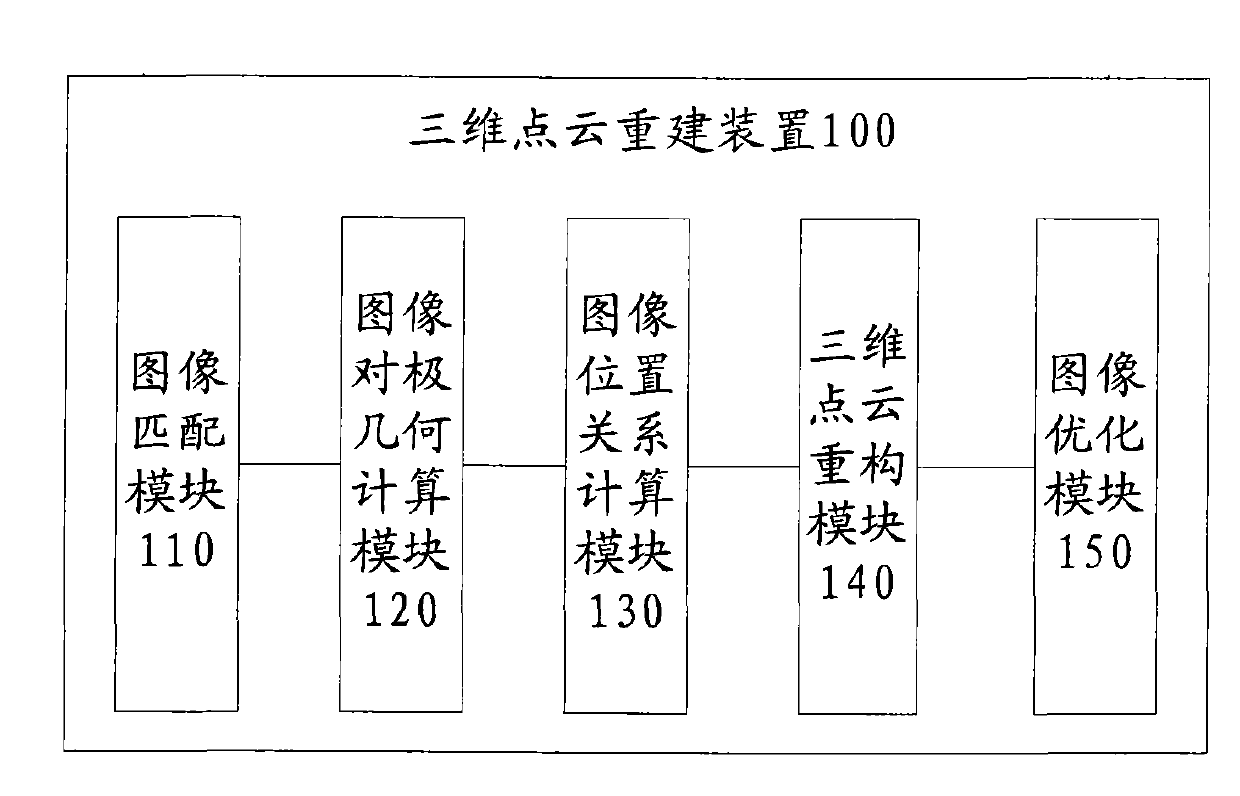
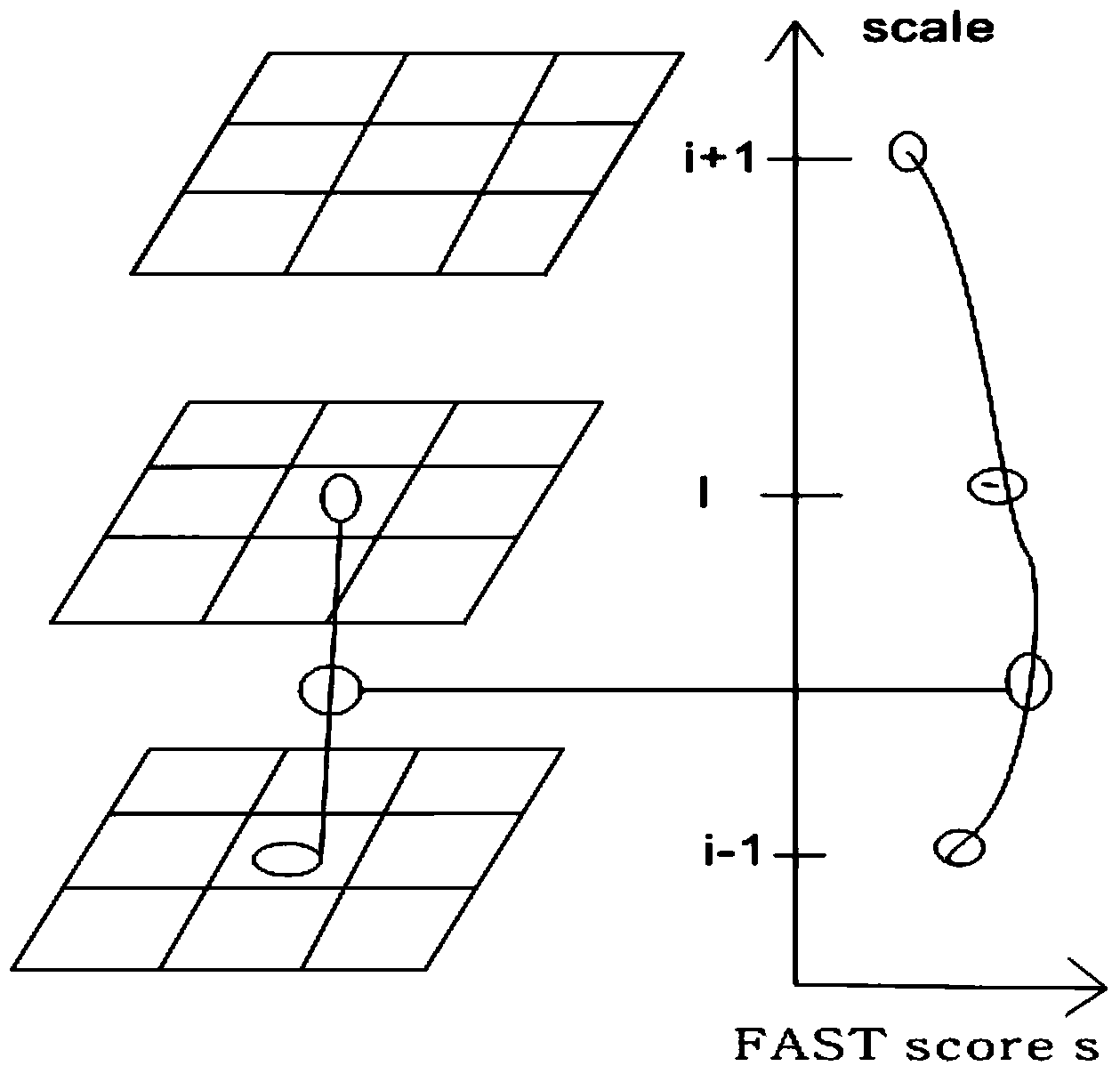
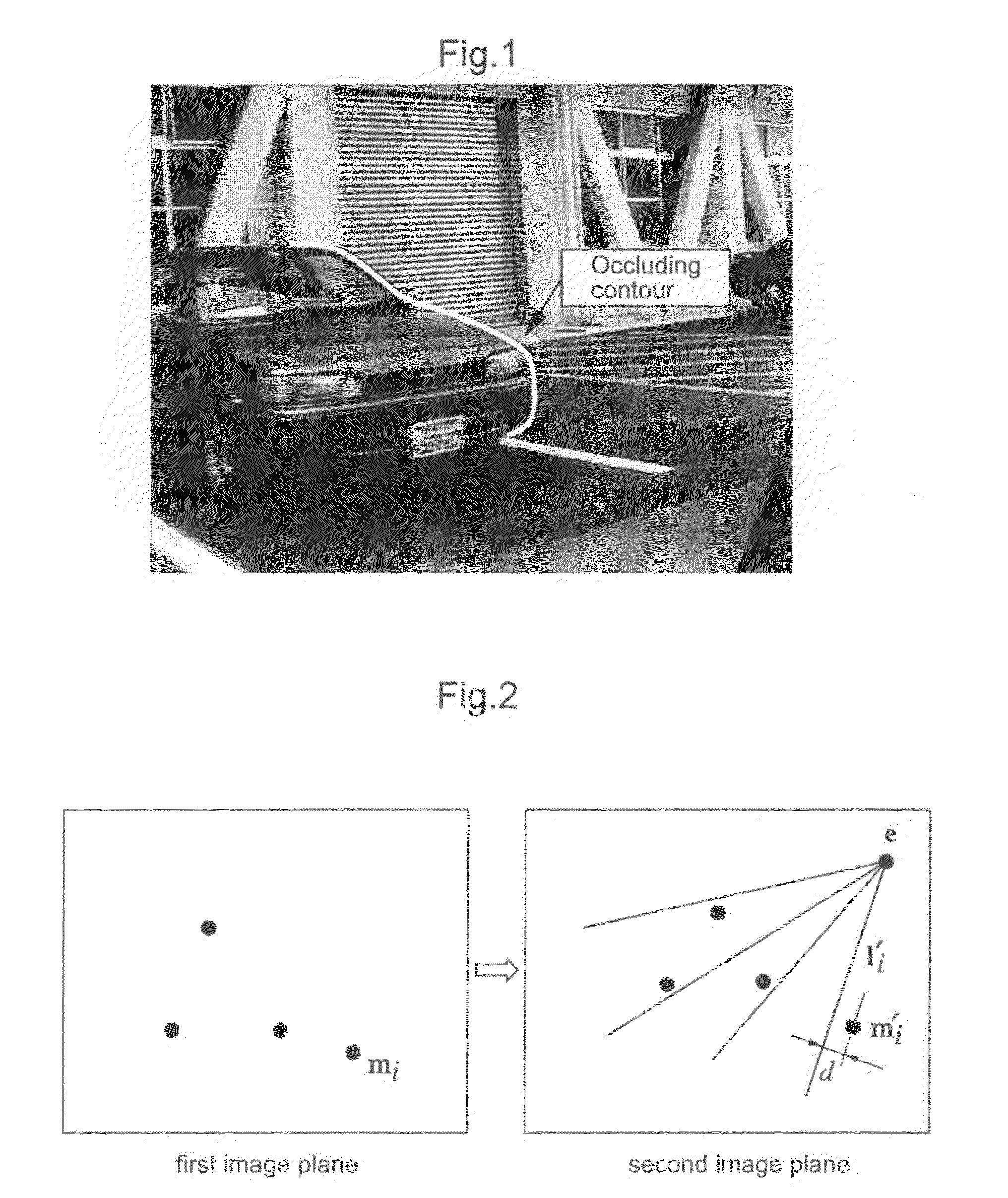
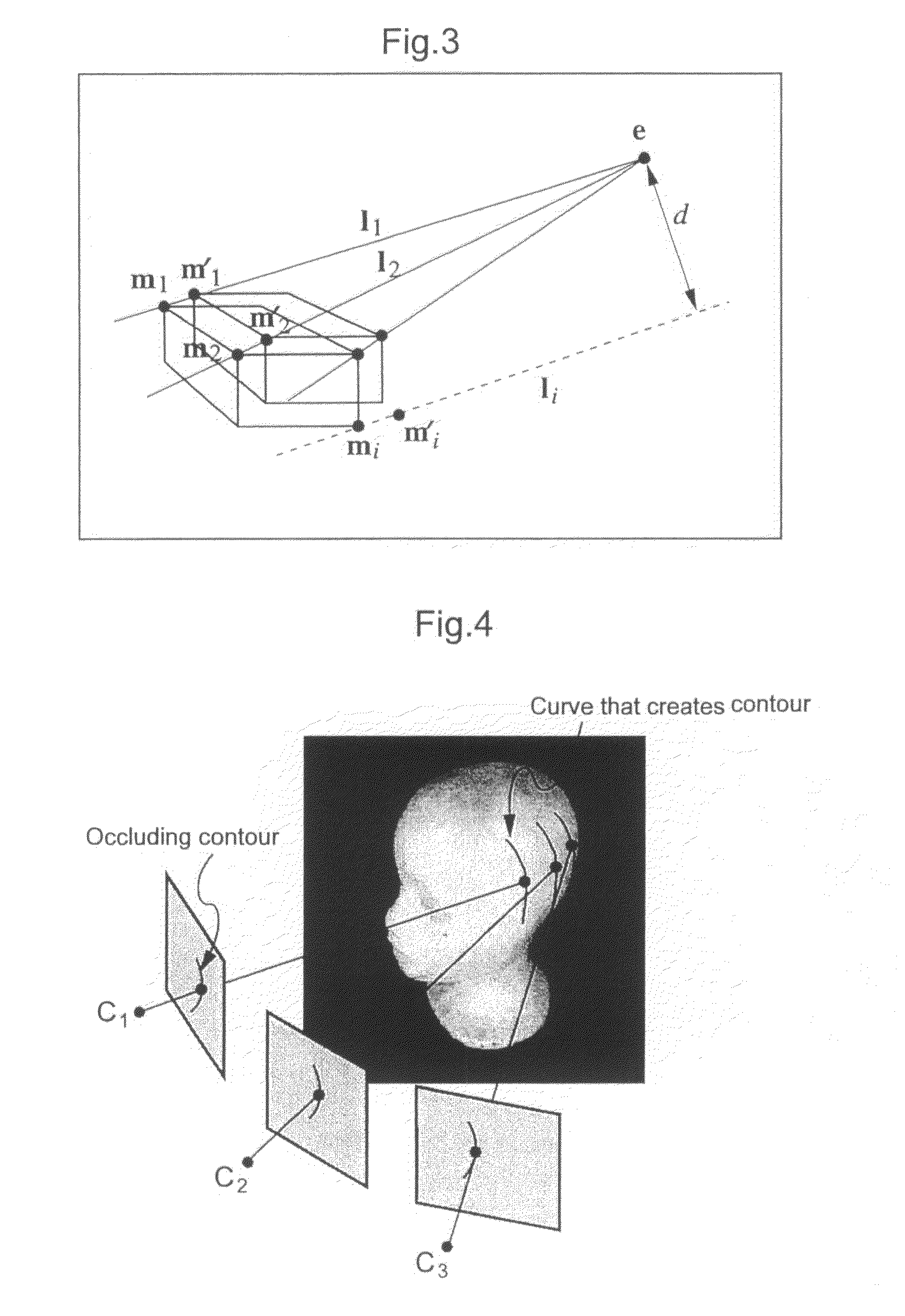
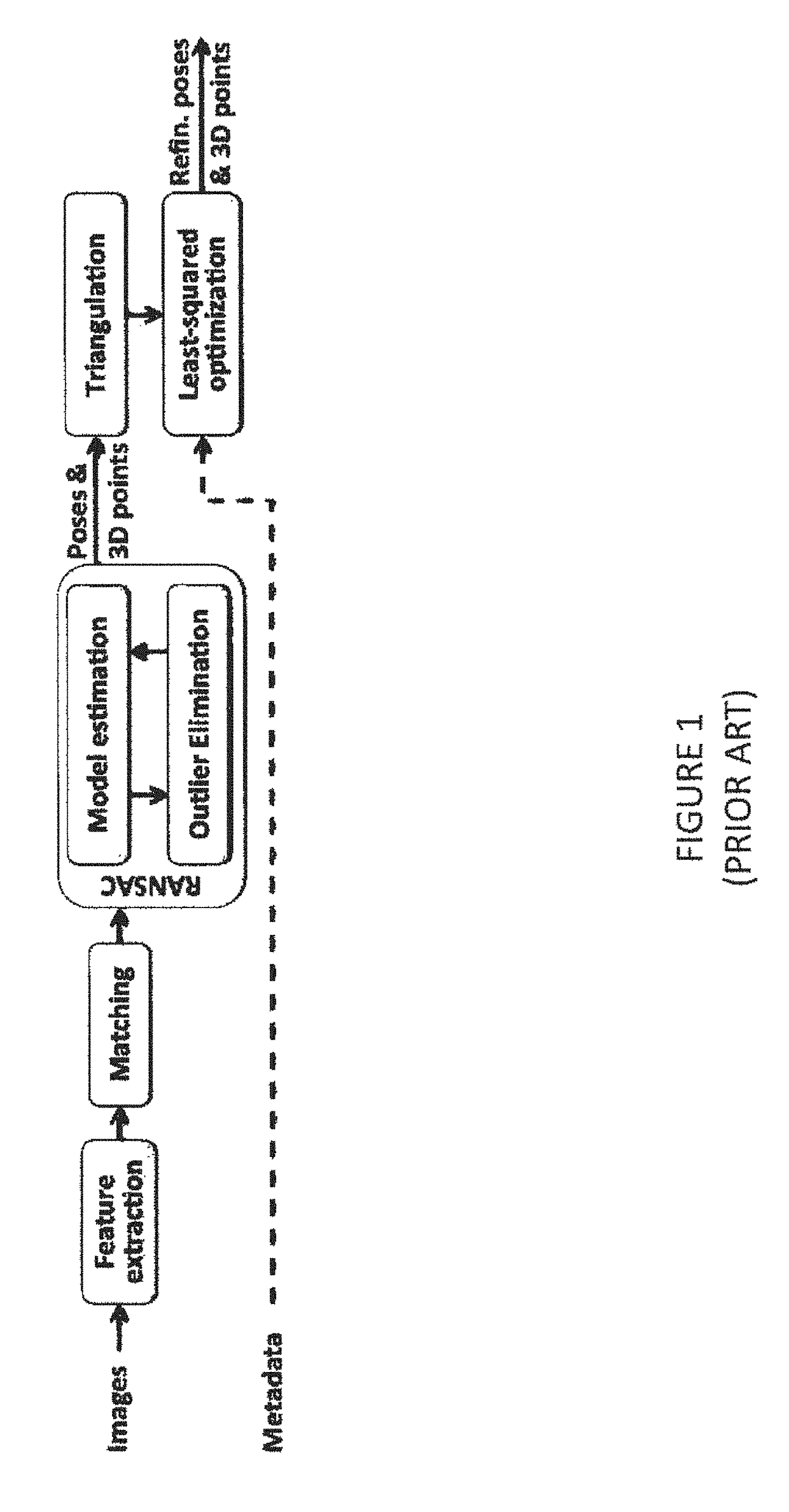
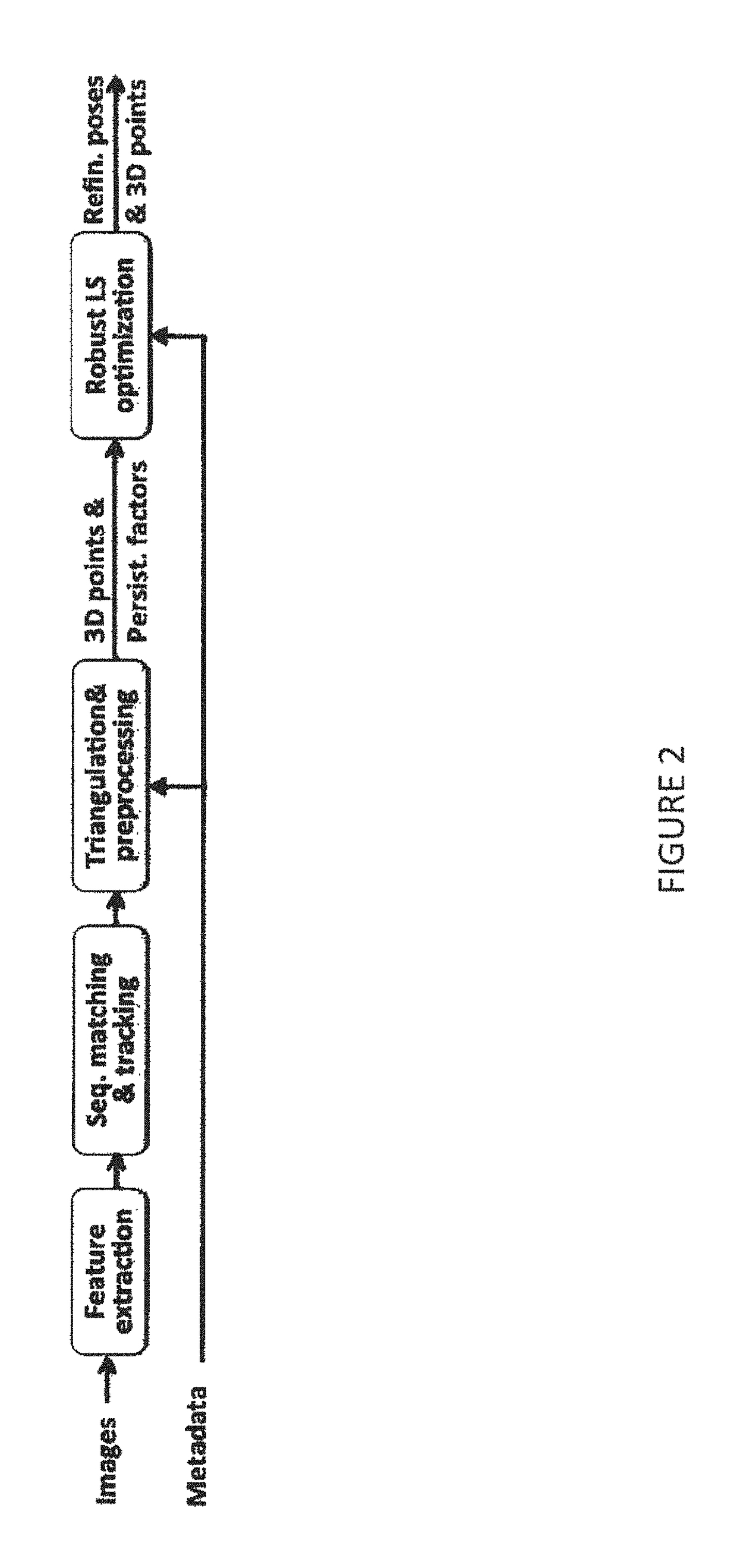
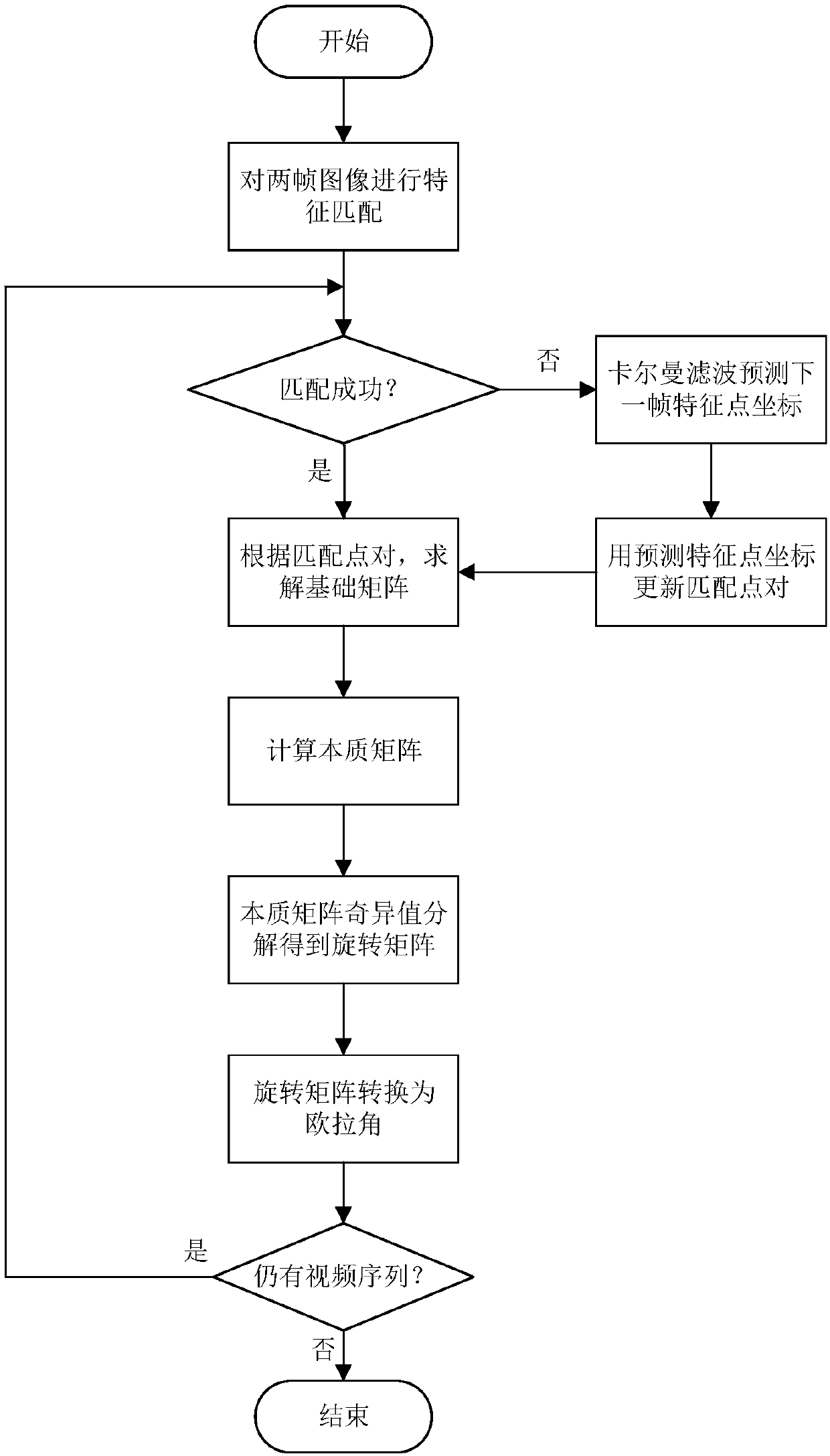
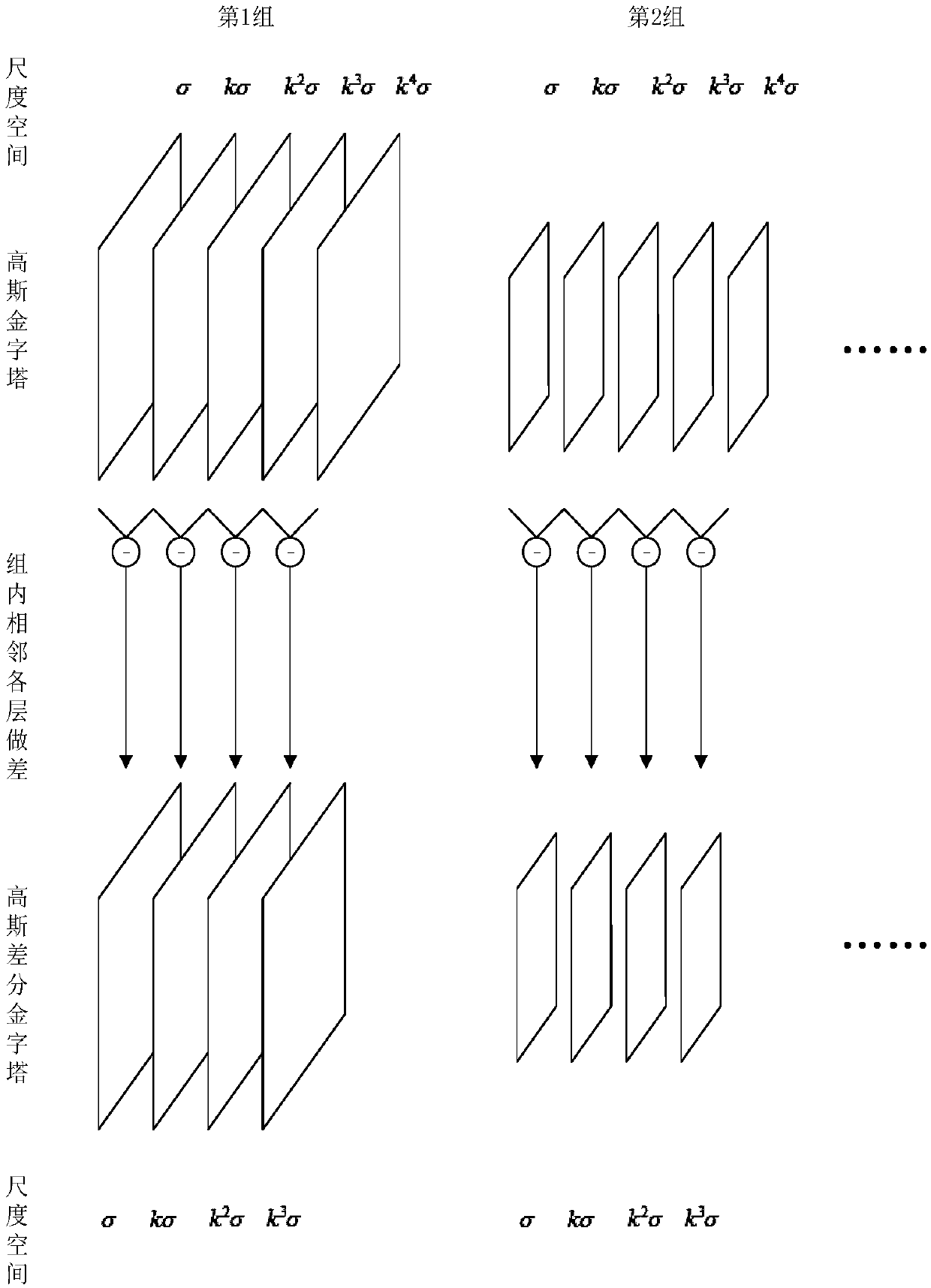
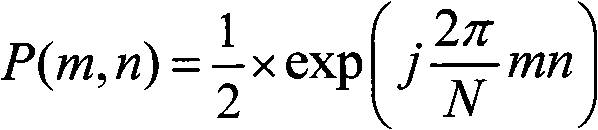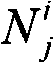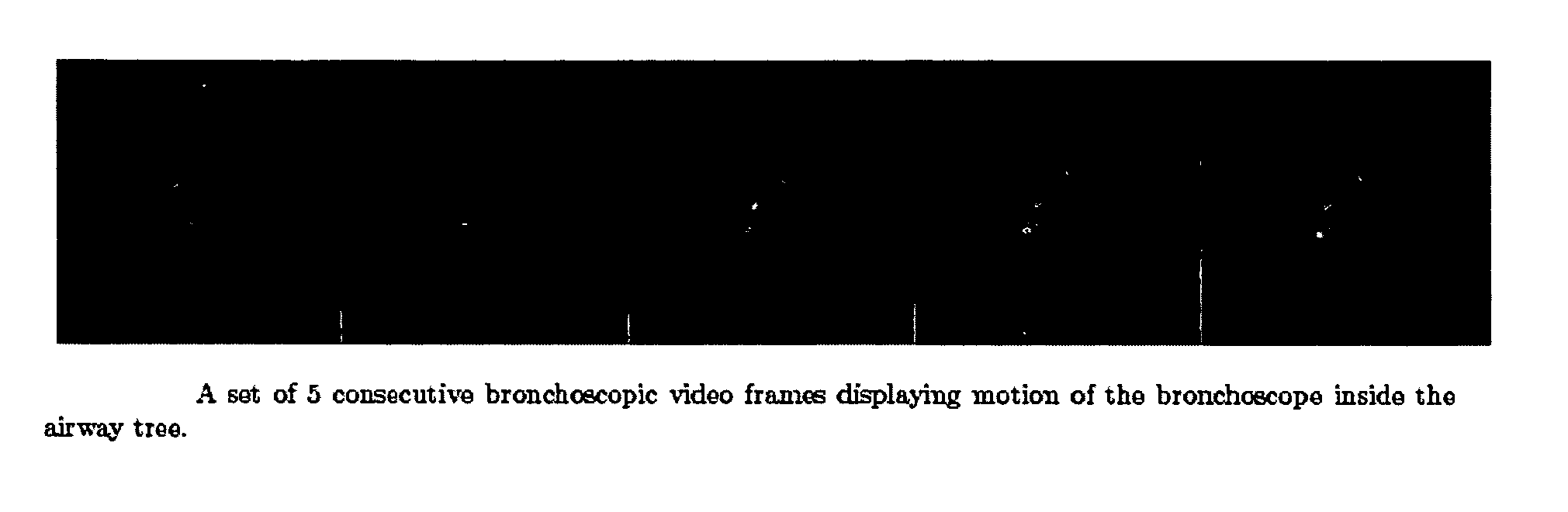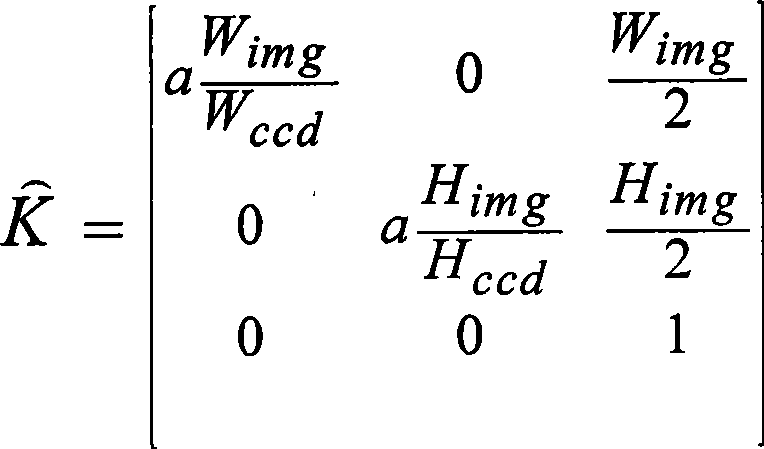Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
