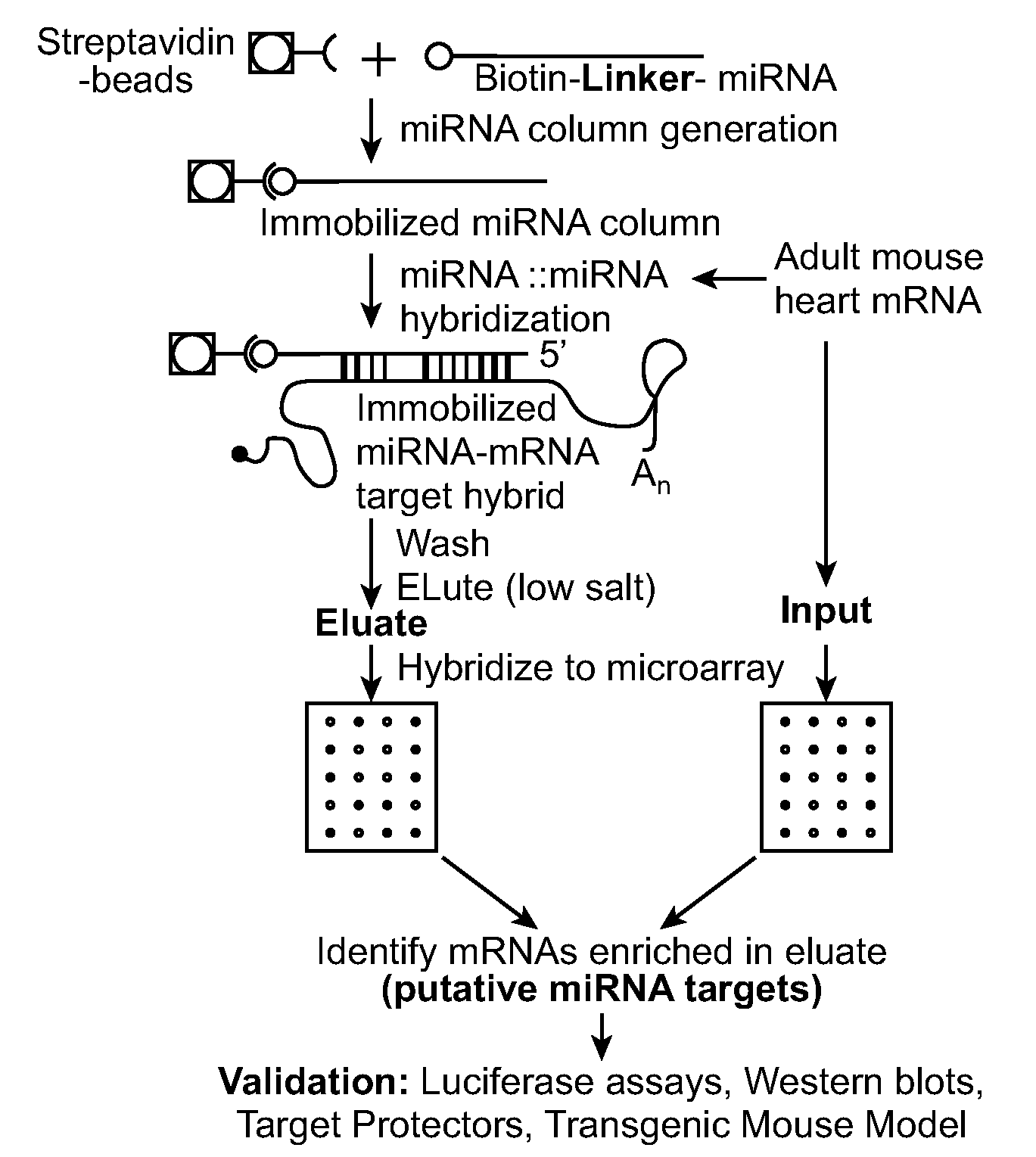
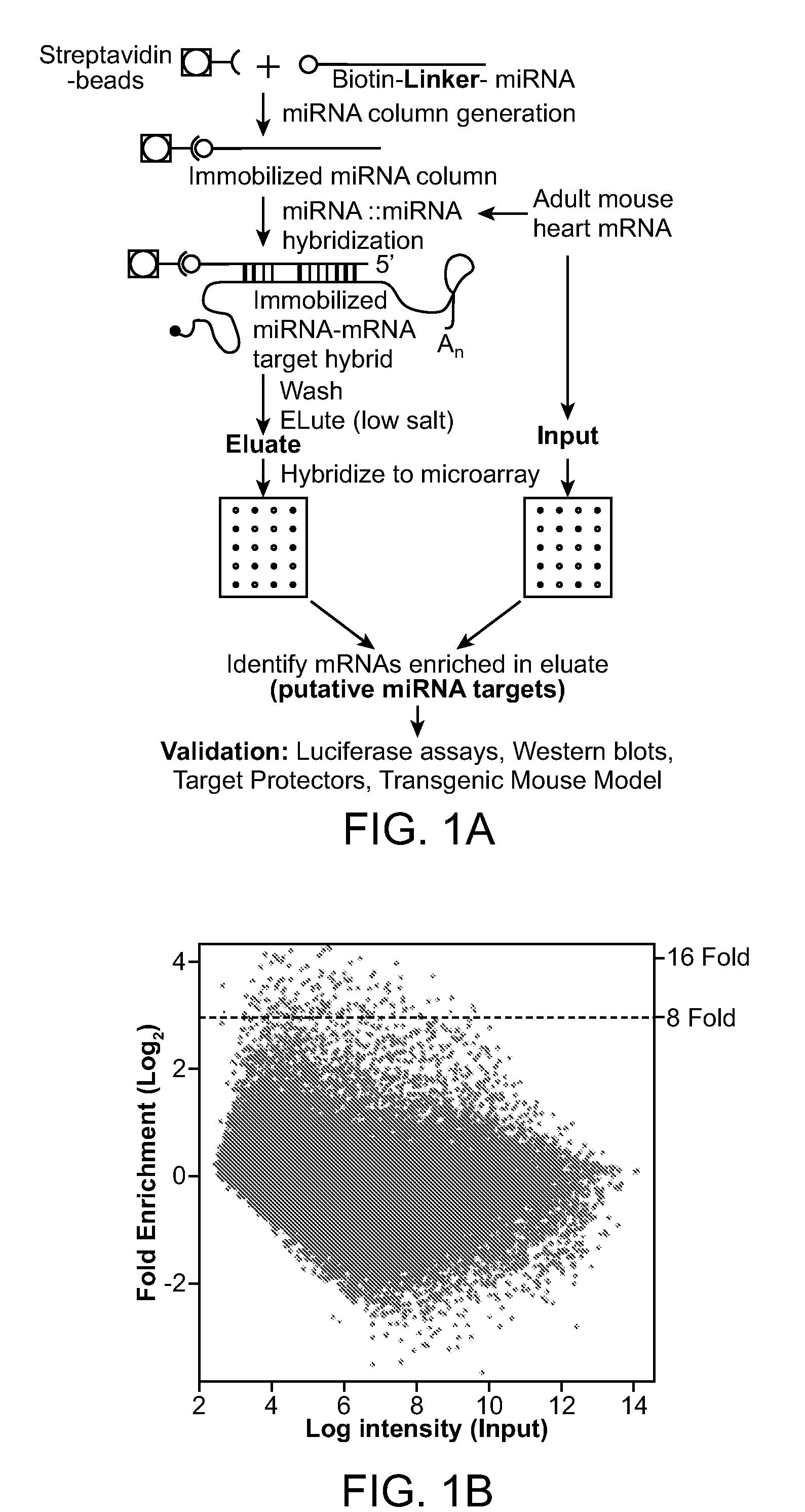
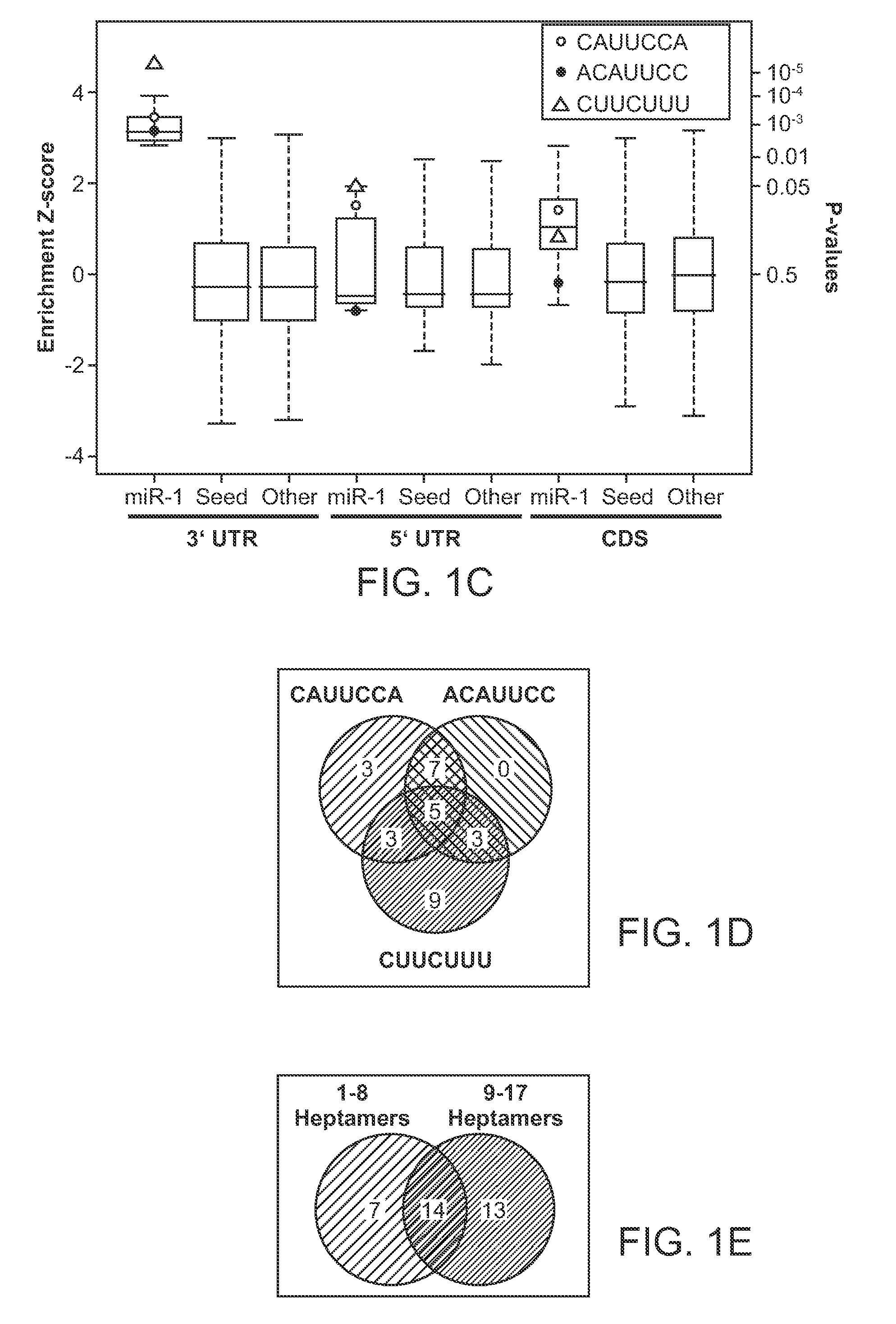
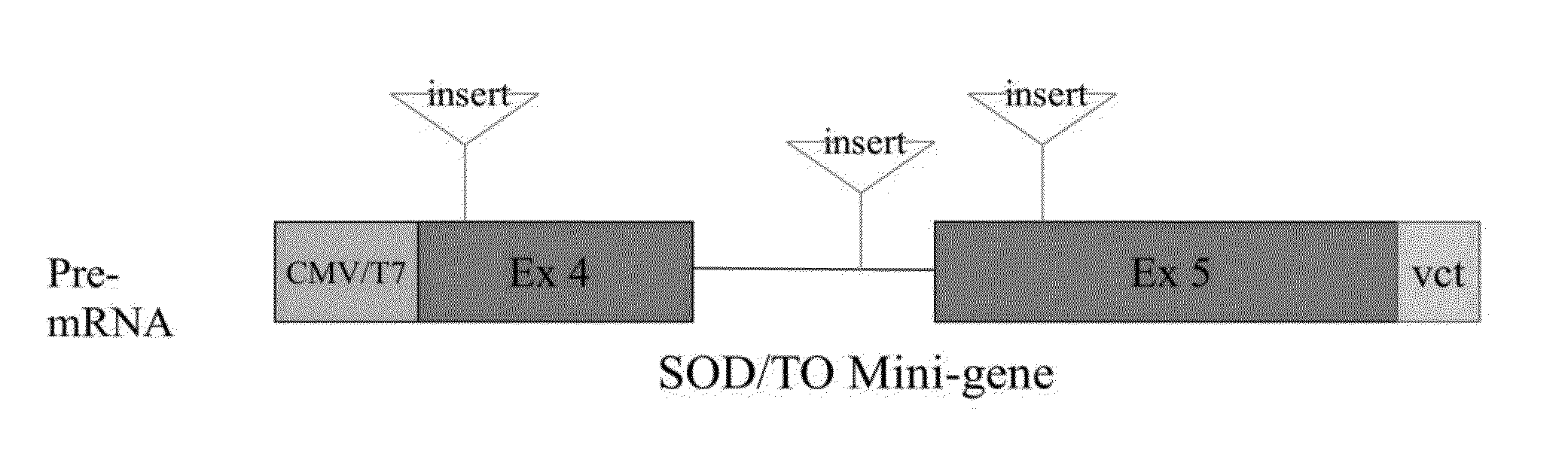
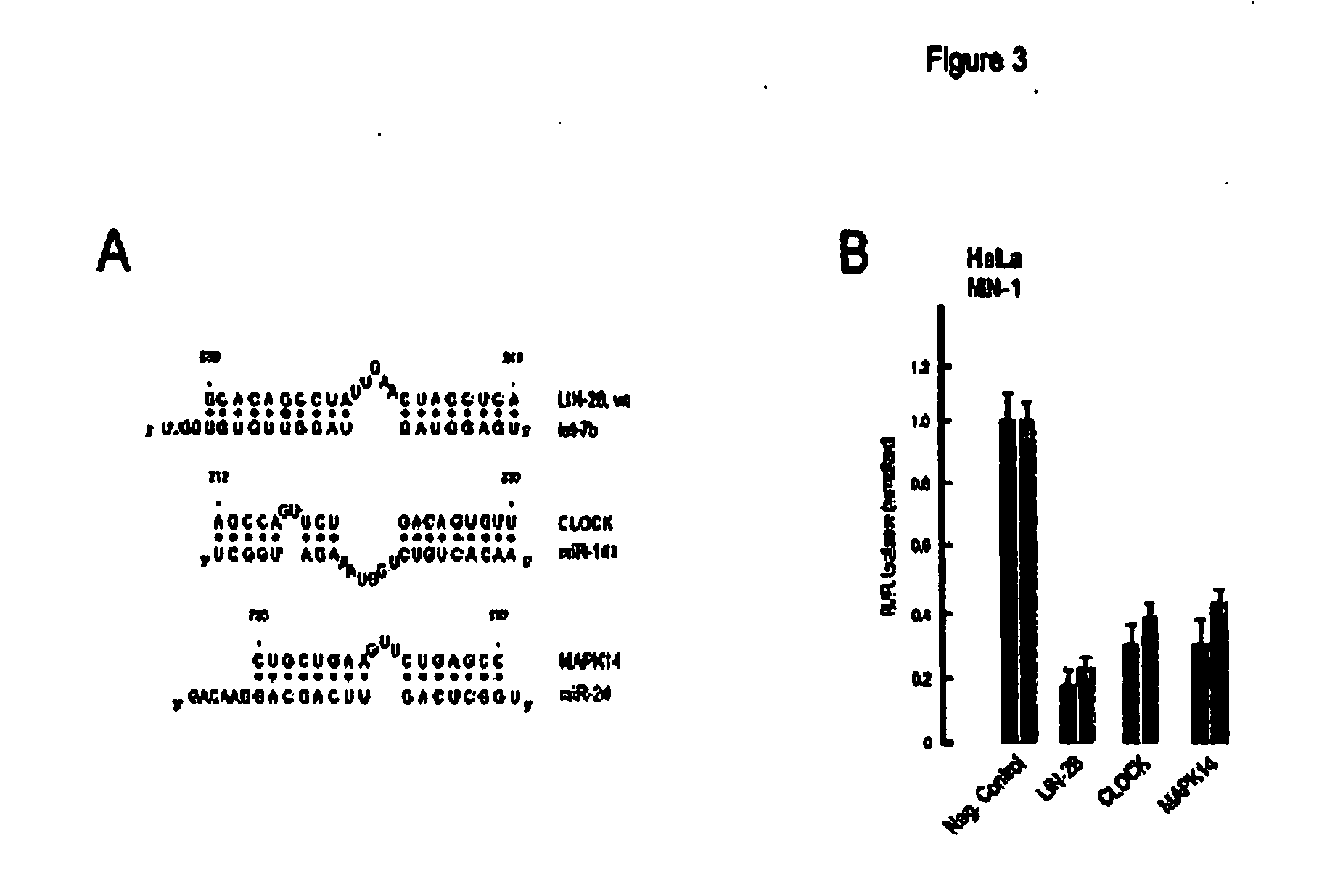
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
137 results about "Rna targeting" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
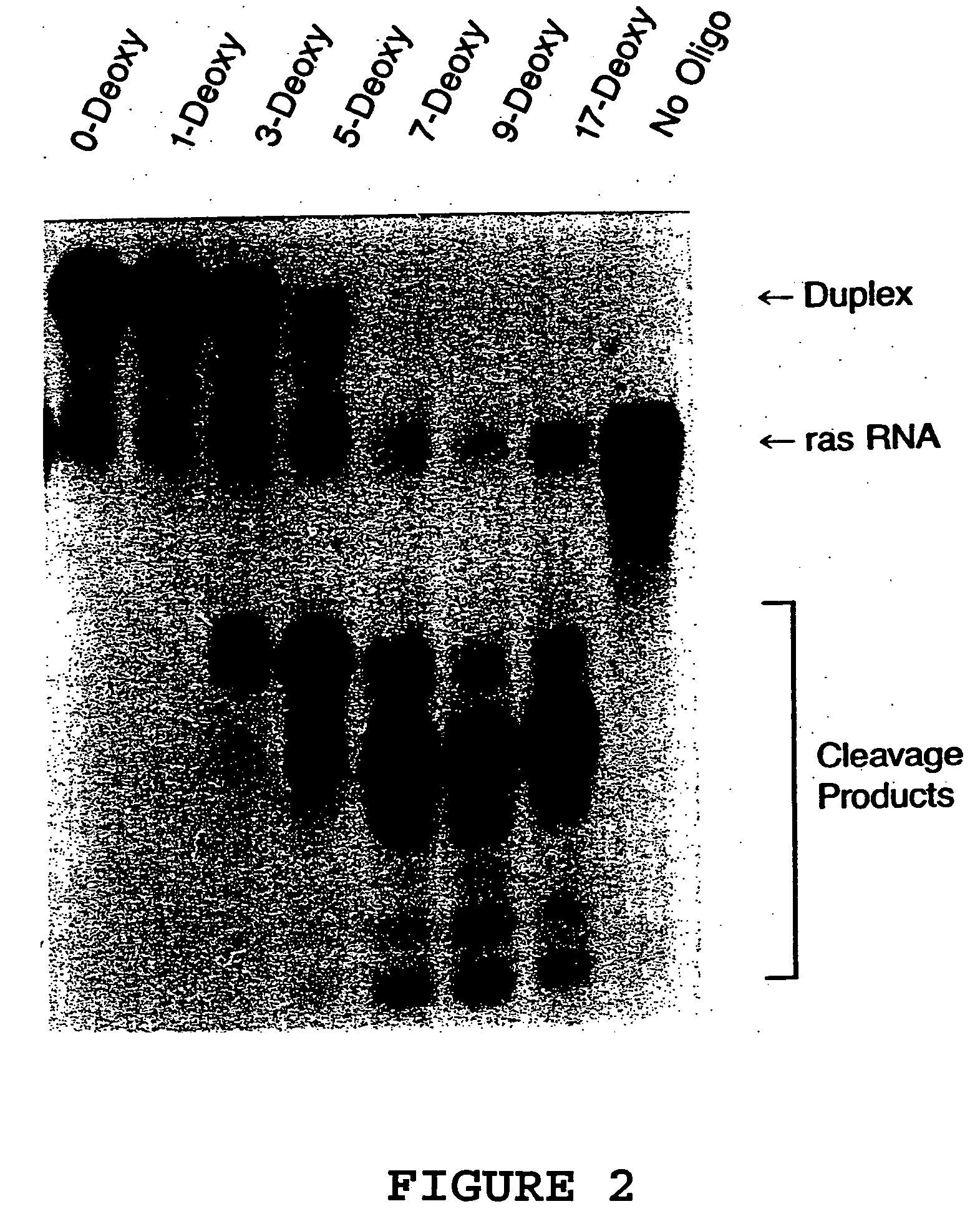
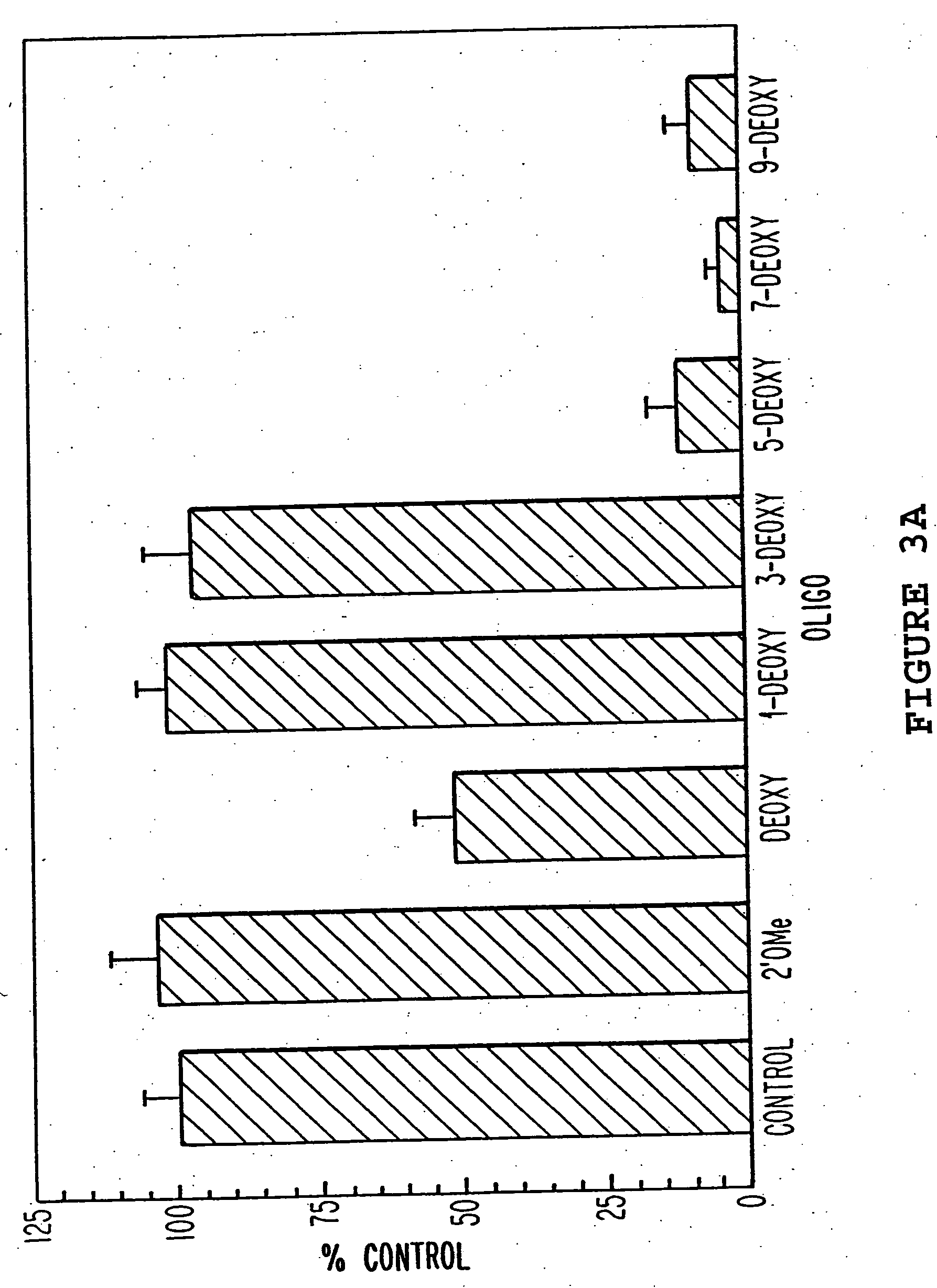
Synthetic oligomers having chirally pure phosphonate internucleosidyl linkages mixed with non-phosphonate internucleosidyl linkages
InactiveUS6028188AHigh binding affinityImprove stabilitySugar derivativesGenetic material ingredientsOligomerRna targeting
Oligomers having chirally pure phosphonate internucleosidyl linkages mixed with non-phosphonate internucleosidyl linkages which hybridize to RNA target sequences and methods for their preparation are provided.
Owner:SIMON LIONEL
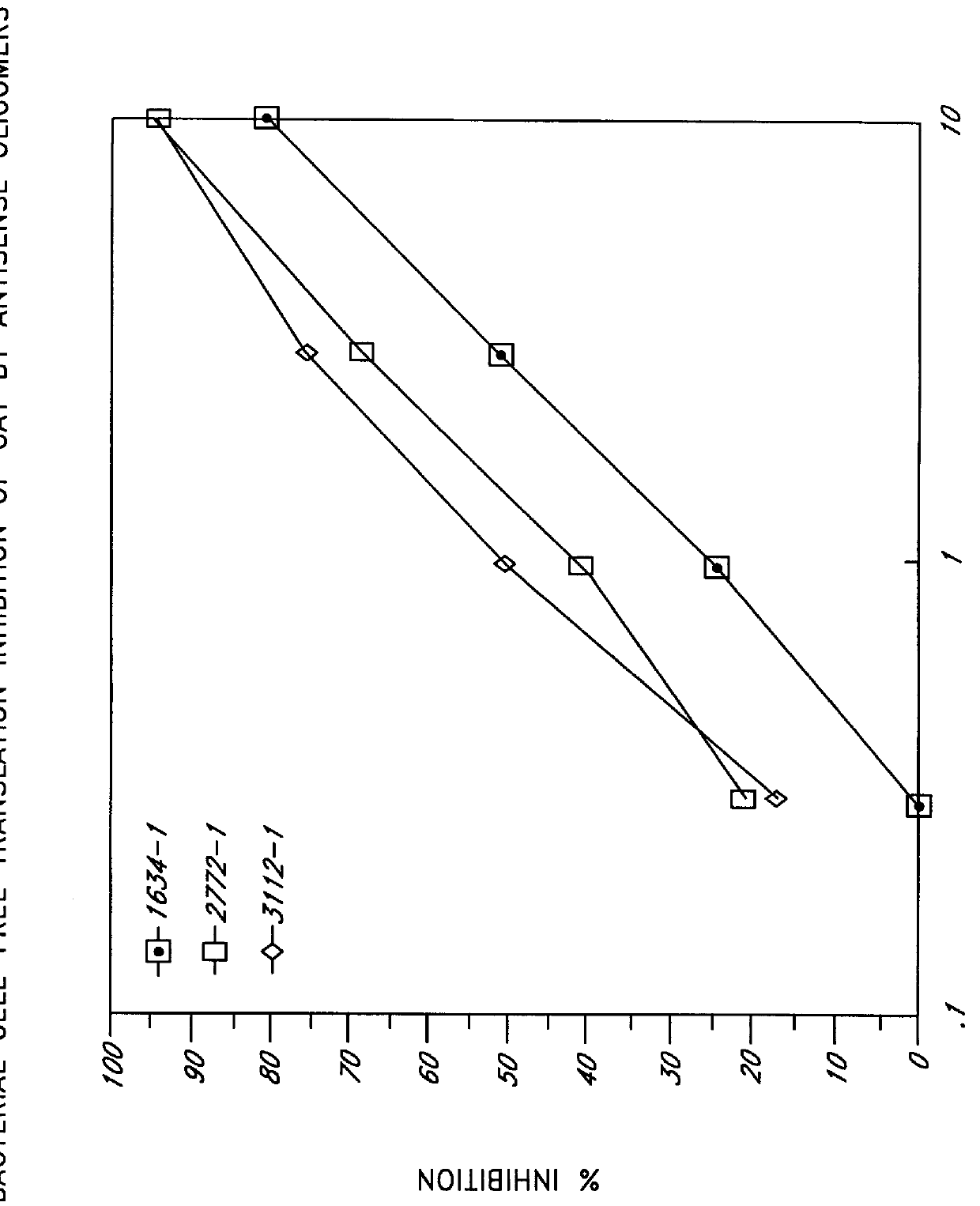
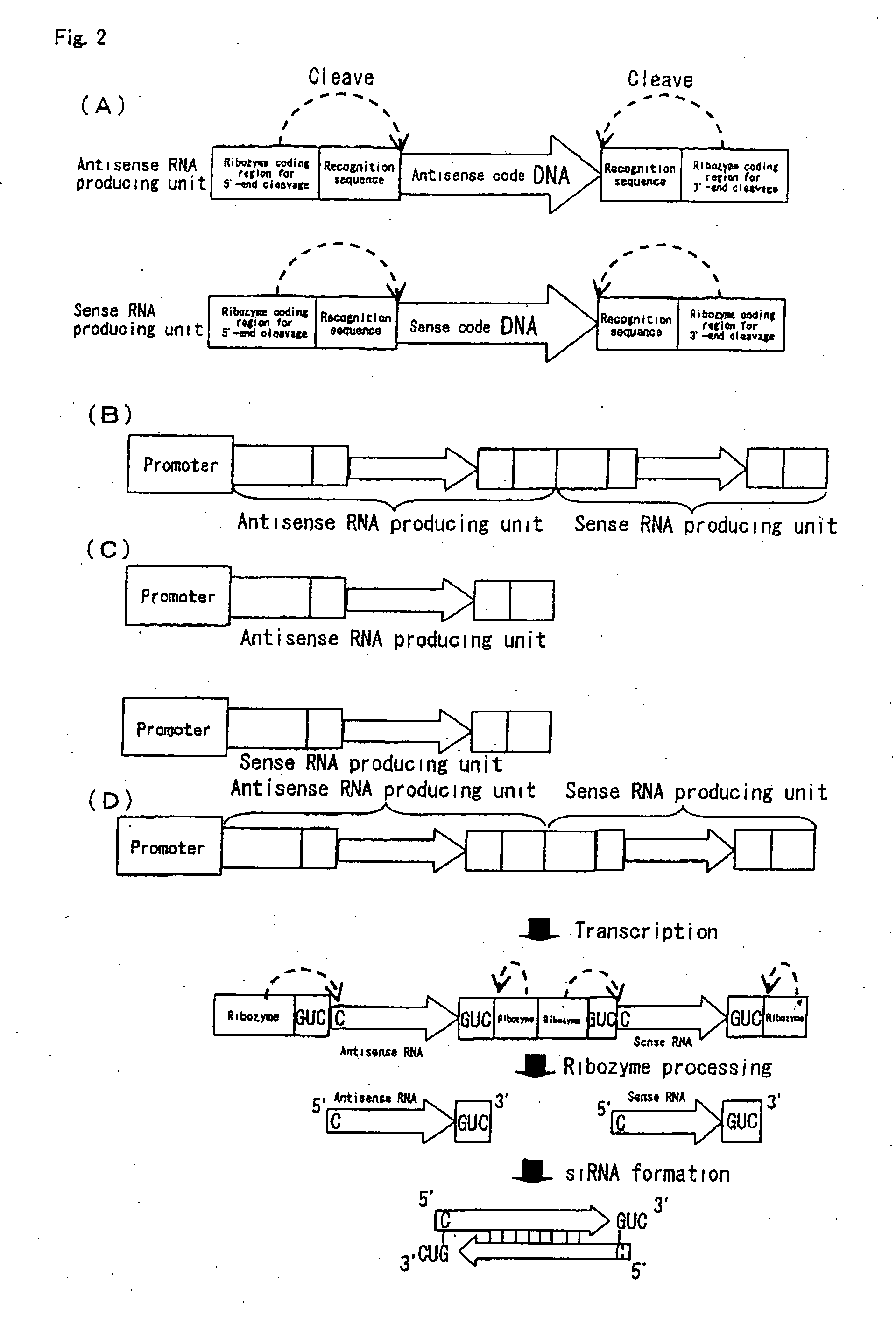
siRNA expression system and method for producing functional gene knock-down cell using the system
InactiveUS20050197315A1Producing RNAi more efficiently, stably, and economically in cellsSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementIn vivoFunctional genes
The in vivo siRNA expression system according to this invention is a system that intracellularly expresses small interfering (si) RNAs and comprises antisense and sense code DNAs coding for antisense and sense RNAs targeting any region of a target gene mRNA and one or more promoters that function to express the antisense and sense RNAs from the antisense and sense code DNAS, respectively.
Owner:TOUDAITLO LTD
Small molecules modulating activity of micro RNA oligonucleotides and micro RNA targets and uses thereof
