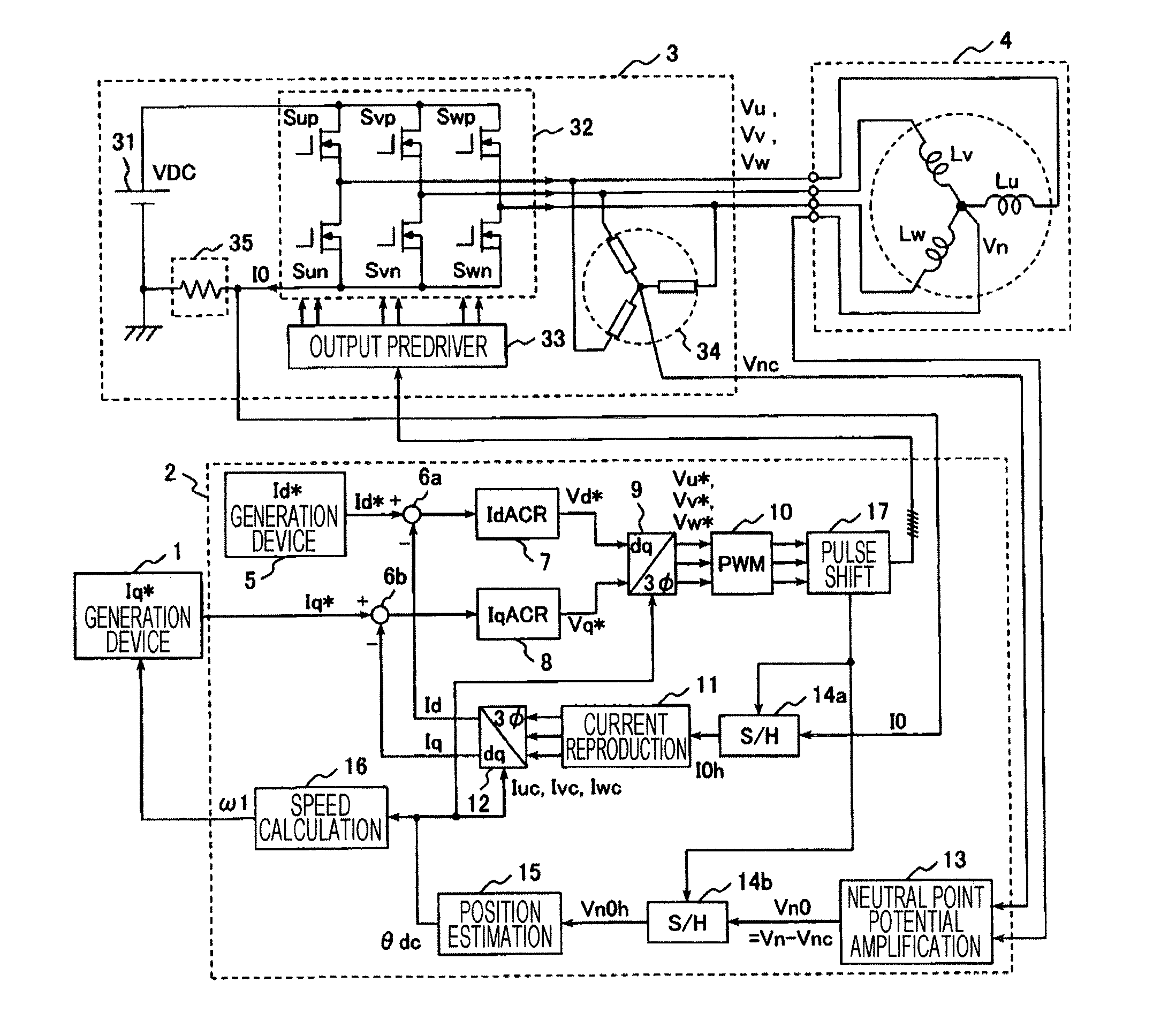
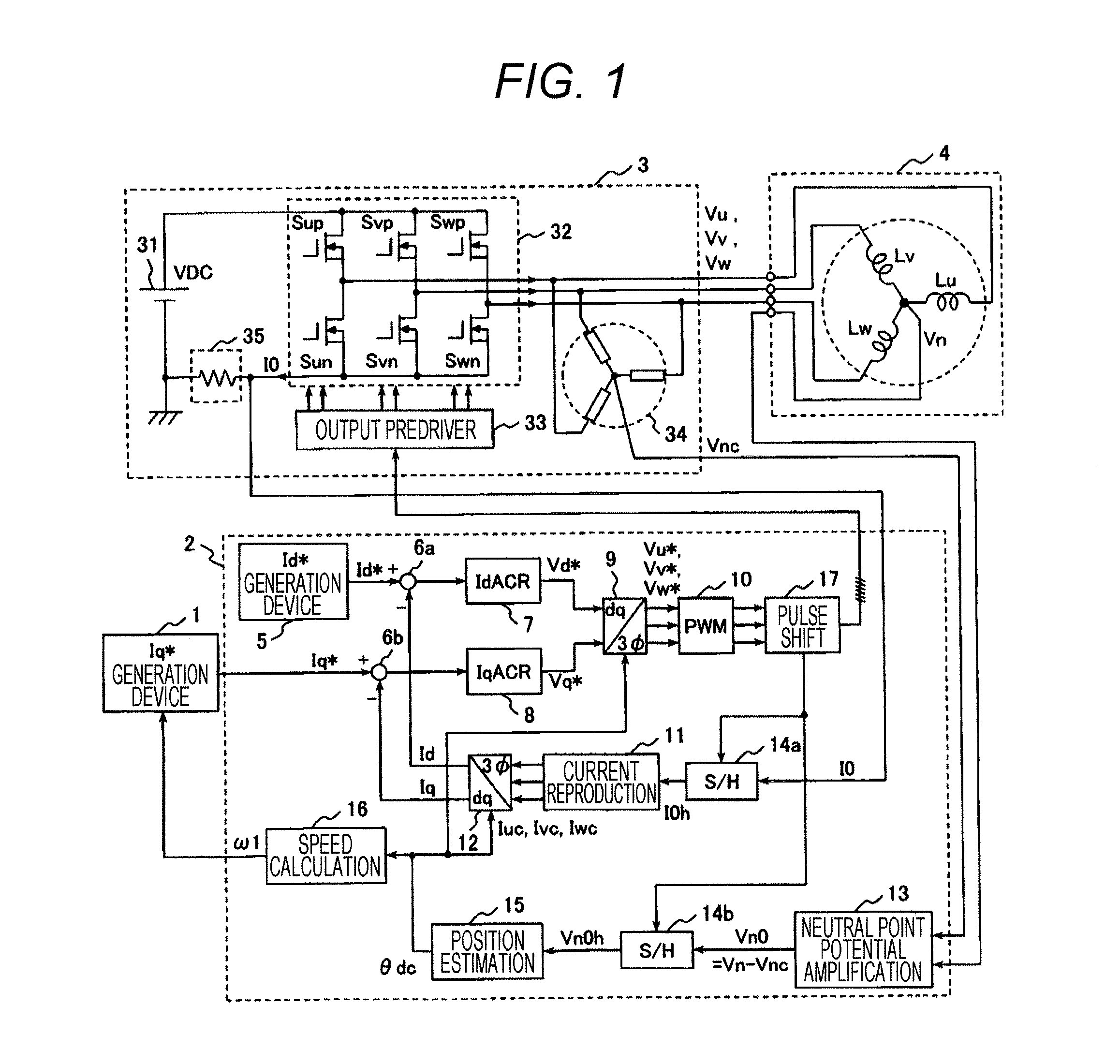
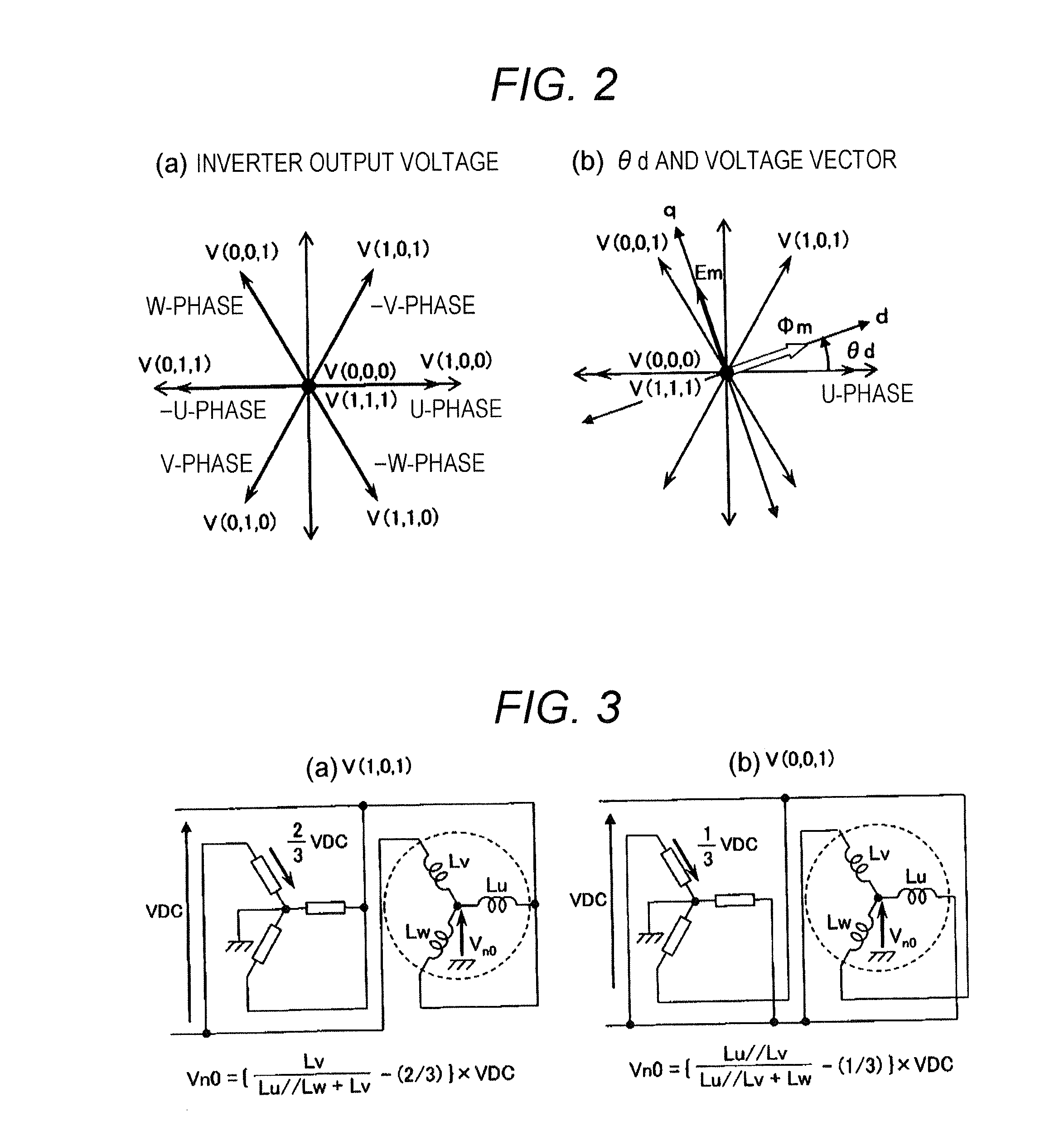
Driving System For Synchronous Motor
InactiveUS20140077738A1Improve efficiencyIncrease the number ofMotor/generator/converter stoppersSynchronous motors startersLow speedSynchronous motor
A position sensor-less driving method is provided that can drive rotation speed / torque control of a permanent magnet motor using an inverter with an ideal sinusoidal current with the minimum number of switching, and can drive at a speed as low as an extremely low speed region close to zero speed. A neutral point potential of a permanent magnet motor is detected in synchronization with PWM waveform of the inverter. A rotor position of the permanent magnet motor is estimated from change of the neutral point potential. When the neutral point potential is detected, timing of each phase of the PWM waveform is shifted to generate three or four types of switch states of which output voltage of the inverter is not zero vector, and neutral point potentials in at least two types of switch states among them are sampled, whereby rotor position of the three-phase synchronous motor is estimated.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
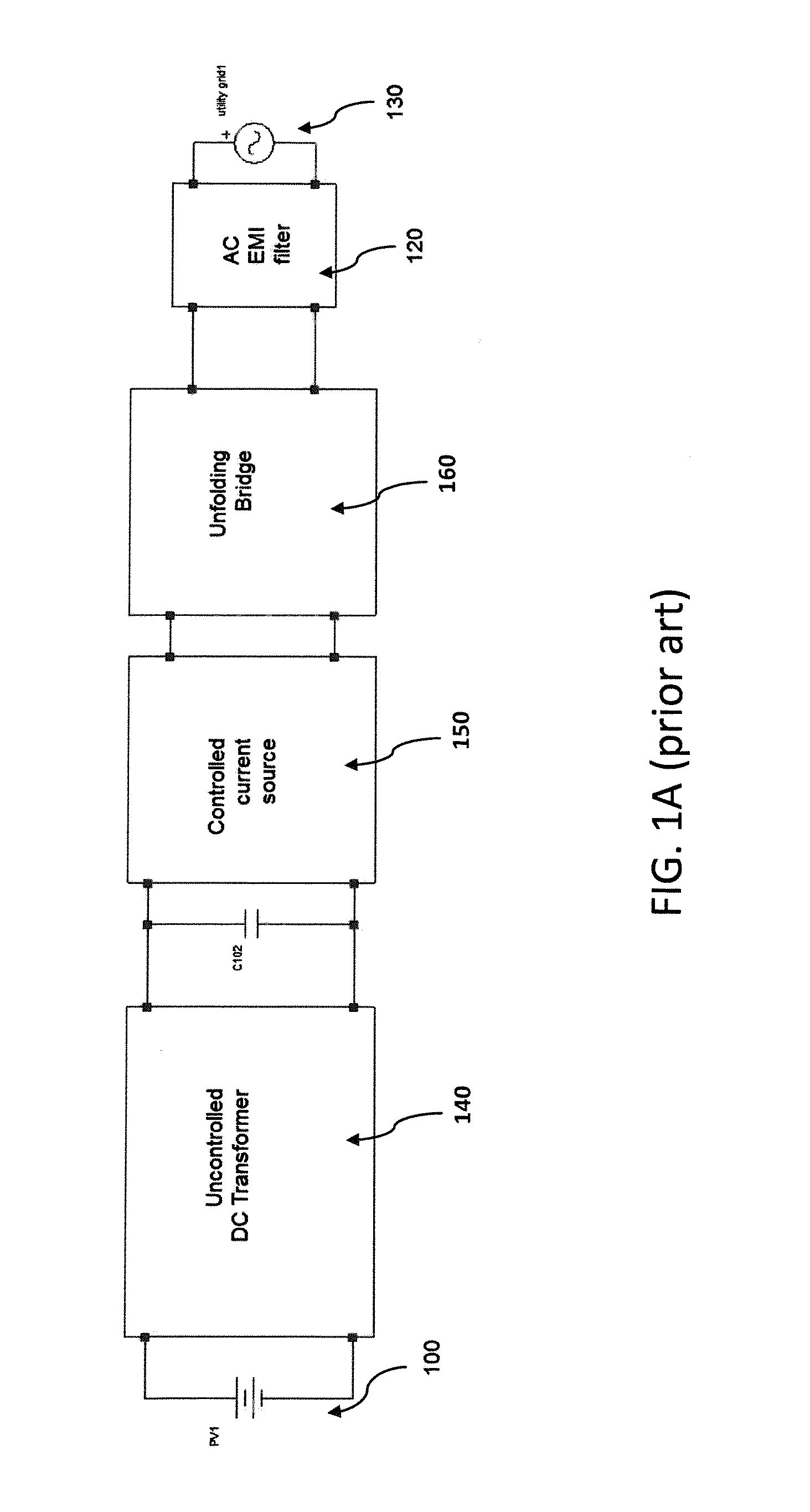
Photovoltaic powered system
InactiveUS20120230066A1Reduce voltage spikesExtensive trackingElectric power transfer ac networkAc-dc conversionPower factorAlternating current
A photovoltaic powered system and an alternating current (AC) module thereof are disclosed. The photovoltaic powered system provides a direct current (DC) power through a photovoltaic module and converts the DC power into an AC power, which is grid-connected to an AC utility power. The AC module of the photovoltaic powered system produces a continuous quasi-sinusoidal current and the quasi-sinusoidal current is converted into a sinusoidal current. The high-frequency harmonic components of the sinusoidal current are filtered to produce a sinusoidal output current in phase with the AC utility power, thus realizing the maximum power point tracking (MPPT) of the photovoltaic module and feeding unity-power-factor power into the AC utility power.
Owner:ALLIS ELECTRIC
Totem-pole PFC (power factor correction) fully-digital control method and device
ActiveCN107863880AImprove the ability to track power frequency sinusoidal currentImprove anti-interference abilityEfficient power electronics conversionAc-dc conversionInner loopComputer module
The invention discloses a totem-pole PFC fully-digital control method and device. The method comprises acquiring corresponding voltage and current information through a sampling module, after digitalphase locking is completed, computing effective value and phase value of input voltage, adjusting error signals through a voltage outer loop adjuster and a current inner loop adjuster, and performingfeed forward compensation on an output duty ratio through duty ratio feed forward. According to the totem-pole PFC fully-digital control method, by introducing the duty ratio feed forward, the currentinner loop adjuster only needs to inhibit small signal disturbance, so that the capability of a controller on tracking power frequency sine-wave current; by collecting the zero crossing point of input voltage for digital phase locking, querying a sine table to acquire the phase value of the input voltage, collecting the real-time value of the input voltage for effective value computation and taking the computed real-time value of the input voltage as input current instruction value and the input value of a feed forward duty ratio computing module, the totem-pole PFC fully-digital control method can eliminate output duty ratio disturbance led by input voltage sampling deviation and improve anti-interference performance and stability of digital control totem PFCs.
Owner:武汉矩阵能源科技有限公司
Asynchronous motor parameter identification method
ActiveCN103281033AAvoid Zero Crossing DistortionMotor parameters estimation/adaptationFrequency changerConductor Coil
