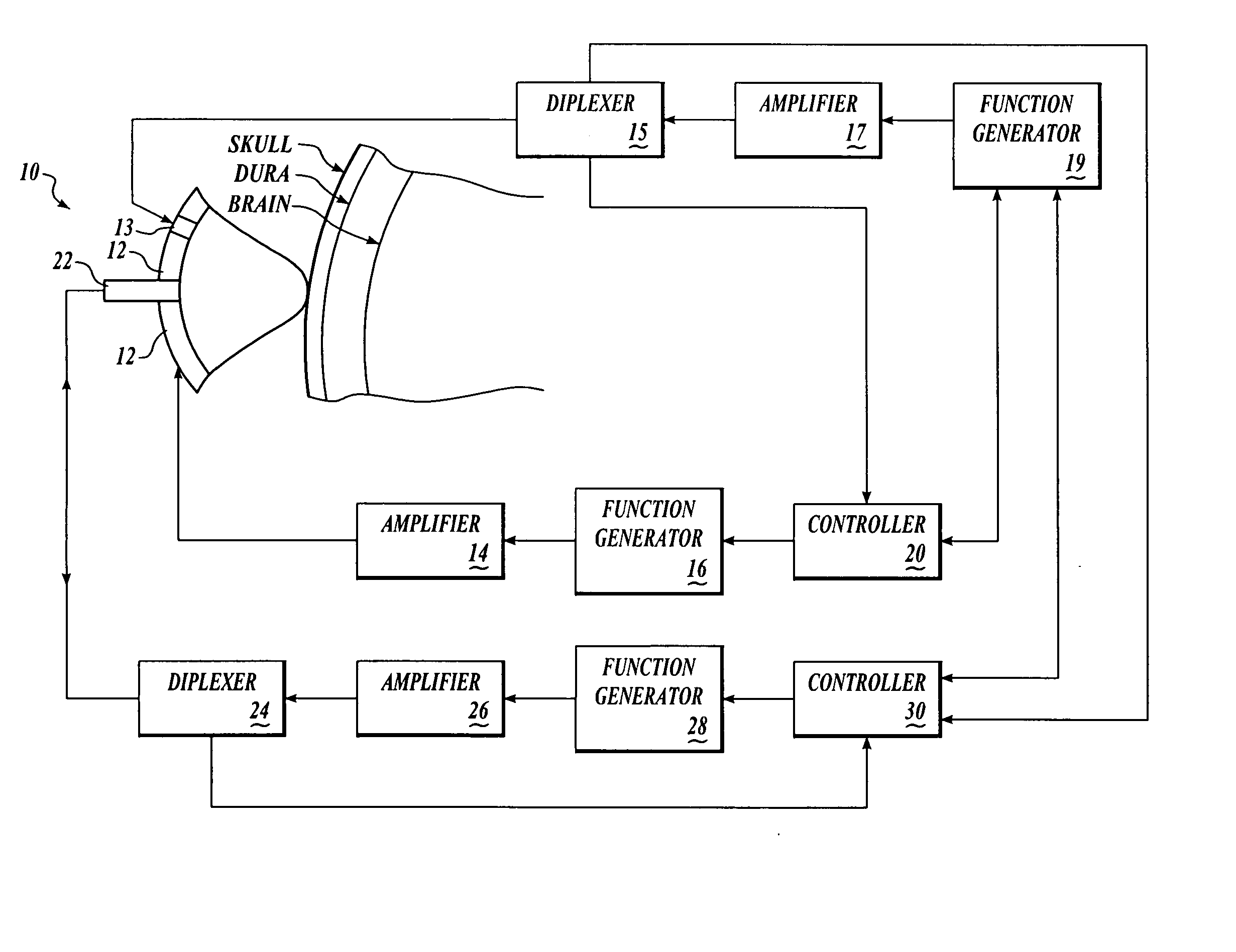
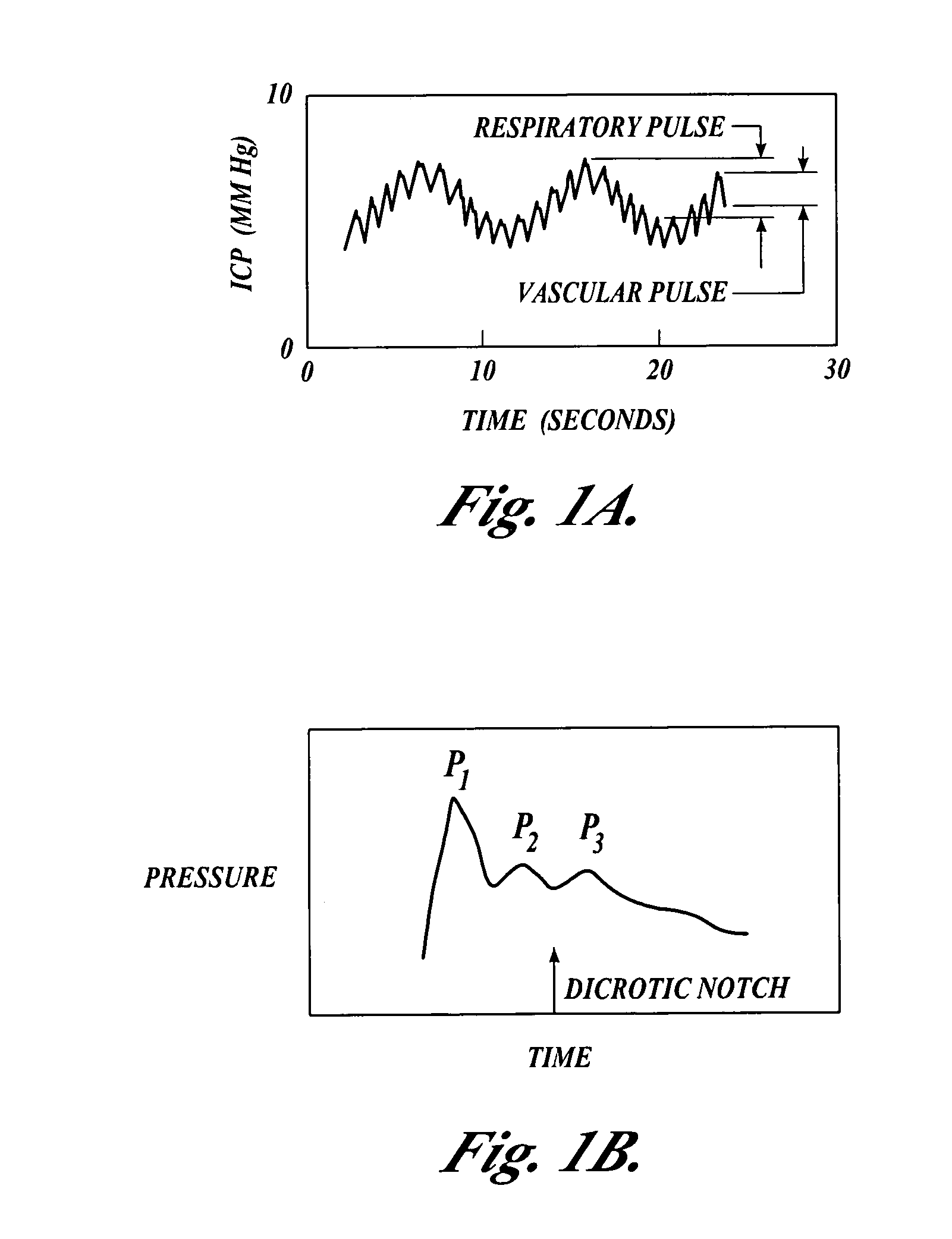
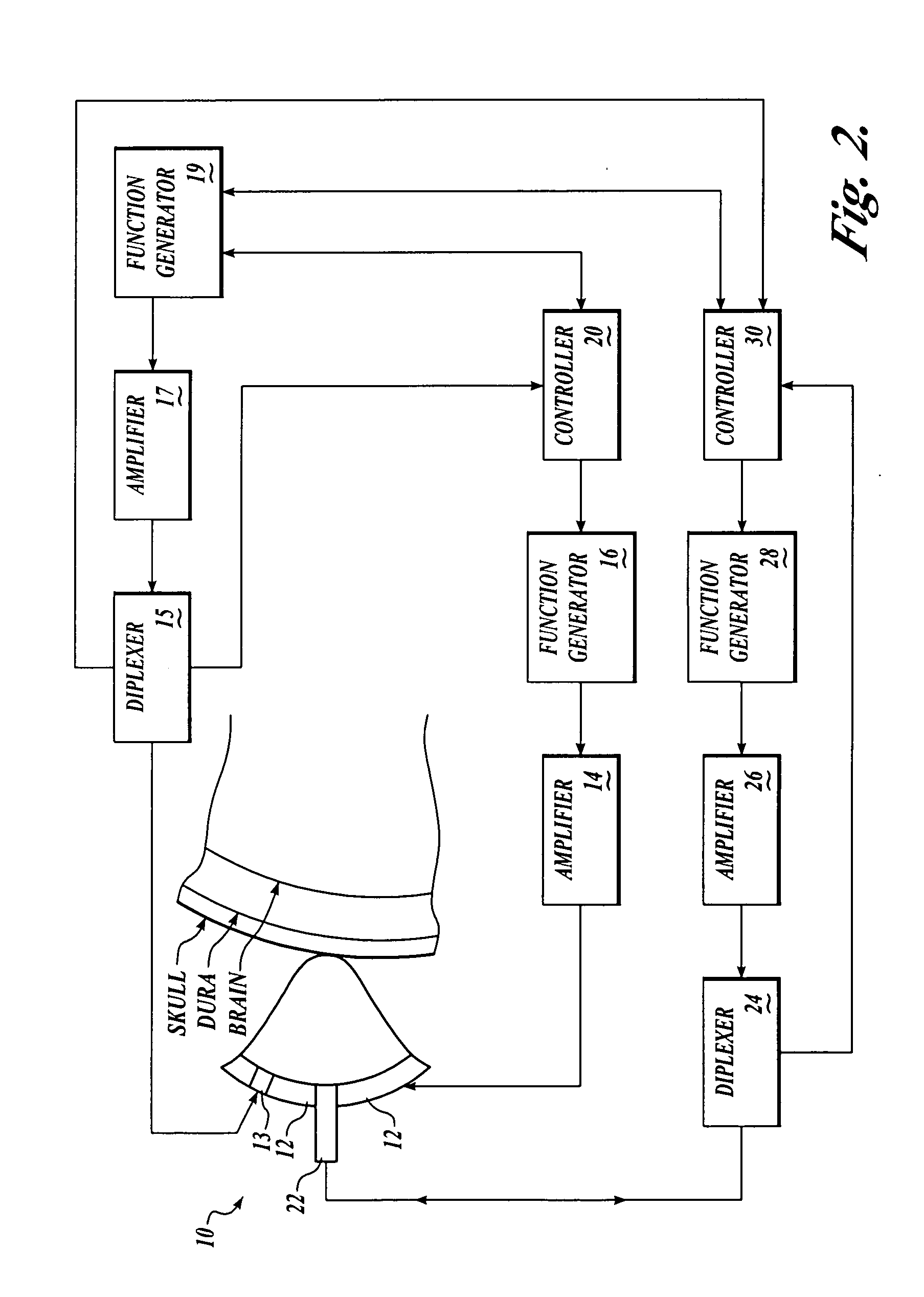
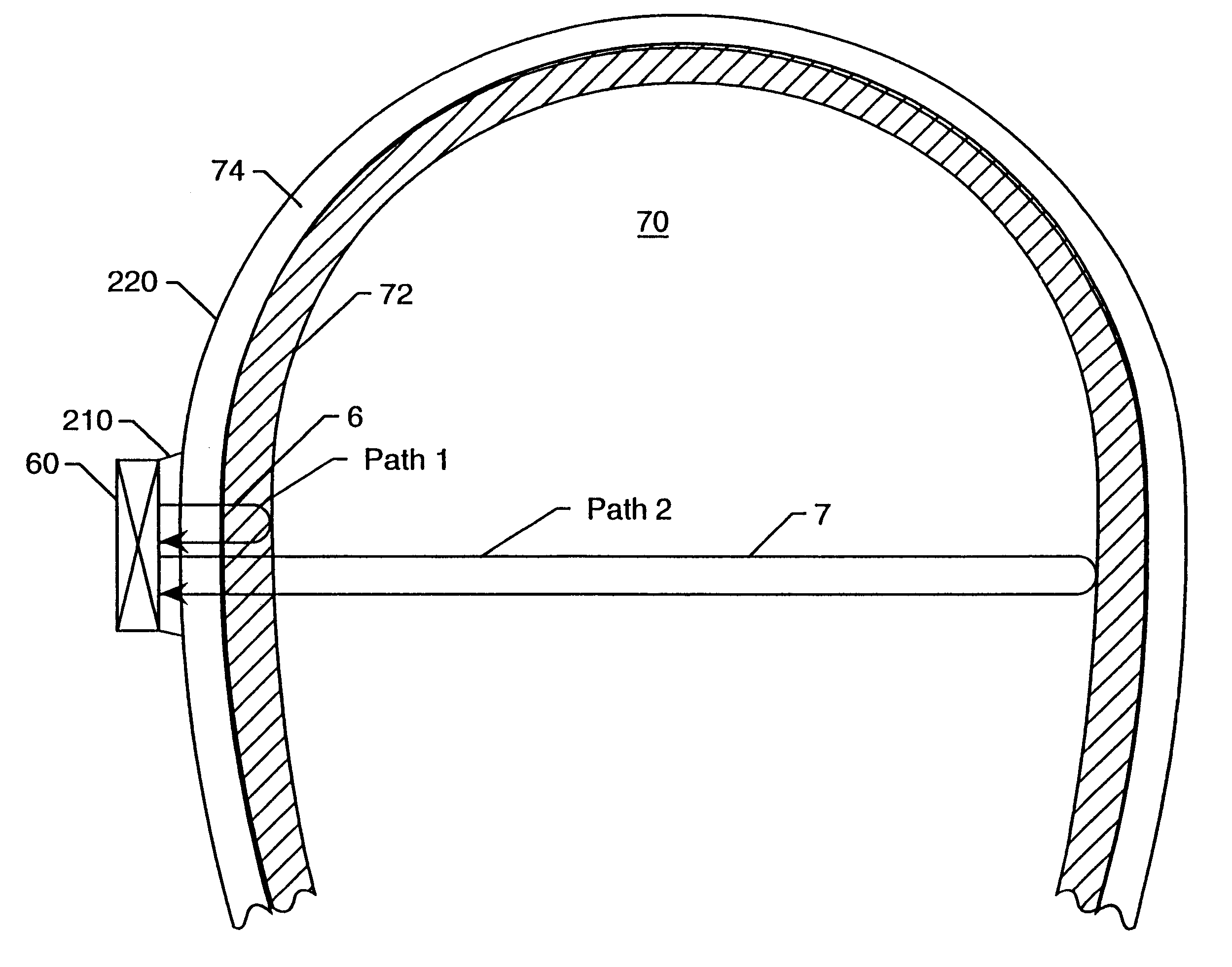
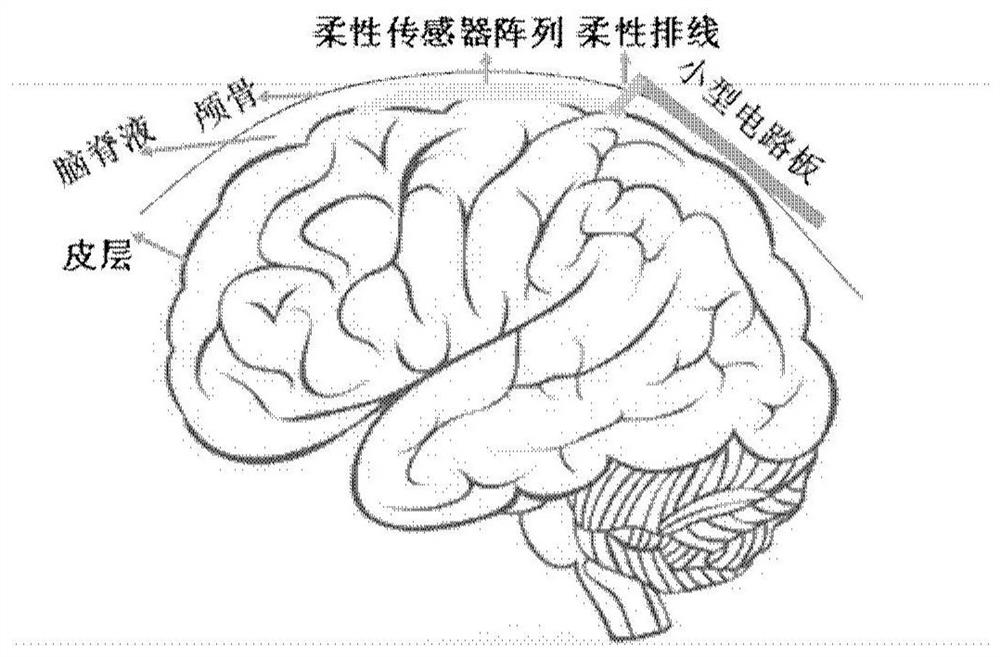
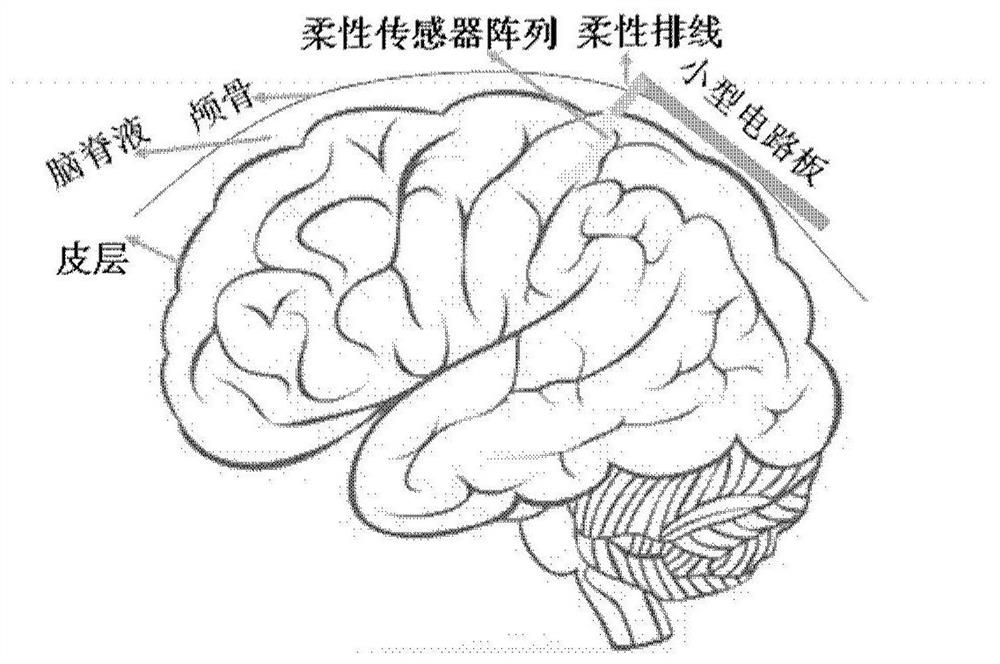
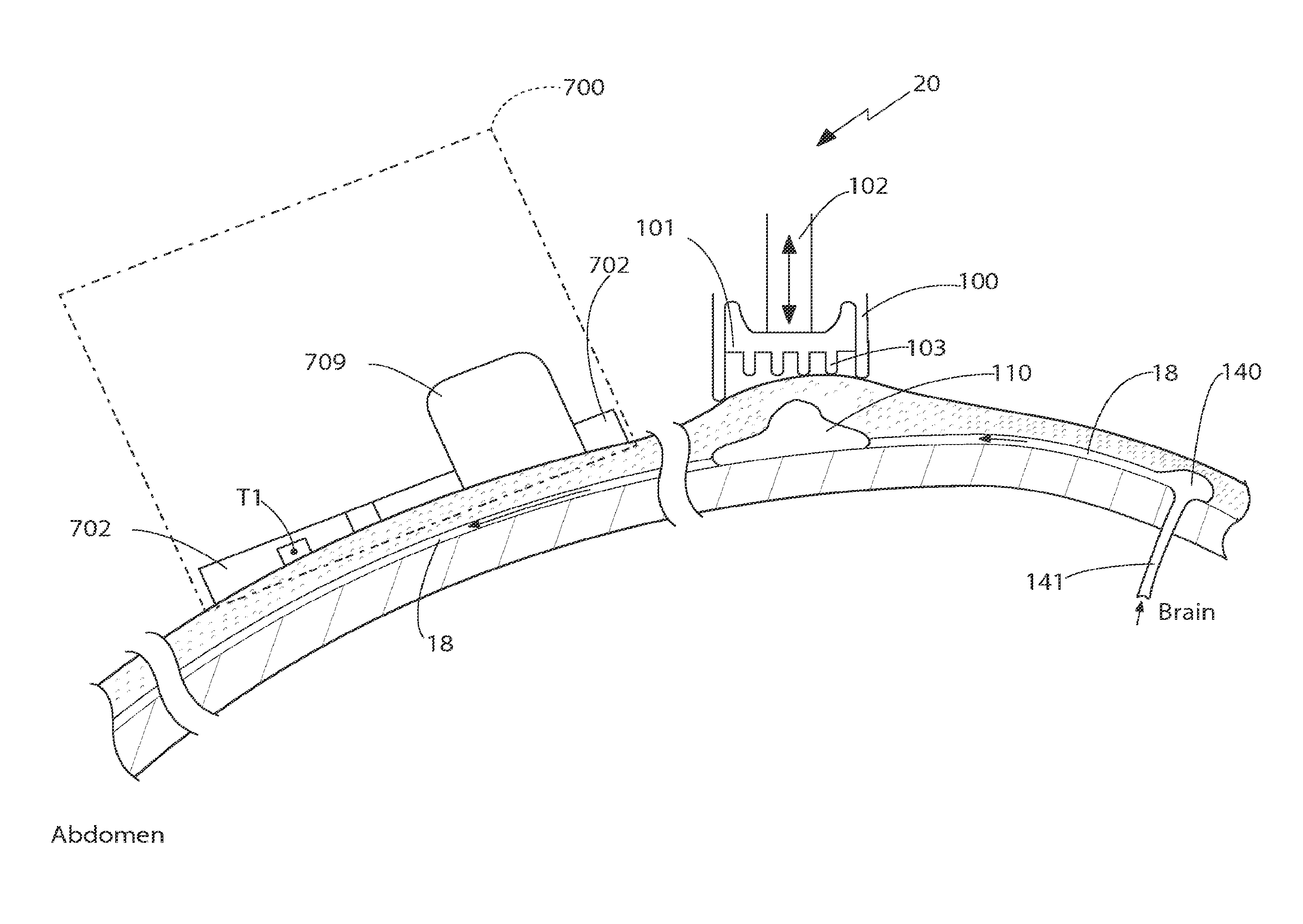
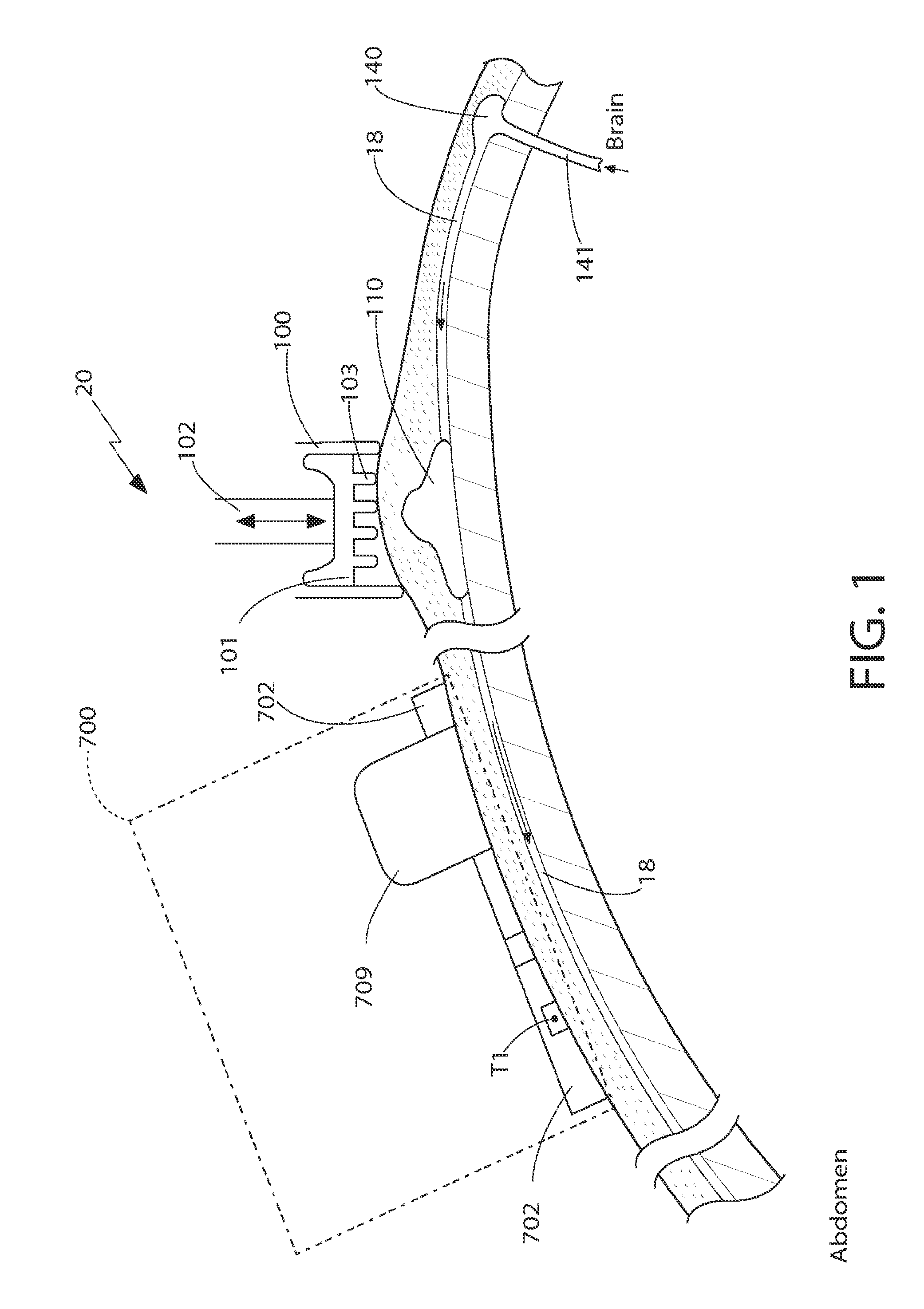
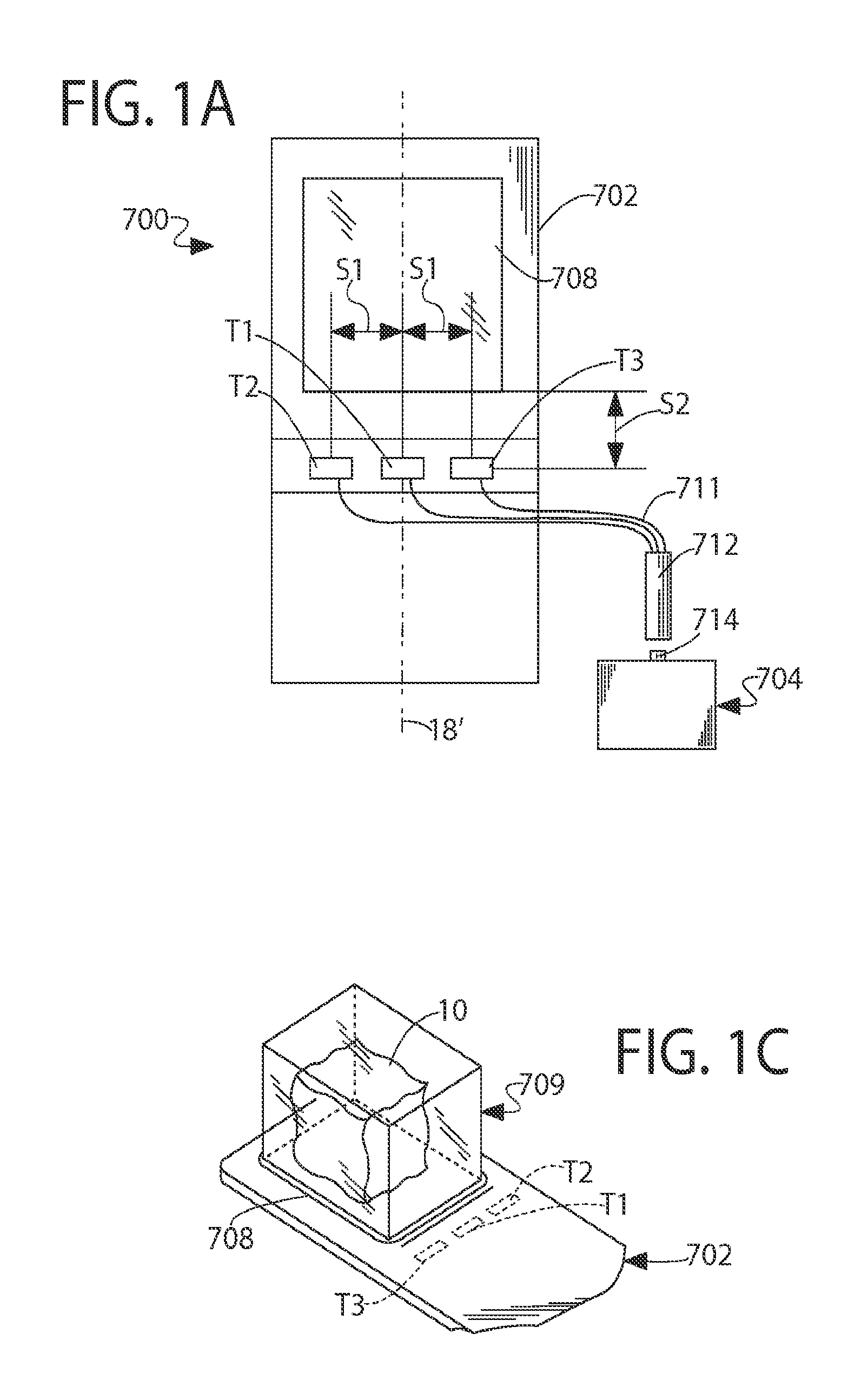
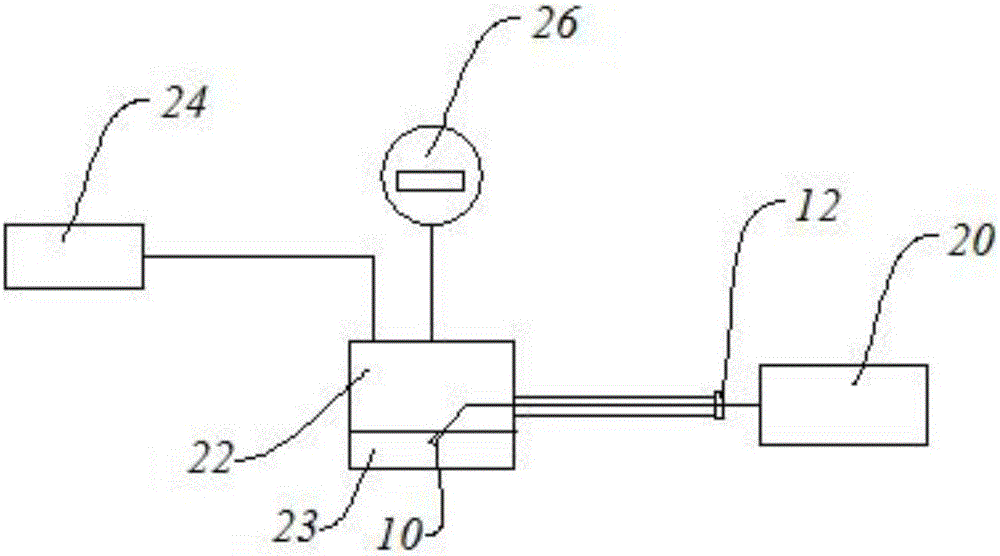
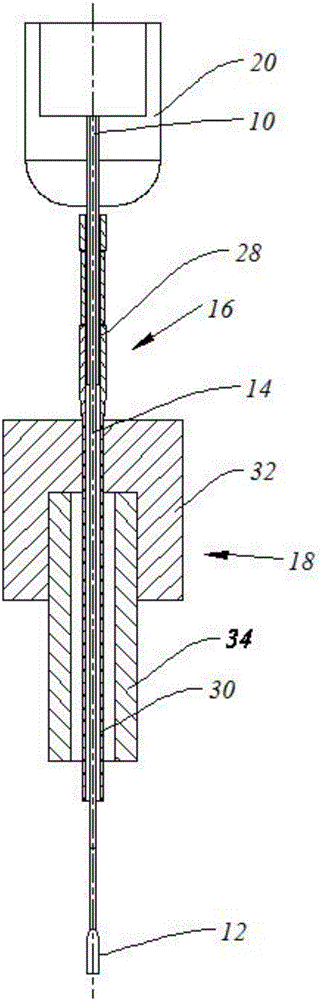
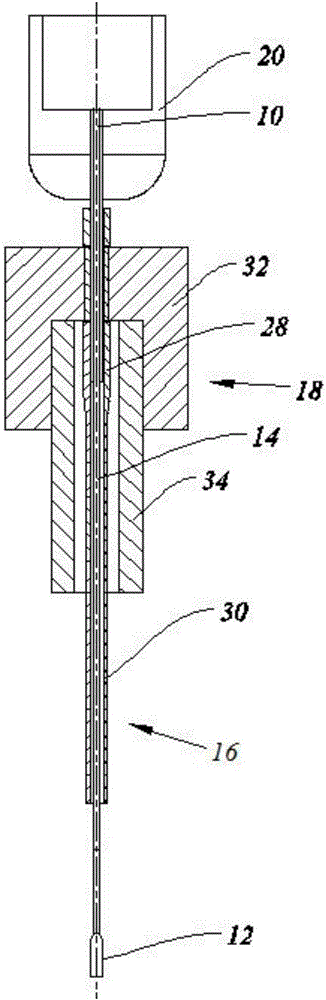
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
117 results about "ICP - Intracranial pressure" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
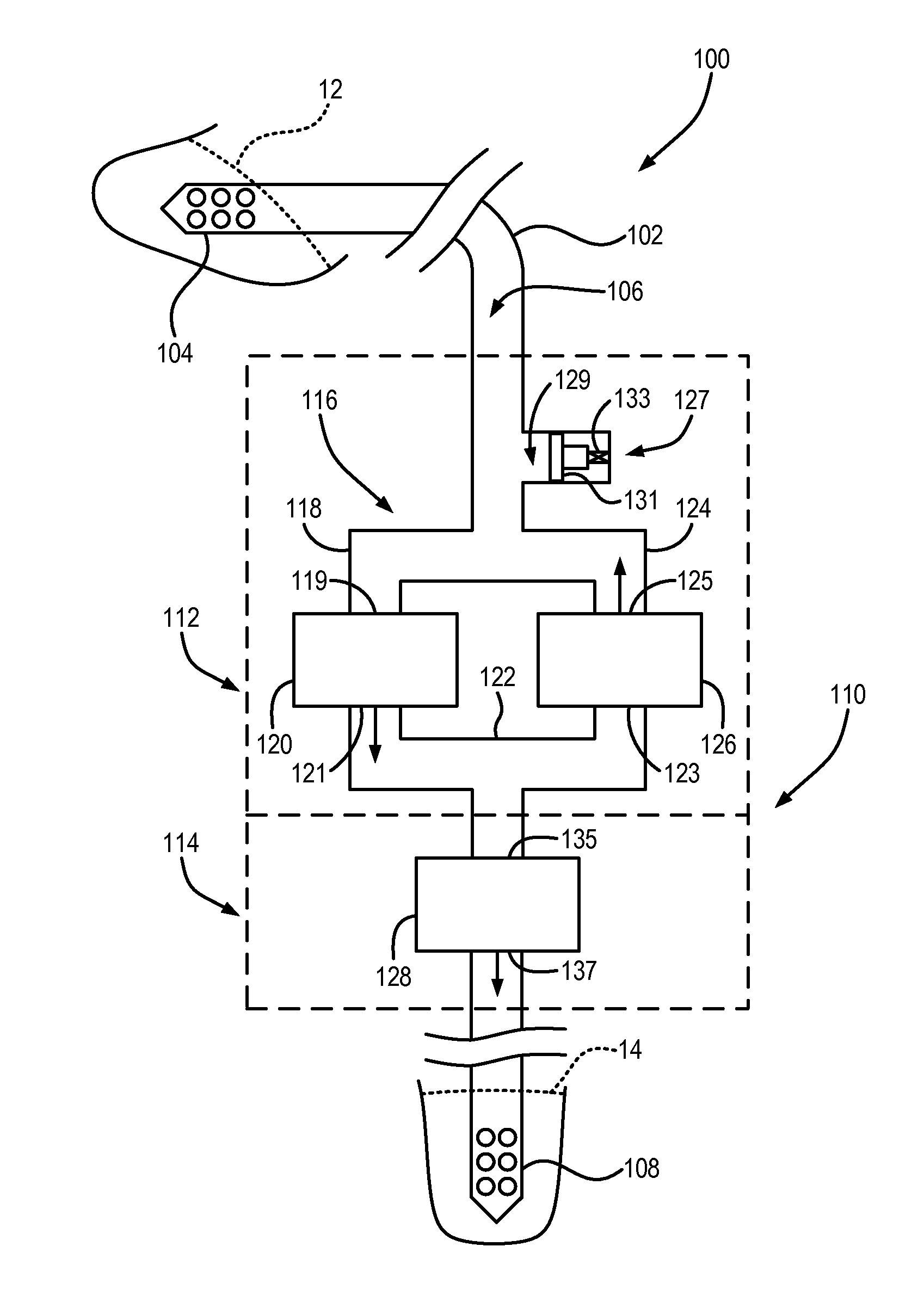
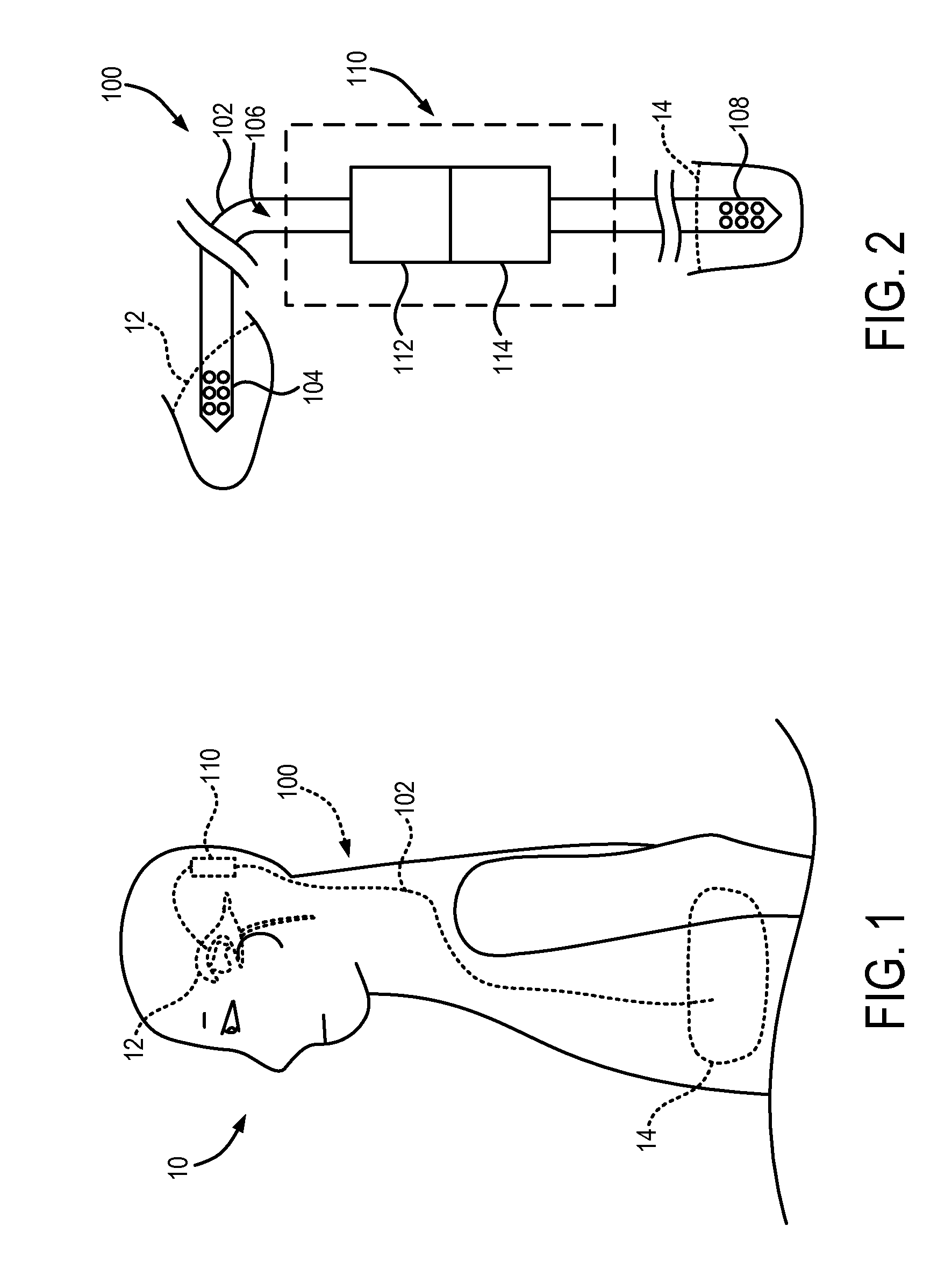
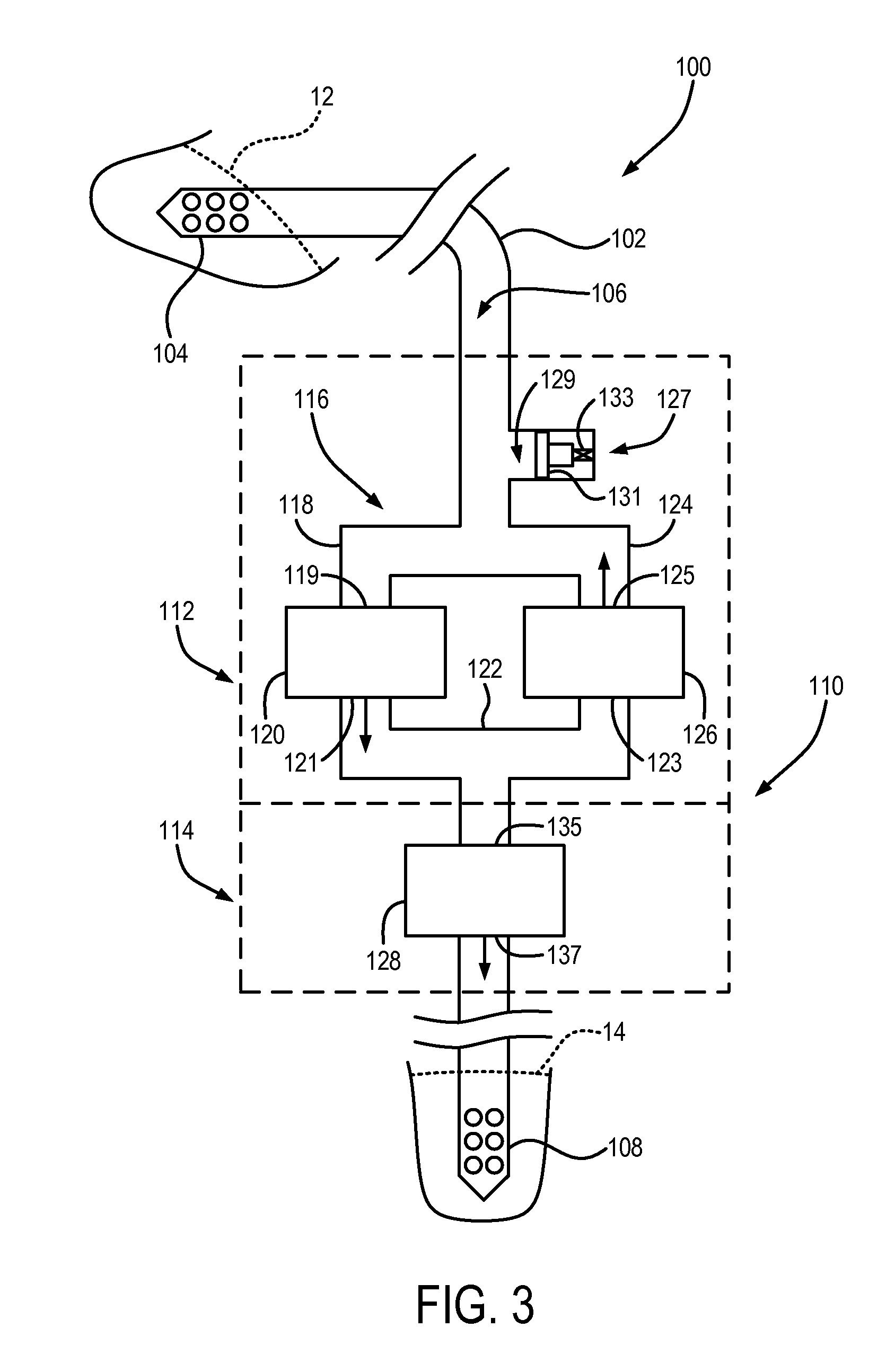
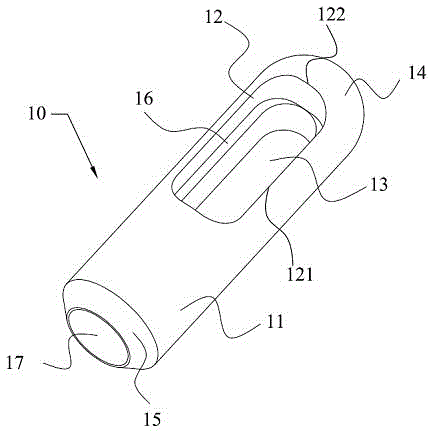
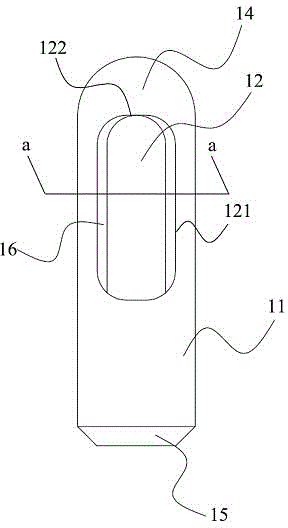
Systems and methods for making non-invasive physiological assessments by detecting induced acoustic emissions
InactiveUS20060079773A1Improve accuracyPositive diagnosisDiagnostics using vibrationsOrgan movement/changes detectionDiseaseNon invasive
Systems and methods for assessing a physiological parameter of a target tissue wherein a pulse of focused ultrasound is applied to a target tissue site thereby inducing oscillation of the target tissue. By these systems and methods, a property of an acoustic signal emitted from the oscillating target tissue is measured and related to a physiological property of the tissue. Specific applications for systems and methods of the present invention include the assessment and monitoring of intracranial pressure (ICP), arterial blood pressure (ABP), CNS autoregulation status, vasospasm, stroke, local edema, infection and vasculitus, as well as diagnosis and monitoring of diseases and conditions that are characterized by physical changes in tissue properties.
