Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
32 results about "Intracellular signaling pathways" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
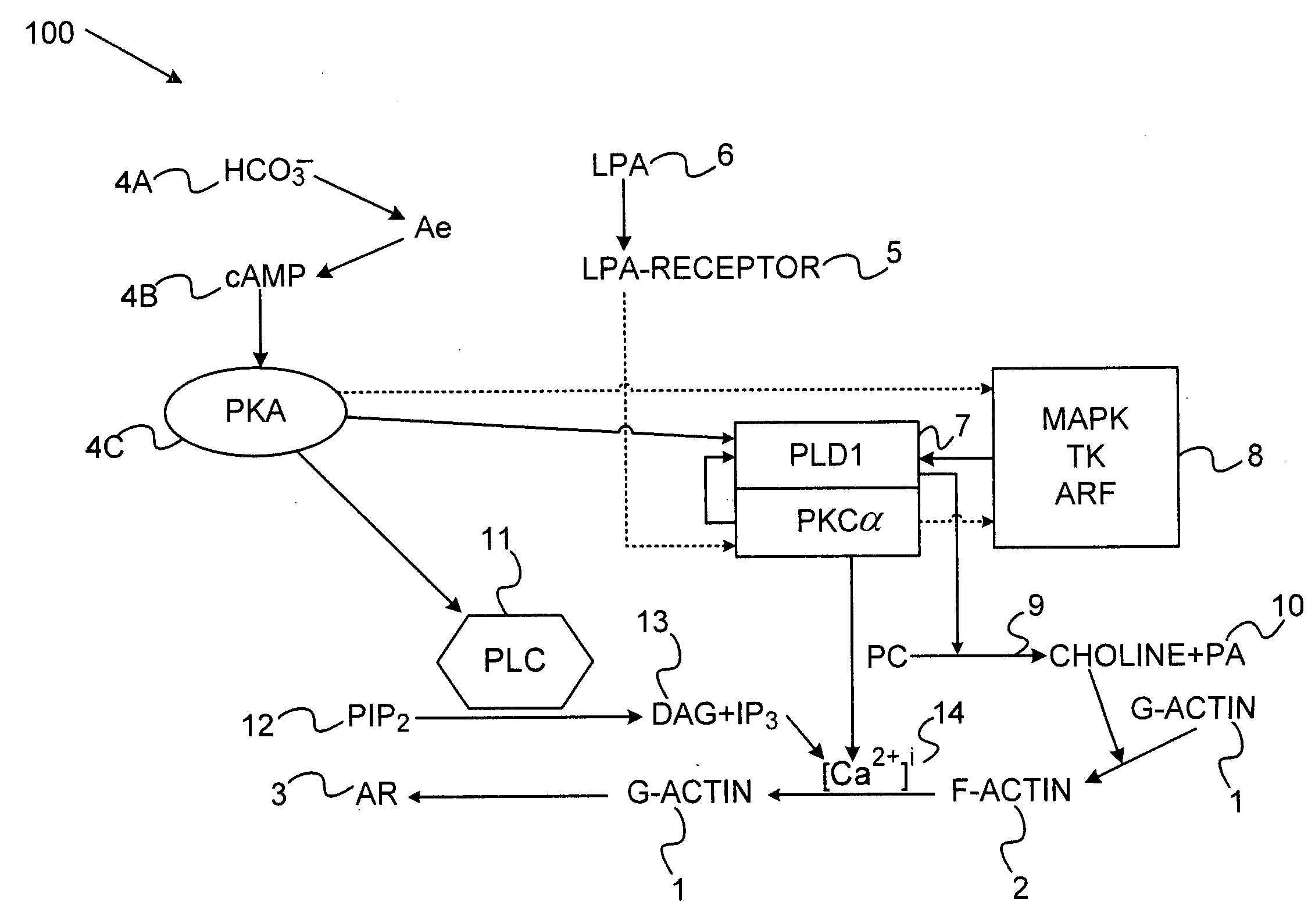
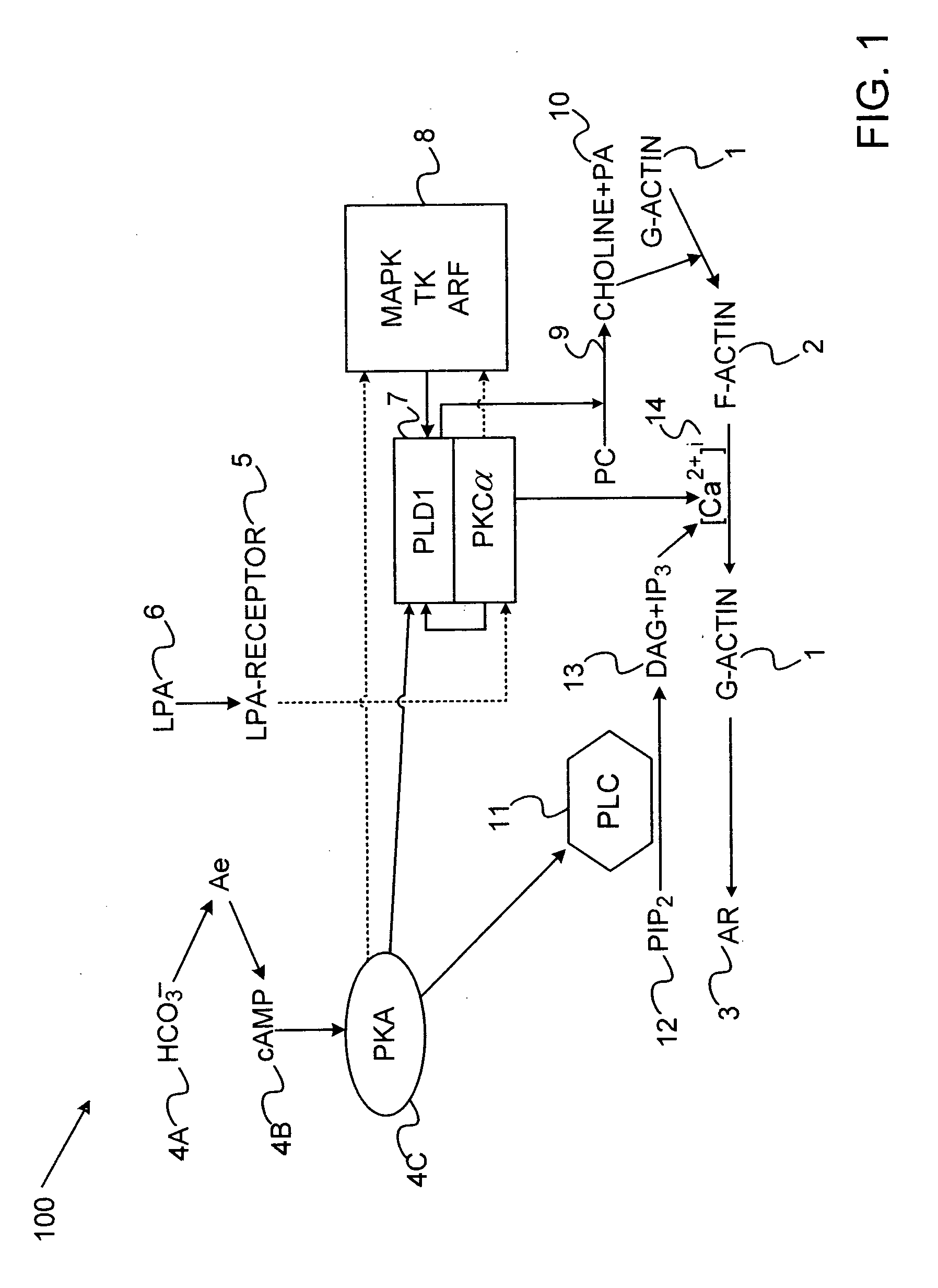
Pathways of Intracellular Signal Transduction Most cell surface receptors stimulate intracellular target enzymes, which may be either directly linked or indirectly coupled to receptors by G proteins.
