Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
100 results about "Imaging brain" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Neuroimaging or brain imaging is the use of various techniques to either directly or indirectly image the structure, function/pharmacology of the nervous system.
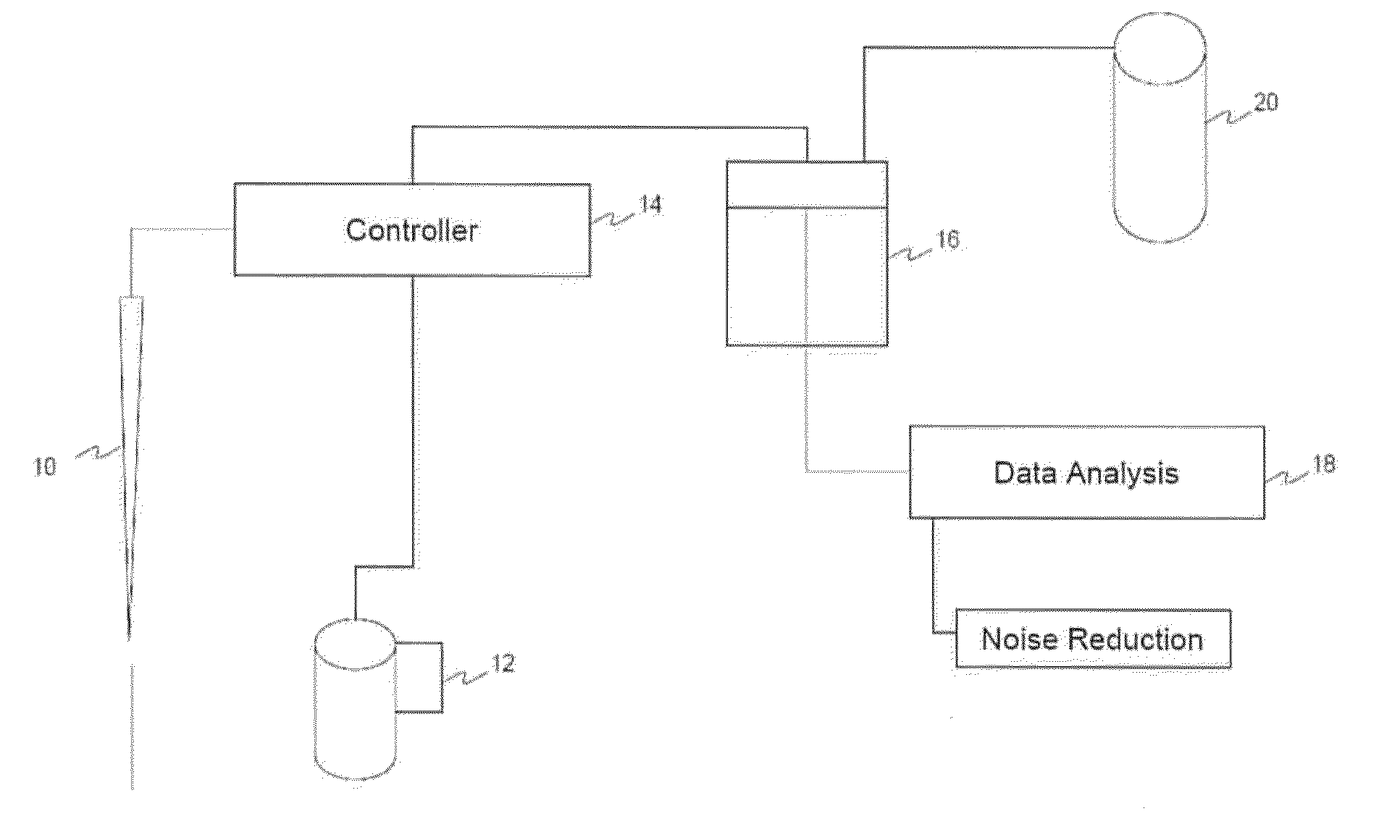
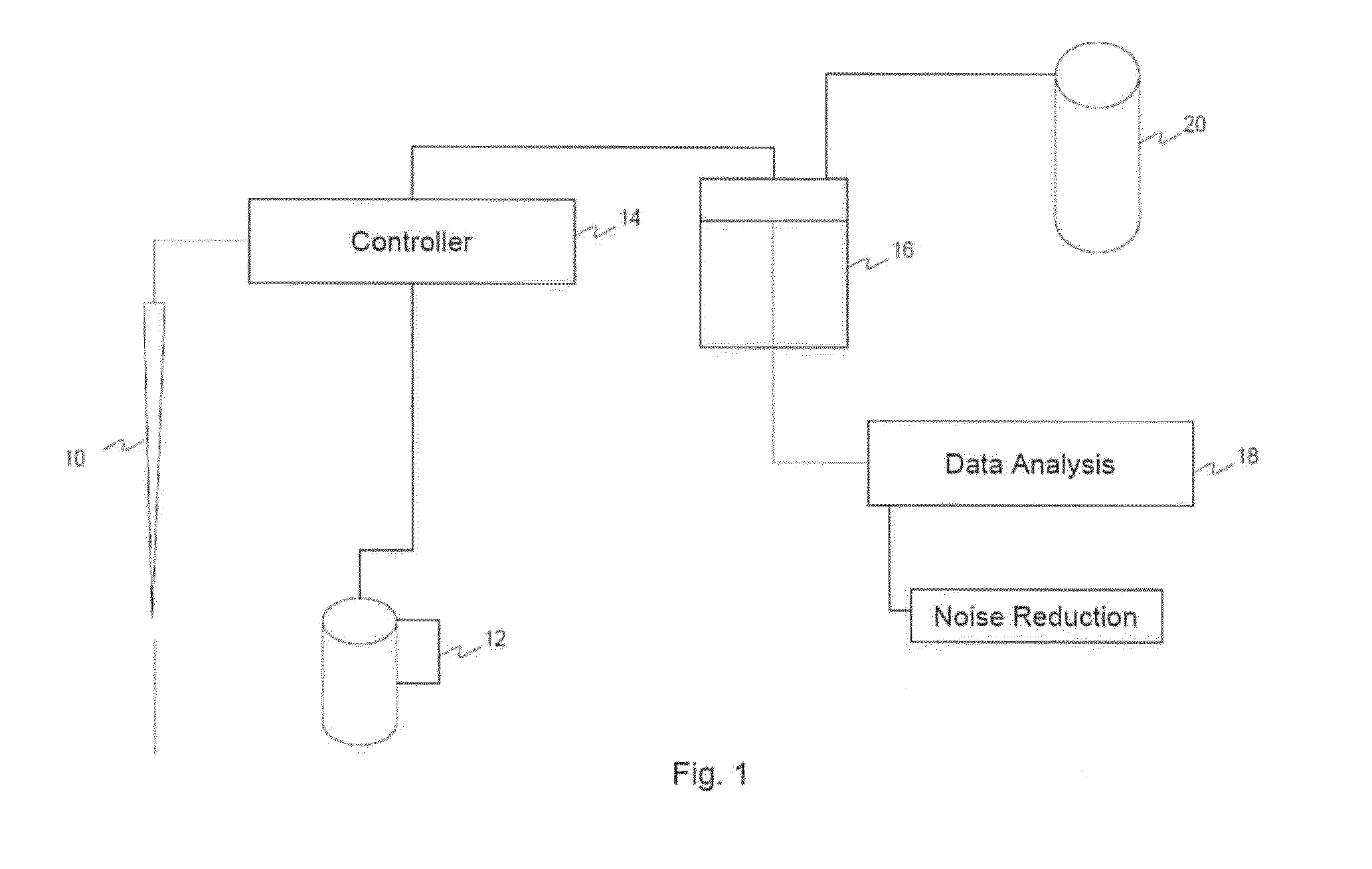
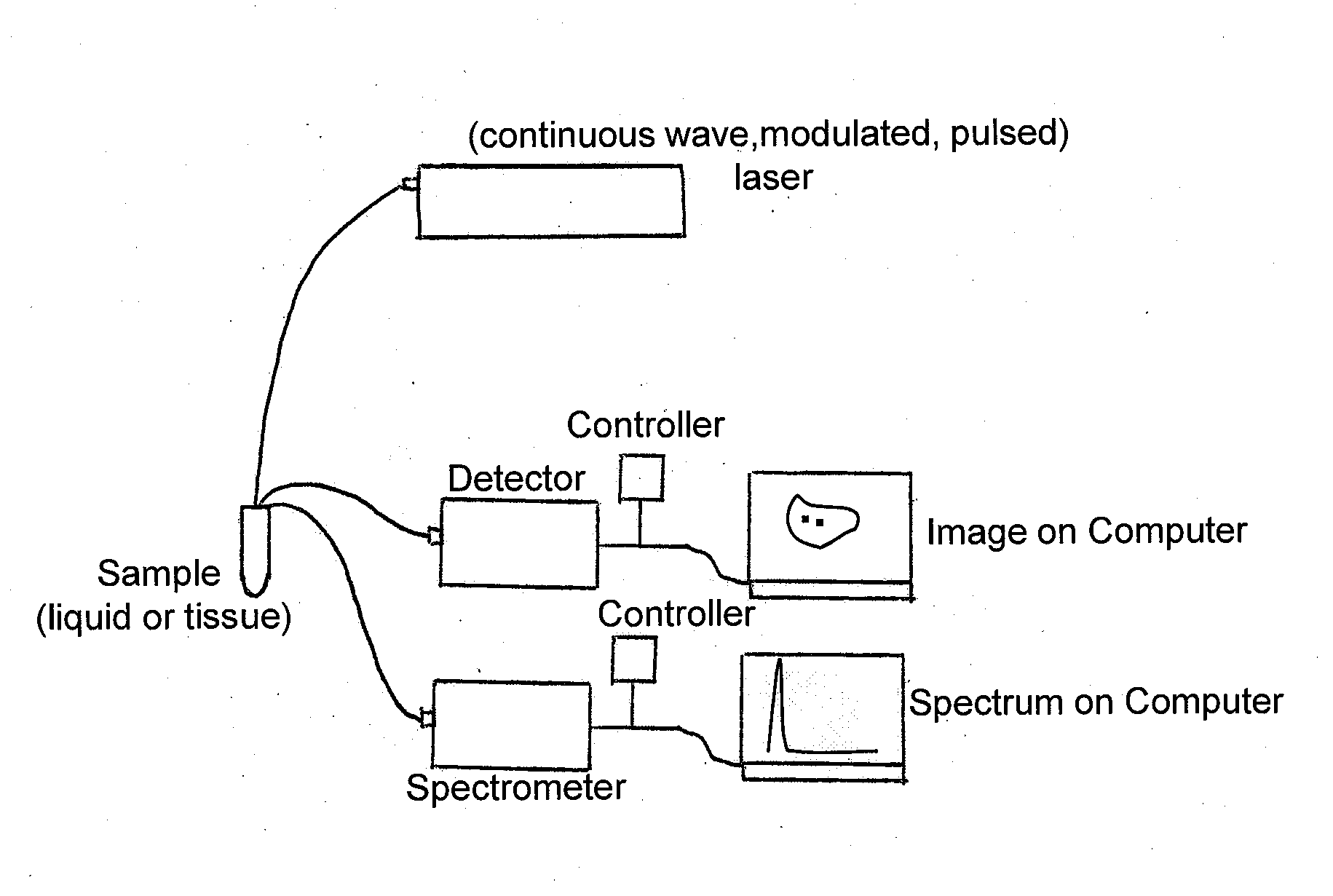
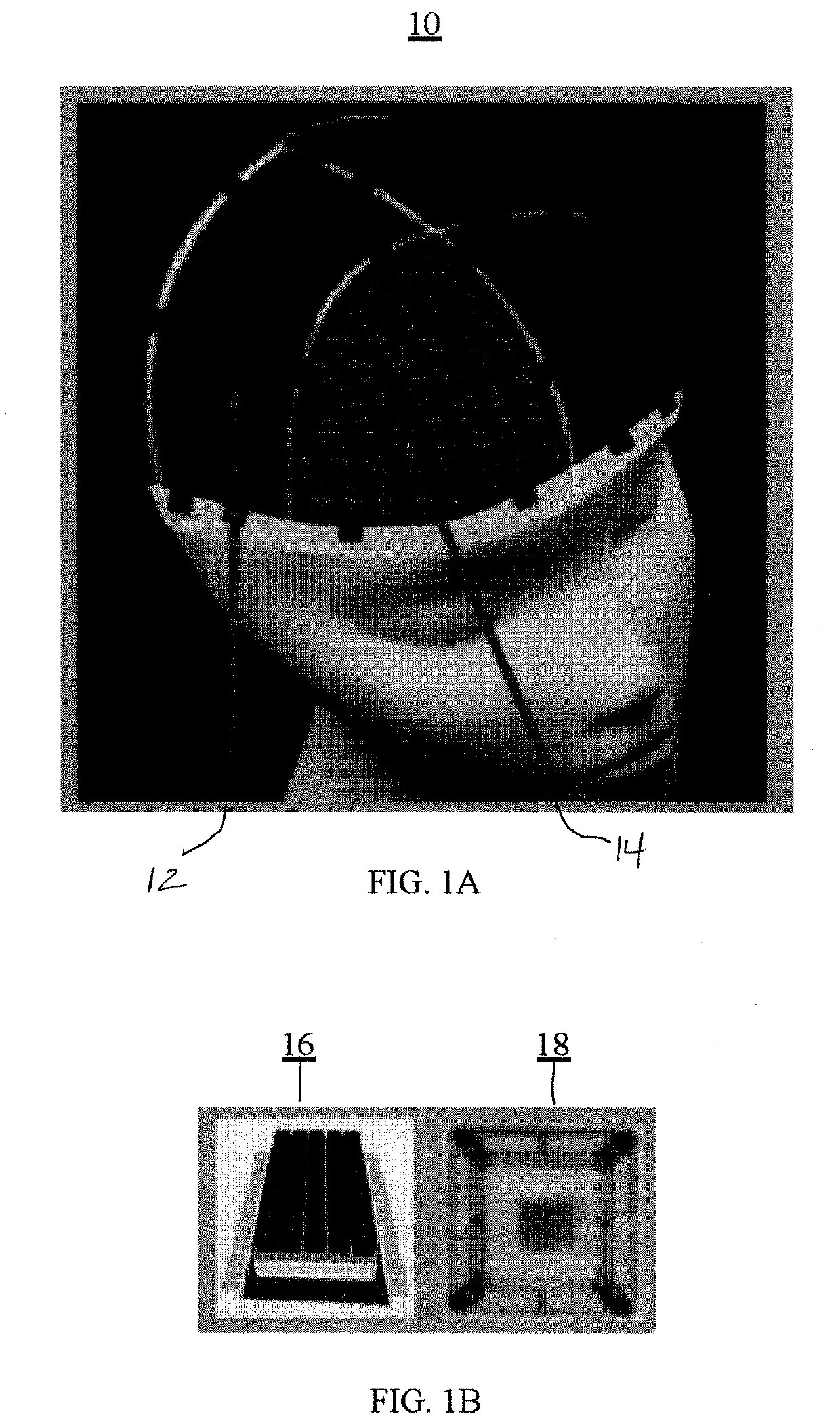
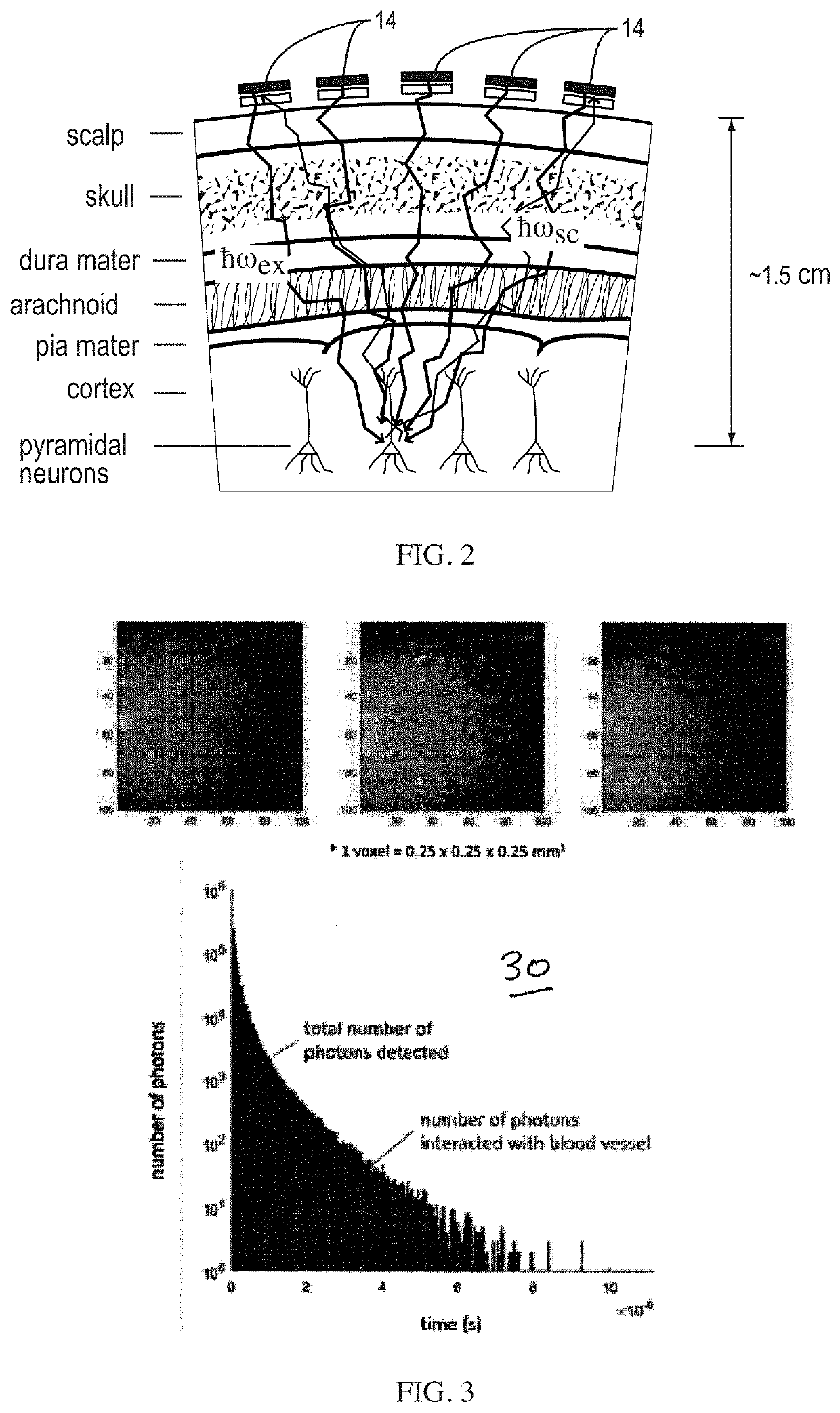
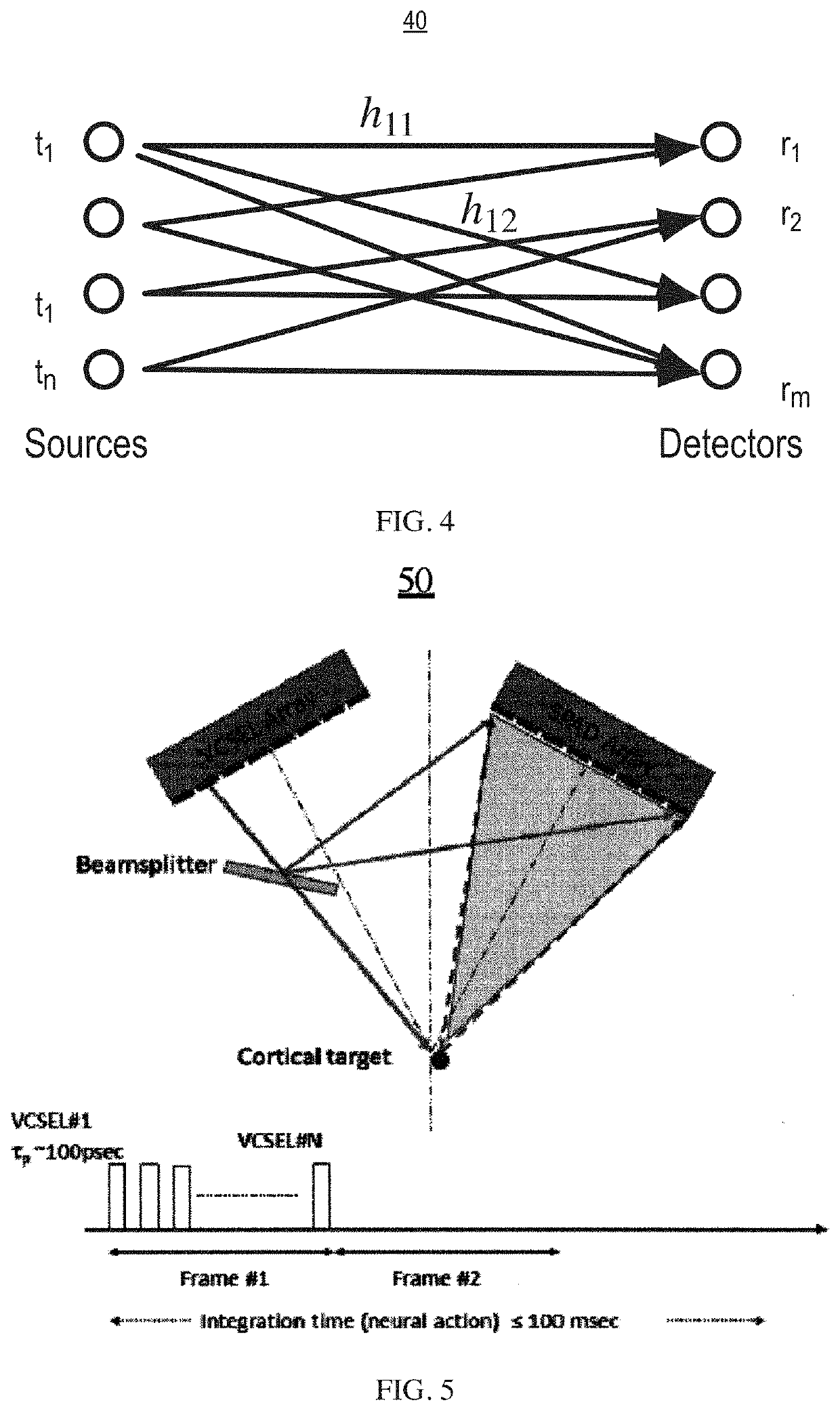
Real-time multimode neurobiophysiology probe
Apparatus and methods in which very small volumes of material may be extracted, delivered, interrogated or stimulated via optical, electromagnetic or mechanical means, in vivo or in vitro, for site-specific detection, characterization, stimulation, diagnostics or therapy, comprising optical, fluidic, chemical, electromagnetic and biological techniques applied via a microprobe in a single intra-parenchymal tissue perforation procedure in the brain. The primary use of the device is in neuroscience research, clinical diagnostics and therapeutics applications in the brain, however, the device may also be beneficially applied to other organs and biological systems. Human clinical applications may include neurosurgical intra-operative monitoring, extra-operative chronic monitoring of devices introduced in an operation, and diagnostic monitoring combined with simultaneous neuroimaging.
