Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
59 results about "Lectin binding" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
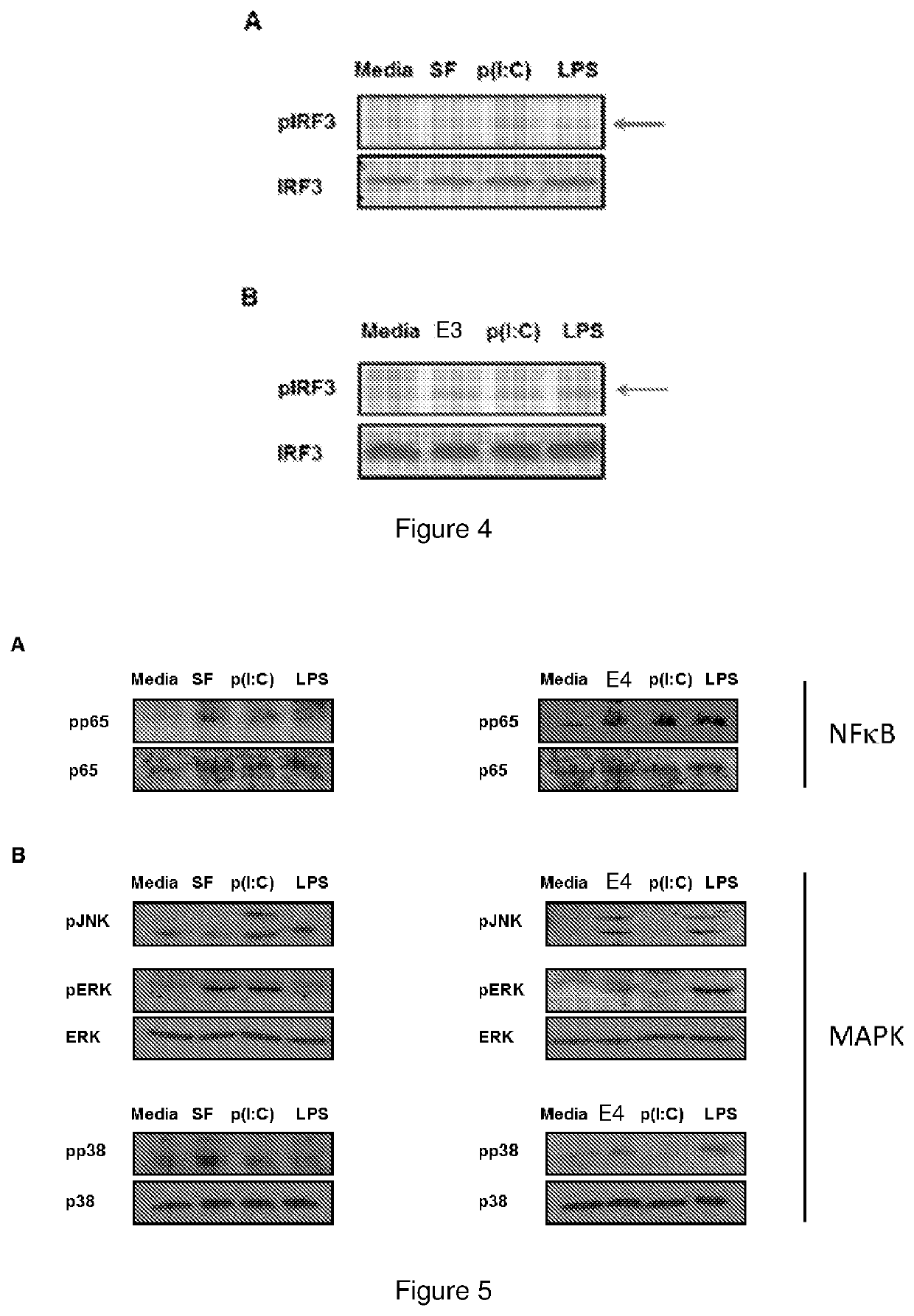
Lectins are a type of protein that can bind to cell membranes. They are sugar-binding and become the “glyco” portion of glycoconjugates on the membranes. Lectins offer a way for molecules to stick together without getting the immune system involved, which can influence cell-cell interaction.
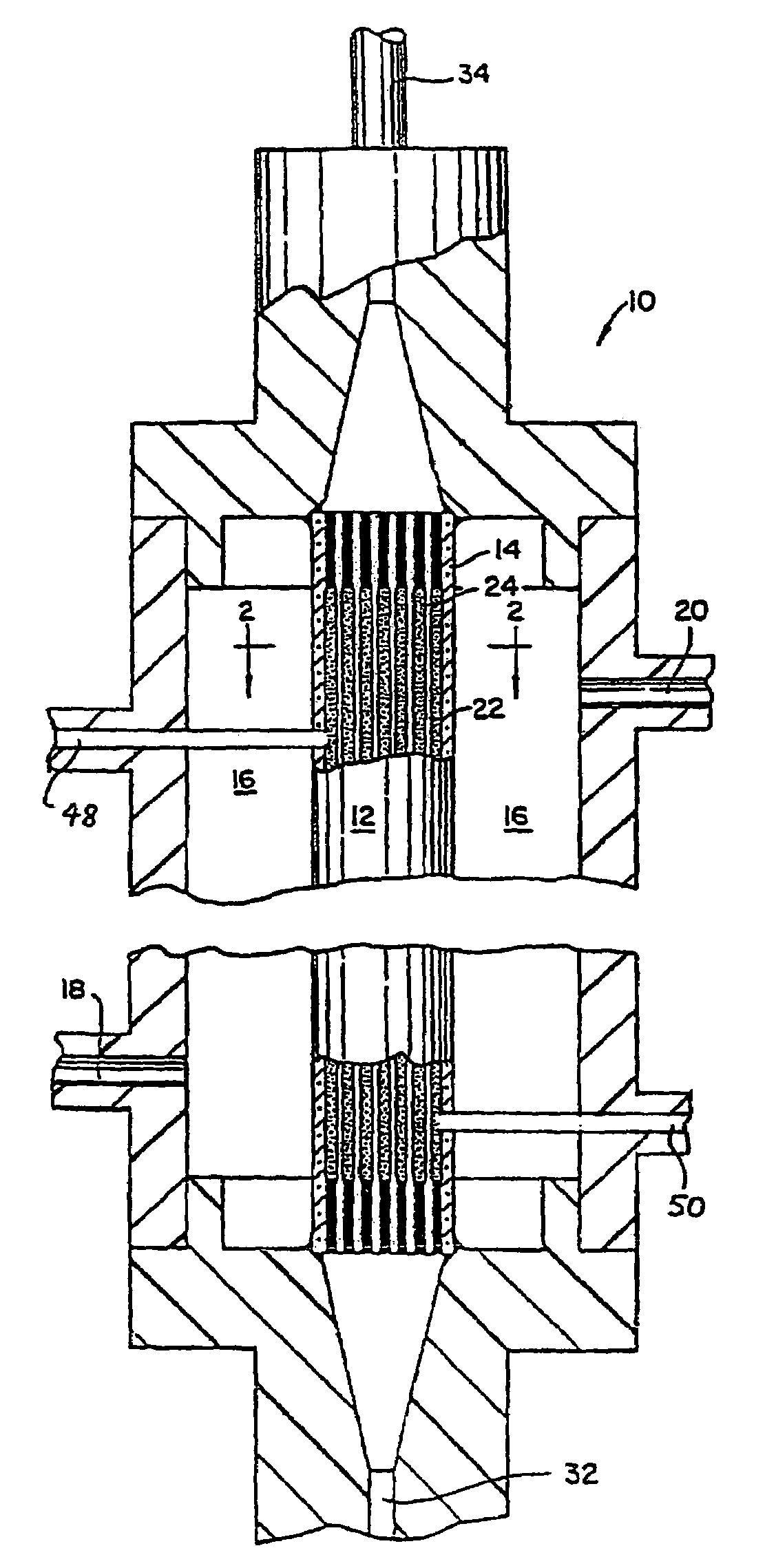
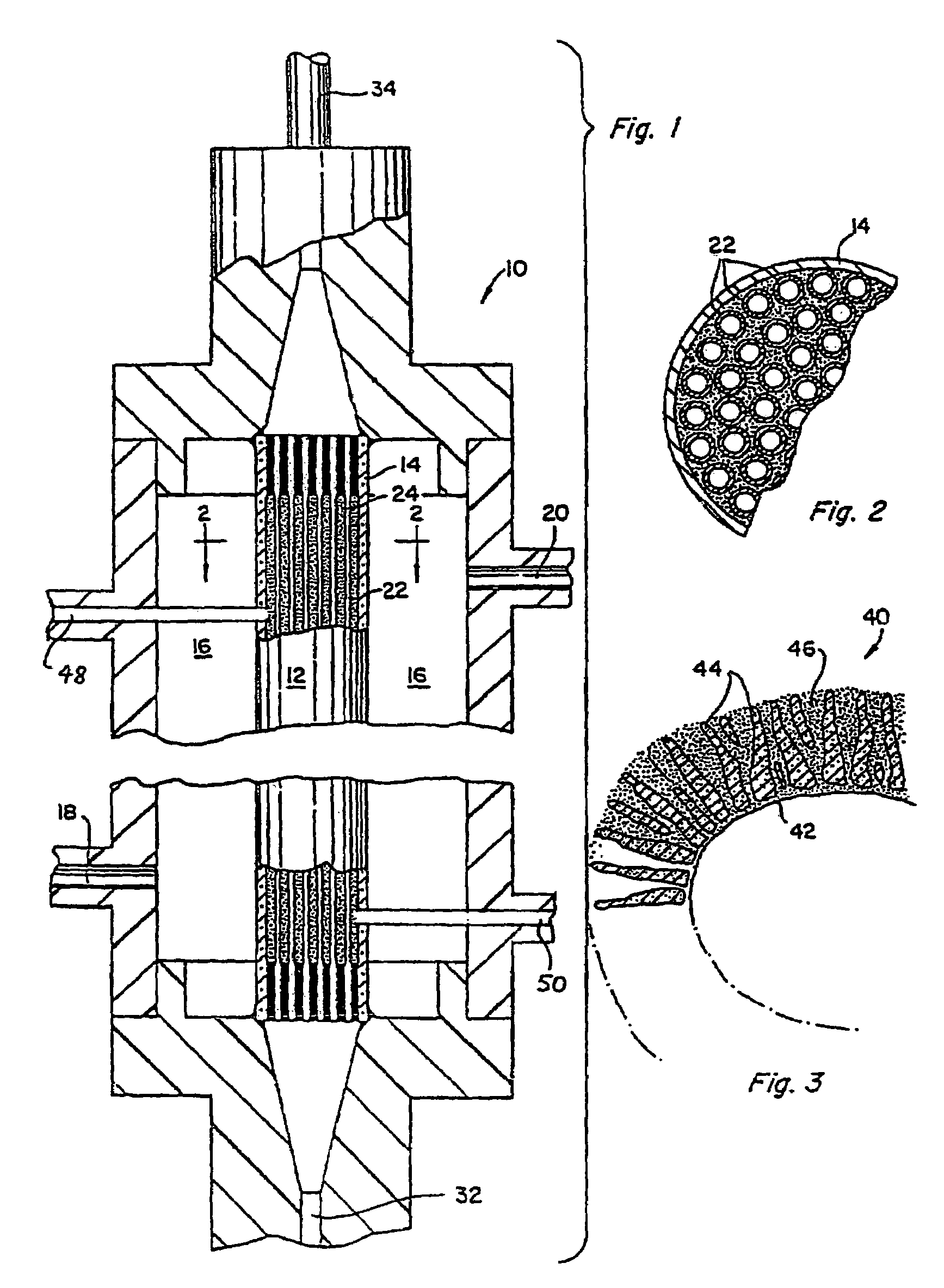
Method for removal of viruses from blood by lectin affinity hemodialysis
ActiveUS7226429B2Reduce loadReduce in quantityOther blood circulation devicesViral antigen ingredientsHemodialysisHigh mannose
The present invention relates to a method for using lectins that bind to pathogens having high mannose surface glycoproteins or fragments thereof which contain high mannose glycoproteins, to remove them from infected blood or plasma in an extracorporeal setting. Accordingly, the present invention provides a method for reducing viral load in an individual comprising the steps of obtaining blood or plasma from the individual, passing the blood or plasma through a porous hollow fiber membrane wherein lectin molecules are immobilized within the porous exterior portion of the membrane, collecting pass-through blood or plasma and reinfusing the pass-through blood or plasma into the individual.
