Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
299 results about "Signaling nodes" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
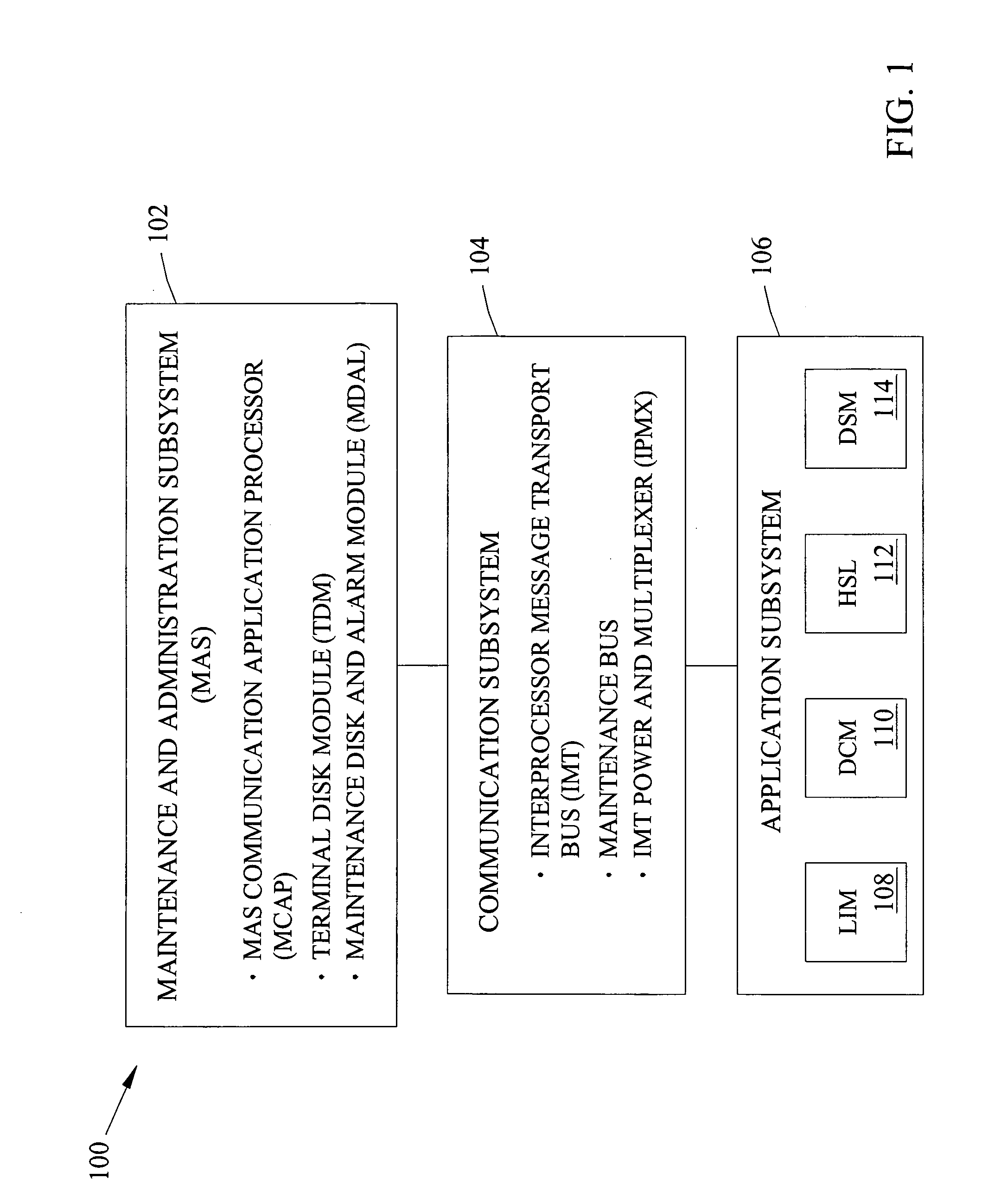
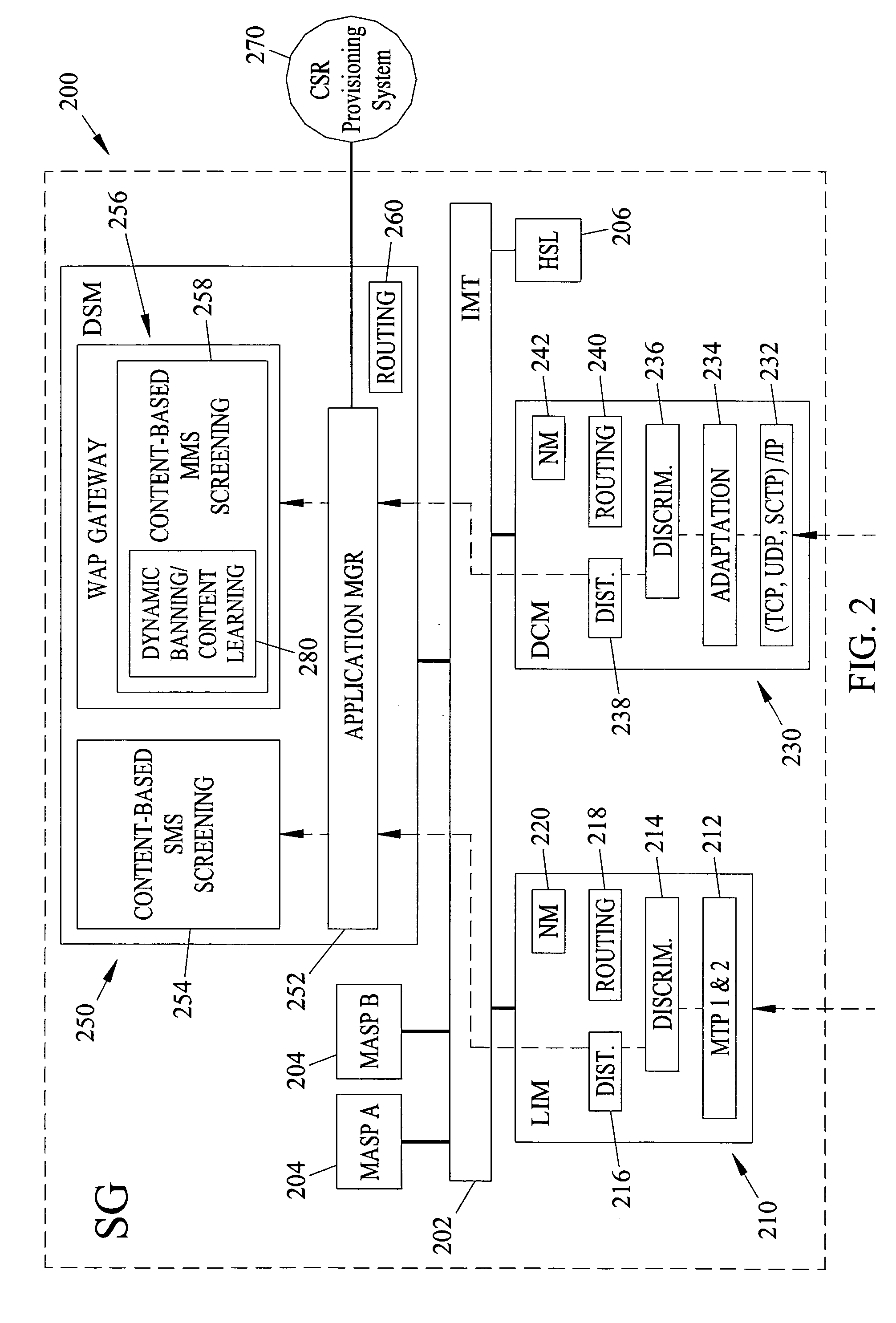
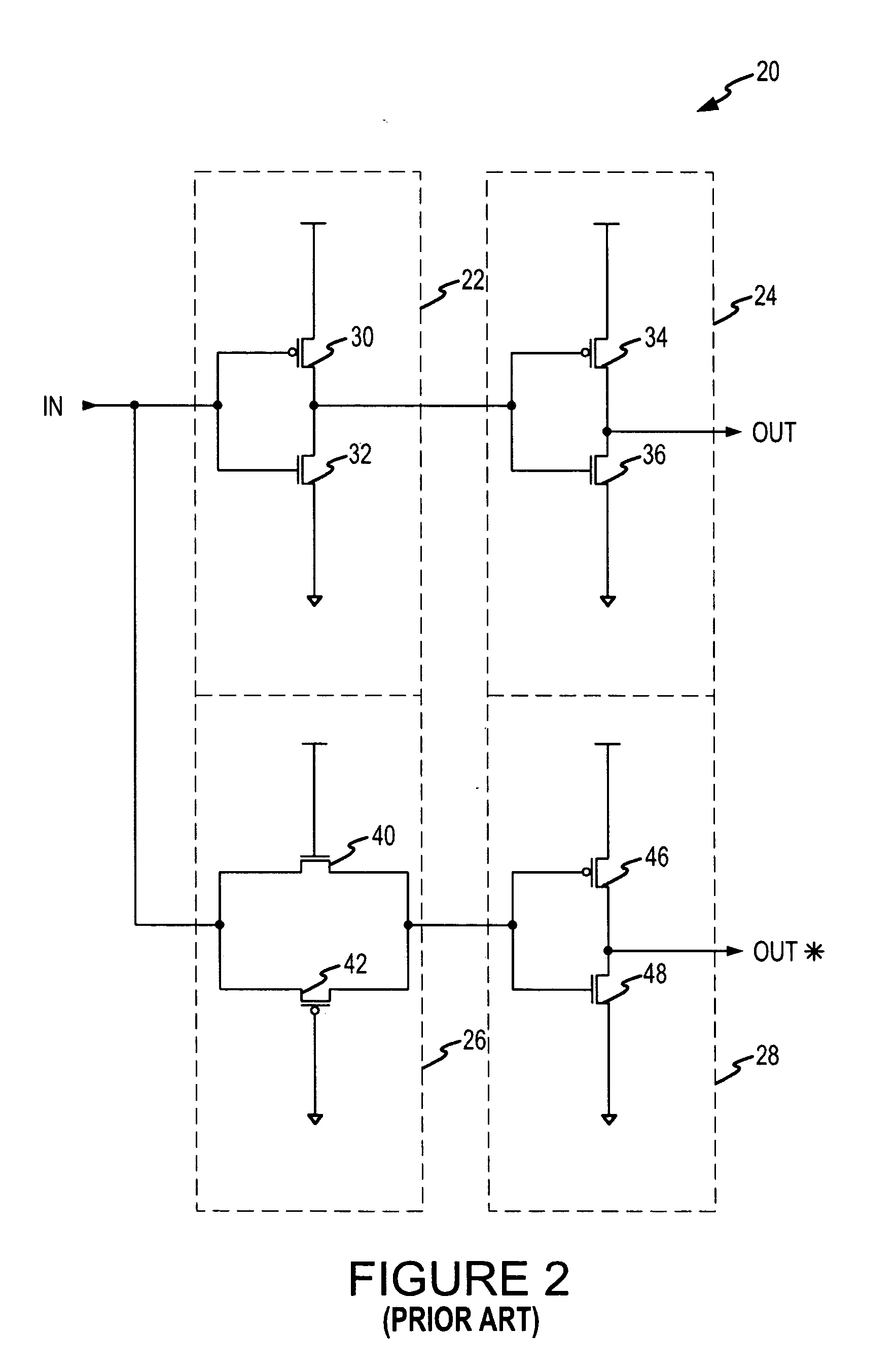
Methods, systems, and computer program products for content-based screening of messaging service messages
ActiveUS7155243B2Reduce loadReduce processing burdenUnauthorised/fraudulent call preventionEavesdropping prevention circuitsSignaling nodesMessage passing
Methods, systems, and computer program products for content-based screening of messaging service (MS) messages, such as short message service messages and multimedia message service messages, are disclosed. MS subscribers may provision specific message content screening rules via a web interface. Content-based MS screening functionality may be applied in the core of a communications network, such as at a network signaling node separate from a short message service center or a mobile terminal.
Owner:TEKELEC GLOBAL INC
Integrated Circuit, Method of Operating an Integrated Circuit, Method of Manufacturing an Integrated Circuit, Memory Module, Stackable Memory Module
InactiveUS20080002481A1Improve performanceIncrease speedCurrent/voltage measurementDigital storageCapacitanceAudio power amplifier
An integrated circuit has a current sense amplifier that includes a voltage comparator having a first input, a second input and an output; a first clamping device coupled between the first input of the voltage comparator and a first input signal node, a second clamping device coupled between the second input of the voltage comparator and a second input signal node, a current mirror having a first side and a second side, the current mirror first side including a first transistor coupled between a voltage source and the first clamping device and the current mirror second side including a second transistor coupled between the voltage source and the second clamping device, and a sensing scheme including an actively balanced capacitance coupled to the source and drain of the second transistor.
Owner:POLARIS INNOVATIONS
Integrated circuit, method of operating an integrated circuit, method of manufacturing an integrated circuit, memory module, stackable memory module
InactiveUS7433253B2Design and efficient manufactureAccurate balanceCurrent/voltage measurementDigital storageCapacitanceEngineering
An integrated circuit has a current sense amplifier that includes a voltage comparator having a first input, a second input and an output; a first clamping device coupled between the first input of the voltage comparator and a first input signal node, a second clamping device coupled between the second input of the voltage comparator and a second input signal node, a current mirror having a first side and a second side, the current mirror first side including a first transistor coupled between a voltage source and the first clamping device and the current mirror second side including a second transistor coupled between the voltage source and the second clamping device, and a sensing scheme including an actively balanced capacitance coupled to the source and drain of the second transistor.
Owner:POLARIS INNOVATIONS LTD
Current sense amplifier
InactiveUS20060050584A1Improve performanceIncrease speedCurrent/voltage measurementDigital storageCapacitanceAudio power amplifier
A high-speed current sense amplifier has complementary reference cells and load devices that eliminate capacitive mismatch contributions. The current sense amplifier includes a voltage comparator, a first clamping device coupled between a first input of the voltage comparator and a first input signal node. The first clamping device is coupled to a reference voltage. A second clamping device is coupled between the second input of the voltage comparator and a second input signal node. The second clamping device is also coupled to the reference voltage. A current mirror is coupled between the first and second input of the voltage comparator and is coupled to an active capacitance balancing circuit. The active capacitance balancing circuit may be combined with the voltage comparator. Equalization devices may be coupled between the first and second inputs of the voltage comparator, and between the first input signal node and the second input signal node.
Owner:POLARIS INNOVATIONS
Indoor fusion positioning system and method based on WiFi and BLUETOOTH
InactiveCN104837118ABest position estimateReduce generationWireless commuication servicesLocation information based servicePhysical addressNavigation system
The invention provides an indoor fusion positioning system and method based on WiFi and BLUETOOTH, and relates to a mobile network wireless positioning and navigation system and method. The system comprises a signal node disposition system, an intelligent terminal system and a positioning server system. The signal node disposition system provides disposition methods of WiFi signal nodes and Bluetooth signal nodes. The system collects surrounding WiFi signal node information comprising WiFi signal strength information, WiFi signal node physical addresses and WiFi coordinate information. The system collects surrounding Bluetooth signal node information Bluetooth signal strength information, Bluetooth signal node physical addresses and Bluetooth coordinate information. The system comprises a fusion positioning model and the positioning algorithm thereof. According to the invention, WiFi and Bluetooth modules in an intelligent terminal are fully used, and WiFi signals and Bluetooth signals of the intelligent terminal are fused for positioning, thereby being significant for utilization and positioning of more and more intelligent terminals.
