Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1133 results about "Processing delay" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In a network based on packet switching, processing delay is the time it takes routers to process the packet header. Processing delay is a key component in network delay. During processing of a packet, routers may check for bit-level errors in the packet that occurred during transmission as well as determining where the packet's next destination is. Processing delays in high-speed routers are typically on the order of microseconds or less. After this nodal processing, the router directs the packet to the queue where further delay can happen (queuing delay).
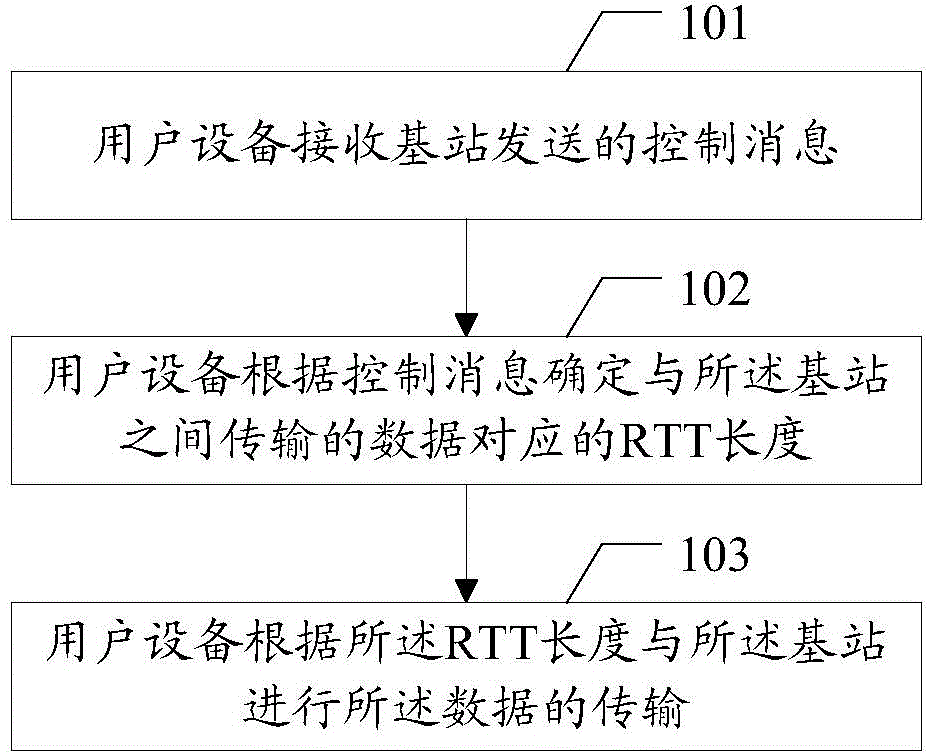
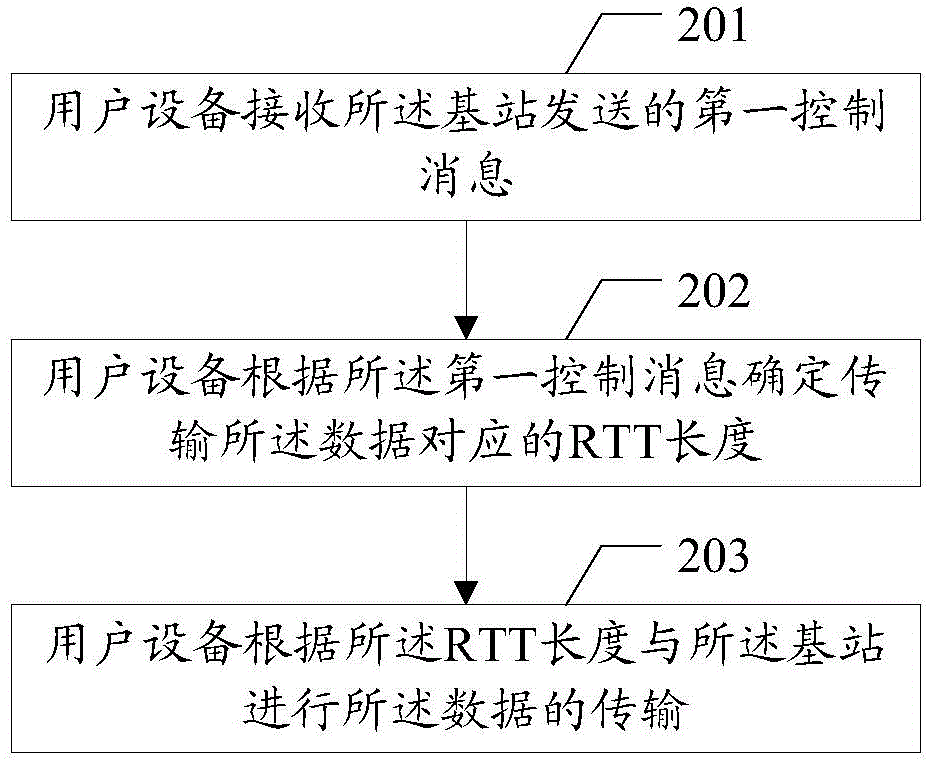
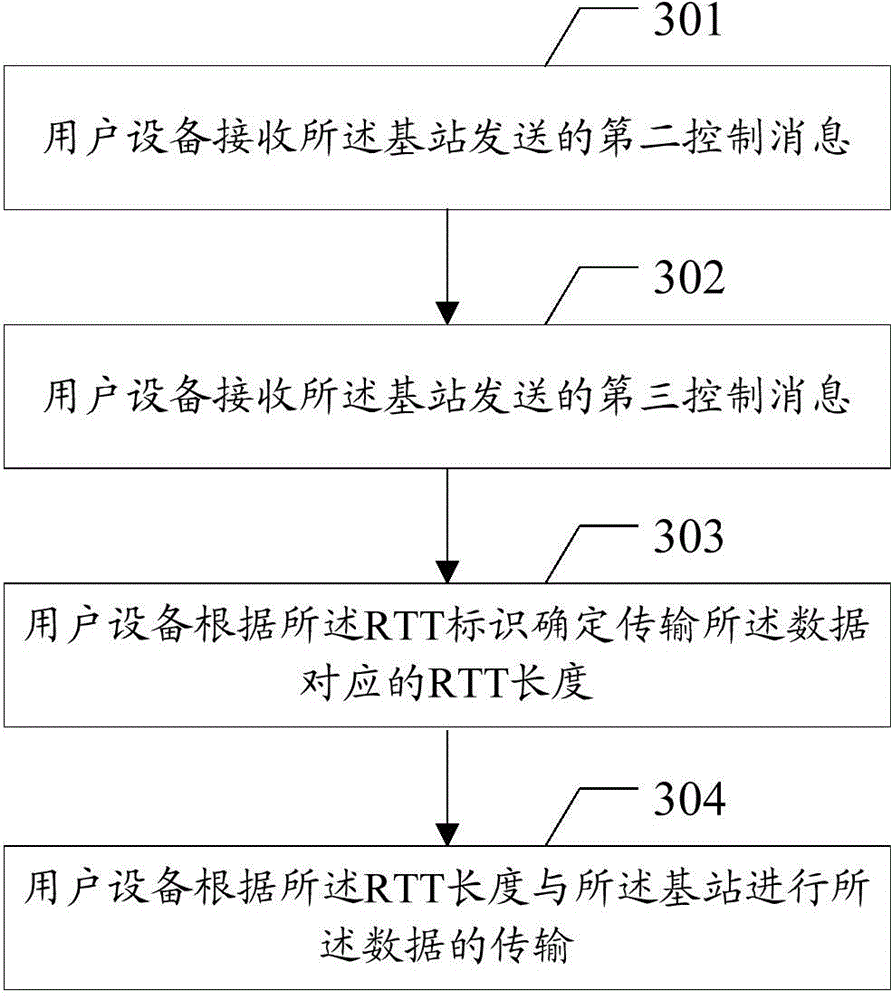
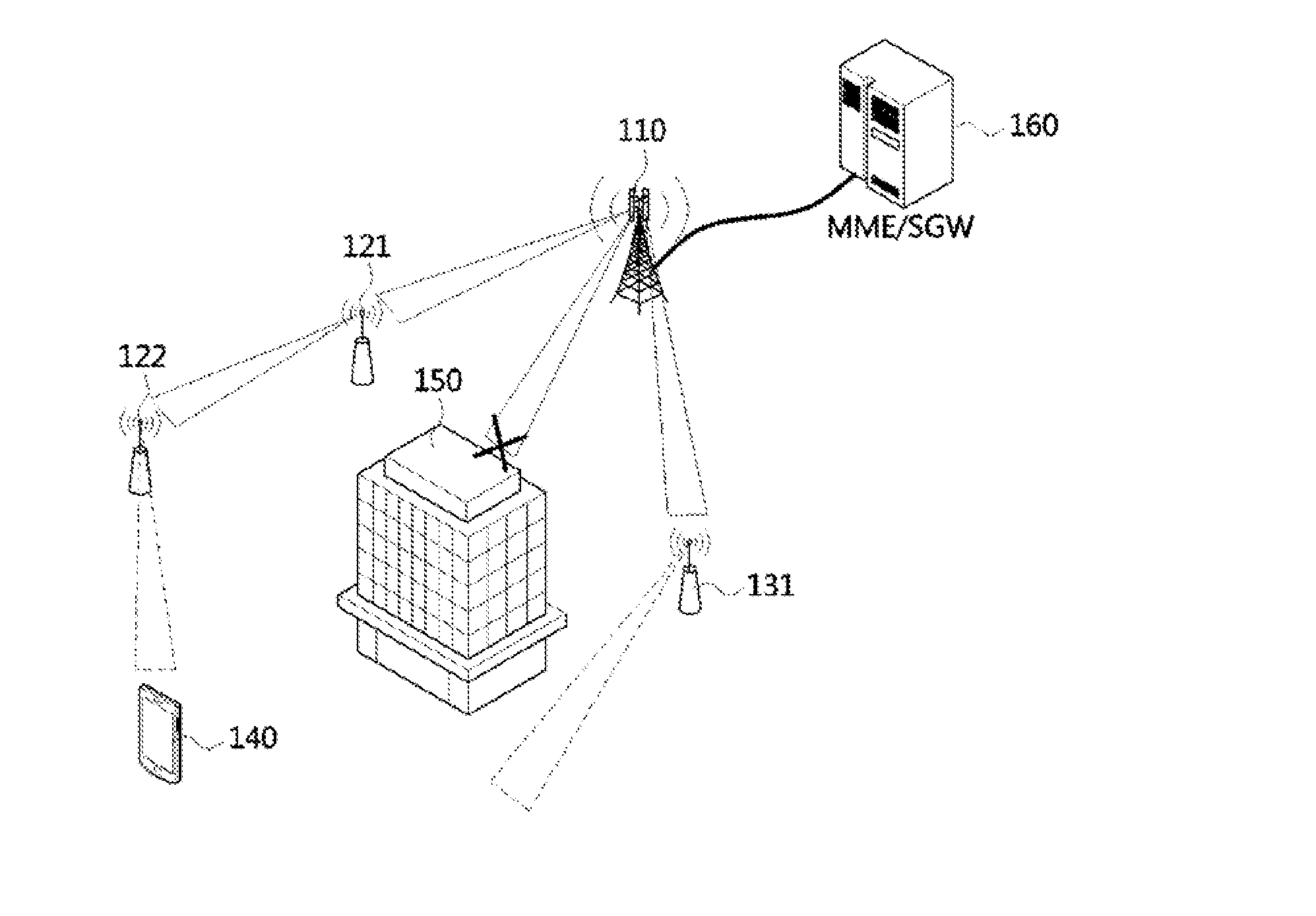
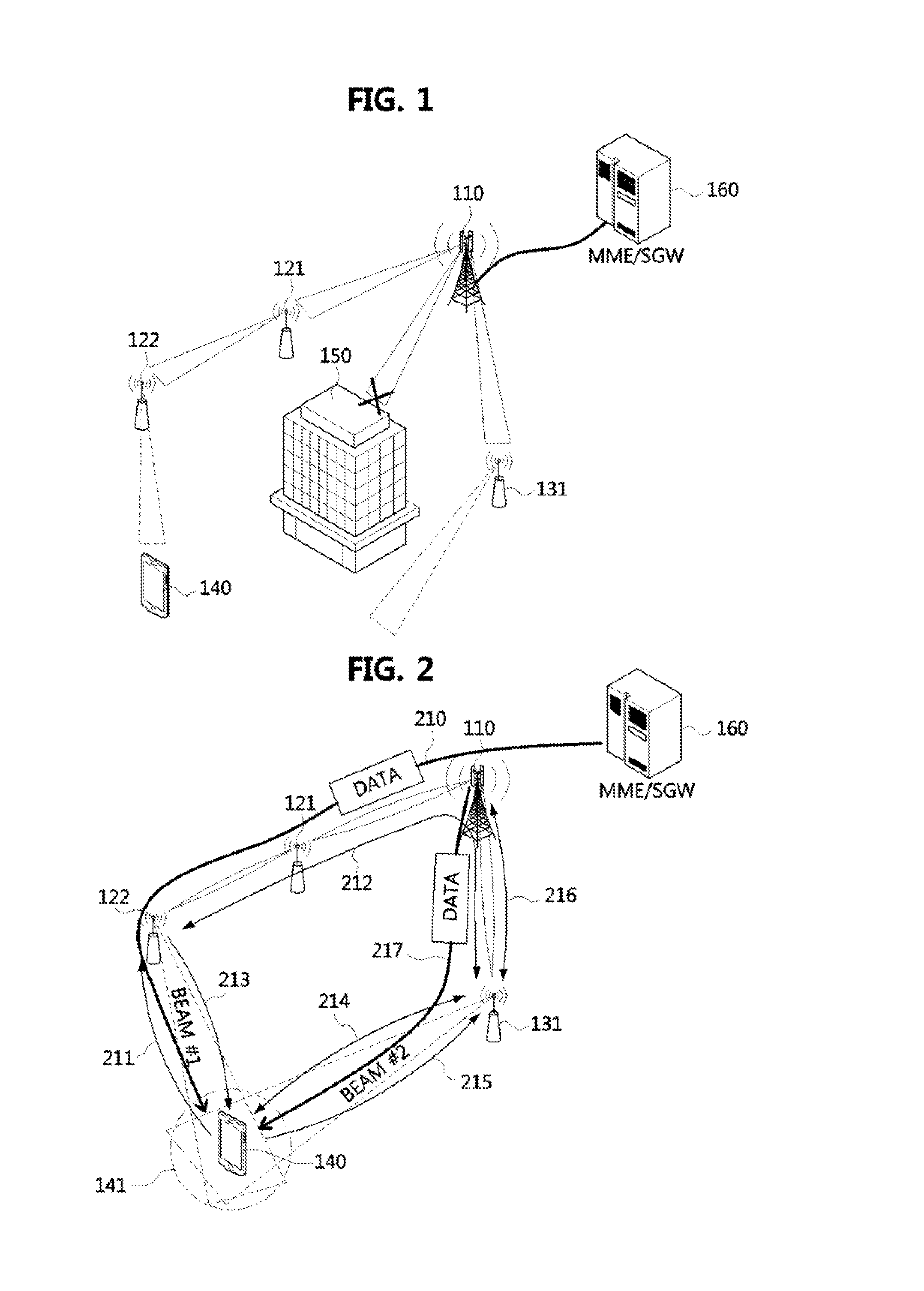
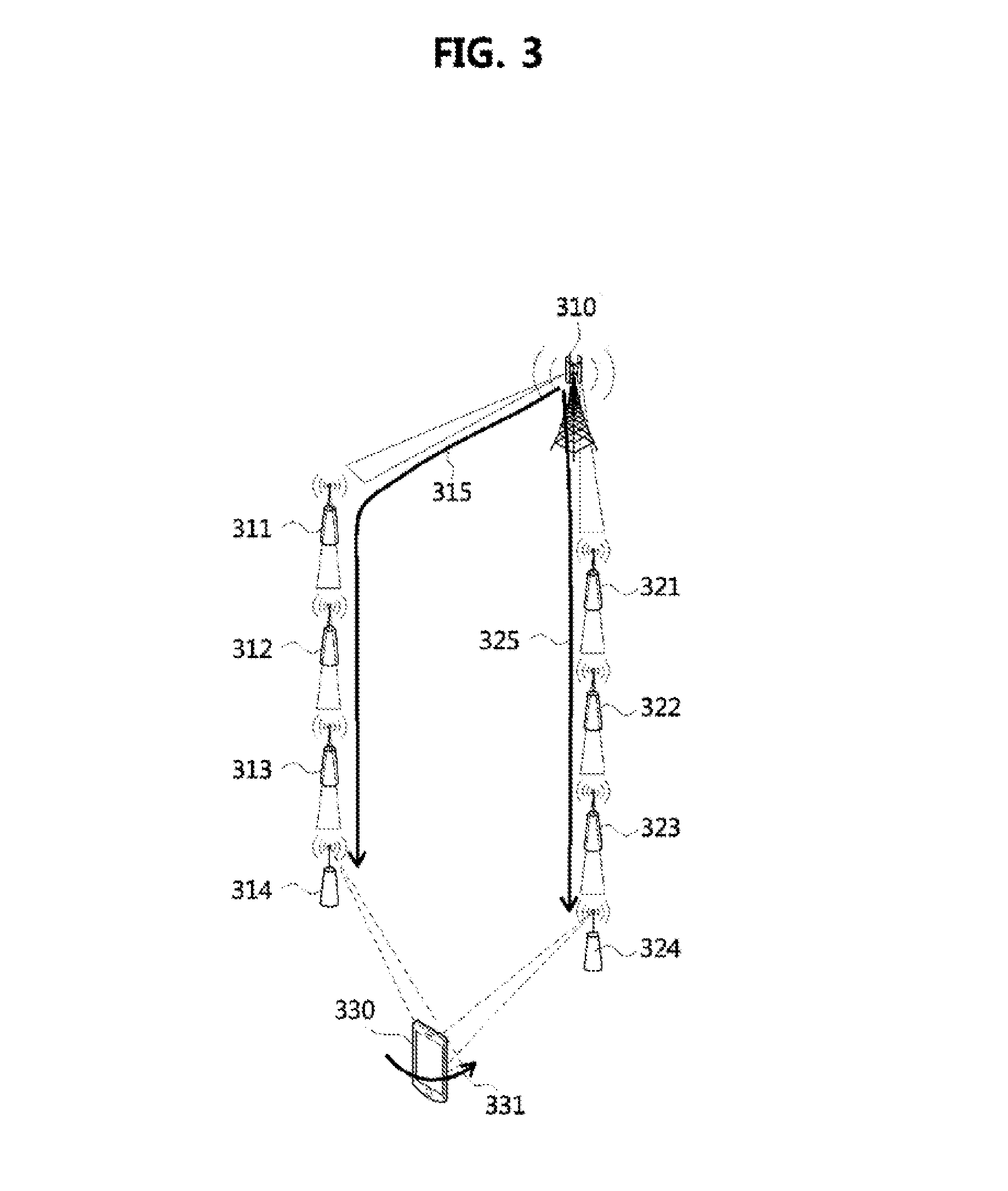
Data transmission method, user equipment and base station
InactiveCN104468030ASolve conflictsError preventionSignal allocationData transmission circuitUser equipment
The embodiment of the invention discloses a data transmission method, user equipment and a base station. The data transmission method, the user equipment and the base station are used for solving the problem about conflicts in the data transmission process under the condition of scene coexistence of different kinds of processing delay. The method includes the steps that the user equipment receives a control message sent by the base station, the control message is used for determining RTT length corresponding to data transmitted between the user equipment and the base station; the user equipment determines the RTT length corresponding to the data transmitted between the user equipment and the base station according to the control message; data transmission between the user equipment and the base station is achieved according to the RTT length.
Owner:SHANGHAI HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
System and method for discovering information objects and information object repositories in computer networks
InactiveUS7162539B2Special service provision for substationDigital data information retrievalInformation repositoryInformation object
An address of an information object repository that should service a client request for an information object is returned in response to a request therefor. The address of the information object repository which is returned is selected according to specified performance metrics regardless of whether or not the information object repository maintains a local copy of the information object that is the client request. In some cases, the address of the information object repository is further selected according to an address of a client making the client request. Further, the address of the information object repository is selected from a number of addresses of information object repositories. The specified performance metrics may include one or more of an average delay from the information object repository to the client, average processing delays at the information object repository, reliability of a path from the information object repository to the client, available bandwidth in said path, and loads on the information object repository. In some cases, the information object repository may be instructed to obtain a copy of the information object after the address of the information object repository is returned in response to the request therefore.
Owner:ADARA NETWORKS
System and method for information object routing in computer networks
InactiveUS7552233B2Reliable transmissionConvenient distanceSpecial service provision for substationMultiple digital computer combinationsInformation objectProcessing delay
An address of a server that should supply an information object or service to a requester is returned in response to a request therefor. The address of the server that is returned is an optimal server selected according to specified performance metrics. The specified performance metrics may include one or more of an average delay from the server to another, average processing delays at the server, reliability of a path from the server to another, available bandwidth in said path, and loads on the server.
Owner:ADARA NETWORKS
System and method for using network layer uniform resource locator routing to locate the closest server carrying specific content
ActiveUS7908337B2Less latencySpecial service provision for substationDigital data information retrievalClient-sideProcessing delay
A request for an information object at an address identified by a uniform resource locator (URL) is received; and the URL is mapped to a corresponding anycast address for the information object. Thereafter, the anycast address for the information object may be resolved to a unicast address for the information object, and the information object sent to the client. The request may be received at an information object repository that is topologically closer to the client than any other information object repository. This closest information object repository may be selected according to specified performance metrics, such as: average delay from the selected information object repository to a source of the request, average processing delay at the selected information object repository, reliability of a path from the selected information object repository, available bandwidth in said path, and loads on the selected information object repository.
