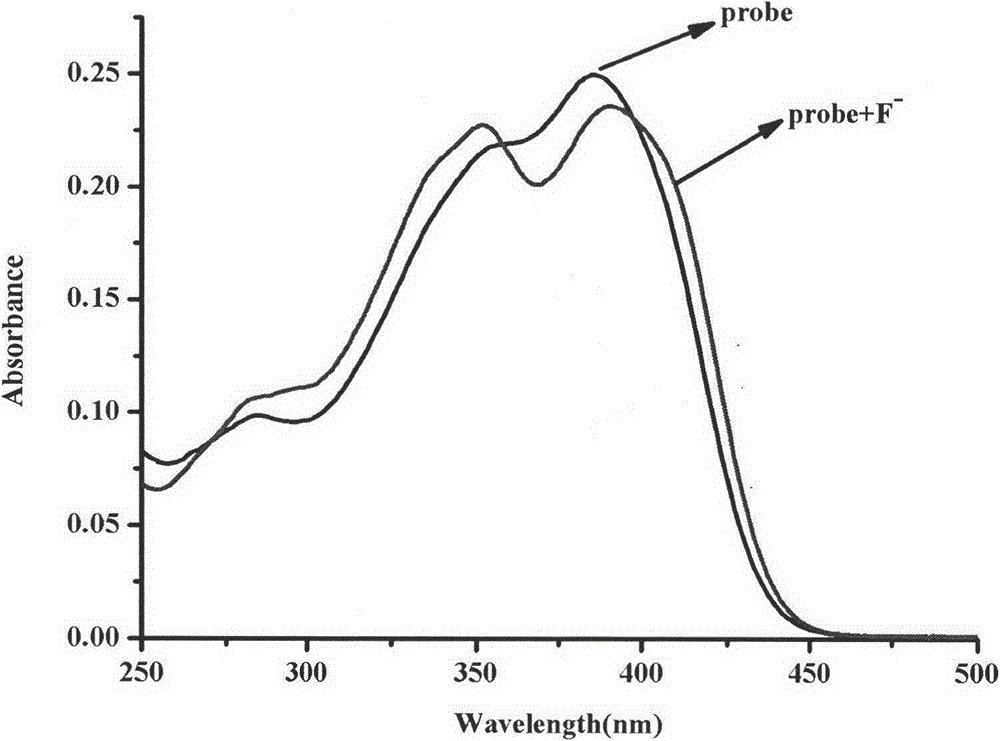
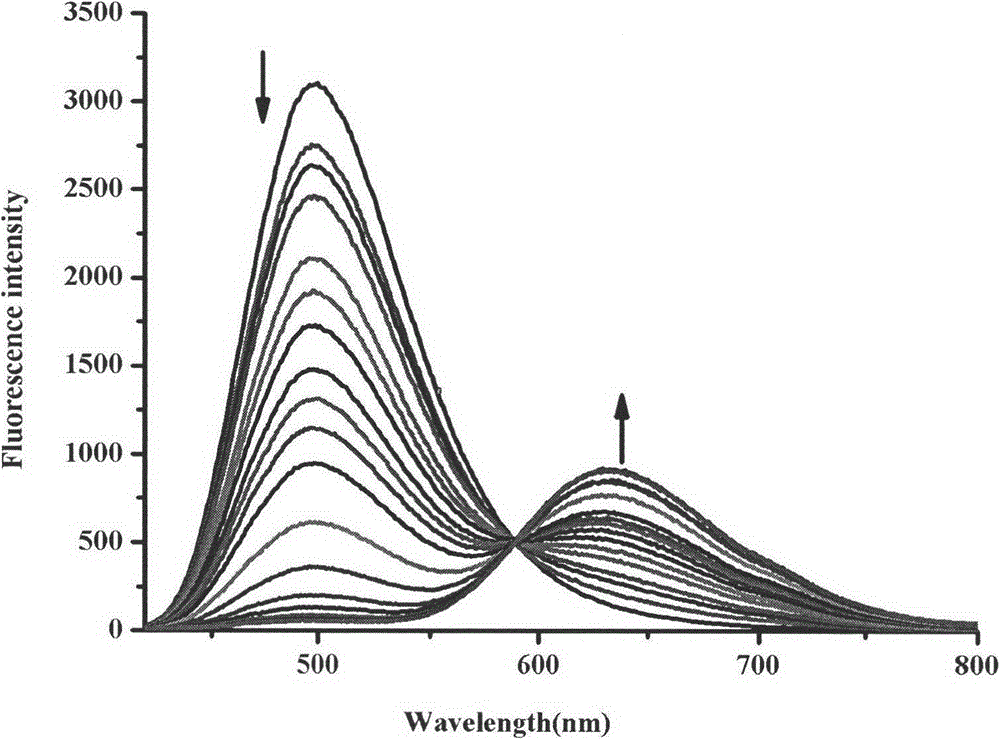
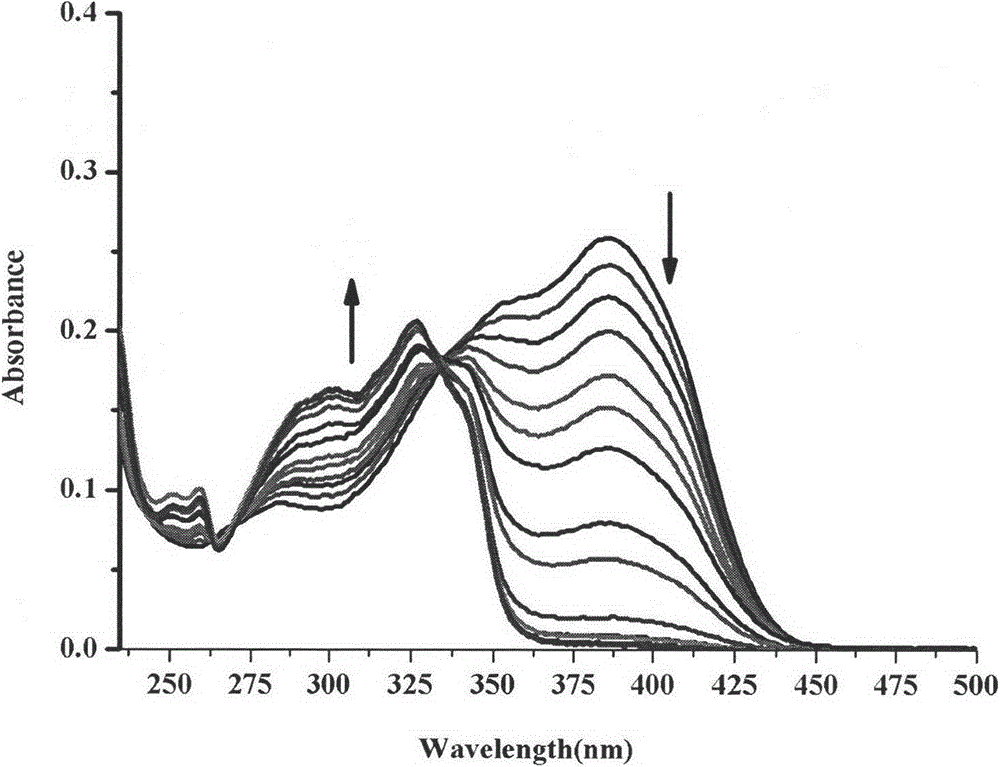
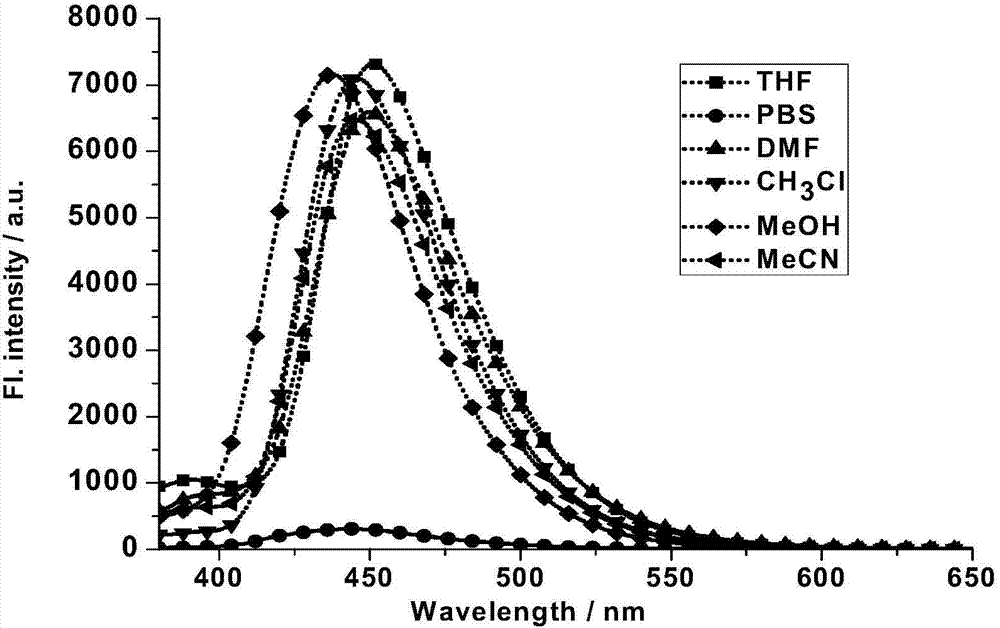
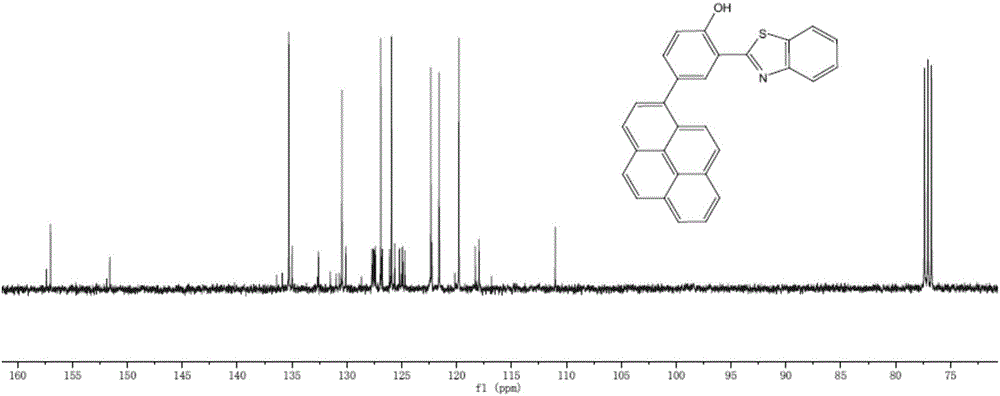
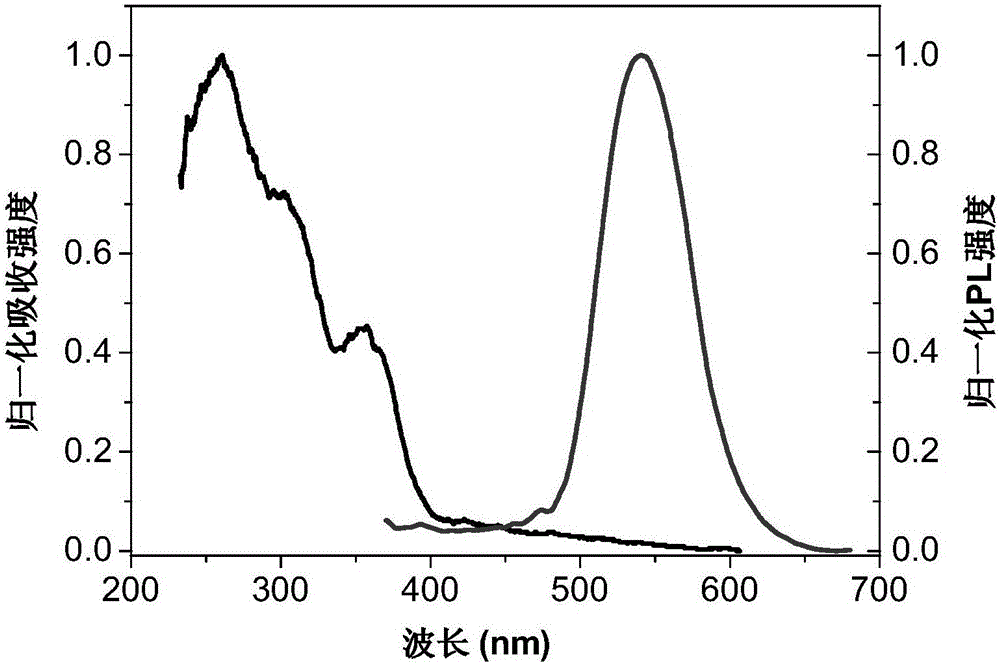
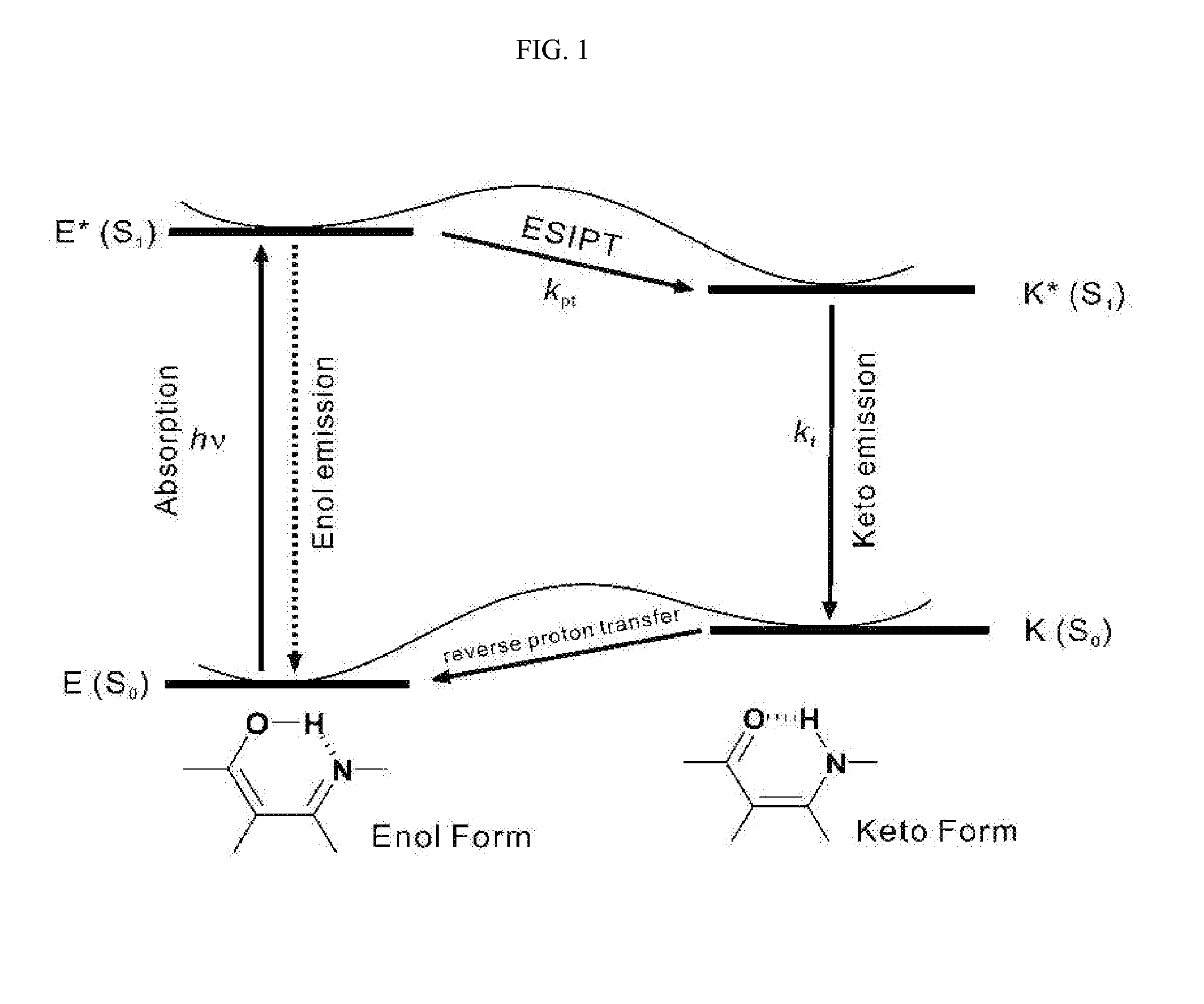
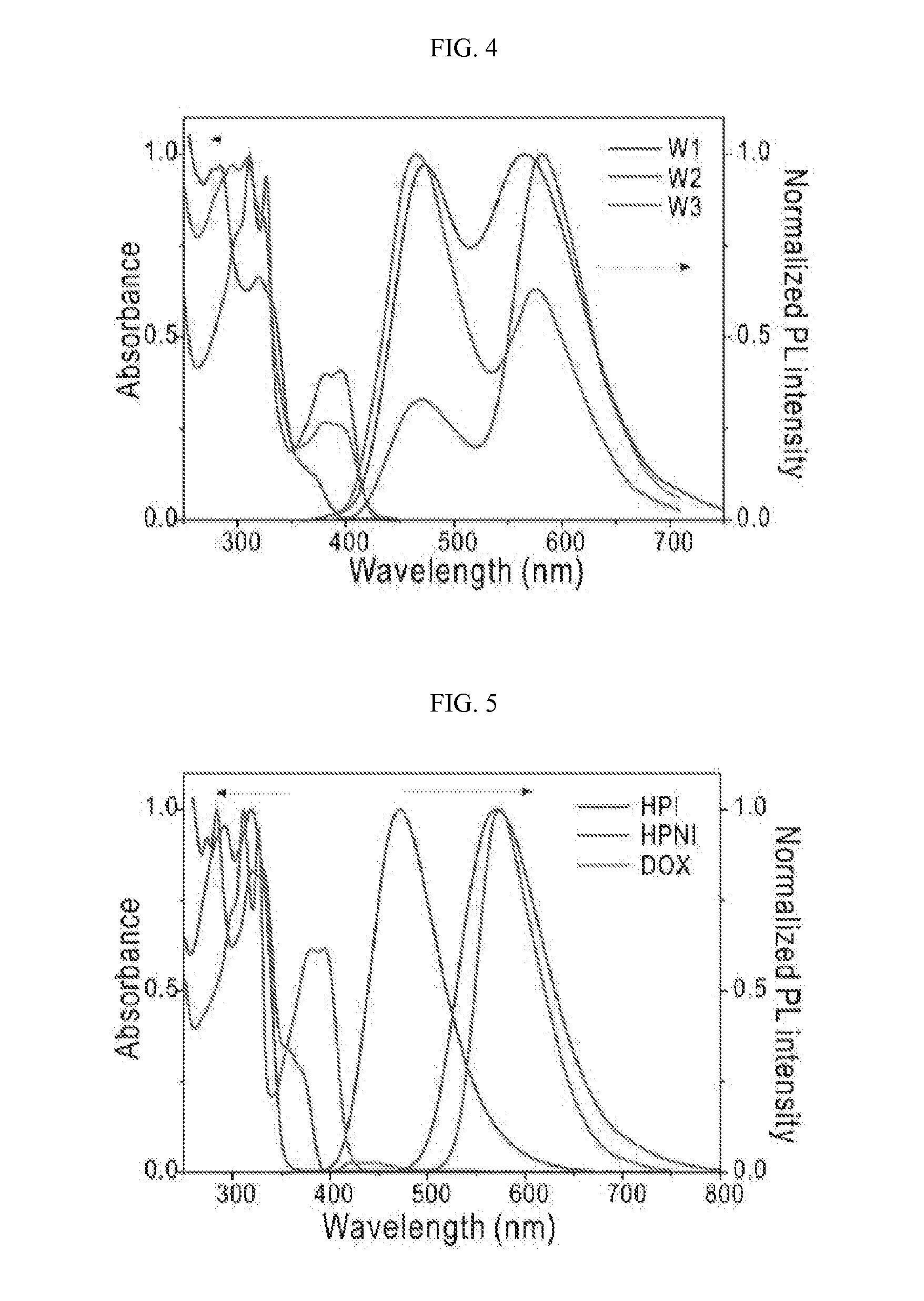
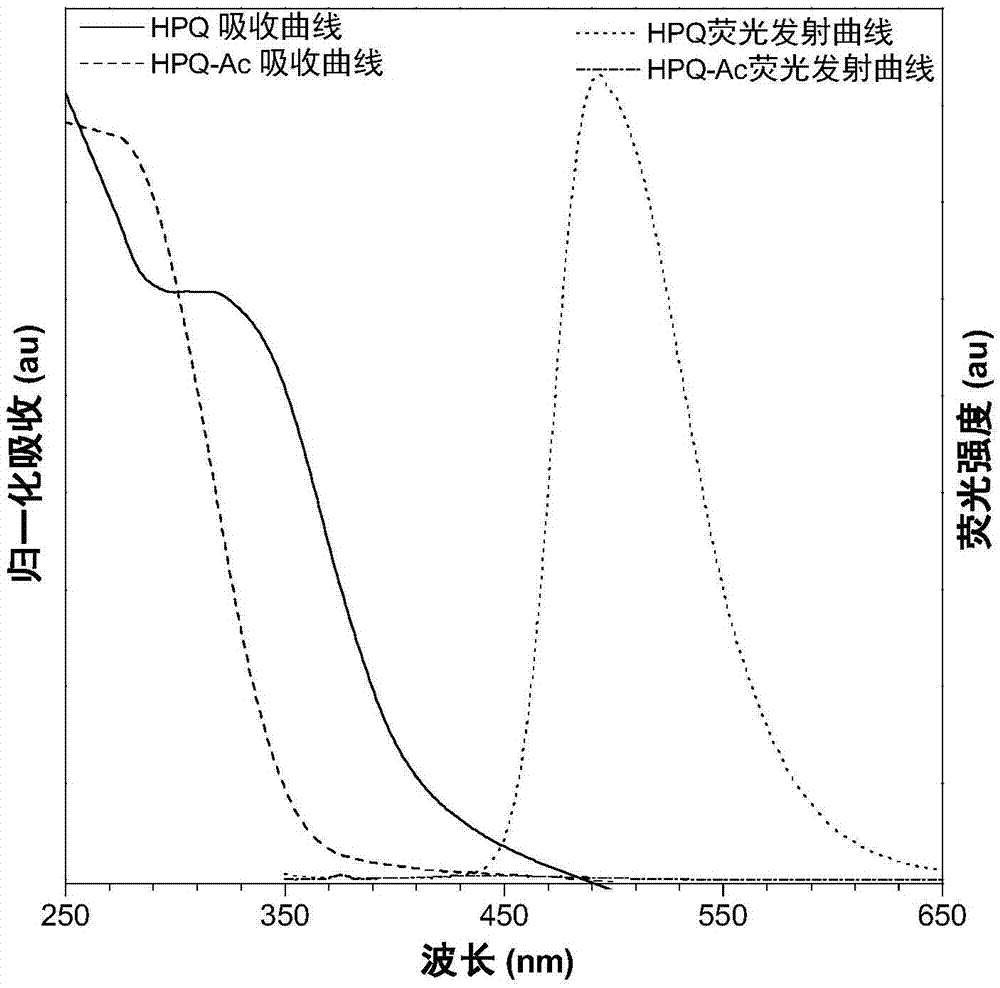
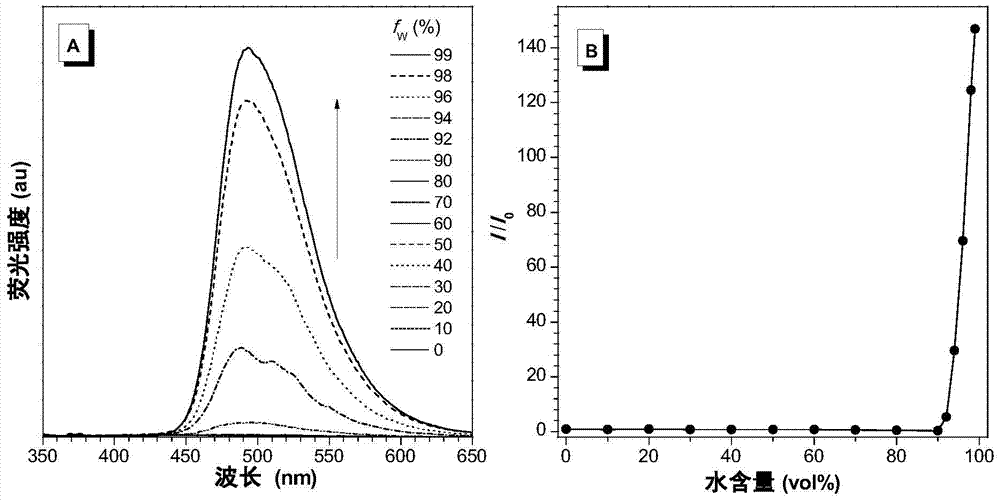
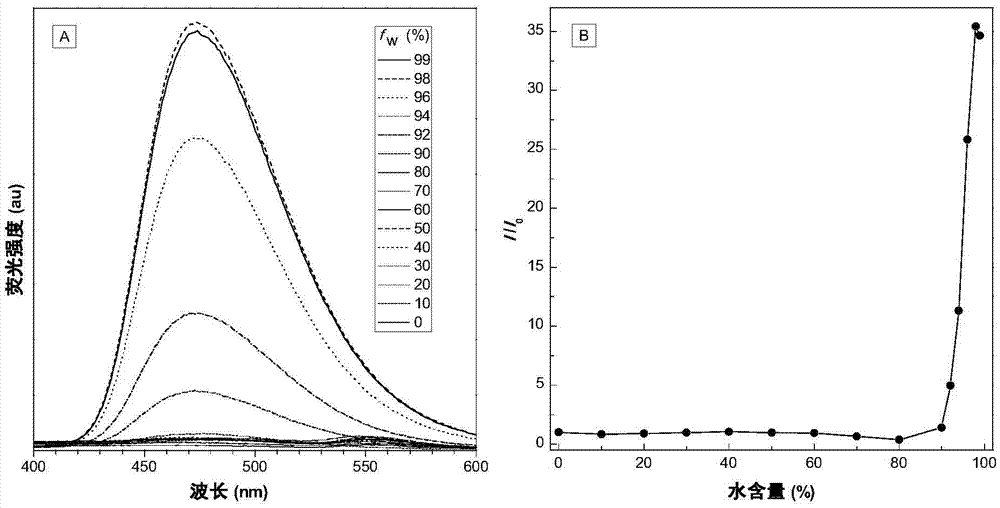
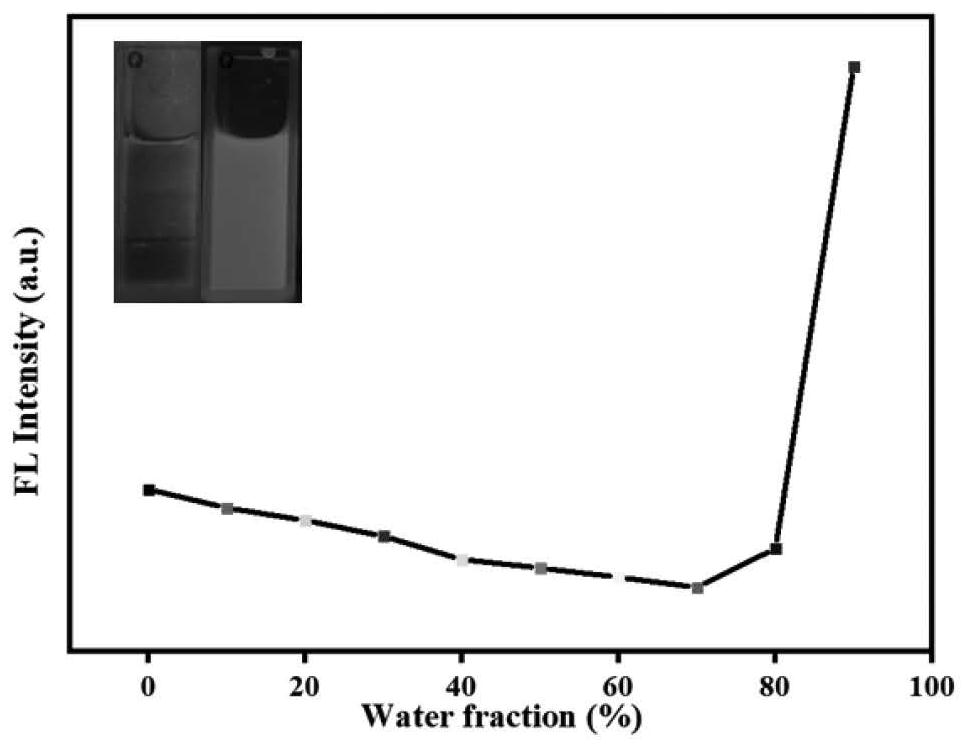