The invention relates to an asynchronous motor parameter identification method, in particular to an asynchronous motor parameter off-line identification method. Sine-wave current signals with different frequencies are accessed to an asynchronous motor stator winding twice; equivalent total leakage inductance and mutual inductance are computed according to a T-shaped equivalent circuit in a motor single phase test; trapezoid current signals are accessed to an asynchronous motor stator resistance; the output voltage of a frequency converter on the ascent stage of the trapezoid current signals is detected; a stator leakage inductance and a rotor leakage inductance of an asynchronous motor are computed; the output voltage V of the frequency converter at the horizontal stage of the trapezoid current signals is detected; and an asynchronous motor rotor resistance is computed. Due to the adoption of the method, the parameters of an asynchronous motor can be rapidly identified, and meanwhile, the output of the frequency converter can track the given current signals through a PI (proportional integral) current controller; and the zero crossing point distortion of current which is caused by the influence of frequency converter tube voltage drop and dead zones can be avoided through adding direct current bias in the input current signals of the frequency converter.
Owner:CHANGZHOU LIANLI AUTOMATION TECH
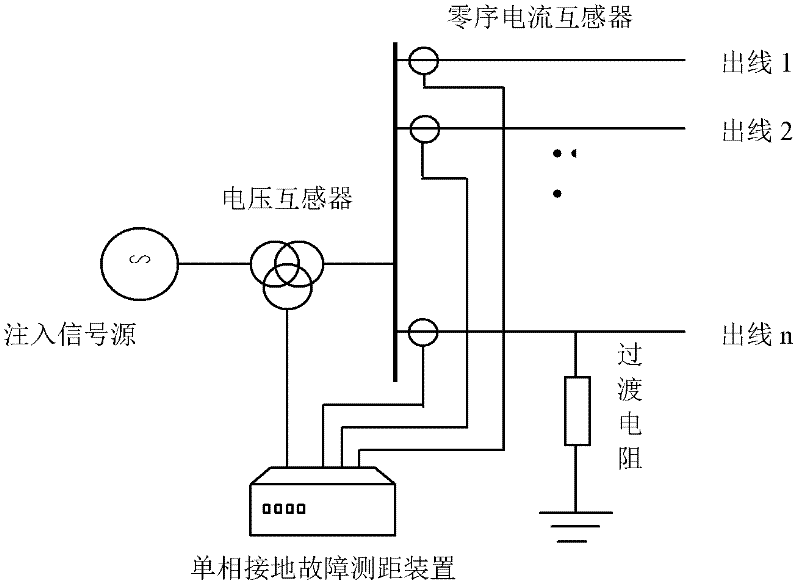
Small-current grounding system single-phase grounding fault distance measurement method based on signal injection method
InactiveCN102288872AImprove applicabilityGuaranteed accuracyFault locationCapacitanceConstant frequency
The invention relates to a small-current grounding system single-phase grounding fault distance measurement method based on a signal injection method. Under a single-phase grounding fault, a constant-frequency sine current signal is injected through a voltage transformer during secondary lateral fault phase short circuit; the current generates a corresponding voltage drop on a faulted line; relational expressions between injection signal voltage and injection signal current at the head end of the line and the injection signal voltage and the injection signal current on a faulted point can be written by adopting a distribution parameter model of the line based on a long-line equation; relational expressions between the injection signal voltage and the injection signal current on the faulted point and transitional resistance can be also written; the virtual part of the transitional resistance is set to be 0 and the plural equations are solved, so that a fault distance can be obtained. The small-current grounding system single-phase grounding fault distance measurement method based on the signal injection method has the advantages that: due to adoption of an injection signal for distance measurement, influences of a system structure, a running mode and an arc suppression coil can be avoided; due to adoption of the distribution parameter model of the line, an influence of a distribution capacitor can be avoided; therefore, a distance measurement result has higher precision, and the small-current grounding system has high anti-transitional-resistance capability.
Owner:SHANDONG ELECTRIC POWER SCHOOL
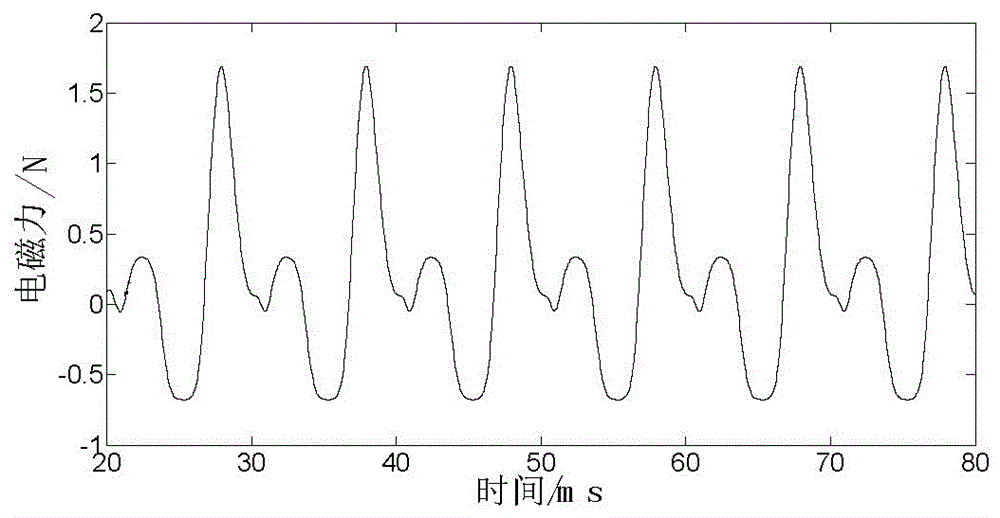
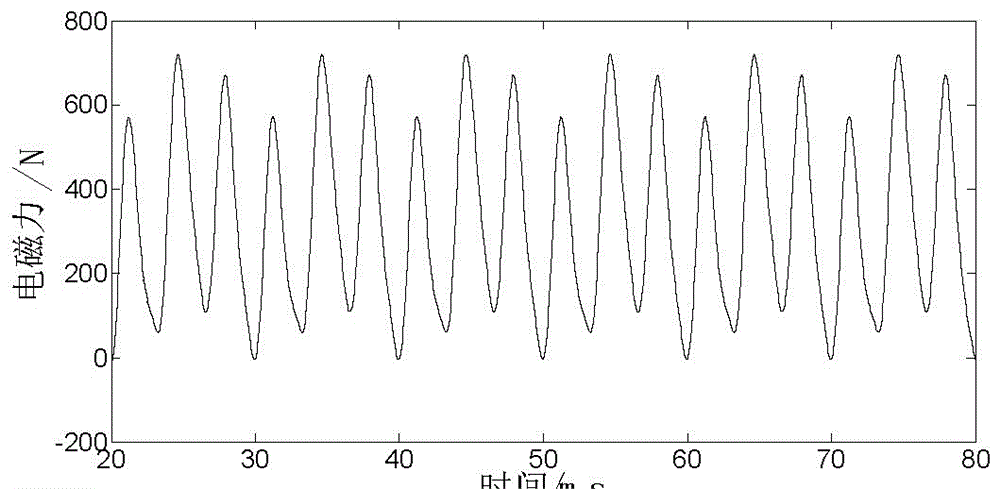
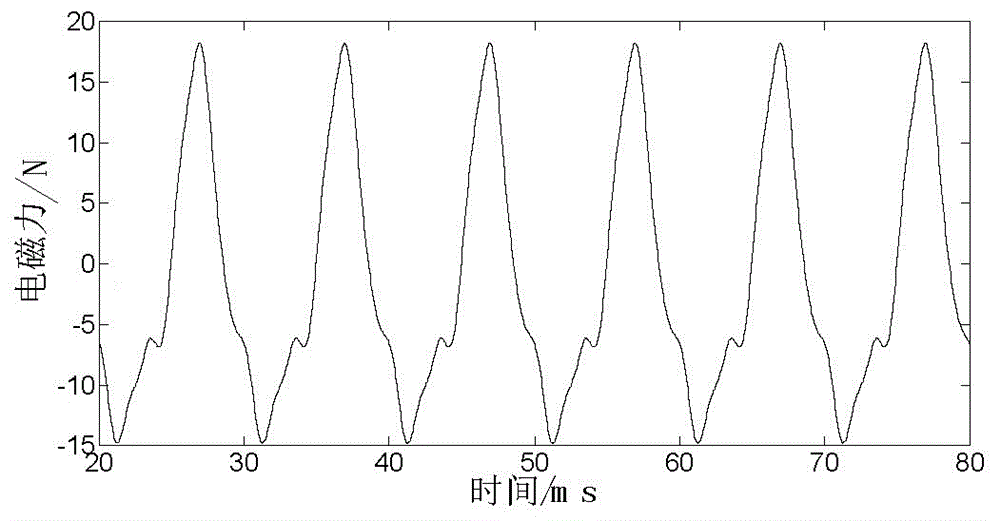
Method for computing electromagnetic force of transformer iron core based on finite element method
InactiveCN106570218ACalculation method directlyCalculation method is simpleDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsTransformerLow voltage
The invention discloses a method for computing electromagnetic force of a transformer iron core based on a finite element method. The method comprises the steps that structural parameters of a winding, the iron core and a fuel tank of a transformer are collected, and then a three-dimensional geometric grid model of the transformer is established; the three-dimensional geometric grid model is input into software, sinusoidal currents with a phase different of 120 DEG are applied to the cross section of the three-phase low voltage winding respectively, and Dirichlet boundary conditions are applied to the outer side of the structural grid model; and an instant electromagnetic field is solved by a virtual displacement method, magnetic field energy is computed, a virtual work method is used to compute instant electromagnetic force borne by the transformer iron core and the winding, FFT is conducted to the instant electromagnetic force, and frequency domain distribution of the electromagnetic force of the iron core can be obtained. The computation method disclosed by the invention is direct and convenient; electromagnetic vibration and force bearing situations of the transformer iron core can be analyzed from the perspective of energy; each influential factor on force bearing of the iron core is considered comprehensively; and computation results are accurate and reliable.
