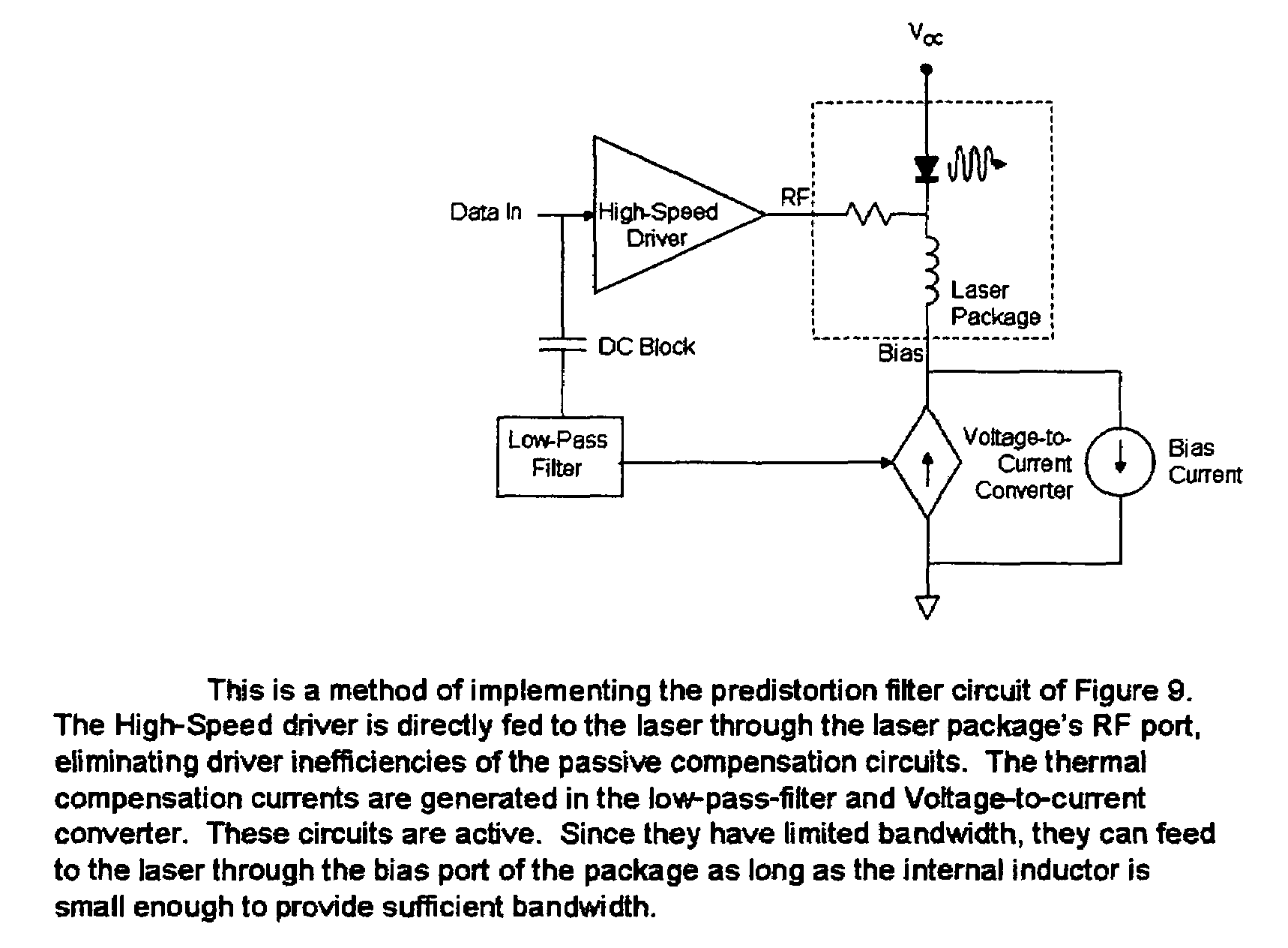
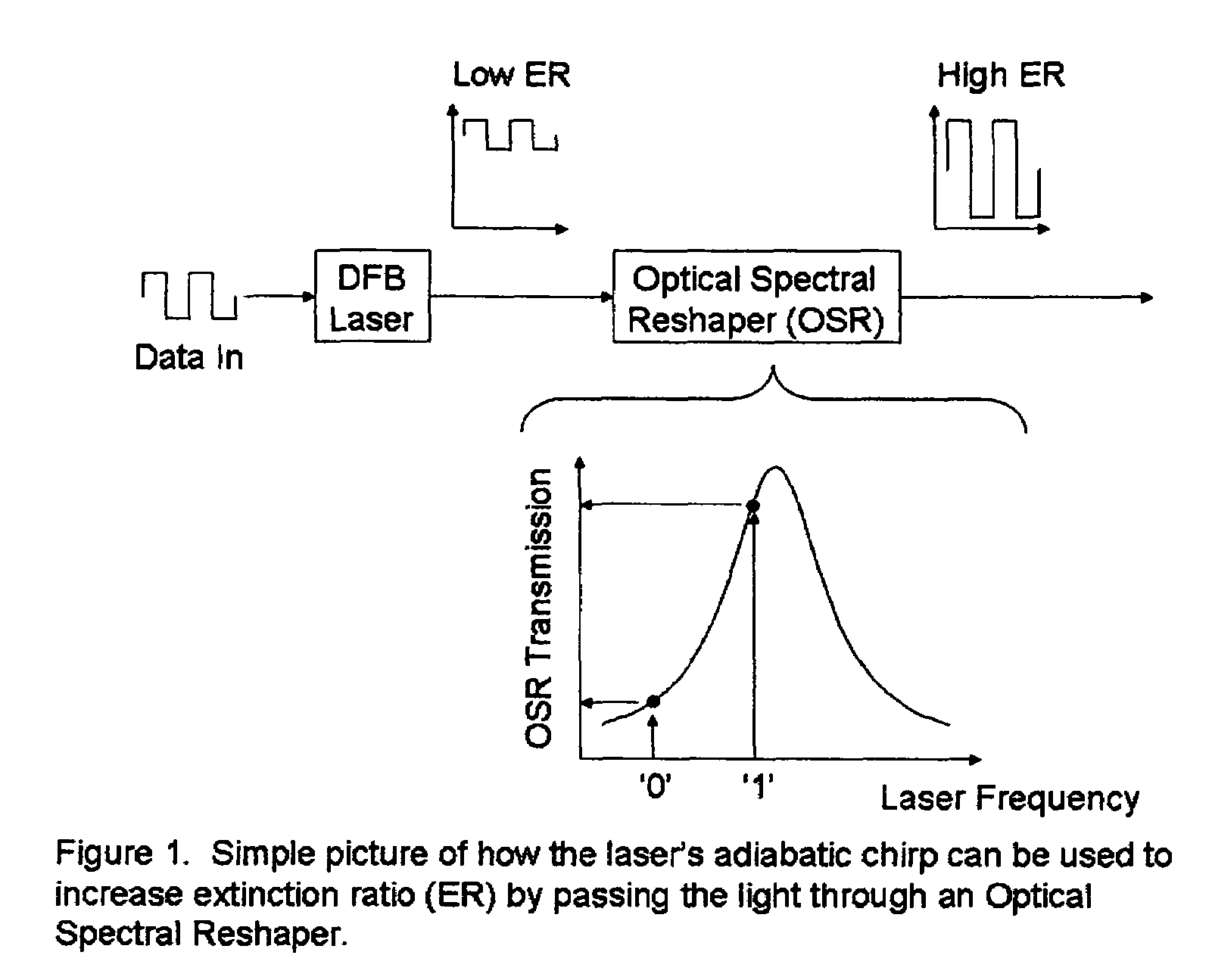
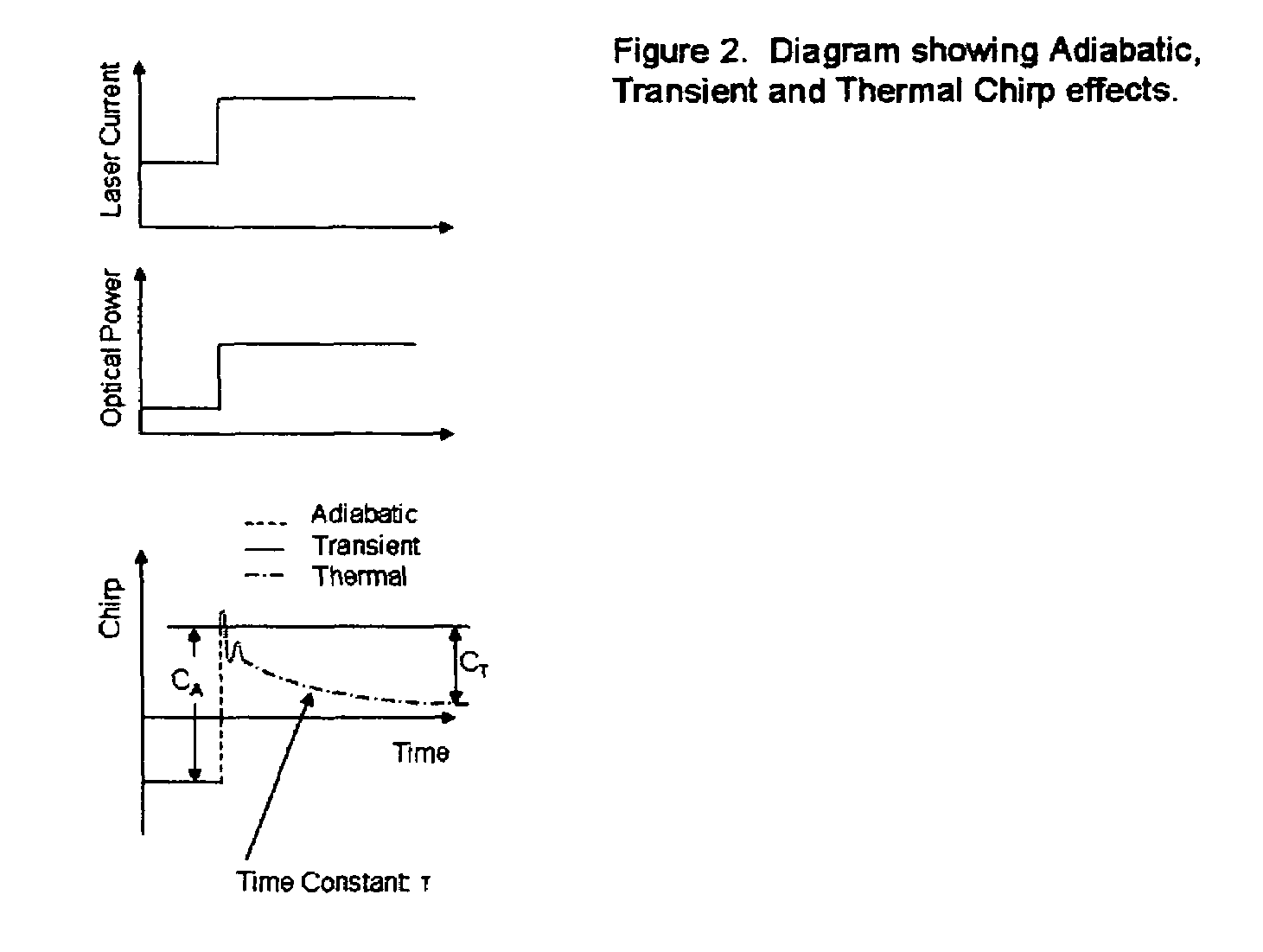
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
131 results about "Fiber optic communication systems" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Fiber optic communication system
Owner:MULLSTEFF DAVID M
Power source for a dispersion compensation fiber optic system
InactiveUS6963685B2Minimize signalingIncrease bitrateCoupling light guidesElectromagnetic transmittersFrequency modulationDispersion compensation
Owner:OPTICAL HORIZONS CORP +1
High-speed transmission system comprising a coupled multi-cavity optical discriminator
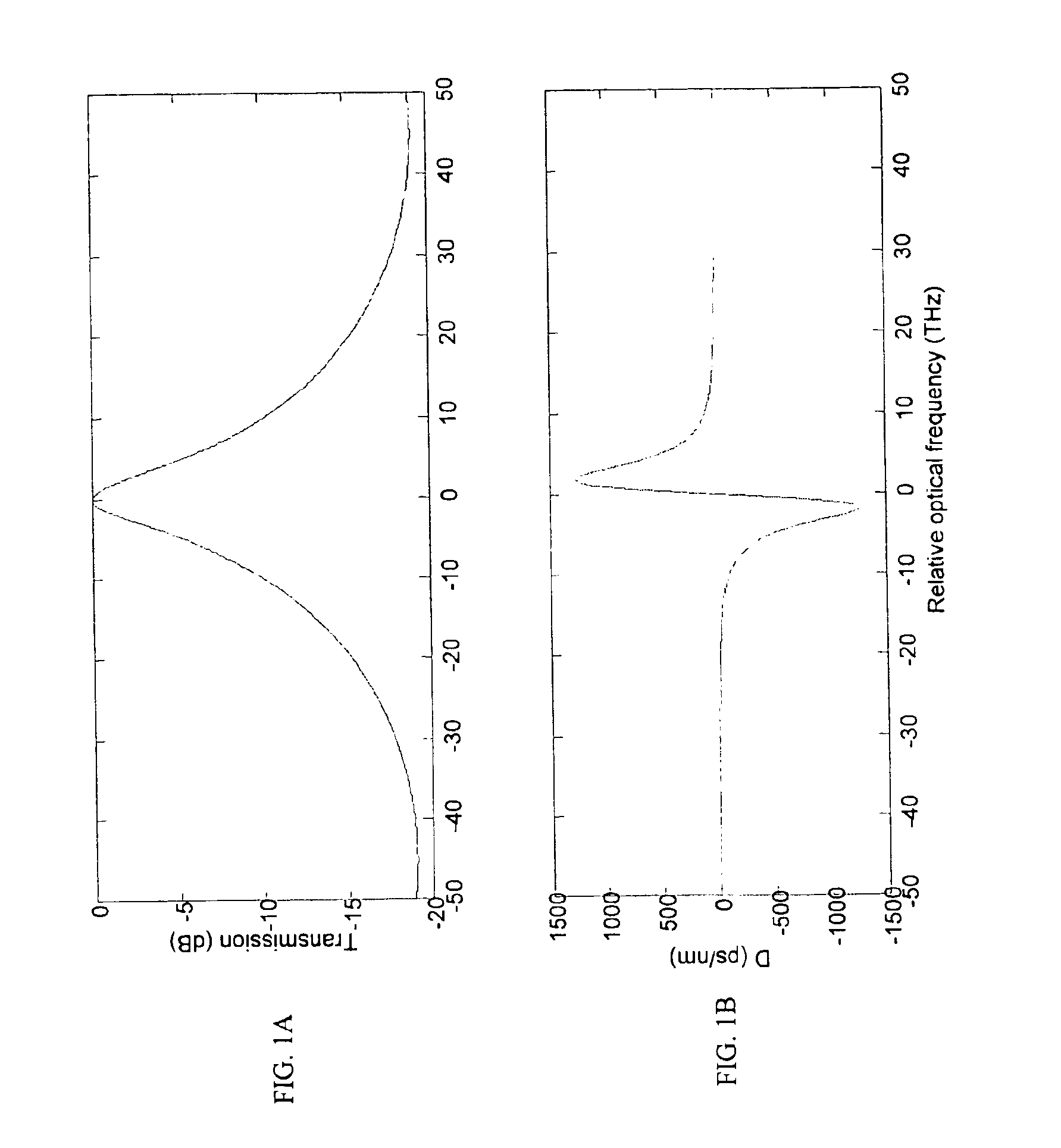
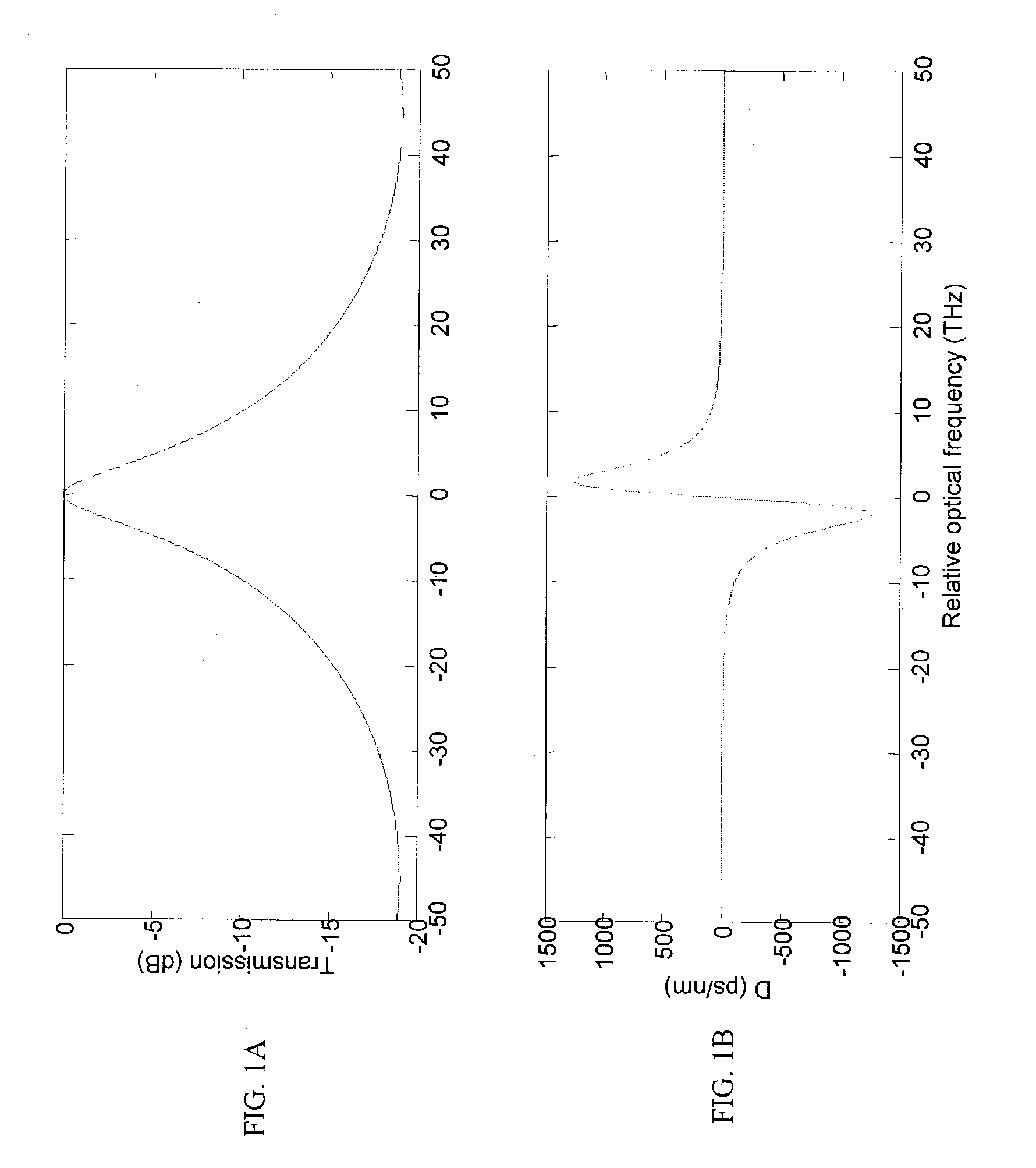
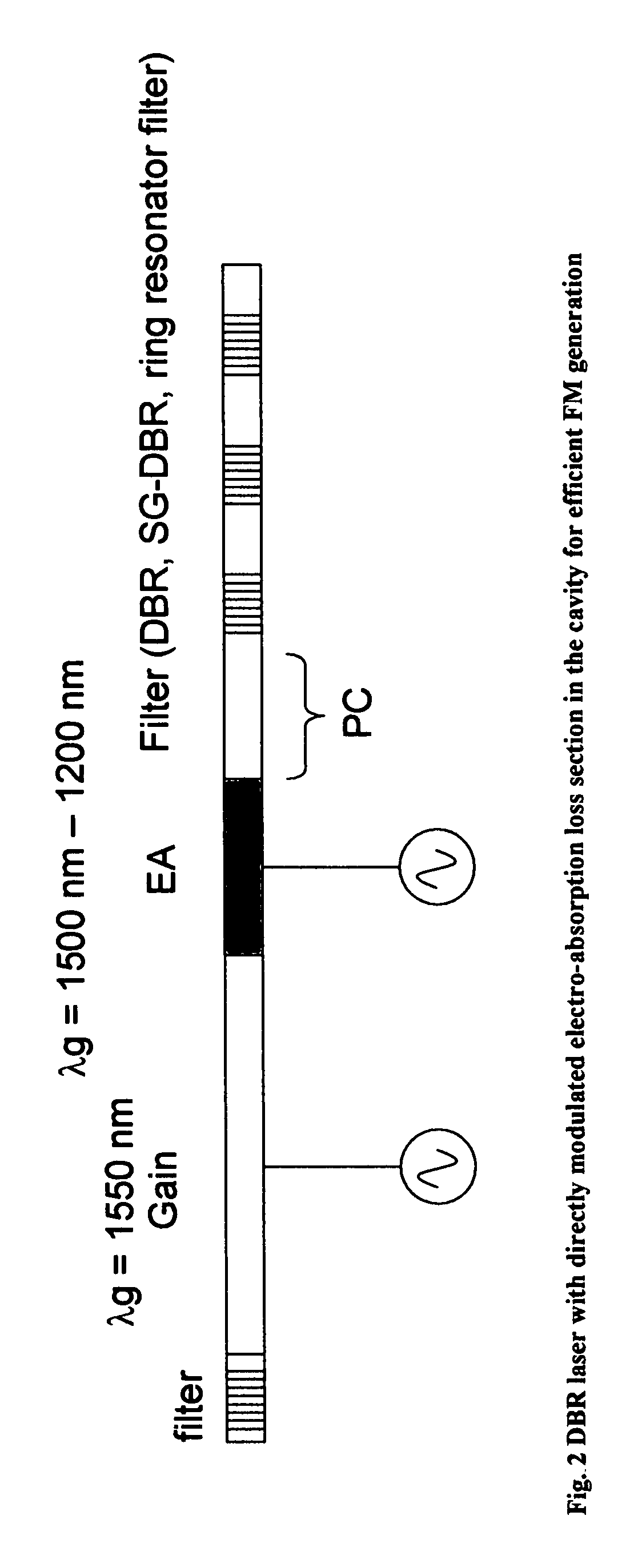
This invention generally relates to an optical filter for a fiber optic communication system. A coupled multi-cavity optical filter may be used, following a directly modulated laser source, and converts a partially frequency modulated signal into a substantially amplitude modulated signal. The optical filter may compensate for the dispersion in the fiber optic transmission medium and may also lock the wavelength of the laser source.
Owner:II VI DELAWARE INC
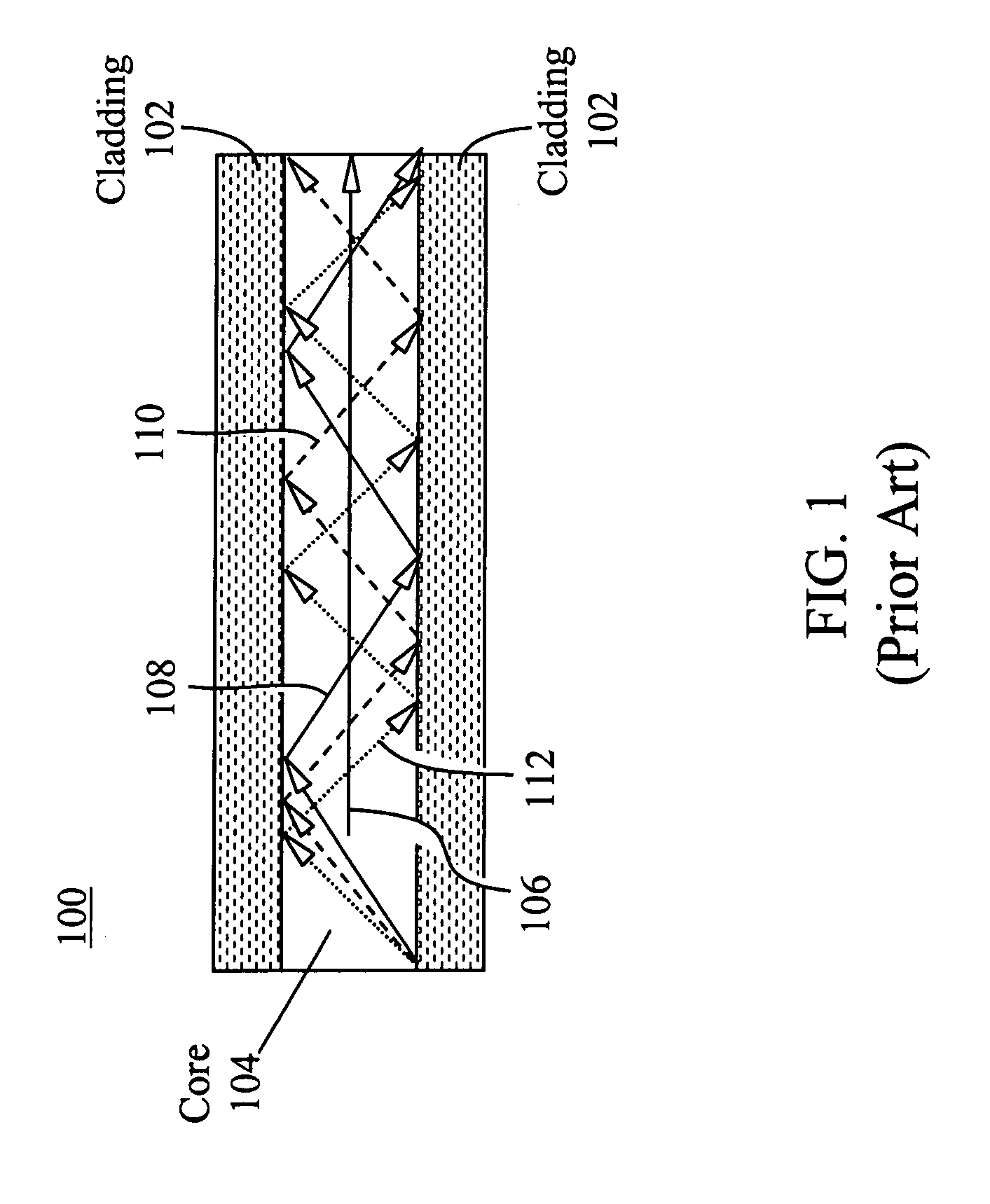
Apparatus, system and method for an adiabatic coupler for multi-mode fiber-optic transmission systems
InactiveUS20050265653A1Low insertion lossIncrease system bandwidthLaser detailsOptical fibre with graded refractive index core/claddingFiberRefractive index
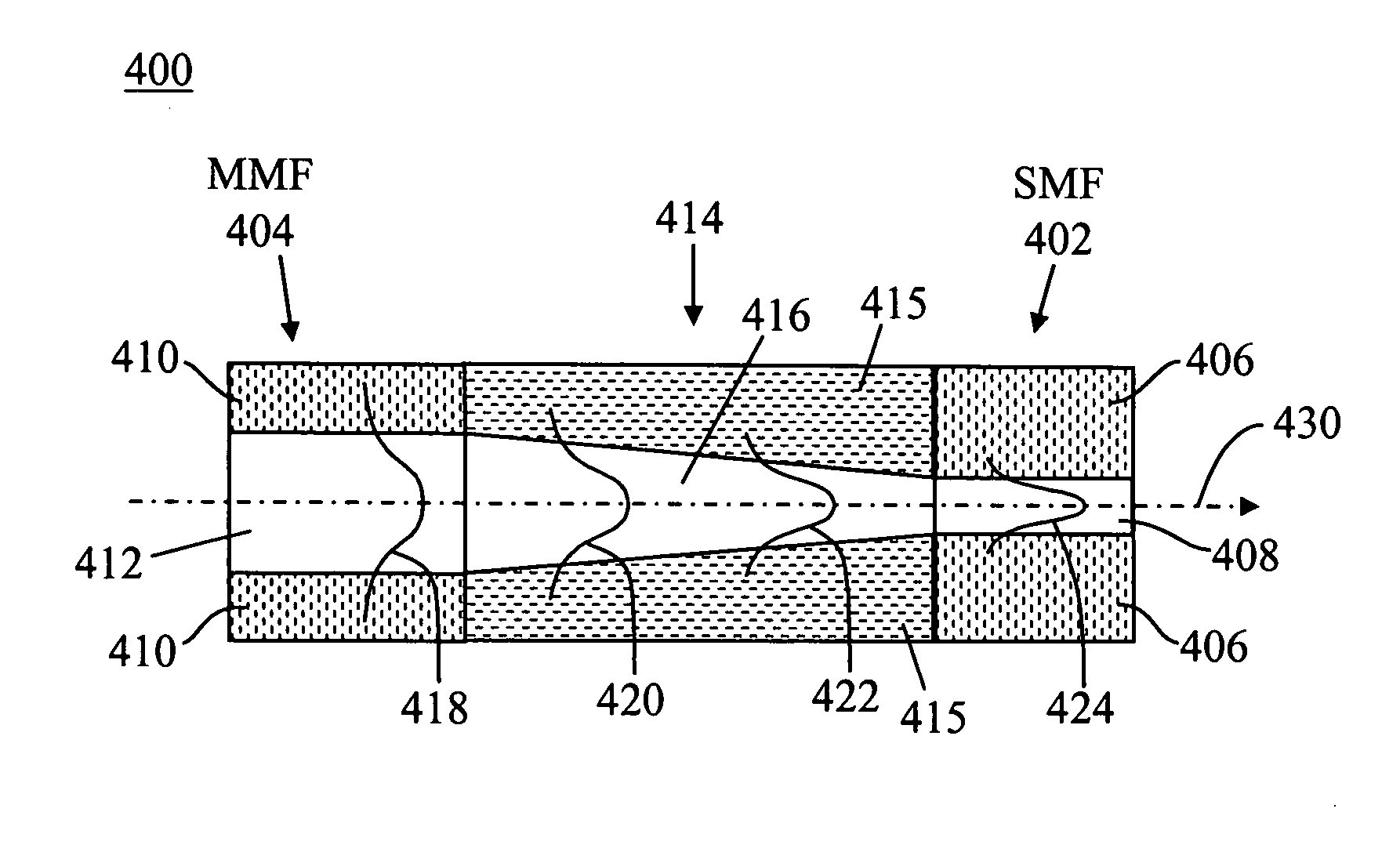
An improved fiber-optic communications system comprises a multi-mode waveguide carrying an optical signal, a single-mode waveguide optically coupled to and receiving the optical signal from the multi-mode waveguide and an adiabatic coupler optically coupled between the multi-mode waveguide and the single-mode waveguide. The multi-mode and single-mode waveguides may be optical fibers. The adiabatic coupler may comprise a tapered core surrounded by a cladding. Alternatively, the adiabatic coupler may comprise a core surrounded by a cladding, wherein the refractive index of at least one of the core and the cladding varies over the length of the adiabatic coupler.
