Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
75 results about "Gaussian approximation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
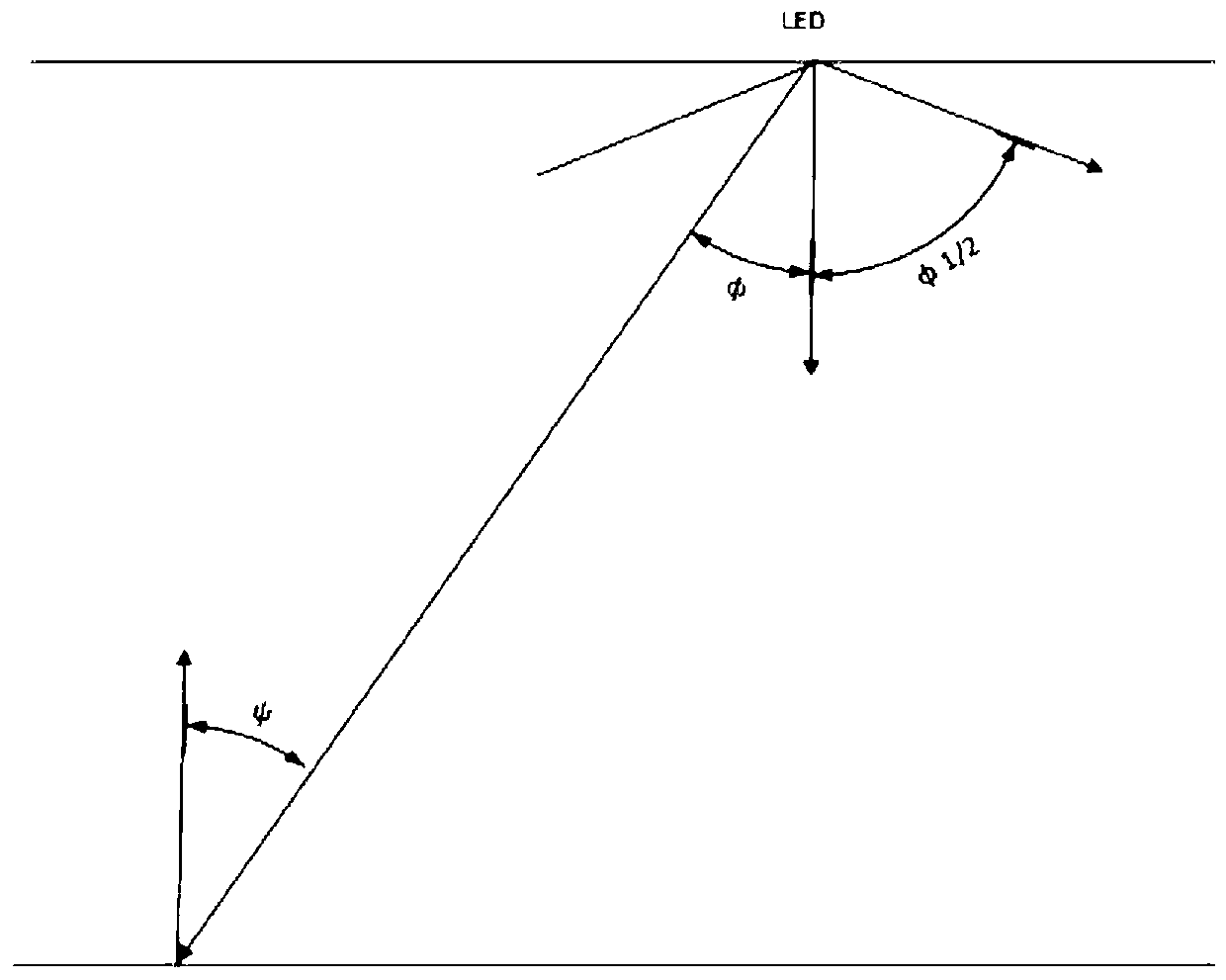
Gaussian approximation is strictly valid only for rays close to the optical axis - paraxial rays - and used to determine their points of convergence. In principle, these points coincide with the points of convergence of a perfect (aberration-free) system.
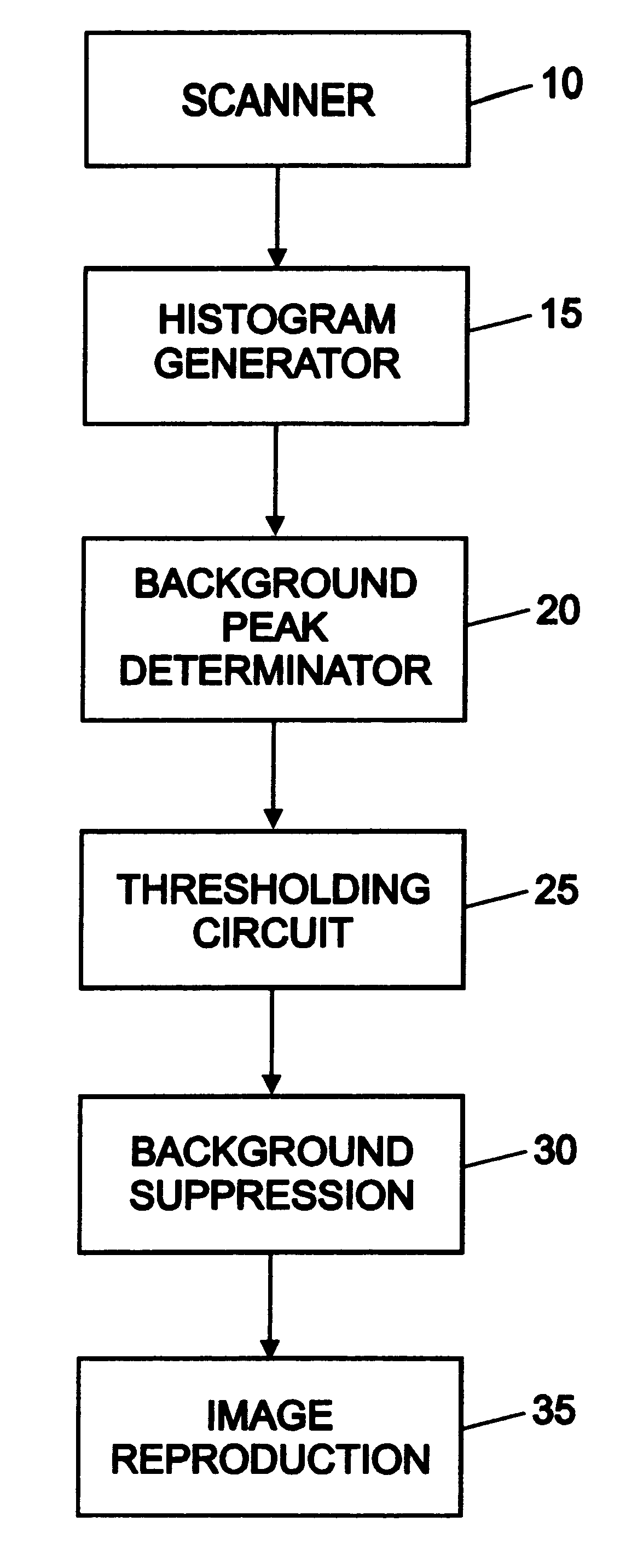
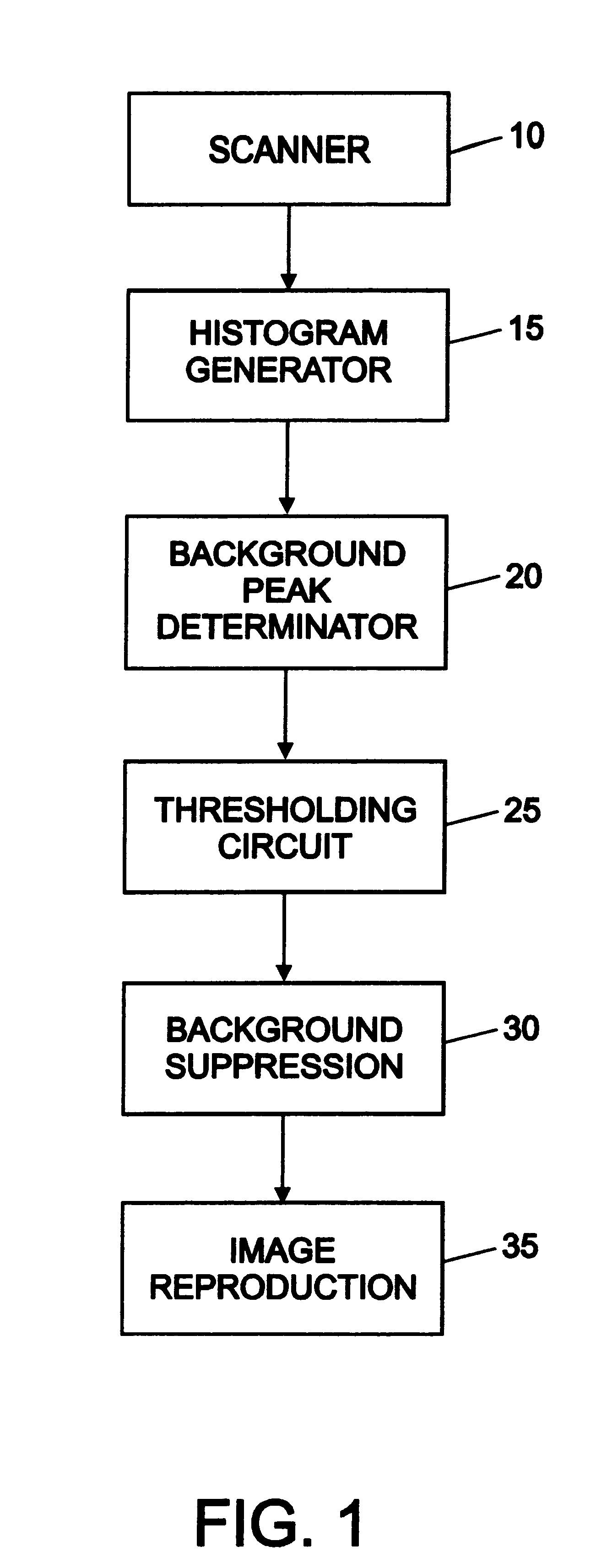
System and method for eliminating background pixels from a scanned image
InactiveUS6222642B1Promote reproductionMore valueImage enhancementDigitally marking record carriersPeak valueHistogram
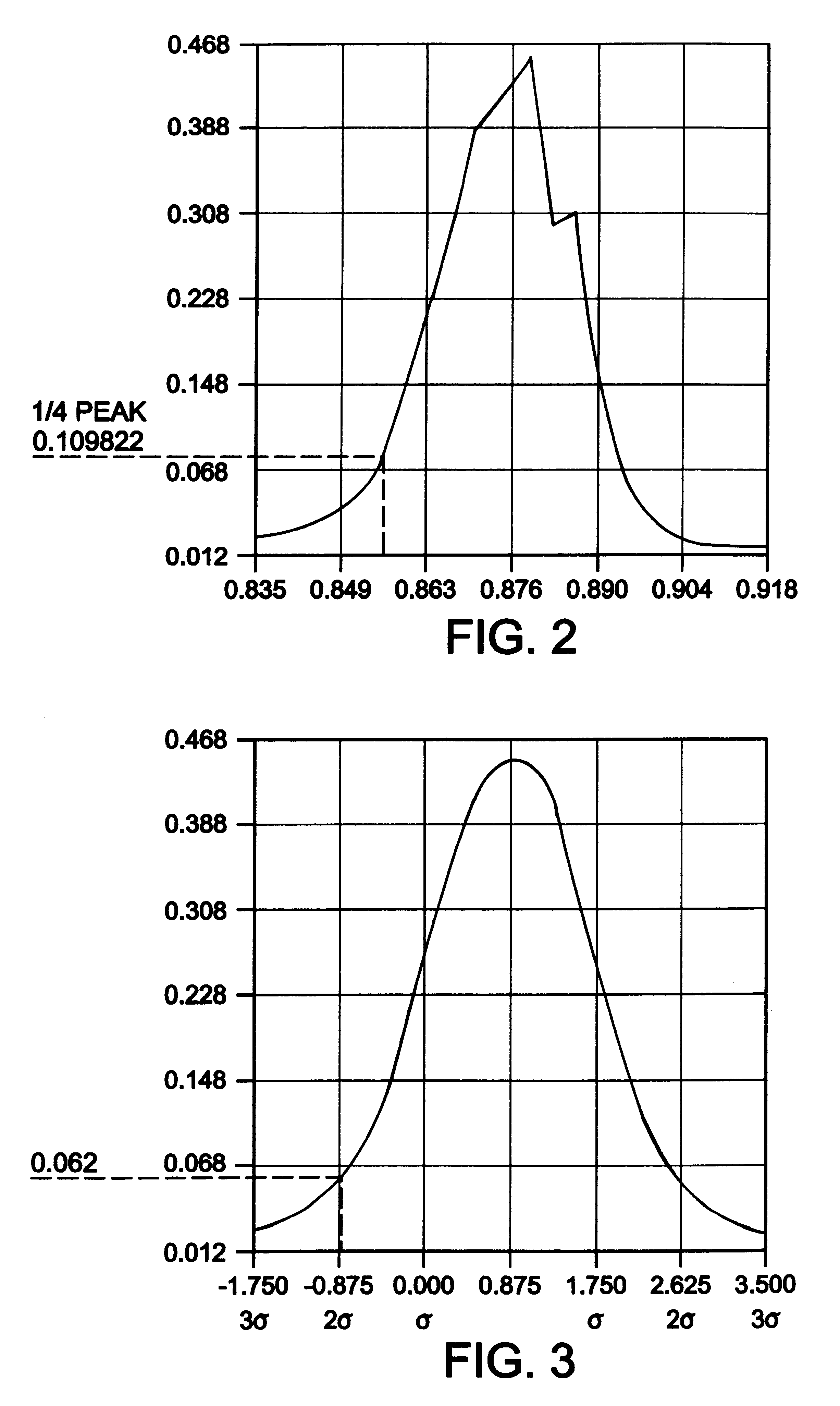
An image desired to be reproduced is scanned to determine its video pixel gray values. A histogram generator generates a histogram distribution representing a frequency of the gray values. The histogram distribution is analyzed to determine a background peak gray value of the image and a standard deviation of the histogram distribution based on a Gaussian approximation. A thresholding circuit dynamically adjusts the background peak value based on the standard deviation and a selected scaling factor to generate a background threshold value. The background threshold value expands a range of background gray values in the image which are eliminated during image reproduction. Eliminating substantially all background gray values improves the quality of the reproduced image.
Owner:XEROX CORP
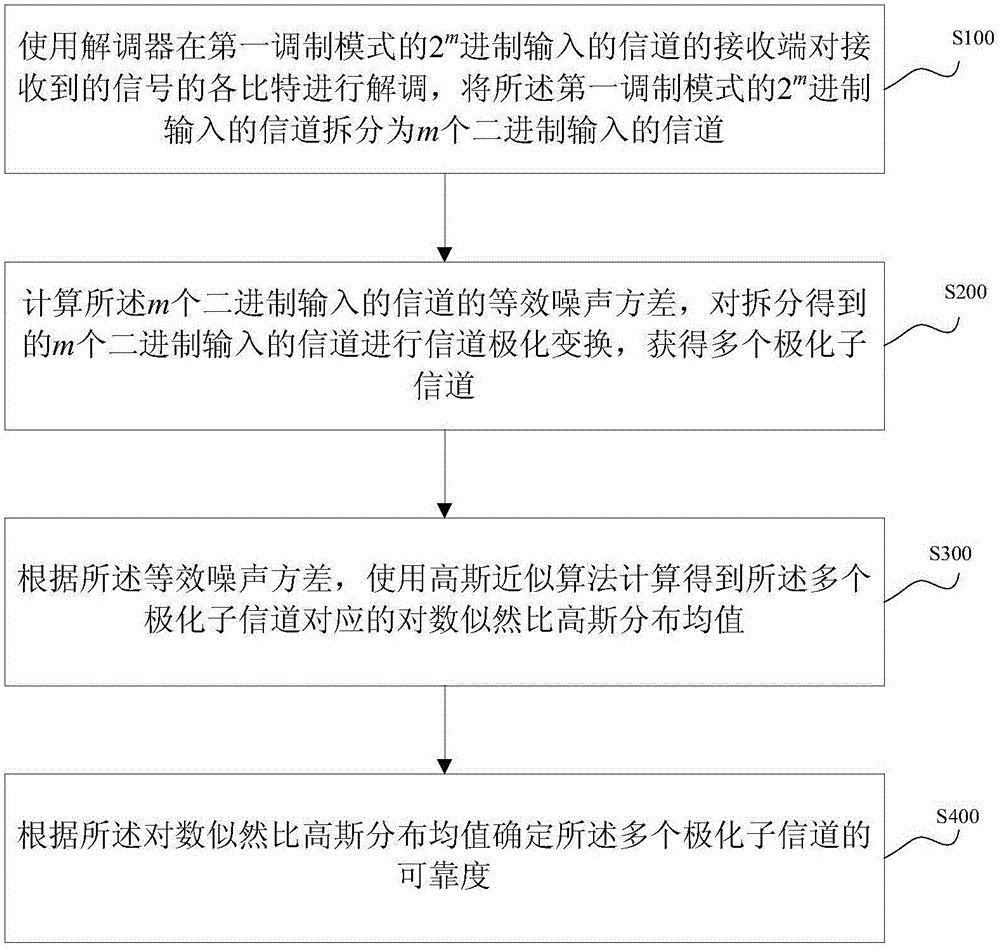
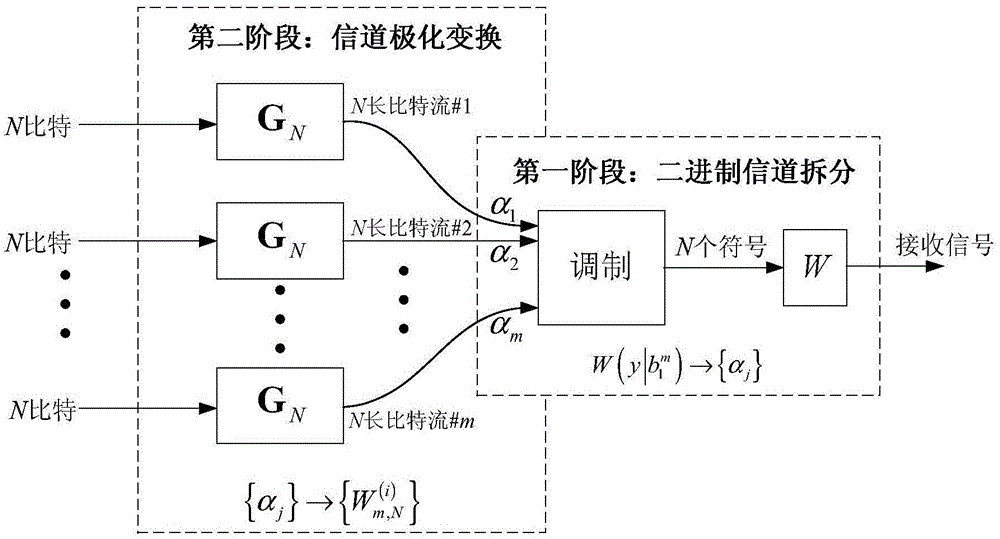
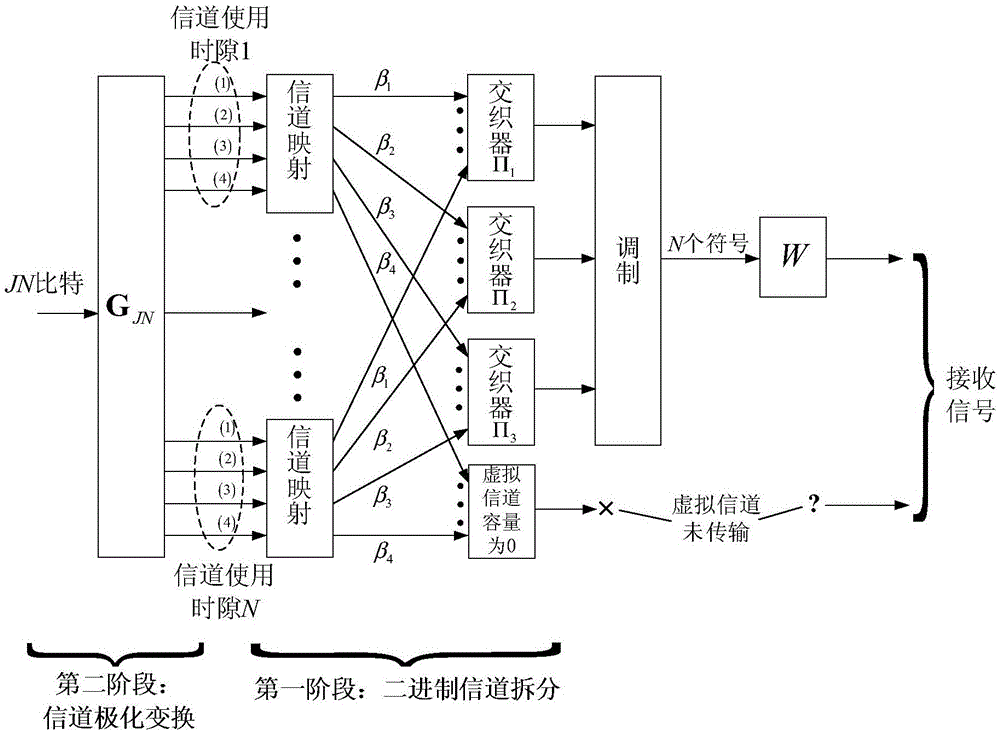
Method and device for determining channel reliability in polarization coding modulation
ActiveCN105099622AAvoid the problem of computational complexityReduce complexityChecking code calculationsChannel coding adaptationComputation complexityChannel polarization
Embodiments of the invention provide a method and device for determining channel reliability in polarization coding modulation. The method comprises: dividing a channel into m binary input channels, carrying out channel polarization transformation, and using a Gaussian approximation algorithm to calculate a log likelihood ratio Gaussian distribution mean corresponding to the polarization sub-channels according to the equivalent noise variance of the binary input channels obtained by splitting, so as to determine the reliability of the polarization sub-channels. Since the method provided by the invention adopts the Gaussian approximation algorithm, the problem of calculation complexity caused by calculating the channel reliability by using a density evolution tool is avoided. Compared with the scheme of calculating the channel reliability by using the density evolution tool, the calculation complexity of the method provided by the invention is obviously reduced.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