ActiveUS7687616B1Inhibition of activityImprove translationSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroRNAPolynucleotide
The present invention describes a novel approach whereby small molecules may be used to modulate activity of microRNA and GAM oligonucleotides. This mode of therapy allows inter alia up regulation of a disease-related target gene of novel GAM oligonucleotides of the present invention, by countering the activity of a GAM oligonucleotides which naturally inhibits expression of that target gene. Nucleic acid molecules are provided respectively encoding 122,764 GAM oligonucleotides and their respective precursors, and 18602 GR polynucleotides, as are vectors and probes both comprising the nucleic acid molecules, and methods and systems for detecting GAM oligonucleotides and GR polynucleotides and specific functions and utilities thereof, for detecting expression of GAM oligonucleotides and GR polynucleotides, and for selectively enhancing and selectively inhibiting translation of the respective target genes thereof.
Owner:ROSETTA GENOMICS
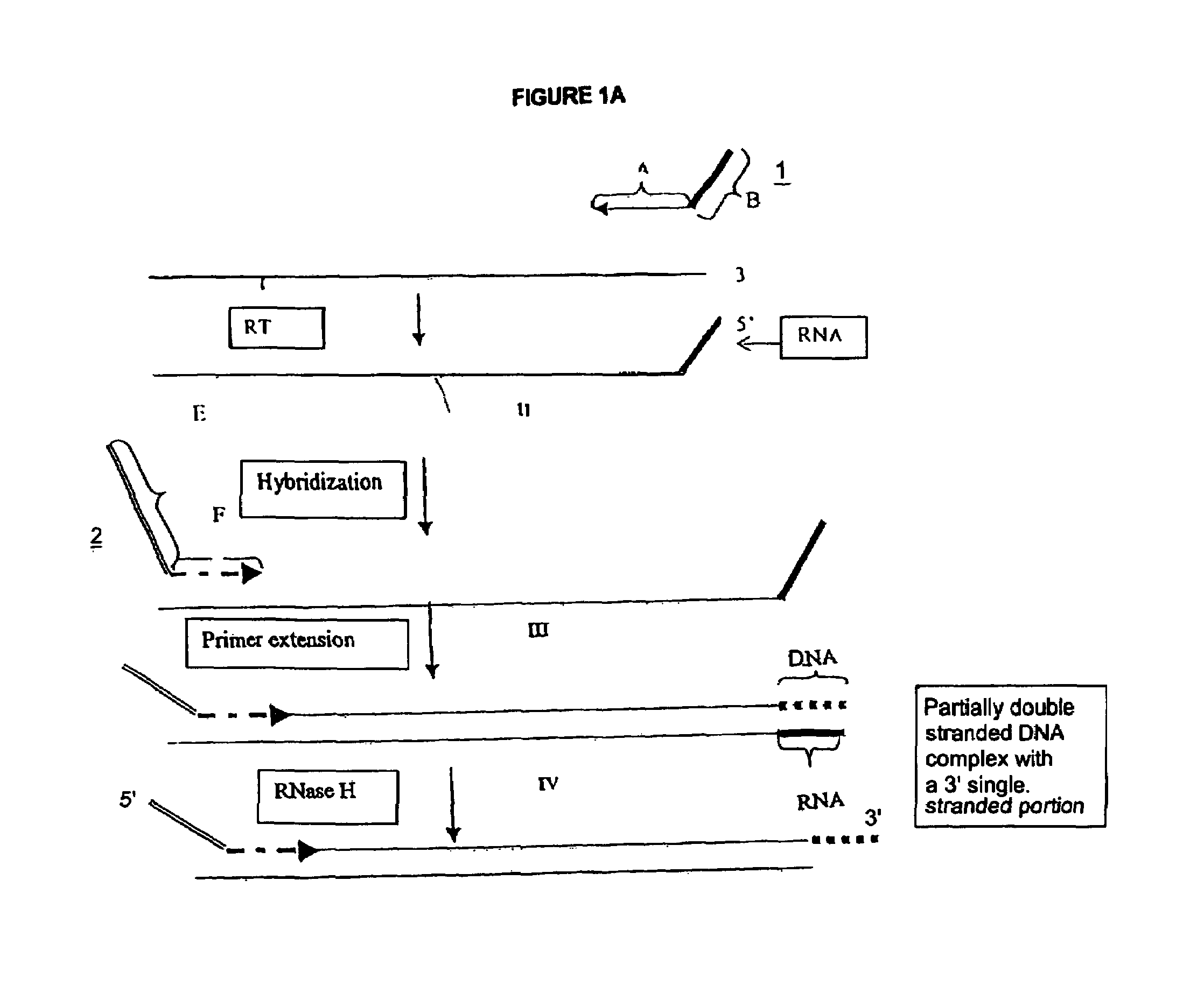
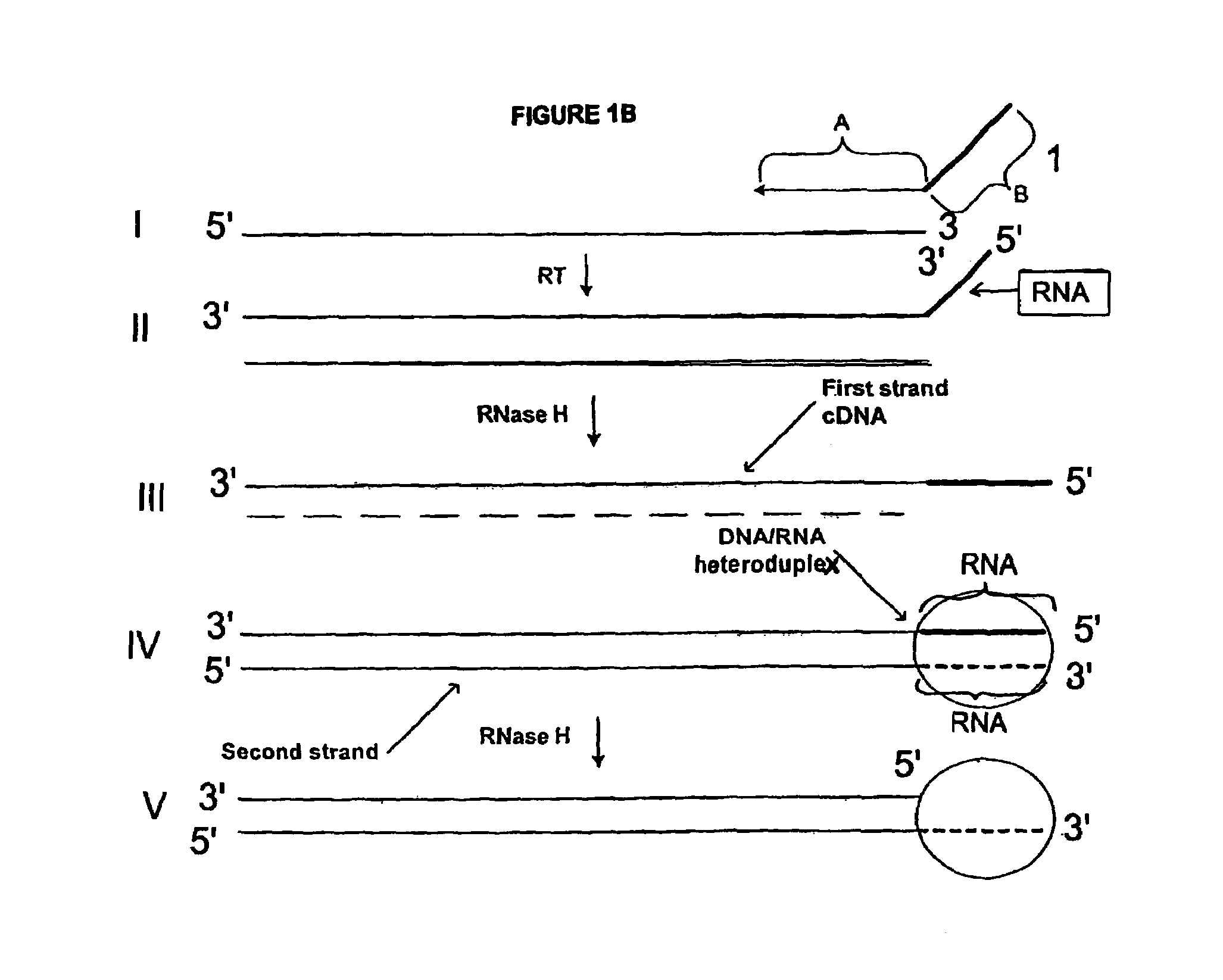
Methods for generating double stranded DNA comprising a 3' single stranded portion and uses of these complexes for recombination
Methods of recombining nucleic acids are provided. In particular, methods for the production of partially double stranded nucleic acids comprising a 3′ overhang from an RNA target and use in methods of recombining polynucleotides is described. These methods do not require thermocycling. The present invention also provides methods of recombining and selection which allow for identification of proteins comprising improved or desired characteristics.