Owner:ADARA NETWORKS
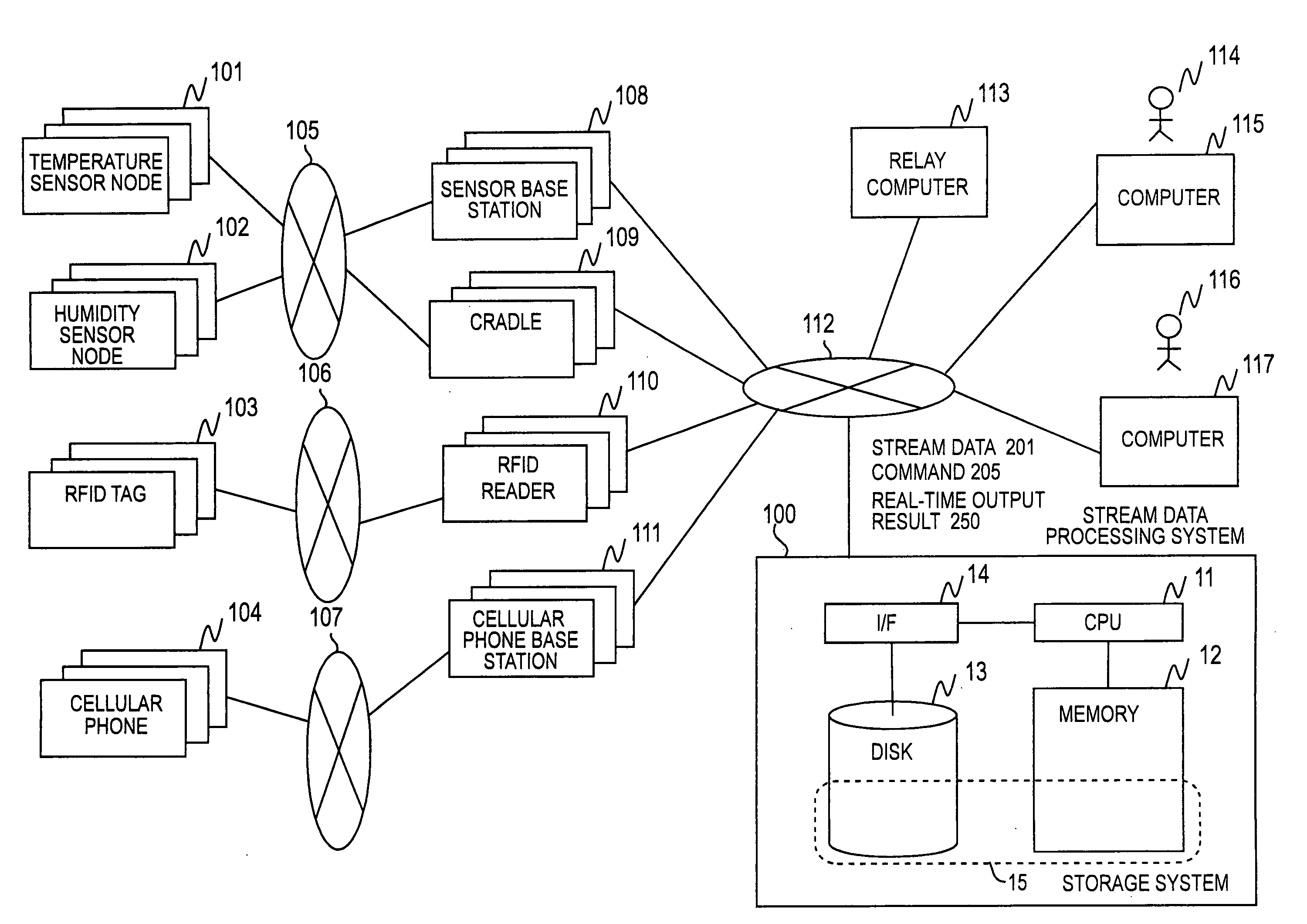
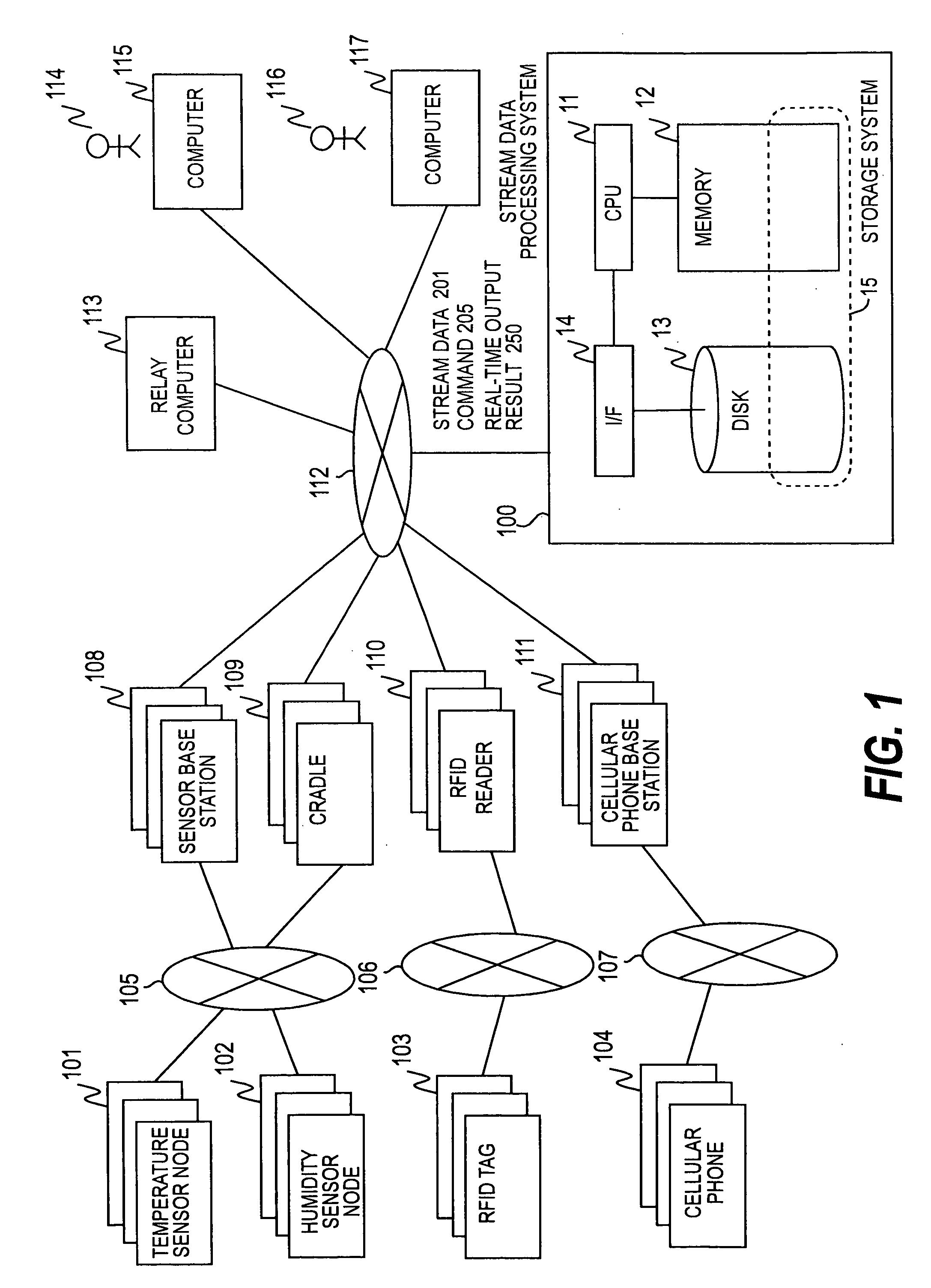
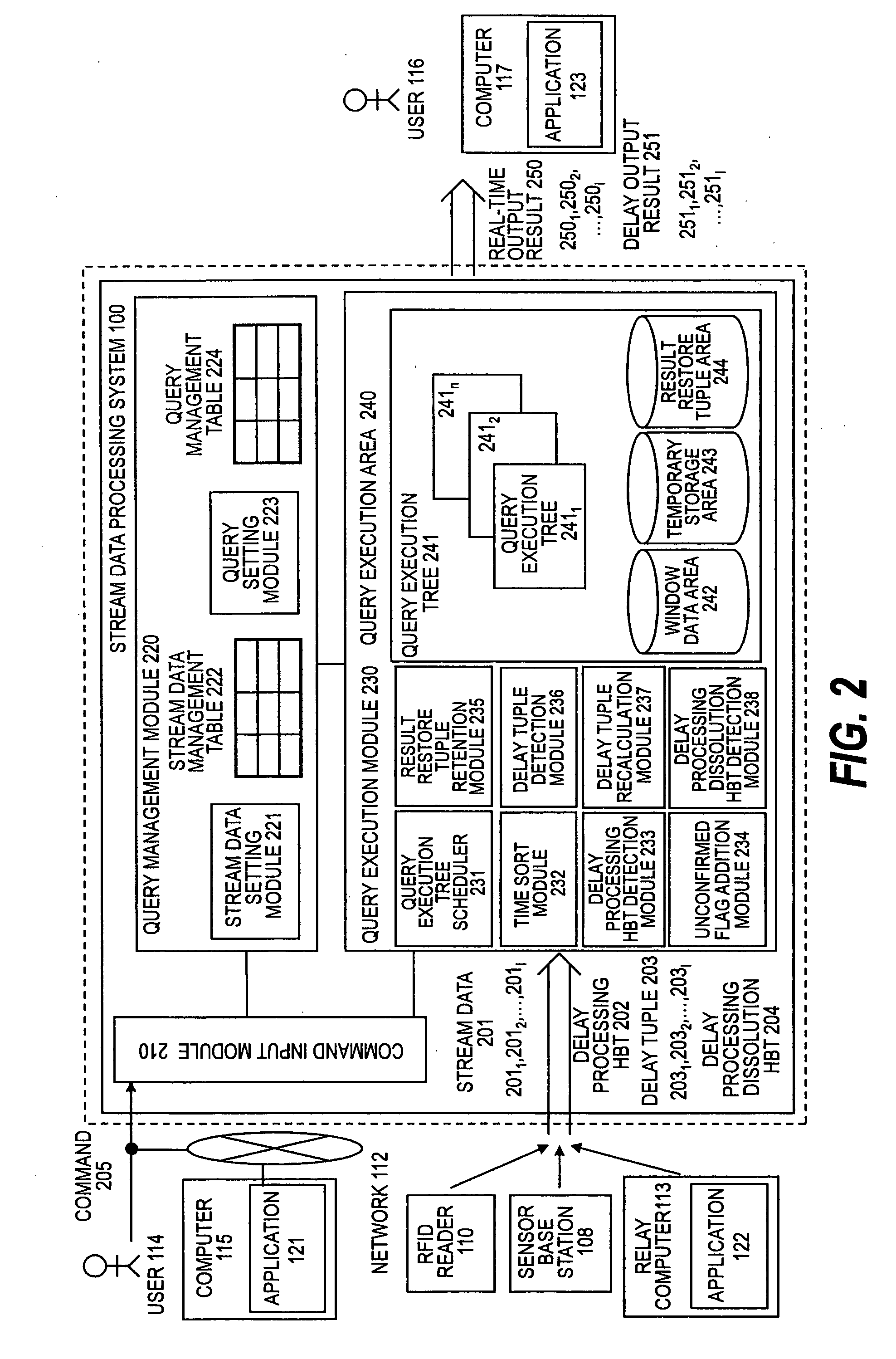
Stream data processing method and computer systems
InactiveUS20090271529A1The processing result is accurateDigital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsStreaming dataParallel computing
Provided is a stream data processing method that can effectively handle delay data. In the stream data processing method of processing data whose lifetime is defined by a window, an operation result excluding a delay tuple is immediately output along with an unconfirmed flag according to delay processing HBT while a midway processing result necessary for reproduction is retained along with the lifetime, and when the delay tuple arrives, a correct processing result is calculated from the delay tuple and the processing result restore tuple.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
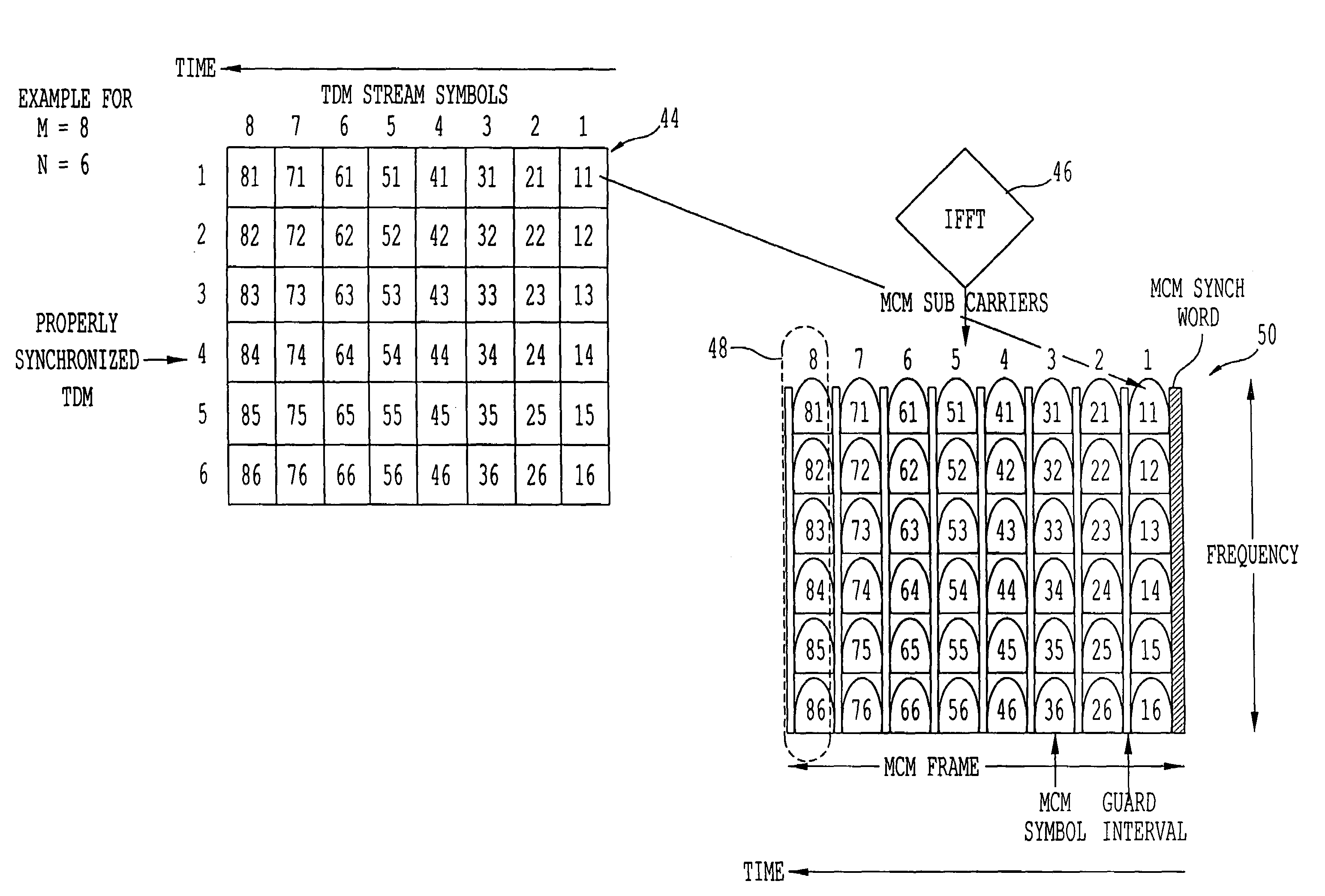
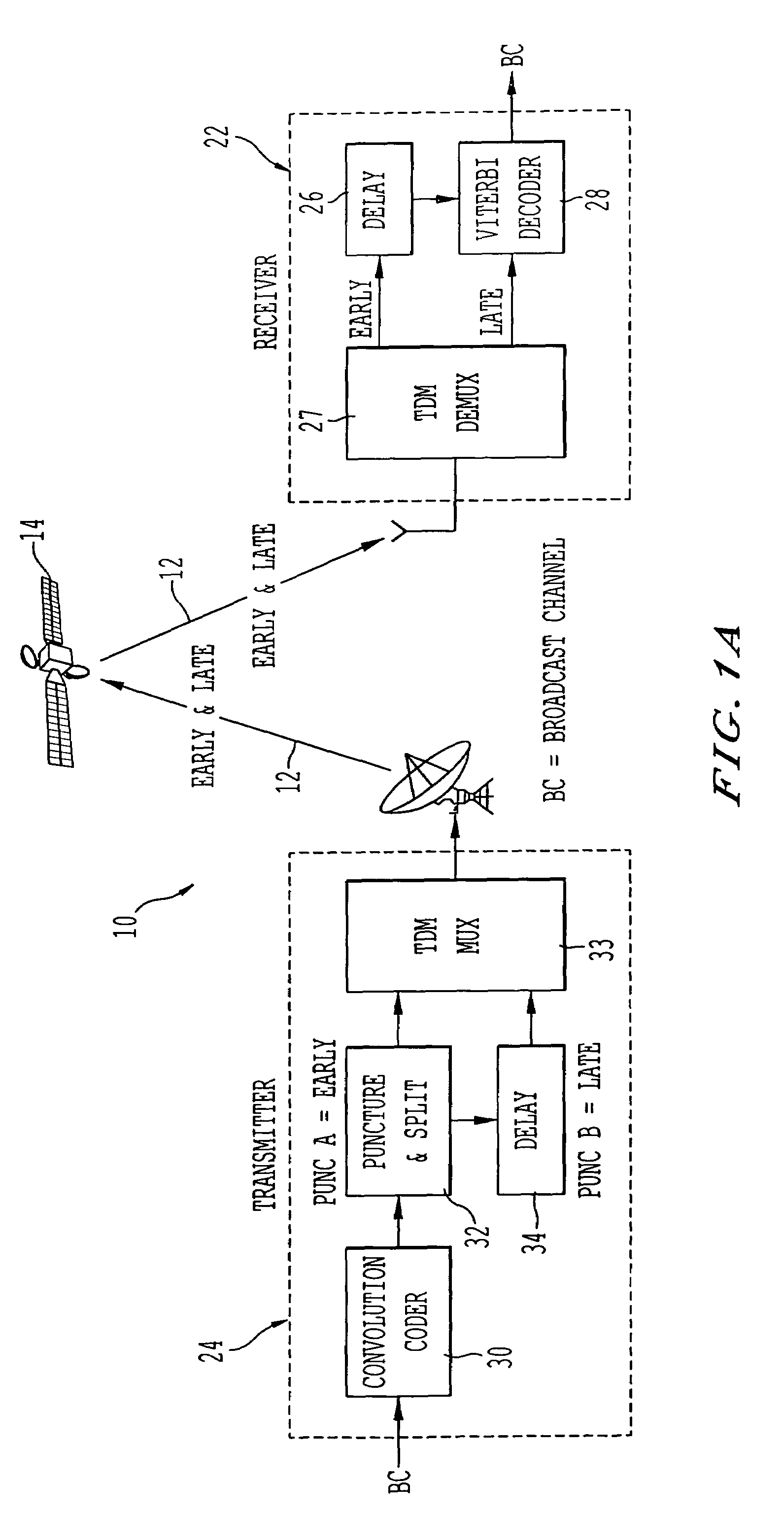
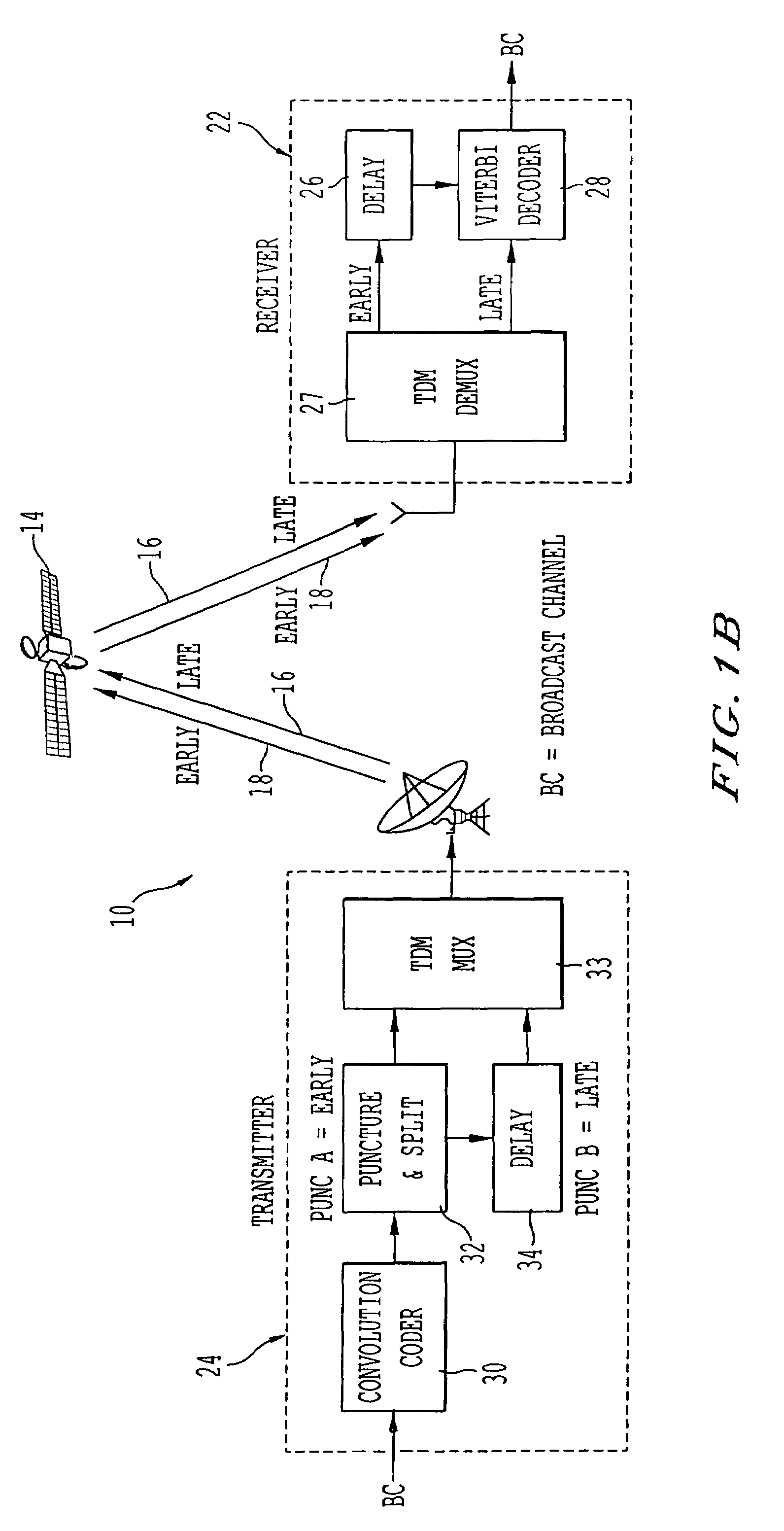
Method and apparatus for mobile platform reception and synchronization in direct digital satellite broadcast system
InactiveUS6956814B1Overcome disadvantagesImprove continuityPolarisation/directional diversityActive radio relay systemsEngineeringDiversity scheme
A satellite system employing time diversity and a single frequency network of terrestrial re-radiation stations is provided wherein each terrestrial re-radiation station inserts a delay into a terrestrial signal. The delay allows the time of arrival of the early time diversity signal at the center of terrestrial coverage to coincide with the arrival of the corresponding late time diversity signal, thereby improving hand-off between terrestrial and satellite signals at a receiver. The delay also adjusts for distance differences between each terrestrial re-radiation station and the satellite and between each station and the center of the terrestrial coverage region. This adjustment optimizes the TDM-MCM reception by synchronizing at the center of the SFN the phase of the MCM signals re-radiated from the re-radiating stations of the SFN. The delay also compensates for the processing delay encountered when converting a satellite LOS TDM stream into a multicarrier modulated stream for transporting the satellite LOS TDM stream to user receivers and for the diversity delay between the early and late signals.
Owner:WORLDSPACE INC
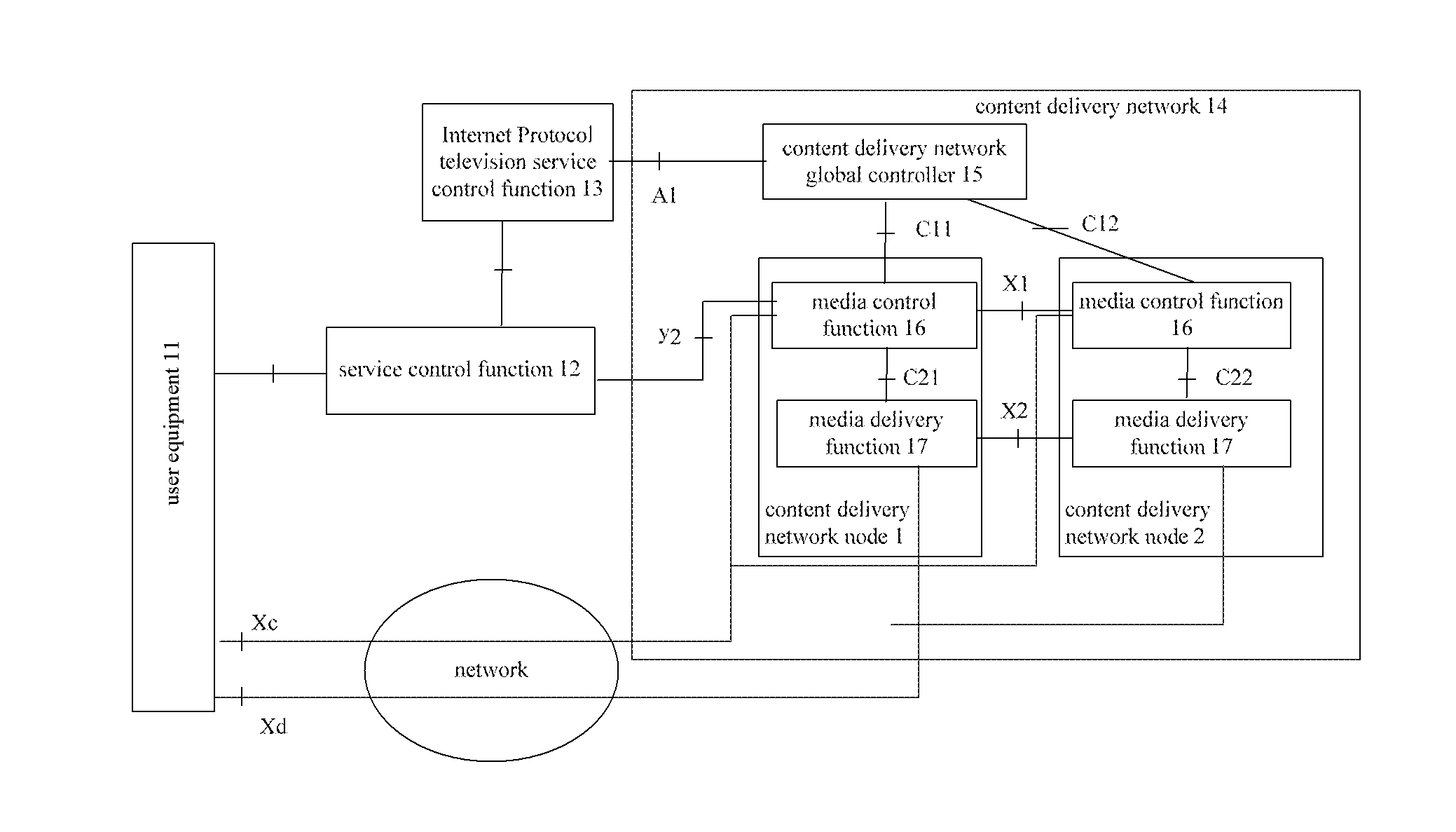
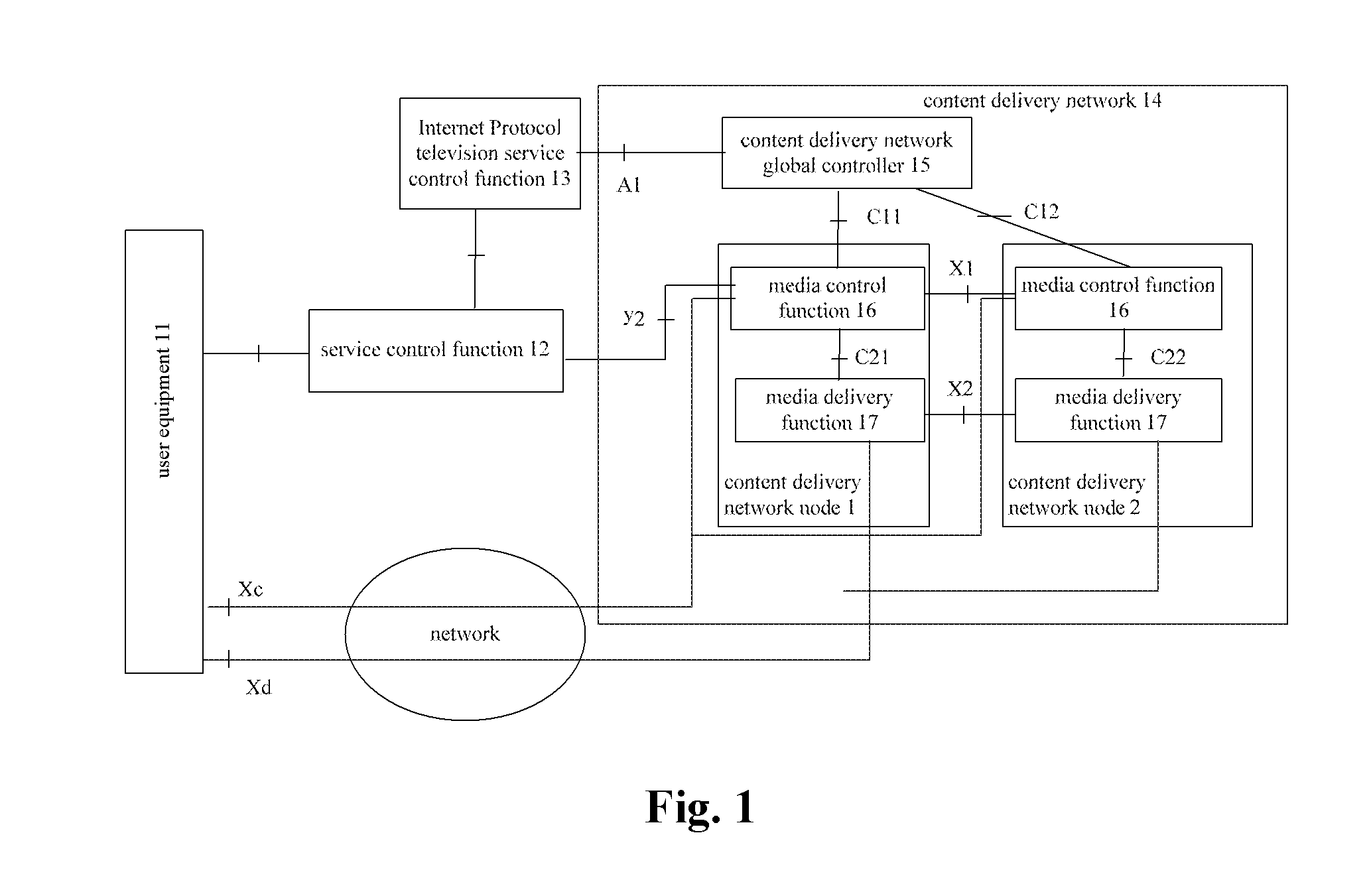
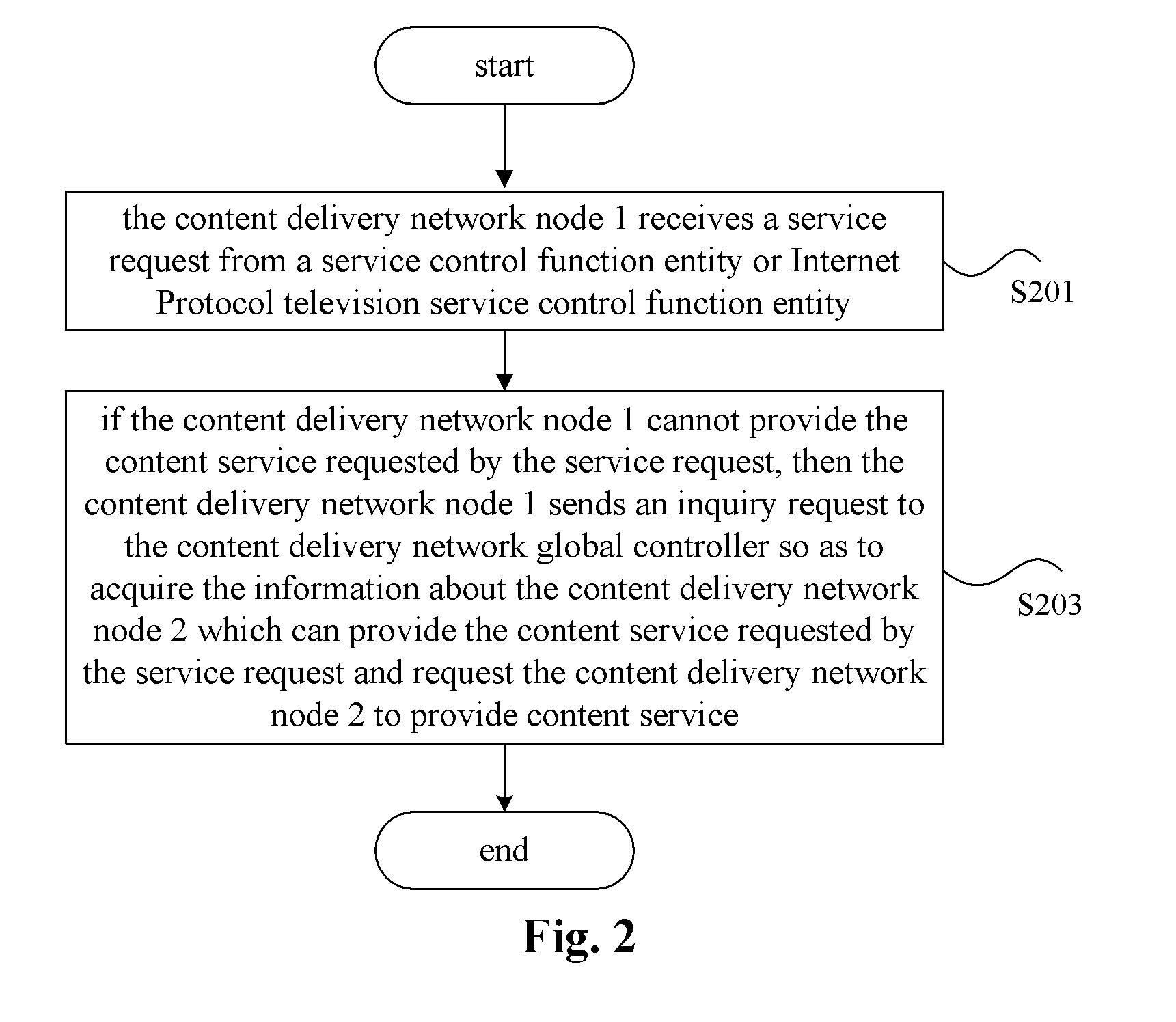
Content location method and content delivery network node
ActiveUS20120023530A1Long processing delayLow costTwo-way working systemsTransmissionContent IdentifierContent distribution
The present invention provides a content locating method and a content delivery network node. In this case, the content locating method provided by the present invention comprises: receiving by a first content delivery network CDN node a service request sent by a service control function entity or an IPTV service control function entity, wherein this service request carries a content identifier which is used to indicate requesting content corresponding to this content identifier; if the first CDN node cannot provide the content service requested by the service request, then the first CDN node sends an inquiry request to a CDN global controller so as to acquire the information about a second CDN node which can provide the content service requested by the service request and request the second CDN node to provide the content service. By way of the present invention, the pressure of the CDN global controller can be reduced and the processing delay of CDN can be shortened.