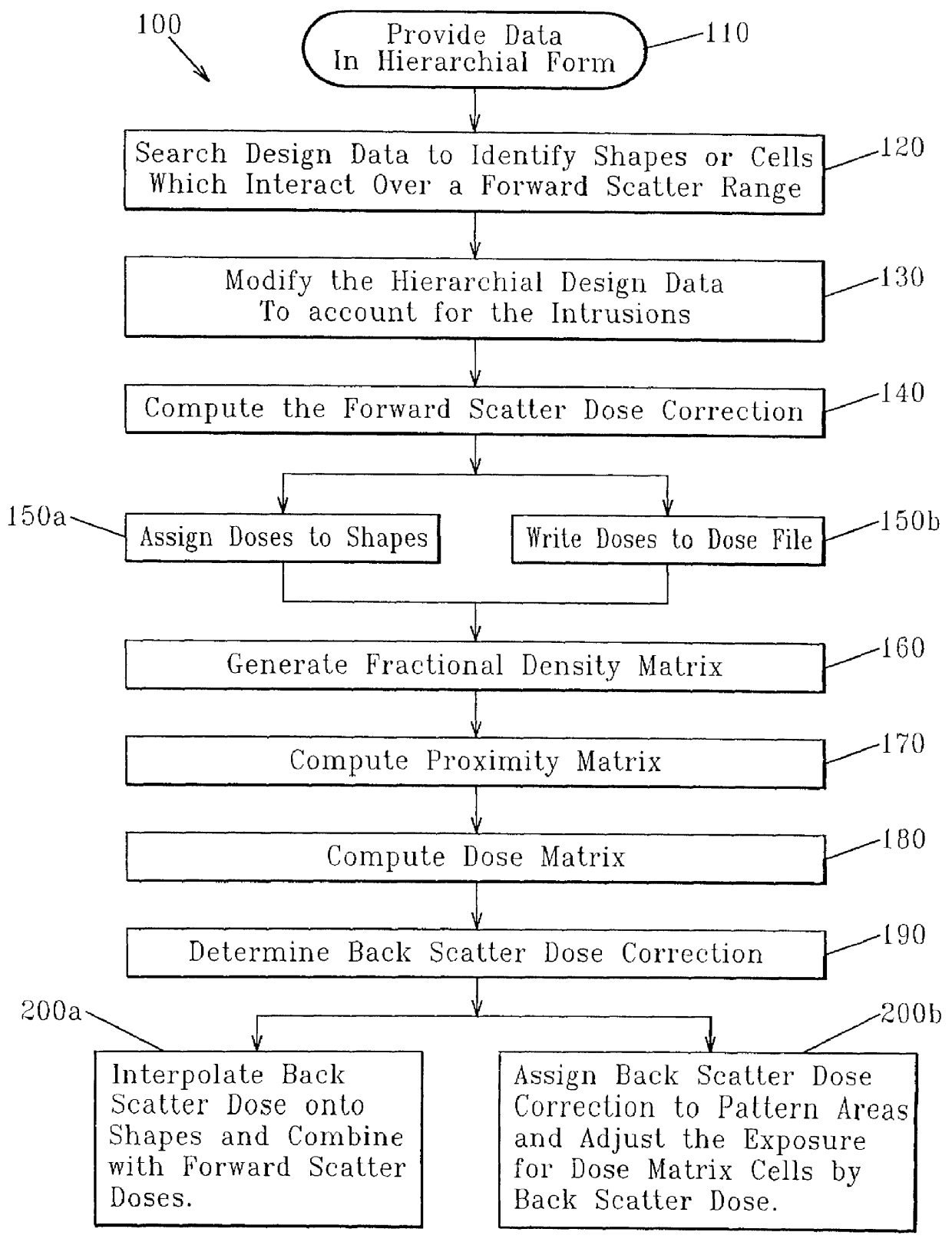
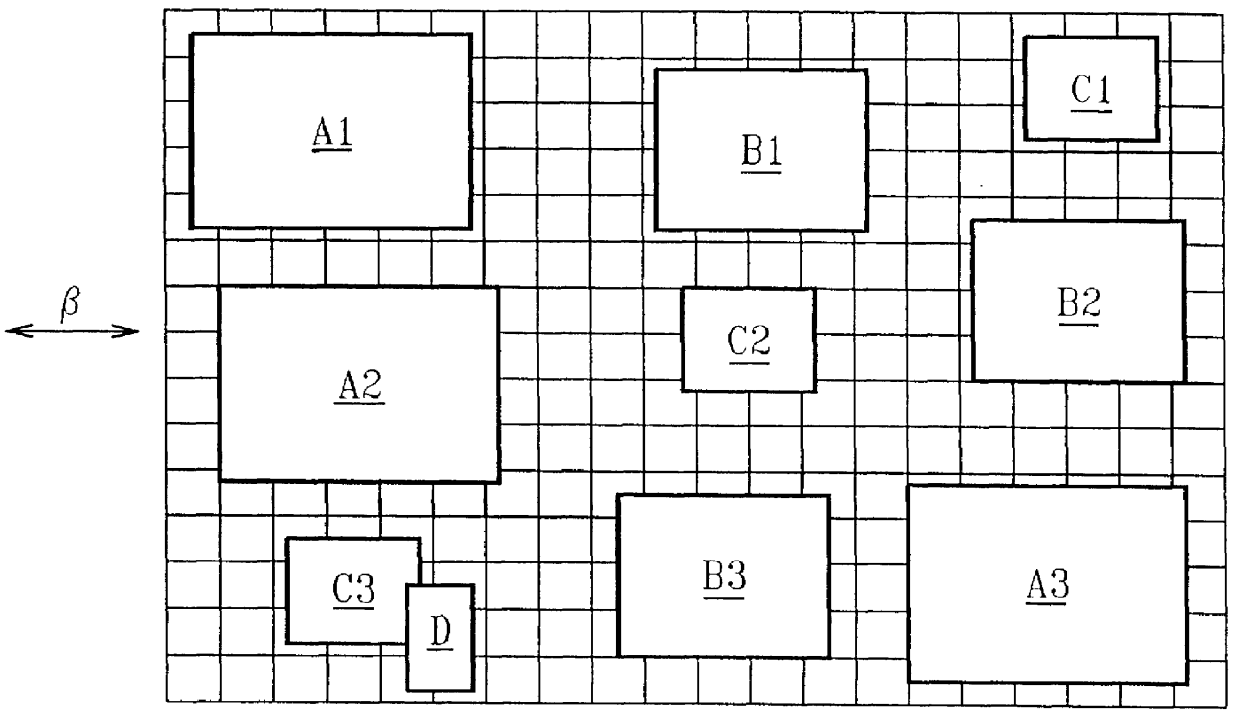
Electron beam proximity correction method for hierarchical design data
InactiveUS6035113AReduce proximity effectImprove computing efficiencyElectric discharge tubesSpecial data processing applicationsForward scatterResist
A method for formulating an exposure dose for an electron beam on a resist film for a pattern of geometric shapes which compensates for electron scattering effects utilizing hierarchial design data which is preserved to as great as an extent as possible in the computation of the exposure dose. The exposure dose is corrected for both the forward scatter and backscatter effects of the electron beam in which the design data is modified for interactions of shapes which are affected only over the forward scatter range. In another version of the method, a multiple Gaussian approximation is used where the short term Gaussian terms are treated as the forward scatter terms and the long term Gaussian terms are treated as the back scatter terms.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
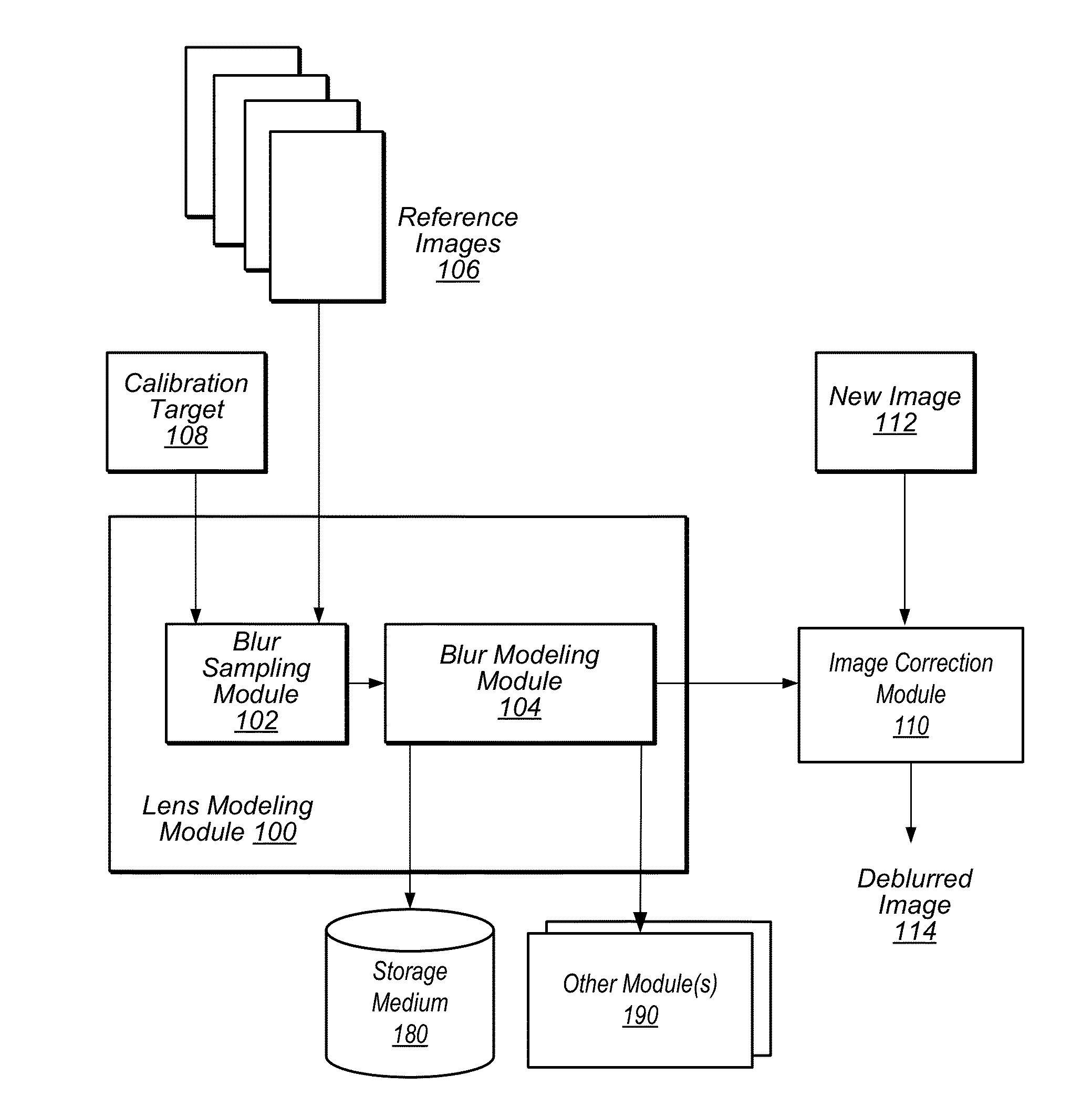
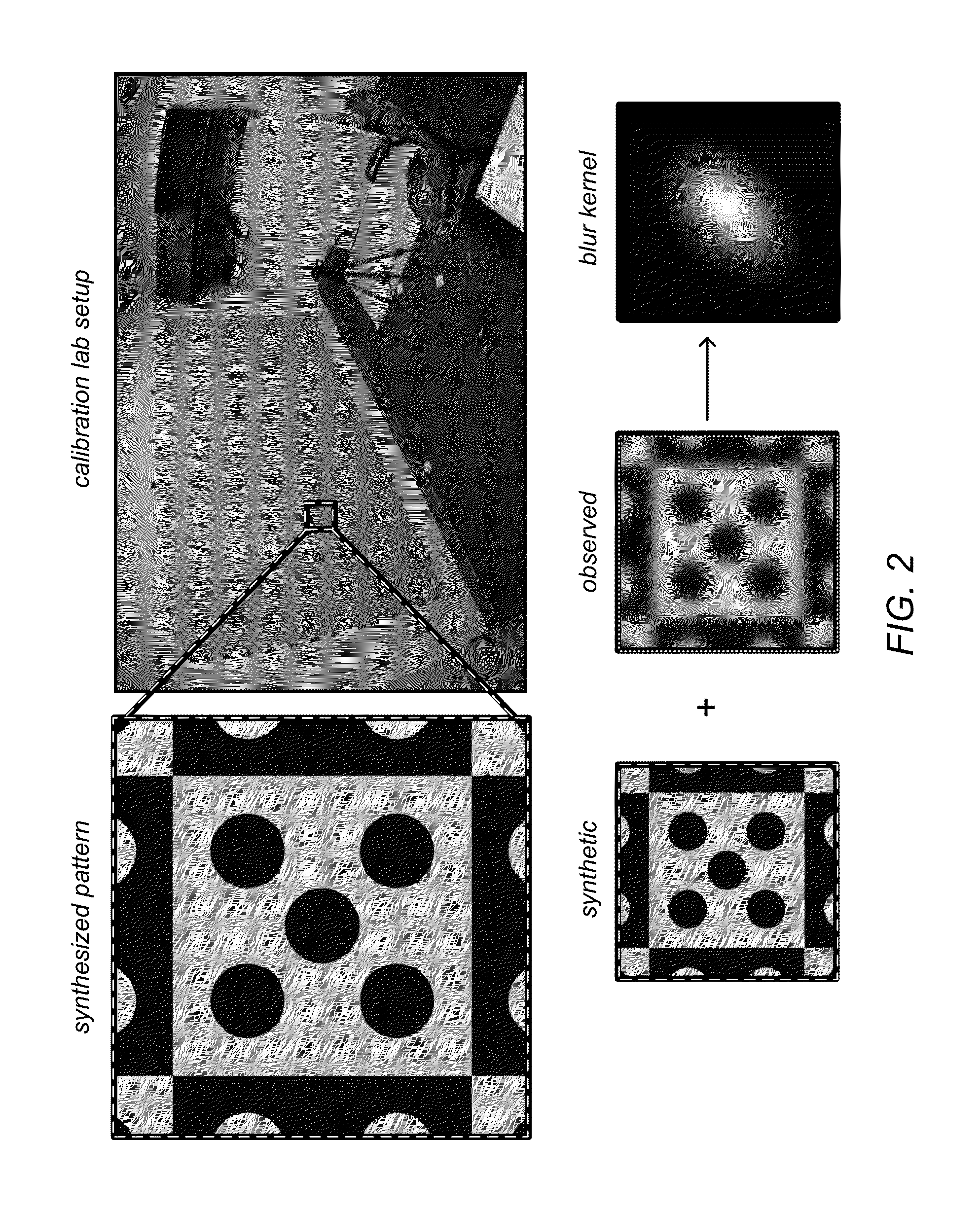
Lens Modeling
ActiveUS20130132044A1Save computing resourcesComputation using non-denominational number representationOptical partsReference imageImage field
Techniques are disclosed relating to lens modeling. In one embodiment, a lens model may be generated based on reference images of a pre-determined, known geometric pattern. The lens model may represent a spatially variant blur pattern across the image field of the lens used to capture the reference images. In one embodiment, the lens model may include Gaussian approximations of the blur that may minimize the difference between a location within a reference image and a corresponding location of a pre-determined, known geometric pattern. In one embodiment, the generated lens model may be applied to deblur a new image.
Owner:ADOBE SYST INC
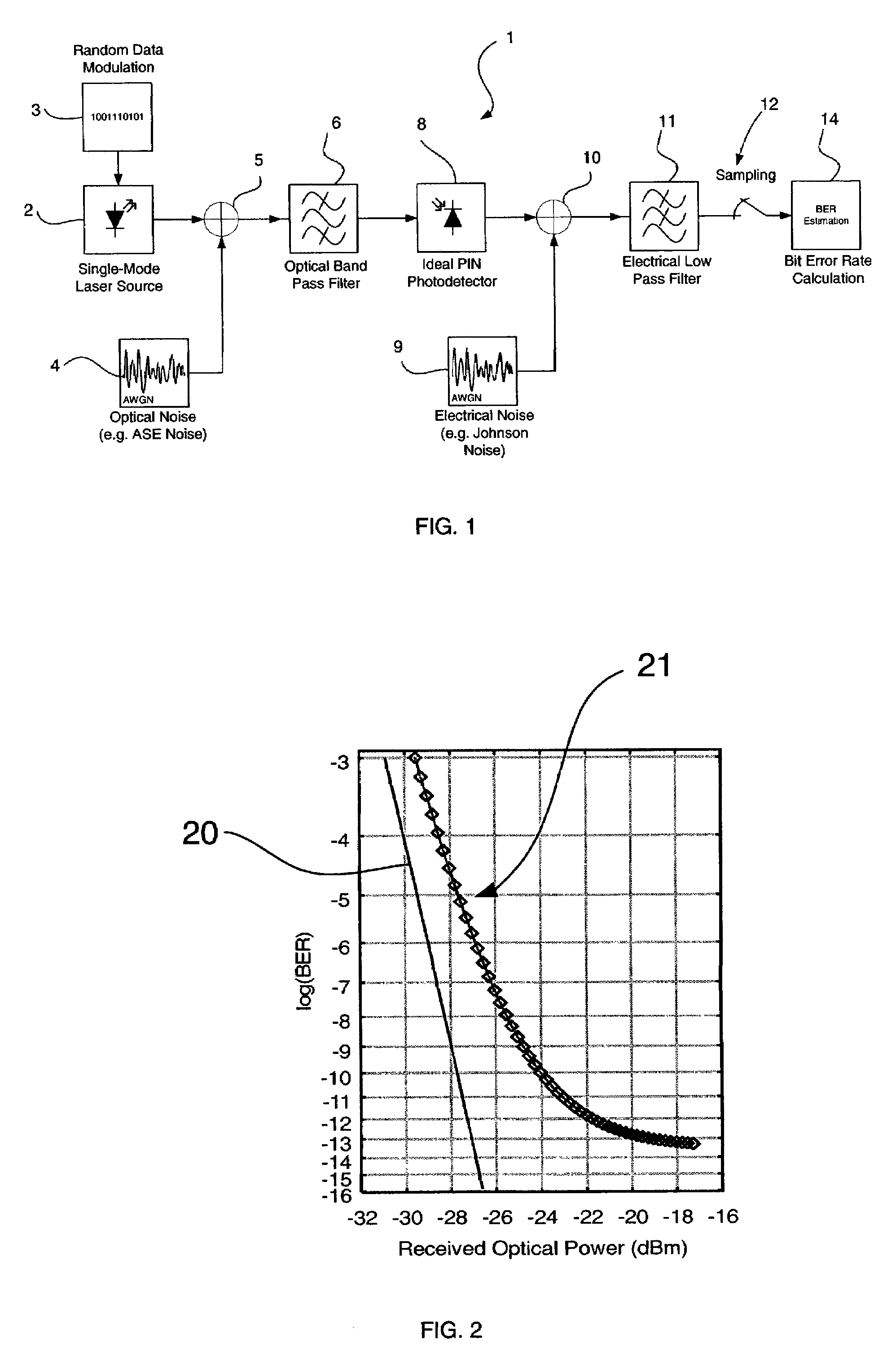
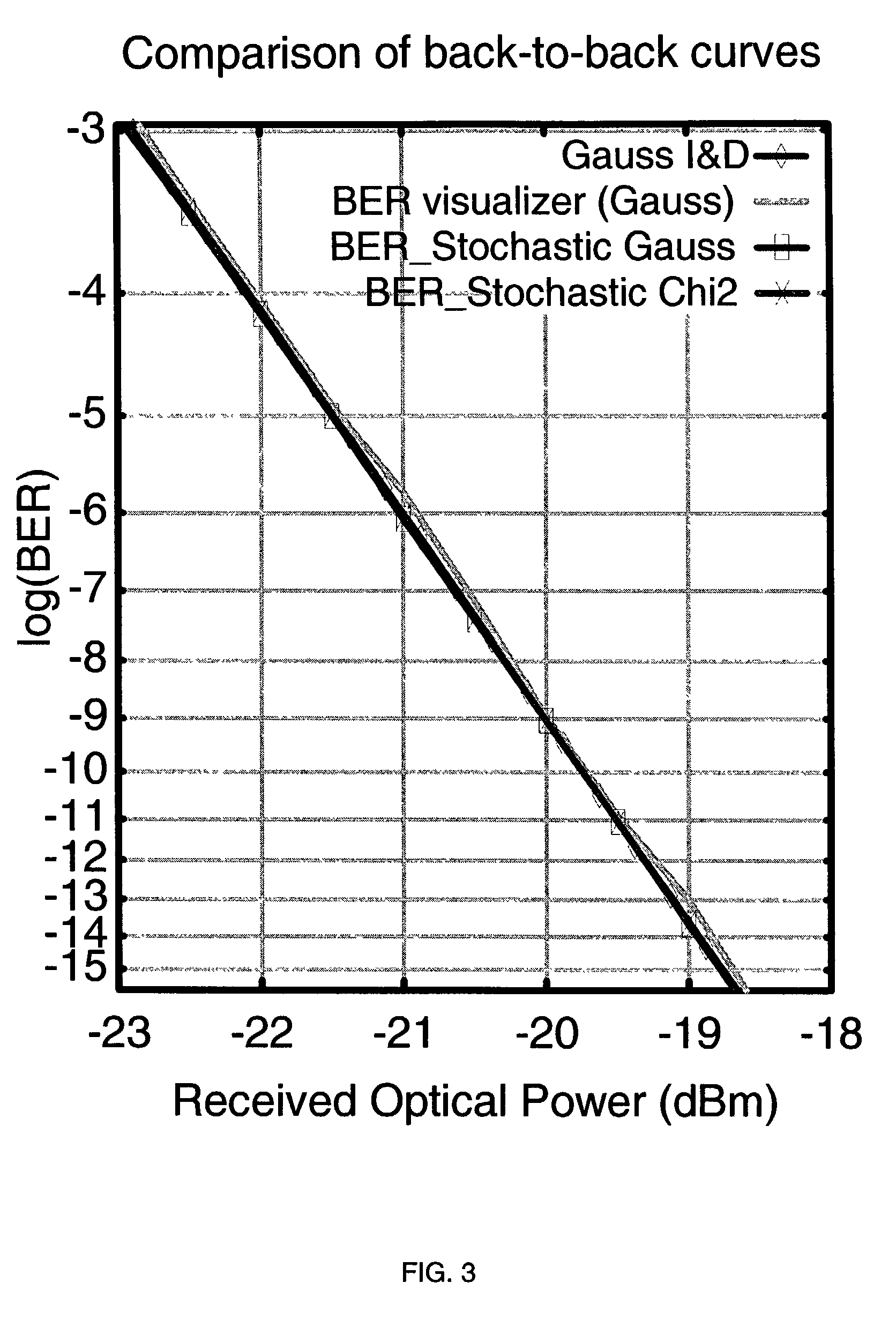
Optical error simulation system
ActiveUS7233962B2Accurate estimateShorten the construction periodTransmission monitoringPicture interpretationCommunications systemOptical communication
There is disclosed a method and computer program product for estimating a measure of the quality of the received signal in a computer simulation of an optical transmission system, wherein the simulation includes additive optical noise generated by components within the transmission system. The method and product are able to account for non-Gaussian statistics of noise fluctuations observed in the receivers of optical communications systems, in order to provide for the more accurate simulation of system performance than may be the case using prior art methods based on Gaussian approximation.
