Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
59 results about "Myotonic dystrophy" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Myotonic dystrophy is a long-term genetic disorder that affects muscle function. Symptoms include gradually worsening muscle loss and weakness. Muscles often contract and are unable to relax. Other symptoms may include cataracts, intellectual disability and heart conduction problems. In men, there may be early balding and an inability to have children.
Compound and method for treating myotonic dystrophy
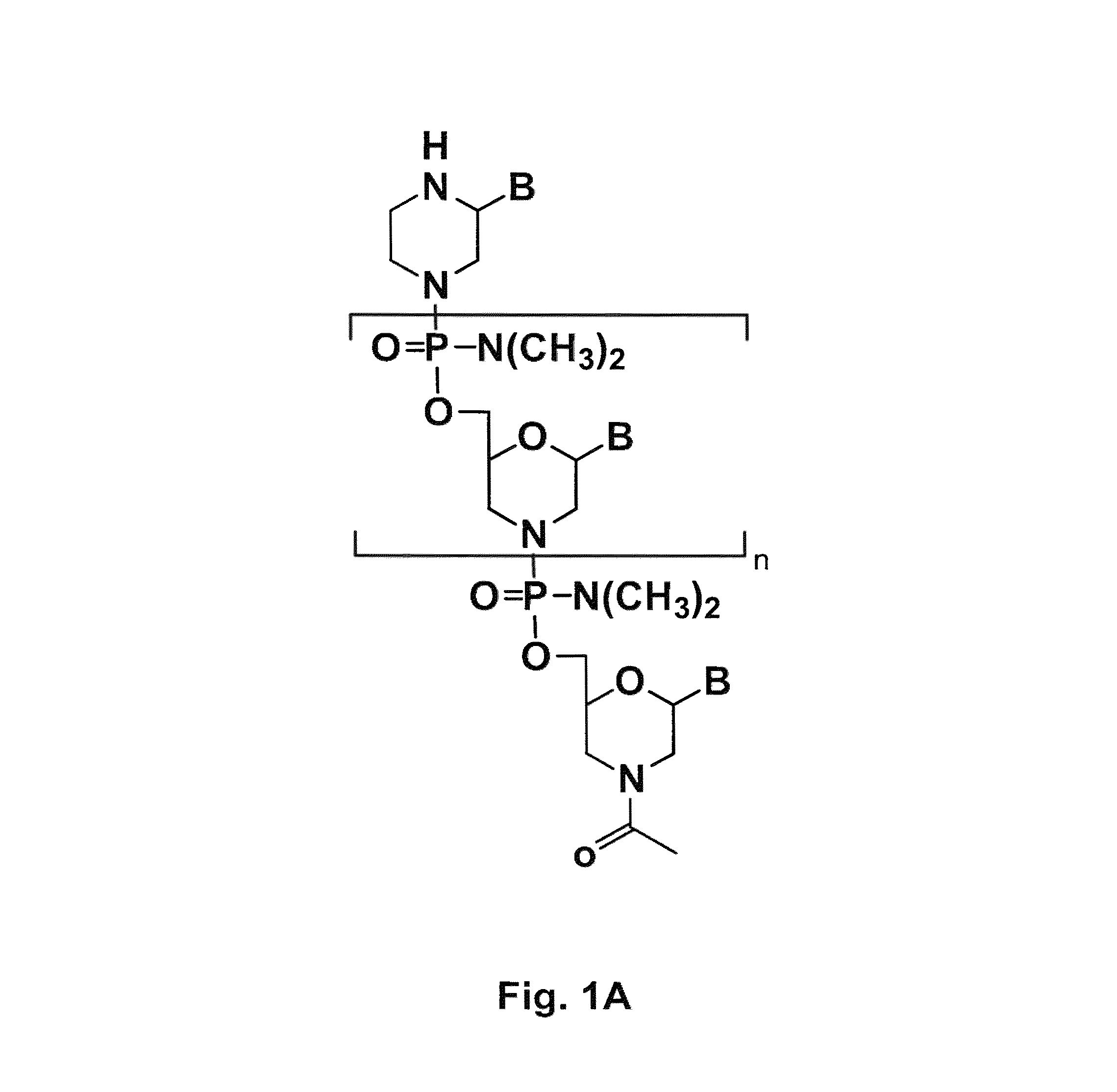
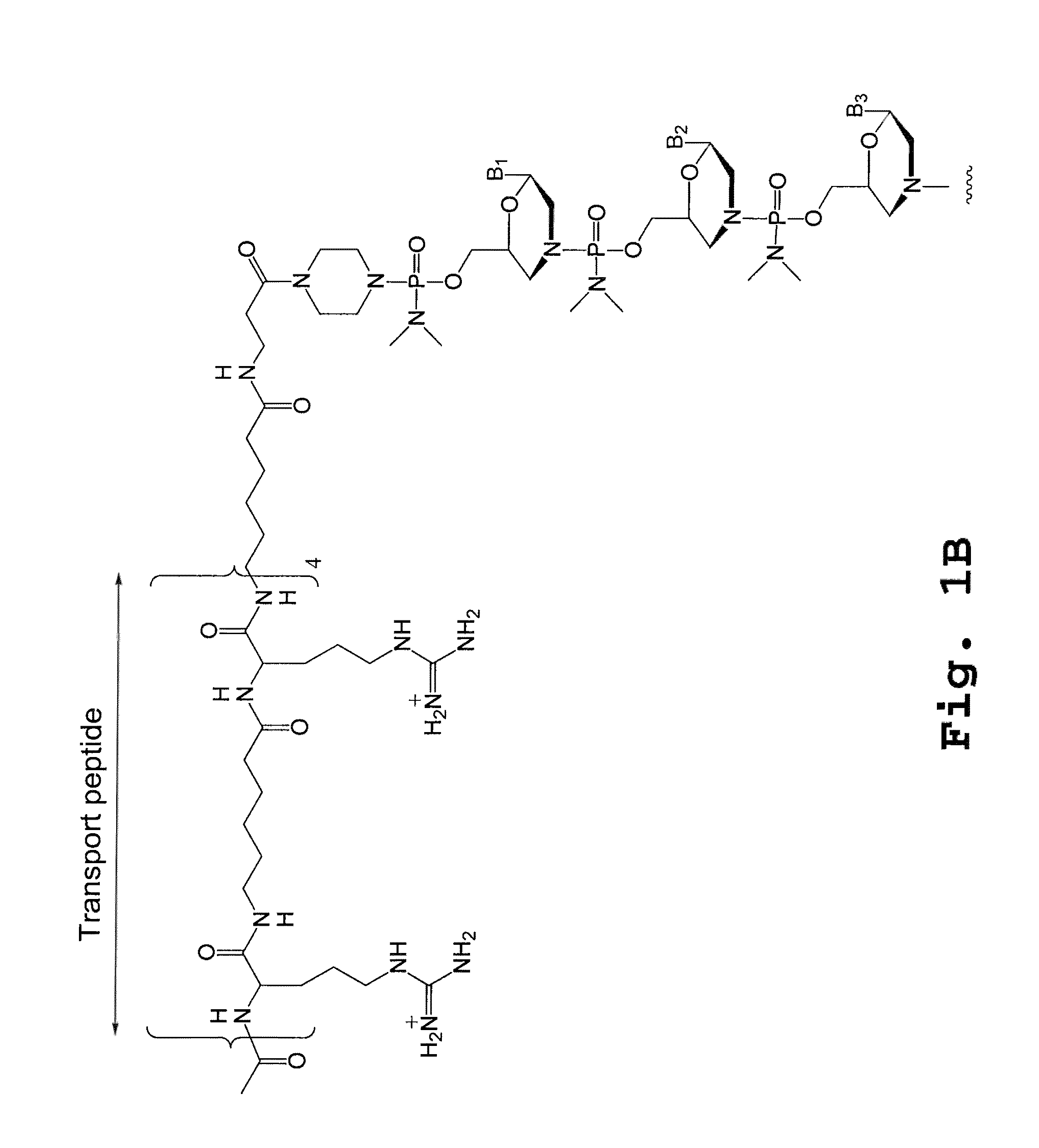
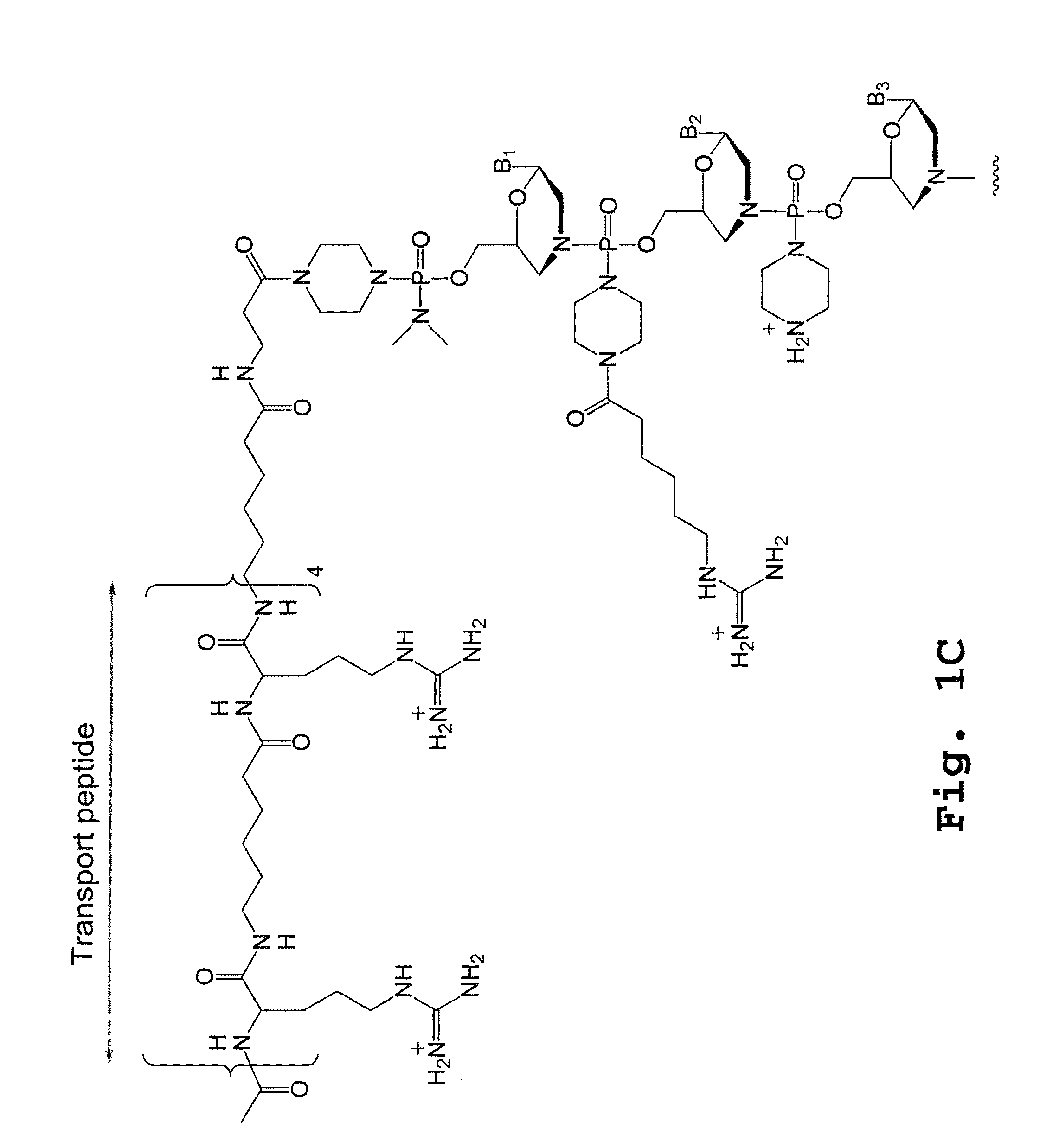
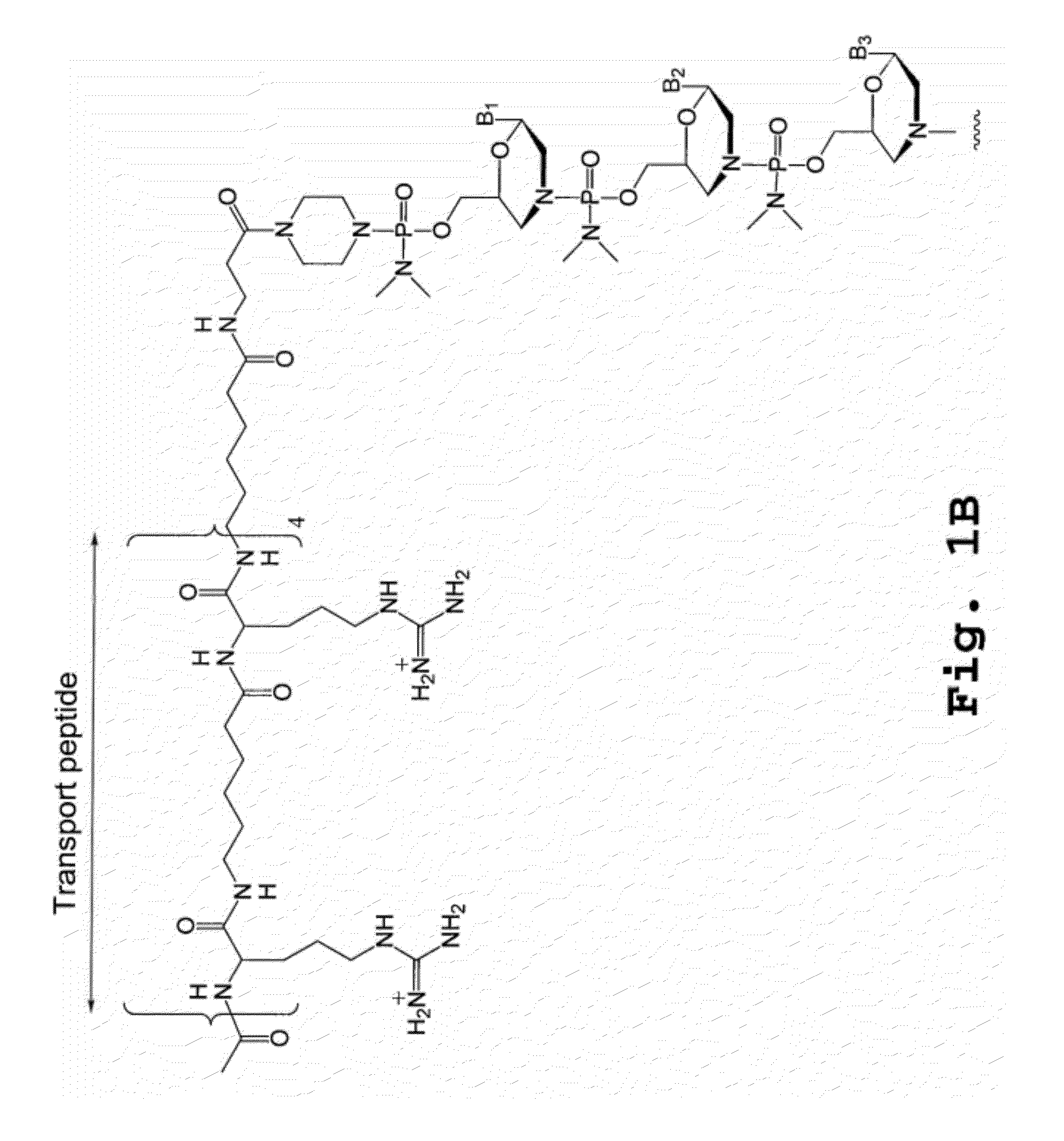
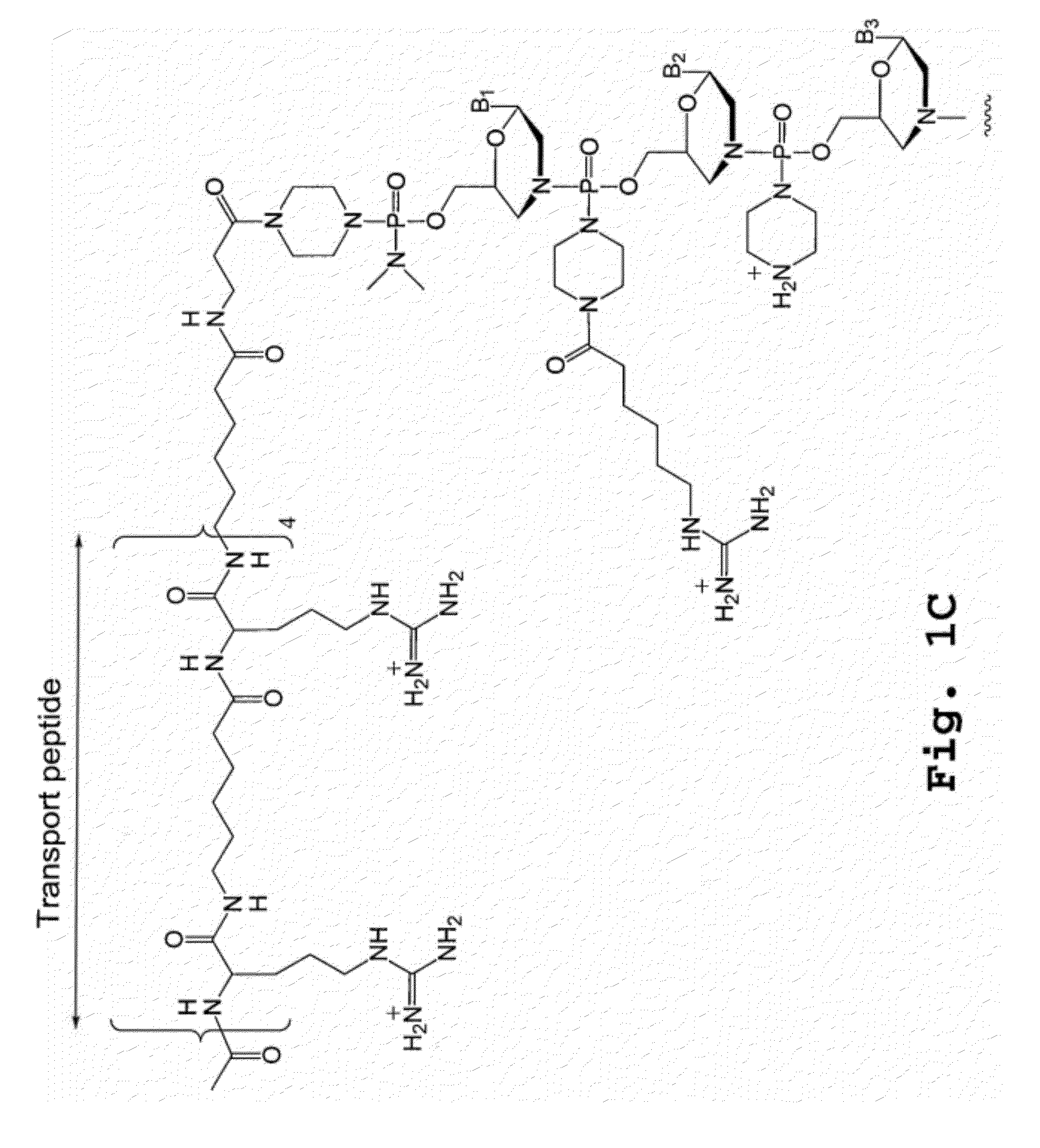
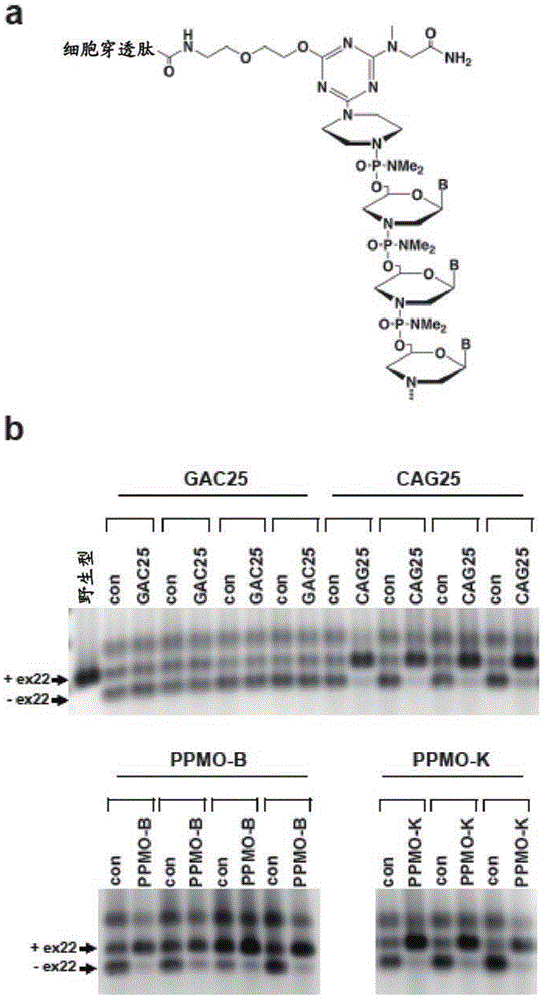
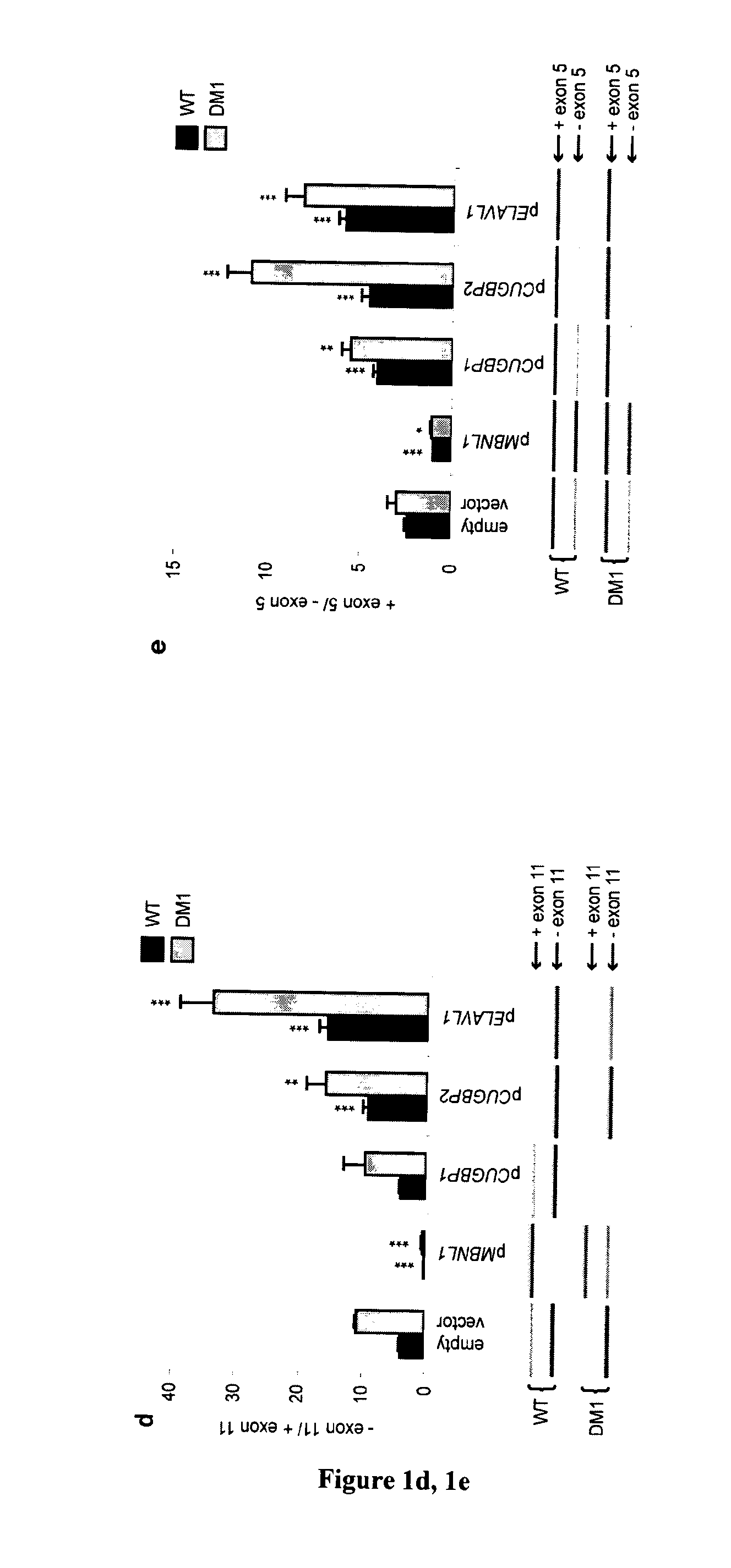
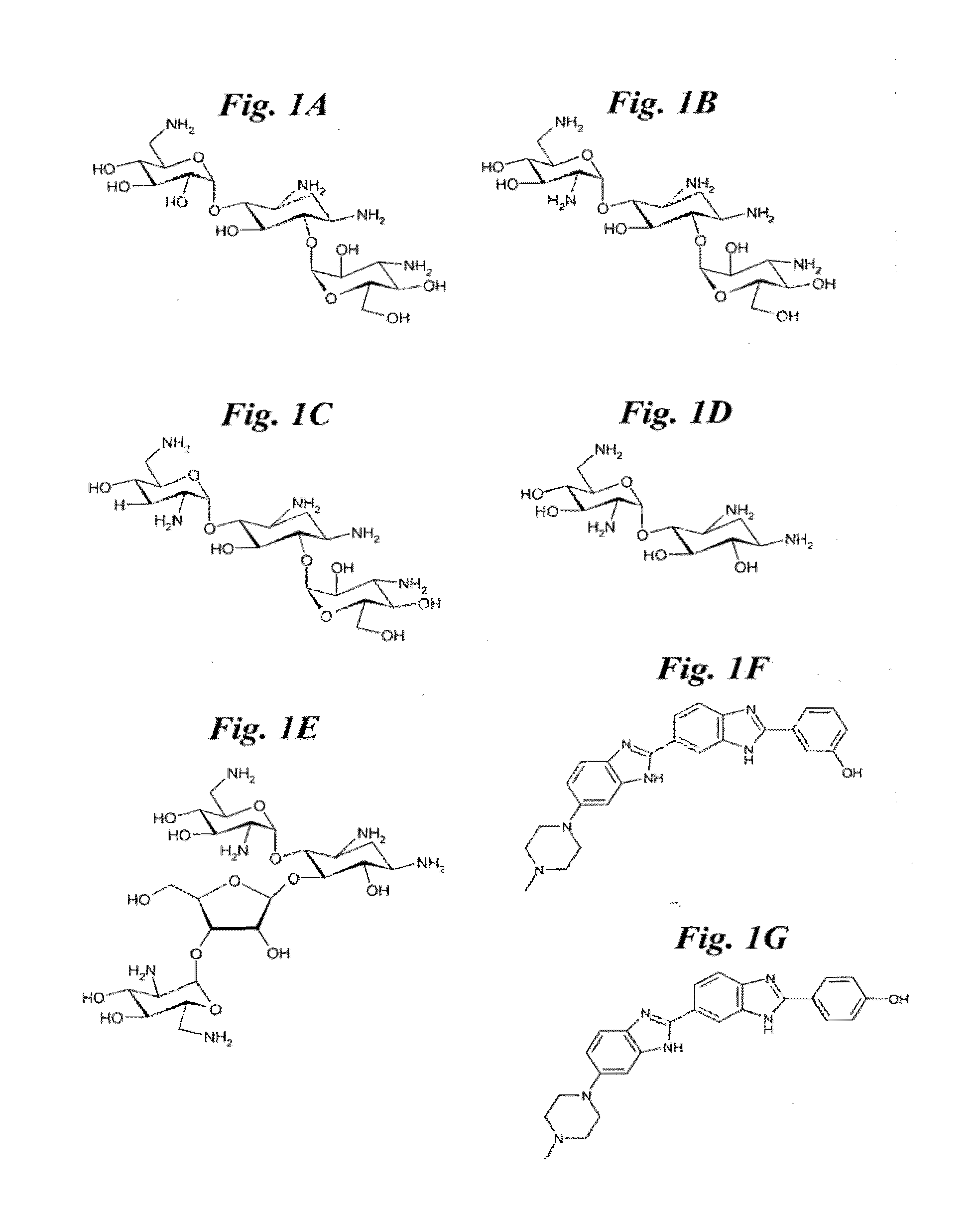
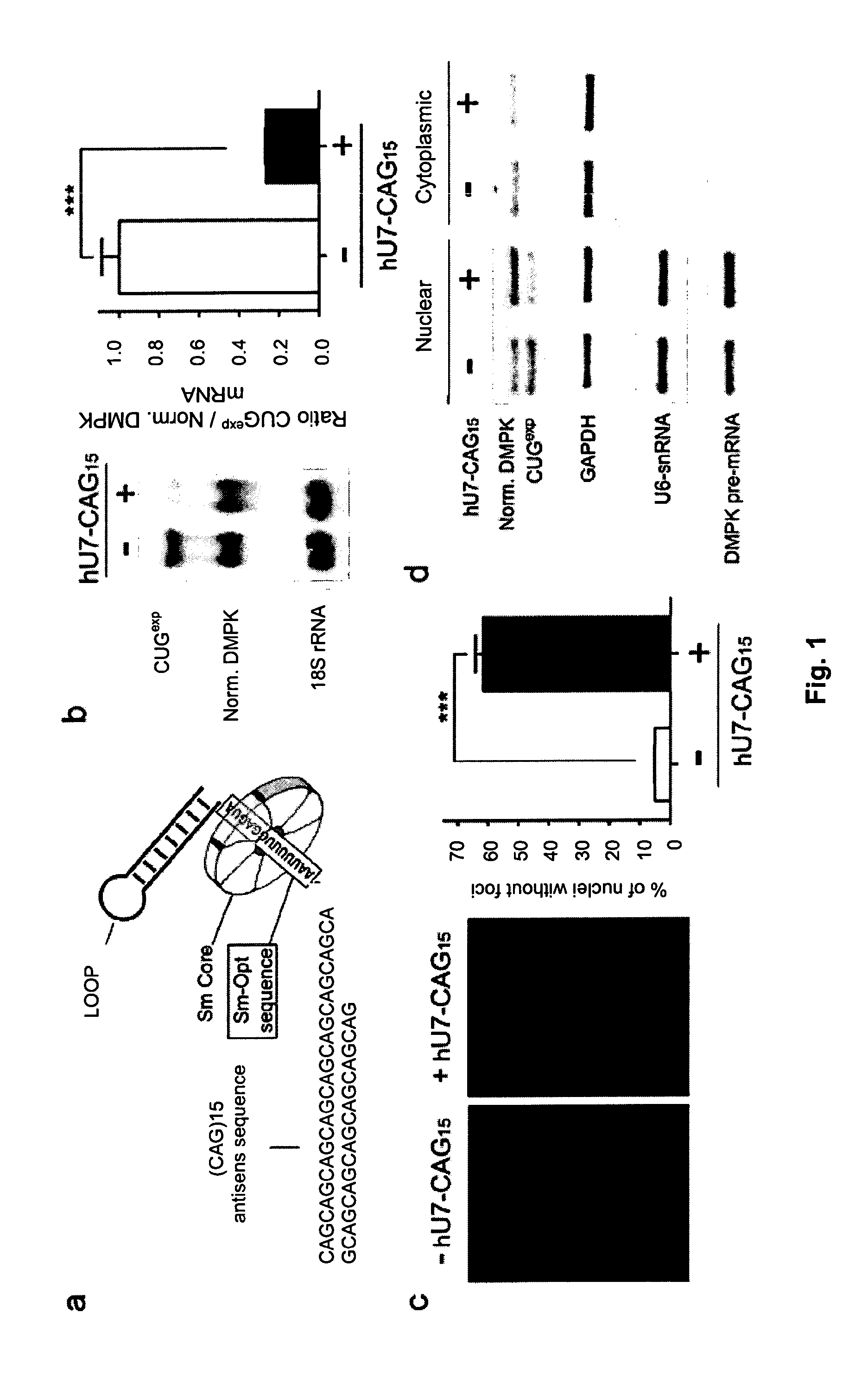
