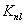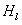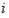Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
220 results about "Planar projection" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
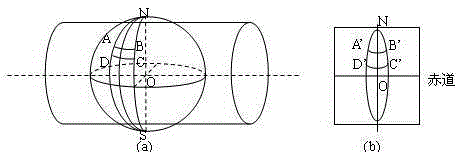
Planar projections are the subset of 3D graphical projections constructed by linearly mapping points in three-dimensional space to points on a two-dimensional projection plane. The projected point on the plane is chosen such that it is collinear with the corresponding three-dimensional point and the centre of projection. The lines connecting these points are commonly referred to as projectors.
Systems and methods for optically projecting three-dimensional text, images and/or symbols onto three-dimensional objects
ActiveUS20110169924A1Efficiently and rapidly and accurately assembleLow costColor television detailsSteroscopic systemsGuidance systemComputer graphics (images)
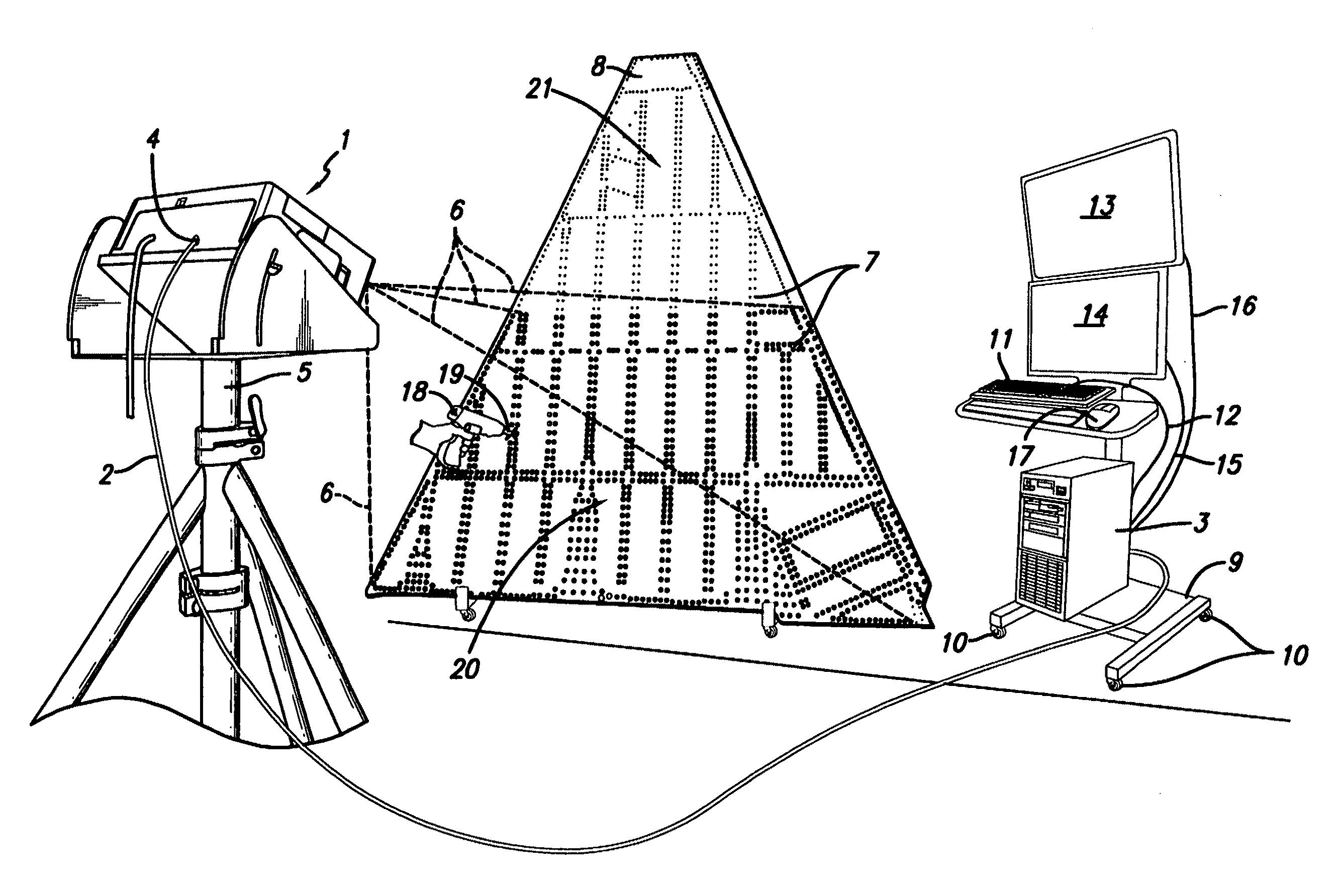
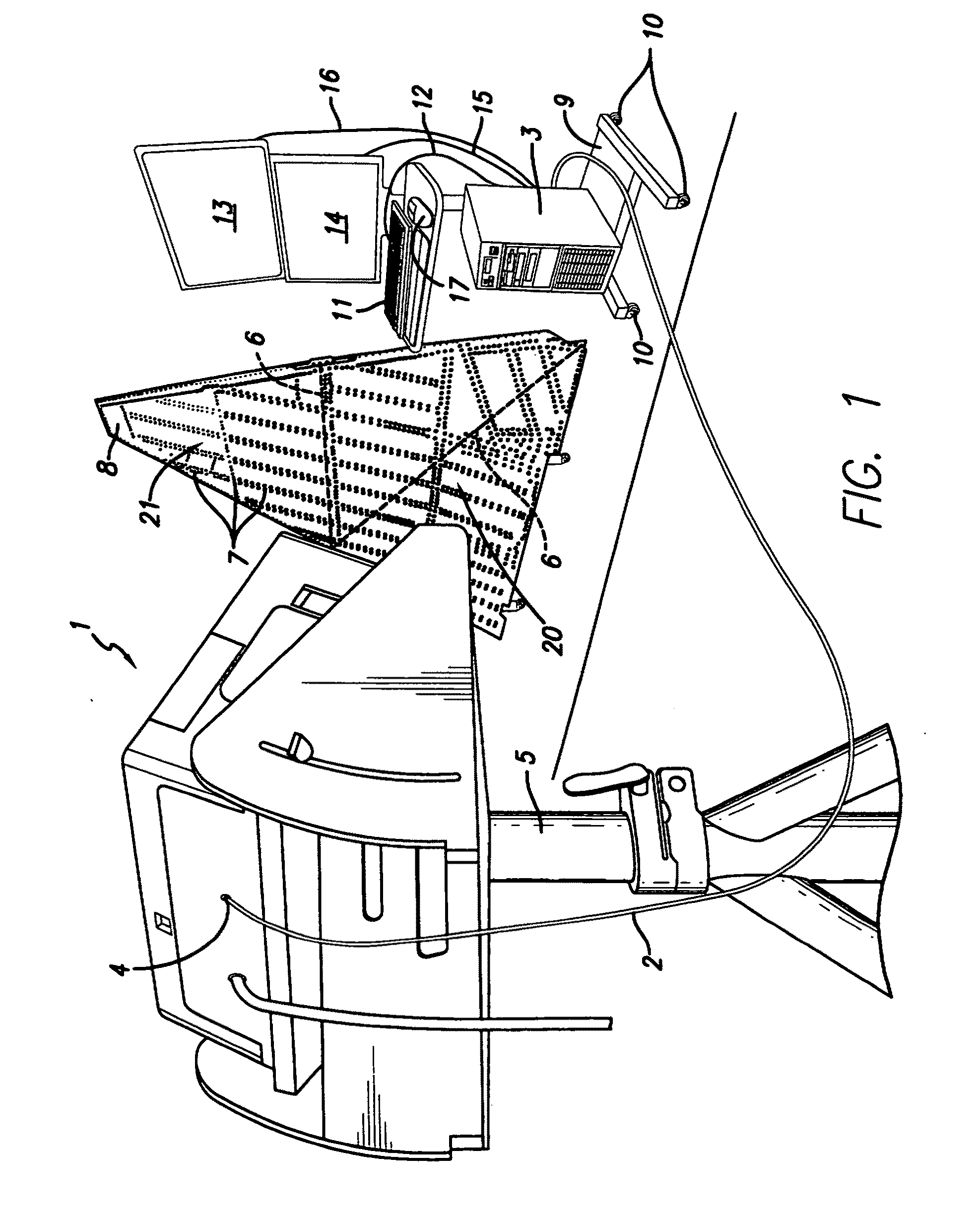
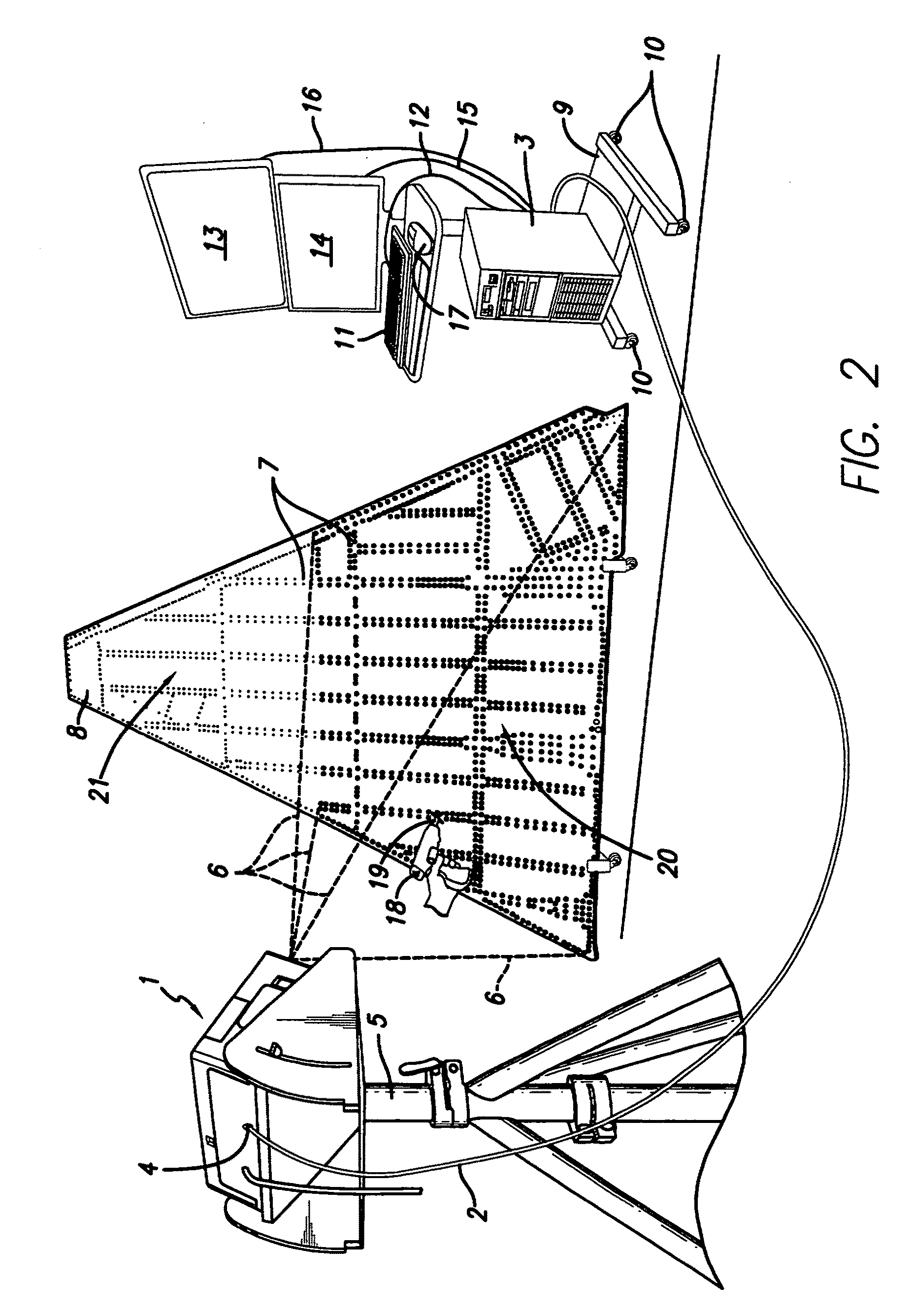
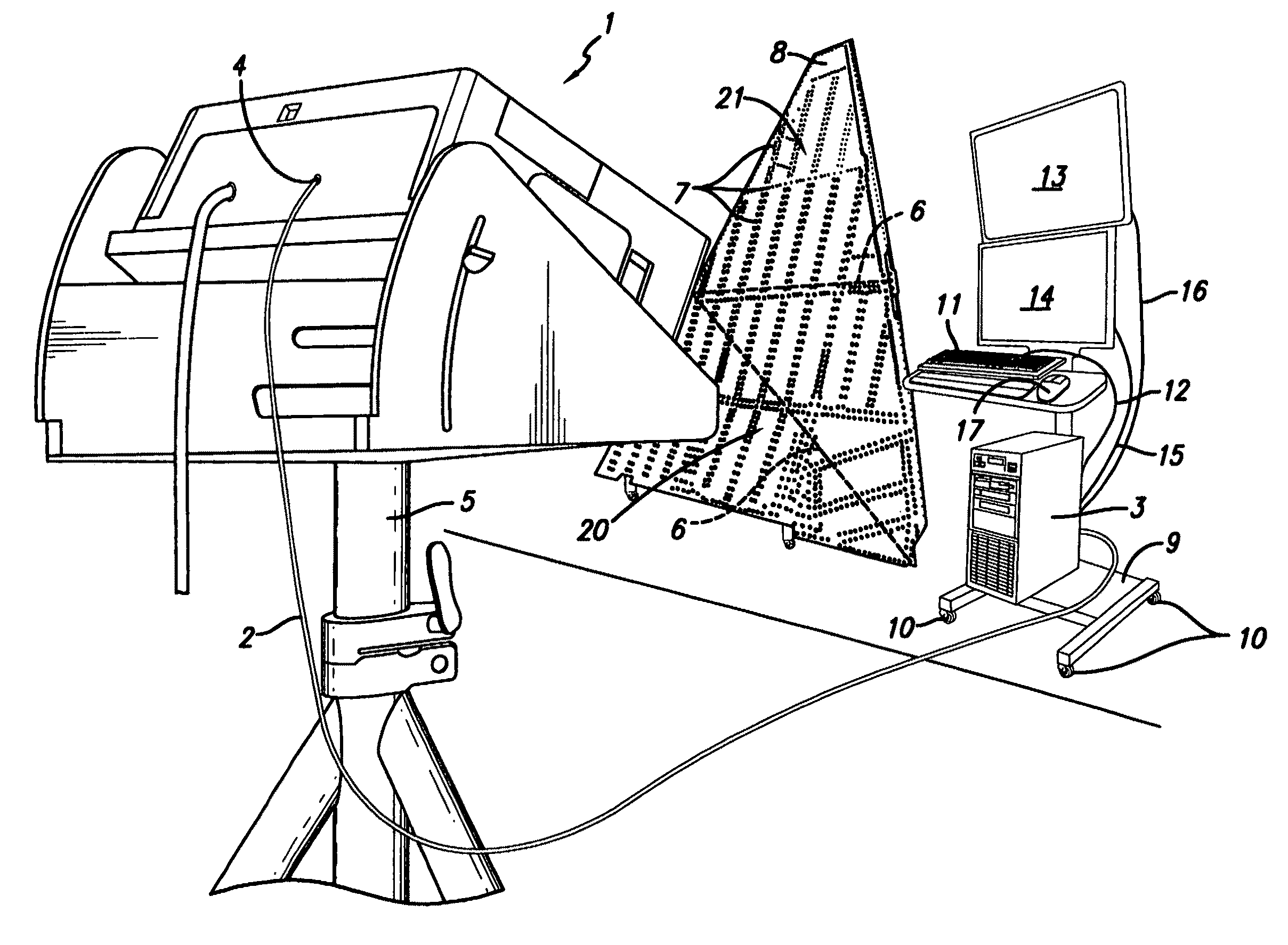
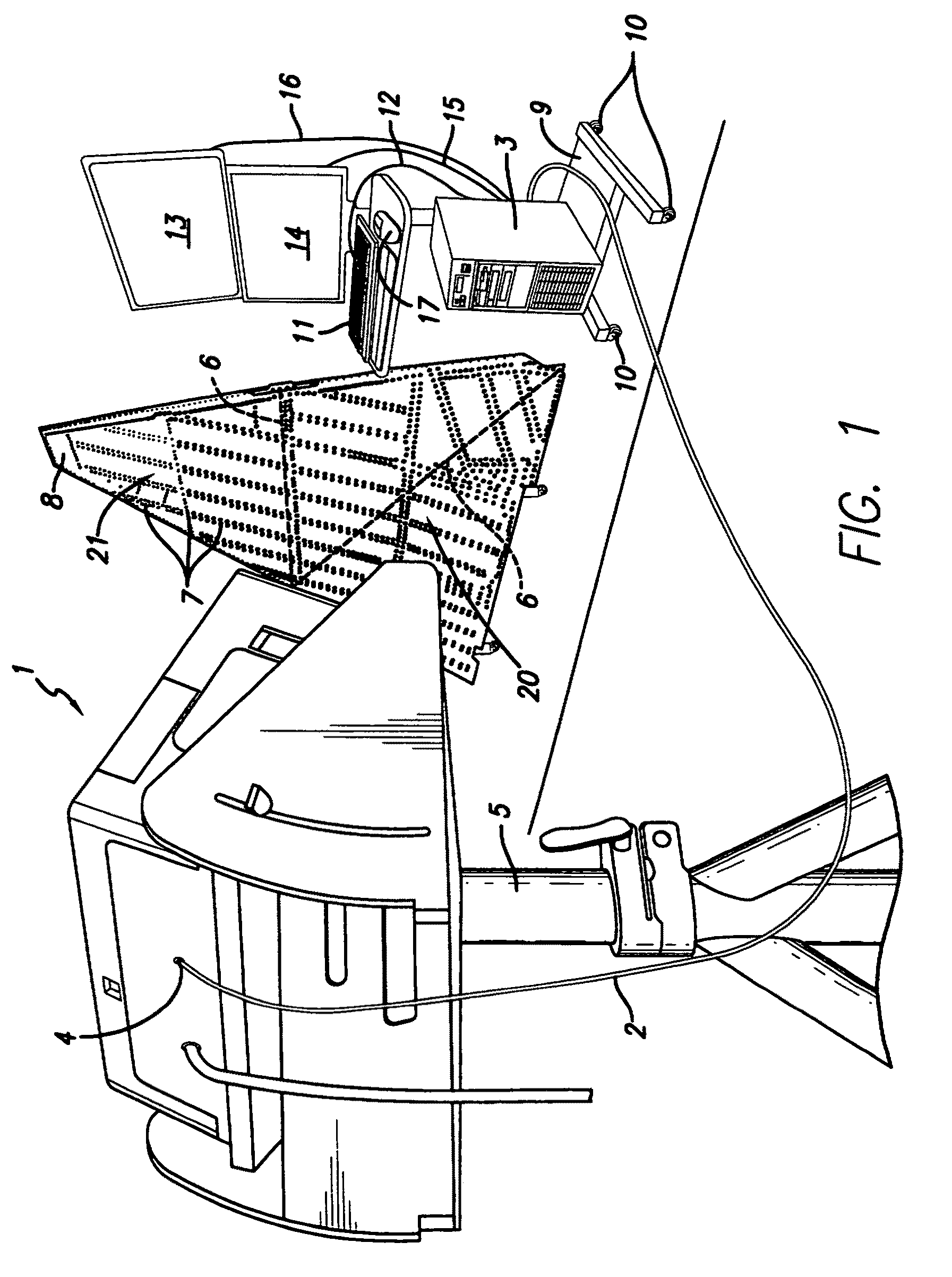
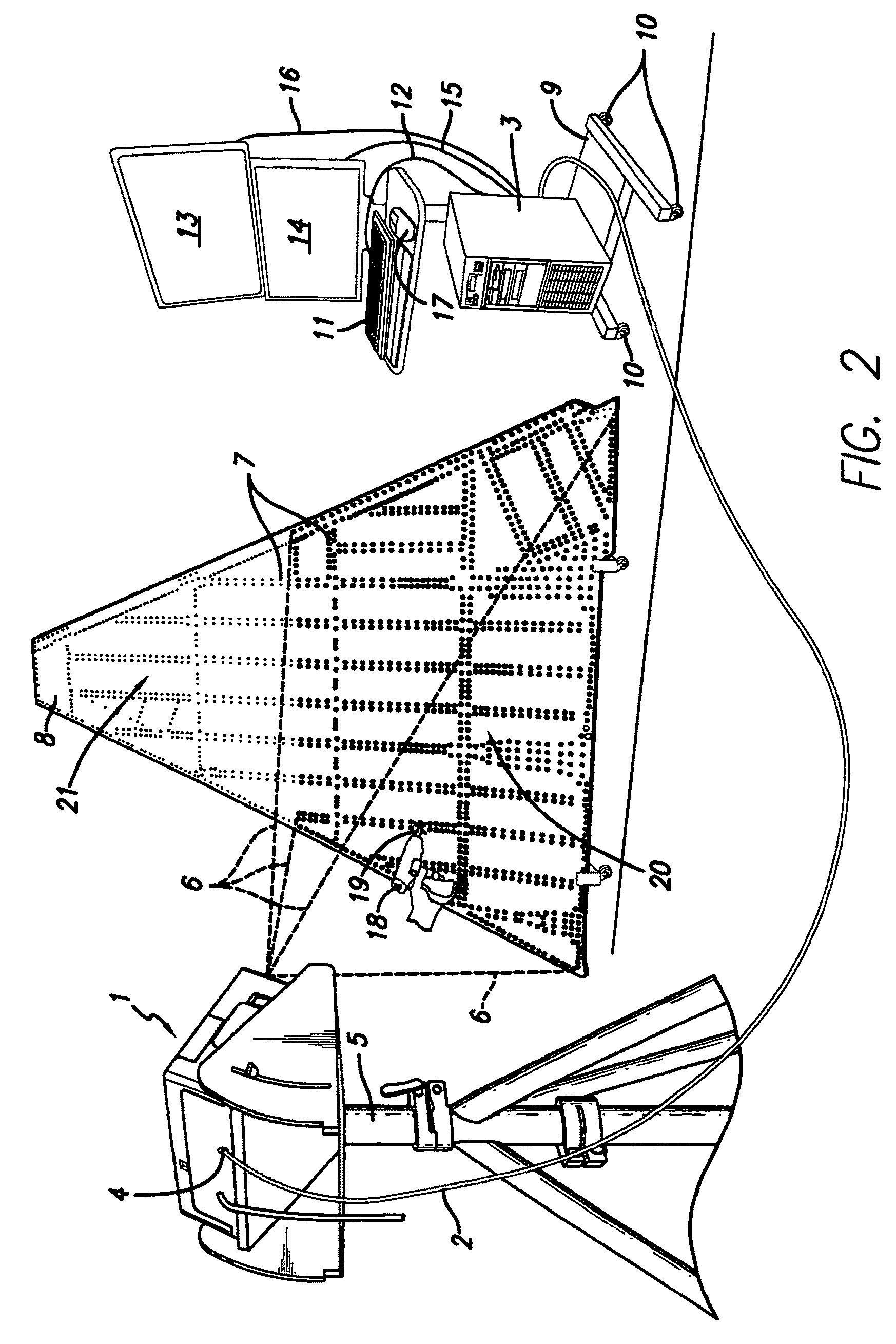
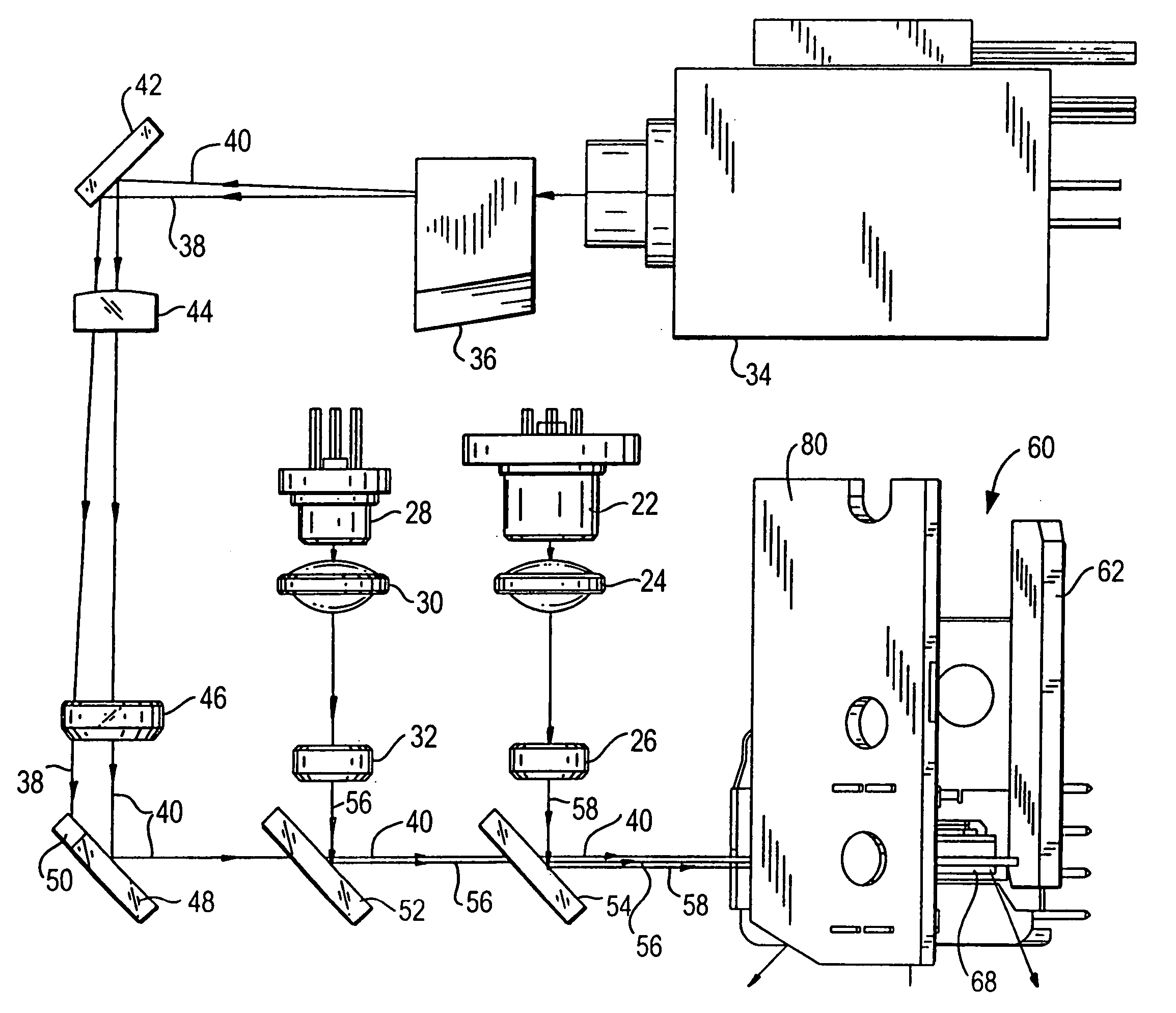
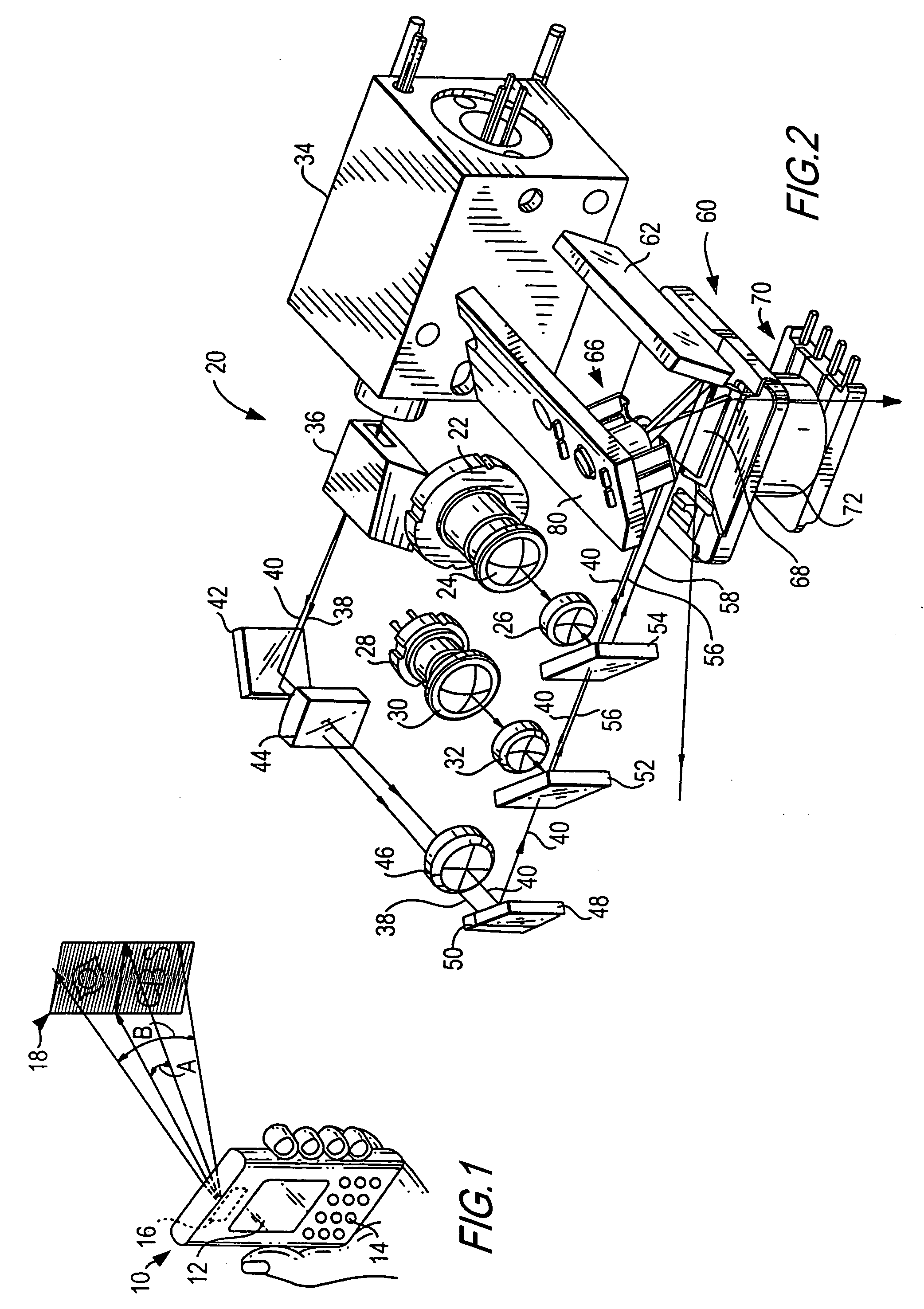
The present invention provides a method whereby the spatial relationship and orientations of one or more three-dimensional objects being illuminated by an optical projector, and the optical projector itself, can be very accurately defined both quickly and easily. The present invention also provides a novel computerized optical projection system whereby three dimensional data when viewed by the human eye projected onto three dimensional objects is not deformed as a result of the non-planar projection surface. The present invention could have many applications in many industries that include entertainment, apparel, marketing, and many others. In one embodiment, the invention provides computerized optical assembly or manufacturing guidance systems, and related methods, that provide step-by-step assembly or manufacturing instructions for instructing technicians how to assemble or manufacture three-dimensional objects or systems, or parts thereof, which may be extremely complex, such as an aircraft, or a part thereof (a vertical stabilizer, or the like), in a very efficient, rapid and accurate manner. The assembly instructions are in the form of calibrated three-dimensional text, images and / or symbols, and are projected by one or a plurality of optical projectors that are in operable communication with one or a plurality of computers onto the three-dimensional objects or systems, or component parts or skins thereof.