Owner:OCLARO NORTH AMERICA
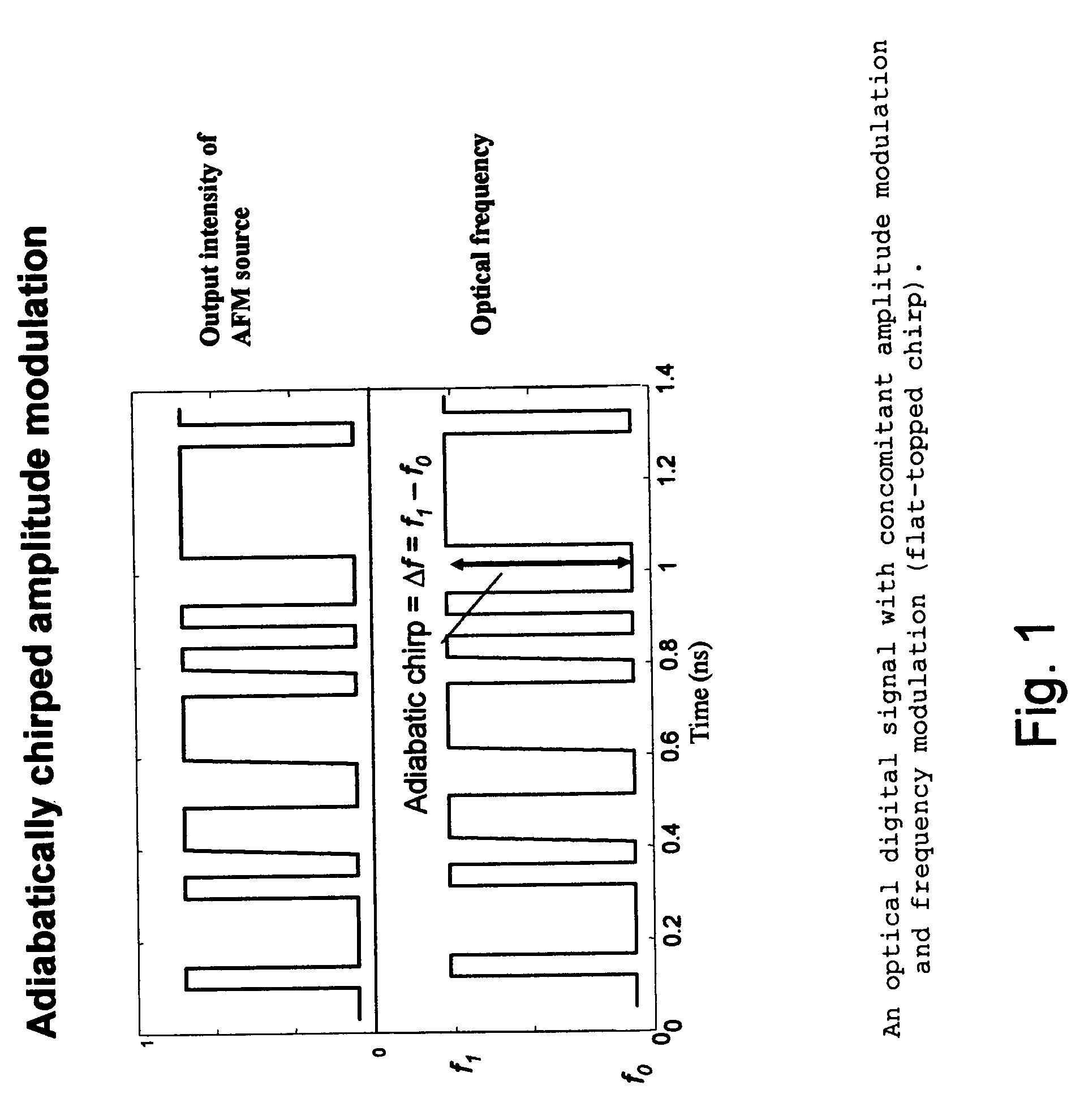
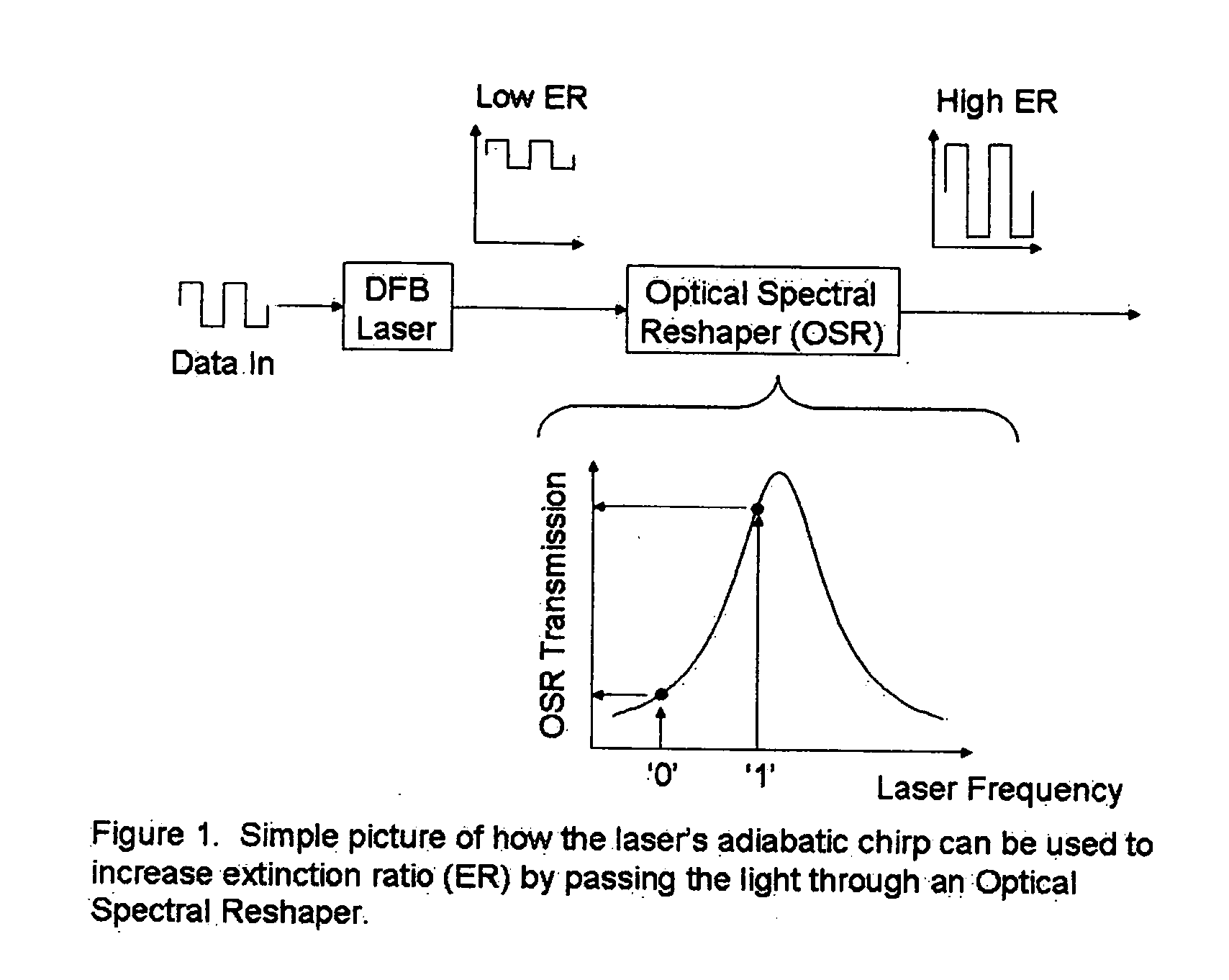
Optical system comprising an FM source and a spectral reshaping element
InactiveUS20060029358A1Extending optical transmission lengthImprove toleranceColor television with bandwidth reductionColor television signals processingOptical propertyFrequency modulation
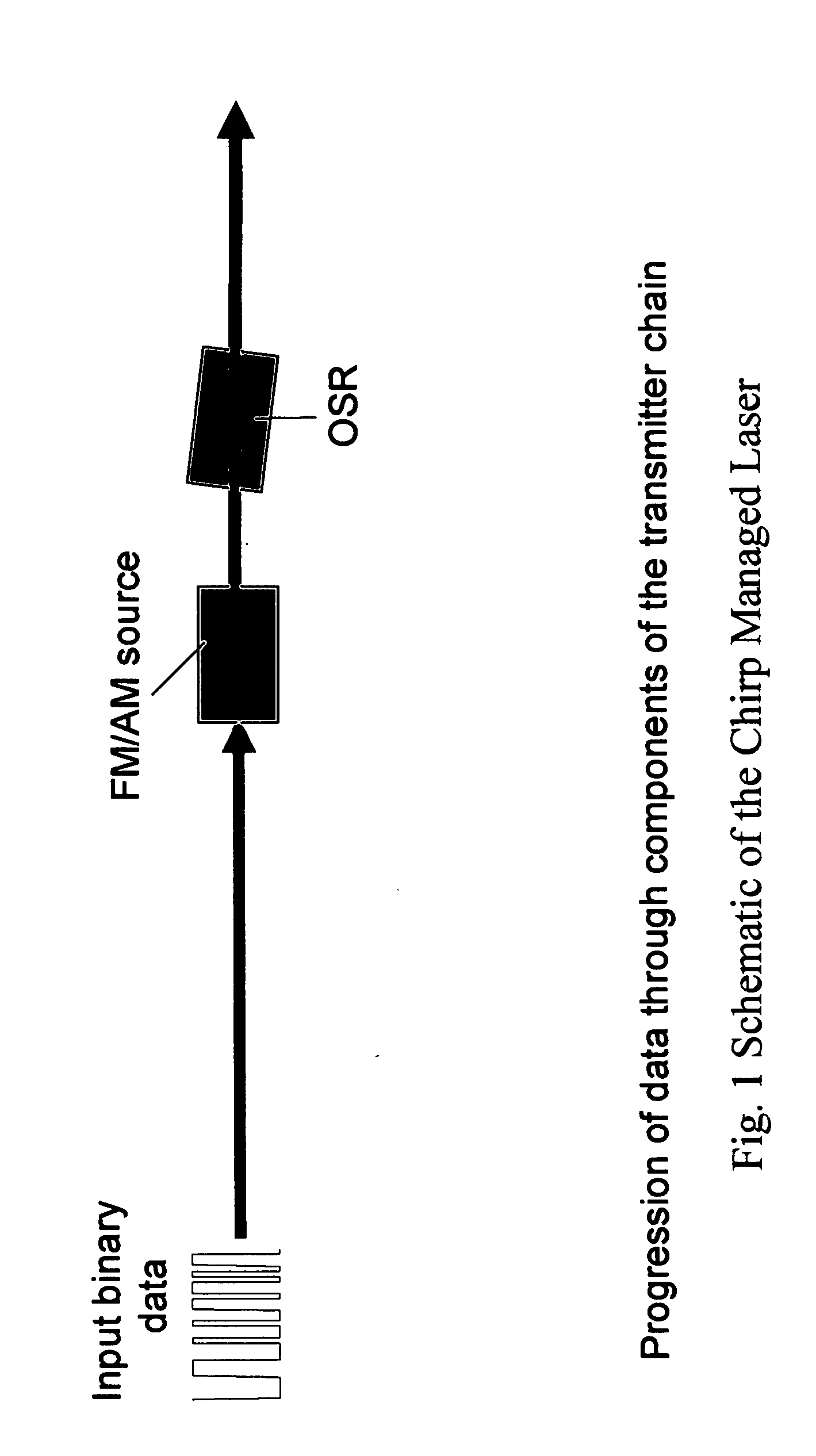
In one form of the present invention, there is provided a fiber optic communication system comprising: an optical signal source adapted to receive a base binary signal and produce a first signal, said first signal being frequency modulated; and an optical spectrum reshaper adapted to reshape the first signal into a second signal, said second signal being amplitude modulated and frequency modulated; characterized in that: the frequency characteristics of said first signal, and the optical characteristics of said optical spectrum reshaper, being such that the frequency characteristics of said second signal are configured so as to increase the tolerance of the second signal to dispersion in a transmission fiber. In another form of the present invention, there is provided an optical transmitter comprising: a frequency modulated source for generating a first frequency modulated signal, and an amplitude modulator for receiving the first frequency modulated signal and for generating a second amplitude and frequency modulated signal. In another form of the present invention, there is provided a method for transmitting an optical signal through a transmission fiber comprising: receiving a base binary signal; operating an optical signal source using the base binary signal to produce a first signal, said first signal being frequency modulated; passing the frequency modulated signal through an optical spectrum reshaper so as to reshape the first signal into a second signal, said second signal being amplitude modulated and frequency modulated; the frequency characteristics of said first signal, and the optical characteristics of said optical spectrum reshaper, being such that the frequency characteristics of said second signal are configured so as to increase the tolerance of the second signal to dispersion in a transmission fiber; and passing the second signal through a transmission fiber. In another form of the present invention, there is provided a method for transmitting a base signal, comprising: using the base signal to produce a frequency modulated signal; and providing an amplitude modulator for receiving the frequency modulated signal and for generating an amplitude and frequency modulated signal.
Owner:II VI DELAWARE INC
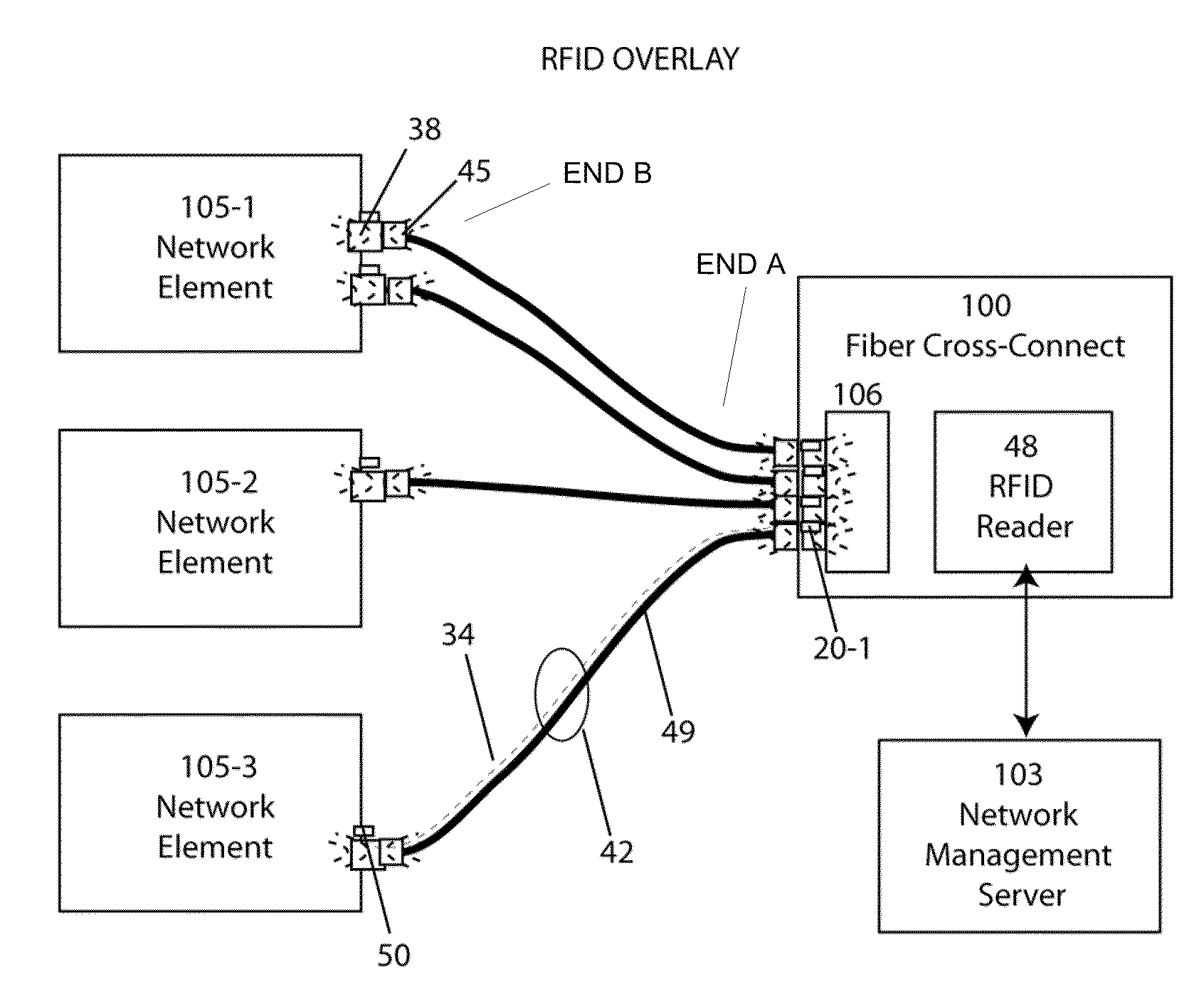
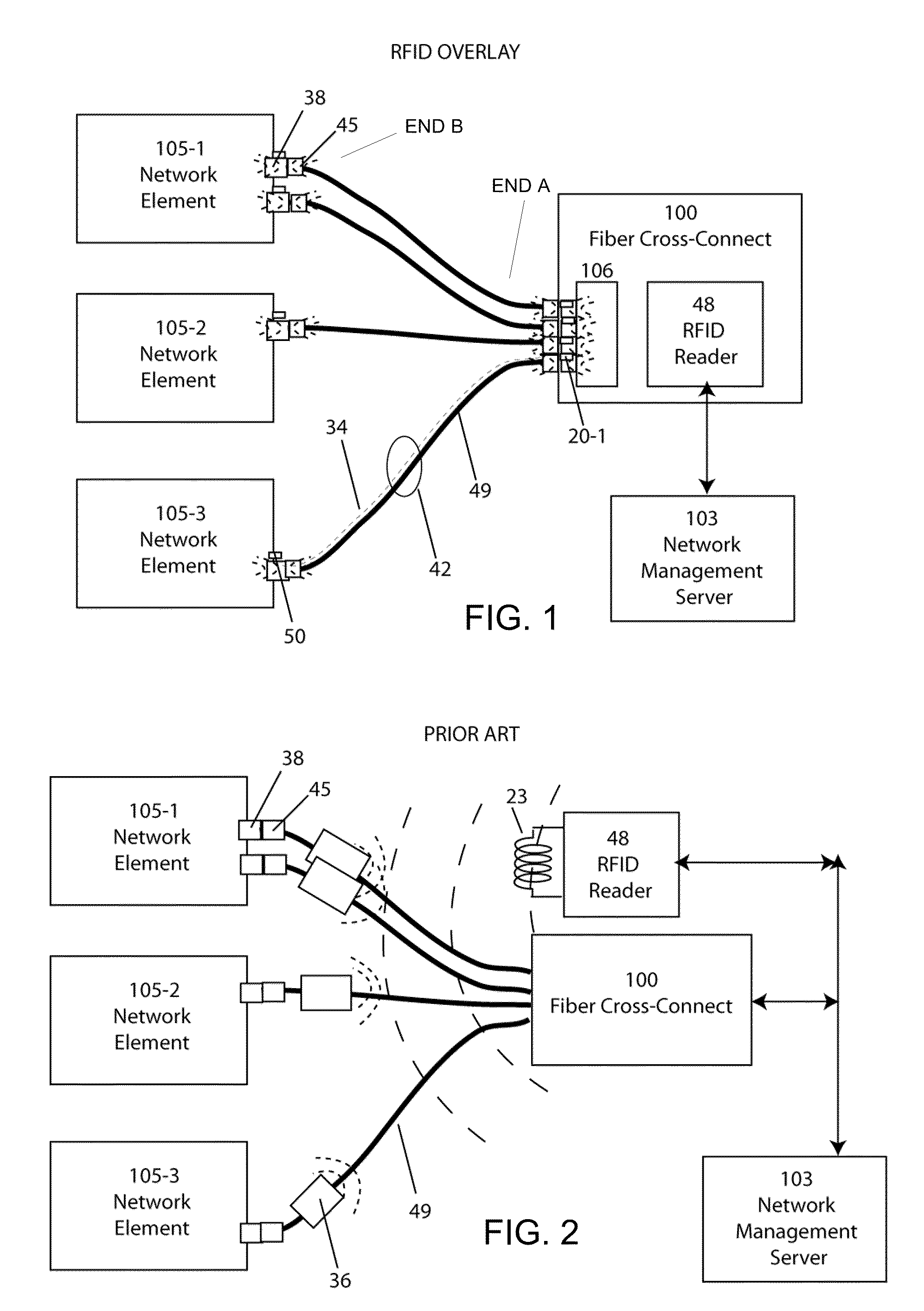
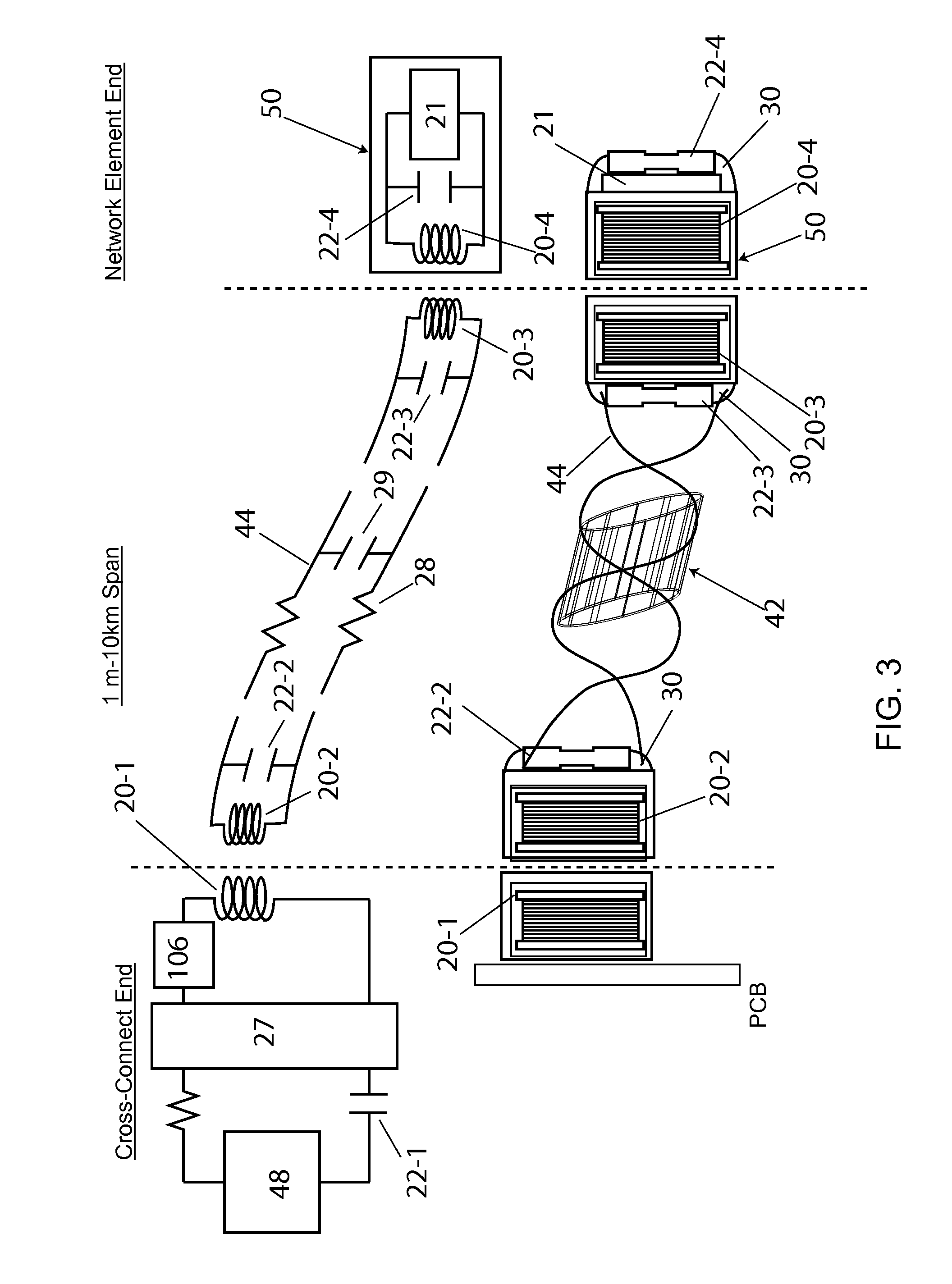
Radio frequency identification overlay network for fiber optic communication systems
ActiveUS20100098425A1Eliminate needSensing record carriersElectromagnetic transmissionFiberEngineering
In this invention, a radio frequency identification overlay network that automates the discovery and configuration management of all physical fiber optic connections within a distributed communications network is disclosed. Miniaturized, low crosstalk RFID tags at a first fiber optic receptacle location and miniature, distributed, multiplexed reader antenna at a distant, second fiber optic receptacle location are joined by a fiber optic link which transmits both optical data and RF electronic signals. This electronic-fiber optic interface is comprised of two separated, miniaturized resonant antenna in communication with another through a resonant RF transmission line integral to the fiber optic cable. This RFID overlay network is comprised of multiplexed RFID readers, RF resonant fiber optic cables, and miniaturized RFID tags attached to the connector receptacles of network elements. The RFID overlay network interrogates tags automatically and remotely through the RF transmissive and optically transmissive fiber optic patch cords, eliminating the need for manual readout by technicians.