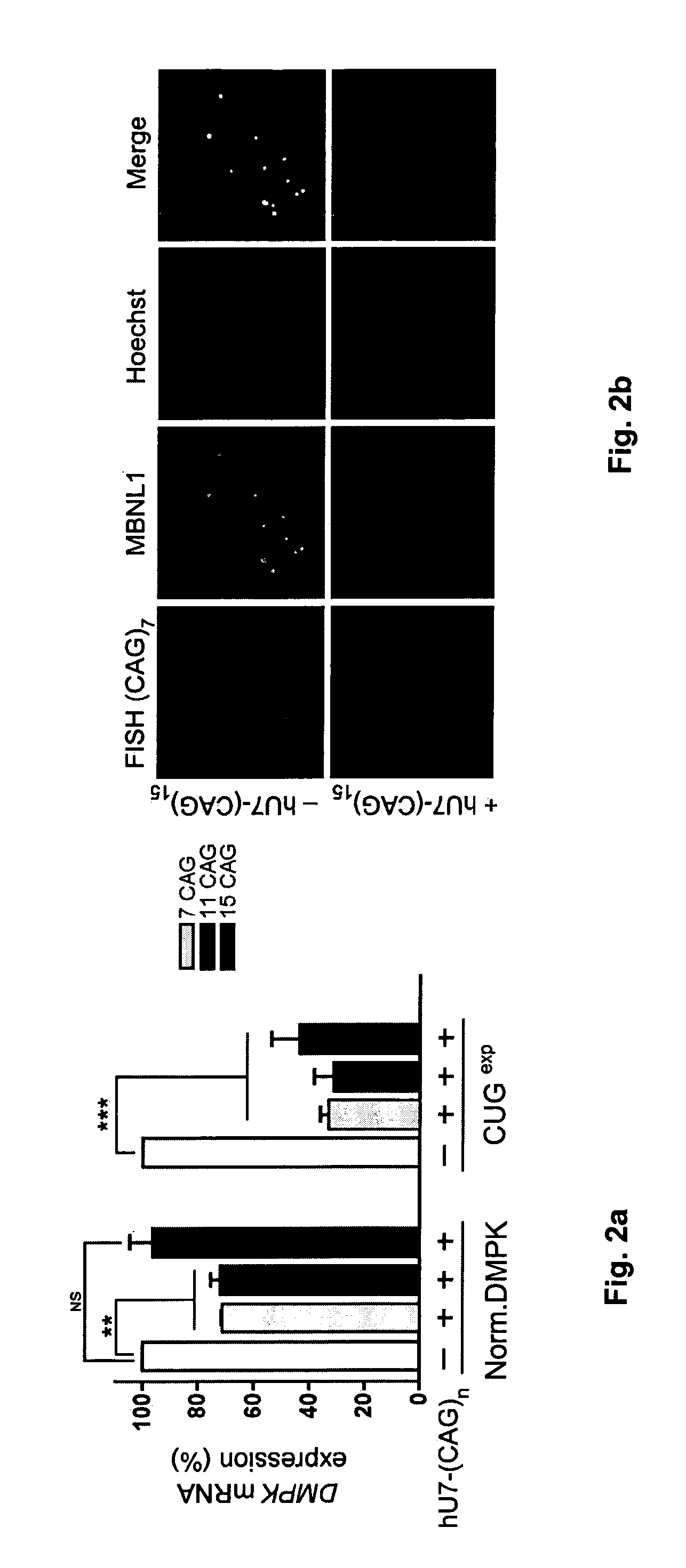
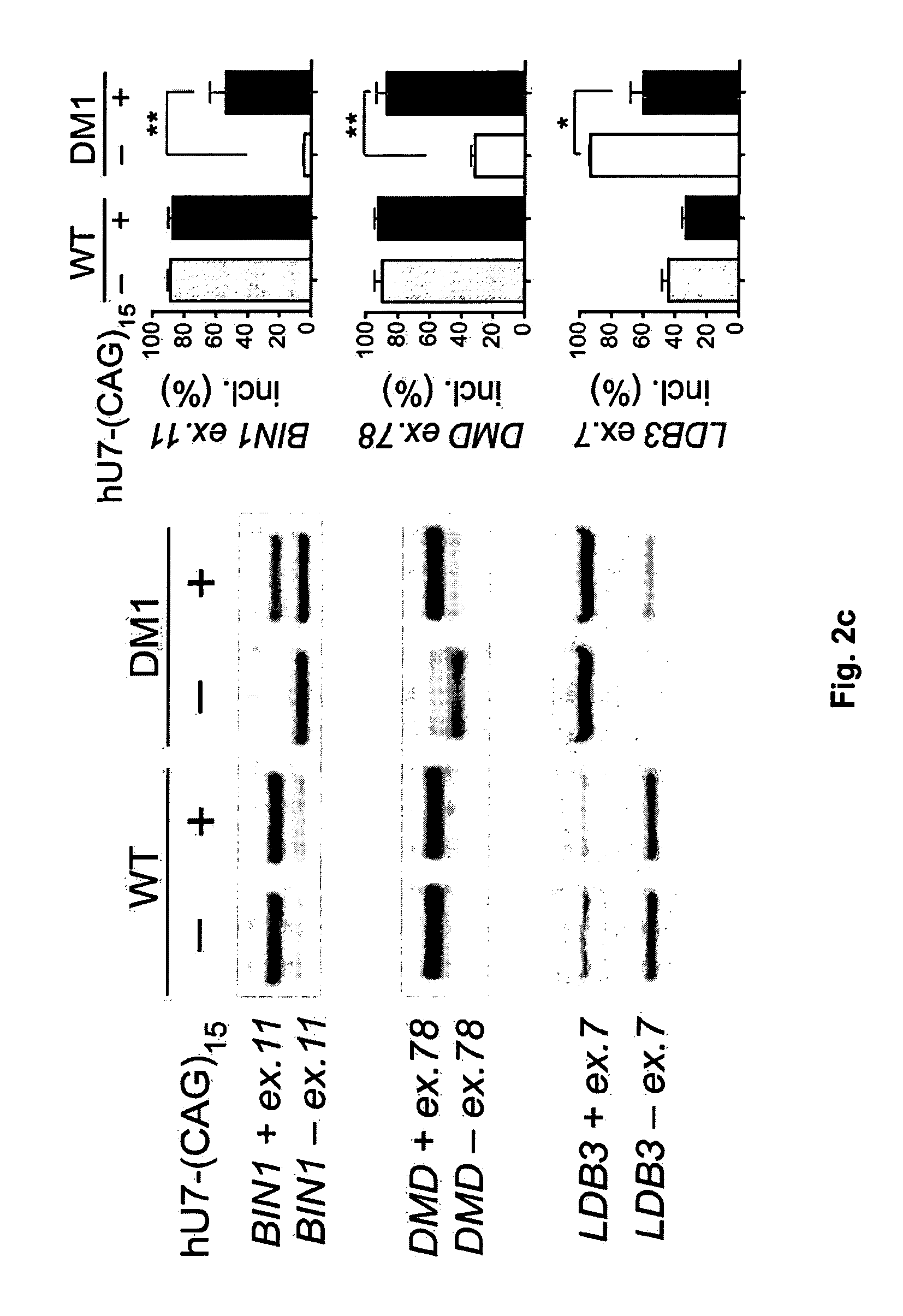
An antisense compound for use in treating myotonic dystrophy DM1 or DM2, a method of enhancing antisense targeting to heart and quadricep muscles, and a method for treating DM1 or DM2 in a mammalian subject are disclosed. The oligonucleotide has 8-30 bases, with at least 8 contiguous bases being complementary to the polyCUG or polyCCUG repeats in the 3′UTR region of dystrophia myotonica protein kinase (DMPK) mRNA in DM1 or DM2, respectively. Conjugated to the oligonucleotide is a cell-penetrating peptide having the sequence (RXRR(B / X)R)2XB, where R is arginine; B is β-alanine; and each X is —C(O)—(CH2)n—NH—, where n is 4-6. The antisense compound is effective to selectively block the sequestration of muscleblind-like 1 protein (MBNL1) and / or CUGBP, in heart and quadricep muscle in a myotonic dystrophy animal model.