Owner:BLUMENFELD WALTER +2
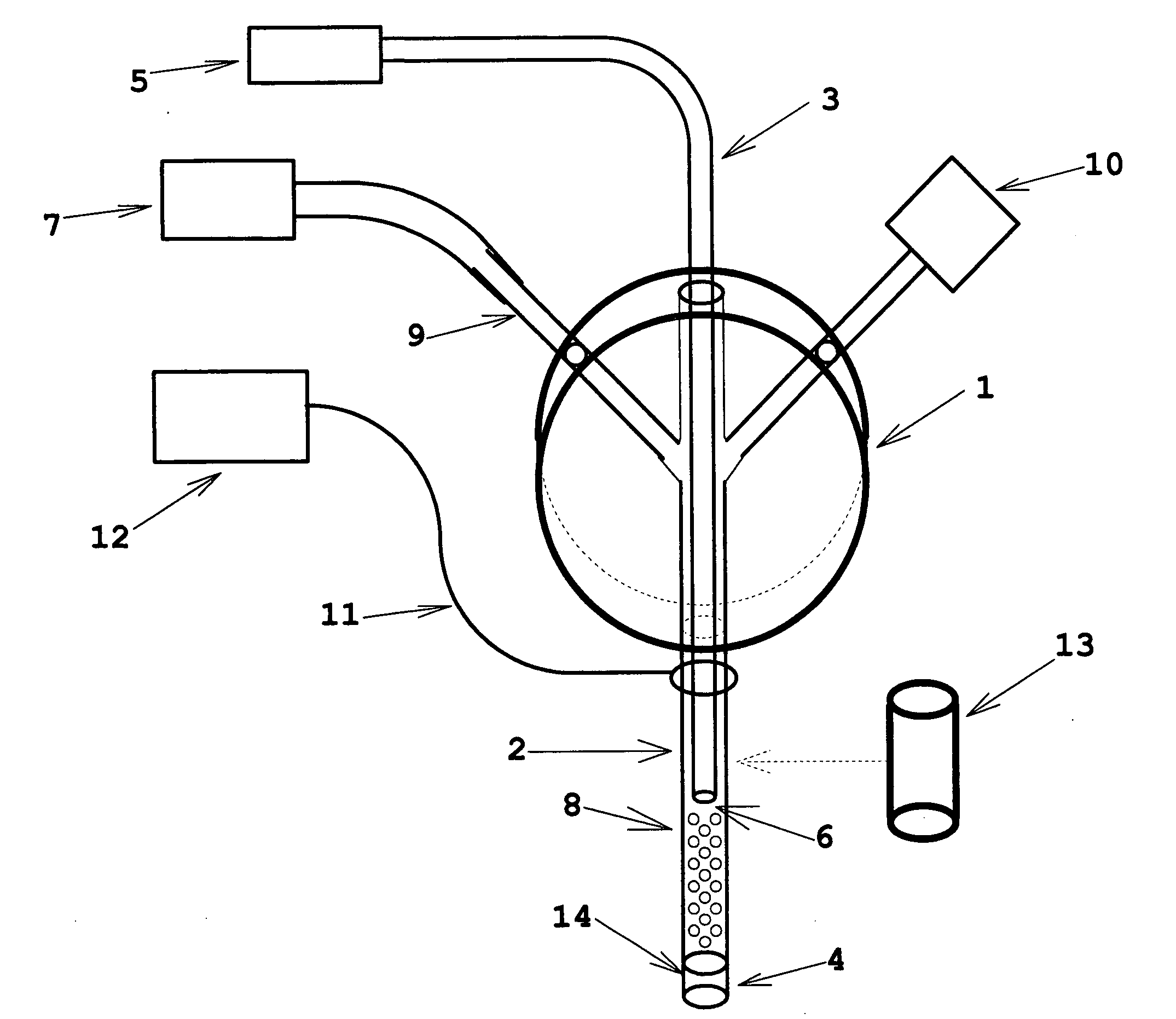
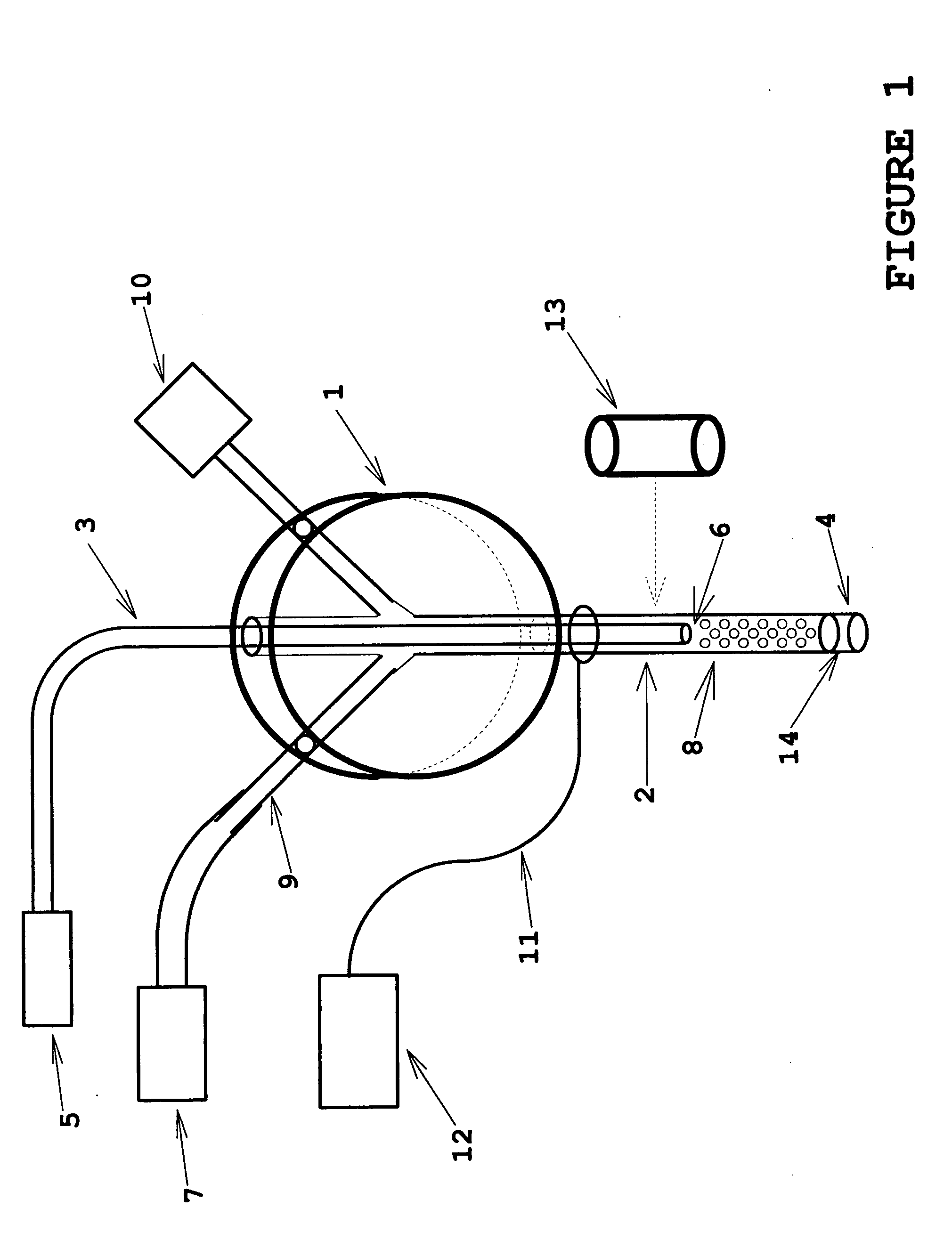
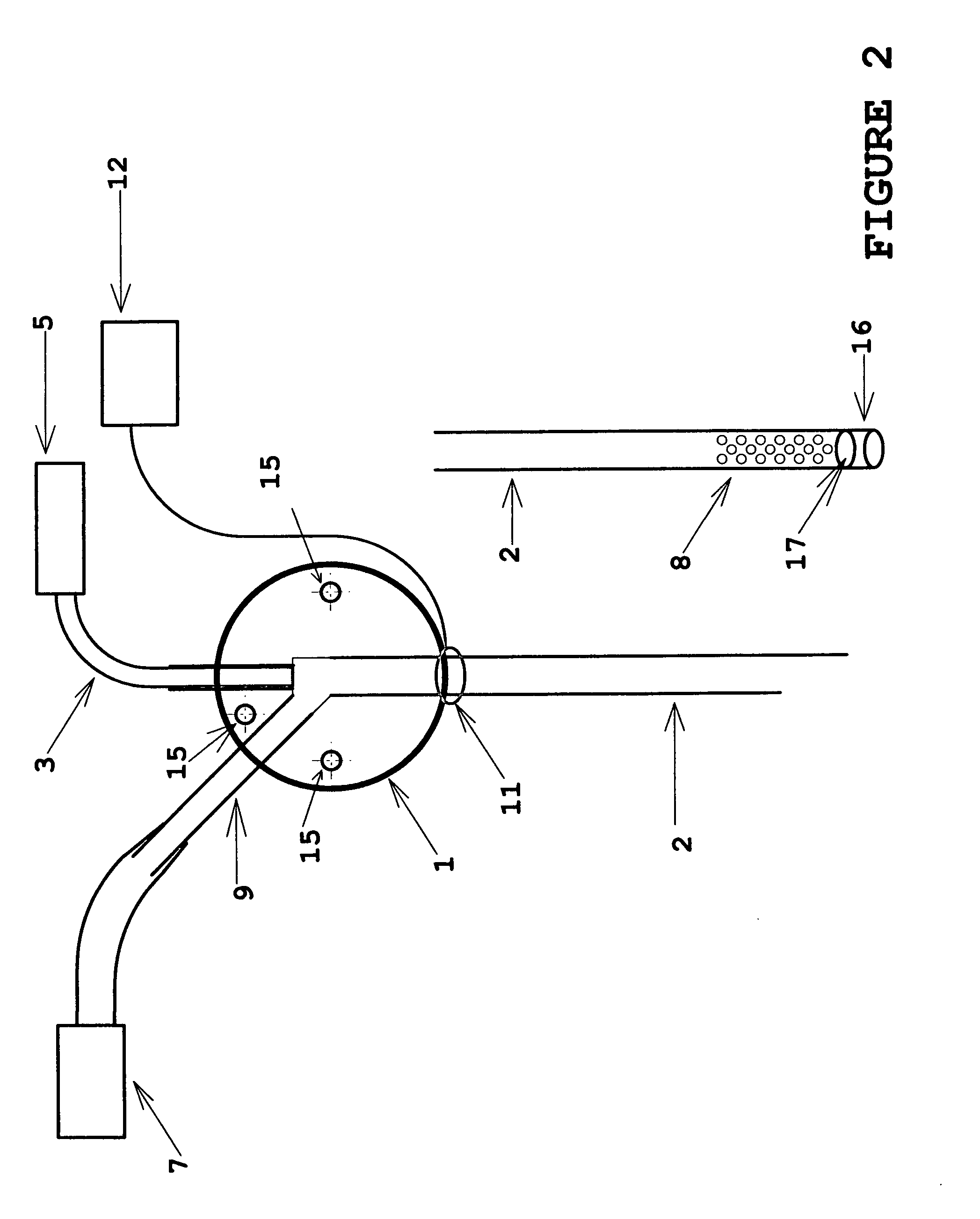
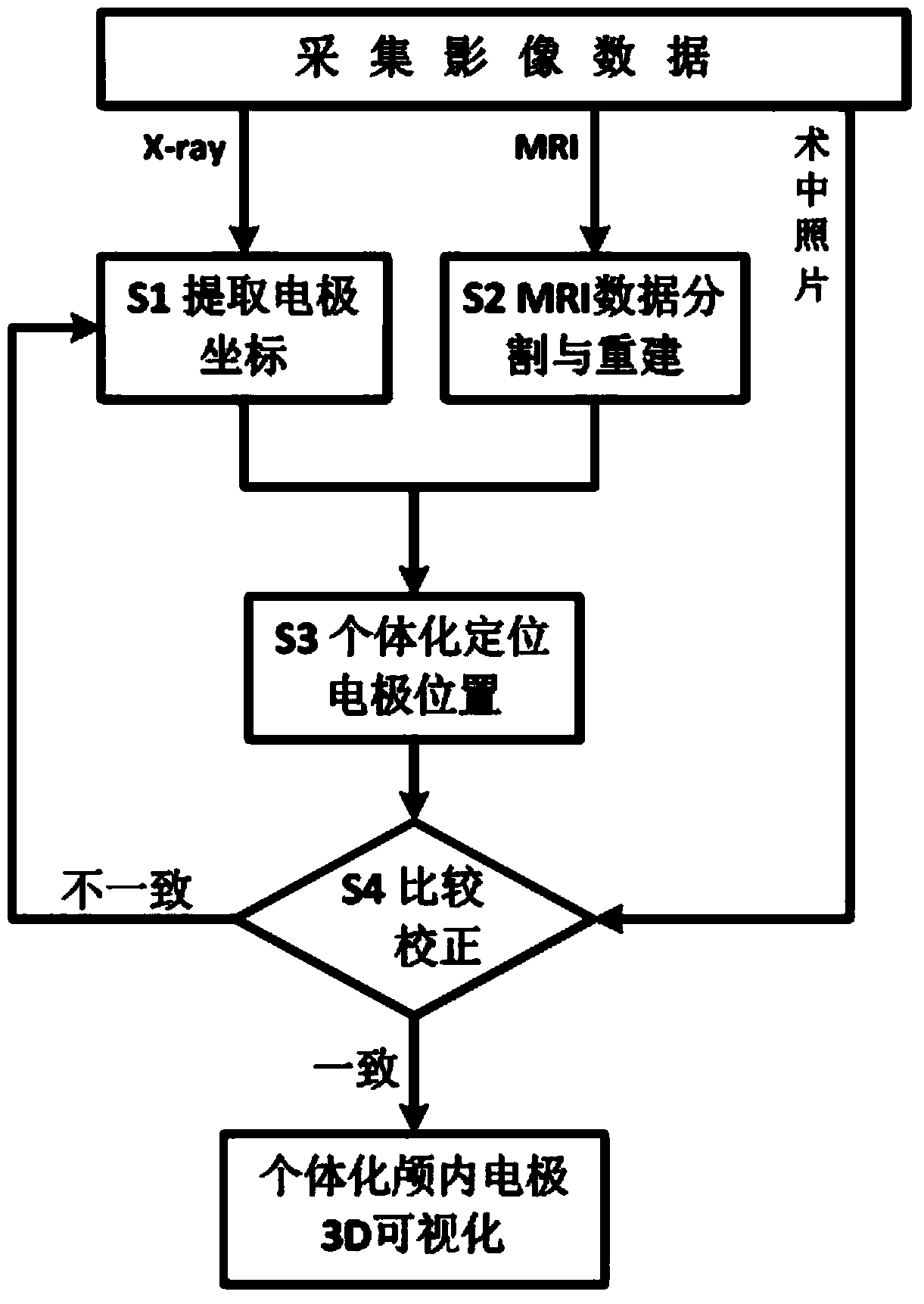
Encephalic electrode individualization locating method based on multimode medical image data fusion
InactiveCN103932796ARealize high-precision individual positioningPrecise positioningDiagnosticsSurgeryDiagnostic Radiology ModalityAnatomical structures
An encephalic electrode individualization locating method based on multimode medical image data fusion relates to the fields of medical instruments and medical image processing and neuroimaging. By means of multimode medical image data including magnetic resonance images, X-ray images and intranperative optical photos, the space position relation of an encephalic electrode and a brain tissue structure is comprehensively measured, a relation between the position of the encephalic electrode and a brain anatomical structure is established, and accurate and fast individualization locating of the encephalic electrode is achieved. The encephalic electrode individualization locating method based on multimode medical image data fusion can be used in the fields of cognitive neuroscience basic research, clinic neurosciences and the like, provide accurate brain space position information for an encephalic electroencephalogram signal, and enhance application value in the aspect of electrophysiological basis research.
Owner:BEIJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
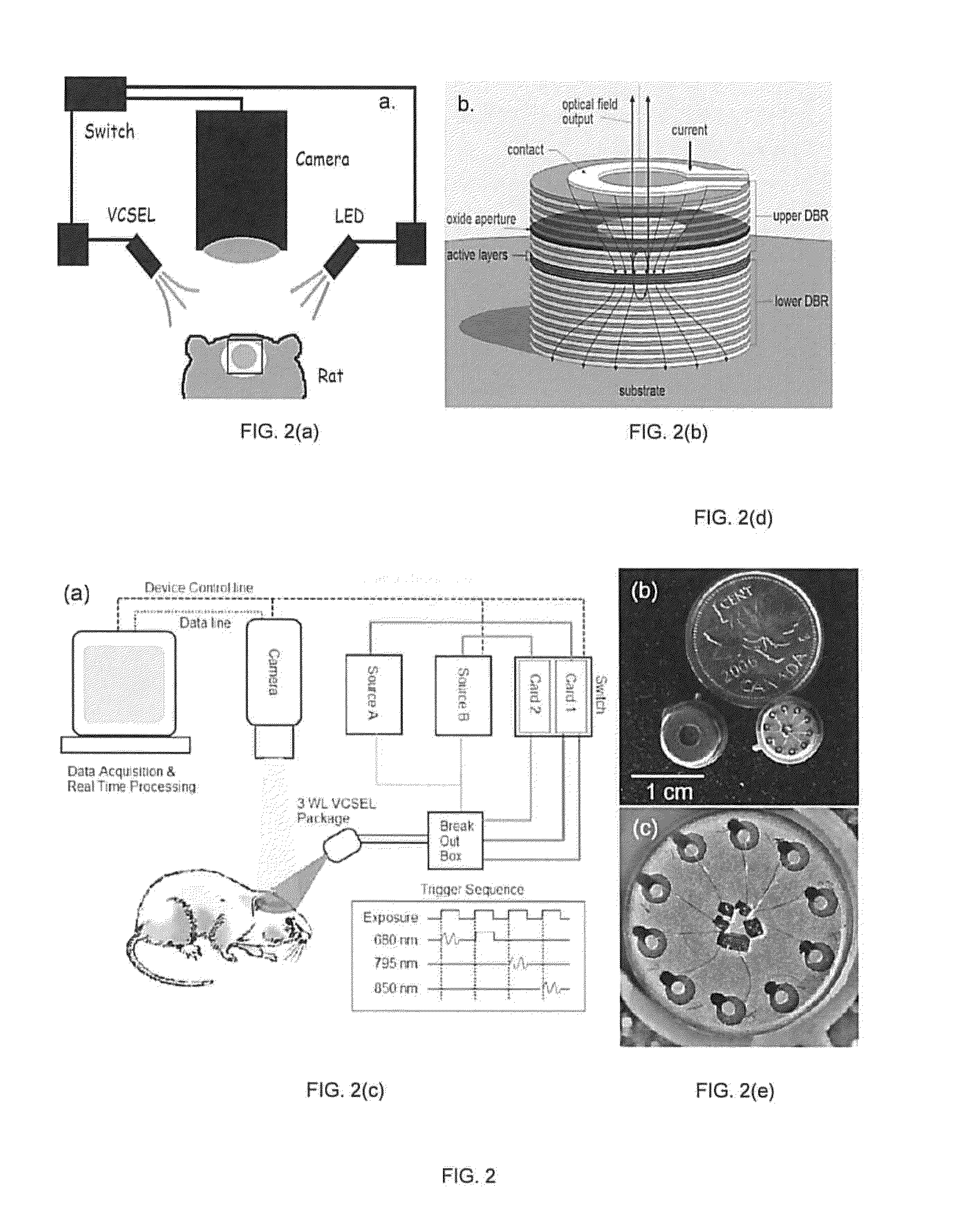
System and method for optical imaging with vertical cavity surface emitting lasers
ActiveUS20120188354A1Reduce spatial noiseReduce temporal noiseTelevision system detailsColor television detailsLow noiseDiagnostic Radiology Modality
The present invention uses vertical-cavity surface-emitting lasers (VCSELs) as illumination source for simultaneous imaging of blood flow and tissue oxygenation dynamics in vivo, or a means to monitor neural activity in brain slices ex vivo. The speckle pattern on the brain tissue due to a VCSEL's coherence properties is the main challenge to producing low-noise high-brightness illumination, required for evaluating tissue oxygenation. Moreover, using oxide-confined VCSELs we show a fast switching from a single-mode operation scheme to a special multi-modal, multi-wavelength rapid sweep scheme. The multi-modal, multi-wavelength rapid sweep scheme reduces noise values to within a factor of 40% compared to non-coherent LED illumination, enabling high-brightness VCSELs to act as efficient miniature light sources for various brain imaging modalities and other imaging applications. These VCSELs are promising for long-term portable continuous monitoring of brain dynamics in freely moving animals.
