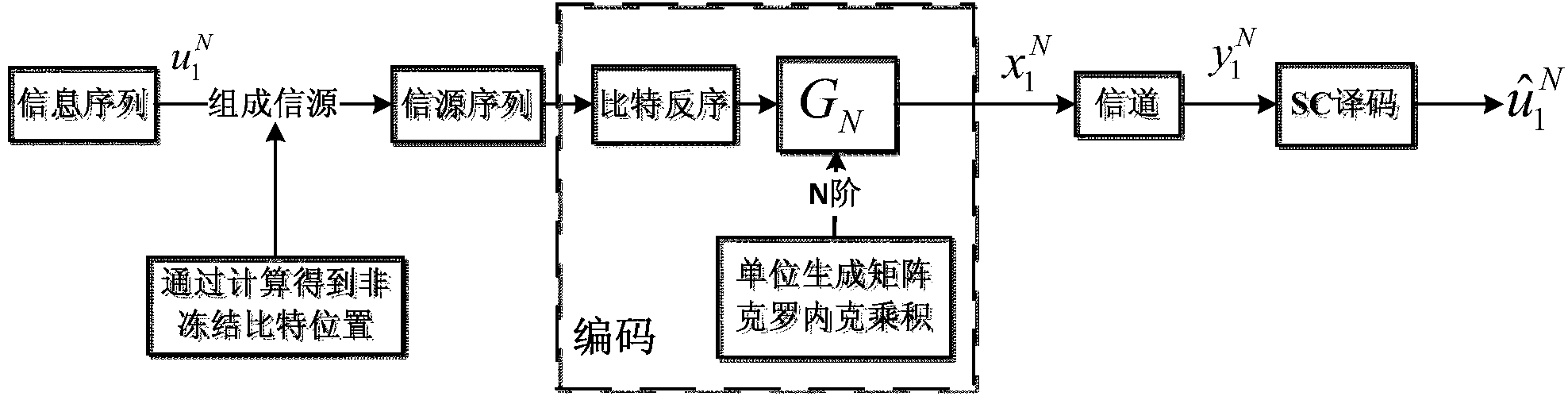
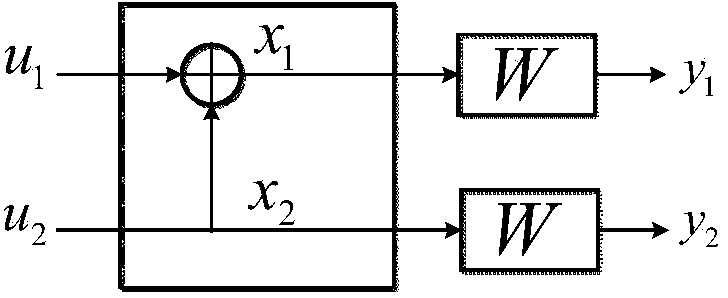
Polar code decoder and polar code decoding method based on probability calculation
A technology of probability calculation and polar code, which is applied in the field of channel coding, can solve the problem of unoptimistic decoder throughput and achieve the effect of improving the overall throughput, good versatility, and good practical prospects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach 1
[0041] Embodiment 1: bipolar probability calculation (BSC-SC) decoder, see Figure 9 , introducing the specific steps of the process:
[0042] Step 1, converting fixed-point numbers into probability sequences: After receiving the soft information output by the demodulator, these soft information need to be converted into probability sequences and sent to the decoder for iterative calculation. The probability sequence in this method is the simplest Bernoulli sequence, that is, a randomly generated 01 bit sequence. The code length of the polar code used is N, the set of information subchannels required by the polar code is A, and each soft information value is transformed into a probability sequence of length M. Wherein, N is the nth power of 2, n is a positive integer, and M is the length of the initial probability sequence set by the decoding system. Parameters A, N and M are preset. This step 1 specifically includes:
[0043] (11) Store the received soft information value...
Embodiment approach 2
[0053] Embodiment 2: low bit probability calculation (LBSC-SC) decoder, the basic purpose of each step in the method is the same as the corresponding steps in method 1, and the algorithm used in each step in the method is the essential difference between this method and method 1 . see Figure 11 , introducing the specific steps of the process:
[0054] Step 1: This step converts the values received by the channel into a sequence of probabilities. The code length of the polar code used is N, the set of information channels required by the polar code is A, and each soft information value is transformed into a probability sequence of length M. Wherein, N is the nth power of 2, n is a positive integer, and M is the length of the initial probability sequence set by the decoding system. Parameters A, N and M are preset. Step 1 specifically includes:
[0055] (11) Store the received soft information value, and scale it according to the signal-to-noise ratio, so that all soft i...
Embodiment approach 3
[0066] Embodiment 3: multi-stage probability calculation decoder, see Figure 14 , taking a simple special case of a multi-stage probability calculation decoder (in the special case, the decoding algorithm is divided into two stages, but in fact it can be divided into more stages) as an example to introduce the specific steps of the method:
[0067] Step 1: This step converts the values received by the channel into a sequence of probabilities. The code length of the polar code used is N, the set of information channels required by the polar code is A, and each soft information value is transformed into a probability sequence of length M. In the first n of the decoder 0 level, all soft information values are represented by probability sequences of length M, and in the remaining (n-n 0 ) level, all soft information lengths are represented by probability sequences with a length of M / 2 to improve system throughput. where n is a positive integer, n 0 The value is N is the...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com