135 results about "Essential matrix" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
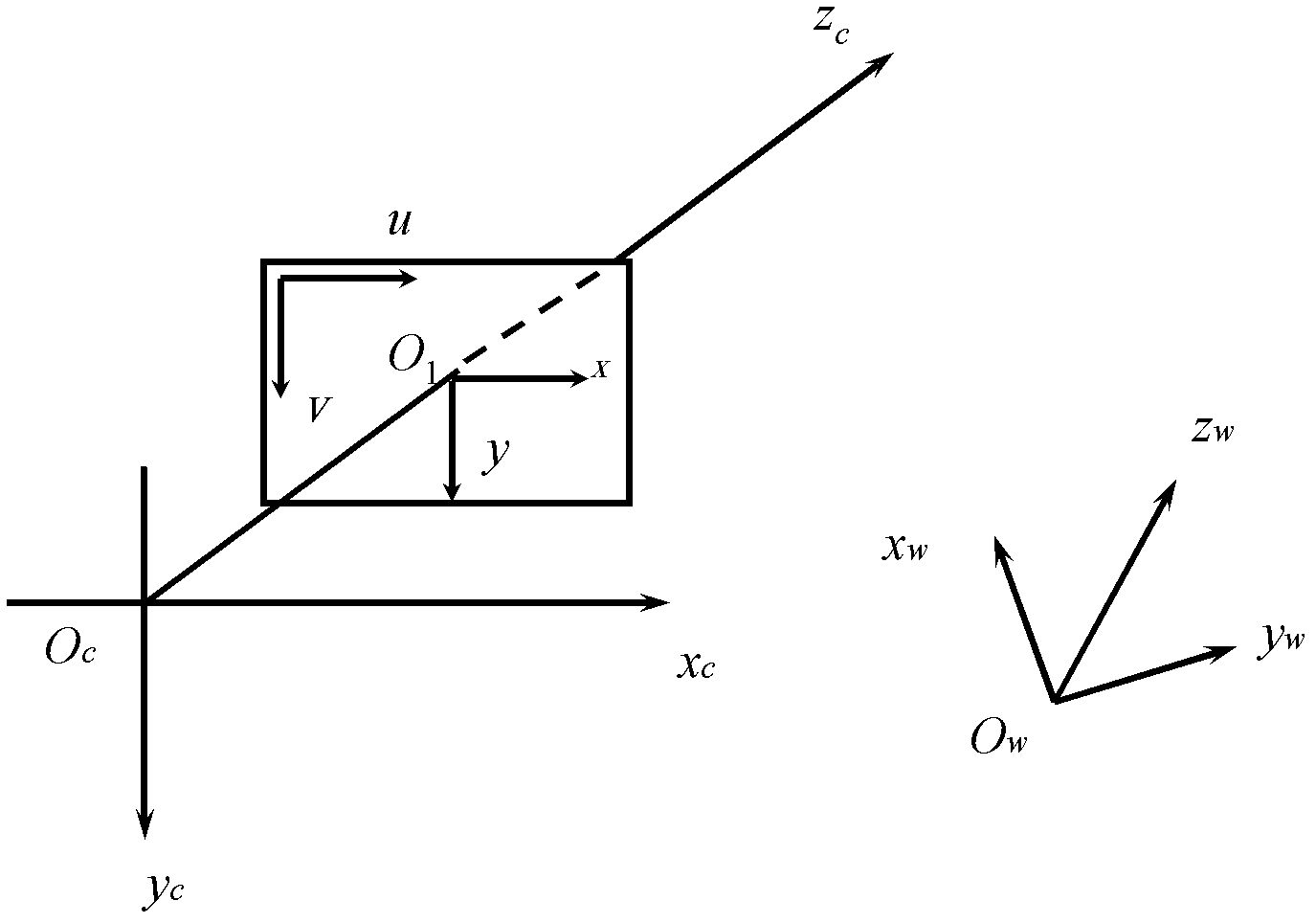
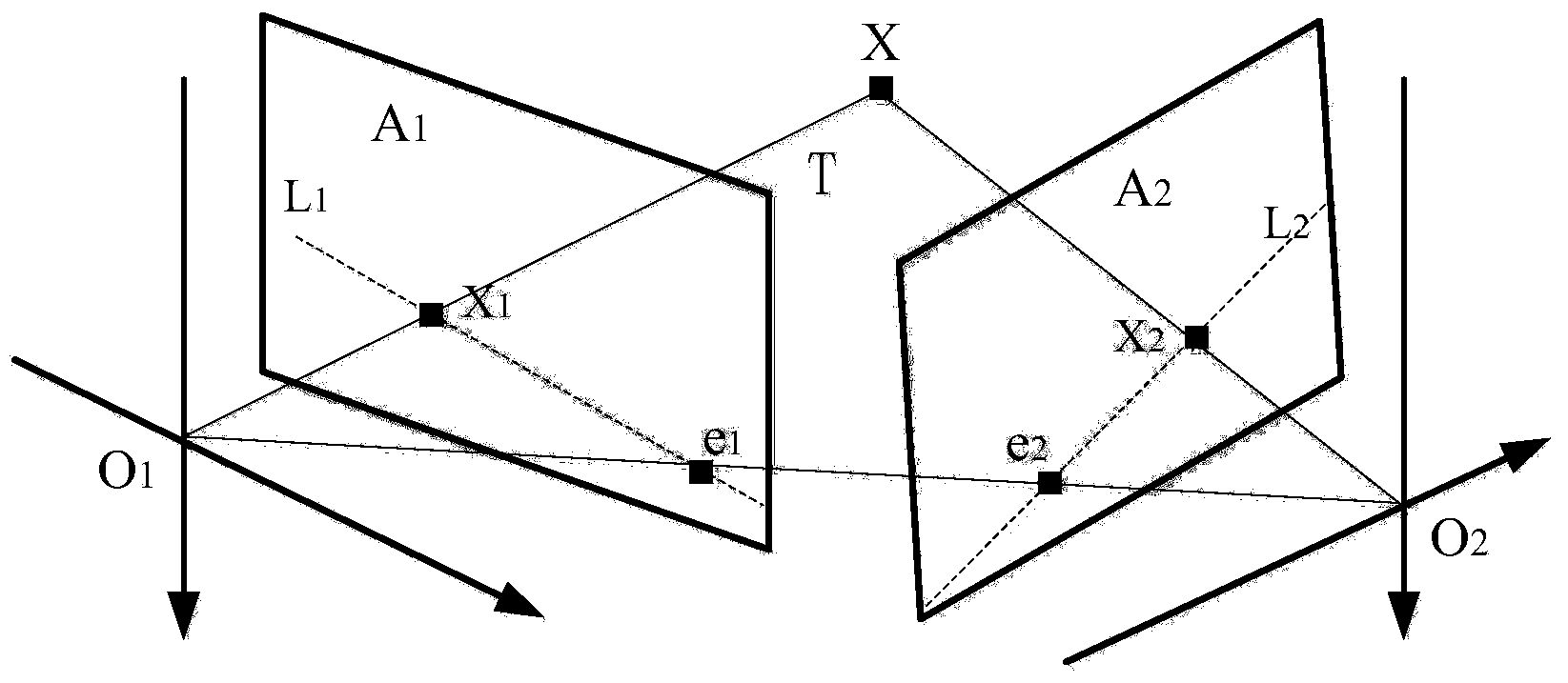
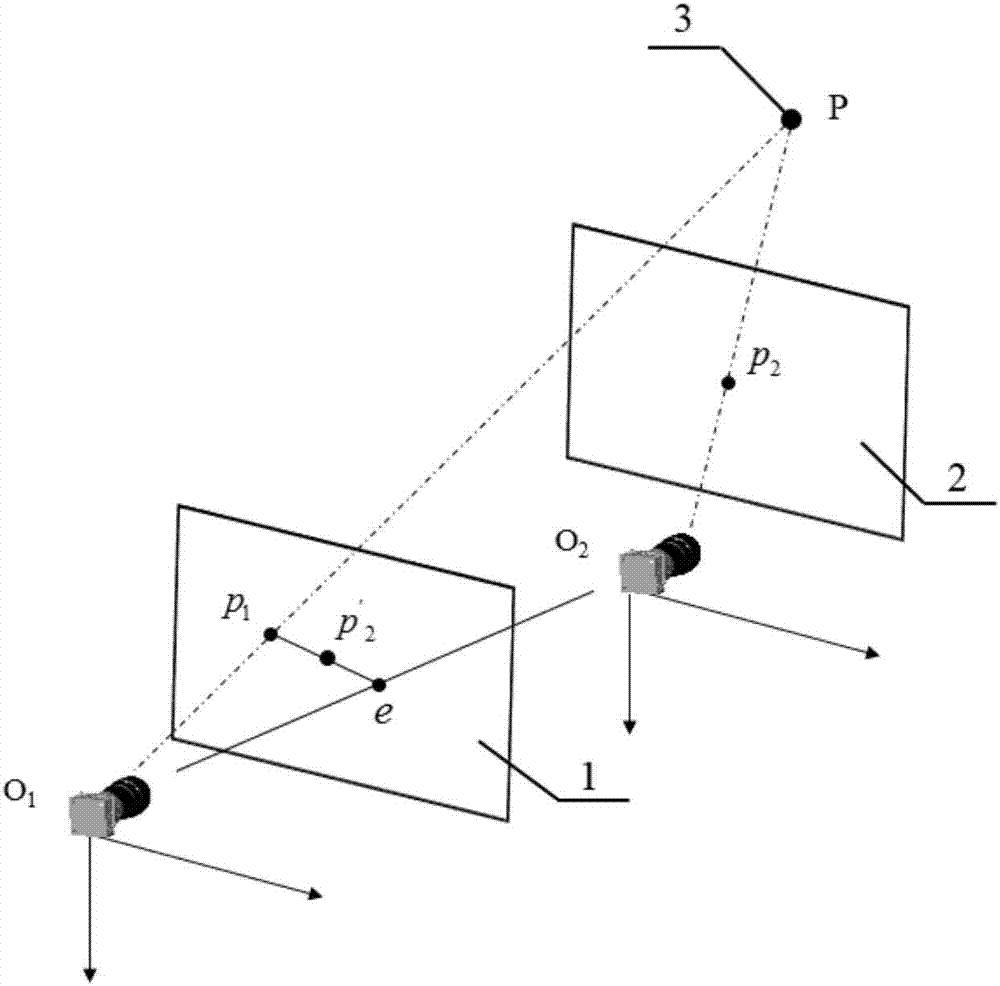
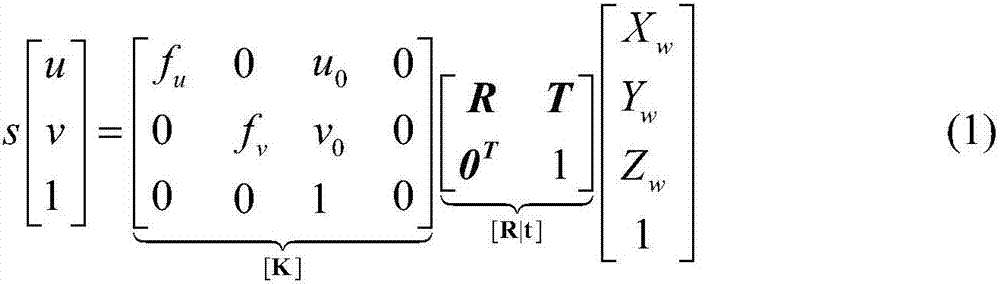
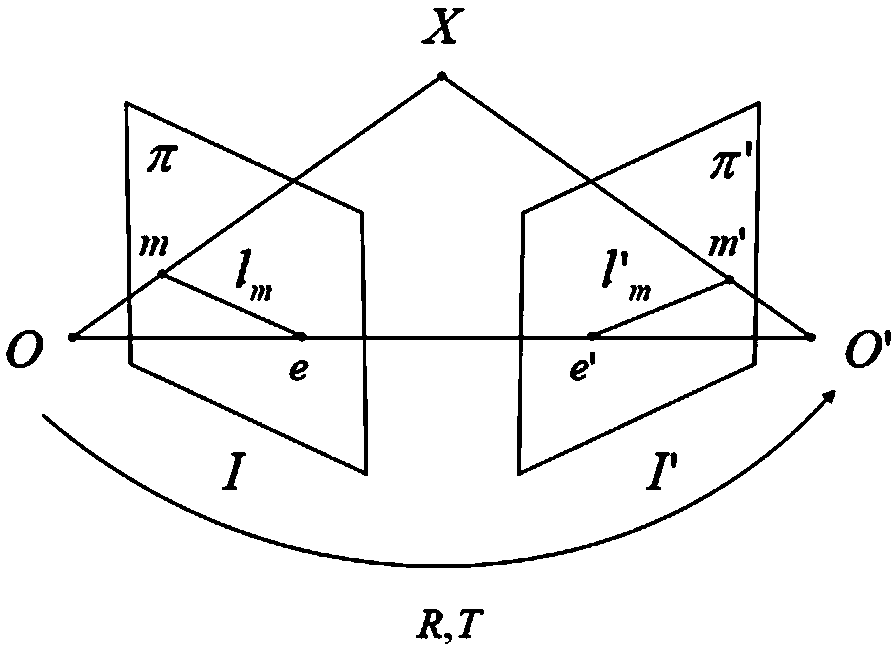
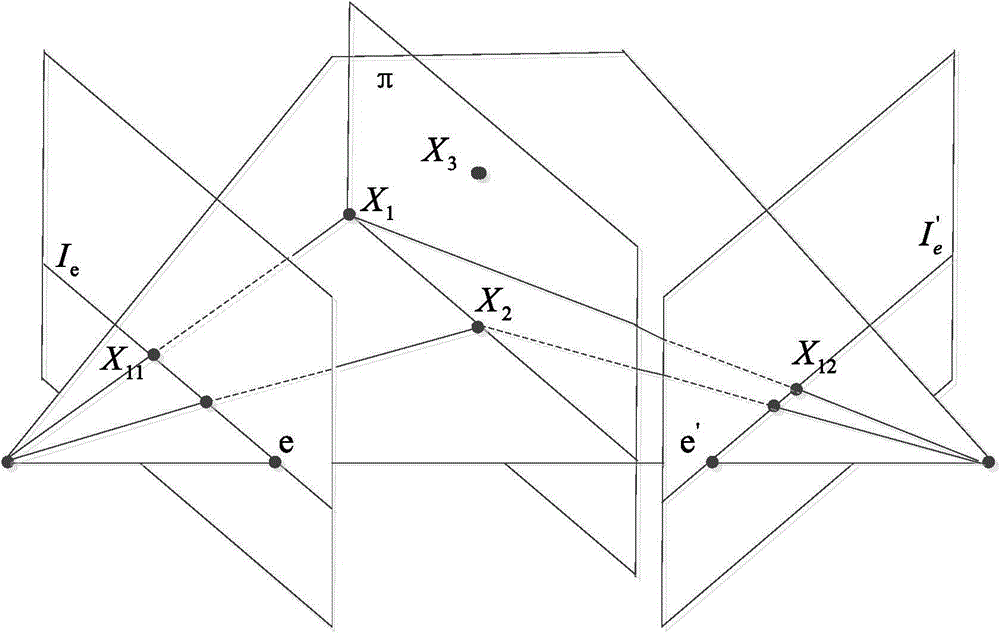
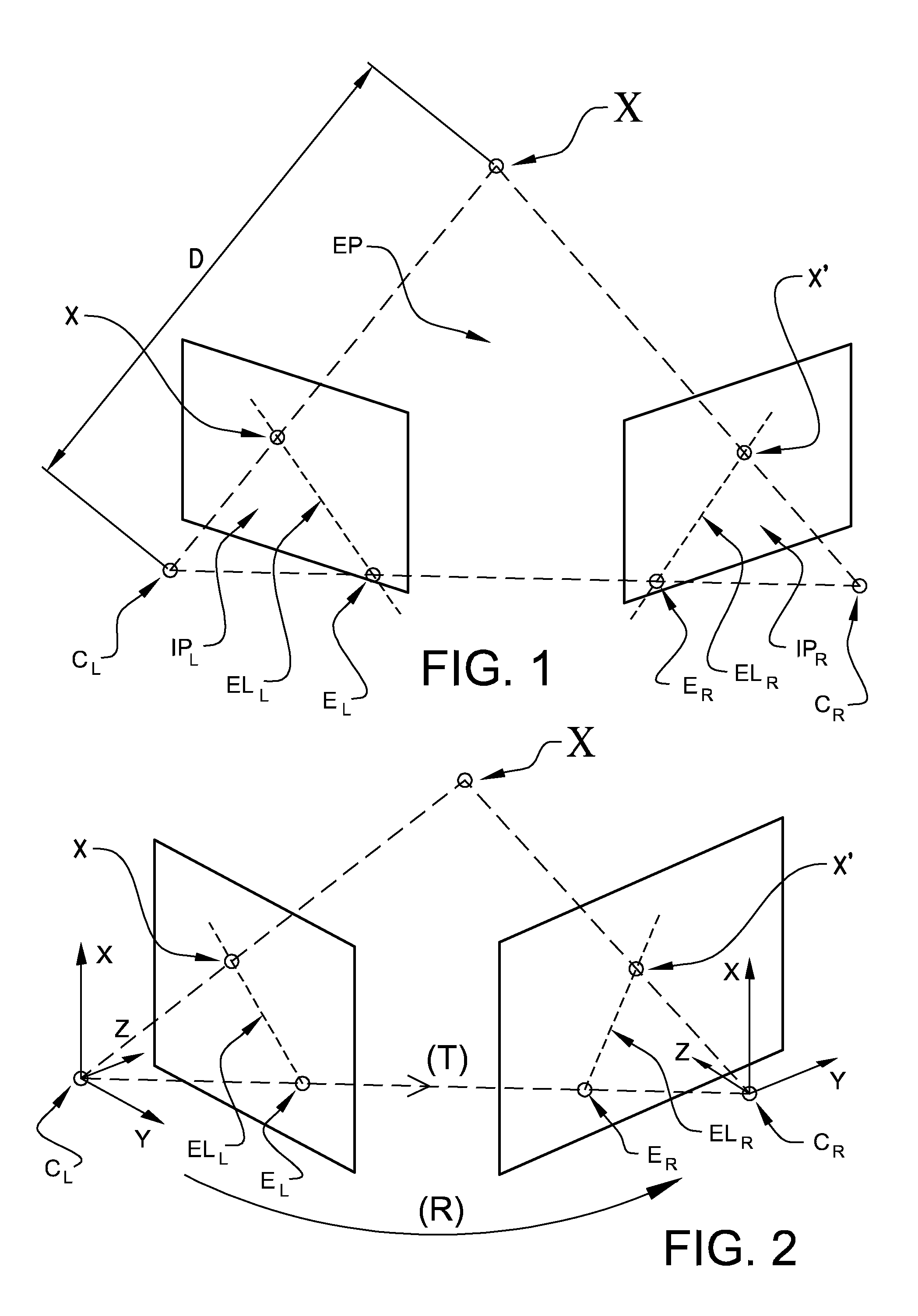
In computer vision, the essential matrix is a 3×3 matrix, 𝐄, with some additional properties described below, which relates corresponding points in stereo images assuming that the cameras satisfy the pinhole camera model.