Owner:TELESCENT
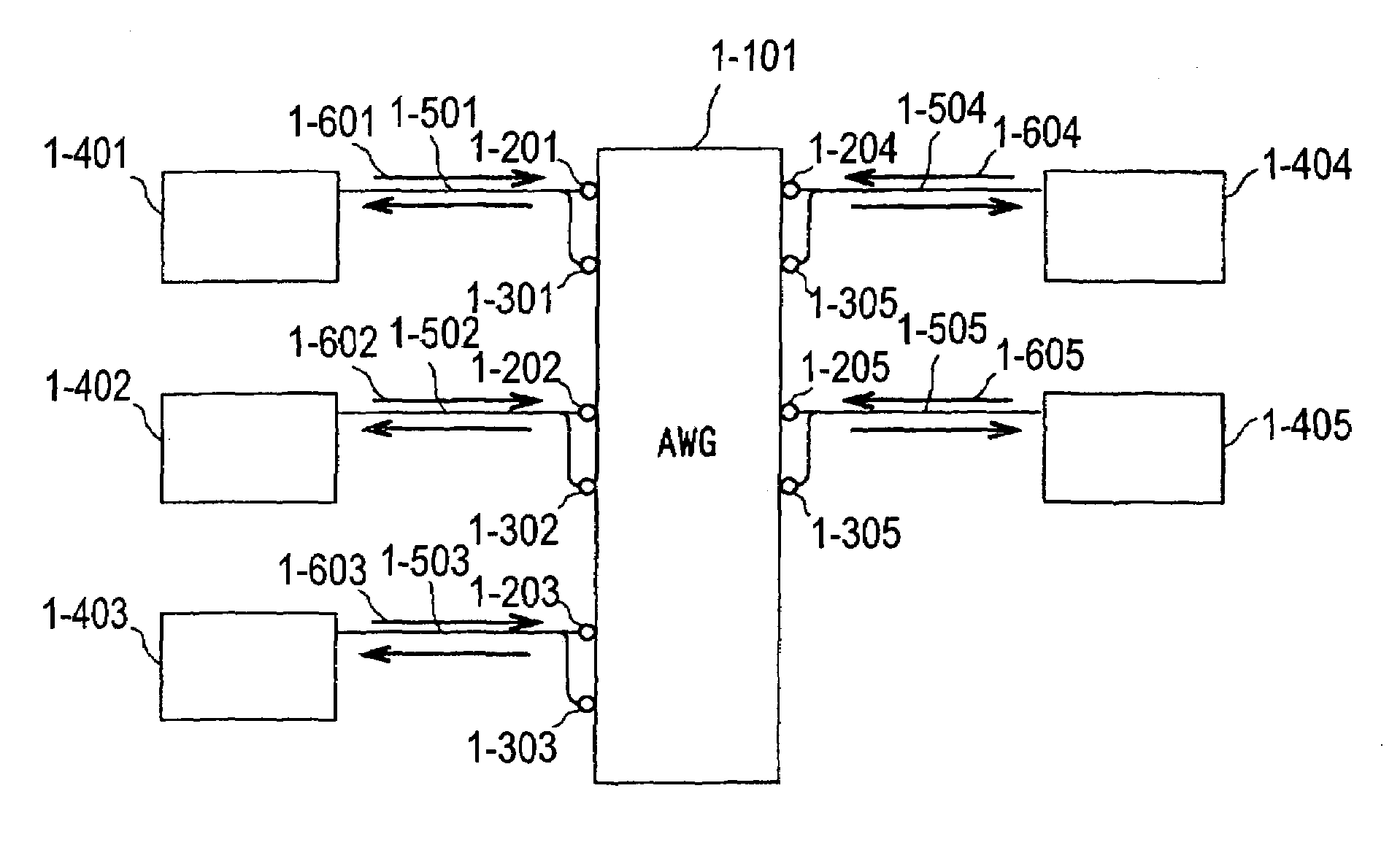
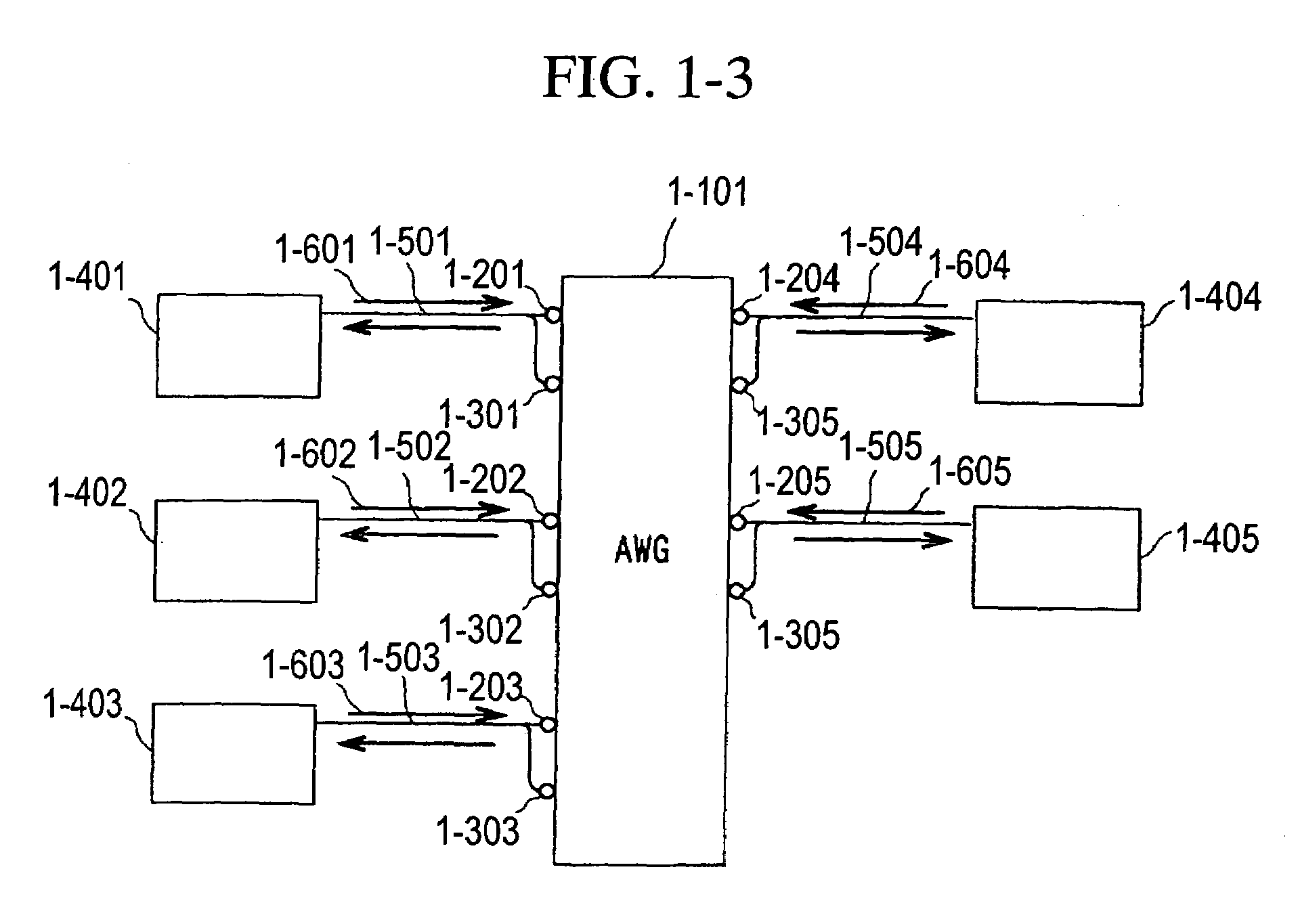
Optical communication network system
ActiveUS20060153496A1Quickly reconfiguredOptimizationMultiplex system selection arrangementsRing-type electromagnetic networksGratingLength wave
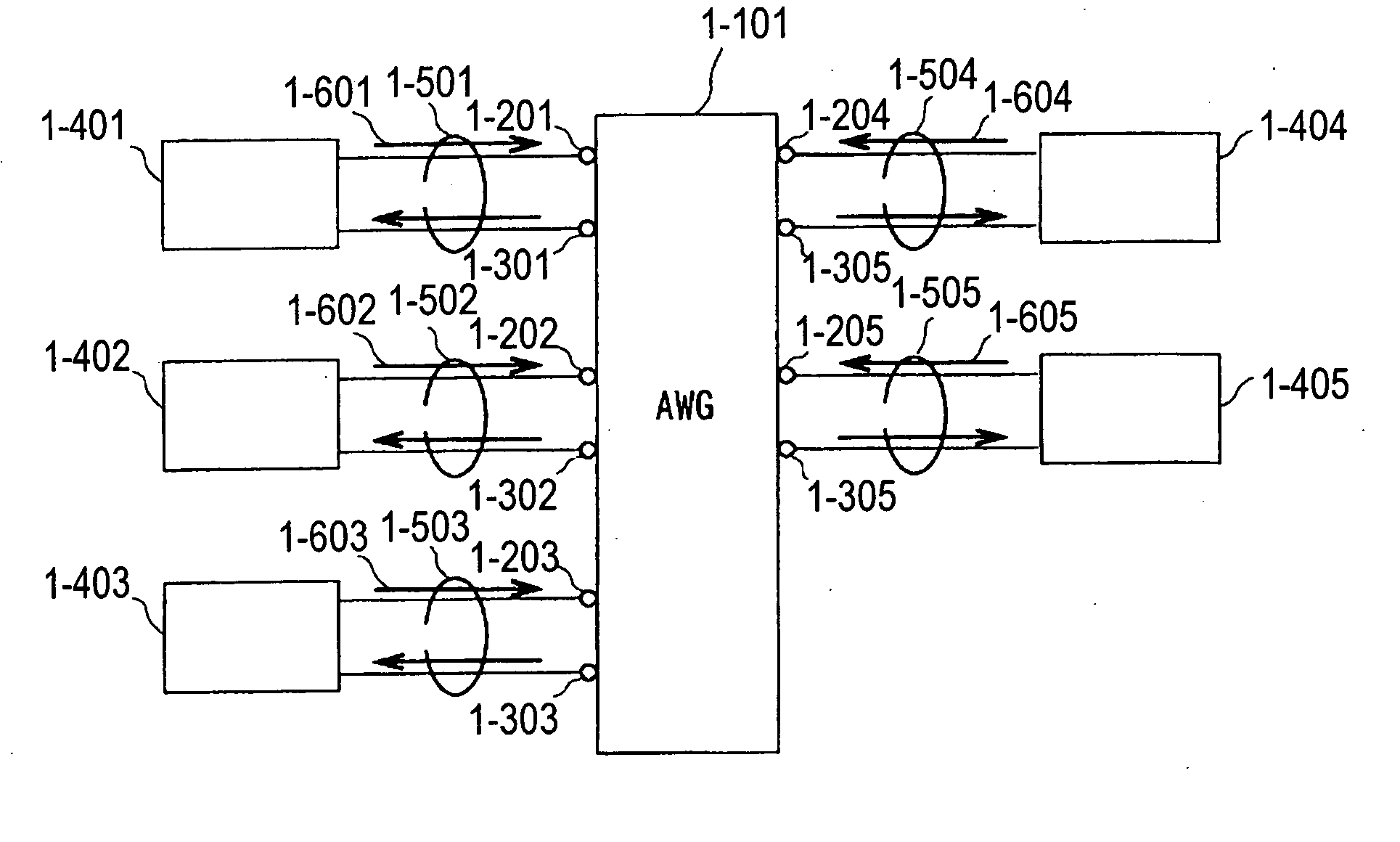
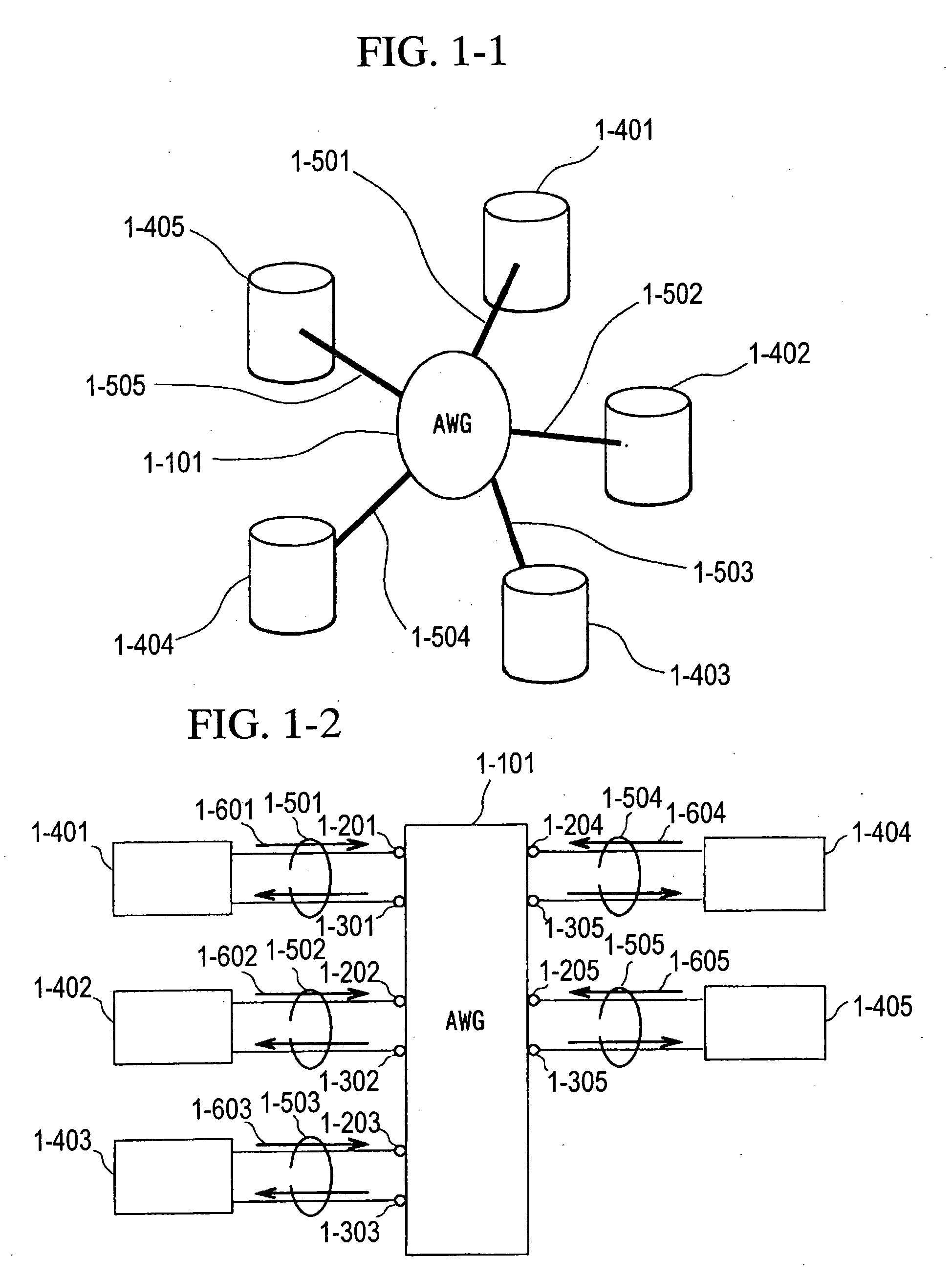
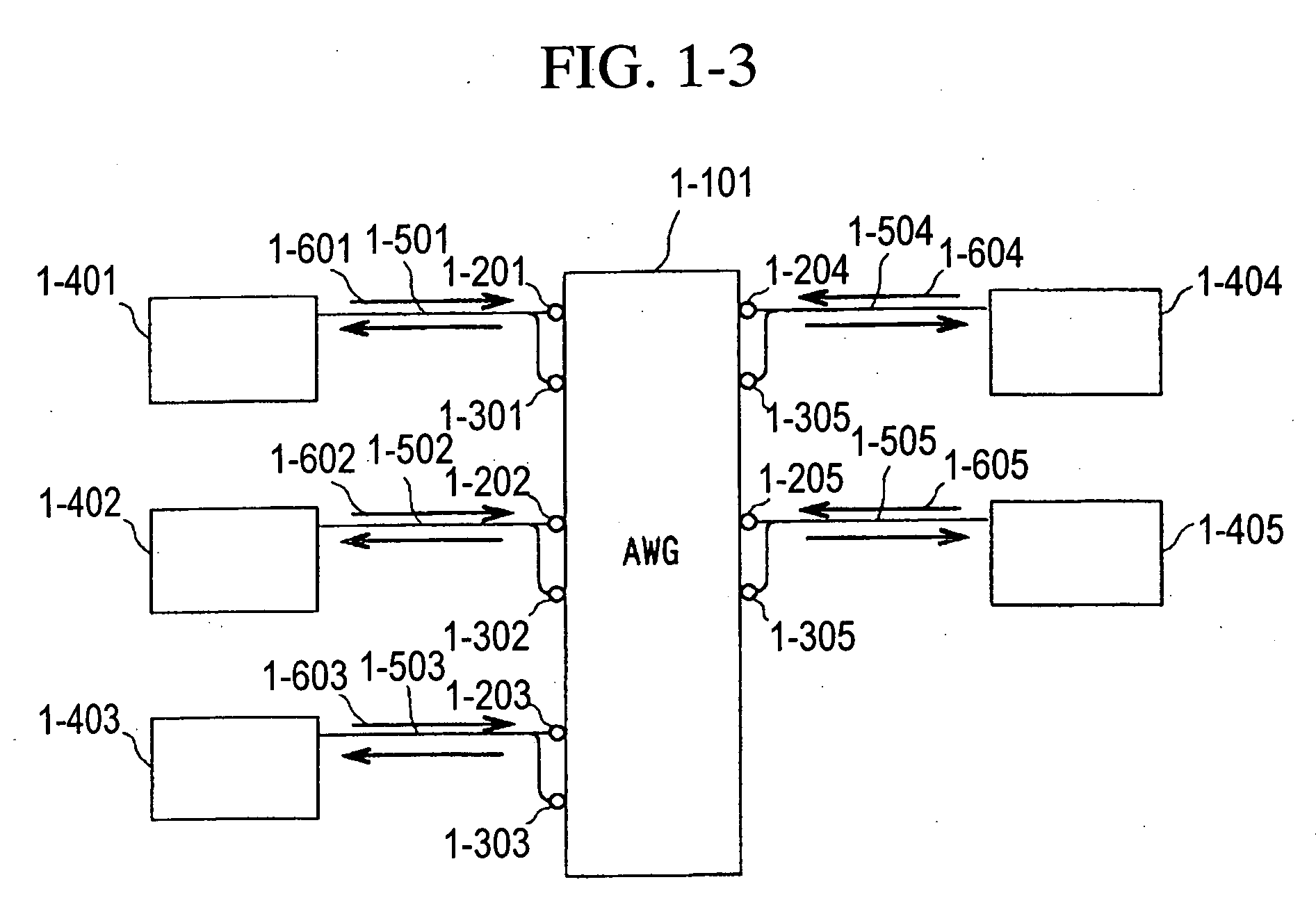
A fiber optic communication system includes a device of switching and setting wavelength of optical signals used in communication by network-node equipments, which sets the mapping of the wavelength of the optical signal used in communication by the network node equipments, and the input / output ports of an array waveguide grating (AWG), so as to construct a predetermined logical network topology by a plurality of network node equipments which are connected via optical fibers to the array waveguide grating that outputs optical signals inputted to optical input ports, to predetermined optical output ports in accordance with the wavelength thereof. As well as enabling a simple construction, it is easy to realize flexible network design, construction, and operation, and different network groups can also be easily connected to each other. Moreover, a fiber optic communication system having robust security and which can be stably operated even at the time of failure is realized at low cost.
Owner:NIPPON TELEGRAPH & TELEPHONE CORP
Error mitigation system using line coding for optical WDM communications
InactiveUS7016606B2Error detection/correctionWavelength-division multiplex systemsData streamEngineering
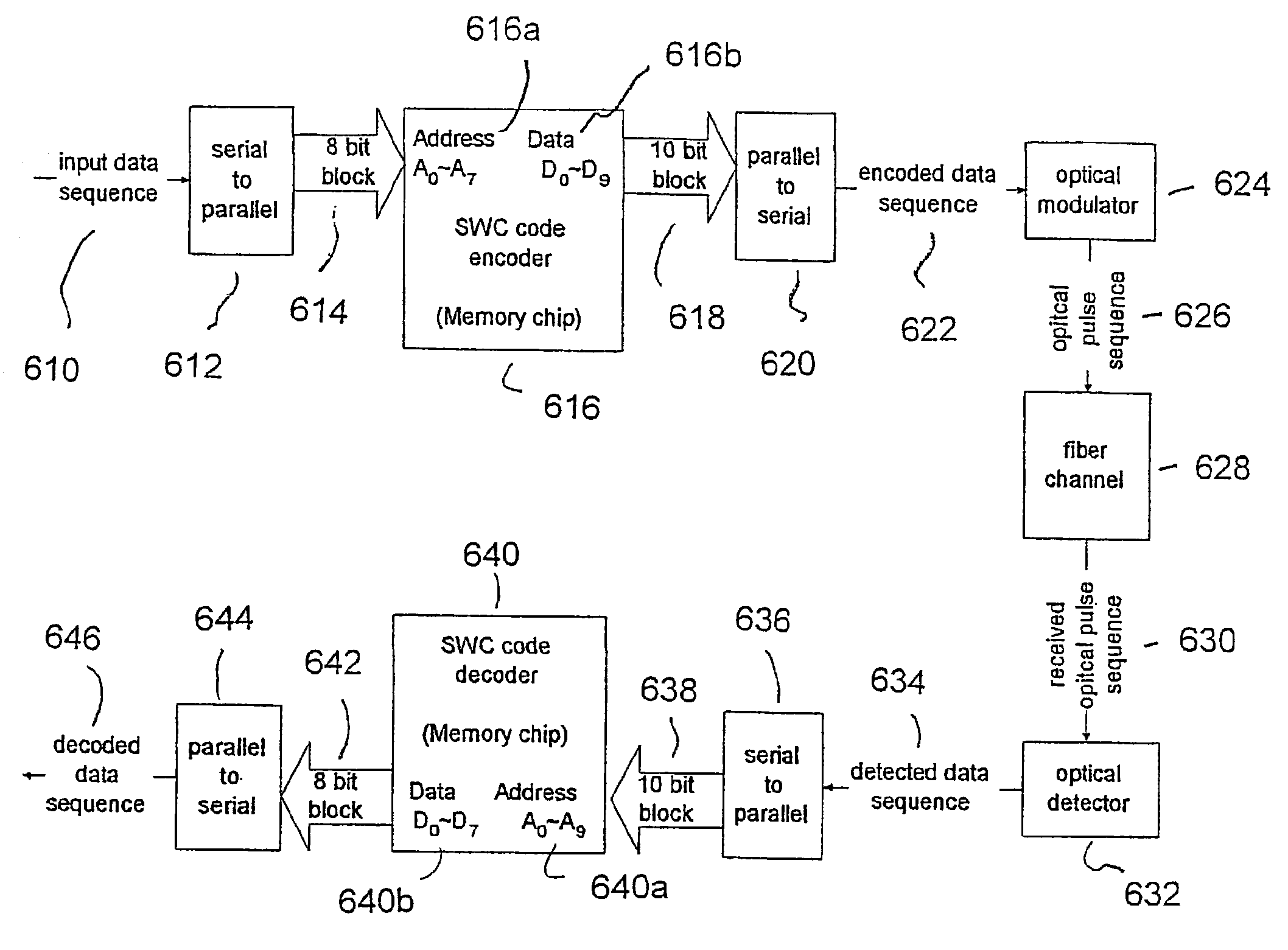
An apparatus and method of line coding to mitigate collision induced errors in Wavelength Division Multiplexing (WDM) optical communications systems is disclosed. The apparatus and method prevents Soliton-Soliton-Collision induced errors by reducing a variance in a number of possible collisions between solitons in multiple channels in a WDM fiber optic communication system using a sliding window criterion. The sliding window criterion defines a set of parametric values based on physical properties of the transmission network, a transmission frequency and a defined data block size. N-bit codes are iteratively selected and sequentially assigned to segments of a mapping table indexed by all possible unique combinations of “1”s and “0”s in a block of data. Input data blocks are mapped to corresponding code words having a reduced number of transitions for transmission on the fiber optic network. Received code words are converted back to a data stream corresponding to the input data stream.
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND BALTIMORE COUNTY
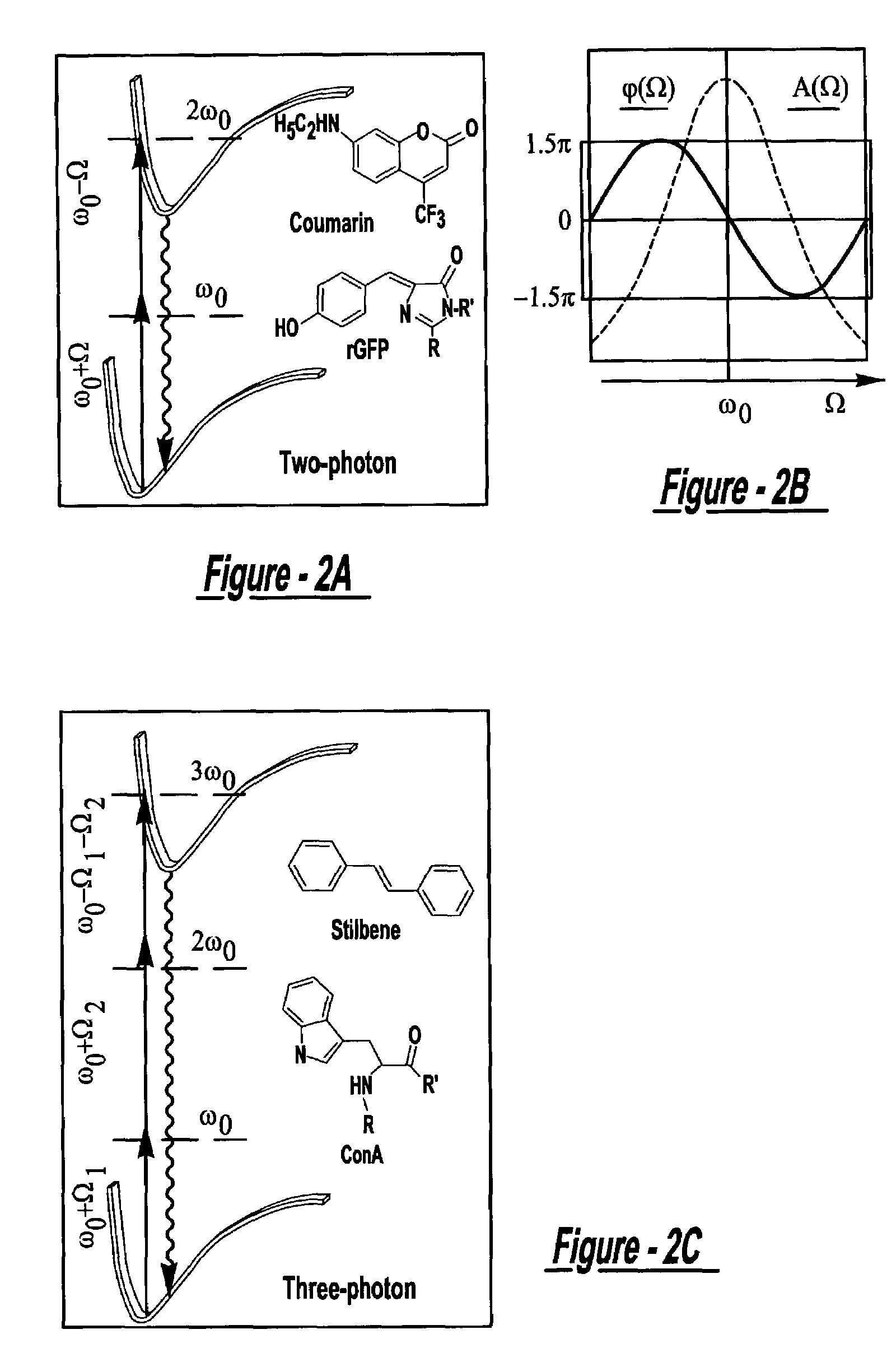
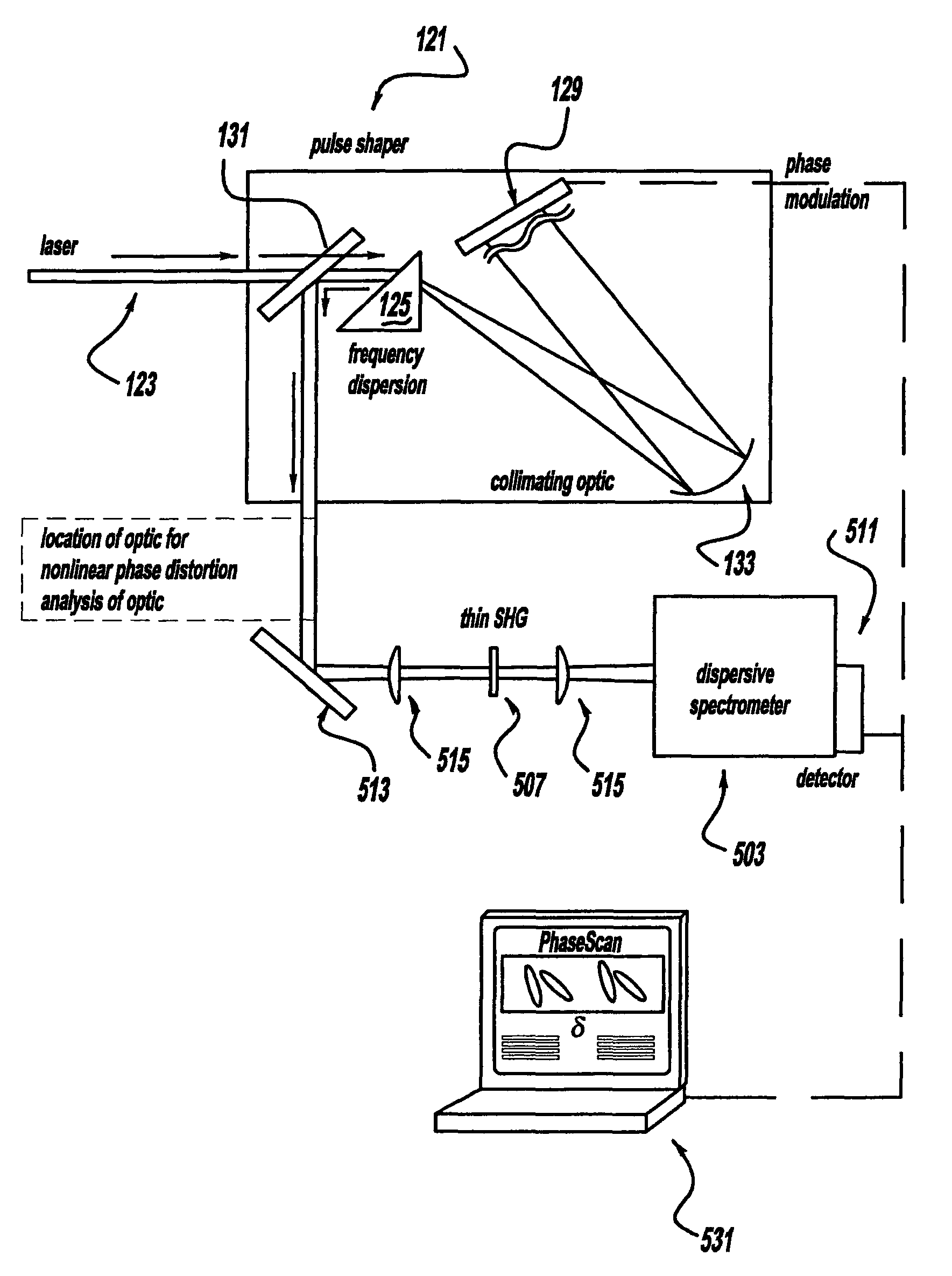
Laser system using ultrashort laser pulses
ActiveUS7450618B2Easy to set upEasy to useLaser detailsMaterial analysis by optical meansFemto second laserCharacterization test
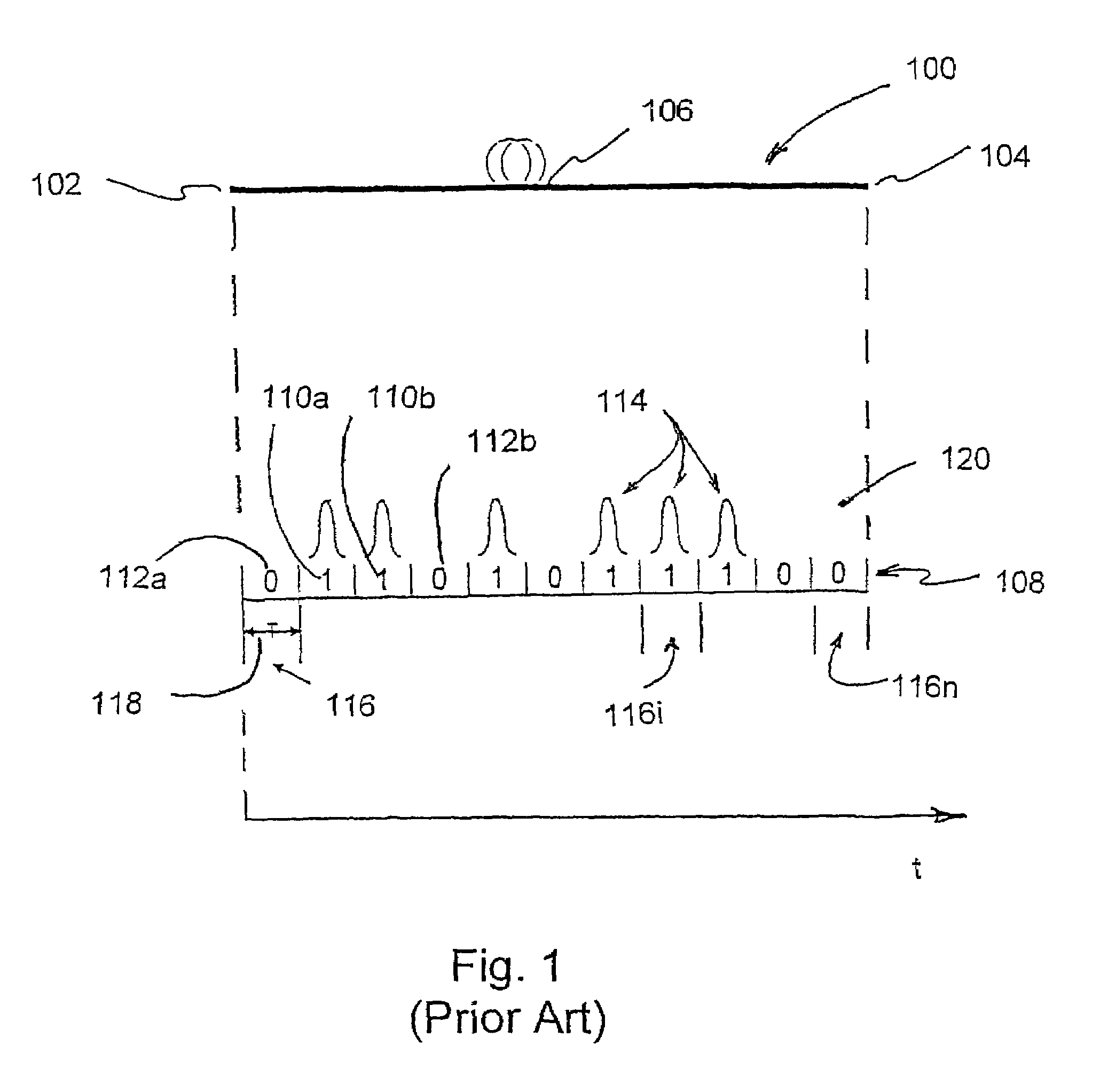
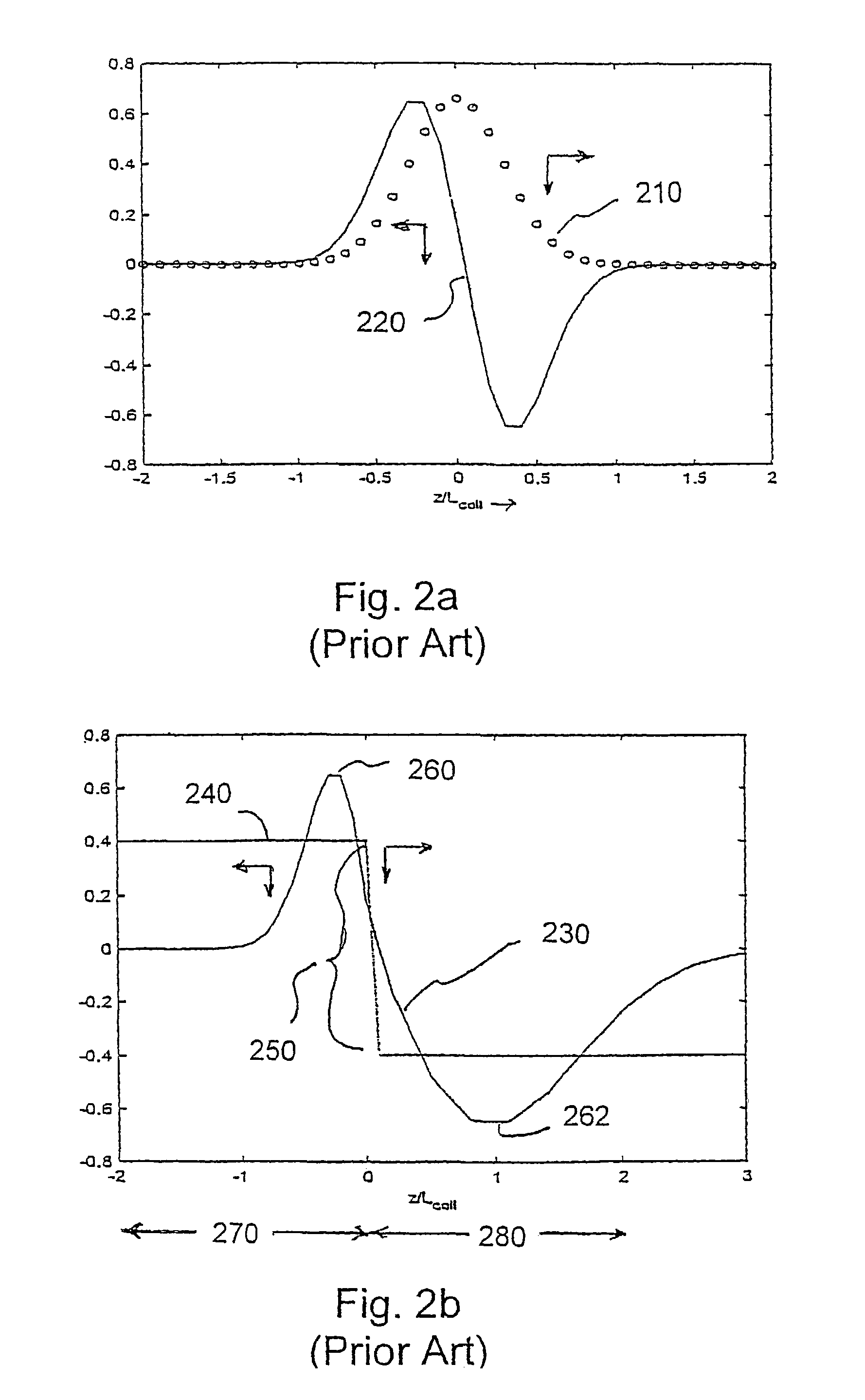
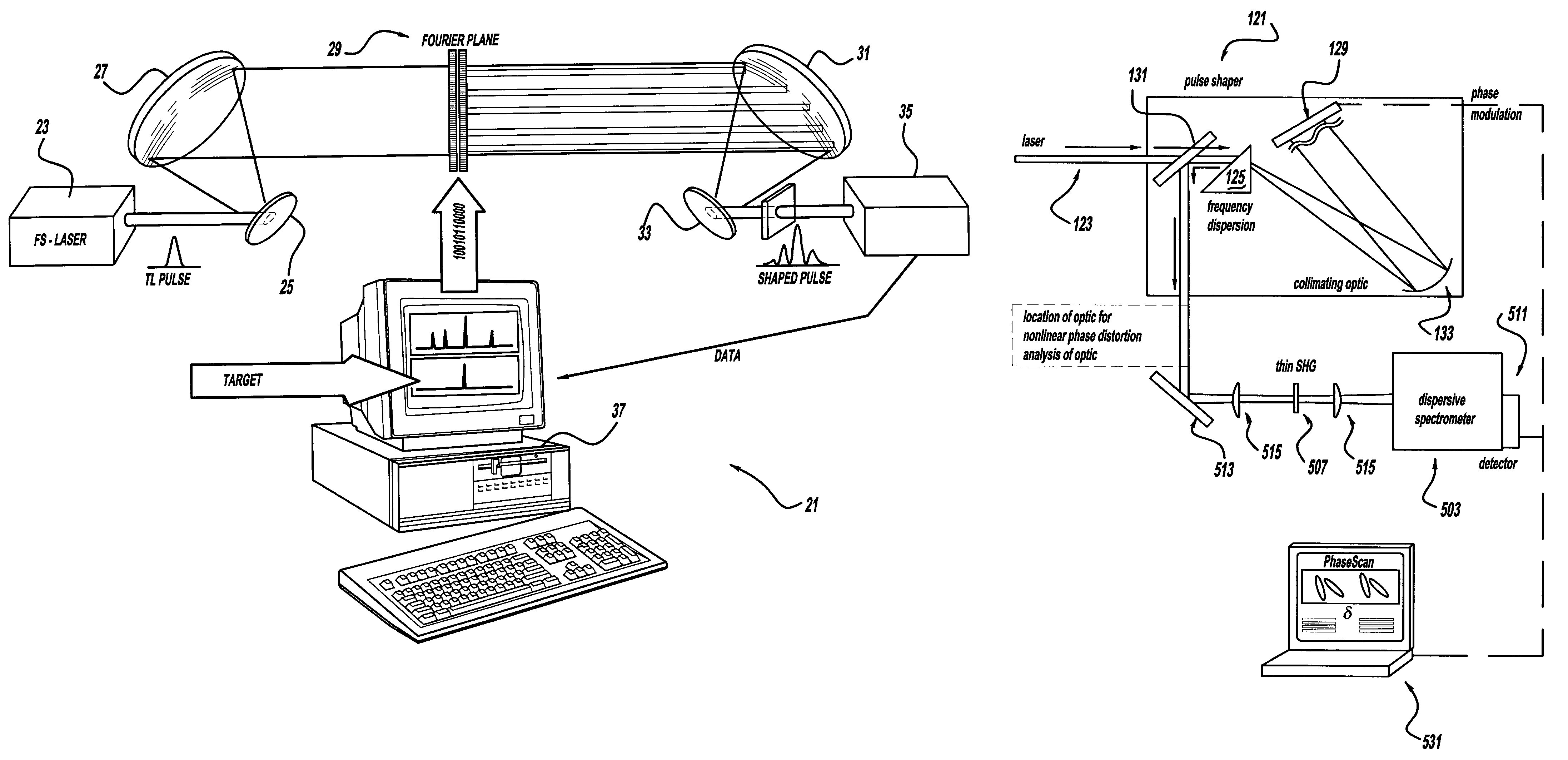
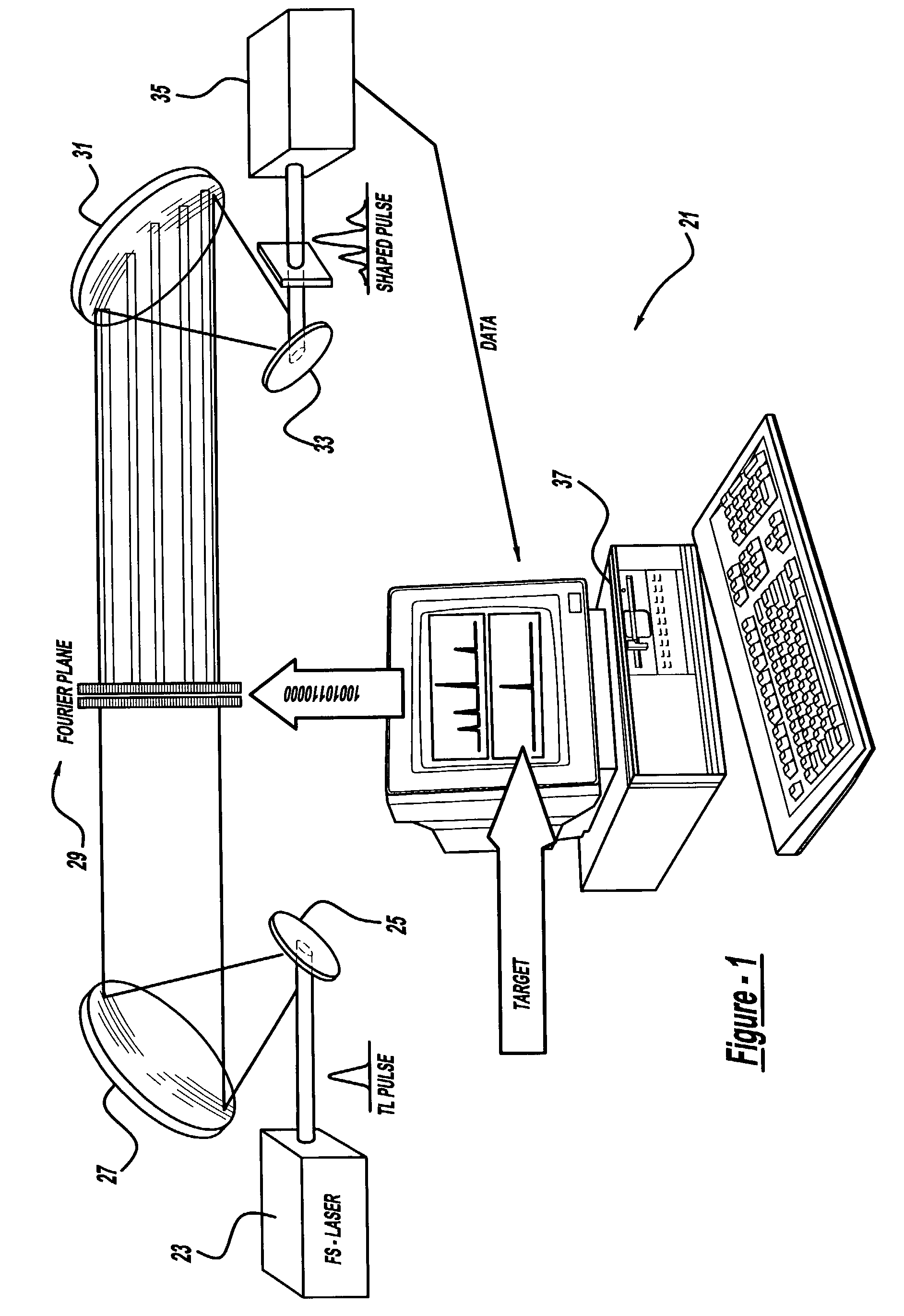
A laser system using ultrashort laser pulses is provided. In another aspect of the present invention, the system includes a laser, pulse shaper and detection device. A further aspect of the present invention employs a femtosecond laser and a spectrometer. Still another aspect of the present invention uses a laser beam pulse, a pulse shaper and a SHG crystal. In yet another aspect of the present invention, a multiphoton intrapulse interference phase scan system and method characterize the spectral phase of femtosecond laser pulses. Fiber optic communication systems, photodynamic therapy and pulse characterization tests use the laser system with additional aspects of the present invention.
