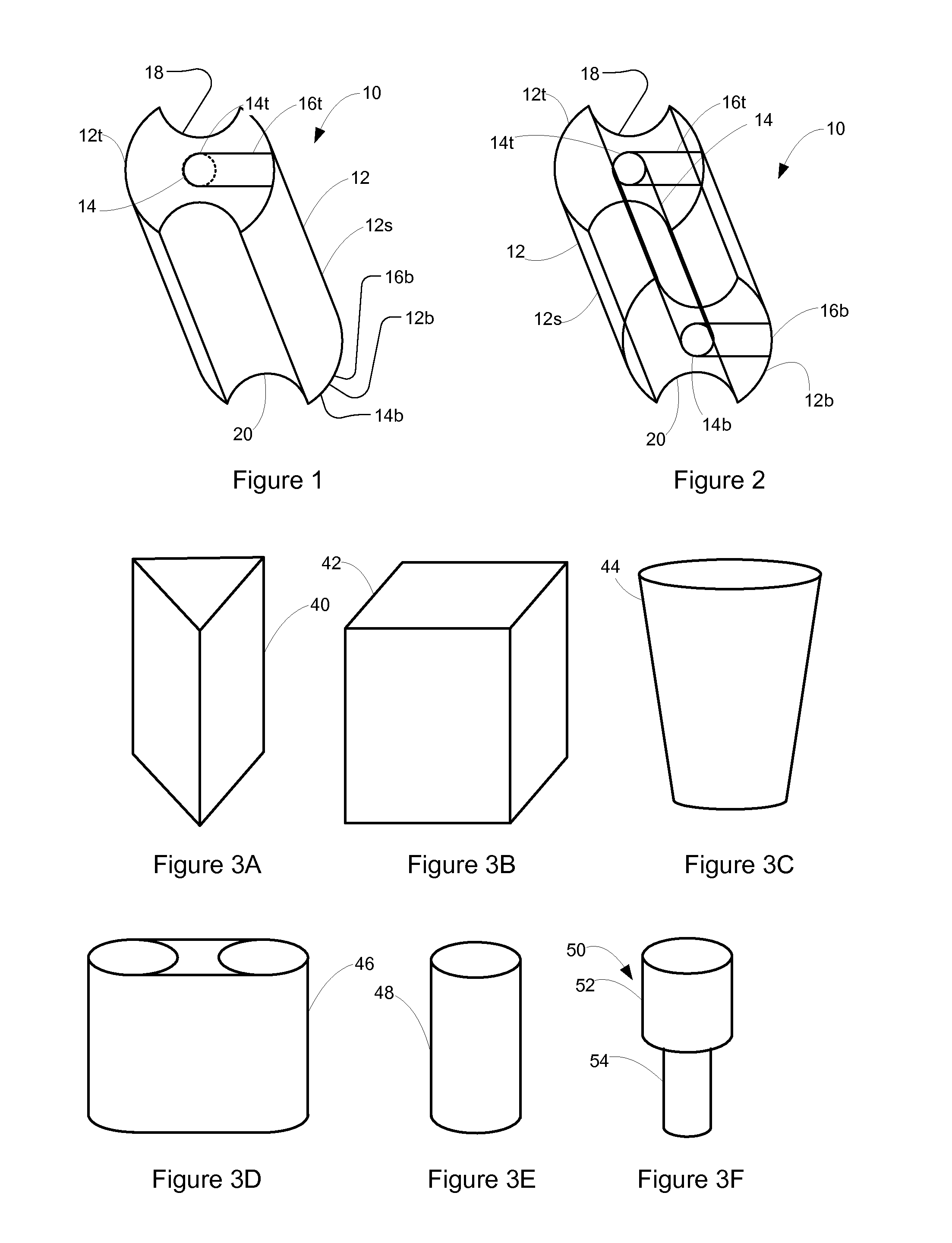
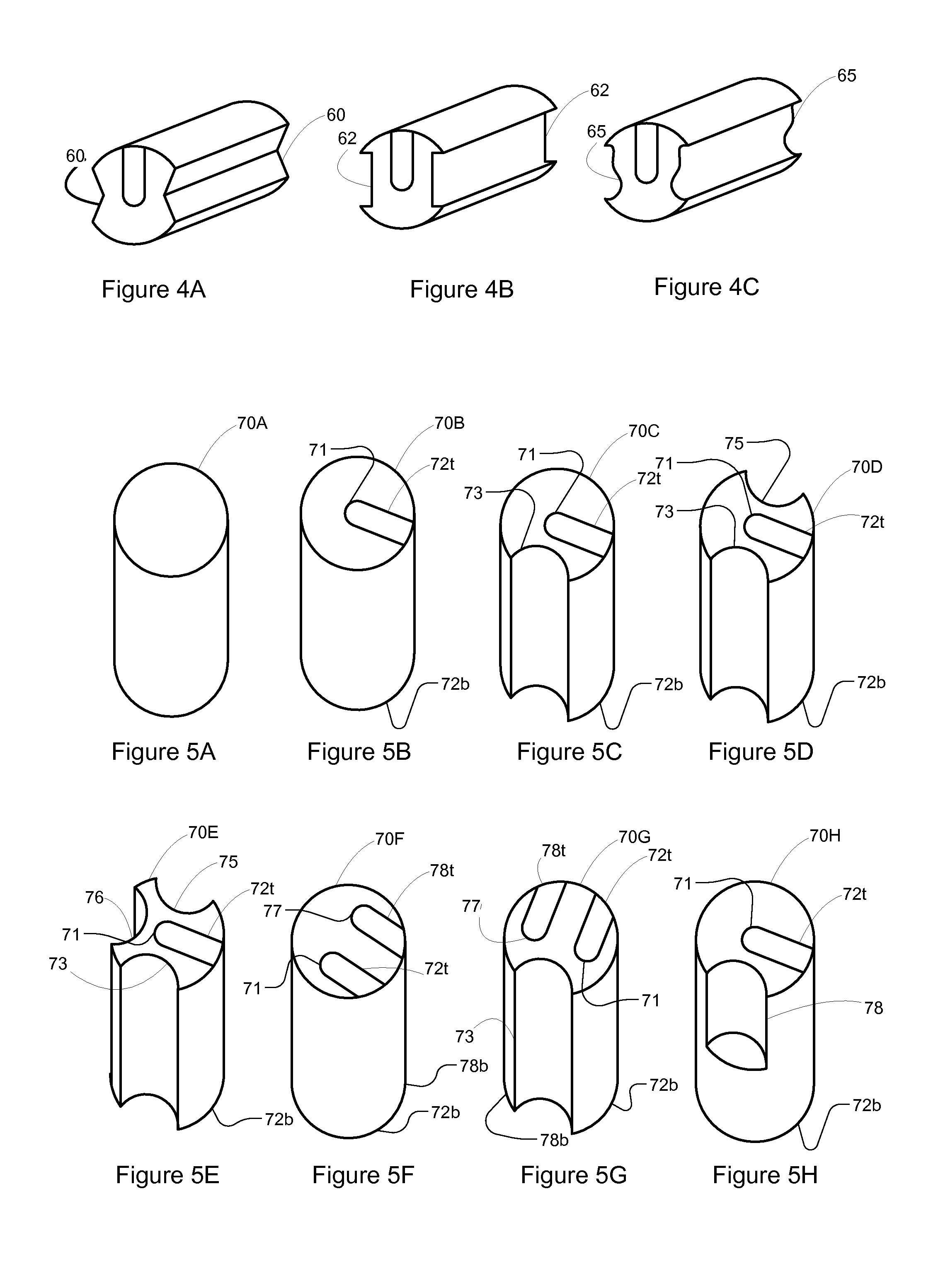
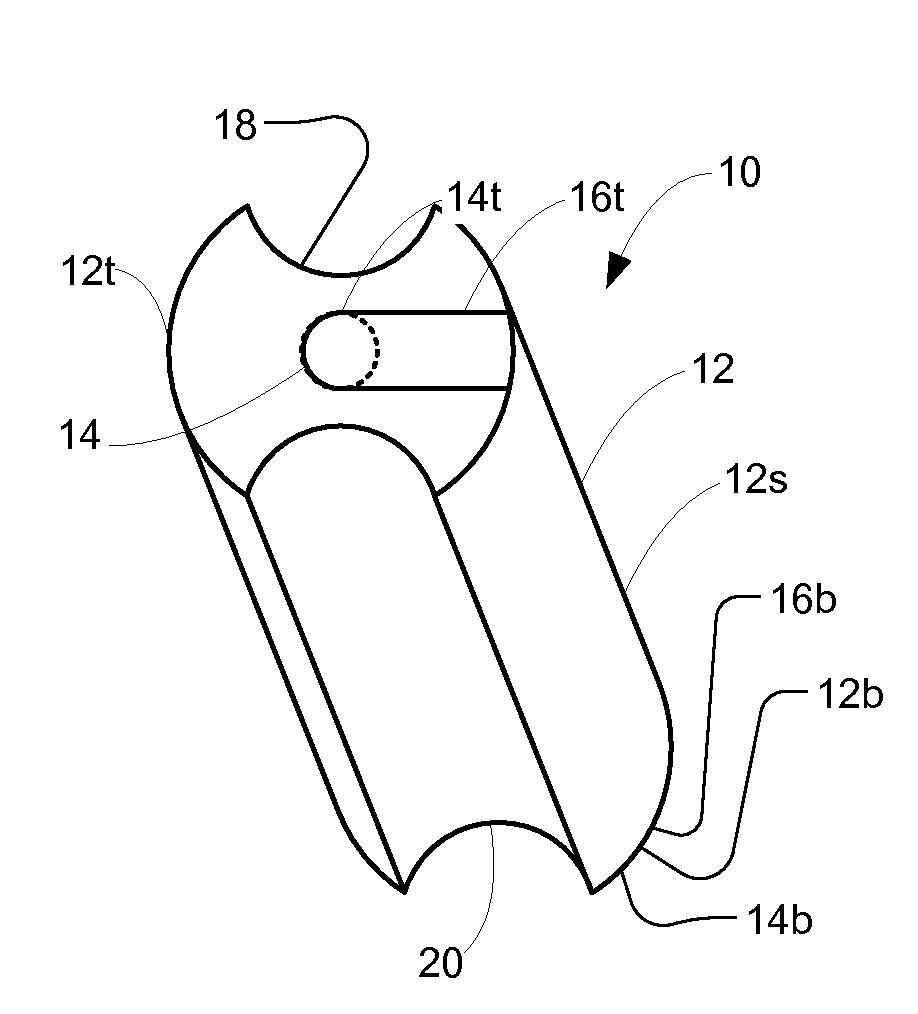
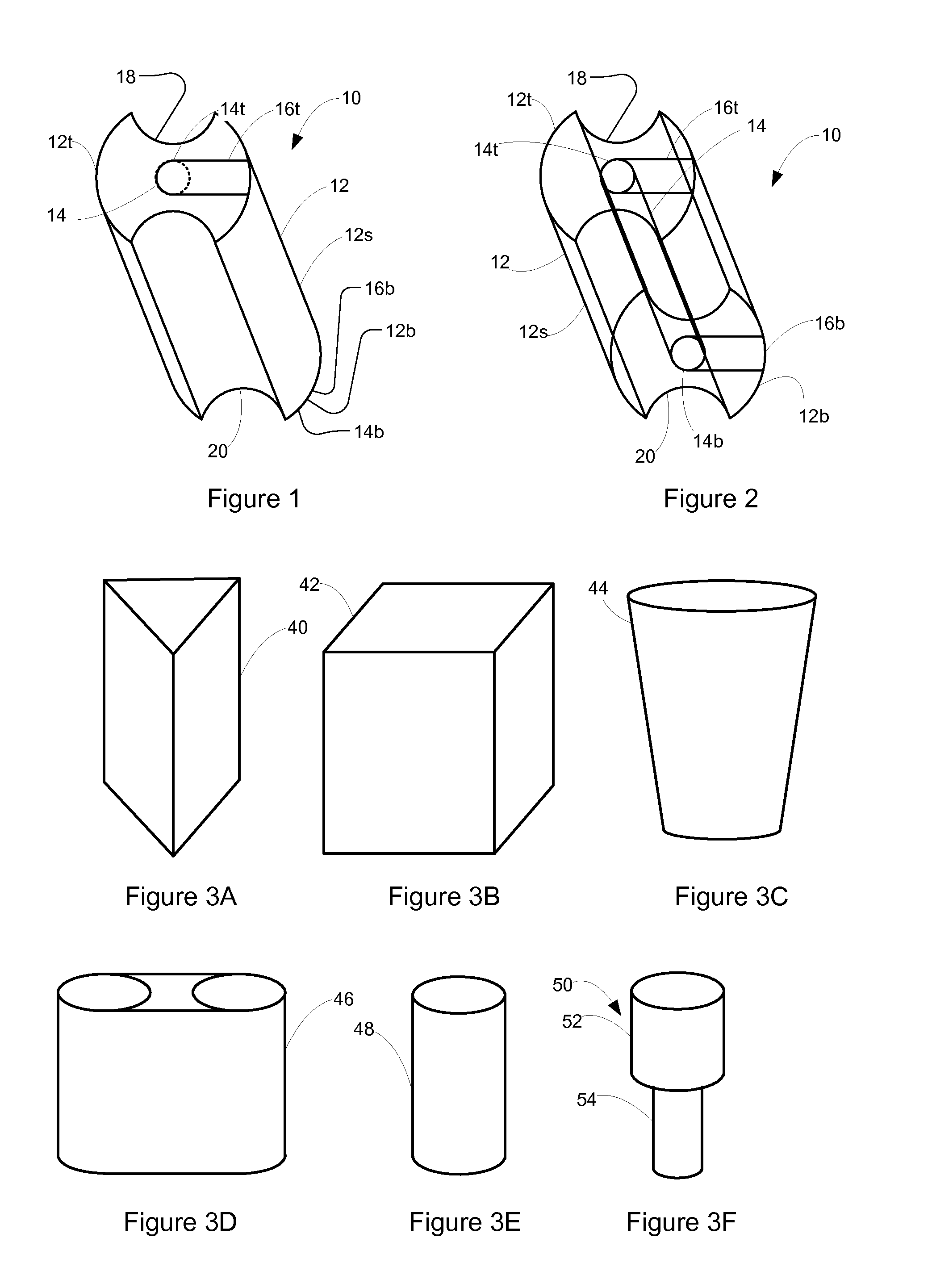
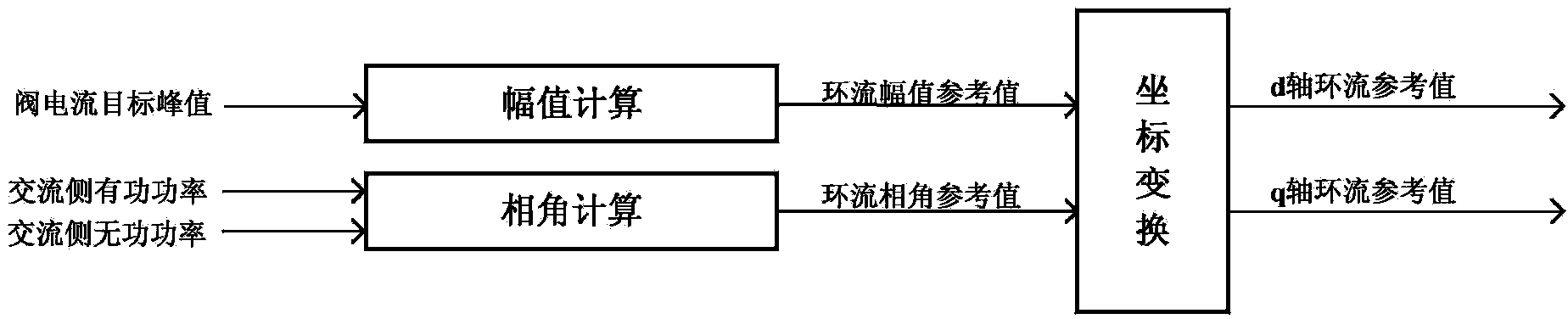
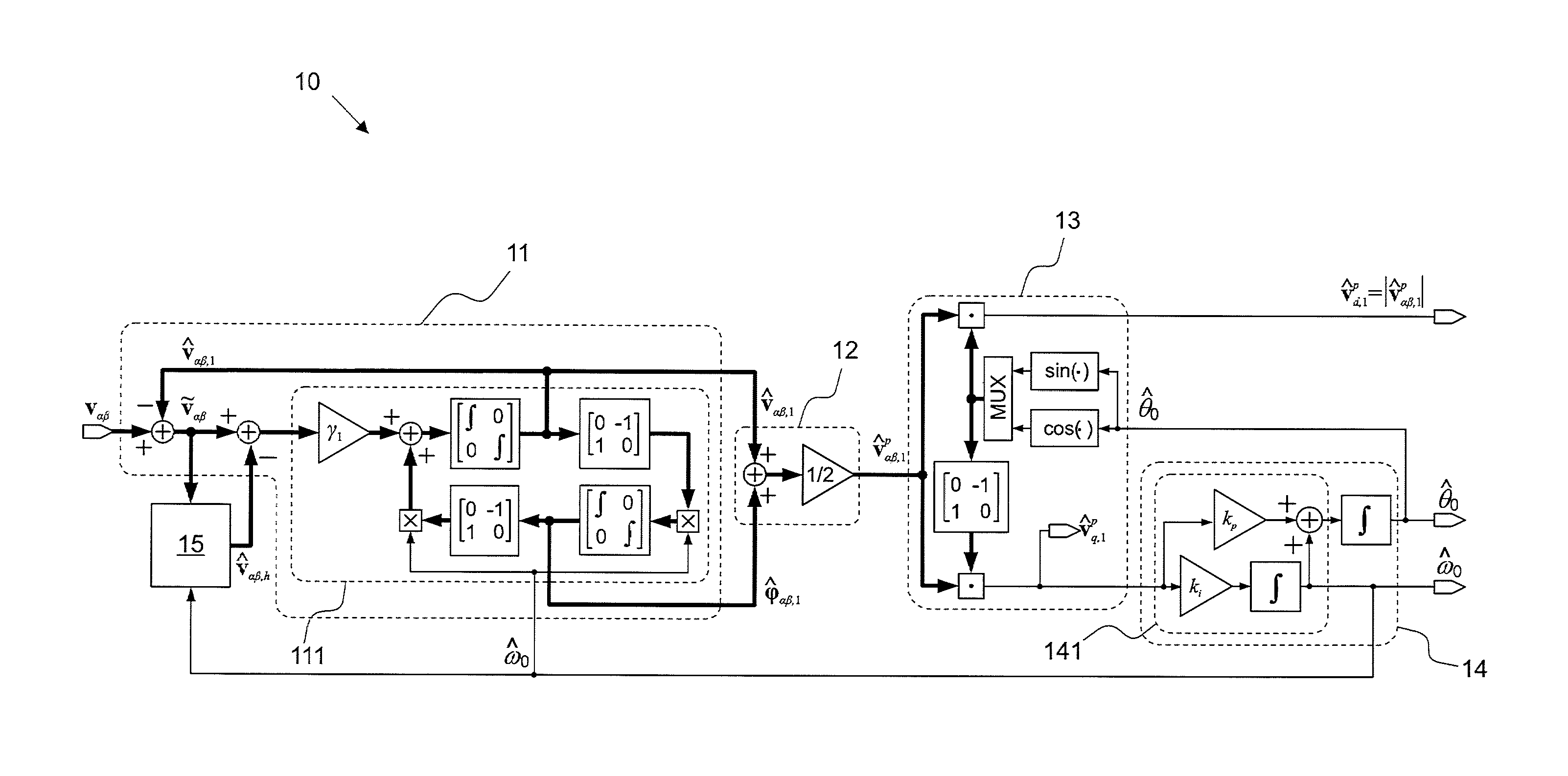
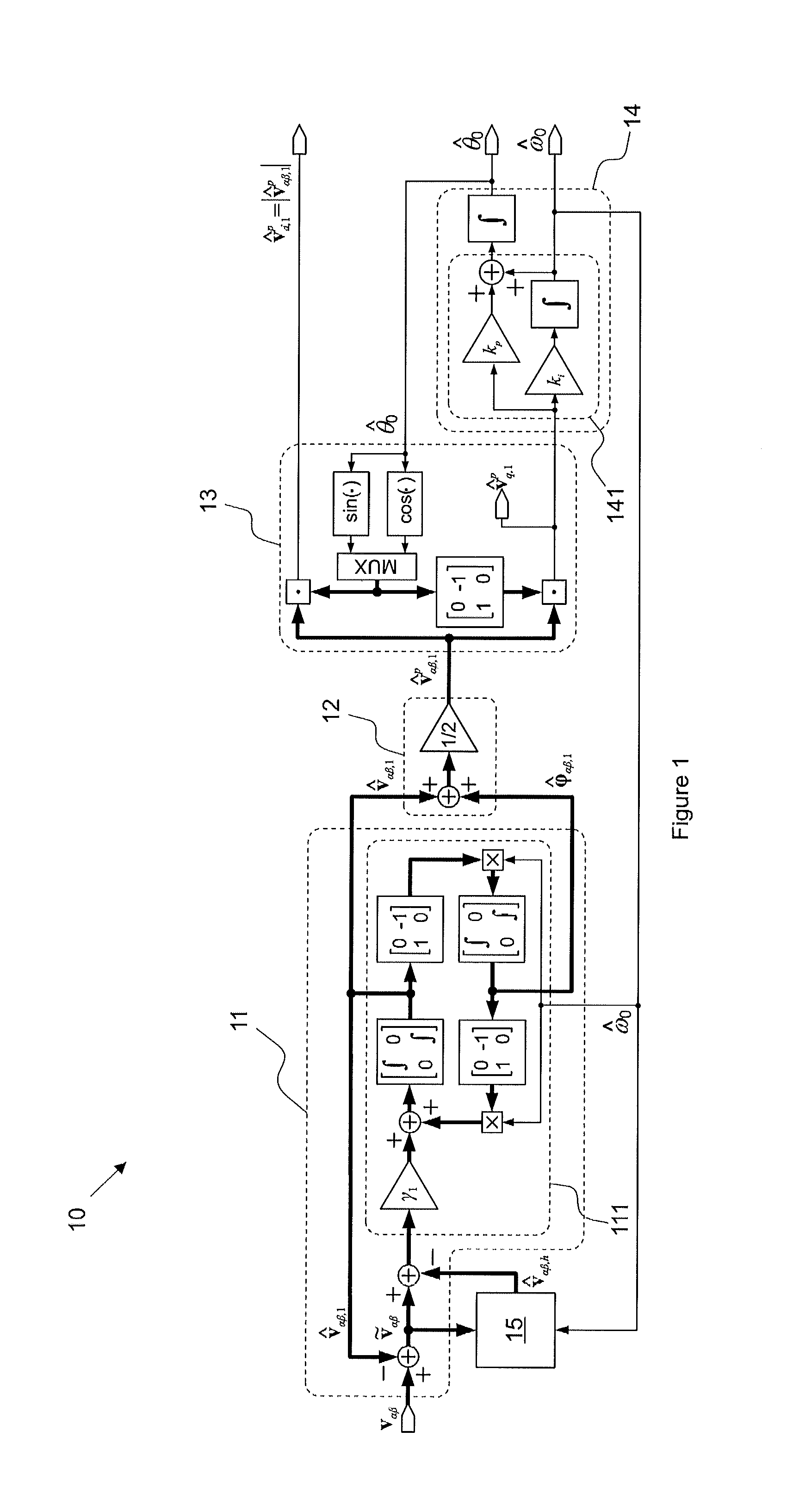
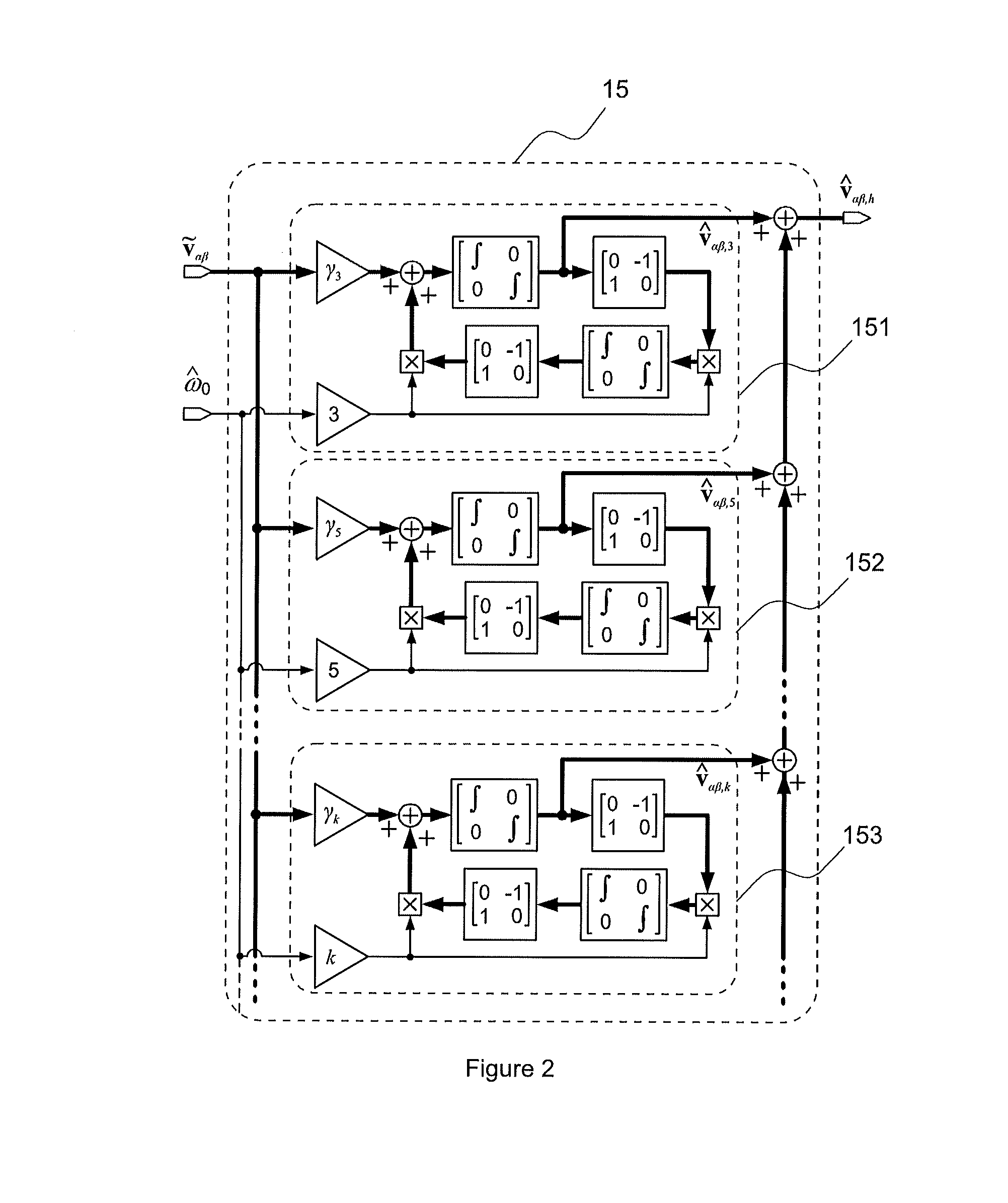
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
186 results about "Direct component" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
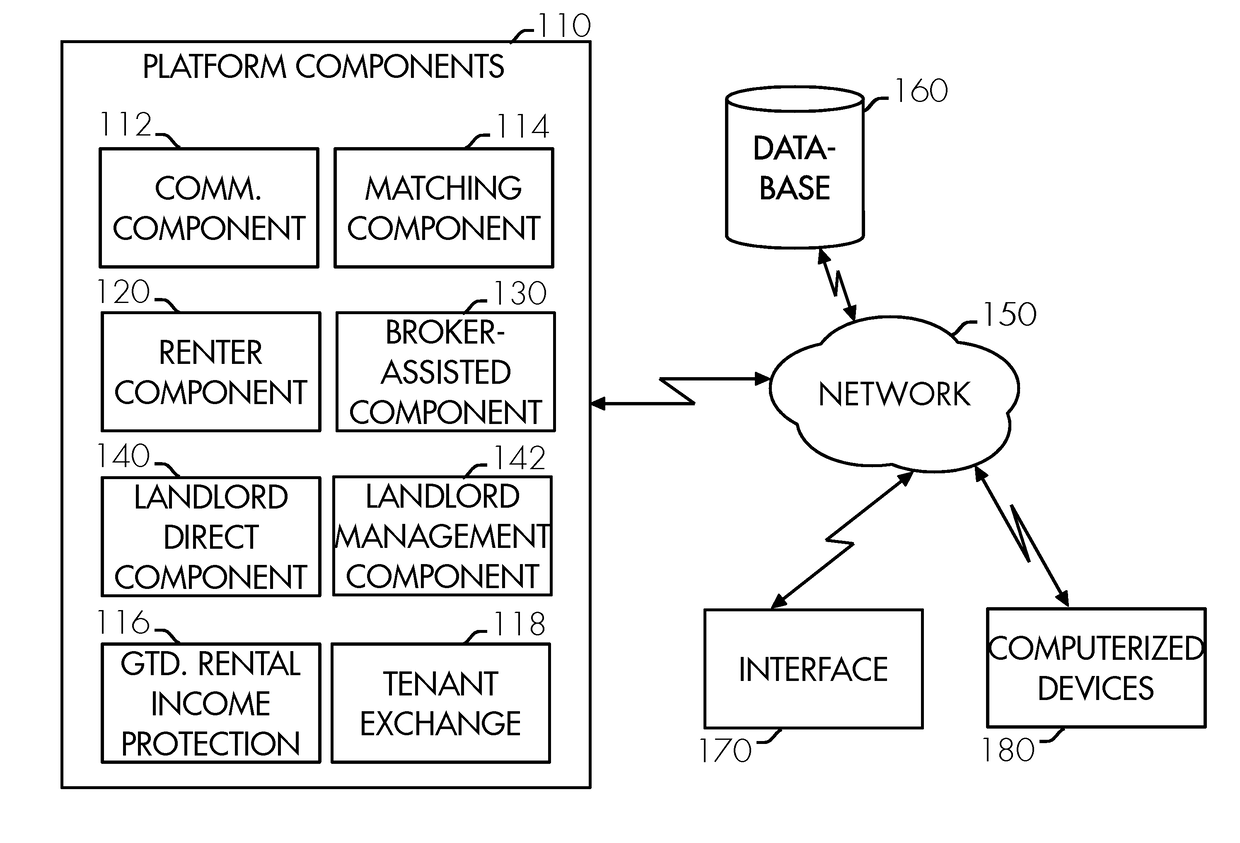
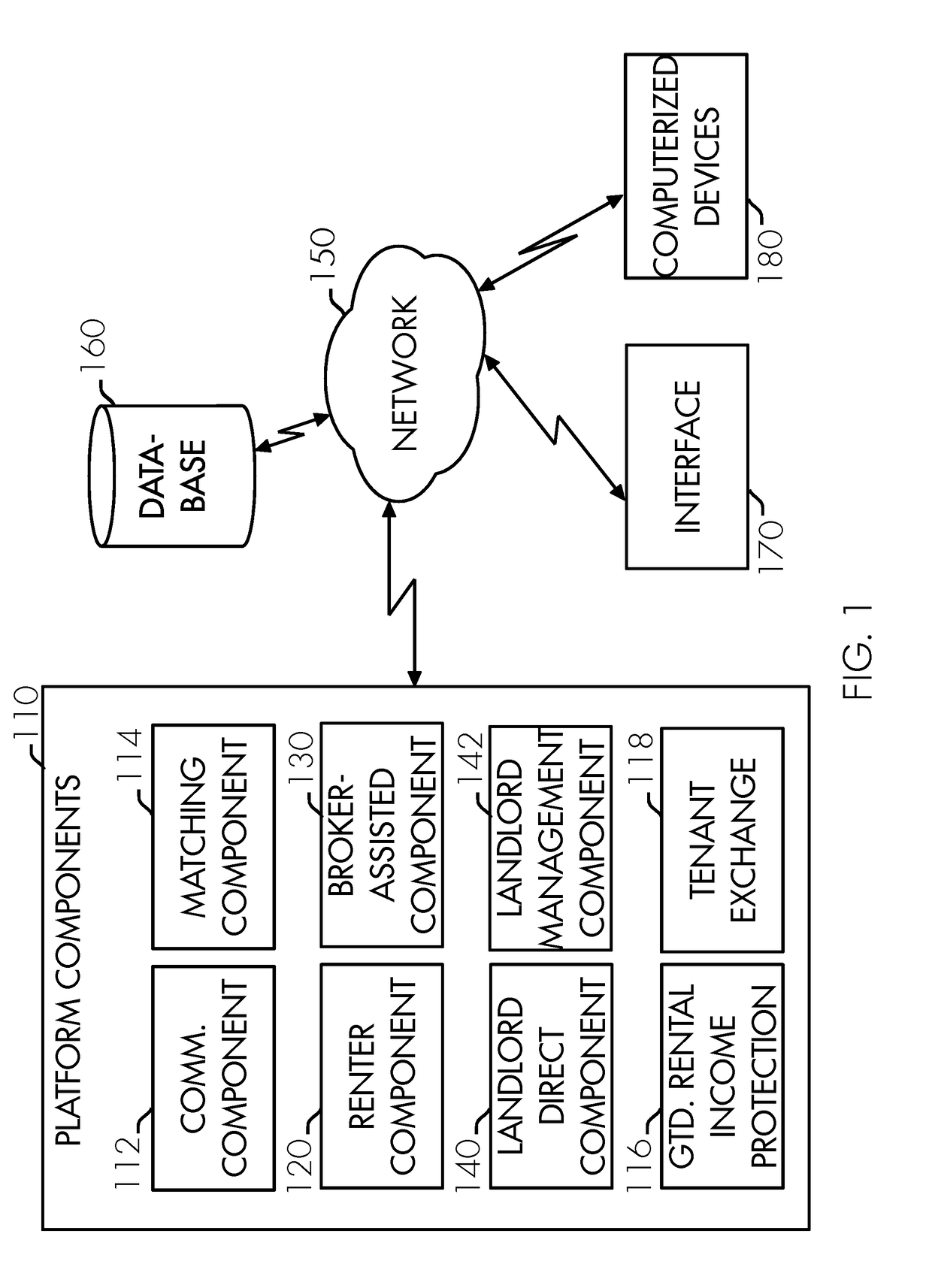
Decentralized cryptographic real estate transaction assistance system and method
InactiveUS20180322597A1Easy to manageEasy to analyzeFinanceOffice automationDirect componentReal-time computing
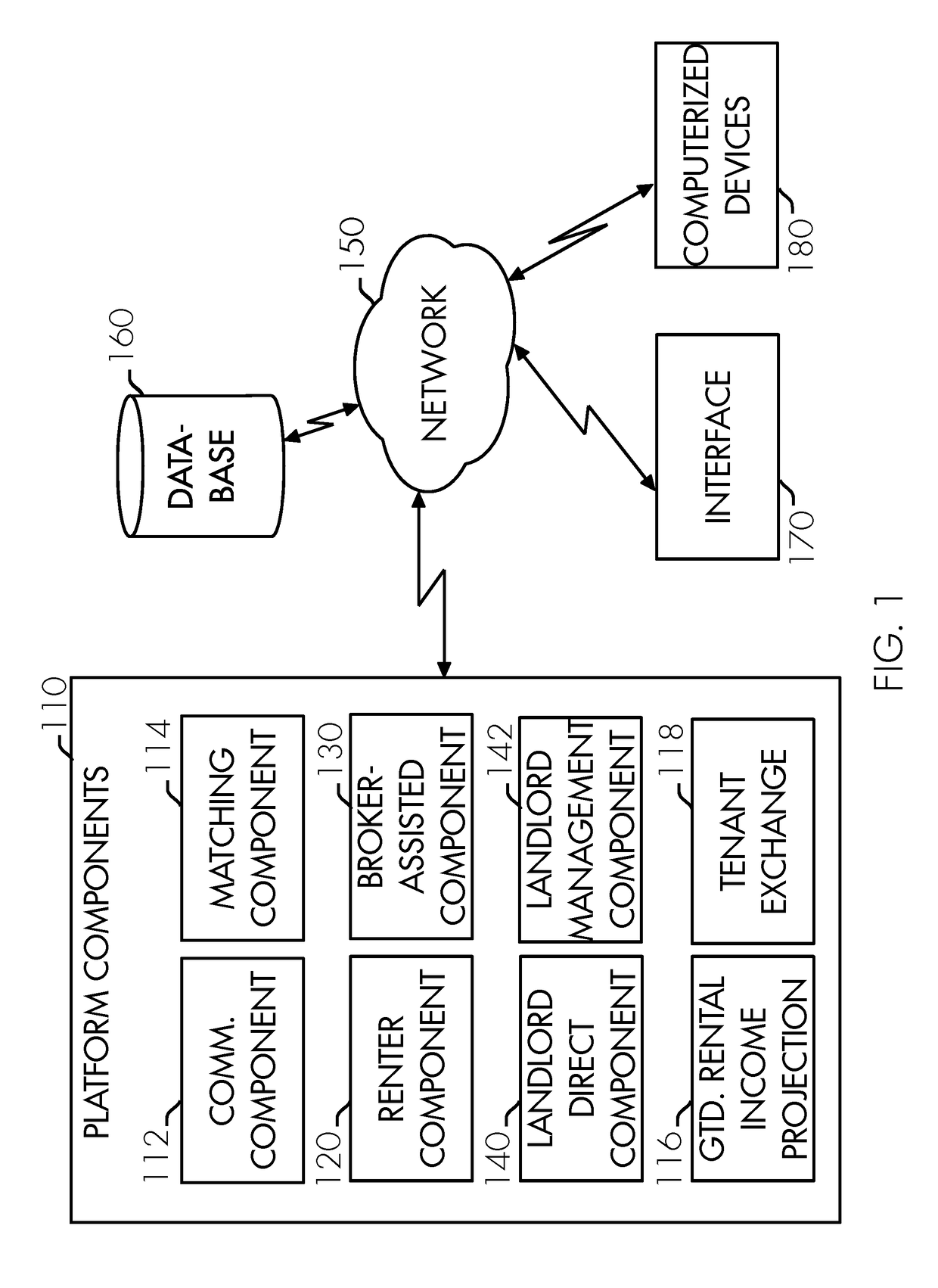
A decentralized cryptographic real estate transaction assistance system and method is provided to facilitate matching, engaging, contracting, and communicating between parties to a real estate and / or property rental transaction by a network-leveraged system. The decentralized cryptographic real estate transaction assistance system and method may include a property rental and real estate transaction assistance platform, database, platform components, renter component, matching component, communication component, broker-assisted component, landlord direct component, landlord management component, vendor portal, lead marketplace component, guaranteed rental income protection, renter profile validation aspect, and tenant exchange. A method for facilitating matching, engaging, contracting, and communicating between parties to a real estate and / or property rental transaction by a network-leveraged system using the decentralized cryptographic real estate transaction assistance system and method is also provided.
Owner:SHER ROBERT
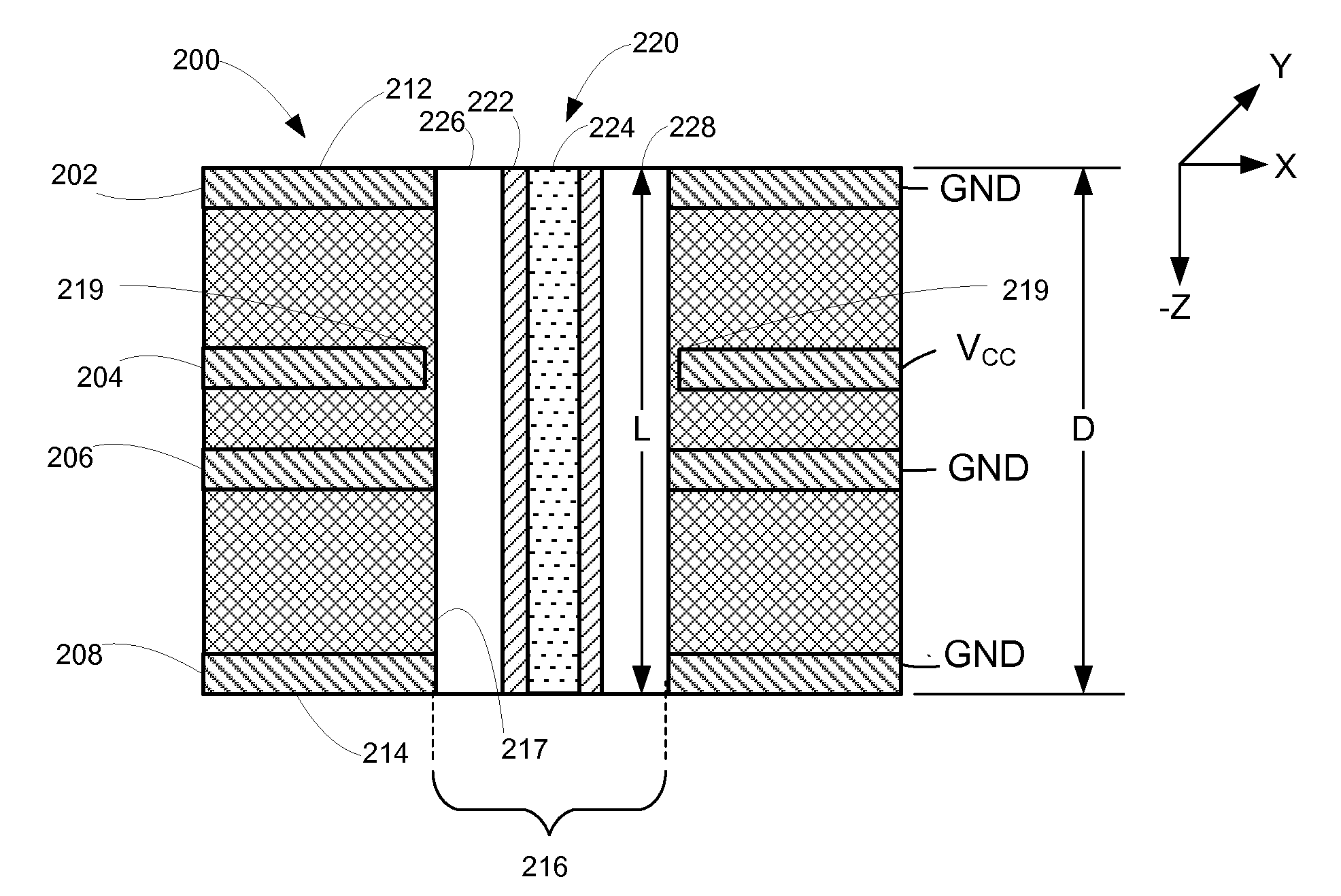
Z-Directed Variable Value Components for Printed Circuit Boards
ActiveUS20110017507A1Printed electric component incorporationSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsElectricityElectrical resistance and conductance
A Z-directed variable value component for insertion into a printed circuit board while allowing electrical connection to internal conductive planes contained with the PCB. The Z-directed variable value component mounts in a printed circuit board (PCB) having a mounting hole having a depth D therein and a plurality of conductive traces and comprises an insulative body of a length L comprising a top surface; a bottom surface; a side surface between the top and bottom surfaces; a cross-sectional shape that is insertable into the mounting hole in the PCB; and a first and a second electrically conductive channels on the side surface with the first channel and second channel both extending from one of the top and bottom surfaces; a plateable strip disposed on the side surface intermediate the top and bottom surfaces; and a first and second conductor disposed within the body, the first conductor electrically connected to the first channel and one end of the plateable strip and the second conductor electrically connected to the second channel and the other end of the plateable strip. In one form the plateable strip is comprised of a resistive material. In another form the plateable strip is comprised of a material having an electrical characteristic that changes when plating is applied to the strip after installation of the Z-directed component in the mounting hole of the PCB.