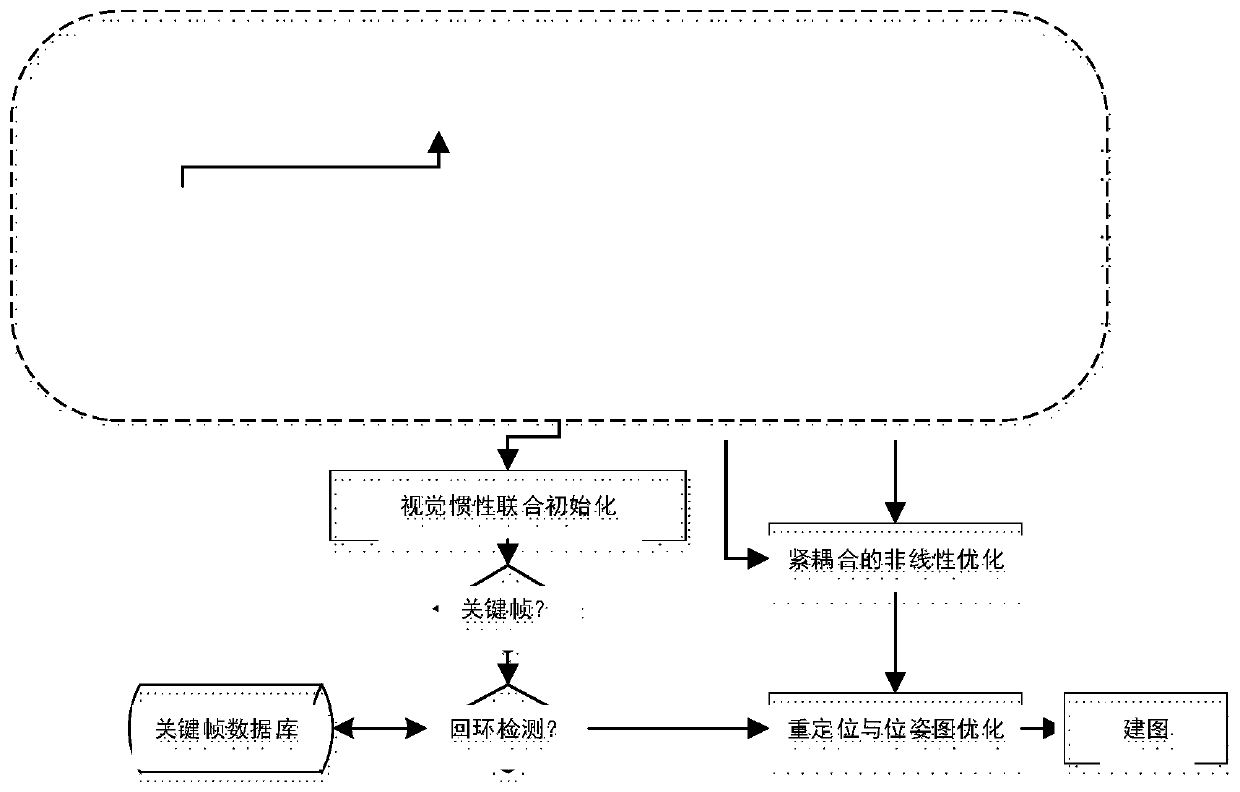
Monocular vision/inertia autonomous navigation method for indoor environment
ActiveCN102435188ALow costSimple algorithmNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsParallaxEssential matrix
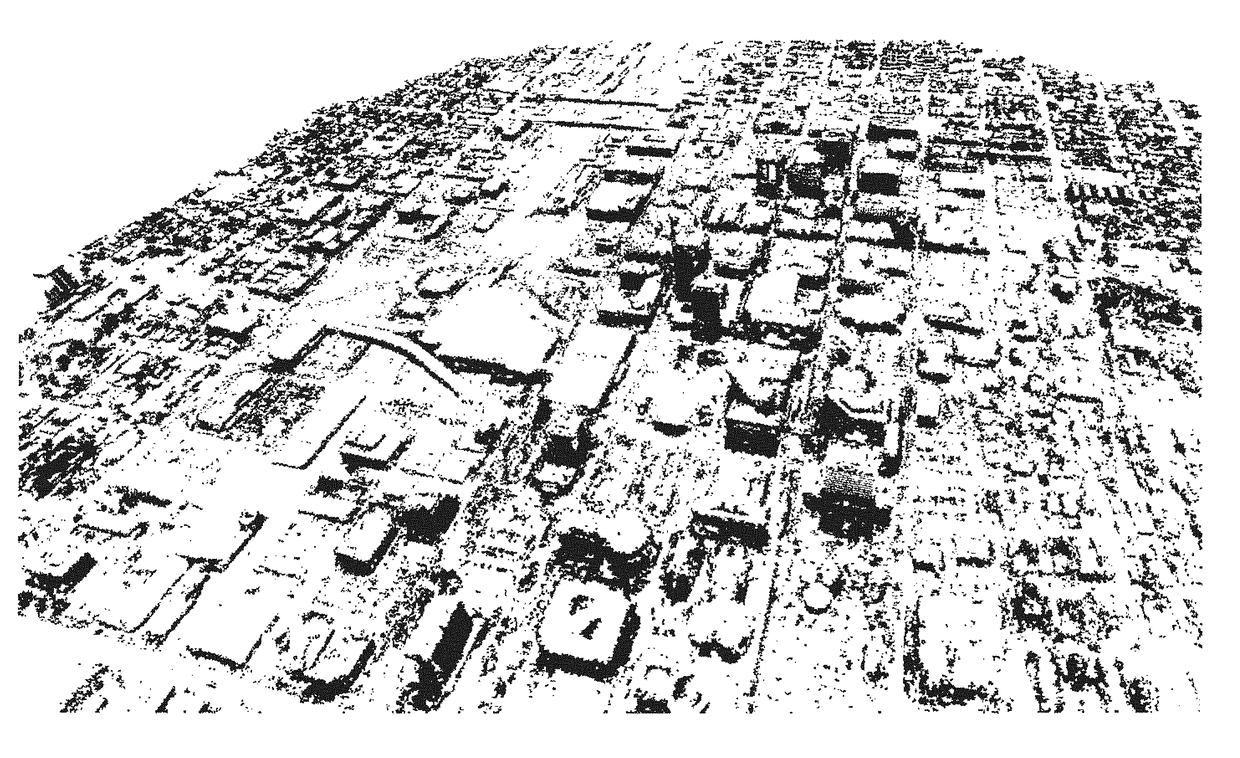
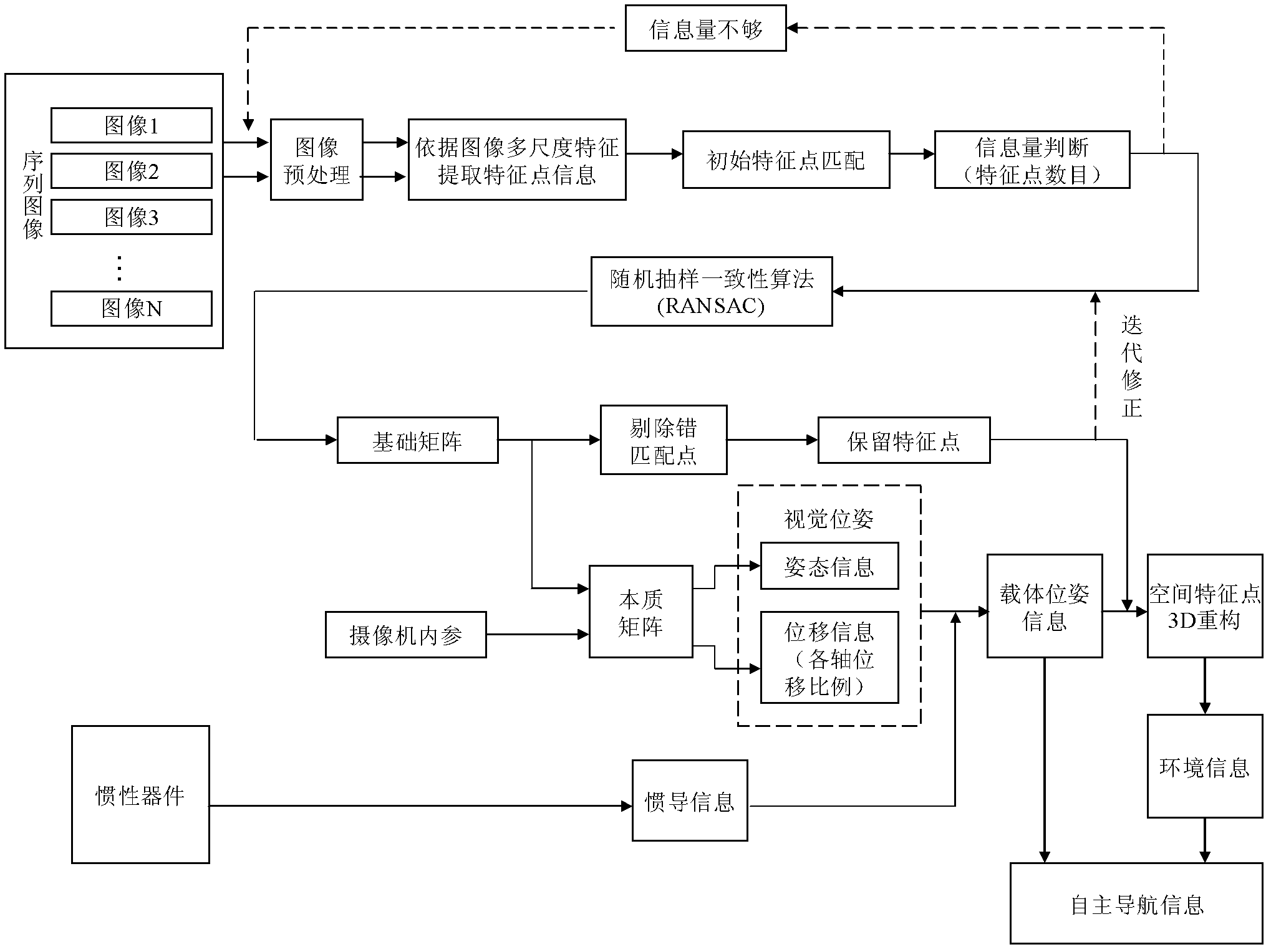
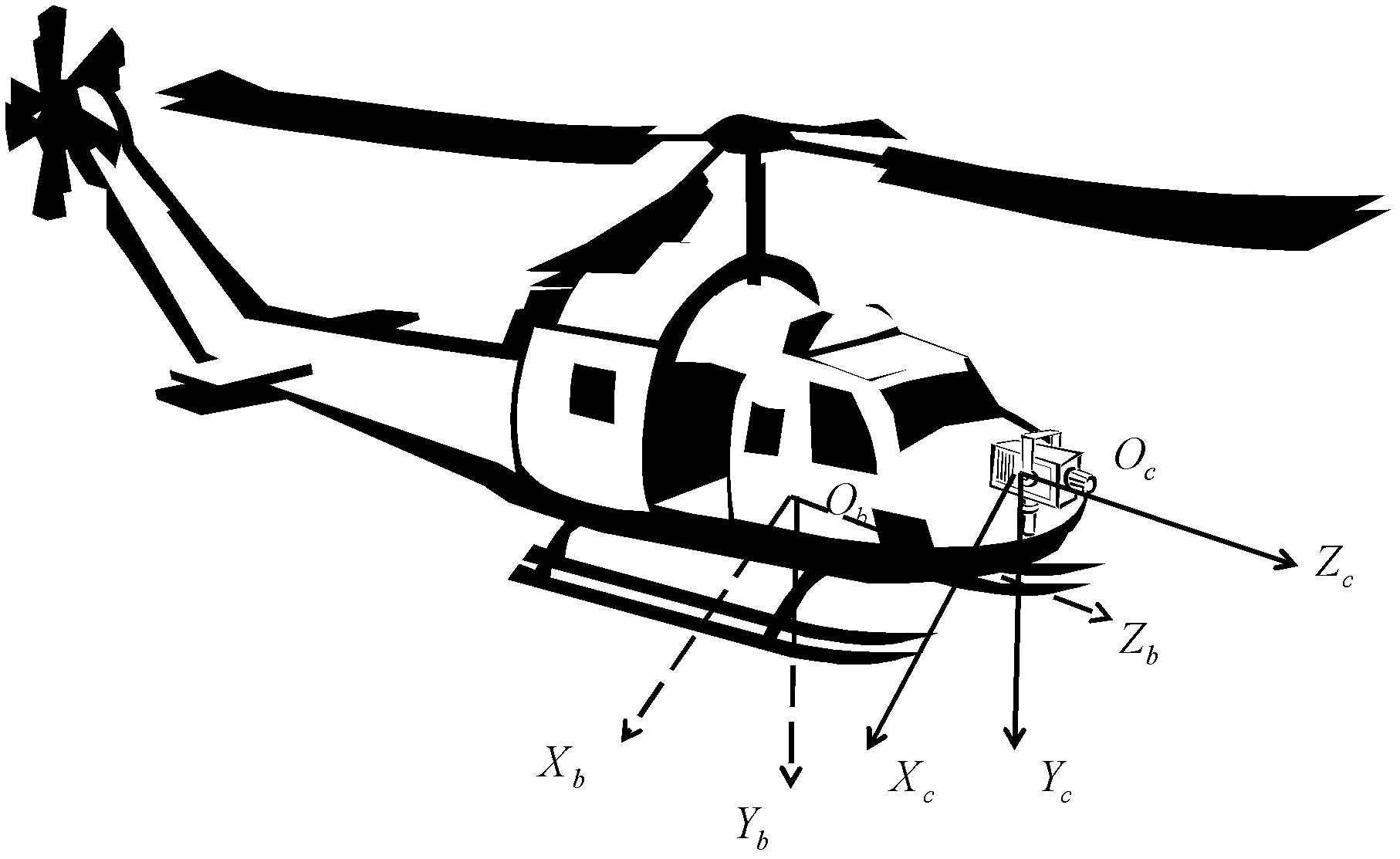
The invention discloses a monocular vision / inertia autonomous navigation method for an indoor environment, belonging to the field of vision navigation and inertia navigation. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring feature point information based on local invariant features of images, solving a basis matrix by using an epipolar geometry formed by a parallax generated by camera movements, solving an essential matrix by using calibrated camera internal parameters, acquiring camera position information according to the essential matrix, finally combining the vision navigation information with the inertia navigation information to obtain accurate and reliable navigation information, and carrying out 3D reconstruction on space feature points to obtain an environment information mapto complete the autonomous navigation of a carrier. According to the invention, the autonomous navigation of the carrier in a strange indoor environment is realized with independent of a cooperative target, and the method has the advantages of high reliability and low cost of implementation.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
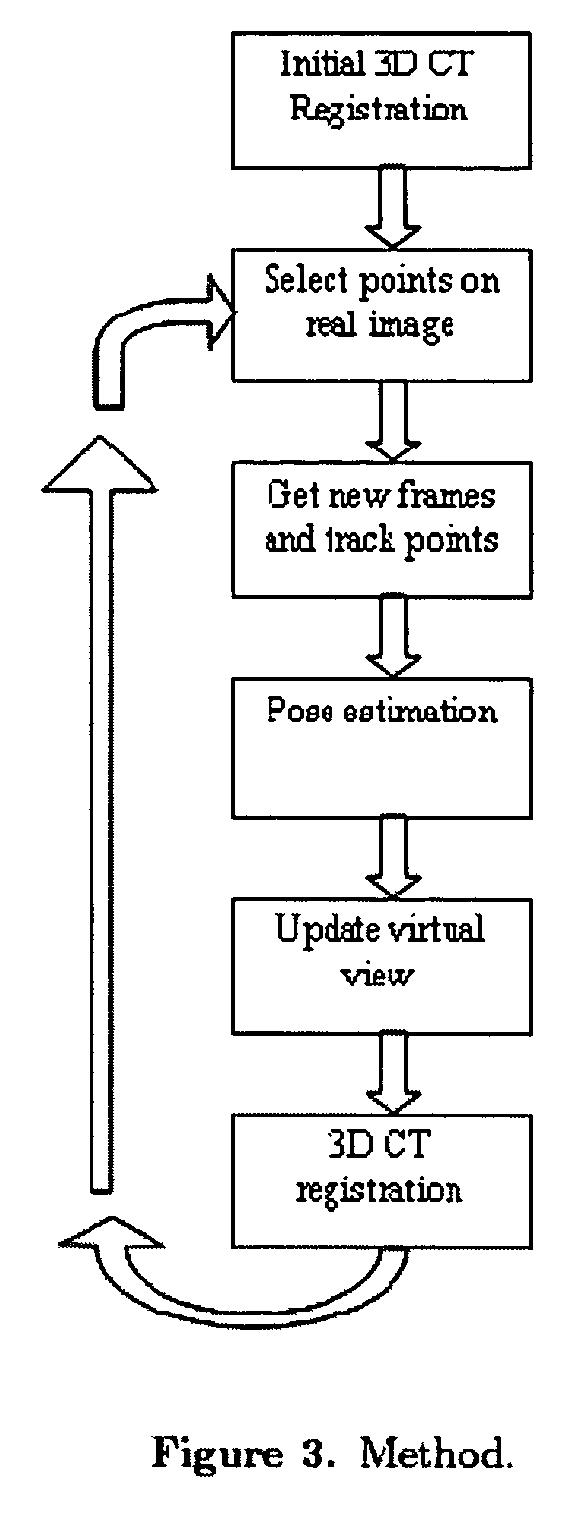
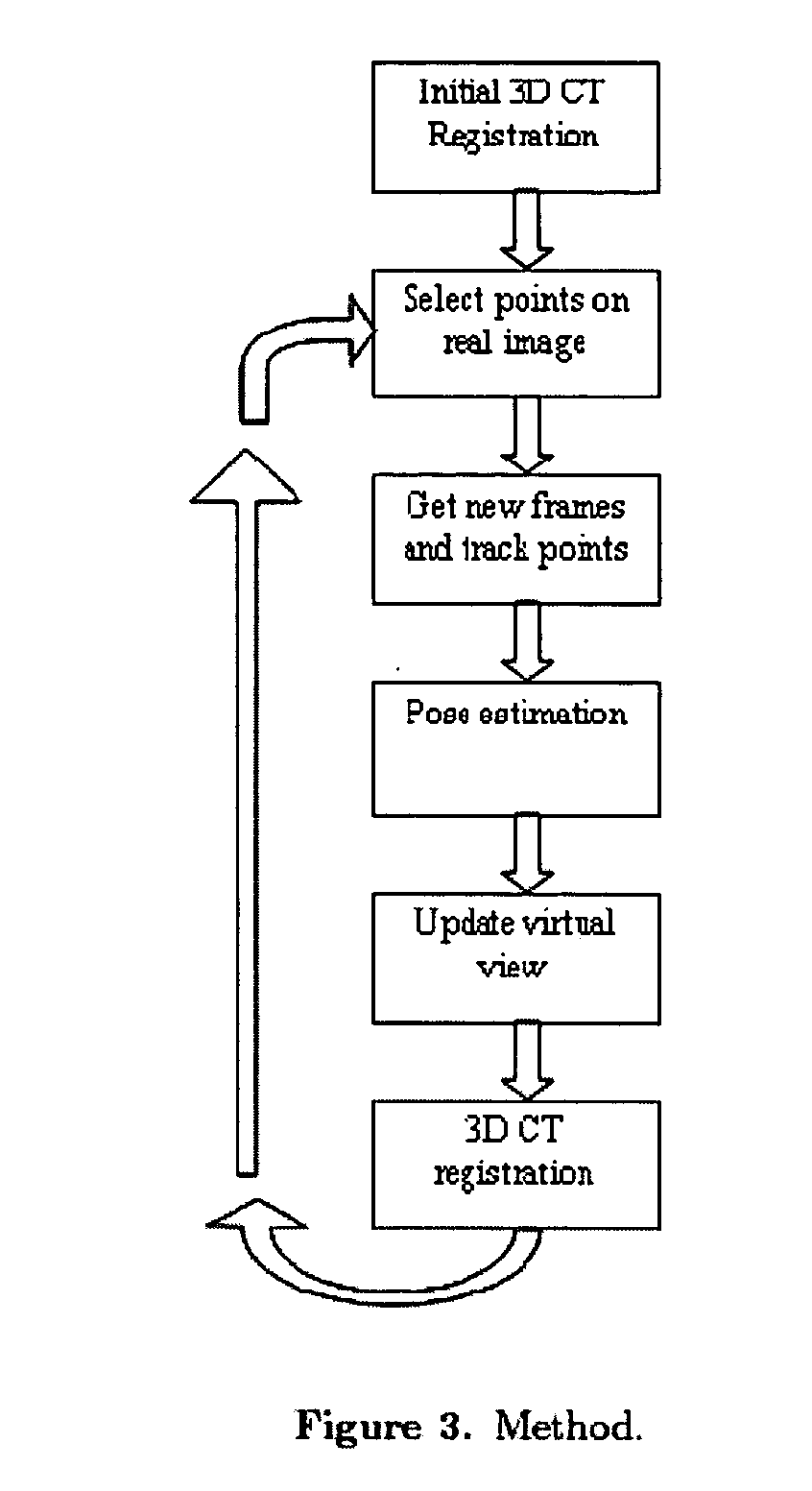
Guidance method based on 3D-2D pose estimation and 3D-CT registration with application to live bronchoscopy
ActiveUS7756563B2Maximizing costEasy to useRadiation diagnostic clinical applicationsSurgical navigation systemsGauss newton methodEndoscopic Procedure
A method provides guidance to the physician during a live bronchoscopy or other endoscopic procedures. The 3D motion of the bronchoscope is estimated using a fast coarse tracking step followed by a fine registration step. The tracking is based on finding a set of corresponding feature points across a plurality of consecutive bronchoscopic video frames, then estimating for the new pose of the bronchoscope. In the preferred embodiment the pose estimation is based on linearization of the rotation matrix. By giving a set of corresponding points across the current bronchoscopic video image, and the CT-based virtual image as an input, the same method can also be used for manual registration. The fine registration step is preferably a gradient-based Gauss-Newton method that maximizes the correlation between the bronchoscopic video image and the CT-based virtual image. The continuous guidance is provided by estimating the 3D motion of the bronchoscope in a loop. Since depth-map information is available, tracking can be done by solving a 3D-2D pose estimation problem. A 3D-2D pose estimation problem is more constrained than a 2D-2D pose estimation problem and does not suffer from the limitations associated with computing an essential matrix. The use of correlation-based cost, instead of mutual information as a registration cost, makes it simpler to use gradient-based methods for registration.