Owner:CHINA ELECTRIC POWER RES INST +1
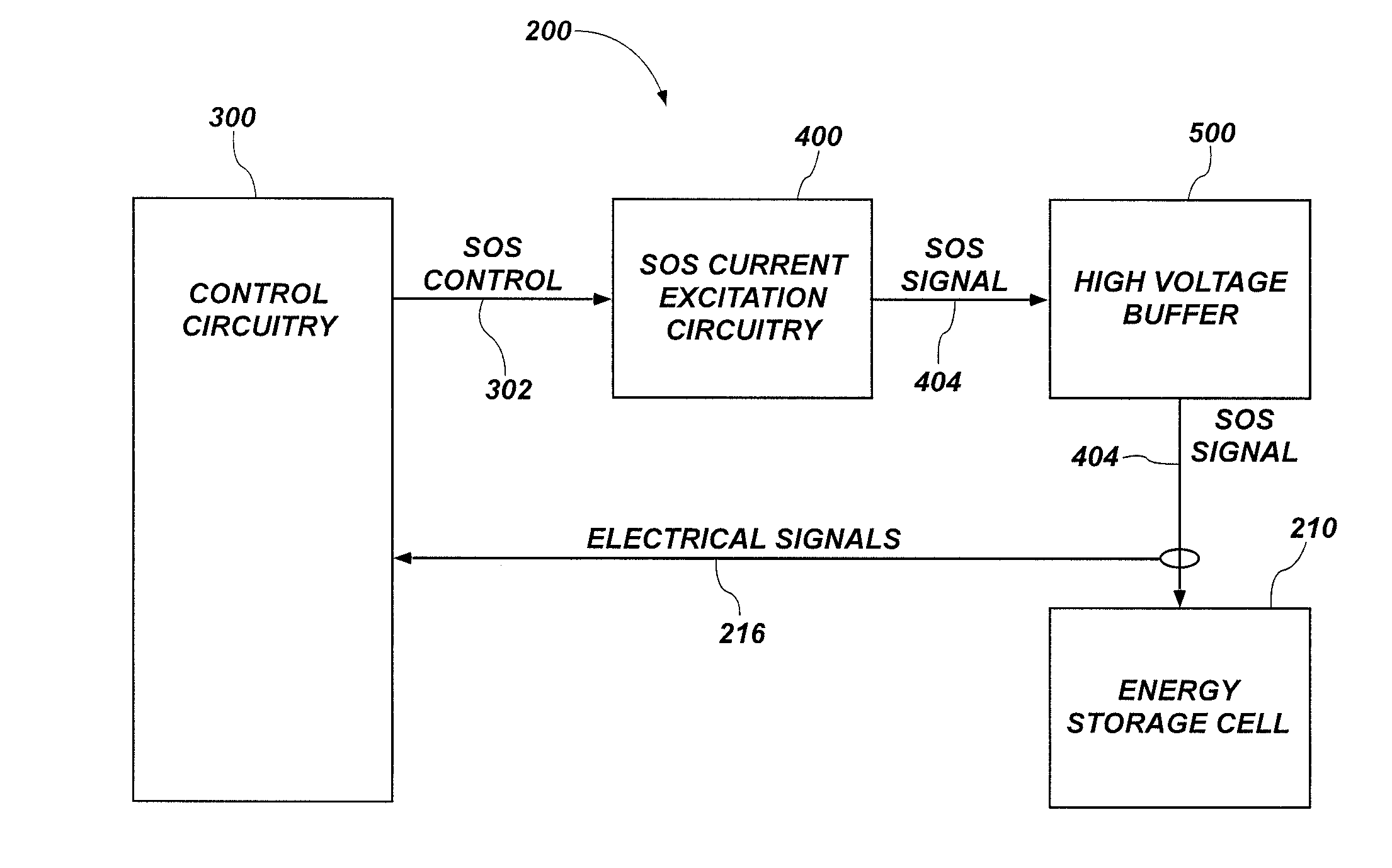
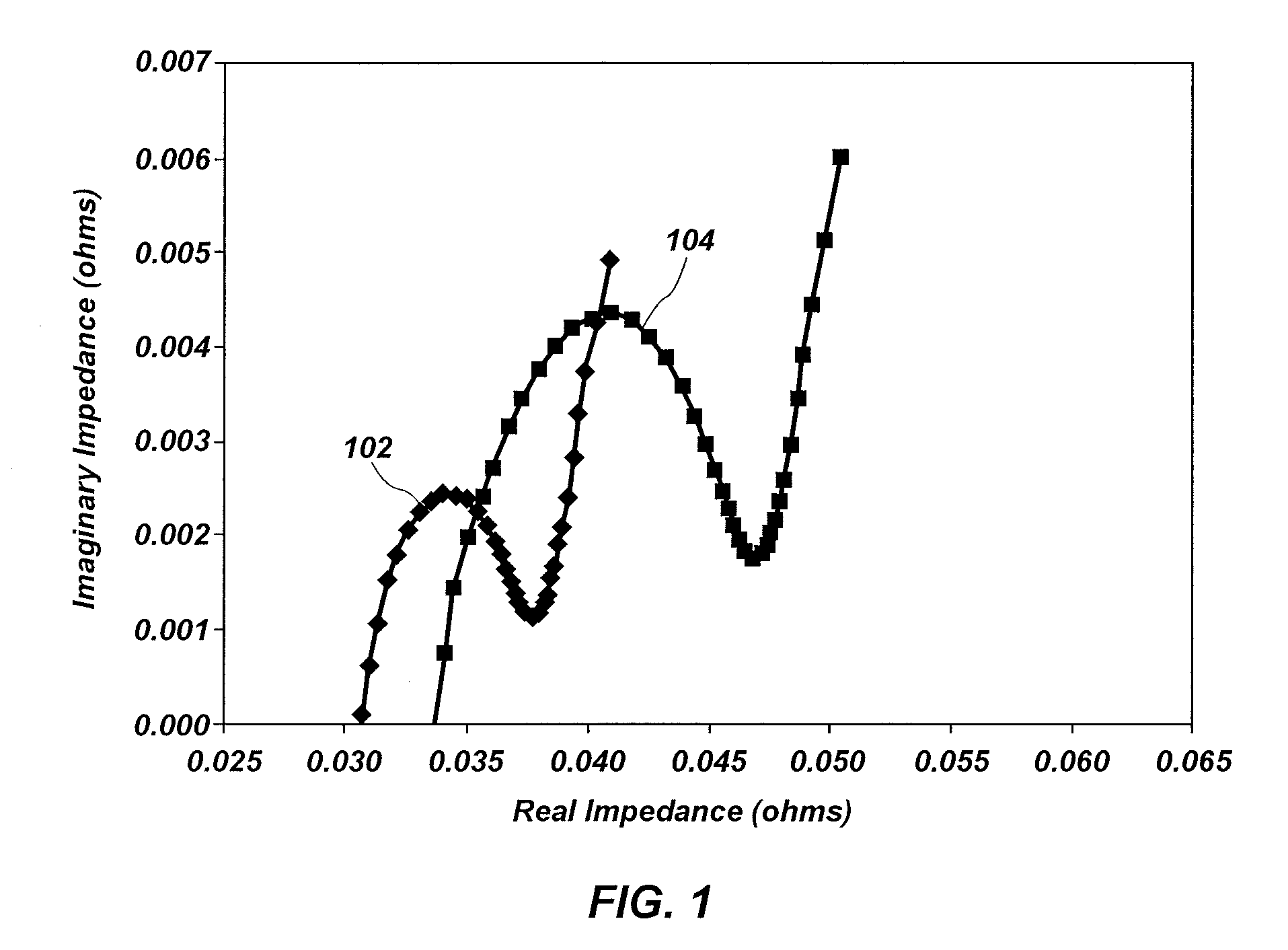
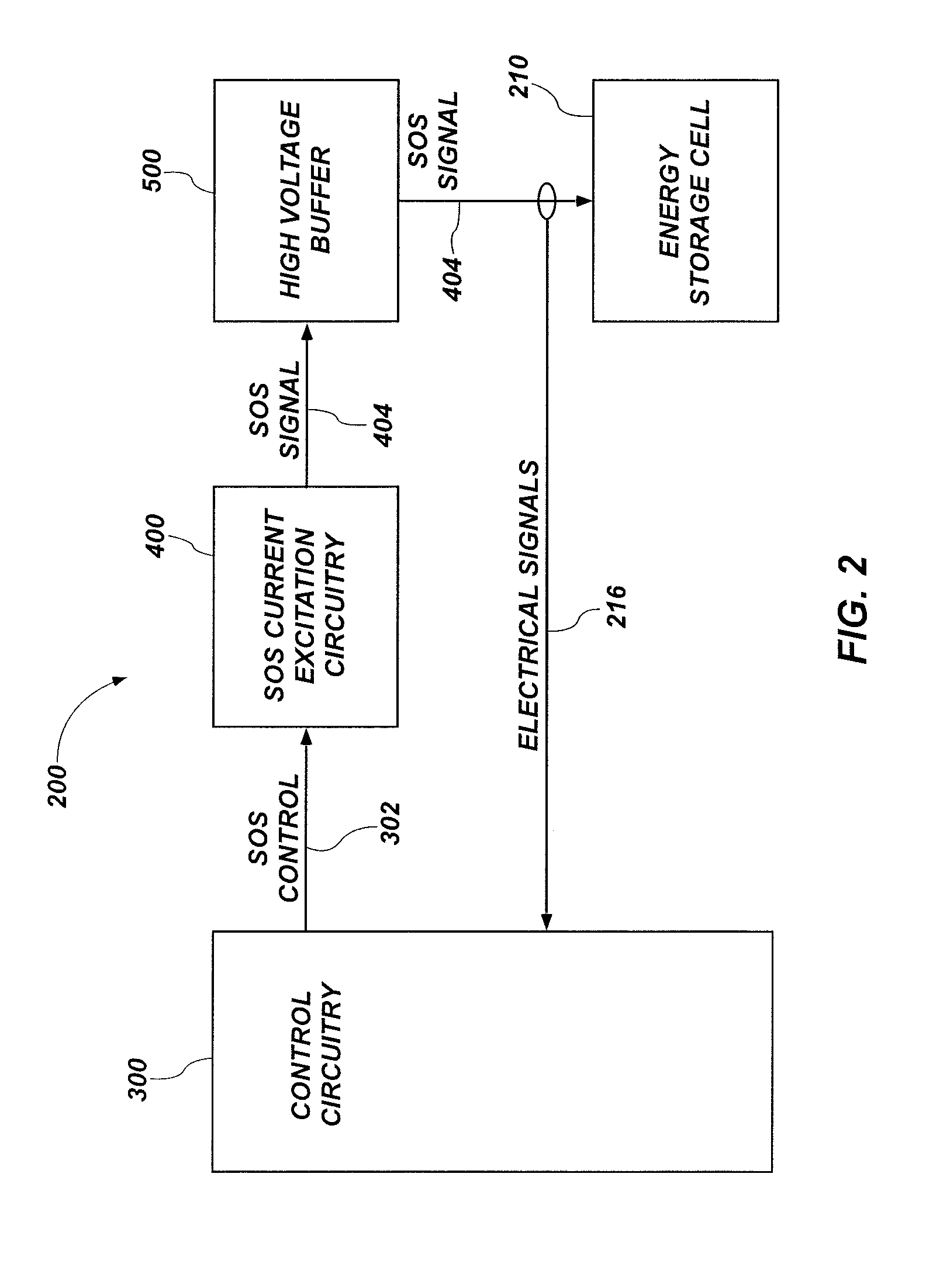
Energy storage cell impedance measuring apparatus, methods and related systems
Energy storage cell impedance testing devices, circuits, and related methods are disclosed. An energy storage cell impedance measuring device includes a sum of sinusoids (SOS) current excitation circuit including differential current sources configured to isolate a ground terminal of the differential current sources from a positive terminal and a negative terminal of an energy storage cell. A method includes applying an SOS signal comprising a sum of sinusoidal current signals to the energy storage cell with the SOS current excitation circuit, each of the sinusoidal current signals oscillating at a different one of a plurality of different frequencies. The method also includes measuring an electrical signal at a positive terminal and a negative terminal of the energy storage cell, and computing an impedance of the energy storage cell at each of the plurality of different frequencies using the measured electrical signal.