Owner:PHYSIOSONICS +1
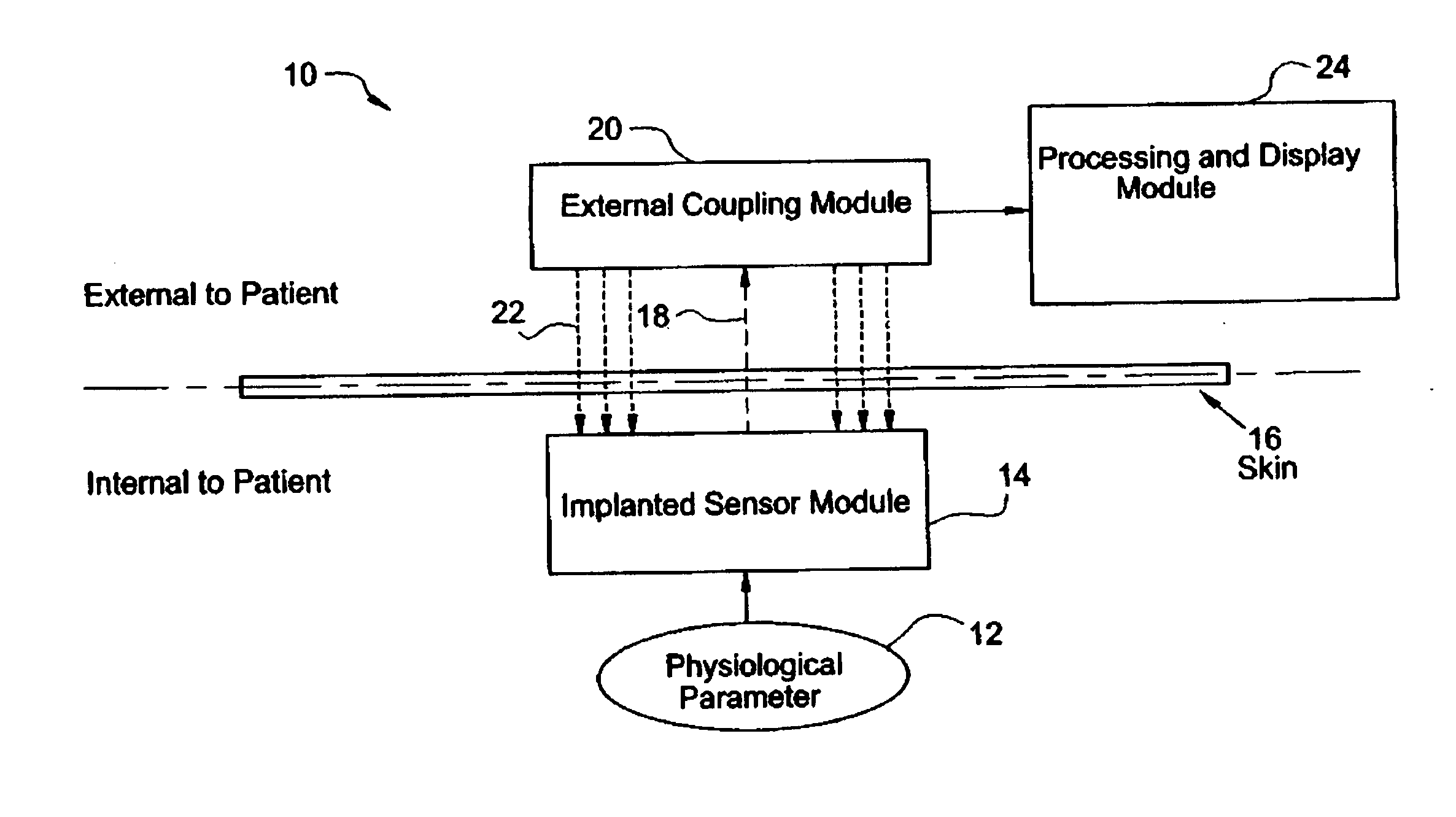
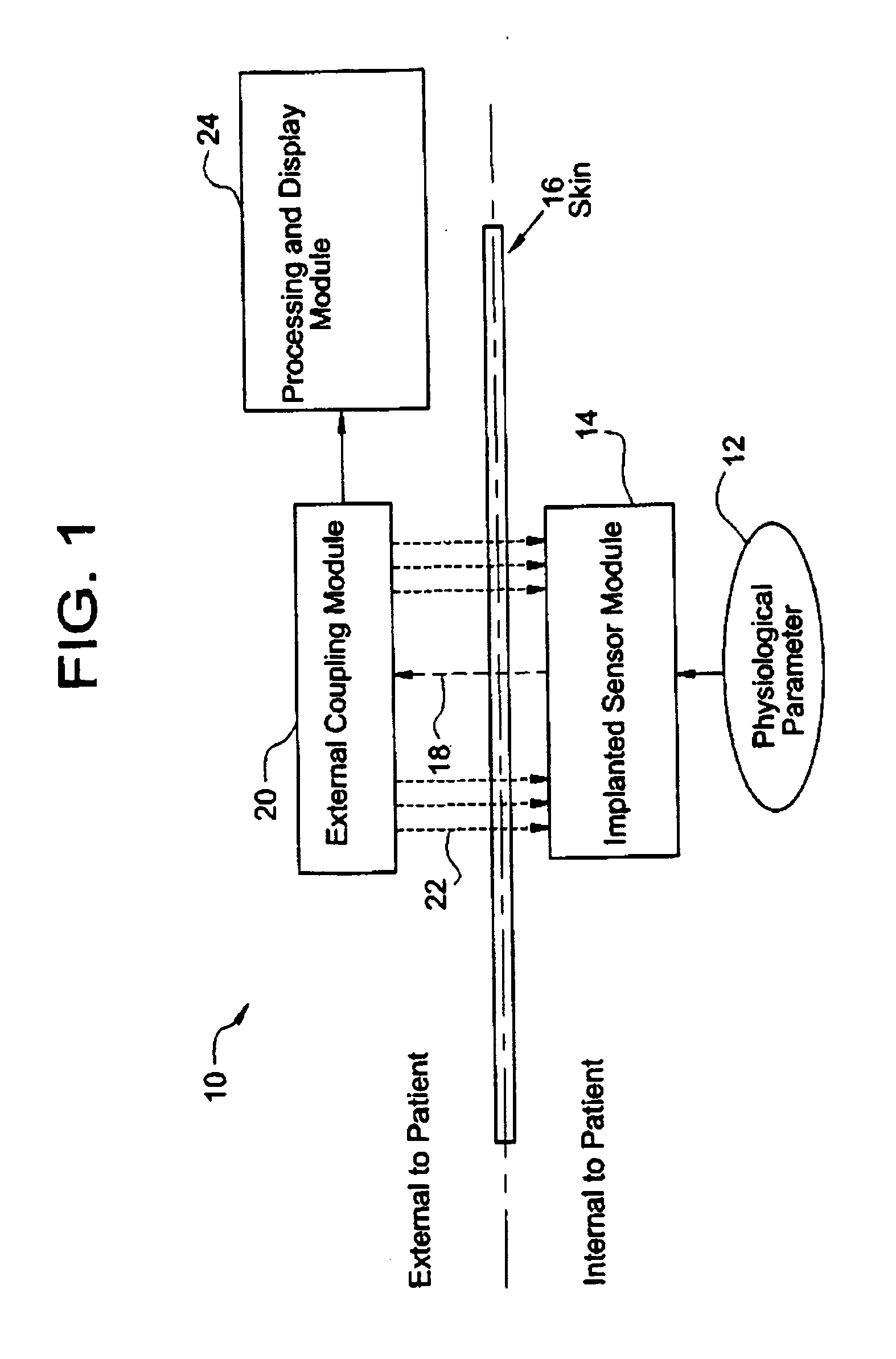
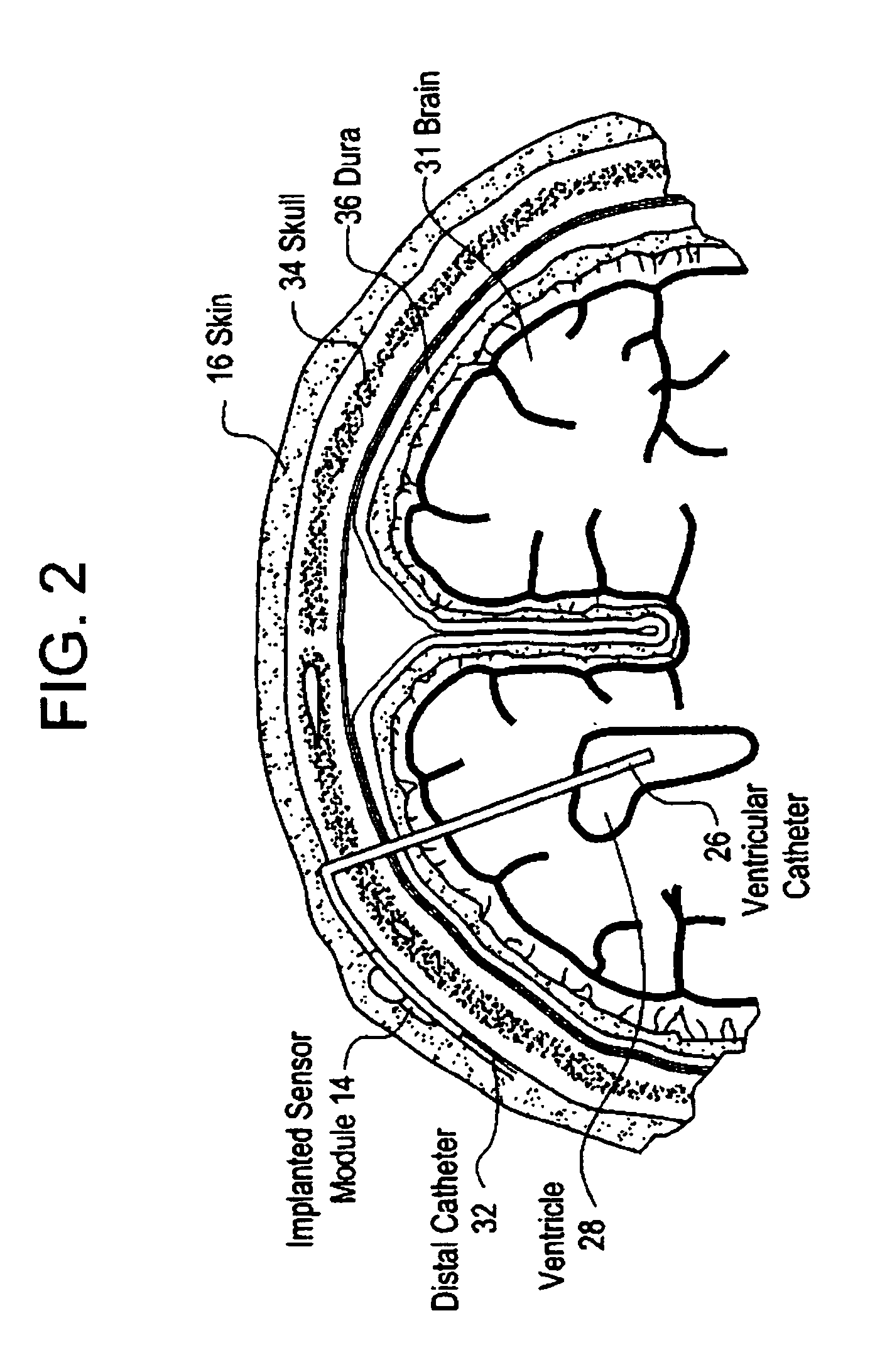
System for transcutaneous monitoring of intracranial pressure (ICP) using near infrared (NIR) telemetry
ActiveUS20050187488A1Small sizeTransmission easilyFluid pressure measurement using inductance variationDiagnostics using spectroscopyInfraredGraphics
A system for measuring and converting to an observer intelligible form an internal physiological parameter of a medical patient. The invention allows transcutaneous telemetry of the measured information intracranial pressure via a system which includes a patient implanted sensor module and a processing and display module which is external of the patient and optically coupled to the sensor module via an external coupling module. A sensor within the implanted module transduces the measured information and a near infrared (NIR) emitter transmits this telemetry information when interrogated by the complementary external coupling module. Power for the sensor module is derived inductively through rectification of a transcutaneously-applied high-frequency alternating electromagnetic field which is generated by a power source within the external coupling module, in concept much like a conventional electrical transformer. A computer within the processing and display module calculates the parameter value from the NIR telemetry signal and represents this data either in numerical, graphical, or analog format.
Owner:WOLF ERICH W
Method and apparatus for assessment of changes in intracranial pressure
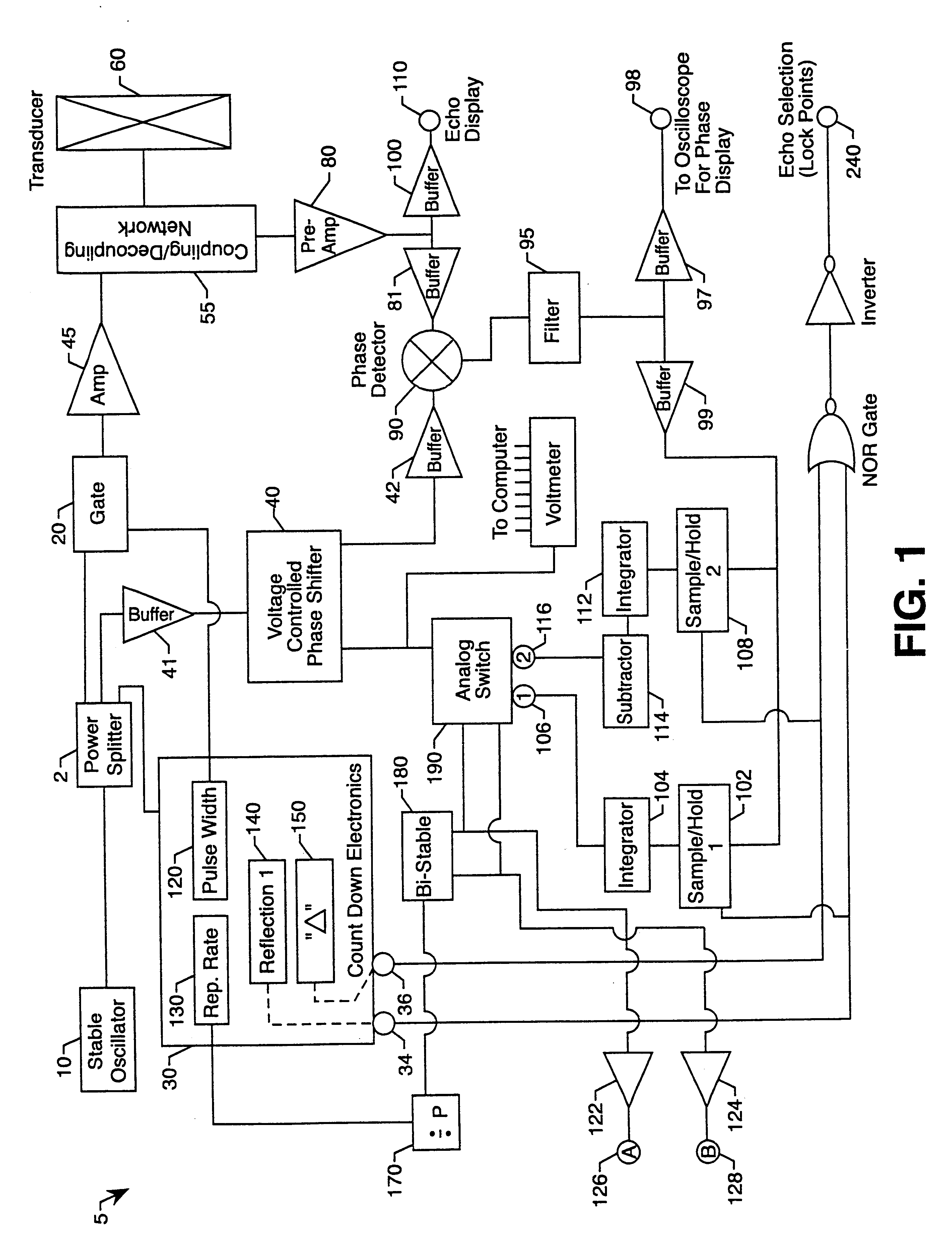
InactiveUS6413227B1Eliminate the effects ofOrgan movement/changes detectionIntracranial pressure measurementElectricityPhase shifted
A non-invasive method and apparatus for monitoring changes in intracranial pressure which removes extracranial effects from the measurements. The method and apparatus can include the supplying of a fixed frequency electrical output to a transducer coupled to the patient's head, thereby generating an acoustical tone burst in the patient's head which generates a first echo and a second echo, the first echo reflecting from a first interface in the side of the patient's head coupled to the transducer, and the second echo reflecting from a second interface at the opposite side of the patient's head. The first and second echoes are received by the transducer which can generate a first electrical signal and a second electrical signal, wherein the first and second electrical signals vary in accordance with the corresponding first and second echoes. The counterbalancing phase shifts required to bring about quadrature between each of the first and second electrical signals and the fixed frequency electrical output can be measured, and values for the change in intracranial distance based on the changes in the counterbalancing phase shifts can be obtained.
Owner:NASA
Non-invasive monitoring of intracranial pressure
InactiveUS20090234245A1Diagnostics using lightIntracranial pressure measurementOptical radiationTemporal change
Methods, systems, and related computer program products for are described for non-invasive detection of intracranial pressure (ICP) variations in an intracranial compartment of a patient. Optical radiation is propagated transcranially into the intracranial compartment, and optical radiation that has migrated through at least a portion of the intracranial compartment and back out of the cranium is detected. At least one signal representative of the detected optical radiation is processed to extract therefrom at least one component signal that varies in time according to at least one of an intrinsic physiological oscillation and an externally driven oscillation in the patient. Examples of suitable intrinsic physiological oscillations include intrinsic respiratory and cardiac oscillations. Examples of suitable externally driven oscillations include ventilated respiratory oscillations and externally mechanically induced oscillations. The extracted component signal is then processed to generate an output signal representative of the ICP variations in the intracranial compartment.
Owner:O2 MEDTECH
Conpositions and method to prevent and treat brain and spinal cord injuries
The cerebrospinal fluid and intracranial pressure are two major reasons why central nervous system is so vulnerable to injuries. A composition and method for treating injured central nervous tissue, or preventing injury to central nervous system tissue is provided. The composition is comprised of a combination of colloidal osmotic agents and crystal osmotic agents. The method comprise of: a). Withdrawing cerebrospinal fluid from the subarachnoid spaces around the tissue to be treated or protected and b). Injecting the composition which is dissolved by patient's own cerebrospinal fluid into subarachnoid spaces. The treatment can be augmented with agents that suppress production of cerebrospinal fluid, or with other known neuroprotective agents.
Owner:WANG YANMING
Systems and Methods for Controlling Cerebrospinal Fluid in a Subject's Ventricular System
A system for draining excess cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) from the head of a subject includes a drainage shunt and a valve assembly that selectively permits the shunt to drain CSF. The valve assembly also compensates for multiple factors that can affect the subject's intracranial pressure (ICP) and compliance, and could otherwise lead to CSF over-drainage or other undesirable conditions.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Cerebrospinal fluid drainage device and intracranial pressure monitoring system
InactiveCN105641758AAvoid backflow) phenomenonPrevent backflowWound drainsMedical devicesAirbagControl valves
The invention provides a cerebrospinal fluid drainage device and an intracranial pressure monitoring system. The cerebrospinal fluid drainage device comprises a cerebrospinal fluid drainage tube and a drainage bag used for collecting fluid in the cerebrospinal fluid drainage tube, a guide tube used for being connected with a pressure sensor is communicated on the cerebrospinal fluid drainage tube, a first control valve is arranged at a position, between the guide tube and the drainage bag, of the cerebrospinal fluid drainage tube, and a buffering airbag is arranged at a position, close to a joint of the guide tube and the cerebrospinal fluid drainage tube, of the guide tube. Through the buffering airbag arranged on the guide tube, cerebrospinal fluid in the cerebrospinal fluid drainage tube can be effectively avoided being sucked back into the guide tube, so that failing of the pressure sensor caused by the fact that the cerebrospinal fluid flows back to the pressure sensor can be effectively prevented, accuracy of intracranial pressure detected by the pressure sensor is guaranteed, the pressure sensor is prevented from being polluted by the cerebrospinal fluid, and cross infection caused by reuse of the sensor is avoided.
Owner:王学建
Multi-parameter-based intracranial pressure noninvasive detection method and device
InactiveCN102429651AHigh precisionGood clinical applicabilityUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsDiagnostic recording/measuringEcg signalSonification
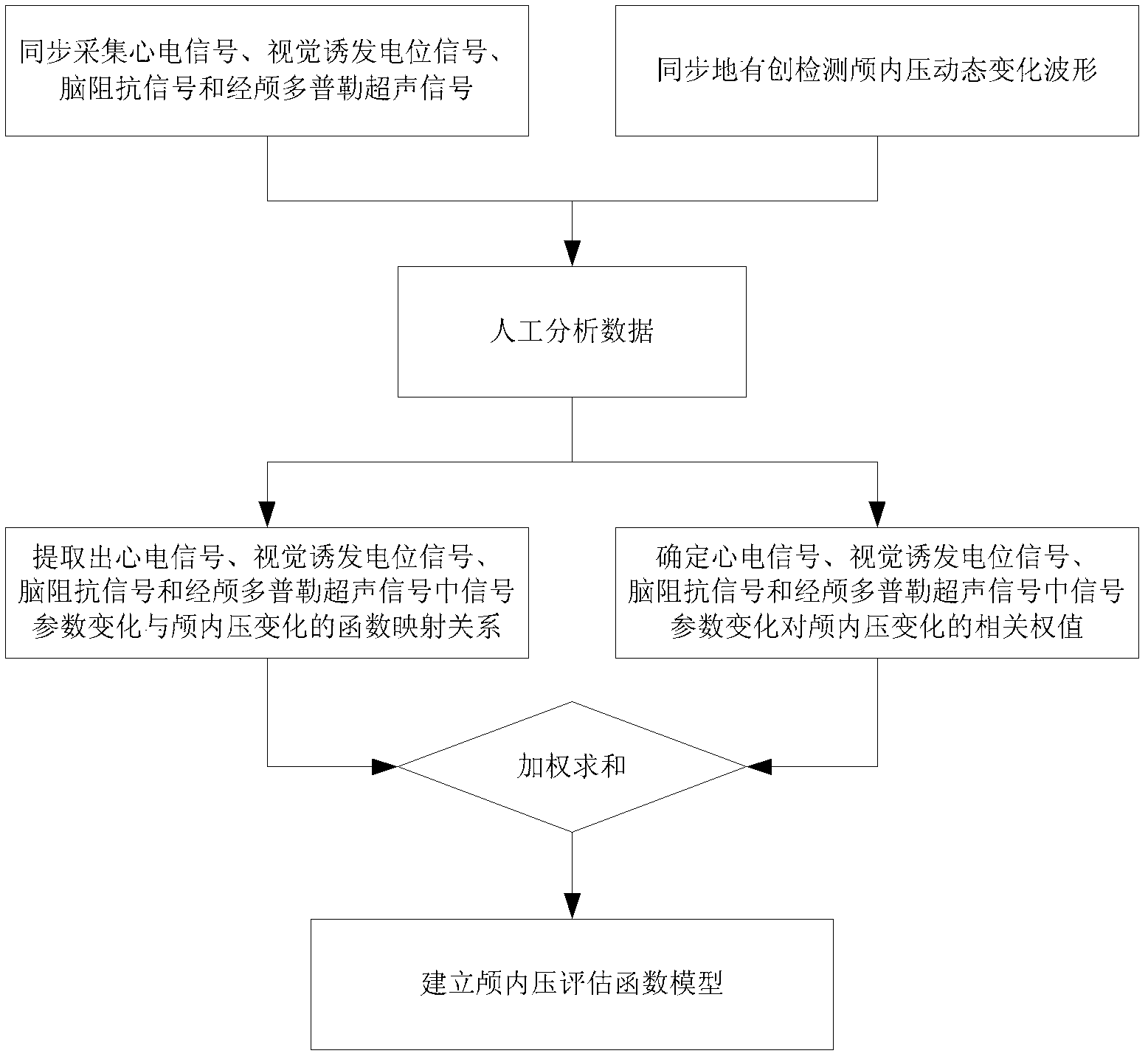
The invention provides a multi-parameter-based intracranial pressure noninvasive detection method and device. The method comprises the following steps of: pre-establishing an intracranial pressure evaluation function model for recording a function mapping relation between the change of the intracranial pressure and the changes of an electrocardiosignal, a visual evoked potential signal, a brain impedance signal and a transcranial Doppler ultrasonic signal and setting in a computer; and synchronously acquiring the electrocardiosignal, the visual evoked potential signal, the brain impedance signal and the transcranial Doppler ultrasonic signal into a computer and inputting the signals serving as the intracranial pressure evaluation function model to obtain the dynamic change process waveform of the intracranial pressure of an inspected object by performing multi-parameter and multi-direction operation. Due to the adoption of the method, invasive intracranial pressure detection is avoided; the device for implementing the method is easy to obtain; and meanwhile, various physiological and pathological signal parameters causing the change of the intracranial pressure are considered comprehensively in the intracranial pressure evaluation function model, so that the intracranial pressure noninvasive detection method has higher clinical detection accuracy.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV +1
Wound-frce intracranial pressure monitoring method and apparatus
InactiveCN1404793AAccurate monitoringEasy to monitorDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsNegative phaseNon invasive
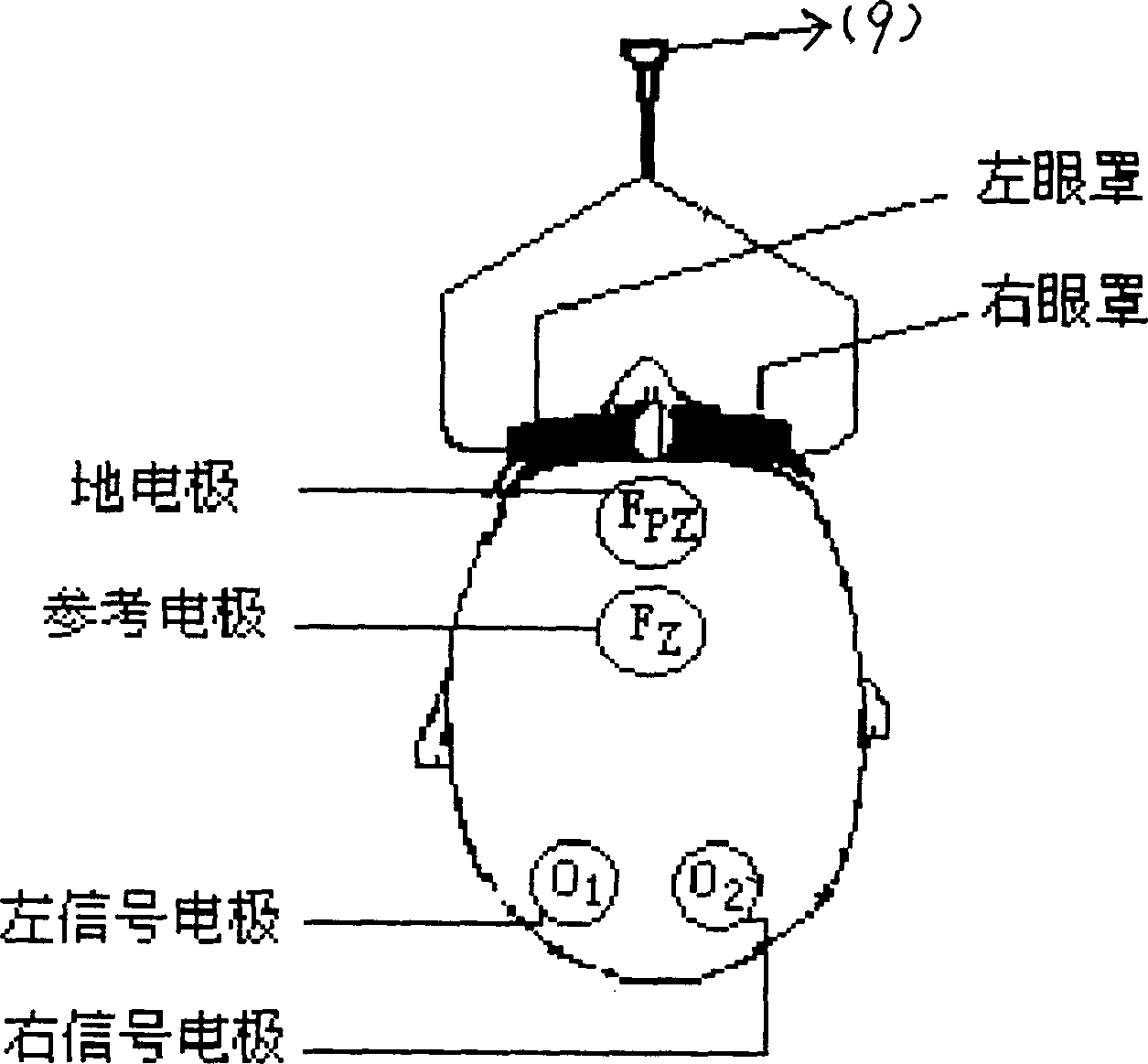
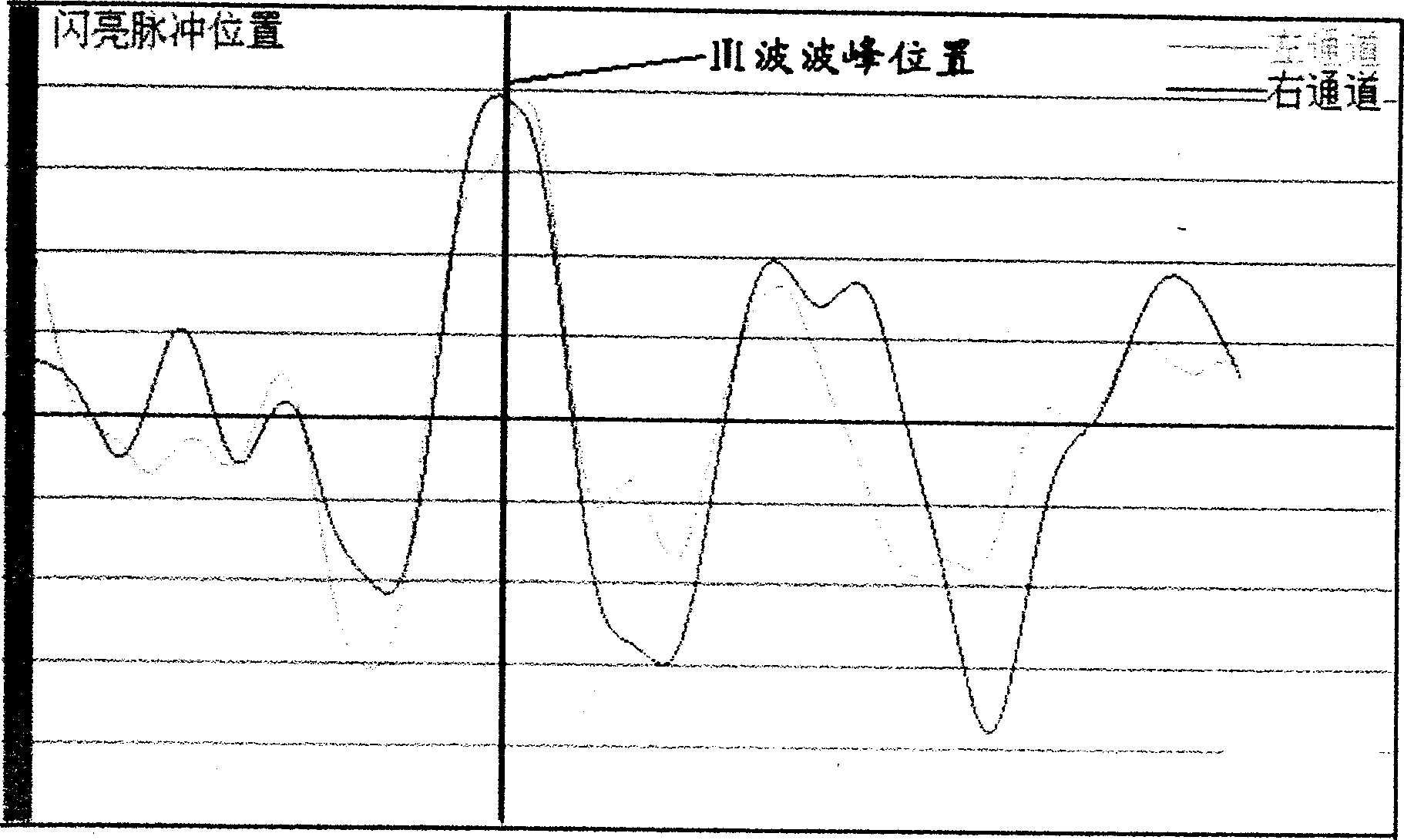
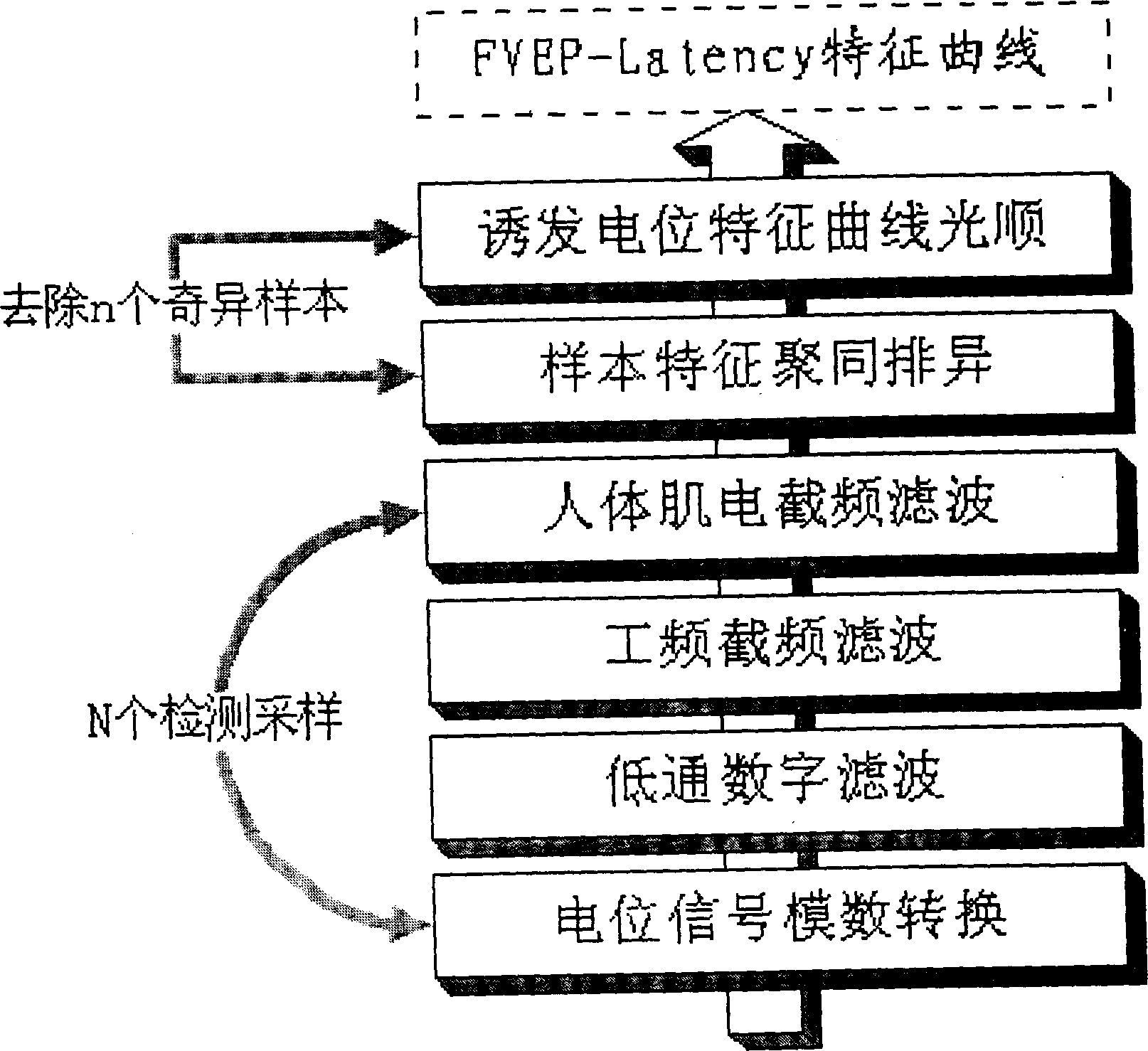
The non-invasive intracranial pressure monitoring method adopts the flash eye-shield to give out standard photostimulation signal to human eye, said signal is sensed by retina and converted into electric signal, said electric signal can be picked up by detection electrode and undergone the process of amplifier treatment, then inputted into computer to display flashing visual evoked potential (FVEP) characteristic curve and define the peak latency of III wave, then the function relationship of intracranial pressure and peak latency of III wave, ICP=f(III Latency) can be used to display intracranial pressure value correspondent to wave peak (negative phase) point of III wave on the FVEP-Latency curve on the display screen.