Owner:SAREPTA THERAPEUTICS INC
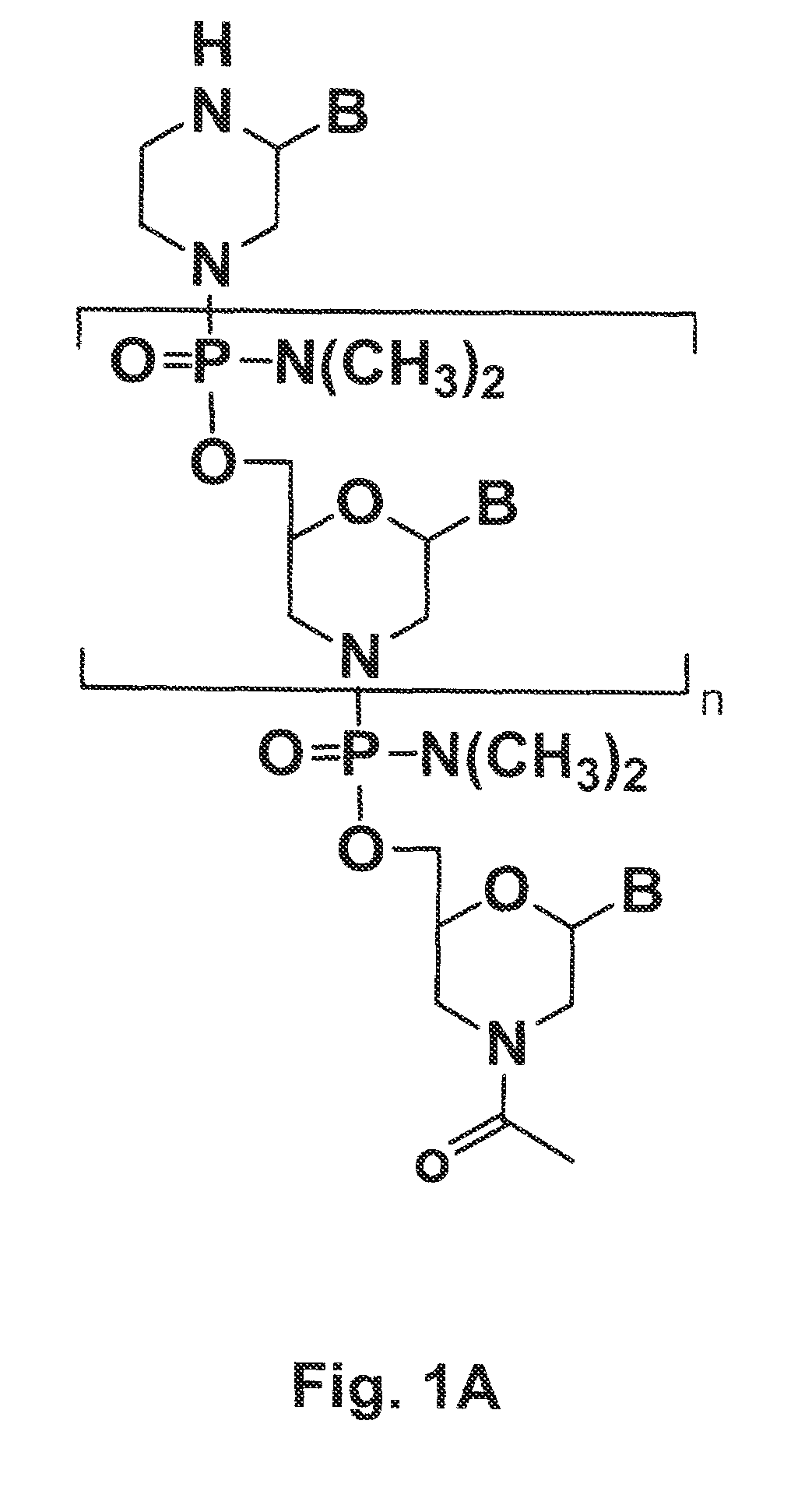
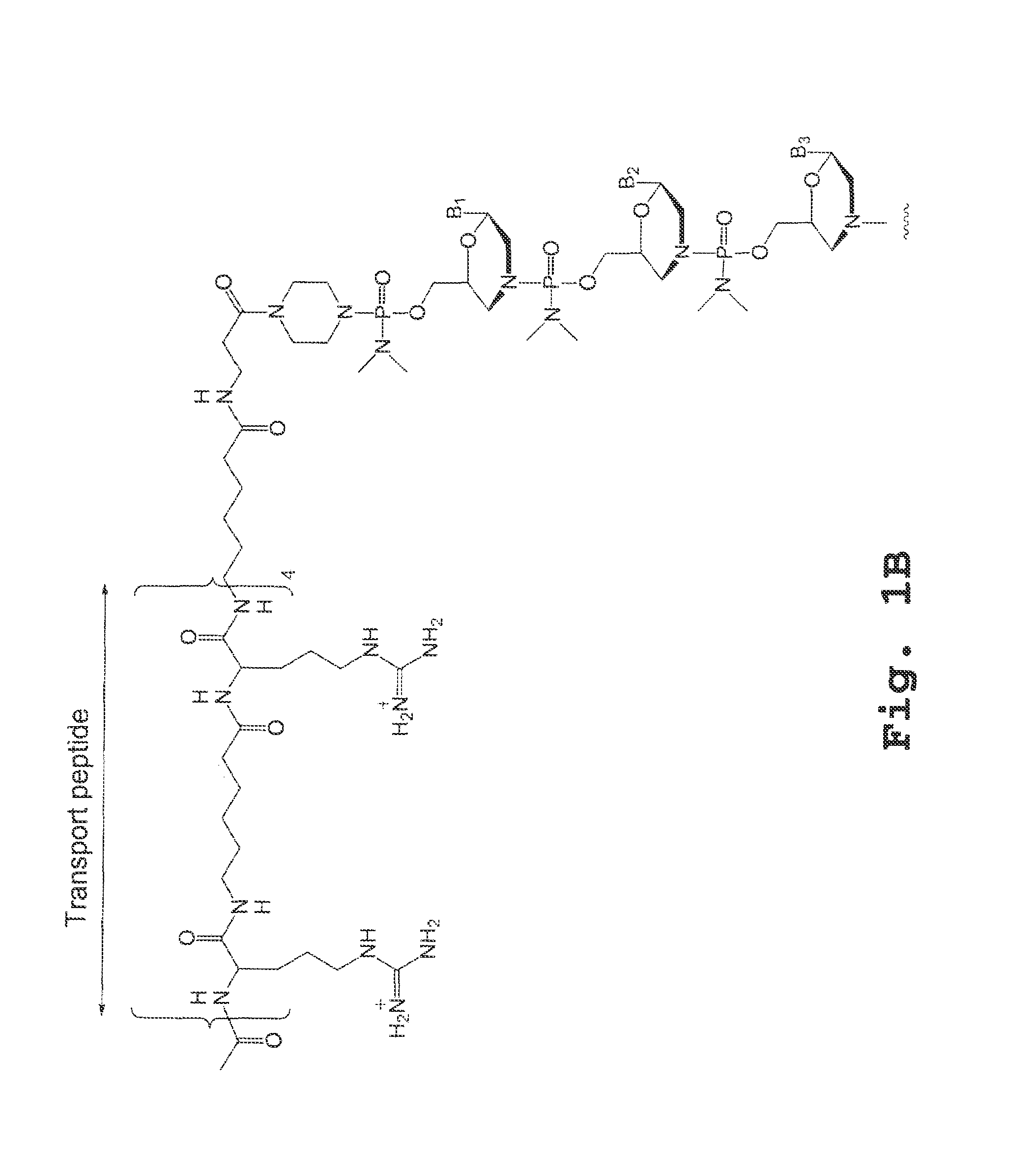
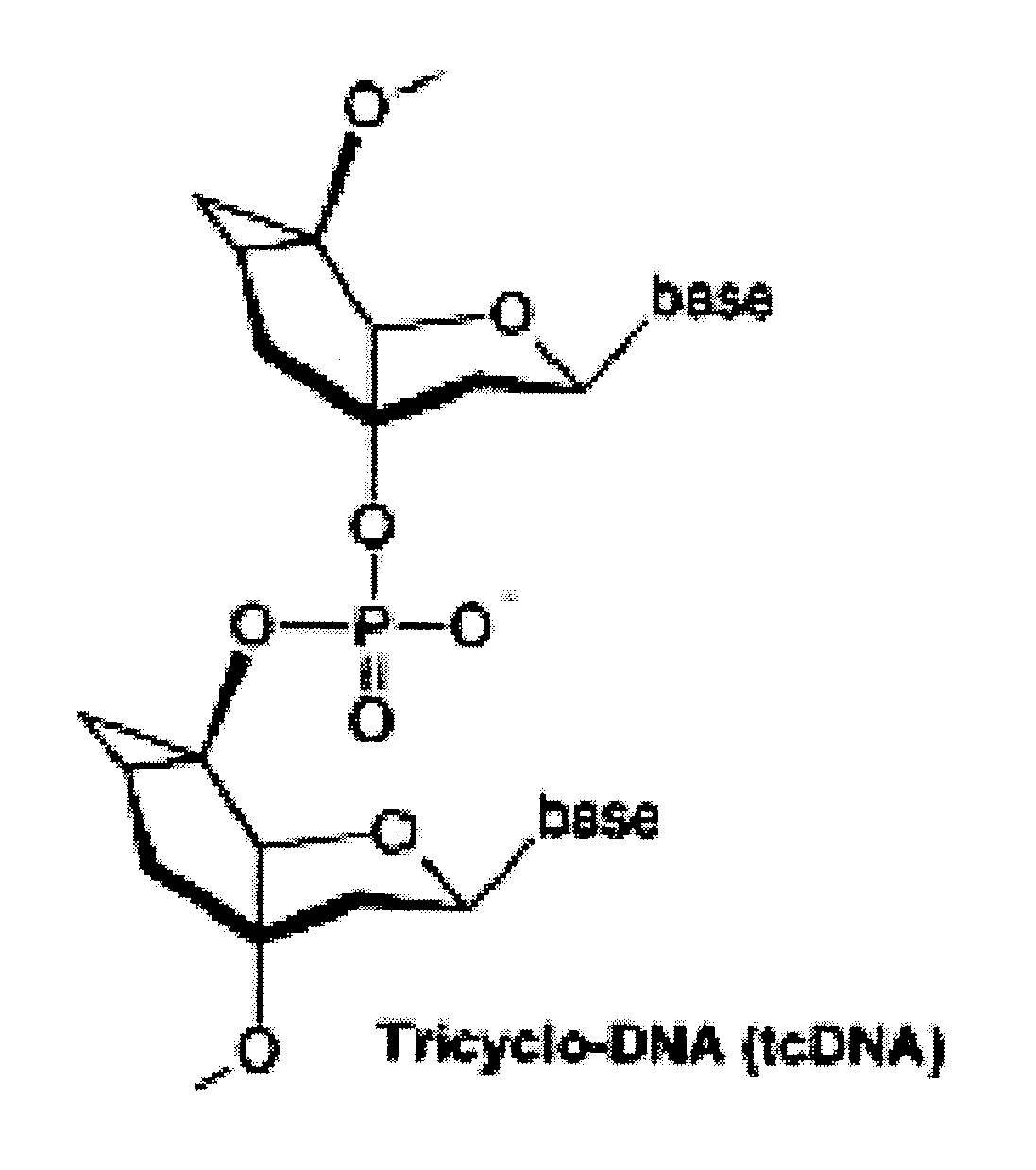
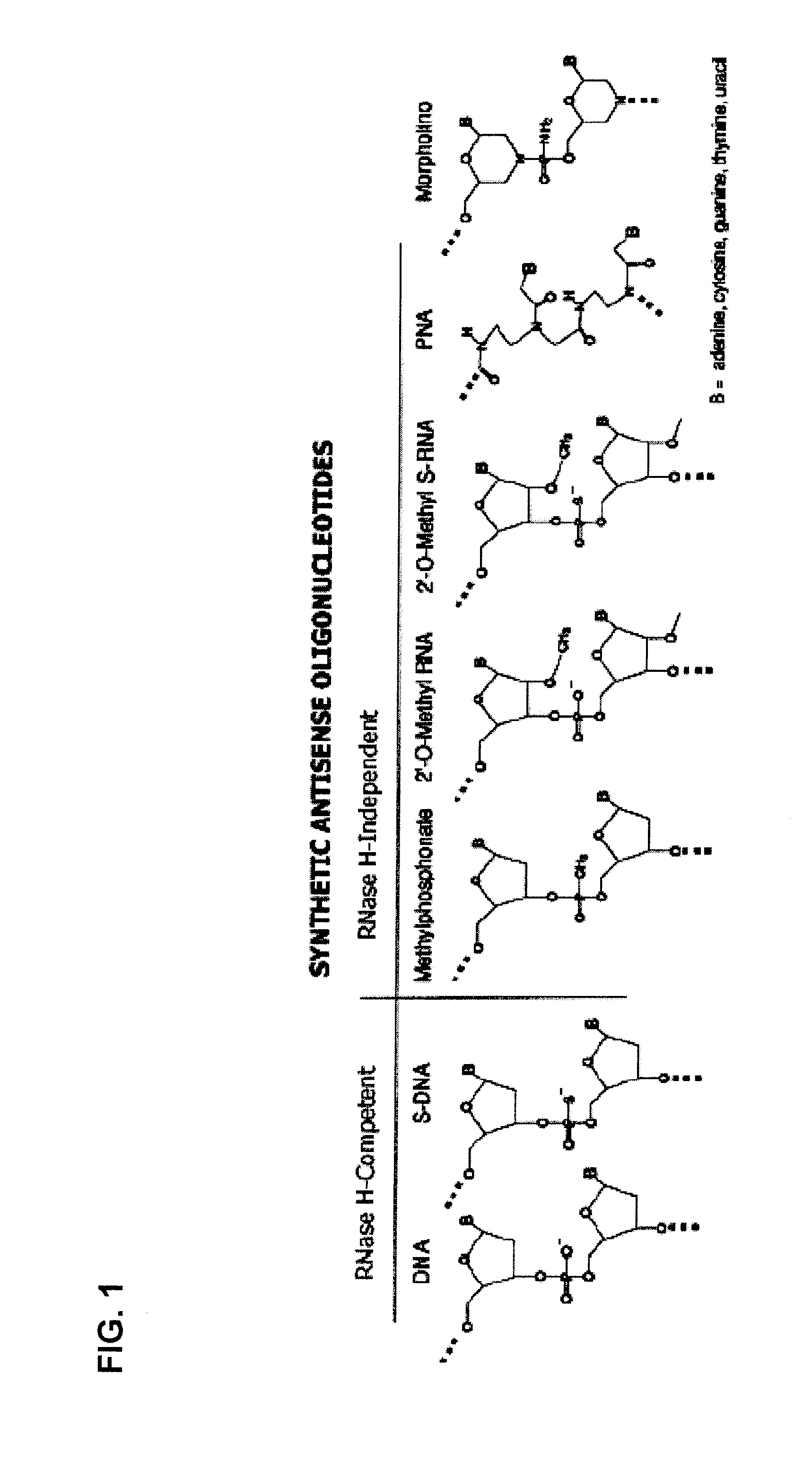
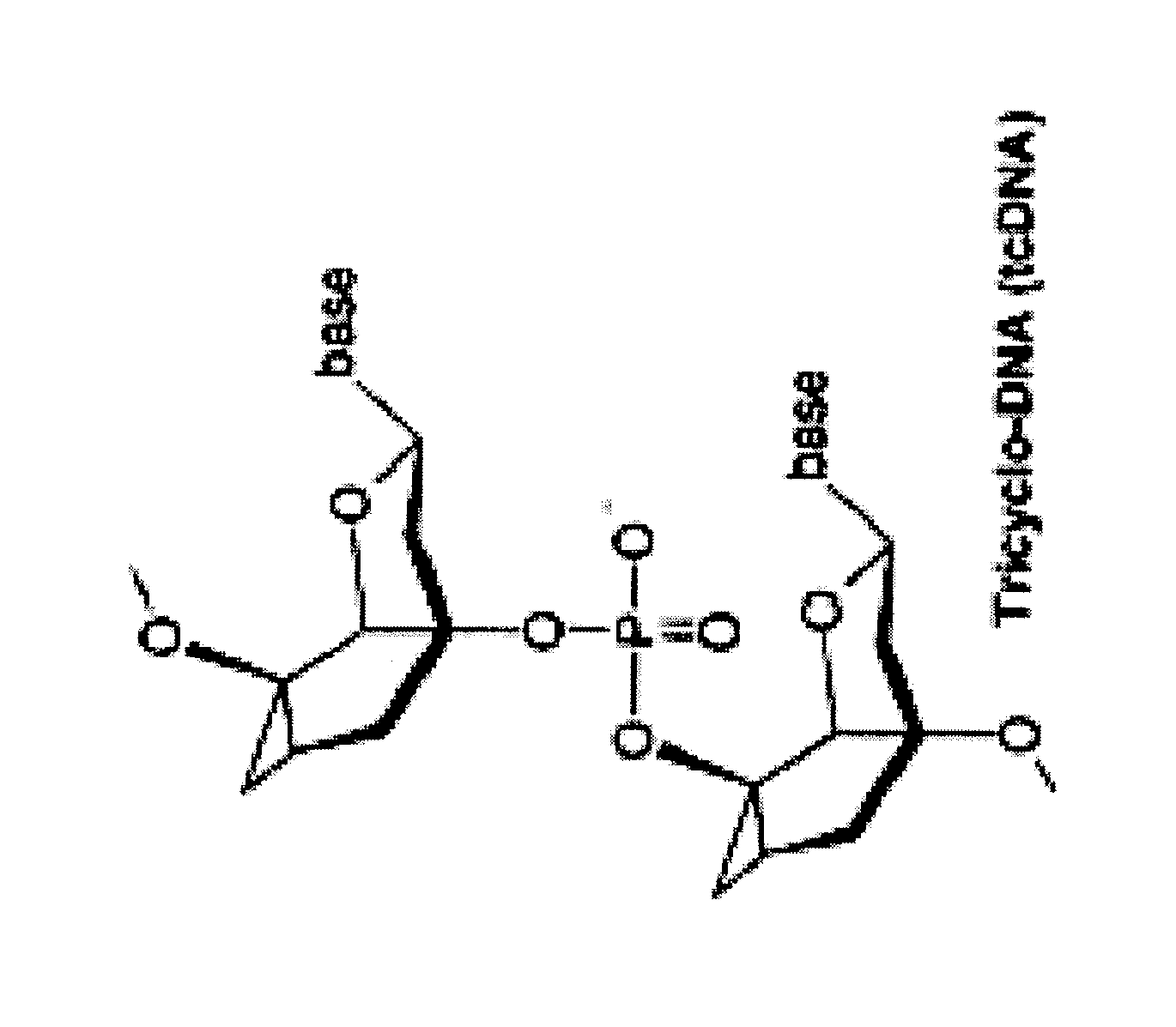
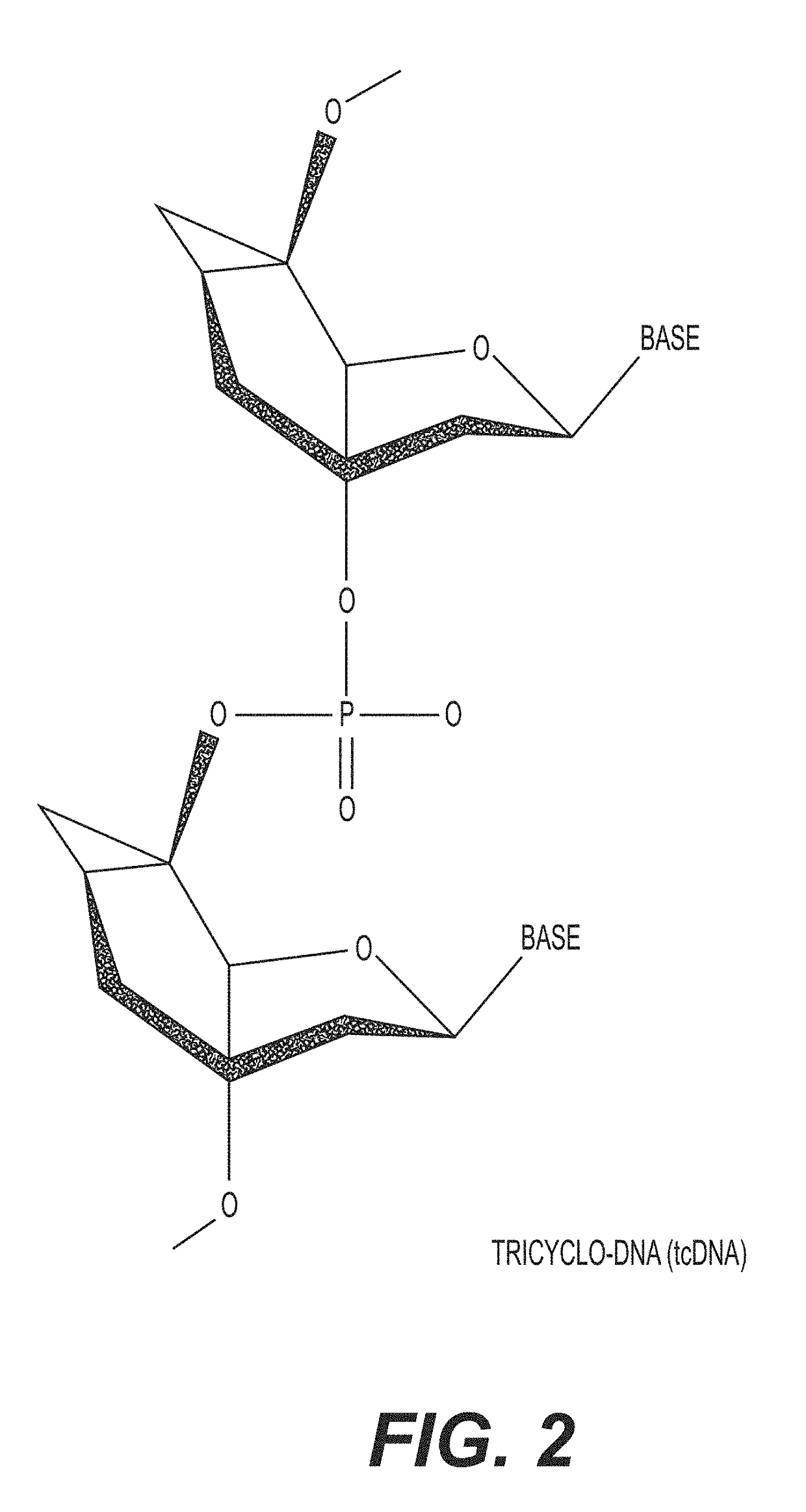
Tricyclo-dna antisense oligonucleotides, compositions, and methods for the treatment of disease
InactiveUS20120149756A1Find utilityFacilitates inclusionOrganic active ingredientsSplicing alterationDiseasePre mrna processing
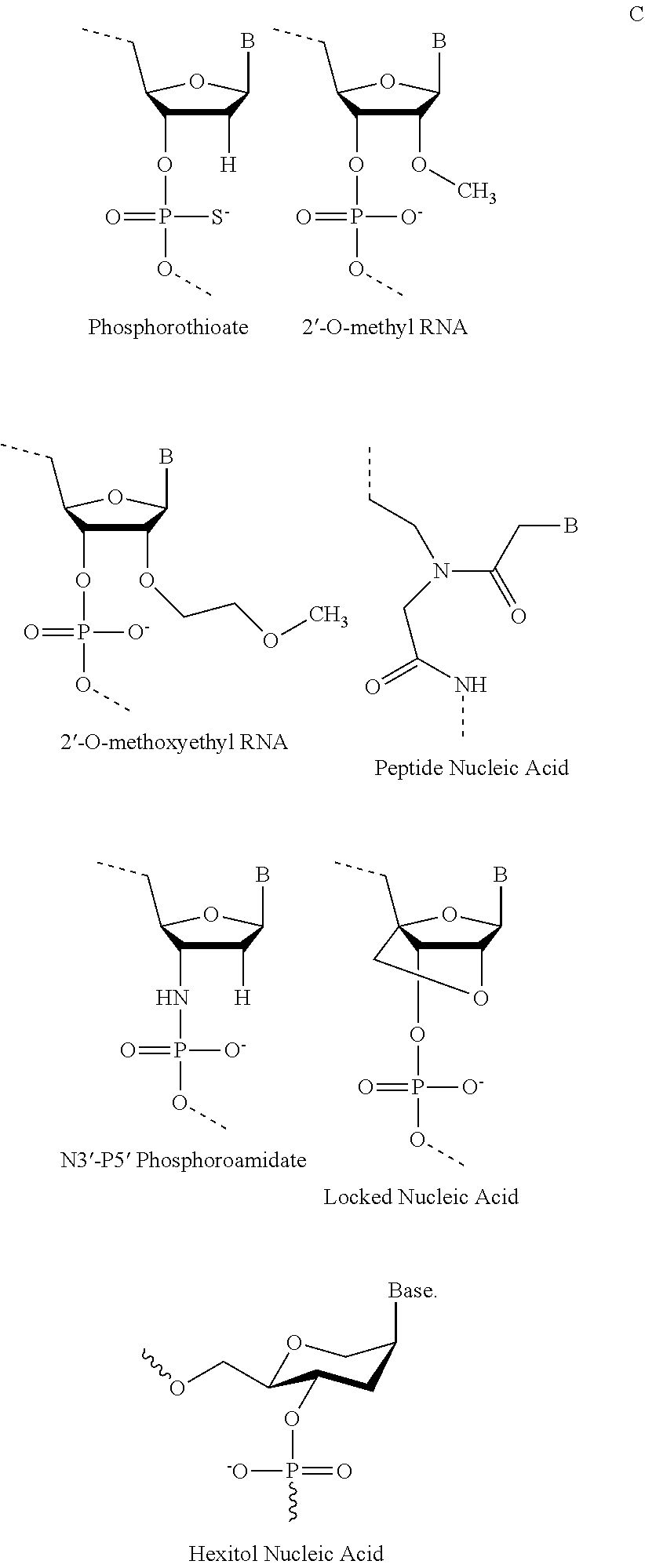
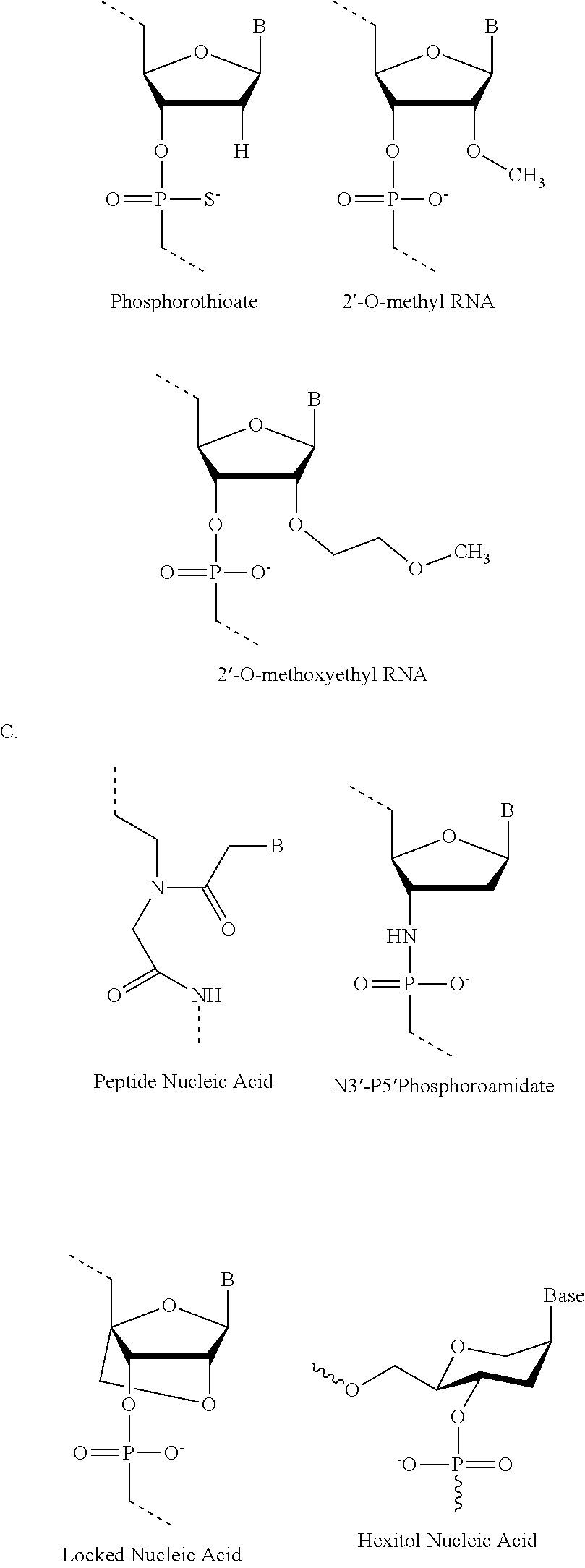
Provided are tricyclo-DNA (tc-DNA) AON and methods employing tc-DNA AON for modifying splicing events that occur during pre-mRNA processing. Tricyclo-DNA (tc-DNA) AON are described that may be used to facilitate exon skipping or to mask intronic silencer sequences and / or terminal stem-loop sequences during pre-mRNA processing and to target RNase-mediated destruction of processed mRNA. Tc-DNA AON described herein may be used in methods for the treatment of Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy by skipping a mutated exon 23 or exon 51 within a dystrophin gene to restore functionality of a dystrophin protein; in methods for the treatment of Spinal Muscular Atrophy by masking an intronic silencing sequence and / or a terminal stem-loop sequence within an SMN2 gene to yield modified functional SMN2 protein, including an amino acid sequence encoded by exon 7, which is capable of at least partially complementing a non-functional SMN1 protein; and in methods for the treatment of Steinert's Myotonic Dystrophy by targeting the destruction of a mutated DM1 mRNA comprising 3′-terminal CUG repeats.