Owner:AETHLON MEDICAL INC
Lectin conjugates
InactiveUS20060251580A1Easy diagnosisLow toxic loadNanomedicineNMR/MRI constrast preparationsSelectinLanthanide
A conjugate includes at least one target-seeking unit, which specifically binds to receptors on the surface of endothelial cells, and at least one effector unit which is coupled to the unit by a linker. The effector unit exhibits at least one signal unit and optionally at least one therapeutic active substance. The target-seeking unit includes a lectin or a fragment or derivative thereof, wherein the lectin is not L-selectin and the signal unit includes a lanthanide ion.
Owner:FAUSTUS FORSCHUNGS CIE TRANSLATIONAL CANCER RES
Medicinal composition for treatment of chronic hepatitis c
InactiveUS20070110714A1Enhance immune functionPreventing sideration of hepatic cirrhosisBiocideOrganic active ingredientsChronic hepatitisBULK ACTIVE INGREDIENT
The present invention provides a pharmaceutical composition for treating chronic hepatitis C characterized by comprising at least one active ingredient selected from the group consisting of IL-15, myeloid dendritic cell maturation stimulators (for example, CpG oligo deoxynucleotide, GM-CSF, IL-4, LPS, CD40L, polyI:C, TNF-a and IFN-?) and lectin-binding substances (for example, mannose carbohydrate, fucose carbohydrate and anti-lectin antibody); and a method of treating chronic hepatitis C by using such active ingredient(s). In the above pharmaceutical composition and therapeutic method, it is possible to use INF-a together with these active ingredients.
Owner:INTPROP CONSULTING +1
Caries risk test for predicting and assessing the risk of disease
Provided are methods, test devices, and diagnostic kits for predicting, assessing, and diagnosing the risk of a disease using salivary analysis. The method comprises providing a whole (unfractionated) saliva sample from a subject; contacting an aliquot of said saliva with one or more lectins under conditions that allow said one or more lectins to bind to a lectin-binding component of said saliva; detecting the amount of bound lectin; and comparing the amount of bound lectin to the amount known to bind a saliva sample from a control patient, to predict the risk of a disease in the subject. Also provided are methods for reducing the risk of a disease and a method for assessing the risk of the disease at a defined level.
Owner:PROACTIVE ORAL SOLUTIONS +1
Pathogen vaccines and methods of producing and using the same
ActiveCN108697778AFree from attackAntibacterial agentsCosmetic preparationsResistant bacteriaVaccination
The present invention provides vaccine compositions and methods of producing such compositions. Other embodiments of the invention include methods of treating a pathogen infection, methods of vaccinating a subject against a pathogen infection, and methods for treating an antibiotic-resistance bacterial infection in a subject in need thereof. In further embodiments, the invention includes methods of decreasing the level of a pathogen in a subject having a pathogen infection, methods of increasing the surviving rate of a subject having a pathogen infection, methods of reducing the level of painassociated with a pathogen infection, and methods of reducing the level of distress associated with a pathogen infection in a subject in need thereof. Novel scaffold compositions and opsonin-bound orlectin-bound pathogen compositions, and uses thereof, are also provided herein.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
Compositions and methods for detecting oral neoplasm
InactiveUS20100234762A1Simplified and cost-effective detectionUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsSurgical furnitureMedicineSialic acid
Methods and kits for assessing the presence of, and for detecting cancer, notably oral cancer, are disclosed. Such methods and kits use one or more lectins operably linked to a fluorophore, wherein the lectin binds differentially to cancerous and non-cancerous tissues, and wherein the fluorophore facilitates visualizing the differential binding. The lectins are applied to the oral mucosa of a subject, the fluorophore is exposed to light, and cancerous regions of the mucosa are visualized. In certain embodiments, the lectin specifically binds to one or more of a β-galactoside, an α- or β-N-acetylglucosamine, or a sialic acid moiety.
Owner:INTERMED
Antigen detection method which uses lectin and comprises enzyme treatment step
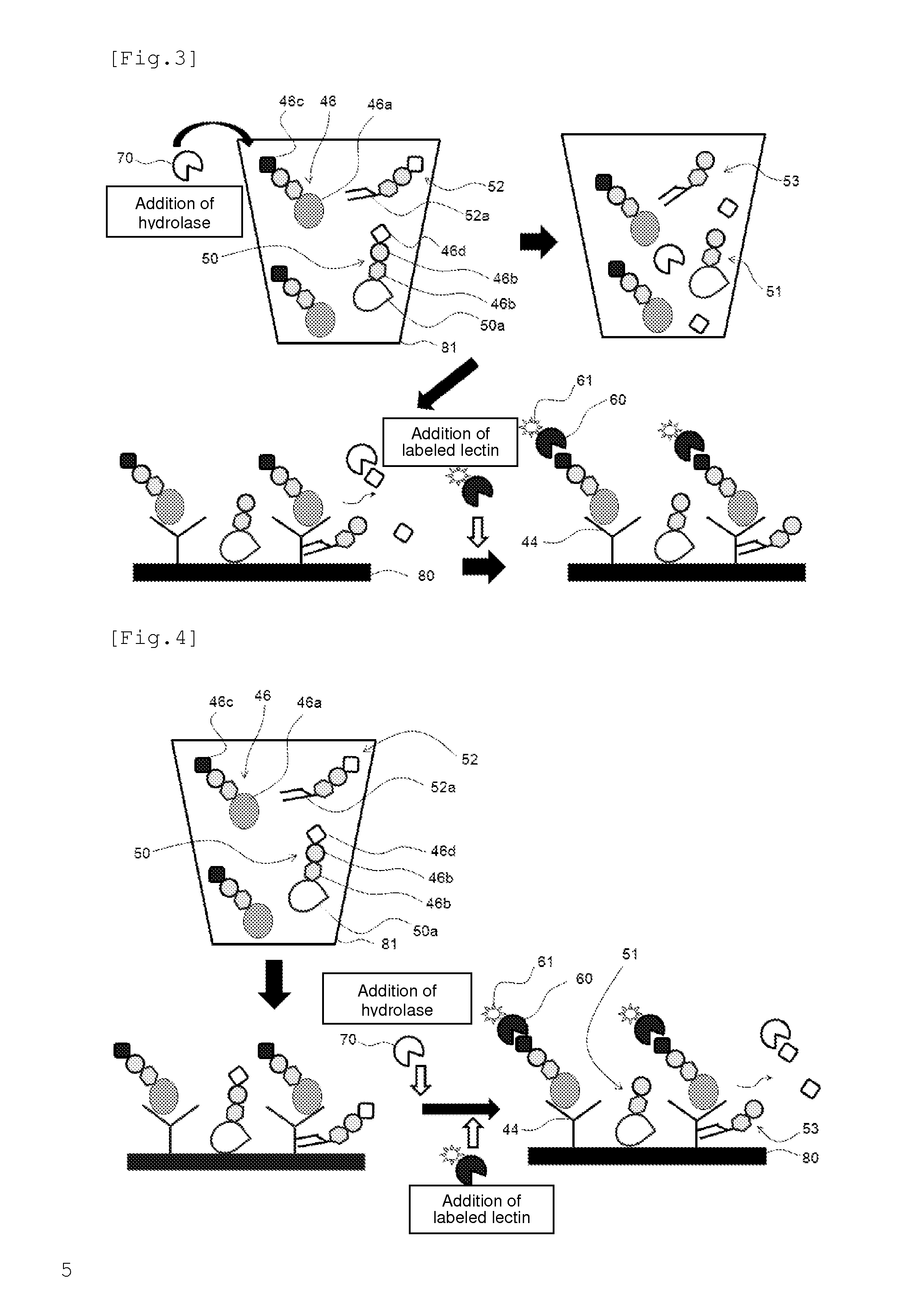
ActiveUS20150140571A1Suppress increase in backgroundImprove performanceMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisAntigenSugar
An antigen detection method detects an antigen having a specific sugar chain in a sample with a lectin that binds to plural kinds of sugar chains including the specific sugar chain. The detection method includes: a first step of bringing the lectin into contact with the sample; a second step of bringing a glycohydrolase capable of cleaving at least one kind of sugar chain to which the lectin can bind into contact with the sample, the at least one kind of sugar chain excluding the specific sugar chain among the plural kinds of sugar chains; and a step of detecting the antigen bound with the lectin after the first and second steps.