Owner:重庆海威康医疗仪器有限公司
Intracranial pressure non-invasive measuring method and system
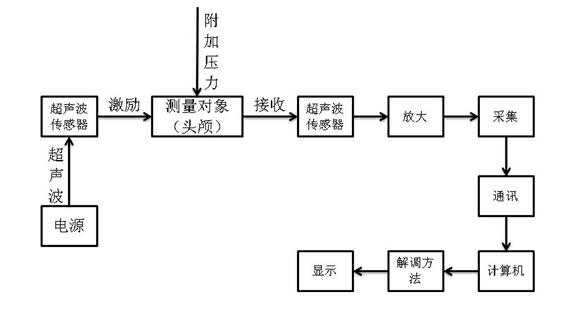
InactiveCN102670252AAchieve non-destructive ultrasonic testingUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsInfrasonic diagnosticsHuman bodyICP - Intracranial pressure
The invention discloses an intracranial pressure non-invasive measuring method. The method includes the following steps that step one, at least two ultrasonic sensors with a same specification are utilized to obtain a normal ultrasonic amplitude value and a phase reference signal; and step two, the ultrasonic sensors are arranged at temple positions of two sides of a head to be measured respectively, an incentive ultrasonic signal parameter which is same to that of the step one is utilized, the signal collected by the ultrasonic sensors is processed again and then transmitted to a computer, and an additional pressure value, namely an intracranial pressure can be detected by a differential demodulation method. Beside, the invention further discloses a system for intracranial pressure non-invasive measuring. By means of the intracranial pressure non-invasive measuring method and the system, the sensors are not required to be extended to the interior of a measured object (the head), and the ultrasonic wave is harmless to human body, so that a nondestructive ultrasonic testing for the measured object (the head) can be achieved, and the defect that the non-invasive testing for the measured object (the head) can not be achieved in terms of existing detection devices is overcome.
Owner:重庆朗普科技有限公司
Method and System for Determining Intracranial Pressure
ActiveUS20170065193A1Overall stabilityImprove accuracyEvaluation of blood vesselsIntracranial pressure measurementSupporting systemNegative feedback
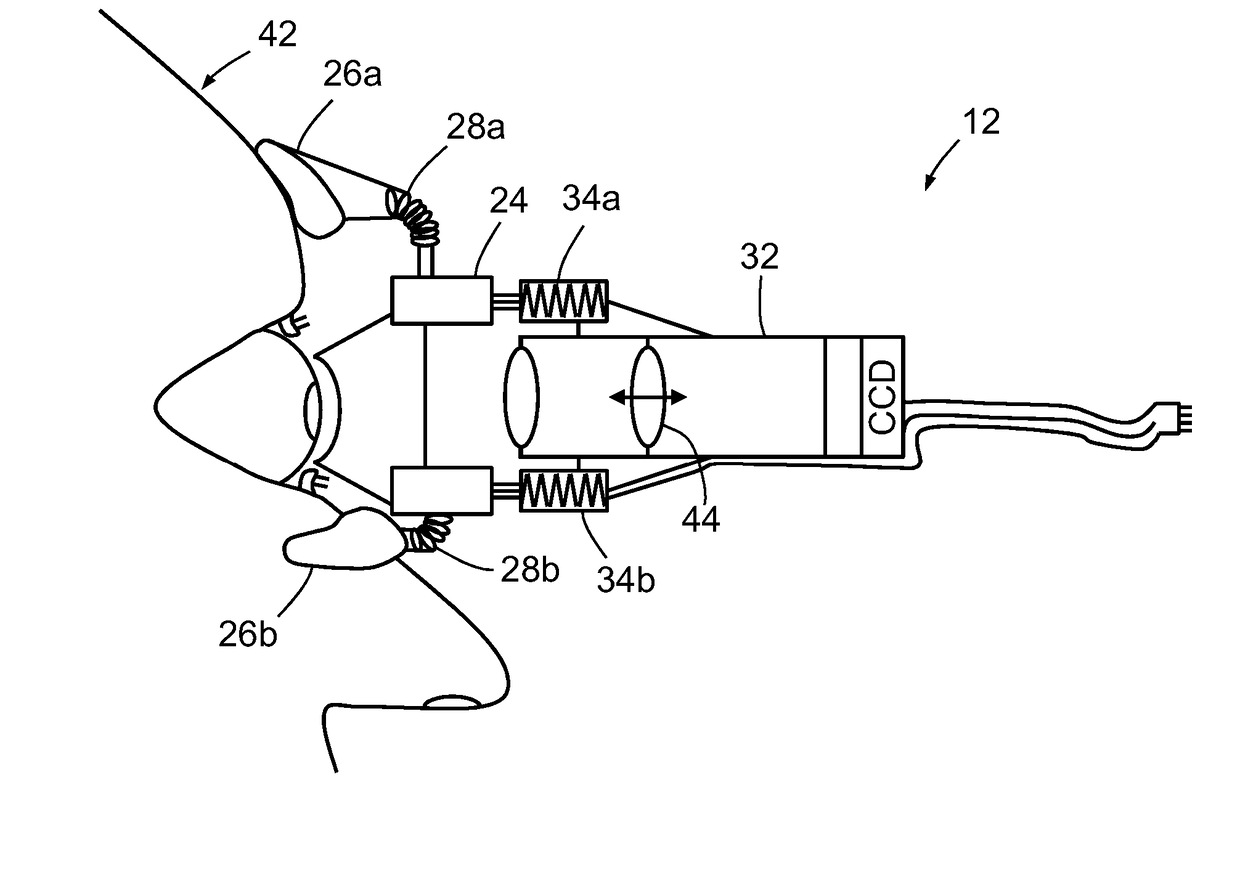
A method and apparatus for determining intracranial pressure, includes a contact lens; a camera for making a plurality of images of at least one eye of a subject; one or more force transducers for controllably applying a force to the eye via the contact lens; a support system for supporting the camera, the contact lens and the one or more force transducers against the eye; and a computing device for controlling the force applied to the eye by the force transducers and stabilizing the force by negative feedback.
Owner:LIONS EYE INST OF WESTERN AUSTRALIA
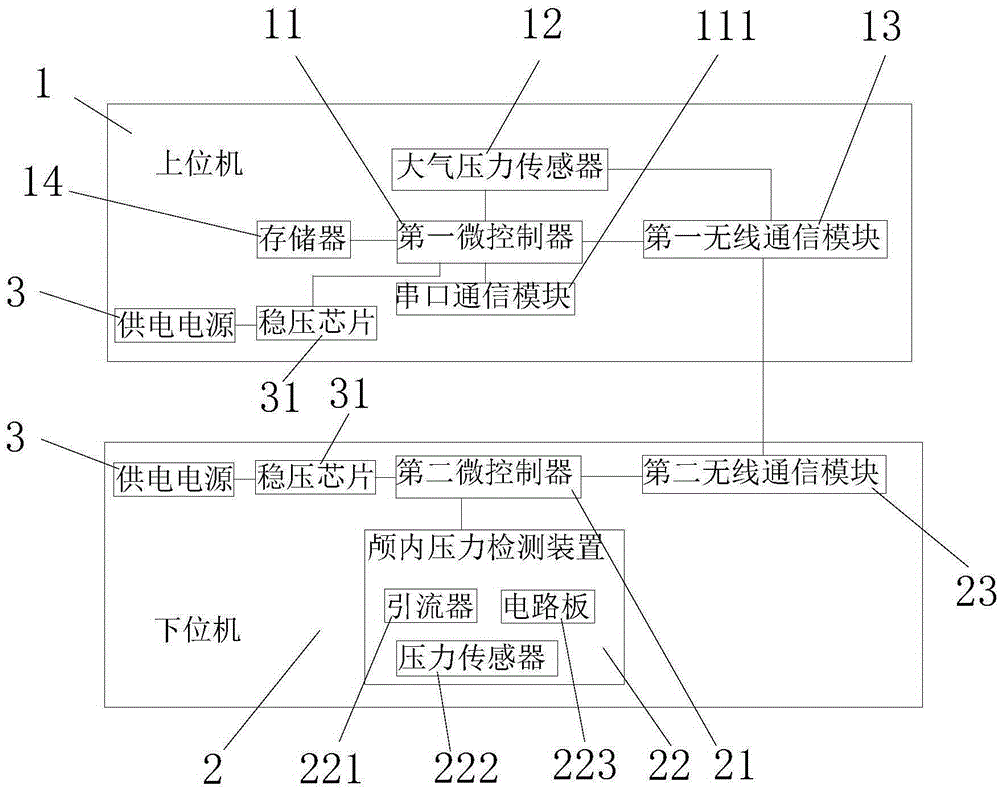
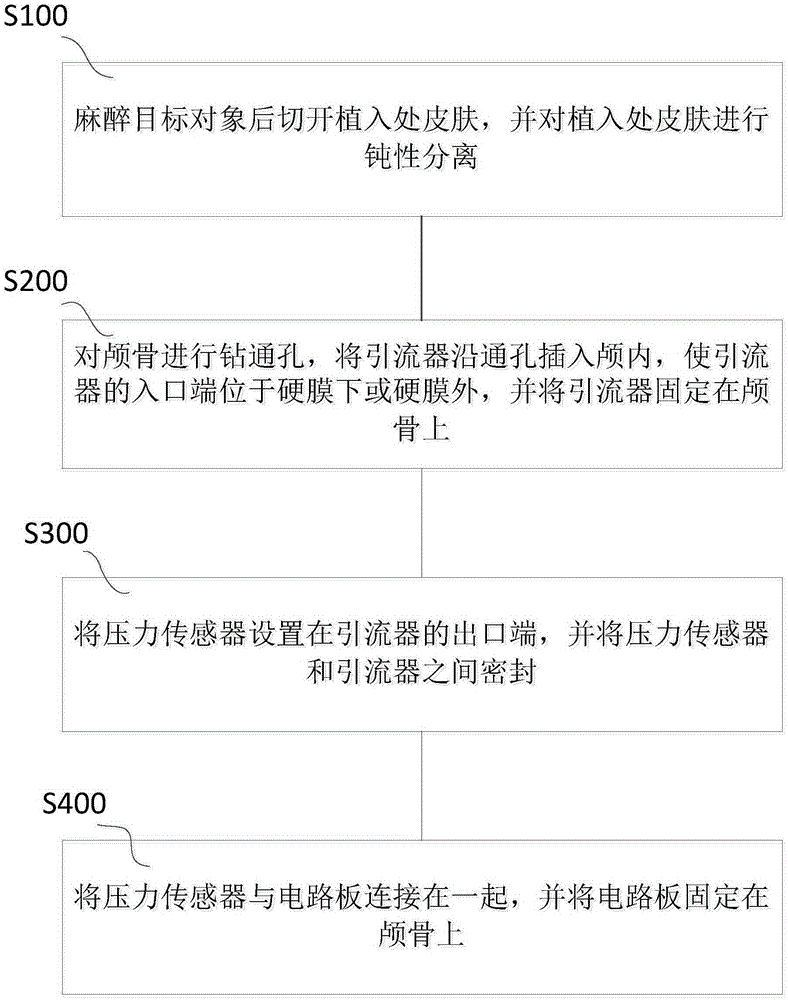
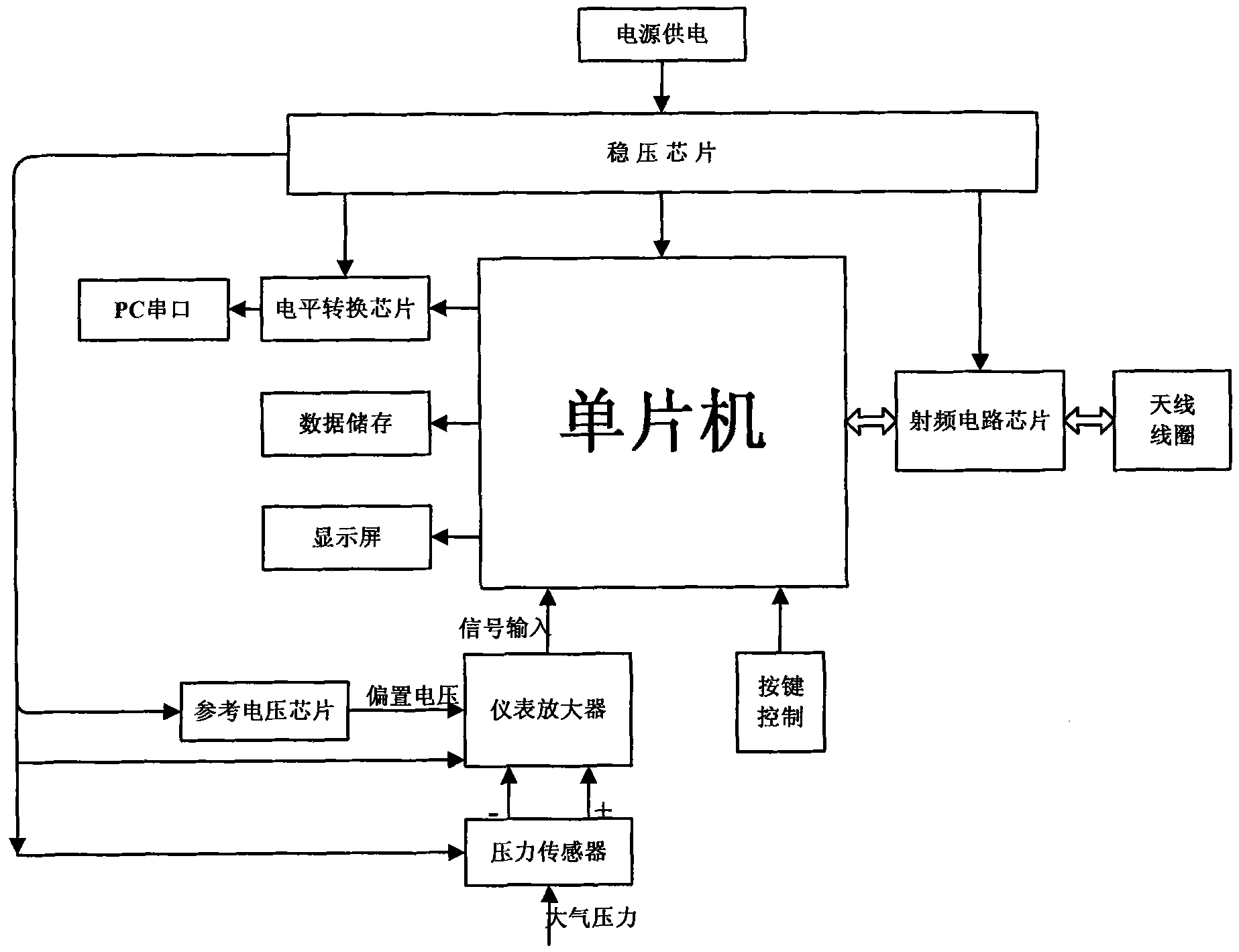
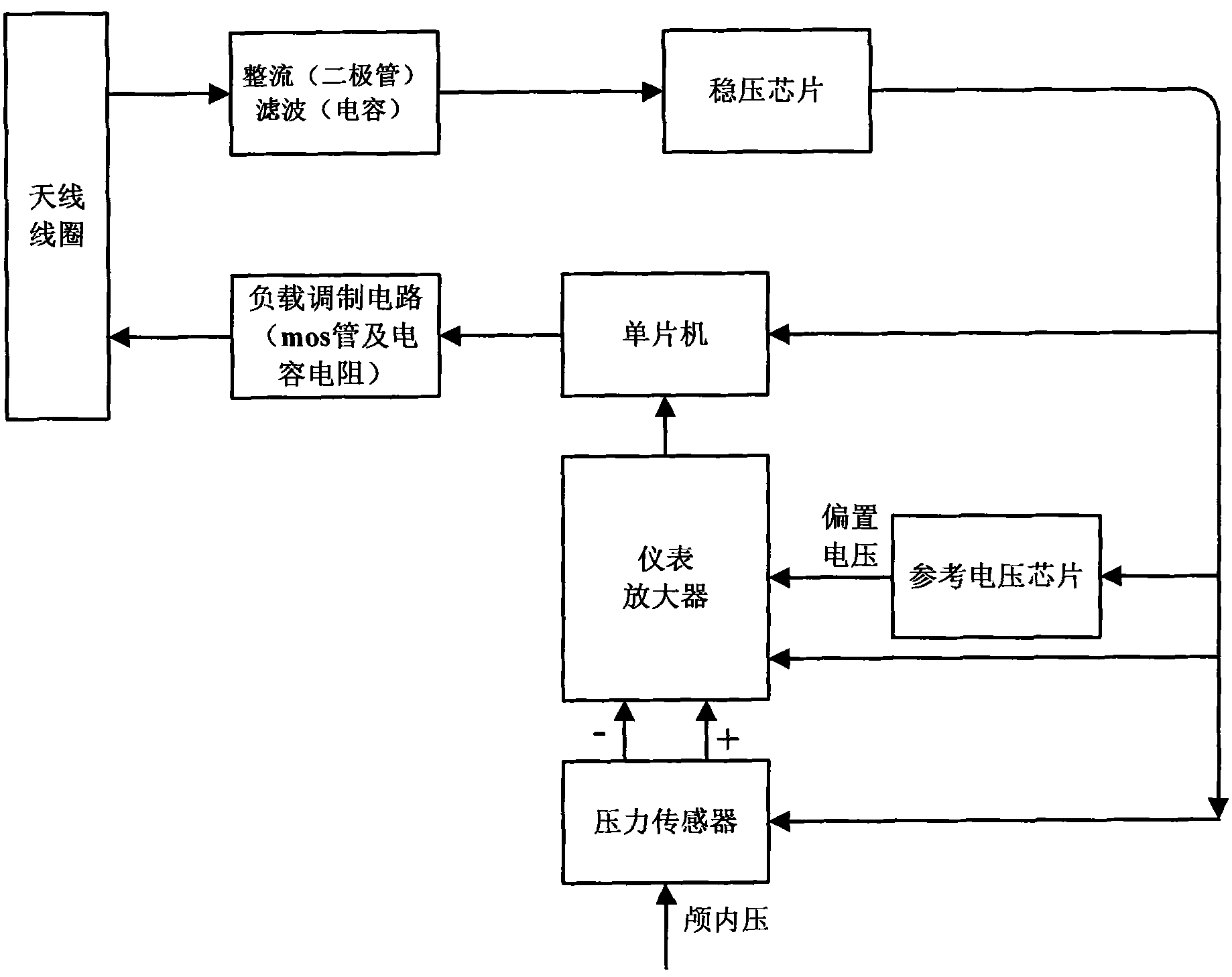
Intracranial pressure detecting system and implantation method of intracranial pressure detecting device
The invention provides an intracranial pressure detecting system and an implantation method of an intracranial pressure detecting device. The intracranial pressure detecting system comprises an upper computer and a lower computer. The upper computer comprises a first microcontroller, a barometric pressure sensor and a first wireless communication module. The lower computer comprises a second microcontroller, the intracranial pressure detecting device and a second wireless communication module. The intracranial pressure detecting device comprises a drainage apparatus, a pressure sensor and a circuit board, and the second wireless communication module and the first wireless communication module are connected in a wireless communication mode. The implantation method of the intracranial pressure detecting device comprises the steps that the skull is drilled to form a through hole, the drainage apparatus is inserted into the skull through the through hole to enable the inlet end of the drainage apparatus to be located under the dura mater or outside the dura mater, the pressure sensor is arranged at the outlet end of the drainage apparatus, and sealing is performed between the pressure sensor and the drainage apparatus. The intracranial pressure detecting system can conduct continuous intracranial pressure detection on an astronaut in a space micro-gravity environment or an experimental animal on the ground and accordingly fills the bank in the field.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
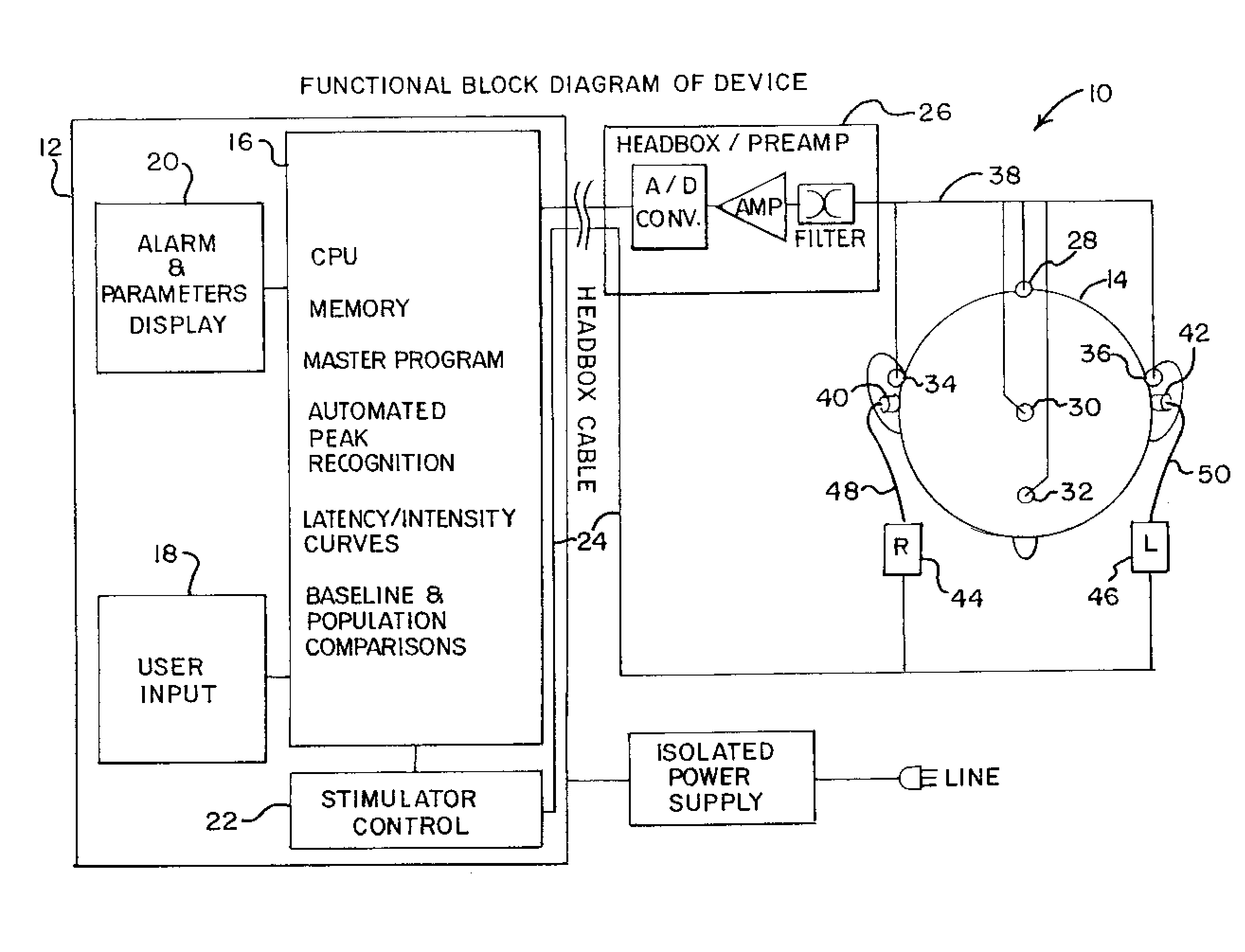
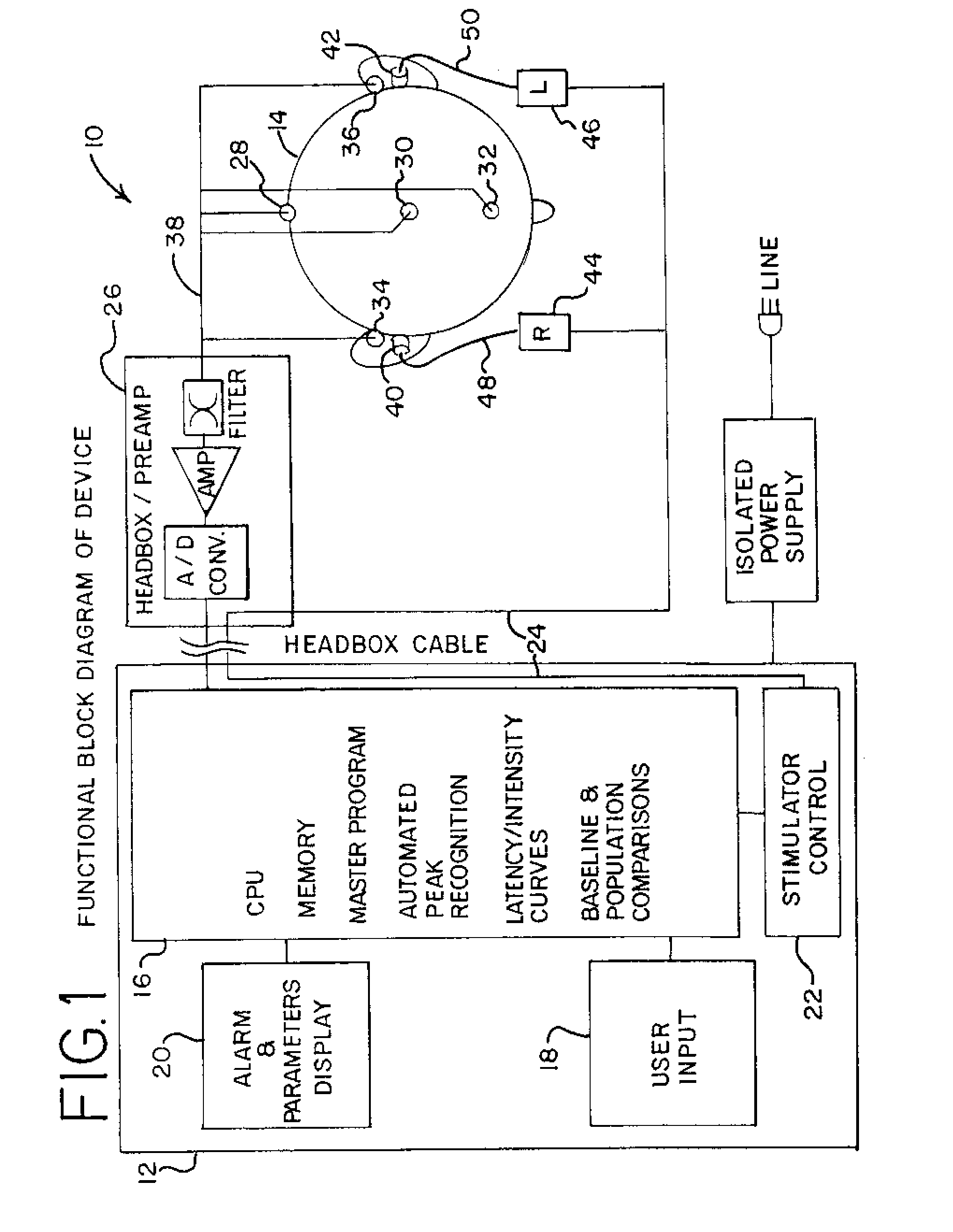
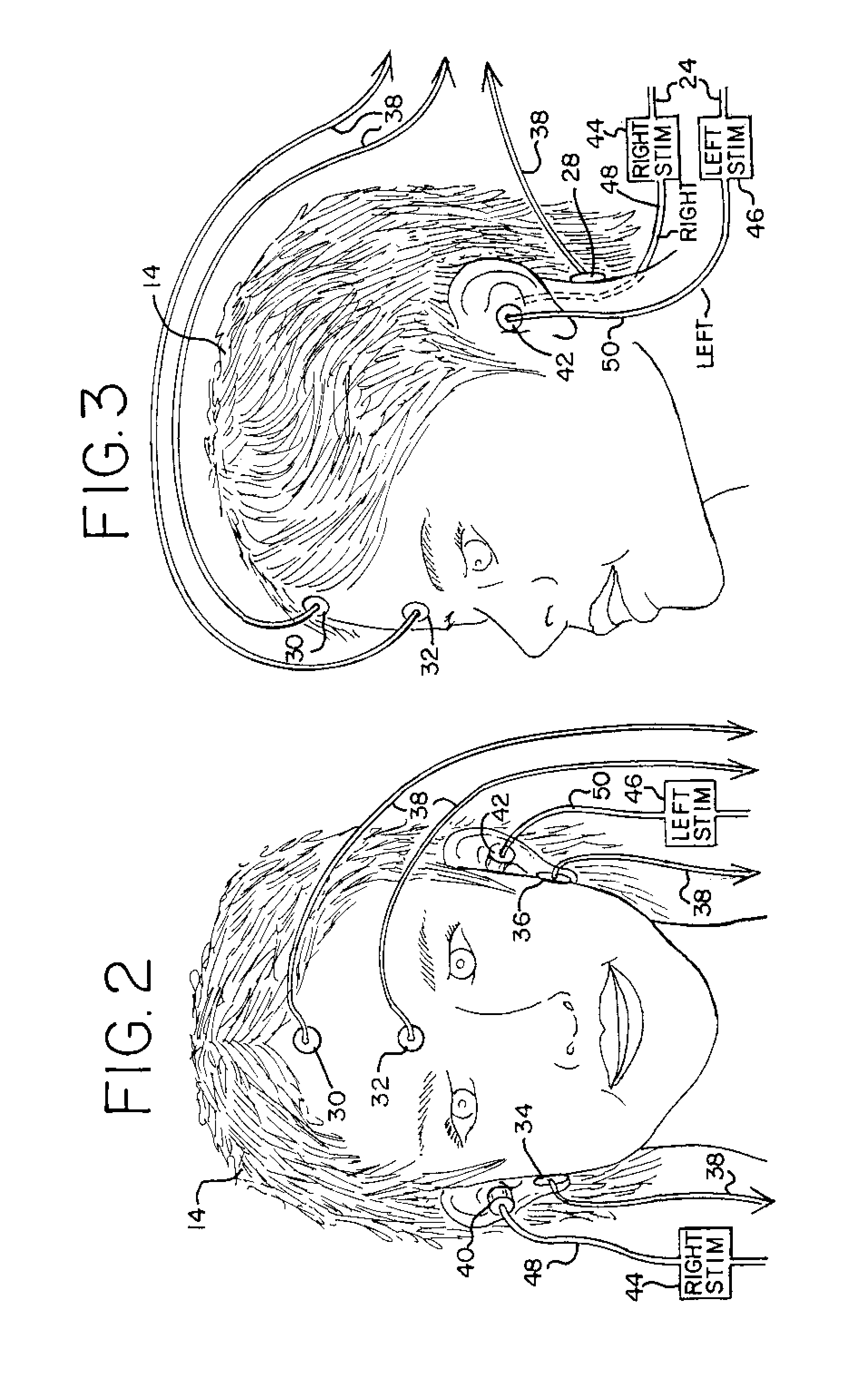
Non-invasive, bedside intra-cranial pressure and brain shift/herniation monitoring unit utilizing early onset auditory evoked responses
ActiveUS8632475B2ElectroencephalographyIntracranial pressure measurementAuditory evoked responsesICP - Intracranial pressure
An intracranial pressure monitoring system and method. The system includes an auditory stimulation and recording unit, which includes a stimulation controller, a memory for storing waveforms, a device for comparing received waveforms with stored waveforms, and an alarm operable based upon that comparison. The system includes at least one cranial electrode attachable to a patient, and an auditory stimulation device, operable by the stimulation controller. The stimulation device is a pair of acoustic ear inserts, each of which is connected to and operated by an auditory stimulator activated by the stimulation controller. In the method, a patient is auditorially stimulated to evoke a received waveform indicative of intracranial pressure, a comparison is generated by comparing the received waveform with one of an established patient baseline waveform and an established normal waveform, and an alarm is generated responsive to that comparison.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