Owner:DELTA SIGMA
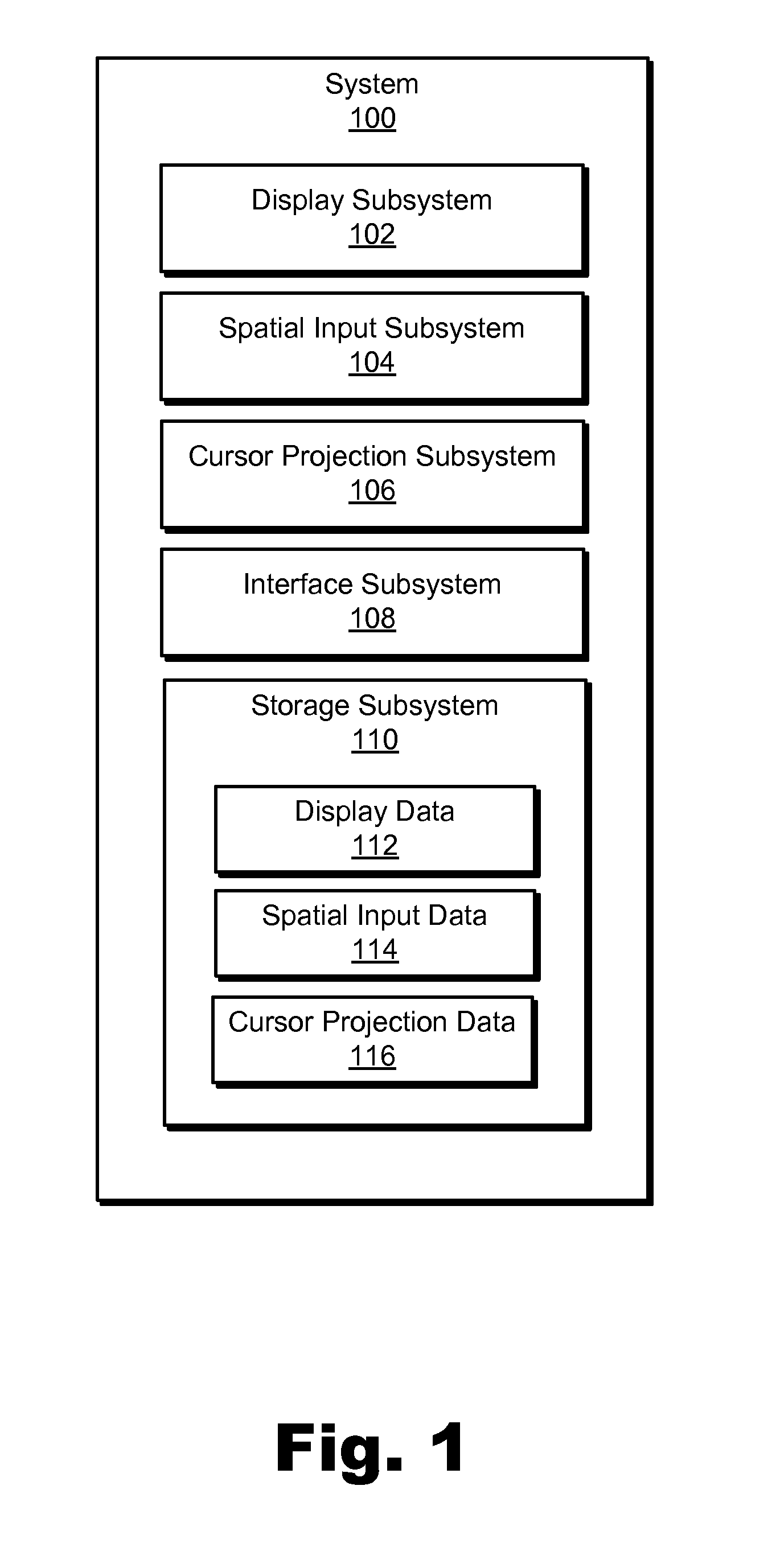
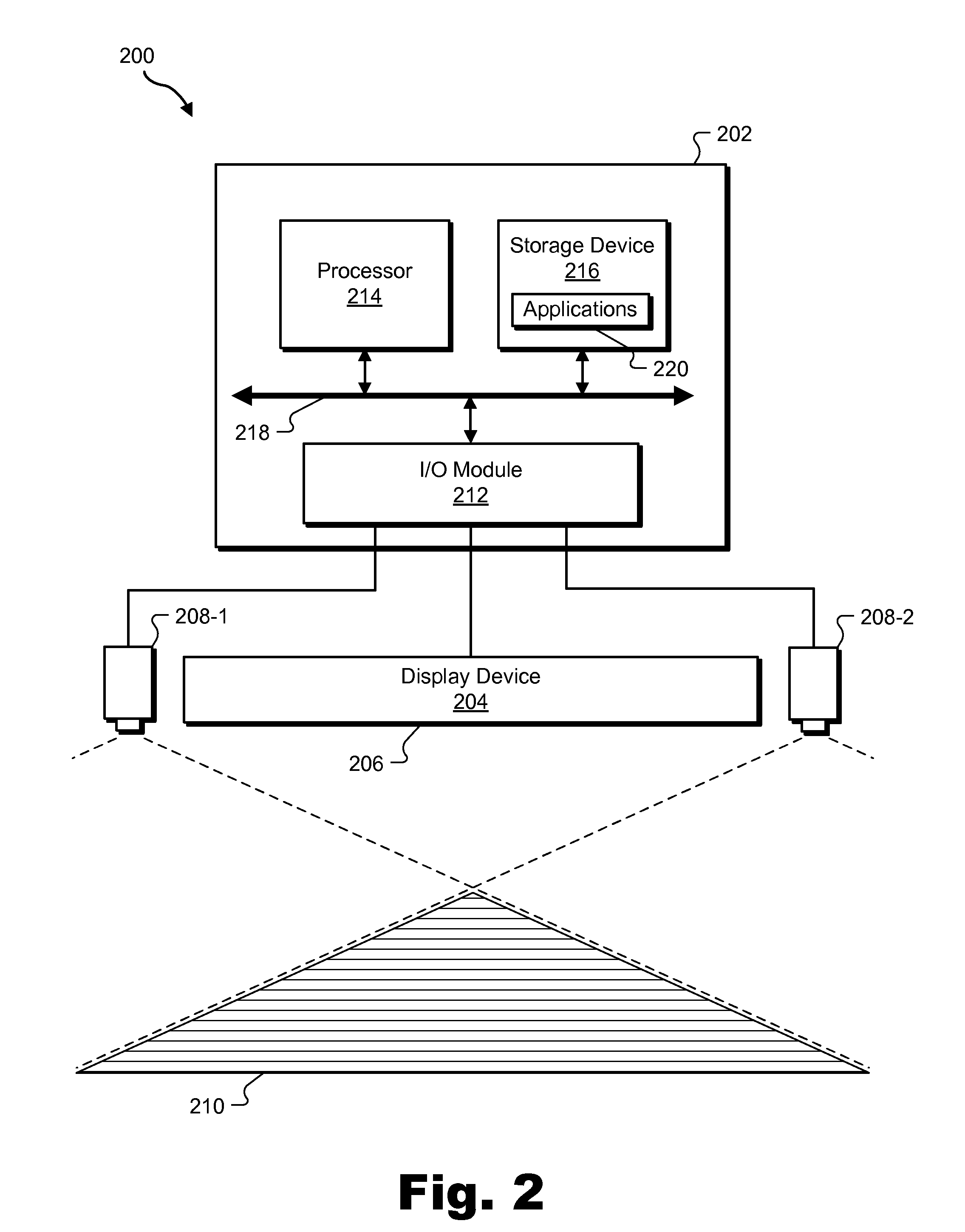
Spatial-input-based cursor projection systems and methods
ActiveUS20110267265A1Cathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingPattern recognitionComputer graphics (images)
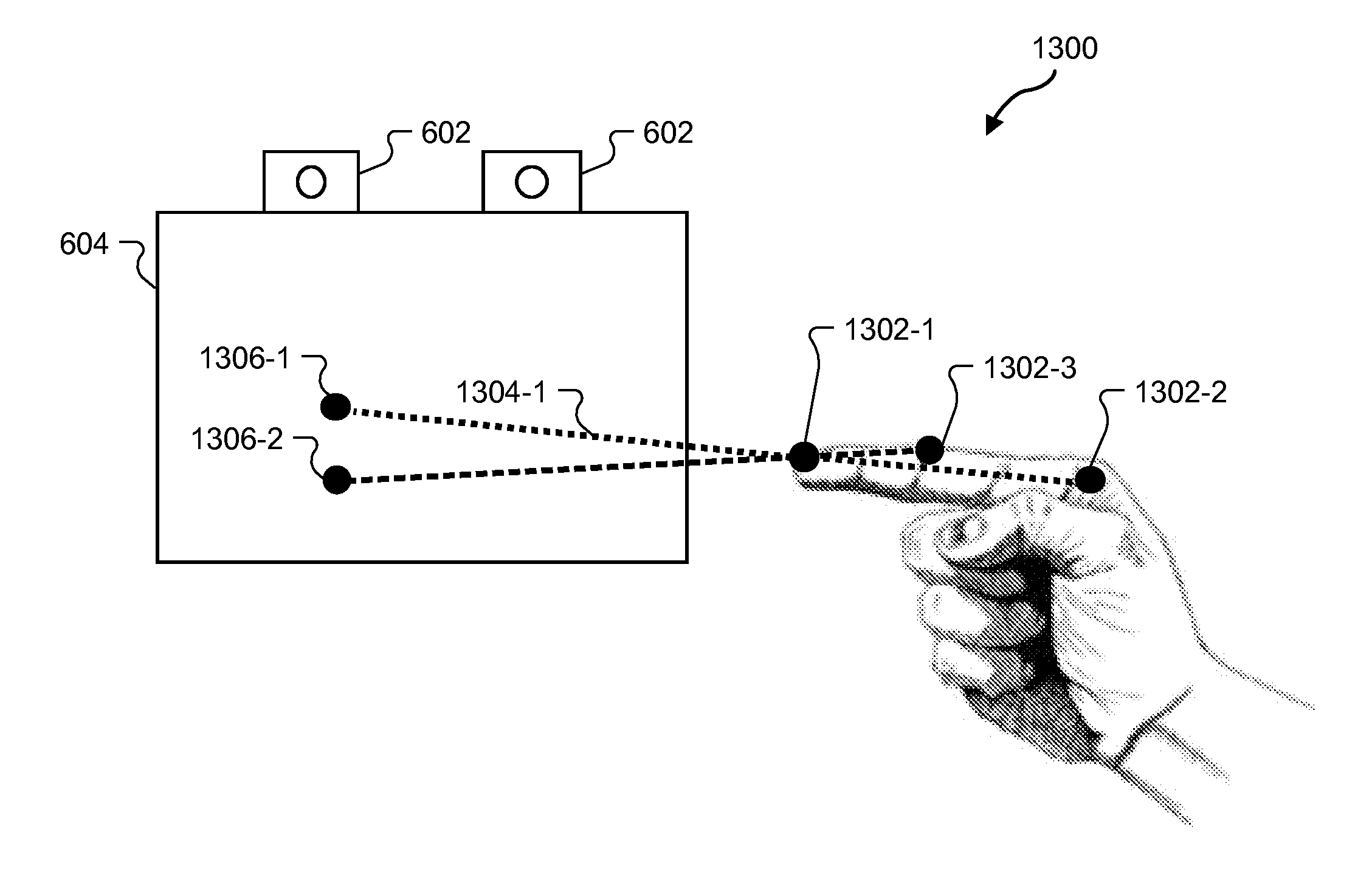
Exemplary spatial-input-based cursor projection systems and methods are disclosed herein. An exemplary method includes a cursor projection system detecting spatial input provided by a user within a physical user space associated with a display screen, determining that the spatial input is associated with a request for cursor projection, and mapping the spatial input to at least one cursor position on the display screen based on at least one of a plane projection heuristic and a vector projection heuristic. Corresponding systems and methods are also disclosed.
Owner:VERIZON PATENT & LICENSING INC
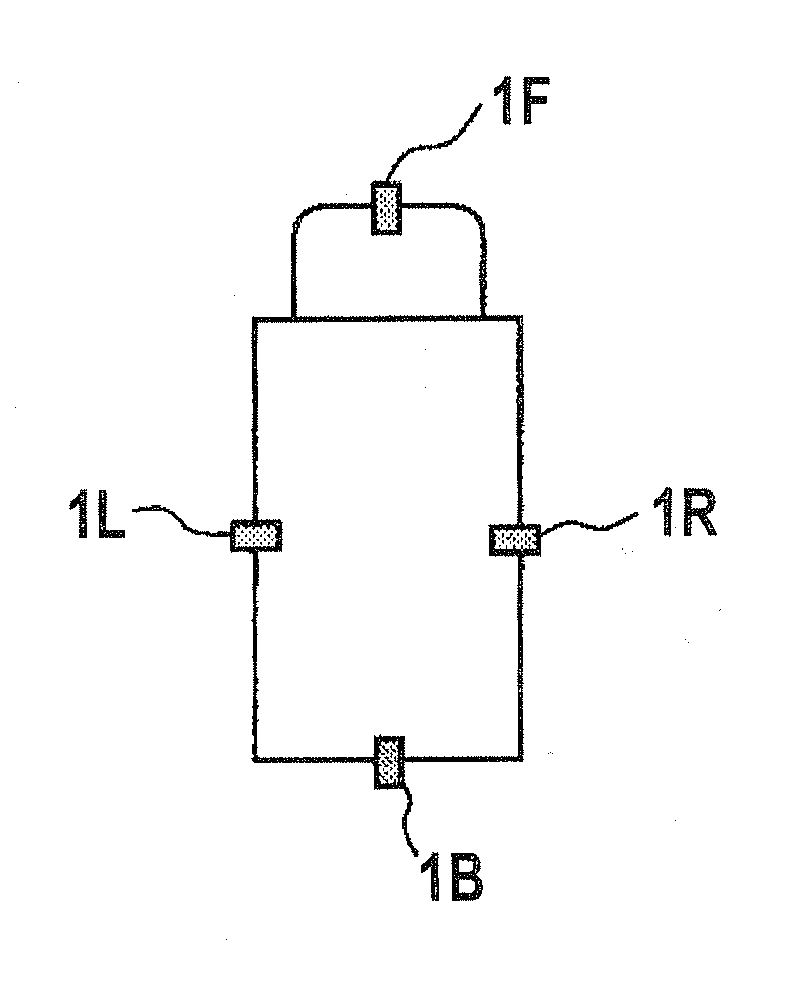
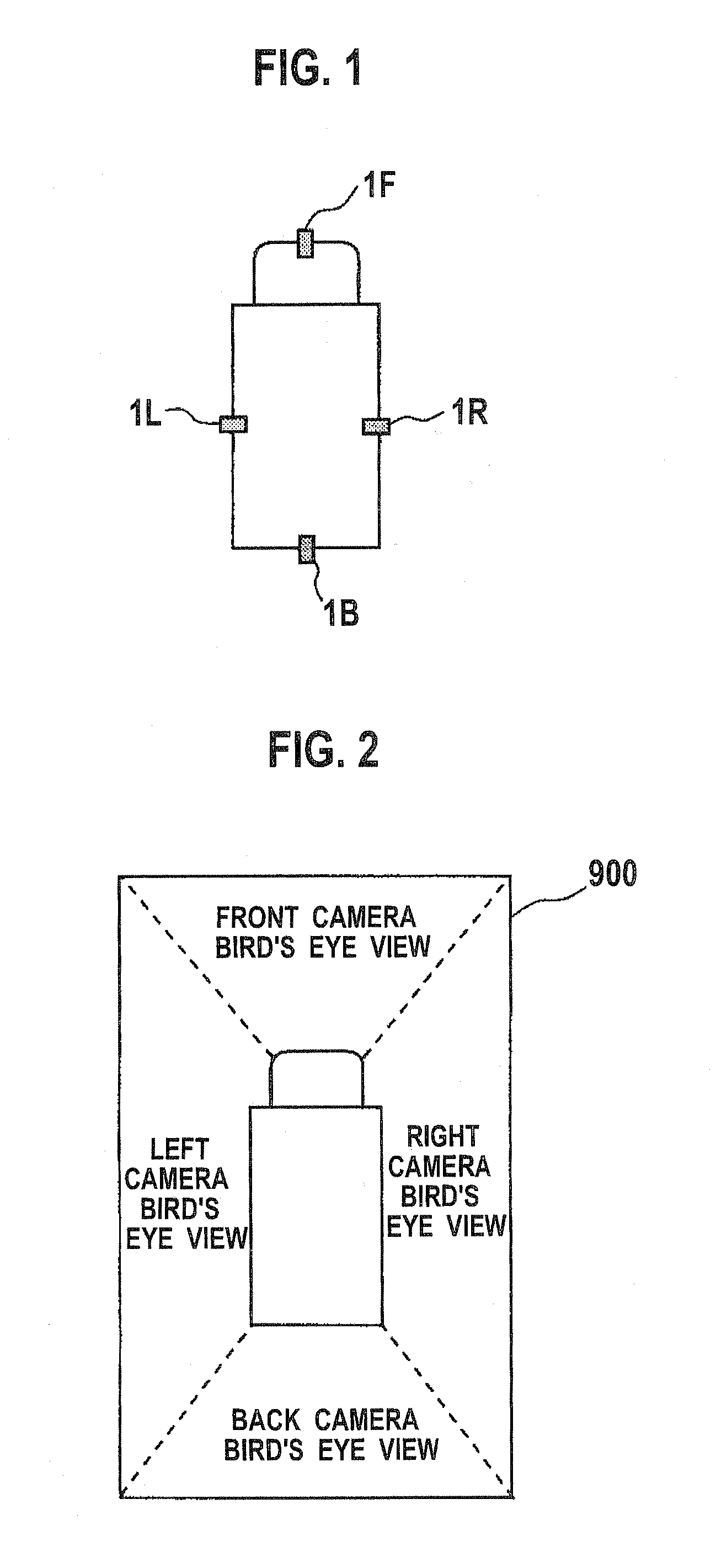
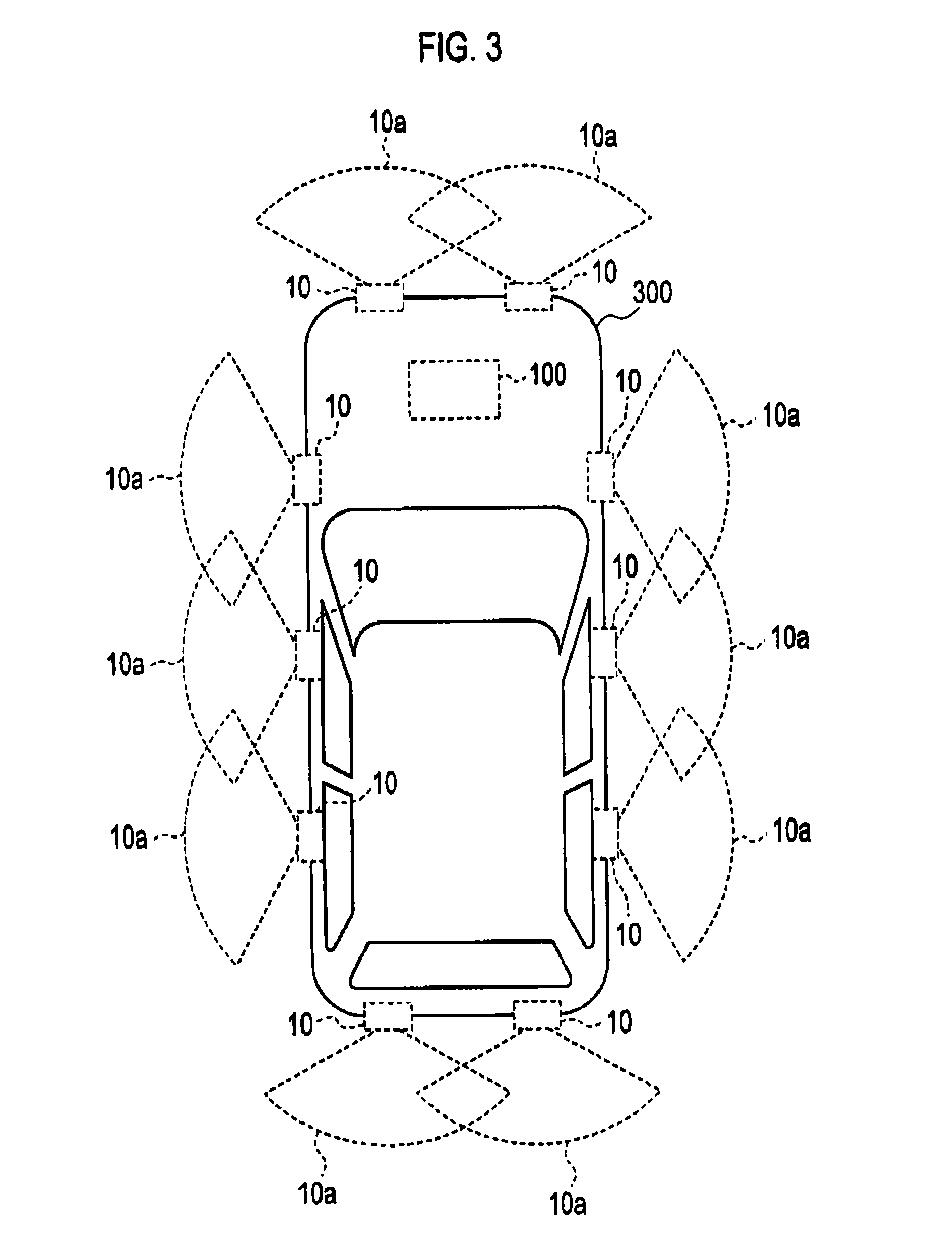
Camera calibration device, camera calibration method, and vehicle having the calibration device
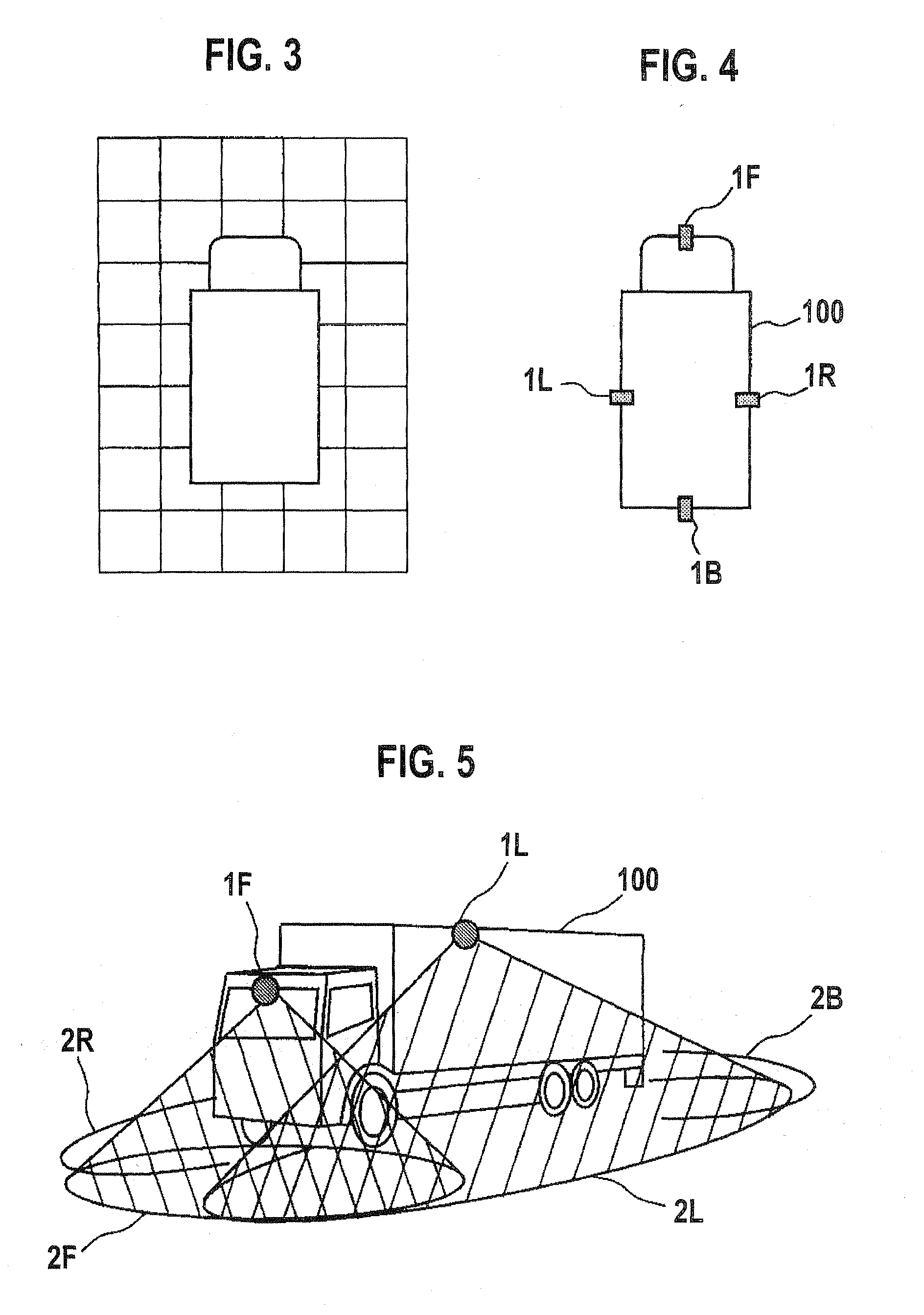
InactiveUS20080181488A1Reduce image degradationEasy maintenanceCharacter and pattern recognitionOptical viewingTransformation parameterField of view
Cameras are installed at the front, right, left, and back side of a vehicle, and two feature points are located at each of the common field of view areas between the front-right cameras, front-left cameras, back-right cameras, and back-left cameras. A camera calibration device includes a parameter extraction unit for extracting transformation parameters for projecting each camera's captured image on the ground and synthesizing them. After transformation parameters for the left and right cameras are obtained by a perspective projection transformation, transformation parameters for the front and back cameras are obtained by a planar projective transformation so as to accommodate transformation parameters for the front and back cameras with the transformation parameters for the left and right cameras.