Owner:THE GOVERNINIG COUNCIL OF THE UNIV OF TORANTO
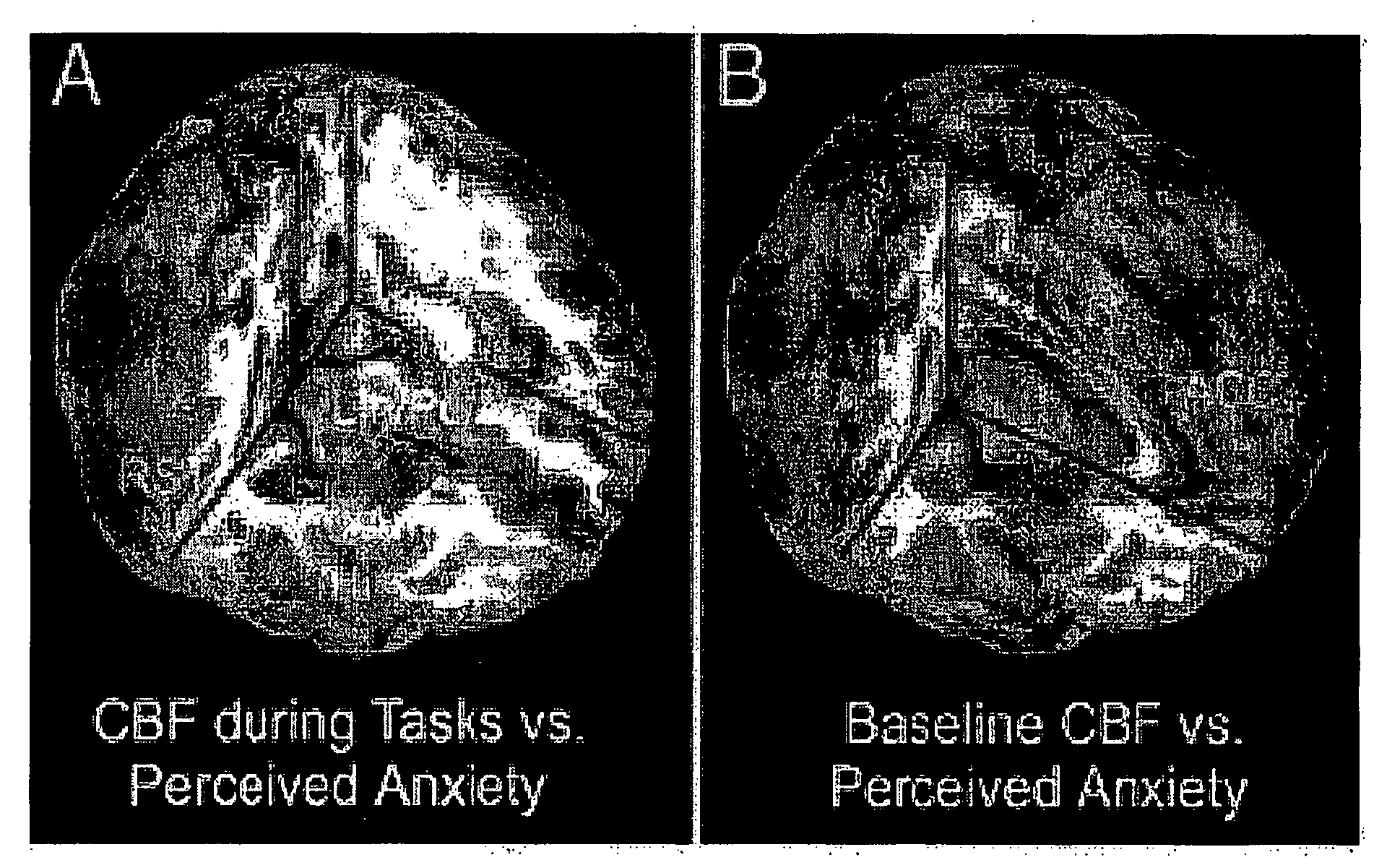
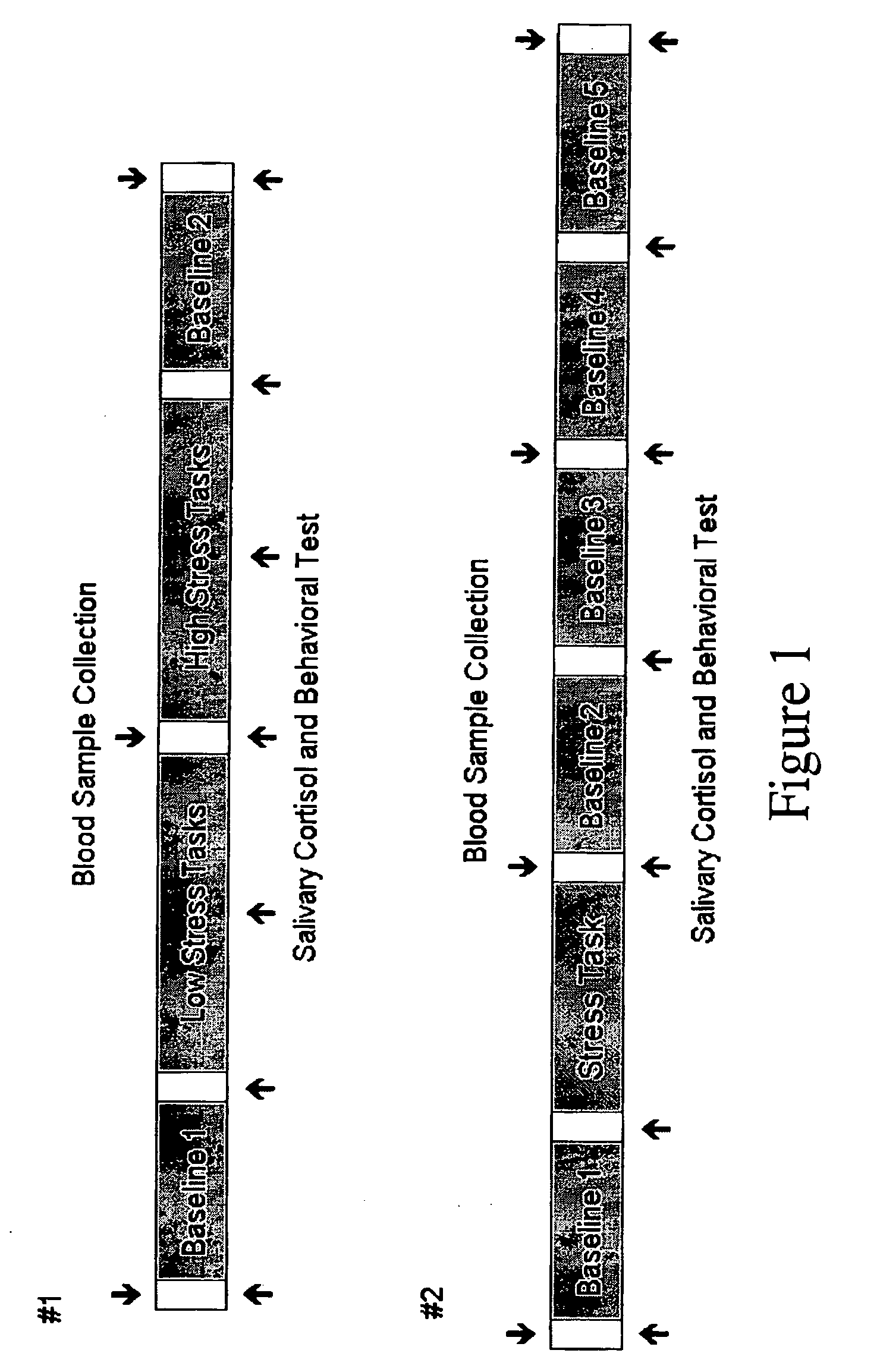
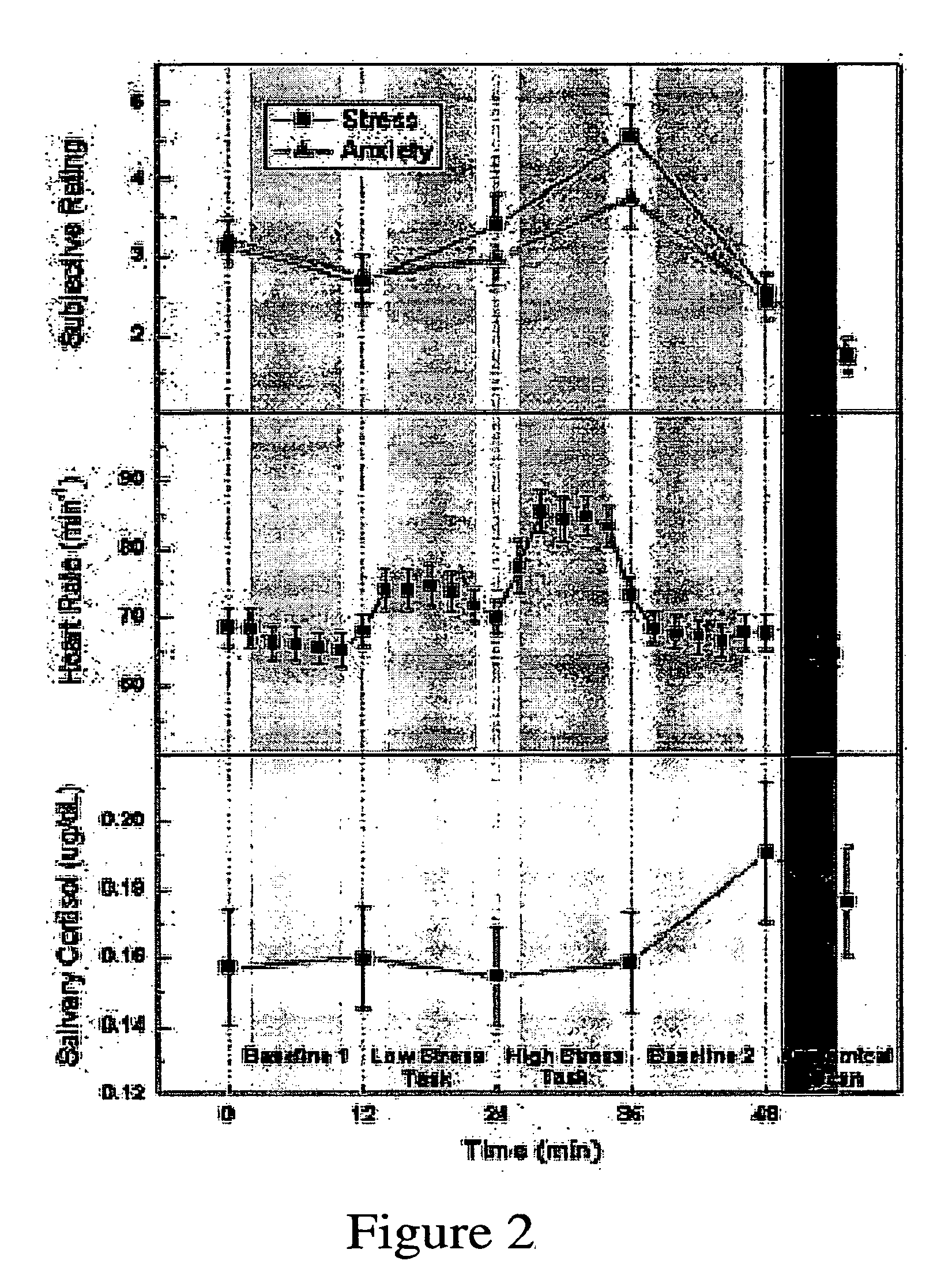
Assessing subject's reactivity to psychological stress using fmri
This invention relates to the use of a quantitative functional MRI (fMRI)—arterial spin-labeling perfusion MRI or absolute T2 mapping MRI or a combination thereof in the non-invasive neuroimaging of a subject's brain in response to stress-inducing psychological stimuli, which can be utilized to predict individual stress reactivity as well as to be used as a human model for testing or optimizing psychopharmacological agents.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
Linear Velocity Imaging Tomography
ActiveUS20170188874A1Strong specificityHigh sensitivityMaterial analysis using microwave meansMicrowave sensorsTomographyImaging brain
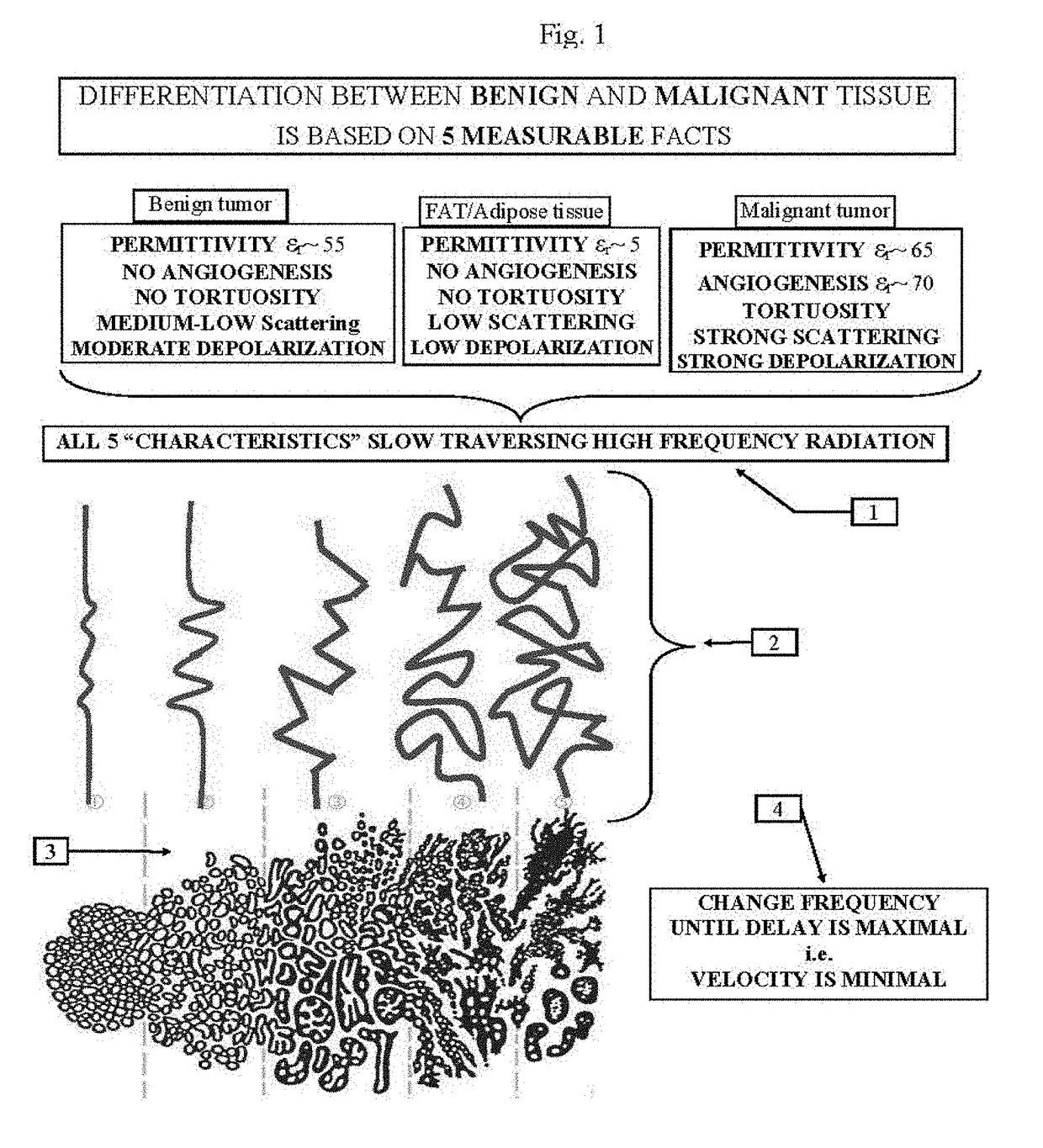
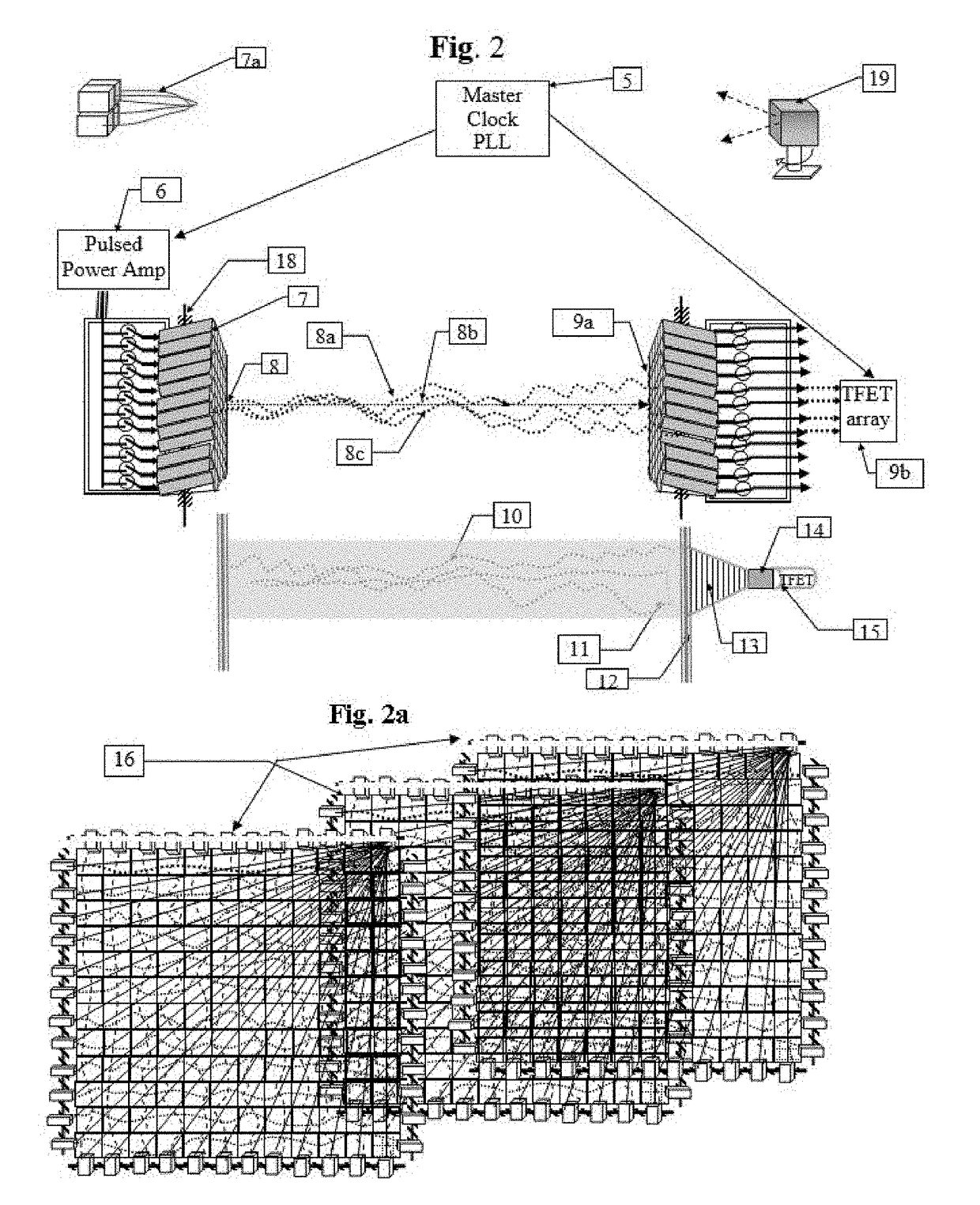
The invention describes a new Imaging modality based on Linear Velocity Imaging Tomography; its applications include differentiating between malignant and benign tissues, the ability to correlate an ECG trace with actual disorders of the heart and Imaging Brain communications.
Owner:SUHAMI AVRAHAM
Screening, Diagnosis and Prognosis of Autism and Other Developmental Disorders
ActiveUS20150227681A1Improve accuracyHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningDevelopmental disorderCrowds
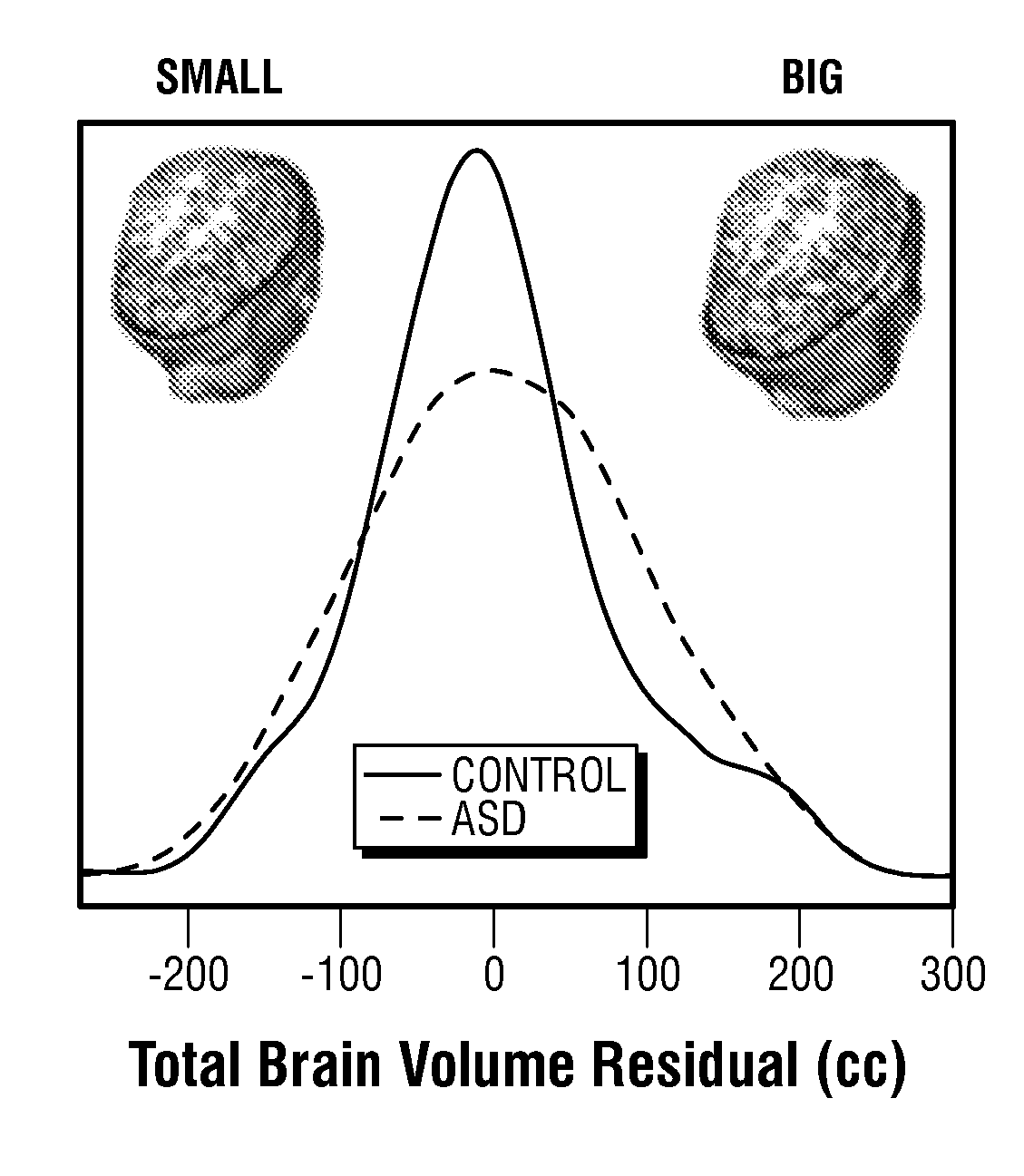
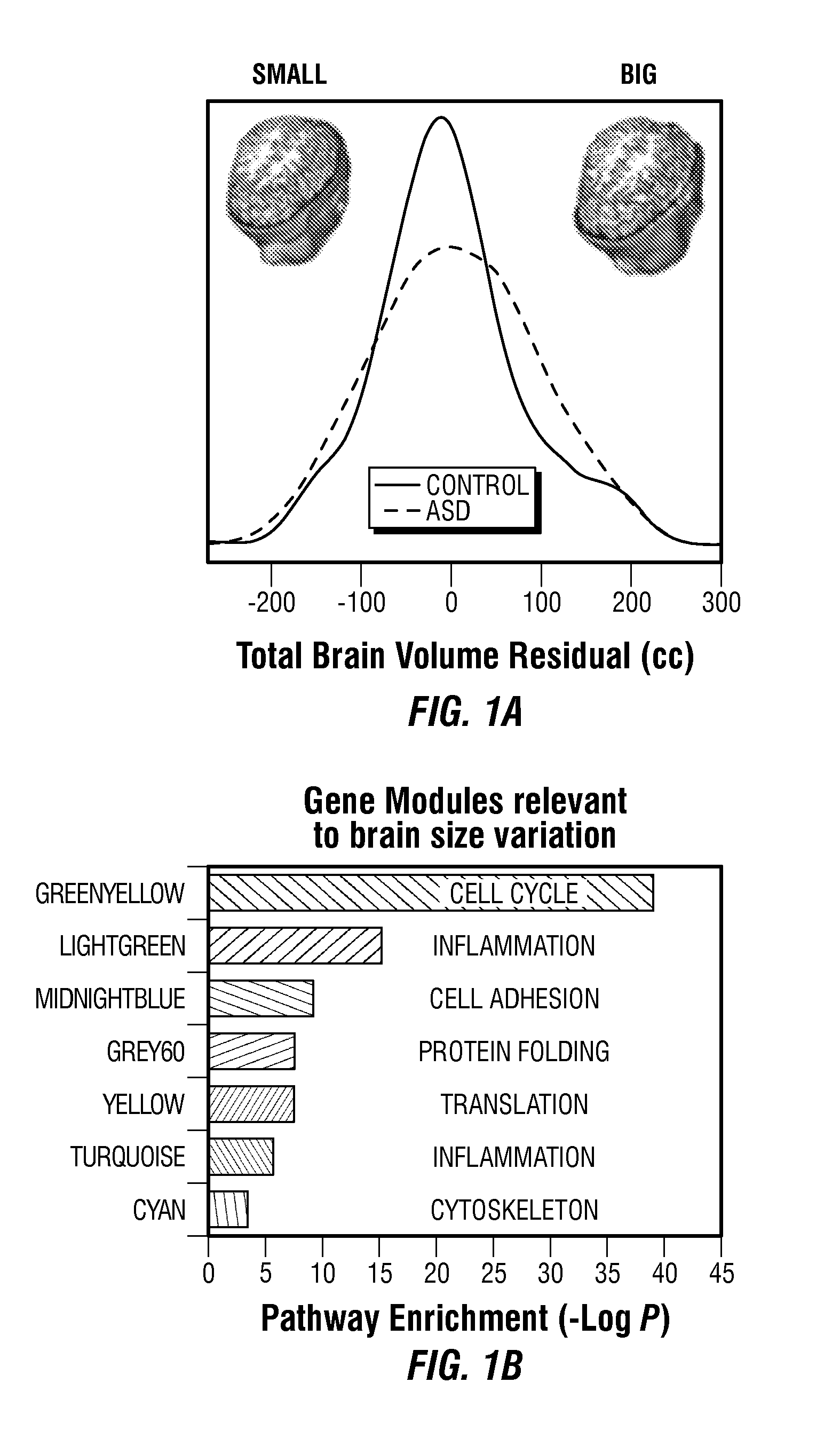
The invention provides a method and system combining functional genomic and genetic, proteomic, anatomic neuroimaging, functional neuroimaging, behavioral and clinical measurements and data analyses for autism pediatric population screening, diagnosis or prognosis. More specifically, the invention provides a weighted gene and feature test for autism which uses a