Owner:LEXMARK INT INC
Z-Directed Filter Components for Printed Circuit Boards
ActiveUS20110019376A1Cross-talk/noise/interference reductionPrinted electric component incorporationElectrical conductorElectrical connection
A Z-directed filter component for insertion into a printed circuit board while allowing electrical connection to internal conductive planes contained with the PCB. In one embodiment the Z-directed filter component is mounted within the thickness of the PCB allowing other components to be mounted over it. The filter may be T-filter or a Pi-filter within the body of the Z-directed component. The body may also contain one or more conductors and may include one or more surface channels or wells extending along at least a portion of the length of the body. Methods for mounting Z-directed components are also provided.
Owner:LEXMARK INT INC
Z-Directed Capacitor Components for Printed Circuit Boards
ActiveUS20110017503A1Printed electric component incorporationCross-talk/noise/interference reductionElectricityElectrical conductor
A Z-directed capacitor component for insertion into a printed circuit board while allowing electrical connection to internal conductive planes contained within the PCB. In one embodiment the Z-directed capacitor component utilizes semi-cylindrical metallic sheets. In another embodiment, stack annular metallic disks are used. The Z-directed capacitor component mounts within the thickness of the PCB allowing other components to be mounted over it. The body may contain one or more conductors and may include one or more surface channels or wells extending along at least a portion of the length of the body. Methods for mounting Z-directed components are also provided.
Owner:LEXMARK INT INC
Communication Terminal Apparatus And Wireless Transmission Method
InactiveUS20070171418A1Avoid radiationSolar heating energySolar heat collector controllersWireless transmissionRefractive index
A collector for propagating incident radiation to a remote location. The collector comprises, a light directing component coupled to a buffer component, a first propagation component coupled to the buffer component and configured to transmit the incident radiation into a collector region through one of a plurality of windows, and an optical transport assembly coupled to an end of the collector region and having a second propagation component. Each light directing component is configured to redirect the incident radiation from a first direction to a second direction, and the collector region includes a plurality of regions exhibiting a refractive index value that gradually transitions from about 1.5 to about 2.0. The second propagation component is further configured to retain the incident radiation.
Owner:BIOSYNERGETICS INC
Z-Directed Components for Printed Circuit Boards
InactiveUS20110017502A1Printed electric component incorporationHigh frequency circuit adaptationsElectrical conductorElectrical connection