Owner:ZTE CORP
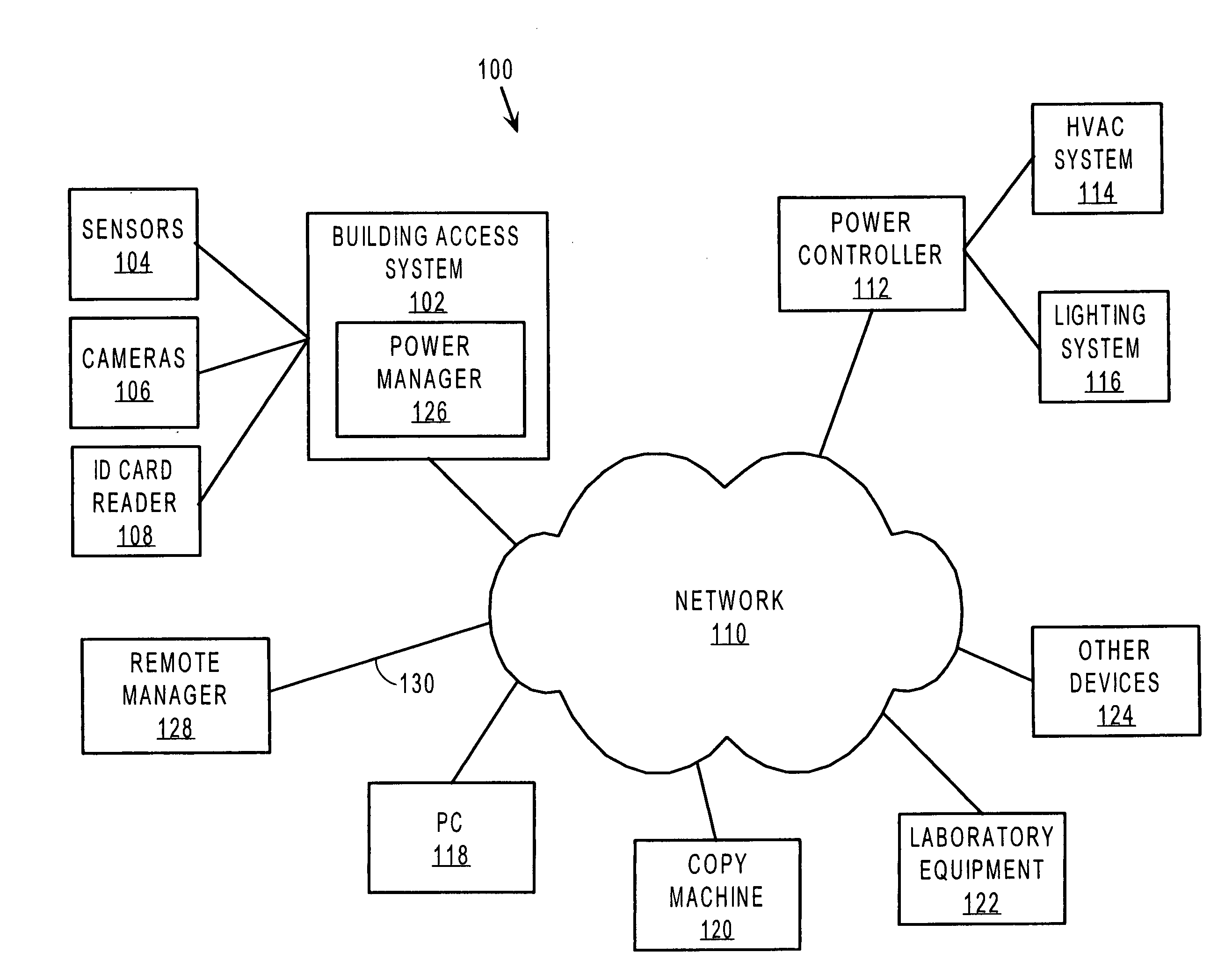
Method of pre-activating network devices based upon previous usage data
An approach for pre-activating network devices includes using prior usage of a network device to estimate times when the network device will be used in the future. The network device is then pre-activated, i.e., transitioned to an active operational state, prior to the estimated times so that the network device will be ready when needed. This reduces or eliminates delays in processing attributable to having to wait for the network device to transition to the active operational state.
Owner:RICOH KK
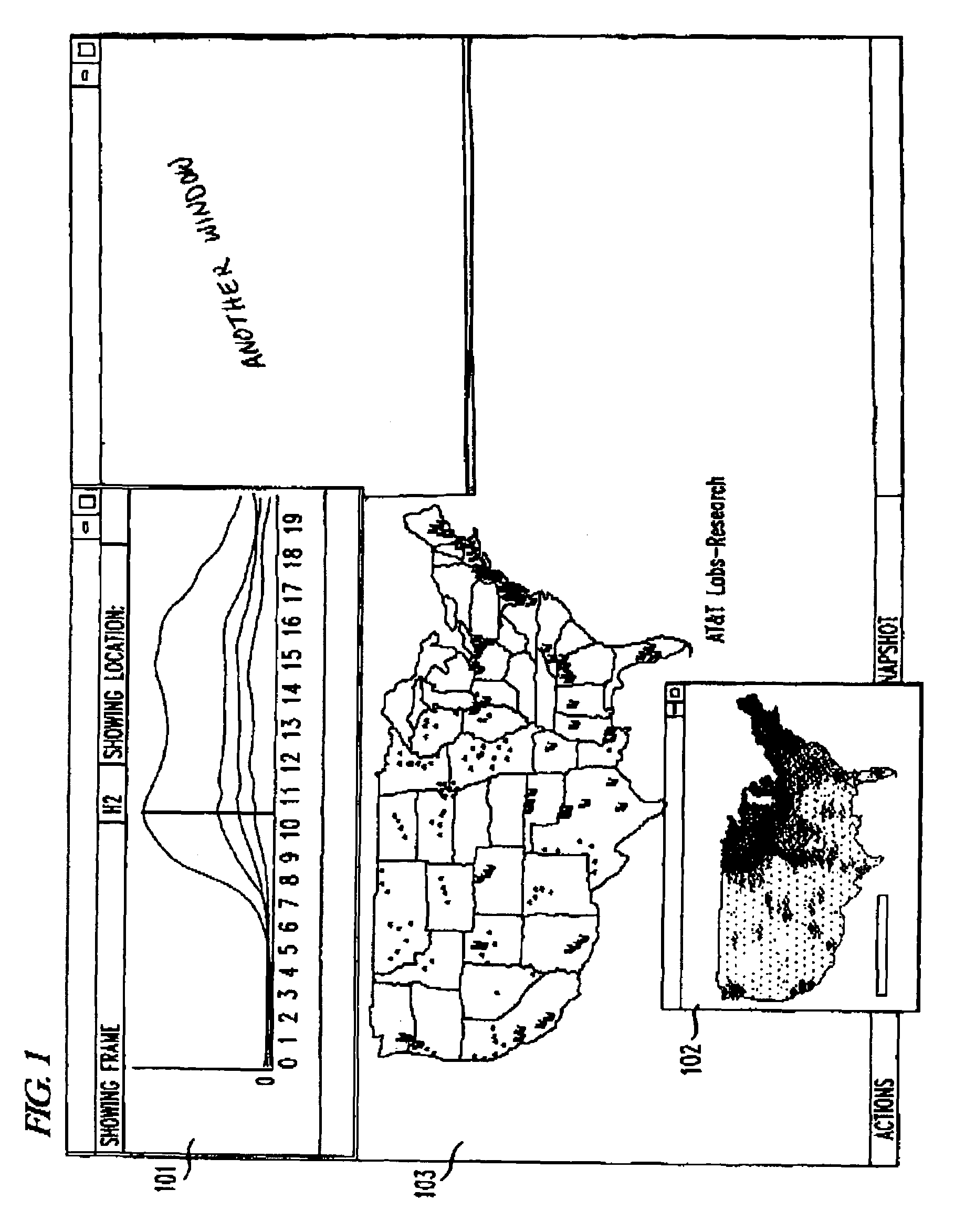
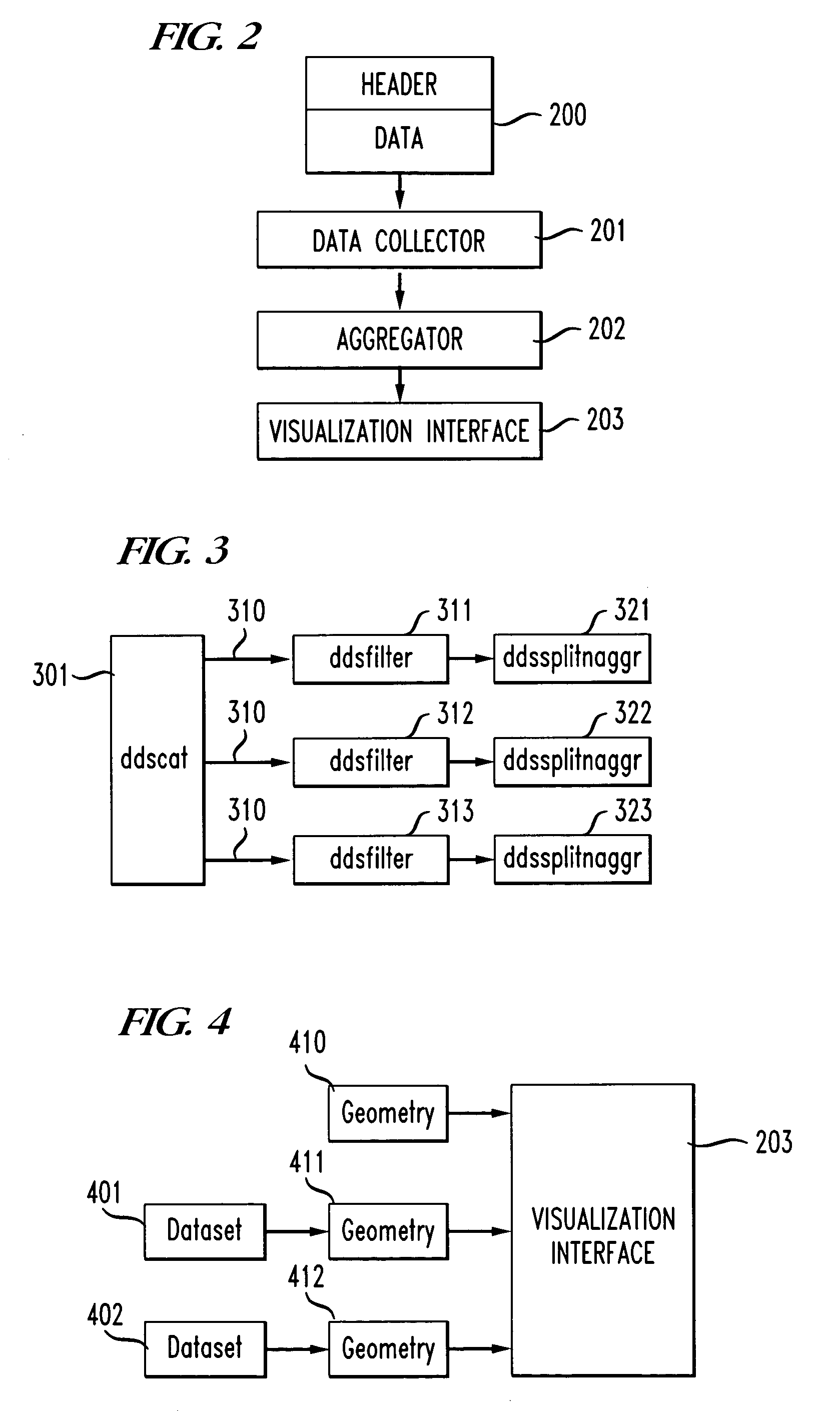
System and method for large-scale data visualization
ActiveUS7454439B1Minimize processing delayComprehensive supportDigital data processing detailsTransmissionData setData exploration
The present invention is directed to a new visualization platform for the interactive exploration of large datasets. The present invention integrates a collection of relevant visualization techniques to provide a new visual metaphor for viewing large datasets. It is capable of providing comprehensive support for data exploration, integrating large-scale data visualization with querying, browsing, and statistical evaluation. A variety of techniques are utilized to minimize processing delays and the use of system resources, including processing pipelines, direct IO, memory mapping, and dynamic linking of “on-the-fly” generated code.
Owner:AMERICAN TELEPHONE & TELEGRAPH CO
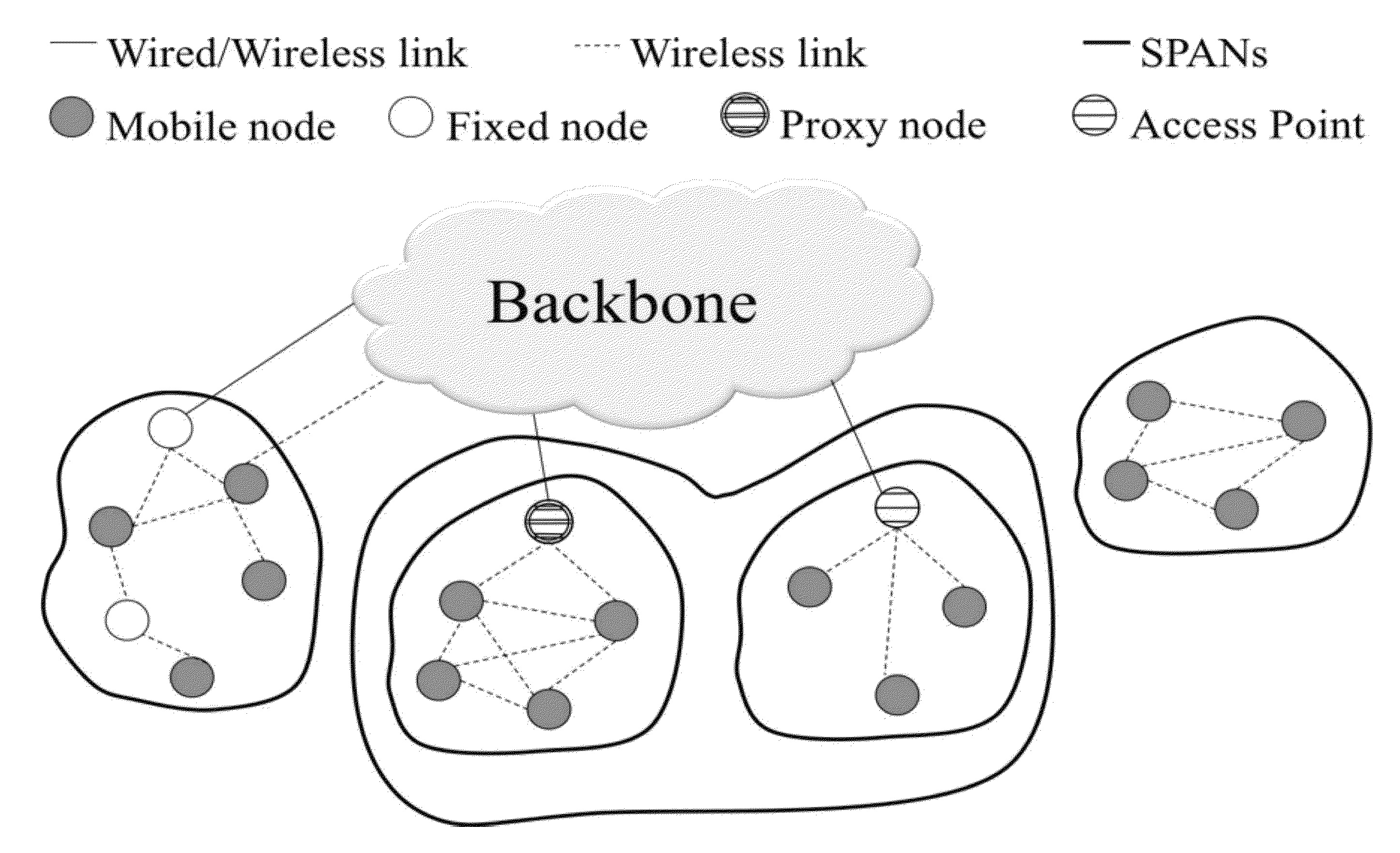
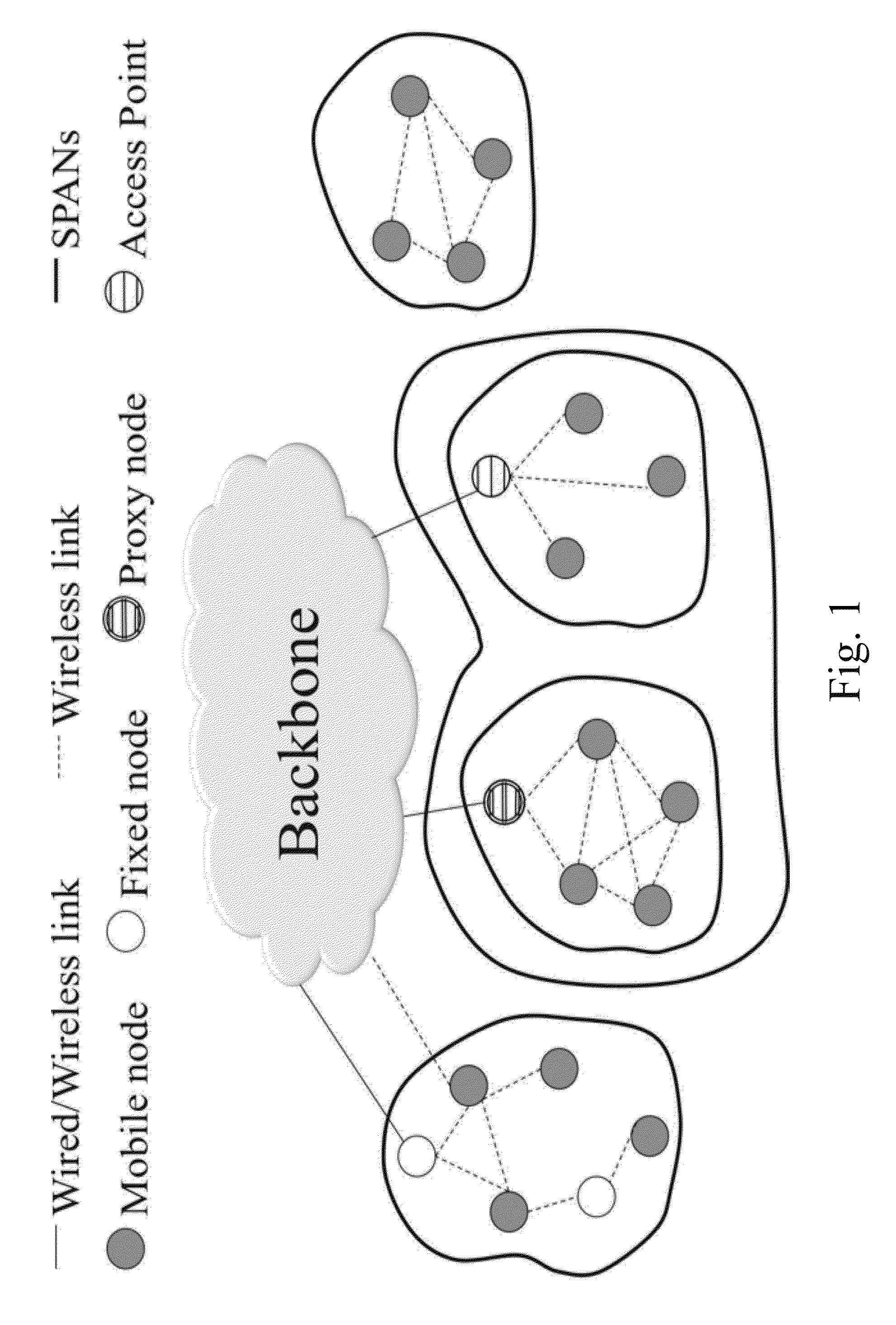
Systems and Methods for Creating, Managing and Communicating Users and Applications on Spontaneous Area Networks
ActiveUS20100208662A1Network topologiesWireless commuication servicesInformation typeWireless transmission
A Spontaneous Area Network (SPAN) is formed by mobile and fixed nodes using wireless transmission links between nodes, usually in a nearby geographical area. Applications allow users to create, join, leave, and manage SPANs and groups in a SPAN. Automatic procedures allow nodes to join other SPANs. Transmission power of the wireless network interface is dynamic, varying depending on battery level, type of information to transmit, state and topology of the network. A delay tolerant object layer abstraction creates, modifies, deletes, publishes, and handles Delay Tolerant Distributed Objects (DTDOs). A Patient Transport Protocol (PTP) ensures a reliable transport of information through the network while avoiding congestion conditions. An aggressive and explosive network protocol (AGENET) has routing and forwarding capacities and uses datagrams to establish communication between different nodes of the SPAN. Cooperation and diversity are exploited to react to node mobility that causes frequent changes in network topology and disconnections.
Owner:MIRAVEO
Redundancy-based methods, apparatus and articles-of-manufacture for providing improved quality-of-service in an always-live distributed computing environment
InactiveUS20020023117A1Increased riskReduce decreaseDigital computer detailsMemory systemsQuality of serviceDistributed Computing Environment
Improved methods, apparatus and articles-of-manufacture for providing distributed computing in a peer-to-peer network of processing elements utilize redundancy to improve quality-of-service and / or mitigate processing delays attributable to failures or slowdowns of processing elements or network connections.