weighted gene signature matrix for comparison to a reference database of healthy and afflicted individuals. The invention also provides normalized gene expression value signatures for comparison to a reference database. The invention additionally combines either the weighted gene or the normalized gene analysis with comparisons to a gene-networks signature matrix, a multi-modal signature matrix, and a collateral features signature matrix for improved accuracy in screening, diagnostic and prognostic relevance for autism, particularly for newborns, babies ages birth to 1 year, toddlers ages 1 to 2 years, toddlers ages 2 to 3 years and young children ages 3 through 4 years.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
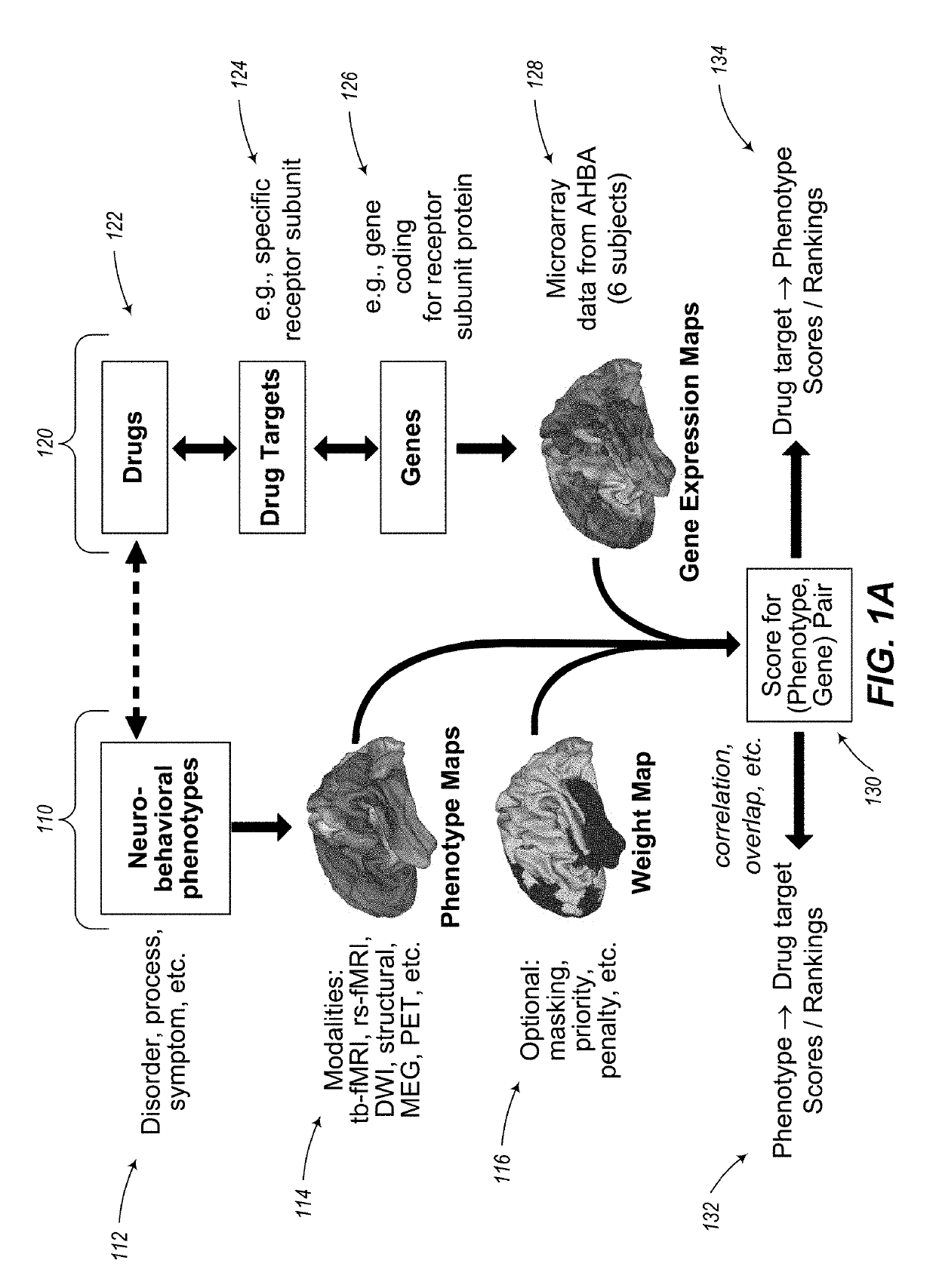
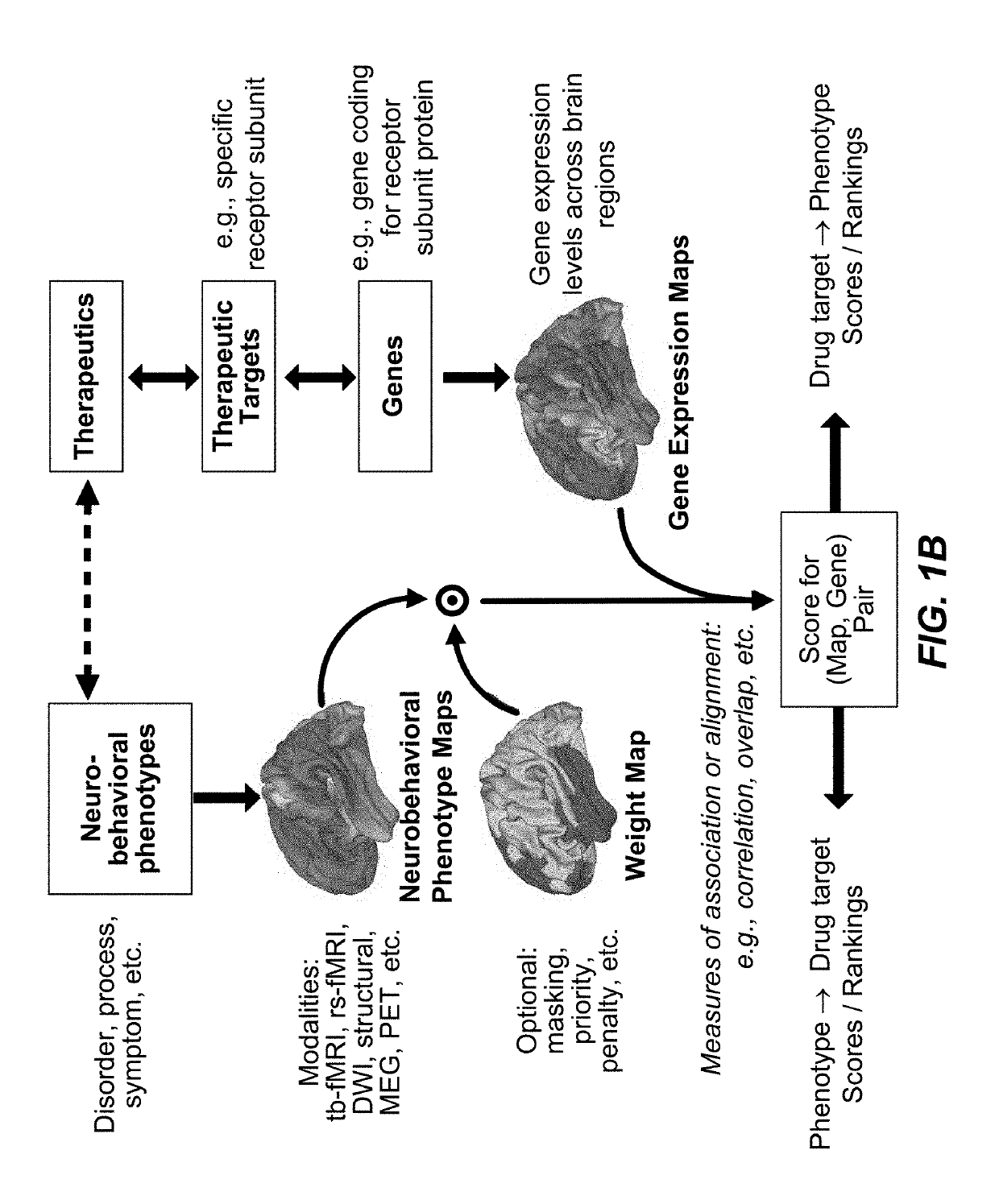
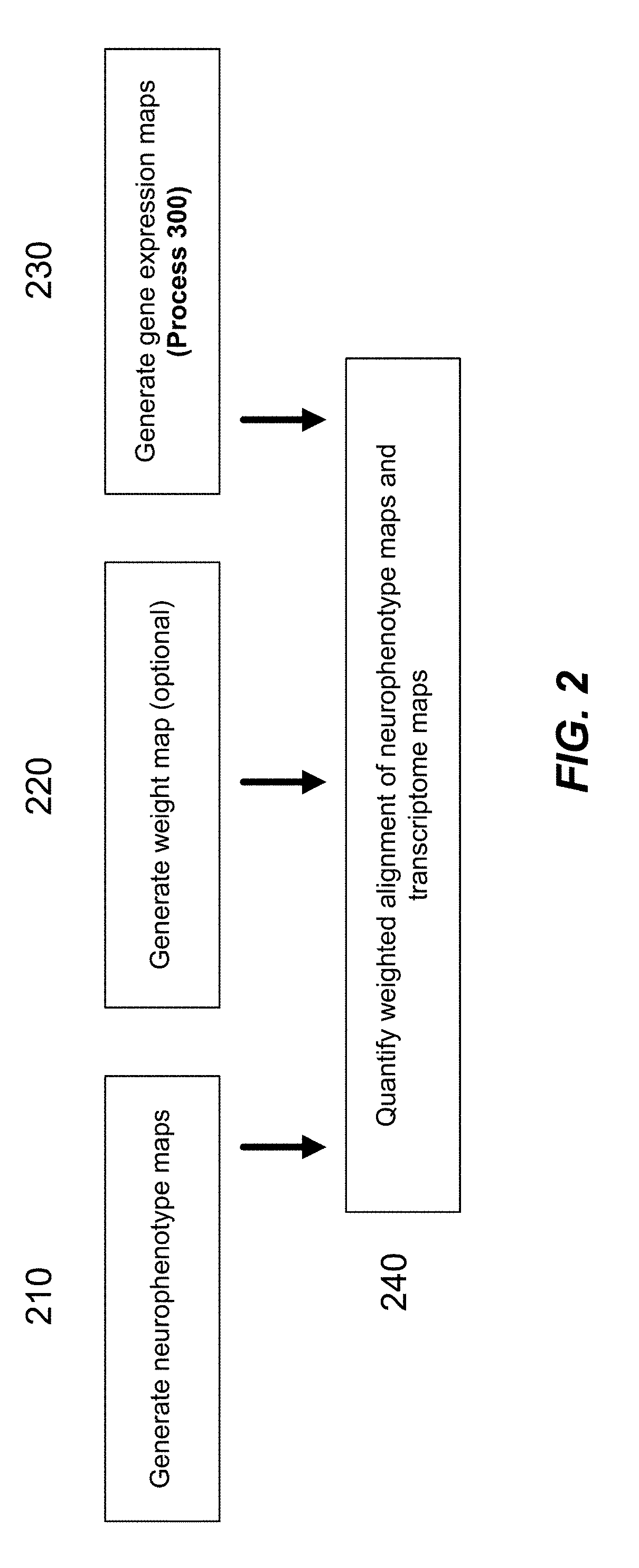
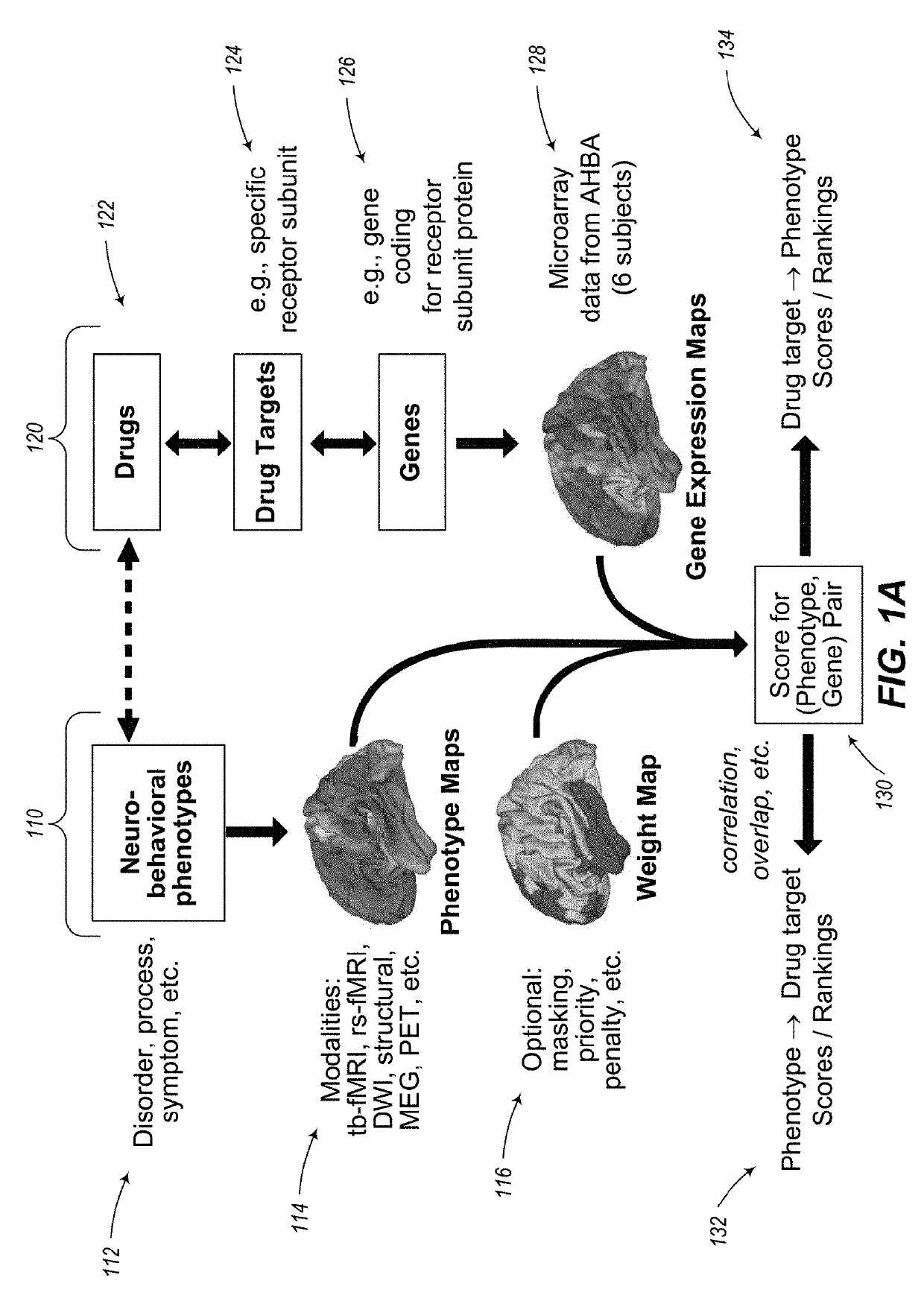
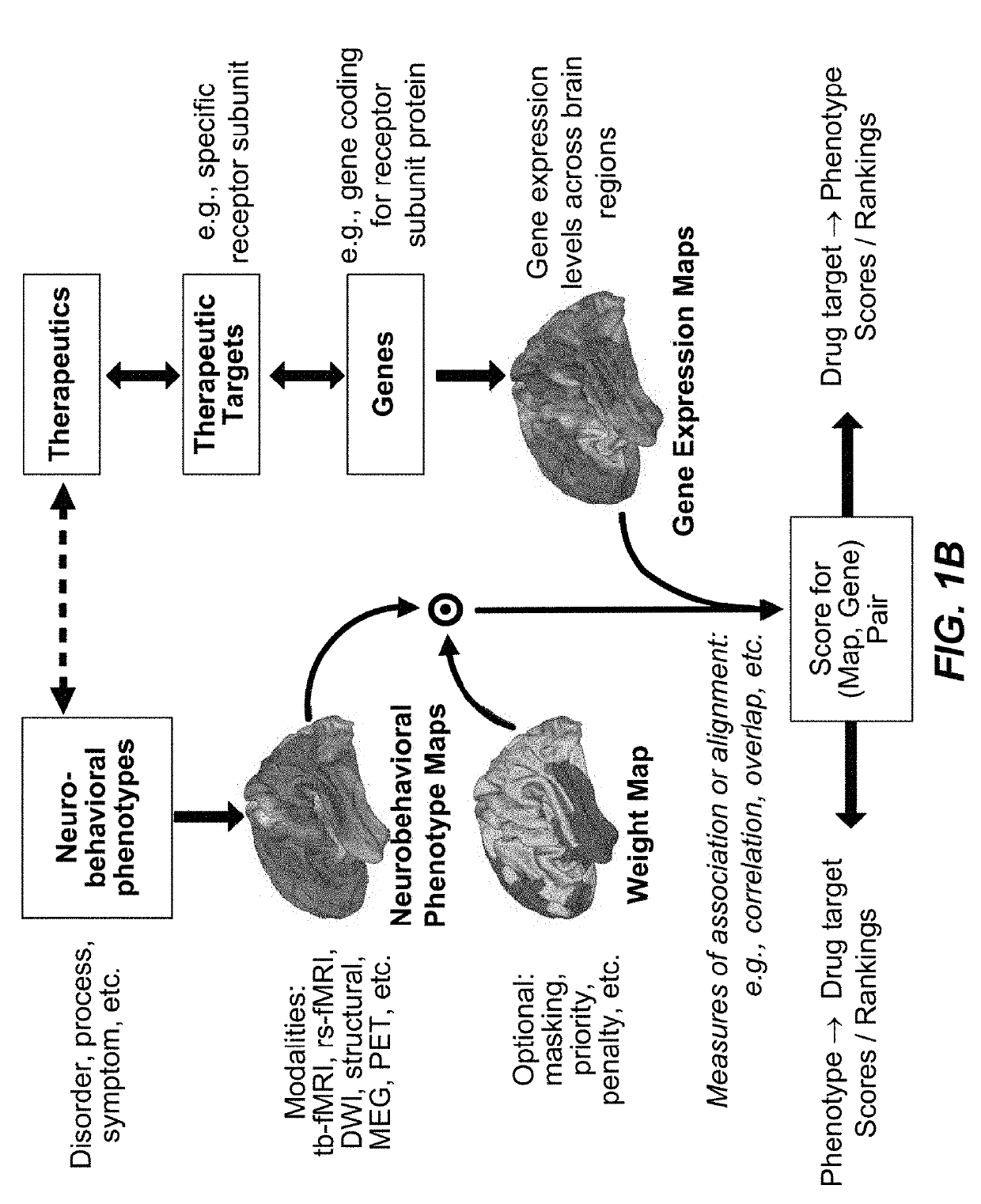
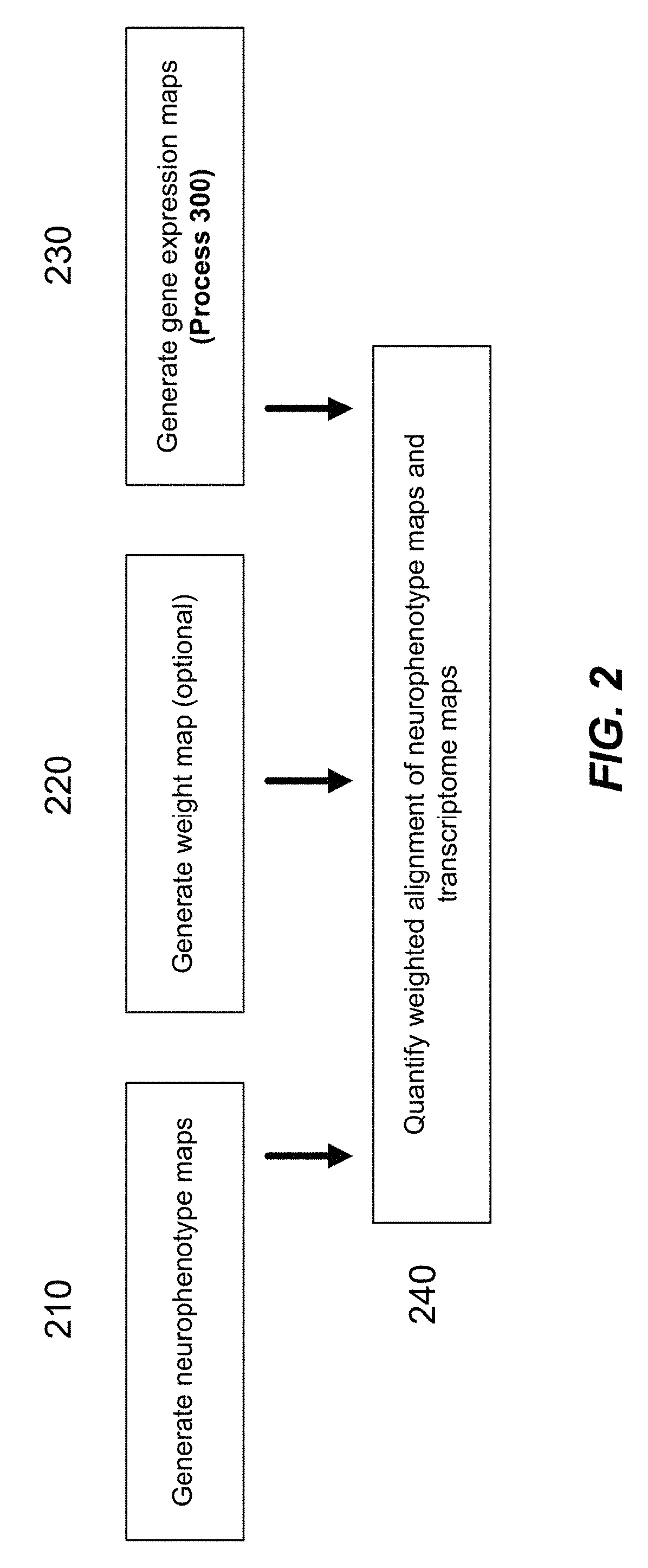
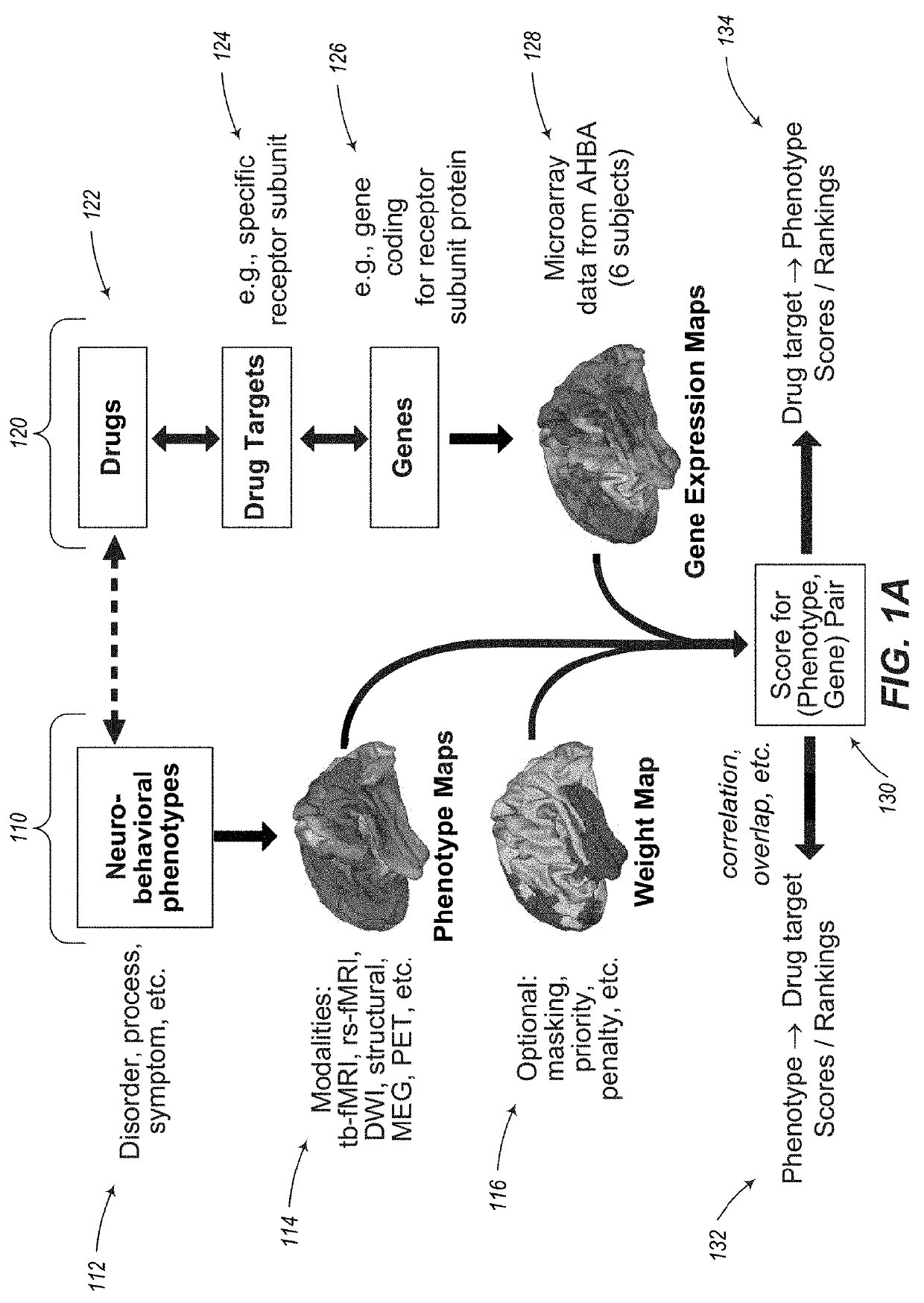
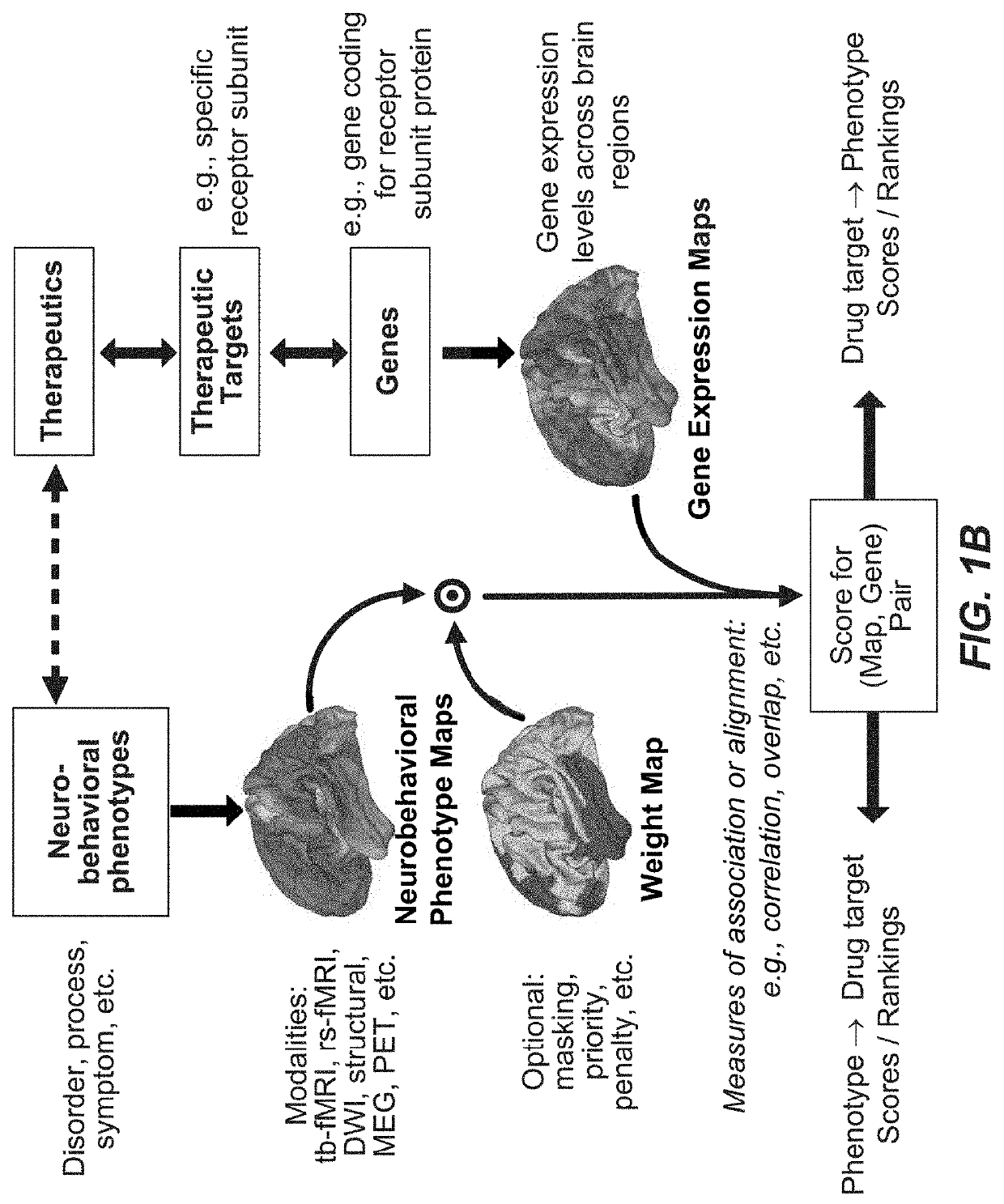
Methods and tools for detecting, diagnosing, predicting, prognosticating, or treating a neurobehavioral phenotype in a subject
InactiveUS20190102511A1Efficient designPrecise positioningDrug and medicationsBiostatisticsPharmacometricsGenotype
The present tools and methods for detecting, diagnosing, predicting, prognosticating, or treating a neurobehavioral phenotype in a subject. These tools and methods relates to a genotype and neurophenotype topography-based approach for analyzing brain neuroimaging and gene expression maps to identify drug targets associated with neurobehavioral phenotypes and, conversely, neurobehavioral phenotypes associated with potential drug targets, to develop rational design and application of pharmacological therapeutics for brain disorders, and to provide methods and tools for treatment of subjects in need of neurological therapy.