A design for a Z-directed component for insertion into a printed circuit board while allowing electrical connection to internal conductive planes contained with the PCB. In one embodiment the Z-directed component is mounted within the thickness of the PCB allowing other components to be mounted over it. The body may contain one or more conductors and may include one or more surface channels or wells extending along at least a portion of the length of the body. Z-directed components include high frequency signal pass throughs, capacitors, diodes, transistors, transmission lines, delay lines. Methods for mounting Z-directed components are also provided.
Owner:LEXMARK INT INC
Z-Directed Delay Line Components for Printed Circuit Boards
ActiveUS20110019374A1Printed circuit aspectsDetails of conductive coresElectricityElectrical conductor
A Z-directed signal delay line component for insertion into a printed circuit board while allowing electrical connection to internal conductive planes contained with the PCB. In one embodiment the Z-directed delay line component is housed within the thickness of the PCB allowing other components to be mounted over it. The delay line embodiments include a W-like line and a plurality of spaced apart, semi-circular line segment connected such that current flow direction alternates in direction between adjacent semi-circular line segments, each of which in other embodiments can be varied by use of shorting bars. Several Z-directed delay line components may be mounted into a PCB and serially connected to provide for longer delays. The body may contain one or more conductors and may include one or more surface channels or wells extending along at least a portion of the length of the body. Methods for mounting Z-directed components are also provided.
Owner:LEXMARK INT INC
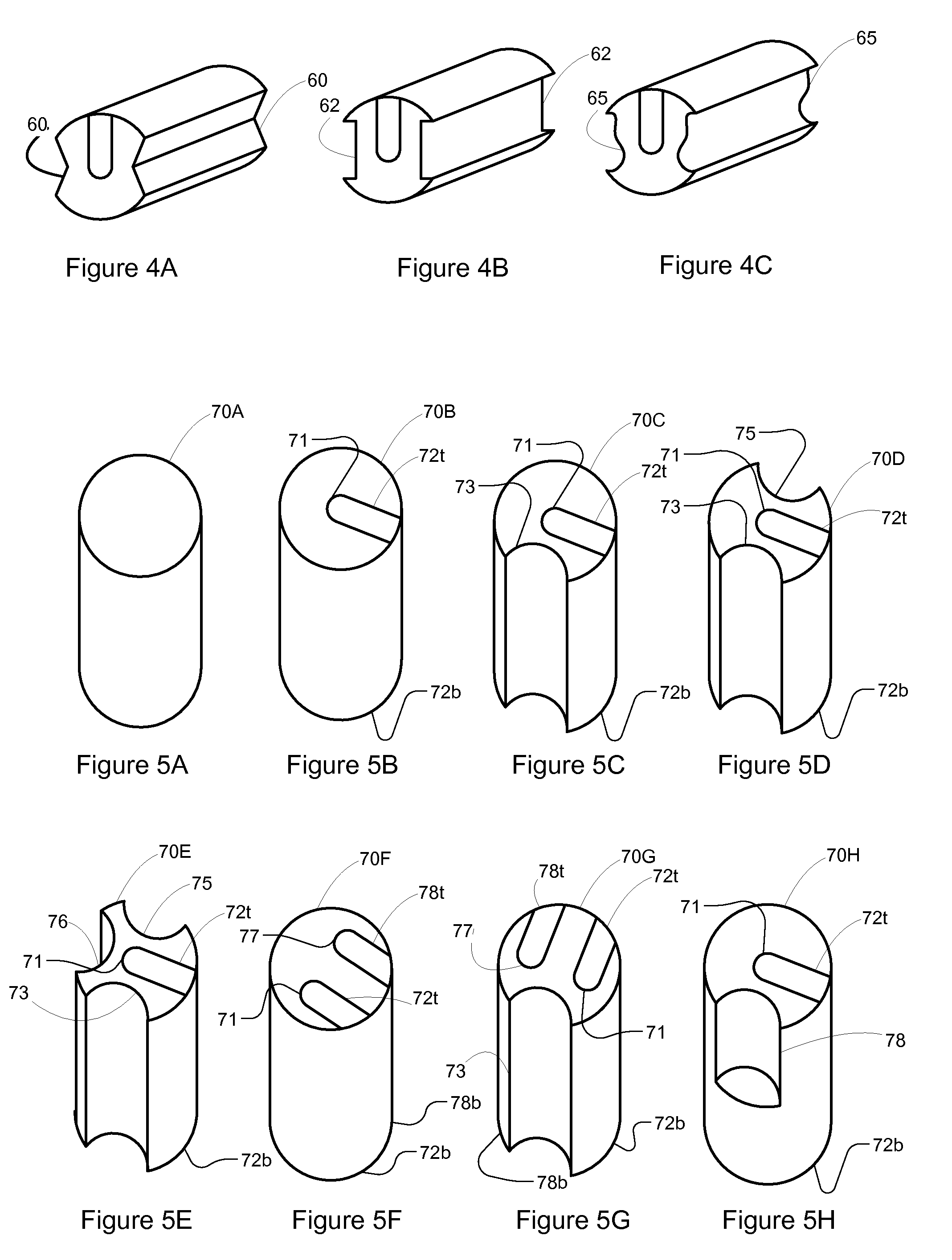
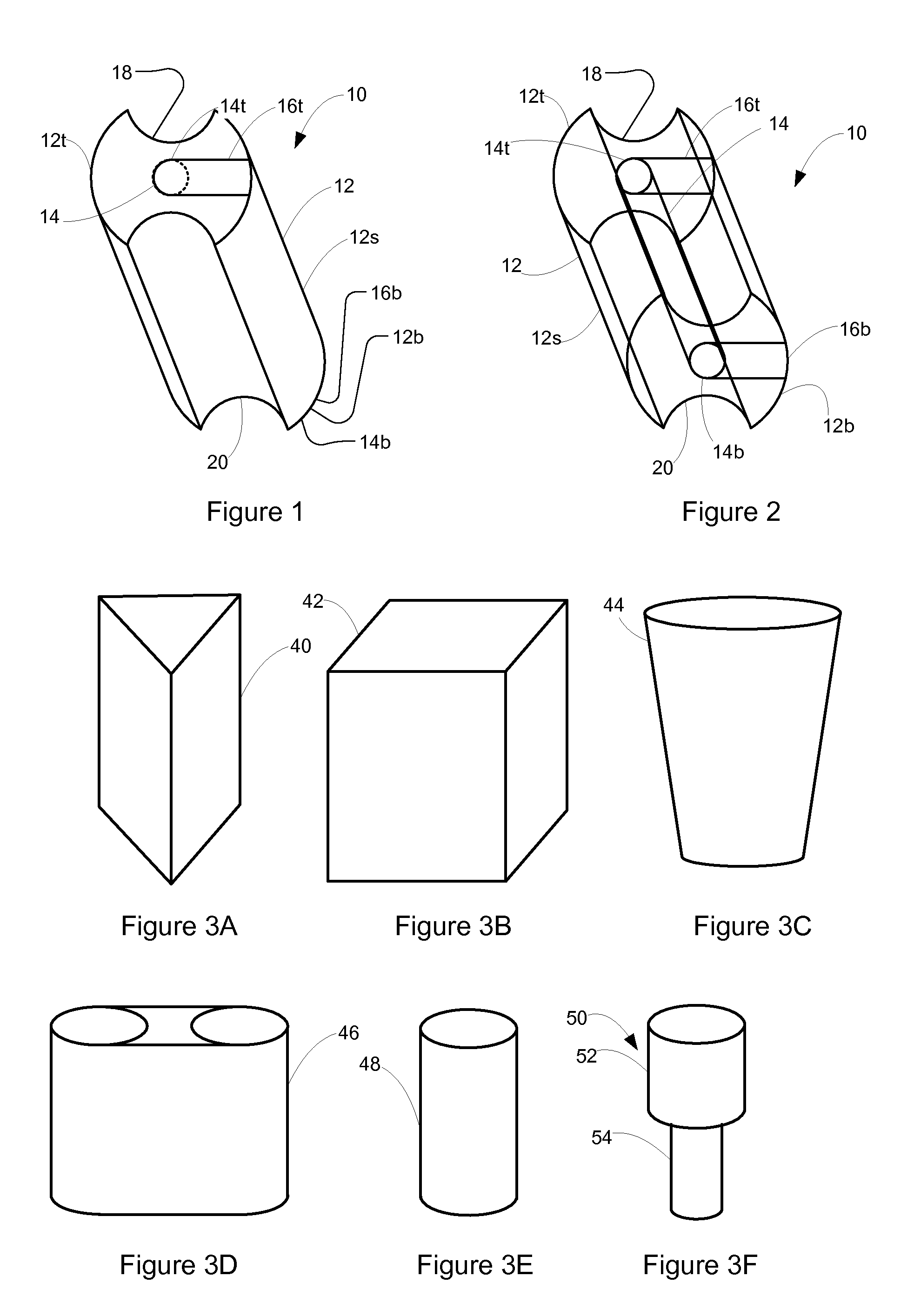
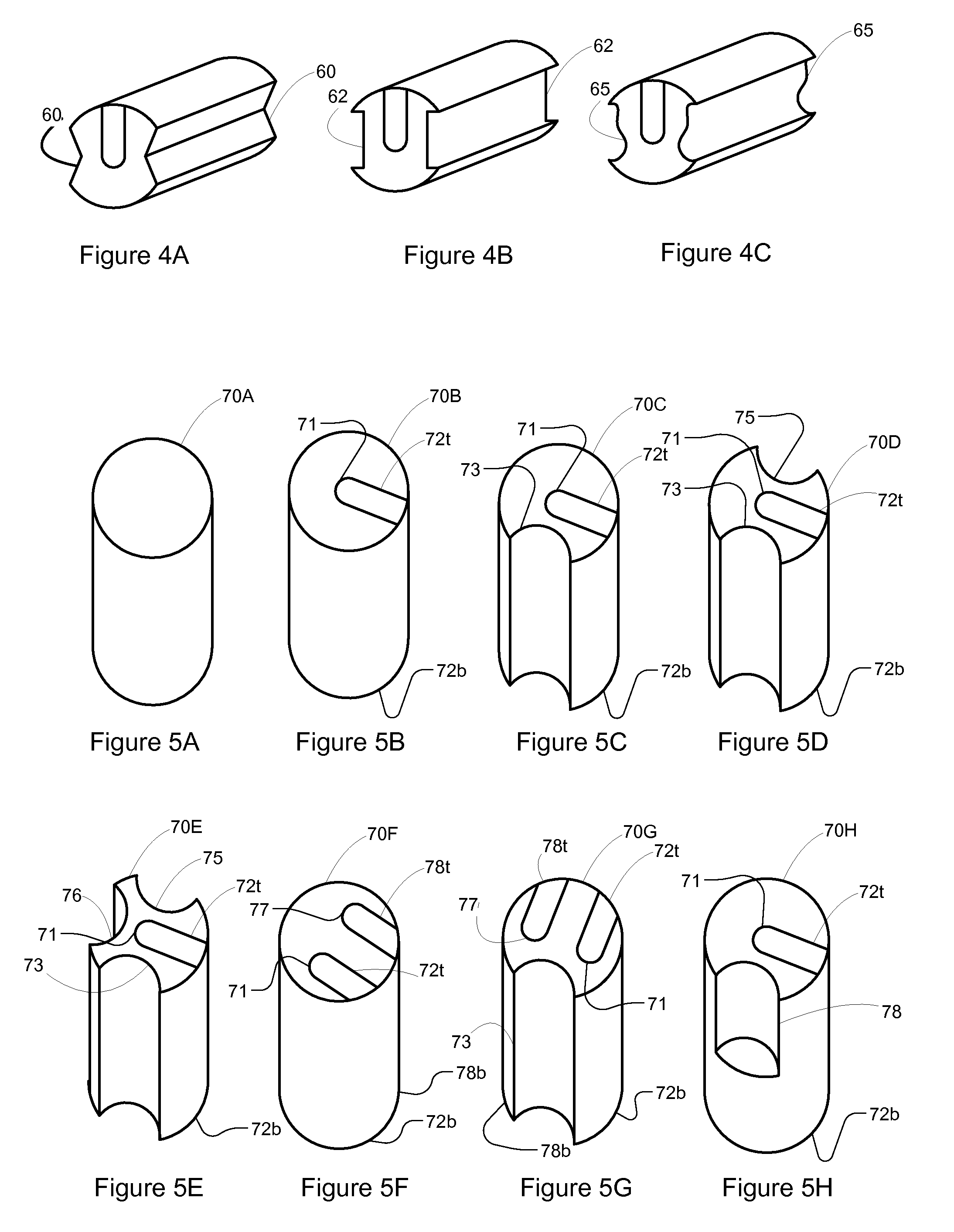
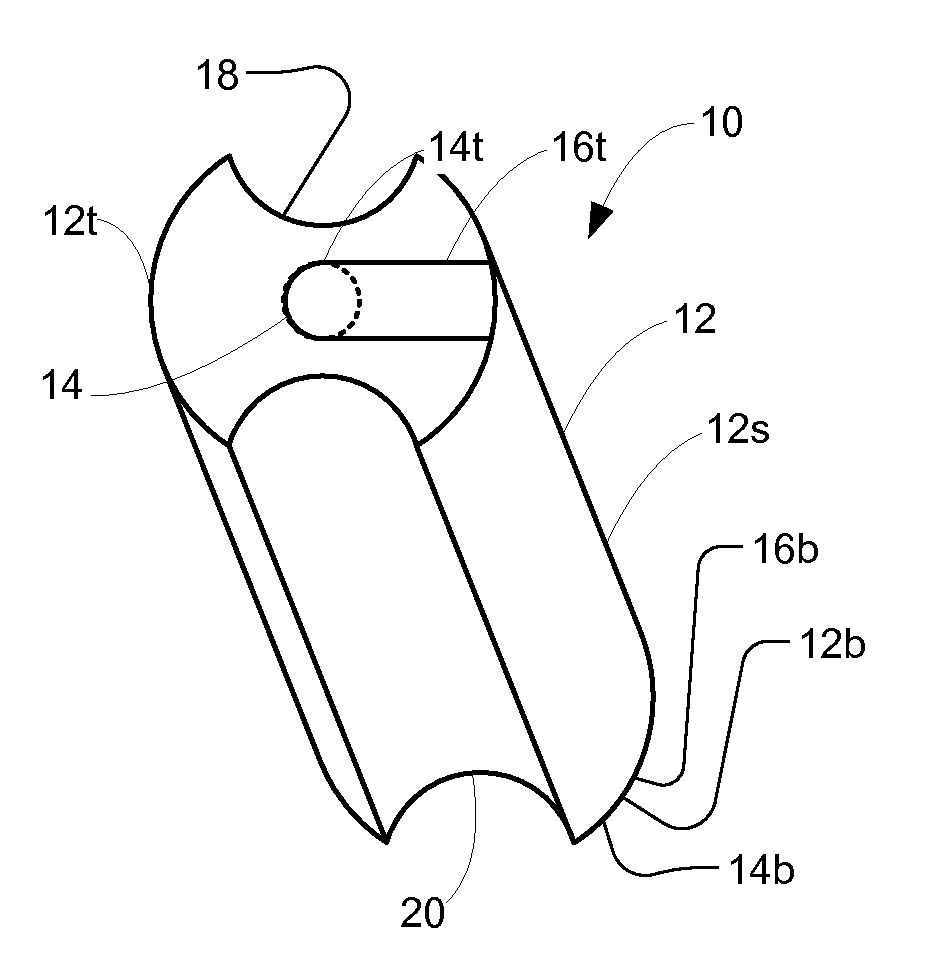
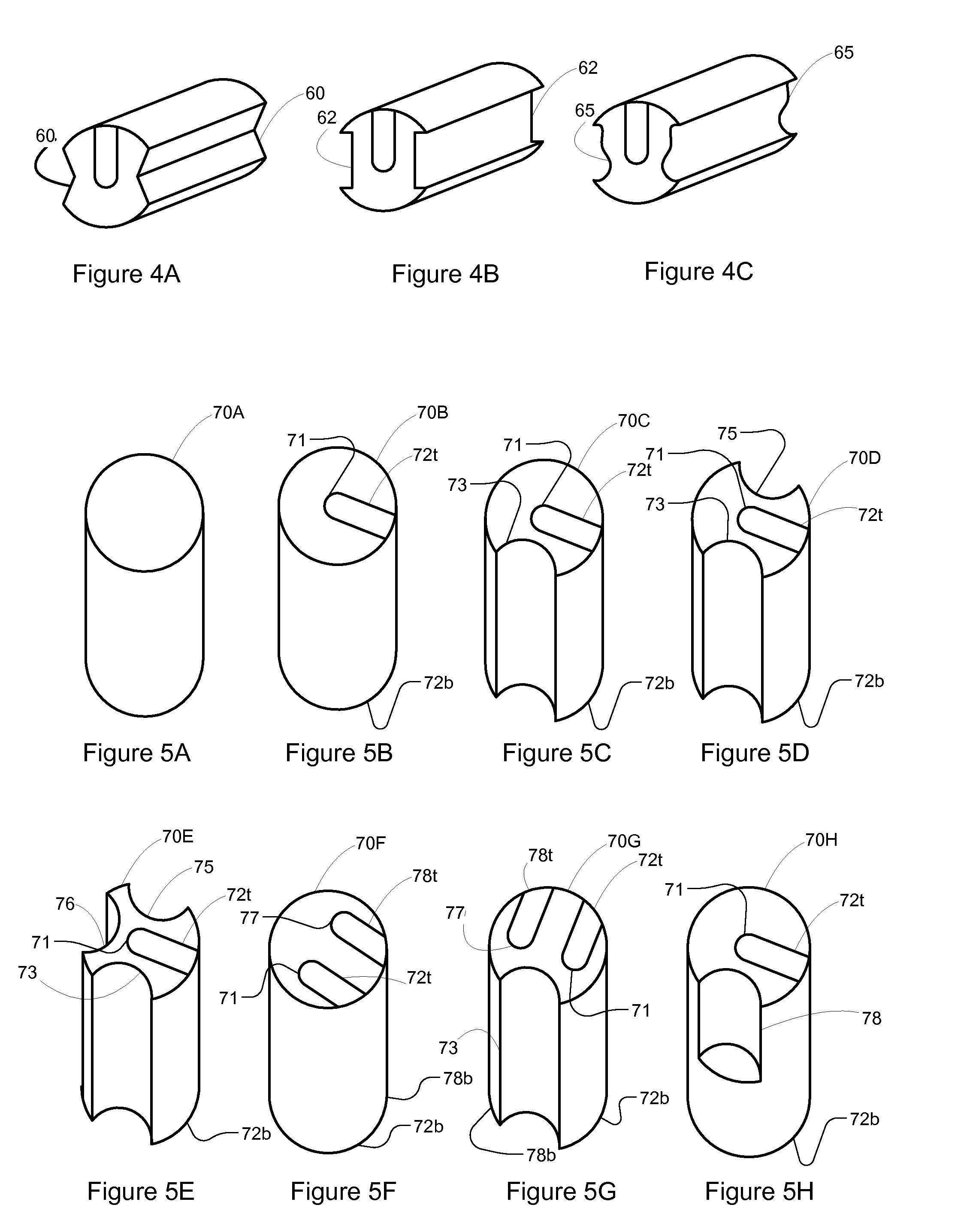
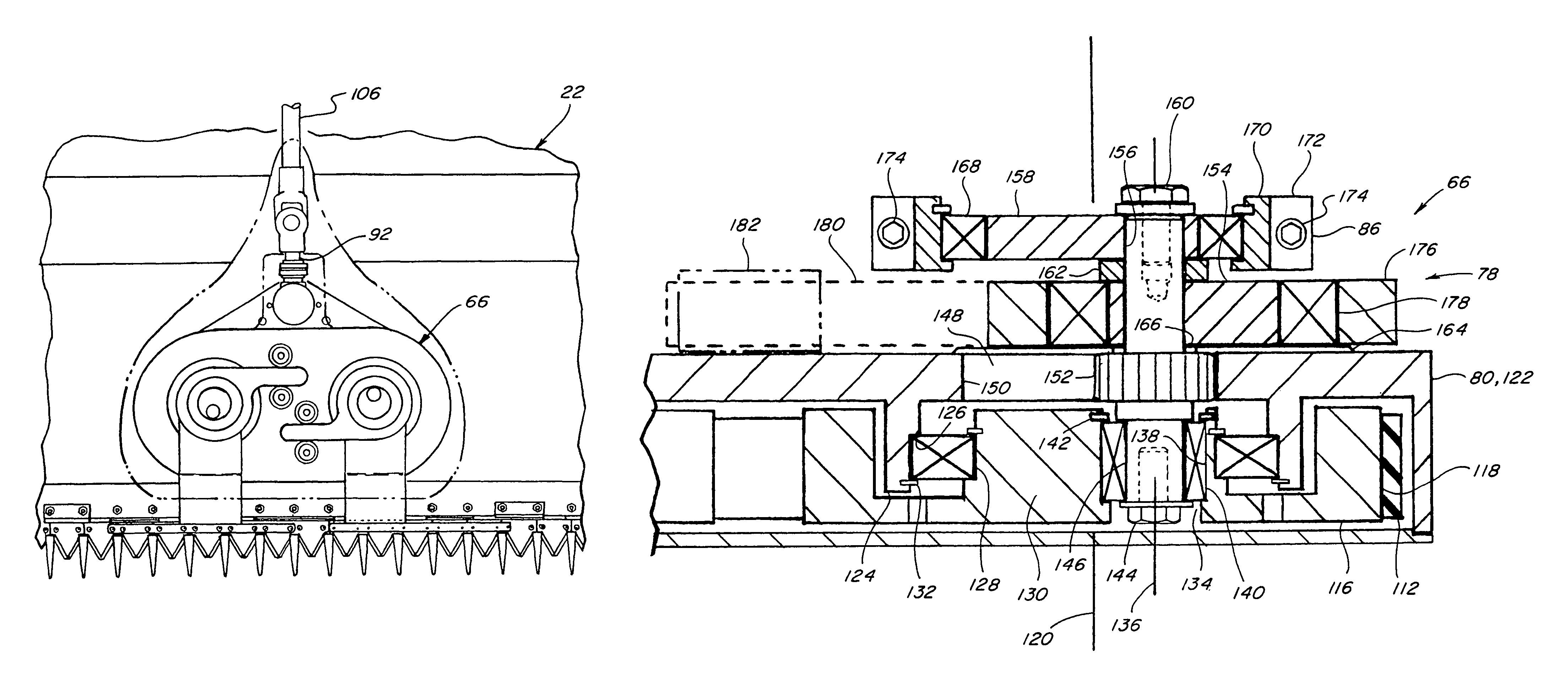
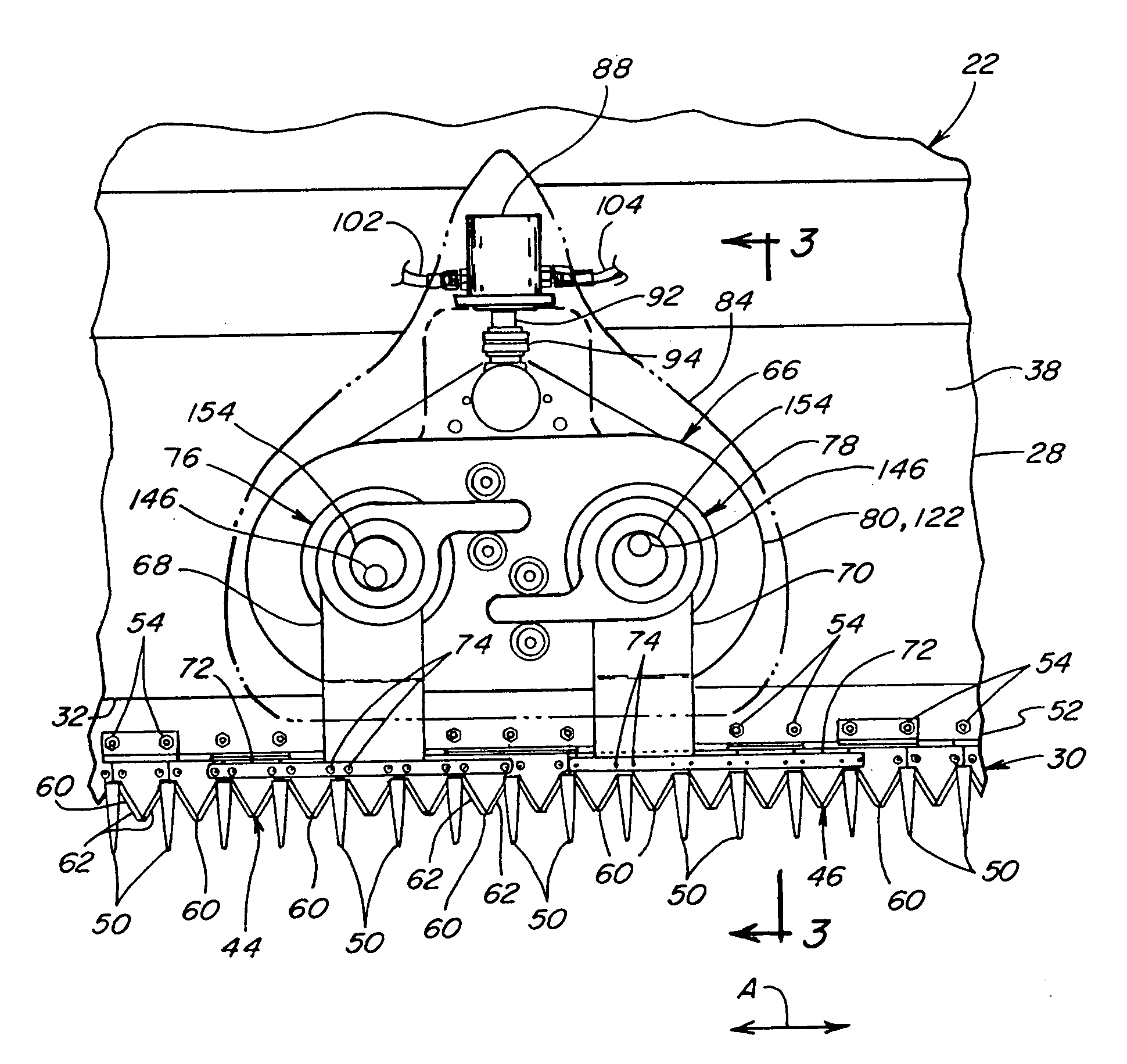
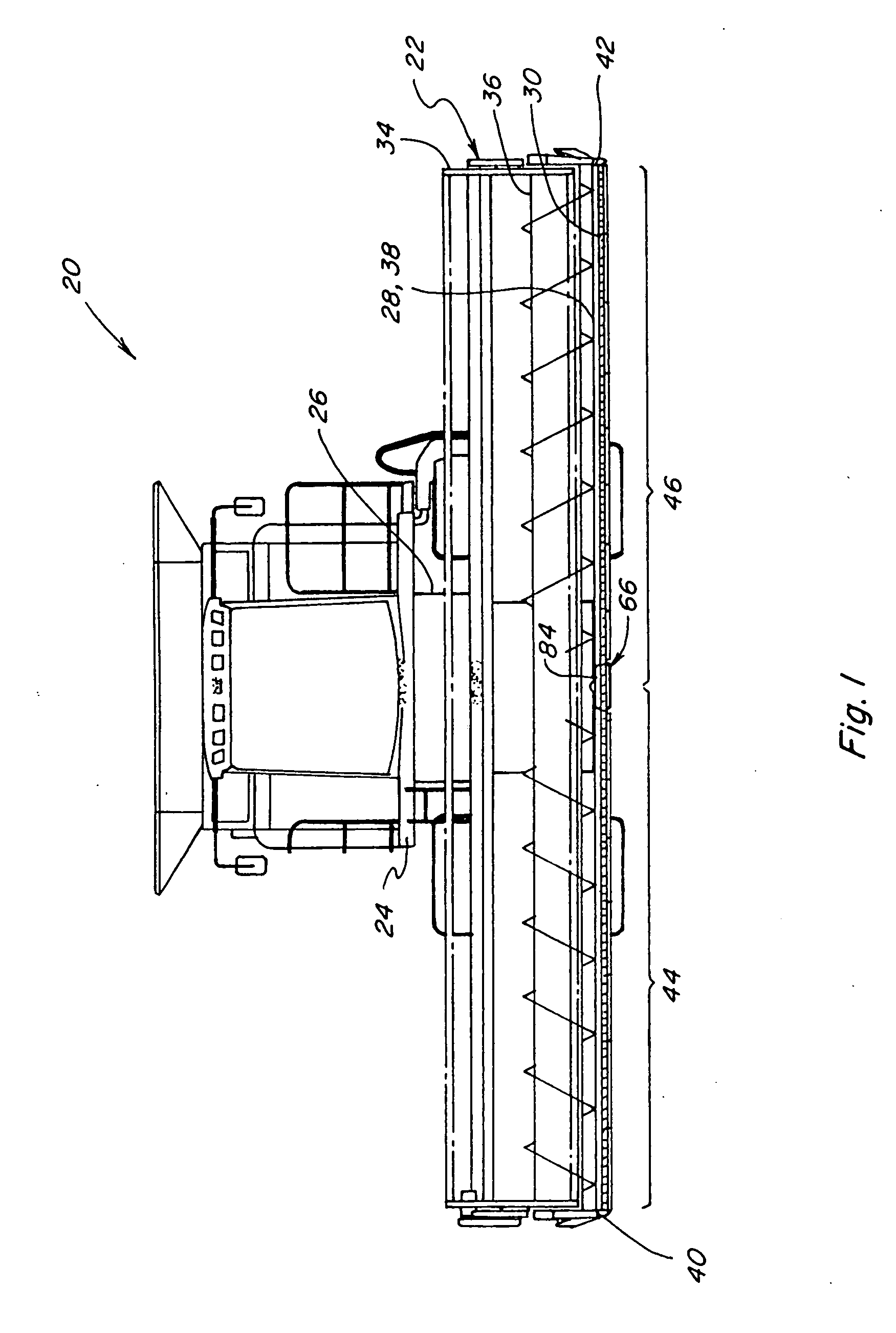
Compact knife head assembly, bearing and eccentric for a sickle drive for a header of an agricultural plant cutting machine
A compact epicyclic drive includes a pinion rotatable about a ring gear and an eccentric element fixedly connected to the pinion so as to be rotated thereby, a knife head bearing supported on and extending around the eccentric element, and a knife head assembly connected in driving relation to a sickle knife assembly. The knife head assembly includes an element supported on and extending around the knife head bearing and configured so as to transfer sidewardly directed components of rotations of the eccentric element into sideward reciprocating movements of the sickle knife assembly. The eccentric element, knife head bearing, and knife head assembly are generally flat and axially coextensive, contributing to the compactness of the drive. The sickle drive is adapted to incorporated into or beneath a floor or pan of a header of an agricultural harvesting machine.