Owner:BERNARDIN JAMES +1
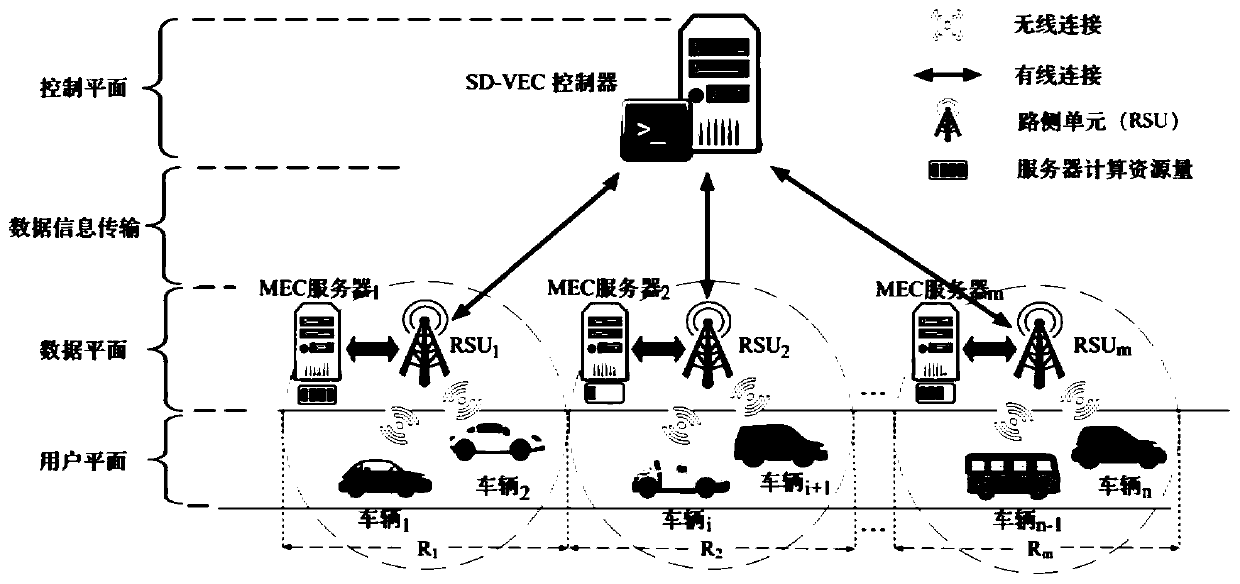
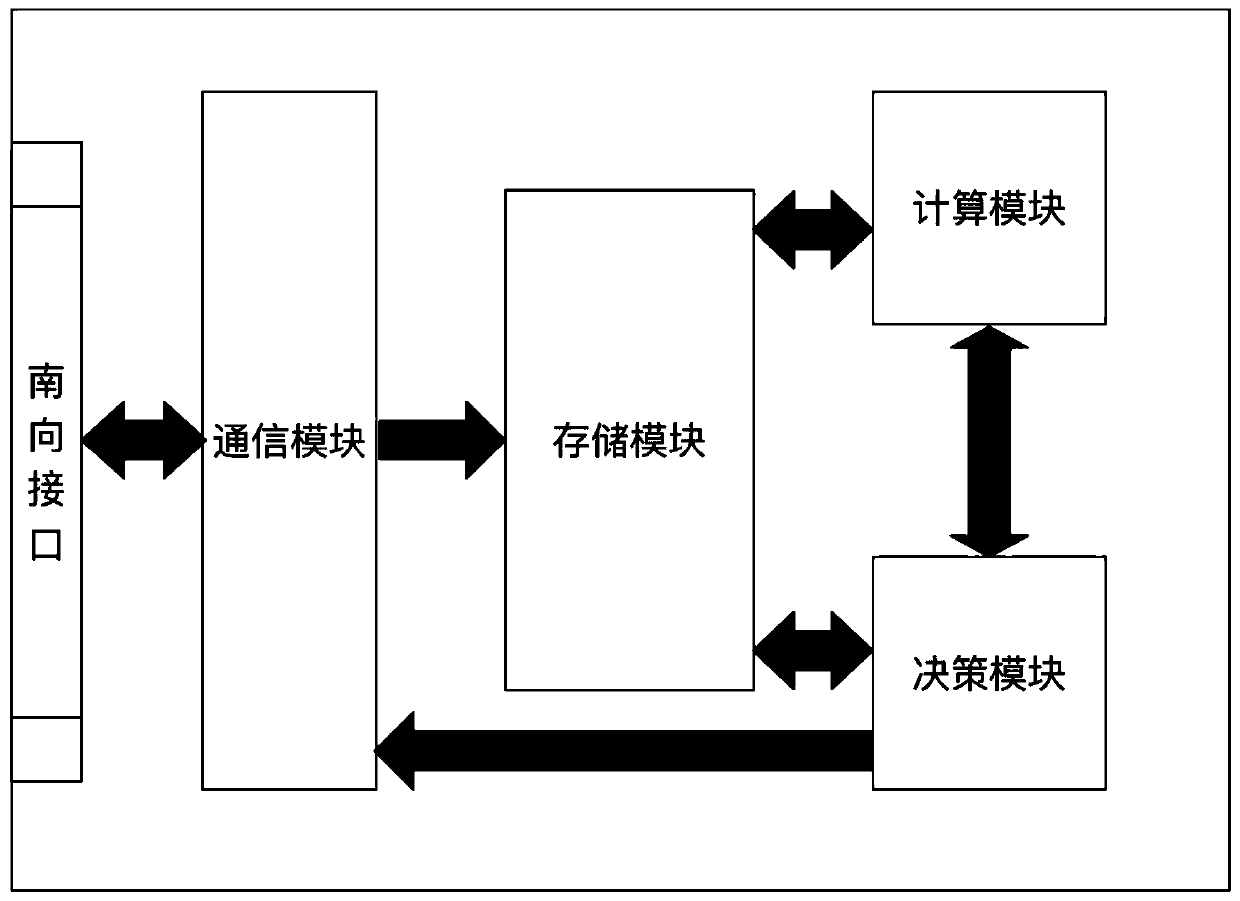
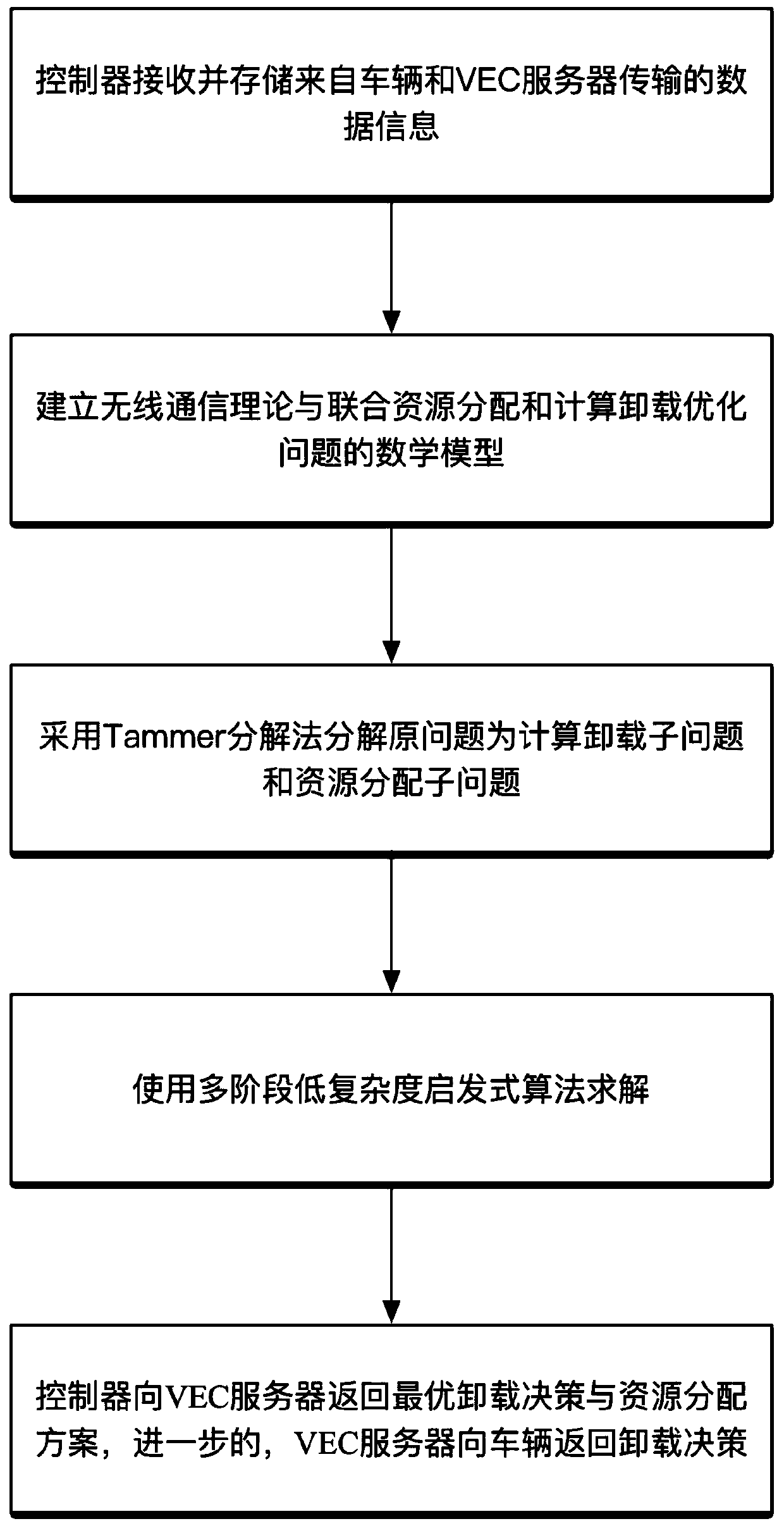
Method and system for joint resource allocation and computing unloading in software defined vehicle-mounted edge network
ActiveCN110035410AGood decisionMinimize the total processing delay of on-board tasksResource allocationParticular environment based servicesData informationMathematical model
The invention discloses a method and a system for joint resource allocation and computing unloading in a software defined vehicle-mounted edge network. The method comprises the following steps: establishing a mathematical model of a wireless communication theory according to data information, and modeling a joint resource allocation and calculation unloading problem as a mixed integer nonlinear programming problem (MINLP) according to the mathematical model; decomposing an original problem into a resource allocation sub-problem and a calculation unloading sub-problem through a Tammer decomposition method, and adopting function monotonicity definition, Lagrangian duality and KKT (Karush-Kahn-Tucker) to obtain optimal resource distribution, and obtaining an optimal unloading strategy by adopting a multi-stage low-complexity heuristic algorithm; wherein the server can allocate computing resources to the vehicle according to the scheme of the controller, and the vehicle selects the serverto unload the computing task according to the strategy of the controller. According to the invention, an optimal unloading strategy and an optimal resource allocation scheme are provided for vehicles,and the total processing delay of vehicle-mounted tasks in a system range is reduced.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
System and method for discovering information objects and information object repositories in computer networks
ActiveUS20060271705A1Special service provision for substationDigital data information retrievalInformation objectObject store
An address of an information object repository that should service a client request for an information object is returned in response to a request therefor. The address of the information object repository which is returned is selected according to specified performance metrics regardless of whether or not the information object repository maintains a local copy of the information object that is the client request. In some cases, the address of the information object repository is further selected according to an address of a client making the client request. Further, the address of the information object repository is selected from a number of addresses of information object repositories. The specified performance metrics may include one or more of an average delay from the information object repository to the client, average processing delays at the information object repository, reliability of a path from the information object repository to the client, available bandwidth in said path, and loads on the information object repository. In some cases, the information object repository may be instructed to obtain a copy of the information object after the address of the information object repository is returned in response to the request therefore.
Owner:ADARA NETWORKS
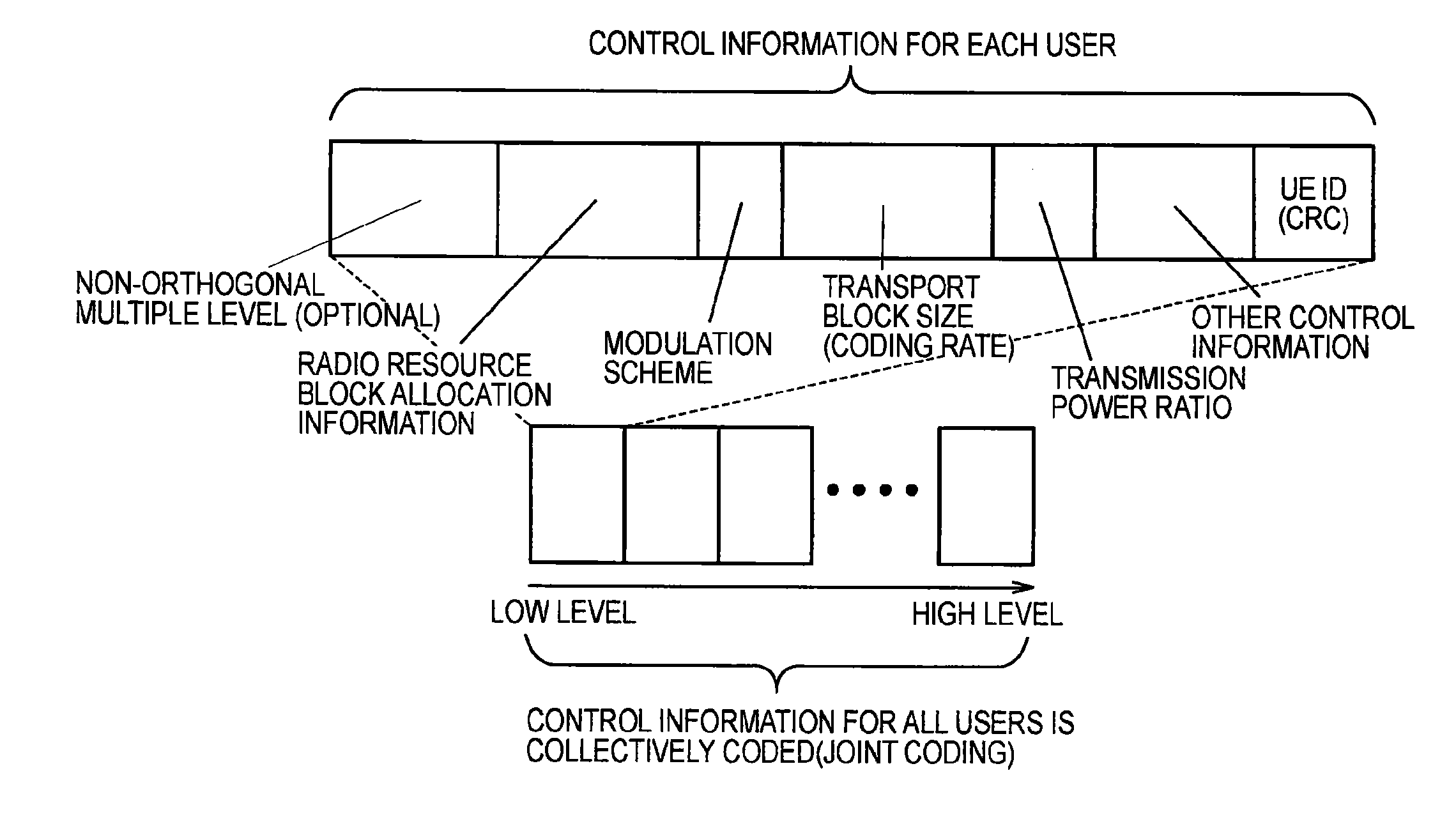
Receiver, transmitter and radio communication method
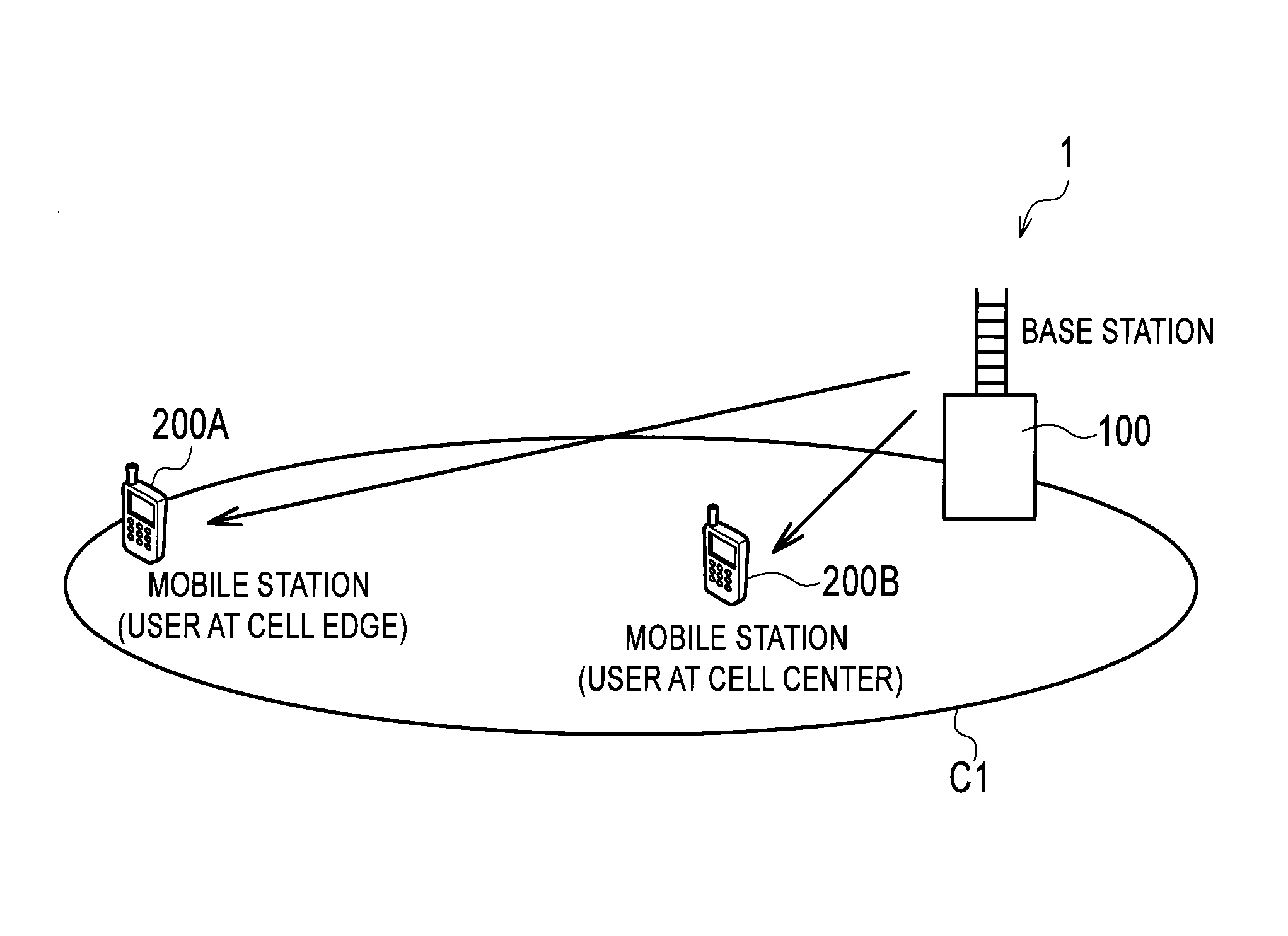
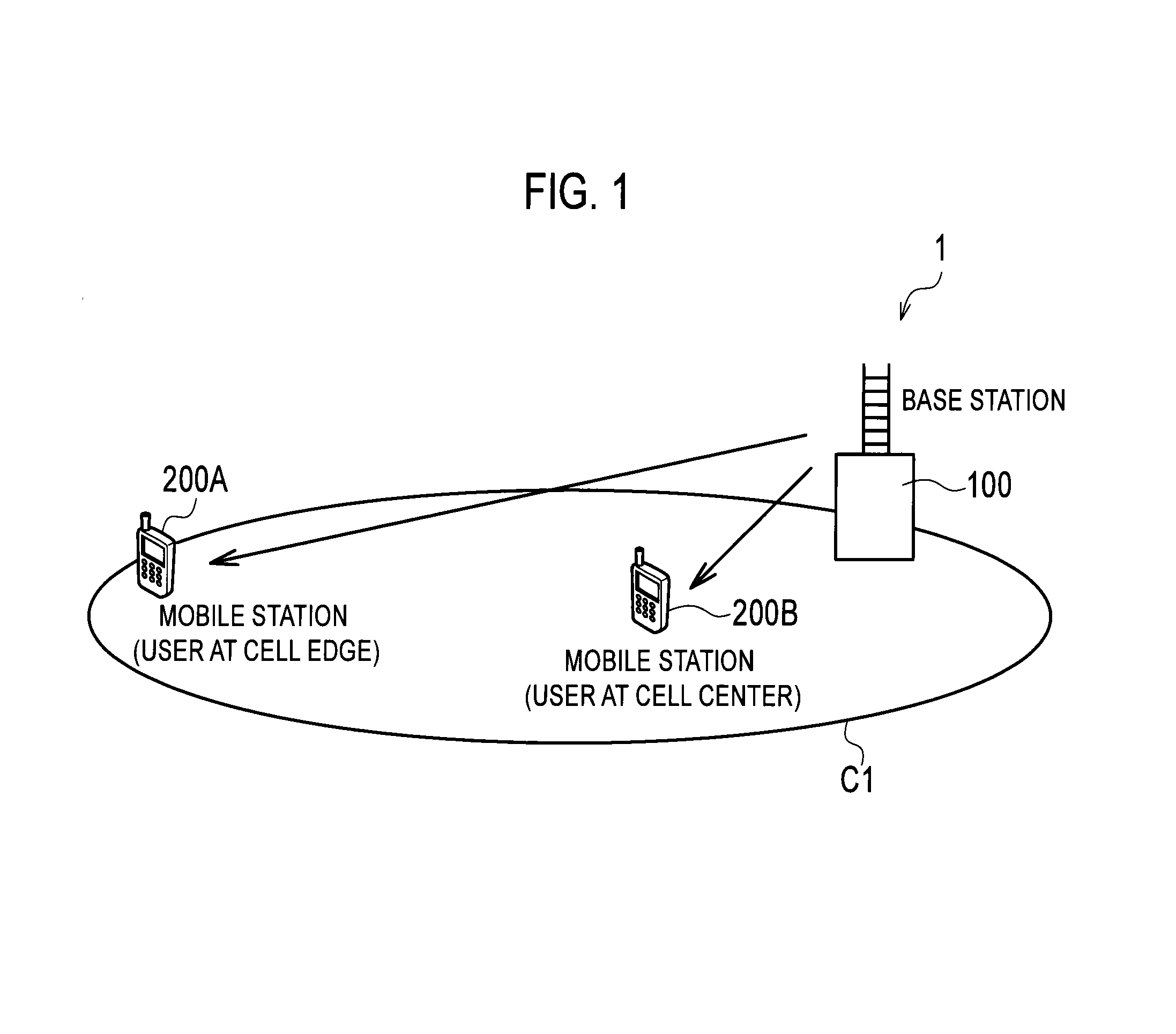
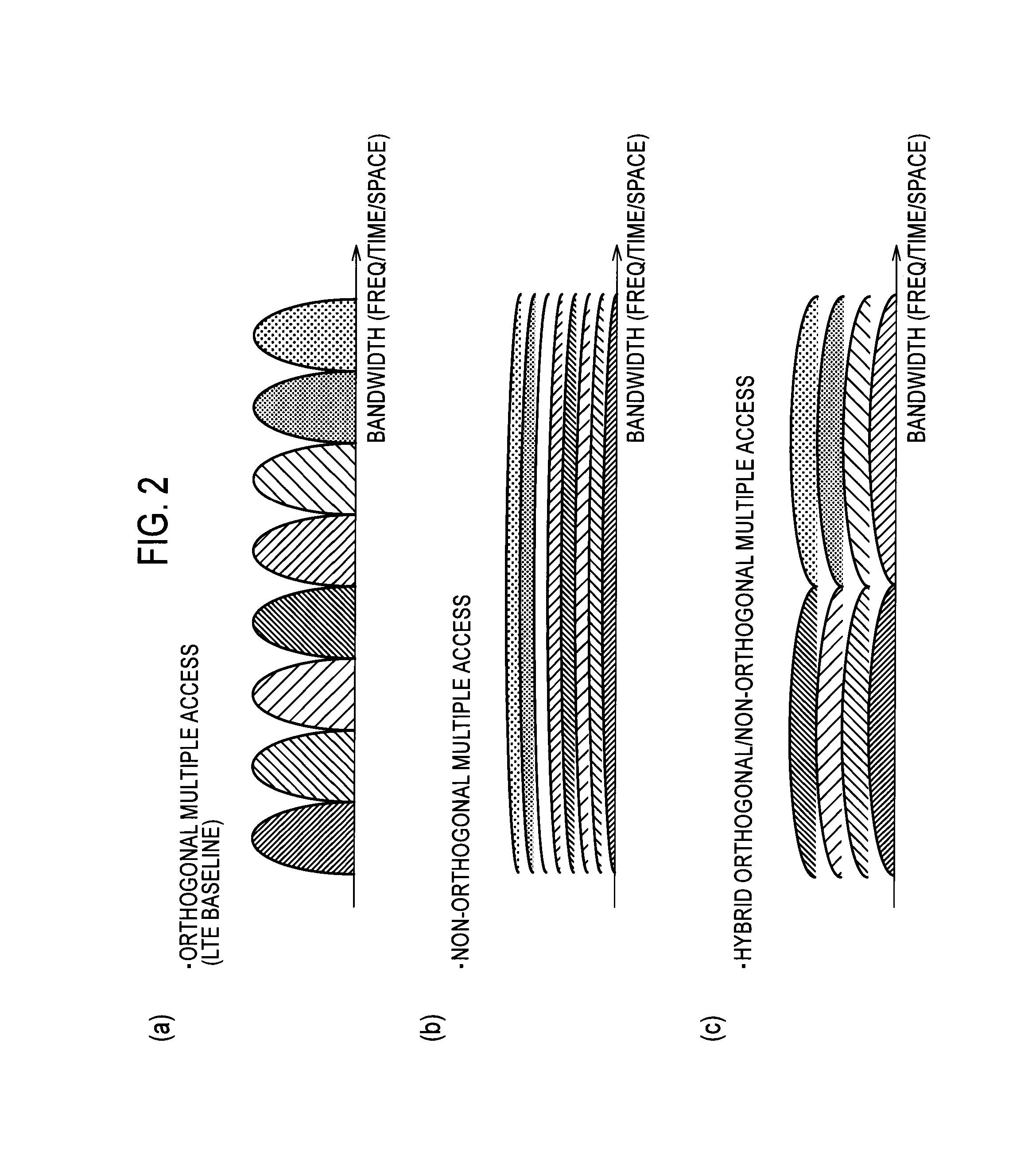
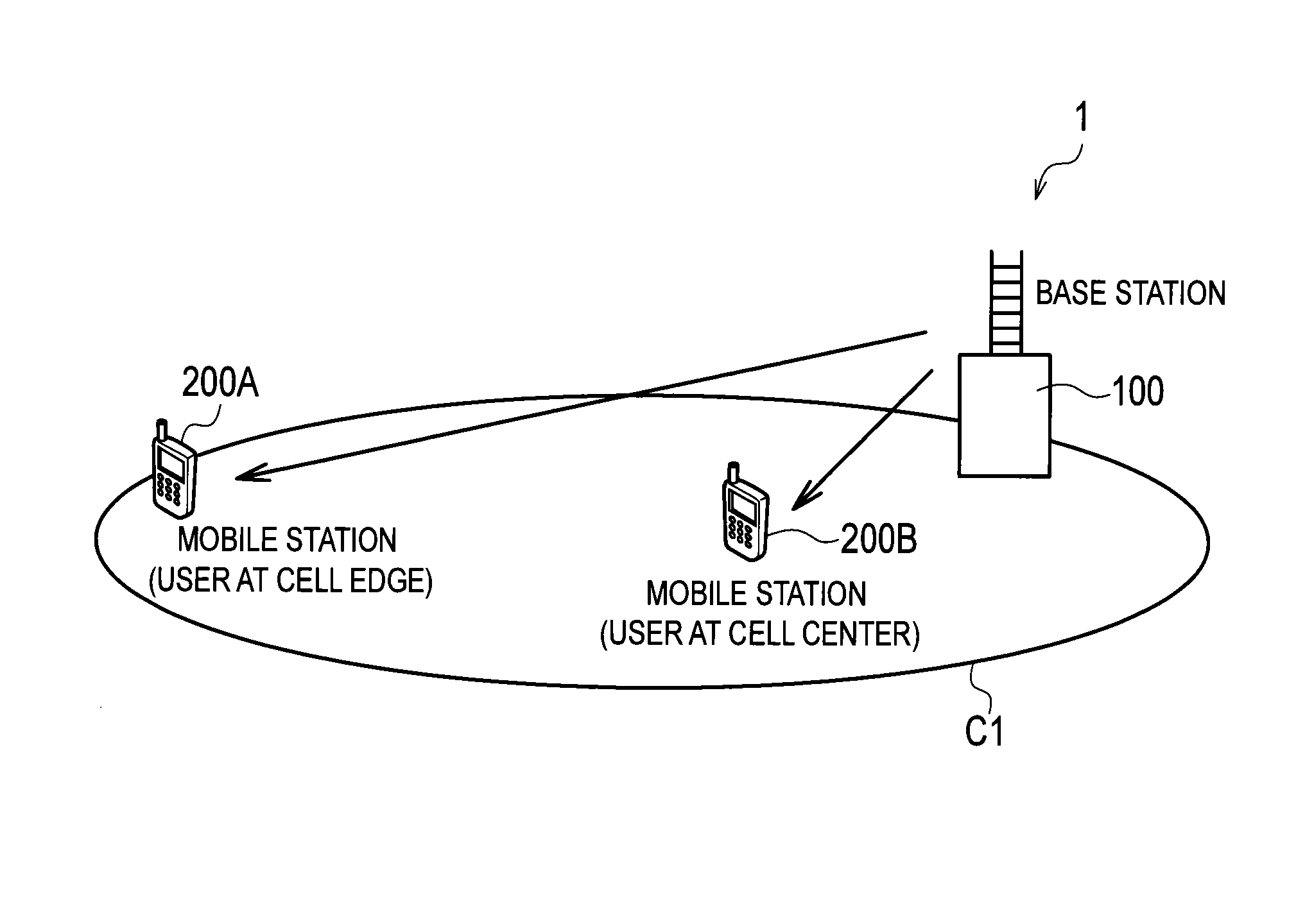
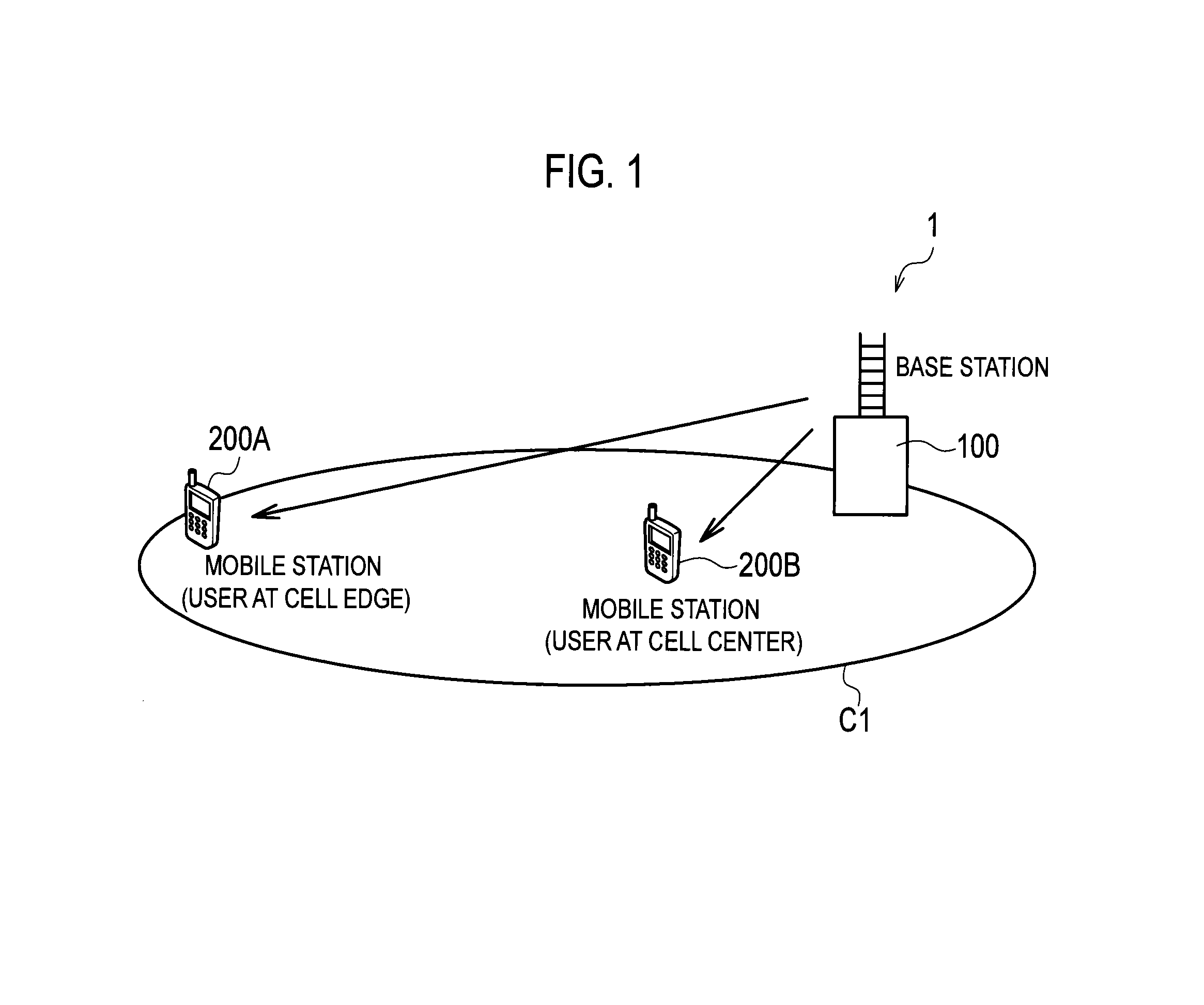
InactiveUS20140050279A1Suppressing cost increaseSuppress processing delayModulated-carrier systemsSecret communicationResource blockMobile station
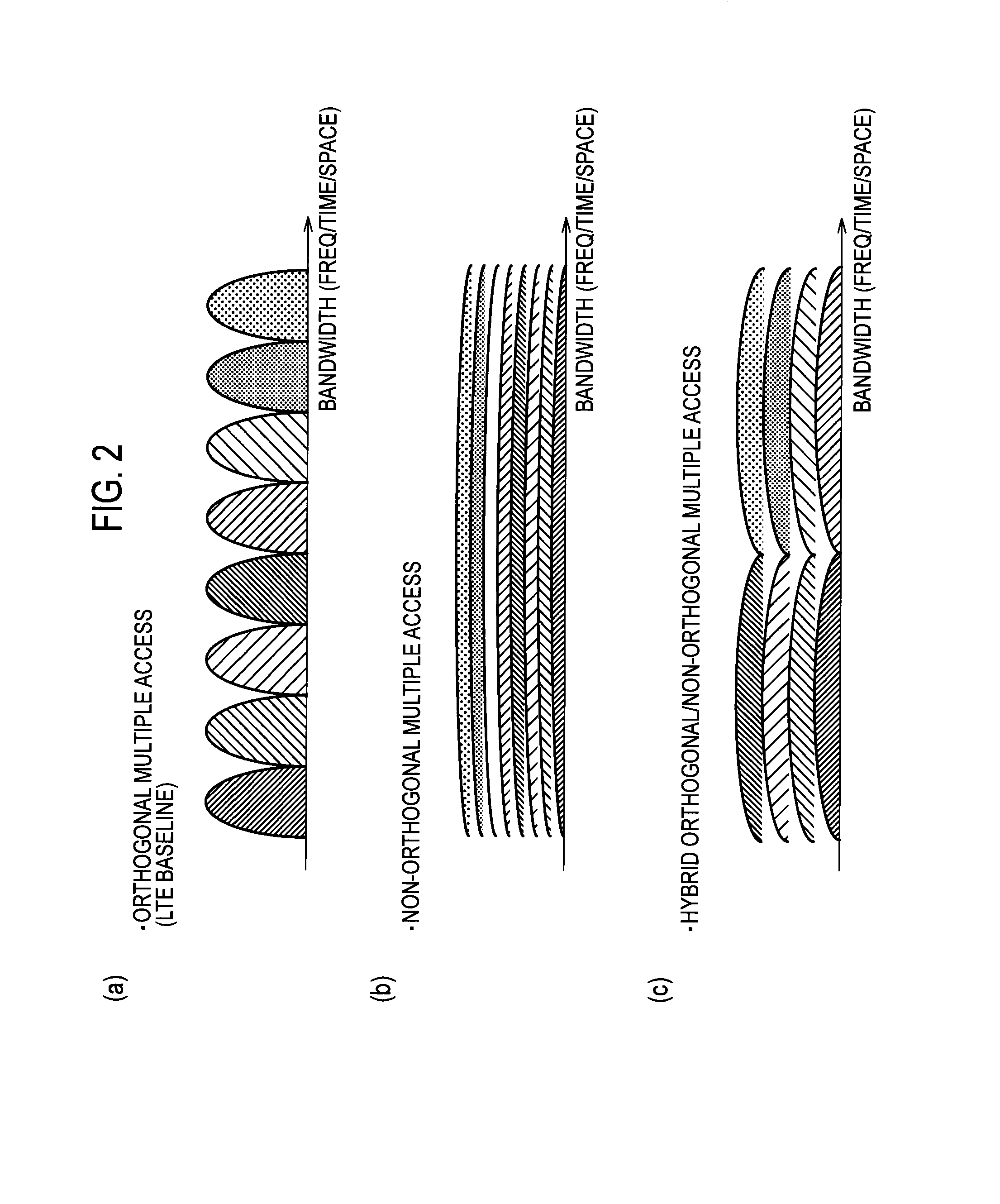
Provided are a receiver, a transmitter and a radio communication method capable of using non-orthogonal multiple access while suppressing cost increase and processing delay. A mobile station 200A receives non-orthogonal signals, also receives a reference signal to be used for interference cancellation, and extracts the non-orthogonal signal addressed to the mobile station 200A from the received non-orthogonal signals by demodulating and cancelling the radio signal addressed to another mobile station. In addition, the mobile station 200A demodulates the extracted non-orthogonal signal addressed to the mobile station 200A on the basis of the reference signal. The reference signal is multiplexed in the same radio resource block as a resource block allocated to the non-orthogonal signals, and is multiplexed in the radio resource block only when at least one signal is scheduled in the radio resource block.