Owner:NUGEN TECH
Process of knocking out Wnt3a gene and verification method thereof
InactiveCN106434752AHigh targeting accuracyShort experiment cycleFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionValidation methodsWNT3A gene
The invention discloses a process of knocking out Wnt3a gene and a verification method thereof. The knockout and verification of Wnt3a gene are finished through the following steps: establishment of a Cas9 lentiviral vector for Wnt3a gene, culture and passage of HepG2 cell, lentivirus infection and screening of target cell, verification of gene knockout efficiency through a mispairing enzyme method, cell protein analysis and cell proliferation detection by a CCK-8 method. The invention has the following advantages: the Wnt3a gene is knocked out by establishing a Cas9 double-vector lentivirus system for the first time; Crispr / Cas9 is a technology for accurately editing specific site of the genome of any species, and the cell-level single gene or multiple genes can be knocked out by the technology; compared with other gene editing technologies, the method has the advantages that the targeting accuracy is higher; only if the RNA target sequence is completely matched with the genome sequence, can the Cas9 cut the DNA and realize simultaneous knockout of multiple sites of the target gene; and moreover, the experimental period of vector establishment is short, the time and the cost are remarkably saved, and species limit is avoided.
Owner:AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF NANTONG UNIV
Methods and compositions for detection of small rnas
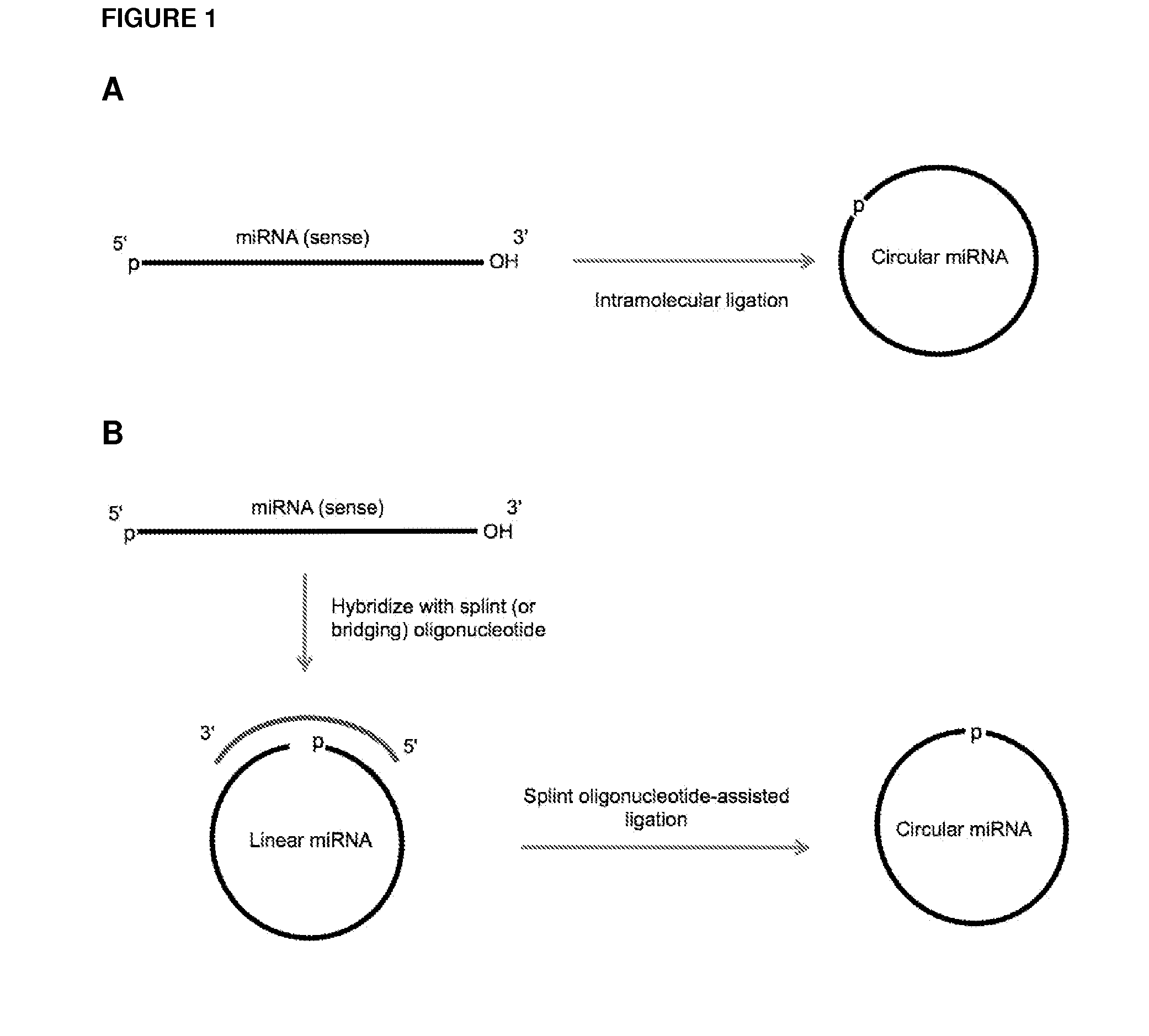
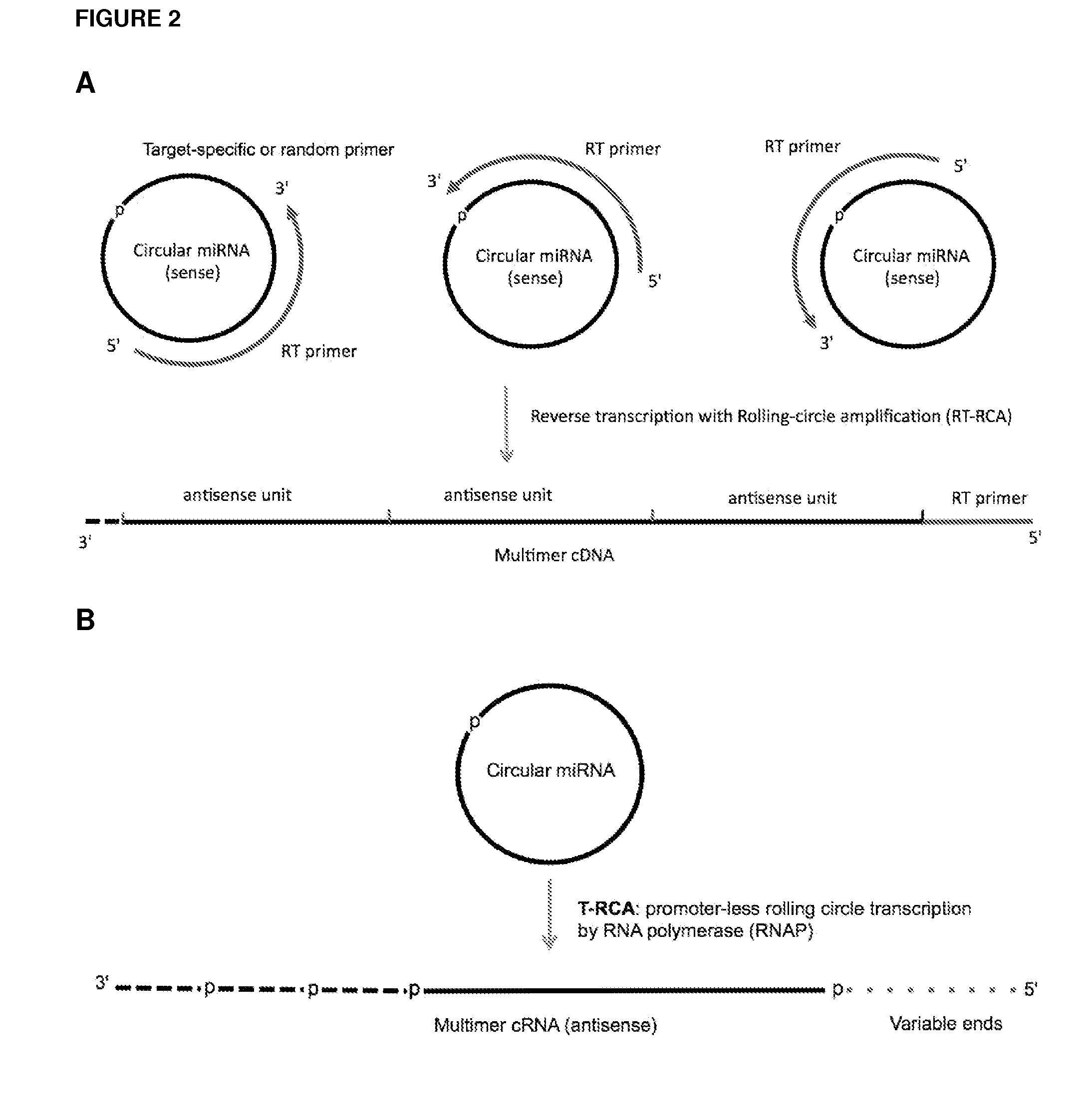
ActiveUS20120164651A1Improve efficiencySimilar efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementTrue positive rateCircular RNA
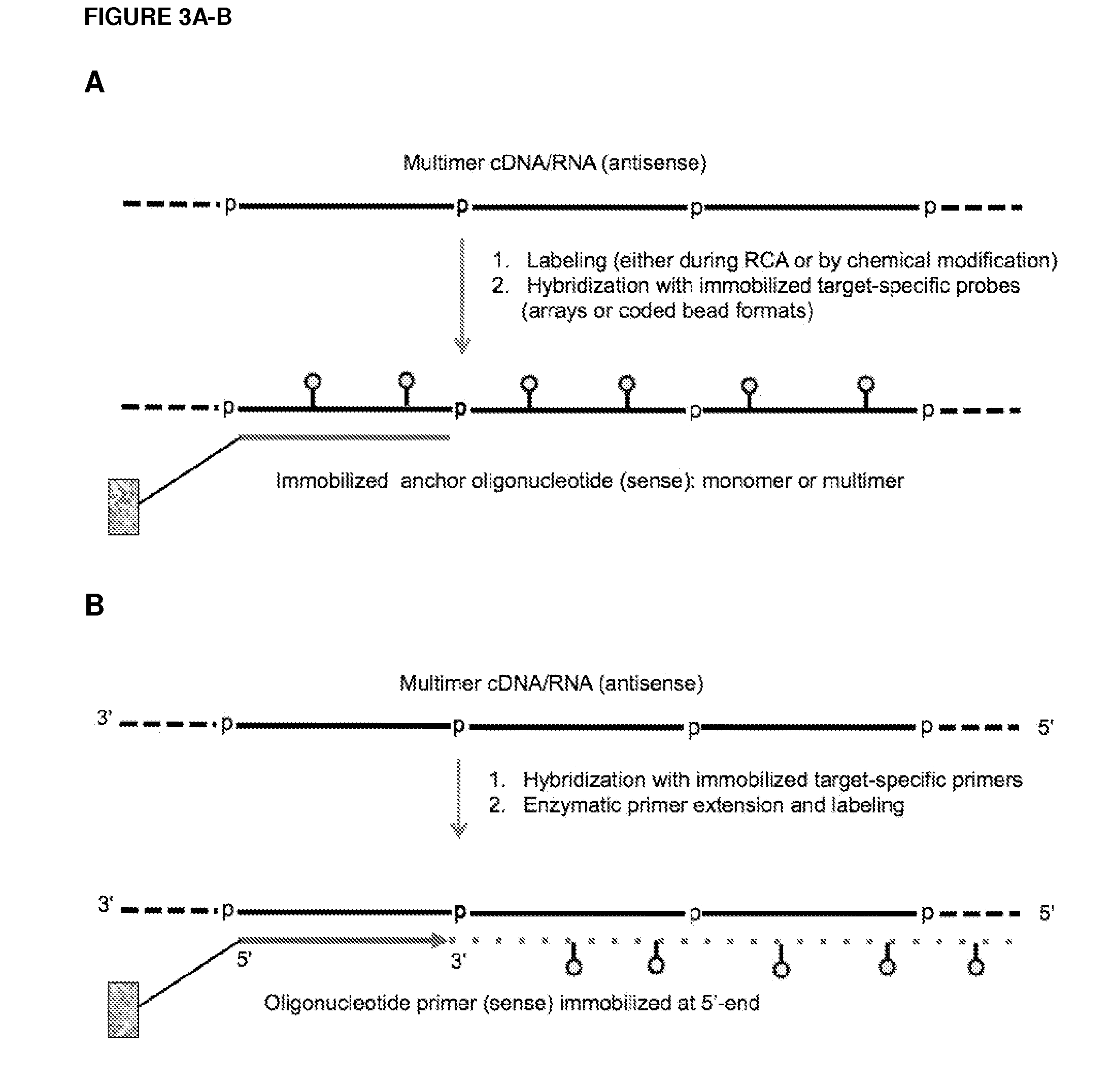
Currently, the circularization of small RNAs is broadly regarded as an obstacle in ligation-related assays and explicitly avoided while short lengths of linear RNA targets is broadly recognized as a factor limiting use of conventional primers in PCR-related assays. In contrast, the disclosed invention capitalizes on circularization of small RNA targets or their conjugates with oligonucleotide adapters. The circular RNA templates provide amplification of the target sequences via synthesis of multimer nucleic acids that can be either labeled for direct detection or subjected to PCR amplification and detection. Structure of small circular RNAs and corresponding multimeric nucleic acids provide certain advantages over current methods including flexibility in design of conventional RT and PCR primers as well as use of 5′-overlapping dimer-primers for efficient and sequence-specific amplification of short target sequences. Our invention also reduces number of steps and reagents while increasing sensitivity and accuracy of detection of small RNAs with both 2′OH and 2′-OMe at their 3′ ends. Our invention increase sensitivity and specificity of detection of microRNAs and other small RNAs with both 2′OH and 2′-OMe at their 3′ ends while allowing us to distinguish these two forms from each other.
Owner:REALSEQ BIOSCI INC
Methods of detecting dna, RNA and protein in biological samples
InactiveUS20140024024A1Microbiological testing/measurementBiological testingIn situ hybridisationProteinase activity
Novel methods of probing multiple targets in a biological sample are provide whereby the targets are DNA, RNA and protein. The method comprises subjecting the sample to an in situ hybridization reaction using a labeled nucleic acid probe that binds an RNA target, observing a signal, and optionally removing the signal. The method further comprises an antigen retrieval protocol, observing a signal, removing the signal, and optionally applying a protease treatment to access the sample's DNA targets by subjecting the sample to an in situ hybridization reaction using a labeled nucleic acid probe, observing a signal from the labeled DNA targets, and optionally removing the signal.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Circular RNA for inhibition of microrna
InactiveUS20150299702A1Avoid interactionControl degradationOrganic active ingredientsSugar derivativesDecoyCircular RNA
The present invention relates to inhibition of microRNAs (miRNA), other types of RNA and RNA-binding proteins. In particular the present invention relates to nucleic acid sequences that are circular and allow inhibition of the interactions between microRNAs and their RNA target and being resistant to degradation by exonucleases. Also, the present invention relates to nucleic acid sequence that are circular and acts as an RNA blocker or protein decoy.