Owner:ASTORIA CONSULTANCY LTD
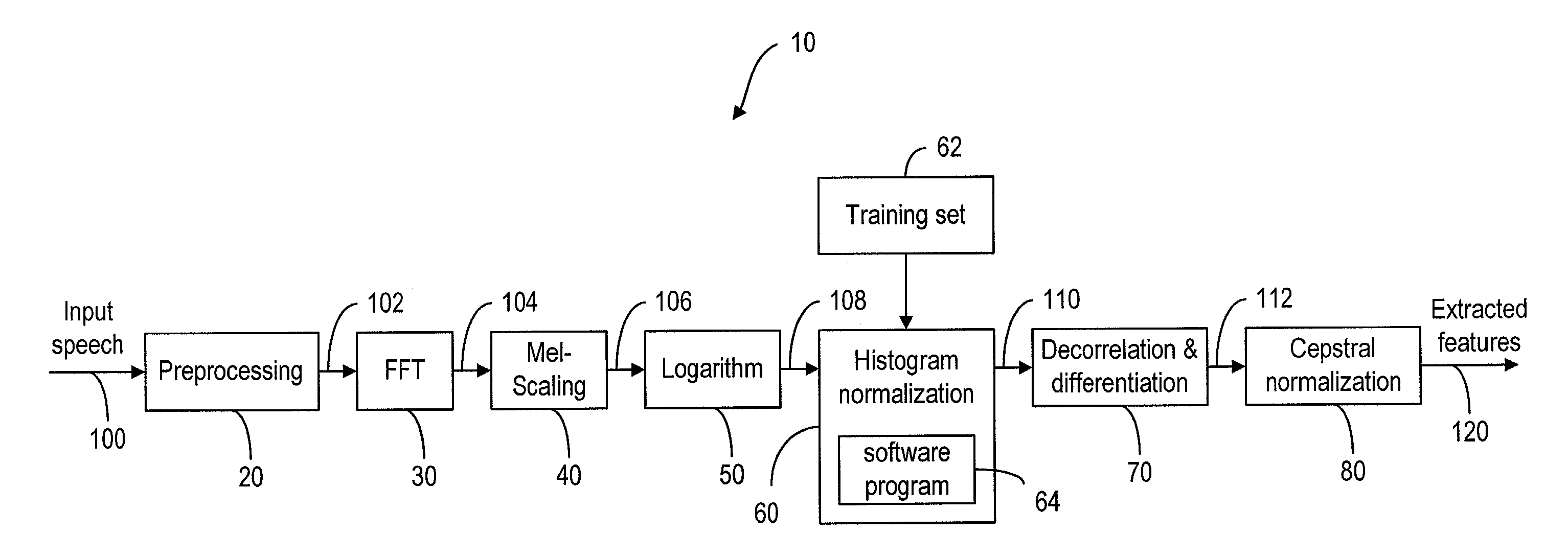
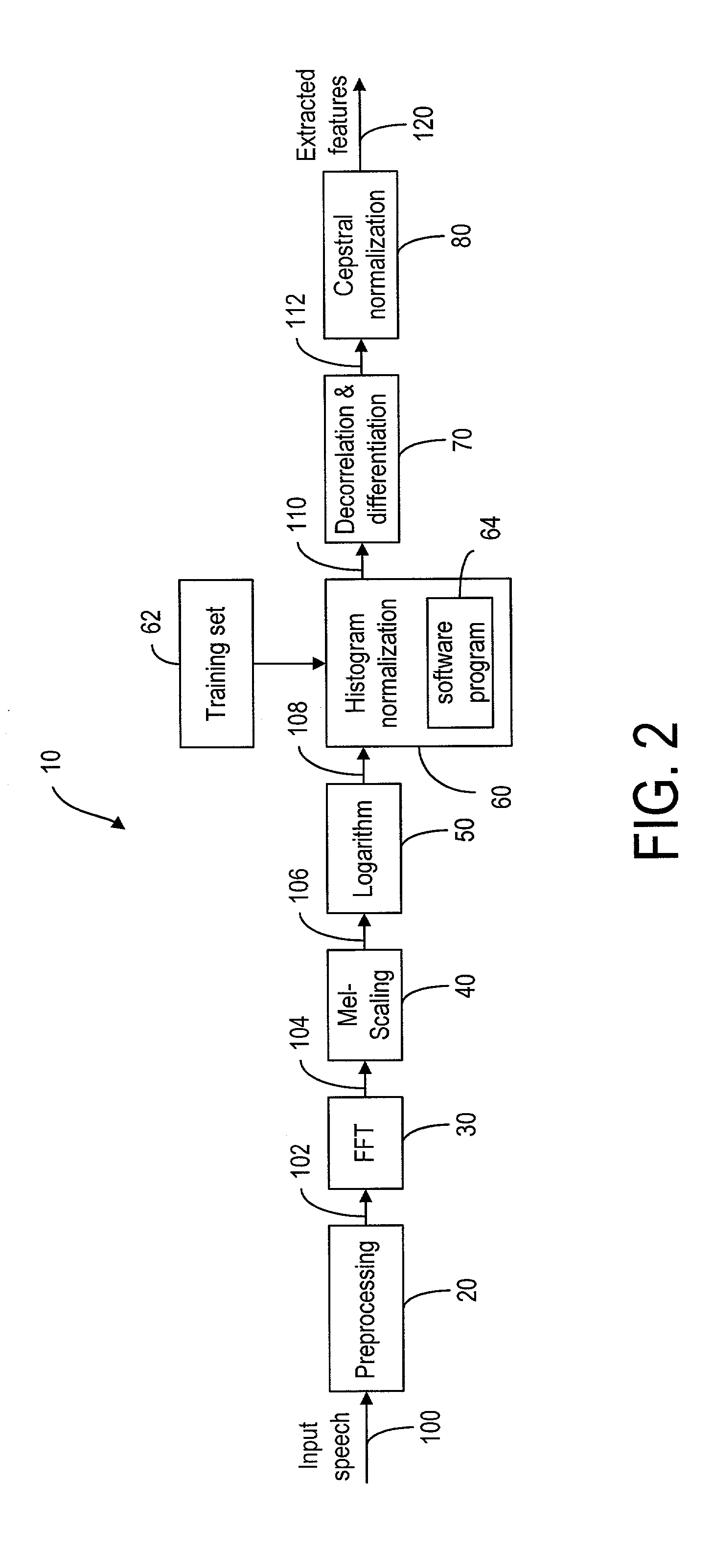
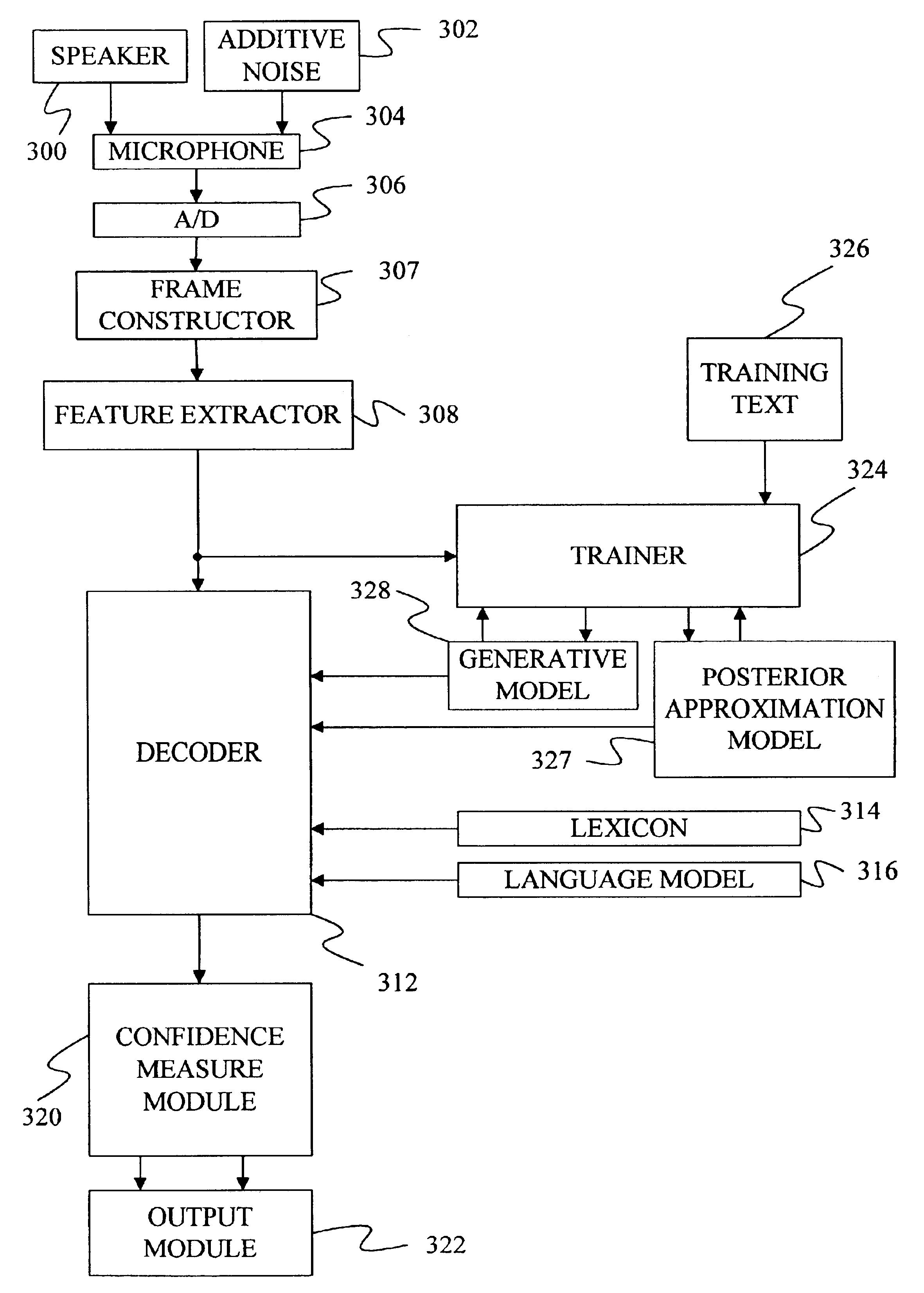
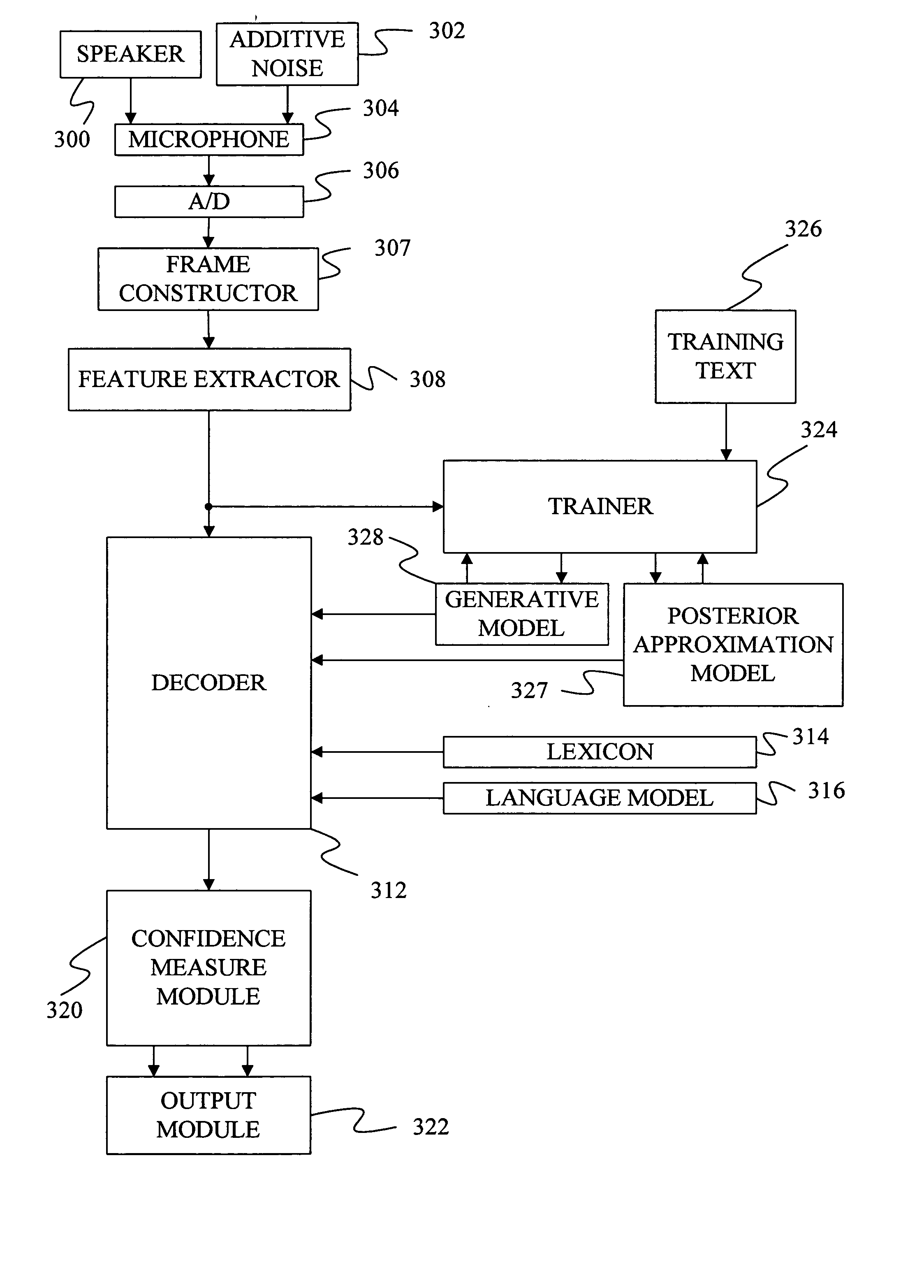
On-line parametric histogram normalization for noise robust speech recognition
A method for improving noise robustness in speech recognition, wherein a front-end is used for extracting speech feature from an input speech and for providing a plurality of scaled spectral coefficients. The histogram of the scaled spectral coefficients is normalized to the histogram of a training set using Gaussian approximations. The normalized spectral coefficients are then converted into a set of cepstrum coefficients by a decorrelation module and further subjected to ceptral domain feature-vector normalization.