Owner:PENN STATE RES FOUND
Dynamic target position and attitude measurement method based on monocular vision at tail end of mechanical arm
ActiveCN103759716ASimplified Calculation Process MethodOvercome deficienciesPicture interpretationEssential matrixFeature point matching
The invention relates to a dynamic target position and attitude measurement method based on monocular vision at the tail end of a mechanical arm and belongs to the field of vision measurement. The method comprises the following steps: firstly calibrating with a video camera and calibrating with hands and eyes; then shooting two pictures with the video camera, extracting spatial feature points in target areas in the pictures by utilizing a scale-invariant feature extraction method and matching the feature points; resolving a fundamental matrix between the two pictures by utilizing an epipolar geometry constraint method to obtain an essential matrix, and further resolving a rotation transformation matrix and a displacement transformation matrix of the video camera; then performing three-dimensional reconstruction and scale correction on the feature points; and finally constructing a target coordinate system by utilizing the feature points after reconstruction so as to obtain the position and the attitude of a target relative to the video camera. According to the method provided by the invention, the monocular vision is adopted, the calculation process is simplified, the calibration with the hands and the eyes is used, and the elimination of error solutions in the measurement process of the position and the attitude of the video camera can be simplified. The method is suitable for measuring the relative positions and attitudes of stationery targets and low-dynamic targets.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Method for pre-encoding multi-input multi-output transmission and codebook encoding
InactiveCN101330479AReduce Feedback OverheadAvoid multiplicationTransmitter/receiver shaping networksError prevention/detection by diversity receptionMulti inputEssential matrix
The invention discloses a method for multi-input multi-output transmission for precoding. The method comprises the following steps: a fundamental matrix is selected, a column vector is selected from the fundamental matrix according to the dimension of a precoding matrix under each rank, the precoding matrixes are combined into codebooks, and the codebooks are respectively stored into the transmitting end and the receiving end of a multi-input multi-output transmission system; the receiving end selects precoding matrixes from the codebooks, and feeds back the indexes thereof to the transmitting end; the transmitting end uses the precoding matrixes corresponding to the indexes when the next transmission is performed, performs linear transformation in spatial domain to signals to be transmitted and then transmits the signals. The invention also discloses a method for multi-input multi-output codebook coding for precoding. The method enables the system to meet the feedback expenses and obtains good performance gain.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Multi-camera system calibrating method based on optical imaging test head and visual graph structure
ActiveCN102034238AHigh precisionImprove robustnessImage analysisStereoscopic photographyEssential matrixMulti camera
The invention provides a multi-camera system calibrating method based on an optical imaging test head and a visual graph structure. The method comprises the following steps: independently calibrating each camera by the optical imaging test head to obtain the initial values of the internal parameter and aberration parameter of each camera; calibrating the multiple cameras two by two, and obtaining the fundamental matrix, polar constraint, rotation matrix and translation vector between every two cameras with a plurality of overlapped regions at a view field by means of linear estimation; building the connection relationship among the multiple cameras according to the graph theory and the visual graph structure, and estimating the rotation vector quantity initial value and translation vector quantity initial value of each camera relative to the referred cameras by a shortest path method; and optimally estimating all the internal parameters and external parameters of the all cameras and the acquired three-dimensional sign point set of the optical imaging test head by a sparse bundling and adjusting algorithm to obtain a high-precision calibrating result. The multi-camera system calibrating method is simple in a calibrating process from the partial situation to the overall situation and from the robust to the precise, ensures high-precise and robust calibration, and is applied to calibrating multi-camera systems with different measurement ranges and different distribution structures.
Owner:SUZHOU DEKA TESTING TECH CO LTD
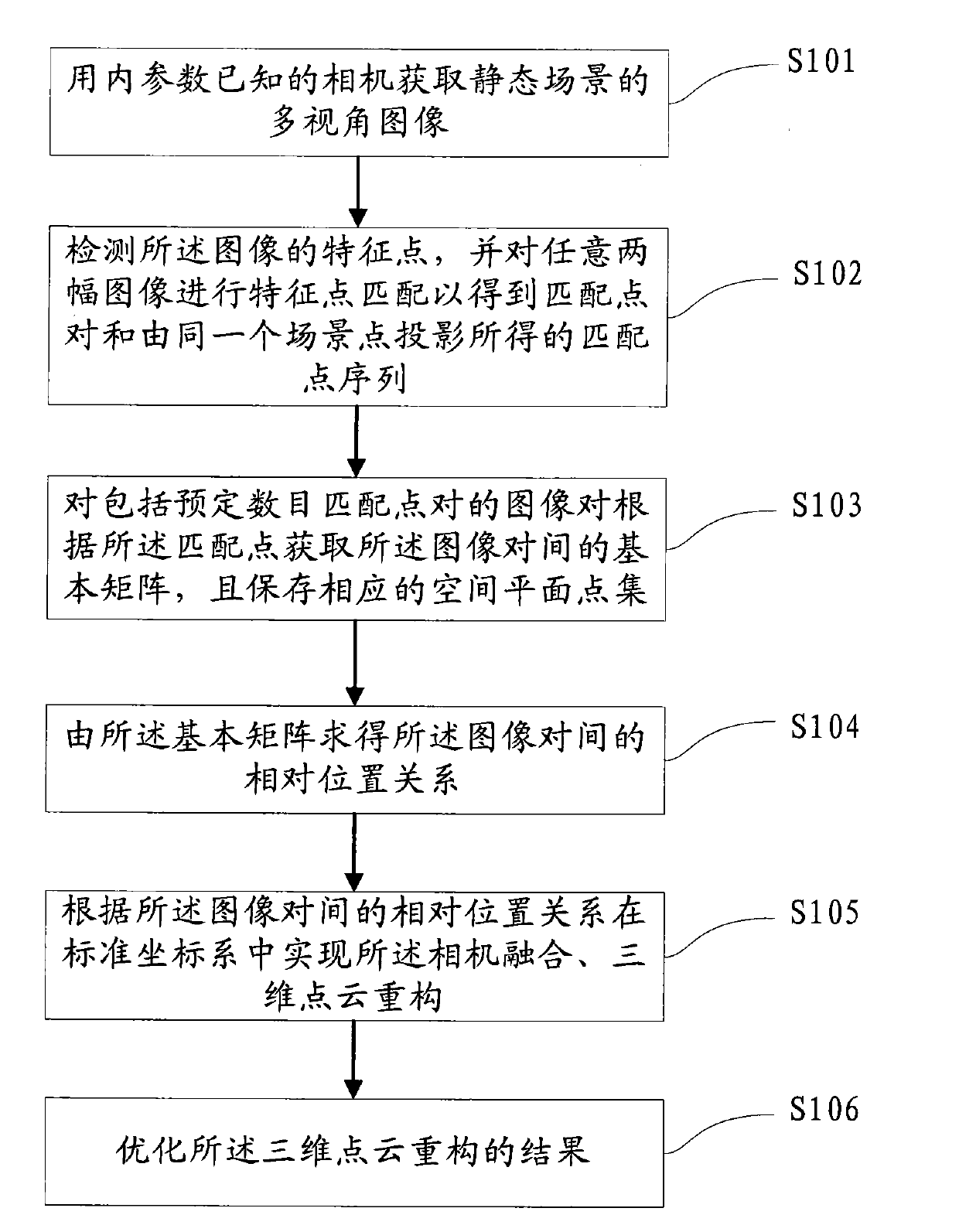
Reconstruction method and system for processing three-dimensional point cloud containing main plane scene
The invention proposes a reconstruction method and system for processing three-dimensional point cloud containing a main plane scene. The method comprises the following steps of obtaining a multi-angle image of a static scene by using a camera with known internal parameters; detecting characteristic points of the image, and matching characteristic points of any two images to obtain a matched point pairs and obtaining a matched point sequence by projecting the same scene point; for image pairs containing the preset number of matched point pairs, obtaining a basic array between the image pairs according to the matched points, and storing corresponding space plane point sets; determining the corresponding position relationship between the image pairs according to the basic array; realizing camera fusion and three-dimensional point reconstruction in a standard coordinate frame according to the corresponding position relationship between the image pairs; and optimizing the reconstruction result of the three-dimensional point cloud. The reconstruction method for processing three-dimensional point cloud containing main plane scene of the invention can overcome defects of the existing reconstruction method for processing three-dimensional point cloud and can realize the three-dimensional reconstruction not depending on the scene.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Guidance method based on 3D-2D pose estimation and 3D-CT registration with application to live bronchoscopy
ActiveUS20070015997A1Maximizing costEasy to useRadiation diagnostic clinical applicationsSurgical navigation systemsGauss newton methodEndoscopic Procedure
A method provides guidance to the physician during a live bronchoscopy or other endoscopic procedures. The 3D motion of the bronchoscope is estimated using a fast coarse tracking step followed by a fine registration step. The tracking is based on finding a set of corresponding feature points across a plurality of consecutive bronchoscopic video frames, then estimating for the new pose of the bronchoscope. In the preferred embodiment the pose estimation is based on linearization of the rotation matrix. By giving a set of corresponding points across the current bronchoscopic video image, and the CT-based virtual image as an input, the same method can also be used for manual registration. The fine registration step is preferably a gradient-based Gauss-Newton method that maximizes the correlation between the bronchoscopic video image and the CT-based virtual image. The continuous guidance is provided by estimating the 3D motion of the bronchoscope in a loop. Since depth-map information is available, tracking can be done by solving a 3D-2D pose estimation problem. A 3D-2D pose estimation problem is more constrained than a 2D-2D pose estimation problem and does not suffer from the limitations associated with computing an essential matrix. The use of correlation-based cost, instead of mutual information as a registration cost, makes it simpler to use gradient-based methods for registration.
Owner:PENN STATE RES FOUND
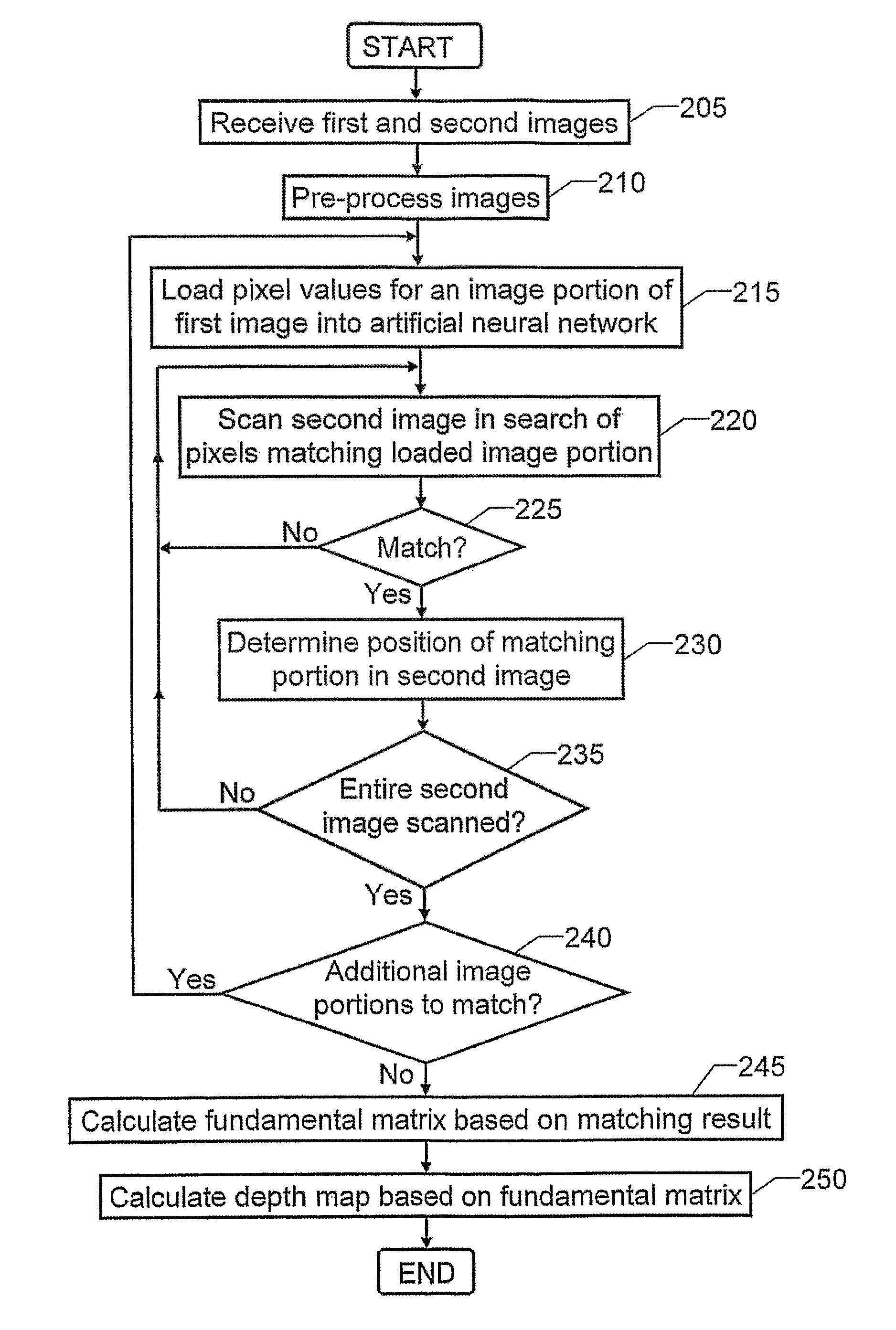
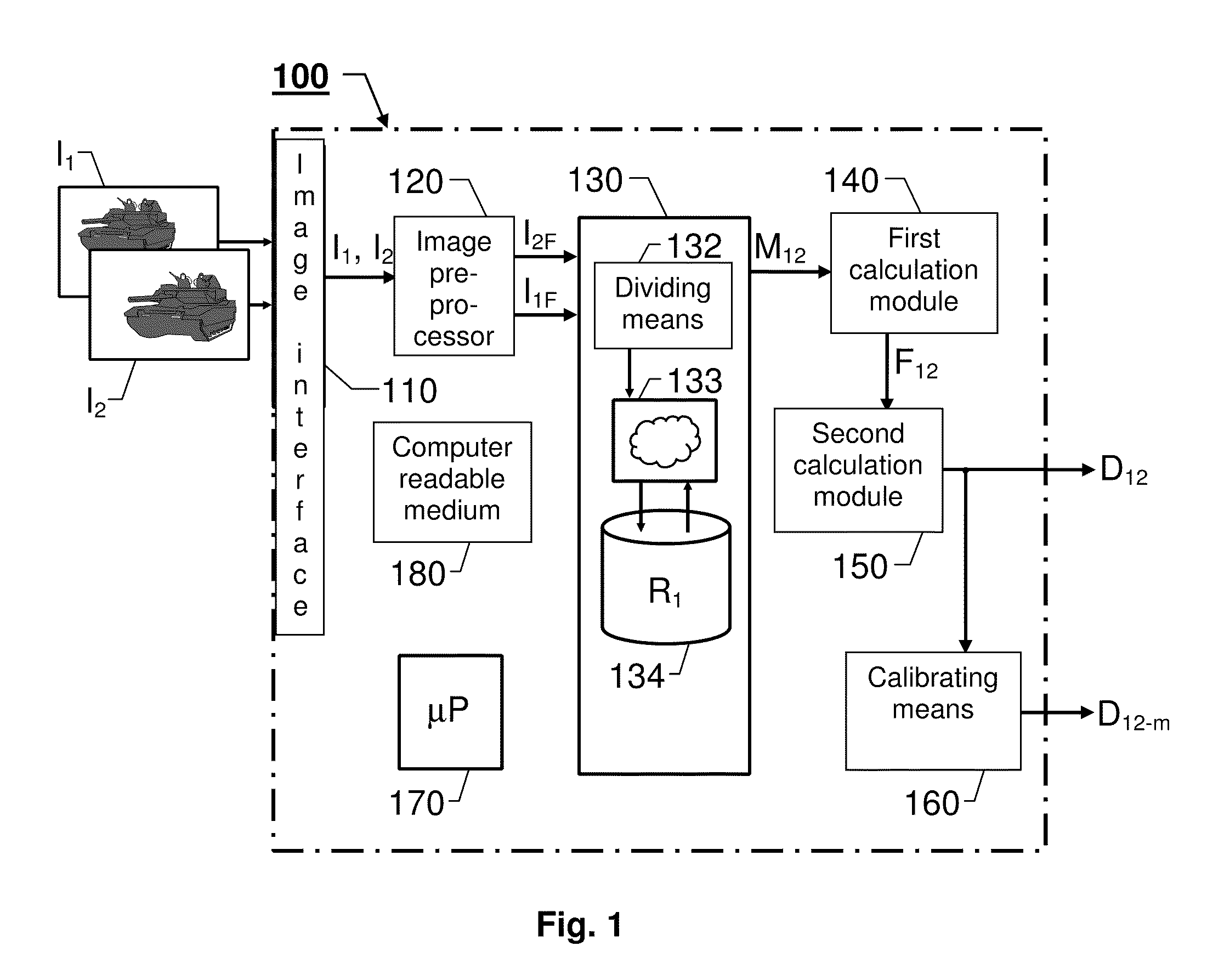
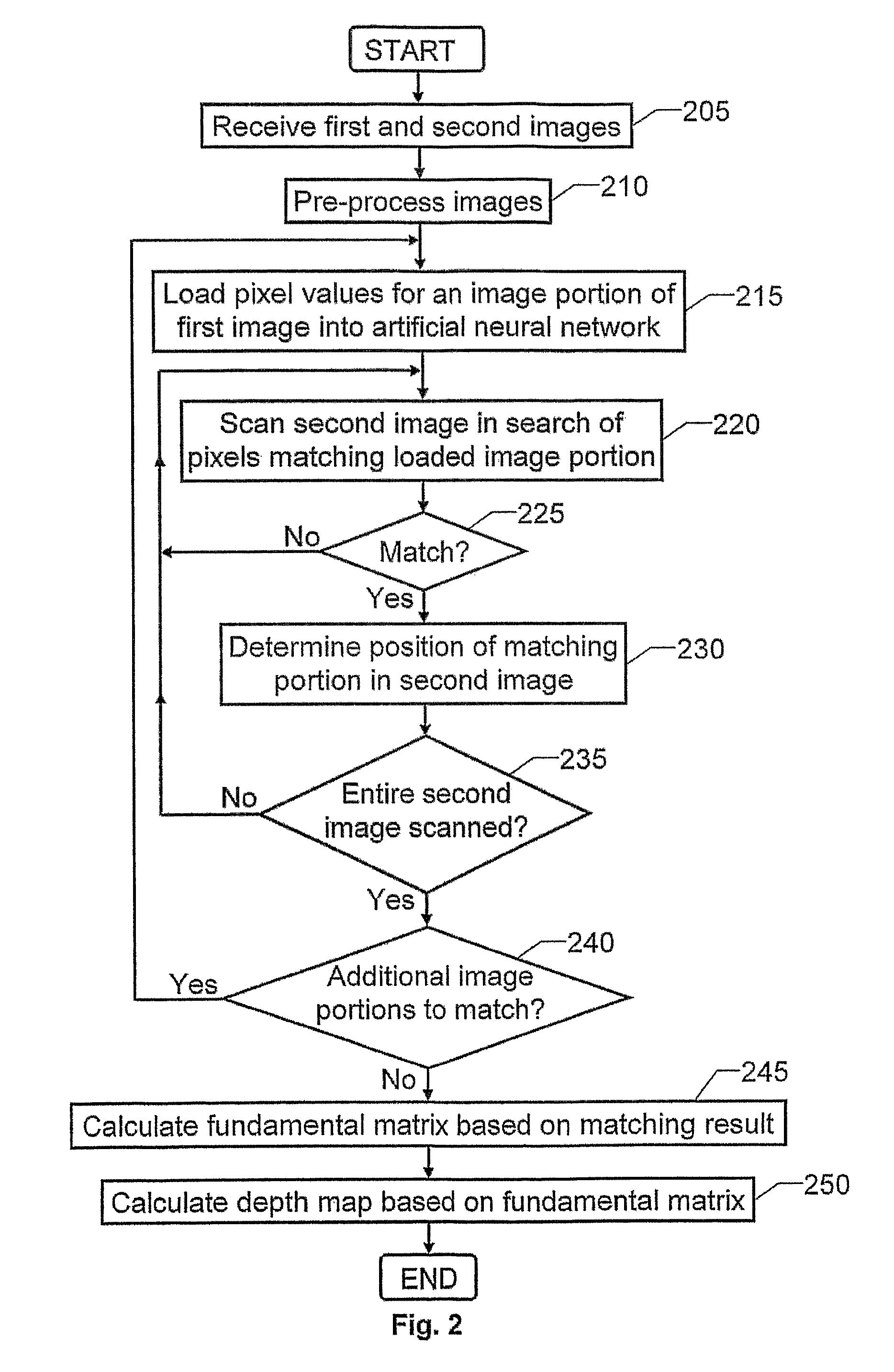
Computer modeling of physical scenes
The present invention relates to automatic modeling of a physical scene. At least two images (I1, I2) of the scene are received, which are taken from different angles and / or positions. A matching module (130) matches image objects in the first image (I1) against image objects in the second image (I2), by first loading pixel values for at least one first portion of the first image (I1) into an artificial neural network (133). Then, the artificial neural network (133) scans the second image (I2) in search of pixels representing a respective second portion corresponding to each of the at least one first portion; determines a position of the respective second portion upon fulfillment of a match criterion; and produces a representative matching result (M12). Based on the matching result (M12), a first calculation module (140) calculates a fundamental matrix (F12), which defines a relationship between the first and second images (I1, I2). Based on the fundamental matrix (F12), in turn, a second calculation module (150) calculates a depth map (D12), which describes distance differences between a set of image points in the first image (I1) and a corresponding set of image points in the second image (I2). Finally, the depth map (D12) constitutes a basis for a synthetic model of the scene.
