Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
31 results about "Reservoir computing" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
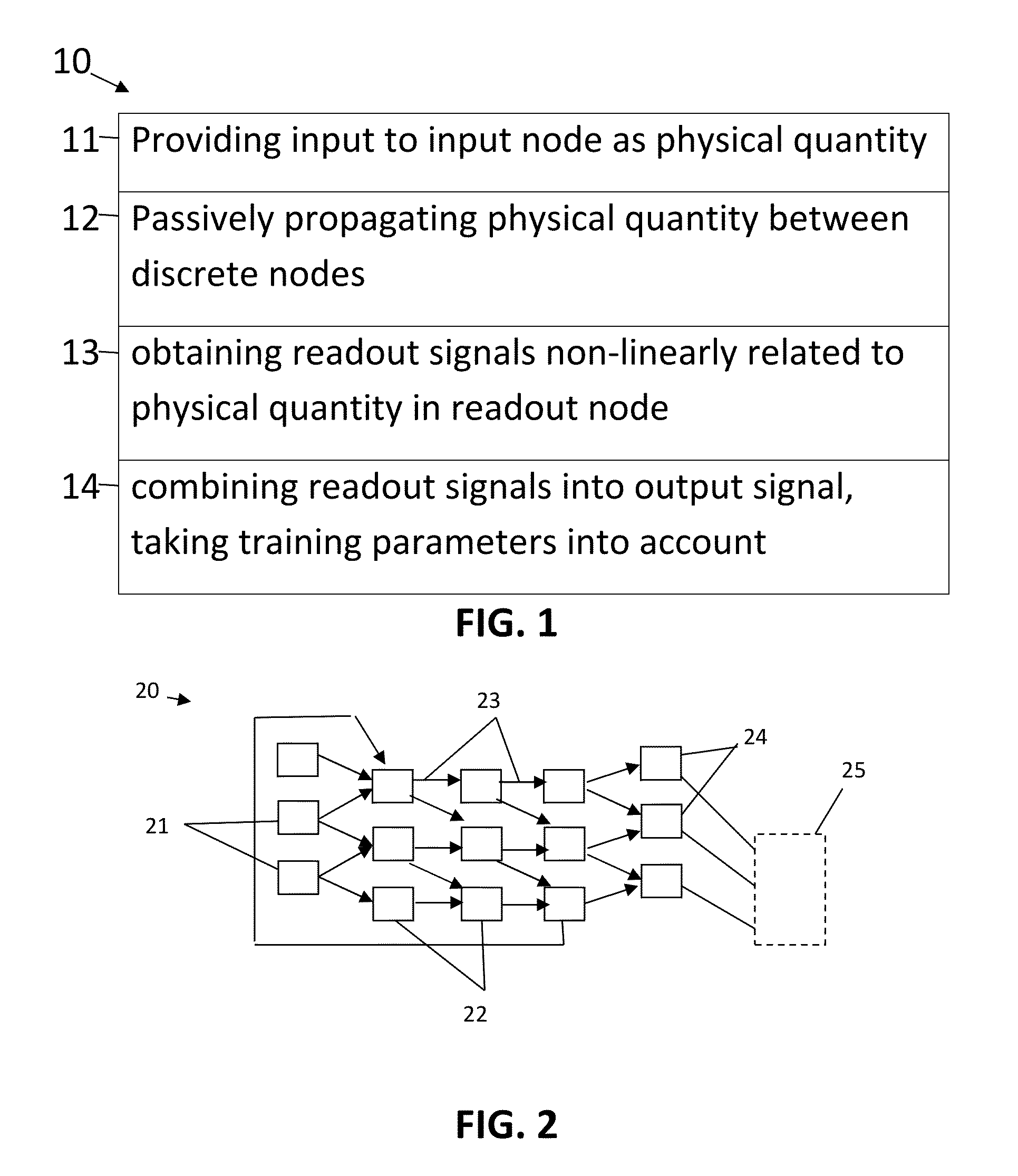
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
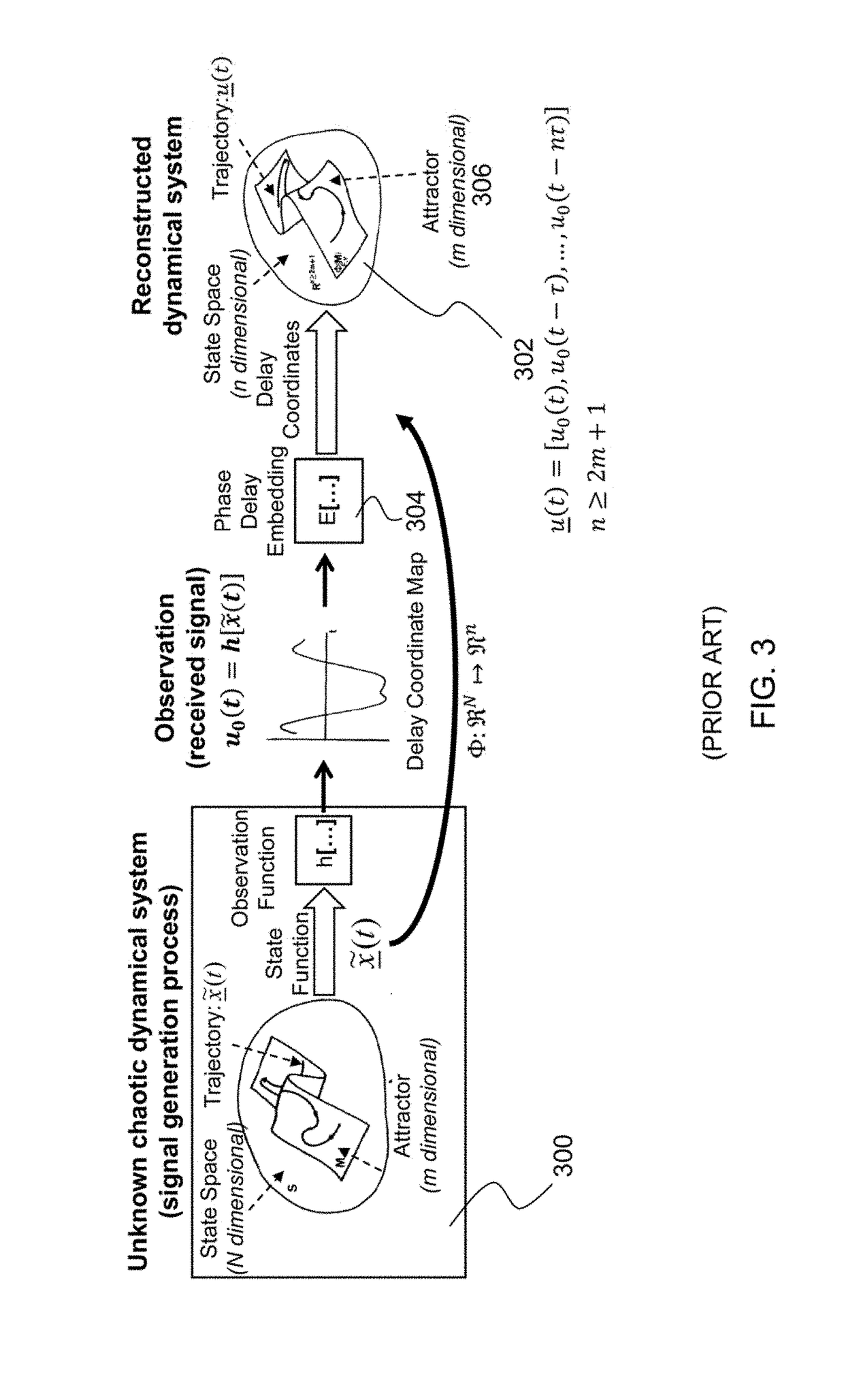
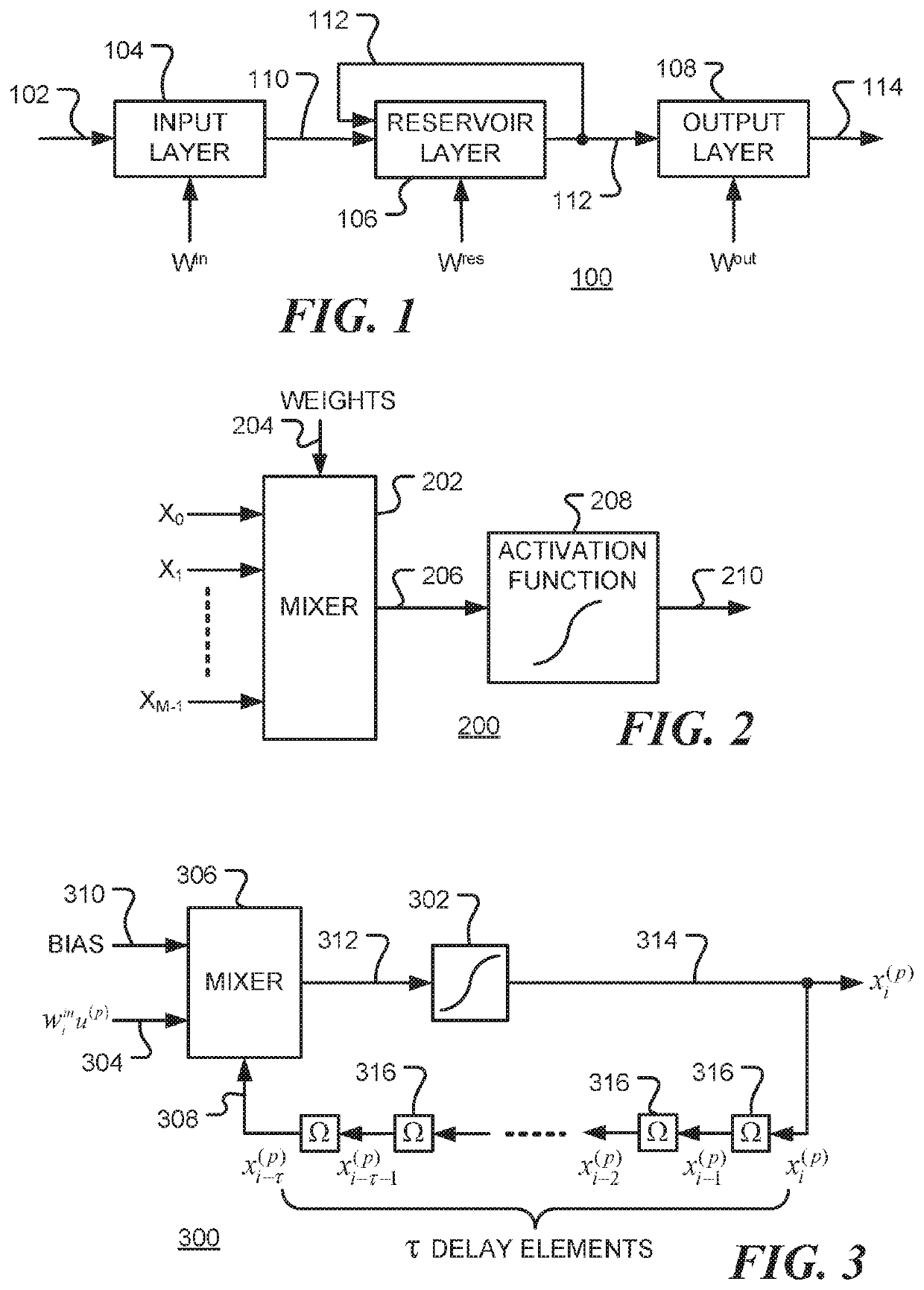
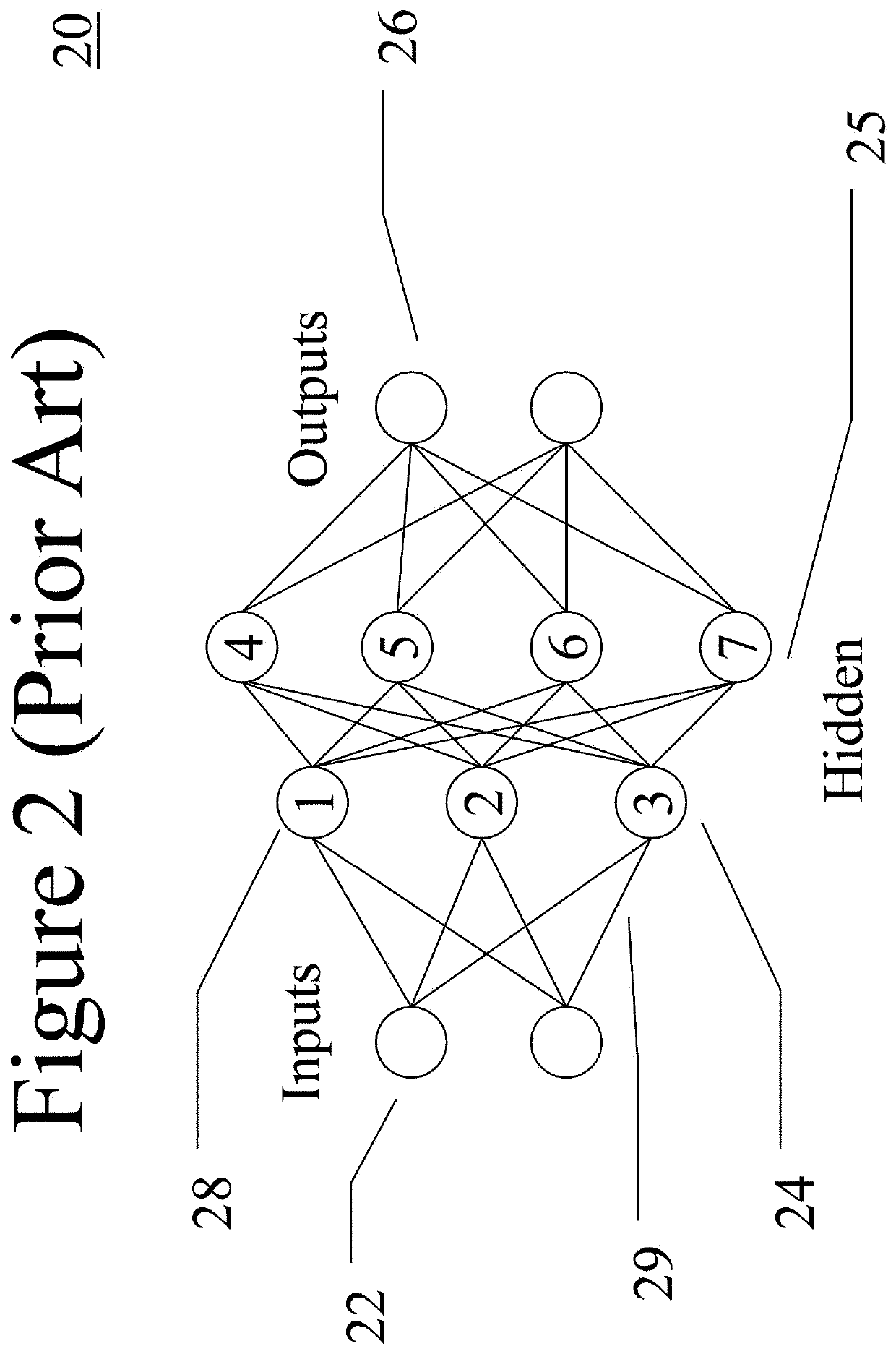
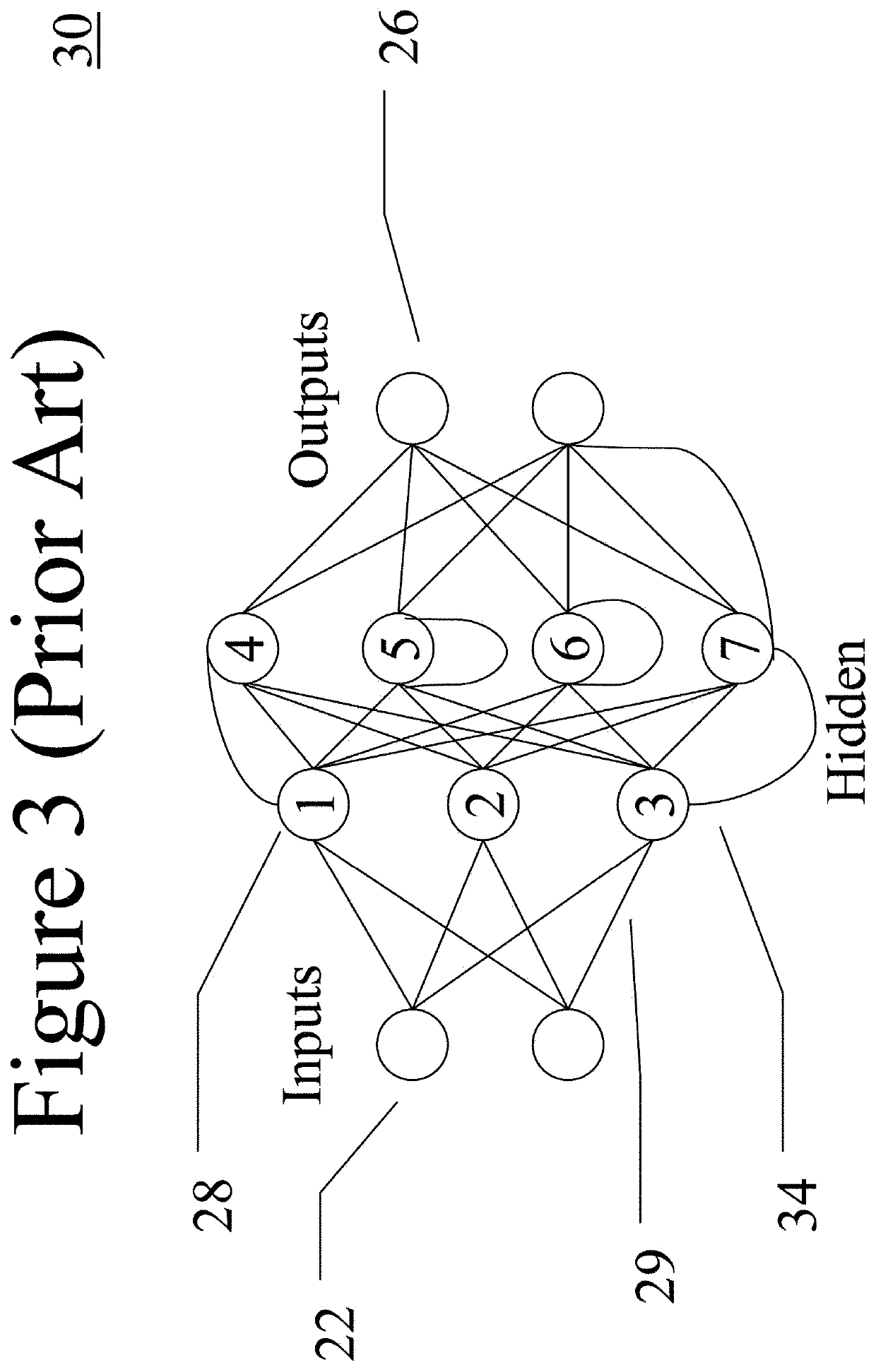
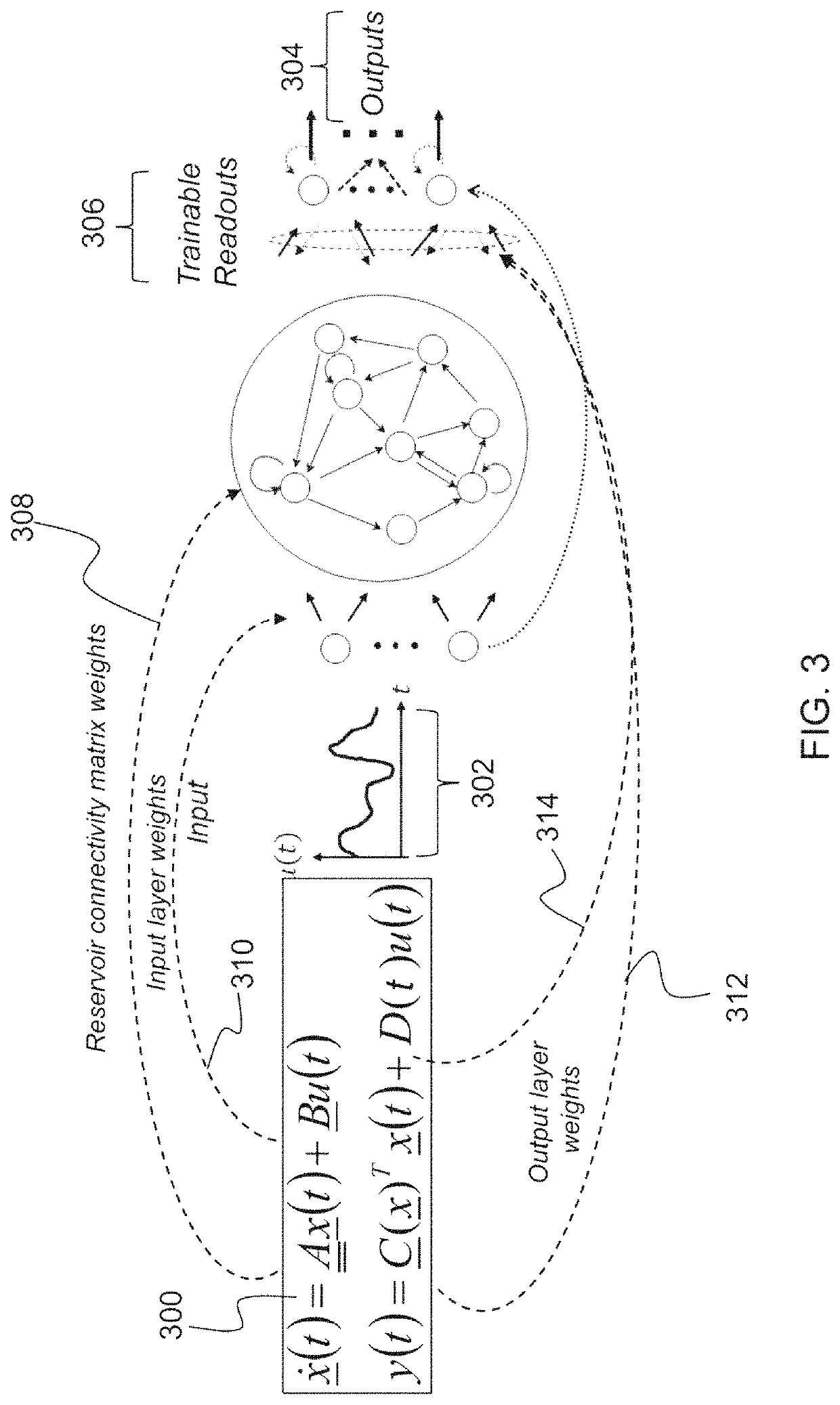
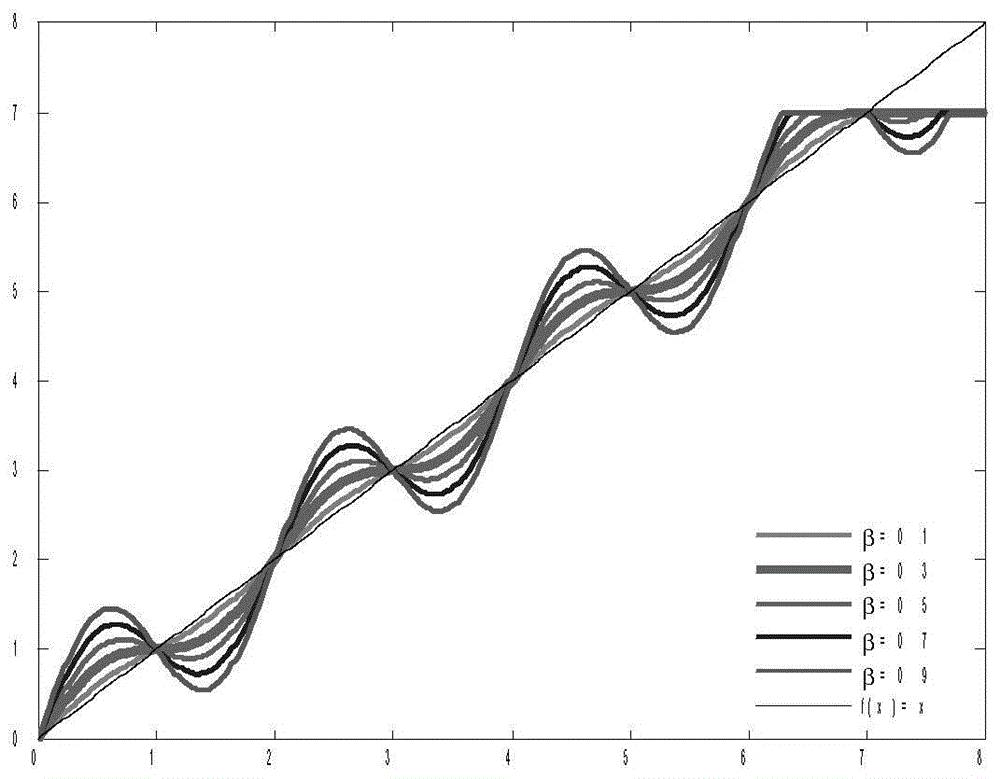
Reservoir computing is a framework for computation that may be viewed as an extension of neural networks. Typically an input signal is fed into a fixed (random) dynamical system called a reservoir and the dynamics of the reservoir map the input to a higher dimension. Then a simple readout mechanism is trained to read the state of the reservoir and map it to the desired output. The main benefit is that training is performed only at the readout stage and the reservoir is fixed. Liquid-state machines and echo state networks are two major types of reservoir computing. One important feature of this system is that it can use the computational power of naturally available systems which is different from the neural networks and it reduces the computational cost.