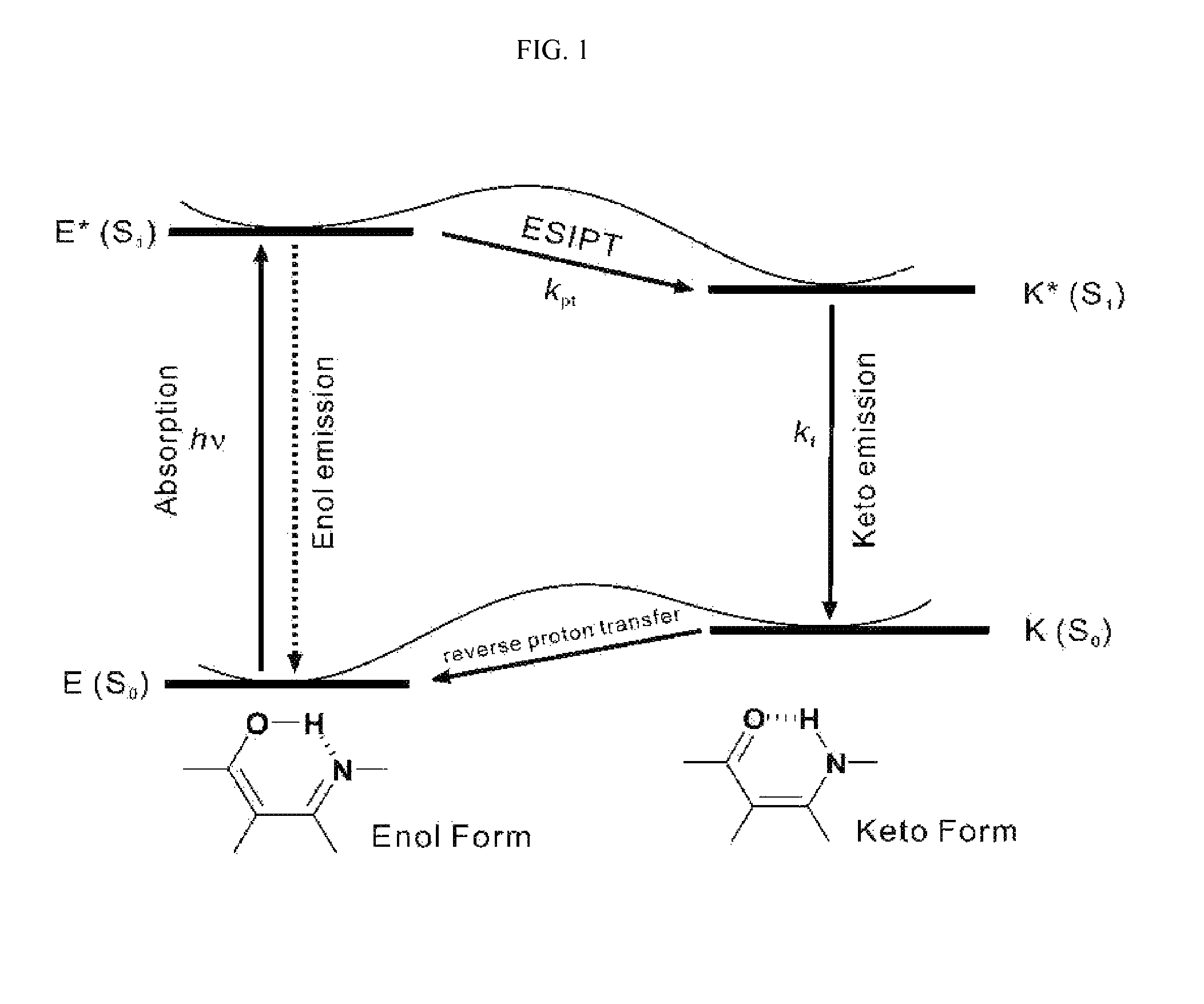
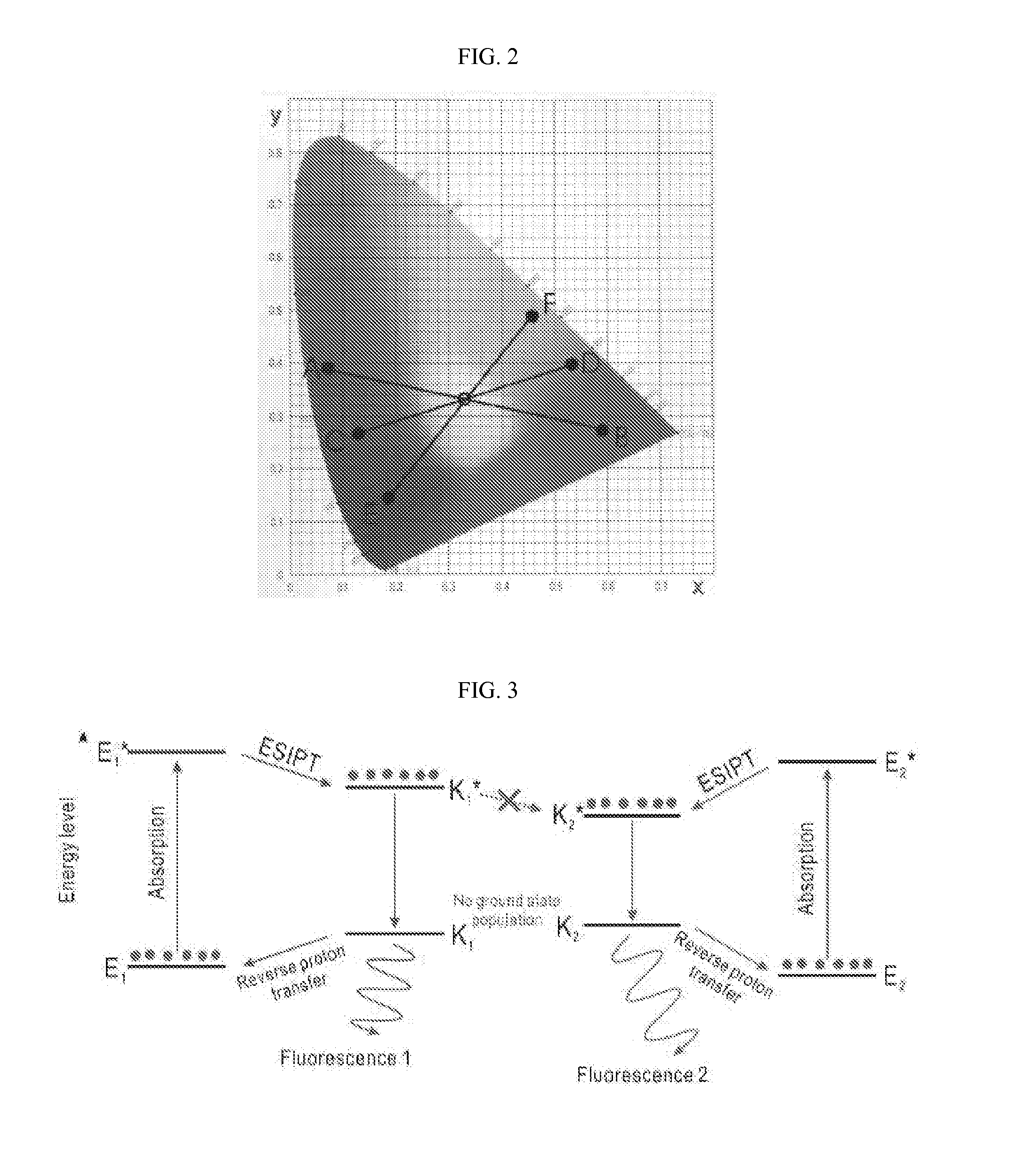
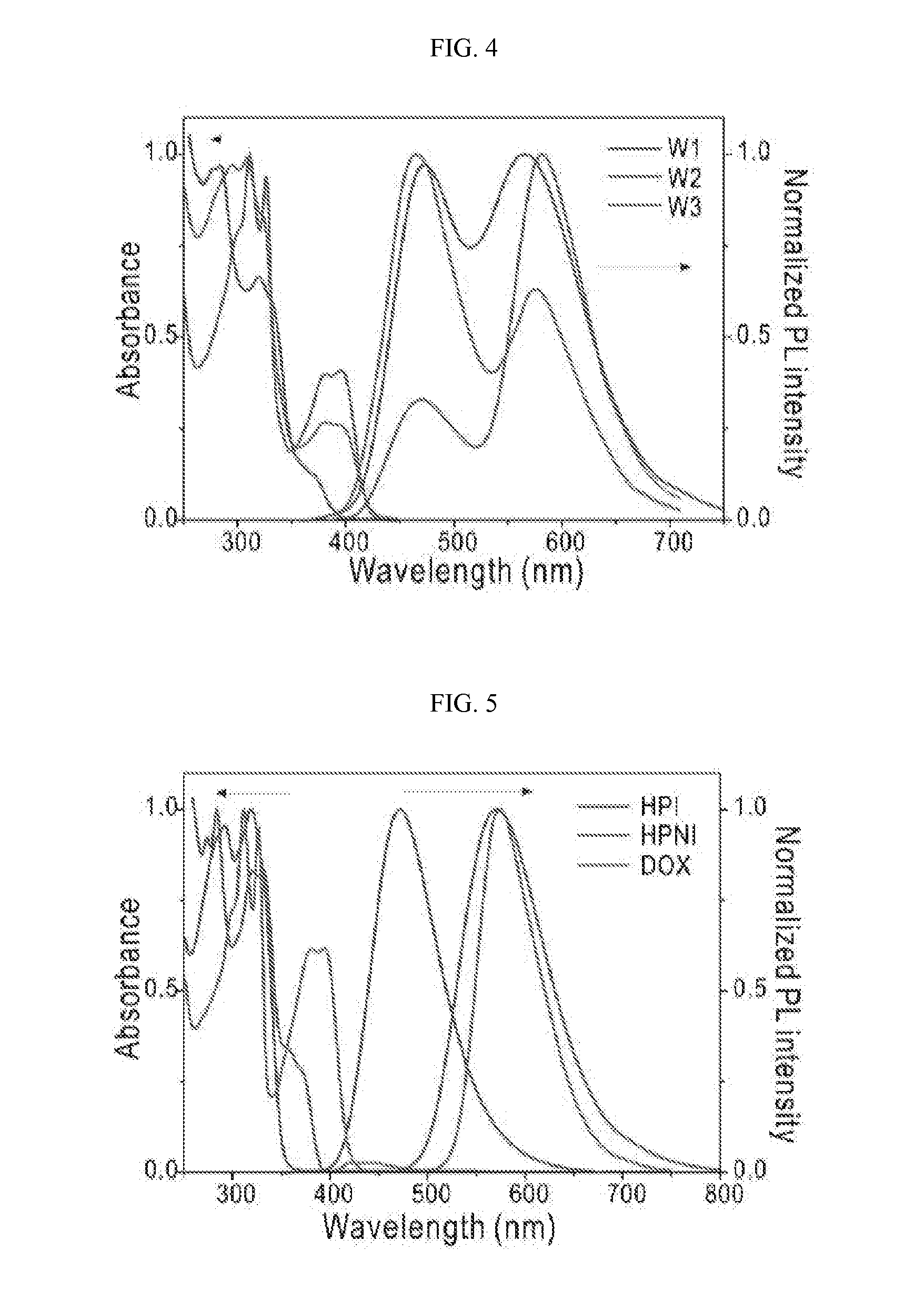
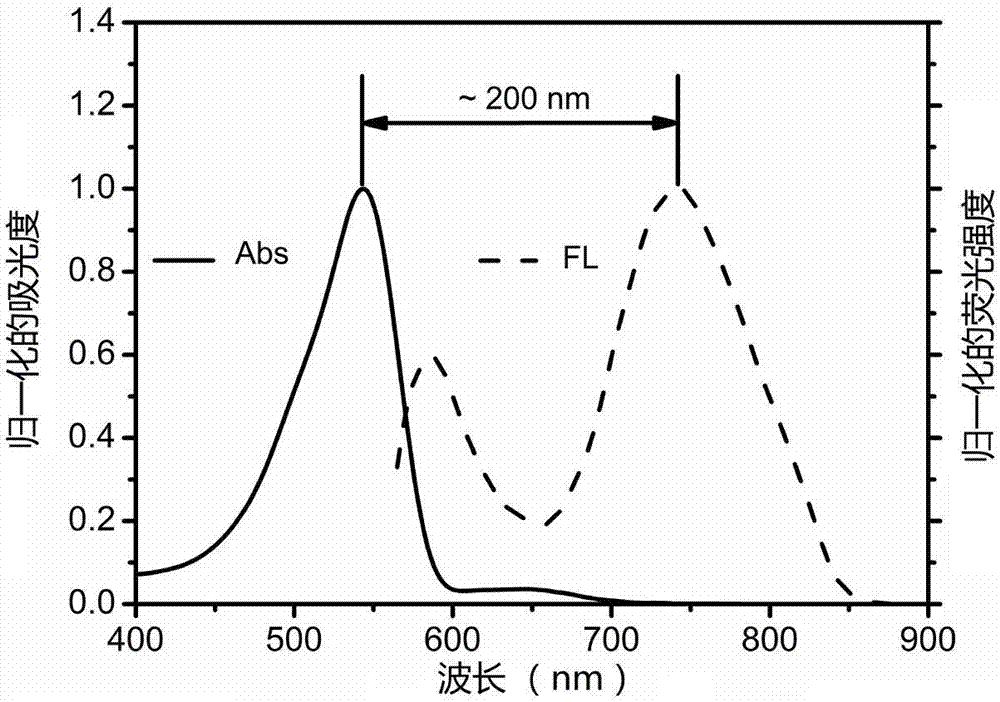
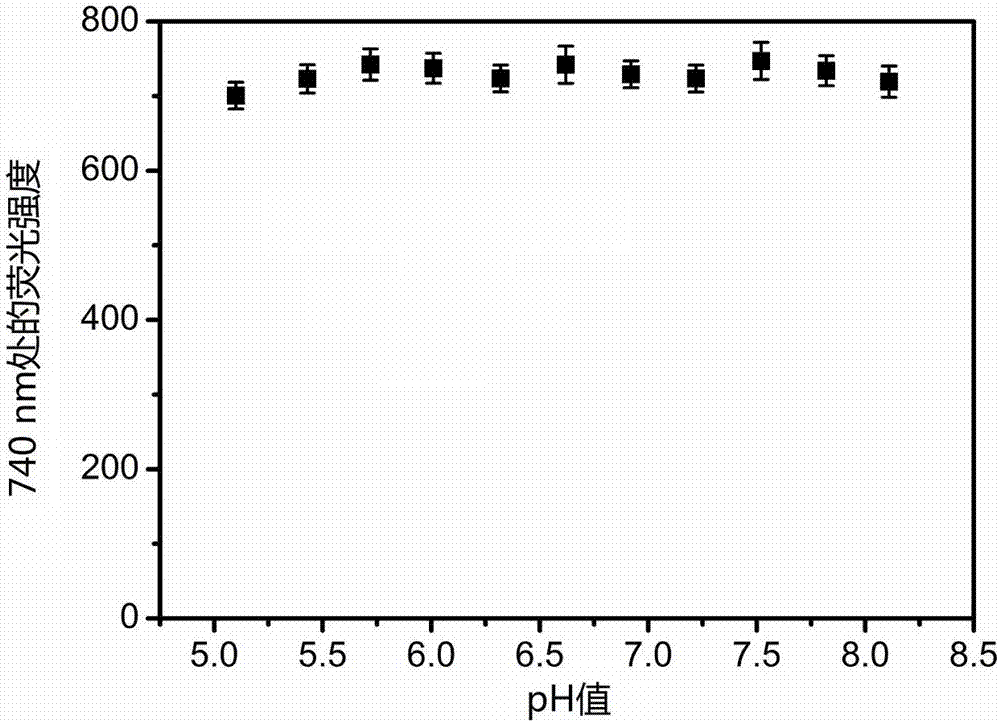
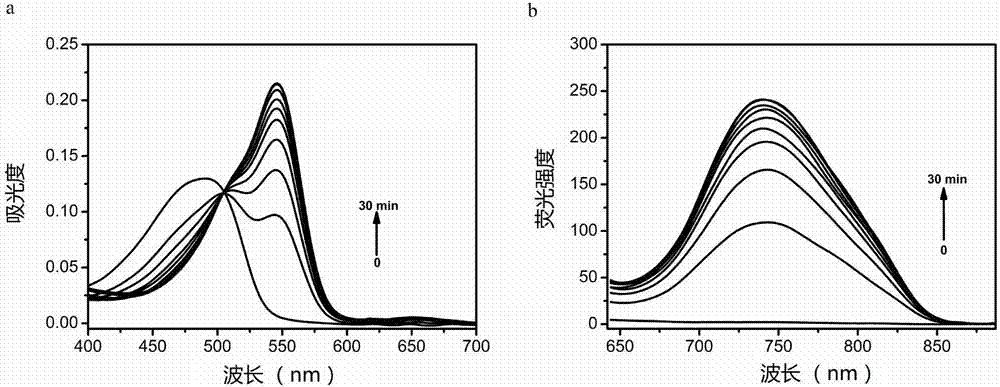
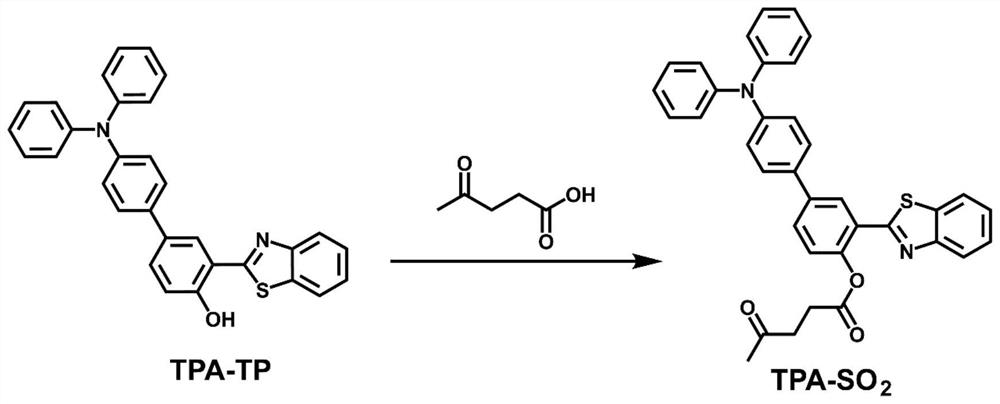
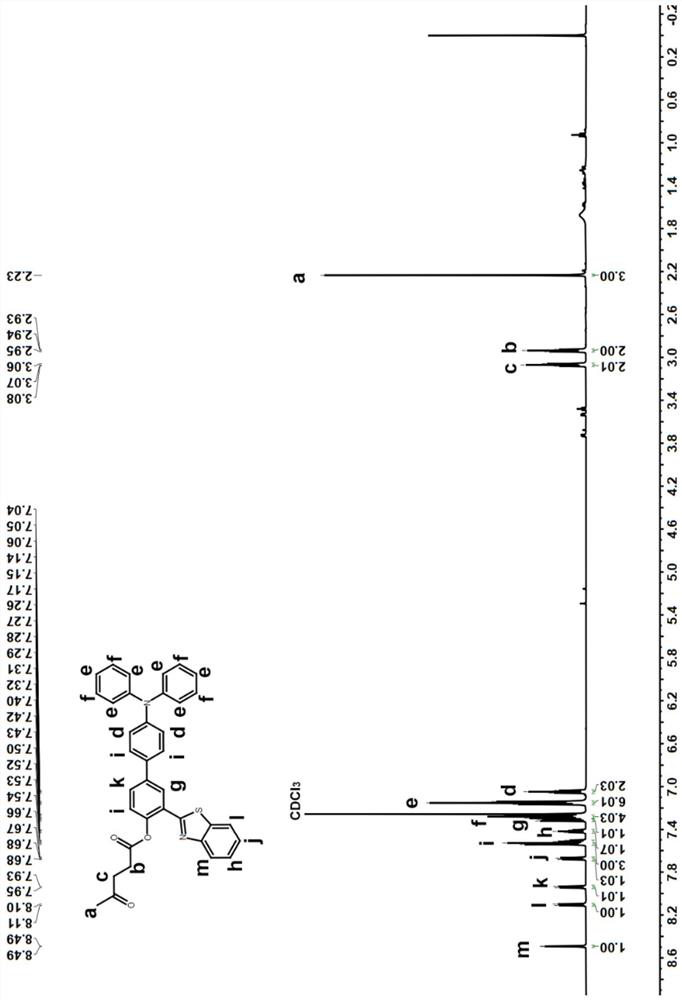
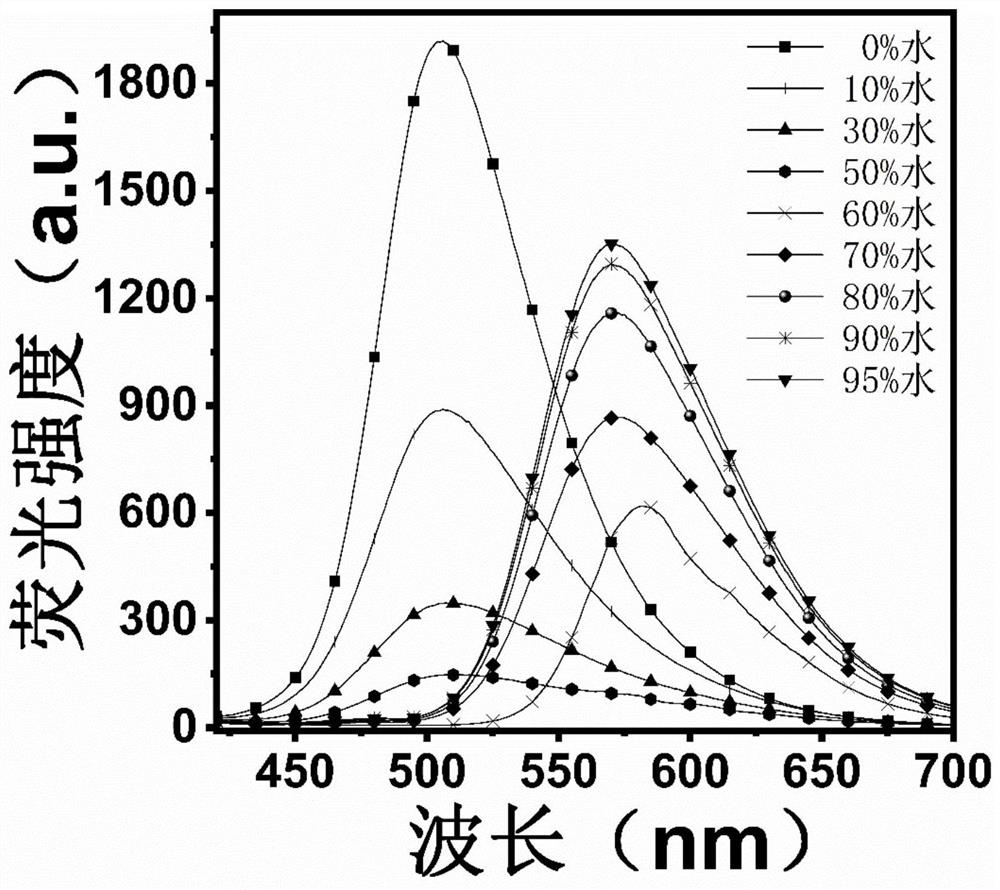
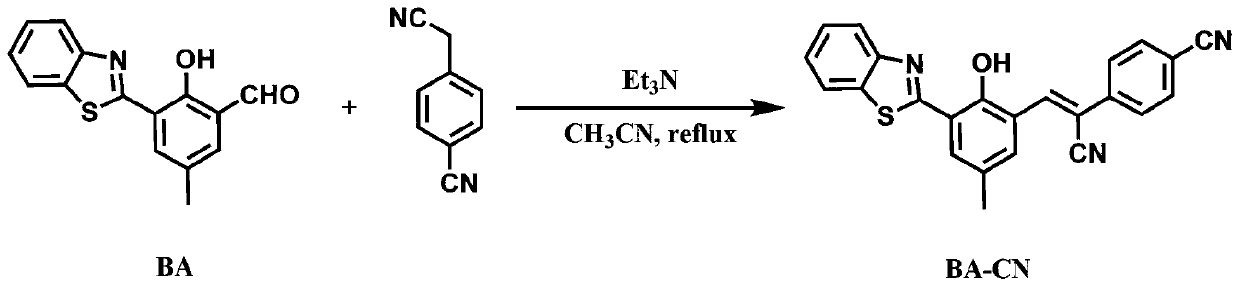
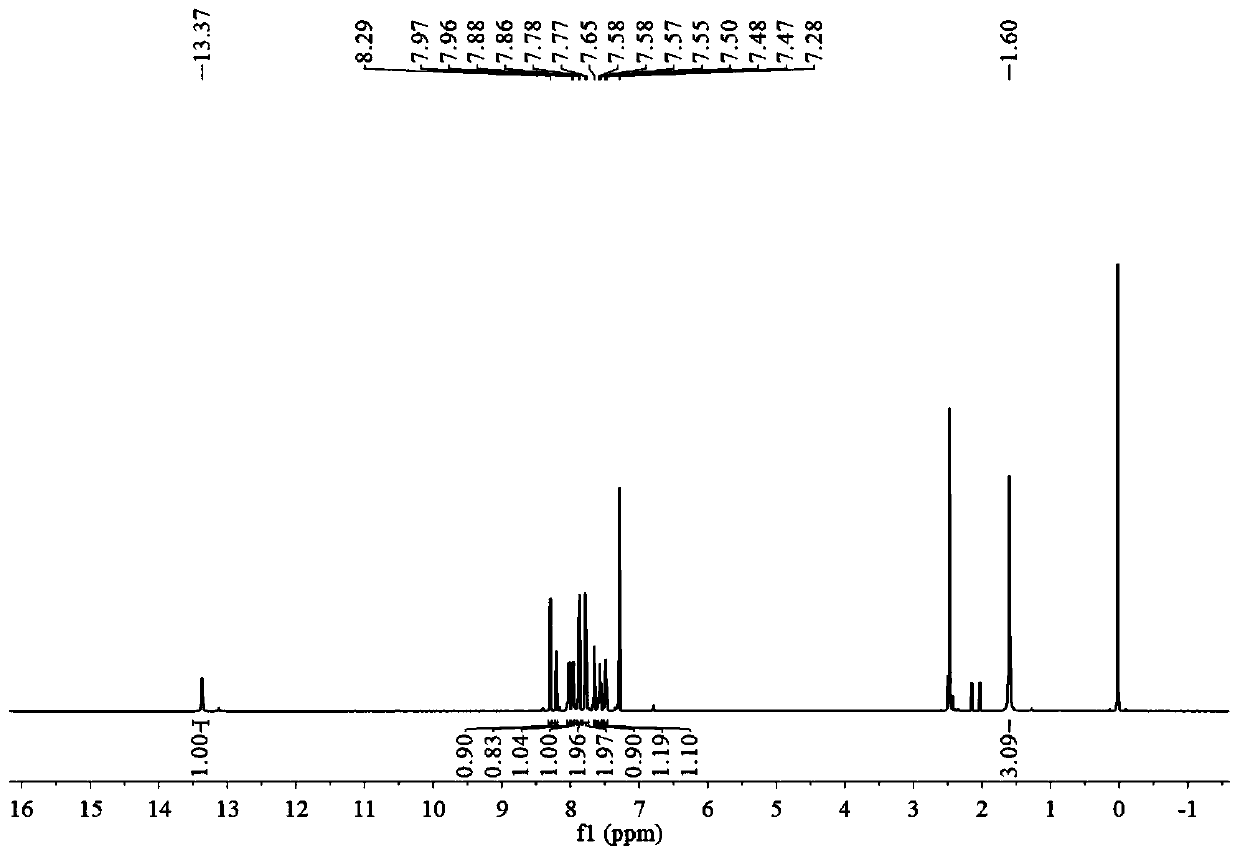
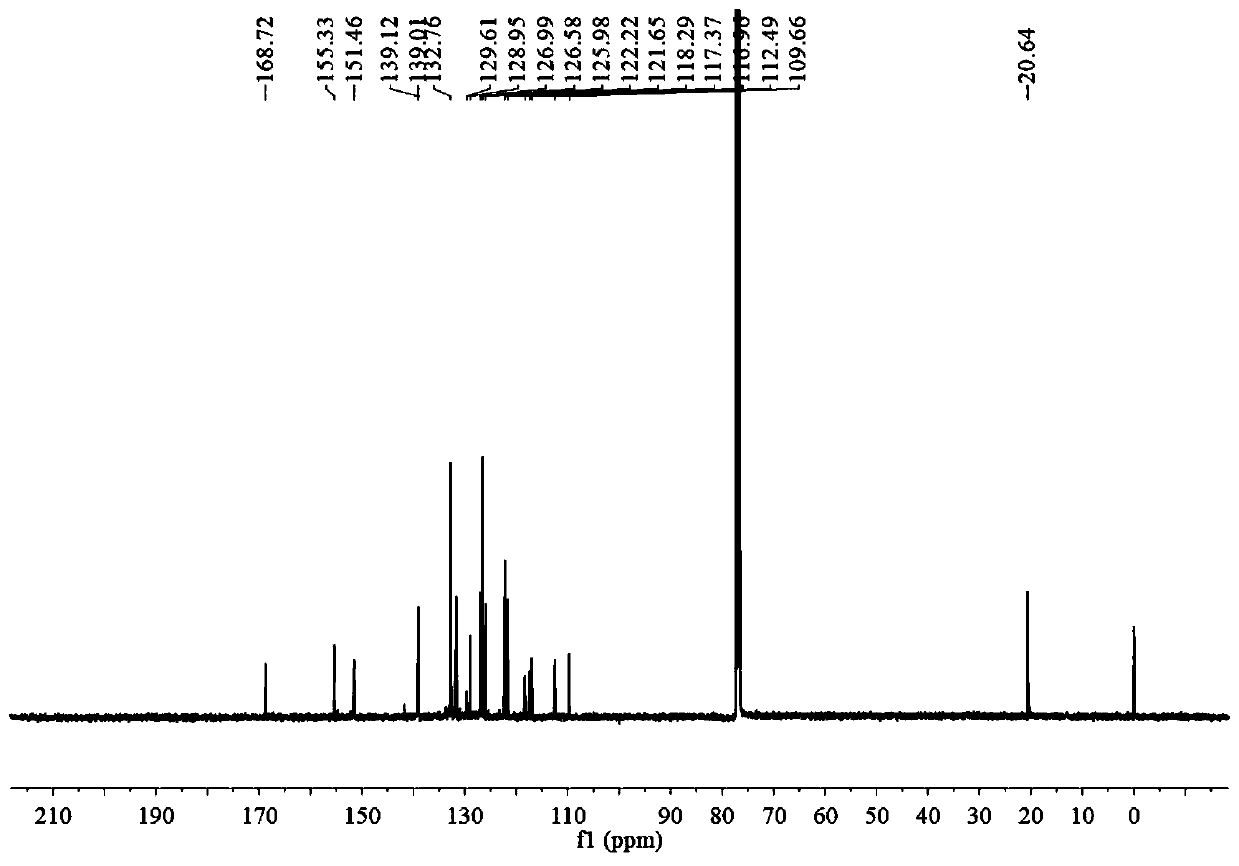