Owner:BOARD OF TRUSTEES OPERATING MICHIGAN STATE UNIV
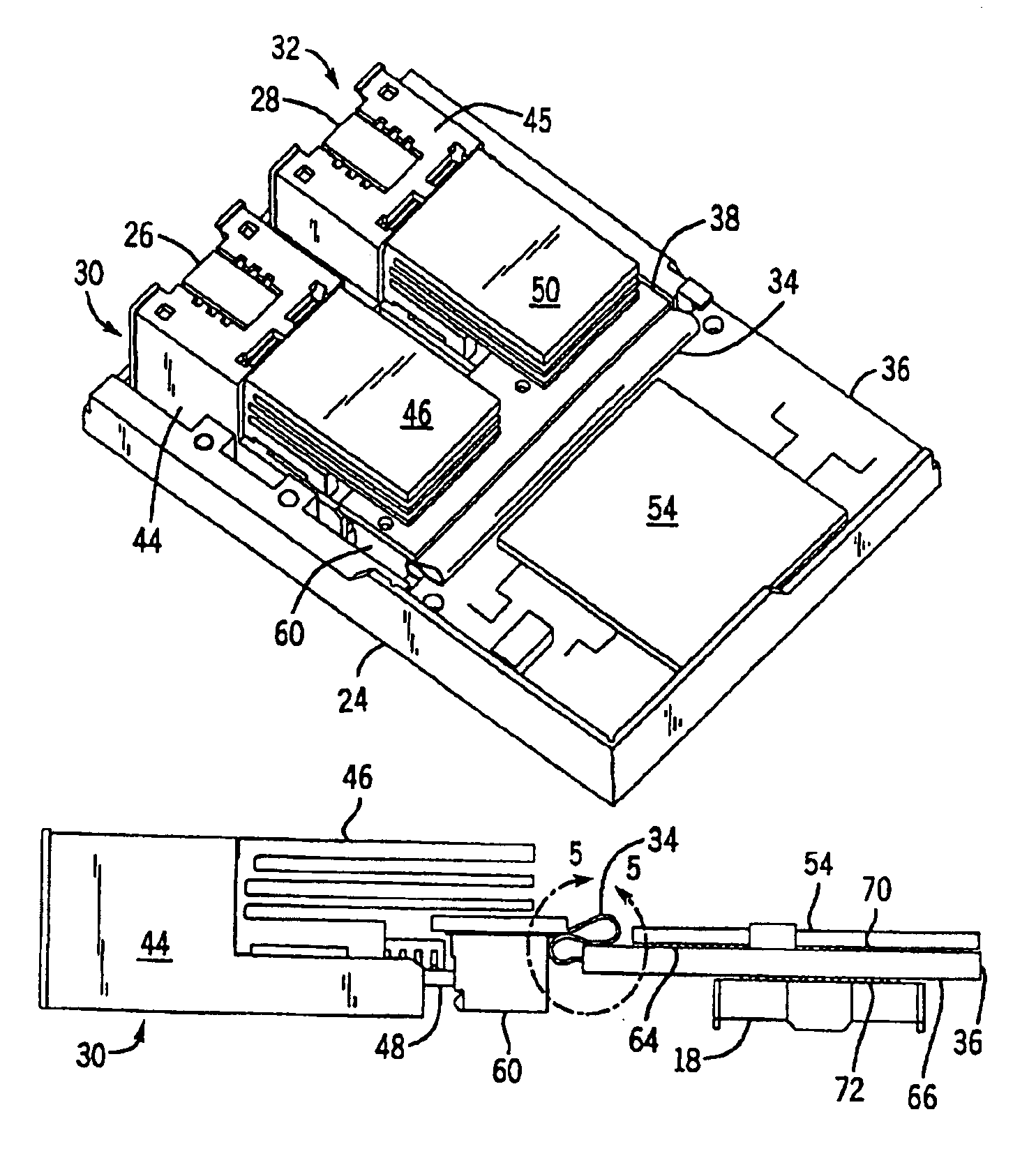
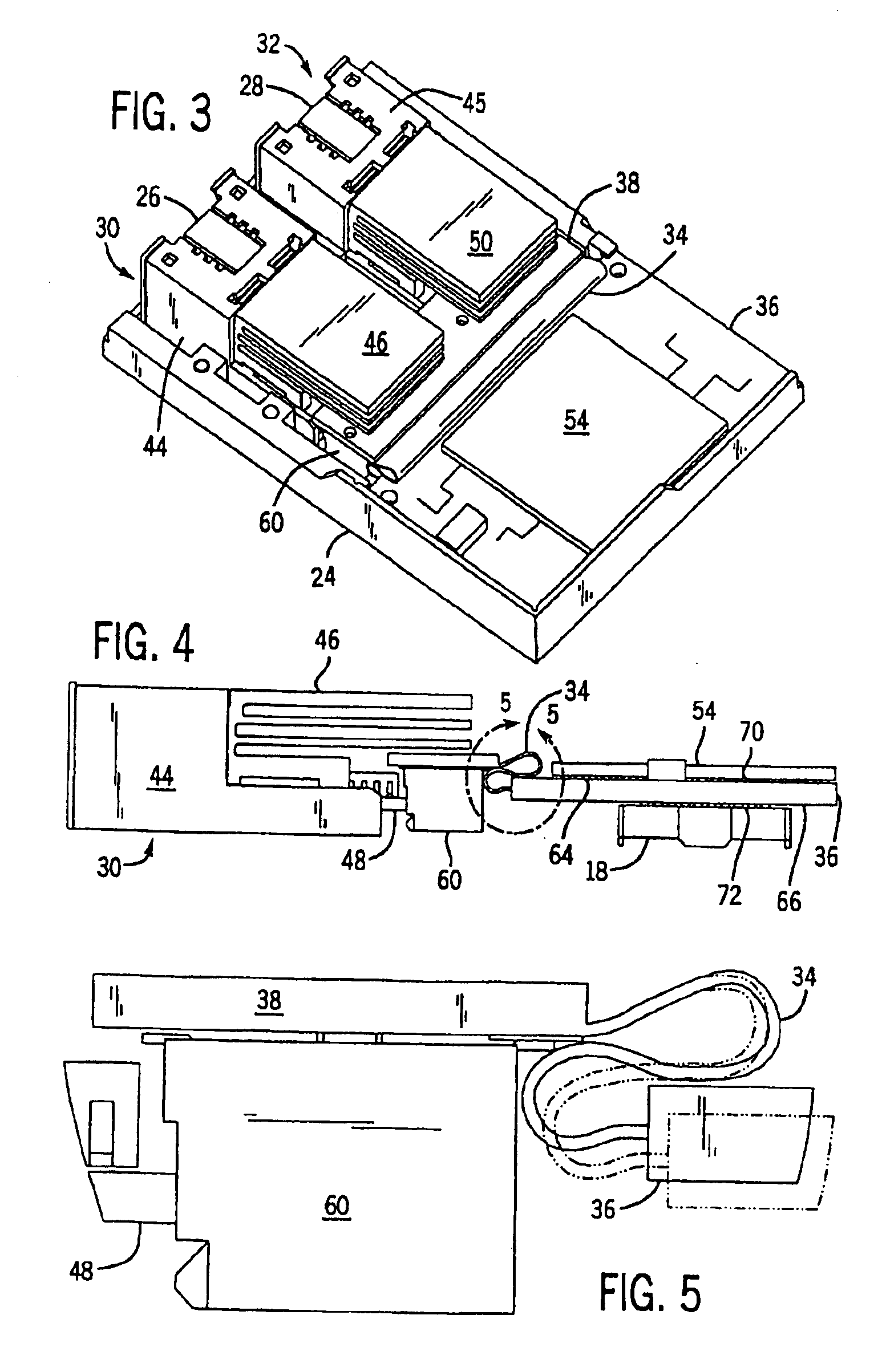
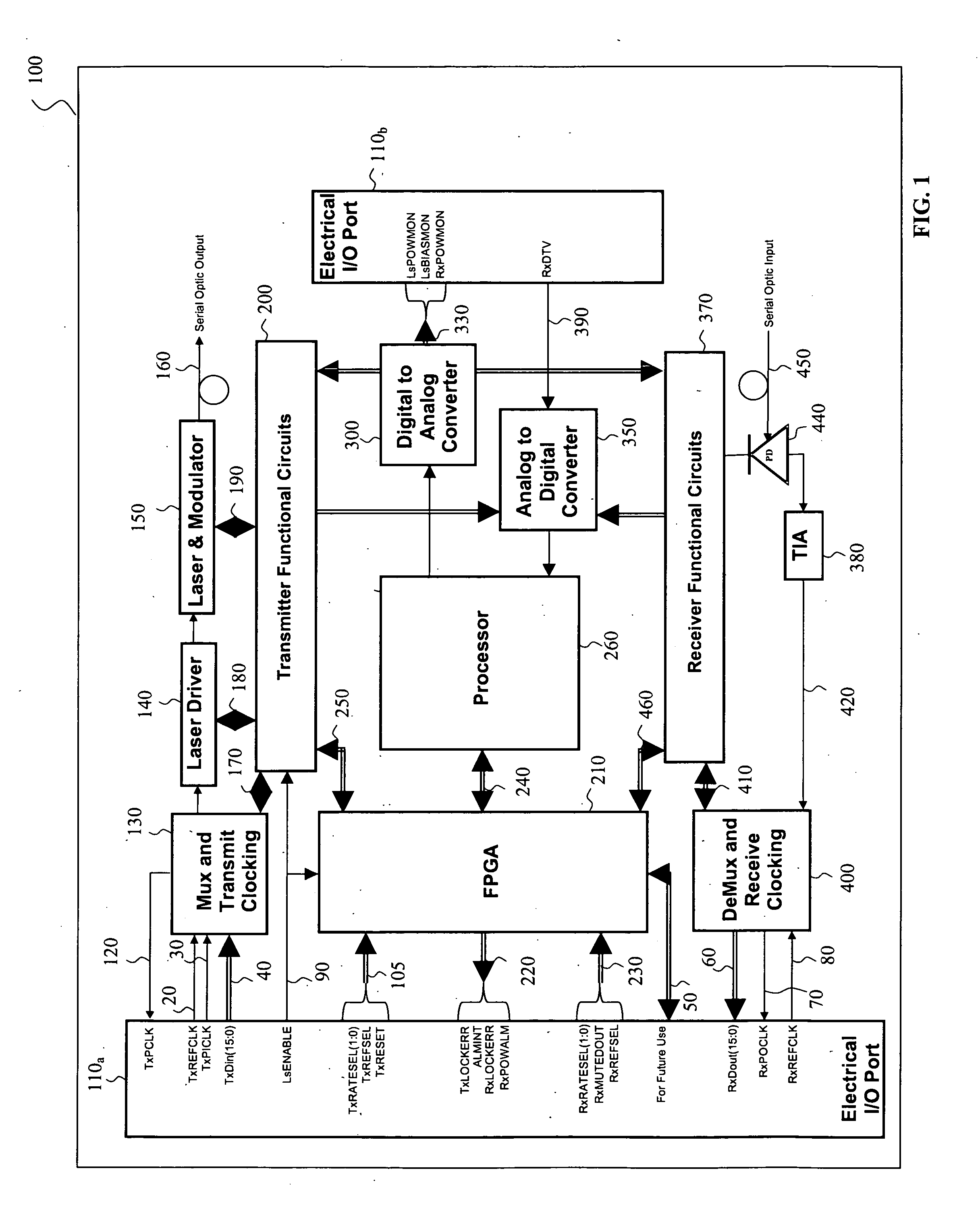
Circuit board construction for use in small form factor fiber optic communication system transponders
InactiveUS6903934B2Efficient and effectiveSmall sizePrinted circuit aspectsCoupling light guidesFiberSmall form factor
A transponder assembly for use with fiber optic digital communication cables having multiple parallel optic fiber elements. The transponder assembly features separate transmitter and receiver ports and an electrical connector for connecting with computer or communication systems. The transponder assembly includes a parallel optic transmitter module and a parallel optic receiver module. The assembly also includes a circuit board on which a semiconductor chip useful for signal processing and the electrical connector are mounted. A Flex circuit is used in connecting the circuit board to the parallel optic modules. The semiconductor chip and electrical connector are mounted directly across from one another on opposite surfaces of the circuit board using ball grid arrays having overlapping attachment structures.
Owner:STRATOS INT
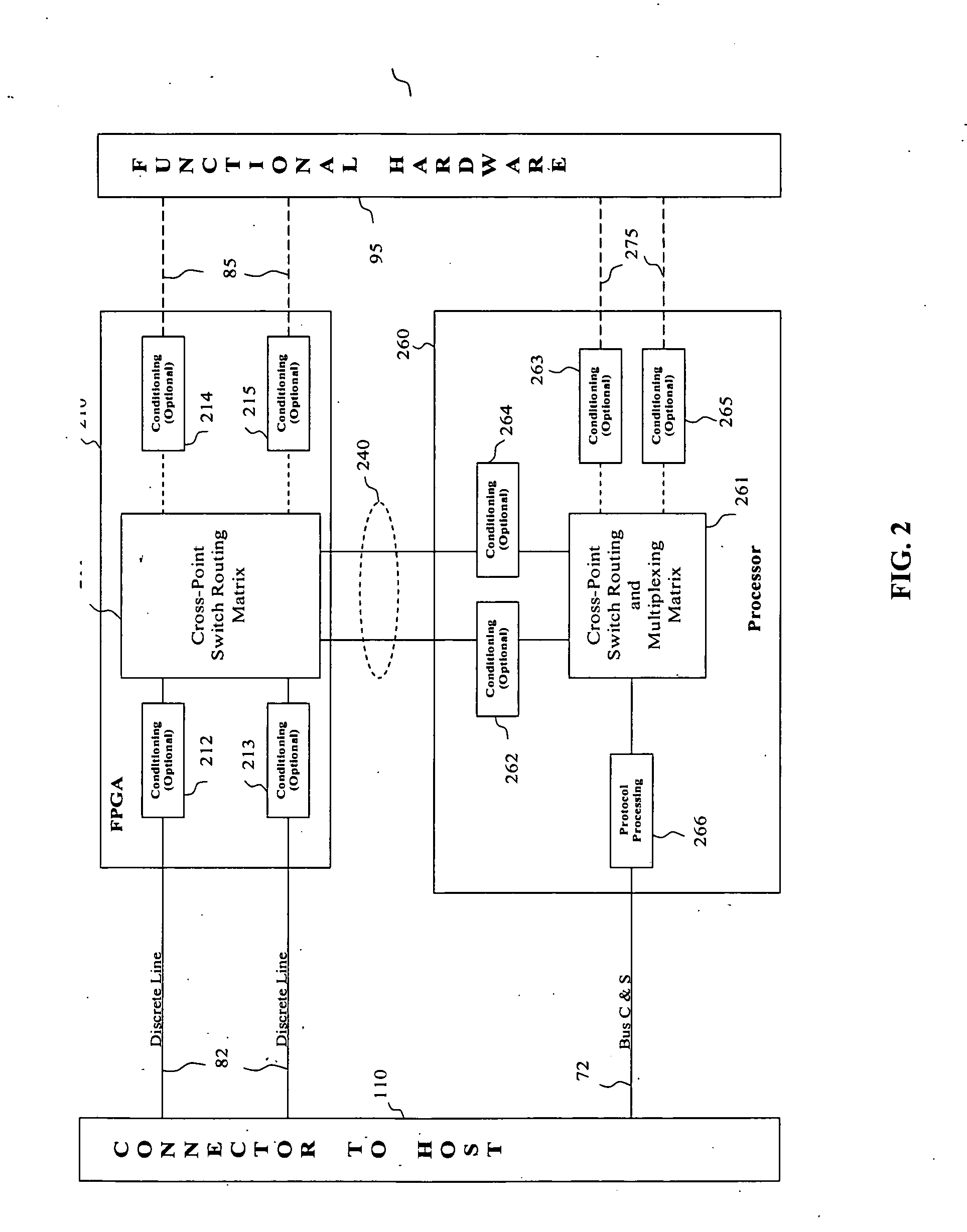
Flexible control and status architecture for optical modules
InactiveUS20050286902A1Electromagnetic transmittersElectromagnetic receiversReconfigurabilityTransceiver
Owner:LUMENTUM OPERATIONS LLC
Optical communication network system
ActiveUS7298974B2Quickly reconfiguredOptimizationMultiplex system selection arrangementsRing-type electromagnetic networksNetworked systemFiber-optic communication
A fiber optic communication system includes a device of switching and setting wavelength of optical signals used in communication by network-node equipments, which sets the mapping of the wavelength of the optical signal used in communication by the network node equipments, and the input / output ports of an array waveguide grating (AWG), so as to construct a predetermined logical network topology by a plurality of network node equipments which are connected via optical fibers to the array waveguide grating that outputs optical signals inputted to optical input ports, to predetermined optical output ports in accordance with the wavelength thereof. As well as enabling a simple construction, it is easy to realize flexible network design, construction, and operation, and different network groups can also be easily connected to each other. Moreover, a fiber optic communication system having robust security and which can be stably operated even at the time of failure is realized at low cost.
Owner:NIPPON TELEGRAPH & TELEPHONE CORP
Radio-over-fiber (RoF) system for protocol-independent wired and/or wireless communication
ActiveUS8280259B2Reduce lossHigh bandwidthTelevision conference systemsData switching by path configurationRadio over fiberFiber
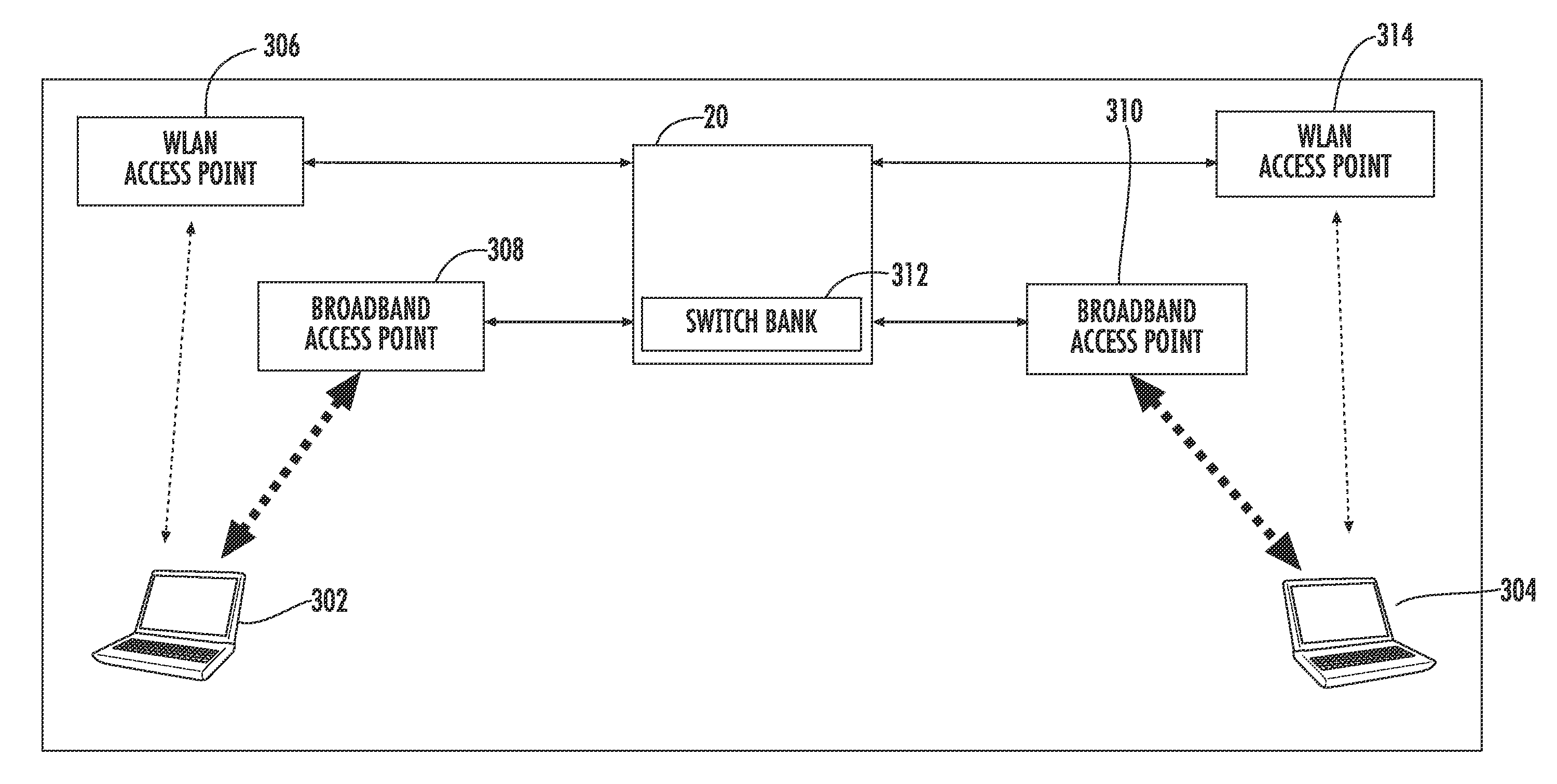
An optically-switched fiber optic communication system, such as a Radio-over-Fiber (RoF) based optical fiber link system, may be used to increase the range of peer-to-peer communications. The optically-switched fiber optic communication system may include a head-end unit (HEU) having an optical switch bank. Fiber optic cables comprising optical fibers optically couple the HEU to one or more remote access points in different coverage areas. The optical switch bank in the HEU provides a link between the remote access points in the different coverage areas such that devices in the different cellular coverage areas can communicate with each other over the optical fibers through the HEU. By using the optically-switched fiber optic communication system, the range and coverage of communication between devices may be extended such that devices in different coverage areas and devices using different communication protocols can communicate.
Owner:CORNING OPTICAL COMM LLC
Apparatus, system and method for an adiabatic coupler for multi-mode fiber-optic transmission systems
InactiveUS7184623B2Low insertion lossIncrease system bandwidthLaser detailsOptical fibre with graded refractive index core/claddingFiberRefractive index
An improved fiber-optic communications system comprises a multi-mode waveguide carrying an optical signal, a single-mode waveguide optically coupled to and receiving the optical signal from the multi-mode waveguide and an adiabatic coupler optically coupled between the multi-mode waveguide and the single-mode waveguide. The multi-mode and single-mode waveguides may be optical fibers. The adiabatic coupler may comprise a tapered core surrounded by a cladding. Alternatively, the adiabatic coupler may comprise a core surrounded by a cladding, wherein the refractive index of at least one of the core and the cladding varies over the length of the adiabatic coupler.