Owner:SAAB AB
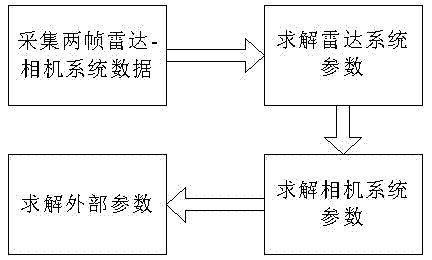
Random trihedron-based radar-camera system external parameter calibration method
InactiveCN103049912ALow noise immunityLow operational complexity requirementsImage analysisEssential matrixRadar systems
The invention discloses a random trihedron-based radar-camera system external parameter calibration method. According to the method, an external parameter of a system can be solved with only two frames of data by using a trihedron scene a natural environment. The method comprises the following steps of: stipulating a world coordinate system by using a trihedron; performing planar fitting on the trihedron observed in a radar system to obtain a parameter of each plane and solving conversion relation of the world coordinate system and the radar coordinate system and relative motion between the two frames of data under the radar coordinate system; and in a camera system, solving an essential matrix by using matching characteristic points extracted by front and rear frames, then solving relation motion under the camera coordinate system, solving the plane parameter under the camera coordinate system by using the parameter under the radar coordinate system, finally solving an external parameter of a radar-camera, and performing final optimization by using coplanarity of points on corresponding planes under the two coordinate systems. A scene required by the method is simpler; and the method has the characteristics of high anti-interference performance, simple experimental equipment and high flexibility.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
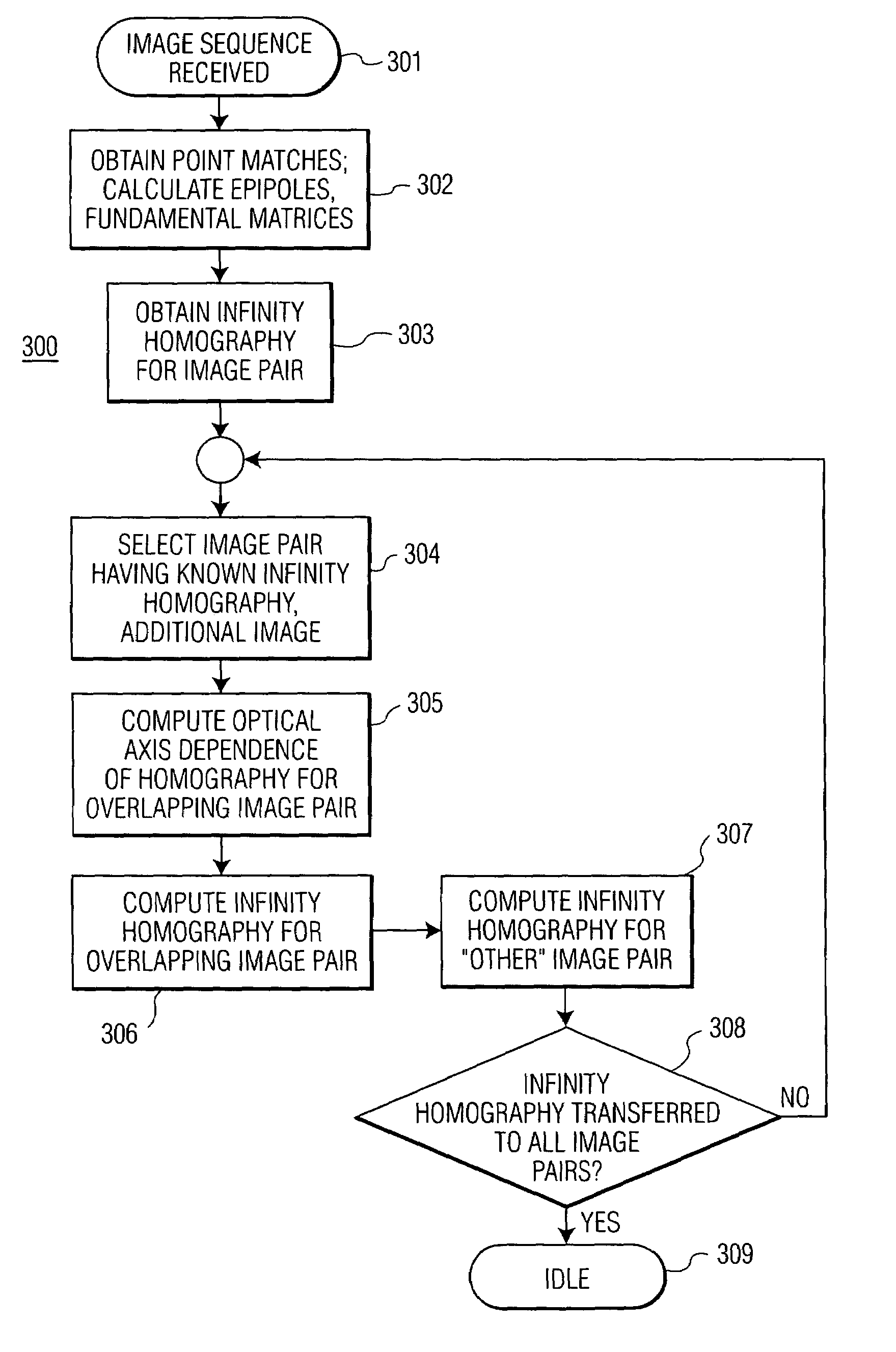
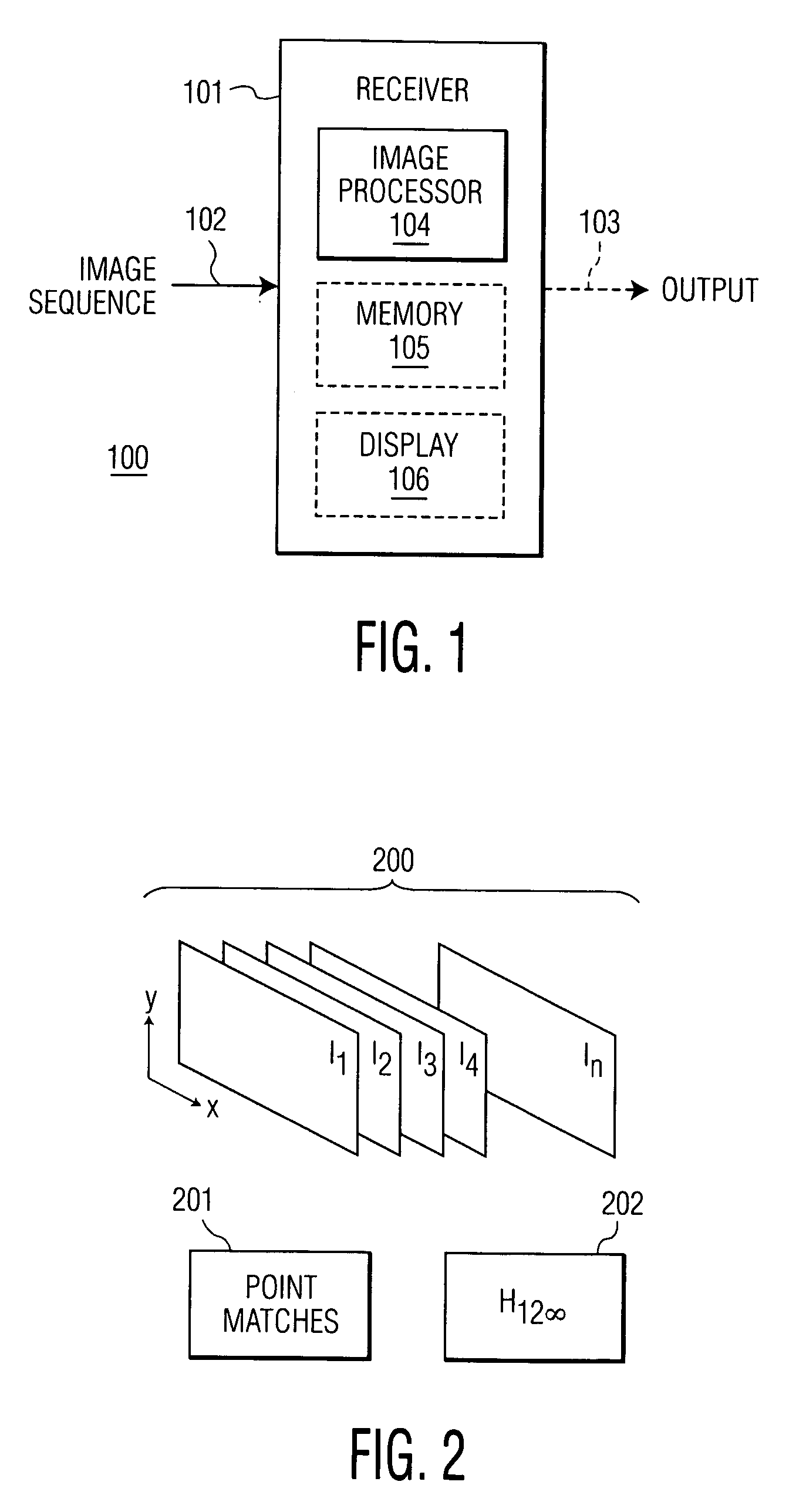
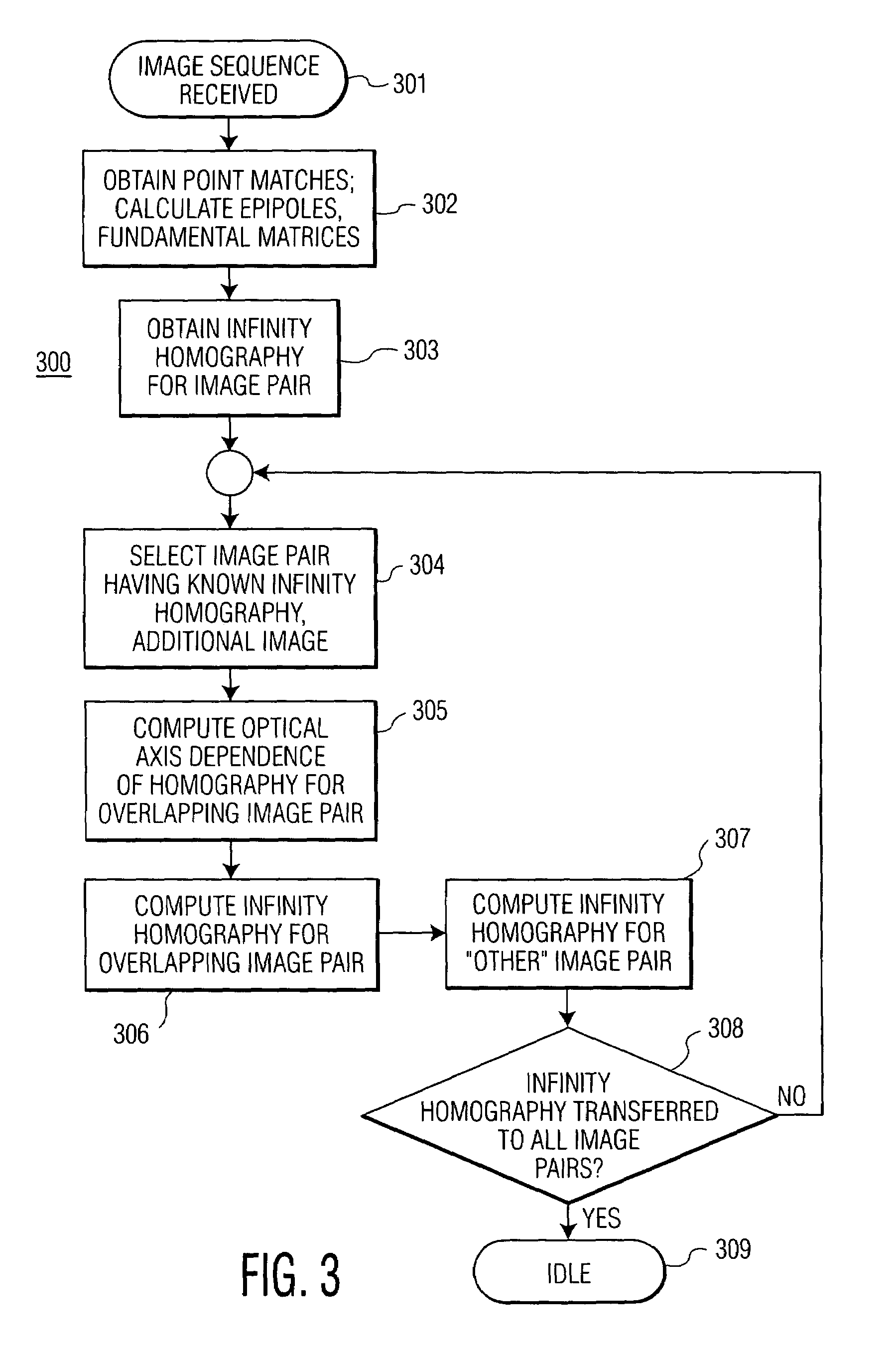
Homography transfer from point matches
InactiveUS7003150B2Image analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionPattern recognitionEssential matrix
An infinity homography for an image pair within an image sequence is transferred to other image pairs within the image sequence utilizing point matches for the subject image pairs. An image set including the image pair for which the infinity homography is known and a third image are selected. Then intermediate parameters for homography transfer for one image pair overlapping the known infinity homography image pair is computed from the known infinity homography and epipoles and fundamental matrices of the overlapping image pairs, to derive the infinity homography for the selected overlapping image pair. The process may then be repeated until infinity homographies for all image pairs of interest within the image sequence have been derived.
Owner:UNILOC 2017 LLC
Method of generating 3D house type model by 2D house type model based on camera shooting
InactiveCN104821011AAccurately Responds to Structural InformationThe generation method is simple3D modellingEssential matrixComputer graphics (images)
The invention discloses a method of generating a 3D house type model by a 2D house type model based on camera shooting. The method comprises steps: 1, a 2D house type picture is acquired through camera shooting; 2, an essential matrix reduction method is used for correcting the 2D house type picture acquired in the first step; 3, image enhancement processing is carried out on the2D house type picture after processing of the second step; 4, a contour line of the 2D image after processing of the third step is extracted; 5, a door and window model base is built, matching is carried out according to the contour line extracted in the fourth step, and door and window positions are recognized; 6, a wall structure is stretched to a fixed height position, and generation of a 3D house type model is completed. The method has the following advantages that automatic generation of the 3D house type model from the 2D house type model is realized, the generation method is simple, applicability is universal, the generation method can be embedded in a portable mobile device to form APP application software to be combined with a camera of the portable mobile device, and practicability is provided.
Owner:郭小虎
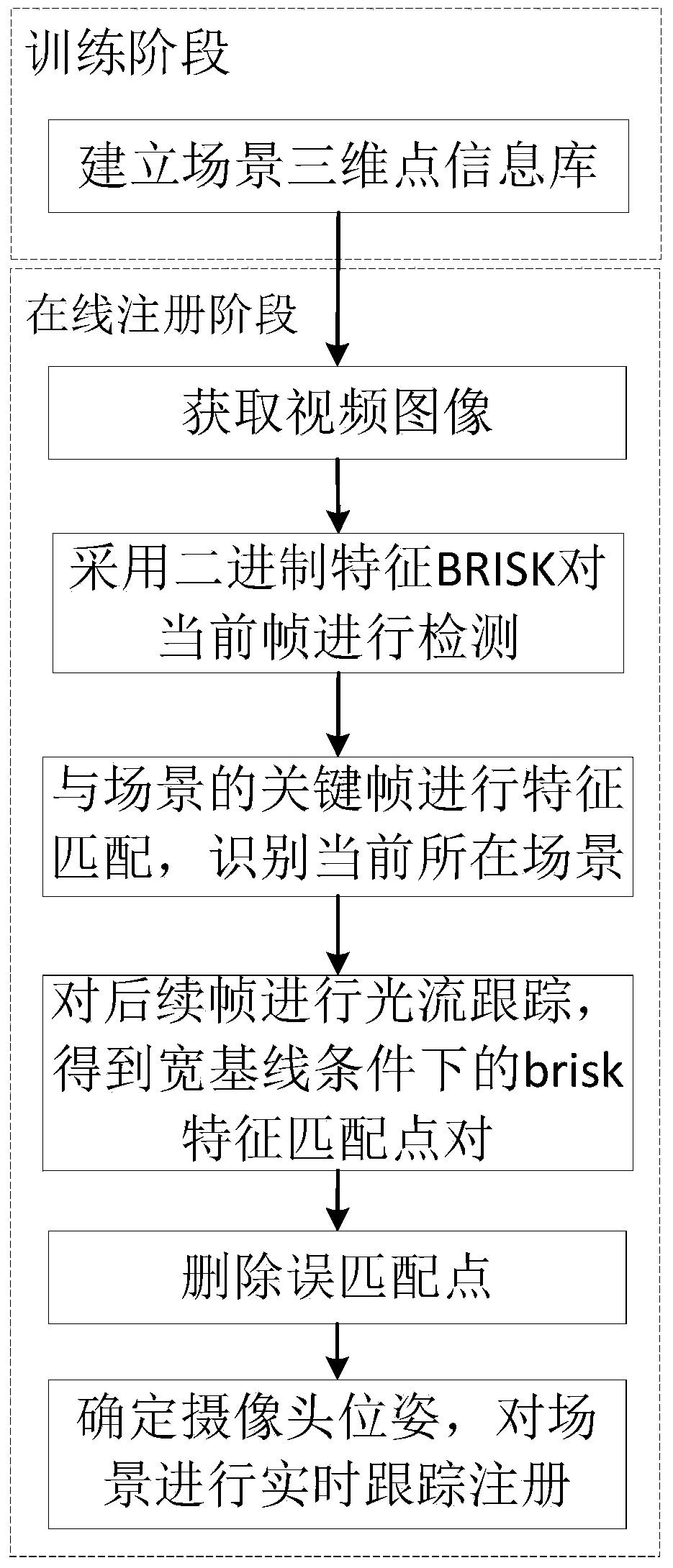
Mobile augmented reality registration method of outdoor wide-range natural scene
ActiveCN103839277AImprove stabilityPrecise registrationImage analysisEssential matrixExternal reference
The invention provides a mobile augmented reality registration method of an outdoor wide-range natural scene. The mobile augmented reality registration method comprises the steps that three-dimensional reconstruction of feature points is accomplished through an Euclidean reconstruction method on the basis of combination between an essential matrix and triangulation, the initial external reference of a camera is calculated by using the essential matrix, a coordinate system of a virtual three-dimensional object and a coordinate system of the scene plane are built, feature detection and tracking are carried out by using a BRISK operator, tracking is only carried out on an image which is successfully recognized, and the speed of real-time updating of registration information is further increased. Tracking is carried out on the detected scene feature points through a light stream tracking method, scene feature information can be updated in real time, and real-time performance of augmented reality registration is further improved.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Object Recognition Apparatus and Object Recognition Method Using Epipolar Geometry
An object recognition apparatus that processes images, as acquired by an imaging means (10) mounted on a moving object, in a first image plane and a second image plane of different points of view, and recognizes an object in the vicinity of the moving object. The object recognition apparatus comprises: a feature point detection means (42) that detects feature points in first and second image planes of an object image; a fundamental matrix determination means (43a) that determines, based on calculation of an epipole through the auto-epipolar property, a fundamental matrix that expresses a geometrically corresponding relationship based on translational camera movement, with not less than two pairs of feature points corresponding between the first and second image planes; and a three-dimensional position calculation means (43b) that calculates a three-dimensional position of an object based on the coordinates of the object in the first and second image planes and the determined fundamental matrix.
Owner:AISIN SEIKI KK
Large-scale part three-dimensional reconstruction method based on image sequence
ActiveCN111815757AImprove matching speedAddresses issues prone to error conditionsImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionEssential matrix
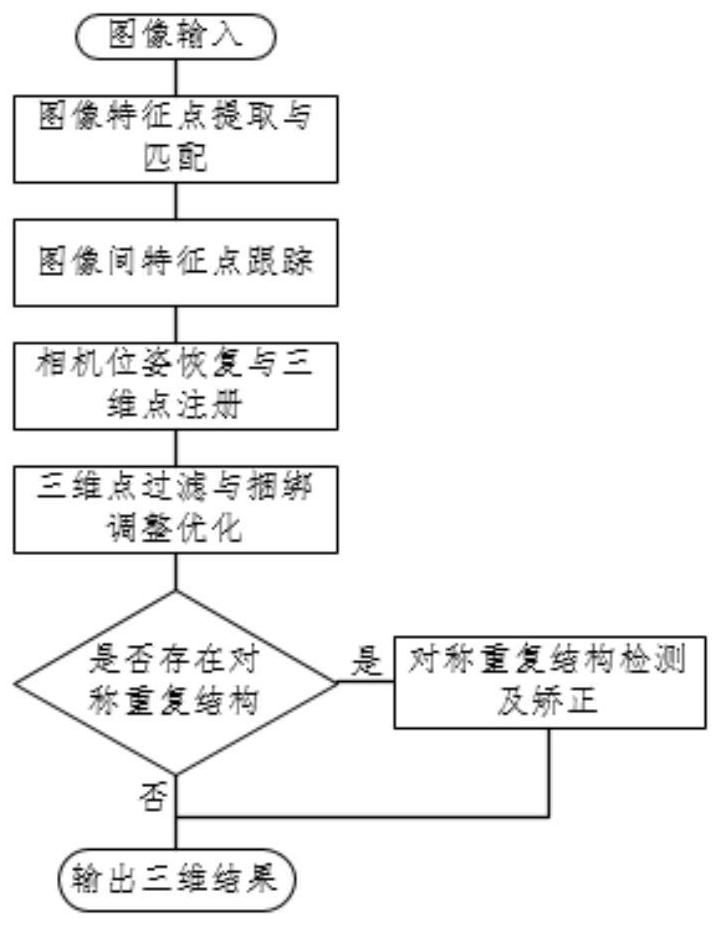
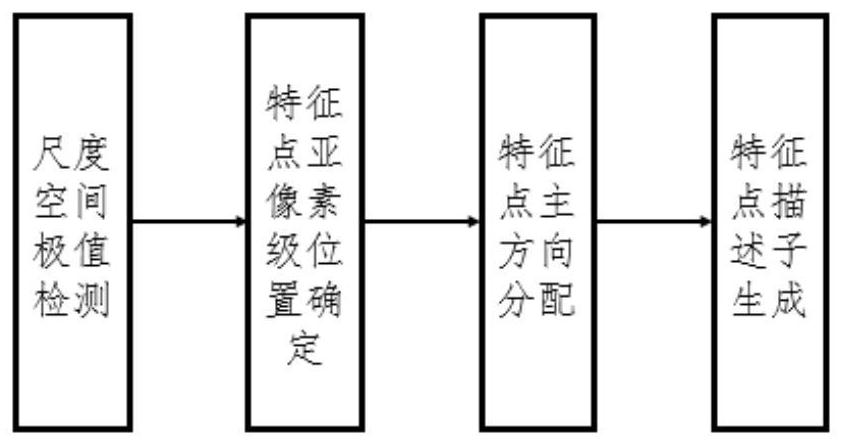
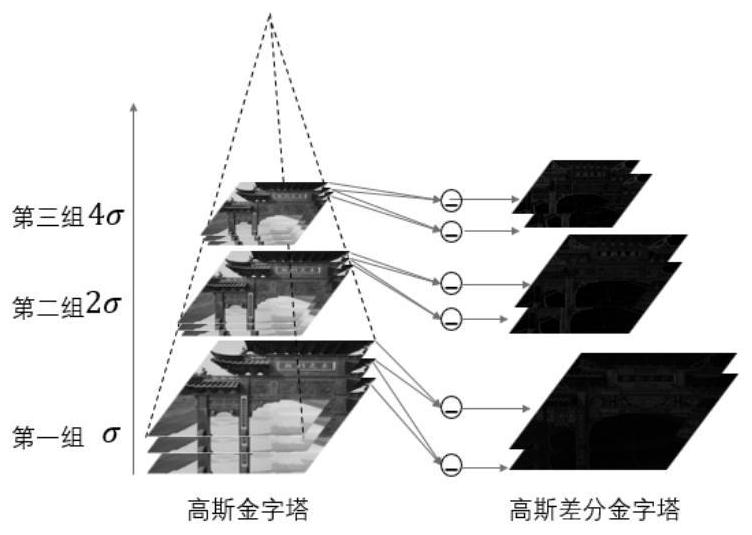
The large part three-dimensional reconstruction method based on the image sequence comprises the following steps that S1, an unmanned aerial vehicle carrying a camera flies around a target part, and ato-be-reconstructed image sequence is obtained; s2, adopting an SIFT algorithm and an SURF algorithm to jointly extract image feature points; s3, estimating camera motion by calculating an essentialmatrix and a basic matrix based on the sparse feature points obtained by the SIFT corner points and the SURF corner points, and registering three-dimensional space points to obtain sparse point cloudof a three-dimensional scene; s4, judging whether the optimized sparse point cloud has a symmetrical repeated structure or not; and S5, taking the sparse point cloud as seed point and reference imageinput, and performing dense reconstruction based on a dense three-dimensional point construction method of multiple views to obtain a low-resolution depth map. The three-dimensional point recovery andcorrection method based on the image sequence has the advantages that the three-dimensional point recovery and correction method based on the image sequence is provided, and construction from the image sequence to the space sparse three-dimensional points is achieved.