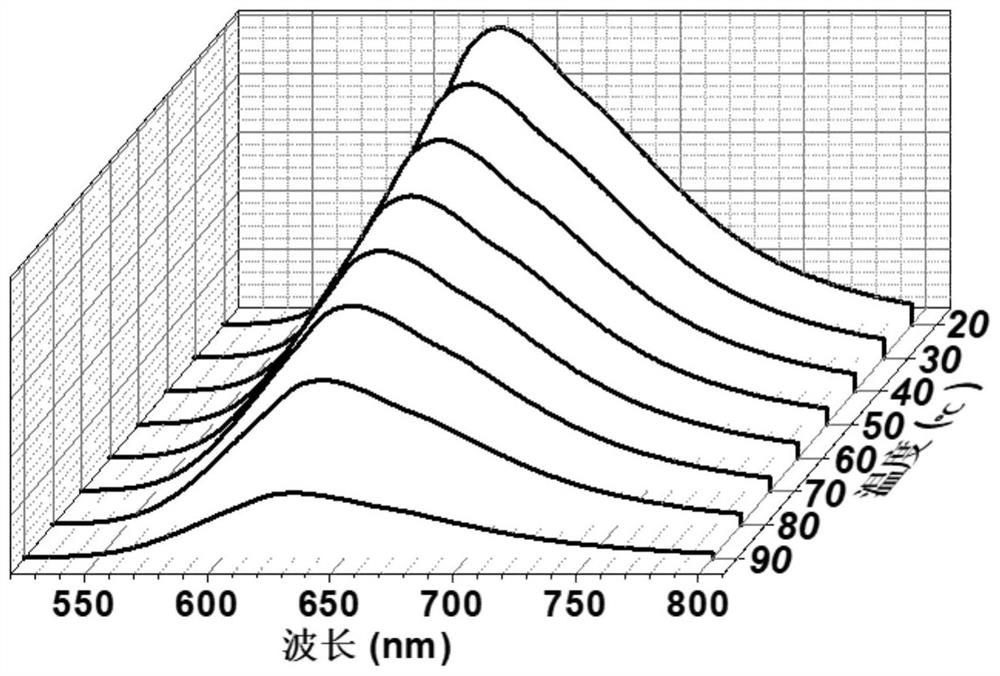
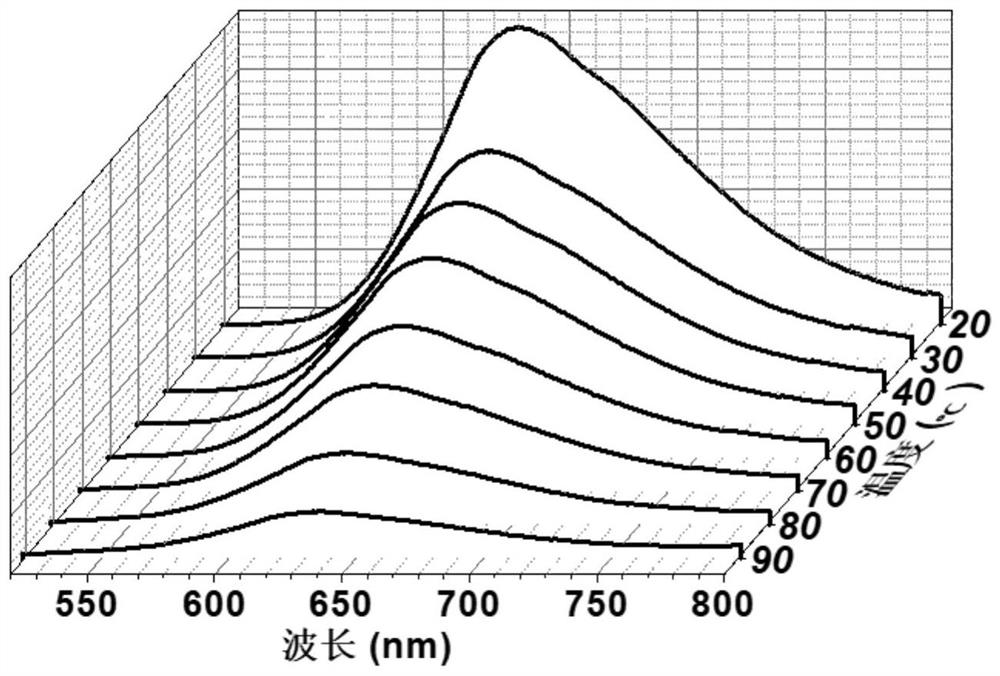
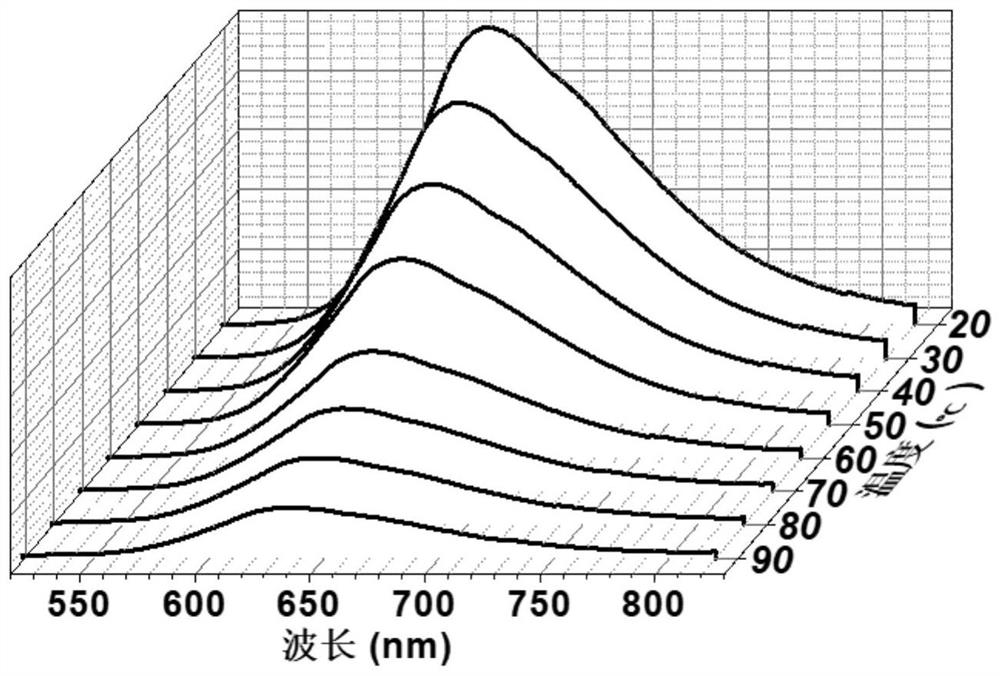
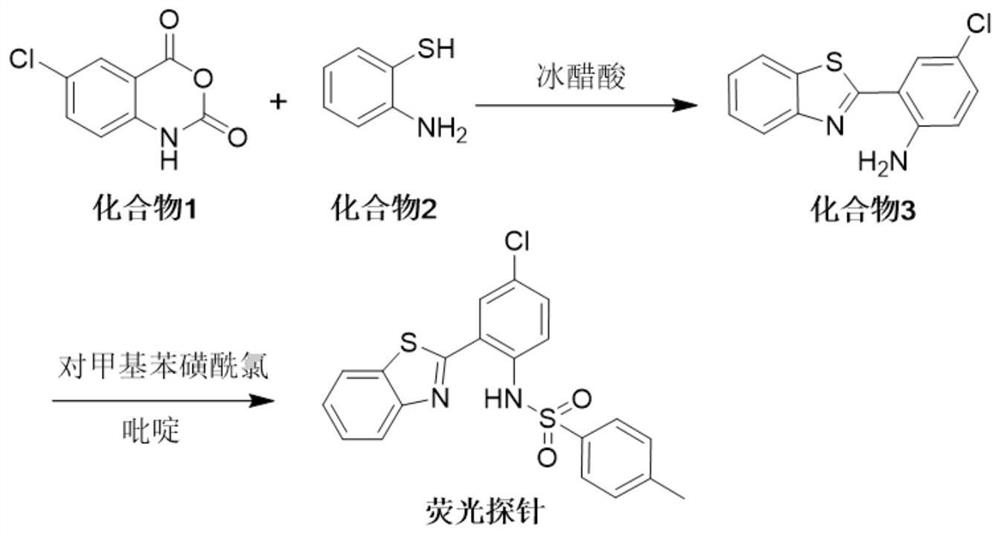
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
47 results about "Excited state intramolecular proton transfer" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
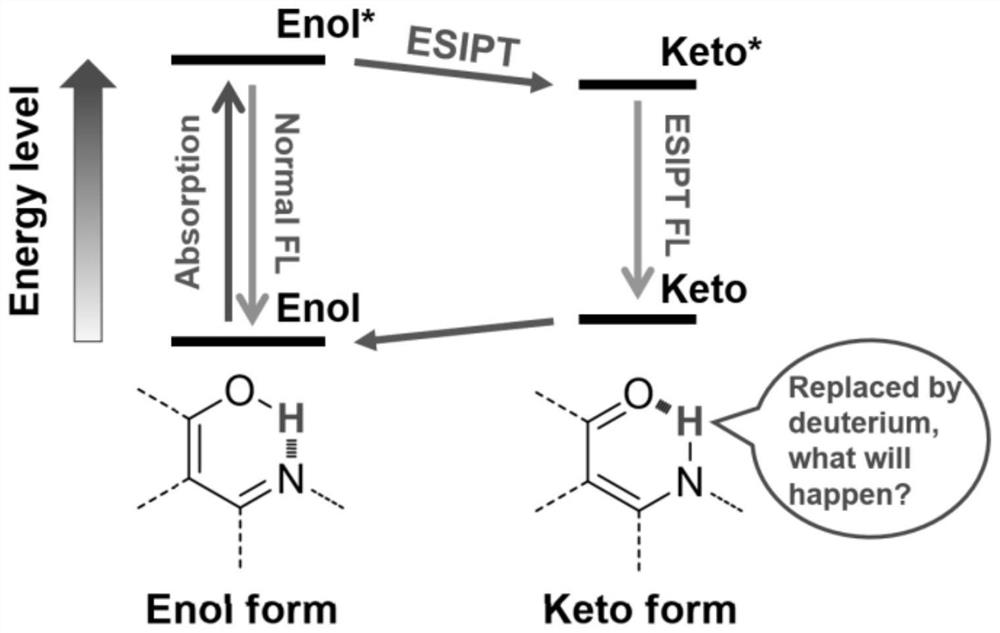
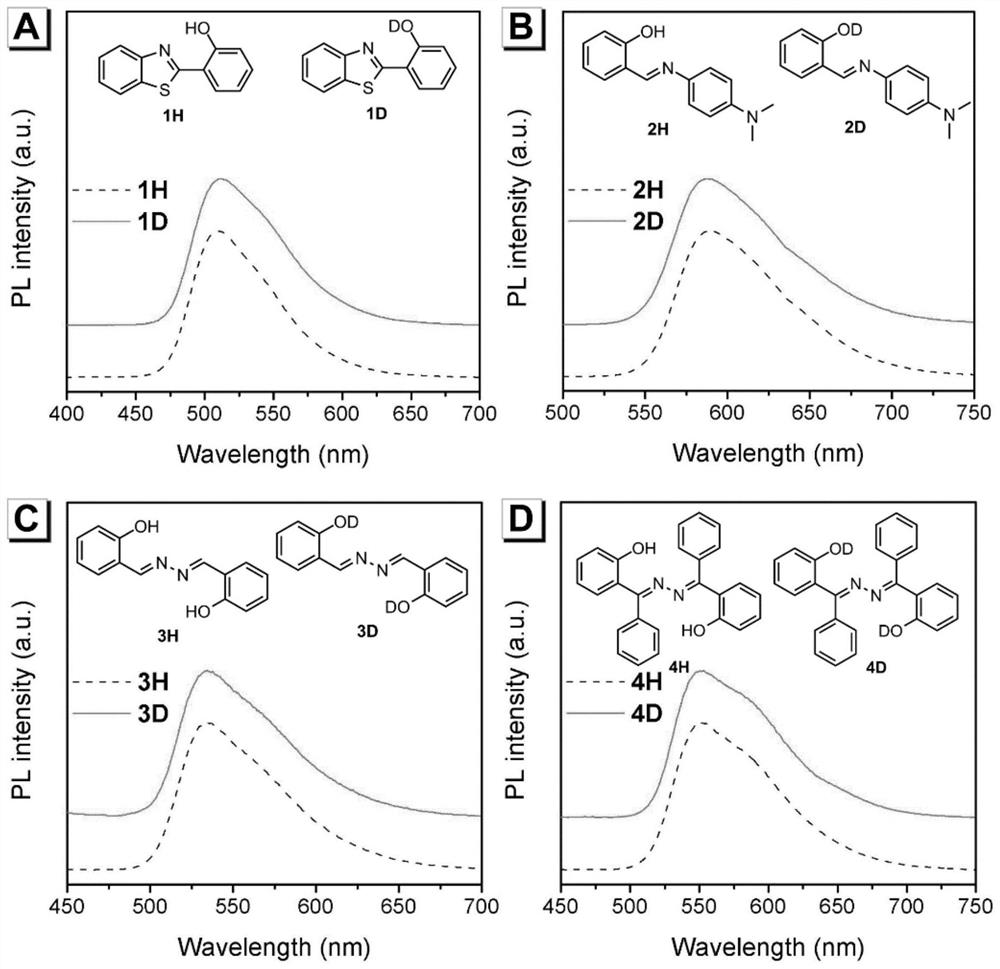
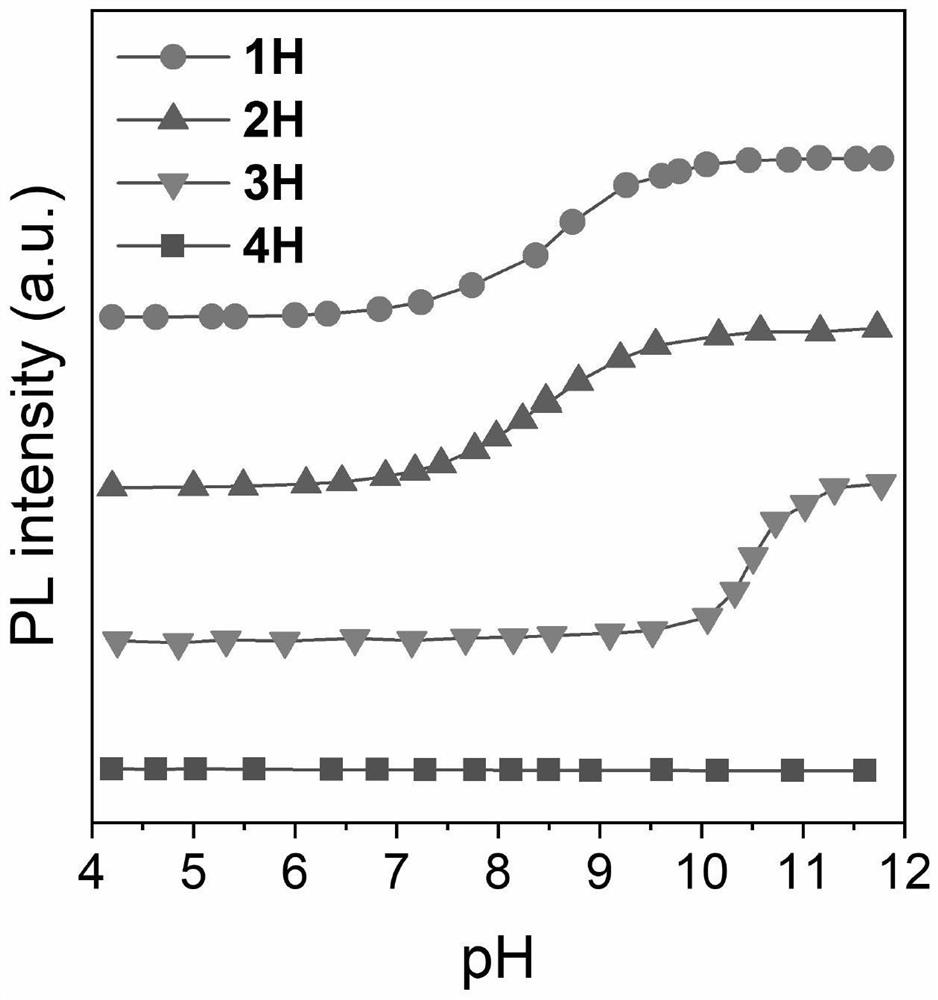
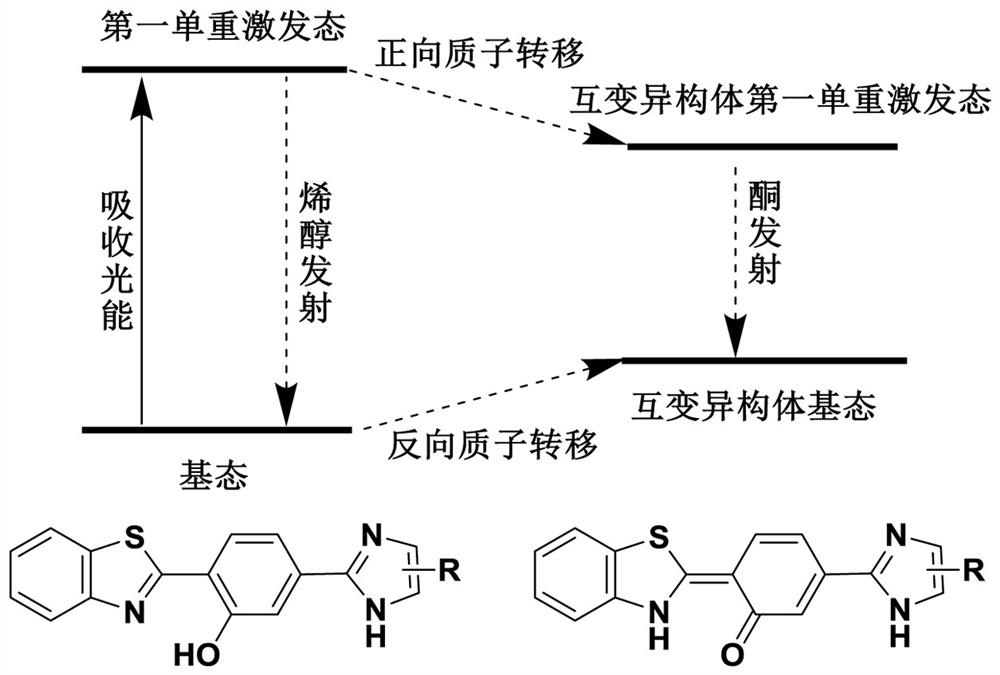
Excited state intramolecular proton transfer (ESIPT) is a process in which photoexcited molecules relax their energy through tautomerization by transfer of protons. Some kinds of molecules could have different minimum-energy tautomers in different electronic states, and if the molecular structure of minimum-energy tautomer in the excited state is proton-transferred geometry between neighboring atoms, proton transfer in excited state can occur. The tautomerization often takes the form of keto-enol tautomerism.