Owner:SANYO ELECTRIC CO LTD
Systems and methods for optically projecting three-dimensional text, images and/or symbols onto three-dimensional objects
ActiveUS8610761B2Efficiently and rapidly and accurately assembleLow costProjectorsColor television detailsGuidance systemProjection system
Owner:DELTA SIGMA
Three-dimensional terrain model real-time smooth drawing method with combination of GPU technology
InactiveCN105336003ATroubleshoot preprocessing issuesEliminate noise3D modellingVideo memoryEngineering
The invention provides a three-dimensional terrain model real-time smooth drawing method with combination of a GPU technology, and belongs to the technical field of image processing. The objective of the invention is to provide the three-dimensional terrain model real-time smooth drawing method with combination of the GPU technology so that cache reuse in multiple times of drawing can be realized based on the current popular programmable GPU technology with a global digital elevation model acting as a data source, and load of computation space is effectively reduced. The method comprises the steps of construction of a multi-resolution pyramid model, elimination of image noise points, filtering of images, partitioning of planar projection of the earth according to equal latitude and longitude, and construction of different hierarchical levels of pyramid layers according to a mode from the top to the bottom. Acceleration and enhancement of terrain rendering are realized based on the programmable GPU technology, i.e. all phases of a graphical drawing pipeline are controlled by using shader languages, two and textures are respectively generated by vertex information and index information of elevation data to be stored in video memory for scheduling of whole terrain drawing; and vertex interpolation and migration are performed in the geometric phase by utilizing a curved surface subdivision and fractal technology so that procedural details are generated and the phenomenon of edges and corners of the terrain mesh when resolution is insufficient can be compensated.
Owner:PLA AIR FORCE AVIATION UNIVERSITY
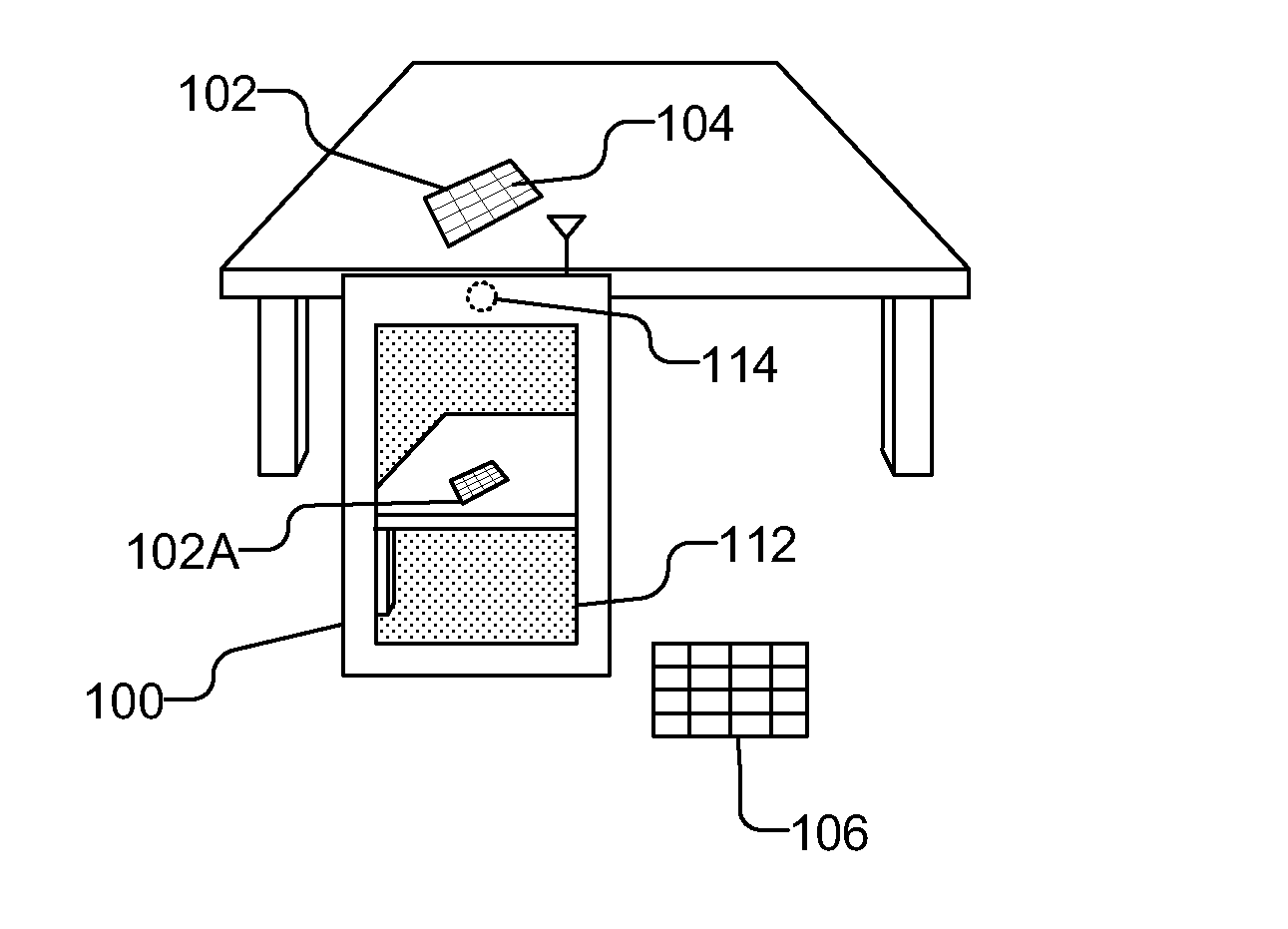
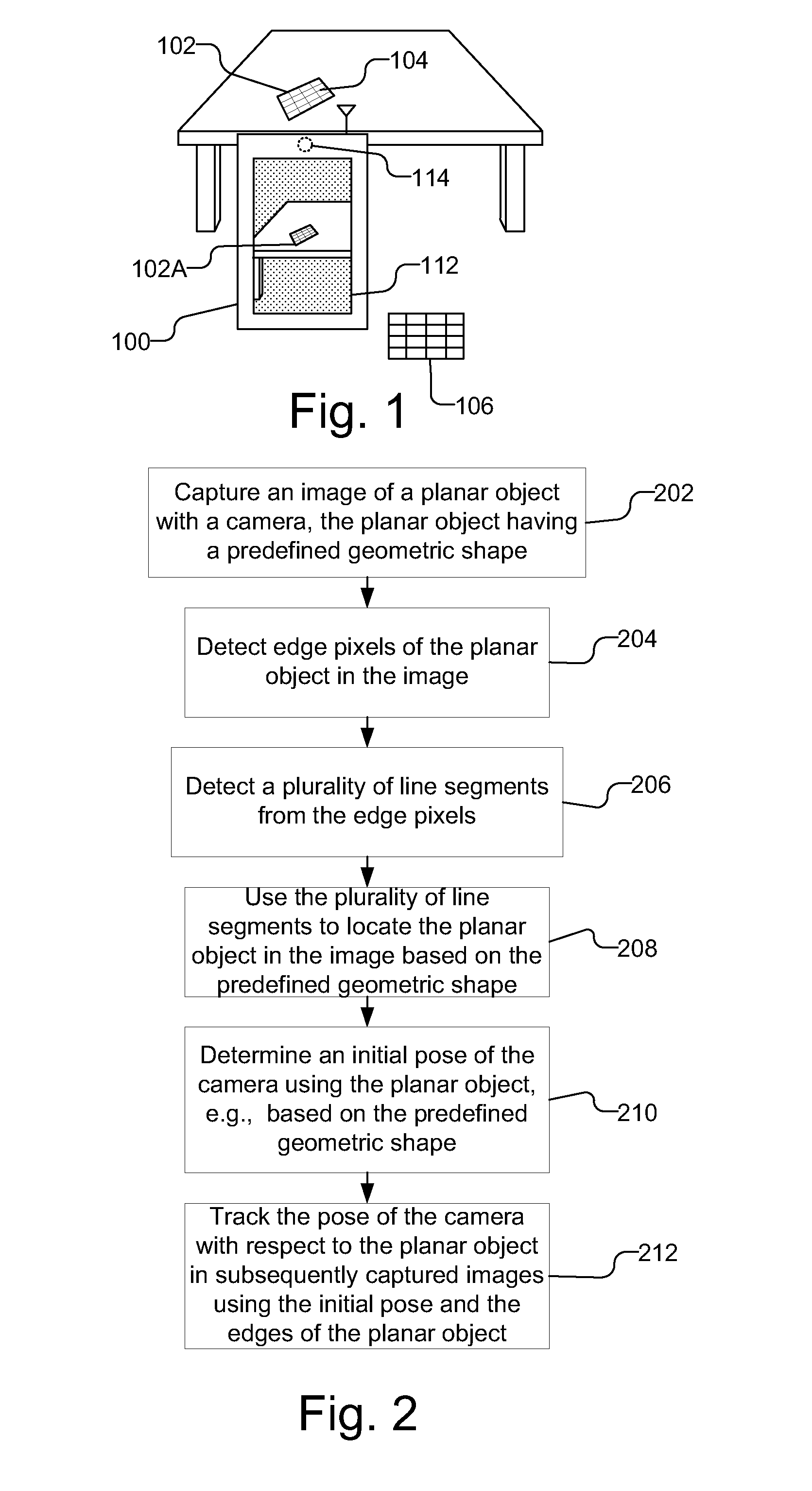
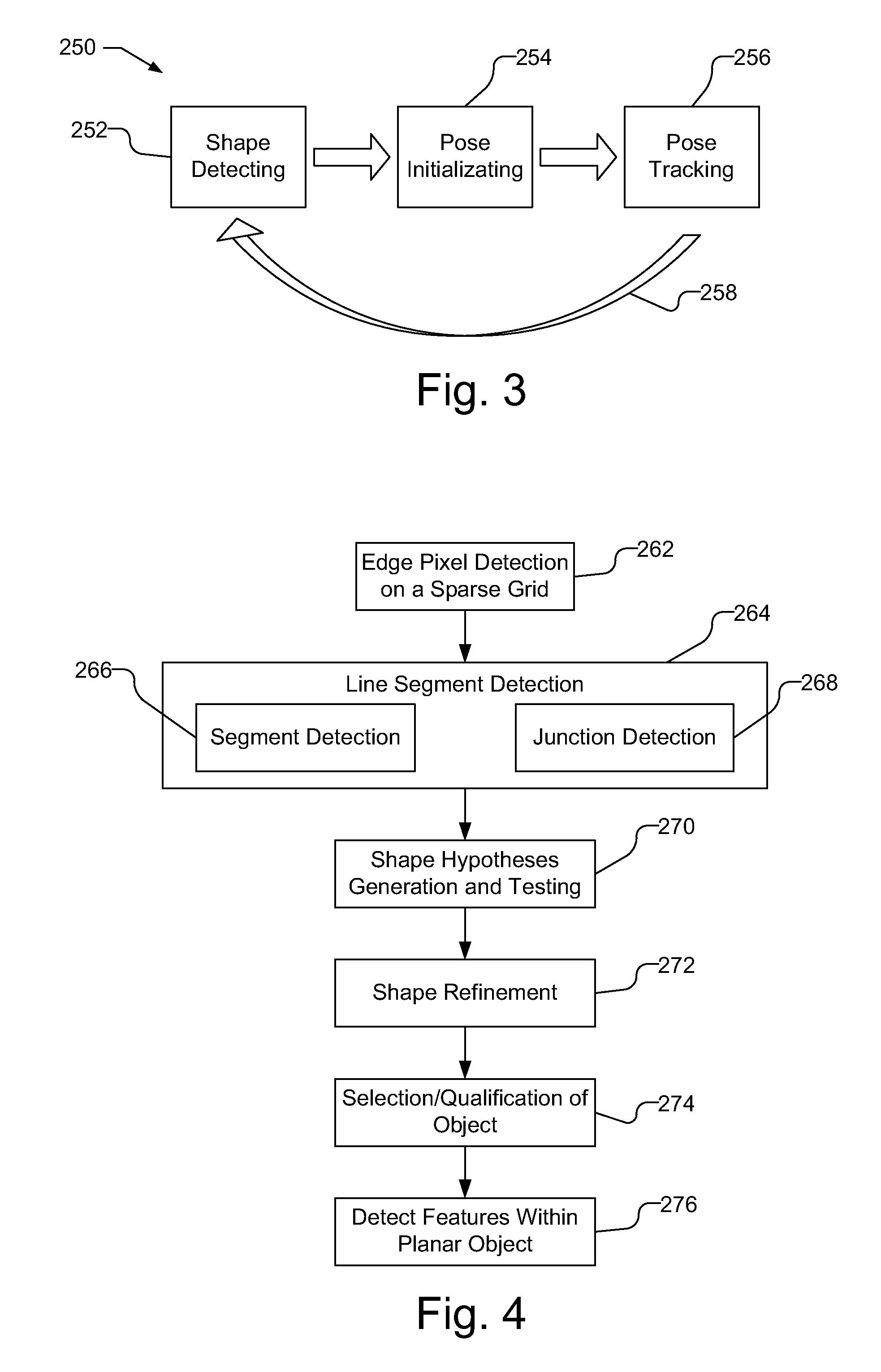
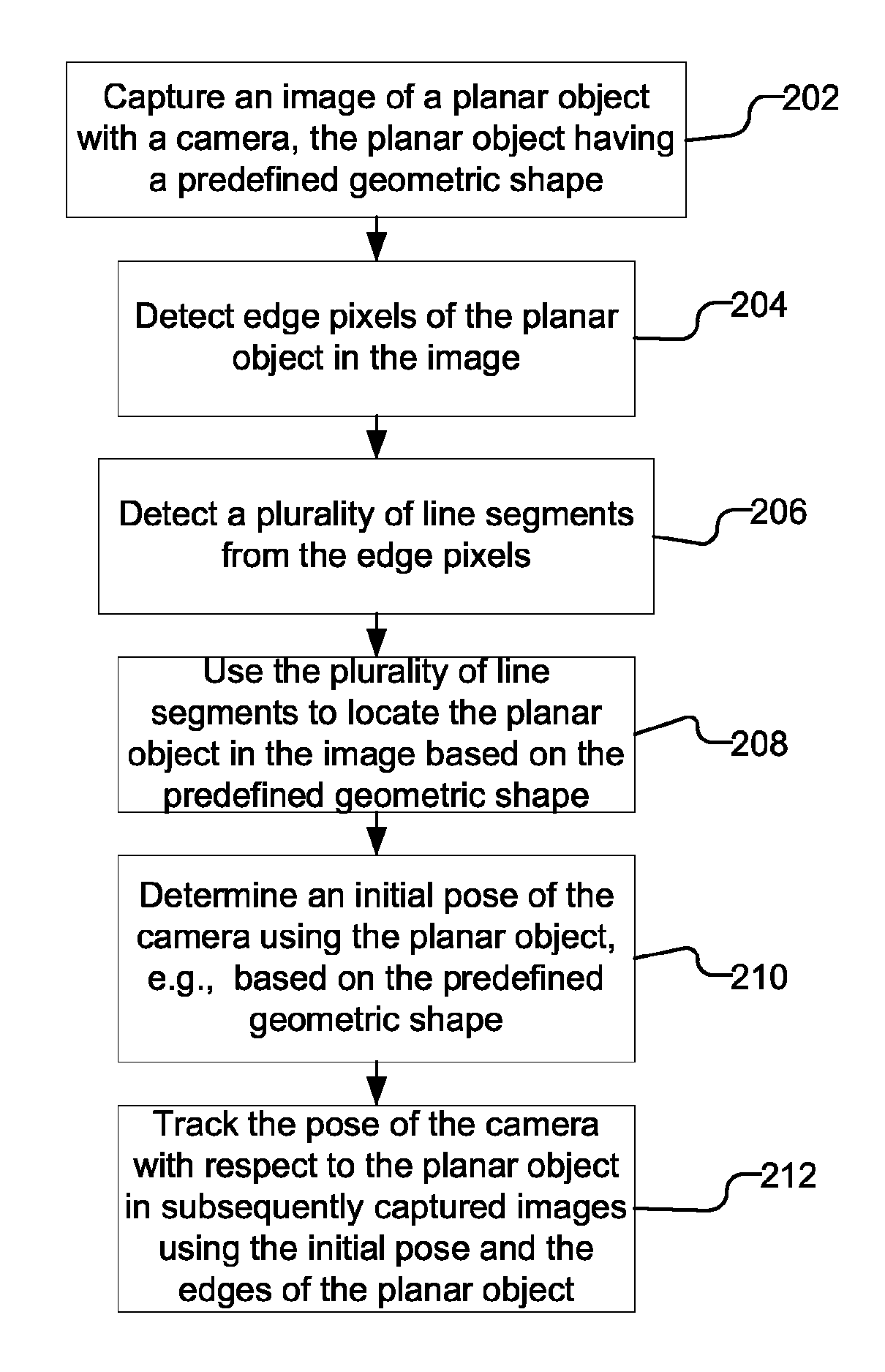
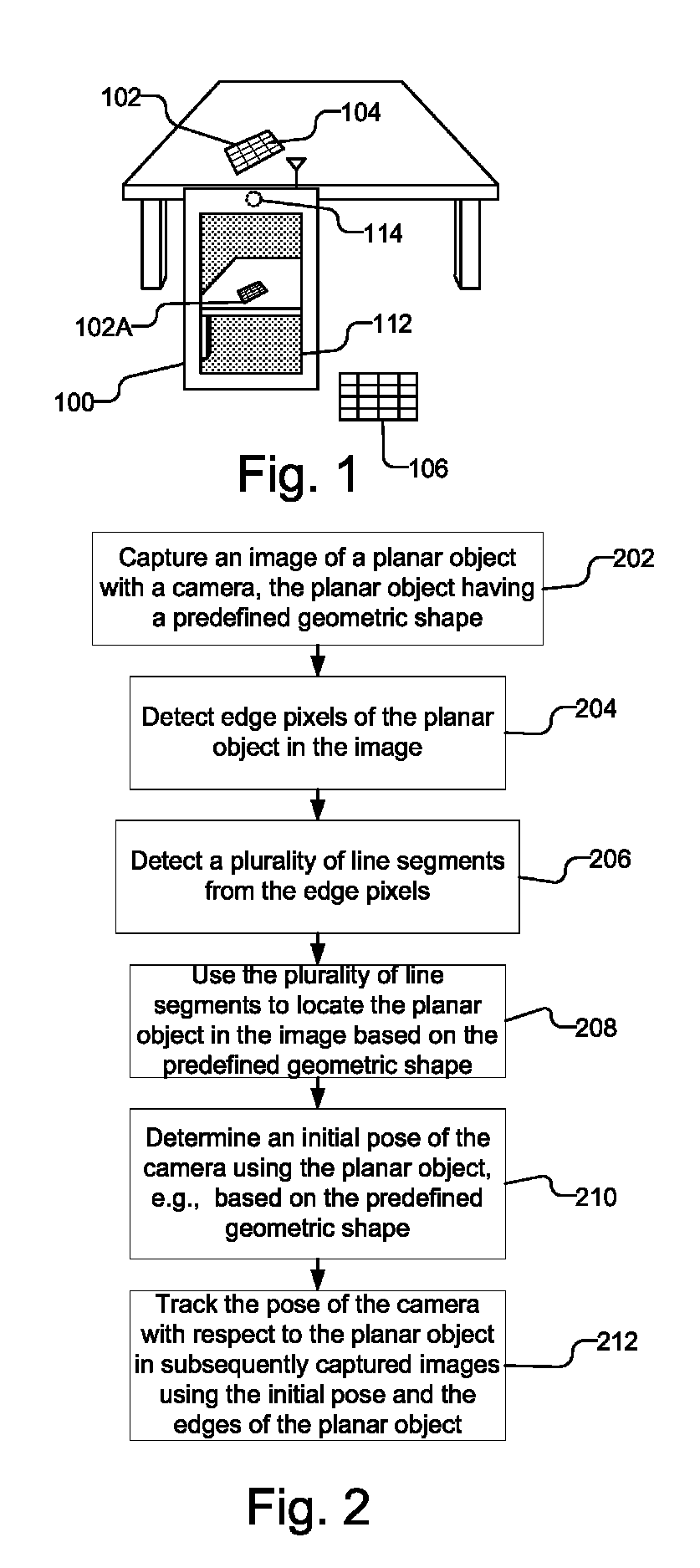
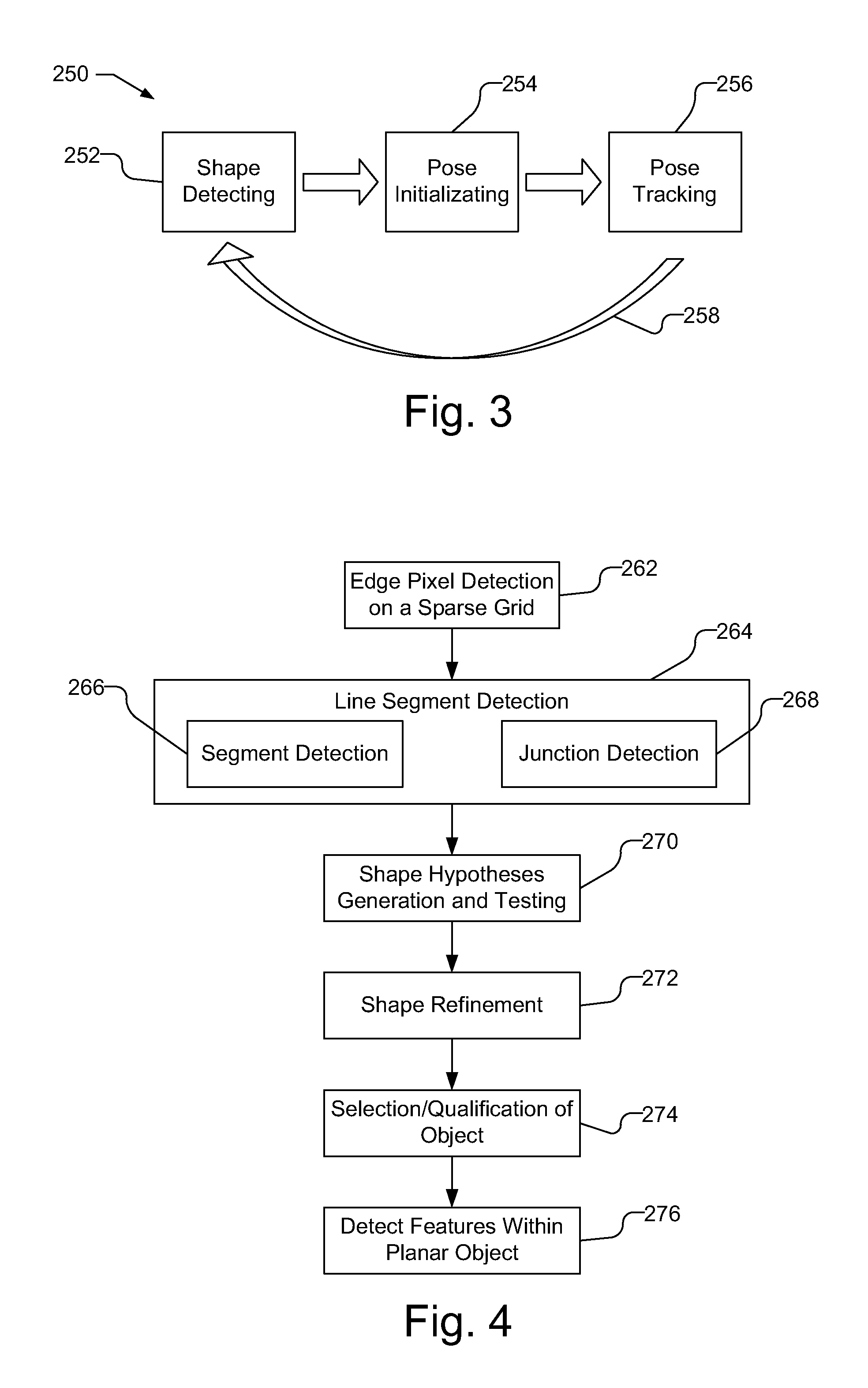
Accelerated geometric shape detection and accurate pose tracking
A reference in an unknown environment is generated on the fly for positioning and tracking. The reference is produced in a top down process by capturing an image of a planar object with a predefined geometric shape, detecting edge pixels of the planar object, then detecting a plurality of line segments from the edge pixels. The plurality of line segments may then be used to detect the planar object in the image based on the predefined geometric shape. An initial pose of the camera with respect to the planar object is determined and tracked using the edges of the planar object.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Uncalibrated multi-viewpoint image correction method for parallel camera array
InactiveCN102065313AFreely adjust horizontal parallaxIncrease the use range of multi-look correctionImage analysisSteroscopic systemsParallaxScale-invariant feature transform