Owner:OCLARO NORTH AMERICA
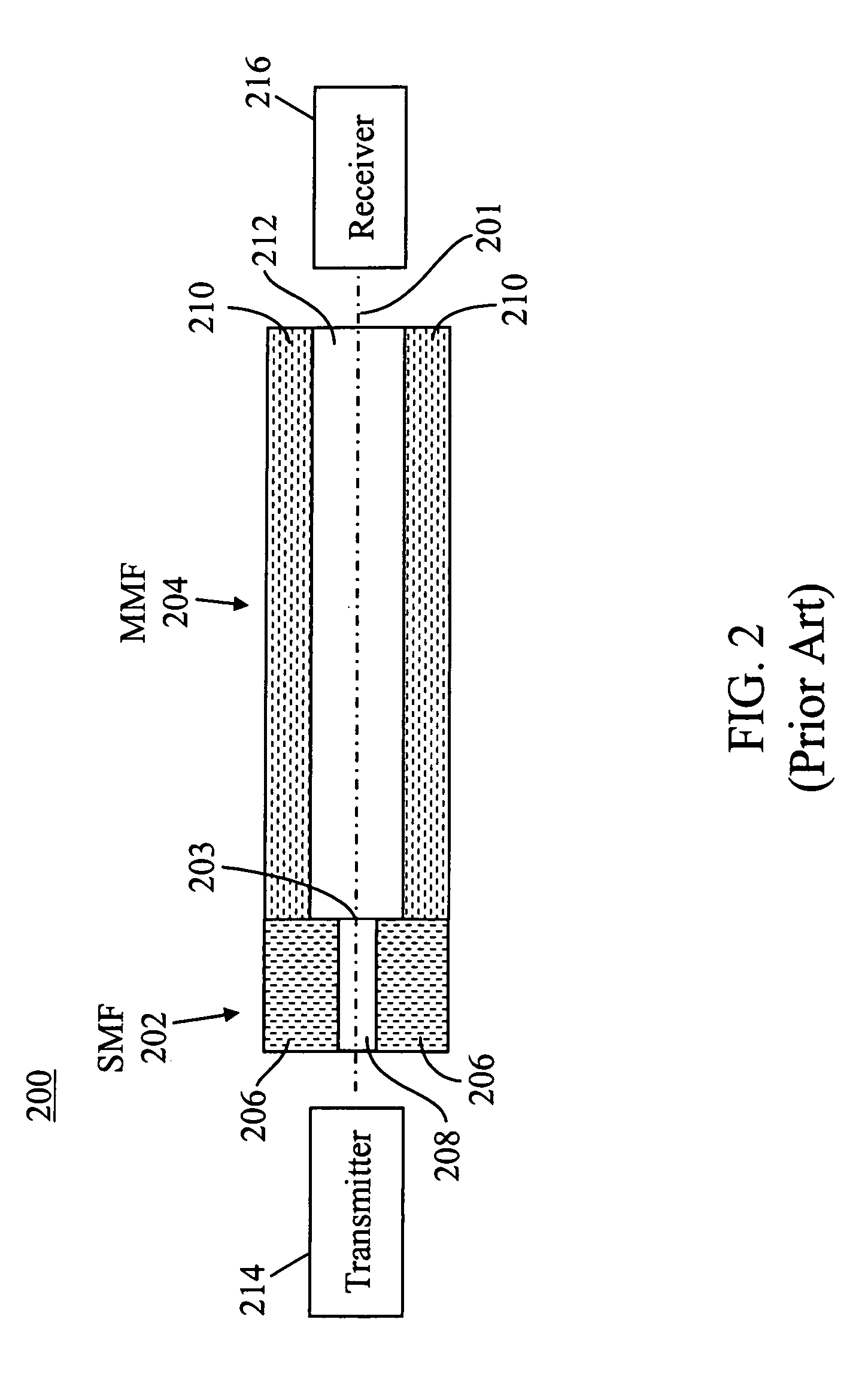
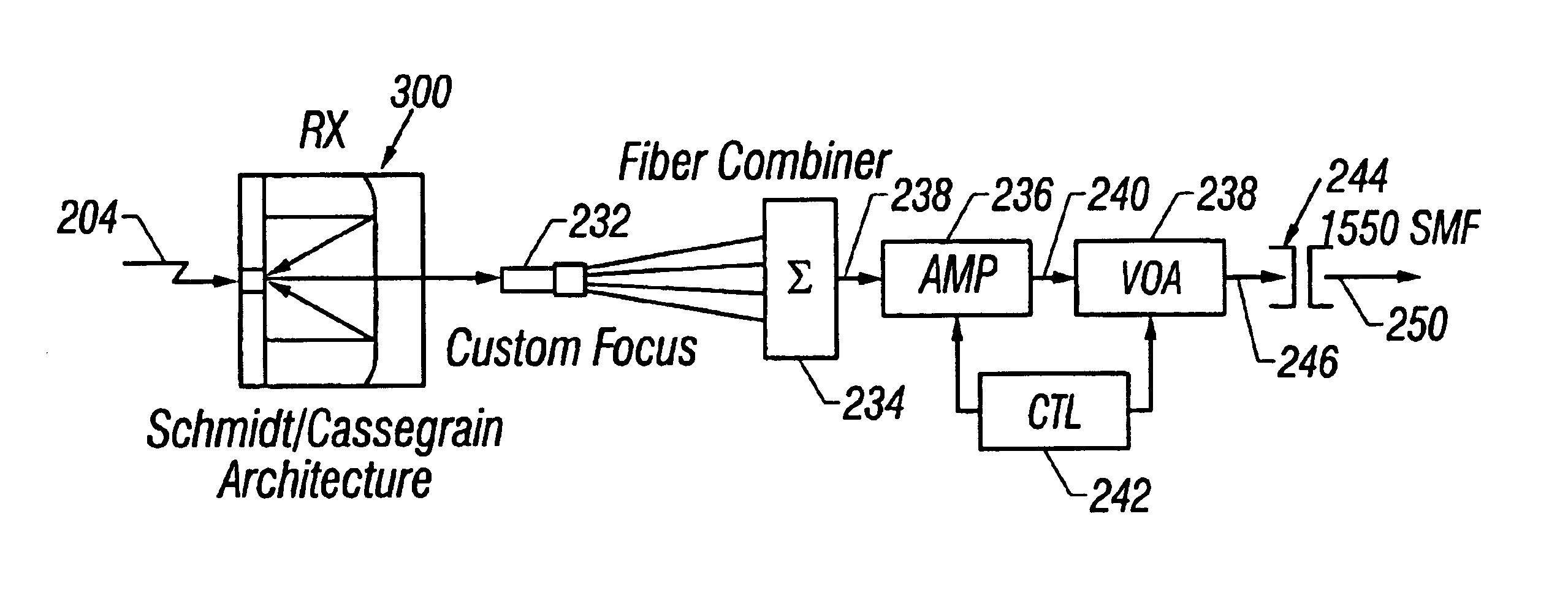
Terrestrial optical communication network of integrated fiber and free-space links which requires no electro-optical conversion between links
InactiveUS6868237B2Multiplex system selection arrangementsLaser detailsUltrasound attenuationLight beam
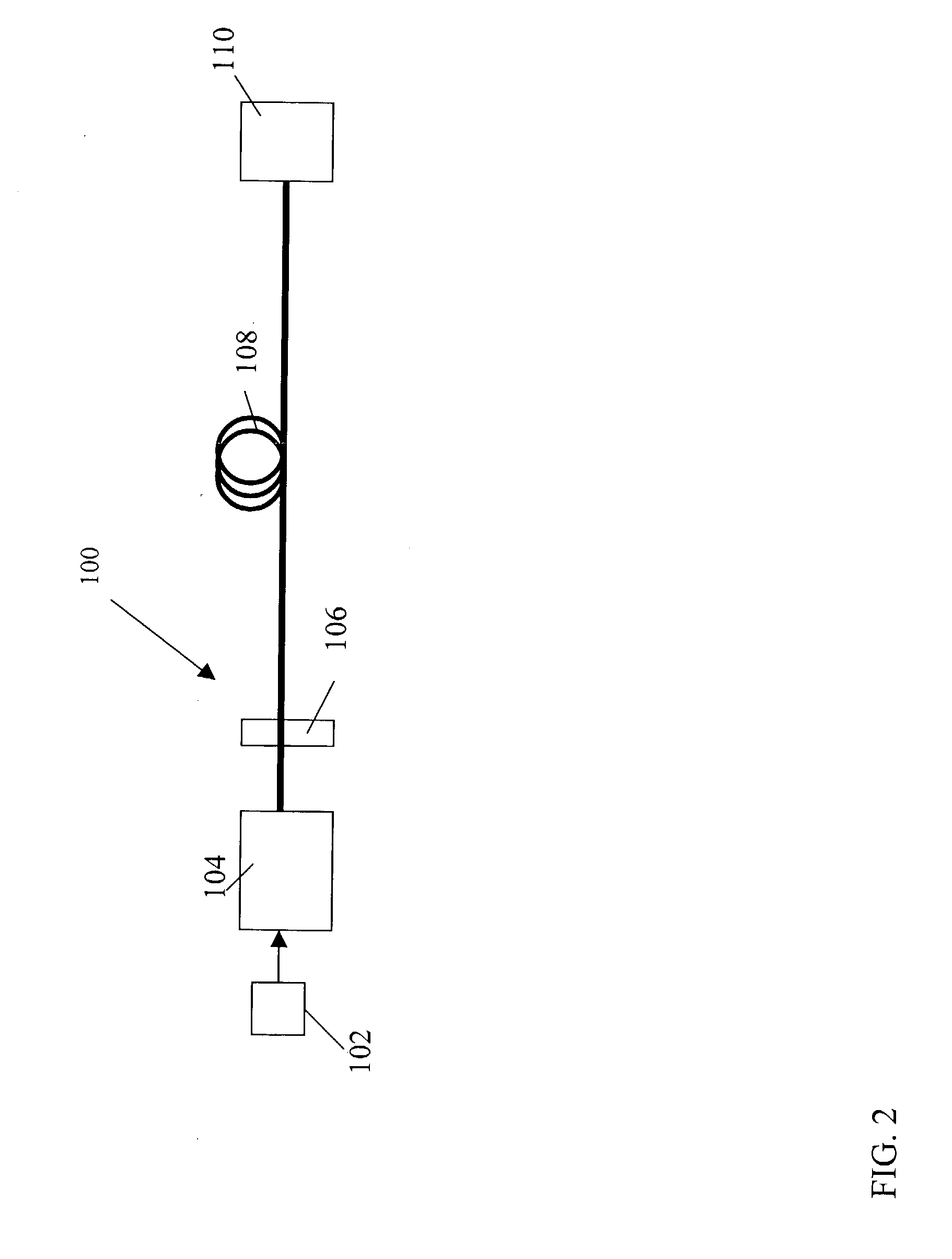
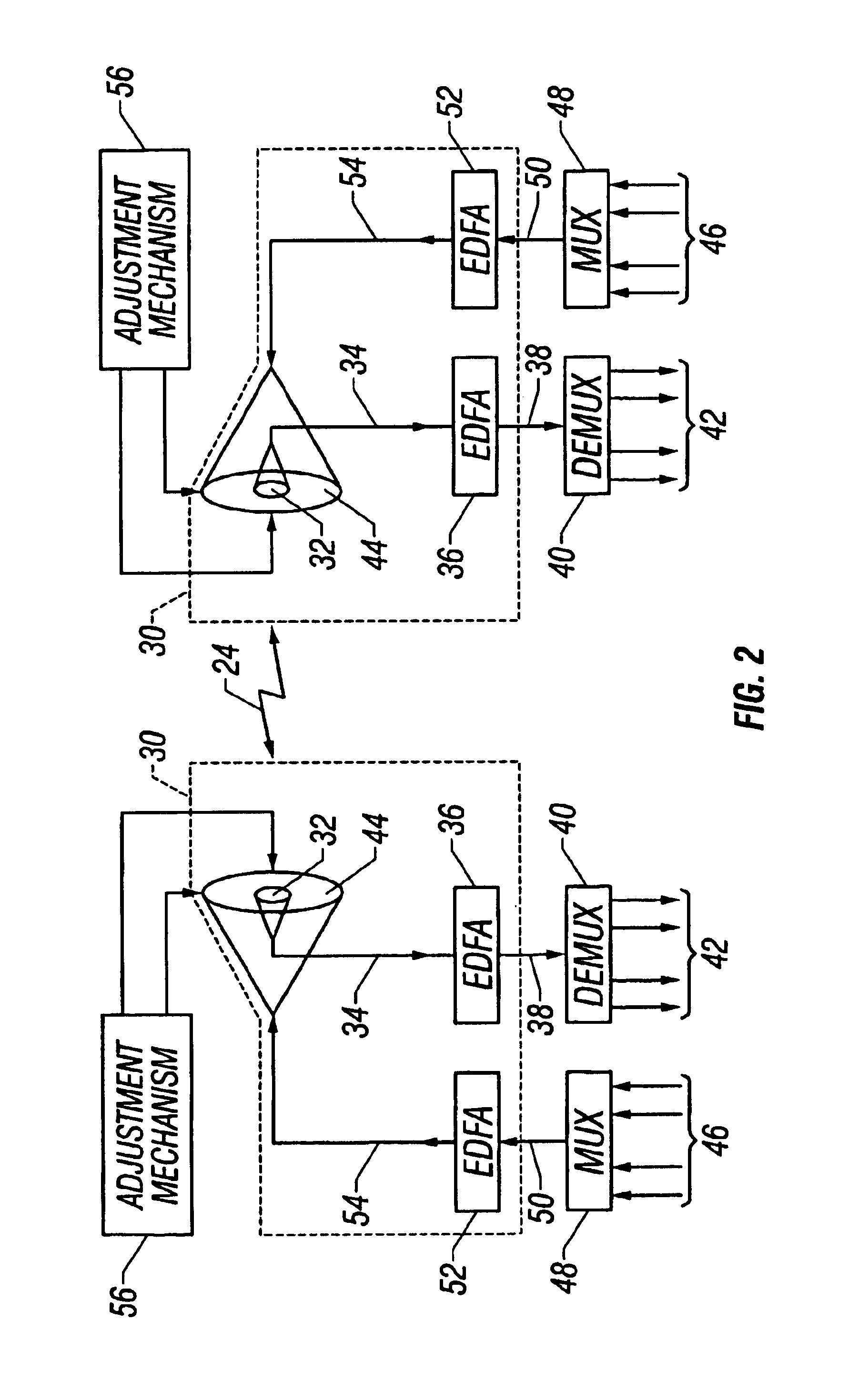
Optical signals are received from a free-space link by directing received light onto a plurality of microlenses and then directing light received through each of the microlenses into a respective single mode optical fiber (SMF). Light beams from the SMFs are combined into a single light beam in one SMF. The single light beam is amplified with a multi-wavelength fiber amplifier and attenuated with a variable optical attenuator. The power gain of the multi-wavelength fiber amplifier and the attenuation of the variable optical attenuator are controlled. The single light beam is directed into a fiber optic communication system that is optically coupled to the variable optical attenuator.
Owner:LIGHTPOINTE COMM
Retrofit heater for erbium fiber in an erbium-doped fiber amplifier (EDFA)
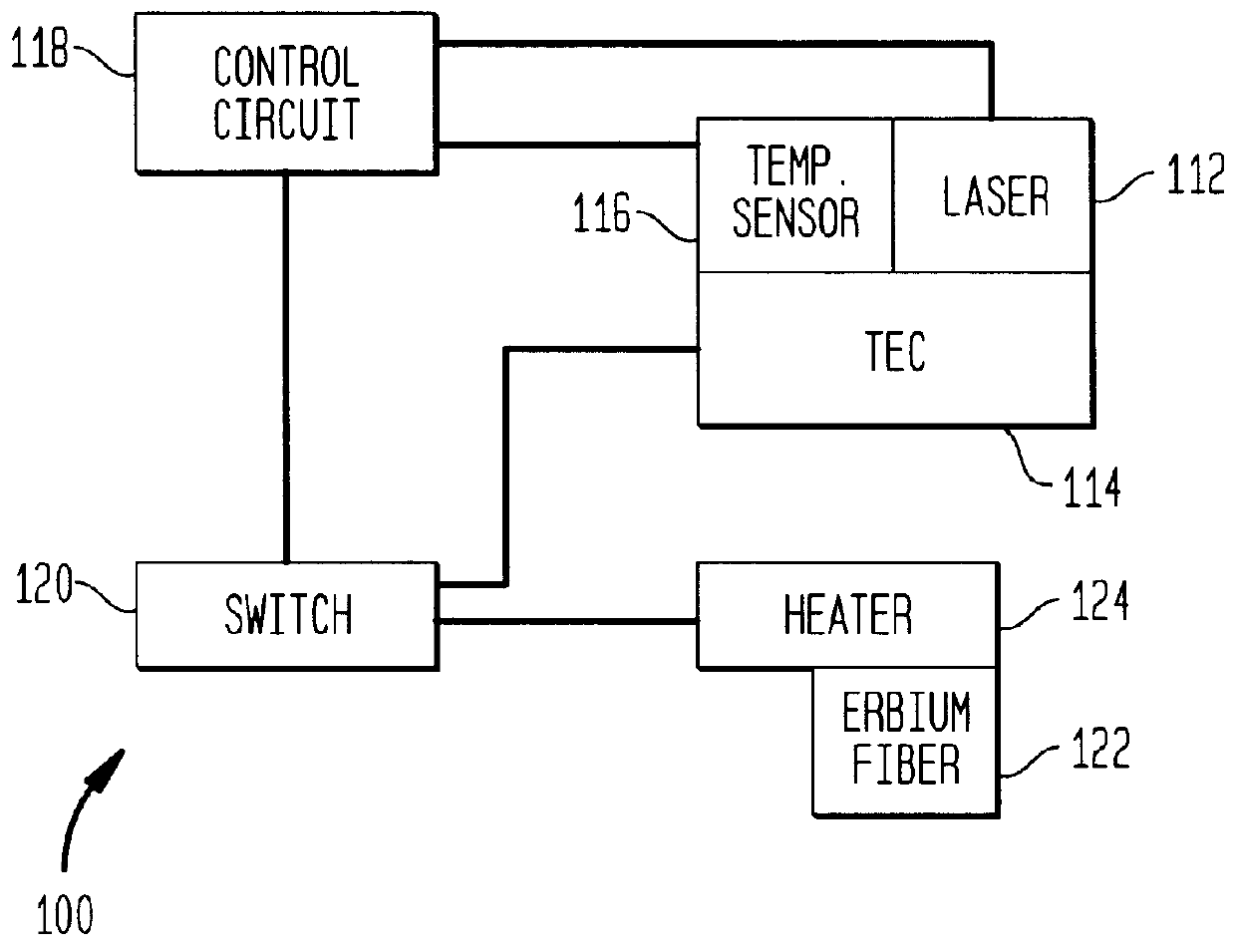
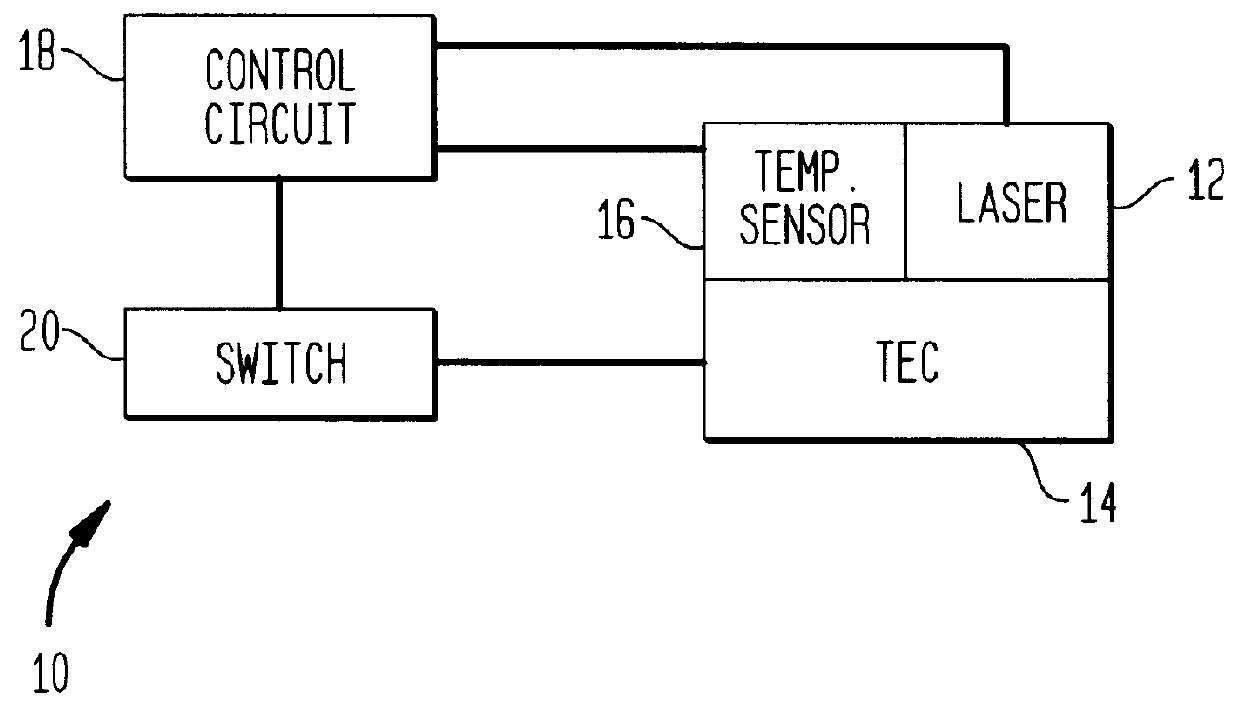
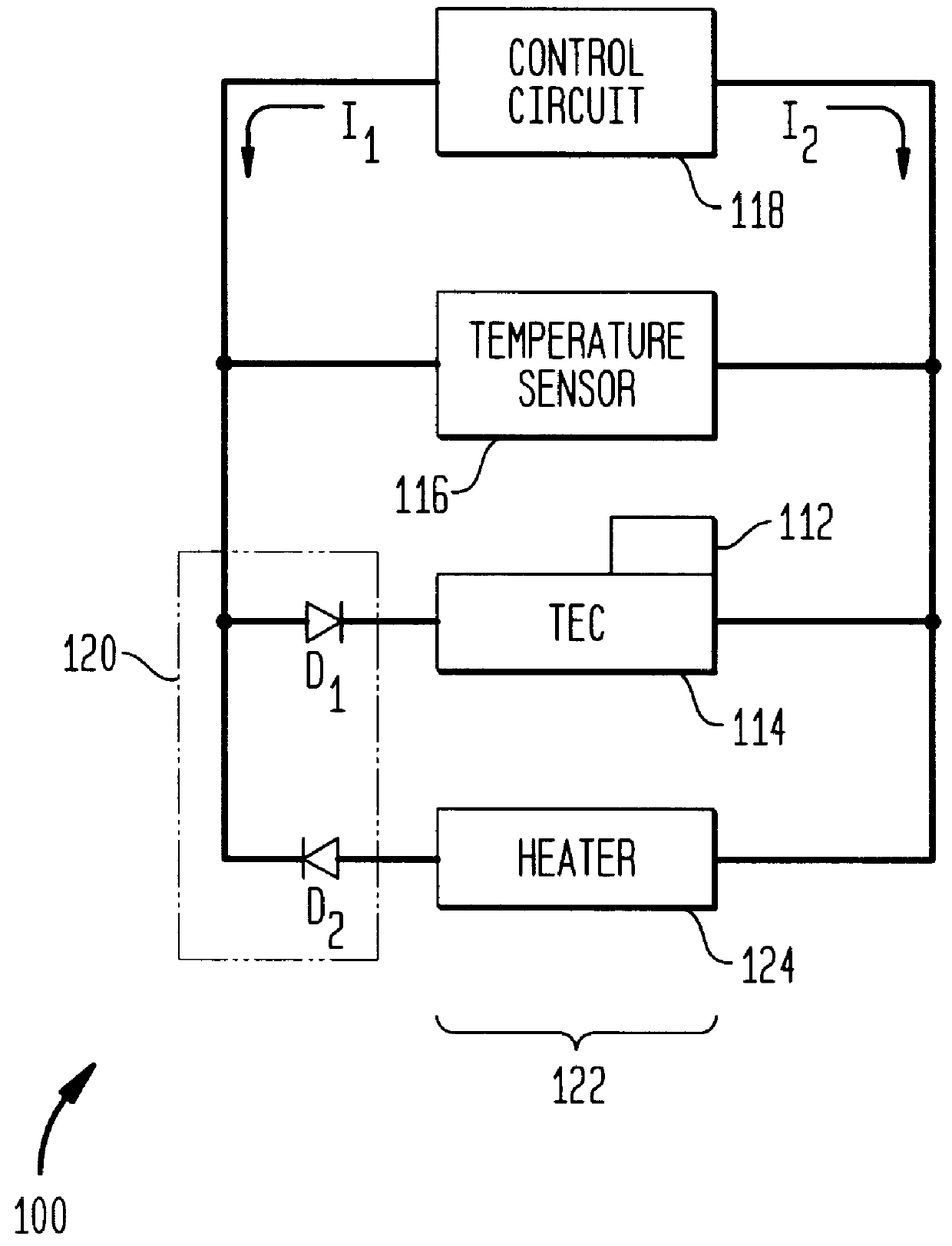
A heater system for heating an erbium-doped fiber amplifier (EDFA) of a fiber optic communication system operable in an environment. The heater system includes a pump laser for providing optical power to an erbium fiber in the EDFA. The pump laser is cooled by a thermoelectric cooler (TEC) when a predetermined maximum temperature is reached to maintain the temperature of the laser below the maximum temperature value. The temperature of the laser is sensed by a temperature sensor and is conveyed to a control circuit for generating a control signal. A heater unit is thermally connected to the erbium fiber and is controlled by the control signal in the event that the sensed temperature falls below a predetermined minimum value to maintain the temperature of the fiber above the minimum temperature value. A switch is connected between the control circuit, the TEC and the heater to automatically direct current to either the heater or the TEC depending on the sensed temperature.