Owner:OTSUKA PHARM CO LTD
Caries risk test for predicting and assessing the risk of disease
Provided are methods, test devices, and diagnostic kits for predicting, assessing, and diagnosing the risk of a disease using salivary analysis. The methods comprise providing a whole (unfractionated) saliva sample from a subject; contacting an aliquot of the saliva with two or more lectins under conditions that allow the two or more lectins to bind to a lectin-binding component of the saliva; detecting the amount of bound lectin; and comparing the amount of bound lectin to the amount known to bind a saliva sample from a control patient, to predict the risk of a disease in the subject. Also provided are methods for reducing the risk of a disease and a method for assessing the risk of the disease at a defined level.
Owner:PROACTIVE ORAL SOLUTIONS +1
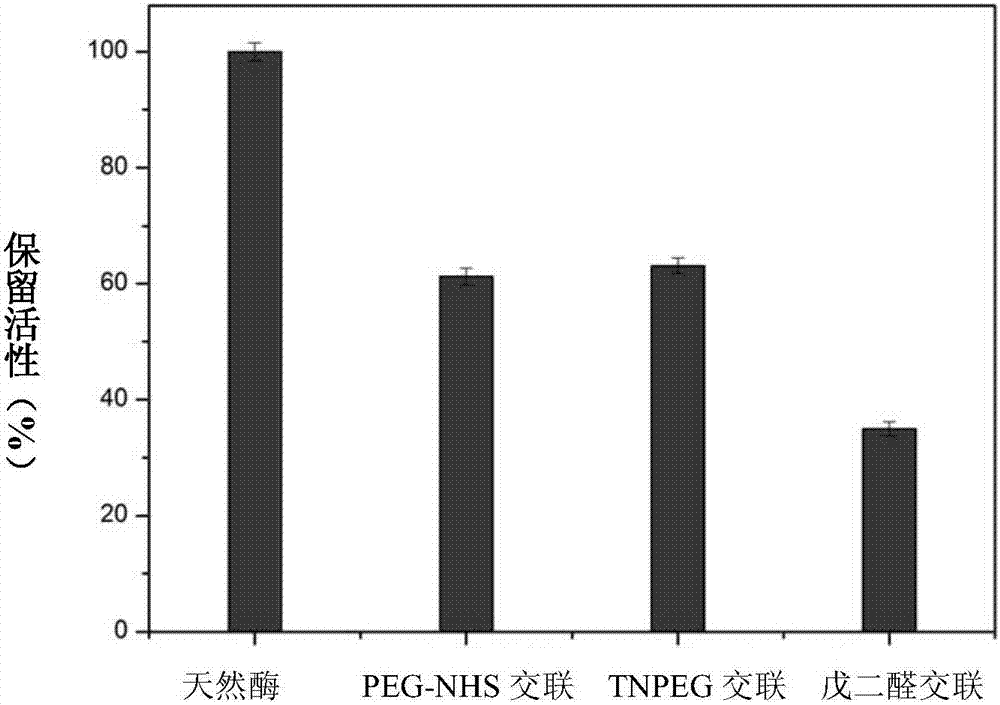
Enzyme-lectin conjugate nano-particles and preparing method thereof
ActiveCN107034206AHigh catalytic activityGood repeatabilityOxidoreductasesOn/in organic carrierCross-linkReaction temperature
The invention discloses enzyme-lectin conjugate nano-particles and a preparing method thereof. According to the preparing method, raw materials for preparing the enzyme-lectin conjugate nano-particles include enzyme, lectin and a cross-linking agent, as well as magnetic nano-particles and / or a reductant. The enzyme-lectin conjugate nano-particles can be prepared from, by weight, 10 parts of enzyme, 50-500 parts of lectin, 0.1-300 parts of cross-linking agent and 0-1 parts of reductant. The enzyme-lectin conjugate nano-particles can also be prepared from, by weight, 10 parts of enzyme, 50-500 parts of lectin, 1-100 parts of magnetic nano-particles, 0.1-300 parts of cross-linking agent and 0-1 parts of reductant. The enzyme-lectin conjugate nano-particles are dispersed in aqueous solution at a conventional catalytic reaction temperature and have high catalytic activity. Lectin combined with enzyme can attract saccharides substrates, so that the aqueous-phase activity of the conjugate can be further improved. Enzyme molecules in enzyme-lectin-magnetic nano-particle conjugate nano-particles are adsorbed by lectin, covalent cross-linking occurs between enzyme molecules and lectin and magnetic nano-particles, and therefore recoverability of the catalyst is realized based on the realization of high catalytic activity.
Owner:北京德润天勤生物工程技术有限公司 +1
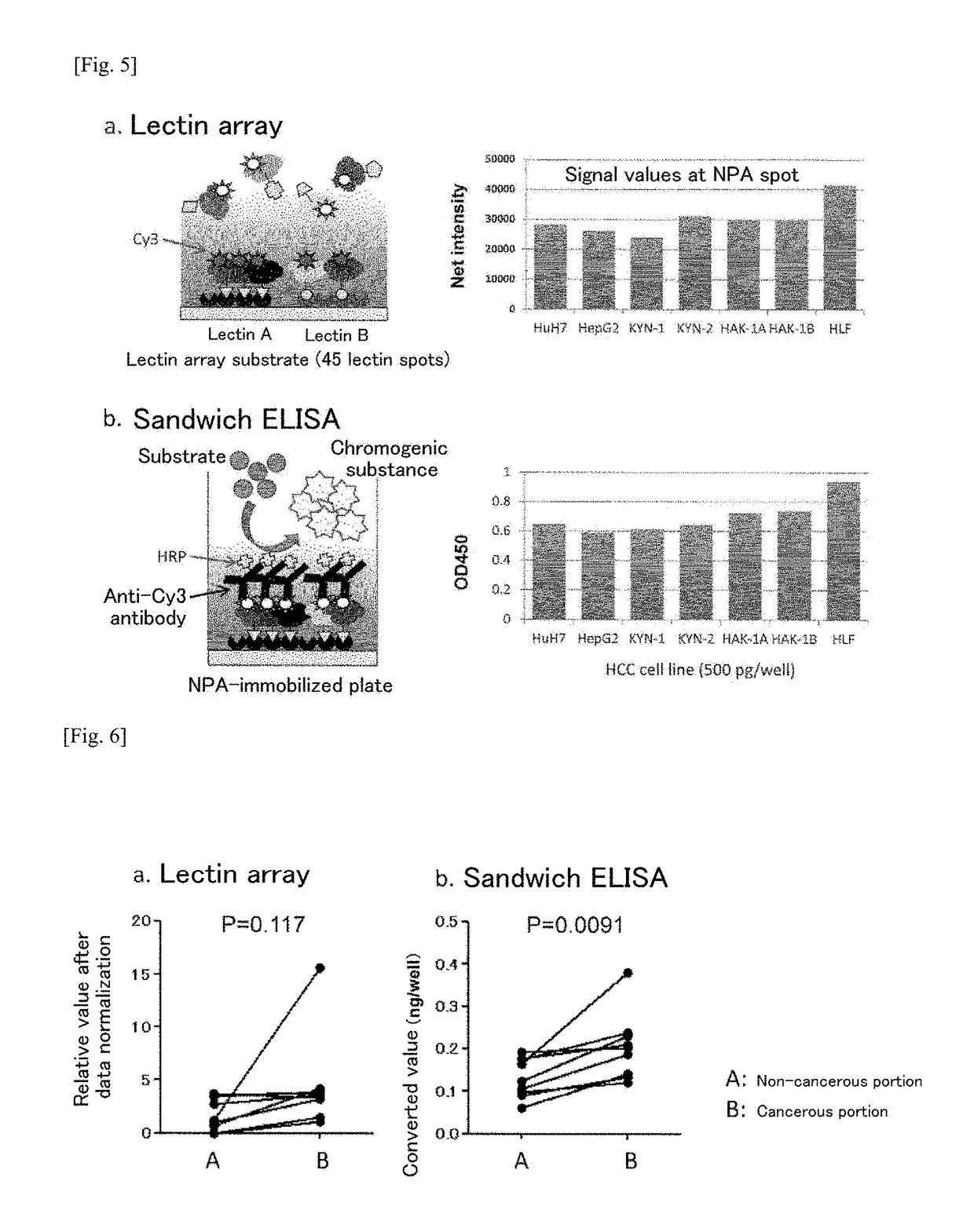
Hepatocellular carcinoma marker
InactiveUS20170219590A1Library screeningPreparing sample for investigationHigh mannoseHepatocellular carcinoma
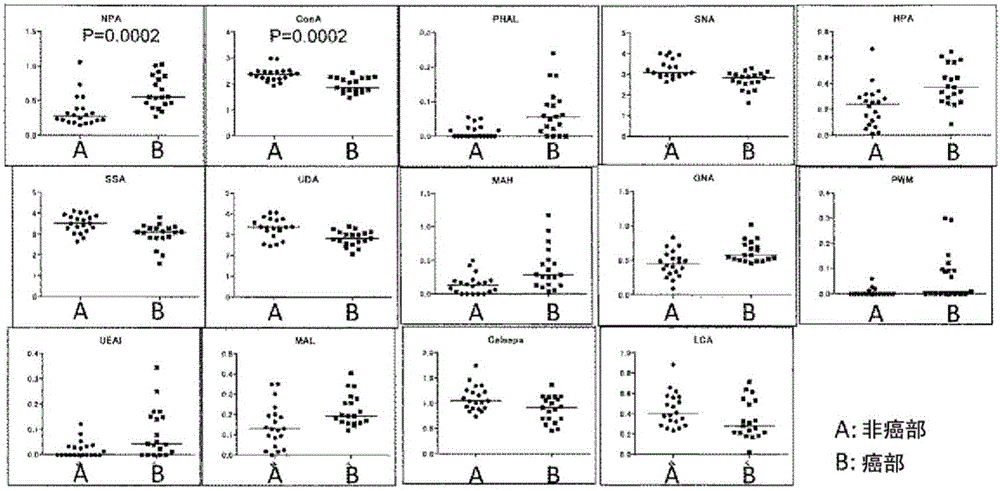
The problem addressed by the present invention is to provide a marker for detecting hepatocellular carcinoma, wherein the hepatocellular carcinoma marker comprises a glycoprotein that first becomes present in the liver with the occurrence of cancer, without depending on changes in the state of the liver. The present invention provides a hepatocellular carcinoma marker comprising an NPA lectin-binding glycoprotein having an NPA lectin-binding glycan epitope that has at least one of the following properties (1) to (5): (1) the glycan epitope does not include core fucose (fucose α1→6 glycan); (2) the glycan epitope comprises a complex-type glycan having three (four or fewer) mannoses; (3) the glycan epitope does not include a high-mannose-type glycan having five or more mannoses; (4) the glycan epitope comprises a complex-type glycan that does not depend on the property of binding to LCA lectin; and (5) the glycan epitope comprises a complex-type glycan that does not depend on the property of binding to ConA lectin. By detecting the hepatocellular carcinoma marker of the present invention in a test sample, it is possible to determine the presence of hepatocellular carcinoma or the level of progression or malignancy of carcinoma.