Owner:LIAONING UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
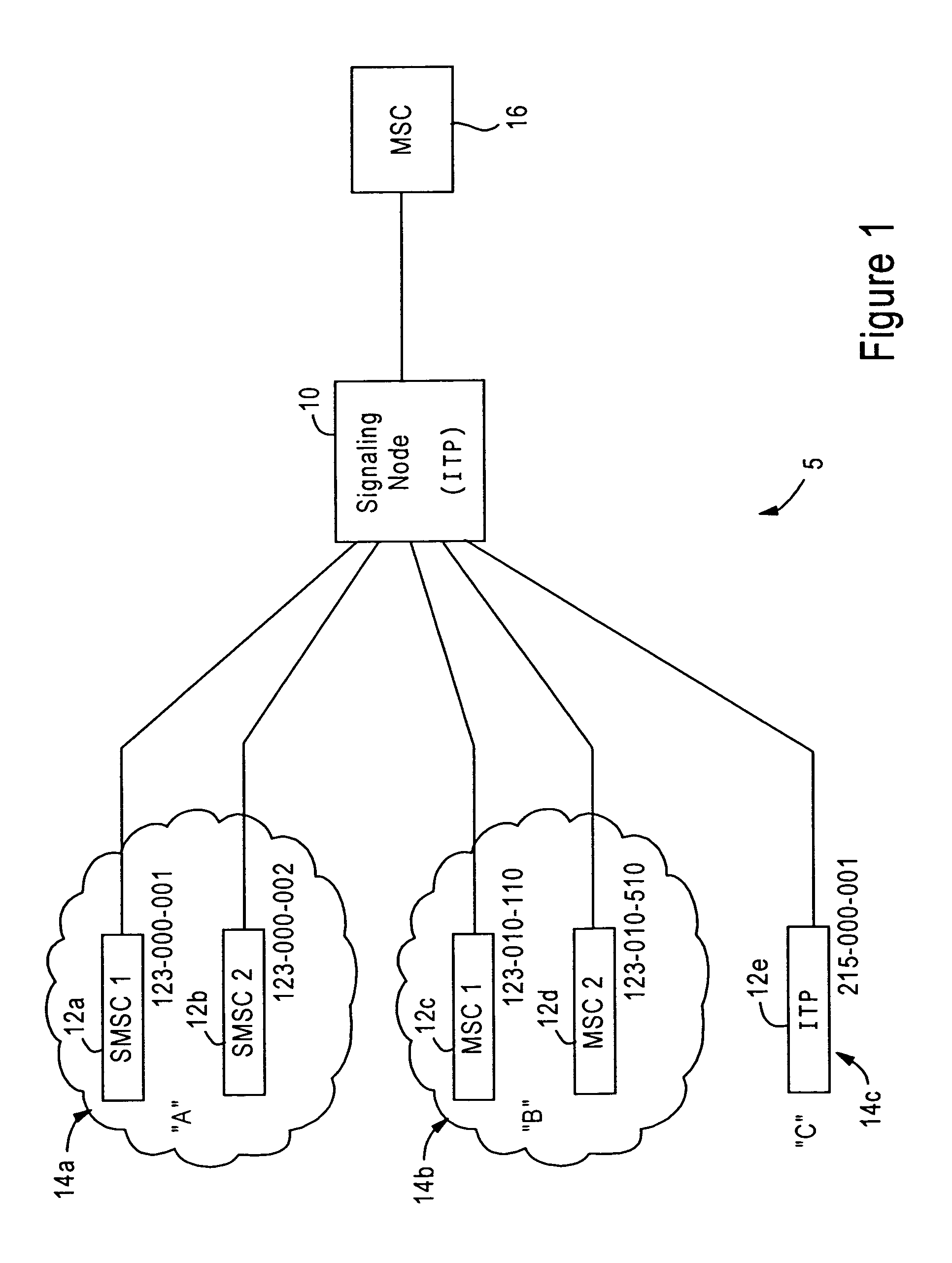
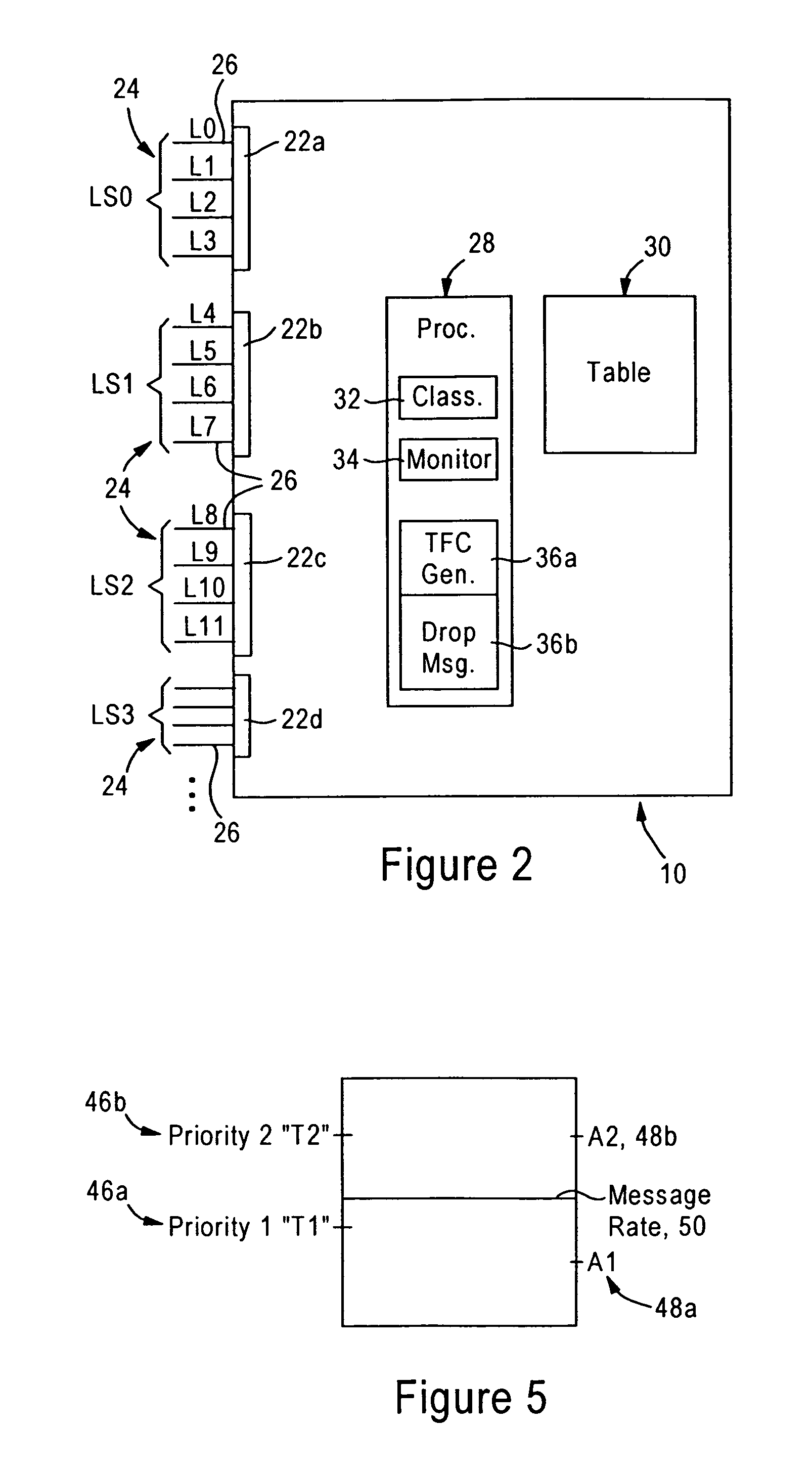
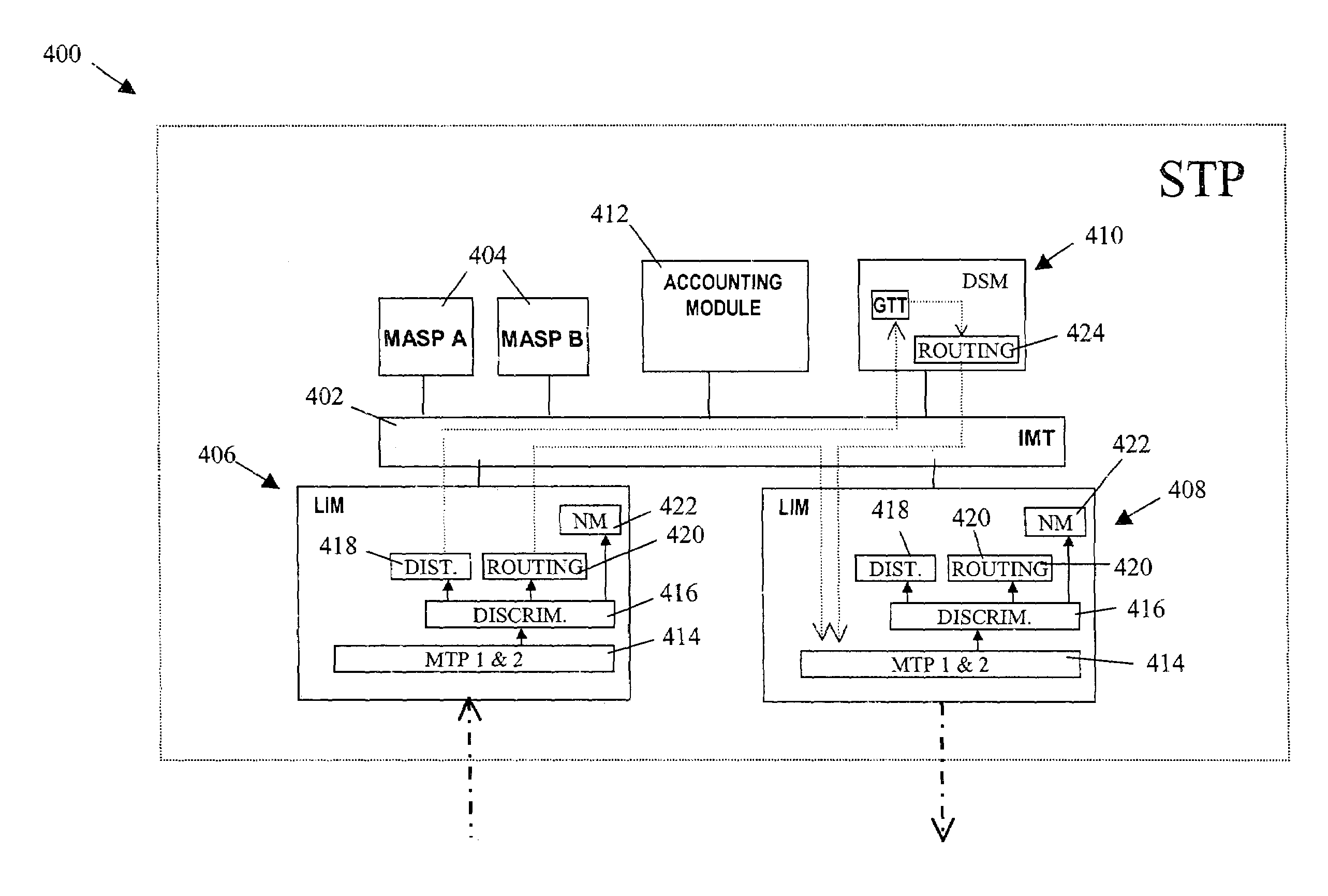
Arrangement for controlling congestion in an SS7 signaling node based on packet classification
ActiveUS6996225B1Minimize network congestionReduce congestionInterconnection arrangementsData switching networksSignaling networkSelection criterion
A signaling network node is configured for identifying a received signaling message as belonging to one of a plurality of prescribed originating node groups, based on prescribed message class selection criteria. Each originating node group has at least one originating node and is assigned at least one congestion threshold relative to a message rate (e.g., messages per unit time or number of bytes per unit time). The signaling network node determines the message rate for each corresponding originating node group; if the message rate for an originating node group exceeds the corresponding at least one congestion threshold, the signaling network node outputs a congestion signaling message to the originating node having sent the signaling message, for reduction of the corresponding message rate.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
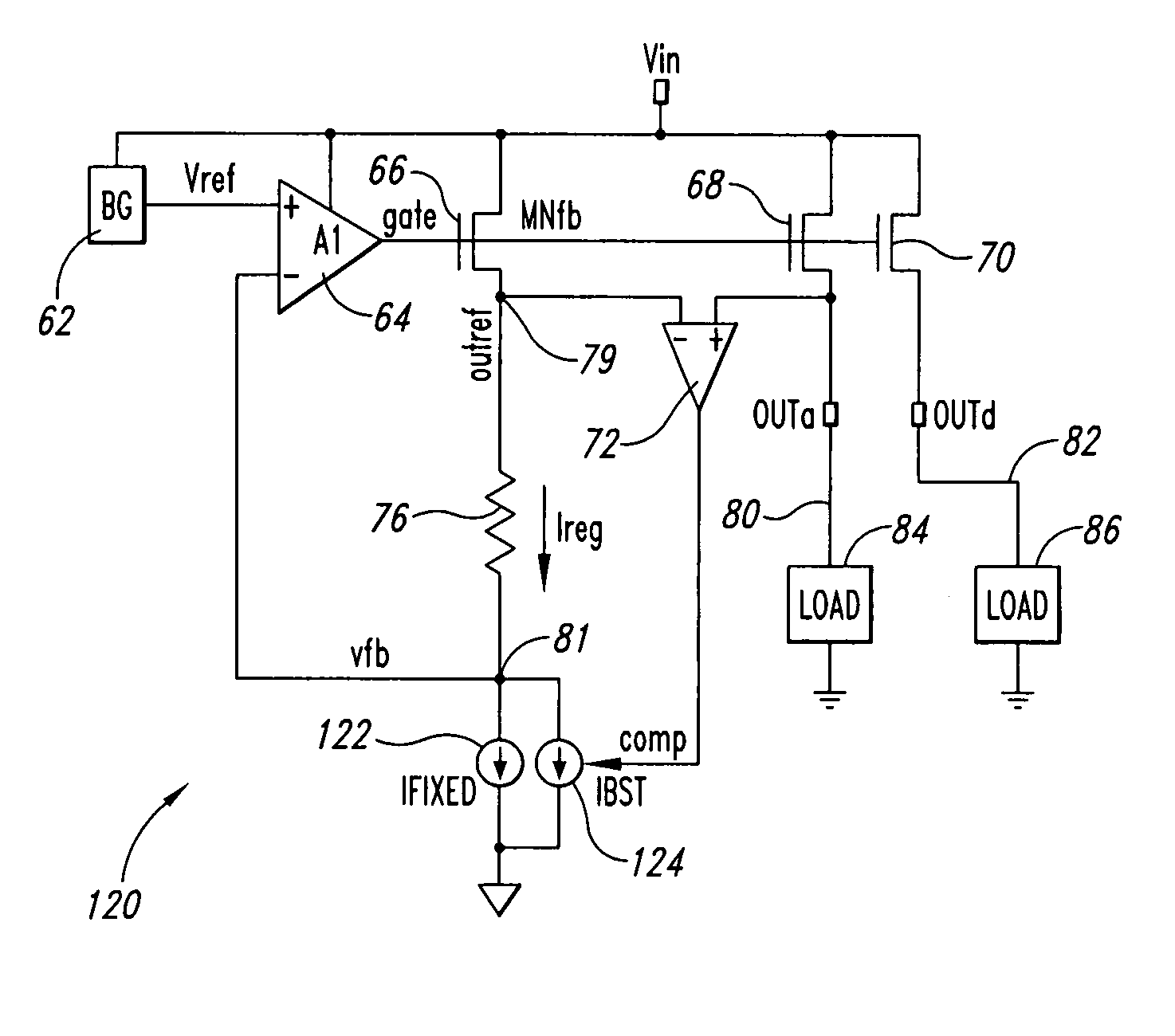
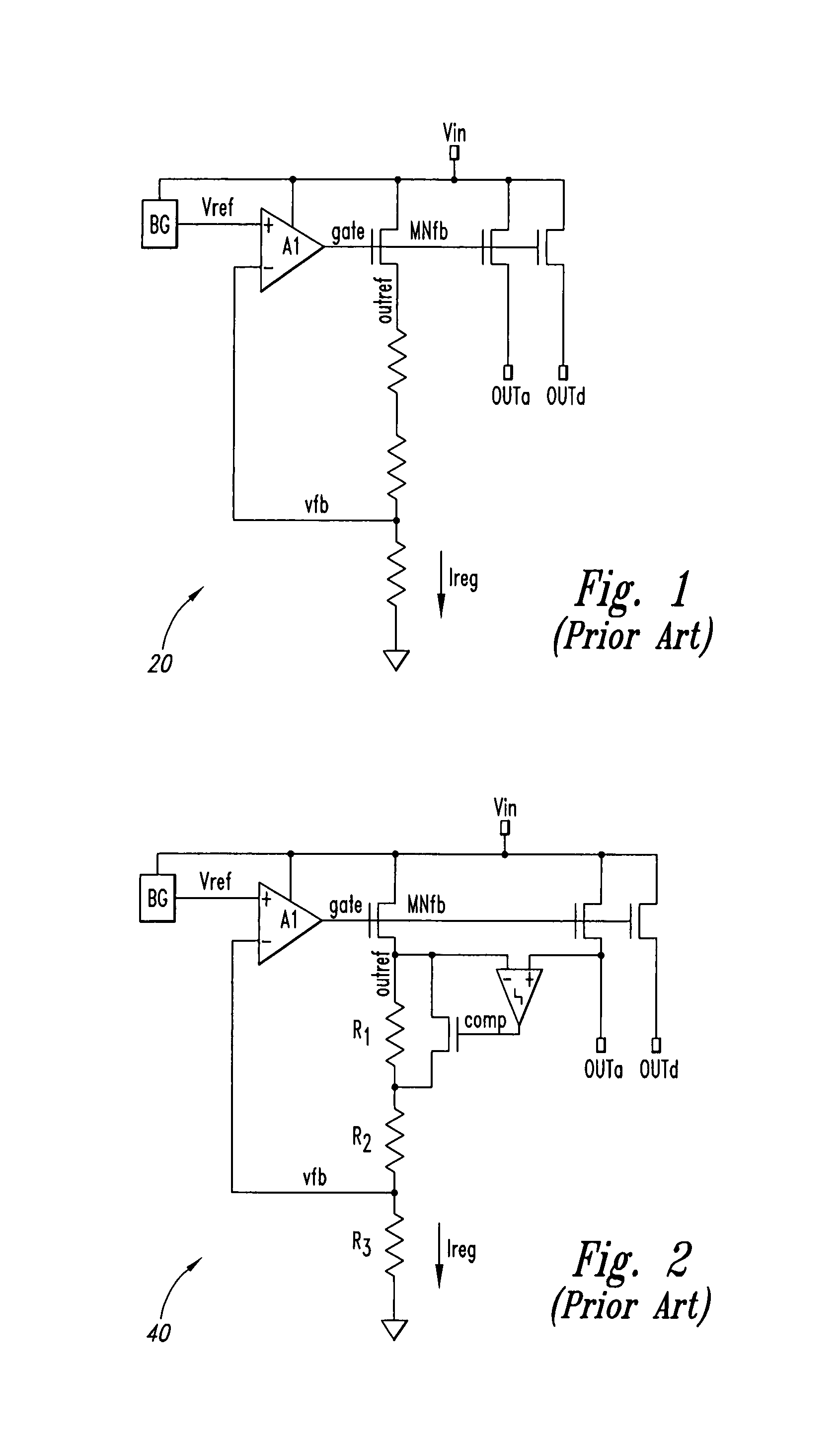
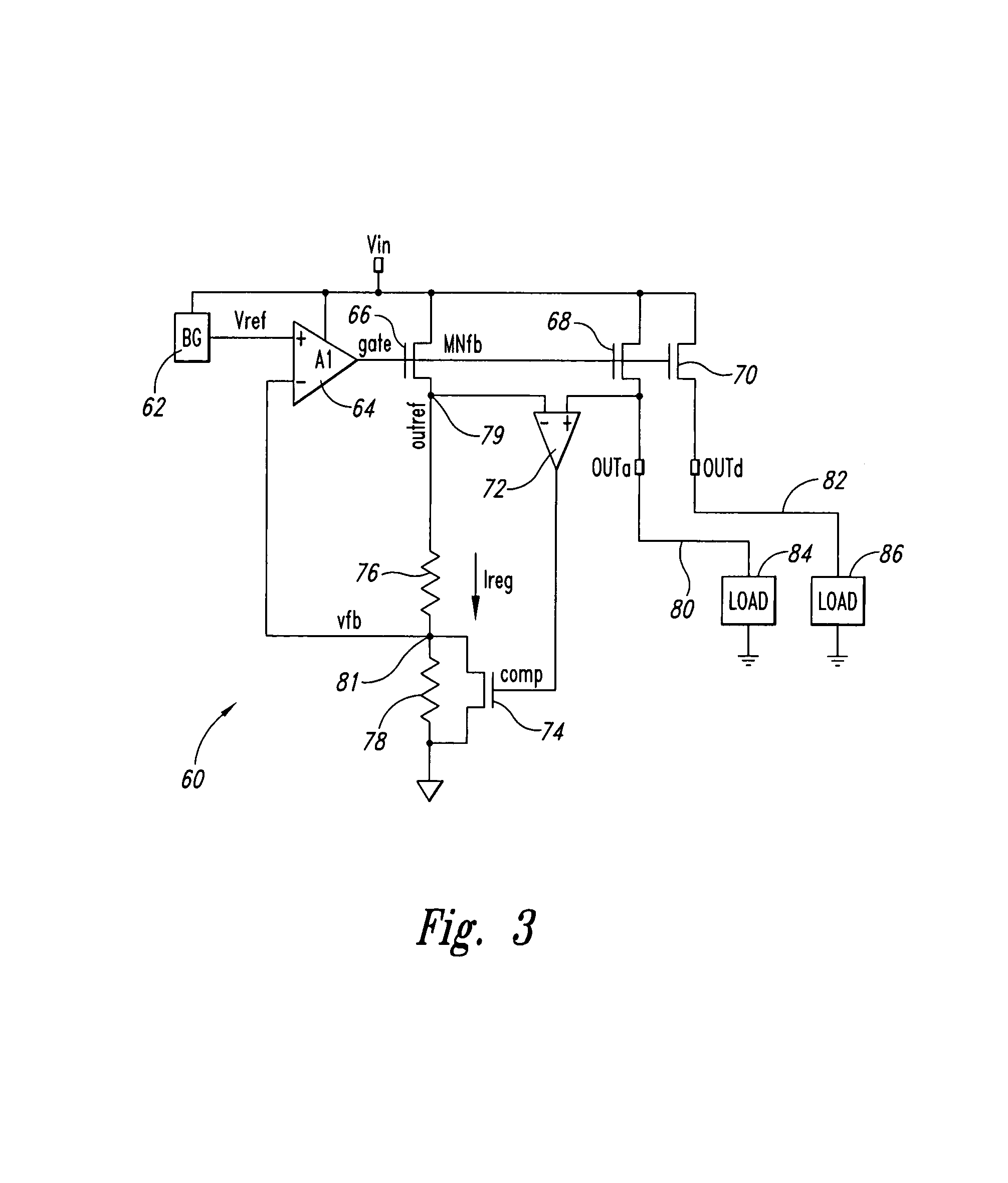
Replica regulator with continuous output correction
Circuits for regulating a voltage or current to a load(s). In one example, a circuit may include a first amplifier providing an amplifier output signal, the first amplifier having at least a first input and a second input, the first input receiving a voltage reference signal; a first transistor receiving the amplifier output signal, the first transistor having a transistor output; at least one resistor coupled between the transistor output and the second input of the first amplifier and defining a feedback voltage signal node; a second transistor in parallel with the first transistor, the second transistor receiving the amplifier output signal, the second transistor providing a regulated output signal of the circuit; a second amplifier receiving the output signal of the second transistor and the transistor output of the first transistor, the second amplifier providing a control signal; and a circuit element coupled between the feedback voltage signal node and ground, the circuit element receiving as a control the control signal of the second amplifier.