Owner:BLUE LEAF I P INC
All-reflective optical systems for broadband wafer inspection
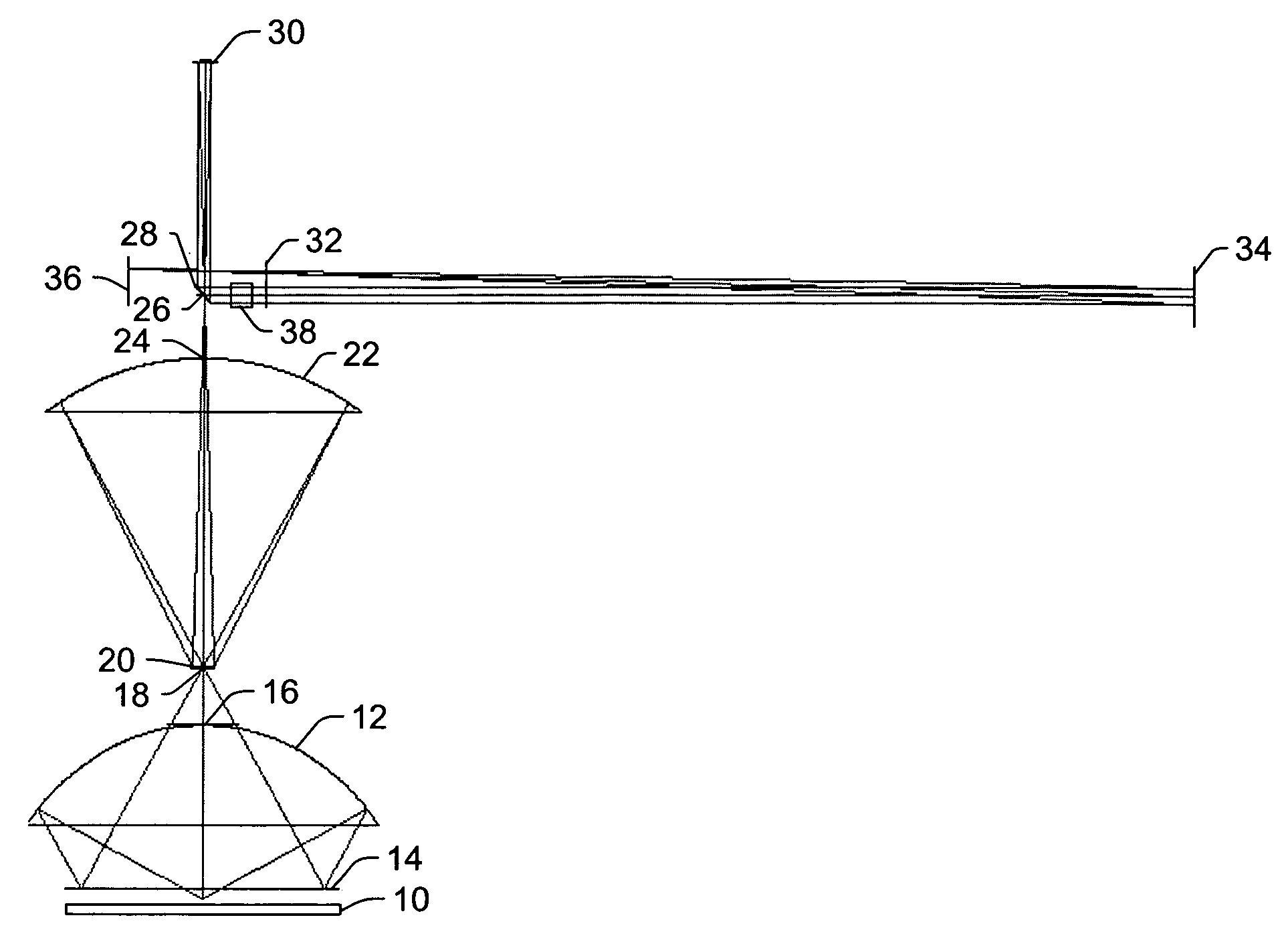
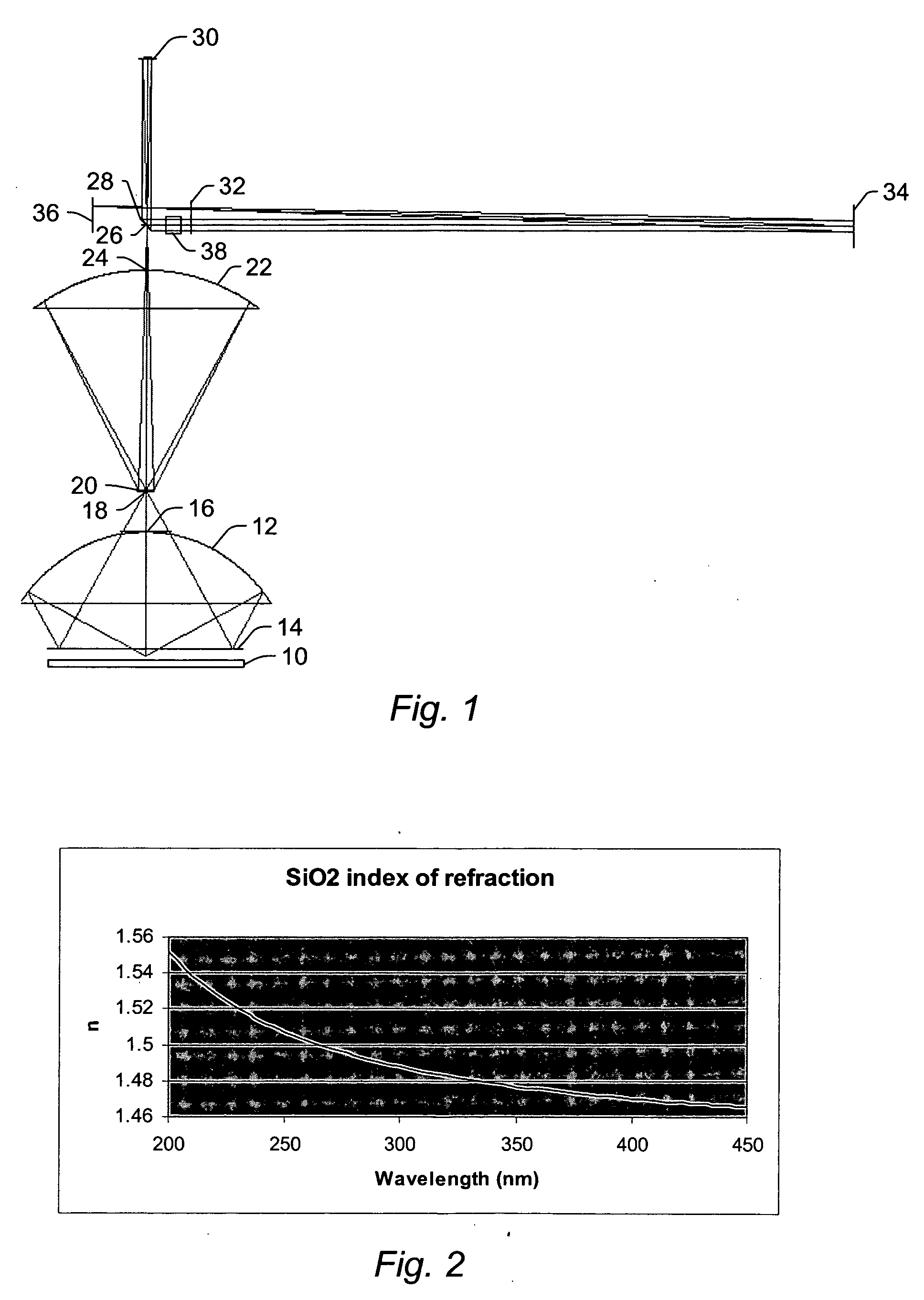
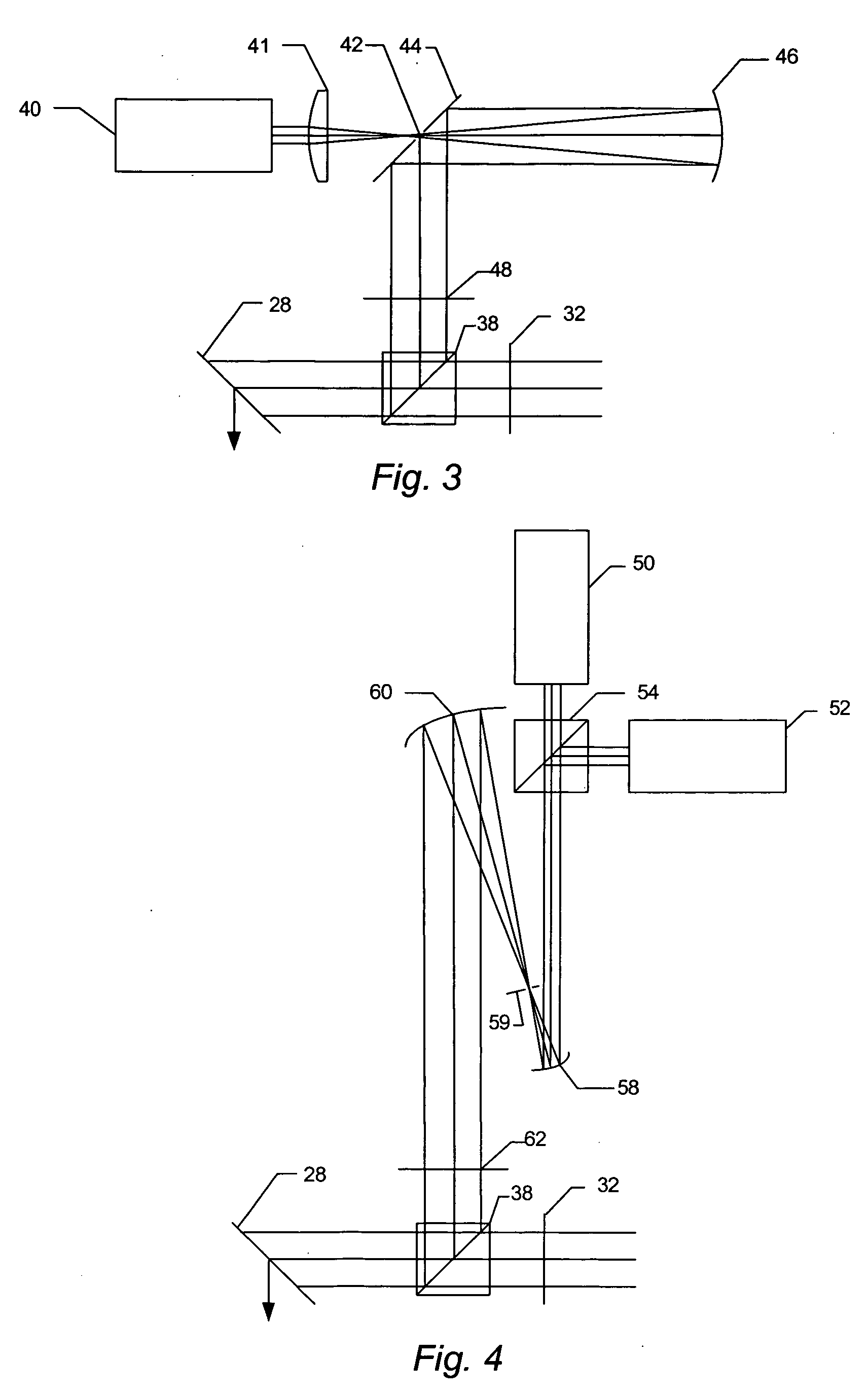
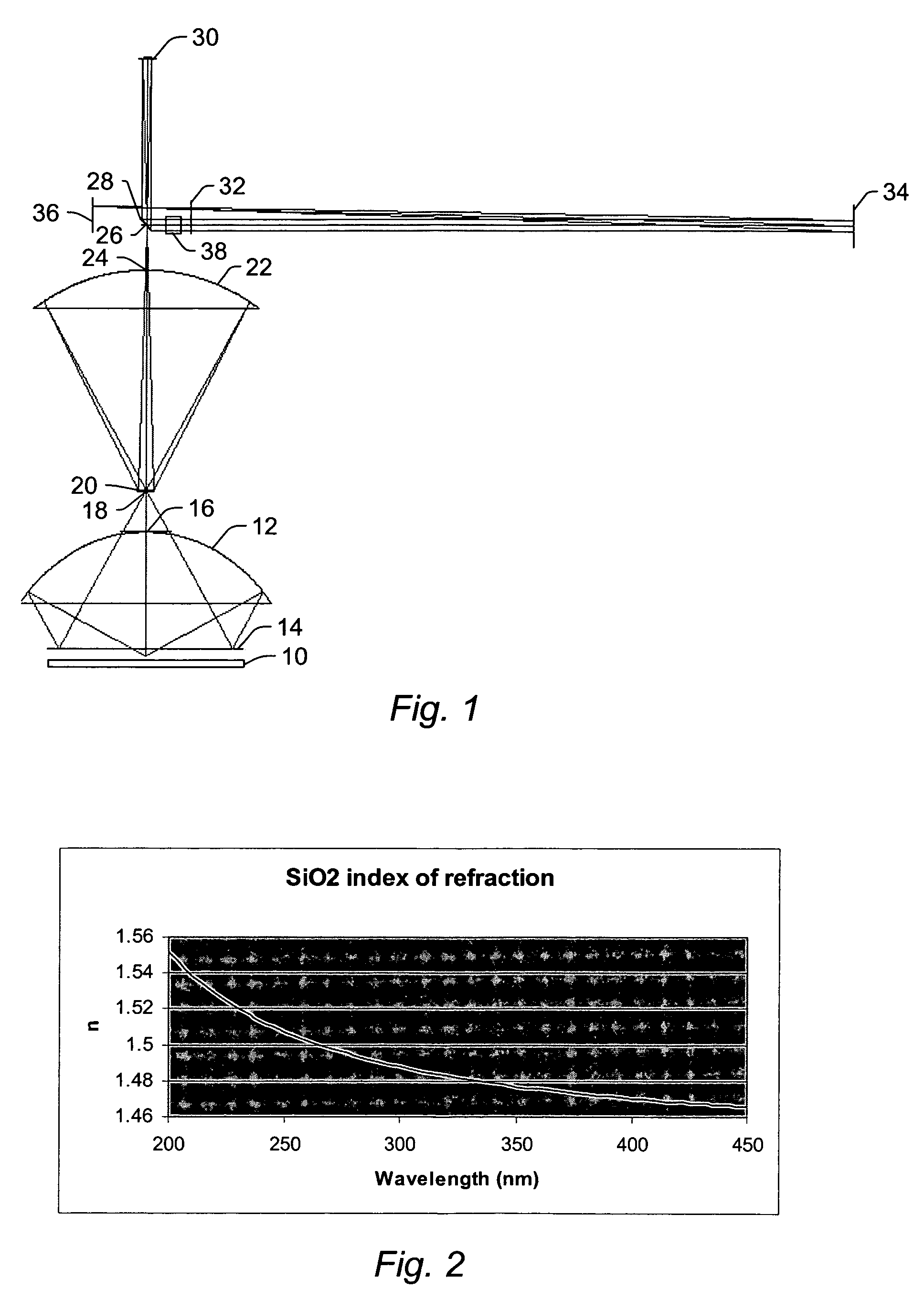
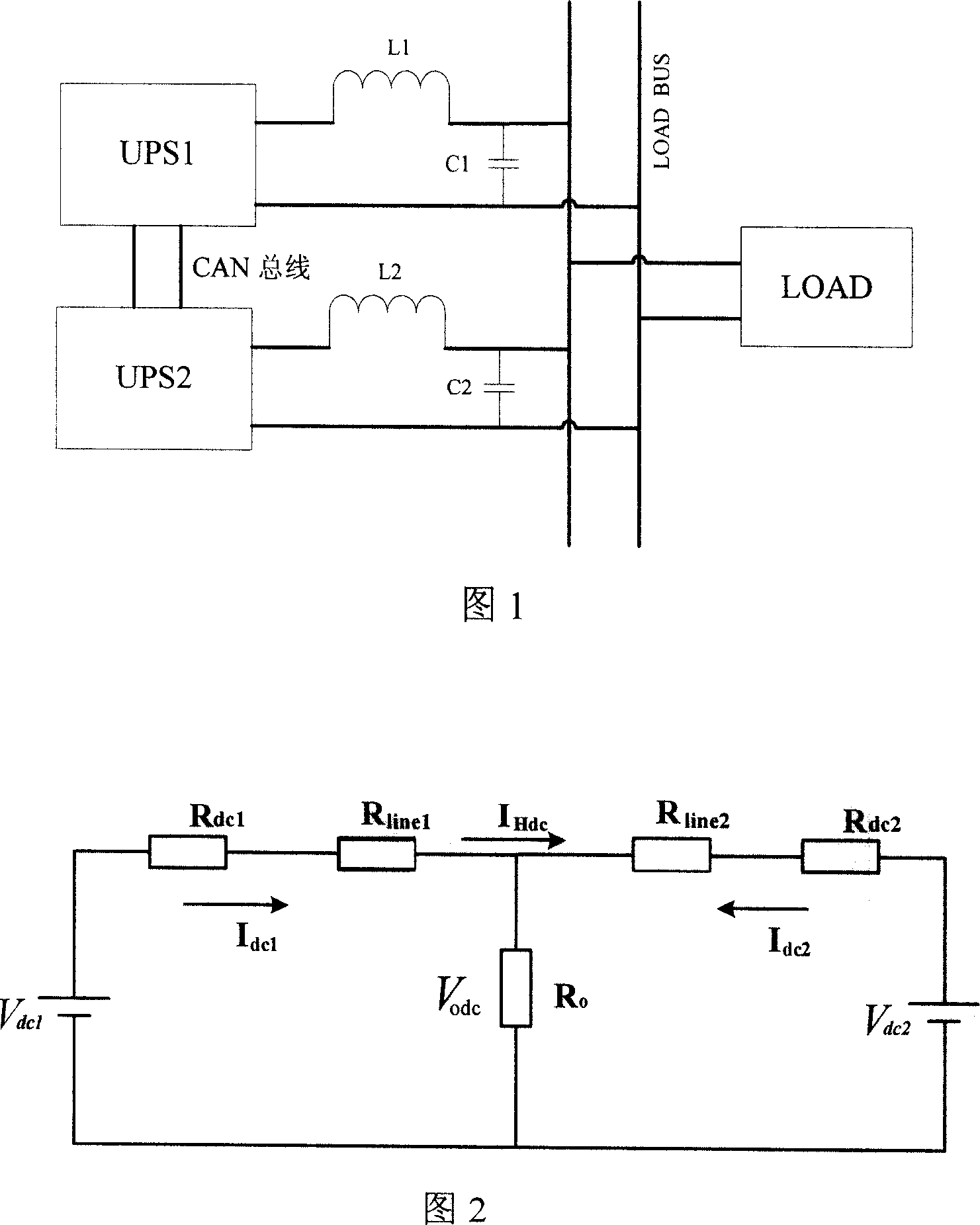
ActiveUS20060219930A1Low central obscurationReduce distortion problemsOptically investigating flaws/contaminationPhotometry using electric radiation detectorsCatoptricsBroadband
All-reflective optical systems for broadband wafer inspection are provided. One system configured to inspect a wafer includes an optical subsystem. All light-directing components of the optical subsystem are reflective optical components except for one or more refractive optical components, which are located only in substantially collimated space. The refractive optical component(s) may include, for example, a refractive beamsplitter element that can be used to separate illumination and collection pupils. The optical subsystem may also include one or more reflective optical components located in substantially collimated space. The optical subsystem is configured for inspection of the wafer across a waveband of greater than 20 nm. In some embodiments, the optical subsystem is configured for inspection of the wafer at wavelengths less than and greater than 200 nm.
Owner:KLA TENCOR TECH CORP
Method for dynamically measuring the state of health and charge of a car battery and device for implementing said method
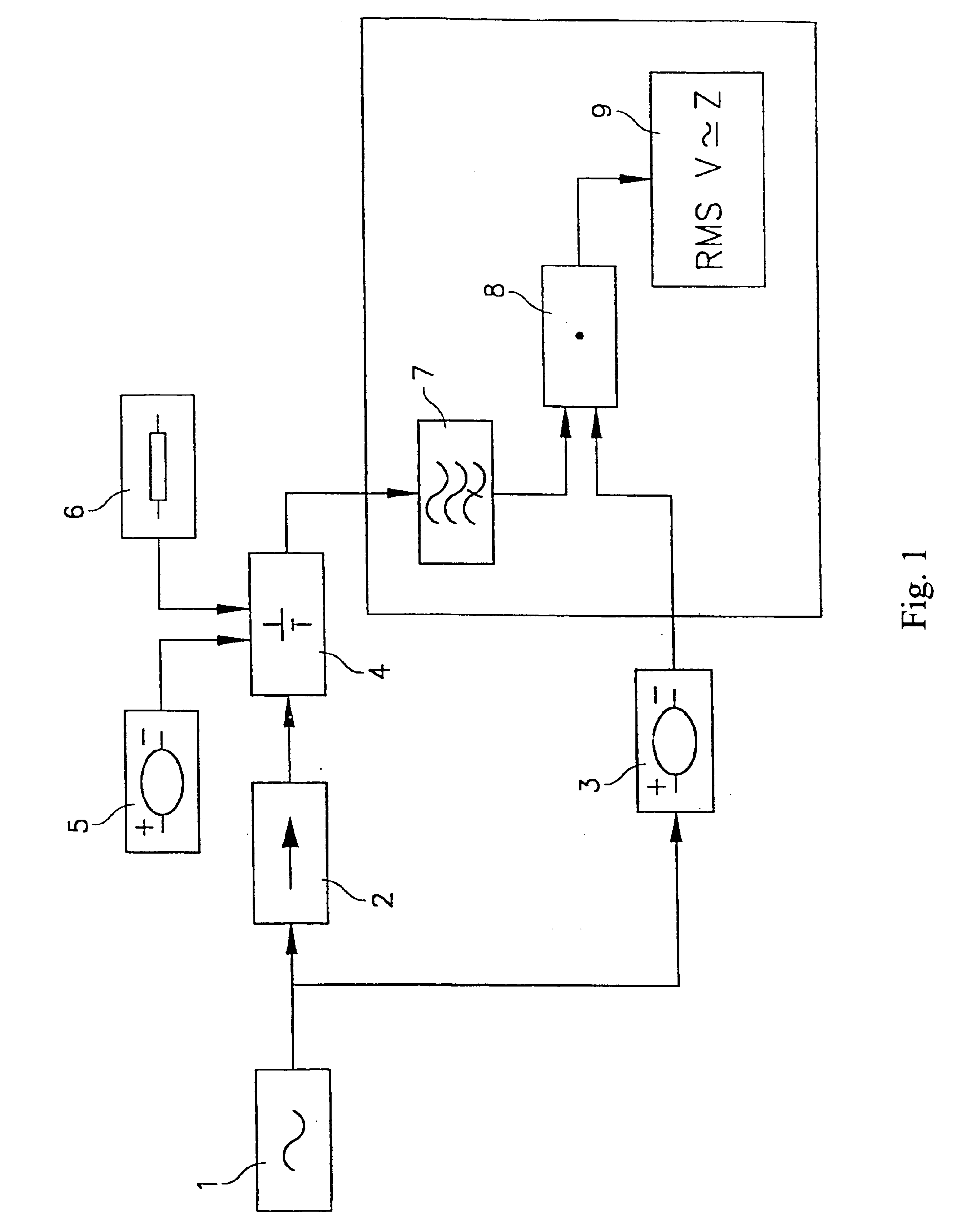
InactiveUS6876174B1Batteries circuit arrangementsElectrical testingAutomotive batteryElectrical battery
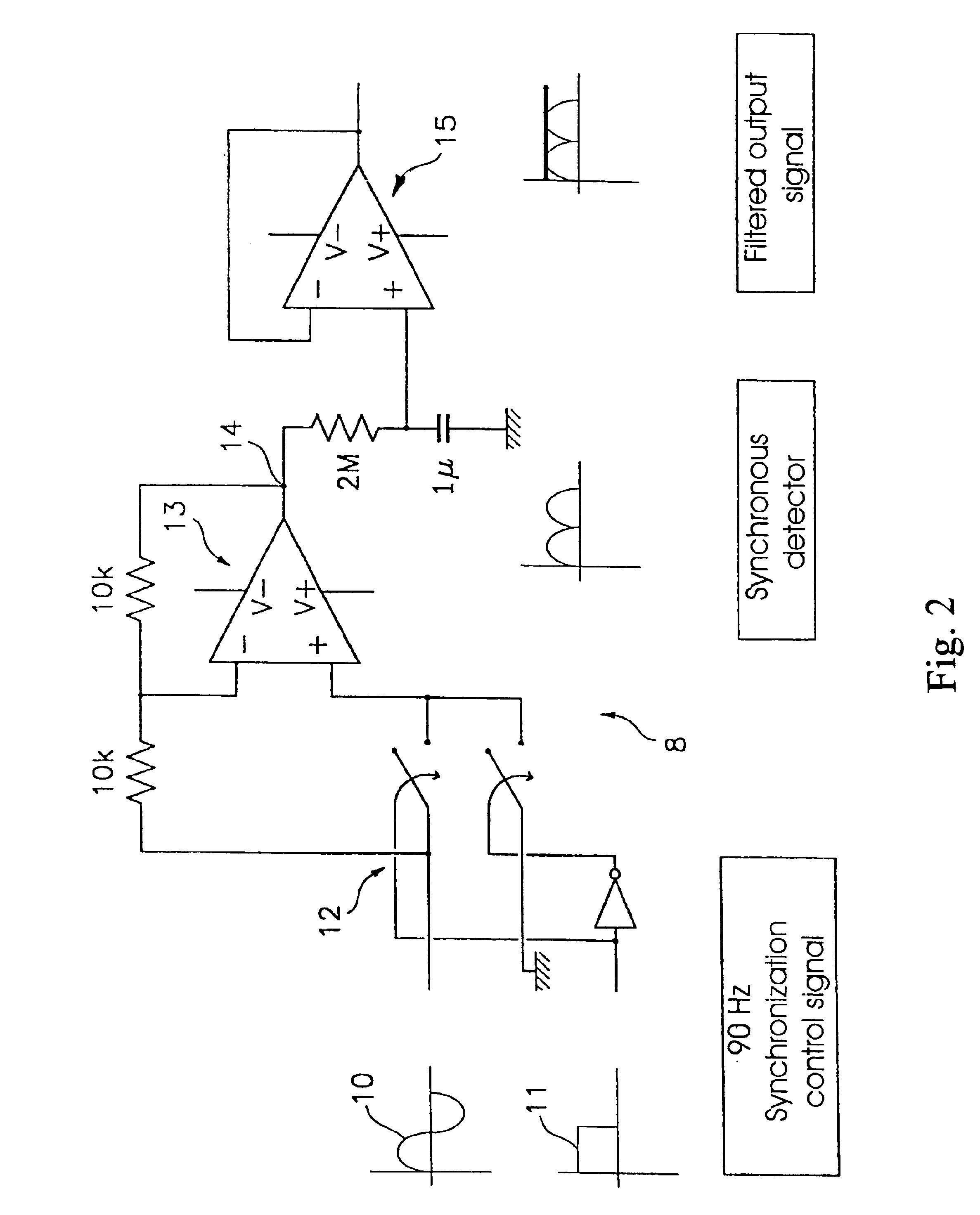
Based on the measurement of the increase of sinusoidal voltage ΔV=Vmaxsine(2πft) on adding a sinusoidal current ΔI=Imaxsine(2πft+φ) to the battery current, where f is the frequency and Imax, the amplitude of the superimposed current, with whose magnitudes the electrochemical impedance of the battery Z(f)=Vmax / Imaxejφ is calculated, comprising the application of a first sinusoidal signal of prefixed frequency to the battery which generates an alternate voltage component superimposed over the direct one; eliminating the direct component of the response signal; applying a second periodic voltage signal with a frequency identical to that of said first signal and carrying out a synchronous detection of the alternate component generated by the application of said first signal to obtain the voltage proportional to the electrochemical impedance and evaluate the state of health and charge of the battery.
Owner:LEAR AUTOMOTIVE (EEDS) SPAIN SL
Compact knife head assembly, bearing and eccentric for a sickle drive for a header of an agricultural plant cutting machine
A compact epicyclic drive includes a pinion rotatable about a ring gear and an eccentric element fixedly connected to the pinion so as to be rotated thereby, a knife head bearing supported on and extending around the eccentric element, and a knife head assembly connected in driving relation to a sickle knife assembly. The knife head assembly includes an element supported on and extending around the knife head bearing and configured so as to transfer sidewardly directed components of rotations of the eccentric element into sideward reciprocating movements of the sickle knife assembly. The eccentric element, knife head bearing, and knife head assembly are generally flat and axially coextensive, contributing to the compactness of the drive. The sickle drive is adapted to incorporated into or beneath a floor or pan of a header of an agricultural harvesting machine.