Owner:NTT DOCOMO INC
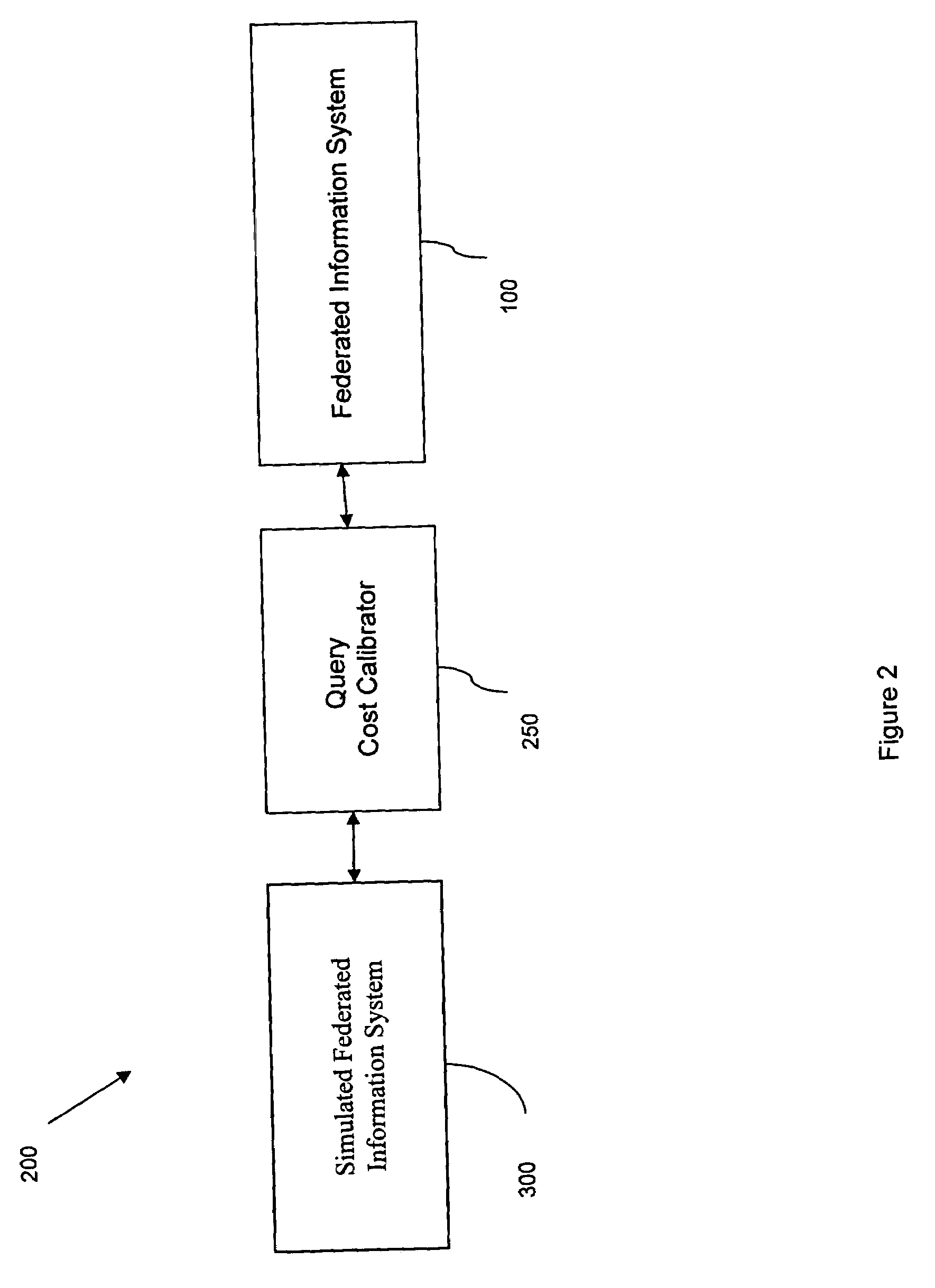
Query routing of federated information systems for fast response time, load balance, availability, and reliability
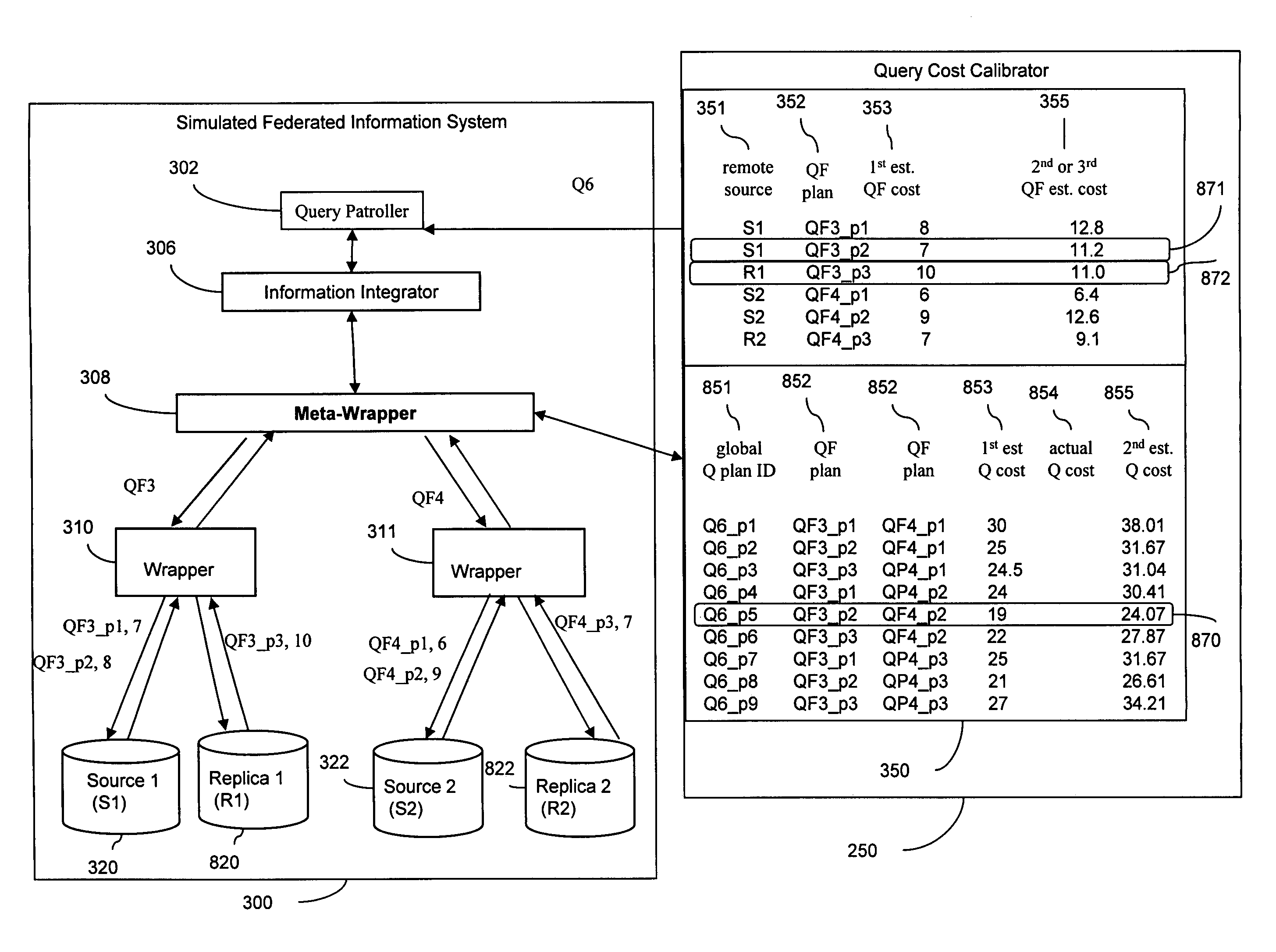
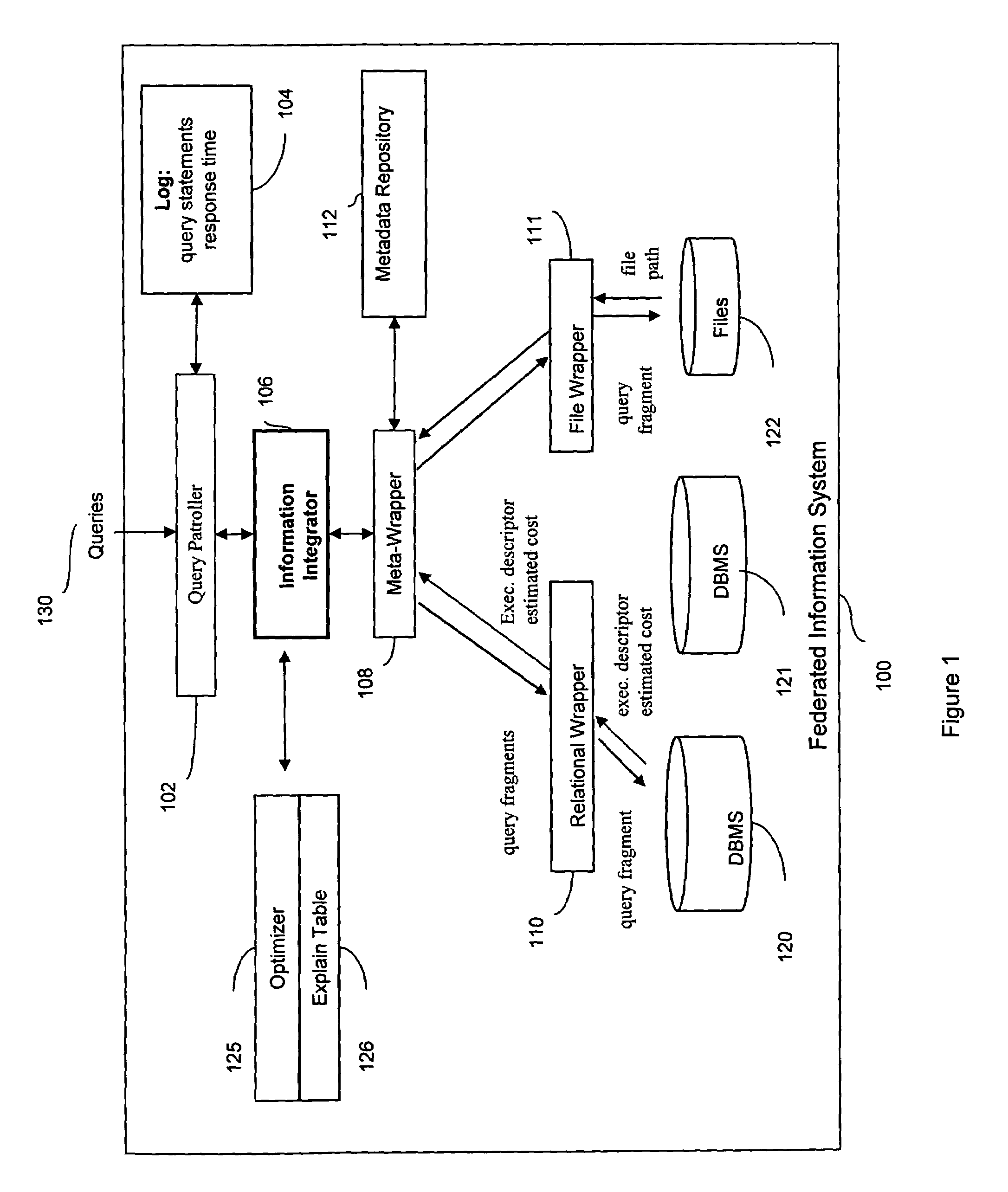
InactiveUS7383247B2Digital data information retrievalData processing applicationsLoad distributionQuery statement
Disclosed are embodiments of a system for optimizing query processing in a federated information system. The system may be used to identify alternative query plans in a simulated environment and to calculate cost estimates associated with the alternative query plans, based not only on database statistics and query statements, but also based on workload and processing latencies associated with specific data source and with the federated information system as a whole. In addition the calculated cost estimates may also factor in data source availability and reliability. The system may use the alternative query plans and the associated cost estimates to influence query processing in a federated information system by feeding to the federated information system query plans that allow for cost-efficient query plan-level load distribution, cost-efficient query fragment plan-level load distribution, and load distribution based upon quality of service cost constraints.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
System for Proximity Determination
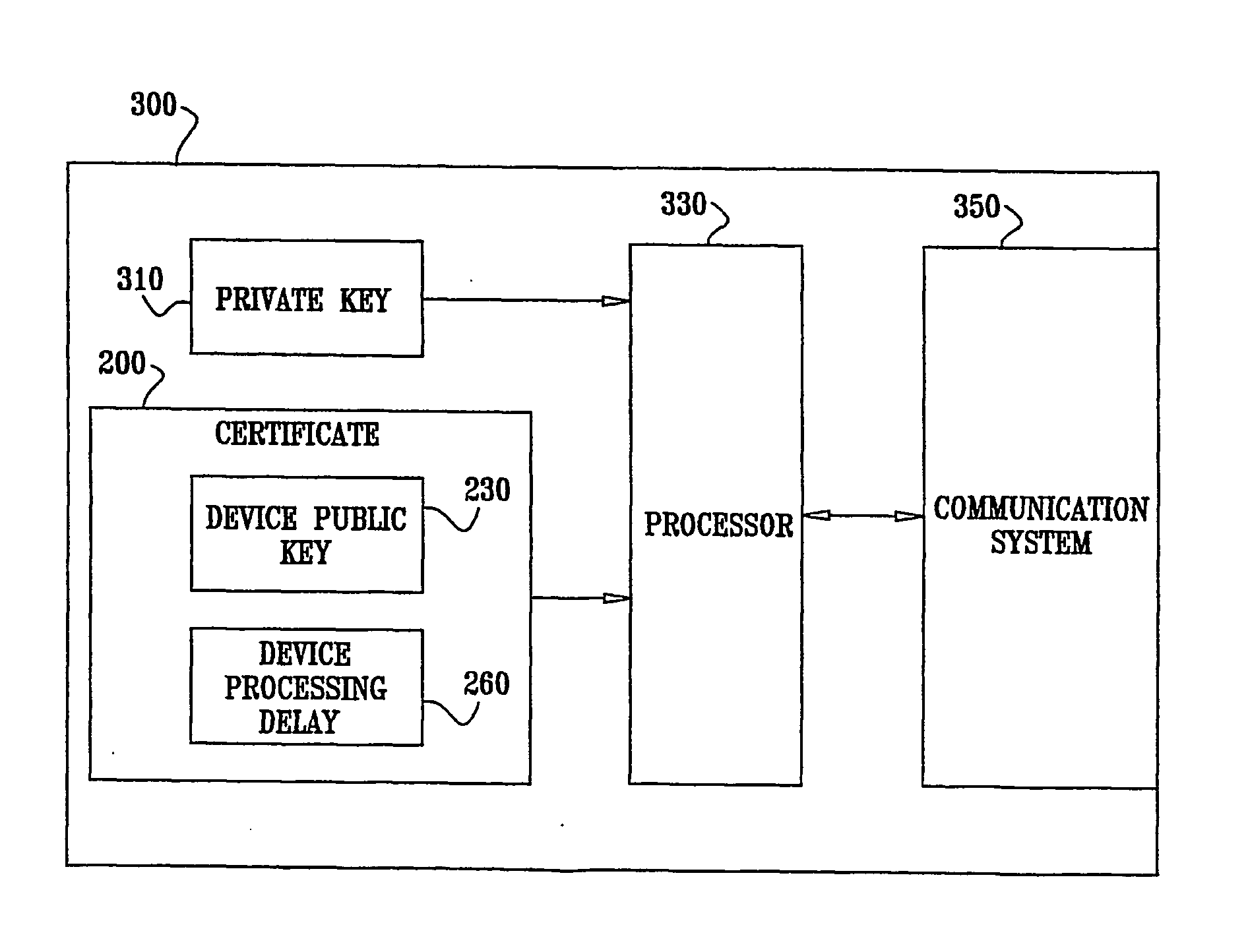
ActiveUS20070300070A1Minimizes hardware requirementSimple methodDigital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationTime processingProcessing delay
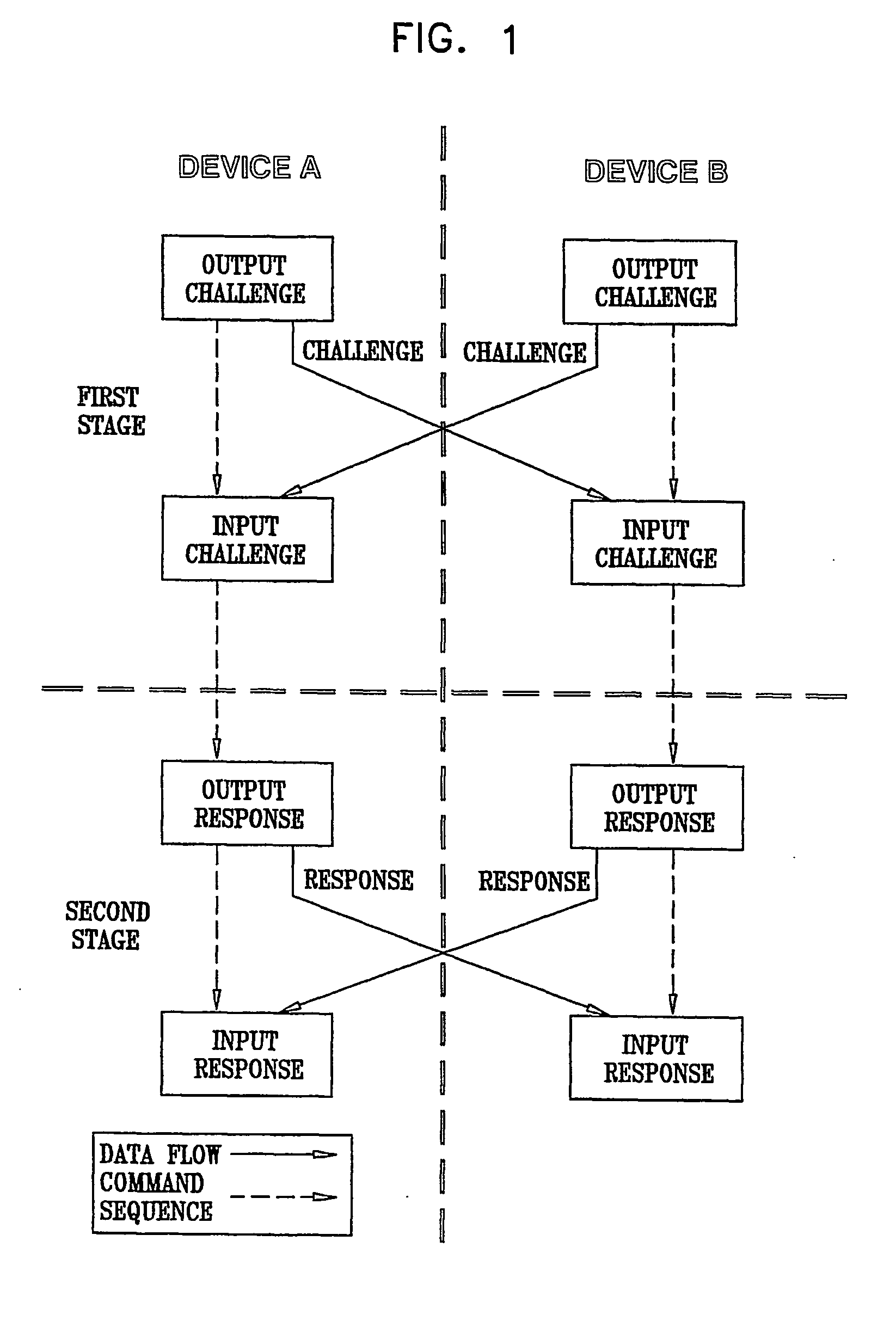
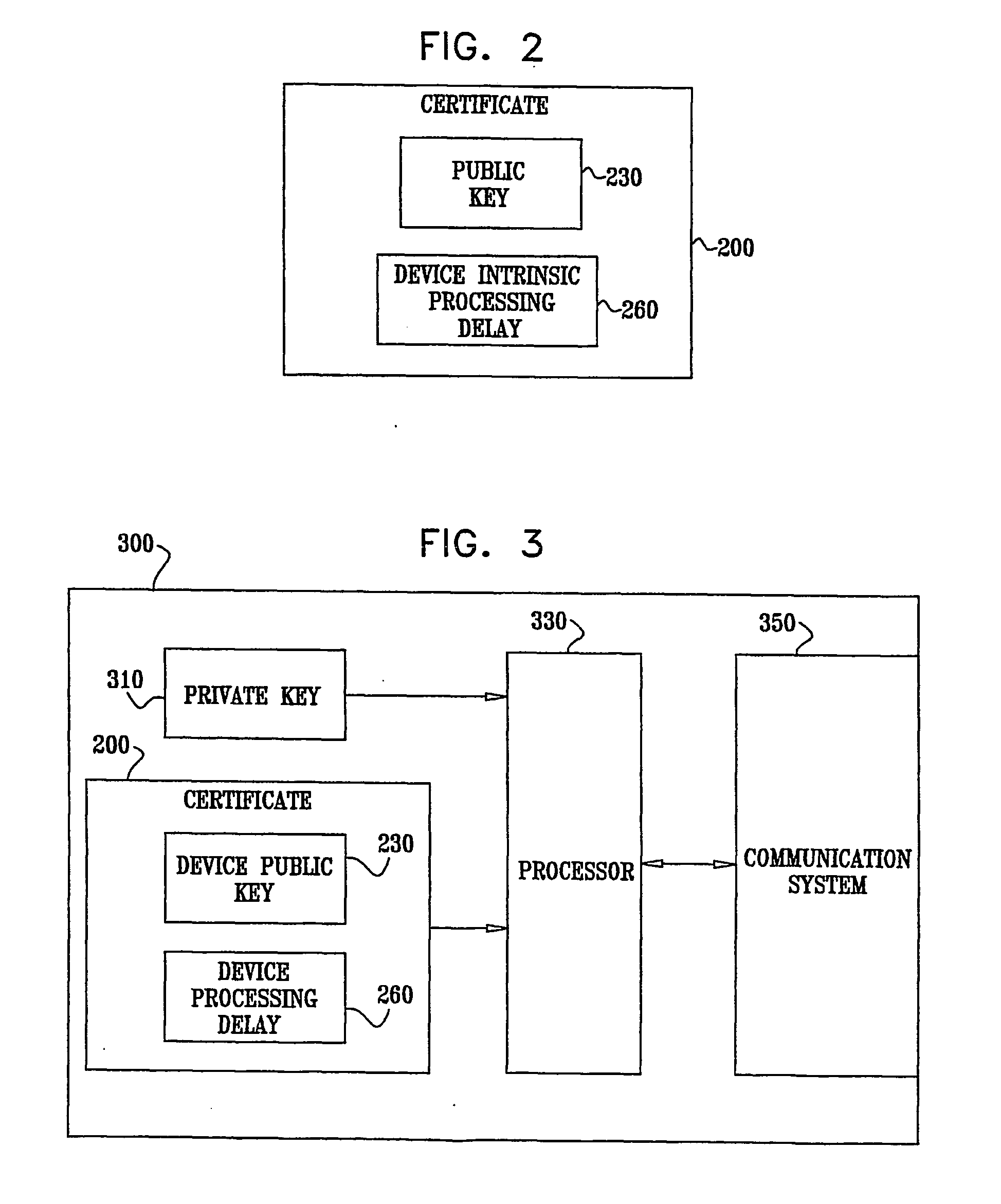
A method for determining proximity between a first device and a second device, the method comprising providing a first device storing a first device private key, the first device having an associated secure first device certificate storing secured information, the secured information comprising a first device public key corresponding to the first device private key, providing a second device storing a second device private key, the second device having an associated secure second device certificate storing secured information, the secured information comprising a second device public key corresponding to the second device private key, and a second device processing delay, providing a copy of the second device certificate to the first device, establishing a secure authenticated channel between the first device and the second device, sending a proximity challenge from the first device to the second device, the proximity challenge including a numeric challenge value, receiving the proximity challenge at the second device, processing the proximity challenge at the second device to produce the response to the proximity challenge, and sending the response to the proximity challenge from the second device to the first device, receiving the response to the proximity challenge at the first device, and performing the following at the first device verifying, at the first device, that the response to the proximity challenge is legitimate, determining a gross time between sending the proximity challenge and receiving the response to the proximity challenge, subtracting the second device processing delay from the gross time to produce a net response time, and comparing the net response time to a first threshold and determining whether the first device and the second device are in proximity based on a result of the comparing. Related methods and apparatus are also described.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Method for conducting HARQ with a wireless communications system
InactiveUS20110055652A1Error prevention/detection by using return channelTransmission systemsCommunications systemHybrid automatic repeat request
Provided is a method of performing hybrid automatic repeat request (HARQ) of a receiver in a wireless communication system. The method includes: receiving data in a transmission time interval (TTI) unit consisting of a plurality of consecutive subframes; and transmitting acknowledgment (ACK) / non-acknowledgment (NACK) for the received data, wherein the data is received using a plurality of redundancy versions respectively allocated to the plurality of subframes, and the ACK / NACK is transmitted with an interval of a predetermined processing delay from a transmission time of a specific redundancy version among the plurality of redundancy versions.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