Owner:MONTEREY RES LLC
Current sense amplifier
InactiveUS7251178B2Faster sensingDesign and efficient manufactureCurrent/voltage measurementDigital storageCapacitanceAudio power amplifier
A high-speed current sense amplifier has complementary reference cells and load devices that eliminate capacitive mismatch contributions. The current sense amplifier includes a voltage comparator, a first clamping device coupled between a first input of the voltage comparator and a first input signal node. The first clamping device is coupled to a reference voltage. A second clamping device is coupled between the second input of the voltage comparator and a second input signal node. The second clamping device is also coupled to the reference voltage. A current mirror is coupled between the first and second input of the voltage comparator and is coupled to an active capacitance balancing circuit. The active capacitance balancing circuit may be combined with the voltage comparator. Equalization devices may be coupled between the first and second inputs of the voltage comparator, and between the first input signal node and the second input signal node.
Owner:POLARIS INNOVATIONS LTD
Optical burst switch network system and method with just-in-time signaling
InactiveUS20050013613A1Lower latencyRich varietyMultiplex system selection arrangementsFibre transmissionNetwork terminationOptical burst switching
Optical burst switch network system and method with Just-in-Time (JIT) signaling and advanced data transmission and memory access and management. The system and method allow concurrent data transmission having arbitrary signal types, such as analog and digital signal types, in which the JIT signaling allows for subsequent simultaneous transmission of optical signals that do not require electro-optical conversion. The system includes an optical signal bus having a passive star coupler. A plurality of network adapters that are in optical communication with the optical signal bus and in network communication with network terminal devices are provided. The network adapters include receivers, transmitters and control logic that allows for bi-directional movement of data signals as bursts between the terminal equipment and the network system. The transmitter and receiver may be fixed or tunable. The system further includes an optical bus controller in optical communication with the optical signal bus that processes signals from the optical signal bus to connect a requested network adapter to a requesting network adapter in accordance with the user-to-network protocol. The network system implements a just-in-time signaling protocol to signal nodes in the network that burst communications are forthcoming. Optionally, the system allows comprehensive memory access in a Local Area Network (LAN). The nodes in the network are capable of seamlessly addressing memories of all other nodes that comprise the network.
Owner:RES TRIANGLE INST
Techniques for integrated routing of call circuit signaling and the internet protocol
InactiveUS20070248103A1Data switching by path configurationSelection arrangementsTTEthernetNetwork link
Techniques for processing an IP packet at a router that supports SS7 signaling include receiving IP routing data that associates a network link and a destination IP address for a node in a signaling network that includes a plurality of signaling nodes. When an ingress IP data packet is received, it is determined whether conditions are satisfied for locally processing an SS7 payload within the ingress IP data packet. If it is determined that conditions are satisfied for locally processing the SS7 payload, then the SS7 payload is processed locally, i.e., without sending the SS7 payload over a network link to a different node in the signaling network. If it is determined that conditions are not satisfied for locally processing the SS7 payload, then the ingress IP data packet is routed normally. These techniques allow reduced numbers of expensive STP devices and expanded routing options in a signaling network.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
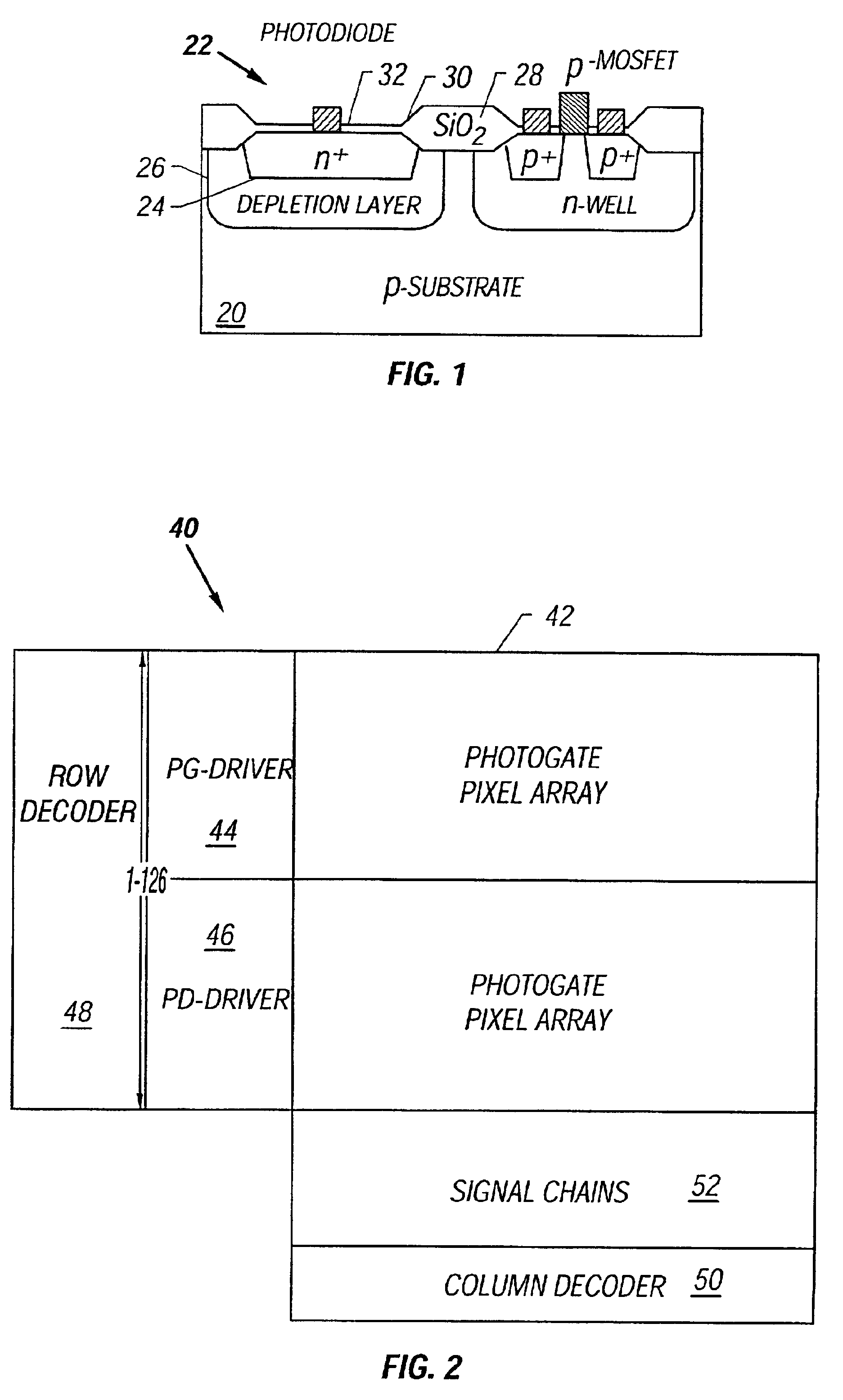
Silicon-on-insulator (SOI) active pixel sensors with the photosite implemented in the substrate
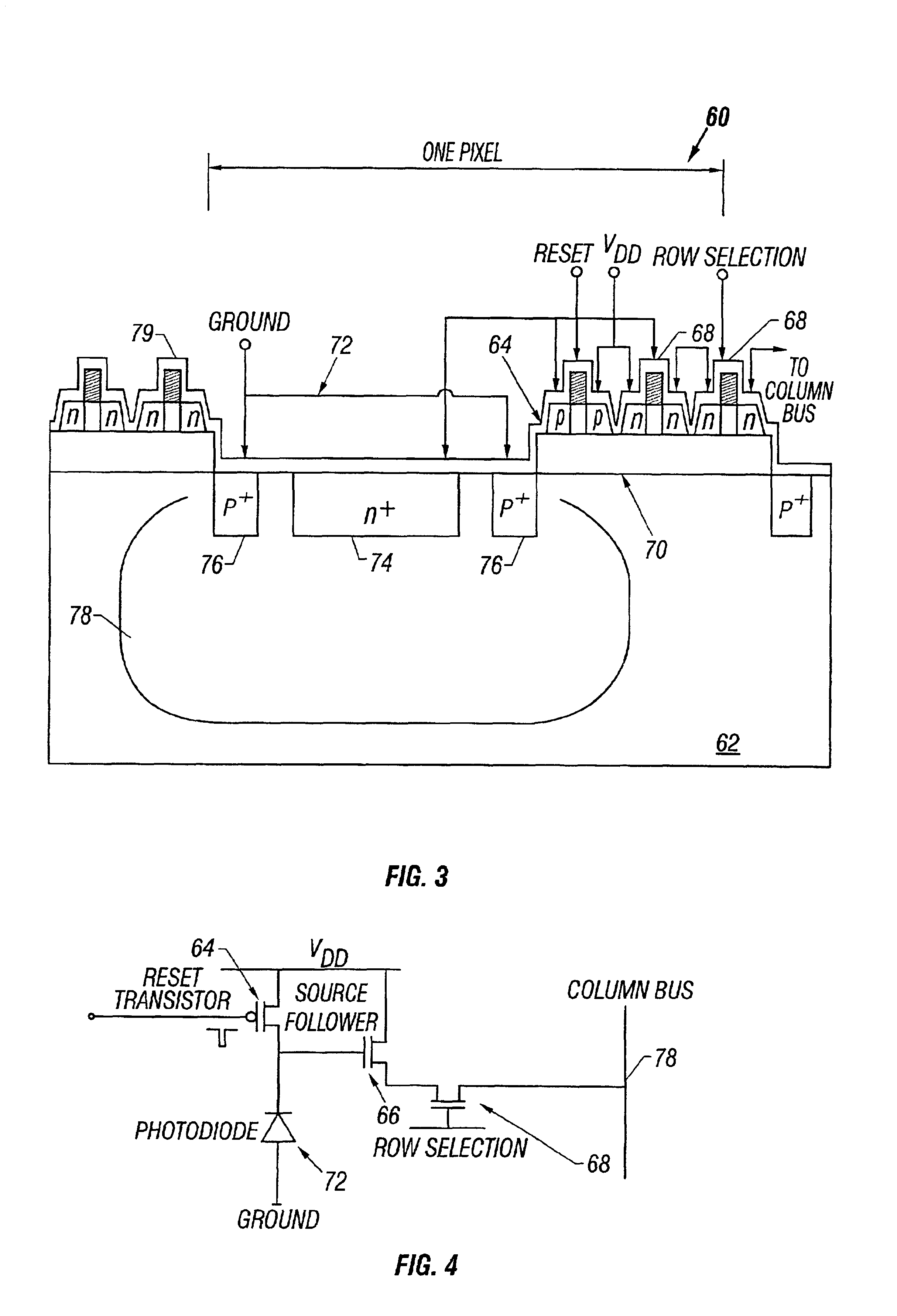
Active pixel sensors for a high quality imager are fabricated using a silicon-on-insulator (SOI) process by integrating the photodetectors on the SOI substrate and forming pixel readout transistors on the SOI thin-film. The technique can include forming silicon islands on a buried insulator layer disposed on a silicon substrate and selectively etching away the buried insulator layer over a region of the substrate to define a photodetector area. Dopants of a first conductivity type are implanted to form a signal node in the photodetector area and to form simultaneously drain / source regions for a first transistor in at least a first one of the silicon islands. Dopants of a second conductivity type are implanted to form drain / source regions for a second transistor in at least a second one of the silicon islands. Isolation rings around the photodetector also can be formed when dopants of the second conductivity type are implanted. Interconnections among the transistors and the photodetector are provided to allow signals sensed by the photodetector to be read out via the transistors formed on the silicon islands.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Combination ESD protection circuits and methods
Circuits, integrated circuits, apparatuses, and methods, such as those for protecting circuits against electrostatic discharge events are disclosed. In an example method, a thyristor is triggered to conduct current from a signal node to a reference voltage node using leakage currents provided by a transistor formed in a semiconductor doped well shared with the base of the thyristor. The leakage currents are responsive to a noise event (e.g., electrostatic discharge (ESD) event) at the signal node, and increase the voltage of the semiconductor doped well to forward bias the base and the collector of the thyristor. The triggered thyristor conducts the current resulting from the ESD event to the reference voltage node.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Level shifter with balanced rise and fall times
A level shifting circuit can include a shift stage that latches first and second internal nodes to opposite shifted logic potentials in response to different transitions at an input signal node. The input signal node can vary between non-shifted logic potentials. An output stage can enable a first controllable impedance path coupled between an output node and a first shifted power supply node in response to a first type transition at the first internal node, and can enable a second controllable impedance path coupled between the output node and a second shifted power supply node in response to the first type transition at the second internal node.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Methods and systems for routing signaling messages to the same destination over different routes using message origination information associated with non-adjacent signaling nodes
InactiveUS7088728B2Eliminate requirementsInterconnection arrangementsData switching by path configurationQuality of serviceNetwork addressing
Methods and systems for associating a plurality of different routes with the same destination and for routing signaling messages to the destination based on originating information associated with non-adjacent signaling nodes are disclosed. A routing database in a signal transfer point includes multiple routes to the same destination. The routes are distinguishable from each other in the routing database using message origination information associated with signaling nodes that are not adjacent to the signal transfer point. When a signaling message is received, origination and destination information in the signaling message are used in combination to select among multiple routes to a destination having a network address corresponding to the destination information in the signaling message. The signaling message is then routed over the route selected using the originating information. The selected route may be a high-speed route used to provide a particular quality of service.
Owner:TEKELEC GLOBAL INC
Multiple function power domain level shifter
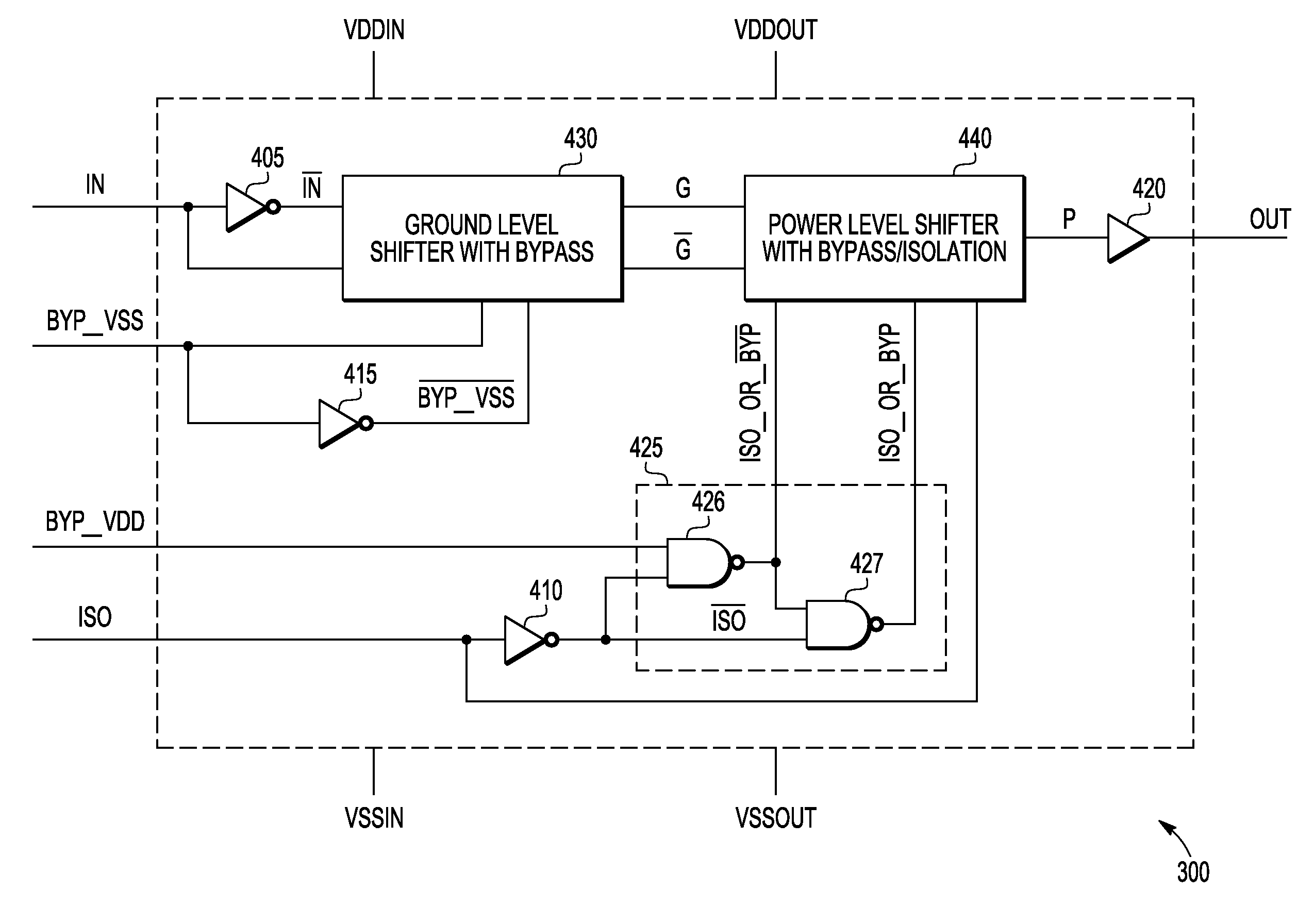
A level shifter including input and output power nodes, input and output reference nodes, input and output signal nodes, and a lever shifter network. The input power and input reference nodes operate within a first power domain and the output power and output reference nodes operate within a second power domain. The level shifter network receives an input signal operable within the first power domain, performs voltage shifting between the input and output power nodes and between the input and output reference nodes, and provides an output signal output signal indicative of the input signal that operates within the second power domain. The level shifter may include power and / or ground bypass such that either one or both of power and ground voltage shifting may be bypassed for faster switching. The level shifter may include an isolation input to assert the output to a known level.
