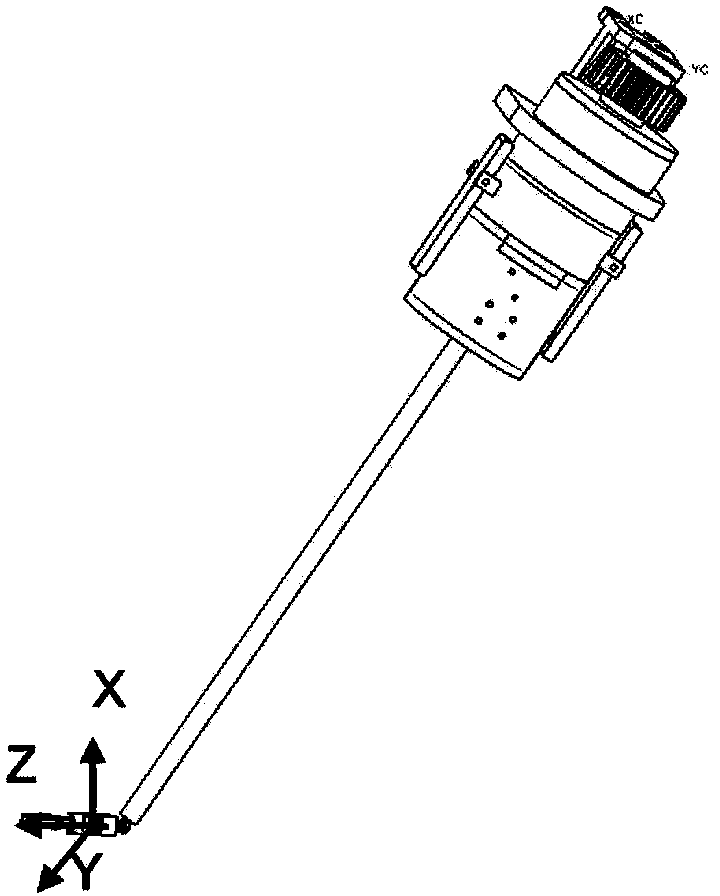Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
990 results about "Heat-shrink tubing" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
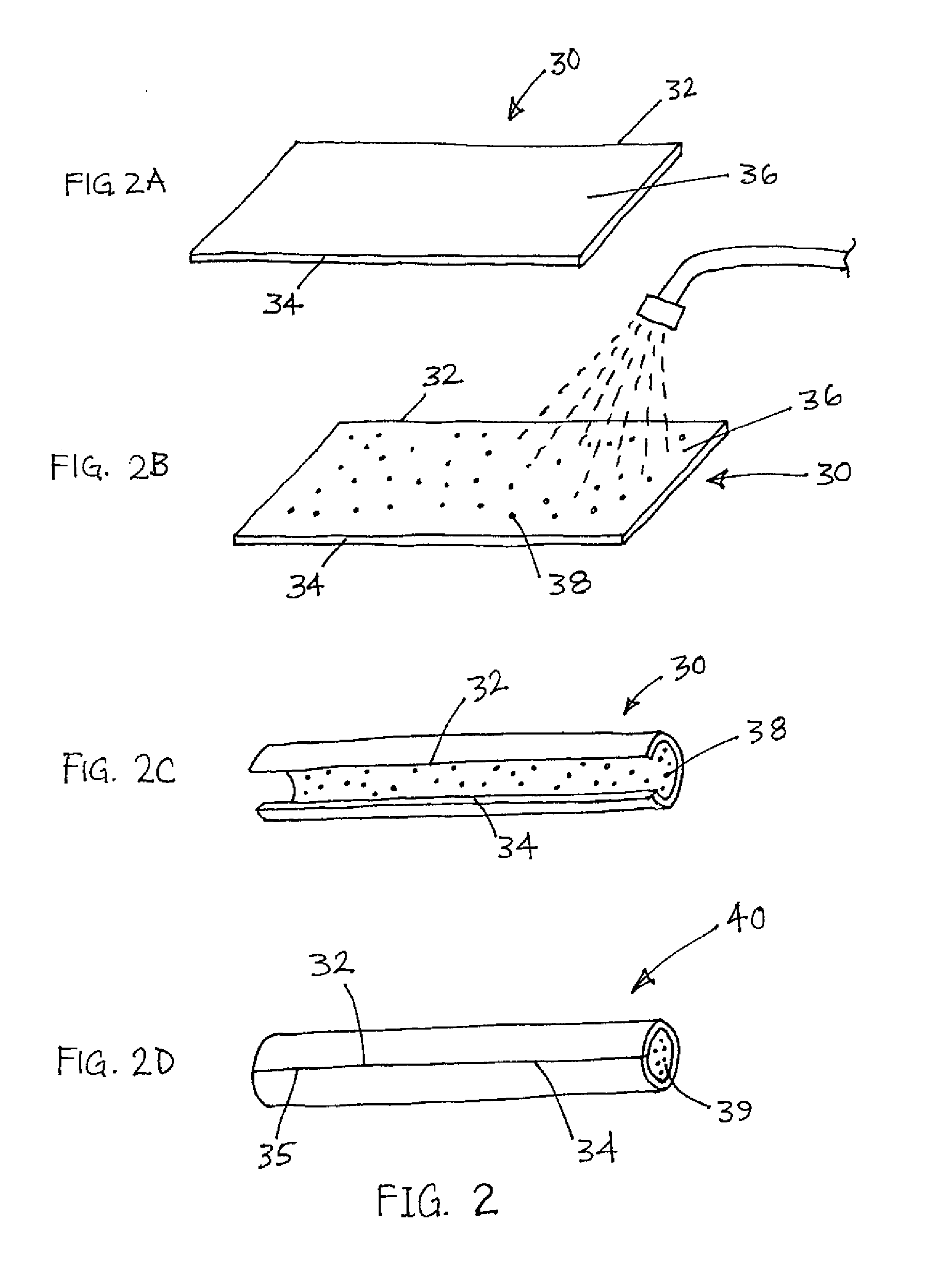
Heat-shrink tubing (or, commonly, heat shrink or heatshrink) is a shrinkable plastic tube used to insulate wires, providing abrasion resistance and environmental protection for stranded and solid wire conductors, connections, joints and terminals in electrical work. It can also be used to repair the insulation on wires or to bundle them together, to protect wires or small parts from minor abrasion, and to create cable entry seals, offering environmental sealing protection. Heat-shrink tubing is ordinarily made of polyolefin, which shrinks radially (but not longitudinally) when heated, to between one-half and one-sixth of its diameter.
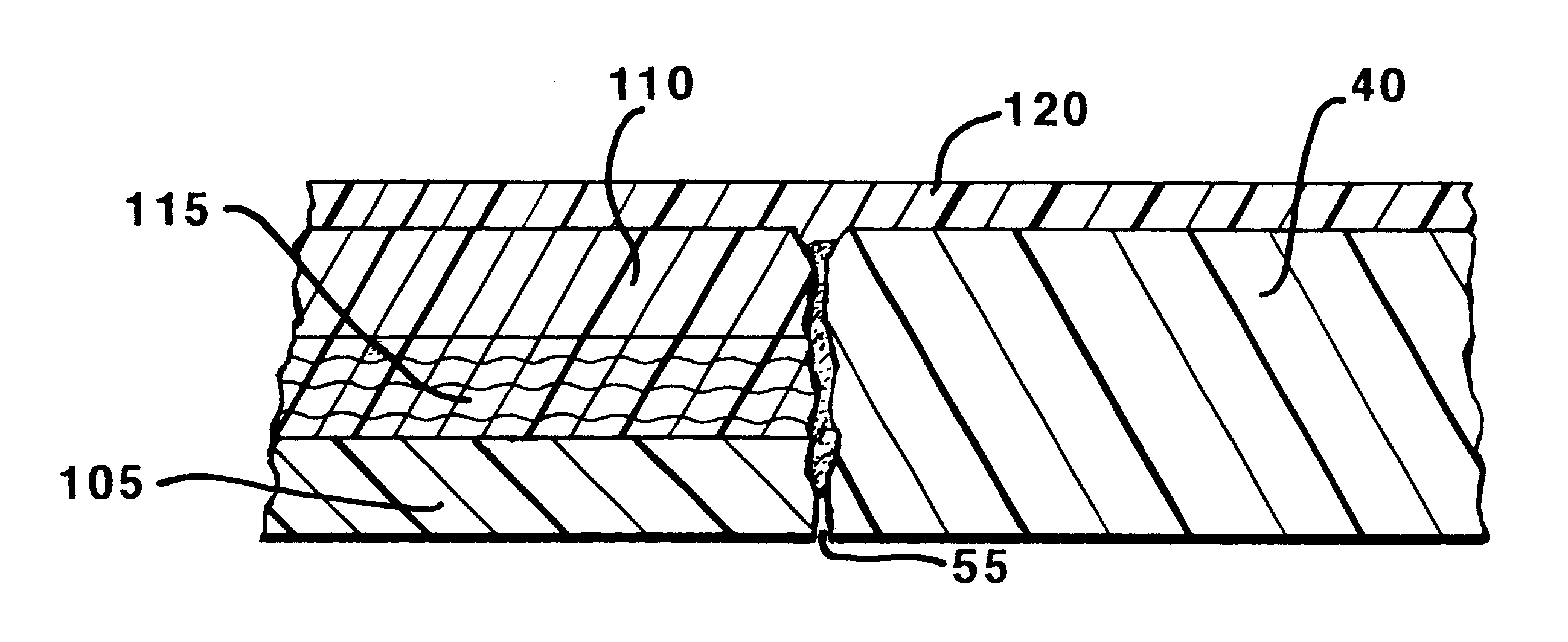
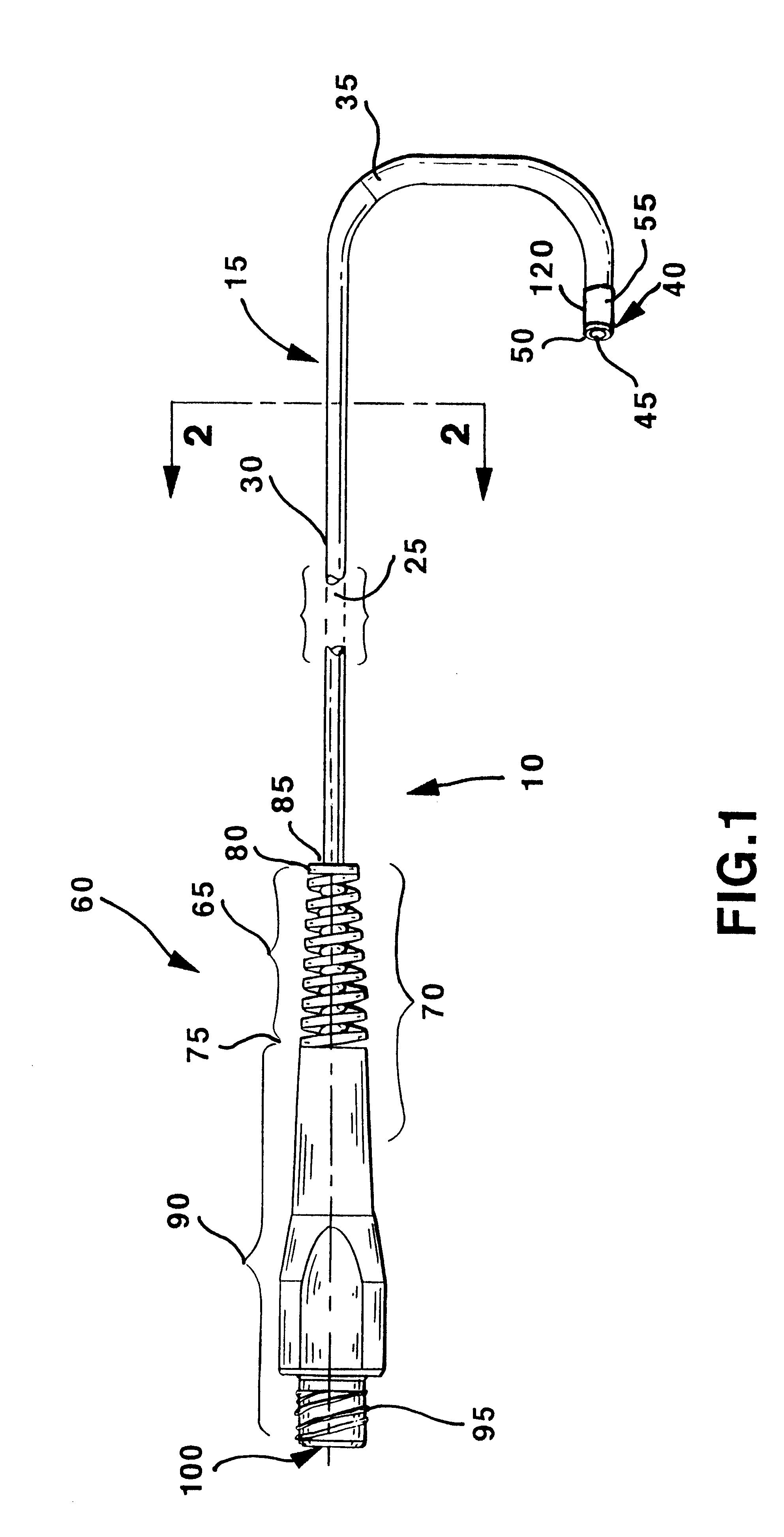
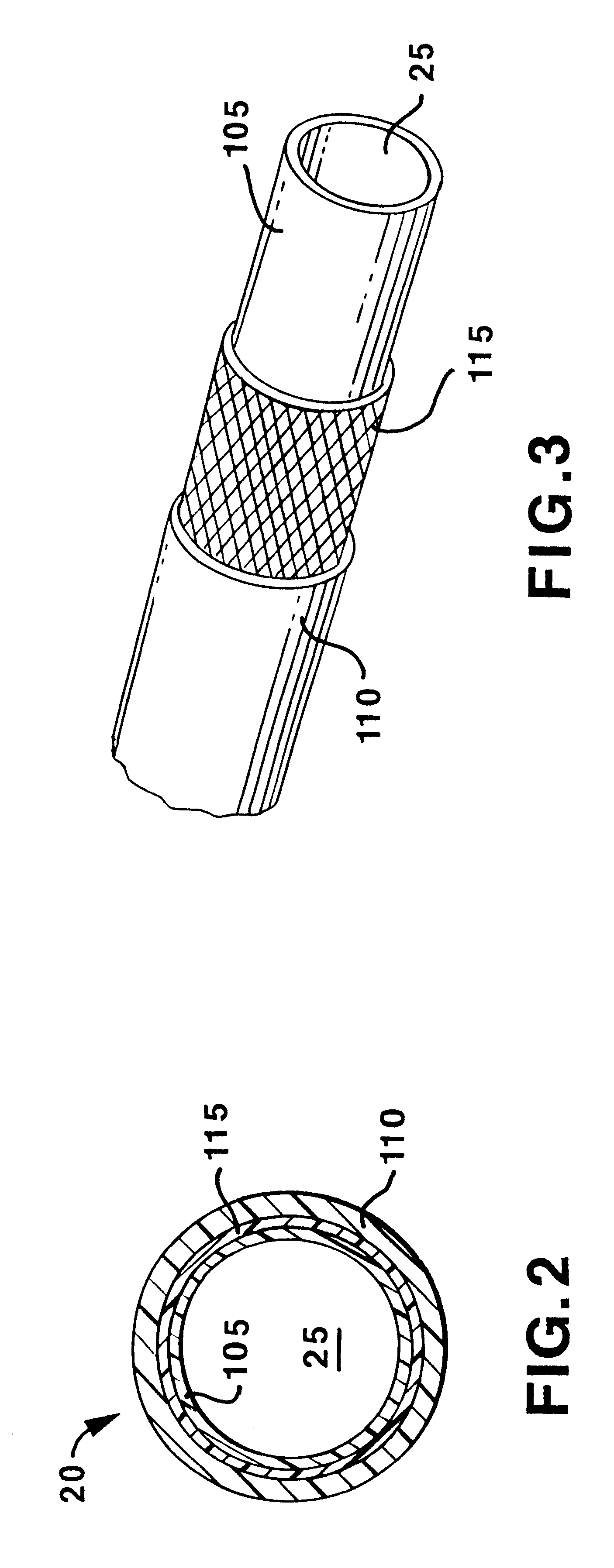
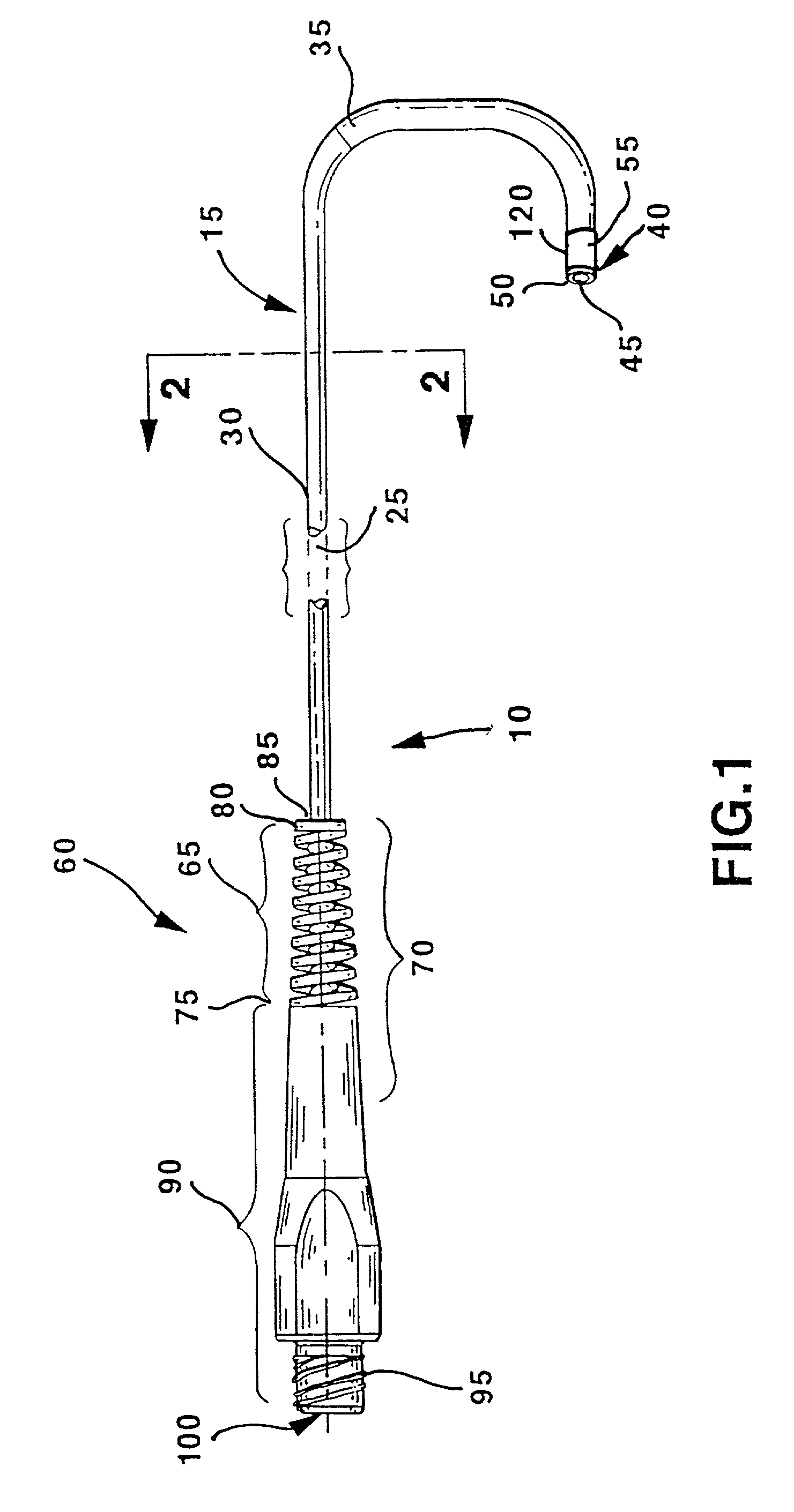
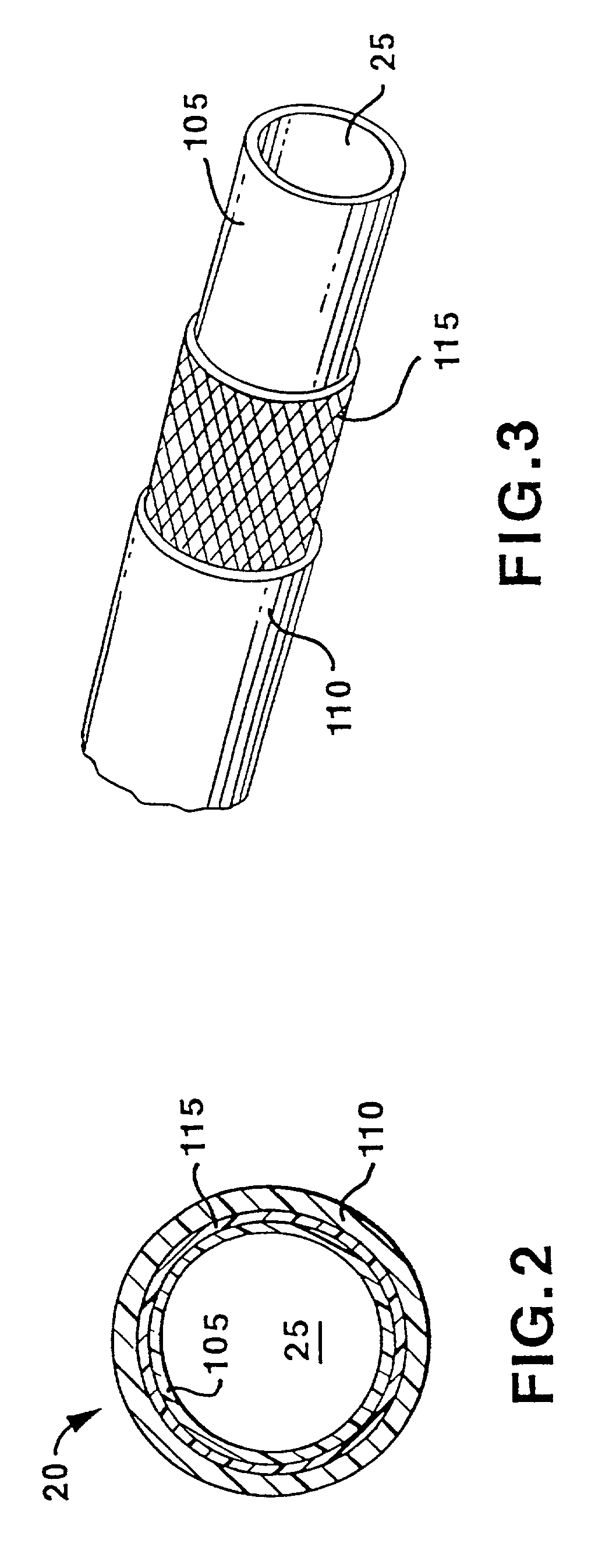
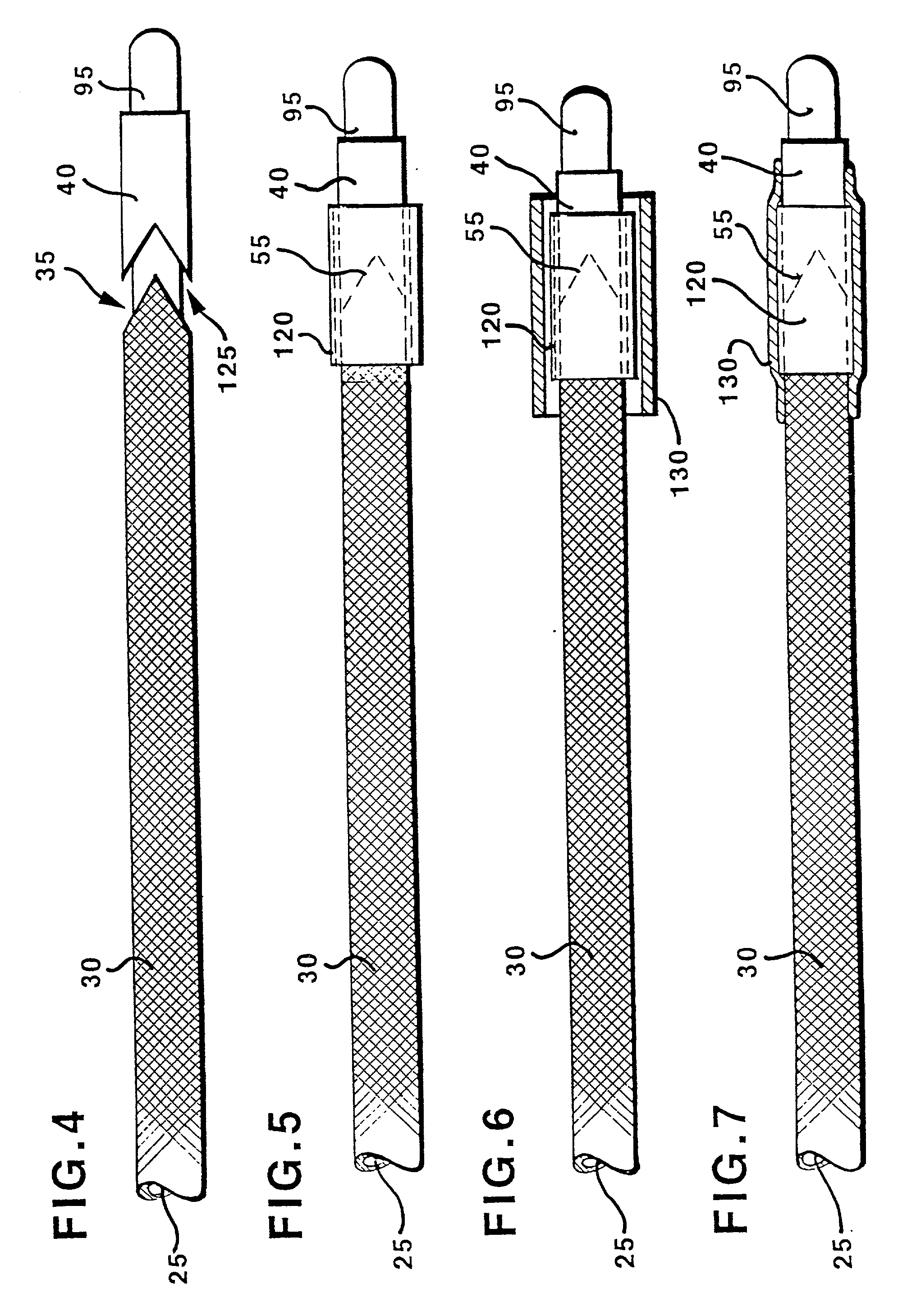
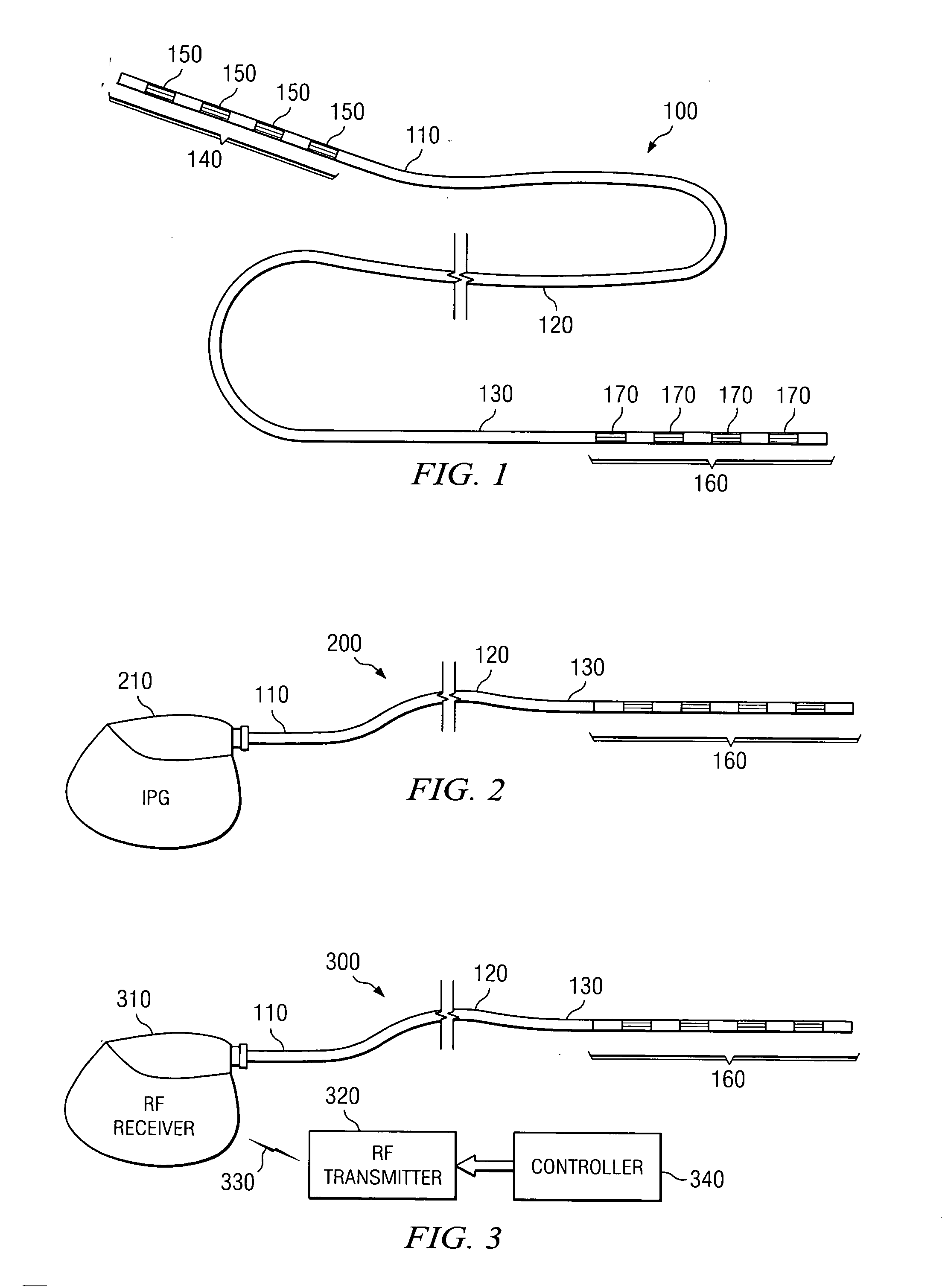
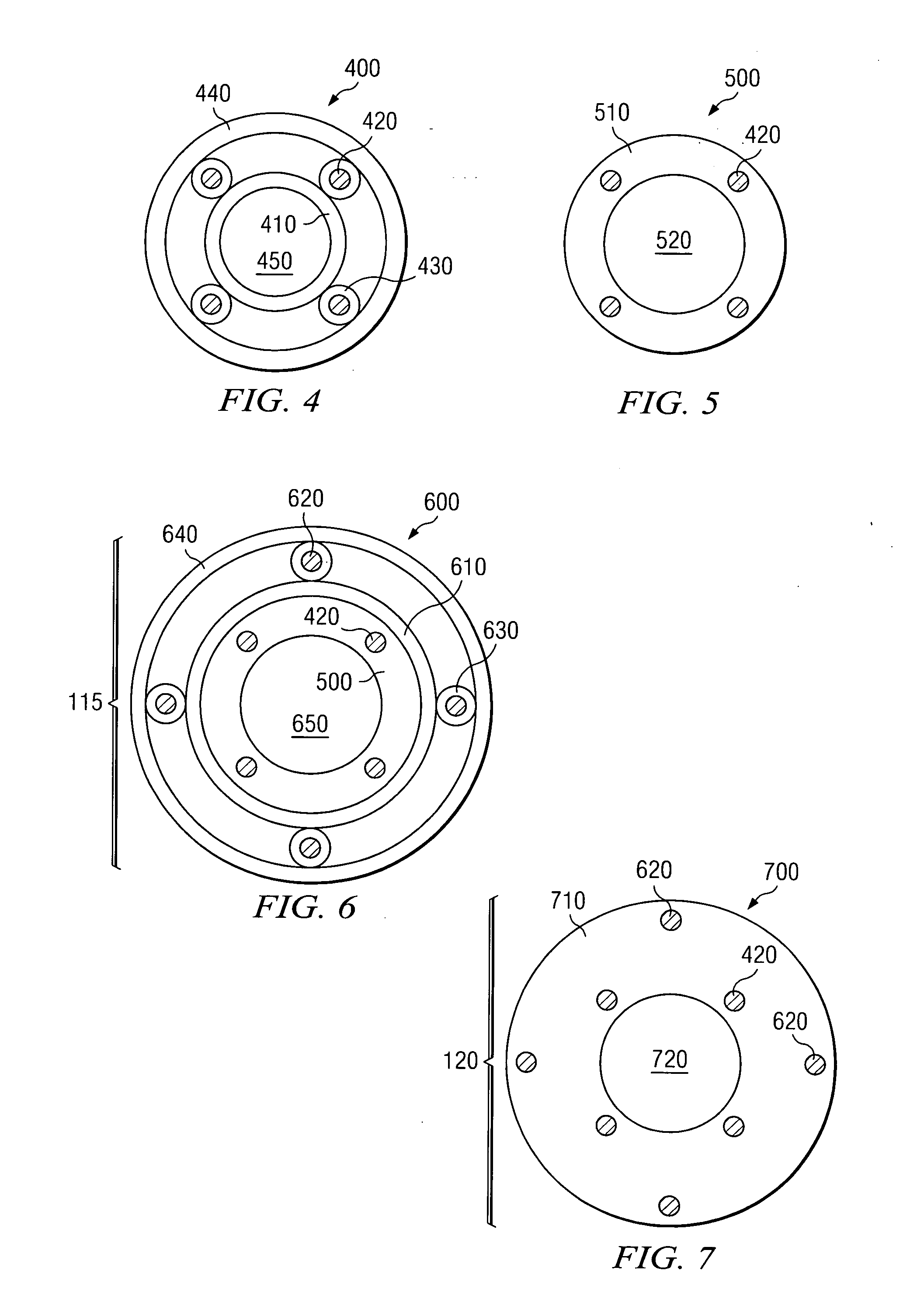