Owner:NAT INST OF ADVANCED IND SCI & TECH
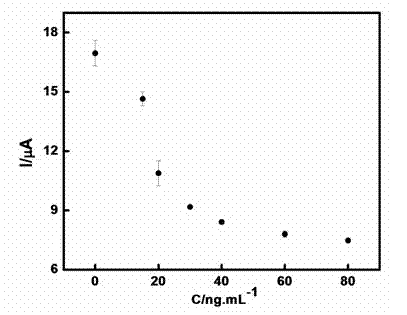
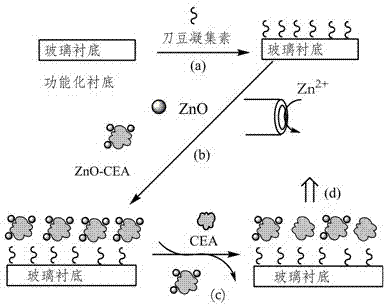
Method for detecting glycoprotein
InactiveCN102520162AMaintain biological activityImprove bindingMaterial electrochemical variablesZinc ionPhysical chemistry
The invention discloses a method for detecting glycoprotein. The method comprises the following steps of: marking the glycoprotein by using zinc oxide quantum dots; meanwhile, immobilizing an agglutinin layer on a chip in an electrolytic cell; specifically binding the glycoprotein marked by the zinc oxide quantum dots with agglutinin on the chip in a series of glycoprotein solutions to be determined of known concentrations; connecting the zinc oxide quantum dots marked on the glycoprotein to the chip; and determining the agglutinin by using dissolving voltammetry of marking the glycoprotein with the zinc oxide quantum dots. Since the marked glycoprotein has different binding capacities to the glycoprotein to be determined and the agglutinin, the glycoprotein marked on the chip is substituted by the glycoprotein to be determined of different concentrations, and the concentration of zinc ions which are remained on the chip and dissolved out is determined by using the dissolving voltammetry to establish relation between the concentration of the zinc ions and the concentration of the glycoprotein so as to determine the concentration of the glycoprotein to be determined.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
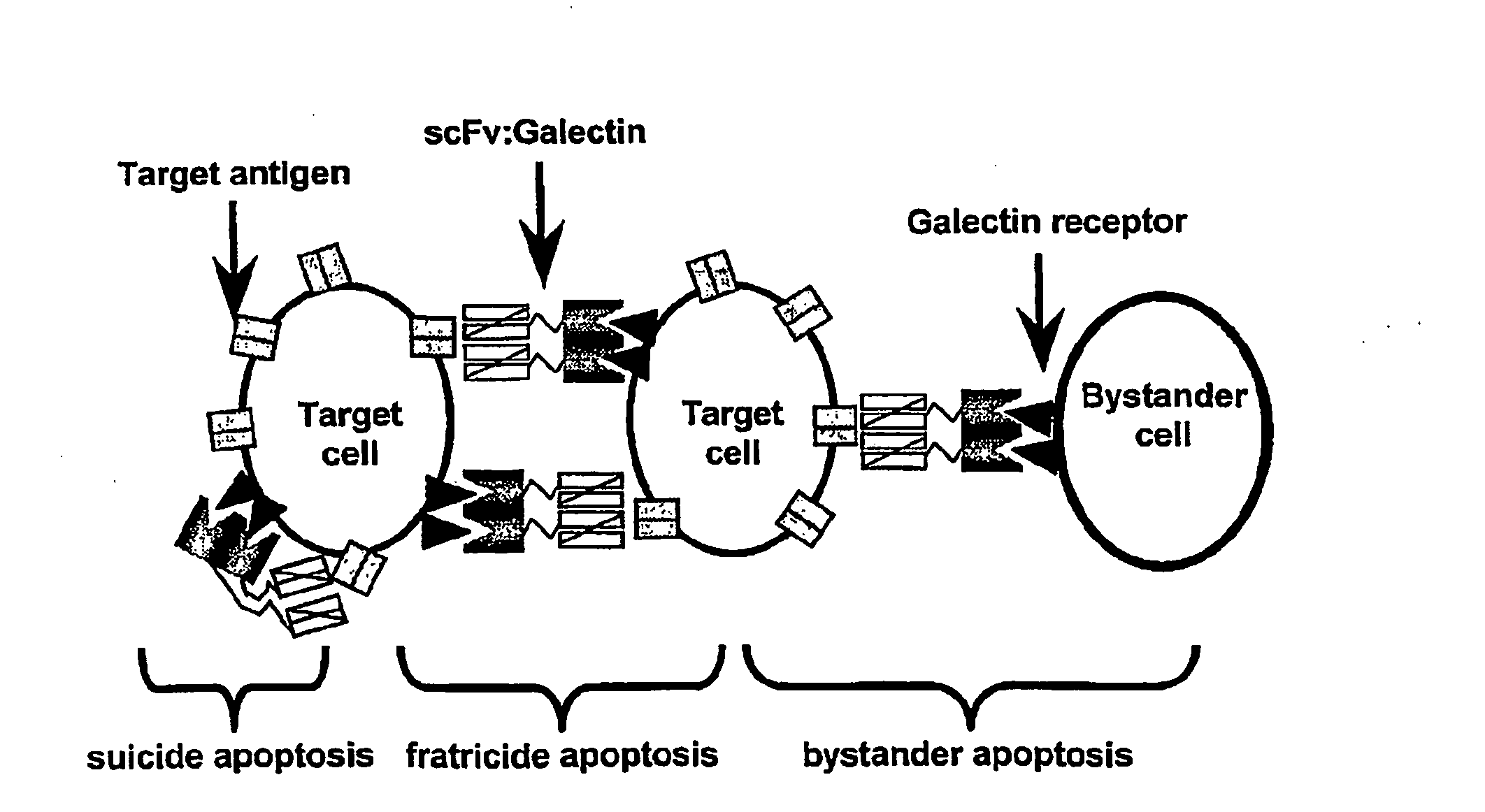
Targeting-enhanced activation of galectins
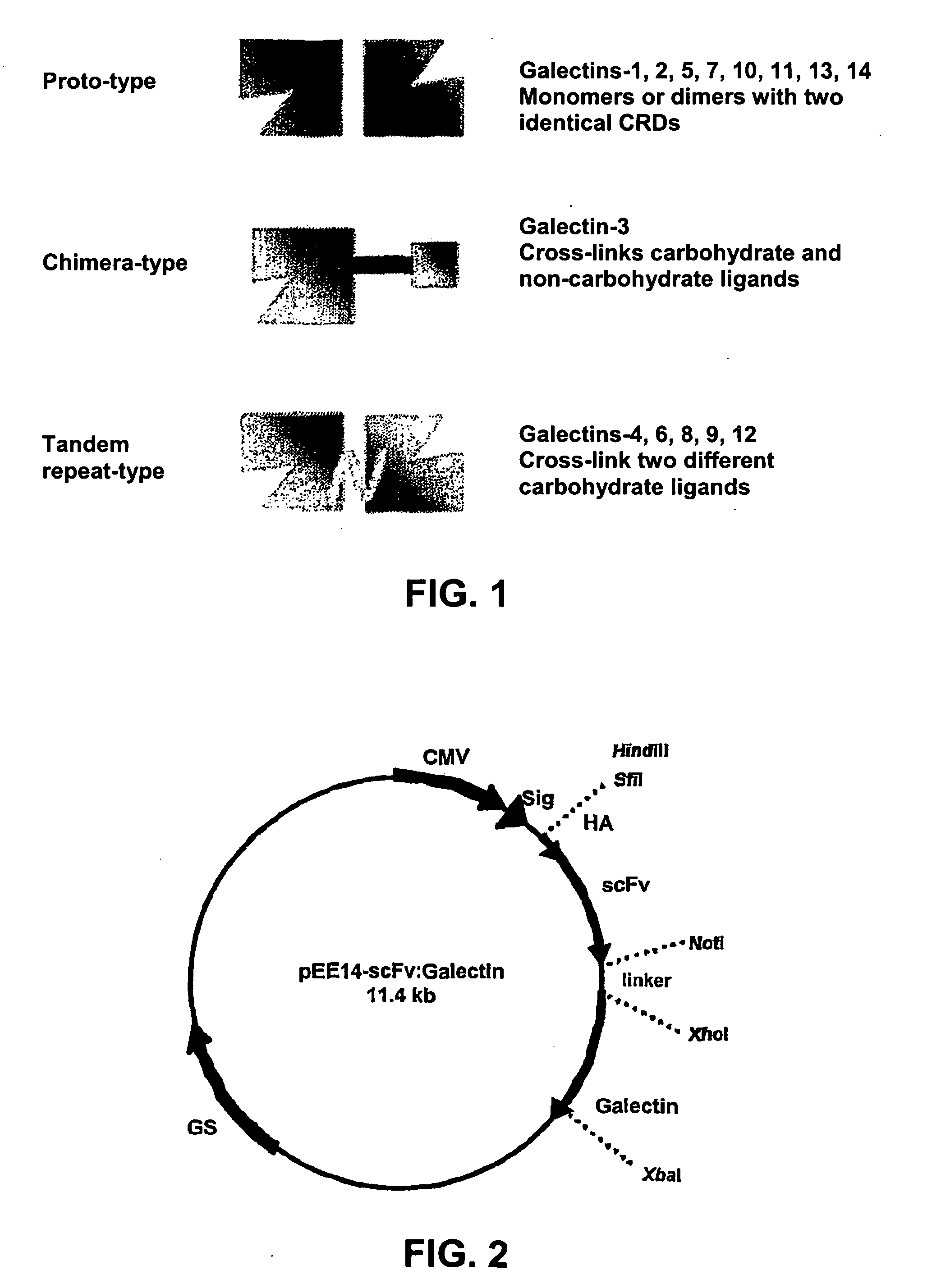
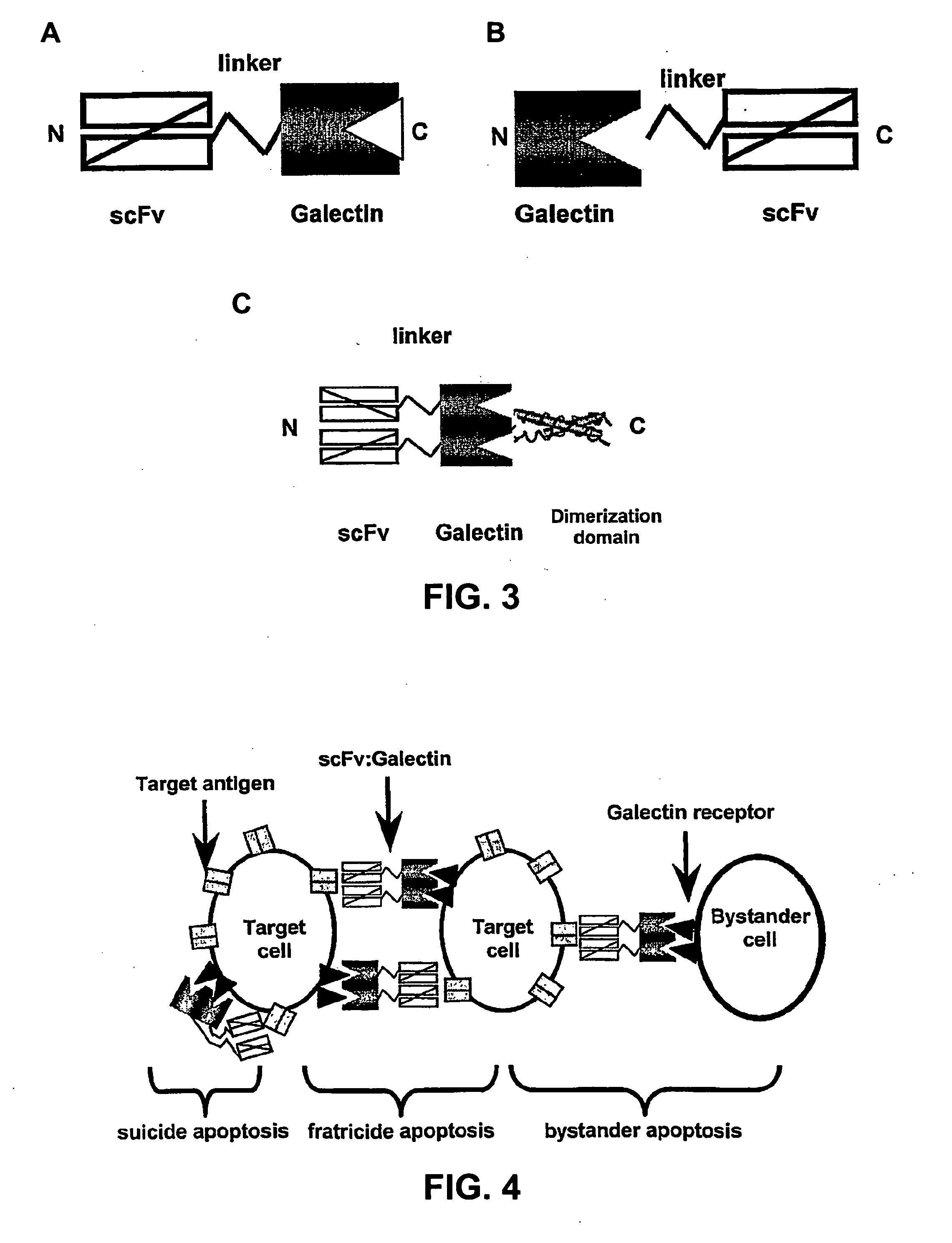
InactiveUS20080234177A1Enhancing vivo efficacyHigh in vivo efficacyNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsArthritisTnf family
Lectin-binding proteins and their therapeutic use. In particular, described are the targeting and targeting-enhanced multimerization and activation of galectins. Provided is a galectin-conjugate including at least one galectin molecule conjugated to a non-galectin cell targeting means. Exemplary targeting means include targeting means able to bind EGP2, a pancarcinoma-associated cell surface target antigen, CD antigen, such as CD7 or CD38, or a TNF family member, such as TRAIL-R. The targeting means may comprise an antibody or a functional fragment thereof, such as a single chain variable antibody fragment (scFv). Also provided is the use of a galectin-conjugate for treating a disease, like cancer or an immune disorder, such as auto-immune disease, allergic disorder, auto-immune encephalomyelitis, arthritis, colitis, hepatitis, asthma, multiple sclerosis, transplant rejection, Graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) and / or inflammatory bowel disease.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF GRONINGEN
Hepatocellular carcinoma marker
ActiveCN106662588AReduce functionPreparing sample for investigationBiological material analysisEpitopeHigh mannose
The present invention addresses the problem of providing a hepatocellular carcinoma marker which can be used for detecting the presence of hepatocellular carcinoma and comprises a glycoprotein that can occur in the liver only when the carcinoma is developed regardless of the change in the condition of the liver. The present invention provides a hepatocellular carcinoma marker which comprises an NPA lectin-binding glycoprotein containing an NPA lectin-binding sugar chain epitope having at least one property selected from the following properties (1) to (5) (1) the sugar chain epitope does not contain core fucose (a fucose alpha 1(arrow) 6 sugar chain); (2) the sugar chain epitope contains a composite sugar chain that contains three (less than four) mannose molecules; (3) the sugar chain epitope does not contain a high-mannose-type sugar chain containing five or more mannose molecules; (4) the sugar chain epitope comprises a composite sugar chain that does not rely on the bindability to LCA lectin; and (5) the sugar chain epitope comprises a composite sugar chain that does not rely on the bindability to ConA lectin. The presence of the development of hepatocellular carcinoma or the degree of the progression or malignancy of the carcinoma can be determined by detecting the hepatocellular carcinoma marker of the present invention in a sample of interest.