The invention relates to an uncalibrated multi-viewpoint image correction method for parallel camera array. The method comprises the steps of: at first, extracting a set of characteristic points in viewpoint images and determining matching point pairs of every two adjacent images; then introducing RANSAC (Random Sample Consensus) algorithm to enhance the matching precision of SIFT (Scale Invariant Feature Transform) characteristic points, and providing a blocking characteristic extraction method to take the fined positional information of the characteristic points as the input in the subsequent correction processes so as to calculate a correction matrix of uncalibrated stereoscopic image pairs; then projecting a plurality of non-coplanar correction planes onto the same common correction plane and calculating the horizontal distance between the adjacent viewpoints on the common correction plane; and finally, adjusting the positions of the viewpoints horizontally until parallaxes are uniform, namely completing the correction. The composite stereoscopic image after the multi-viewpoint uncalibrated correction of the invention has quite strong sense of width and breadth, prominently enhanced stereoscopic effect compared with the image before the correction, and can be applied to front-end signal processing of a great many of 3DTV application devices.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
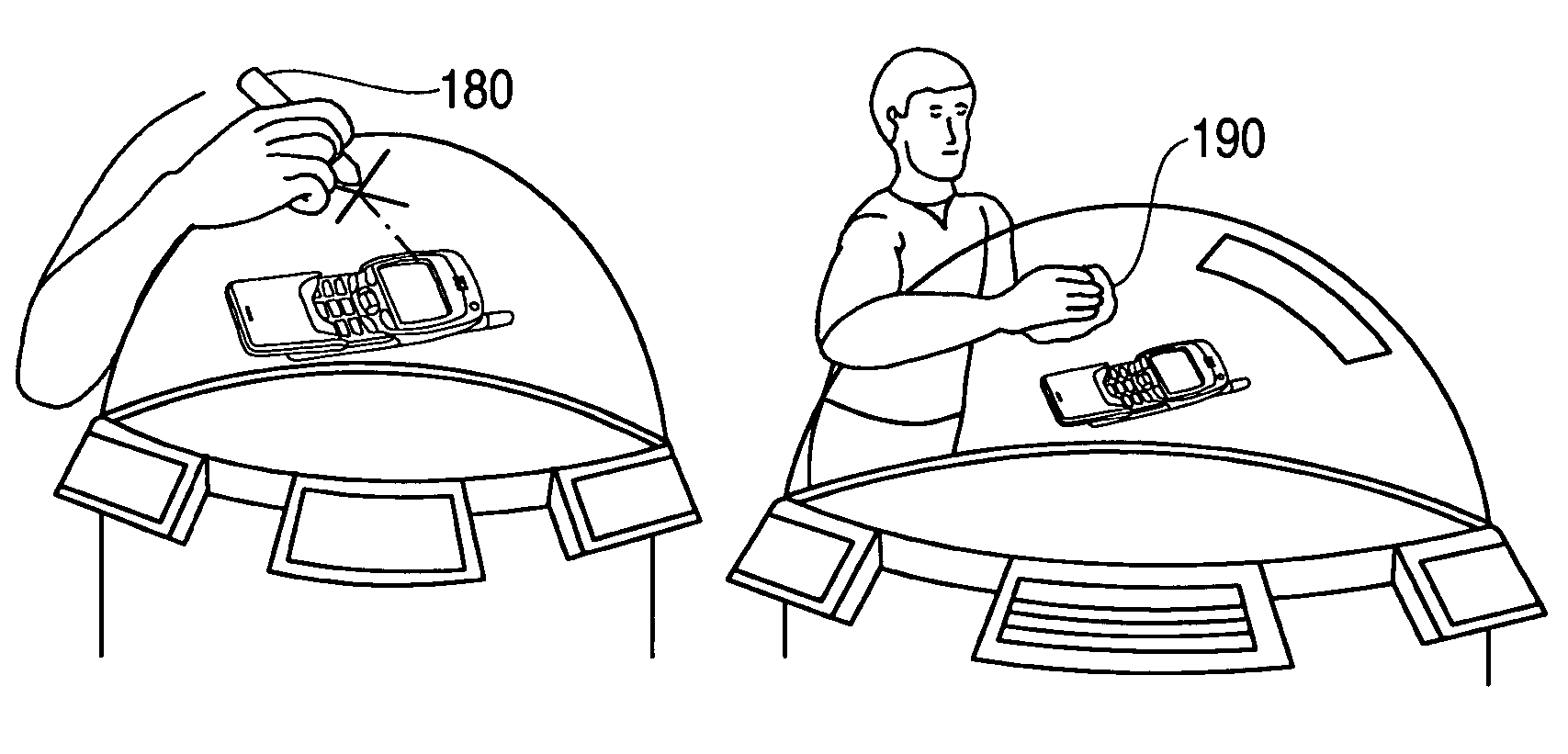
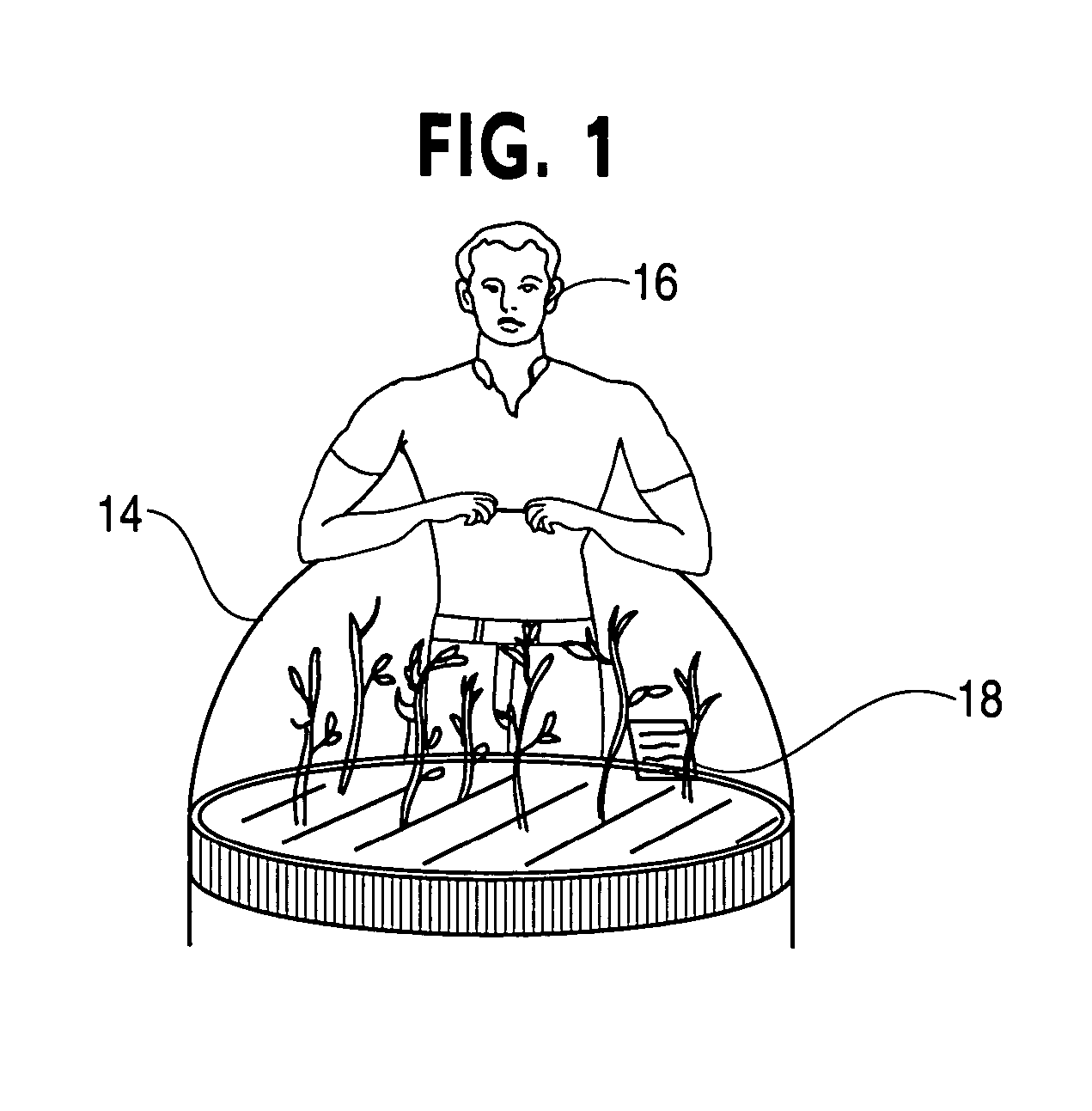
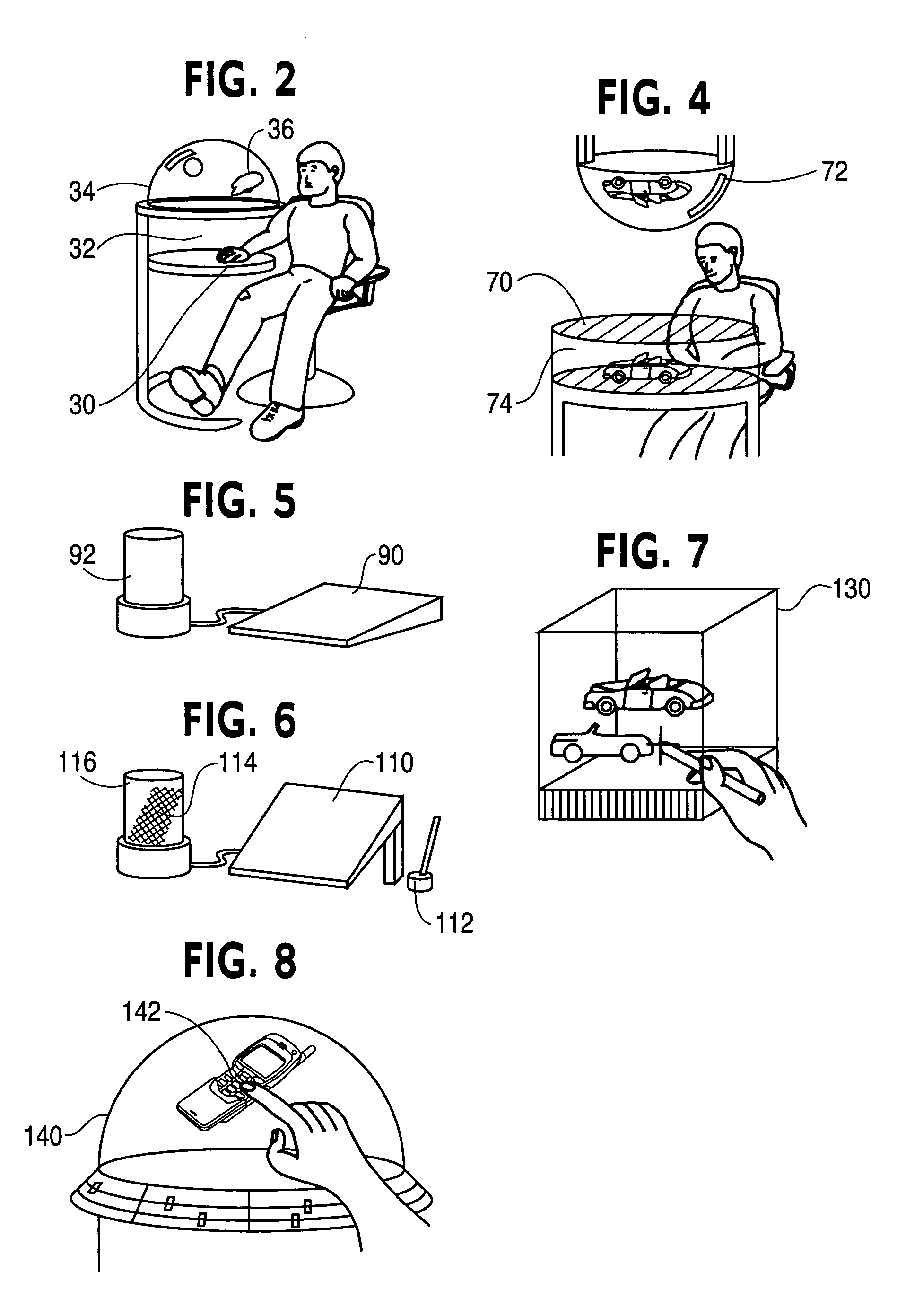
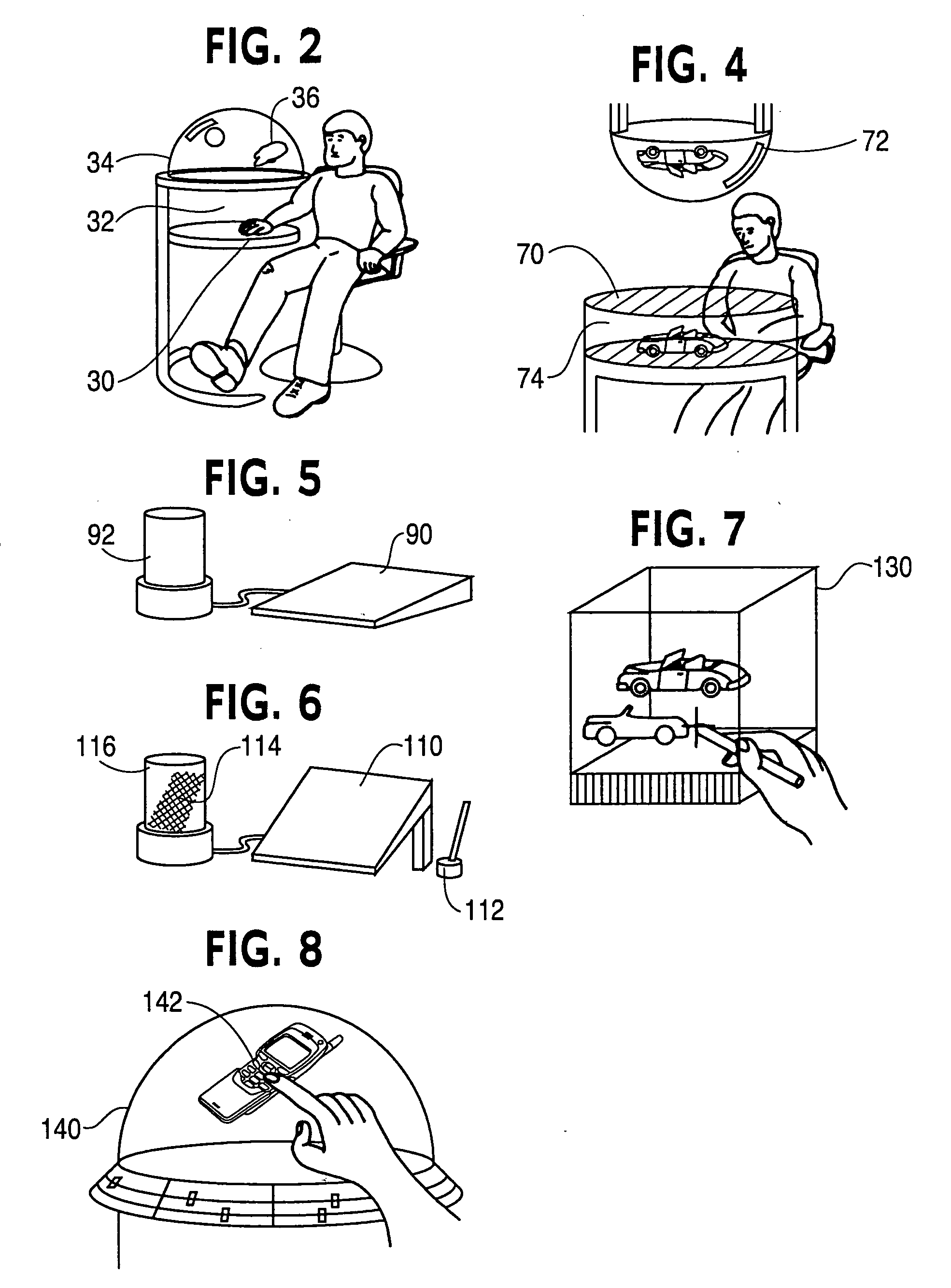
Three dimensional volumetric display input and output configurations
InactiveUS7583252B2Input/output for user-computer interactionDigital data processing detailsEngineeringPlanar projection
The present invention is a system that allows a number of 3D volumetric display or output configurations, such as dome, cubical and cylindrical volumetric displays, to interact with a number of different input configurations, such as a three-dimensional position sensing system having a volume sensing field, a planar position sensing system having a digitizing tablet, and a non-planar position sensing system having a sensing grid formed on a dome. The user interacts via the input configurations, such as by moving a digitizing stylus on the sensing grid formed on the dome enclosure surface. This interaction affects the content of the volumetric display by mapping positions and corresponding vectors of the stylus to a moving cursor within the 3D display space of the volumetric display that is offset from a tip of the stylus along the vector.
Owner:AUTODESK INC
Catadioptric 1x projection system and method
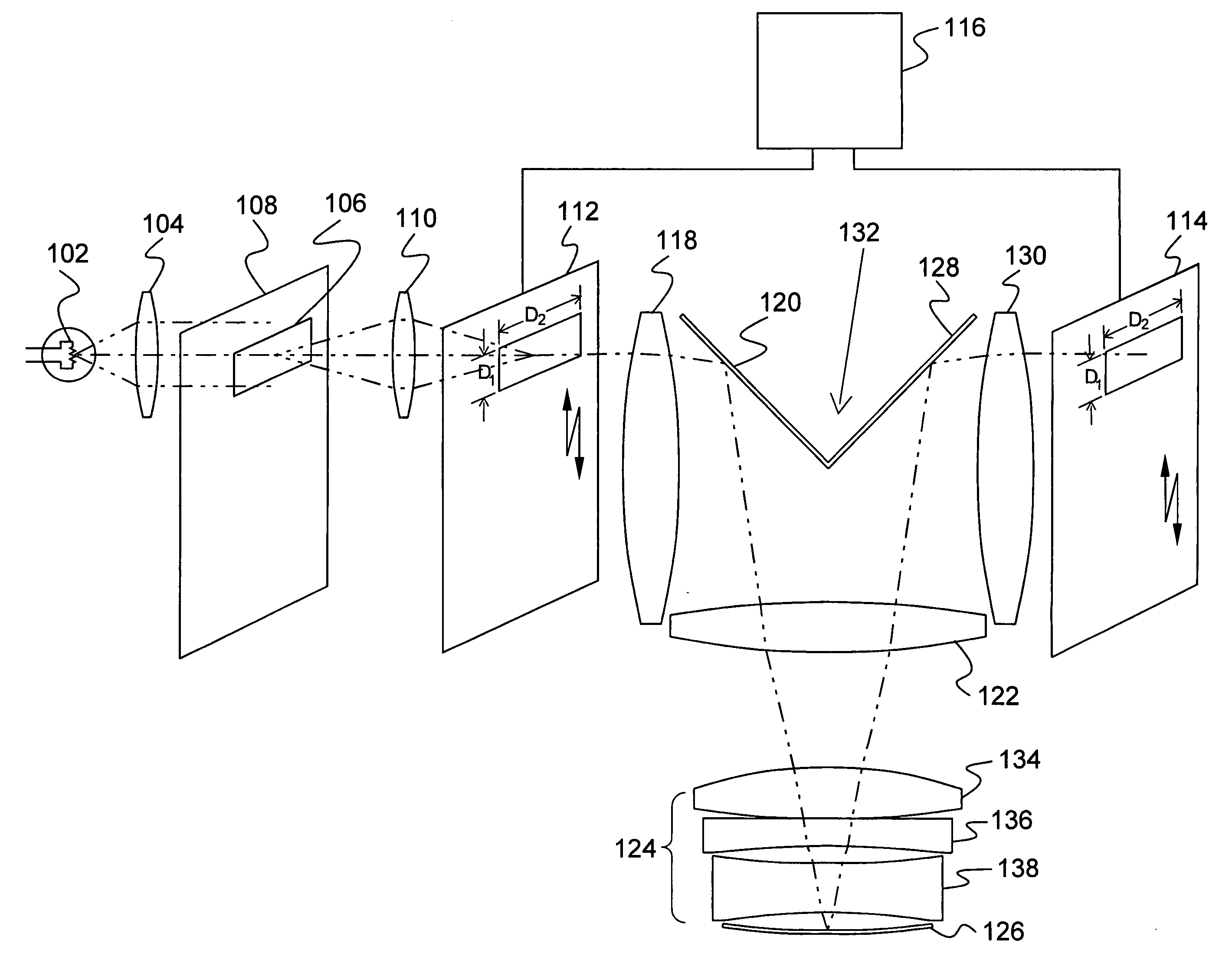
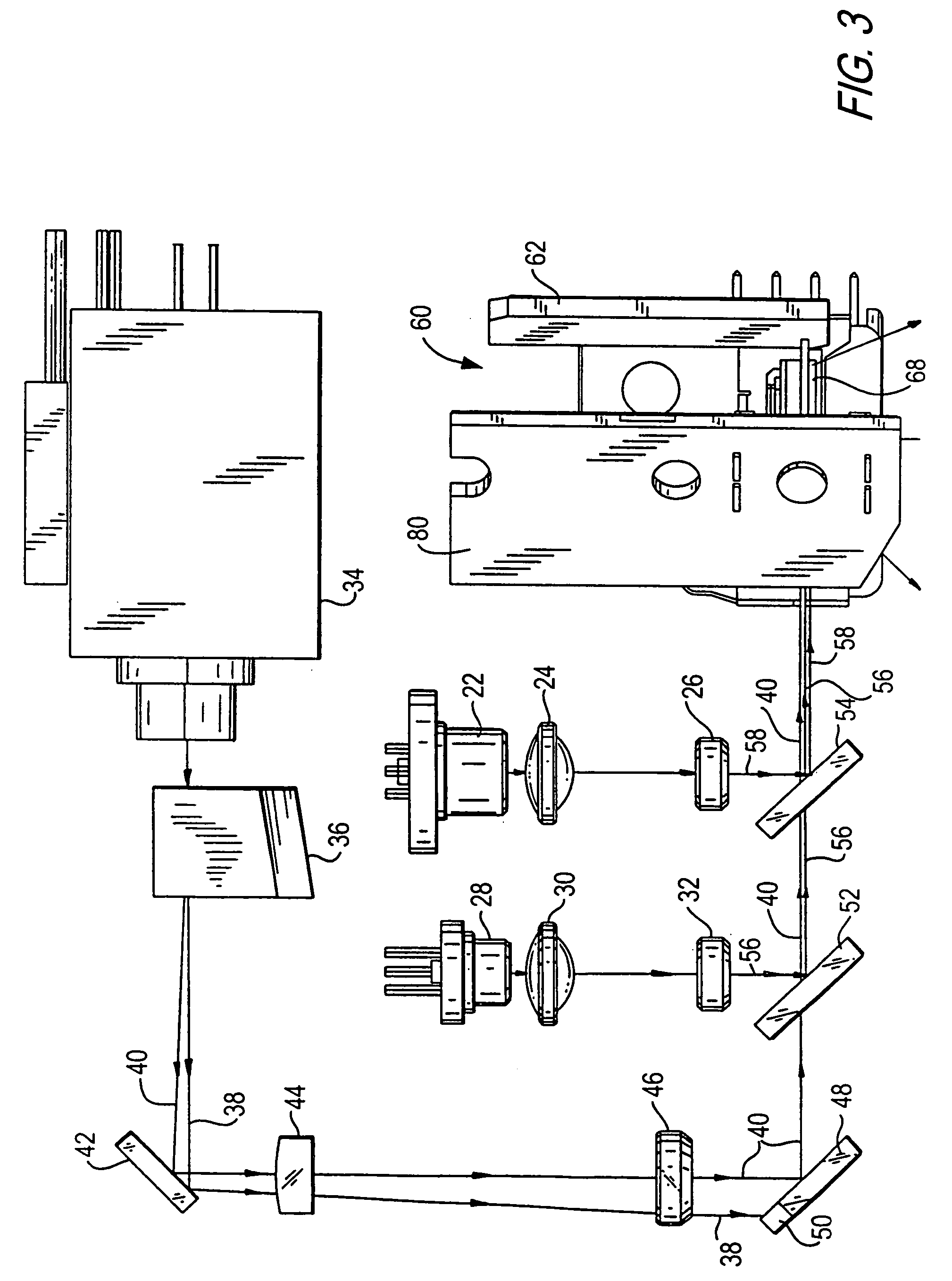
A new and useful method and projection system for projecting an image from an object plane to an image plane is provided. The method and system is designed to operate at a 1× magnification, a relatively high NA, with a relatively large instantaneous scanning field, and to achieve sub-micron resolution at high optical throughput. An object plane is scanned across an instantaneous rectangular field at least 40 mm in the direction of scan and at least 132 mm in a direction that is perpendicular to the scan, and the scanned image is projected onto the image plane through a catadioptric projection system configured for a 1× magnification and a numerical aperture of at least 0.23. The catadioptric projection system includes (i) a first field lens group configured to transmit an image ray bundle from the object plane, (ii) a first plane reflector configured to reflect and redirect the image ray bundle projected from the first field lens group, (iii) a second lens group in the optical path of the reflected, redirected image ray bundle, and a concave reflector following the second lens group, the concave reflector configured to reflect and return the reflected image ray bundle through the second lens group, (iv) a second plane reflector configured to reflect and redirect the returned image ray bundle, and (v) a third field lens group configured to receive and project the reflected, returned image ray bundle onto the image plane.