Owner:AARHUS UNIV
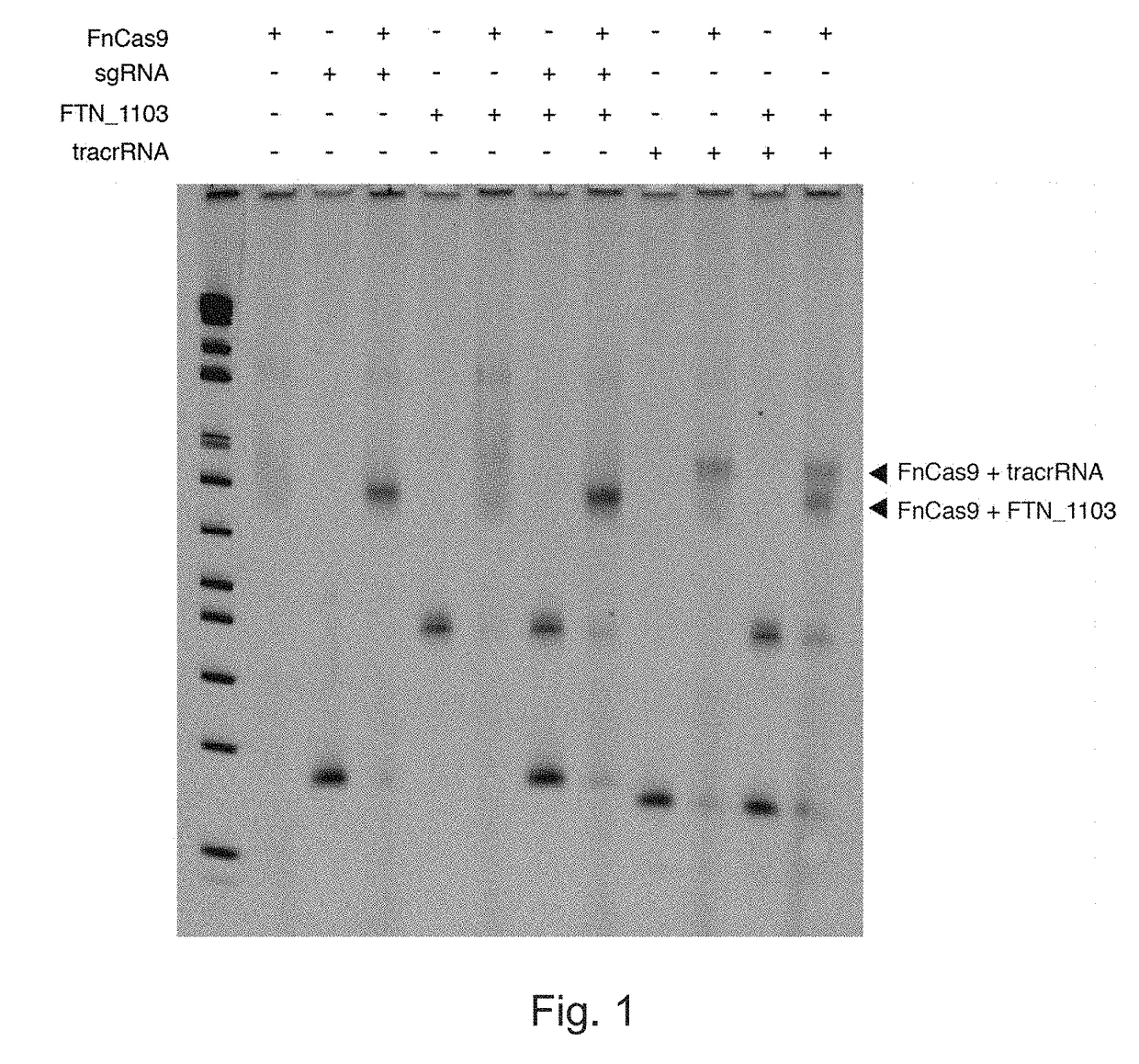
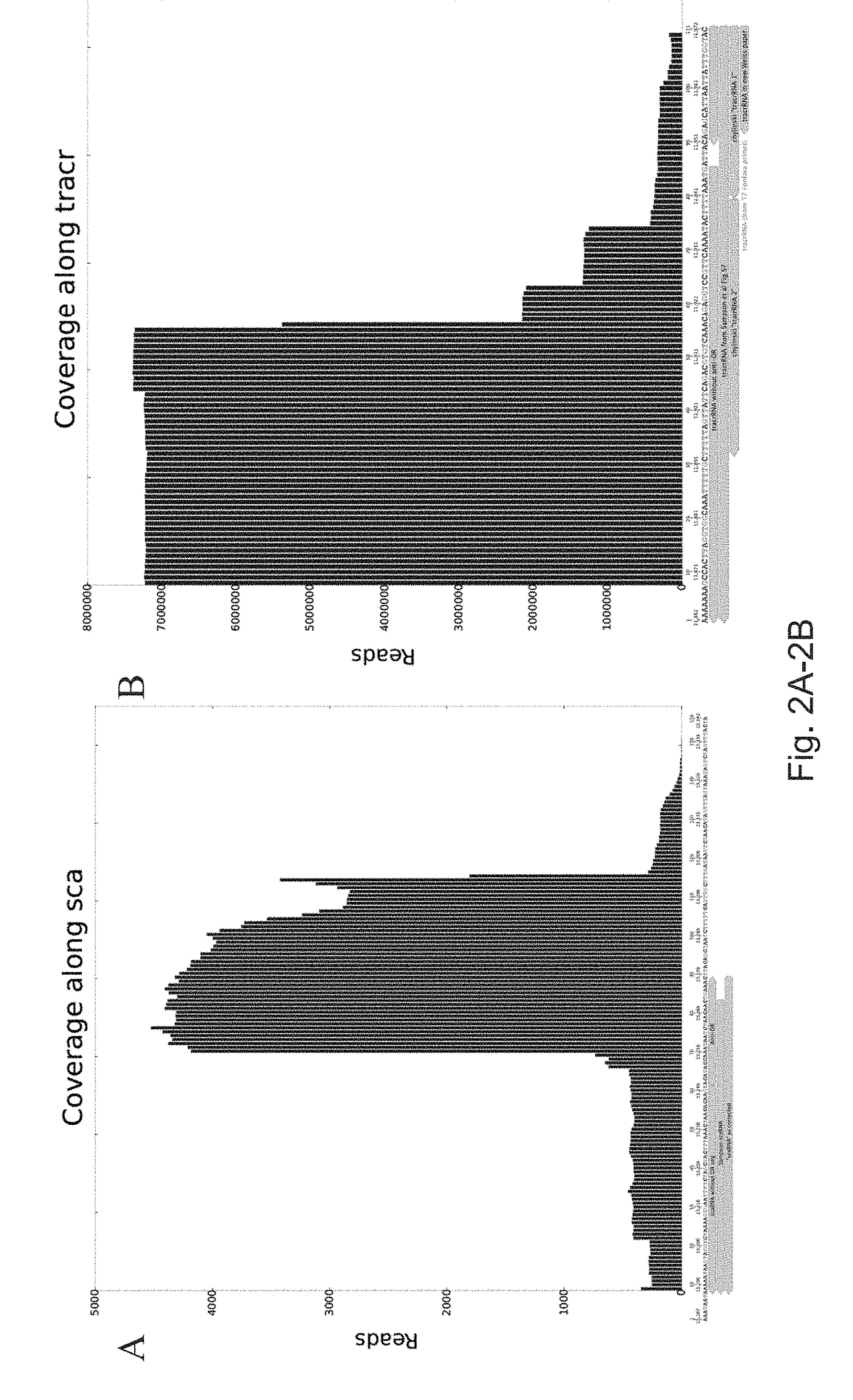
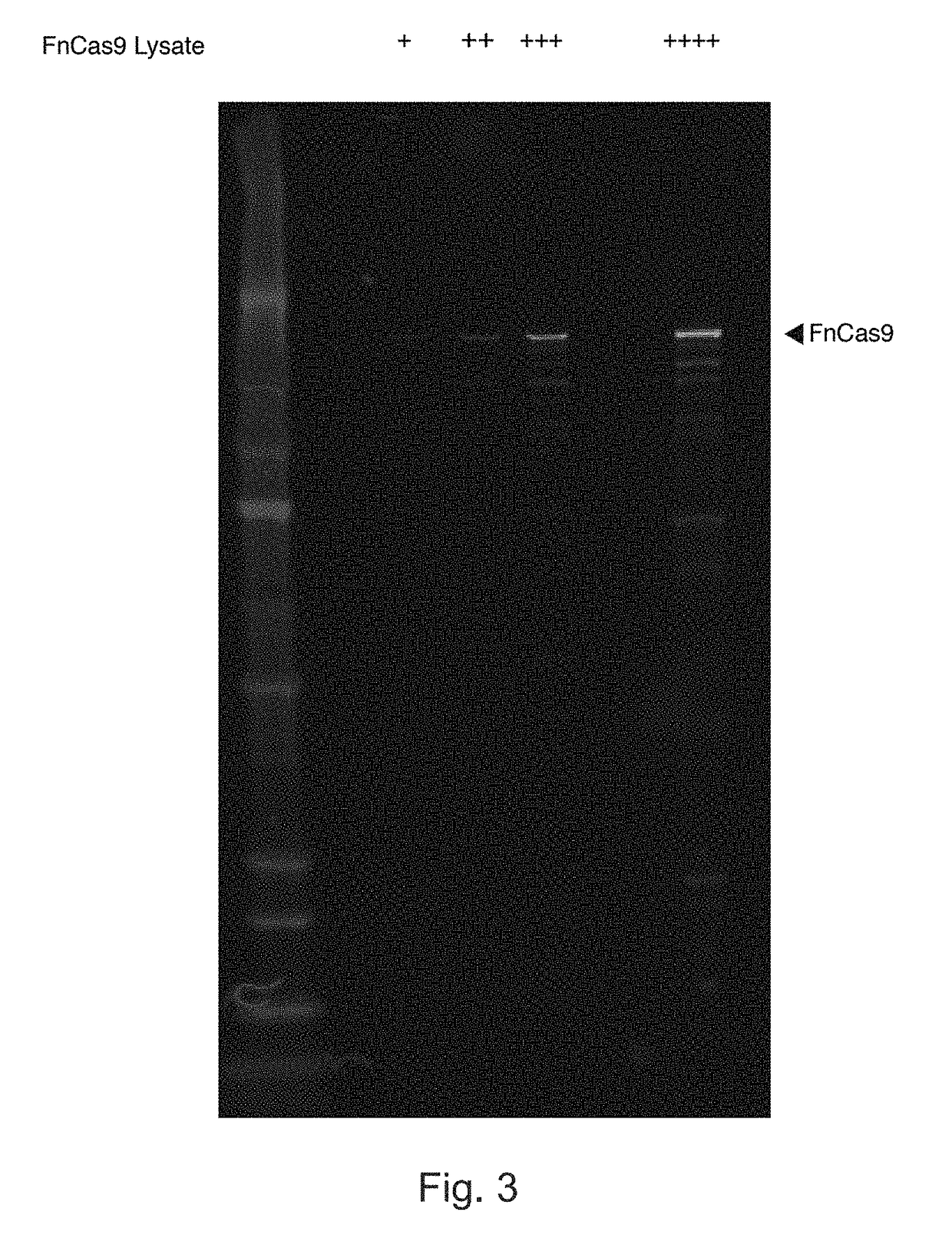
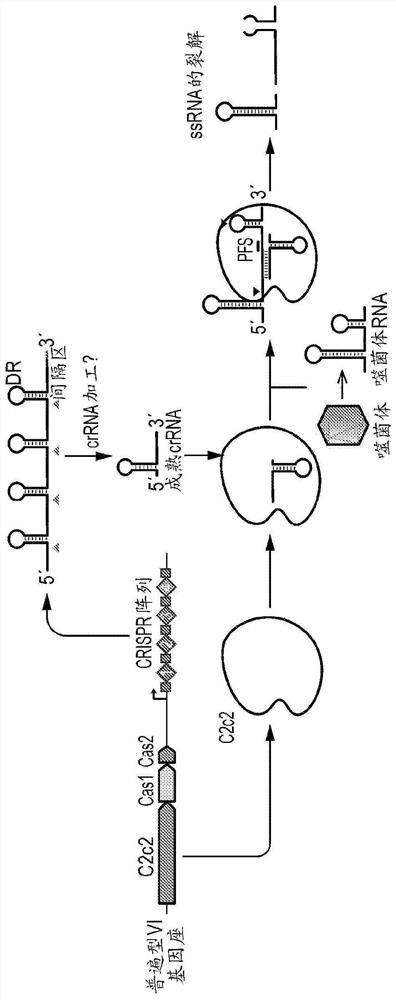
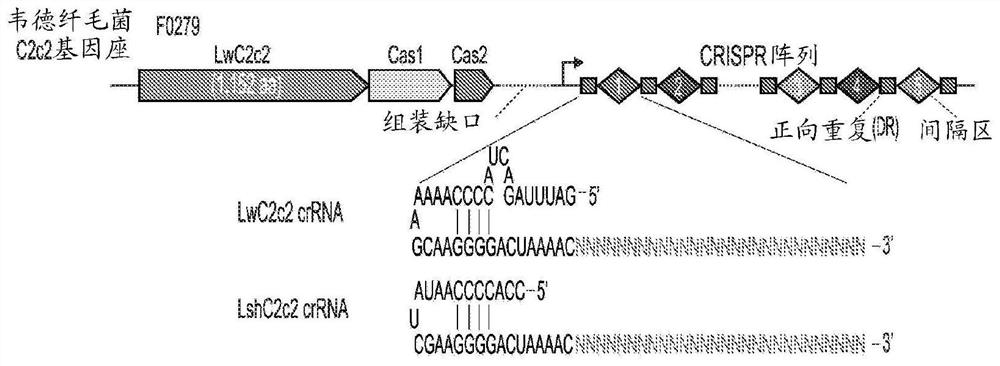
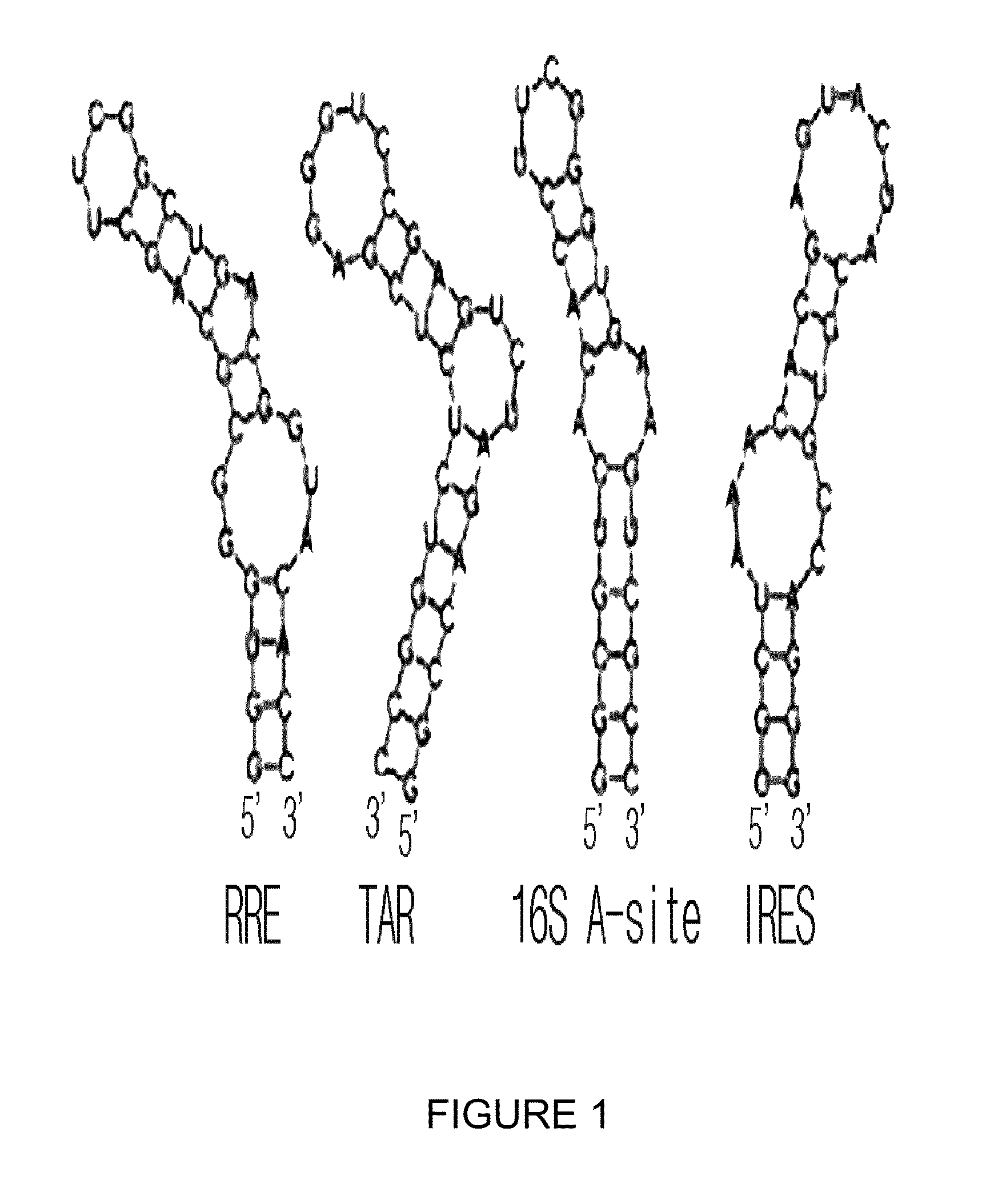
Rna-targeting system
PendingUS20170306335A1Efficient use ofStrong specificityPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifHydrolasesGuide RNARna hybridization
The invention provides for systems, methods, and compositions for targeting RNA. In particular, the invention provides a non-naturally occurring or engineered RNA-targeting system comprising an RNA-targeting Cas protein and at least one RNA-targeting guide RNA, wherein said RNA-targeting guide RNA is capable of hybridizing with a target RNA in a cell.