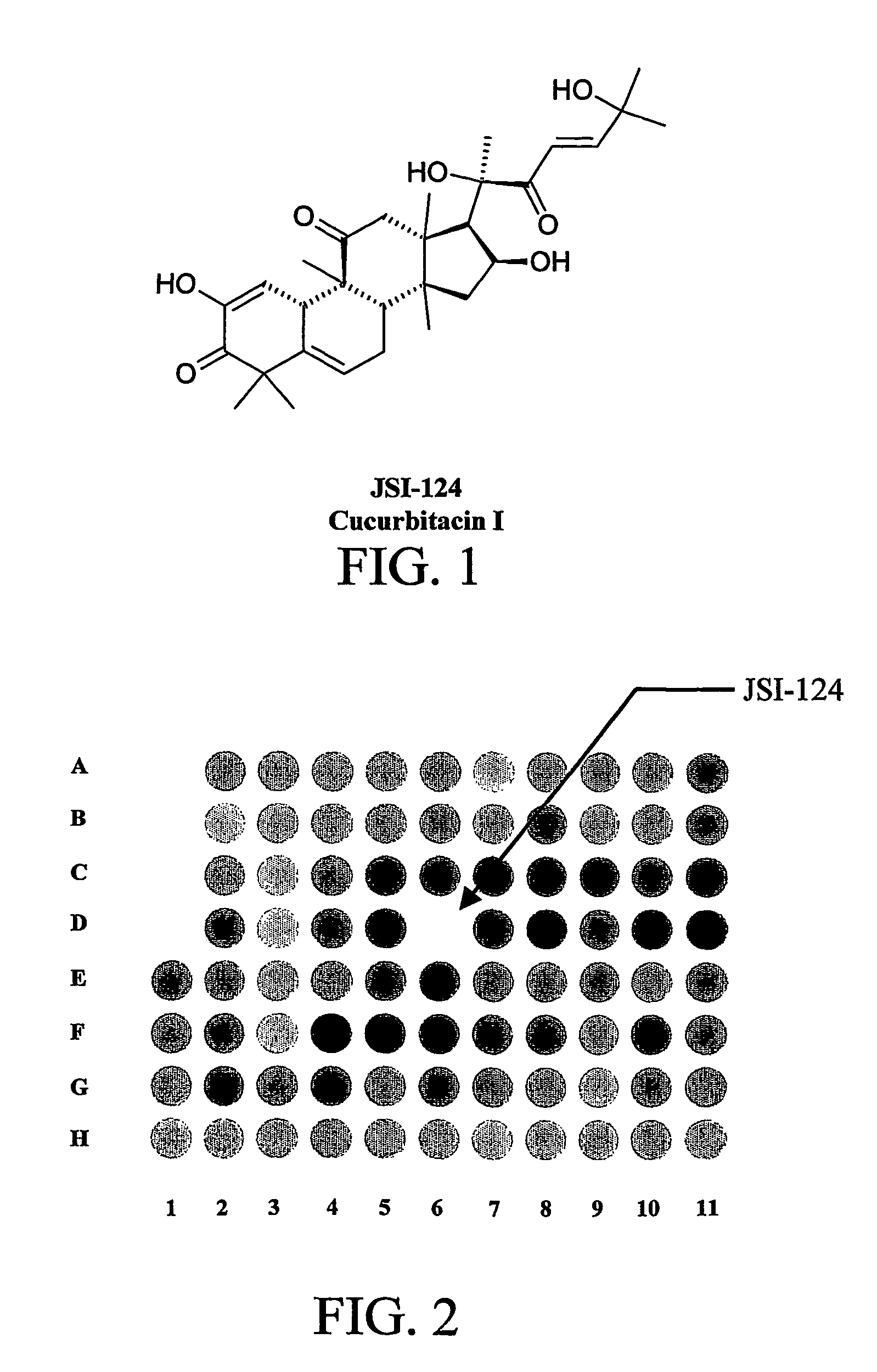
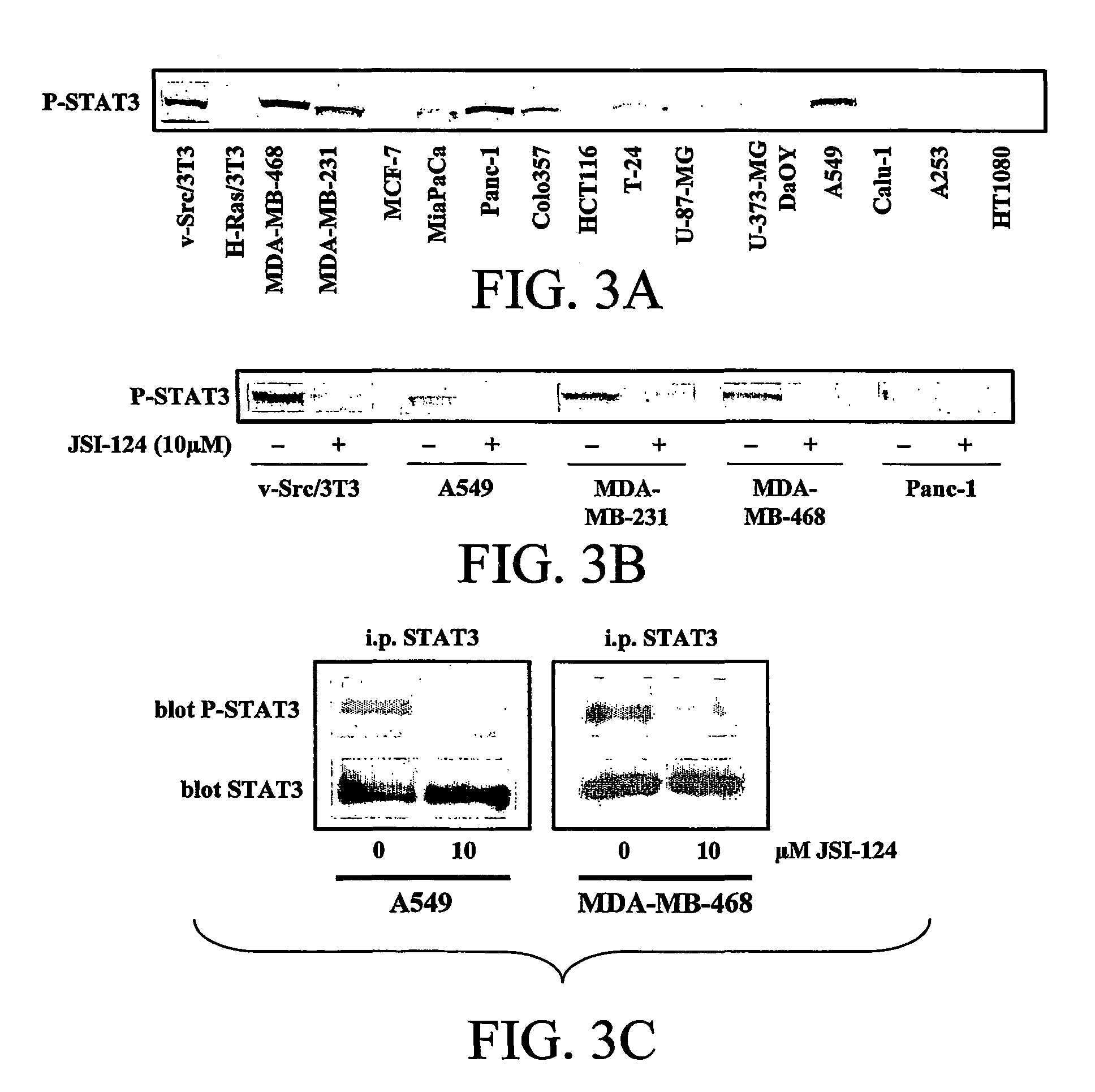
Materials and methods for treatment of cancer and identification of anti-cancer compounds
The subject invention pertains to the treatment of tumors and cancerous tissues and the prevention of tumorigenesis and malignant transformation through the modulation of JAK / STAT3 intracellular signaling. The subject invention concerns pharmaceutical compositions containing cucurbitacin I, or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt or analog thereof, to a patient, wherein the tumor is characterized by the constitutive activation of the JAK / STAT3 intracellular signaling pathway. The present invention further pertains to methods of moderating the JAK and / or STAT3 signaling pathwaysin vitro or in vivo using cucurbitacin I, or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt or analog therof. Another aspect of the present invention concerns a method for screening candidate compoudns for JAK AND / or STAT3 inhibition and anti-tumor activity.