Owner:BATTELLE ENERGY ALLIANCE LLC
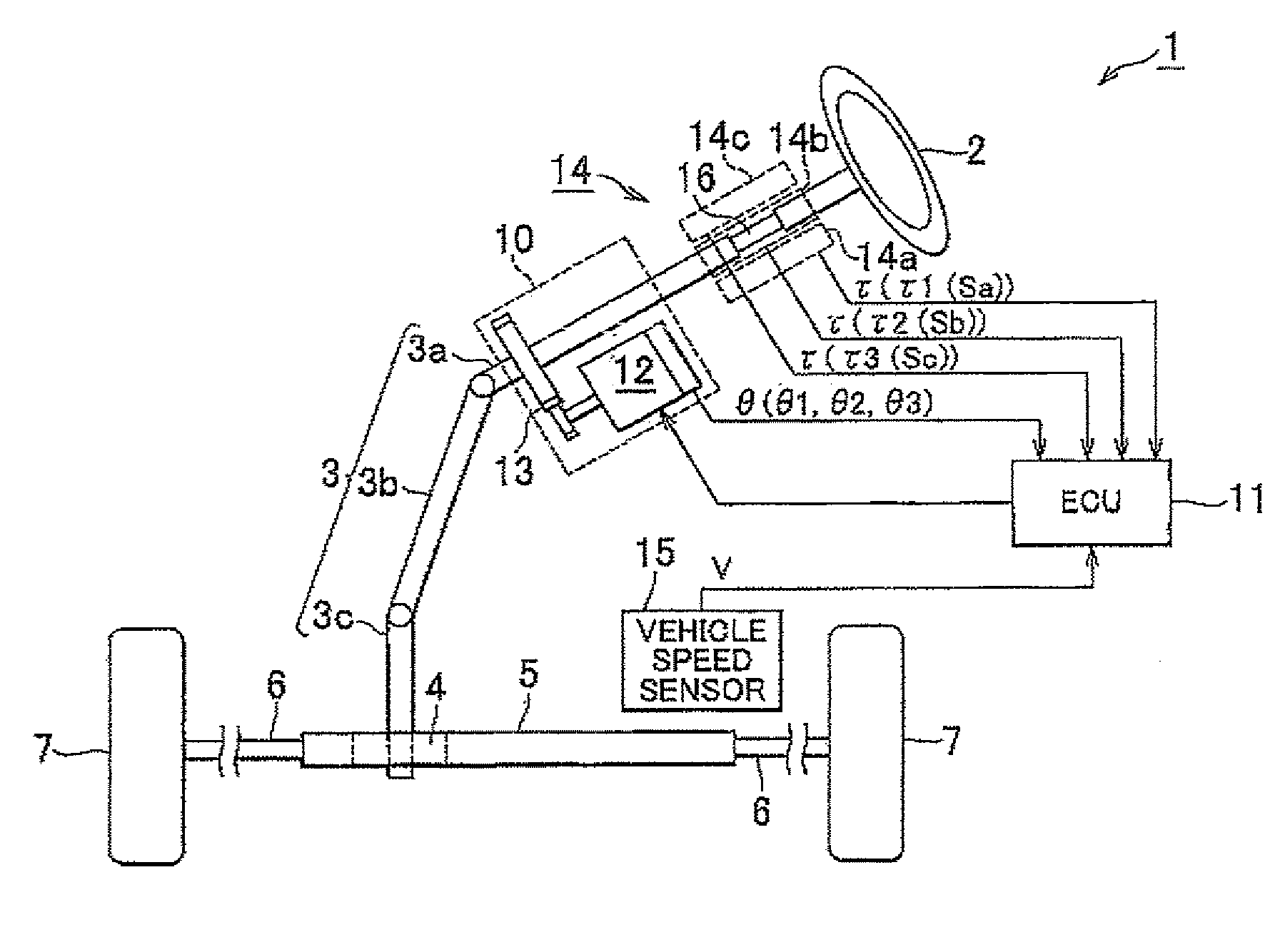
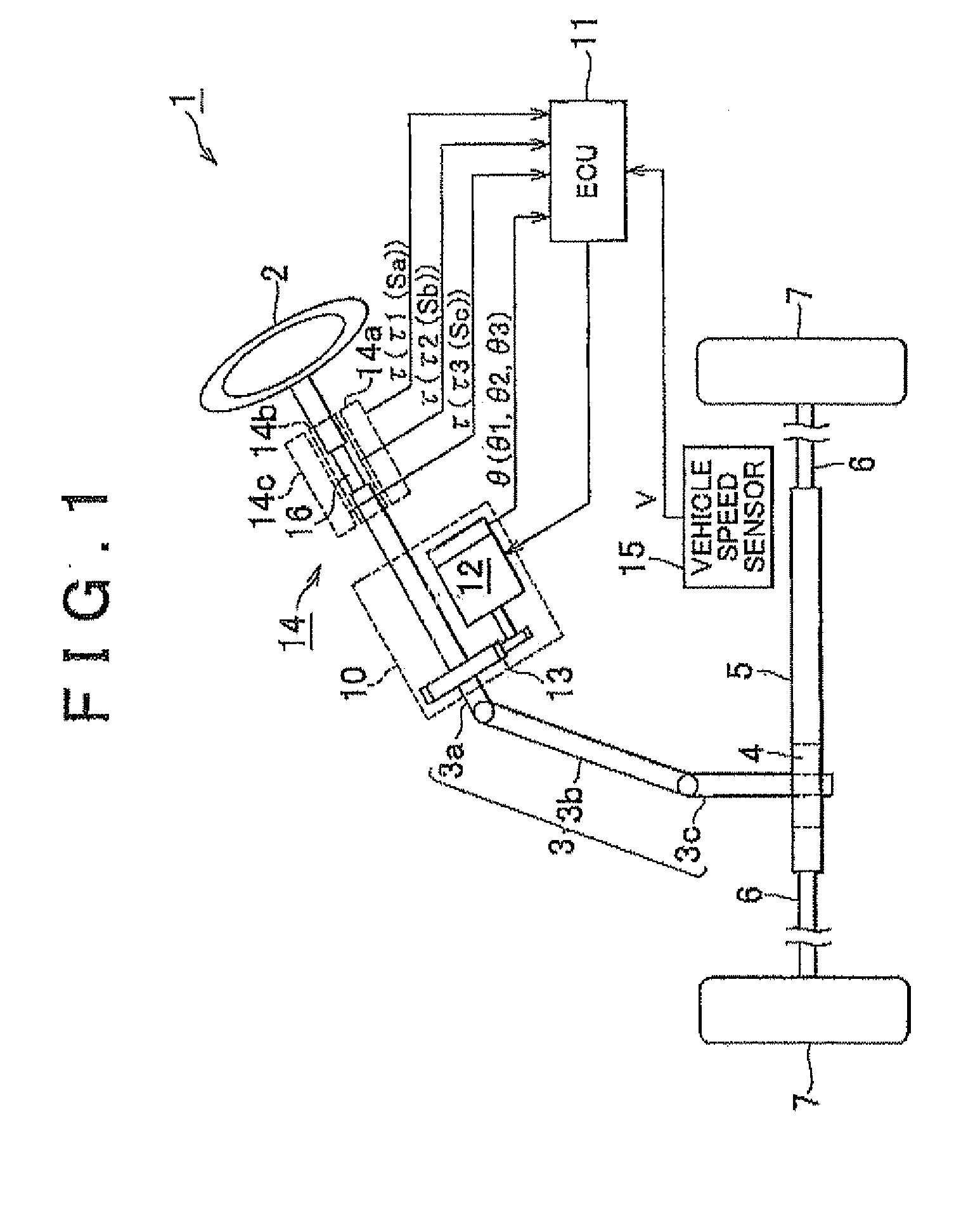
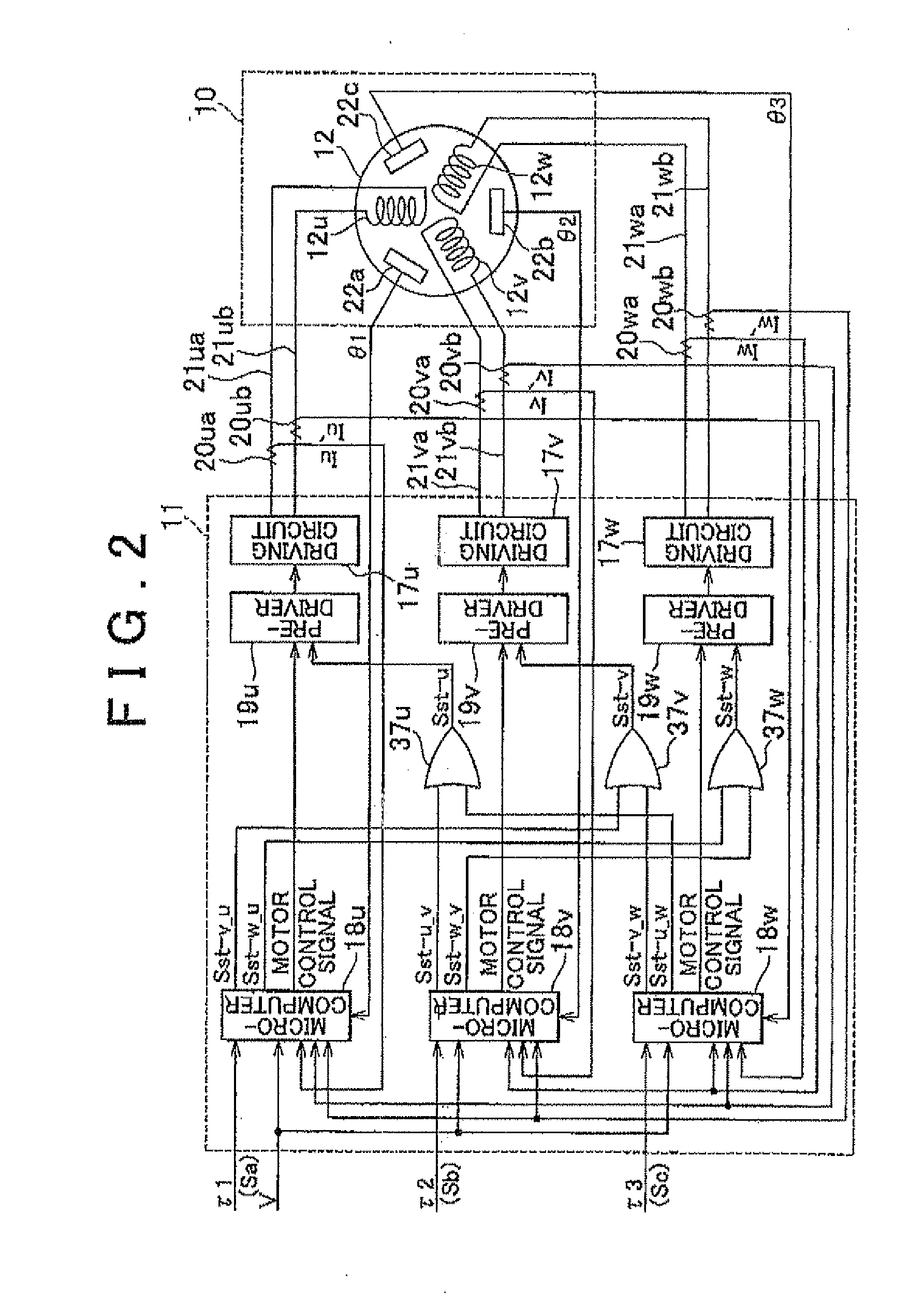
Electric Power Steering System
InactiveUS20110025244A1Improve reliabilityDetected as abnormalityCommutation monitoringAC motor controlMicrocomputerElectric power steering
In an electric power steering system, an ECU 11 that controls the operation of the system includes three independent microcomputers 18u, 18v, 18w that perform phase current feedback control with respect to the corresponding phases, so that sinusoidal current is applied to each phase of the motor 12 as a non-connected motor. Also, each of the microcomputers 18u, 18v, 18w monitors a deviation of an actual current value from a phase current command value, with respect to each of two phases other than the corresponding phase, and determines that an abnormality occurs in the phase in question when the deviation exceeds a predetermined threshold value. When two of the microcomputers 18u, 18v, 18w determine that the abnormality occurs in the remaining one phase, the ECU 11 confirms the determination that the phase in question is in an abnormal condition.