Synthesis method and application of ratiometric fluorescent molecular probe for simultaneously detecting fluorine ion and sulfite radical
InactiveCN104610955AHigh sensitivityGood optical performanceGroup 4/14 element organic compoundsFluorescence/phosphorescenceSynthesis methodsPhotochemistry
The invention relates to a synthesis method and application of a ratiometric fluorescent molecular probe for simultaneously detecting a fluorine ion and a sulfite radical. The ratiometric fluorescent molecular probe adopts a 2-(2-hydroxyphenyl)benzothiazole derivative as a matrix structure, and detects the fluorine ion and the sulfite radical based on excited-state intramolecular proton transfer (ESIPT) and intramolecular charge transfer (ICT) mechanisms, respectively. The probe has a maximum emission wavelength of 498 nm in an acetonitrile solution with a concentration of 80%, when the fluorine ion is added, the fluorescence spectrum of the probe has a red shift of 136 nm; and when the sulfite radical is added, the fluorescence spectrum of the probe has a blue shift of 127 nm. The differentiated detection of the two ions can be realized by the fact that the fluorescence spectrum of the probe has an obvious red shift or blue shift after the fluorine ion or sulfite radical is added, respectively, showing different fluorescence response signals. The inventive fluorescent probe has the advantages of simple operation, mild reaction conditions, easy purification, high synthesis yield, good selectivity, high sensitivity and stable optical performances. At the same time, the design and synthesis of the fluorescent probe provide an important foundation for development of multi-functional fluorescent probes in the future.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Fluorescent probe for specially identifying bivalent copper ions in water phase and application thereof
InactiveCN104774607AHigh fluorescence quantum yieldOrganic chemistryFluorescence/phosphorescenceChemical structureStructural formula
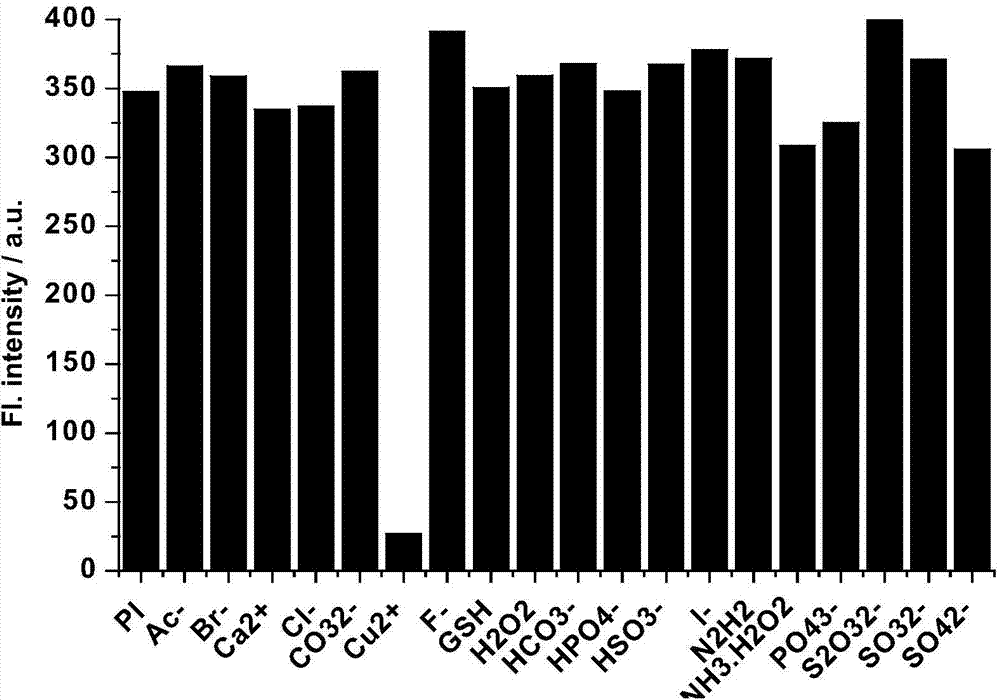
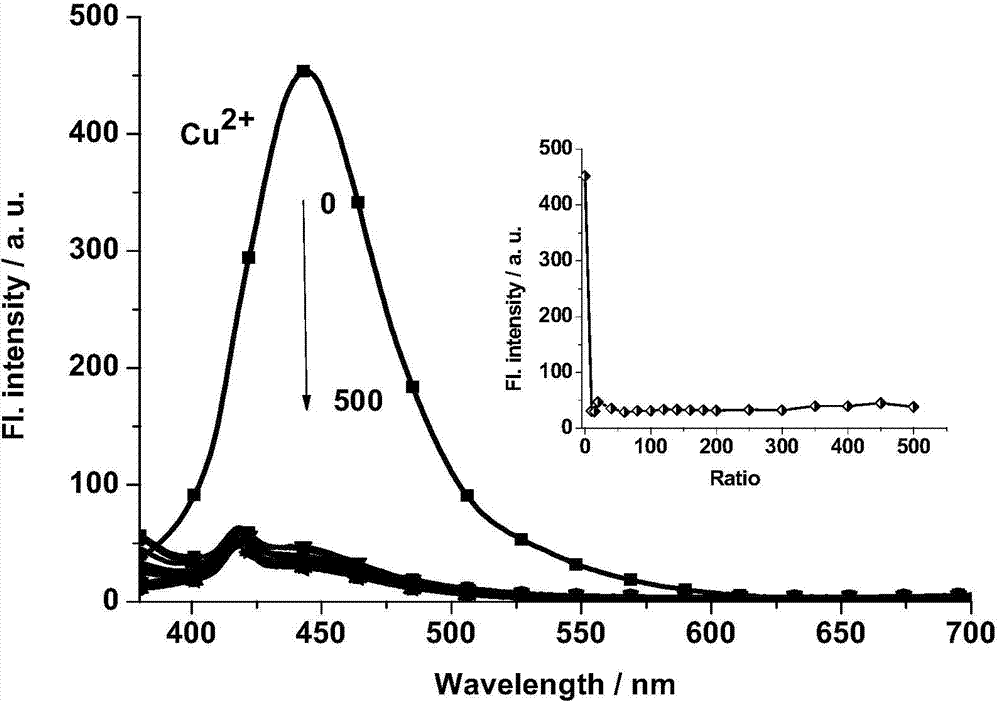
The invention discloses a fluorescent probe suitable for specially identifying bivalent copper ions in a water phase. The fluorescent probe is 3-hydroxy-4-(1H-phenanthrenequinone[9,10-d]imidazol-2-ethyl)phenyl-4-oxo-valerate (Pi for short) and has a chemical structural formula represented by a formula (1) (shown in the specification). The invention further discloses an application of the fluorescent probe for detecting whether water contains bivalent copper ions. An experiment proves that the copper ion fluorescent probe can be used for selectively detecting copper ions in the water phase based on an ESIPT (Excited-State Intramolecular Proton Transfer) mechanism and carrying out fluorescence quenching, and the fluorescence recovery is enhanced when meeting biological mercaptan. According to the characteristics of the fluorescent probe, the fluorescent probe has an outstanding advantage for detecting the heavy metal ion level in an environment and living bodies as well as a latent application value in the field of laser excitation fluorescence biomarkers.
Owner:UNIV OF JINAN
ESIPT (excited state intramolecular proton transfer) type fluorescent probe for biological mercaptan detection and application
ActiveCN107602502AThe synthesis steps are simpleEasy to operateOrganic chemistryFluorescence/phosphorescenceThiolDinitrophenyl
The invention discloses an ESIPT (excited state intramolecular proton transfer) type fluorescent probe for biological mercaptan detection. The ESIPT type fluorescent probe is 2-(4-(2,4-dinitrophenyl sulfonyloxy)-3-formylphenyl)-4-methylthiazole-5-ethyl carboxylate, wherein 2,4-dinitrophenyl sulfonyl serves as a recognition group, and 2-(3-formyl-4-hydroxyphenyl)-4-methylthiazole-2-ethyl formate serves as an information reporter group. A preparation method of the ESIPT type fluorescent probe is simple, the fluorescent probe can enter cells simply and rapidly and specifically bound with biological mercaptan in the cells, so that the fluorescent probe has an obvious fluorescence enhancement effect, can realize distinguishing by naked eyes, has high anti-interference capacity on common biological molecules, has quite efficient selectivity and can perform analysis through ultraviolet absorption and fluorescence spectrophotometry. The ESIPT type fluorescent probe is good in stability, can bestored and used for a long time, is applicable to growing environments of various living cells, can realize high-sensitivity detection of trace biological mercaptan in the cells, can be applied to cell and living imaging and has quite important application value.
Owner:ANHUI AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
2-(2'-hydroxyphenyl) benzoxazole compound containing substituent at 4-site and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN106749094AHigh yieldLarge Stokes shiftOrganic chemistrySolid-state devicesBenzoxazoleChemistry
The invention belongs to the technical field of organic semiconductor photoelectricity, and provides a 2-(2'-hydroxyphenyl) benzoxazole compound containing substituent at 4-site and a preparation method and application thereof. The general formula of the 2-(2'-hydroxyphenyl) benzoxazole compound containing the substituent at the 4-site is as shown in description, wherein X is S, O or NH, Ar is an aromatic hydrocarbon-containing conjugated structure unit. The compound is prepared from 2-(2'-4-bromophenol) benzoxazole and a polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon compound containing bromine through Suzuki reaction. The compound disclosed by the invention has a four energy level transition fluorescence property of excited-state molecular proton transfer compound, can be used as a luminescent material, and can be applied to an organic white-light diode device. The compound disclosed by the invention has the advantages of being large in Stokes shift, good in luminescent quantum efficiency, simple in preparation, and high in synthetic yield.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Micromolecular fluorescent probe taking 3-hydroxyflavone as fluorophore as well as preparation method and application of micromolecular fluorescent probe
ActiveCN110563685AEasy to useHigh selective responseOrganic chemistryFluorescence/phosphorescence3-HydroxyflavoneSynthesis methods
The invention discloses a small-molecule fluorescent probe taking 3-hydroxyflavone as a fluorophore and application of the small-molecule fluorescent probe. An excited state intramolecular proton transfer (ESIPT) strategy system is adopted in a DMSO / H2O (5: 1, v / v) solution, high-selectivity response to group IIIA metal ions is shown relative to other cations, green fluorescence is converted intoblue fluorescence, ultraviolet absorption peaks are subjected to red shift, and along with the increase of the concentrations of Ga, Al and In ions, the metal ions are strongly combined with the probe, so that the Ga, Al and In ions are accurately detected by a fluorescence technology, and endogenous and exogenous Ga, Al and In ions in living cells can be detected. Therefore, the method has a goodapplication prospect in the aspect of Ga, Al and In ion detection, and meanwhile, the synthesis method disclosed by the invention is simple and convenient to operate, and does not need harsh conditions.
Owner:WENZHOU MEDICAL UNIV
White-emitting compounds using excited-state intramolecular proton transfer, organic electroluminescent element and laser material using the same
InactiveUS20120046472A1Good reproducibilityImprove life characteristicsOrganic chemistryLaser active region structureChemical compoundExcited state intramolecular proton transfer
Provided are a white-emitting monomolecular compound using excited-state intramolecular proton transfer (ESIPT) characteristics, and an organic electroluminescence device and a laser device comprising same. The white-emitting monomolecular compound according to the present invention is prepared by covalently bonding at least two types of molecules which produce different colors and have excited-state intramolecular proton transfer (ESIPT) characteristics. The white-emitting monomolecular compound according to the present invention achieves white luminescence irrespective of the concentration thereof and of the state of the materials thereof, and therefore can be used in a variety of fields including an organic electroluminescence device and a laser device.
Owner:DONGWOO FINE CHEM CO LTD +1
Fluorescent probe for detecting hydrazine or amine substance gas and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN106929002ASimple structureEasy to synthesizeOrganic chemistryFluorescence/phosphorescenceChemical compoundExcited state intramolecular proton transfer
The invention relates to a quinazolinone compound. The compound does not laminate in a solid state, and in the effects of hydrazine or amine substance gas, aminolysis or hydrolysis reaction of ester function group-O-C(O)-R3 is carried out, hydroxy is released, interaction between O-H of hydroxy and N of C=N in a quinazolinone ring is carried out, and an intramolecular six-membered ring hydrogen bond is formed; because of intramolecular rotation limit and excitation state intramolecular proton transfer mechanism, strong fluorescence is emit in a solid state. The compound can be used as a fluorescent probe for detecting hydrazine or amine substance gas.