Owner:SOUTH FLORIDA UNIVESITY OF
Stat3 as a theranostic indicator
This invention relates, e.g., to a method for predicting the response of a subject having estrogen-receptor-positive breast cancer to an inhibitor of the estrogen signaling pathway (e.g. tamoxifen), comprising measuring in a cancer sample from the subject the level of phosphorylation, compared to a baseline value, of one or more of the following members of an interconnected intracellular signaling pathway: (a) 4EBP1, and / or (b) p70S6, and / or (c) STAT3, and / or (d) FAK, wherein a significantly elevated level of phosphorylation of 4EBP1, and / or p70S6 and / or STAT3, and / or a significantly decreased level of phosphorylation of FAK, compared to the baseline value, indicates that the subject is likely to be a non-responder to the inhibitor and / or has a poor prognosis. Additional members of the intracellular signaling pathway whose phosphorylation can be measured are also described. Also described is a method for treating breast cancer in a subject in need thereof, wherein the subject exhibits an elevated level of phosphorylation of these markers, comprising administering to the subject an effective amount of one or more inhibitors of members of the interconnected intracellular signaling pathway.
Owner:GEORGE MASON INTPROP OF FAIRFAX VIRGINIA
Method for producing peptide libraries and use thereof
Screening libraries of peptides in different assays offers an opportunity to simultaneously interrogate intracellular signaling pathways, create reagents to further the understanding of the pathway, and to create novel forms of therapies.Many, if not all, biologically active peptides (e.g. peptide hormones) have profound effects both in health and disease, either by growth stimulating roles, growth inhibitory roles, or the regulation of critical metabolic pathways.The present invention is directed to novel bioactive peptides, an in silico method to identify these peptides and a peptide library containing these peptides.
Owner:SANOFI SA
Peptides causing formation of compact structure
The present invention relates to compositions and methods comprising peptides with high mutual affinity that, when attached to a protein, assist the protein to fold into a compact structure. By virtue of its stability and binding, this scaffold extends the activity of any contained protein sequence in the presence of cellular and other proteases. This compact structure may have other included functional sequences, which are superior to linear and less constrained peptides for library screening, building structure-biased peptide libraries, and targeting specific intracellular and extracellular compartments. The compositions of the present invention can be displayed on viral, archaeal, prokaryotic and eukaryotic cell surfaces for library screening, drug screening and display. The methods of the present invention are useful for in vivo screening of intracellular effector proteins that modulate signaling pathways, and for identification of interacting proteins in vitro. Therefore, the present invention can be used as a scaffold for gene therapy, for the isolation of new therapeutic drugs, and has potential utilization value for use as a therapeutic agent in physiological fluids.
Owner:RIGEL PHARMA
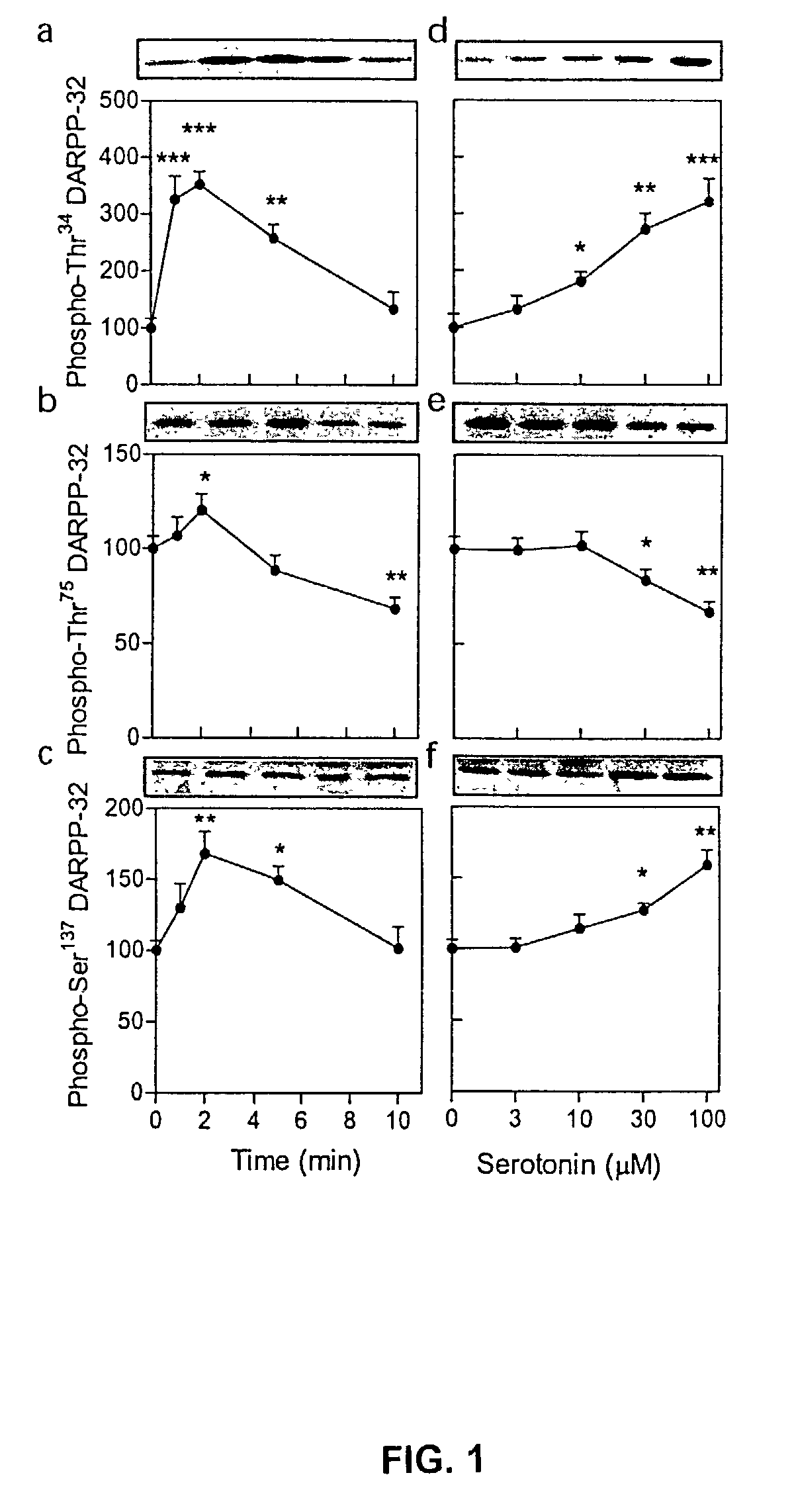
Compositions and methods for modulation of DARPP-32 phosphorylation
InactiveUS7320785B2Easy to optimizeModulate activityBiocideOrganic active ingredientsSignalling moleculesSignalling pathways
The present invention provides methods and compositions for modulating the phosphorylation of DARPP-32 in a serotonergic receptor intracellular signaling pathway. The invention provides methods and compositions for modulating the activities of DARPP-32, casein kinase 1 (CK1), cyclin-dependent kinase 5 (Cdk5), AMPA receptors, protein phosphatase-1 (PP-1), protein phosphatase 2C (PP2C), protein phosphatase 2B (PP2B) and / or protein phosphatase 2A (PP2A) in cells or tissues. The invention provides methods of treating serotonergic intracellular signaling pathway disorders, e.g., depression. The invention provides methods of treating dopamine-related disorders. The invention provides methods of identifying agents that modulate the activities of serotonergic receptor intracellular signaling molecules, DARPP-32, casein kinase 1, cyclin-dependent kinase 5, AMPA receptors, protein phosphatase-1, protein phosphatase 2C, protein phosphatase 2B and / or protein phosphatase 2A, for use in such treatments. The invention also provides methods of modulating phosphorylation-dependent activation of AMPA receptors for use in such treatments.