Owner:AGERE SYST INC
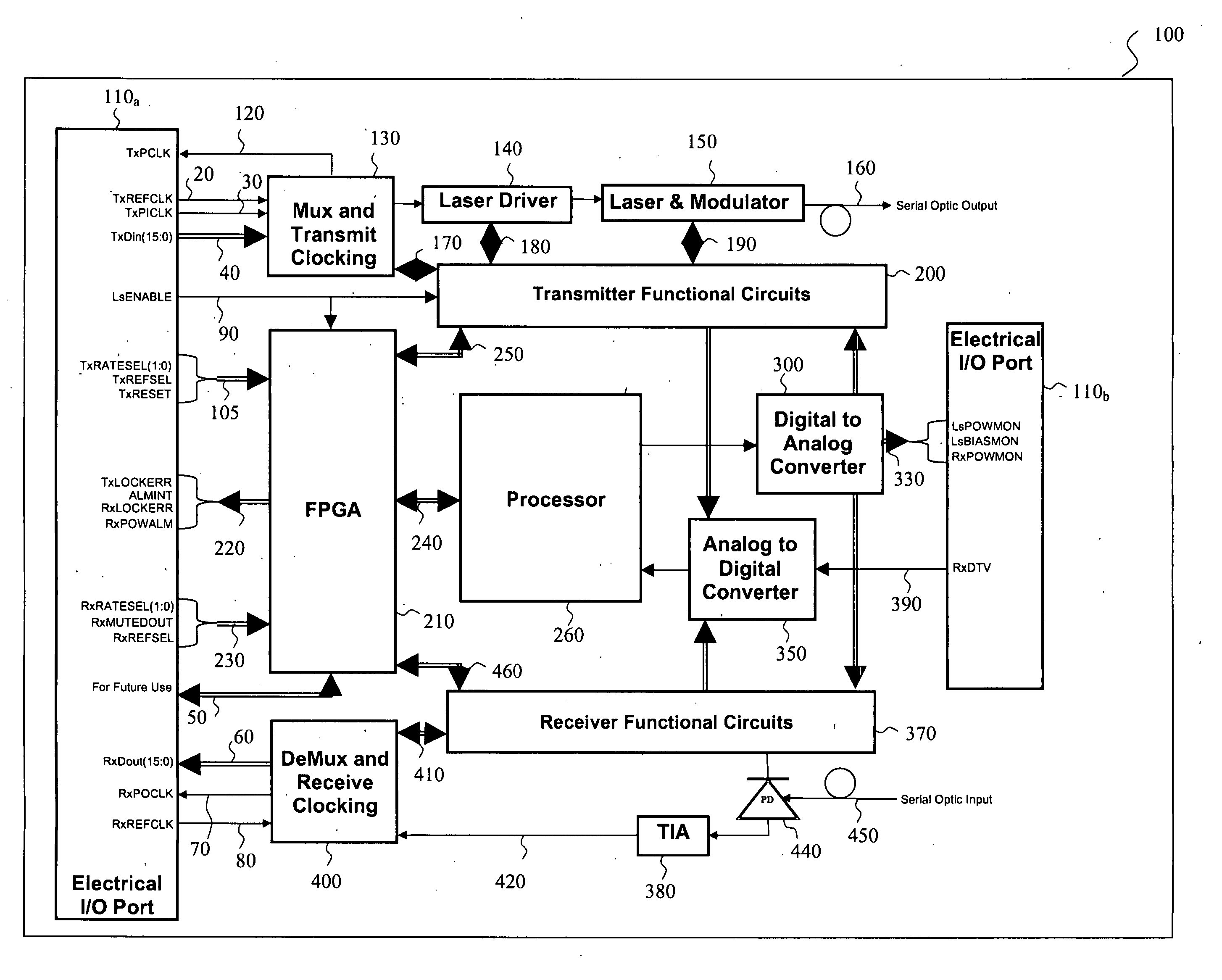
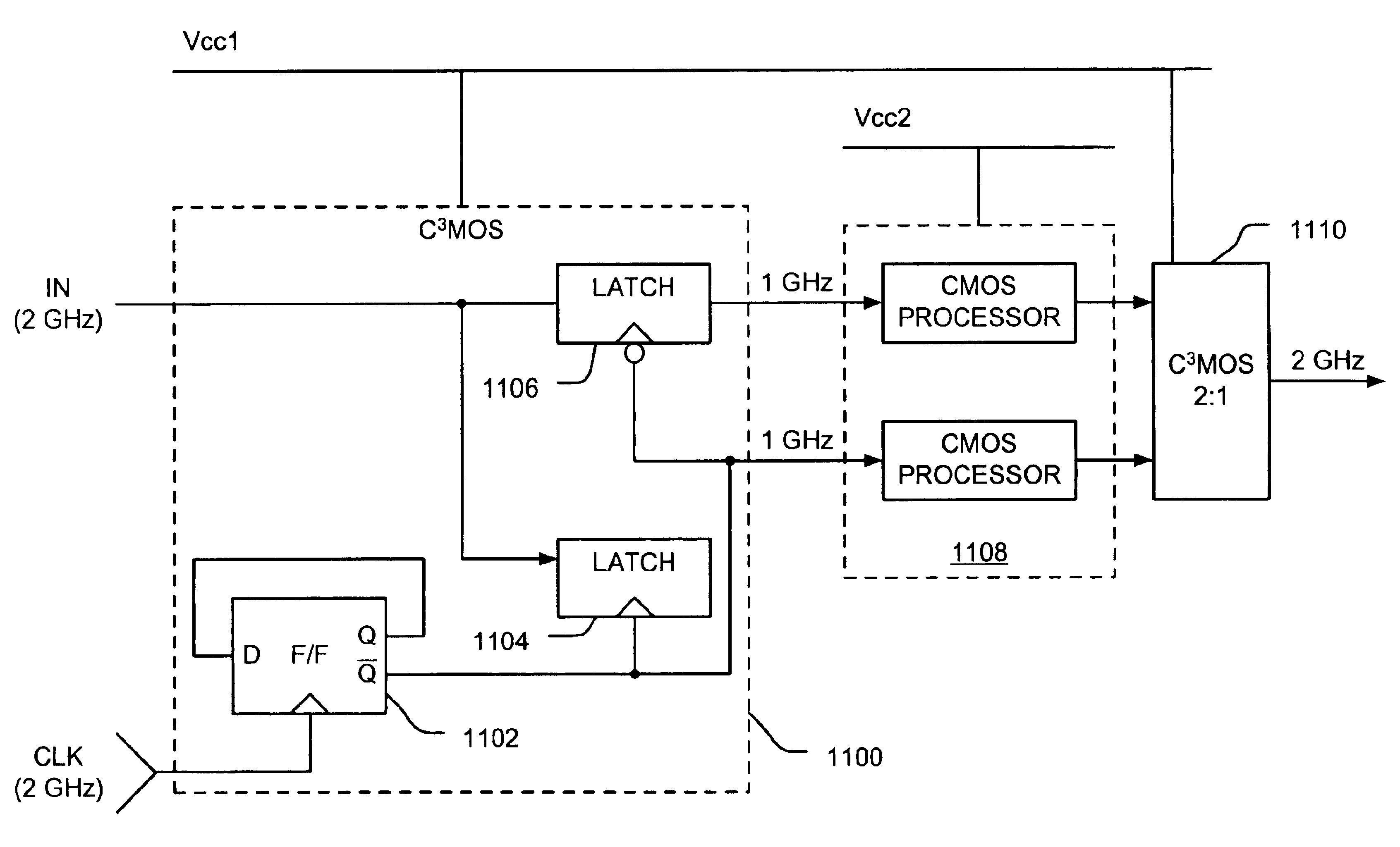
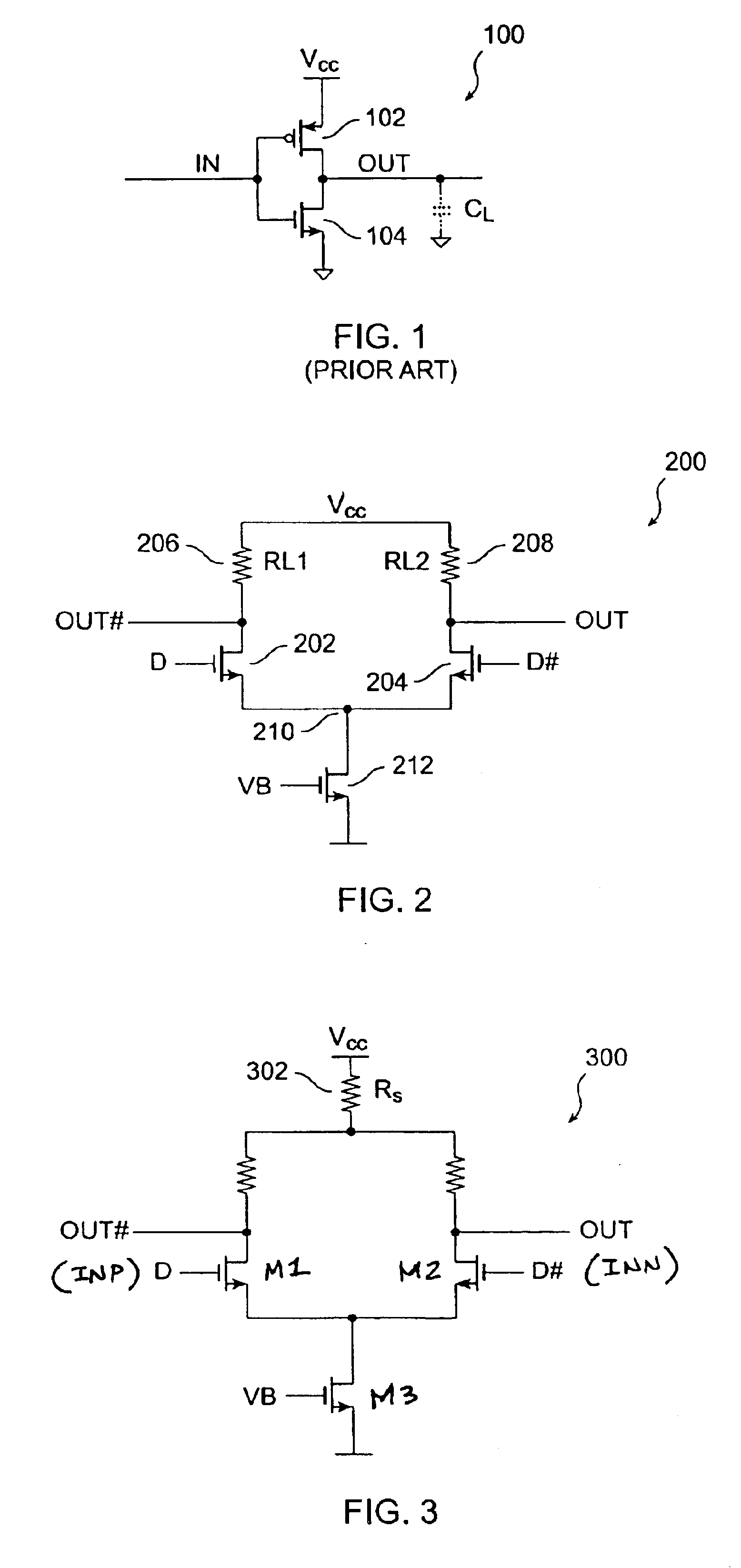
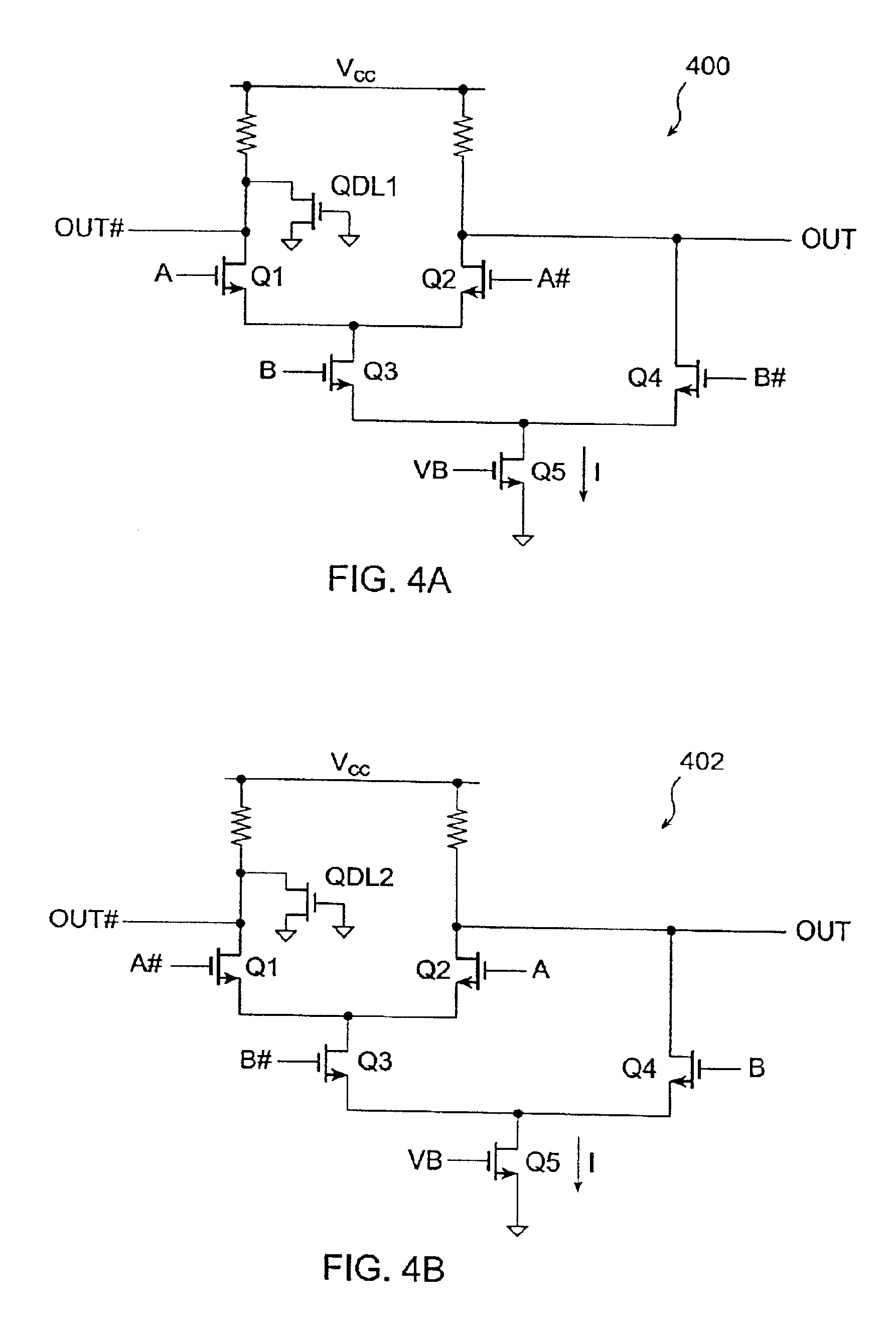
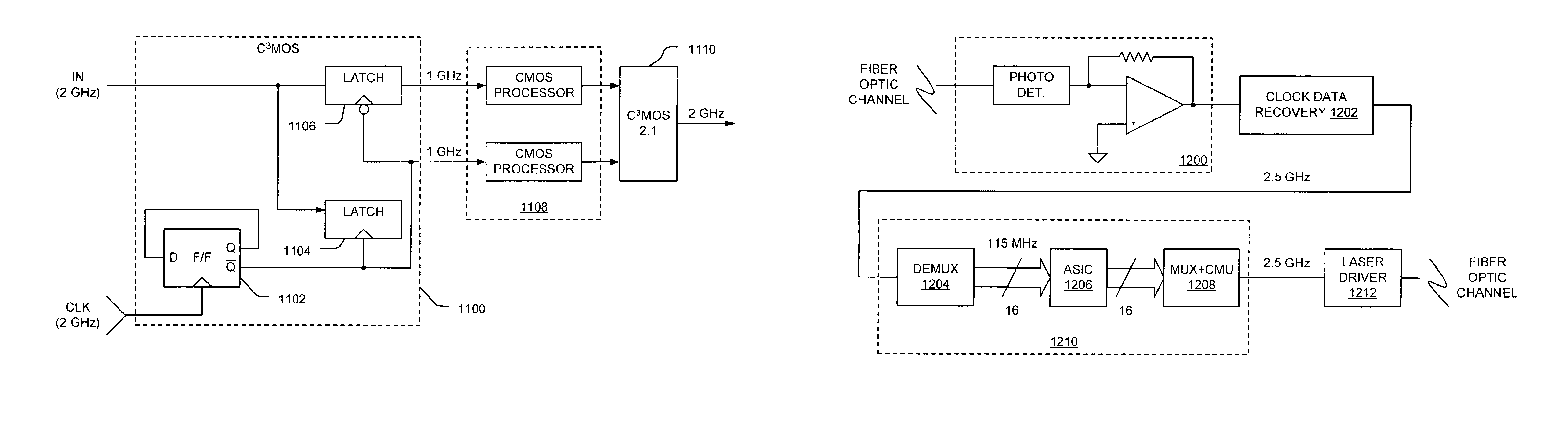
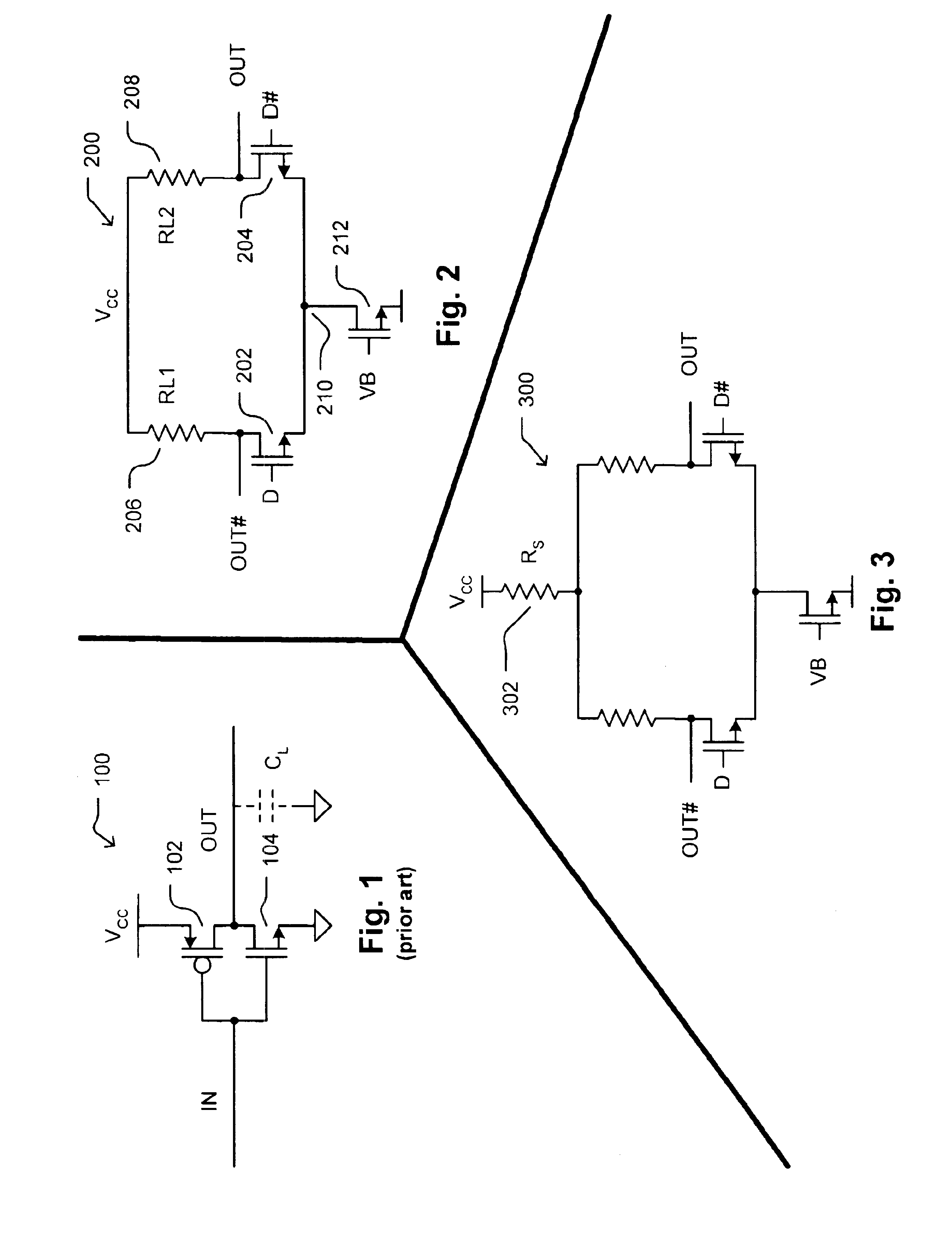
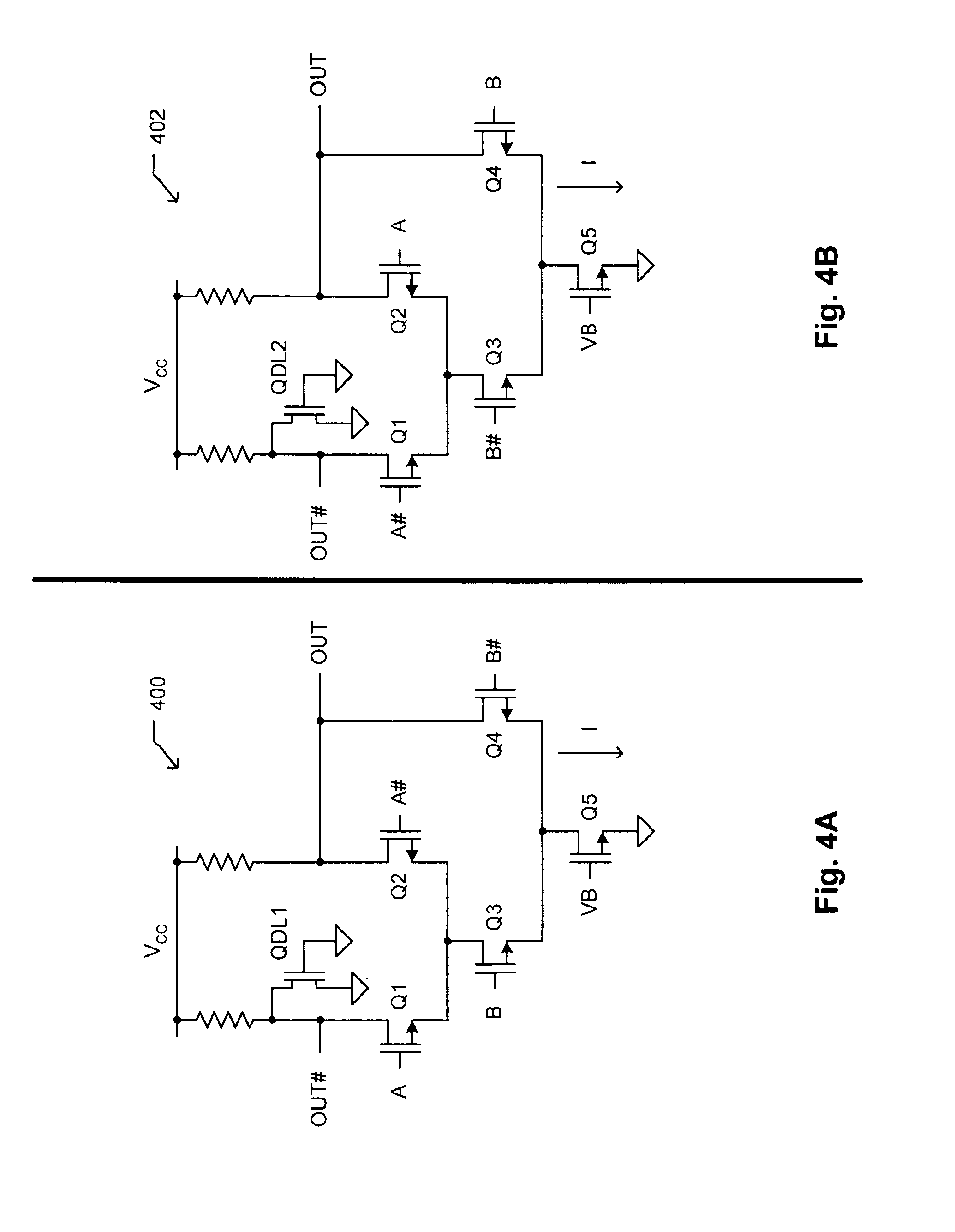
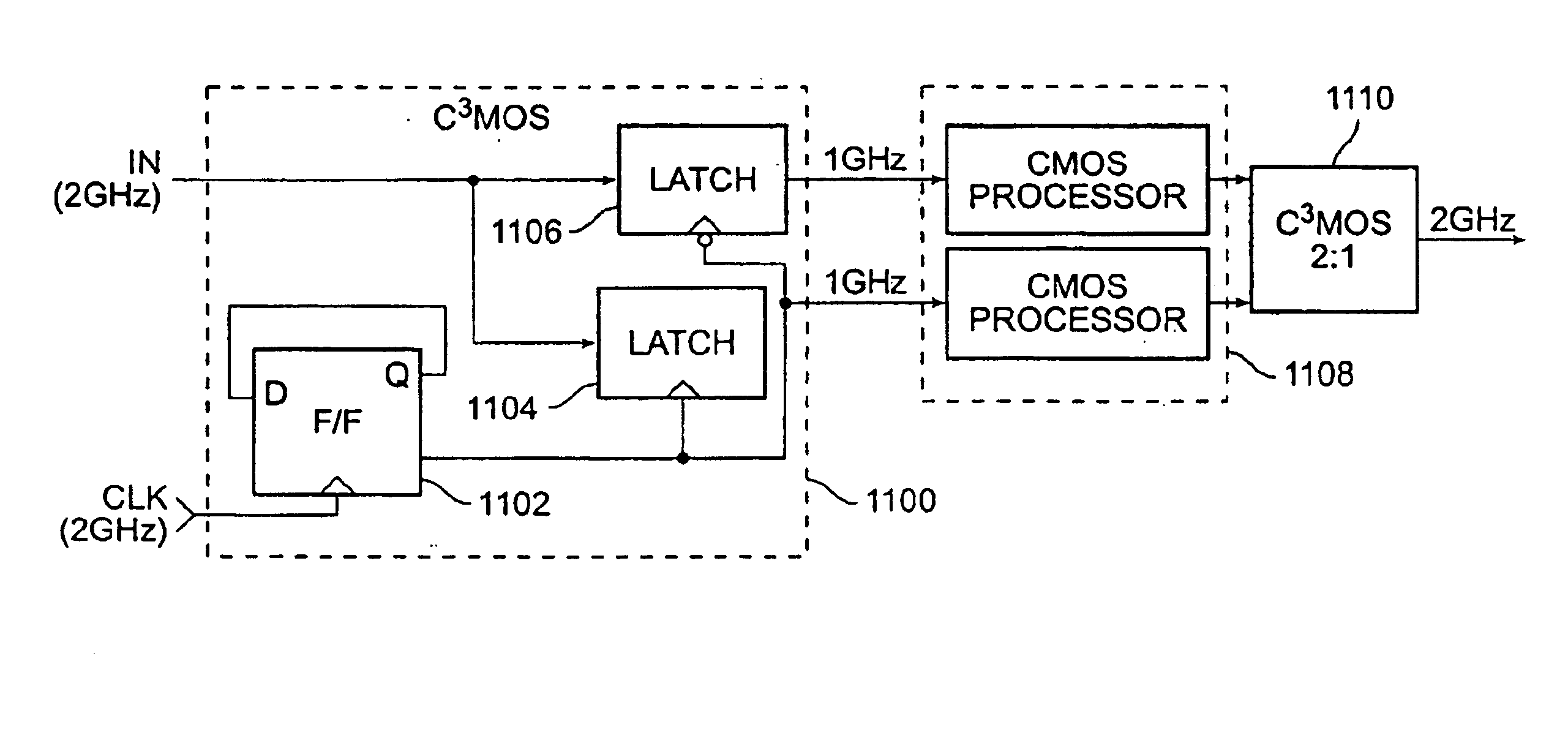
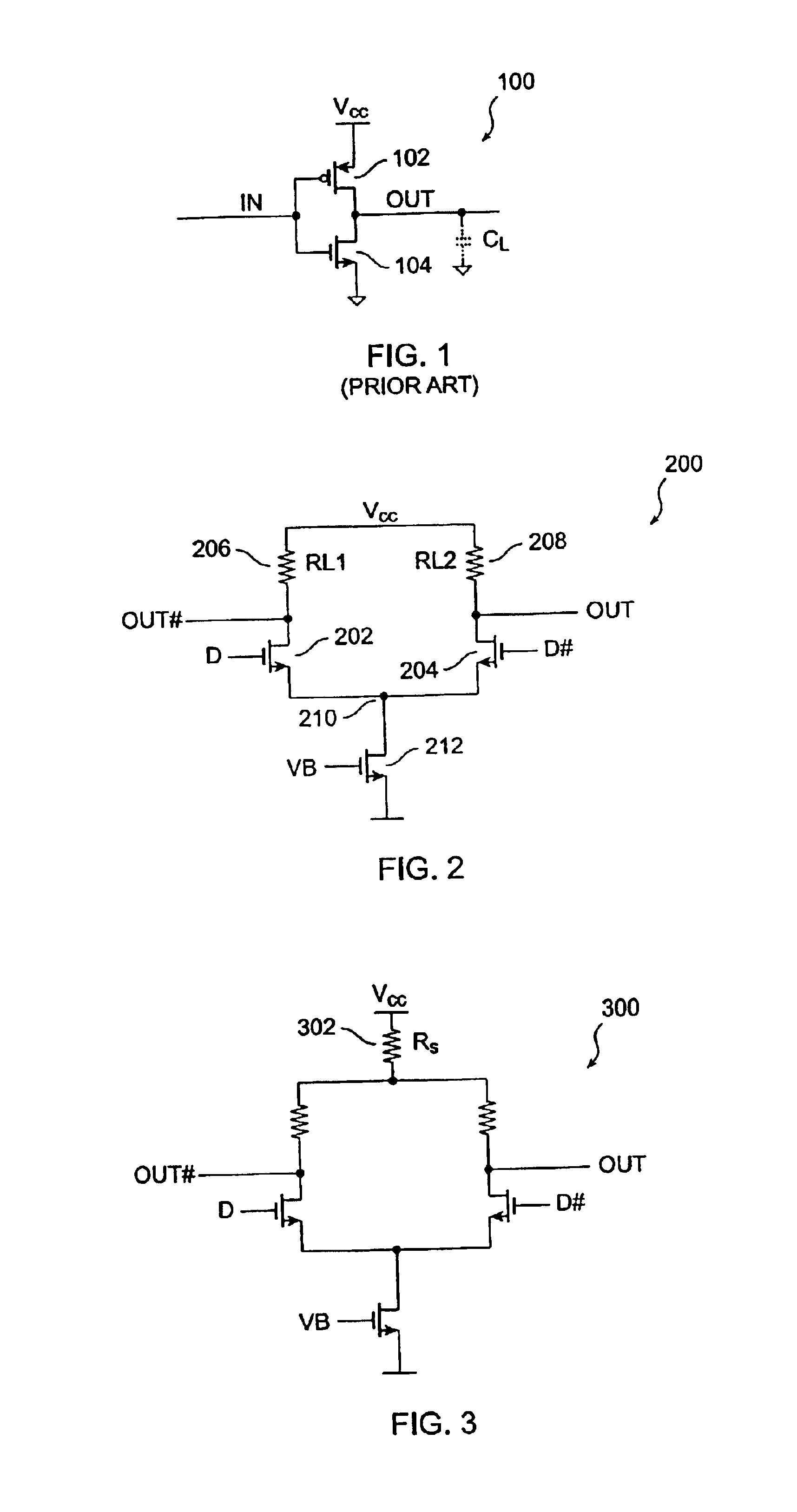
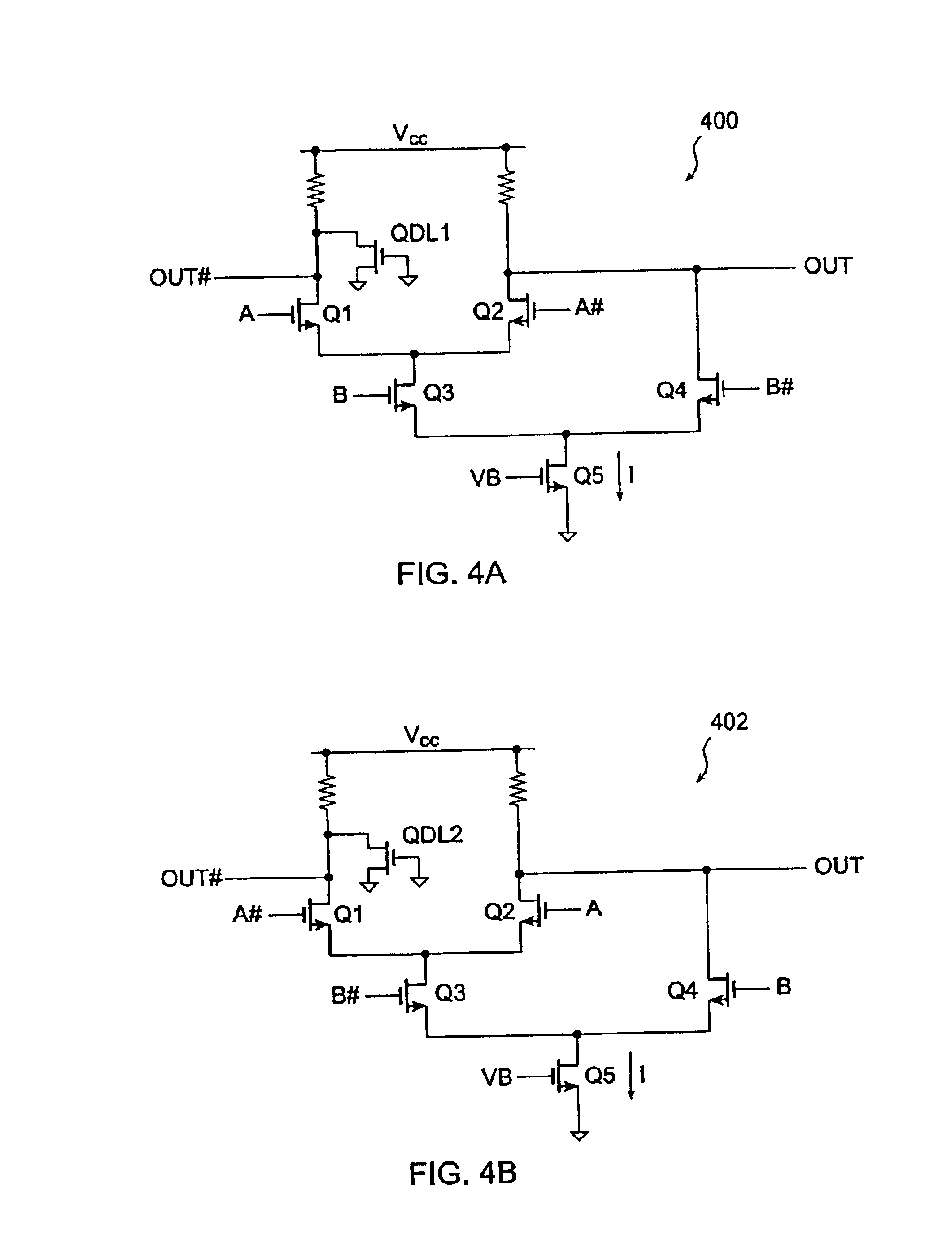
Current-controlled CMOS circuit using higher voltage supply in low voltage CMOS process
InactiveUS6911855B2Speed maximizationDissipates static currentElectronic switchingElectric pulse generatorTransceiverEngineering
Various circuit techniques for implementing ultra high speed circuits use current-controlled CMOS (C3MOS) logic fabricated in conventional CMOS process technology. An entire family of logic elements including inverter / buffers, level shifters, NAND, NOR, XOR gates, latches, flip-flops and the like are implemented using C3MOS techniques. Optimum balance between power consumption and speed for each circuit application is achieve by combining high speed C3MOS logic with low power conventional CMOS logic. The combined C3MOS / CMOS logic allows greater integration of circuits such as high speed transceivers used in fiber optic communication systems. The C3MOS structure enables the use of a power supply voltage that may be larger than the voltage required by the CMOS fabrication process, further enhancing the performance of the circuit.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Laser Pulse Shaping System
ActiveUS20090122819A1Increase productionWide bandwidthLaser detailsMaterial analysis by optical meansCharacterization testUltrashort laser
A laser system using ultrashort laser pulses is provided. In another aspect of the present invention, the system includes a laser, pulse shaper and detection device. A further aspect of the present invention employs a femtosecond laser and a spectrometer. Still another aspect of the present invention uses a laser beam pulse, a pulse shaper and a SHG crystal. In yet another aspect of the present invention, a multiphoton intrapulse interference phase scan system and method characterize the spectral phase of femtosecond laser pulses. Fiber optic communication systems, photodynamic therapy and pulse characterization tests use the laser system with additional aspects of the present invention.
Owner:BOARD OF TRUSTEES OPERATING MICHIGAN STATE UNIV
Optical transmission using semiconductor optical amplifier (SOA)
InactiveUS20080159751A1Reduces and eliminates thermal chirpImprove FM efficiencyElectromagnetic transmittersSemiconductor amplifier structureAudio power amplifierHigh intensity
A fiber optic communication system comprising:an optical signal source adapted to receive a binary first signal and generate a binary second signal, wherein the binary first signal has an amplitude modulated component, wherein the binary second signal has an amplitude modulated component and a frequency modulated component, and further wherein the binary second signal is characterized in that the higher intensity 1 bits are red shifted relative to the lower intensity 0 bits;a semiconductor optical amplifier (SOA) adapted to receive the binary second signal and generate a binary third signal, wherein the binary third signal has an amplitude modulated component and a frequency modulated component, and further wherein the semiconductor optical amplifier operates in saturation; andan optical spectrum reshaper (OSR) adapted to reshape the binary third signal into a binary fourth signal, wherein the binary fourth signal has an amplitude modulated component and a frequency modulated component.A method for transmitting a signal, comprising:receiving a binary first signal having an amplitude modulated component and generating a binary second signal having an amplitude modulated component and a frequency modulated component, wherein the binary second signal is characterized in that the higher intensity 1 bits are red shifted relative to the lower intensity 0 bits;passing the binary second signal through a semiconductor optical amplifier (SOA) operating in saturation so as to generate a binary third signal, wherein the binary third signal has an amplitude modulated component and a frequency modulated component; andreshaping the binary third signal into a binary fourth signal, wherein the binary fourth signal has an amplitude modulated component and a frequency modulated component.
Owner:II VI DELAWARE INC
Current-controlled CMOS circuit using higher voltage supply in low voltage CMOS process
InactiveUS6982583B2Speed maximizationIncrease circuit speedExclusive-OR circuitsMultiple input and output pulse circuitsTransceiverHigh voltage
Various circuit techniques for implementing ultra high speed circuits use current-controlled CMOS (C3MOS) logic fabricated in conventional CMOS process technology. An entire family of logic elements including inverter / buffers, level shifters, NAND, NOR, XOR gates, latches, flip-flops and the like are implemented using C3MOS techniques. Optimum balance between power consumption and speed for each circuit application is achieve by combining high speed C3MOS logic with low power conventional CMOS logic. The combined C3MOS / CMOS logic allows greater integration of circuits such as high speed transceivers used in fiber optic communication systems. The C3MOS structure enables the use of a power supply voltage that may be larger than the voltage required by the CMOS fabrication process, further enhancing the performance of the circuit.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Laser pulse shaping system
InactiveUS8208504B2Increase productionWide bandwidthLaser detailsMaterial analysis by optical meansCharacterization testUltrashort laser
A laser system using ultrashort laser pulses is provided. In another aspect of the present invention, the system includes a laser, pulse shaper and detection device. A further aspect of the present invention employs a femtosecond laser and a spectrometer. Still another aspect of the present invention uses a laser beam pulse, a pulse shaper and a SHG crystal. In yet another aspect of the present invention, a multiphoton intrapulse interference phase scan system and method characterize the spectral phase of femtosecond laser pulses. Fiber optic communication systems, photodynamic therapy and pulse characterization tests use the laser system with additional aspects of the present invention.