Owner:SHANDONG IND TECH RES INST OF ZHEJIANG UNIV
Step-by-step calibration method for camera parameters of binocular stereoscopic vision system
ActiveCN106981083AReal-time calibrationApplicable calibration requirementsImage analysisDimension measurementElectric control
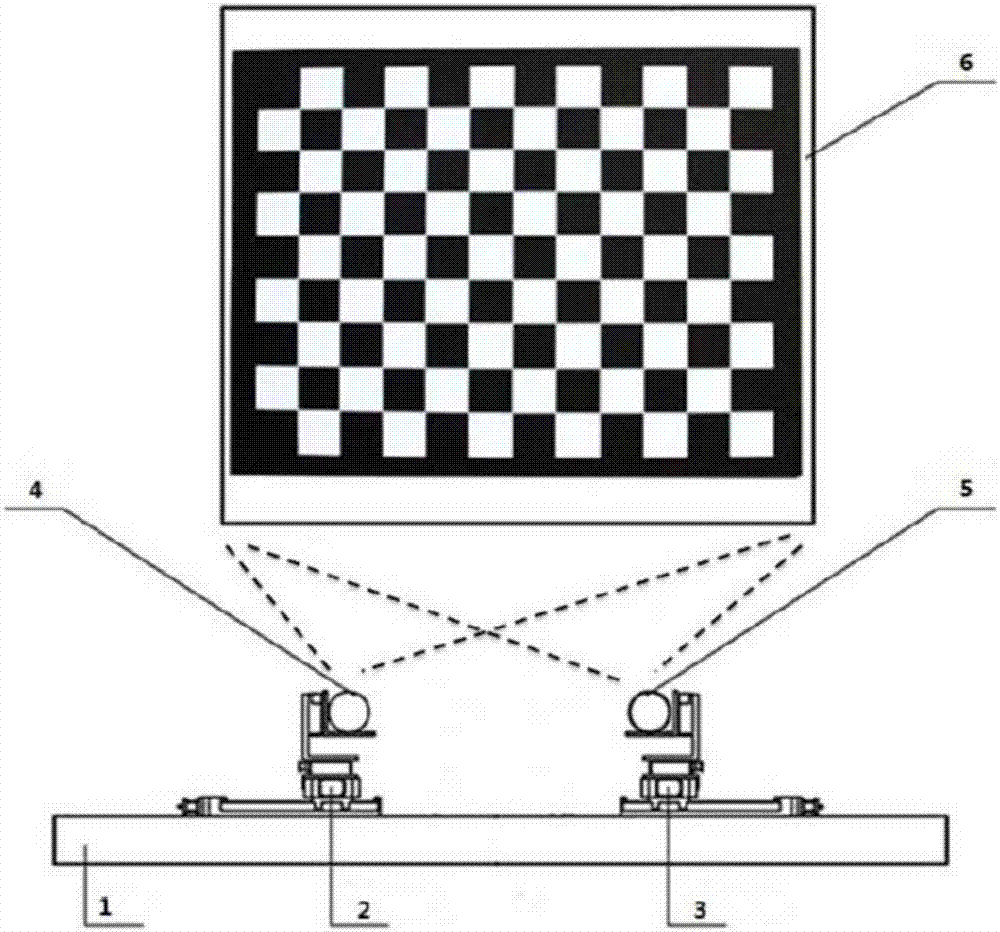
The invention relates to a step-by-step calibration method for the camera parameters of a binocular stereoscopic vision system and belongs to the field of image processing and computer vision detection, which relates to a step-by-step calibration method for the camera intrinsic and external parameters of a dimension measurement system for large-scale forgings. According to the calibration method, firstly, the intrinsic parameter matrix of a camera is calibrated in the off-line manner in a laboratory, and the camera is driven to conduct two sets of mutually independent triorthogonal motions by a high-precision electric control platform. Secondly, based on the properties of FOD points, the intrinsic parameters of the camera are listed through the unique solution of a linear equation. At a forging experiment site, a basic matrix between two images is figured out through the 8-point method, and the method of decomposing of an essential matrix is conducted. In this way, the real-time on-line calibration for the external parameters of the camera is realized. Finally, based on the image information, the length of a high-precision three-dimensional scale is reconstructed, so that the solution of a camera scale factor is realized. The above method is simple and convenient in calibration process, short in calibration time and high in precision. The calibration of the camera of the binocular vision measurement system at the forging site can be precisely realized by adopting fewer images.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
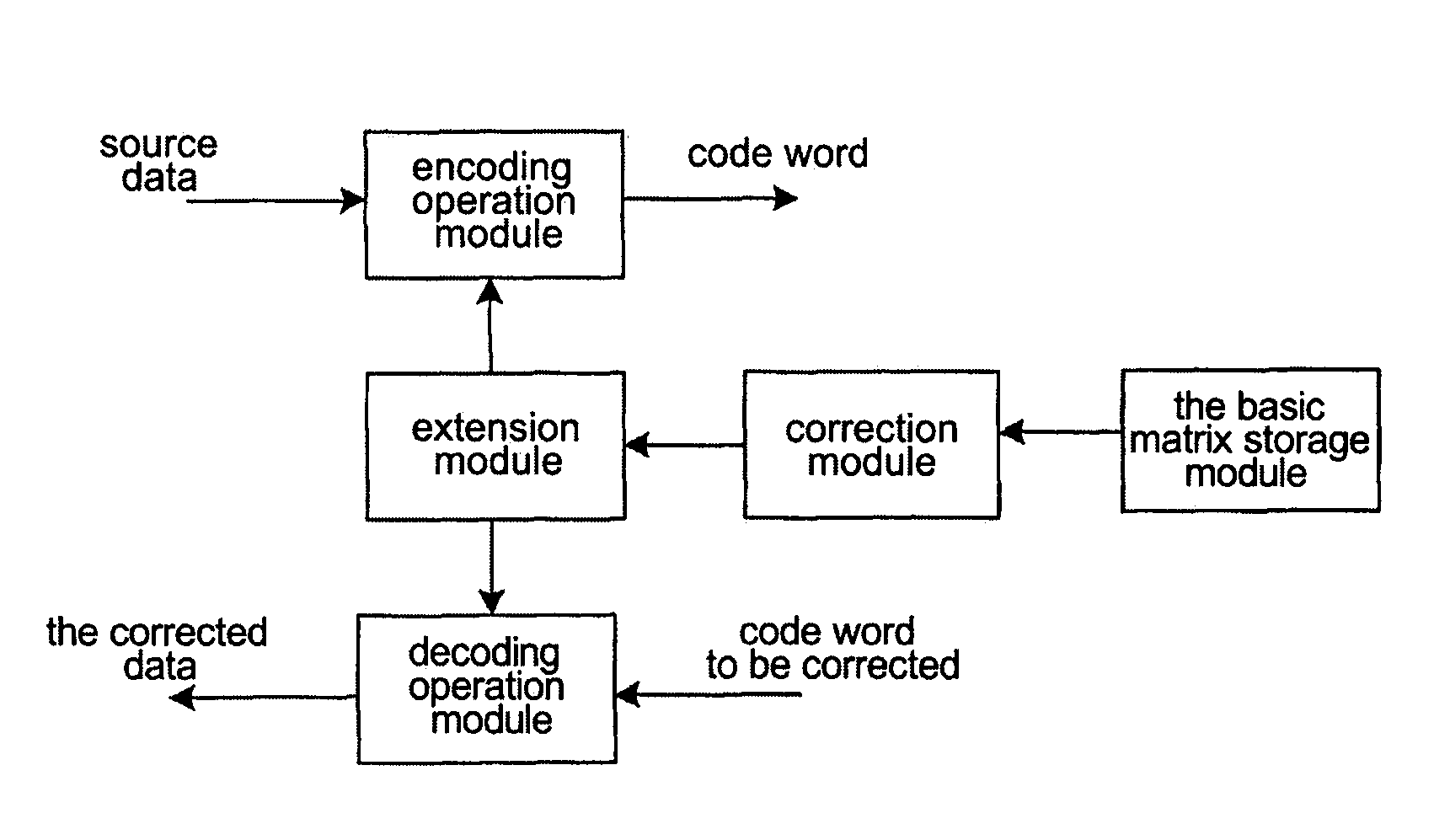
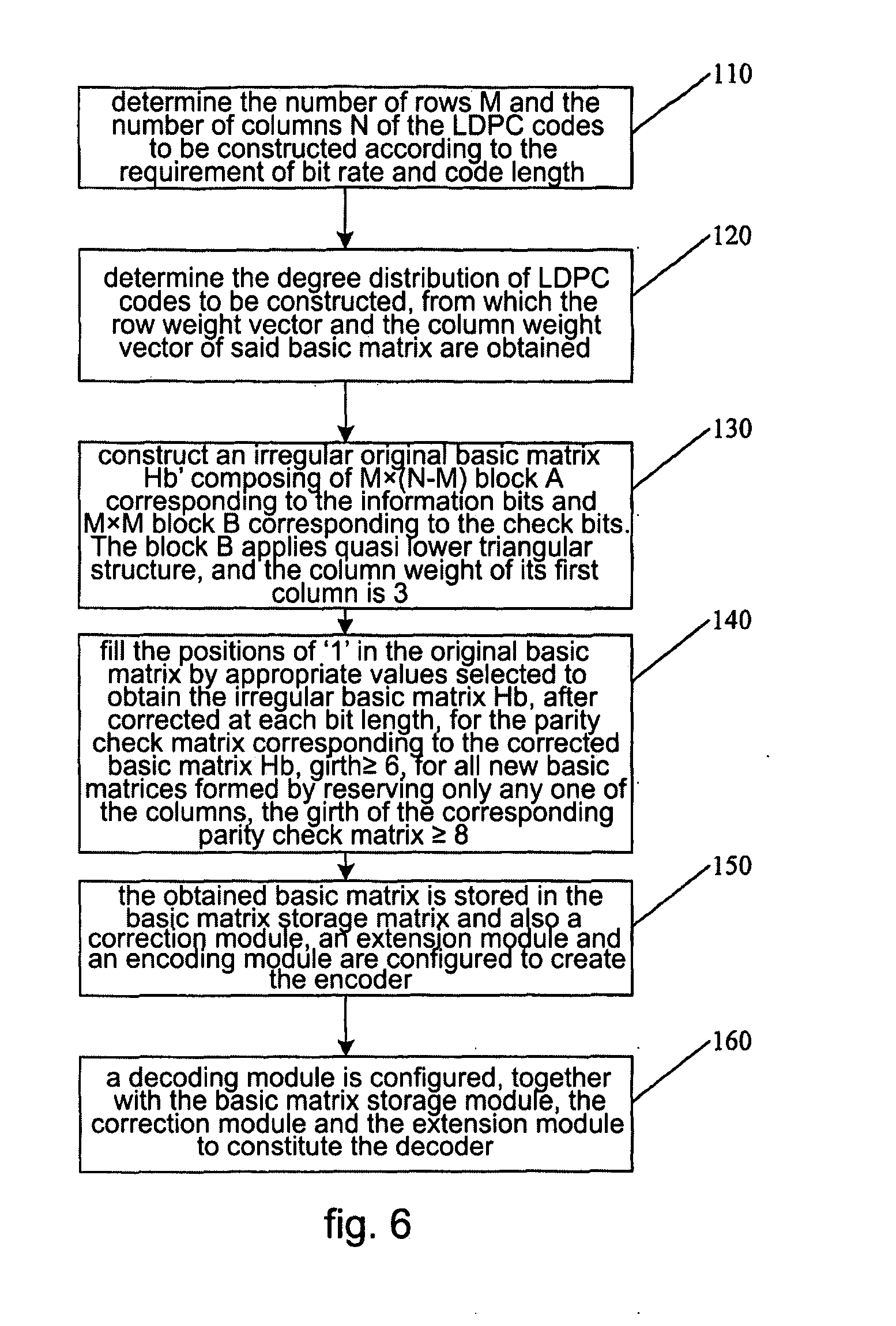
Basic Matrix Based on Irregular Ldpc, Codec and Generation Method Thereof
ActiveUS20080168324A1Eliminate phenomenonSpeed up the fallError detection/correctionParty-line systemsEssential matrixEuclidean vector
Basic matrix based on irregular LDPC codes, codec and generation method thereof. The codec includes an encoding / decoding operation module and a basic matrix storage module. In the stored basic matrix Hb, for all girths with length of 4, any element of i, j, k or l constituting the girths in anti-clockwise or clockwise always satisfies inequality: mod(i−j+k−l, z)≠0, wherein z is the extension factor. When generating the basic matrix, firstly the number of rows M, number of columns N, and weight vectors of the rows and columns are determined, an irregularly original basic matrix is constructed; then the position of ‘1’ is filled by a value chosen from set {0, 1, 2, . . . , z−1} to obtain the basic matrix Hb, which is made to satisfy the above-mentioned inequality. The basic matrix Hb obtained by storing, which is configured with corresponding encoding / decoding operation module, constitutes the desired encoder / decoder. The encoder / decoder according to the present invention can effectively eliminate error-floor phenomenon of LDPC codes and accelerate the falling speed of BER curve.
Owner:ZTE CORP
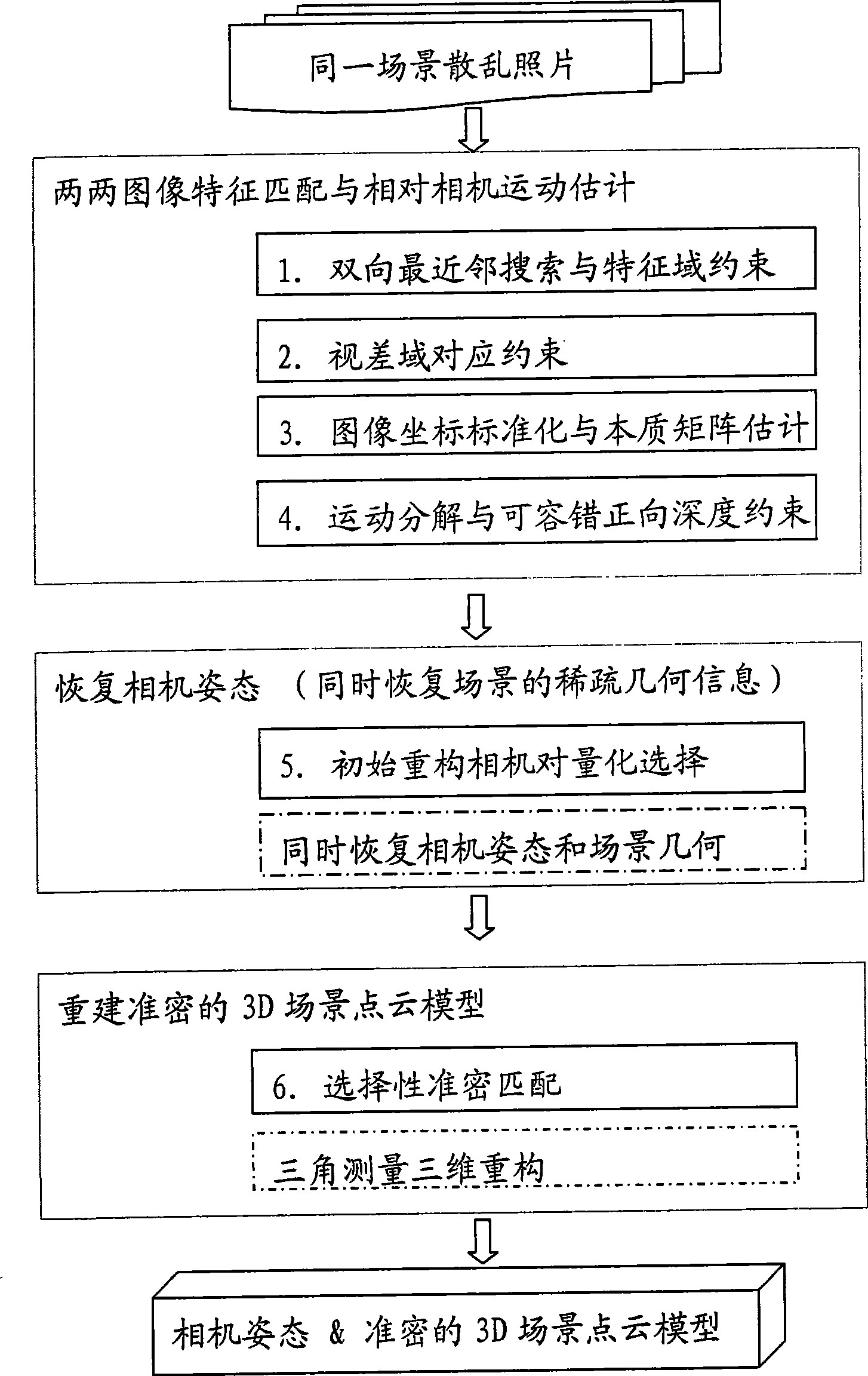
Three-dimensional reconstruction method based on fringe photograph collection of same scene
InactiveCN101398937AImprove stabilityImprove accuracy2D-image generationNearest neighbor searchEssential matrix
A 3D reconstruction method based on scattered photo sets of the same scene is divided into three stages: the first stage: every pairwsie image feature matching and relative camera motion are estimated; and the stage is divided into 4 steps: (1) every two images are subject to the bidirectional nearest neighbor search and feature domain constraint to obtain a candidate correspondence; (2) the candidate correspondence is subject to parallax domain correspondence constraint to obtain a hypothesis correspondence; (3) the image coordinates of the hypothesis correspondence are standardized to solve an essential matrix estimation meeting the hypothesis correspondence; (4) the essential matrix is decomposed to obtain four groups of possible solutions of the camera motion, and the final solution is determined by the fault-tolerant forward depth constraint; the second stage: the optimized initial reconstruction camera pair is selected according to the results of the first stage, the standard sparse reconstruction method is applied, and the camera pose and the sparse geometric information of the scene are restored; the third stage: selective accurate and dense matching is carried out based on the results of second stage, and an accurate and dense 3D scene point cloud model is reconstructed by the triangulation method. The method has the advantages of obtaining reliable camera pose and high-density scene geometric information, greatly shortening the reconstruction time, having relatively high reconstruction efficiency, and is applicable to processing the scattered photo set with large data size.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
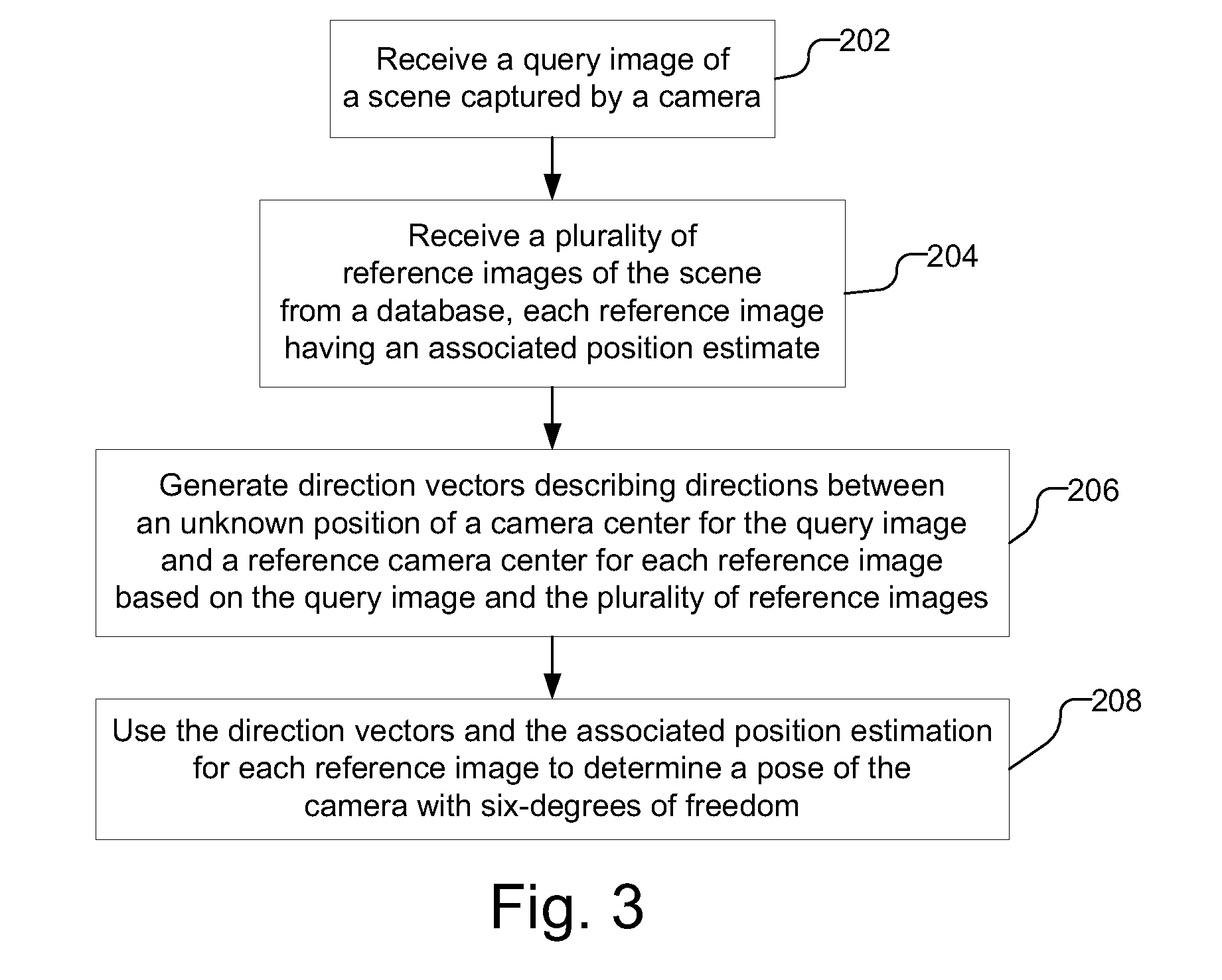
Scene structure-based self-pose estimation
Pose estimation is performed using a scene structure captured in a query image and reference images from a database. Each of the reference images has an associated position estimate. Direction vectors are generated that describe directions between an unknown position of a camera center for the query image and a reference camera center for each reference image based on the query image and the plurality of reference images. The direction vectors may be generated using, e.g., homographies, essential matrices, or fundamental matrices. A pose estimation with six degrees of freedom is determined using the direction vectors and the associated position estimate for each reference image. The pose estimation, for example, may be determined by solving a three-point pose problem using the direction vectors and the associated position estimate for each reference image.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Monocular real-time three-dimensional reconstruction method based on loop testing
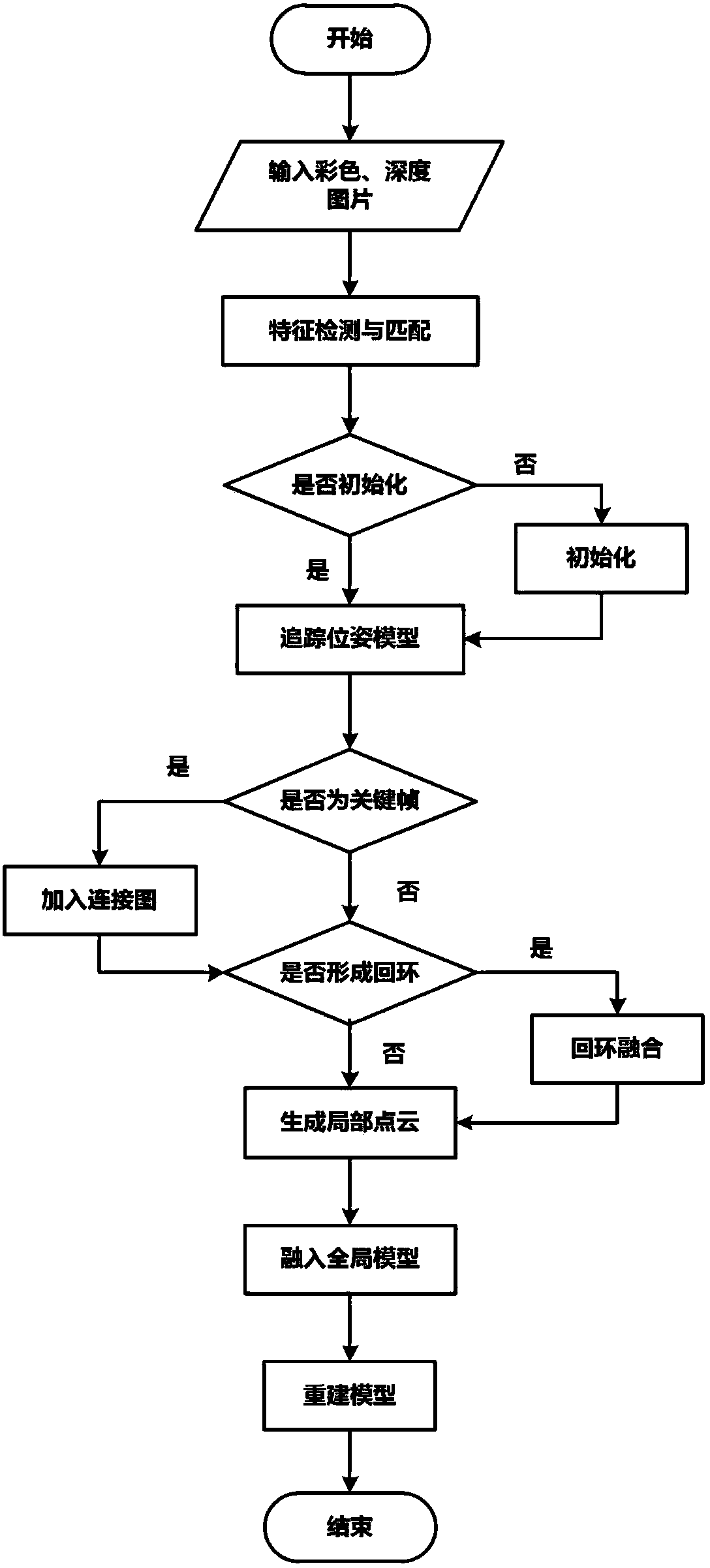
InactiveCN108364344AImprove accuracyPrevent deviationImage enhancementImage analysisSingular value decompositionReconstruction method
The invention relates to a monocular real-time three-dimensional reconstruction method based on loop testing, and belongs to the technical field of three-dimensional reconstruction. The method comprises: carrying out pairwise matching in an image sequence of a specified scene on the basis of an image feature point matching theory to obtain image matching point pairs; solving an essential matrix, and then utilizing a singular-value decomposition theory to acquire an initial pose; utilizing the initial pose or a previous-frame pose to obtain an estimated pose through a pose tracking model; judging whether a current frame is a key frame; then utilizing a random fern algorithm to calculate similarity of the current frame and the key frame, and if the similarity reaches a threshold value, it isconsidered that a loop is formed; utilizing a pose of the key frame to optimize the current pose if the loop is formed; utilizing the above-obtained pose to obtain a point cloud, and fusing the sameinto a TSDF global-model; and adopting a light ray projection algorithm to visualize a surface. According to the method, accuracy of the acquired pose is enabled to be high, the cumulative-error problem in three-dimensional-reconstruction processes is eliminated, and a real-time reconstruction result has higher accuracy.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Monocular vision inertia SLAM method for dynamic scene
ActiveCN111156984ANavigational calculation instrumentsNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsGyroscopeEssential matrix