Owner:MOBILITY +1
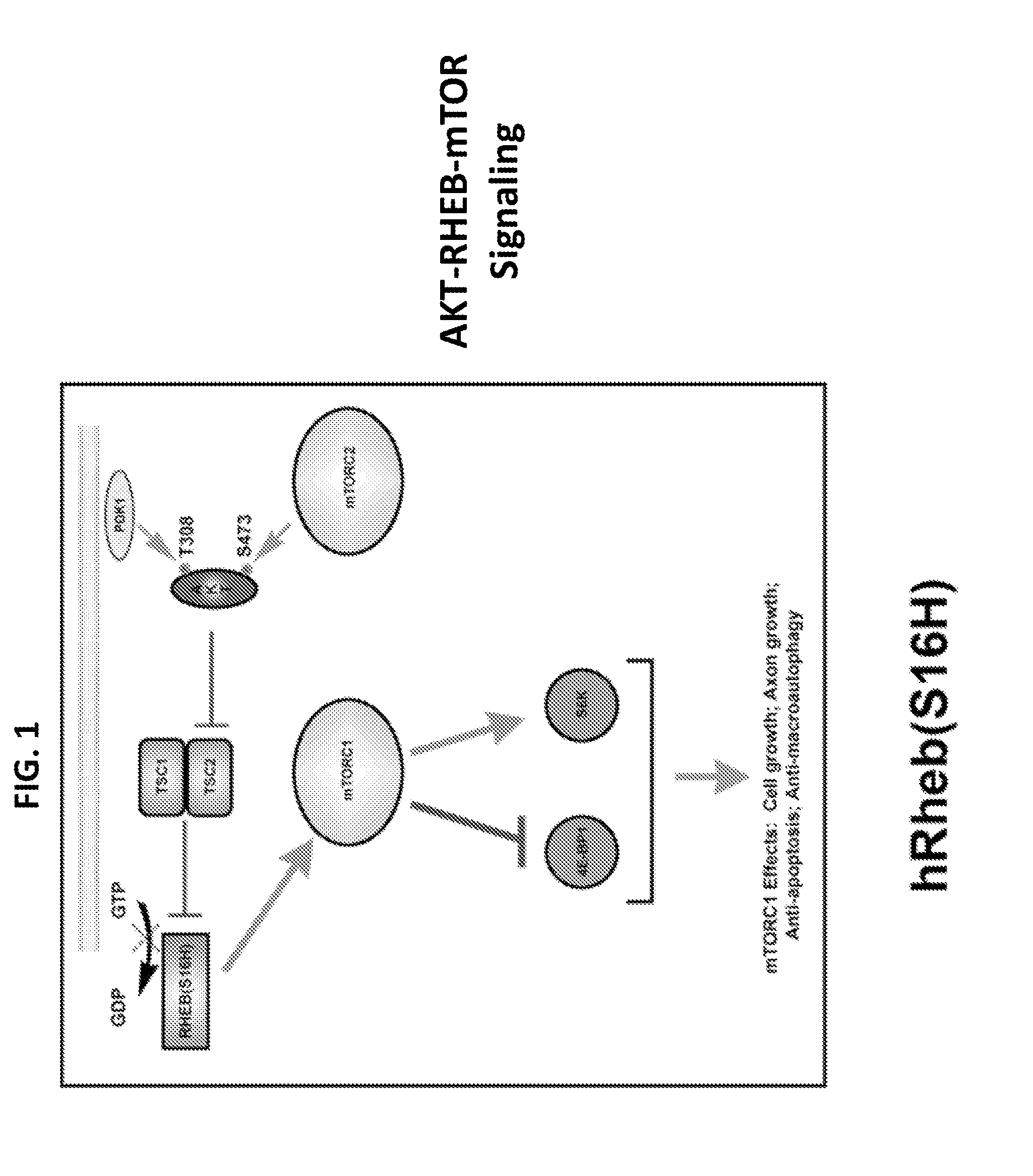
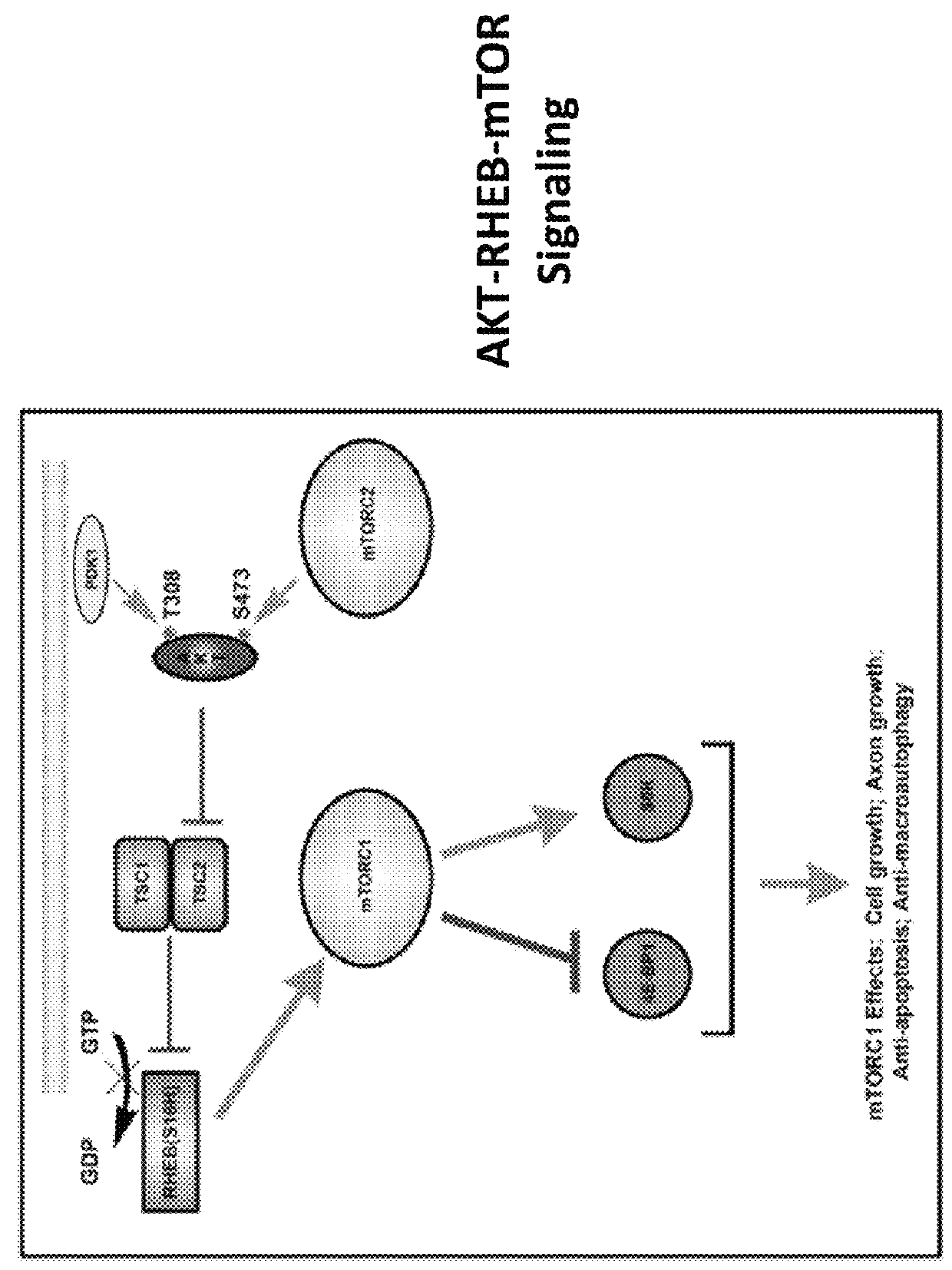
Gene Delivery Vehicles in the Treatment of Neurodegenerative Diseases
ActiveUS20140100265A1Promoting axon regenerationSugar derivativesPeptide/protein ingredientsGene deliveryAxon growth
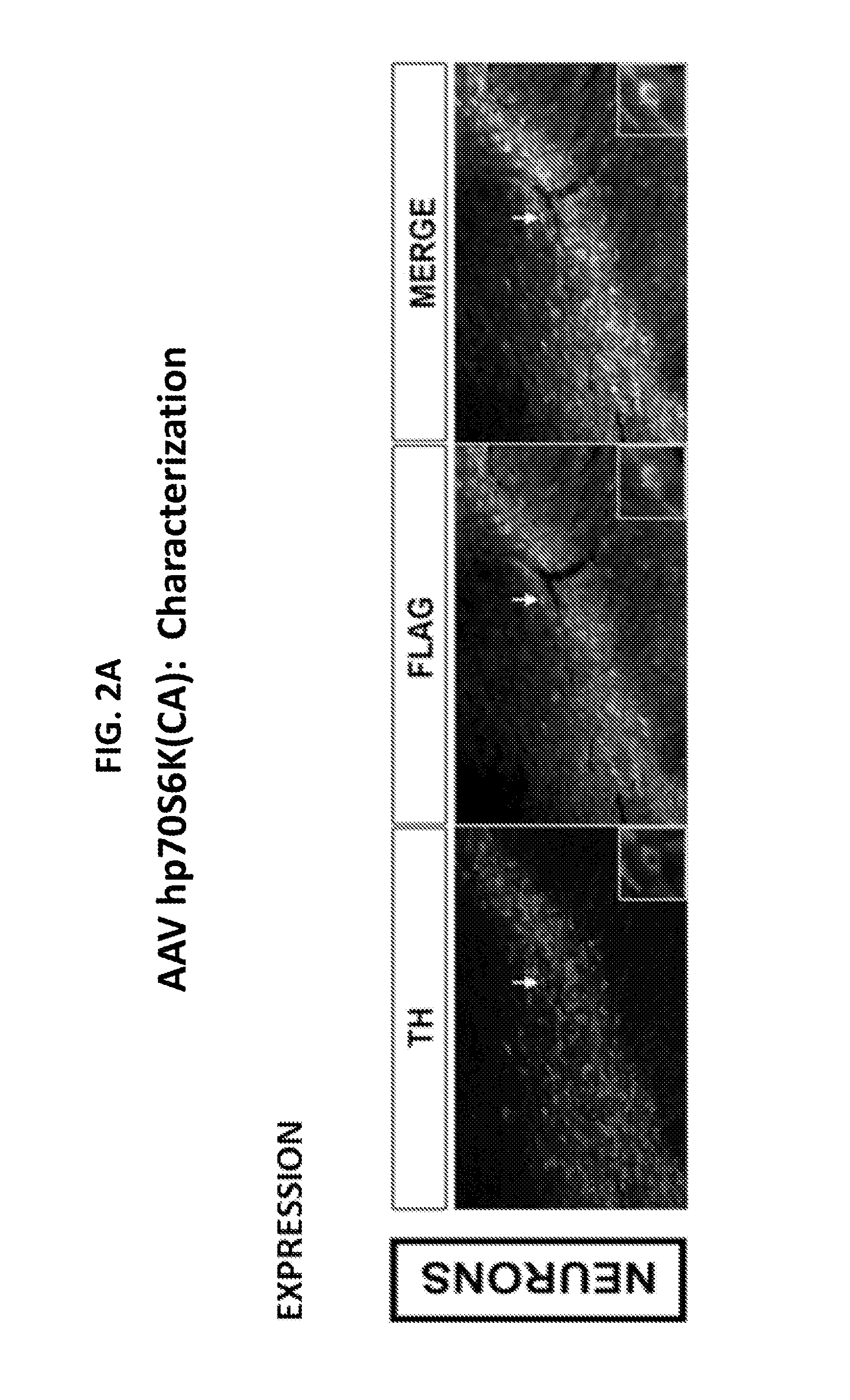
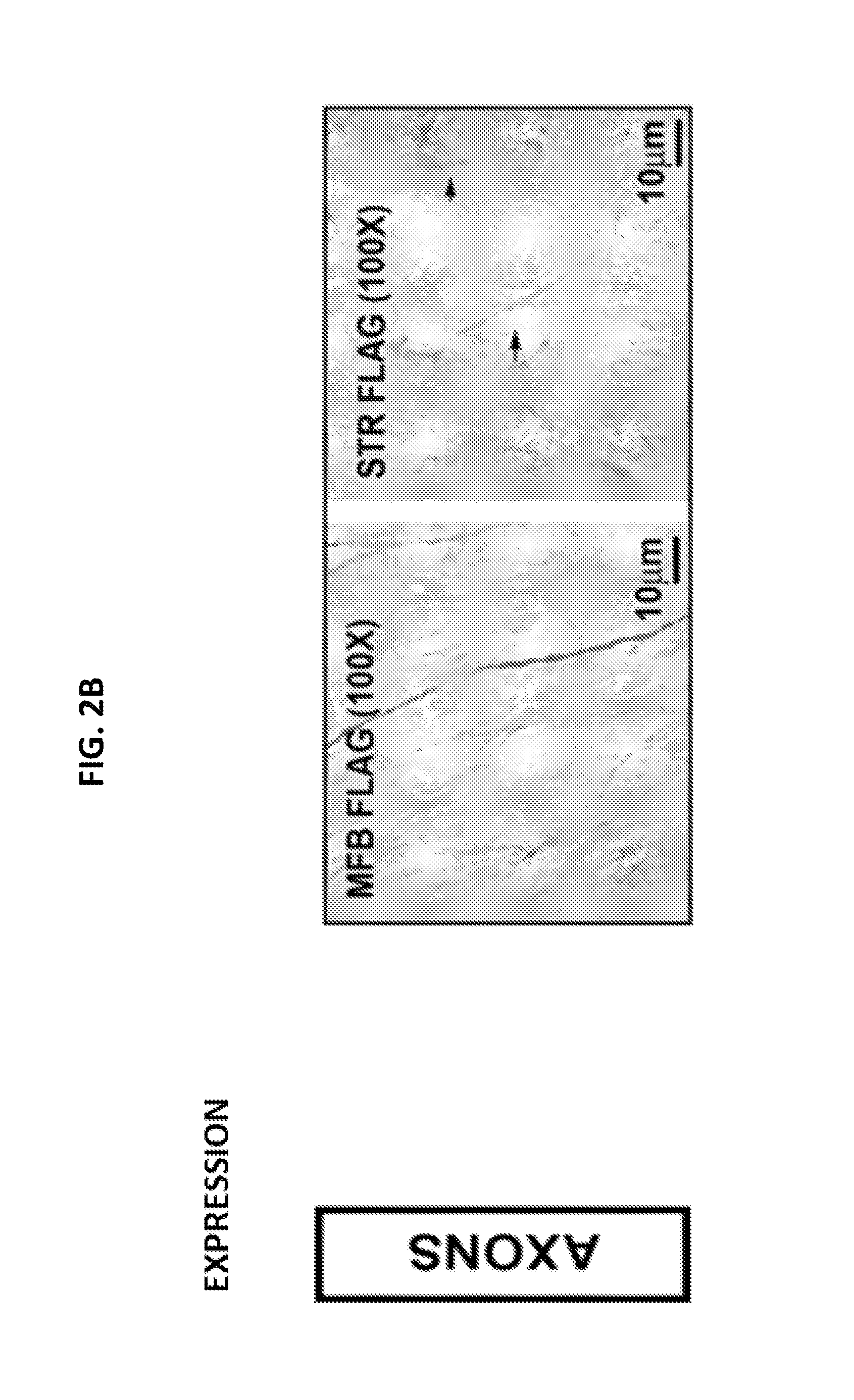
Currently no therapies that provide either protection or restoration of neuronal function for adult onset neurodegenerative diseases such as Parkinson's disease exist. Many clinical efforts to provide such benefits by infusion of neurotropic factors have failed. An alternative approach such as viral construct transduction may be used to directly activate the intracellular signaling pathways that mediate neurotrophic effects and induce axon growth. Viral construct transduction of dopaminergic neurons with a constitutively active human form of the p70S6K gene—hp70S6K (CA)—was shown to induce axon regeneration from living dopaminergic cell bodies that had no living axons.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
Bone mineralization protein expression systems, and methods of studying intracellular signaling pathways induced thereby
The present invention is directed to methods of switching a differentiation of a cell from a non-osteogenic lineage into an osteogenic lineage. The present invention is also directed to methods of generating a model system for assessing the intracellular signaling pathways of bone growth factors.
Owner:EMORY UNIVERSITY
Cell signal pathway detection kit and detection method based on mass spectrum flow technology
PendingCN111189761AAdd depthHigh precisionPreparing sample for investigationBiological particle analysisCell signaling pathwaysBiochemistry
The invention discloses a cell signal pathway detection kit and a detection method based on a mass spectrum flow technology. Through the kit and a matched signal pathway stimulant and a detection antibody, and by utilizing a mass spectrum flow detection technology, an intracellular signal path activation level can be specifically and effectively detected at a high throughput and a single cell level, the sample detection precision is greatly improved, and a false negative analysis result possibly existing in a traditional detection means is avoided to a great extent.