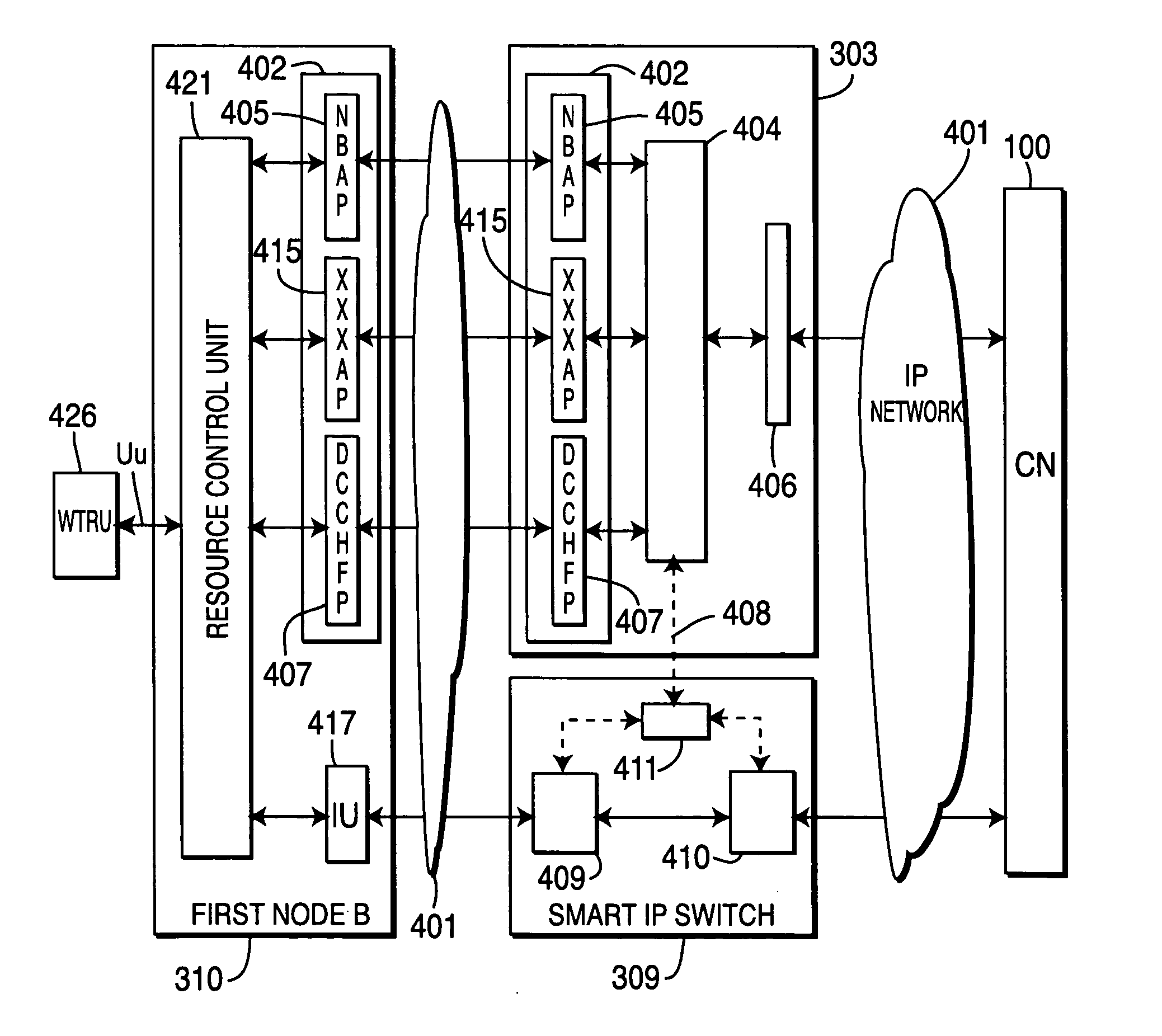
Centralized radio network controller
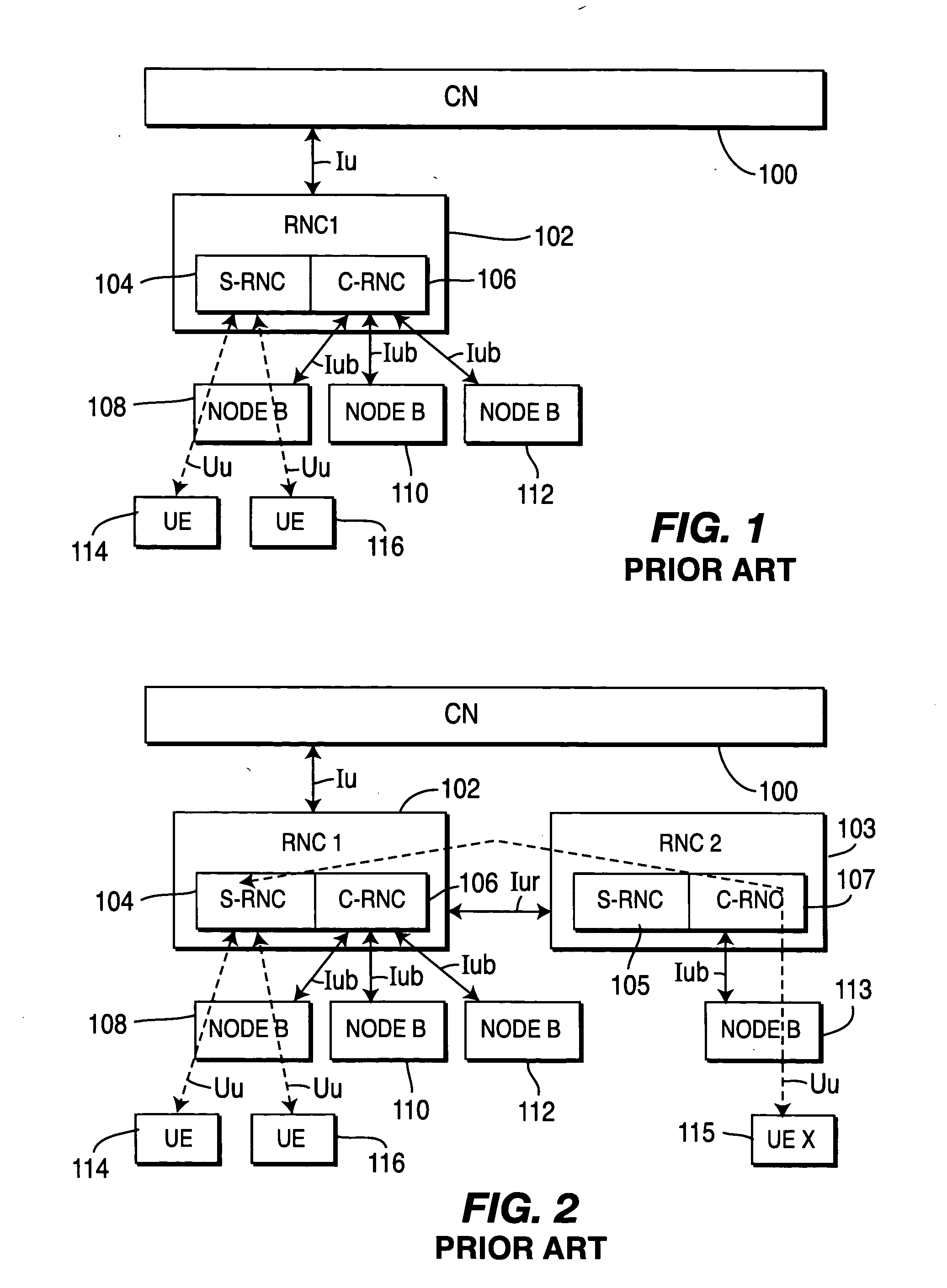
InactiveUS20050068967A1Efficient processingImprove Radio Resource Management (RRM)Multiplex system selection arrangementsData switching by path configurationWireless resource managementRadio access network
In a radio access network, novel systems and methods reduce processing delay, and improve integration with IP networks, by separating user data from connection management and control data at a Node B or at a base station. The user data are routed to an IP (Internet Protocol) switch, whereas the connection management and control data are routed to a centralized radio network controller (RNC). Pursuant to a second embodiment of the invention, a centralized RNC provides improved radio resource management (RRM) functionality by handing all connection management and control data for a plurality of Node B's, thereby simplifying the switching of user data throughout the radio access network. Pursuant to a third embodiment of the invention, a smart IP switch is equipped to switch user data without core network (CN) involvement. Downlink user data are switched independently of uplink user data.
Owner:INTERDIGITAL TECH CORP
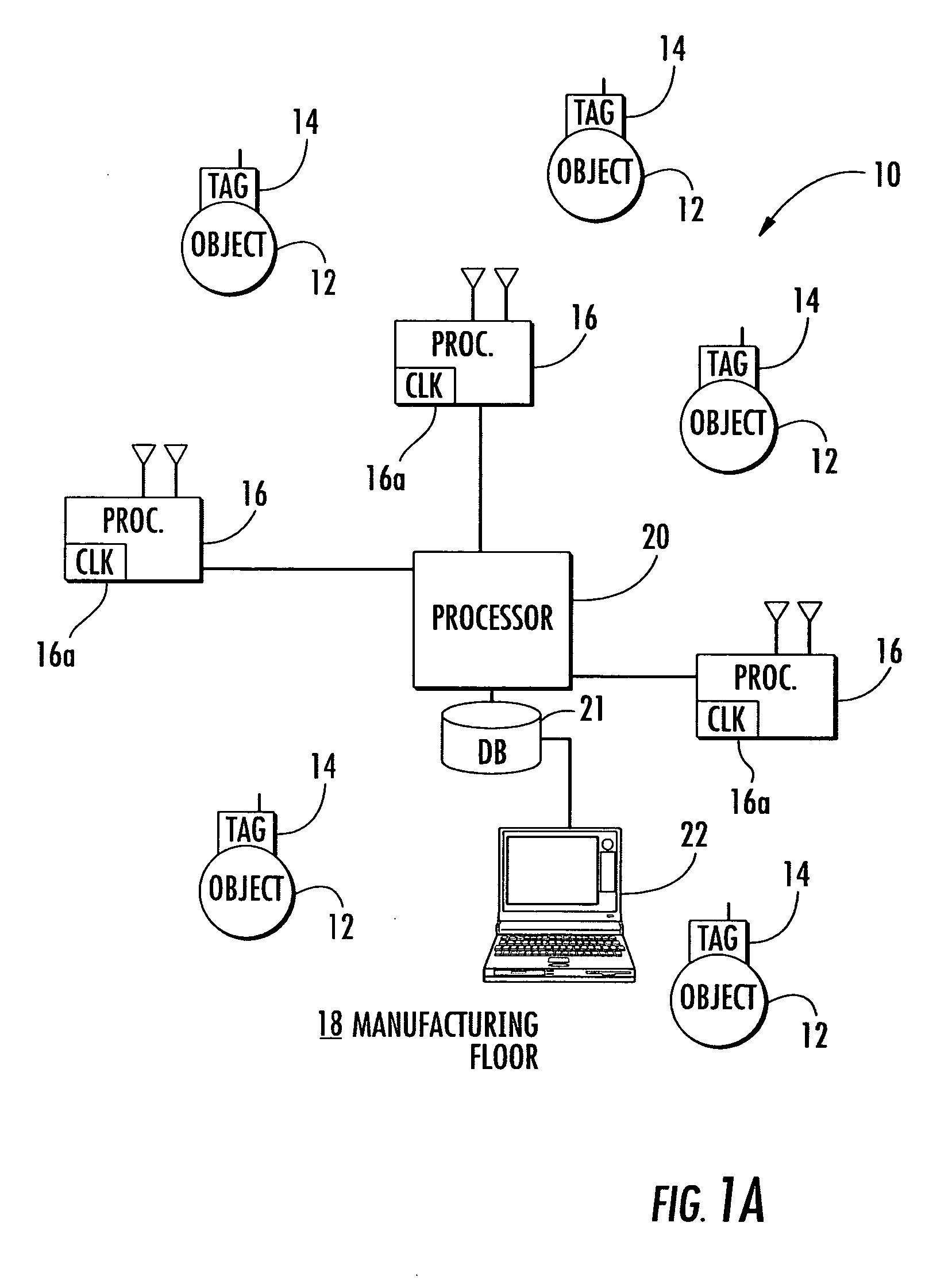
Location system and method that achieves time synchronized network performance using unsynchronized receiver clocks
ActiveUS7190271B2Synchronisation arrangementDirection finders using radio wavesPositioning systemTransmitter
A system for locating an object within a monitored environment includes a tag transmitter that transmits an RF signal to receivers having unsynchronized clocks. A processor is operative with each receiver and determines clock timing relationships for the clocks based on one of at least propagation or processing delays in the receivers to synchronize receiver performance.
Owner:ZEBRA TECH CORP
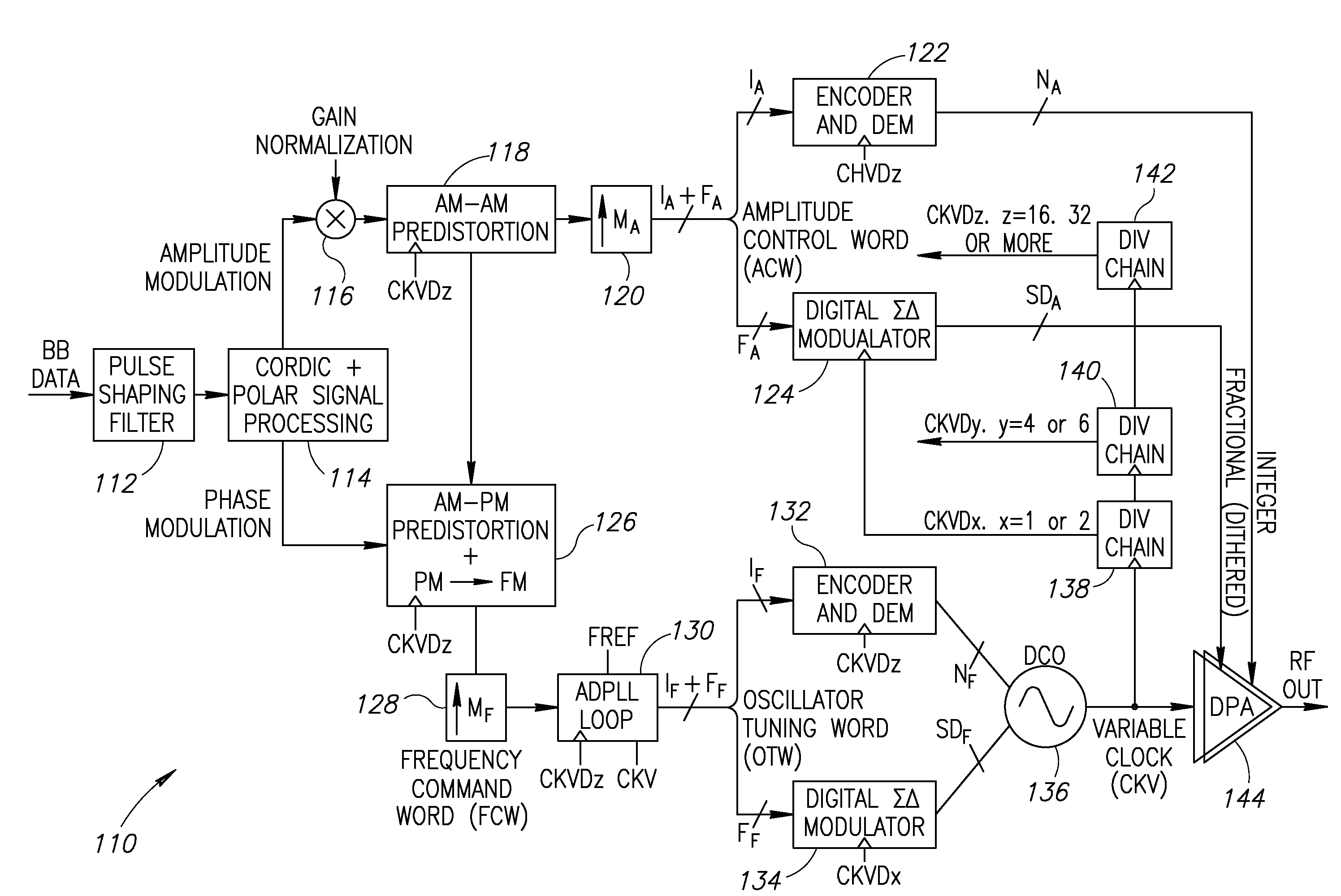
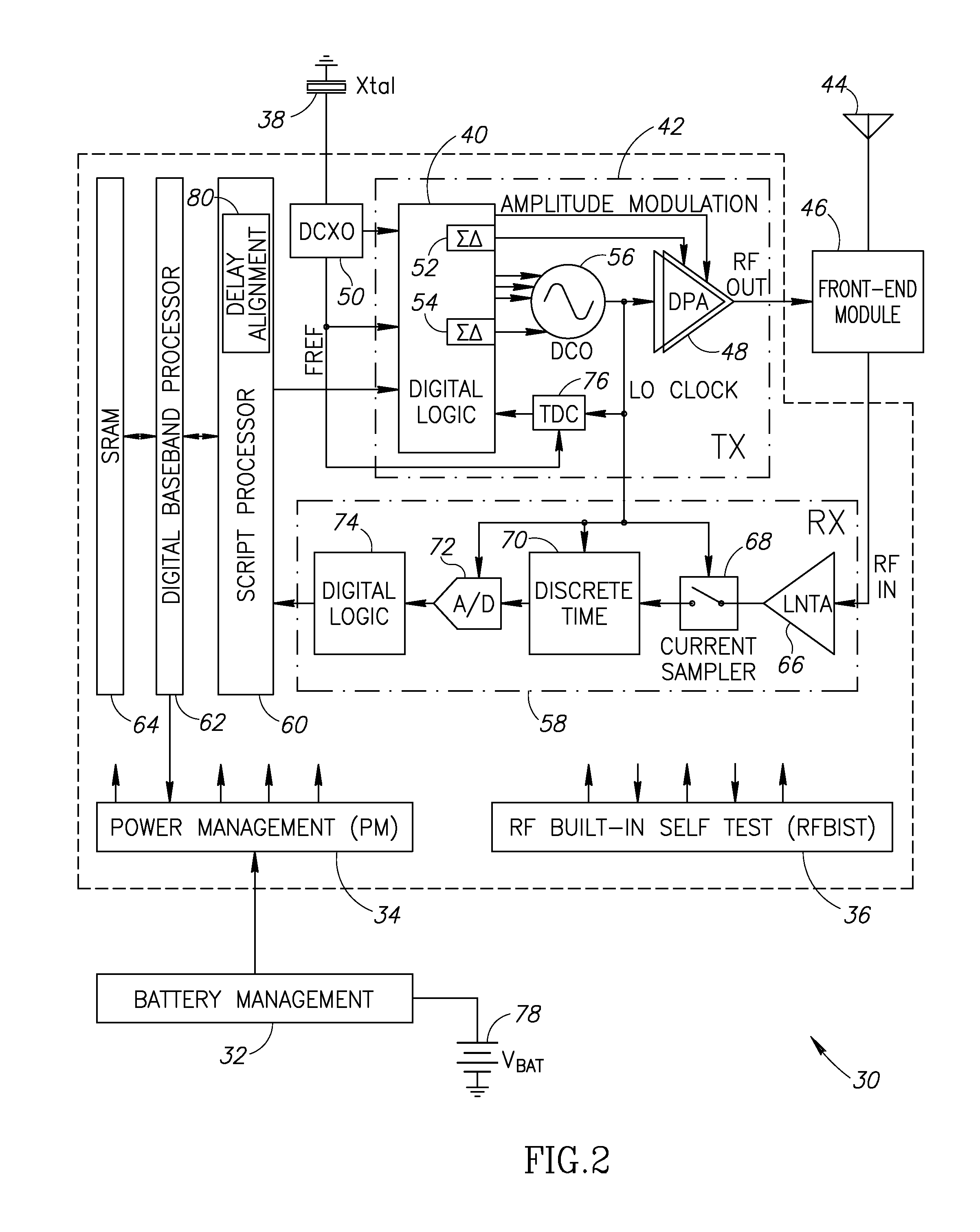
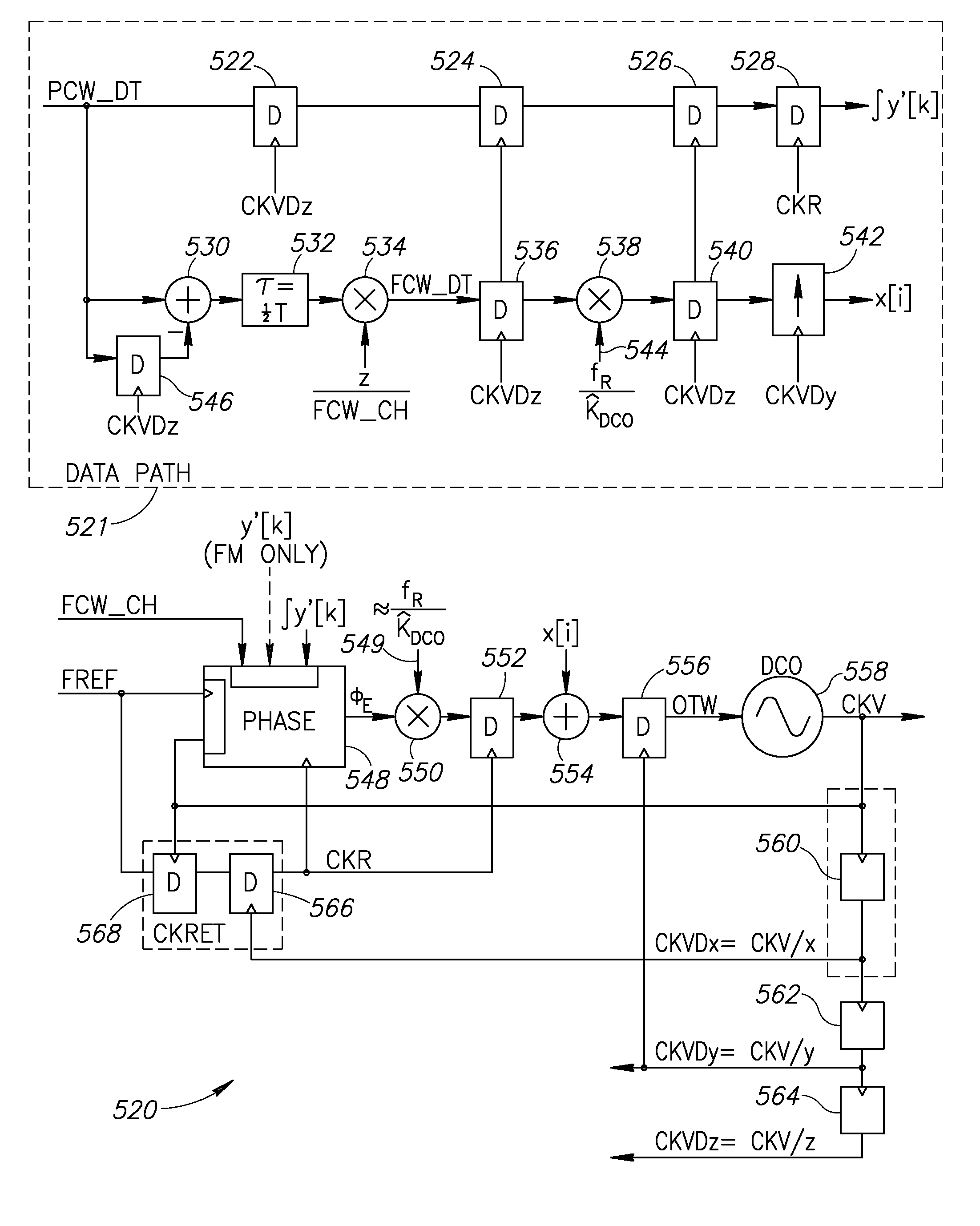
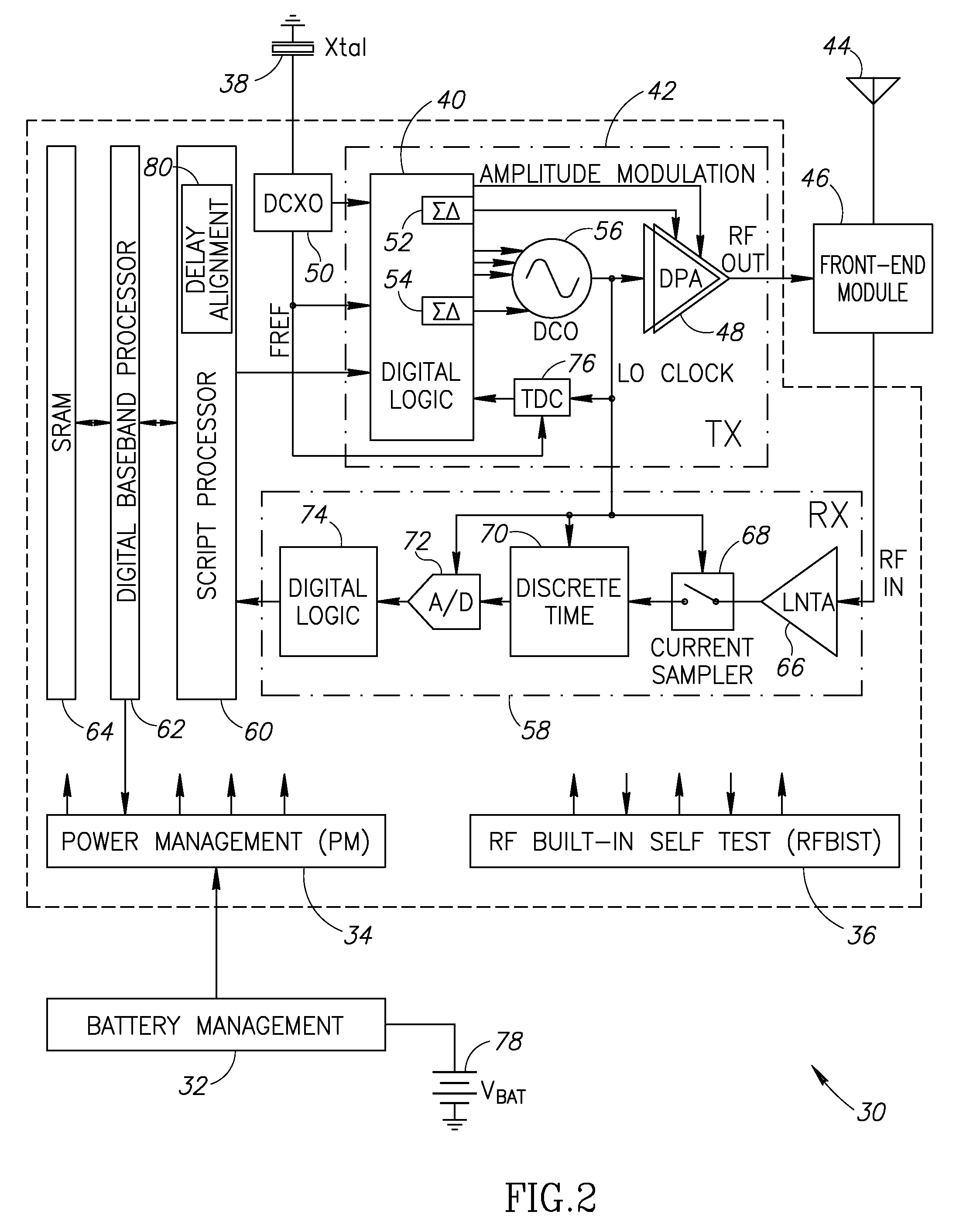
Precise delay alignment between amplitude and phase/frequency modulation paths in a digital polar transmitter
ActiveUS20070189417A1Achieve alignmentHigh phase modulation accuracy requirementSimultaneous amplitude and angle modulationModulation with suppressed carrierAudio power amplifierNanosecond
A novel apparatus for and method of delay alignment between amplitude and phase / frequency modulation paths in a digital polar transmitter. The invention provides a fully digital delay alignment mechanism where better than nanosecond alignment is achieved by accounting for processing delays in the digital circuit modules of the transmitter and by the use of programmable delay elements spread across several clock domains. Tapped delay lines compensate for propagation and settling delays in analog elements such as the DCO, dividers, quad switch, buffers, level shifters and digital pre-power amplifier (DPA). A signal correlative mechanism is provided whereby data from the amplitude and phase / frequency modulation paths to be matched is first interpolated and then cross-correlated to achieve accuracy better than the clock domain of comparison. Within the ADPLL portion of the transmitter, precise alignment of reference and direct point injection points in the ADPLL is provded using multiple clock domains, tapped delay lines and clock adjustment circuits.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Receiver, transmitter and radio communication method
InactiveUS20140044091A1Suppressing cost increaseSuppress processing delayPower managementTransmission monitoringInterference cancellerControl signal
Provided are a receiver, a transmitter and a radio communication method capable of using non-orthogonal multiple access while suppressing cost increase and processing delay. A mobile station 200A includes a target user control signal detector 230 and an interfering user control signal detector 240 which are configured to receive a control signal to be used to cancel a non-orthogonal signal by interference canceller. The control signal includes control information containing a radio resource block allocated to the non-orthogonal signal addressed to another mobile station. The mobile station 200A demodulates and cancels the radio signal addressed to the other mobile station on the basis of the control signal.