Owner:NAT INST OF ADVANCED IND SCI & TECH
Device and method for purifying virally infected blood
InactiveUS20110284463A1Reduction of antigenic assault on the immune systemMembranesSemi-permeable membranesProximateBlood plasma
The present invention relates to a method for using lectins that bind to pathogens having surface glycoproteins or fragments thereof which contain glycoproteins, to remove them from infected blood or plasma or other fluids in an extracorporeal setting. Accordingly, the present invention provides a methods and devices for reducing viral load or plaque forming units in blood or plasma from one or more infected individuals. A preferred embodiment of the method comprises passing the blood or plasma through a porous hollow fiber membrane wherein lectin molecules are disposed proximate to the membrane, collecting pass-through blood or plasma and optionally reinfusing the pass-through blood or plasma into the individual. Additionally, the present invention provides a methods and devices for the reduction of plaque forming units, cleared more rapidly and more efficiently than overall viral load.
Owner:AETHLON MEDICAL INC
Device and method for purifying virally infected blood
InactiveUS20160000987A1Reduction of antigenic assault on the immune systemMembranesOther blood circulation devicesBlood plasmaViral infection
The present invention relates to a method for using lectins that bind to pathogens having surface glycoproteins or fragments thereof which contain glycoproteins, to remove them from infected blood or plasma or other fluids in an extracorporeal setting. Accordingly, the present invention provides a methods and devices for reducing viral load or plaque forming units in blood or plasma from one or more infected individuals. A preferred embodiment of the method comprises passing the blood or plasma through a porous hollow fiber membrane wherein lectin molecules are disposed proximate to the membrane, collecting pass-through blood or plasma and optionally reinfusing the pass-through blood or plasma into the individual. Additionally, the present invention provides a methods and devices for the reduction of plaque forming units, cleared more rapidly and more efficiently than overall viral load.
Owner:AETHLON MEDICAL INC
Method for extracting CEL I nuclease in celery
InactiveCN101538561ANo significant difference in purityNo significant difference in activityHydrolasesSulfite saltFiltration
The invention relates to a method for extracting CEL I nuclease in celery and discards measures adopting a plurality of high-speed or ultra-speed centrifugation and a plurality of gel filtration and ion exchange chromatography in the prior art. The method comprises the following steps: adding a small amount of sodium sulfite to extract so as to reduce and clear colored substances in the extract; adopting a thermal denaturation physical method to rapidly clear a great amount of foreign protein with poor temperature toleration; utilizing the characteristic that CEL I is the combination of glycoprotein and activated concanavalin to combine CEL I nuclease and concanavalin so as to remove the foreign protein and further purify the CEL I; and finally, selecting DEAE-Sepharose FF as a suitable medium for the CEL I by once chromatography purification. Accordingly, the extraction method replaces the time-consuming and expensive measures adopting a plurality of high-speed even ultra-speed refrigerated centrifugation, a plurality of gel filtration and ion exchange chromatography, and the like and achieves the aims that the CEL I nuclease is rapidly extracted from the celery and purified.