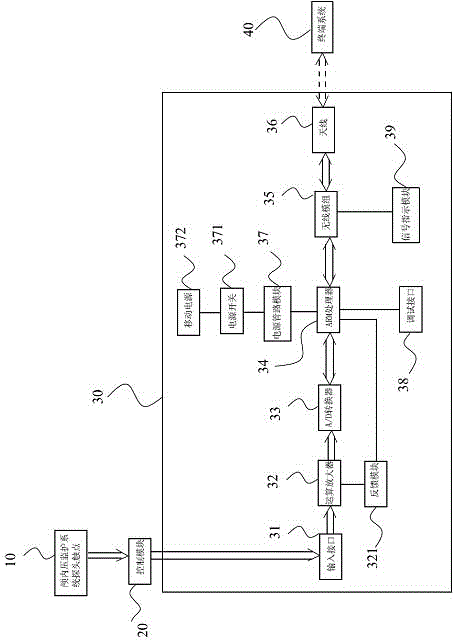
Intracranial pressure monitoring system
InactiveCN104352232AAvoid pullingEliminate potential safety hazardsTransmission systemsIntracranial pressure measurementICP - Intracranial pressureTerminal equipment
The invention discloses an intracranial pressure monitoring system. The intracranial pressure monitoring system comprises a probe, a wireless receiving-transmitting device connected with the probe, and a terminal system which is in wireless communication with the wireless receiving-transmitting device, wherein the wireless receiving-transmitting device is at least used for wirelessly transmitting physiological data which are obtained by the probe and can represent an intracranial state to the terminal system. Compared with the prior art, the physiological data which are obtained by the probe and can represent the intracranial state are transmitted to the terminal equipment by the wireless receiving-transmitting device, and the pulling of the probe, caused by the fact that a patient move improperly can be effectively prevented; the potential safety hazards in a use process of the monitoring system are eliminated.
Owner:SCENERAY
System for transcutaneous monitoring of intracranial pressure
ActiveUS20120059238A1Small sizeTransmission easilyFluid pressure measurement using inductance variationDiagnostics using spectroscopyICP - Intracranial pressureIntensive care medicine
A system for measuring and converting to an observer intelligible form an internal physiological parameter of a patient. The invention allows transcutaneous telemetry of intracranial pressure via a system which includes a patient implanted sensor module and an external processing module, optically coupled to the sensor module via an external coupling module. A sensor within the sensor module transduces the measured pressure and a near infrared emitter transmits the telemetry when interrogated by the external coupling module. A set of tuned inductor-crystal circuits comprised in part of a cylindrical crystal oscillator whose resonant frequency is sensed by a dipper circuit arrangement is provided. Power for the sensor module is derived inductively through rectification of a transcutaneously-applied high-frequency alternating electromagnetic field generated within the external coupling module. A computer within the processing module calculates the physiological parameter from the telemetry signal and represents this data in numerical, graphical, or analog format.
Owner:WOLF ERICH
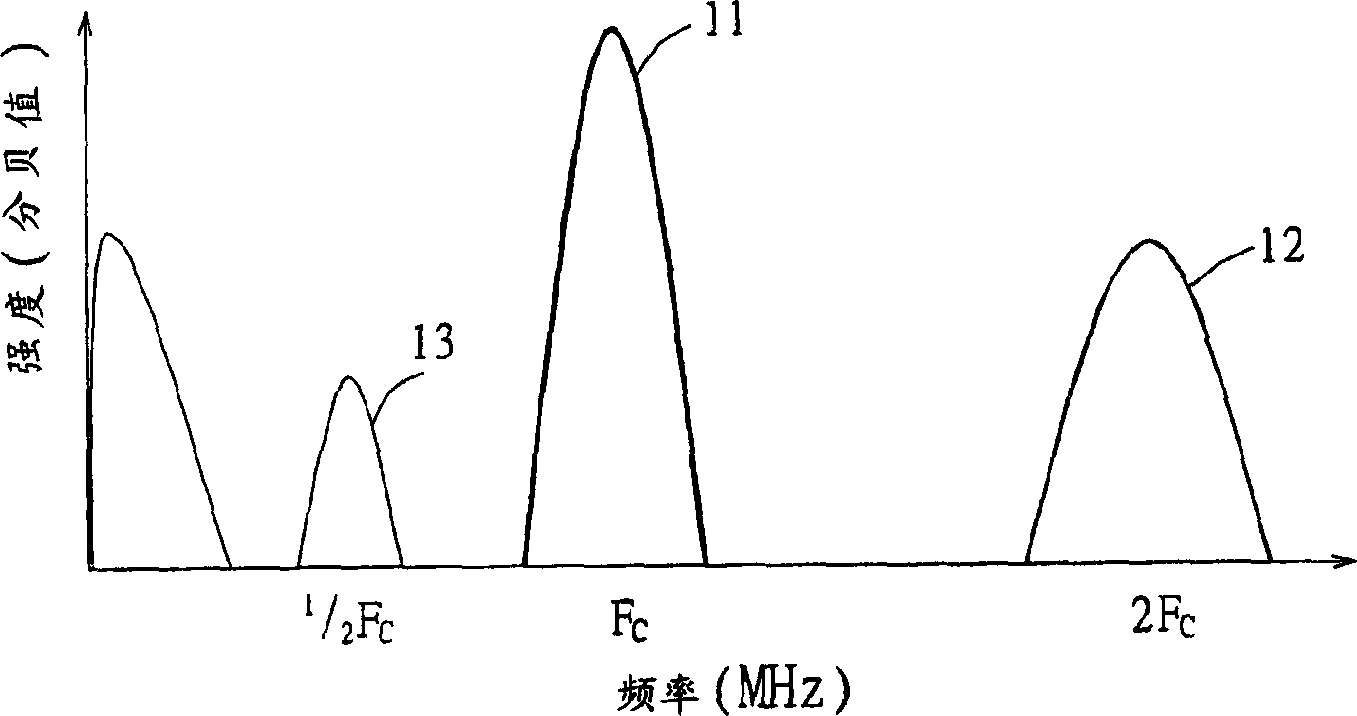
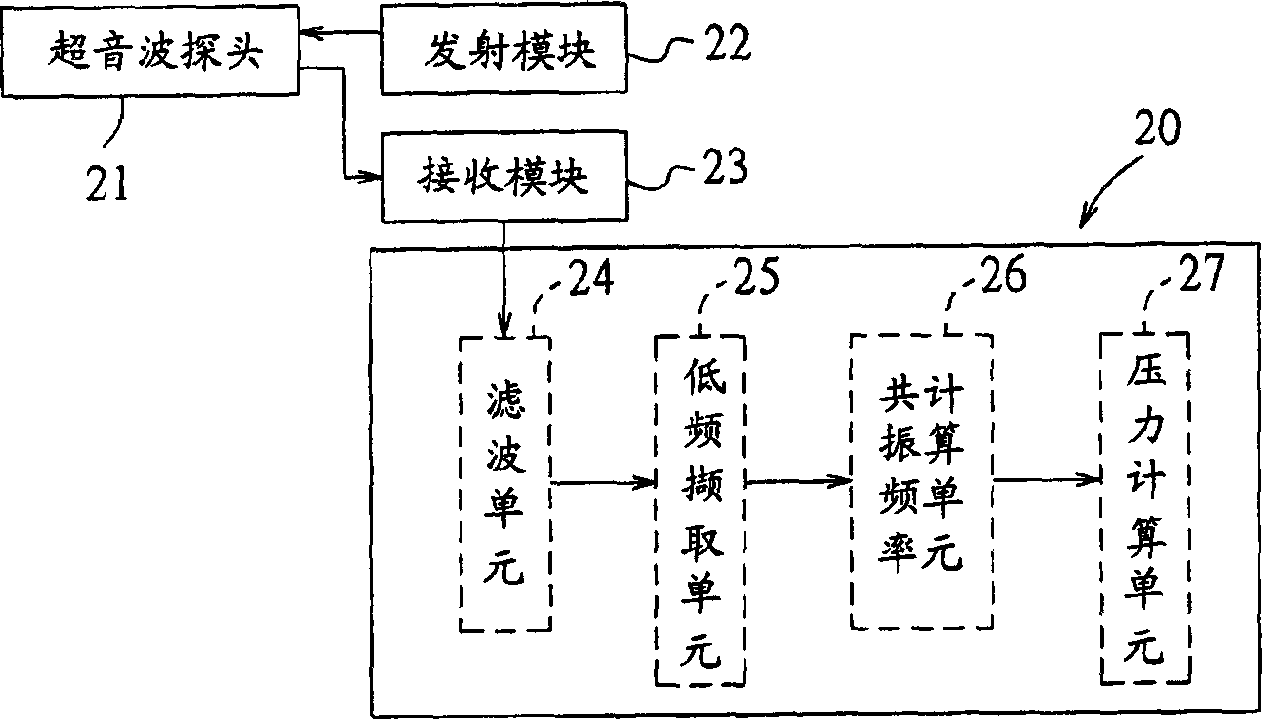
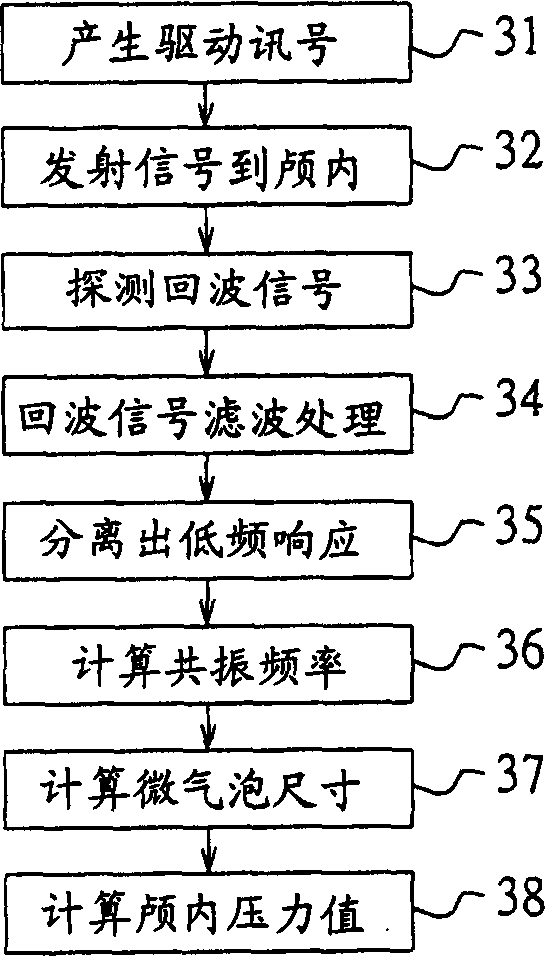
Intracranial pressure measuring method and system
ActiveCN1806760ADegree of reductionImprove signal qualityUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsInfrasonic diagnosticsFrequency spectrumMicro bubble
A method for measuring cranial pressure, which can be used to measure cranial inner area which is injected with contrast-medium and forms micro bubble, comprising following steps: (1) emitting a ultrasonic transmitted signal of broad band to cranial inner area; (2) detecting echo-signal from micro bubble;(3) spectrum analyzing the echo-signal to get low-frequency response near to direct current part, the bandwidth of which is near to transmitted signal; (4) calculating the resonance frequency of micro bubble taking the performance feature of bandwidth and strength of low-frequency response as parameter; (5) calculating out the size of micro bubble according to the resonance frequency and cooperating the property of contrast-medium; (6) calculating cranial pressure.
Owner:MICRO-STAR INTERNATIONAL
Implantable wireless intracranial pressure automatic monitoring method
InactiveCN101849822AEasy to monitorQuick monitoringDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsMonitoring systemE communication
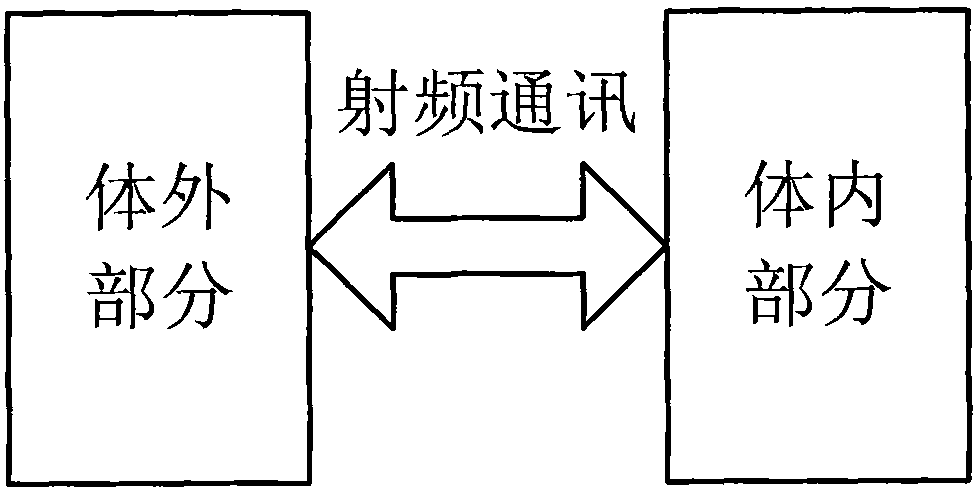
The invention relates to an implantable wireless intracranial pressure automatic monitoring method. In the monitoring method, a monitoring system which is formed by an internal part and an external part completely independently of each other is used. When in use, the two parts are communicated with each other through radio frequency so as to fulfill the aim of monitoring intracranial pressure automatically. The method comprises the following steps that: (1) the external part provides energy for the internal part through radio electromagnetic waves; (2) the internal part receives the energy and starts to operate; (3) the external part sends a command to the internal part through electromagnetic waves; (4) after receiving the command, the internal part acquires intracranial pressure data, encodes the intracranial pressure data and transmits the encoded intracranial pressure data to the external part; and (5) the external part receives the data, decodes and acquires the intracranial pressure data after processing. The automatic monitoring method of the invention has the characteristics of more convenience, rapidness, accuracy, safety, reliability and effectiveness, less infection and high applicability.