Owner:INST NAT DE LA SANTE & DE LA RECHERCHE MEDICALE (INSERM) +4
Compound and method for treating myotonic dystrophy
ActiveUS8741863B2Organic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsArginineMyotonic dystrophy gene
An antisense compound for use in treating myotonic dystrophy DM1 or DM2, a method of enhancing antisense targeting to heart and quadricep muscles, and a method for treating DM1 or DM2 in a mammalian subject are disclosed. The oligonucleotide has 8-30 bases, with at least 8 contiguous bases being complementary to the polyCUG or polyCCUG repeats in the 3′UTR region of dystrophia myotonica protein kinase (DMPK) mRNA in DM1 or DM2, respectively. Conjugated to the oligonucleotide is a cell-penetrating peptide having the sequence (RXRR(B / X)R)2XB, where R is arginine; B is β-alanine; and each X is —C(O)—(CH2)n—NH—, where n is 4-6. The antisense compound is effective to selectively block the sequestration of muscleblind-like 1 protein (MBNL1) and / or CUGBP, in heart and quadricep muscle in a myotonic dystrophy animal model.
Owner:SAREPTA THERAPEUTICS INC
RNA targeting compounds and methods for making and using same
ActiveUS20080227213A1Peptide-nucleic acidsOrganic active ingredientsSide chainMyotonic dystrophy gene
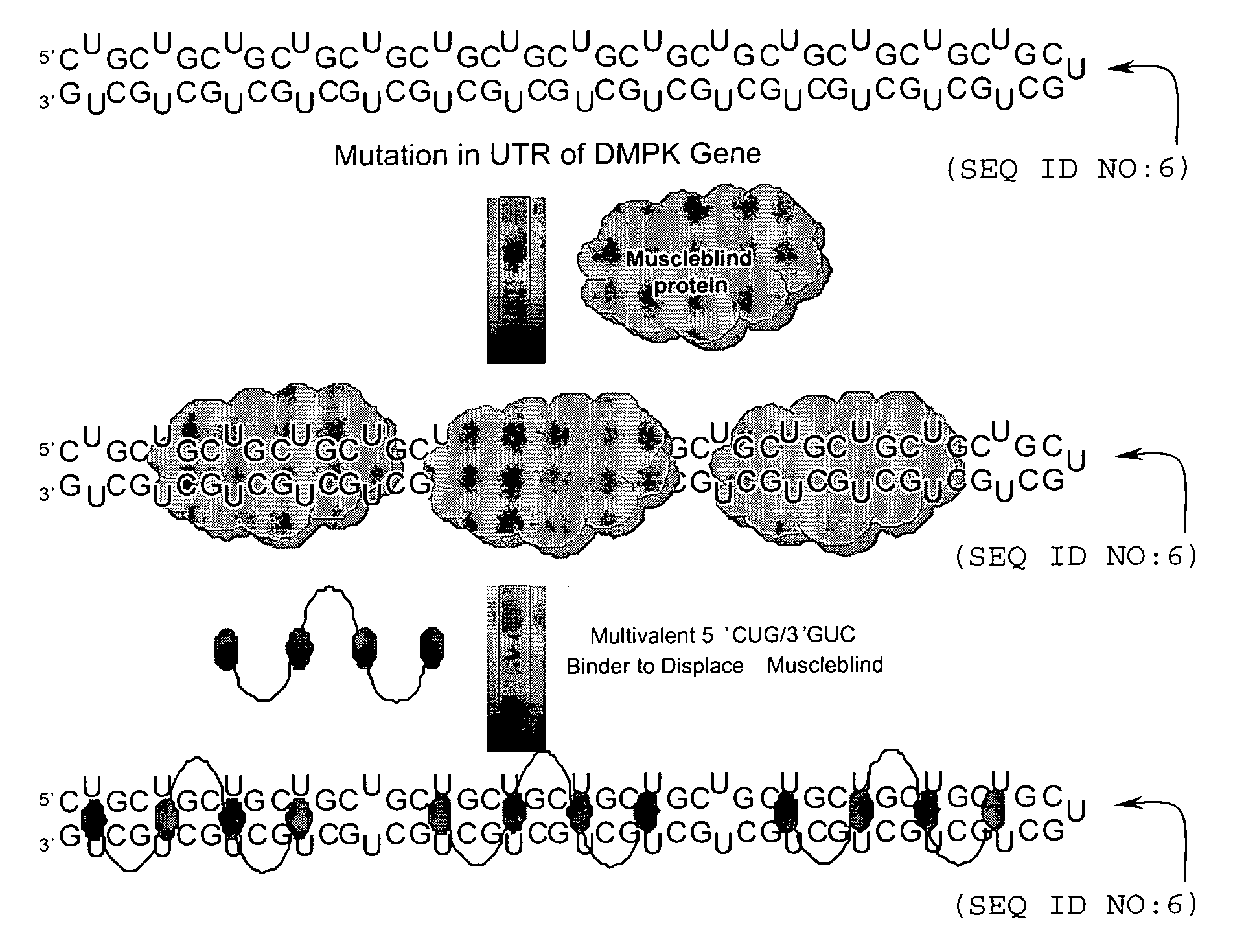
Disclosed are RNA targeting compounds having the formula:wherein j is an integer from 1 to 100; each i is the same or different and is zero or an integer from 1 to 100; each Z1 represents the same or different linking moiety; each R1 is the same or different and represents an alkyl group or an aryl group; each Q1 represents the same or different RNA binding ligand; Q2 is an alkyl group; Q3 is a halogen, an alkyl group, an aryl group, or an amine. Also disclosed are RNA targeting compounds that include a polymer backbone and two or more pendant RNA binding ligands that are bound to the polymer backbone. Methods for using the subject RNA targeting compounds to treat myotonic dystrophy and other diseases are also disclosed, as are compounds that can be used to prepare the subject RNA targeting compounds.
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK
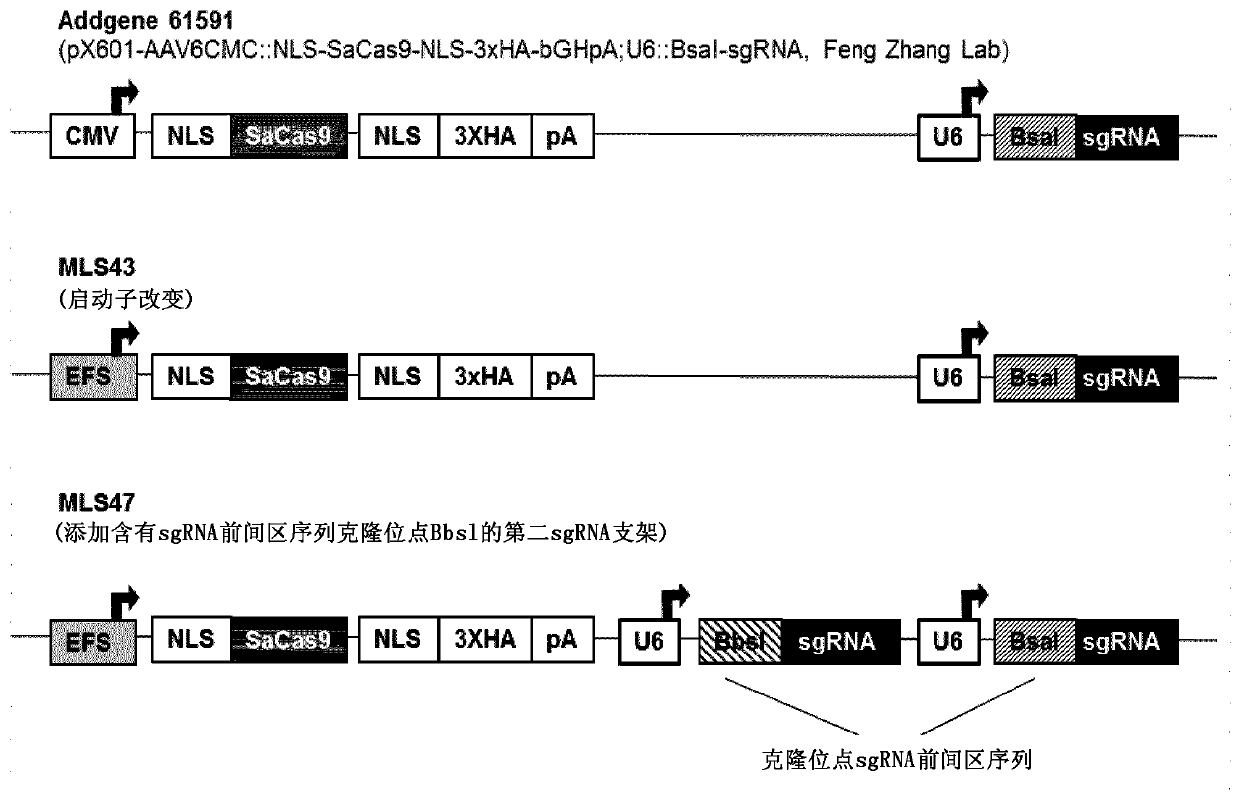
Genetic correction of myotonic dystrophy type 1
InactiveUS20170088819A1Reduced proliferative capacityLimited life-spanGenetic material ingredientsTransferasesProtein kinase domainNucleotide
The invention relates to polynucleotides suitable for reducing or eliminating the expression of expanded repeat RNA (CUGexp) of the dystrophy myotonic-protein kinase (DMPK) gene in a cell of a DM-1 patient. The polynucleotides are a combination of a polynucleotide for a site specific nuclease targeting the dystrophy myotonic-protein kinase (DMPK) gene locus, and a donor polynucleotide having 5′ and 3′ regions which are homologous with the sequence of DMPK gene which flank the target site of the nuclease. The invention further relate to in vivo and in vitro methods to reduce or eliminate CTG repeats in the DMPK gene. The invention further relates to the medical use of polynucleotides and cells for treating DM-1 patient.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP +1
Antisense conjugates for decreasing expression of dmpk
InactiveUS20150064181A1Constipation lowReduce difficultyOrganic active ingredientsTransferasesMBNL1Myotonic dystrophy gene
The disclosure provides novel conjugates comprising antisense oligonucleotides that hybridize to a DMPK transcript and a 3E10 antibody or binding fragment thereof. Also considered are these conjugates further comprising MBNL1 polypeptides. Methods of treating myotonic dystrophy using these conjugates and kits comprising these conjugates are also considered. Wherein the conjugates are suitable for delivery to muscle cells.
Owner:VALERION THERAPEUTICS
Oligomers
InactiveUS20130085139A1Improve securityLasting effectOrganic active ingredientsSplicing alterationMyostatinPrecursor mRNA
Certain disclosed oligomers induce exon skipping during processing of myostatin pre-mRNA. The oligomers may be in a vector or encoded by the vector. The vector is used for inducing exon skipping during processing of myostatin pre-mRNA. A therapeutically effective amount of the oligomer may be administered to a subject patient such that exon skipping during processing of myostatin pre-mRNA is induced. The administration to a subject may be used in order to increase or maintain muscle mass, or slowing degeneration of muscle mass in the subject. The administration to a subject may ameliorate muscle wasting conditions, such as muscular dystrophy. Examples of such muscular dystrophies which may be so treated include Becker's muscular dystrophy, congenital muscular dystrophy, Duchenne muscular dystrophy, distal muscular dystrophy, Emery-Dreifuss muscular dystrophy, facioscapulohumeral muscular dystrophy (FSHD), limb-girdle muscular dystrophy, myotonic muscular dystrophy, and oculopharyngeal muscular dystrophy
Owner:ROYAL HOLLOWAY & BEDFORD NEW COLLEGE
Compound and method for treating myotonic dystrophy
ActiveUS20120058946A1Organic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsArginineMyotonic dystrophy gene
An antisense compound for use in treating myotonic dystrophy DM1 or DM2, a method of enhancing antisense targeting to heart and quadricep muscles, and a method for treating DM1 or DM2 in a mammalian subject are disclosed. The oligonucleotide has 8-30 bases, with at least 8 contiguous bases being complementary to the polyCUG or polyCCUG repeats in the 3′UTR region of dystrophia myotonica protein kinase (DMPK) mRNA in DM1 or DM2, respectively. Conjugated to the oligonucleotide is a cell-penetrating peptide having the sequence (RXRR(B / X)R)2XB, where R is arginine; B is β-alanine; and each X is —C(O)—(CH2)n—NH—, where n is 4-6. The antisense compound is effective to selectively block the sequestration of muscleblind-like 1 protein (MBNL1) and / or CUGBP, in heart and quadricep muscle in a myotonic dystrophy animal model.
Owner:SAREPTA THERAPEUTICS INC
Antisense conjugates for decreasing expression of dmpk
ActiveUS20180021449A1Constipation lowReduce difficultyOrganic active ingredientsTransferasesMBNL1Myotonic dystrophy gene
The disclosure provides novel conjugates comprising antisense oligonucleotides that hybridize to a DMPK transcript and a 3E10 antibody or binding fragment thereof. Also considered are these conjugates further comprising MBNL1 polypeptides. Methods of treating myotonic dystrophy using these conjugates and kits comprising these conjugates are also considered. Wherein the conjugates are suitable for delivery to muscle cells.
Owner:VALERION THERAPEUTICS
Antisense conjugates for decreasing expression of DMPK
InactiveUS9610362B2Organic active ingredientsSugar derivativesMyotonic dystrophy geneMyotonic dystrophy
The disclosure provides novel conjugates comprising antisense oligonucleotides that hybridize to a DMPK transcript and a 3E10 antibody or binding fragment thereof. Also considered are these conjugates further comprising MBNL1 polypeptides. Methods of treating myotonic dystrophy using these conjugates and kits comprising these conjugates are also considered. Wherein the conjugates are suitable for delivery to muscle cells.
Owner:VALERION THERAPEUTICS
Methods of Generating Stem Cells and Embryonic Bodies Carrying Disease-Causing Mutations and Methods of Using same for Studying Genetic Disorders
InactiveUS20070269790A1Microbiological testing/measurementGenetically modified cellsStem cell lineWaardenburg syndrome
Stem cells, stem cell lines and differentiated cells, tissues and organs which carry disease-causing mutations are provided. There is also provided a method of identifying agents suitable for treating disorders associated with at least one disease-causing mutations such as myotonic dystrophy and van Waardenburg syndrome.
Owner:TECHNION RES & DEV FOUND LTD
Therapeutic methods and agents for treating myotonic dystrophy
ActiveUS8754084B2Less effectiveLow toxicityBiocideDispersion deliveryMedicineMyotonic dystrophy gene
The invention provides compounds, compositions and methods for treating myotonic dystrophy. The compounds can selectively bind to CUG repeats in RNA, or to CTG repeats in DNA, and inhibit replication of the nucleic acids.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
Methods and compositions for treatment of myotonic dystrophy
InactiveUS20100111977A1Easy to transportReduce deliveryPeptide/protein ingredientsMuscular disorderMedicineMyotonic dystrophy gene
In certain embodiments, the present invention provides compositions and methods for treating myotonic dystrophy.
Owner:VALERION THERAPEUTICS
Compositions and Methods for Treating Myotonic Dystrophy Type 1
Disclosed is a compound for treatment of Myotonic Dystrophy type 1 having the formula:Wherein X is selected from the group consisting of O, N, C, or S, Y is a homo- or heteroatomic 5-membered ring comprising one or more atoms selected from the group consisting of N, O, S, and C, Z is an optionally substituted aryl group or optionally substituted heteroaryl, including but not limited to halogenated benzenes, pyridines, substituted benzene, substituted pyridine, R2=hydroxy, acyl, alkoxyl, esters, ethers, cyclic ethers, and lactones, R3=H, alkyl, an optionally substituted alkyl, aliphatic ether, ester, cyclic unsaturated and aromatic ring groups, and R1, R4 and R5 are independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen, alkyl, and alkoxyl or a pharmaceutically or cosmetically acceptable salt, solvate, or hydrate thereof.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA
Methods and compositions for treatment of myotonic dystrophy
InactiveUS8609615B2Improve in vivo stabilityIncreasing MBNL bioactivityPeptide/protein ingredientsMuscular disorderMedicineMyotonic dystrophy gene
In certain embodiments, the present invention provides compositions and methods for treating myotonic dystrophy.