Owner:GUANGZHOU UNIVERSITY
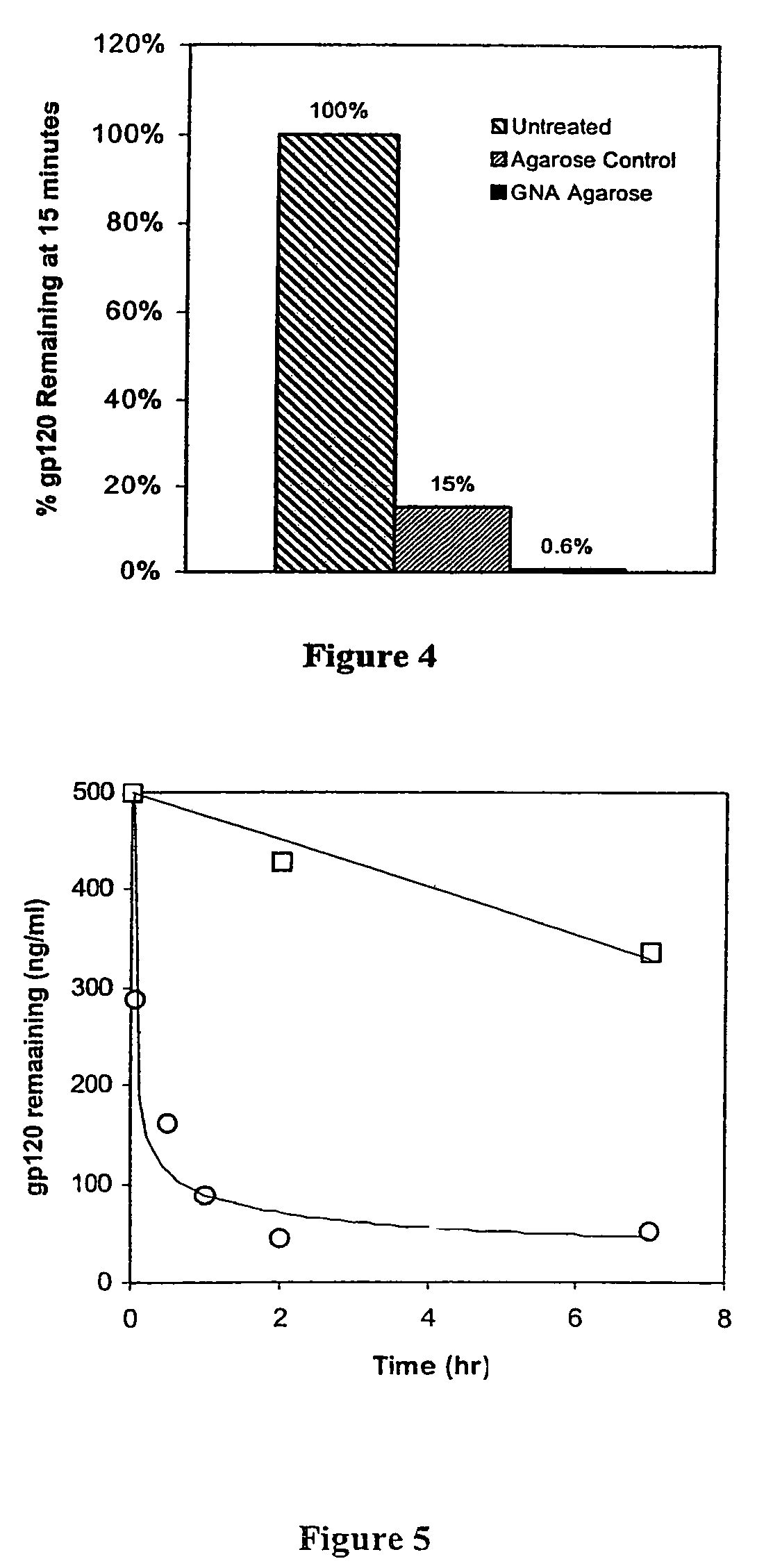
Lectin binding to choroidal neovascularization
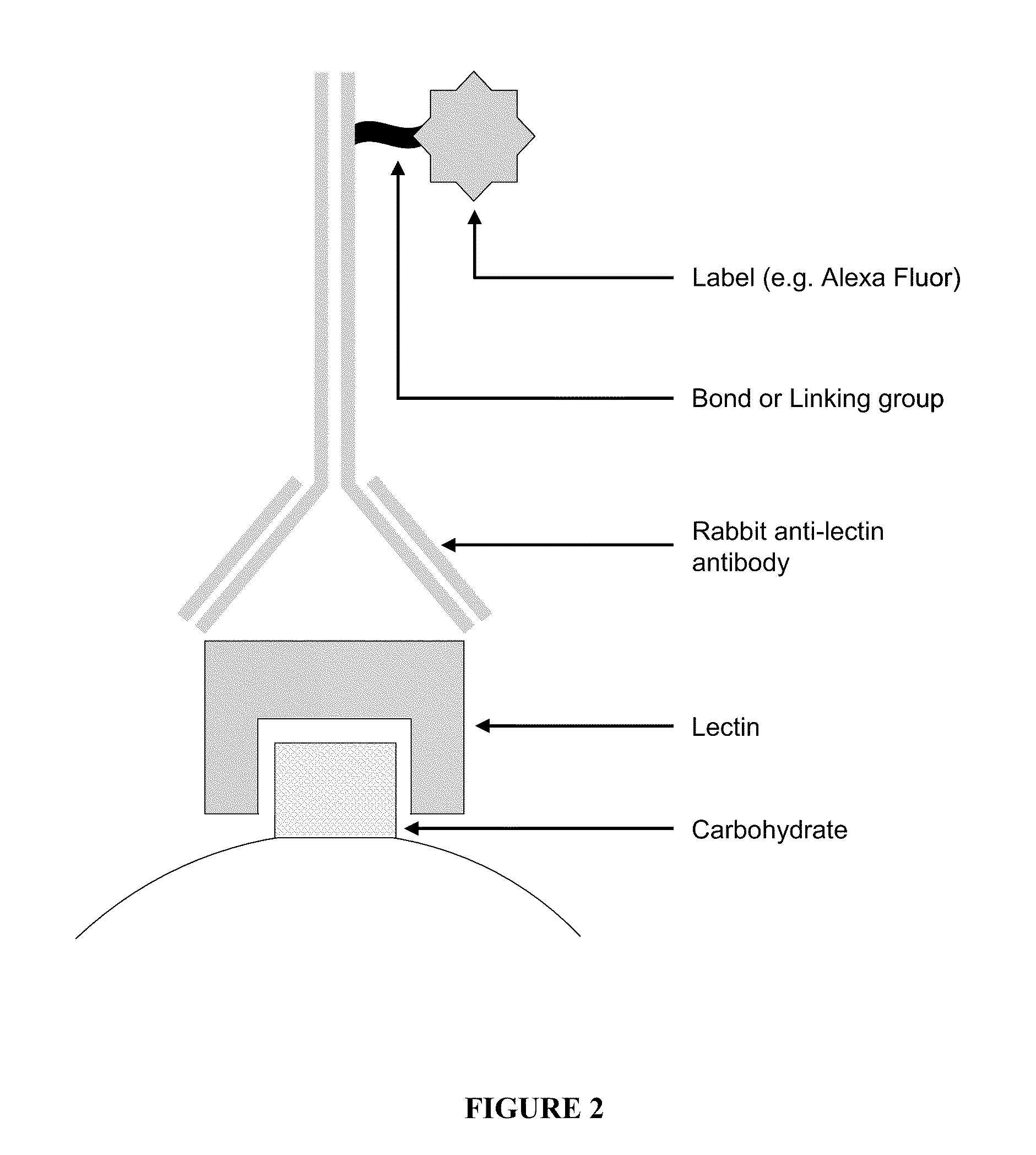
InactiveUS20060286604A1Saccharide peptide ingredientsDisease diagnosisLectin bindingChoroidal neovascularization
The present invention involves the identification of choroidal neovascularization (CNV) based on lectin binding patterns in choroidal and / or Bruch's membranes. The use of lectins to target therapeutic agents to CNV also is disclosed.
Owner:UNIV OF IOWA RES FOUND
Immunoassay method less affected by impurities
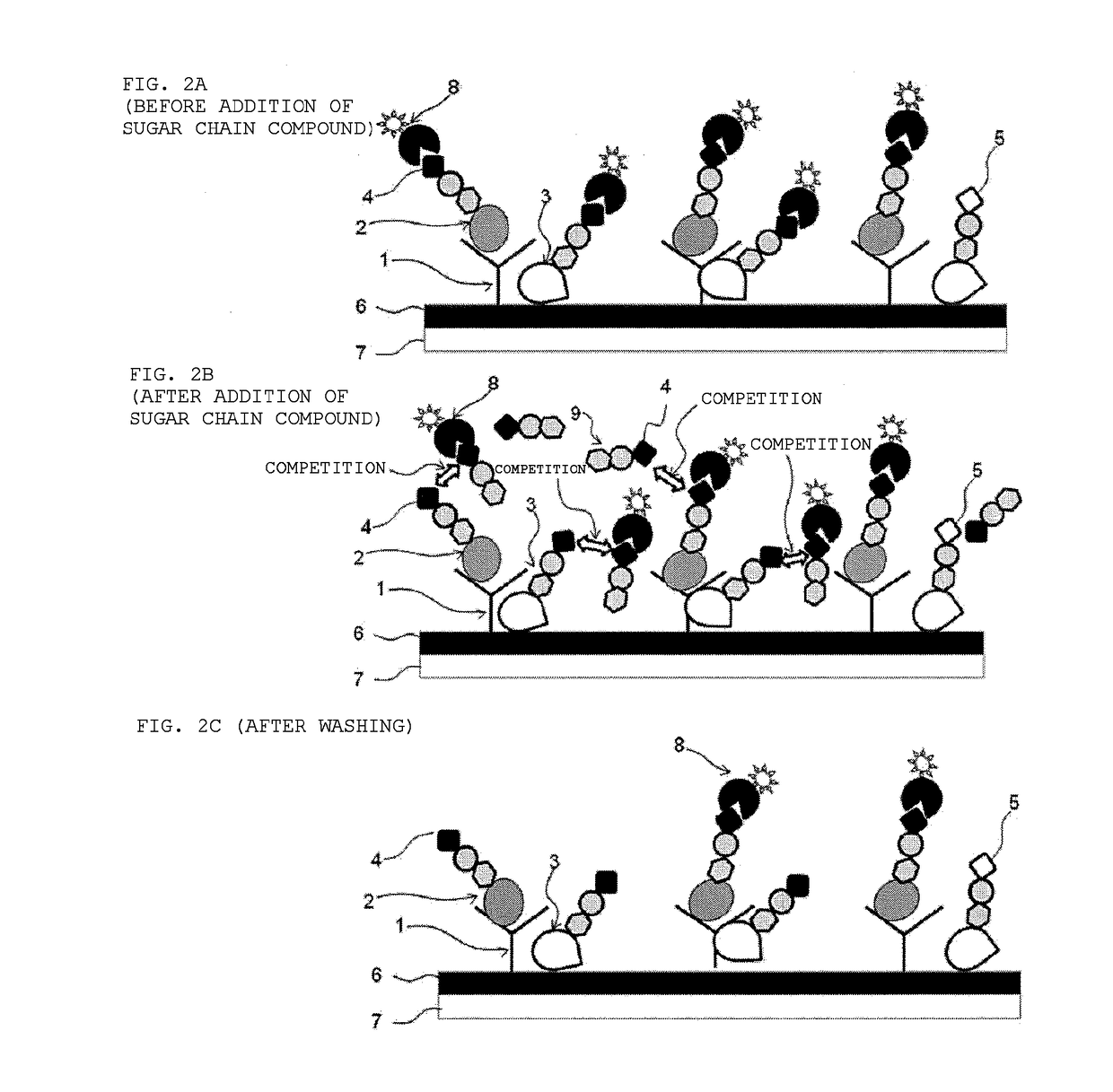
An object of the present invention is to provide a method of measuring the amount of a compound containing a sugar chain in a biological sample by a sandwich immunoassay method using a labeled lectin, which method is suitable for reduction of noise originating from impurities and determination of the exact amount of a target compound. The present invention provides a method of measuring the amount of a target compound containing a sugar chain in a biological sample by a sandwich immunoassay method using a labeled lectin (including cases where a target compound-capturing substance other than an antibody is used as a ligand), the method containing adding a sugar chain compound which competes (crosses) with impurities contained in the biological sample in binding with the labeled lectin.