Owner:北京锐致聪科技有限公司
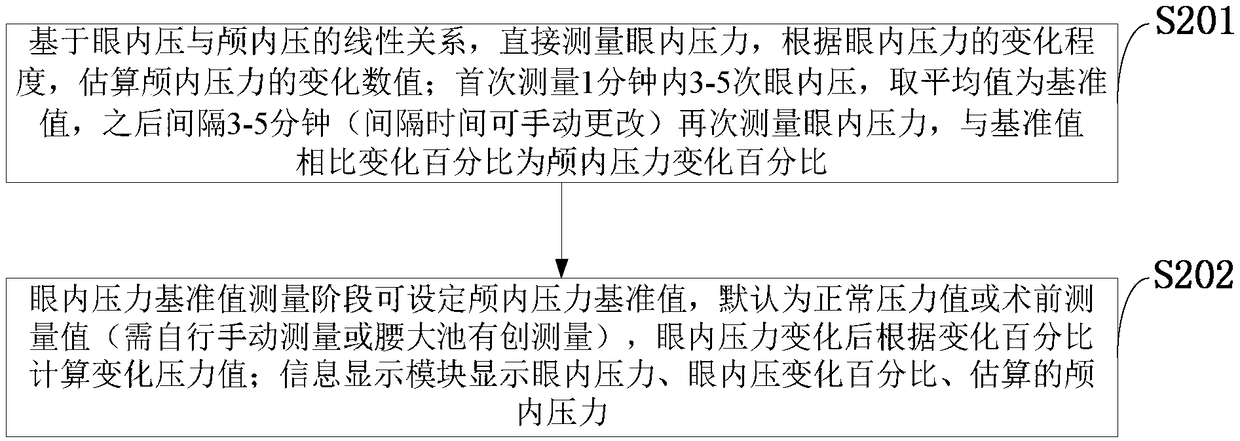
A monitoring system and method based on linear relationship between intraocular pressure and intracranial pressure
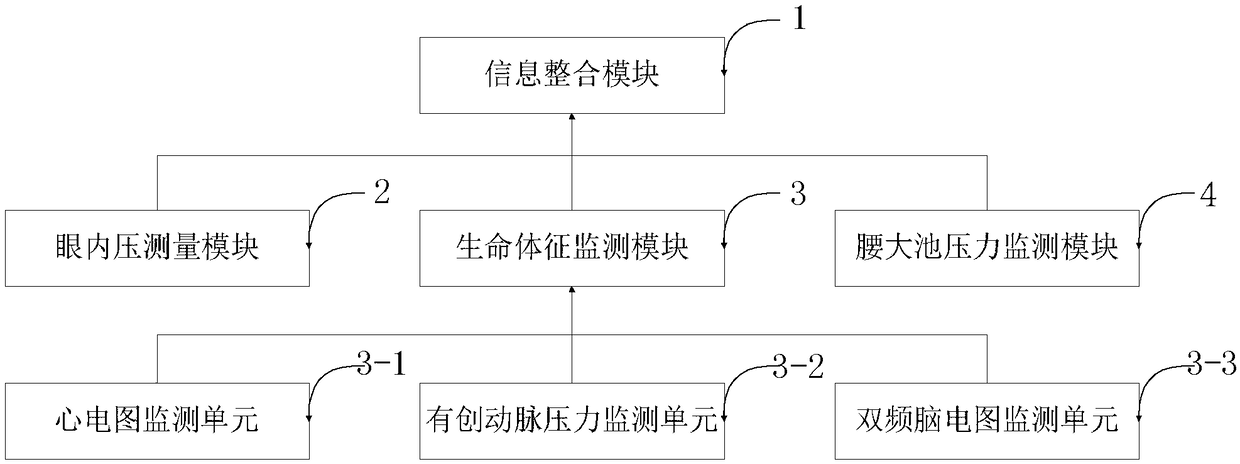
InactiveCN109124567AEffective non-invasive monitoring meansCatheterIntracranial pressure measurementMedical equipmentIntraocular pressure
The invention belongs to the technical field of medical equipment and discloses a monitoring system and a method based on the linear relationship between intraocular pressure and intracranial pressure. The monitoring system comprises an information integration module, an intraocular pressure measurement module, a vital signs monitoring module, and a lumbar cistern pressure monitoring module. The intraocular pressure measuring module, the vital signs monitoring module, and the lumbar cistern pressure monitoring module are mutually independently connected with the information integrating moduleand do not affect each other. The vital sign monitoring module comprises an electrocardiogram monitoring unit, an invasive artery pressure monitoring unit and a dual-frequency electroencephalogram monitoring unit. The data are integrated through an information integration module for information display, information storage and integration with the information. Based on the linear relationship between intraocular pressure (IOP) and intracranial pressure (ICP), the system indirectly reflects the change of ICP by measuring IOP, and provides an effective non-invasive monitoring method for ICP during general anesthesia.
Owner:PEKING UNIV THIRD HOSPITAL
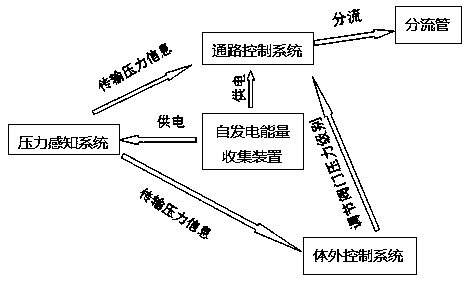
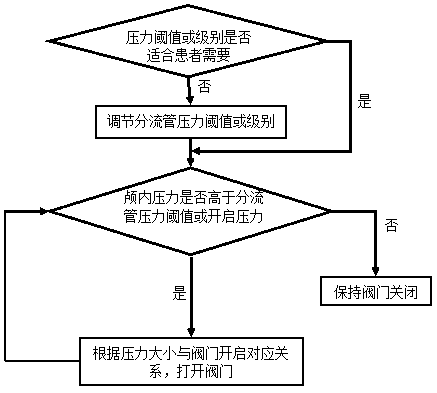
Rechargeable implantable automatic pressure regulating and diverting system with program control function
The invention discloses a rechargeable implantable automatic pressure regulating and diverting system with a program control function, and belongs to the field of medical instruments. The system includes a passage control valve, a pressure sensing system, a self-generating energy collecting system, an external control system and a drainage tube. Through the pressure feedback of the pressure sensing system and the adjustment of the external control system, the passage control valve adjusts the opening pressure or flow of a hydrocephalus valve, and drains intracranial cerebrospinal fluid to another suitable position in the body through the drainage tube, electricity required by various systems is supplied by the self-generating energy collecting system, and the drain tube is provided with ananti-freezing and antibacterial drug coating layer. The system can monitor the intracranial pressure in real time, adjust the pressure autonomously, effectively reduce related complications such as excessive or insufficient diversion, drain tube clogging, infection and the like.
Owner:SHANDONG BRANDEN MEDICAL DEVICE
SonoVue-based non-invasive transcranial ultrasonic blood pressure measuring device and method
ActiveCN112641467AControl pressureAccurate intracranial blood pressureOrgan movement/changes detectionInfrasonic diagnosticsMicrobubblesICP - Intracranial pressure
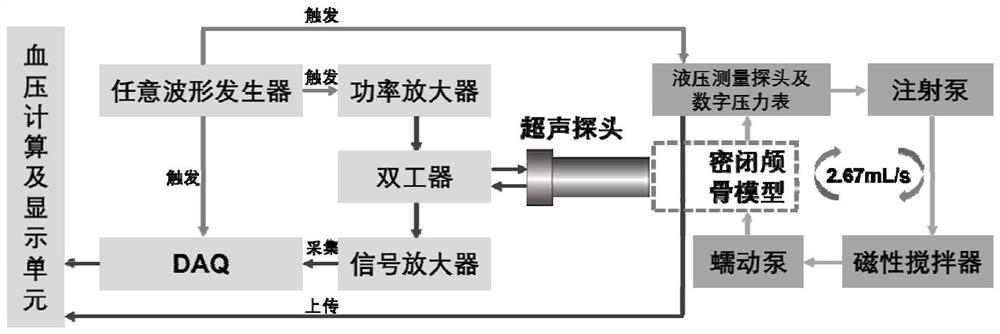
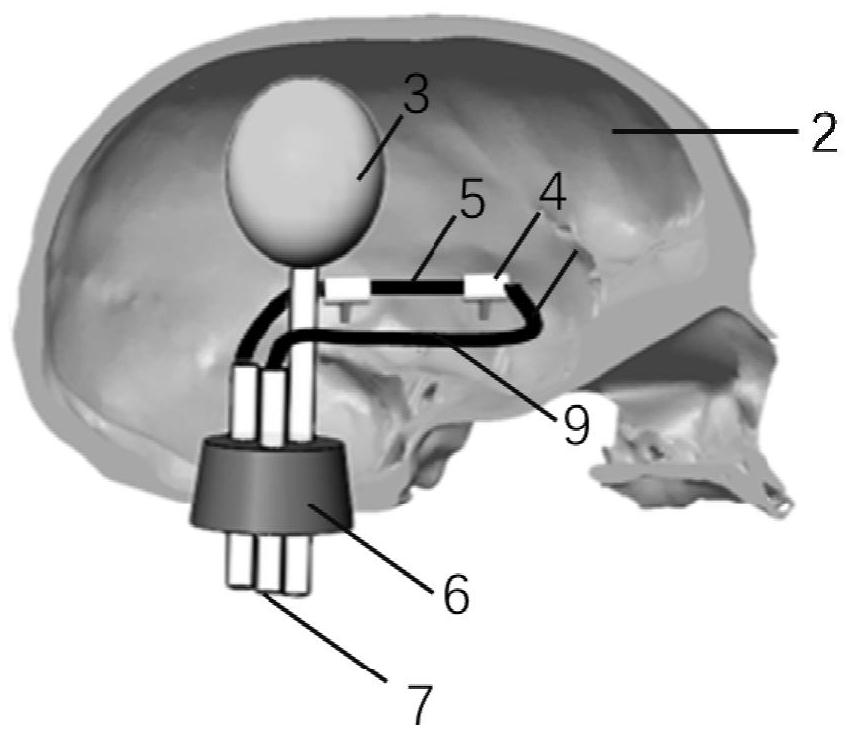
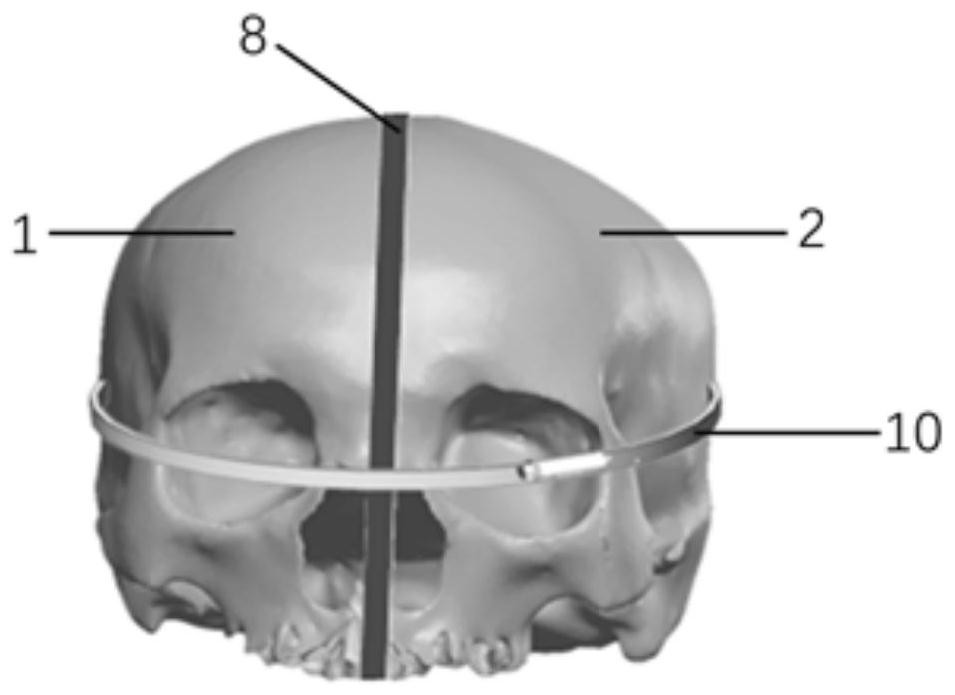
The invention discloses a SonoVue-based non-invasive transcranial ultrasonic blood pressure measuring device and method. The device comprises a skull phantom bionic module, a blood circulation pressurizing system and a pressure measuring unit; a blood vessel phantom is arranged in a skull phantom; the blood vessel phantom is connected with the blood circulation pressurizing system; a SonoVue microbubble solution is injected into the blood vessel phantom to operate instead of the blood, and the pressure of the blood vessel phantom is controlled by the blood circulation pressurization system; an arbitrary waveform generator and an ultrasonic probe are employed to emit different incident sound pressure to the skull phantom; and meanwhile, the pressure of the blood vessel phantom is controlled, then the relationship between the different incident sound pressure, a sound scattered signal of the blood vessel phantom and the pressure of the blood vessel phantom is acquired, and then the intracranial blood pressure is determined according to the relationship therebetween. Convenient intracranial pressurization and pressure measurement are realized, and the relationship between intracranial blood pressure and injection pressure rise is reflected, so that the relationship between the SonoVue subharmonic amplitude and hydrostatic pressure presents the optimal linear relationship, and thus, not only is accurate noninvasive measurement of intracranial blood pressure realized, but also the relationship between intracranial blood pressure and intracranial pressure can be studied.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Brain disease judgment system based on intracranial multi-modal information fusion of machine learning
ActiveCN113180605ADoes not affect function usageEasy to integrateDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsICP - Intracranial pressurePhysical therapy
The invention provides a brain disease judgment system based on intracranial multi-modal information fusion of machine learning. The judgment system comprises an input layer and an output layer, wherein intracranial information is input into the input layer, multi-level processing of data is carried out, various intracranial injury types are automatically judged and output. An intervention treatment combination is specified according to the type combination of the output layer, wherein the intracranial information comprises intracranial pressure, intracranial oxygen partial pressure, intracranial temperature, intracranial electroneurographic signals, intracranial sodium ion concentration and intracranial potassium ion concentration.
Owner:AEROSPACE INFORMATION RES INST CAS
CSF shunt flow enhancer, method for generating CSF flow in shunts and assessment of partial and complete occlusion of CSF shunt systems
An apparatus capable of generating flow in cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) shunt systems by vibrating the shunt, tubing or shunt valve dome, or applying cyclical pressure to the various parts of the shunt system. A method of generating flow and method of using the apparatus in shunt patency assessment, for example, hydraulic resistance assessment, is also disclosed. The apparatus allows, in conjunction with a thermal dilution method or radionuclide method, a quick CSF shunt patency assessment based upon CSF shunt resistance and not upon CSF flow or intracranial pressure (ICP) separately. This provides a more objective measure of shunt obstruction compared to other methods. Furthermore, the apparatus can be used to enhance flow in shunts, identify partial occlusion before symptoms occur, differentiate between patent, partially-occluded and occluded shunts. The apparatus can be used to generate flow in shunts if there is a need to lower ICP or move drugs administered via an injection chamber or a shunt dome.
Owner:SHUNTCHECK +1
Probe sealing structure and testing system
ActiveCN106343998AGood sealing effectImprove product qualityIntracranial pressure measurementSensorsIntracranial pressureElectrical and Electronics engineering
The invention discloses a probe sealing structure and a testing system. A probe is used for detecting an intracranial pressure and comprises a sensor, a probe connector and a lead for connecting the sensor and the probe connector, wherein the sealing structure comprises a protective pipe surrounding the periphery of the lead and a sealing connector surrounding the periphery of the protective pipe. The probe sealing structure and the testing system are good in sealing effect, high in product quality and higher in working efficiency.
Owner:SCENERAY
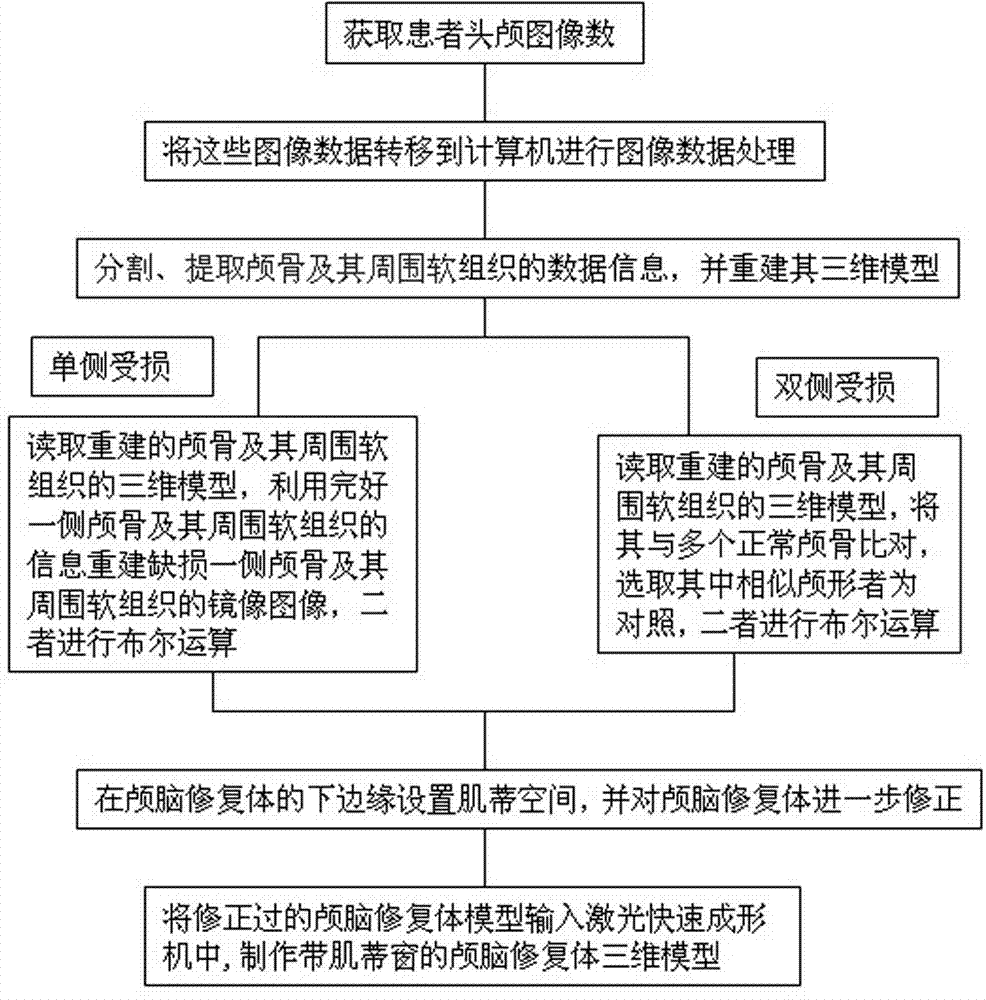
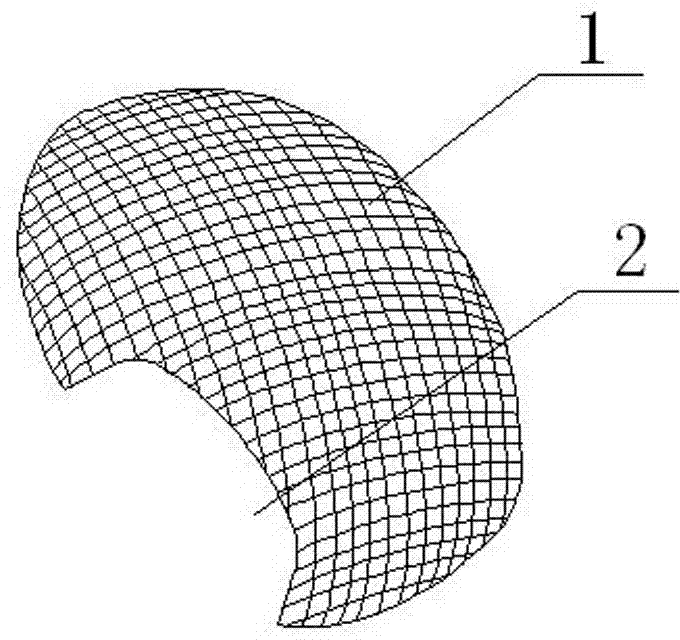
Craniocerebral three-dimensional forming restoration with muscle base window and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a craniocerebral three-dimensional forming restoration with a muscle base window. According to the craniocerebral three-dimensional forming restoration with the muscle base window, a medical three-dimensional forming material serves as a substrate, multiple mesh holes are formed in the substrate, the craniocerebral three-dimensional forming restoration with the muscle base window is provided with a smooth outline edge, a suitable individualized muscle base window three-dimensional structure is reserved for the skull defect zone muscular tissue of a patient at the edge, close to the base of skull, of an outline, the tissue combinations such as the muscles, the meninx and the brain which are attached to a skull defect zone are located at the inner side of the craniocerebral three-dimensional forming restoration with the muscle base window, the outline radian of the craniocerebral three-dimensional forming restoration with the muscle base window are formed with the consideration of the distribution condition of the tissue combinations such as the muscles, the meninx and the brain in the skull defect zone, so that it is guaranteed that the skull and the brain are repaired and protected together, and symmetry and beauty of the skull and the brain at the two sides are considered. Compared with the prior art, the craniocerebral three-dimensional forming restoration with the muscle base window has the following advantages that the internal environments such as brain blood supply and intracranial pressure maintenance are improved and recovery of the brain functions is facilitated.
Owner:步星耀
Intracranial pressure monitoring method and device
PendingCN111990986AAddress operational complexityEasy to operateIntracranial pressure measurementPressure sensorsICP - Intracranial pressureSurgery
The invention discloses an intracranial pressure monitoring method and device. The monitoring method comprises the steps that a pressure sensor is connected with a pressure measuring probe, and a pressure transmission path from a thin film to the pressure sensor is formed; the pressure measuring probe is implanted into the ventricle of a patient, and intracranial pressure is conducted to the thinfilm of the pressure measuring probe by using cerebrospinal fluid in the ventricle; the cerebrospinal fluid pressure change is converted into a grating signal through the pressure sensor; the gratingsignal is transmitted to a photoelectric analysis module through an optical fiber, so that the photoelectric analysis module converts the grating signal into an electric signal; and digital-to-analogue conversion is carried out on the electric signal to obtain a pressure waveform representing the intracranial pressure and the pressure waveform is displayed. Operation such as drainage can be carried out while monitoring is carried out, due to the fact that the size of the pressure measuring probe is relatively small, and meanwhile an optical fiber sensor and the corresponding optical fiber arerelatively thin, drilling insertion of the pressure measuring probe can be achieved, detection is carried out according to the medium conduction principle, the principle of a communicating vessel is not needed, operation is easy, and cerebrospinal fluid drainage can be carried out synchronously.