Owner:NTT DOCOMO INC
Method for handover of terminal using multi-connection in cellular communication system
InactiveUS20140153423A1Problems can be minimizedProcess be minimizedError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsCellular communication systemsExtremely high frequency
A method for handover of a terminal using a multi-connection in a cellular communication system is disclosed. The method for handover according to the present invention includes a multi-connection setting procedure of setting a connection to a second base station in addition to a connection to a first base station according to movement of a terminal in a direction from the first base station to the second base station, and a connection release procedure of releasing the connection to the first base station. Specifically, the present invention may be applied in a multi-beam management environment of super high frequency (SHF) and extremely high frequency (EHF) bandwidths, and may obtain an effect of decreasing signaling overhead and process latency of a conventional handover method.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
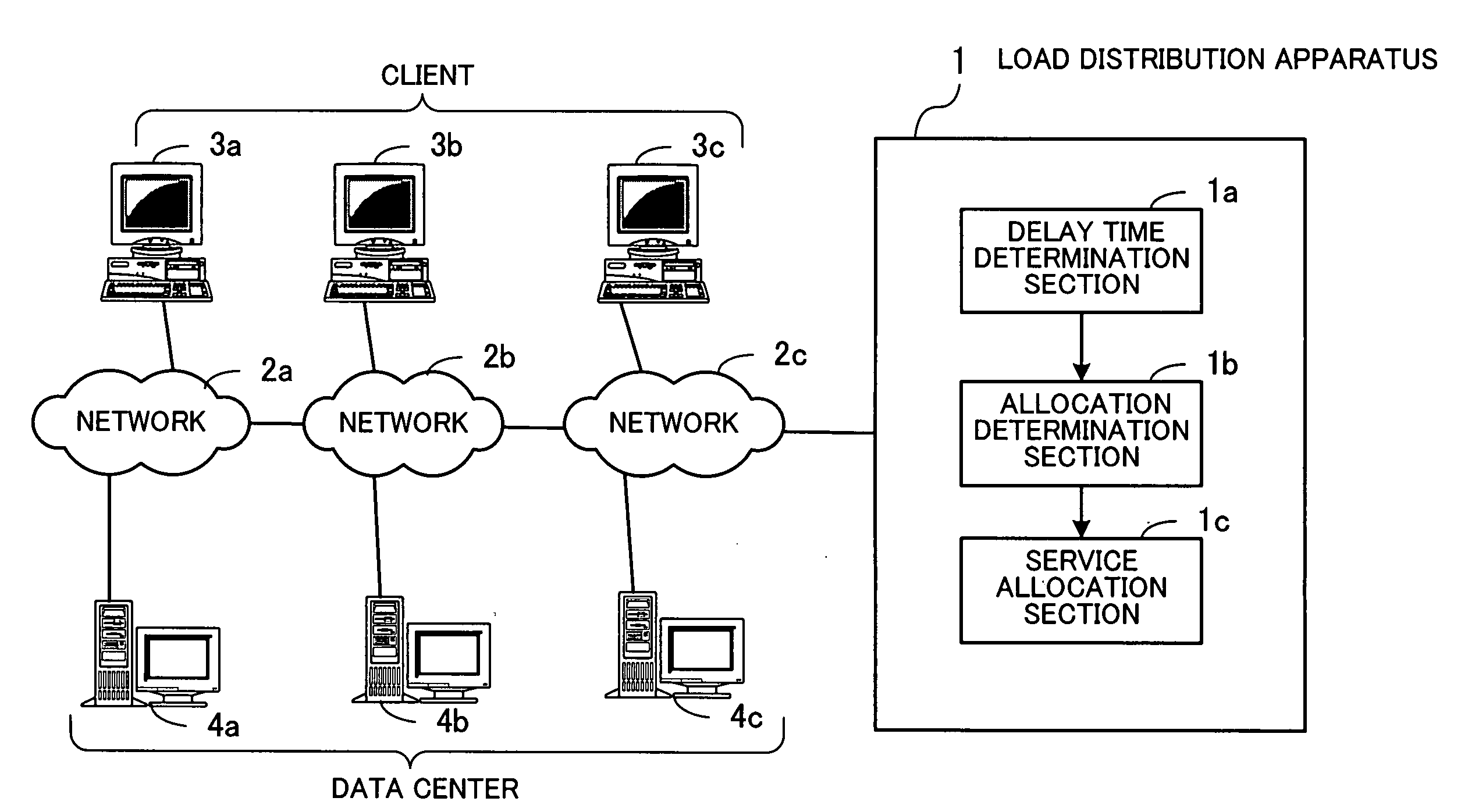
Record medium with a load distribution program recorded thereon, load distribution method, and load distribution apparatus
InactiveUS20060271700A1Quality improvementMultiple digital computer combinationsData switching networksData centerDelayed time
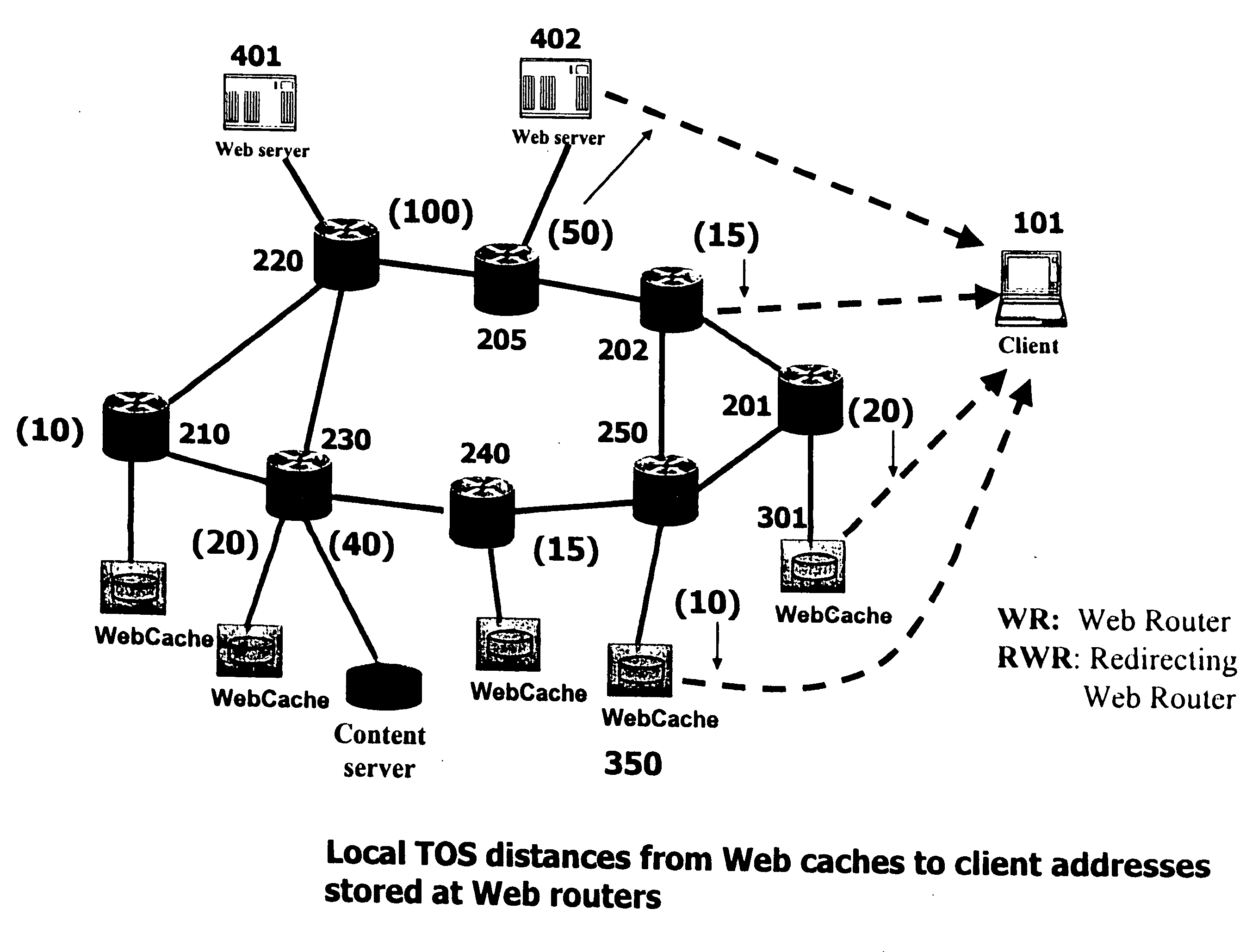
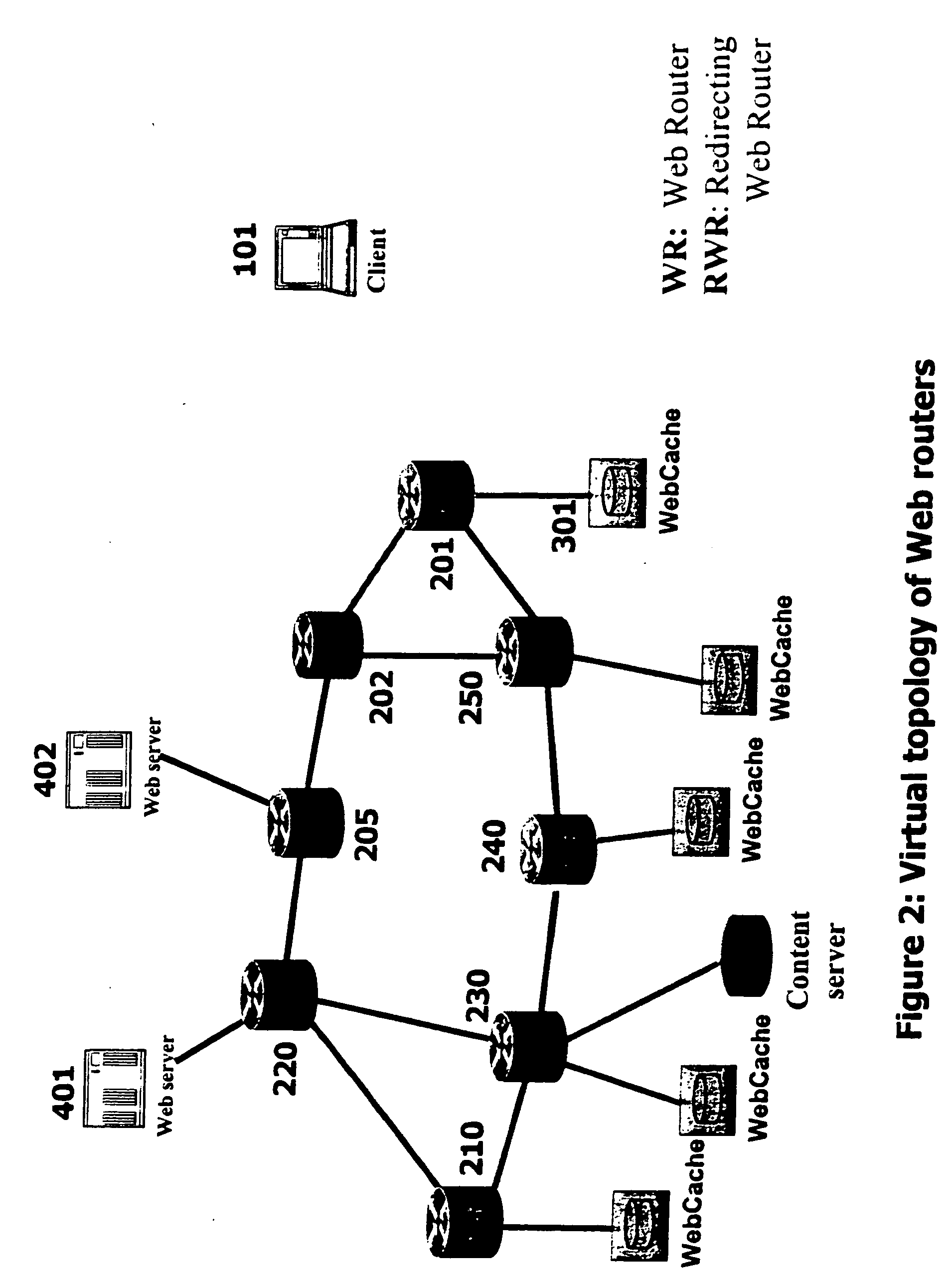
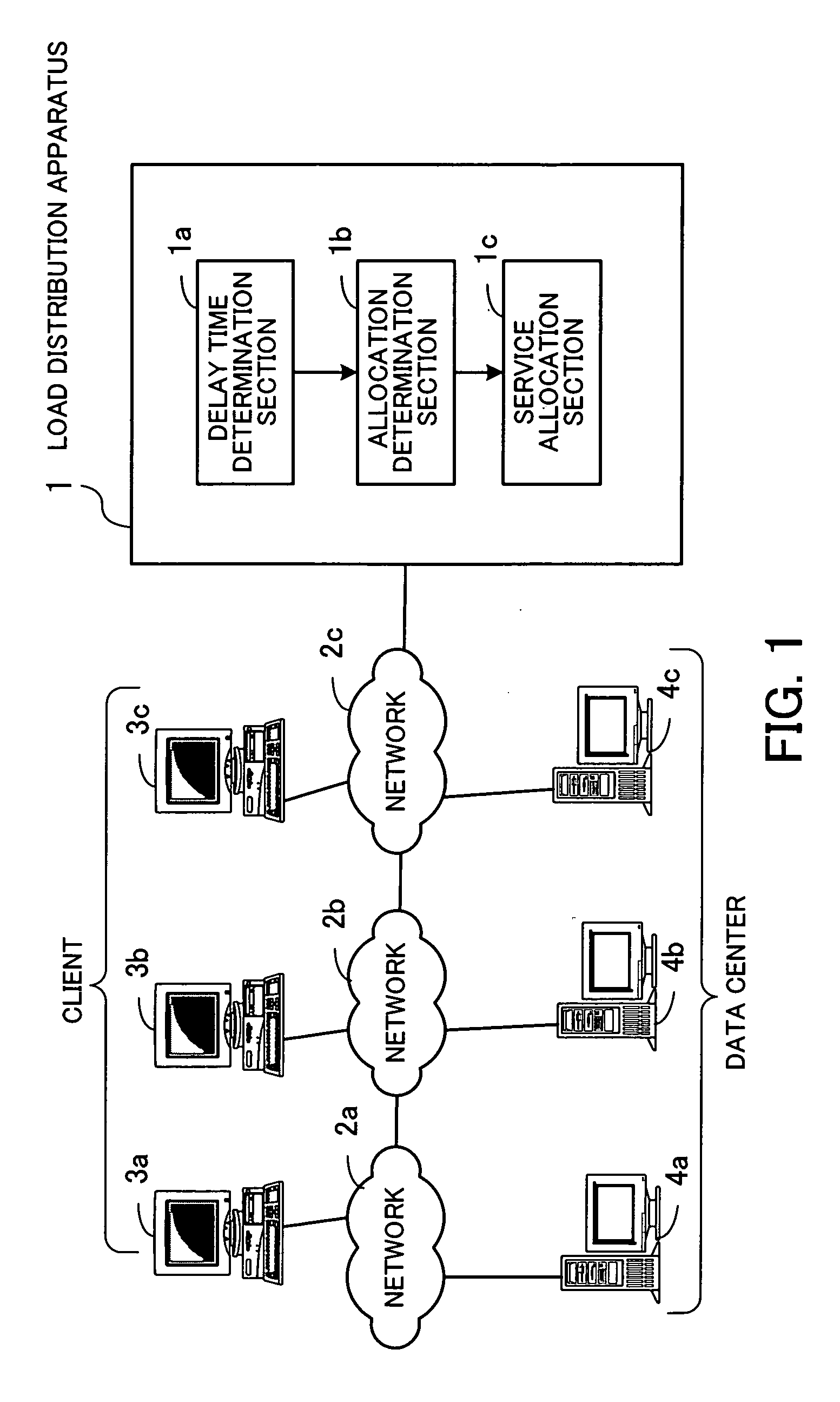
A record medium on which a load distribution program capable of dynamically determining a service providing server which can provide a service of high quality according to a place where a client is installed is recorded. A delay time determination section analyzes a request sent from a client, identifies a position on a network of the client, and determines processing delay time the client takes to receive a response from each data center on the basis of a communication path between the position of the client and a position on the network of each data center. An allocation determination section preferentially selects a data center which can provide a service to the client after shortest processing delay time as a recommended data center on the basis of the processing delay time determined by the delay time determination section. A service allocation section makes a server in the recommended data center provide the service to the client which outputted the request.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Receiver, transmitter and radio communication method
ActiveUS20140029562A1Suppressing cost increaseSuppress processing delayModulated-carrier systemsCriteria allocationInterference cancellerInterference (communication)
Provided are a receiver, a transmitter and a radio communication method capable of using non-orthogonal multiple access while suppressing cost increase and processing delay. A mobile station 200A includes a physical channel segmentation unit 210 and data demodulating / decoding units 220. A radio resource block allocated to non-orthogonal signals is defined in a frequency domain, a time domain and a non-orthogonal multiplex domain. The non-orthogonal multiplex domain has multiple levels corresponding to the number of interference cancellations by the data demodulating / decoding units 220. Interference canceller of the mobile station 200A cancels a non-orthogonal signal whose allocated radio resource block is at a lower level than that of the mobile station 200A.
Owner:NTT DOCOMO INC
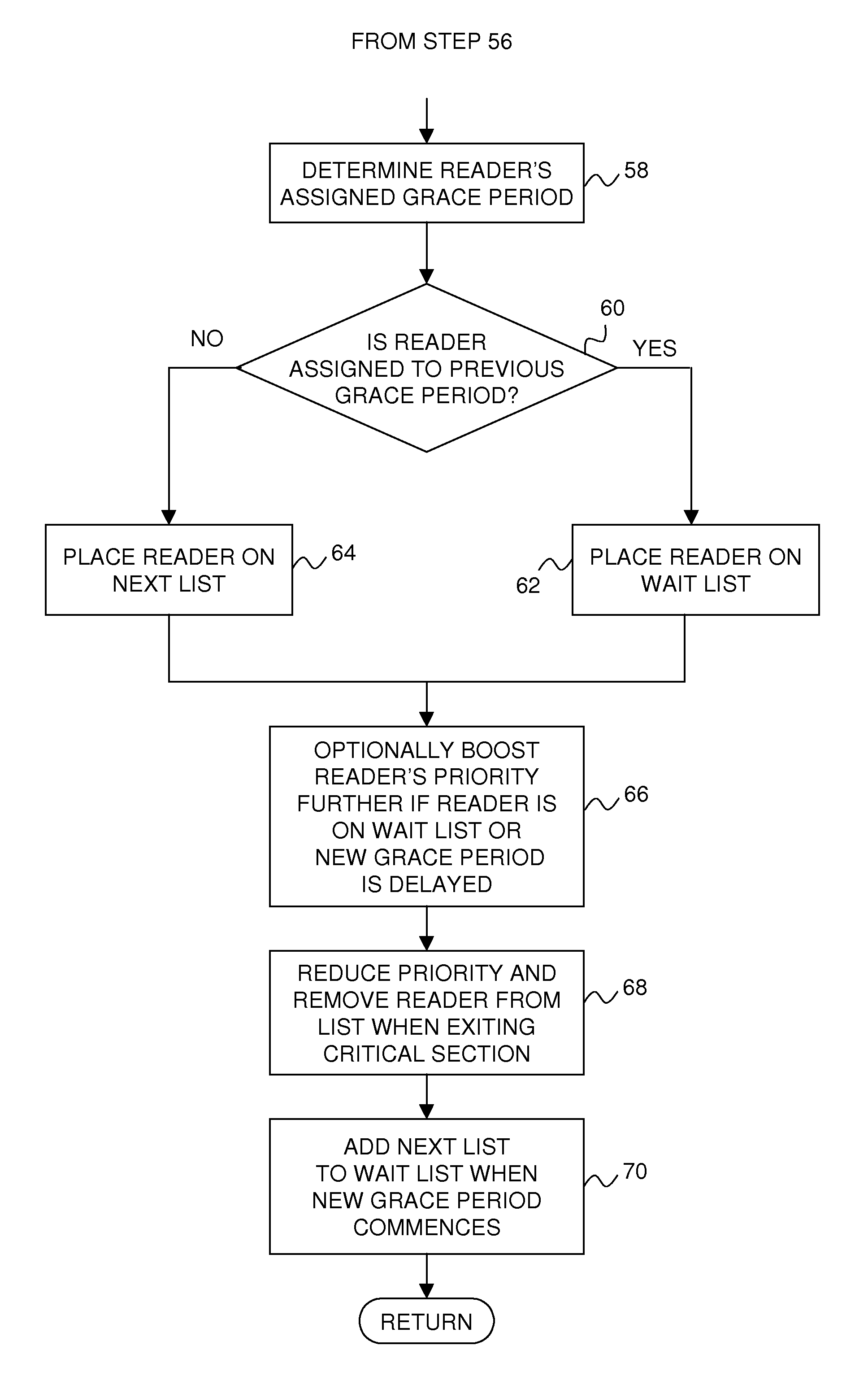
Efficiently boosting priority of read-copy update readers in a real-time data processing system
ActiveUS7734879B2Raise priorityMinimum of processing overheadProgram synchronisationMemory systemsReal-time dataRead-copy-update
A technique for efficiently boosting the priority of a preemptable data reader in order to eliminate impediments to grace period processing that defers the destruction of one or more shared data elements that may be referenced by the reader until the reader is no longer capable of referencing the data elements. Upon the reader being subject to preemption or blocking, it is determined whether the reader is in a read-side critical section referencing any of the shared data elements. If it is, the reader's priority is boosted in order to expedite completion of the critical section. The reader's priority is subsequently decreased after the critical section has completed. In this way, delays in grace period processing due to reader preemption within the critical section, which can result in an out-of-memory condition, can be minimized efficiently with minimal processing overhead.