The invention discloses a monocular vision inertia SLAM method for a dynamic scene. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, extracting ORB feature points by a visual front end, performing target identification by using a YOLO-v3 neural network, further extracting a potential static feature point set, removing RANSAC outer points of an essential matrix, screening out final static featurepoints, and tracking the final static feature points; meanwhile, in order to improve the data processing efficiency, carrying out pre-integration on IMU measurement values; initializing, and calculating initial values including attitude, speed, gravity vector and gyroscope offset; then, carrying out nonlinear optimization of visual inertia tight coupling, and establishing a map; meanwhile, carrying out loopback detection and repositioning, and finally carrying out global pose graph optimization. According to the method, deep learning and visual inertia SLAM are fused, the influence of a dynamic object on SLAM positioning and mapping can be eliminated to a certain extent, and the stability of long-time work of the system is improved.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
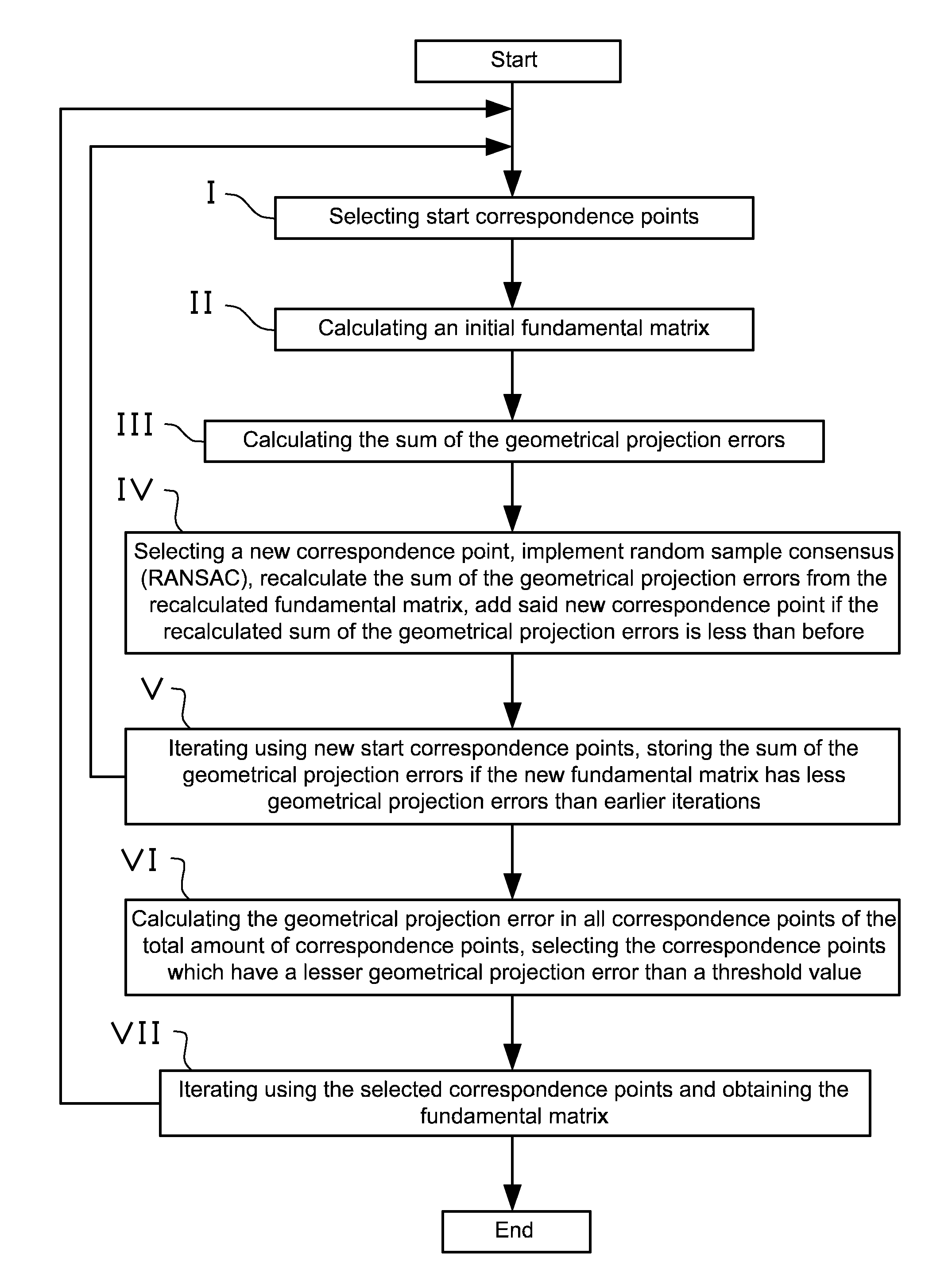
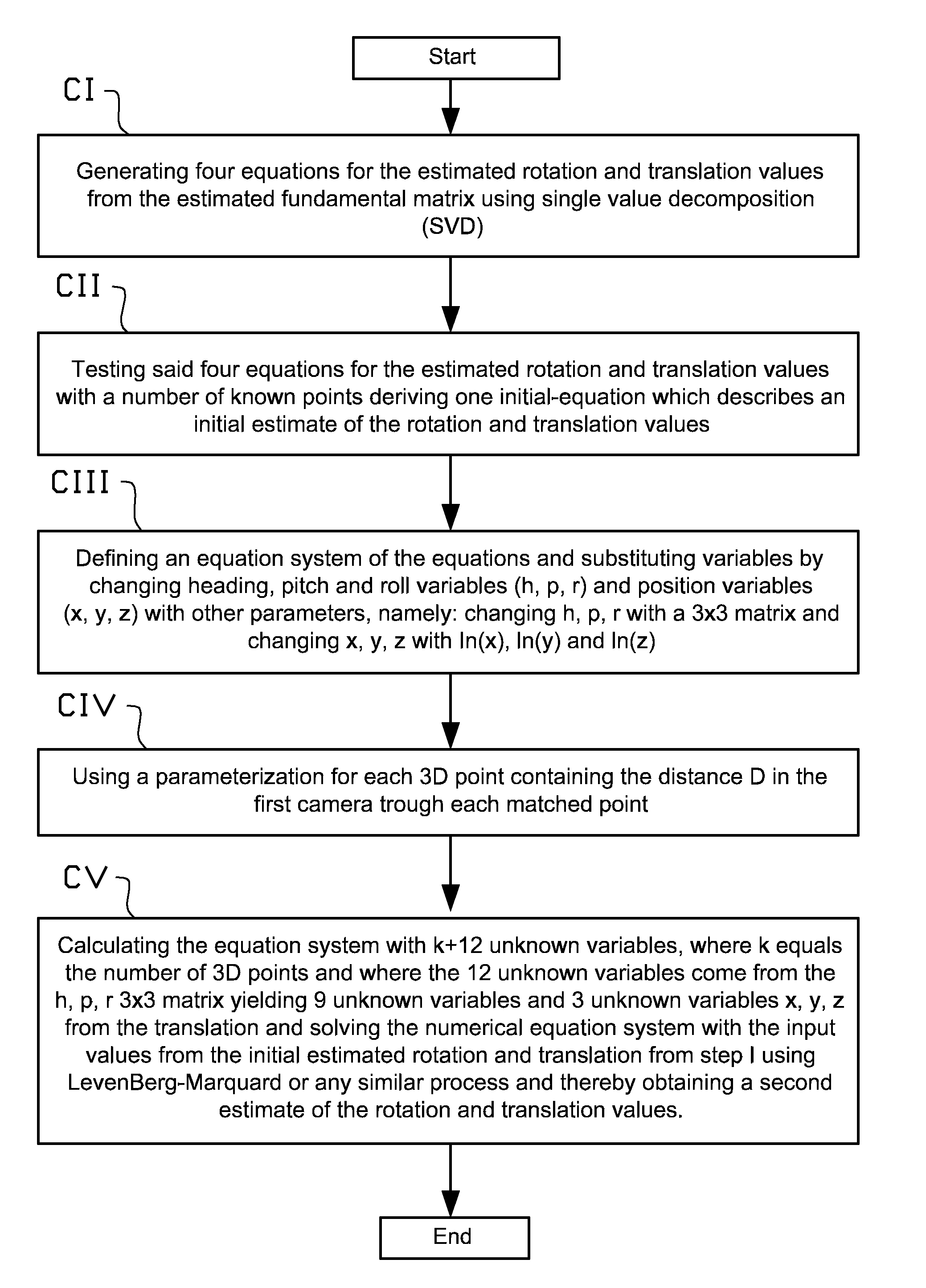
Method and apparatus for solving position and orientation from correlated point features in images
ActiveUS20130272581A1Mitigate, alleviate, or eliminate oneImage enhancementImage analysisEssential matrixRapid convergence
A method and apparatus for determining a position and attitude of at least one camera by calculating and extracting estimated rotation and translation values from an estimated fundamental matrix based on information from at least a first and second 2D image. Variable substitution is utilized to strengthen derivatives and provide a more rapid convergence. A solution is provided for solving position and orientation from correlated point features in images using a method that solves for both rotation and translation simultaneously.
Owner:SAAB AB
Virtual view synthesis method based on homographic matrix partition
ActiveCN104809719AImprove real-time performanceRebuild fastImage analysisSteroscopic systemsSingular value decompositionEssential matrix
The invention discloses a virtual view synthesis method based on homographic matrix partition. The virtual view synthesis method based on homographic matrix partition comprises the following steps of 1) calibrating left and right neighboring view cameras to obtain the internal reference matrixes of the left and right neighboring view cameras and a basis matrix between the left and right neighboring view cameras, deriving an essential matrix from the basis matrix, performing singular value decomposition on the essential matrix, and computing the motion parameters including a rotation matrix and a translation matrix between the left and right neighboring view cameras; 2) performing interpolation division on the rotation matrix and the translation matrix to obtain sub homographic matrixes from left and right neighboring views to a middle virtual view; 3) applying the forward mapping technology to map two view images to a middle virtual view image respectively through the sub homographic matrixes, taking the mapping graph of one of the images as a reference coordinate system and performing interpolation fusion on the mapped two images to synthesize a middle virtual view image. The virtual view synthesis method based on the homographic matrix partition has the advantages of being high in synthesis speed, simple and effective in process and high in practical engineering value.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
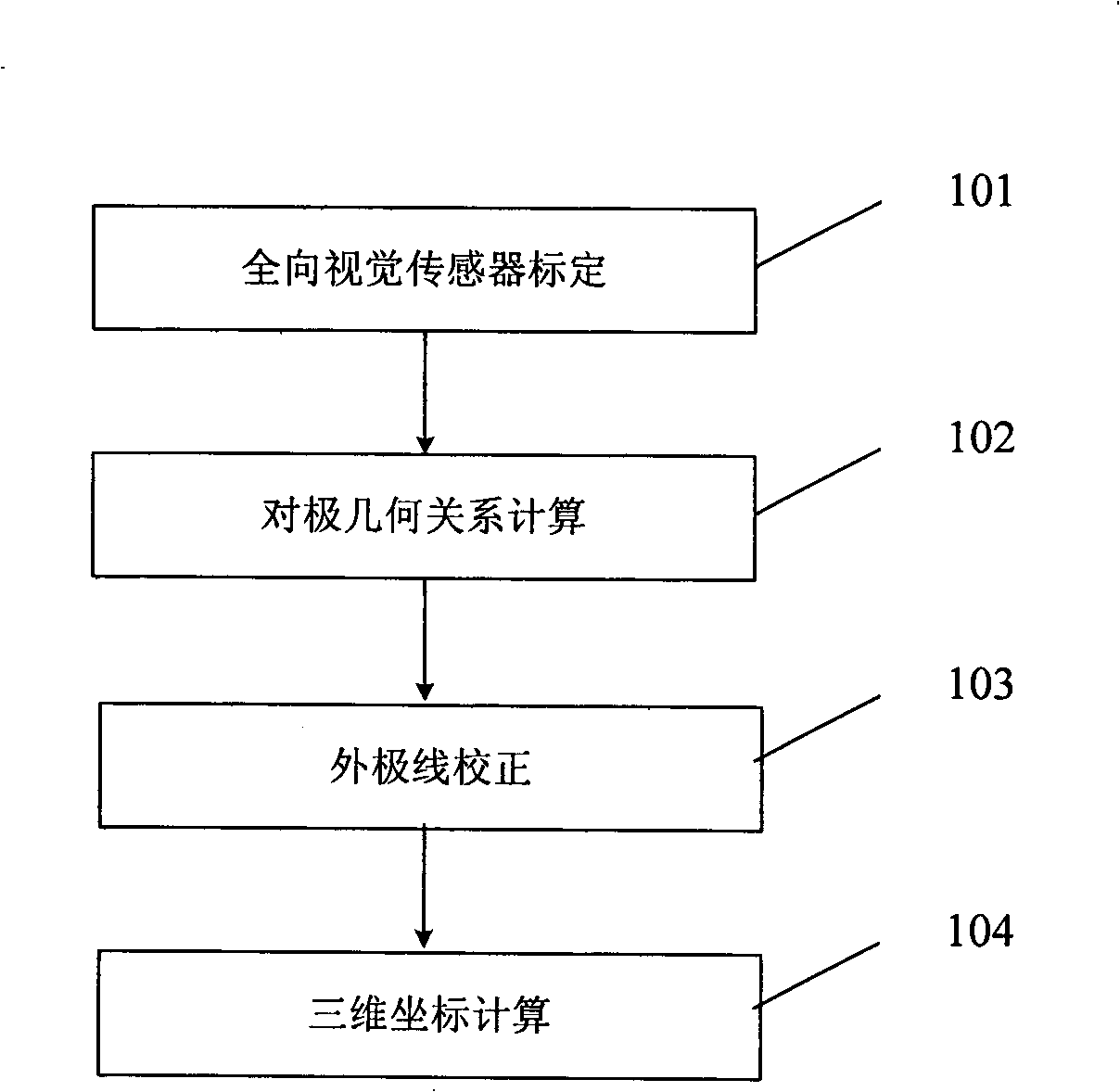
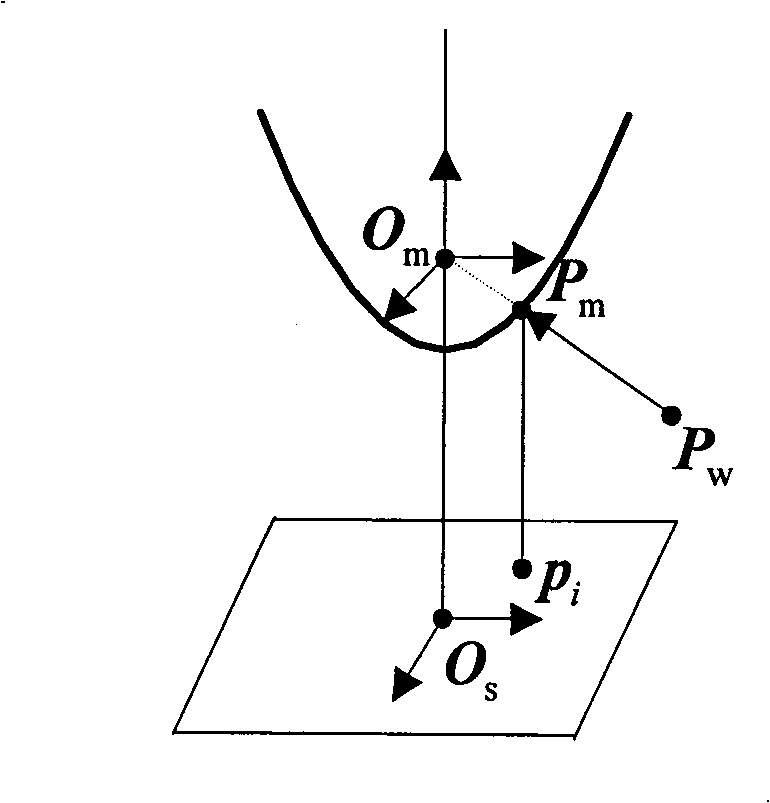
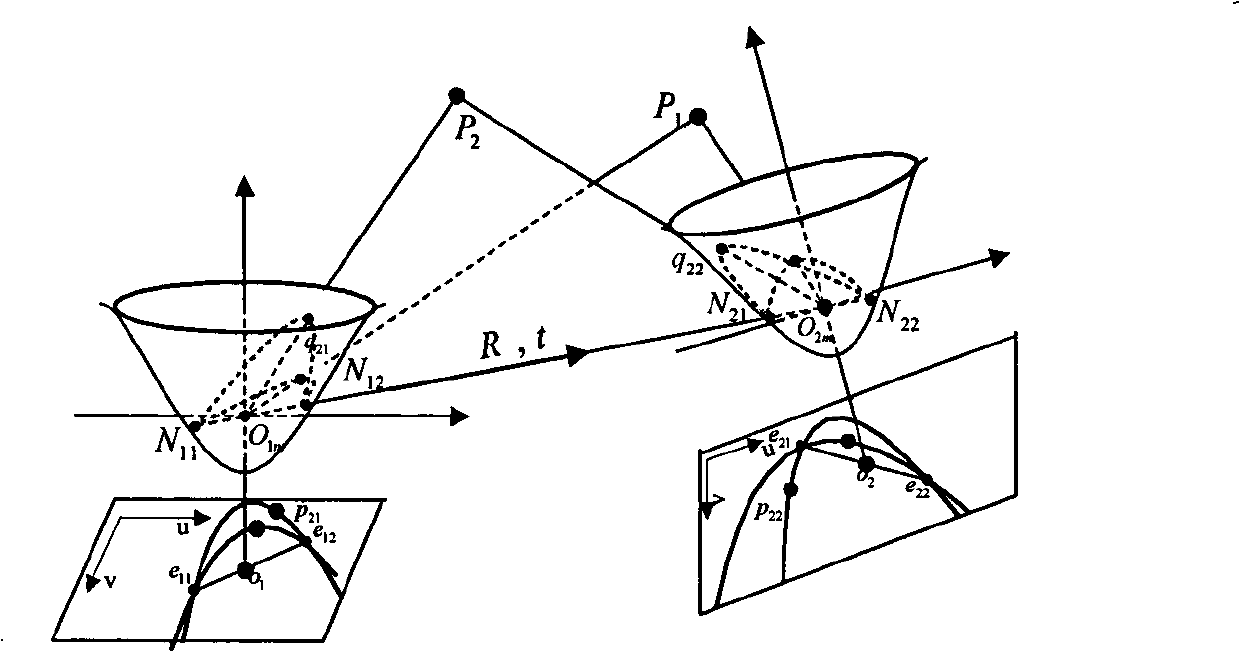
Omnidirectional stereo vision three-dimensional rebuilding method based on Taylor series model
InactiveCN101354796AHigh precision3D reconstruction worksImage analysis3D modellingReconstruction methodDirectional antenna
The invention discloses an omni-directional stereo vision three-dimensional reconstruction method based on Taylor series models. The method comprises the following: a step of calibrating a camera, which is to utilize a Taylor series model to calibrate an omni-directional vision sensor so as to obtain internal parameters of the camera; a step of obtaining epipolar geometric relation, which comprises the steps of calculating an essential matrix between binocular omni-directional cameras and extracting the rotation and translation component of the cameras; a step of correcting an outer polar line, which is to correct the outer polar line of a shot omni-directional stereo image so as to allow a corrected polar quadratic curve to coincide with an image scan line; and a step of three-dimensional reconstruction, which is to carry out feature point matching to the corrected stereo image and calculate the three-dimensional coordinates of points according to matching results. The method can be applicable to various omni-directional vision sensors, has the characteristics of wide application range and high precision, and can carry out effective three-dimensional reconstruction under the condition that the parameters of the omni-directional vision sensors are unknown.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Method and apparatus for solving position and orientation from correlated point features in images
ActiveUS8953847B2Mitigate, alleviate, or eliminate oneImage enhancementImage analysisEssential matrixRapid convergence
A method and apparatus for determining a position and attitude of at least one camera by calculating and extracting estimated rotation and translation values from an estimated fundamental matrix based on information from at least a first and second 2D image. Variable substitution is utilized to strengthen derivatives and provide a more rapid convergence. A solution is provided for solving position and orientation from correlated point features in images using a method that solves for both rotation and translation simultaneously.
Owner:SAAB AB
Data-clustering-based adaptive image SIFT (Scale Invariant Feature Transform) feature matching method
InactiveCN102194133ARealize the combinationImprove adaptabilityCharacter and pattern recognitionFeature setEssential matrix
The invention discloses a data-clustering-based adaptive image SIFT (Scale Invariant Feature Transform) feature matching method, which comprises the following steps of: (1) acquiring a reference image sequence, extracting image SIFT feature sets and clustering all image SIFT feature sets by adopting a k-d (k-dimensional) tree; (2) organizing all the image SIFT feature sets by adopting a cascaded vocabulary tree and carrying out secondary feature clustering on the feature sets contained in vocabulary tree nodes; (3) matching BBF (Best Bin First) purified based on a specific value with a dual-mode clustering feature based on comentropy by using the cascaded vocabulary tree to finish the first-stage feature matching; and (4) finishing the second-stage feature matching by using a key image and combining the feature matching results of the two stages; and finally rejecting exterior points by adopting RANSAC (Random Sample Consensus), basic matrix and other technologies. By using the matching method, the robustness of the feature matching can be greatly improved and the adaptability of the feature matching can be effectively enhanced.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
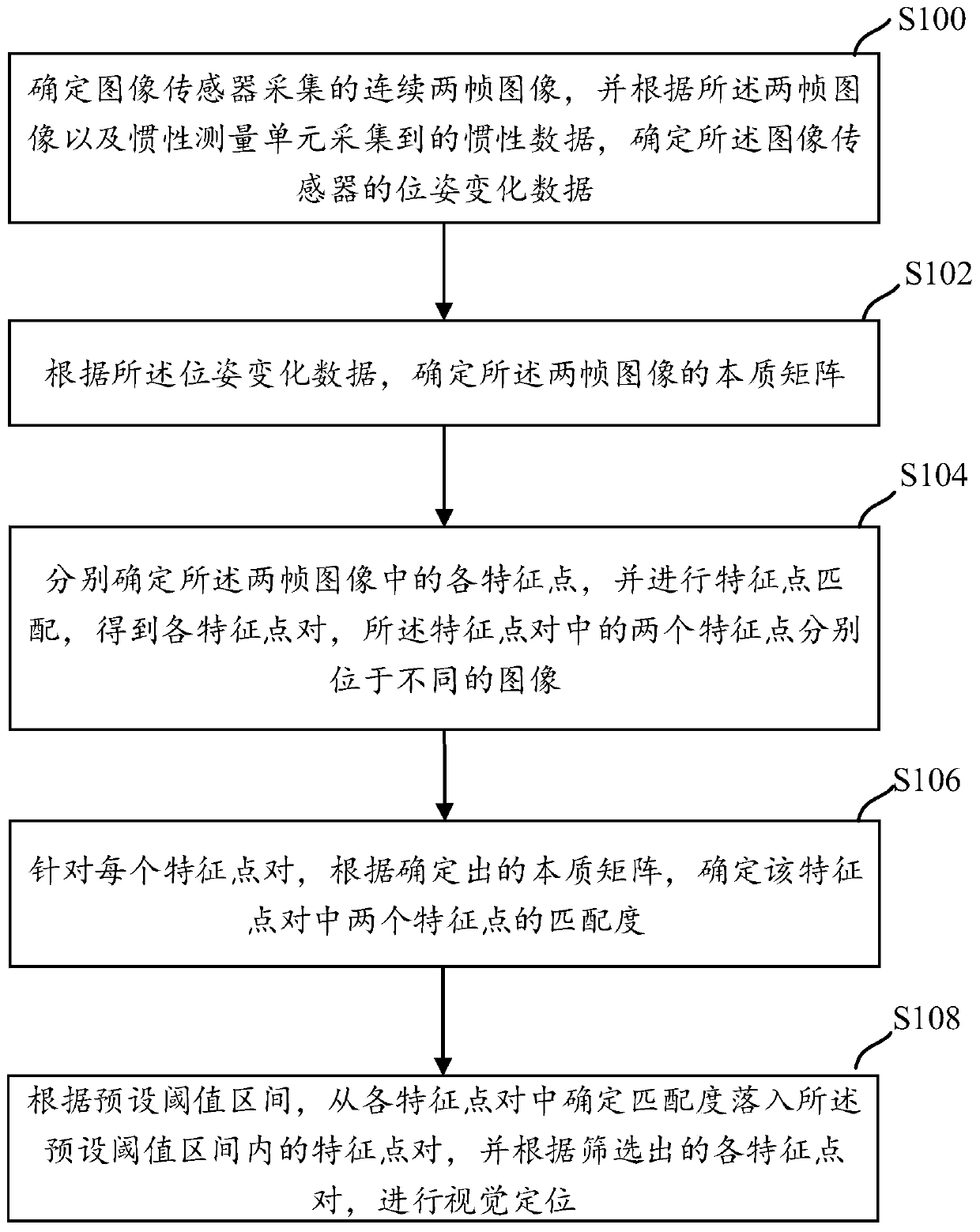
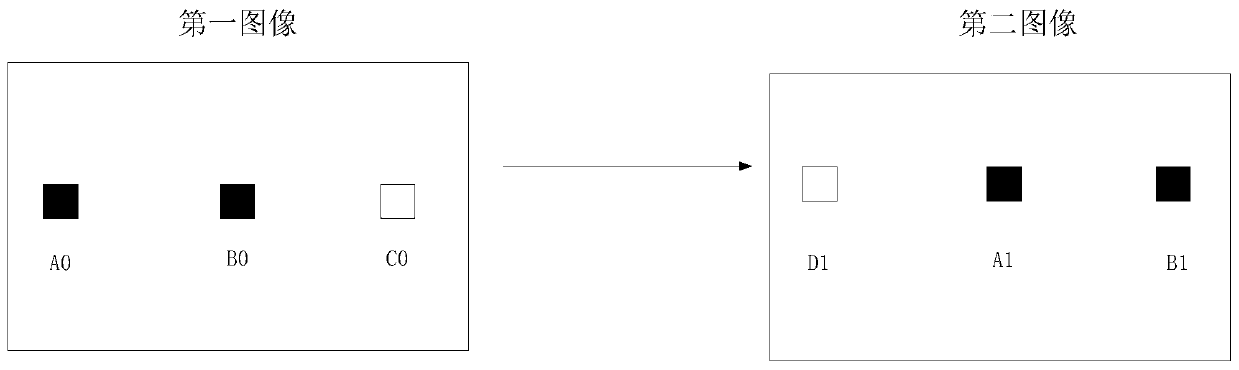
Visual positioning method and device
InactiveCN111260726AHigh precisionPrecise positioningImage analysisNavigational calculation instrumentsEssential matrixRadiology
The invention discloses a visual positioning method and device. The method comprises the following steps of firstly determining continuous frames of images collected by an image sensor according to the two frames of images and inertia data, determining pose change data of the image sensor; determining an essential matrix of the two frames of images; respectively determining each feature point in the two frames of images; matching feature points to obtain each feature point pair; for each feature point pair, determining the matching degree of two feature points in the feature point pair according to the determined essential matrix, finally determining the feature point pair of which the matching degree is within the preset threshold interval from the feature point pairs according to the preset threshold interval, and performing visual positioning according to the screened feature point pairs. The matching degree of each feature point pair is determined through the essential matrix, so that the feature points with higher matching degree are screened out and sent to the rear end, the rear end performs visual positioning according to the feature points with higher matching degree, thepositioning is more accurate, and the map construction precision is higher.