Owner:合肥中纳医学仪器有限公司
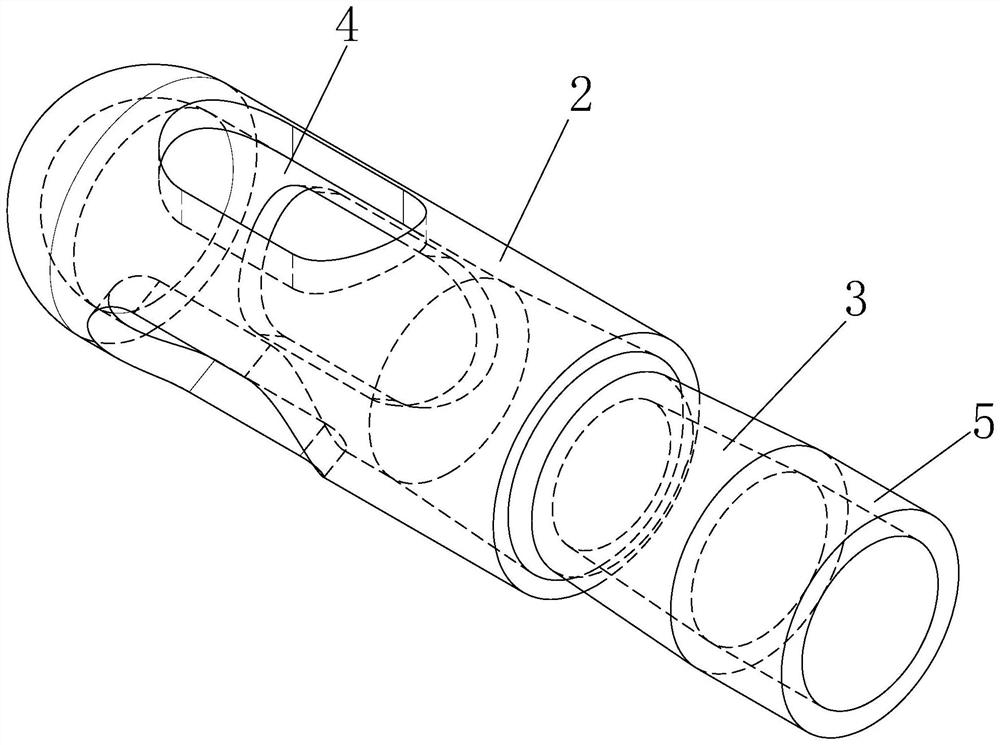
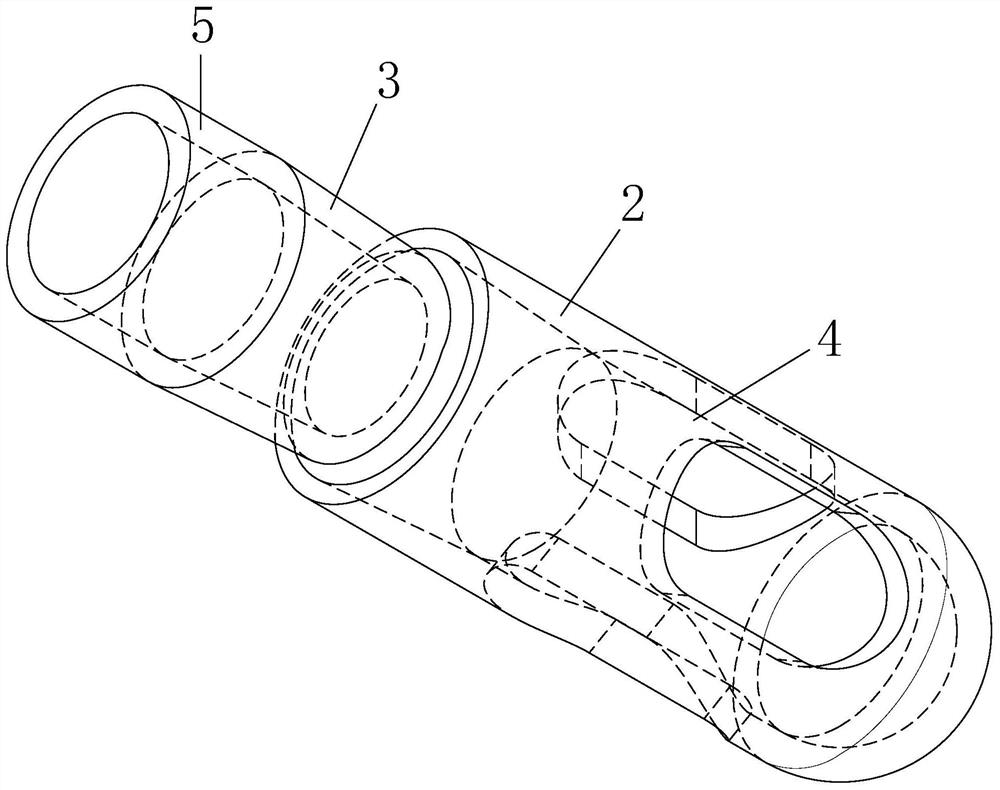
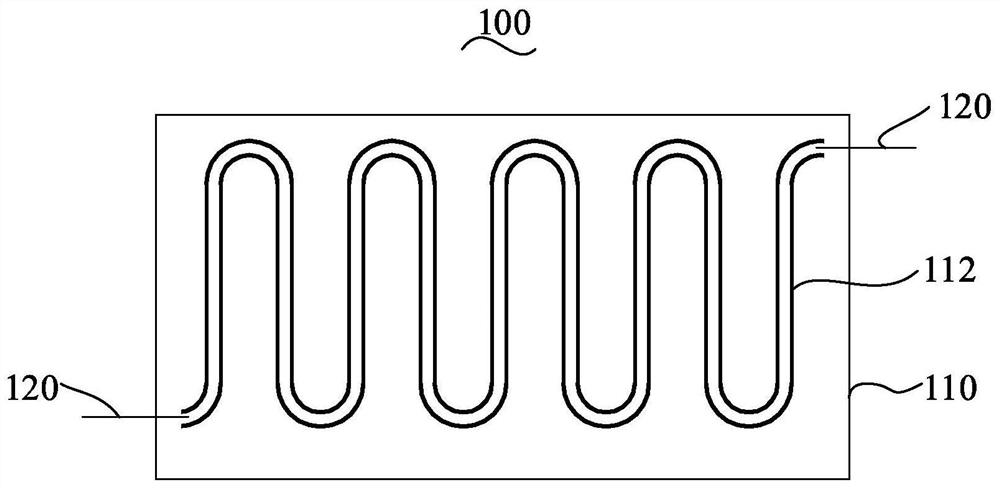
Pressure sensor, preparation method and application thereof and intracranial pressure detection equipment
ActiveCN111990985AFlexibleHigh sensitivityIntracranial pressure measurementSensorsMedicineICP - Intracranial pressure
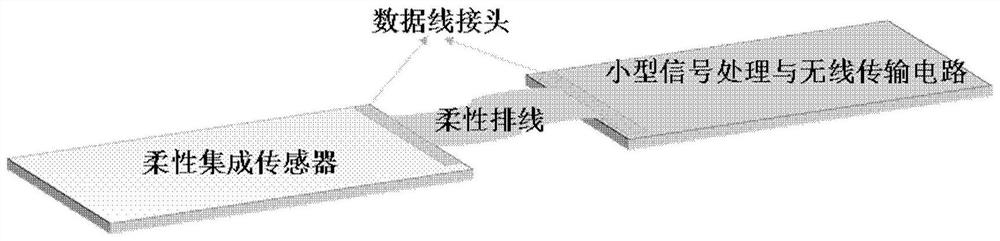
The invention relates to a pressure sensor, a preparation method and application thereof and intracranial detection equipment. The pressure sensor comprises an elastic polymer layer and a liquid metalfilled in the elastic polymer layer, a serpentine channel is arranged in the elastic polymer layer, and the liquid metal is filled in the serpentine channel. The pressure sensor is flexible and highin sensitivity.
Owner:SOUTH UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY OF CHINA
Ventricular drainage device
PendingCN111375093AImprove securityImprove convenienceMedical devicesIntravenous devicesCerebral ventricularICP - Intracranial pressure
The invention relates to the technical field of ventricular drainage devices, and discloses a ventricular device. The device comprises a drainage tube, a drainage bag and a controller. The drainage end of the drainage tube is placed in the cerebral ventricle, the other end of the drainage tube is connected to the drainage bag, the drainage tube is provided with an electromagnetic pinch valve and afirst pressure sensor, the first pressure sensor and the electromagnetic pinch valve are connected to the controller, the controller is connected with a prompt device and a control input device, thecontroller is also connected with an intracranial pressure monitoring device, and the intracranial pressure monitoring device comprises an intracranial pressure monitoring probe extending into the brain. According to the ventricular drainage device of the present invention, the adjustment and control of drainage can be realized according to the set pressure value, the drainage is not affected by the posture of patients, the medical staff can be reminded in time when the drainage tube is not smooth, the use safety is ensured, the intracranial pressure of patients can be more accurately controlled, and the device is conducive to the improvement of the prognosis of patients.
Owner:THE SECOND HOSPITAL OF HEBEI MEDICAL UNIV
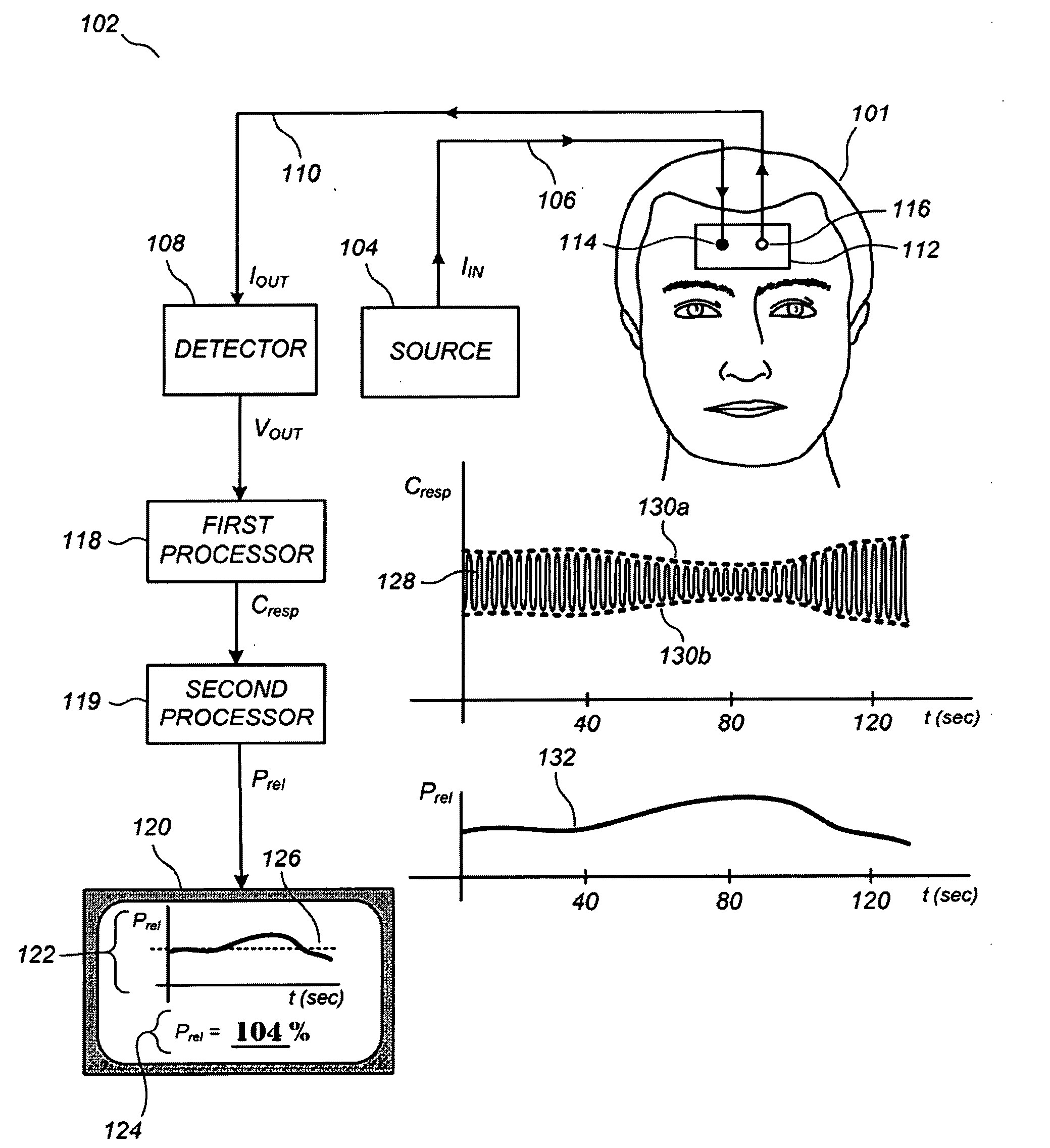
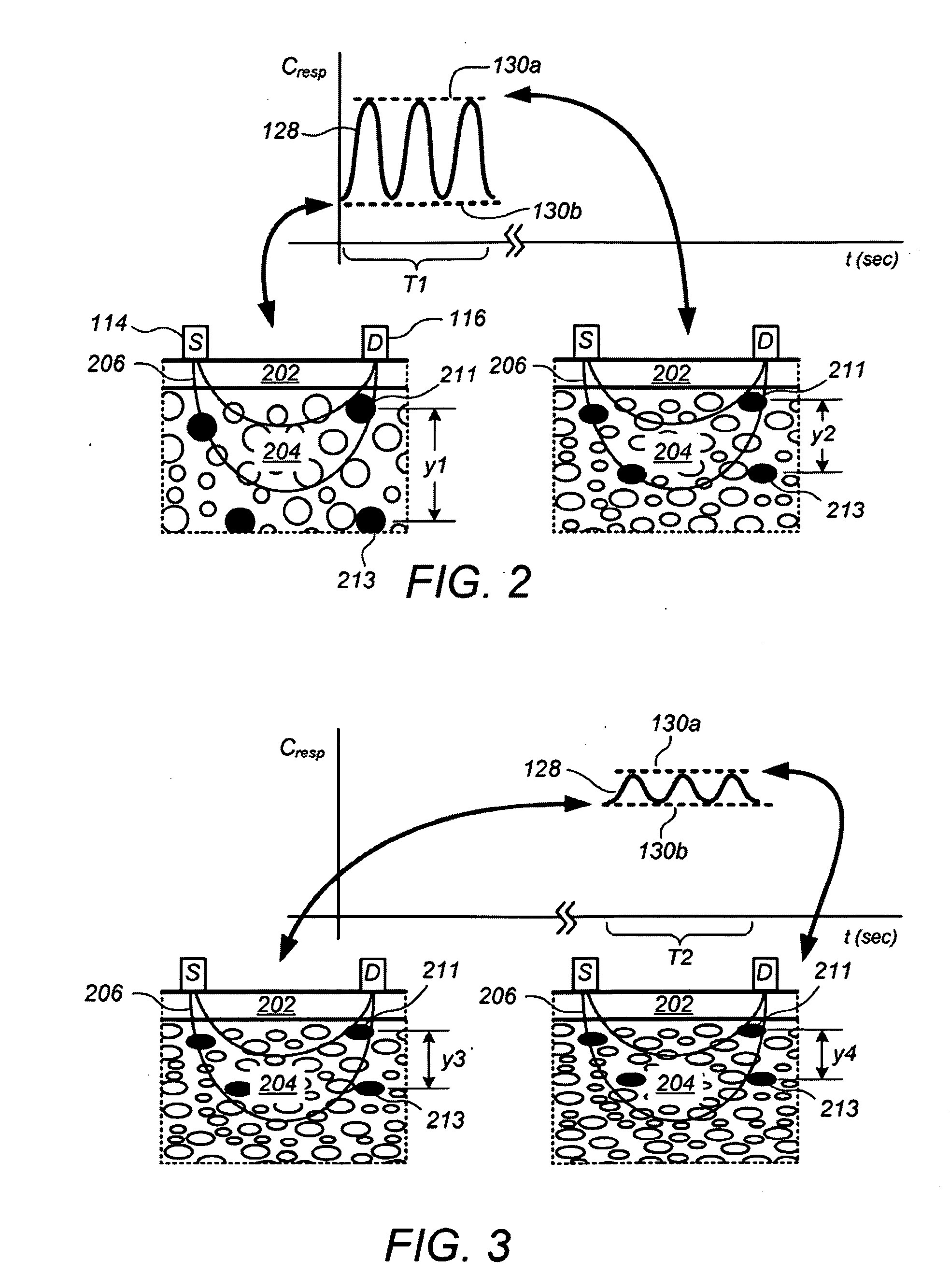
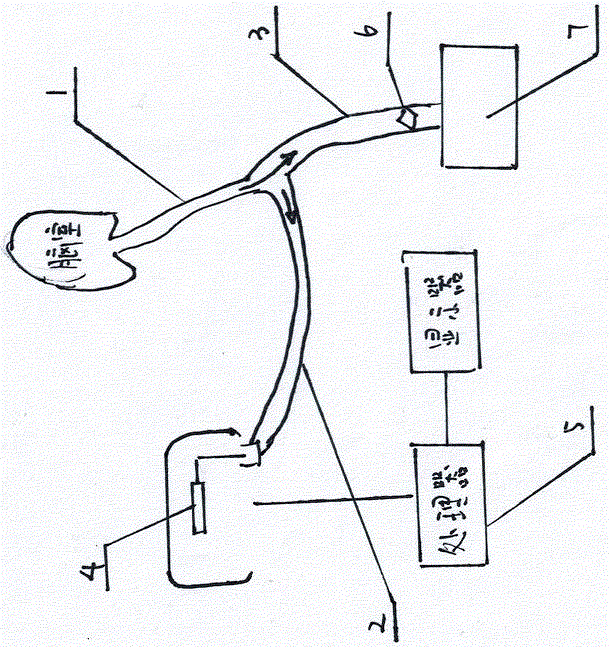
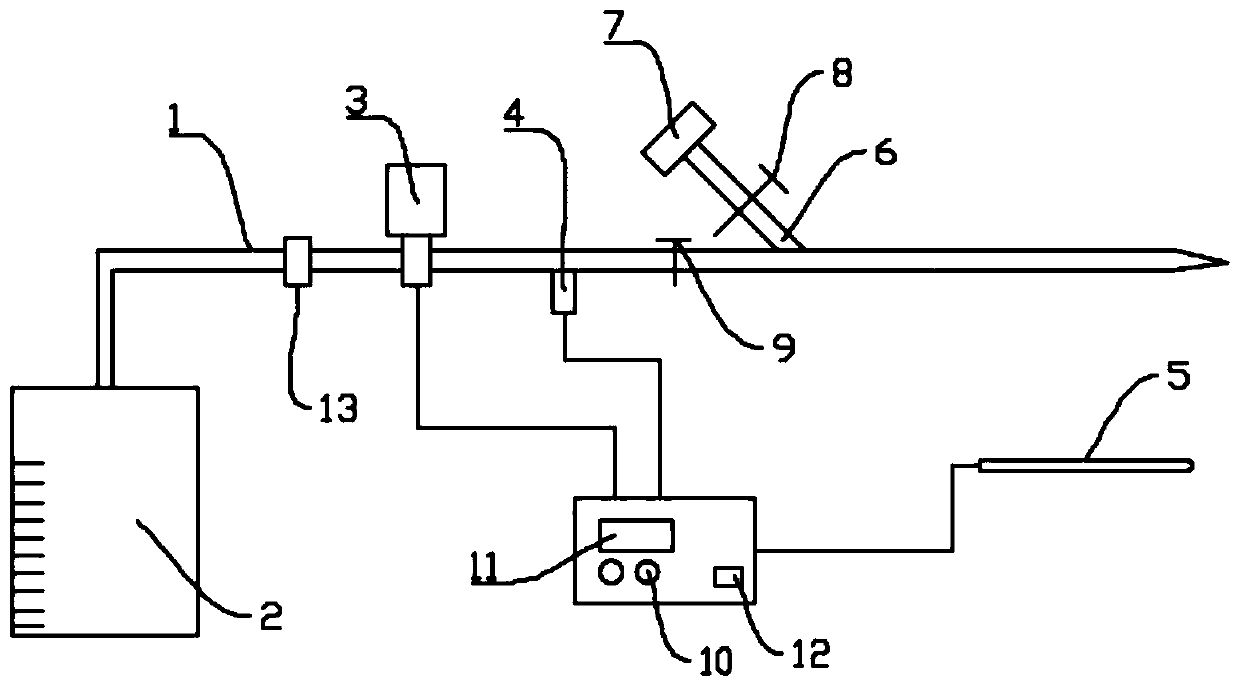
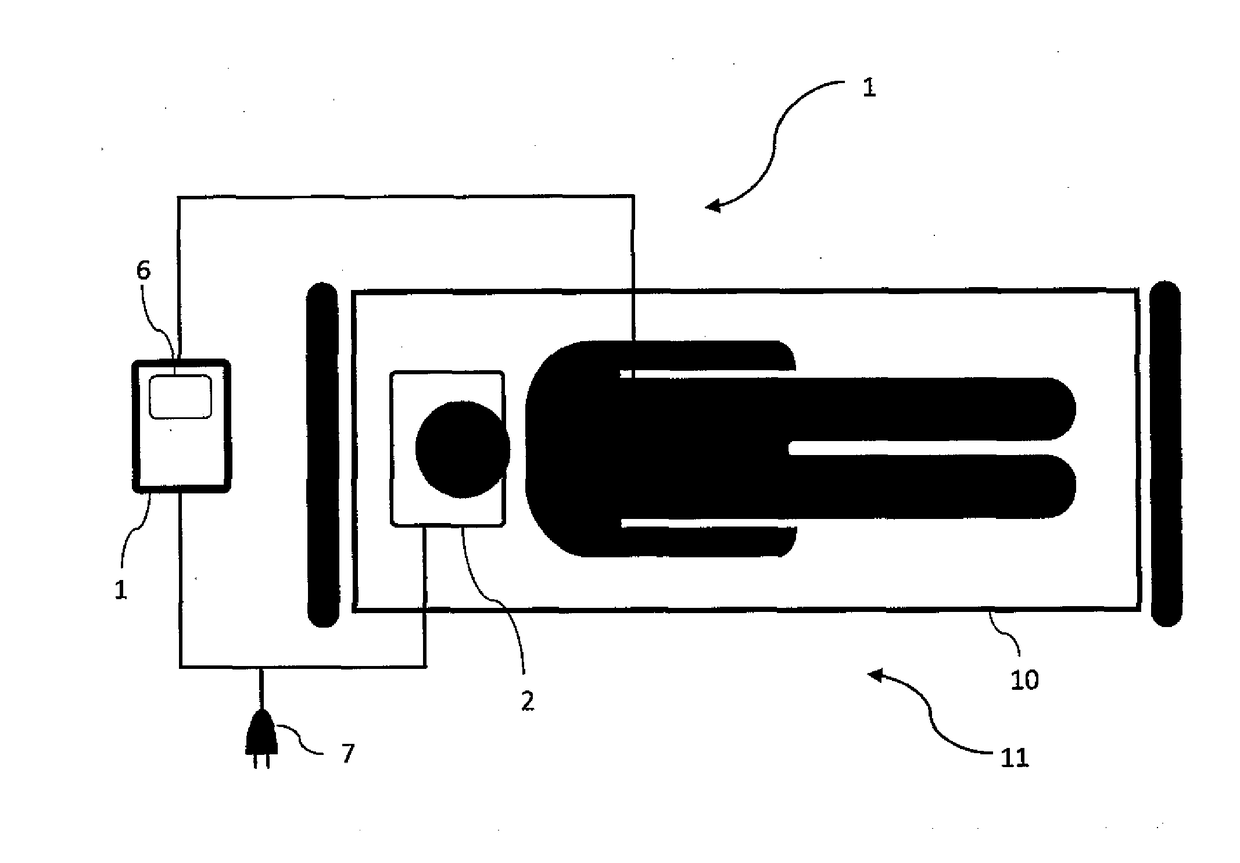
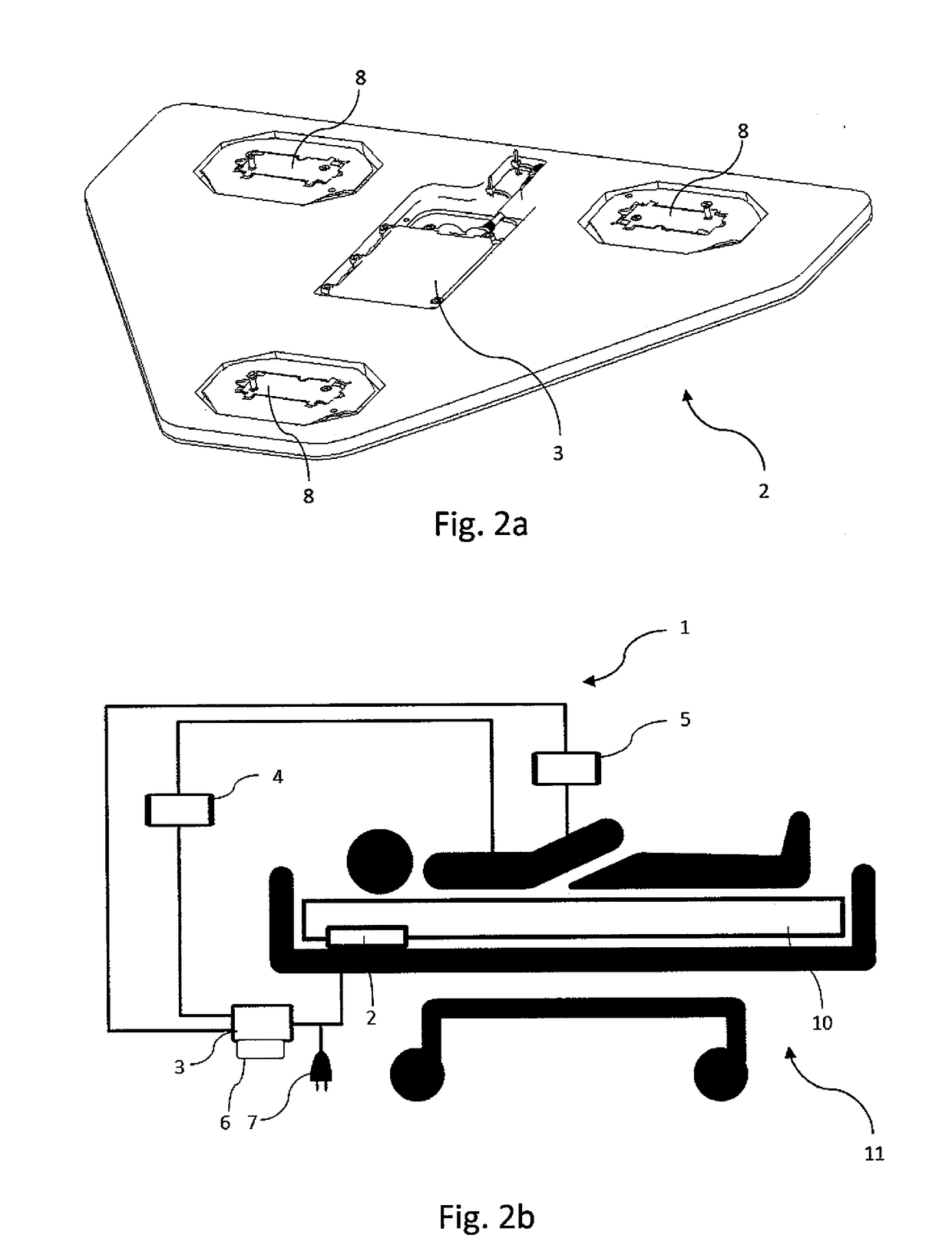
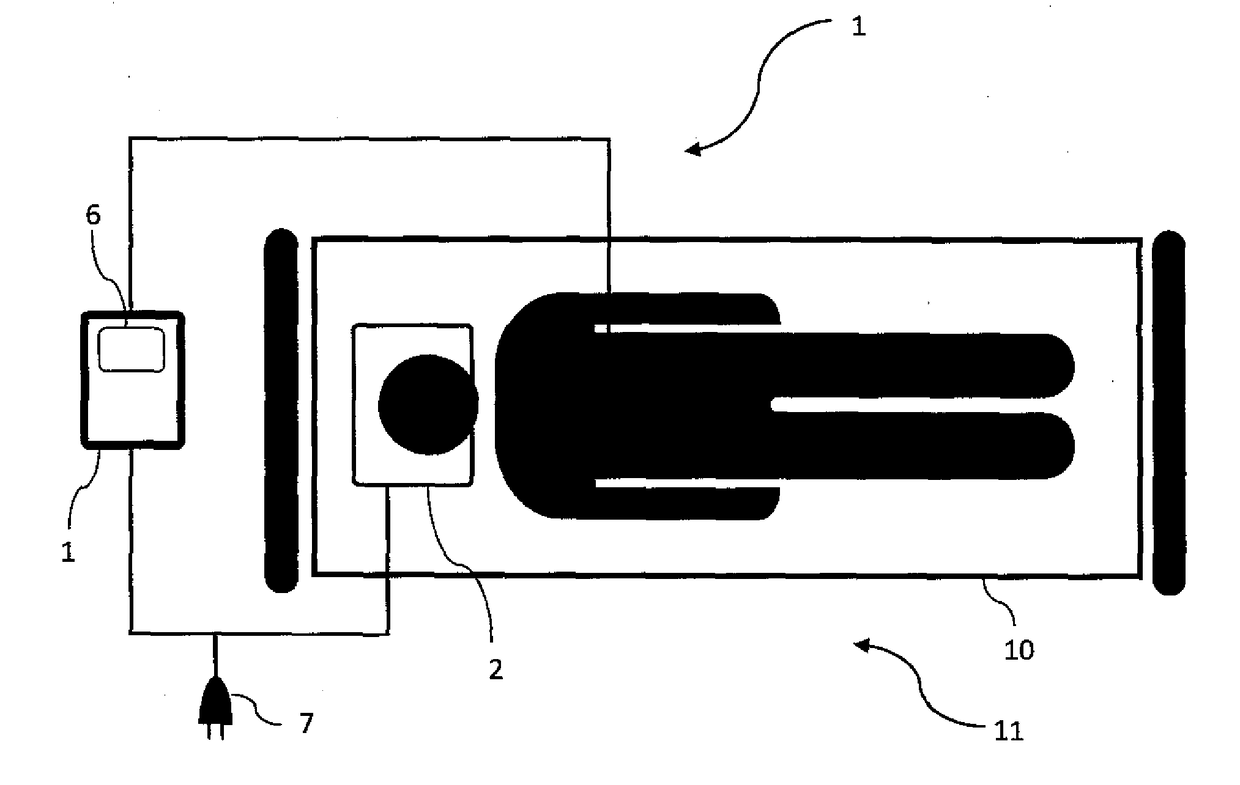
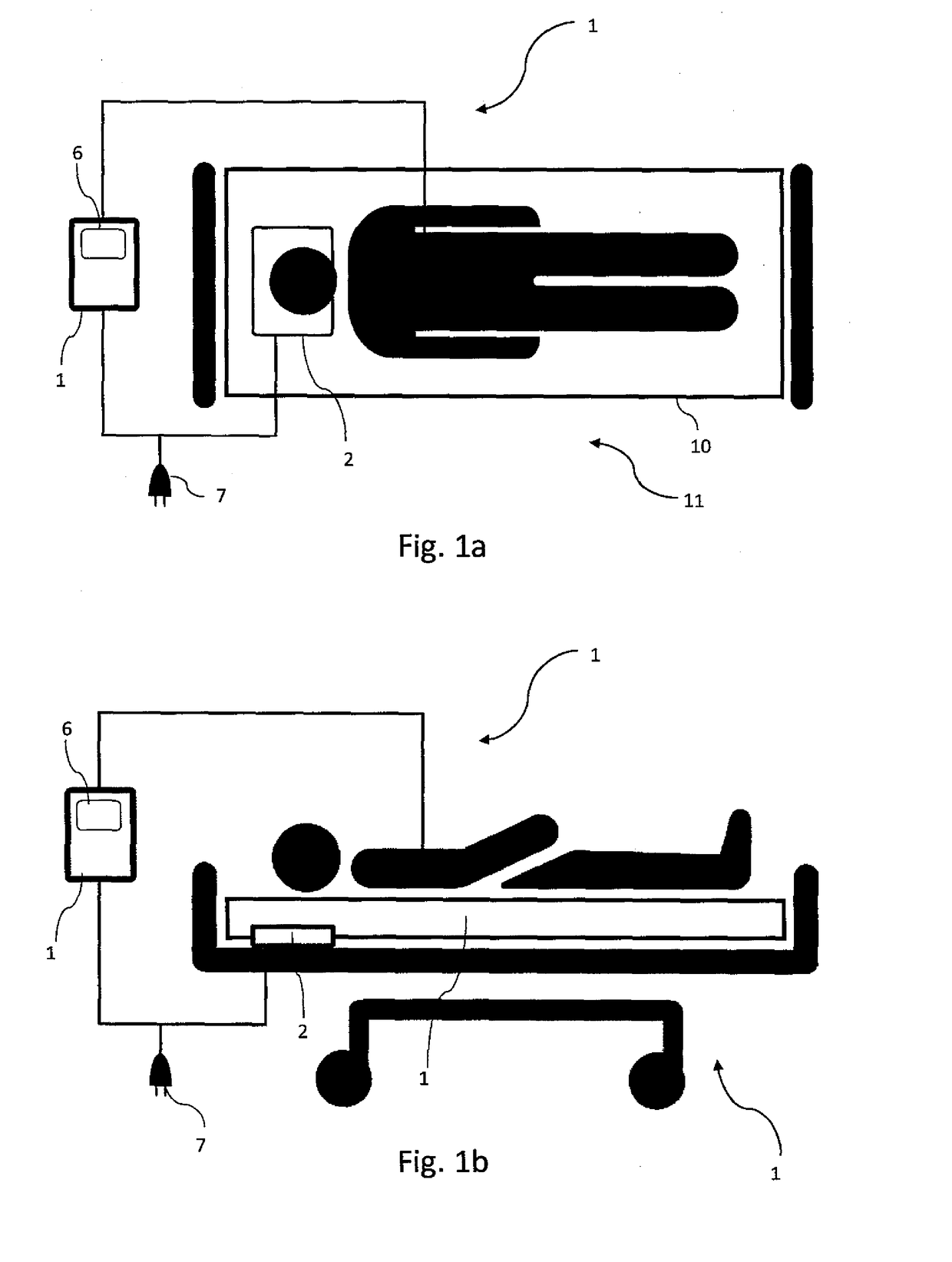
Device and method for measurement of intracranial pressure
The device for non-invasive monitoring of intracranial pressure (1) includes a measuring mat (2), processor unit (3), displaying device (6) and a network connector (7). The measuring mat includes the processor unit (3) and sensors, at least one sensor (8) monitoring mechanical movement caused by the bloodstream dynamics. The ICP calculation methods use the Windkessel model and the relationship between the first and second signal, which is related to the reflection of the pulse wave in the head. The method of relative changes of the intracranial pressure is based on an analysis of the bloodstream dynamics using the Moens-Kortweg equation.