Owner:NORTH STAR INNOVATIONS
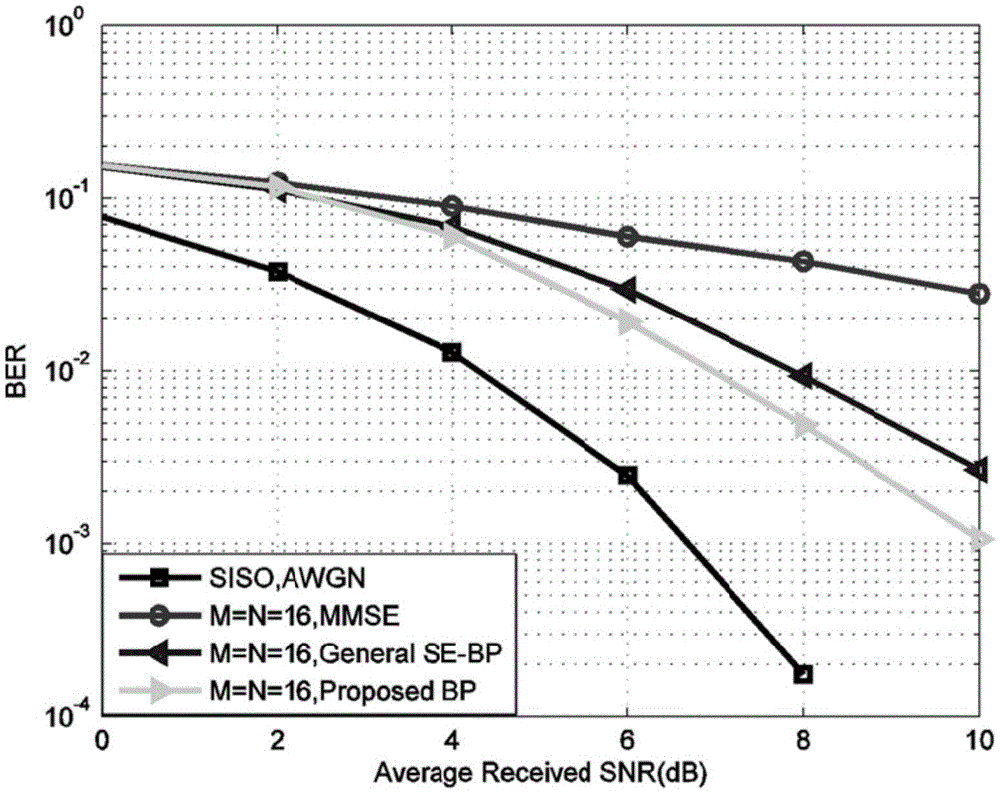
Low-complexity belief propagation detection algorithm for large-scale MIMO system
InactiveCN105656538AImprove performancePrevent inversionSpatial transmit diversityNODALPrior information
The invention discloses a low-complexity belief propagation detection algorithm for a large-scale MIMO system. A corresponding factor graph is built by utilizing an equivalent real number field model, and complex number field operation is translated into real number field operation, thereby implementing BP-based iteration detection; wherein the factor graph is used for representing a dependency relation between a receiving signal and a transmitting signal, the transmitting signal is utilized as a signal node, and the receiving signal is utilized as an observation node; each signal node updates prior information according to posterior information obtained from the observation node, and then transmits the updated prior information to all observation nodes connected with the signal node; each observation node calculates updates posterior information according to prior information obtained from the signal node, and then transmits the updated posterior information to a signal node connected with the observation node. According to the low-complexity belief propagation detection algorithm for the large-scale MIMO system, a symbol-based large-scale MIMO detection algorithm is implemented; high-dimensional matrix inversion is avoided, and the low-complexity belief propagation detection algorithm can be greatly suitable for application scenarios of the large-scale MIMO.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
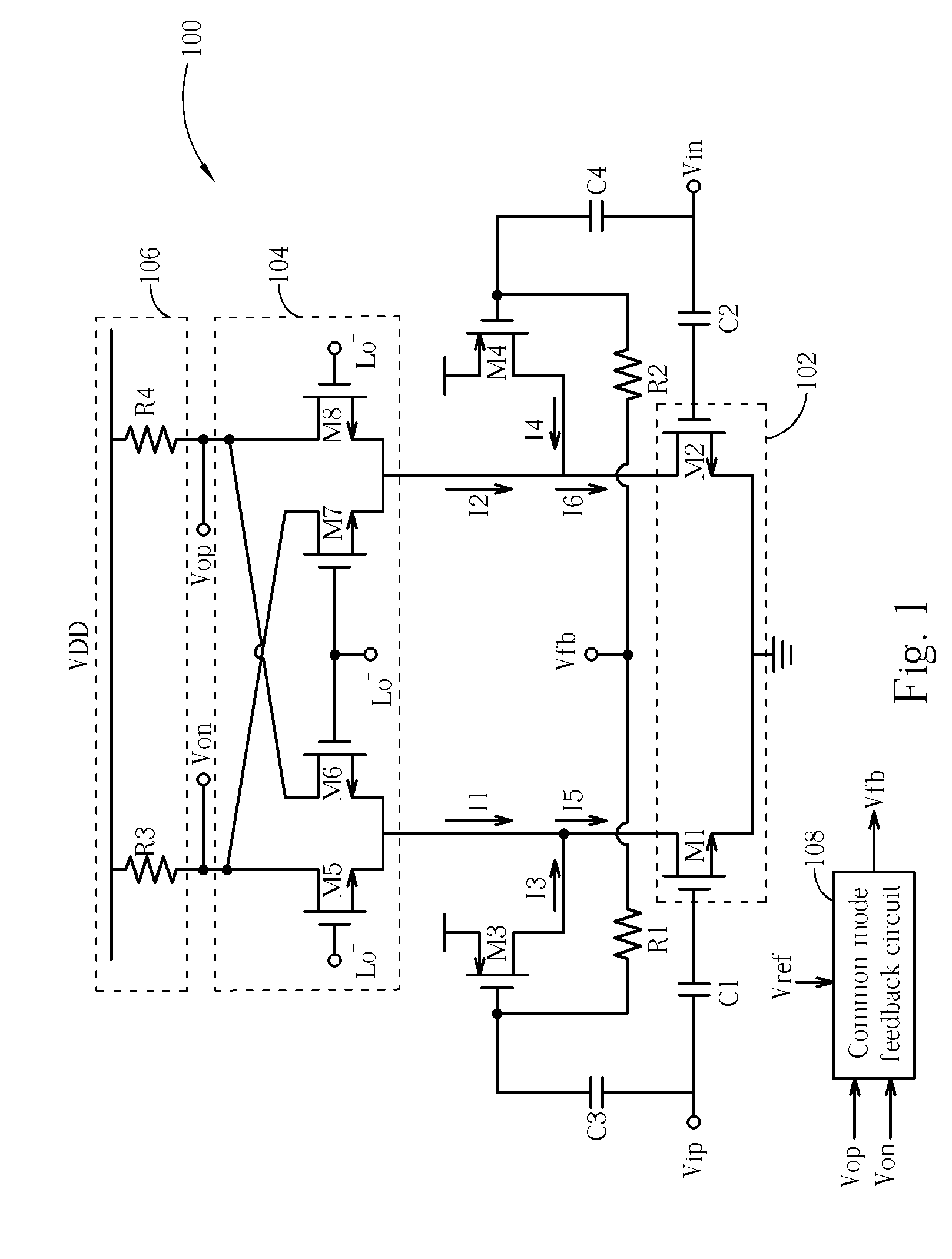
Low noise mixer
ActiveUS20070142018A1Decreasing flicker noise phenomenonModulation transferenceTransmissionLow noiseLoad circuit
Disclosed is a mixer comprising: a switching circuit, having a first pair of differential signal nodes and a second pair of differential signal nodes, for switching according to a local oscillation signal; an amplifying stage circuit, for receiving an input signal and amplifying the input signal; a load circuit, for serving as the loading of the mixer and generating an output signal of the mixer; a common-mode feedback circuit, for receiving the output signal and generating a feedback signal according to the output signal; a first current source, for receiving the feedback signal and generating a first current according to the feedback signal; and a second current source, for receiving the feedback signal and generating a second current according to the feedback signal.
Owner:REALTEK SEMICON CORP
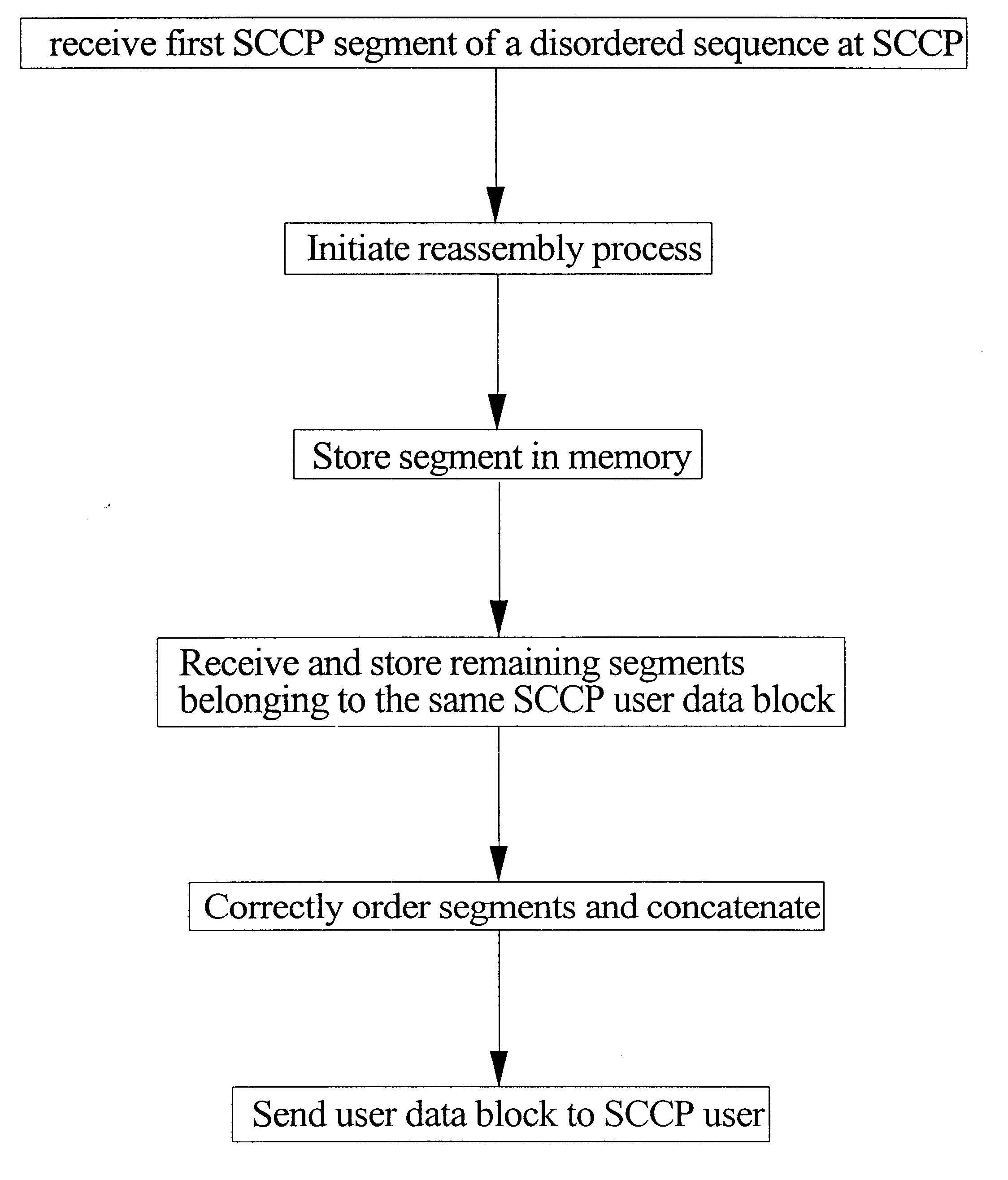
Signalling in a telecommunications network
InactiveUS6628672B1Time-division multiplexData switching by path configurationTelecommunications networkTelecommunications link
A method of reassembling an ordered sequence of Signalling Connection and Control Part (SCCP) message segments at the SCCP of a signalling node of a telecommunications network, where said message segments are received out of order at the signalling node. The method comprises the steps of receiving a first of the message segments at the SCCP and initiating a reassembly process for the sequence to which the received segment belongs. The received segment is stored in a memory as part of said initiated process, and thereafter the remaining segments of the SCCP message are also received and stored in the same memory. The received segments are then concatenated in the correct order to obtain an SCCP user data block. The reassembled SCCP user data block is passed to an SCCP user.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Network switching method and device
ActiveCN105992293AReduce interactionReduce loadWireless communicationRadio networksComputer terminal
Owner:DATANG MOBILE COMM EQUIP CO LTD
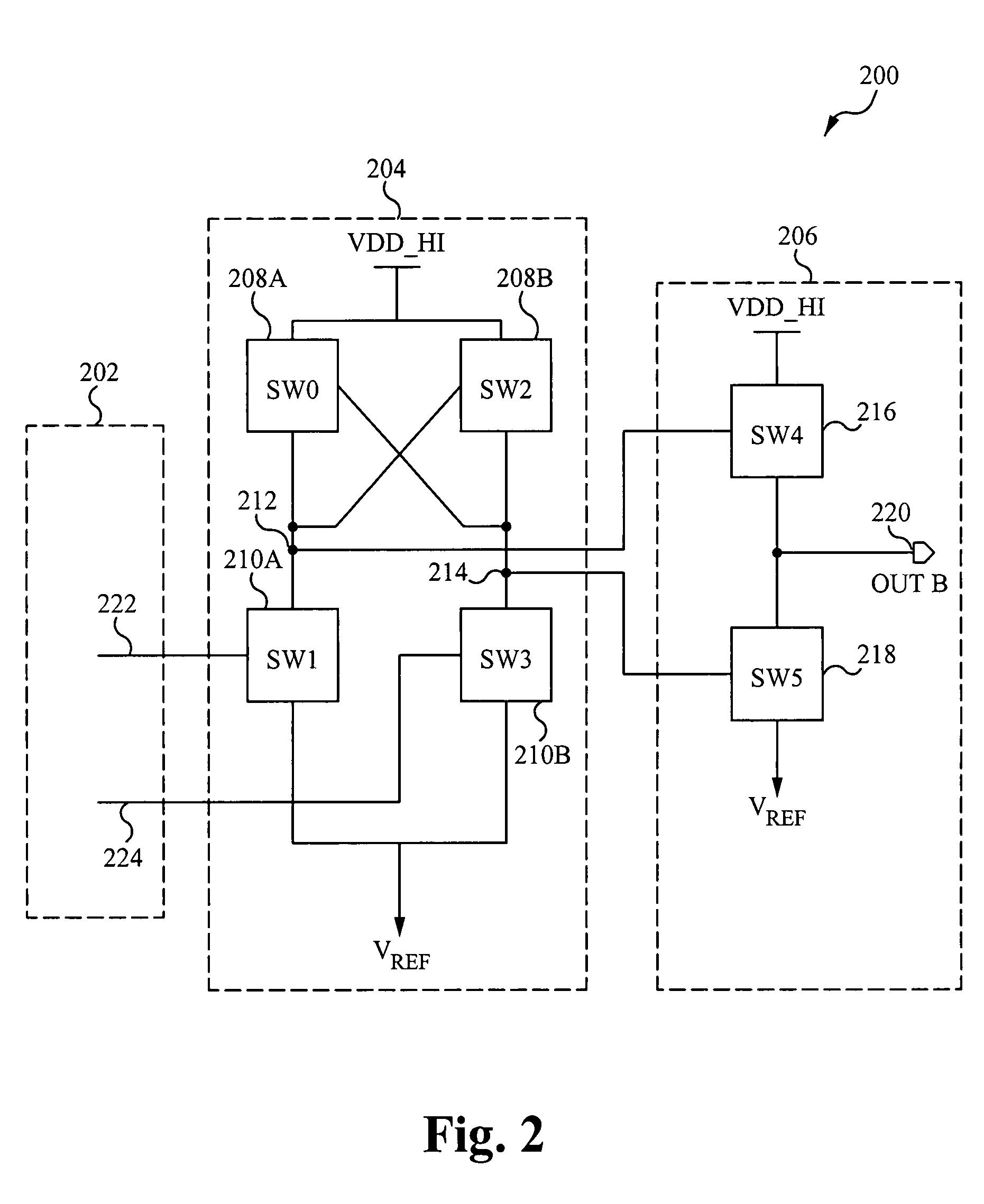
Arrangement for controlling congestion for multiple host groups sharing a single signaling point code in an IP-based network using respective group congestion levels
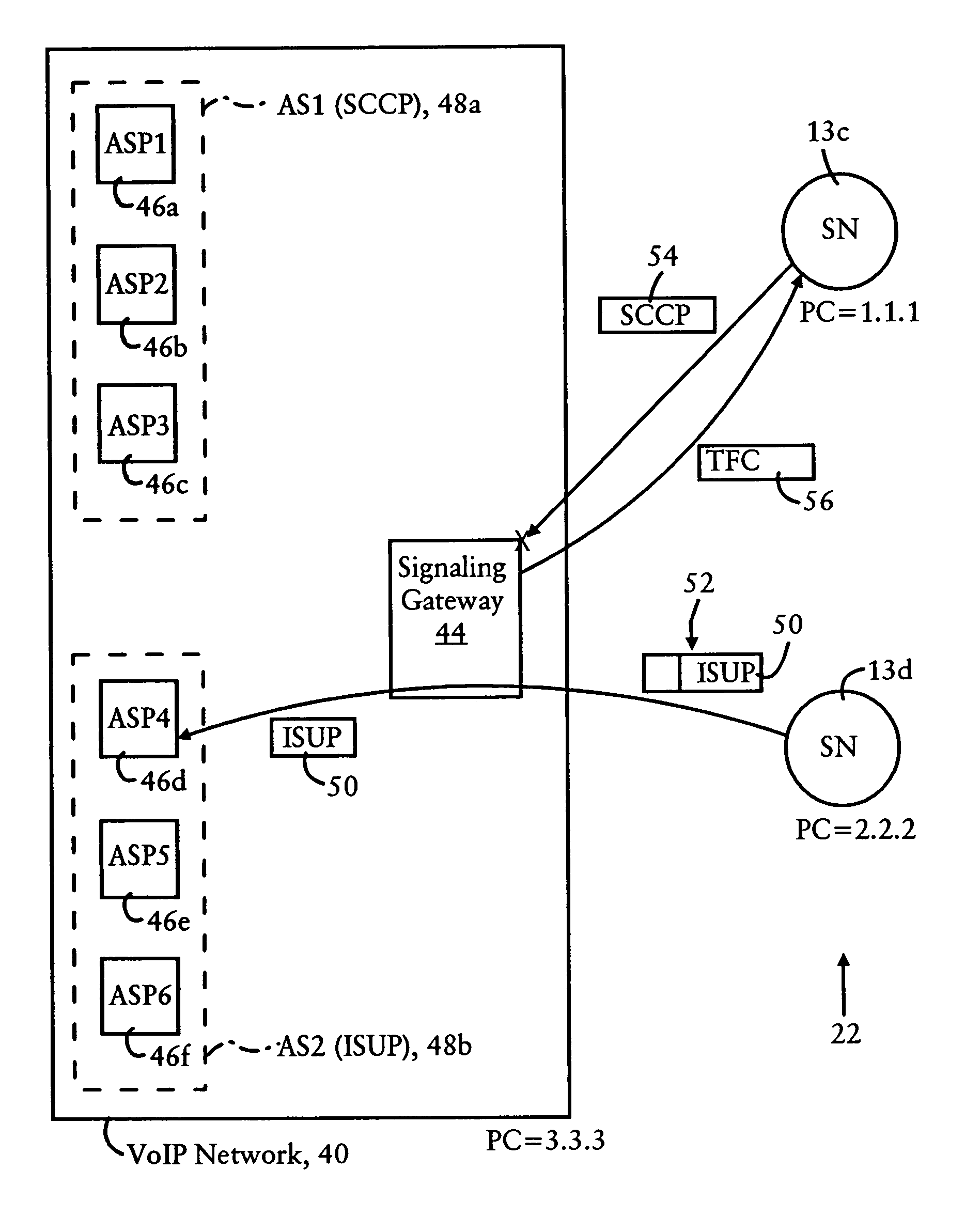
ActiveUS7477646B1Minimizing interruptionOptimizationError preventionTransmission systemsSignaling nodesMultiple applications