Owner:NIKON CORP
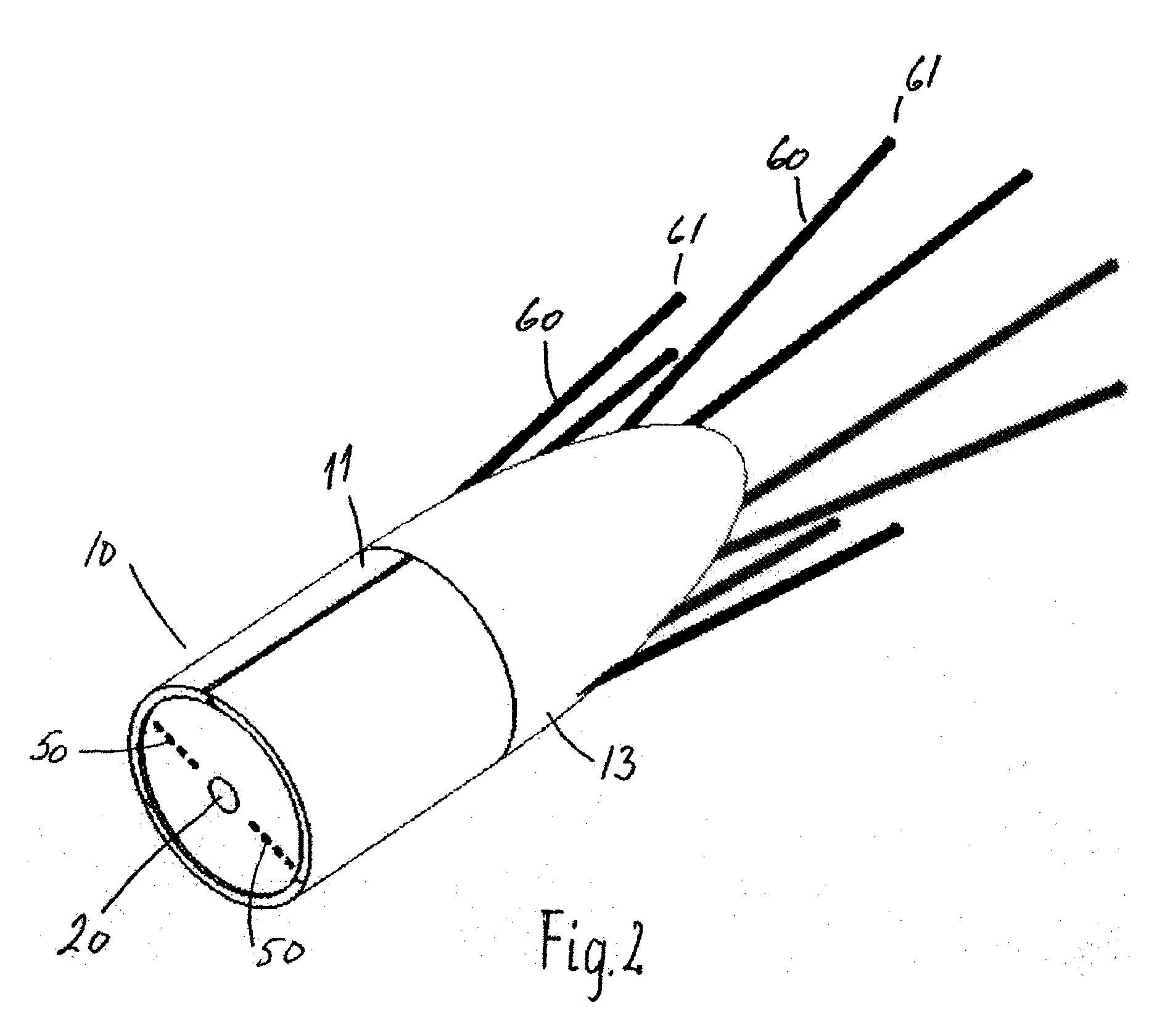
Electrode introducer device
InactiveUS20090254019A1Least amount of injuryImproved and flexible and efficient electric fieldSurgical needlesSkin piercing electrodesElectroporationBiomedical engineering
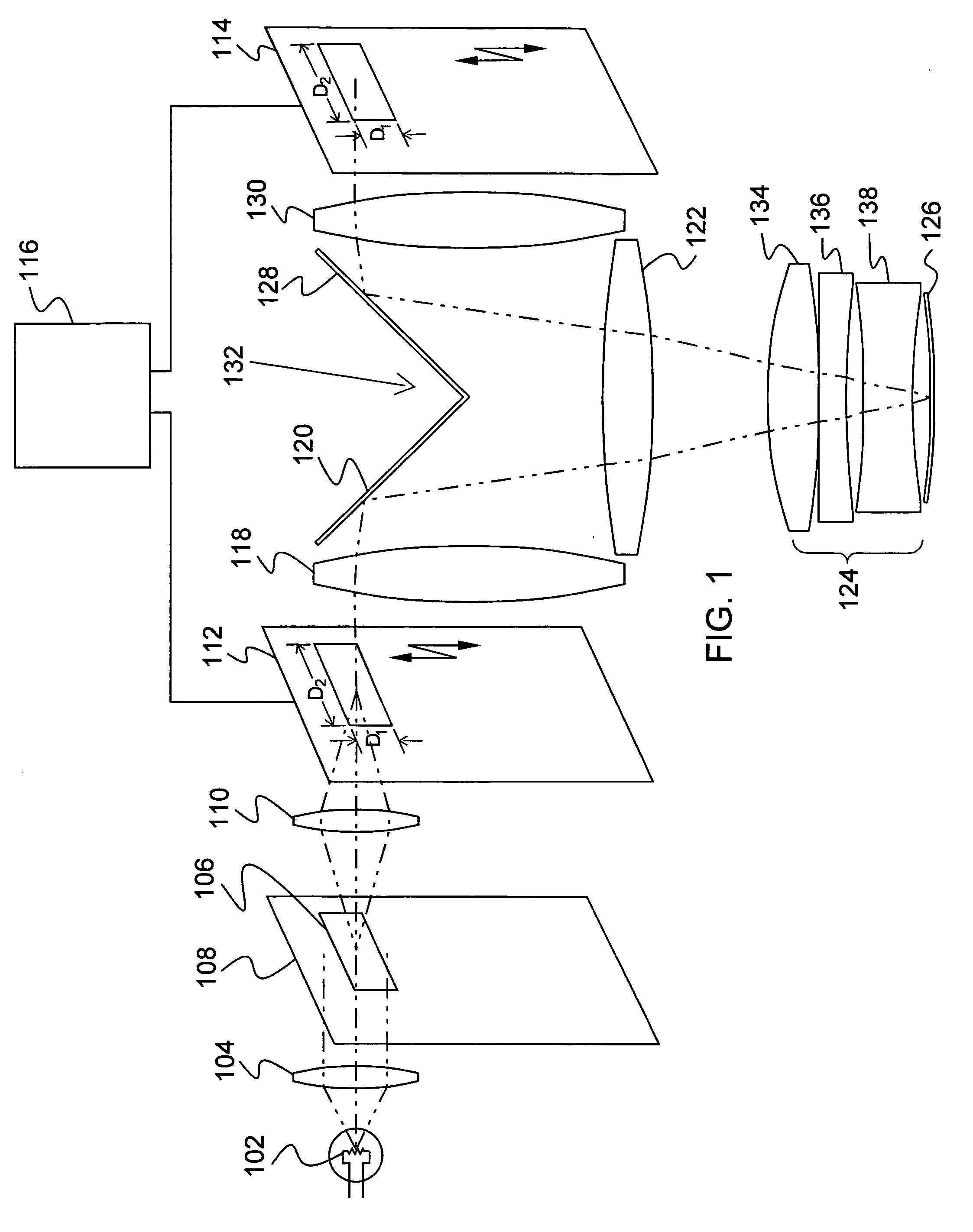
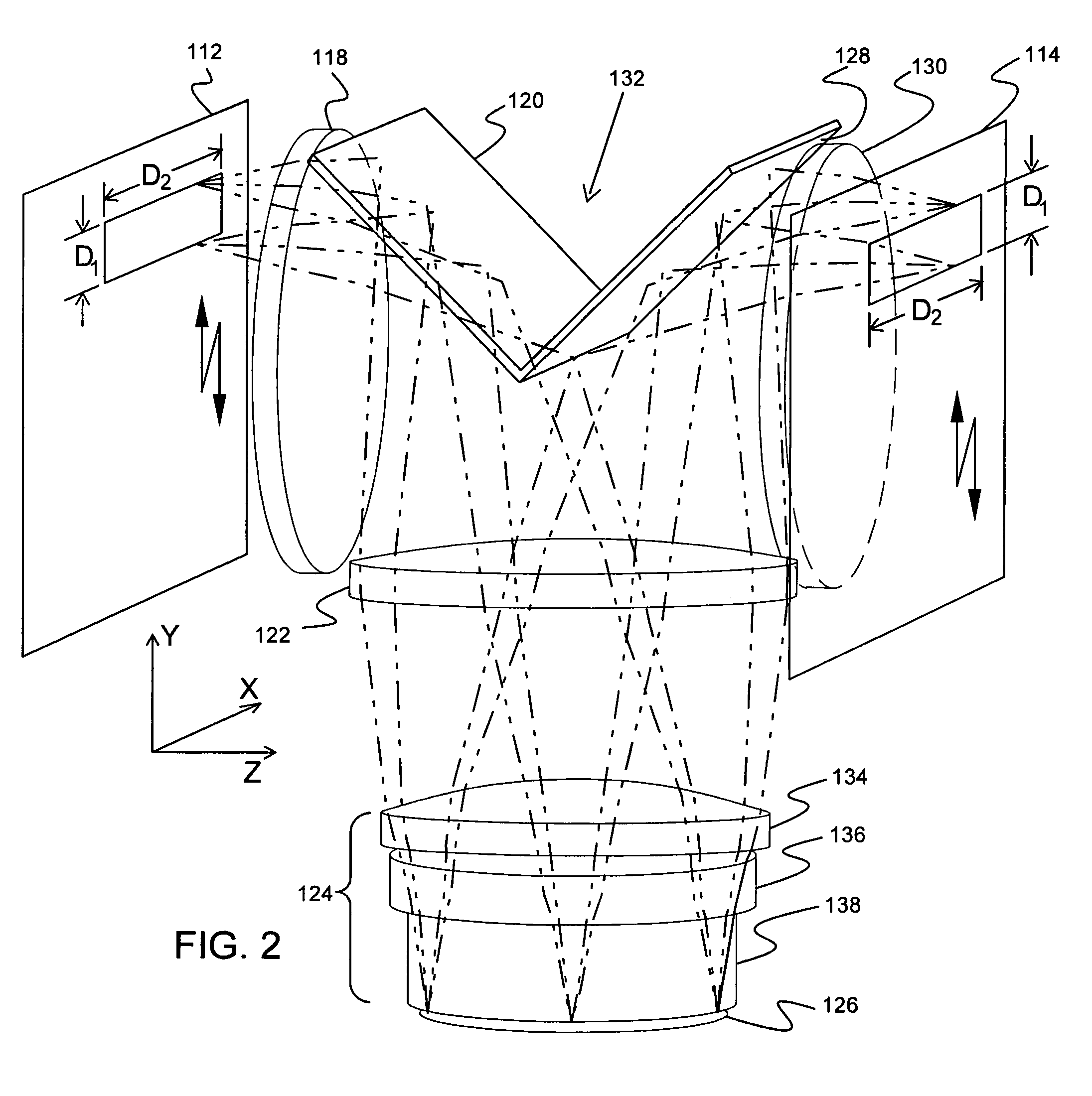
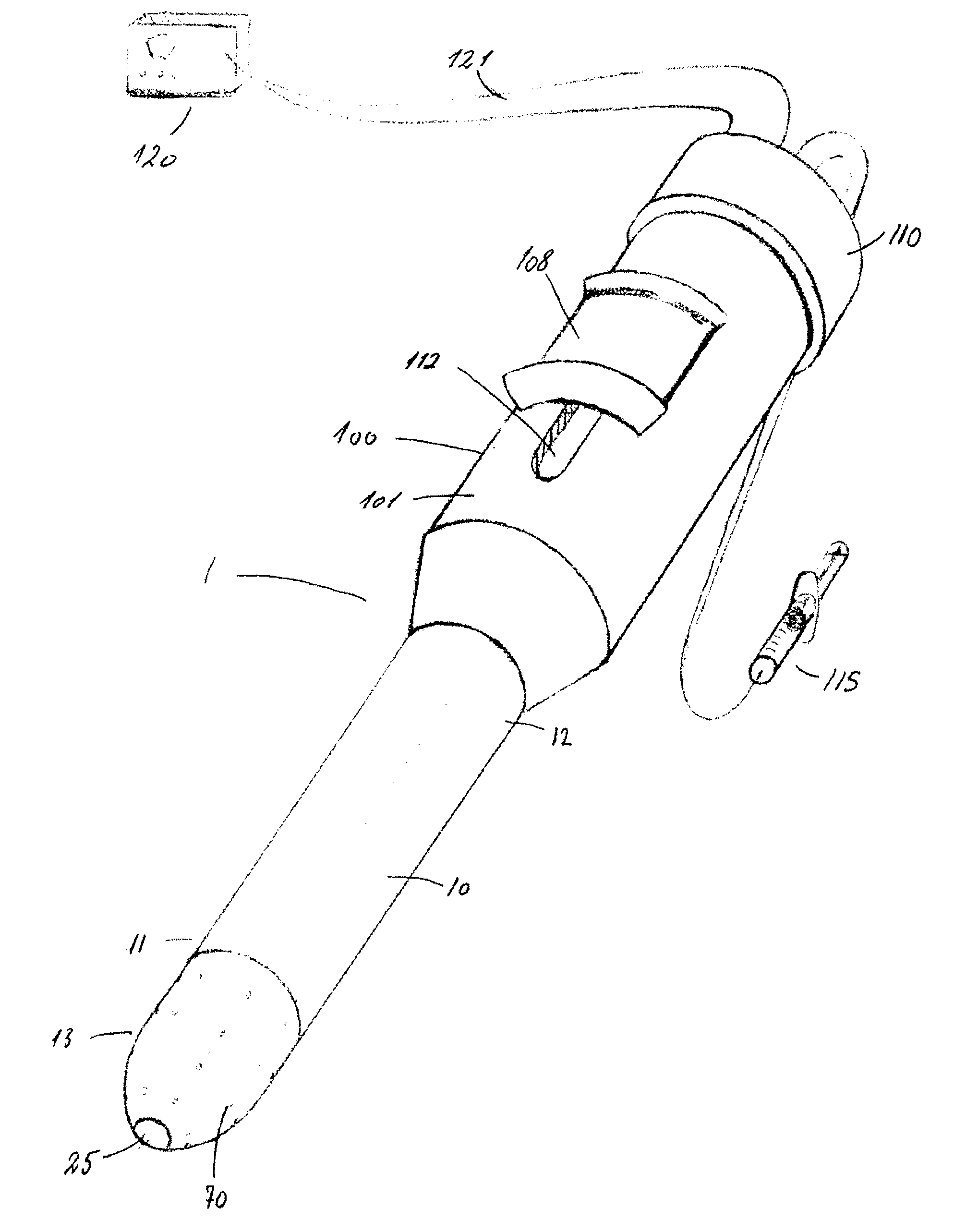
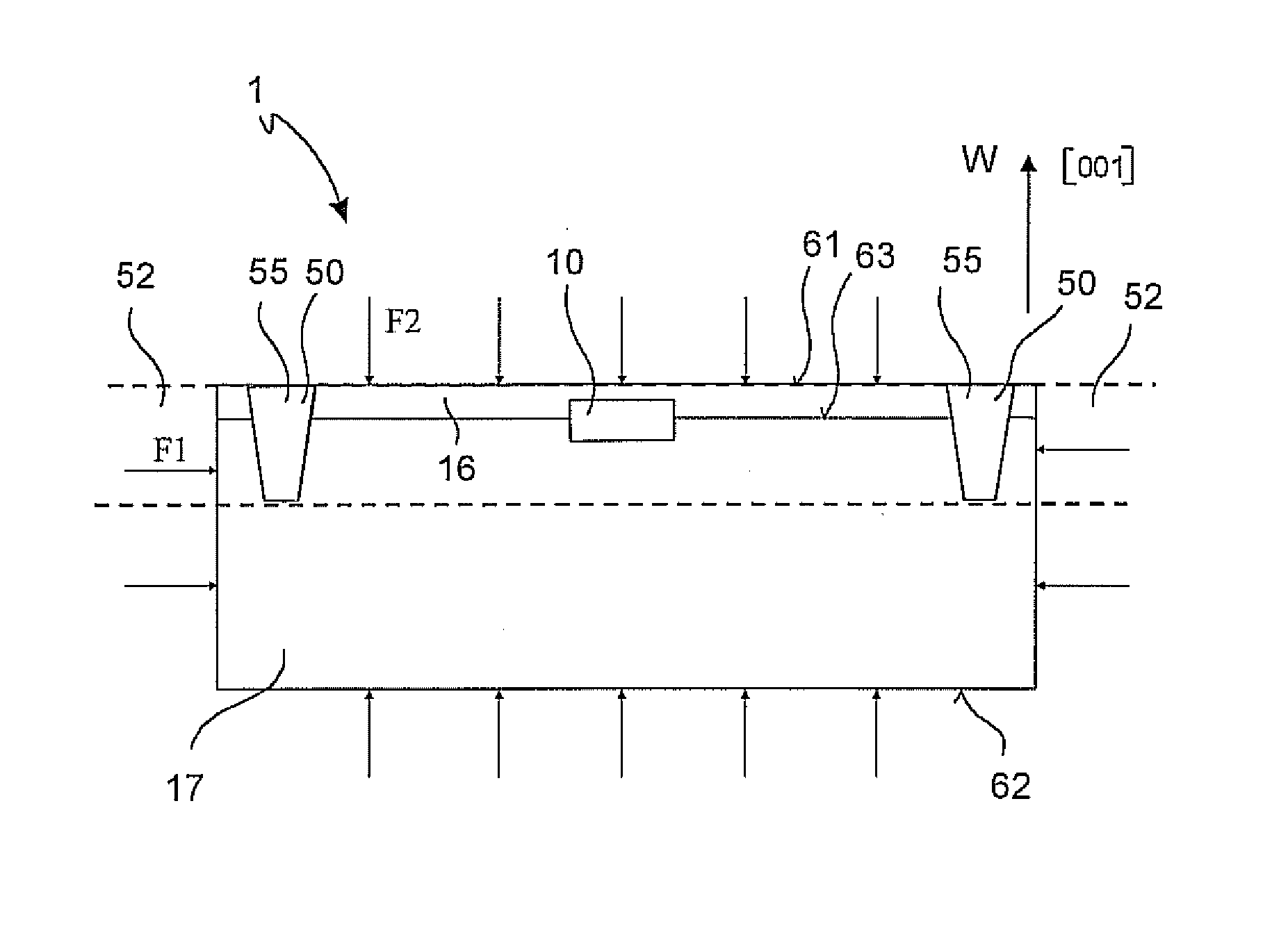
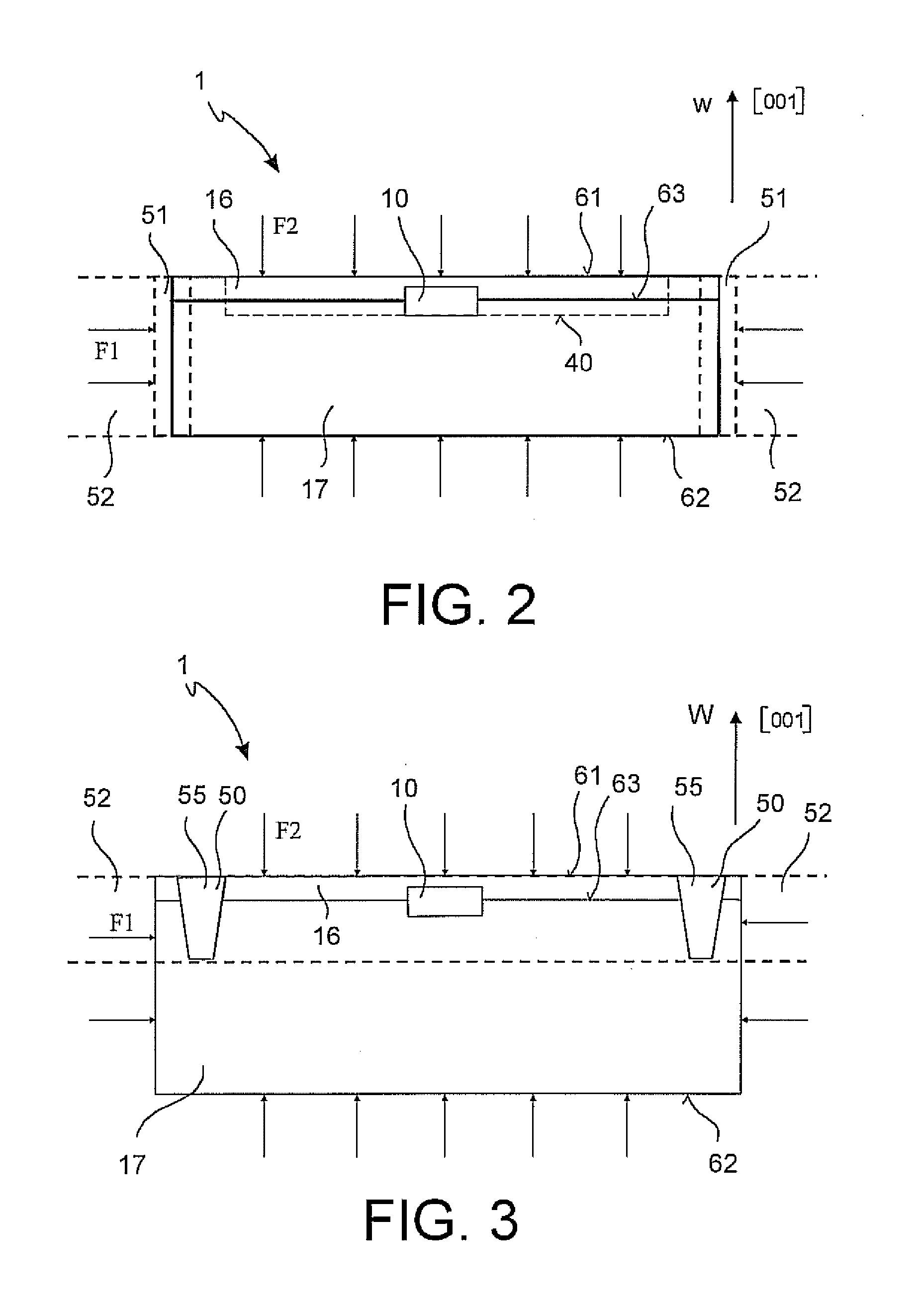
An electroporation device 1 comprising a handle section 100; an elongate introducer shaft 10 connected to said handle section 100, said introducer shaft 10 having a distal tip 13; and a set of electrodes 60 having respective distal ends 61, each electrode 60 being slidably arranged within said introducer shaft 10 from a retracted position, where said distal ends 61 are enclosed within said introducer shaft 10, to an exposed position, where said distal ends 61 extend from said distal tip 13; wherein said electrode distal ends 61 are deflectable away from a longitudinal axis L of said shaft 10 when deployed / extended to their extended position, such that at least one planar projection taken in a plane perpendicular to said longitudinal axis L of distance D1 between a pair of distal ends 61 of said electrodes 60 is larger than a maximal extent D2 of a cross-section of said introducer shaft 10, said cross-section taken in a plane perpendicular to said longitudinal axis L at a distal end 11 of said introducer shaft 10.
Owner:REGION HOVEDSTADEN VHERLEV HOSPITAL
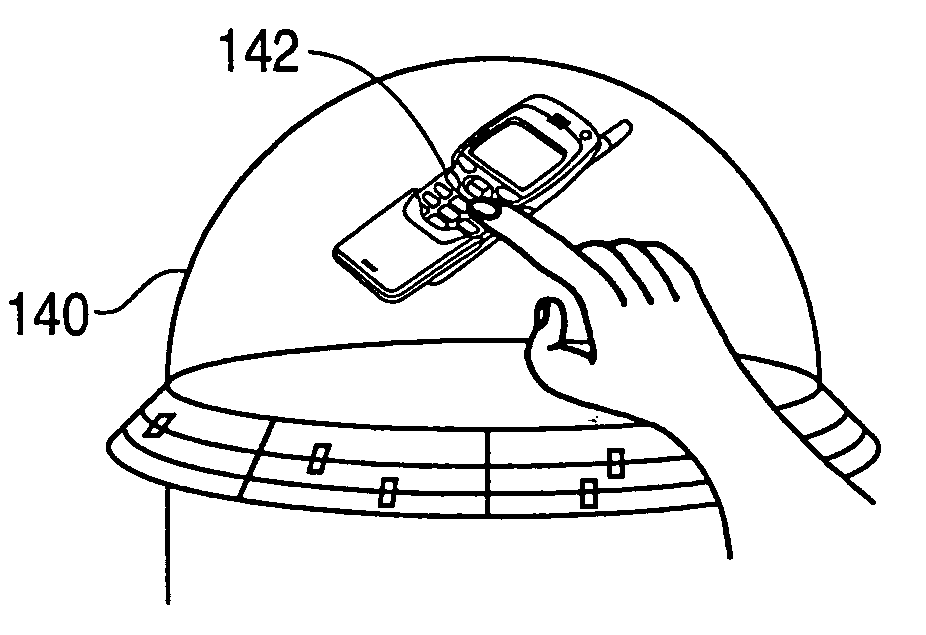
Three dimensional volumetric display input and output configurations
ActiveUS20080284729A1Efficient mechanismInput/output for user-computer interactionDigital data processing detailsEngineeringPlanar projection
The present invention is a system that allows a number of 3D volumetric display or output configurations, such as dome, cubical and cylindrical volumetric displays, to interact with a number of different input configurations, such as a three-dimensional position sensing system having a volume sensing field, a planar position sensing system having a digitizing tablet, and a non-planar position sensing system having a sensing grid formed on a dome. The user interacts via the input configurations, such as by moving a digitizing stylus on the sensing grid formed on the dome enclosure surface. This interaction affects the content of the volumetric display by mapping positions and corresponding vectors of the stylus to a moving cursor within the 3D display space of the volumetric display that is offset from a tip of the stylus along the vector.