Owner:YALE UNIV +1
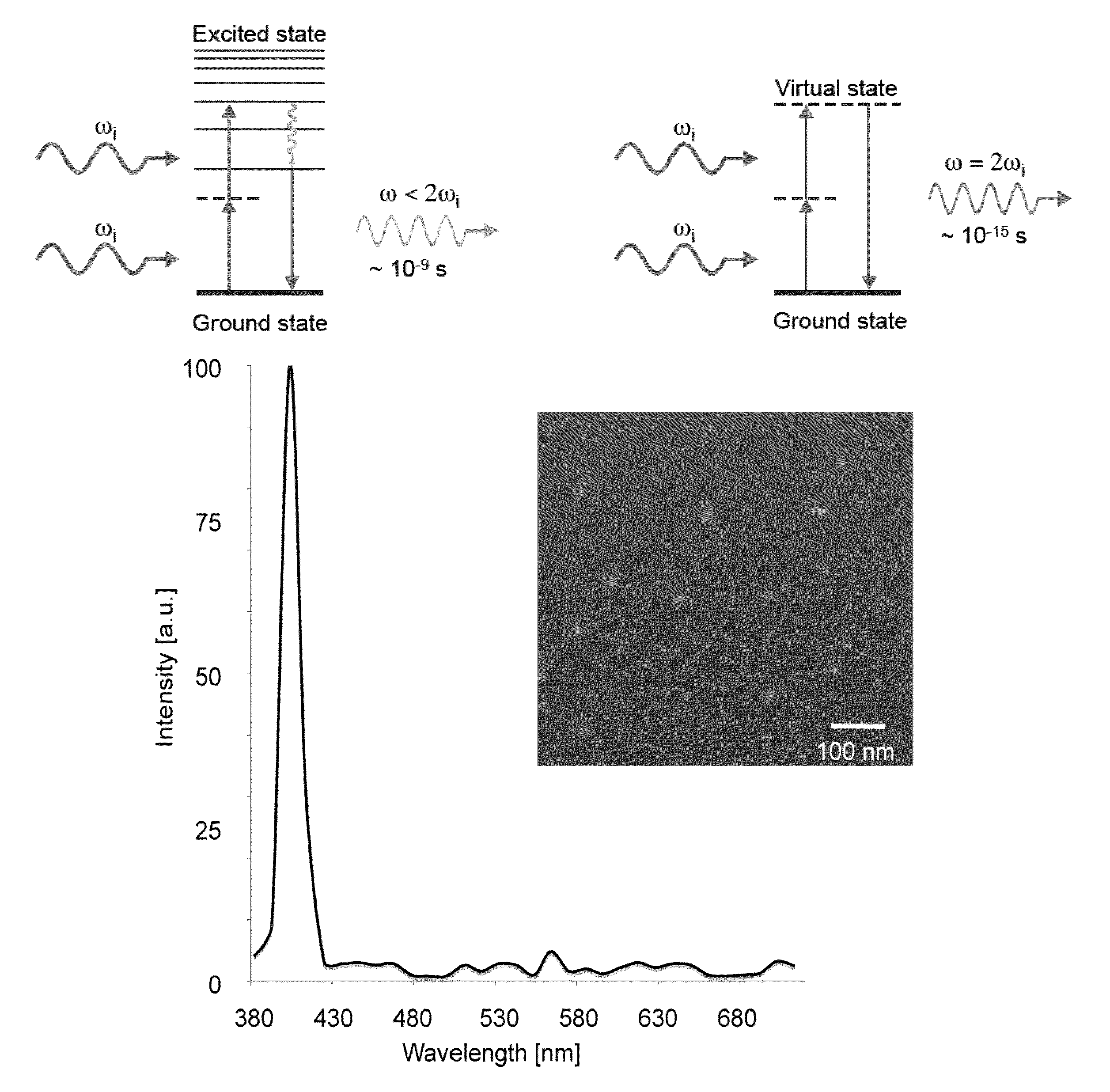
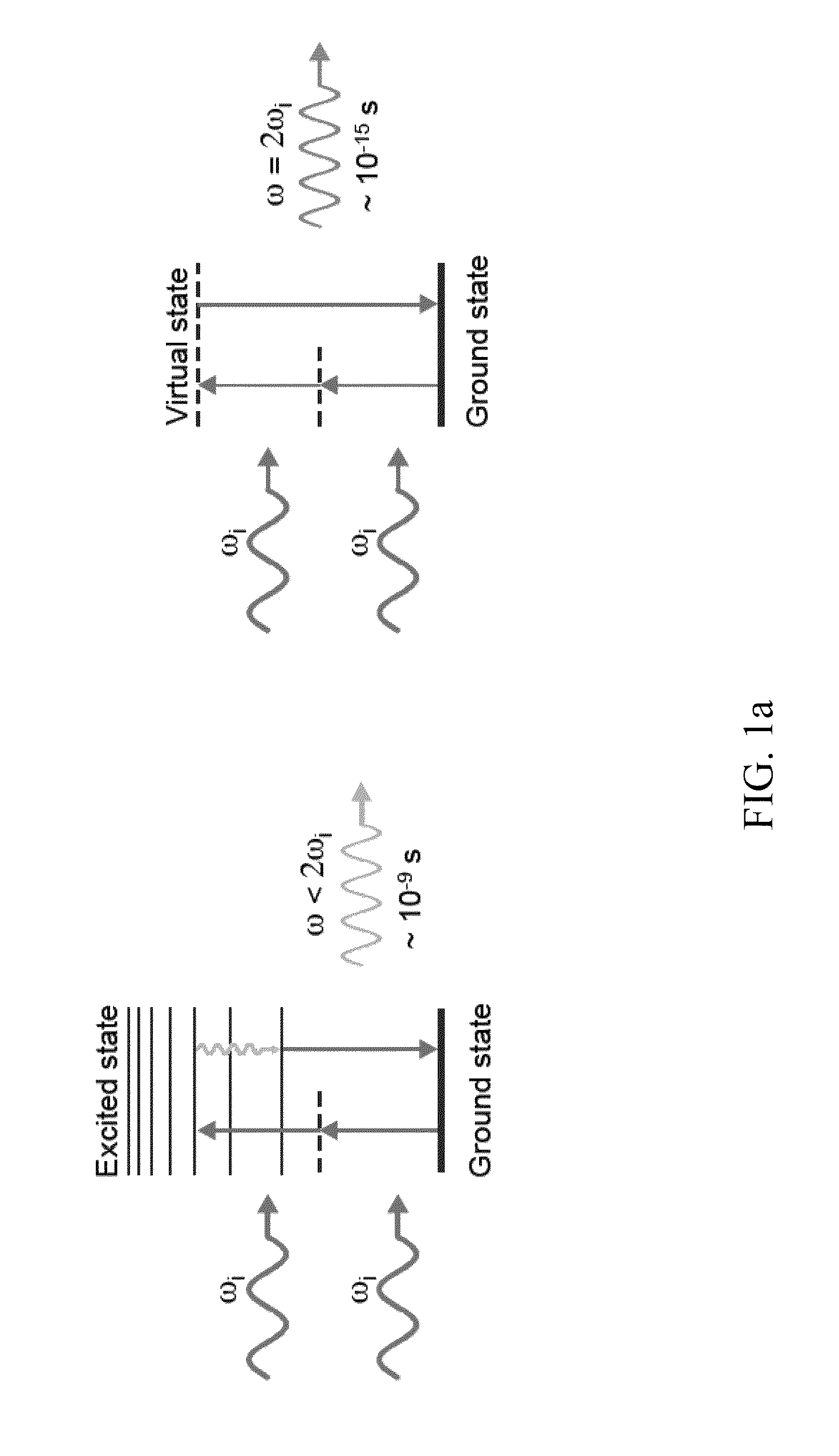
Second harmonic imaging nanoprobes and techniques for use thereof
ActiveUS20120141981A1Enhances electric fieldBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsCell signalingPhoton
Second harmonic nanoprobes for imaging biological samples and a method of using such probes to monitor the dynamics of biological process using a field resonance enhanced second harmonic (FRESH) technique are provided. The second harmonic generating (SHG) nanoprobes are comprised of various kinds of nanocrystals that do not possess an inversion symmetry and therefore are capable of generating second harmonic signals that can then be detected by conventional two-photon microscopy for in vivo imaging of biological processes and structures such as cell signaling, neuroimaging, protein conformation probing, DNA conformation probing, gene transcription, virus infection and replication in cells, protein dynamics, tumor imaging and cancer therapy evaluation and diagnosis as well as quantification in optical imaging.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
High spatiotemporal resolution brain imaging
PendingUS20200253479A1Improve rendering capabilitiesImprove permeabilityHolographic light sources/light beam propertiesHolographic optical componentsVertical-cavity surface-emitting laserEngineering
An ultra high-resolution near infrared brain imager system includes a modular cap housing closely spaced multiple vertical-cavity surface-emitting laser—single-photon avalanche photodiode array (VCSEL-SPAD) modules, each one of the VCSEL-SPAD modules including a linear VCSEL array and a SPAD detector.
Owner:BROWN UNIVERSITY
Methods and tools for detecting, diagnosing, predicting, prognosticating, or treating a neurobehavioral phenotype in a subject
ActiveUS20190272889A1Efficient designPrecise positioningDrug and medicationsBiostatisticsDiseasePharmacometrics
Owner:YALE UNIV +1
Ultra-dense electrode-based brain imaging system
ActiveUS20180276822A1Fully captureImprove accuracyElectroencephalographyImage enhancementTemporal resolutionImage resolution
An ultra-dense electrode-based brain imaging system with high spatial and temporal resolution. A Sparsity and Smoothness enhanced Method Of Optimized electrical TomograpHy (s-SMOOTH) based reconstruction technique to improve the spatial resolution and localization accuracy of reconstructed brain images is described. Also described is a graph Fractional-Order Total Variation (gFOTV) based reconstruction technique to improve the spatial resolution and localization accuracy of reconstructed brain images.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Multipurpose analysis using second harmonic generating nanoprobes
ActiveUS20100233820A1Microbiological testing/measurementMaterial analysis by optical meansDiagnostic Radiology ModalityCell signaling
Second harmonic nanoprobes for multipurpose imaging of samples and a method of using such probes to monitor nucleotide sequencing in a Multi-SHG Detection Imaging (MSDI) modality and to monitor external electric field using voltage sensitive second harmonic generating (SHG) nanoprobes are provided. The SHG nanoprobes are comprised of various kinds of nanocrystals that do not possess an inversion symmetry and therefore are capable of generating second harmonic signals that can then be detected by conventional two-photon microscopy for in vivo imaging of biological processes and structures such as cell signaling, neuroimaging, protein conformation probing, DNA conformation probing, gene transcription, virus infection and replication in cells, protein dynamics, tumor imaging and cancer therapy evaluation and diagnosis as well as quantification in optical imaging for a wide-range of biological and non-biological processes and devices.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
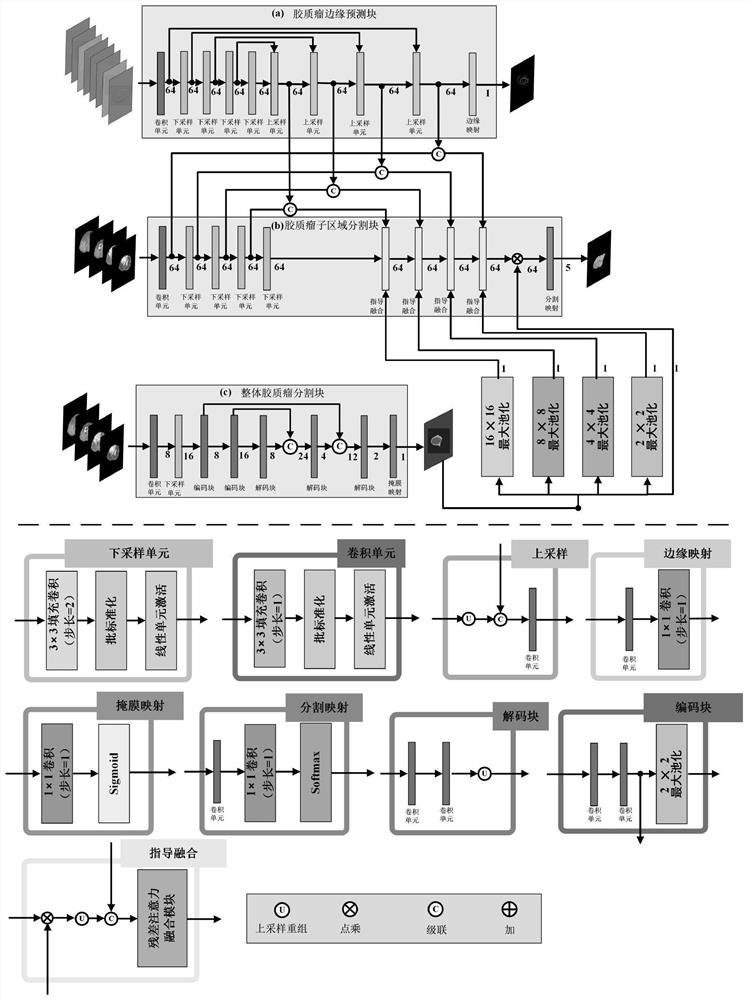
Multi-modal MR image brain tumor segmentation method based on deep learning and multi-guidance
ActiveCN112365496AReduce the amount of parametersImage enhancementImage analysisImaging brainImaging processing
The invention discloses a multi-modal MR image brain tumor segmentation method based on deep learning and multi-guidance, belongs to the field of image processing, and solves three problems in a multi-modal MRI brain glioma segmentation process: (1) the problem of inaccurate segmentation caused by unclear brain glioma boundary; (2) some discrete wrong segmentation points appear in a segmentation result due to uneven brightness distribution of the multi-mode MRI; and (3) the problem of carrying out feature fusion on various kinds of guide information in a brain glioma MRI segmentation network.Feature fusion is carried out on an overall brain glioma segmentation result and a brain glioma edge prediction result through a proposed fusion mechanism, so that multi-mode MRI brain glioma segmentation under multi-feature map guidance and fusion is realized. According to the deep segmentation network, high-accuracy segmentation is realized with less parameter quantity, so that the method is convenient to embed into edge equipment to assist doctors in diagnosing and analyzing brain glioma.
Owner:ZHONGBEI UNIV
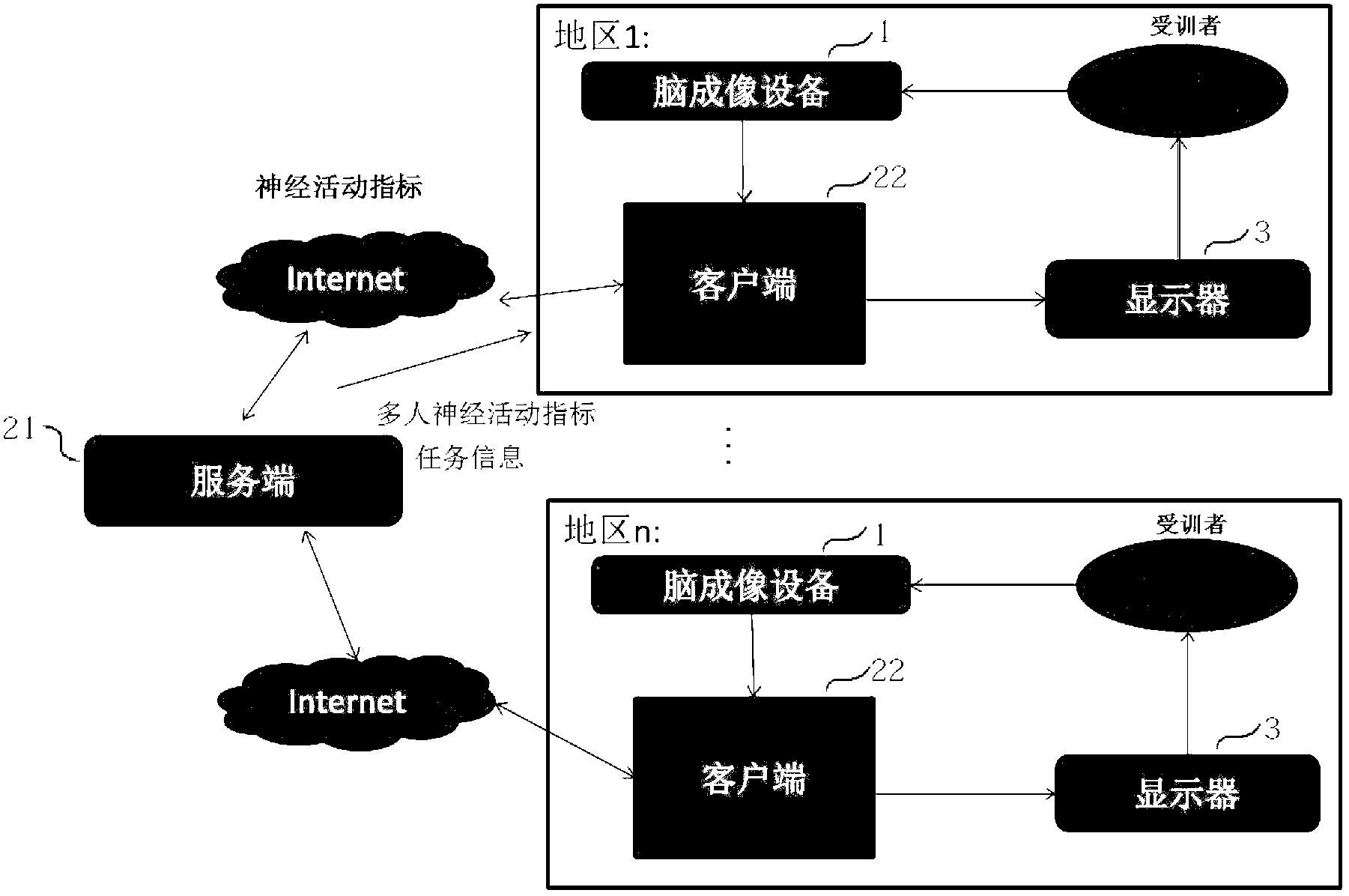
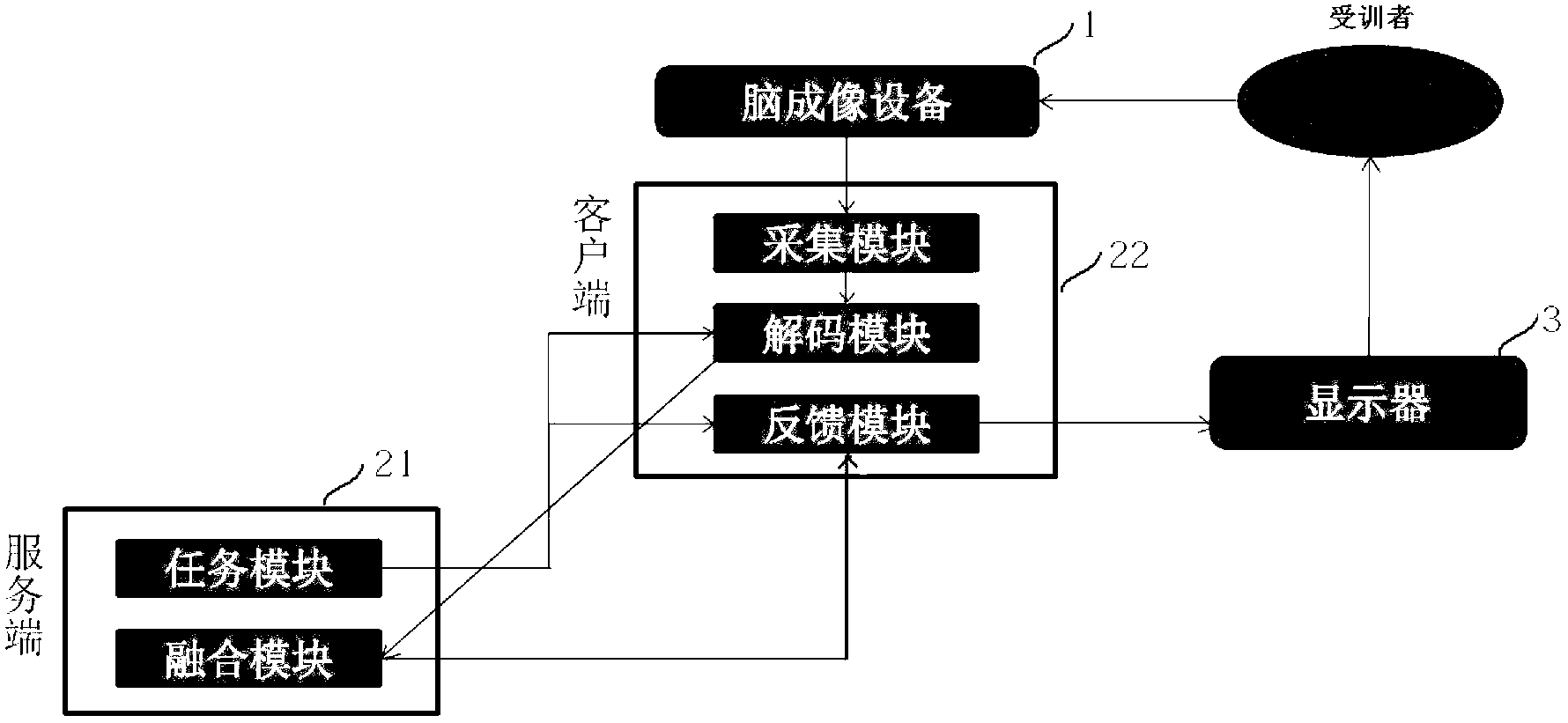
Group neural feedback training method and group neural feedback training system
ActiveCN103169470AChange cognitive behaviorDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsPhysical medicine and rehabilitationDisplay device
The invention discloses a group neural feedback training method and a group neural feedback training system. The group neural feedback training system comprises at least two brain imaging devices, at least three central processing units and a plurality of display devices. Each of the central processing units comprises a server-side processing unit and at least two client-side processing units. An output end of each brain imaging device is connected with an input end of a corresponding client-side processing unit. An output end of each client-side processing unit is connected with an input end of each corresponding display device. A plurality of client-side processing units are respectively connected with the server-side processing units. In the group neural feedback training system, the client-side processing units are used for obtaining a brain neural activity indicator of a local trainee and the server-side processing units are used for obtaining a brain neural activity interactivity indicator of the local trainee. Through feeding the brain neural activity interactivity indicator back to the trainee, the trainee can regulate a training strategy autonomously, so that the aim that group cognitive behaviors are changed can be achieved.