Owner:JTEKT CORP
Power factor correction circuits
InactiveUS20050201124A1Efficient power electronics conversionAc-dc conversionEngineeringPower factor control
A bi-directional boost circuit for power factor correction includes a power factor control circuit and a pair of diodes, a pair of inductors, and a pair of switches. A first diode, a second diode, a first inductor, a second inductor, a first switch, and a second switch convert the AC input voltage, rectify the AC input voltage, and output an intermediate DC voltage. The power factor control circuit receives the AC input voltage and receives the intermediate DC voltage. The power factor control circuit regulates the DC output voltage. Based on the AC input voltage and the intermediate DC output voltage, the power factor control circuit controls an inductor current waveform by driving the first switch and the second switch to create a substantially sinusoidal current as seen by the power source that is in phase with the AC input voltage.
Owner:COMARCO WIRELESS TECH
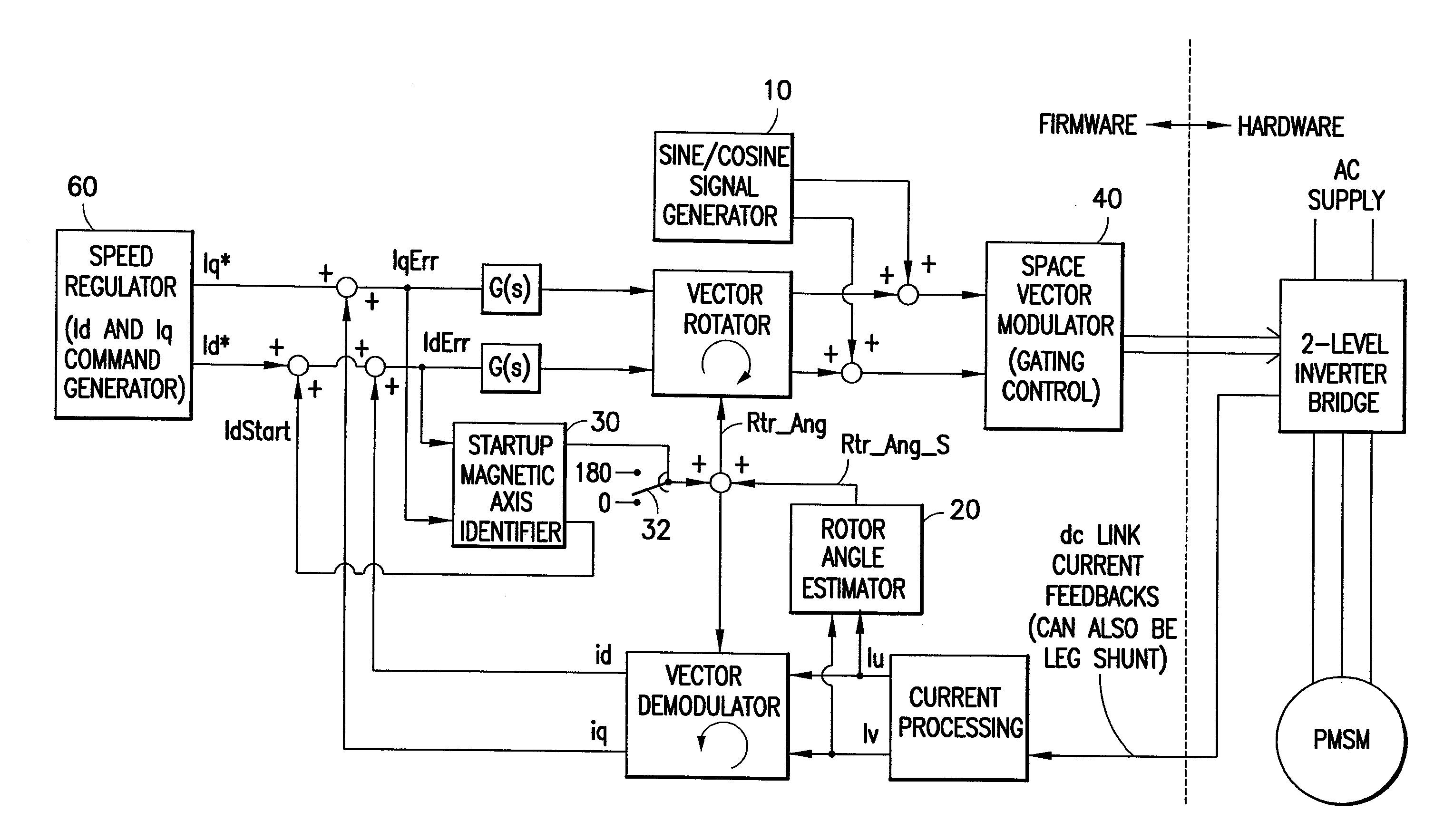
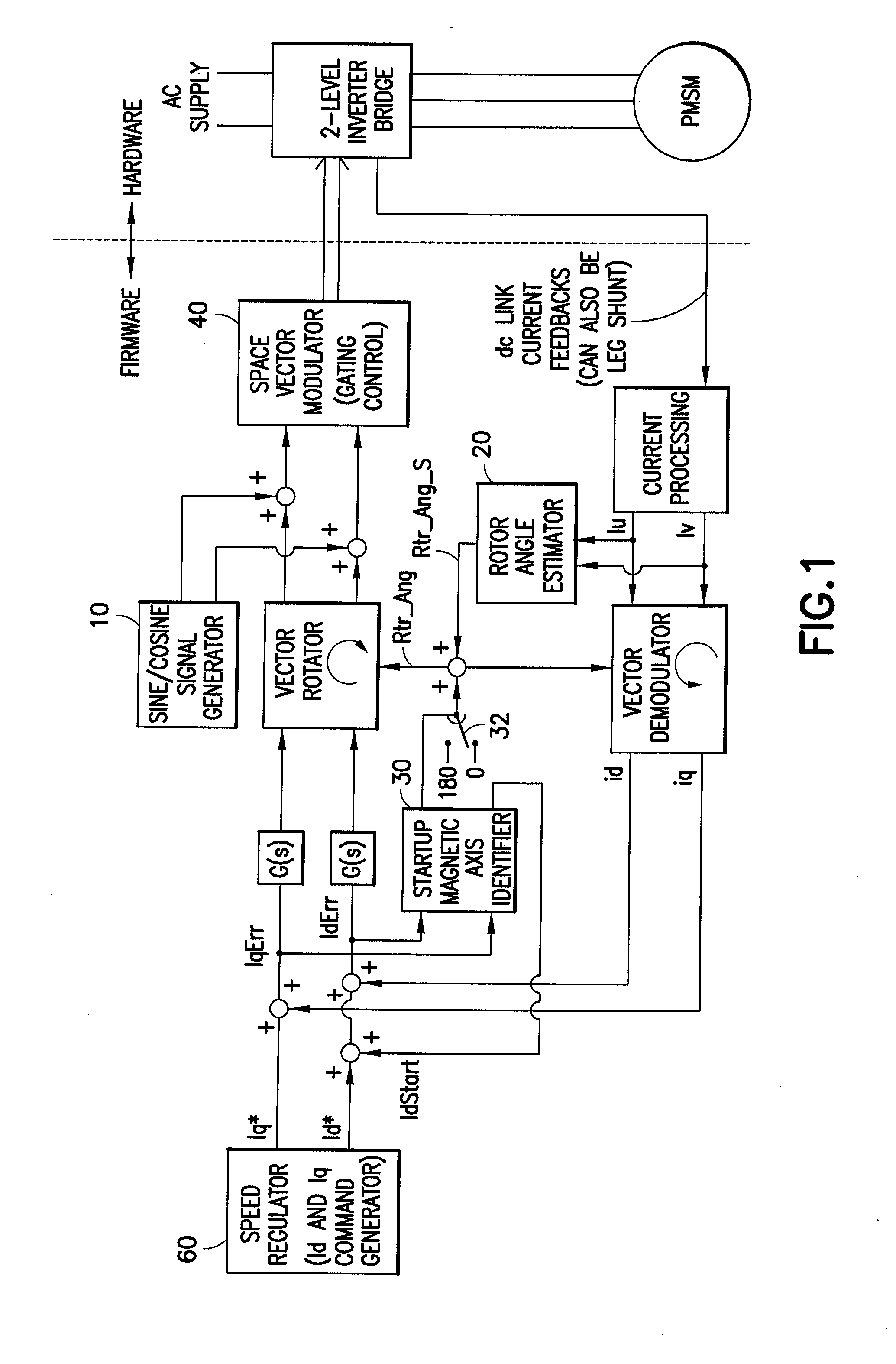
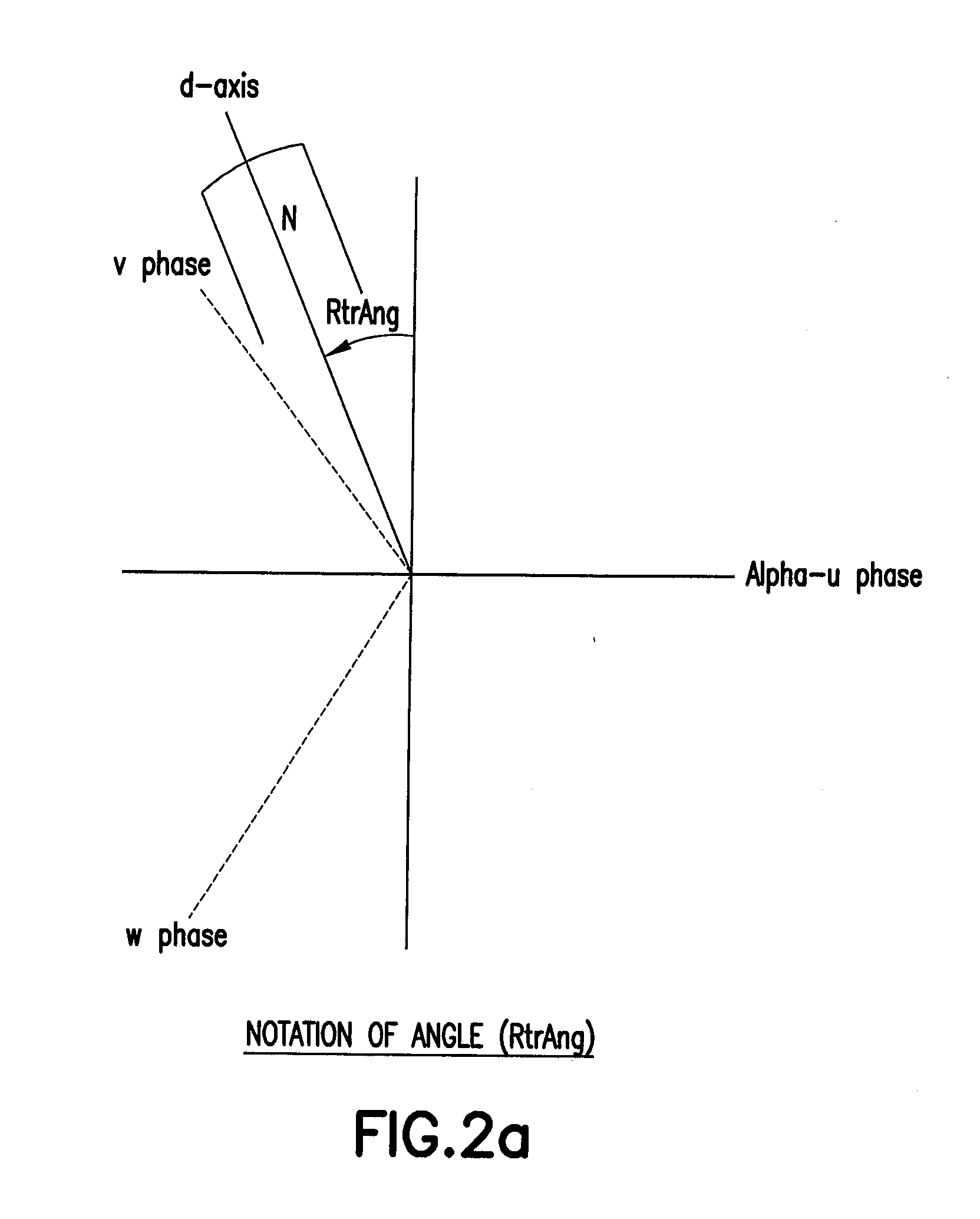
Signal conditioning apparatus and method for determination of permanent magnet motor rotor position
ActiveUS20080048599A1Fast trackSimple technologyElectronic commutation motor controlMotor/generator/converter stoppersLow speedCurrent amplitude
An apparatus and method for estimating rotor angle information for the control of permanent magnet AC motors having sinusoidal current excitation. The disclosed motor drive can provide full load operation at very low speeds including zero speed without the use of a shaft position sensing device. The rotor angle is estimated through injection of high frequency current, and rotor angle is extracted by a signal-conditioning algorithm, which utilizes current amplitude differential to discriminate the rotor angle. Rotor angle magnetic axis orientation (North or South pole) at startup is detected by comparing time average current ripple (at signal injection frequency) content between two different levels of d-axis current injection.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AMERICAS CORP
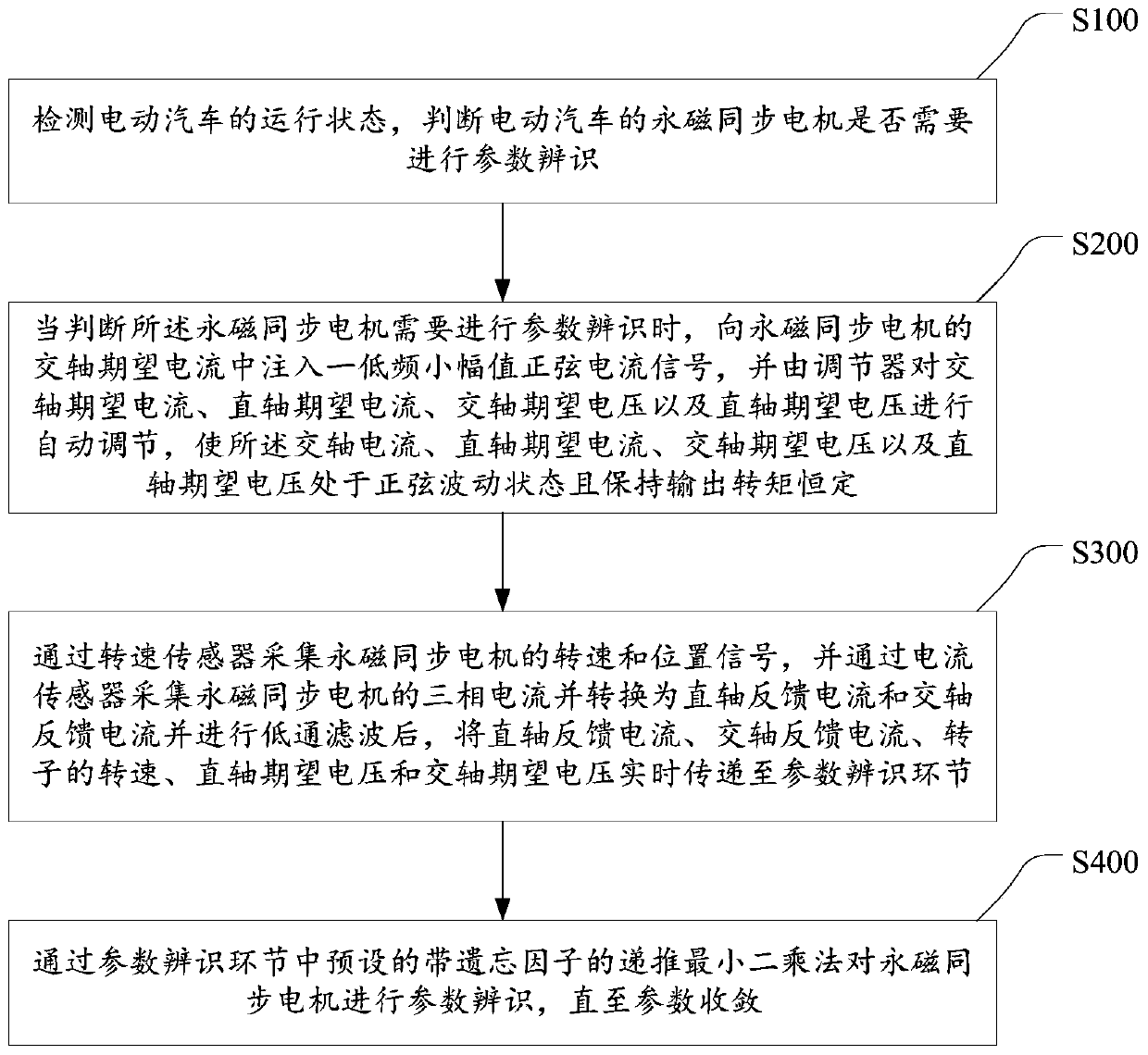
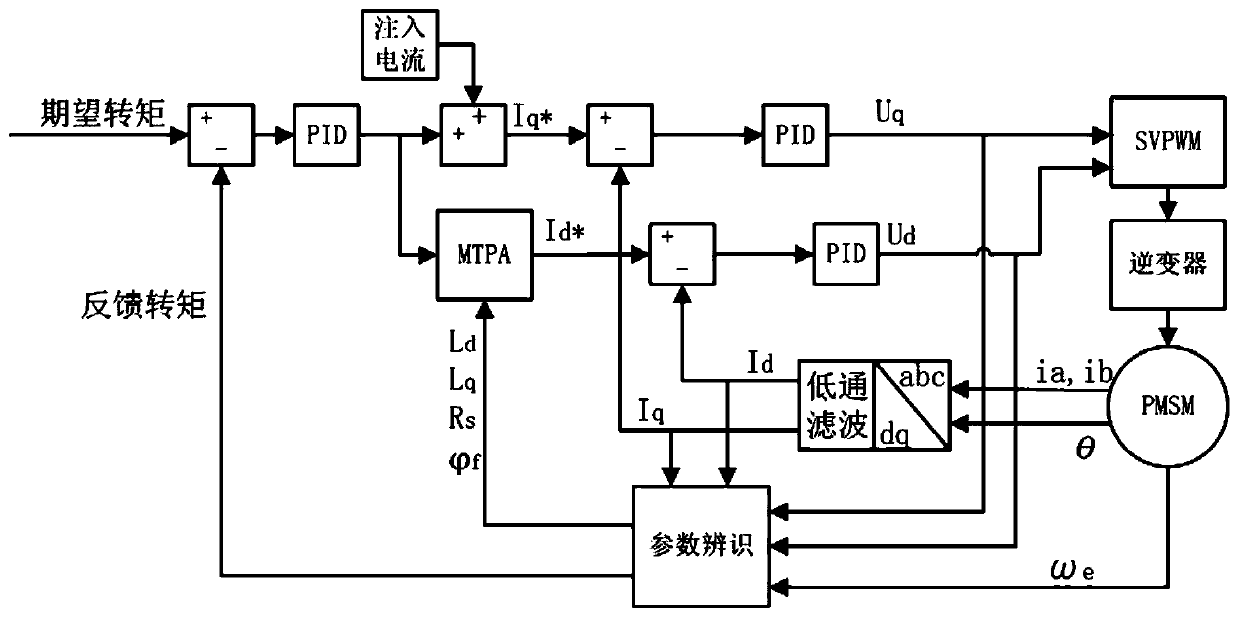
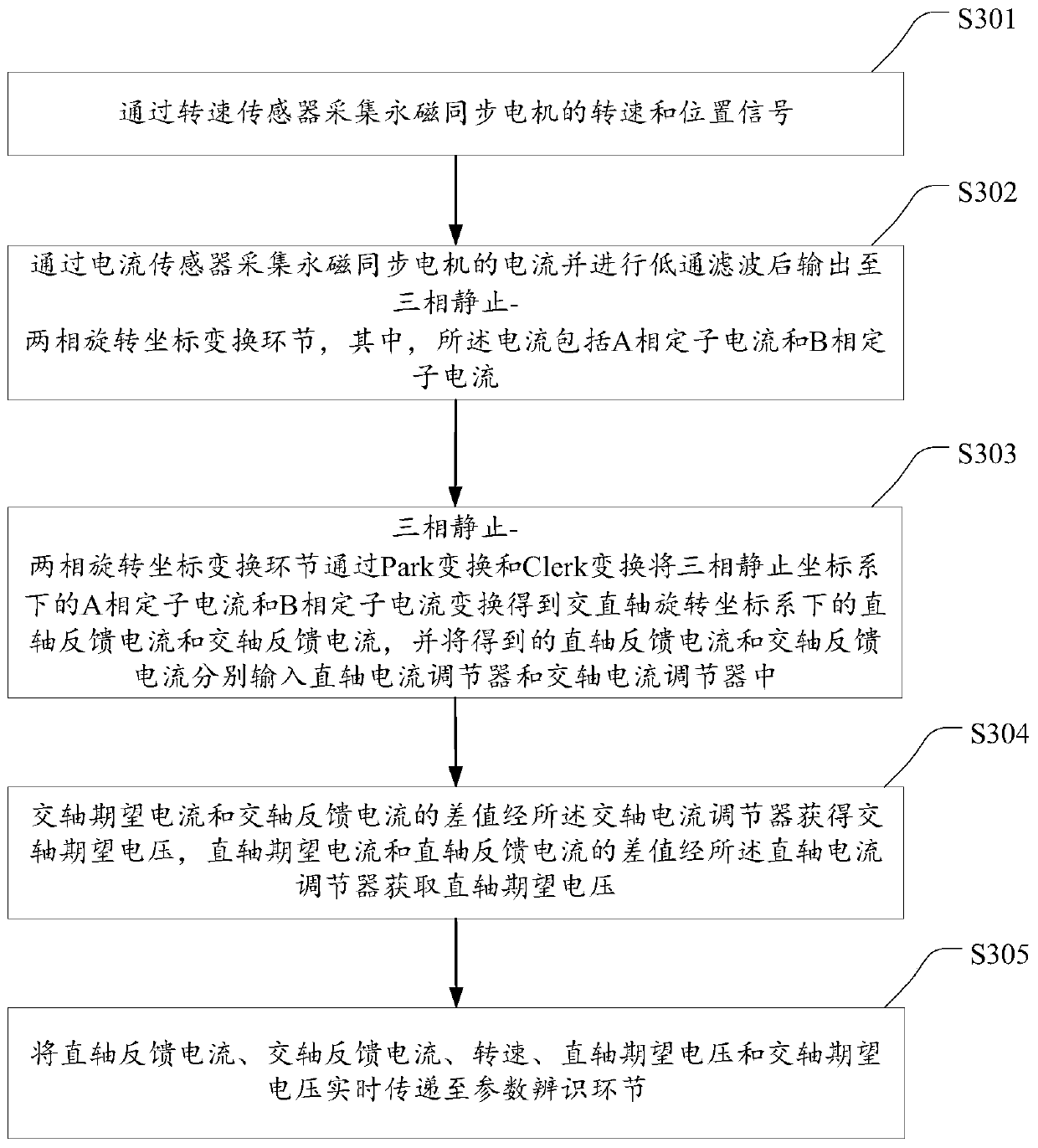
Parameter recognition method for permanent magnet synchronous motor of electric vehicle
InactiveCN110890855AMeet control requirementsAccurate identificationElectronic commutation motor controlAC motor controlElectric machinePermanent magnet synchronous motor