Owner:浙江普罗亭健康科技有限公司
Methods, systems, compositions and dosage forms for diagnosing and treating male infertility
Methods and systems are provided for diagnosing male infertility relating to inadequate production of phosphatidic acid and are complementary to the routine tests, assessing sperm count, motility, viability, head morphology, and white blood cell count. Additional therapeutic methods, compositions and dosage forms are provided for treating male infertility that is related to inadequate production of phosphatidic acid. Such therapeutic approaches involve the use of phosphatidic acid or at least one of its precursors in the sperm intracellular signaling pathway.
Owner:PEERION MEDICAL TECH
Brain blood vessel endothelial cell line for quickly detecting activity of classical Wnt signal channel
PendingCN110218740AImprove screening efficiencyImprove accuracyCompound screeningApoptosis detectionVirusSlow virus
The invention provides a preparing method of a brain blood vessel endothelial cell line for stably expressing TOP-Flash / Renilla dual-luciferase reporter genes. The preparing method comprises the following steps of 1, selecting cerebral microvascular endothelial cells, infecting the cerebral microvascular endothelial cells with a slow virus carrying a Renilla gene, and conducting screening to obtain a cell line for stably expressing Renilla; 2, infecting the cell line obtained in step 1 with a slow virus carrying a TOP-Flash gene, and conducting screening to obtain the brain blood vessel endothelial cell line for simultaneously stably expressing the Renilla and TOP-Flash dual-luciferase reporter genes. The brain blood vessel endothelial cell line can be used for screening active substancesfor activating the activity of a Wnt signal channel in the brain blood vessel endothelial cells, the screening efficiency and accuracy are improved, and the preparing method is simple.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH
Natural immune receptor TLR5S gene of Saddletail grouper and novel application of protein encoded with natural immune receptor TLR5S gene
InactiveCN108997491AAntibacterial agentsCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsBiotechnologyInflammatory factors
The invention discloses a natural immune receptor TLR5S gene of Saddletail grouper and application of a protein encoded with the natural immune receptor TLR5S gene in the aspects of identifying bacterial flagellum, regulating intracellular signal pathways and adjusting inflammatory factors. The natural immune receptor TLR5S gene has the advantages of being beneficial for knowing pathogenic microorganisms resistant to a fish body and even a physiological process of vibrio invasion and providing a scientific evidence and a practice foundation for studies on fish immunology, prevention of diseases and the like in production application. Additionally, the natural immune receptor TLR5S gene can be prepared into a drug with an effect of resisting the multiplication of vibrio patahaemolyticus inthe production application, and the natural immune receptor TLR5S gene can also be applied as an immunopotentiator.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Novel application of dictamnine
InactiveCN108159046ANo obvious side effectsInhibition of activationOrganic active ingredientsImmunological disordersPhosphorylationBiological activation
The invention discloses novel application of dictamnine, in particular to application of the dictamnine in preparing type I hypersensitivity reaction drugs caused by mast cell activation, and belongsto the field of pharmaceuticals. According to the dictamnine disclosed by the invention, by constructing a C48 / 80 induced P815 mast cell in vitro inflammatory model, the dictamnine is found to have the effects of inhibiting the activation of mast cells, effectively inhibiting the degranulation degree of the mast cells in a sensitized state and alleviating the release of beta-hexosaminidase; the expression of inflammatory genes IL-4, IL-6, IL-12 and IL-13 in the mRNA level can be inhibited; in addition, the phosphorylation level of ERK in an intracellular signaling pathway can be significantlyinhibited.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Application of METTL3 inhibitor in preparation of medicine for inhibiting PI3K/Akt and ERK1/2 signal channels
PendingCN114177297ASpeed up progressPrevent proliferationOrganic active ingredientsAntineoplastic agentsSide effectPharmaceutical drug
The invention discloses application of an METTL3 inhibitor in preparation of a medicine for inhibiting PI3K / Akt and ERK1 / 2 signal channels, belongs to the technical field of intracellular signal channels, and aims to solve the problem that the existing PI3K / Akt and ERK1 / 2 signal channel inhibitors have side effects. The invention relates to an application of an METTL3 inhibitor in preparation of drugs for inhibiting PI3K / Akt and ERK1 / 2 signal pathways. Knock-down of METTL3 can inhibit proliferation of colon cancer cells, invasion, migration and clone formation of colon cancer cells, expression of EphA2 and VEGFA, and formation of vascular mimicry. The method is applied to the field of screening of colon cancer targeted drugs.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Application of cyclic erythropoietin-derived peptide in protection of renal injury and cyclosporine A injury
PendingCN112076309AImprove survival rateCompounds screening/testingMicroencapsulation basedApoptosisThelial cell
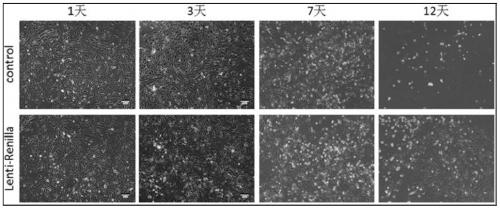
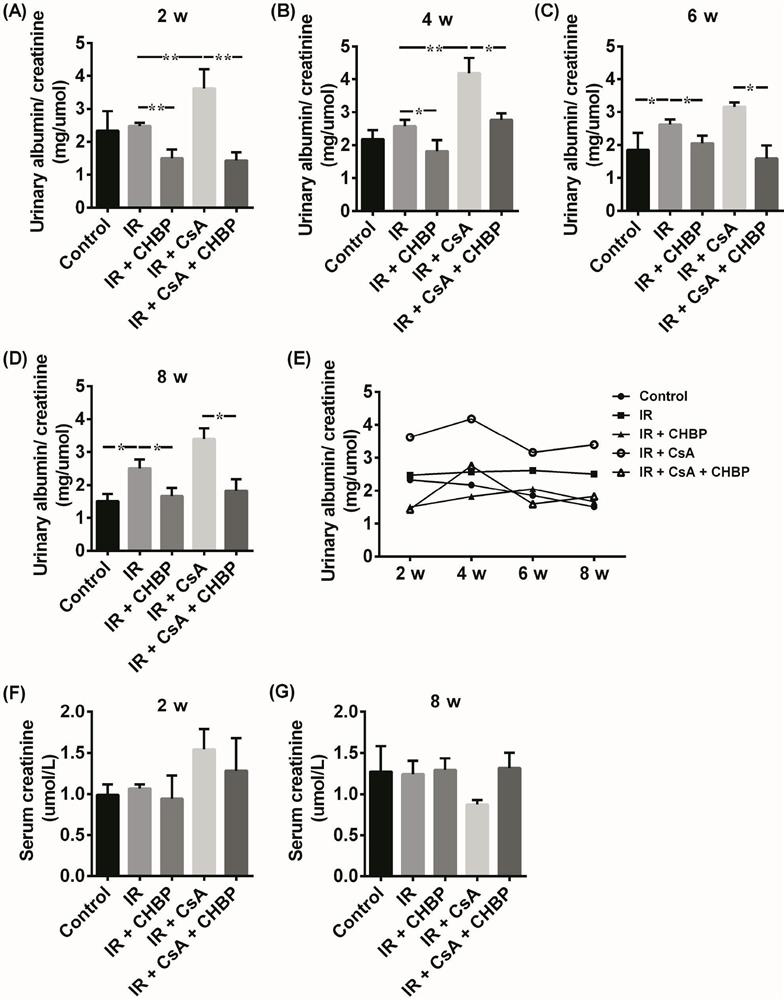
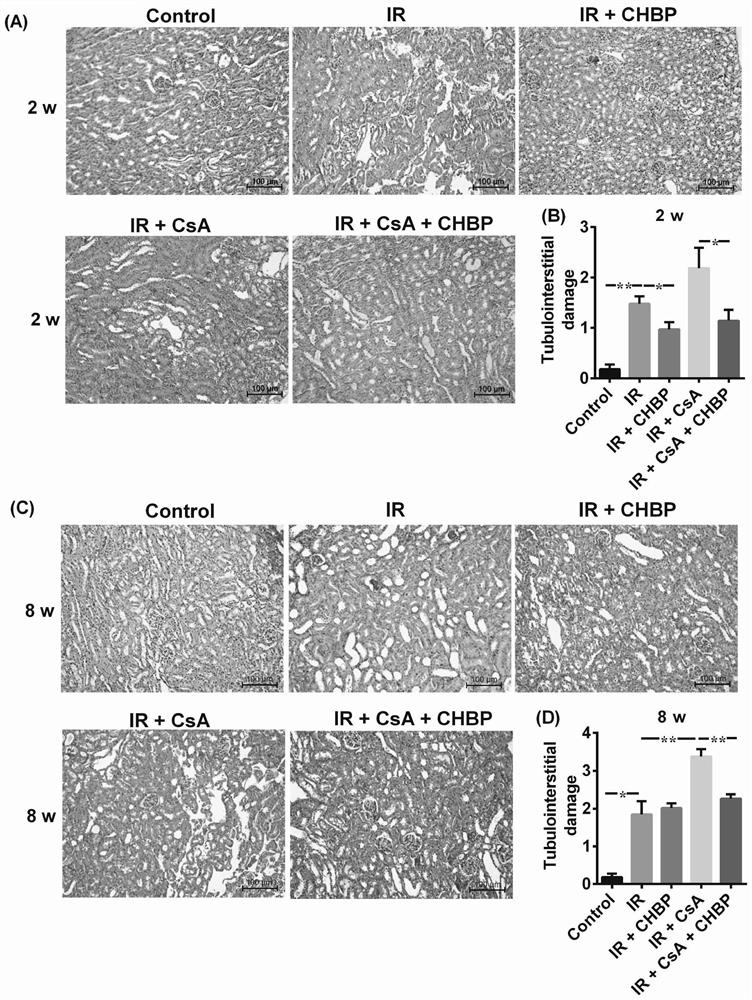
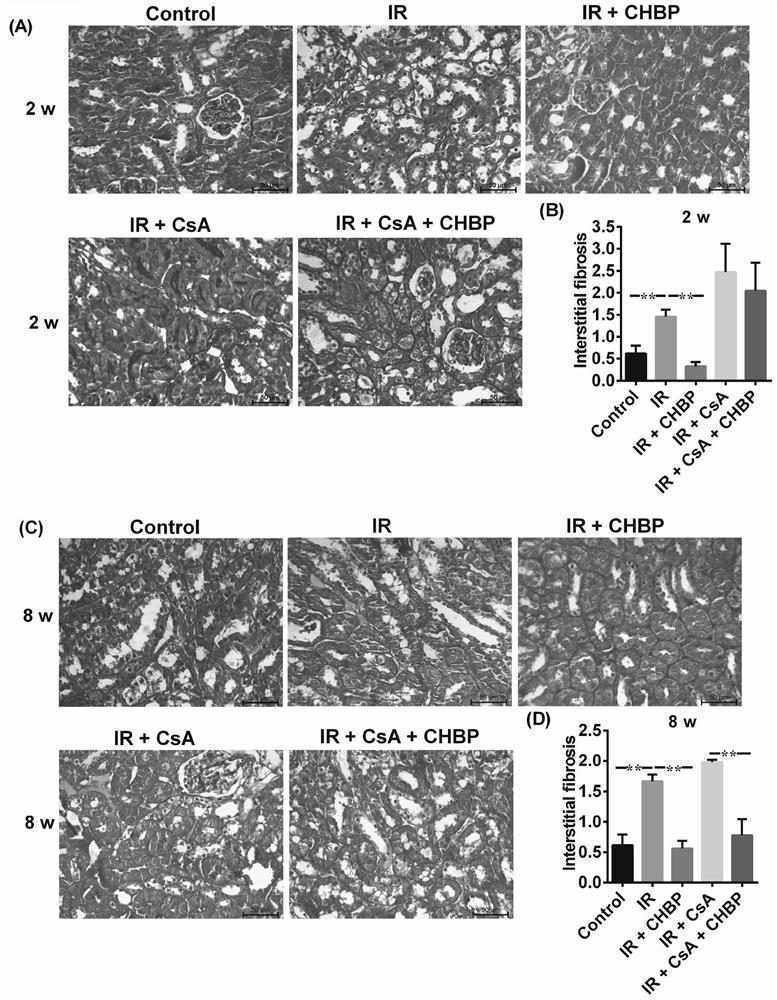