Owner:THE BROAD INST INC +2
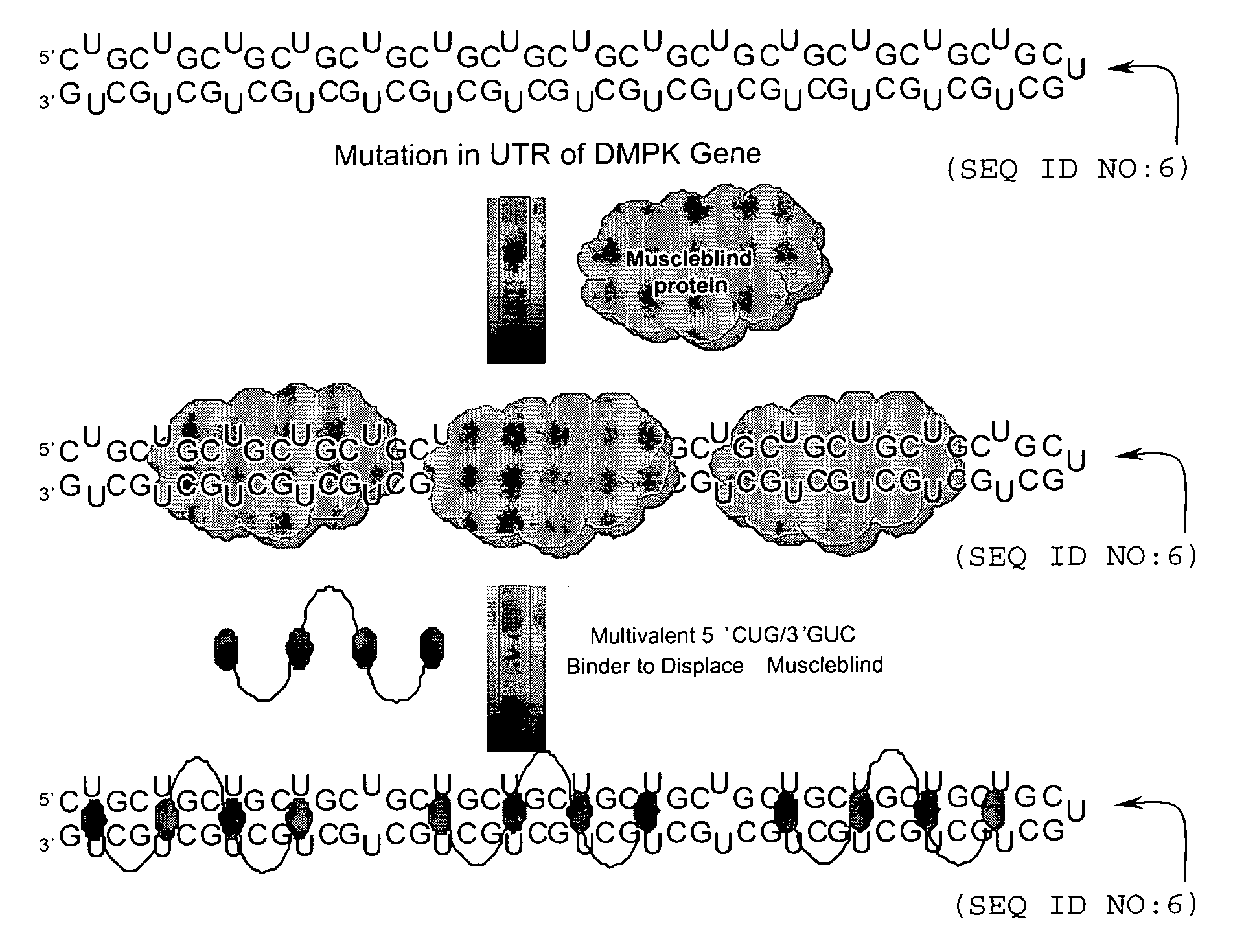
RNA targeting compounds and methods for making and using same
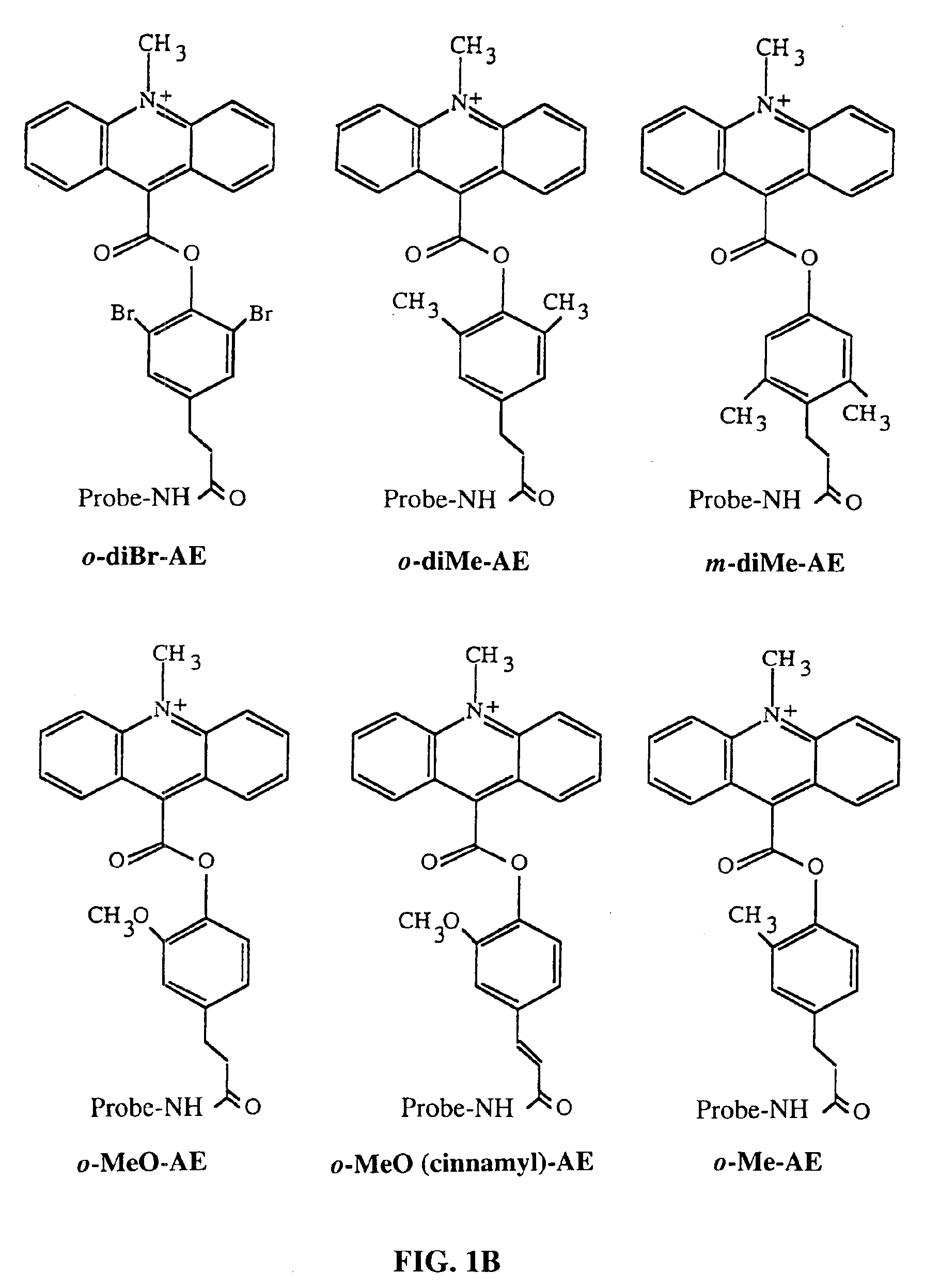
ActiveUS20080227213A1Peptide-nucleic acidsOrganic active ingredientsSide chainMyotonic dystrophy gene
Disclosed are RNA targeting compounds having the formula:wherein j is an integer from 1 to 100; each i is the same or different and is zero or an integer from 1 to 100; each Z1 represents the same or different linking moiety; each R1 is the same or different and represents an alkyl group or an aryl group; each Q1 represents the same or different RNA binding ligand; Q2 is an alkyl group; Q3 is a halogen, an alkyl group, an aryl group, or an amine. Also disclosed are RNA targeting compounds that include a polymer backbone and two or more pendant RNA binding ligands that are bound to the polymer backbone. Methods for using the subject RNA targeting compounds to treat myotonic dystrophy and other diseases are also disclosed, as are compounds that can be used to prepare the subject RNA targeting compounds.
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK
Novel microarray techniques for nucleic acid expression analyses
ActiveUS20060078925A1Eliminate biasConvenient experimentMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationMiRNA GeneExonuclease I
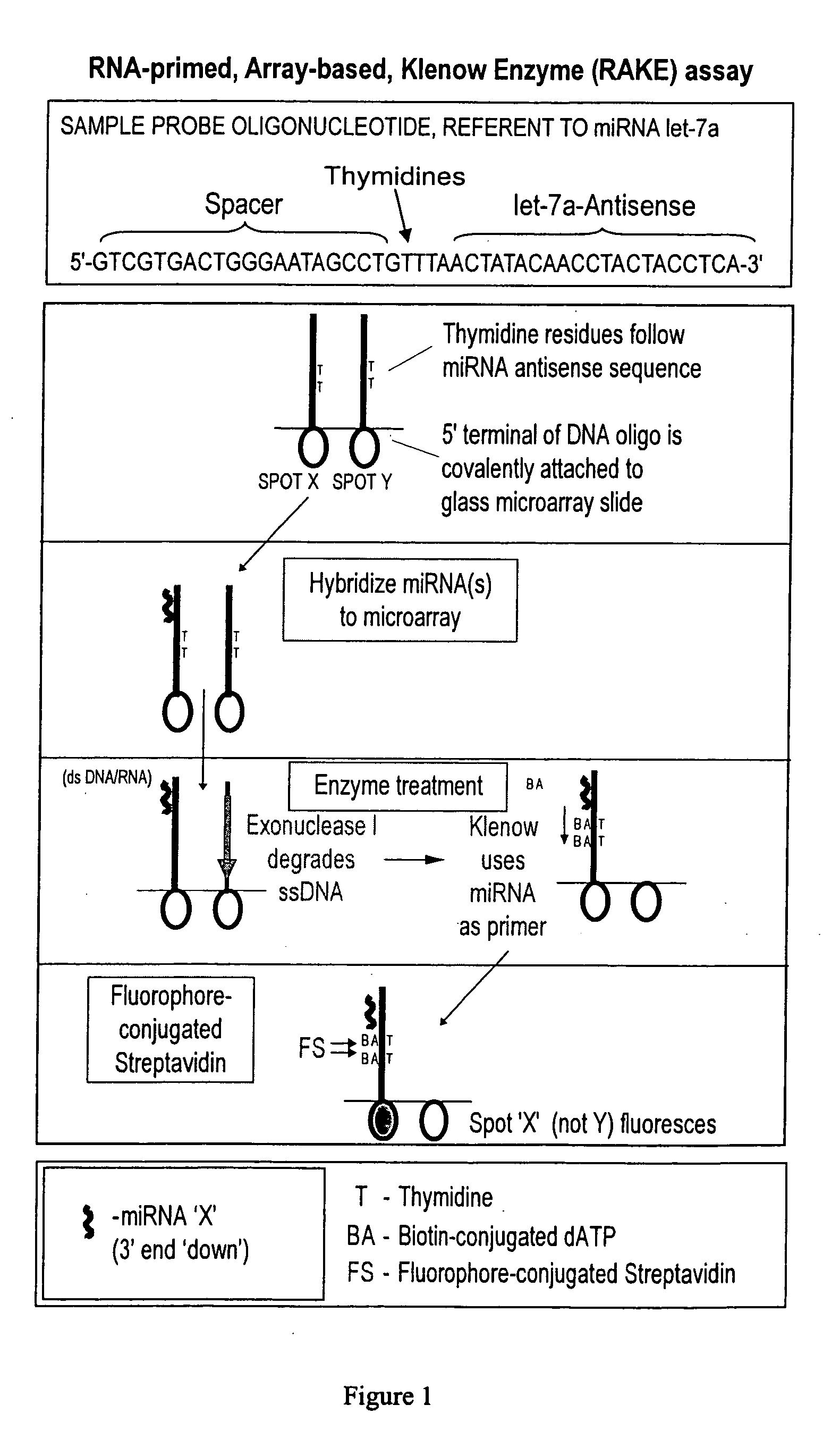
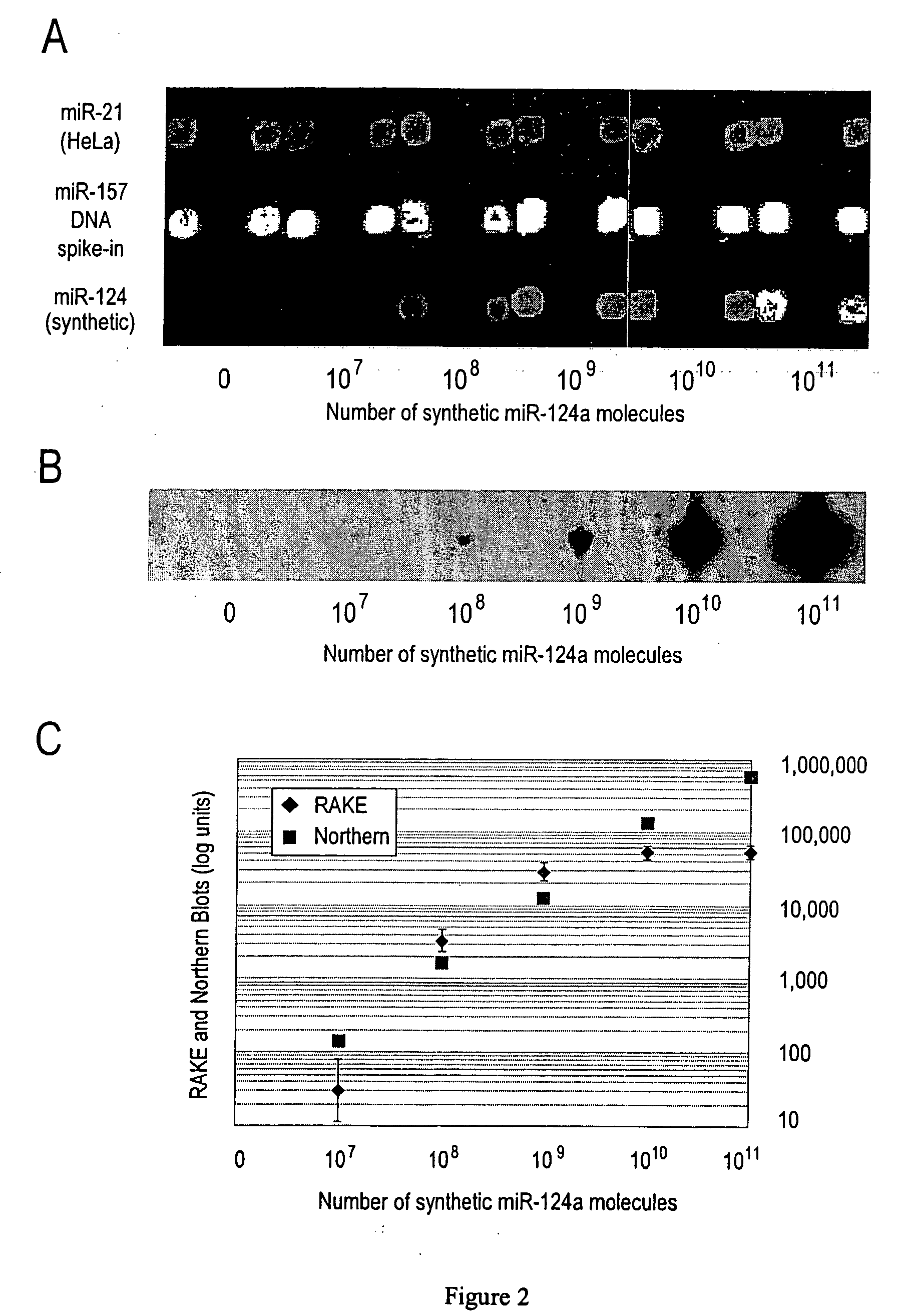
Provided are DNA microarray techniques that allow hybridization without RNA amplification, without using cDNA, and without labeling the nucleic acid prior to hybridization. Referred to as the Double-stranded Exonuclease Protection (DEP) assay, the technique permits the sample RNA to be used directly for hybridization, without manipulation in any way. Further provided is a microarray technique for high-throughput miRNA gene expression analyses, termed the RNA-primed, Array-based, Klenow Enzyme (RAKE) assay. The RAKE assay is a sensitive and specific technique for assessing single-stranded DNA and RNA targets, and offers specific advantages over Northern blots.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
Kits for amplifying target nucleic acid sequences using modified oligonucleotides
InactiveUS6903206B1Increase ratingsEfficiently strand invade double-stranded regionsSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleic acid sequencingNitrogenous base
The present invention concerns oligonucleotides containing one or more modified nucleotides which increase the binding affinity of the oligonucleotides to target nucleic acids having a complementary nucleotide base sequence. These modified oligonucleotides hybridize to the target sequence at a faster rate than unmodified oligonucleotides having an identical nucleotide base sequence. Such modified oligonucleotides include oligonucleotides containing at least one 2′-O-methylribofuranosyl moiety joined to a nitrogenous base. Oligonucleotides can be modified in accordance with the present invention to preferentially bind RNA targets. The present invention also concerns methods of using these modified oligonucleotides and kits containing the same.
Owner:GEN PROBE INC
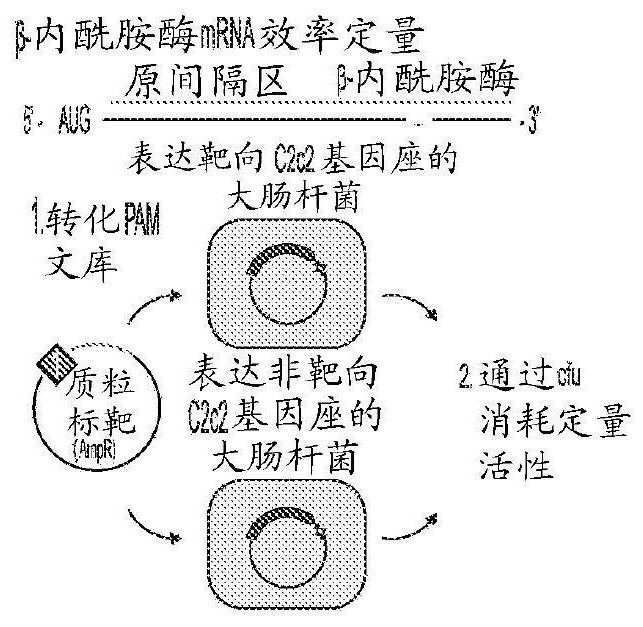
Crispr effector system based diagnostics
The embodiments disclosed herein utilized RNA targeting effectors to provide a robust CRISPR-based diagnostic with attomolar sensitivity. Embodiments disclosed herein can detect both DNA and RNA withcomparable levels of sensitivity and can differentiate targets from non-targets based on single base pair differences. Moreover, the embodiments disclosed herein can be prepared in freeze-dried formatfor convenient distribution and point-of-care (POC) applications. Such embodiments are useful in multiple scenarios in human health including, for example, viral detection, bacterial strain typing, sensitive genotyping, and detection of disease-associated cell free DNA.
Owner:THE BROAD INST INC +2
Crispr effector system based multiplex diagnostics
The embodiments disclosed herein utilized RNA targeting effectors to provide a robust CRISPR-based diagnostic with attomolar sensitivity. Embodiments disclosed herein can detect broth DNA and RNA withcomparable levels of sensitivity and can differentiate targets from non-targets based on single base pair differences. Moreover, the embodiments disclosed herein can be prepared in freeze-dried format for convenient distribution and point-of-care (POC) applications. Such embodiments are useful in multiple scenarios in human health including, for example, viral detection, bacterial strain typing,sensitive genotyping, and detection of disease-associated cell free DNA.
Owner:THE BROAD INST INC +2
Replication Stable and RNase Resistant Chimeras of Pestivirus with Insertion in 3' Nontranslated Region (3'NTR)
The invention relates to the field of nucleic acid amplification, particularly to quality control materials for use in viral RNA assays. It specifically relates to the construction of a recombinant Pestivirus by the identification of a region in the 3′NTR of the viral RNA genome where additional sequence elements can be stably inserted. Chimeric Pestivirus with sequence insertions in the 3′ nontranslated region (3′NTR) of the viral RNA genome were stable in replication and capable of forming infectious, RNase resistant virus particles. This chimeric Pestivirus with a 3′NTR insertion can be utilized as a quality control material in analytical assays for RNA targets, including external, internal controls, quantitative standards in PCR and NAT nucleic acid assays.