AVoice over IP network, having multiple application server processes (ASPs) and at least one signaling gateway, communicates with switched circuit network nodes using a prescribed point code. The ASPs are arranged into ASP groups, each ASP group identifying the ASPs configured for processing prescribed message signaling unit (MSU) types. The signaling gateway determines a congestion level for each ASP group. Upon receiving an SS7 message specifying the prescribed point code as the destination point code and carrying a MSU, the signaling gateway selects one of the ASP groups based on identifying a matching MSU type. If the signaling gateway determines that the priority of the MSU is less than the determined congestion level for the ASP group, the signaling gateway drops the MSU and sends back a Transfer Controlled message to the originating signaling node.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
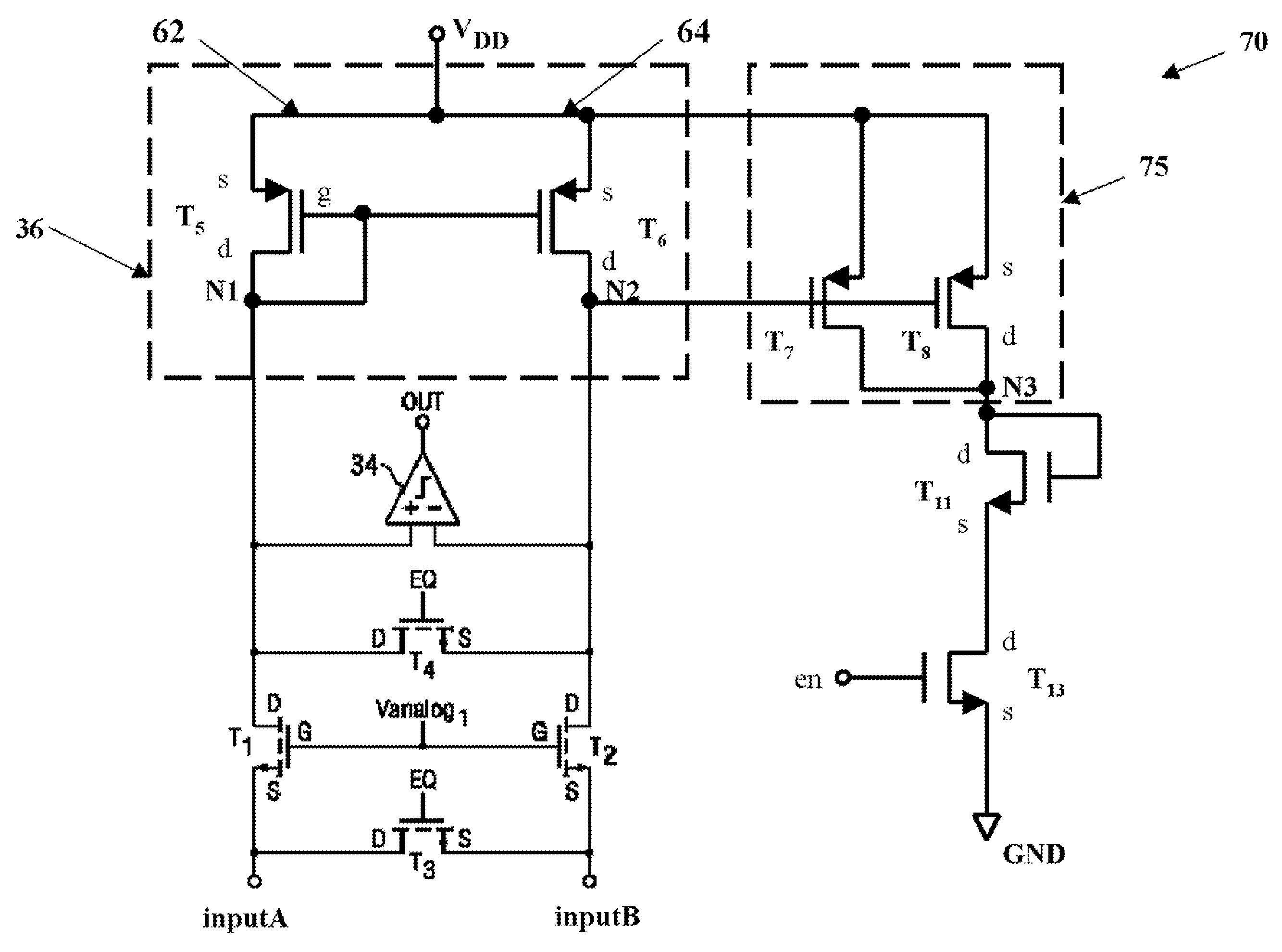
Method and circuit for producing symmetrical output signals tolerant to input timing skew, output delay/slewrate-mismatch, and complementary device mismatch
InactiveUS20080054944A1Pulse manipulationLogic circuit coupling/interface arrangementsSignal generatorSignaling nodes
An electronic circuit, including a signal transmitter, a signal generator and a ring oscillator, has a topography that is entirely symmetrical so that signals transmitted or produced by the circuit have symmetrical output signals tolerant to input timing skew, output delay / slewrate-mismatch, and complementary device-mismatch. Each P-type transistor in the circuit has a correspondingly connected P-type transistor connected to signal nodes and supply voltage nodes in a complementary manner. Similarly, each N-type transistor in the circuit has a correspondingly connected N-type transistor connected to signal nodes and supply voltage nodes in a complementary manner.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
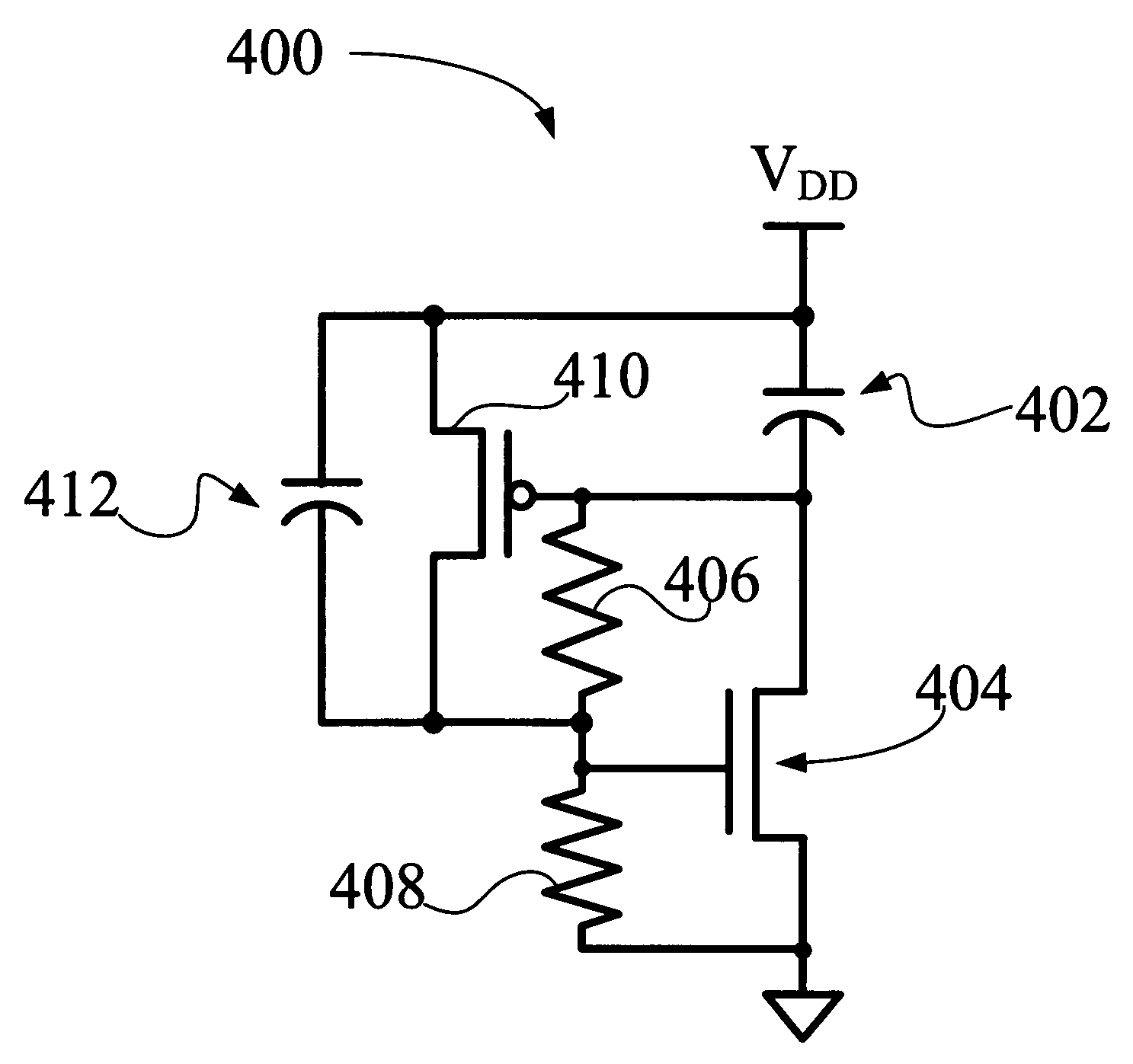
Decoupling capacitor control circuit and method for enhanced ESD performance
ActiveUS7495878B2TransistorEmergency protective arrangements for limiting excess voltage/currentVoltage referenceSignaling nodes
A decoupling capacitor control circuit is configured to be coupled between supply voltage and reference voltage planes. The control circuit includes a decoupling capacitor having a first node configured to be coupled to the supply voltage plane and having a second node. A first switching element has a first signal node coupled to the second node of the decoupling capacitor and has a second signal node and a control node. A second switching element has a first signal node coupled to the first node of the decoupling capacitor and has a second signal node coupled to the control node of the first switching element, and has a control node. A biasing circuit is coupled to the control nodes of the first and second switching elements. The biasing circuit activates both switching elements when the decoupling capacitor is not defective and deactivates both switching elements when the decoupling capacitor is defective.
Owner:BAE SYST INFORMATION & ELECTRONICS SYST INTEGRATION INC
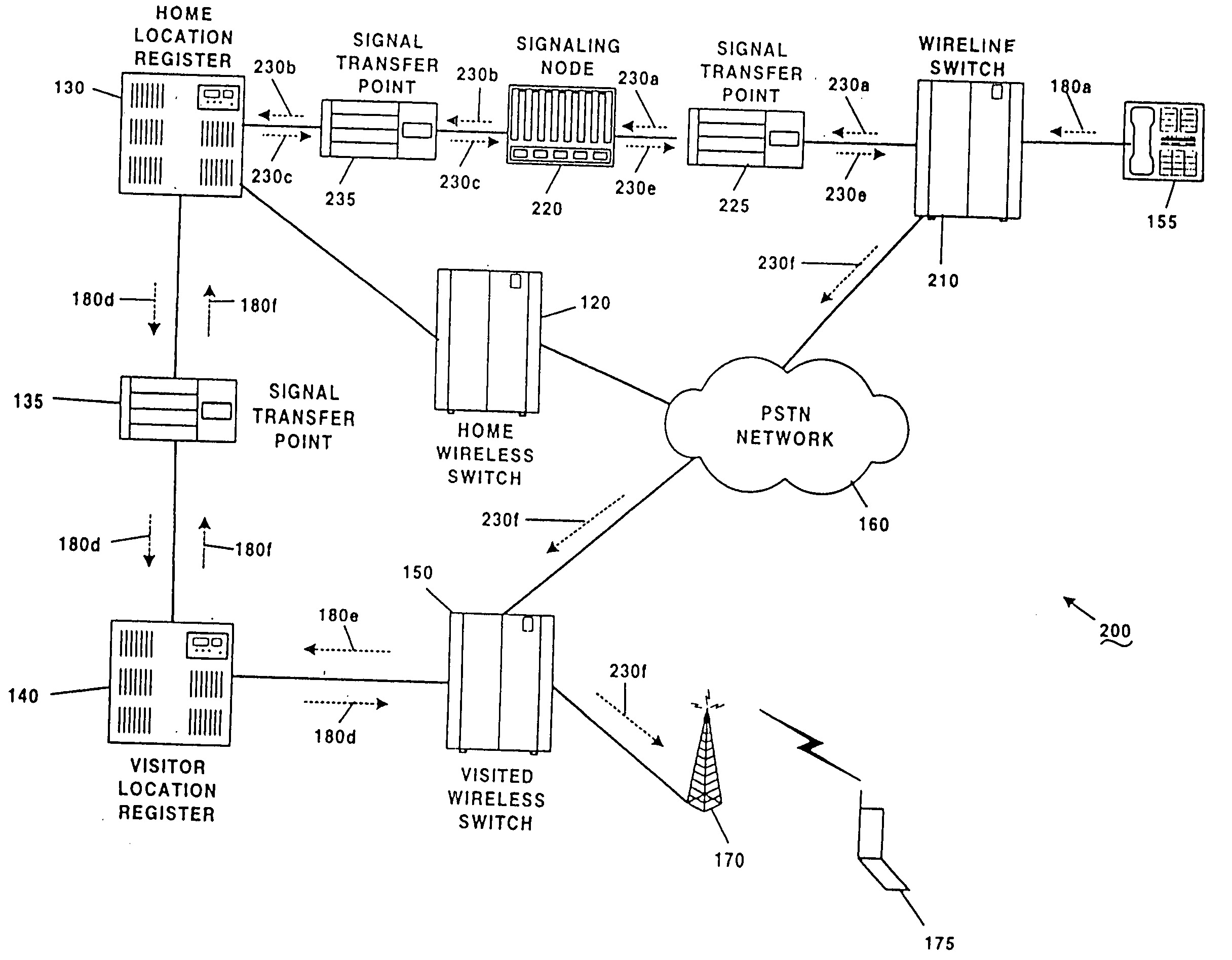
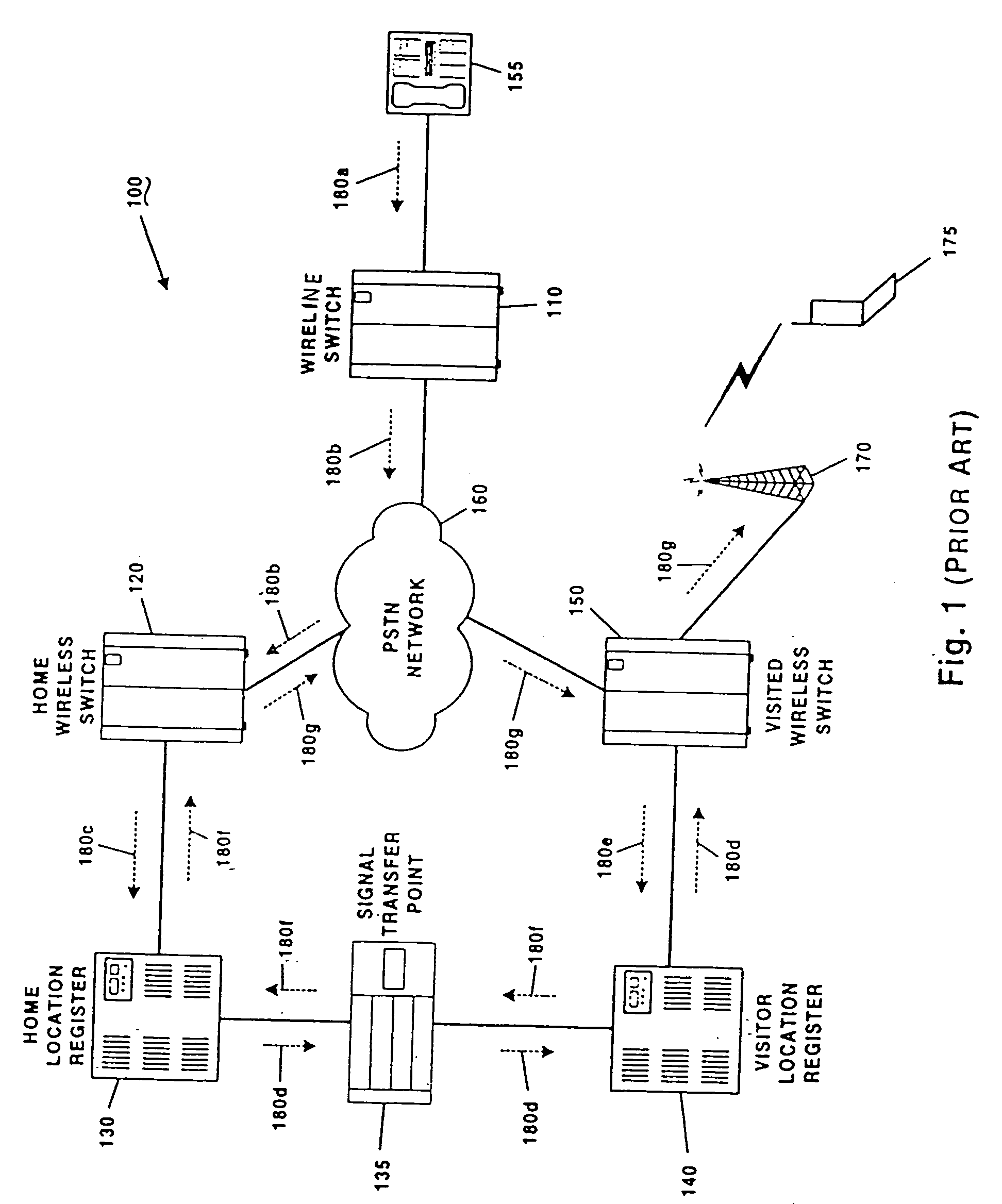
Wireless mobile call location and delivery for non-geographic numbers
InactiveUS20050221863A1Reduce in quantityIncrease capacitySpecial service for subscribersConnection managementSignaling nodesDirectory number
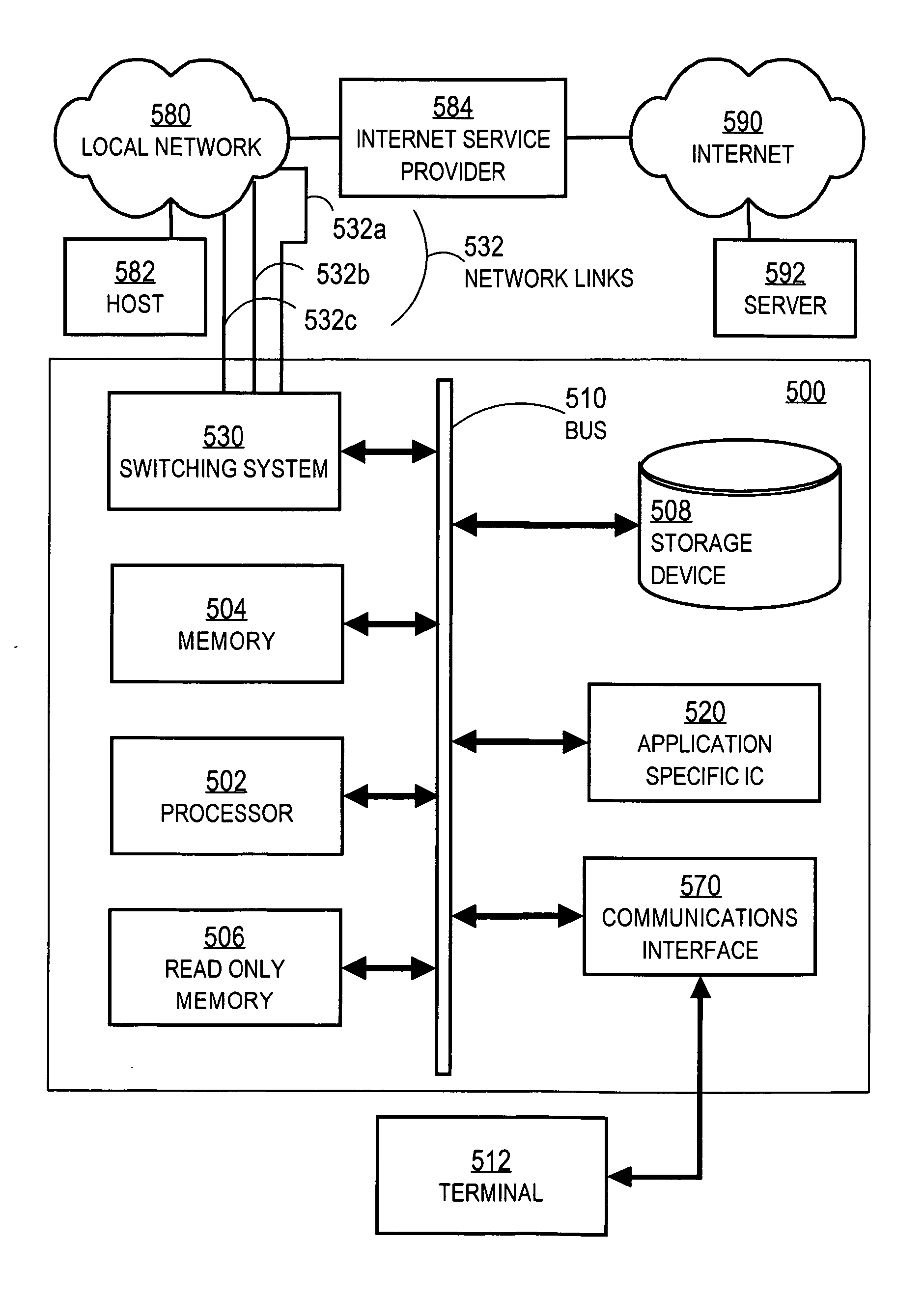
