Enzyme-lectin conjugate nano-particles and preparing method thereof
A nanoparticle and lectin technology, applied in the direction of biochemical equipment and methods, enzymes, enzymes, etc., can solve the problems of inability to construct efficient multi-enzyme-magnetic nanoparticle systems, enzyme molecule inactivation, etc., to achieve easy industrial implementation and Scale-up, mild reaction conditions, and easy reusability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0060] Embodiment 1, preparation enzyme-lectin conjugate nanoparticle
[0061] 1. Raw material ratio
[0062] In parts by weight, the proportioning of each raw material in the present embodiment is as follows:
[0063] 2 parts of glucose oxidase, 8 parts of horseradish peroxidase, 110 parts of concanavalin A (lectin), 0.4 parts of glutaraldehyde (crosslinking agent), 0.4 parts of sodium borohydride (reducing agent).
[0064] 2. Preparation method
[0065] Prepare the enzyme-lectin conjugate nanoparticles according to the following steps with the raw materials of the above ratio:
[0066] 1) Add enzyme and lectin to 10mM phosphate buffer solution with pH 7 (add 1mL buffer solution for every 1mg lectin), and stir (250rad / min) at 25°C for 2 hours;
[0067] 2) Add a cross-linking agent to the system obtained in step 1), continue to react for 2 hours, add a reducing agent after the cross-linking reaction, and continue to react for 24 hours;
[0068] 3) The system obtained in st...
Embodiment 2
[0073] Embodiment 2, preparation enzyme-lectin conjugate nanoparticle
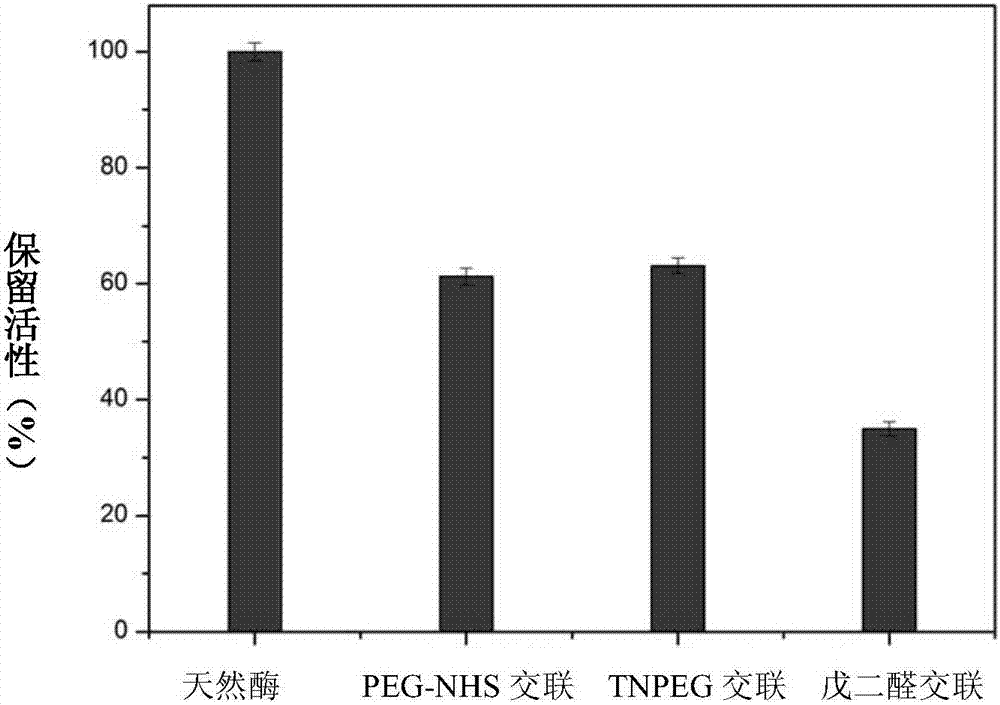
[0074] The operation steps are the same as in Example 1, except that 0.4 parts of glutaraldehyde crosslinking agent is replaced by 300 parts of terminal aldehyde group PEG (i.e. aldehyde group-polyethylene glycol-aldehyde group, CHO-PEG-CHO) (Mn= 2000), the photos of the high-resolution transmission electron microscope of the prepared enzyme-lectin conjugate nanoparticles have no substantial difference from Example 1, and the biocatalytic activity is 61% of the equivalent natural enzyme, such as figure 2 shown.
Embodiment 3
[0075] Example 3, preparation of enzyme-lectin conjugate nanoparticles
[0076] The operation steps are the same as in Example 1, except that 0.4 parts of glutaraldehyde crosslinking agent is replaced by 200 parts of terminal succinimide ester PEG (succinimide ester-polyethylene glycol-succinimide ester, NHS -PEG-NHS) (Mn=2000), without using a reducing agent, the high-resolution transmission electron microscope photos of the prepared enzyme-lectin conjugate nanoparticles have no substantial difference from Example 1, and its biocatalytic activity is equivalent to natural 63% of enzymes, such as figure 2 shown.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com