Owner:KONICA MINOLTA INC
Pathogen vaccines and methods of producing and using the same
ActiveUS10813988B2Create quicklyPrevent leakageAntibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsVaccinationOpsonin binding
The present invention provides vaccine compositions and methods of producing such compositions. Other embodiments of the invention include methods of treating a pathogen infection, methods of vaccinating a subject against a pathogen infection, and methods for treating an antibiotic-resistance bacterial infection in a subject in need thereof. In further embodiments, the invention includes methods of decreasing the level of a pathogen in a subject having a pathogen infection, methods of increasing the surviving rate of a subject having a pathogen infection, methods of reducing the level of pain associated with a pathogen infection, and methods of reducing the level of distress associated with a pathogen infection in a subject in need thereof. Novel scaffold compositions and opsonin-bound or lectin-bound pathogen compositions, and uses thereof, are also provided herein.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
Rabbit Klebsiella pneumoniae agglutinogen and application of rabbit Klebsiella pneumoniae agglutinogen
The invention relates to the technical field of organisms, in particular to a rabbit Klebsiella pneumoniae agglutination reaction experimental technique. A rabbit Klebsiella pneumoniae agglutinogen is prepared from rabbit Klebsiella pneumoniae liquid dyed by fuchsin dye liquid. An application method concretely belongs to an application method in agglutination reaction experiments: the rabbit Klebsiella pneumoniae agglutination is combined with agglutinin, and the agglutination result is judged. The rabbit Klebsiella pneumoniae agglutinogen has the advantages that expensive instruments and reagents are not needed, the cost is low, the speed is high, the operation is simple and convenient, the technical requirements on operators are low, the result is intuitional, the rabbit Klebsiella pneumoniae agglutinogen is applied to basic level site detection application, the detection antigen of a rabbit Klebsiella pneumoniae microagglutination reagent kit is dyed, agglutination particles or agglutination blocks are red, the observation is easier, and the detecting method can be used for quantificationally detecting the rabbit serum antibody valence, can also be used for qualitatively detecting the rabbit Klebsiella pneumoniae antigen and is particularly suitable for on-site rabbit Klebsiella pneumoniae diagnosis for basic level veterinary stations and warrens.
Owner:CHONGQING ACAD OF ANIMAL SCI
Lectin conjugates for mucin hydration
The invention provides, inter alia, conjugates of a hydratable polymer (such as PEG, polyethylene glycol) and a lectin (such as wheat germ agglutinin, WGA), compositions comprising these conjugates, as well as methods and targeted uses of these conjugates and compositions for, e.g., lubricating, maintaining hydration of, rehydrating, and / or inhibiting microorganism colonization of a biological surface in need thereof.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
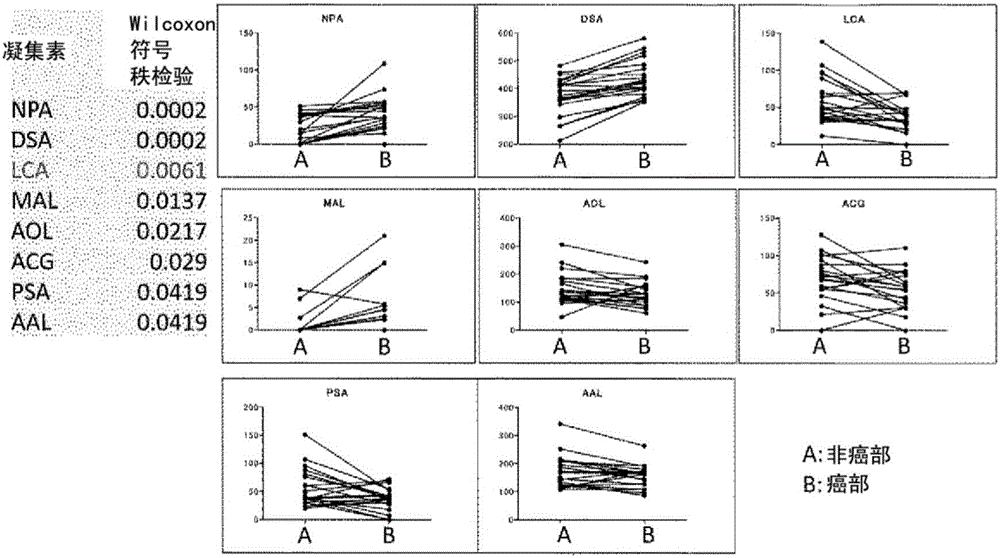
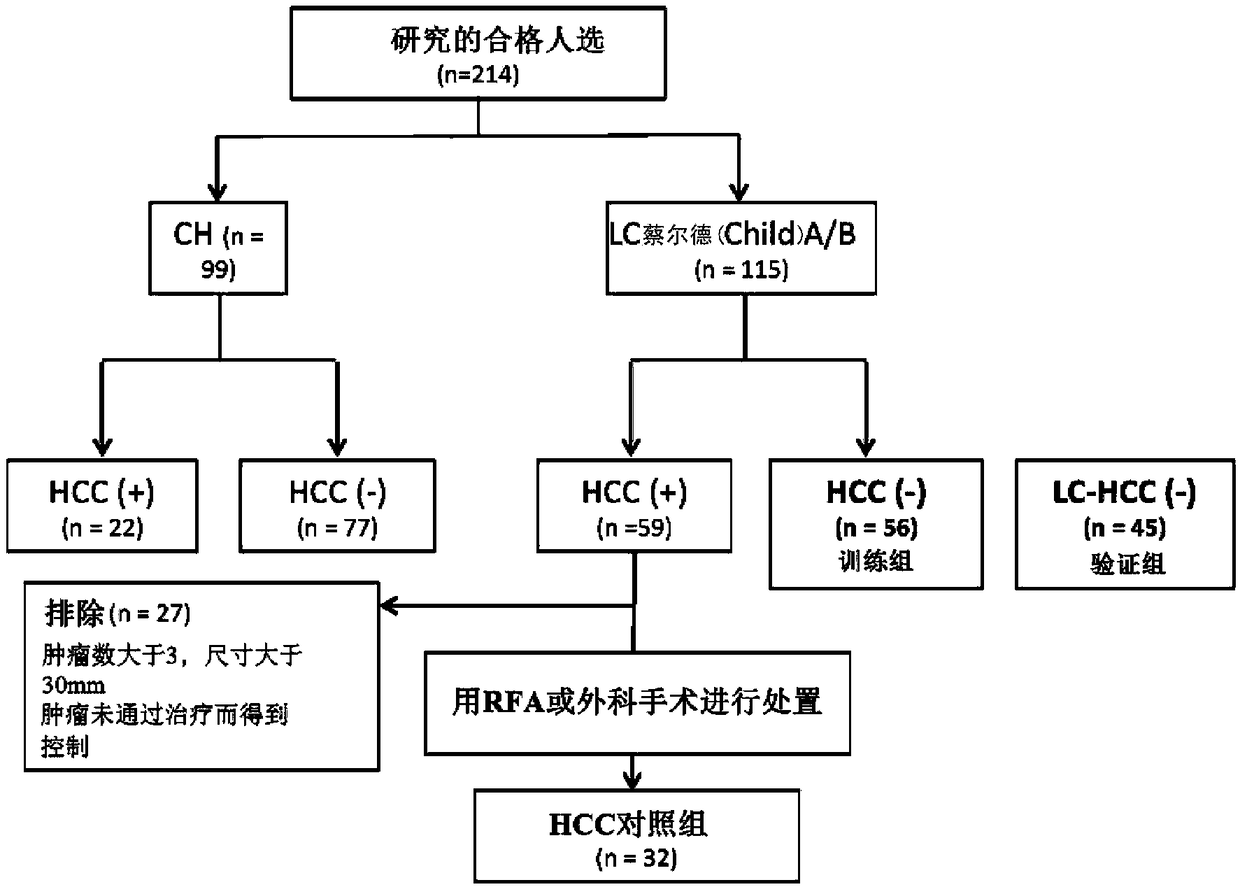
Method for predicting prognosis and risk of developing hepatocellular carcinoma in liver cirrhosis patient
The present invention provides a method and a kit for accurately predicting the prognosis (mortality rate) and risk of developing hepatocellular carcinoma in liver cirrhosis patients. The present invention provides: a method by which an 'index for evaluating the risk of developing hepatocellular carcinoma, 'which is used for predicting the prognosis and risk of developing hepatocellular carcinomain liver cirrhosis patients, is calculated as the ratio of CSF1R that contains WFA / VVA-binding sugars relative to the total CSF1R content of bodily fluid (blood serum) (WFA+-CSF1R%); and a method by which a 'prognosis evaluation index ' is calculated as the amount of CSF1R that contains WFA / VVA-binding sugars (WFA+-CSF1R ng / mL). Furthermore, an optimal cutoff value was determined for each of the indices, and it was proven that: the risk of developing hepatocellular carcinoma was significantly high when the 'index for evaluating the risk of developing hepatocellular carcinoma ' in a subject wasequal to or greater than the optimal cutoff value; and the prognosis was significantly poor when the 'prognosis evaluation index ' was equal to or greater than the optimal cutoff value. In addition,anti-CSF1R antibodies (CSR-1-30), which are exceptional for detecting CSF1Rs such as CSF1Rs that contain WFA / VVA-binding sugars in a bodily fluid sample, were provided. It was discovered that srWFA and VVA lectins other than WFA lectins can be used, and it was additionally proven that measuring the amount of CSF1R that binds to a CSF1R-specific lectin is preferable to measuring the total amount ofCSF1R. It was also possible to provide, inter alia, a kit for measuring the 'prognosis evaluation index ' and / or 'index for evaluating the risk of developing hepatocellular carcinoma ' in a liver cirrhosis patient, the kit including these anti-CSF1R antibodies and lectins as constituent elements.
Owner:NAT INST OF ADVANCED IND SCI & TECH
Immunological extract and method of production
PendingUS20210361720A1High purityEffective and quick deliveryOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsPentraxin bindingComplement S-Protein
The present invention relates to a method of preparing an extract from edible bird's nest, a bird's nest extract and uses of the bird's nest extract. The method comprises preparing an edible bird's nest (EBN) mixture; and contacting the mixture with an extraction solution to bind a molecule in the mixture, wherein the extraction solution comprises at least one binding moiety selected from the group comprising an opsonin binding moiety, a complement protein binding moiety, a lectin binding moiety, a ficolin binding moiety, a collectin binding moiety, and a pentraxin binding moiety.