Owner:BEIJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Wear-type microscopy device for imaging brain function of small active animal
ActiveCN101991406AShort rejection timeDoes not affect activity behaviorDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsMicrocontrollerRefractive index
The invention discloses a wear-type microscopy device for imaging cortex of a small active animal under the waking activity state, comprising an imaging module, an illumination module and a system support base. The imaging module consists of an imaging cavity made of metal as well as an image carrying optical fibre and a gradient refractive index lens arranged inside the imaging cavity; the illumination module is an optical fibre derived compound optical source system and consists of a light source, a light source adjusting circuit, a control driving circuit and an output optical fibre; the light source consists of a semiconductor laser device (LD) and a high-power light emitting diode (LED); two drivers are controlled by a microcontroller so as to output light rays and laser with different wavelengths in a separated or mixed way; the system support base is a special metal structural body fixed on the head of the small animal to be tested and right above a target observation region, is equipped with the imaging module inside and introduces an illumination optical fibre to support the whole imaging system. The invention realizes imaging of various forms by introducing different illumination light rays.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
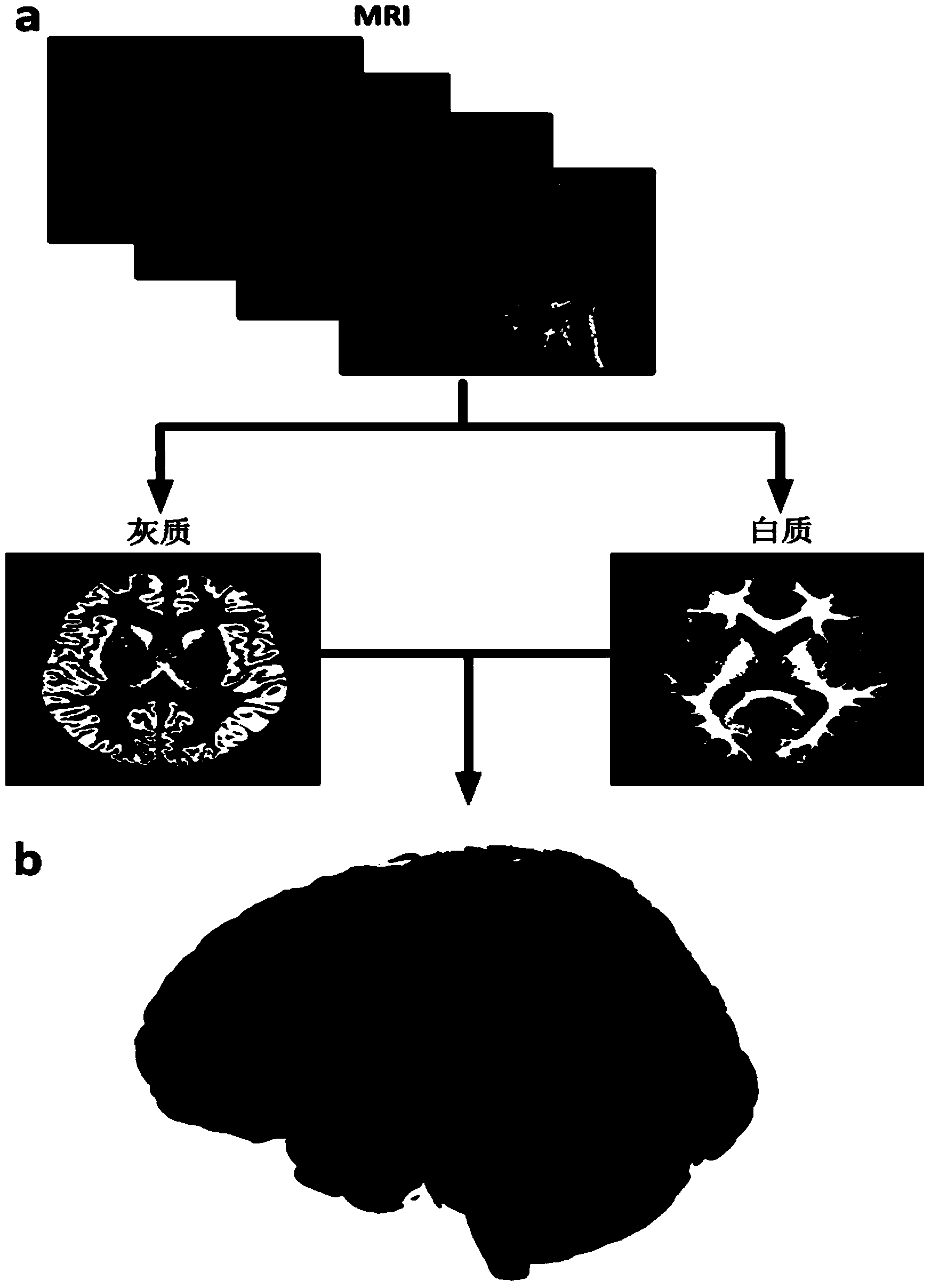
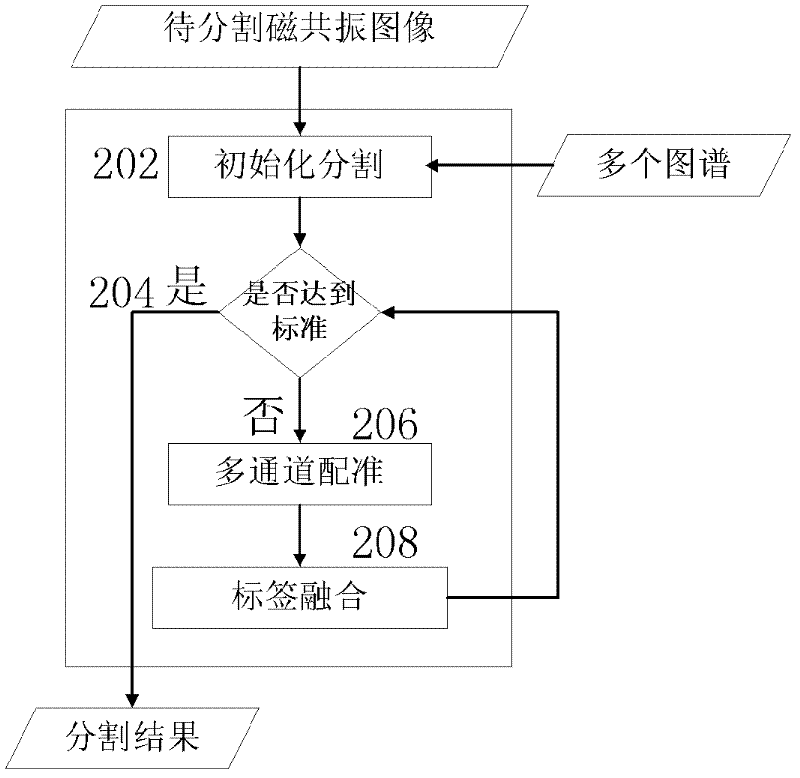
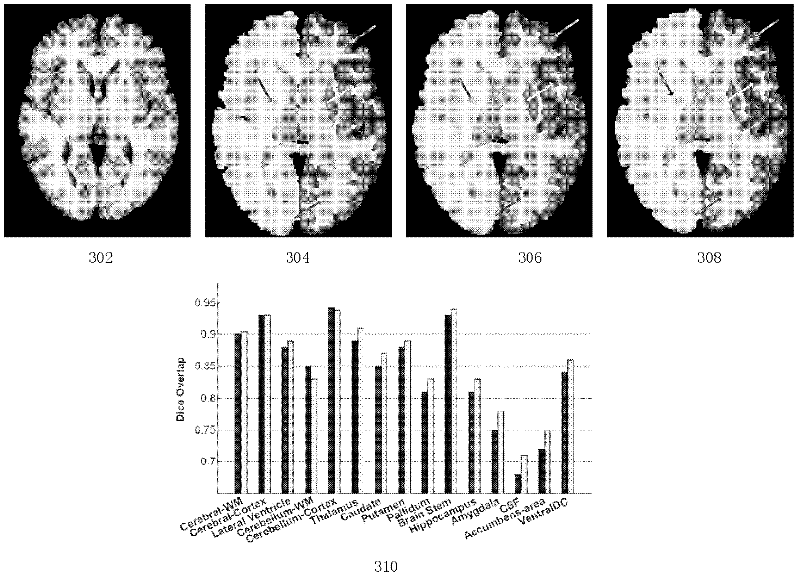
Magnetic resonance image brain structure automatic dividing method based on statistics multi-map registration optimization
InactiveCN102646268AImprove registration accuracyGood segmentation resultImage enhancementImaging brainResonance
The invention relates to a magnetic resonance image brain structure automatic dividing method based on statistics multi-map registration optimization. A manual image dividing method is utilized for obtaining a plurality of maps; the maps are registered to images to be divided one by one; the images to be divided are subjected to initial dividing; the initial dividing images are subjected to iteration optimization processing; a registration field between each map and the images to be divided is calculated by using multi-channel image registration, and the registration field is used for registering the images of the maps and the dividing results to image spaces to be divided; and the final dividing results are calculated. The iteration method is utilized for simultaneously optimizing the registration precision of the maps and the dividing images and the dividing results of the images to be divided, so that the final dividing results are obviously superior to those of the traditional multi-map dividing method.
Owner:INST OF AUTOMATION CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
4D transcranial focused ultrasonic neuroimaging method based on acoustoelectric effect
ActiveCN109645999AImprove time resolutionImprove spatial resolutionUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsDiagnostic recording/measuringPhase correlationSonification
The invention discloses a 4D transcranial focused ultrasonic neuroimaging method based on an acoustoelectric effect. The method includes the steps that a focused ultrasonic signal generator and an energy converter are adopted to achieve generation and emission of focused ultrasonic signals, and focused ultrasonic characteristics under different parameters are determined; an electroneurographic signal collecting device composed of an electroencephalogram collecting system provided with an electroencephalogram electrode, an electroencephalogram amplifier and an electroencephalogram filter and anelectroneurographic-signal measuring system based on ultrasonic modulation is installed and connected; ultrasonic waves are spread through the cranium and focused on a certain position, and based onthe acoustoelectric effect principle, scalp electroencephalogram signals after ultrasonic modulation, namely, acoustoelectric signals are collected; through the amplitude values, the frequency and thephase position relevance of the acoustoelectric signals and activation source signals, the electroencephalogram signals are subjected to spatial encoding and demodulation, 4D neuroimaging of high space-time resolution is achieved, and multiple requirements in practical application are met.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
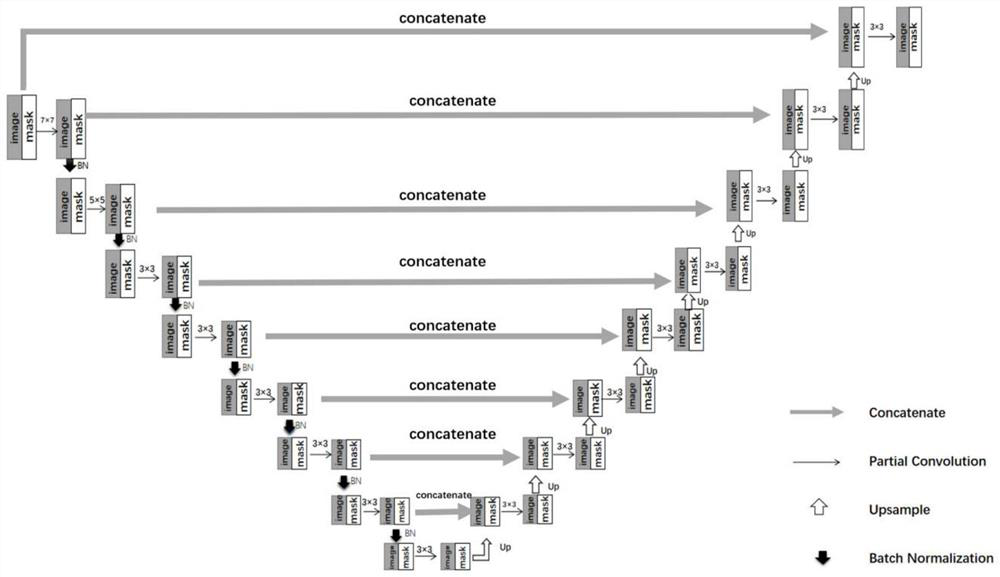
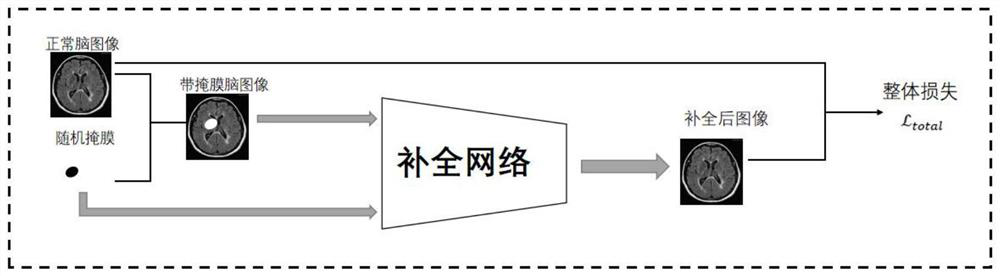
Tumor image brain region segmentation method and system based on image completion
PendingCN112529909AAchieve segmentationImprove accuracyImage enhancementImage analysisImaging brainRadiology
The invention discloses a tumor image brain region segmentation method and system based on image completion. The method comprises the steps of obtaining a to-be-segmented tumor image and a tumor mask;inputting the to-be-segmented tumor image and the tumor mask into a completion network to obtain a completed to-be-segmented image; wherein the completion network is obtained by training a PconvUnetnetwork by taking a normal brain image and a random mask as a training set and taking the minimum overall loss function as a target; inputting the completed to-be-segmented image into the segmentationnetwork to obtain brain partitions of the to-be-segmented tumor image; wherein the segmentation network is obtained by training the Unet network by taking a normal brain image and a corresponding image label as a training set and taking the minimum similarity measure loss function or the minimum cross entropy loss function as a target. The accuracy of brain region segmentation of the tumor imagecan be improved.
Owner:BEIJING ANDE YIZHI TECH CO LTD
Multipurpose analysis using second harmonic generating nanoprobes
ActiveUS8945471B2Microbiological testing/measurementChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceDiagnostic Radiology ModalityCell signaling
Second harmonic nanoprobes for multipurpose imaging of samples and a method of using such probes to monitor nucleotide sequencing in a Multi-SHG Detection Imaging (MSDI) modality and to monitor external electric field using voltage sensitive second harmonic generating (SHG) nanoprobes are provided. The SHG nanoprobes are comprised of various kinds of nanocrystals that do not possess an inversion symmetry and therefore are capable of generating second harmonic signals that can then be detected by conventional two-photon microscopy for in vivo imaging of biological processes and structures such as cell signaling, neuroimaging, protein conformation probing, DNA conformation probing, gene transcription, virus infection and replication in cells, protein dynamics, tumor imaging and cancer therapy evaluation and diagnosis as well as quantification in optical imaging for a wide-range of biological and non-biological processes and devices.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Composition and processes for crossing the blood-brain barrier with polypeptides for in vivo neuroimaging
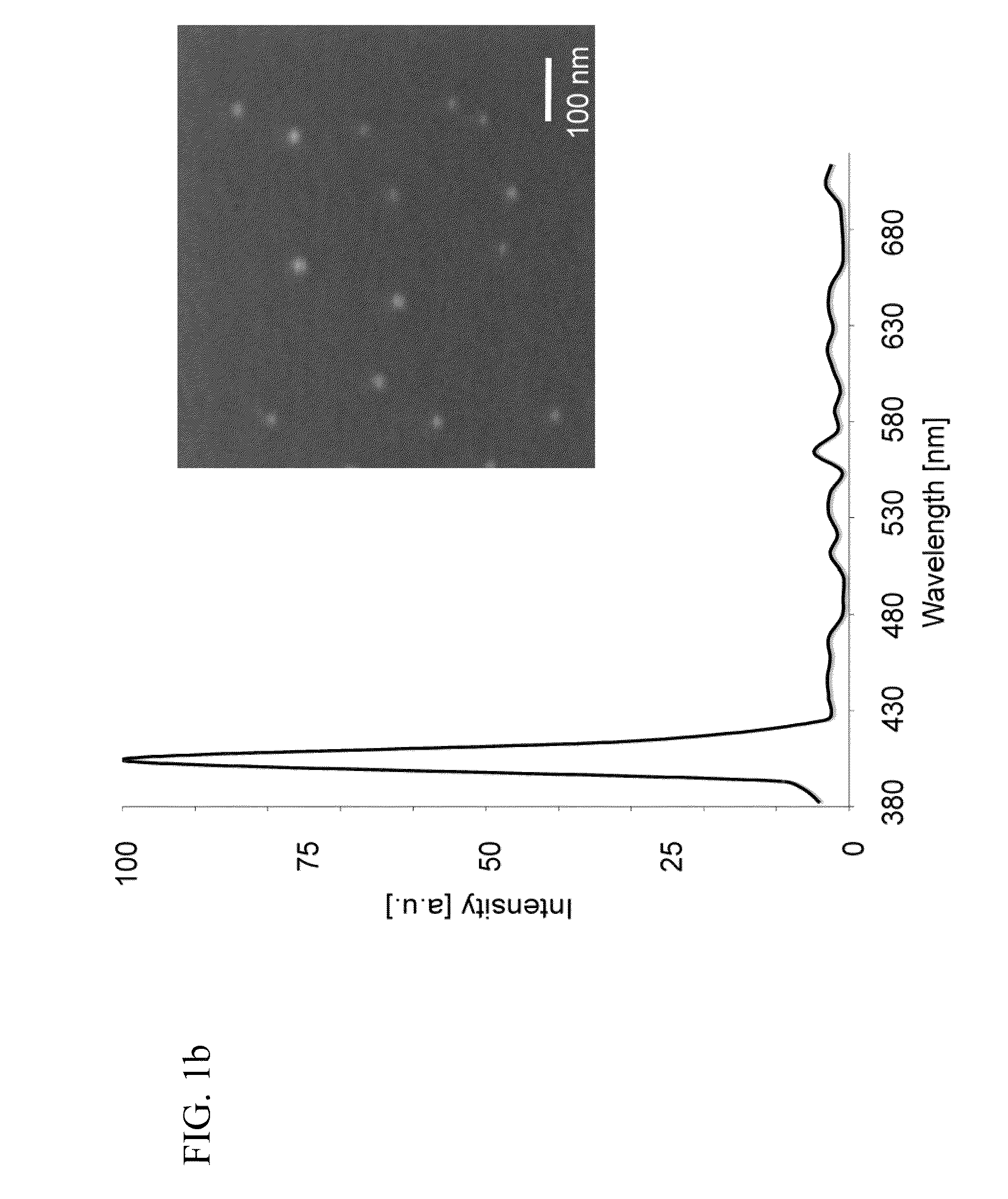
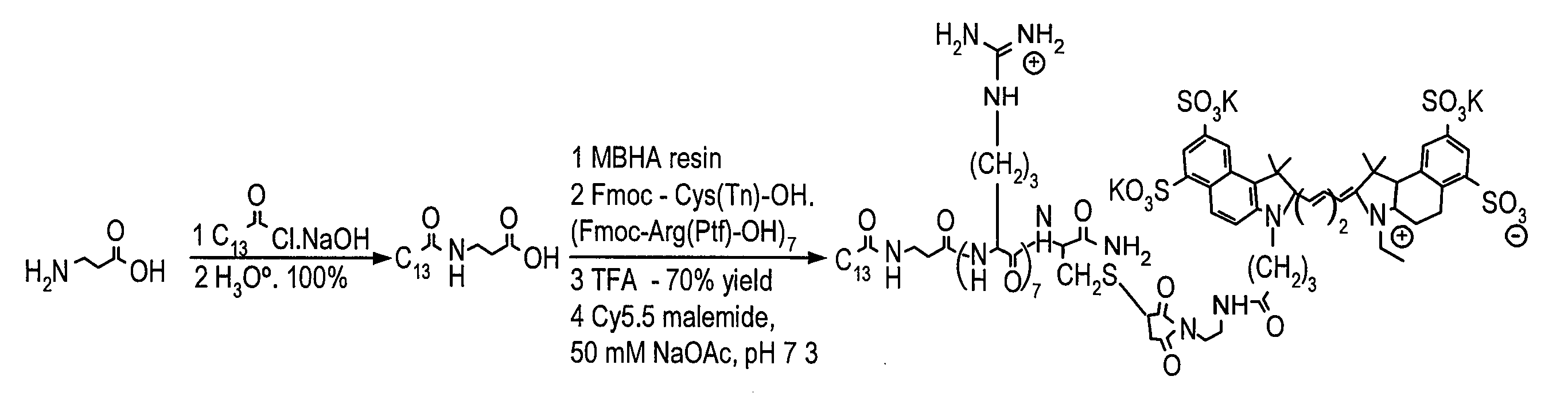
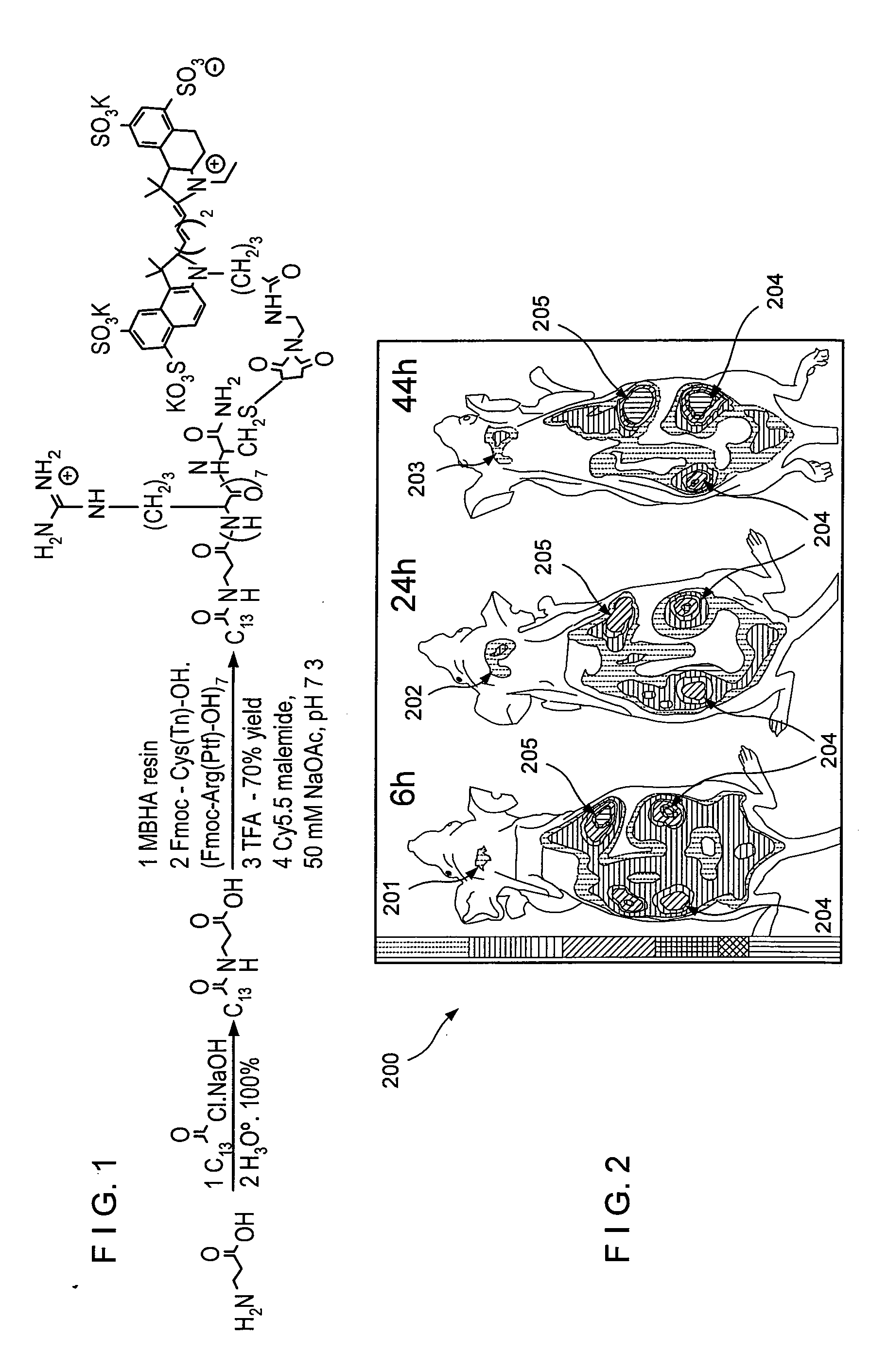
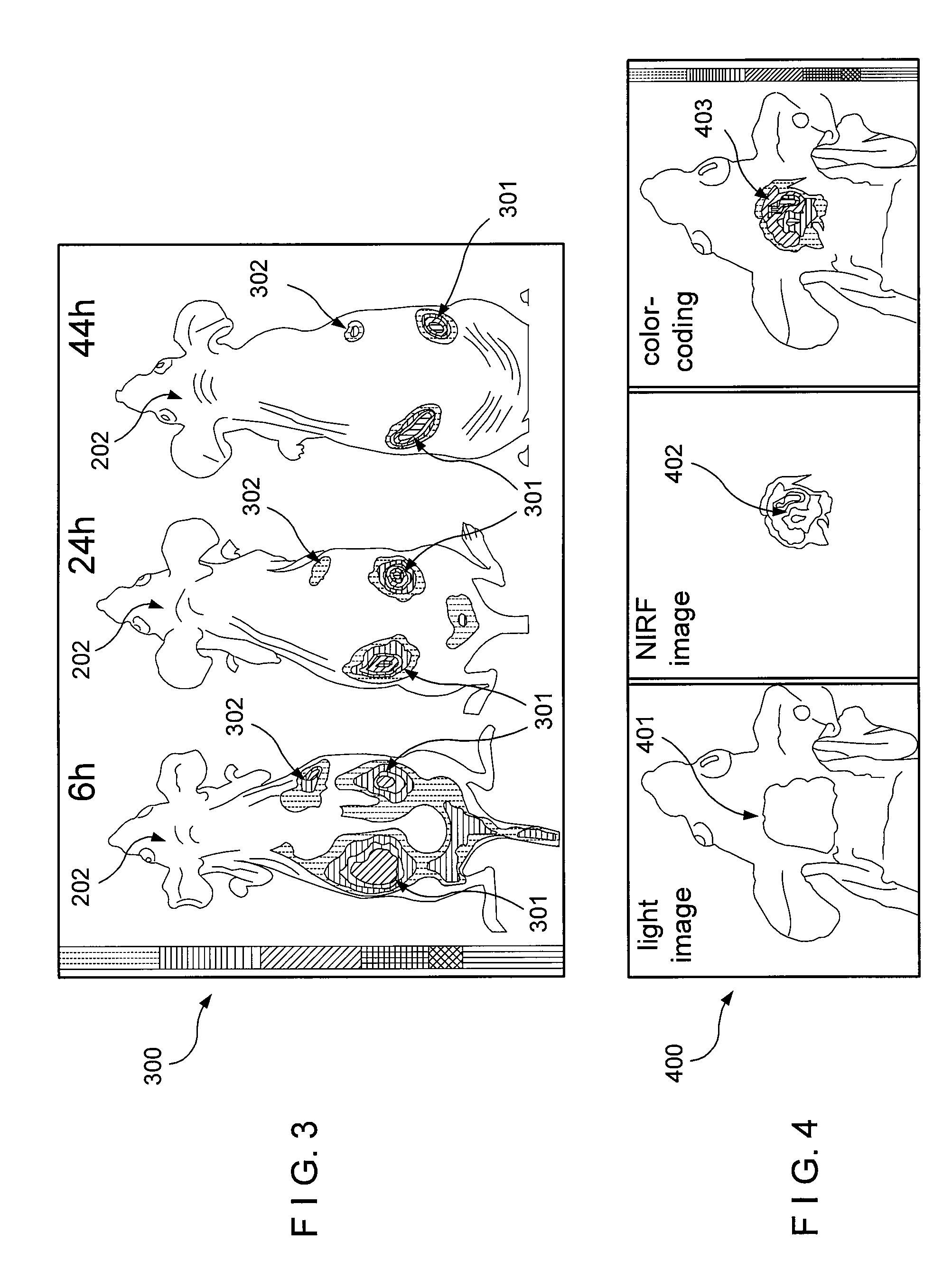
According to an exemplary embodiment of the present invention, a versatile delivery module based on a myristoylated polyarginine backbone can be provided to cross a blood-brain barrier (“BBB”). An incorporation of a fatty acid group can be achieved using a Schotten-Bauman reaction with quantitative yield, and a peptide can be further synthesized by conventional solid phase peptide synthesis (“SPPS”). An in vivo distribution of the delivery module into a brain over time using near-infrared (“NIR”) fluorescence imaging can be obtained. A fluorescent cargo can be detected in vivo after an intravenous injection and can be further characterized in perfused brains. A staining of an excised brain can show that the delivery module can primarily accumulate in neurons with occasional localization in astrocytes and endothelial cells. This exemplary approach can be used for the delivery of imaging probes and targeted therapeutics across the BBB.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
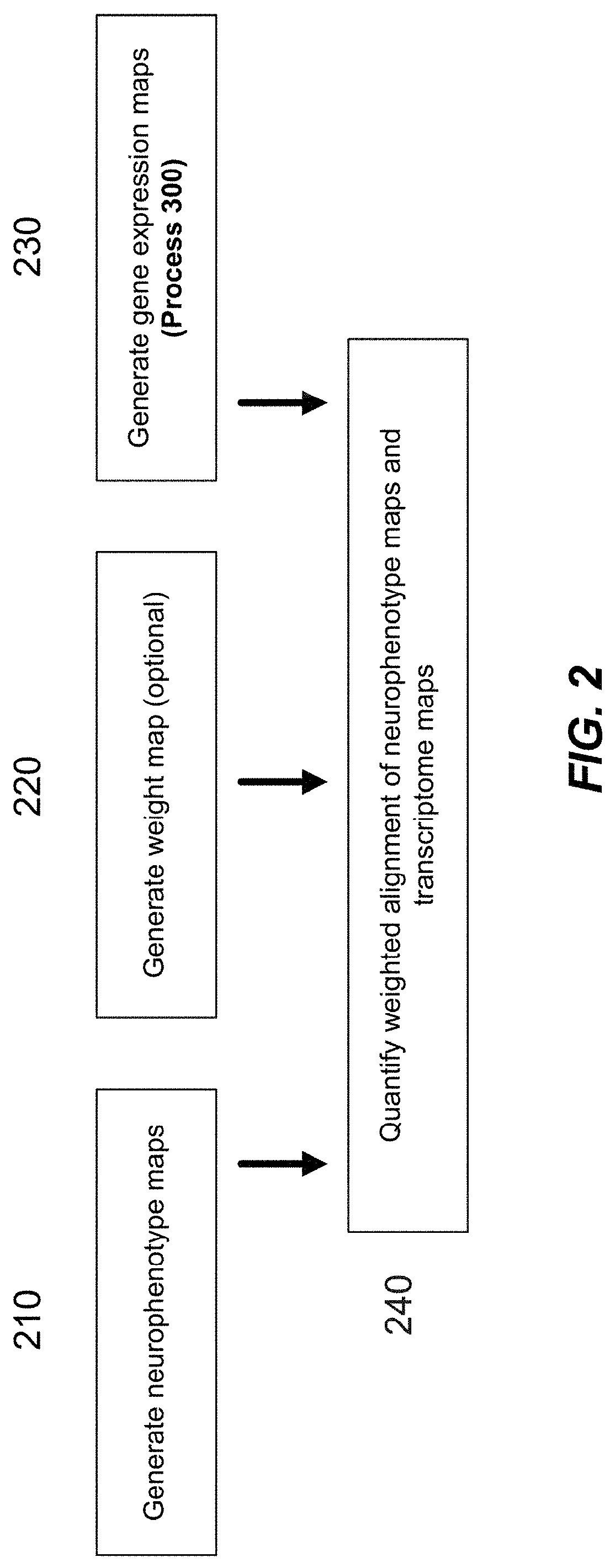
Methods and systems for computer-generated predictive application of neuroimaging and gene expression mapping data
ActiveUS20190355439A1Efficient designPrecise positioningDrug and medicationsBiostatisticsImaging brainTopography