Owner:BLUE LEAF I P INC
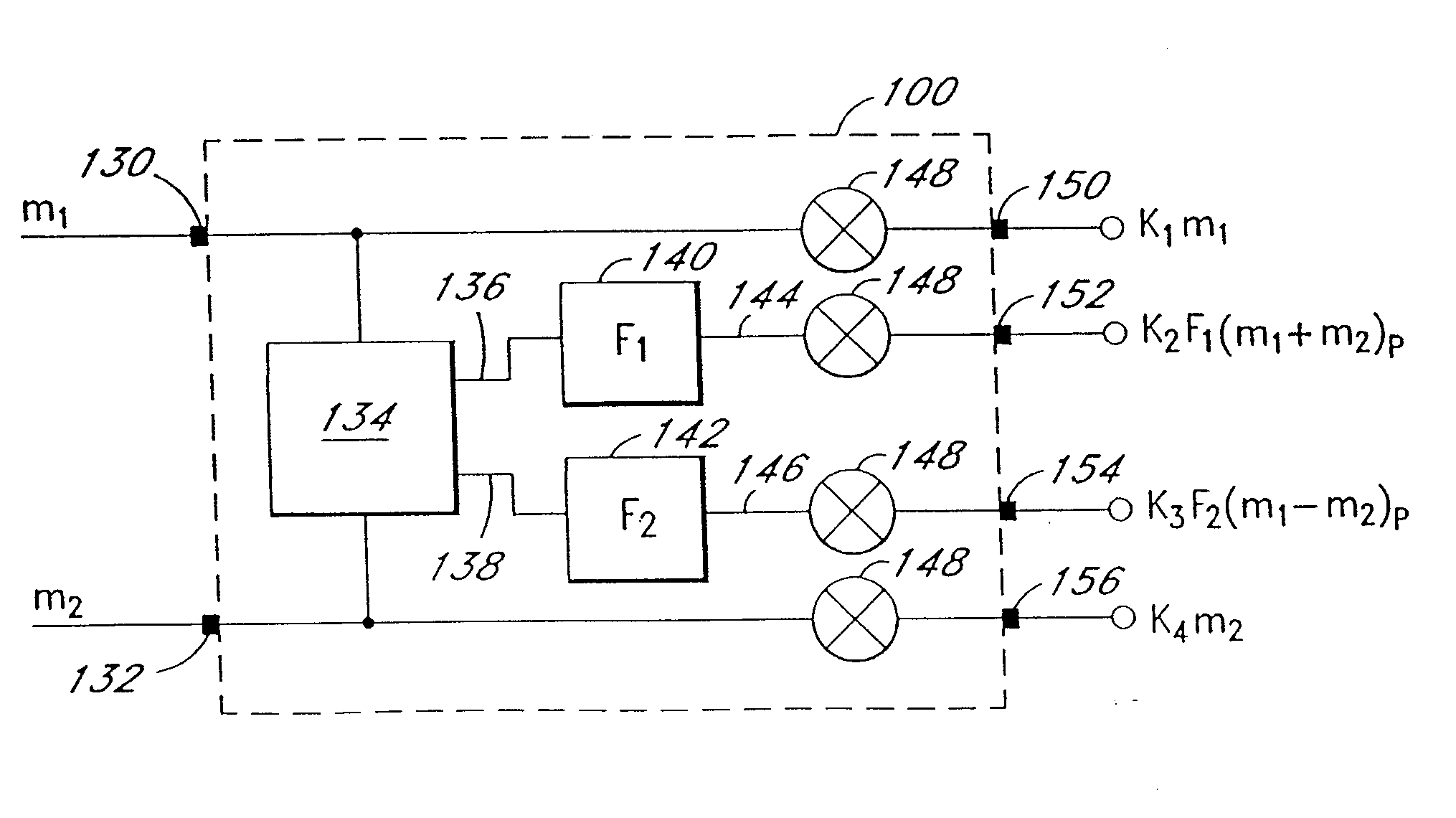
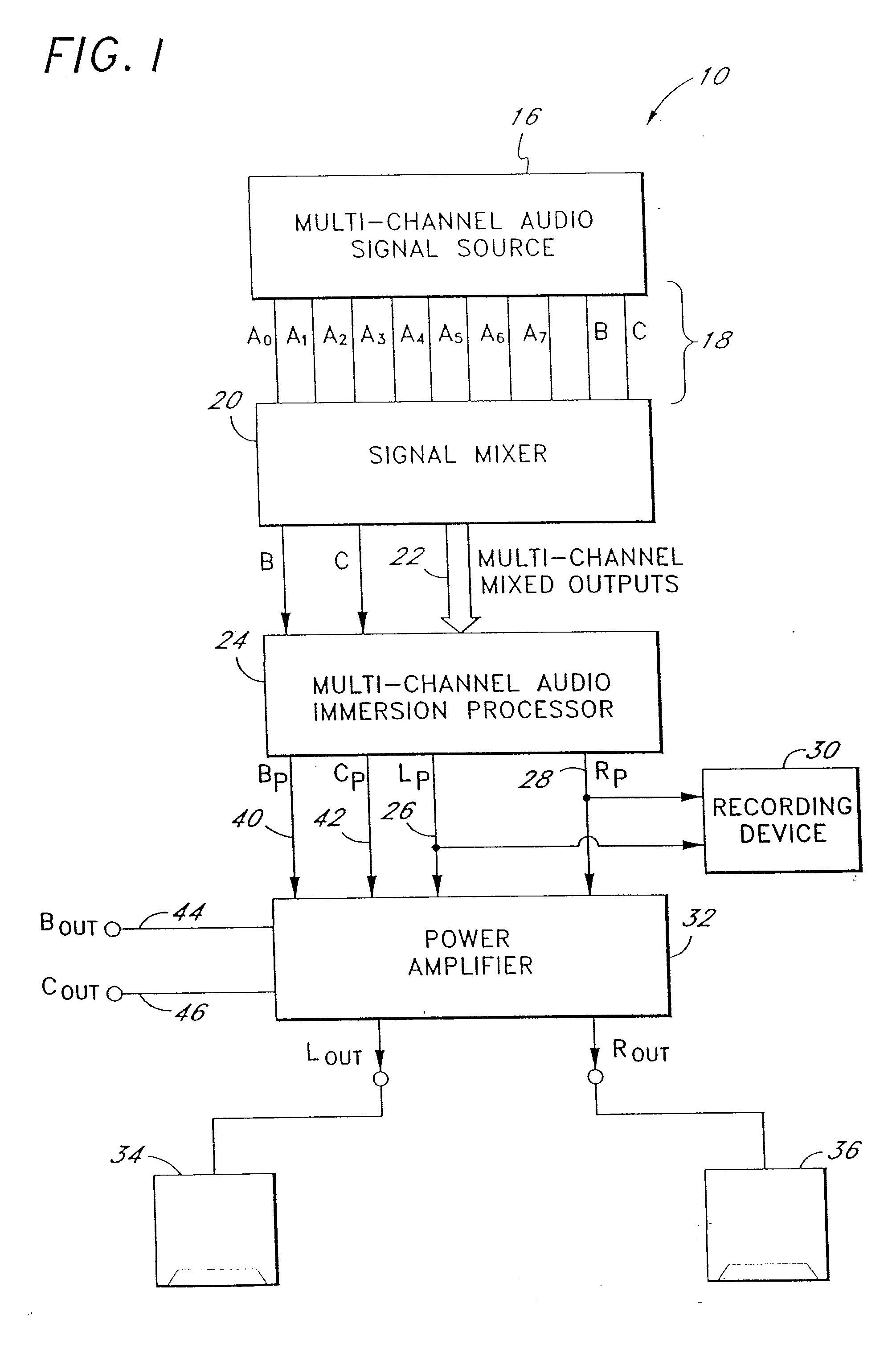
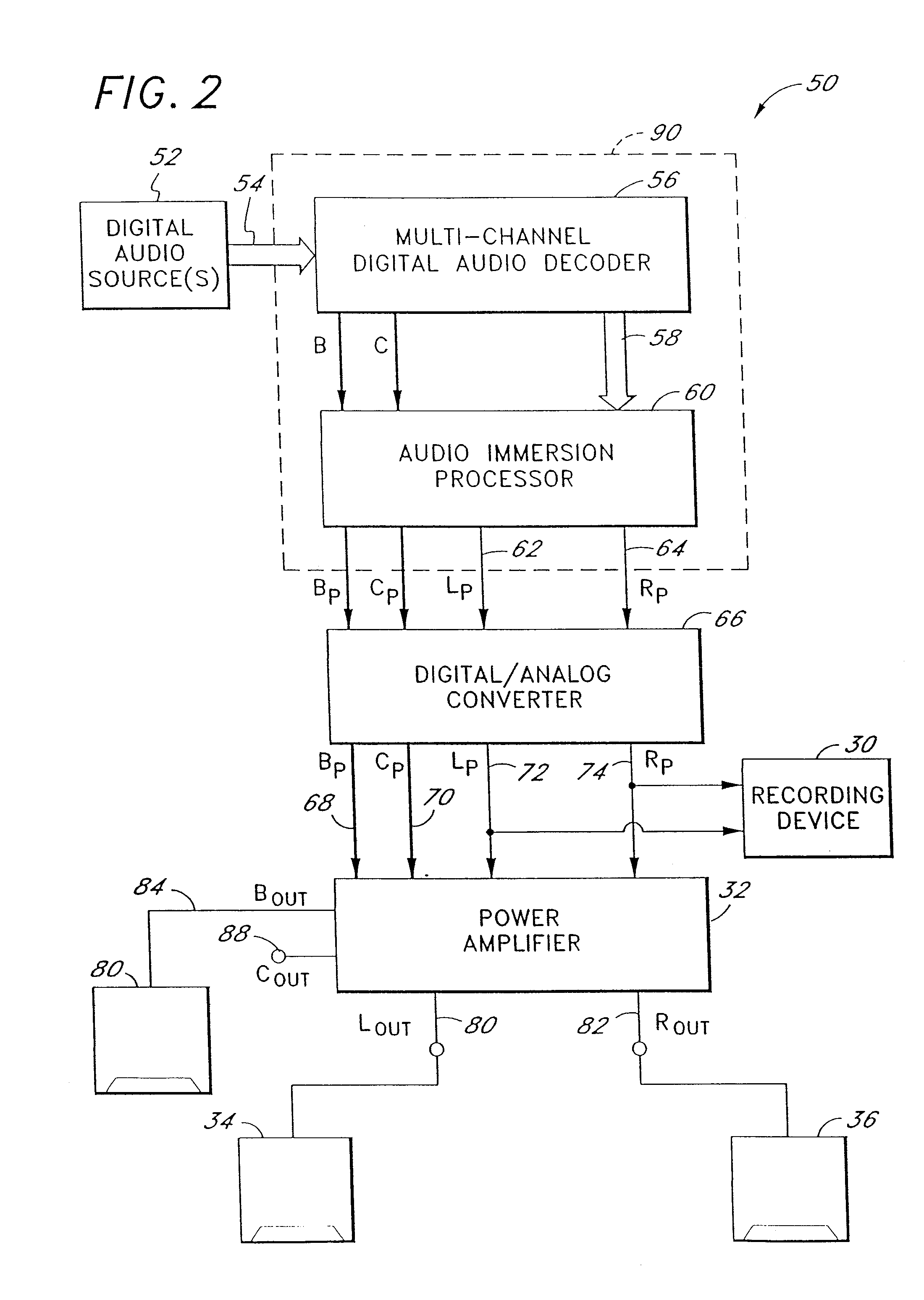
Multi-channel audio enhancement system for use in recording and playback and methods for providing same
InactiveUS20070165868A1Enhance sounds perceivedPseudo-stereo systemsTransmissionDirect componentComputer science
An audio enhancement system and method for use receives a group of multi-channel audio signals and provides a simulated surround sound environment through playback of only two output signals. The multi-channel audio signals comprise a pair of front signals intended for playback from a forward sound stage and a pair of rear signals intended for playback from a rear sound stage. The front and rear signals are modified in pairs by separating an ambient component of each pair of signals from a direct component and processing at least some of the components with a head-related transfer function. Processing of the individual audio signal components is determined by an intended playback position of the corresponding original audio signals. The individual audio signal components are then selectively combined with the original audio signals to form two enhanced output signals for generating a surround sound experience upon playback.
Owner:DTS
All-reflective optical systems for broadband wafer inspection
ActiveUS7351980B2Color/spectral properties measurementsPhotometry using electric radiation detectorsCatoptricsBroadband
All-reflective optical systems for broadband wafer inspection are provided. One system configured to inspect a wafer includes an optical subsystem. All light-directing components of the optical subsystem are reflective optical components except for one or more refractive optical components, which are located only in substantially collimated space. The refractive optical component(s) may include, for example, a refractive beamsplitter element that can be used to separate illumination and collection pupils. The optical subsystem may also include one or more reflective optical components located in substantially collimated space. The optical subsystem is configured for inspection of the wafer across a waveband of greater than 20 nm. In some embodiments, the optical subsystem is configured for inspection of the wafer at wavelengths less than and greater than 200 nm.
Owner:KLA TENCOR TECH CORP
An improved control method for UPS parallel connection average current
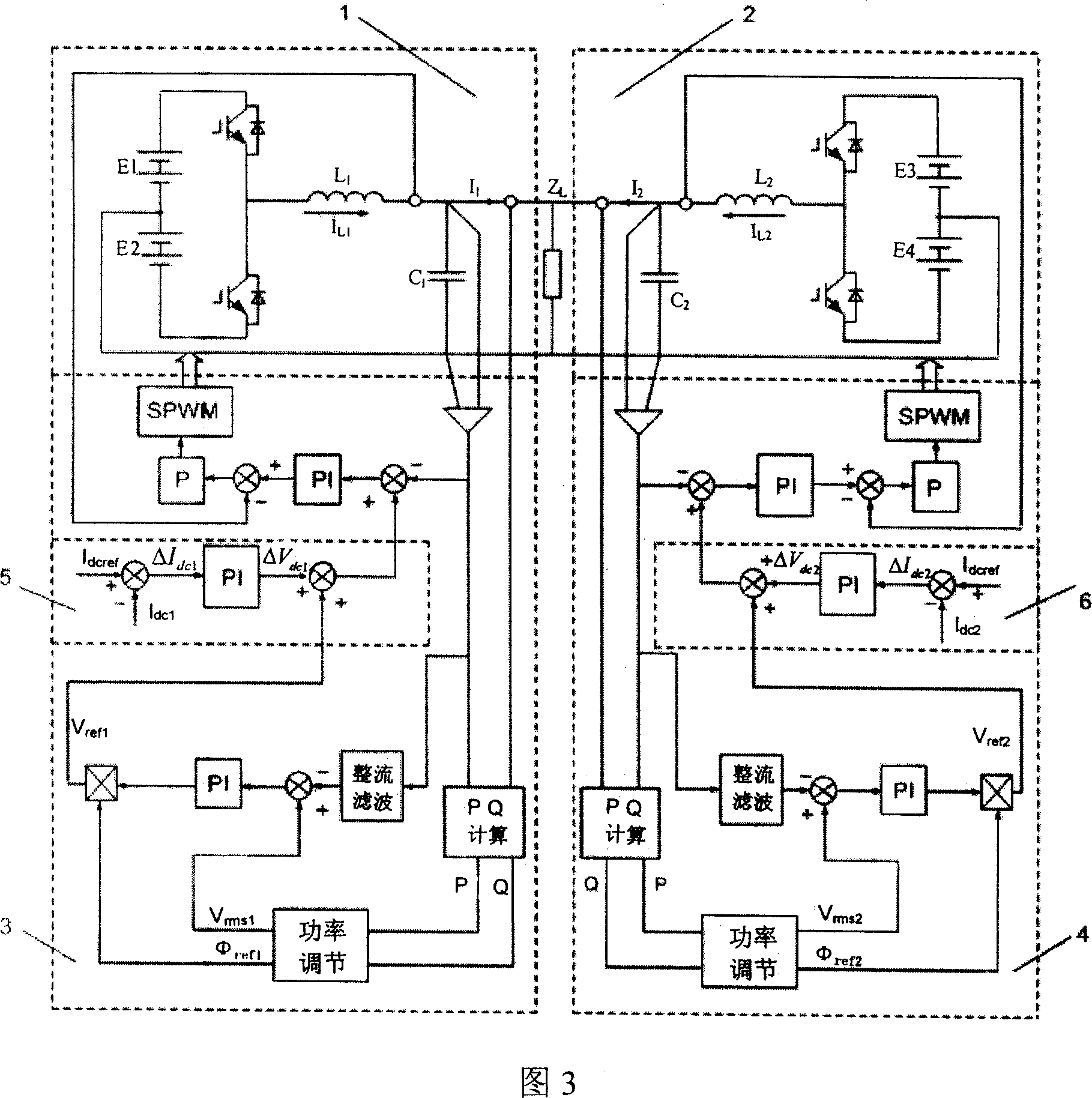
InactiveCN101009436AEliminate DC circulationImprove featuresBatteries circuit arrangementsElectric powerPower controllerAverage current
The invention relates to UPS parallel connection equal current control method, the real power controller and the idle power controller are adopted to control the UPS contravariant reference voltage, inductance current direct component is added into the UPS contravariant reference voltage, inductance current direct component of the other UPS in system can be obtained by CAN bus, after DSP calculation of every UPS, the average value of the parallel connection system inductance current direct component is calculated to as the system direct current component, then the given value of the direct current is compared with the direct current component of the UPS inductance current to obtain the difference of the inductance current, the difference passes PI adjustor to obtain the regulated quantity needed by the contravariant reference voltage, and the regulated quantity is used to control the UPS output voltage. So the effective control of the inductance current direct component can be realized, and the direct loop current of UPSs can be eliminated, the flow equalization property and stability of integral UPS parallel connection system can be improved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
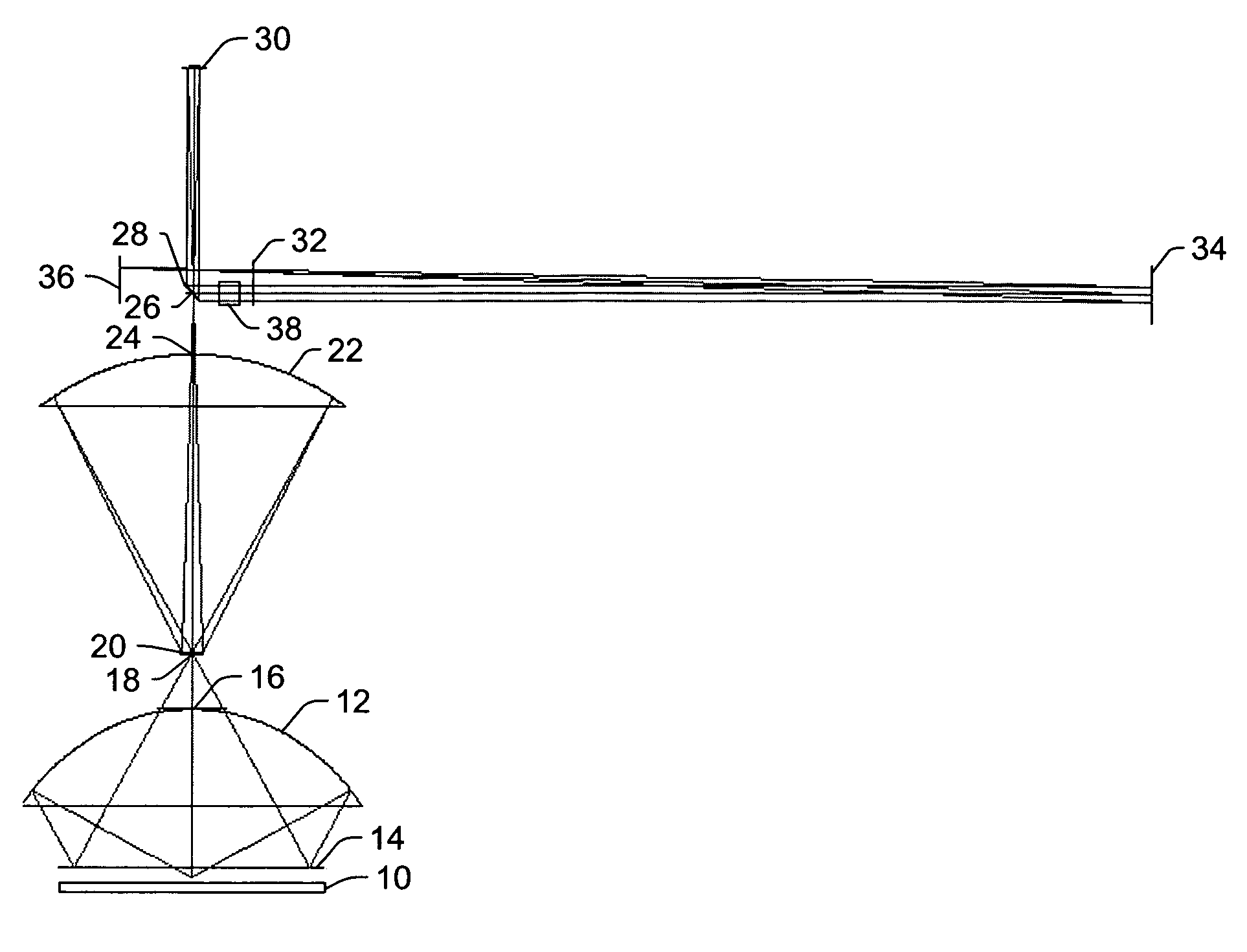
Electromagnetic radiation collector and transport system
InactiveUS6957650B2Avoid radiationRoof covering using slabs/sheetsSolar heating energyTransport systemElectromagnetic radiation
The present invention includes a radiation collector configured to collect incident radiation. The radiation collector includes a radiation directing component configured to redirect the incident radiation, a buffer component configured to receive the radiation redirected by the radiation directing component, and a propagation component configured to receive the radiation from the buffer component and to propagate the radiation towards a first end of the propagation component.
Owner:BIOSYNERGETICS INC
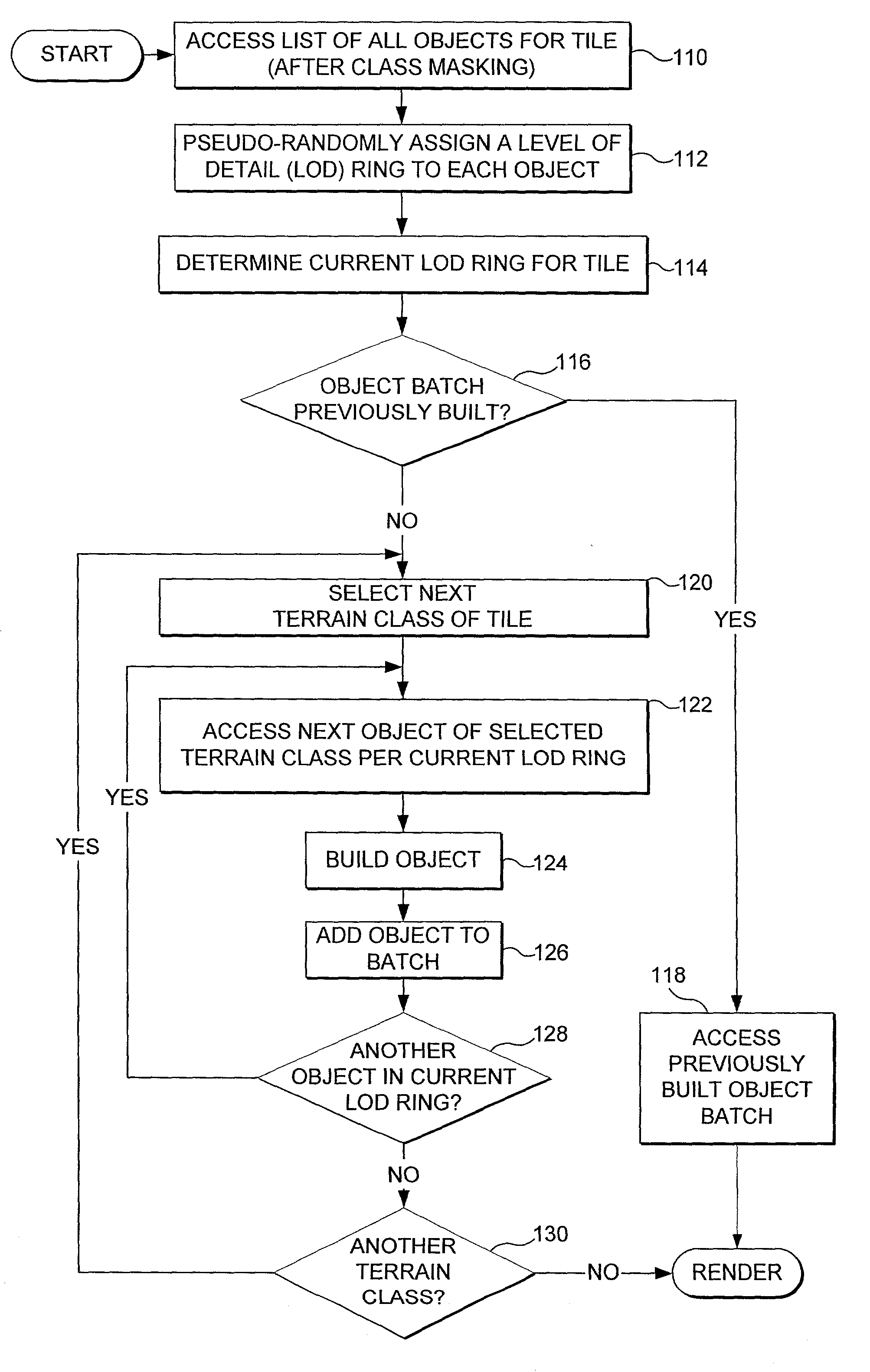
Efficient scenery object rendering
InactiveUS20050156928A1Avoid sudden changesElectric/magnetic detectionSpecial data processing applicationsGraphicsViewpoints
The number of graphic objects in a visual tile rendered varies as a function of distance between the tile and a viewpoint in a simulation. Fewer objects are rendered when the tile is far from the viewpoint, and vise versa. A level of detail (LOD) value is pseudo-randomly selected and associated with each object, indicating the maximum distance at which the object will be visible. A current LOD value is determined for the tile. An object is rendered if its LOD value is equal or greater than the current LOD value of the tile. Objects are faded into and out of view by modulating an opacity value as the current LOD value changes. Texture values of an object are adjusted as a function of ambient and direct components of light on the object, to achieve lighting corresponding to time of day, current season, and / or region in the simulated world.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Efficient scenery object rendering
InactiveUS6952207B1Avoid sudden changesElectric/magnetic detectionSpecial data processing applicationsGraphicsViewpoints
The number of graphic objects in a visual tile rendered varies as a function of distance between the tile and a viewpoint in a simulation. Fewer objects are rendered when the tile is far from the viewpoint, and vise versa. A level of detail (LOD) value is pseudo-randomly selected and associated with each object, indicating the maximum distance at which the object will be visible. A current LOD value is determined for the tile. An object is rendered if its LOD value is equal or greater than the current LOD value of the tile. Objects are faded into and out of view by modulating an opacity value as the current LOD value changes. Texture values of an object are adjusted as a function of ambient and direct components of light on the object, to achieve lighting corresponding to time of day, current season, and / or region in the simulated world.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
LED Light Module
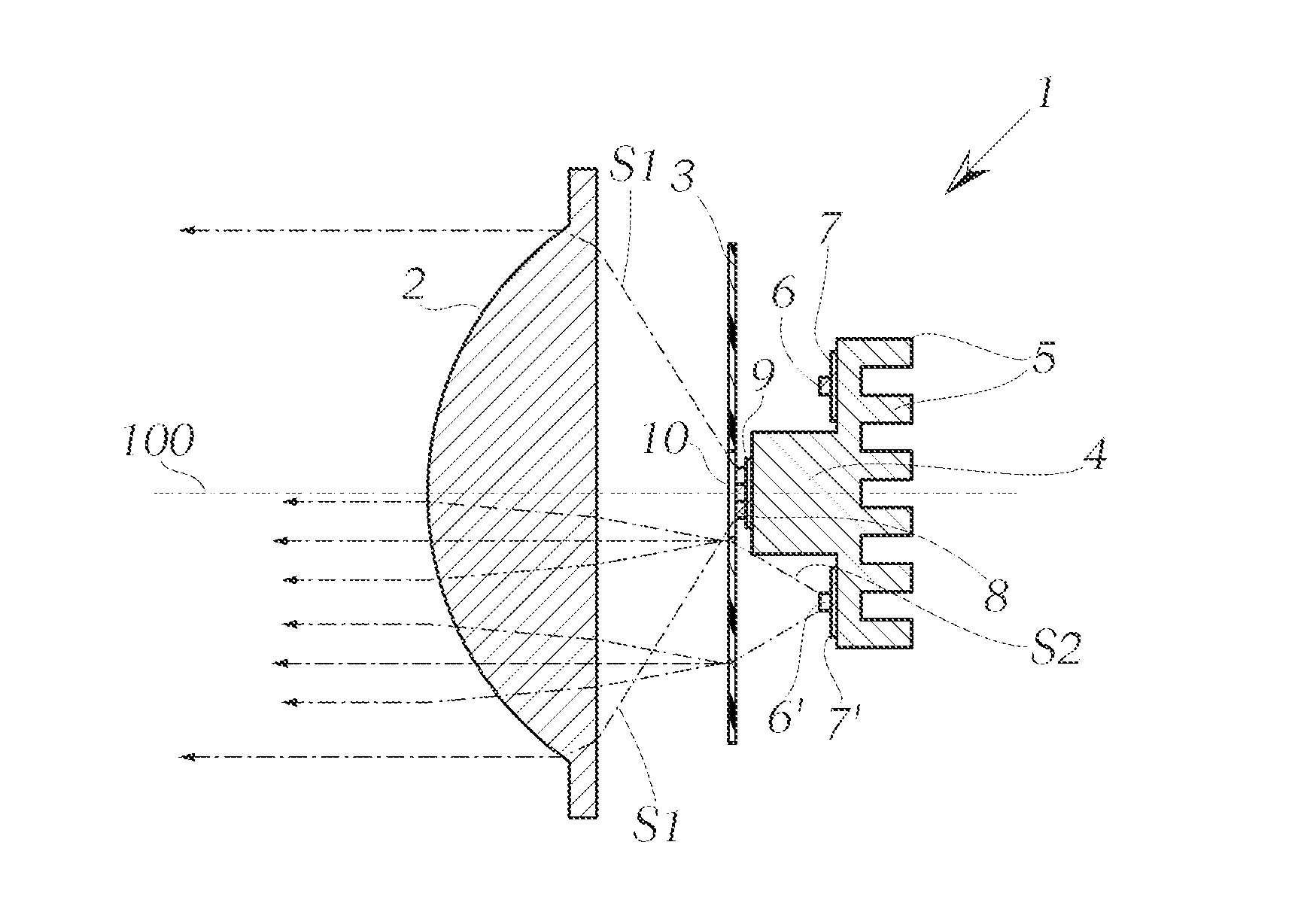
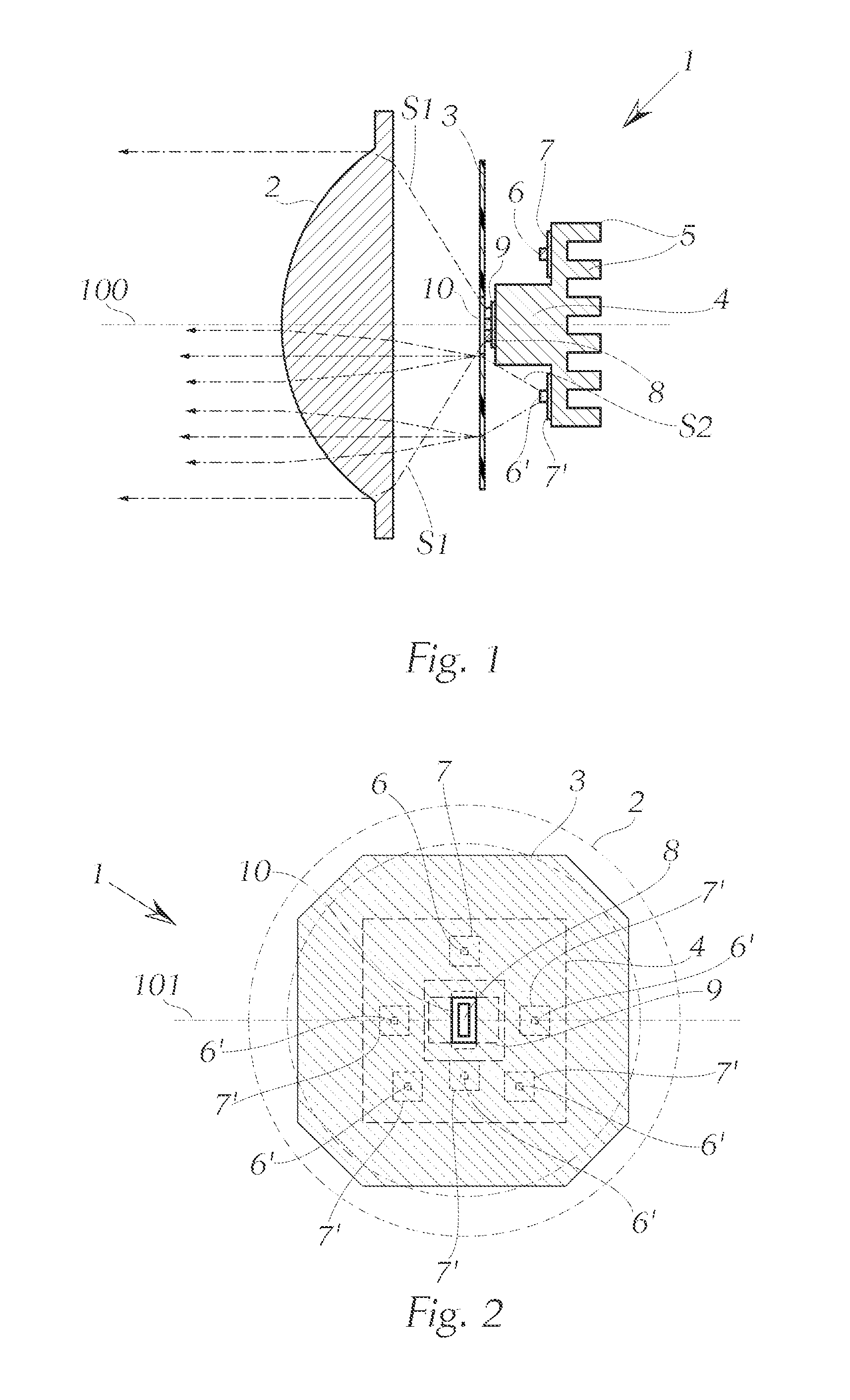
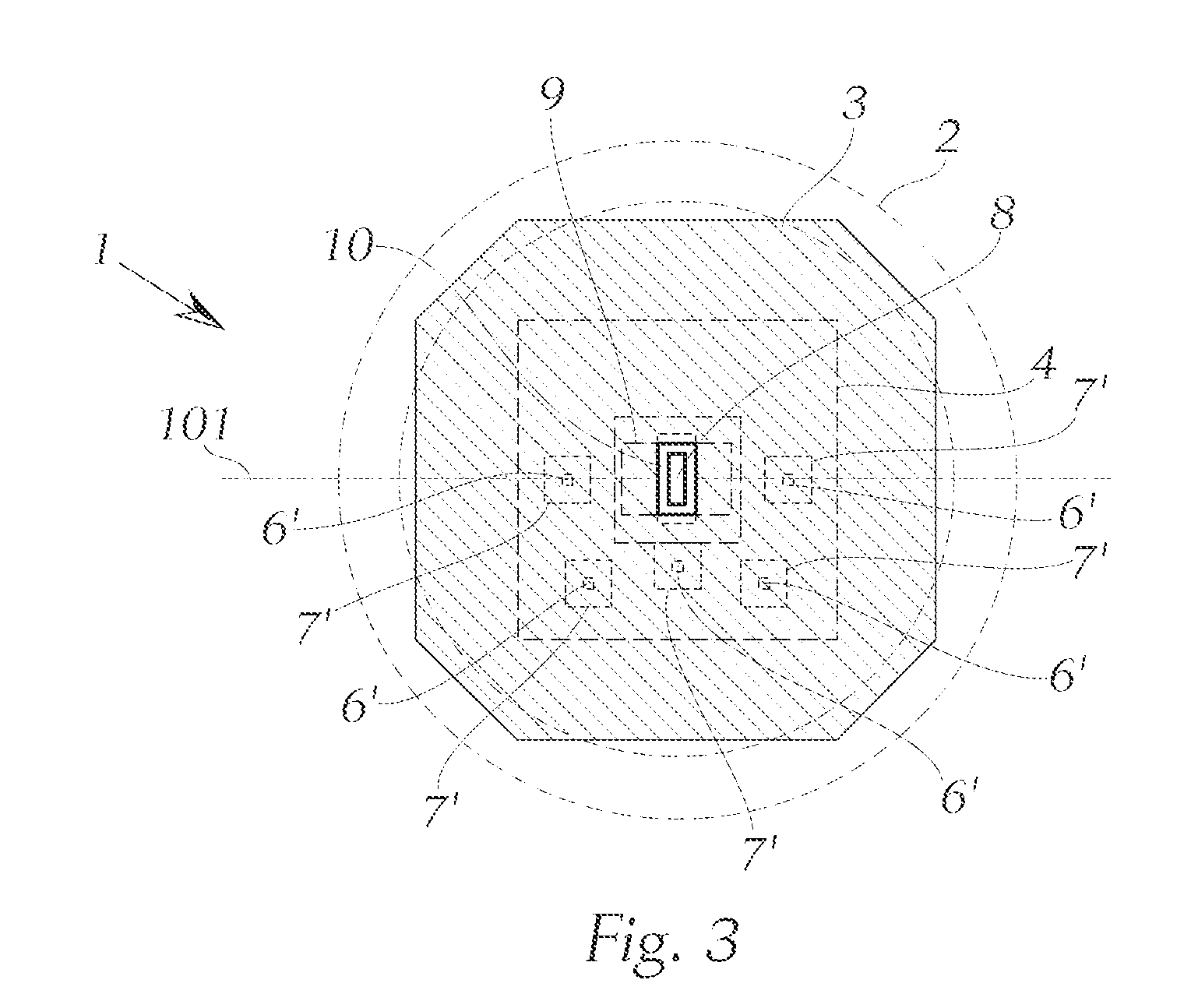
The invention relates to an LED light module for a motor vehicle, or for a headlight for a motor vehicle, wherein the light module comprises a lens and an LED light source, wherein according to the invention a diffusion disk is disposed between the LED light source and the lens as viewed in the light exit direction, wherein the diffusion disk has at least one aperture for the direct passage of at least one component of the light emitted by the LED light source, and wherein the direct component of the light emitted by the LED light source, which component emerges through the aperture of the diffusion disk, is projected through the lens so as to generate a lighting function in the region in front of the motor vehicle.