Owner:VALERION THERAPEUTICS
RNA targeting compounds and methods for making and using same
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK
Compounds and methods for myotonic dystrophy therapy
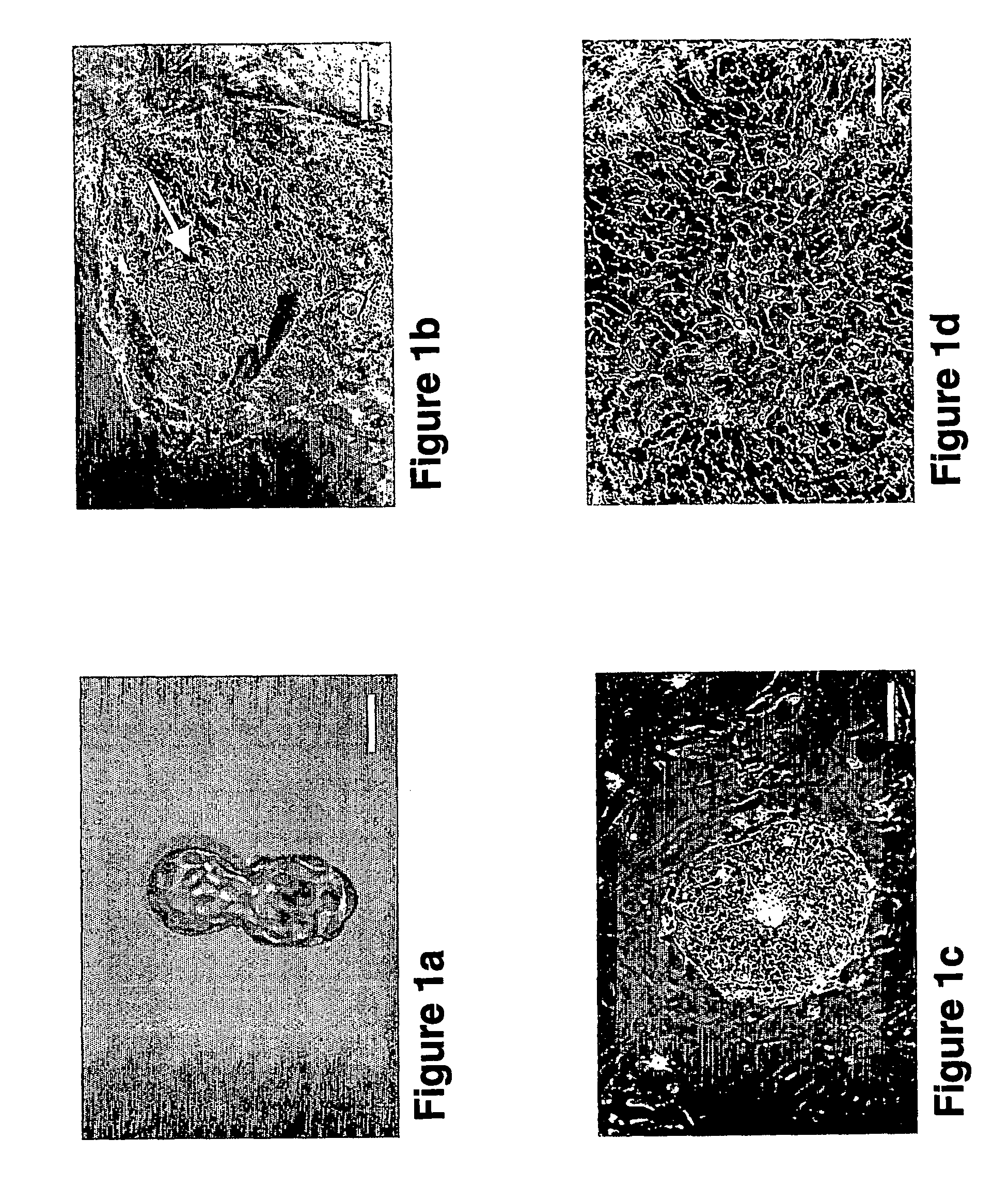
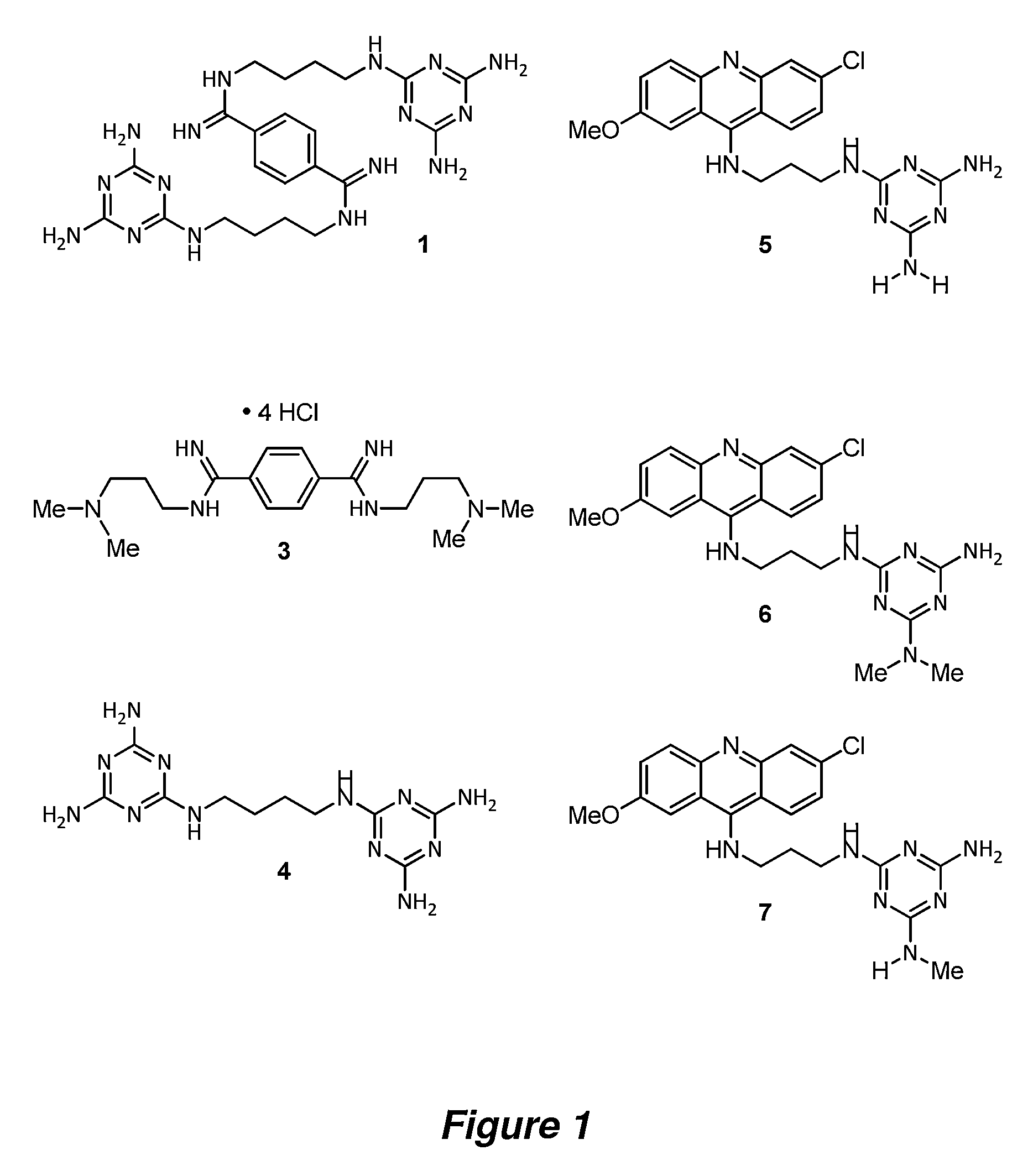
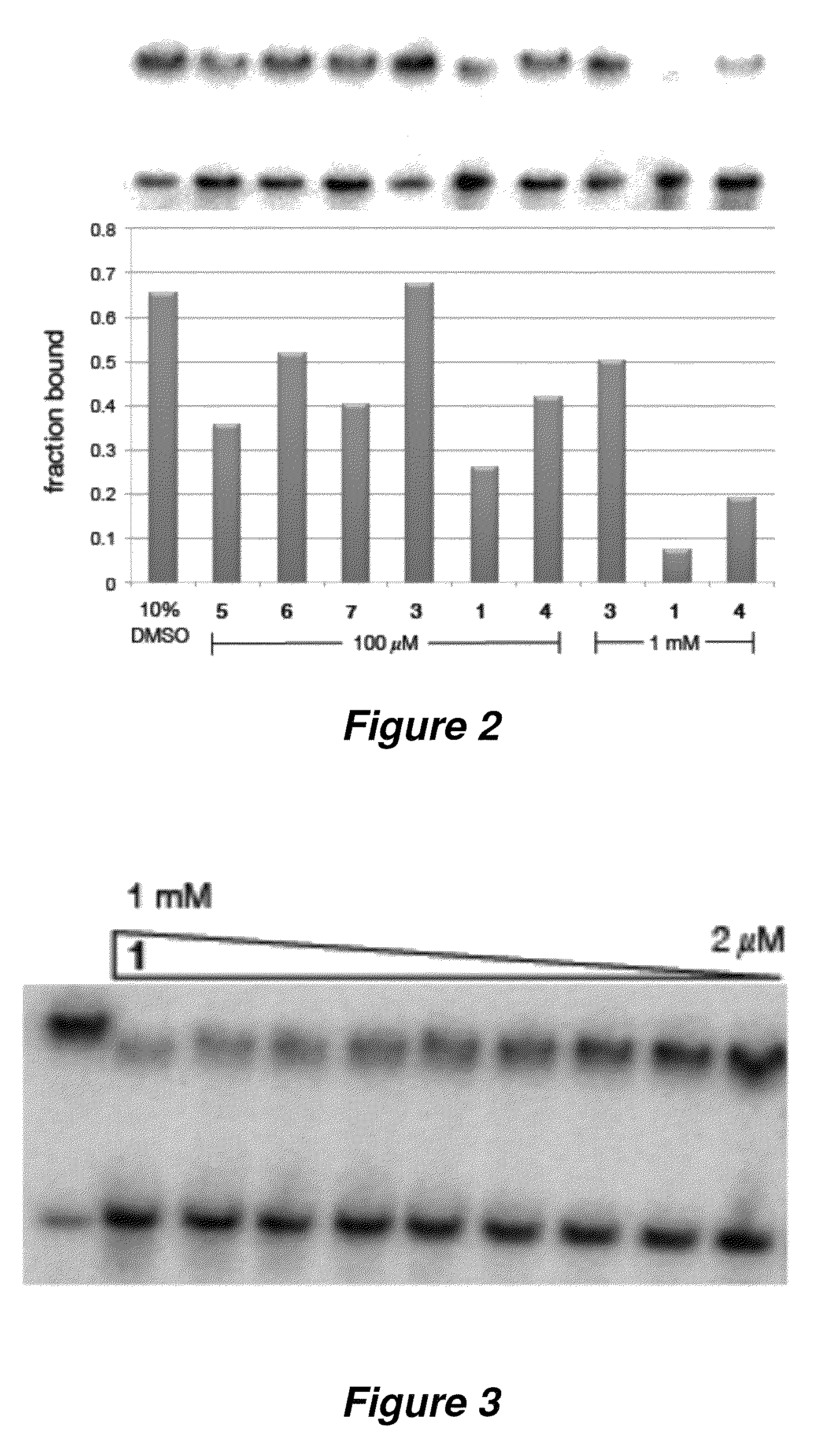
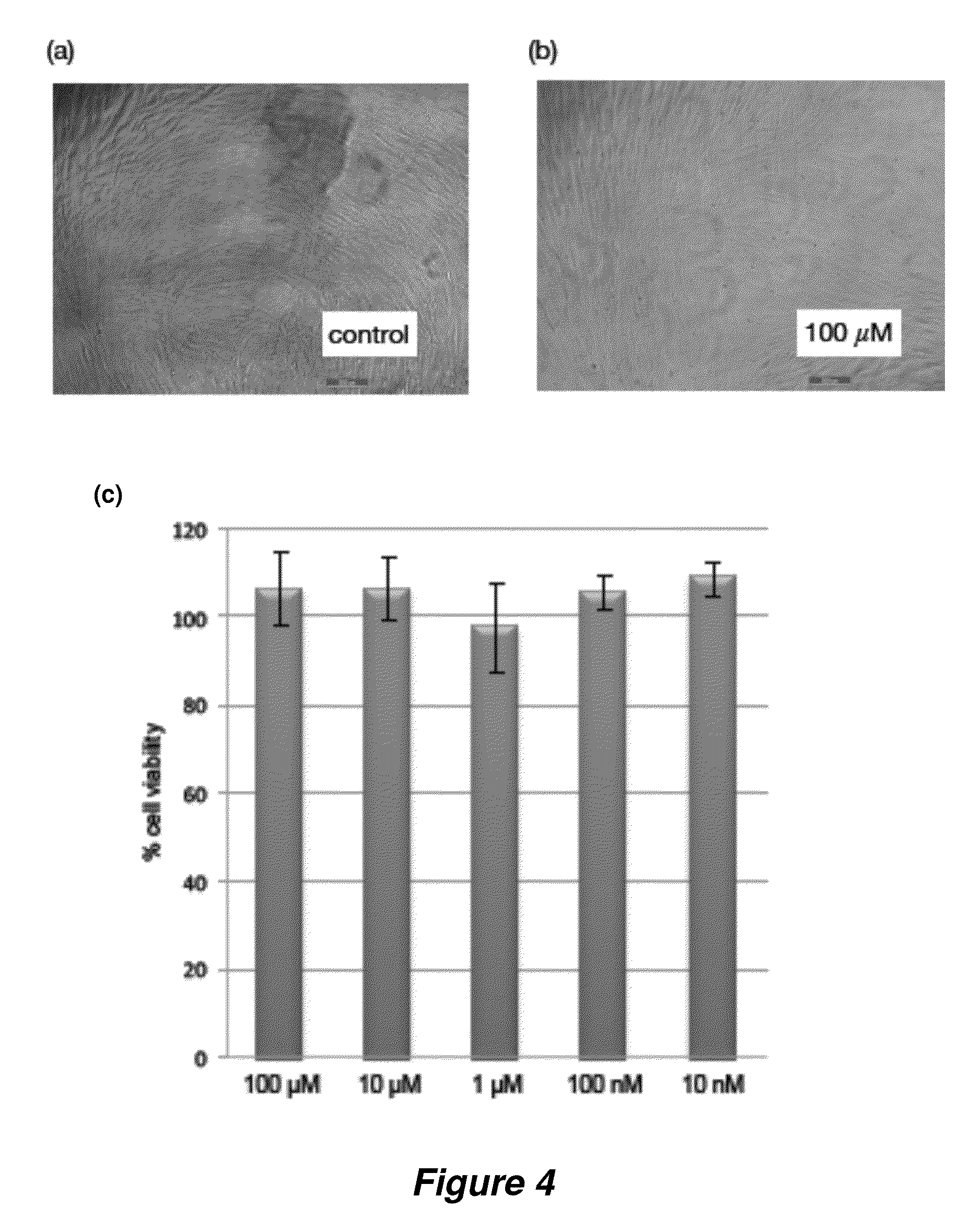
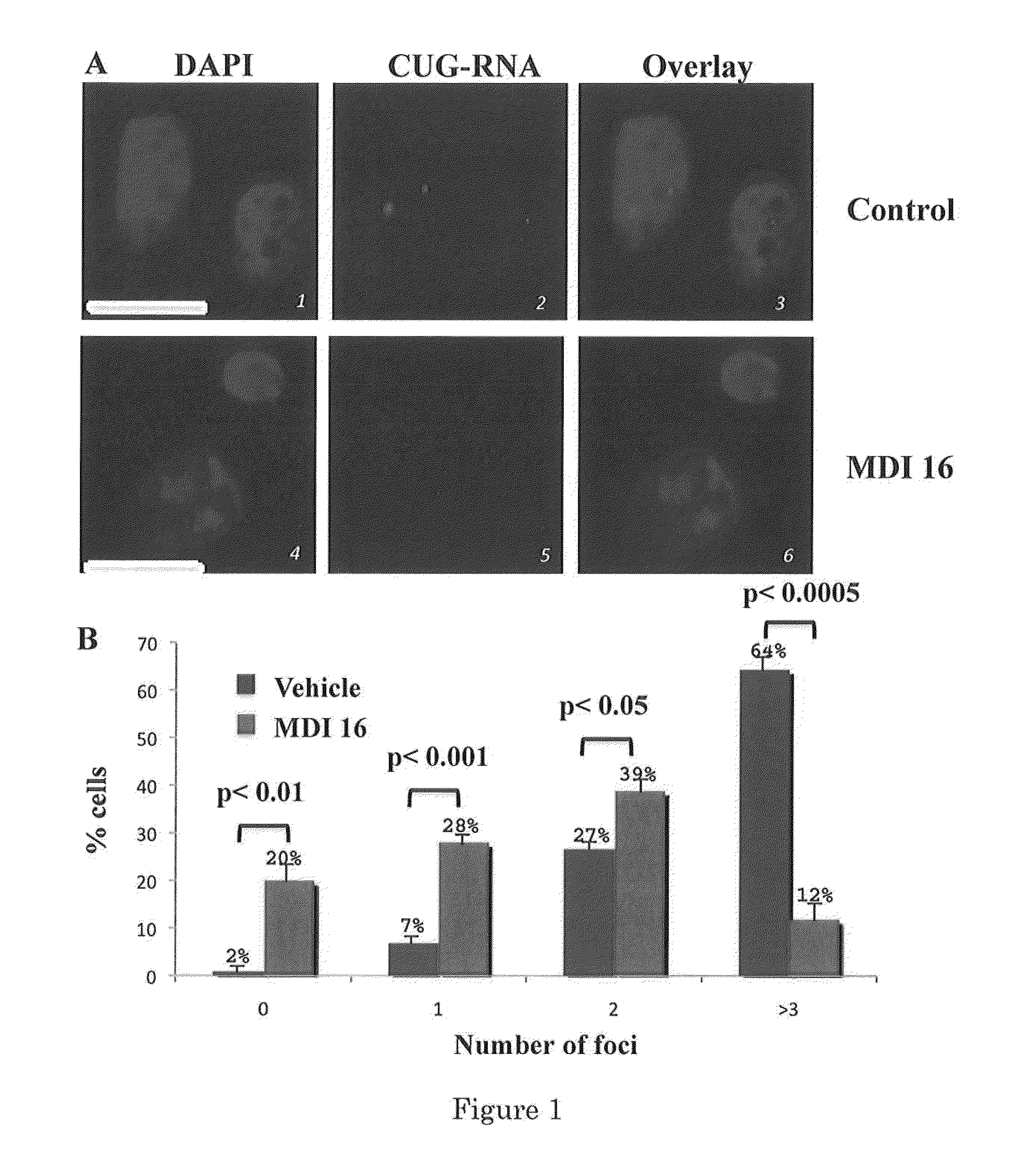
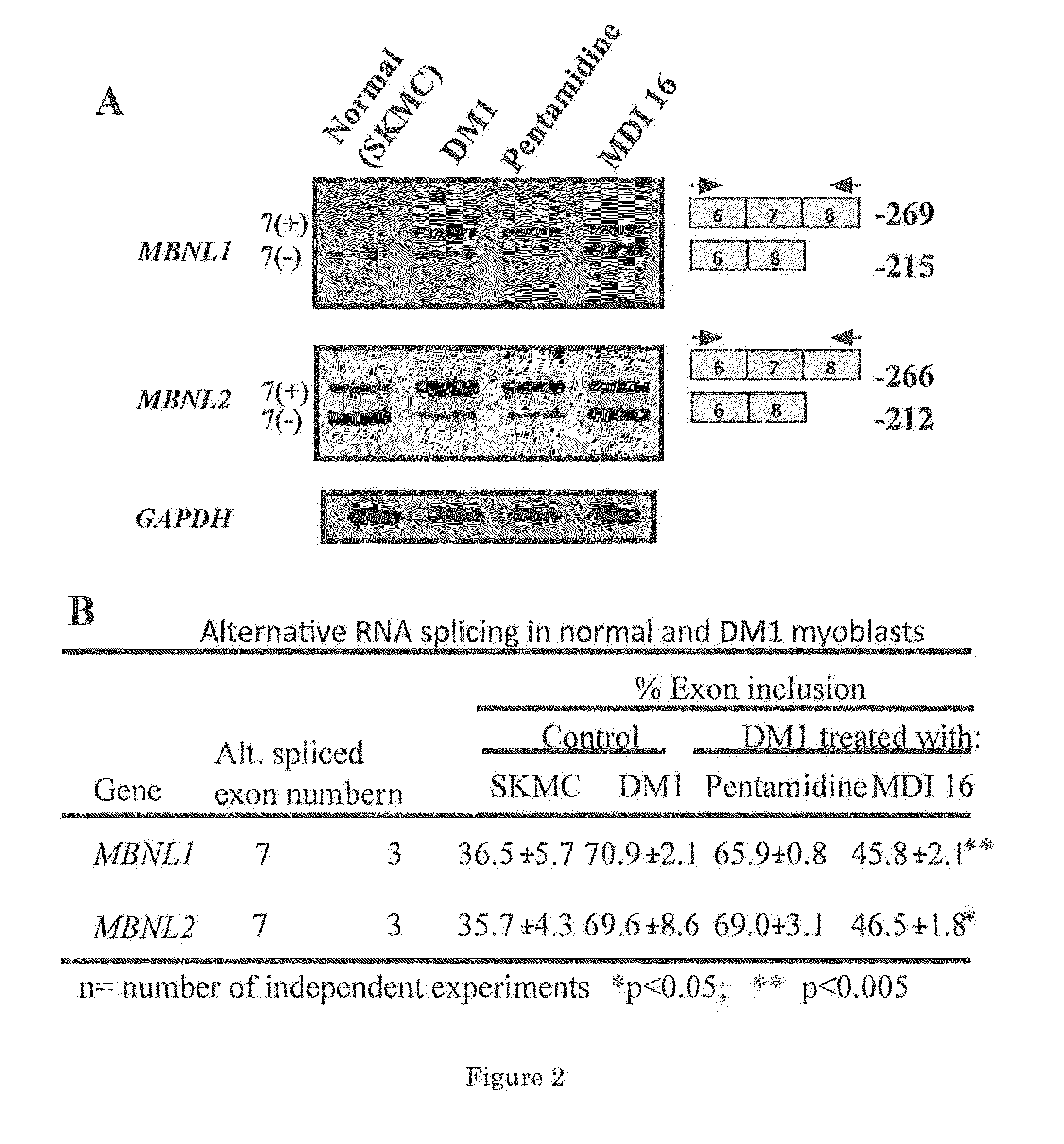
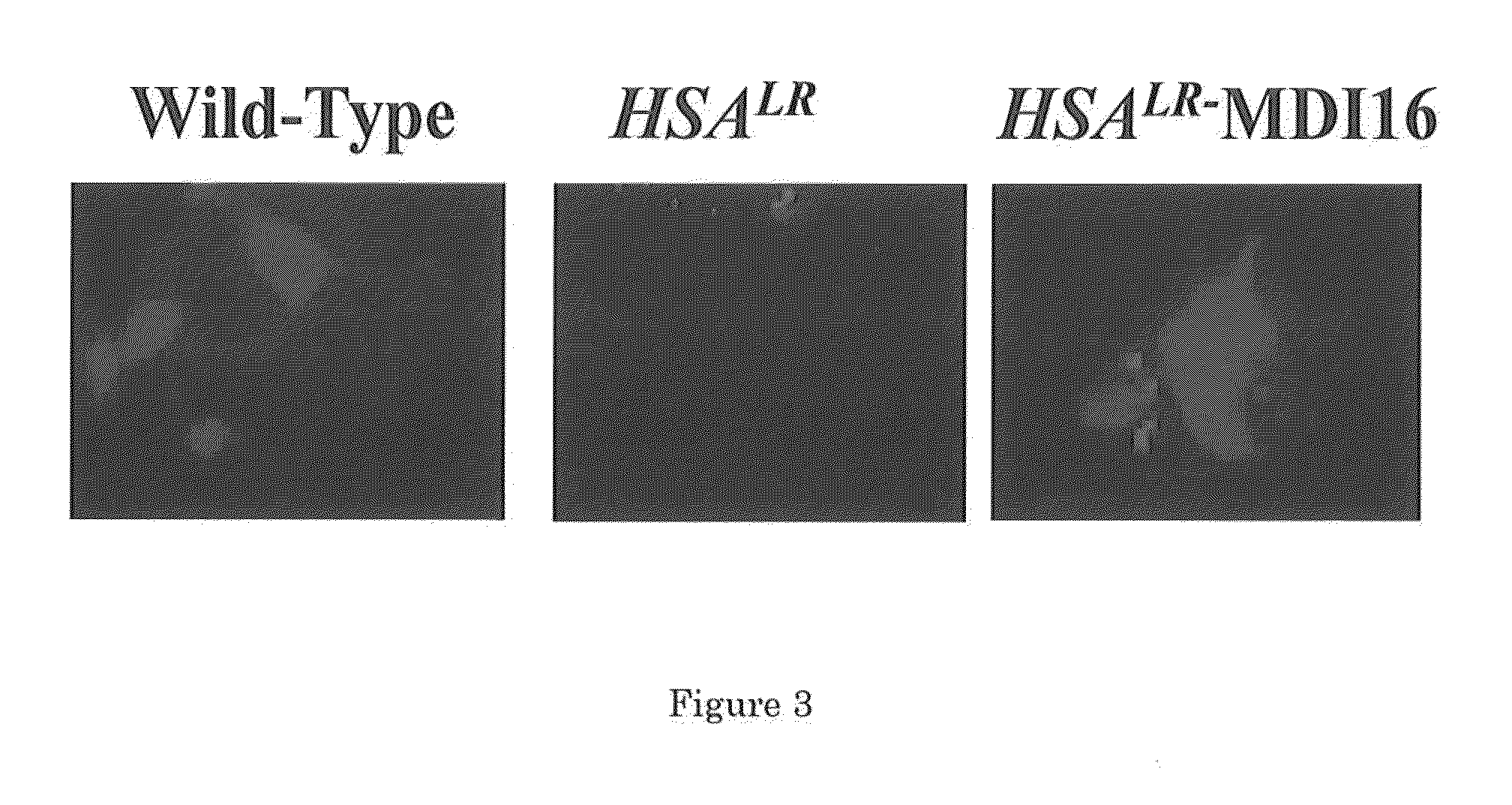
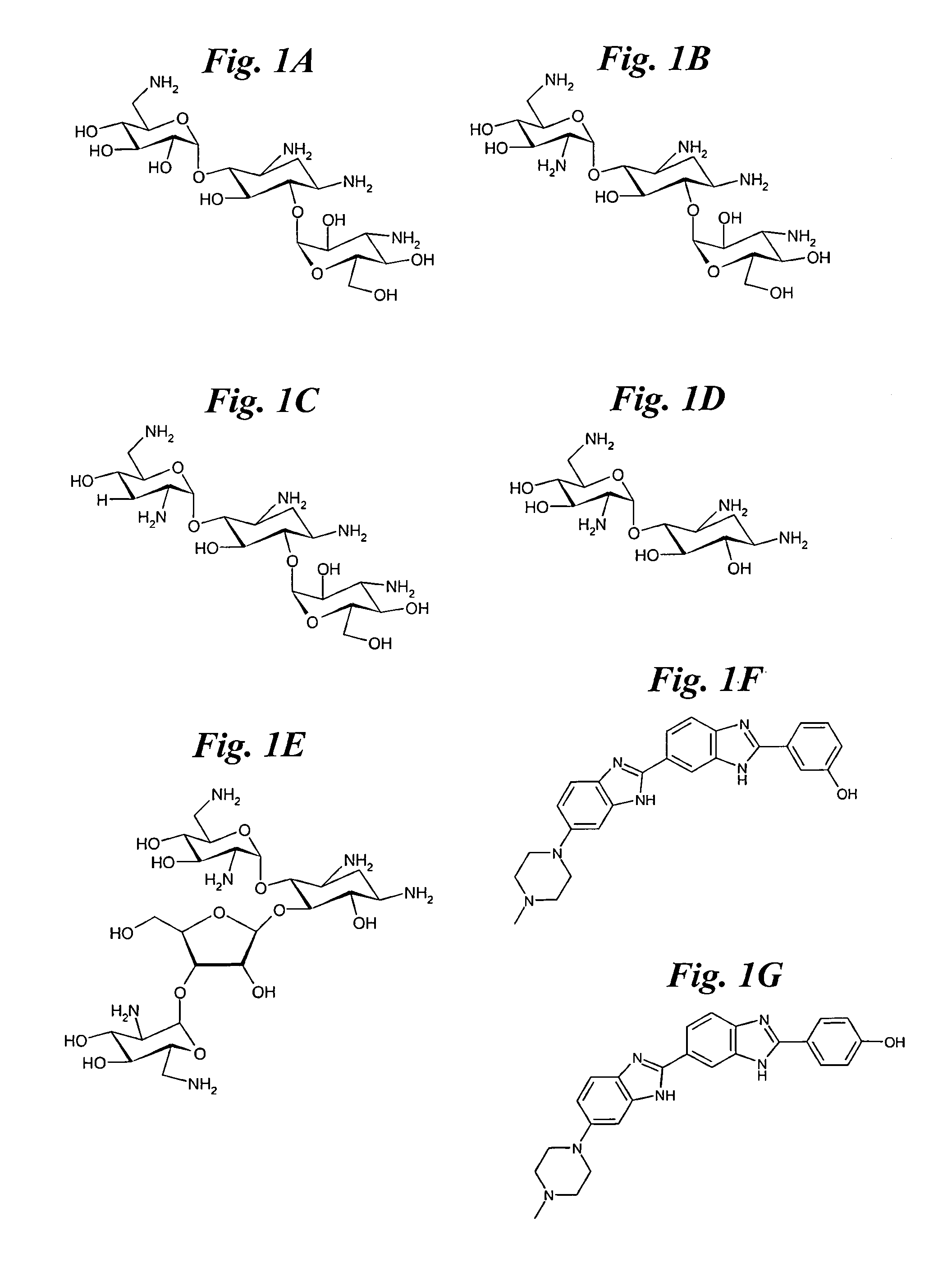
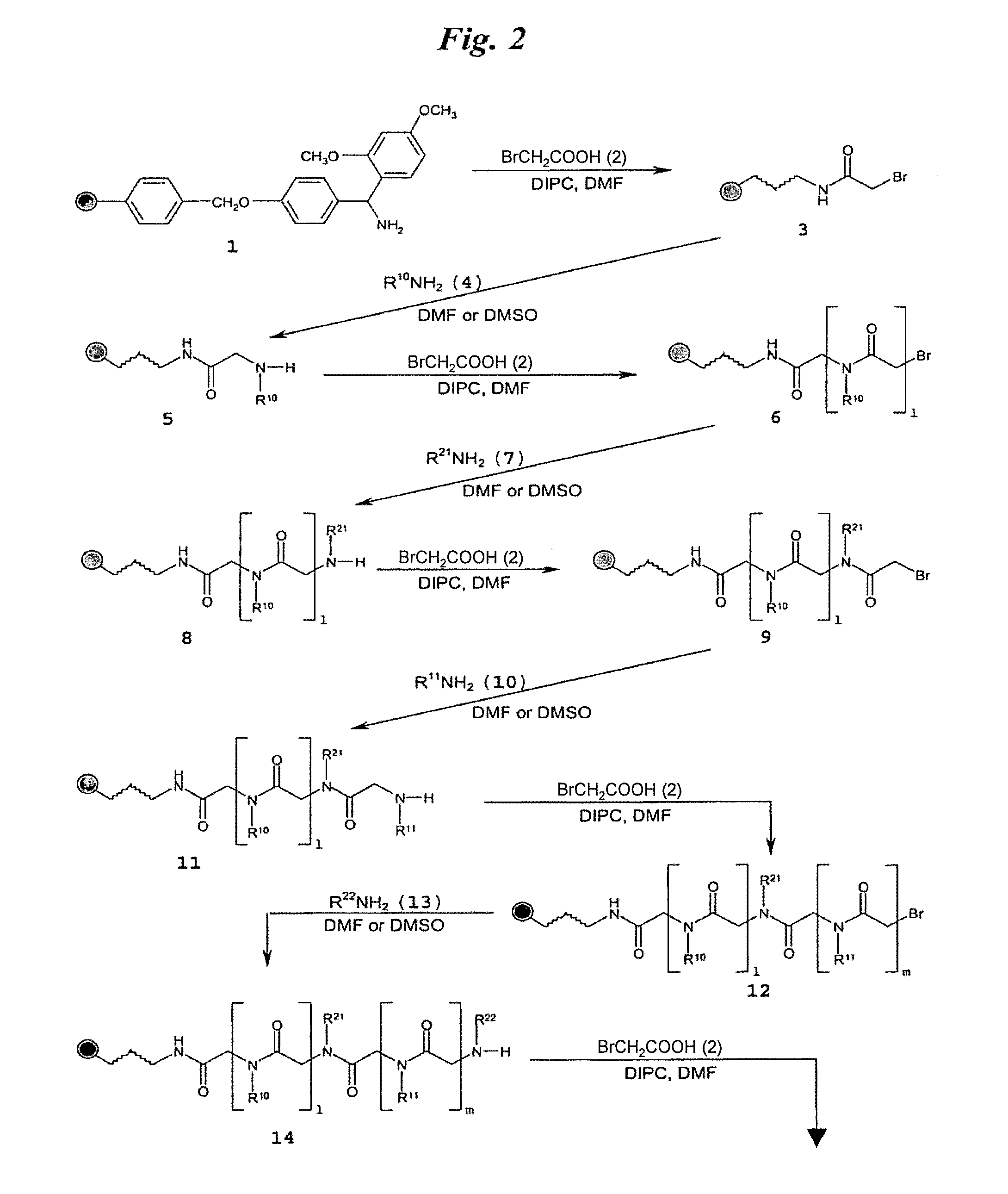
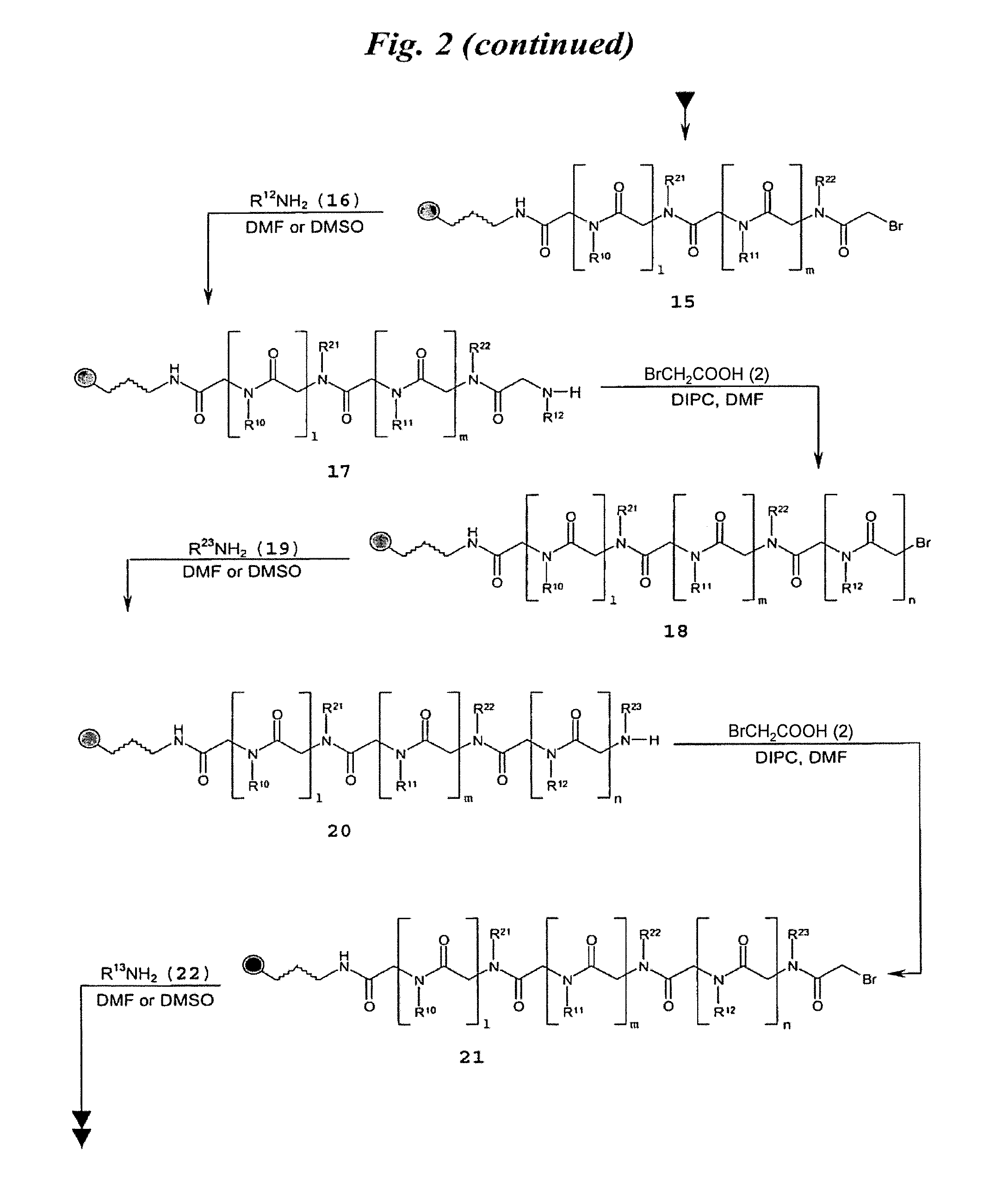
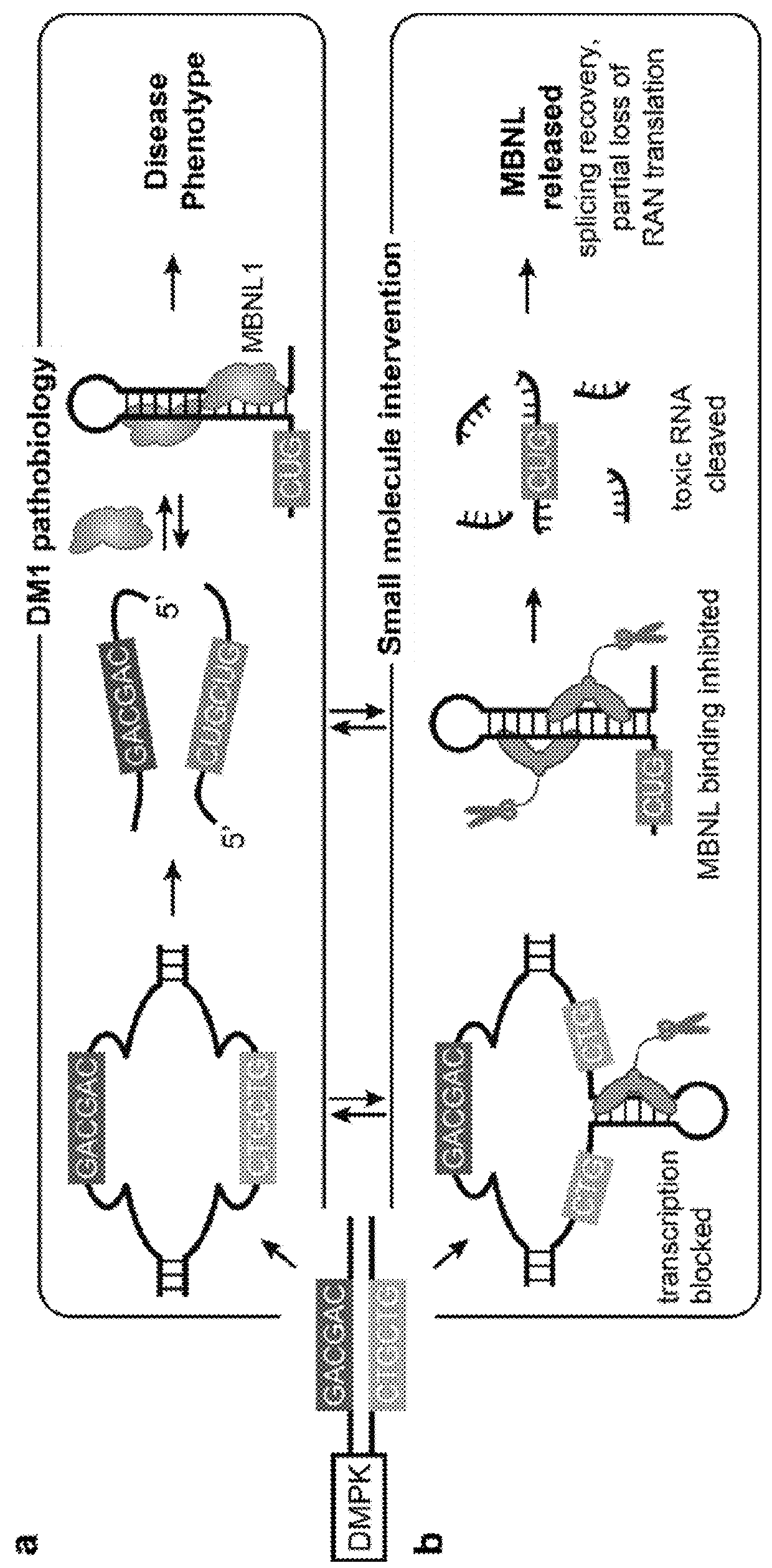
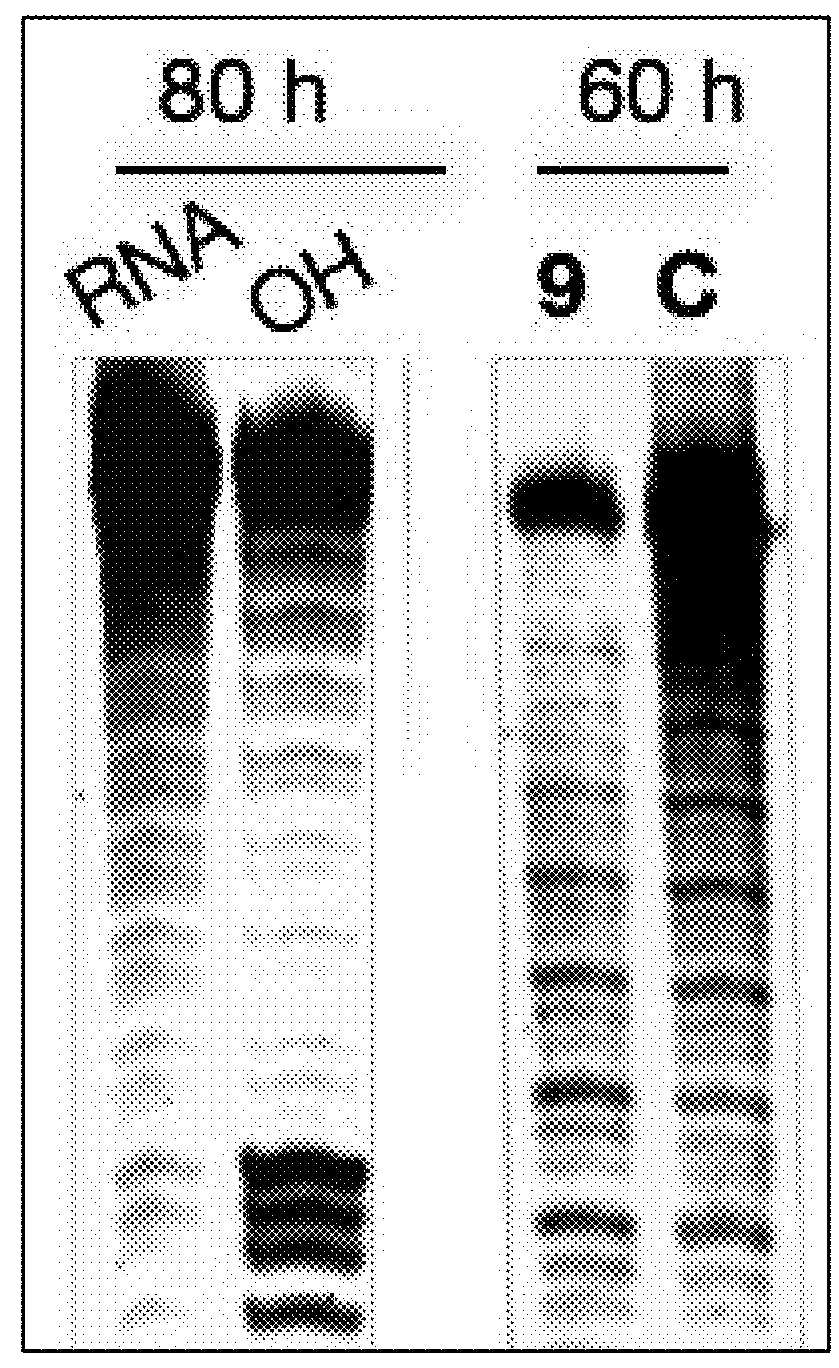
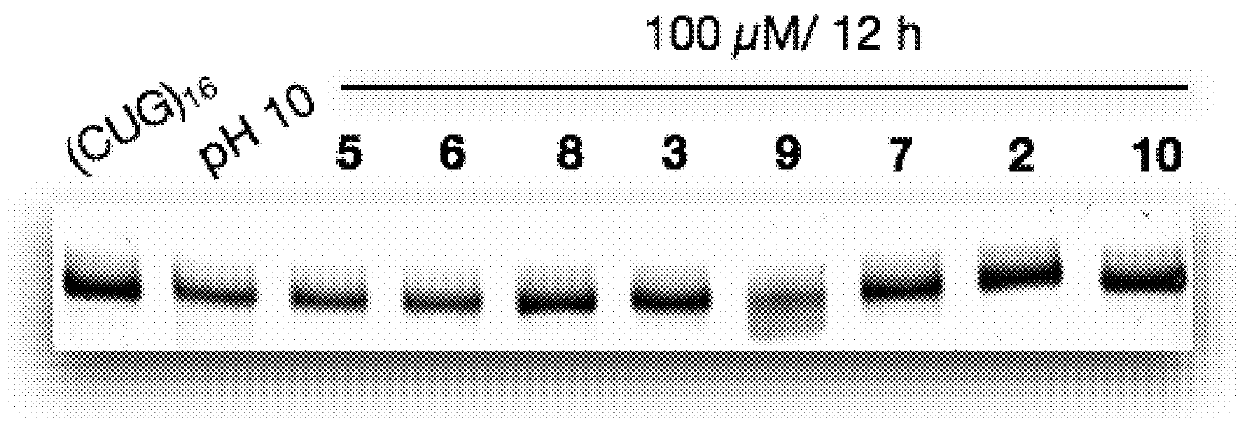
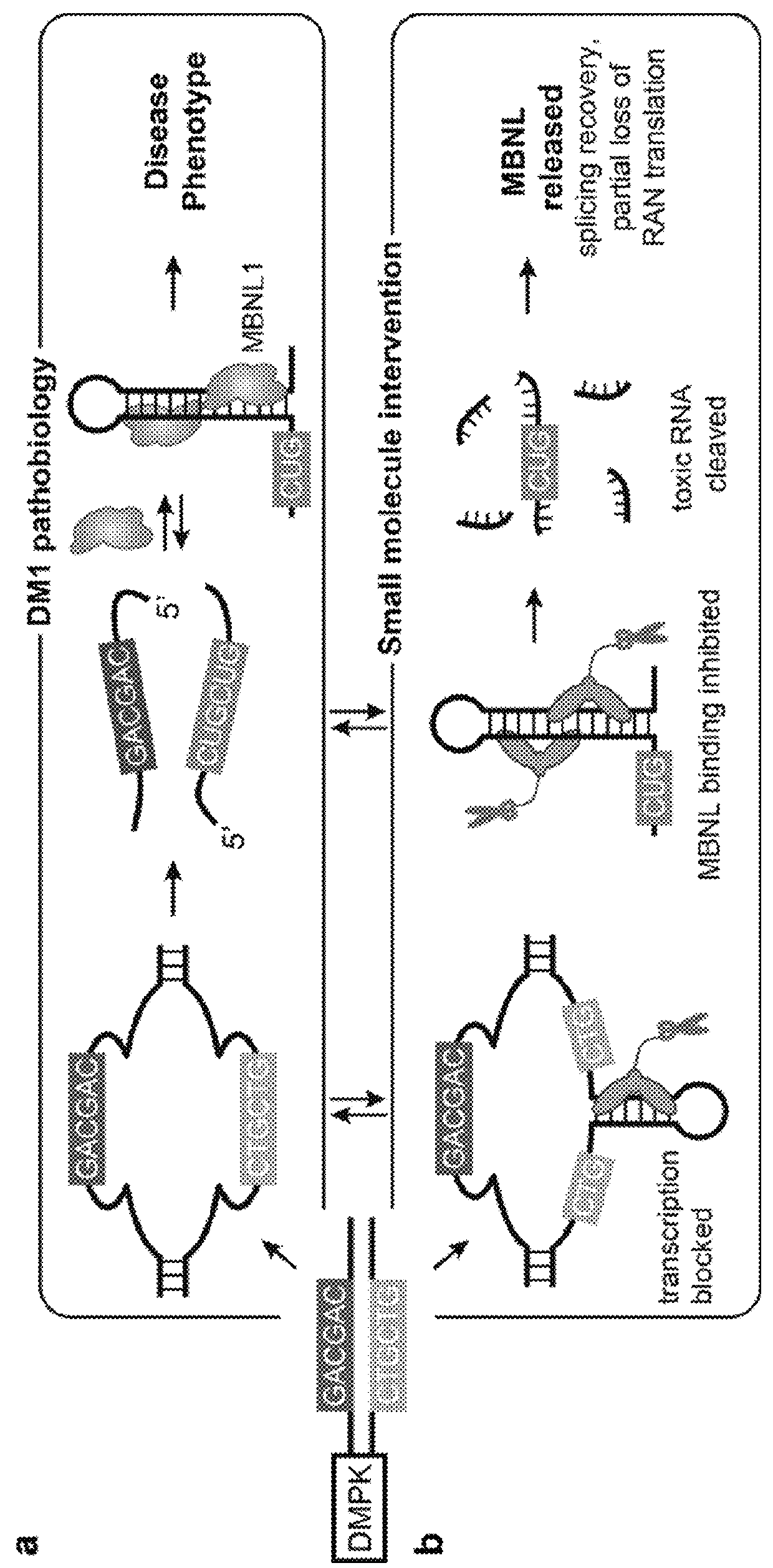
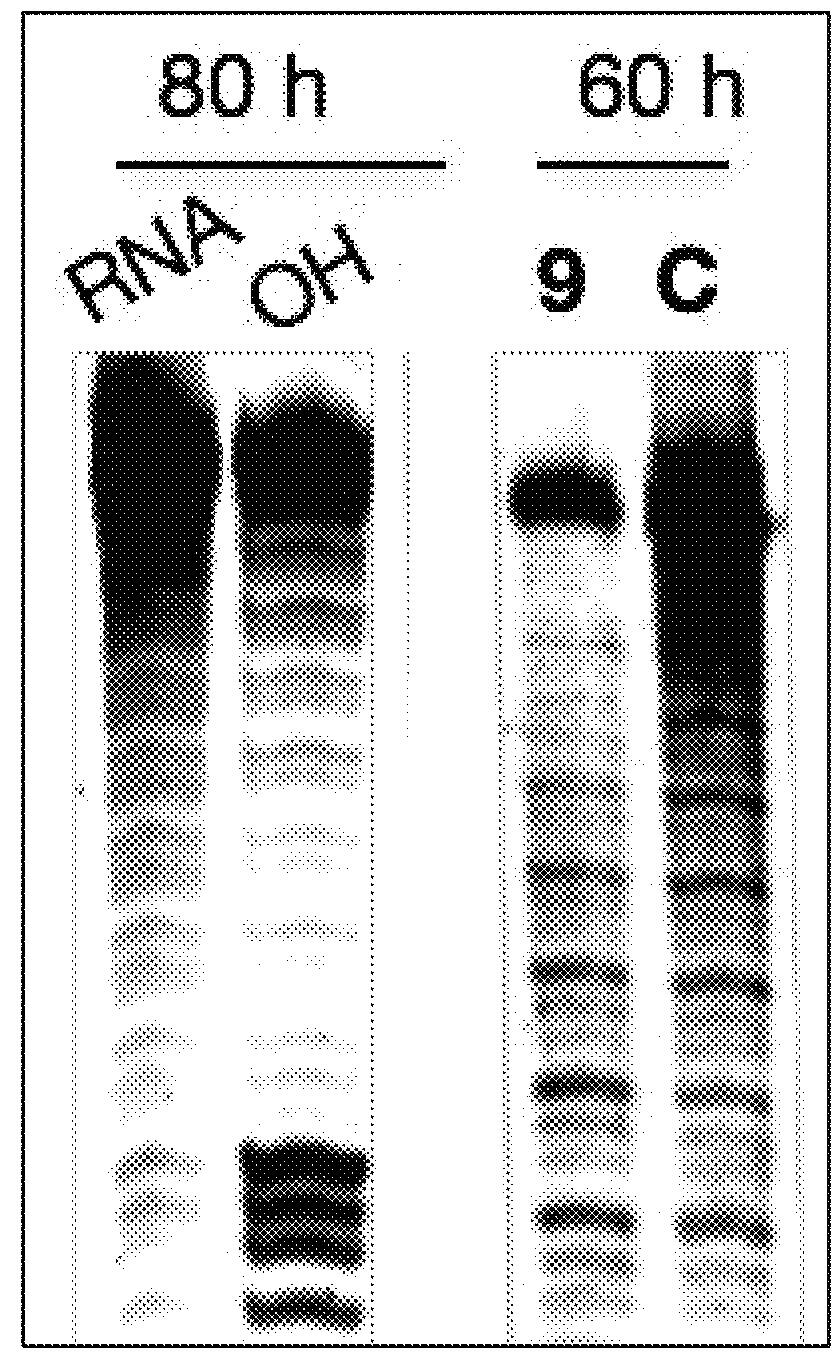
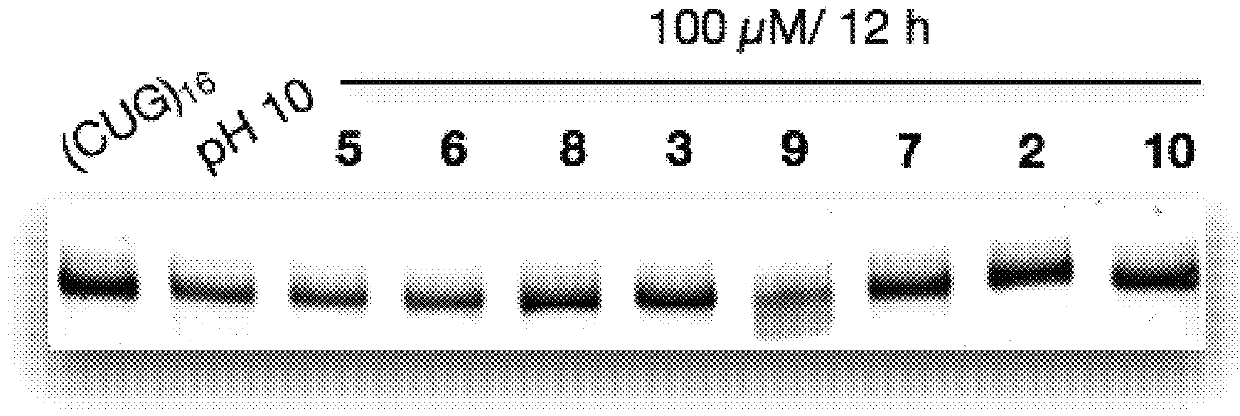
The invention provides rationally designed multi-targeting therapeutic agents for myotonic dystrophy type 1 (DM1), an incurable neuromuscular disease that originates in an abnormal expansion of CTG repeats (CTGexp) in the DMPK gene. The rationally designed small molecules target the DM1 pathobiology in three distinct ways: (1) binding the expanded trinucleotide repeat, CTGexp, and inhibiting its transcription to the toxic CUGexp RNA, (2) binding the CUGexp RNA and releasing sequestered muscleblind-like protein (MBNL1), and (3) cleaving the toxic CUGexp in an RNase-like manner. Importantly, the compounds can reduce the levels of CUGexp in DM1 model cells and reverse two separate CUGexp-induced phenotypes of DM1.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
Methods and Compositions for Treating Aging-Associated Impairments Using CCR3-Inhibitors
ActiveUS20190105314A1Improve cognitionImproved motor activityPowder deliveryOrganic active ingredientsHuntingtons choreaMyotonic dystrophy gene
Methods of improving neurodegenerative disease with CCR3 modulating agents are provided. The methods include administering a therapeutically effective amount of the CCR3 modulating agent to the subject, with a concomitant improvement in cognition, motor, or other neurodegenerative-affected function. Cognitive and motor diseases upon which the methods of the invention can improve cognition include Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, frontotemporal dementia, Huntington's disease, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, multiple sclerosis, glaucoma, myotonic dystrophy, vascular dementia, progressive supranuclear palsy.
