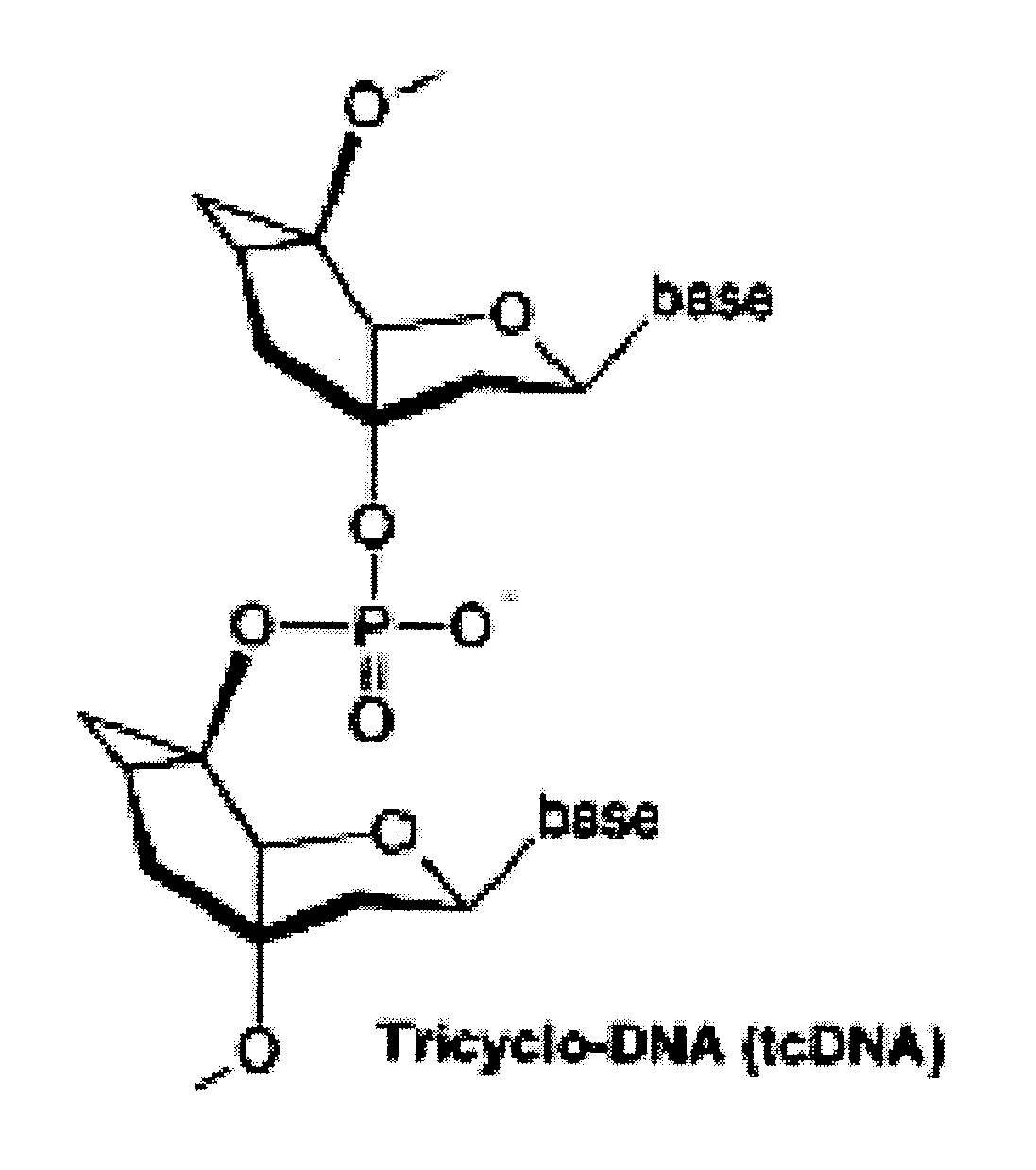
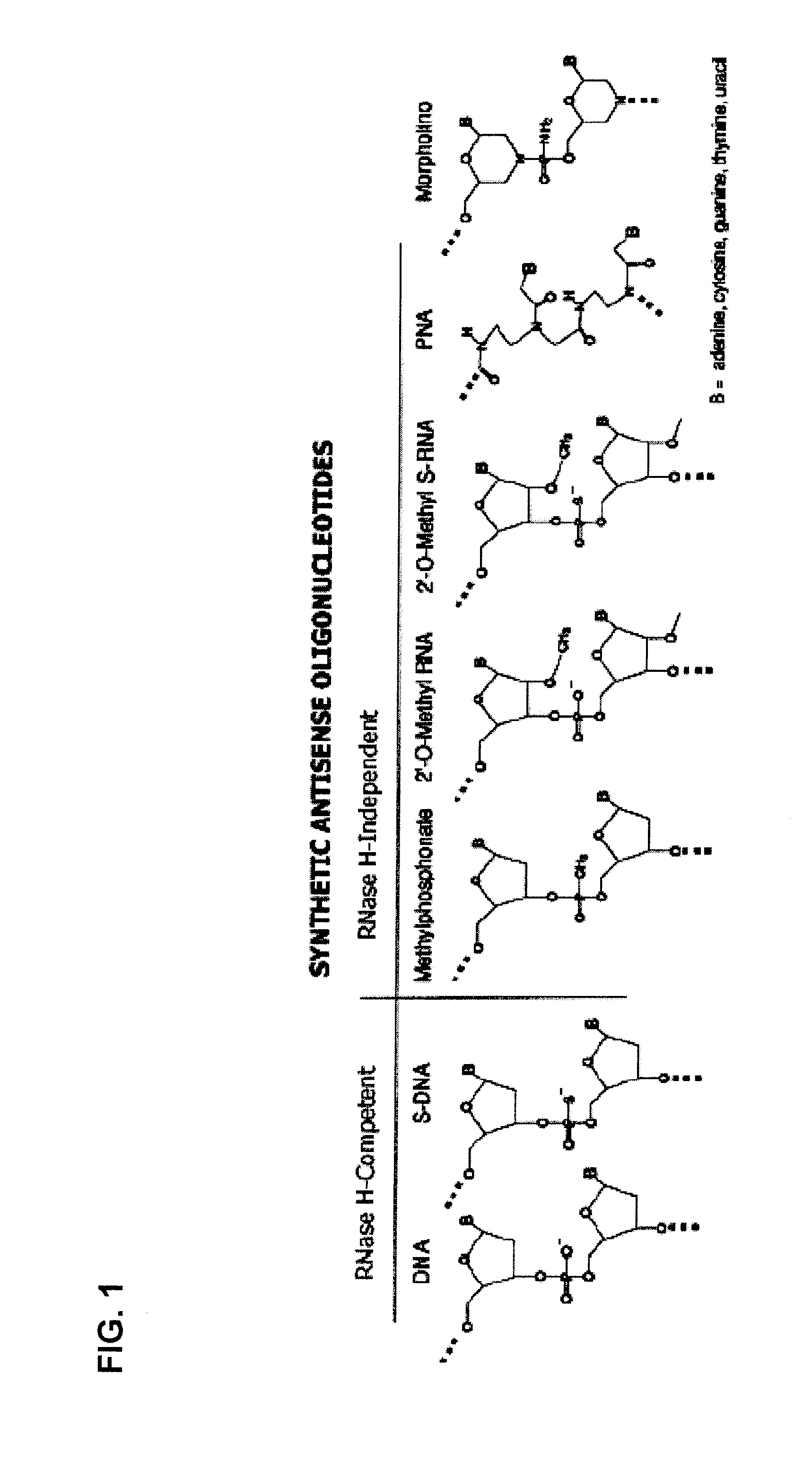
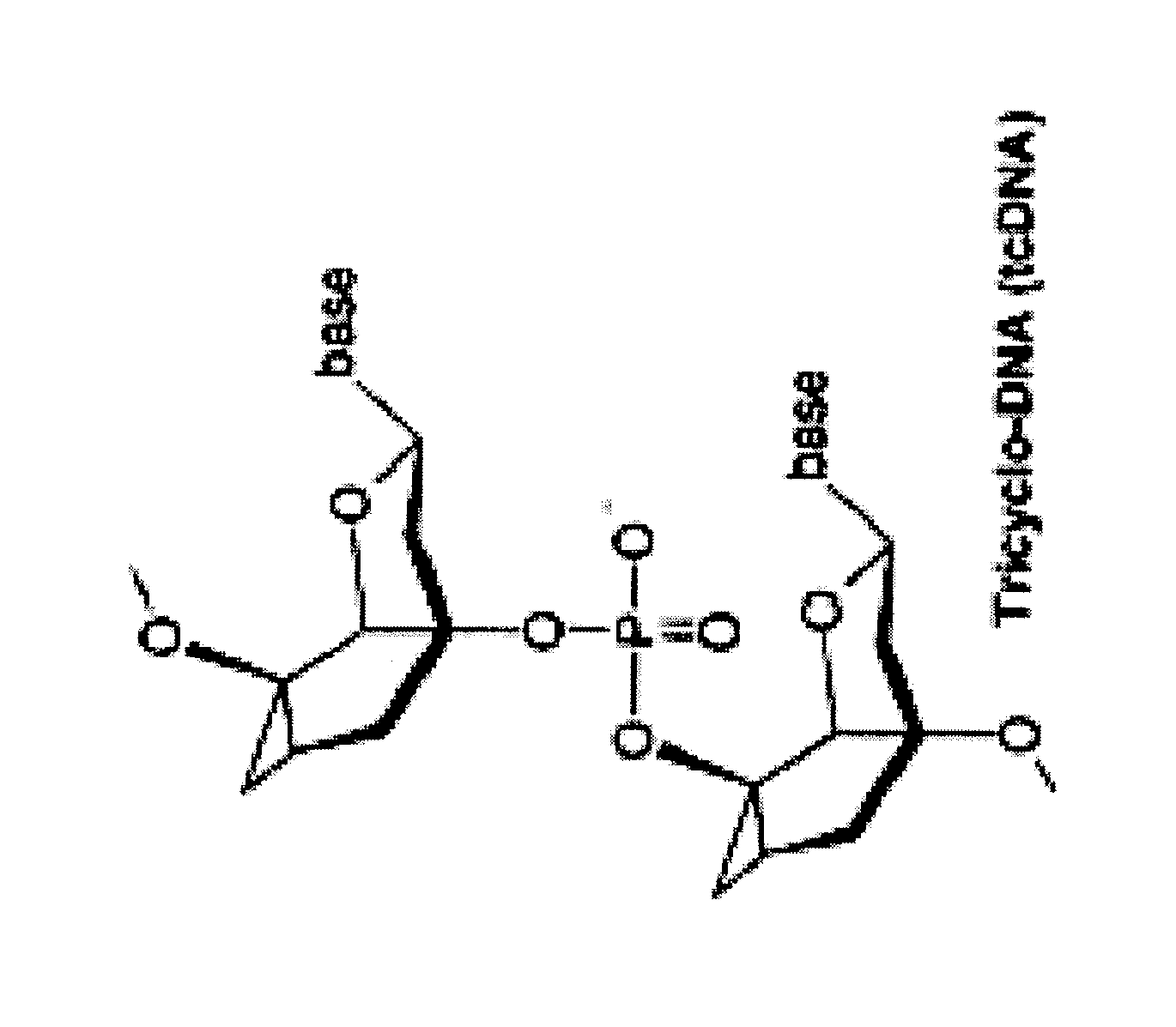
Tricyclo-dna antisense oligonucleotides, compositions, and methods for the treatment of disease
a technology of antisense oligonucleotides and tricyclodna, applied in the field of synthetic antisense oligonucleotides (aon), can solve the problems of inability to produce dystrophin in striated muscles, affecting the function of striated muscles, and affecting the function of muscle fibers, etc., and achieve the effect of finding utility
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Use of Tricyclo-DNA Antisense Oligonucleotides to Rescue Dystrophin in Dystrophic Muscle Fibers
[0142]Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy (DMD) is an X-linked recessive disorder that results from mutations in the gene encoding dystrophin. Out-of-frame deletions within the dystrophin gene that encode a truncated dystrophin protein deficiency lead to severe DMD phenotypes. Exon-skipping strategies using tricyclo-DNA (tc-DNA) antisense oligonucleotides (AON) were