Owner:BOARD OF TRUSTEES OPERATING MICHIGAN STATE UNIV
Current-controlled CMOS circuit using higher voltage supply in low voltage CMOS process
InactiveUS6897697B2Speed maximizationDissipates static currentExclusive-OR circuitsElectronic switchingTransceiverEngineering
Various circuit techniques for implementing ultra high speed circuits use current-controlled CMOS (C3MOS) logic fabricated in conventional CMOS process technology. An entire family of logic elements including inverter / buffers, level shifters, NAND, NOR, XOR gates, latches, flip-flops and the like are implemented using C3MOS techniques. Optimum balance between power consumption and speed for each circuit application is achieve by combining high speed C3MOS logic with low power conventional CMOS logic. The combined C3MOS / CMOS logic allows greater integration of circuits such as high speed transceivers used in fiber optic communication systems. The C3MOS structure enables the use of a power supply voltage that may be larger than the voltage required by the CMOS fabrication process, further enhancing the performance of the circuit.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
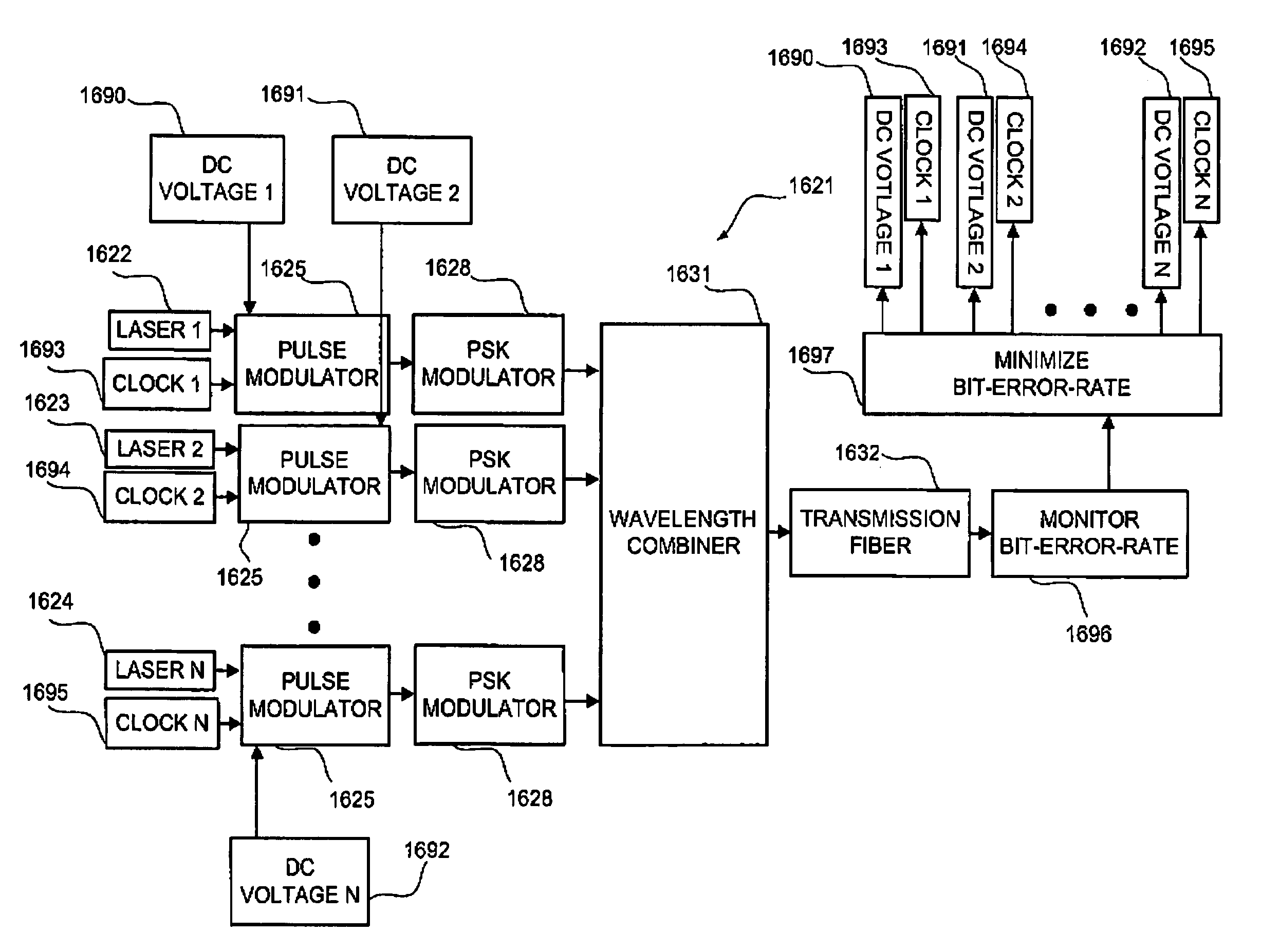
Method and system for mitigating nonlinear transmission impairments in fiber-optic communications systems
InactiveUS7224906B2Time-division optical multiplex systemsSynchronisation by photonic/optical meansFiberReturn-to-zero
The present invention relates to a method for transmitting data. An optical pulse stream comprising a plurality of return-to-zero optical pulses is prepared by modulating a phase of light output by an optical source to thereby encode data from a data source. The light of the optical pulse stream has a wavelength. The optical pulse stream is transmitted along an optical fiber of an optical network. Optical pulse streams of the invention enhance transmission performance at least in part by reducing noise at the receiver caused by fiber non-linearities.
Owner:CELIGHT
Radio-Over-Fiber (RoF) System for Protocol-Independent Wired and/or Wireless Communication
ActiveUS20110116794A1Expand coverageReduce lossTelevision conference systemsData switching by path configurationFiberRadio over fiber
An optically-switched fiber optic communication system, such as a Radio-over-Fiber (RoF) based optical fiber link system, may be used to increase the range of peer-to-peer communications. The optically-switched fiber optic communication system may include a head-end unit (HEU) having an optical switch bank. Fiber optic cables comprising optical fibers optically couple the HEU to one or more remote access points in different coverage areas. The optical switch bank in the HEU provides a link between the remote access points in the different coverage areas such that devices in the different cellular coverage areas can communicate with each other over the optical fibers through the HEU. By using the optically-switched fiber optic communication system, the range and coverage of communication between devices may be extended such that devices in different coverage areas and devices using different communication protocols can communicate.
Owner:CORNING OPTICAL COMM LLC
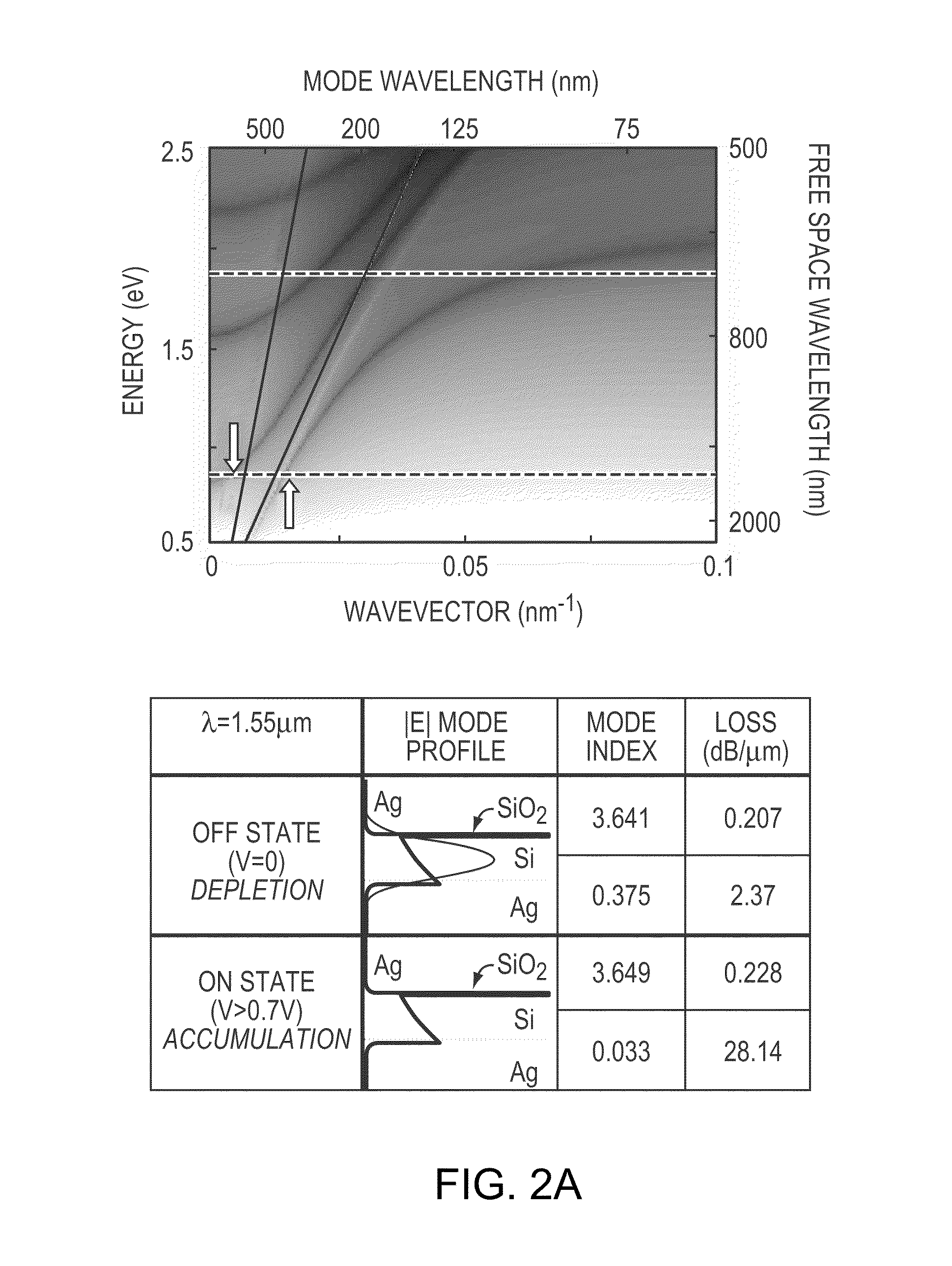
Plasmostor: a-metal-oxide-si field effect plasmonic modulator
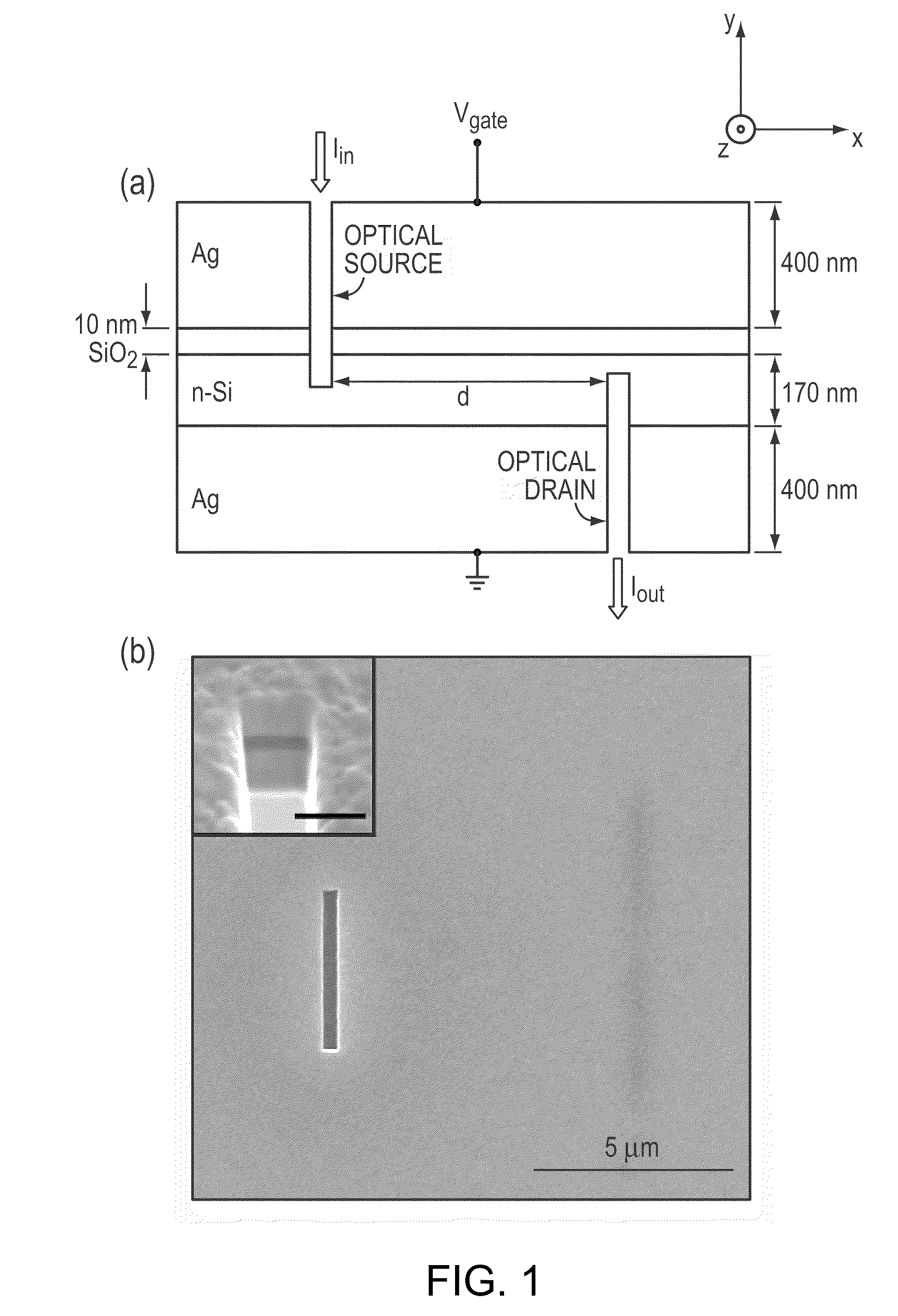
InactiveUS20090273820A1Optical waveguide light guideNon-linear opticsPhotovoltaic detectorsPhotodetector
The invention is a system and method for performing all-optical modulation. A semiconductor layer having a defined thickness has an insulator adjacent one surface of the semiconductor. Conductive layers are provided adjacent the semiconductor layer and the insulator. A photodetector is provided to generate an electric field across the conductive layers in response to an input optical gate signal. An input optical signal is modulated by interaction with a plasmon wave generated at the semiconductor / conductive layer interface. By defining the thickness of the semiconductor layer, a desired wavelength of light supports the plasmon waves. Operation of the all-optical modulator requires the provision of an input optical signal of a desired wavelength and the provision of a gate optical signal. An output optical signal is recovered and can be used to store, display or transmit information, for example over a fiber optic communication system, such as a telecommunication system.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
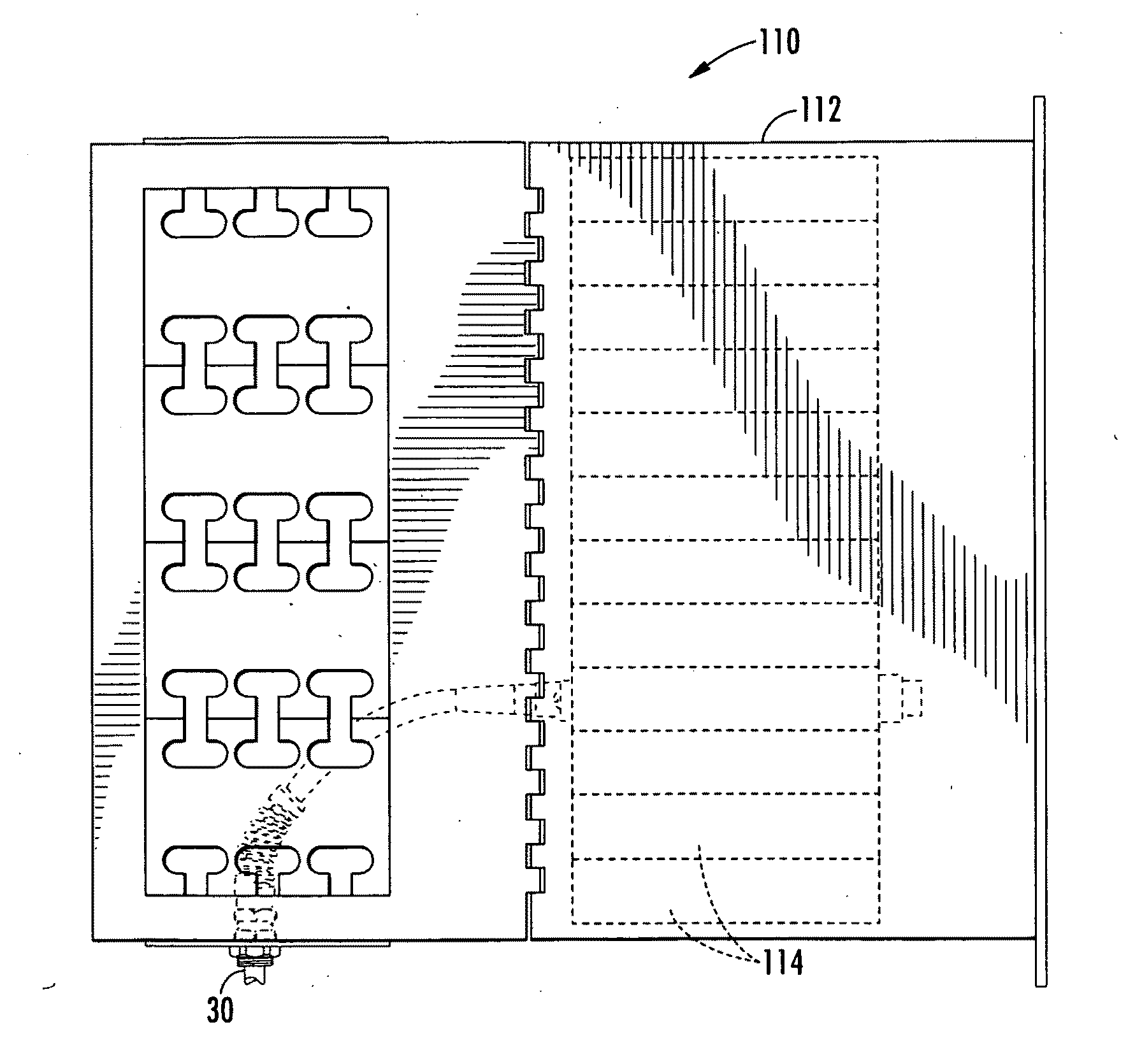
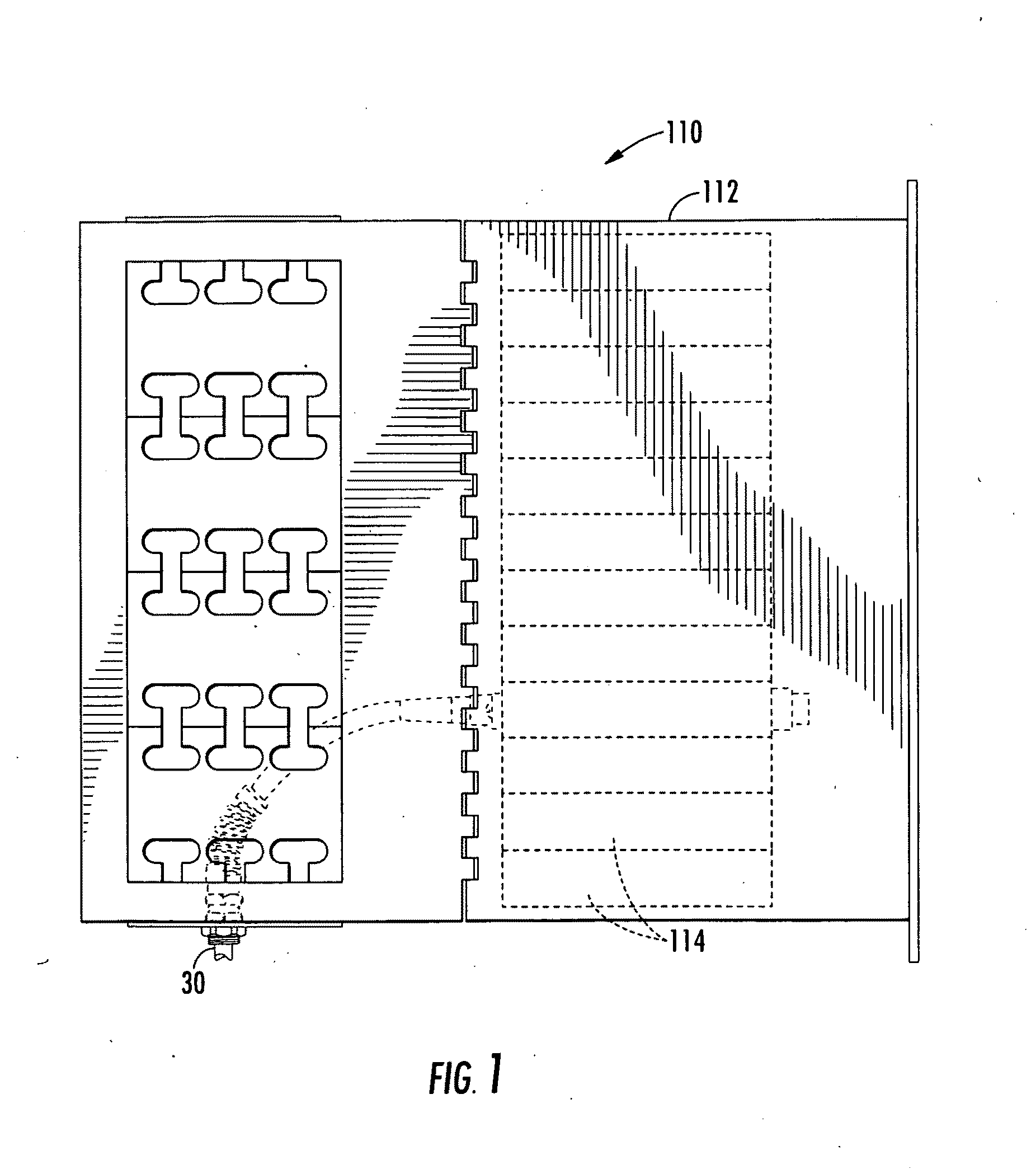
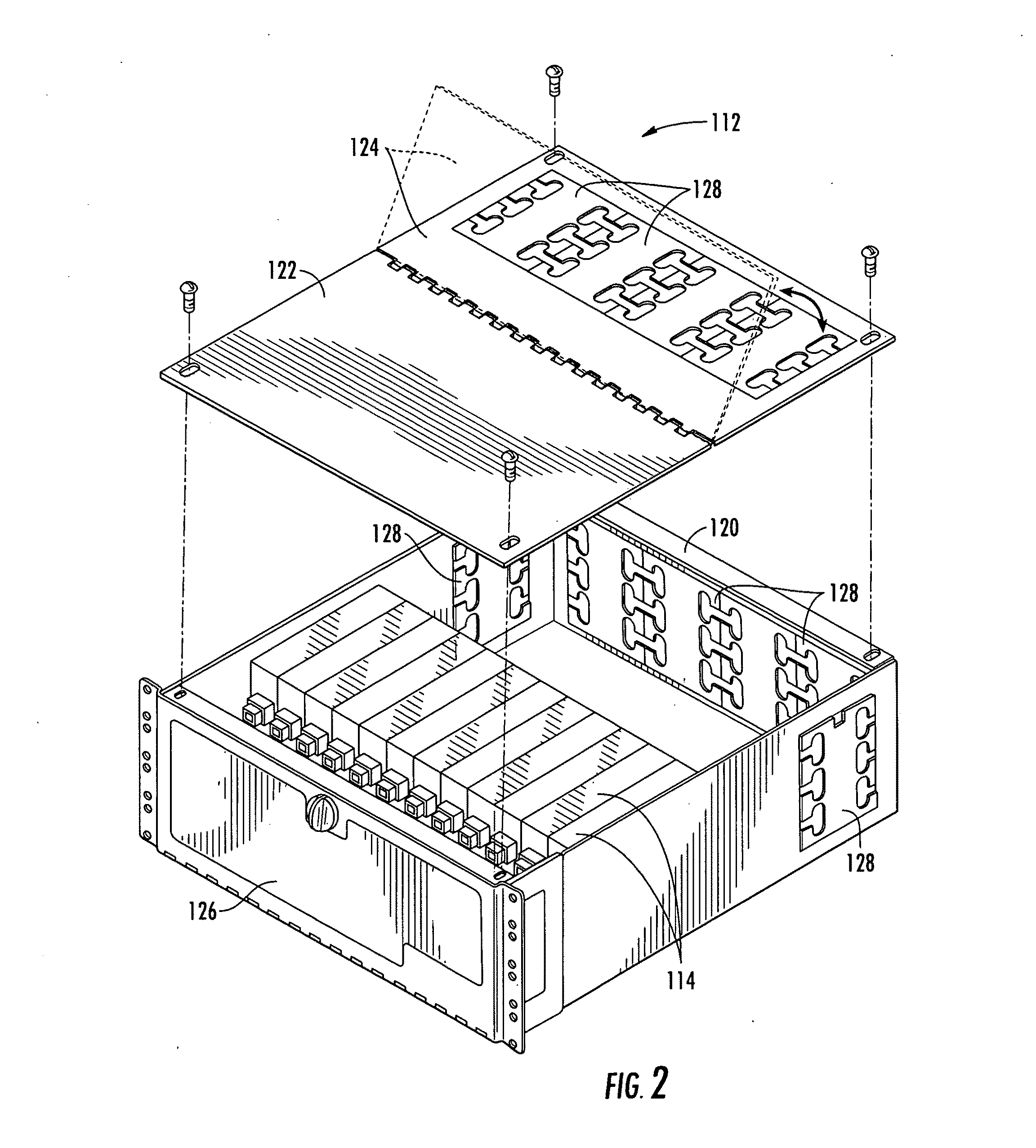
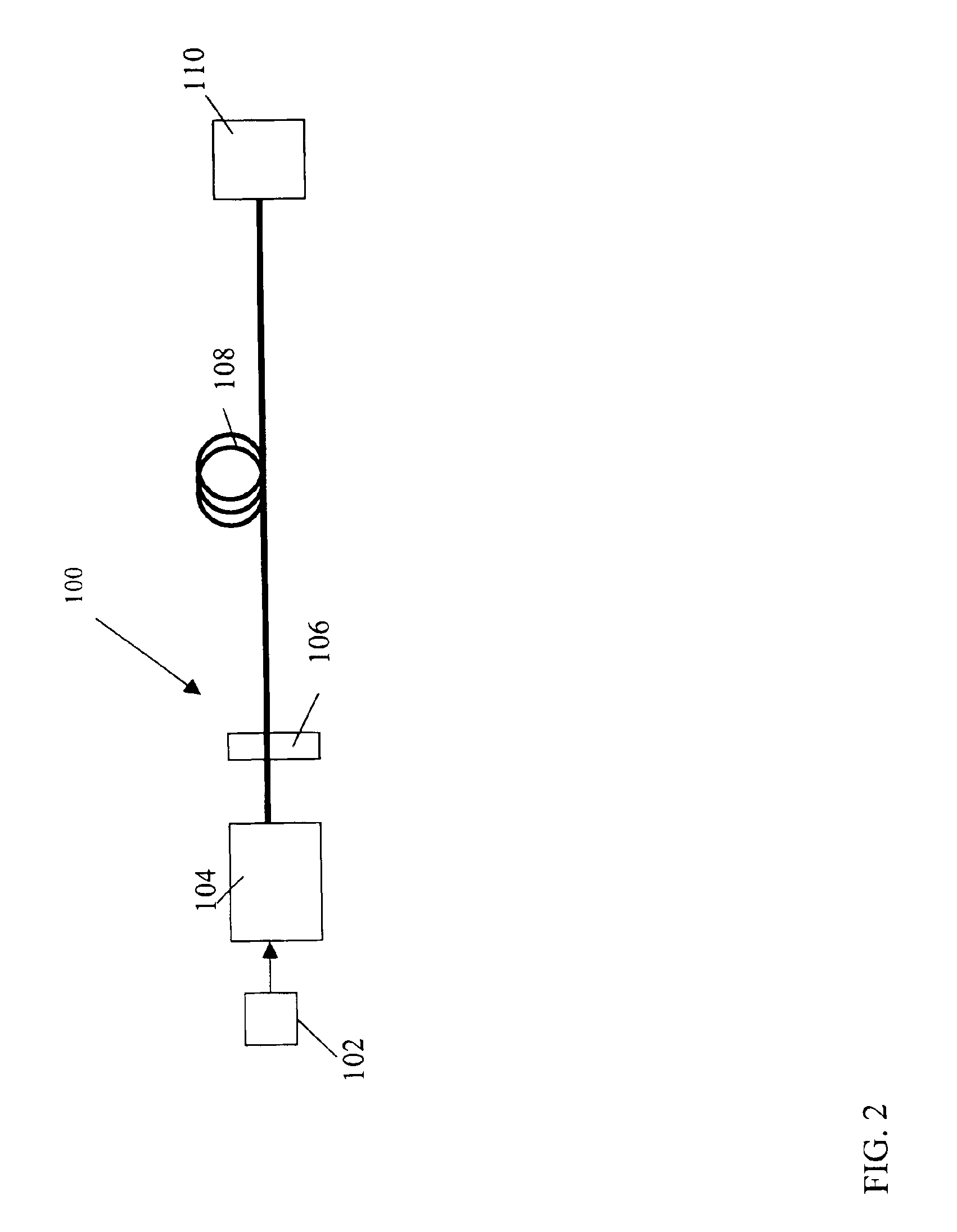
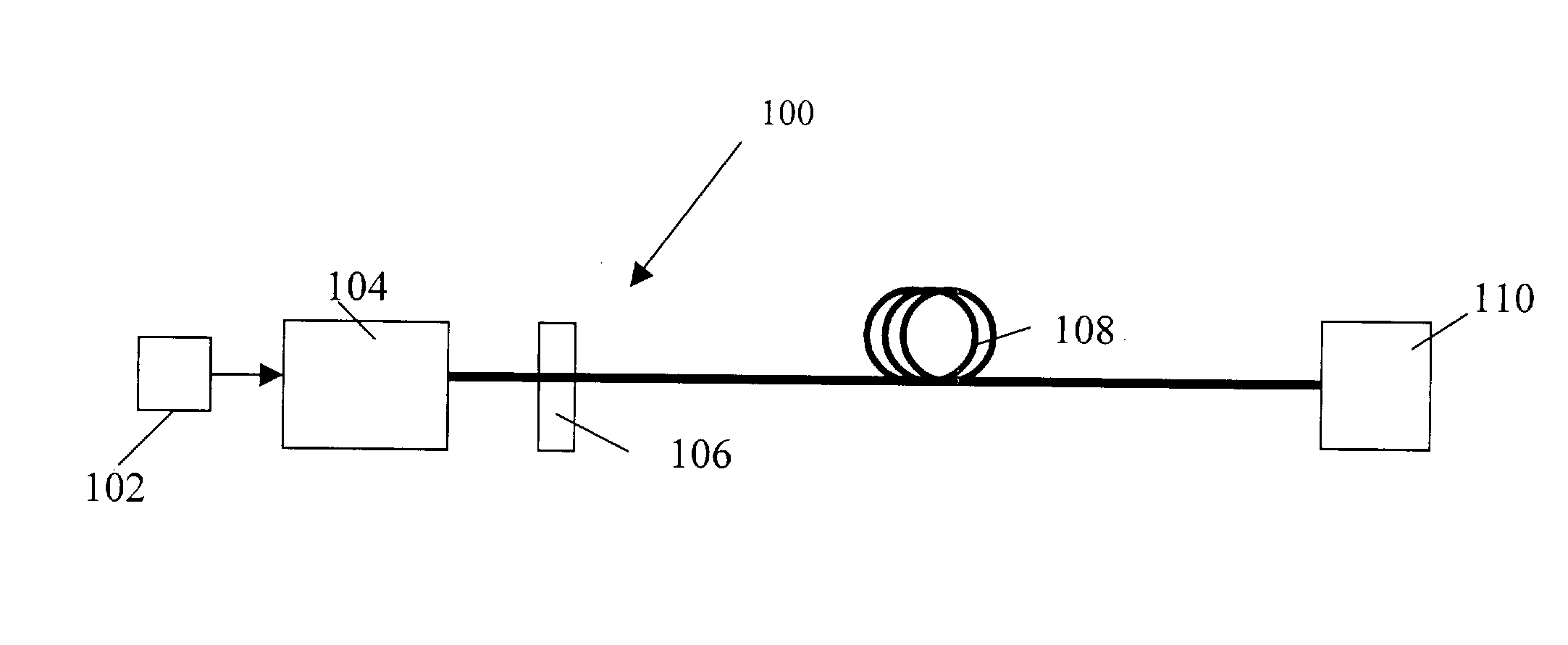
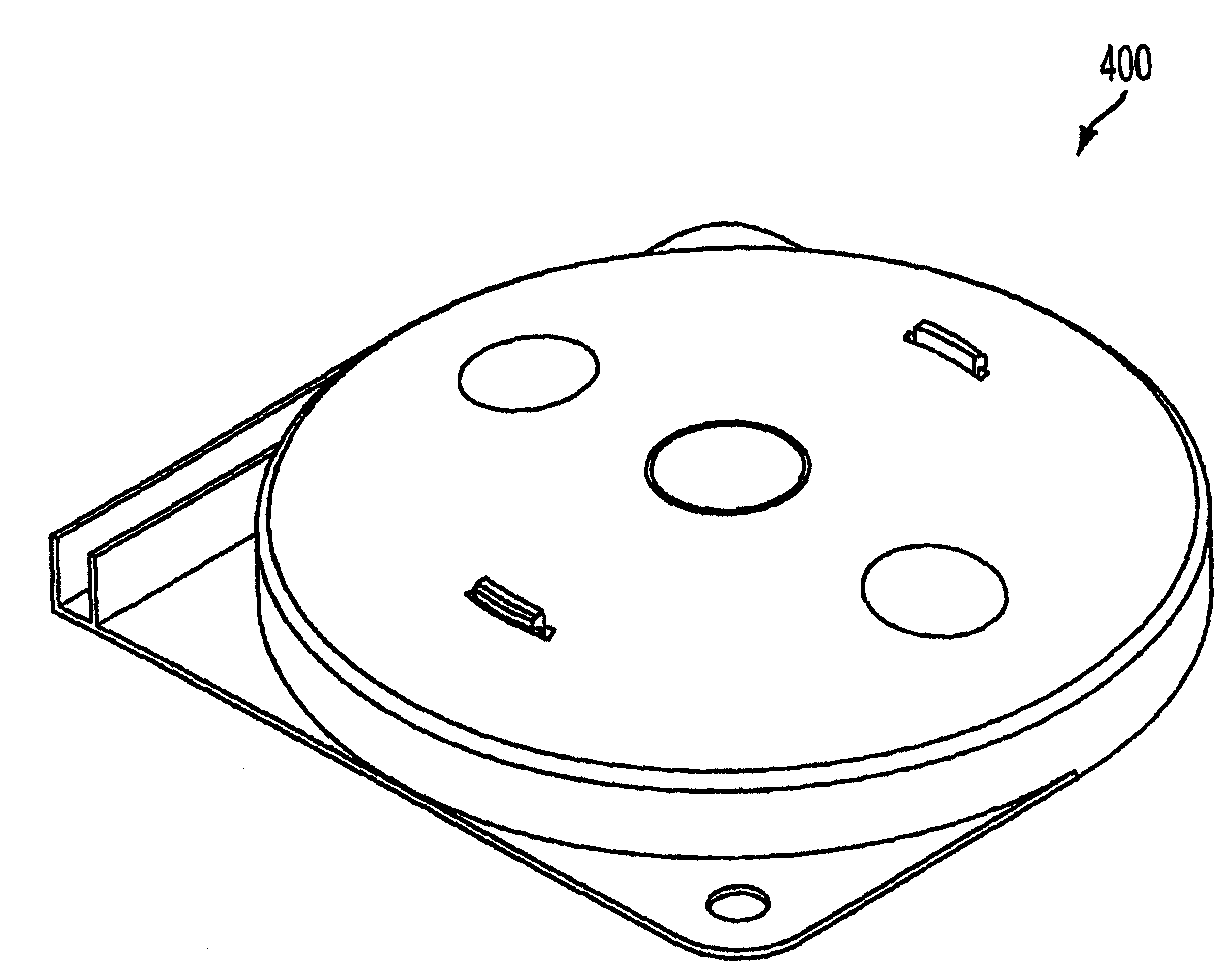
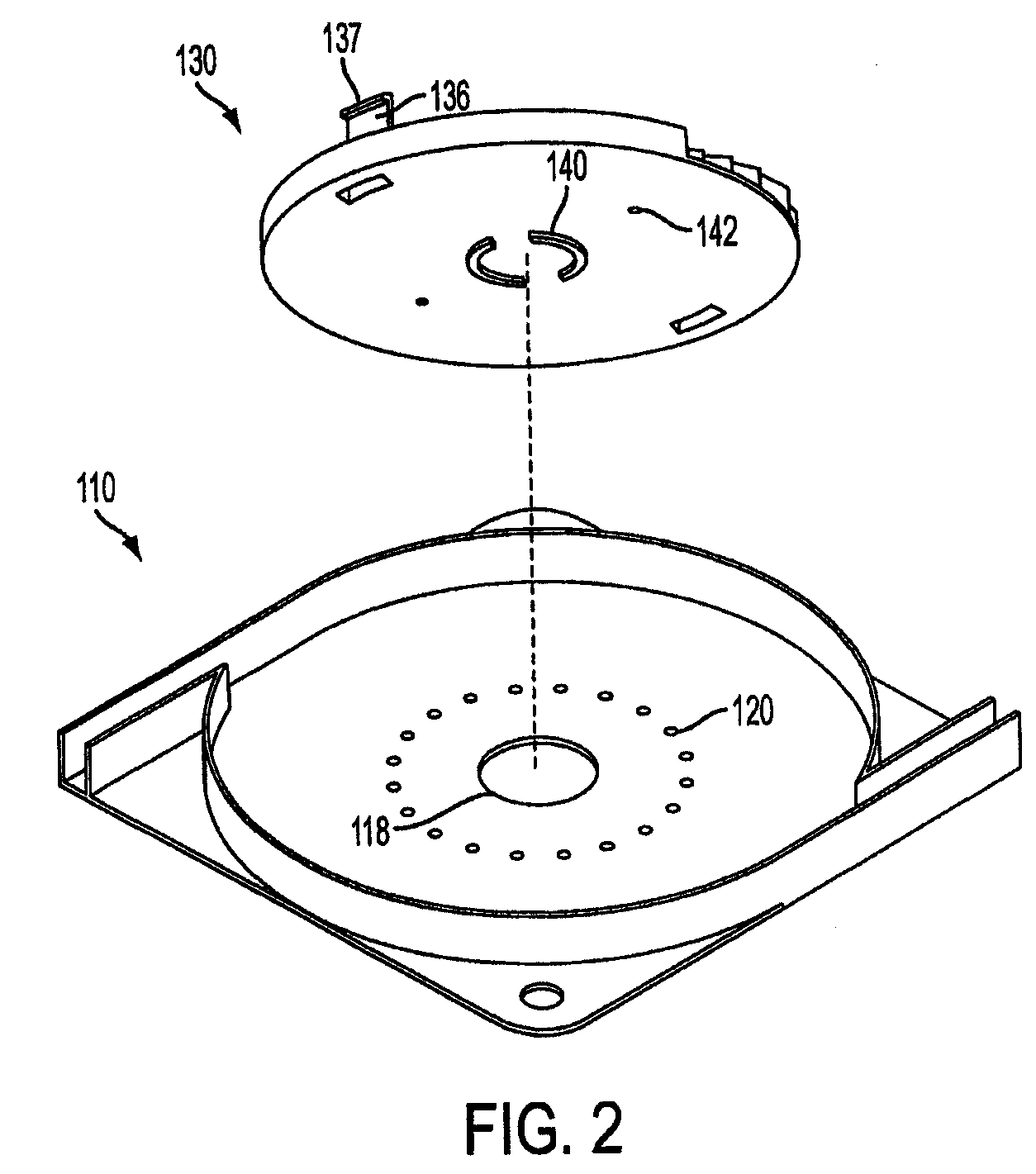
Storage Device for Use in Fiber Optic Communication Systems and Method of Using the Same
A storage device for storing cable or fiber, rotating element, and method of using the same are provided. The storage device includes a housing, having an inner cavity and at least one opening; and a rotating element which is rotatably and removably placed within the inner cavity and has at least one receptacle. The rotating element includes a base member; a receptacle for holding at least one splice sleeve containing a sliced fiber; and a plurality of guide ridges, which are disposed on the base member, one of the plurality of guide ridges disposed at either end of each of the at least one receptacle. The method includes placing the fiber or cable into the receptacle; draping excess fiber or cable through guide fins; and rotating the rotating element to retract or dispense the excess fiber or cable into or out of the storage device through the at least one opening in the housing.