The invention discloses a parameter recognition method for a permanent magnet synchronous motor of an electric vehicle. The method comprises the steps of judging whether the permanent magnet synchronous motor of the electric vehicle needs parameter recognition or not; when parameter recognition needs to be carried out, injecting a low-frequency small-amplitude sinusoidal current signal into quadrature-axis expected current of the permanent magnet synchronous motor, and automatically adjusting the quadrature-axis expected current, direct-axis expected current, quadrature-axis voltage and direct-axis voltage by an adjuster; the rotating speed and position signals of the permanent magnet synchronous motor are measured through a rotating speed sensor, three-phase current of the permanent magnet synchronous motor is collected through a current sensor and converted into direct-axis feedback current and quadrature-axis feedback current, and data are transmitted to a parameter recognition linkin real time; and performing parameter recognition on the permanent magnet synchronous motor through the parameter recognition link until the parameters converge. According to the method, parameter recognition can be carried out under any operation state of the motor, the control requirements of the permanent magnet synchronous motors with different structures can be well met, the identified parameters are accurate, and the application range is wide.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF TECH
Electronic ballast with feed-forward control
InactiveUS6424101B1Increasing costIncreasing performanceEfficient power electronics conversionAc-dc conversionVoltage dropEngineering
An electronic ballast which is capable of compactly powering a discharge lamp from a source of rectified, but unregulated, power having a varying DC voltage. The ballast includes a selfoscillating converter powered by the DC voltage for producing pulses at a nominal operating frequency which is determined by a resonant tank. The resonant tank converts the pulses to a sinusoidal current for powering the discharge lamp and includes an inductive impedance.in series with the lamp for providing a voltage drop which varies with the operating frequency. A feed-forward control circuit is coupled to the converter for automatically varying the operating frequency directly with variations in the DC source voltage. The voltage drop across the inductive impedance is substantially proportional to the magnitude of the DC source voltage. This enables regulation of the voltage supplied to the discharge lamp by the ballast without sensing the lamp voltage itself.