Owner:ALKAHEST INC
Heterocyclyl substituted pyrrolopyridines that are inhibitors of the cdk12 kinase
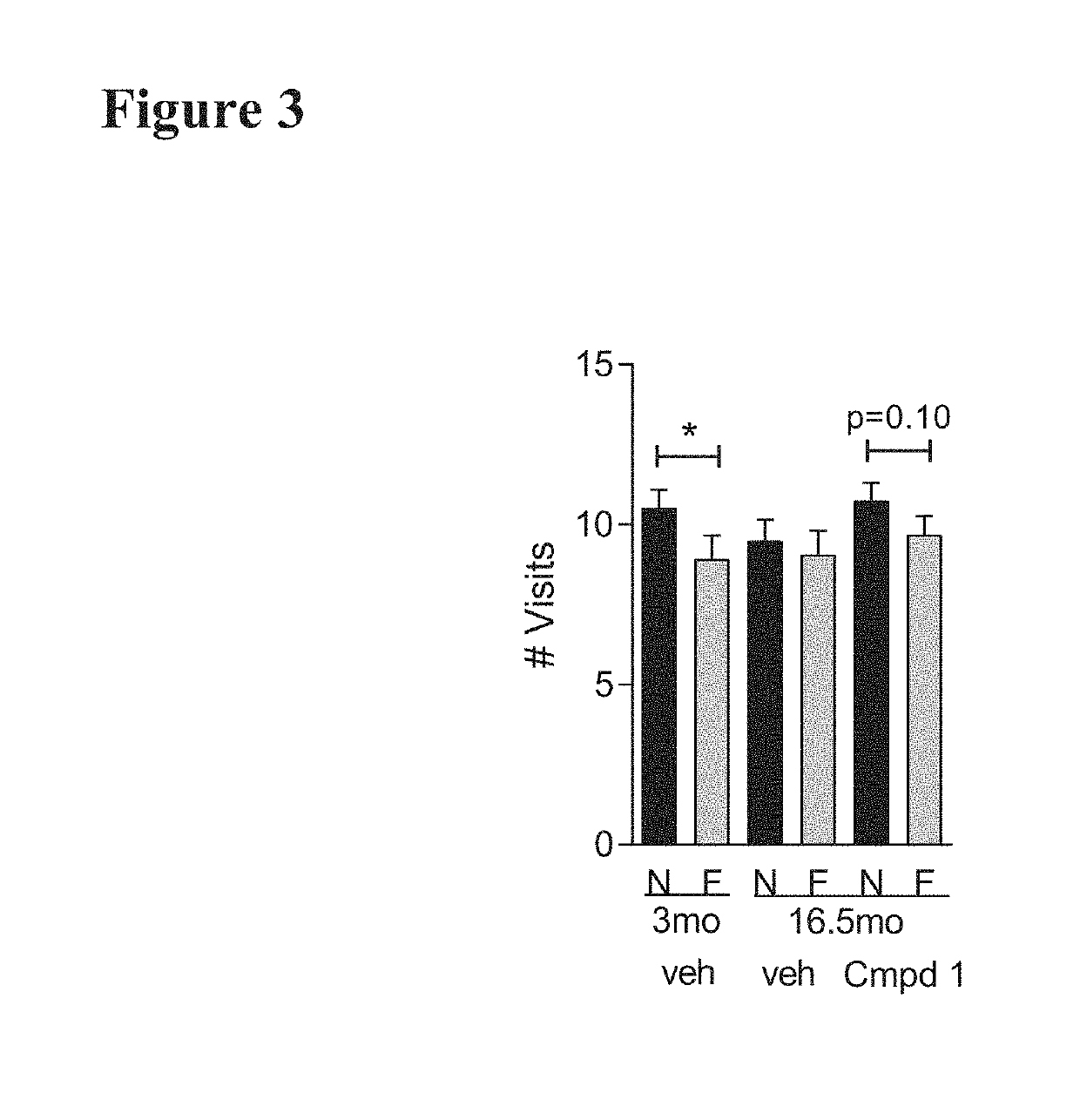
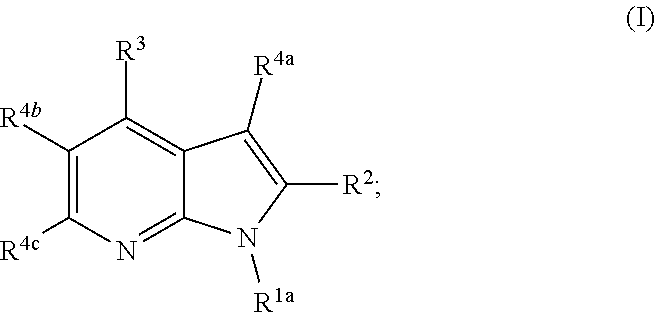
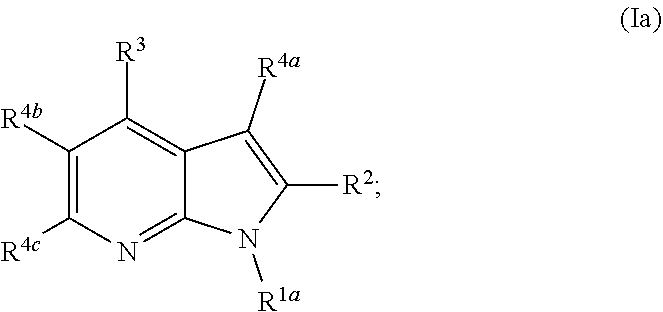
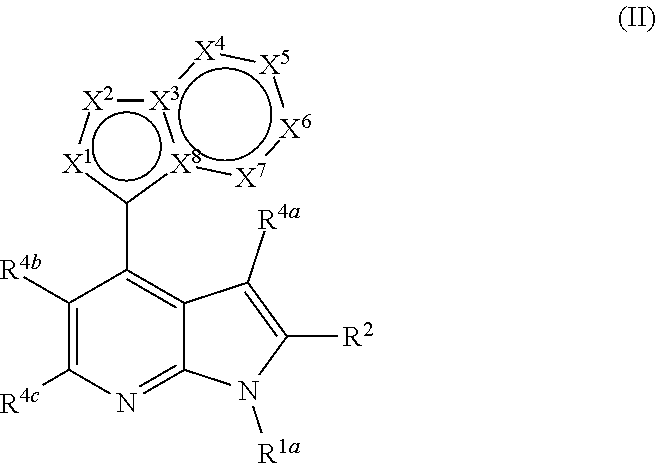
ActiveUS20200247824A1Inhibitory activityOrganic chemistryMuscular disorderMyotonic dystrophy genePharmaceutical medicine
This invention related to compounds that are inhibitors of the CDK12 kinase. The compounds are useful in the treatment of disorders mediated by the CDK12 kinase including myotonic dystrophy type 1 (DM1) and other disorders caused by the generation of RNA repeat expansion transcripts. In particular, the invention relates to compounds of the formula (I), or a pharmaceutically acceptable salts or N-oxides thereof, wherein R1a, R2, R3, R4a, R4b and R4c are as defined herein.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF NOTTINGHAM
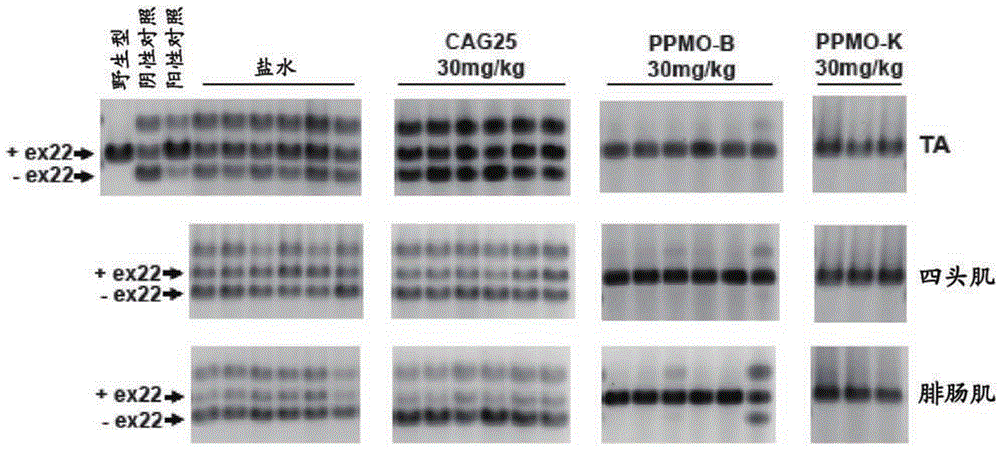
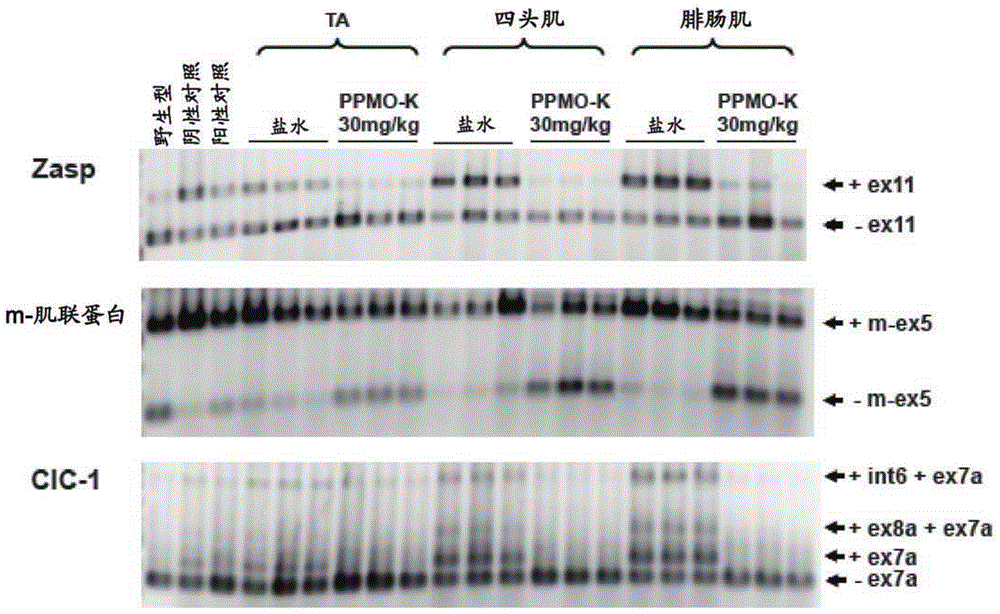
Peptide-linked morpholino antisense oligonucleotides for treatment of myotonic dystrophy
Provided herein are peptide-linked morpholino (PPMO) antisense oligonucleotides that target the poly CUG repeat tract in the 3' untranslated region of the gene encoding dystrophia myotonica-protein kinase (DMPK) and methods for systemic administration of the same for the treatment of mytonic dystrophy type I (DM1).
Owner:GENZYME CORP
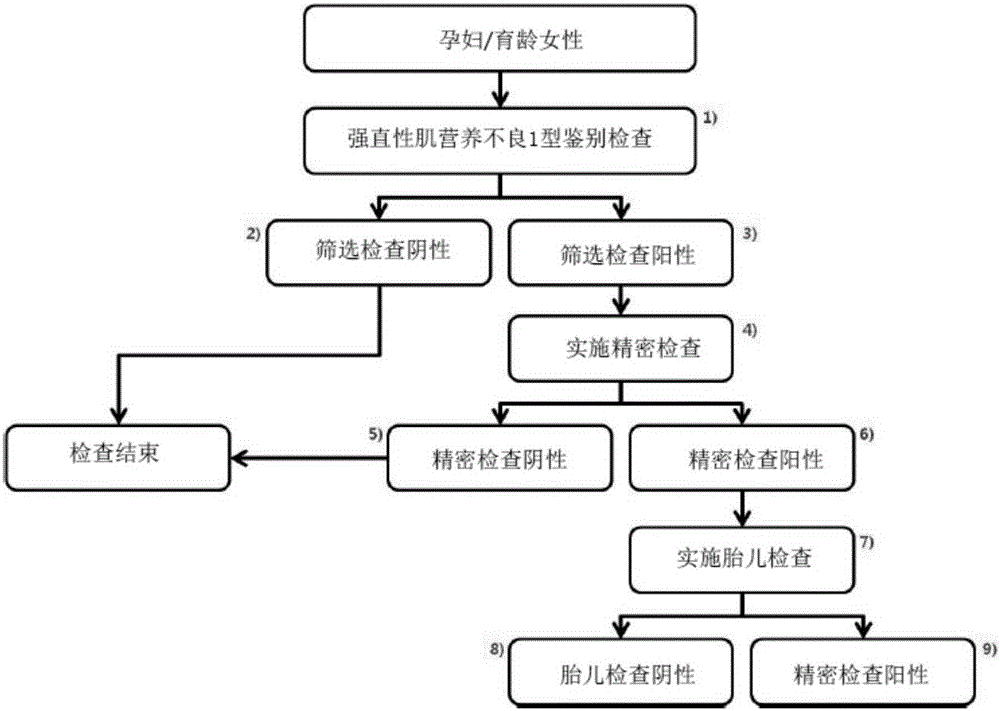
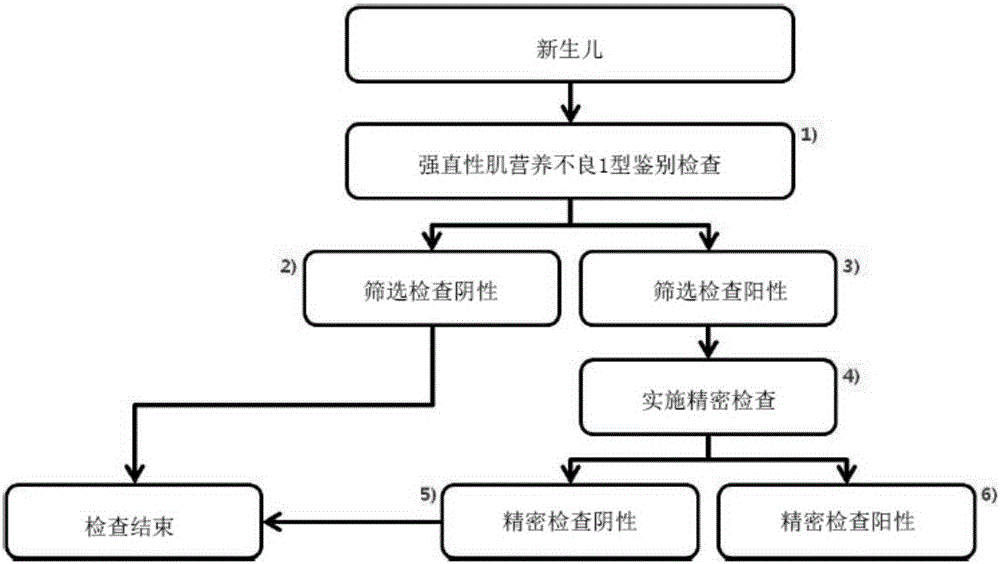
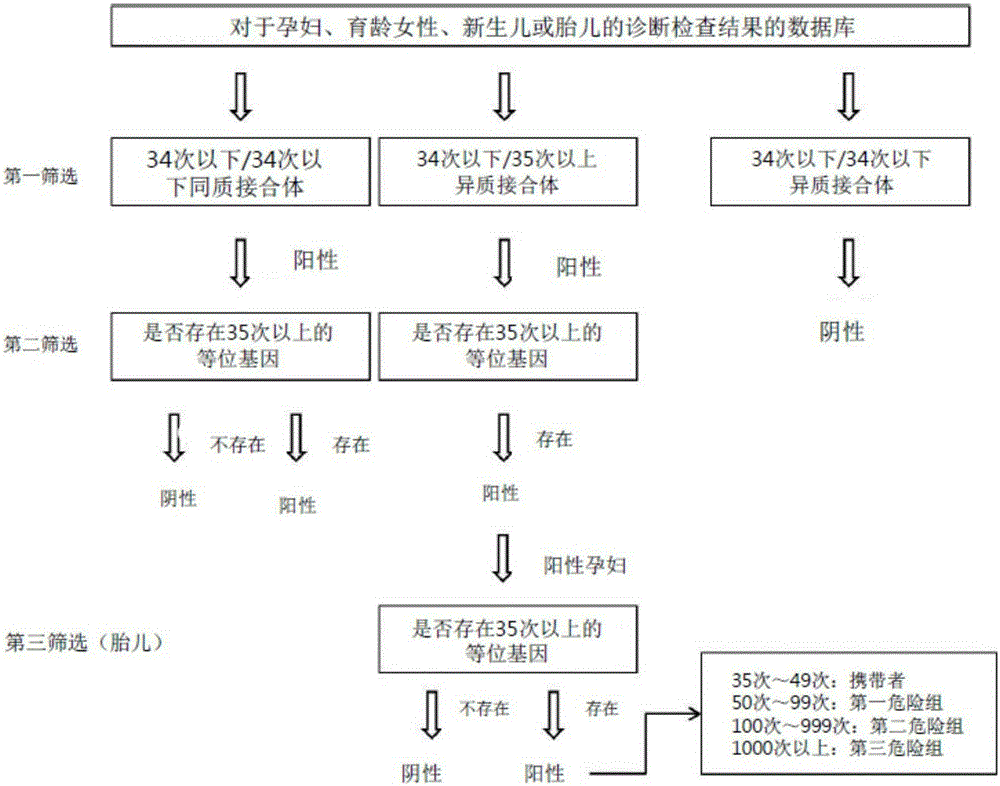
Method for diagnosing myotonic dystrophy type 1
InactiveCN105164278AGrasp the level of dangerMicrobiological testing/measurementProteomicsMyotonic dystrophy geneMyotonic dystrophy
The present invention relates to a method for diagnosing myotonic dystrophy type 1 or a method for identifying myotonic dystrophy type 1 patients by using a computer processor. The method of the present invention is an early diagnosis method of a genetic disorder having no effective prevention method except prevention in the early months of pregnancy, and can be applied to a method for diagnosing various dominant or recessive genetic disorders in which a specific repeating base sequence of a specific gene is abnormal. According to the method of the present invention, it is possible to take suitable measures related to symptoms, which will occur later, by classifying a genetic carrier and first to third risk groups according to the repetition number of the CTF sequence of 3'-noncoding region of the DDMPK gene. Particularly, the method of the present invention numerically provides a genetic carrier or the approximate prevalence of a disease with respect to an unborn baby, thereby allowing the risk of disorders to be accurately understood.
Owner:SAMSUNG LIFE PUBLIC WELFARE FOUND +1
Methods and compositions comprising ampk activator (metformin/troglitazone) for the treatment of myotonic dystrophy type 1 (DM1)
InactiveUS20130085169A1Dosage of each AMPK activator may be reducedControlling the riskBiocideOrganic active ingredientsTroglitazoneMedicine
The present invention relates to methods and compositions for the treatment of Myotonic Dystrophy type 1 (DM1) with an AMPK activator <eq.metformin or troglizazone>.