Owner:AFL COMM LLC
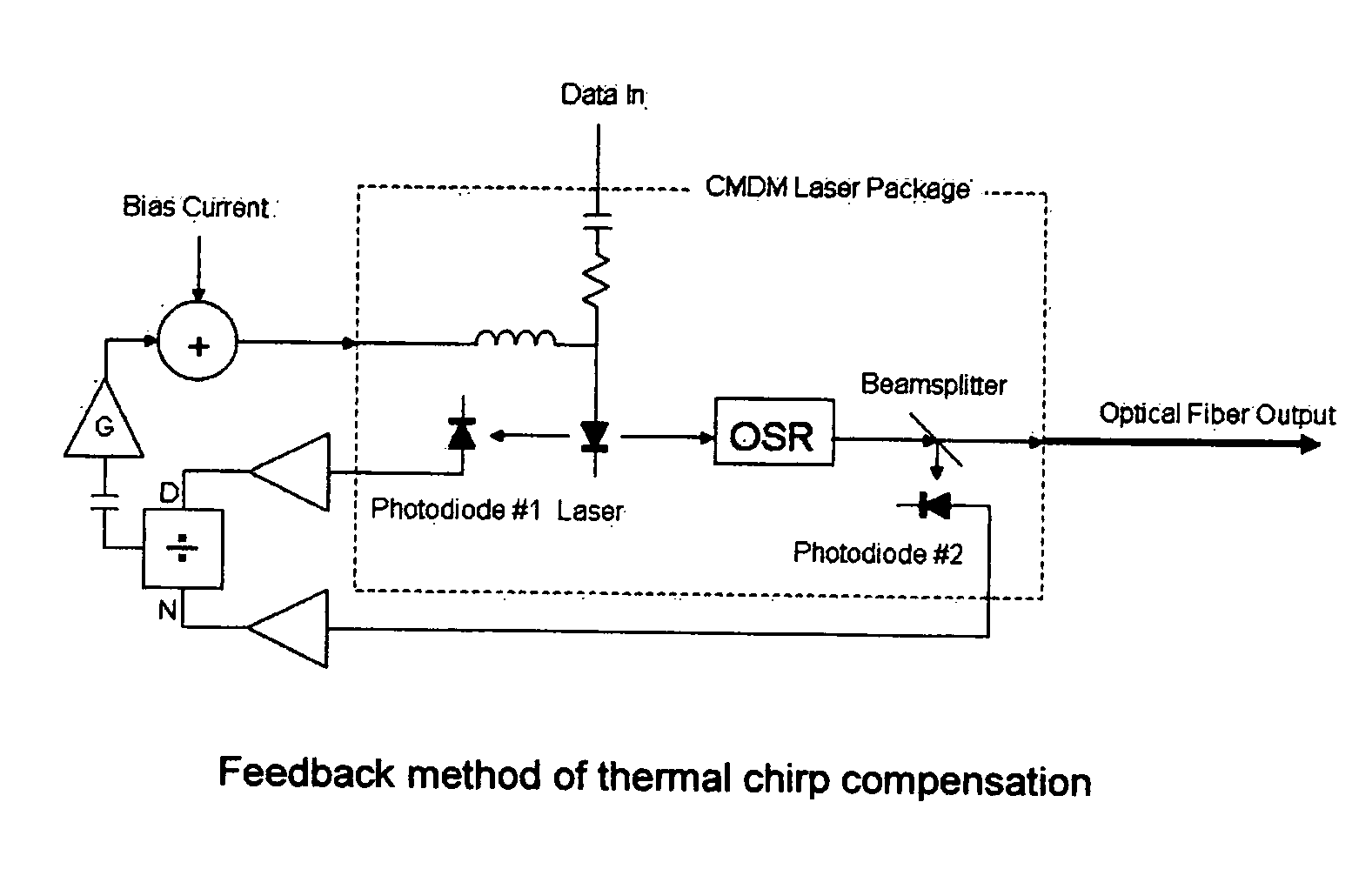
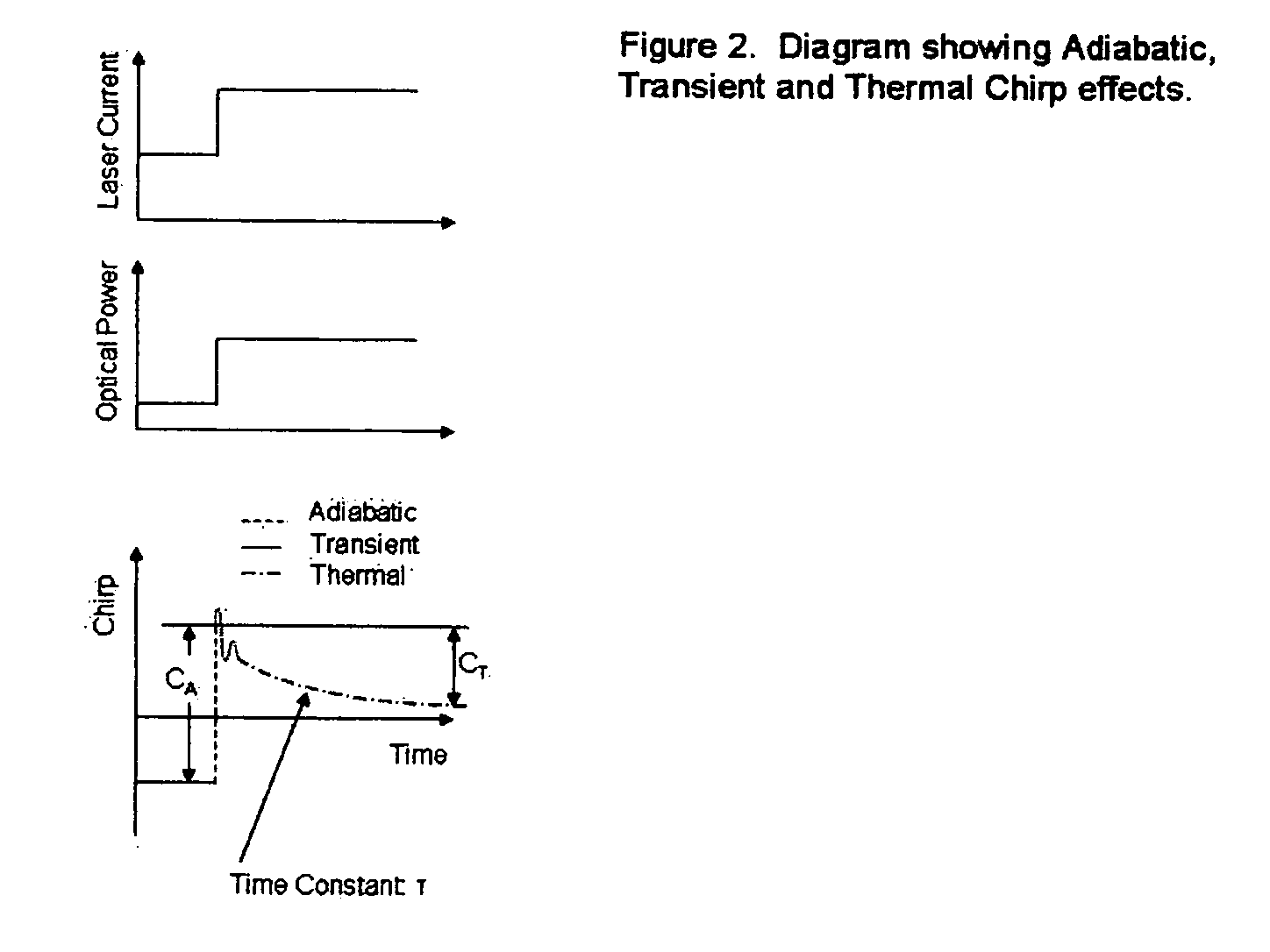
Thermal chirp compensation systems for a chirp managed directly modulated laser (CML(TM)) data Link
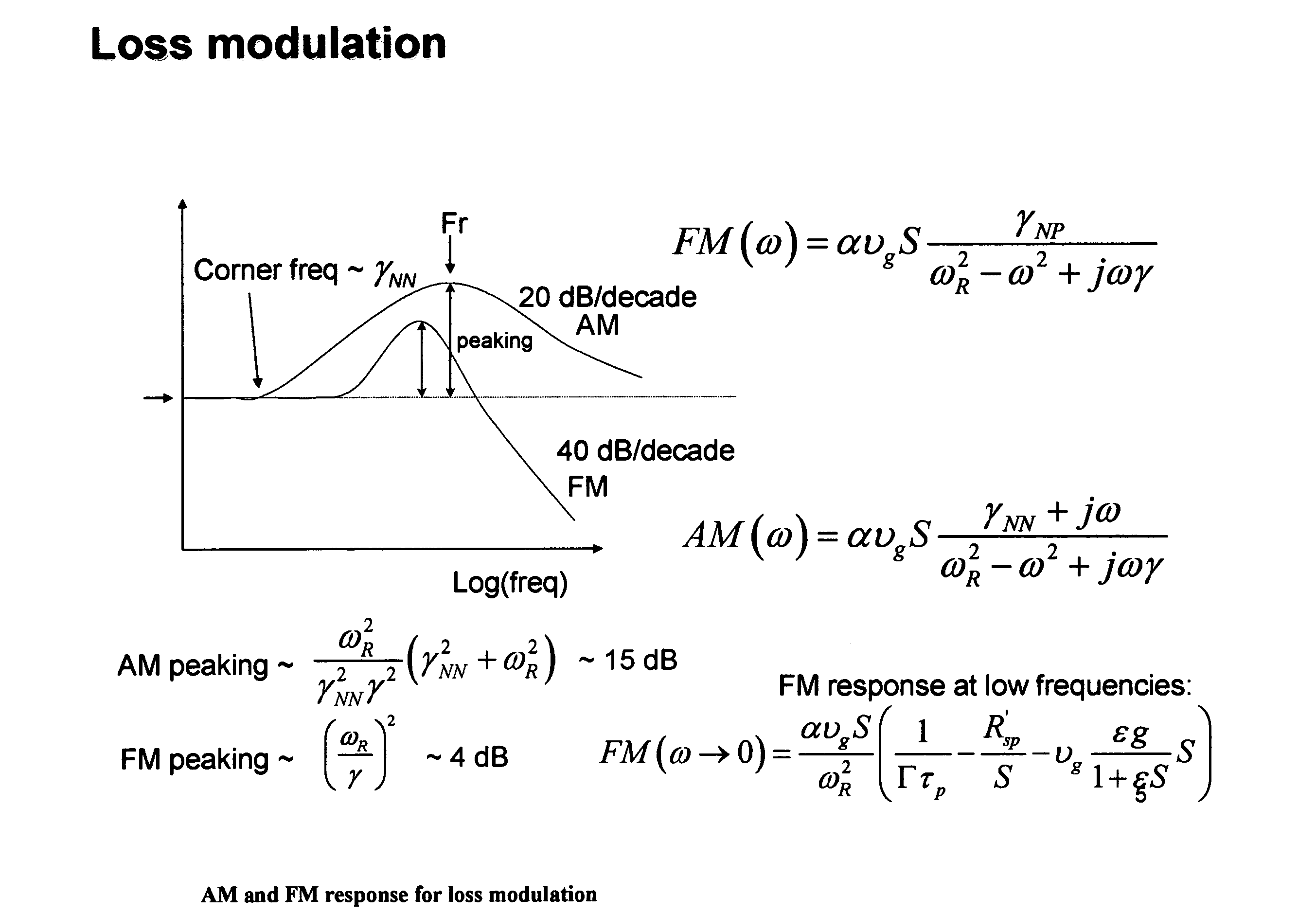
ActiveUS20060078338A1Reduce the impactReduce the amplitudeElectromagnetic transmittersSemiconductor lasersDigital dataFrequency modulation
A fiber optic communication system for receiving an electronic digital data signal and transmitting the same, comprising an optical signal source adapted to receive the digital data signal and to produce a frequency modulated optical signal from a directly modulated semiconductor laser; an optical spectrum reshaper adapted to convert the frequency modulated optical signal into an amplitude modulated optical signal; and compensation apparatus for compensating for the adverse effects of the thermal chirp normally induced in the frequency modulated optical signal by modulating the semiconductor laser with the electronic digital data signal.
Owner:II VI DELAWARE INC
Systems and methods for the compensation of nonlinear cross polarization and cross phase modulation in dual polarization coherent channels
ActiveUS20140050476A1Improve toleranceOptimize channel performancePolarisation multiplex systemsDistortion/dispersion eliminationPolarization multiplexedEngineering
The present disclosure provides systems and methods for the compensation of signal distortion in fiber optic communication systems and the like. More specifically, the present disclosure provides an orthogonal polarization detection and broadband pilot (OPDBP) technique for the compensation of nonlinear cross polarization (i.e. nonlinear cross polarization modulation) (XPolM) induced noise and nonlinear nonlinear cross phase modulation (XPM) induced noise in a high data rate polarization multiplexed (PM) multilevel-quadrature amplitude modulated (M-QAM) channel due to neighboring channels. This approach allows for the compensation of both XPolM and XPM simultaneously, providing several dBs of optical reach extension. The approach uses a pilot tone based orthogonal polarization detection scheme with broadband (i.e. a few GHz wide) filtering of the pilot tones.
Owner:CIENA
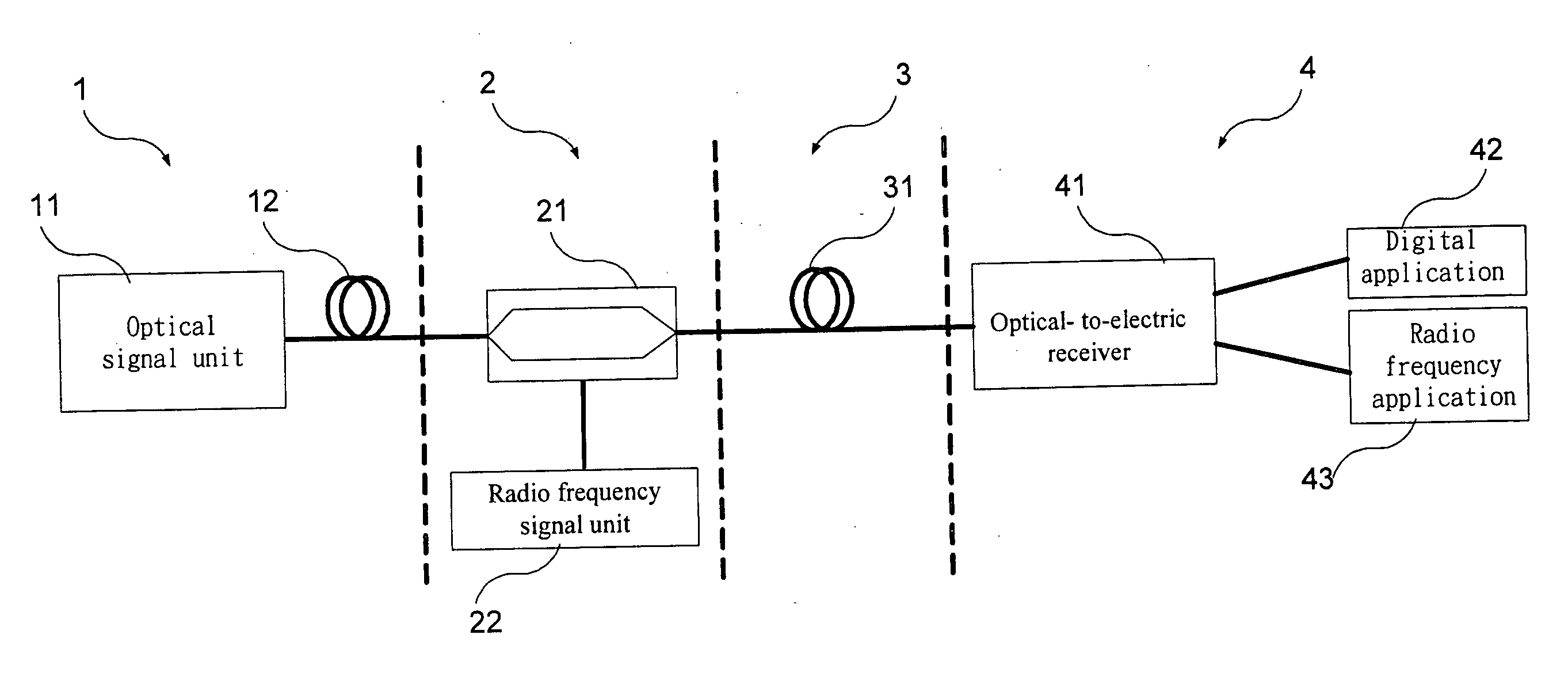
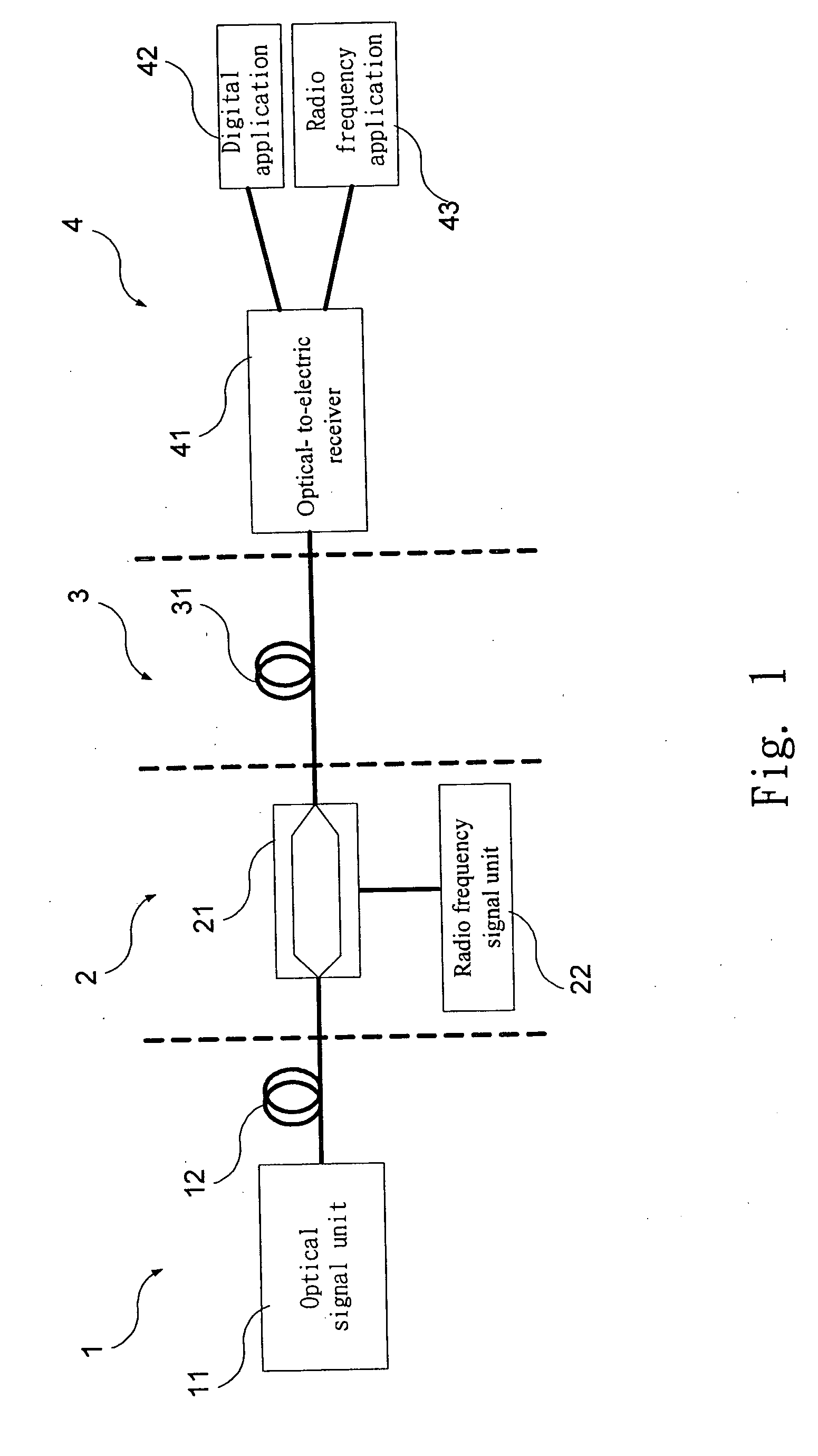
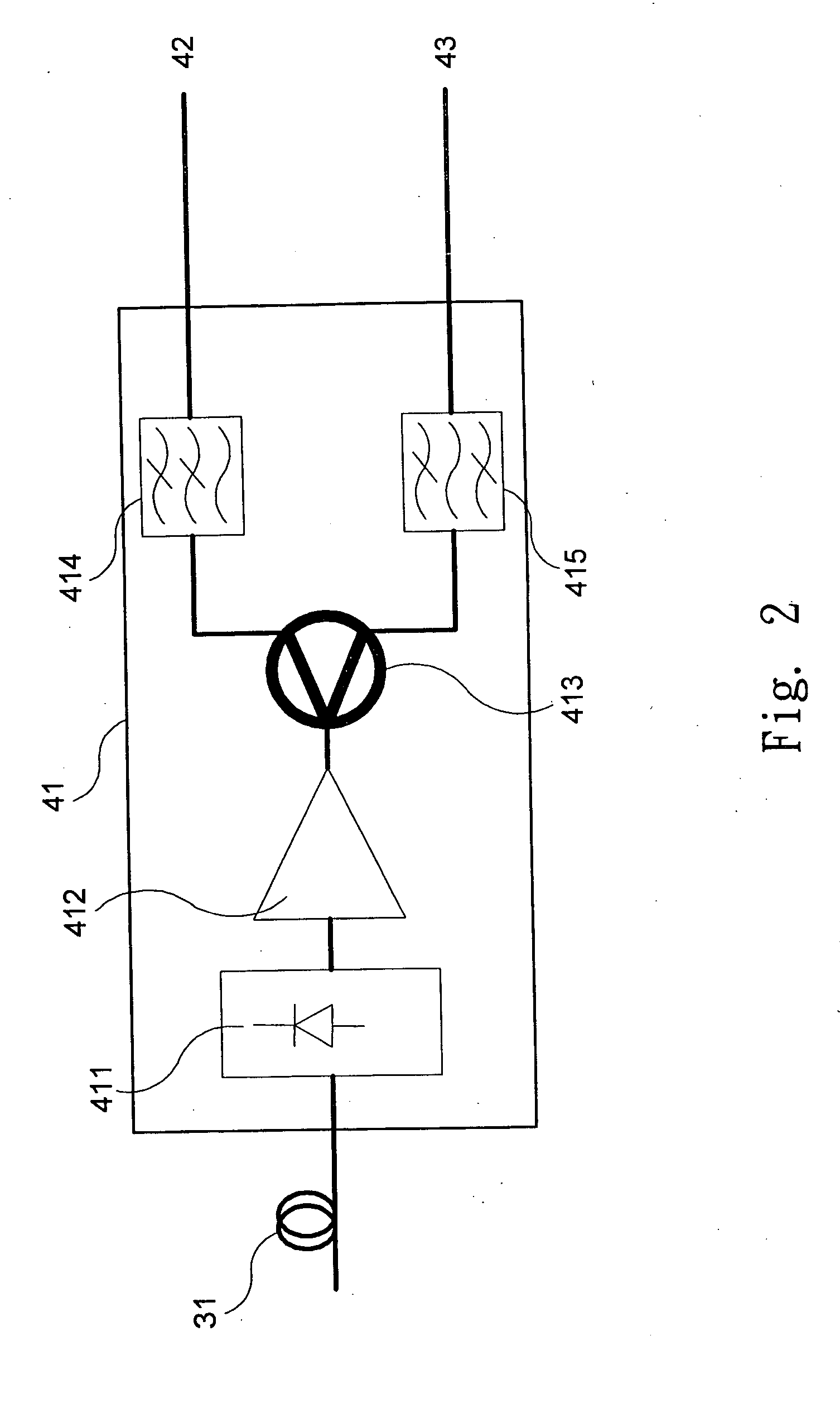
Method and apparatus for transporting ethernet and radio frequency signals in fiber-optic system
InactiveUS20060291863A1Increase bitrateSimple and inexpensive structureRadio-over-fibreElectromagnetic transmittersFiberRadio frequency signal
A single wavelength fiber-optic communication system that mixes an Ethernet signal with a radio frequency signal is disclosed. The system includes an Ethernet signal module, a radio frequency signal module, a mixer module and a receiver module. The Ethernet signal module provides an Ethernet signal. The radio frequency signal module provides a radio frequency signal. The mixer module provides an optical mixed signal by means of mixing the Ethernet signal with the radio signal at a single wavelength. The receiver module transforms the optical mixed signal into the radio frequency signal and a digital signal that contains the Ethernet signal.
Owner:NAT CENT UNIV
Thermal chirp compensation systems for a chirp managed directly modulated laser (CML(TM)) data link
ActiveUS7505694B2Reduce the amplitudeLower Level RequirementsElectromagnetic transmittersSemiconductor lasersDigital dataData signal
A fiber optic communication system for receiving an electronic digital data signal and transmitting the same, comprising an optical signal source adapted to receive the digital data signal and to produce a frequency modulated optical signal from a directly modulated semiconductor laser; an optical spectrum reshaper adapted to convert the frequency modulated optical signal into an amplitude modulated optical signal; and compensation apparatus for compensating for the adverse effects of the thermal chirp normally induced in the frequency modulated optical signal by modulating the semiconductor laser with the electronic digital data signal.
Owner:II VI DELAWARE INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com