A system and method is provided for establishing a call to a wireless directory number (982) which is either a non-geographic directory number or a non-dialable directory number. A call is initiated from a wireline telephone (155) to a geographic-based local access directory number (994, 996). An originating switching node (810) recognizes the local access directory number (994, 996) as an AIN trigger, and thereafter identifies a signaling node (820) that is associated with the dialed local access DN (994, 996). The signaling node (820) sends a location request that includes the local access DN (994, 996) to an HLR (130). The HLR (130) obtains the wireless DN (982) from an internal database (990) in which the wireless DN (982) is associated with the local access DN (994, 996). The HLR (130) utilizes the wireless DN (982) to receive a temporary local directory number (TLDN) from visitor location register (140). The HLR (130) associates the TLDN with the local access DN (994, 996) and subsequently forwards the TLDN to the signaling node (820), which in turn relays the TLDN to the originating switching node (810). The call connection is thereafter established directly from the originating switching node in the end office to a visited cellular switch using the TLDN.
Owner:GTE WIRELESS
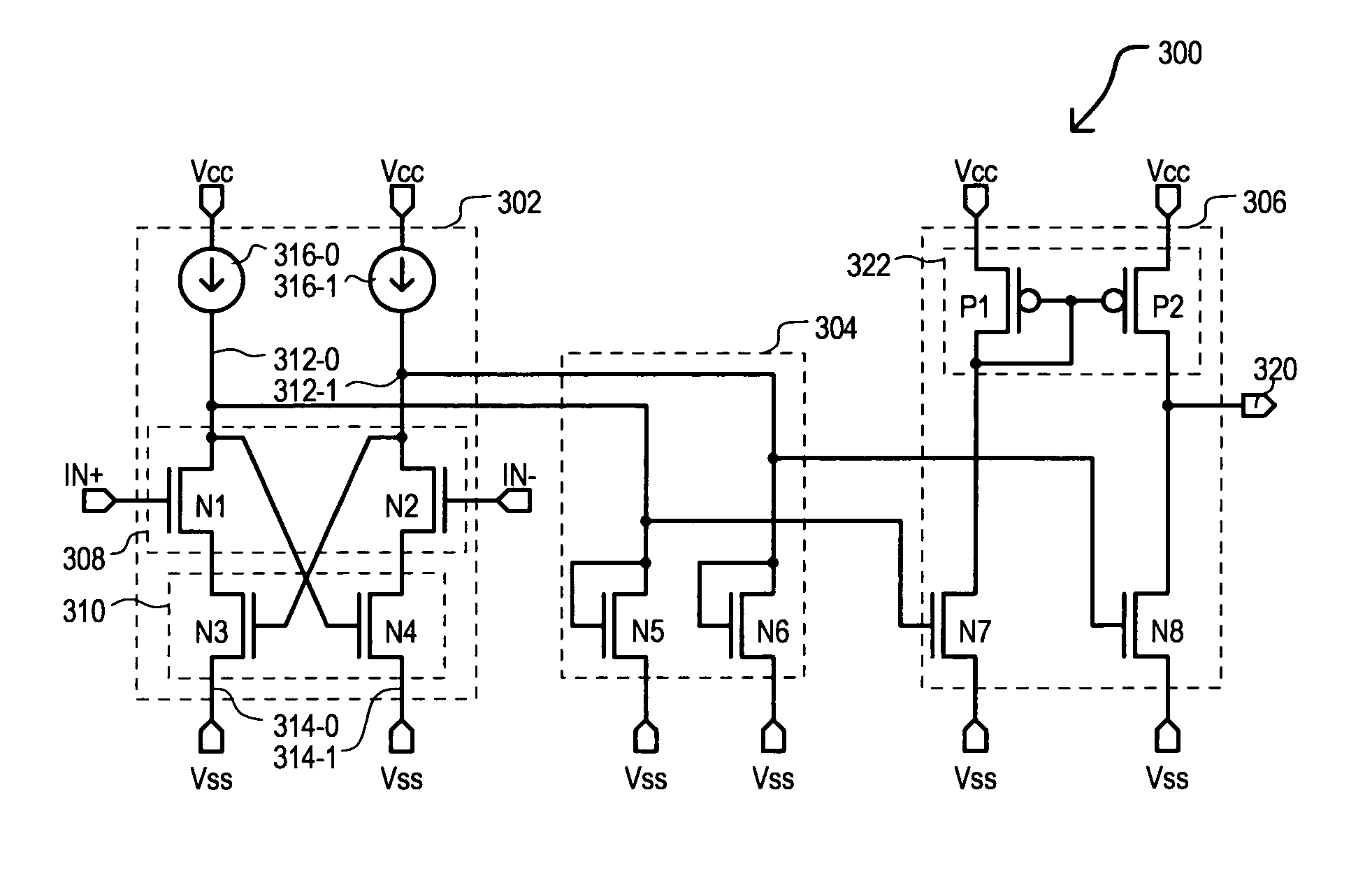
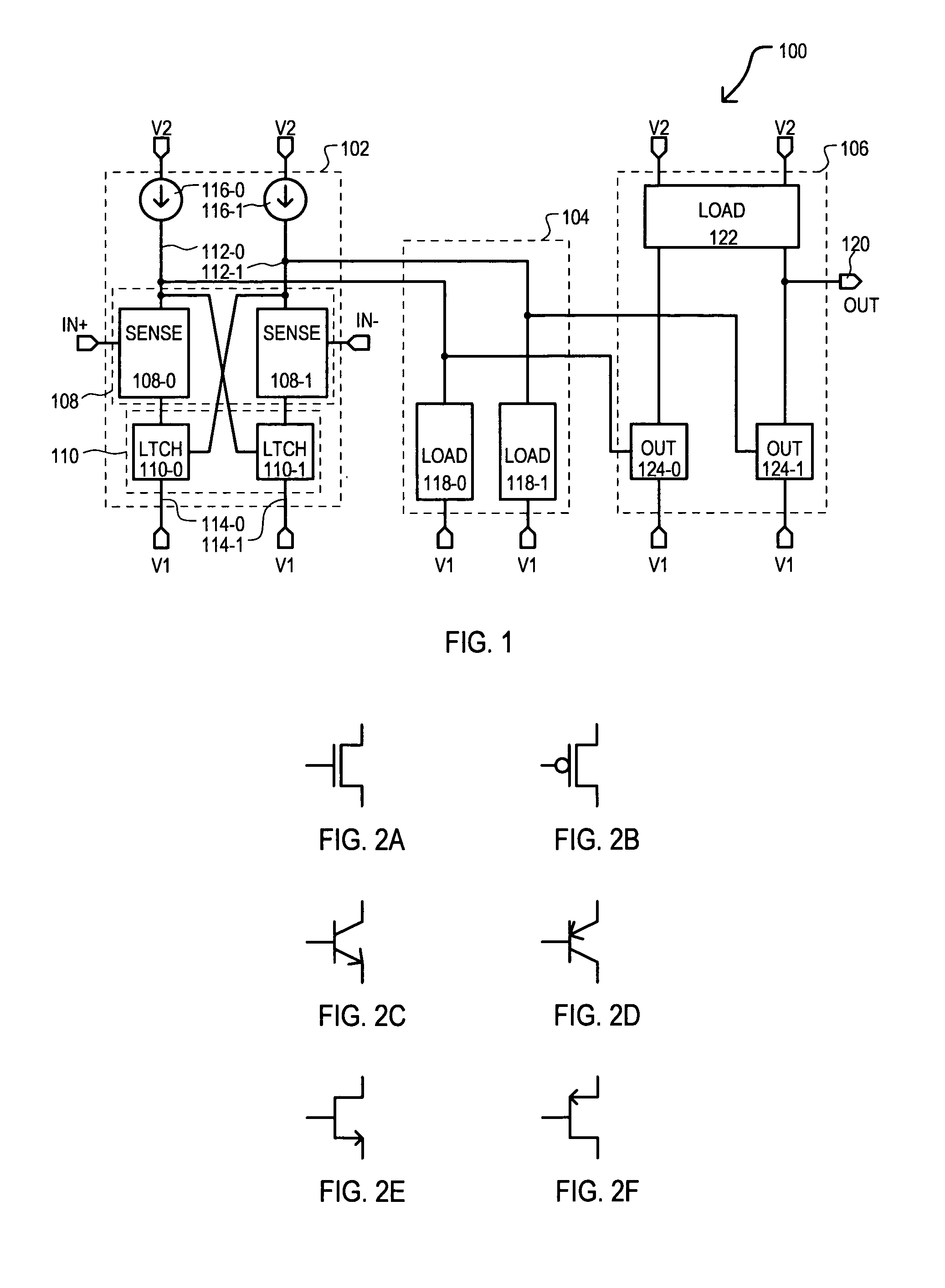
Differential-to-single ended signal converter circuit and method
ActiveUS8085067B1Multiple input and output pulse circuitsCurrent/voltage measurementPower flowSignaling nodes
A differential-to-single ended converter circuit can include a latching circuit having first and second latch field effect transistors (FETs) with drains and gates cross-coupled between a first latch node and a second latch node. The source-drain paths of the first and second latch FETs are coupled to a first reference potential node via separate current paths. A sense circuit can include a first sense FET having a source-drain path coupled between the first sense node and the first reference potential node, and a gate coupled to a first input node. A second sense FET has a source-drain path coupled between the second sense node and the first reference potential node, and a gate coupled to a second input node. An output circuit can have a first output FET with a source-drain path coupled between a first output supply node and an output signal node, and a gate coupled to the first latch node, and a second output FET with a source-drain path coupled between the output signal node and a second output supply node.
Owner:MONTEREY RES LLC
Decoupling capacitor control circuit and method for enhanced ESD performance
ActiveUS20080232019A1TransistorEmergency protective arrangements for limiting excess voltage/currentEngineeringVoltage reference
A decoupling capacitor control circuit is configured to be coupled between supply voltage and reference voltage planes. The control circuit includes a decoupling capacitor having a first node configured to be coupled to the supply voltage plane and having a second node. A first switching element has a first signal node coupled to the second node of the decoupling capacitor and has a second signal node and a control node. A second switching element has a first signal node coupled to the first node of the decoupling capacitor and has a second signal node coupled to the control node of the first switching element, and has a control node. A biasing circuit is coupled to the control nodes of the first and second switching elements. The biasing circuit activates both switching elements when the decoupling capacitor is not defective and deactivates both switching elements when the decoupling capacitor is defective.
Owner:BAE SYST INFORMATION & ELECTRONICS SYST INTERGRATION INC
Information perception method based on knowledge base of operation and maintenance
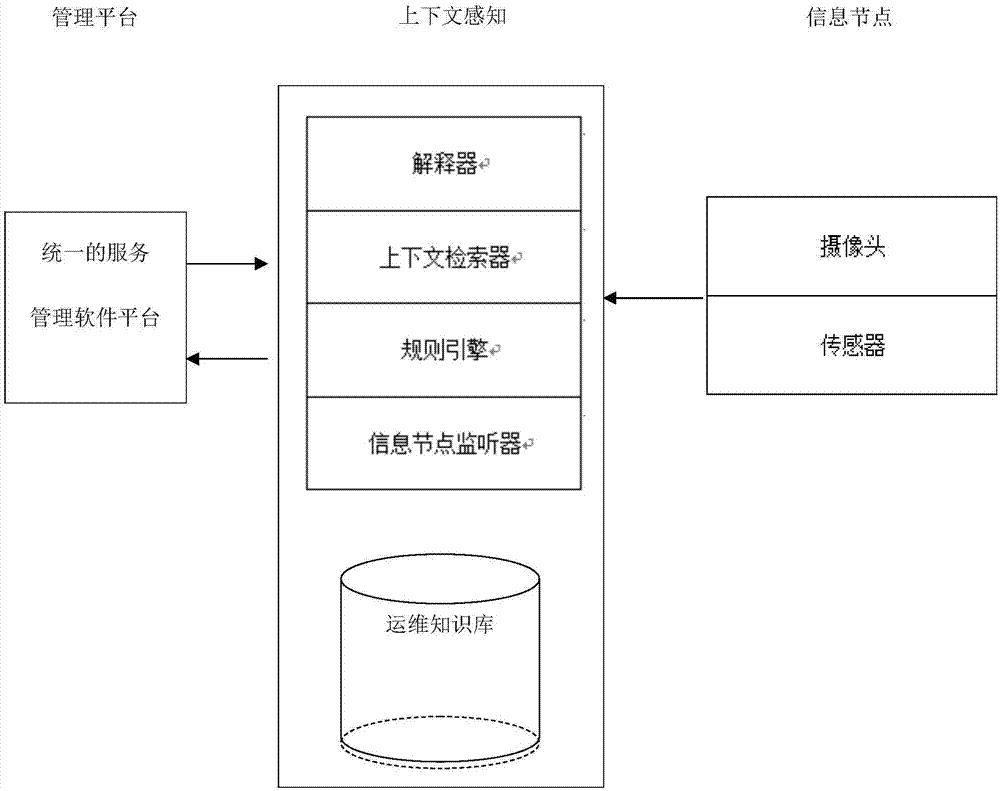
InactiveCN107066577ASpecial data processing applicationsDatabase design/maintainanceSignaling nodesComputer science
The invention discloses an information perception method based on a knowledge base of operation and maintenance. An information node monitor is responsible for monitoring update of distributed information nodes and stored context information; a context retriever is responsible for indexing and retrieving the stored context information; an interpreter is used to provide services for a signal node monitor and the context retriever; and when occurrence of context changes is retrieved, a rule engine will be used for self-adaption management, will deduce a senior context according to rules in the knowledge base of the operation and maintenance, and will provide a uniform service management software platform, so that automatic early waning and prevention of accidents could be achieved.