developed to permit the efficient rescue of out-of-frame dystrophin gene mutations thereby restoring the translational reading-frame and hence the production of functionally active dystrophin protein. Tc-DNA AON are described that, for example, hybridize to an exon 23 / intron 23 junction and interfere with pre-mRNA processing such that exon 23 is spliced out of the resulting processed mRNA. Alternatively, tc-DNA AON that hybridize to an exon 51 / intron 51 junction similarly interfere with pre-mRNA processing such that exon 51 is spliced...
example 2
The Mdx Mouse Model
[0143]The mdx mouse is a murine model of DMD that lacks the full length dystrophin protein, but retains all the smaller dystrophin isoforms. Bulfield et al., Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 81:1189-1192 (1984). The mdx mouse carries a non-sense mutation in exon 23 of the dystrophin gene, which precludes functional dystrophin synthesis (see, FIG. 3). Exon 23 partially encodes repeats R6 and R7 in which a C to T mutation creates a stop codon (TAA).
example 3
In Vitro Studies
[0144]This example demonstrates that mdx myotubes transfected with a 15-nucleotide tc-DNA AON designated M23D (+02−13) having the nucleotide sequence 5′-AACCTCGGCTTACCT-3′ undergo exon skipping at the downstream donor splice site of exon 23 such that dystrophin pre-mRNA is processed to mRNA that are deleted in exon 23.
[0145]The tc-DNA AON designated M23D (+02−13), was designed such that it hybridizes to the target sequence intron 22—ttttgag[GCTC . . . EXON 23 . . . TCAG]gtaagccgaggtttggcc—intron 23 at the exon 23 / intron 23 splice junction.
[0146]Mdx myotubes were transfected with tc-DNA AON M23D (+02−13) (1, 2 and 10 μg) with or without oligofectamine. One sample was left untreated, as a negative control. After 48 hours, cultures were harvested and mRNA was extracted using the RNeasy mini kit (Qiagen). mRNA was then reverse transcribed, as follows. Eight microliters of extracted RNA (500 ng to 1 μg) was mixed with 1 μL dNTP and 1 μL random hexamers, and the mixture w...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Gene expression profile | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com