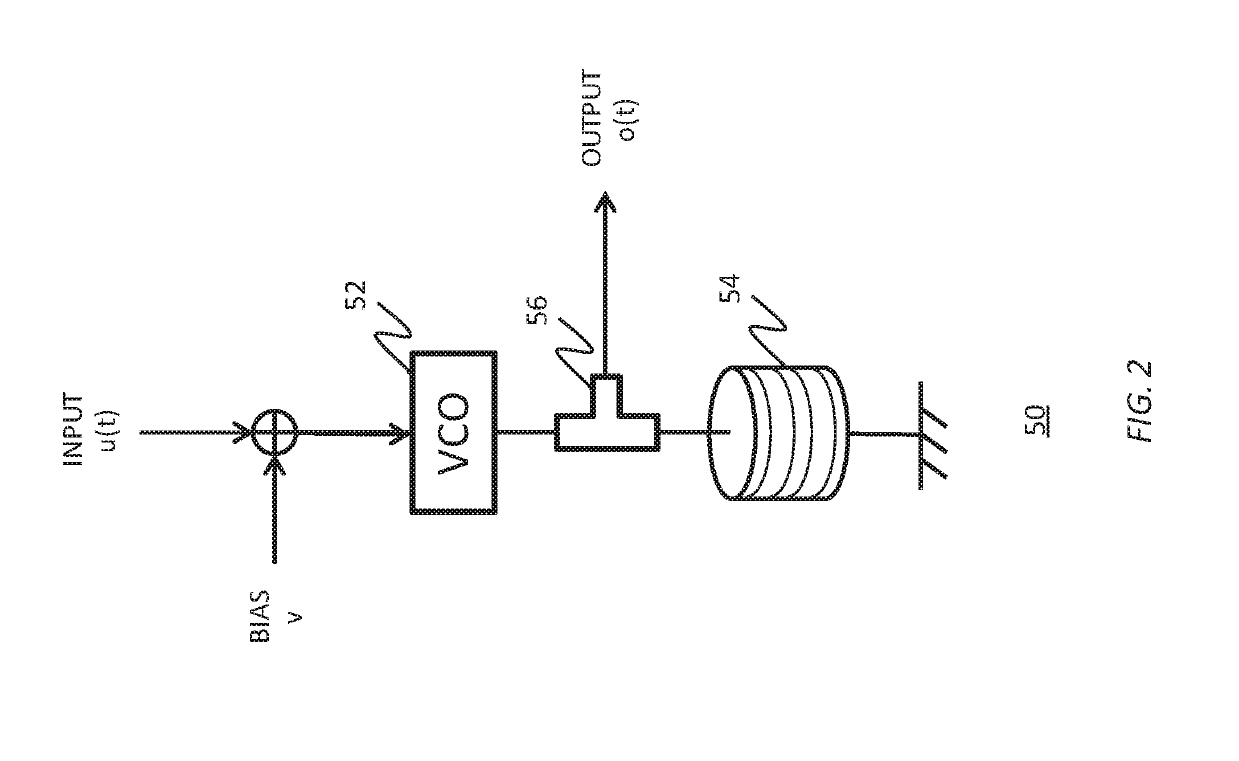
Reservoir Computing Using Passive Optical Systems
ActiveUS20150009548A1Improve efficiencyLogic circuits using opto-electronic devicesPhysical realisationPhotonicsInterconnection
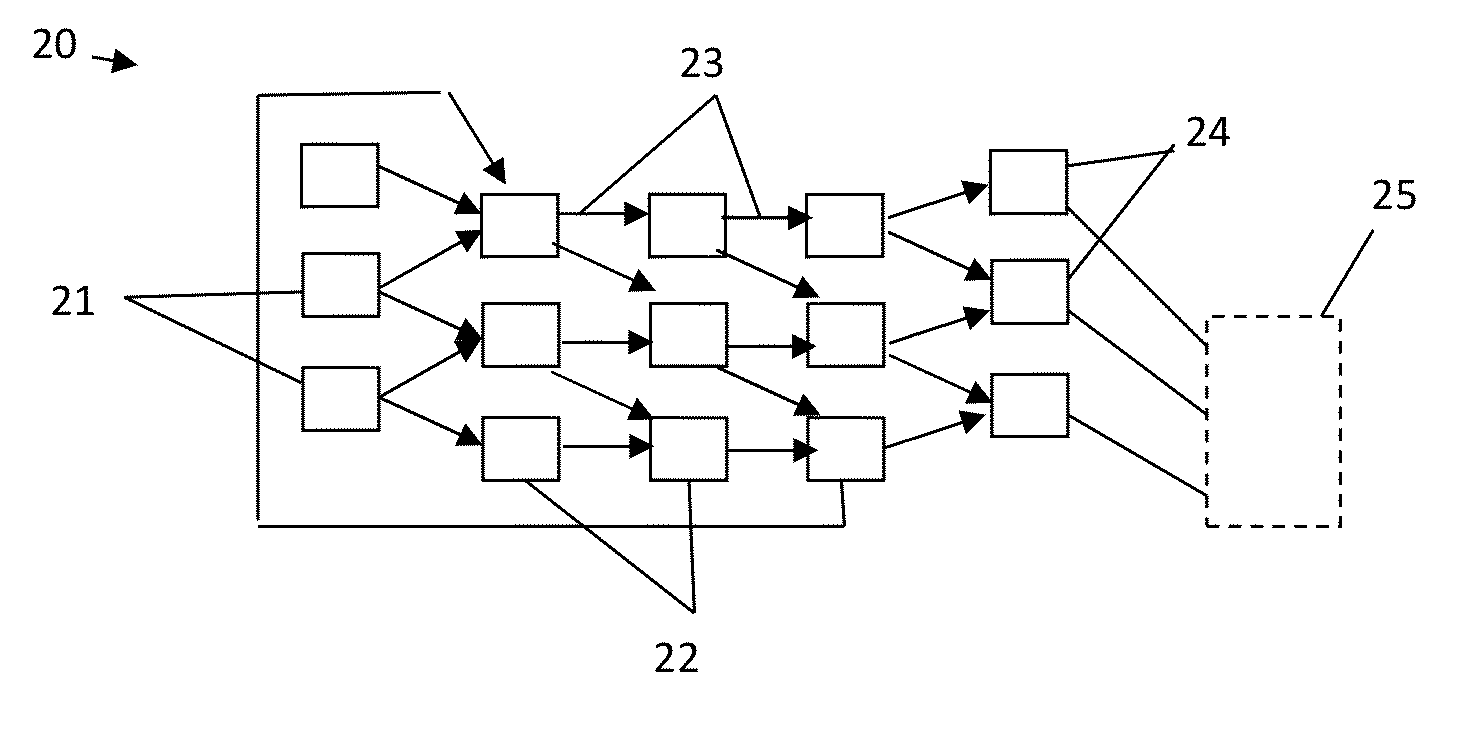
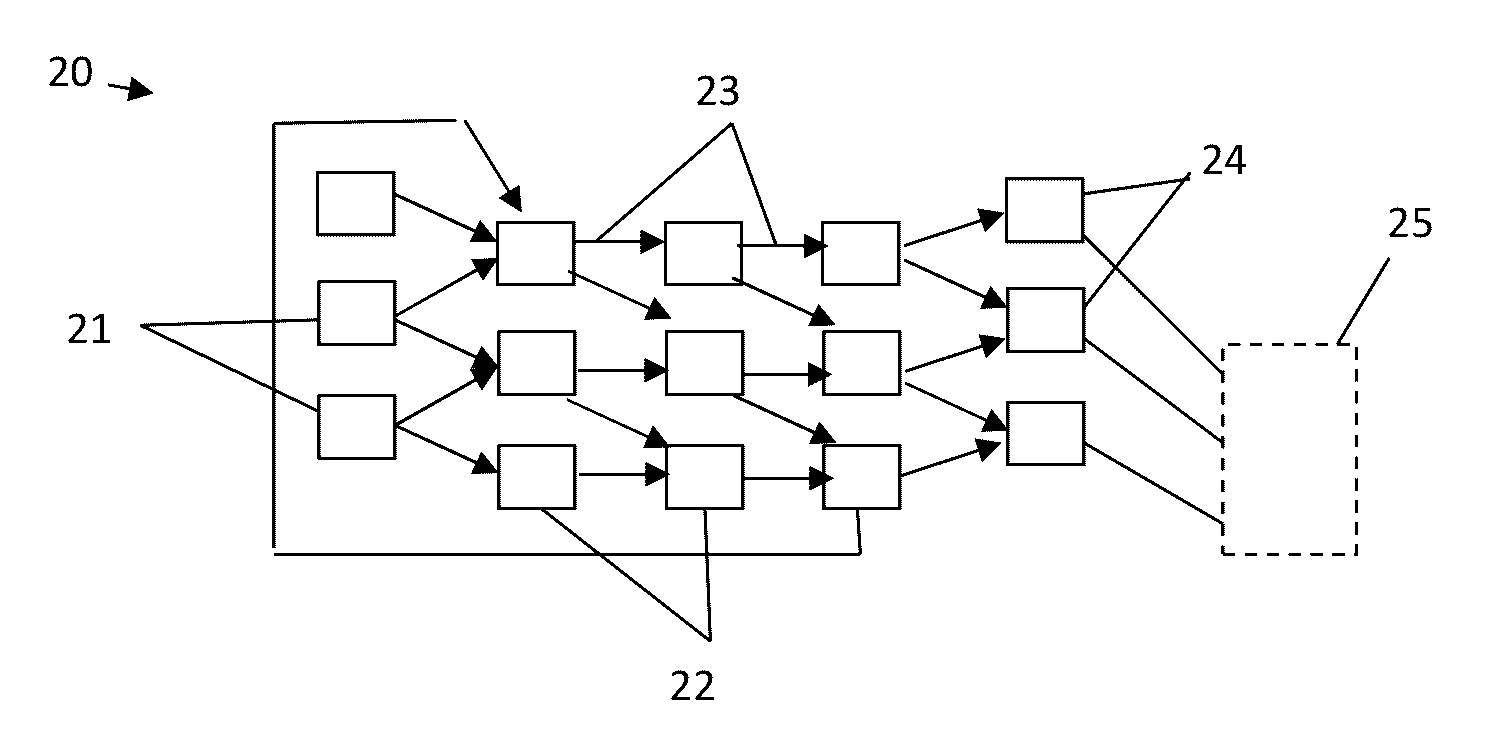
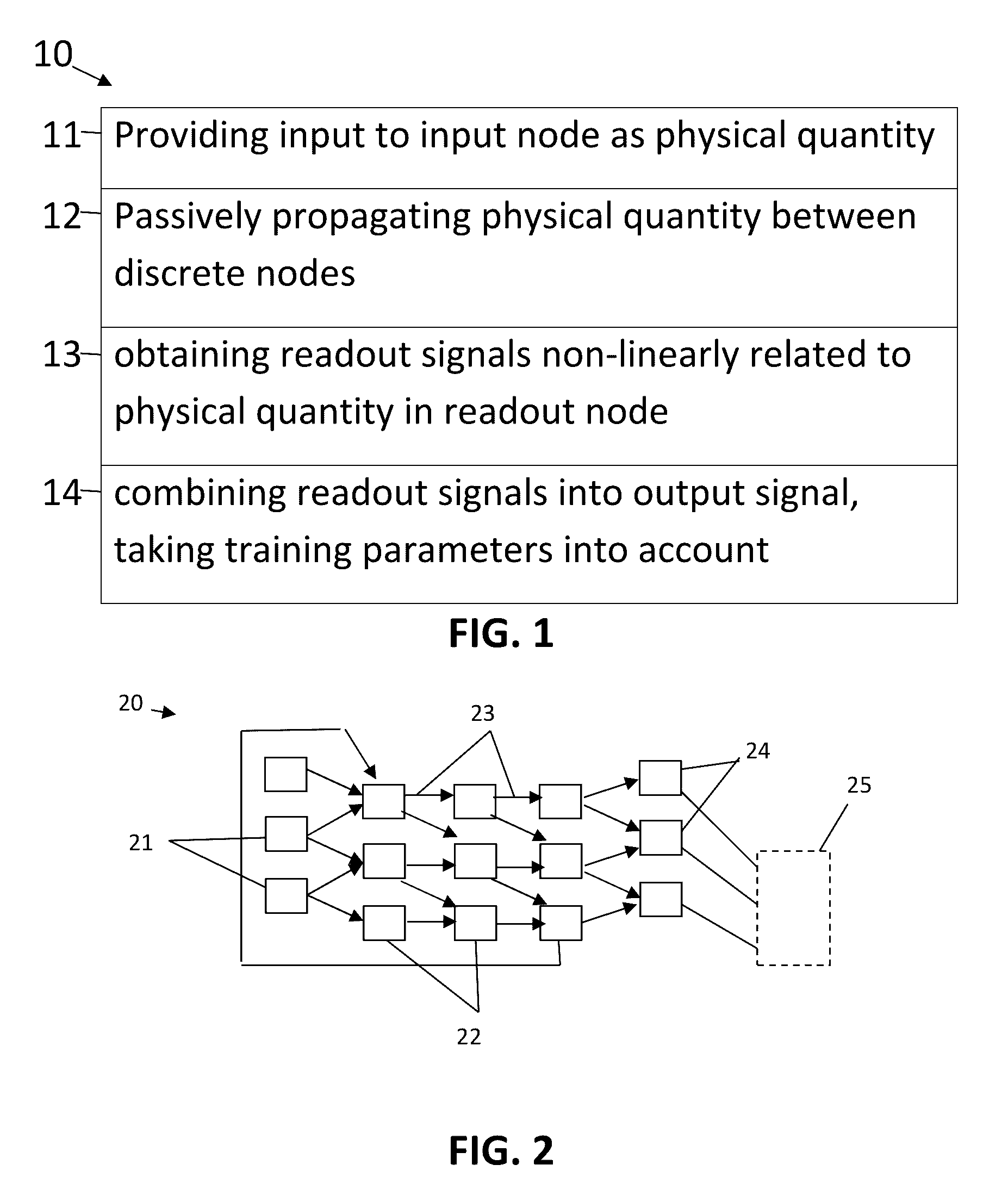
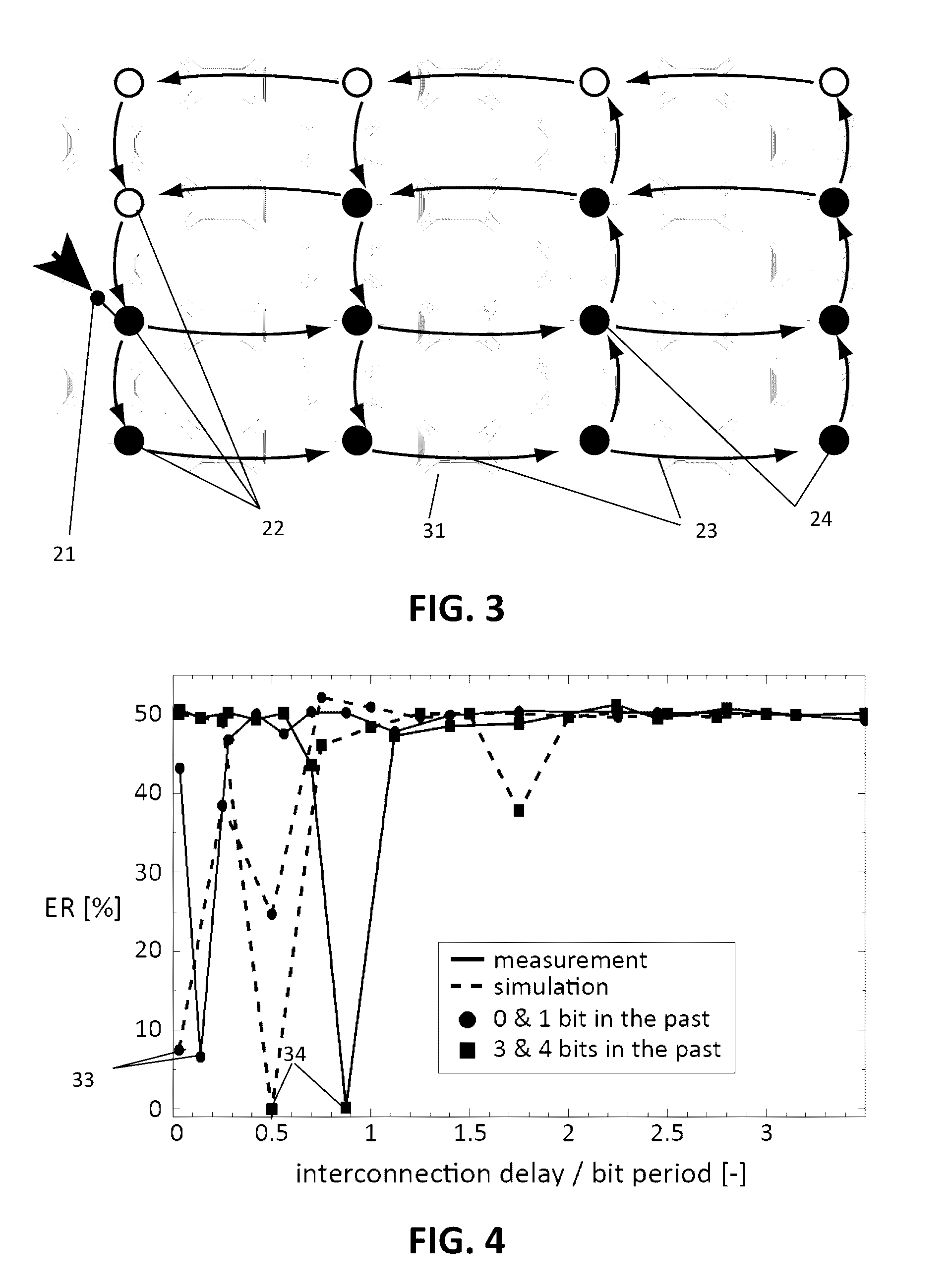
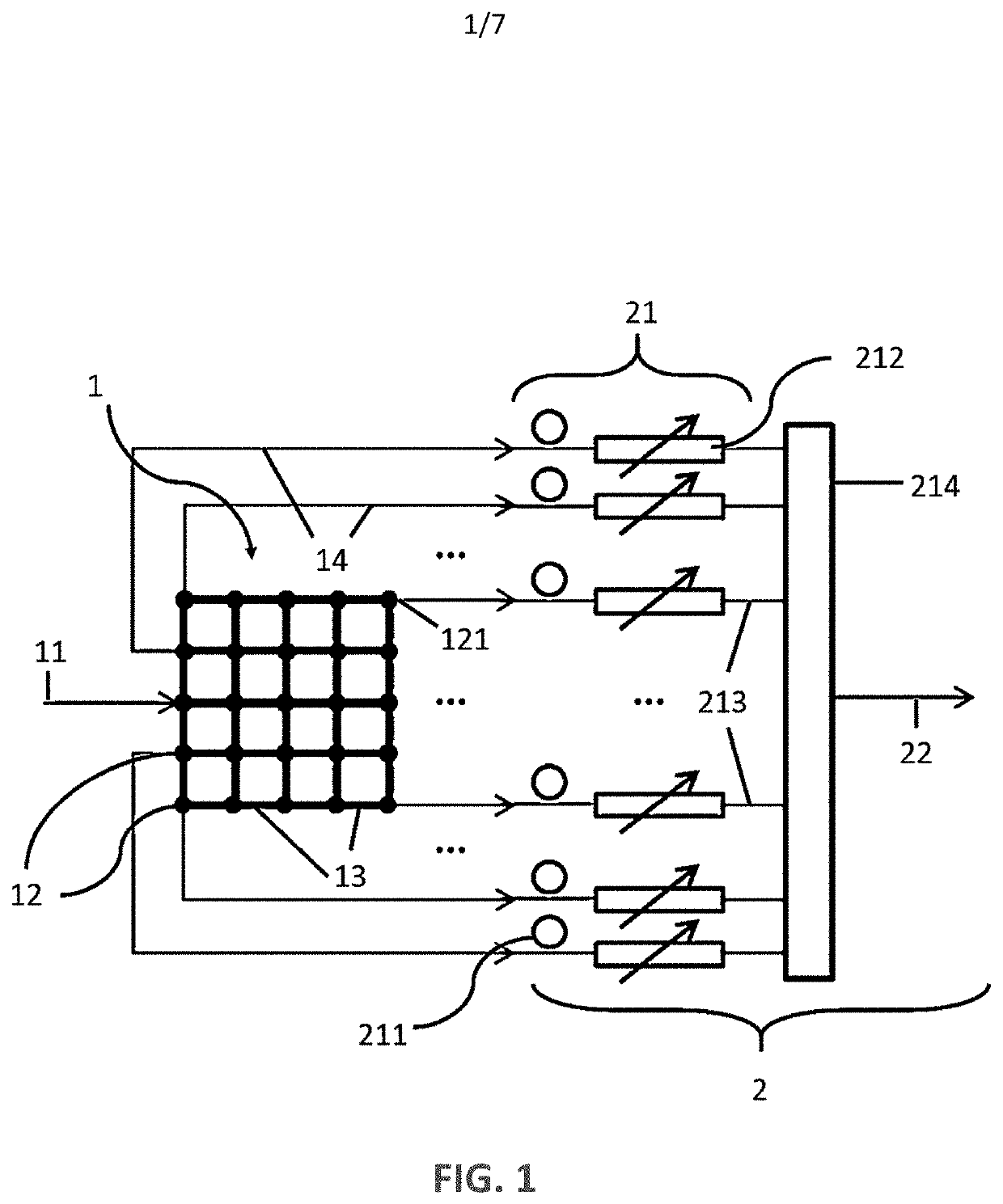
A method comprising providing an input signal to at least one input node of a computing reservoir by temporally encoding the input signal by modulating the at least one photonic wave as function of the input signal is described. The method further comprises propagating the at least one photonic wave via passive guided or unguided propagation between discrete nodes of the computing reservoir, in which each discrete node is adapted for passively relaying the at least one photonic wave over the passive interconnections connected thereto. The method also comprises obtaining a plurality of readout signals, in which each readout signal is determined by a non-linear relation to the at least one photonic wave in at least one readout node of the computing reservoir, and combining this plurality of readout signals into an output signal by taking into account a plurality of training parameters.
Owner:UNIV GENT +1
Reservoir computing using passive optical systems
ActiveUS9477136B2Improve efficiencyLogic circuits using opto-electronic devicesPhysical realisationPhotonicsInterconnection
A method comprising providing an input signal to at least one input node of a computing reservoir by temporally encoding the input signal by modulating the at least one photonic wave as function of the input signal is described. The method further comprises propagating the at least one photonic wave via passive guided or unguided propagation between discrete nodes of the computing reservoir, in which each discrete node is adapted for passively relaying the at least one photonic wave over the passive interconnections connected thereto. The method also comprises obtaining a plurality of readout signals, in which each readout signal is determined by a non-linear relation to the at least one photonic wave in at least one readout node of the computing reservoir, and combining this plurality of readout signals into an output signal by taking into account a plurality of training parameters.
Owner:UNIV GENT +1
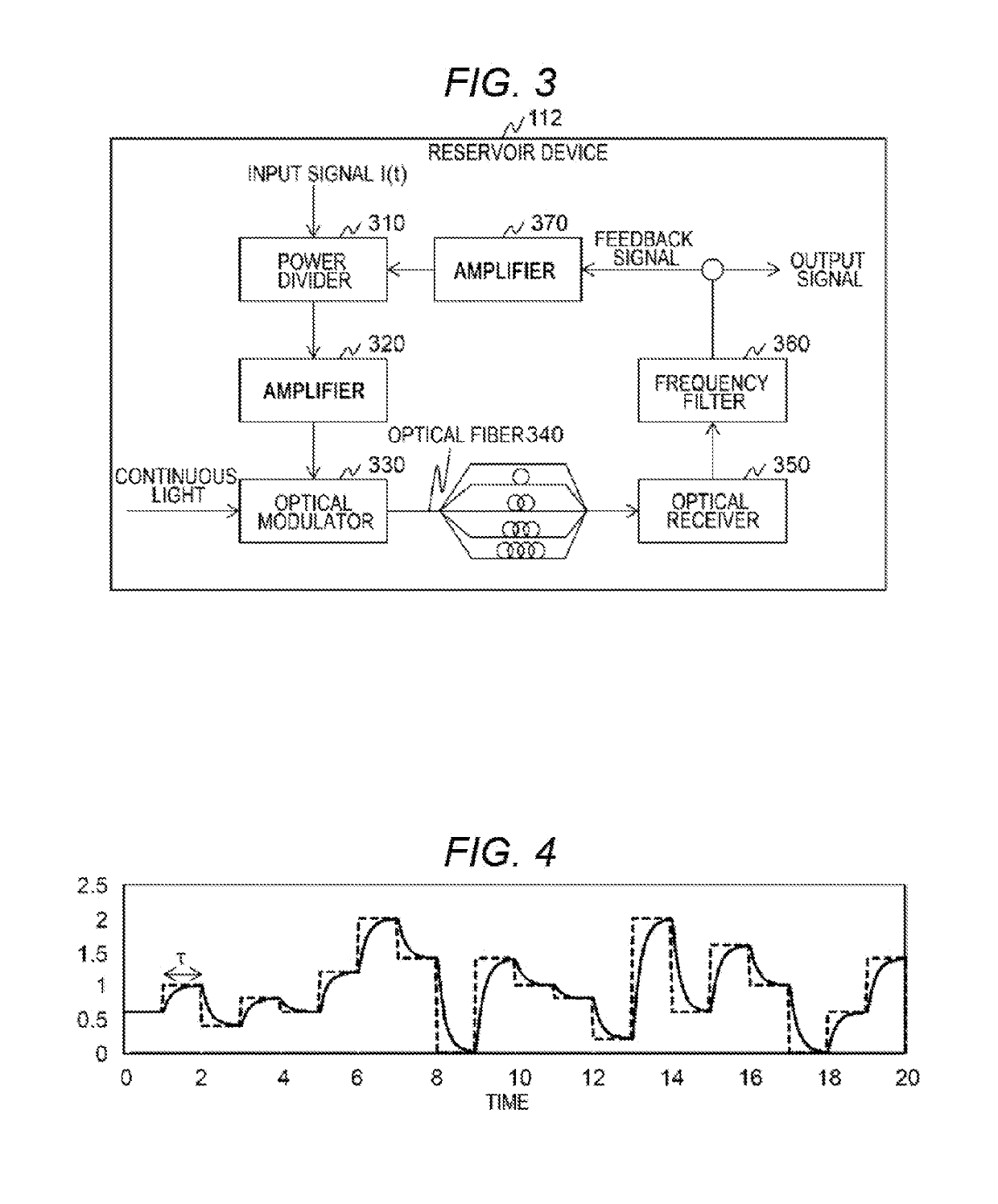
Laser apparatus and reservoir computing system
ActiveUS20180309266A1Laser detailsLaser optical resonator constructionErbium lasersReservoir computing
To realize a reservoir computing system with a small size and reduced learning cost, provided is a laser apparatus including a laser; a feedback waveguide that is operable to feed light output from the laser back to the laser; an optical splitter that is provided in a path of the feedback waveguide and is operable to output a portion of light propagated in the feedback waveguide to outside; and a first ring resonator that is operable to be optically connected to the feedback waveguide, as well as a reservoir computing system including this laser apparatus.