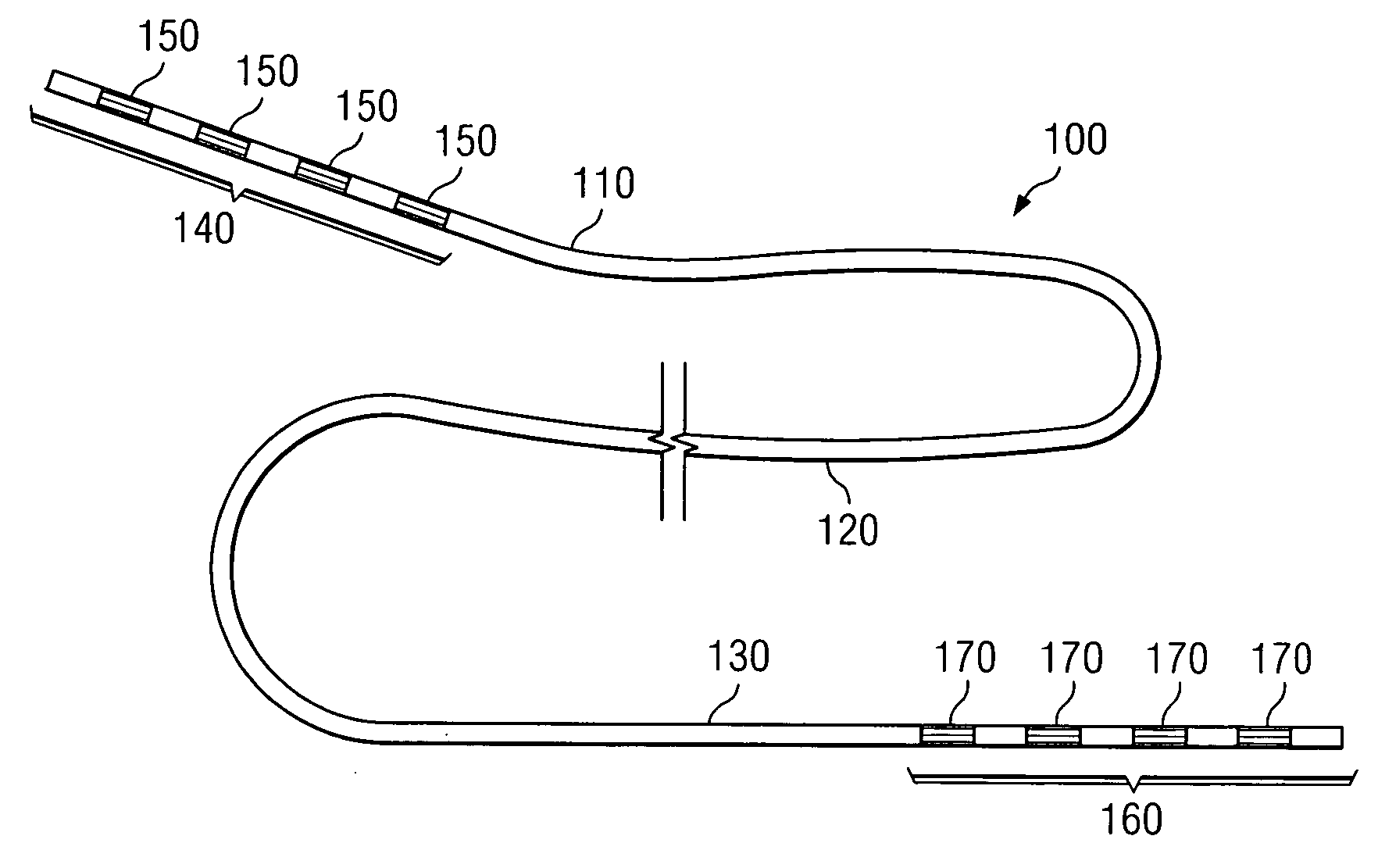
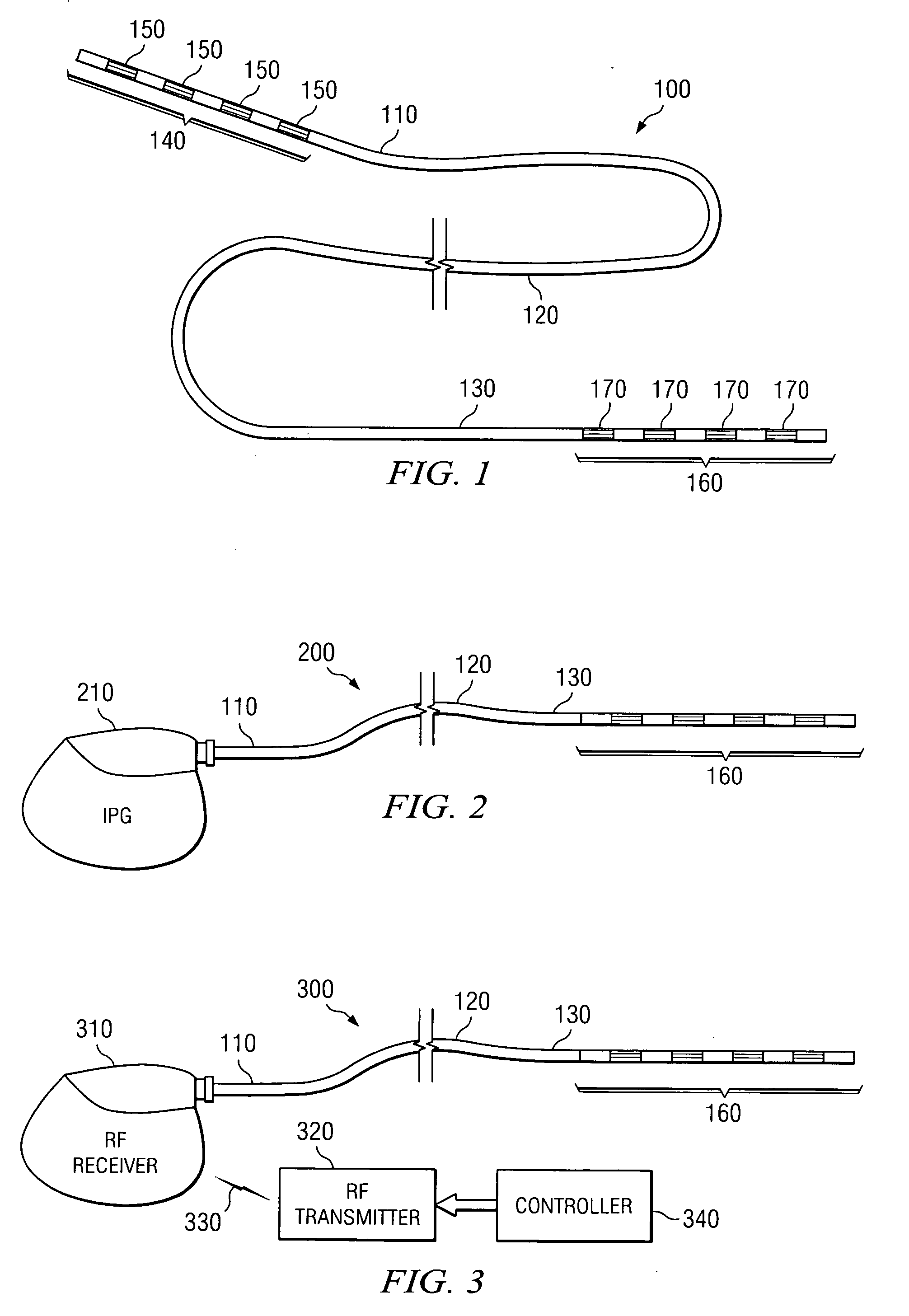
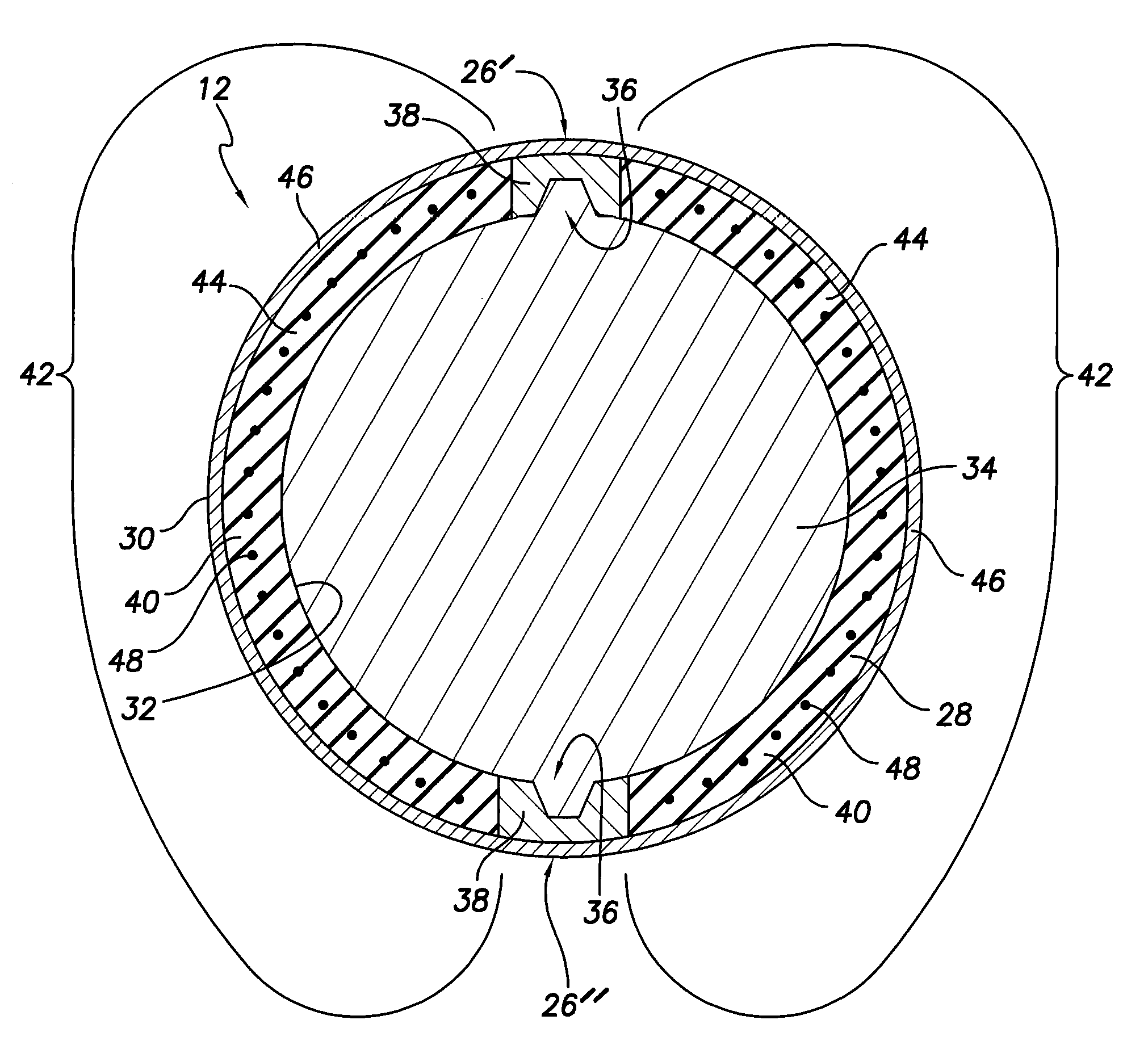
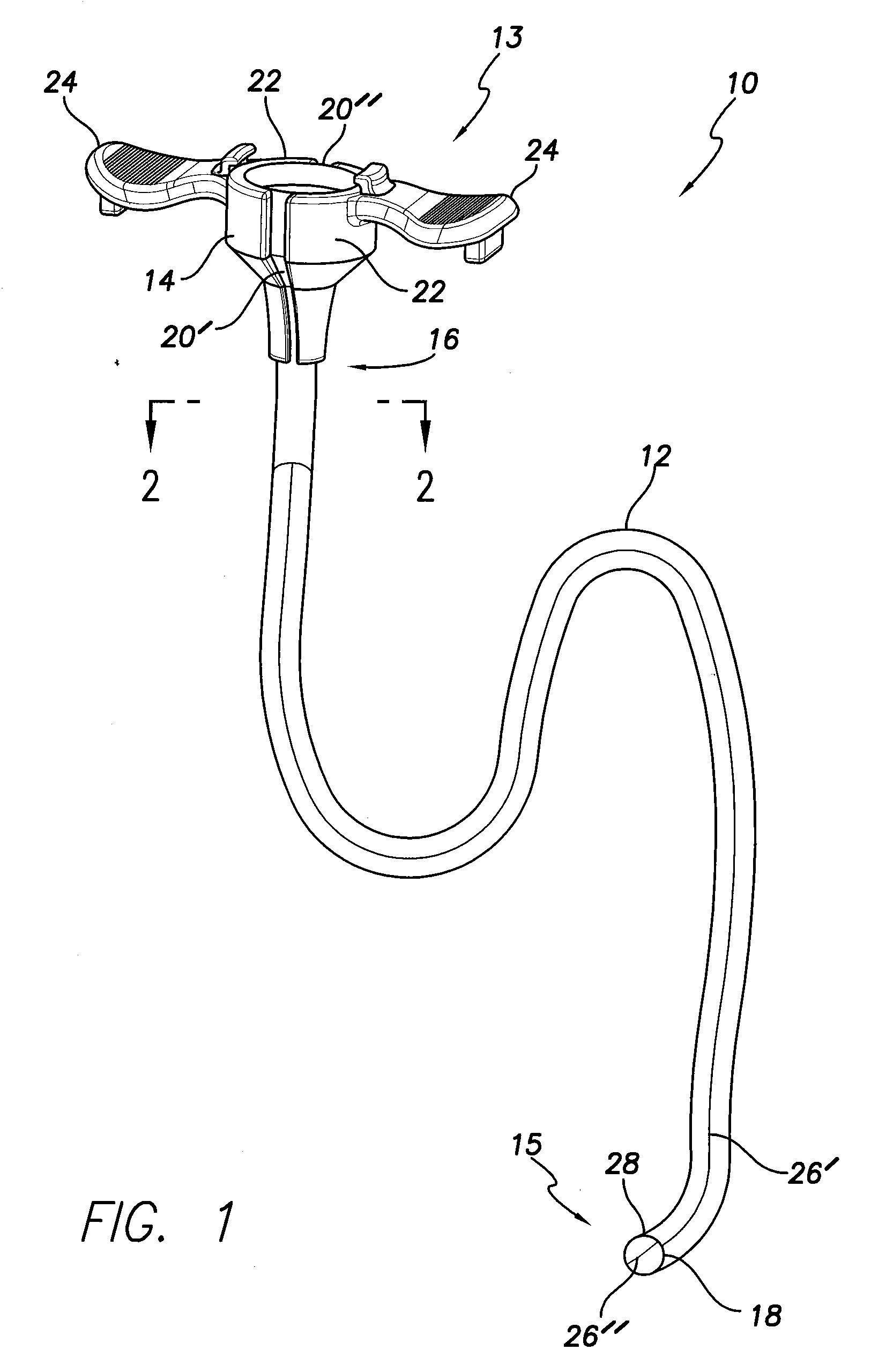
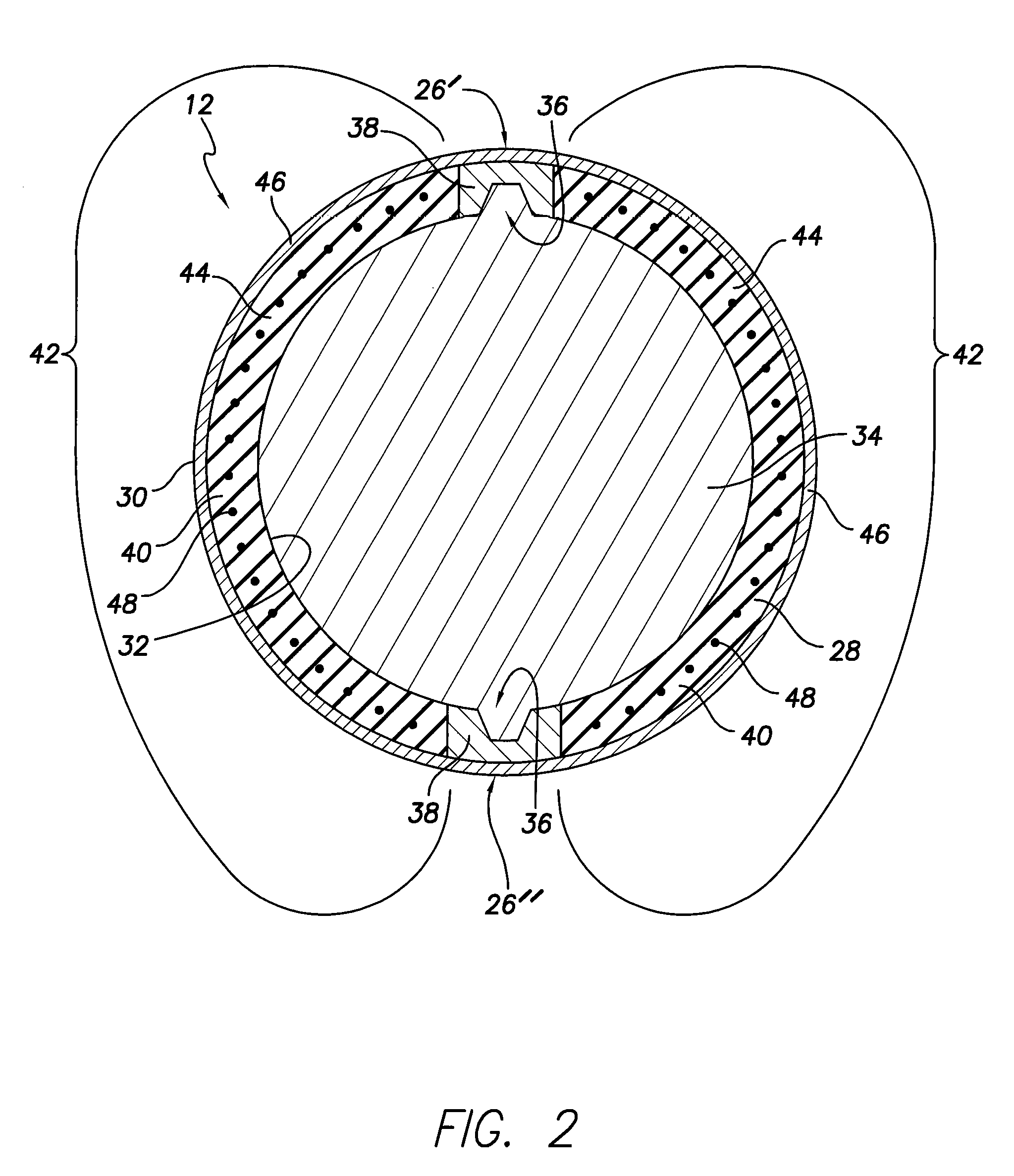
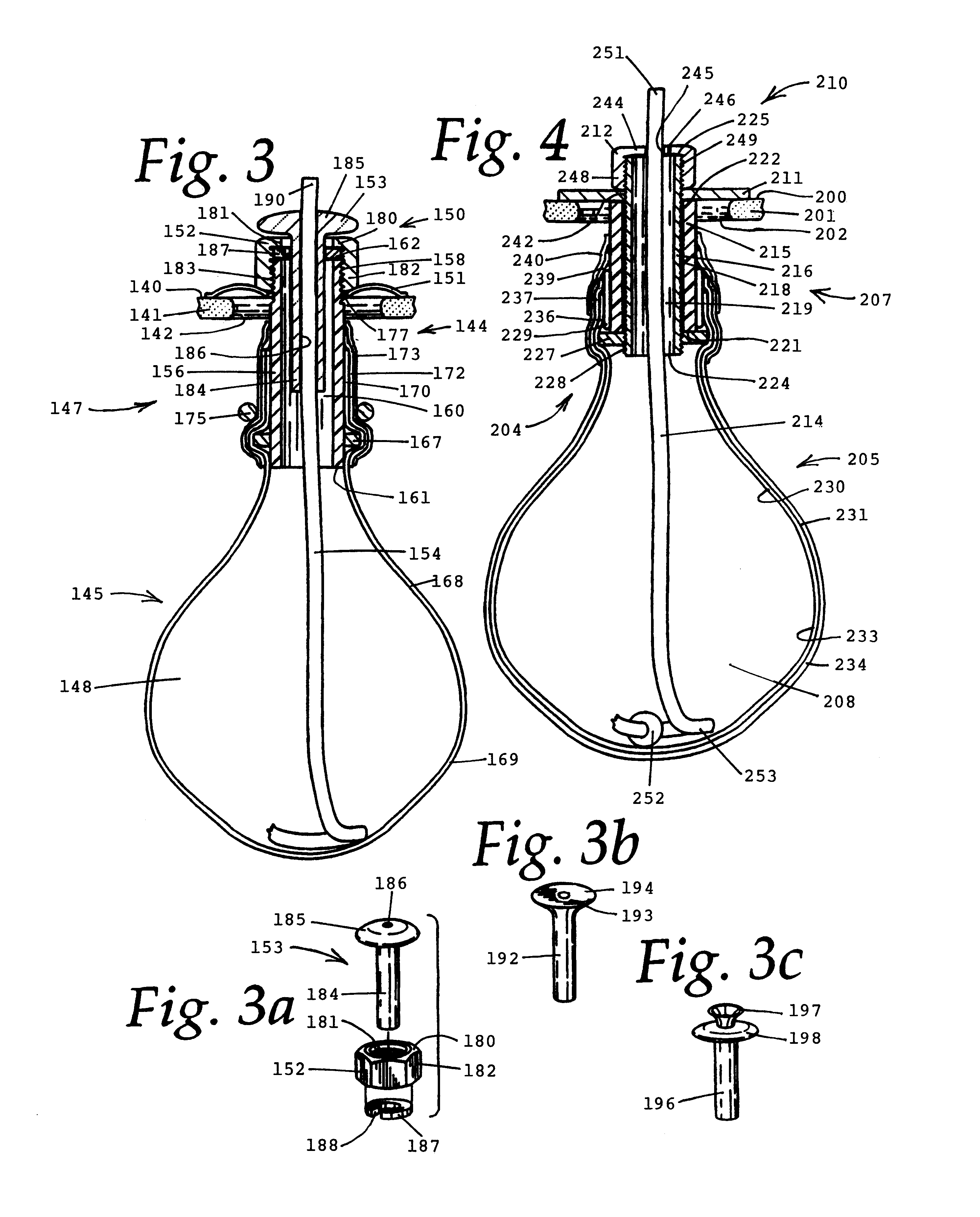
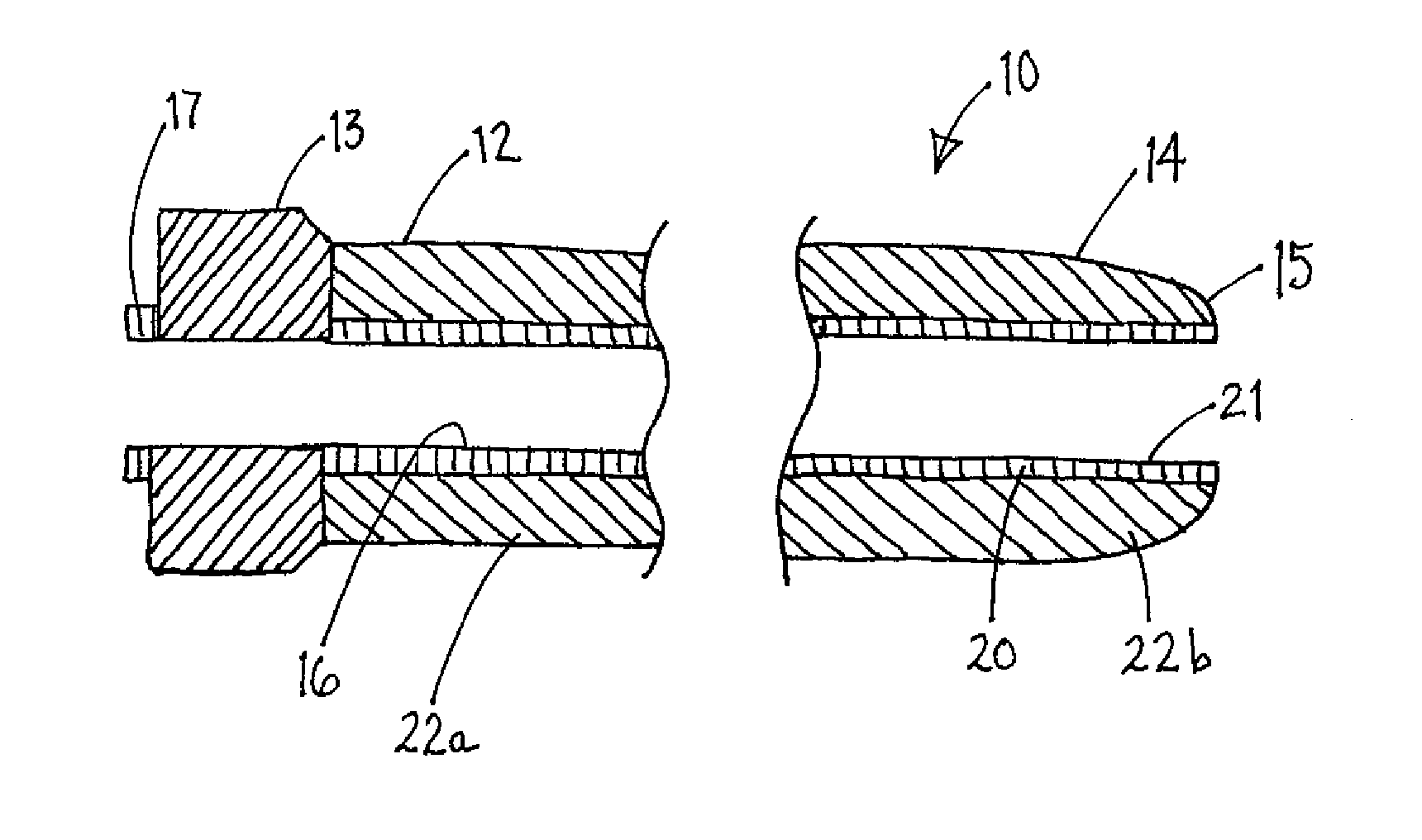
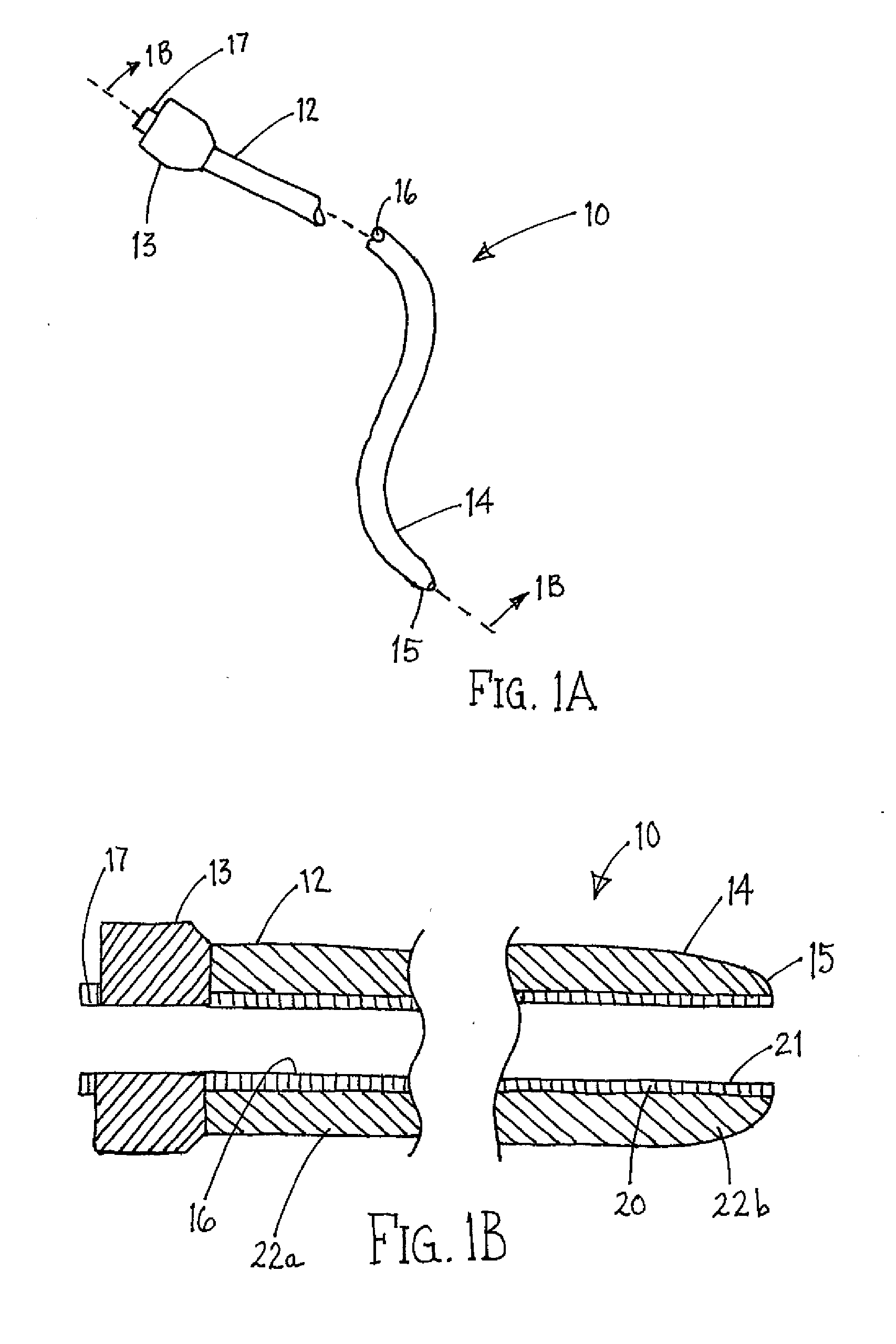
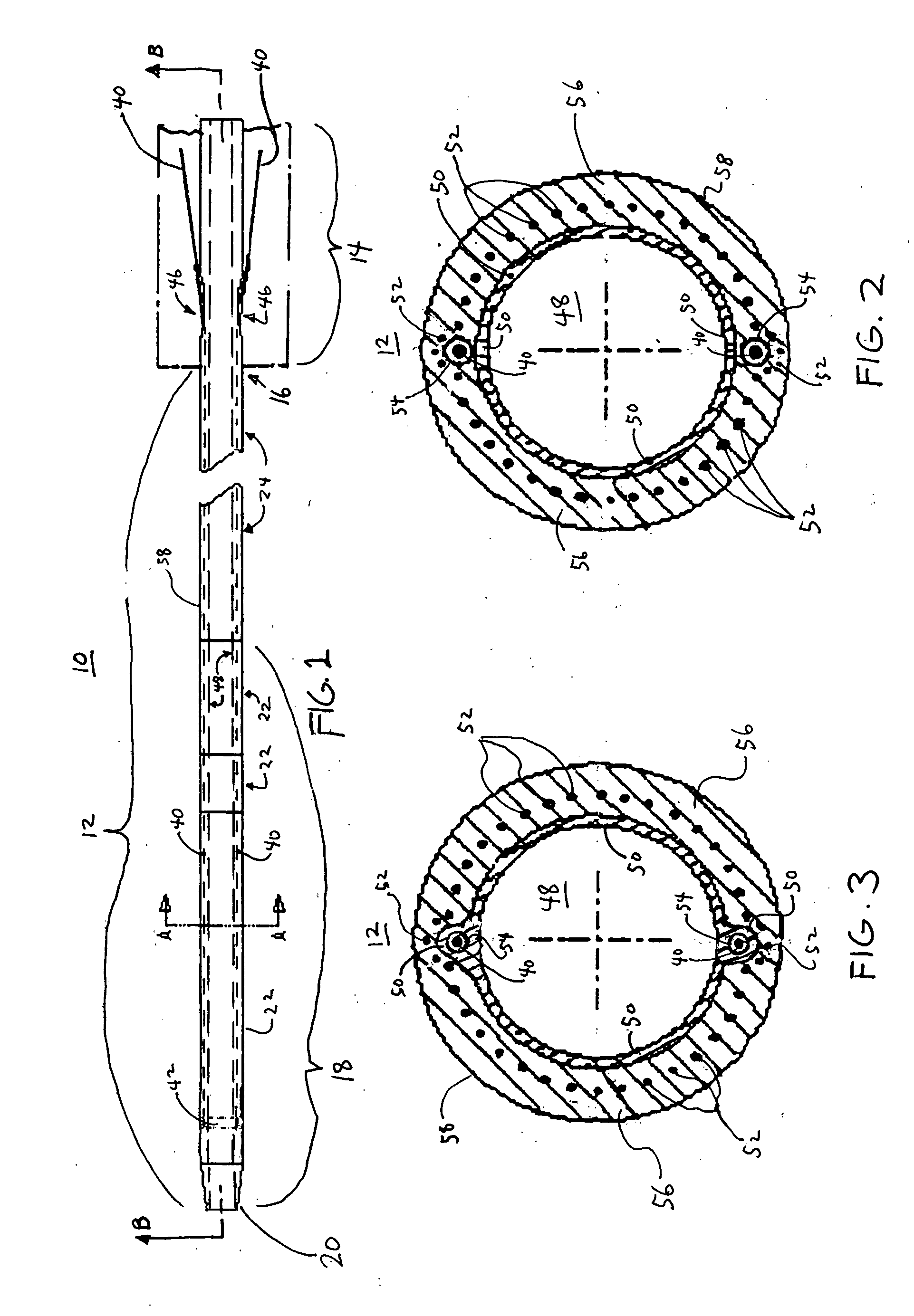
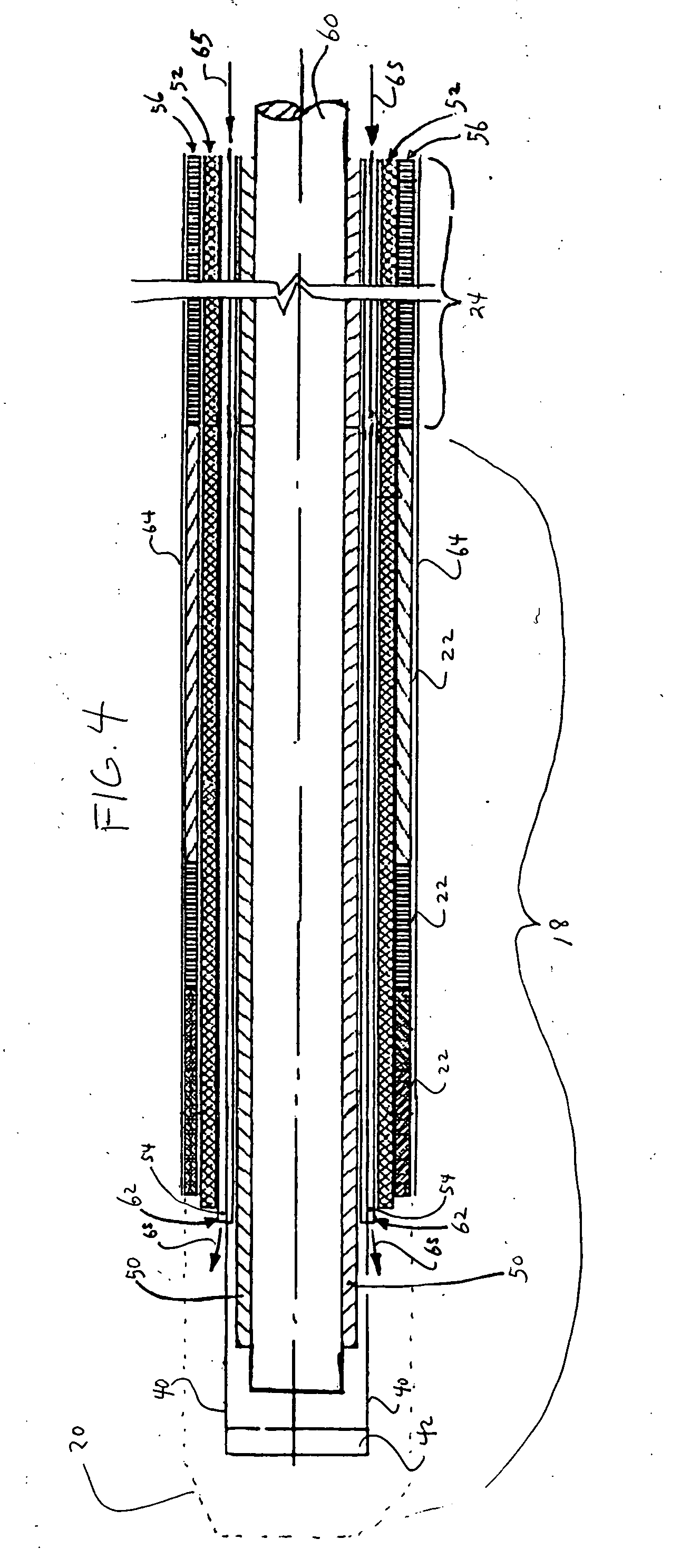
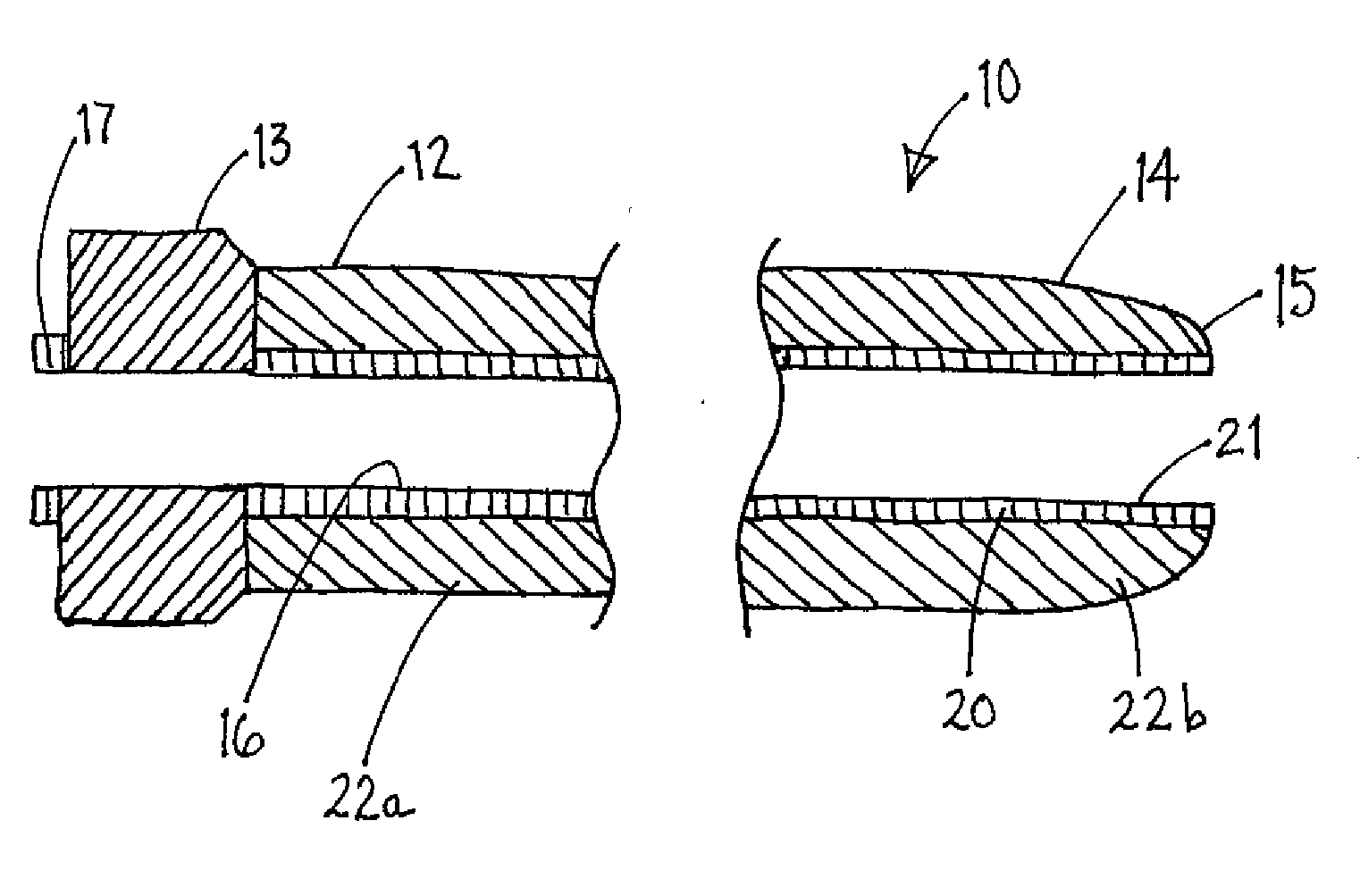
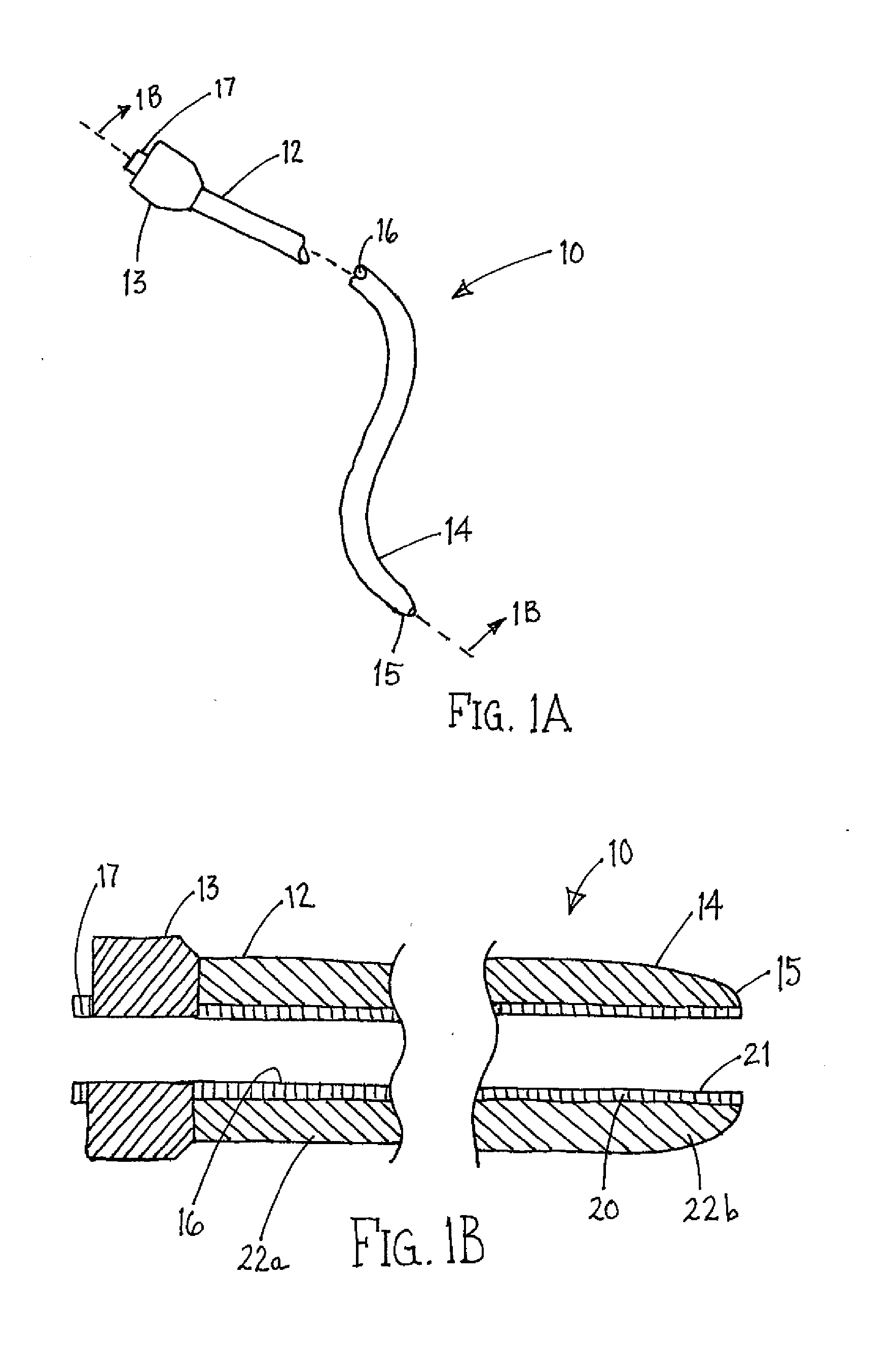
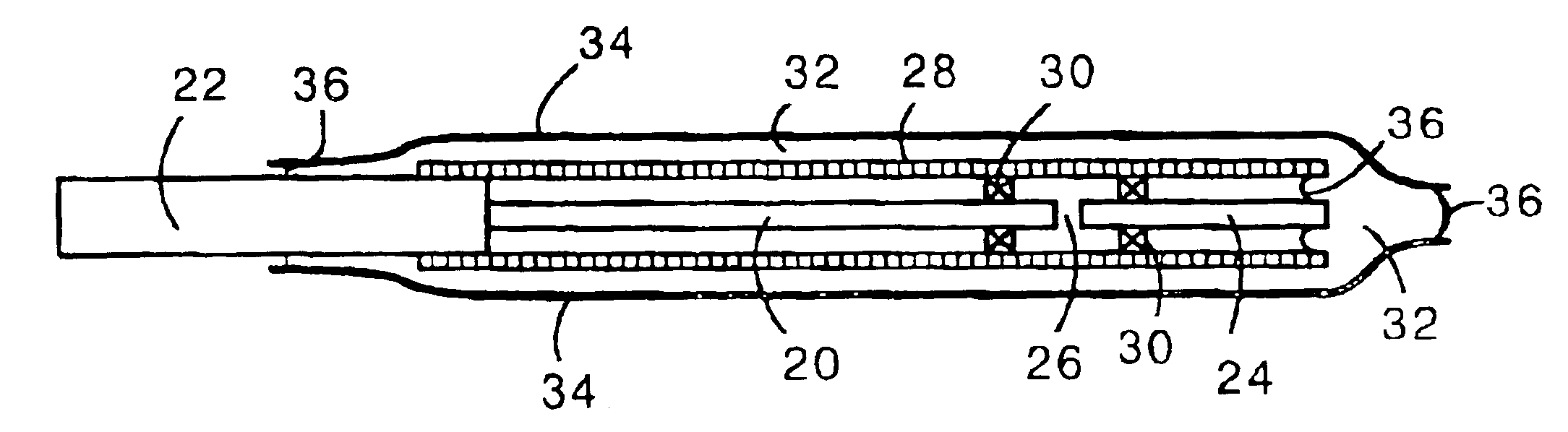
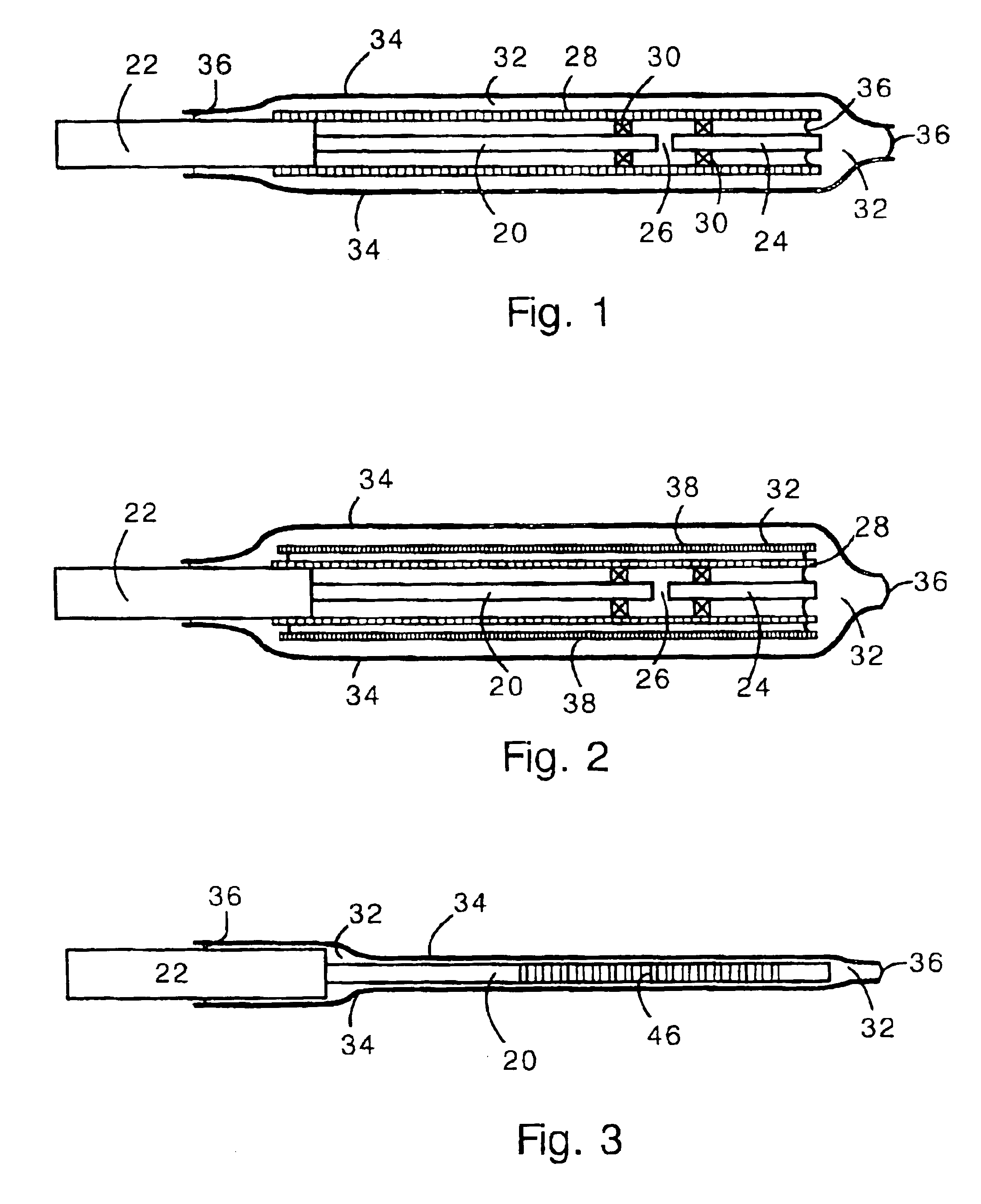
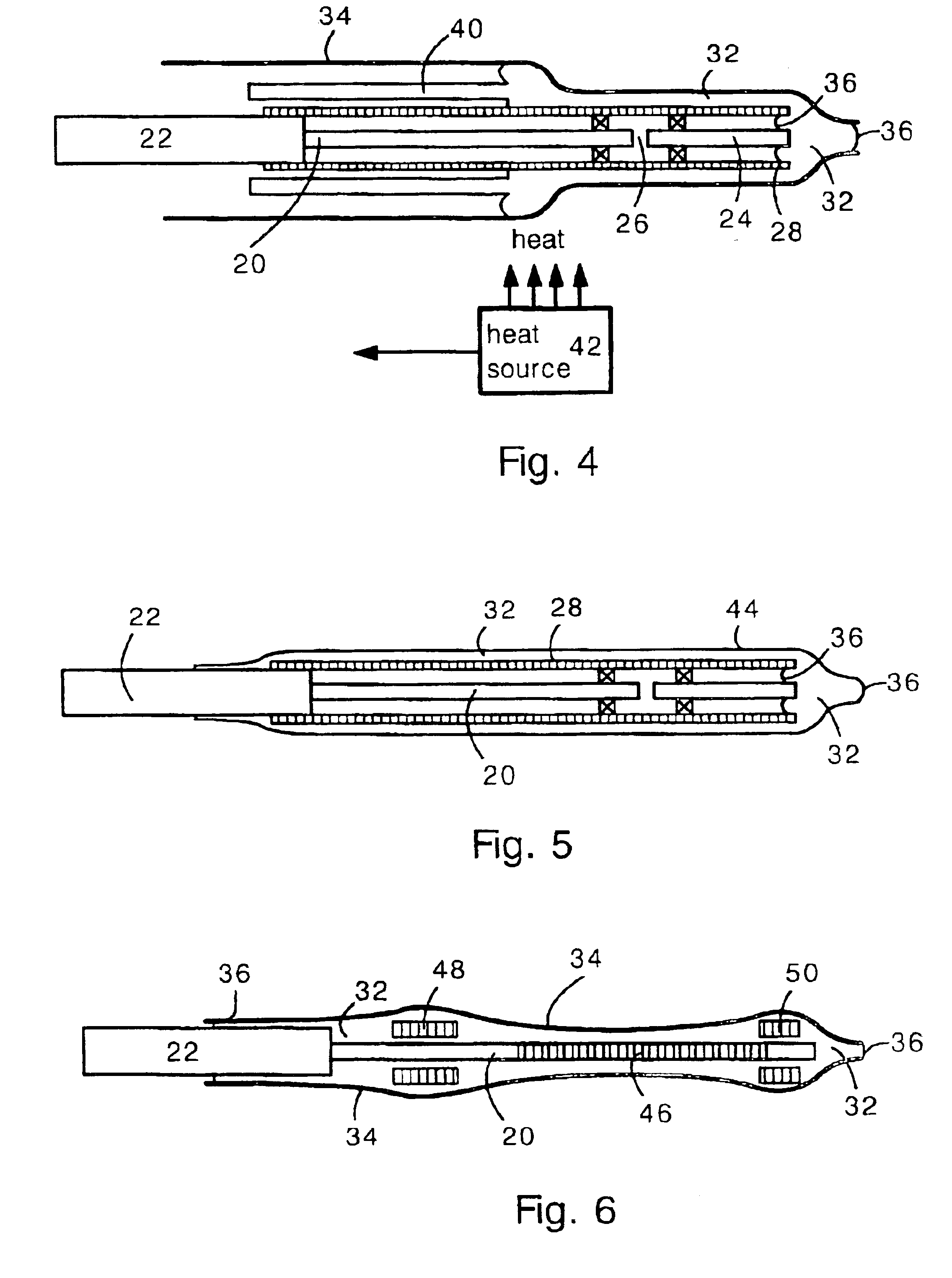
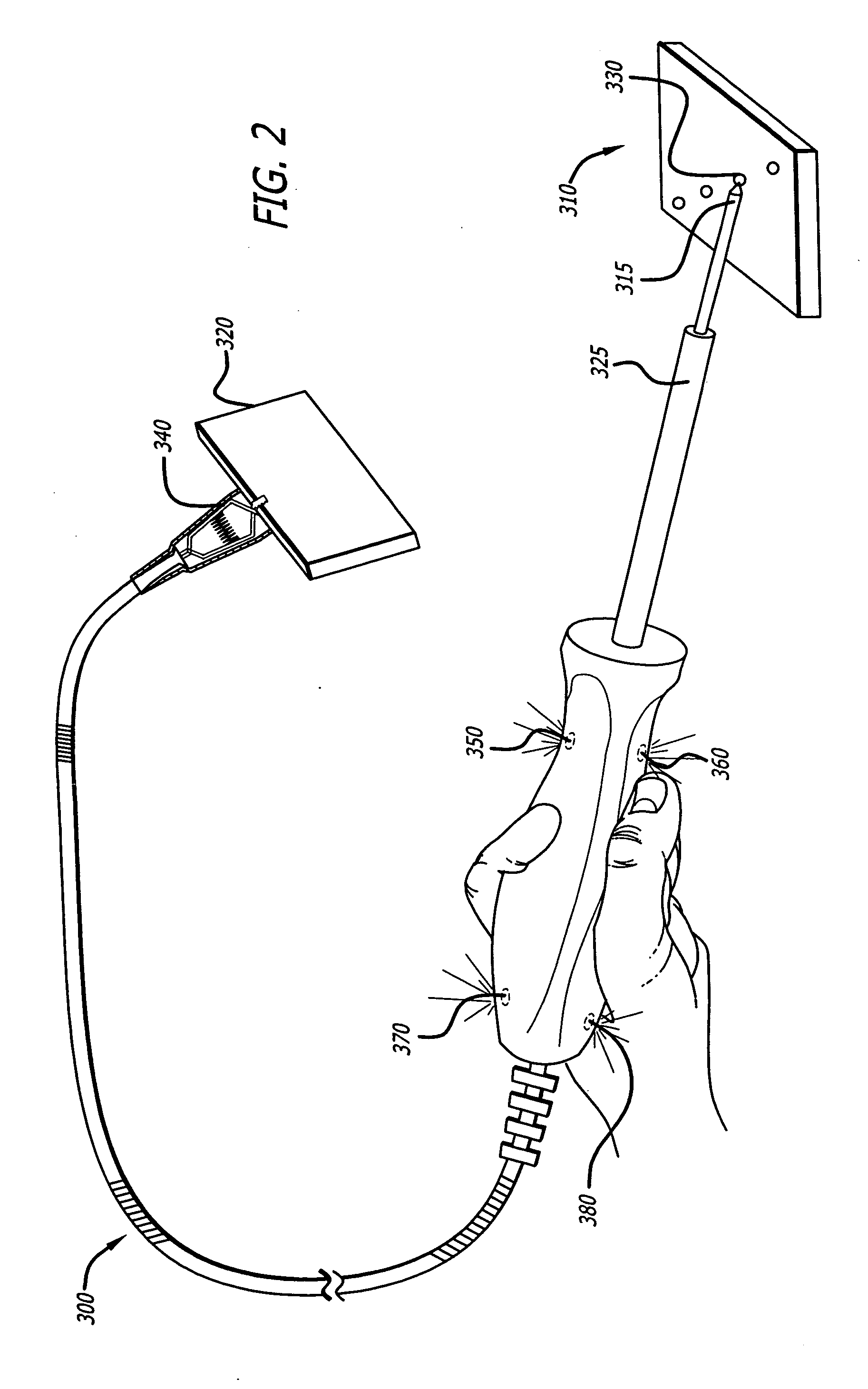
Soft tip guiding catheter and method of fabrication
The present invention relates to medical vascular catheters adapted to be inserted into a blood vessel from an incision through the skin of a patient for introducing ther devices or fluids for diagnostic or therapeutic purposes, and particularly to an improved distal soft tip or segment attachment with a relatively stiff proximal catheter shaft. A tubular sleeve is bonded through the application of pressure and heat to a distal portion of the catheter shaft and a proximal portion of the