Owner:LIFE TECH CORP
RNA interfered target sequence of HBV and use thereof
InactiveCN1667120AHighly conservativeNo homologyGenetic material ingredientsDigestive systemVirus ProteinIn vivo
This invention belongs to molecule biology and biomedicine technique field. It relates to 9 target points of RNA disturbing to HBV and applications of preparing hepatitis B medicine according to these target sequence. Plasmid is expressed through shRNA and siRNA transfection cell and animal cell is chemical synthesized. Then 16 RNA target point on HBV tissue is sieved, 9 of them can obvious restrain HBV protein expression at cell level. Expression and virus duplication of HBV protein inside cell can be stably restrained by 11 target point, and expression of HBV transgene little mouse in vivo virus protein can be restrained. Medicine curing hepatitis B can be made according to these target sequence.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Method of identifying micro-rna targets
The present invention provides methods of identifying an mRNA target of a microRNA. The present invention further provides kits and systems for carrying out a subject method.
Owner:THE J DAVID GLADSTONE INST A TESTAMENTARY TRUST ESTABLISHED UNDER THE WILL OF J DAVID GLADS
Modulation of RNA by repeat targeting
Disclosed herein are antisense compounds, compositions and methods for modulating an RNA target by targeting a repetitive sequence in the RNA target and modulating an associated disease, disorder and / or condition related to such RNA target. Also disclosed herein are methods of identifying such compounds and compositions.
Owner:IONIS PHARMA INC
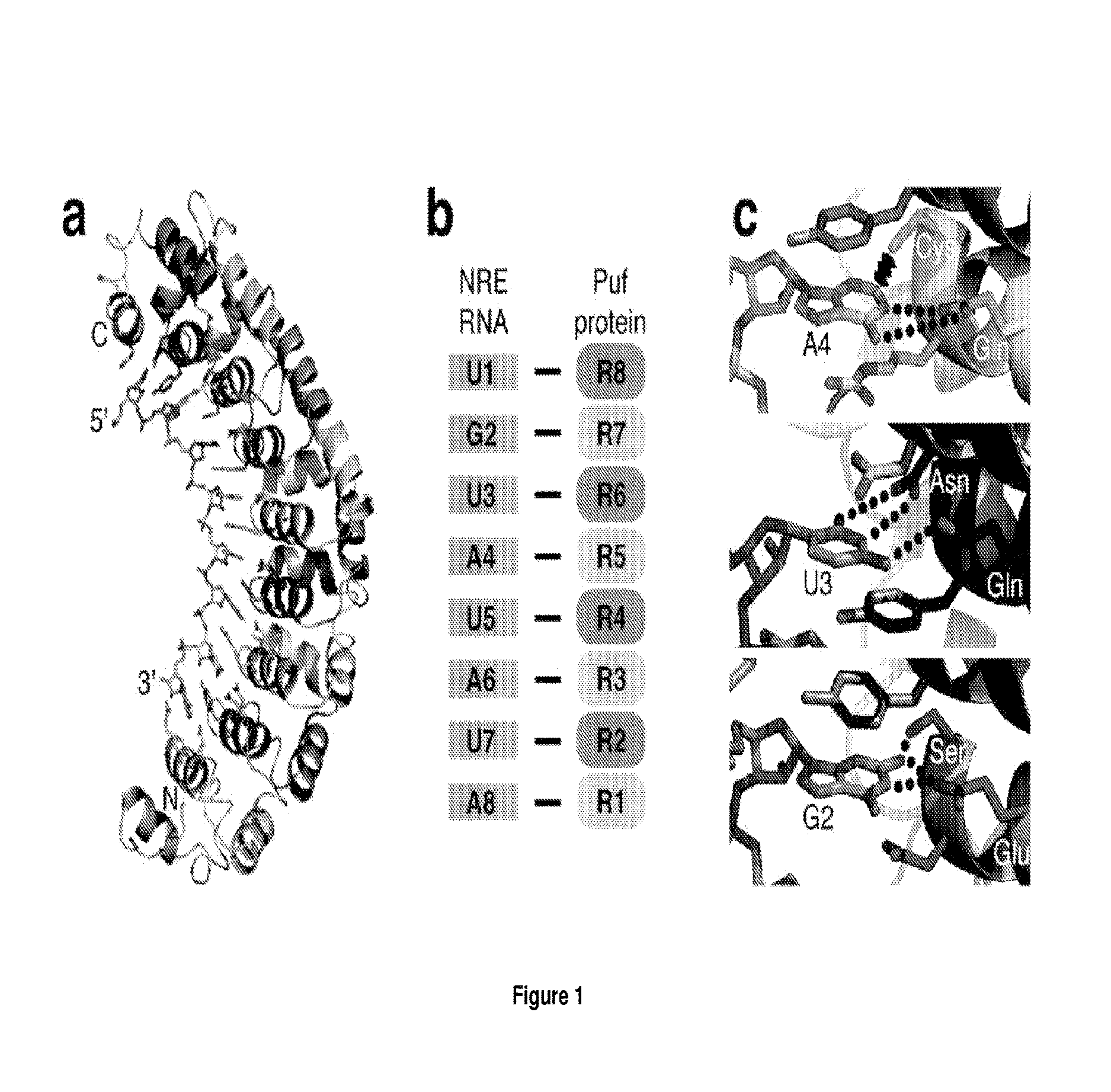
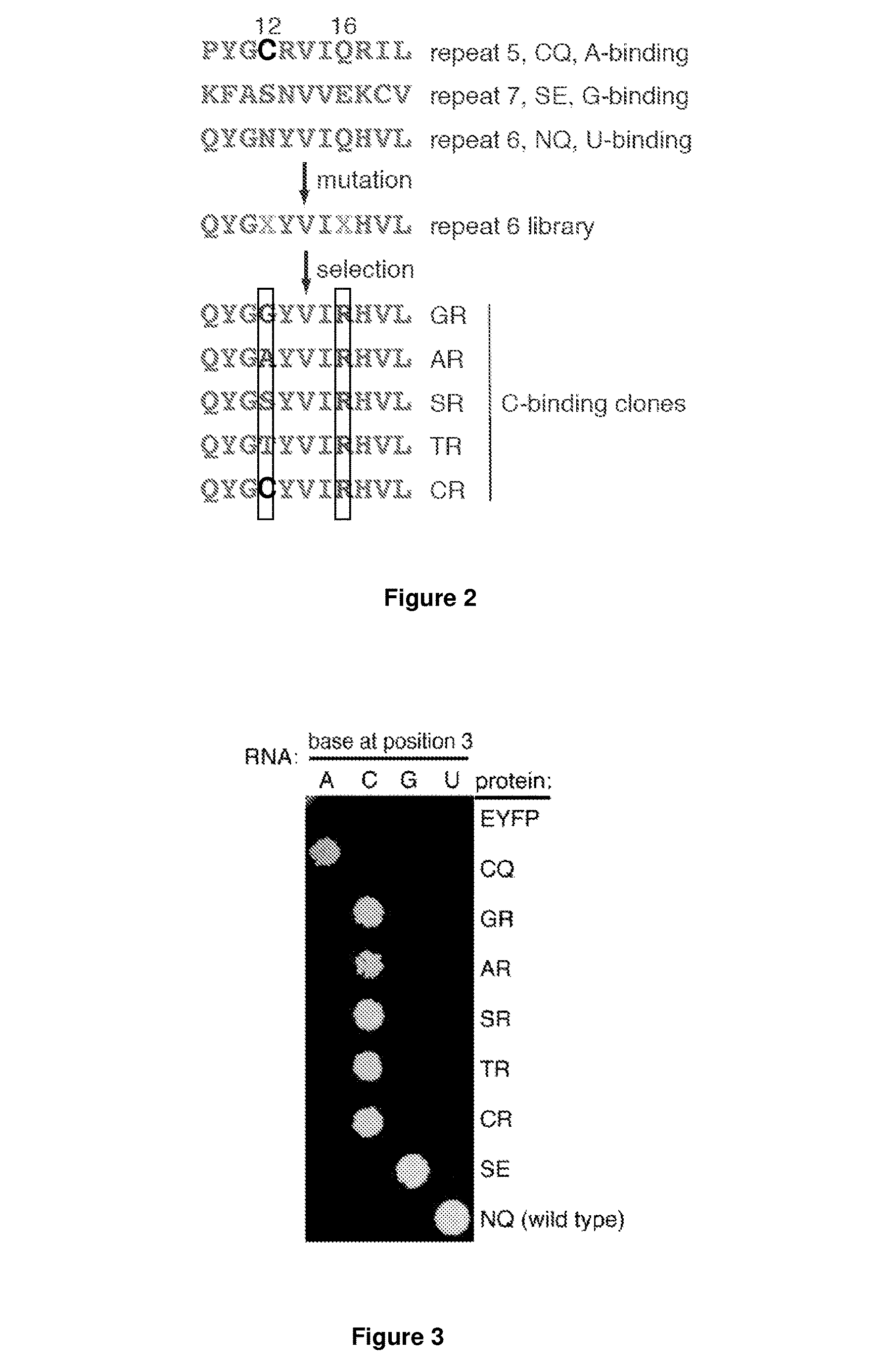
Peptides for the specific binding of RNA targets
A recombinant polypeptide is described including at least one PUF RNA-binding domain capable of specifically binding to a cytosine RNA base. The PUF RNA-binding domain of the polypeptide includes at least one RNA base-binding motif of the general formula X1X2X3X4X5X6X7X8X9X10X11 wherein X1 is selected from a defined group and wherein the RNA base-binding motif is operably capable of specifically binding to a cytosine RNA base.
Owner:UNIV OF WESTERN AUSTRALIA
Methods for preparation of nucleic acid-containing samples using clay minerals and alkaline solutions
ActiveUS20160102340A1Reduce riskThe process is simple and fastMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA preparationLysisMolecular analysis
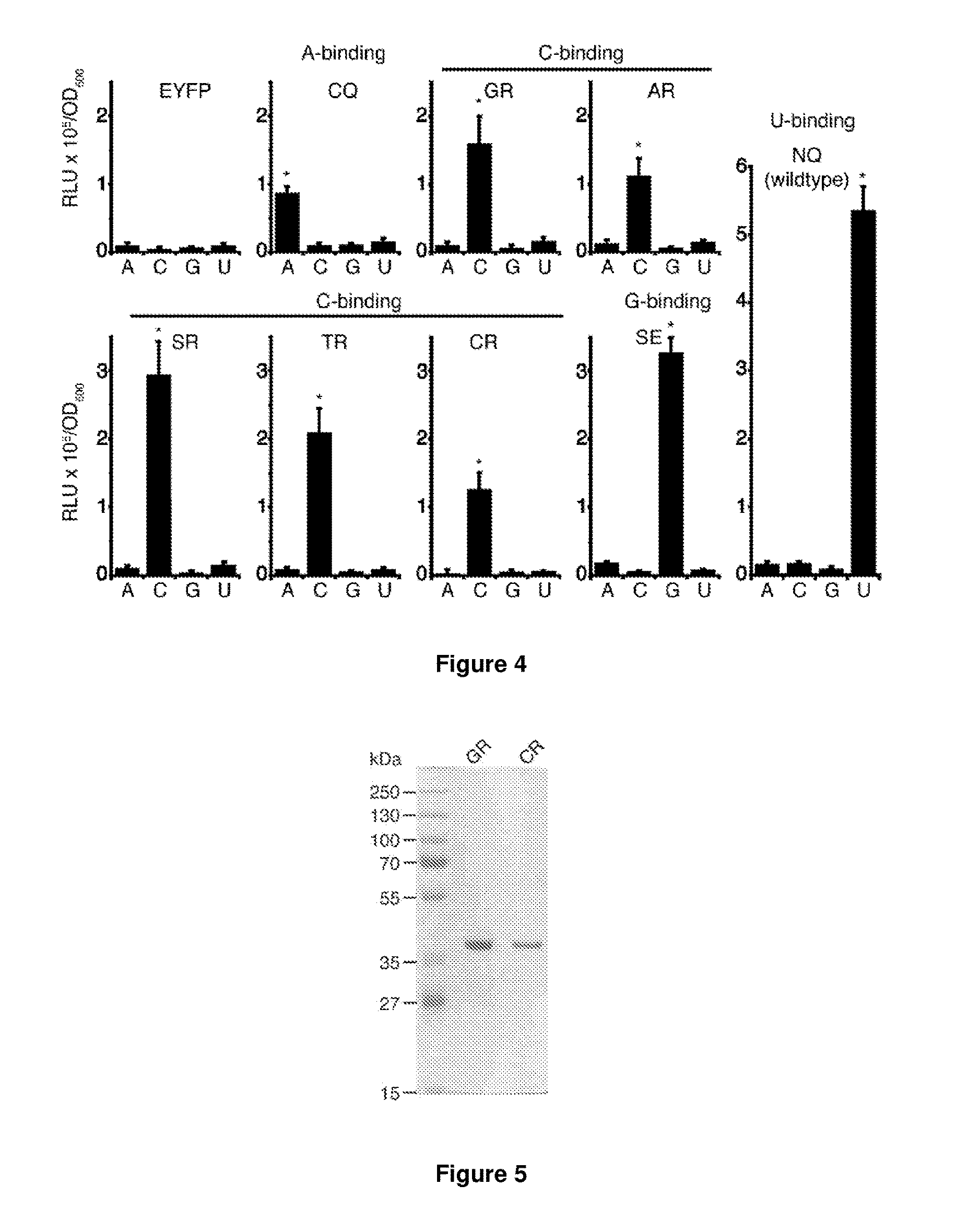
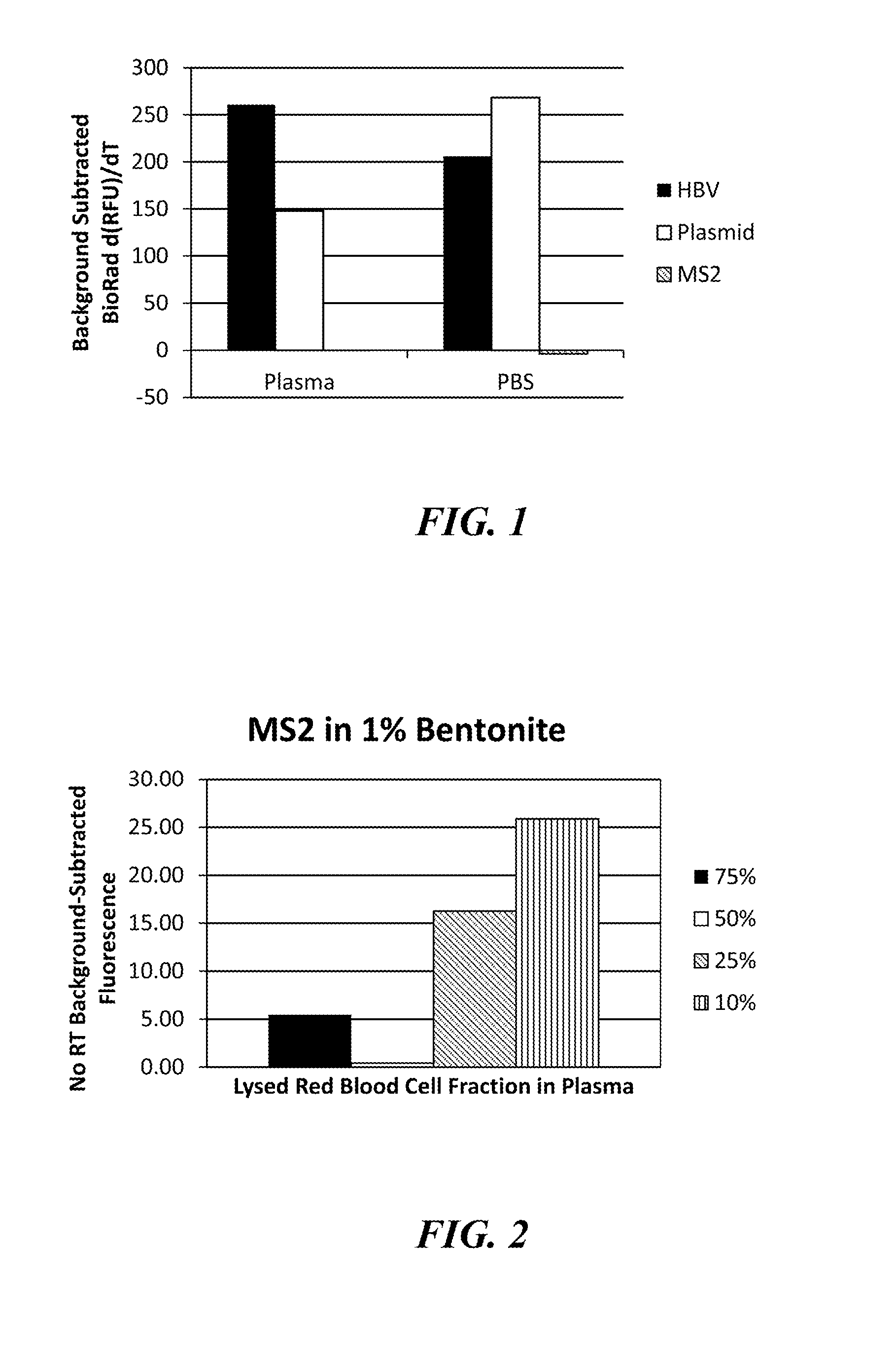
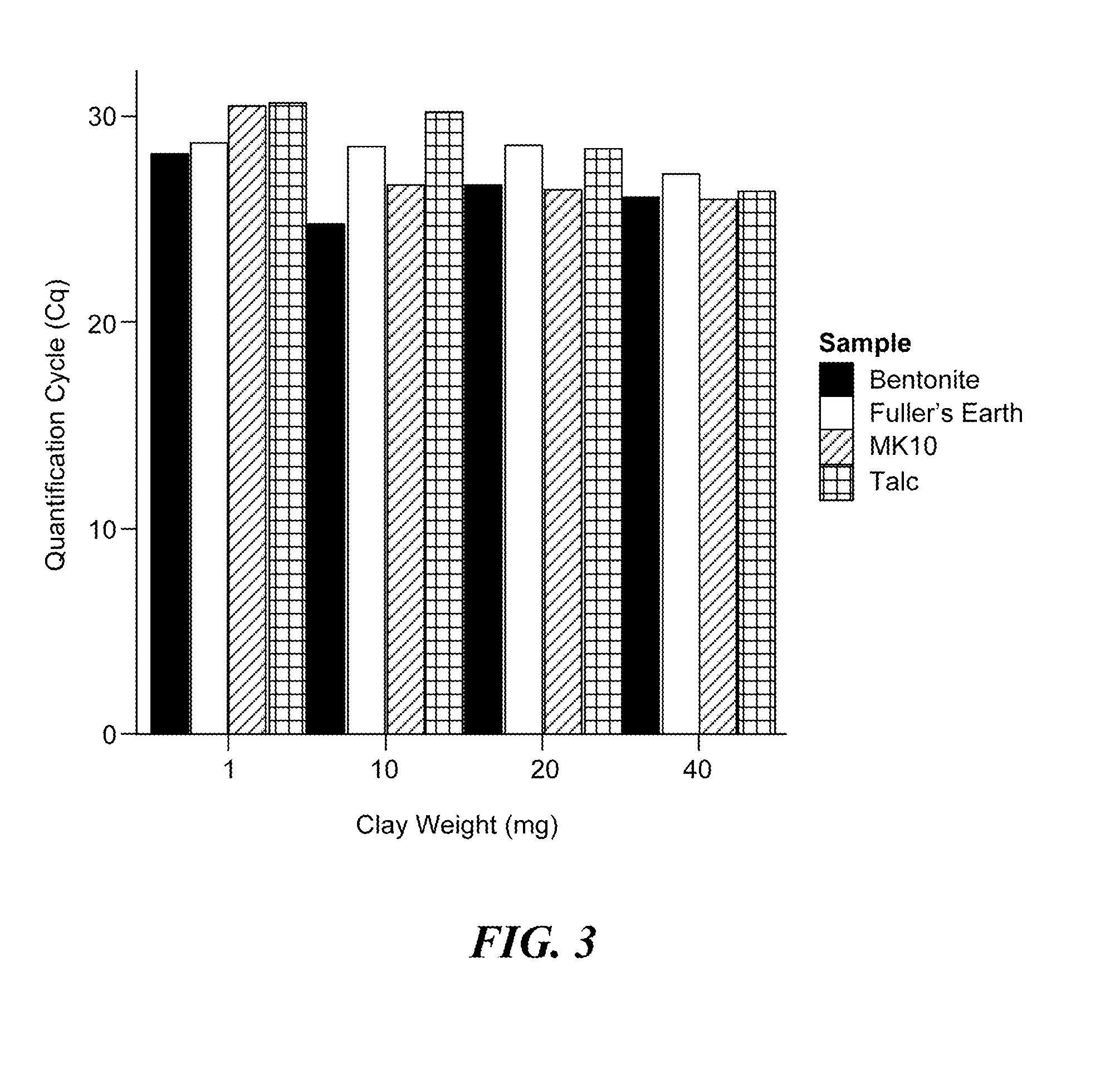
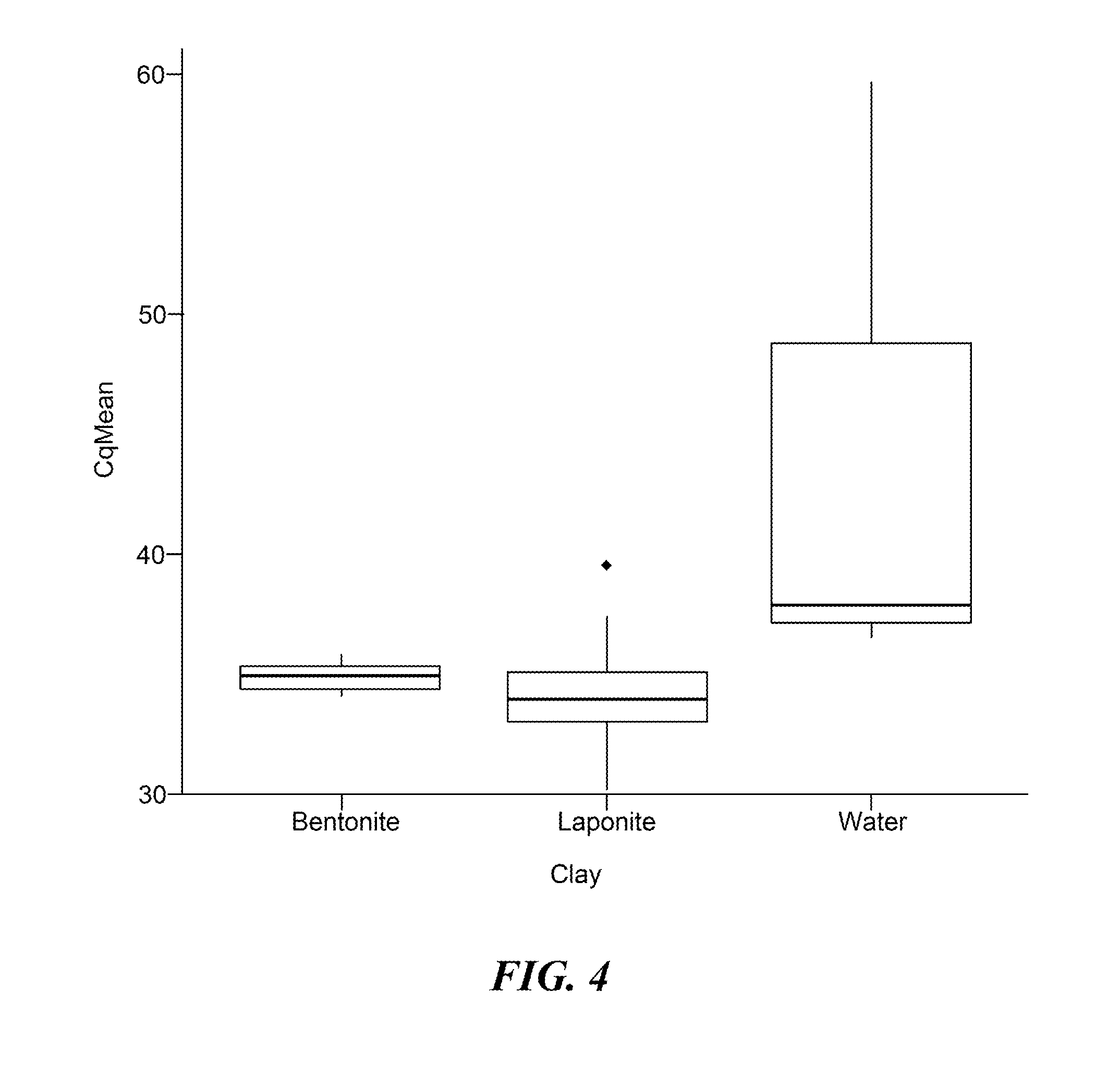
The present invention provides a rapid and highly effective method for the preparation of biological samples for detection of both DNA and RNA target molecules. The method comprises treatment of the sample with a clay mineral followed by lysis of the sample with an alkaline solution. The method is particularly suited for preparing complex biological samples, such as blood or plasma, for the simultaneous detection of DNA and RNA targets. Samples prepared by the method of the invention may be directly used as targets in PCR amplification. The method of the invention may conveniently be coupled with further steps and devices to perform molecular analyses for diagnostic and other applications.