Owner:IBM CORP
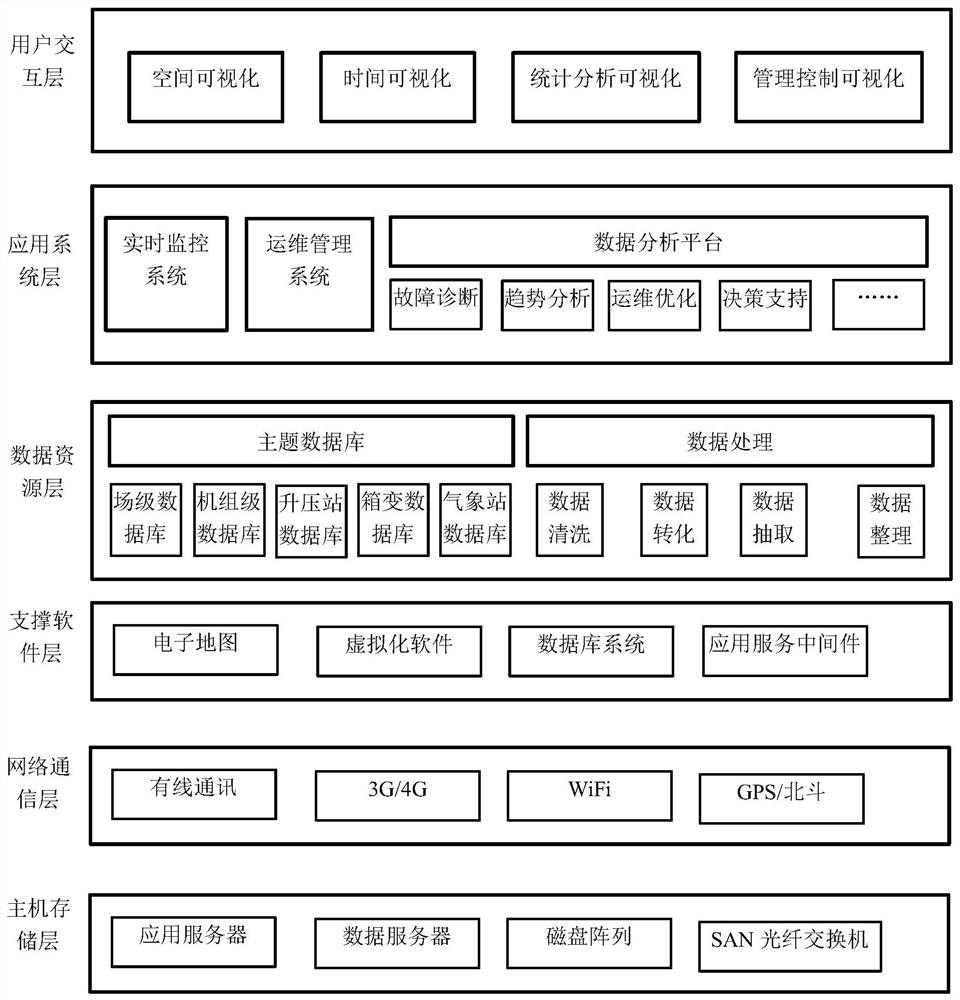
New energy power plant station management platform
ActiveCN107968482ARealize collection and displayAchieve transparencyCircuit arrangementsInformation technology support systemInteraction layerRelational database
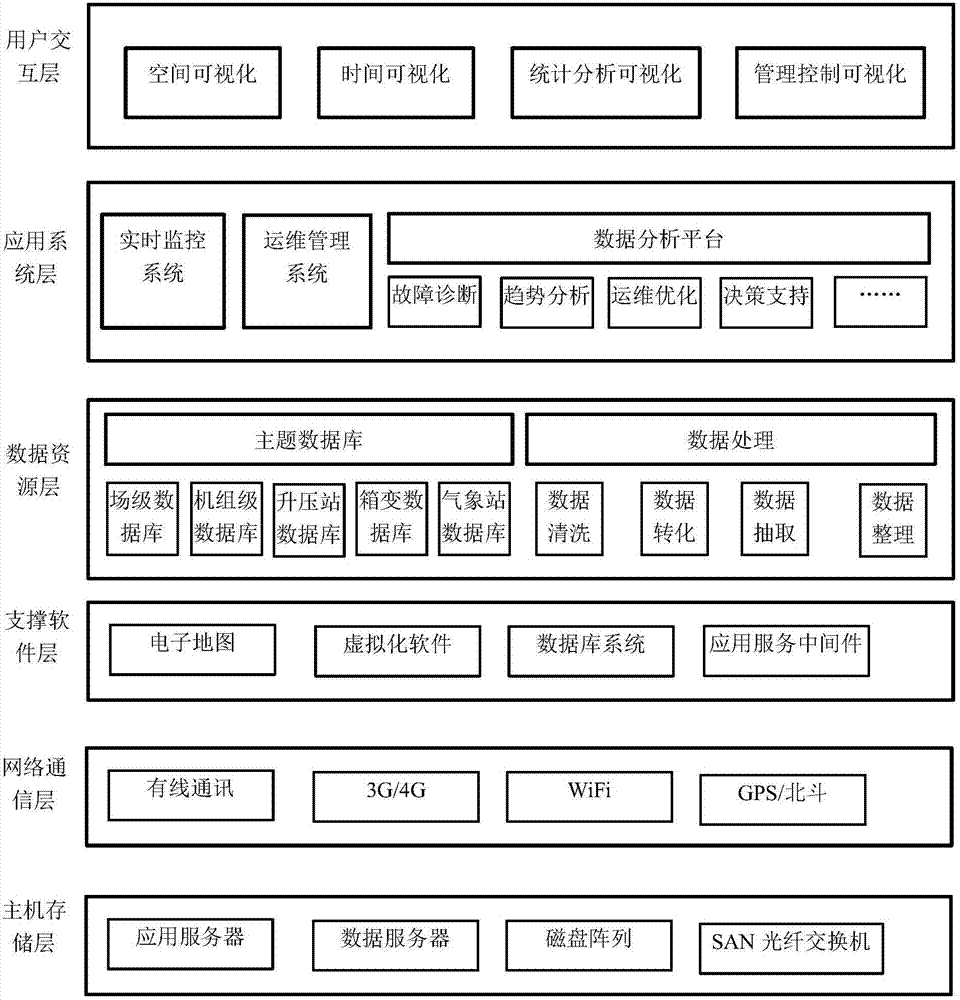
The invention discloses a new energy power plant station management platform, which comprises a host storage layer, a network communication layer, a support software layer, a data resource layer, an application system layer and a user interaction layer. The host storage layer provides computing, storage and disaster recovery resources. The network communication layer completes operating data access of a field new energy power plant station, and supports data transmission and exchange in wireless and wired manners. The support software layer is used for scheduling and expanding the computing and storage resources of the host storage layer by means of virtualization software. The data resource layer realizes persistent storage and use of various types of business subject data by adopting a traditional relational database and various NoSQL databases according to different data features. The application system layer transmits new energy power plant data to the management personnel in realtime, provides online control and plant station management, and utilizes data of the data resource layer to perform fault prediction and diagnosis by means of data pattern identification and adoptinga model training algorithm. The user interaction layer is used for establishing user interaction channels for different application scenarios.
Owner:CRRC WIND POWER(SHANDONG) CO LTD
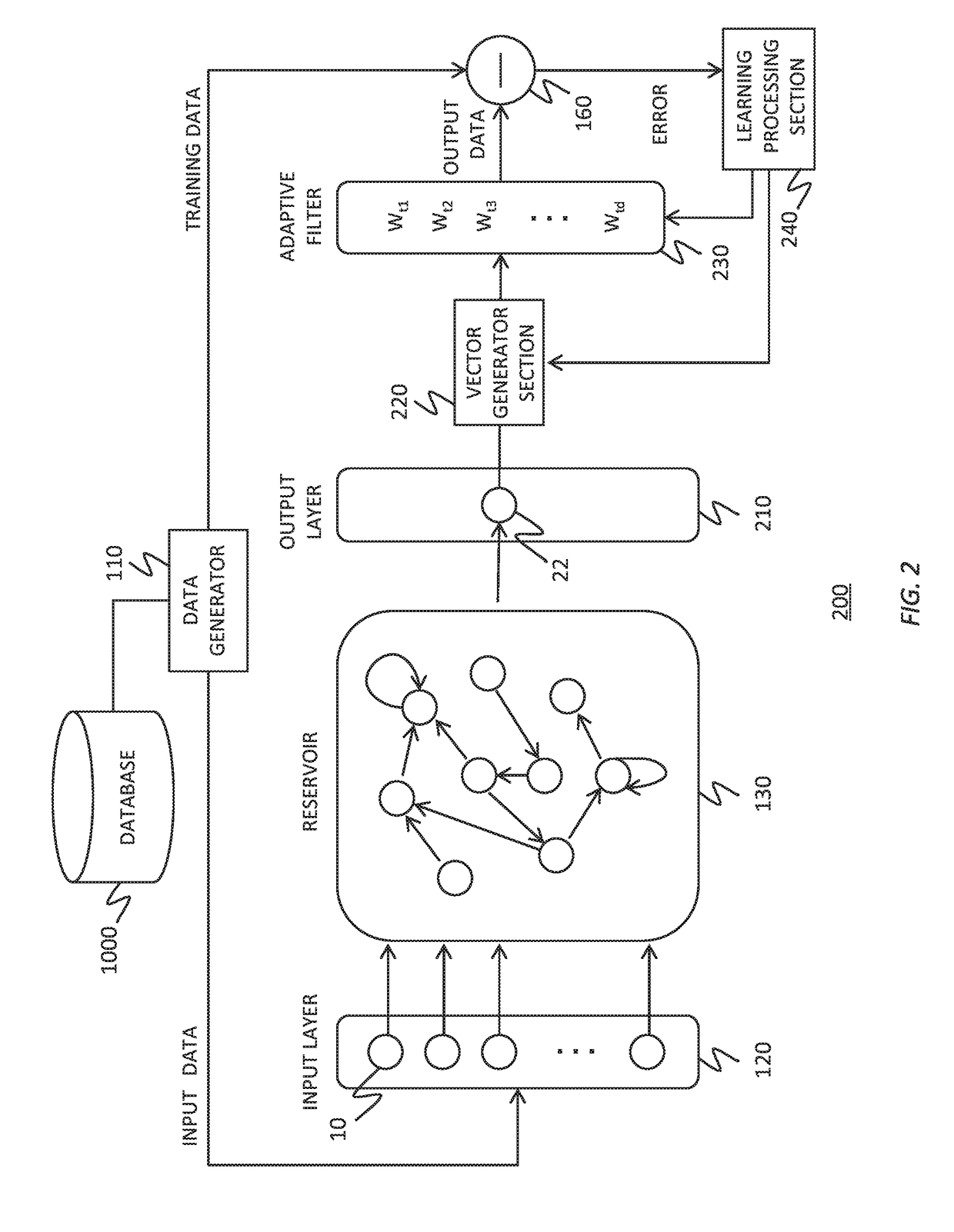
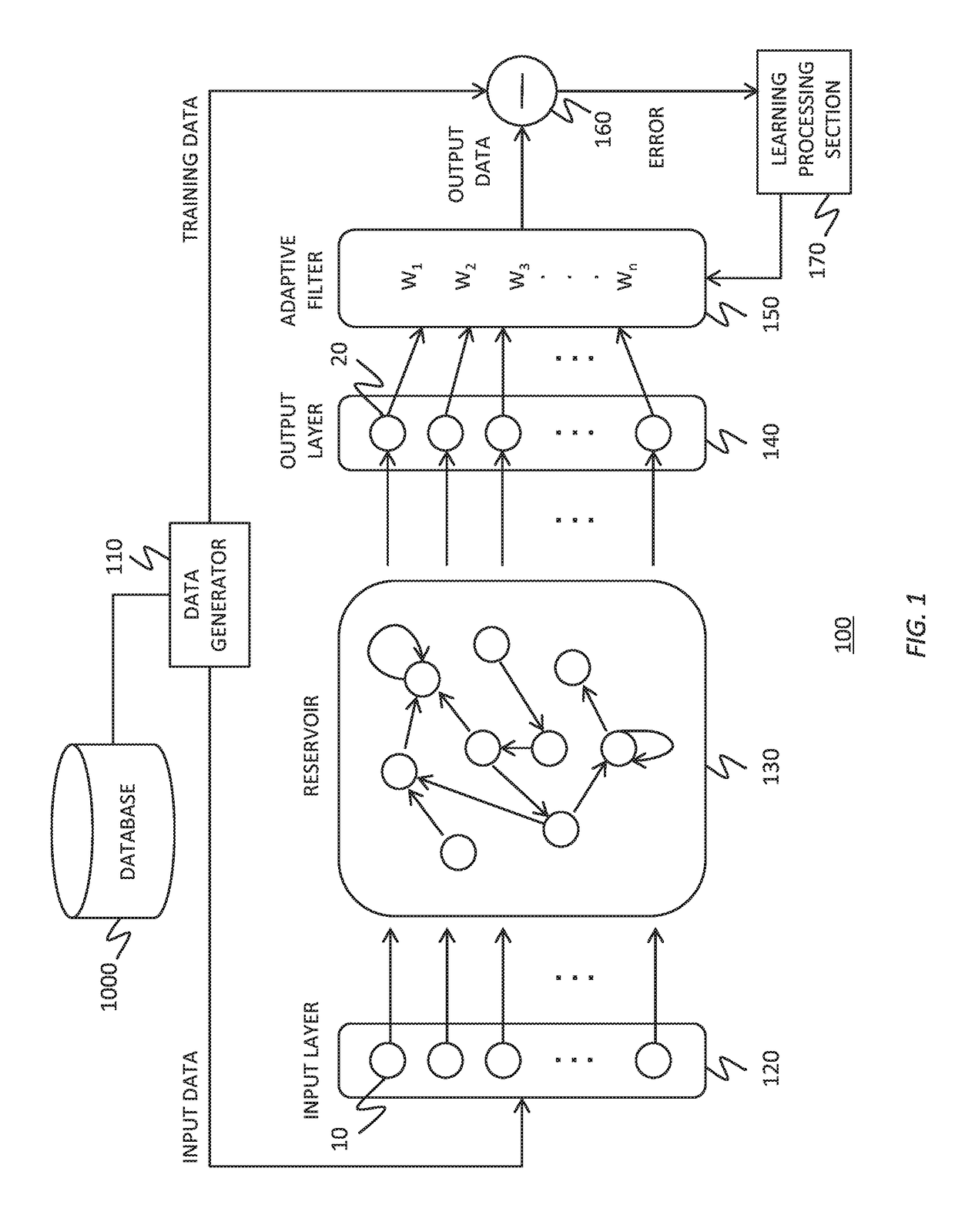
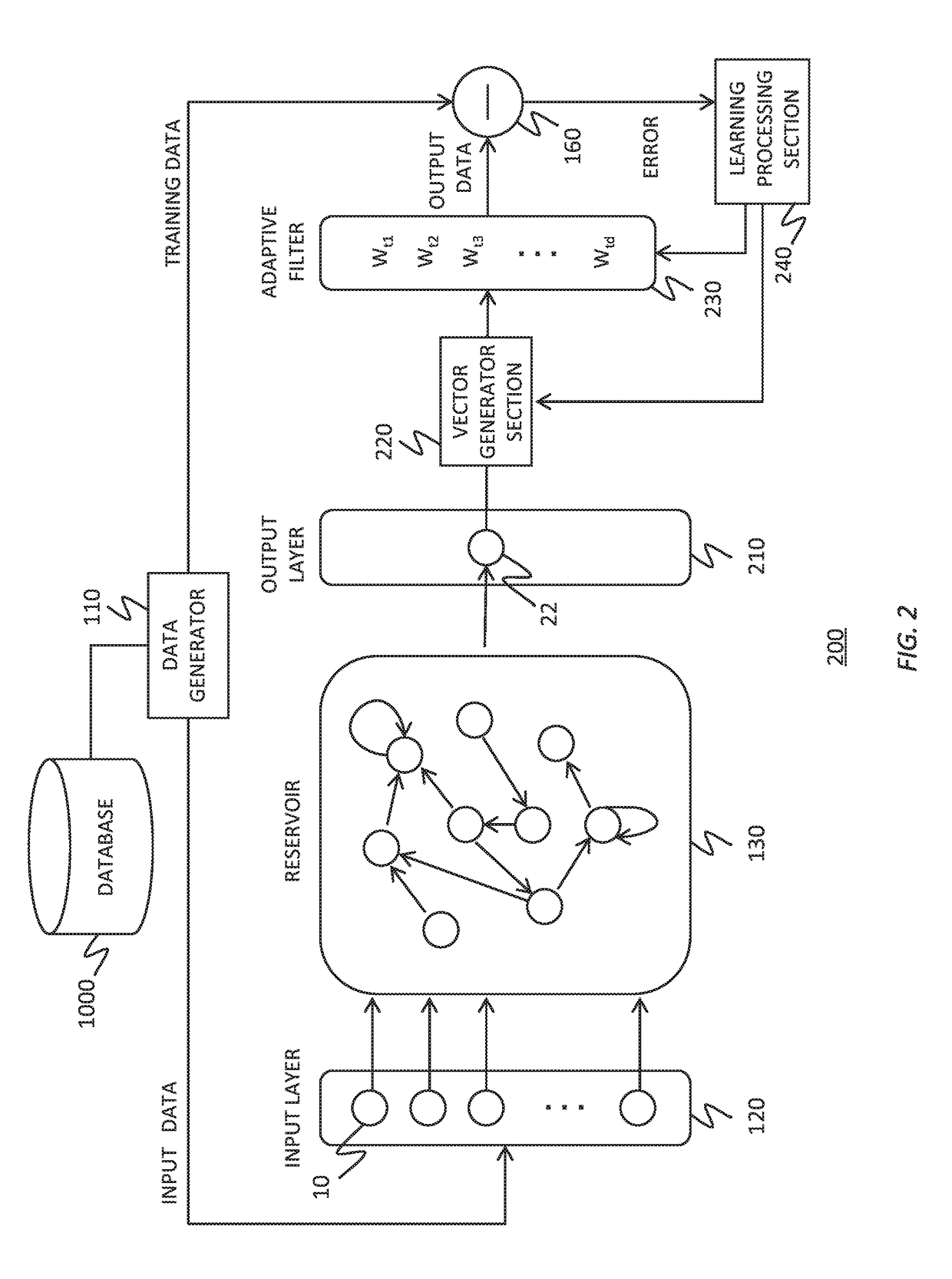
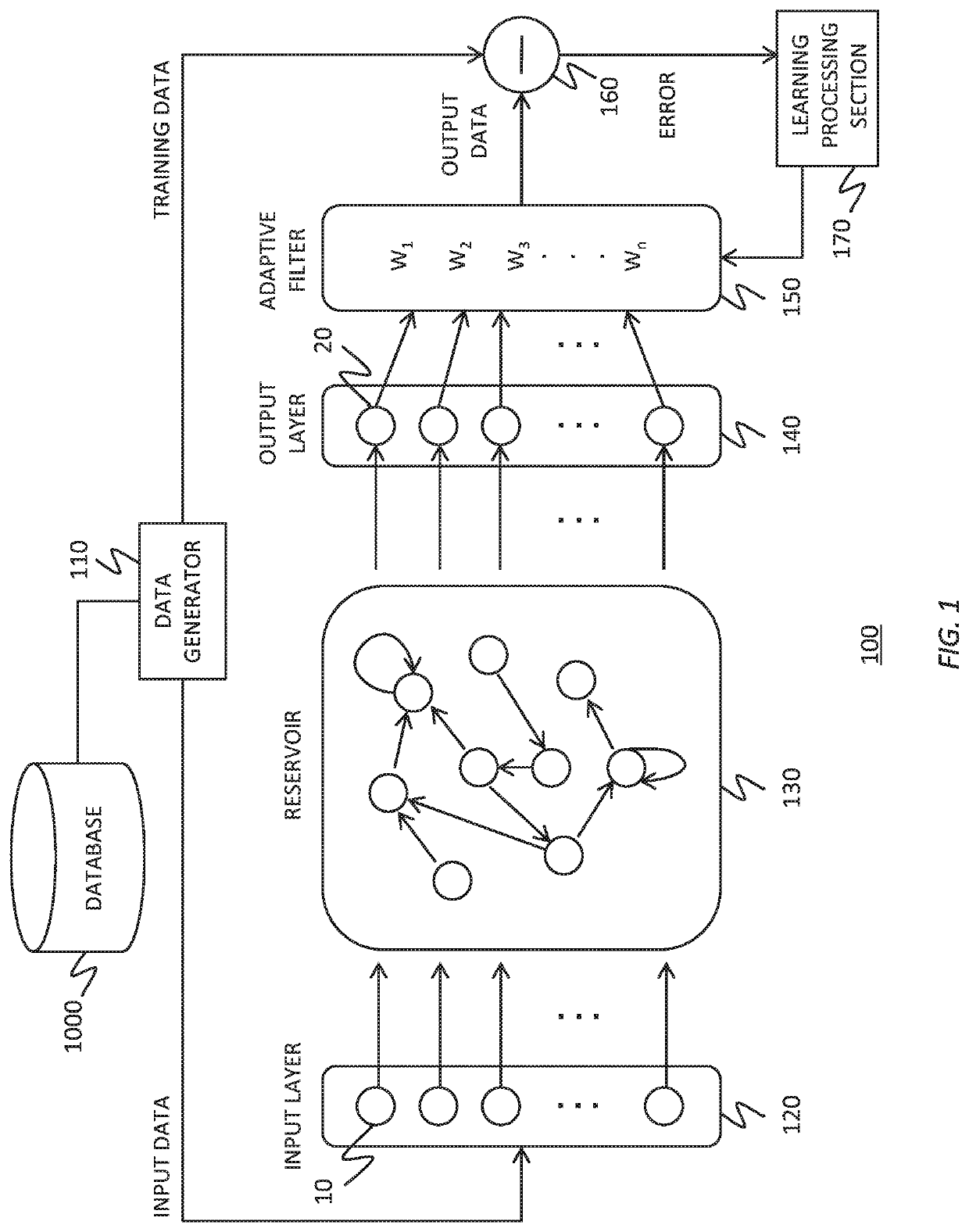
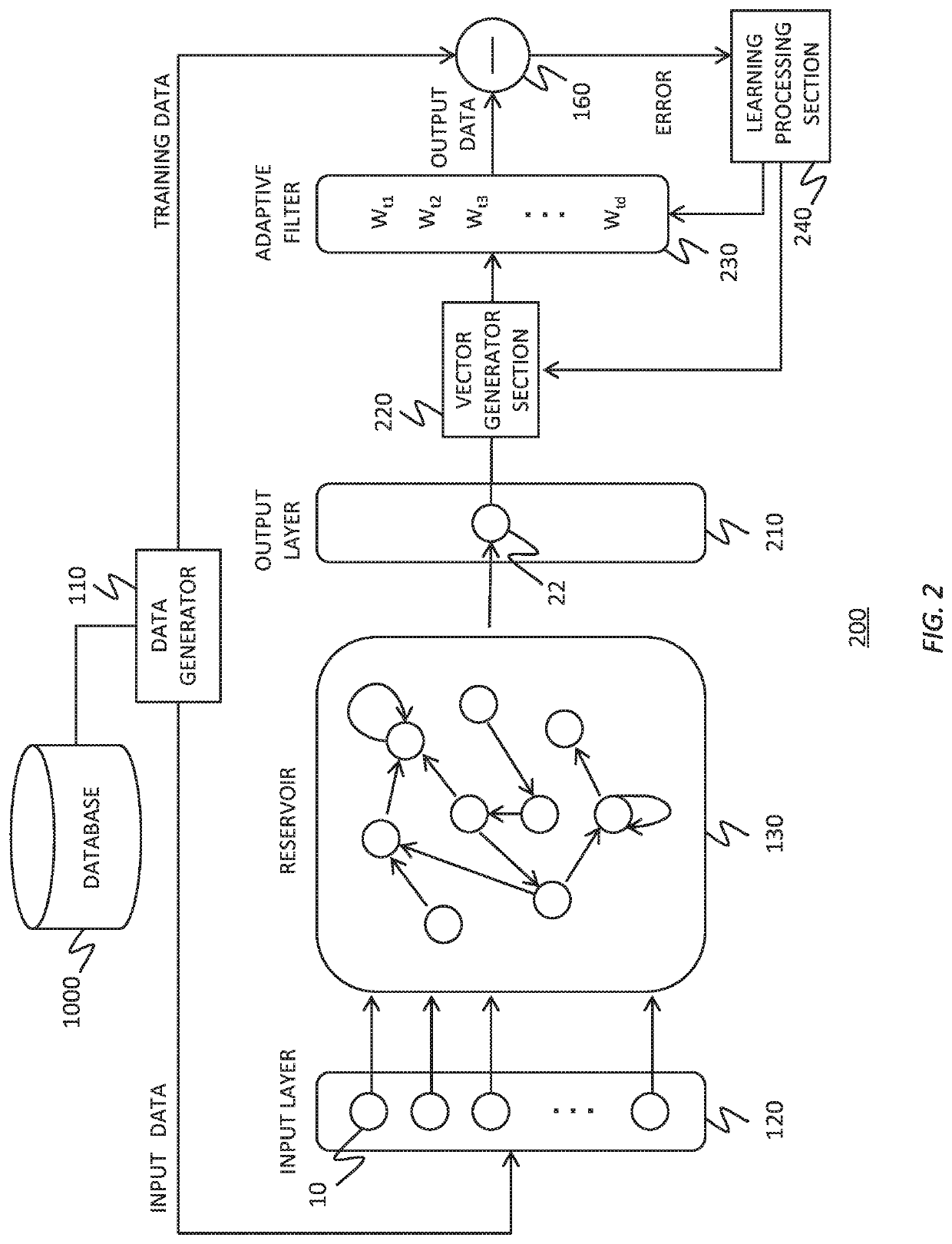
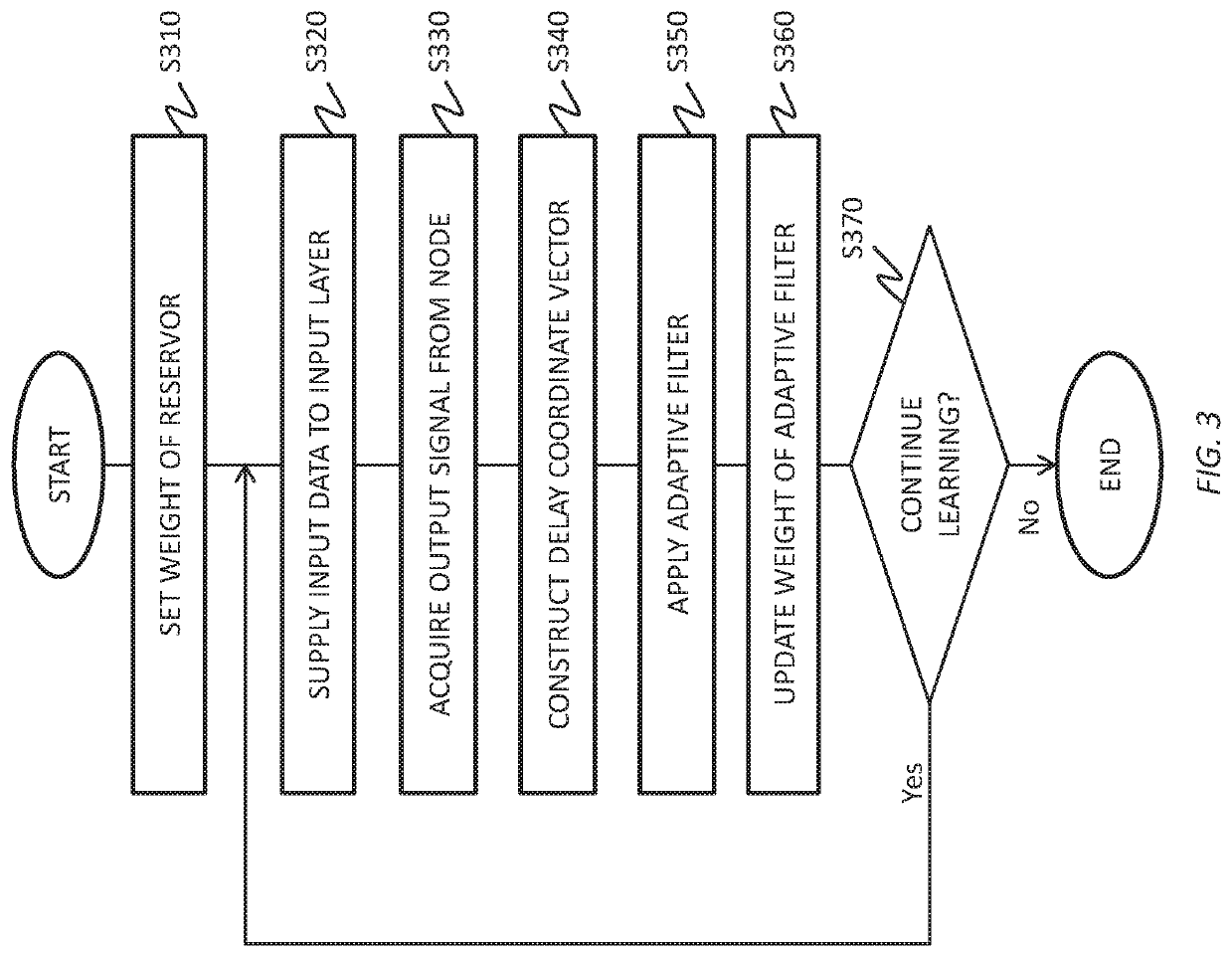
Reservoir computing system
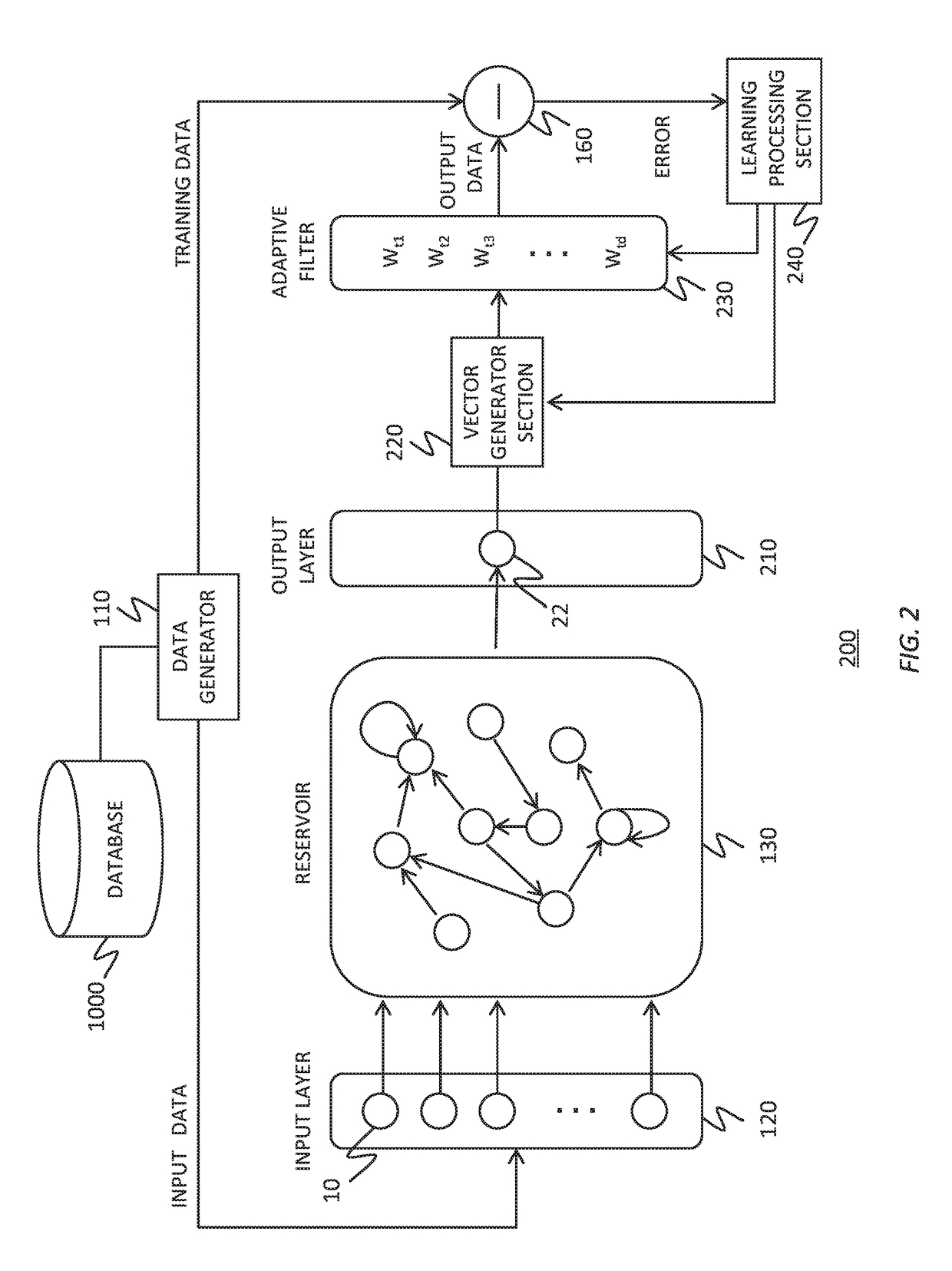
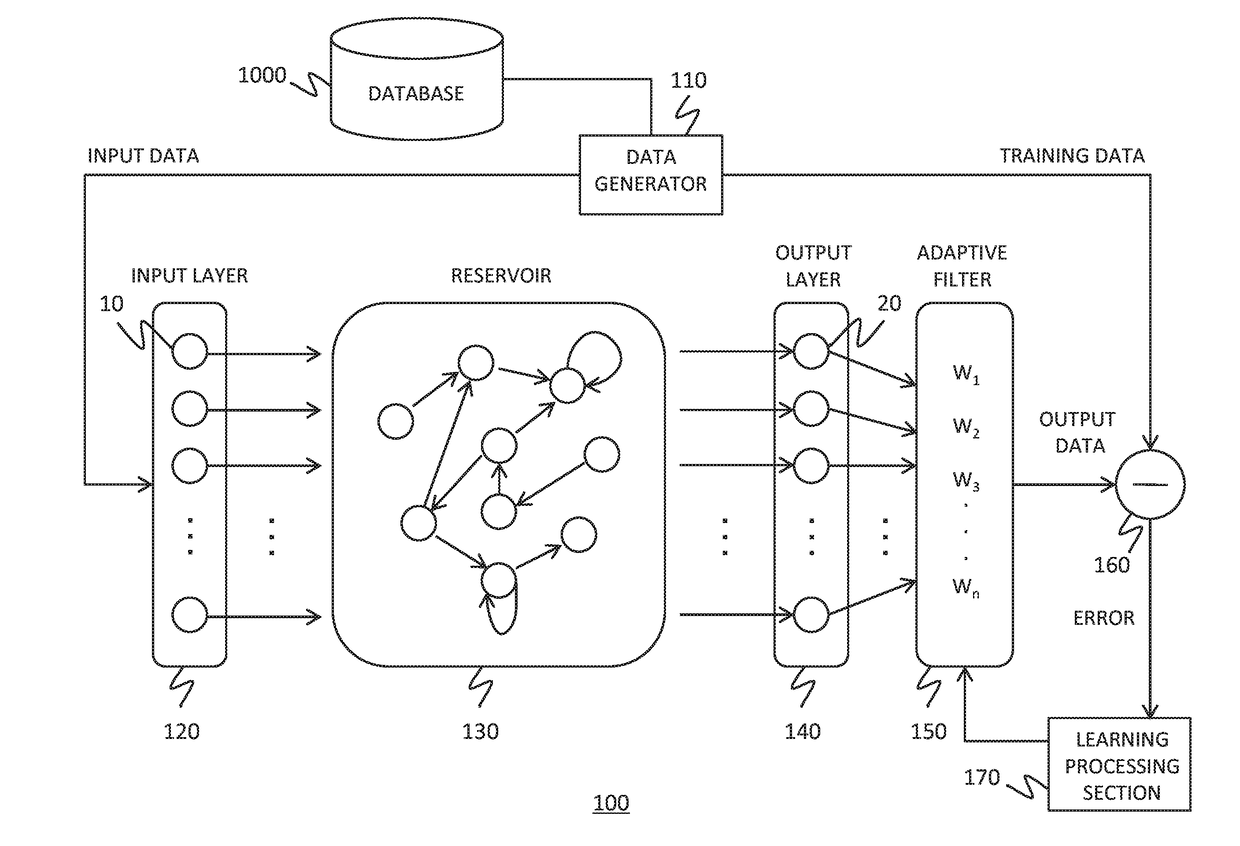
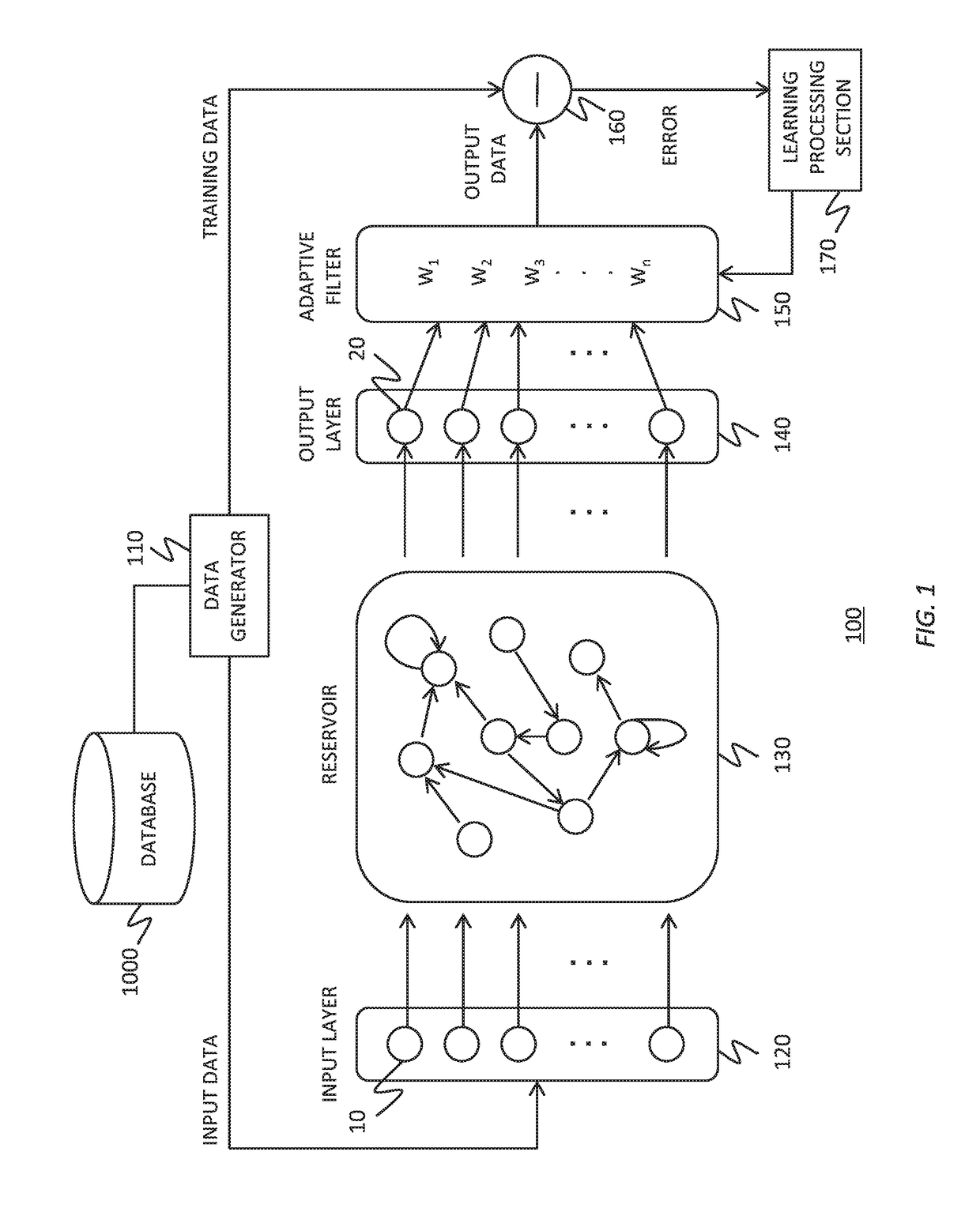
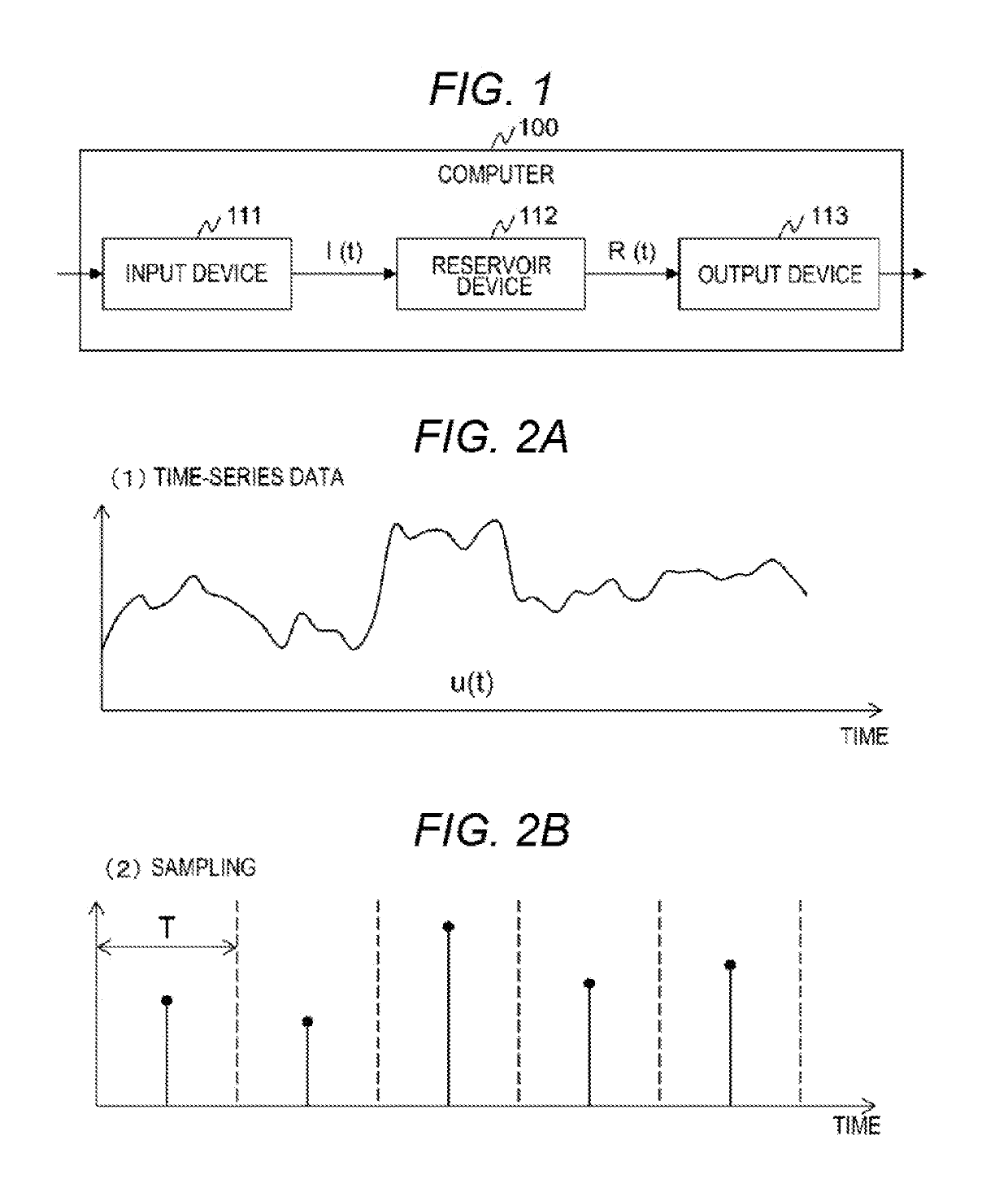
