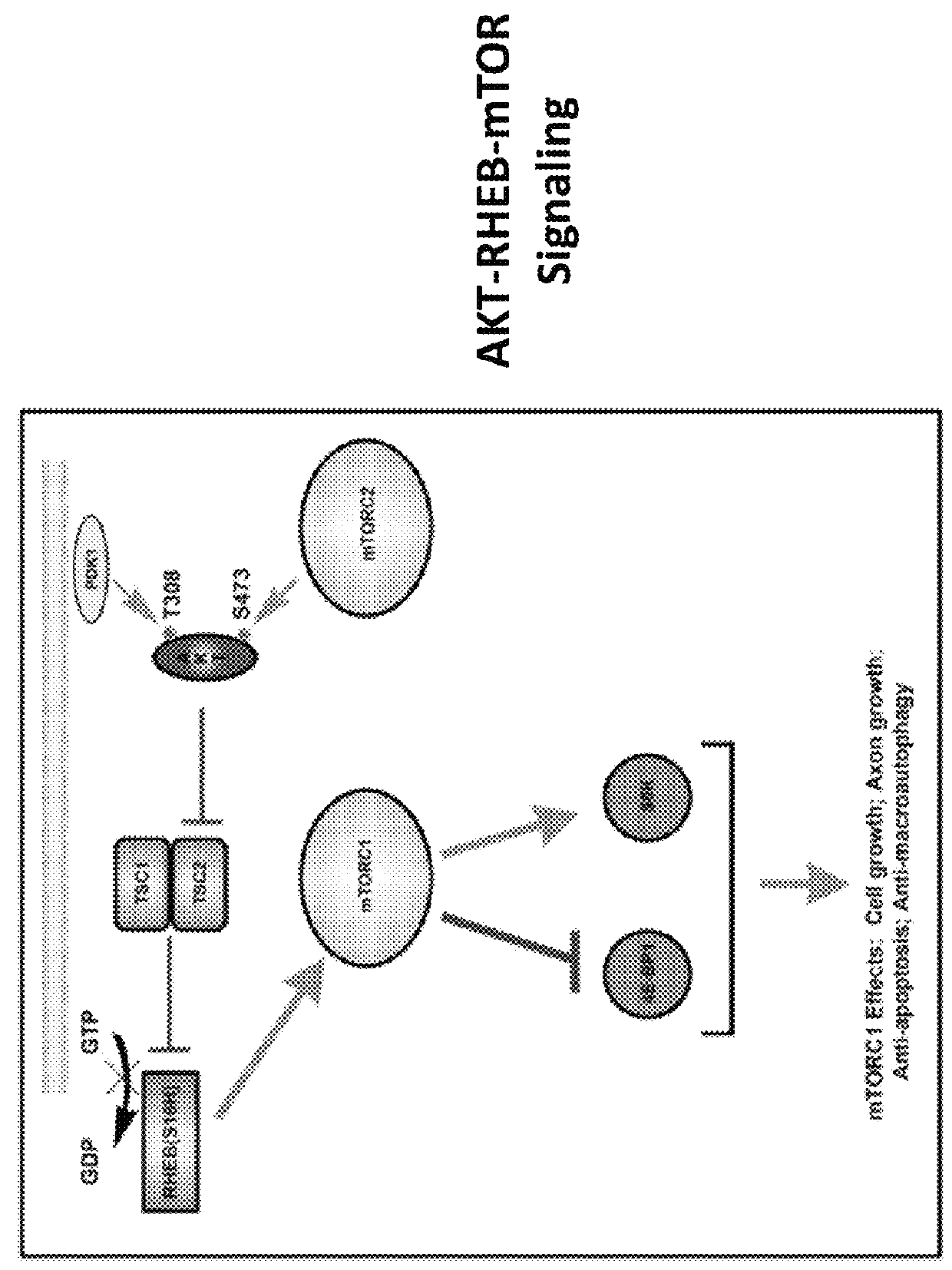
Gene delivery vehicles in the treatment of neurodegenerative diseases
a technology for neurodegenerative diseases and gene delivery, applied in the direction of genetic material ingredients, peptide/protein ingredients, transferases, etc., can solve the problems of no treatment that prevents deterioration, dyskinesia of involuntary abnormal movements in pd patients, cognitive impairment, etc., and achieve the effect of promoting axon regeneration
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Materials and Methods
Chemical Reagents
[0136]Chemical reagents were obtained from SIGMA. 6OHDA was obtained from Regis Laboratories in Illinois, but may be obtained from other companies.
Mice and Animal Care
[0137]Adult (8 week) male C57B1 / 6 mice weighing ˜25 g were obtained from Charles River Laboratories (Wilmington, Mass.). TH-GFP transgenic mice, which express green fluorescent protein driven by the tyrosine hydroxylase (TH) promoter (11) were generously made available by Drs. K. Kobayashi and H. Okano and maintained on a C57B1 / 6 background.
Institutional Review of Animal Protocols
[0138]All injection procedures, described below, were approved by the Columbia University Animal Care and Use Committee.