Owner:PERKINELMER HEALTH SCIENCES INC
Device for preparation and analysis of nucleic acids
ActiveUS10087440B2Superior substrate for modifying enzymeMicrobiological testing/measurementLaboratory glasswaresAnalysis dnaWhole blood product
Owner:PERKINELMER HEALTH SCIENCES INC
Method and systems for identifying micro-rna targets and synthesizing novel micro-rnas and uses of the same
Method of identifying a microRNA-recognition element and of generating microRNAs are disclosed. System and computer programs for performing such methods are disclosed. Recombinant nucleic acid molecule comprising a heterologous coding sequences and one or more MREs are also disclosed as are isolated nucleic acid molecule comprising one or more MRE sequences and being free of a coding sequence operably linked to regulatory elements. MicroRNA generated by a methods of the invention and the use of the microRNAs to downregulate gene expression are disclosed.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
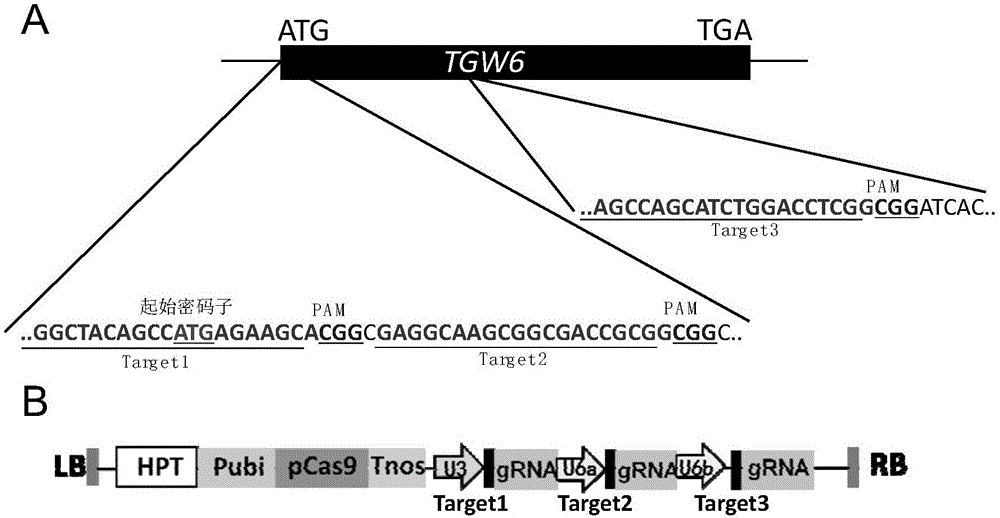
Rice thousand kernel weight gene TGW6 guided RNA target sequence and application thereof
InactiveCN105063026AEasy to editEfficient editingFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionMutation frequencyGermplasm
The invention belongs to the field of plant biotechnology, and in particular relates to rice thousand kernel weight gene TGW6 guided RNA target sequences and application thereof. The oligonucleotide sequences of the rice thousand kernel weight gene TGW6 guided RNA target sequences are as shown in SEQ ID NO.1-6. The group of the target sequences is applicable to the editing of rice genome, and has the advantages of being convenient, efficient and the like. When the rice thousand kernel weight gene TGW6 guided RNA target sequences provided by the invention are used for editing the rice genome, the mutation frequency of rice thousand kernel weight gene tgw6 is 90% or above, including more than 50% of fragment-deleted homozygous mutants and around 40% of diallelic heterozygous mutants. The invention provides an important reference for the rapid establishment of high-quality new rice germplasm having an important application value on rice quality and like production, and is expected to provide a safe and efficient new way for the innovation of rice germplasm resources; and the invention has important theoretical and practical significance.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
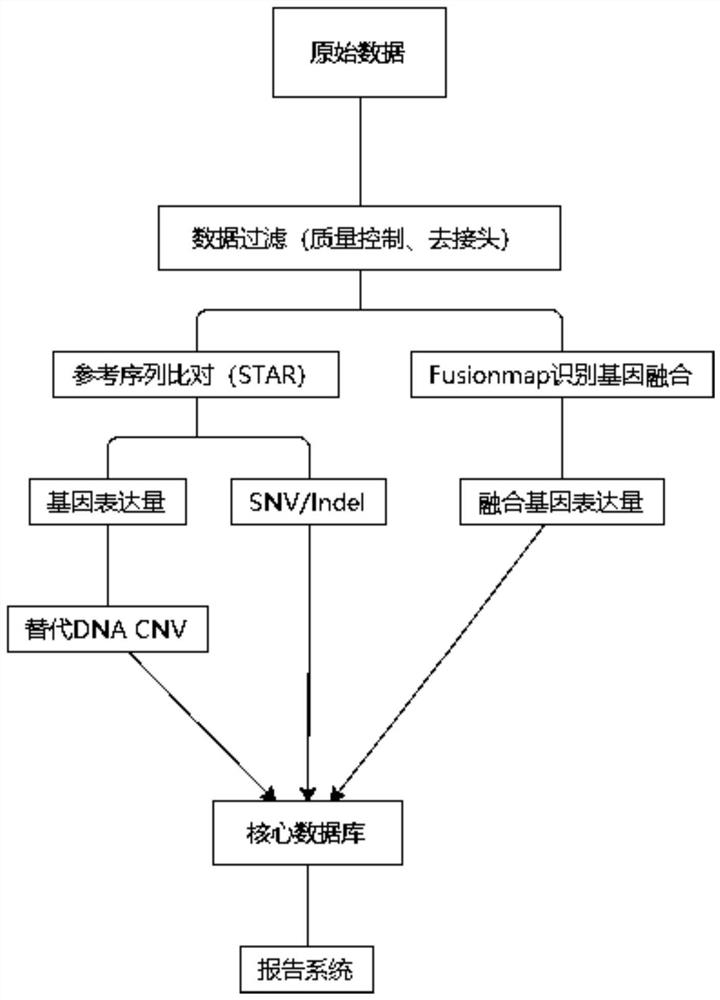
Method and device for detecting gene mutation and expression quantity
ActiveCN112397144AEfficient enrichmentApplicable developmentMicrobiological testing/measurementProteomicsNucleotideRelated gene
The invention discloses a method and a device for detecting gene mutation and expression quantity. The method comprises the following steps: S1, extracting RNA, interrupting, and carrying out reversetranscription to obtain cDNA; S2, constructing a gene library by adopting cDNA; S3, capturing and enriching a target gene from the gene library by utilizing specific hybridization of a capture probe and the target region; S4, sequencing by using a high-throughput sequencer to obtain RNA targeted sequencing data; S5, analyzing changes of gene mutation and expression quantity in the RNA targeted sequencing data, wherein the step S5 specifically comprises the following substeps: S51, analyzing the gene expression quantity; S52, analyzing gene overexpression; S53, carrying out gene fusion analysis; S54, carrying out the fusion mutation expression quantity analysis; S55, carrying out the single nucleotide variation analysis; S56, analyzing the expression quantity of the mononucleotide variationmutation. RNA transcripts expressed by tumor-related genes can be efficiently enriched, and the expression quantity and mutation conditions of the tumor genes in tumor tissues are analyzed.
Owner:ZHENYUE BIOTECHNOLOGY JIANGSU CO LTD
Method for determining the presence of an RNA analyte in a sample using a modified oligonucleotide probe
InactiveUS7070925B1Great ability to discriminateHigh TmSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementAnalyteNitrogenous base
The present invention concerns oligonucleotides containing one or more modified nucleotides which increase the binding affinity of the oligonucleotides to target nucleic acids having a complementary nucleotide base sequence. These modified oligonucleotides hybridize to the target sequence at a faster rate than unmodified oligonucleotides having an identical nucleotide base sequence. Such modified oligonucleotides include oligonucleotides containing at least one 2′-O-methylribofuranosyl moiety joined to a nitrogenous base. Oligonucleotides can be modified in accordance with the present invention to preferentially bind RNA targets. The present invention also concerns methods of using these modified oligonucleotides and kits containing the same.
Owner:GEN PROBE INC
Process for screening of a binding amphiphilic peptides specific for hairpin RNA
ActiveUS8084399B2Easy to useImprove bindingPeptide librariesSugar derivativesScreening methodPeptide library
The present invention relates to a screening method of an amphiphilic peptide specifically binding to hairpin RNA, more precisely a screening method of an amphiphilic peptide having specificity and strong binding strength to target hairpin RNA using peptide library comprising those peptides having modifications of both hydrophilic face and hydrophobic face. The method of the present invention provides a screening method of an amphiphilic peptide which is specific to hairpin RNA. So, the peptide selected by the method of the present invention can be effectively used for the study of hairpin RNA functions and for the production of a novel drug using an artificial peptide binding to a hairpin RNA target.
Owner:SEOUL NAT UNIV R&DB FOUND
Liquid-stage chip constant-temperature detection method for tiny RNA
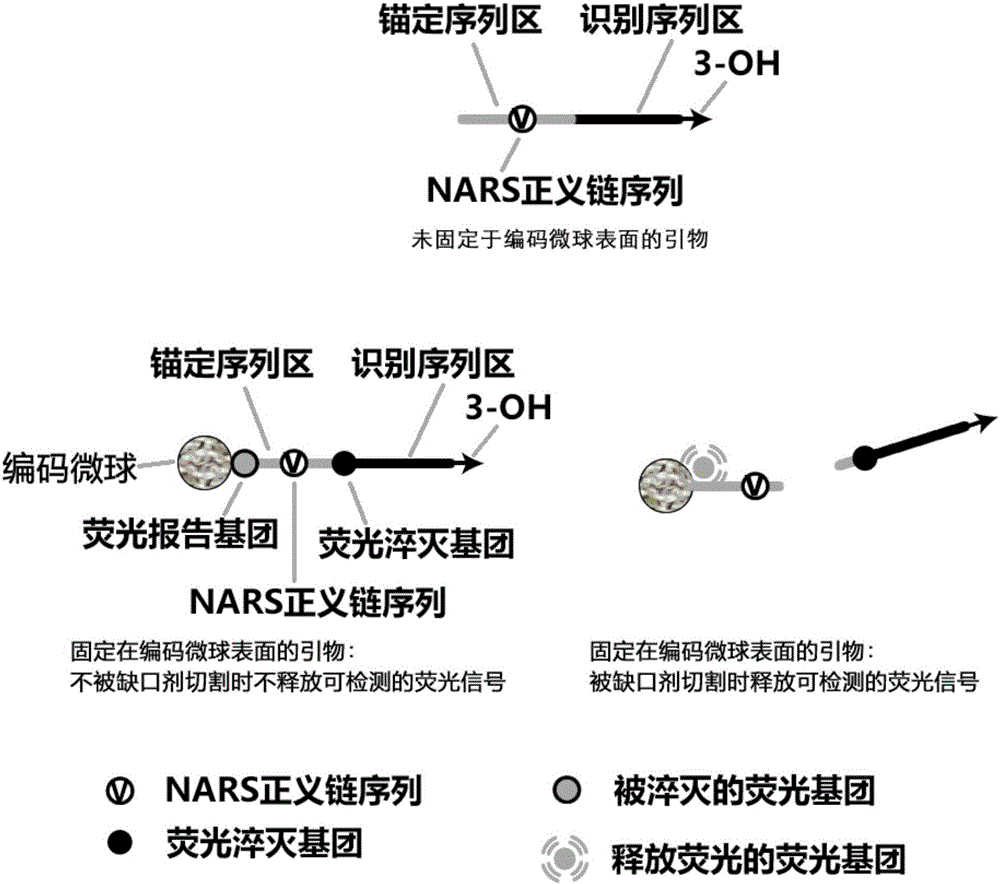
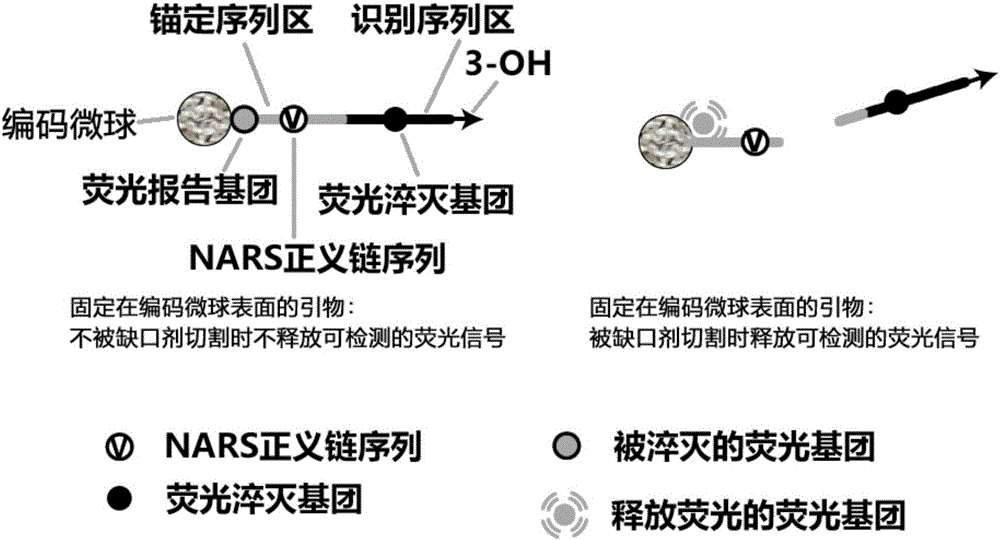
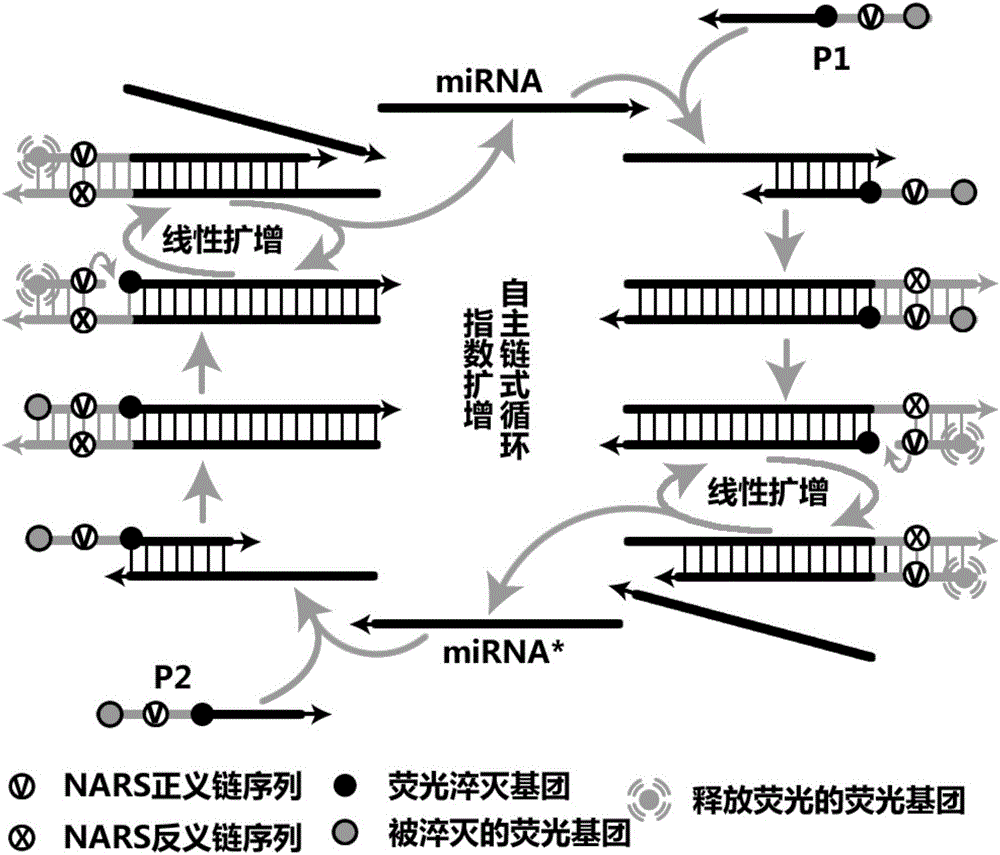
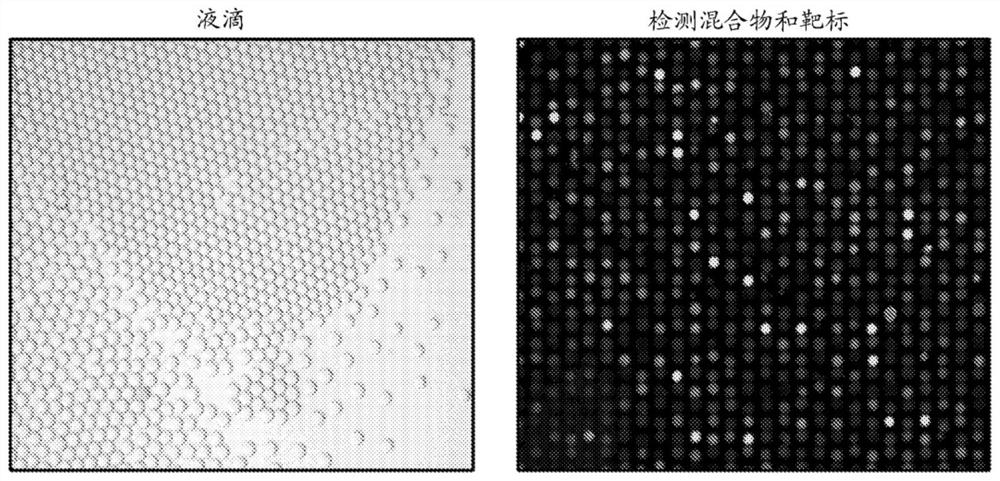
InactiveCN105002285AAchieving Exponential ScalingHigh detection energyMicrobiological testing/measurementMicrosphereOligonucleotide primers
The invention discloses a liquid-stage chip constant-temperature index amplification and detection method for tiny RNA target molecules. By fixing upstream and / or downstream primers to the surfaces of encoding microspheres and marking the two sides of notch agent recognition sequences of the primers fixed to the surfaces of the encoding microspheres with fluorescence report molecules which have the fluorescence resonance energy transfer effect and cancellation molecules, finally the high-throughput detection of various target molecules is achieved through target molecule specificity detectable fluorescence signals on the surfaces of the encoding microspheres. The design difficulty of miRNA inherent attributes on the amplification detection method for the target molecules is lowered, a liquid-state constant-temperature index amplification and detection system based on oligonucleotides primers is provided, and the method for achieving constant-temperature index amplification and absolute quantification under the constant-temperature condition can be achieved.