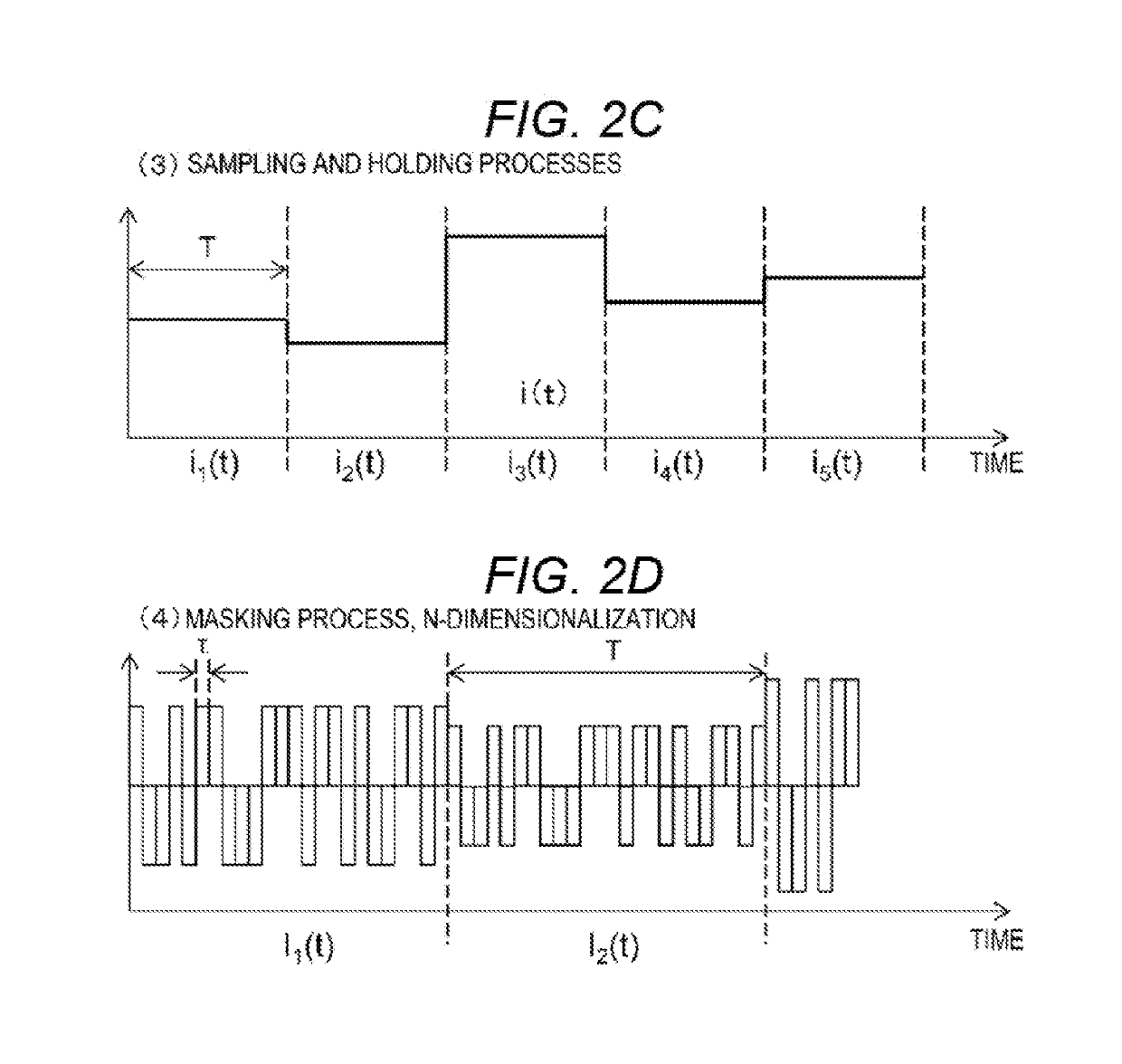
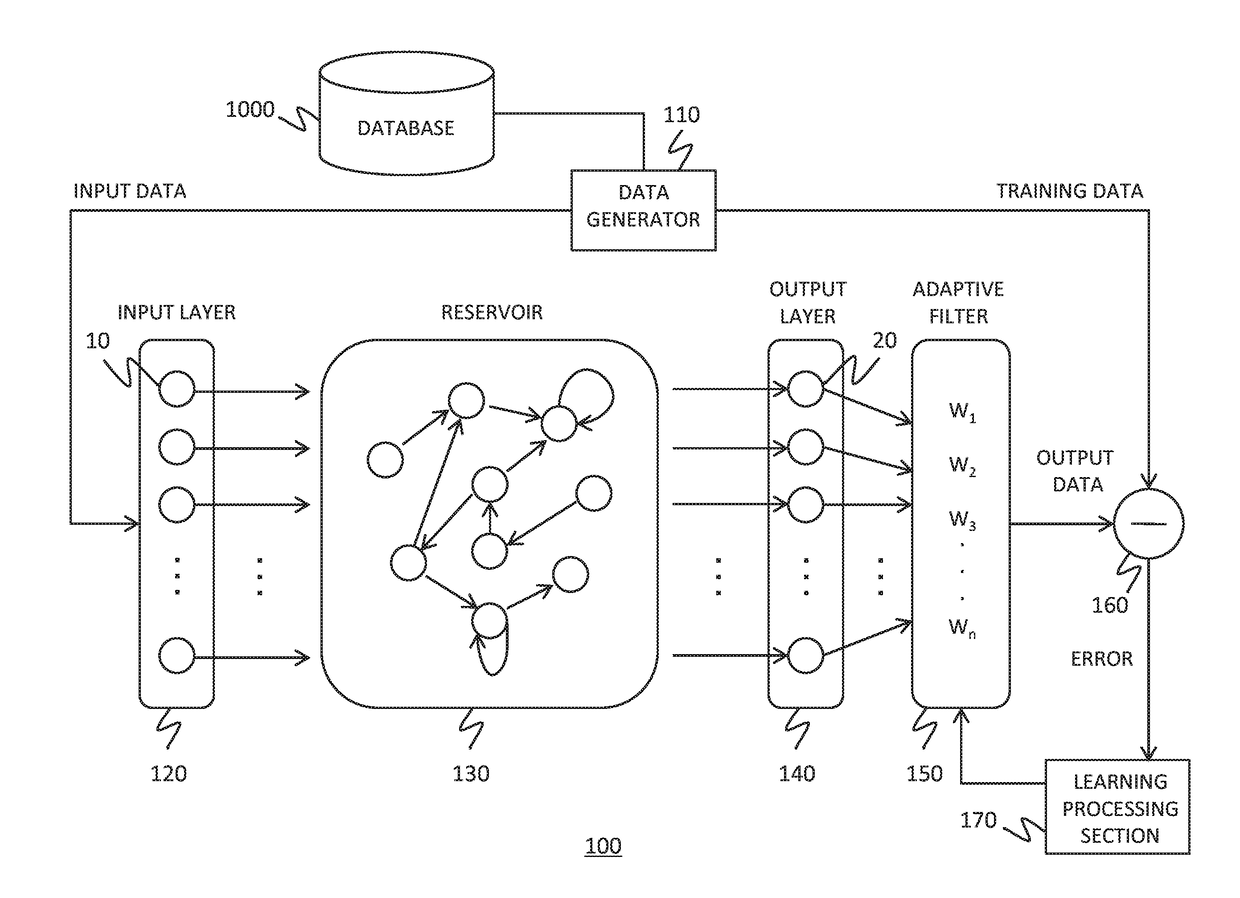
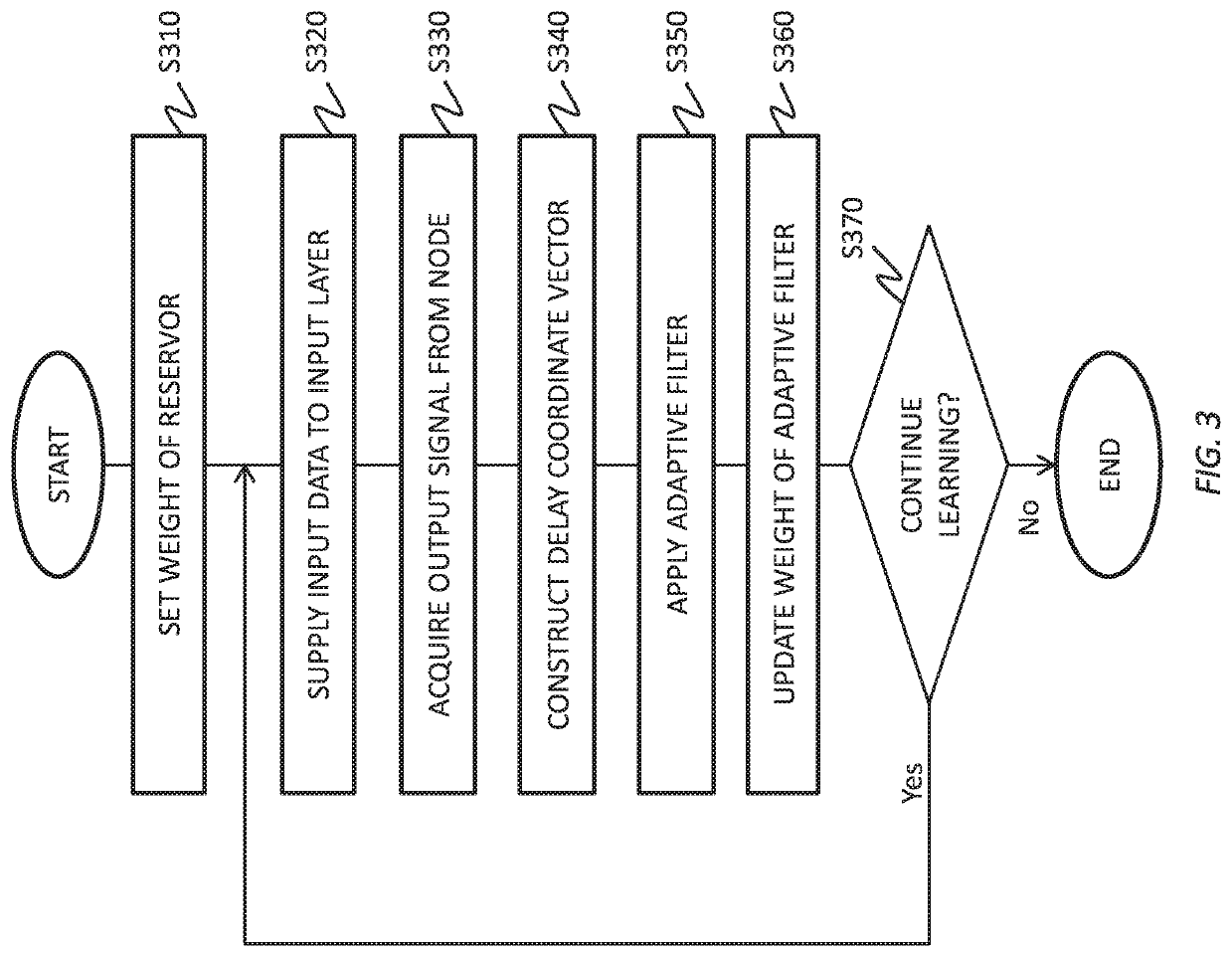
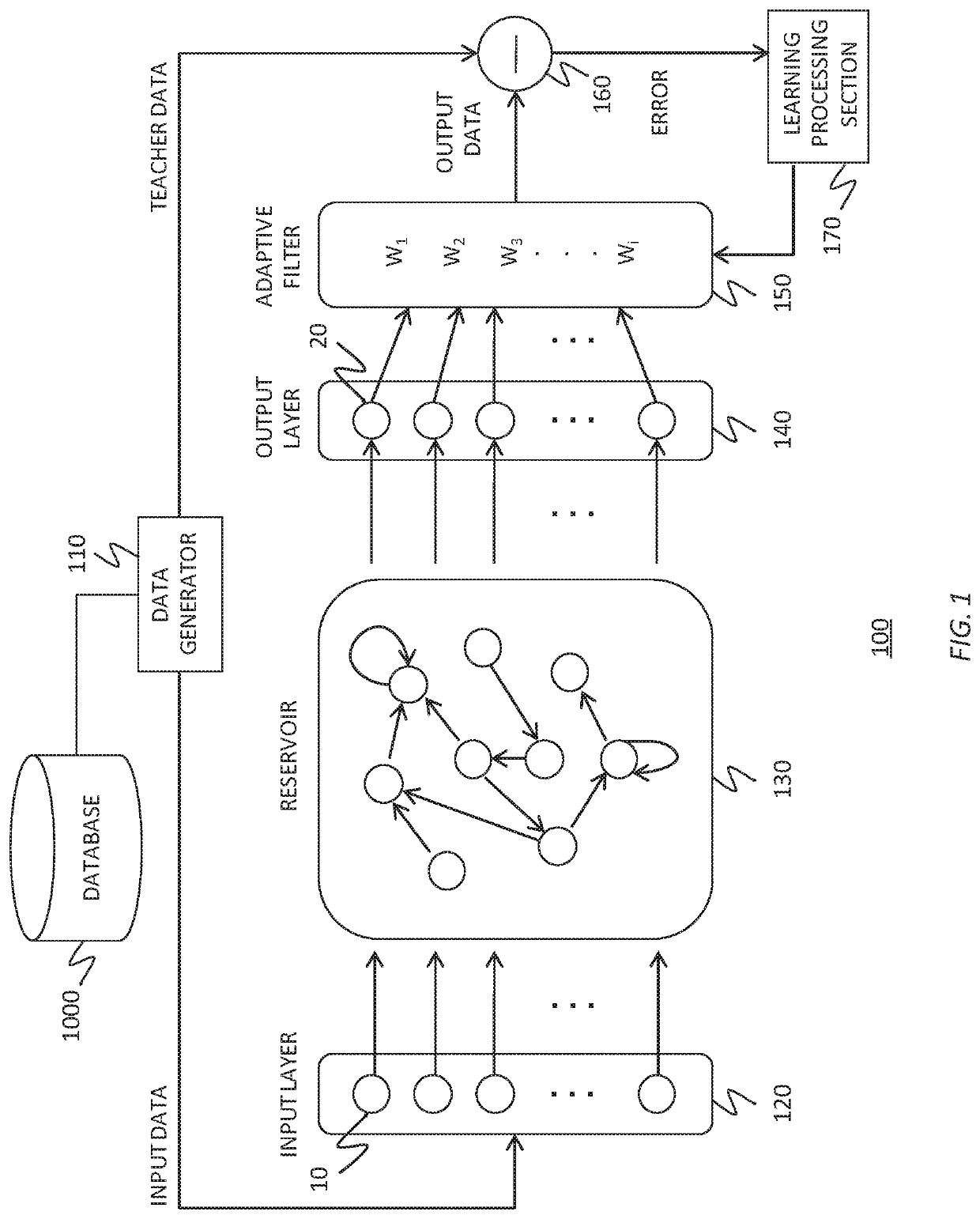
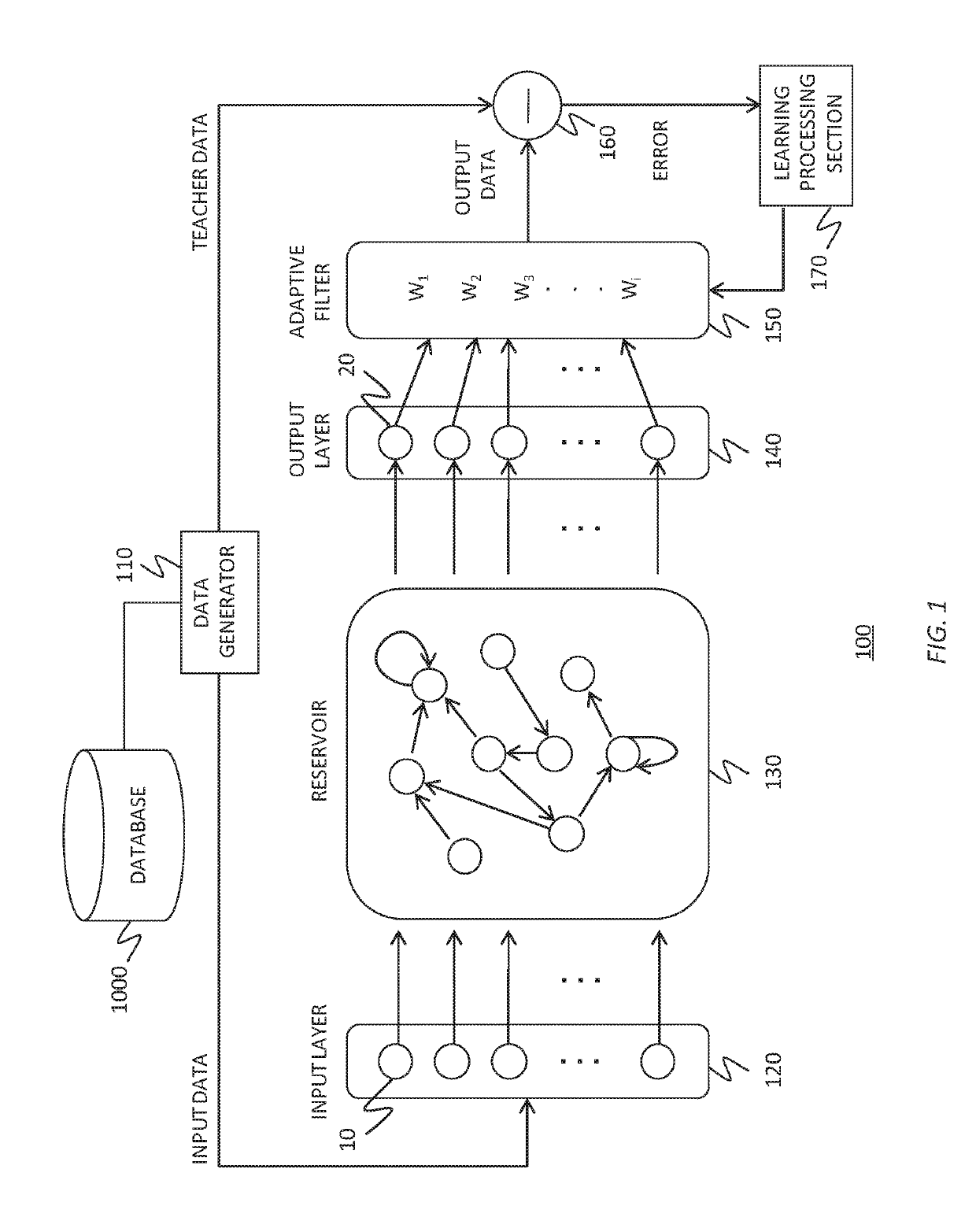
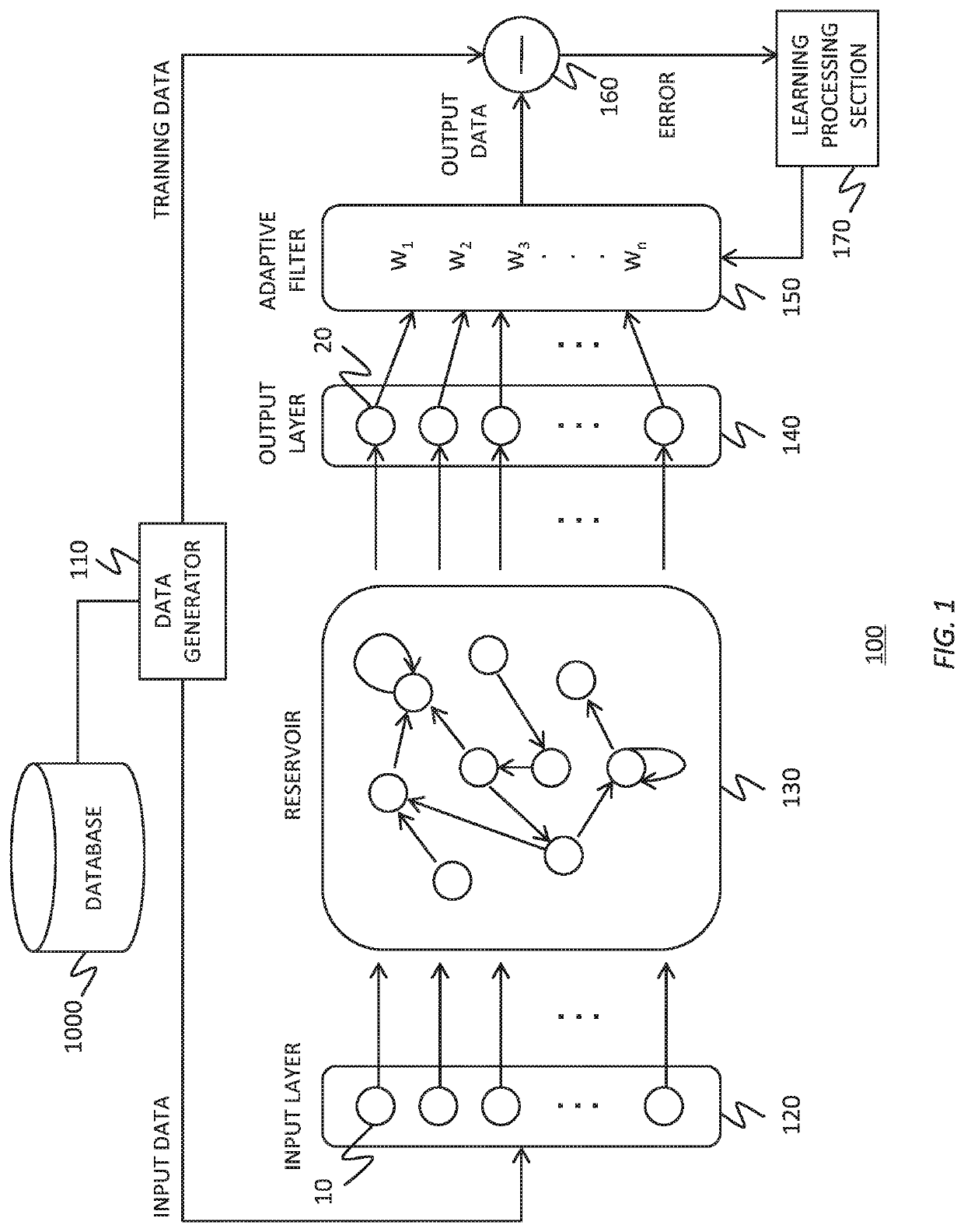
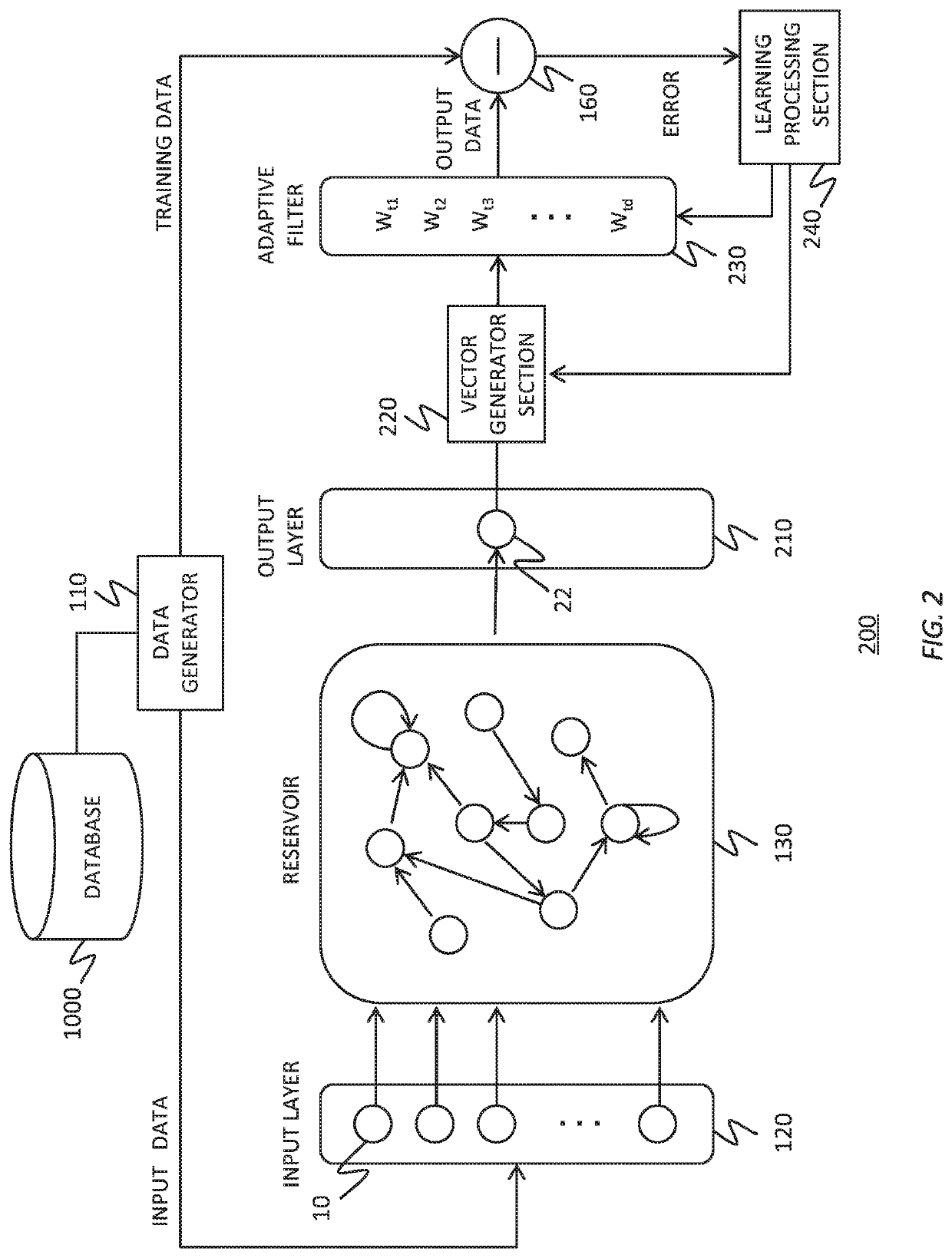
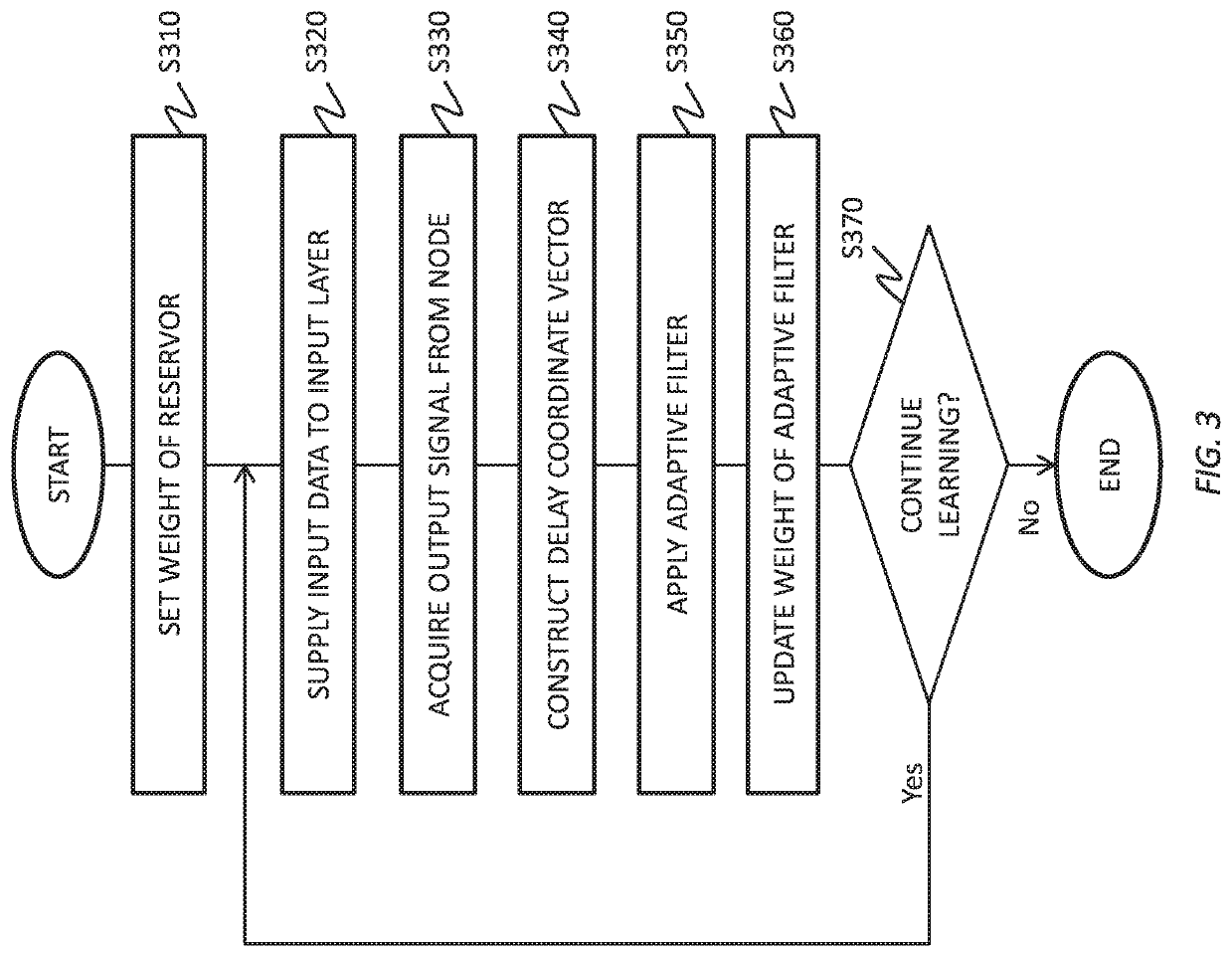
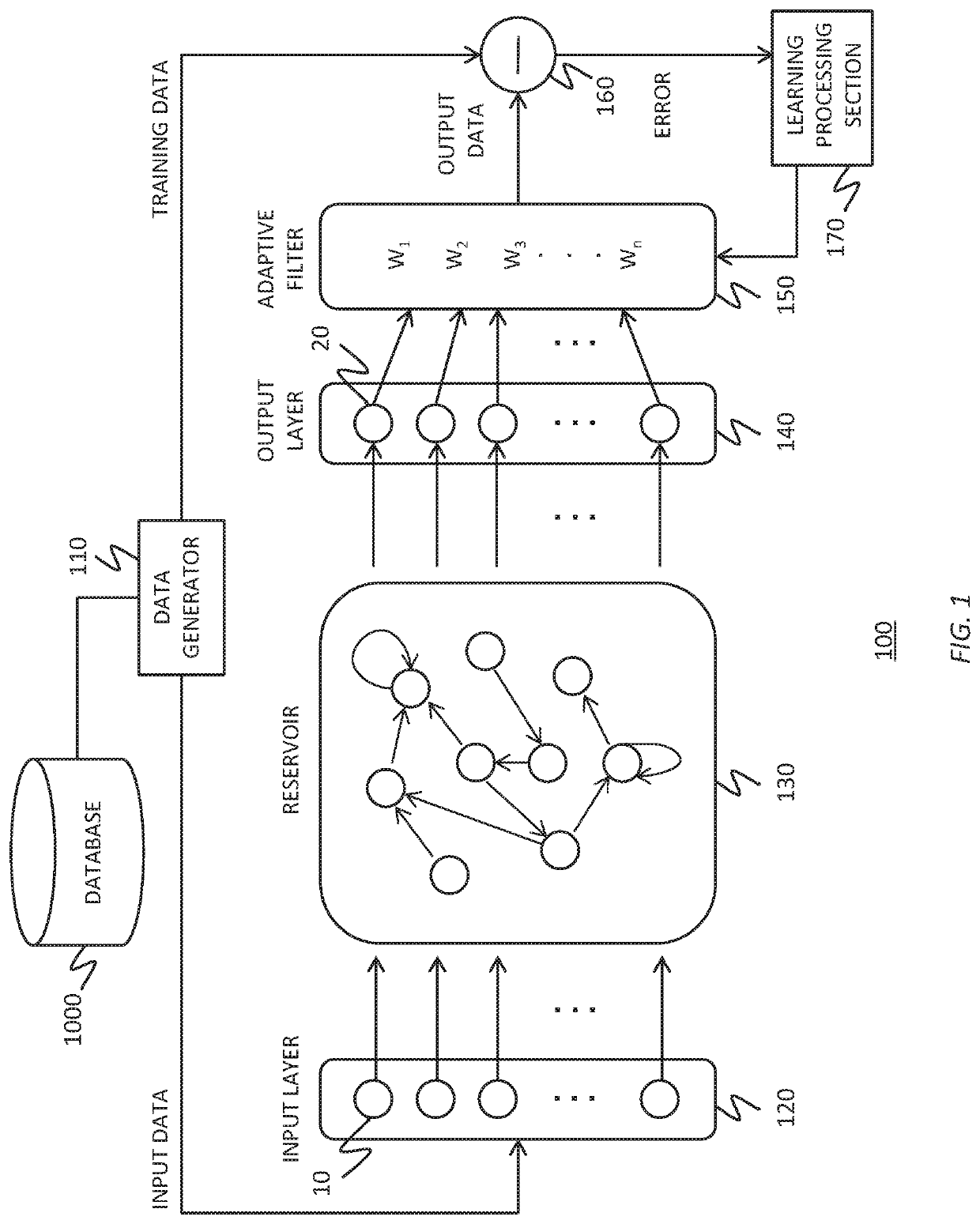
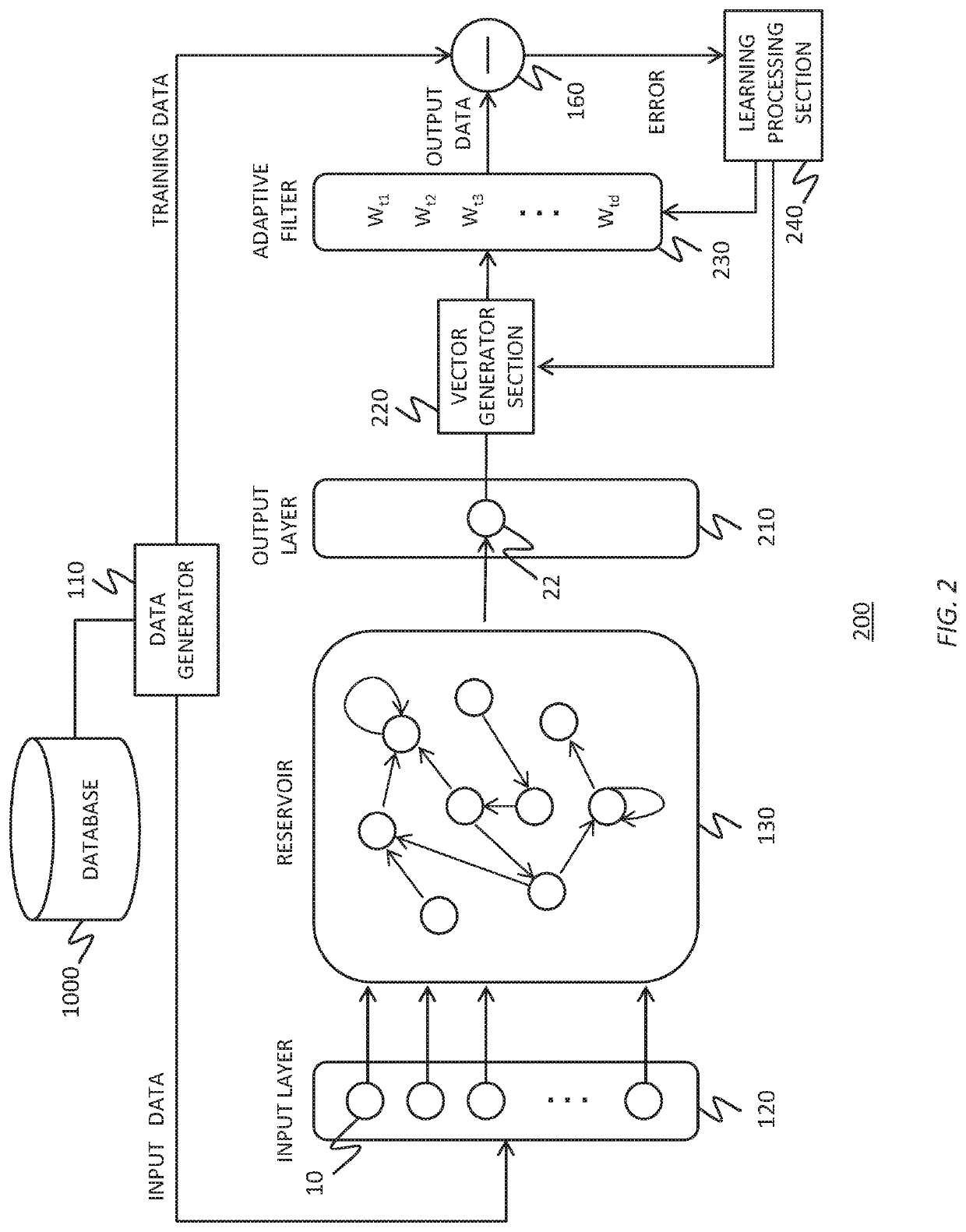
To realize a reservoir computing system easily implemented as hardware, provided is a reservoir computing system including a reservoir operable to output an inherent output signal in response to an input signal. An input node is operable to supply the reservoir with an input signal corresponding to input data, and an output node is operable to output an output value corresponding to an output signal that is output by the reservoir in response to the input data. An adaptive filter is operable to output output data based on a result obtained by weighting a plurality of the output values output from the output node at a plurality of timings with a plurality of weights. Also provided are a learning method and a computer program product.
Owner:IBM CORP
Parallel dual optical feedback semiconductor laser reservoir computing system
ActiveCN110247299AReduce cache sizeLow costLaser detailsLaser output parameters controlFiberPhotovoltaic detectors
The invention discloses a parallel dual optical feedback semiconductor laser reservoir computing system which comprises an input layer, a reservoir layer and an output layer. The input layer includes a driving laser, an arbitrary waveform generator, a modulator, and a coupler I and is used for dividing an input signal into two parts to be input into the reservoir layer. The reservoir layer consists of two response lasers with dual optical feedback loops and is used for generating a rich nonlinear dynamic response. Each optical feedback loop is composed of a circulator, a delay fiber, and an adjustable attenuator. Each response laser has a feedback loop and two couplers and is used for receiving the input signal and outputting a portion of light to the output layer. The