The present disclosure relates to computer generated topographies from computer correlations of neurobehavioral phenotype mapping data and gene expression mapping data. Neurobehavioral phenotype mapping data is obtained for a selected phenotype and correlated with gene expression mapping data for one or more genes to define a phenotype-gene pair topography for each phenotype-gene pair. A score for each phenotype-gene pair is determined based on the correlation. The scores are used to identify genes, or drug targets, associated with the respective gene of the respective phenotype-gene pair. Conversely, gene expression mapping data is obtained for a selected gene and correlated with neurobehavioral phenotype mapping data for one or more phenotypes to define a gene-phenotype topography for each gene-phenotype pair. A score for each gene-phenotype pair is determined based on the correlation. The scores are used to identify a phenotype associated with the respective phenotype-gene pair.
Owner:YALE UNIV +1
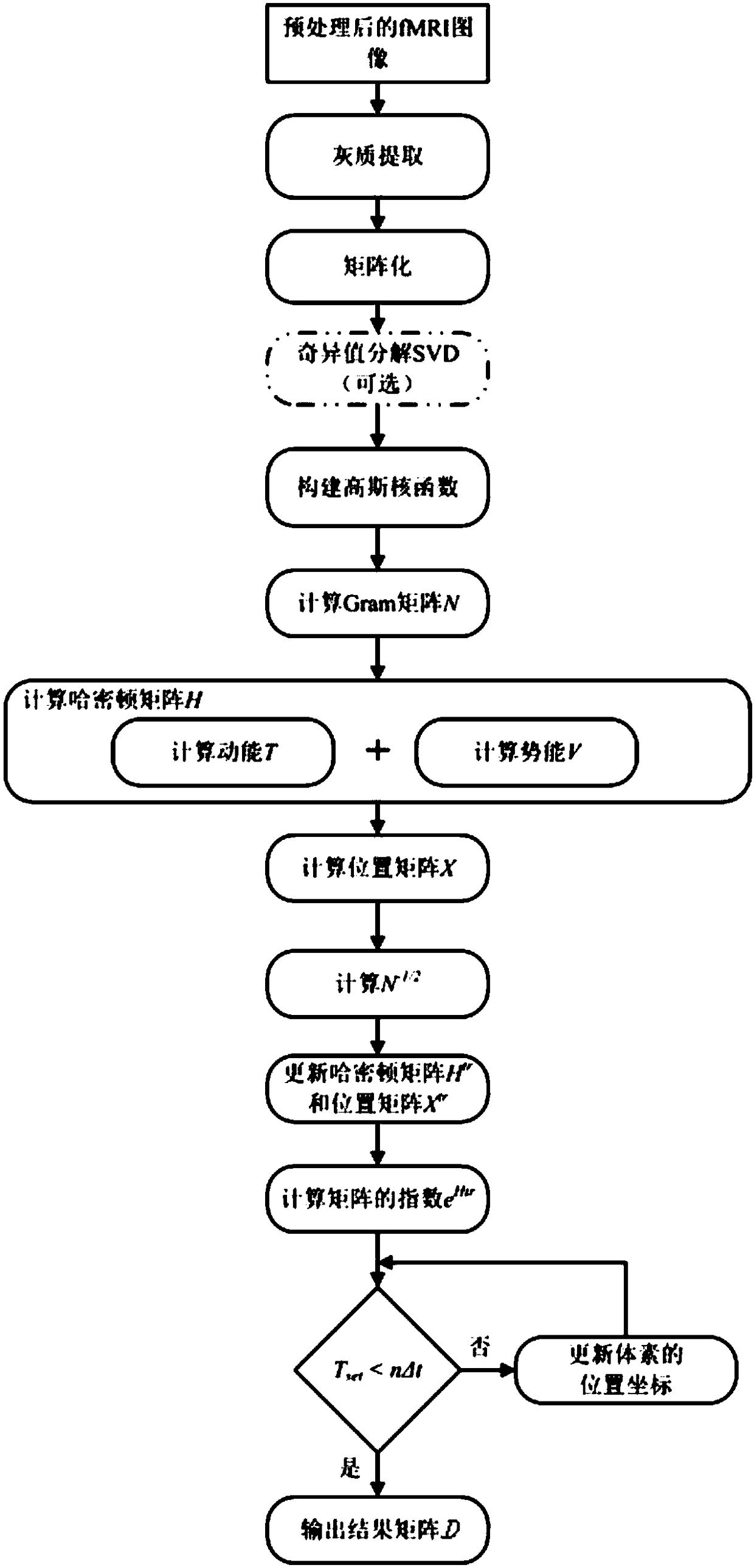
A magnetic resonance image brain zoning method and system
ActiveCN109410195AImprove processing efficiencyHigh precisionImage enhancementImage analysisImaging brainQuantum modeling
A magnetic resonance image brain zoning method and system are disclosed. The magnetic resonance image brain zoning method comprises: preprocessing fMRI brain images; the dynamic evolution of quantum system is used to partition the preprocessed fMRI brain images. The invention converts brain regions into a dynamic evolution process of a quantum system. The fMRI images of a single individual or multiple individuals are partitioned by quantum process, which makes use of the advantages of quantum model and quantum algorithm in processing big data with high dimension, and is suitable for fMRI imageprocessing and brain functional partitioning, and improves the processing efficiency of fMRI images and the precision of brain partitioning results.
Owner:SHANDONG FIRST MEDICAL UNIV & SHANDONG ACADEMY OF MEDICAL SCI
Methods for measuring the distribution, metabolism and clearance of traceable small molecule compounds in the brain
InactiveCN102293634AThe calculation method is accurateDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsTissue fluidMolecular property
The invention provides a method for measuring the distribution, metabolism and clearance of traceable small molecule compounds in the brain, the method comprising: placing the brain of the subject under test in an imaging device; using the imaging device to form the basis of the brain of the subject under test Imaging; introduce the compound into the interstitial fluid of the brain of the subject; use the imaging device to form a dynamic image of the brain of the subject; perform temporal and spatial preprocessing on the dynamic image and the basic image to obtain the net concentration image of the compound in the brain; Model estimation and analysis are performed on the net concentration images to obtain information on the distribution, metabolism and clearance process of compounds in the brain after they diffuse in the interstitial fluid of the brain. The present invention introduces a traceable small molecule compound of a corresponding size, dynamically displays and quantitatively measures the process of distribution, metabolism and clearance of the molecule and small molecules with similar molecular weight and properties in the brain through the brain tissue fluid in the living body.
Owner:PEKING UNIV THIRD HOSPITAL
Carp brain electrode implantation method through magnetic-resonance positioning and navigation
InactiveCN106974653AAccurately obtain scale parametersReduce positioning errorsHead electrodesSensorsFast spin echoImplantable Stimulation Electrodes
The invention discloses a carp brain electrode implantation method by means of magnetic resonance positioning and navigation. Taking the first fish scale (the junction of the head and the trunk) as the origin, reference scratches are made on the surface of the skull based on the characteristics of the carp skull to establish Space coordinate system; with the help of the T2WI fast spin echo scanning sequence of the magnetic resonance equipment, the brain is scanned and imaged, the two-dimensional coordinates of the electrode stimulation site are converted into three-dimensional space coordinates, and the spatial coordinates of the brain stimulation electrode implantation site are determined The coordinate value of the system; according to the coordinate value, the brain stimulation electrode is implanted for positioning and navigation. The invention can not only locate and navigate for the implantation of the carp aquatic animal robot brain stimulation electrodes, but also provide new positioning and navigation means for the implantation of various animal robot brain stimulation electrodes.
Owner:YANSHAN UNIV
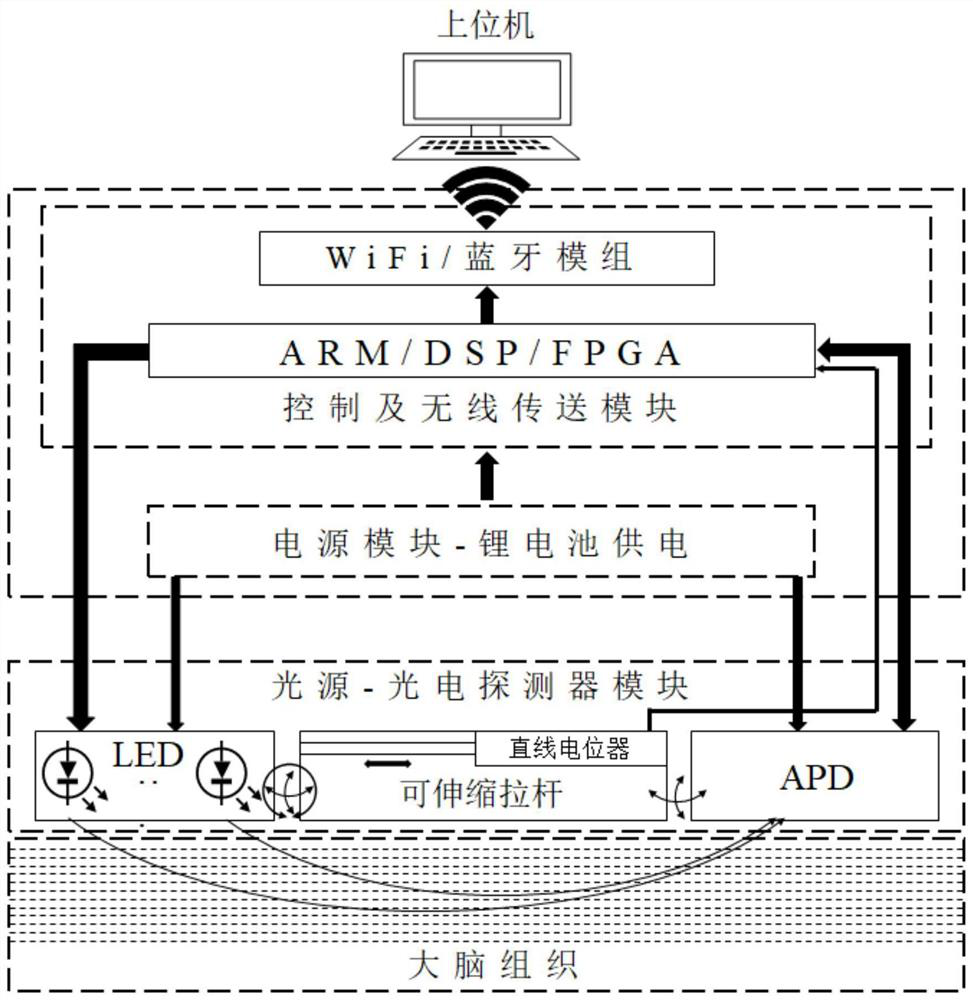
Worn type fNIRS brain imaging system
ActiveCN112401881AReduce measurement errorEnabling Multimodal Brain ImagingDiagnostics using spectroscopySensorsImaging brainPhotovoltaic detectors
The invention discloses a worn type fNIRS brain imaging system. The worn type fNIRS brain imaging system comprises a light source-photodetector module, a control and wireless transmitting module, a power supply module and an upper computer. According to the worn type fNIRS brain imaging system disclosed by the invention, the problem of worn type fNIRS brain imaging systems or EEG-fNIRS multimode brain imaging systems that relative positions of probes cannot be adjusted freely and detectable regions are limited can be solved; according to the system disclosed by the invention, relative positions of a light source probe and a photodetector can be adjusted freely according to actual situations, the spacing between the light source probe and the photodetector is measured automatically, measurement errors of brain blood oxygen signals can be reduced, and detectable regions of a brain can be adjusted flexibly; and the system disclosed by the invention can be matched with brain electric signal detection, brain electric sensors can be mounted around cylindrical bottom faces of the light source probe and the photodetectors, spacing among the brain electric sensors changes synchronously along with the probes, so that EEG-fNIRS multimode brain imaging is achieved, and brain electric signals of different densities can also be acquired.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
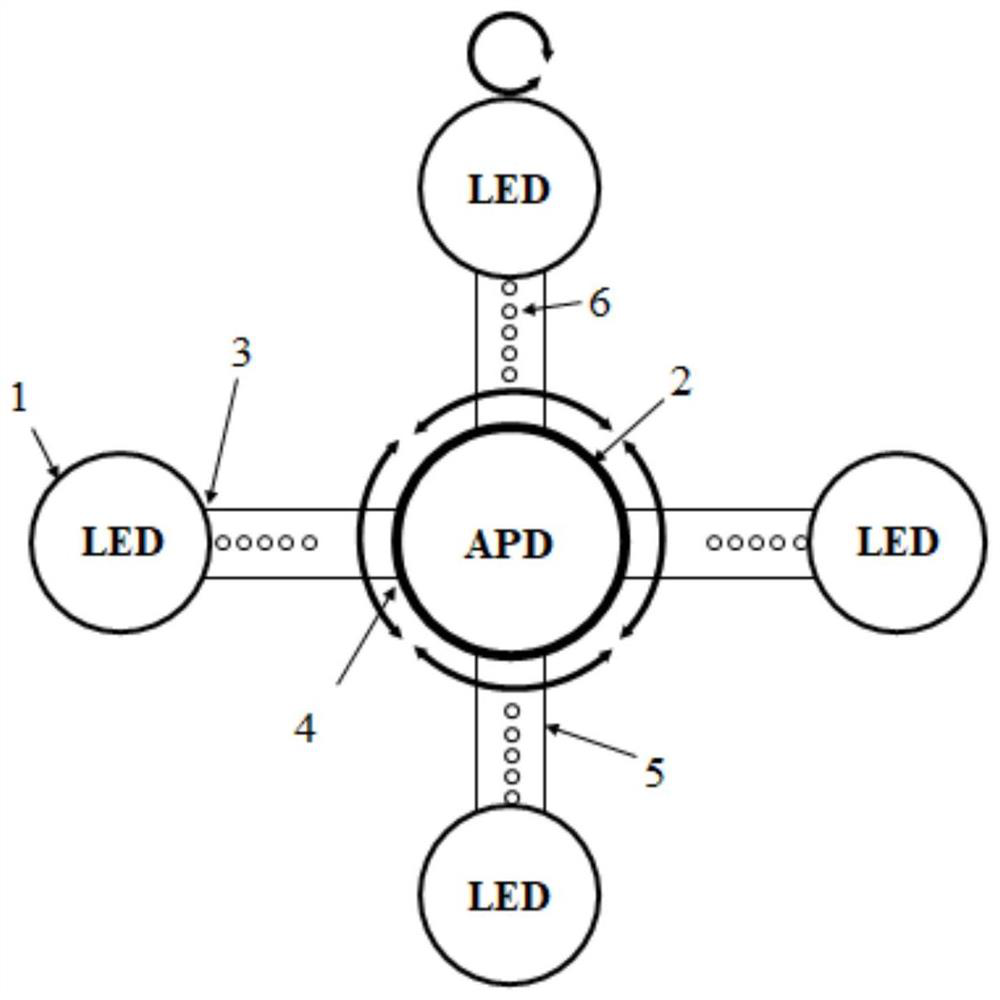
Brain imaging detection device
PendingCN111053536ASimple structureSimple and convenient distributionDiagnostics using spectroscopySensorsImaging brainImage detection
The invention relates to the field of brain imaging, in particular to a brain imaging detection device. The brain imaging detection device comprises a head sleeve, a plurality of detectors and a plurality of near-infrared light sources, wherein a plurality of contact parts are raised on the surface of the inner side of the head sleeve in the thickness direction of the head sleeve, and the detectors and the near-infrared light sources are arranged at the tops of the contact parts. The device has the advantages as follows: the contact parts can push the hair of the human head aside to make the detectors and the near-infrared light sources to be in contact with the scalp, so that the detectors can accurately detect information in the brain; and the device has few parts and is simple in structure.
Owner:INST OF FLEXIBLE ELECTRONICS TECH OF THU ZHEJIANG +1
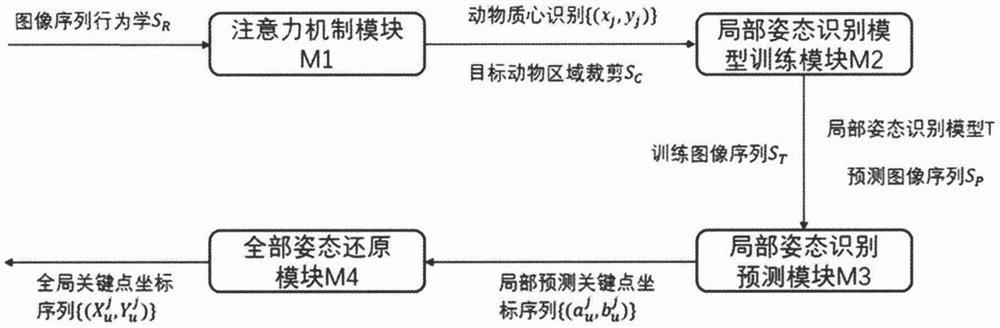
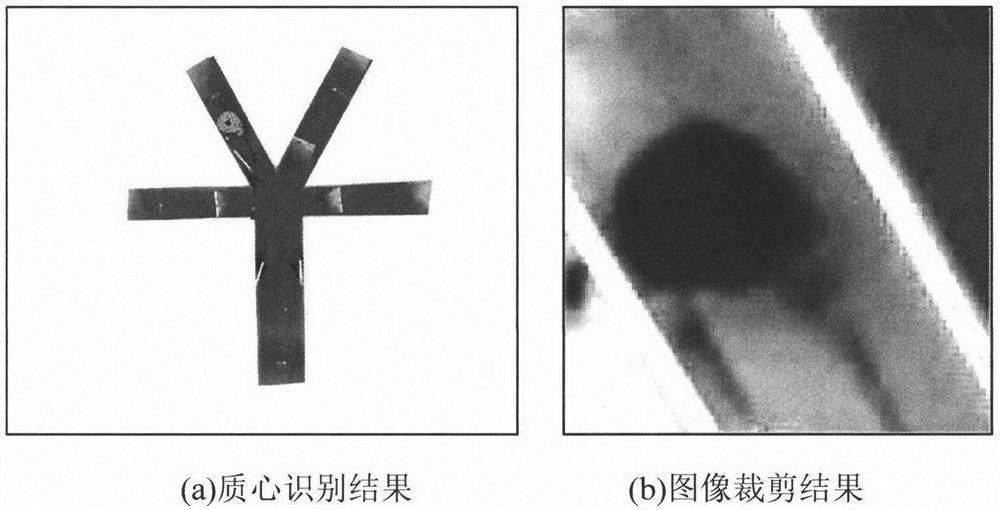
Animal long-time posture recognition system based on infrared image and wearable optical fiber
PendingCN112184734AAchieve high-precision recognitionShorten the durationImage enhancementImage analysisImaging brainMedicine
The invention discloses an animal long-time posture recognition system based on an infrared image and a wearable optical fiber. The system comprises an attention mechanism module M1, a local posture recognition model training module M2, a local posture recognition prediction module M3, and a global posture restoration module M4. According to the invention, high-precision identification of the keynode of the animal behavioral infrared low-resolution video wearing the optical fiber equipment is realized, the time length of manual verification is greatly reduced, the influence of animal curling,rotation, shooting illumination fluctuation and the like is solved, and the system can be widely applied to the field of brain imaging.