Owner:THE FIRST AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF THIRD MILITARY MEDICAL UNIVERSITY OF PLA
Crispr system based droplet diagnostic systems and methods
PendingCN113474456AMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysis by optical meansBacterial strain typingViral test
RNA targeting proteins are utilized to provide a robust massively multiplexed CRISPR-based diagnostic by detection in droplets with attomolar sensitivity. Detection of both DNA and RNA with comparable levels of sensitivity at nanoliter volumes can differentiate targets from non-targets based on single base pair differences, with applications in multiple scenarios in human health including, for example, viral detection, bacterial strain typing, and sensitive genotyping.
Owner:THE BROAD INST INC +3
Nanoparticle probes with raman spectroscopic fingerprints for analyte detection
ActiveUS7985539B2Increase in stainBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsRaman microspectroscopyOligonucleotide
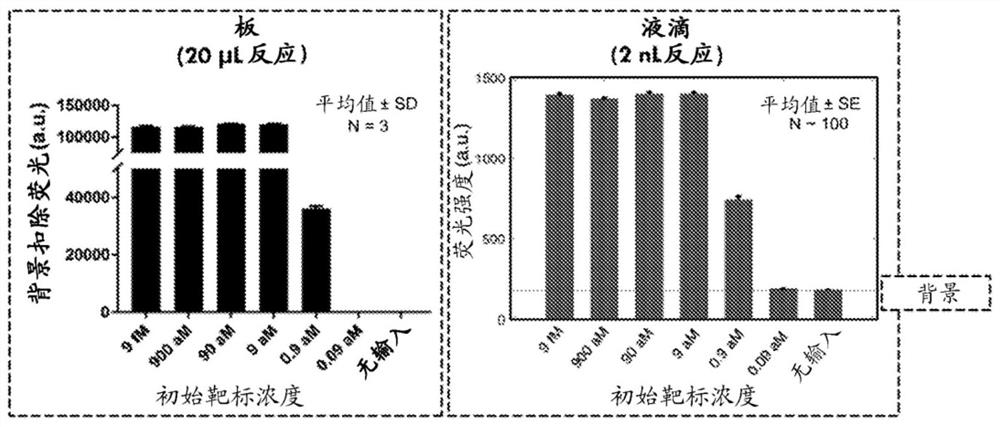
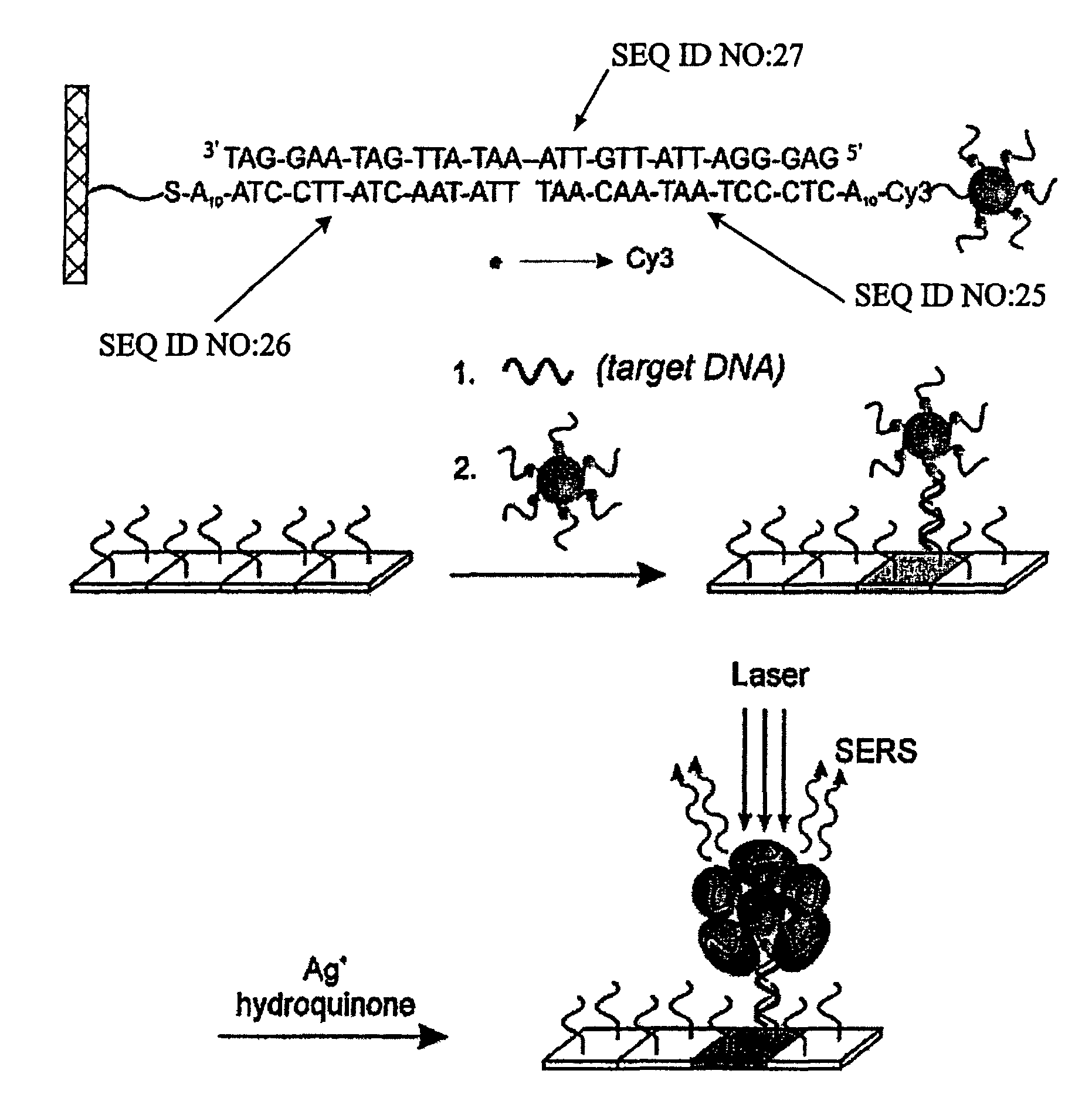
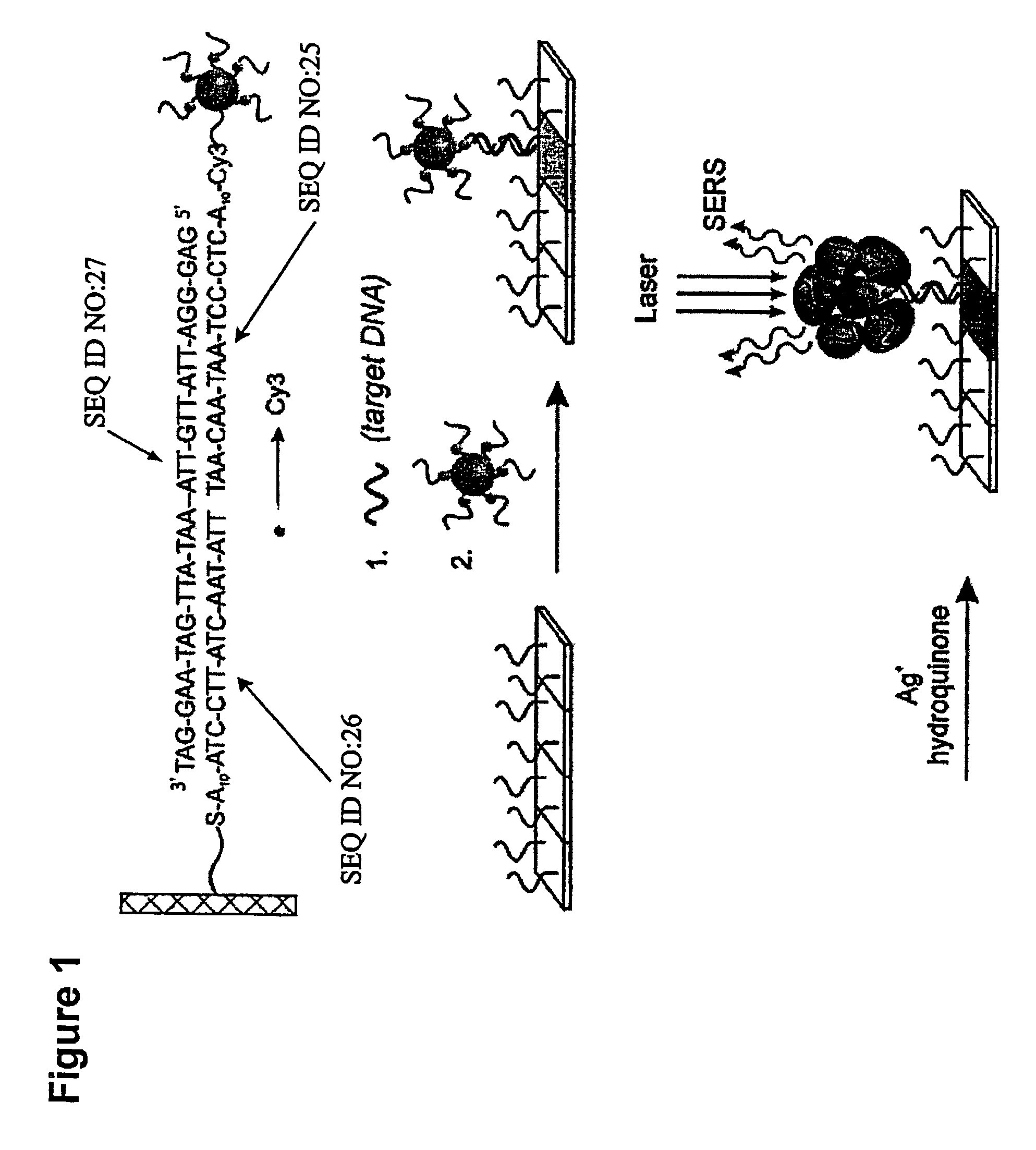
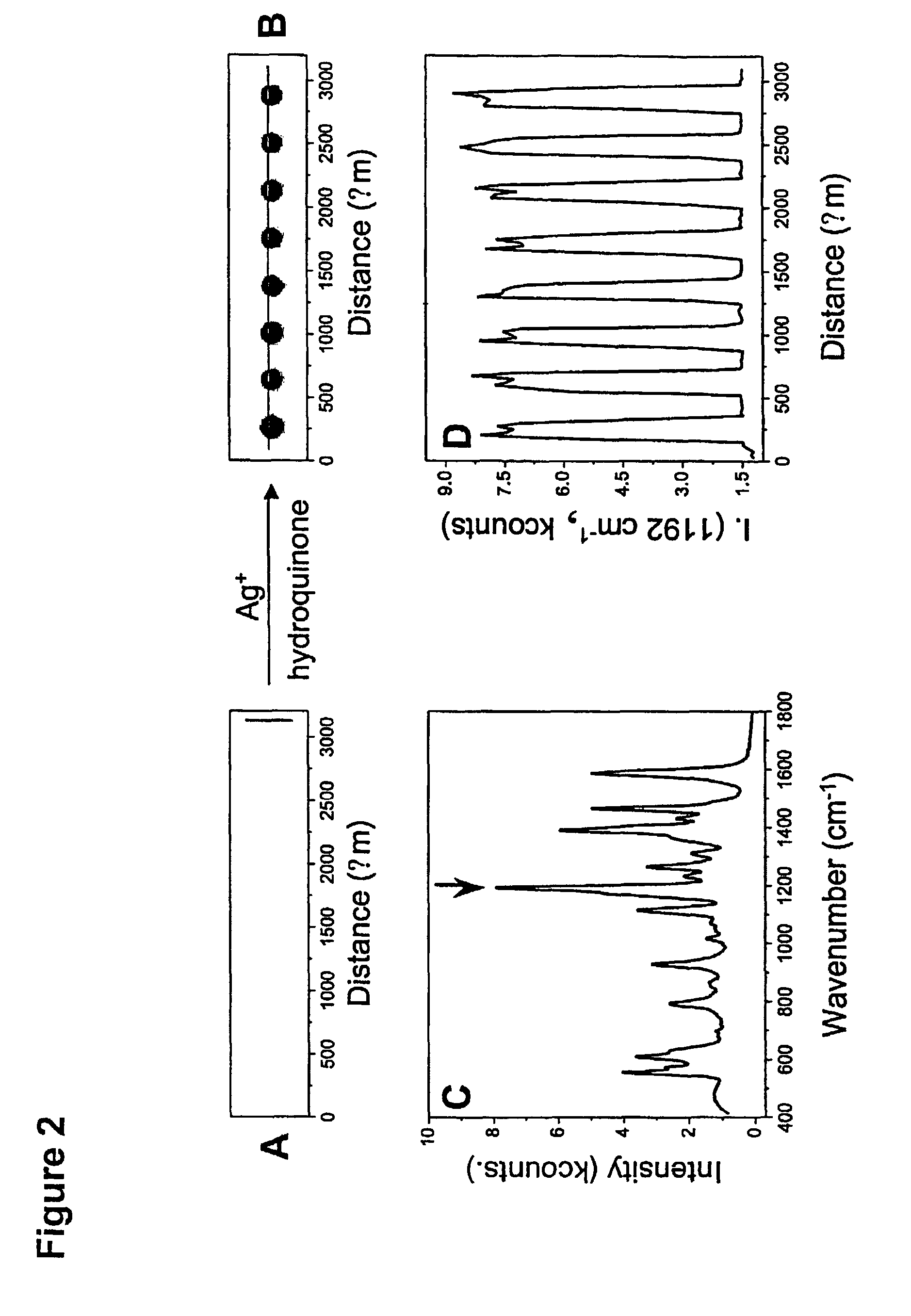
The invention encompasses reagents comprising particles with at least one Raman dye and a specific binding members bound thereto and methods of using such reagents. The invention also encompasses reagents of a specific binding member and two or more different Raman dyes and methods for using such reagents. New types of particle probes having a specific binding member bound thereto are described. These reagents are used in a novel detection strategy that utilizes the catalytic properties of the Au nanoparticles to generate a silver coating that can behave as a surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) promoter for the dye-labeled particles that have been captured by target and an underlying chip in microarray format. The strategy provides the high sensitivity and high selectivity attributes of grey-scale scanometric detection but provides a route to multiplexing and ratioing capabilities since a very large number of probes can be designed based upon the concept of using a Raman tag as a spectroscopic fingerprint in detection. These spectra are used as fingerprints to differentiate oligonucleotide or other targets in one solution. This method has been used to distinguish six dissimilar DNA targets with six Raman labeled nanoparticle probes, and also two RNA targets with single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs).
Owner:NORTHWESTERN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com