output layer includes a pair of photoelectric detectors and a dual-channel digitizer to obtain the response status of the reservoir. The parallel dual optical feedback semiconductor laser reservoir computing system can reduce the number of virtual nodes of the feedback loop receiving the input signal and the period of a mask signal without degrading the performance, thereby reducing the requirement of the reservoir for the cache size of the arbitrary waveform generator.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
Reconfigurable event driven hardware using reservoir computing for monitoring an electronic sensor and waking a processor
ActiveUS9541982B2Low powerGood for conservationEnergy efficient ICTBiological neural network modelsReconfigurable antennaGeneral purpose
The present inventors have recognized that proper utilization of reconfigurable event driven hardware may achieve optimum power conservation in energy constrained environments including a low power general purpose primary processor and one or more electronic sensors. Aspects of neurobiology and neuroscience, for example, may be utilized to provide such reconfigurable event driven hardware, thereby achieving energy-efficient continuous sensing and signature reporting in conjunction with the one or more electronic sensors while the primary processor enters a low power consumption mode. Such hardware is event driven and operates with extremely low energy requirements.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
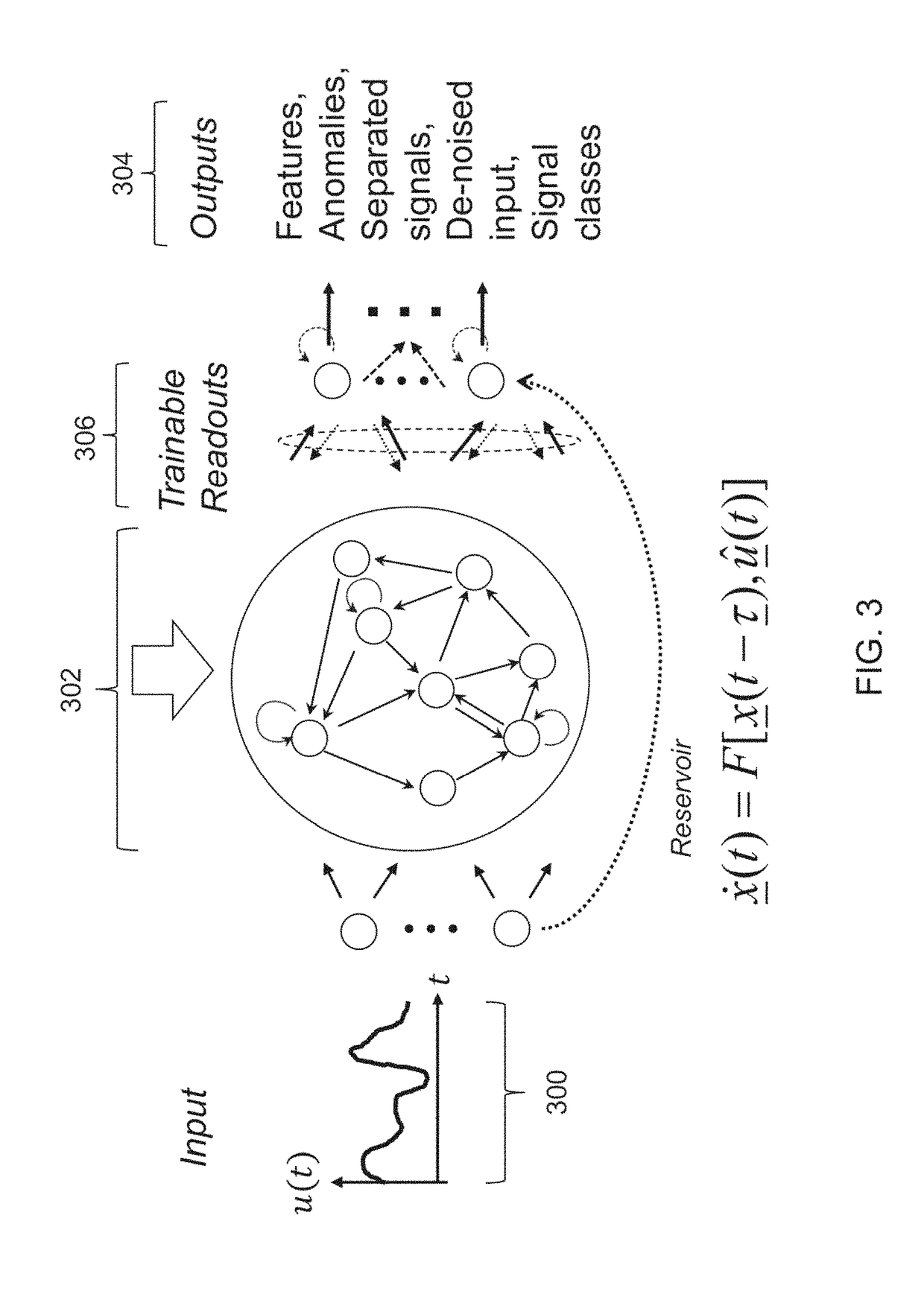
Cognitive architecture for wideband, low-power, real-time signal denoising
Described is a cognitive signal processor that can denoise an input signal that contains a mixture of waveforms over a large bandwidth. Delay-embedded mixture signals are generated from a mixture of input signals. The delay-embedded mixture signals are mapped with a reservoir computer to reservoir states of a dynamical reservoir having output layer weights. The output layer weights are adapted based on short-time linear prediction. Finally, a denoised output of the mixture of input signals is generated.