Owner:INST NAT DE LA SANTE & DE LA RECHERCHE MEDICALE (INSERM)
RNA targeting compounds and methods for making and using same
Disclosed are RNA targeting compounds, methods for using the subject RNA targeting compounds to treat myotonic dystrophy and other diseases are also disclosed.
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK
Modified U7 snRNAs for treatment of neuromuscular diseases
ActiveUS9080170B2Inefficient sequencingSplicing alterationNervous disorderDiseaseNeuromuscular disease
The present invention relates to a method to improve the activity of engineered U7 snRNAs used in the context of RNA-based therapeutics; particularly in exon skipping, exon inclusion, and mRNA eradication strategies. The resulting modified U7 snRNAs are useful for treating neuromuscular diseases, in particular Duchenne neuromuscular dystrophy, myotonic dystrophy DM1 and spinal muscular atrophy.
Owner:ASSOC INST DE MYOLOGIE +3
Enhancing epithelial or endothelial barrier function
PendingUS20220062391A1Cell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsPeptide/protein ingredientsEndothelial barrierMyotonic dystrophy gene
The present invention relates to improvement of epithelial or endothelial barrier function by increasing a level of myotonic dystrophy kinase-related Cdc42-binding kinases a (MRCKalpha) in one or more cells in the barrier.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER
Tricyclo-dna antisense oligonucleotides, compositions, and methods for the treatment of disease
ActiveUS20170260524A1Facilitates inclusionPromote skippingOrganic active ingredientsSplicing alterationDiseasePre mrna processing
Provided are tricyclo-DNA (tc-DNA) AON and methods employing tc-DNA AON for modifying splicing events that occur during pre-mRNA processing. Tricyclo-DNA (tc-DNA) AON are described that may be used to facilitate exon skipping or to mask intronic silencer sequences and / or terminal stein-loop sequences during pre-mRNA processing and to target RNase-mediated destruction of processed mRNA. Tc-DNA AON described herein may be used in methods for the treatment of Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy by skipping a mutated exon 23 or exon 51 within a dystrophin gene to restore functionality of a dystrophin protein; in methods for the treatment of Spinal Muscular Atrophy by masking an intronic silencing sequence and / or a terminal stem-loop sequence within an SMN2 gene to yield modified functional SMN2 protein, including an amino acid sequence encoded by exon 7, which is capable of at least partially complementing a non-functional SMN1 protein; and in methods for the treatment of Steinert's Myotonic Dystrophy by targeting the destruction of a mutated DM1 mRNA comprising 3′-terminal CUG repeats.
Owner:ASSOC INST DE MYOLOGIE +3
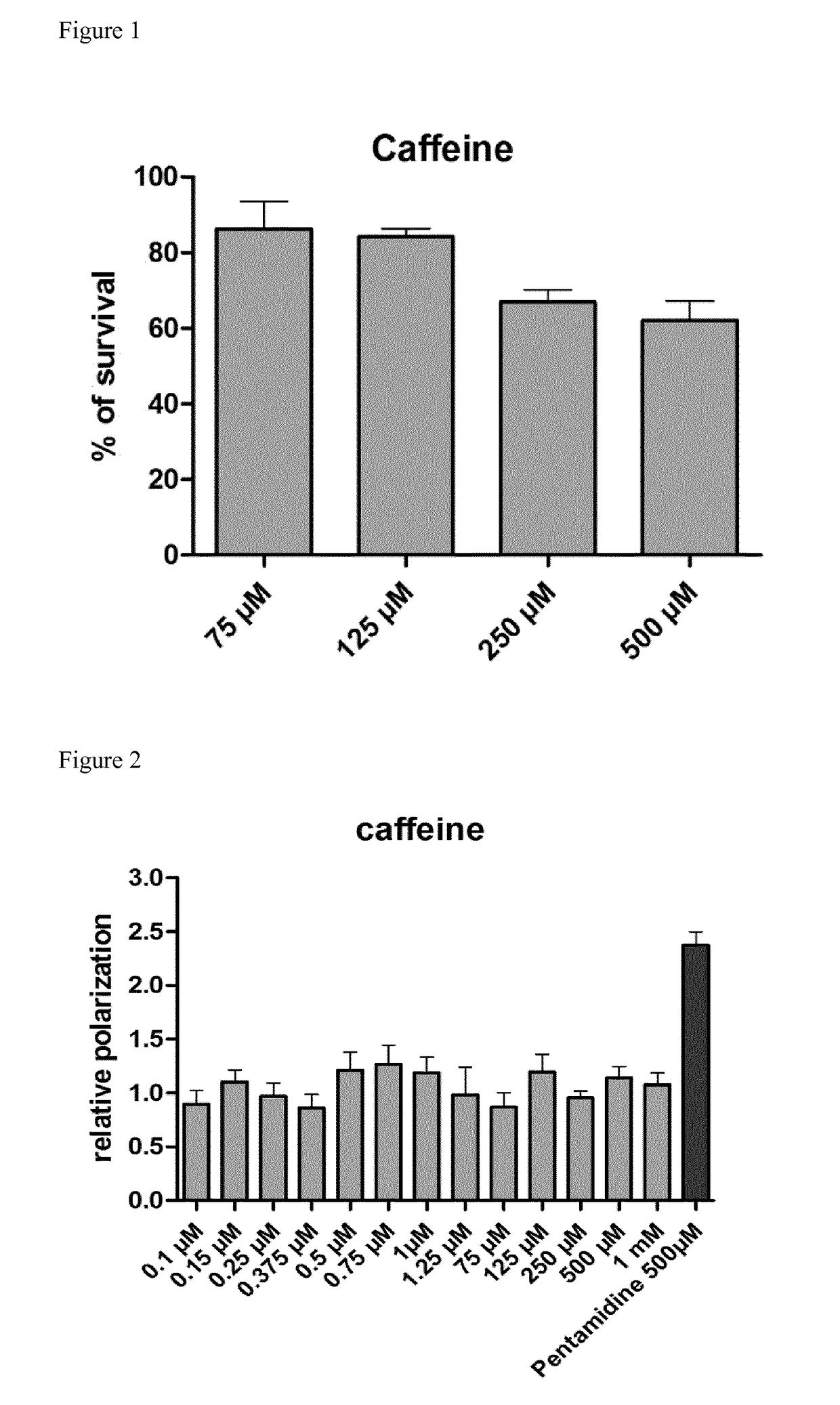
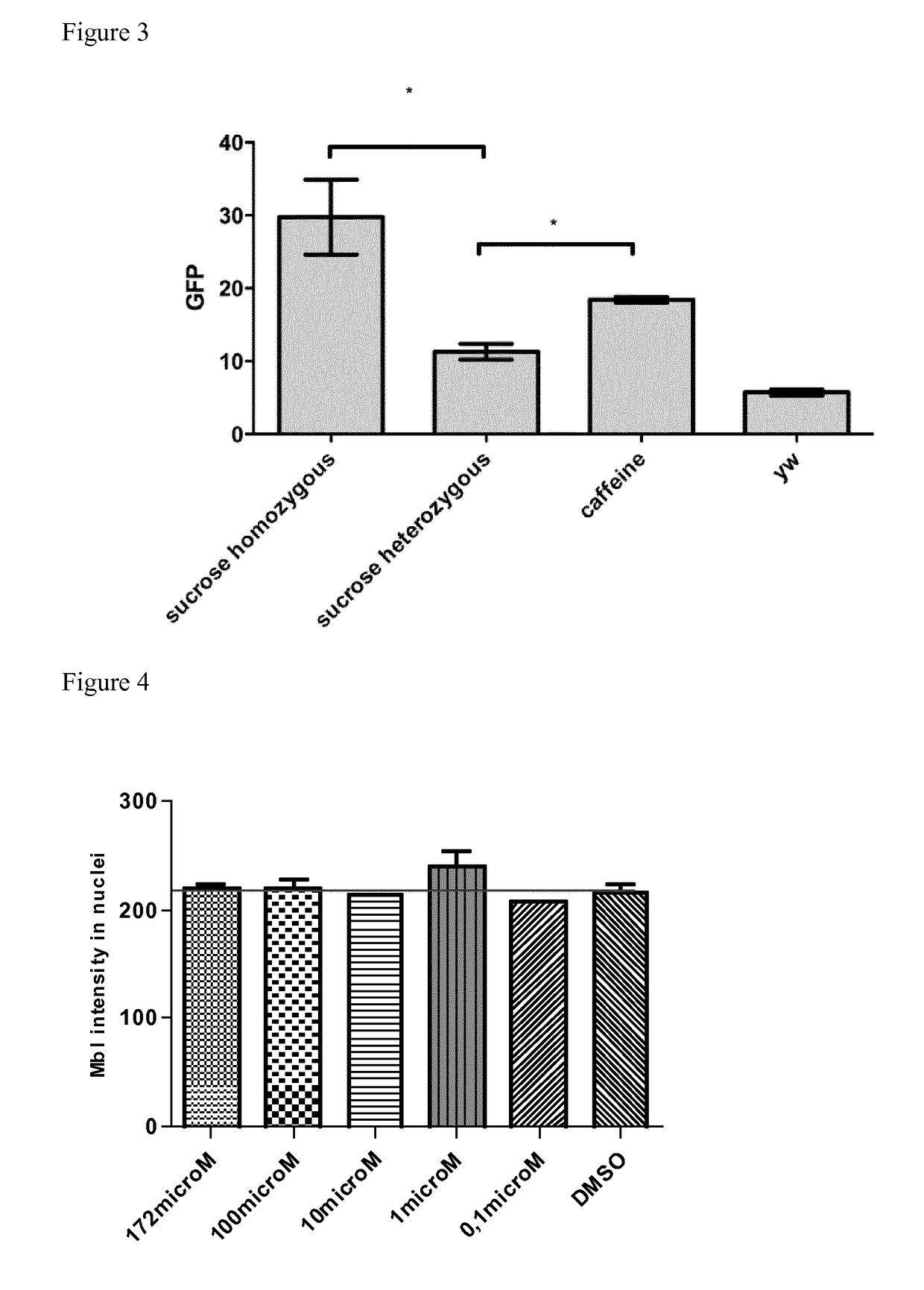
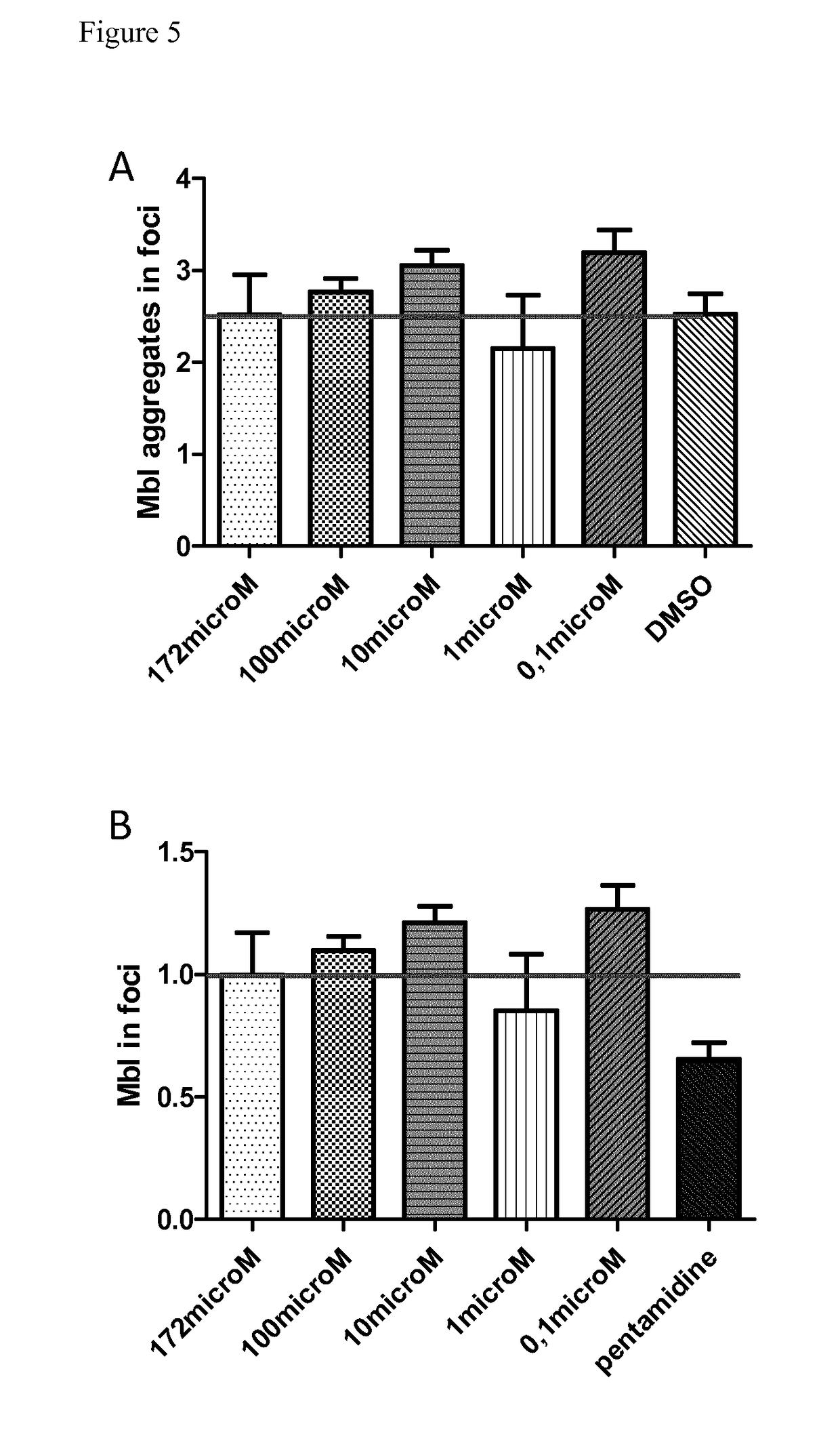
Caffeine for the treatment of myotonic dystrophy type 1 and type 2
InactiveUS20170304309A1Milk preparationMuscular disorderMyotonia chondrodystrophicaMyotonic dystrophy gene
The present invention relates to caffeine for use in the treatment of myotonic dystrophy type 1 and type 2. The present invention also relates to compositions comprising caffeine for use in the treatment of myotonic dystrophy type 1 and type 2.
Owner:INST UNIV DE CIENCIA I TECH SA +2
Compositions and methods for the treatment of myotonic dystrophy
Owner:GENETHON +1
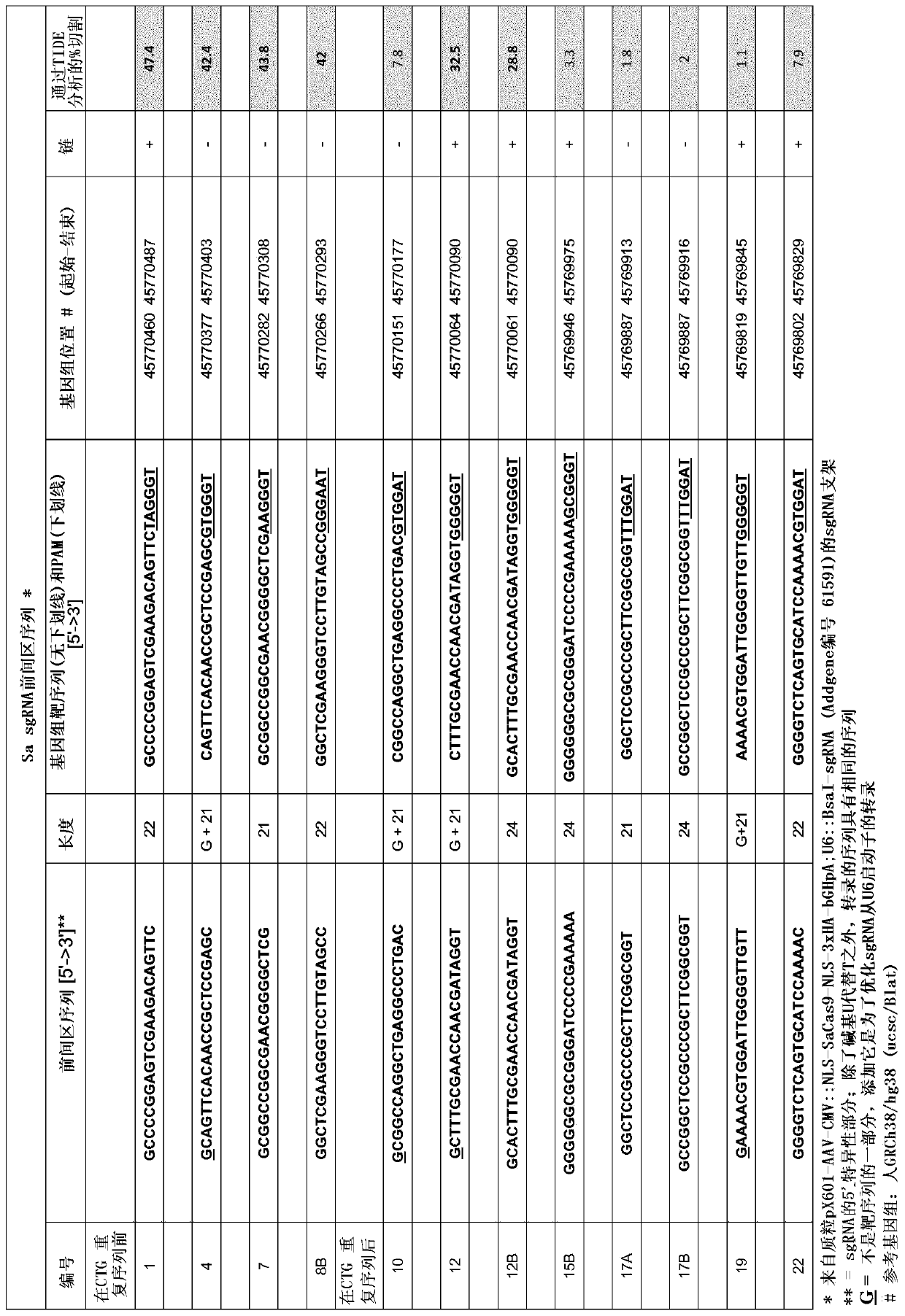
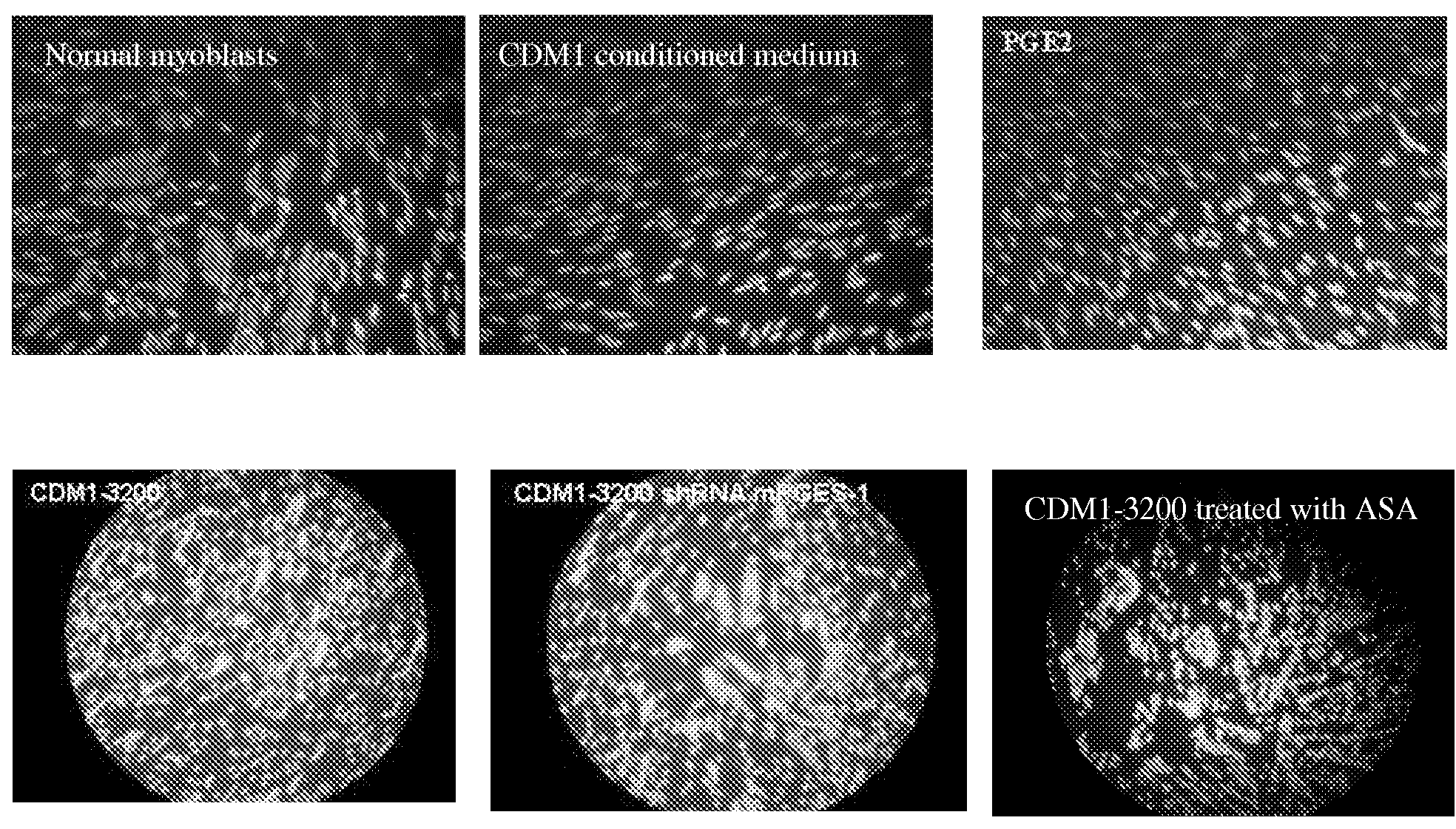
Prostaglandin e2 modulation and uses thereof
Methods, uses, kits and products are described for the prognosis, diagnosis, prevention and treatment of myotronic dystrophy type 1 (DM1), and more particularly for the prognosis, diagnosis, prevention and treatment of the congenital form of myotronic dystrophy type 1 (cDM1), based on changes in / modulation of prostaglandin E2 (PGE2).
Owner:UNIV LAVAL
Compounds and methods for myotonic dystrophy therapy
The invention provides rationally designed multi-targeting therapeutic agents for myotonic dystrophy type 1 (DM1), an incurable neuromuscular disease that originates in an abnormal expansion of CTG repeats (CTGexp) in the DMPK gene. The rationally designed small molecules target the DM1 pathobiology in three distinct ways: (1) binding the expanded trinucleotide repeat, CTGexp, and inhibiting its transcription to the toxic CUGexp RNA, (2) binding the CUGexp RNA and releasing sequestered muscleblind-like protein (MBNL1), and (3) cleaving the toxic CUGexp in an RNase-like manner. Importantly, the compounds can reduce the levels of CUGexp in DM1 model cells and reverse two separate CUGexp-induced phenotypes of DM1.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com