Owner:LIM KAH MENG
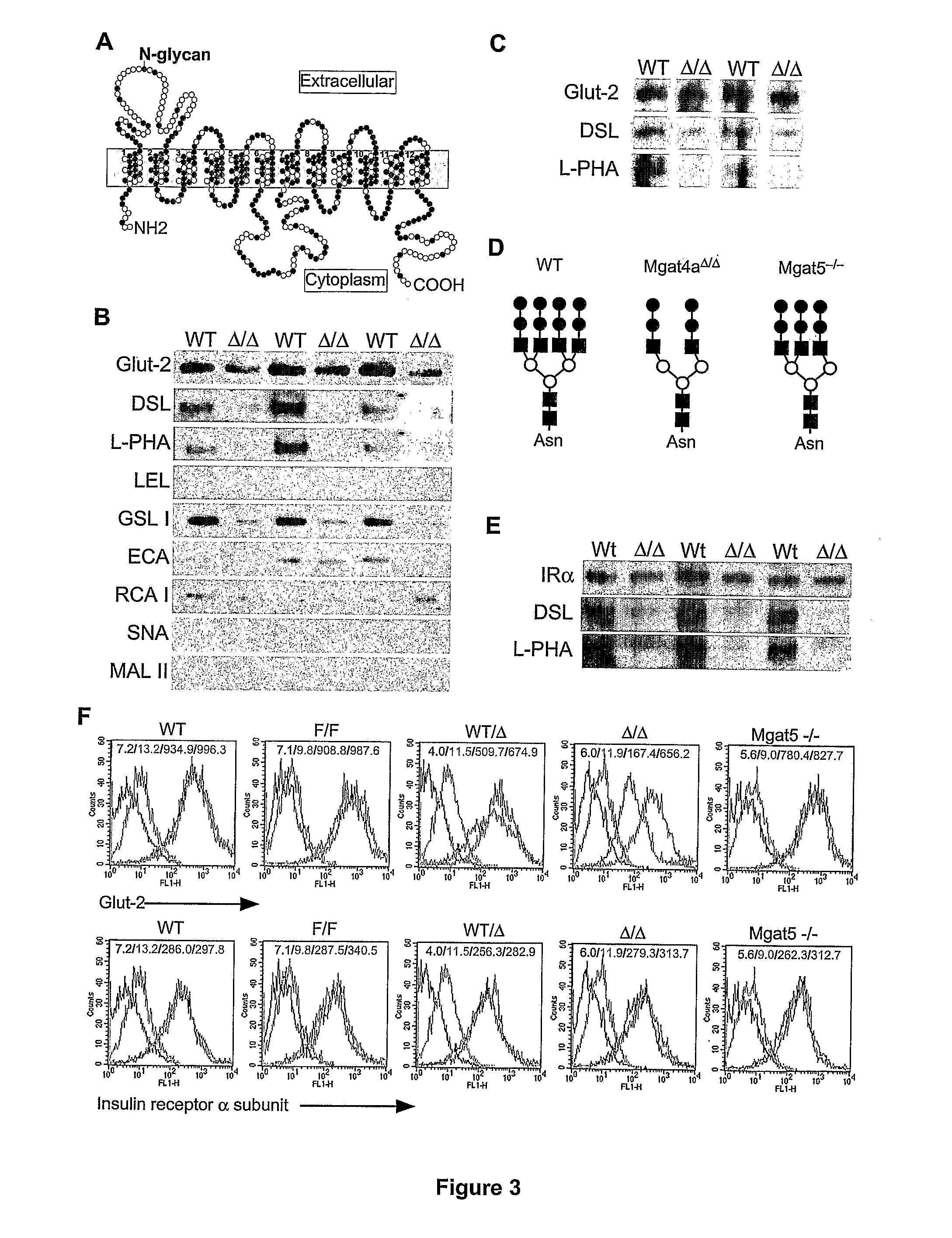
Regulation of glucose and insulin levels by gnt-4 glycosyltransferase activity
InactiveUS20070259379A1Reduce transportationIncrease metabolic ratePeptide/protein ingredientsPancreatic cellsGlycosyltransferase activityPre diabetes
The invention is based on the discovery that the gylcosylation enzyme GnT-4 increases glyocsylation and the stability of glucose transporter (Glut) family members, e.g., by increasing lectin binding. Modulators of GnT-4 activity can therefore be identified and used for the treatment of diabetes or pre-diabetes. In addition, inhibitors of GnT-4 activity can be used for the treatment of cancer.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Caries risk test for predicting and assessing the risk of disease
InactiveUS20140274876A1Reduce disease riskPredict disease riskAntibacterial agentsBiocideDisease riskSaliva sample
Provided are methods, test devices, and diagnostic kits for predicting, assessing, and diagnosing the risk of a disease using salivary analysis. The methods comprise providing a whole (unfractionated) saliva sample from a subject; contacting an aliquot of the saliva with two or more lectins under conditions that allow the two or more lectins to bind to a lectin-binding component of the saliva; detecting the amount of bound lectin; and comparing the amount of bound lectin to the amount known to bind a saliva sample from a control patient, to predict the risk of a disease in the subject. Also provided are methods for reducing the risk of a disease and a method for assessing the risk of the disease at a defined level.
Owner:PROACTIVE ORAL SOLUTIONS +1
Compositions and methods for detecting oral neoplasm
Methods and kits for assessing the presence of, and for detecting cancer, notably oral cancer, are disclosed. Such methods and kits use one or more lectins operably linked to a fluorophore, wherein the lectin binds differentially to cancerous and non-cancerous tissues, and wherein the fluorophore facilitates visualizing the differential binding. The lectins are applied to the oral mucosa of a subject, the fluorophore is exposed to light, and cancerous regions of the mucosa are visualized. In certain embodiments, the lectin specifically binds to one or more of a β-galactoside, an α- or β-N-acetylglucosamine, or a sialic acid moiety.
Owner:VSL ACQUISITION LLC
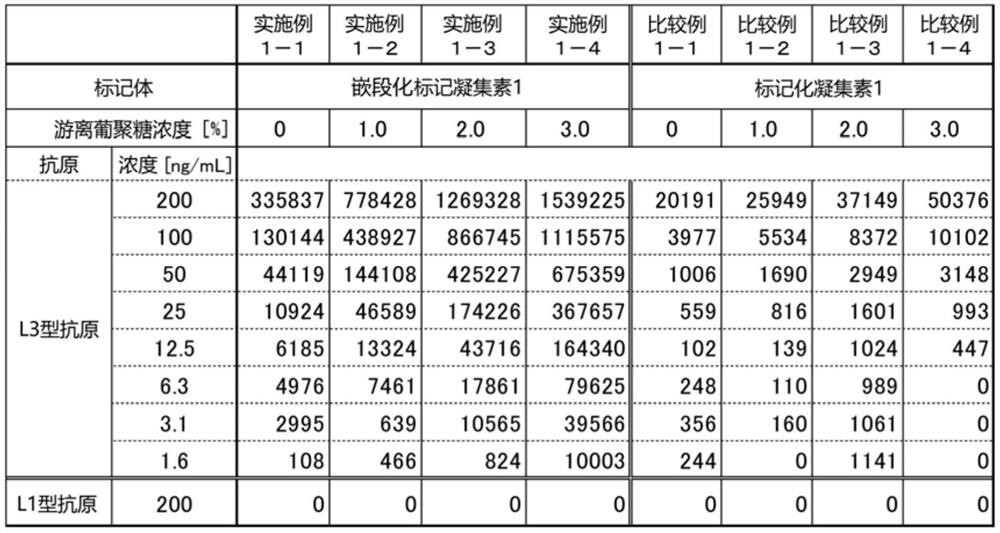
Method for measuring lectin-binding substance, kit for measuring lectin-binding substance, and block-labeled lectin used in said method and kit
A method for measuring a lectin-binding substance in a sample, said method comprising: a measurement step in which a block-labeled lectin is brought into contact with the sample to measure a lectin-binding substance in the sample; the block-labeled lectin comprises a water-soluble carrier containing a first water-soluble polymer, and a marker and lectin immobilized on the water-soluble carrier.
Owner:FUJIREBIO CO LTD
Method for extracting CEL I nuclease in celery
The invention relates to a method for extracting CEL I nuclease in celery and discards measures adopting a plurality of high-speed or ultra-speed centrifugation and a plurality of gel filtration and ion exchange chromatography in the prior art. The method comprises the following steps: adding a small amount of sodium sulfite to extract so as to reduce and clear colored substances in the extract; adopting a thermal denaturation physical method to rapidly clear a great amount of foreign protein with poor temperature toleration; utilizing the characteristic that CEL I is the combination of glycoprotein and activated concanavalin to combine CEL I nuclease and concanavalin so as to remove the foreign protein and further purify the CEL I; and finally, selecting DEAE-Sepharose FF as a suitable medium for the CEL I by once chromatography purification. Accordingly, the extraction method replaces the time-consuming and expensive measures adopting a plurality of high-speed even ultra-speed refrigerated centrifugation, a plurality of gel filtration and ion exchange chromatography, and the like and achieves the aims that the CEL I nuclease is rapidly extracted from the celery and purified.
Owner:GUANGZHOU UNIVERSITY
Regulation of glucose and insulin levels by GnT-4 glycosyltransferase activity
InactiveUS8034556B2Reduce transportationIncrease metabolic rateSugar derivativesPeptide/protein ingredientsGlycosyltransferase activityLevel insulin
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Biomarker for diagnosing primary sicca syndrome and application of biomarker
The invention relates to a biomarker for diagnosing primary sicca syndrome and application of the biomarker. According to the biomarker for diagnosing primary sicca syndrome and application of the biomarker of the invention, a lectin microarray containing 56 types of lectins is adopted to detect a glycan spectrum of specific binding of the serum IgG and the lectin of a patient with the primary sicca syndrome (PSS). The results show that LCA lectin binding glycan content is increased in the patient with primary biliary cholangitis (PBC) compared with that of a healthy person. As the LCA lectin is specific binding fucose, the expression of the fucose level in the patient withPSS is increased. A lectin immunoblotting verification result shows that the content of the LCA lectin binding glycan is still increased in the patient with the PSS. Therefore, the LCA lectin binding glycan level in the serum IgG can be used as a marker of the primary sicca syndrome (PSS).
Owner:PEKING UNION MEDICAL COLLEGE HOSPITAL CHINESE ACAD OF MEDICAL SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com