Owner:HRL LAB
Neuromorphic processor for wideband signal analysis
ActiveUS10162378B1Generating/distributing signalsNeural architecturesFinite impulse responseUnit impulse response
Described is a neuromorphic processor for signal denoising and separation. The neuromorphic processor generates delay-embedded mixture signals from an input mixture of pulses. Using a reservoir computer, the delay-embedded mixture signals are mapped to reservoir states of a dynamical reservoir having output layer weights. The output layer weights are adapted based on short-time linear prediction, and a denoised output of the mixture of input signals us generated. The denoised output is filtered through a set of adaptable finite impulse response (FIR) filters to extract a set of separated narrowband pulses.
Owner:HRL LAB
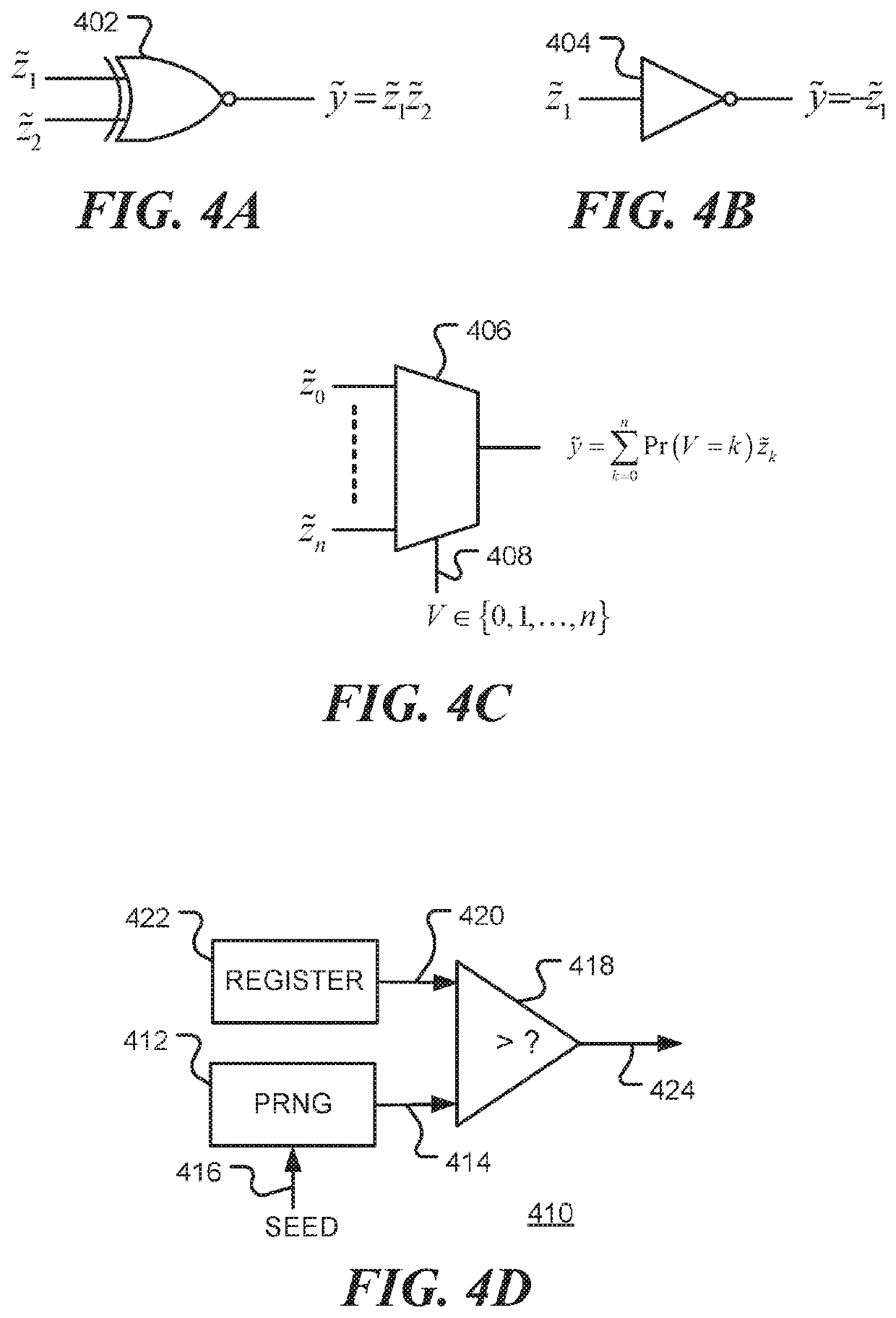
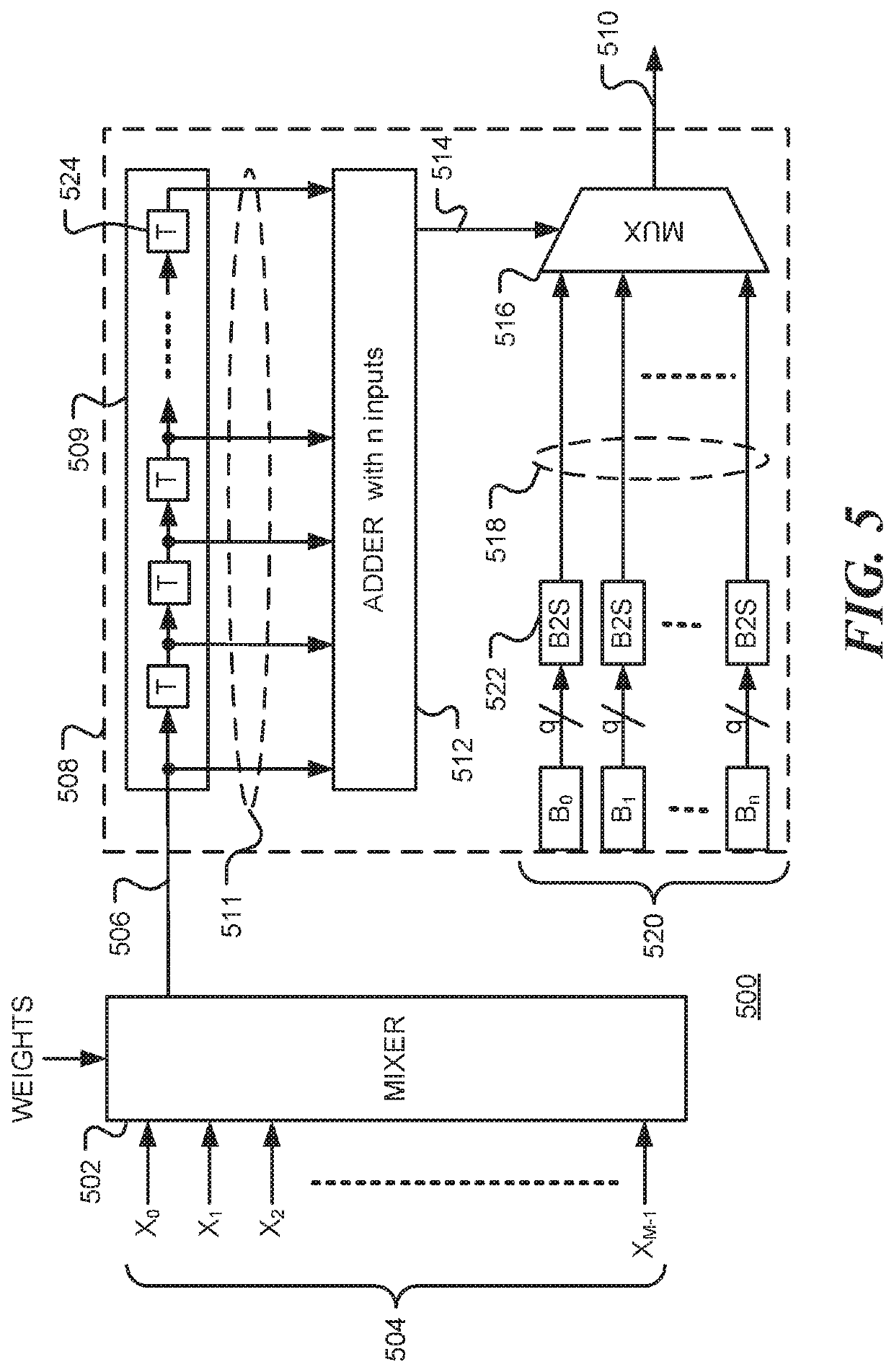
Artificial neural network for reservoir computing using stochastic logic
An artificial neuron includes a signal mixer that combines input signals to provide a first stochastic bit-stream as output and a stochastic activation function circuit configured to receive the first stochastic bit-stream from the signal mixer and to generate therefrom a second stochastic bit-stream. The first stochastic bit-stream is representative of a first output value. In the stochastic activation function circuit, n independent stochastic bit-streams, each representative of the first output value, are summed to provide a selection signal that is provided to a multiplexer to select between n+1 coefficient bit-streams and provide the second stochastic bit-stream. The activation function has a characteristic determined by the proportion of ones in each of the n+1 coefficients bit-streams. One or more artificial neurons may be used in an Artificial Neural Network, such as a Time Delay Reservoir network.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESETNED BY THE SEC OF THE AIR FORCE
Wave propagation computing devices for machine learning
Embodiments of the present technology may be directed to wave propagation computing (WPC) device(s), such as an acoustic wave reservoir computing (AWRC) device, that performs computations by random projection. In some embodiments, the AWRC device is used as part of a machine learning system or as part of a more generic signal analysis system. The AWRC device takes in multiple electrical input signals and delivers multiple output signals. It performs computations on these input signals to generate the output signals. It performs the computations using acoustic (or electro-mechanical) components and techniques, rather than using electronic components (such as CMOS logic gates or MOSFET transistors) as is commonly done in digital reservoirs.
Owner:CYMATICS LAB CORP
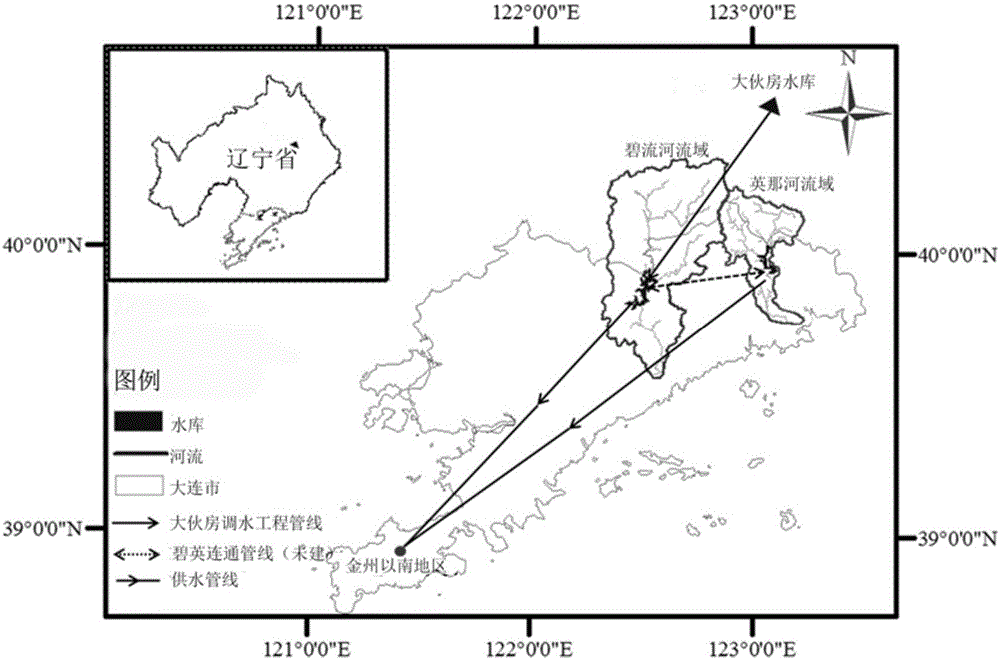
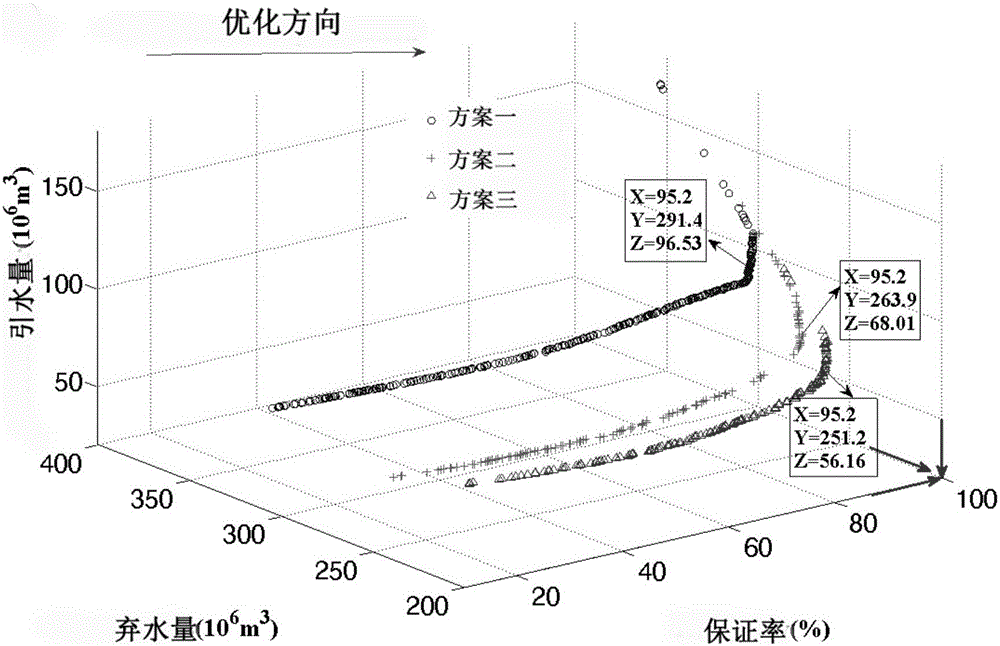
Reservoir connectivity analysis method based on multi-target analysis
InactiveCN105825308AConnectivity Analysis ConvincingFacilitate decision-makingForecastingHydraulic engineering apparatusCompensation effectDecision taking
The present invention discloses a reservoir connectivity analysis method based on multi-target analysis. The method comprises the following steps of S1 determining reservoirs and the basic situations of the reservoirs which are involved in a connecting engineering needing to be demonstrated; S2 designing corresponding connecting schemes according to the conditions, such as the reservoir distribution situation, the reservoir water supply tasks, etc.; S3 applying a multi-target decision method to establish a reservoir multi-target joint scheduling model; S4 adopting a multi-target genetic algorithm epsilon-NSGAII to optimize and obtain the multi-target tradeoff solution sets of the reservoir scheduling under the schemes; S5 utilizing the visualized analysis to compare the multi-target solution sets of the schemes, and evaluating the advantages and disadvantages of the multi-target solution sets of the schemes, thereby giving out a reservoir connecting feasibility analysis result. The reservoir connectivity analysis method based on multi-target analysis of the present invention fully considers a watershed hydrology compensation effect and an inter-reservoir storage capacity compensation effect, has stronger persuasion for the feasibility analysis of the connecting engineering, and facilitates guiding the management decision personnel to make the reasonable decisions about the reservoir connectivity problem.
Owner:INVESTIGATION & DESIGN INST OF WATER RESOURCES & HYDROPOWER LIAONING PROVINCE +1
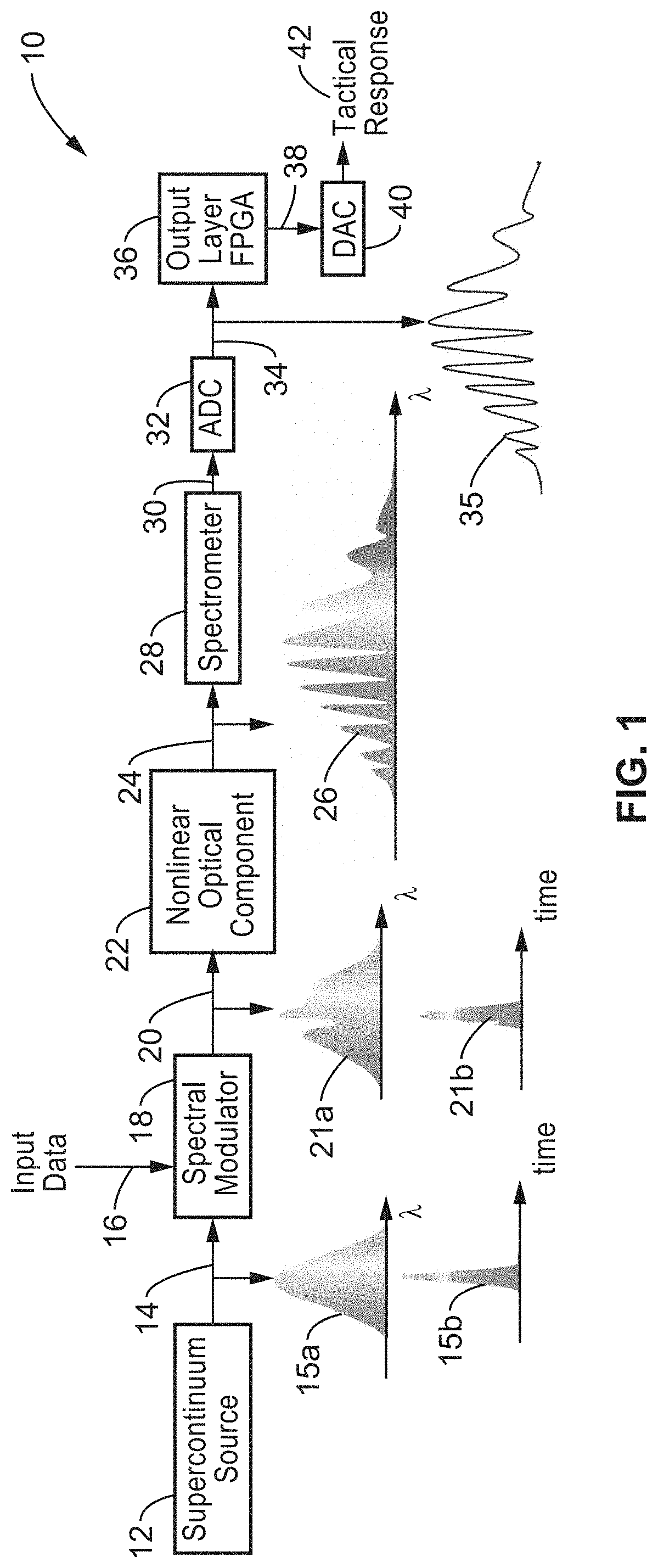
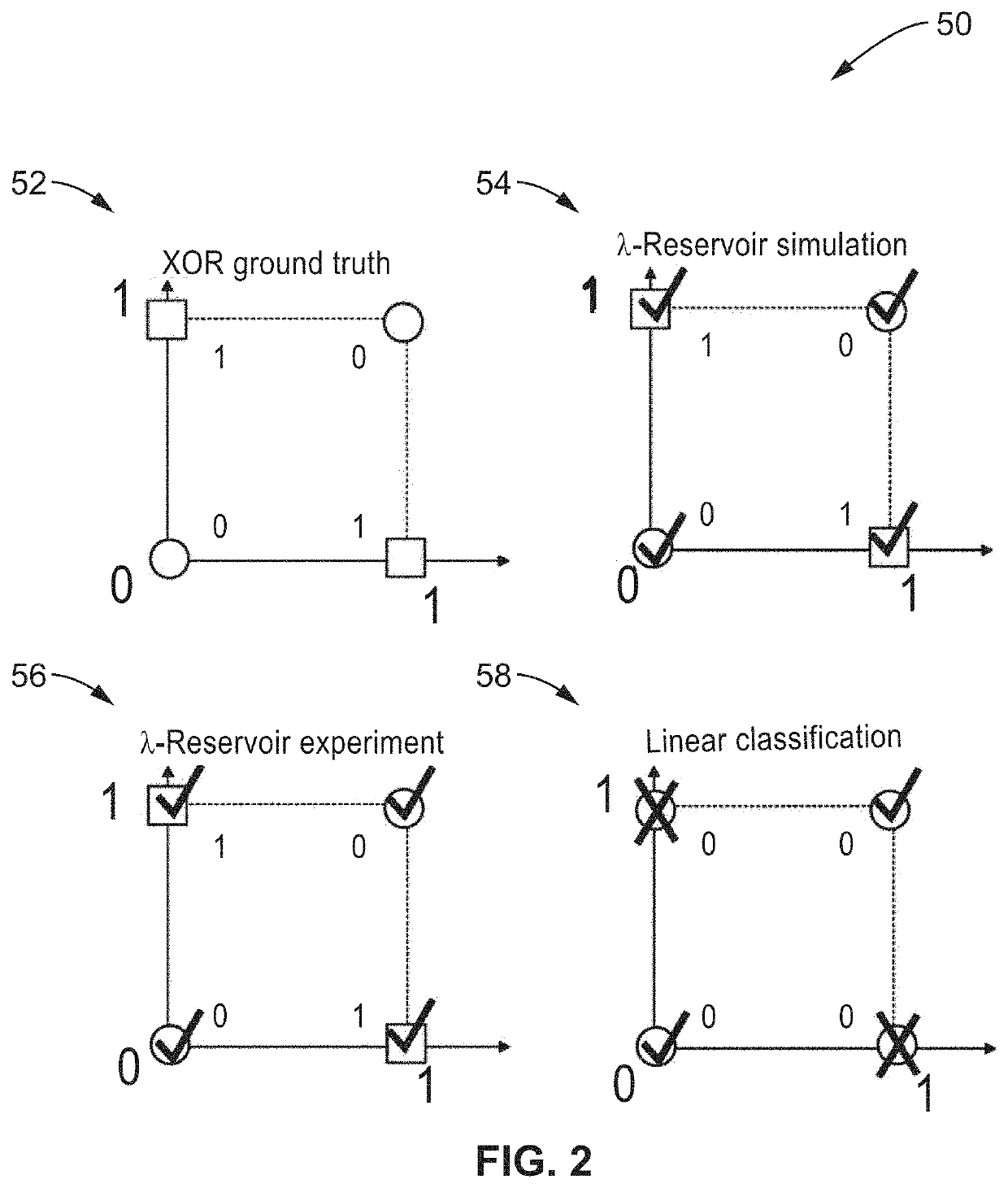
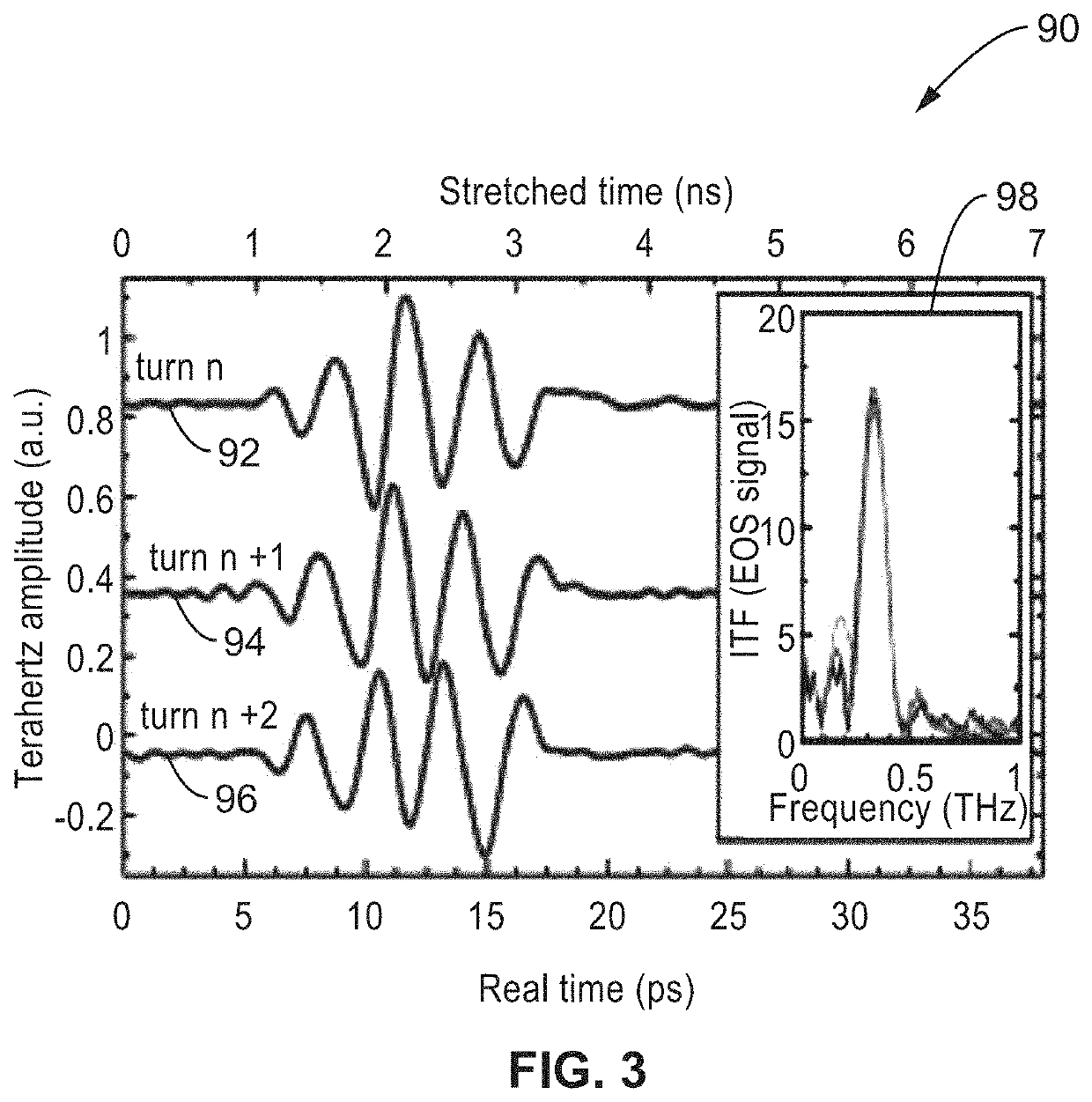
Lambda-reservoir computing
InactiveUS20200311532A1Sacrifice speedSimplifies the necessary hardwareAcquiring/recognising microscopic objectsMachine learningData transformationEngineering
A Lambda reservoir computing system that can readily handle shifts in the distribution of input and output data. Data is modulated onto the spectrum of a broadband optical pulse which is subjected to nonlinear optical effects transforming the data to a higher optical dimensional space. The optical information is converted to electronic signals for processing by an electronic machine learning stage which then generates an output based on the data processed by the learning stage.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
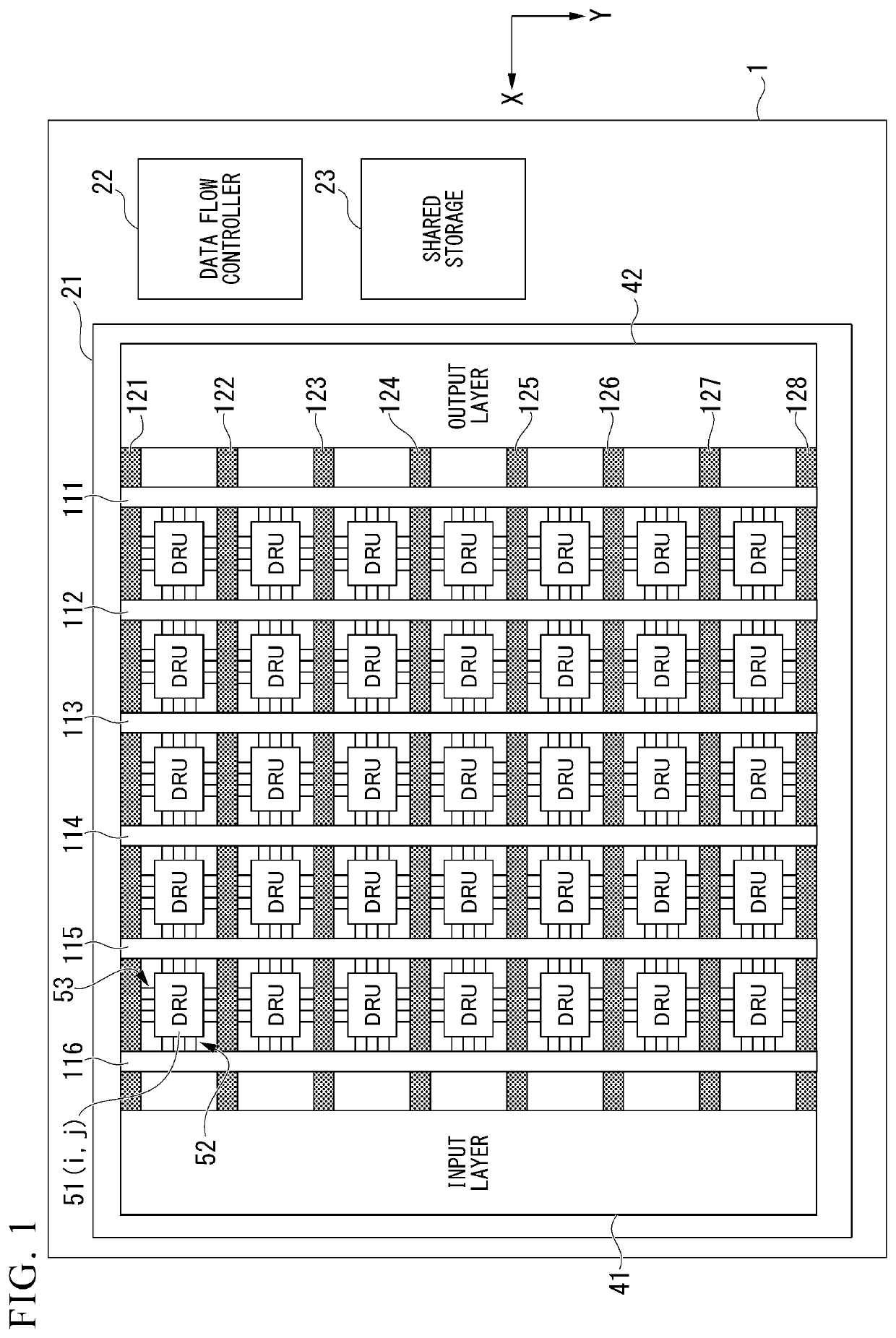
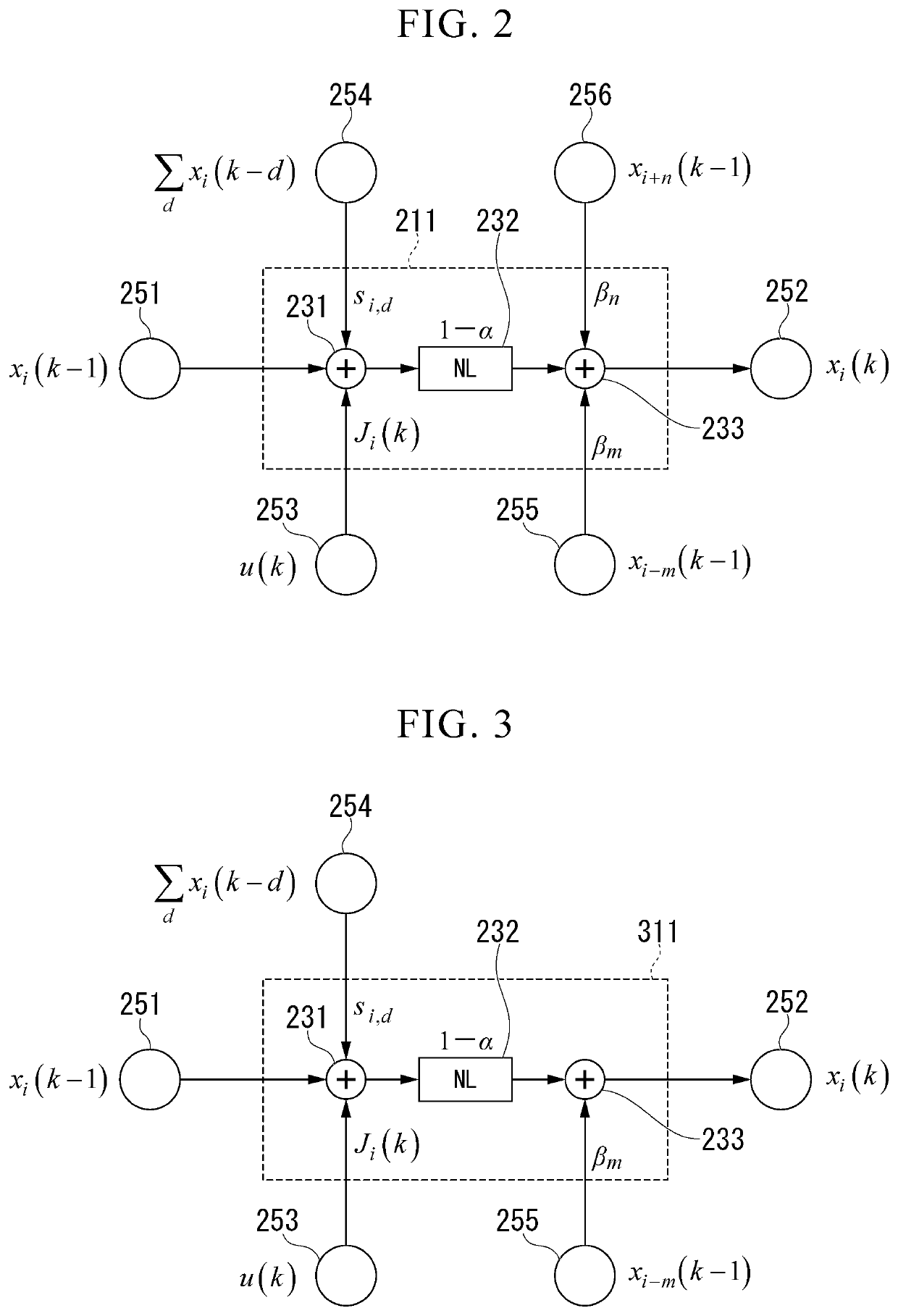
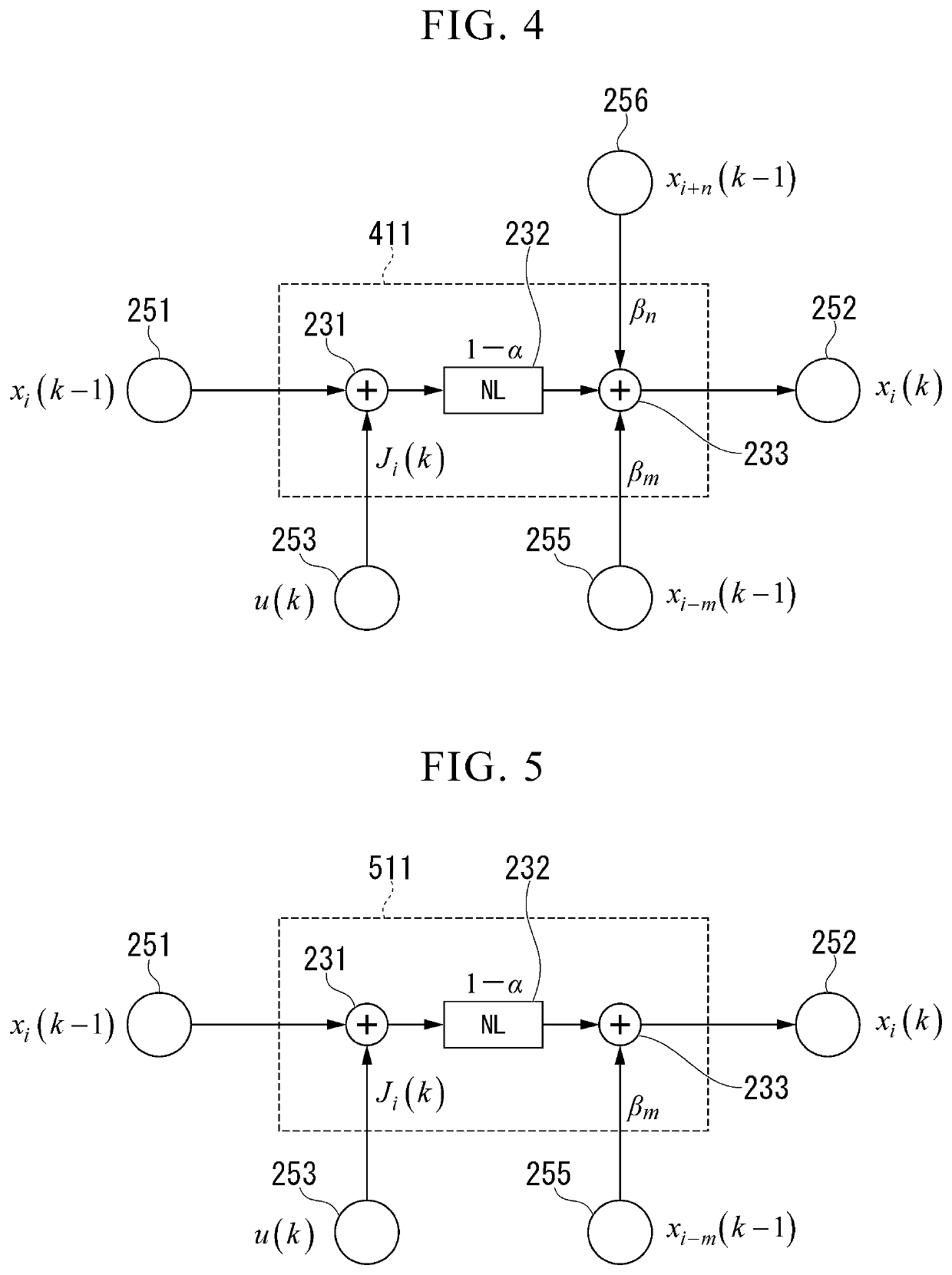
Device and Computer Realizing Calculation of Reservoir Layer of Reservoir Computing
ActiveUS20190164053A1Reduce diversitySimple configurationNeural learning methodsNon-linear opticsReservoir computingDelayed time
A device includes an input unit, a nonlinear converter, and an output unit. The nonlinear converter and the output unit are connected via a connection path having a delay mechanism that realizes a feedback loop giving a delay to a signal. The delay mechanism includes a conversion mechanism that generates a plurality of signals with different delay times using the signal output from the nonlinear converter, generates a new signal by superimposing the plurality of signals, and outputs the generated signal to the output unit.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Reservoir computing system
To realize a reservoir computing system easily implemented as hardware, provided is a reservoir computing system including a reservoir operable to output an inherent output signal in response to an input signal. An input node is operable to supply the reservoir with an input signal corresponding to input data, and an output node is operable to output an output value corresponding to an output signal that is output by the reservoir in response to the input data. An adaptive filter is operable to output output data based on a result obtained by weighting a plurality of the output values output from the output node at a plurality of timings with a plurality of weights. Also provided are a learning method and a computer program product.
Owner:IBM CORP
Reservoir computing system