Owner:PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NORTH AMERICA
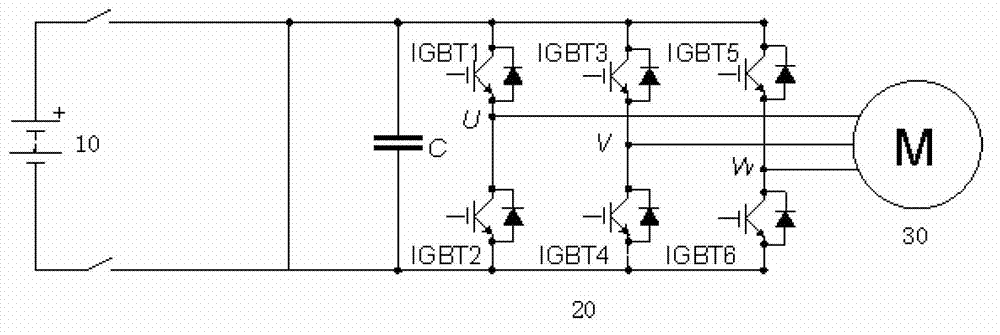
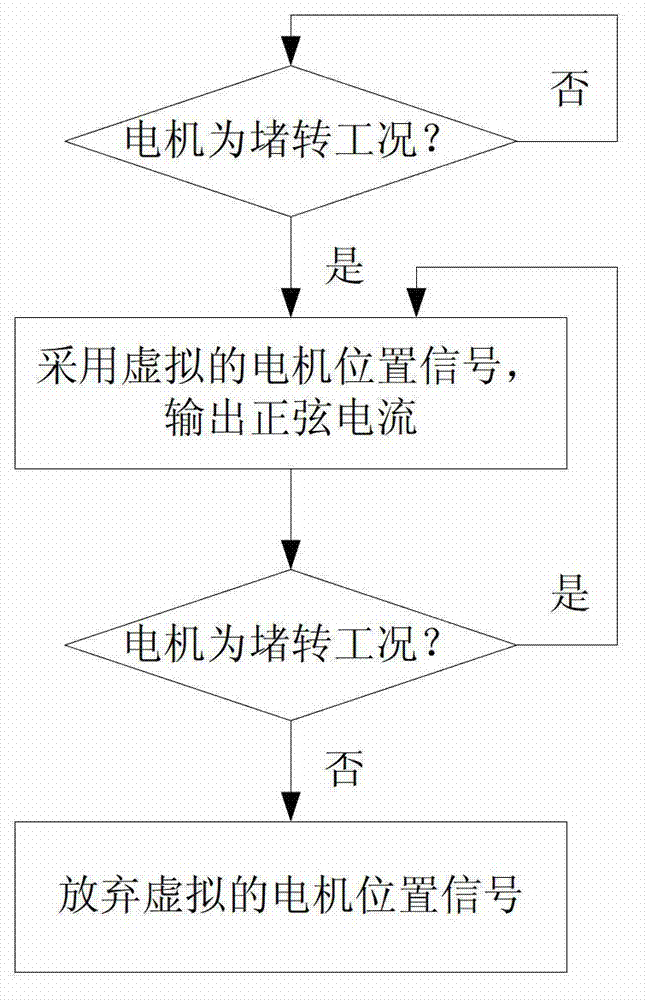
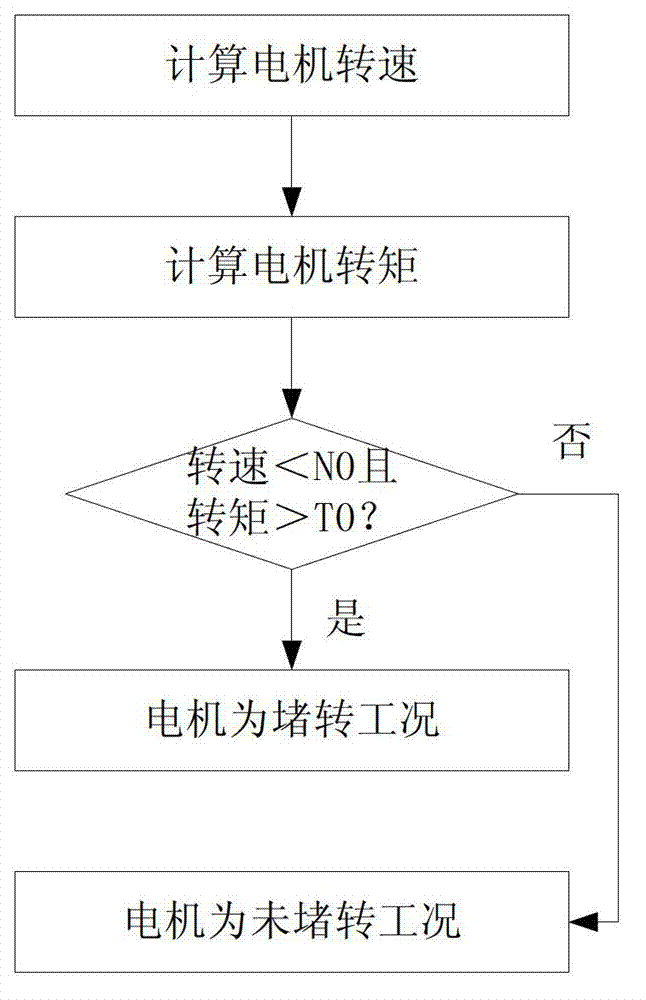
Control method of new energy automobile in motor-stalling working condition
ActiveCN103085680AMeet the needs of high torqueAvoid resistanceSpeed controllerElectric machinesDrive wheelElectric machine
The invention discloses a control method of a new energy automobile in a motor-stalling working condition. Once a motor controller judges the fact that a permanent magnet synchronous motor works in the motor-stalling working condition, virtual motor position signals serve as input of the motor controller, and therefore, the motor controller outputs sinusoidal current to the permanent magnet synchronous motor. The fact that the virtual motor position signals serve as the input of the motor controller is stopped until the motor controller judges the fact that the permanent magnet synchronous motor does not work in the motor-stalling working condition. According to the control method, output torque of the permanent magnet synchronous motor in the motor-stalling working condition achieves or approaches the maximal torque in the non-motor-stalling working condition, therefore short large-torque requirements on the condition that an automobile starts on a slope or driving wheels are blocked by barriers are met, resistance is overcome by the automobile, and the permanent magnet synchronous motor can break away from the motor-stalling working condition.
Owner:UNITED AUTOMOTIVE ELECTRONICS SYST
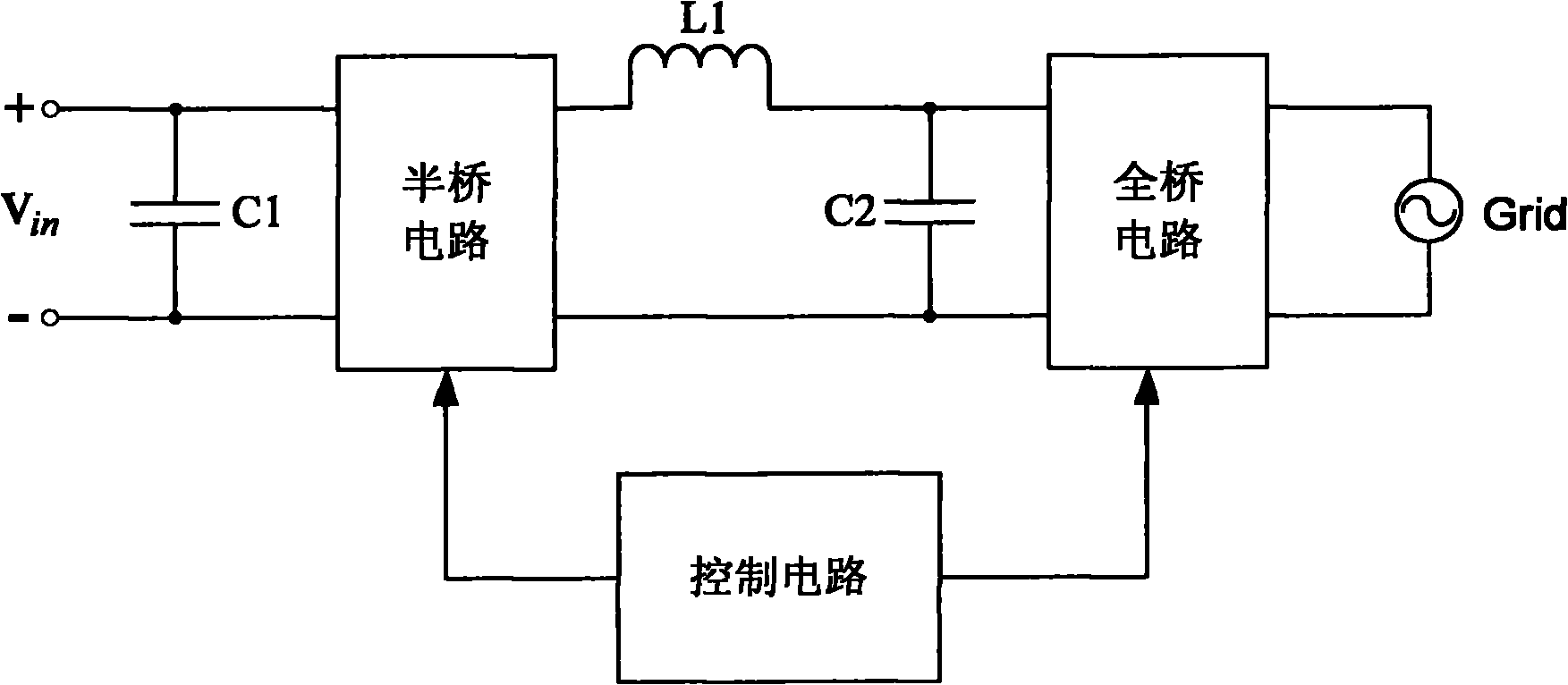
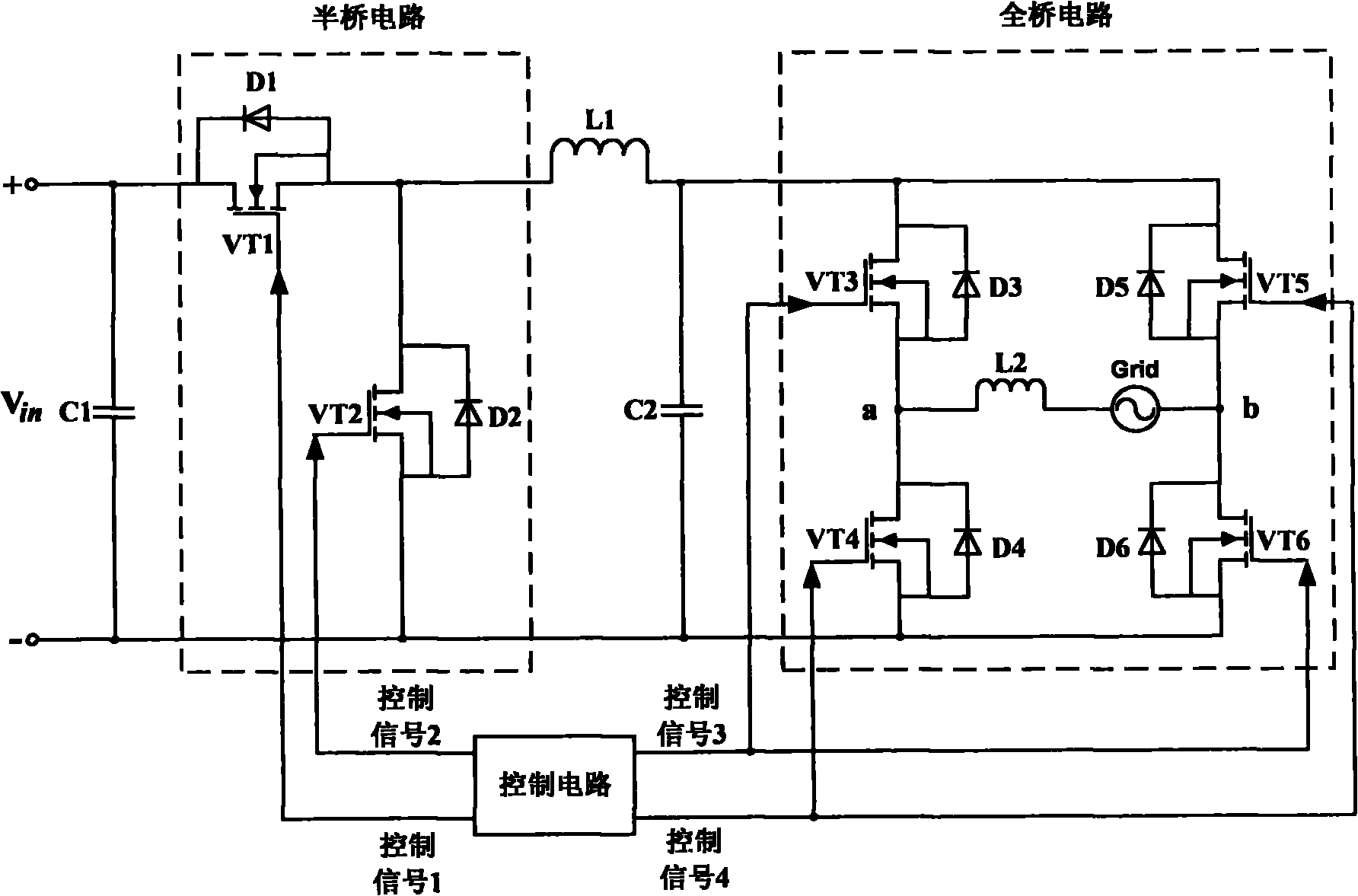
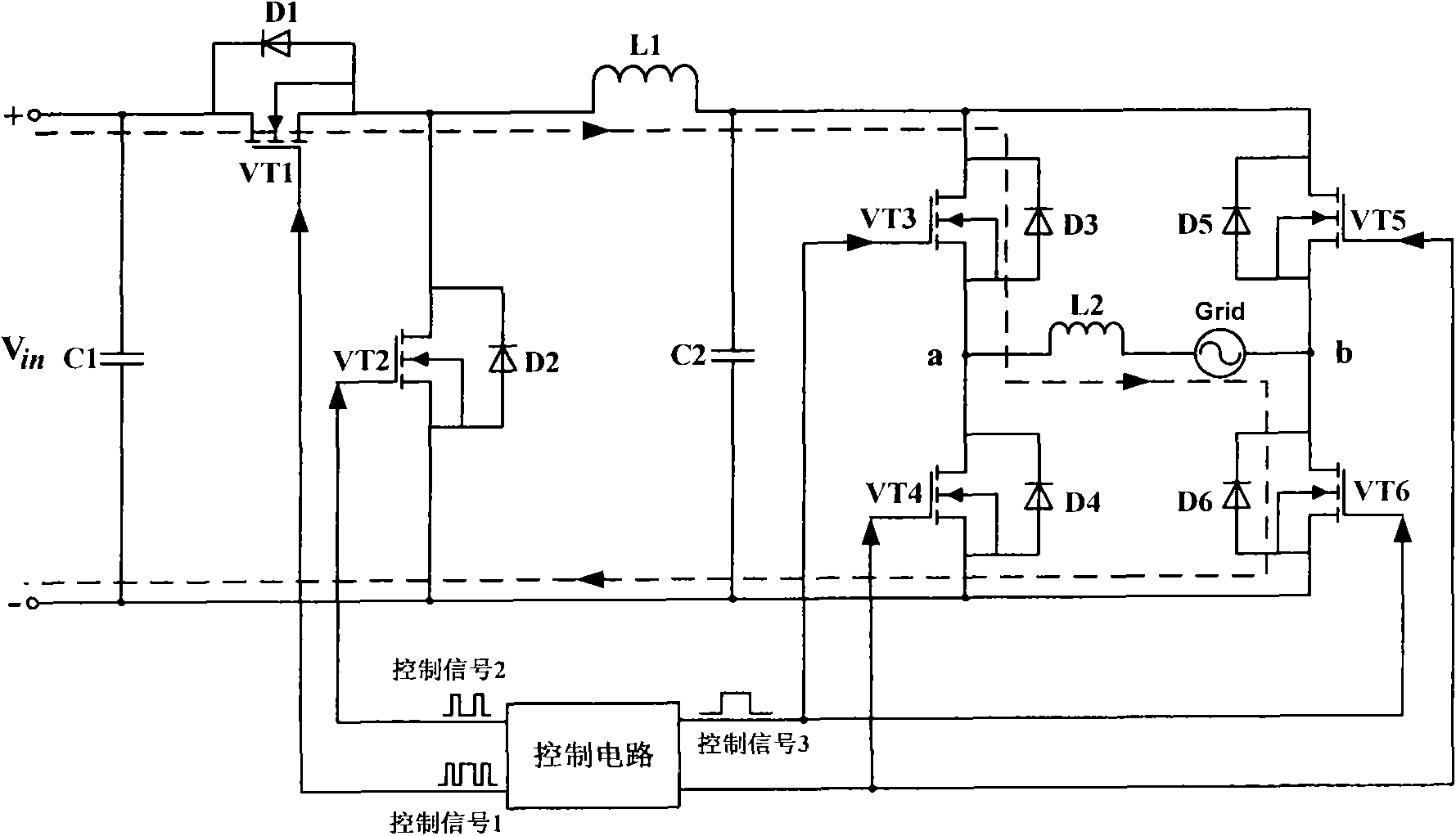
Single-phase non-isolated photovoltaic grid-connected inverter and control method
ActiveCN102005954AAvoid it happening againSmall distortionPhotovoltaic energy generationDc-ac conversion without reversalFull bridgeEngineering