Owner:SHANGHAI DATACENT SCI CO LTD
System and Method for a Transformer and a Phase-Shift Network
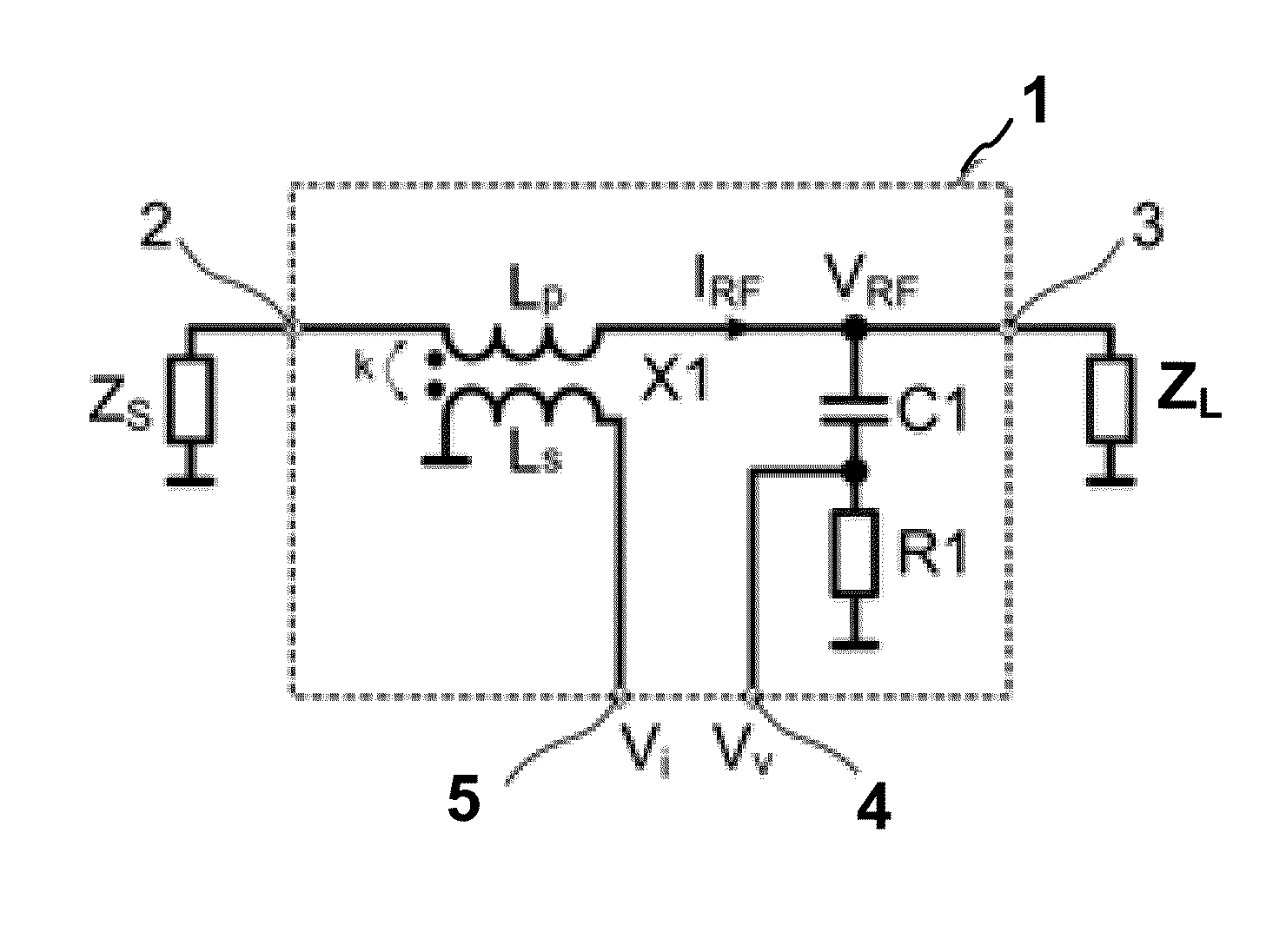
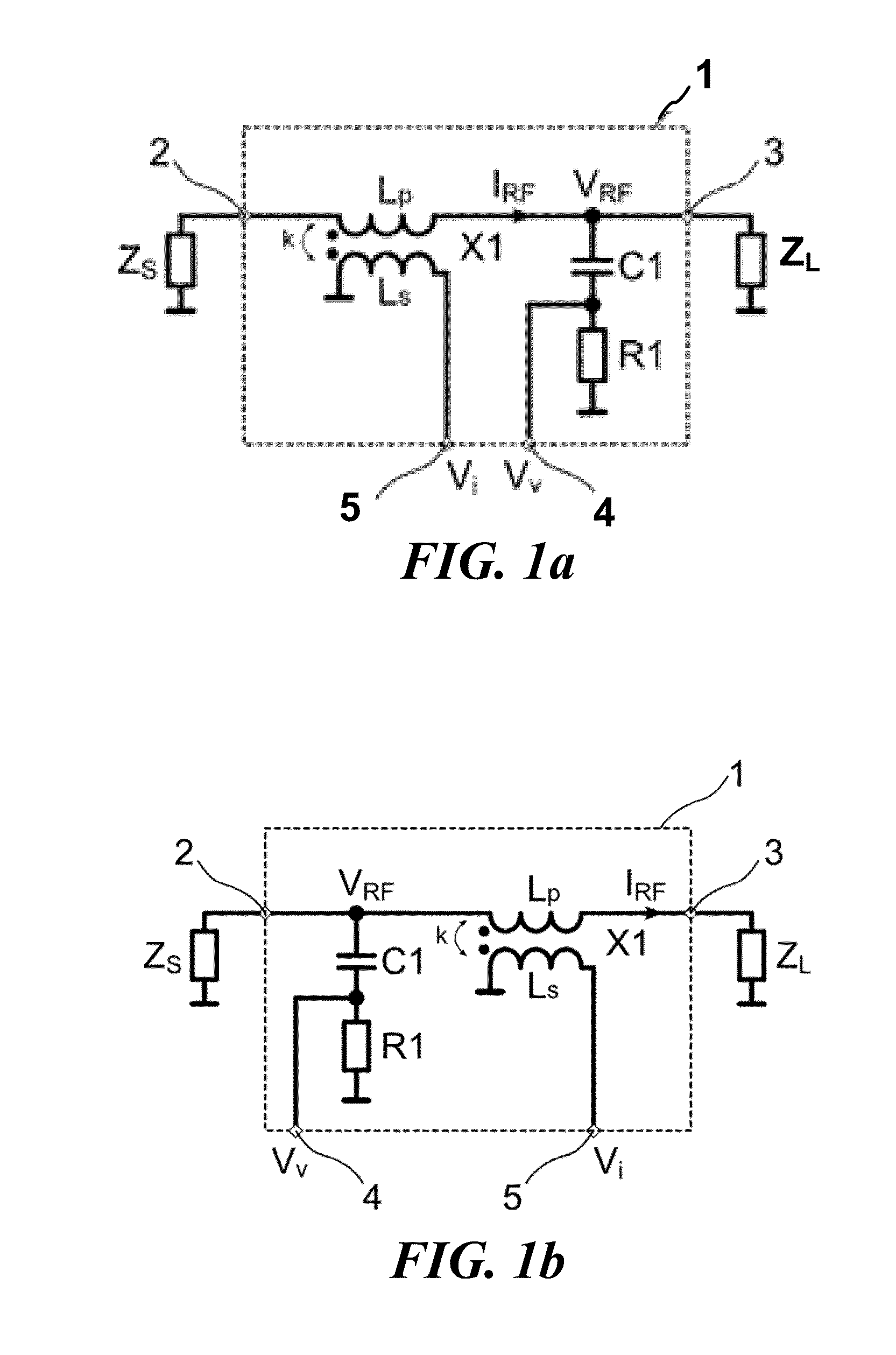
ActiveUS20150002146A1Multiple-port networksMagnitude/direction of magnetic fieldsPhase shiftedPhase difference
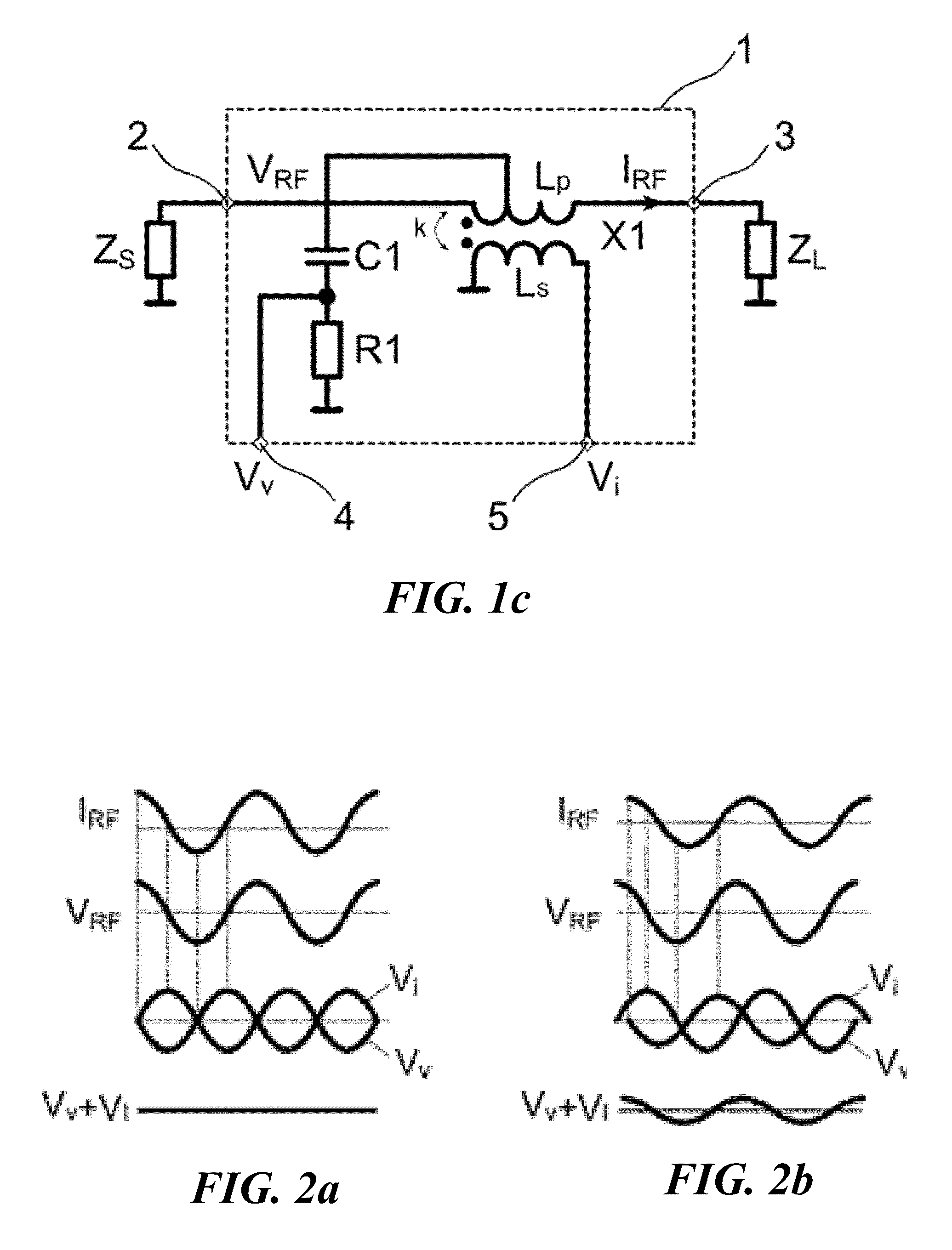
In accordance with an embodiment, a circuit includes a magnetic transformer having a first winding coupled between a first signal node and a second signal node, and a second winding coupled between a first reference node and a current measurement node. A phase shift network is coupled between the second node and a voltage measurement node, and the circuit is configured to indicate an impedance matching condition based on an amplitude difference and a phase difference between the voltage measurement node and the current measurement node.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AG
AT (Autotransformer) line fault ranging system with built-bin GPS (Global Positioning System) module
ActiveCN101923138AImprove ranging accuracyGuaranteed synchronizationSatellite radio beaconingFault locationAutotransformerEconomic benefits
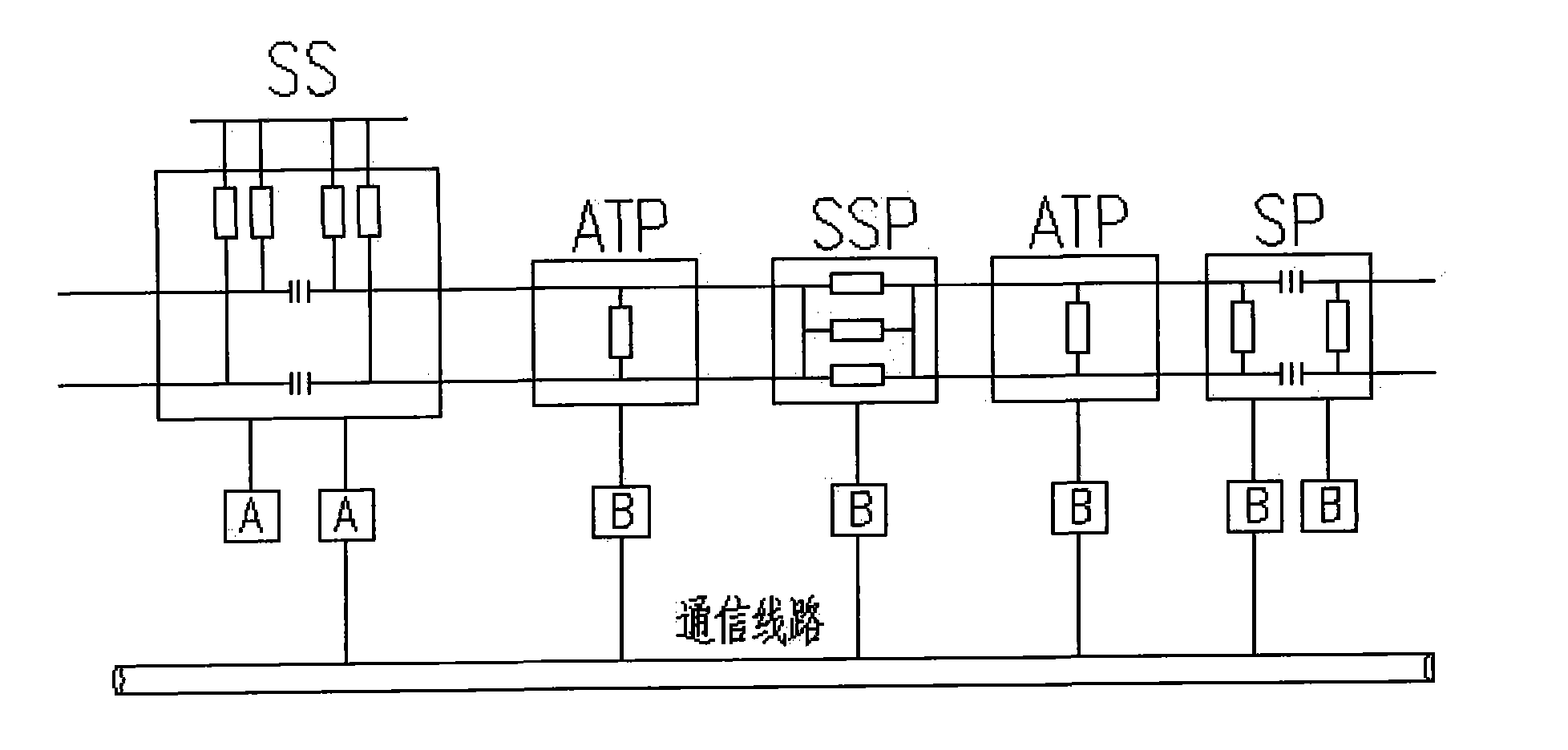
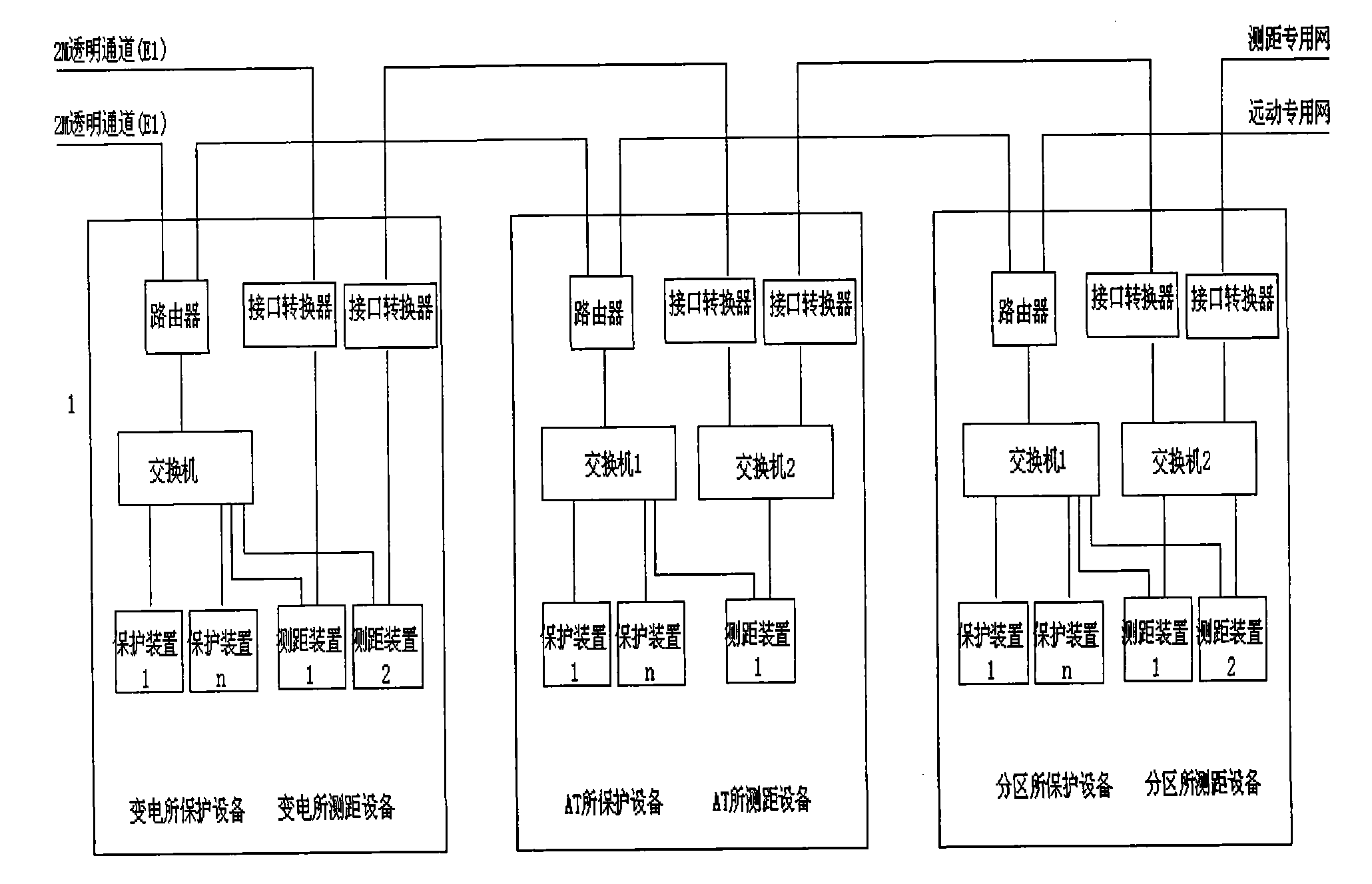
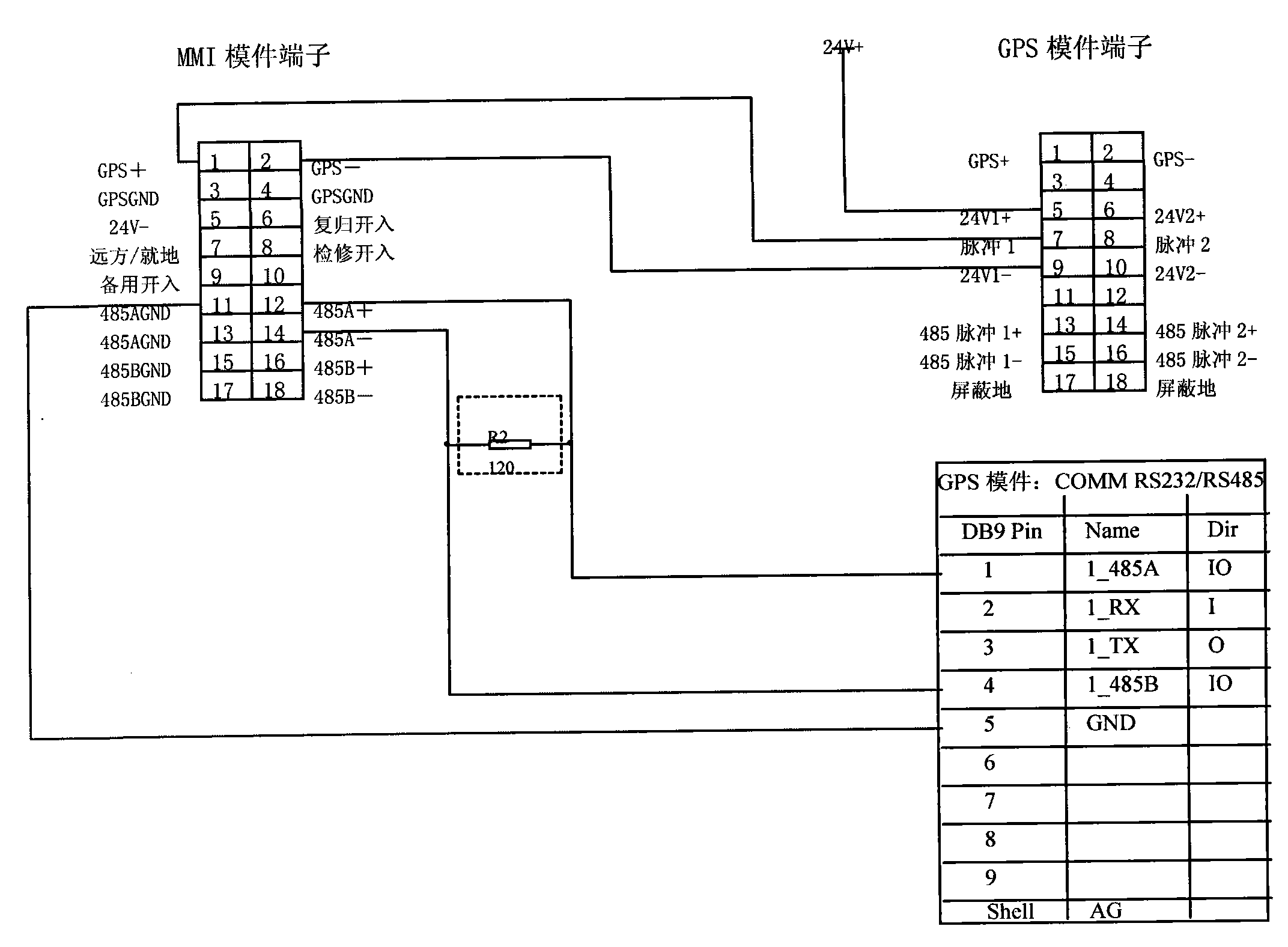
The invention discloses a fault ranging system scheme with a built-bin GPS (Global Positioning System) module of a high-speed electric railway in an AT (Autotransformer) power supply mode. The ranging system can realize the accurate synchronization of a clock without the match of a GPS pulse signal node of another device, has simple external wiring and is practical and convenient, and the accurate clock synchronization of the built-in GPS is an important link for ensuring the ranging accuracy, can greatly save human and material resources for searching fault points, lighten the labor intensity of a railway power supply maintenance department, troubleshoot as soon as possible, recover power supply and reduce loss due to power failures. Under the background that high-speed railways are the focus of railway construction, the invention inevitably creates favorable economic benefits.