distal segment of soft distal tip bridging the attachment junction. In the preferred method, the catheter shaft distal end is aligned with the distal segment or soft tip proximal end and the sleeve is fitted over the attachment junction. A heat shrink tube is fitted over the sleeve and adjoining portions of the catheter shaft and the distal segment or distal soft tip and heat is applied. The shrinkage force of the heat shrink tube over the assembly of the tubular sleeve overlying and bridging the attachment junction and the applied heat melts and force the materials of the tubular sleeve and the catheter shaft and the distal segment or distal soft tip together to fill interstitial spaces of the attachment junction and reduces the outer diameter of the sleeve. The heat shrink tube is removed after the assembly cools and solidifies. Preferably, the catheter shaft distal end and the soft tip or intermediate segment proximal end are each formed with a like plurality of ungular cut sections that are complementary in shape to one another, whereby the ungular cut sections are aligned with and mated together along the attachment junction.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
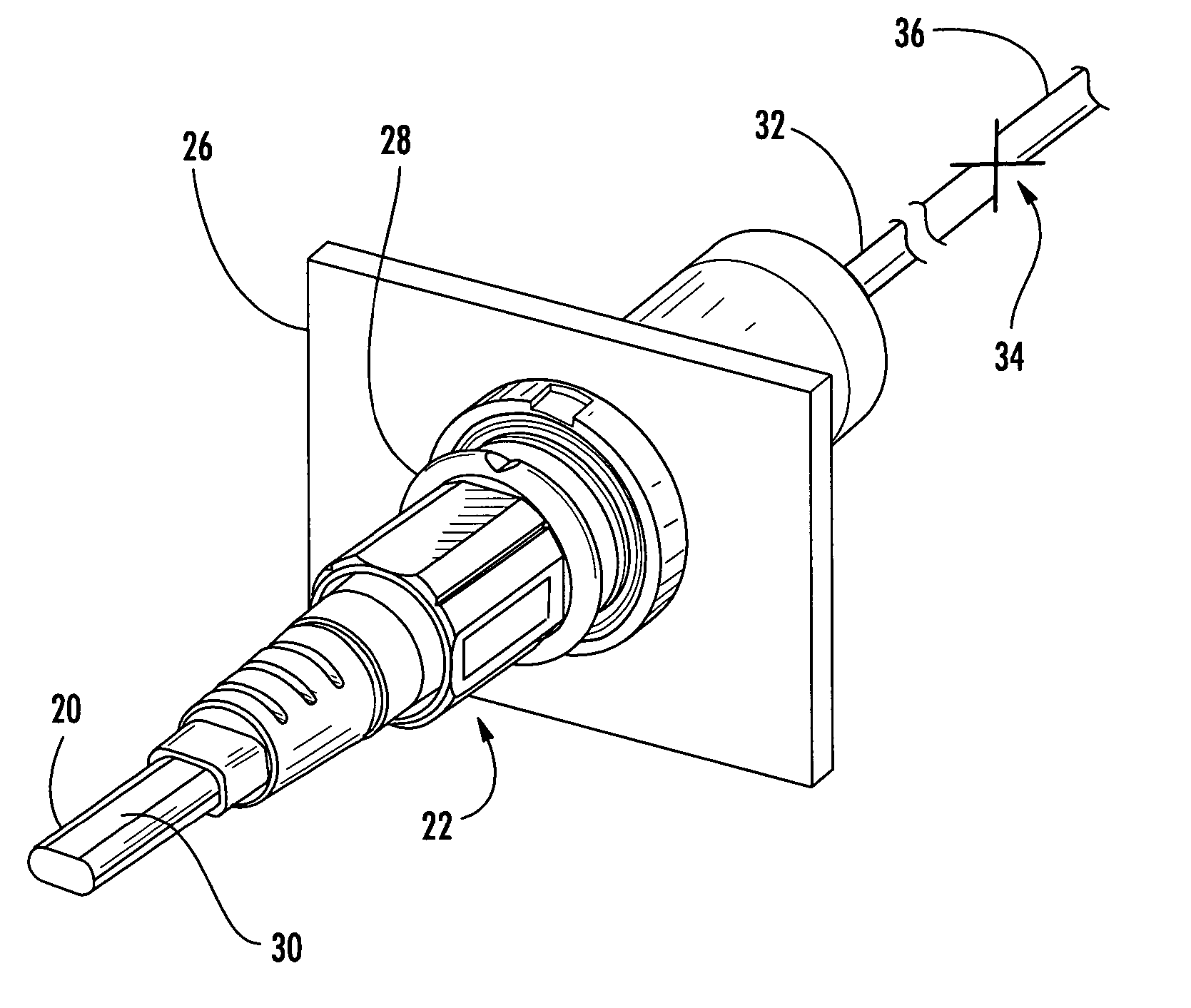
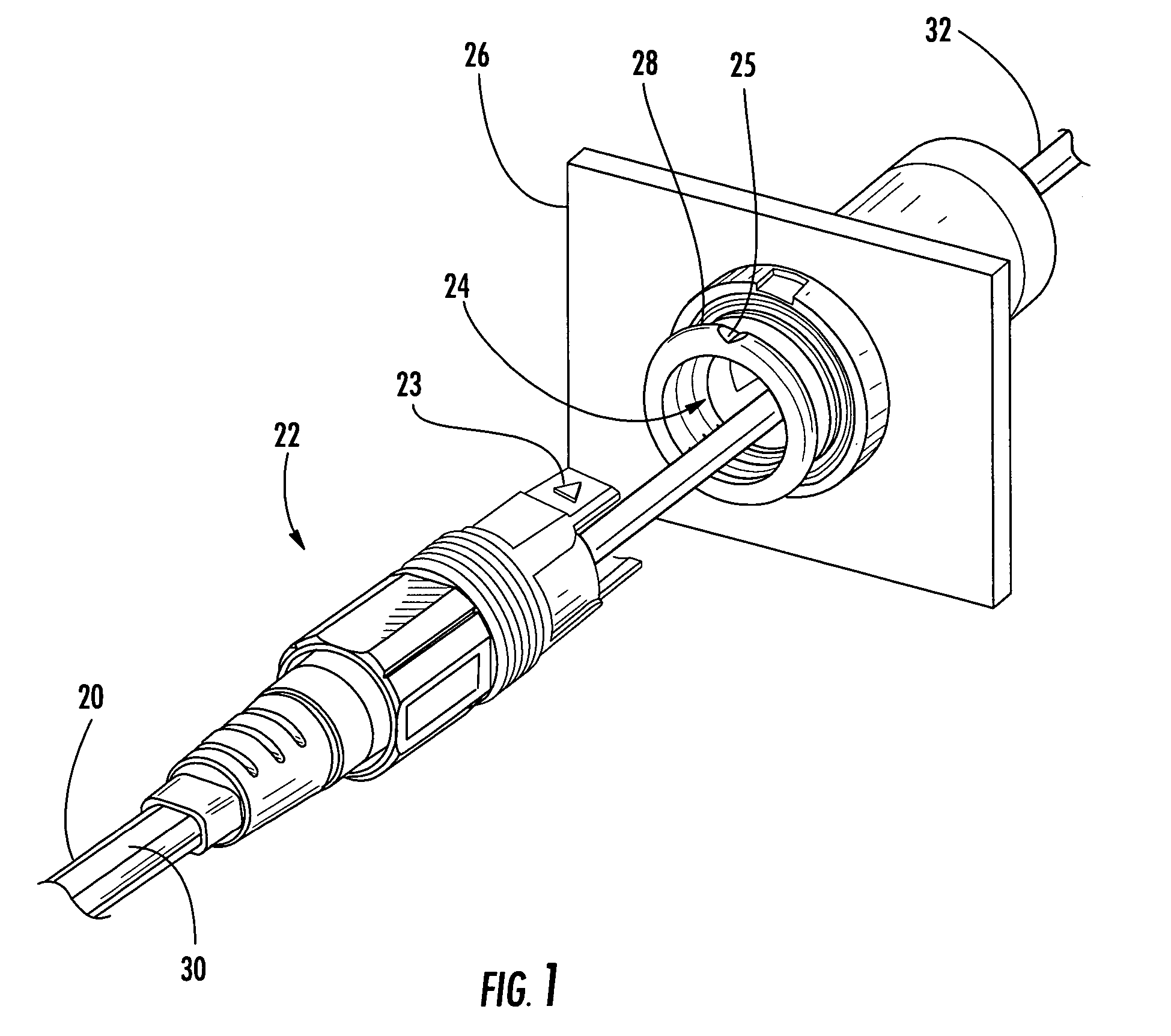
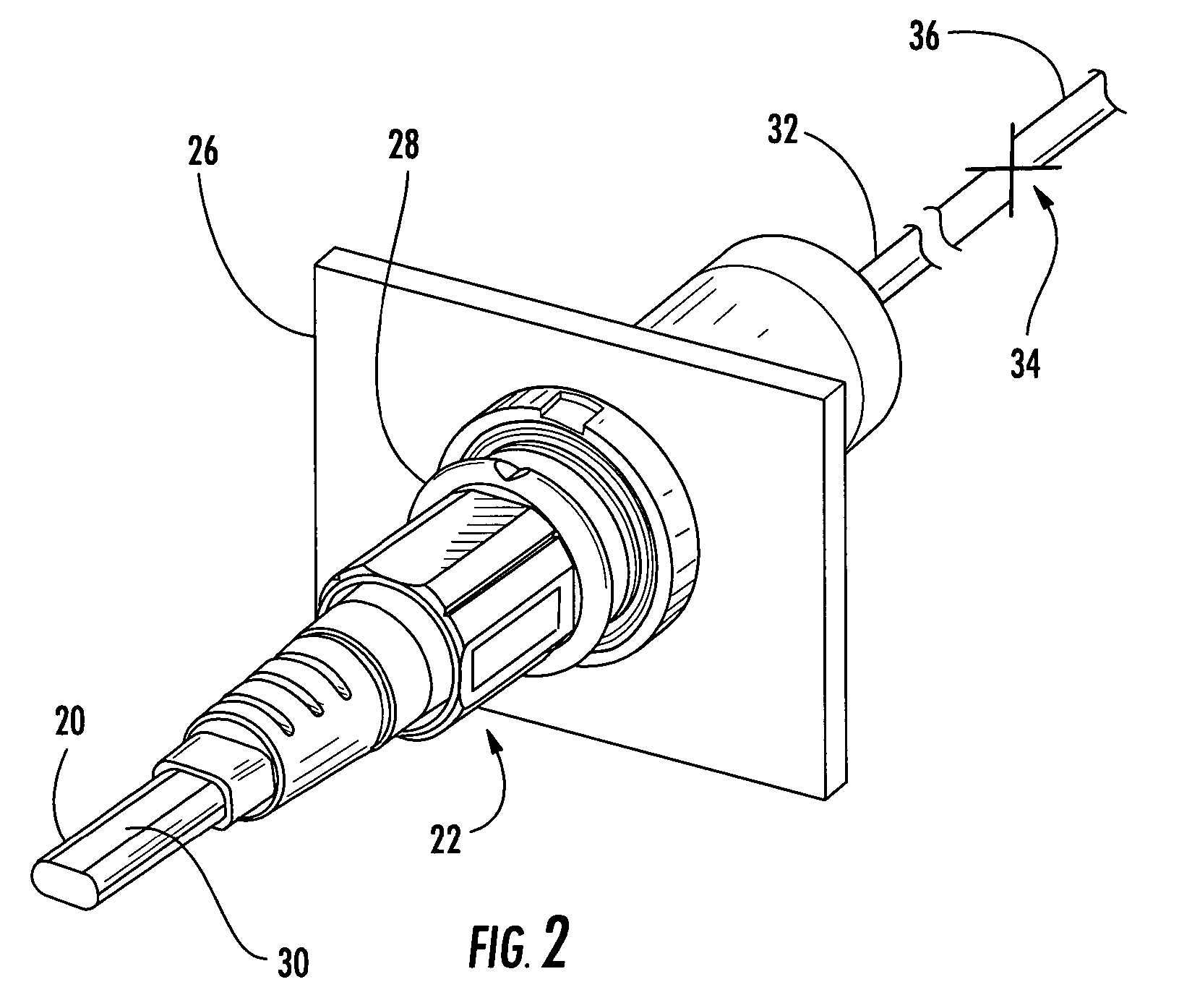
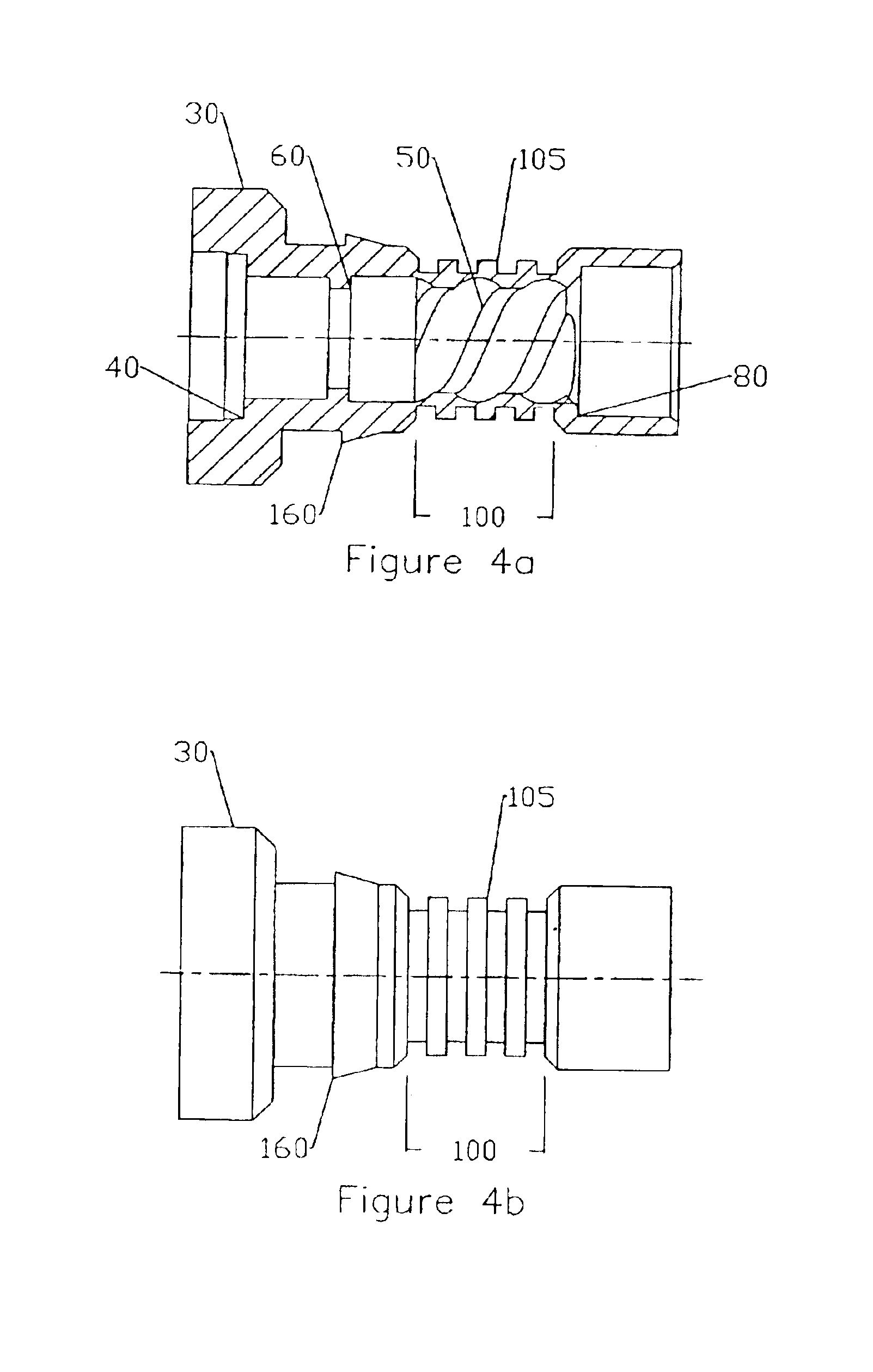
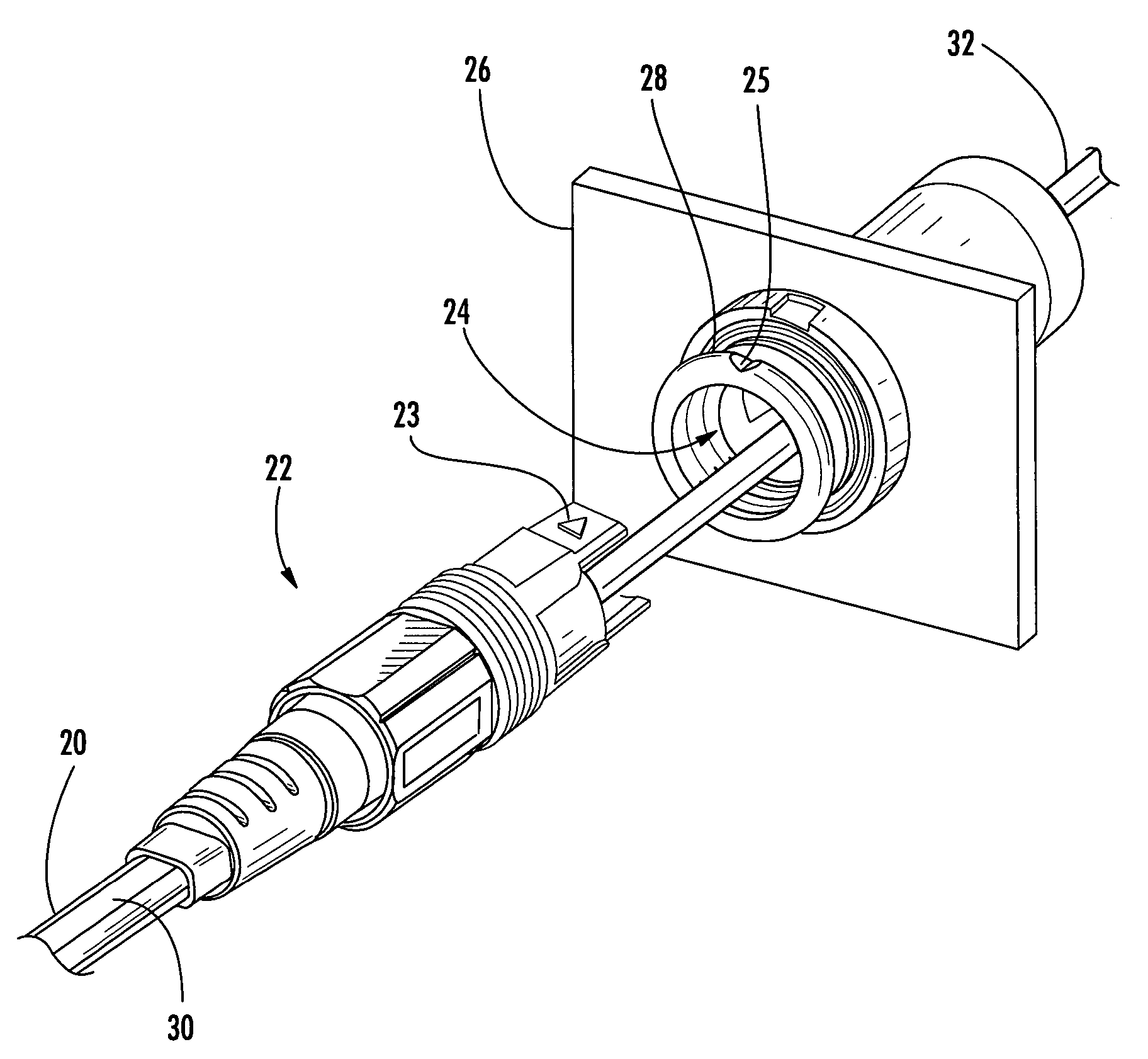
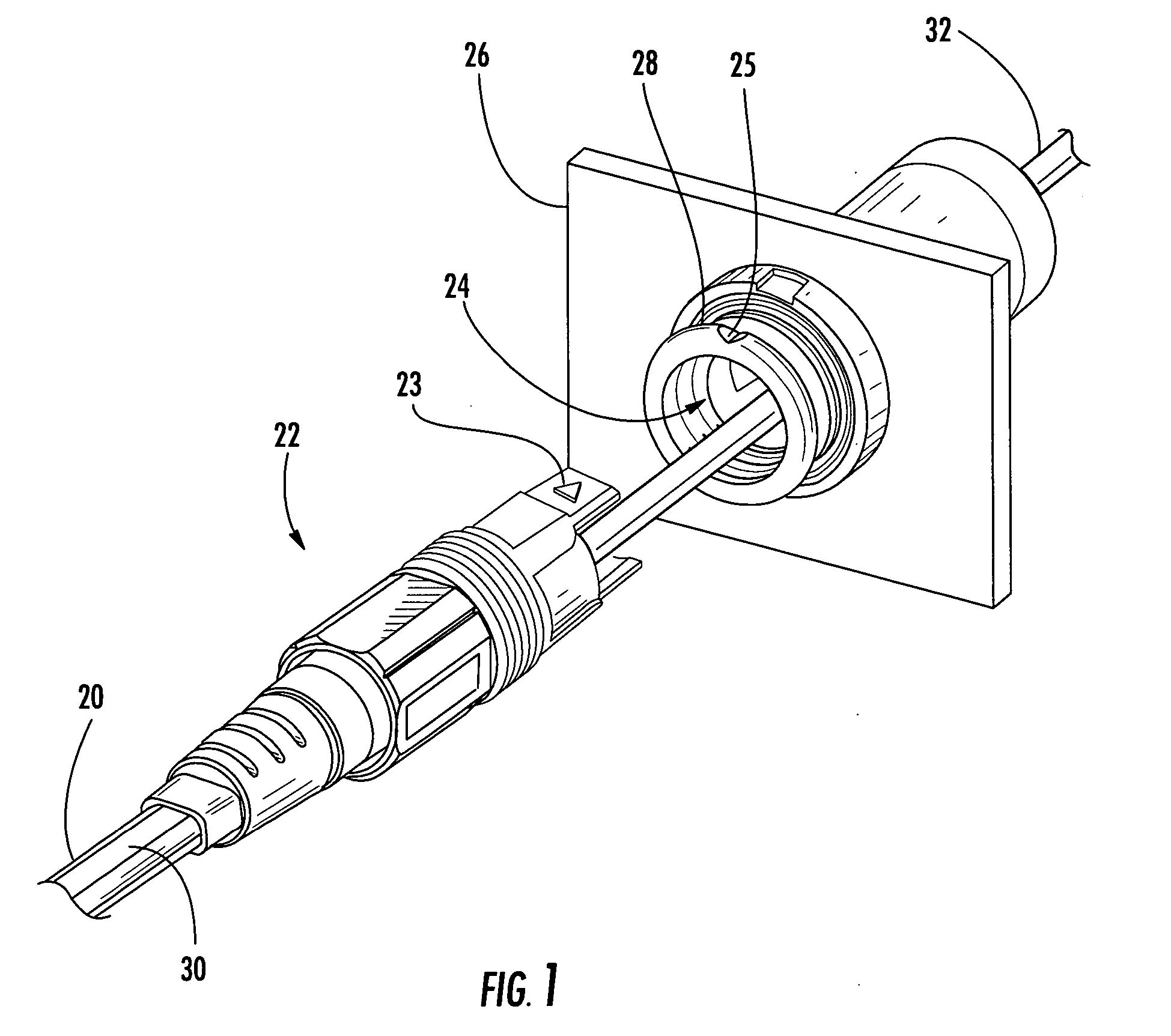
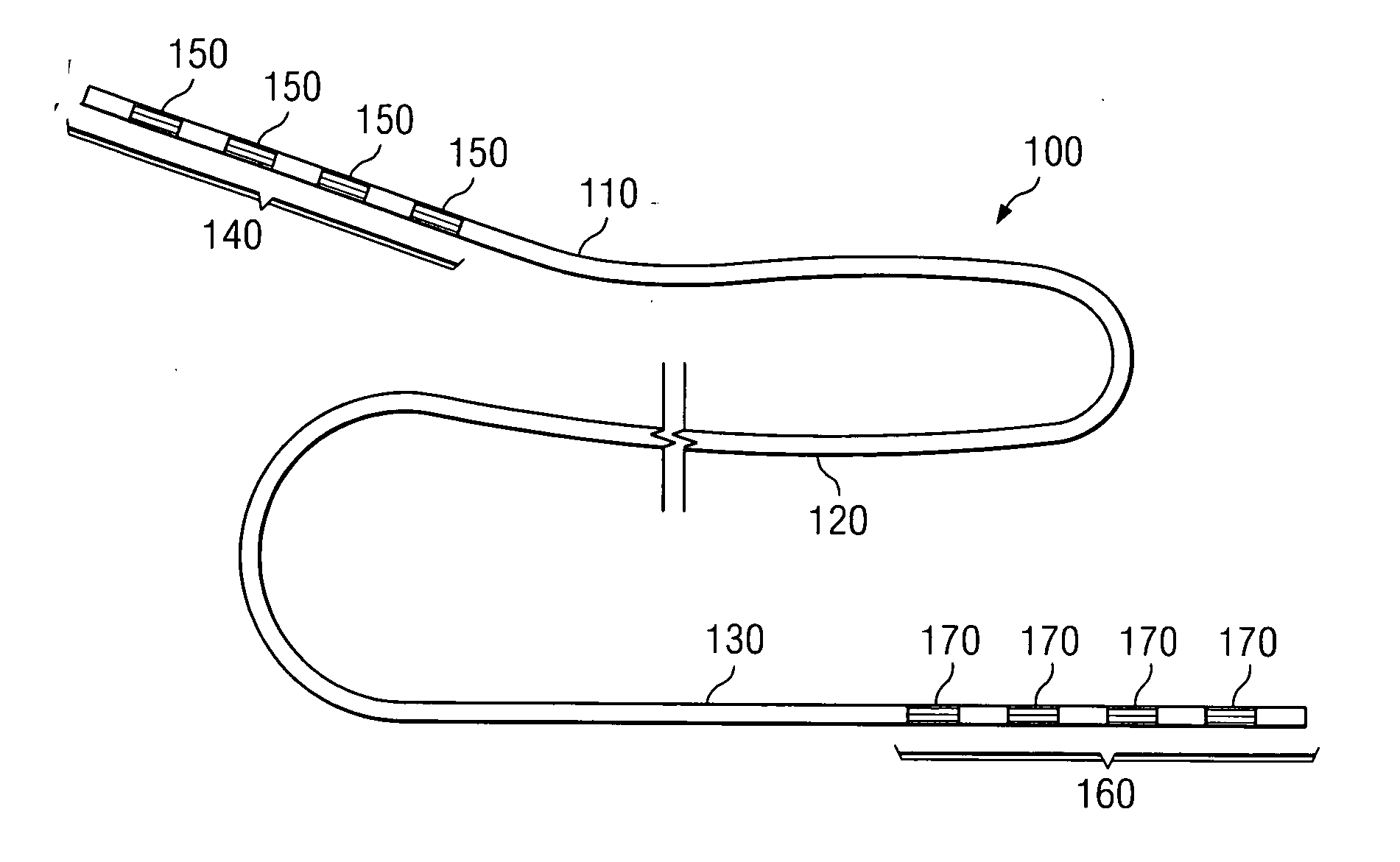
Fiber optic cable and plug assembly
A fiber optic cable has a plug assembly that may be positioned and secured at any desired location along the length of the cable to engage a receptacle disposed within a connector port provided in a wall of a connection terminal. The plug assembly includes a shroud, a coupling nut, a heat shrink tube for sealing the cable and a boot for providing bending strain relief. At least a portion of the cable passes through the connector port for interconnection with optical fibers of a distribution cable or optical equipment. A method for routing a fiber optic cable into a connection terminal includes using a connector port provided in a wall of the terminal, determining a desired length of the cable, positioning and securing a plug assembly at a desired location along the length of the cable, and mating the plug assembly with a receptacle disposed within the connector port.