Owner:RPX CORP
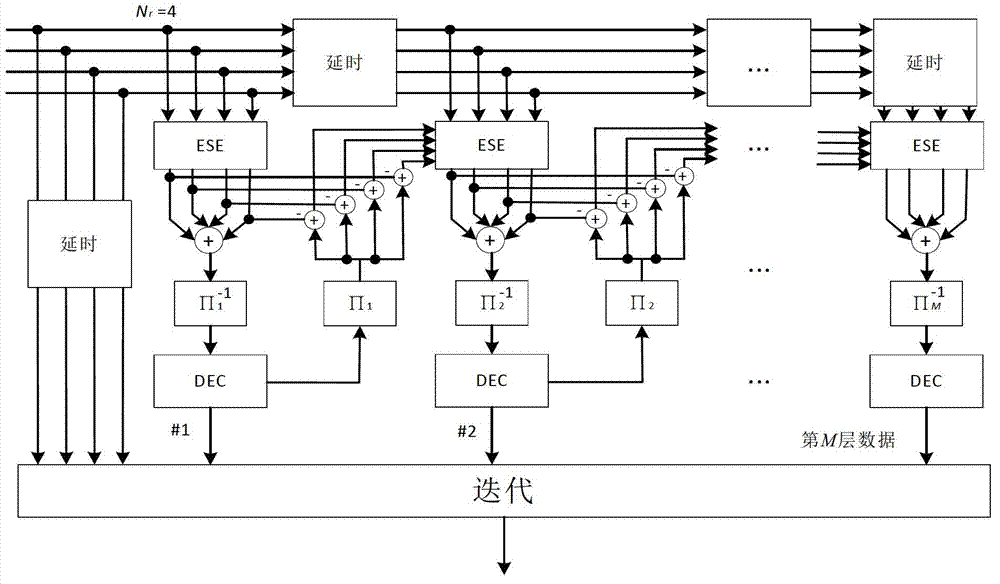
Methods and apparatus for iterative decoding in multiple-input-multiple-output (mimo) communication systems
InactiveCN102835055AModulated-carrier systemsTransmitter/receiver shaping networksRound complexityCommunications system
Methods and apparatus for receiving, processing, and decoding MIMO transmissions in communications systems are described. A non-Gaussian approximation method for simplifying processing complexity where summations are used is described. Use of a priori information to facilitate determination of log likelihood ratios (LLRs) in receivers using iterative decoders is further described. A Gaussian or non-Gaussian approximation method using a priori information may be used to determine a K-best list of values for summation to generate an LLR is also described.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Method of speech recognition using variational inference with switching state space models
InactiveUS6931374B2Fatty/oily/floating substances removal devicesSedimentation separationState spaceSpeech identification
A method is developed which includes 1) defining a switching state space model for a continuous valued hidden production-related parameter and the observed speech acoustics, and 2) approximating a posterior probability that provides the likelihood of a sequence of the hidden production-related parameters and a sequence of speech units based on a sequence of observed input values. In approximating the posterior probability, the boundaries of the speech units are not fixed but are optimally determined. Under one embodiment, a mixture of Gaussian approximation is used. In another embodiment, an HMM posterior approximation is used.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
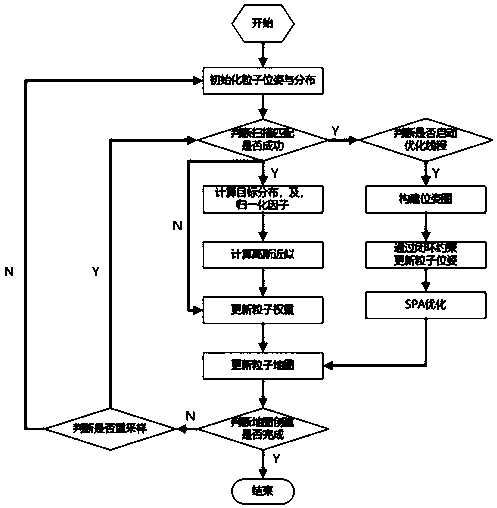
Gmapping mapping method of mobile robot based on sparse pose adjustment
ActiveCN111427370ANavigational calculation instrumentsElectromagnetic wave reradiationTarget distributionMobile robot
The invention relates to the field of robots, and particularly provides a Gmapping mapping method of a mobile robot based on sparse pose adjustment, which comprises the following steps of S1, initializing particle poses and distribution, S2, scanning and matching, S3, calculating target distribution of sampling positions, S4, calculating Gaussian approximation, S5, updating the weight of the ith particle, and S6, updating the particle map. S3'pose map construction and S4' closed-loop constraint are implemented simultaneously with S3 and S4. According to the method, the technical problems of fuzzy boundaries, missing and slippage of an original Gmapping algorithm under the condition of few particles are solved, the construction precision is high, the boundaries are clear and complete, and the stability is good.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CIVIL ENG & ARCHITECTURE
Sparse code multiple access detection method with low complexity
InactiveCN106130688AThe effective degree d is reducedReduce complexityForward error control useComputation complexityRound complexity
The invention discloses a sparse code multiple access detection method with low complexity and belongs to the field of signal detection of a wireless communication system. Classification is carried out by utilizing channel coefficient module values of the adjacent edges, namely the edge and the edge with the larger module value in the adjacent edges of the edge are selected to be in the same class to participate in information updating; other edges with the smaller module values are classified to the same class and are approximate to noise by utilizing a Gaussian approximation principle. According to the classification, an original sparse factor graph becomes a dynamic and sparser factor graph. Meanwhile, each iteration process utilizes mean and variance of the approximate noise in the last iteration process to carry out information feedback in order to make up for the information loss caused by the edge which does not participate in the information updating process. In comparison with the computation complexity in the background technology, the computation complexity is reduced in an exponential form under the condition of little BER performance loss. The result proves that the computation complexity and the BER performance are well balanced.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
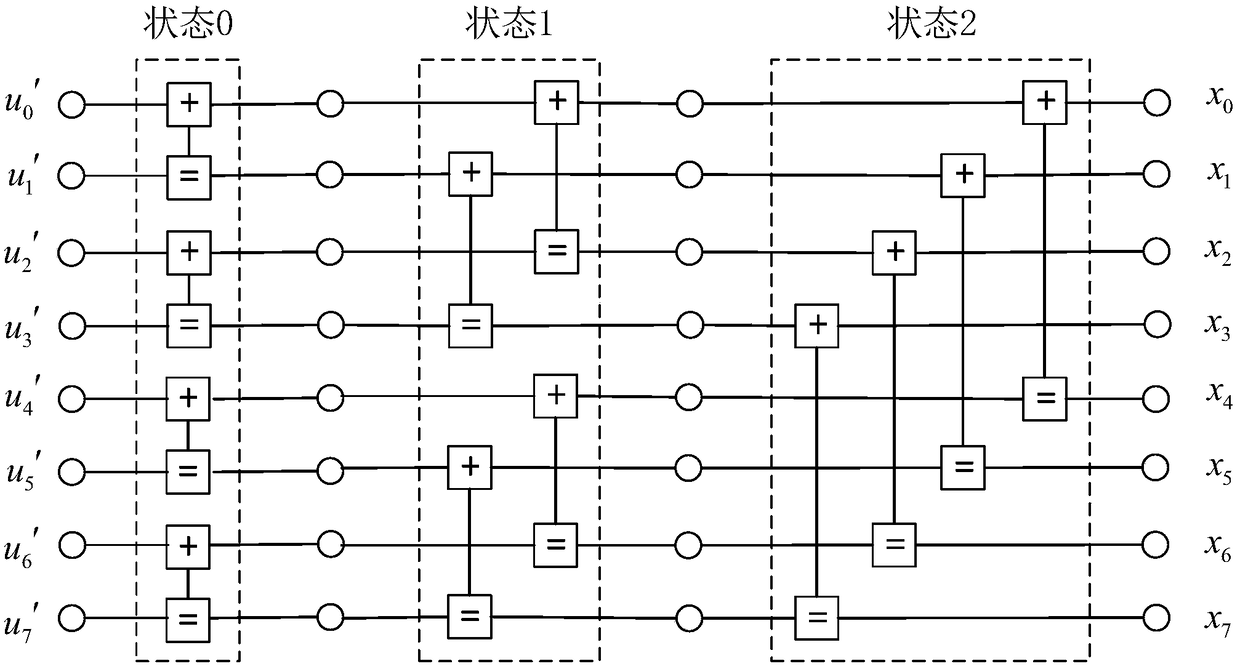
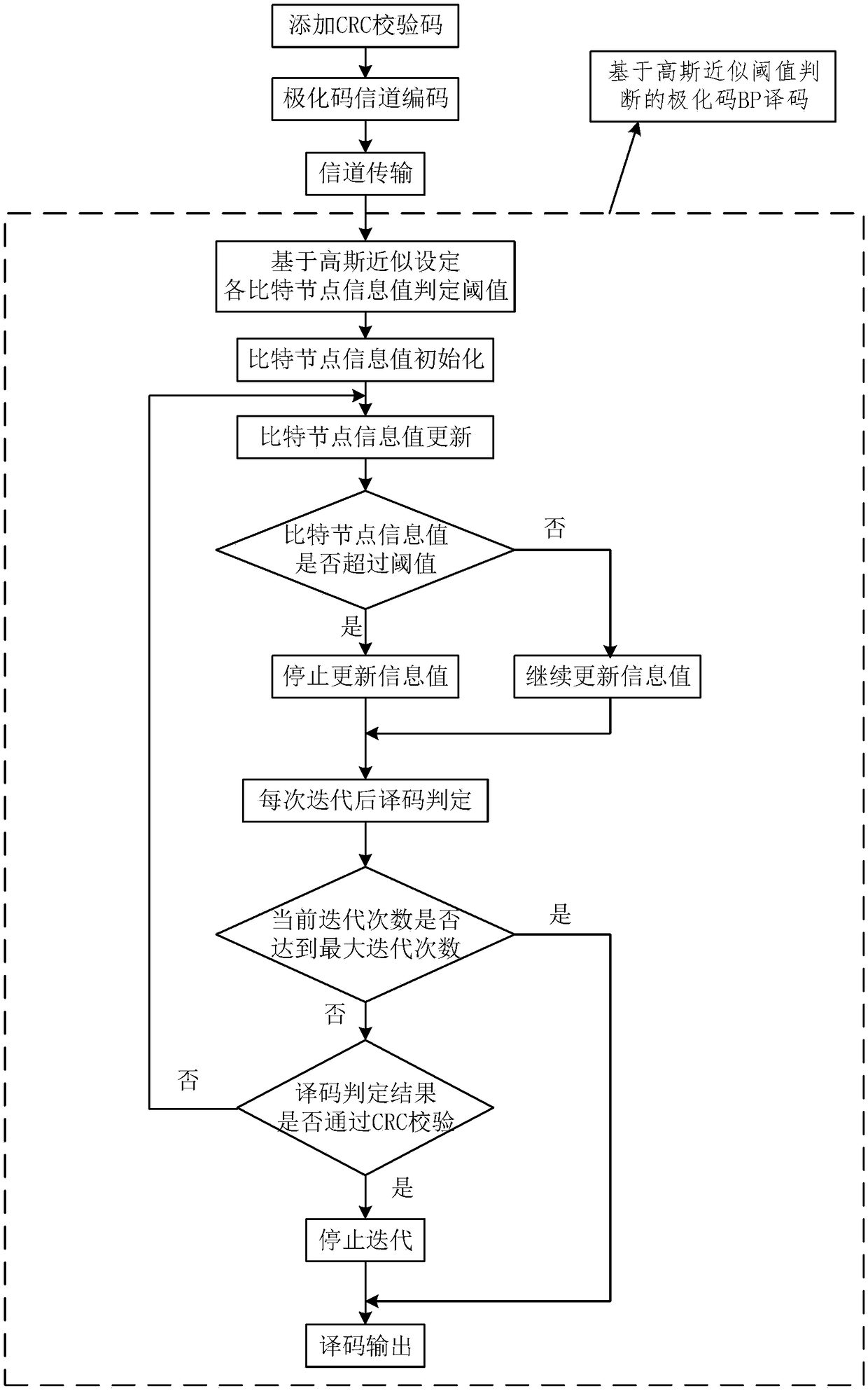
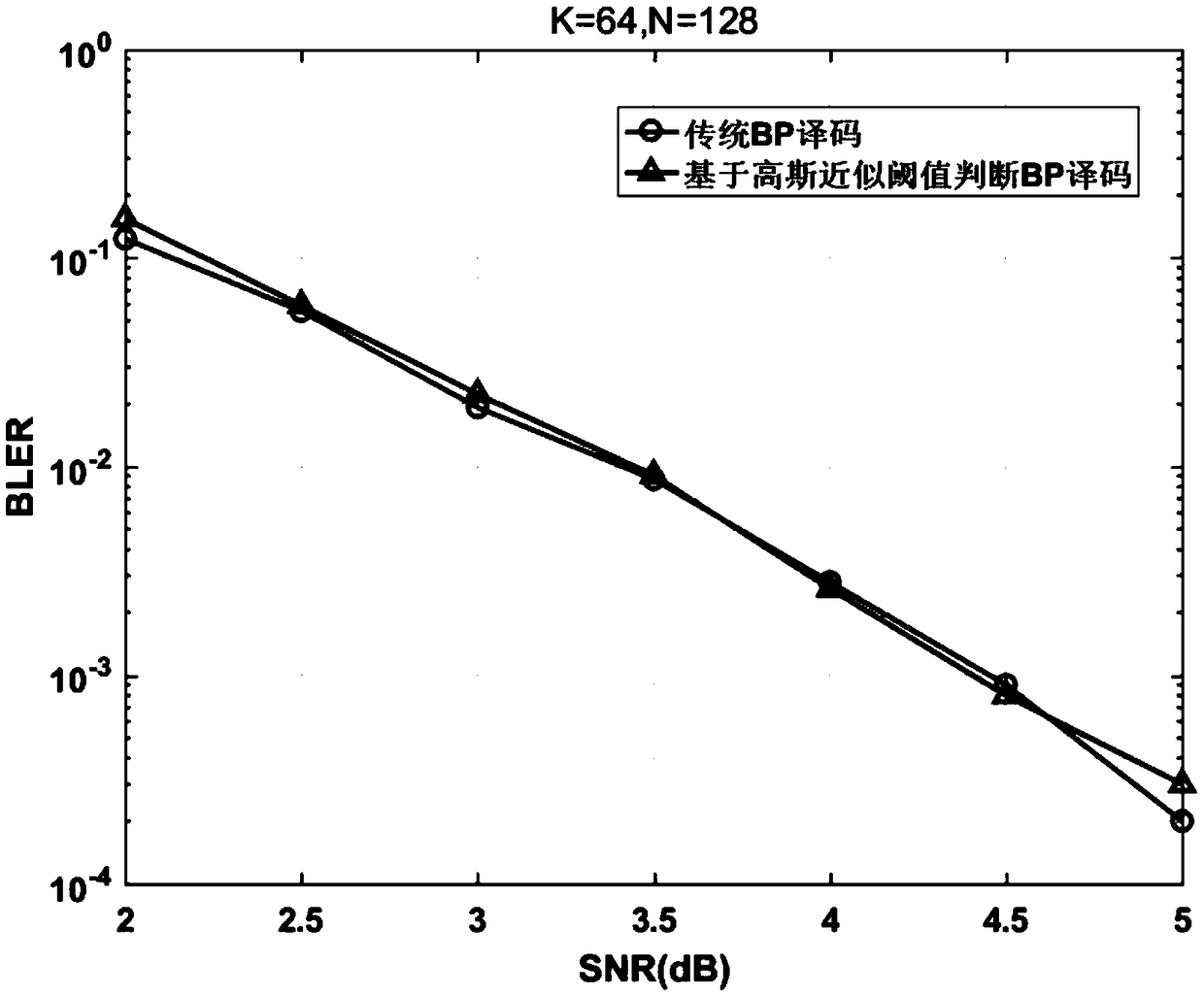
Polarization code BP decoding method based on Gaussian approximation threshold judgment
ActiveCN109257148AImprove reliabilityReduce computational complexityError preventionError correction/detection using multiple parity bitsDecoding methodsComputation complexity
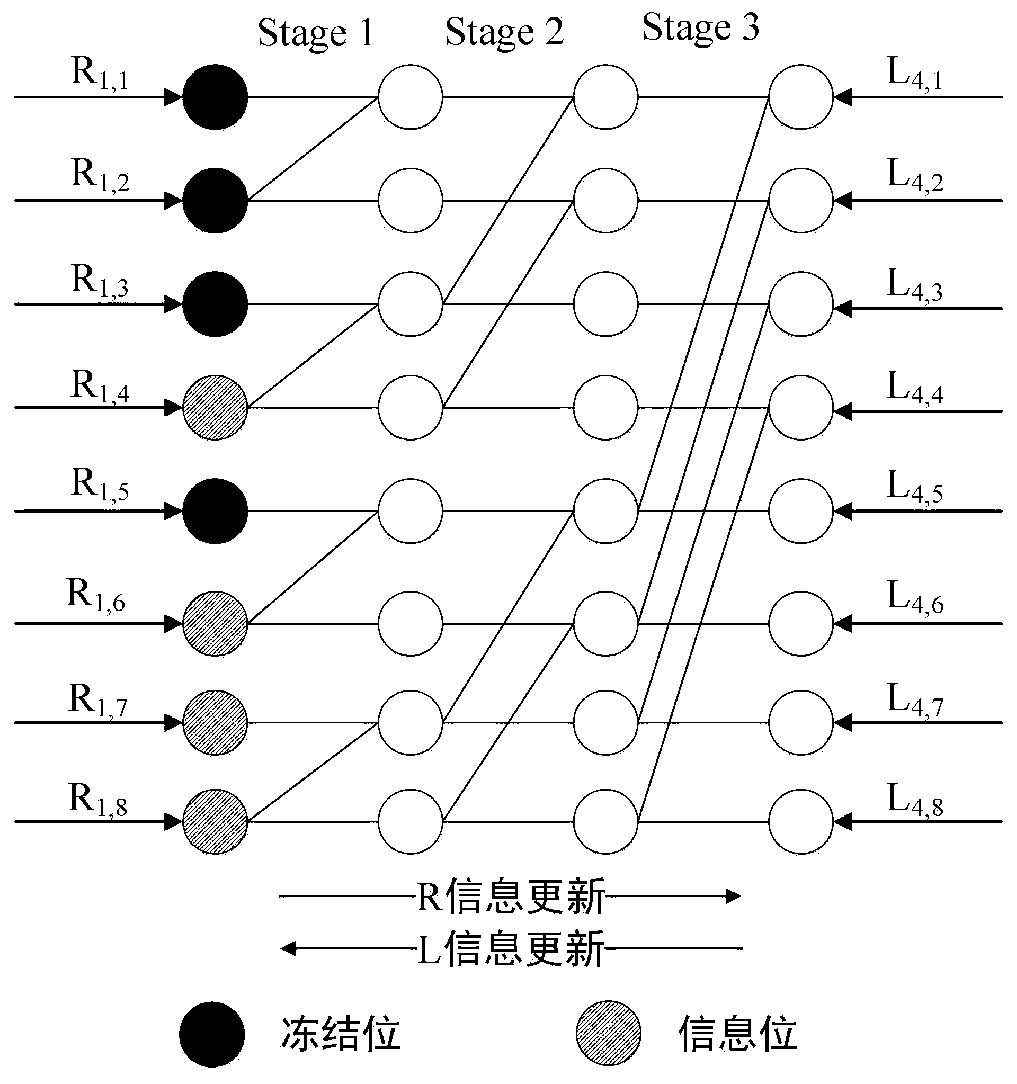
The invention relates to a polarization code BP decoding method based on Gaussian approximation threshold judgment, belonging to the technical field of channel coding and decoding. The invention addsa CRC checking module in the transmission process, and sets the information value judgment threshold value for each bit node at the receiving end according to the Gaussian approximation principle. Ineach iteration process, by comparing the information value of each bit node with the corresponding decision threshold, the bit nodes exceeding the threshold are selected step by step and the update isstopped, and the information value of the bit nodes not exceeding the threshold is updated continuously. At that end of each iteration, the decode result is judged and CRC check is carry out, if thecheck is passed, the iteration is stopped;otherwise, the iteration is continued until the maximum iteration numb is reached. On the basis of guaranteeing the decoding performance, the invention reduces the calculation complexity of the decoding and saves the calculation resources.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Method and apparatus for generating check matrix
InactiveUS7272770B2Error correction/detection using multiple parity bitsCode conversionEssential matrixTheoretical computer science
A method of generating a check matrix for an LDPC code includes determining a coding rate, generating a basic matrix that satisfies predetermined conditions, determining a number of columns of a check matrix, substituting rows of the basic matrix based on a specific relational equation, provisionally searching an ensemble of weights by executing Gaussian approximation, deleting rows of the basic matrix after the permutation in order from the bottom by considering the number of rows after a division, searching an optimal ensemble of weights by executing Gaussian approximation based on a predetermined condition after row deletion, and dividing at random the weights of the basic matrix after the row deletion based on the optimal ensemble.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
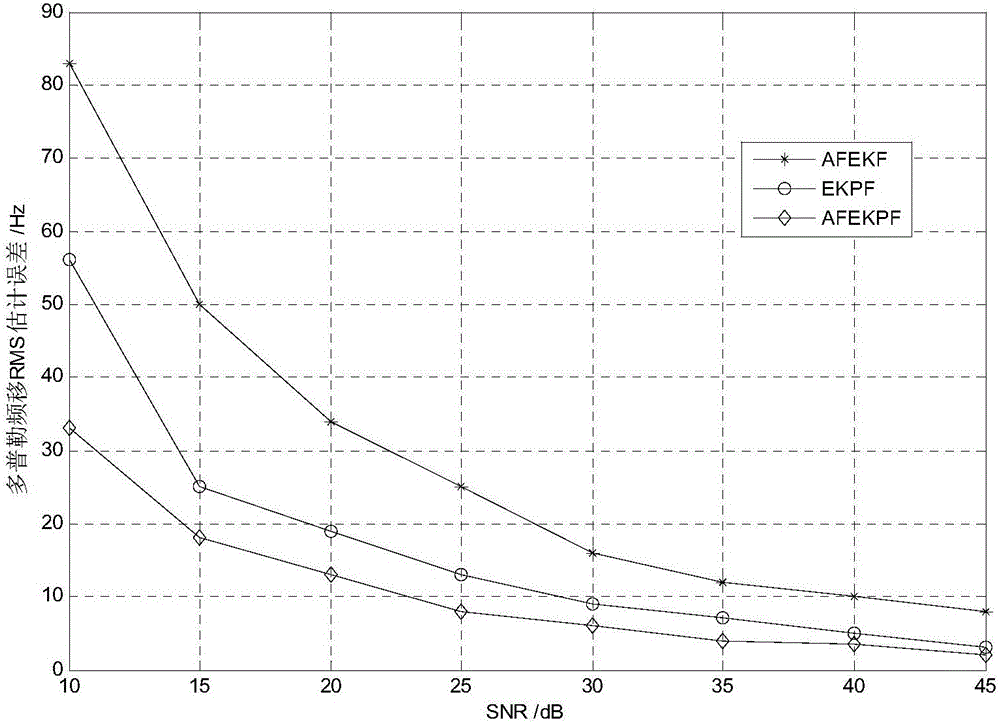
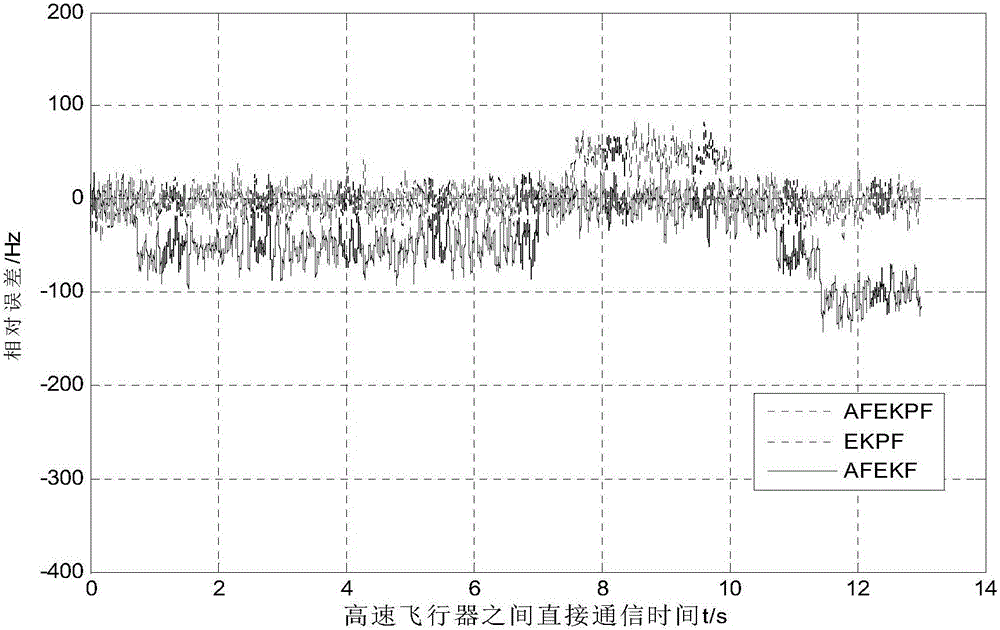
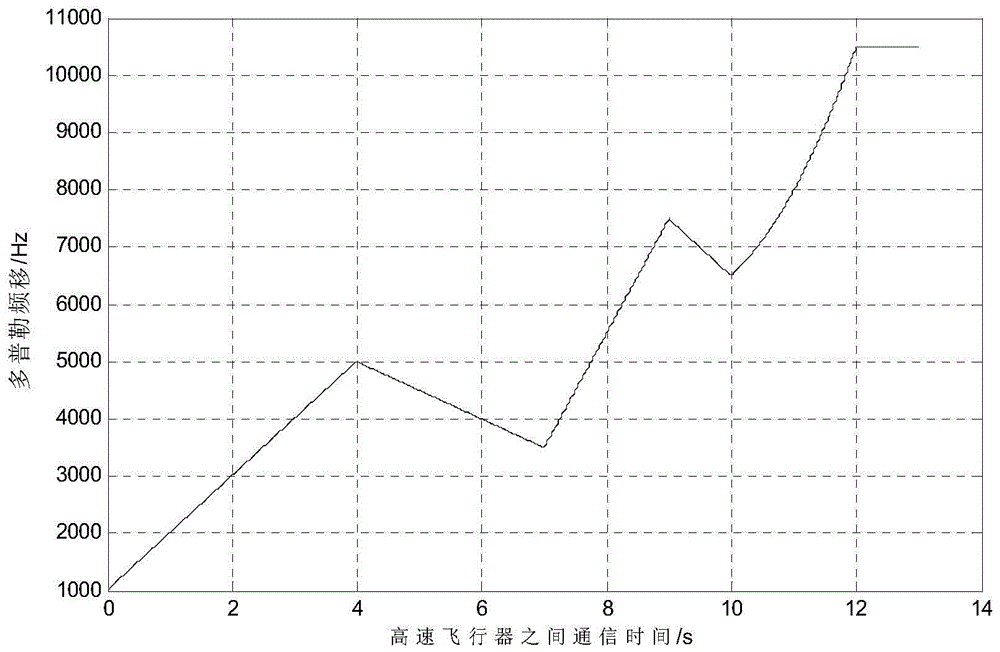
Information-sequence-based adaptive fading extended kalman particle filter (AFEKPF) doppler frequency shift estimation method
The invention discloses an information-sequence-based adaptive fading extended kalman particle filter (AFEKPF) doppler frequency shift estimation method. The method mainly comprises the steps of: firstly, receiving signal parameters by means of an antenna receiver, and defining a sampled signal by adopting a vector table method; secondly, regarding a carrier phase of the sampled signal as a state variable of a particle filter equation, and carrying out dynamic unfolding to obtain a state transition matrix of a system and a covariance matrix of a noise interference vector; estimating a state vector by using adaptive fading kalman with fading particles to obtain optimal filter estimation; and generating an importance density function through AFEKPF, updating posteriori distribution continuously through gaussian approximation to achieve recursive estimation, and completing AFEKPF (adaptive fading extended kalman particle filter).