Owner:AUTODESK INC
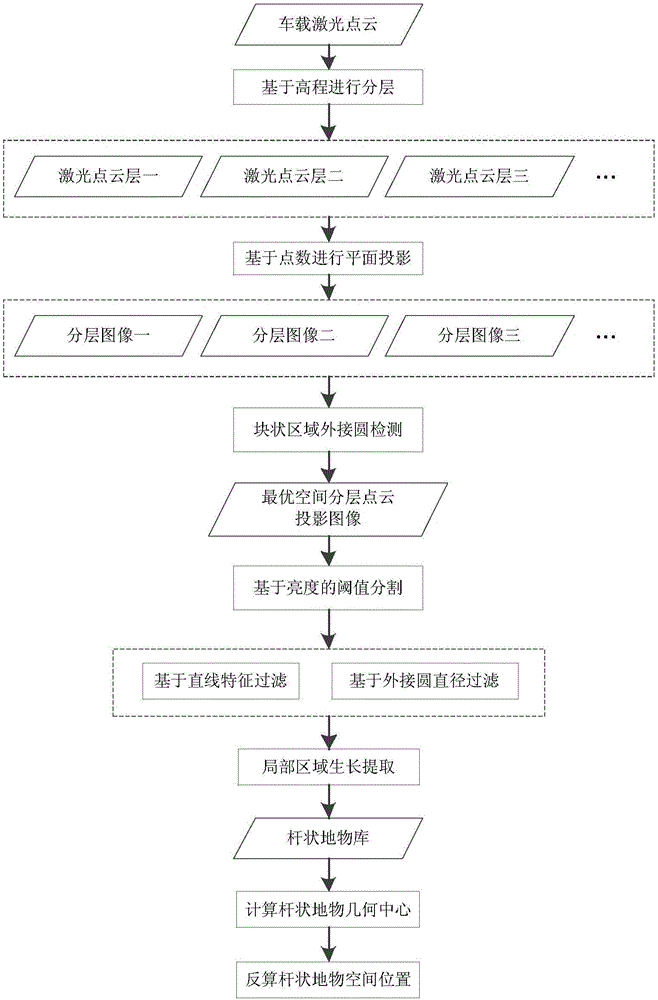
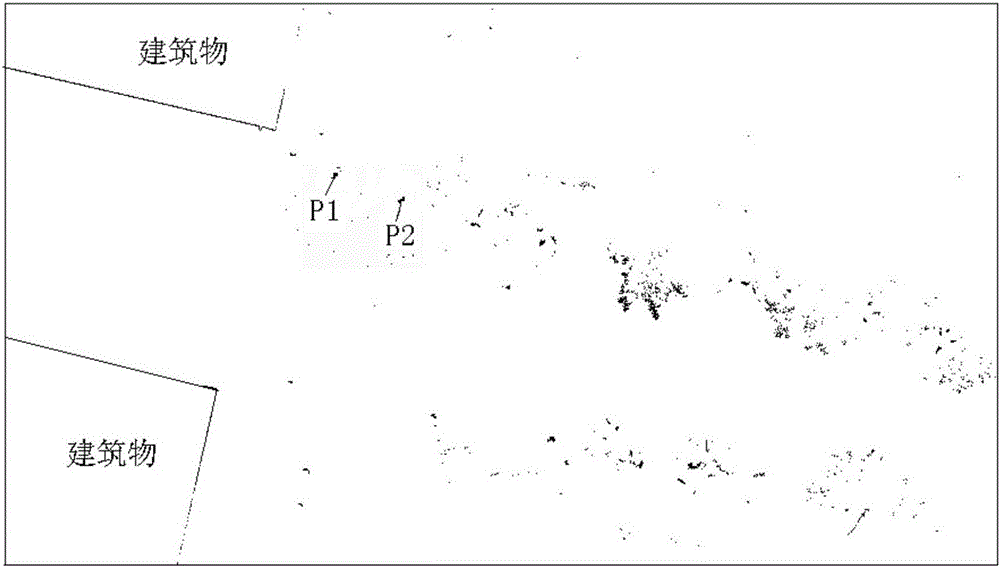
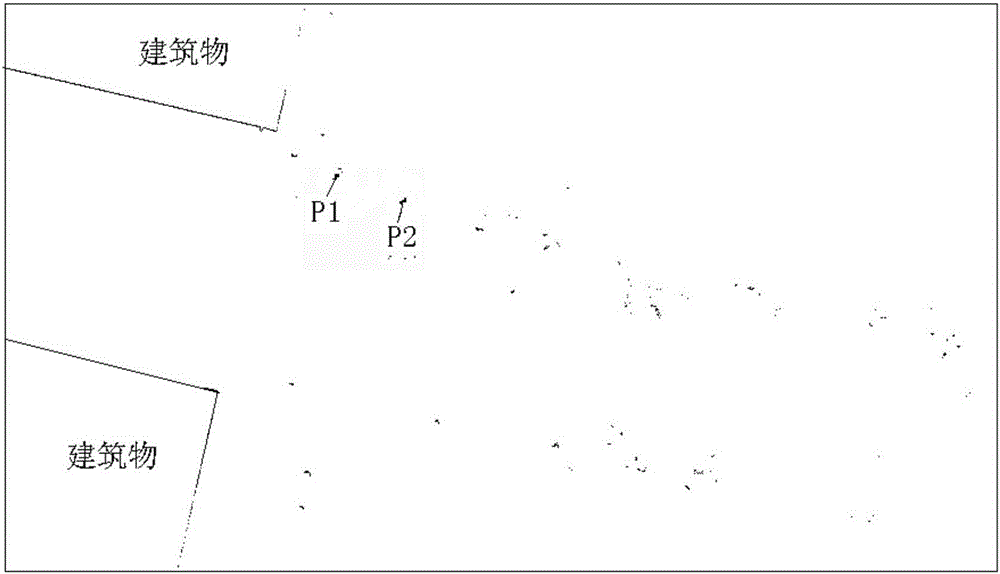
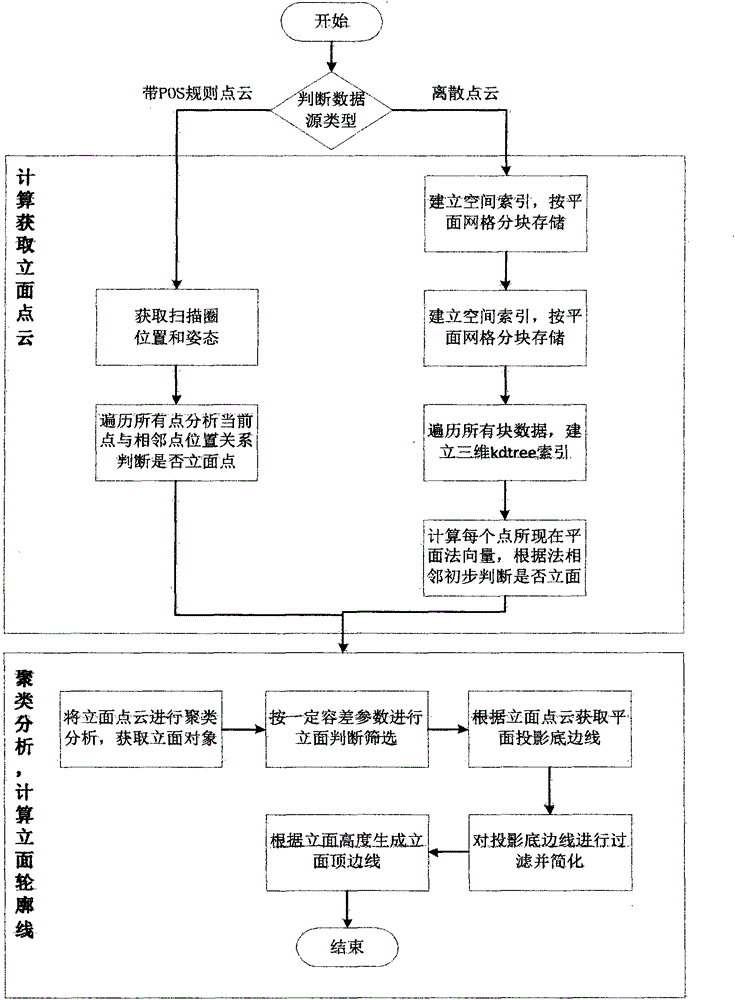
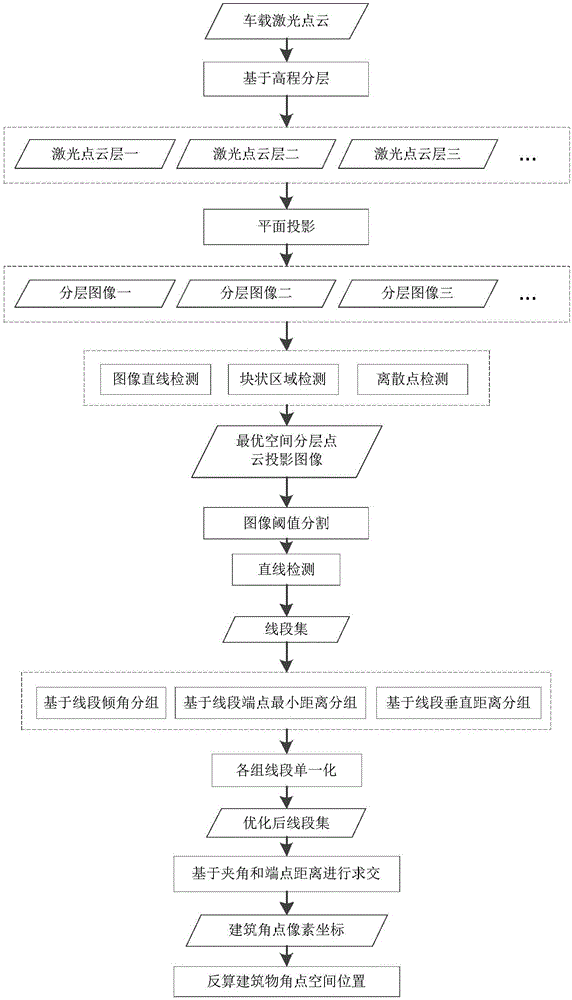
Method for automatically extracting spatial position of rod-shaped ground objects from point clouds in vehicle laser scanning
ActiveCN106204547AHigh degree of automationEasy extractionImage enhancementImage analysisPoint cloudMobile laser scanning
The invention discloses a method for automatically extracting a spatial position of rod-shaped ground objects from point clouds in vehicle laser scanning. The method first acquires the optimal spatial layered point cloud plane projected image from the laser scanning point cloud. Threshold segmentation is performed on the generated optimal spatial layered point cloud plane projection image to remove the low luminance points. The linear detection of the plane projection image after threshold segmentation is carried out, and the data with line features is removed. The image is further extracted to obtain the projection image of the rod-shaped ground object by removing the data part which does not accord with the diameter characteristics of the rod-shaped ground object. Finally, the geometric center of each rod-shaped ground object area is taken as the spatial location point of the rod-shaped ground object from the projected image of the rod-shaped ground object, and the relative position is reduced to the three-dimensional point cloud. The method of the invention is not susceptible to the noise point of data with high automation degree, fully utilizing the morphological characteristics of the point cloud data to achieve a better extraction effect.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
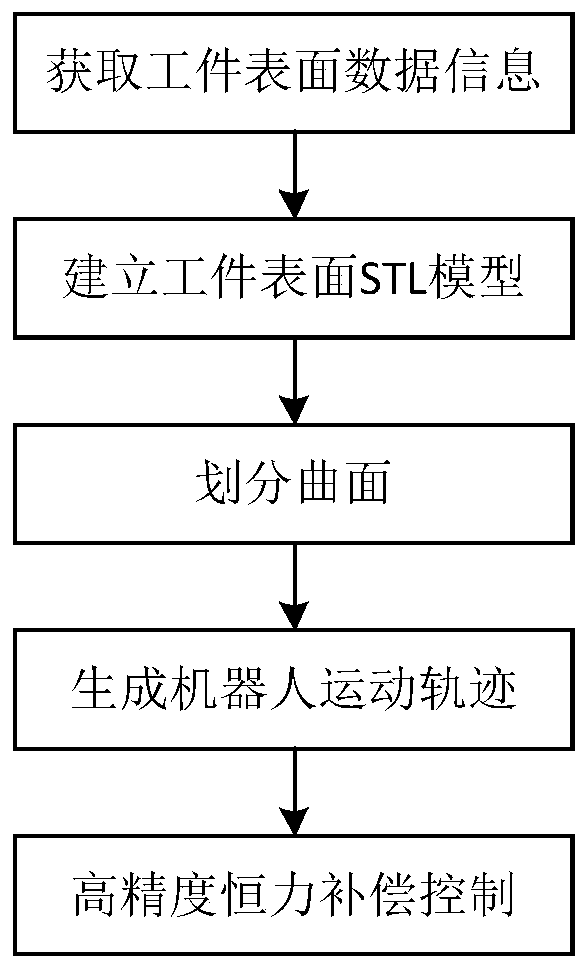
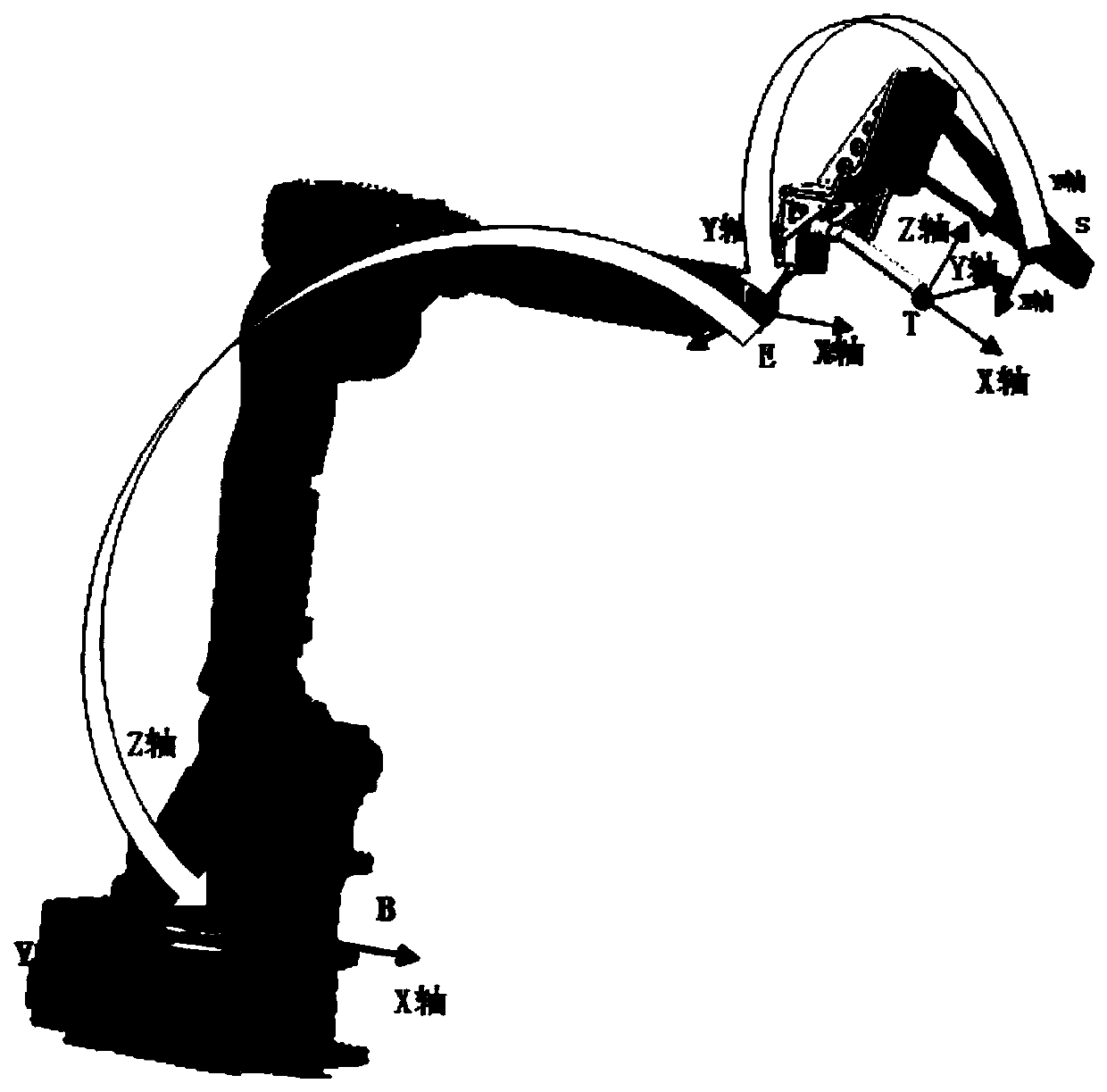
Industrial robot high-precision constant-force grinding method based on curved surface self-adaption
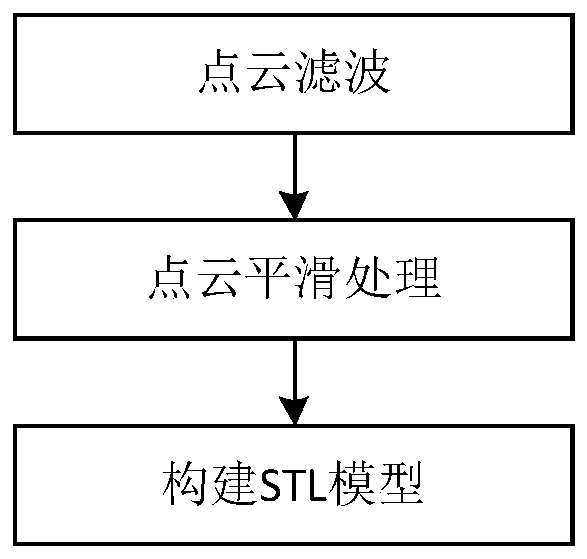
InactiveCN111055293AImprove effectivenessImprove versatilityProgramme-controlled manipulatorModel extractionData information
The invention discloses an industrial robot high-precision constant-force polishing method based on curved surface self-adaption. The method comprises the steps of acquiring scanning sampling point data information of the surface of a workpiece to be polished by adopting a linear structured light scanning mode, and acquiring an ordered point cloud model of the workpiece to be polished; through point cloud preprocessing, establishing an STL model of the surface of the to-be-polished workpiece; extracting and utilizing geometric features and topological features of the STL model on the surface of the to-be-polished workpiece, and dividing the curved surface of the to-be-polished workpiece into a plurality of planes without holes; constructing a feature frame according to the STL model of thesurface of the to-be-polished workpiece, and generating a robot polishing motion track by adopting a cutting plane projection method; and in the robot grinding process, constant-force grinding control is achieved according to real-time force feedback. The method has the beneficial effects that the constant-force grinding task for any curved surface can be achieved; the adaptability of the grinding method to the curved surface is improved; the grinding precision is improved; and therefore the intelligence and the automation level of a robot grinding system can be improved.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Arrangement for and method of projecting an image with linear scan lines
ActiveUS20060279664A1Quality improvementEffective alignmentTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsProjection imageLinearity
A lightweight, compact image projection module, especially for mounting in a housing having a light-transmissive window, is operative for sweeping a composite laser beam as a pattern of linear scan lines on a planar projection surface and for causing selected pixels arranged along each linear scan line to be illuminated to produce an image of high quality and in color.
Owner:MICROVISION
Apparatus and method for indicating target by image processing without three-dimensional modeling
InactiveCN1380996AInput/output for user-computer interactionImage analysisReference frame3D modeling
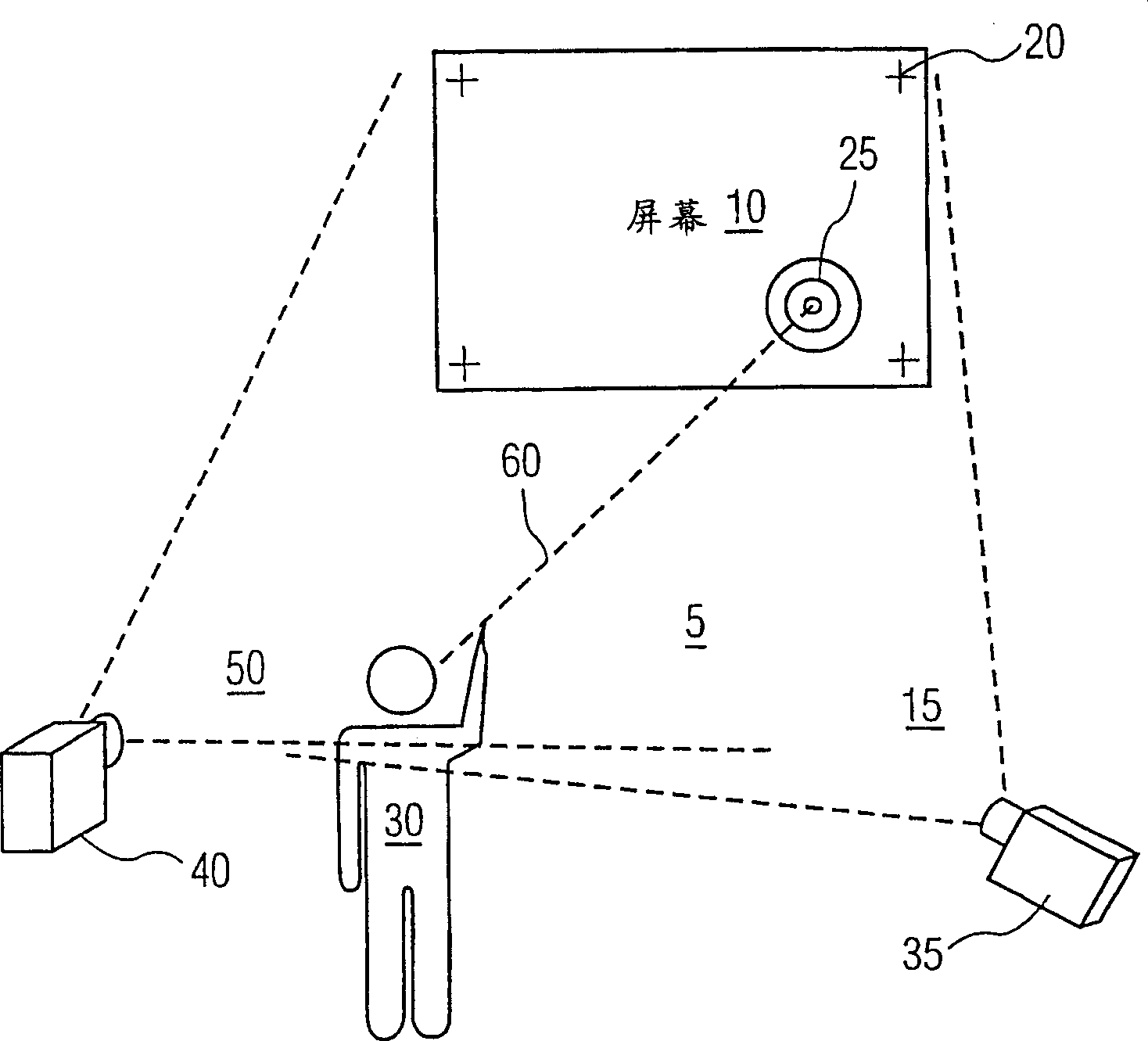
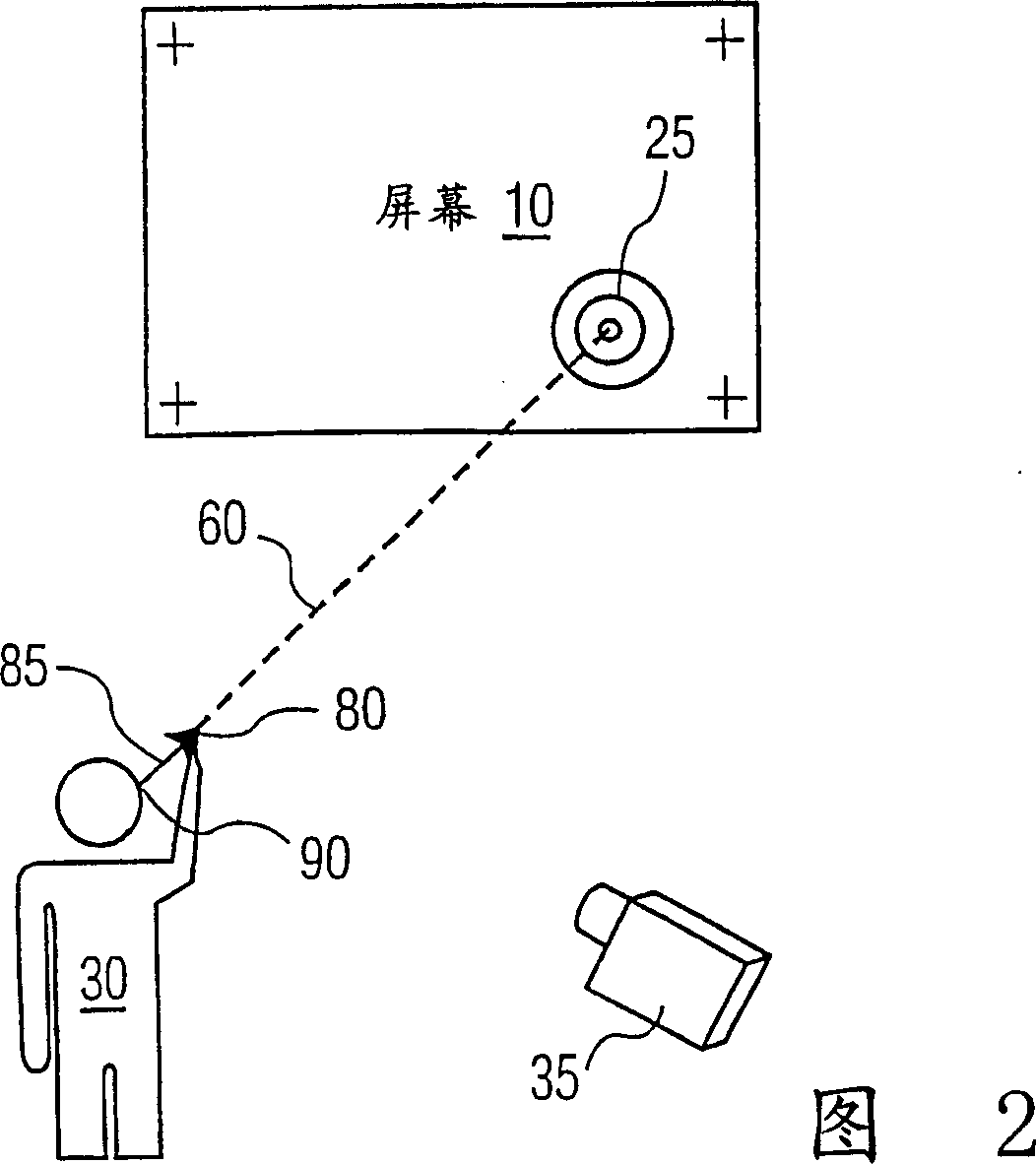
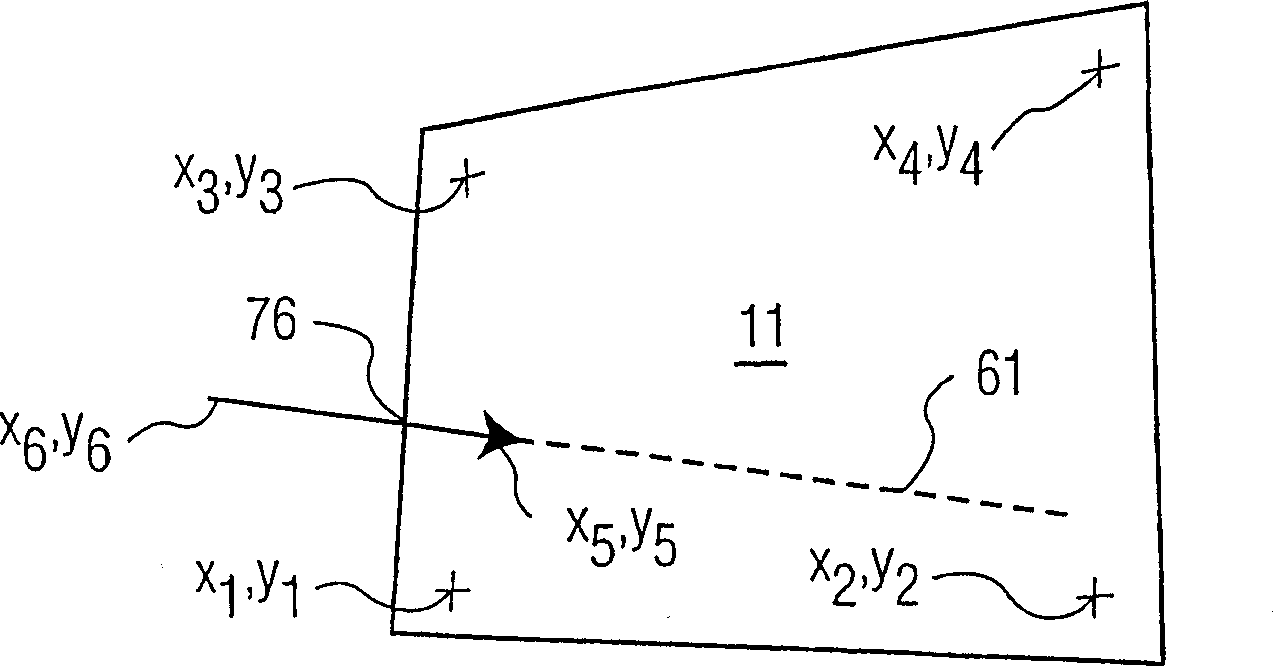
Using a pair of cameras, the coordinates of a target on a plane to which a user is pointing may be obtained without three-dimensional modeling and using only data derived from the respective images and no three-dimensional scene data. Each camera views at least four registration points on the plane and an indicator of a direction along which the target lies. A linear transform of a first image maps the planar projection of the direction indication into the second image. The coordinates, in the second image, of the target are determined from the intersection of the projection of the direction in the second image and the transformed projection from the first image. In another embodiment, the directions are mapped to a third reference frame or image by respective linear transforms. An application of the system would allow a user to indicate a location on a projection or television screen using a static pointing gesture. No information about the locations of the cameras is required, so the system can be set up quickly.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Projection algorithm for generating curved surface non-interference five-axis processing locus
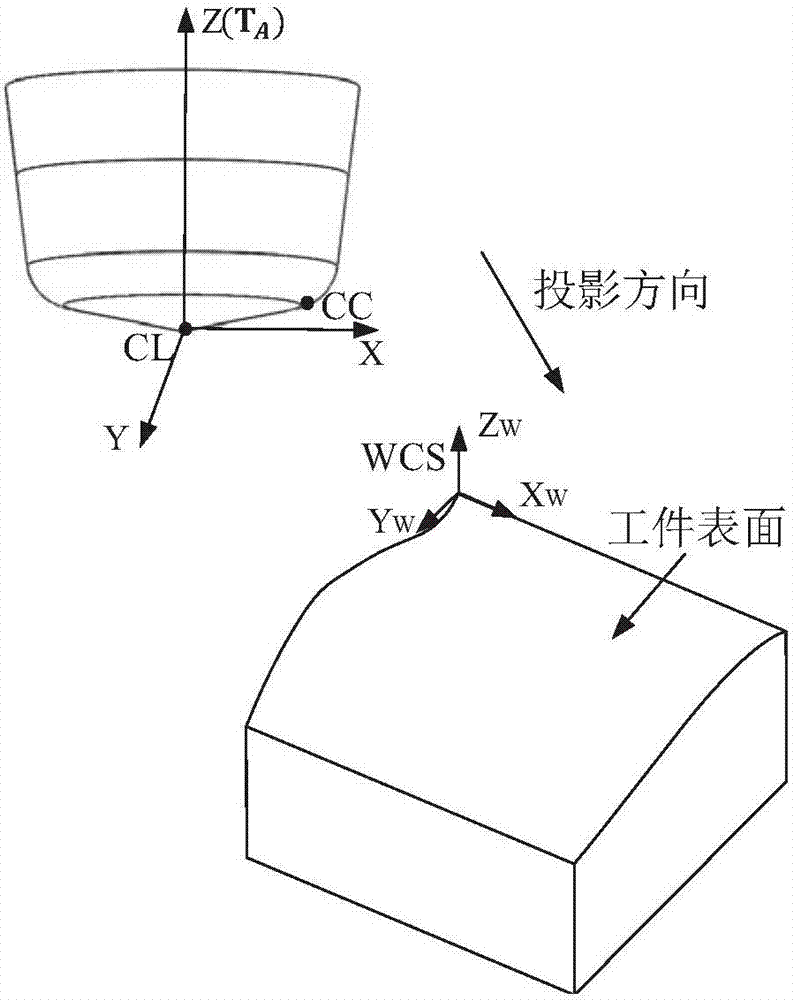
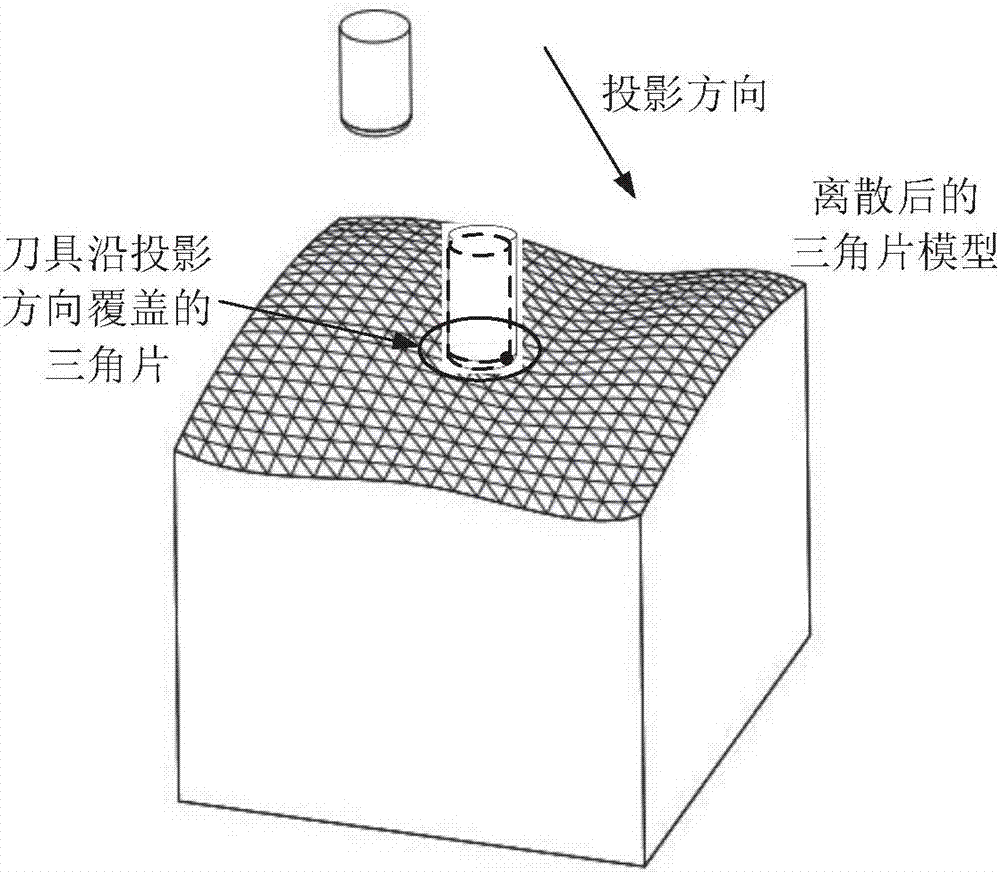
ActiveCN107247444AImprove calculation accuracySolving Convergence Oscillation ProblemsNumerical controlShortest distanceProjection algorithms
The invention relates to a projection algorithm for generating curved surface non-interference five-axis processing locus, belongs to the milling processing technology field and aims to guarantee that a final knife contact point is on an original workpiece curved surface, improve processing precision and guarantee relatively good processing surface quality. According to the algorithm, a knife contact point of a cutter projected on a triangular sheet model is selected as an initial point; the shortest distance from the initial point to a workpiece curved surface is calculated, and a corresponding point on the workpiece curved surface is further calculated; a tangent plane on the workpiece curved surface passing the corresponding point is established; the cutter is projected to the tangent plane to acquire projection points on the tangent plane; an adjusting search step algorithm is executed for an oscillation convergence problem; the projection point on the tangent plane satisfying an error is taken as the knife contact point. The algorithm is advantaged in that based on a Newton-Raphson algorithm, a continuous iteration method based on the tangent plane is employed, that the knife contact point is on the original workpiece curved surface is guaranteed, and calculation precision of the cutter contact point is improved.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH +1
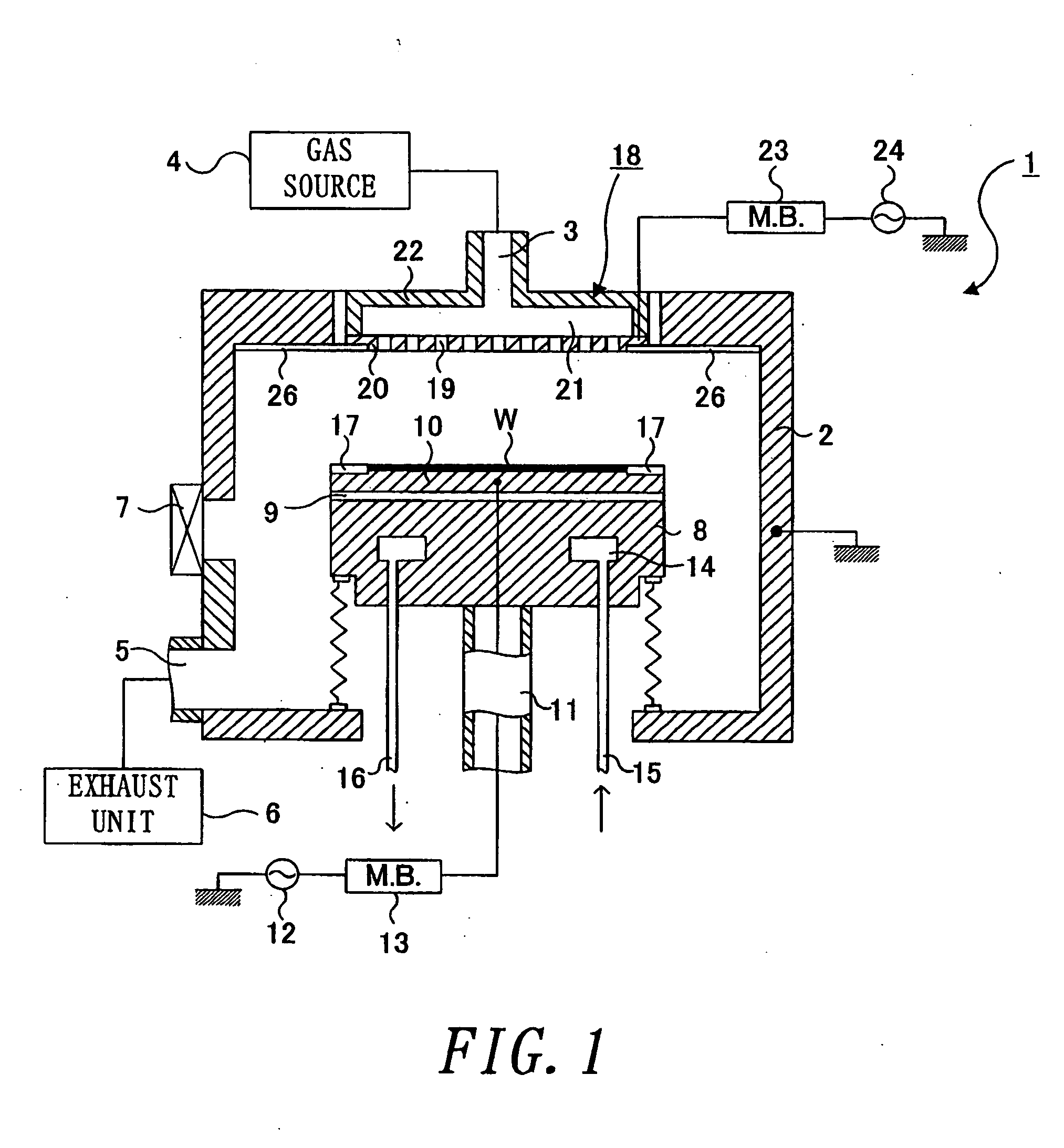
Plasma process device and plasma process method
InactiveUS20070131171A1Improve uniformityElectric discharge tubesDecorative surface effectsWaferingSusceptor
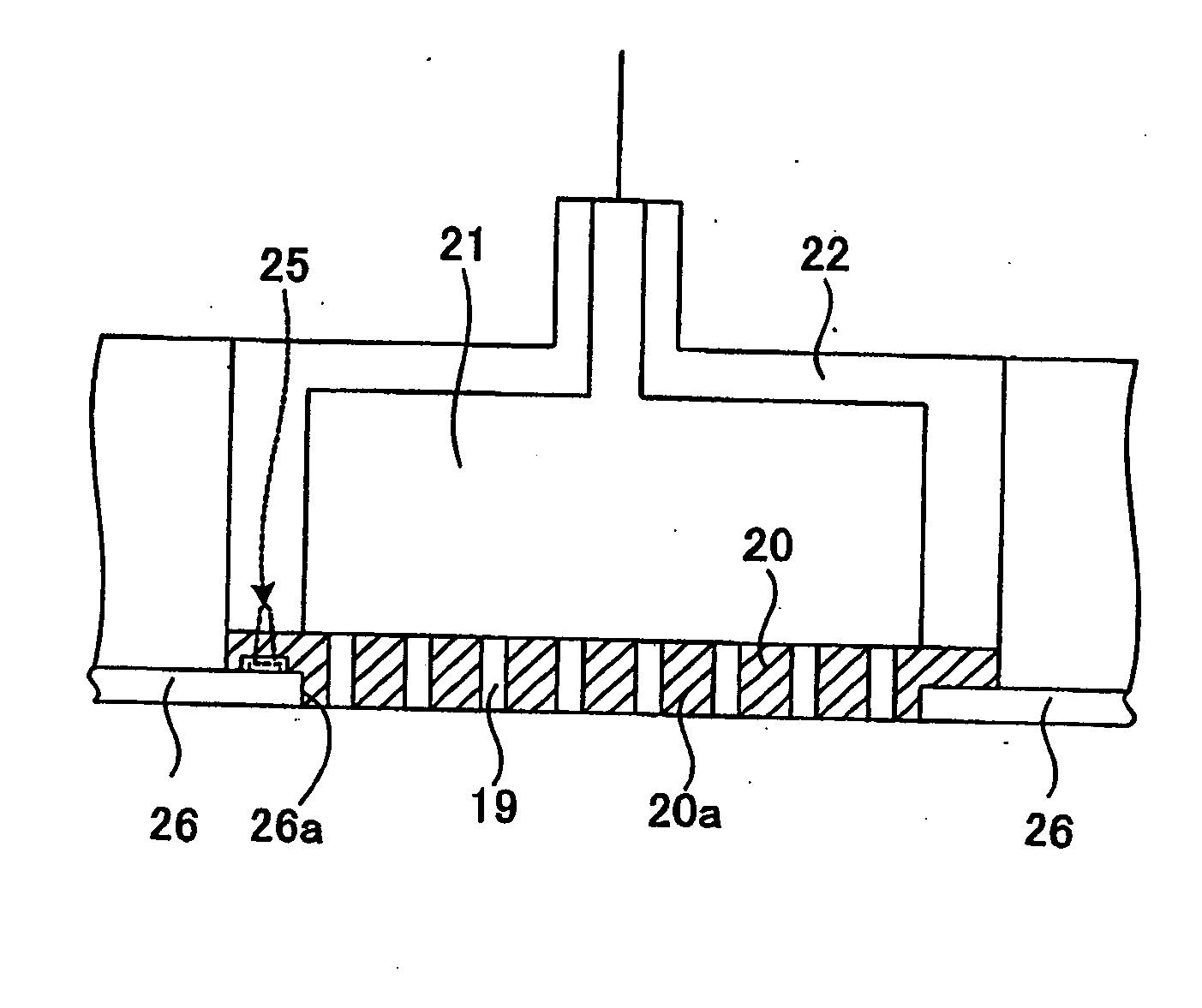
That surface of an electrode plate 20 which is opposite to a susceptor 10 has a projection shape. The electrode plate 20 is fitted in an opening 26a of shield ring 26 at a projection 20a. At this time, die thickness of the projection 20a is approximately the same as the thickness of the shield ring 26. Accordingly, the electrode plate 20 and the shield ring 26 form substantially the same plane. The major surface of the projection 20a has a diameter 1.2 to 1.5 times the diameter of a wafer W. The electrode plate 20 is formed of, for example, SiC.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