Owner:CORNING OPTICAL COMM LLC
Crimp connector for corrugated cable
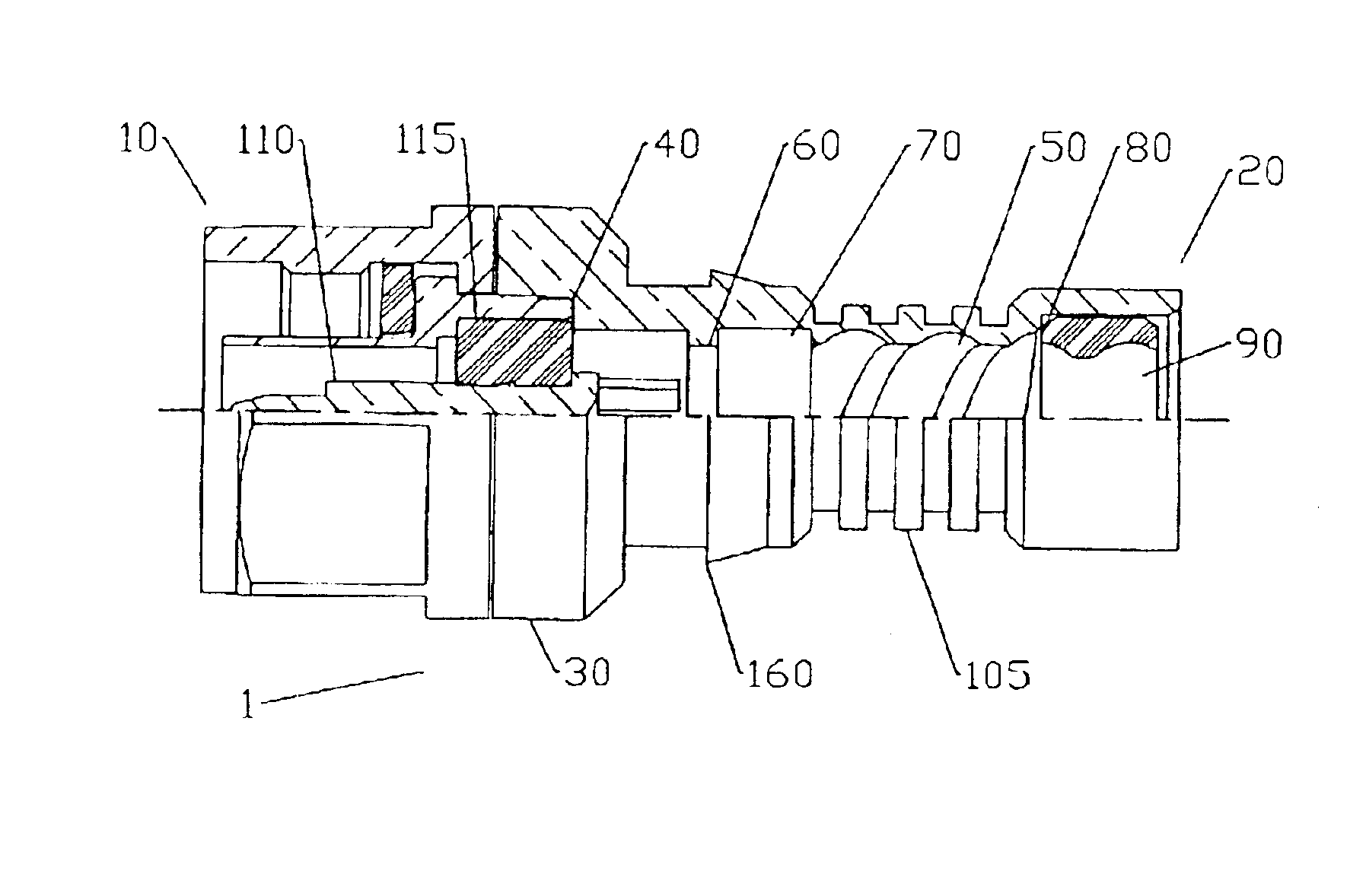
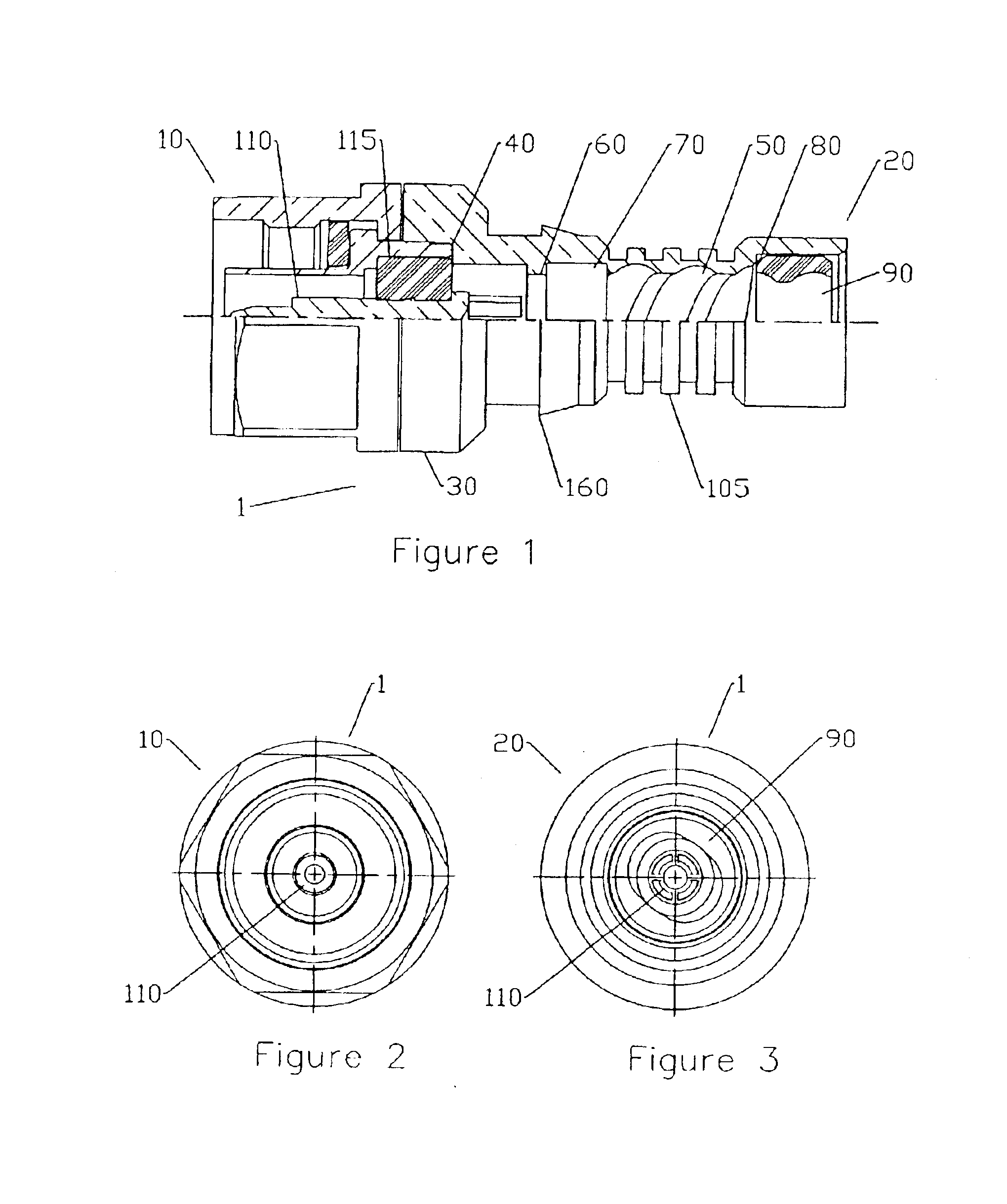
InactiveUS6840803B2Minimizing reactionAdvantageous strength and flexibility and weight characteristicElectrically conductive connectionsTwo pole connectionsElectrical conductorCoaxial cable
A corrugated coaxial cable connector, field installable with a hand crimp tool has a connector interface coupled to the connector end of a hollow cylindrical body; an inner surface of the body is adapted to thread onto the helical corrugations on the outer conductor of the cable. A plurality of ridges on an outer surface of the body corresponding to an internal threaded section forms a crimp surface. An inner contact located coaxially within the body has a socket contact section at the cable end dimensioned for insertion of the inner conductor of the cable and electrical connection therewith. A body barb located on the outer surface of the body provides an acute surface for heat shrink tubing to seal against.
Owner:ANDREW LLC
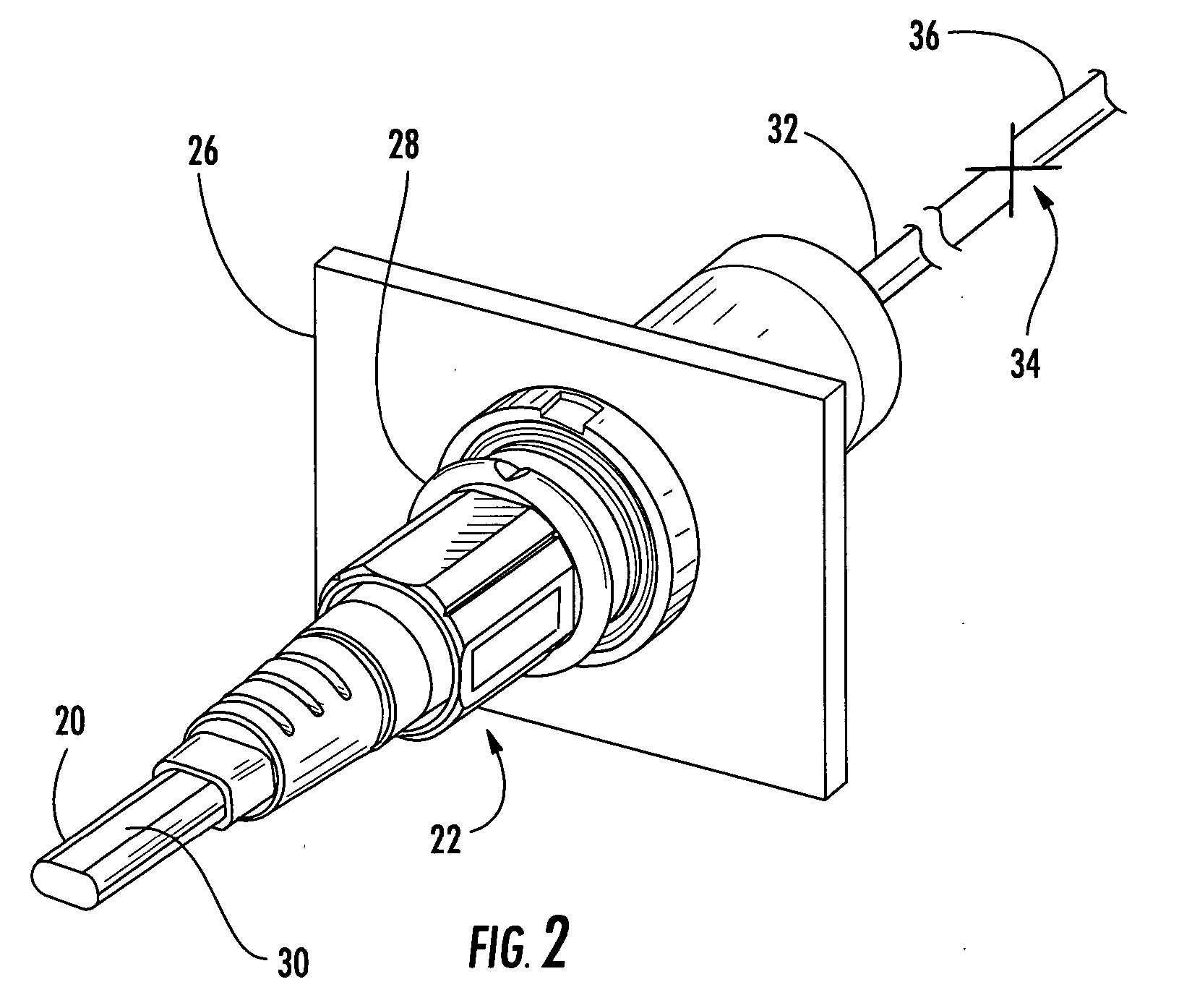
Fiber optic cable and plug assembly
ActiveUS20050281510A1Easy to adjustCoupling light guidesFibre mechanical structuresFiberBending strain
A fiber optic cable has a plug assembly that may be positioned and secured at any desired location along the length of the cable to engage a receptacle disposed within a connector port provided in a wall of a connection terminal. The plug assembly includes a shroud, a coupling nut, a heat shrink tube for sealing the cable and a boot for providing bending strain relief. At least a portion of the cable passes through the connector port for interconnection with optical fibers of a distribution cable or optical equipment. A method for routing a fiber optic cable into a connection terminal includes using a connector port provided in a wall of the terminal, determining a desired length of the cable, positioning and securing a plug assembly at a desired location along the length of the cable, and mating the plug assembly with a receptacle disposed within the connector port.
Owner:CORNING OPTICAL COMM LLC
Soft tip guiding catheter and method of fabrication
The present invention relates to medical vascular catheters adapted to be inserted into a blood vessel from an incision through the skin of a patient for introducing other devices or fluids for diagnostic or therapeutic purposes, and particularly to an improved distal soft tip or segment attachment with a relatively stiff proximal catheter shaft. A tubular sleeve is bonded through the application of pressure and heat to a distal portion of the catheter shaft and a proximal portion of the distal segment of soft distal tip bridging the attachment junction. In the preferred method, the catheter shaft distal end is aligned with the distal segment or soft tip proximal end and the sleeve is fitted over the attachment junction. A heat shrink tube is fitted over the sleeve and adjoining portions of the catheter shaft and the distal segment or distal soft tip and heat is applied. The shrinkage force of the heat shrink tube over the assembly of the tubular sleeve overlying and bridging the attachment junction and the applied heat melts and force the materials of the tubular sleeve and the catheter shaft and the distal segment or distal soft tip together to fill interstitial spaces of the attachment junction and reduces the outer diameter of the sleeve. The heat shrink tube is removed after the assembly cools and solidifies. Preferably, the catheter shaft distal end and the soft tip or intermediate segment proximal end are each formed with a like plurality of ungular cut sections that are complementary in shape to one another, whereby the ungular cut sections are aligned with and mated together along the attachment junction.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
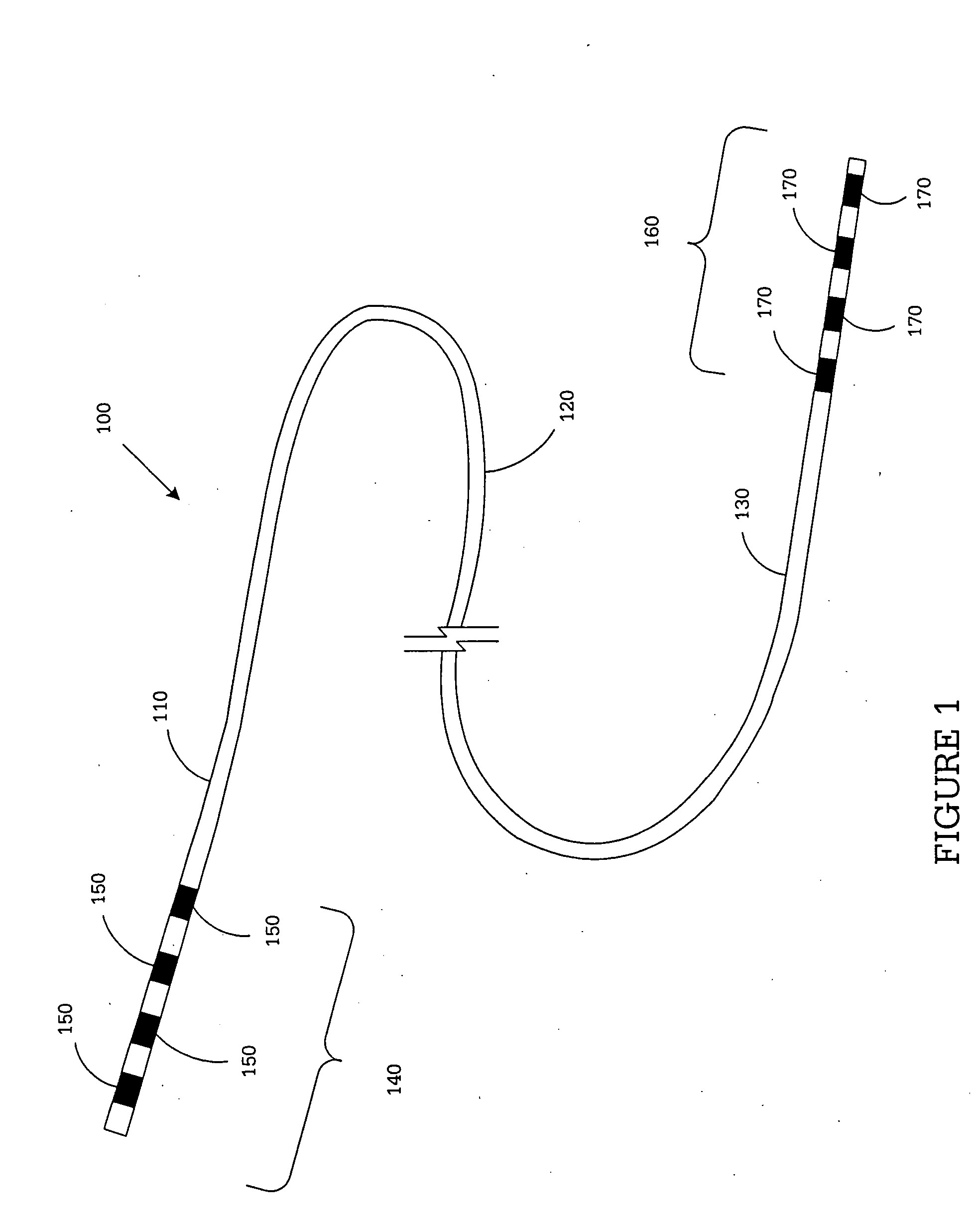
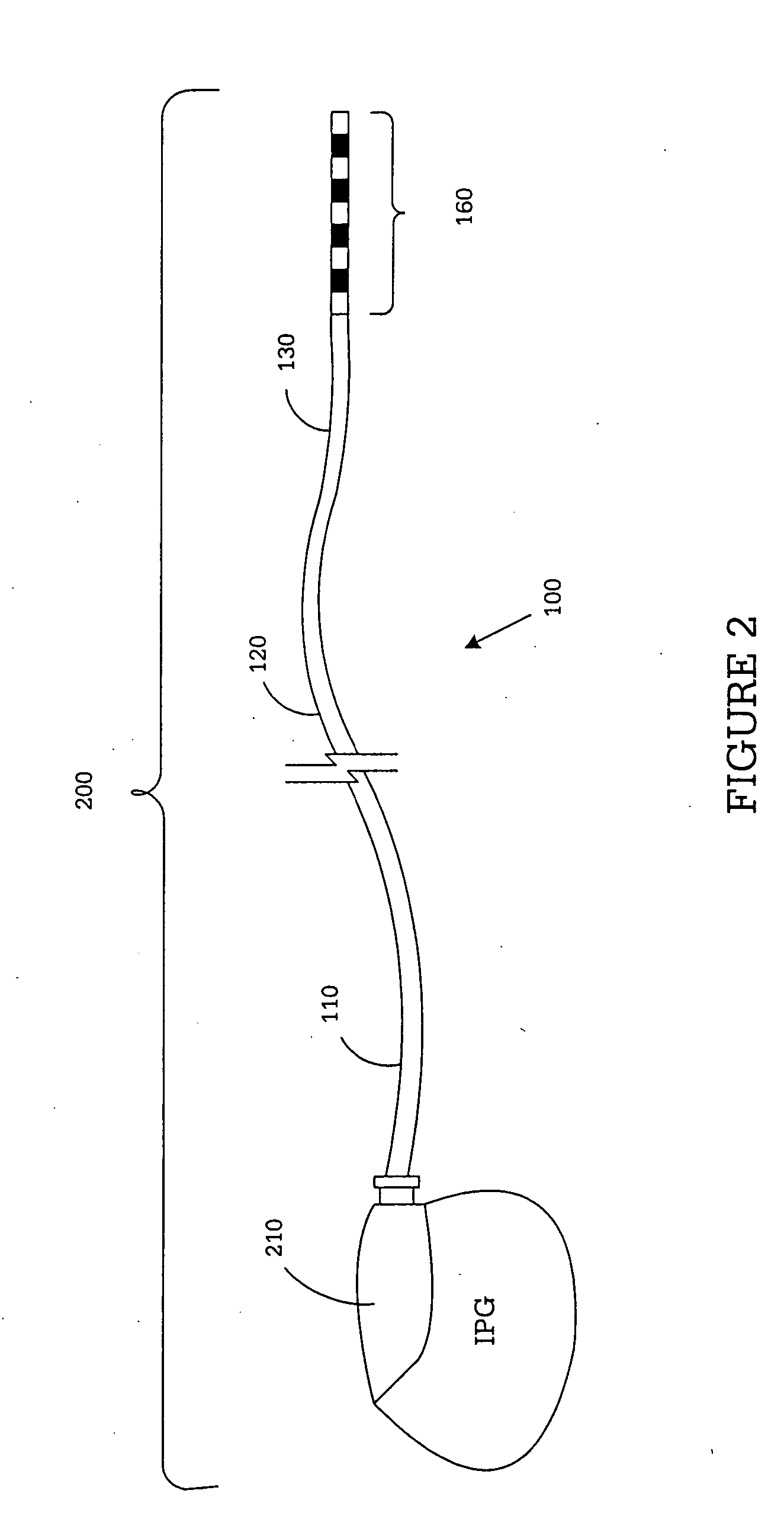
System and method for providing a medical lead body having dual conductor layers
InactiveUS20050027340A1Spinal electrodesExternal electrodesElectrical conductorBiomedical engineering
An implantable medical lead and lead body, method of manufacturing the same, and a system and method for stimulating a portion of a body is disclosed. In one advantageous embodiment, a lead body assembly is formed by preparing a first layer unitary body comprising a first plurality of conductors. An inner layer of extrusion material is placed on the first layer unitary body. A second plurality of conductors coated with extrusion material is placed on the inner layer. An outer layer of extrusion material is placed over the second plurality of conductors. Heat shrink tubing is placed over the assembly and the assembly is heated to melt the extrusion material. The extrusion material is compressed around the conductors. The assembly is cooled and the heat shrink tubing is removed. The solidified extrusion material forms a protective wall that encapsulates the first and second plurality of conductors in the lead body.