To realize a reservoir computing system easily implemented as hardware, provided is a reservoir computing system including a reservoir operable to output an inherent output signal in response to an input signal. An input node is operable to supply the reservoir with an input signal corresponding to input data, and an output node is operable to output an output value corresponding to an output signal that is output by the reservoir in response to the input data. An adaptive filter is operable to output output data based on a result obtained by weighting a plurality of the output values output from the output node at a plurality of timings with a plurality of weights. Also provided are a learning method and a computer program product.
Owner:IBM CORP
Implementation model of self-organizing reservoir based on lorentzian nonlinearity
ActiveUS11295198B2Neural architecturesNeural learning methodsComputational physicsReservoir computing
To realize a reservoir computing system in which the reservoir is configured to be suitable for various learning targets, provided is a self-organizing reservoir computing system, including an input layer that outputs an input layer signal corresponding to input data; a reservoir layer that includes therein a nonlinear signal path using physical resonance phenomena and is operable to output an inherent reservoir layer signal in response to the input layer signal; and an output layer that outputs output data corresponding to the reservoir layer signal. Also provided is a self-organizing method.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Implementation model of self-organizing reservoir based on lorentzian nonlinearity
To realize a reservoir computing system in which the reservoir is configured to be suitable for various learning targets, provided is a self-organizing reservoir computing system, including an input layer that outputs an input layer signal corresponding to input data; a reservoir layer that includes therein a nonlinear signal path using physical resonance phenomena and is operable to output an inherent reservoir layer signal in response to the input layer signal; and an output layer that outputs output data corresponding to the reservoir layer signal. Also provided is a self-organizing method.
Owner:IBM CORP
Laser apparatus and reservoir computing system
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Cognitive denoising of nonstationary signals using time varying reservoir computer
ActiveUS10712425B1Reduce computationReduce hardware complexityMathematical modelsNeural architecturesEngineeringAcoustics
Described is a system for signal denoising using a cognitive signal processor having a time-varying reservoir. The system receives a noisy input signal of a time-series of data points from a mixture of waveform signals. The noisy input signal is linearly mapped into the time-varying reservoir. A high-dimensional state-space representation of the mixture of waveform signals is generated by combining the noisy input signal with a plurality of reservoir states. The system then generates a denoised signal corresponding to the noisy input signal.
Owner:HRL LAB
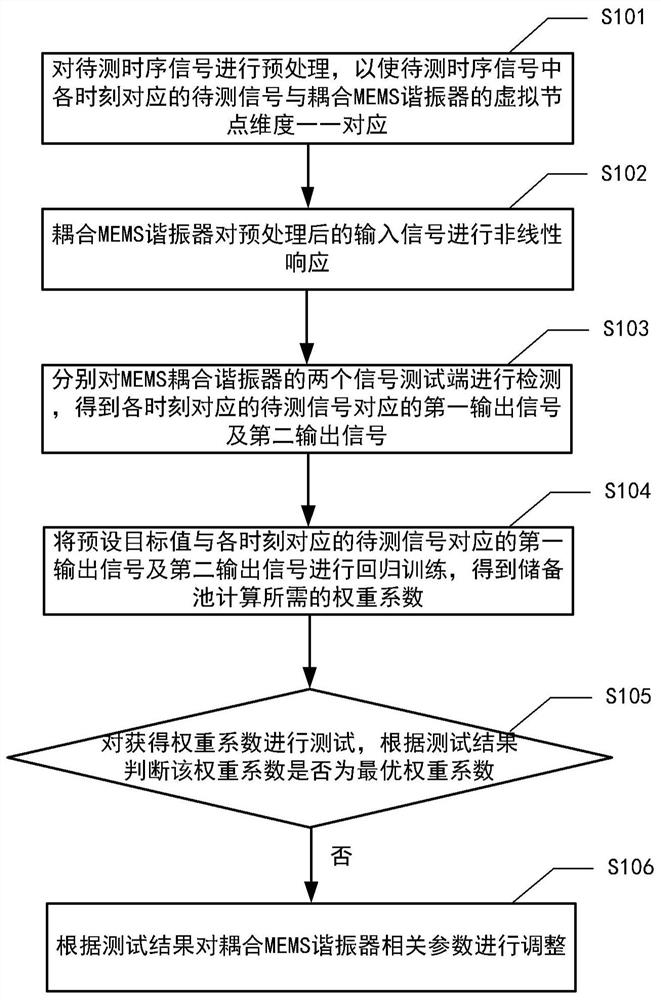
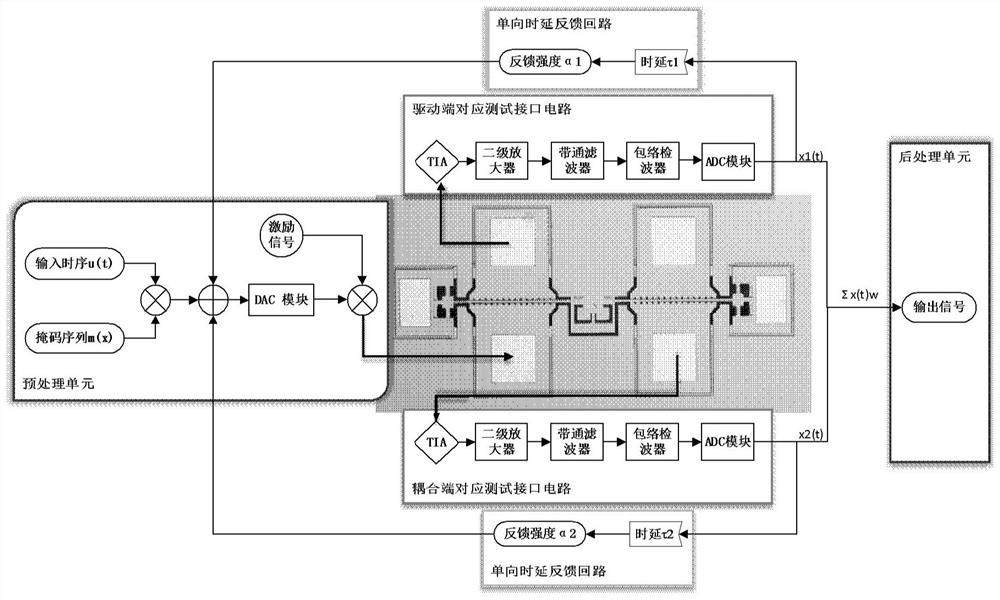
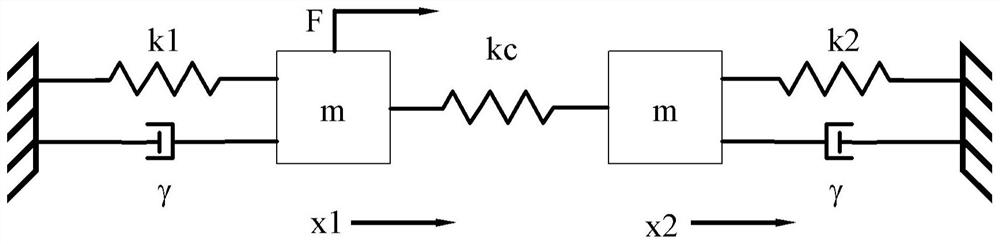
Reservoir computing hardware implementation method and device based on coupled MEMS resonator
PendingCN112163358AImprove dynamic mapping capabilitiesImprove classification recognition abilityDesign optimisation/simulationCAD numerical modellingComputer hardwareTime delays
The invention discloses a reservoir computing hardware implementation method and device based on a coupled MEMS resonator, and the method comprises the steps: carrying out the preprocessing of a to-be-detected time sequence signal, so as to enable the to-be-detected time sequence signal to correspond to a virtual node of the coupled MEMS resonator; designing a nonlinear vibration equation of the coupled MEMS resonator, and regulating and controlling the coupled MEMS resonator to a preset nonlinear working point according to the equation; respectively detecting two signal test ends of the MEMScoupled resonator to obtain a first output signal and a second output signal corresponding to the to-be-tested signal corresponding to each moment, and feeding back the output signal corresponding tothe to-be-tested signal at the current moment to the virtual node corresponding to the next moment through a bidirectional time delay feedback loop; and performing regression training on the preset target value and the first output signal and the second output signal corresponding to the to-be-measured signal corresponding to each moment to obtain a weight coefficient required by calculation of the storage pool. According to the method, the data mapping dimension and the memory performance are enhanced, and richer nonlinear characteristics are provided for reserve pool calculation.
Owner:AEROSPACE INFORMATION RES INST CAS
A new energy power station management platform
ActiveCN107968482BRealize collection and displayAchieve transparencyCircuit arrangementsInformation technology support systemRelational databaseExchange network
The invention discloses a new energy power station management platform, which includes a host storage layer that provides computing, storage and disaster recovery resources; and completes on-site new energy power station operation data access and supports wireless and wired data transmission , the network communication layer for switching; and, the supporting software layer that schedules and expands the computing and storage resources of the host storage layer through virtualization software; and, adopts traditional relational databases and various NoSQL databases according to different data characteristics to achieve Persistent storage of various business subject data, the data resource layer used; and, real-time transmission of new energy electric field data to managers, providing online control and station management, using data resource layer data through data pattern recognition and model training algorithms The application system layer for fault prediction and diagnosis; and, the user interaction layer for building user interaction channels for different application scenarios.
Owner:CRRC WIND POWER(SHANDONG) CO LTD
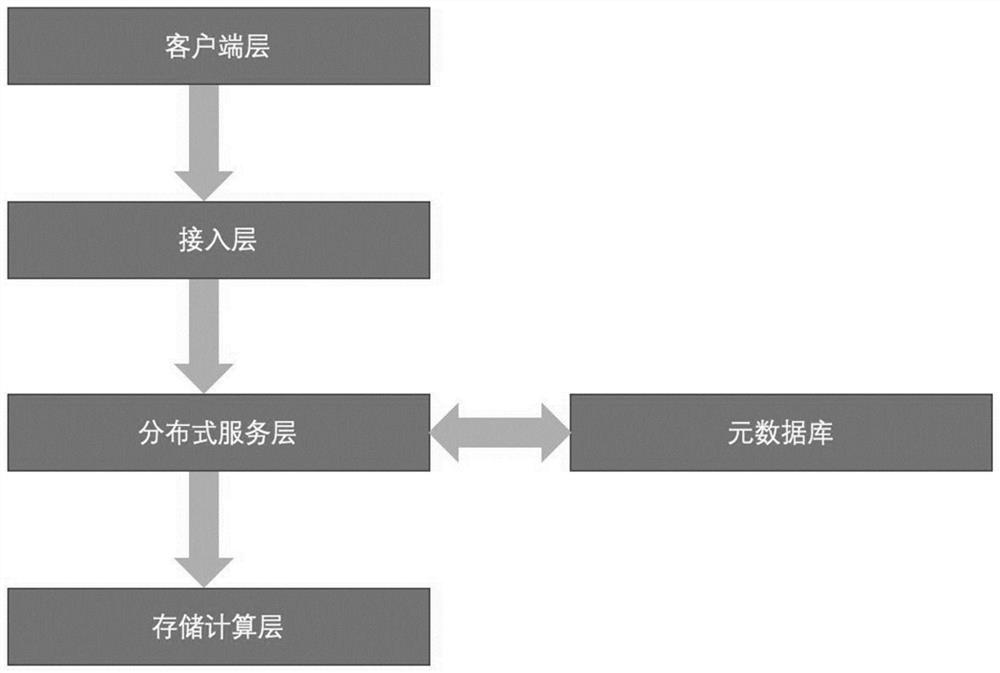
Virtual database system and query method
InactiveCN112163029ADon't care about how to useRealize the use effectDatabase management systemsDatabase distribution/replicationDatabase queryTheoretical computer science
The invention discloses a virtual database system and a query method, and the system comprises a client layer which is used for submitting an SQL code to achieve a business demand, an access layer which receives and authenticates the SQL code, a distributed service layer which analyzes the SQL code, a storage layer calculation layer which executes an SQL code request, and a meta-database which isused for storing actual physical data. The client layer is connected with the access layer, the access layer is connected with the distributed service layer, and the distributed service layer is connected with the reservoir calculation layer and the meta-database. According to the invention, the bottom layer use of the physical database is shielded, the heterogeneous cross-database query and mixedcalculation can be carried out as long as the unified SQL is written, developers can concentrate on the business logic development, and various bottom layer use methods of the database do not need tobe concerned.