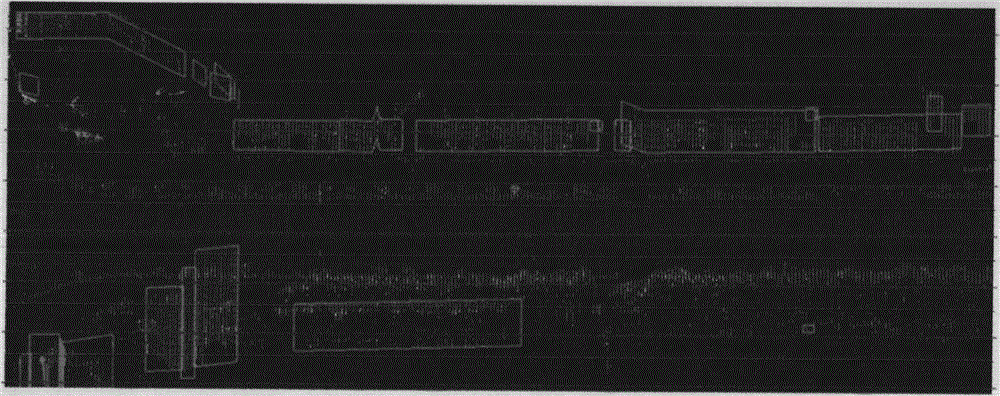
Automatic vehicle-mounted three-dimensional laser point cloud facade classification and outline extraction method
ActiveCN104657968AQuick extractionReduce collection workloadImage enhancementImage analysisPoint cloudImage resolution
The invention relates to an automatic vehicle-mounted three-dimensional laser point cloud facade classification and outline extraction method which comprises the following steps: (1) acquiring corresponding position and posture of a three-dimensional laser scanner at each scanning ring; (2) calculating the position relationship of adjacent points under theoretic vertical condition according to the position and the angular resolution of the scanner; (3) performing clustering analysis on facade points, thereby obtaining a building facade object list; (4) analyzing each facade object, screening, and excluding objects which do not belong to the building facade; (5) sequencing point cloud of each facade object in the length direction of the bottom side of the an outer box, and constructing a planar projection line object; (6) screening planar projection lines; (7) simplifying the planar projection lines, thereby obtaining a final projection line. Through the adoption of the method, facade point cloud and facade outline can be rapidly extracted, the processing process can be completely automatic without artificial interference, the facade acquisition workload in streetscape data production is greatly reduced, and the production cost is reduced.
Owner:WUHAN HI TARGET DIGITAL CLOUD TECH CO LTD
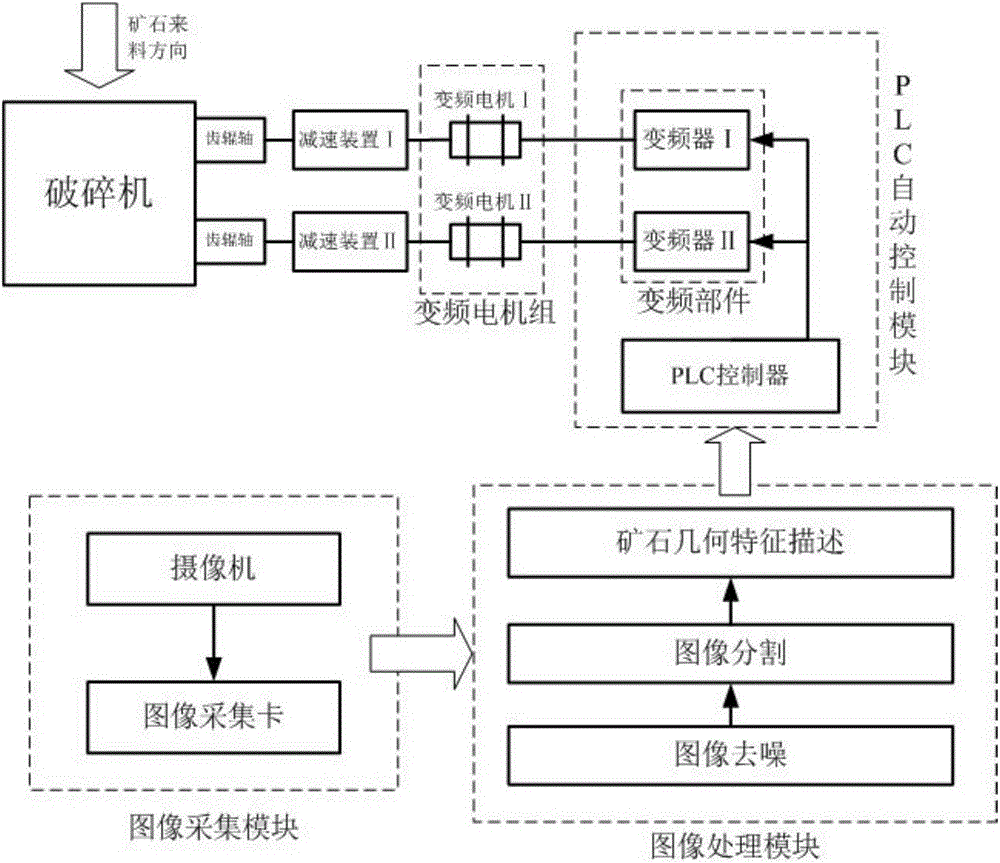
Automatic speed adjustment control system of toothed roll crusher and control method
InactiveCN105251563ATake full advantage of performanceAvoid wastingGrain treatmentsAutomatic controlCrusher
The invention discloses an automatic speed adjustment control system of a toothed roll crusher and a control method. An image collecting module carries out image pre-treatment on ore pictures. The planar projection area S of a single ore body and the overall planar projection area SZ of the whole stack of ore are obtained through an image processing module. A programmable logic controller (PLC) automatic control module is used for controlling the rotation speed of a motor. The geometric shape of the ore and the coverage rate of coming materials are judged through an image recognition method and then compared with preset parameters in a PLC so that the rotation speed of the motor can be automatically controlled. Therefore the toothed roll crusher can operate reasonably under different work conditions, the resource waste and use failures caused by underload and overload are effectively avoided, the repairing workloads of equipment are reduced, the economic benefits are improved, and the performance advantages of the crusher are brought into full play. The PLC is used for automatically controlling the rotation speed of the motor through programming, the original electromechanical system of the crusher is not changed, the automation degree is high, and the method is simple and reliable.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF MINING & TECH +1
Integrated electronic device for monitoring mechanical stress within a solid structure
ActiveUS20140182390A1Acceleration measurement using interia forcesSolid-state devicesSolid structureEngineering
The integrated electronic device is for detecting a local parameter related to a force observed in a given direction, within a solid structure. The device includes at least one sensor configured to detect the above-mentioned local parameter at least in the given direction through piezo-resistive effect. At least one damping element, integrated in the device, is arranged within a frame-shaped region that is disposed around the at least one sensor and belongs to a substantially planar region comprising a plane passing through the sensor and perpendicular to the given direction. Such at least one damping element is configured to damp forces acting in the planar region and substantially perpendicular to the given direction.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS INT NV
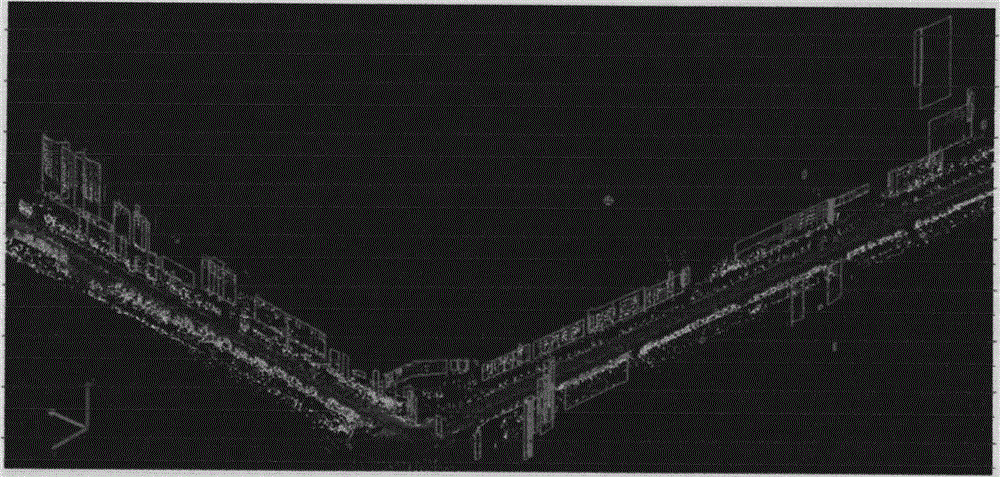
Building corner space position automatic extraction method in vehicle laser scanning point cloud
ActiveCN106056659ANot easy to influenceHigh degree of automationImage analysisImage generationPoint cloudIn vehicle
The present invention discloses a building corner space position automatic extraction method in a vehicle laser scanning point cloud. The method comprises: obtaining the space layering point cloud in a vehicle direction in a local range according to the height of a local building, performing planar projection of the space layering point cloud, and projecting the dispersed laser scanning point cloud to a plane according to the range of the space layering point cloud and the plane coordinates of the space layering point cloud; defining the brightness value of a pixel according to the number of the laser scanning point cloud in a unit pixel on the plane, converting the brightness value of the pixel to a planar projection image; performing linear detection of an area having high brightness in the plane projection image, extracting the line sections having linear features, and merging the line sections; and analyzing the relative position relation and the intersecting angle of the extracted line sections, screening out the line sections which accord with the building corner features through intersecting, solving the coordinates of the line section intersecting corner points in the planar projection image, and calculating the space position information of a corner object according to the coordinates of the line section intersecting corner points in the planar projection image.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Accelerated geometric shape detection and accurate pose tracking
A reference in an unknown environment is generated on the fly for positioning and tracking. The reference is produced in a top down process by capturing an image of a planar object with a predefined geometric shape, detecting edge pixels of the planar object, then detecting a plurality of line segments from the edge pixels. The plurality of line segments may then be used to detect the planar object in the image based on the predefined geometric shape. An initial pose of the camera with respect to the planar object is determined and tracked using the edges of the planar object.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
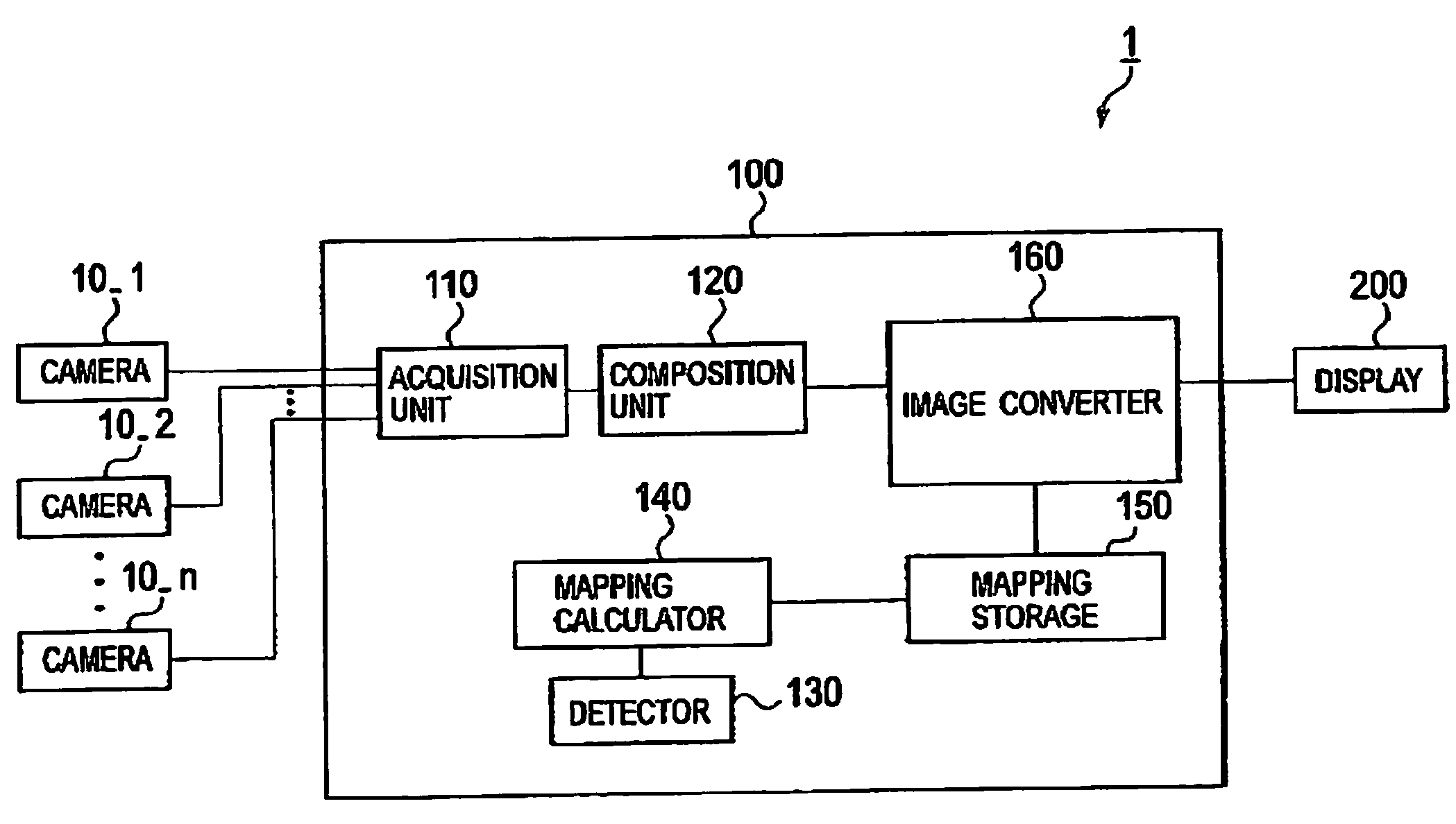
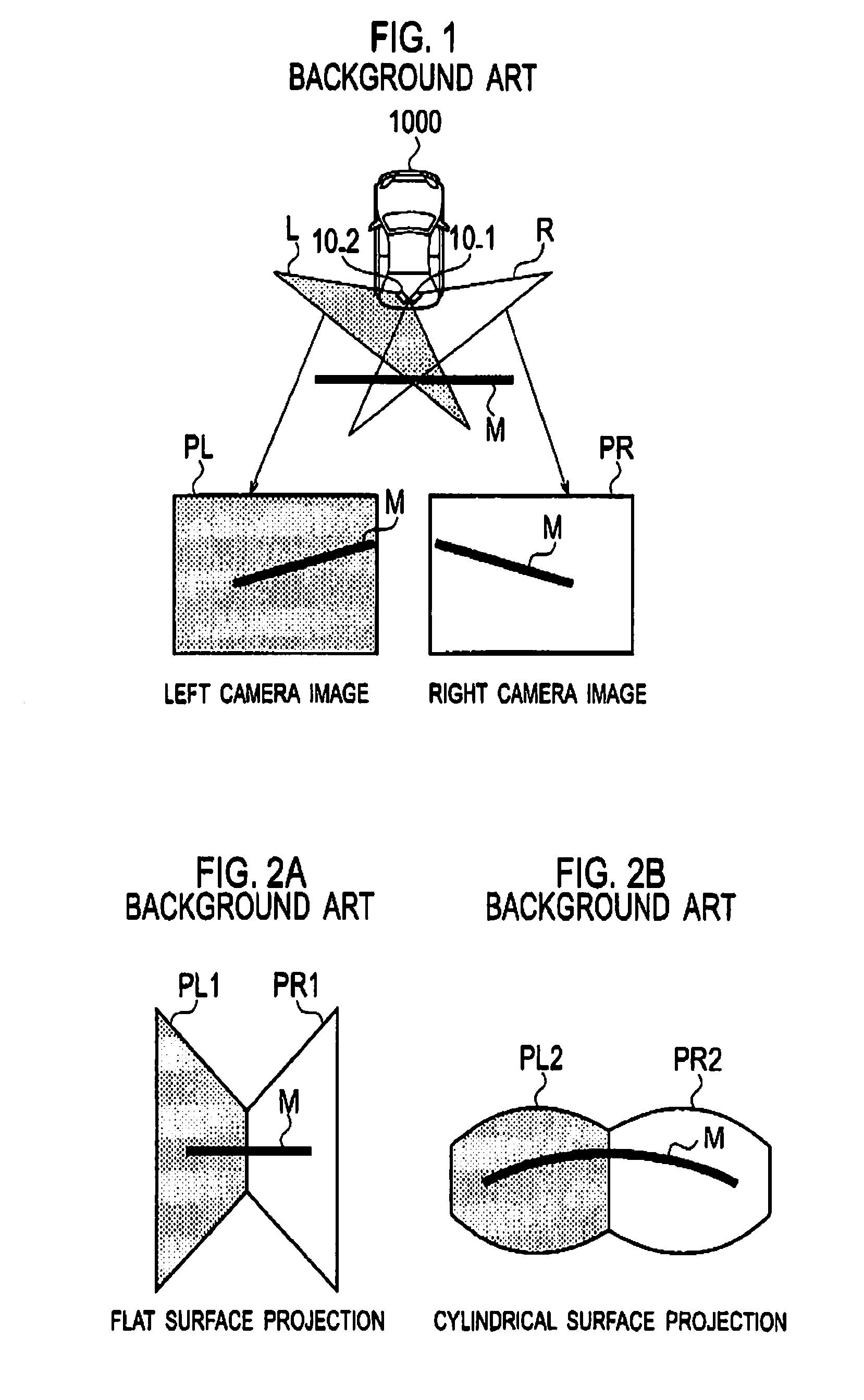
Image processor, vehicle, and image processing method
ActiveUS20080175436A1Geometric image transformationCharacter and pattern recognitionCamera imageImaging processing
An image processor includes an acquisition unit configured to acquire a camera image captured by a camera provided on a vehicle, a first image converter configured to project the camera image onto a flat surface to convert the camera image into a flat surface projection image, and a second image converter configured to project the camera image onto a curved surface to convert the camera image into a curved surface projection image. The first image converter converts a first image region having a predetermined width within the camera image into the flat surface projection image, and the second image converter converts a second image region outside the first image region in a width direction, within the camera image, into the curved surface projection image.