Owner:DALIAN UNIV
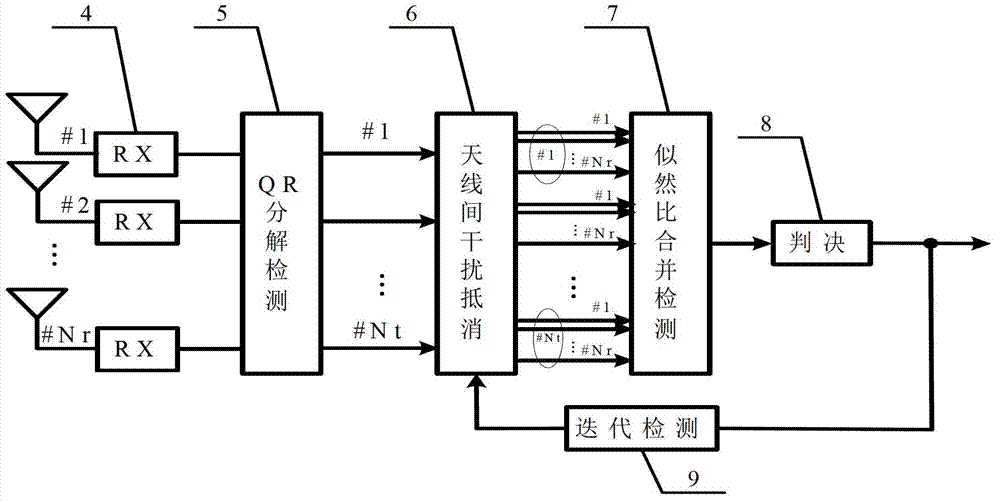
Detection method for multi-antenna superimposing coding modulation system
InactiveCN102820938ASolve the problem that the noise will be amplified when mergingImprove bit error rate performanceTransmission monitoringWireless communicationPattern recognitionDecomposition
The invention discloses a detection method for a multi-antenna superimposing coding modulation system, and the detection method comprises the following steps of decomposition detection, inter-antenna interference counteraction, likelihood ratio combined detection, judgment and iteration detection. The method utilizes a likelihood ratio combination scheme, the influence of noise on a signal is considered when the likelihood ratio of the signal is calculated, the Gaussian distribution characteristics of the noise are also utilized by adopting Gaussian approximation, the likelihood ratio represents the confidence level of the received signal, the superimposing of the confidence level only enables the useful signal to be accurate, no influence on the noise is produced, and the problem that the noise is amplified when combining conventional antennas can be effectively solved, so that the error-rate performance of the system is improved.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
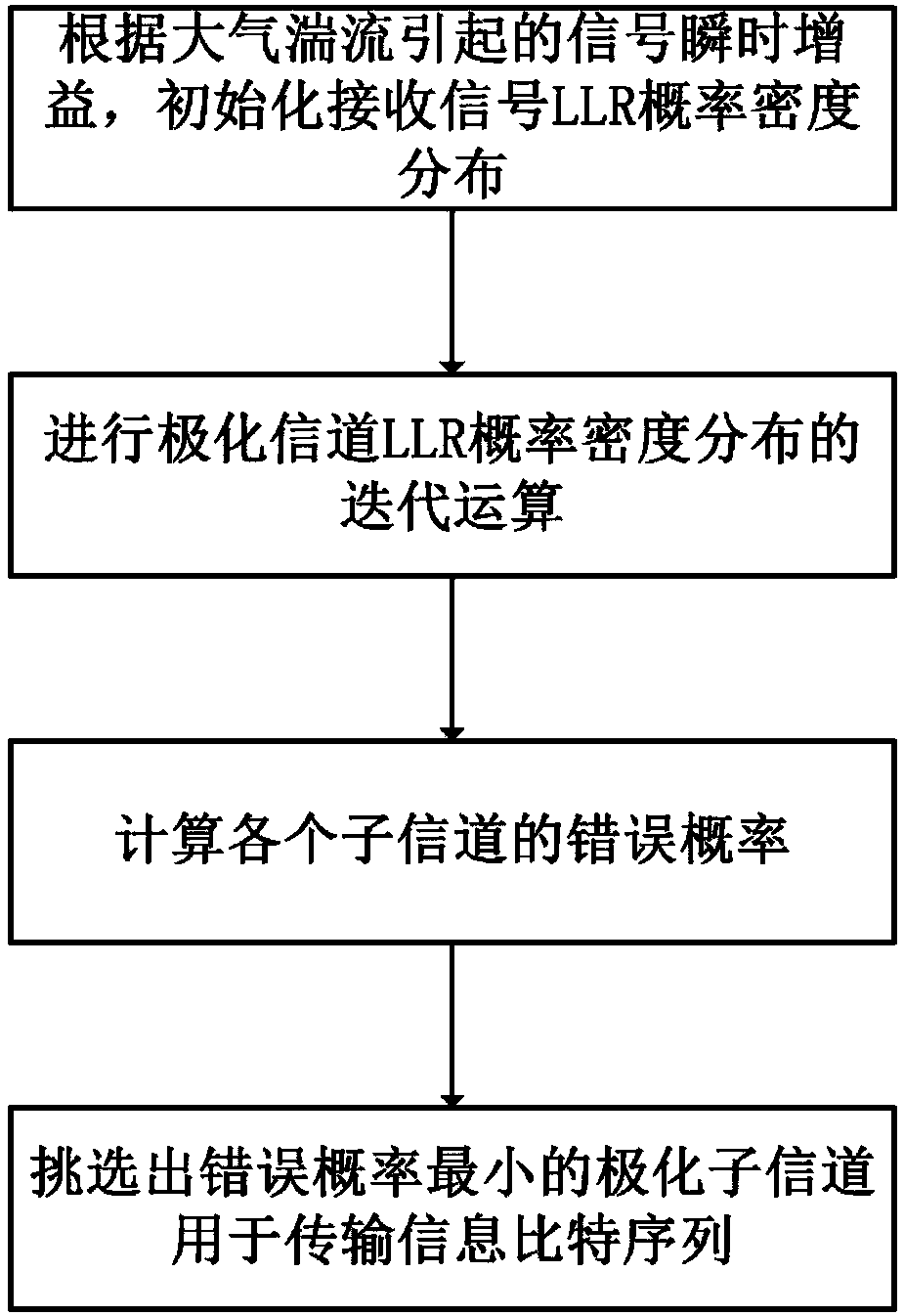
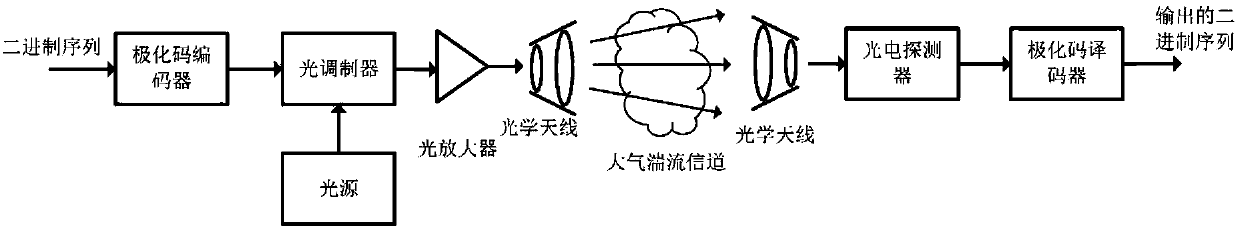
Polarization code building method capable of resisting atmospheric turbulence decline based on Gaussian approximation theory
InactiveCN108259135ALarge decoding performance improvementBuild changesError preventionFree-space transmissionCommunications systemLog likelihood
The invention provides a polarization code building method capable of resisting atmospheric turbulence decline based on a Gaussian approximation theory. Polarization code coding is applied to a free space optical communication system, a polarization sub-channel with relatively low atmospheric turbulence gain error probability is selected to be applied to transmitting an information bit sequence, and a polarization sub-channel with relatively high atmospheric turbulence gain error probability is selected to be applied to transmitting a known fixed bit sequence. The method provided by the invention comprises the specific steps of initializing a probability density distribution of a received signal log-likelihood ratio according to a signal transient gain caused by atmospheric turbulence; performing iteration computing on log-likelihood ratio probability density distribution of the polarization channels; computing the error probability of each polarization sub-channel; and selecting the polarization sub-channel with the relatively low error probability to be applied to transmitting the information bit sequence. According to the method provided by the invention, the problem of buildingthe polarization code under the atmospheric turbulence decline channel is mainly solved, decrease of the system performance caused by atmospheric turbulence decline can be effectively suppressed, andthe stability of the free space optimal communication system is improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
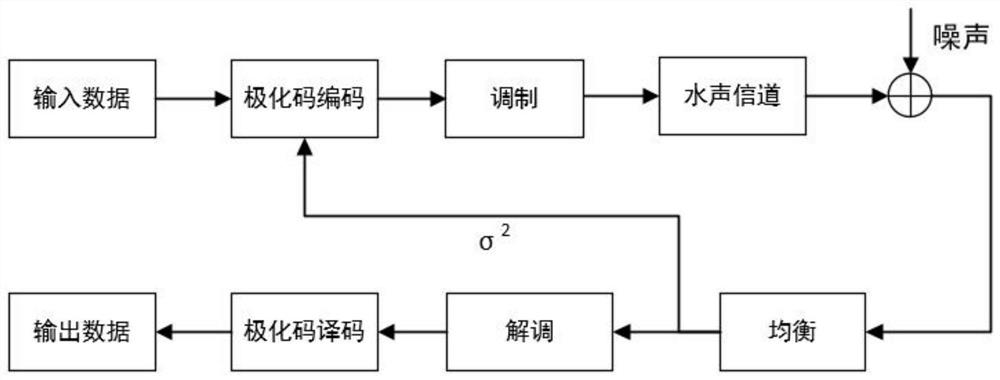
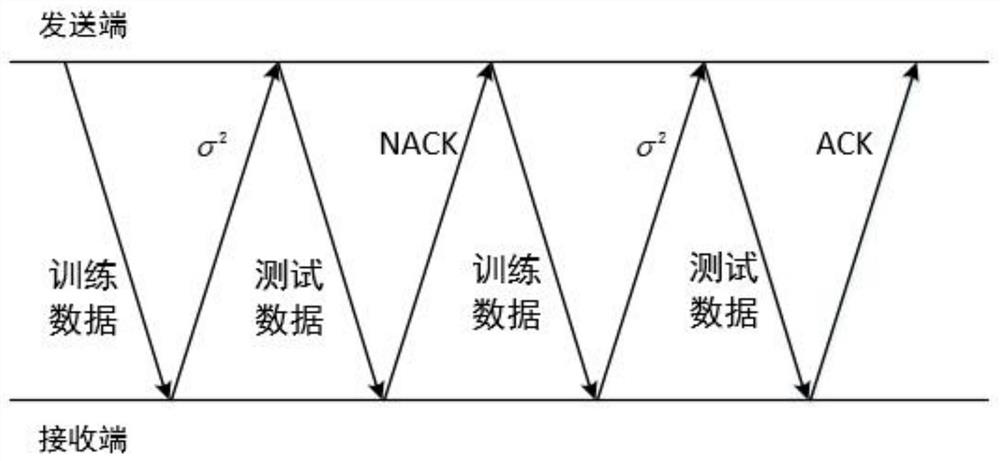
Underwater acoustic communication method using polarization code and equalizer
InactiveCN113542167ASimple coding structureGood bit error rate performanceError prevention/detection by using return channelTransmitter/receiver shaping networksEqualizationControl theory
The invention provides an underwater acoustic communication method using a polarization code and an equalizer. An underwater acoustic channel is converted into a Gaussian channel through the equalizer to construct the polarization code, and an HARQ mechanism is added to improve the performance of the scheme. According to the scheme, the bit error rate performance is superior to the result of turbo equalization iteration for five times, the decoding complexity is low, the coding structure is simple, and only noise variance information needs to be fed back when a polarization code receiving end is constructed by using a Gaussian approximation method.
Owner:SHANGHAI MARITIME UNIVERSITY
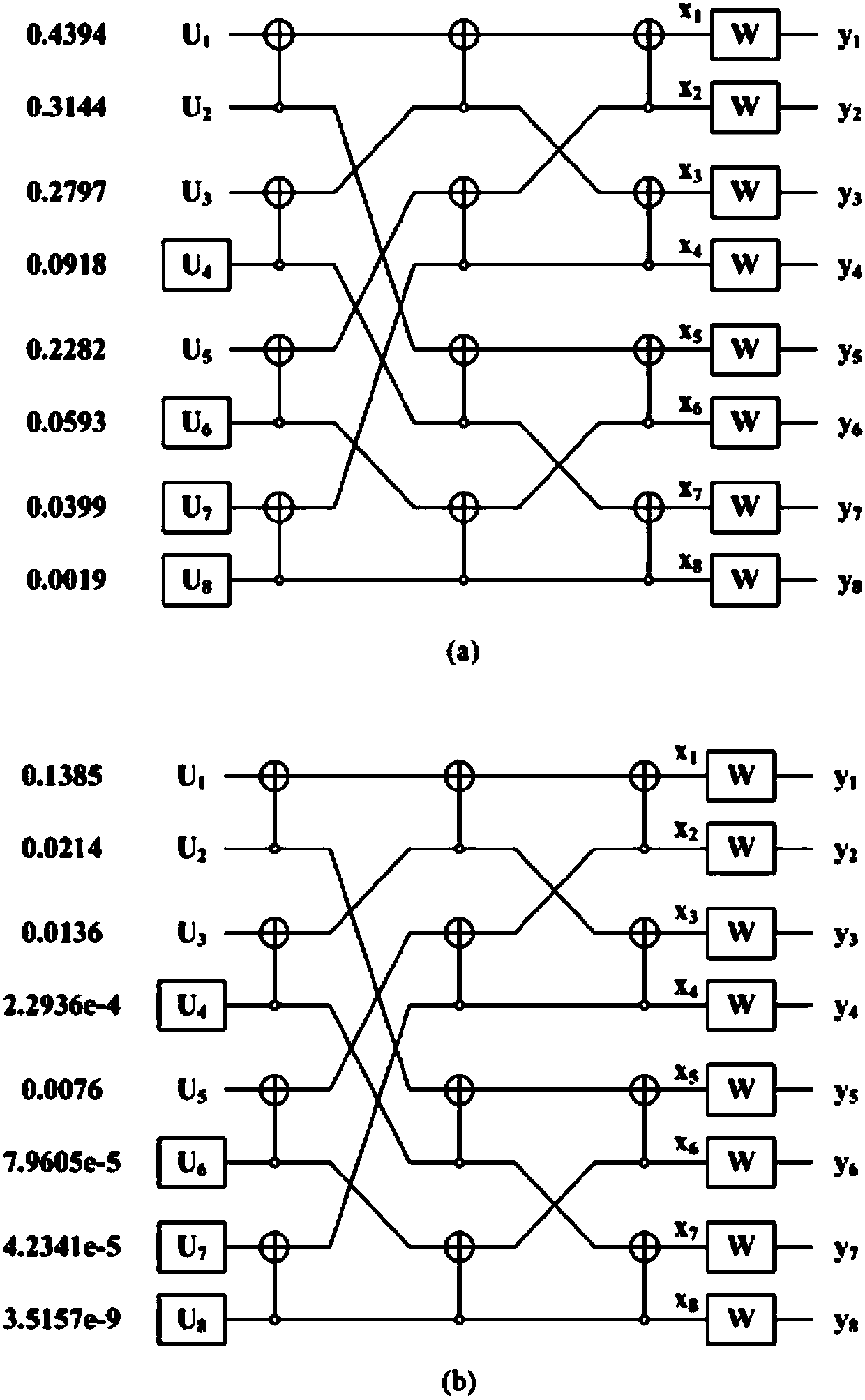
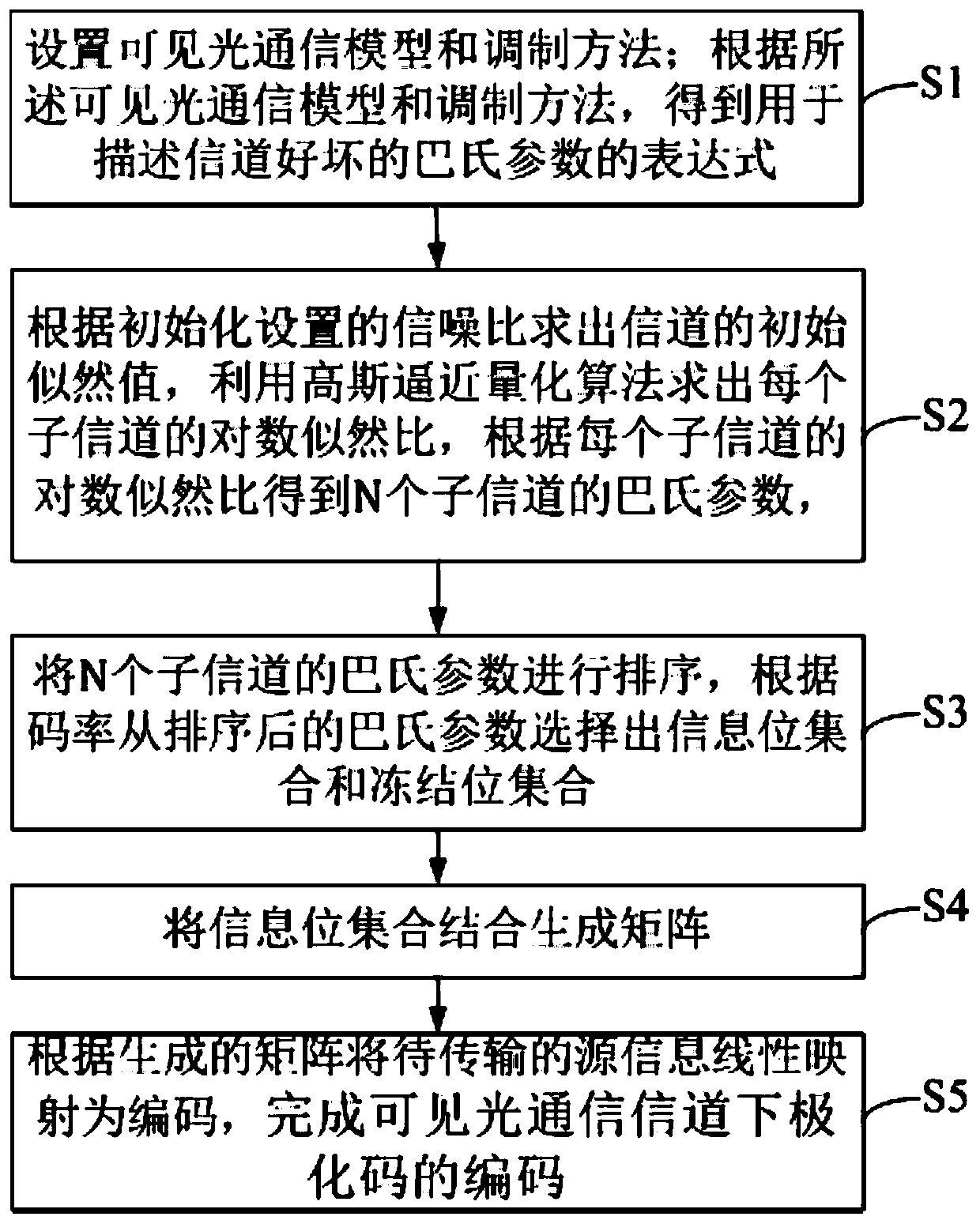
Polarization coding method and system of visible light communication channel based on Gaussian approximation
ActiveCN109889266AShorten the timeExcellent channel capacityError preventionClose-range type systemsPattern recognitionSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)
The invention discloses a polarization coding method of a visible light communication channel based on Gaussian approximation. The method comprises: S2, determining an initial likelihood value of a channel according to a signal to noise ratio of an initial setting, and determining a frequency of each subchannel by using a Gaussian approximation quantization algorithm Log likelihood ratio accordingto the log likelihood ratio of each subchannel obtains the Pap parameter Z(W) of N subchannels, N is the code length of the set polarization code; S3, sorts the Pap parameters of the N subchannels, sorts according to the code rate The latter Pap s parameter selects the information bit set and the frozen bit set; thereby analyzing the quality of each subchannel; the smaller the Pap s parameter, the larger the channel capacity of the representative channel, so that a better channel can be selected. S4, combining the information bit set to generate the matrix GN; S5, linearly mapping the sourceinformation to be transmitted according to the generated matrix GN into a coding sequence The encoding of the polarization code in the visible light communication channel is completed.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
NDT point cloud registration algorithm and device based on GPU, and electronic equipment
ActiveCN112837354AImprove work efficiencyLower latencyImage enhancementImage analysisComputational scienceSingular value decomposition
The embodiment of the invention provides an NDT point cloud registration algorithm and device based on a GPU, and electronic equipment, and belongs to the technical field of point cloud registration computers, and the algorithm comprises the steps of extracting target point cloud data, extracting source point cloud data, calculating a Gaussian approximation constant, giving an initial guess pose, transforming points in a source point cloud, calculating a Jacobian matrix and a Hessian matrix, judging whether points in the source point cloud after pose transformation are effective points, calculating a gradient vector of each effective point and a Hessian matrix H, respectively adding the gradient vector and the Hessian matrix H, and adding the sum to Hapos; a Jacobi method is used to realize a singular value decomposition equation to solve a pose increment and a norm thereof, the pose increment is normalized, a line search algorithm is used to update the pose increment, a source point cloud is transformed according to new pose transformation, the solving process of a gradient vector, a Hessian matrix and the pose increment is repeated, and an optimal transformation pose is obtained through iteration. Through the processing scheme provided by the invention, the problem of high delay of the algorithm at the CPU end is reduced, and the working efficiency of the GPU is improved.