Owner:ZKW GRP GMBH
A display device and image display method
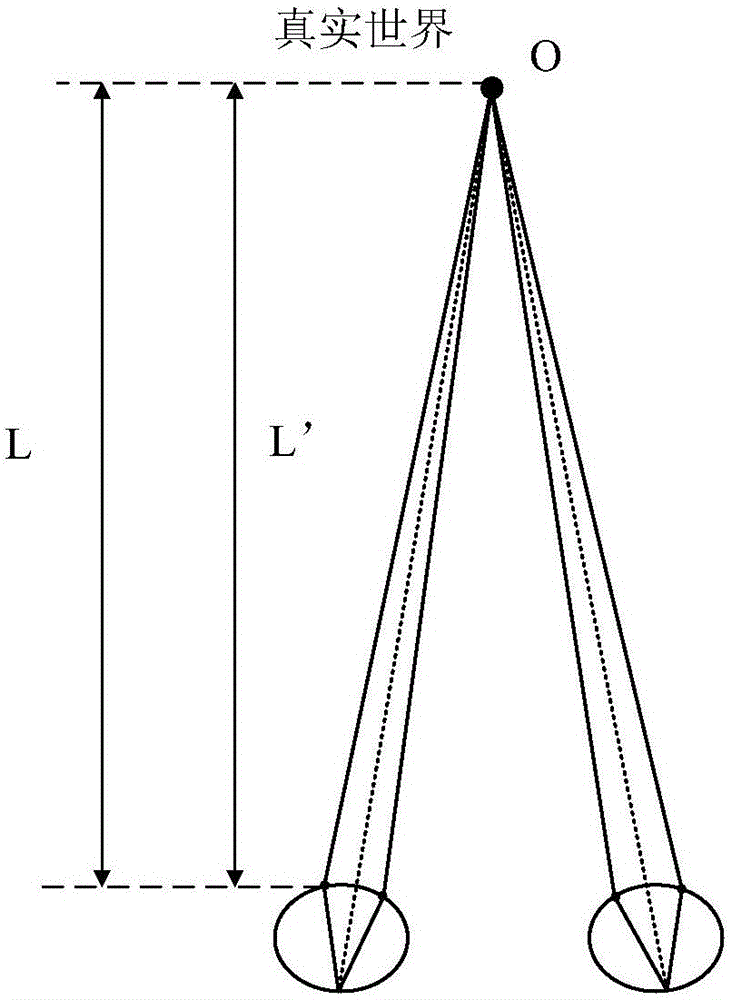
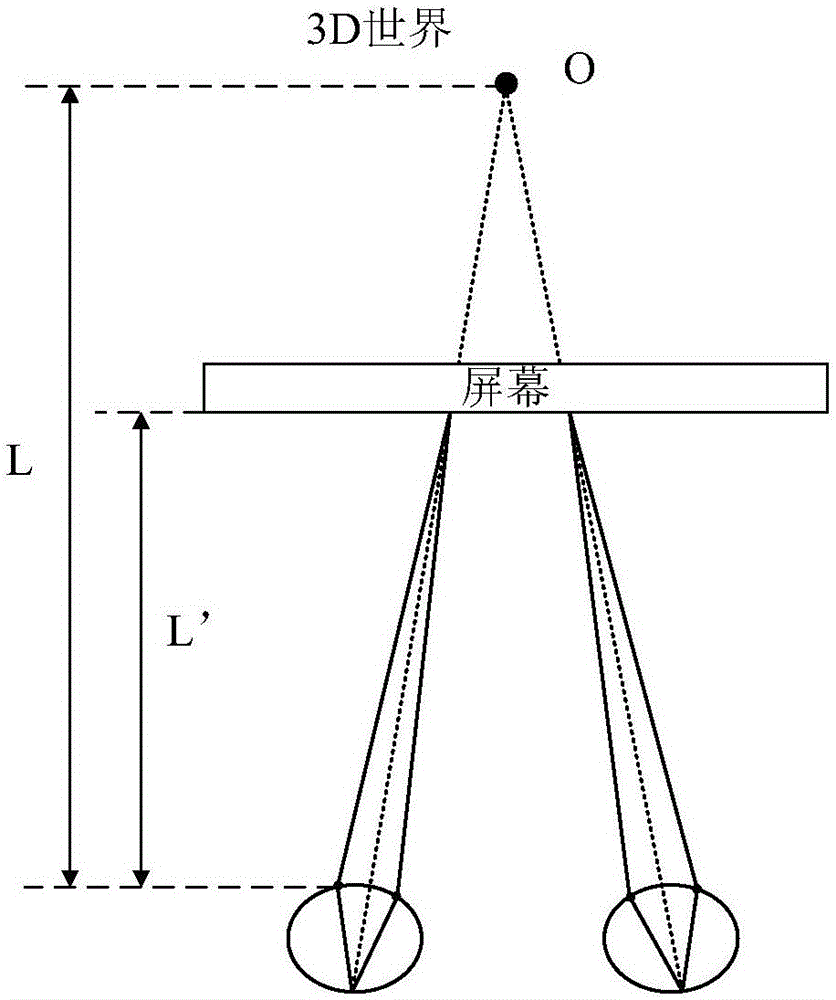
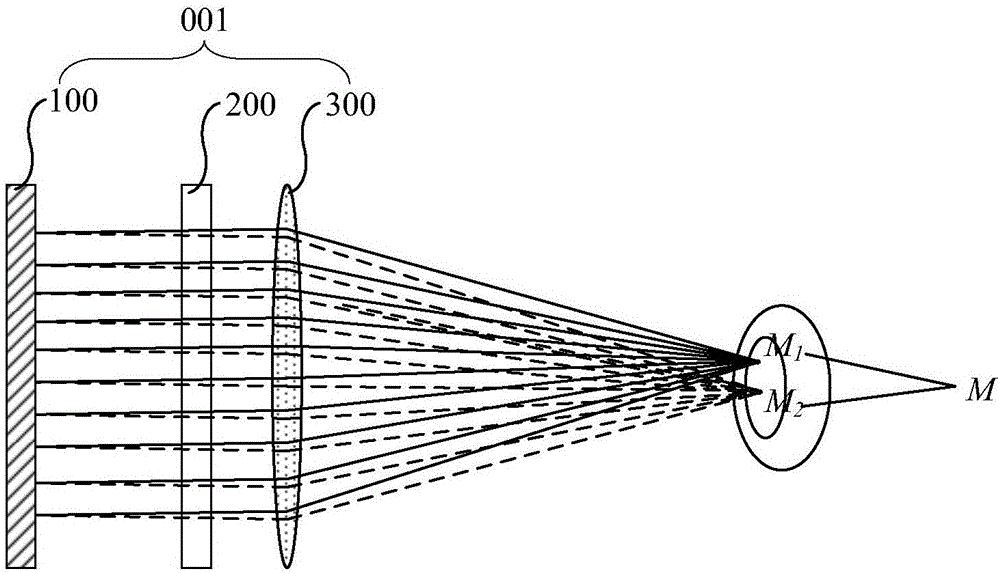
ActiveCN106291958ASolve vertigoPlanar/plate-like light guidesSteroscopic systemsViewpointsDisplay device
The invention provides a display device and image display method which is related to display technology filed. The display device is able to provide hardware support for the same monocular focus distance and binocular convergence distance. The display device comprises sequentially set backlight module, display module and light directing component. The backlight module is used for periodically sending out S collimated lights in different directions. The collimated lights in different directions go through the display module to reach the light directing component, wherein S>=2. The light directing component is used for collecting the collimated lights with the same incident direction to the same preset viewpoint, and different incident directions to the different preset viewpoints. Wherein, the preset viewpoints belonging to the same eye among S preset viewpoints constitute a viewpoint group, and the viewpoint group contains at least two preset viewpoints, while different viewpoint groups locate in different eyeballs.
Owner:BOE TECH GRP CO LTD
Apparatus for the collection and transmission of electromagnetic radiation
InactiveUS7369735B2Avoid radiationSolar heating energySolar heat collector controllersRefractive indexDirect component
Owner:BIOSYNERGETICS INC
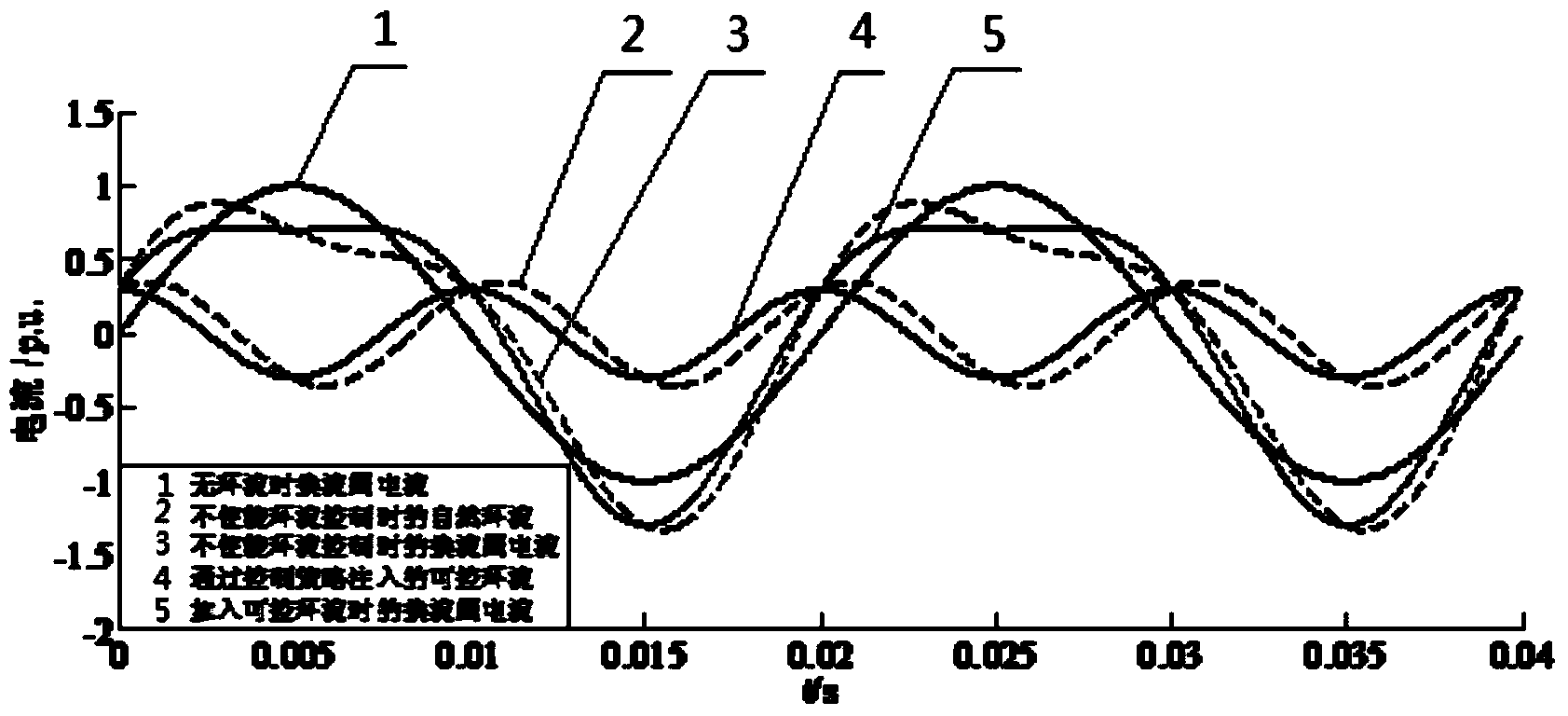
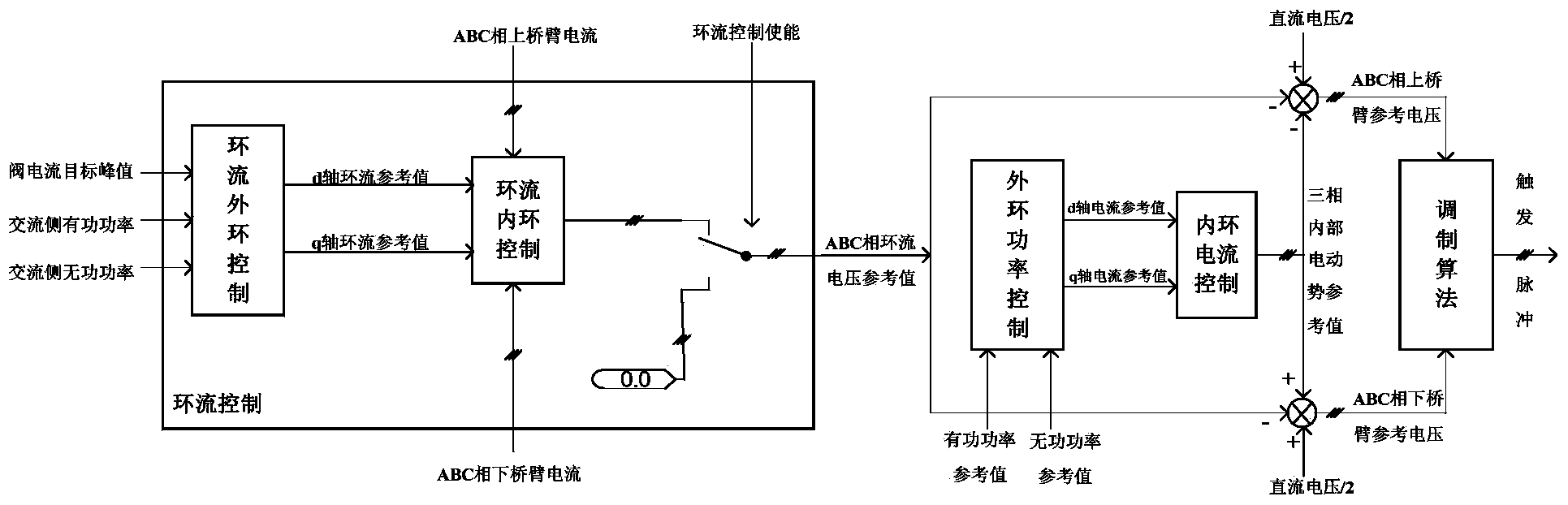
Circulation control strategy for reducing current peak of flexible HVDC (High Voltage Direct Current Transmission) converter valve
ActiveCN104333032AReduce peak currentImprove traversal abilityElectric power transfer ac networkPeak valueEngineering
The invention discloses a circulation control strategy for reducing the current peak of a flexible HVDC (High Voltage Direct Current Transmission) converter valve. The flexible HVDC converter valve is a modular multi-level voltage source type converter valve. According to the circulation control strategy, second harmonic frequency circulation components are superimposed on the basis of fundamental currents and direct components of the converter valve, and the second harmonic frequency circulation components are circulation components generated by the circulation control strategy with controllable amplitude and phase angle, or natural circulation introduced under the control of not-enabled circulation. The circulation control strategy can reduce the current peak of the converter valve, especially reduce the current peak of a faulted rear axle arm on the alternating current side so that the current peak of the faulted rear axle arm cannot exceed the overcurrent protection threshold of the axle arm, and the alternating current fault ride-through capability of the HVDC system is improved. The circulation control strategy is simple in principle, clear in thinking and easy to achieve.
Owner:BEIJING RONGXIN HUIKE TECH
Phase-locked loop
InactiveUS20140043014A1Pulse automatic controlVoltage-current phase angleFundamental frequencyThree-phase
A phase-locked loop and method for estimating a phase angle of a three-phase reference signal is disclosed, which includes an adaptive quadrature signal generator configured to calculate an estimated first state and an estimated second state of a model of an unbalanced three-phase system at a fundamental frequency of the reference signal on a basis of the reference signal and an estimated fundamental frequency; a reference frame transformation block configured to calculate a direct component and a quadrature component in a rotating reference frame synchronous with an estimated phase angle on a basis of the fundamental positive sequence component and the estimated phase angle, and configured to determine an estimate of an amplitude of the fundamental positive sequence component on the basis of the direct component; and an estimator configured to determine estimates of the estimated fundamental frequency and the estimated phase angle on the basis of the quadrature component.