Owner:南京国电南自轨道交通工程有限公司
Integrated Switch and Limiter Circuit
ActiveUS20150162901A1Fast response timeAdjustable voltageResonant circuit tuningPulse automatic controlCouplingEngineering
A fast response time, self-activating, adjustable threshold limiter including a limiting element LE, a first coupling element CE1 electrically connected from a signal node of LE to a control input of LE, and a second coupling element CE2 electrically connected from the control input of LE to a nominal node of LE. An initial bias (control) voltage is also supplied to the control input of LE to dynamically control the limiting threshold for the limiter. Embodiments include usage of self-activating adjustable power limiters in combination with series switch components in a switch circuit in lieu of conventional shunt switches.
Owner:PSEMI CORP
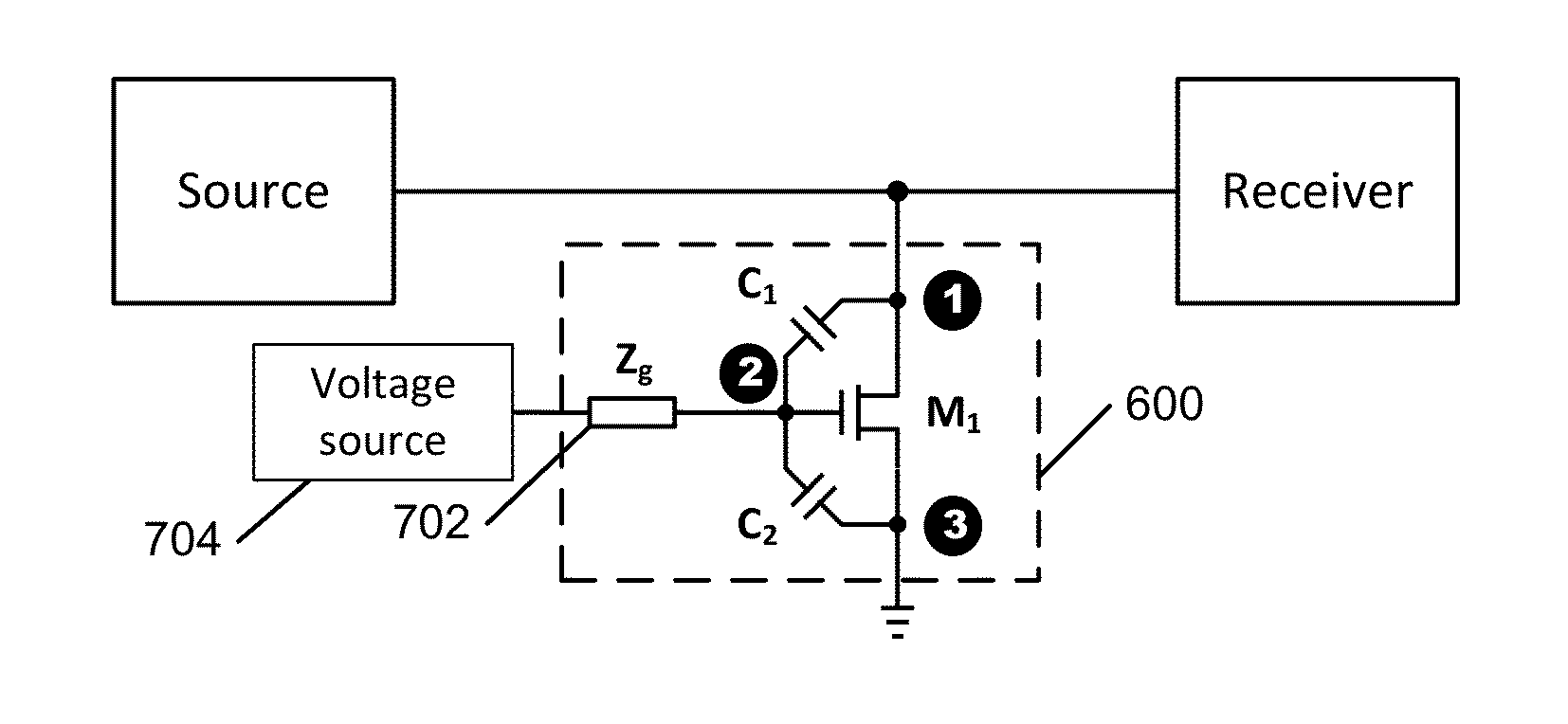
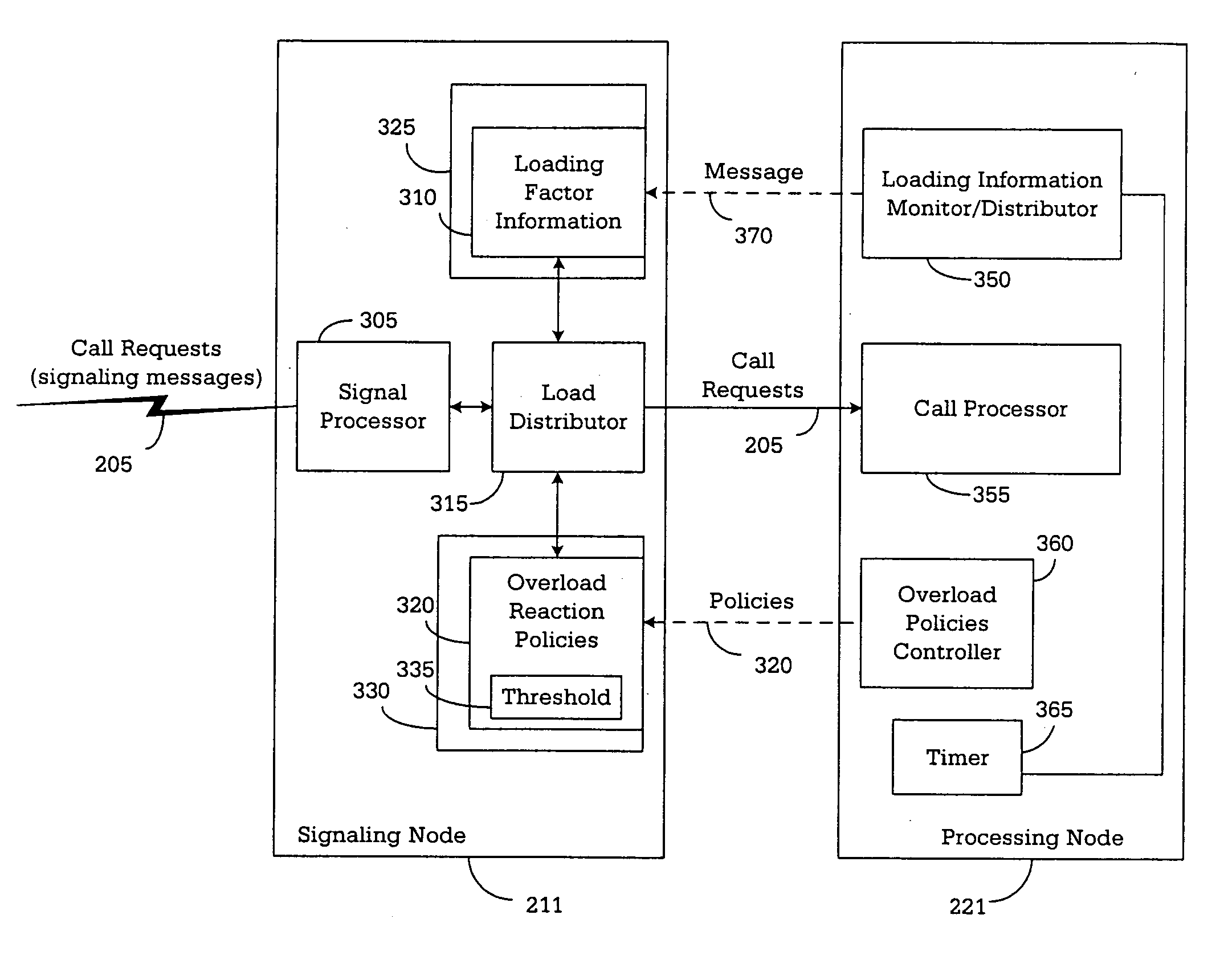
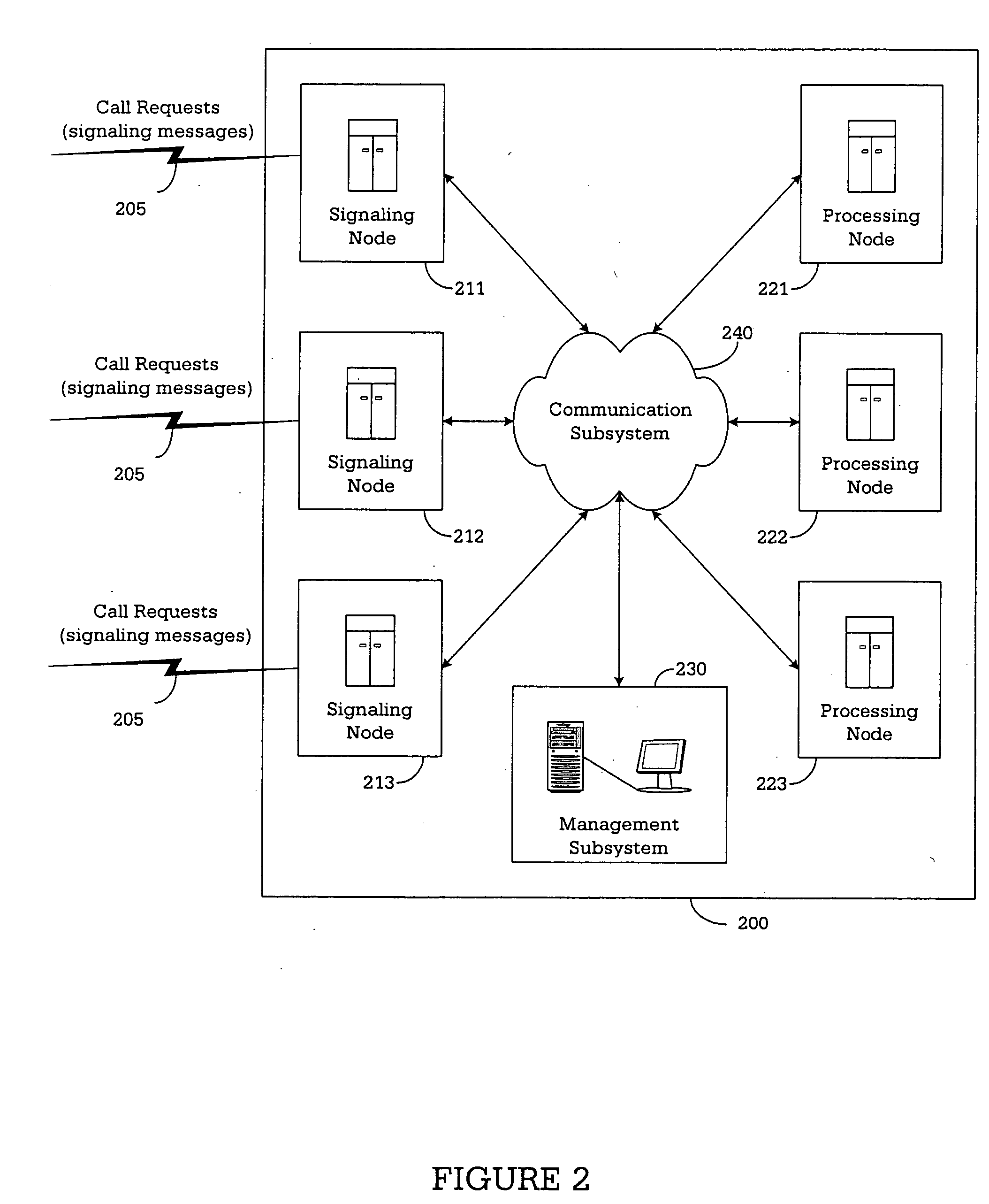
Apparatus and method for real-time overload control in a distributed call-processing environment
A telecommunication node controls overload conditions in a distributed processing environment using processing nodes that include: (i) a load monitor configured to monitor a loading factor for the processing node and produce real-time loading factor information; and (ii) a call processor operable to process signaling messages. In addition, the telecommunication node uses signaling nodes that include: (i) a load information list including the real-time loading factor information received from each of the processing nodes; (ii) an overload policy list including programmable overload reaction policies for each of the processing nodes, in which the overload reaction policies control overload conditions of the processing nodes based on the real-time loading factor information; and (iii) a load distributor configured to select one of the processing nodes to process one of the signaling messages based on the real-time loading factor information and the overload reaction policies.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com