Owner:北京知元科技有限公司 +1
Aggregation-induced emission probe based on quinazolinones compound as well as preparation method and application of aggregation-induced emission probe
ActiveCN106632088ASimple structureEasy to synthesizeOrganic chemistryInksAggregation-induced emissionExcited state intramolecular proton transfer
The invention relates to a quinazolinones compound. The compound does not emit light under a solid state; however, an ester functional group -O-C(O)-R3 is subjected to ammonolysis reaction under the action of ammonia gas to realize hydroxyl; O-H of the hydroxyl and N of C=N in a quinazolinone ring have a mutual effect to form an intramolecular six-membered ring hydrogen bond; strong fluorescent light is emitted under the solid state due to an intramolecular rotation restricted and excited-state intramolecular proton transferring mechanism. The compound can be used as a fluorescent probe and is used for detecting the ammonia gas; furthermore, the compound can be used as a detection reagent for detecting the corrosion degree of foods and an invisible ink material with an AND logic gate.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Cd<2+> fluorescence probe with AIE (aggregation-induced emission) property as well as preparation method and application of Cd<2+> fluorescence probe
ActiveCN110003095AHigh yieldEasy to operateOrganic chemistryFluorescence/phosphorescenceAggregation-induced emissionExcited state intramolecular proton transfer
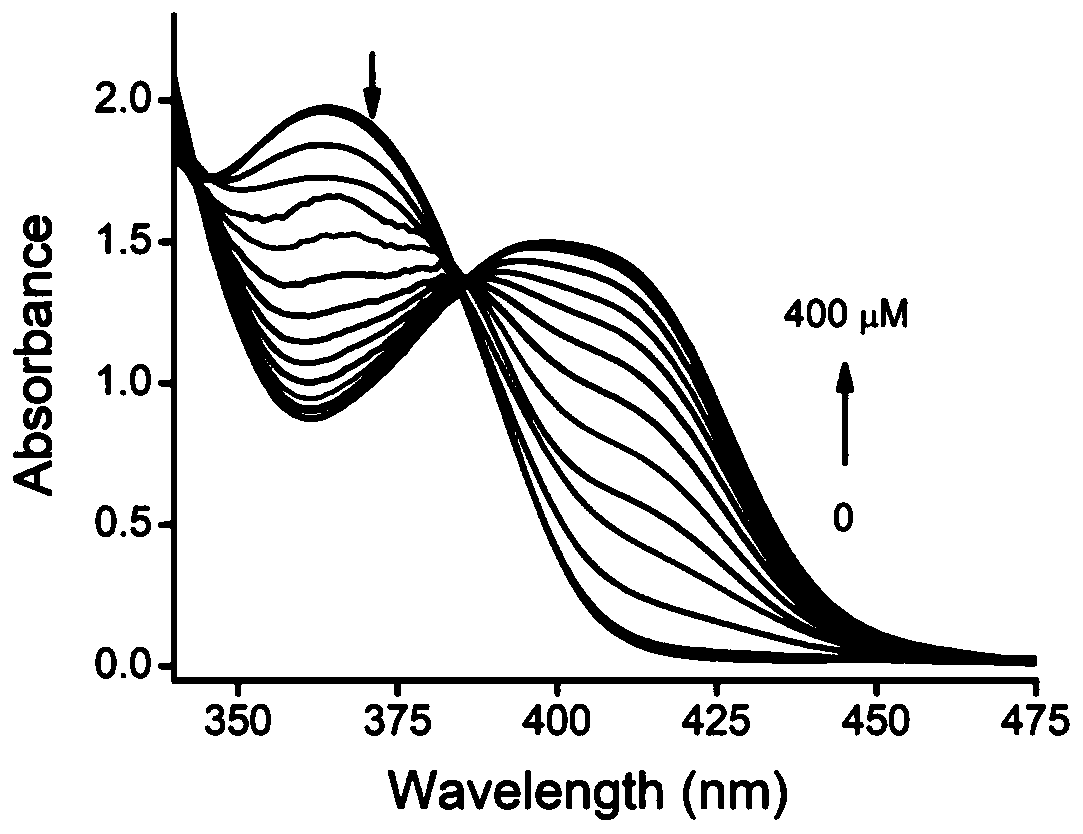
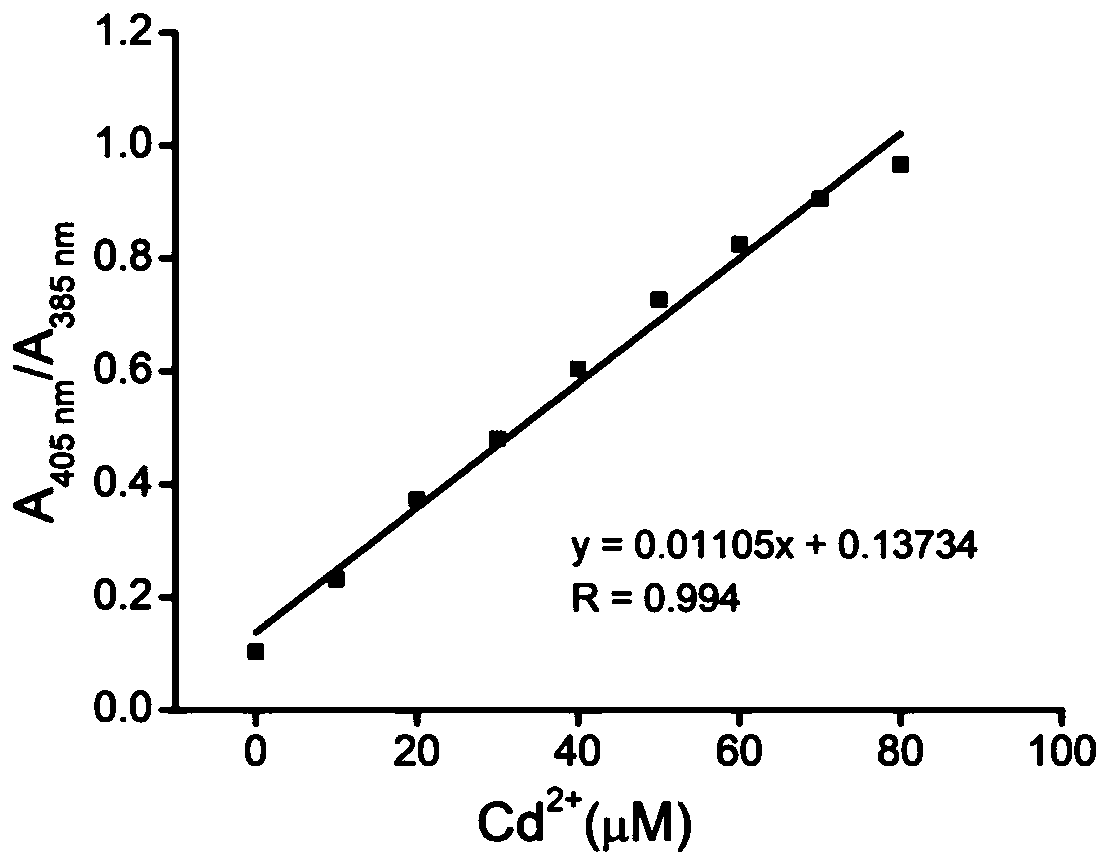
The invention discloses a Cd<2+> fluorescence probe with an AIE (aggregation-induced emission) property as well as a preparation method and an application of the Cd<2+> fluorescence probe. 2-hydroxy-5-methylisophthalaldehyde and 2-aminopyridine react in the ratio of amount of substances being 1:2, and the Cd<2+> fluorescence probe with the AIE property is prepared at a low cost. In a CH3CN-H2O(95:5,v / v) solution, the fluorescence probe has ESIPT (excited state intramolecular proton transfer) property, during high-selectivity and high-sensitivity detection of Cd<2+>, the emission peak has blueshift, and fluorescence turns blue green from yellow. Besides, the fluorescence probe is successfully applied to quantitative detection of Cd<2+> in aqueous solutions.
Owner:SHAANXI UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Novel compound, and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN111825634ALong emission wavelengthExcellent fluorescence quantum yieldOrganic chemistryFluorescence/phosphorescenceBenzoxazoleExcited state intramolecular proton transfer
The invention discloses a novel compound and a preparation method and application thereof. Specifically, the invention provides a 2-(2 '-hydroxyphenyl) benzoxazole compound which has an excited stateintramolecular proton transfer and aggregation-induced emission characteristic and has a skeleton structure as shown in a general formula I. In the general formula I, R2 is independently selected fromhydrogen, an aldehyde group or an electron-withdrawing unit conjugated with a benzene ring through double bonds; the invention provides a preparation method of a 2-(2 '-hydroxyphenyl) benzoxazole compound. In addition, the invention also provides an application of the 2-(2 '-hydroxyphenyl) benzoxazole compound containing the nitrogen positive ion structure in living cell mitochondrion imaging. The 2-(2 '-hydroxyphenyl) benzoxazole compound with excited state intramolecular proton transfer and aggregation-induced emission effects has a good application prospect in the fields of photoelectricity, sensing, biomedicine and the like.
Owner:XIEHE HOSPITAL ATTACHED TO TONGJI MEDICAL COLLEGE HUAZHONG SCI & TECH UNIV
Excited state intramolecular proton transfer regulation based fluorescence probe, and synthetic method and applications thereof
ActiveCN103333679AEasy to separate and purifyRaw materials are easy to obtainOrganic chemistryFluorescence/phosphorescenceSolubilitySynthesis methods
The invention discloses an excited state intramolecular proton transfer regulation based fluorescence probe, and a synthetic method and applications thereof. The structural formula of the fluorescence probe is shown in the patent specification of the invention. Specific synthetic steps are as following: DMF is taken as a solvent; molar ratio of N-(2-(1H-benzimidazolyl)phenyl)-2-chloroacetamide to picolylamine, which are used as raw materials, is 1:1.5-1.3; the mixture is stirred at room temperature for 5 to 10 h; the mixture is diluted with distilled water, pH value of the mixture is adjusted to 6.5 to 7.5 with dilute hydrochloric acid, the mixture is filtered, produced sediment is collected and is recrystallized with acetonitrile, so that the fluorescence probe N-(2-(1H-benzimidazolyl)phenyl)-2-(2- picolylamine)acetamide is obtained. Advantages are that: synthesis is simple; water solubility is high; the fluorescence probe is friendly to the environment, and can be used for monitoring, analyzing and tracking Zn<2+> and S<2-> in water environment system and biological cell system; sensitivity is high, and anti-interference capability is excellent.
Owner:BOHAI UNIV
Phenanthroimidazole derivative with ESIPT (excited-state intramolecular proton transfer) and AIE (aggregation-induced emission) properties and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN109134382AWith ESIPTHas AIE effectOrganic chemistryFluorescence/phosphorescenceAggregation-induced emissionExcited state intramolecular proton transfer
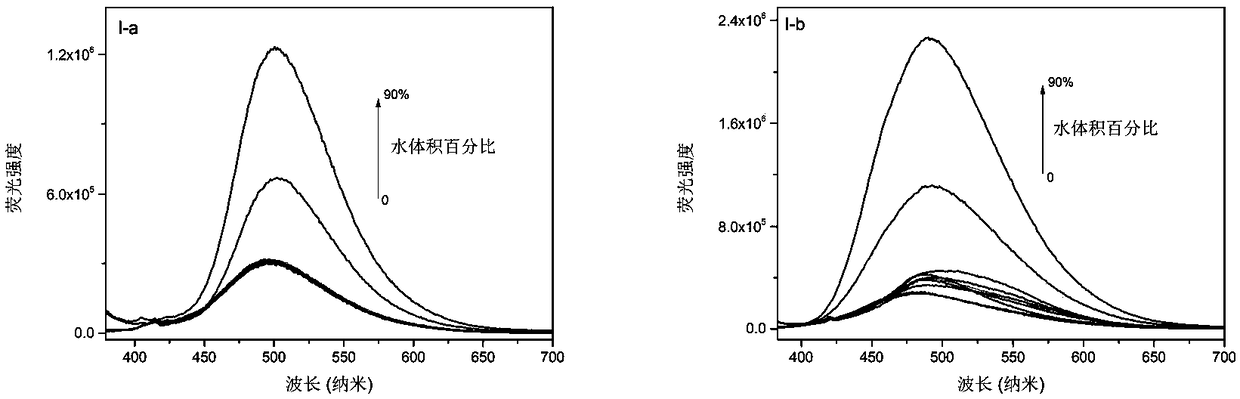
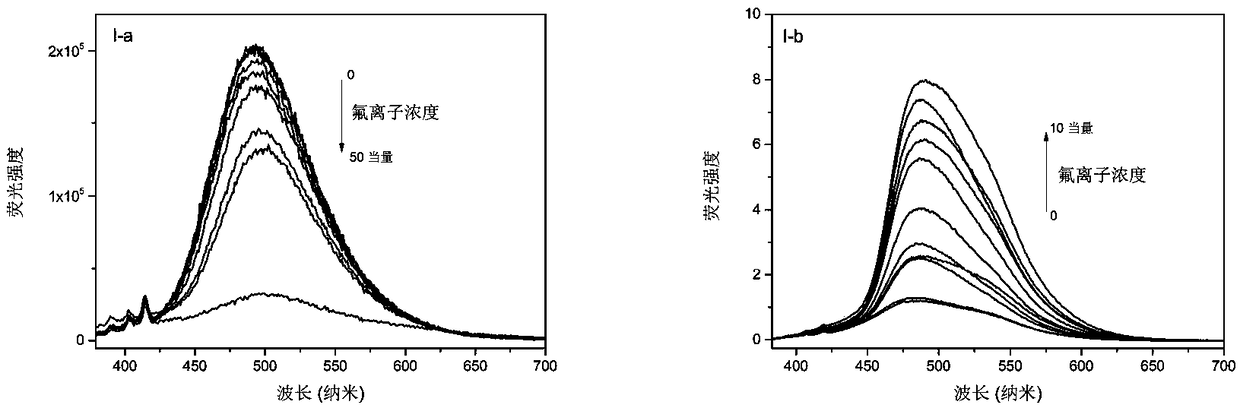
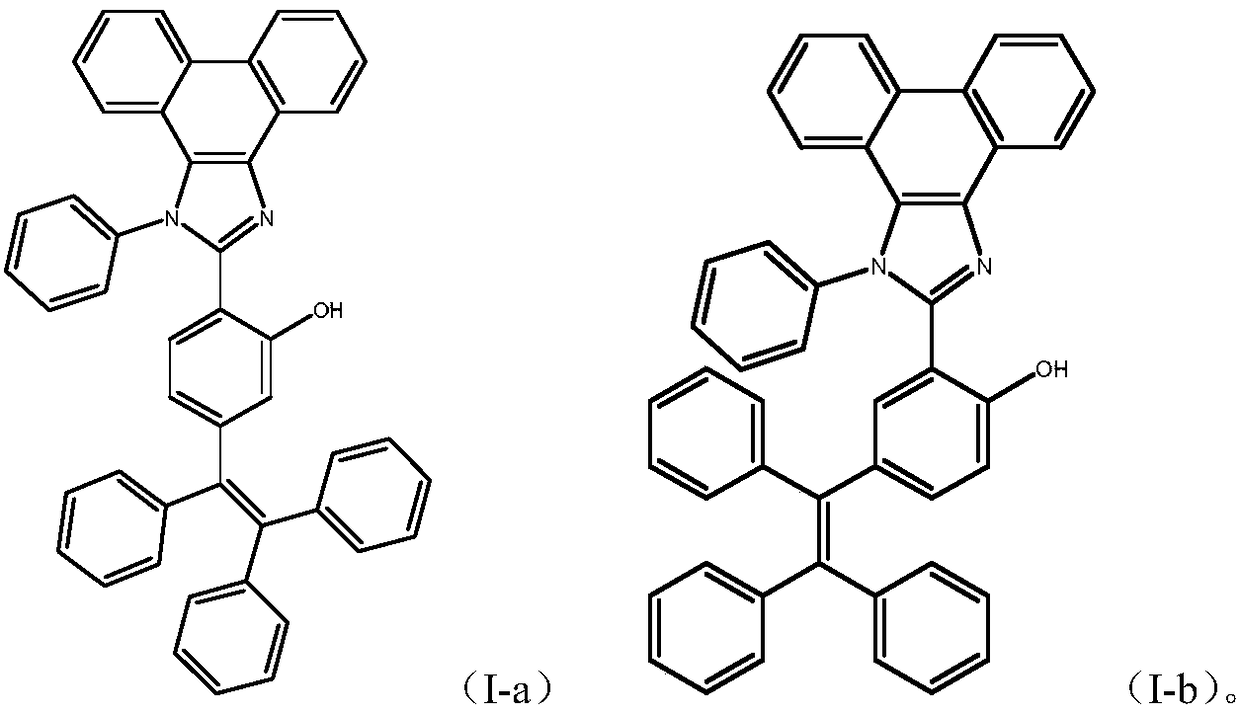
The invention provides a phenanthroimidazole derivative with ESIPT (excited-state intramolecular proton transfer) and AIE (aggregation-induced emission) properties, shown as formula (I-a) or (I-b) which is shown in the description, and a preparation method and application thereof. The phenanthroimidazole derivative synthesized by the preparation method has both ESIPT and AIE effects. The phenanthroimidazole derivative herein is suitable for fluorine ion detection and is a potential fluorescence sensor material.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Method for detecting content of heavy water by utilizing aggregation-induced emission molecules
ActiveCN113030056AAccurate identificationQuick identificationGeneral water supply conservationFluorescence/phosphorescenceChemical compoundExcited state intramolecular proton transfer
The invention provides a method for detecting the content of heavy water by utilizing aggregation-induced emission molecules, which comprises the following steps: preparing a compound with intramolecular hydrogen bonds by utilizing a condensation reaction of an amino compound and a carbonyl compound, and preparing a stock solution with the concentration of 10<-3> mol / L from the compound which is the aggregation-induced emission molecules with excited-state intramolecular proton transfer property; and respectively adding the stock solution into D2O / H2O mixed standard water samples with different heavy water contents and a water sample to be detected, determining the fluorescence lifetime by using a transient fluorescence spectrometer to obtain a linear relationship between the fluorescence lifetime and the heavy water content, and calculating the heavy water content of the water sample to be detected. The invention provides a novel heavy water detection technology which overcomes many defects in the traditional D2O detection means. According to the technology, after active hydrogen in AIE molecules with excited-state intramolecular proton transfer property is substituted by deuterium hydrogen, the obvious change of fluorescence lifetime is used as a signal for heavy water detection and is used for distinguishing D2O and H2O signals.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU UNIV