Owner:MICRONET MEDICAL
Halogen-free flame-retardant thermal-shrinkage sleeve materials and sleeve prepared thereby
ActiveCN1629216AWon't happenRaw materials are readily availableTubular articlesLow-density polyethyleneLinear low-density polyethylene
The invention provides a bittern-free flame-proof thermal contraction sleeve which comprises (by weight ratio), (1) 100 parts of one or more selected from ethane-vinyl acetate copolymer (EVA), ethene-ethyl acrylate copolymer (EEA), low density polyethylene (LDPE), linear low density polyethylene (LLDPE), (2) 5-50 parts of one or more selected from ethylene-propylene terpolymerisate rubber (EPDM), ethylene propylene rubber (EPM), dimethyl silicone rubber (MQ), methylvinyl silicone rubber (VMQ), methylsilicone rubber with phenyl and vinyl Group (PVMQ), thermoplastic elastomer styrene - butadiene - styrene blocked copolymer (SBS), styrene-isoprene blocked copolymer (SIS), (3) 50-100 parts of bittern-free flame retardant, and (4) 0.5-6 parts of coupling agent.
Owner:深圳市沃尔热缩有限公司
System and method for providing a medical lead body having conductors that are wound in opposite directions
InactiveUS20050027341A1Spinal electrodesExternal electrodesElectrical conductorBiomedical engineering
An implantable medical lead and lead body, method of manufacturing the same, and a system and method for stimulating a portion of a body are disclosed. A lead body assembly is formed by preparing a first layer unitary body comprising a first plurality of conductors wound in a first direction. An inner layer of extrusion material is placed on the first layer unitary body. A second plurality of conductors coated with extrusion material is placed on the inner layer. The second plurality of conductors is wound in a second opposite direction. An outer layer of extrusion material is placed over the second plurality of conductors. Heat shrink tubing is placed over the assembly. The extrusion material is heated and melted and compressed around the conductors. When the heat shrink tubing is removed, the solidified extrusion material forms a protective wall that encapsulates the conductors in the lead body.
Owner:MICRONET MEDICAL
Waterproofing method for wire and wire having waterproof part formed by the waterproofing method
InactiveUS20110048762A1Water penetration into a connector can be more reliably preventedPrevent water penetrationSoldering apparatusInsulated cablesEngineeringHot melt
A waterproofing method is provided for a wire to be arranged in a water susceptible area of a vehicle. An insulating coating layer is removed in a lengthwise intermediate part of the wire to expose a core. A heat shrinkable tube with an inner layer made of a hot-melt waterproofing agent is mounted on the exposed core section and parts of the insulating coating layer adjacent to the exposed core section and heated. As a result, the hot-melt waterproofing agent of the inner layer is melted and infiltrates into clearances between strands of the exposed core section. In addition, negative pressure is introduced into the inside of the insulating coating layer from an end of the wire, thereby sucking the waterproofing agent into the inside of the insulating coating layer to infiltrate the waterproofing agent also between the strands of the core inside the insulating coating layer.
Owner:SUMITOMO WIRING SYST LTD
Braided peelable catheter and method of manufacture
InactiveUS20100268196A1Lamination ancillary operationsLaminationHeat-shrink tubingBiomedical engineering
A method of manufacturing a braid-reinforced peelable tubular body is disclosed herein. In one embodiment, the method includes: providing a braided tubular body; forming at least one longitudinally extending slit in tho braided tubular body, resulting in a longitudinally slit braided tubular body, the at least one longitudinally extending slit including slit edges and a severed braid layer of the braided tubular body; placing the longitudinally slit braided tubular body on a mandrel; placing a heat shrink tube about the longitudinally slit braided tubular body; subjecting the heat shrink tube and longitudinally slit braided tubular body to bonding conditions, such as, for example, reflow, laser bonding, thermoforming, etc., thereby causing the slit edges to be joined to each other and resulting in a braid-reinforced peelable tubular body; and removing the braid-reinforced peelable tubular body from the mandrel.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
System and method for providing a medical lead body
InactiveUS20050027339A1Internal electrodesExternal electrodesElectrical conductorBiomedical engineering
An implantable lead and lead body, method of manufacturing the same, and a system and method for stimulating a portion of a body is disclosed. In one advantageous embodiment, a lead body assembly is formed by placing an inner layer of extrusion material on a mandrel, wrapping a plurality of conductors coated with extrusion material around the inner layer, and placing an outer layer of extrusion material over the plurality of conductors. Heat shrink tubing is placed over the lead body assembly and the lead body assembly is heated to melt the extrusion material. The melted extrusion material is compressed around the plurality of conductors. The assembly is then cooled and the heat shrink tubing is removed. The solidified extrusion material forms a protective wall that encapsulates the plurality of conductors in the lead body.
Owner:MICRONET MEDICAL
Liquid fuel burner
InactiveUS6579090B1Easily refilled and reusedEasy to installFuel lightersCapillary burnersCombustorLiquid fuel
A liquid fuel burner adapted to be inserted into an opening of a supporting base, such as a statue or other art work, includes a container to hold combustible fuel, a tube having one end attached to an opening in the container, a collar assembly secured to the other end of the tube and having a cap closing the end of the tube and a flange part to support the burner in the opening, and a wick extending from the container through the tube and being held within an opening defined in the cap. The cap may include a glass wick holder to support the wick in burning position thereabove. The fuel container may be defined by one or more flexible bladders which are attached to the tube by insulation, tape, heat-shrink tubing, or a wire clamp.
Owner:TAUBITZ ROBERT +2
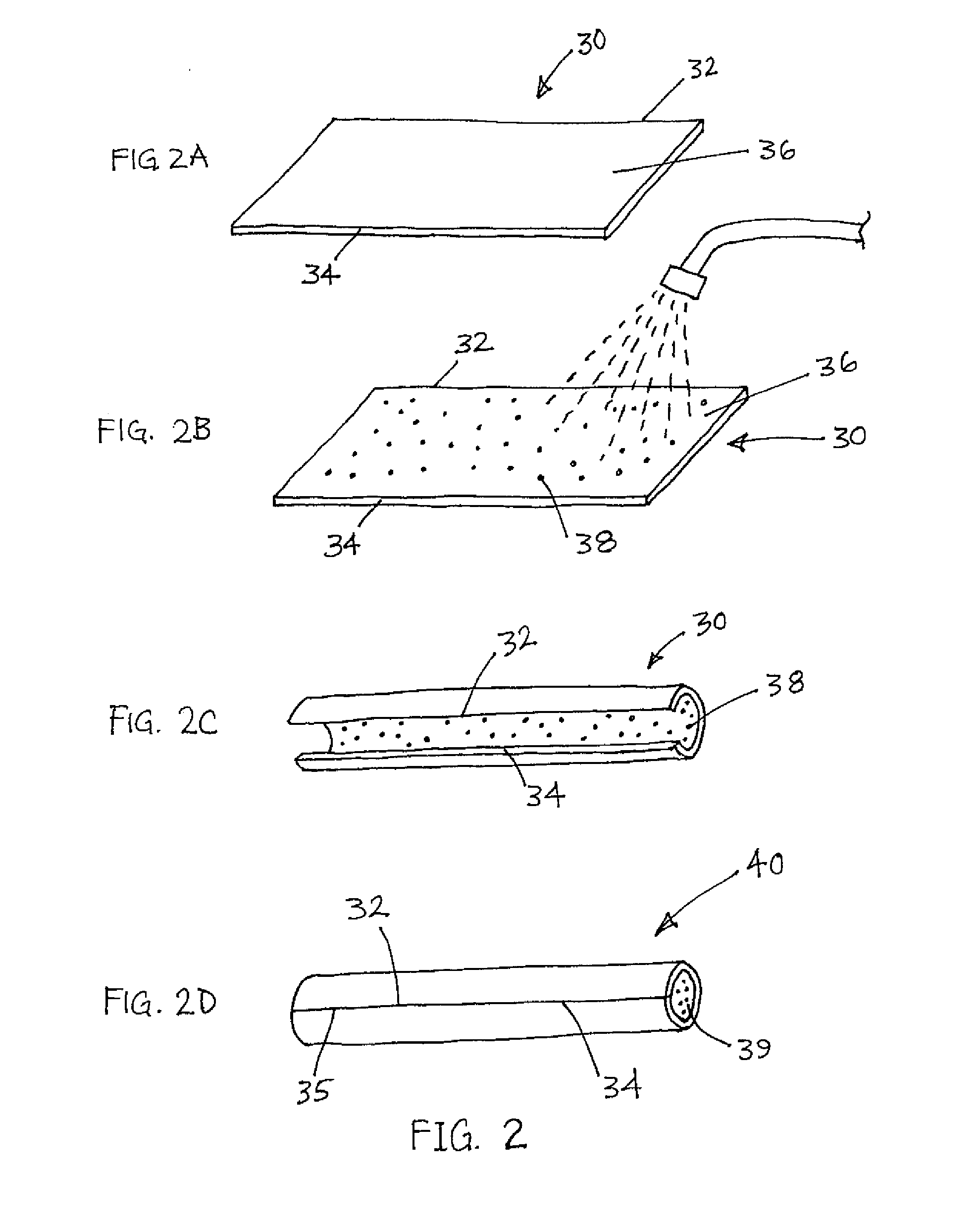
Catheters with lubricious linings and methods for making and using them
ActiveUS20110264057A1Improve cross linkingImprove adhesionTransvascular endocardial electrodesSynthetic resin layered productsBiomedical engineeringCatheter device
Apparatus and methods are provided for creating tubular devices, e.g., as components for catheters, sheaths, and or other devices sized for introduction into a patient. In one embodiment, a method is provided for making a tubular device using a sheet of material including a coated first surface. The sheet is rolled around a mandrel until longitudinal edges of the sheet are disposed near or adjacent one another, e.g., without attaching the longitudinal edges together. A tubular braid is positioned over the sheet-wrapped mandrel, one or more tubular segments are positioned over the tubular braid, and heat shrink tubing is positioned over the tubular segments. The resulting assembly is heated to cause the tubular segments to at least partially reflow and / or otherwise laminate the tubular segments to the tubular braid and sheet. The heat shrink tubing and mandrel are then removed to create the tubular device.
Owner:CLPH
Catheters with lubricious linings and methods for making and using them
ActiveUS20150320971A1Reduce bondingEnhance the air being evacuatedTransvascular endocardial electrodesGlovesBiomedical engineeringCatheter device
Apparatus and methods are provided for creating tubular devices, e.g., as components for catheters, sheaths, and or other devices sized for introduction into a patient. In one embodiment, a method is provided for making a tubular device using a sheet of material including a coated first surface. The sheet is rolled around a mandrel until longitudinal edges of the sheet are disposed near or adjacent one another, e.g., without attaching the longitudinal edges together. A tubular braid is positioned over the sheet-wrapped mandrel, one or more tubular segments are positioned over the tubular braid, and heat shrink tubing is positioned over the tubular segments. The resulting assembly is heated to cause the tubular segments to at least partially reflow and / or otherwise laminate the tubular segments to the tubular braid and sheet. The heat shrink tubing and mandrel are then removed to create the tubular device.
Owner:CLPH
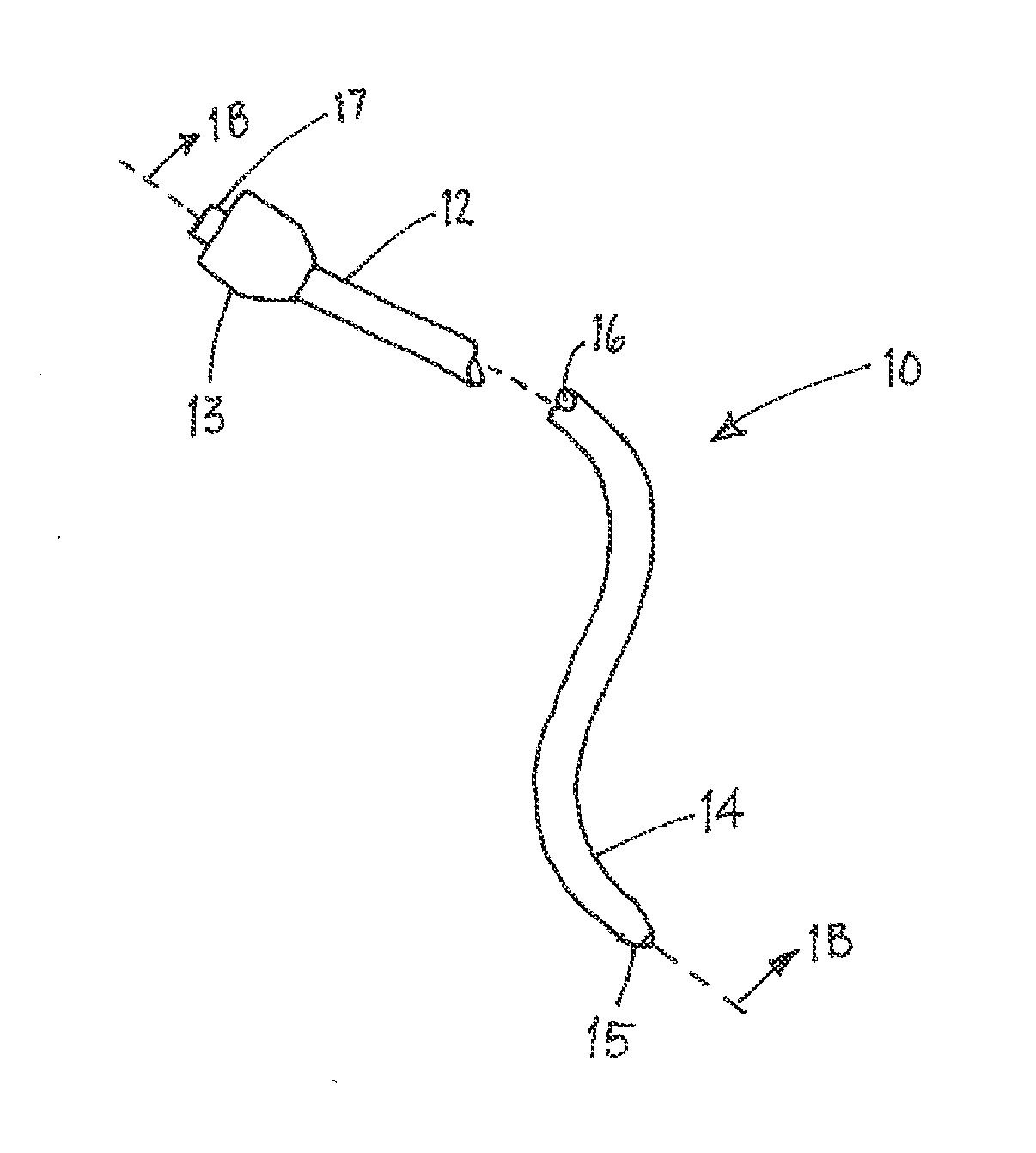
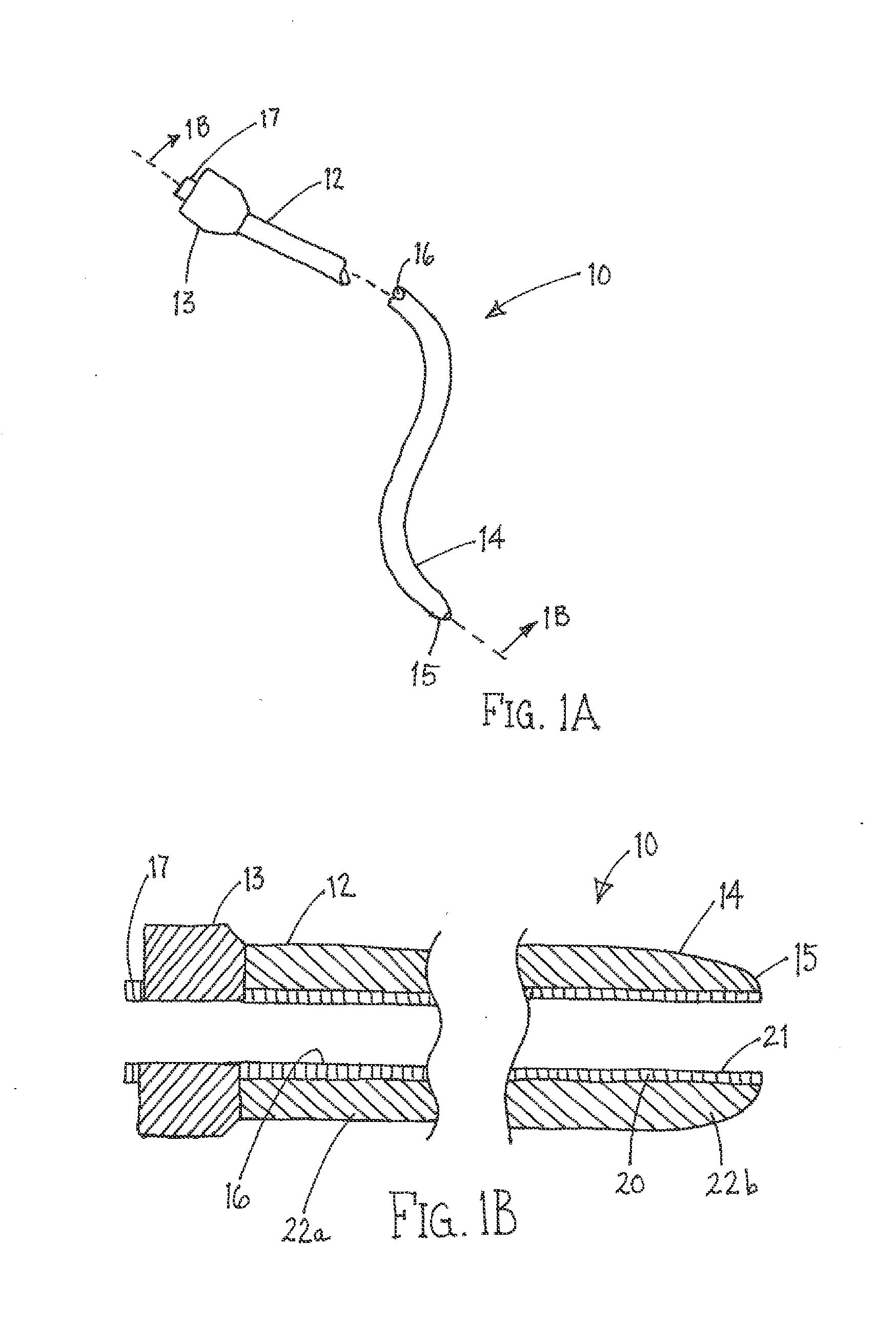
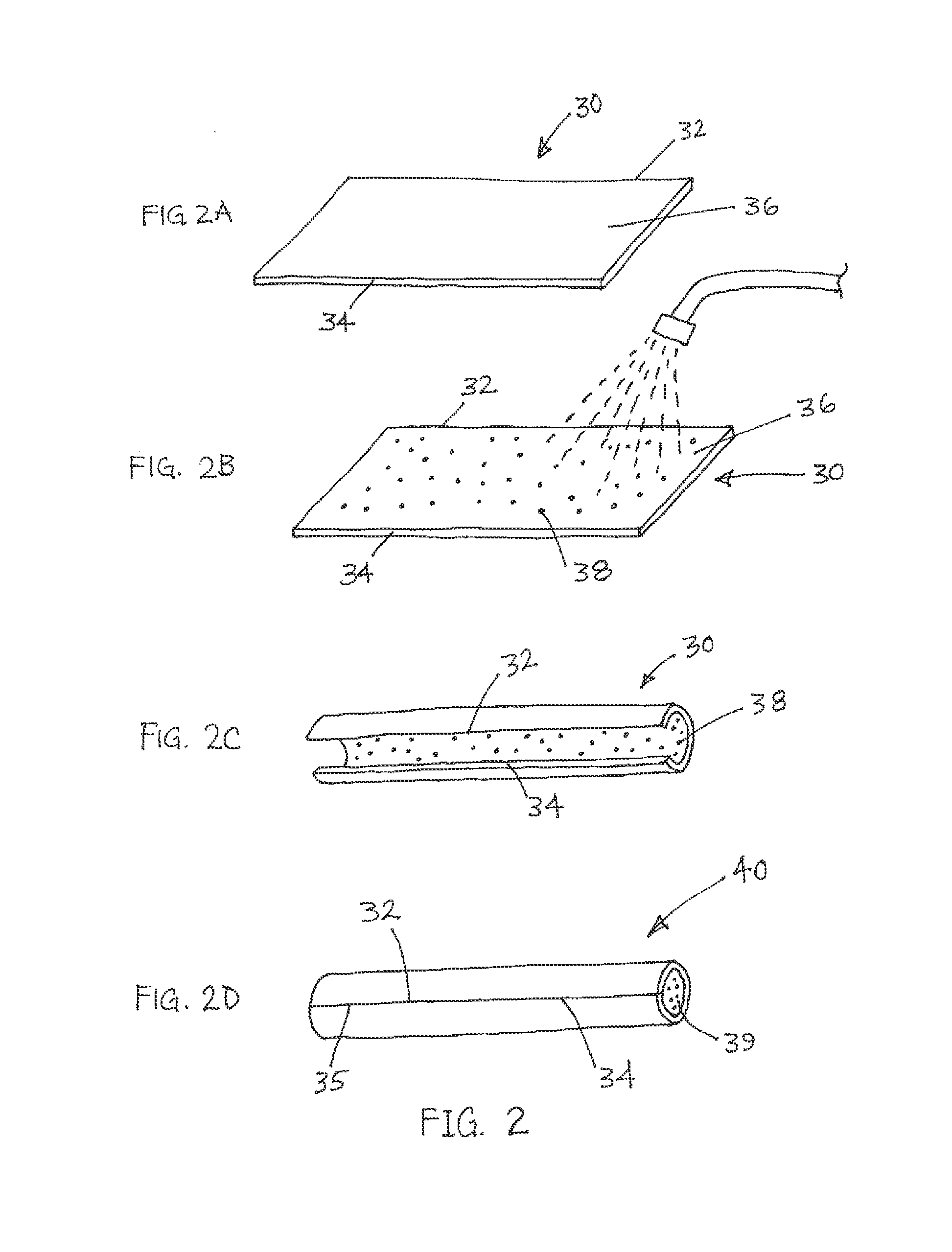
Steerable catheter and methods of making the same
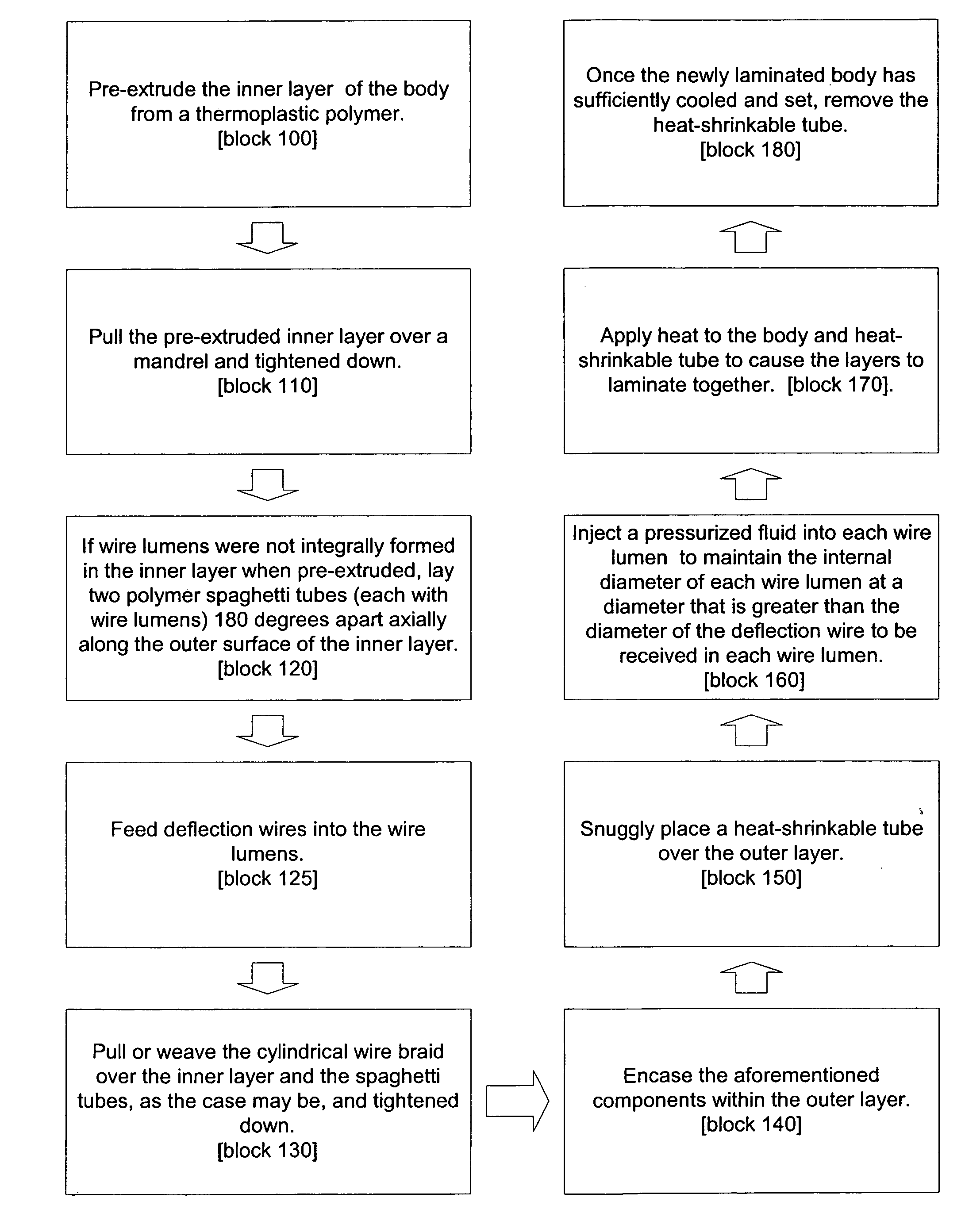
The present invention is a method of manufacturing a flexible tubular body for catheter, sheath or similar medical device. The method comprises pre-extruding an inner layer of the body from a thermoplastic polymer and then pulling the inner layer over a mandrel and tightening the layer down. If wire lumens were not integrally formed in the inner layer when pre-extruded, then two polymer spaghetti tubes, each with wire lumens, are laid 180 degrees apart axially along the outer surface of the inner layer. Deflection wires are then fed into the wire lumens. A cylindrical wire braid is woven or pulled over the inner layer (and the spaghetti tubes, as the case may be) and tightened down. The aforementioned components are then encased in an outer polymer layer. A heat-shrinkable tube is then placed over the outer layer. A pressurized fluid is injected into each wire lumen to maintain the internal diameter of each wire lumen at a diameter that is greater than the diameter of the deflection wire received in each wire lumen. Heat is then applied to the body and heat-shrinkable tube to cause the layers to laminate together. Once the newly laminated body has sufficiently cooled, the heat-shrinkable tube is removed from the body.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL ATRIAL FIBRILLATION DIV
Material used for halogen-free flame retardant heat shrinkable sheathing and cross-linking cable wire and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to a material used for a halogen-free, flame retardant and thermal shrinkage sleeve and crosslinked wires and cables as well as the preparation method, aiming to provide a material and the preparation preparation method for halogen-free, flame retardant and thermal shrinkage sleeve and crosslinked wires and cables in diversified colors. The preparation method comprises the following steps: first, evenly mixing the compound formed by polyolefin copolymer, silicon rubber, halogen-free ammonium polyphosphate composite fire retardant, lubricant, colorant color master batch and antioxidant in specific proportions through a high speed mixer, then extruding and granulating the compound by means of the mechanical blending, finally turning out the material for producing the halogen-free flame retardant and thermal shrinkage sleeve and crosslinked wires and cables.