Owner:NANJING RAYGEN HEALTH CO LTD
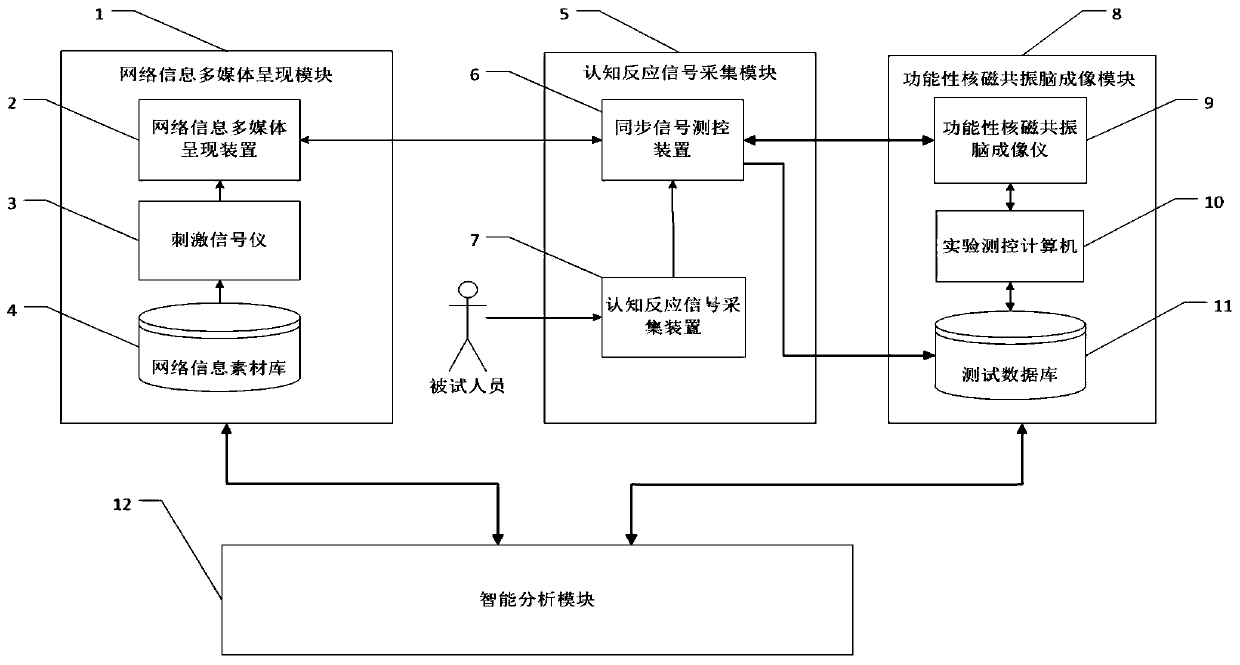
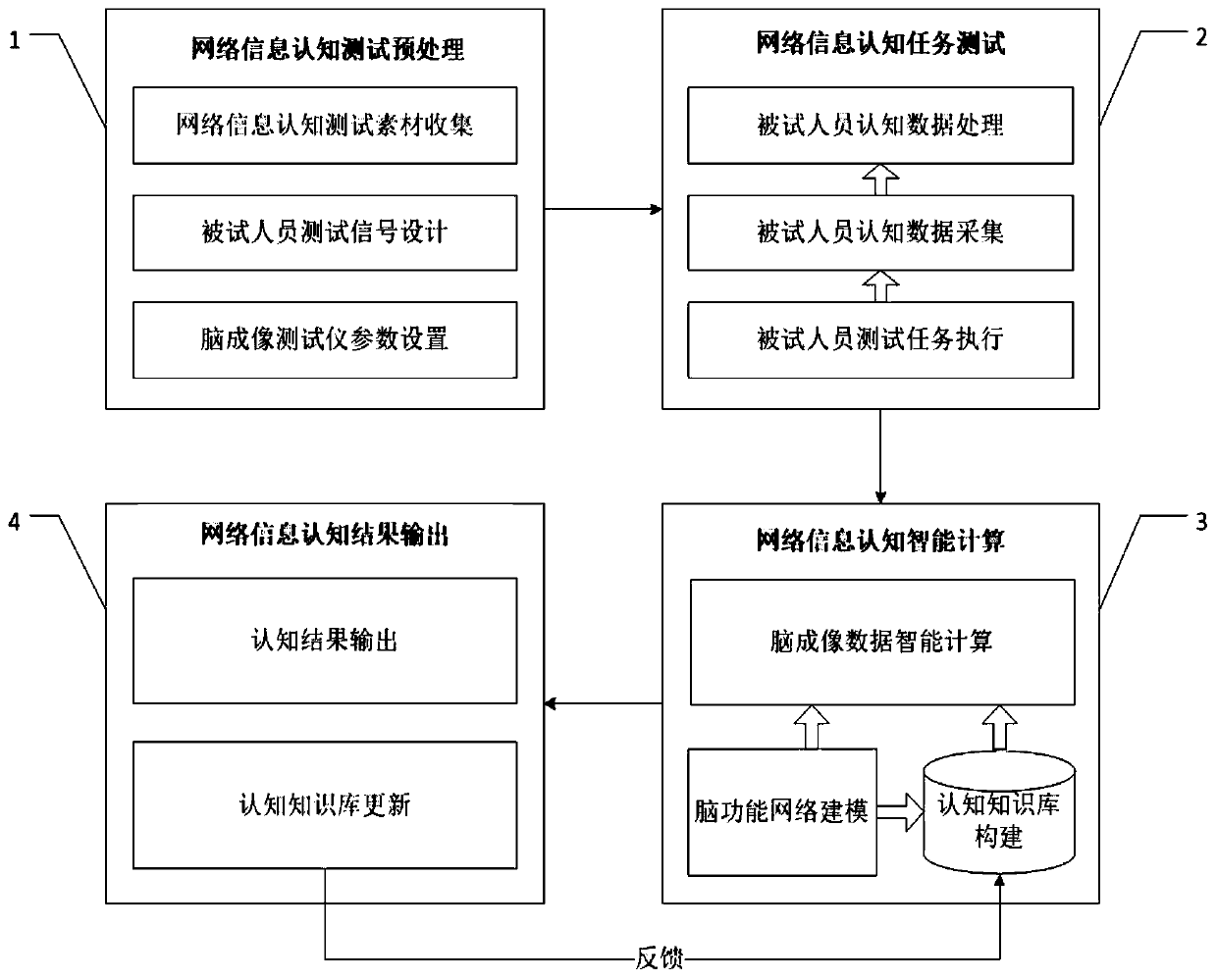
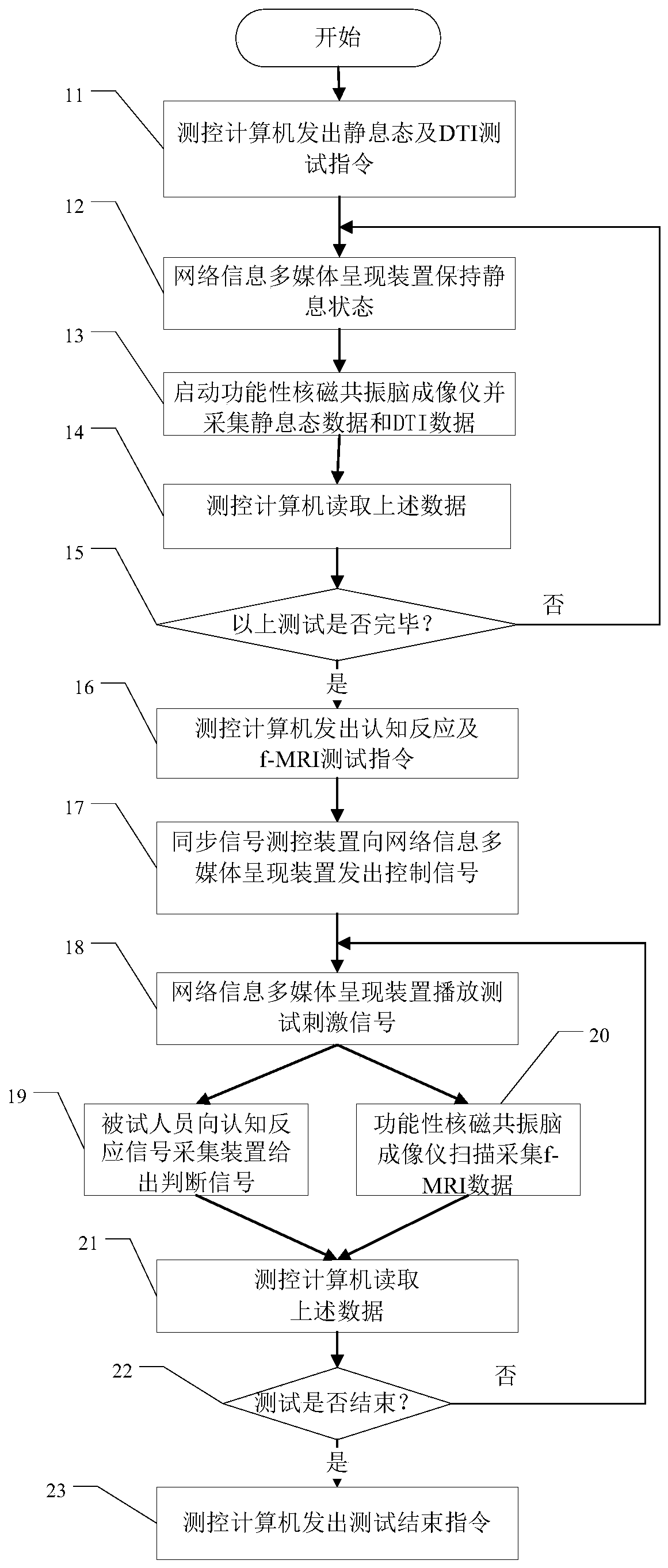
Brain imaging intelligent test analysis method for network information cognition and system thereof
ActiveCN110192860AImprove design qualityImprove effectivenessDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsHardware modulesEngineering
The invention belongs to the technical field of information, and specifically relates to a brain imaging intelligent test analysis method for network information recognition and a system thereof. Themethod of the invention comprises four steps of network information cognition test preprocessing, network information cognition task testing, brain imaging data cognition calculation, and network information cognition result output. The test analysis system of the invention comprises four software modules corresponding to four steps, and four hardware modules of a network information multimedia presentation module, a cognitive response signal acquisition module, a functional nuclear magnetic resonance brain imaging module and an intelligent analysis module. The method has the advantages of designing a network information test signal by using a virtual reality technology, modeling a brain function network based on a neural network model, and performing fusion analysis of a brain rest state,DTI and f-MRI test data; and realizing intelligent calculation through an artificial intelligence technology. More accurate test analysis results can be obtained by the method.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
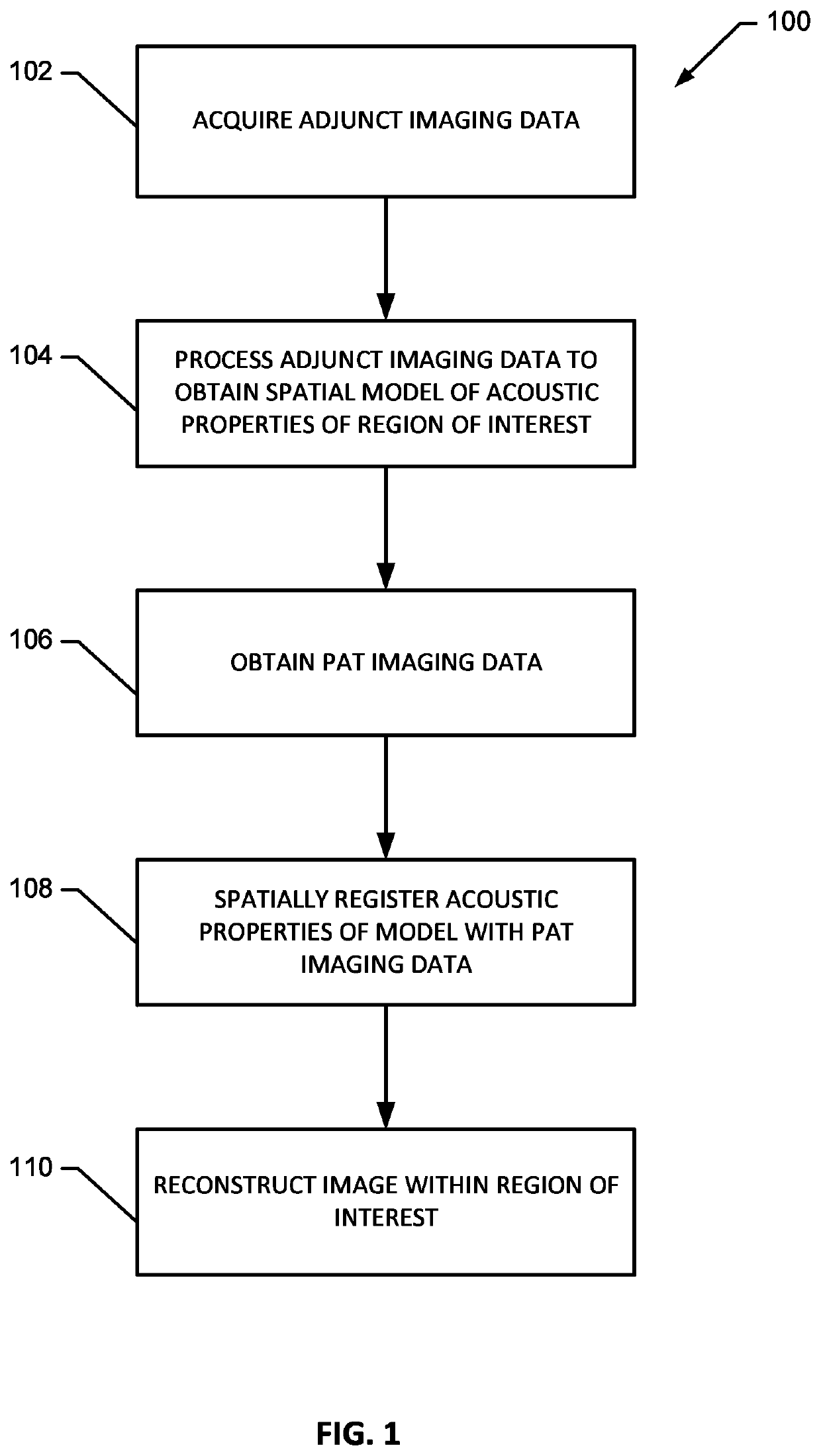
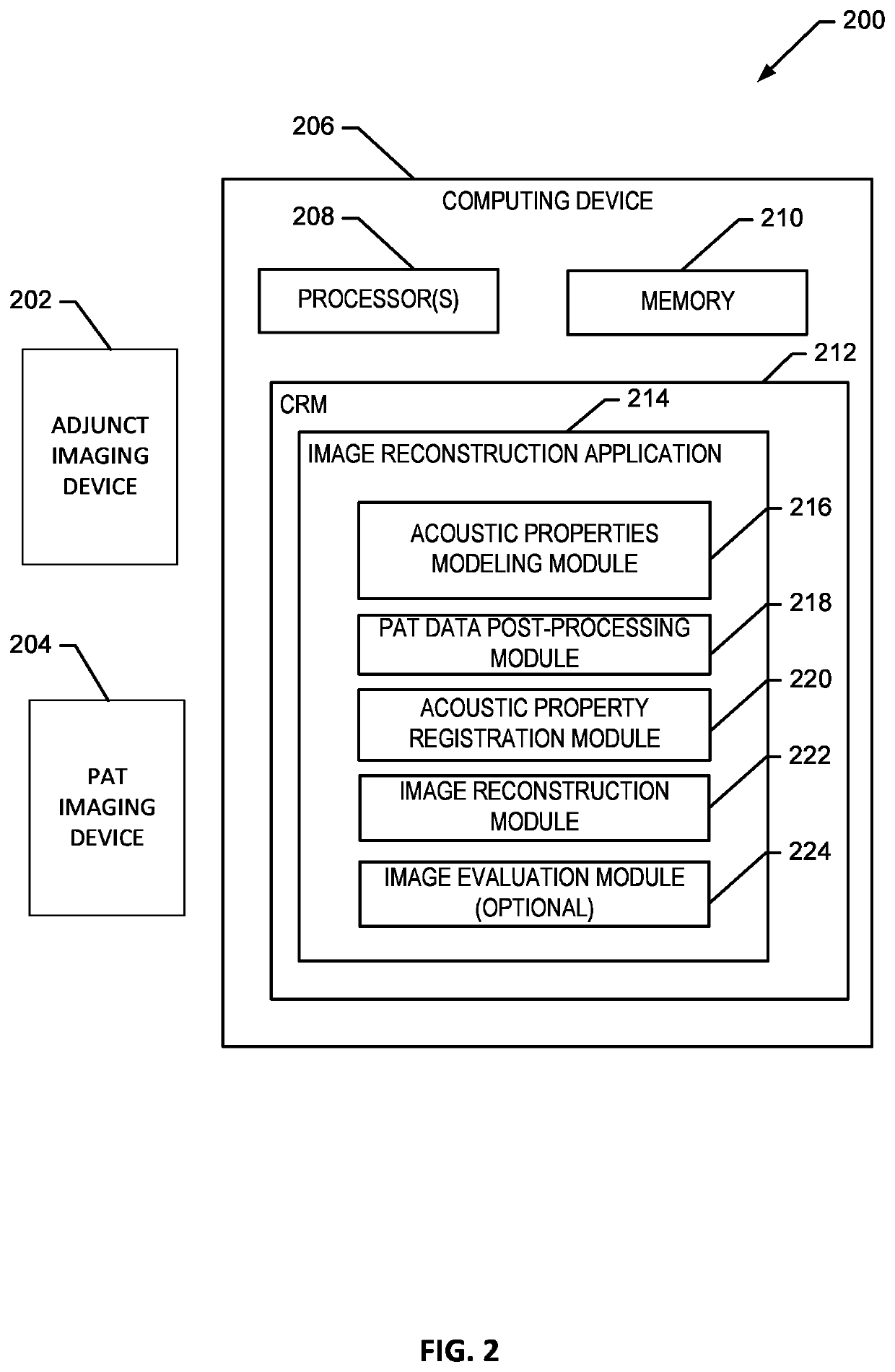
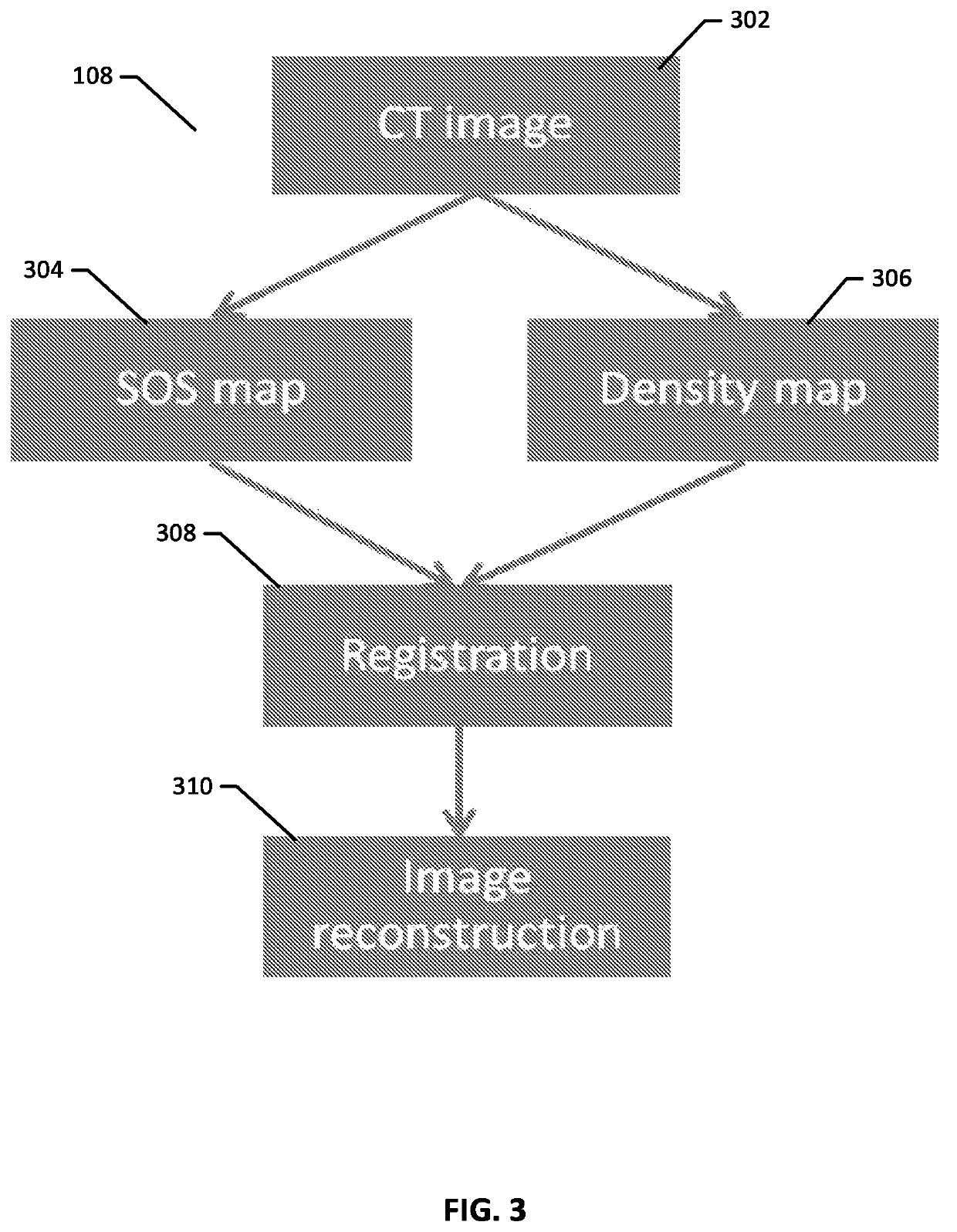
Transcranial photoacoustic/thermoacoustic tomography brain imaging informed by adjunct image data
ActiveUS11020006B2Medical imagingMaterial analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesImaging brainPhotoacoustic imaging in biomedicine
Systems and methods of reconstructing photoacoustic imaging data corresponding to a brain of a subject through a skull of a subject utilizing a reconstruction method that incorporates a spatial model of one or more acoustic properties of the brain and skull of the subject derived from an adjunct imaging dataset.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Three-dimensional brain magnetic resonance image brain cortex surface maximum principal direction field diffusion method
InactiveCN101866485AGeometrically preciseExact topologyImage analysisDiagnostic recording/measuringDifferential coefficientDiffusion methods
The invention relates to a three-dimensional brain magnetic resonance image brain cortex surface maximum principal direction field diffusion method, which has the technical scheme that the method comprises the following steps: carrying out pretreatment and brain cortex surface reconstruction on three-dimensional brain magnetic resonance images; calculating the principal curvature, the principal direction and the differential coefficient of the principal curvature of a peak on the brain cortex surface; using an alpha-expanon graph cut method for minimizing an energy function to carry out diffusion on the maximum principal direction field; and projecting the diffused maximum principal direction field into a tangent plane. The invention has the advantages that: 1. the method sets the weights of smooth items and data items in different regions on the brain cortex surface into different values, so the inherent geometrical structure and discontinuity in the maximum principal direction field can be perfectly maintained; and 2. the principal direction field diffusion is regarded as an energy minimization problem which is converted into a diffusion marking problem, and the alpha-expanon graph cut method can be used for effectively working out the strong local optimum solution of the energy function.
Owner:JIANGSU SHUANGNENG SOLAR ENERGY +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com