Owner:SANYO ELECTRIC CO LTD
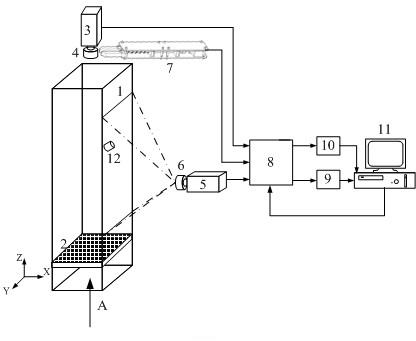
Measuring device and measuring method for drag coefficient of irregular particle
The invention provides an accurate measuring method for a drag coefficient of an irregular particle. A vertical charge coupled device (CCD) high-speed camera of which the shooting direction is vertical downwards is arranged right above a transparent square pipeline, and meanwhile, a horizontal CCD high-speed camera of which the shooting direction is vertical with the wall face of the square pipeline is horizontally arranged outside the square pipeline. One particle is freely released against the airflow direction of the square pipeline by utilizing a particle electromagnetic holding device, and the drag coefficient of the particle is obtained through analyzing an XOY planar projection image sequence and an XOZ planar projection image sequence which are shot by the two CCD high-speed cameras. Under the condition that a convection field is not disturbed, the drag coefficient of the particle is accurately measured in real time.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
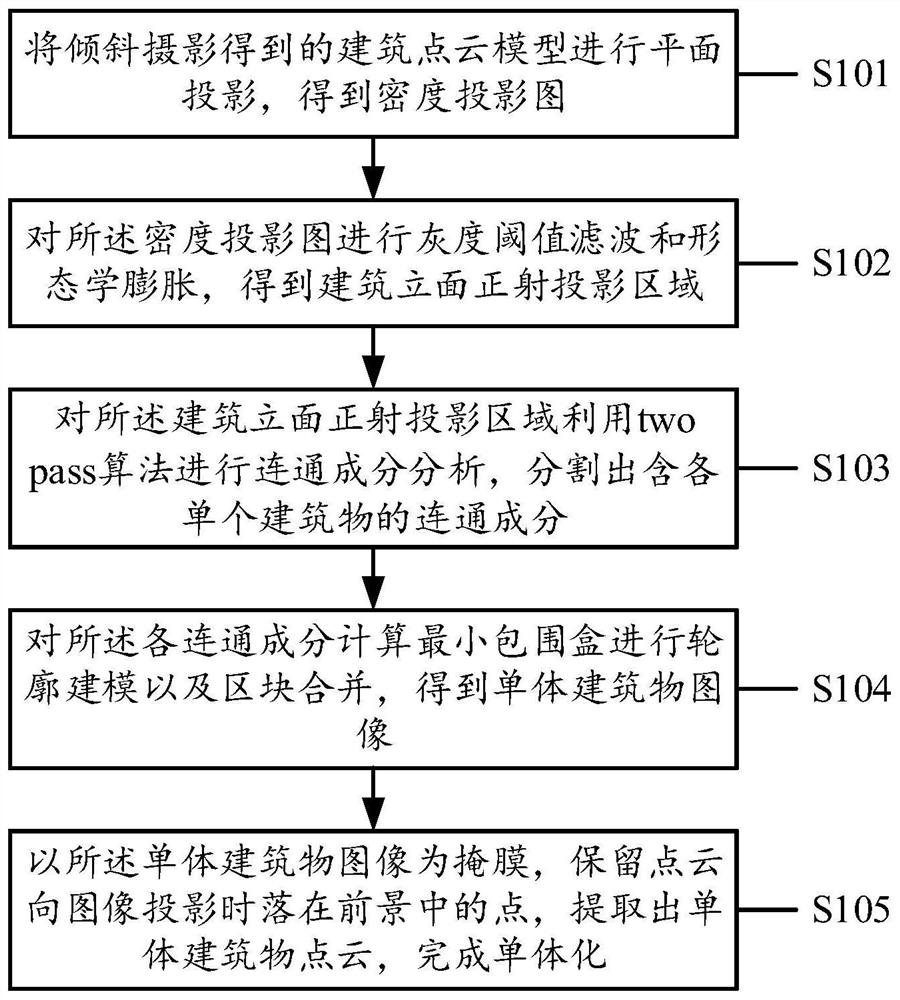
Building model monomerization method, device, storage medium and electronic equipment
ActiveCN112163251AQuick extractionReduce labor costsGeometric CADGeographical information databasesMinimum bounding boxPoint cloud
The embodiment of the invention discloses an oblique photography building model monomerization method and device based on point density projection, a storage medium and electronic equipment. The method comprises the steps: carrying out the planar projection of a building point cloud model obtained through oblique photography, obtaining a density projection drawing, carrying out the gray thresholdfiltering and morphological expansion of the density projection drawing, and obtaining a gray threshold value of the density projection drawing; obtaining a building facade orthographic projection area, carrying out connected component analysis on the building facade orthographic projection area by utilizing a two pass algorithm, segmenting connected components containing each single building, calculating a minimum bounding box for each connected component, and carrying out contour modeling and block merging to obtain a single building image; and taking the single building image as a mask, reserving points falling in the foreground when the point cloud is projected to the image, extracting the single building point cloud, and completing the monomerization. By adopting the embodiment of theinvention, the oblique photography building model monomerization device automatically extracts each single building from the building point cloud model, and the efficiency is improved.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Method for the detection of an obstacle
The invention concerns a method for the detection of an obstacle located in a path of a motor vehicle, in particular a person, in which by means of a camera a first image and, with a time interval from the latter, a second image of the environment of the vehicle located in the direction of travel, are recorded, a first transformed image is generated by projection of the first recorded image out of the camera image plane into the plane of the ground, and a second transformed image is generated by projection of the second recorded image out of the camera image plane into the plane of the ground, a differential image is determined from the first and second transformed images, and by evaluation of the differential image it is determined whether an obstacle is located in the path of the vehicle.
Owner:DELPHI TECH INC
Automatic spraying system coordinate transform method based on point cloud and image matching
ActiveCN106651894AReduce downtimeShorten the timeImage enhancementImage analysisProduction ratePoint cloud
The invention provides an automatic spraying system coordinate transform method based on point cloud and image matching. The method comprises the steps of building a robot coordinate system R, an image coordinate system U and a point cloud coordinate system V; collecting an image Q of a spraying object on a spraying platform, and acquiring description of the spraying object in the robot coordinate R, wherein RQ is equal to RTUUQ; acquiring geometric attributes of the closed image edge of the image Q; acquiring geometric attributes of the edge of the projection of a point cloud model; forming the geometric attributes of the closed image edge of the image Q and the geometric attributes of the edge of the planar projection of the point cloud model into chain codes and matching with each other, and acquiring a transformation relation from the point cloud coordinate system V to the robot coordinate system R according to transformation from the point cloud coordinate system V to the image coordinate system U and transformation from the image coordinate system U to the robot coordinate system. According to the method provided by the invention, a calculation amount can be effectively reduced, time consumed during a path planning process of a spraying robot is shortened, efficiency is improved, downtime of the spraying robot is effectively reduced, and productivity is ensured.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
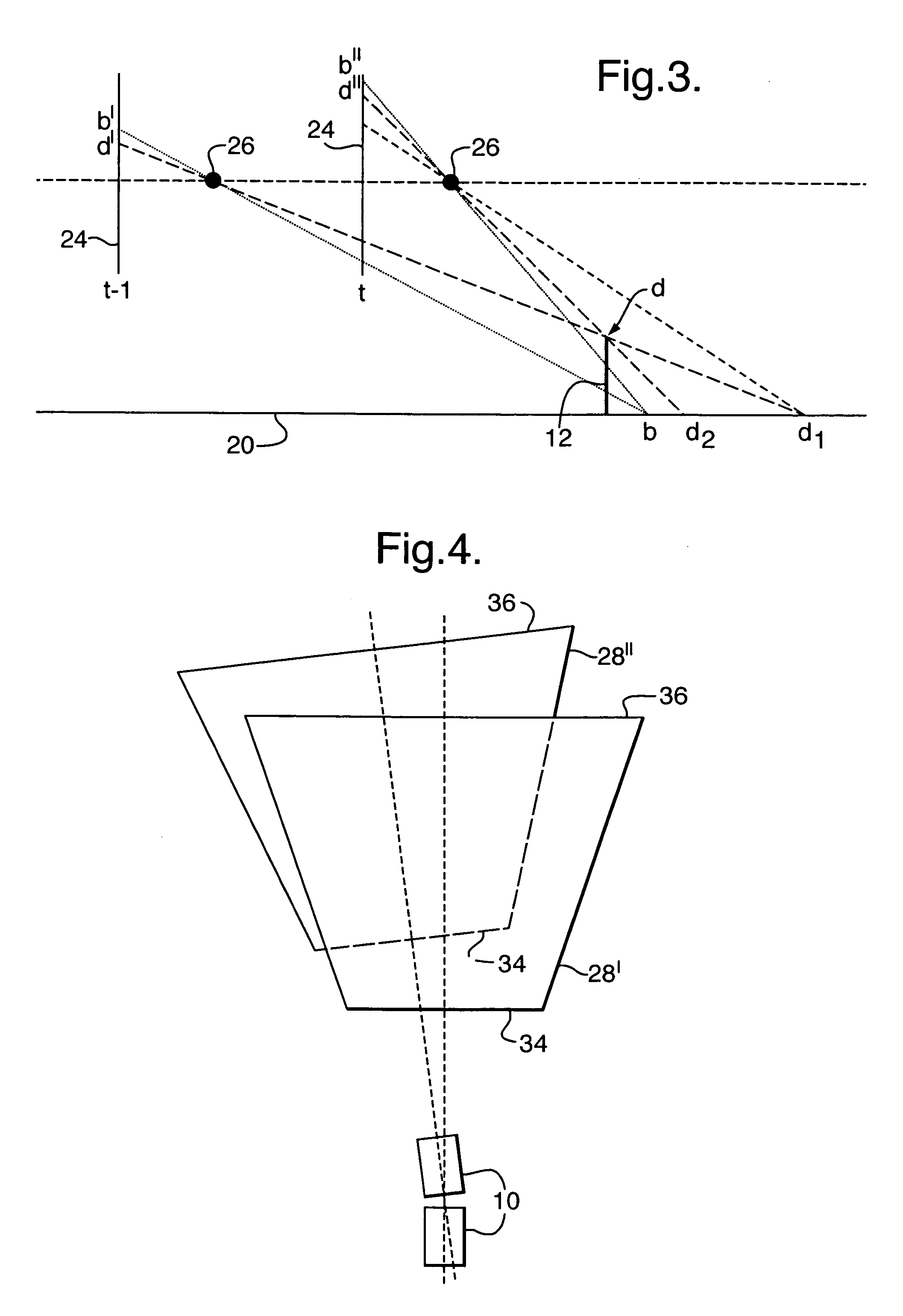
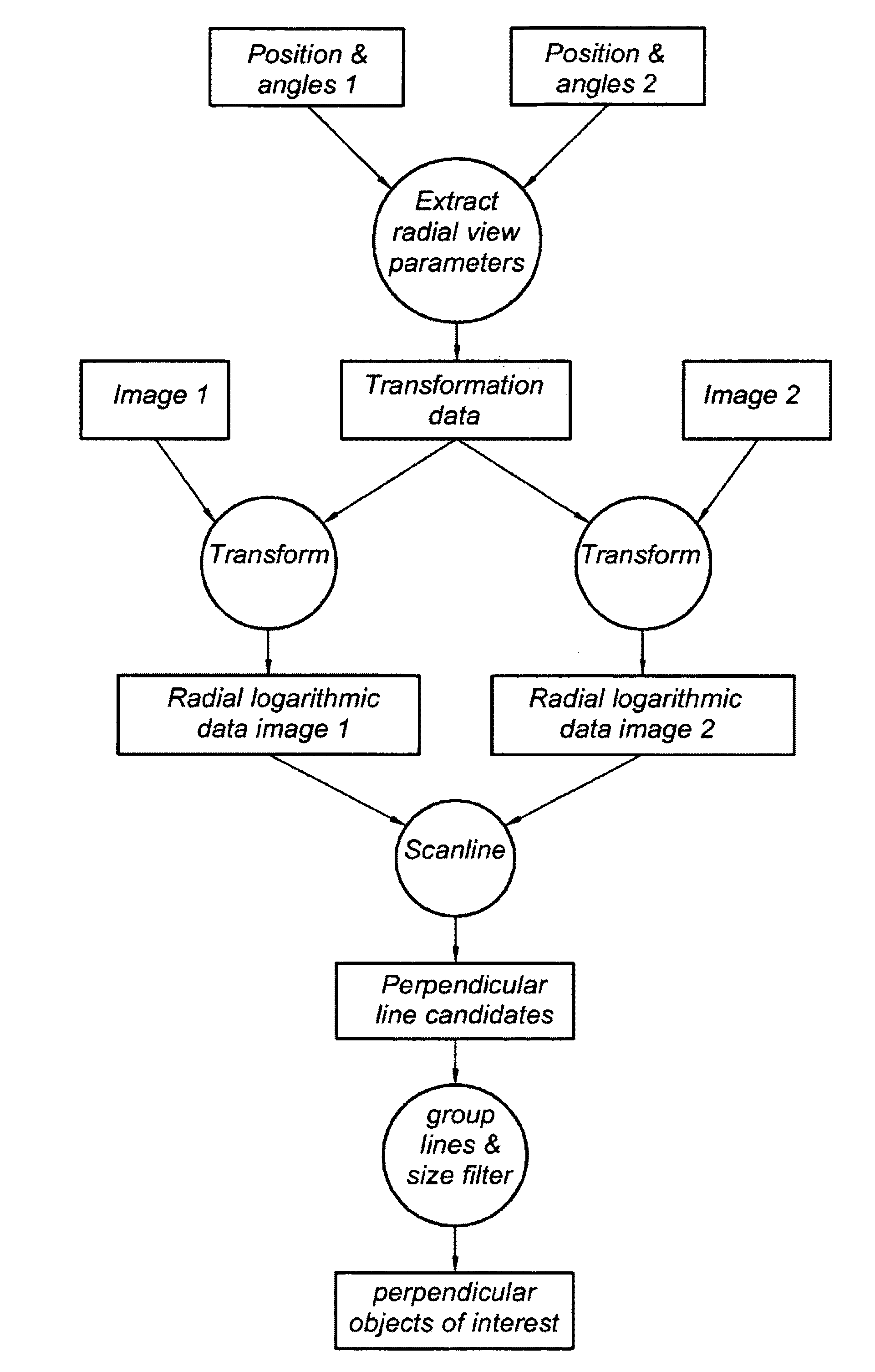
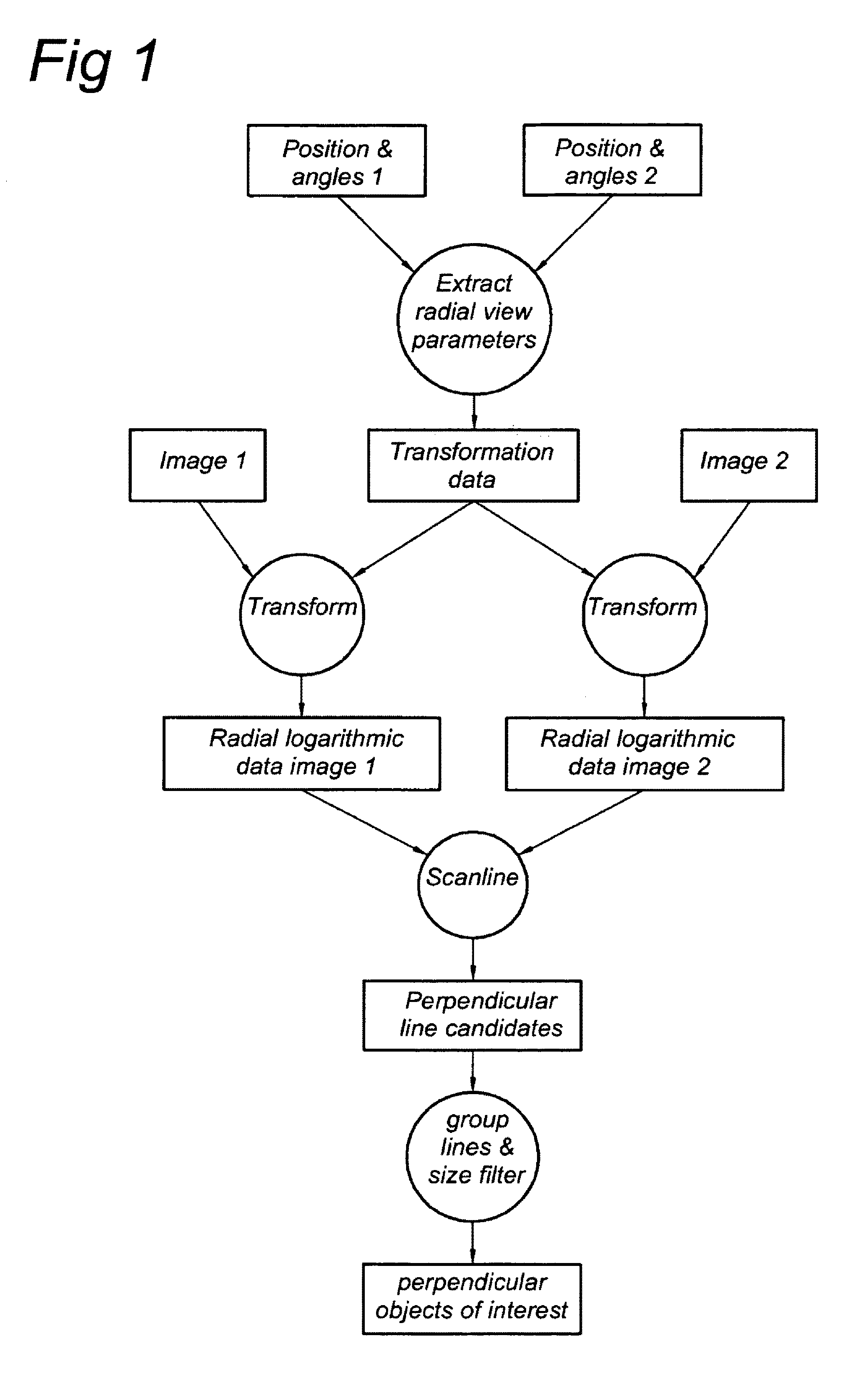
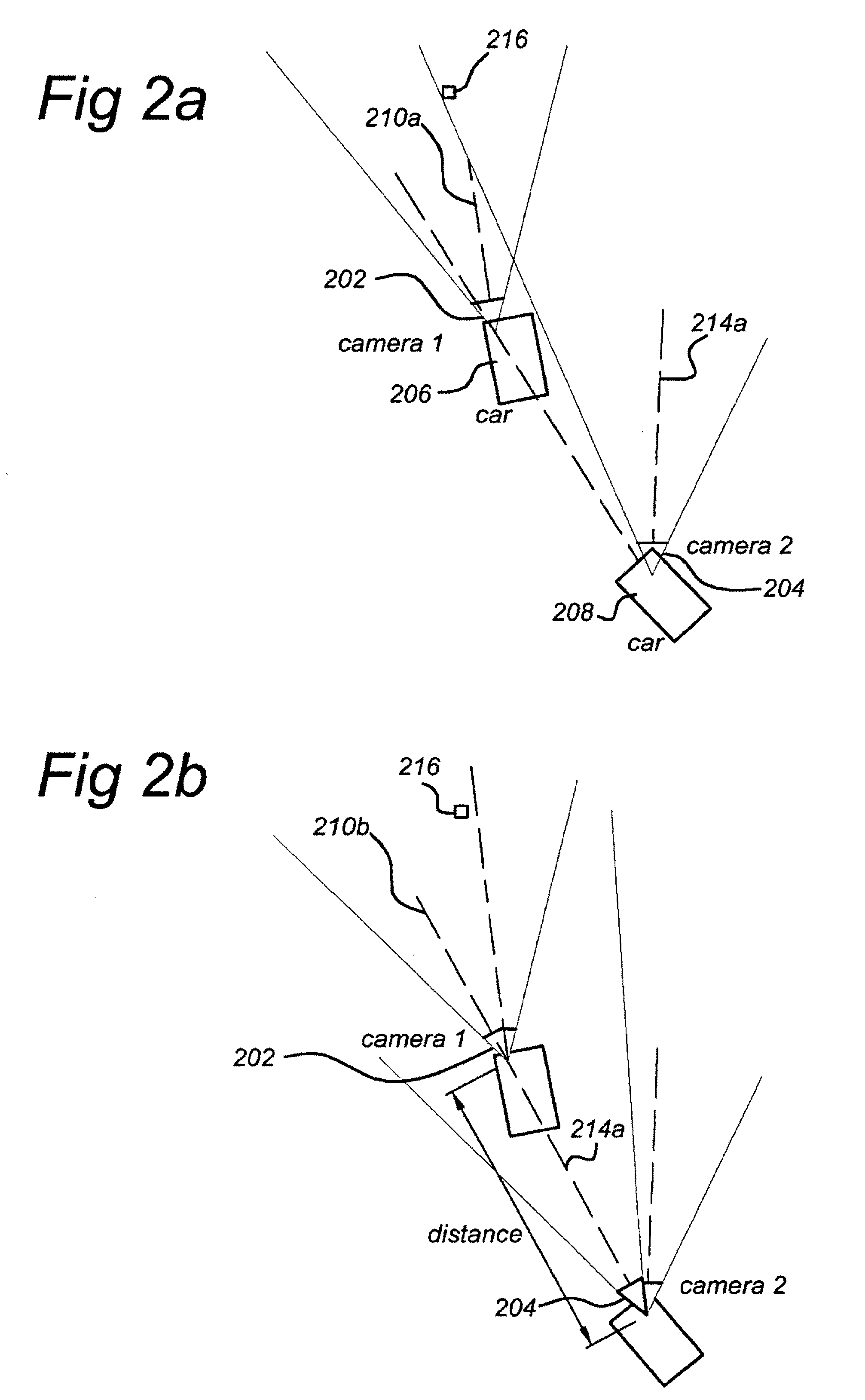
Method and apparatus for identification and position determination of planar objects in images
A method of identifying a planar object in source images is disclosed. In at least one embodiment, the method includes: retrieving a first source image obtained by a first terrestrial based camera; retrieving a second source image obtained by a second terrestrial based camera; retrieving position data associated with the first and second source image; retrieving orientation data associated with the first and second source image; performing a looking axis rotation transformation on the first and second source image by use of the associated position data and orientation data to obtain first and second intermediate images, wherein the first and second intermediate images have an identical looking axis; performing a radial logarithmic space transformation on the first and second intermediate images to obtain first and second radial logarithmic data images; detecting an area in the first image potentially being a planar object; comparing the potential planar object having similar dimensions in the second radial logarithmic data image and similar rgb characteristics; and finally, identifying the area as a planar object and determining its position. At least one embodiment of the method enables the engineer to detect very efficiently planar perpendicular objects in subsequent images.
Owner:TOMTOM GLOBAL CONTENT
Transparent lampshade and lens module of high-power LED streetlamp
InactiveCN102588878AUniform middleUniform edgingPlanar light sourcesPoint-like light sourceLight spotOptical lens design
The invention discloses a lens module of a high-power LED streetlamp, which comprises a projected spherical surface similar to a semielliptical surface. The bottom of the projected spherical surface is connected with a planar bottom plate, a hollow spherical surface groove similar to a semielliptical surface is arranged at the center of the bottom of the projected spherical surface, the projected spherical surface is divided into a left semi-spherical surface and a right semi-spherical surface by centering the long axis, and a smooth-transition groove is arranged at the center of the left spherical surface. The long axis of the projected spherical surface is parallel to the short axis of the hollow spherical surface groove, and the distance delta d between projections on the horizontal plane of the two axes is larger than zero. All 180-degree light emitted from LED chips can be collected by a lampshade designed by fully-refractive secondary optical lens and can be redistributed to the assigned areas. Far-field angular distribution of light intensity of the LED streetlamp can be in bat wing distribution and light spot can be rectangular by the aid of light distribution of free curved surfaces, and further, the middle and the edges of the rectangular light spot can be more uniform, light cutting design of the lens can be realized and flare can be eliminated by means of the principle of marginal light rays.
Owner:DEW & KEN OPTOELECTRONICS ZHENGZHOU
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com