Owner:LINET SPOL
Automated measurement of brain injury indices using brain CT images, injury data, and machine learning
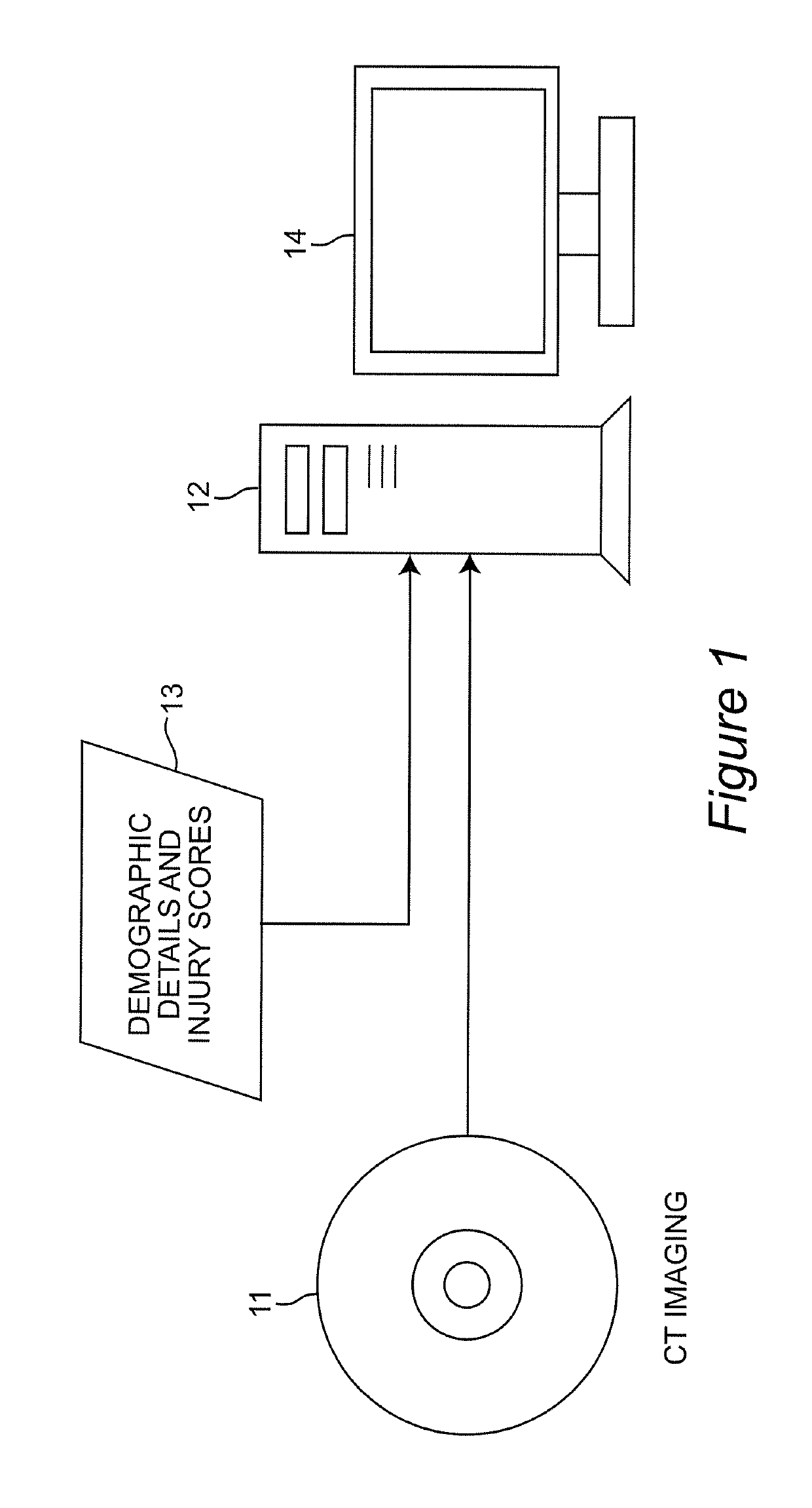
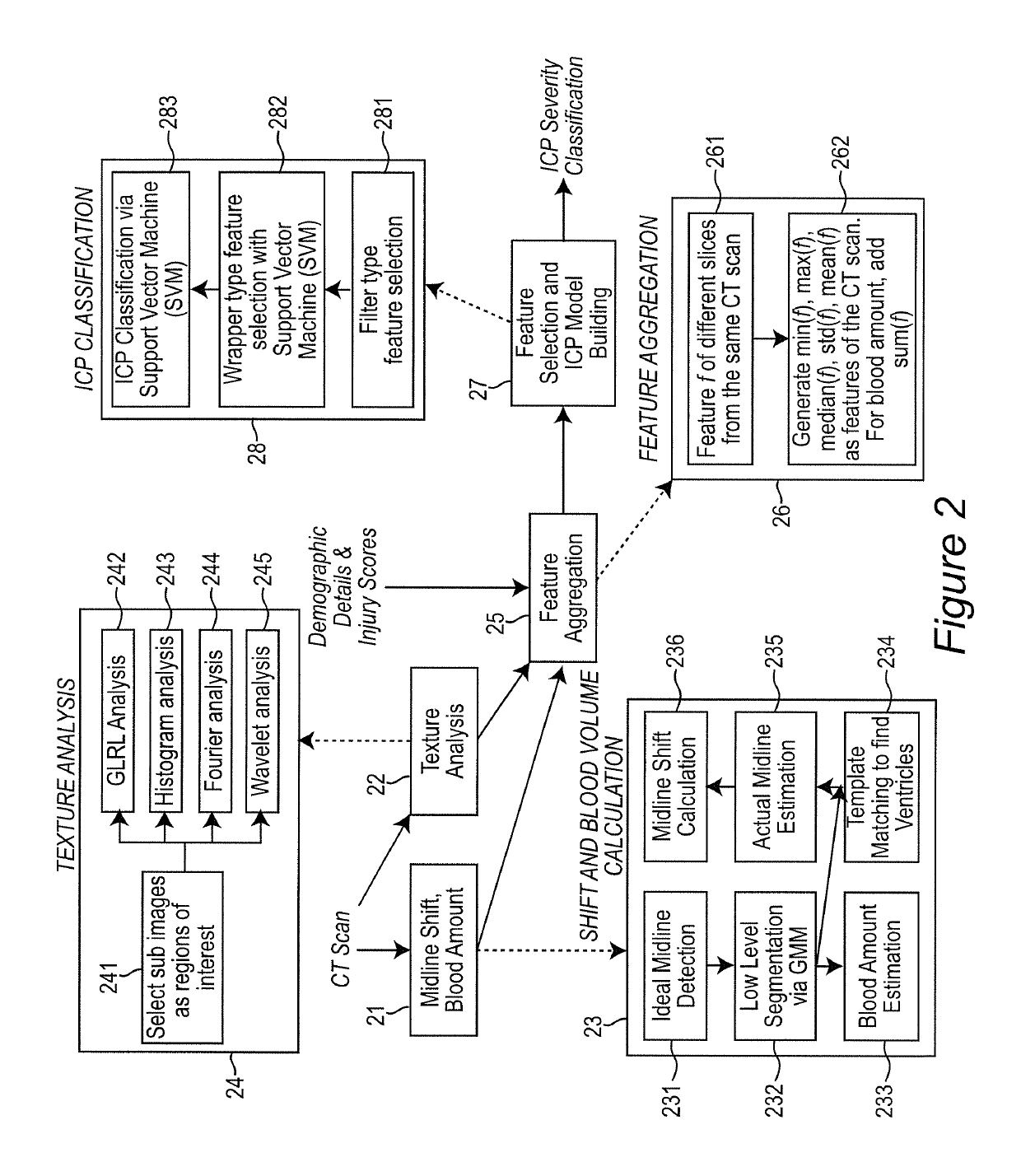
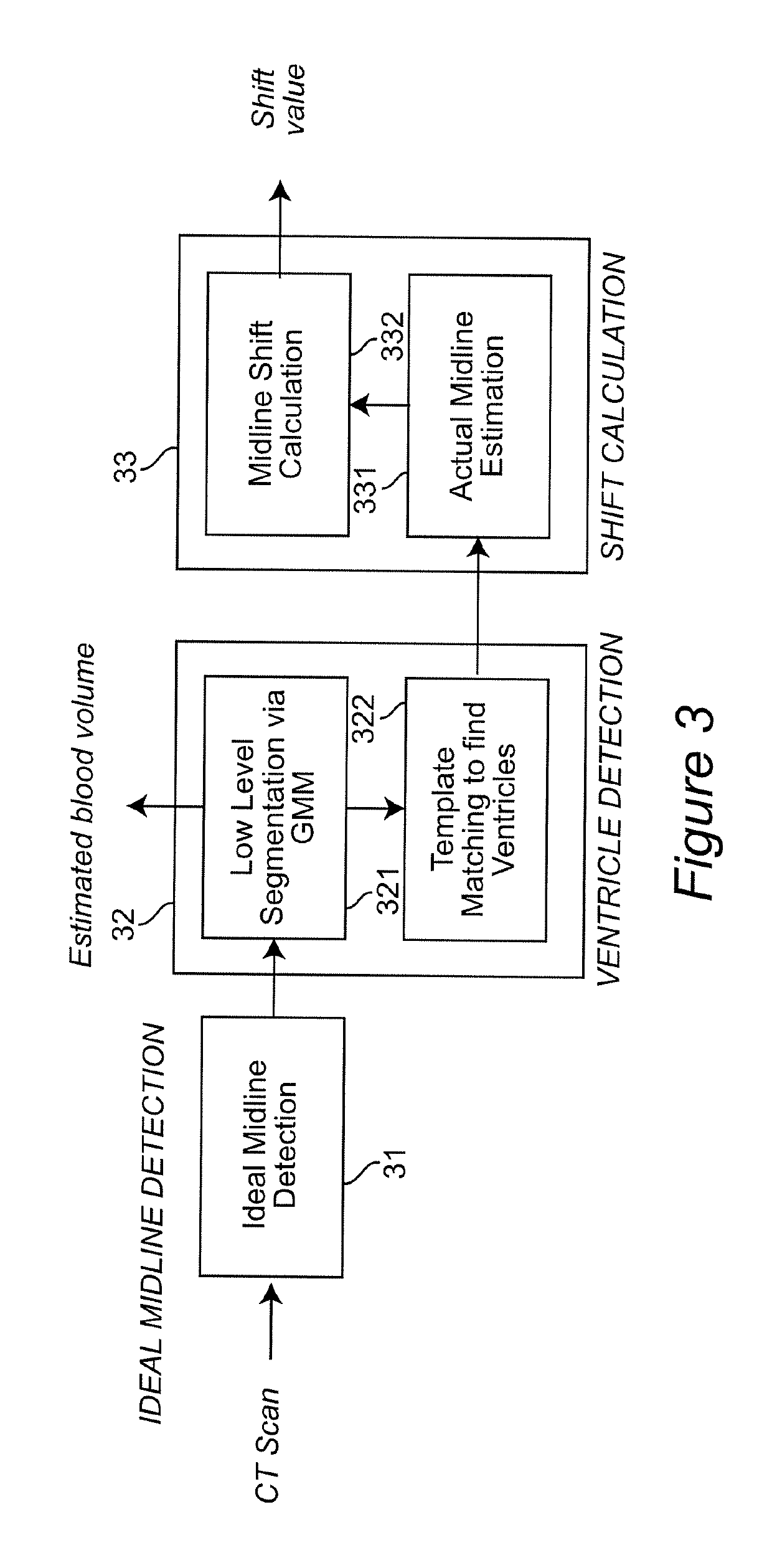
ActiveUS10303986B2Accurate detectionIncrease speedImage enhancementImage analysisInjury brainDecision taking
A decision-support system and computer implemented method automatically measures the midline shift in a patient's brain using Computed Tomography (CT) images. The decision-support system and computer implemented method applies machine learning methods to features extracted from multiple sources, including midline shift, blood amount, texture pattern and other injury data, to provide a physician an estimate of intracranial pressure (ICP) levels. A hierarchical segmentation method, based on Gaussian Mixture Model (GMM), is used. In this approach, first an Magnetic Resonance Image (MRI) ventricle template, as prior knowledge, is used to estimate the region for each ventricle. Then, by matching the ventricle shape in CT images to the MRI ventricle template set, the corresponding MRI slice is selected. From the shape matching result, the feature points for midline estimation in CT slices, such as the center edge points of the lateral ventricles, are detected. The amount of shift, along with other information such as brain tissue texture features, volume of blood accumulated in the brain, patient demographics, injury information, and features extracted from physiological signals, are used to train a machine learning method to predict a variety of important clinical factors, such as intracranial pressure (ICP), likelihood of success a particular treatment, and the need and / or dosage of particular drugs.
Owner:VIRGINIA COMMONWEALTH UNIV
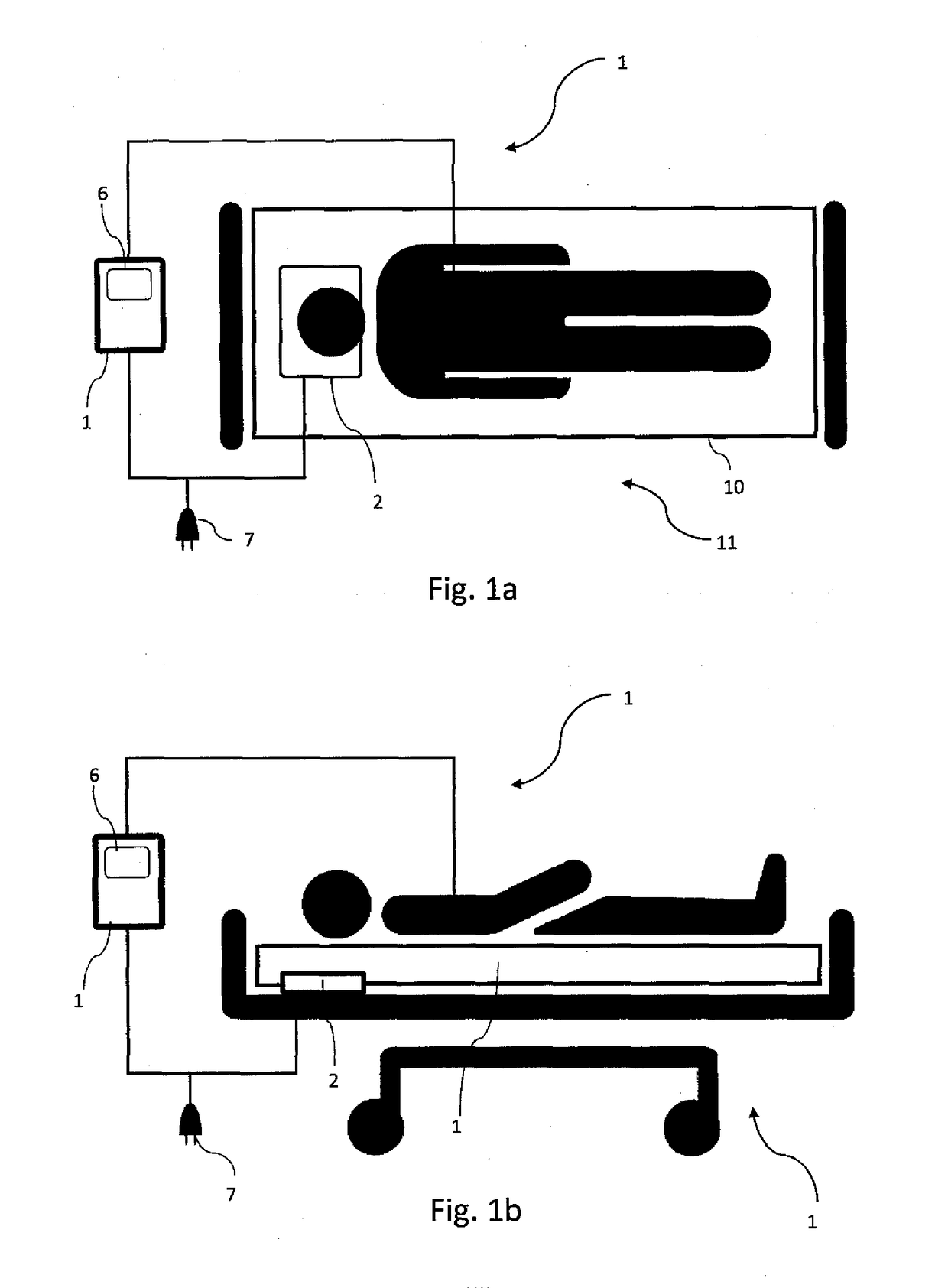
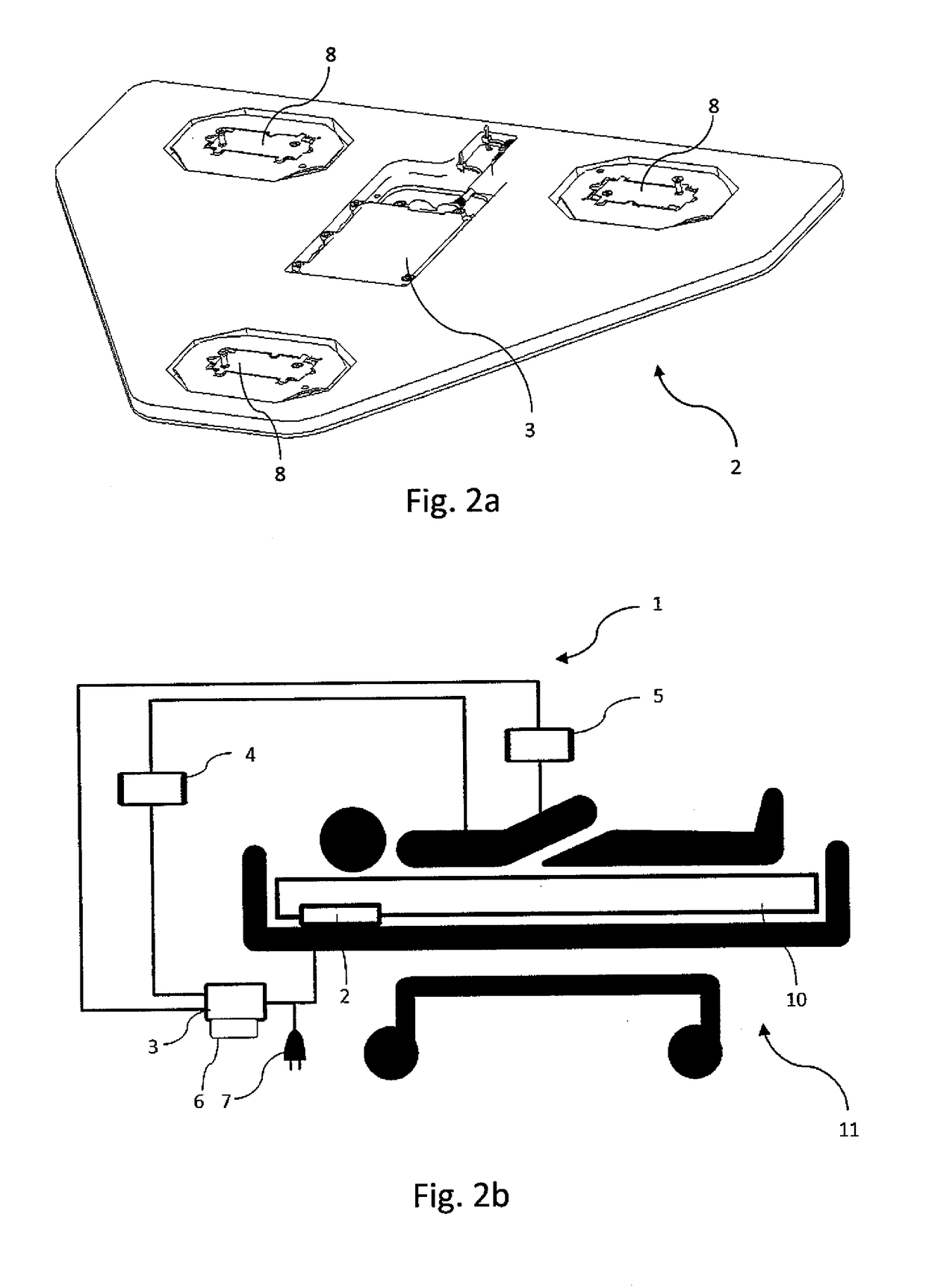
Device and method for measurement of intracranial pressure
The device for non-invasive monitoring of intracranial pressure (1) includes a measuring mat (2), processor unit (3), device for recording electrical activity of the heart (4), device for invasive measurement of arterial blood pressure (5), imaging device 6 and network connector (7). The measuring mat includes the processor unit (3) and sensors, at least one sensor (8) monitoring mechanical movement caused by the bloodstream dynamics. The ICP calculation methods use the Windkessel model and the relation between the start of the R-wave and the time delay of the mechanical movement of the head, which is related to the reflection of the pulse wave in the head.
Owner:LINET SPOL
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com