Owner:浙江百应科技有限公司
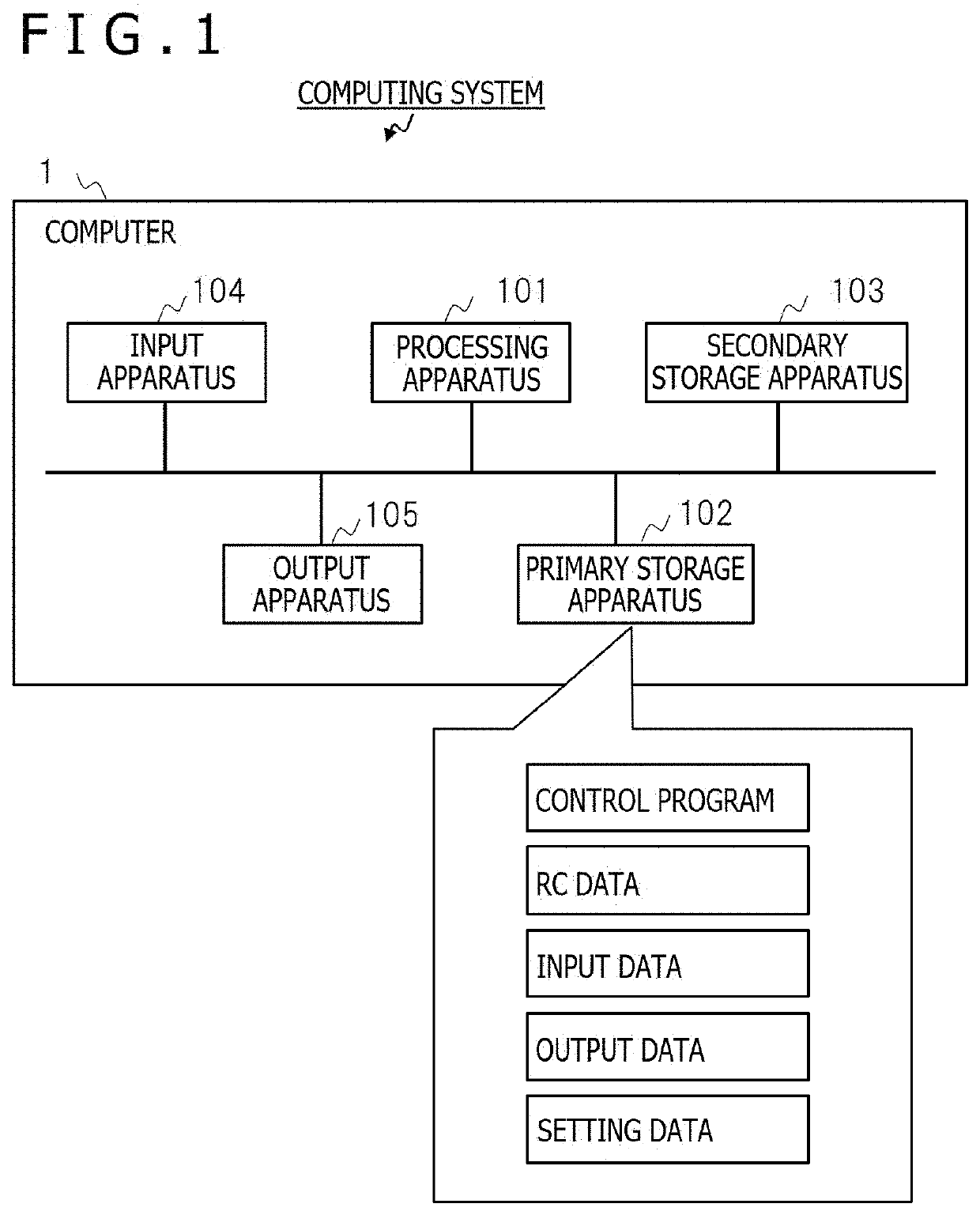
Computing system and method
ActiveUS20200387775A1Improve computing powerSignal identificationNeural architecturesPhysical realisationActivation functionAlgorithm
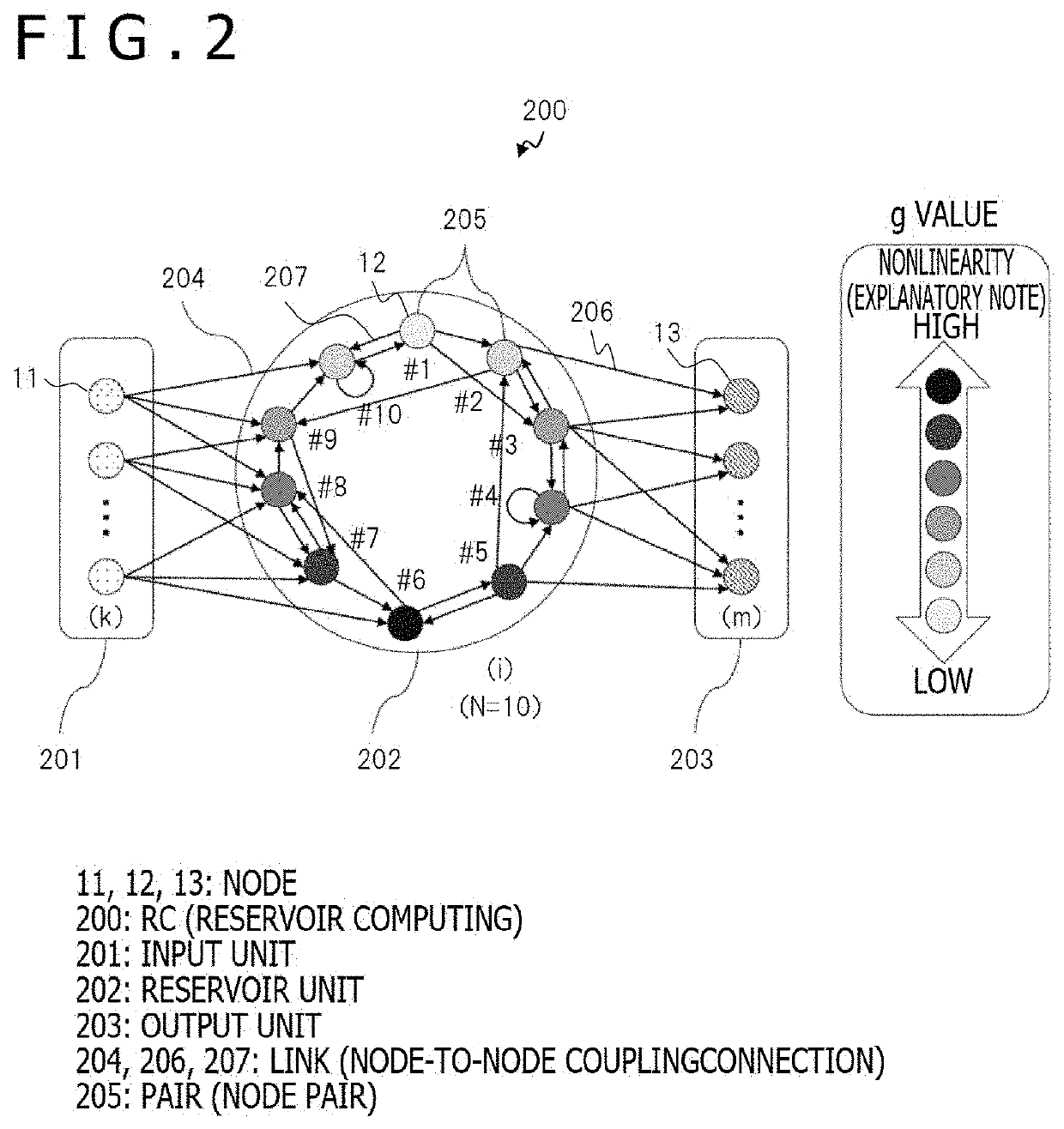
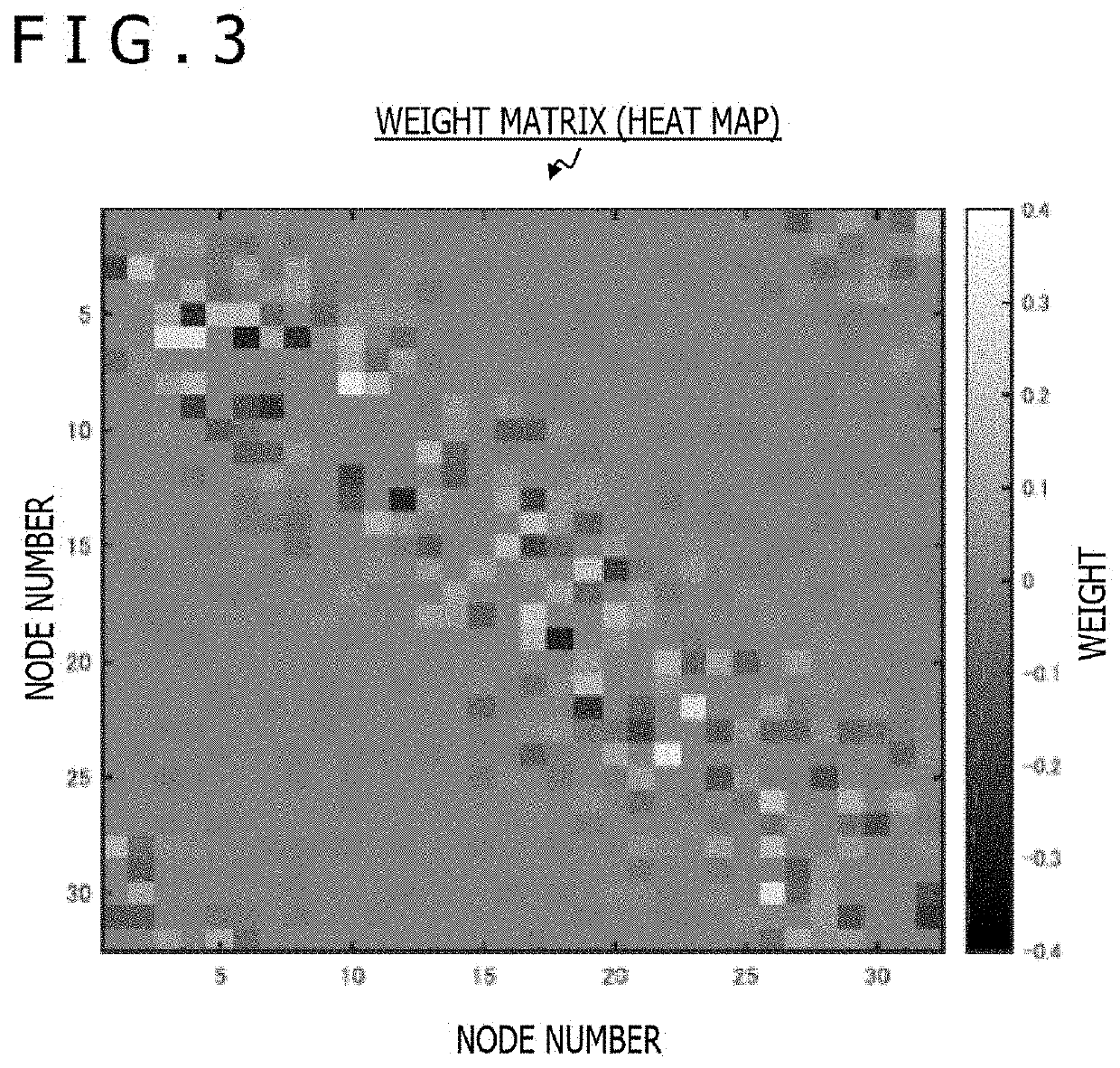
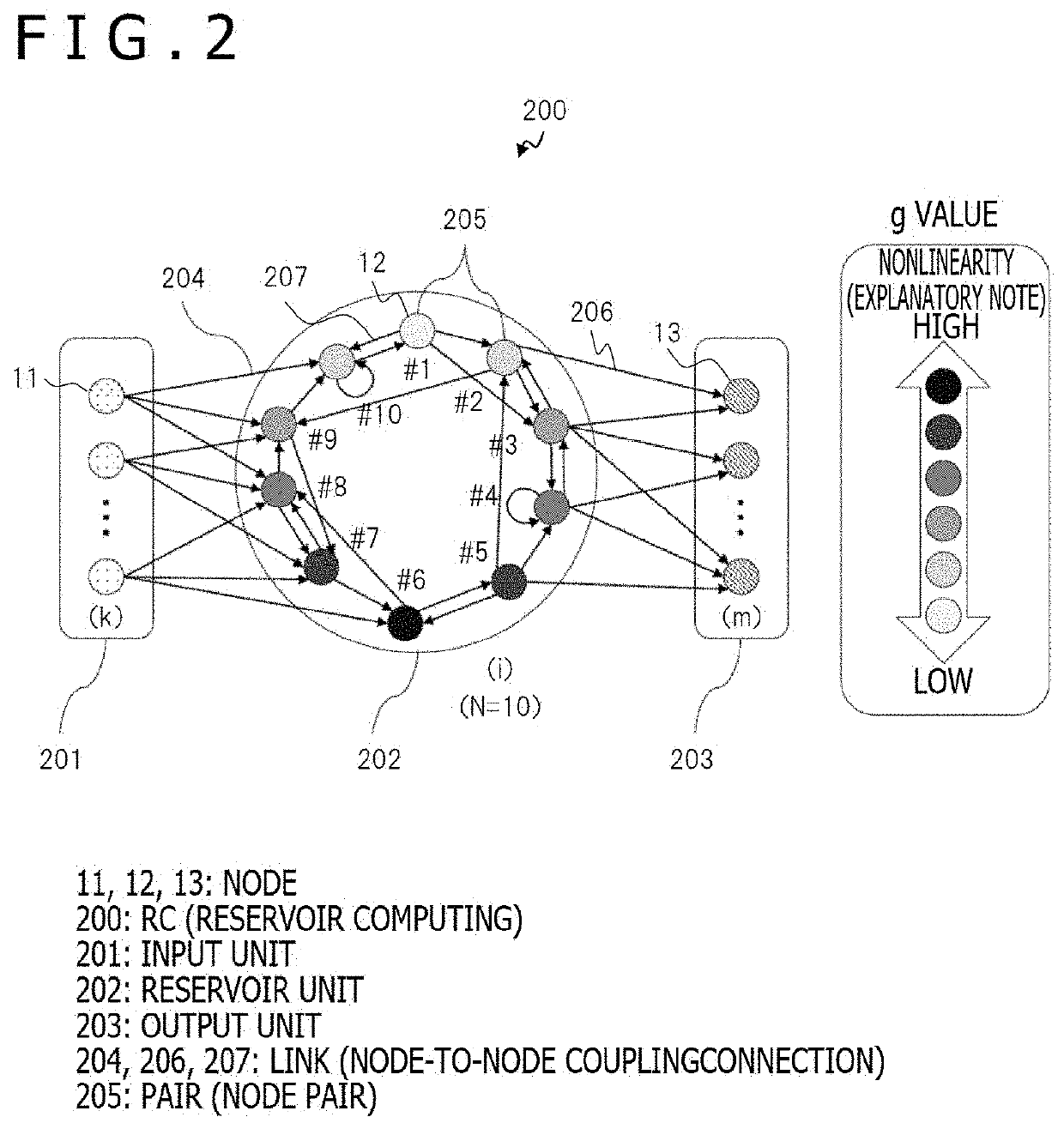
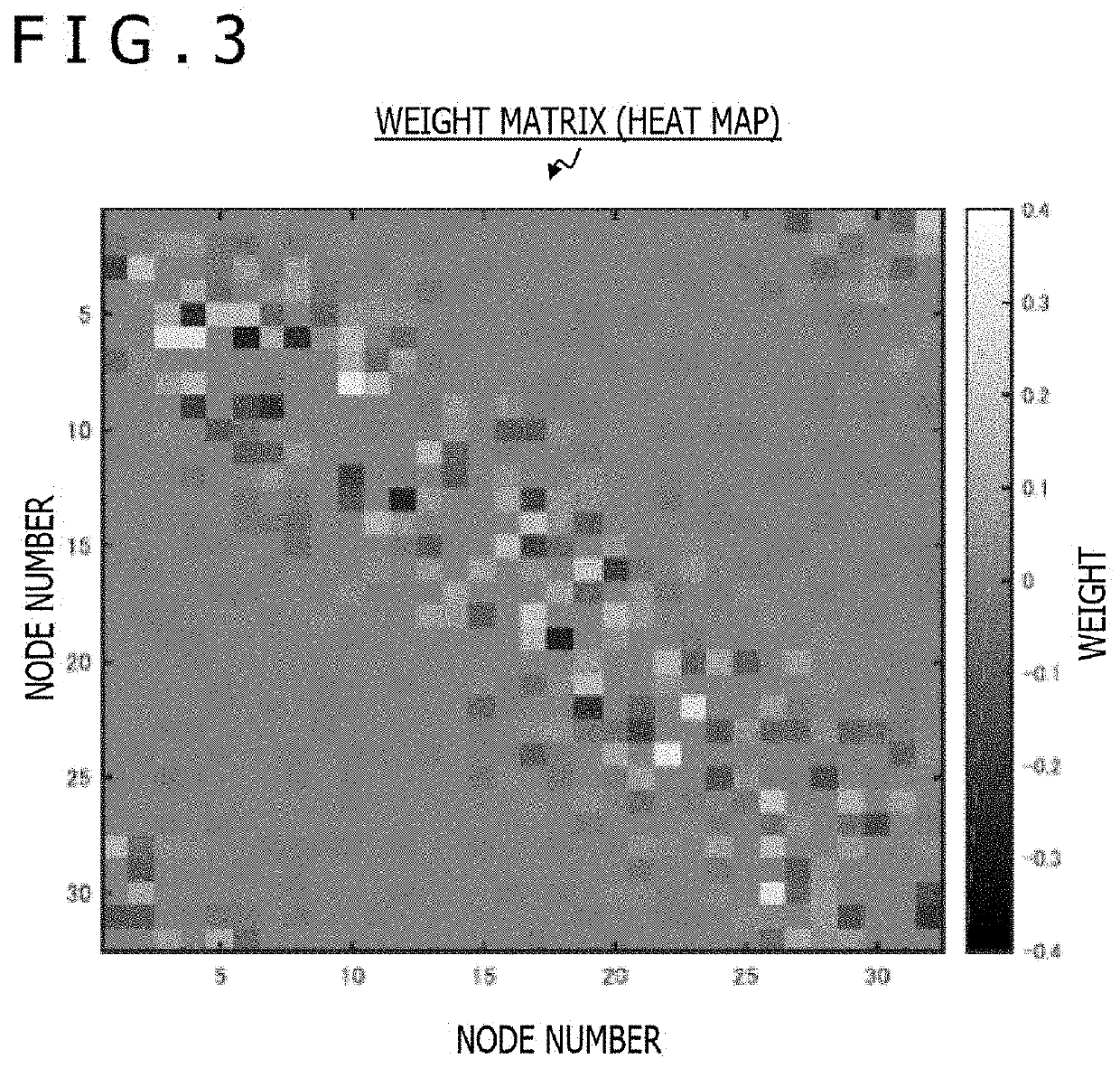
A technology that can enhance the computing performance of a computing system using reservoir computing (RC), includes a computing system which performs computation using a recurrent neural network (RNN) including an input unit, a reservoir unit, and an output unit. The reservoir unit includes a plurality of nodes circularly connected to each other. The circular connection has a weight matrix for determining a weight between the nodes of the plurality of nodes, in which a weight between the nodes closely arranged on the circle is larger than a weight between the nodes arranged away from each other on the circle. The plurality of nodes each have a g value that is a parameter for designating nonlinearity of an activation function of each of the nodes, and that is set so as to periodically change in a direction on the circle.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Computing system and method
ActiveUS11423286B2Improve computing powerSignal identificationNeural architecturesPhysical realisationActivation functionAlgorithm
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Training of photonic reservoir computing systems
A photonics reservoir computing system is described. The system is configured for propagating at least one optical signal so as to create resulting radiation signals in the output channels. The photonics reservoir computing system further comprises weighting elements for weighting signals from the output channels, and at least one optical detector for optically detecting signals from the output channels. The system is adapted for estimating signals from the output channels through an output of the optical detector.
Owner:UNIV GENT +1
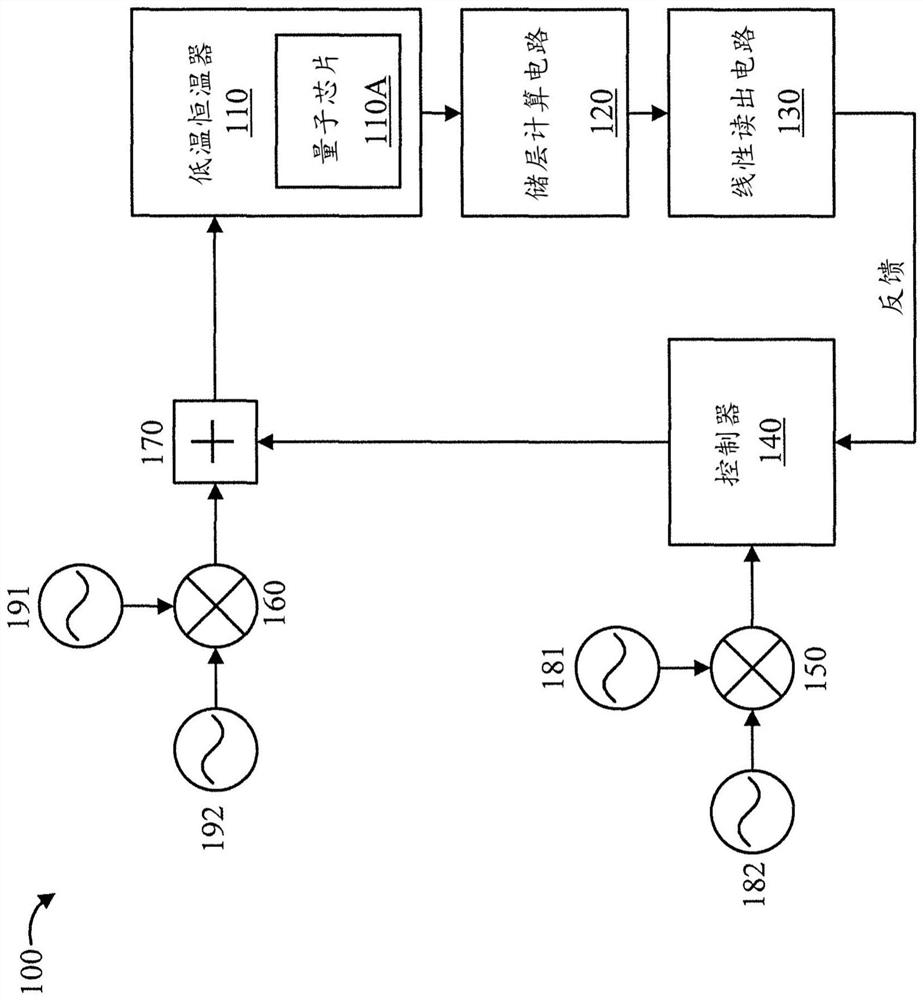
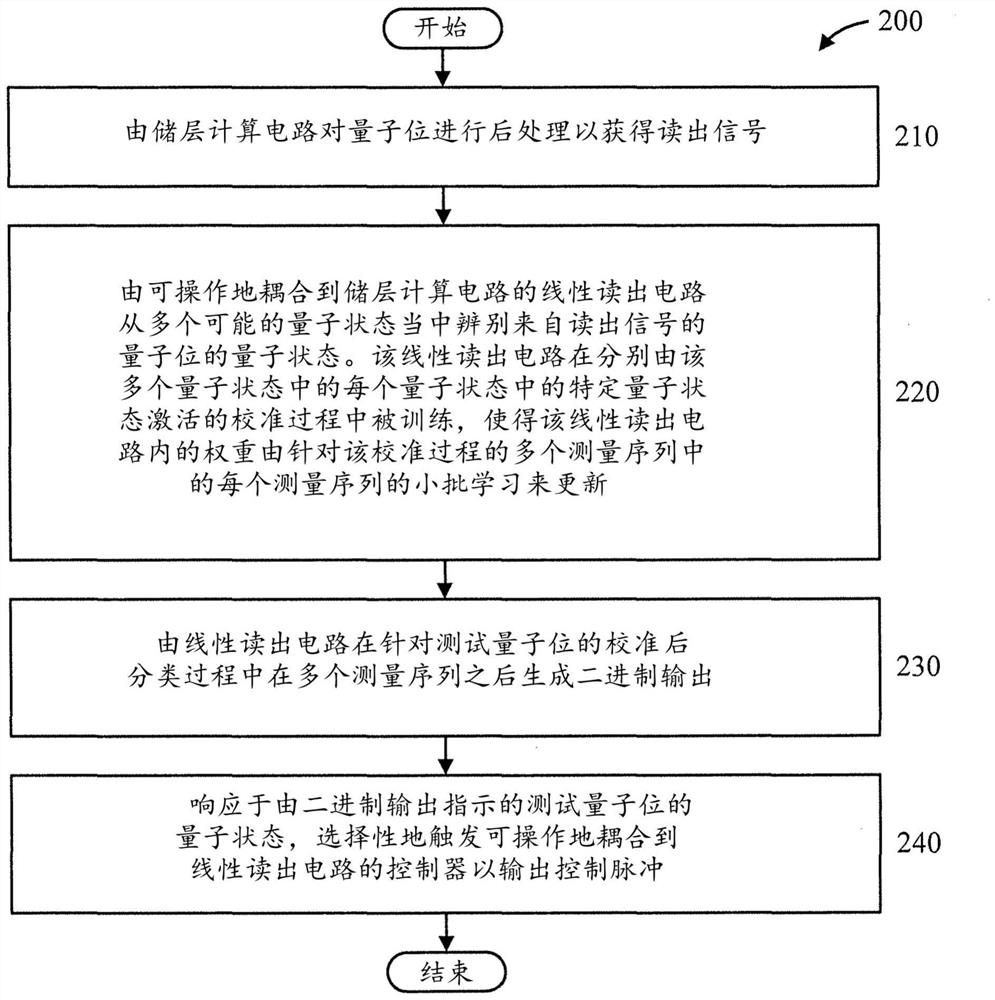
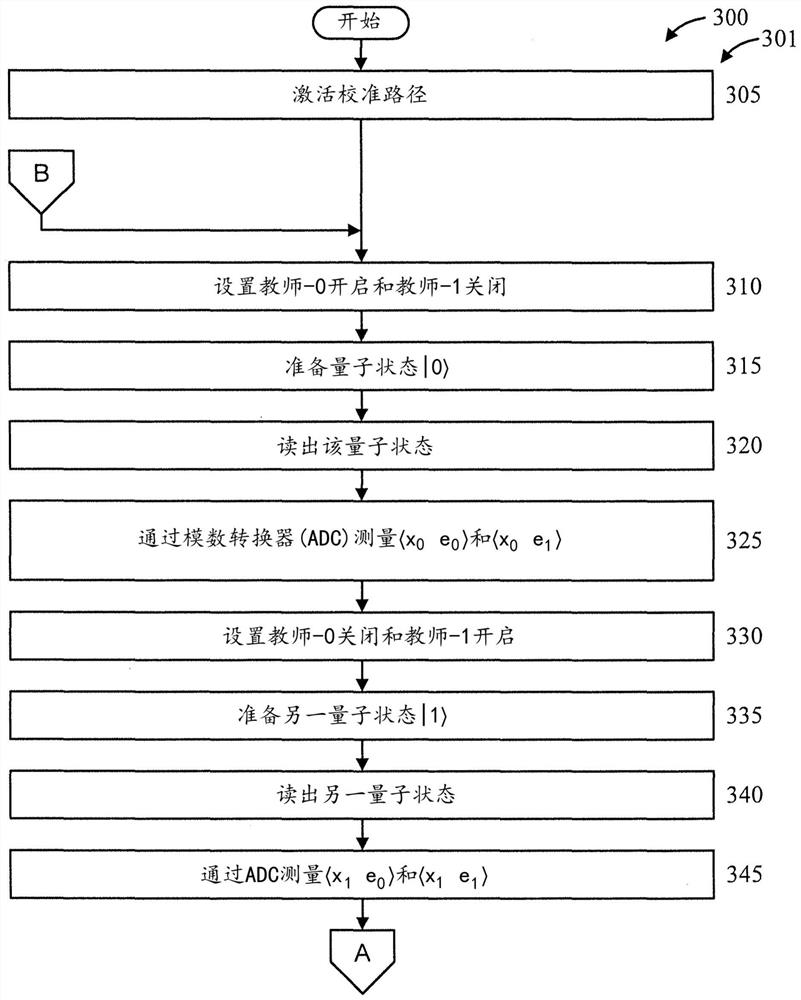
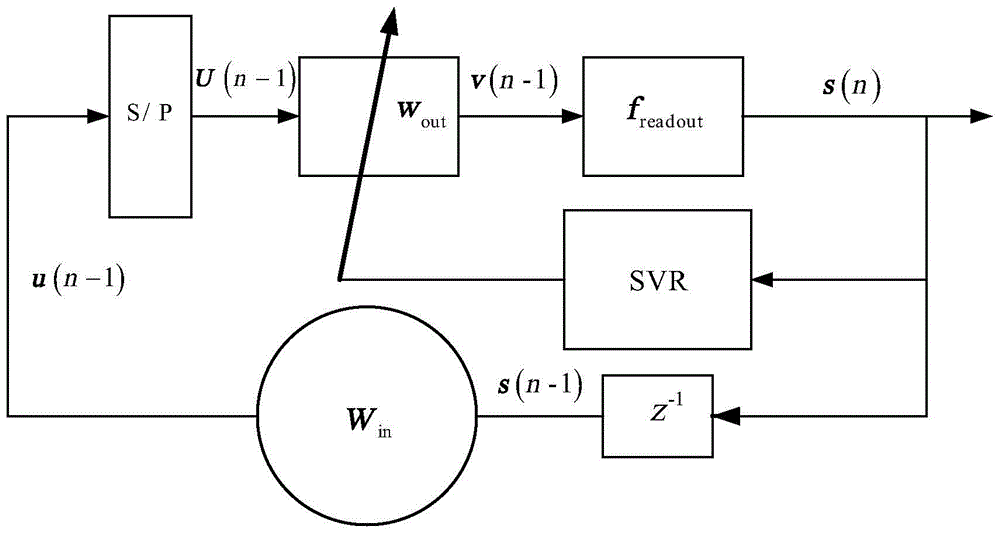
Quantum state classifier using reservoir computation
PendingCN114341893AQuantum computersCharacter and pattern recognitionComputational physicsReservoir computing
A quantum state classifier comprises: a reservoir computing circuit for post-processing a quantum bit to obtain a readout signal; and a readout circuit, coupled to the reservoir computing circuit, for discriminating a quantum state of a qubit from the readout signal from among a plurality of possible quantum states. The readout circuitry is trained in a calibration process activated by a particular quantum state of each of the plurality of quantum states, respectively, such that the weights within the linear readout circuitry are updated by a small batch learning of each of the plurality of measurement sequences for the calibration process. The readout circuit generates a binary output after the plurality of measurement sequences during a post-calibration classification process for the test qubits. The quantum state classifier also includes a controller coupled to the readout circuitry, selectively actuatable to output a control pulse in response to a quantum state of the test qubit indicated by the binary output.
Owner:IBM CORP
Blind detection method of multi-valued communication signals in complex domain based on reserve pool calculation
ActiveCN103581080BError preventionTransmitter/receiver shaping networksQR decompositionSignal subspace
The invention discloses a complex number field multiple-valued communication signal blind detection method based on reservoir computing (RC). According to the technical scheme, a reservoir network suitable for signal direct blind detection is established and does not abide by the RC weight array random generation mechanism, a reservoir matrix is designed through QR decomposition from the angle of receiving terminal signal subspace, a support vector regression method is used for updating training of weight value reading of the reservoir network, and a design method of an RC network nonlinearity reading function is given. The method can be suitable for the situation of blind detection of complex number field multiple-valued signals with dense constellation maps and short data frames.
Owner:温州晶彩光电有限公司
Reservoir and reservoir computing system
Provided is a reservoir computing system that is miniaturized and has a reduced learning cost. The reservoir computing system uses a reservoir that includes a first optical output section that outputs a first optical signal; a first optical waveguide that propagates the first optical signal output by the first optical output section; an optical receiving section that receives the first optical signal from the first optical waveguide; a storage section that stores received optical data corresponding to the first optical signal and output by the optical receiving section; and a feedback section that applies, to the first optical signal, feedback corresponding to the received optical data stored in the storage section.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Reservoir computing data flow processor
PendingUS20210263884A1Improve computing efficiencyHigh of resourceDataflow computersConstructionsData streamControl engineering
A reservoir computing data flow processor includes a plurality of reservoir units to be units constituting a reservoir. The reservoir is able to be reconfigured by changing a connection relationship between the reservoir units. Each of the reservoir units is an operation unit block configured to execute a predetermined operation. The operation unit block includes a first adder configured to perform an addition operation on at least two inputs, a nonlinear operator configured to apply a nonlinear function to an output from the first adder or a result of multiplying the output by a predetermined coefficient, and a second adder configured to perform an addition operation on at least two inputs including an output from the nonlinear operator or a result of multiplying the output by a predetermined coefficient.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com