The invention discloses application of a cyclic erythropoietin-derived peptide in protection of renal injury and cyclosporine A injury. In a control group, the abdominal cavity and renal pedicle are exposed; in IR, two renal pedicles are separated, and are clipped with a vessel clamp for 30 minutes to enable color of the kidneys to be changed, and refilling is performed for 2 or 8 weeks; in IR plus CsA, CsA is dissolved in olive oil, and IR mice are subjected to intragastric administration every day; in IR plus CHBP, CHBP is dissolved in saline water, and the IR mice are subjected to intraperitoneal injection every three days; in IR plus CsA plus CHBP, CsA and CHBP are used for treating the IR mice at the same time; urine albumin / creatinine, serum creatinine, histology, apoptosis, caspase-3 and HMGB1 are evaluated, and intracellular signal channels are screened through a protein chip; and a renal epithelial cell model is established, renal injury is simulated, and the influence of CsA,CHBP and / or caspase-3 siRNA on TCMK1 is studied.
Owner:NANTONG UNIVERSITY +1
Methods, Systems, Compositions And Dosage Forms For Diagnosing And Treating Male Infertility
InactiveUS20110002907A1Increase opportunitiesImprove abilitiesBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsWhite blood cellMALE INFERTILITY DISORDERS
Methods and systems are provided for diagnosing male infertility relating to inadequate production of phosphatidic acid and are complementary to the routine tests, assessing sperm count, motility, viability, head morphology, and white blood cell count. Additional therapeutic methods, compositions and dosage forms are provided for treating male infertility that is related to inadequate production of phosphatidic acid. Such therapeutic approaches involve the use of phosphatidic acid or at least one of its precursors in the sperm intracellular signaling pathway.
Owner:PEERION MEDICAL TECH
System, method and software for analysis of intracellular signaling pathway activation using transcriptomic data
InactiveUS20170262576A1Rapid personalized analysisMicrobiological testing/measurementSystems biologySignalling pathwaysGene product
The present invention provides systems, methods and software for analysis of the intracellular signaling pathway activation (SPA), the method including analyzing activator and repressor roles of a plurality of gene expression gene products in a plurality of pathways in a sample of a subject to determine a pathway activation strength (PAS) for each of the plurality of pathways and comparing the pathway activation strength (PAS) in at least one sick subject with at least one healthy subject to determine intracellular signaling pathway activation (SPA) associated with a disease or disorder in the at least one sick subject.
Owner:ALFA LTD
System, method and software for analysis of intracellular signaling pathway activation using transcriptomic data
The present invention provides systems, methods and software for analysis of the intracellular signaling pathway activation (SPA), the method including analyzing activator and repressor roles of a plurality of gene products in a plurality of pathways in a sample of a subject to determine a pathway activation strength (PAS) for each of the plurality of pathways and comparing the pathway activation strength (PAS) in at least one sick subject with at least one healthy subject to determine intracellular signaling pathway activation (SPA) associated with a disease or disorder in the at least one sick subject.
Owner:ALFA LTD
Anti-il1rap antibodies and methods of use thereof
The present invention provides binding proteins, such as antibodies and antigen-binding fragments, which specifically bind to human interleukin-1 receptor accessory protein (hu-IL1RAP) and fully block the IL-1, IL-33, and IL-36 intracellular signaling pathways. Compositions comprising such binding proteins and methods of making and using such binding proteins are also provided.
Owner:23和我公司
Novel bone mineralization protein expression systems, and methods of studying their intracellular signaling pathways
InactiveUS20080254001A9Good curative effectEasy assessment processBiocideVirusesModel systemBone growth factor
Owner:EMORY UNIVERSITY
Materials and methods for treatment of cancer and identification of anti-cancer compounds
Owner:SOUTH FLORIDA UNIVESITY OF
Use of L-Plastin gene
InactiveCN109234377AMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationInflammatory factorsPhosphorylation
The invention discloses the use of an L-Plastin gene, which is an application of the L-Plastin gene as a drug target in screening a type I hypersensitivity targeted therapeutic inhibitor, and the invention is induced by constructing a sensitizer C48 / 80 The P815 mast cell in vitro allergy model found that L-Plastin knockdown has the effect of inhibiting mast cell activation, can effectively inhibitthe degree of degranulation of mast cells in sensitized state, and relieve the release of histamine and beta-hexosaminidase Represses the synthesis and secretion of inflammatory factors; inhibits theexpression of inflammatory genes and the expression of key receptors in the mast cell activation pathway, and significantly inhibits the RAF-MEK-ERK signaling pathway and inhibits AKT in the intracellular signaling pathway. Phosphorylation levels have been shown to have anti-allergic effects at the cellular level, providing a theoretical basis for clinical treatment of type I hypersensitivity reactions and the application of screening for new drug targets.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Intracellular signaling pathways in diabetic subjects
The present invention provides for methods of identifying subjects with a predisposition towards, or the existing condition of, type II diabetes. The methods involve examination of at least three human gene products—Fab1p, Vac14p and Fig4p—each of which play an important role in the insulin-response pathway. In addition, the invention provides methods for screening of potential therapeutic compounds, and methods for the treatment of type I and II diabetes.