Production of Adeno-Associated Virus (AAV) Viral Construct Hp70S6K(CA)
[0139]All viral constructs used for these studies were AAV1 serotype. The cDNA clone for wild type human p70S6K was obtained from OriGene Technologies (Catalogue No.; Accession No. NM_003161). A constitutively active mu...
example 2
Mediators of Axon Growth in the Dopaminergic Nigro-Striatal Projection
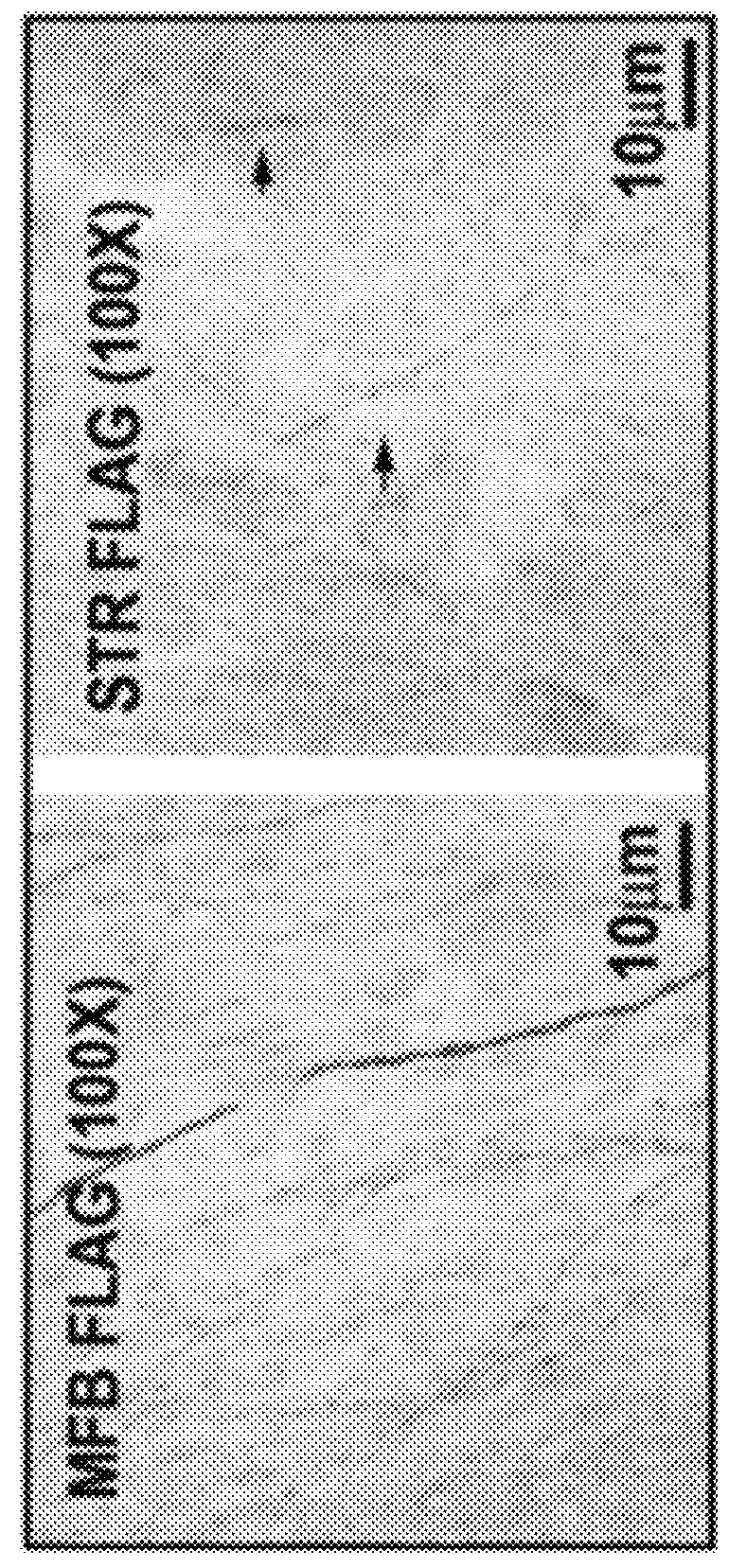
[0147]At time=0, mice received a unilateral intra-striatal injection of 6-OHDA. At time=3 weeks, the mice received either AAV-p70S6K(WT) or AAV-p70S6K(delC / T389E) (also referred to herein as AAV-p70S6K (CA)) or control AAV-GFP. At Time=15 weeks (12 weeks post AAV) mice were sacrificed by perfusion fixation and immunostaining for TH on coronal SN and striatal sections were performed. Transduction of the substantia nigra pars compacta (SNpc) dopamine neurons with AAV-hp70S6K(CA) was demonstrated by immunoperoxidase staining for the FLAG epitope, and by double immunofluorescence labeling for FLAG and tyrosine hydroxylase (TH) (FIG. 2A).
[0148]The number of remaining SN dopamine neurons were determined by sterologic counting. The density of TH immunoperoxidase staining in the lesioned striatum was determined, and expressed as a percent of the optical density of the contralateral, non-lesioned striatum, which serves as ...
example 3
AAV-hp70S6K(CA) Effects in Normal Adult Mice
[0150]The effects of AAV-hp70S6K(CA) transduction of normal adult, non-lesioned mice are shown in FIG. 3A-D. An increased density of immunostaining for TH in the striatum was seen and it is most likely due to the induction of sprouting of dopaminergic nerve fibers in the striatum. In normal mice, AAV-hp70S6K(CA) did not induce the formation of new axons. Morphologic analysis of SN dopamine neurons at 5-6 weeks after intranigral injection of AAV-hp70S6K(CA) was conducted using tyrosine hydroxylase (TH) immunoperoxidase staining and thionin counterstaining. The experimental side injected with AAV-hp70S6K(CA) shows an increased density of staining that is associated with an increase in the mean area of the TH-positive neurons FIG. 3(A). A morphologic analysis of the striatum of these AAV-hp70S6K(CA) transduced animals at 5-6 weeks is shown in FIG. 3B. FIG. 3C is a morphologic analysis of the corpus striatum at 5-6 weeks after intranigral inje...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| time | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| volume | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com