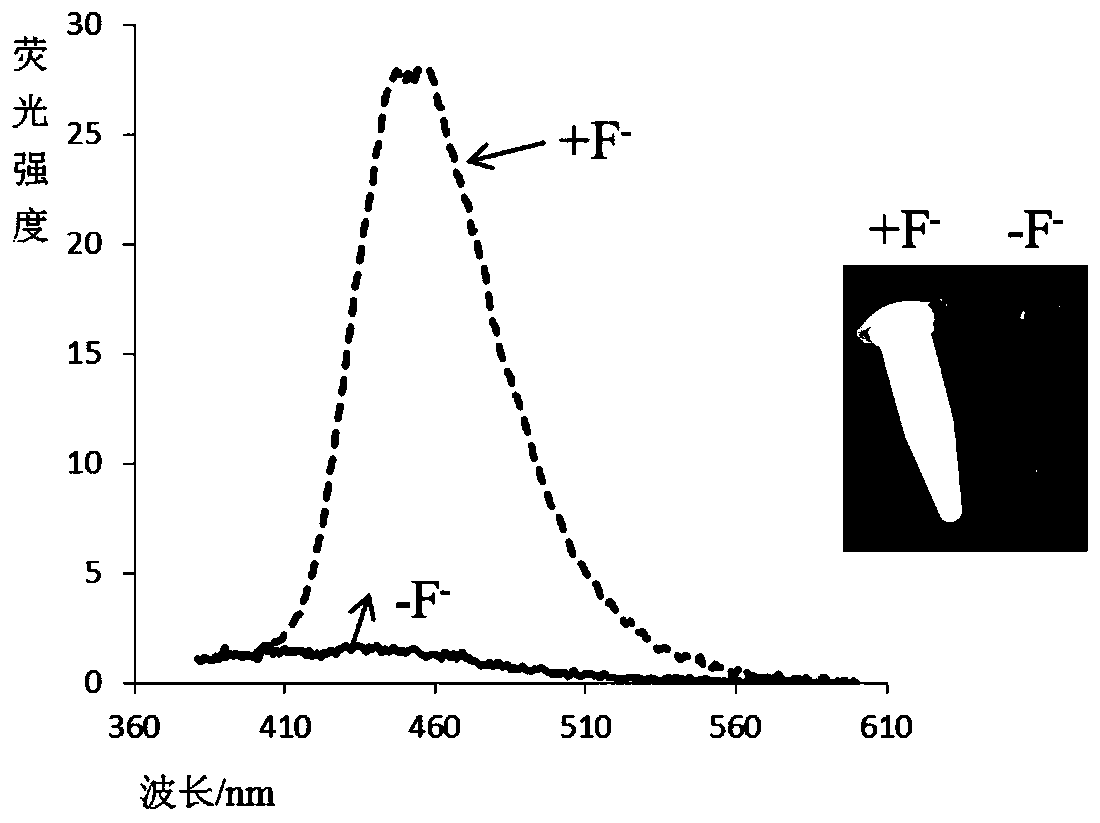
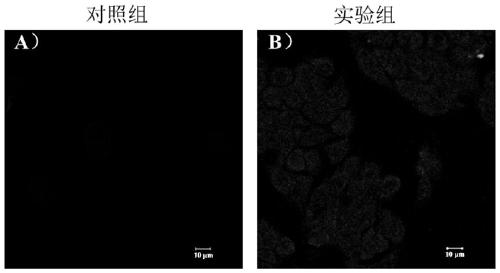
Fluorescent probe for detecting fluorine ions in living cells and method for preparing fluorescent probe
InactiveCN107365326AHigh yieldThe synthesis method is simpleGroup 4/14 element organic compoundsFluorescence/phosphorescenceCell membraneUltraviolet
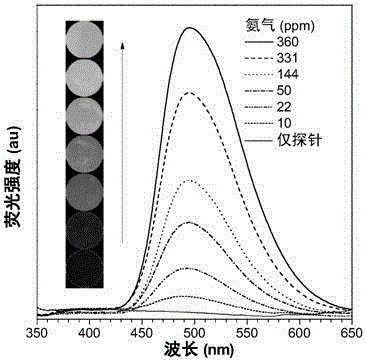
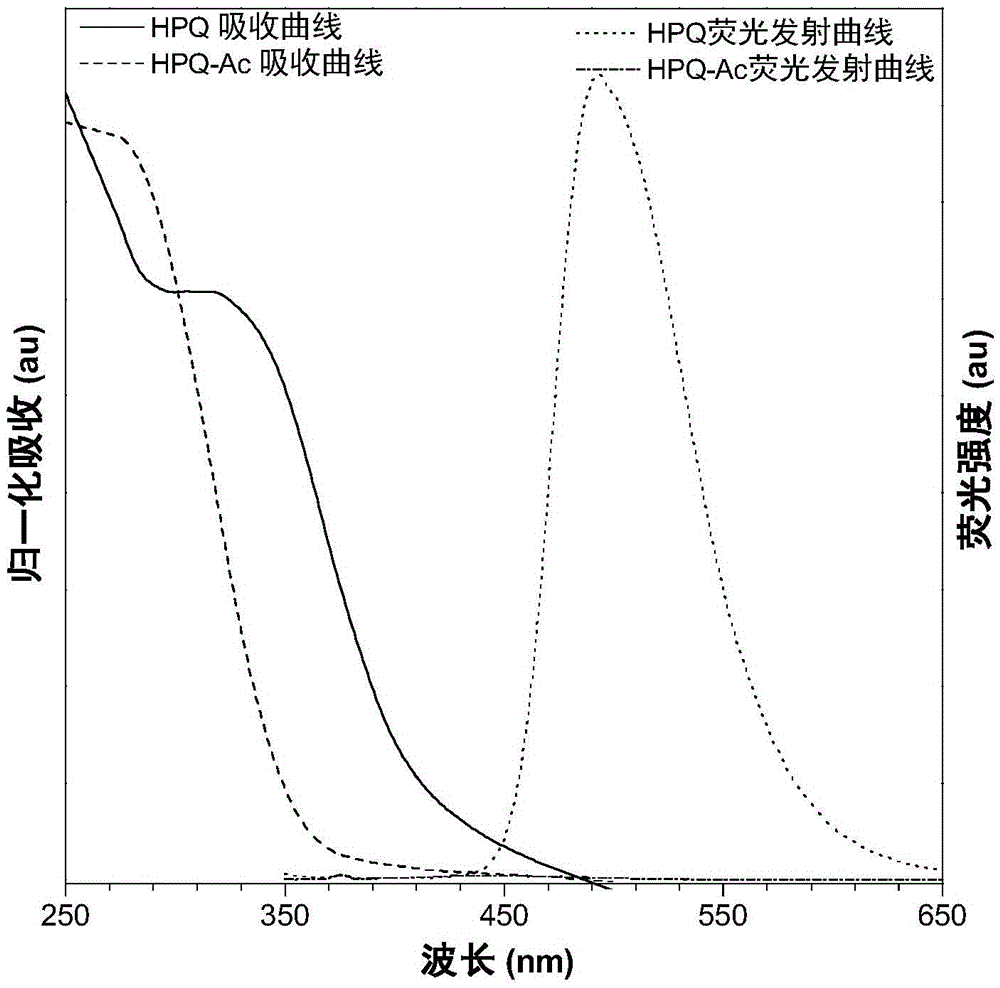
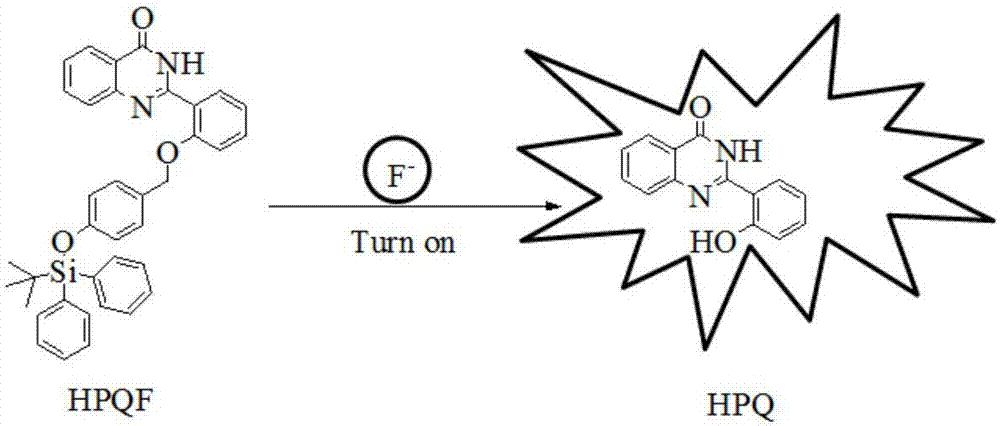
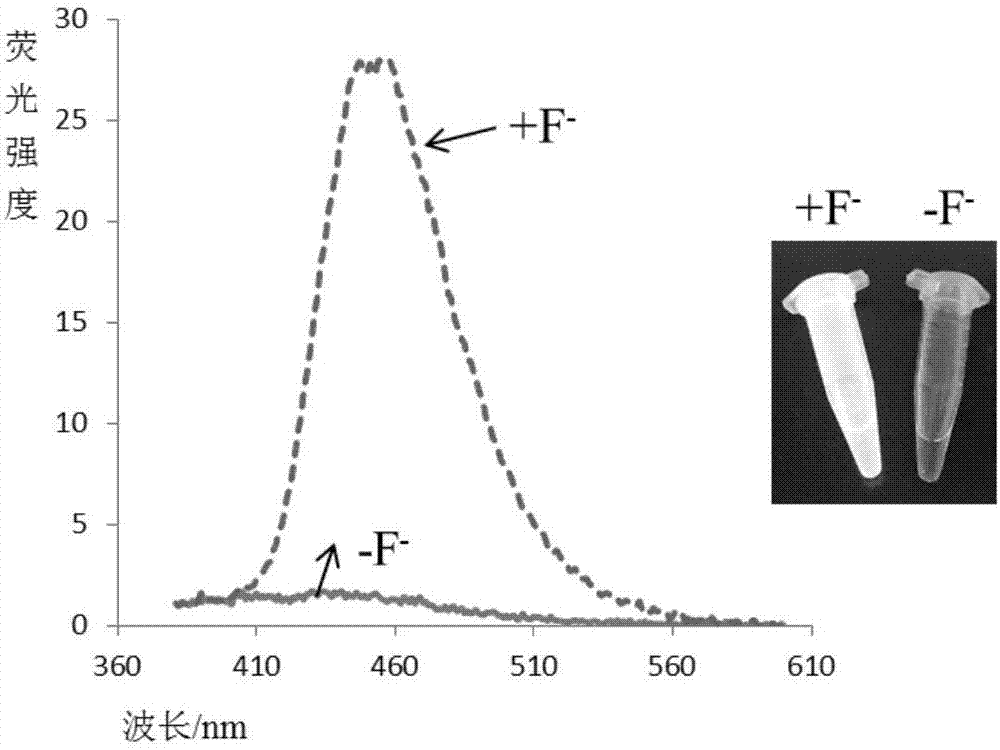
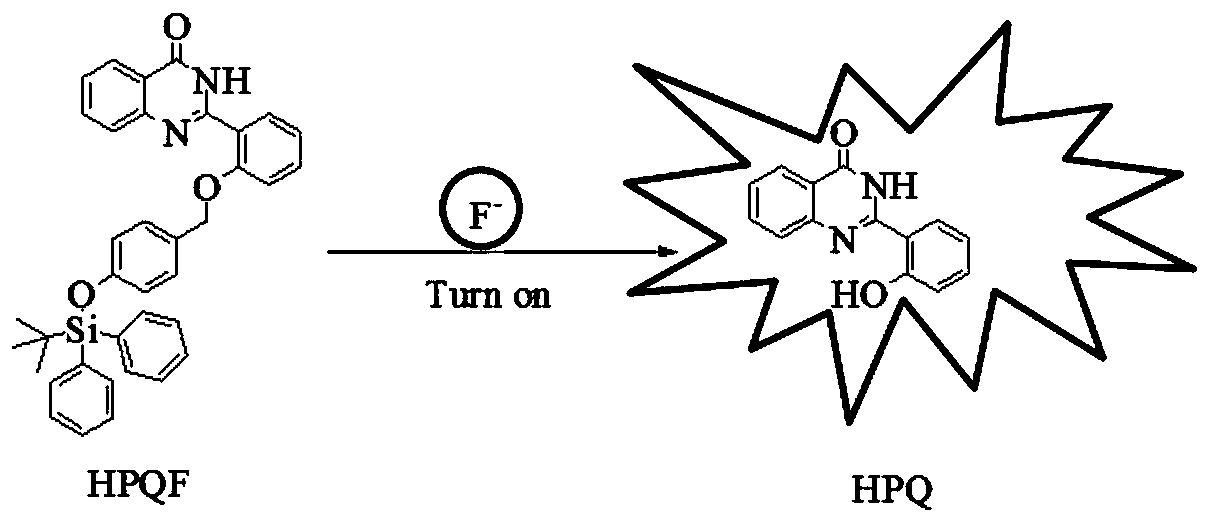
The invention discloses a fluorescent probe for detecting fluorine ions in living cells and a method for preparing the fluorescent probe. The fluorescent probe is of a structure shown as a formula I. The fluorescent probe and the method have the advantages that the fluorescent probe is nearly free of optional fluorescent light, but Si-O bonds can be broken under induction of the fluorine ions, TBDPS (tert-butyl diphenyl silicon-based) protecting groups can be removed, phenolic hydroxy can be generated, HPQ (hydroxypiperaquine) can be released, accordingly, effects of transferring protons in excited-state molecules can be realized, phenomena of greatly enhancing fluorescent light can occur, and strategies for detecting the fluorine ions by means of fluorescent light 'turn-on' can be implemented; the phenomena of enhancing the fluorescent light of the probe can be observed by naked eyes under illumination of ultraviolet lamps when the fluorine ions have the low concentration of 20 micro-M, the fluorescent probe is excellent in biocompatibility, can be permeated through cell membranes and can be combined with laser confocal microscopes, and accordingly response of the fluorescent probe to the micromole-level fluorine ions in the living cells can be observed; the method for synthesizing the fluorescent probe is simple, post-treatment is simple and convenient, and ultimate products with high yields can be obtained without column chromatographic purification.
Owner:HUBEI UNIV
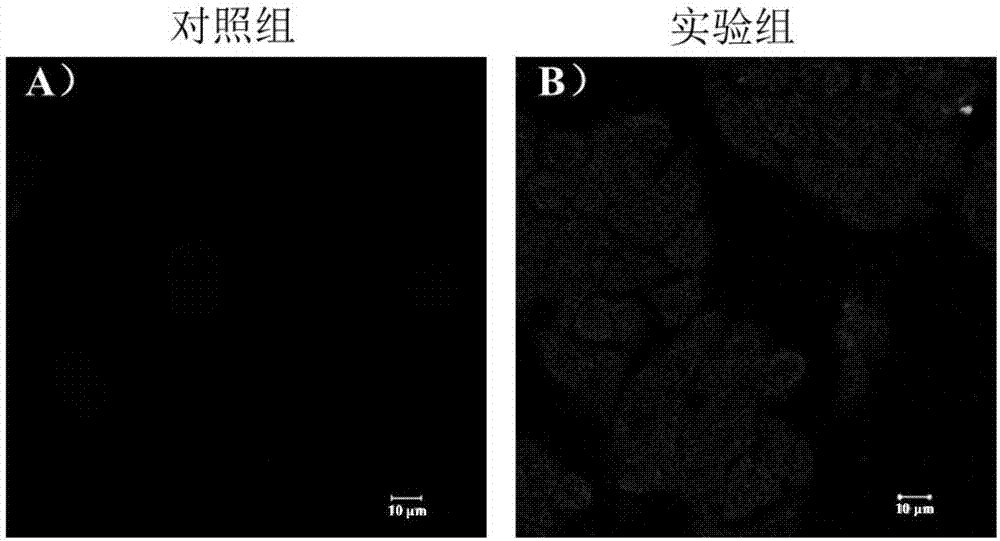
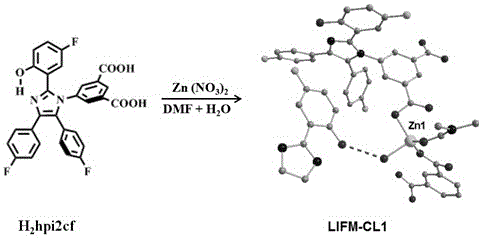
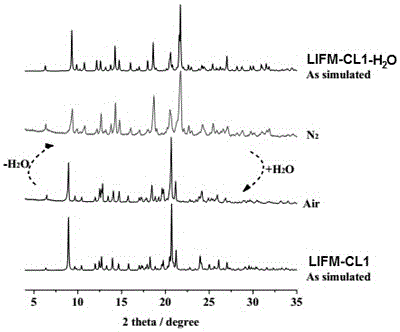
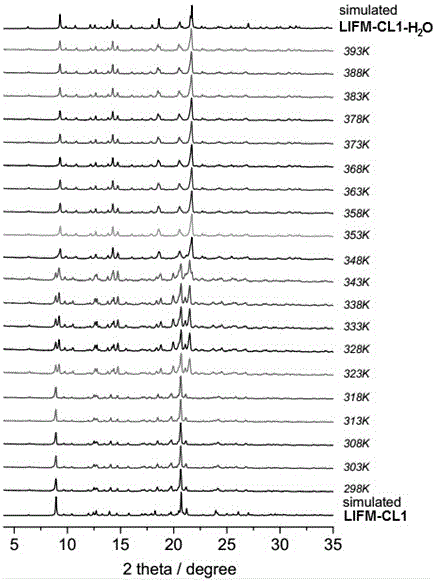
Coordination compound LIFM-CL1 based on ESIPT (excited state intramolecular proton transfer) characteristics and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN105777645ARealize detectionUltra-fast response processFluorescence/phosphorescenceLuminescent compositionsFluoProbesSingle crystal
The invention discloses organic ligand H2hpi2cf based on ESIPT (excited state intramolecular proton transfer) characteristics and a preparation method and application of its Zn2+ complex (complex LIFM-CL1). The organic ligand H2hpi2cf has a molecular formula: 5-(2-(5-fluoro-2-2-hydroxyphenyl)-4,5-bis(4-fluorophenyl)-1H-imidazole-1-yl) isophthalic acid; on this basis, the complex LIFM-CL1 and a fluorescent water responsive film under in-situ single crystal conversion based on this complex are prepared, and the organic ligand has a promising application prospect in terms of heat-sensitive fluorescence, vapor-in-gas detection or fluorescent detection of trace water in an organic solvent; the organic ligand has the advantages that super-fast reversible water response process can be achieved at room temperature, solvent loss in the organic solvent detection process due to detection material dissolution is never caused, and the detection material is recyclable; a prepared fluorescent probe film has good physical characteristics and light emission stability and is reusable many times for a long time.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Fluorenyl salicylaldehyde buzane derivative and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN106146342AAccurate judgmentRealize monitoringMicrobiological testing/measurementHydrazone preparationSalicylaldehydeExcited state intramolecular proton transfer
The invention relates to the technical field of biochemical detection, in particular to a fluorenyl salicylaldehyde hydrazine derivative and a preparation method and application thereof. This type of compound can freely enter and exit the cell and specifically accumulate in the intracellular lipid droplet, changing from the original no fluorescence to strong fluorescence. Compared with the solid-state fluorescence in vitro, there is basically no displacement, and the localization position of the probe can be accurately judged, so as to realize the study of the structure, behavior and physiology of lipid droplets in cells. Process monitoring has extremely broad application prospects in the fields of biology, medicine, health and energy.
Owner:HKUST SHENZHEN RES INST +1
Acidamide compound based on 2-(2'-hydroxyphenyl) benzoxazole, preparation and use thereof
InactiveCN101298442BHigh decomposition temperatureImprove thermal stabilityOrganic chemistryLuminescent compositionsBenzoxazoleExcited state intramolecular proton transfer
The invention relates to an acid amide compound, in particular to the compound based on ESIPT, namely the acid amide compound of 2-(2'-hydroxyphenyl) benzoxazole; the compound of the invention is obtained by adding carboxylic acid and carbonyl diimidazole into a reaction solvent and reacting for 1 to 3 hours under the temperature of 25 to 40 DEG C; then adding the amine compound of the 2-(2'-hydroxyphenyl) benzoxazole and reacting for 2 to 14 hours under the temperature of 25 to 130 DEG C, filtering and purifying. The separation and purifying operations of the preparation method of the invention are simple and convenient; the reaction has no irritation and causticity and the mono-substituted, bis-substituted and tri-substituted acid amide compounds can be directly prepared. The compound of the invention has higher decomposing temperature and excellent thermal stability and can be used for preparing organic luminous materials. The structural general formula of the invention is seen in formula I, wherein, X refers to S, O or NH; when Y is equal to 1, R refers to 7-carboxyl heptane radical, etc.; when Y is equal to 2, R refers to heptane radical, etc.; when Y is equal to 3, R is triphenyl.
Owner:INST OF CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Fluorescent probe for detecting mercury ions as well as preparation method and use method thereof
InactiveCN110483368AEliminate the effects ofHigh sensitivityOrganic chemistryFluorescence/phosphorescenceExcited state intramolecular proton transferPhthalimide
The invention discloses a fluorescent probe for detecting mercury ions as well as a preparation method and a use method of the fluorescent probe. 3-hydroxyphthalimide is used to construct a classicalexcited state intramolecular proton transfer (ESIPT) system, and a propenyl group is introduced to the 4-site. The probe itself has a classic ESIPT effect and emits green fluorescence at a long wave,but in the presence of mercury ions, the mercury ions promote an intramolecular cyclization reaction of 3-hydroxyl, so that the ESIPT effect of the probe is inhibited, and probe molecules emit strongblue fluorescence. The 'ratio' type mercury ion probe based on N-n-butyl phthalimide dye has good response to a mercury ion solution, can realize sensitive quantitative detection of trace mercury ionsin a sample, and has the advantages of simplicity and convenience in operation, low cost, sensitive response, easiness in popularization and application and the like.