Owner:北京超星未来科技有限公司
A polar code SBP decoder based on G-Matrix verification
PendingCN109831216ACorrectly decoded resultImprove decoding performanceError preventionError correction/detection using linear codesEuclidean vectorComputer science
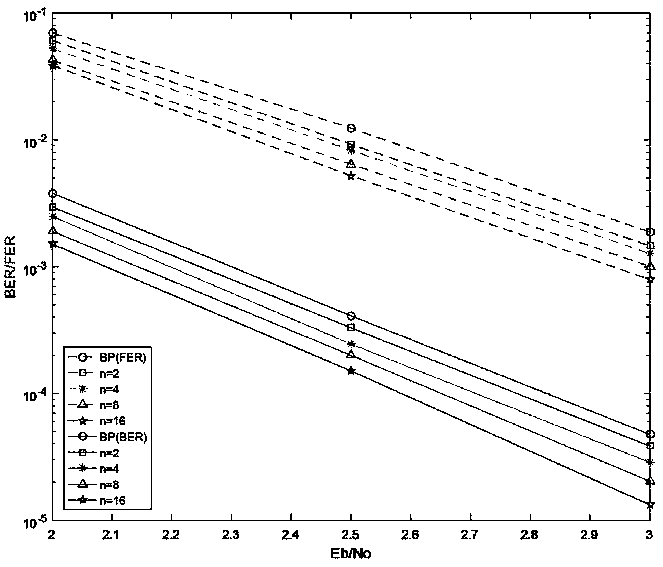
The invention provides an efficient SBP decoder for segmentally increasing an information bit R information initial value. The efficient SBP decoder is composed of an information bit reliability sorting module, an information bit segmentation processing module and a G- Matrix verification module and the like. The invention discloses a method for selecting information bits based on Gaussian approximation, sequencing processing is carried out on the information bit reliability from large to small to obtain an index vector (shown in the specification), and then the index vector (shown in the specification) is subjected to vector alignment (shown in the specification); sequence of the number of subvectors is shown in the specification, the initial value of the information bit R information inthe vector (shown in the specification) is sequentially increased, and finally, re-decoding and utilizing the G-Matrix check to find decoding optimization. The method can be regarded as an informationbit to be converted into a frozen bit to a certain extent, namely, the effect of improving the decoding performance when the code rate is reduced without changing effective information can be achieved. The method is simple and effective, searching, changing and checking are only carried out when decoding is wrong, the error correction capability is greatly improved, the optimization effect of BPdecoding performance is obvious, and the bit error rate performance is improved by 0.25 dB when n is equal to 16.
Owner:CHINA JILIANG UNIV
Adaptive belief propagation list decoding method for polar codes
ActiveCN110233628AImprove bit error rateImproved frame error rate performanceError detection onlyError correction/detection using linear codesBelief propagationComputer science
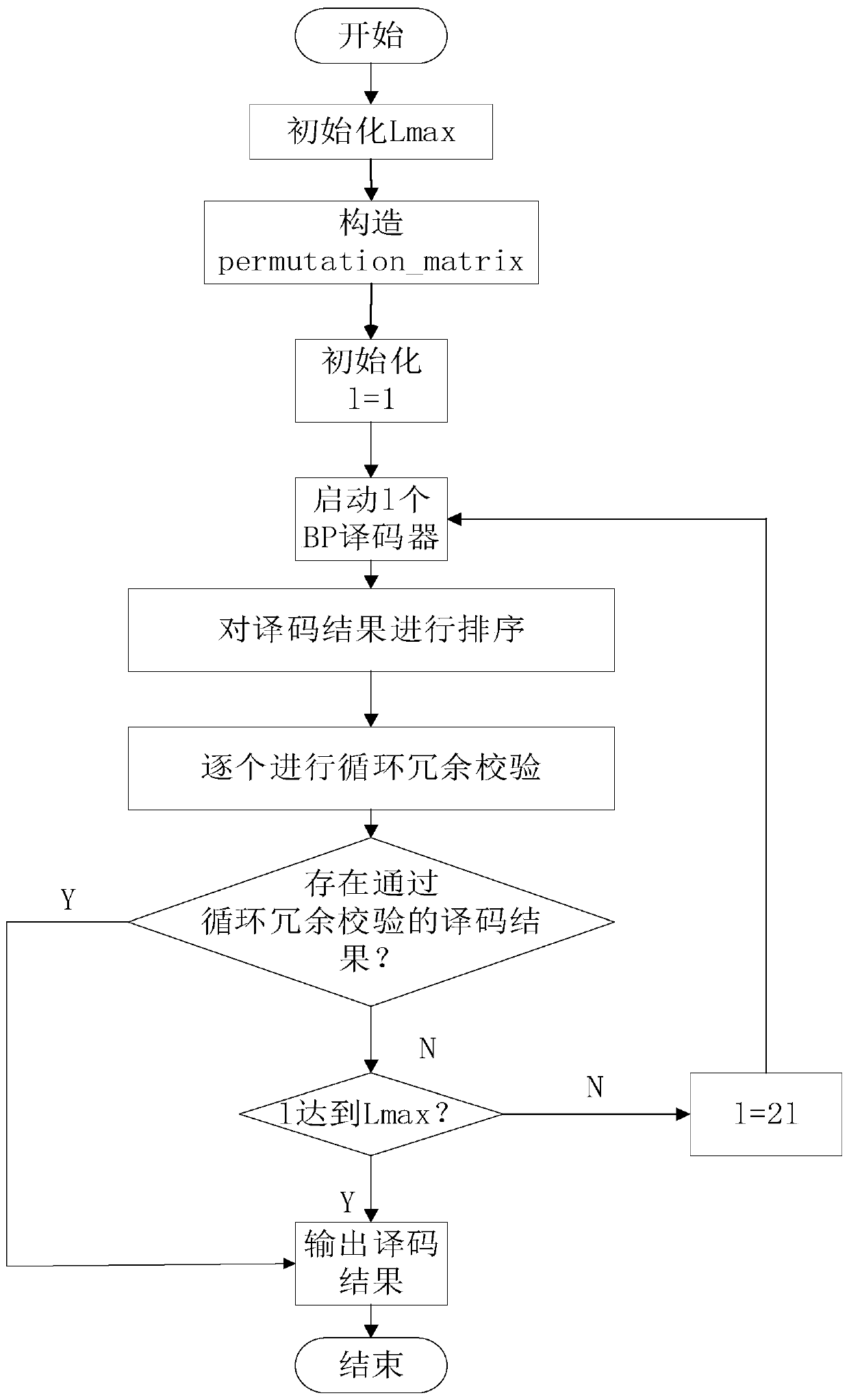
The invention discloses an adaptive belief propagation list decoding method for polar codes. The method comprises: firstly, determining the number of BP decoders owned by a receiving end; determiningthe maximum list number of the method; obtaining a BP decoding factor graph capable of achieving a good decoding effect through calculation by a Gaussian approximation method; then, selecting different BP decoding factor graphs for decoding from the BP decoders recorded in the list; and sequencing the decoding results, then carrying out cyclic redundancy check, if a result passing through the cyclic redundancy check exists, determining that the decoding is successful and stopping the decoding, otherwise, automatically adjusting the size of the list, expanding the number of the list by two times of the original number, and continuing to use the BP decoder in the list to decode.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
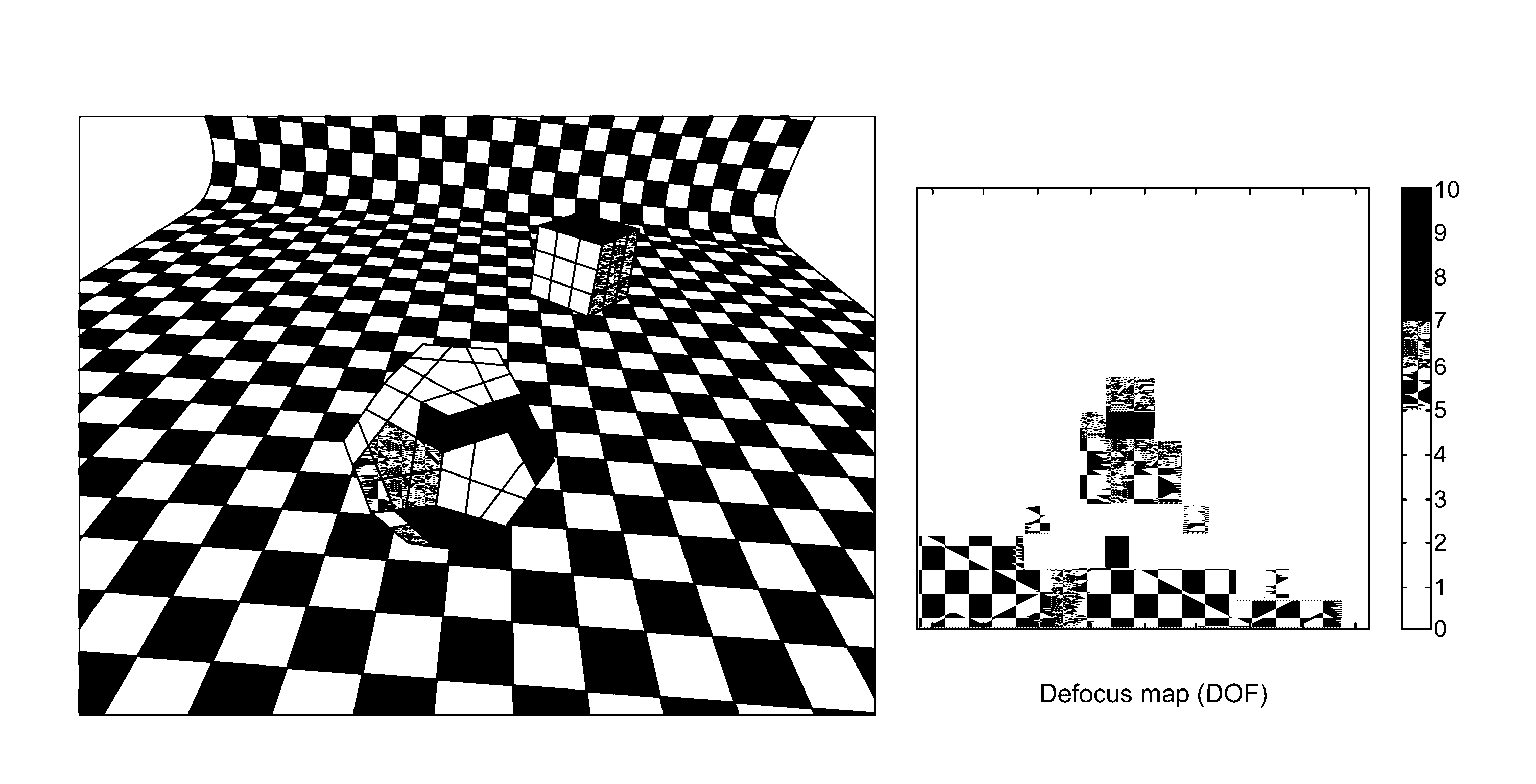
Defocus estimation from single image based on laplacian of gaussian approximation
A defocus estimation algorithm is described herein. The defocus estimation algorithm utilizes a single image. A Laplacian of Gaussian approximation is determined by computing a difference of Gaussian. Defocus blur is able to be estimated by computing a blur difference between two images using the difference of Gaussian.
Owner:SONY CORP
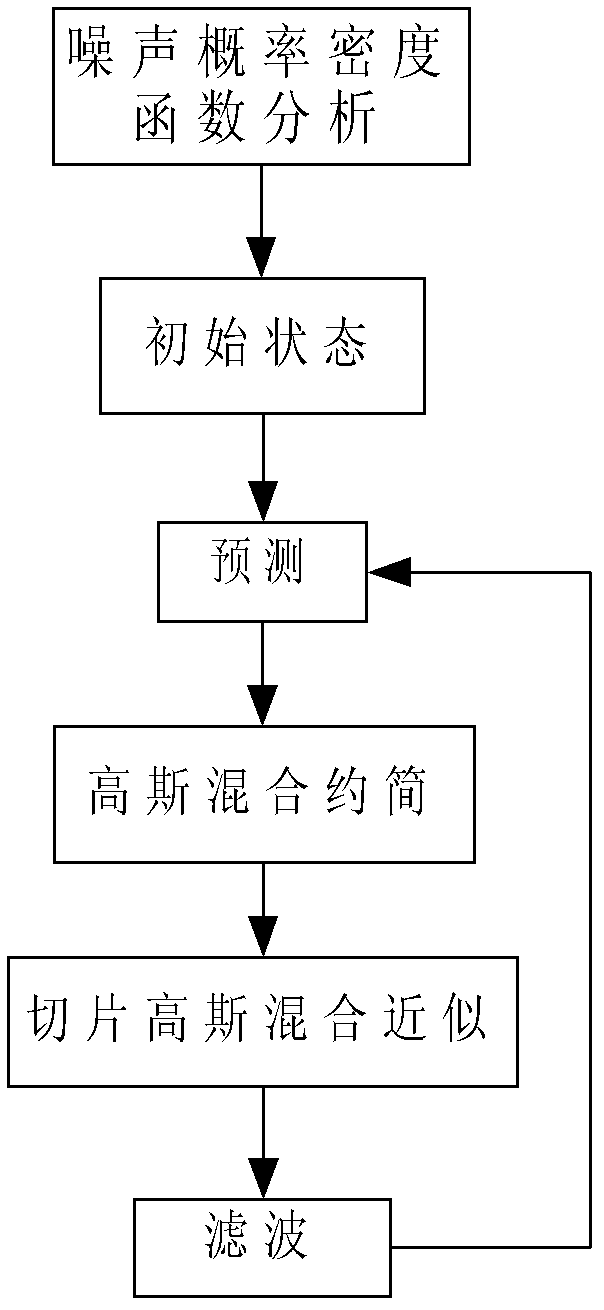
Expanded section Gaussian-mixture filter
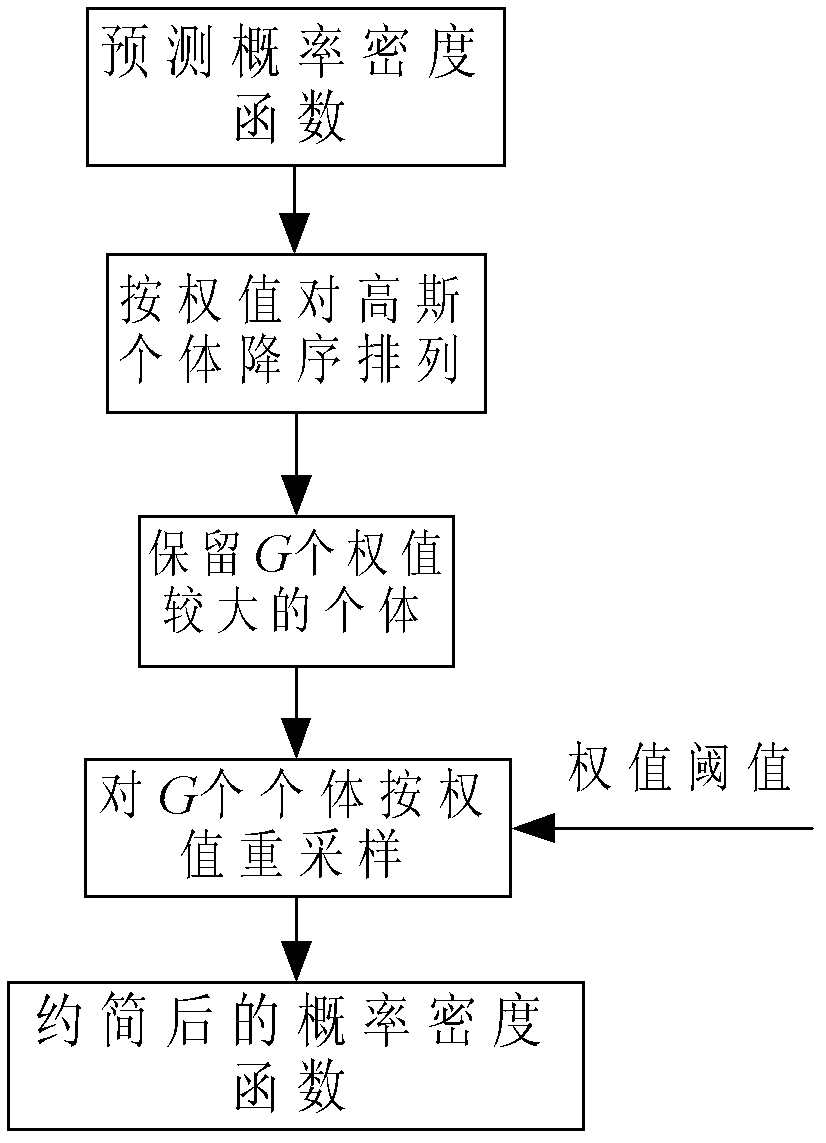
InactiveCN102624358AEasy to transplantCalculation speedDigital technique networkNormal densityComputer science
The invention relates to an expanded section Gaussian-mixture filter, which comprises a Gaussian approximation module, a prediction module, a Gaussian-mixture reduction module, a section Gaussian-mixture approximation module and a filter module, wherein the Gaussian approximation module is used for performing Gaussian-mixture approximation on a probability density function of a received non-Gaussian noise; the prediction module is used for predicting a state of an input signal containing the Gaussian-mixture noise, and the predicted state probability density function is in a Gaussian-mixture form; the Gaussian-mixture reduction module is used for reducing the predicted state probability density function; the section Gaussian-mixture approximation module is used for approximating the predicted state probability density function to a section Gaussian-mixture form; and the filter module is used for updating the state of the input signal. Due to the adoption of the expanded section Gaussian-mixture filter, the state estimation problem of a mixed linear / nonlinear system in a non-Gaussian noise environment can be solved, and a state device in the non-Gaussian noise environment is realized by a paralleling section Gaussian-mixture filter.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
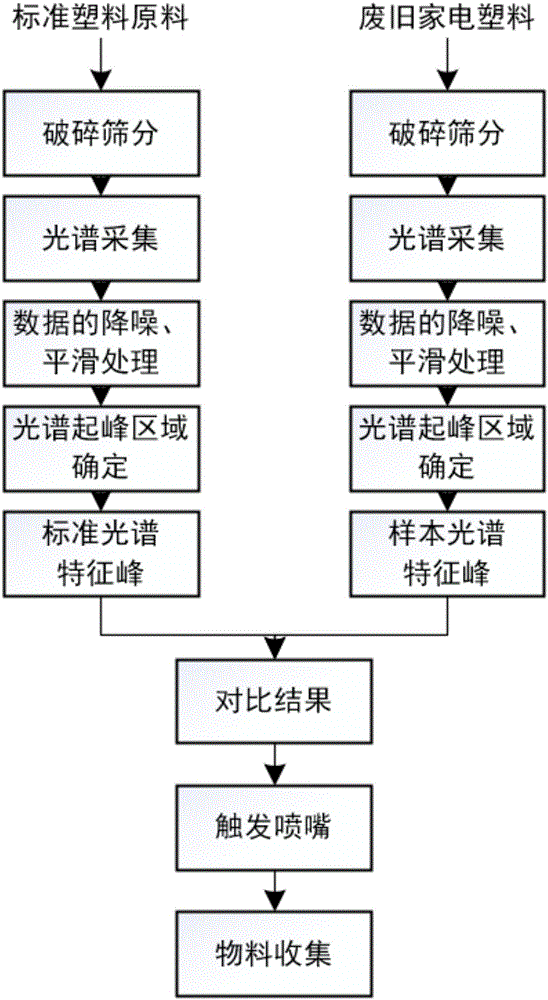
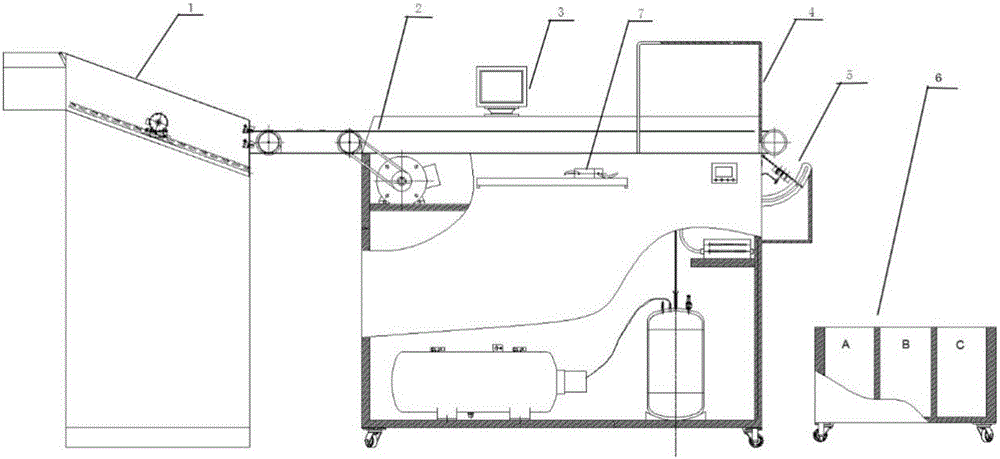
Method for sorting broken plastics in waste household appliances through near infrared absorption spectroscopy analysis device
InactiveCN106426643AAvoid pollutionAvoid health threatsPlastic recyclingSortingSpectroscopyFull width at half maximum