Owner:UNIV OF IOWA RES FOUND
A method for regulating cell pathways by using plant hormone GA and small molecular substance pac
The invention provides a method for regulating cell pathway by using plant hormone GA and small molecular substance PAC, and realizes the regulation switch of signal pathway in human cells. The GA receptor proteins GID1 and GAI in Arabidopsis thaliana were constructed on a human cell expression vector, and then transferred into HEK293T cells together. GA was added to induce the interaction between the two proteins. After adding the inhibitor PAC, the degree of interaction would be weakened. In this way, the key proteins in the human cell signaling pathway are fused and expressed with these two receptor proteins. The two receptor proteins interact under the induction of GA, and the fusion signaling pathway is also induced by GA. The present invention selects the key protein LRP6 on the human Wnt pathway. After the fusion expression of GA receptor and LRP6, LRP6 will aggregate under the induction of GA, thereby promoting the production of β-catenin and opening the intracellular signaling pathway. After adding PAC inhibition, the production of β-catenin is reduced and the cell pathway is closed.
Purpose of Rap1b gene
InactiveCN109295199AHydrolasesMicrobiological testing/measurementInflammatory factorsPhosphorylation
The invention discloses a purpose of a Rap1b gene, which is characterized in that the Rap1b gene is used as a drug target in screening of anti-type I hypersensitivity drugs; by establishing an in-vitro allergy model of P815 mast cells induced by a sensitizer C48 / 80, the knockout of Rap1b has the function of promoting the activation of mast cells, which is characterized in that Rap1b can alleviatea degranulation reaction of mast cells under a sensitized state, inhibits the release of tryptase and beta-hexosaminidase, inhibits the synthesis and secretion of inflammatory factors, and inhibits the expression of inflammatory genes at a mRNA level; knockout of Rap1b activates a MAPK signal pathway and promotes phosphorylation of AKT, which demonstrates that Rap1b inhibits MAPK and AKT signal pathways in intracellular signal pathways, provides a theoretical basis for clinical treatment of type I hypersensitivity reactions, and screens the novel drug targets.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH +1
Use of chemical compounds that can inhibit the toxic activity of sphingomyelinase D from venoms of Loxosceles spiders and pharmaceutical composition comprising said compounds
ActiveUS9833444B2Improve performanceRaise the ratioOrganic active ingredientsAntinoxious agentsFuranHaemolysis
The present invention relates preferably to the use of 4-bromo-N-[(E)-(2-methyl-1H-indol-3-yl)methyleneamino]benzenesulphonamide and 4-methyl-3-oxo-2-(3-pyridylmethylene) benzo[3,4-b]furan-6-yl-4-chlorobenzenesulphonate (compounds 5 and 6, respectively), which are compounds that can inhibit the toxic activity of sphingomyelinase D from Loxosceles venom, controlling the development of cutaneous and systemic loxoscelism; reducing haemolysis; inhibiting the formation of skin lesions; inhibiting skin necrosis; inhibiting intracellular signaling pathways and the production of reactive oxygen species. In addition to the therapeutic potential thereof, said inhibitors can be used to study the activity of sphingomyelinases and phospholipases D. The present invention also relates to a pharmaceutical composition for treating loxoscelism, reducing haemolysis, inhibiting the formation of skin lesions, inhibiting skin necrosis, inhibiting intracellular signaling pathways and the production of reactive oxygen species, comprising said compounds and a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier.
Owner:FUNDACAO BUTANTAN
Application of FAK (focal adhesion kinase) inhibitor in treatment of autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease
PendingCN110201171AInhibition formationGrowth inhibitionOrganic active ingredientsUrinary disorderMadin Darby canine kidney cellFocal adhesion
The invention proves, through the application of an MDCK (Madin-Darby canine kidney cells) vesicular model, that an FAK (focal adhesion kinase) inhibitor can inhibit the generation and growth of vesicles, can determine intrarenal pharmacological activity of the FAK inhibitor through an in-vitro embryonal vesicular model, and can inhibit the progress of intrarenal vesicles significantly. The invention further proves finally, in a polycystic renal mouse model, that the FAK inhibitor can also inhibit the progress of vesicles in vivo, while the in-vitro and in-vivo vesicular inhibitory actions arein dose-effect relationship. The FAK inhibitor never affects the activity of renal cells; it is indicated that the ability of the FAK inhibitor to polycystic kidney is irrelevant to its cytotoxicity,and that the FAK inhibitor can regulate intracellular signal pathways, which may be one of its important mechanisms to inhibit the progress of renal vesicles. The FAK inhibitor is VS4718 which is suitable for treating autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Gene delivery vehicles in the treatment of neurodegenerative diseases
Currently no therapies that provide either protection or restoration of neuronal function for adult onset neurodegenerative diseases such as Parkinson's disease exist. Many clinical efforts to provide such benefits by infusion of neurotropic factors have failed. An alternative approach such as viral construct transduction may be used to directly activate the intracellular signaling pathways that mediate neurotrophic effects and induce axon growth. Viral construct transduction of dopaminergic neurons with a constitutively active human form of the p70S6K gene—hp70S6K (CA)—was shown to induce axon regeneration from living dopaminergic cell bodies that had no living axons.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
Application of compounds inhibiting htr3a and its intracellular signaling pathway in the preparation of drugs for treating and/or preventing AD
The present invention relates to the application of compounds inhibiting Htr3a and its downstream intracellular signaling pathways in the preparation of medicines for treating and / or preventing Alzheimer's disease. The present invention finds for the first time that the expression of Htr3a in Alzheimer's disease transgenic AD animals and AD patients is significantly increased, and the intracellular calcium (Ca 2+ ) and its downstream calcineurin activity (CaN) and transcription factor (NFAT) were significantly increased. In AD transgenic mice, inhibiting the function of Htr3a significantly reduces the production of Aβ-amyloid protein and reverses the intracellular signaling pathway Ca 2+ , CaN, and the transcription factor NFAT inhibited glial cell activation and reduced neuroinflammation. The present invention considers for the first time that Htr3a and its intracellular signaling pathway play an important role in the generation of β-amyloid plaques in AD, and regulating this pathway can prevent the progressive development of AD. Therefore, drugs targeting this pathway can prevent the process of AD, slow down the development of AD, and have great research and application prospects in the treatment of AD.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Judgment or evaluation method of test substance
ActiveCN102959400BGuaranteed efficacyMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisNeurotrophic factorsVaccinia
An object of the present invention is to provide a method for determination or evaluation of an extract from inflamed tissues inoculated with vaccinia virus where the enhancement of activation of neurotrophic factor such as BDNF in cultured cells or the enhancement of activation of proteins participating therein is used as an indicator. The present invention relates to a novel method for determination or evaluation of an extract from inflamed tissues inoculated with vaccinia virus and relates to a method for determination or evaluation of the extract where the enhancement of production of neurotrophic factor such as BDNF in cultured cells or the enhancement of activation of various proteins in intracellular signaling pathway participating in production of BDNF, etc. is used as an indicator. The present invention is highly useful as a simple, convenient and quick method for determination or evaluation for guaranteeing the quality of the extract which is useful as a pharmaceutical agent.
Owner:NIPPON ZOKI PHARM CO LTD
A kind of medicine for preventing or treating hepatitis B virus infection and its preparation method and application
ActiveCN109731095BNo side effectsMechanism diversificationPeptide/protein ingredientsDigestive systemSecreted antigensCell culture supernatant
Owner:佛山病原微生物研究院
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com