Owner:SHENZHEN WOER HEAT SHRINKABLE MATERIAL
Catheters with lubricious linings and methods for making and using them
ActiveUS20090227962A1Improve cross linkingImprove adhesionPaper/cardboard wound articlesTransvascular endocardial electrodesBiomedical engineeringCatheter device
Apparatus and methods are provided for creating tubular devices, e.g., as components for catheters, sheaths, and or other devices sized for introduction into a patient. In one embodiment, a method is provided for making a tubular device using a sheet of material including a coated first surface. The sheet is rolled around a mandrel until longitudinal edges of the sheet are disposed near or adjacent one another, e.g., without attaching the longitudinal edges together. A tubular braid is positioned over the sheet-wrapped mandrel, one or more tubular segments are positioned over the tubular braid, and heat shrink tubing is positioned over the tubular segments. The resulting assembly is heated to cause the tubular segments to at least partially reflow and / or otherwise laminate the tubular segments to the tubular braid and sheet. The heat shrink tubing and mandrel are then removed to create the tubular device.
Owner:CLPH
Waterproof lead and method for making the same
ActiveUS20050095892A1Avoid contactLow costLine/current collector detailsCoupling contact membersAdhesiveEngineering
A waterproof lead includes an electric wire, a terminal, and a heat-shrink tube. The electric wire has an insulative cover and a plurality of exposed core wires. The terminal has a contact member, a core wire crimping section that crimps the plurality of exposed core wires, and an insulative cover crimping section that crimps the insulative cover. The heat-shrink tube covers at least a leading end of the exposed core wires adjacent to the core wire crimping section. An adhesive is provided on an internal surface of the heat-shrink tube. The adhesive seals clearances between adjacent exposed core wires.
Owner:TYCO ELECTRONICS RAYCHEM KK
Method and device for determining radon gas separation in load coal fracture process
InactiveCN104181283AImprove controllabilityPromote migrationFuel testingAdsorption equilibriumAxial pressure
The invention relates to a method and device for determining radon gas separation in the load coal fracture process. The method comprises the following steps: (1) preparing a coal sample into a test piece, installing the test piece between an upper pressure head and a lower pressure head of a three-axis compressor, and arranging a heat shrink tube outside the test piece in a sleeving manner; (2) vacuumizing a sample chamber formed by the upper pressure head, the lower pressure head and the heat shrink tube in an enclosing manner, then continuously introducing carrier gas into the sample chamber; (3) after the coal sample test piece absorbs the carrier gas in a balanced manner, applying a confining pressure and an axial pressure to the test piece, starting the recording of an acoustic emission signal in the determining process; (4) opening an air outlet duct of the sample chamber, collecting gas released from the sample chamber, determining the content of radon in the gas; (5) closing the gas outlet duct of the sample chamber to ensure that the coal sample test piece absorbs the carrier gas again in the balanced manner, increasing the axial pressure; and (6) repeating the steps (4) and (5) until the test piece is damaged, and stopping the recording of the acoustic emission signal.
Owner:HENAN POLYTECHNIC UNIV
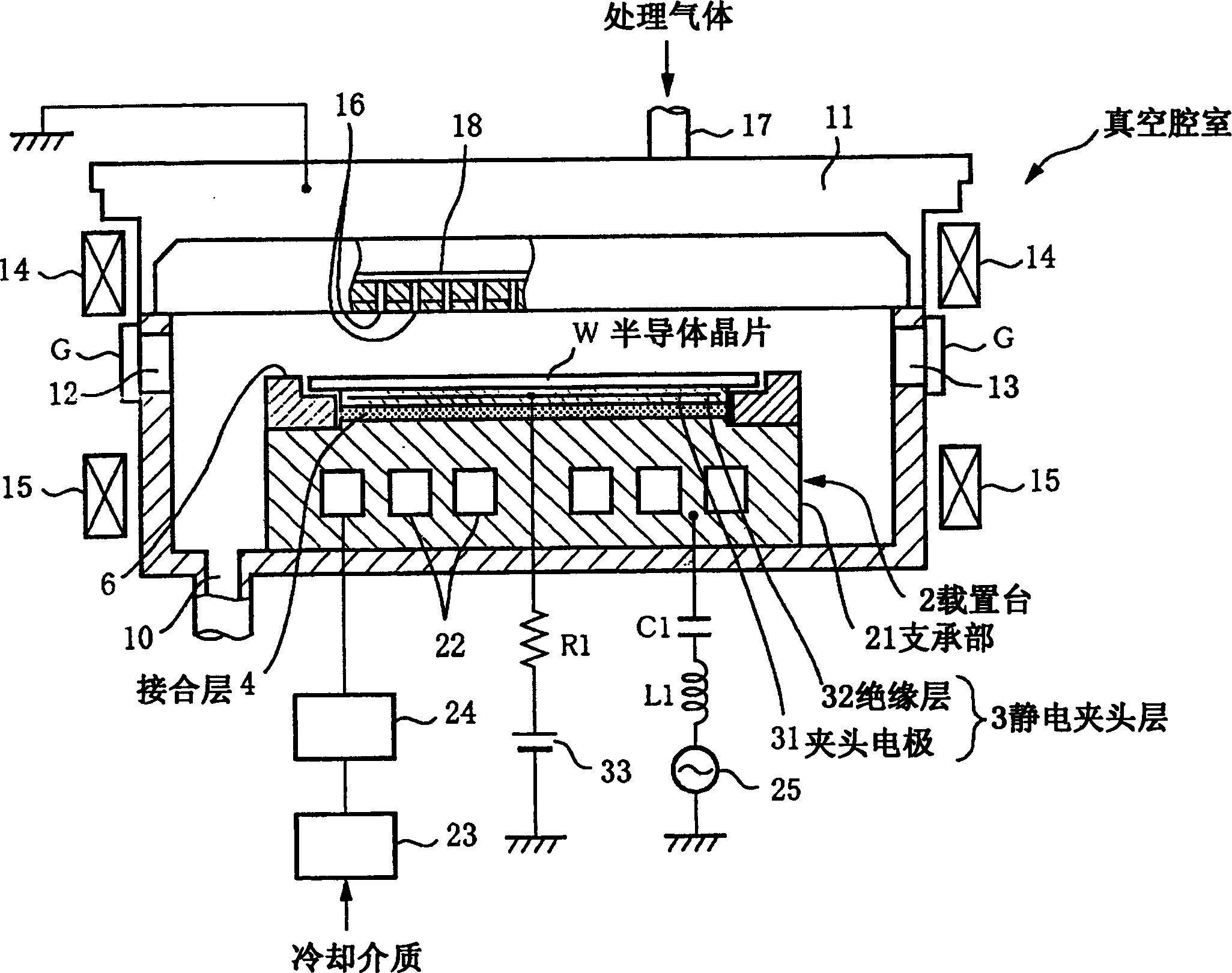
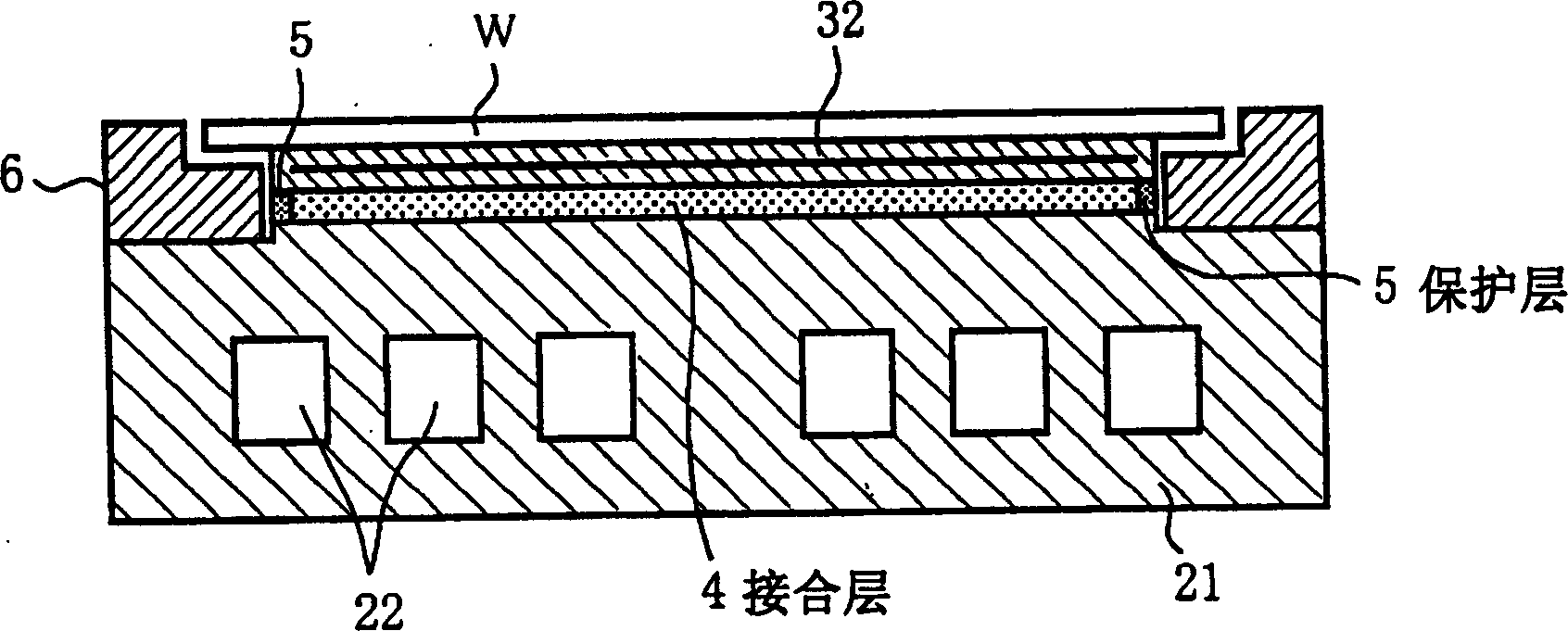
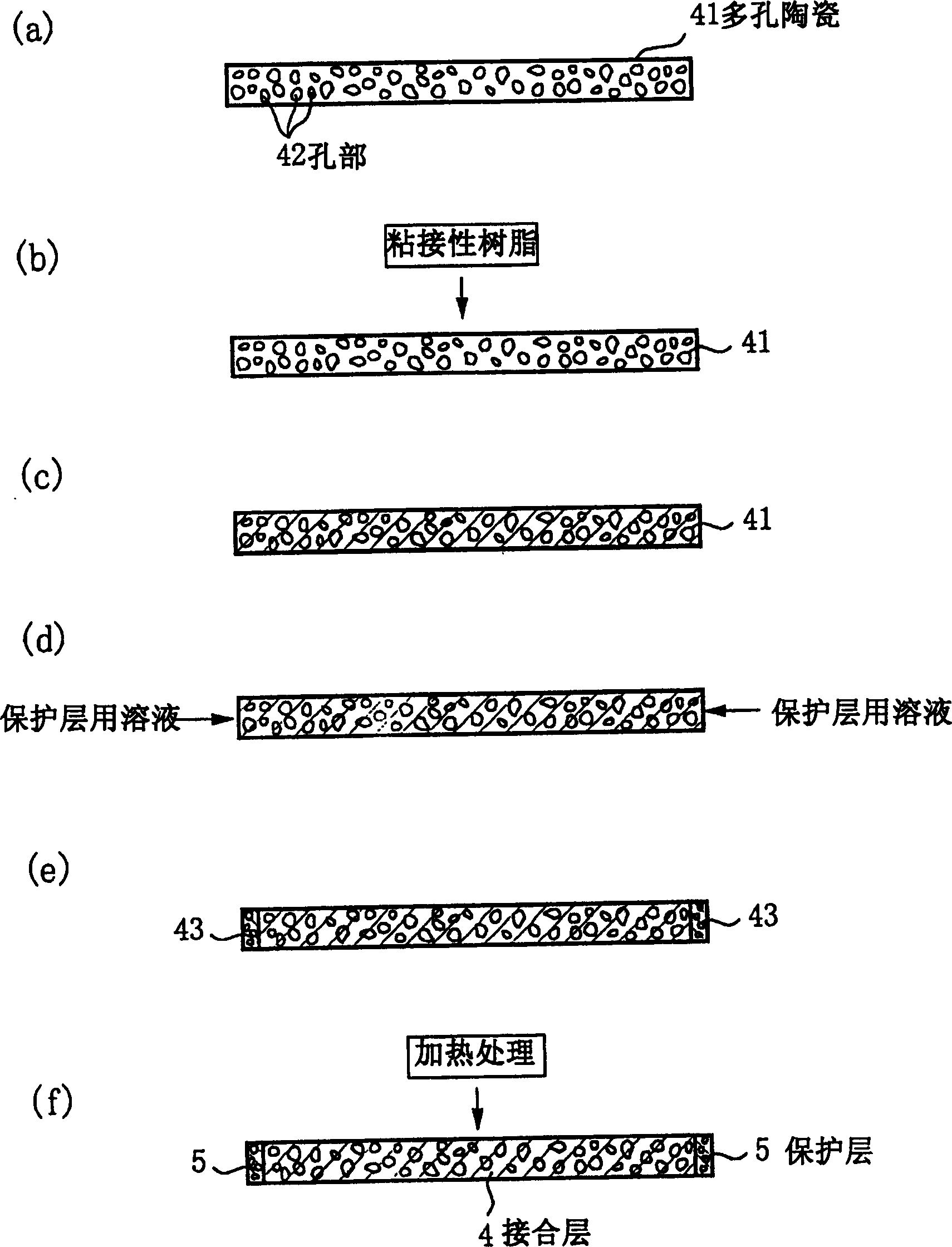
Processing device
InactiveCN1551293AFast heat conductionGood adhesionSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingElectrostatic holding devicesSiliconPorous ceramics
The time period during which a wafer is stabilized to a predetermined temperature by increasing a thermal conductivity of a junction layer for bonding an electrostatic chuck layer and a support together, and the deterioration of the junction layer that is caused by active species generated by plasma is suppressed. Between the electrostatic chuck layer formed by sintering together a chuck electrode made of tungsten and an insulating layer made of alumina and the support, made of aluminum, for supporting the electrostatic chuck layer, the junction layer is provided to bond the electrostatic chuck layer and the support together. The junction layer is formed by impregnating a porous ceramic with a silicone-based adhesive resin. Further, rubber or a heat shrink tube made of a fluoric resin such as PFA is provided as a soft coating member so as to coat a side circumferential surface of the junction layer and the side circumferential surfaces of the electrostatic chuck layer and the support come into a tight contact with the heat shrink tube or rubber.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
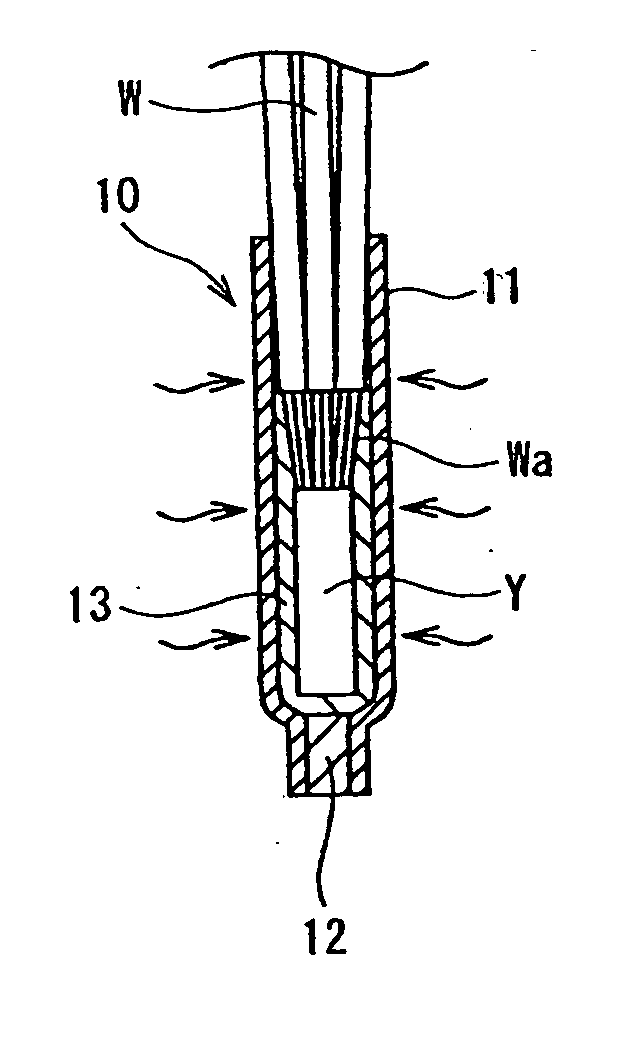
Method and apparatus for packaging optical fiber sensors for harsh environments
InactiveUS6928202B2Quantity minimizationCoupling light guidesFibre mechanical structuresHermetic sealMetal
A package for an optical fiber sensor having a metal jacket surrounding the sensor, and heat-shrink tubing surrounding the metal jacket. The metal jacket is made of a low melting point metal (e.g. lead, tin). The sensor can be disposed in a rigid tube (e.g. stainless steel or glass) that is surrounded by the metal jacket. The metal jacket provides a hermetic, or nearly hermetic seal for the sensor. The package is made by melting the metal jacket and heating the heat shrink tubing at the same time. As the heat-shrink tubing shrinks, it presses the low melting point metal against the sensor, and squeezes out the excess metal.
Owner:VIRGINIA TECH INTPROP INC
Method and structure for waterproofing a terminal splice
ActiveUS20060048965A1Reduce the overall diameterImprove performanceDustproof/splashproof/drip-proof/waterproof/flameproof connectionCouplings bases/casesHeat-shrink tubing
To decrease cap diameter covering a terminal splice and improve workability and waterproof performance, a stopper is inserted in one opening of a heat shrinkable tube. The heat shrinkable tube is heat-shrunk in this state, then a cap having end an closure is formed. A fluid thermosetting waterproofing agent is injected into the cap from a second opening. A thermal splice, which is formed from welded strands stripped from a plurality of wire terminals, is inserted and immersed in the thermosetting waterproofing agent. Then, the entire cap is heated and heat-shrunk at a predetermined temperature and the thermosetting waterproofing agent is heat-hardened.
Owner:SUMITOMO WIRING SYST LTD
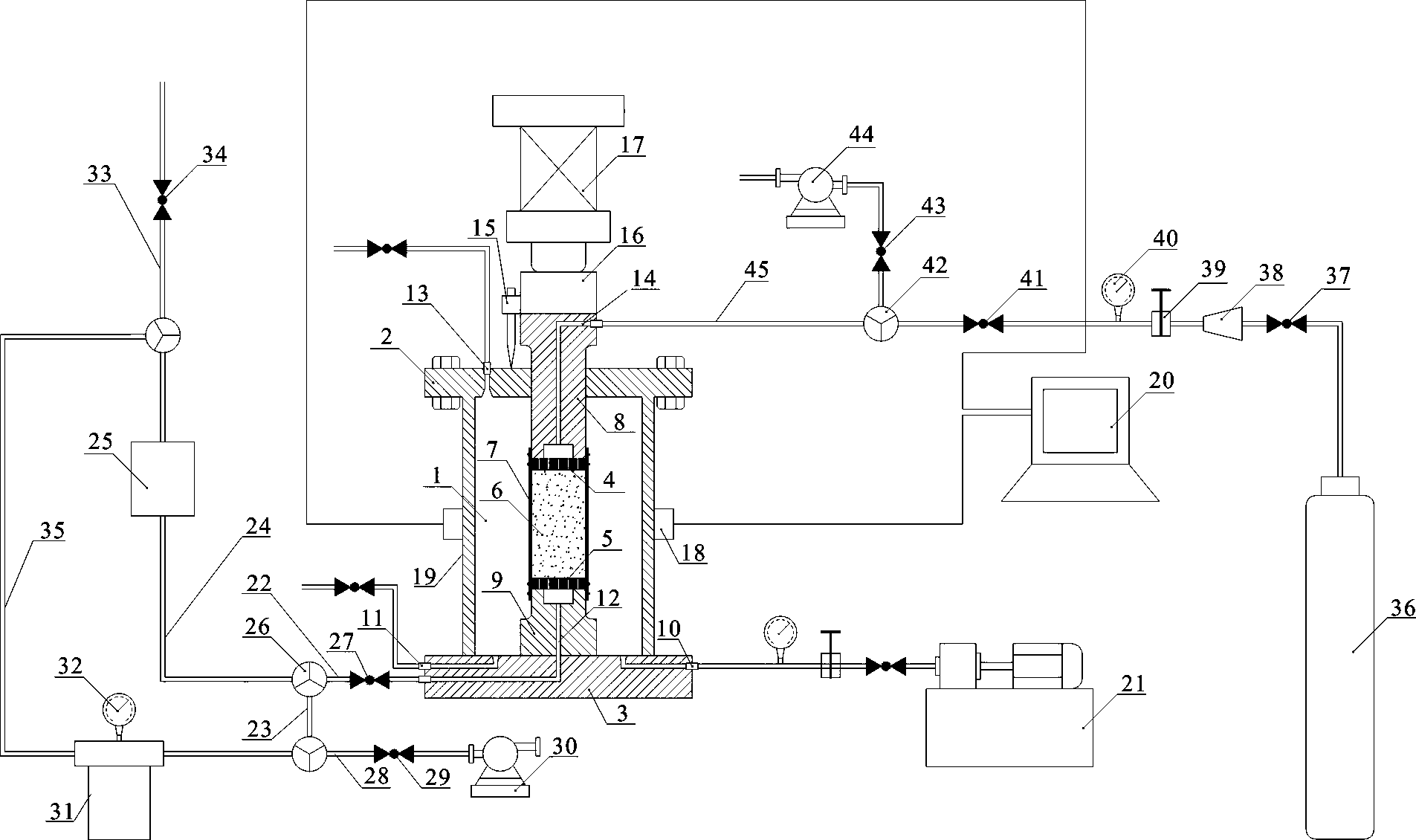
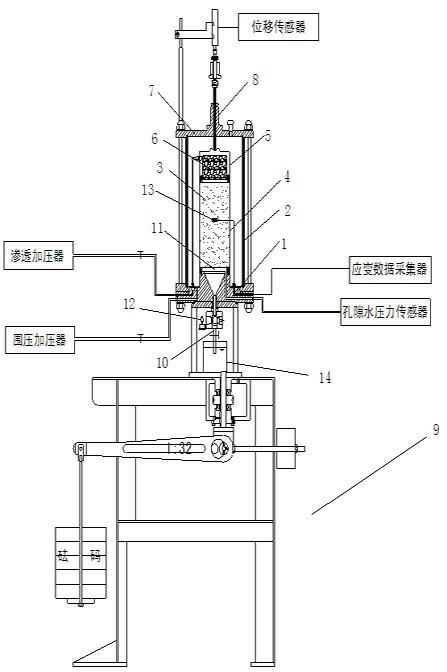
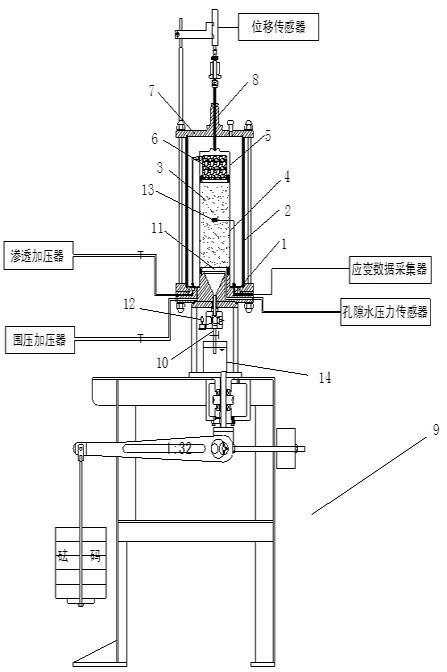
Piping test device of seepage corrosion stress coupling
The invention relates to a piping test device of seepage corrosion stress coupling, wherein a leakage groove is arranged in the base, a pressure chamber is installed on the upper part of the base and a top cover is installed on the upper part of the pressure chamber; one end of the water outlet tube is connected with the bottom outlet of the base and the other end is extended into a measuring pot; a sample is installed in the pressure chamber on the base; a porous steel plate is installed between the sample and the base; a shrinkable tube is closely wrapped on the outside of the sample and a cover cap is arranged at the top part of the sample; a scree filter layer is filled in the cover cap; one end of the axial pressurizing rod is penetrated through the top cover to contact with the cover cap and the other end is connected with an axial pressurizer; a photoelectric sensor is installed on the body of the water outlet tube; a resistance strain gage is installed on the shrinkable tube. The invention researches a piping development process of the soil body under a complex stress state from the seepage corrosion stress coupling aspect, provides a new aspect for the comprehensive understanding of the soil body piping developmental mechanism and also provides an important theoretical basis and a technical support for the prediction and the effective treatment of the dam piping dangerous case.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
1E-grade K1 type halogen-free flame retardant material for nuclear power plants and application thereof
ActiveCN102731895AImprove thermal stabilityStrong absorption capacityPlastic/resin/waxes insulatorsInsulated cablesNuclear powerPhosphoric acid
The invention discloses a 1E-grade K1 type halogen-free flame retardant material for nuclear power plants. The material comprises the following substances: 100 parts of vinyl polymers, 1-20 parts by weight of polymer compatilizer, 0.5-10 parts by weight of organosilicon polymers, 1-10 parts by weight of complex antioxidant, 0.1-10 parts by weight of light stabilizer and 0.1-100 parts by weight of high molecular weight ammonium polyphosphate and / or 0.1-50 parts by weight of phosphate flame retardants and / or 0.1-50 parts by weight of melamine cyanurate and / or 0.1-50 parts by weight of melamine pyrophosphate, wherein the complex antioxidant is a complexing agent formed by blending hindered phenol main antioxidants, thioether auxiliary antioxidants, hindered amine auxiliary antioxidants and an anti-copper agent in a weight ratio of 1:(1-4):(1-2):(0.5-1). The material can serve as the insulating material of 1E-grade K1 type halogen-free flame retardant heat shrink tubes, wires and cables and cable accessories for nuclear power plants.