Owner:TWITTER INC
Delay alignment in a closed loop two-point modulation all digital phase locked loop
InactiveUS20070189431A1Easy to adjustAchieve alignmentSimultaneous amplitude and angle modulationPulse automatic controlNanosecondAudio power amplifier
A novel apparatus for and method of delay alignment in a closed loop two-point modulation all digital phase locked loop (ADPLL). The invention provides a fully digital delay alignment mechanism where better than nanosecond alignment is achieved by accounting for processing delays in the digital circuit modules of the transmitter and by the use of programmable delay elements spread across several clock domains. Tapped delay lines compensate for propagation and settling delays in analog elements such as the DCO, dividers, quad switch, buffers, level shifters and digital pre-power amplifier (DPA). A signal correlative mechanism is provided whereby data from the amplitude and phase / frequency modulation paths to be matched is first interpolated and then cross-correlated to achieve accuracy better than the clock domain of comparison. Within the ADPLL portion of the transmitter, precise alignment of reference and direct point injection points in the ADPLL is provided using multiple clock domains, tapped delay lines and clock adjustment circuits.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
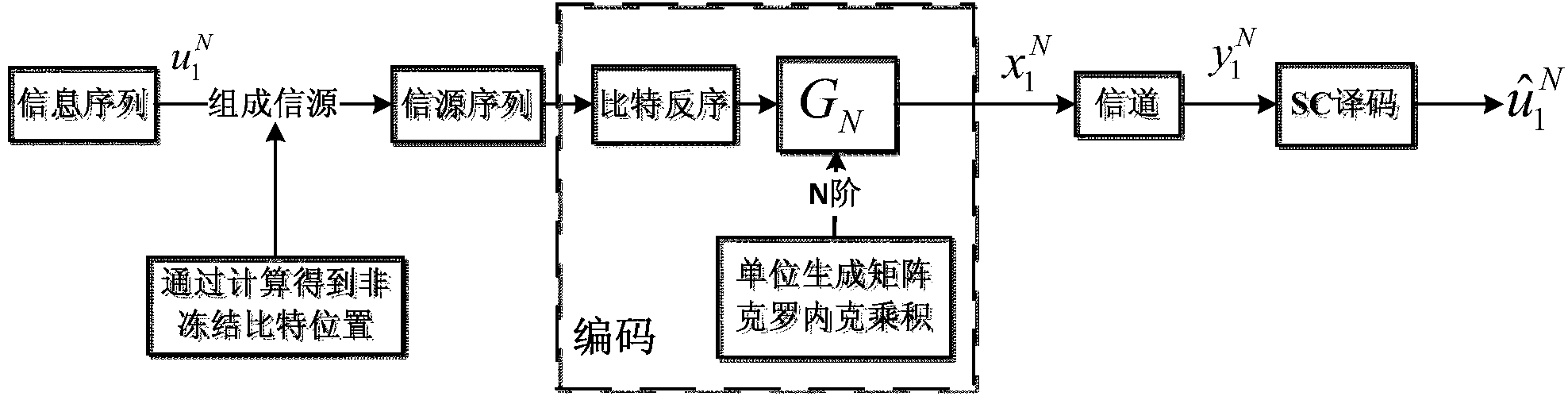
Polar code decoder and polar code decoding method based on probability calculation
ActiveCN104079382AImprove throughputDoes not affect the structureError preventionSequence transformationSoft information
The invention provides a polar code decoder and a polar code decoding method based on probability calculation. The polar code decoder comprises a probability sequence transformation module, a successive interference cancellation decoding module and a decision device, wherein the probability sequence transformation module is used for transforming received channel information into a first probability sequence; the successive interference cancellation decoding module is used for performing iteration processing on the first probability sequence based on a decision result of the decision device so as to obtain a second probability sequence and transforming the second probability sequence into a soft information value; and the decision device is used for performing hard decision on the soft information value and returning the decision result to the decoding module. According to the polar code decoder and the polar code decoding method based on probability calculation, the idea of the probability calculation is applied to the design of the polar code decoder, so that the processing delay of the polar code decoder can be reduced, and the total throughput of the polar code decoder can be increased greatly; and meanwhile, the polar code decoder and the polar code decoding method are simple in operation and good in universality and have better practical prospect.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Base station and mobile communication system
InactiveUS7068637B2Improve processing speedImproved channel efficiencyConnection managementRadio transmissionInterference cancellerSignal on
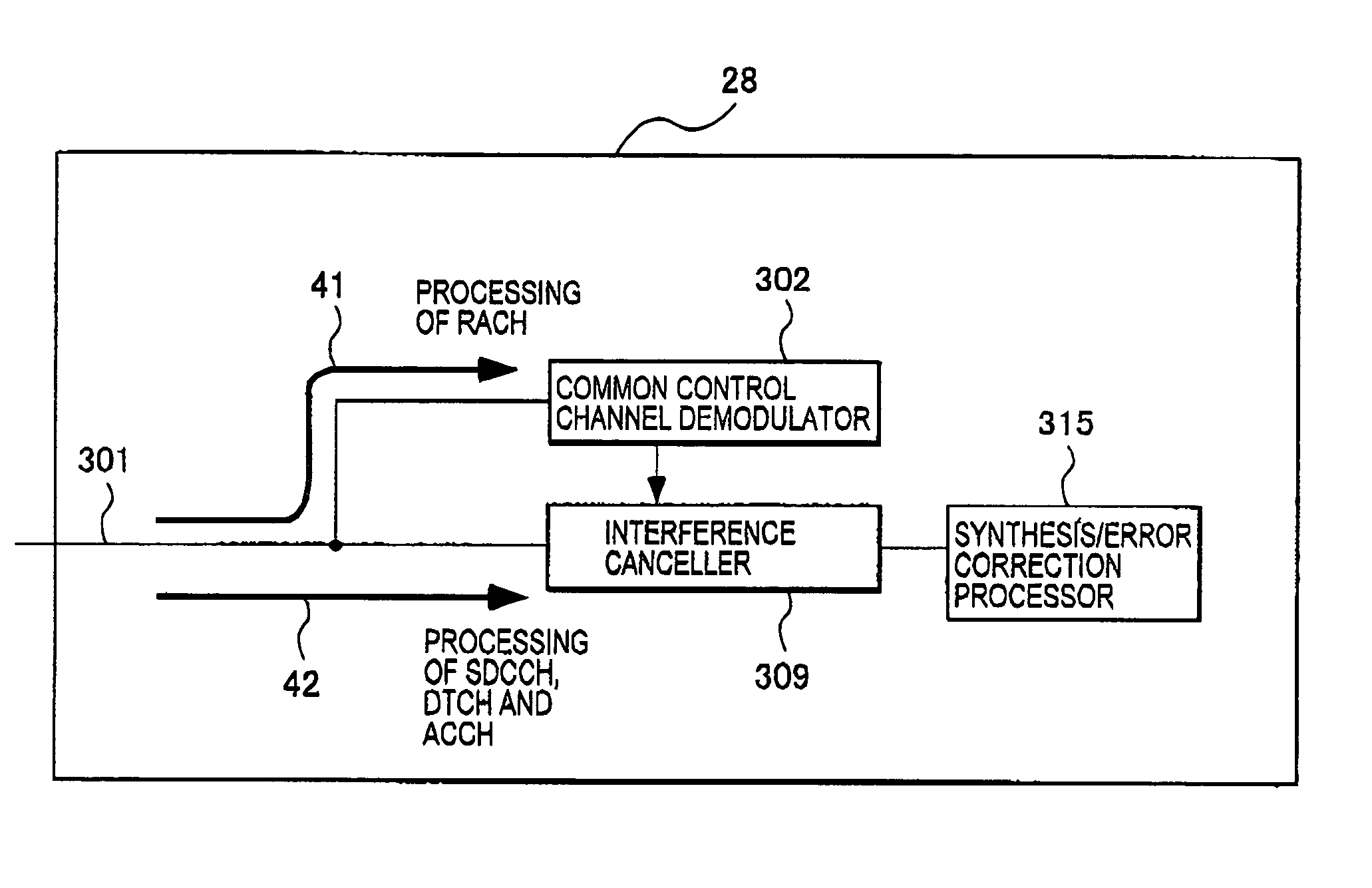
In a mobile communication system employing code division multiple accesses and having radio logical channels such as control channels and traffic channels, for the purpose of interference cancellation processing which is implemented without a large processing delay even under a call control application, the baseband receiving part of the mobile communication system includes a common control channel demodulator 302 which executes the demodulation processing of a common control channel as to a received baseband reception signal 301, an interference canceller 309 which executes interference cancellation processing for a received multiplexed signal on the basis of the notification information of the control channels, and a synthesis / error correction processor 315 which executes error correction processing, etc. as to user information having undergone the interference cancellation processing and thereafter executes frame formation processing. The common control channel is demodulated by the common control channel demodulator 302 and is not submitted to interference cancellation processing, thereby to heighten the processing speed of system information. In the interference canceller 309, cross-correlation interferences are cancelled as to the dedicated control channel and the traffic channel other than the common control channel, thereby to enhance a channel efficiency.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Using transferred operation key status data to synchronize games running on multiple independent game systems
InactiveUS6811487B2Inconsistent contentAvoid inconsistenciesInput/output for user-computer interactionCathode-ray tube indicatorsHuman–computer interactionTransfer operation
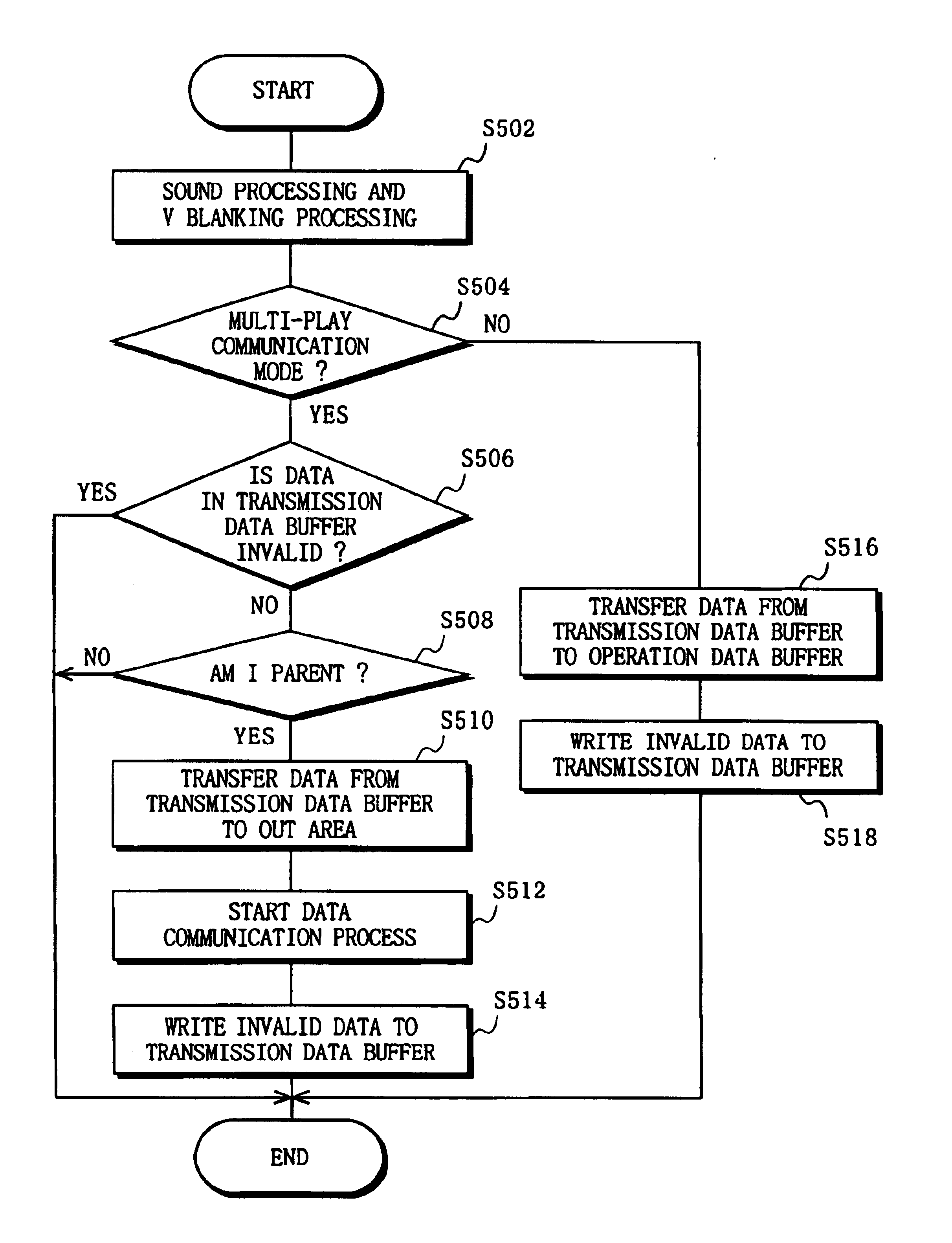
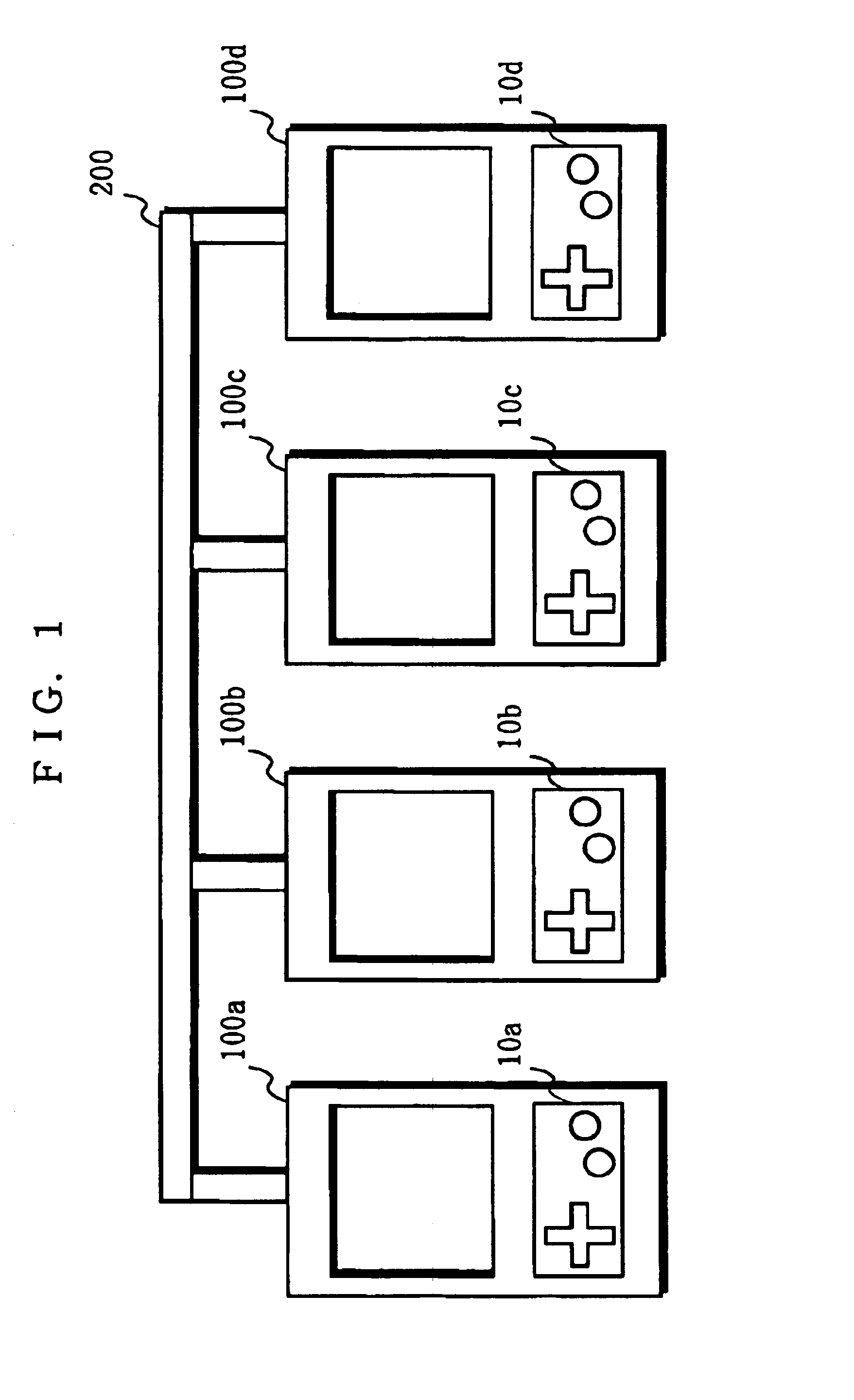
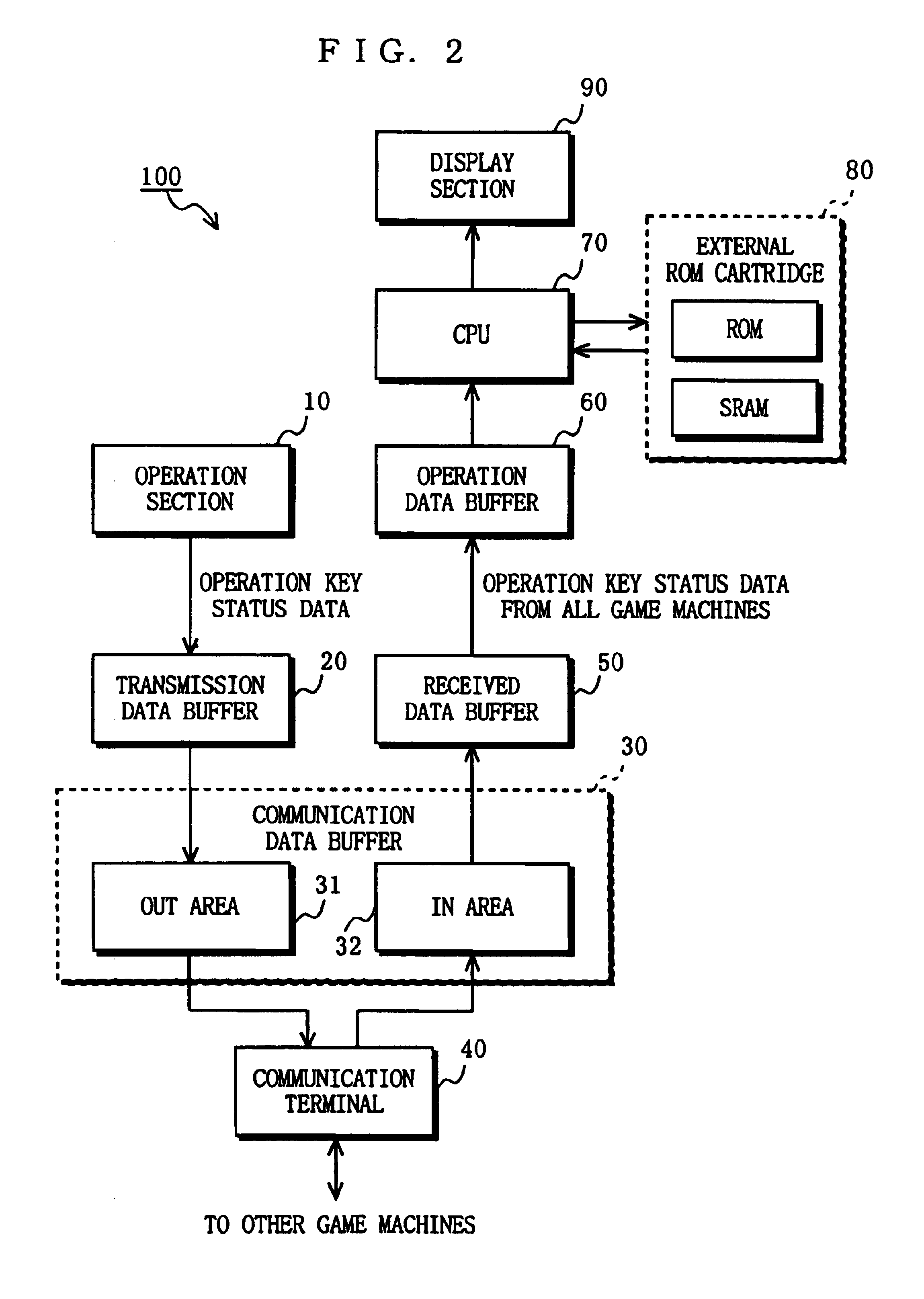
When users simultaneously play the same game with interconnected game machines, processing delays would conventionally cause inconsistencies in game content between different game machines. To solve this problem, the game machines are not synchronized with one another, but each game machine outputs operation key status data representing the state of a set of number of operation controls to the other game machines in accordance with predetermined data communication timing. A received FIFO data buffer in each game machine, sequentially stores operation key status data received from the other game machines. Only valid operation control status data is transferred to an operation data buffer for use in game processing. Inconsistencies in game content between different game machines are prevented through software-based synchronization which does not require hardware-based synchronization.
Owner:NINTENDO CO LTD
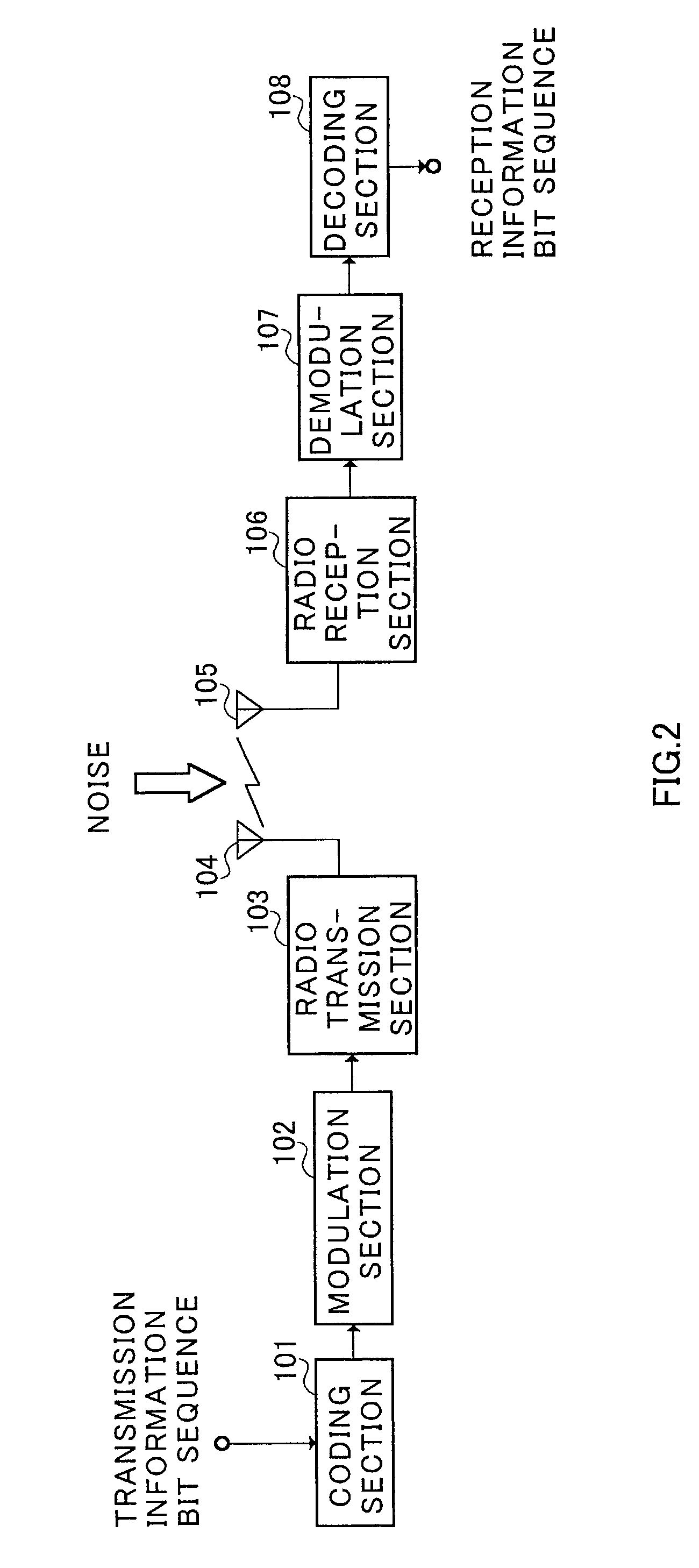
Decoding device and decoding method
InactiveUS6988233B2Securing transmission qualityReduce processing latencyError preventionError detection/correctionTransmission qualityDecodes
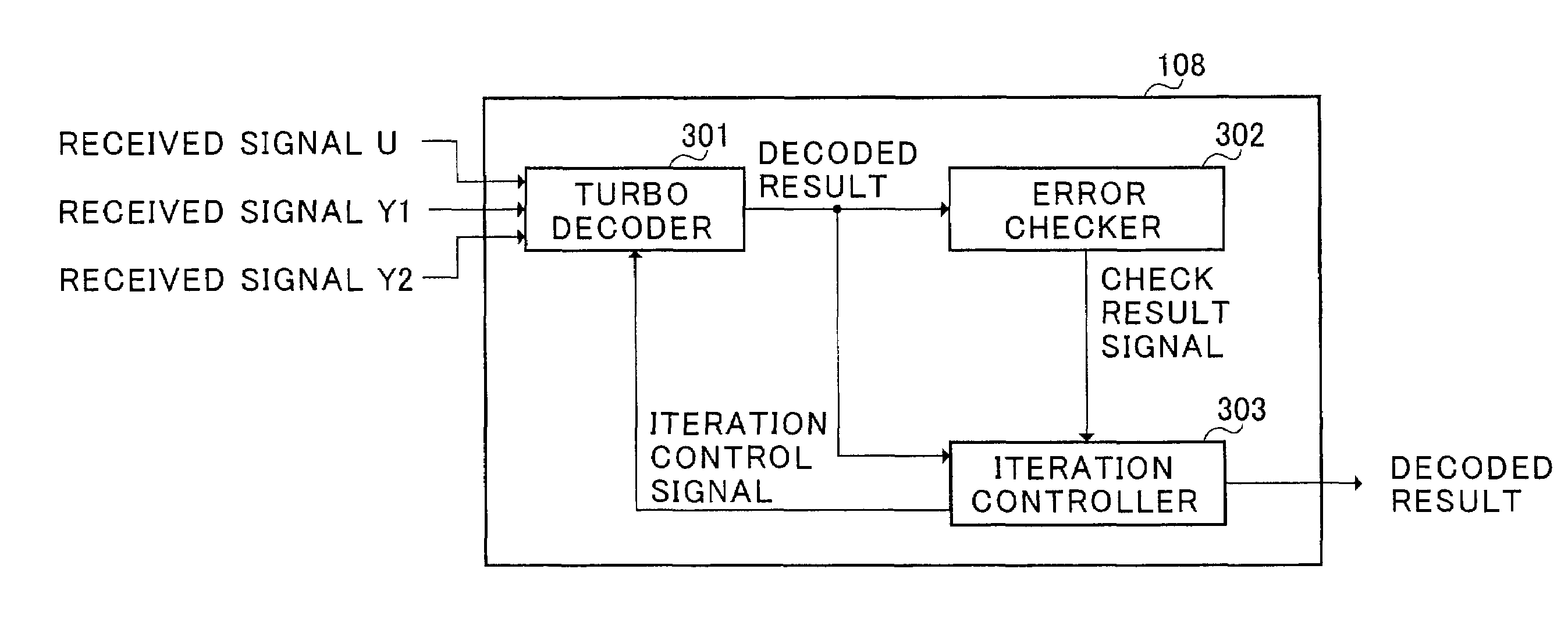
A decoding apparatus and decoding method for performing iteration decoding the suitable number of iterations, and thereby securing the desired transmission quality while decreasing the processing delay. Turbo decoder 301 iterates error correcting decoding on input coded sequences. Error checker 302 decodes an error detecting code contained in a decoded result of the error correcting decoding, and checks whether or not an error remains in the decoded result in turbo decoder 301. Iteration controller 303 instructs turbo decoder 301 to continue the iteration decoding until the number of iterations in the iteration decoding is more than or equal to the constraint number of iterations and error checker 302 determines no error in the decoded result.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com