Owner:ZHEJIANG SCI-TECH UNIV
Preparation and application of aggregation-induced red-light-emitting material with dual pH response
ActiveCN113248456ABright red fluorescenceGood aggregation-induced luminescent propertiesOrganic chemistryMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorProtonationSalicylaldehyde
The invention relates to a preparation method and an application method of an aggregation-induced red-light-emitting material with dual pH response. The red-light-emitting material is prepared from 4-(diethylamino)salicylaldehyde and 4-amino-2,1,3-benzothiadiazole through a Schiff base reaction. On the basis of the synergistic effect of distorted intramolecular charge transfer, intramolecular movement limitation and excited-state intramolecular proton transfer, the red-light-emitting material has bright red fluorescence in an aggregation state and has good aggregation-induced emission performance. As two pH-responsive elements are integrated, in the gradual acidification process of the red-light-emitting material and along with the change of the fluorescence color from red to yellow green and then to fluorescence quenching, a rod-like molecular assembly is firstly converted into microspheres under the condition of high water content, and then the microspheres are damaged under the condition of high acidity. In addition, protonation of a diethylamino group also has application value in the aspects of carbon dioxide visual detection, anti-counterfeiting and information encryption. The preparation method is simple in process, preparation cost is low, and yield is high.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING +1
White-emitting compounds using excited-state intramolecular proton transfer, organic electroluminescent element and laser material using the same
InactiveUS8569510B2Good reproducibilityImprove life characteristicsOrganic chemistryLaser active region structureChemical compoundExcited state intramolecular proton transfer
Provided are a white-emitting monomolecular compound using excited-state intramolecular proton transfer (ESIPT) characteristics, and an organic electroluminescence device and a laser device comprising same. The white-emitting monomolecular compound according to the present invention is prepared by covalently bonding at least two types of molecules which produce different colors and have excited-state intramolecular proton transfer (ESIPT) characteristics. The white-emitting monomolecular compound according to the present invention achieves white luminescence irrespective of the concentration thereof and of the state of the materials thereof, and therefore can be used in a variety of fields including an organic electroluminescence device and a laser device.
Owner:DONGWOO FINE CHEM CO LTD +1
Large-Stokes-displacement near-infrared BODIPY (boron-dipyrromethene) dye and preparation and application thereof
InactiveCN107033621ALight damage is smallReduce fluorescence self-quenchingAzo dyesFluorescence/phosphorescenceInfraredNitrogen
The invention discloses large-Stokes-displacement near-infrared BODIPY (boron-dipyrromethene) dye NIR-BOD and synthesis and application thereof. The dye NIR-BOD herein is prepared via cycling reaction of formyl BODYIPY. Through ESIPIT (excited state intramolecular proton transfer) mechanism and hydrogen-bond interaction between protons on intramolecular hydroxyl and nitrogen atoms on adjourning heterocyclic rings, the dye can emit large-Stokes-displacement (>200 nanometers) near-infrared fluorescence.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Ratio type fluorescent probe and preparation method thereof, and application of ratio type fluorescent probe in sulfite ion detection
ActiveCN112209898AEfficient and accurate identificationEasy to synthesizeOrganic chemistryFluorescence/phosphorescenceFluoProbesThiazole
The invention relates to a ratio type fluorescent probe and a preparation method thereof, and application of the ratio type fluorescent probe in sulfite ion detection. The ratio type fluorescent probecan be used for detecting sulfite ions based on dual mechanisms of excited state intramolecular proton transfer and aggregation-induced emission. A fluorescent probe compound disclosed by the invention is 3-(benzo[d]thiazol-2-yl)-4'-(diphenylamino)-[1,1'-biphenyl]4-yl-4-oxopentanoate. The fluorescence probe has the outstanding characteristics that the fluorescence probe can realize the ratio typedetection of sulfite, the preparation method of the fluorescence probe is simple, the interference of an external environment on a detection result can be effectively avoided, and the fluorescence probe has high sensitivity and good selectivity. The fluorescent probe disclosed by the invention can be used for rapidly detecting sulfite ions in environment and food.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Benzothiazole-benzyl cyanide compound and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN110590701AWith ESIPIWith AIEOrganic chemistryFluorescence/phosphorescenceChemical compoundExcited state intramolecular proton transfer
The invention provides a benzothiazole-benzyl cyanide compound, wherein the molecular formula is as follows. The compound has both excited state intramolecular proton transfer and aggregation inducedluminescence properties. The invention also provides a preparation method of the compound, which has the characteristics of simple synthesis, only one step reaction, mild reaction conditions, high yield reaching more than 80%, large Stokes shift reaching 330nm, emission wavelength 635nm in near infrared region and the like. The compound can be applied to the field of fluorescence detection.
Owner:HENGYANG NORMAL UNIV
Red light emitting material based on excited state proton transfer and preparation method and application thereof
PendingCN114874248AImprove heat sensitivityHigh decomposition temperatureMaterial nanotechnologyGroup 3/13 element organic compoundsOrganosolvP phosphate
The invention discloses a red light emitting material based on excited state proton transfer as well as a preparation method and application of the red light emitting material. An organic boron difluoride complex containing excited state intramolecular proton transfer is prepared and synthesized. The temperature sensing property of the material in an organic solvent diethylene glycol dimethyl ether (MOE) is studied, and the monochromatic temperature sensing property of the material in an aqueous solution and a phosphate (PBS) buffer solution is further studied. The material is doped with temperature-resistant diphenyl (6-(pyrrolidine-1-yl) pyrene-1-yl) phosphine oxide to prepare a non-energy-transfer ratio-type organic fluorescence thermometer, the non-energy-transfer ratio-type organic fluorescence thermometer has excellent sensing characteristics, and temperature indication can be carried out by virtue of fluorescence color change observed by naked eyes. The material disclosed by the invention is simple to prepare, low in price and high in yield. The organic fluorescent temperature sensing probe prepared from the material has high temperature resolution and sensitivity in a wide temperature range, and has very high application value.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Activatable aggregation-induced emission probe and application thereof in sensitive detection of carbaryl
ActiveCN114478457AInhibits esterase activityAdjustment ratioOrganic chemistryFluorescence/phosphorescenceNatural productExcited state intramolecular proton transfer
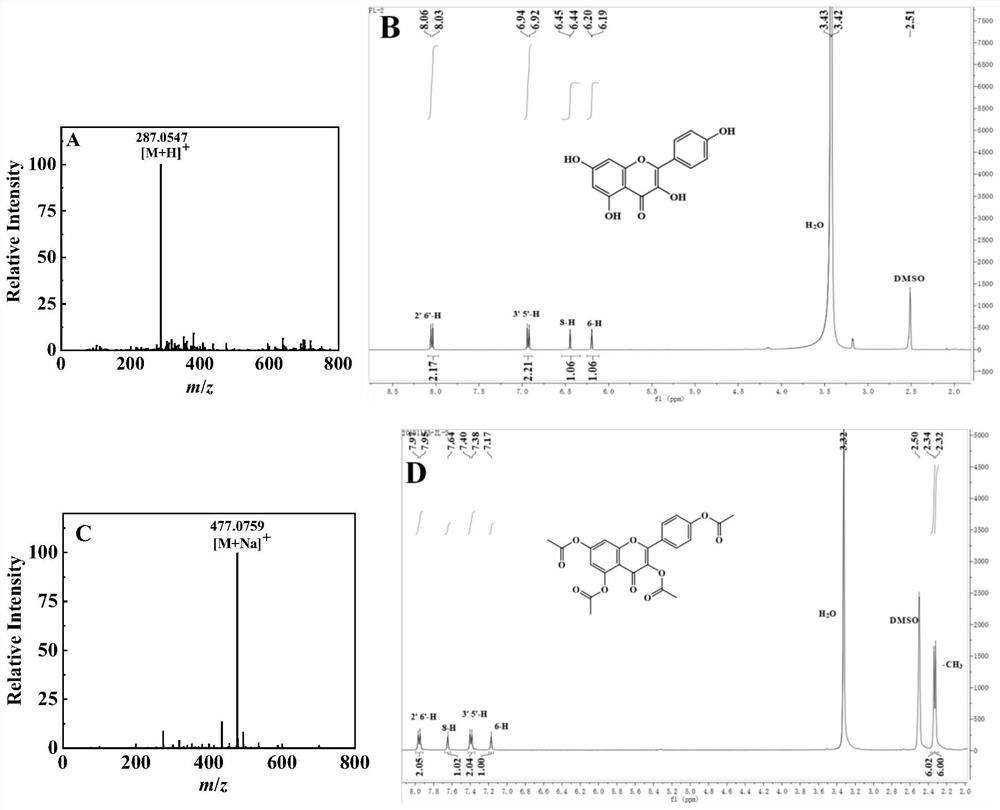
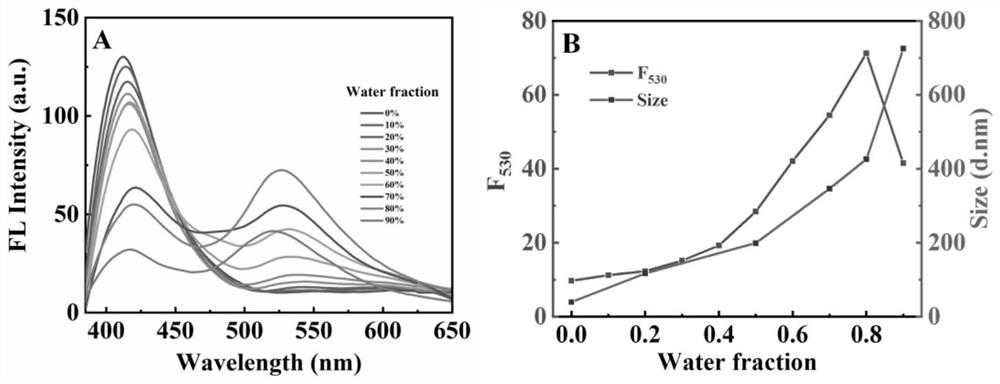
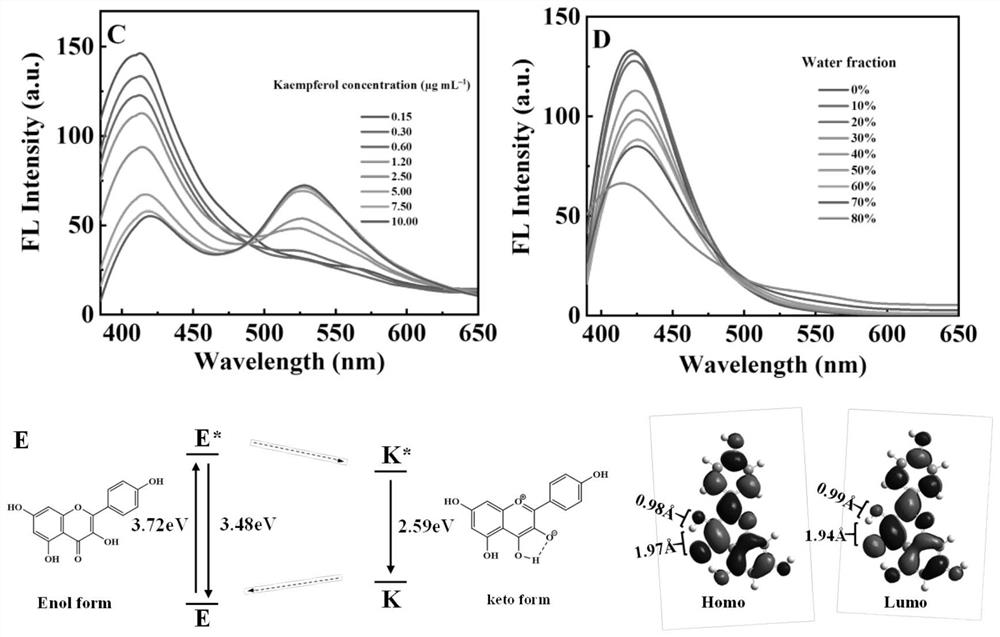
The invention relates to an activatable aggregation-induced emission probe and application of the activatable aggregation-induced emission probe in sensitive detection of carbaryl, a purified natural product kaempferol is used as a raw material, belongs to the field of pesticide detection, and designs and synthesizes a novel esterase activated aggregation-induced emission (AIE) and excited state intramolecular proton transfer (ESIPT) probe kaempferol tetraacetate. The method is used for ratio detection of carbaryl. An acetate group is introduced as an esterase reaction site and an AIE + ESIPT initiator. Kaempferol tetraacetate has an aggregation-induced quenching effect. Esterase specifically hydrolyzes kaempferol tetraacetate to generate kaempferol with AIE and ESIPT characteristics, the kaempferol has obvious fluorescence emission at 530 nm, the Stokes shift is large (165 nm), and the hydrolysis time is short (8 min). Carbaryl can inhibit the activity of esterase, so that the generation of kaempferol is effectively inhibited. Based on the principle, a simple carbaryl ratio detection strategy is constructed, and the strategy has high selectivity and reliability.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
A kind of zinc ion sensor molecule and its preparation and application
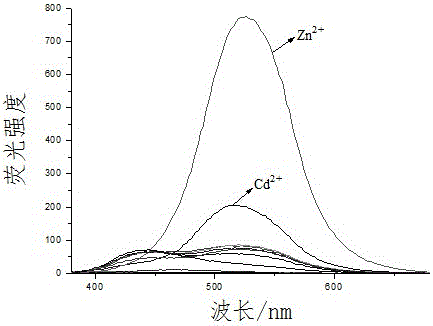
The invention discloses a zinc ion sensor molecule, which belongs to the field of cation detection. The sensor molecules of the present invention contain hydrazone and imine functional groups, based on their strong complexation to metal cations, which hinder excited state intramolecular proton transfer (ESIPT) and -HC=N-isomerization processes, resulting in the opening of fluorescence and Identify and detect Zn2+. Experiments show that the sensor molecule in the HEPES buffer system of DMSO / H2O, only the addition of Zn2+ makes the system emit a significant yellow-green fluorescence under ultraviolet light, and in the corresponding fluorescence spectrum, only the addition of Zn2+ makes the buffer system of the sensor molecule The maximum fluorescence emission peak appears at 524nm. Therefore, the sensor molecule can be used for the rapid fluorescence detection of Zn2+, and its minimum detection limit can reach 1.39×10‑8M, and the recognition of Zn2+ by other cations has no serious interference.
Owner:NORTHWEST NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Ratio type fluorescent molecular probe as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN111995599AImplement ratiometric detectionIncrease acidityOrganic chemistryFluorescence/phosphorescenceFluoProbesExcited state intramolecular proton transfer
The invention discloses a ratio type fluorescent molecular probe as well as a preparation method and an application thereof, the structural formula of the ratio type fluorescent molecular probe is shown as a formula I. The preparation method of the ratio type fluorescent molecular probe for detecting the pH value is simple, raw materials are cheap and easy to obtain, the synthesis process is simple, the yield is high, and the ratio type fluorescent molecular probe is suitable for large-scale production, popularization and application. The fluorescent probe has excited state intramolecular proton transfer property, so that the interference of self-absorption and biological background fluorescence can be effectively avoided, and the error caused by non-uniform probe use concentration, non-uniform probe distribution and the like can be avoided due to ratio type response. In actual detection, the fluorescent probe is quick in response, wide in detection range and high in sensitivity, has high anti-interference performance on common coexisting substances in a sample, has good repeatability on detection of the pH value, and can realize repeated cyclic application by adjusting the pH value. The probe disclosed by the invention has a wide application prospect in the aspect of pH value detection in various scenes such as environmental samples, biological samples and the like.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Compounds with aggregation-induced luminescence function, preparation methods and applications thereof
ActiveCN112480025BHas aggregation-induced luminescent functionSignificant aggregation-induced luminescence functionAntipyreticAnalgesicsChemical structureOrtho position
The present invention relates to a compound with aggregation-induced luminescence function. Its chemical structure is shown in general formula I. The reaction obtains a Schiff base structure intermediate; the intermediate is obtained through recrystallization and purification operation, and then reacts with an oxidant in an organic solvent to obtain a compound with aggregation-induced luminescence function. The compound is further modified to obtain a series of functionalized aggregation-induced luminescent compounds. The synthesis method of such compounds is simple, the reaction conditions are mild and easy to synthesize, the post-processing operation is convenient, the yield is high, and the heating reaction shortens the reaction time. The resulting aggregation-induced luminescent compound has an excited state intramolecular proton transfer effect. There is an intramolecular weak hydrogen bond between the hydroxyl hydrogen atom on the naphthalene ring and the nitrogen atom on the ortho-benzothiazole ring, which has an excited intramolecular proton transfer effect and exhibits a large Stokes shift.
Owner:汉中职业技术学院
Benzothiazole derivative and application thereof as fluorescent dye
InactiveCN112521383AEasy to synthesizeMild reaction conditionsOrganic chemistryAzo dyesFluoProbesDiketone
The invention discloses a benzothiazole derivative and application of the benzothiazole derivative as a fluorescent dye. Specifically, four organic fluorescent dyes with excited state intramolecular proton transfer mechanism respectively react with an aryl diketone derivative through 4-(benzo[d]thiazole-2-yl)-3-hydroxybenzaldehyde to synthesize a series of imidazole ring-containing compounds, theexcited state intramolecular proton transfer mechanism of 4-(benzo[d]thiazole-2-yl)-3-hydroxybenzaldehyde is reserved, and meanwhile a conjugated system of the fluorescent dye is added, the fluorescent dye is simple and convenient to prepare and low in cost, and the series of fluorescent dyes show relatively strong fluorescence, and also have a great application prospect in research on synthesis of a fluorescent probe.
Owner:CHINA THREE GORGES UNIV
A fluorescent probe for detecting fluoride ions in living cells and its preparation method
InactiveCN107365326BHigh yieldThe synthesis method is simpleGroup 4/14 element organic compoundsFluorescence/phosphorescenceUltravioletCell membrane
The invention discloses a fluorescent probe for detecting fluorine ions in living cells and a method for preparing the fluorescent probe. The fluorescent probe is of a structure shown as a formula I. The fluorescent probe and the method have the advantages that the fluorescent probe is nearly free of optional fluorescent light, but Si-O bonds can be broken under induction of the fluorine ions, TBDPS (tert-butyl diphenyl silicon-based) protecting groups can be removed, phenolic hydroxy can be generated, HPQ (hydroxypiperaquine) can be released, accordingly, effects of transferring protons in excited-state molecules can be realized, phenomena of greatly enhancing fluorescent light can occur, and strategies for detecting the fluorine ions by means of fluorescent light 'turn-on' can be implemented; the phenomena of enhancing the fluorescent light of the probe can be observed by naked eyes under illumination of ultraviolet lamps when the fluorine ions have the low concentration of 20 micro-M, the fluorescent probe is excellent in biocompatibility, can be permeated through cell membranes and can be combined with laser confocal microscopes, and accordingly response of the fluorescent probe to the micromole-level fluorine ions in the living cells can be observed; the method for synthesizing the fluorescent probe is simple, post-treatment is simple and convenient, and ultimate products with high yields can be obtained without column chromatographic purification.
Owner:HUBEI UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com