Owner:SHENZHEN WOER HEAT SHRINKABLE MATERIAL
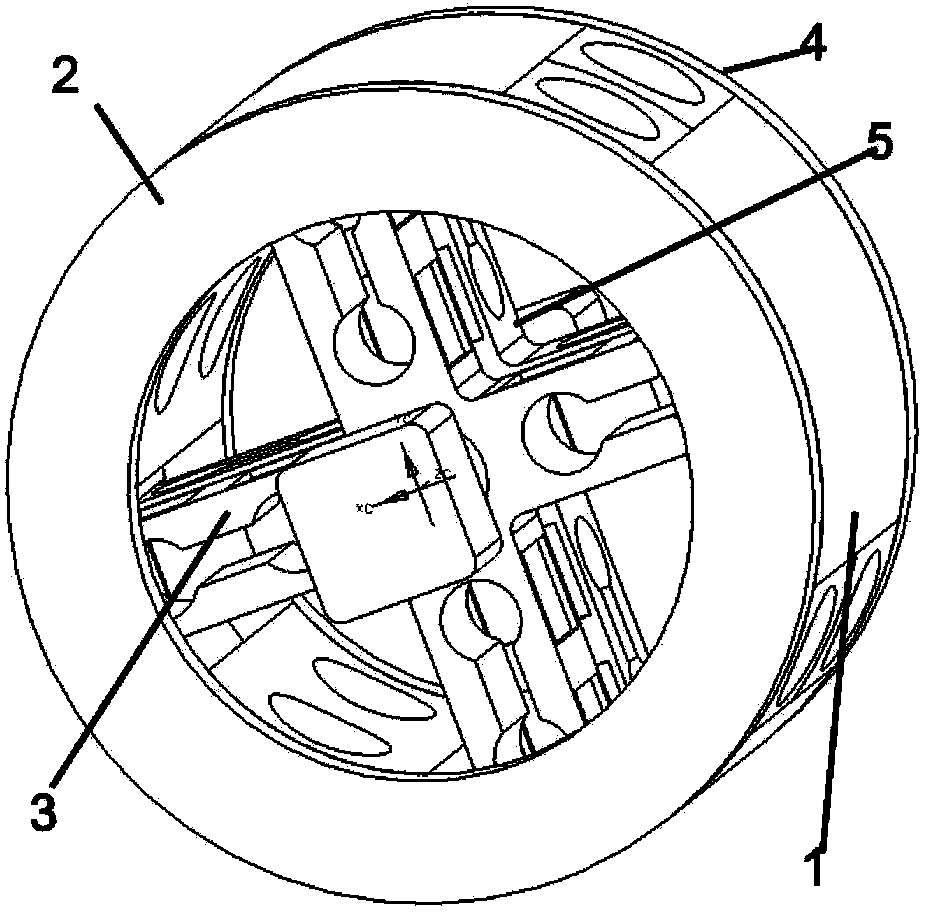
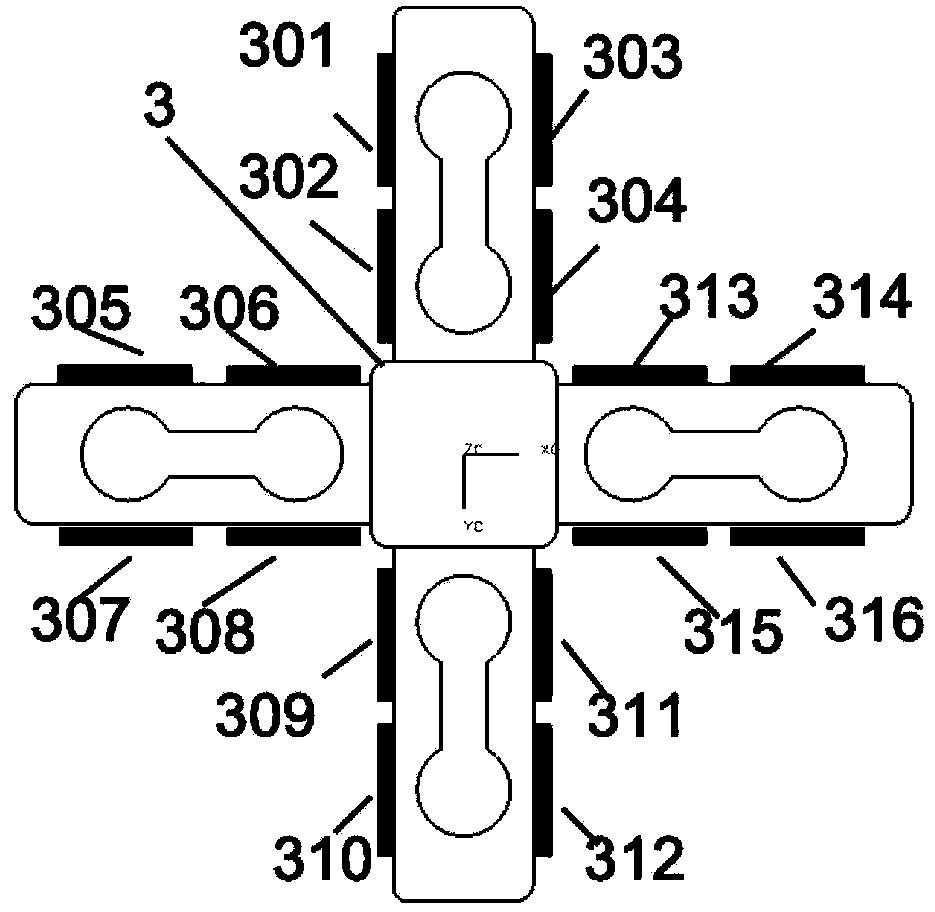
Six-dimensional force sense sensor for minimally invasive surgical robot
ActiveCN103376172AAvoid negative influenceSimple structureSurgeryForce measurementShaped beamSurgical robot
The invention provides a six-dimensional force sense sensor for a minimally invasive surgical robot. The six-dimensional force sense sensor comprises two cross-shaped-shaped beam elastic bodies, two baffles and an elastic body substrate, wherein arc I-shaped holes which are orthogonally distributed are formed in the cross-shaped beam elastic bodies respectively, the elastic bodies are installed at the head end and the tail end of the elastic body substrate in a clearance fit mode in the direction of strut beams stretched out of cross-shaped beams, and the elastic bodies are fixed by the two baffles. Four strain gauges are pasted on each of the four strut beams of each elastic body cross-shaped beam and used for measuring corresponding force or force torque, the four strain gauges on each strut beam form an equal-arm full bridge circuit, four signal lines are led from each equal-arm full bridge circuit and bundled into one bundle after being wrapped by a heat shrink tube in a hot shrinkage mode, and then the bundle is led out of a mechanical hand through a mechanical hand hollow metal round rod from space regions among the cross-shaped beam strum beams. The sensor is installed at the position close to an end effector of the minimally invasive surgical mechanical hand and measures six-dimensional force sense components, and the negative influence of the friction of the mechanical hand and an incision on data measured by the sensor is avoided.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
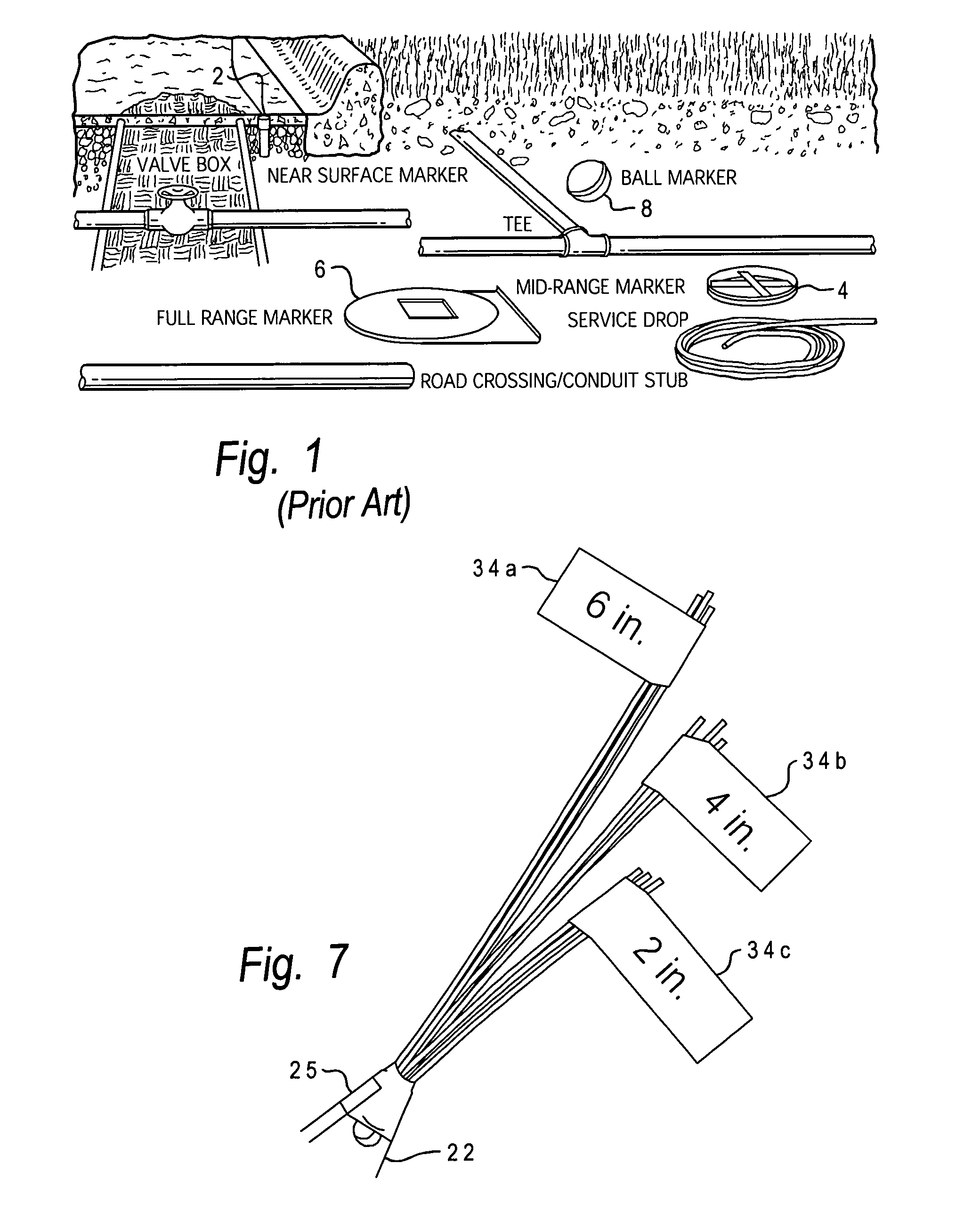
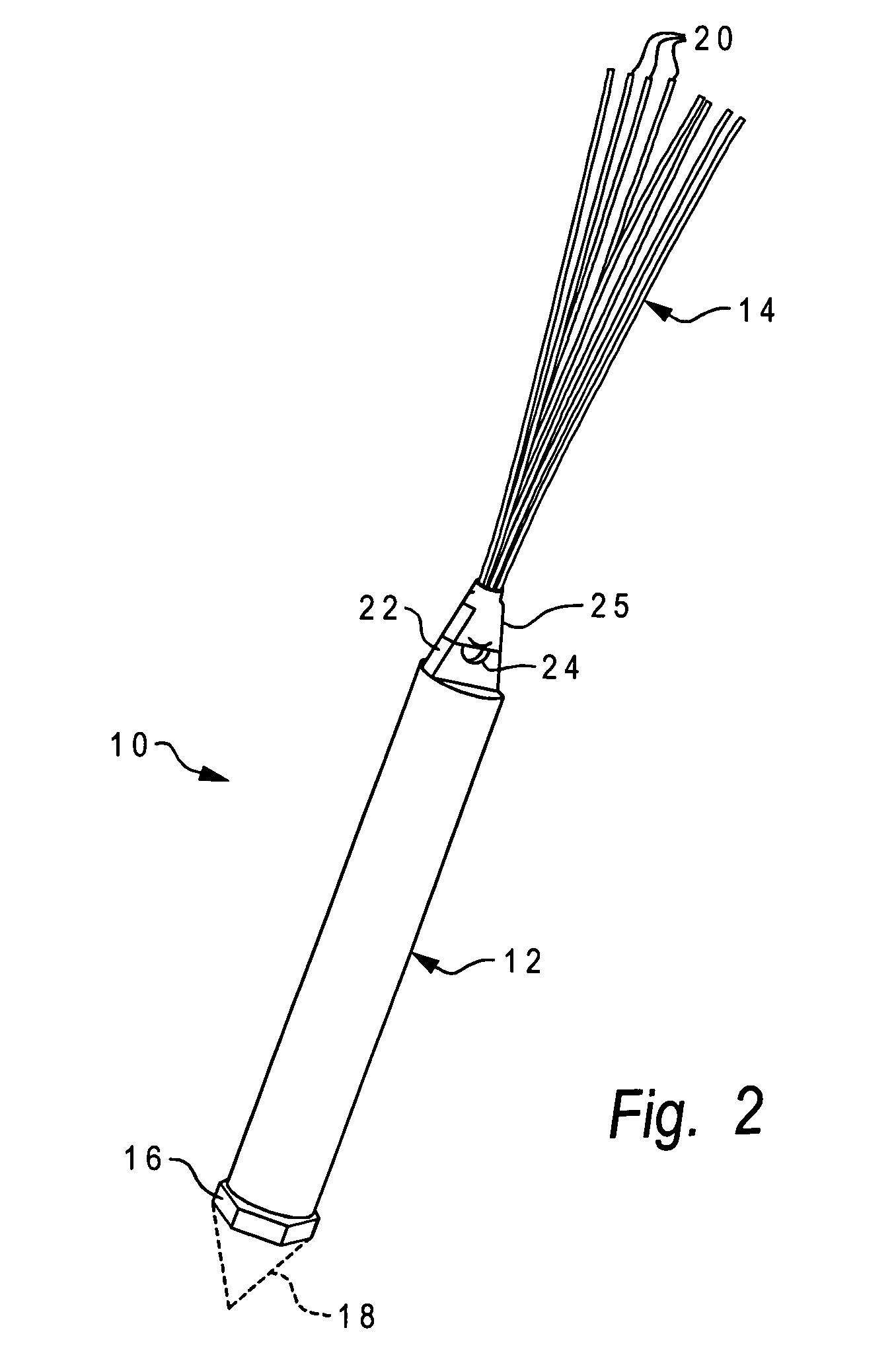
Surface tracker
InactiveUS7081820B2Improve abilitiesAnalysis using chemical indicatorsAntenna arraysAbove groundEngineering
A surface tracker includes a tubular marker body having an interior electronic marker and a visual indicator attached to an upper end of the marker body which extends away from the marker body. When deployed, the marker body is mostly underground and the visual indictor extends upwardly from the ground level to provide above-ground visual recognition. The visual indicator may be a plurality of resilient filaments which pass through a hole in a tab portion of the marker body at the upper end thereof, the filaments being folded about the tab portion and secured to the tab portion using a heat-shrink tube. The visual indication, along with the ability to electronically detect the marker, provides a tracker with superior locating capability.
Owner:MINAROVIC JOE T
Dual voltage circuit tester
InactiveUS20050057243A1Reduce riskProtection from damageElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingDirection of current indicationTester deviceHand held
A handheld dual voltage circuit tester, method and electronic circuit that quickly allows a technician to determine whether an automotive electrical system runs on a 12-14 volt circuit or 36-42 volt circuit. The tester may be used for automobiles having a single voltage electrical system, or automobiles with distinct electrical systems operating on one of a 12-14 volts circuit or a 36-42 volt circuit. The tester includes a screwdriver-type elongated handle and probe tip. The tester also includes electronic circuitry disposed within its handle, heat shrink tubing, a conductive spring assembly, a strain relief, a retractable coil cord, a ground clip and insulation that encloses the ground clip. The tester also includes electronic circuitry that emits light of a first color when a 12-14 volt circuit is sensed, and light of a second color when a 36-42 volt circuit is sensed.
Owner:SNAP ON INC
1E-level K1-type shrinkable tube used in nuclear power station and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN101661803AImprove flame retardant performanceImprove heat aging resistanceNuclear energy generationContainmentAging propertyFire retardant
The invention relates to a 1E-level K1-type shrinkable tube used in a nuclear power station, which comprises the following components by weight: 40 to 60 parts of base resin, 40 to 60 parts of hexyl-propyl rubber, 30 to 60 parts of flame retardant, 5 to 20 parts of antiradiation agent, 4 to 12 parts of antioxidizer, 2 to 5 parts of lubricant, and 3 to 8 parts of color masterbatch. The preparationmethod of the 1E-level K1-type shrinkable tube used in the nuclear power station comprises the following steps of: taking all the components by weight, carrying out mixed granulation by banburying ormixed granulation by a parallel double-screw extruder, then using a single-screw extruder for extrusion to form the tube, and carrying out radiation cross linking of cobalt 60 or electron accelerator50-180KGy to the tube, wherein the tube after the radiation cross linking expands by 2 to 6 times at the temperature of 90 to 150 DEG C. The shrinkable tube reaches and far exceeds the performance requirement of the 1E-level K1-type shrinkable tube used in the nuclear power station. The 1E-level K1-type shrinkable tube used in the nuclear power station has good flame retardant properties, can passV W-1 combustion test; has excellent heat-proof aging property, with the tensile strength and elongation at break of the product far stronger than the performance requirement; and outstanding intenseradiation-resistant function, and can pass AC withstand voltage test.
Owner:CHANGYUAN ELECTRONICS DONGGUAN +1
Working electrode for realizing electrochemical test of high-temperature high-pressure water system
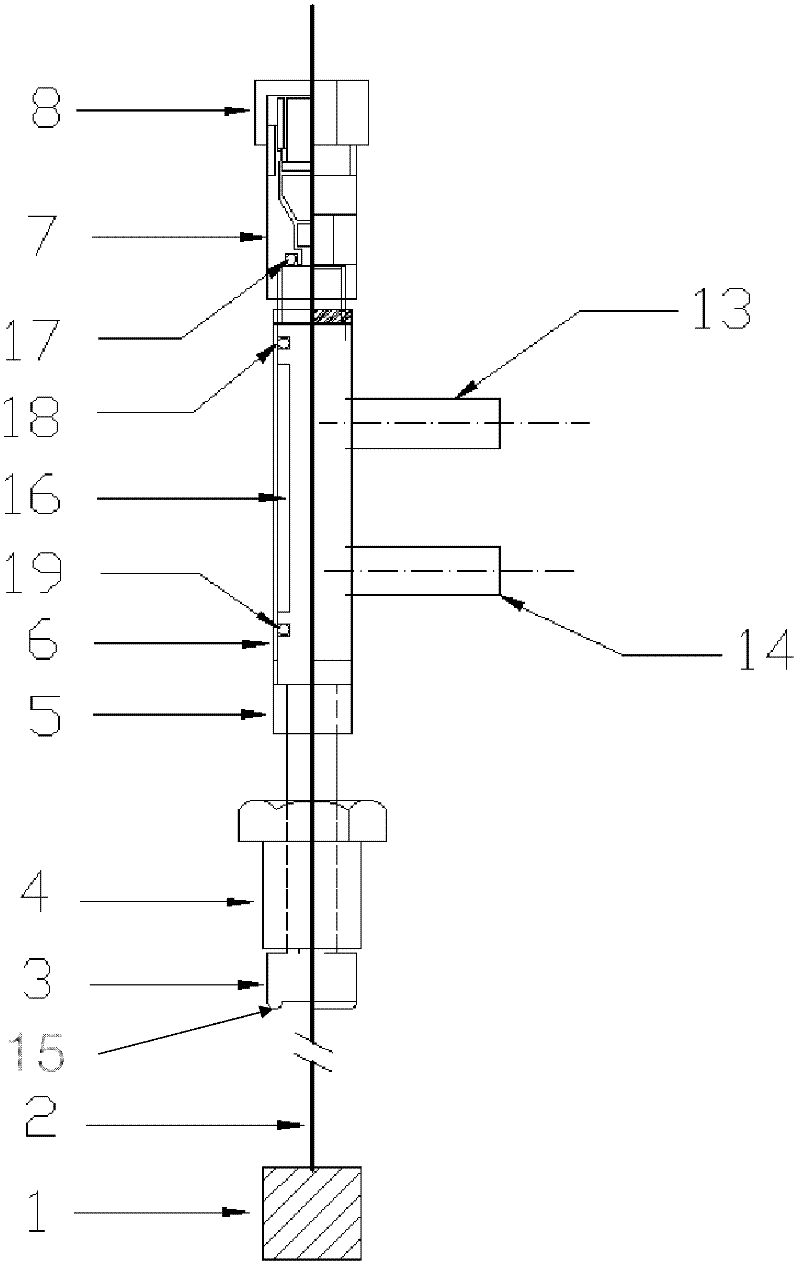
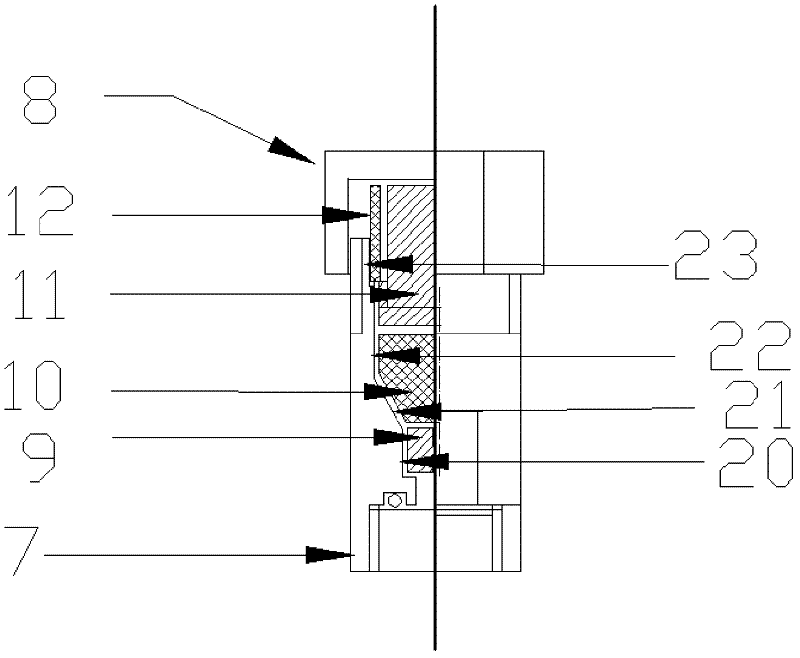
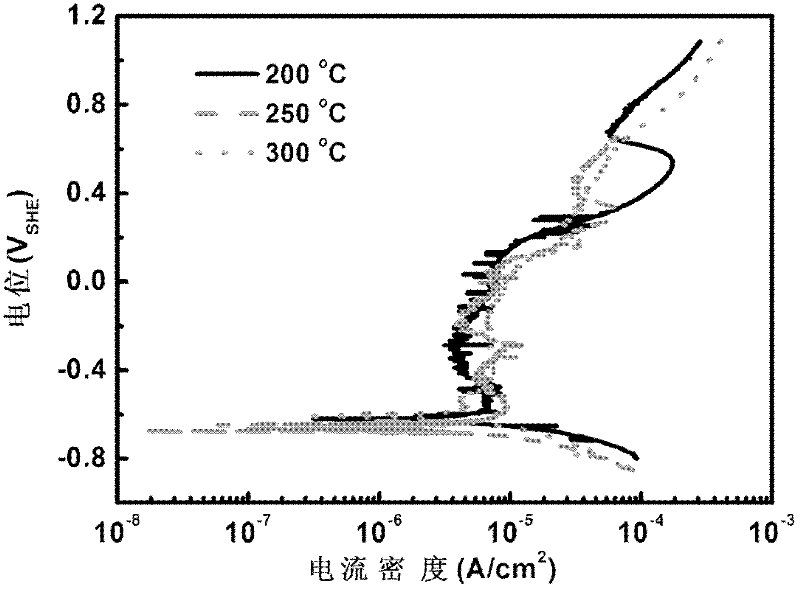
ActiveCN102445478AReduce the difficulty of sealingImproves sealing reliabilityMaterial electrochemical variablesRoom temperatureHigh pressure water
The invention relates to the field of an electrochemical test of a high-temperature high-pressure water system, in particular to a working electrode for realizing the electrochemical test of the high-temperature high-pressure water system. The working electrode comprises a metal electrode, a high-temperature sealing piece, a water cooling device and a low-temperature sealing piece, wherein an electrode lead of the metal electrode is used for wrapping a heat-shrink tube; metal hard sealing is existed between the high-temperature sealing piece and a high-pressure kettle cover; the water coolingdevice is arranged on the high-temperature sealing piece; the low-temperature sealing piece is sealed with the water cooling device through an O-shaped ring; the electrode lead of the metal electrodesequentially penetrates through central holes of the high-temperature sealing piece, the water cooling device and the low-temperature sealing piece; and the low-temperature sealing piece is sealed with the electrode lead through a rubber sealing plug. The working electrode is simple to manufacture, has good sealability, can realize the electrochemical test of the high-temperature high-pressure water system of metal materials under the temperature being between normal temperature and 350 DEG C, and the pressure being between normal pressure and 20MPa, and solves the problems of higher preparation process requirement and difficulty in realization of experimental facilities and the working electrode due to harsh environment of a high-temperature high-pressure water.
Owner:INST OF METAL RESEARCH - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
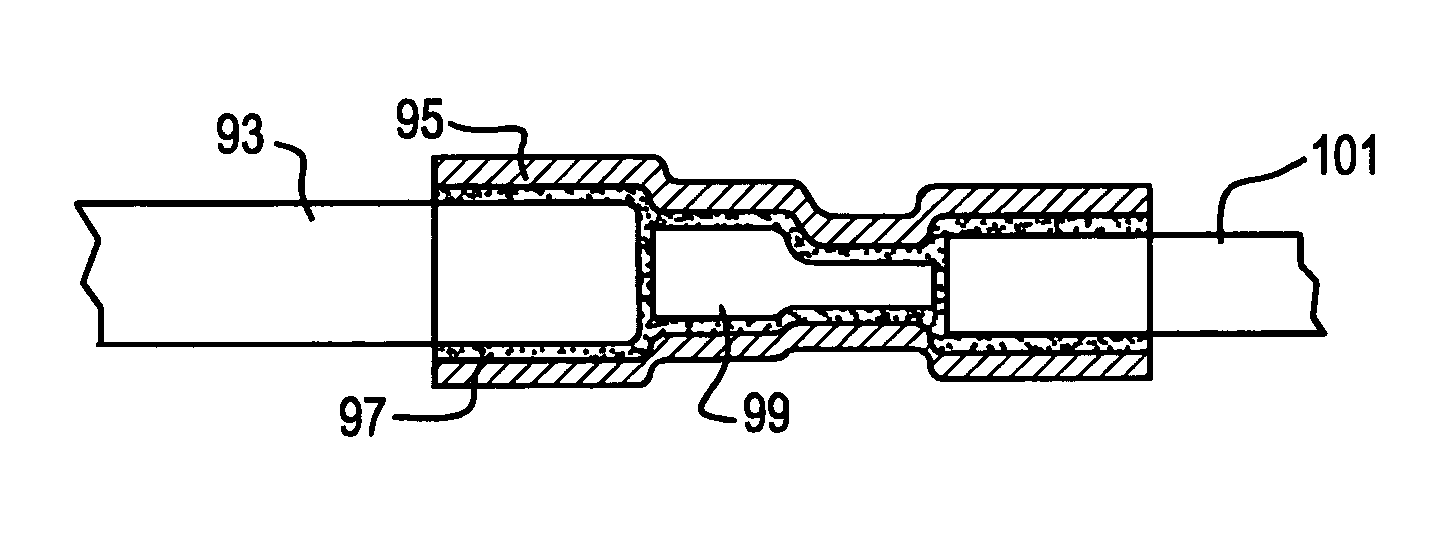
Metal sheathed heater using splice connection assembly with heat shrinkable tubing, and method of use
InactiveUS7230214B2Tougher resistance to cuttingSmall diameterLine/current collector detailsHeater elementsAdhesiveMetal
A metal sheathed heater utilizes splice connections that connects ends of a heater cable with ends of a lead wire. Each splice connection has a connector that connects core wires of the lead wires and heater cable together. Heat shrinkable tubing surrounds the connector and ends of the heater cable and lead wires. An adhesive is interposed between the heat shrinkable tubing and heater cable and lead wire ends to bond with the heat shrinkable tubing and complete the splice connection. The metal sheath of the heater can be formed with an enlarged diameter portion to account for the heat shrinkable tubing surrounding the lead wire and heater cable ends.
Owner:TUTCO
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com