The invention provides a method for sorting broken plastics in waste household appliances through near infrared absorption spectroscopy analysis. The method is characterized in that after being broken and sorted, the broken plastics in the waste household appliances can mainly absorb the light at the infrared wave band while passing through a full-spectrum light source; the rays which are reflected by sheets and are being 720 to 1700 nm in wavelength can be collected through a near infrared spectrometer; the spectral data can be subjected to noise reduction by the least square method through an industrial host computer and smooth processing through Gaussian fitting, and then subjected to Gaussian approximation, so as to extract the wavelength n and the FWHM (Full Width at Half Maximum) corresponding to the data characteristic value; and the wavelength n and the FWHM are compared with the standard characteristic value of the spectrum of the plastics, and the comparing result serves as a triggering condition to control a mechanical sorting structure so as to sort the plastics of different types. With the adoption of the method, the problems of difficult sorting of the broken plastics in the waste household appliances and low accuracy can be solved; the pollution and damage caused by the chemical separation of the waste plastics in the household appliance can be removed; a complete set of recognizing and sorting methods for the waste broken plastics can be created and can be specifically applied to the industry.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
A 5G broadcast channel merging receiving method based on a polarization code
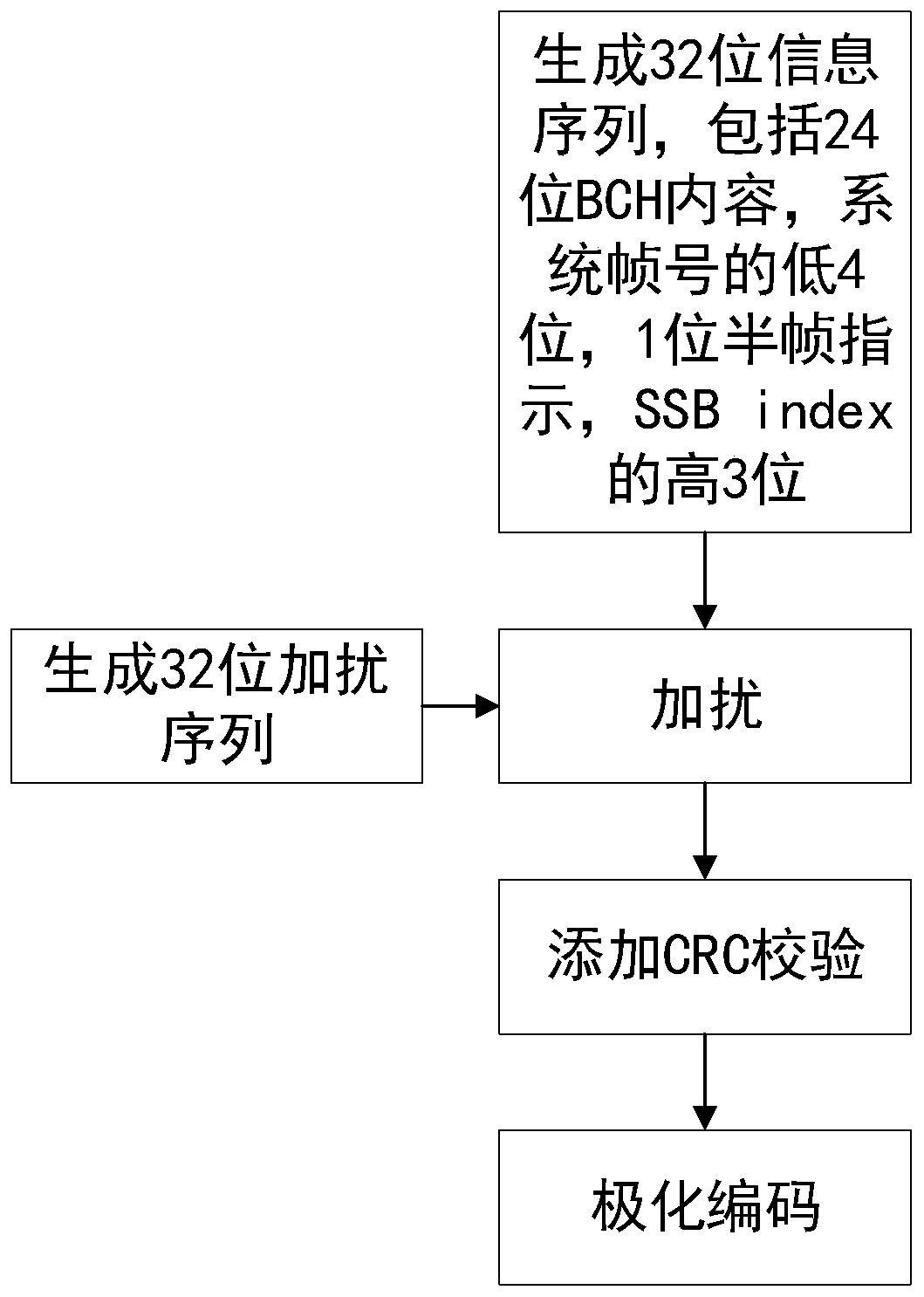
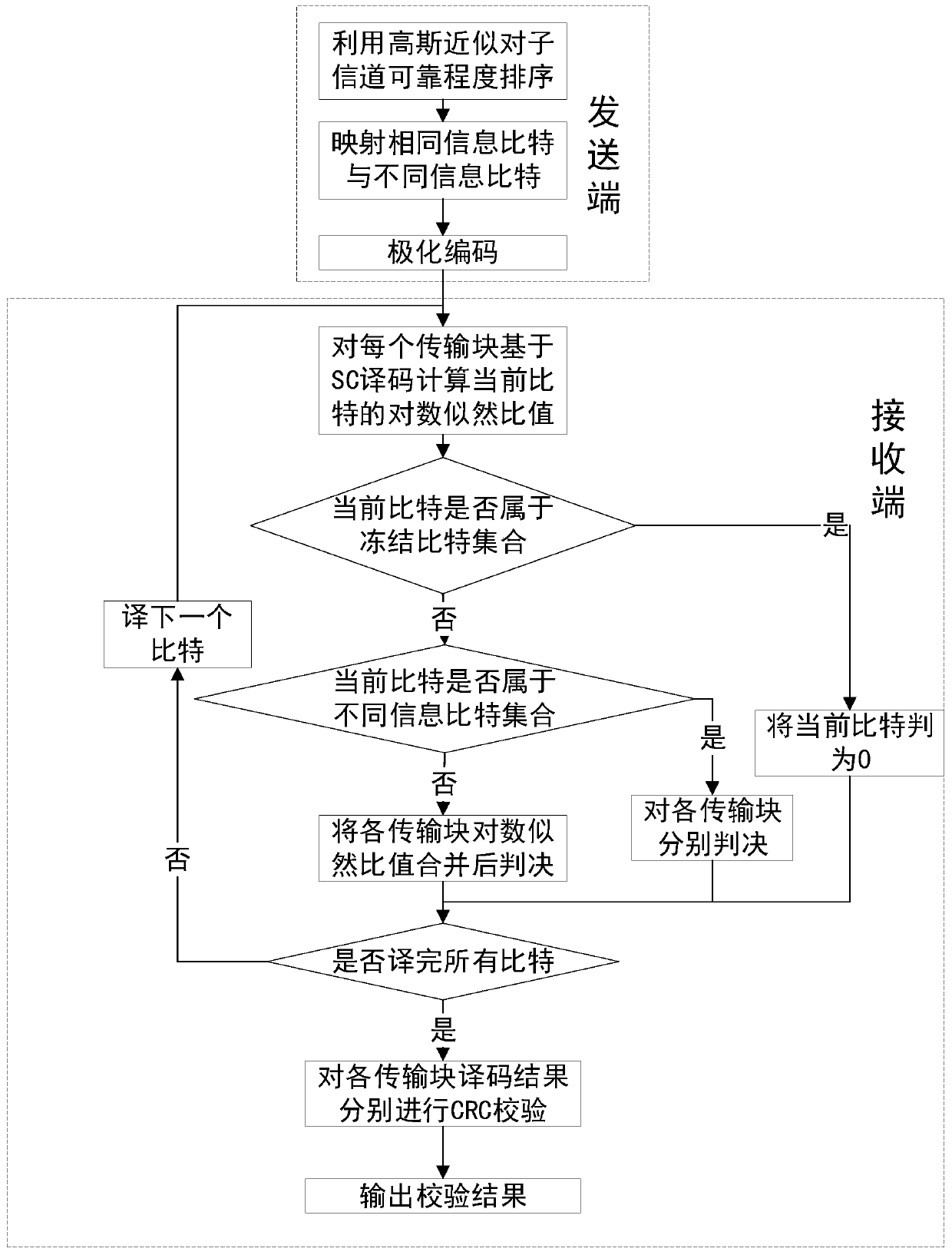
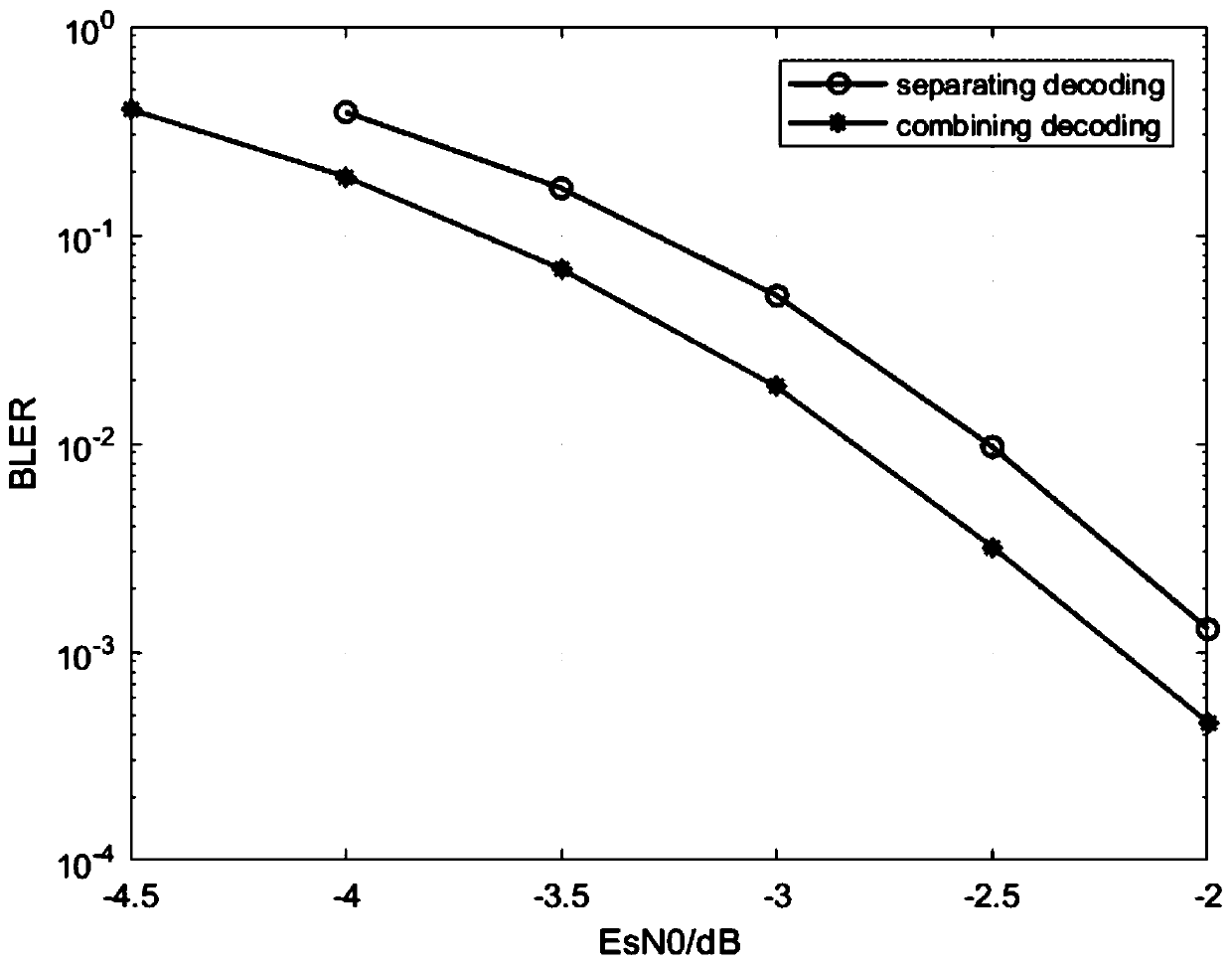
ActiveCN109873686AReduce latencyImprove reliabilityError prevention/detection by using return channelBroadcast channelsTelecommunications
The invention relates to a 5G broadcast channel merging receiving method based on a polarization code, and belongs to the technical field of channel coding and decoding. The method comprises the stepsof estimating the reliability degree of each sub-channel at the sending end by using Gaussian approximation; mapping the same information bit of each transmission block into an information bit sub-channel with lower reliability; mapping different information bits into information bit sub-channels with higher reliability, respectively judging different information bits and transmission blocks at areceiving end, and merging soft information of the transmission blocks and uniformly judging for the same information bit. According to the invention, the decoding accuracy is effectively improved, and the time delay of successful reception of the broadcast channel is reduced.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
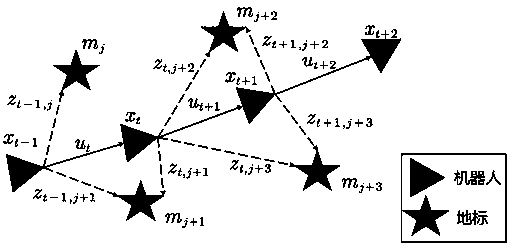
Distributed batch estimation fusion method for asynchronous multistatic radar system
ActiveCN107346020ASolve technical problems that are difficult to integrateEasy to operateWave based measurement systemsRadarParticle filtering algorithm
The present invention discloses a distributed batch estimation fusion method for an asynchronous multistatic radar system. Firstly, an update cycle is set according to a sampling rate of a local radar and an actual requirement of data updating, a particle filtering algorithm is used to carry out local filtering at a multistatic radar, a local posterior estimation result and a local prediction density function of the multistatic radar in the update cycle are obtained, then a Gauss approximation model is used to approximate the local posterior estimation result and the local prediction density function as Gauss distribution, communication is carried out among multiple radars to exchange corresponding Gauss parameters, finally an alignment strategy of using a target state transfer characteristic to carry out recursion to carry out alignment of asynchronous Gauss parameters of the multiple radars, and the distributed batch estimation fusion method is used to fuse the aligned Gauss parameters. According to the method, a problem that the asynchronous data of a synchronous multistatic radar is difficult to fuse can be effectively solved, the calculation quantity of the fusion process is low, and the fusion precision is high.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
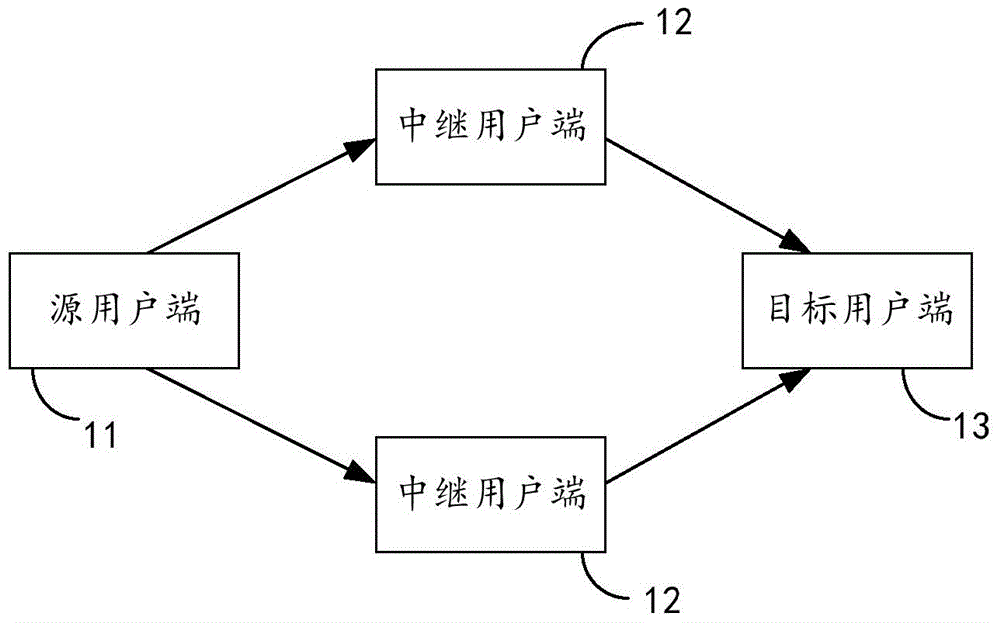
Cooperative communication method and target user end
ActiveCN104821864AOvercome limitationsSimplify complexityError prevention/detection by diversity receptionMimo communicationComputer terminal
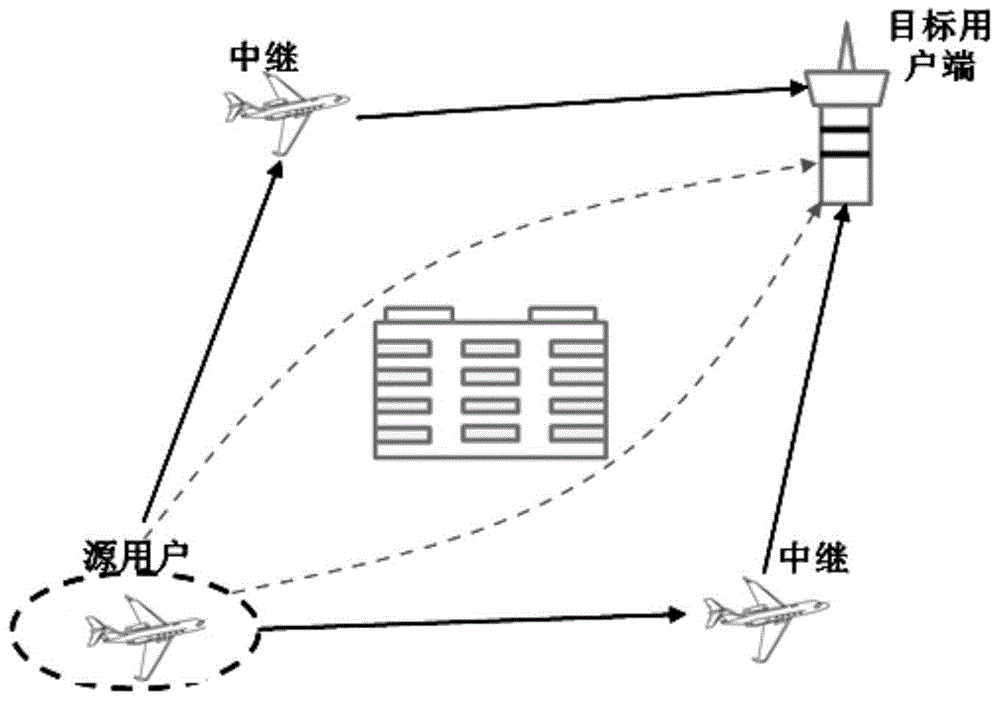
The invention discloses a cooperative communication method and a target user end and belongs to the communication technical field. The method comprises the following steps of: receiving signal vectors forwarded by relay user ends through a channel; detecting the signal vectors according to a minimum mean square error method to obtain first detection signals; approximating target user end noise vectors in the first detection signals according to a Gaussian approximation method to obtain second detection signals; performing log likelihood ratio calculation on the second detection signals; and performing de-interleaving and convolutional code decoding on the signals which have been subjected to the log likelihood ratio calculation so as to obtain original transmitting signals. According to the cooperative communication method of the invention, through cooperative communication of the relay user ends and the target user end, a single antenna can be utilized to transmit and receive signals at each user end, and therefore, limitations of a MIMO communication mode at communication terminals such as handheld communication terminals, aircrafts and vehicles in the aspects such as modification, cost and power consumption can be eliminated.