Owner:ABB TECH AG
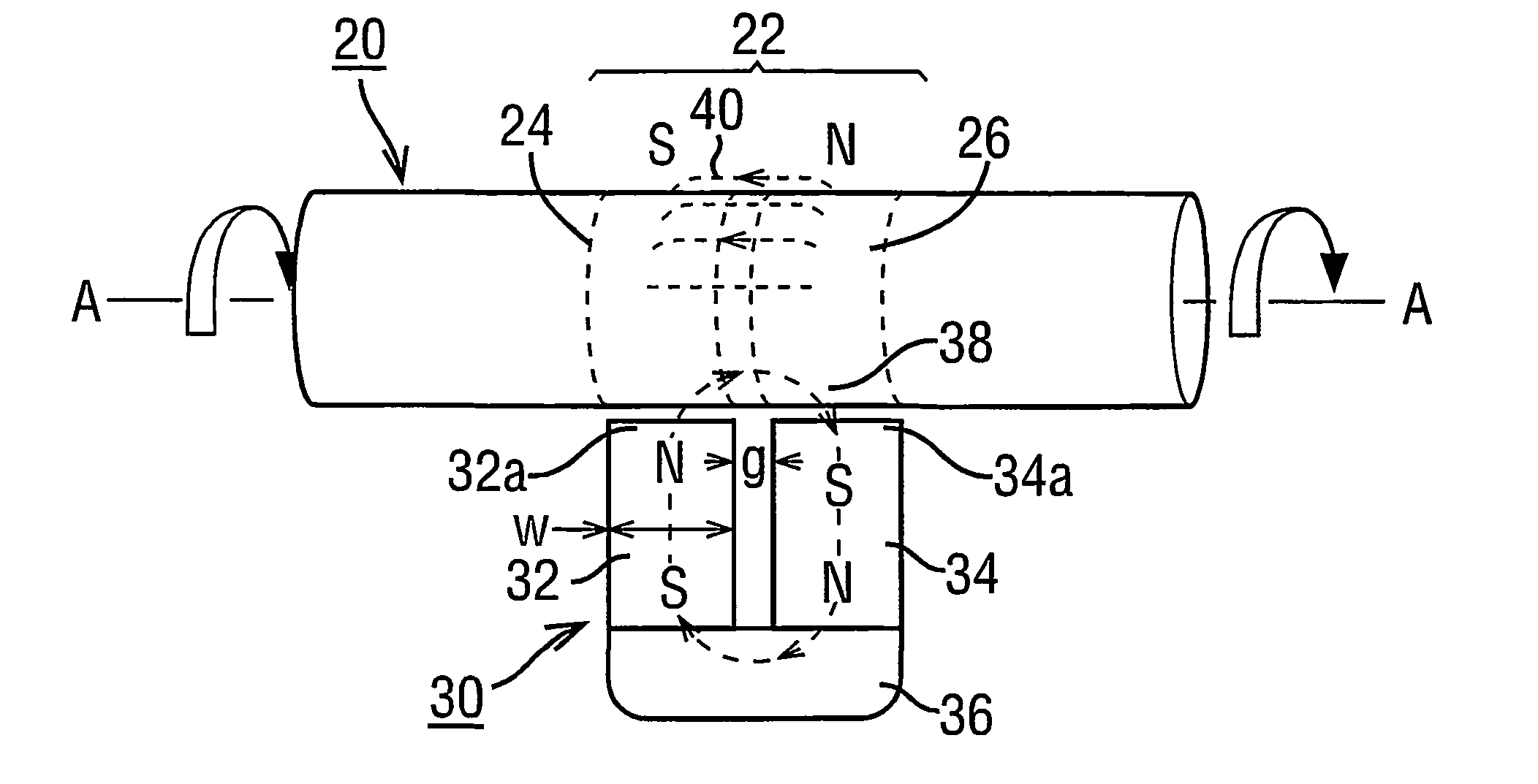
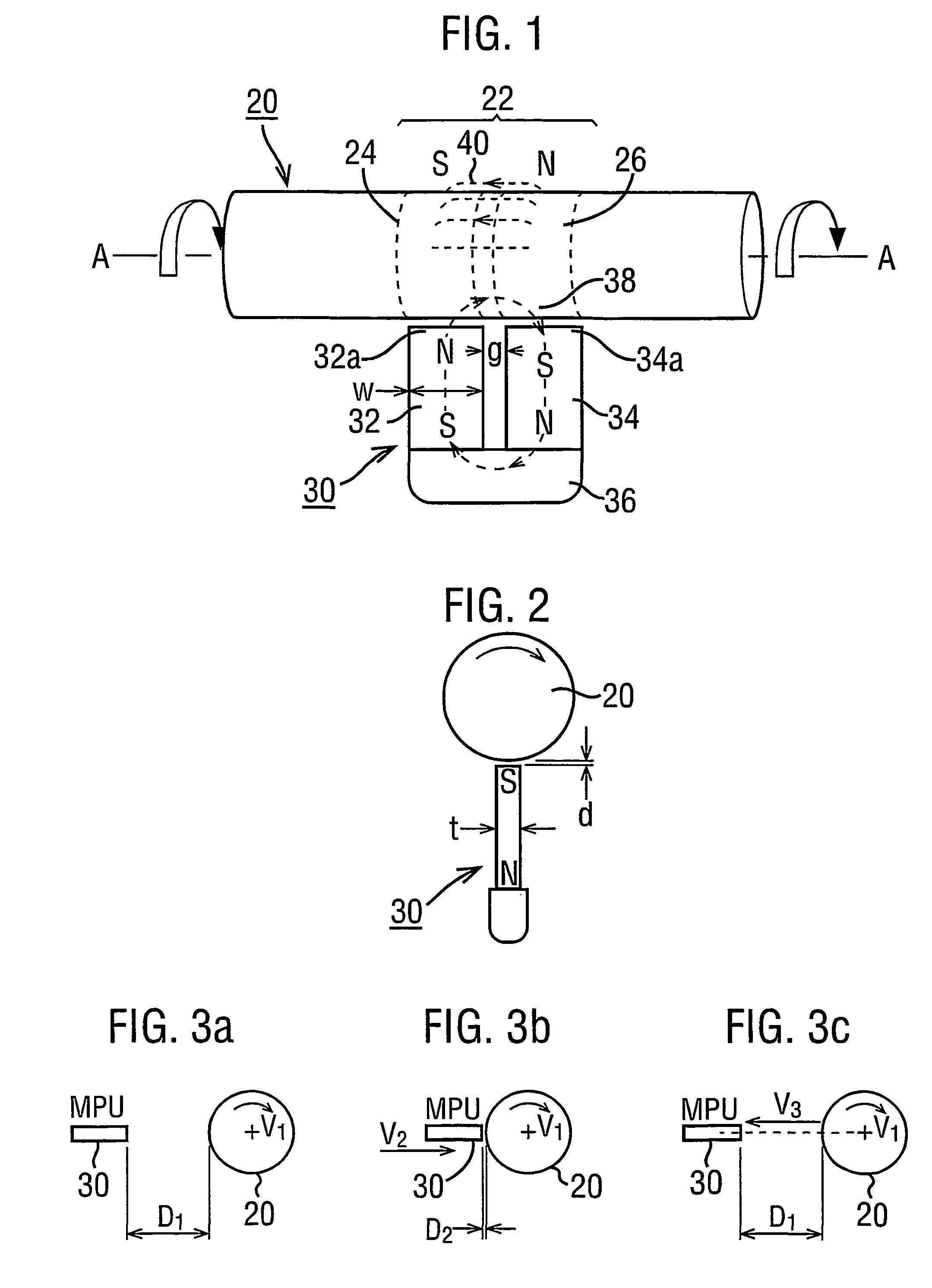
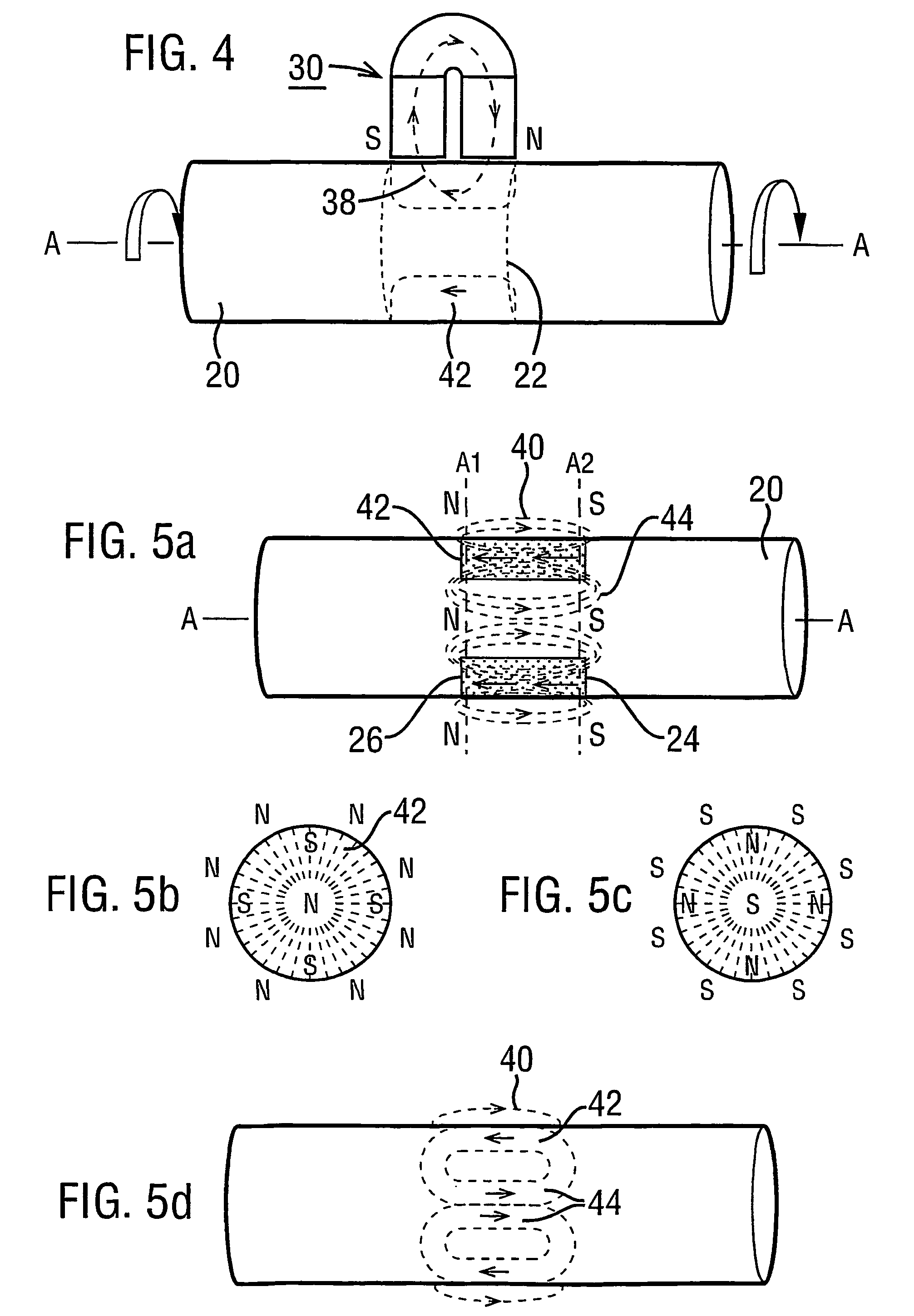
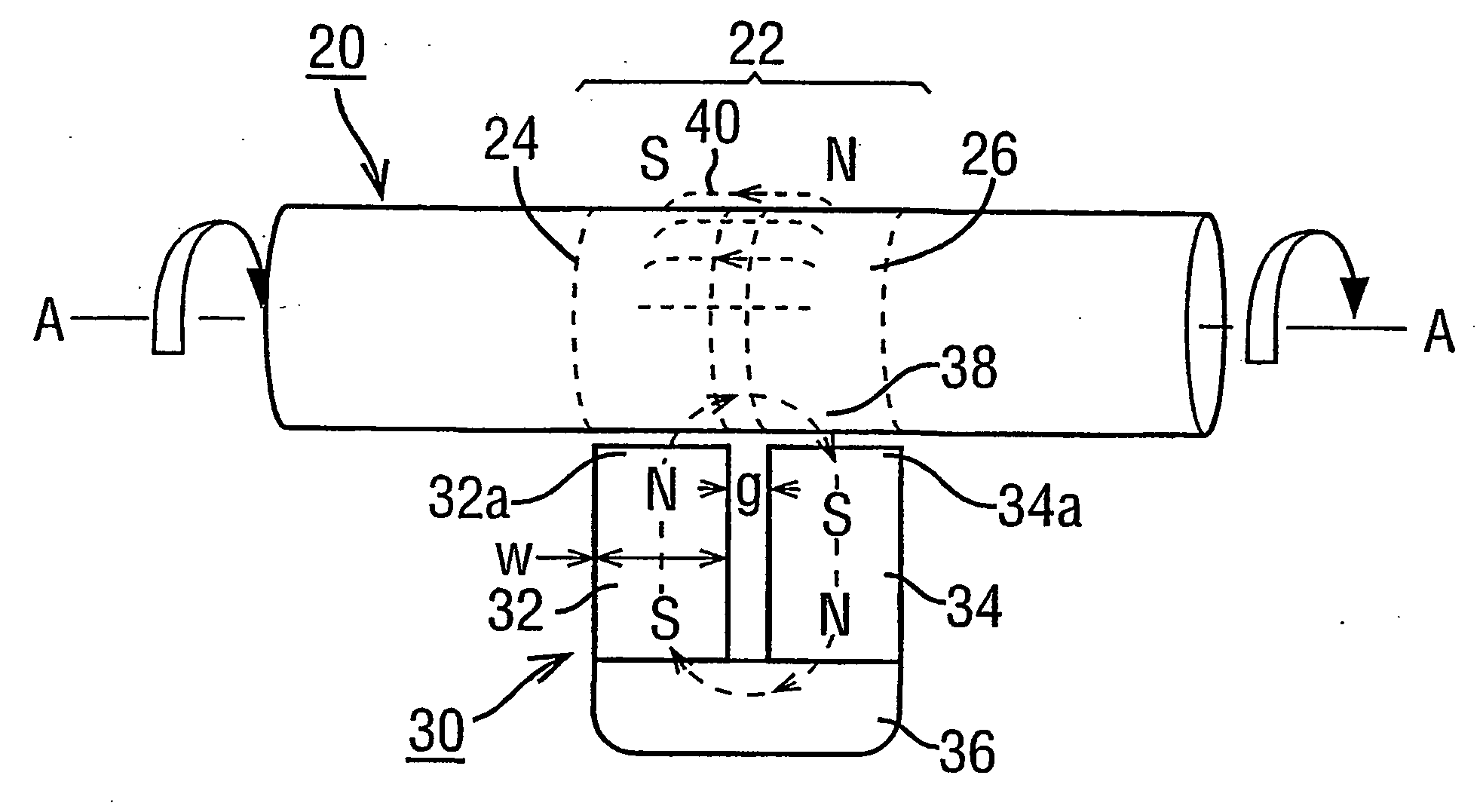
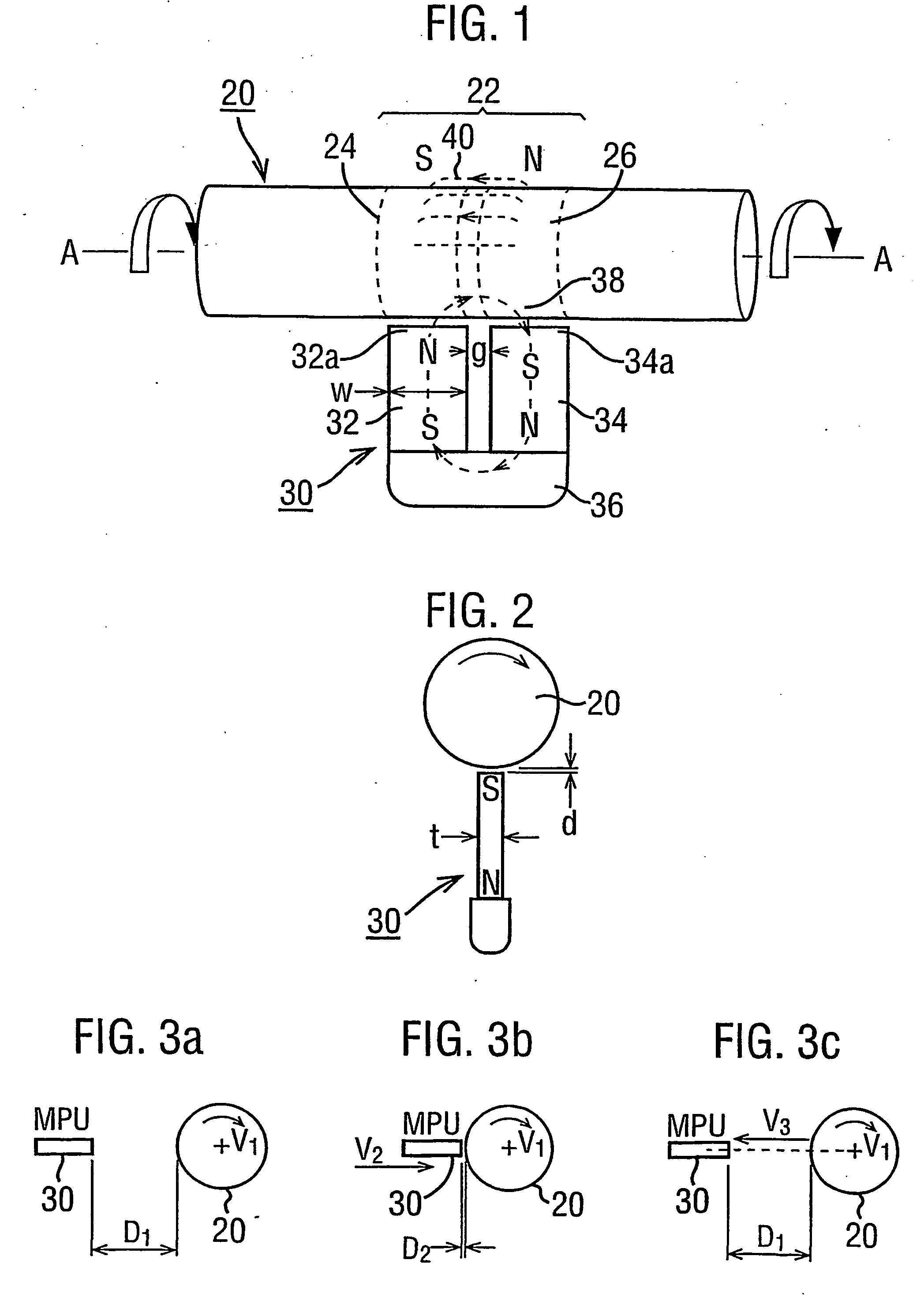
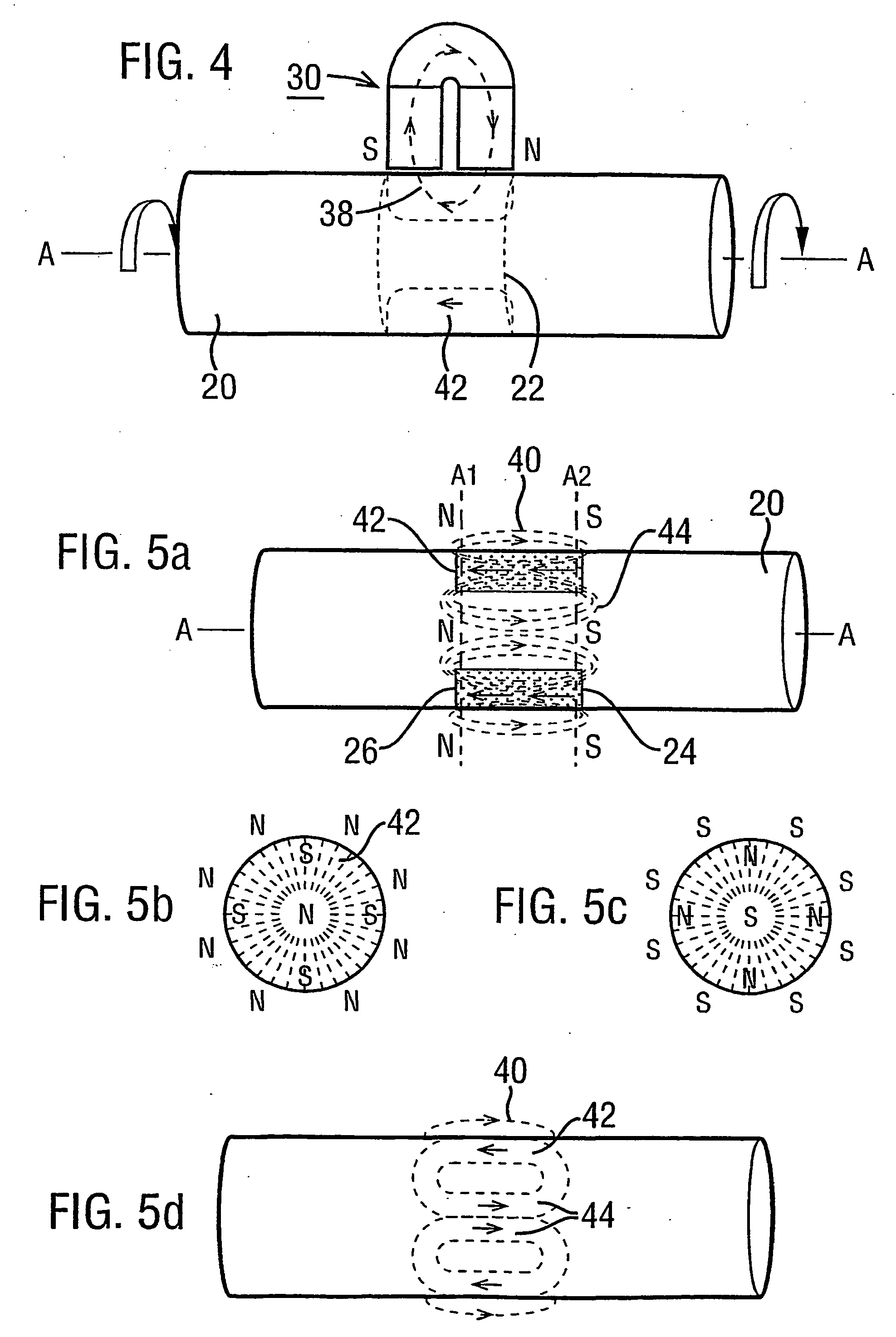
Magnetic transducer torque measurement
A magnetic transducer element (22) is formed by rotating an integral region of a shaft (20) about an axis (A—A) in the presence of a magnetic source (30). An annulus (42) of magnetisation results in having its magnetisation in the axial direction. The exterior magnetic field (40) emanated by the annulus (42) exhibits respective axial magnetic profiles of its axially and radially directed components (FIGS. 7 and 8) which have an axial shift under torque. The direction of profile shift depends on the rotational direction of the shaft (20) while magnetisation proceeds. A pair of regions (122a, 122b: 242, 244) exhibiting opposite shift directions provide signals in which torque-dependent shift is separated from axial displacements of the shaft (FIG. 22, FIG. 24). An annulus (42) of magnetisation may be non-uniform with angle about the shaft axis. Measures to prevent eddy currents generated in the rotating region of the shaft under magnetisation are disclosed as are “sweet spots” (230) for sensor placement (FIG. 30) to mitigate non-uniformity effects.
Owner:ABAS
Magnetic transducer torque measurement
A magnetic transducer element is formed by rotating an integral region of a shaft about an axis in the presence of a magnetic source. An annulus of magnetization results in having its magnetization in the axial direction. The exterior magnetic field emanated by the annulus exhibits respective axial magnetic profiles of its axially and radially directed components which have an axial shift under torque. The direction of profile shift depends on the rotational direction of the shaft while magnetization proceeds. A pair of regions exhibiting opposite shift directions provide signals in which torque-dependent shift is separated from axial displacements of the shaft. An annulus of magnetization may be non-uniform with angle about the shaft axis. Measures to prevent eddy currents generated in the rotting region of the shaft under magnetization are disclosed as we “sweet spots” for sensor placement to mitigate non-uniformity effects.
Owner:ABAS
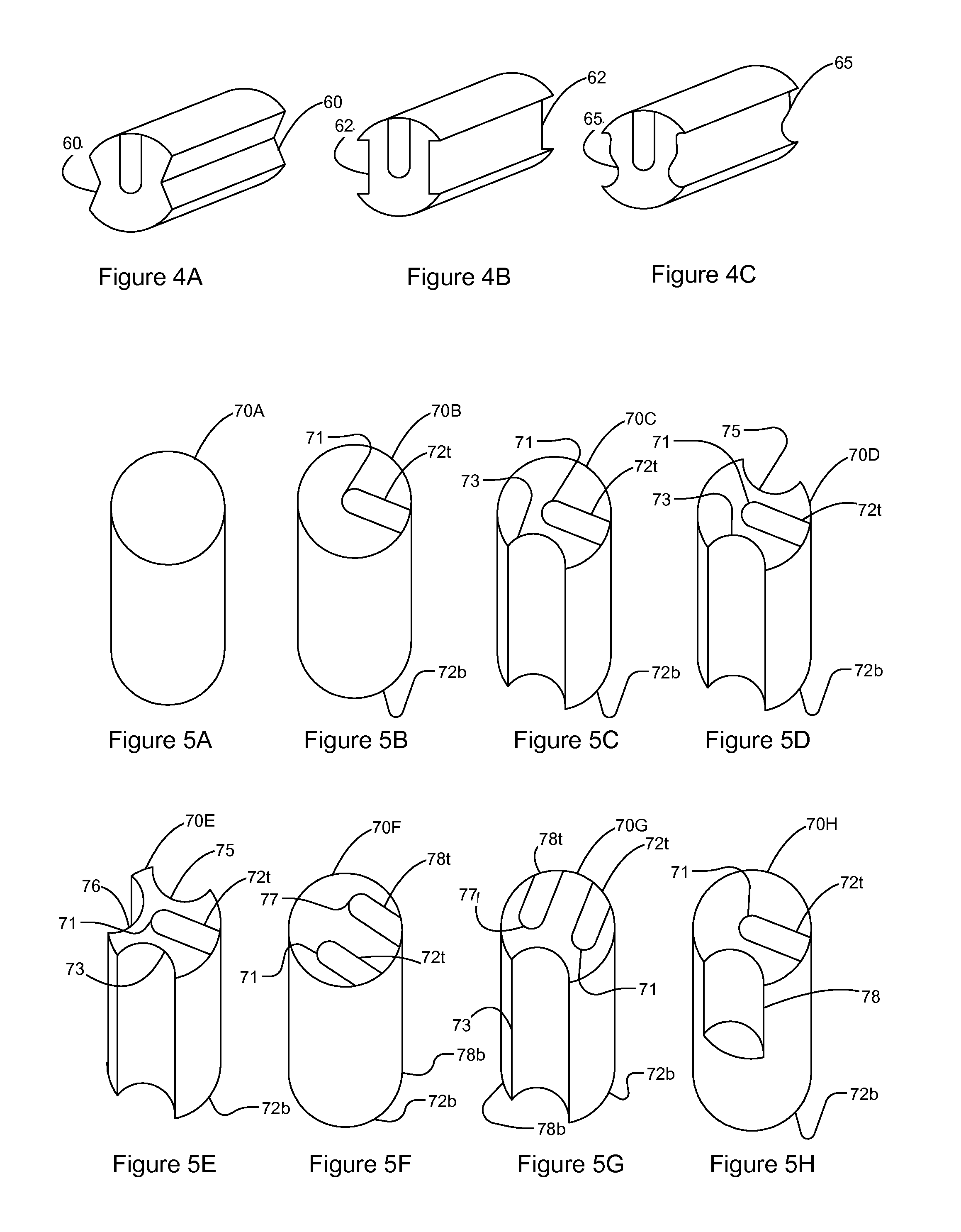
Continuous Extrusion Process for Manufacturing a Z-directed Component for a Printed Circuit Board
A method for manufacturing a Z-directed component for insertion into a mounting hole in a printed circuit board according to one example embodiment includes simultaneously extruding a plurality of materials according to the structure of the Z-directed component to form an extruded object and forming the Z-directed component from the extruded object. In one embodiment, the extruded object is divided into individual Z-directed components. In one embodiment, the timing of extrusion between predetermined sections of one of the materials is varied in order to stagger the sections in the extruded object.