The invention discloses a single-phase non-isolated photovoltaic grid-connected inverter and a control method. The photovoltaic grid-connected inverter mainly comprises a half-bridge circuit, a full-bridge circuit and a control circuit, wherein the control circuit controls the half-bridge circuit and the full-bridge circuit, so that the half-bridge circuit can be modulated in a high-frequency sinusoidal pulse width modulation (SPWM) mode to output half-sinusoidal current, and the full-bridge circuit can commutate in an industrial-frequency mode to commutate the half-sinusoidal current output by the half-bridge circuit and output sinusoidal current required for grid connection. The photovoltaic grid-connected inverter can ensure that the problem of common-mode current in the non-isolated grid-connected inverter circuit is effectively solved, the distortion of the current at the zero crossing point is reduced and the high-frequency switching loss in the circuit is low at any time.
Owner:TBEA SUNOASIS +1
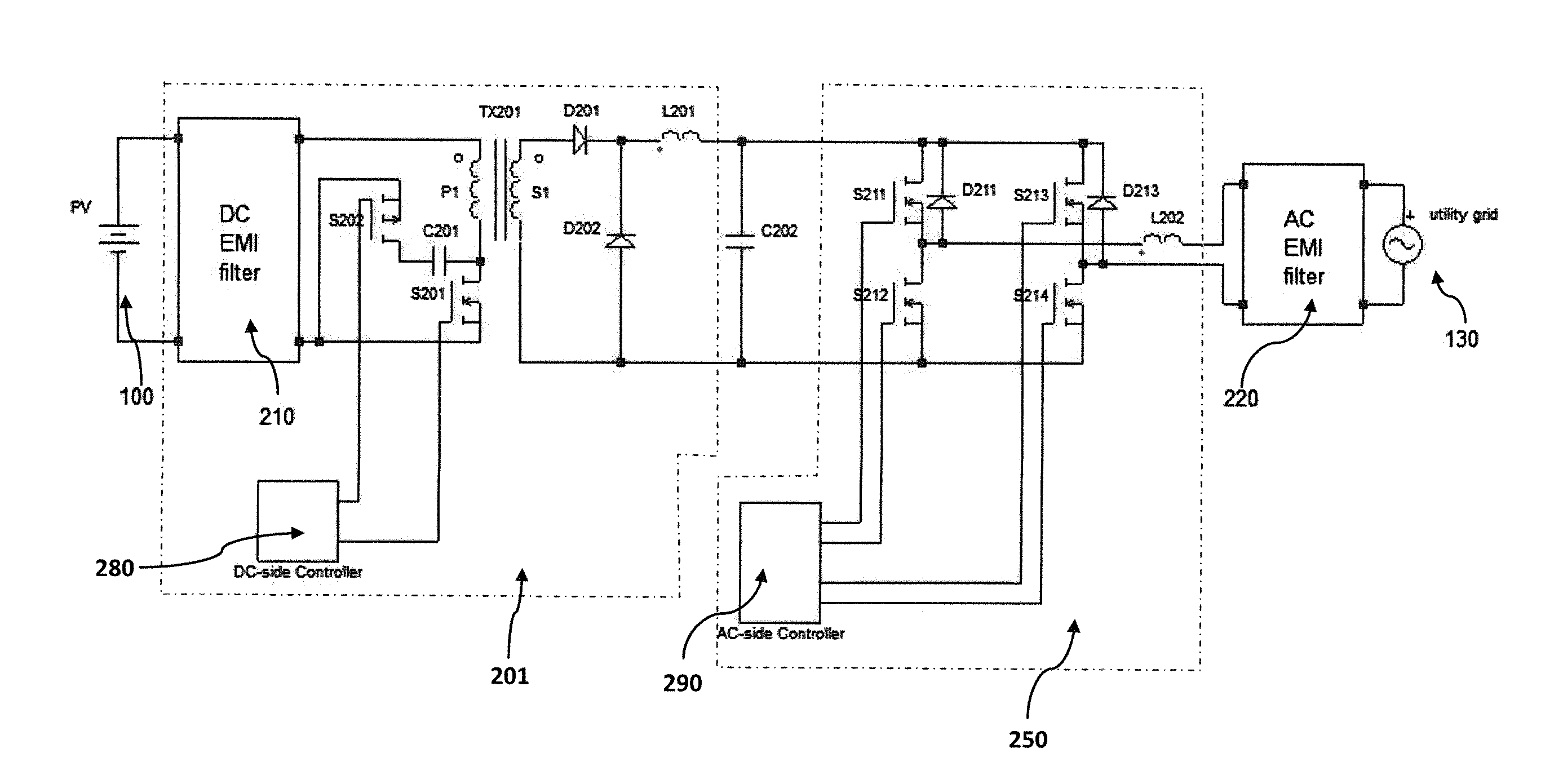
Smart grid power converter
ActiveUS20150109833A1Small sizeMinimal impact performanceEfficient power electronics conversionAc-dc conversionHigh frequency powerSmart grid
A DC-to-AC power converter is disclosed. The power converter has a DC input to receive DC power from a photovoltaic device, an AC output configured for direct connection to an AC mains power supply line, six semiconductor switches, one isolated high-frequency power transformer, two high-frequency inductors, a small resonant capacitor, and a large non-electrolytic (e.g. film) capacitor energy storage component. One of the semiconductor switches located on the primary side of the transformer operates to regulate the voltage across the non-electrolytic capacitor energy storage component. A second semiconductor switch located on the primary side of the transformer provides a resonant reset for the energy stored in the transformer and allows the first semiconductor switch to operate with nearly zero-voltage-switching. The other four semiconductor switches and a high-frequency inductor coupled to the ac output operate with a variable switching frequency to produce a sinusoidal current into the ac output such that the sinusoidal current may be either in phase or out of phase with the ac output voltage.
Owner:GARRITY POWER SERVICES
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com