Owner:THE SECOND RES INST OF CIVIL AVIATION ADMINISTRATION OF CHINA
Heterogeneous sensor information fusion method
ActiveCN111709438AGood Fusion Estimation PerformanceImprove robustnessCharacter and pattern recognitionHigh level techniquesCorrelation coefficientData mining
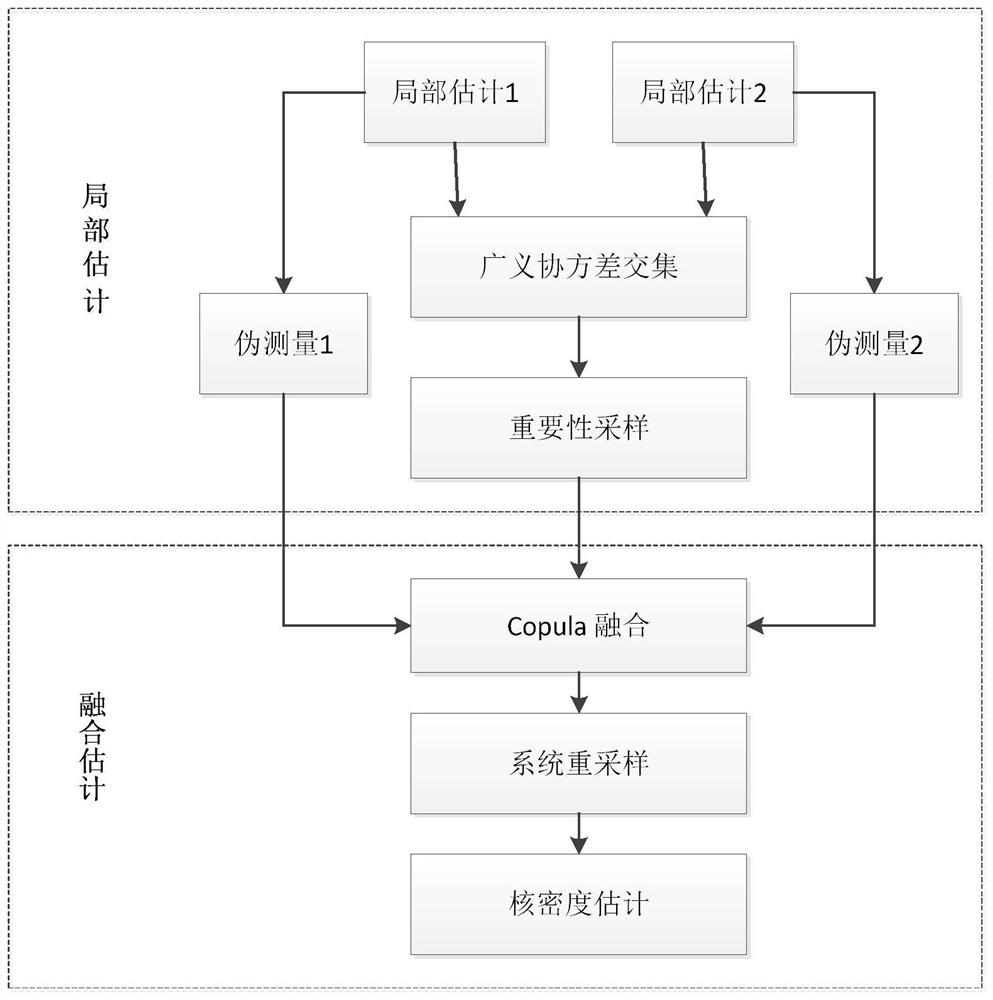
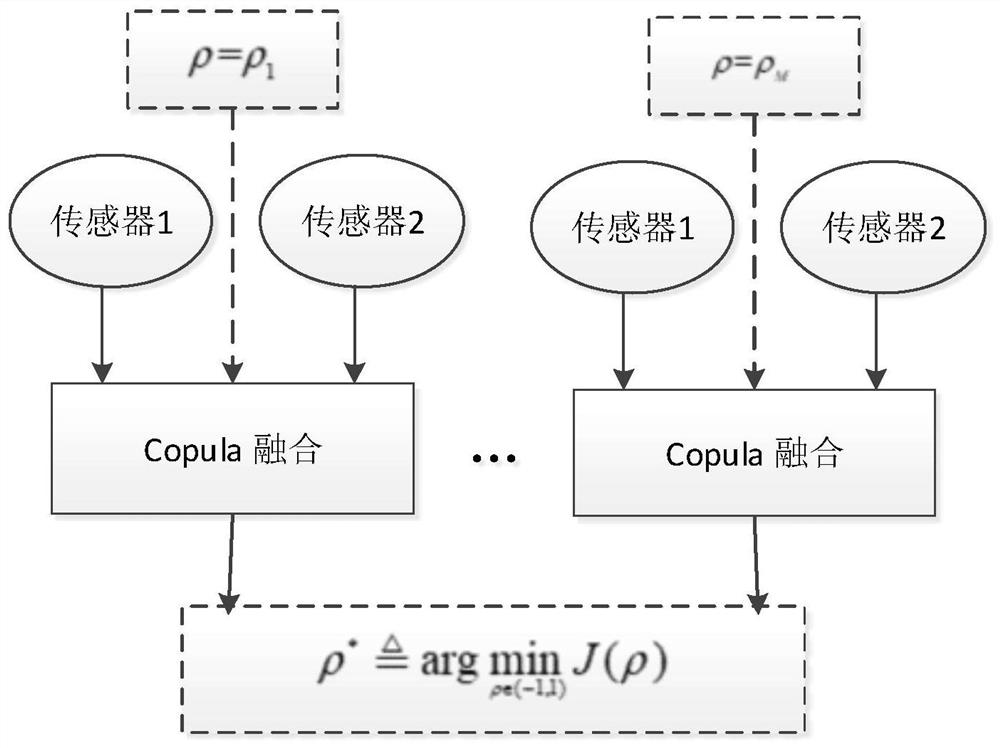
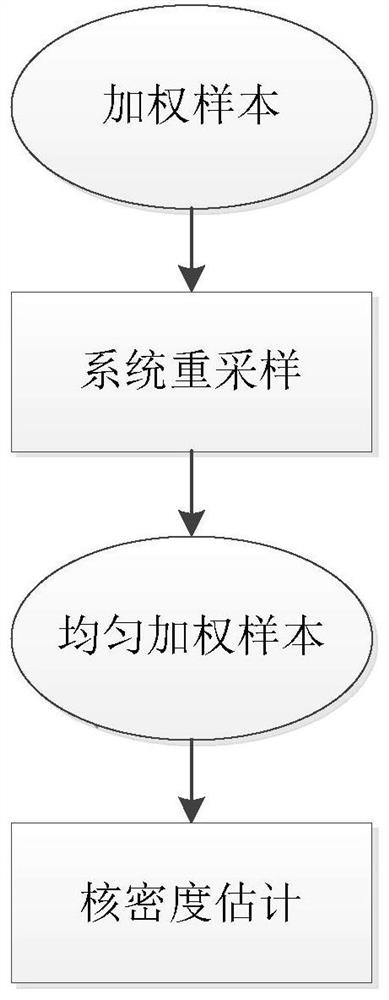
The invention discloses a heterogeneous sensor information fusion method. The method comprises a local estimation part and a fusion estimation part. Each local sensor calculates pseudo measurement toform a local measurement spectrum, and obtains a generalized covariance intersection of local estimation. In the fusion estimation part, based on the Sklar theorem, a Copula function representing thedependency relationship between modes is used for estimating the correlation relationship between random variables of different sensors; optimizing the correlation coefficient of the Copula function according to the minimum resolution information criterion by comparing the Kullback-Leibler divergence between the fusion estimation and the local estimation; performing importance sampling by using the generalized covariance intersection to improve the calculation efficiency, and constructing Gaussian approximation of fusion density by using kernel density estimation; and recursively updating thefusion estimation in a layered manner to realize the fusion of any number of heterogeneous sensors. According to the invention, the requirements on the communication rate and correlation calculation of the local sensor are reduced.
Owner:南京云智控产业技术研究院有限公司
Method of speech recognition using variational inference with switching state space models
InactiveUS20050119887A1Fatty/oily/floating substances removal devicesSedimentation separationState spaceSpeech Acoustics
A method is developed which includes 1) defining a switching state space model for a continuous valued hidden production-related parameter and the observed speech acoustics, and 2) approximating a posterior probability that provides the likelihood of a sequence of the hidden production-related parameters and a sequence of speech units based on a sequence of observed input values. In approximating the posterior probability, the boundaries of the speech units are not fixed but are optimally determined. Under one embodiment, a mixture of Gaussian approximation is used. In another embodiment, an HMM posterior approximation is used.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
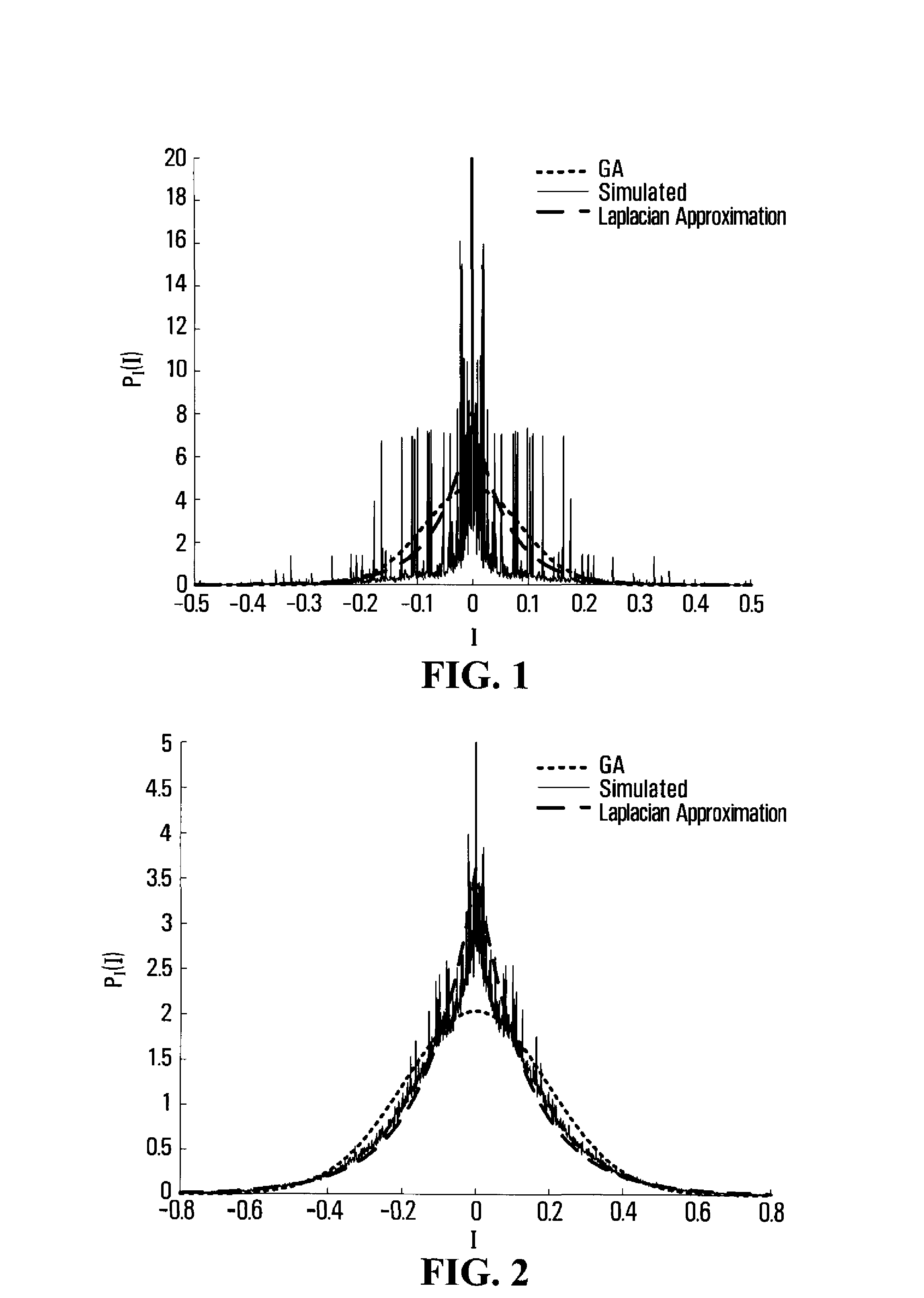
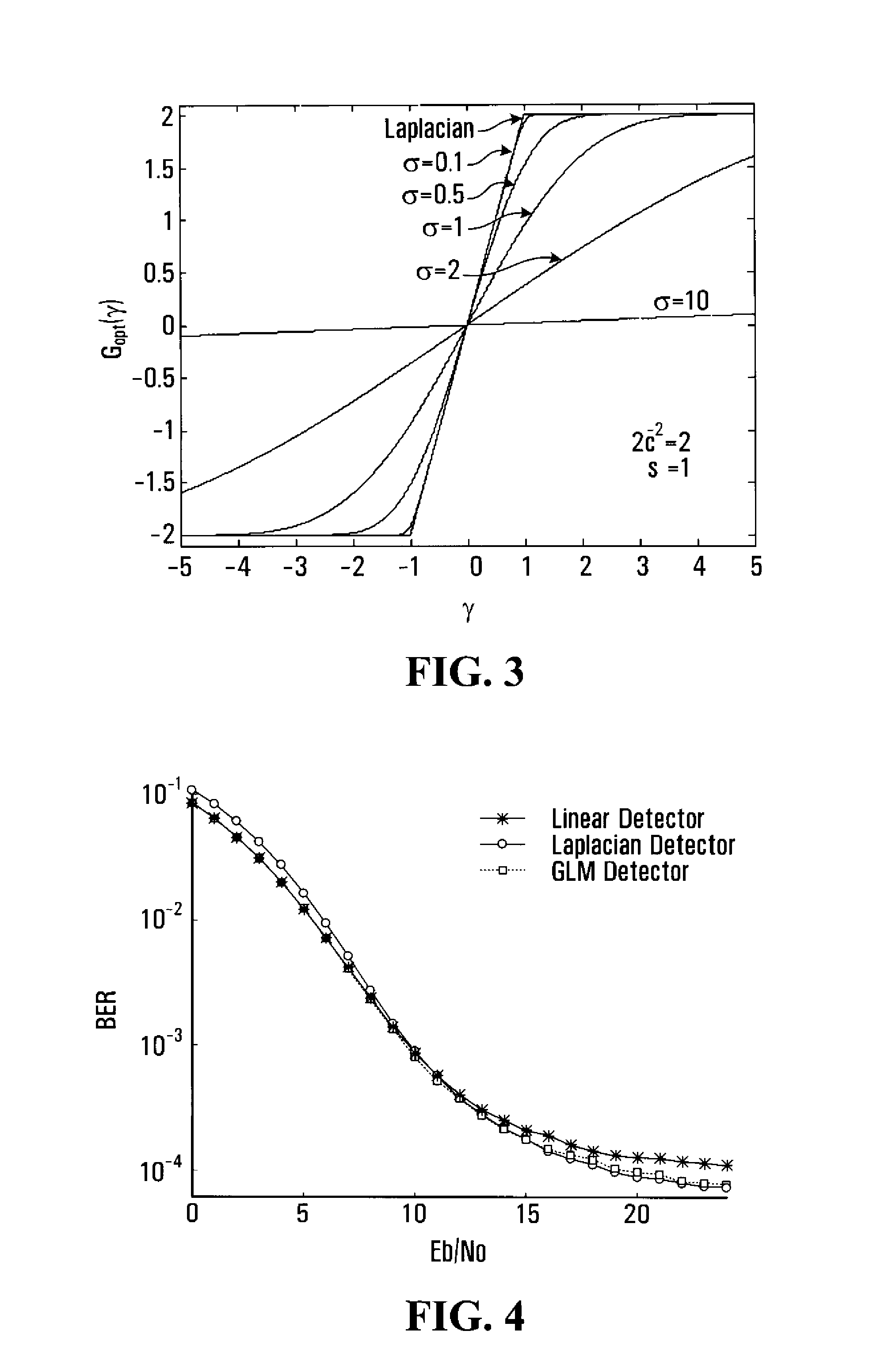
UWB receiver designs based on a gaussian-laplacian noise-plus-mai model
InactiveUS20080273629A1Amplitude-modulated carrier systemsAmplitude demodulationTelecommunicationsMatched filter
Two novel receiver structures which surpass the performance of the conventional matched filter receiver are proposed for ultra-wide bandwidth multiple access communications. The proposed receiver structures are derived based on a more appropriate statistical model for the multiple access interference than the generally used Gaussian approximation.
Owner:THE GOVERNORS OF THE UNIV OF ALBERTA
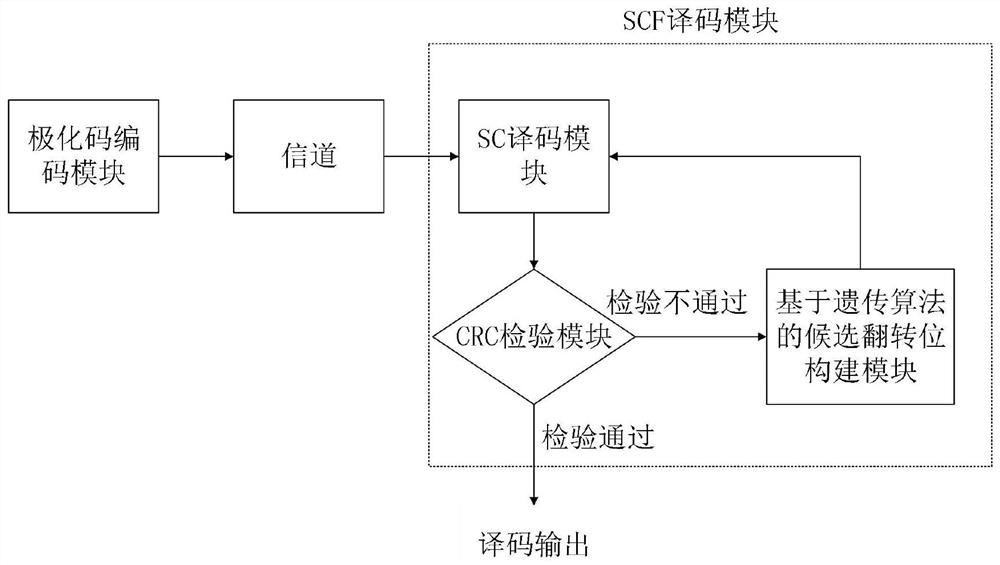
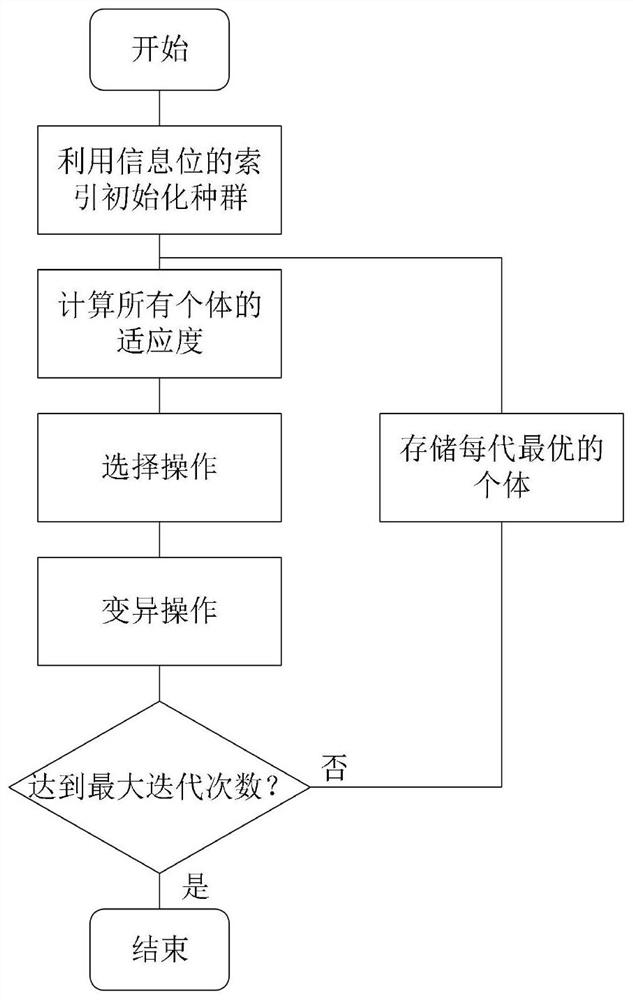
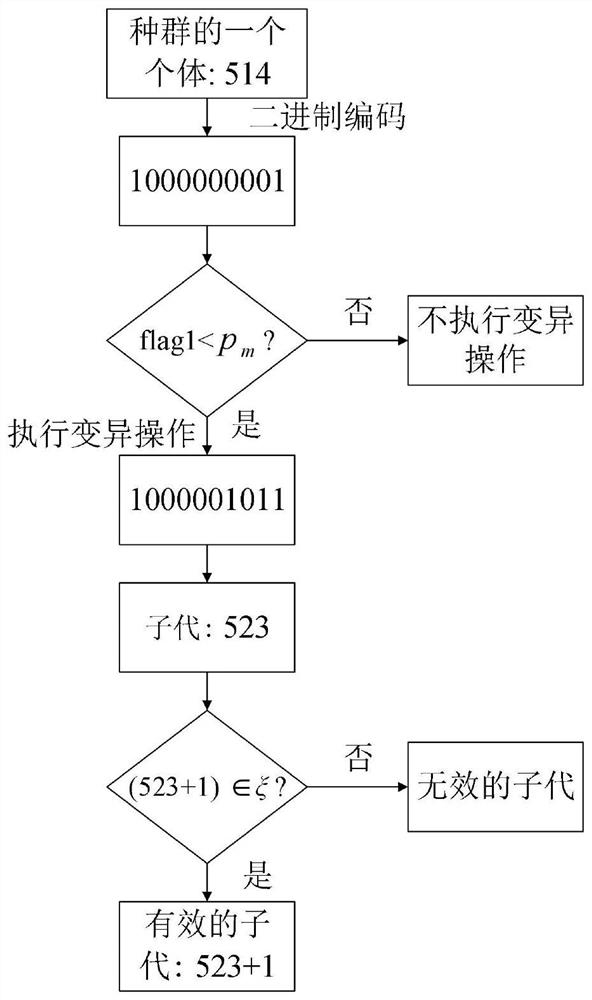
Improved polar code SCF decoder based on genetic algorithm
PendingCN111988045AReduce computational complexityReduce decoding delayCyclic codesGenetic algorithmsComputation complexityTheoretical computer science
The invention provides an improved polar code serial cancellation flip (SCF) decoder based on a genetic algorithm (GA), and particularly relates to a polar code successive cancellation flip (SCF) decoder based on the genetic algorithm (GA). On the basis of an original SCF decoder, aiming at the problem that redundancy exists in an original CFPS (Candidate Flipping Position Set), a new CFPS is constructed by utilizing GA. An initial population of the genetic algorithm is formed by using indexes of all non-frozen bits, and the channel reliability calculated by Gaussian approximation is taken asthe fitness of each individual. Continuous selection, crossover and mutation operations are carried out on the population, and the optimal individual of each generation of population can be stored. Finally, a new candidate flipping position set CFPS-GA is obtained by counting the occurrence frequency of each population in the vector, and SCF decoding is carried out by using the newly constructed candidate flipping position set CFPS-GA. The SCF decoder has the beneficial effects that compared with other similar SCF decoders, the CFPS-GA-based SCF decoder has lower computation complexity and decoding delay on the premise of ensuring the decoding performance.
Owner:CHINA JILIANG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com