Owner:LEXMARK INT INC
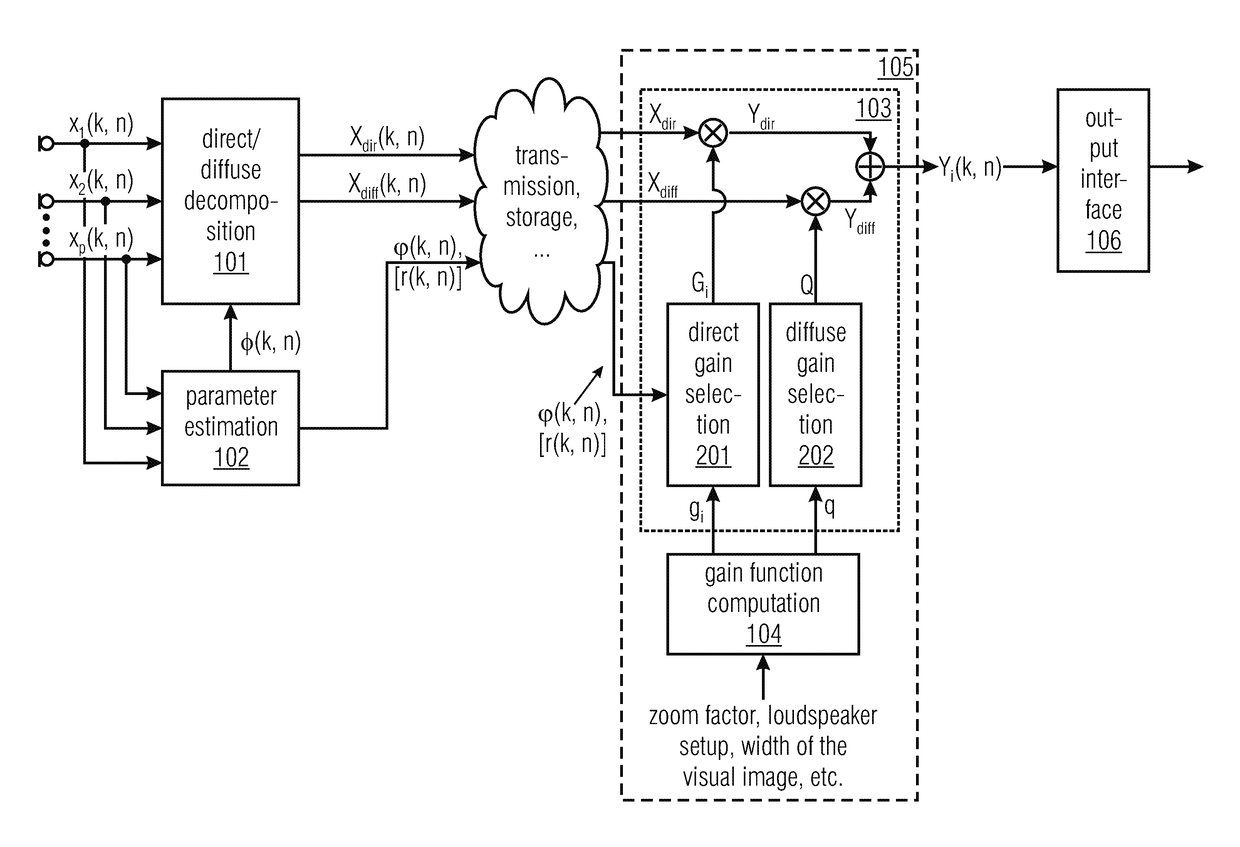
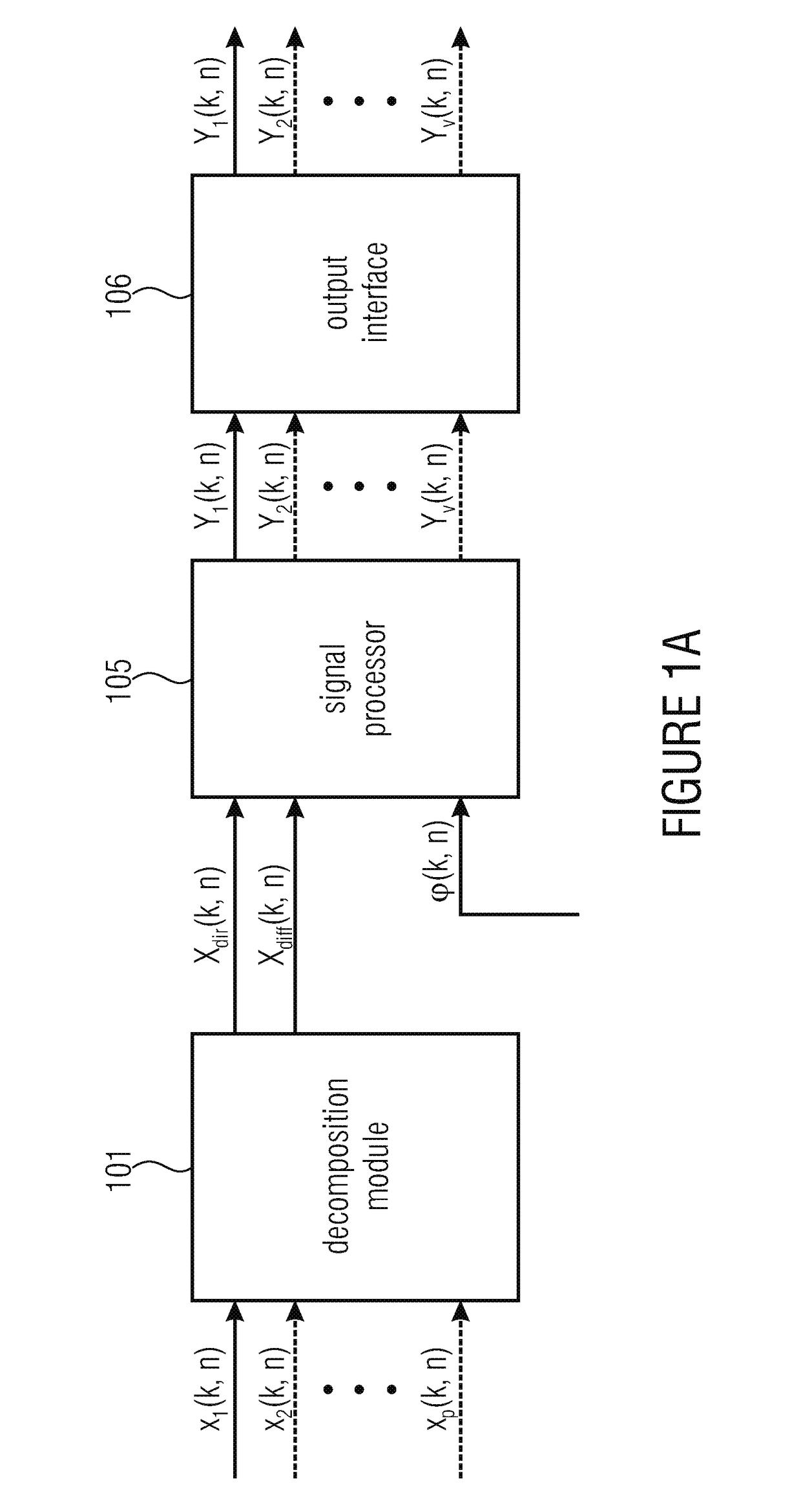
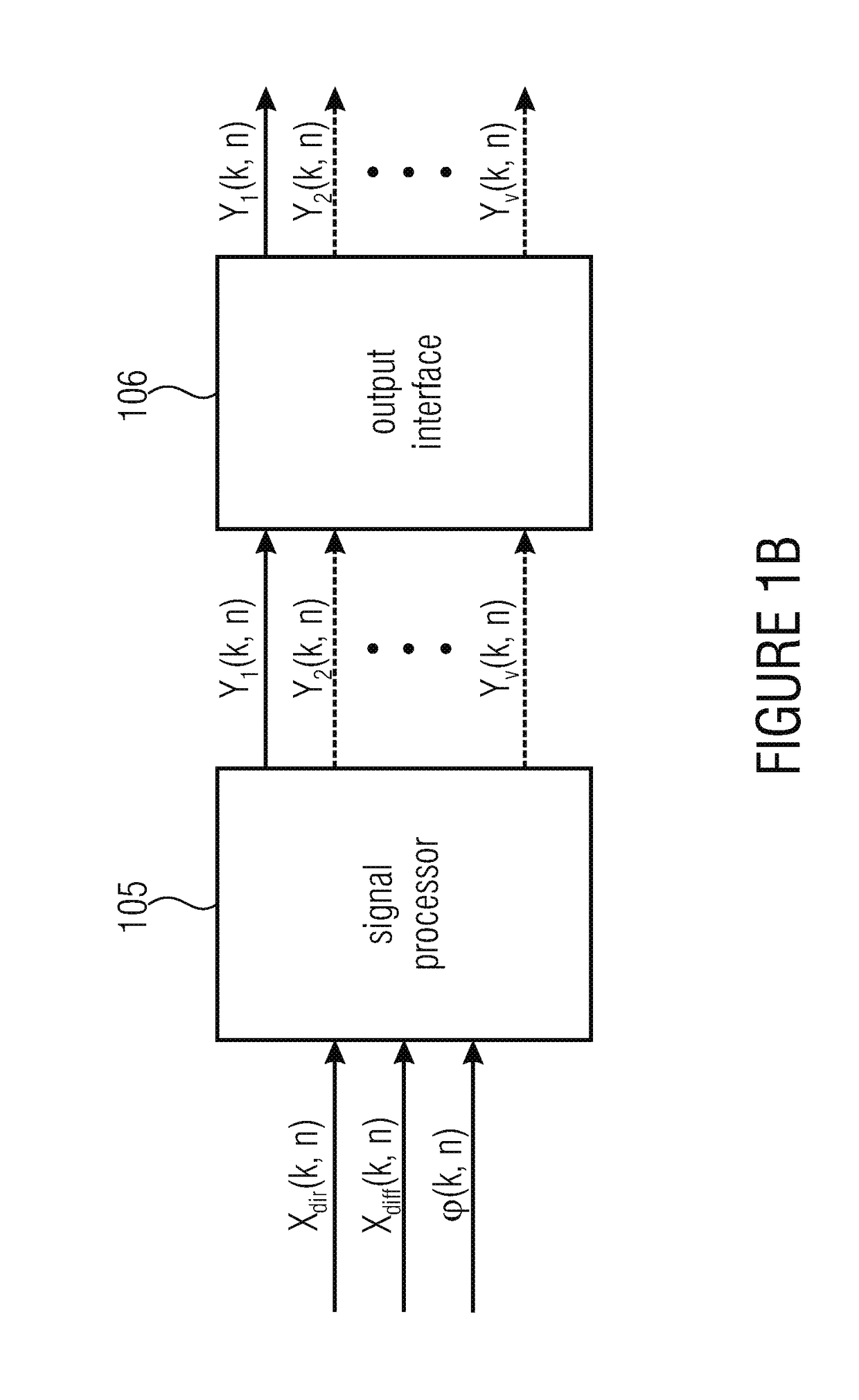
System, apparatus and method for consistent acoustic scene reproduction based on adaptive functions
A system for generating one or more audio output signals is provided, having a decomposition module, a signal processor, and an output interface. The signal processor is configured to receive the direct component signal, the diffuse component signal and direction information. Moreover, the signal processor is configured to generate one or more processed diffuse signals depending on the diffuse component signal. For each audio output signal of the one or more audio output signals, the signal processor is configured to determine a direct gain, the signal processor is configured to apply the direct gain on the direct component signal to obtain a processed direct signal, and the signal processor is configured to combine the processed direct signal and one of the one or more processed diffuse signals to generate the audio output signal. The signal processor further has a gain function computation module and a signal modifier.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
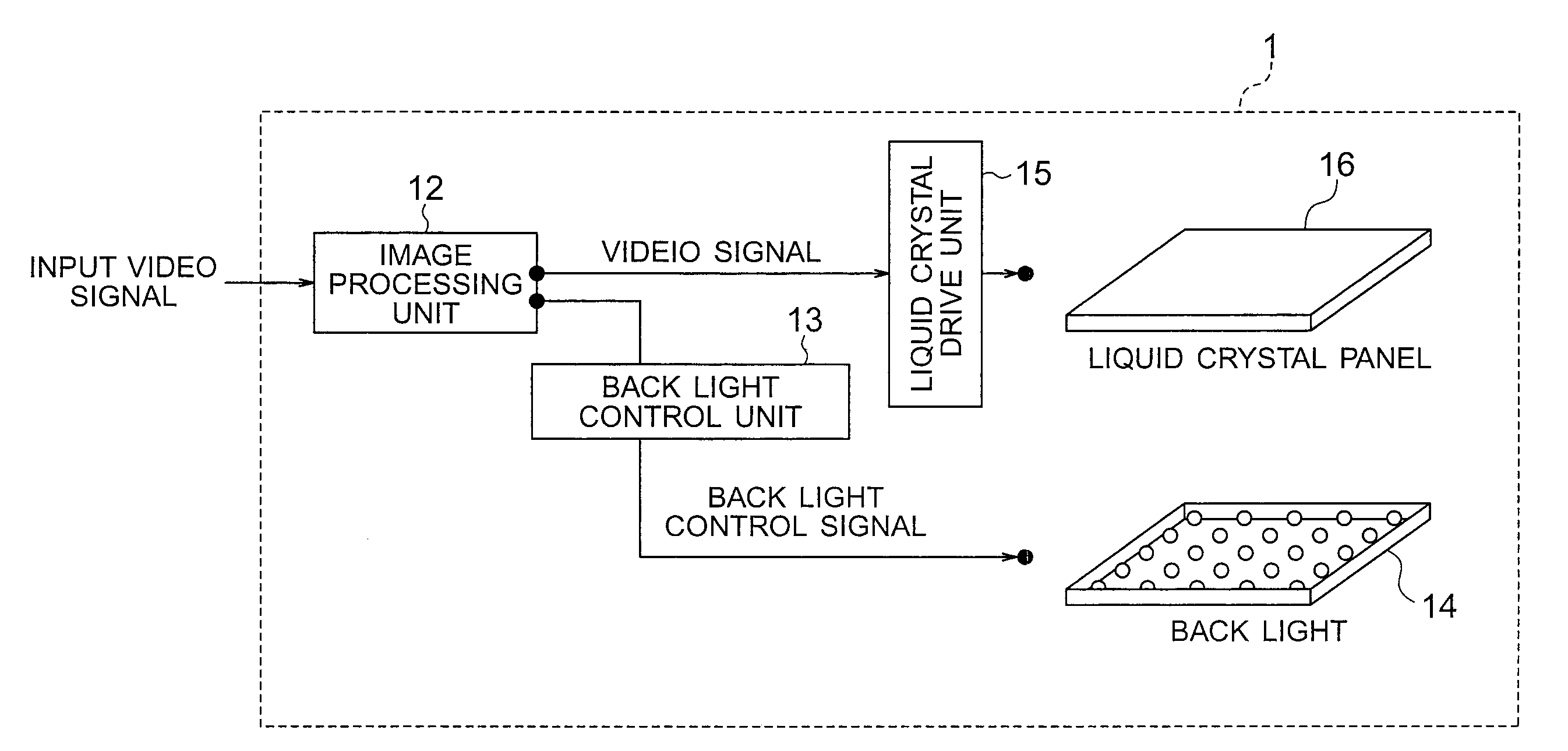
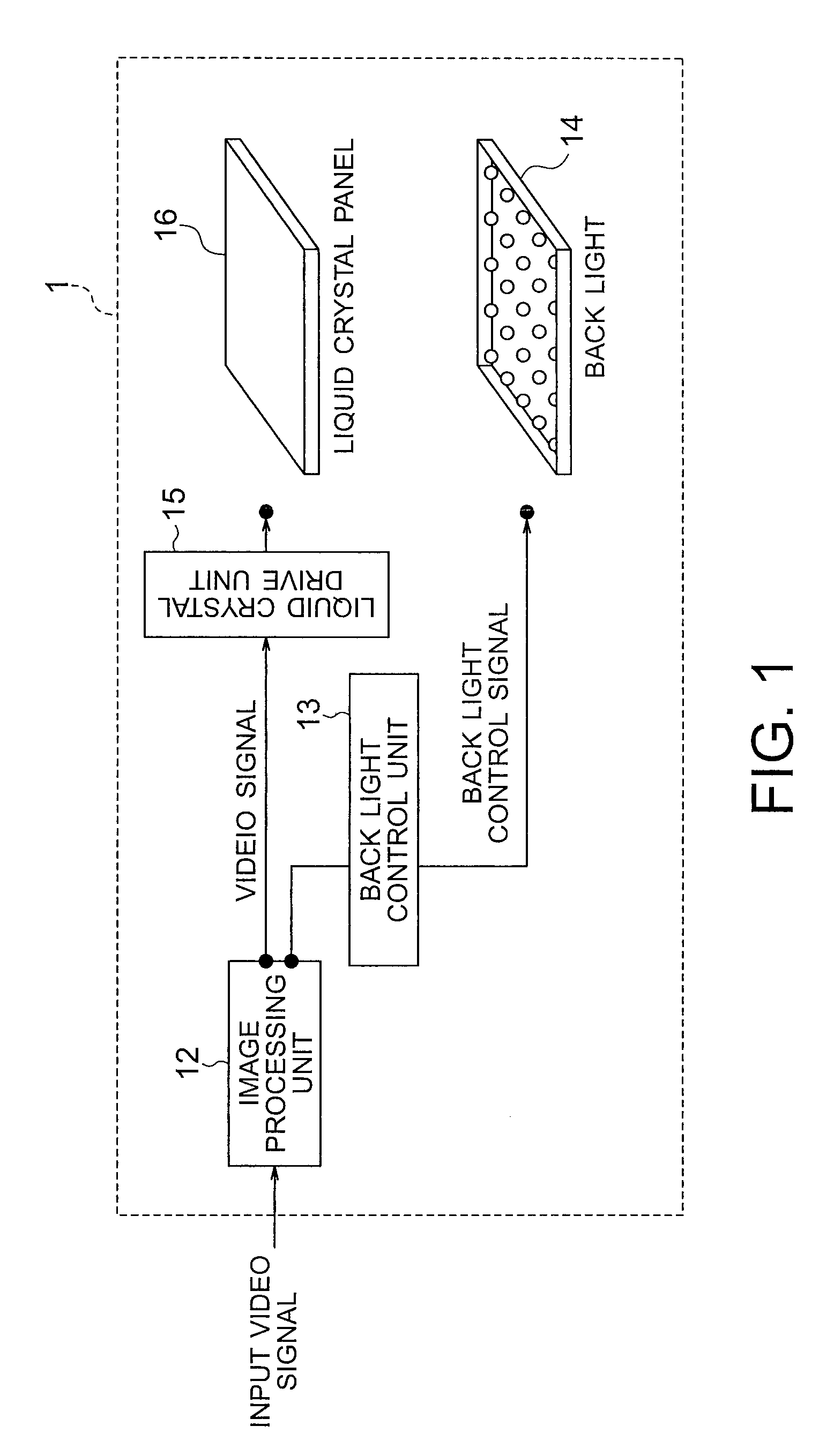
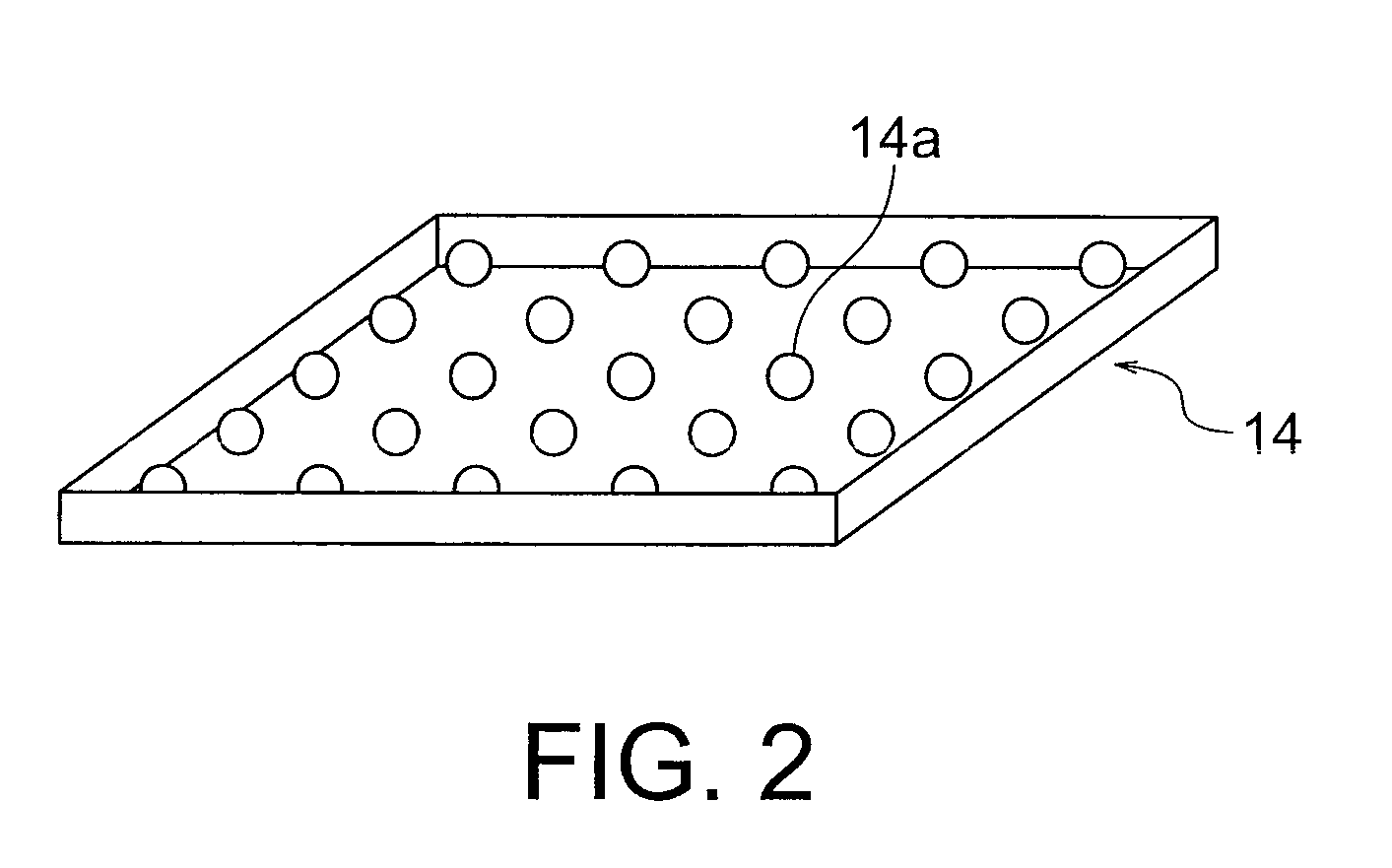
Liquid crystal display apparatus
ActiveUS20090201245A1Suppression of uneven brightnessAvoid convenienceStatic indicating devicesNon-linear opticsLiquid-crystal displayImaging processing
A liquid crystal display apparatus includes: a liquid crystal panel having a plurality of pixels arranged in a matrix form; a back light having a plurality of light sources controlled individually in light emission luminance to supply light to the liquid crystal panel; an image processing unit configured to calculate luminance setting values respectively of the light sources of the back light and correct the video signal; a back light control unit configured to control the back light on the basis of luminance setting values; and a liquid crystal drive unit configured to drive the liquid crystal panel on the basis of the corrected video signal. In strength distribution of light incident, a relative strength compared with a direct component in spatial frequency domain is equal to or less than a first threshold in a spatial frequency region having a value of at least 1.
Owner:HISENSE VISUAL TECH CO LTD
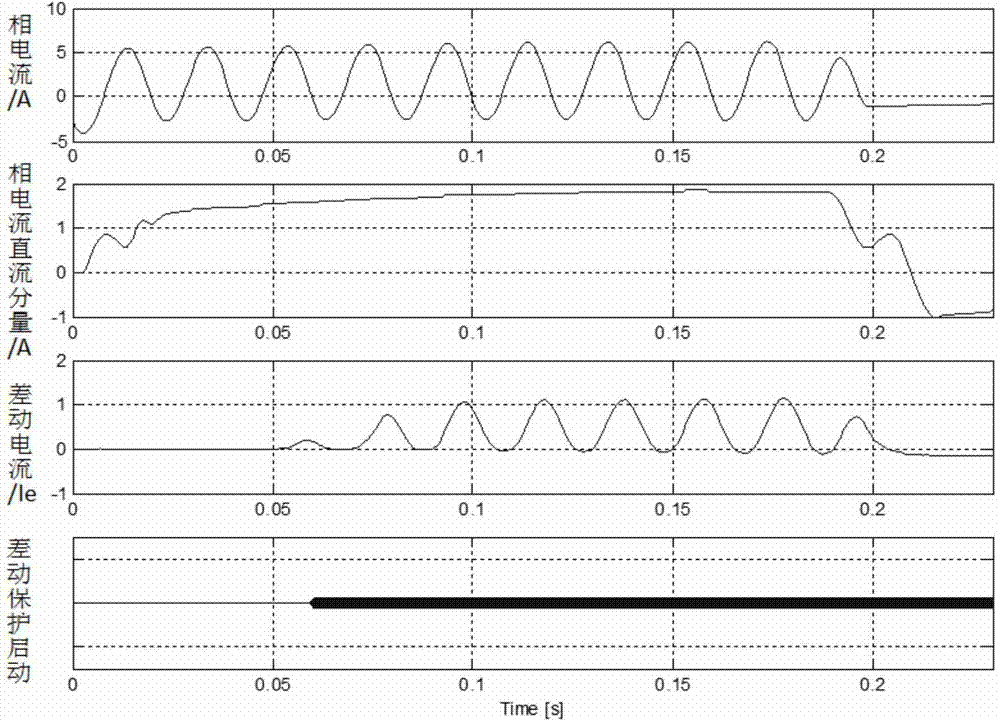
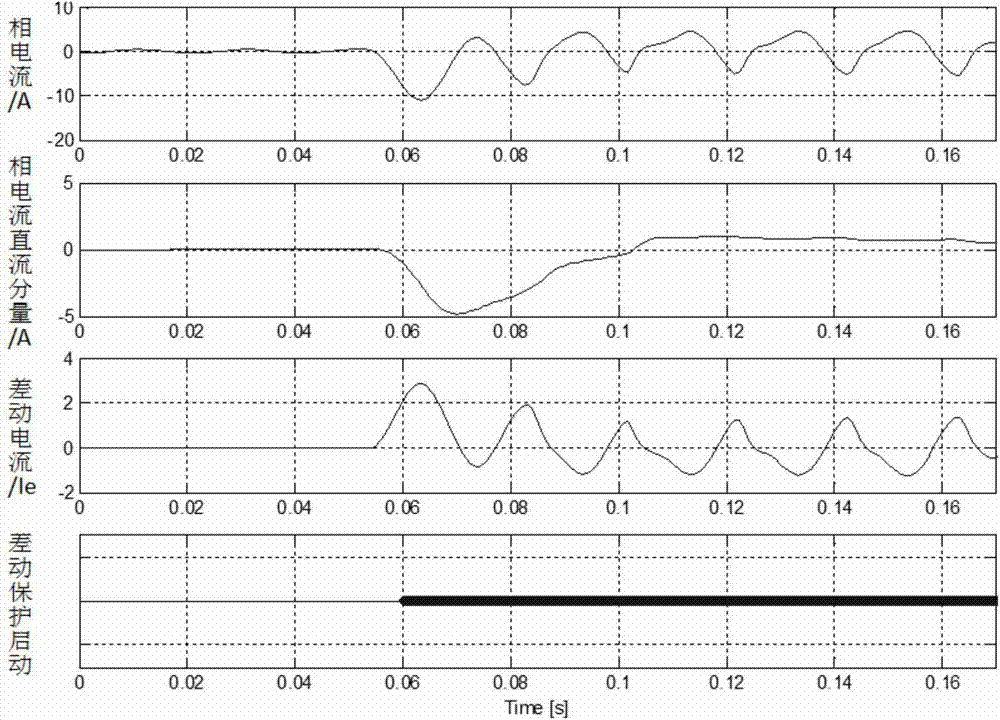
Method for preventing wrong differential protection of motor and transformer caused by induced inrush current
ActiveCN103872646AAvoid misuseThe criterion is simple and reliableEmergency protective circuit arrangementsPhase currentsDirect component
The invention discloses a method for preventing wrong differential protection of a motor and a transformer caused by induced inrush current. The method comprises the steps of detecting the direct component of each phase current of the motor and the transformer, if one phase or multiple phases are rapidly increased and each phase of differential current of differential protection is small than a starting fixed value in the afterward T1 time period, determining the condition that an outer fault and / or the induced inrush current occurs, and performing differential protection with the blocking ratio in the afterward T2 time period; during the blocking period, if the differential current and the phase current are synchronously rapidly increased, determining the internal fault and unblocking. The internal fault and induced inrush current (or external fault) can be distinguished by detecting whether the rapid increment of the direct current component of the phase current and the differential current occur synchronously or not, and the false operation of the ratio differential protection is prevented by a short blocking measure; if the internal fault occurs again in the blocking period, the unblocking is performed to handle the conversion fault. The method is simple, reliable and easy to realize, and the fixed value is still rectified as usual without affecting the sensitivity of the differential protection.
Owner:NR ELECTRIC CO LTD +1
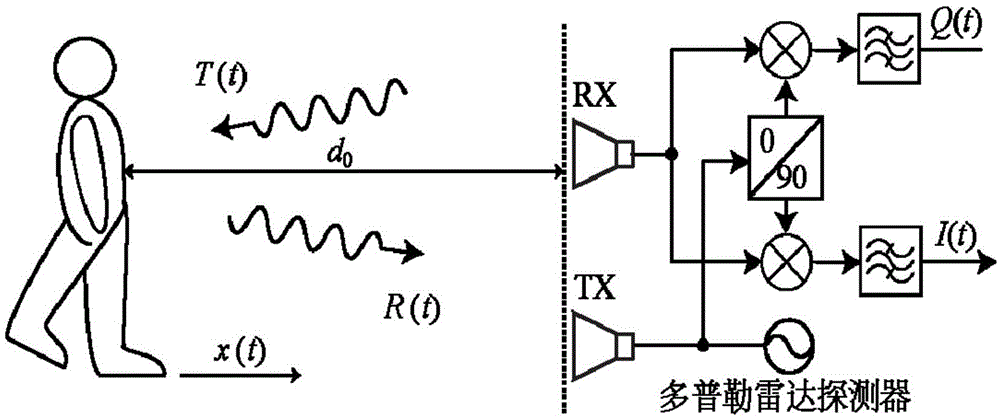
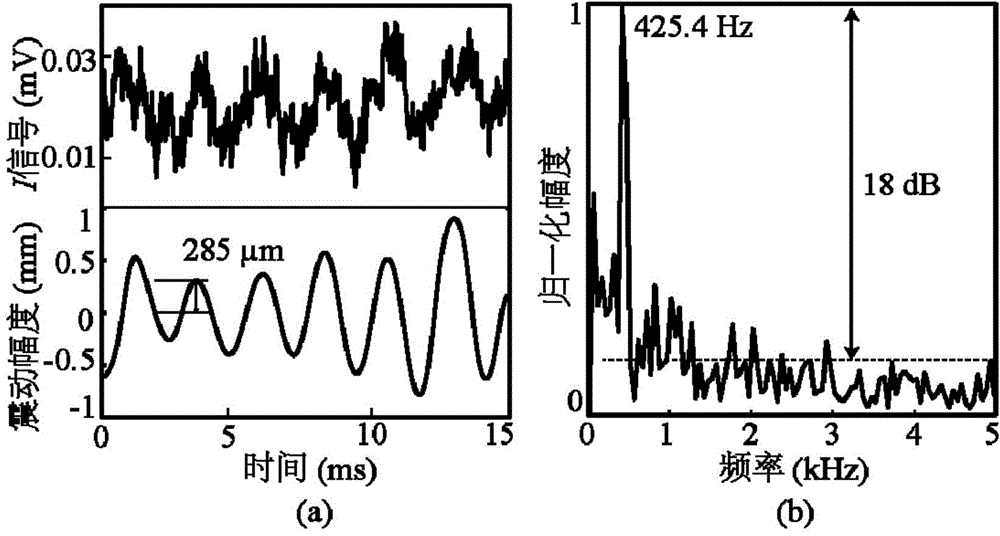
Imaging method for large dynamic range Doppler biological signal
InactiveCN103948381AEnables non-contact large motion detection applicationsSensorsMeasuring/recording heart/pulse rateSmall amplitudeAmbiguity
The invention discloses an imaging method for a large dynamic range Doppler biological signal. A radio frequency front end module emits electromagnetic waves to the surface of a moving living body to be detected by an antenna; a lower frequency conversion module performs digital and orthogonal down-conversion on a signal reflected back to a base band signal; a dynamic circle center tracking algorithm is performed on the base band signal, a useless direct component is removed, a useful direct component is kept, and the characteristic that phase information demodulated by an expanding antitangent algorithm is not limited by phase ambiguity, so that the motion information of the measured object is recovered. Compared with a traditional non-contact biological signal detection system which can only detect small-amplitude motion of the sub-wavelength level, a system related to the method has the advantages of multiple functions and application scenarios, the limitation of the small amplitude motion can be broken through, the method is applied to detection on meter-level multi-wavelength large-amplitude motion, and the related non-contact large-amplitude motion detection applications in the biomedical field and the like are realized.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Network-leveraged real estate transaction assistance system and method
InactiveUS20180060981A1Easy to manageEasy to analyzeGeographical information databasesSpecial data processing applicationsDirect componentComputer science
A network-leveraged real estate transaction assistance system is provided to facilitate matching, engaging, contracting, and communicating between parties to a real estate and / or property rental transaction by a network-leveraged system. The network-leveraged real estate transaction assistance system may include a property rental and real estate transaction assistance platform, database, platform components, renter component, matching component, communication component, broker-assisted component, landlord direct component, landlord management component, lead marketplace component, guaranteed rental income protection, renter profile validation aspect, and tenant exchange. A method for facilitating matching, engaging, contracting, and communicating between parties to a real estate and / or property rental transaction by a network-leveraged system using the network-leveraged real estate transaction assistance system is also provided.
Owner:SHER ROBERT
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com