Owner:BEIJING SANKUAI ONLINE TECH CO LTD
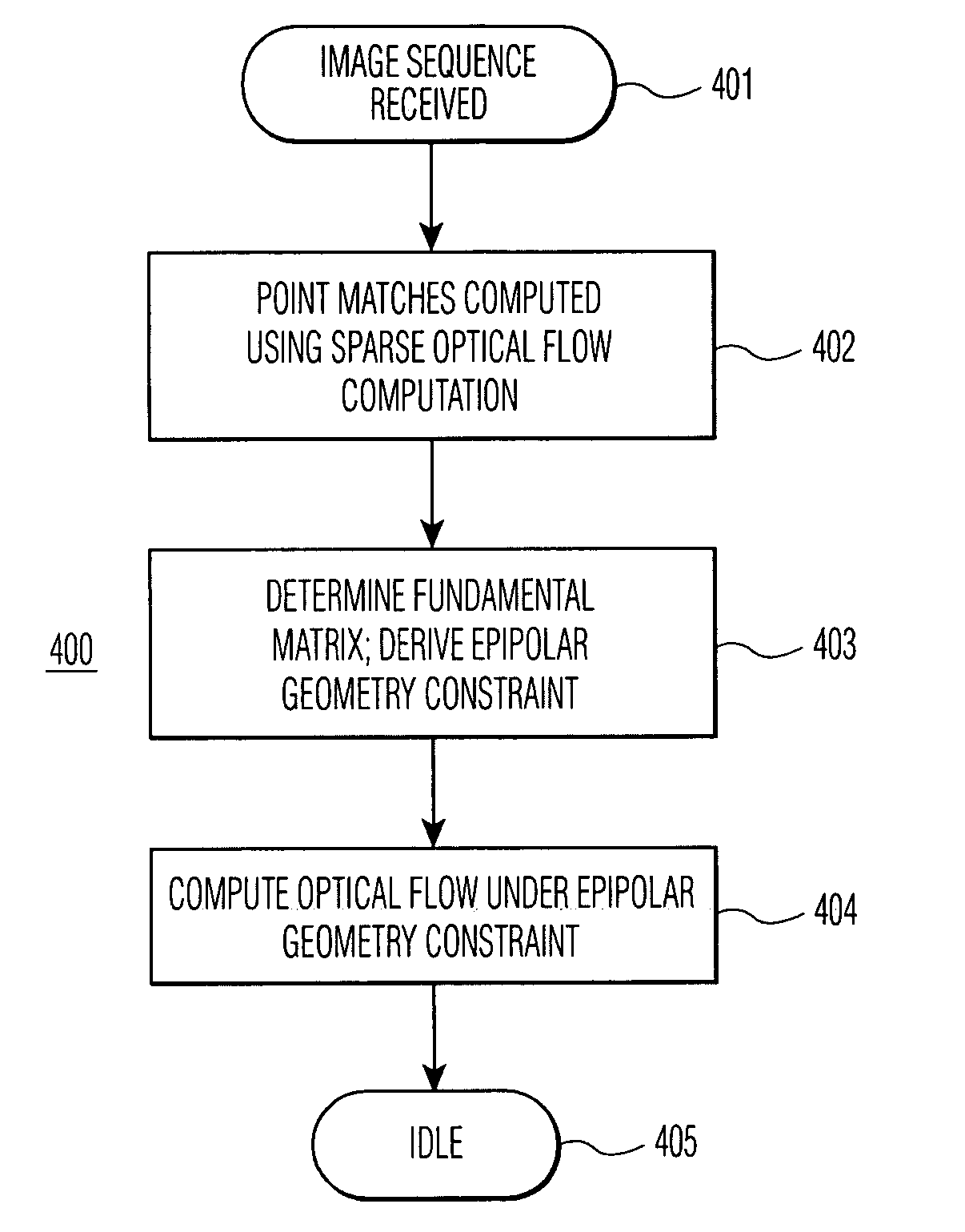
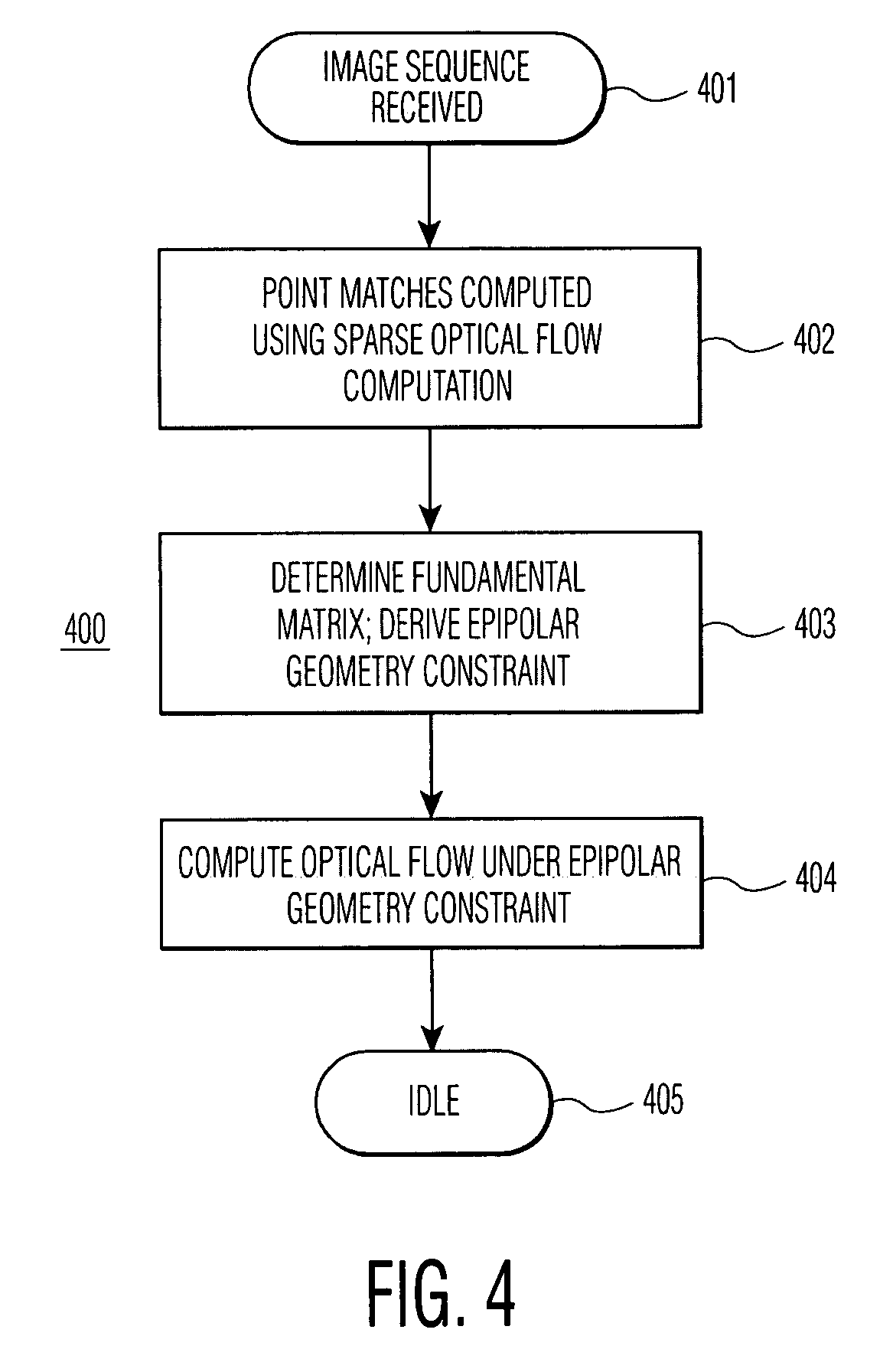
Method for computing optical flow under the epipolar constraint
InactiveUS7031497B2Improve accuracyImprove performanceImage enhancementImage analysisEssential matrixAlgorithm
Point matches between images within an image sequence are identified by sparse optical flow computation and employed to compute a fundamental matrix for the epipolar geometry, which in turn is employed to derive an epipolar geometry constraint for computing dense optical flow for the image sequence. The epipolar geometry constraint may further be combined with local, heuristic constraints or robust statistical methods. Improvements in both accuracy and performance in computing optical flow are achieved utilizing the epipolar geometry constraint.
Owner:UNILOC 2017 LLC
Method for fast camera pose refinement for wide area motion imagery
ActiveUS20170186164A1Not be eliminateReduce impactImage enhancementTelevision system detailsWide areaEssential matrix
The present invention provides a method for fast, robust and efficient BA pipeline (SfM) for wide area motion imagery (WAMI). The invention can, without applying direct outliers filtering (e.g. RANSAC) or re-estimation of the camera parameters (e.g. essential matrix estimation) efficiently refine noisy camera parameters in very short amounts of time. The method is highly robust owing to its adaptivity with the persistency factor of each track. The present invention highly suitable for sequential aerial imagery, particularly for WAMI, where camera parameters are available from onboard sensors.
Owner:THE DEPT OF THE AIR FORCE +1
Method for estimating attitude of carrier aircraft in landing process based on vision guidance
ActiveCN107833249AIncrease flexibilityHigh precisionImage analysisEssential matrixSingular value decomposition
The invention discloses a method for estimating the attitude of a carrier aircraft in the landing process based on vision guidance. Feature points of two successive frames of images acquired by a carrier aircraft are first extracted and matched. According to matching point pairs and pixel coordinates thereof, the epipolar geometrical relationship of the two frames of images are calculated to obtain a basis matrix. An essential matrix is determined by the correspondence between the basis matrix and an intrinsic matrix. After the singular value decomposition of the essential matrix, a rotation matrix is solved. The obtained rotation matrix is converted into Euler angles, so as to estimate attitude information of the carrier aircraft during the descent. The method of the invention can estimate the attitude information of the carrier aircraft simply with two or more frames of observation images, and has more flexibility. Based on the visual guidance mode, the method of the invention has the advantages of low cost, high precision, and strong anti-interference ability.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Visual inertial ranging method and system of tightly coupled vehicle wheel coder data
ActiveCN109764880AReduce mistakesInstruments for road network navigationCamera imageEssential matrix
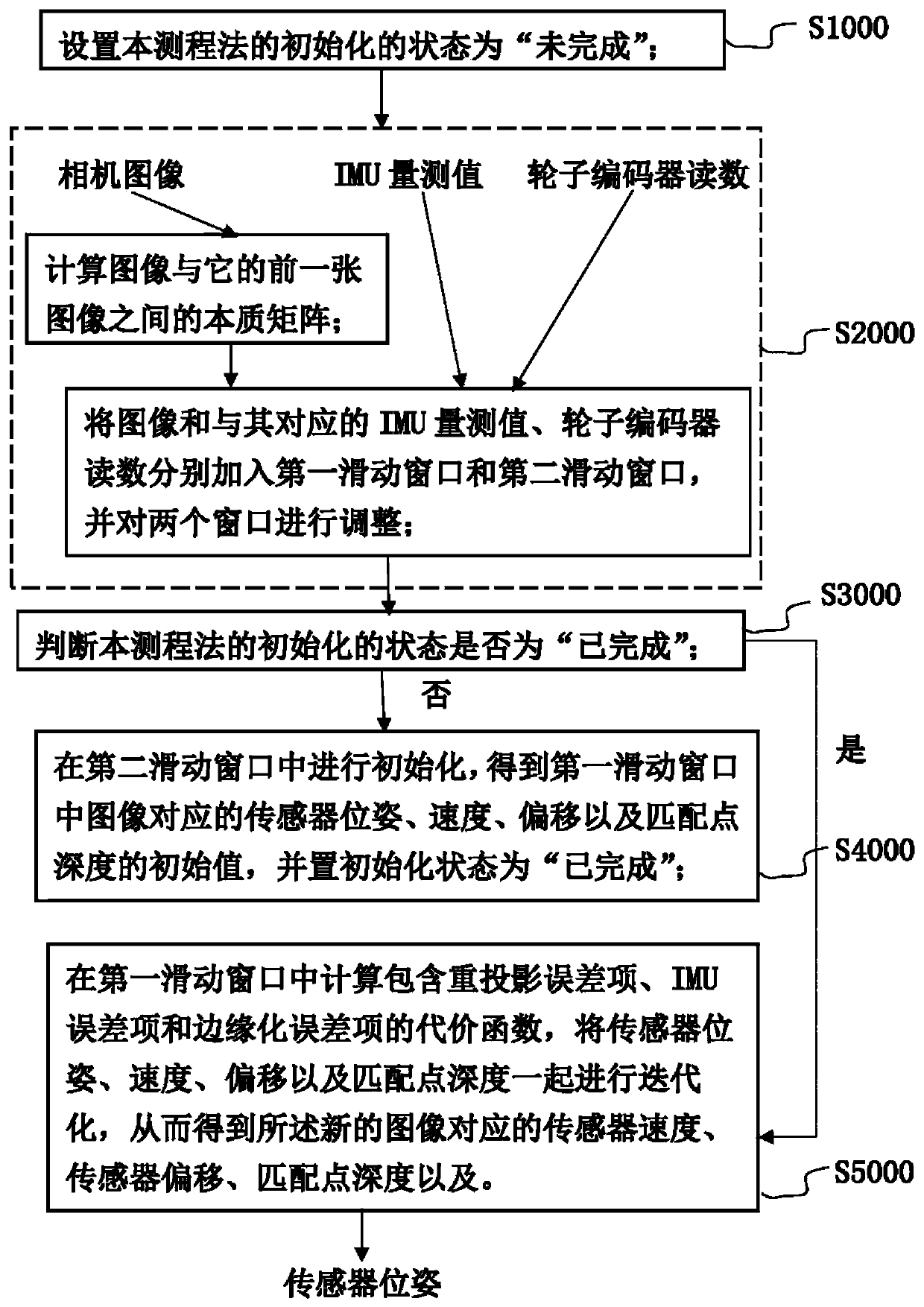
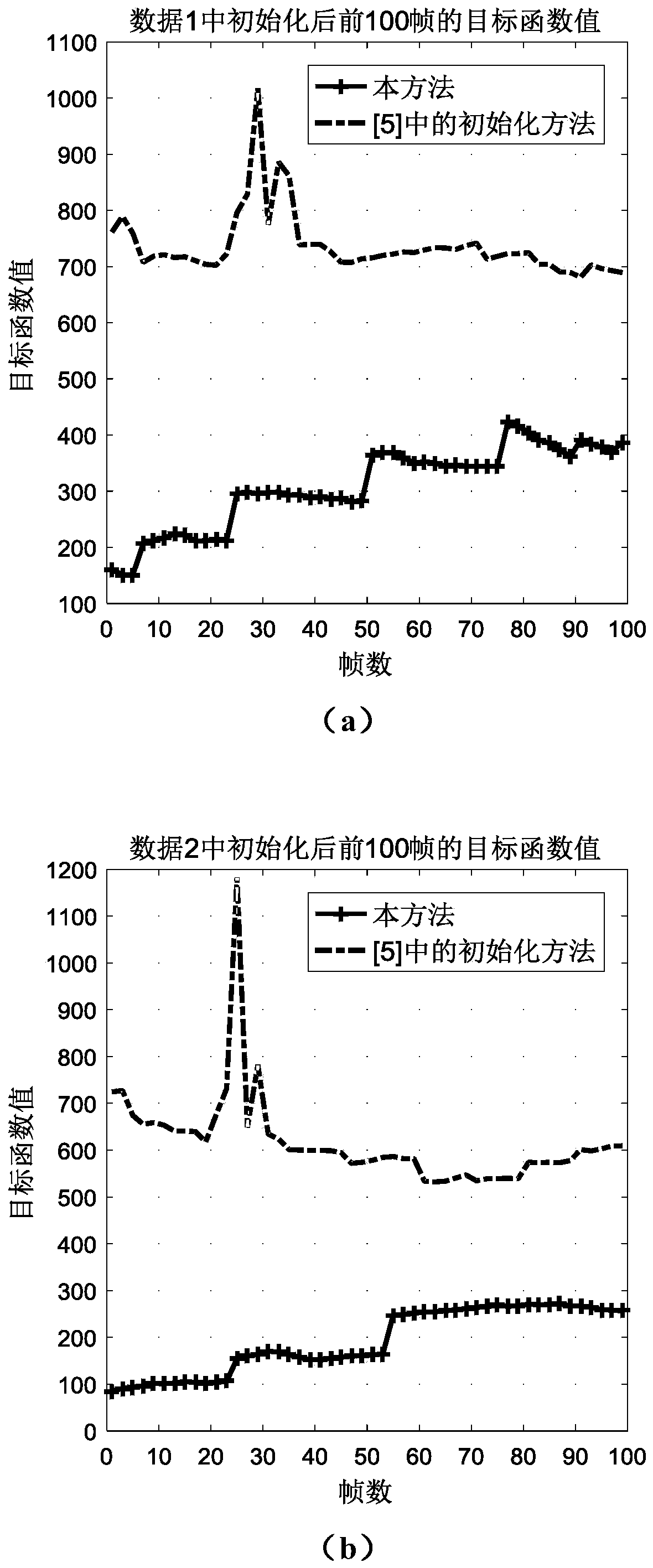
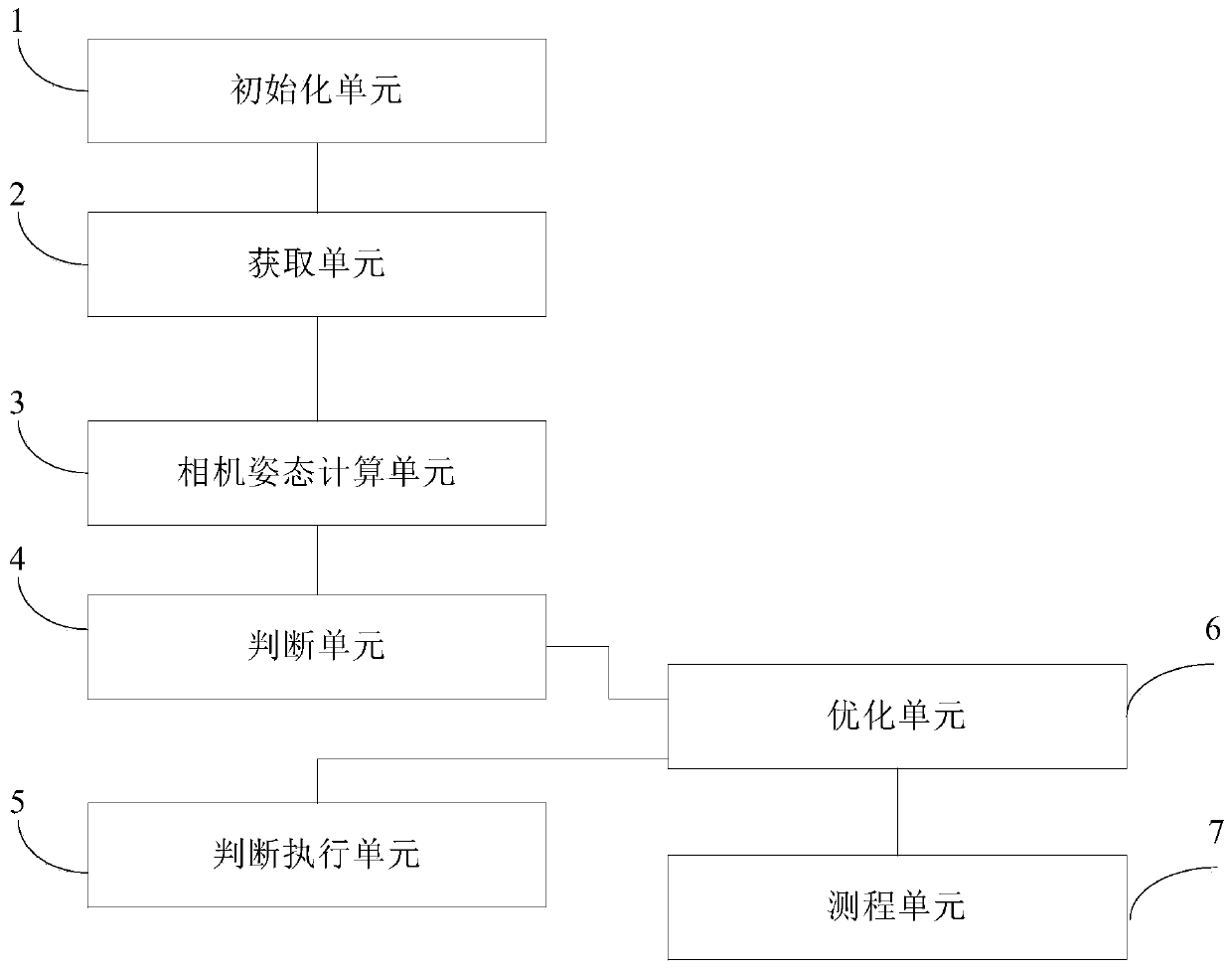
The invention relates to a visual inertial ranging method and system of tightly coupled vehicle wheel coder data. The visual inertial ranging method comprises the steps of: (1), setting the initialization state of the visual inertial ranging method to be unfinished, and obtaining a camera image, an inertial measurement unit IMU measurement value and a wheel coder reading in real time in initialization and measurement processes; (2), calculating an essential matrix between a current image and a previous-frame image, and adding the essential matrix and the corresponding IMU measurement value andwheel coder reading into a first sliding window and a second sliding window at the same time; (3), performing IMU-wheel coder pre-integration on the IMU measurement value and wheel coder reading corresponding to a last-frame image; judging whether the initialization state is finished or not, if so, executing the step (5), and otherwise, executing the step (4); (4), initializing parameters by utilizing a pre-integration result; (5), obtaining parameters corresponding to each image in the first sliding window; and (6), performing visual inertial ranging of the tightly coupled vehicle wheel coder data according to the parameters.
Owner:INST OF AUTOMATION CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com